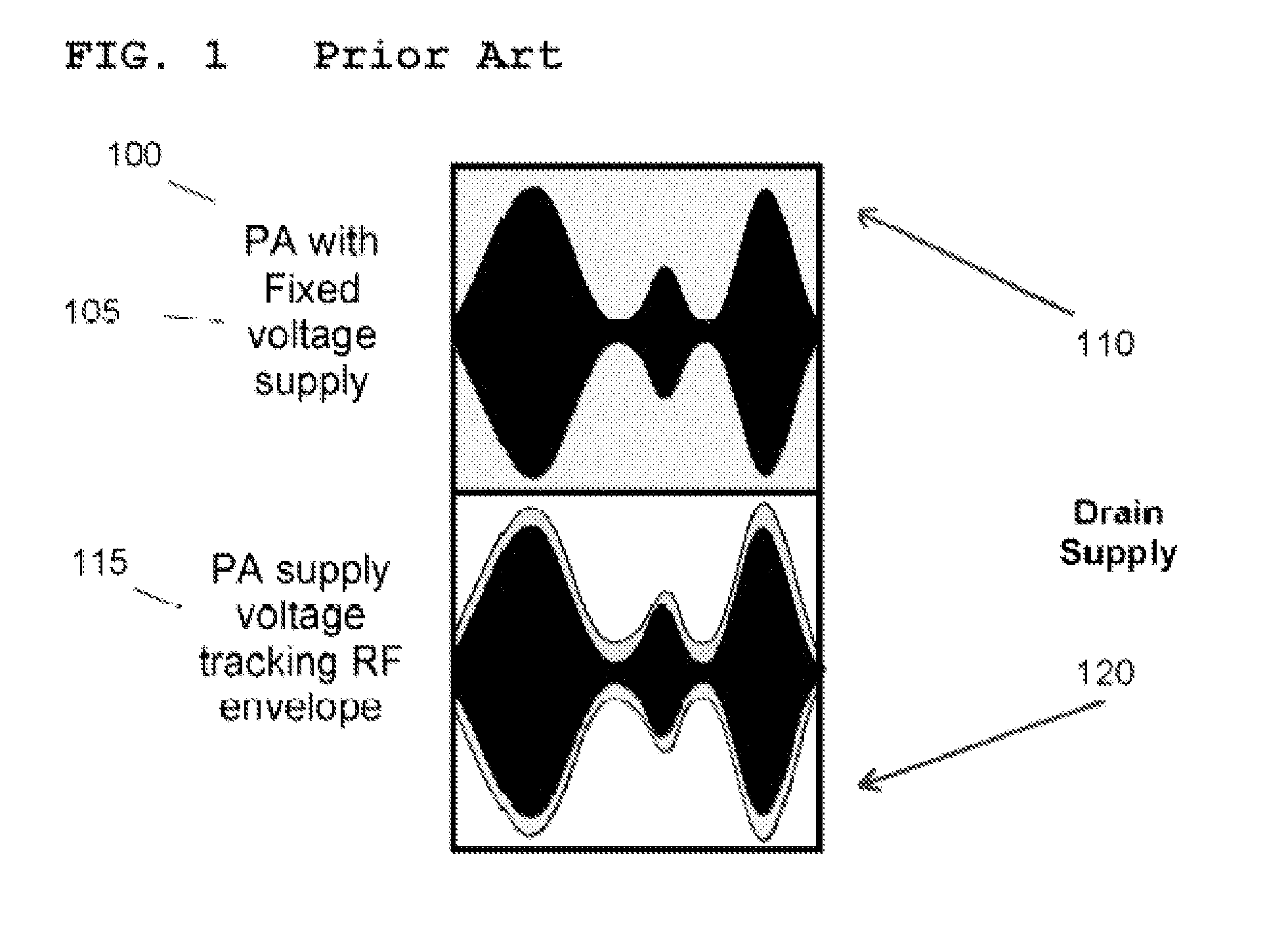
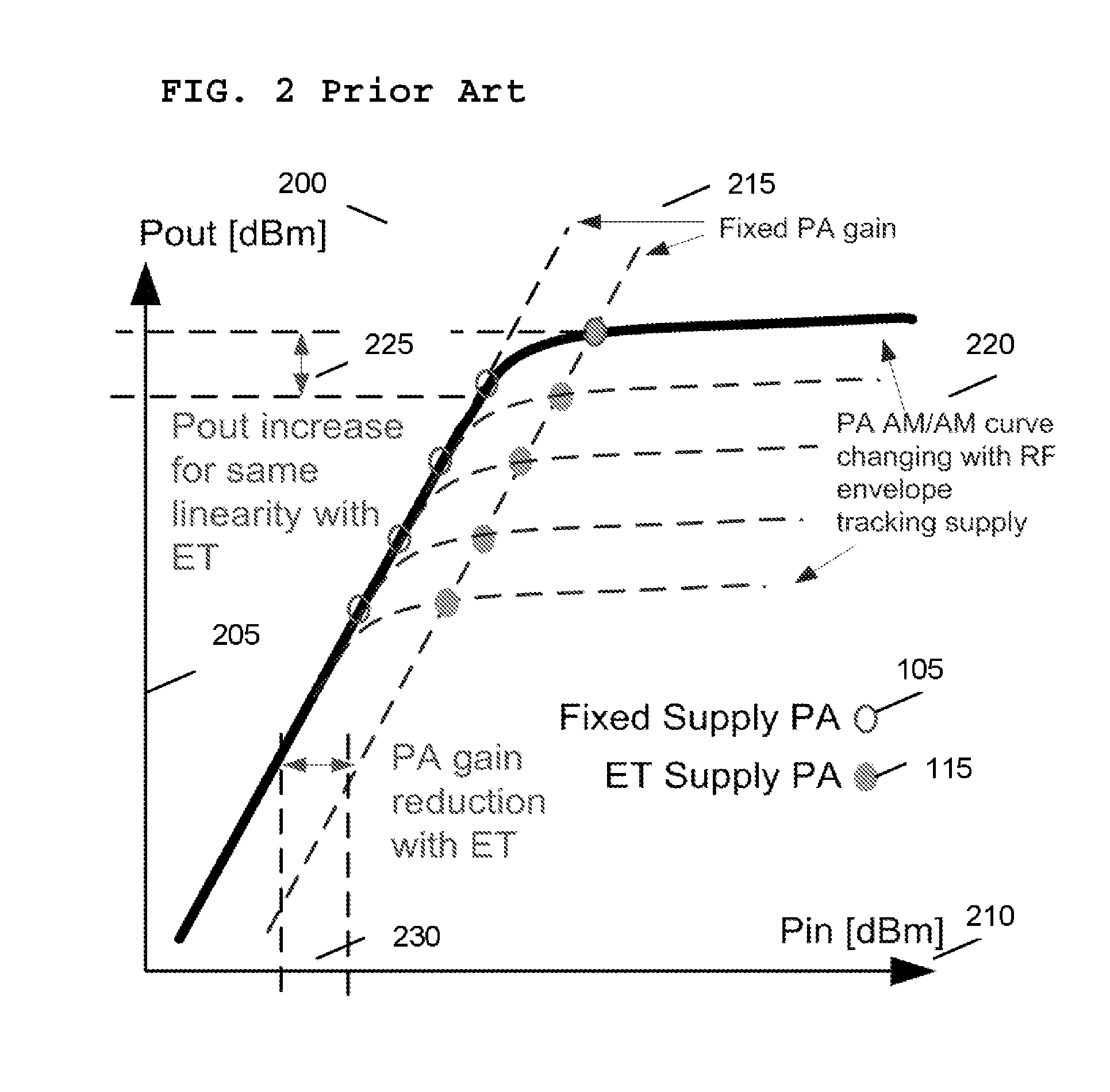
Patents
Literature
4813results about "RF amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
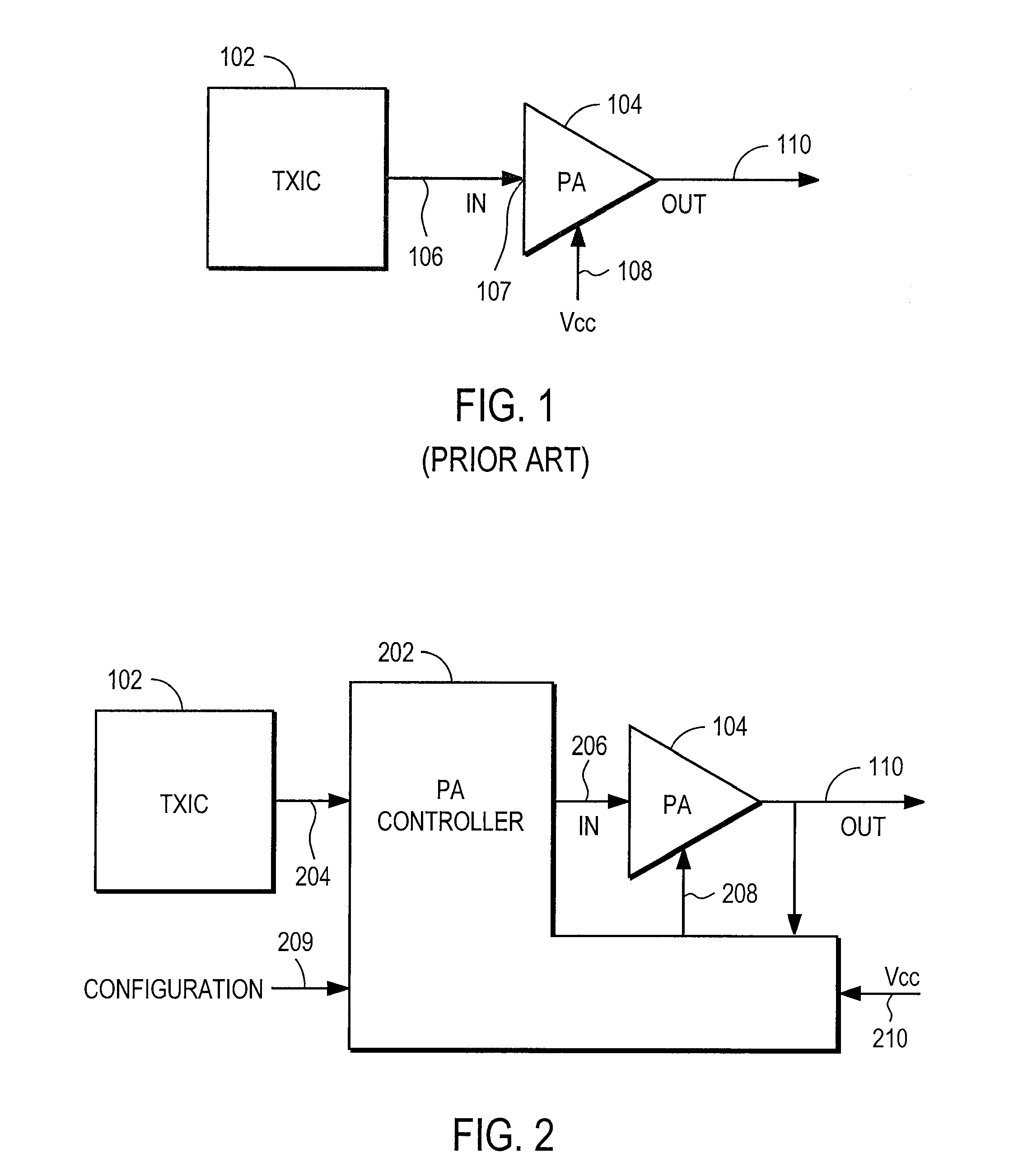
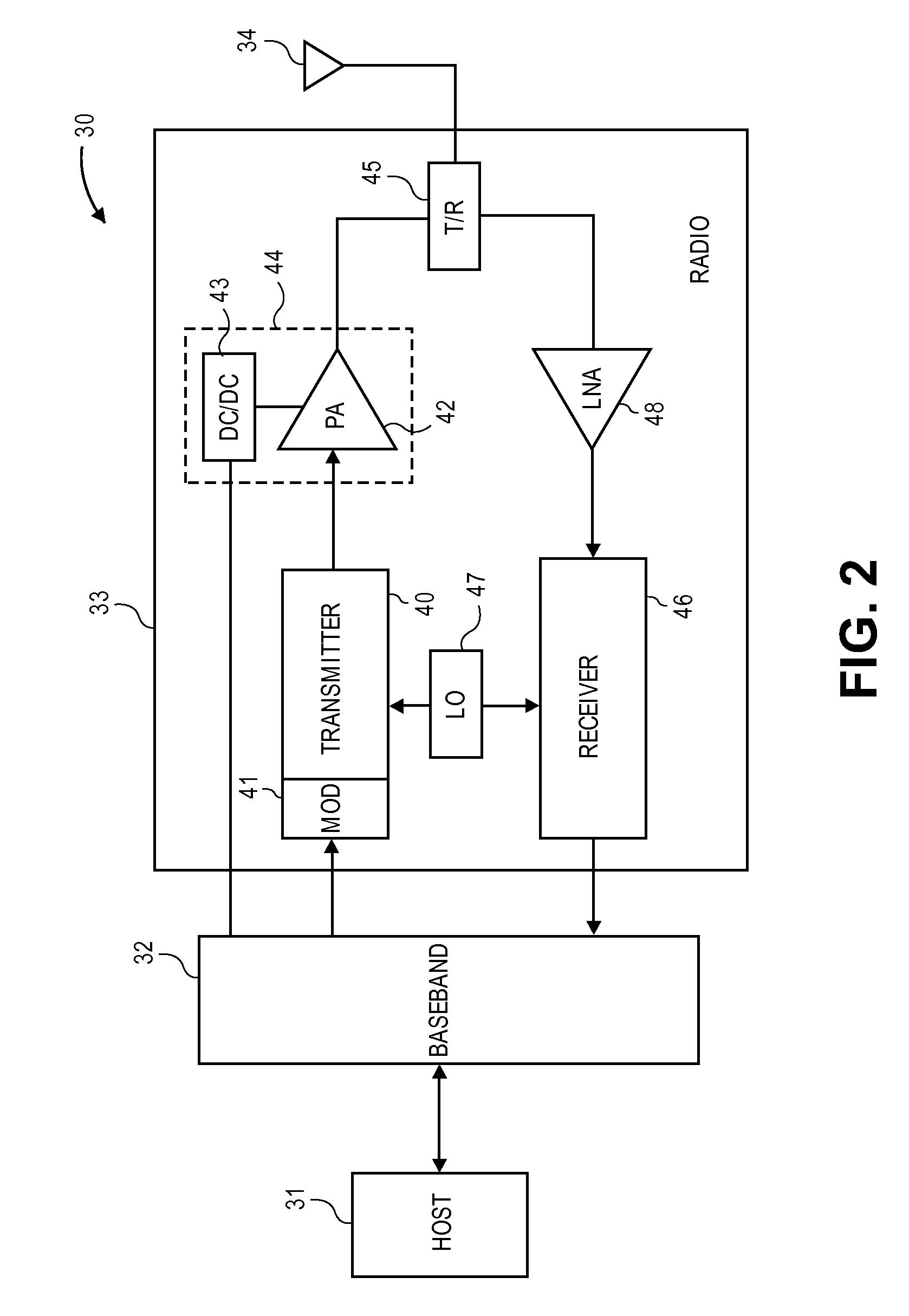
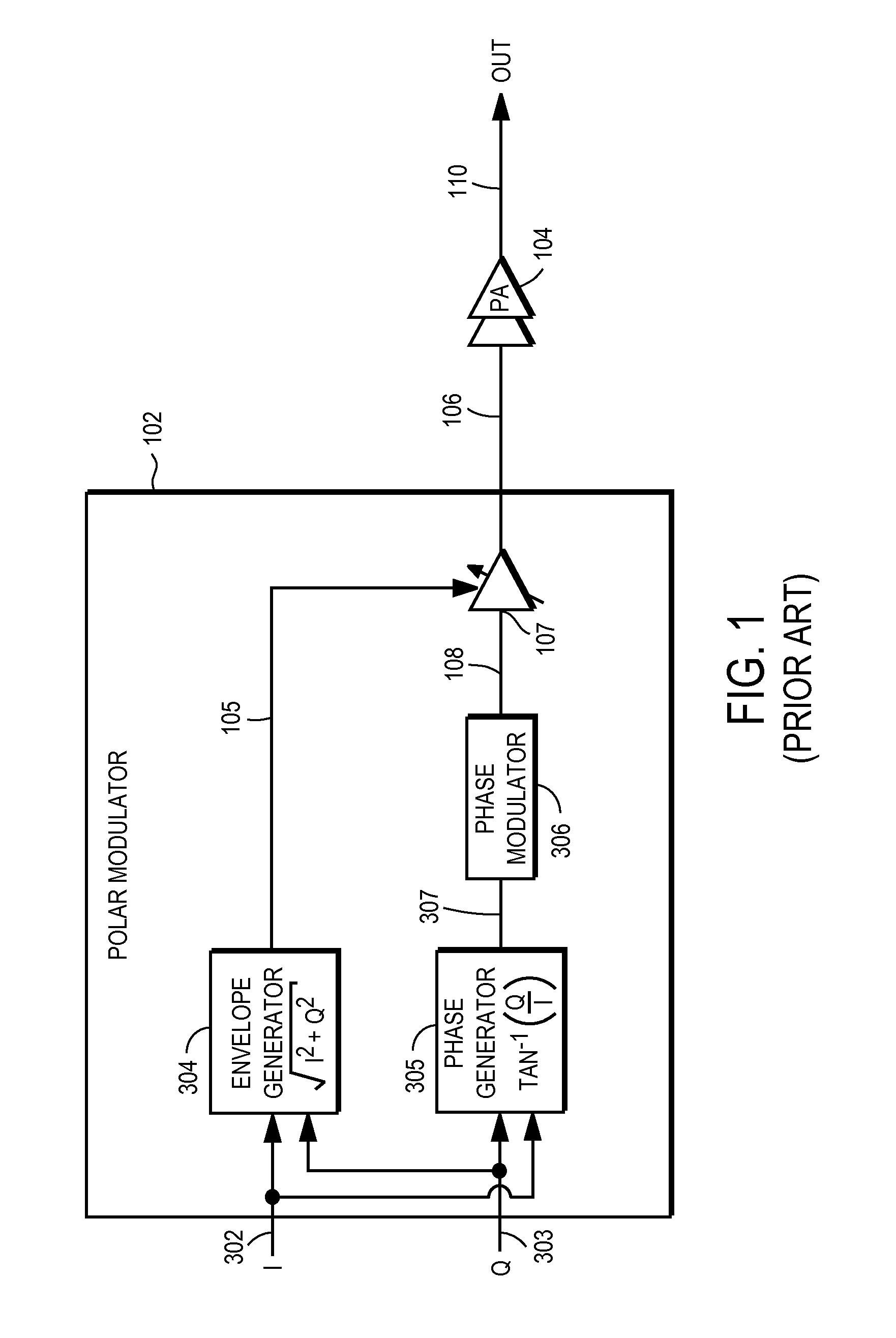
Radio frequency power amplifier and method using a controlled supply
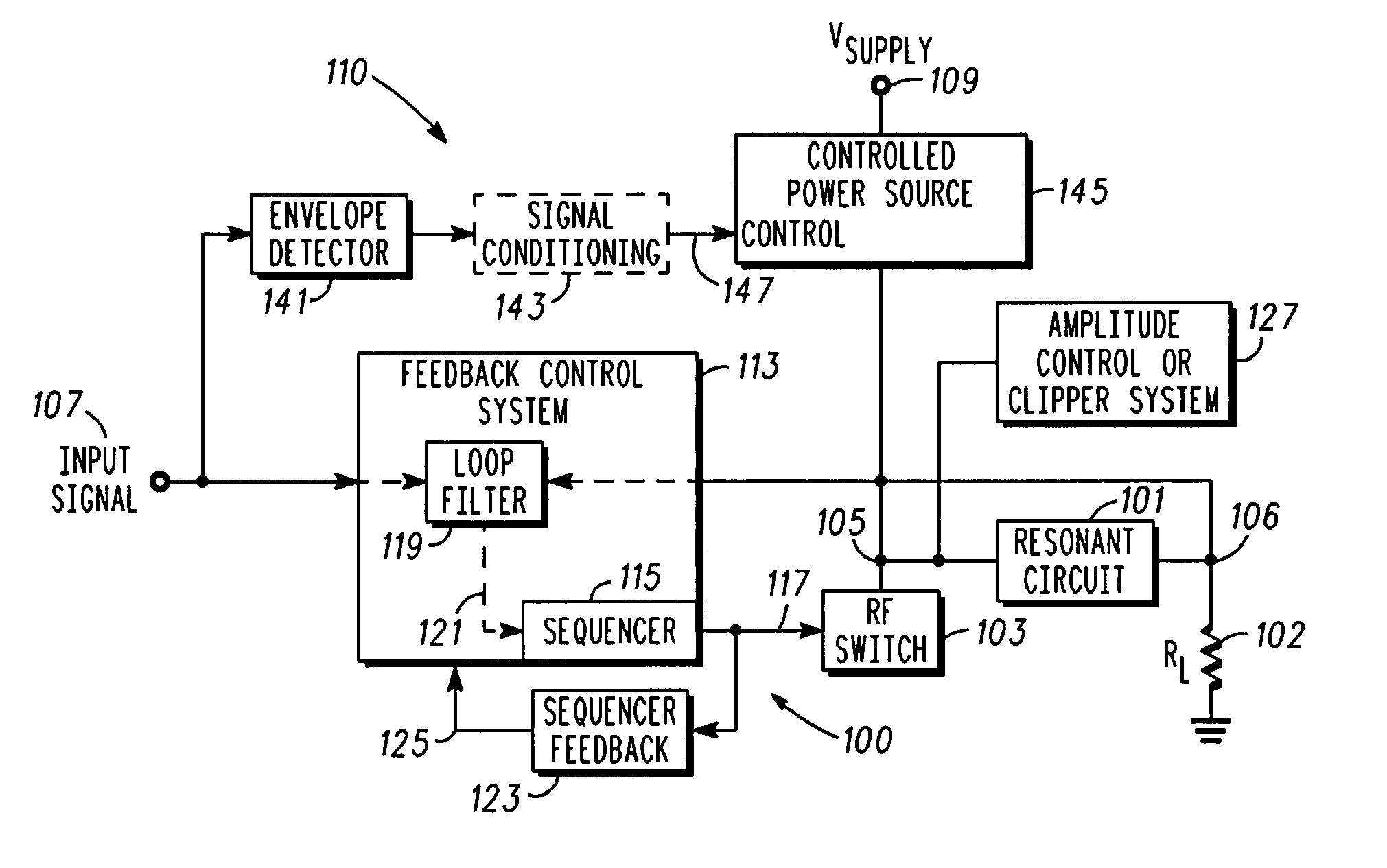
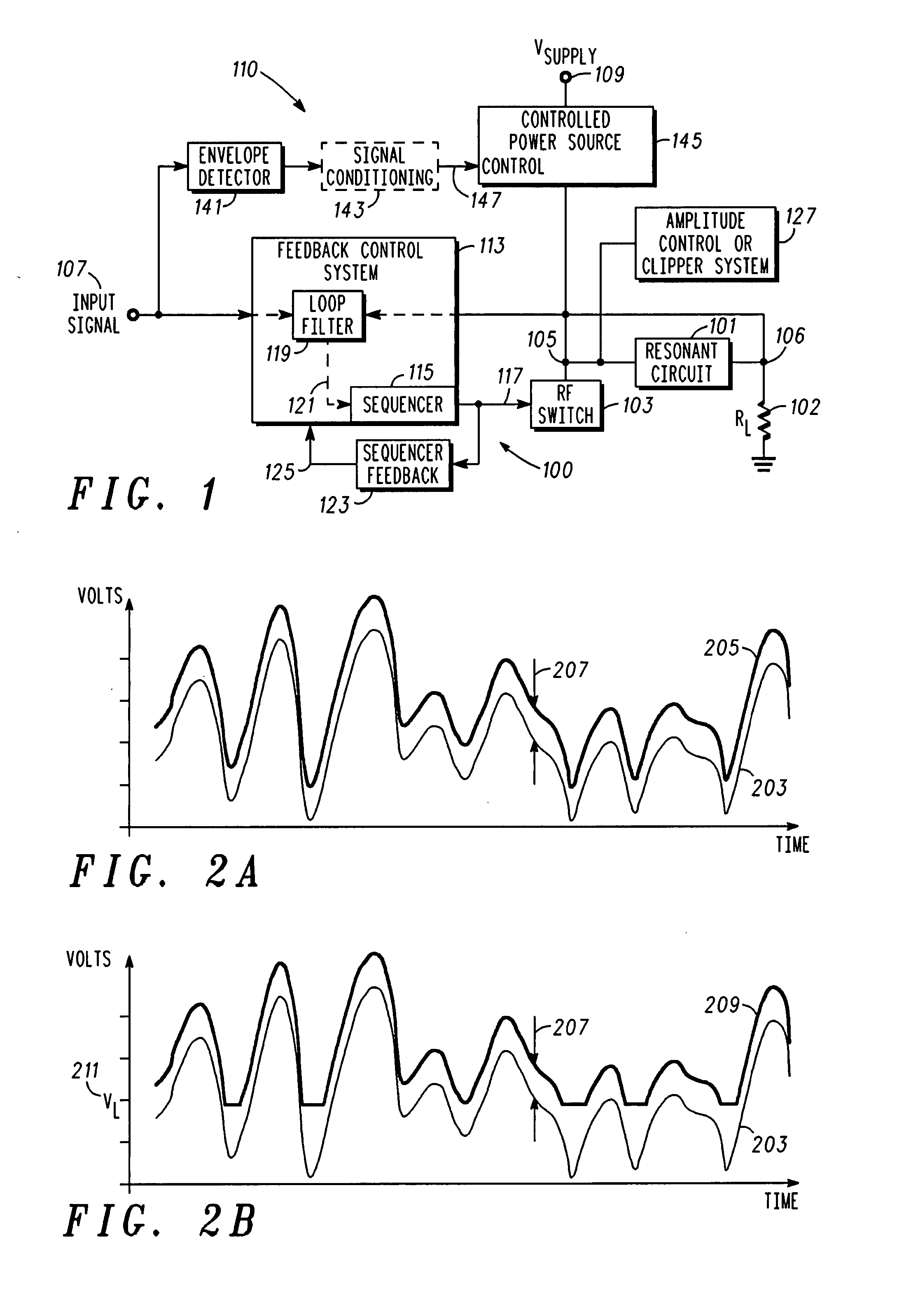
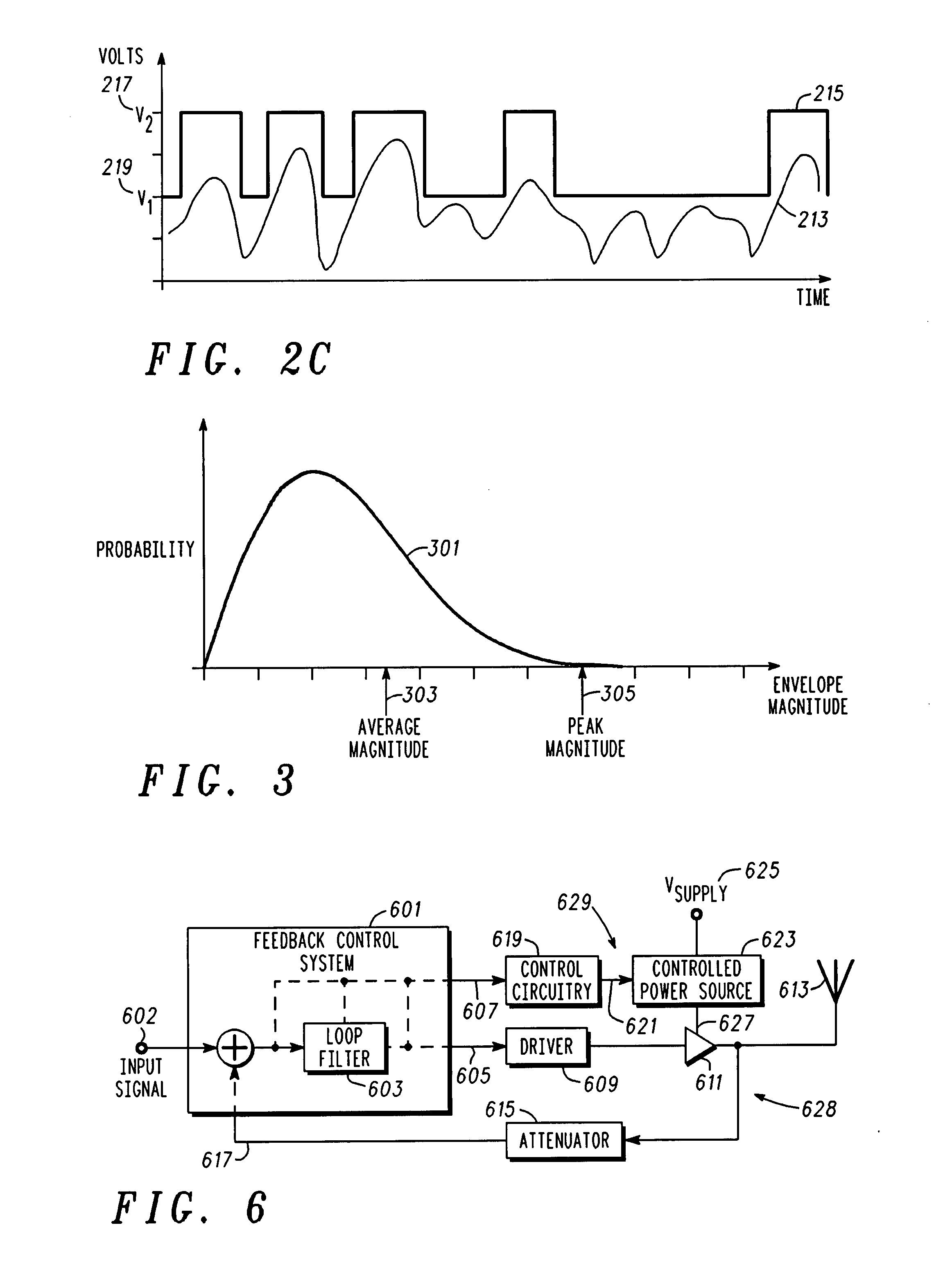
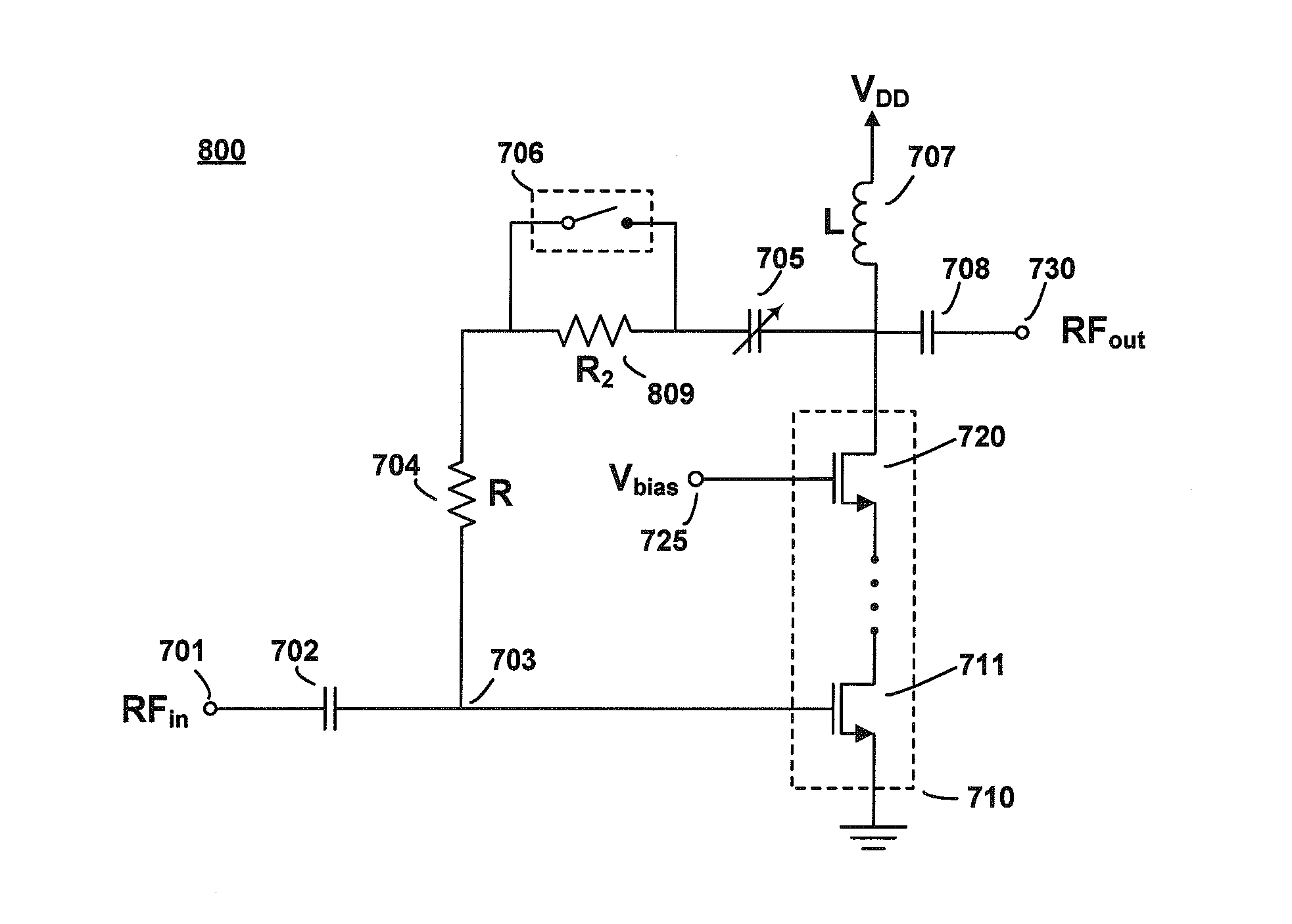
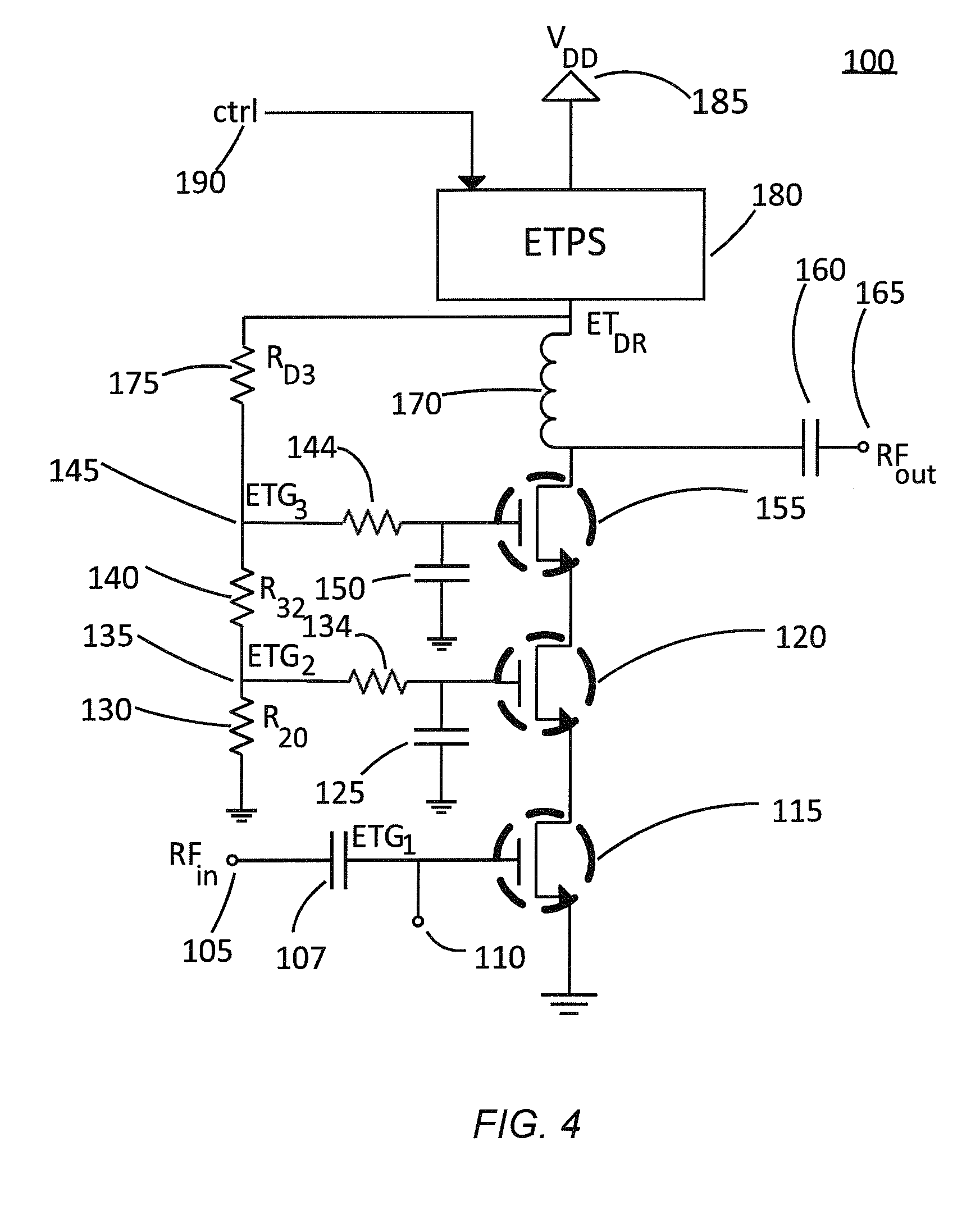
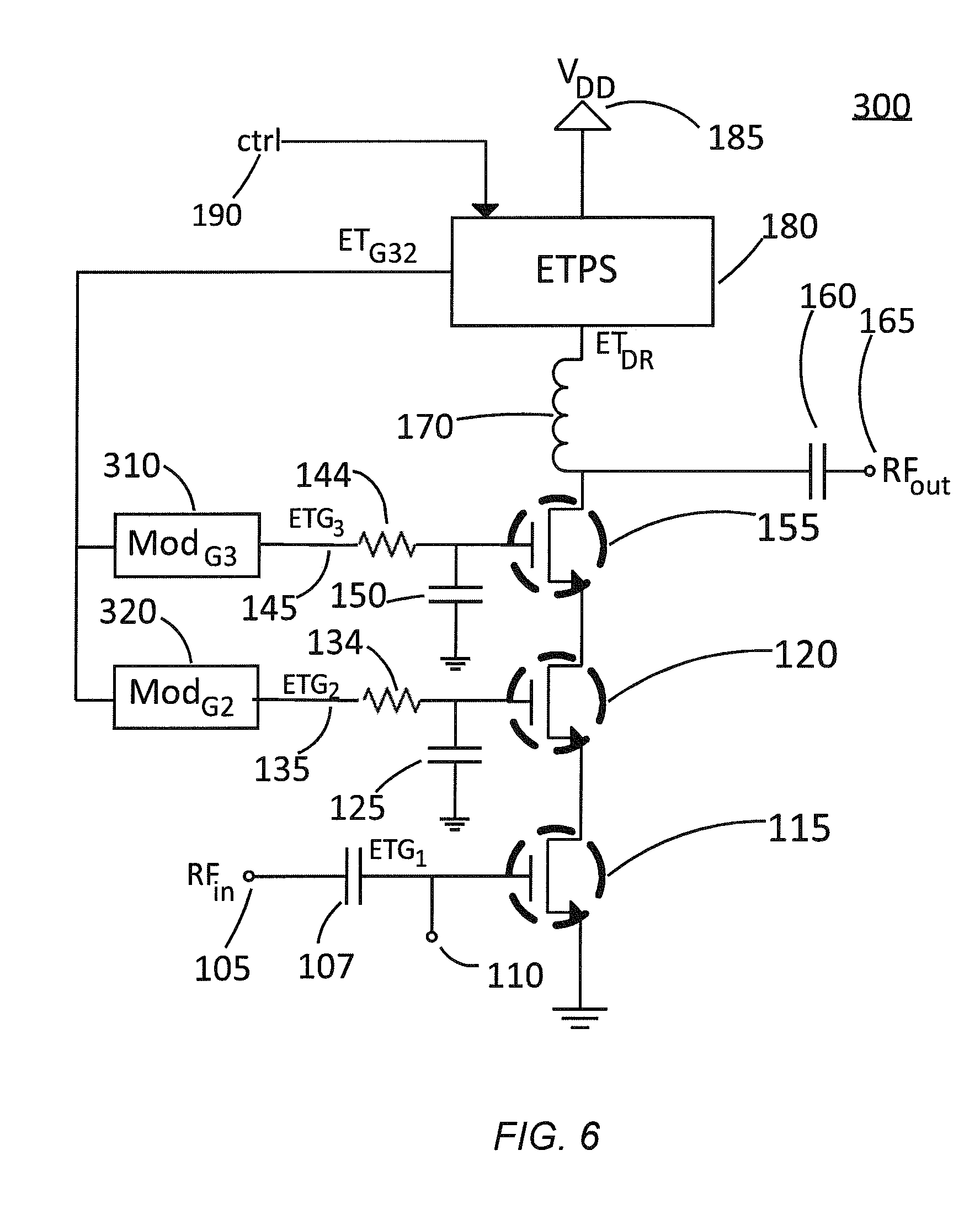
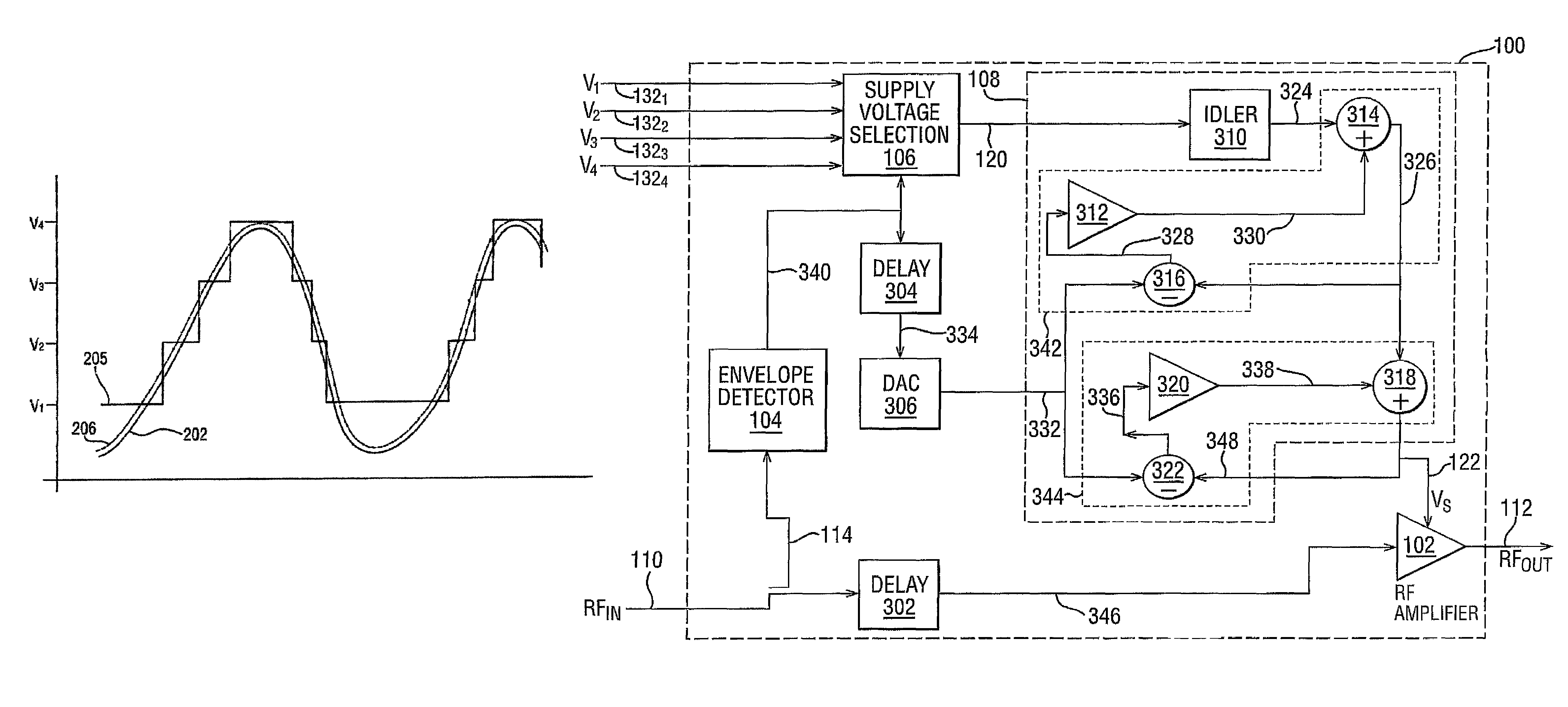
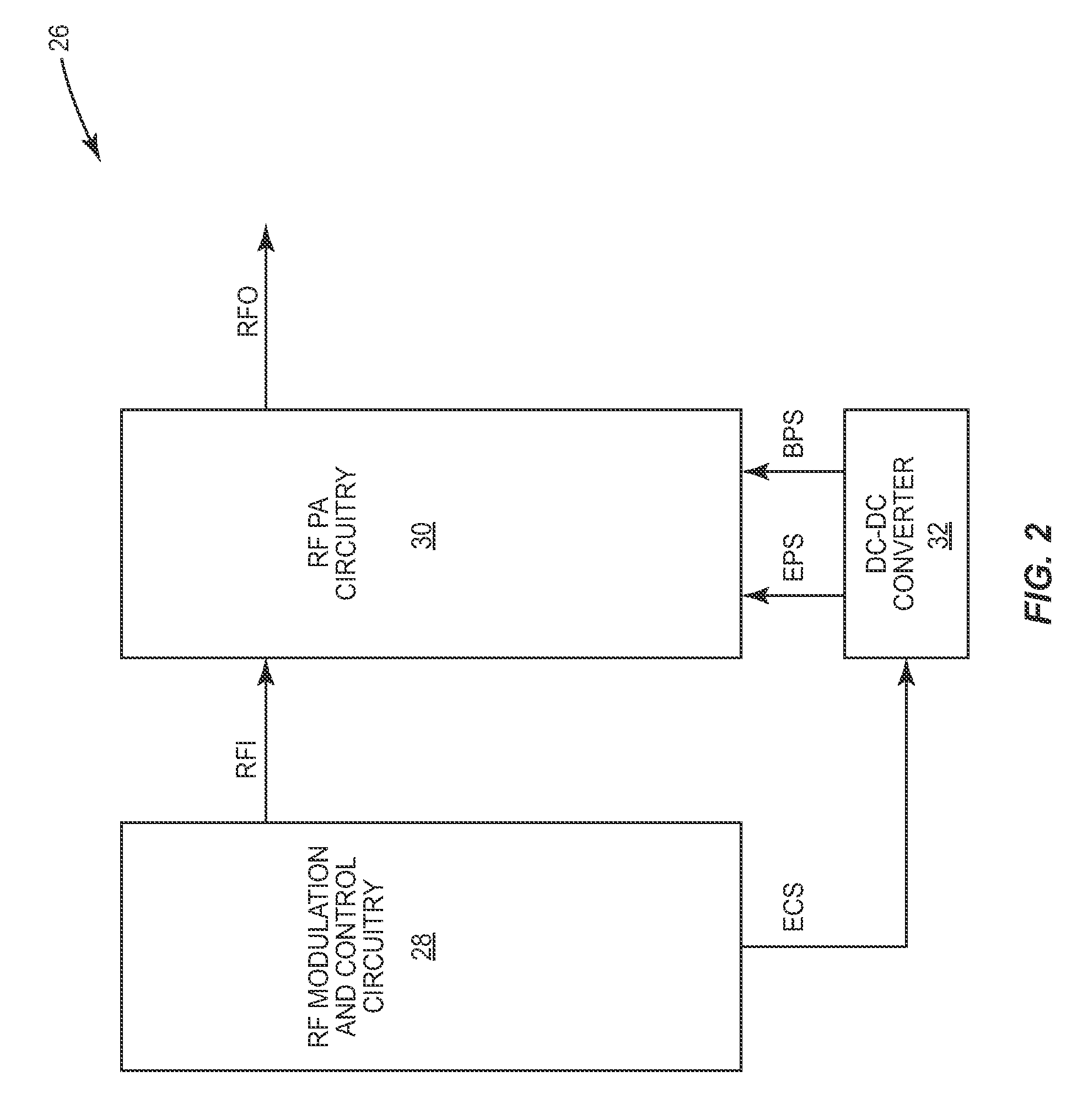
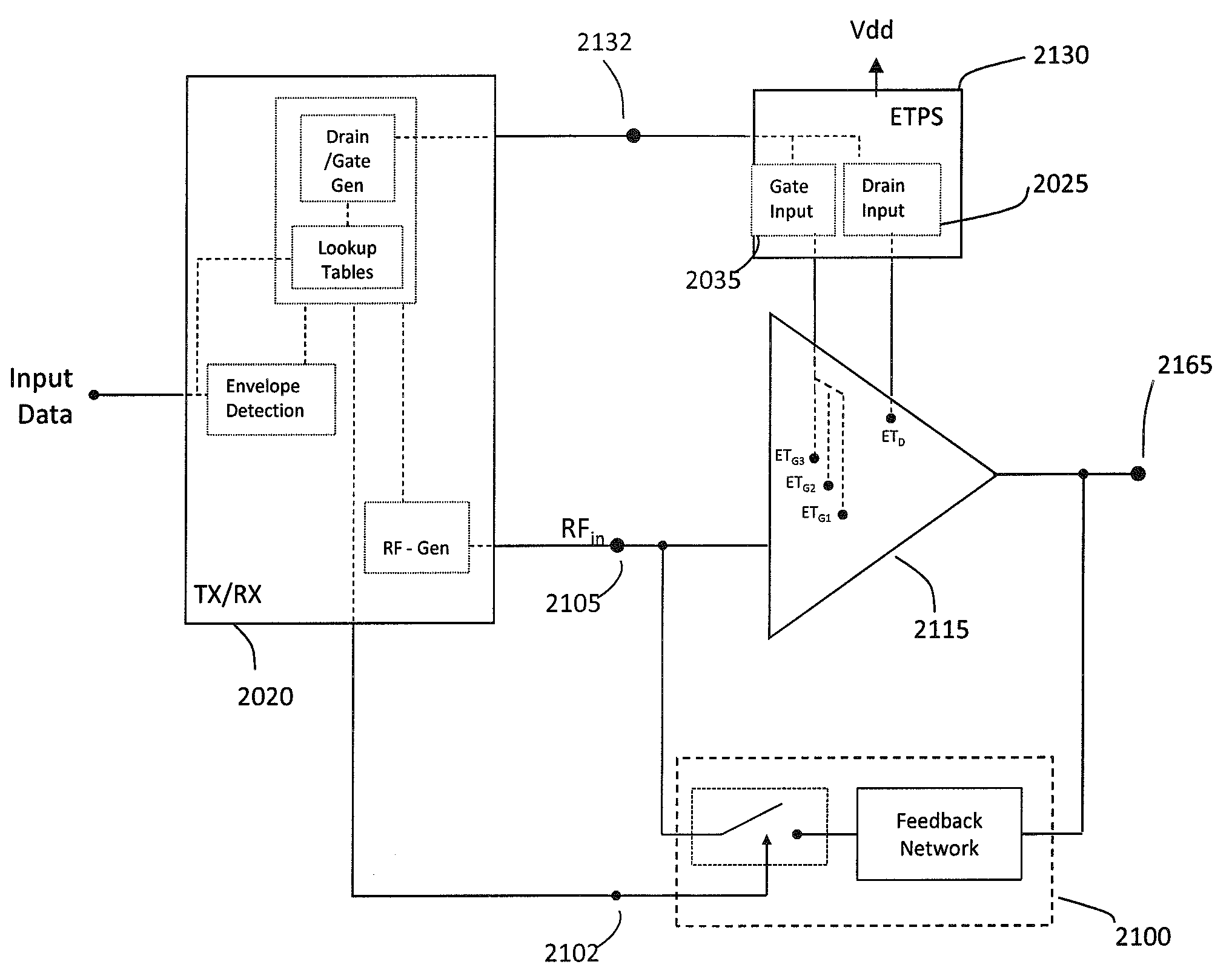
A radio frequency power amplifier includes a feedback control system coupled to an input signal and a first feedback signal and configured to provide an output; a controlled supply configured to provide power that is controlled in accordance with a signal; and a radio frequency