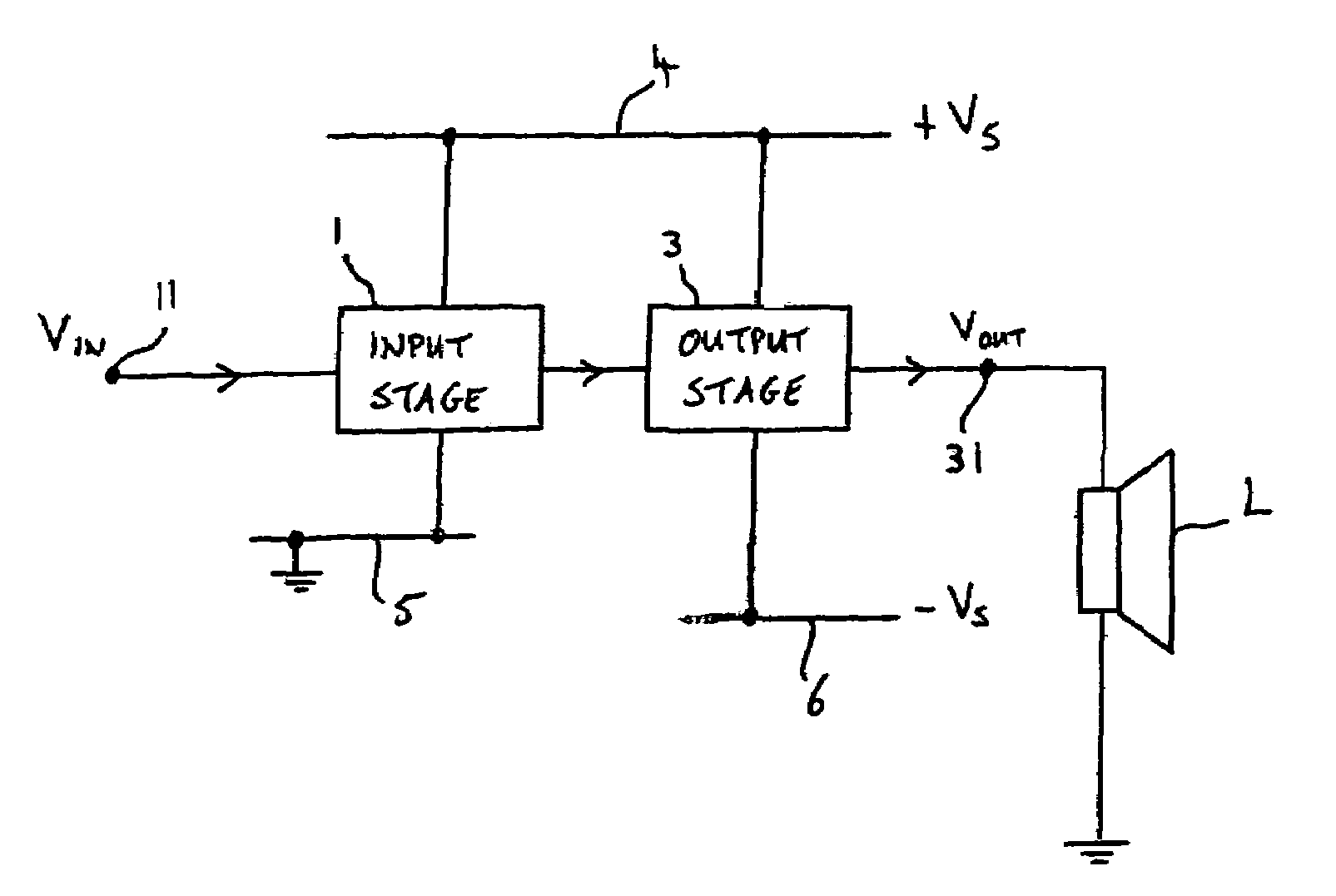
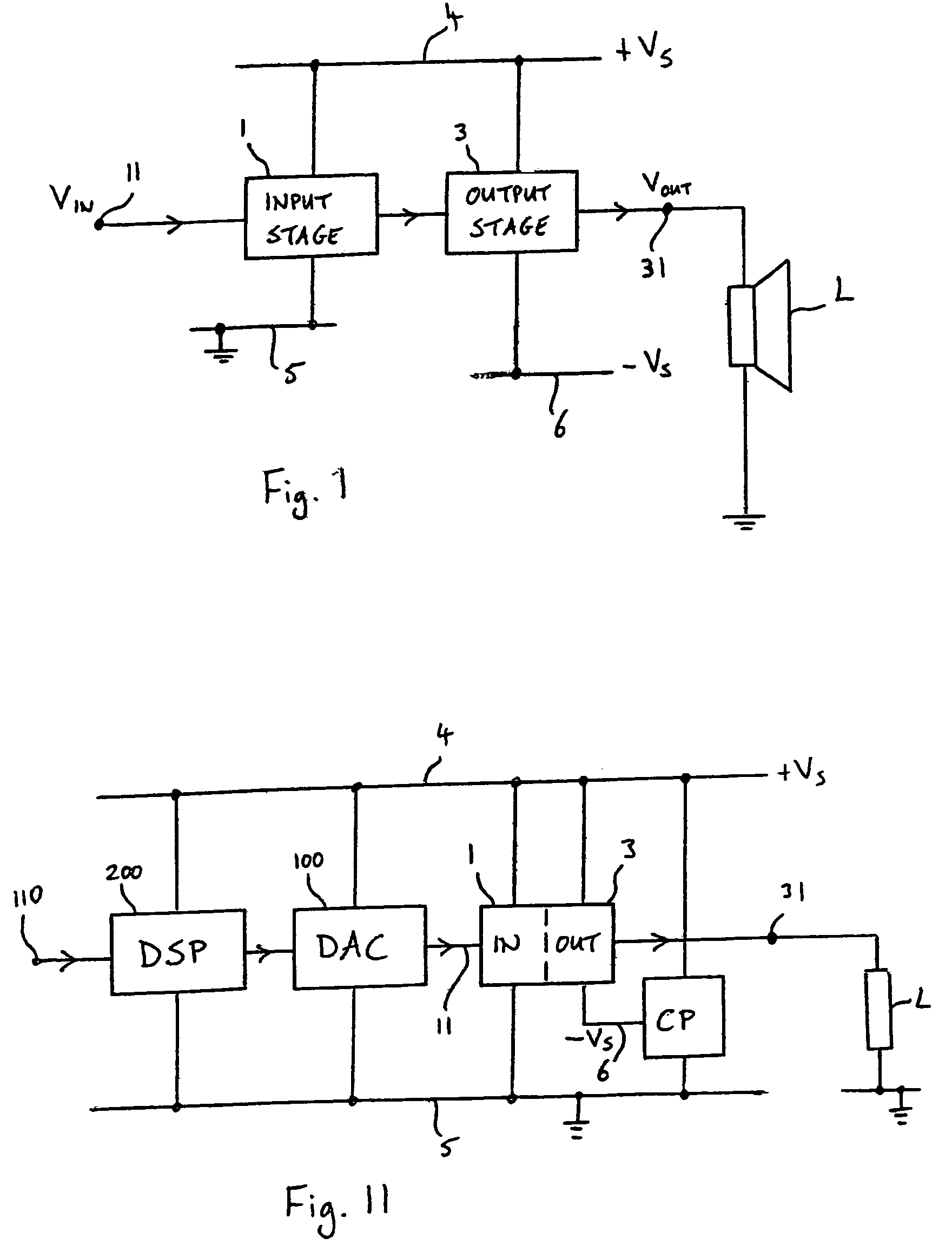
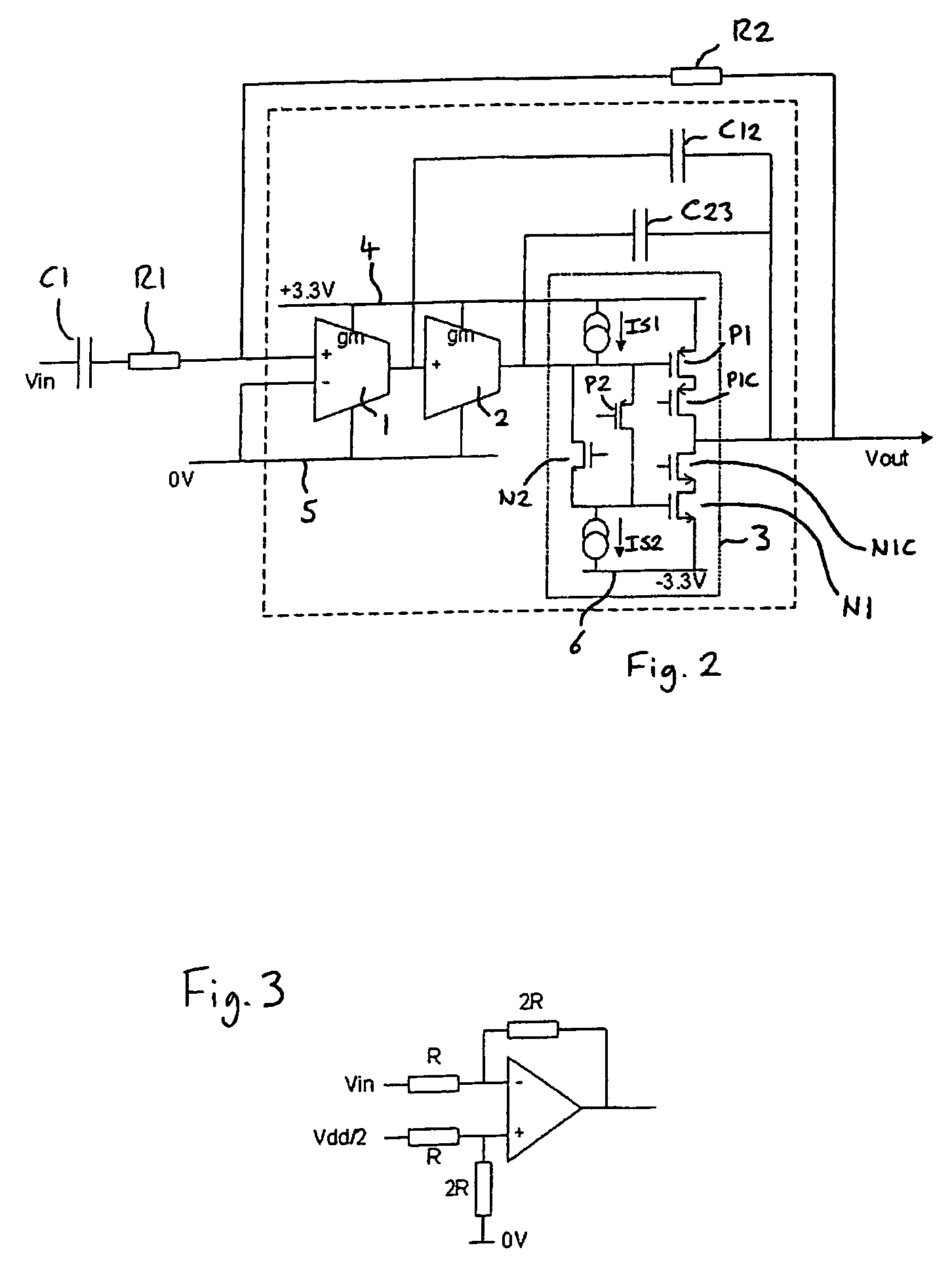
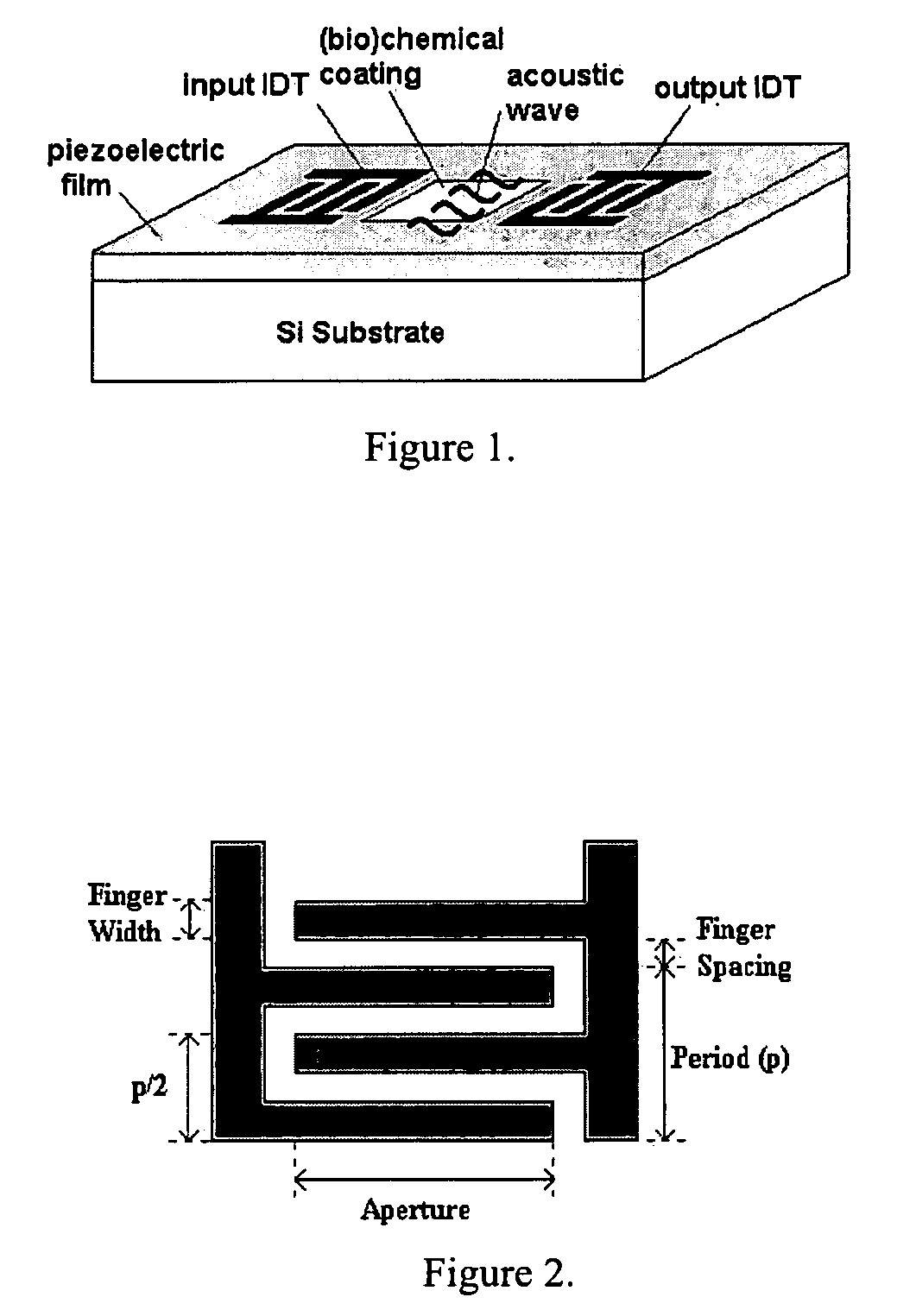
Patents
Literature
305 results about "Soi cmos technology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
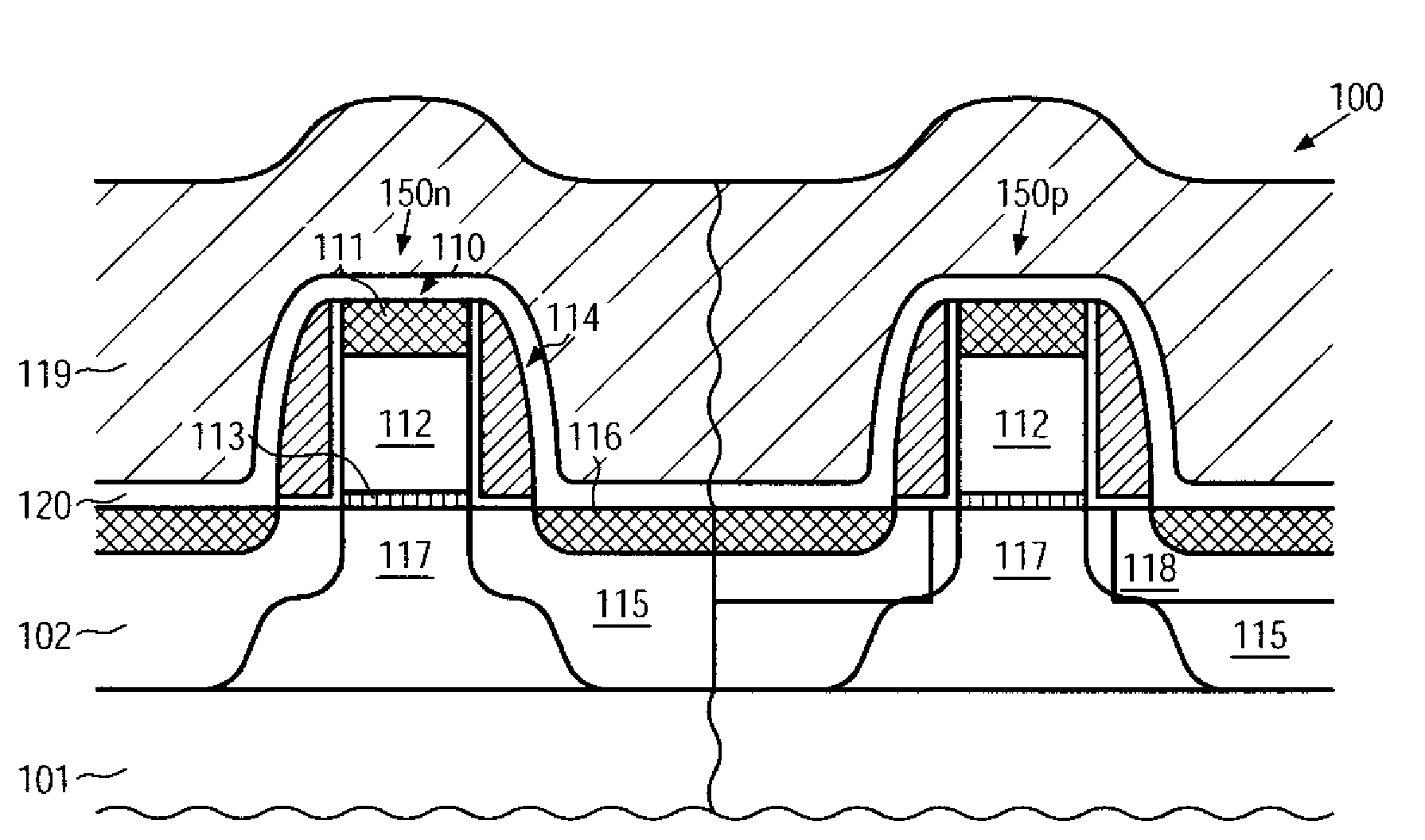
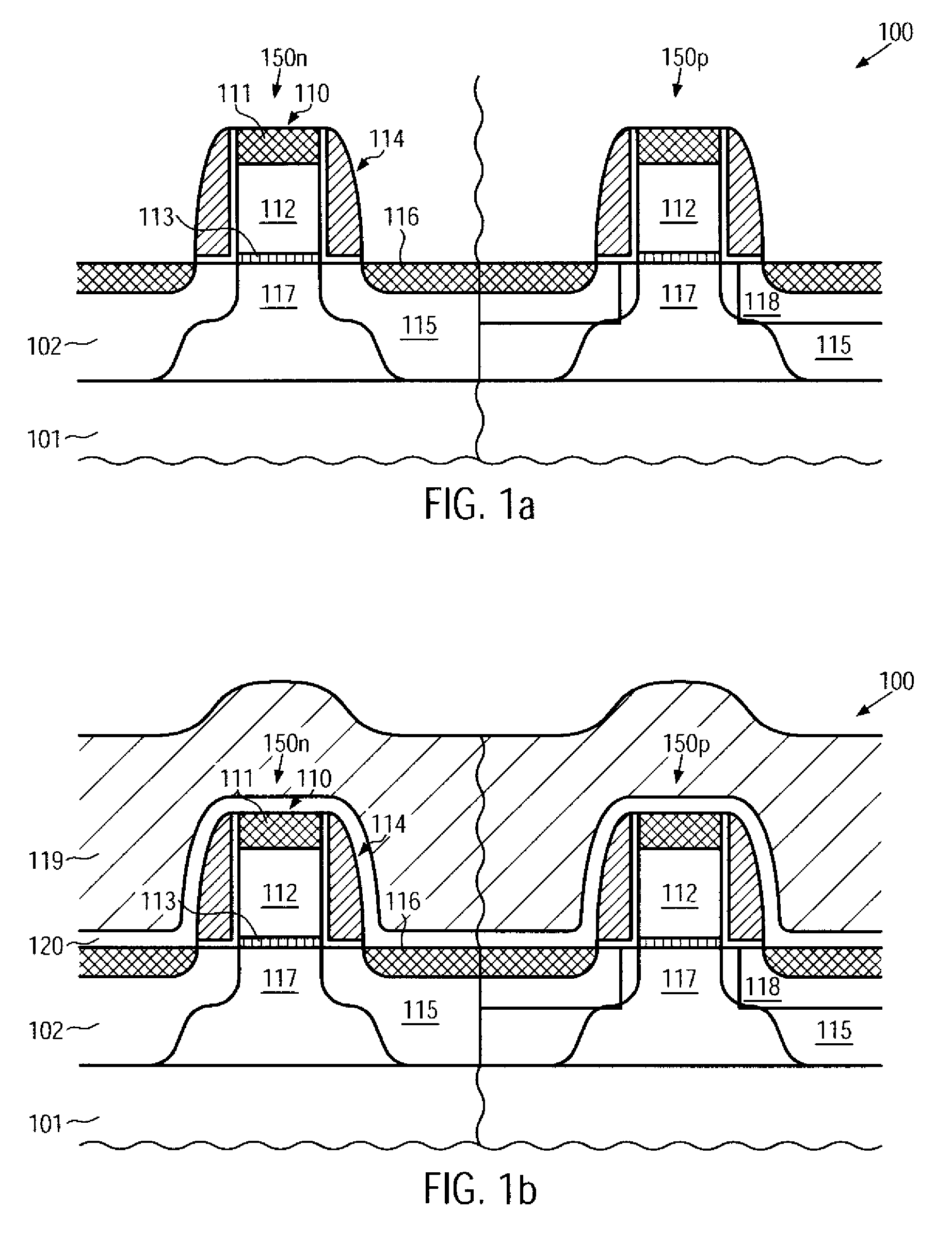
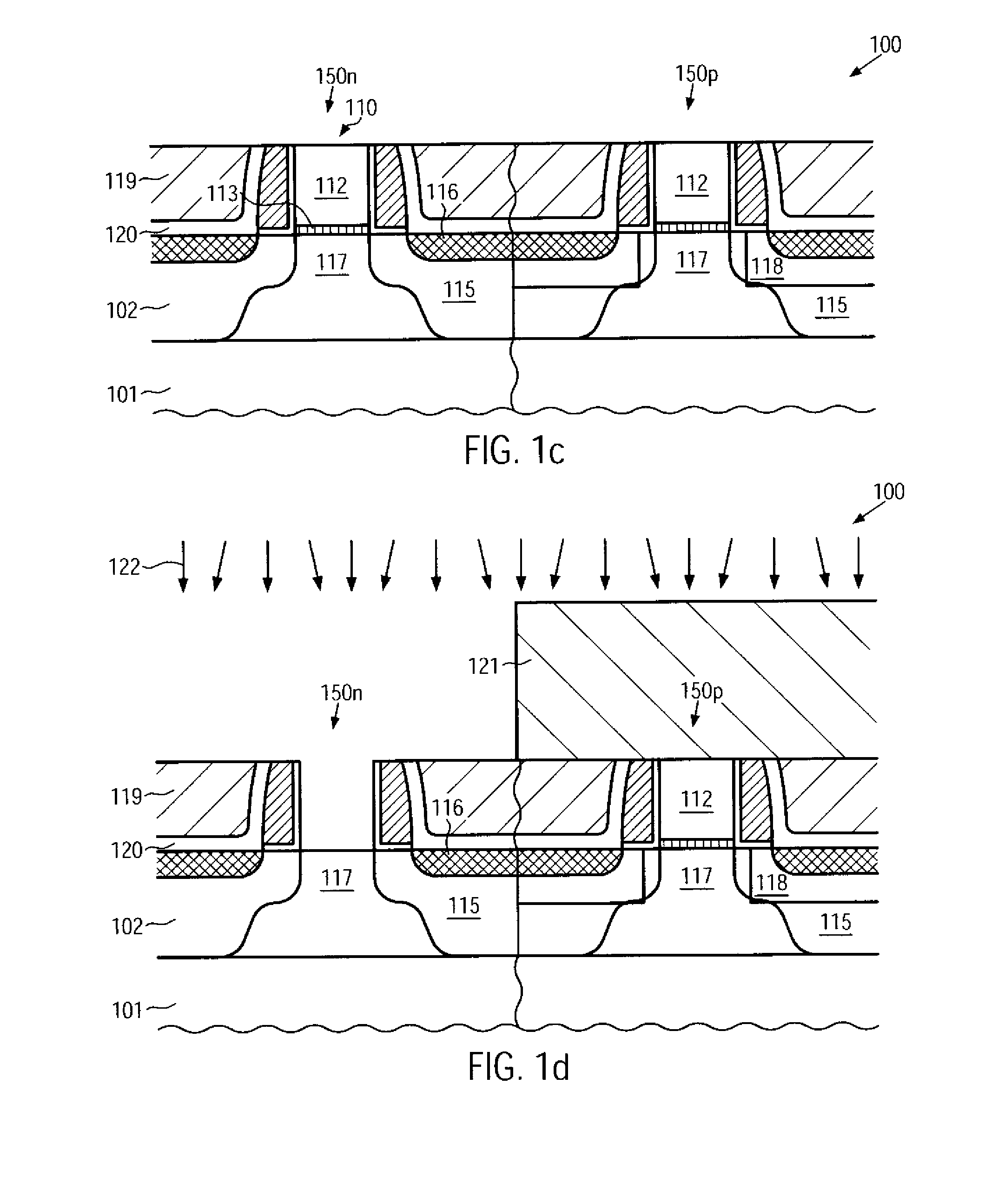
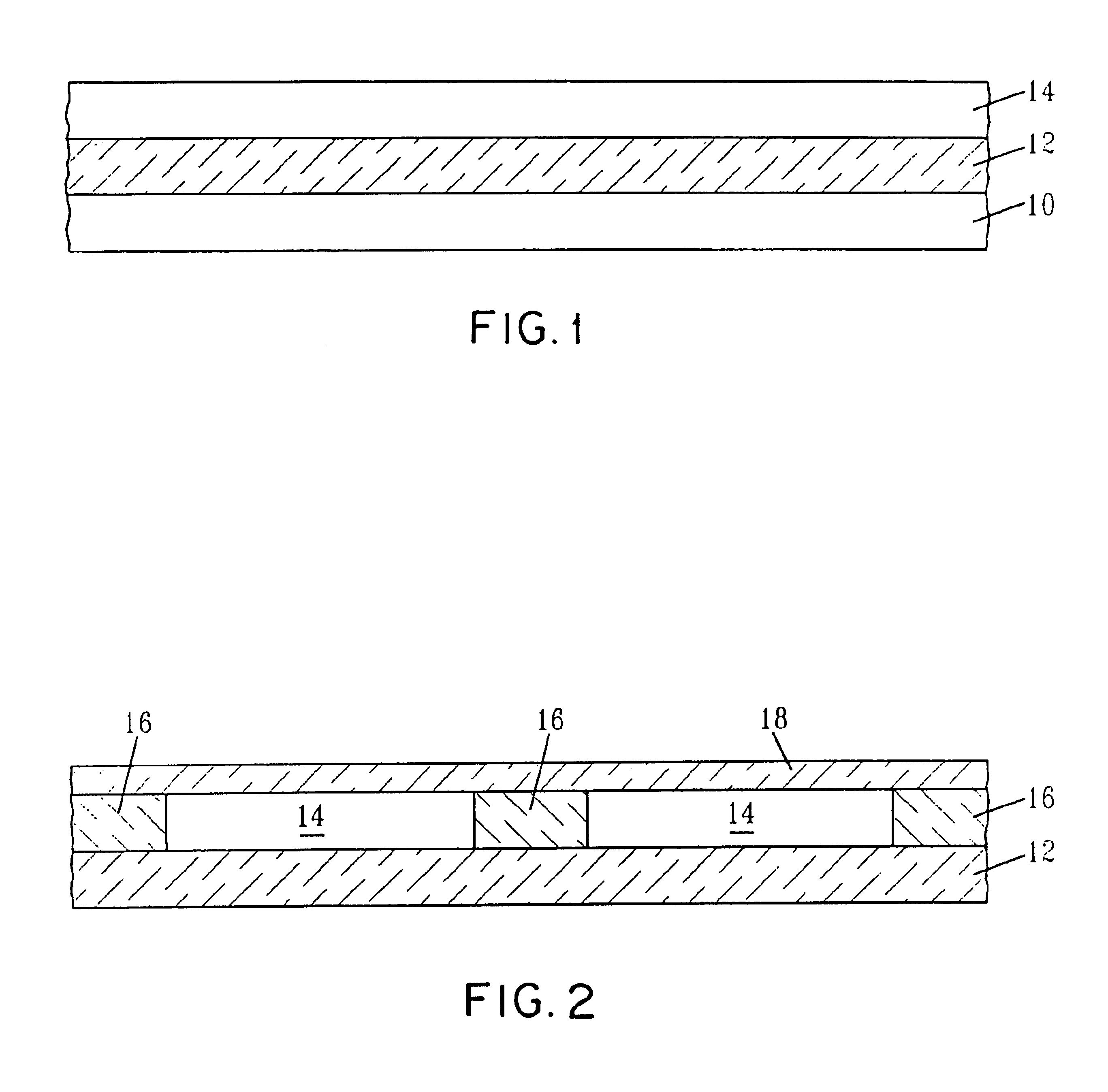
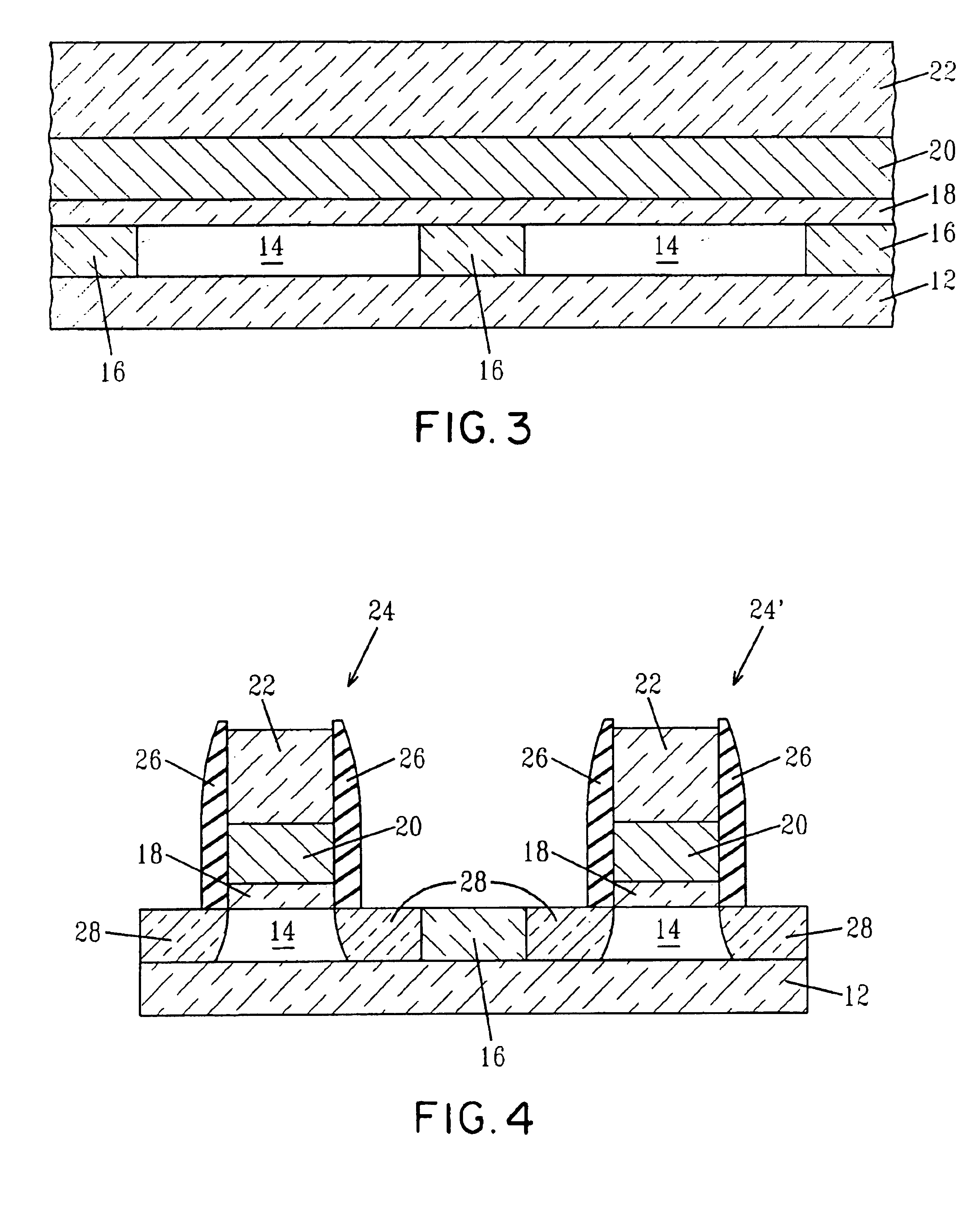
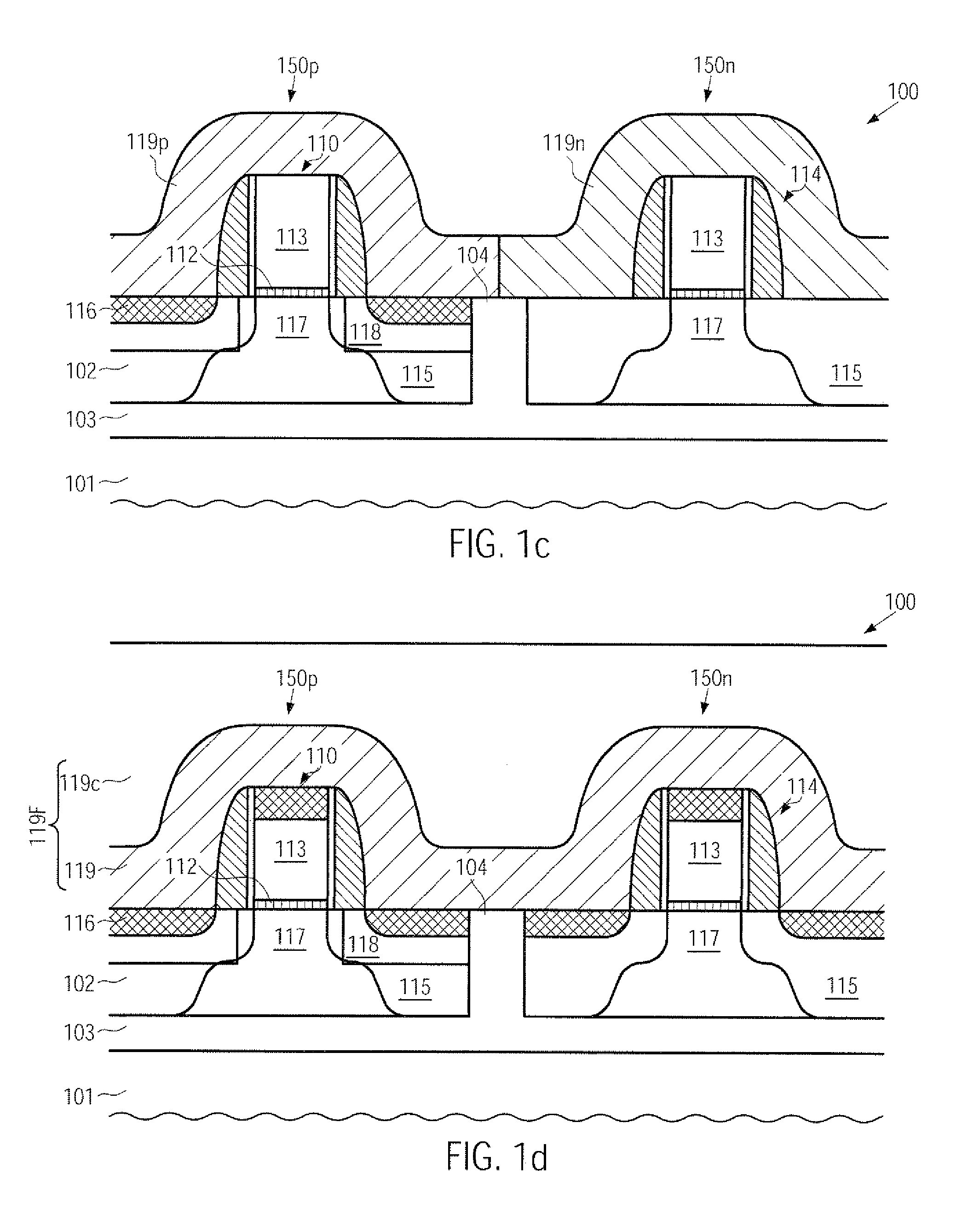
CMOS device having gate insulation layers of different type and thickness and a method of forming the same
ActiveUS20090057769A1Avoid normal workImprove compatibilityTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSInsulation layer
In the process sequence for replacing conventional gate electrode structures by high-k metal gate structures, the number of additional masking steps may be maintained at a low level, for instance by using highly selective etch steps, thereby maintaining a high degree of compatibility with conventional CMOS techniques. Furthermore, the techniques disclosed herein enable compatibility to front-end process techniques and back-end process techniques, thereby allowing the integration of well-established strain-inducing mechanisms in the transistor level as well as in the contact level.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method and process to make multiple-threshold metal gates CMOS technology
Methods of forming complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) devices having multiple-threshold voltages which are easily tunable are provided. Total salicidation with a metal bilayer (representative of the first method of the present invention) or metal alloy (representative of the second method of the present invention) is provided. CMOS devices having multiple-threshold voltages provided by the present methods are also described.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Method of forming high-k gate electrode structures after transistor fabrication
InactiveUS20090087974A1High degreeDeleterious effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCMOSDielectric
A sophisticated high-k metal gate electrode structure may be formed after the deposition of a first part of an interlayer dielectric material, thereby providing a high degree of process compatibility with conventional CMOS techniques. Thus, sophisticated strain-inducing mechanisms may be readily implemented in the overall process flow, while nevertheless avoiding any high temperature processes during the formation of the sophisticated high-k dielectric gate stack.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
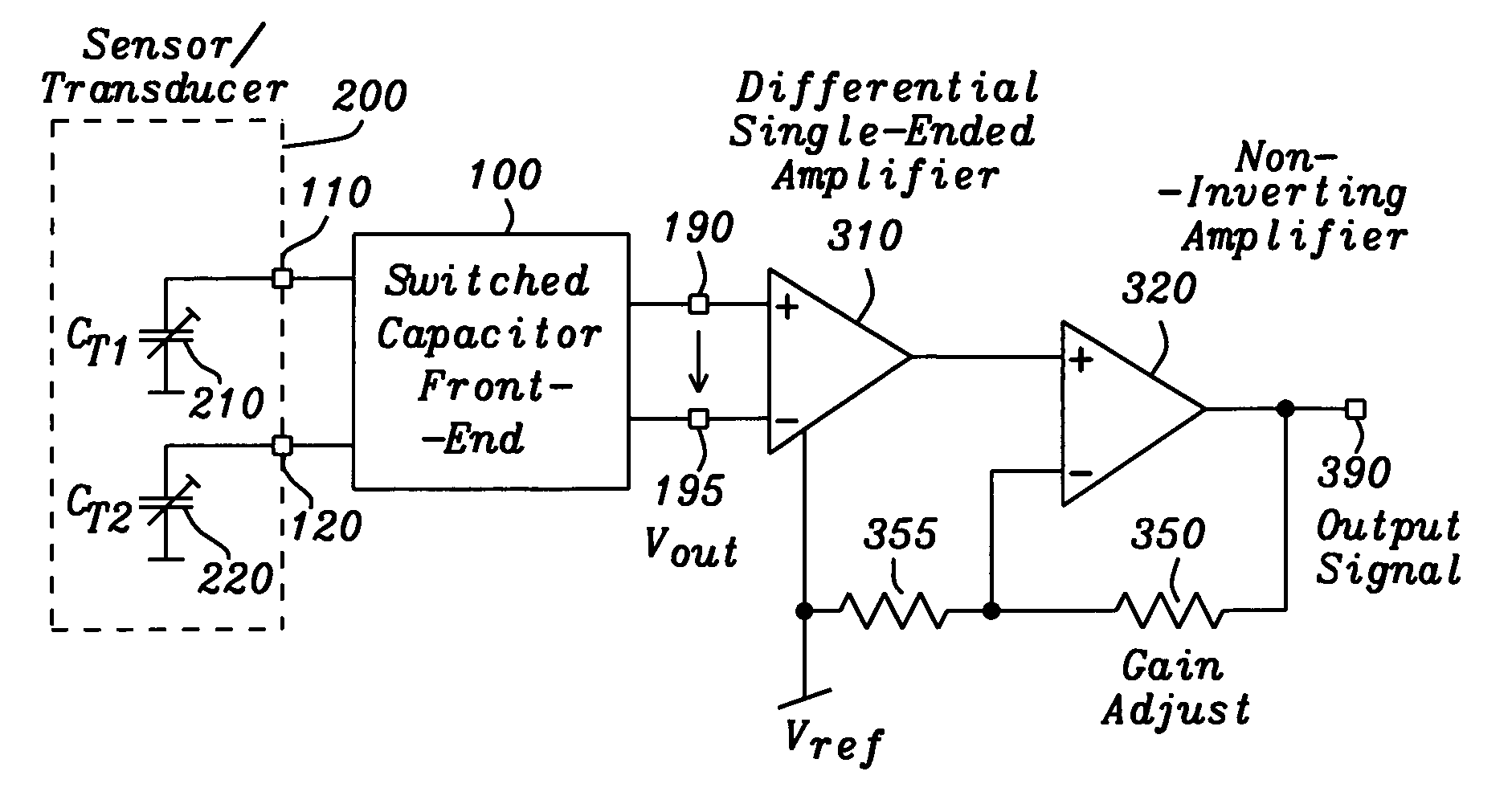
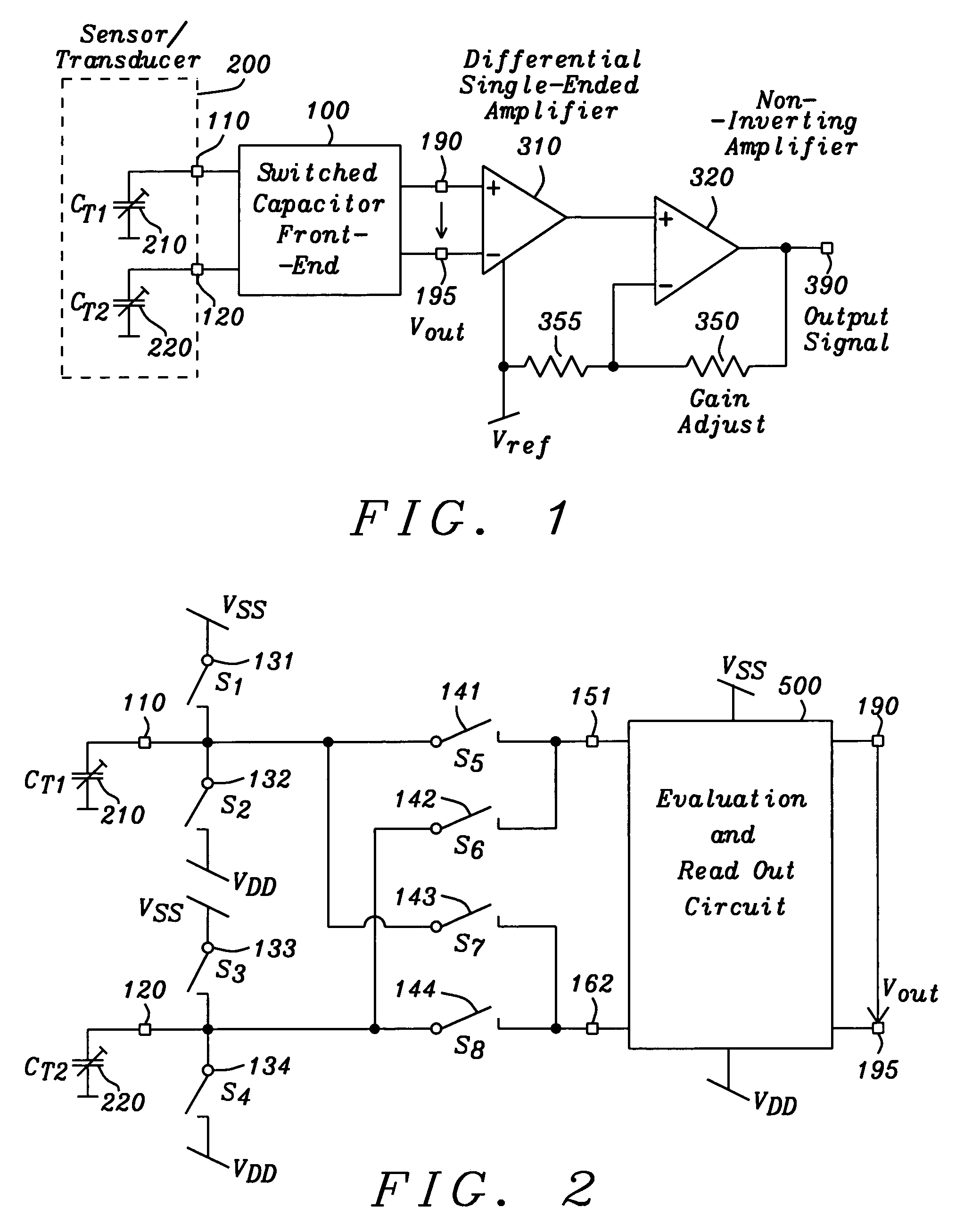
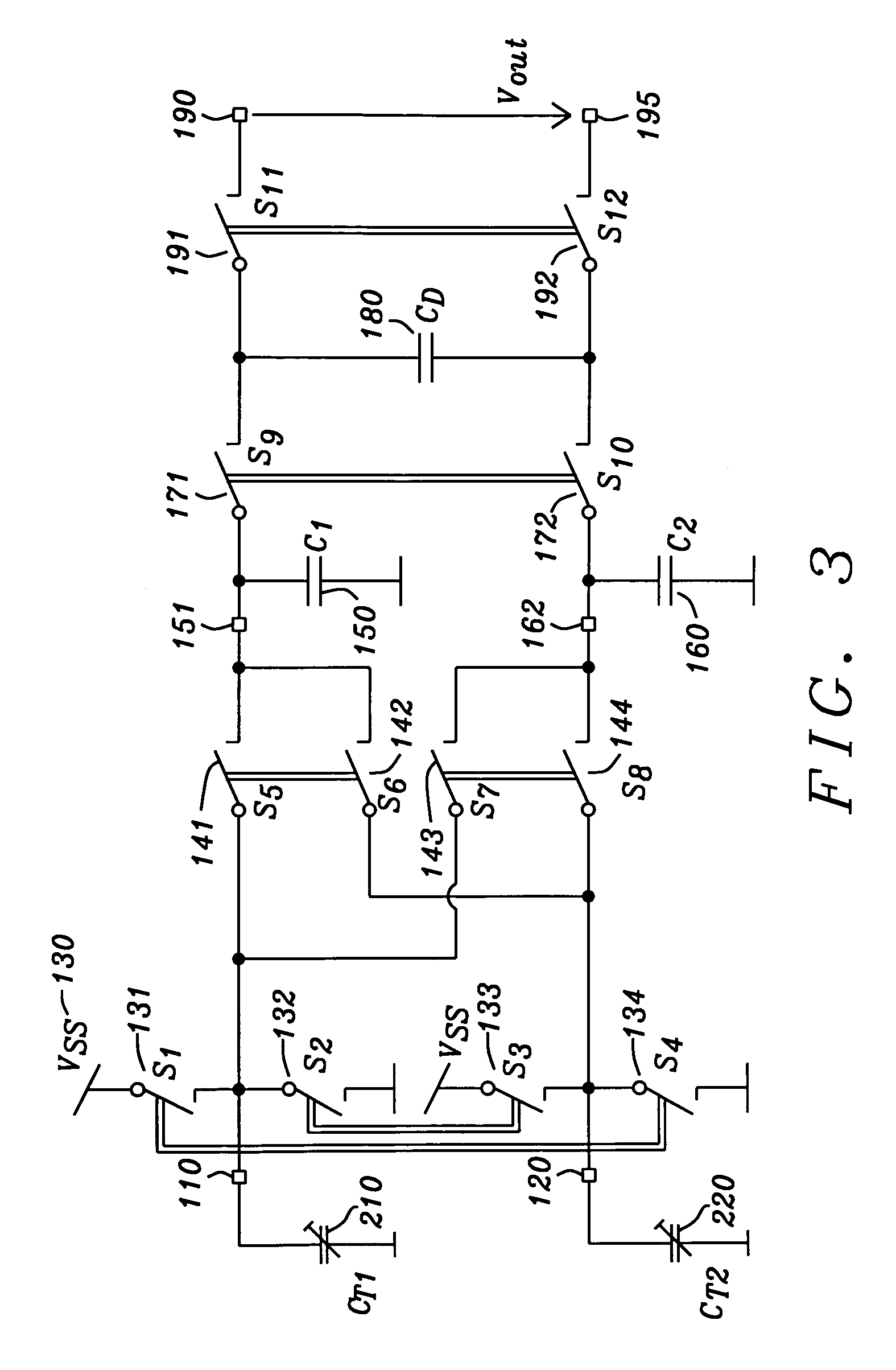
Differential capacitance measurement
InactiveUS6949937B2Efficient methodPrecise and sensitive and yet stable evalutionCapacitance measurementsConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyCMOSSoi cmos technology
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
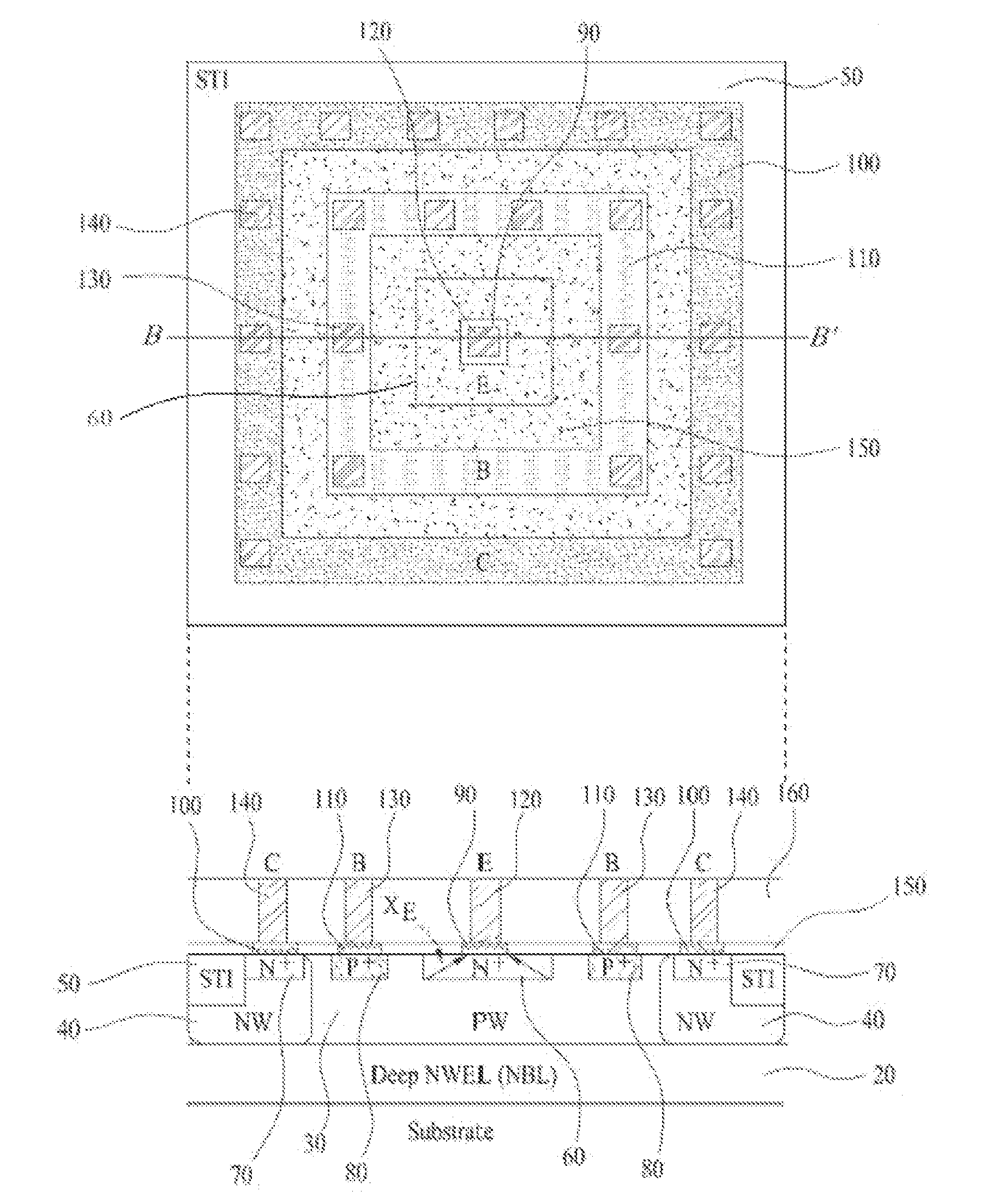
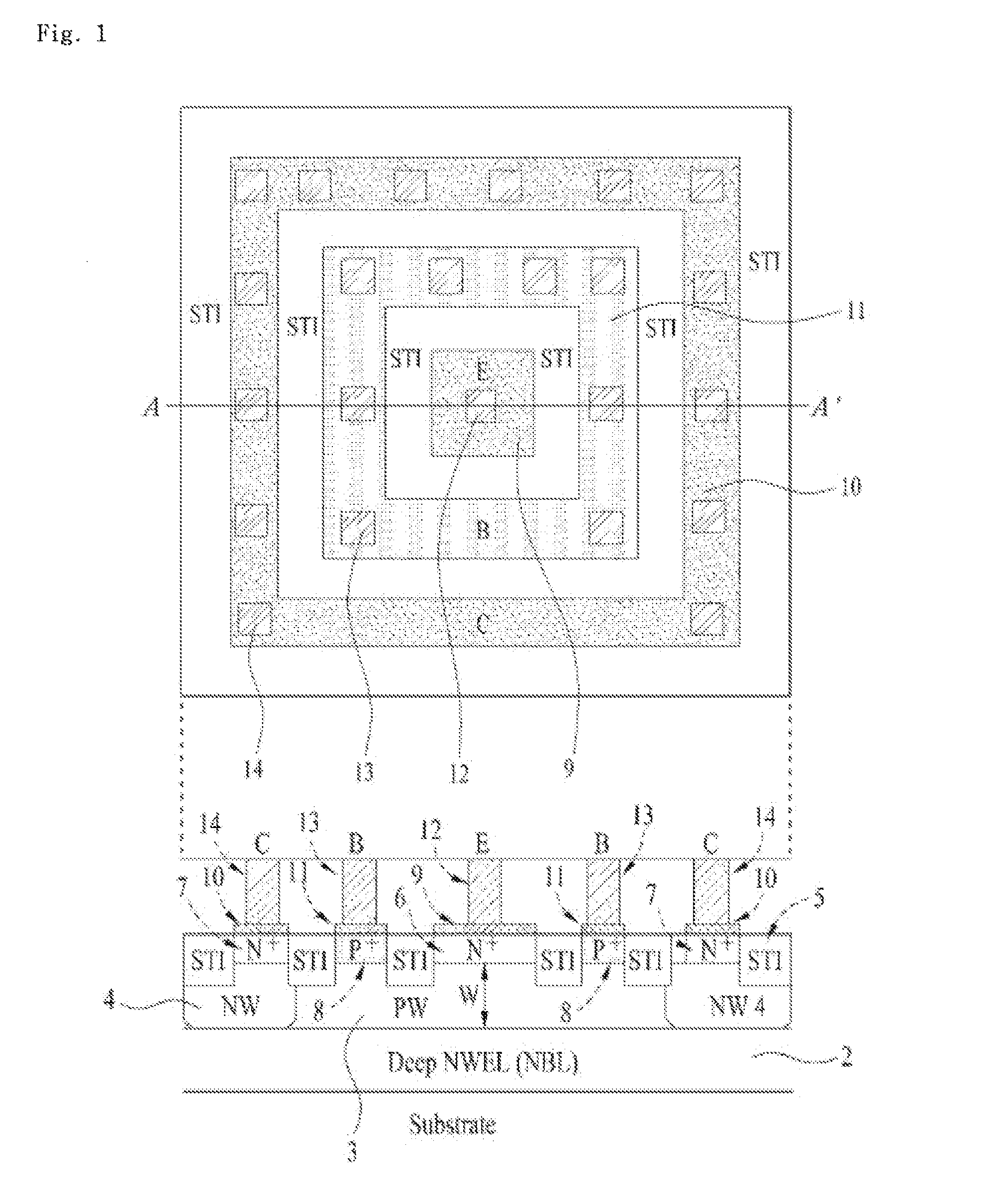
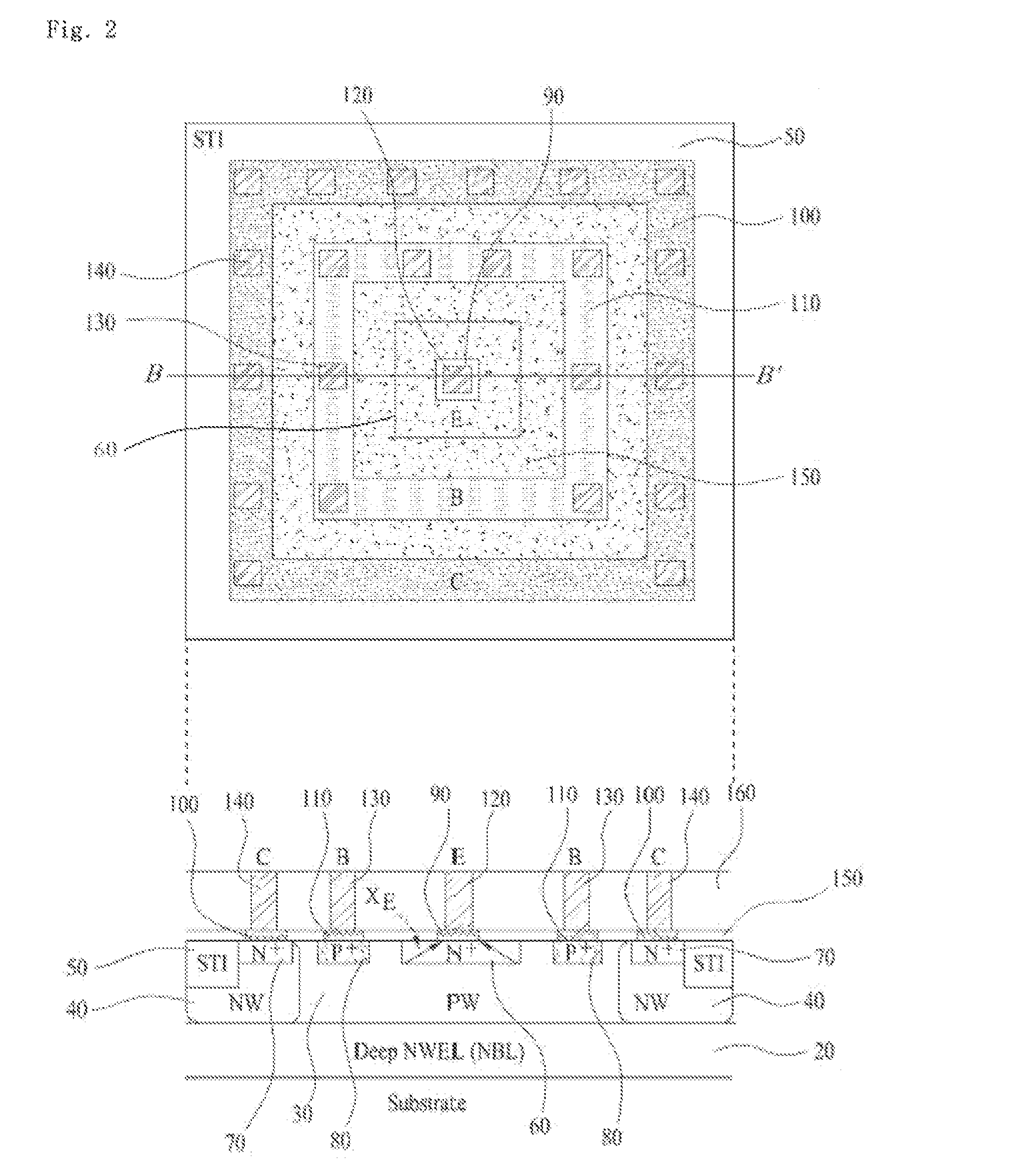
Bipolar Junction Transistor Based on CMOS Technology
InactiveUS20120032303A1Increase currentHigh base resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSEngineering
The present invention relates to semiconductor technologies, and more particularly to a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) in a CMOS base technology and methods of forming the same. The BJT includes a semiconductor substrate having an emitter region, a base having a first contact, and a collector having a second contact and a well plug; a first silicide film on the first contact; a second silicide film on the second contact; a first silicide blocking layer on or over the semiconductor substrate between the first and second silicide films, and a second silicide blocking layer on the semiconductor substrate between the first silicide film and the emitter region.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Integration of strained Ge into advanced CMOS technology
InactiveUS7244958B2Improve mobilityImprove scalabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSoi cmos technology
A structure and method of fabrication for PFET devices in a compressively strained Ge layer is disclosed. The fabrication method of such devices is compatible with standard CMOS technology and it is fully scalable. The processing includes selective epitaxial depositions of an over 50% Ge content buffer layer, a pure Ge layer, and a SiGe top layer. Fabricated buried channel PMOS devices hosted in the compressively strained Ge layer show superior device characteristics relative to similar Si devices.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor structure and method of fabricating the semiconductor structure