gain stage powered from the controlled supply, driven by the output from the feedback control system, and configured to provide an output signal at the radio frequency to a resonant load, where the first feedback signal corresponds to the output signal. Some embodiments include a sequencer in the feedback control system and others utilize an additional feedback loop to control the power provided by the controlled supply.
Owner:PWRF
Amplifier with Variable Feedback Impedance
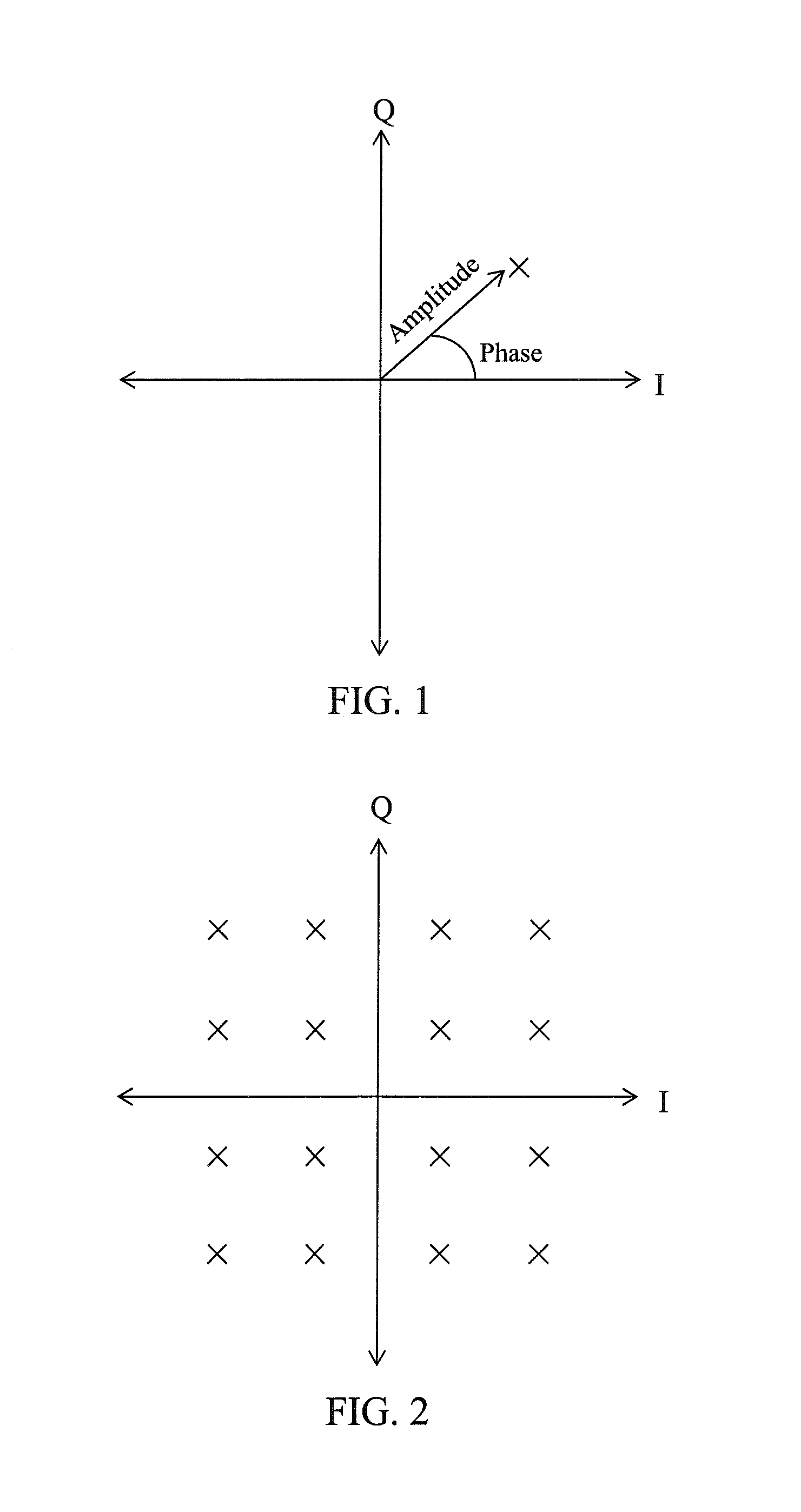
ActiveUS20150091650A1Reducing effect of variableMaintaining the characteristic output voltage range of the RF amplifierAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesRF amplifierVoltage amplitudeAudio power amplifier
A variable feedback impedance is presented capable of providing high linearity (e.g. as represented by 1P2 and 1P3) and high linear range (e.g. as represented by P1dB) when used in a feedback path of an RF amplifier in the presence of high voltage amplitudes.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