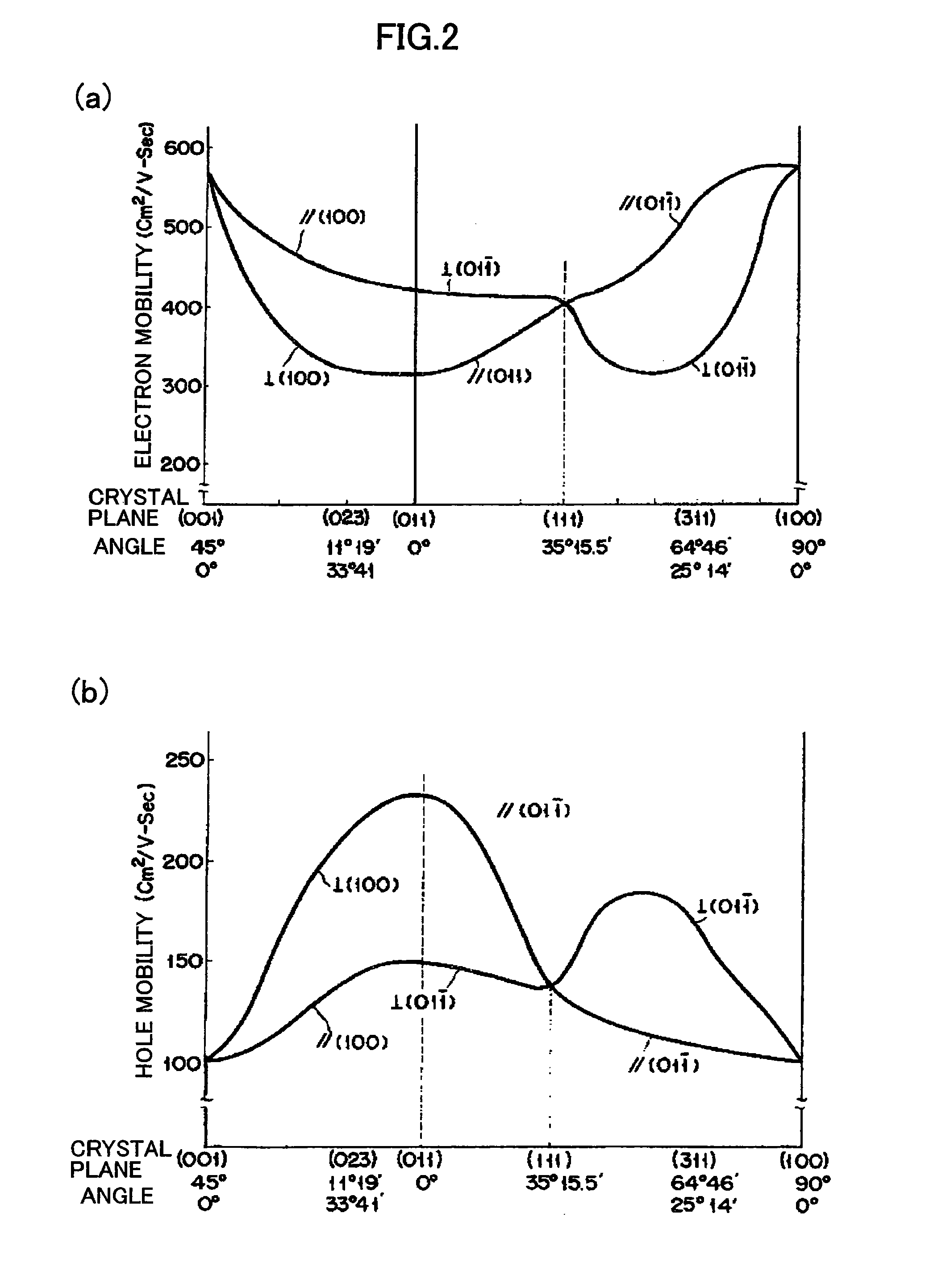
ActiveUS20100207172A1High carrier mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSManufacturing technology
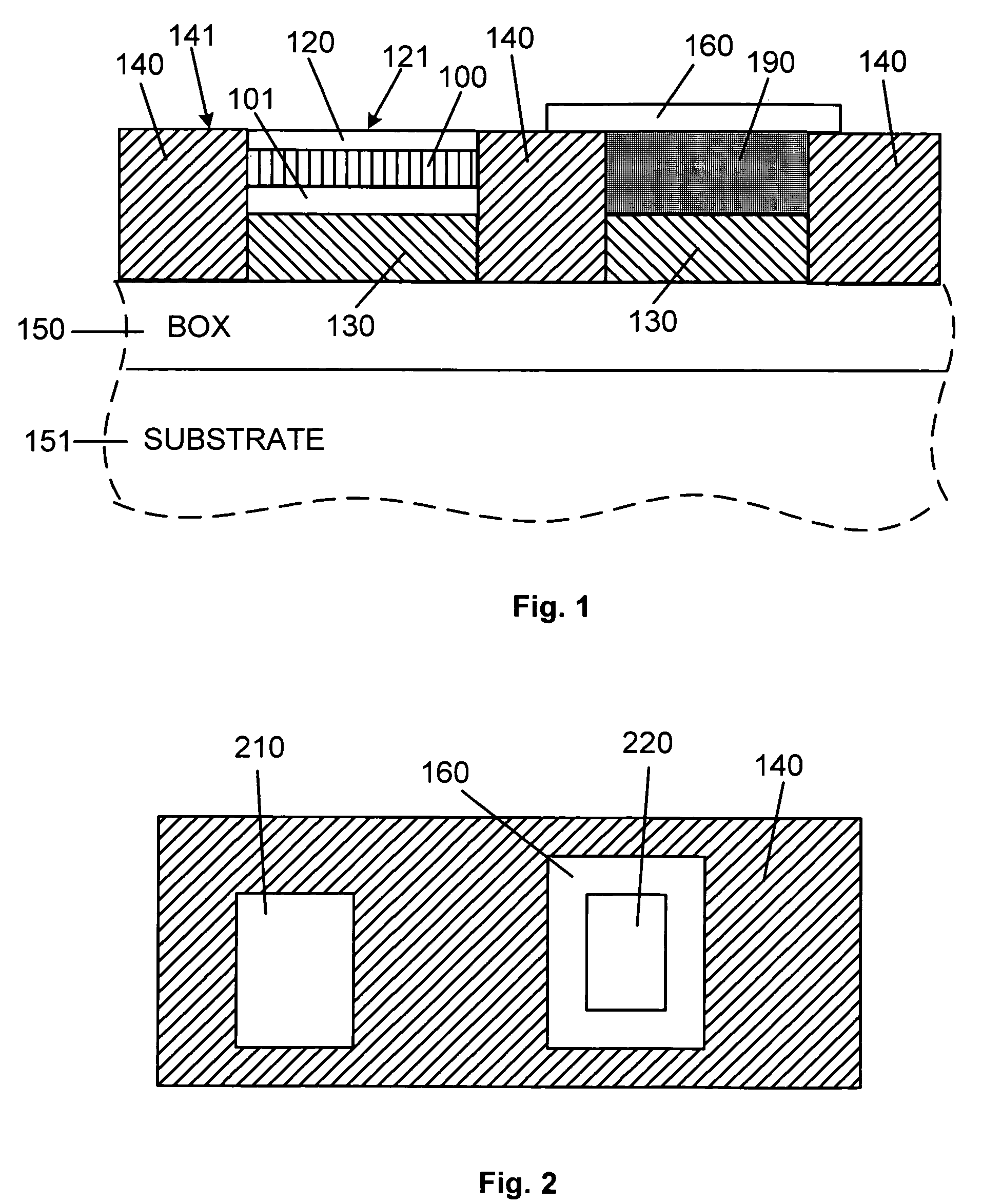
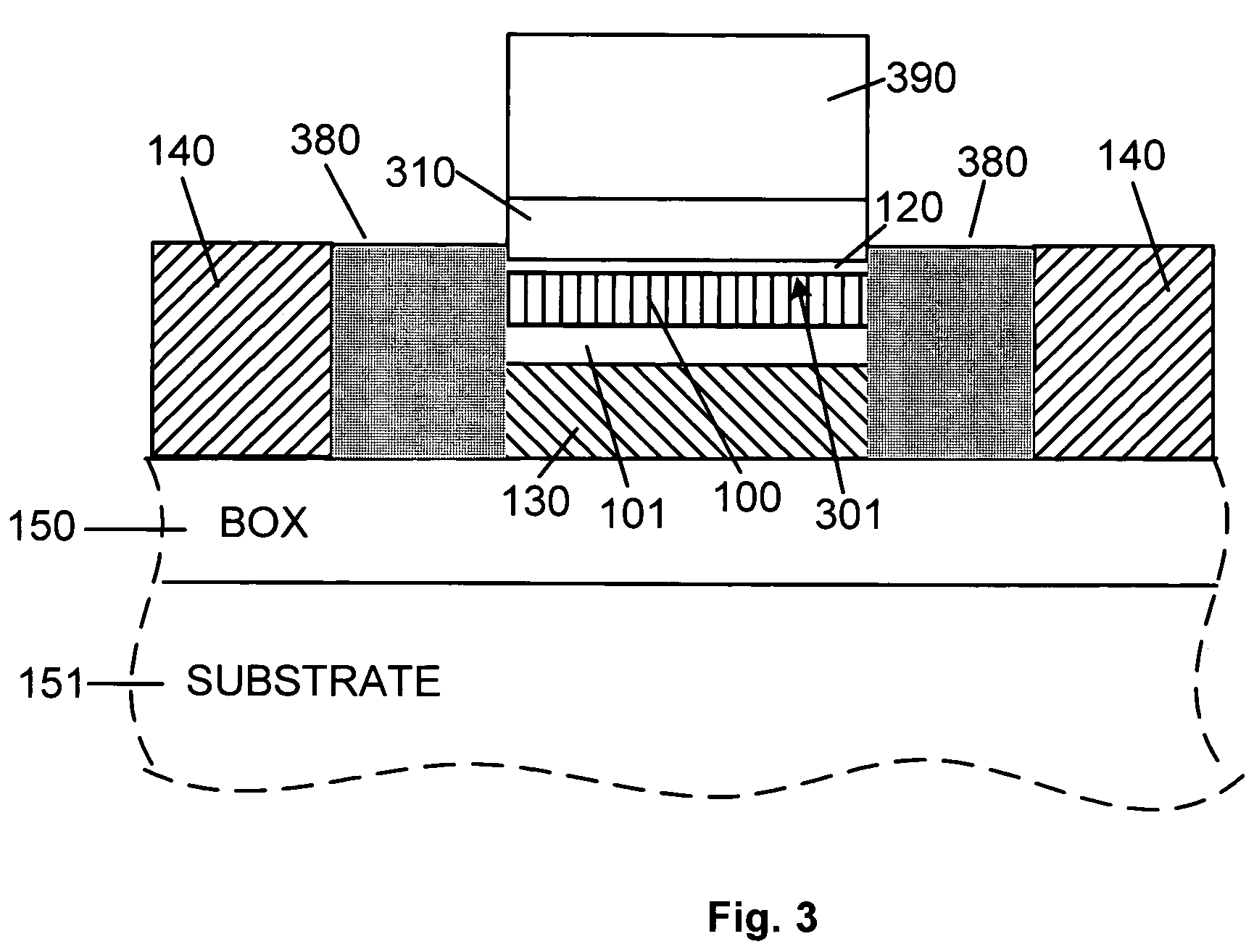
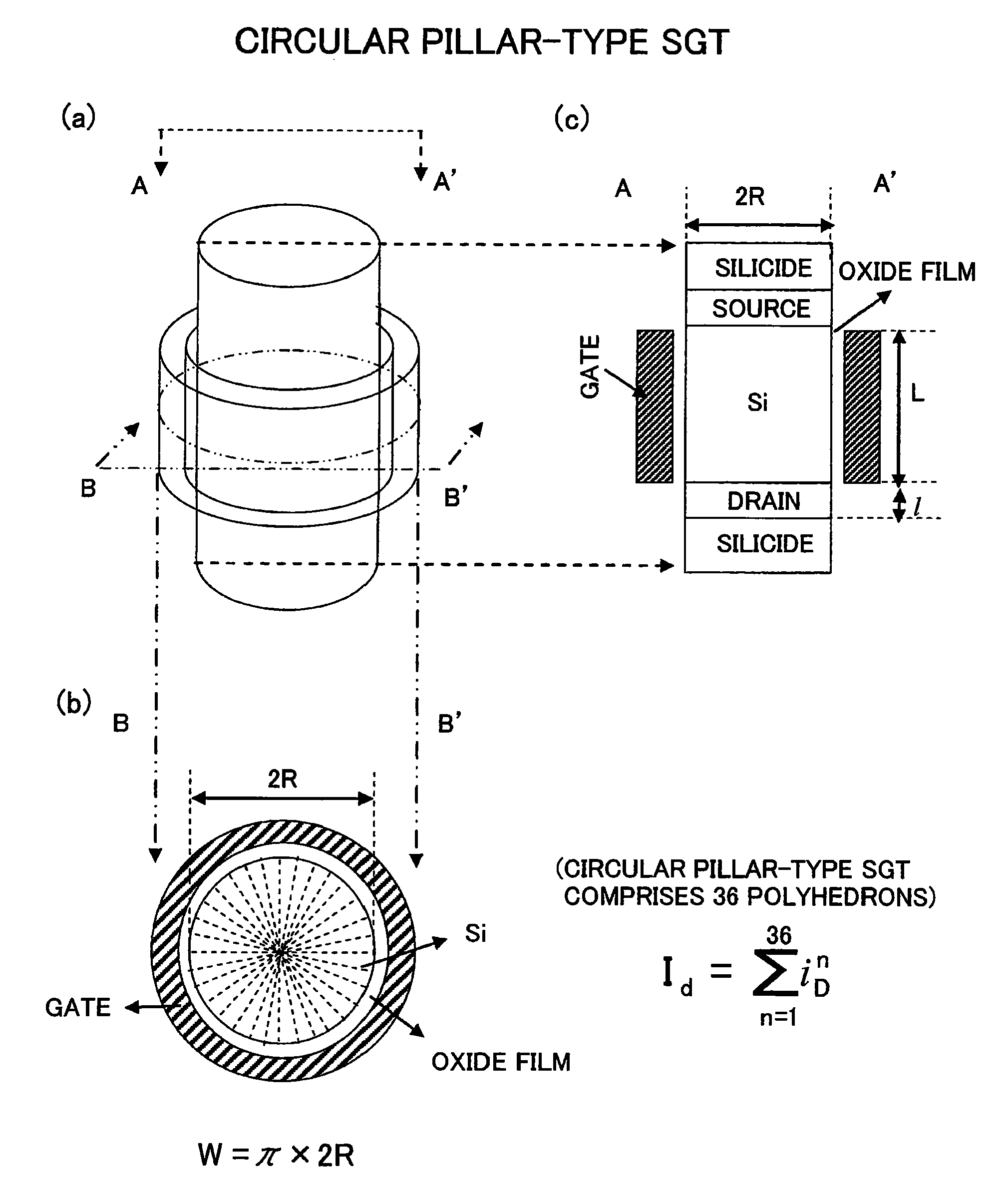
In contrast to a conventional planar CMOS technique in design and fabrication for a field-effect transistor (FET), the present invention provides an SGT CMOS device formed on a conventional substrate using various crystal planes in association with a channel type and a pillar shape of an FET, without a need for a complicated device fabrication process. Further, differently from a design technique of changing a surface orientation in each planar FET, the present invention is designed to change a surface orientation in each SGT to achieve improvement in carrier mobility. Thus, a plurality of SGTs having various crystal planes can be formed on a common substrate to achieve a plurality of different carrier mobilities so as to obtain desired performance.
Owner:UNISANTIS ELECTRONICS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Electronic circuit for ion sensor
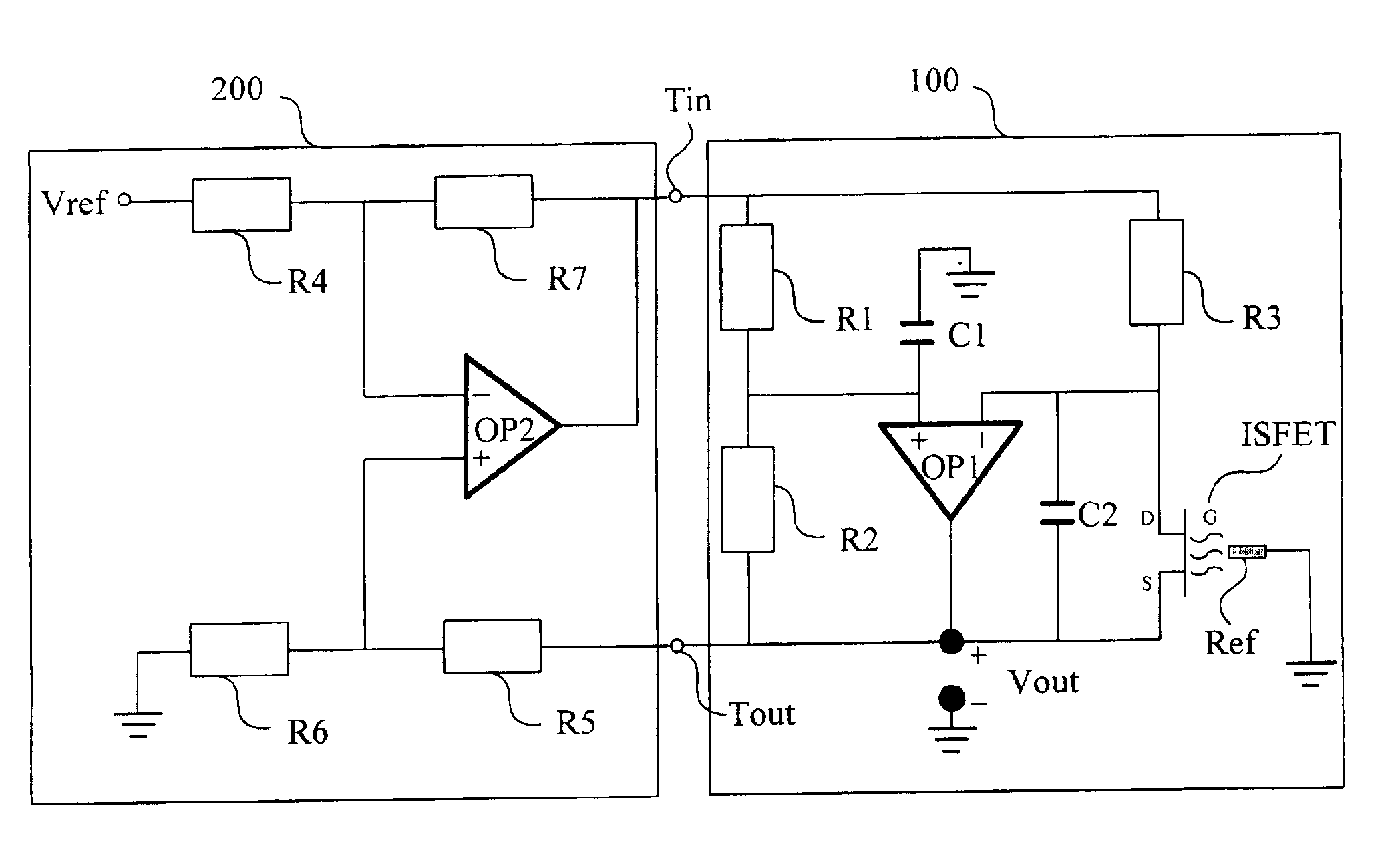
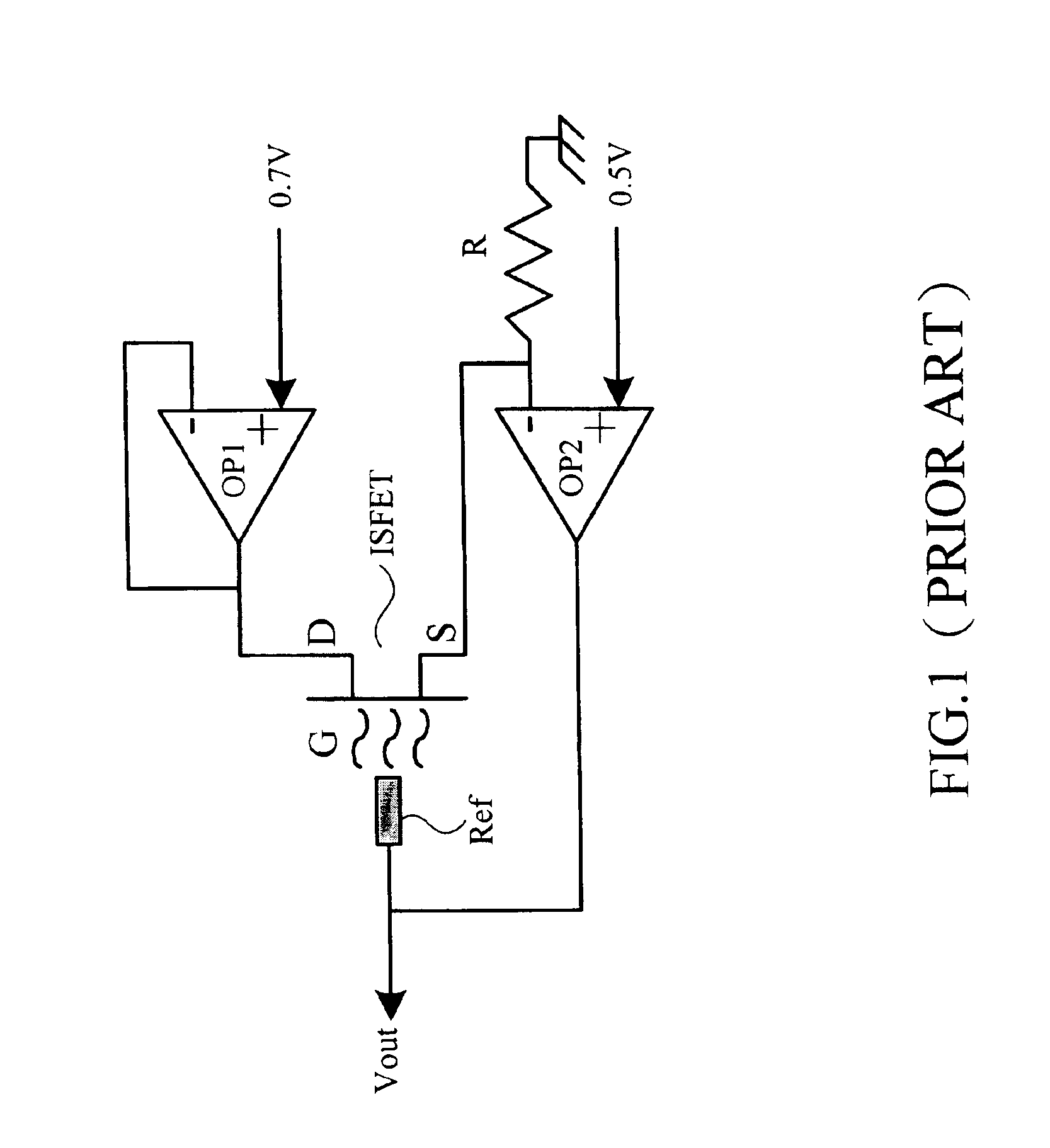
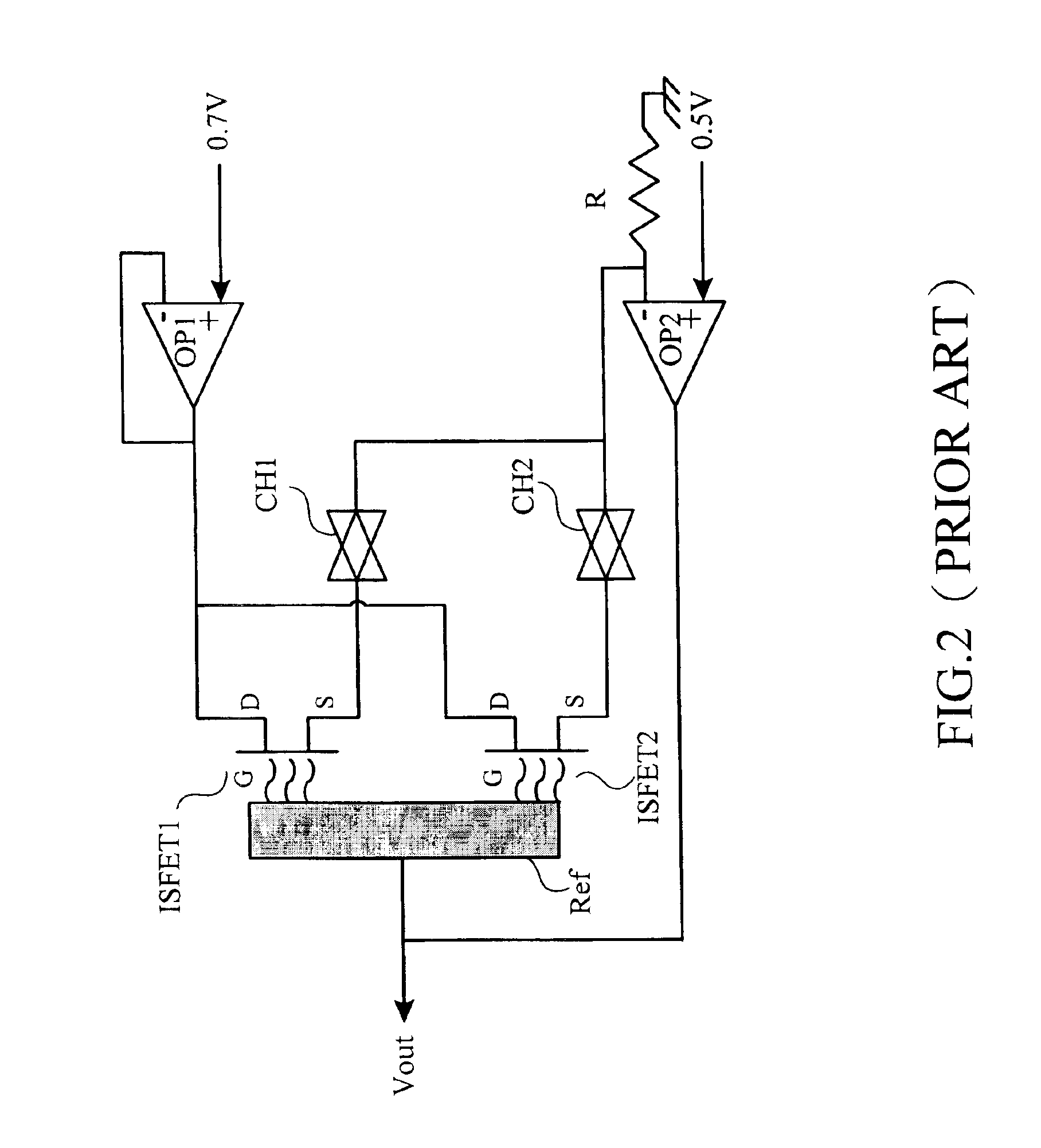
InactiveUS6906524B2Rapid and stable and accurate detectionWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementSensor arrayCMOS
An ion sening circuit comprises a bridge sensing circuit and a differential amplifying circuit. The bridge sensing circuit detects the ion concentration of the solution in the operation mode of constant voltage and constant current. The differential amplifying circuit compares the output of the bridge sensing circuit and a floating reference voltage, thereby the delivered voltage to the bridge sensing circuit, such that the opeation mode of constant voltage and constant current is formed accordingly. The main features of the disclosed circuit are that it grounds the reference electrode and floats the source terminal. The drawbacks of not being manufactured with intergrated circuits by CMOS technology and low benefits when applied to sensor arrays are avoided by the disclosed circuit.
Owner:CHUNG YUAN CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
Method and process to make multiple-threshold metal gates CMOS technology
Methods of forming complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) devices having multiple-threshold voltages which are easily tunable are provided. Total salicidation with a metal bilayer (representative of the first method of the present invention) or metal alloy (representative of the second method of the present invention) is provided. CMOS devices having multiple-threshold voltages provided by the present methods are also described.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
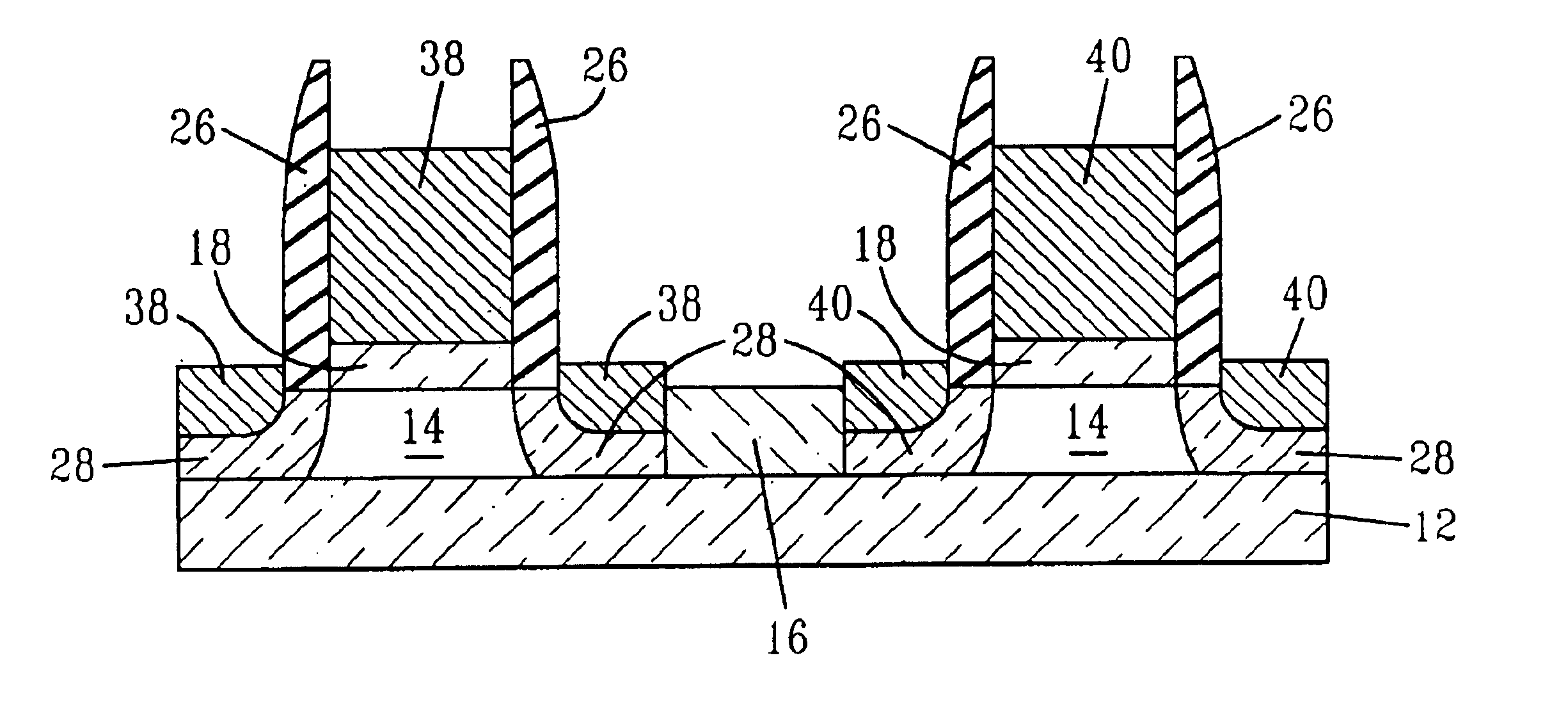
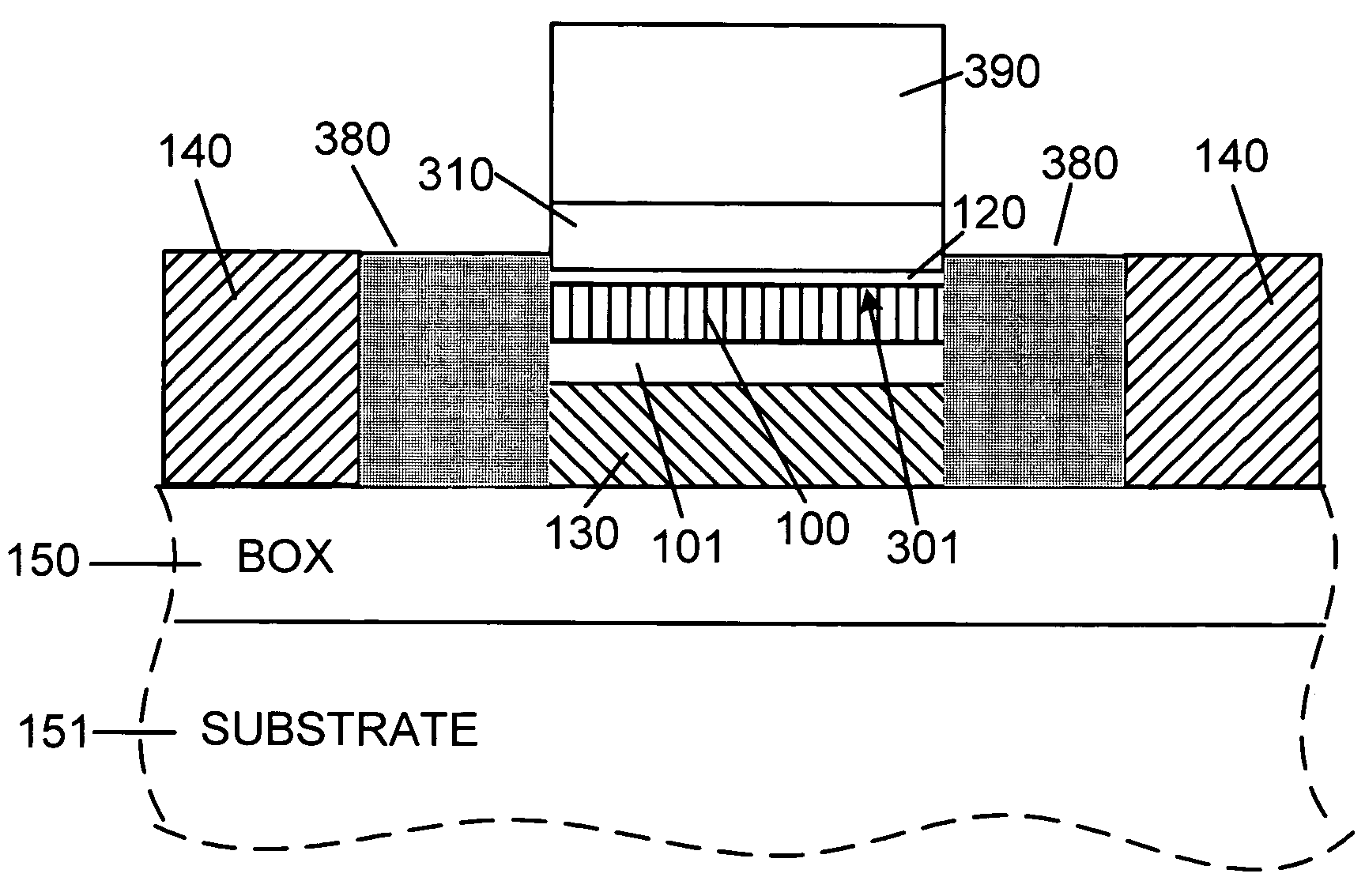
Device threshold control of front-gate silicon-on-insulator mosfet using a self-aligned back-gate
InactiveUS20050037582A1Minimize capacitanceImprove circuit performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceMOSFET
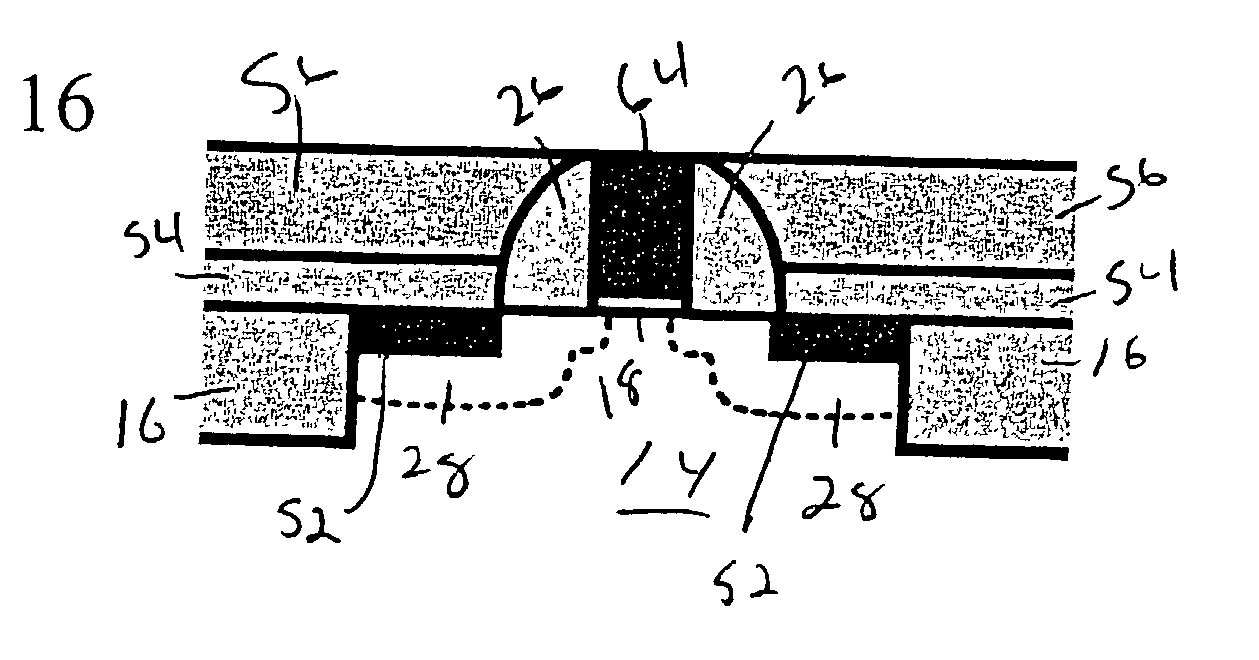
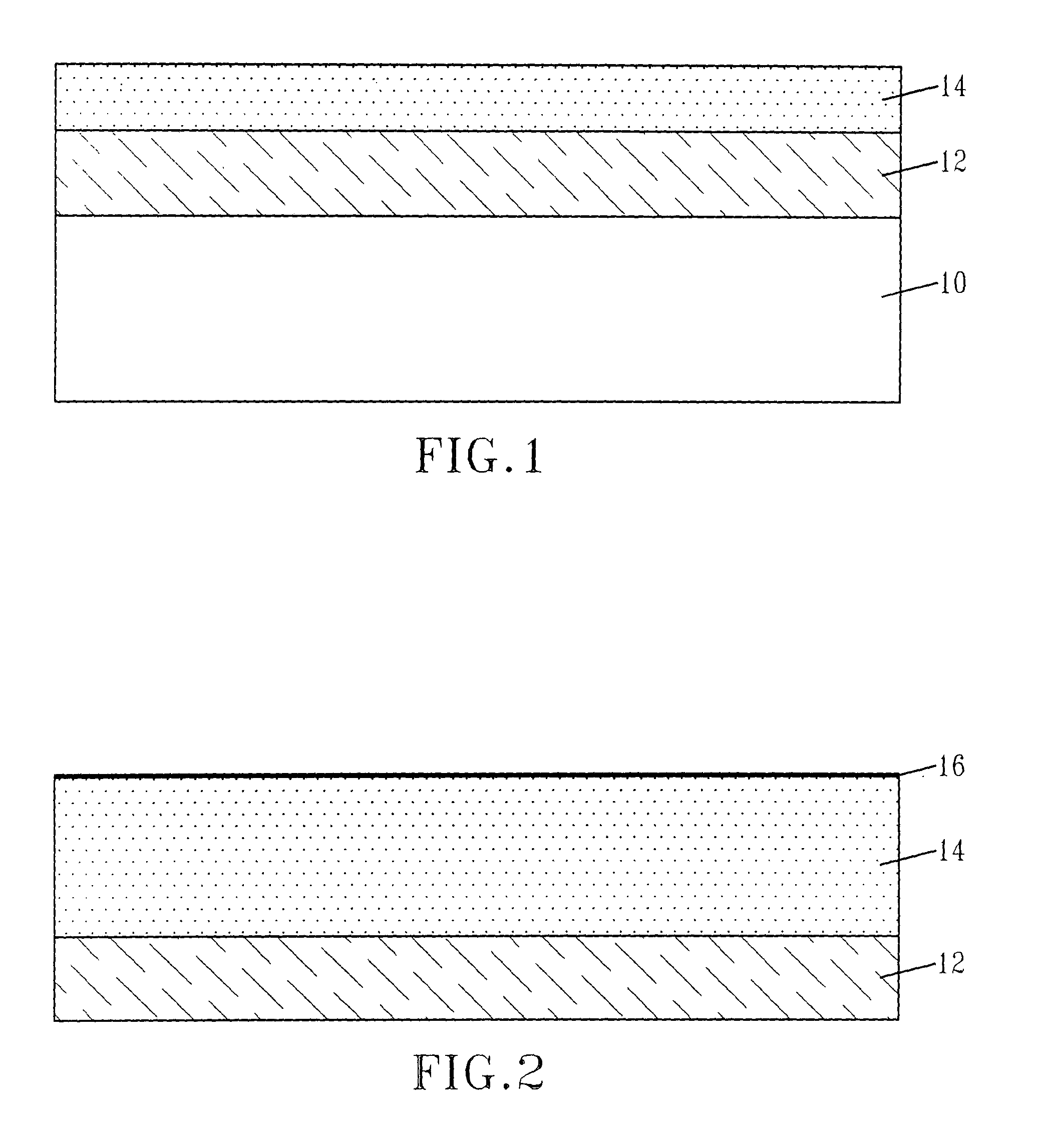
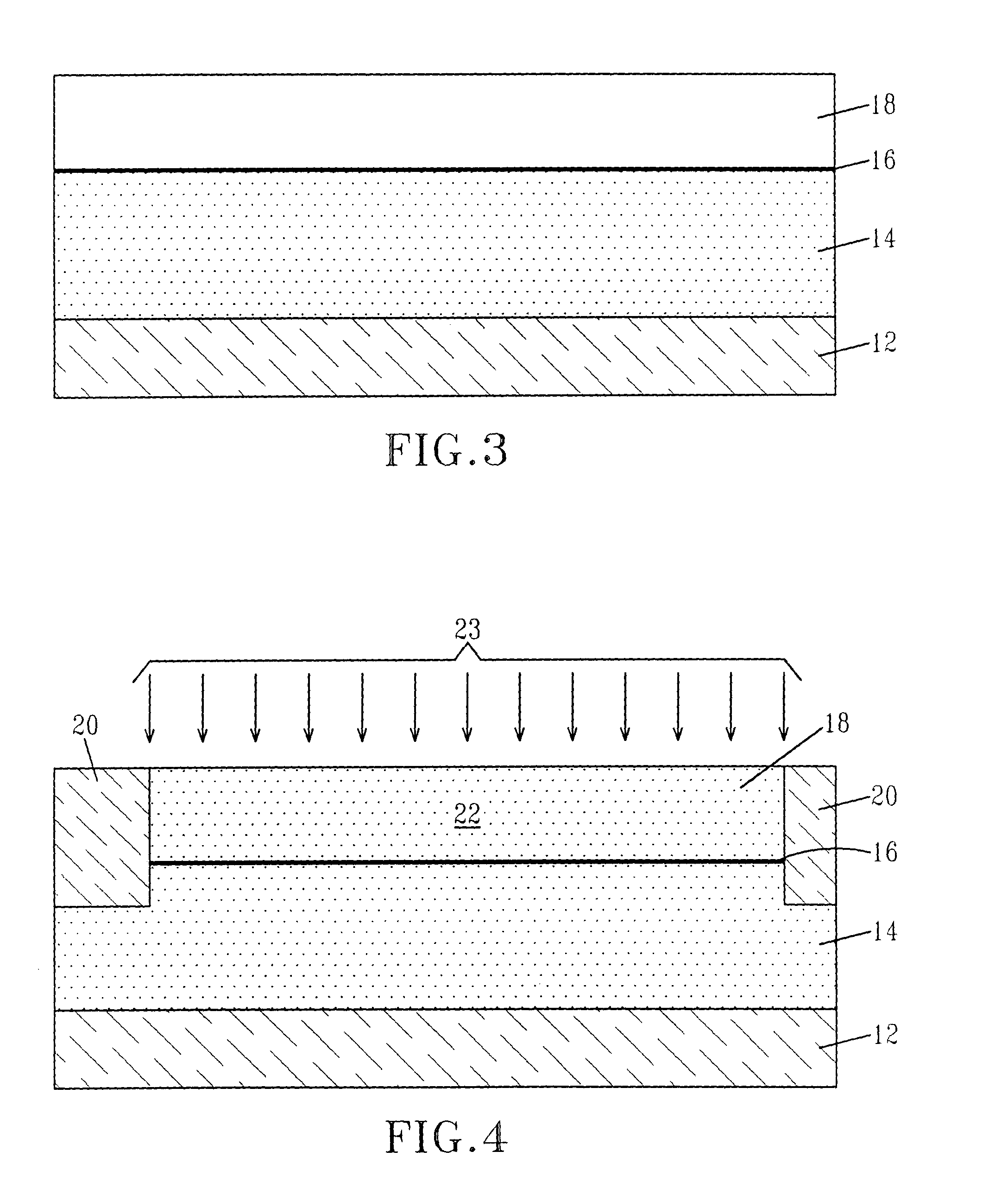
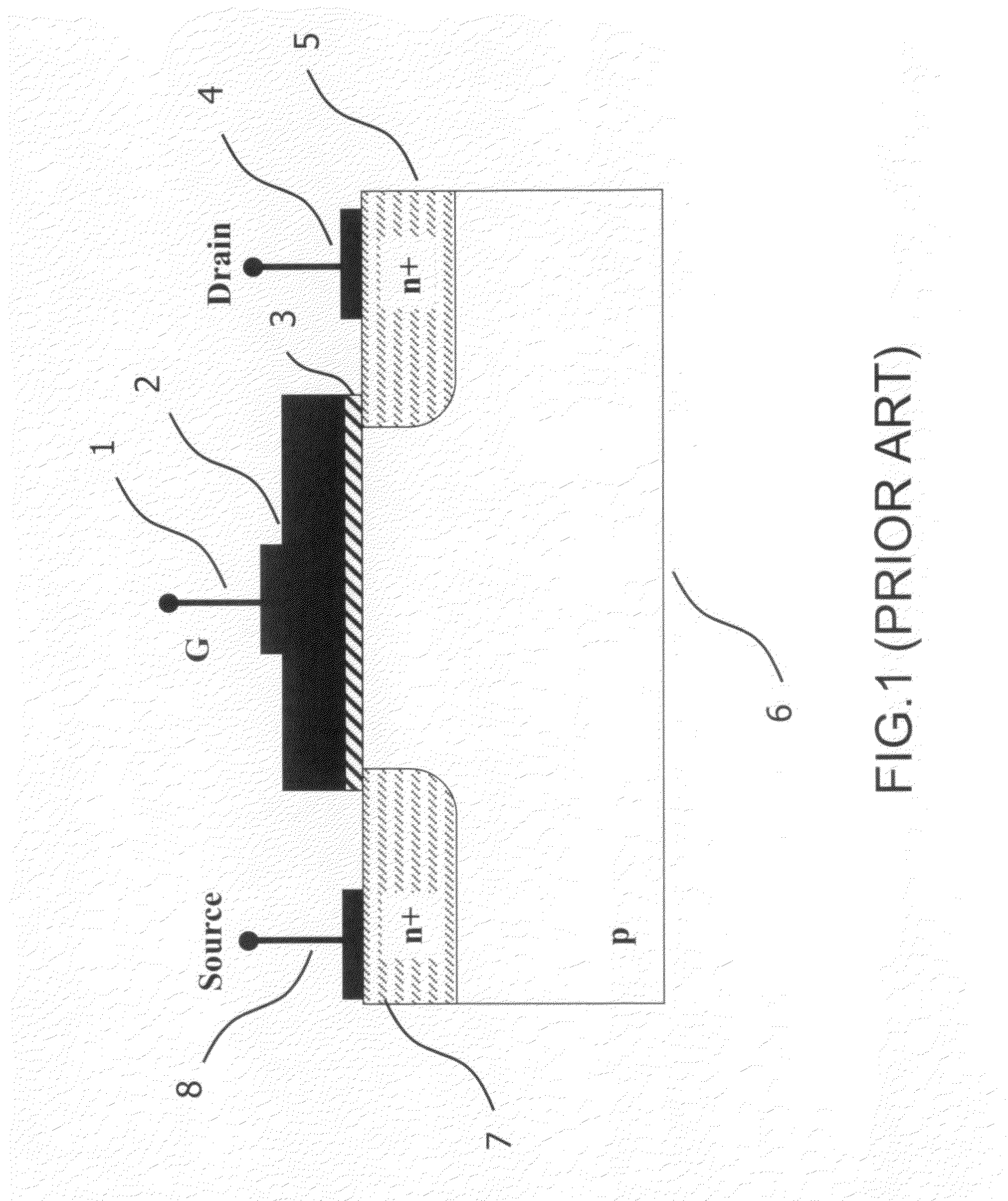
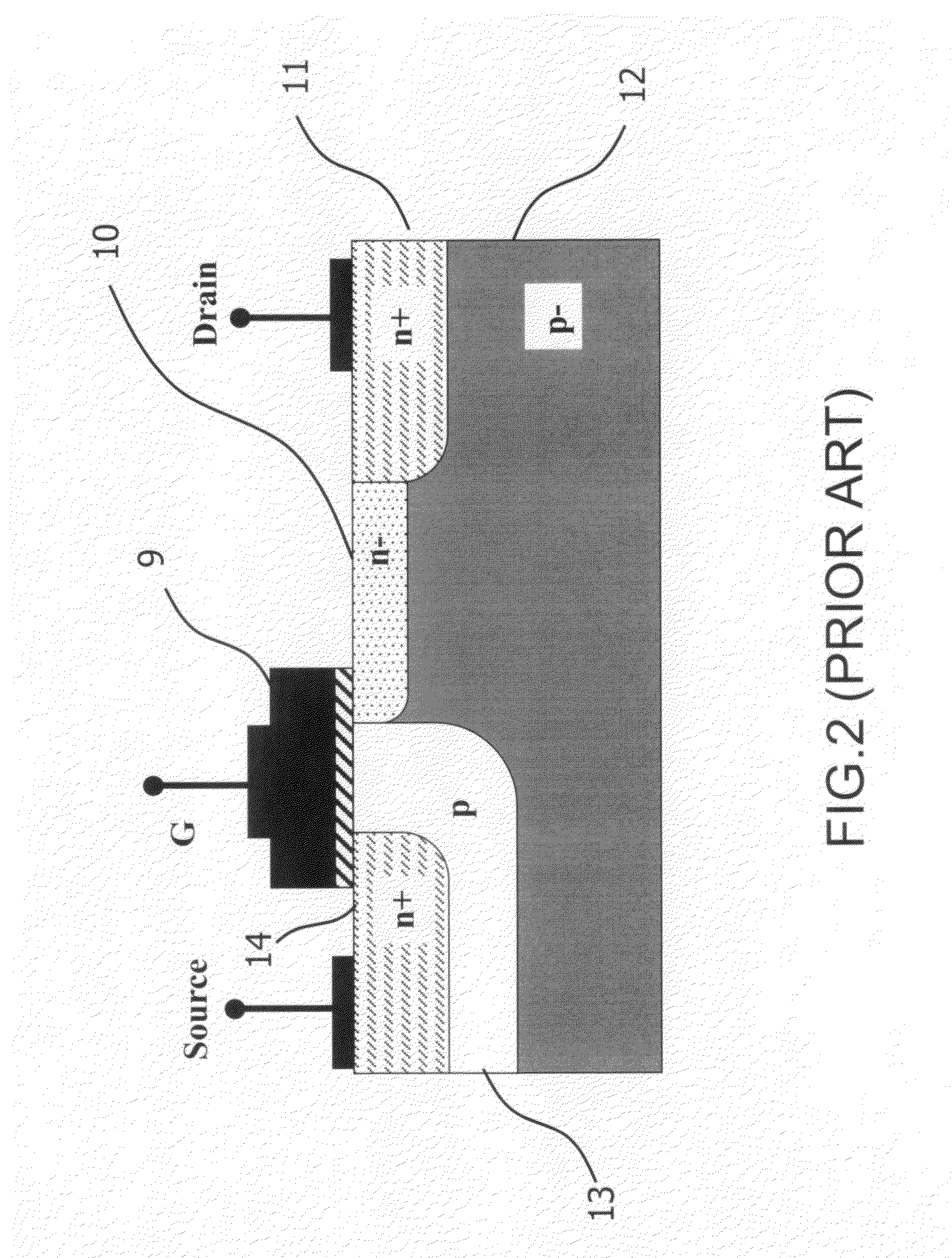
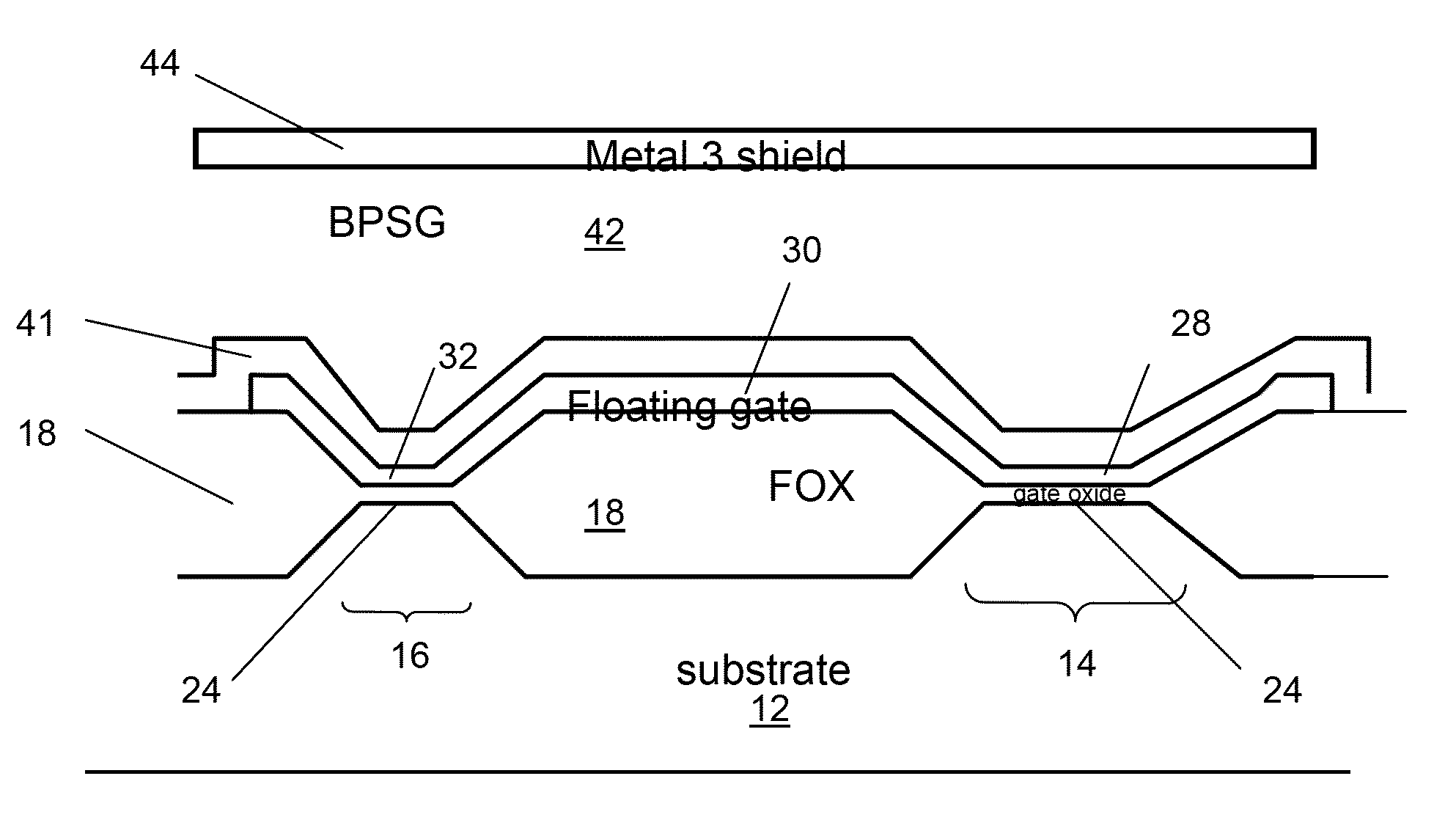
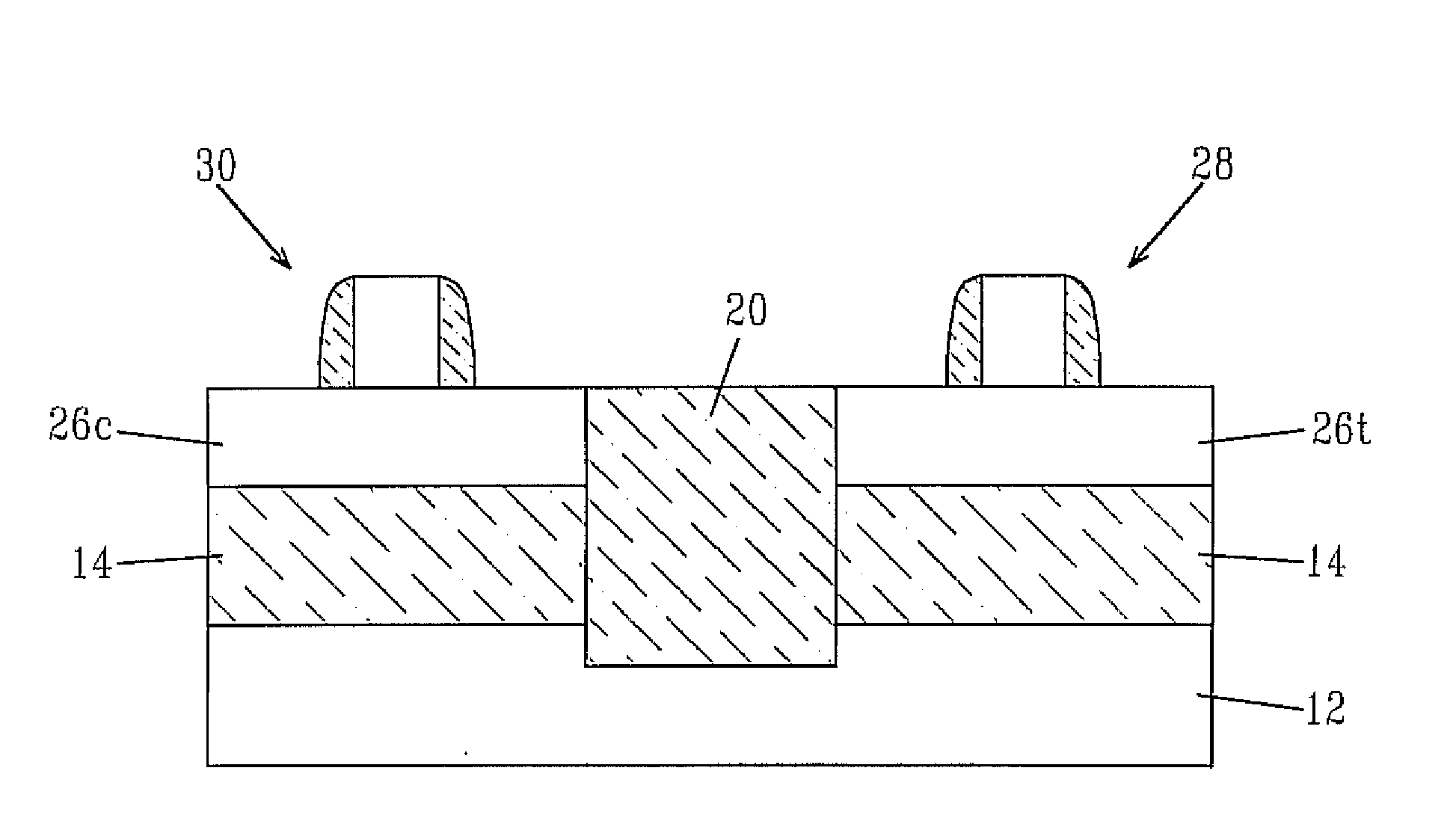
The present invention provides SOI CMOS technology whereby a polysilicon back-gate is used to control the threshold voltage of the front-gate device, and the nMOS and pMOS back-gates are switched independently of each other and the front gates. Specifically, the present invention provides a method of fabricating a back-gated fully depleted CMOS device in which the device's back-gate is self-aligned to the device's front-gate as well as the source / drain extension. Such a structure minimizes the capacitance, while enhancing the device and circuit performance. The back-gated fully depleted CMOS device of the present invention is fabricated using existing SIMOX (separation by ion implantation of oxygen) or bonded SOI wafers, wafer bonding and thinning, polySi etching, low-pressure chemical vapor deposition and chemical-mechanical polishing.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Differential capacitance measurement
InactiveUS20050134292A1Efficient methodPrecise and sensitive and yet stable evalutionCapacitance measurementsConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyCMOSSoi cmos technology
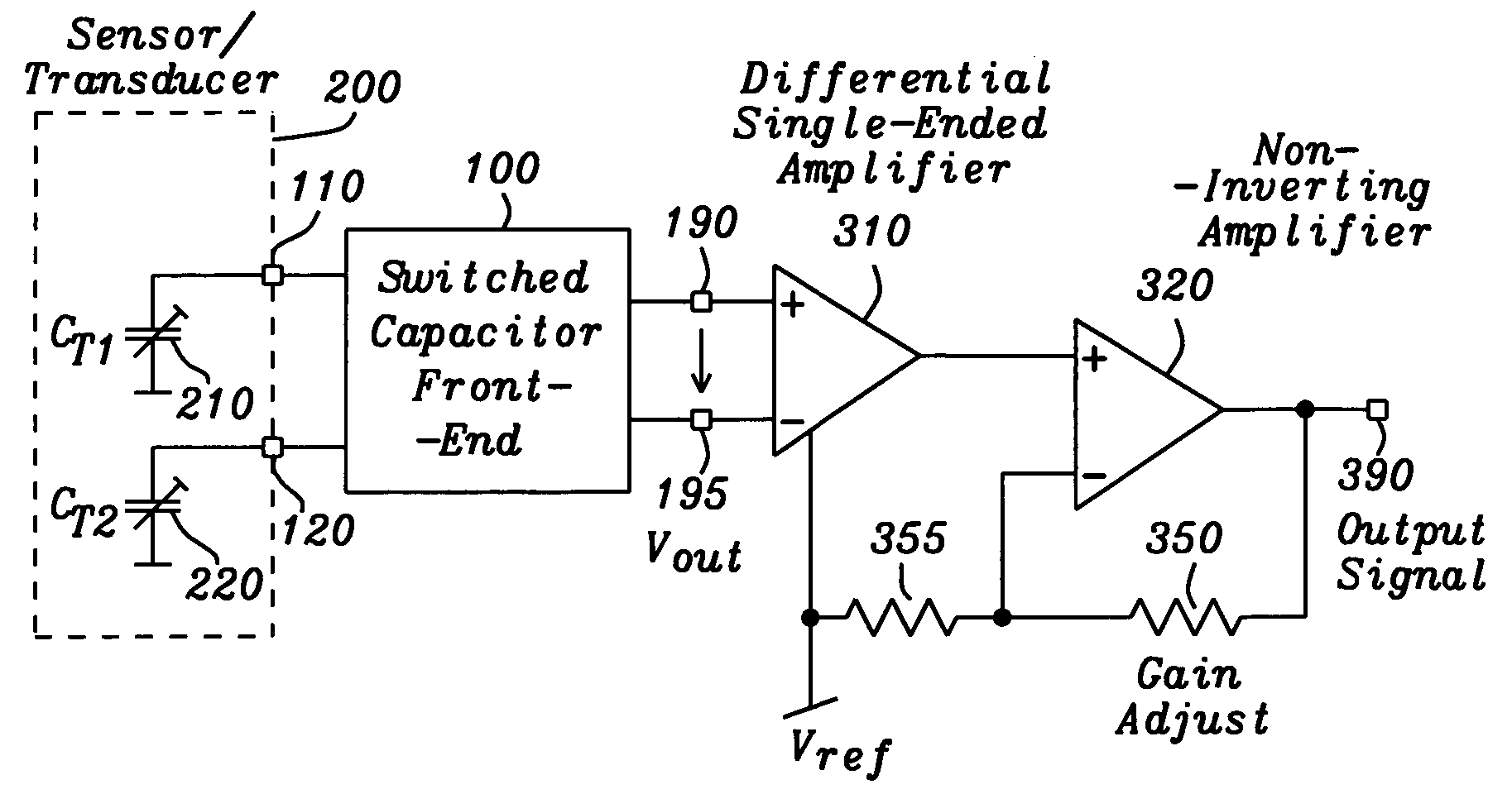
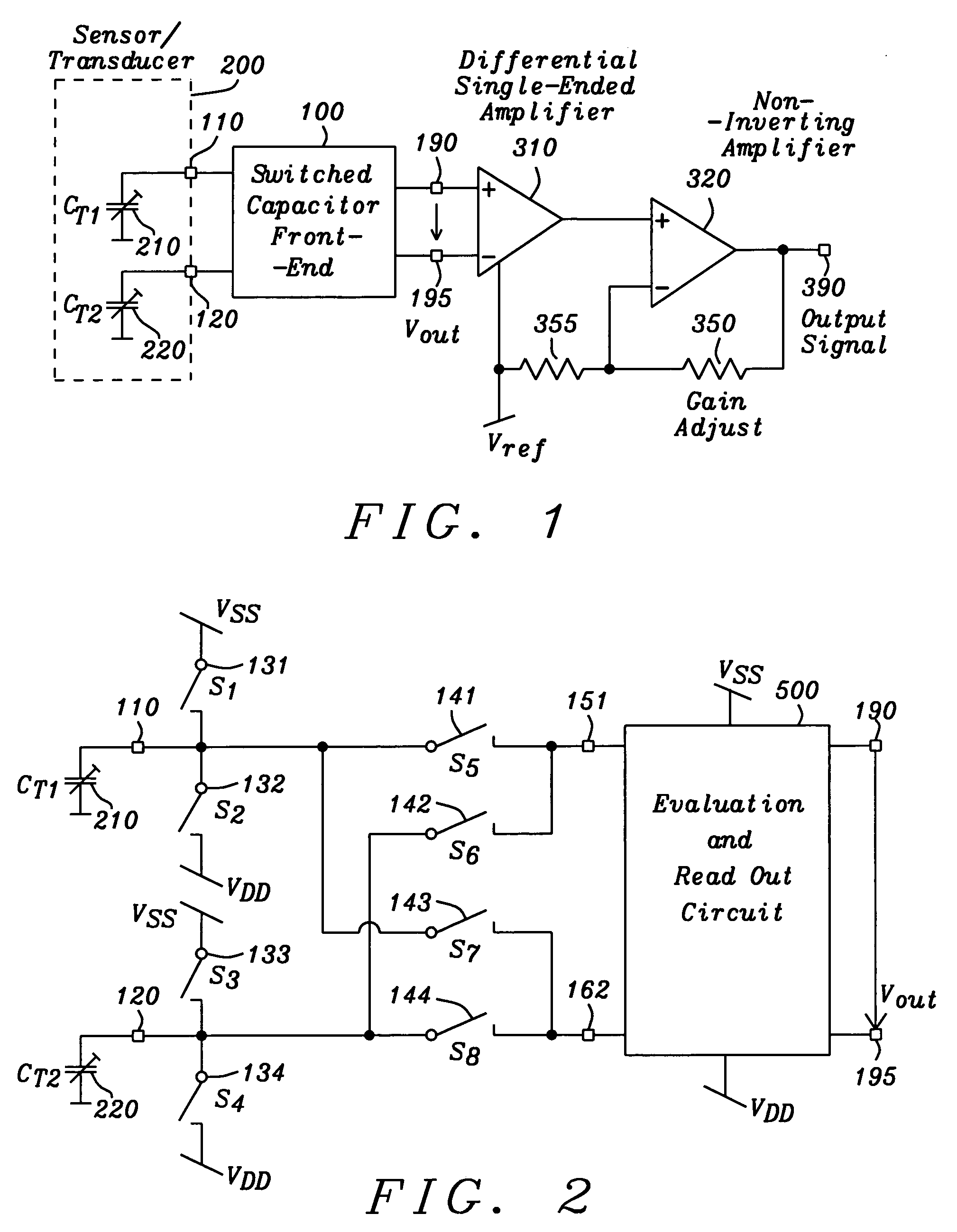
A circuit and method are given, which realizes a stable yet sensitive differential capacitance measuring device with good RF-suppression and with very acceptable noise features for use in capacitive sensor evaluation systems. By evaluating the difference of capacitor values only—with the help of a switched capacitor front-end—large spreads of transducer capacitor values are tolerable. Furthermore a mode of operation can be set up, where no essential galvanic connection between sensor input and the active read-out input at any given time is existing. The solution found exhibits a highly symmetrical construction. Using the intrinsic advantages of that solution the circuit of the invention is manufactured as an integrated circuit with standard CMOS technology at low cost.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Drift Field Demodulation Pixel with Pinned Photo Diode
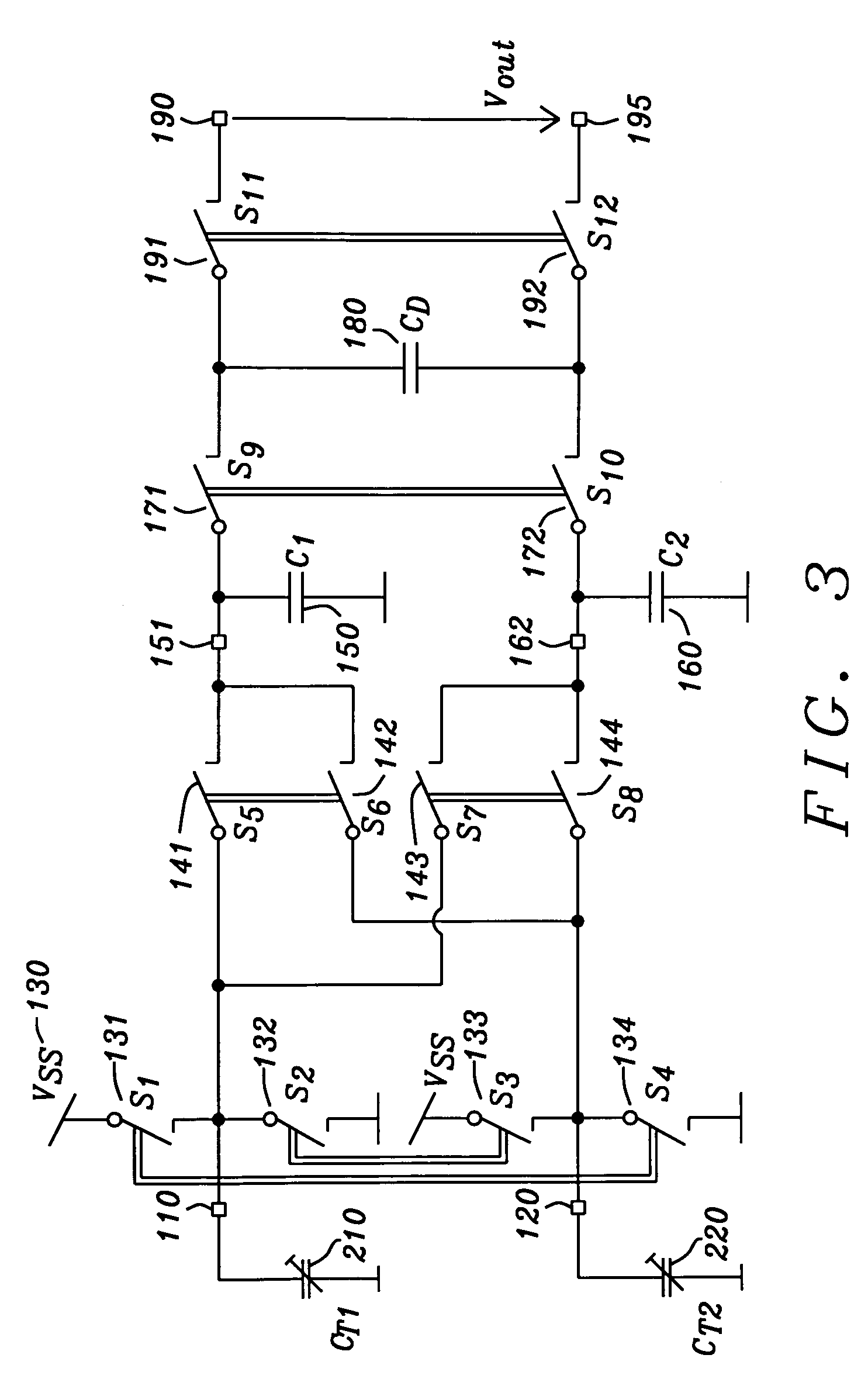
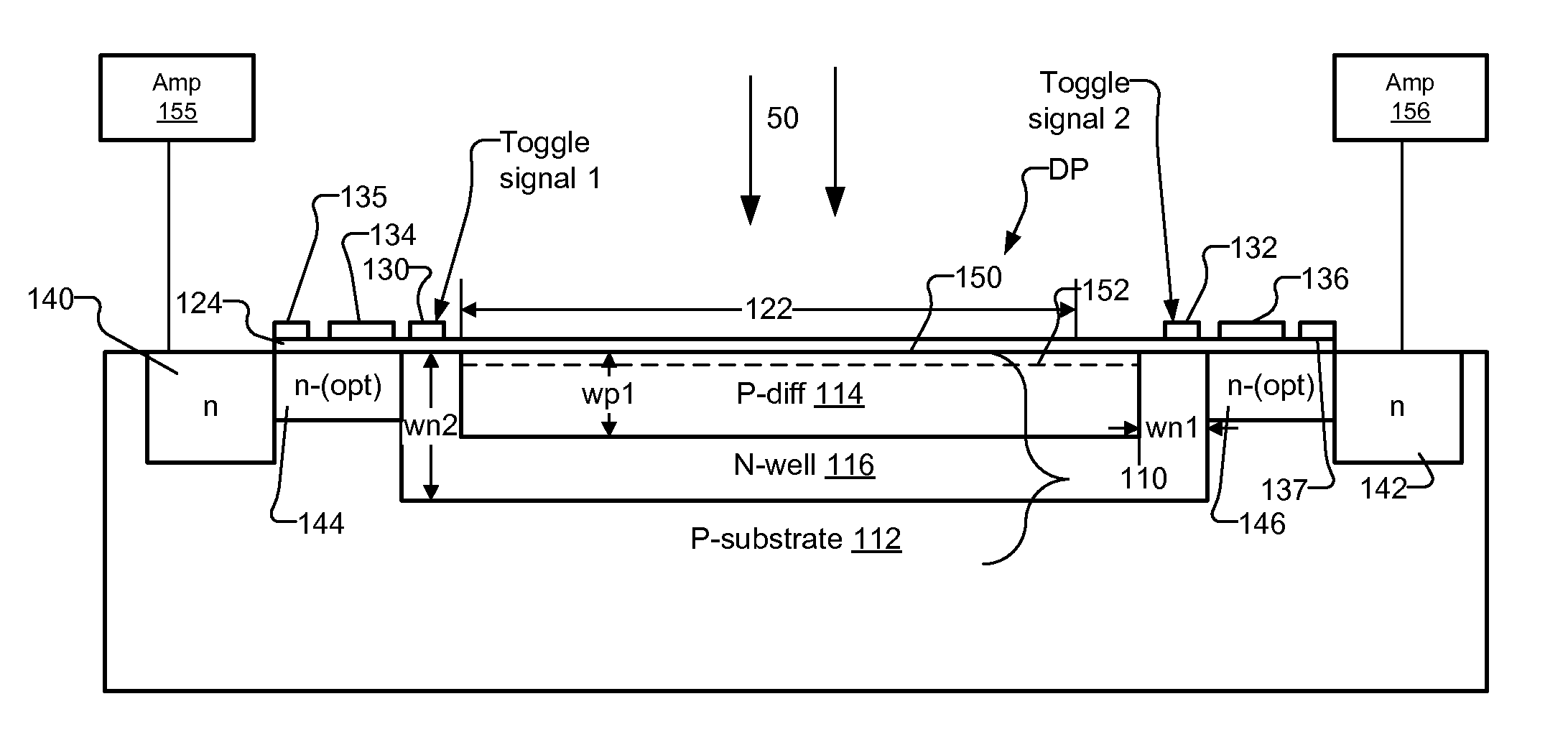
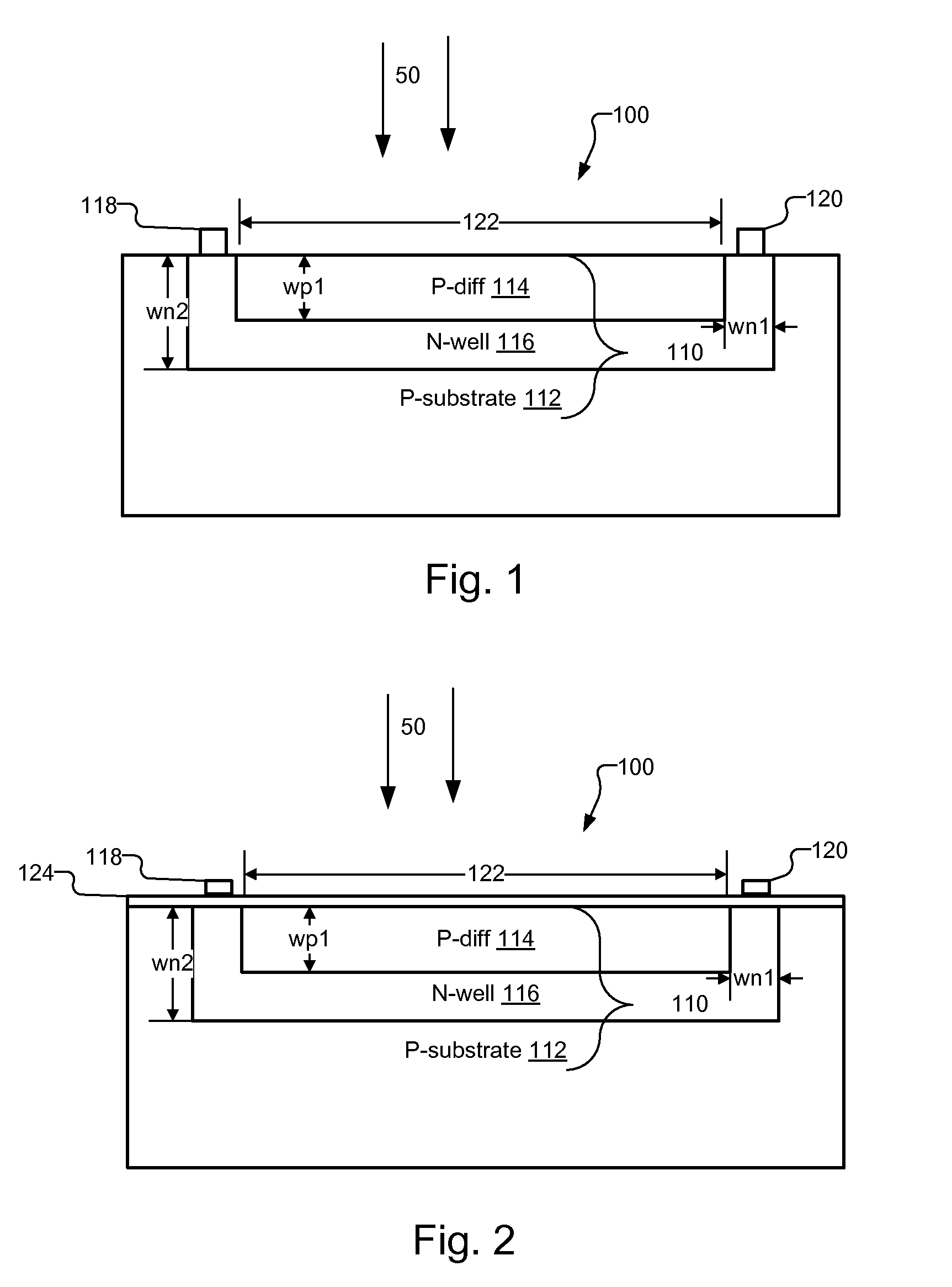
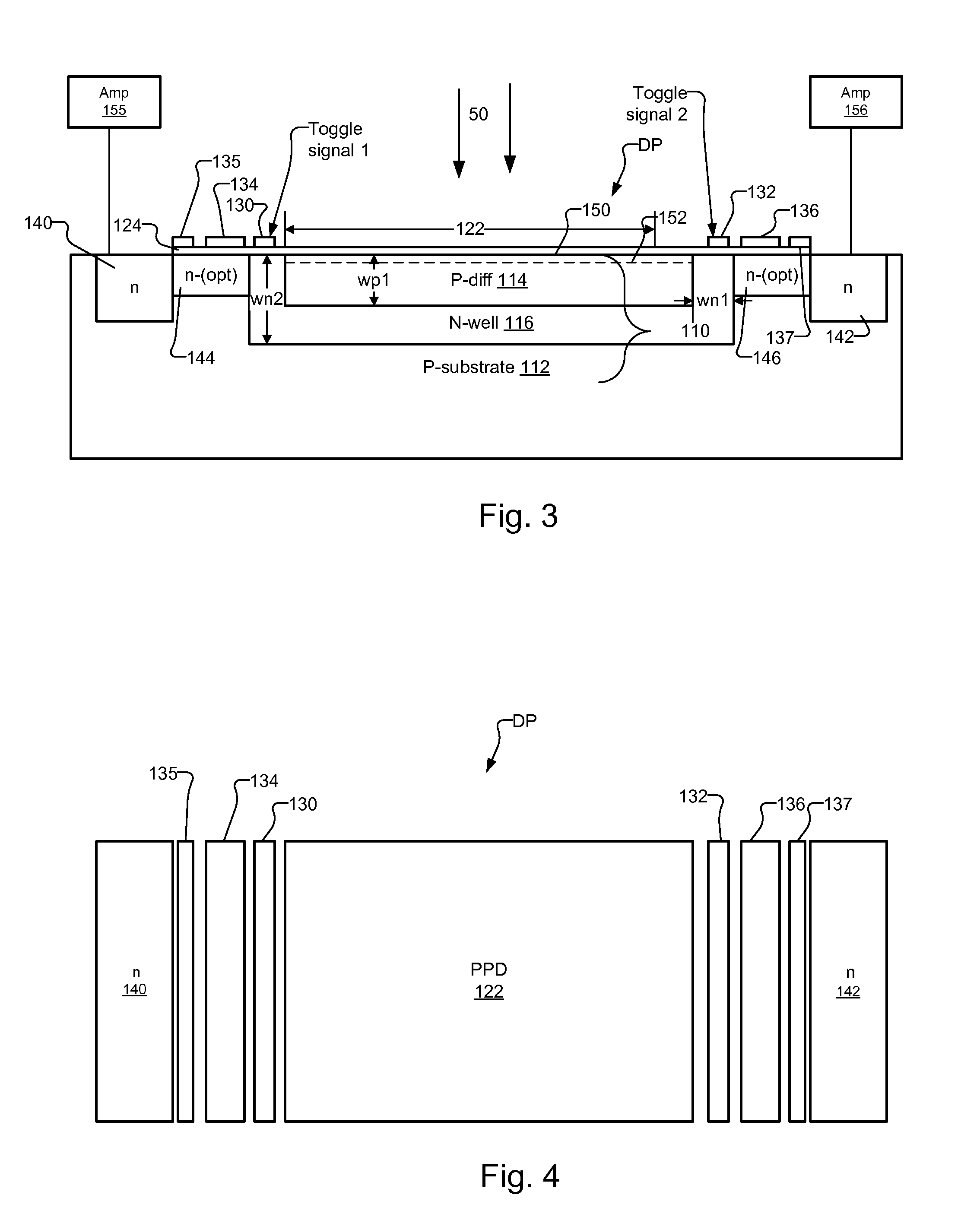
InactiveUS20090224139A1High rateReduce optical sensitivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSoi cmos technologyPhotodiode
A pixel based on a pinned-photodiode structure that creates a lateral electric drift field. The combination of the photodiode with adjacent CCD gates enables the utilization of the drift field device in applications such as 3-D imaging. Compared with recently used demodulation devices in CCD or CMOS technology, the new pinned-photodiode based drift field pixel has its advantages in its wide independence of the quantum efficiency on the optical wavelength, its high optical sensitivity, the opportunity of easily creating arbitrary potential distributions in the semiconductor, the straight-forward routing capabilities and the generation of perfectly linear potential distributions in the semiconductor.
Owner:HEPTAGON MICRO OPTICS
Multi-metal coplanar waveguide
InactiveUS20070241844A1Reduce decreaseImprove performanceMultiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSCoplanar waveguide