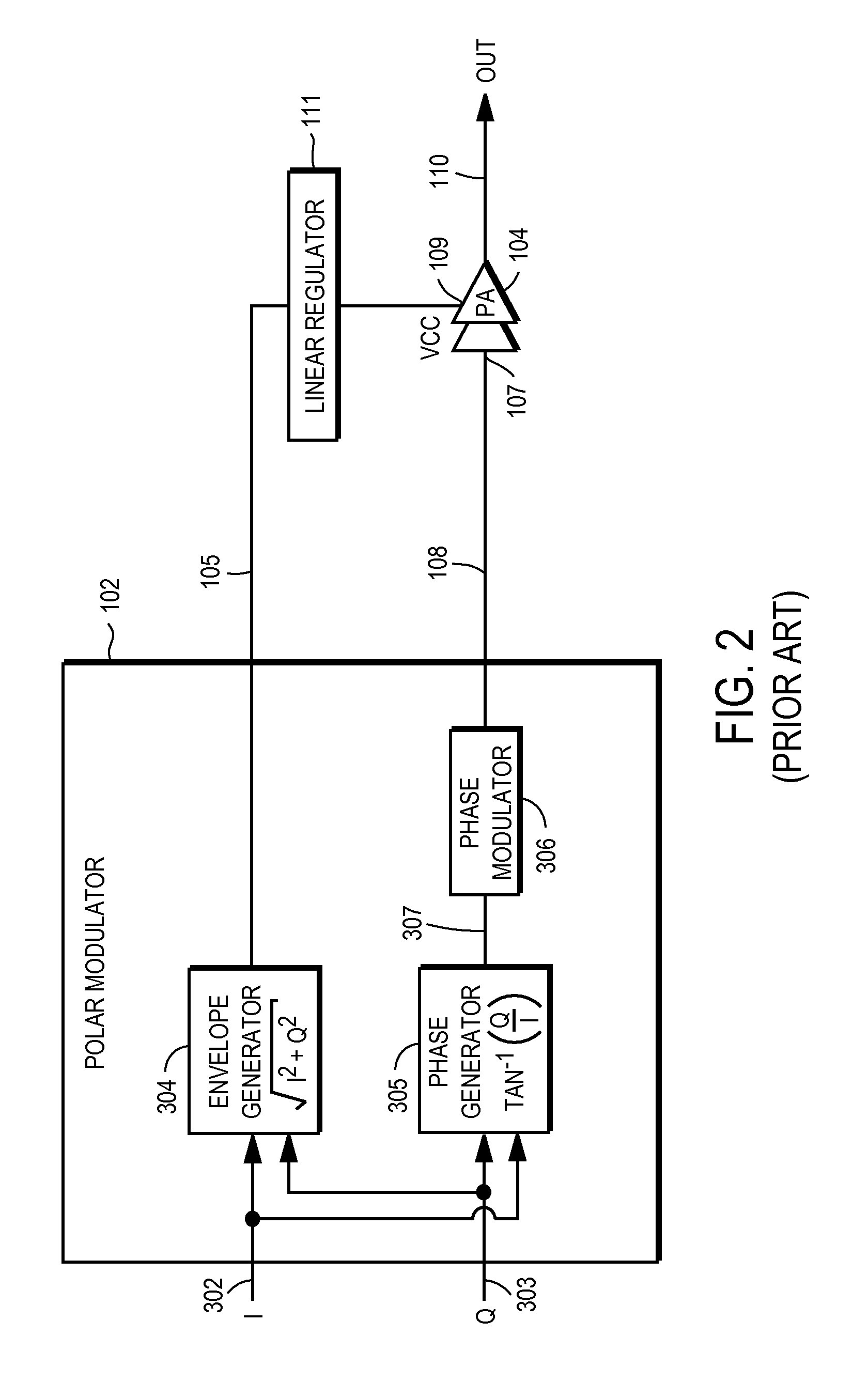
High-Efficiency Envelope Tracking Systems and Methods for Radio Frequency Power Amplifiers
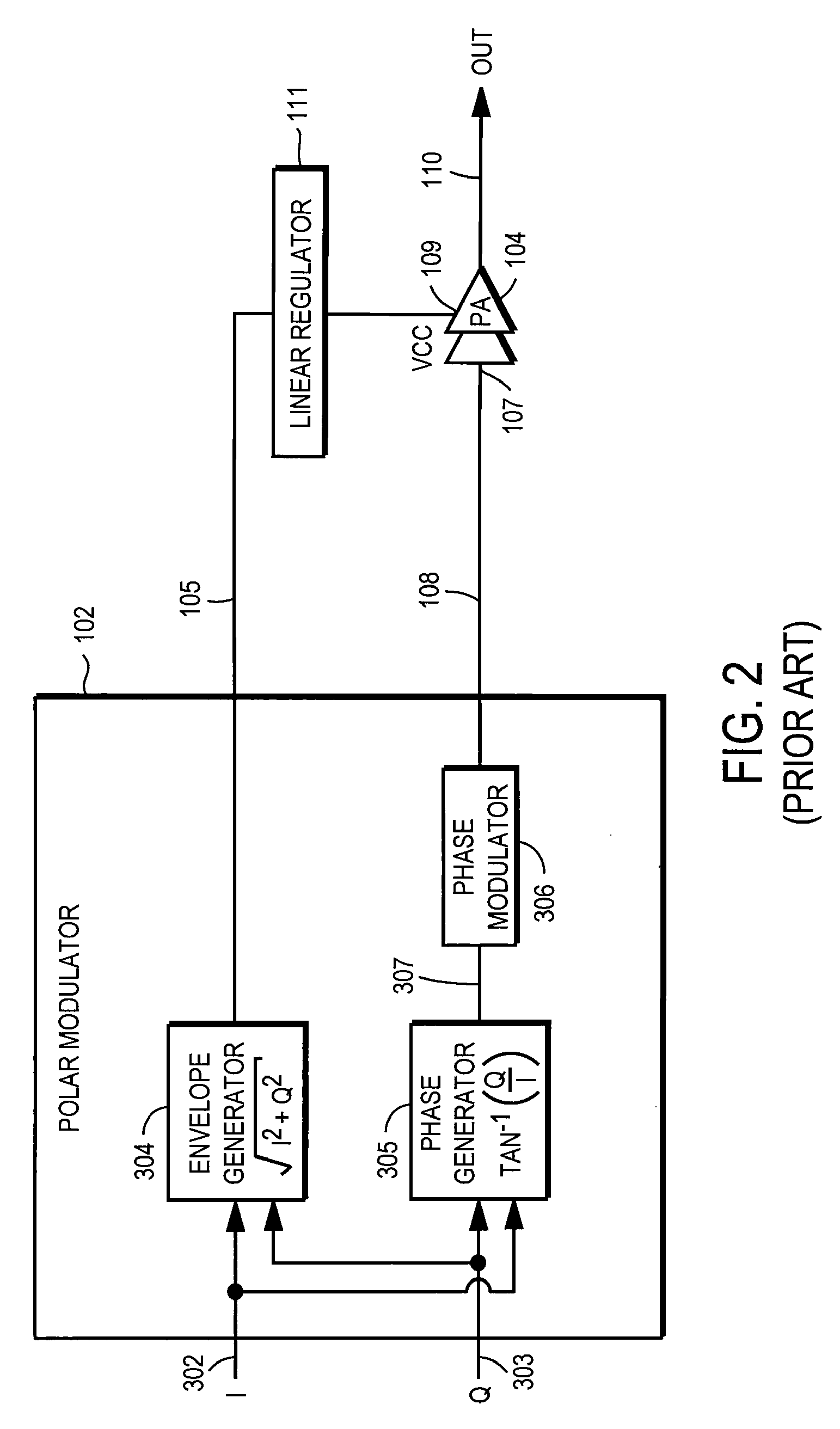
ActiveUS20090289720A1Efficiency penaltyDc network circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersLinear regulatorControl power
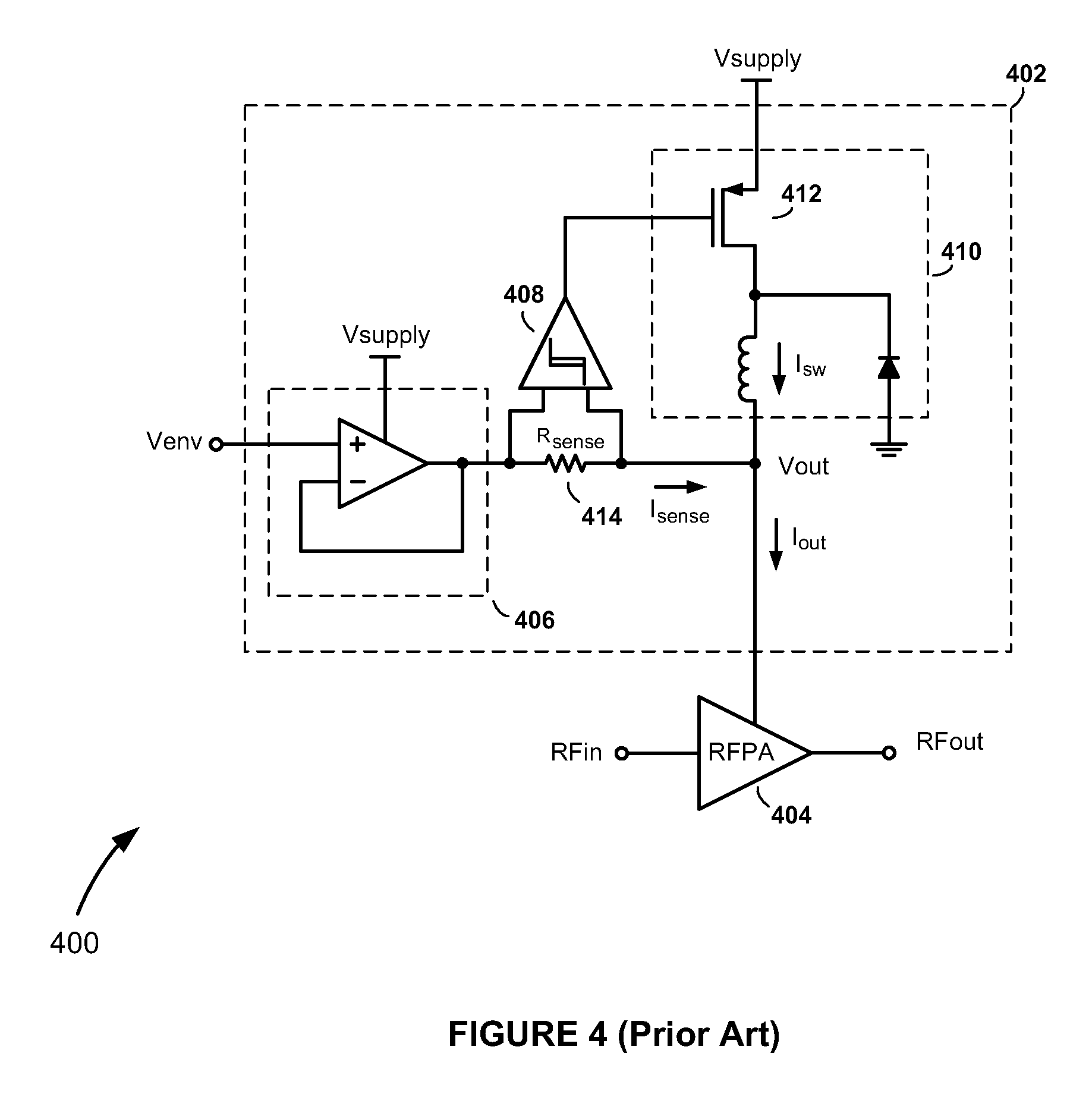
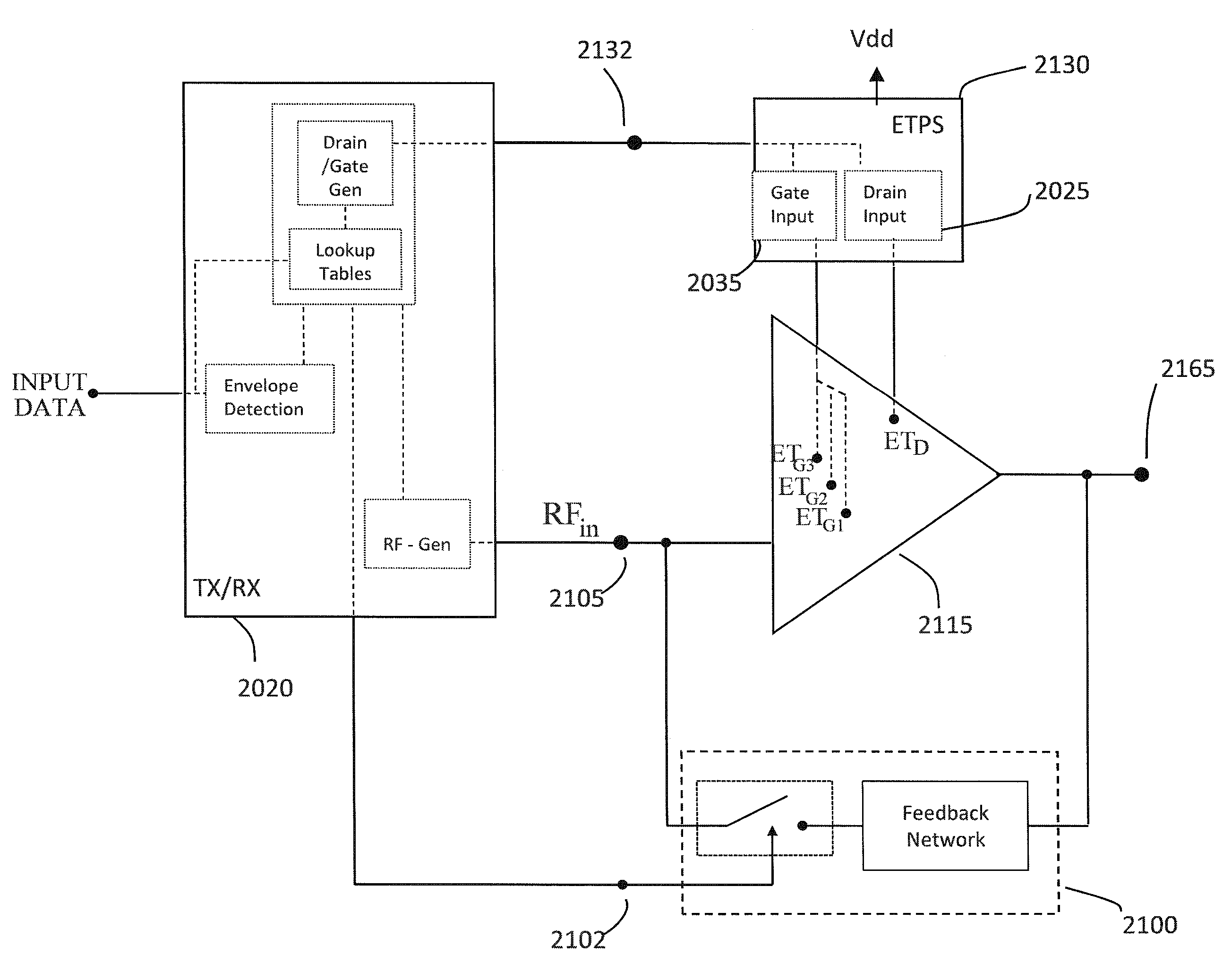
High-efficiency envelope tracking (ET) methods and apparatus for dynamically controlling power supplied to radio frequency power amplifiers (RFPAs). An exemplary ET circuit includes a switch-mode converter coupled in parallel with a split-path linear regulator. The switch-mode converter is configured to generally track an input envelope signal Venv and supply the current needs of a load (e.g., an RFPA). The split-path linear regulator compensates for inaccurate envelope tracking by sourcing or sinking current to the load via a main current path. A current sense path