A coplanar waveguide CPW using multi-layer interconnection CMOS technology is provided. In the CPW including an interlayer insulator disposed on a substrate, metal multilayers disposed on the interlayer insulator, and a ground line-a signal line-a ground line formed of an uppermost metal layer, when a ground line of a lowermost layer is connected to the ground line of the uppermost layer, intermediate metal layers are designed to gradually increase or decrease in width, or to be uneven so as to maximize an area where an ultra-high frequency spreads, thereby minimizing CPW loss and maximizing a slow wave effect. As a result, it is possible to improve performance of an ultra-high frequency circuit and miniaturize the circuit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Single structure cascode device
InactiveUS20120175679A1Without increasing device on-resistanceReduce voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSemiconductor structure
A novel semiconductor power transistor is presented. The semiconductor structure is simple and is based on a MOS configuration with a drift region and an additional gate that modulates the carrier density in the drift region, so that the control on the carrier transport is enhanced and the specific on-resistance per area is reduced. This characteristic enables the use of short gate lengths while maintaining the electric field under the gate within reasonable values in high voltage applications, without increasing the device on-resistance. It offers the advantage of extremely lower on-resistance for the same silicon area while improving on its dynamic performances with respect to the standard CMOS technology. Another inherent advantage is that the switching gate losses are smaller due to lower VGS voltages required to operate the device.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Power-rail ESD clamp circuits with well-triggered PMOS
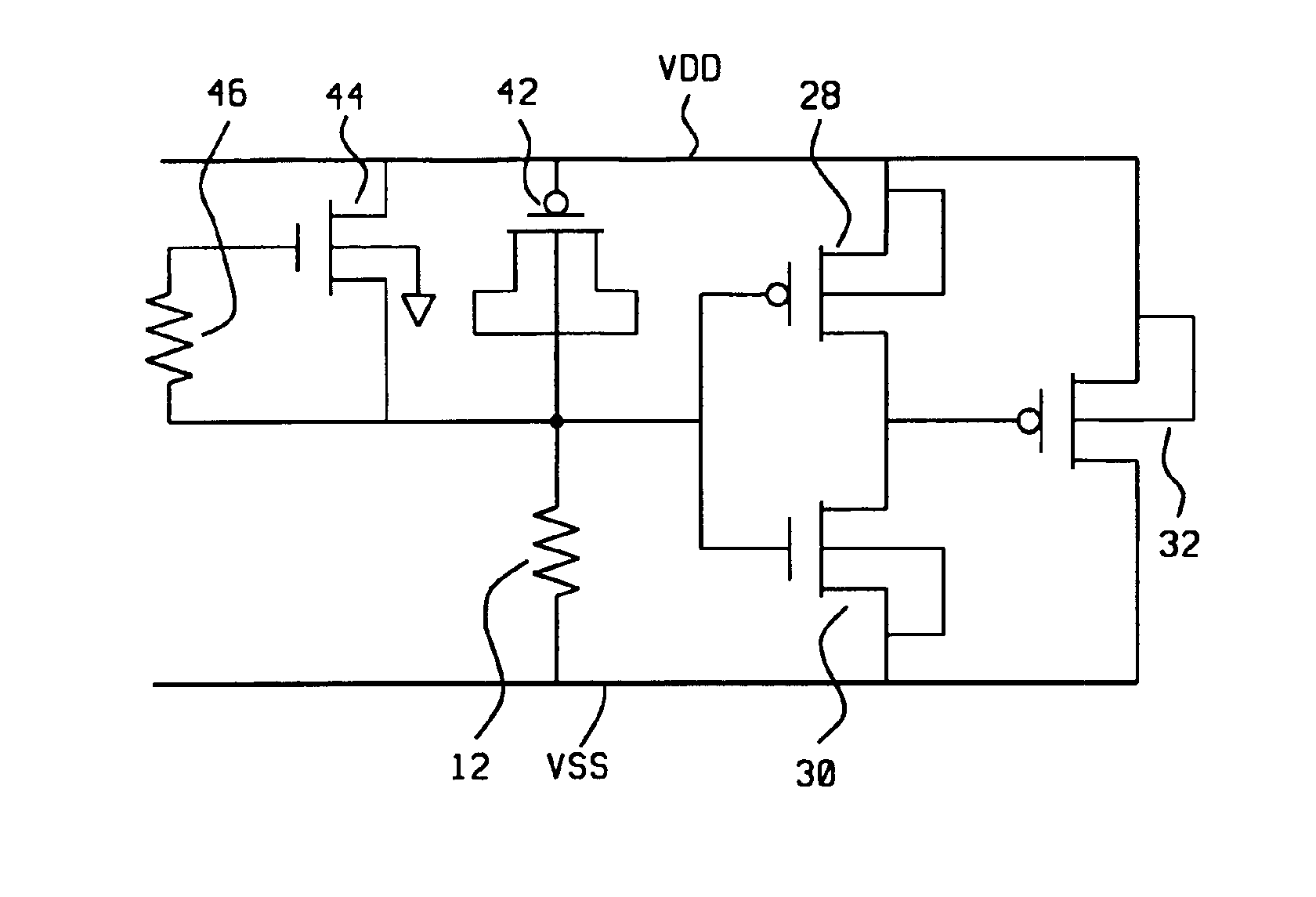
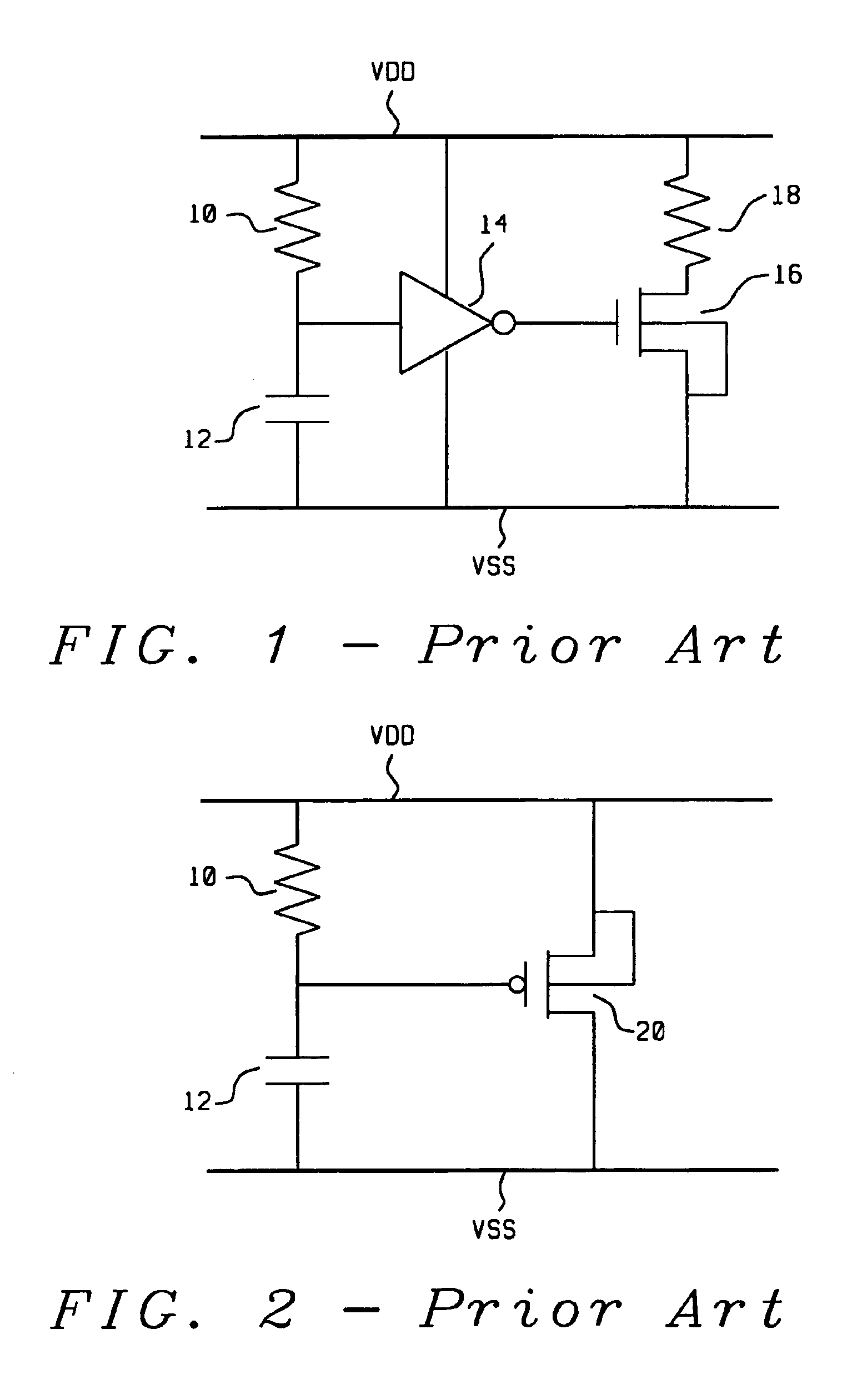
A new ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) protection circuit with well-triggered PMOS is provided for application in power-rail ESD protection. A PMOS device is connected between the VDD and VSS power lines to sustain the ESD overstress current during the time that the ESD voltage is applied between the VDD and the VSS power lines. In deep submicron CMOS p-substrate technology, the weak point of ESD overstress control is typically associated with the NMOS device. For this reason, the invention uses a power-rail ESD clamp circuit that incorporates a PMOS device. Applying gate-coupled and N-well triggering techniques, the PMOS can be turned on more efficiently when the ESD overstress is present between the power lines. For p-substrate CMOS technology, it is difficult to couple a high voltage to the substrate of the NMOS device while high voltage is readily coupled to the N-well of a PMOS device. The proposed ESD clamp circuit can be applied efficiently to protect the ESD overstress between power rails.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
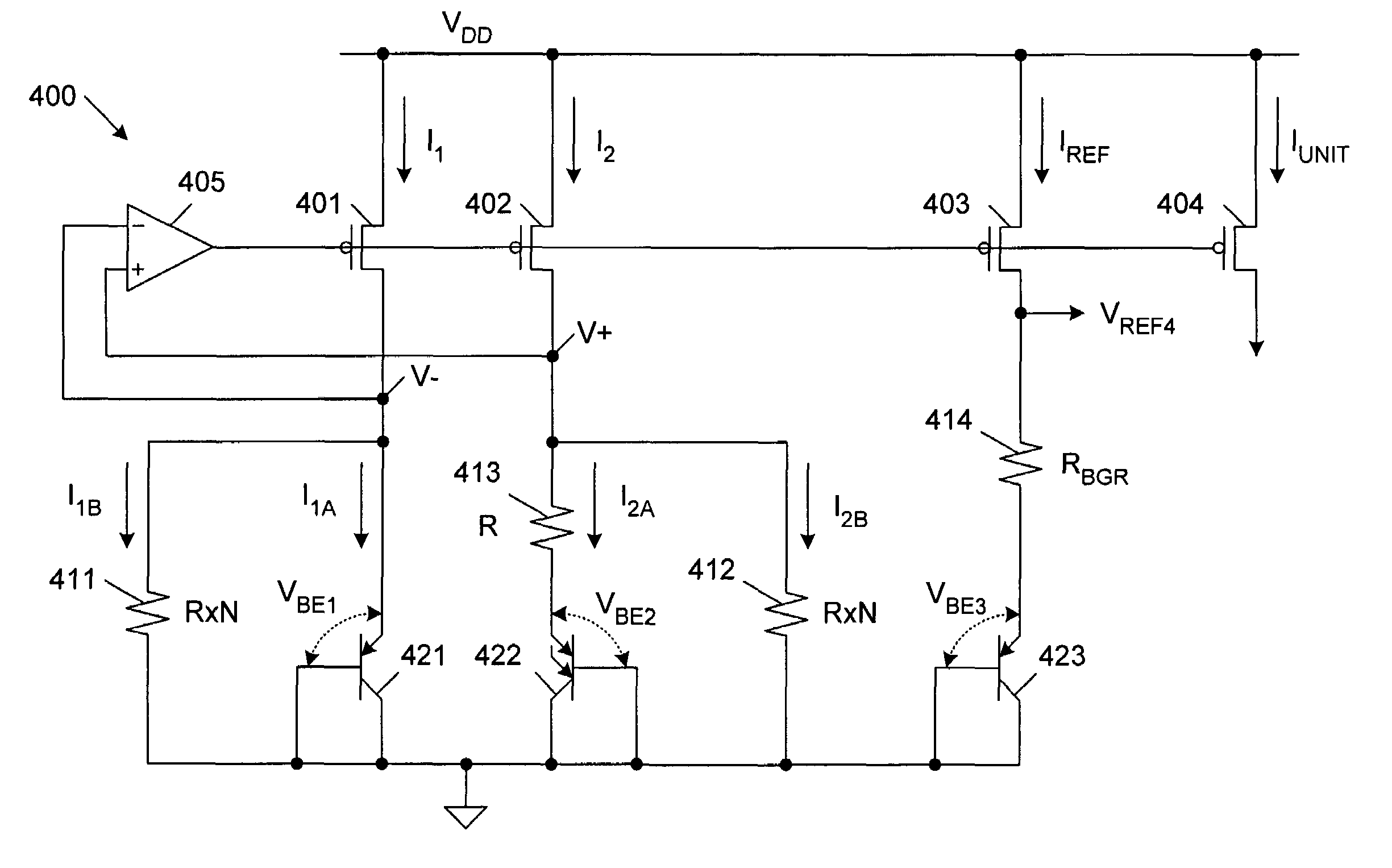
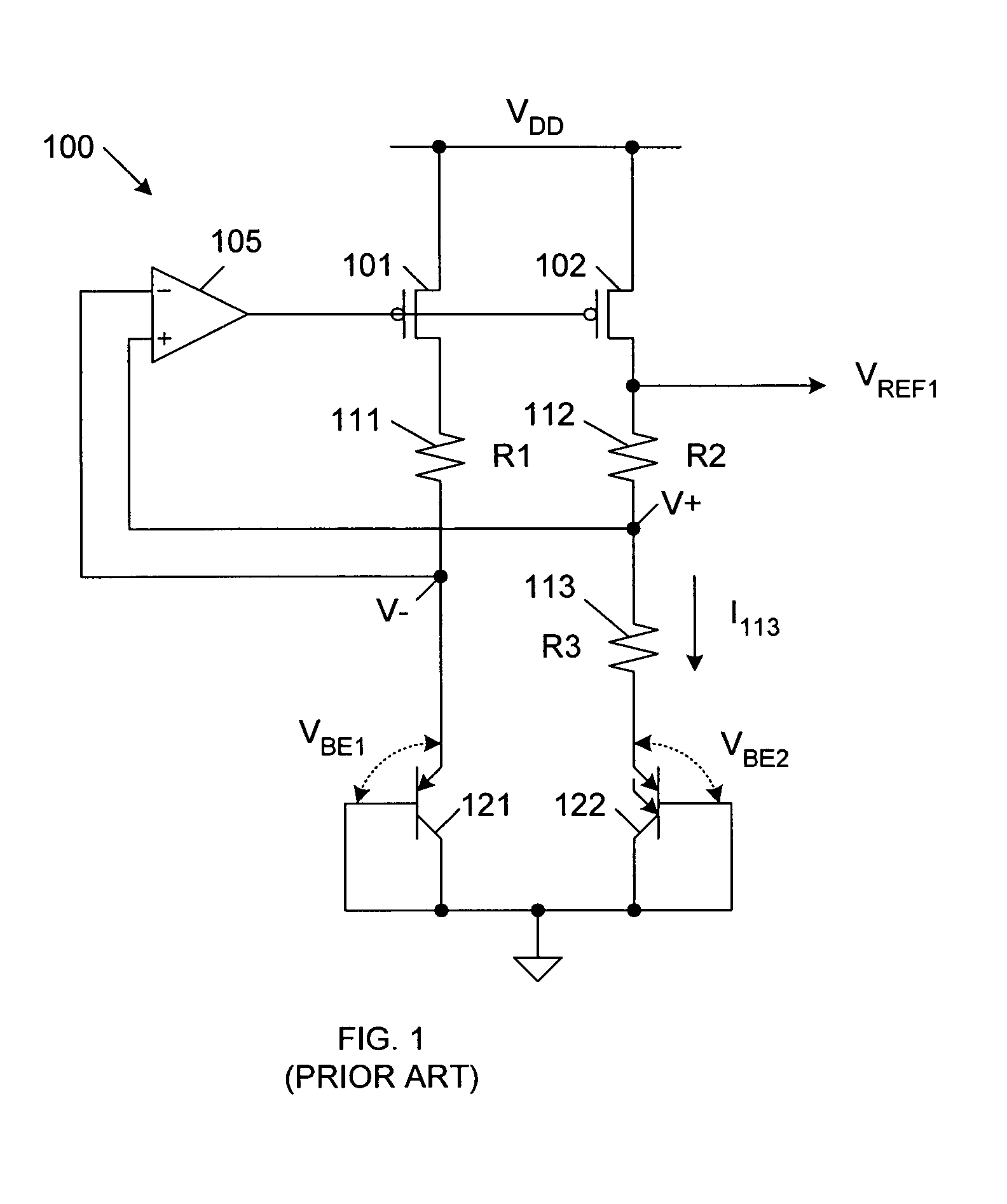
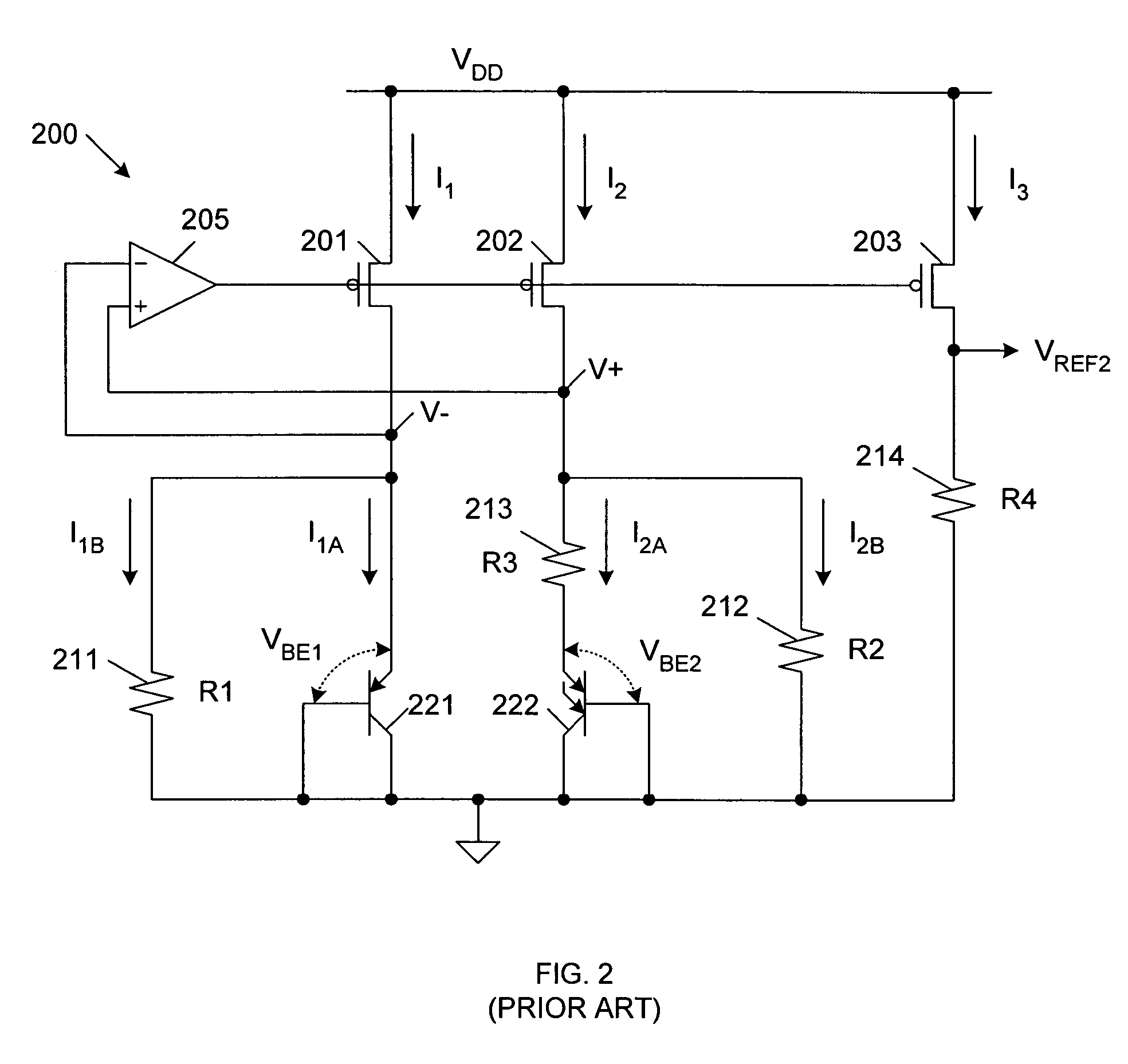
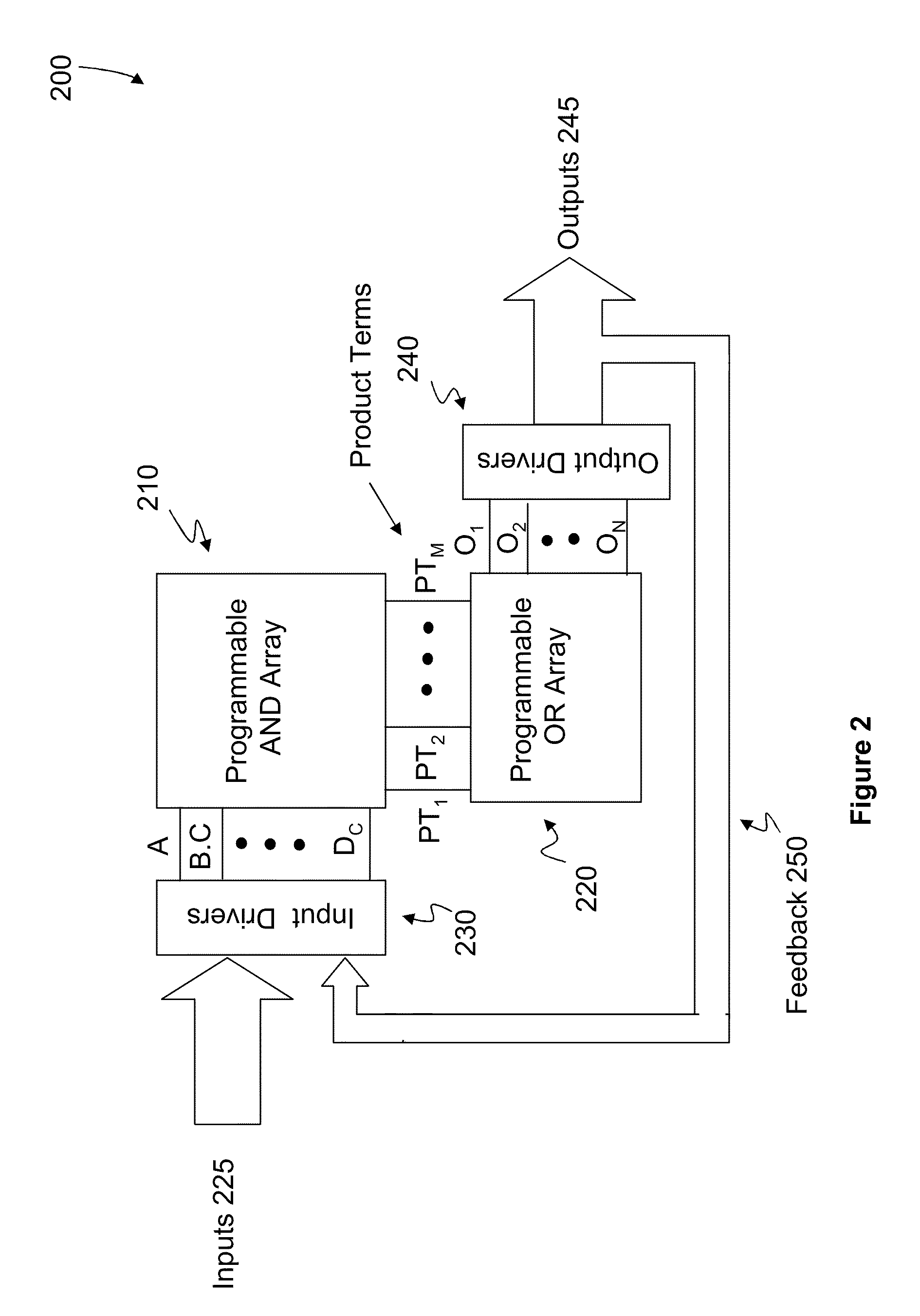
Precise voltage/current reference circuit using current-mode technique in CMOS technology
A voltage / current reference circuit includes a first bipolar transistor and a second bipolar transistor that exhibit a first voltage drop VBE1 and a second voltage drop VBE2, respectively. A first resistor, having a resistance R1, is configured to draw a first current equal to (VBE1−VBE2) / R1. A second resistor, having a resistance R2, is configured to draw a second current equal to VBE1 / R2. A first transistor supplies the first and second currents to the first and second resistors. A second transistor, having a current mirror configuration with respect to the first transistor, directly provides a reference current equal to (VBE1−VBE2) / R1+VBE1 / R2. A third transistor, having a current mirror configuration with respect to the first transistor, provides a current equal to the reference current to a third resistor having a resistance R3 and a third bipolar transistor that exhibits a third voltage drop VBE3, thereby generating a reference voltage.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Nonvolatile nanotube programmable logic devices and a nonvolatile nanotube field programmable gate array using same
Field programmable device (FPD) chips with large logic capacity and field programmability that are in-circuit programmable are described. FPDs use small versatile nonvolatile nanotube switches that enable efficient architectures for dense low power and high performance chip implementations and are compatible with low cost CMOS technologies and simple to integrate.