connected in parallel with the main current path includes a current sense resistor used by a hysteresis comparator to control the switching of the switch-mode converter. The split-path linear regulator is configured so that current flowing in the current sense path is a lower, scaled version of the current flowing in the main current path.
Owner:INTEL CORP
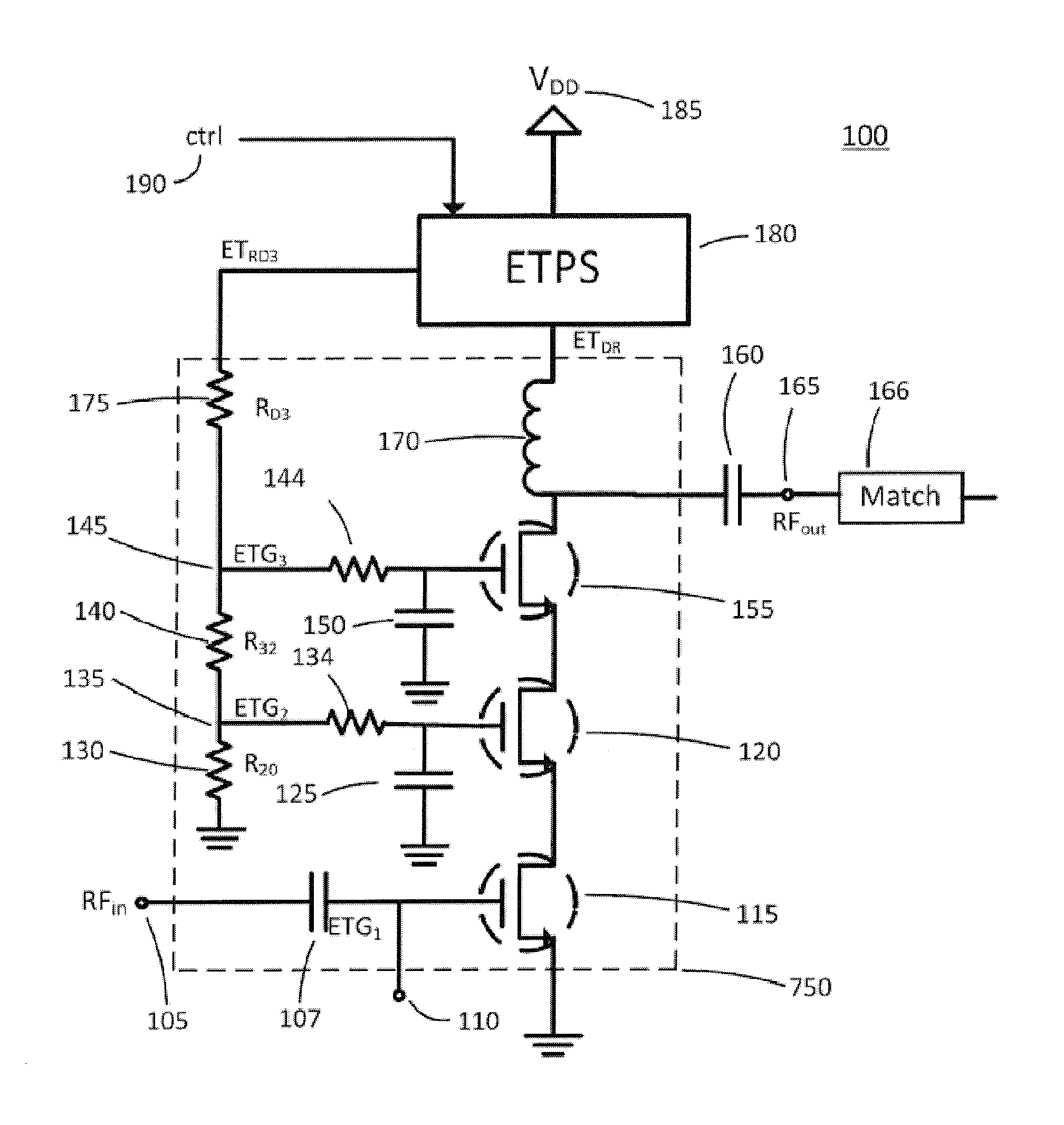
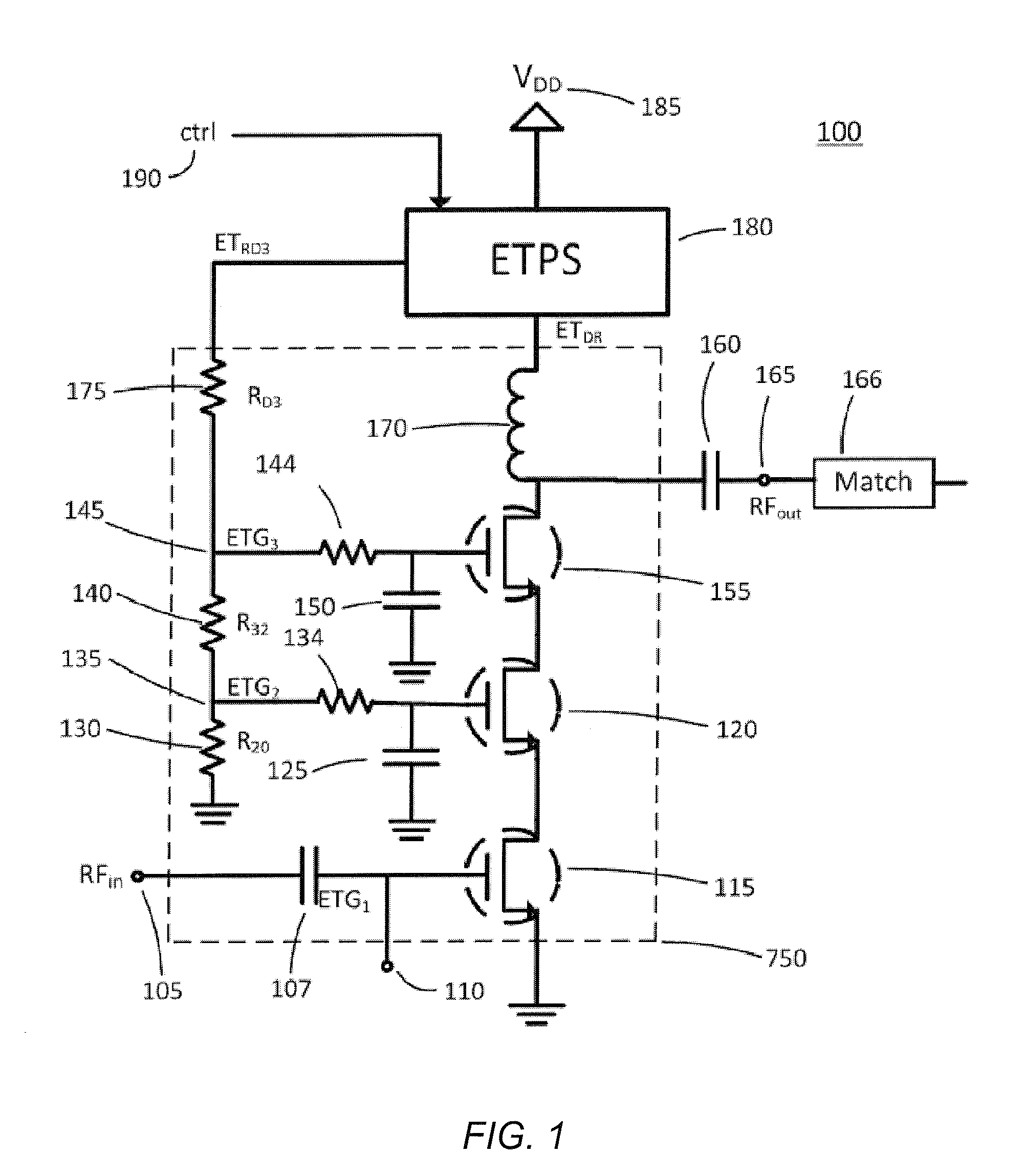
Bias Control for Stacked Transistor Configuration
Various methods and circuital arrangements for biasing one or more gates of stacked transistors of an amplifier are presented, where the amplifier can be an envelope tracking amplifier. Circuital arrangements to generate reference gate-to-source voltages for biasing of the gates of the transistors of the stack are also presented. Particular biasing for a case of an input transistor of the stack is also presented.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
High efficiency linearization power amplifier for wireless communication
ActiveUS20070241812A1Improve efficiencyImprove linearityEnergy efficient ICTAmplifier details to increase power/efficiencyFrequency changerControl signal
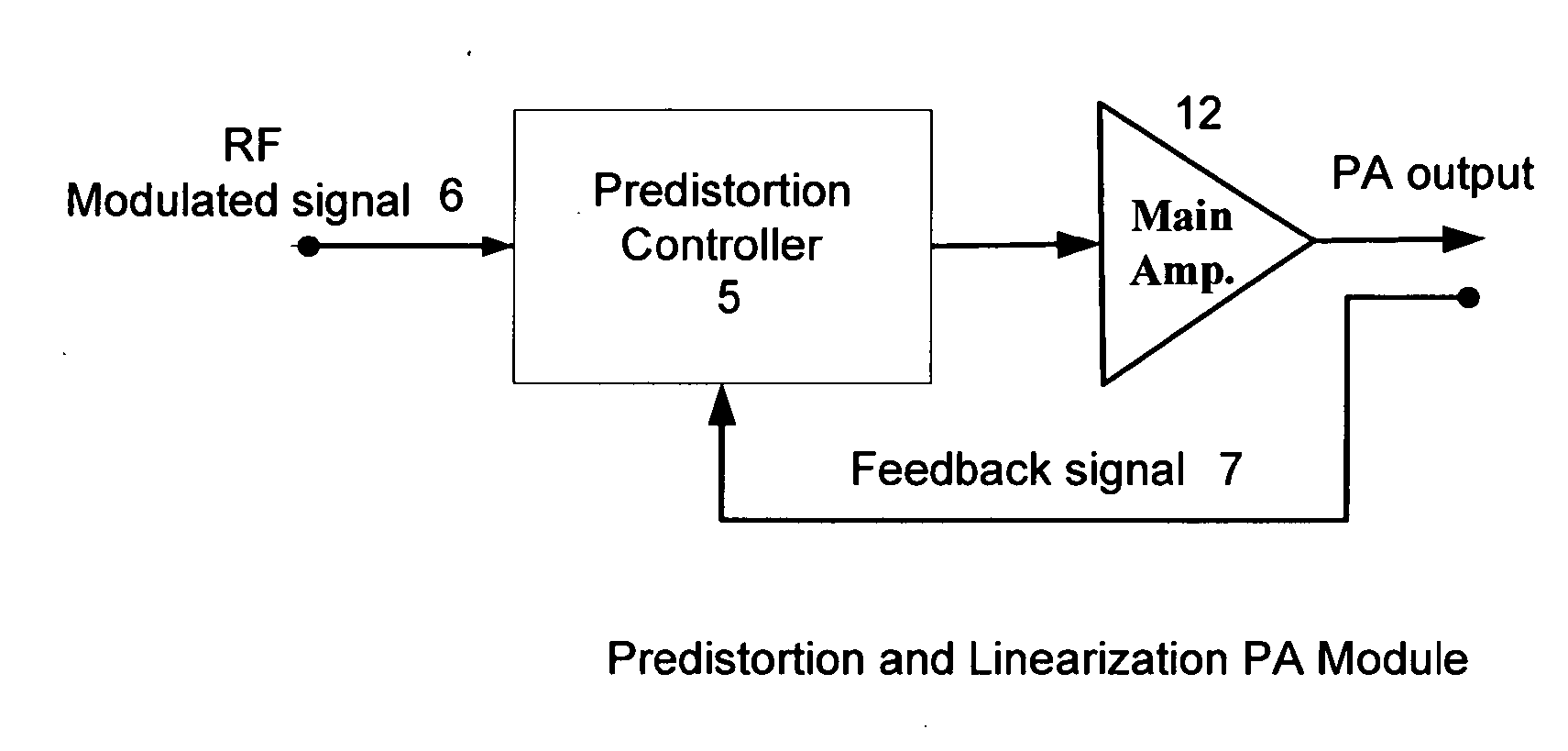
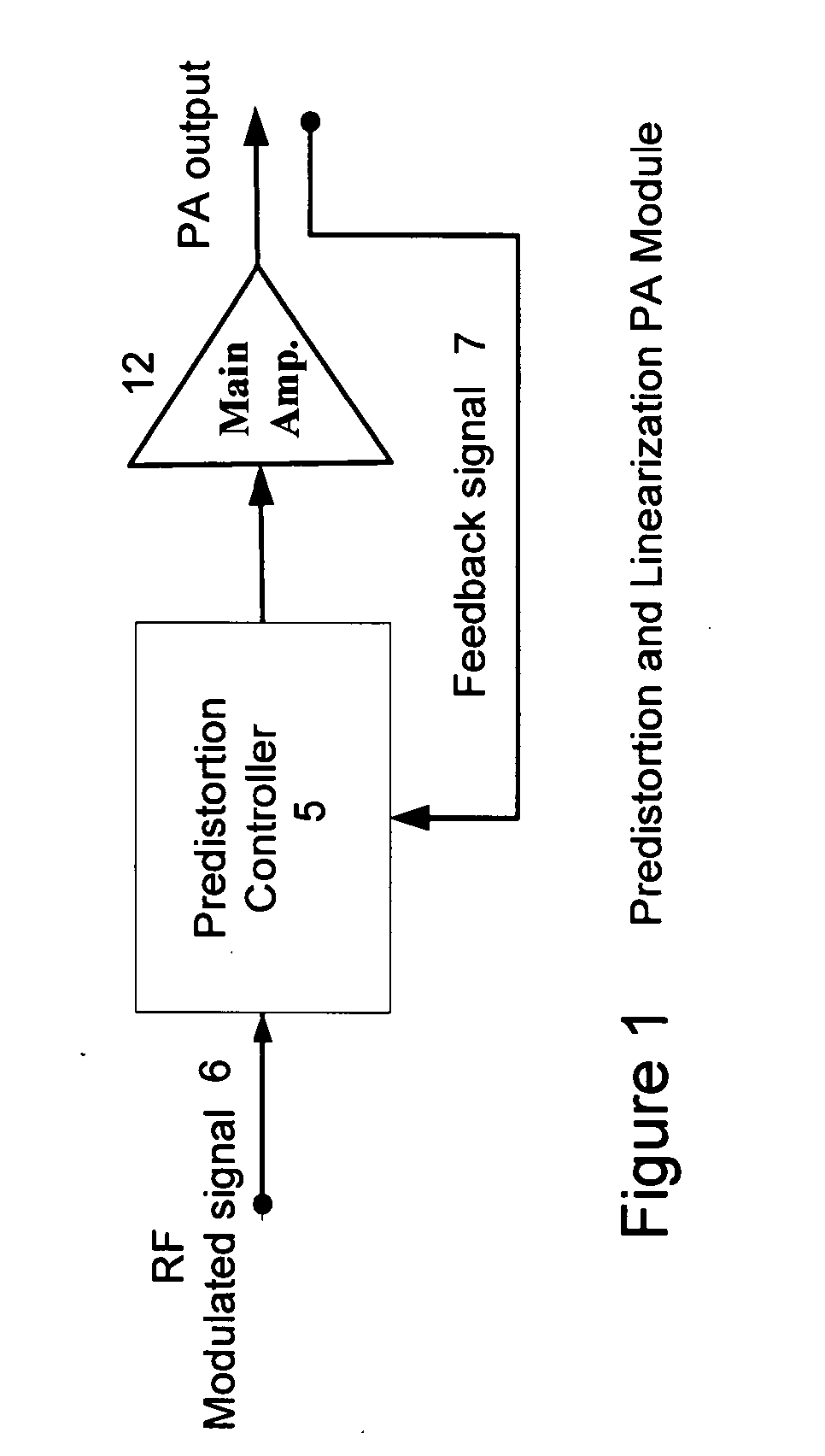
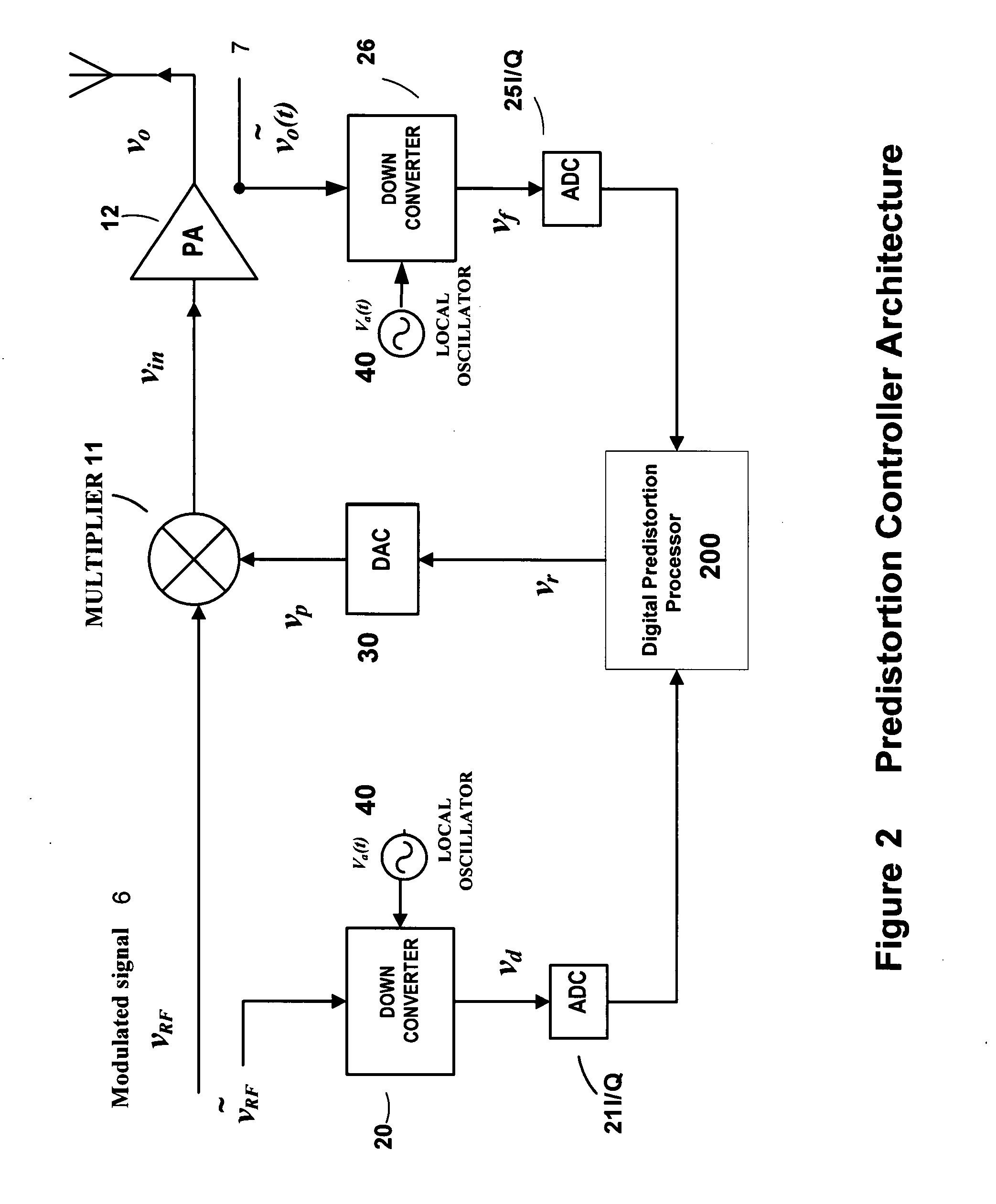
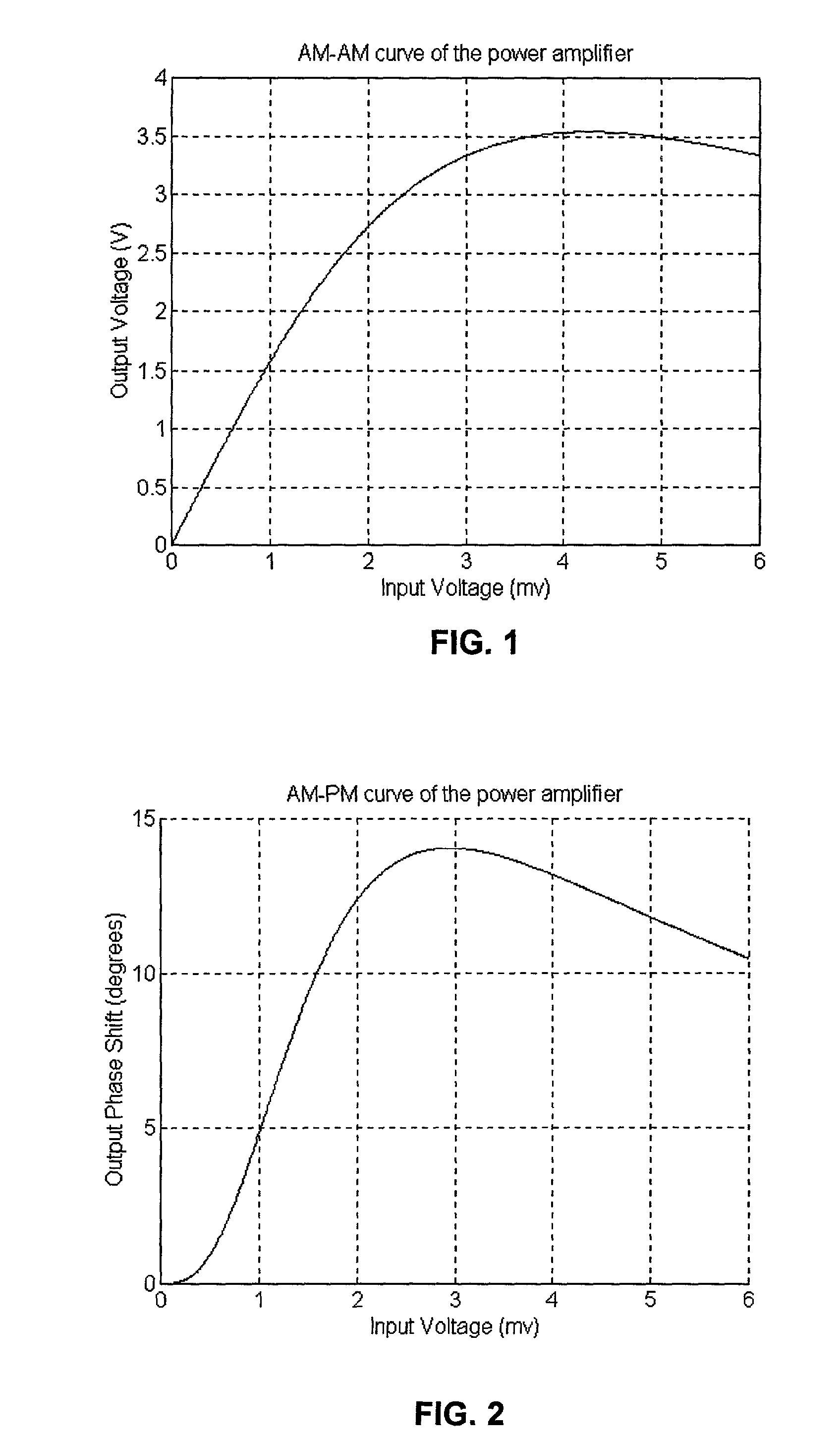
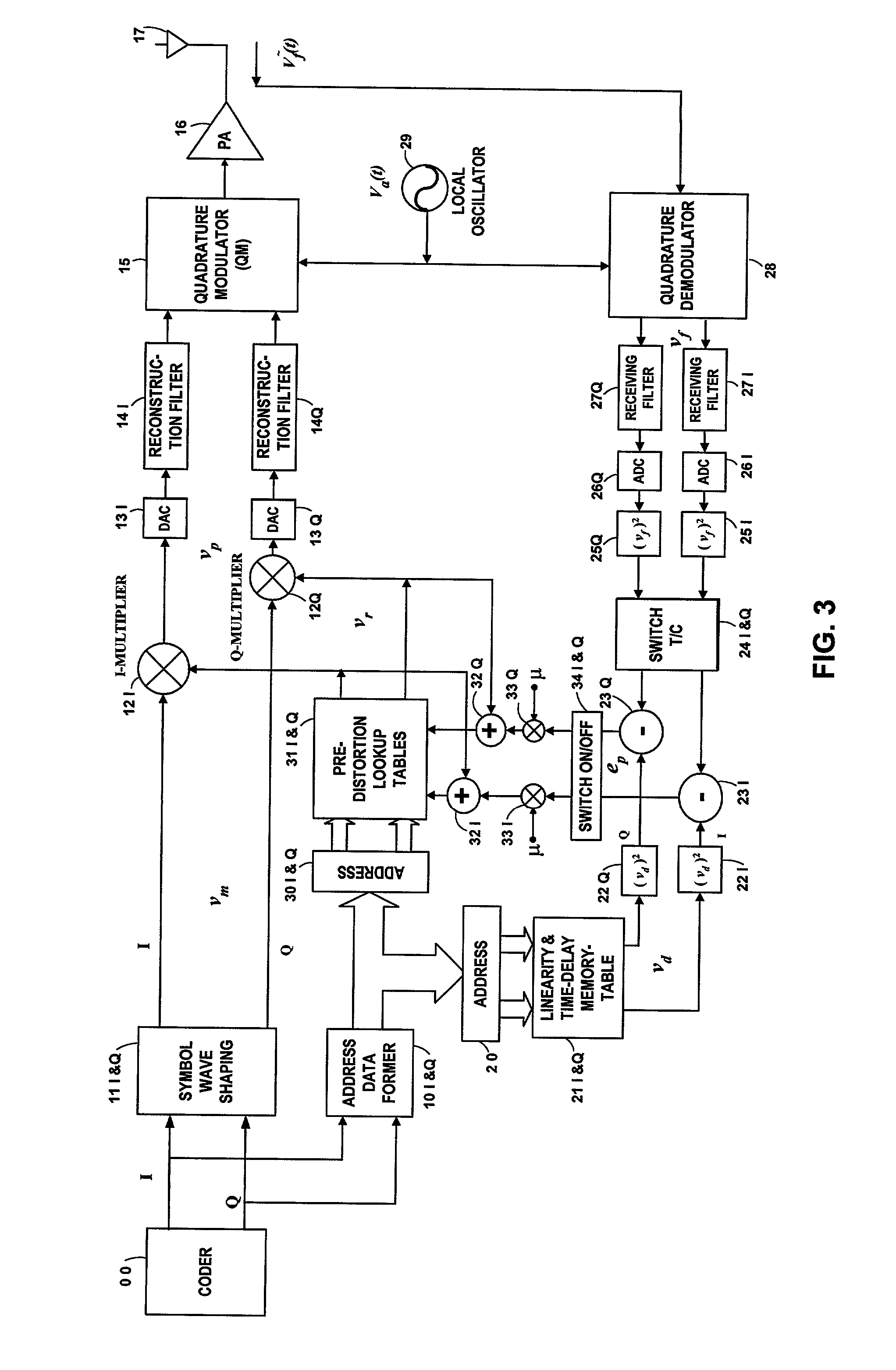
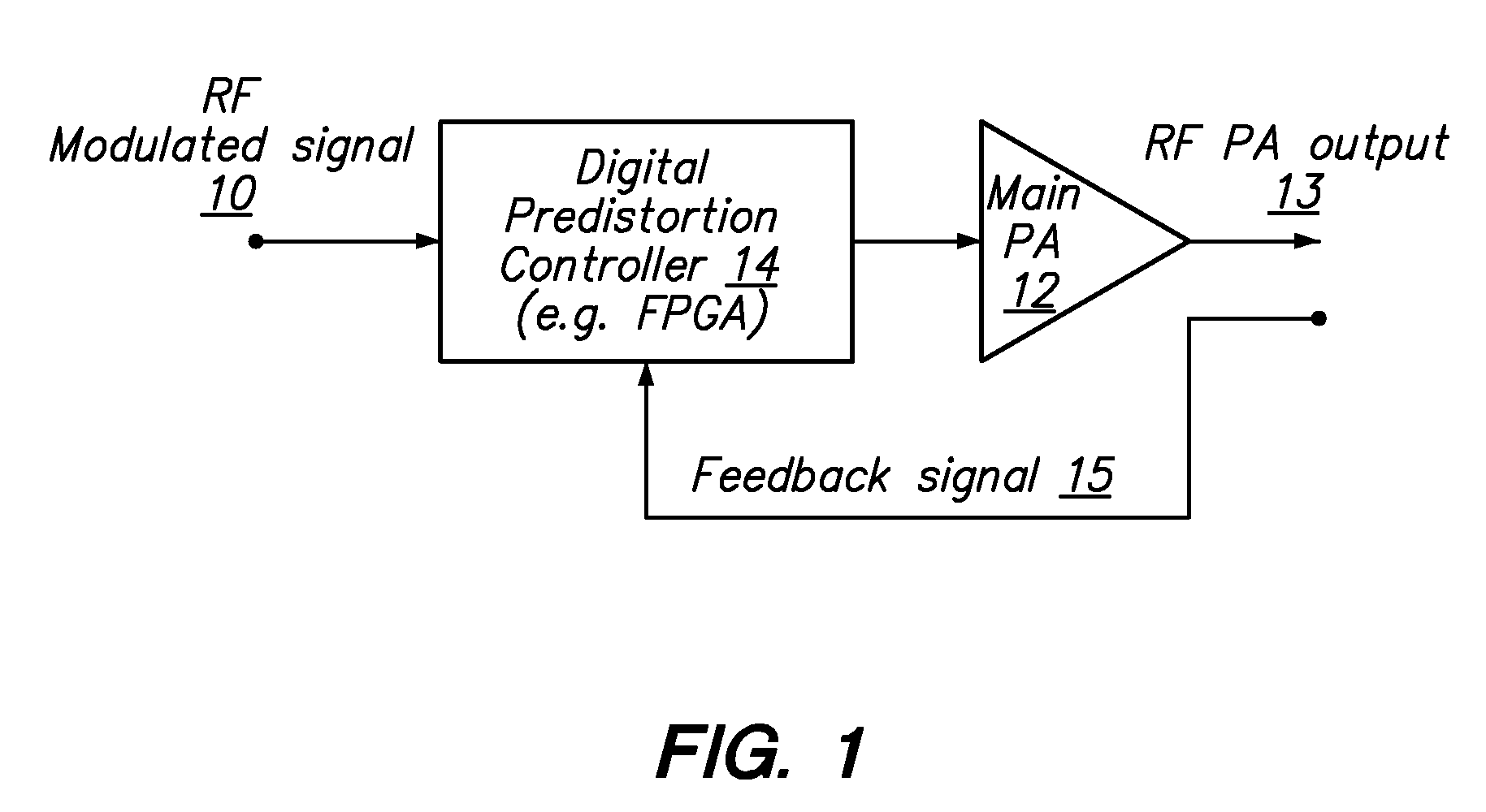
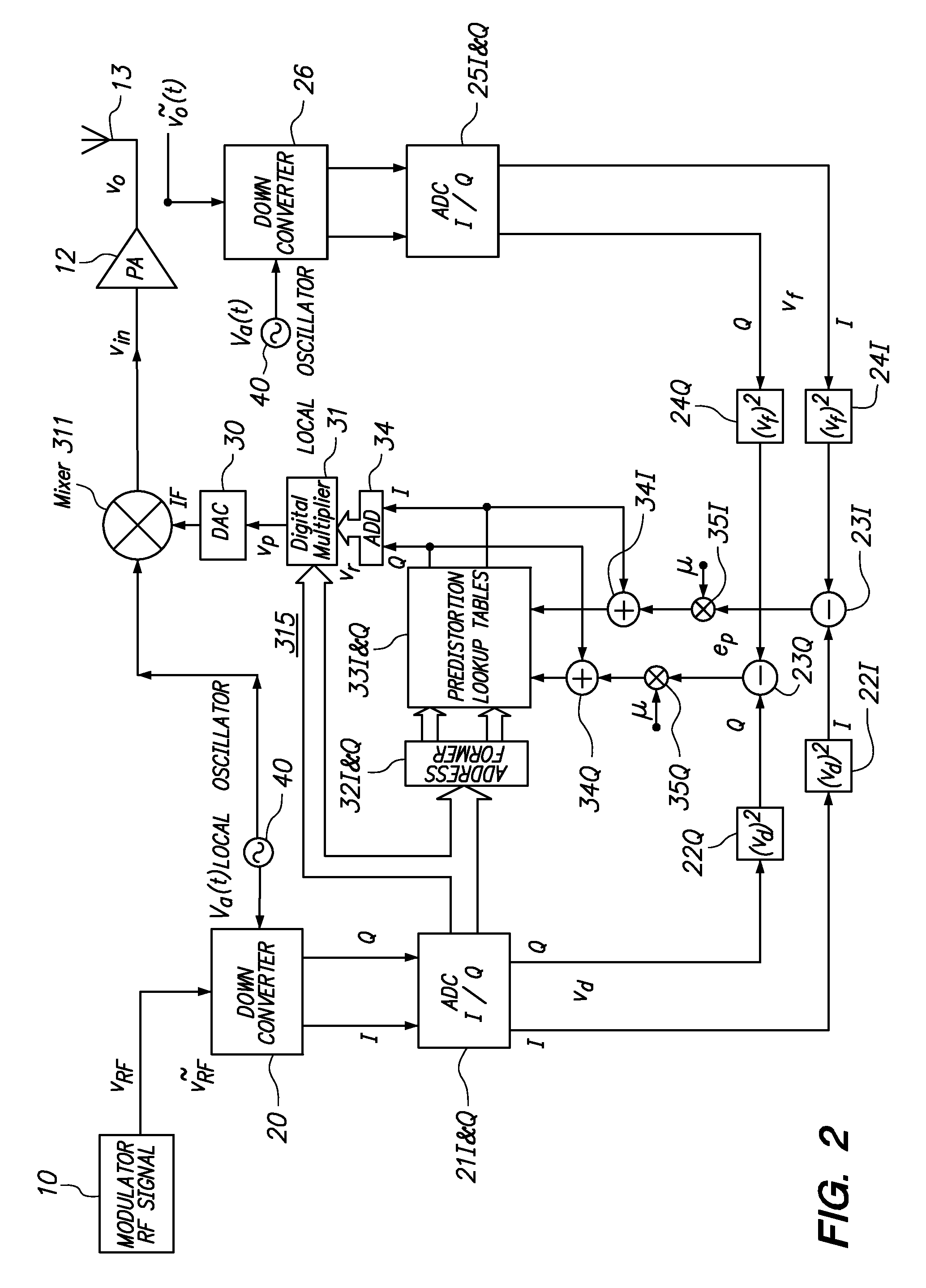
An embodiment of the invention uses a predistortion correction signal to combination the modulated RF signal by an analog multiplier for linearization of power amplifiers having nonlinear characteristics such as those used in wireless RF transmitters. A predistortion controller comprises a plurality of down converters for retrieving both the ideal non-distorted information and the feedback distorted information, together with pre-stored digitally-indexed predistortion information stored, for example, in a look-up table. The digitally-indexed information