Owner:NANTERO
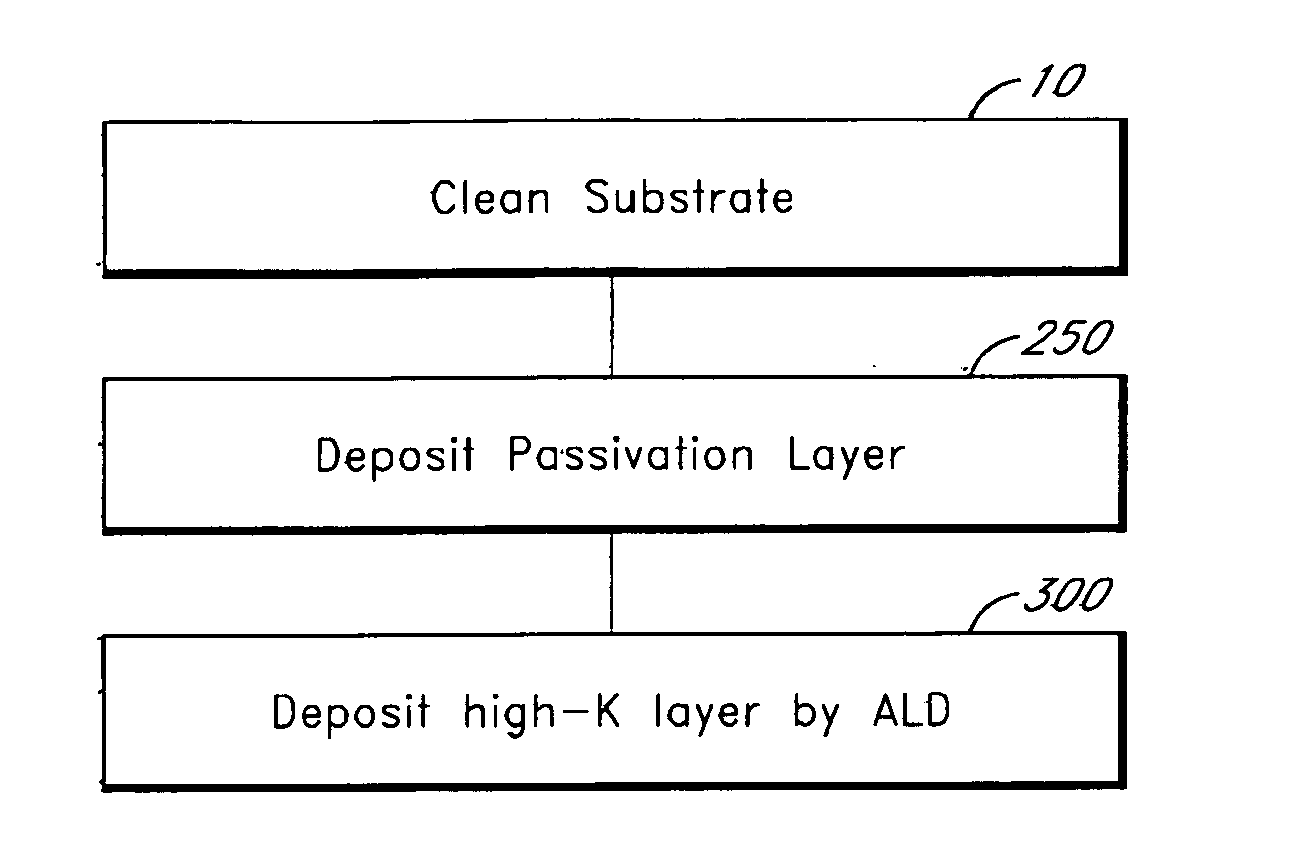
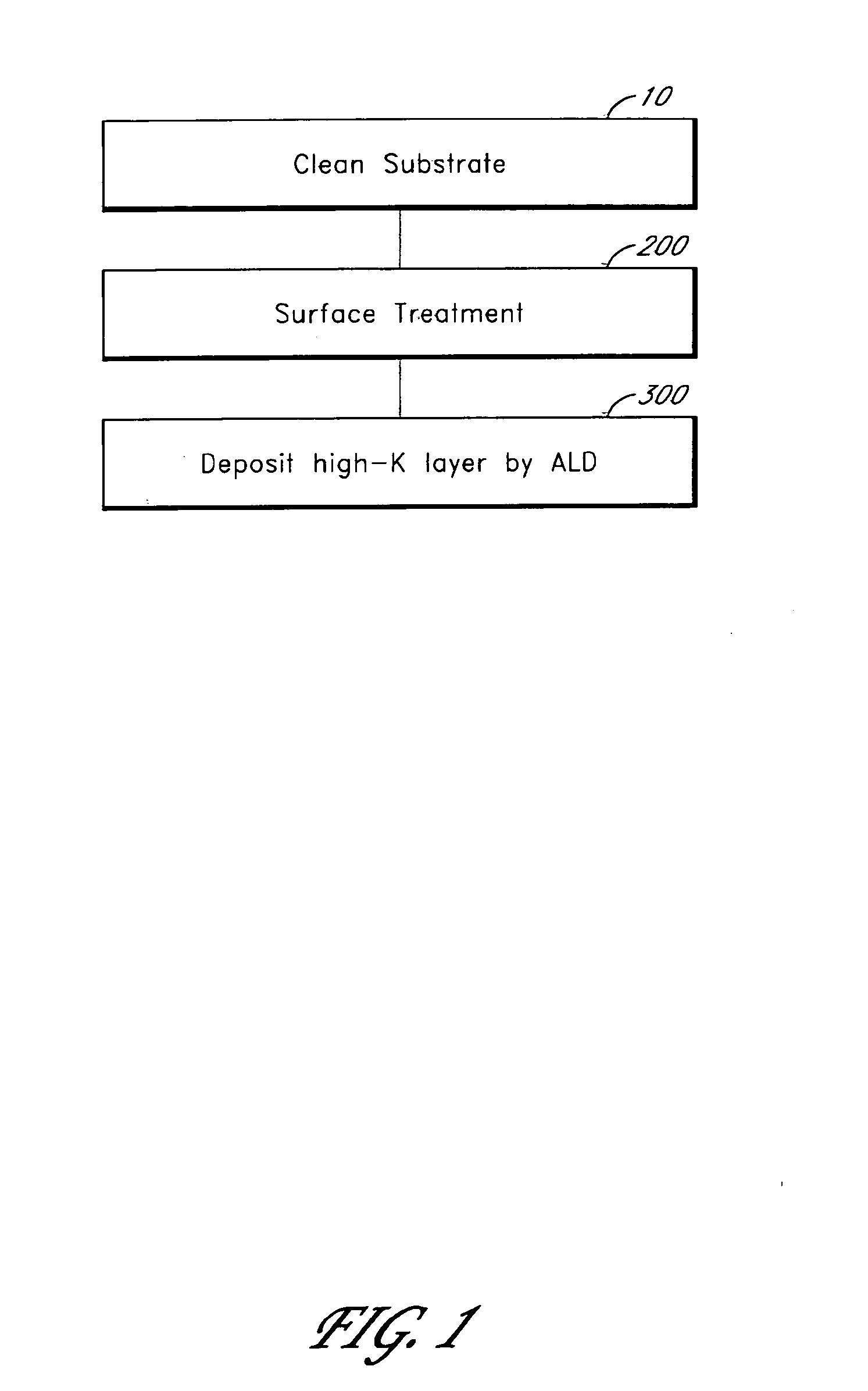
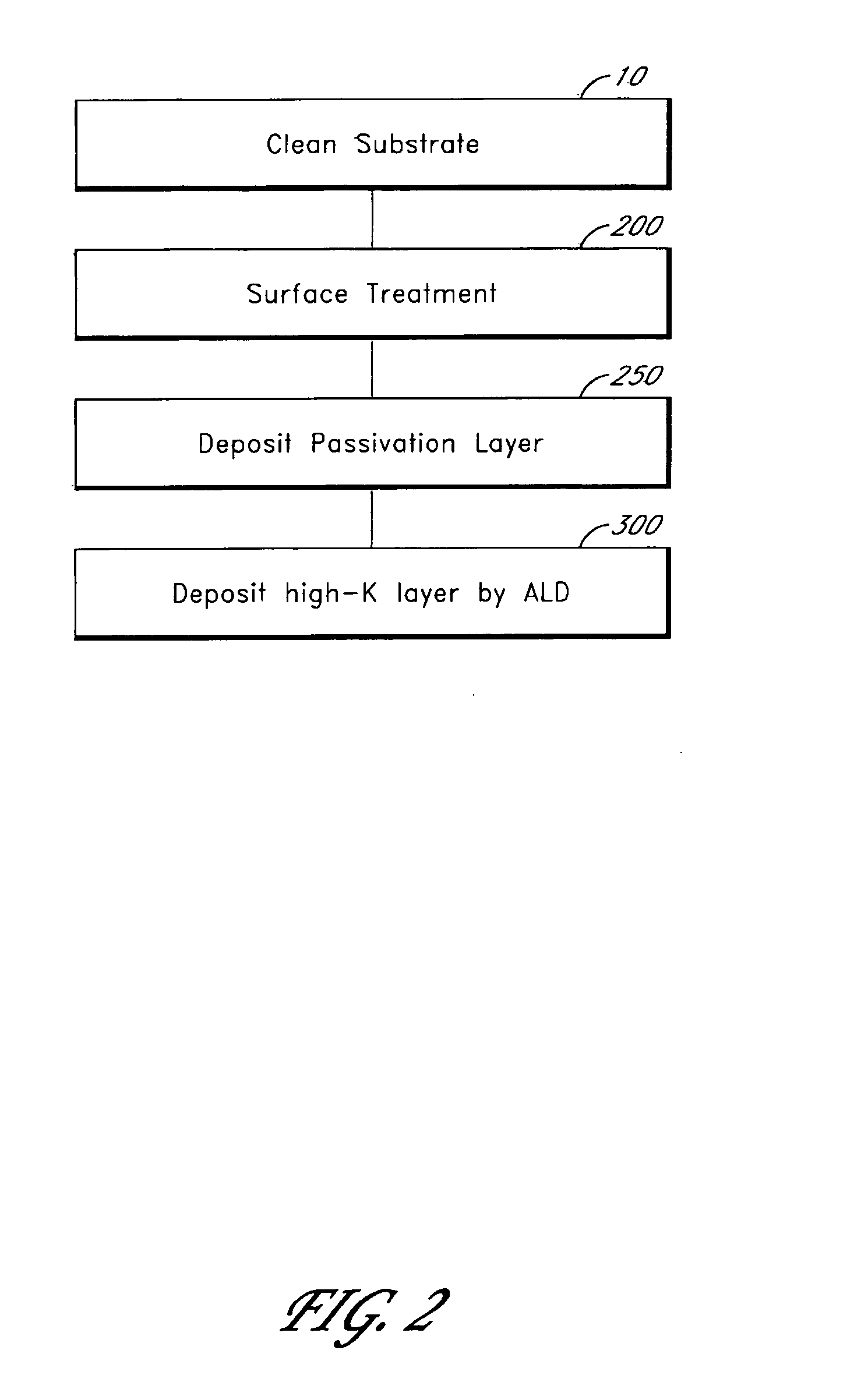
Atomic layer deposition of thin films on germanium
ActiveUS20060292872A1Facilitates subsequent depositionFacilitate ALD on GeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCMOSThin layer
Germanium has higher mobility than silicon and therefore is considered to be a good alternative semiconductor for CMOS technology. Surface treatments a can facilitate atomic layer deposition (ALD) of thin films, such as high-k dielectric layers, on germanium substrates. Surface treatment can comprise the formation of a thin layer of GeOx or GeOxNy. After surface treatment and prior to deposition of the desired thin film, a passivation layer may be deposited on the substrate. The passivation layer may be, for example, a metal oxide layer deposited by ALD.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Method of making a device threshold control of front-gate silicon-on-insulator MOSFET using a self-aligned back-gate
InactiveUS7018873B2Minimize capacitanceImprove performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceMOSFET
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
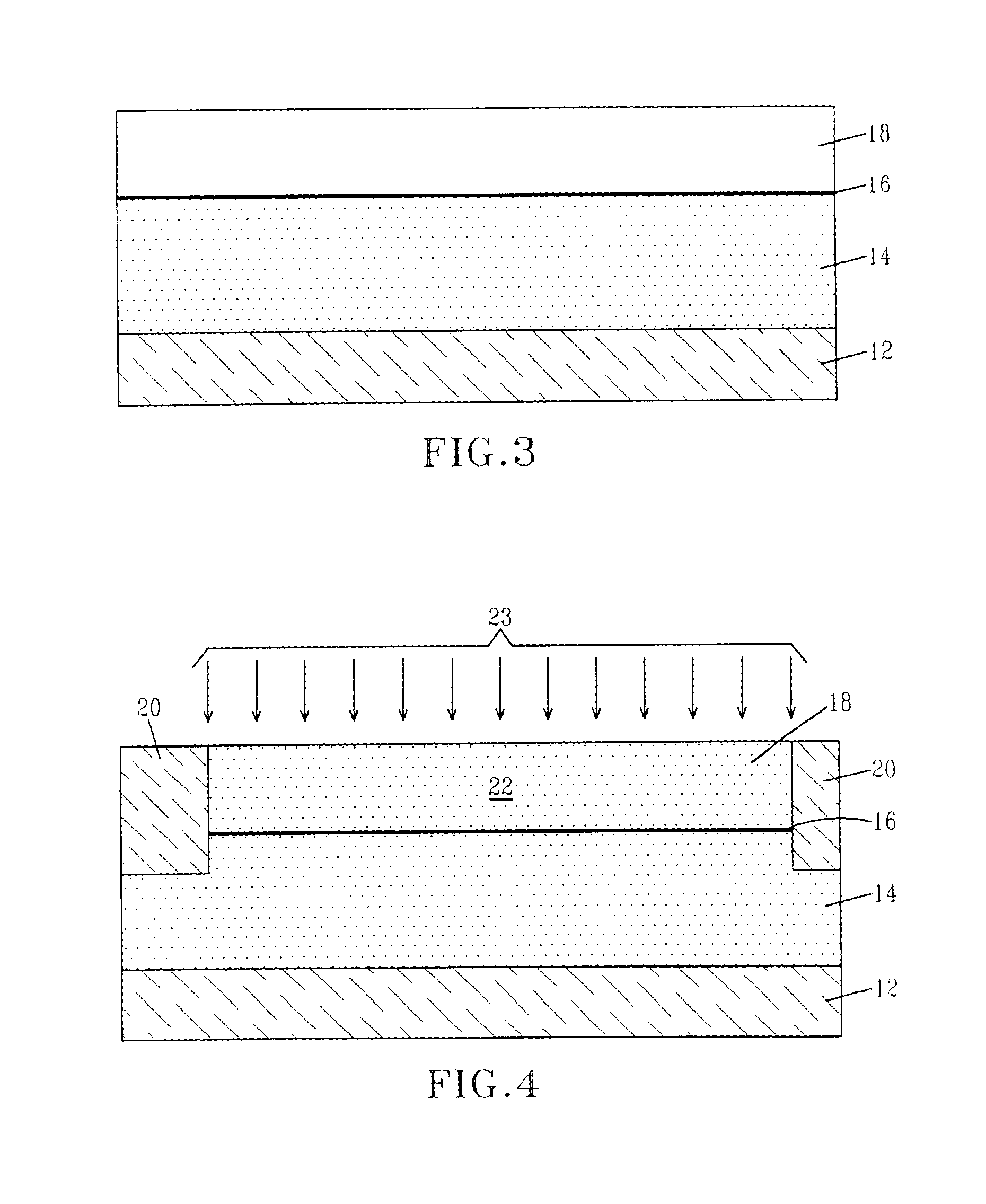
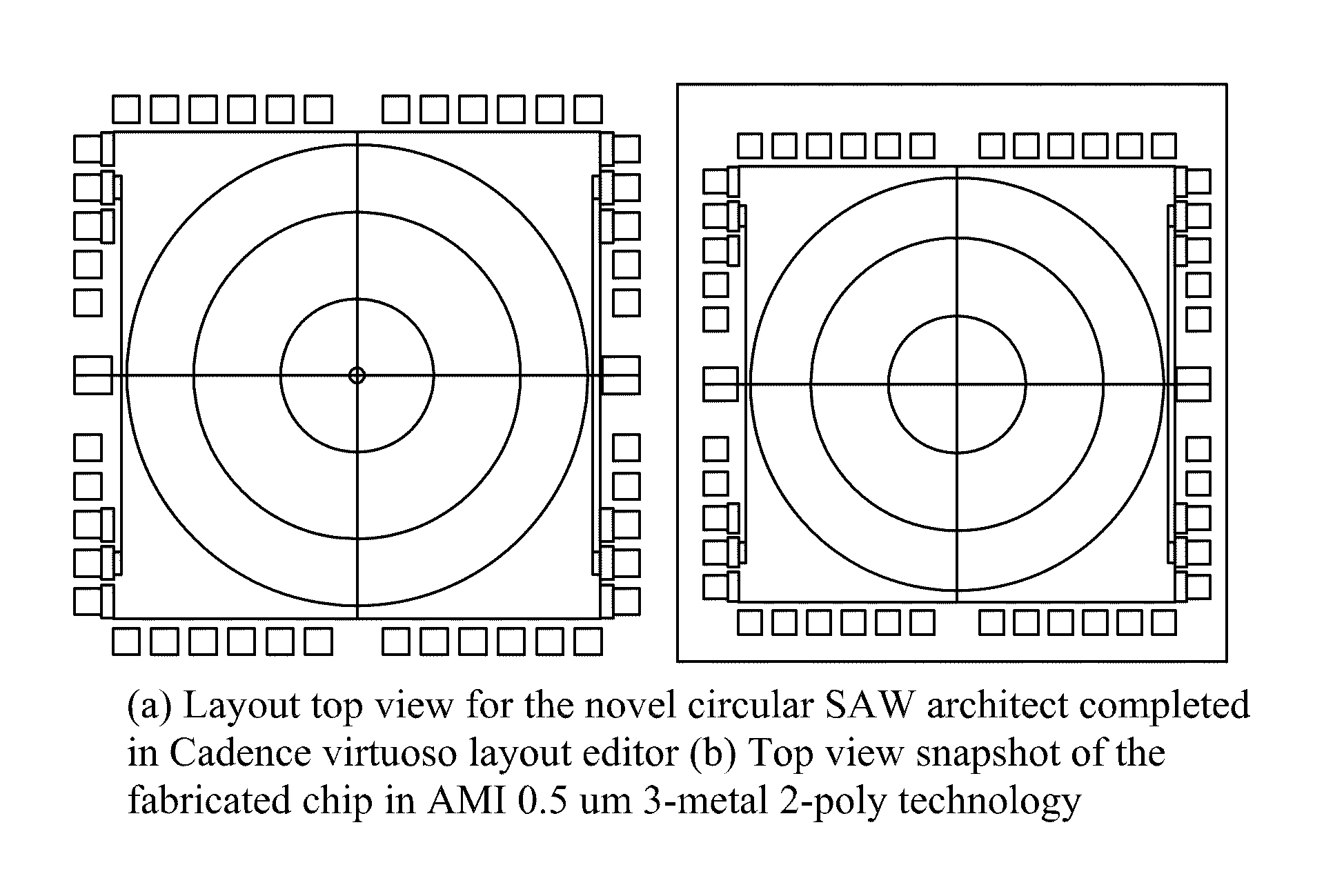
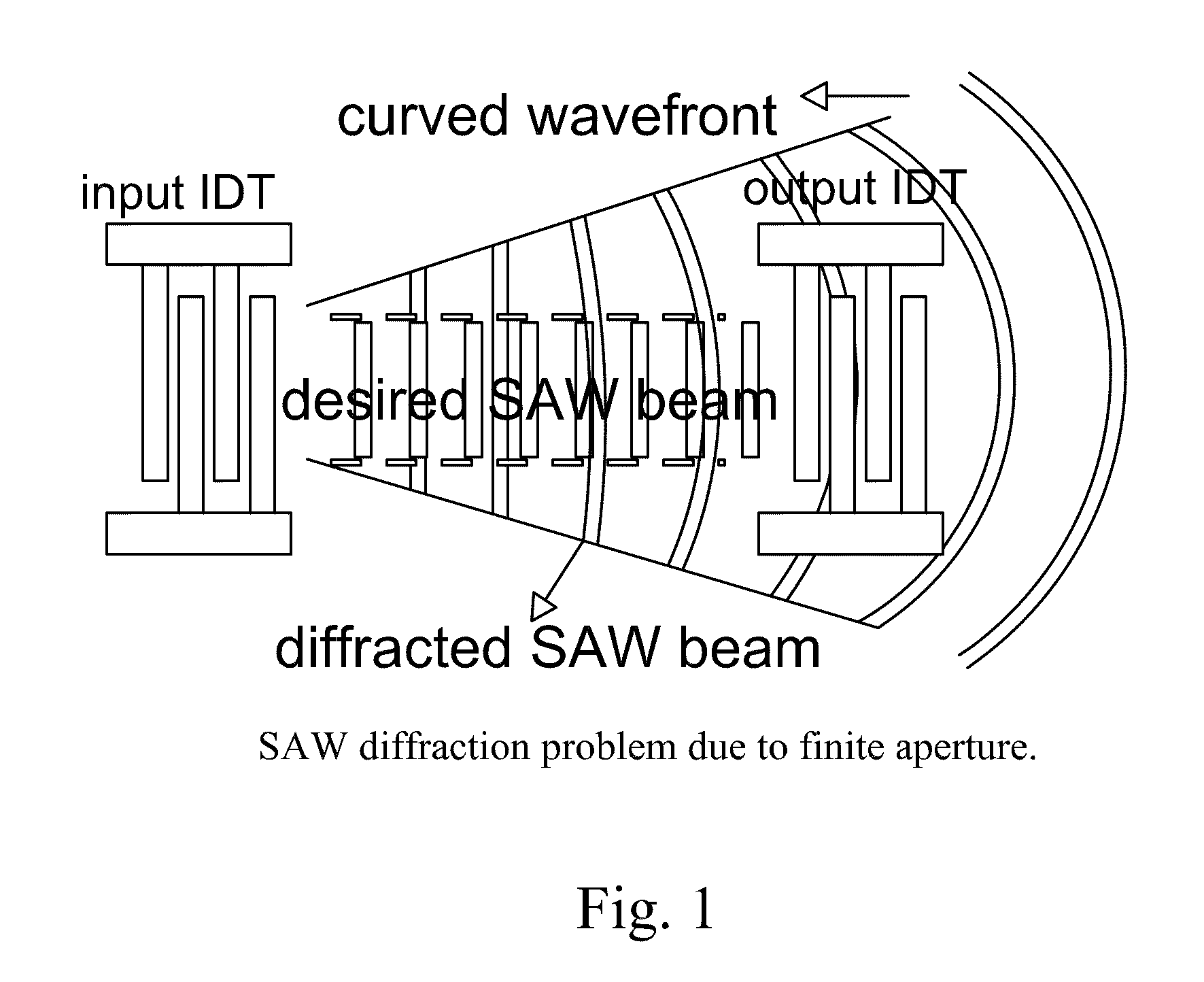
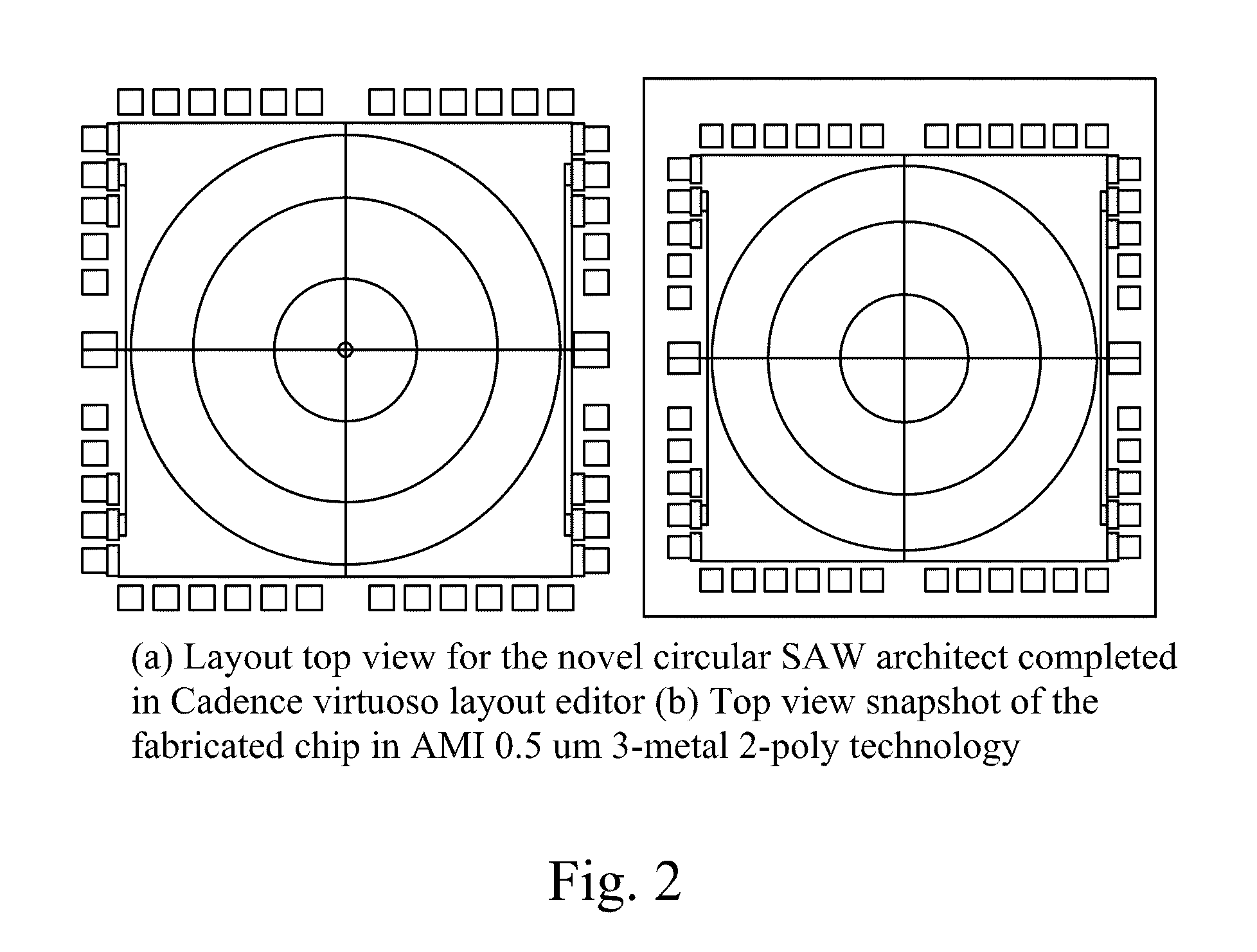
Circular surface acoustic wave (SAW) devices, processes for making them, and methods of use
InactiveUS8018010B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesImpedence networksCMOSTemperature control
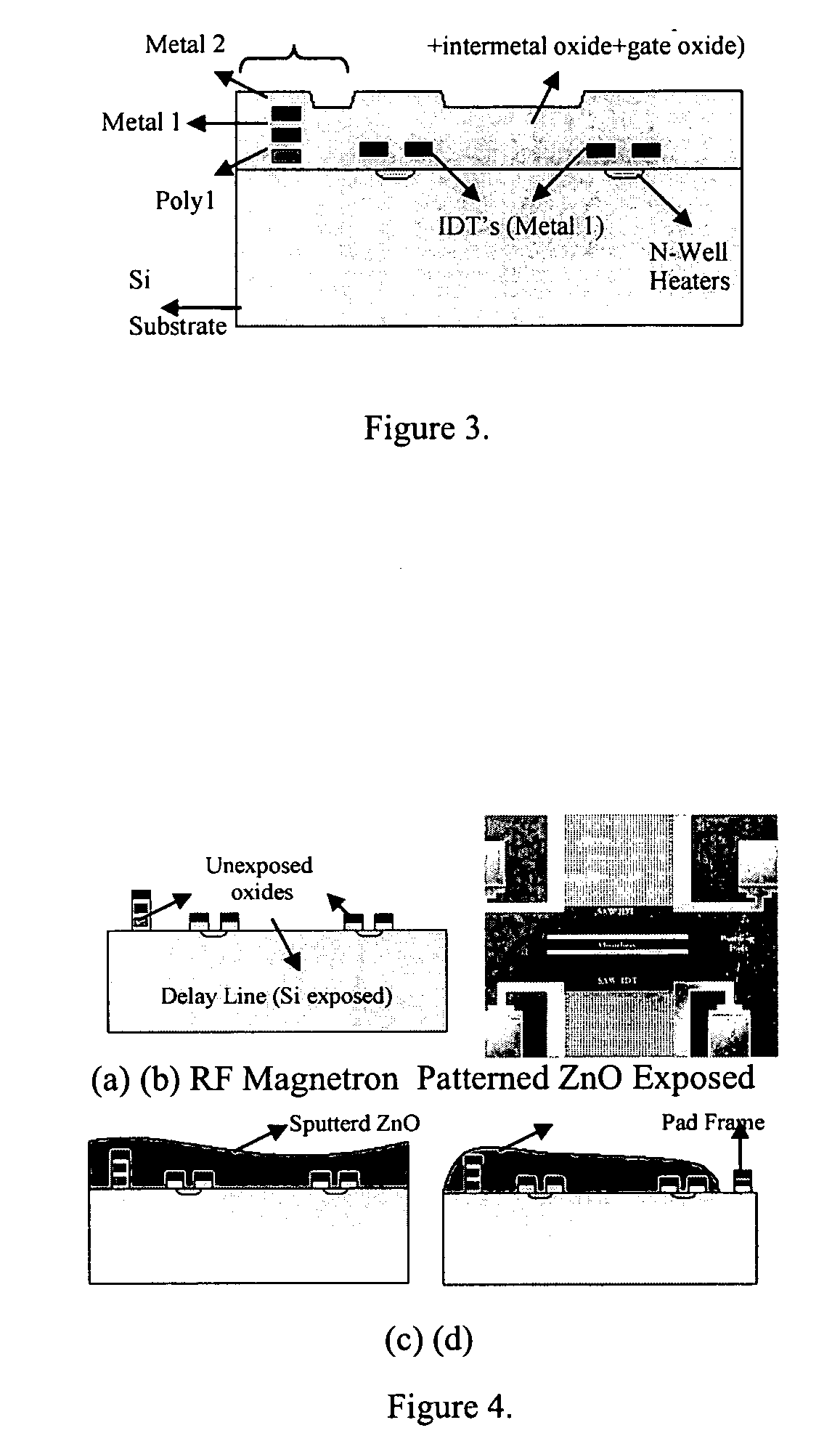
The design, fabrication, post-processing and characterization of a novel circular design SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave) based bio / chemical sensor in CMOS technology is introduced. The sensors are designed in AMI 1.5 μm 2 metal, 2 poly process. A unique maskless post processing sequence is designed and completed. The three post-processing steps are fully compatible with any CMOS technology. This allows any signal control / processing circuitry to be easily integrated on the same chip. ZnO is used as the piezoelectric material for the SAW generation. A thorough characterization and patterning optimization of the sputtered ZnO was carried out. The major novelties that are introduced in the SAW delay line features are: The embedded heater elements for temperature control, compensation and acoustic absorbers that are designed to eliminate edge reflections and minimize triple transit interference. Both of these attributes are designed by using the CMOS layers without disturbing the SAW performance.
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
Amplifier
ActiveUS7030699B2Reduce noiseMore stressStereophonic circuit arrangementsLow frequency amplifiersCMOSAudio power amplifier
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Saw devices, processes for making them, and methods of use
ActiveUS20080230859A1Improved biosensor arrangement performanceQuick checkPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTemperature controlCMOS
The design, fabrication, post-processing and characterization of a novel SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave) based bio / chemical sensor in CMOS technology is introduced. The sensors are designed in AMI 1.5 μm 2 metal, 2 poly process. A unique maskless post processing sequence is designed and completed. The three post-processing steps are fully compatible with any CMOS technology. This allows any signal control / processing circuitry to be easily integrated on the same chip. ZnO is used as the piezoelectric material for the SAW generation. A thorough characterization and patterning optimization of the sputtered ZnO was carried out. The major novelties that are introduced in the SAW delay line features are: The embedded heater elements for temperature control, compensation and acoustic absorbers that are designed to eliminate edge reflections and minimize triple transit interference. Both of these attributes are designed by using the CMOS layers without disturbing the SAW performance.
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
Miniaturized, low power fgmosfet radiation sensor and wireless dosimeter system
ActiveUS20100096556A1Reduce capacitanceHigh sensitivityDosimetersSolid-state devicesCapacitanceMOSFET
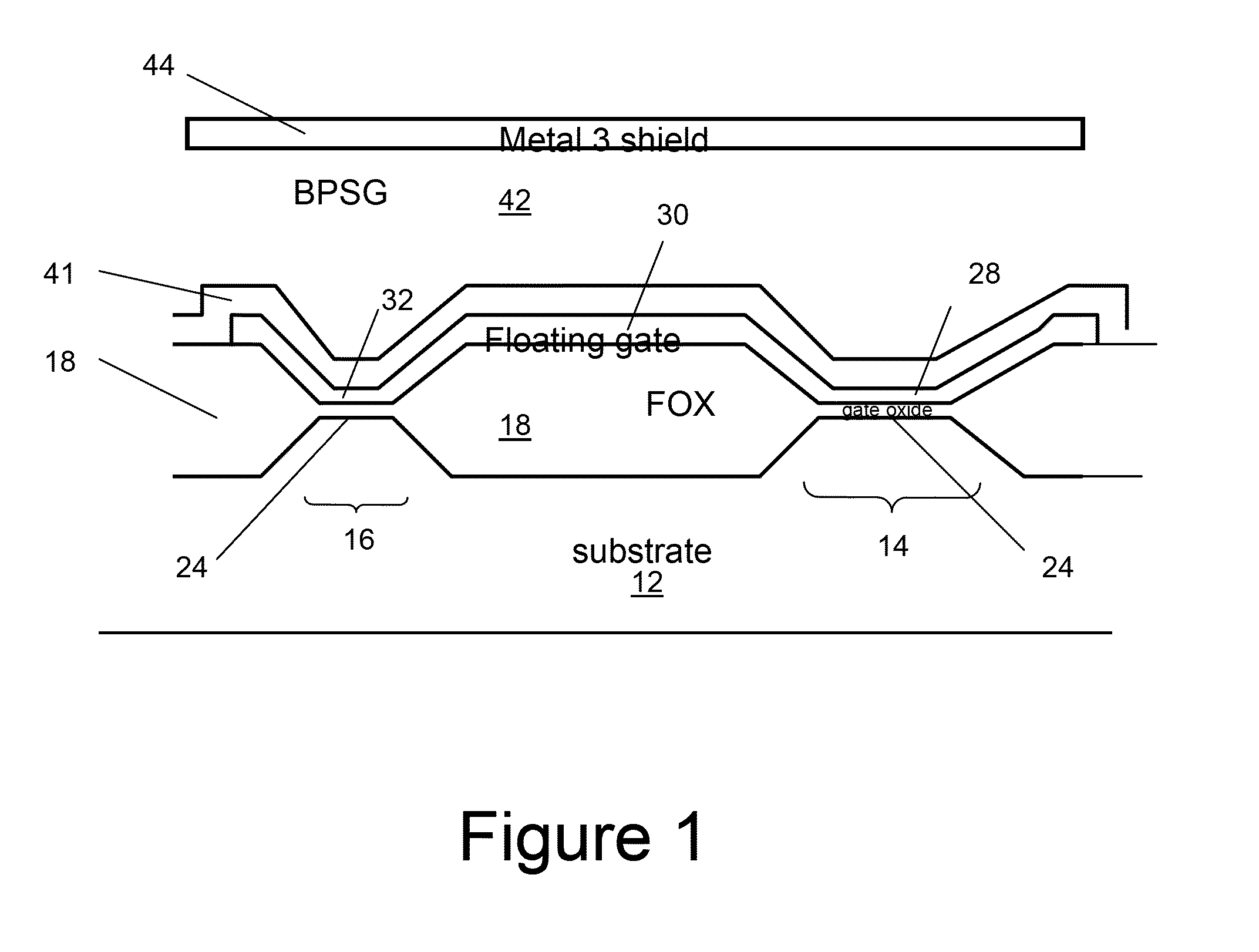
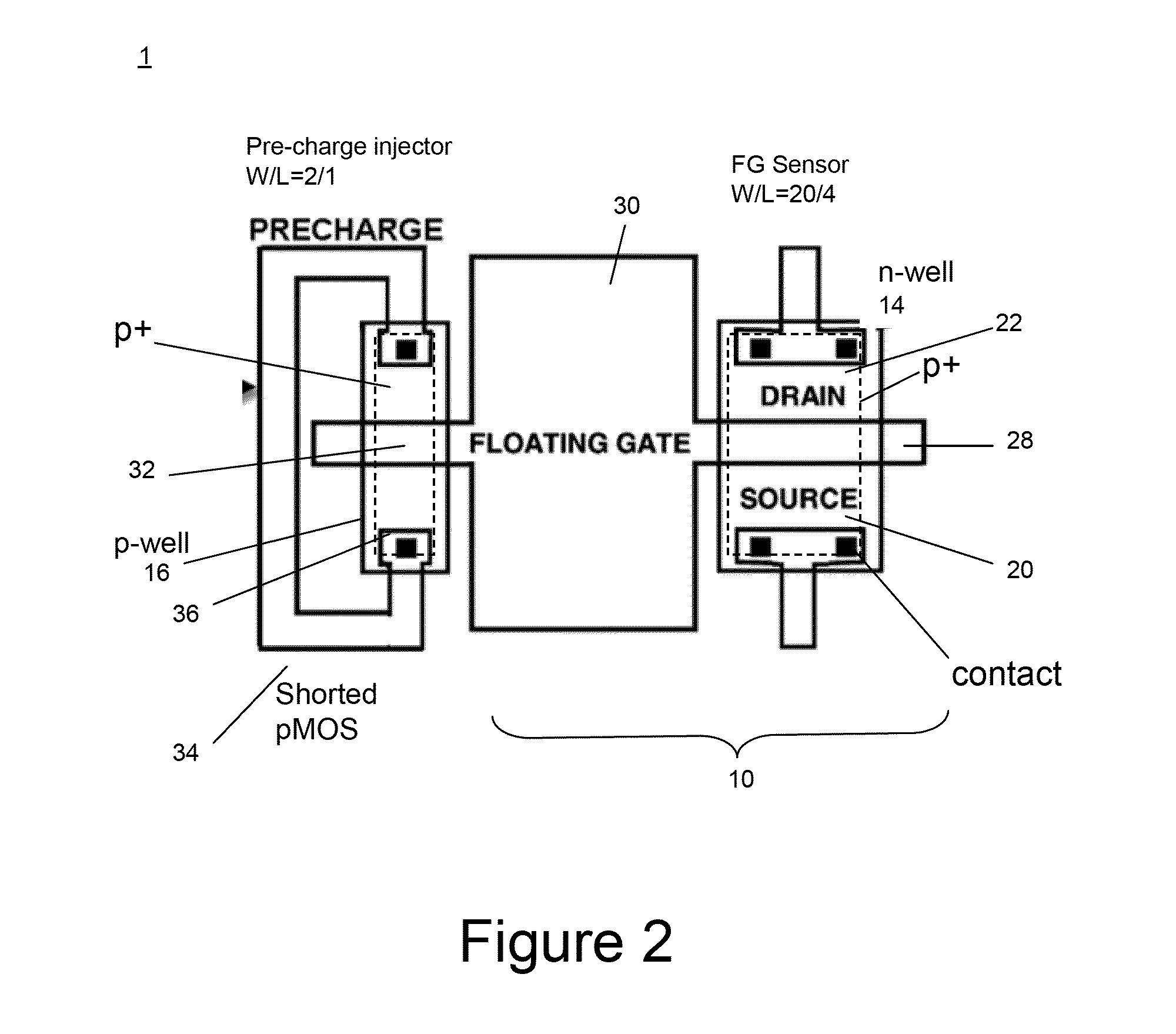
A miniaturized floating gate (FG) MOSFET radiation sensor system is disclosed, The sensor preferably comprises a matched pair of sensor and reference FGMOSFETs wherein the sensor FGMOSFET has a larger area floating gate with an extension over a field oxide layer, for accumulation of charge and increased sensitivity. Elimination of a conventional control gate and injector gate reduces capacitance, and increases sensitivity, and allows for fabrication using standard low cost CMOS technology. A sensor system may be provided with integrated signal processing electronics, for monitoring a change in differential channel current ID, indicative of radiation dose, and an integrated negative bias generator for automatic pre-charging from a low voltage power source. Optionally, the system may be coupled to a wireless transmitter. A compact wireless sensor System on Package solution is presented, suitable for dosimetry for radiotherapy or other biomedical applications.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
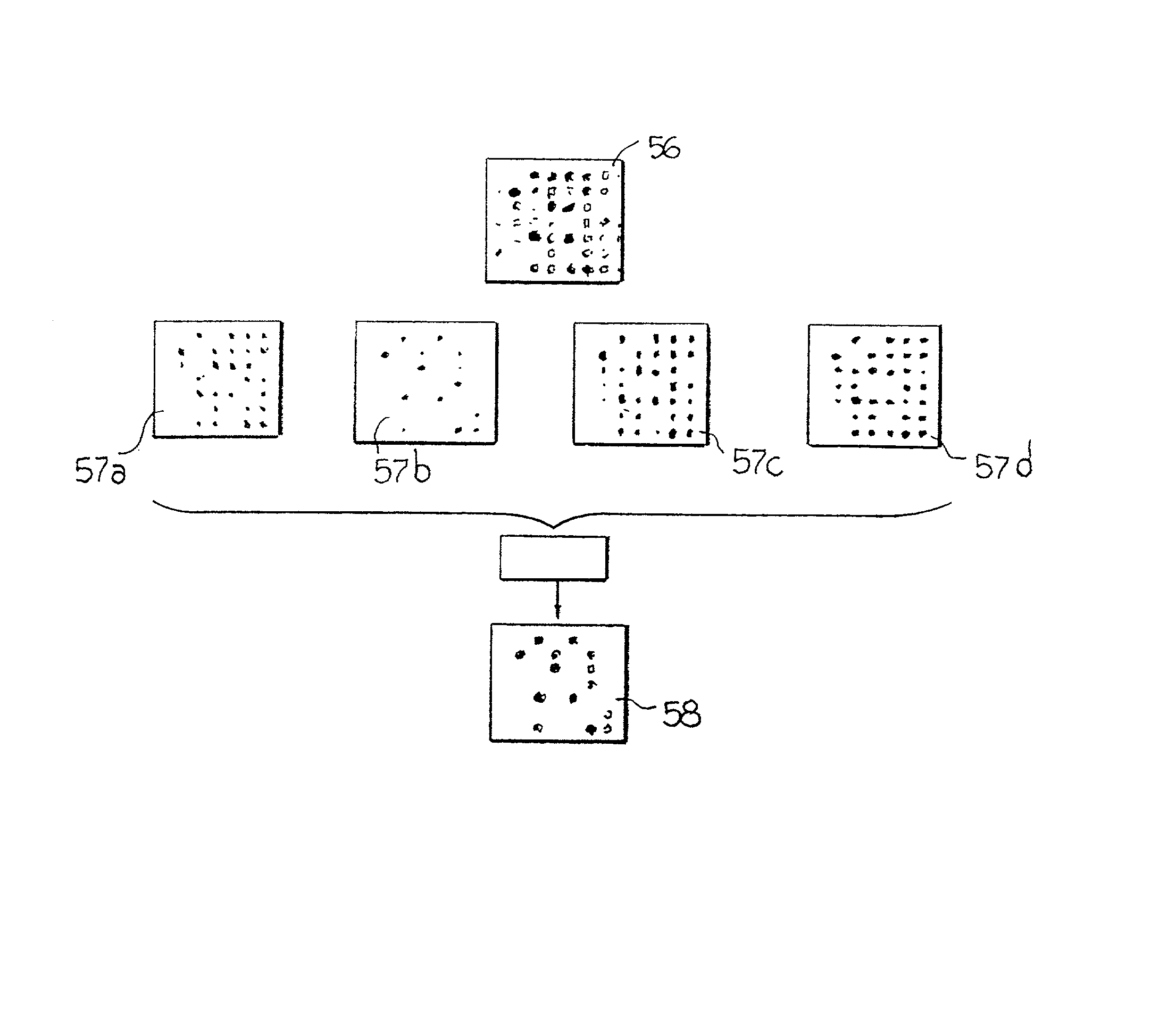
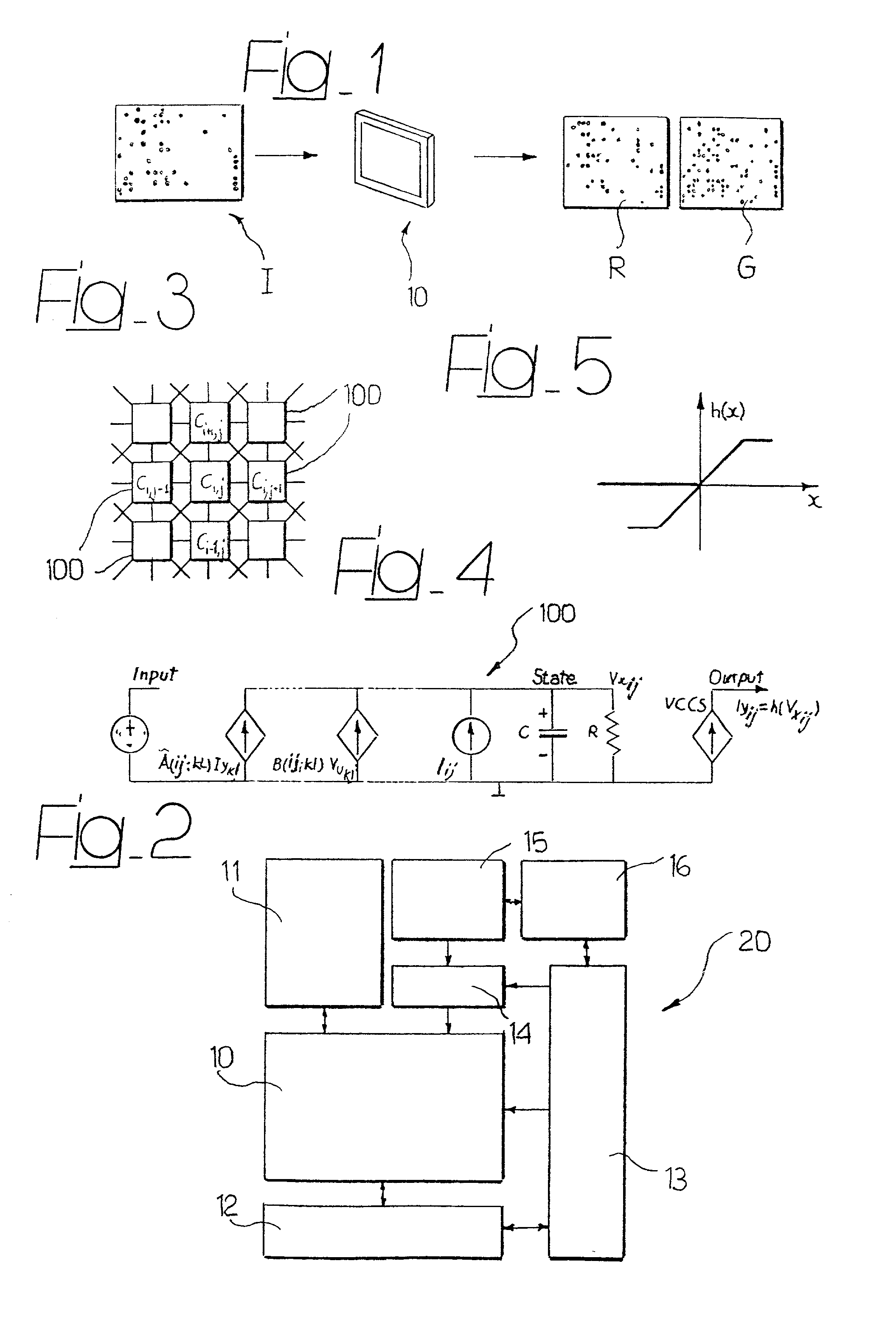
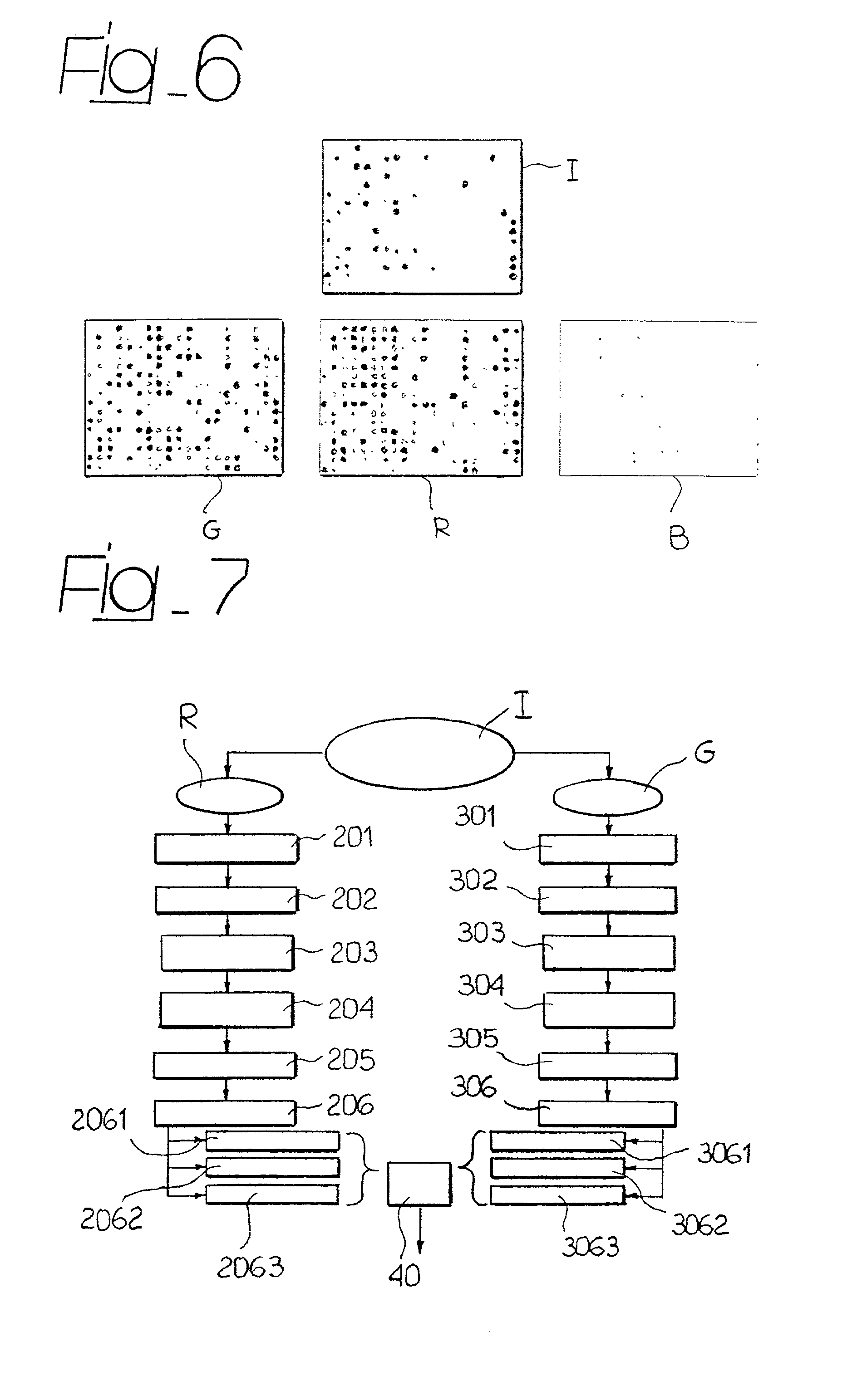
System for the automatic analysis of images such as DNA microarray images
InactiveUS20020097900A1Efficient and rapid automatic analysis of imageImage enhancementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCMOSDNA microarray
The system can be used for the automatic analysis of images (I), comprising a matrix of spots, such as images of DNA microarrays after hybridisation. The system can be associated-and preferably integrated in a single monolithic component implementing VLSI CMOS technology-to a sensor (10) for acquiring said images (I). The system comprises a circuit (20) for processing the signals corresponding to the images (I), configured according to a cellular neural network (CNN) architecture for the parallel analogue processing of signals.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Multi-metal coplanar waveguide
InactiveUS7626476B2Reduce decreaseImprove performanceMultiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSCoplanar waveguide
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
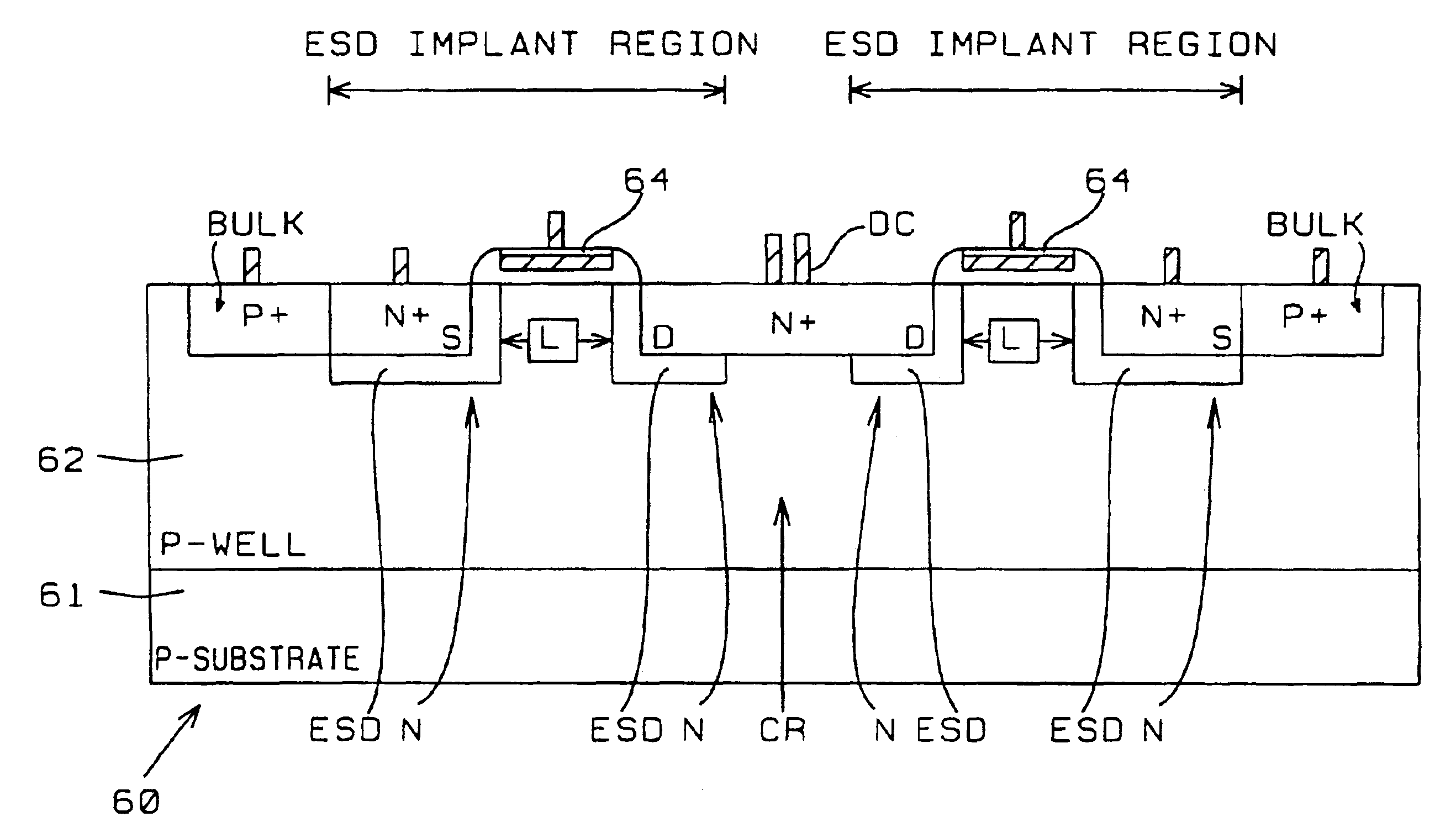
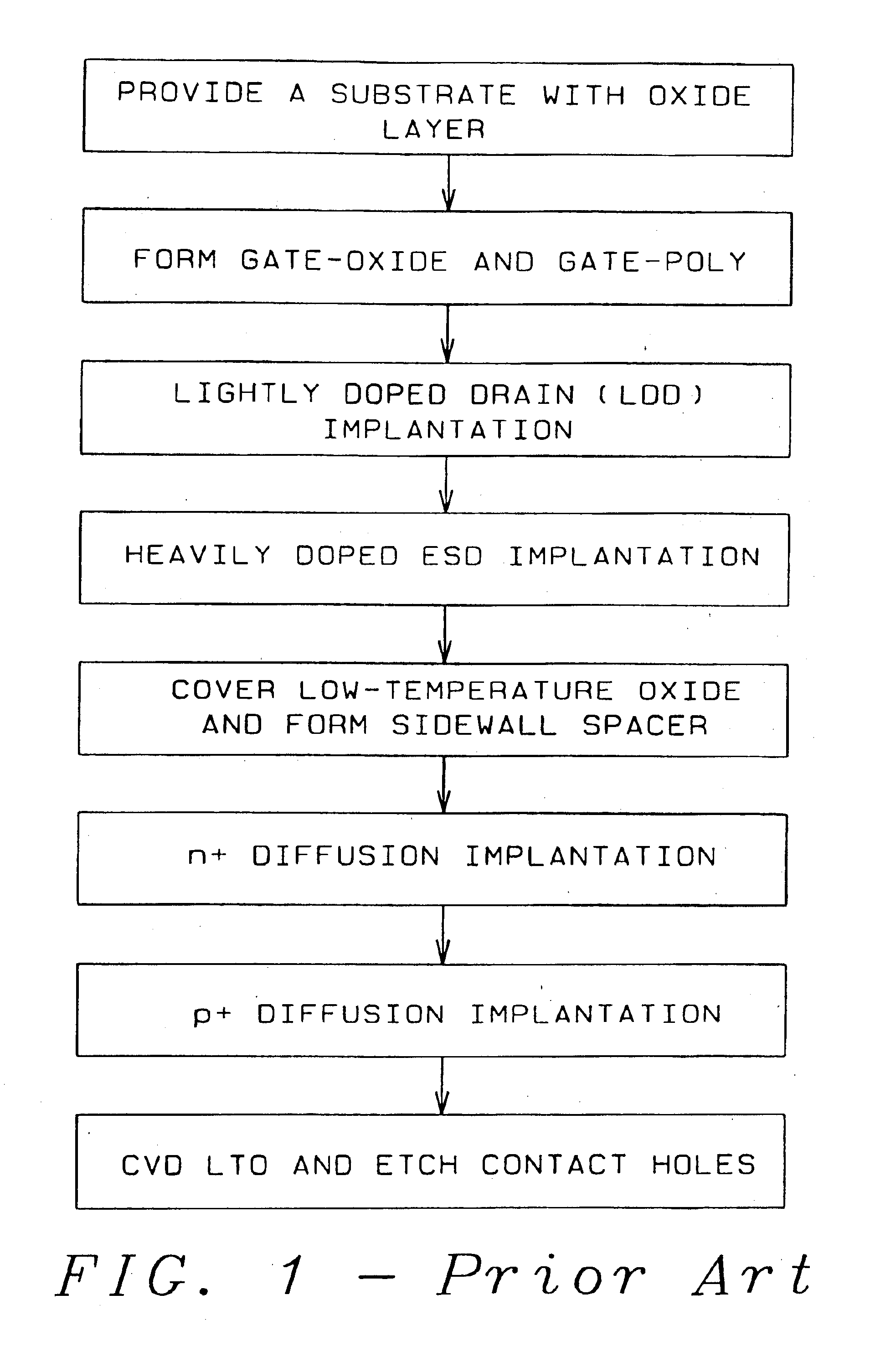
ESD implantation in deep-submicron CMOS technology for high-voltage-tolerant applications
High-voltage-tolerant ESD protection devices (ESDPD) for deep-submicron CMOS process were activated between LDD implanting and forming sidewall spacers. ESD-Implant (ESDI) regions are located at the ESDPD, without covering the center region under the drain contact (DC). The ESDI LDD concentration and doping profile are deep to contain drain diffusion. Regions with the ESDI have a high junction breakdown voltage (JBV) and a low junction capacitance. After forming gate sidewall spacers, high doping concentration ions implanted into active D / S regions formed a shallower doping profile of the D / S diffusion. The drain has a JBV as without this ESDI, so the ESD current (ESDC) is discharged through the center junction region under the DC to bulk, far from the ESDPD surface channel region. The ESDPD sustains a high ESD level. In an original drain JBV of an MOS this ESDI method is unchanged, i.e. the same as that having no such ESDI, so it can be used in I / O circuits with high-voltage signals in the deep-submicron CMOS. The ESD level of the IO ESDPD improves. The ESD discharge current path in the MOS device structure improves the ESD level in the output buffer MOS. ESDI regions are located at the output MOS devices, without covering the region under the DC. Regions under the DC without this ESDI have an unchanged JBV, so the ESDC discharges through the junction region under the DC to bulk. The original drain JBV of the output MOS with this ESDI method is unchanged, which is still the same as that having no such ESDI, to be used in the I / O circuits with high-voltage (5V) input signals in the deep-submicron CMOS with 3.3V or 2.5V VDD. This applies to diodes, FOD and lateral BJT devices.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