models nonlinear characteristics of the high power amplifier, and is stored prior to processing of pre-compensation in the power amplifier. When the predistortion information is combined with the modulated RF signal in the analog multiplier, the result is a substantially linear information transmission from the power amplifier. In an embodiment of the system, the modulated RF input signal and the feedback signal from PA output are down-converted, respectively, by analog devices, such as mixers, after which the analog intermediate frequency (IF) signals are digitized by analog-to-digital converters for digital predistortion correction processing, followed by predistortion processing performed by, for example, a DSP or FPGA chip to generate a digital correction control signal, which is then converted to an analog signal by a digital-to-analog converter, followed by combining the analog correction signal with the RF modulated input signal to yield the input to the power amplifier.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
Amplifiers Operating in Envelope Tracking Mode or Non-Envelope Tracking Mode
ActiveUS20140184335A1Power amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierEngineering
Various envelope tracking amplifiers are presented that can be switched between an ET (envelope tracking) mode and a non-ET mode. Switches and / or tunable components are utilized in constructing the envelope tracking amplifiers that can be switched between the ET mode and the non-ET mode.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Amplifier system and method
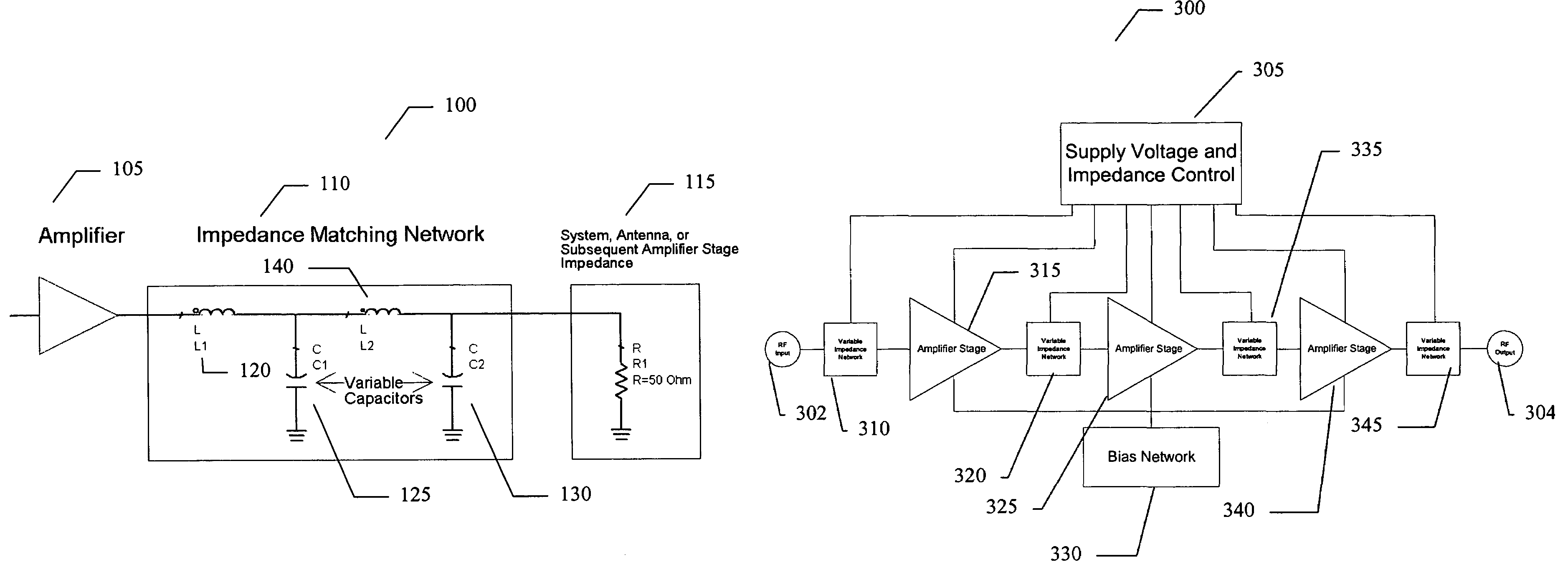
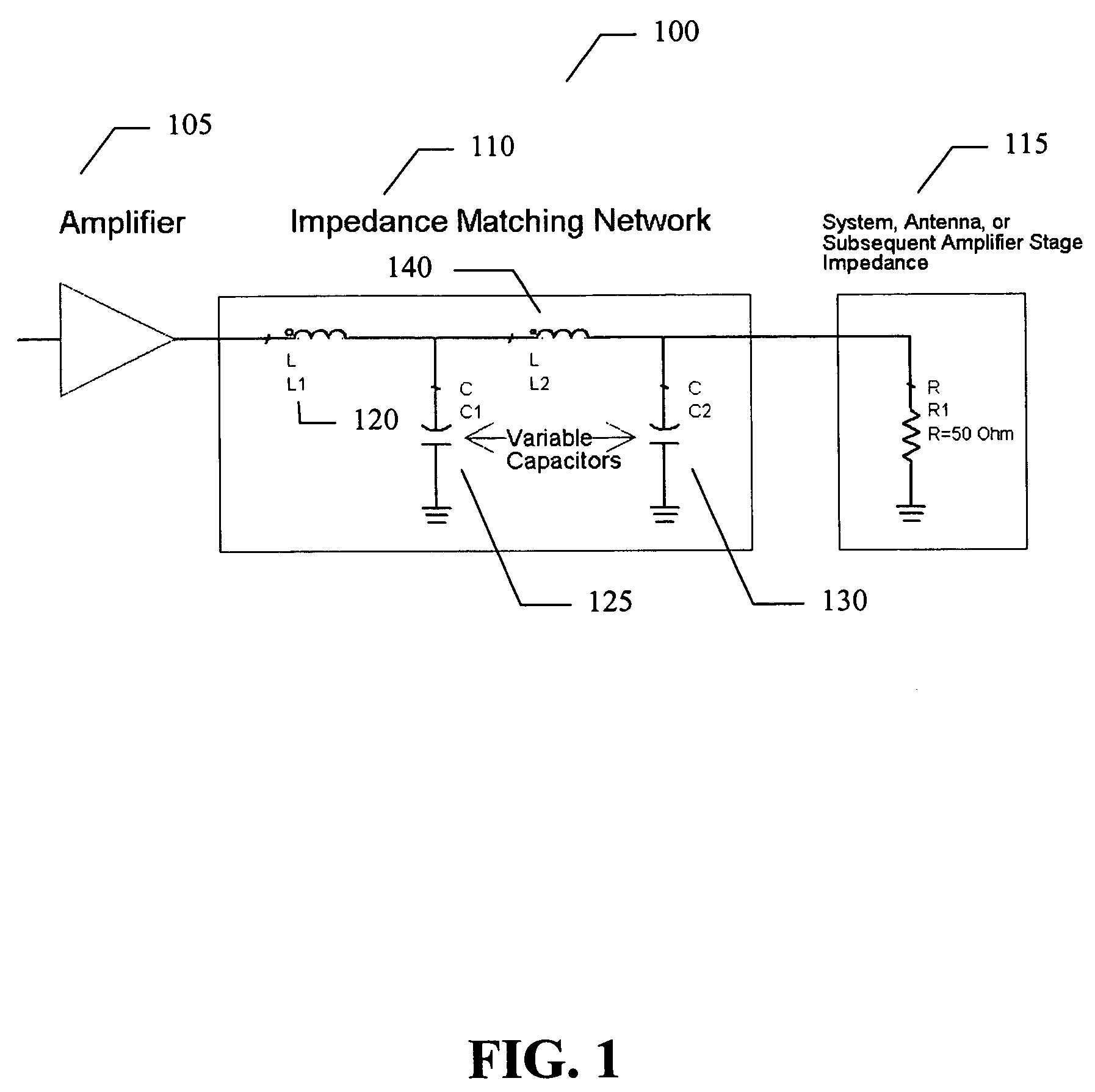
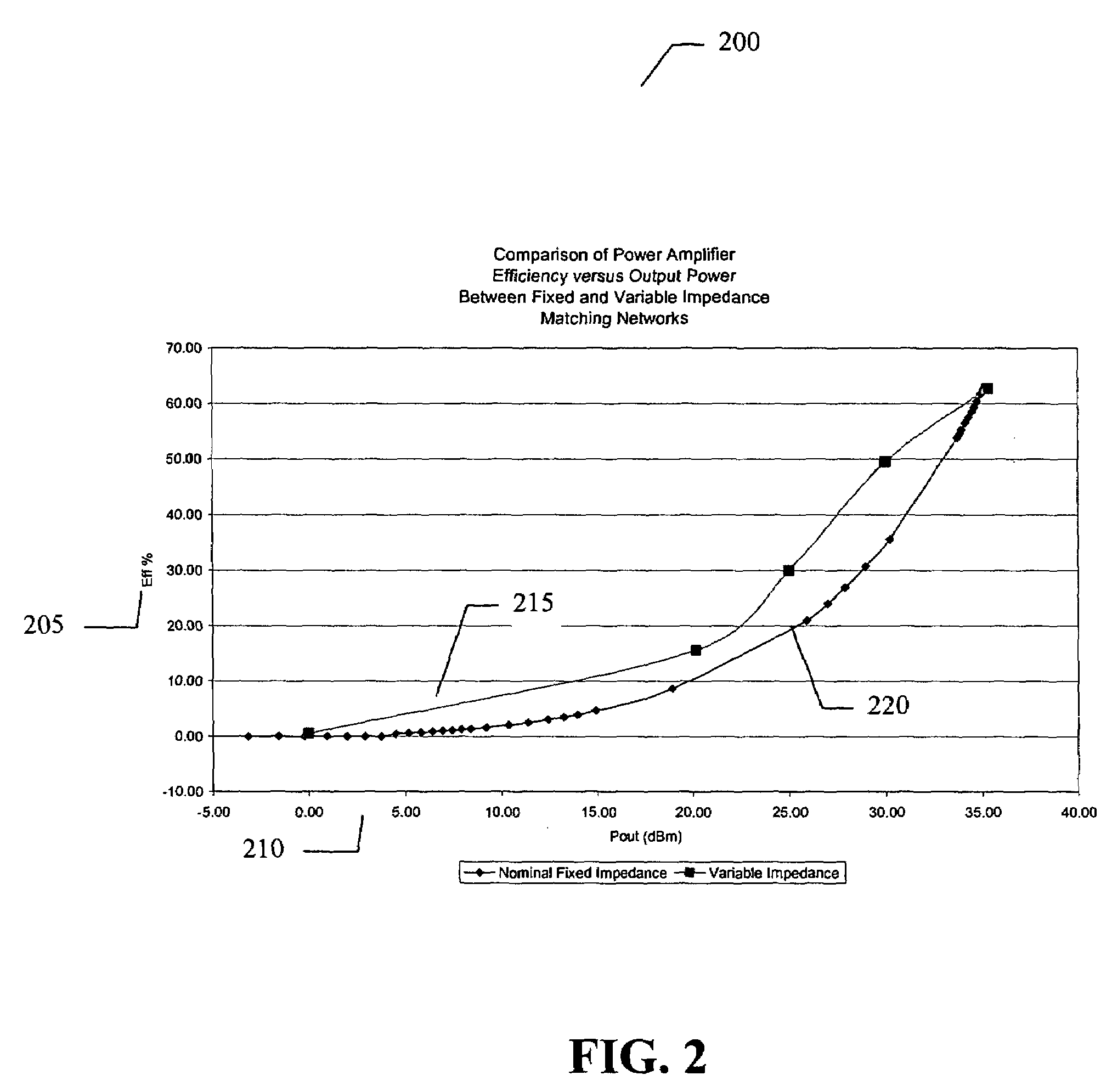
ActiveUS7151411B2High frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierImpedance matching
An embodiment of the present invention provides an amplifier system, comprising at least one variable impedance matching network, the output of which provides the input to at least one amplifier stage or provides