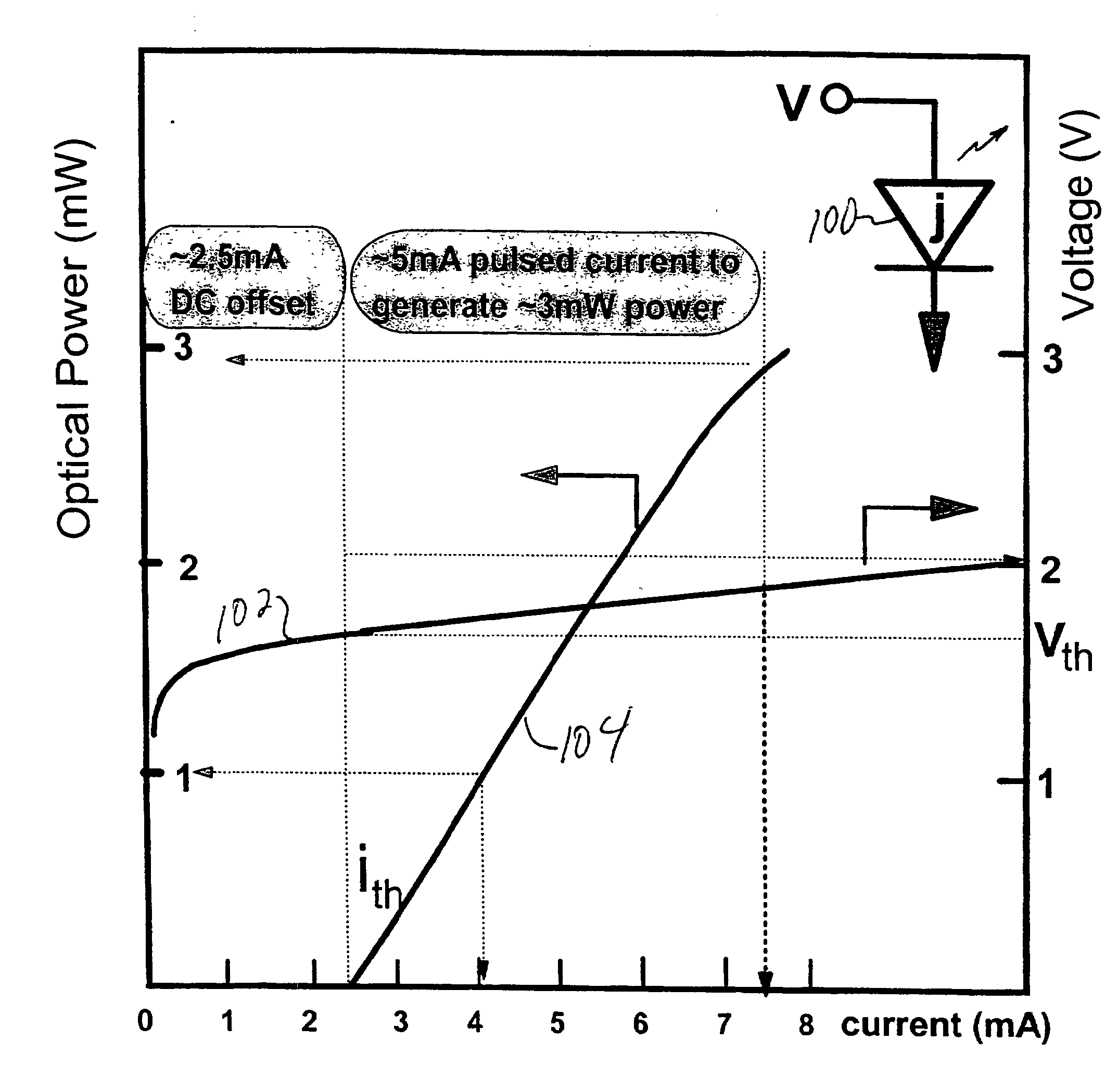
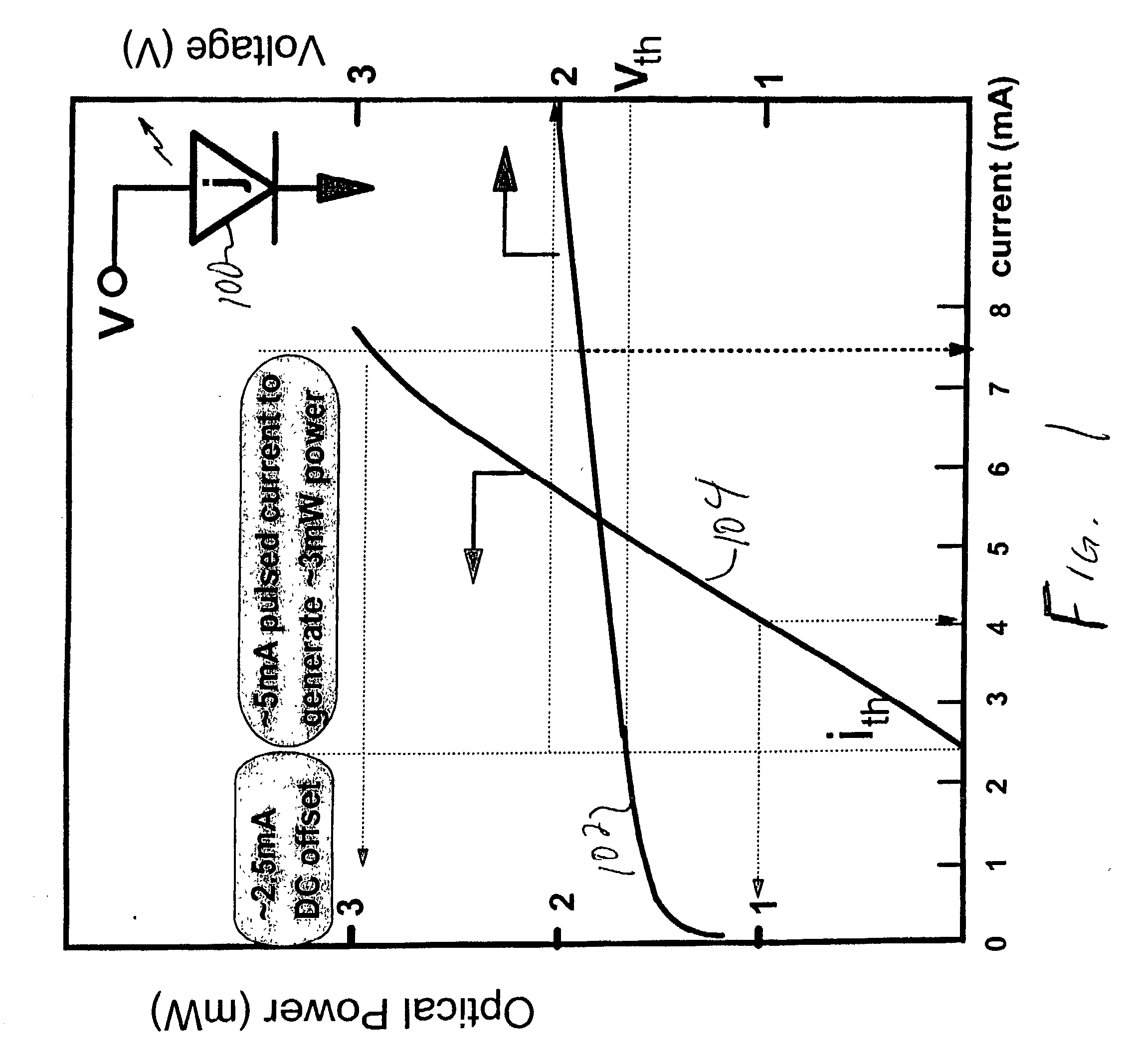
High speed data channel including a CMOS VCSEL driver and a high performance photodetector and CMOS photoreceiver
ActiveUS20040101007A1Laser detailsSolid-state devicesVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserSchottky barrier
A high speed optical channel including an optical driver and a photodetector in a CMOS photoreceiver. The optical channel driver includes a FET driver circuit driving a passive element (e.g., an integrated loop inductor) and a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) diode. The VCSEL diode is biased by a bias supply. The integrated loop inductor may be integrated in CMOS technology and on the same IC chip as either / both of the FET driver and the VCSEL diode. The photodetector is in a semiconductor (silicon) layer that may be on an insulator layer, i.e., SOI. One or more ultrathin metal electrodes (<2000 Å) on the silicon layer forms a Schottky barrier diode junction which in turn forms a quantum well containing a two dimensional electron gas between the ultrathin metal electrode and the Schottky barrier diode junction.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Low-cost strained soi substrate for high-performance CMOS technology
InactiveUS20080171423A1High carrier mobilityInhibit growthTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSCharge carrier mobility
A cost-effective and simple method of fabricating strained semiconductor-on-insulator (SSOI) structures which avoids epitaxial growth and subsequent wafer bonding processing steps is provided. In accordance with the present invention, a strain-memorization technique is used to create strained semiconductor regions on a SOI substrate. The transistors formed on the strained semiconductor regions have higher carrier mobility because the Si regions have been strained. The inventive method includes (i) ion implantation to create a thin amorphization layer, (ii) deposition of a high stress film on the amorphization layer, (iii) a thermal anneal to recrystallize the amorphization layer, and (iv) removal of the stress film. Because the SOI substrate was under stress during the recrystallization process, the final semiconductor layer will be under stress as well. The amount of stress and the polaity (tensile or compressive) of the stress can be controlled by the type and thickness of the stress films.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
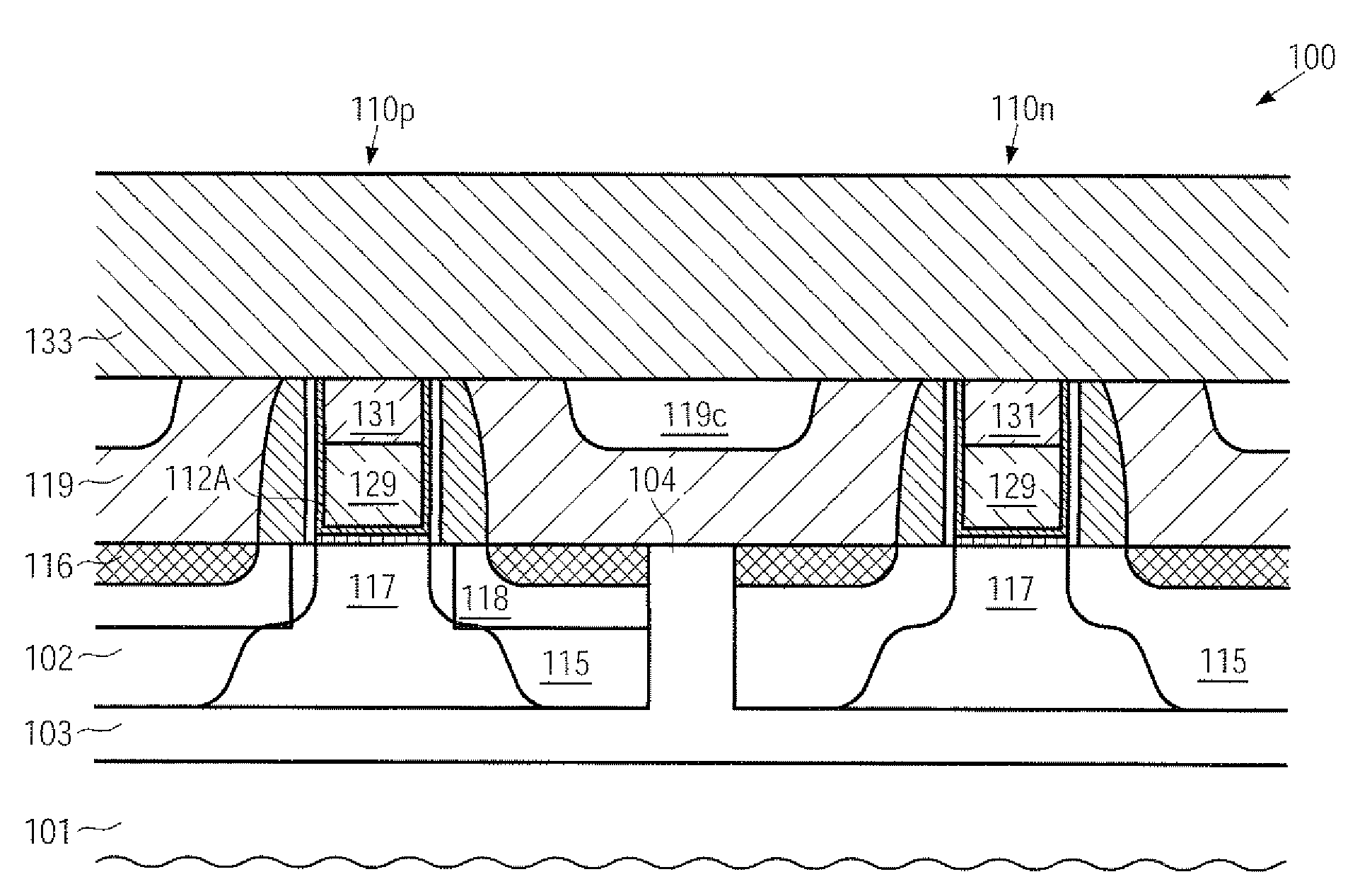
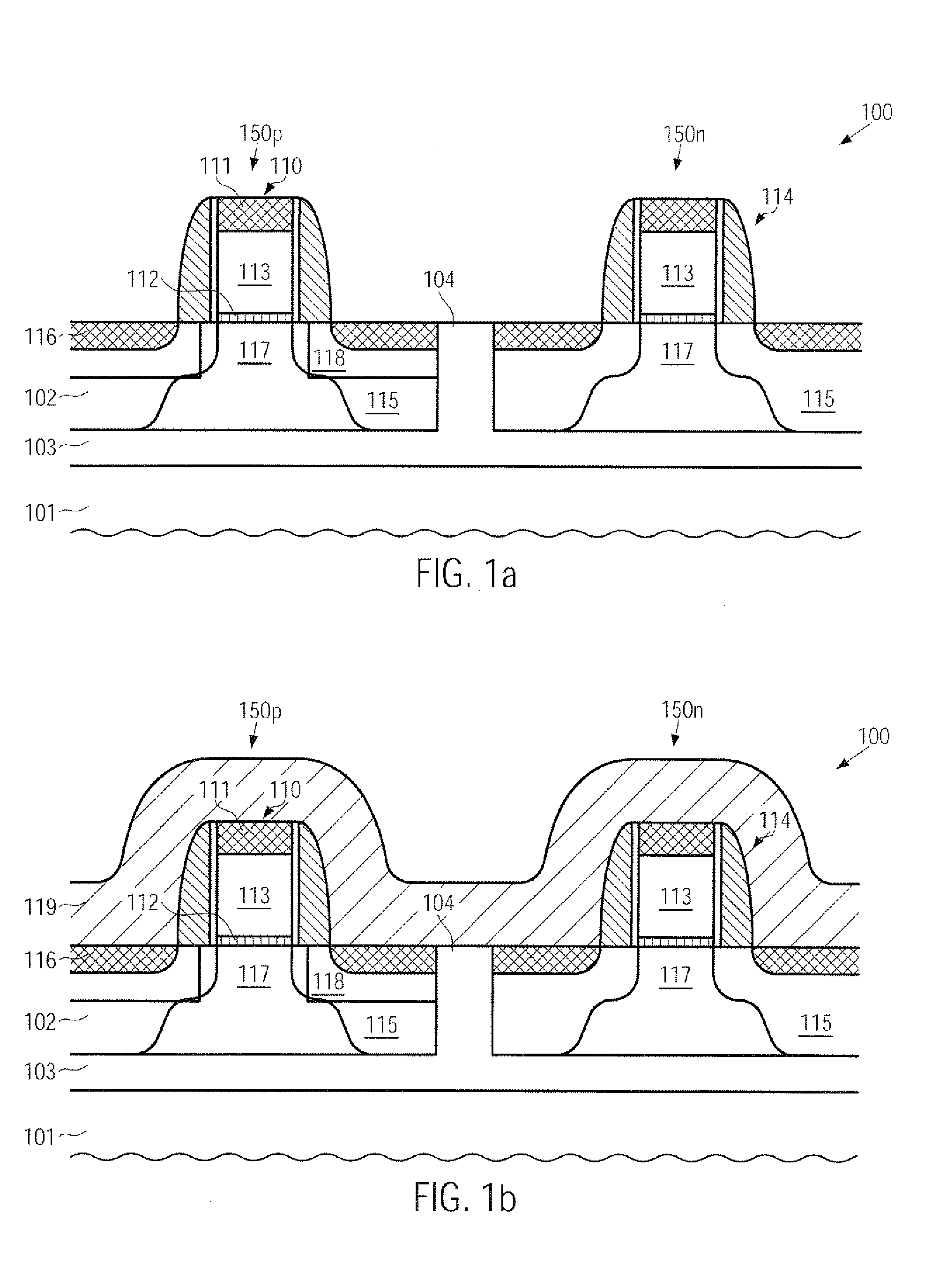
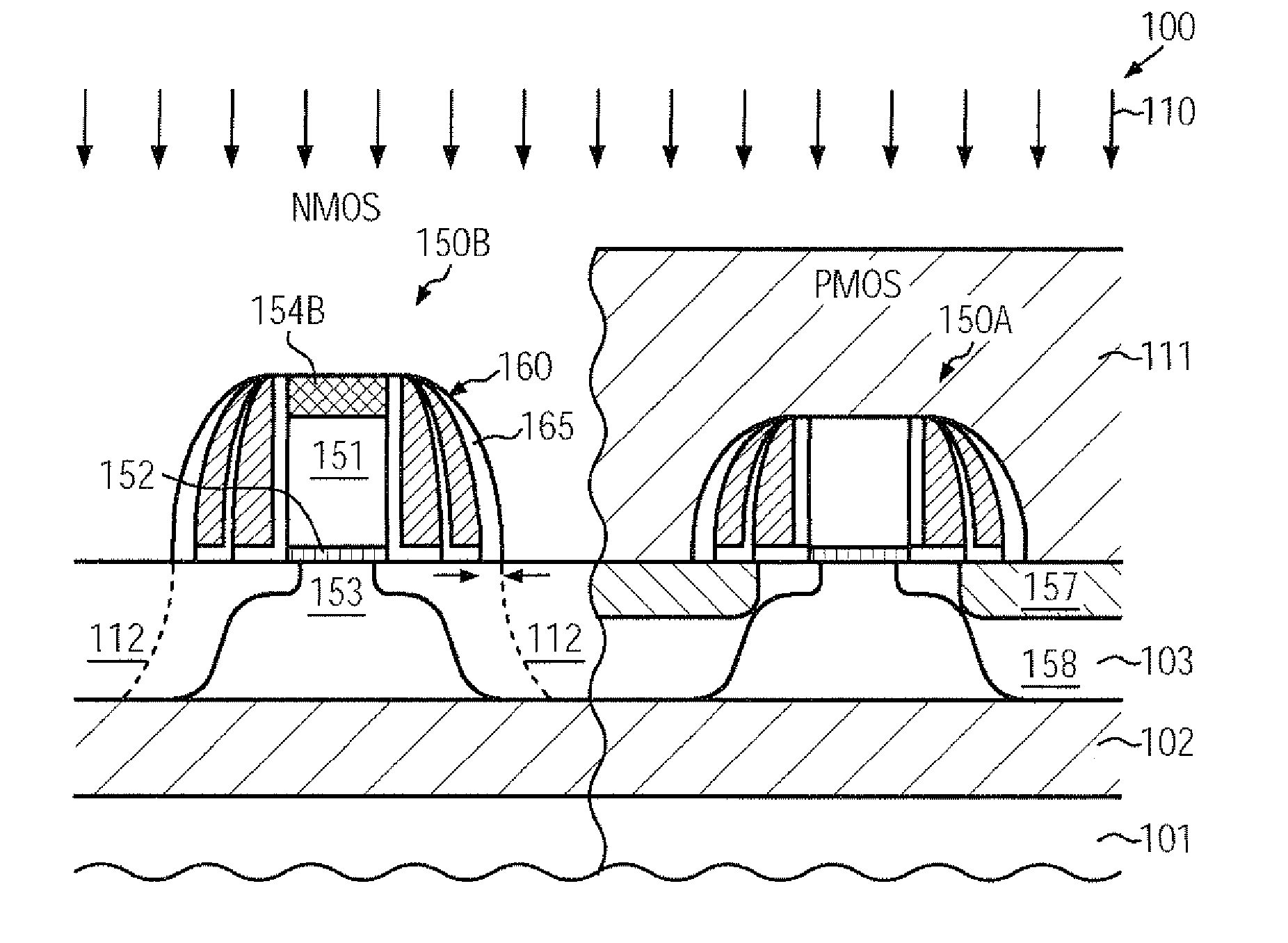
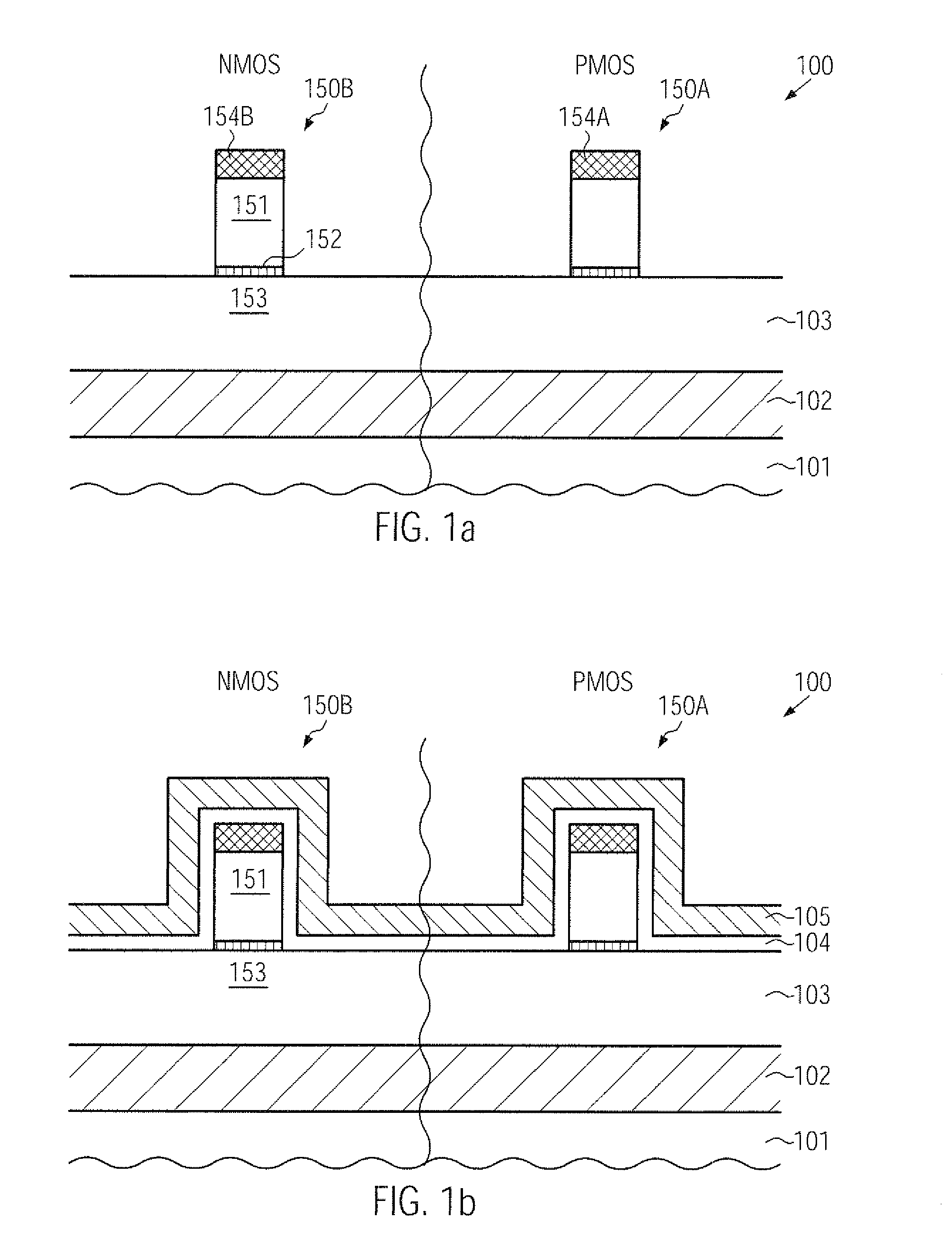
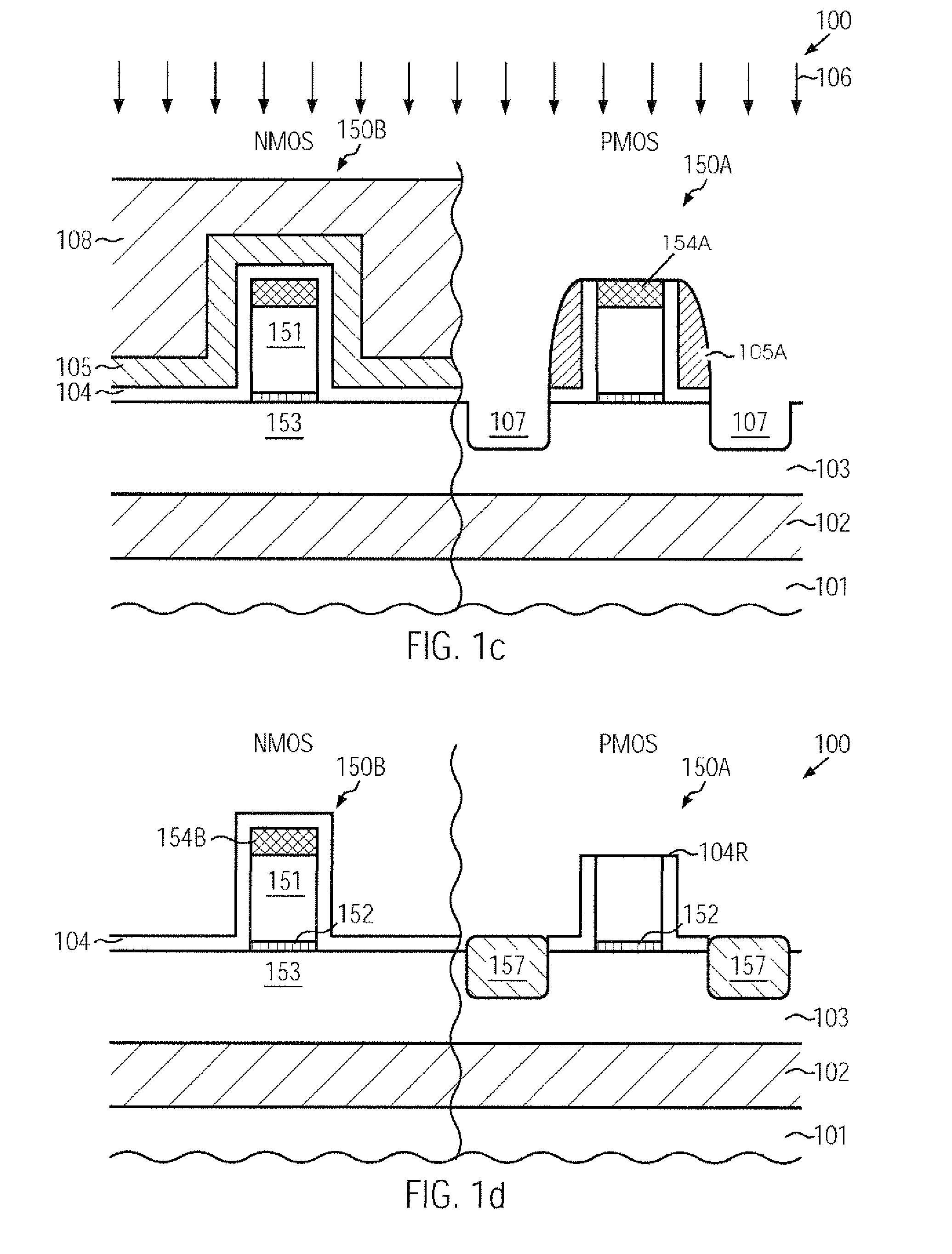
CMOS device comprising an nmos transistor with recessed drain and source areas and a pmos transistor having a silicon/germanium material in the drain and source areas
InactiveUS20090218633A1Enhanced transistor performanceImprove compatibilityTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSSemiconductor alloys
A recessed transistor configuration may be provided selectively for one type of transistor, such as N-channel transistors, thereby enhancing strain-inducing efficiency and series resistance, while a substantially planar configuration or raised drain and source configuration may be provided for other transistors, such as P-channel transistors, which may also include a strained semiconductor alloy, while nevertheless providing a high degree of compatibility with CMOS techniques. For this purpose, an appropriate masking regime may be provided to efficiently cover the gate electrode of one transistor type during the formation of the corresponding recesses, while completely covering the other type of transistor.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Pixel cell design with enhanced voltage control
InactiveUS7443374B2Improve pixel display configurationExpand the scope of operationCathode-ray tube indicatorsColor television detailsMultiplexingCMOS
The present invention discloses a pixel display configuration by providing a voltage controller in each pixel control circuit for controlling the voltage inputted to the pixel electrodes. The controller includes a function of multiplexing the voltage input to the pixel electrodes and also a bit buffering and decoupling function to decouple and flexible change the input voltage level to the pixel electrodes. The controller further includes a first switching stage and a second switching stage and each stage has a P-type transistor and a N-type transistor to expand the range of the switching voltages such that the improvement of the pixel control is further enhanced. The rate of DC balancing can be increased to one KHz and higher to mitigate the possibility of DC offset effects and the image sticking problems caused by slow DC balancing rates. This invention further discloses an enabling technology for switching from one DC balance state to another without rewriting the data onto the panels. Therefore, it is not required to implement a high voltage CMOS designs and standard CMOS technologies can be applied to manufacture the storage cells and control panel for the LCOS displays with lower production cost and higher yields.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com