an output of the power amplifier itself, and a bias network associated with the at least one amplifier stage. The amplifier system may further comprise a controller enabling impedance control to the at least one variable impedance matching network and a supply voltage provided to the at least one variable impedance network and / or the at least one amplifier stage and wherein the at least one variable impedance network and the at least one amplifier stage may be a plurality of impedance networks connected to a plurality of amplifier stages. The at least one variable impedance network may include at least one variable capacitor and the at least one variable capacitor may be a voltage tunable dielectric capacitor which may include Parascan® voltage tunable dielectric material.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Apparatus and method for envelope tracking power amplification in wireless communication system
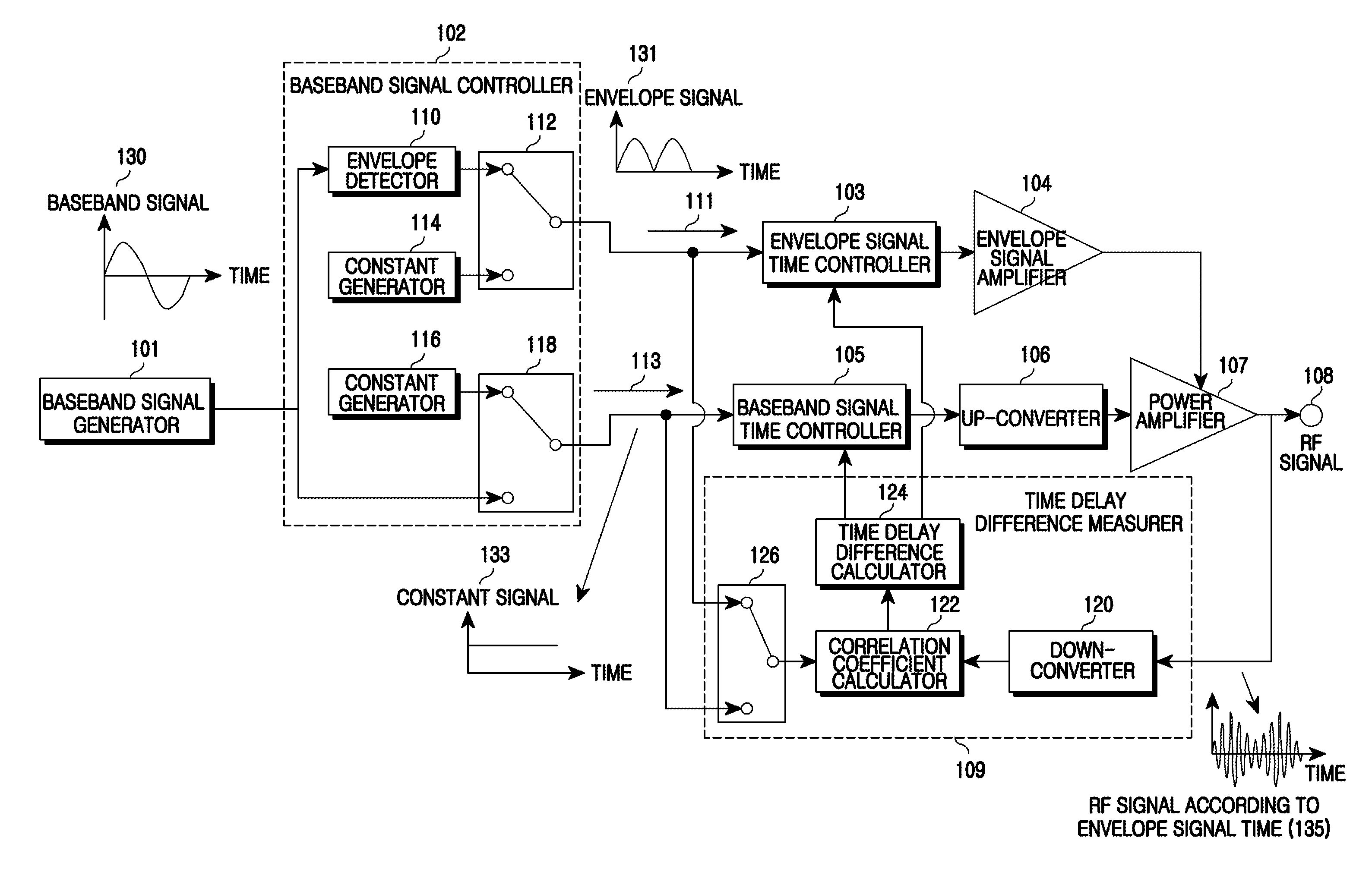
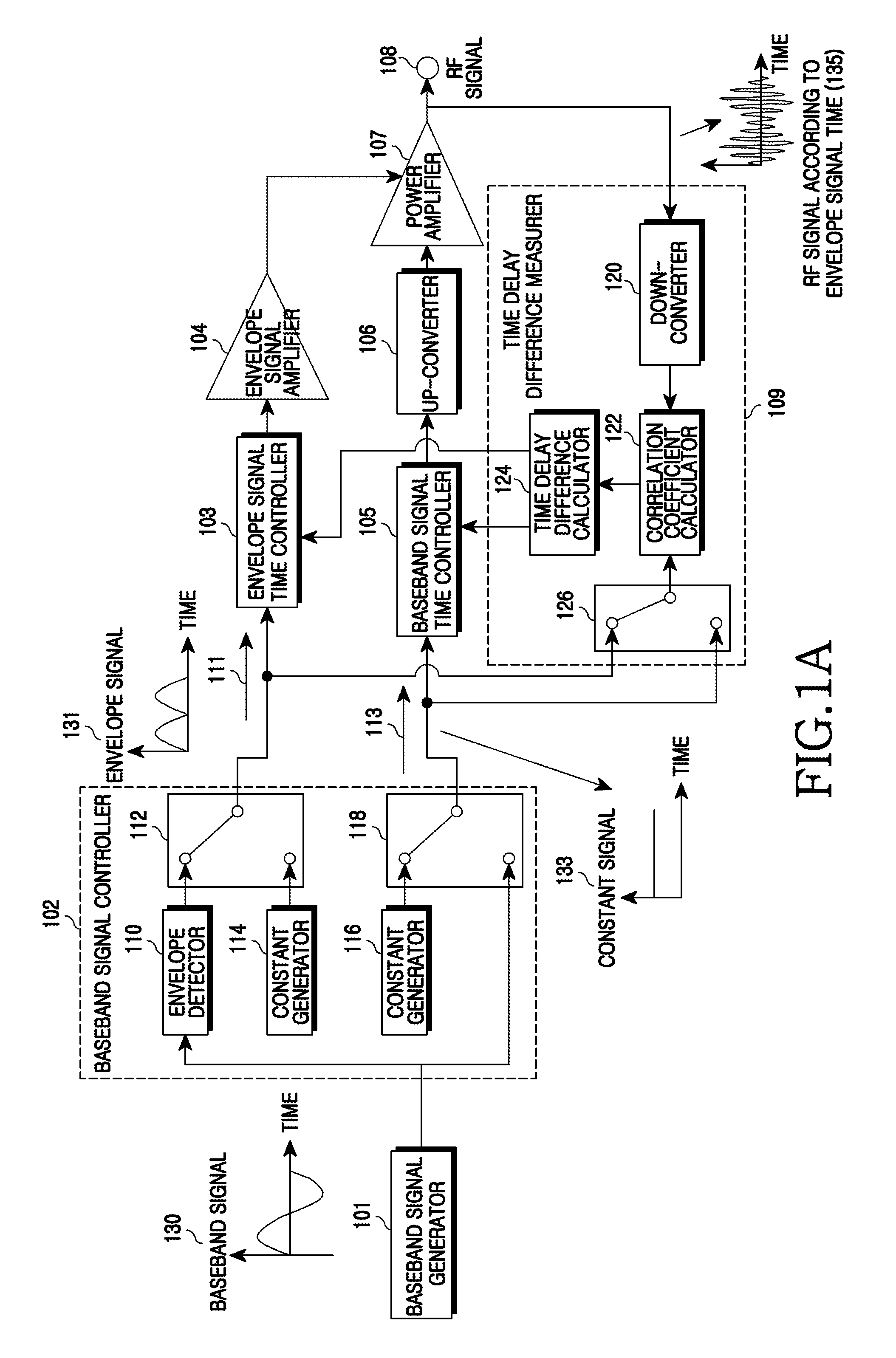
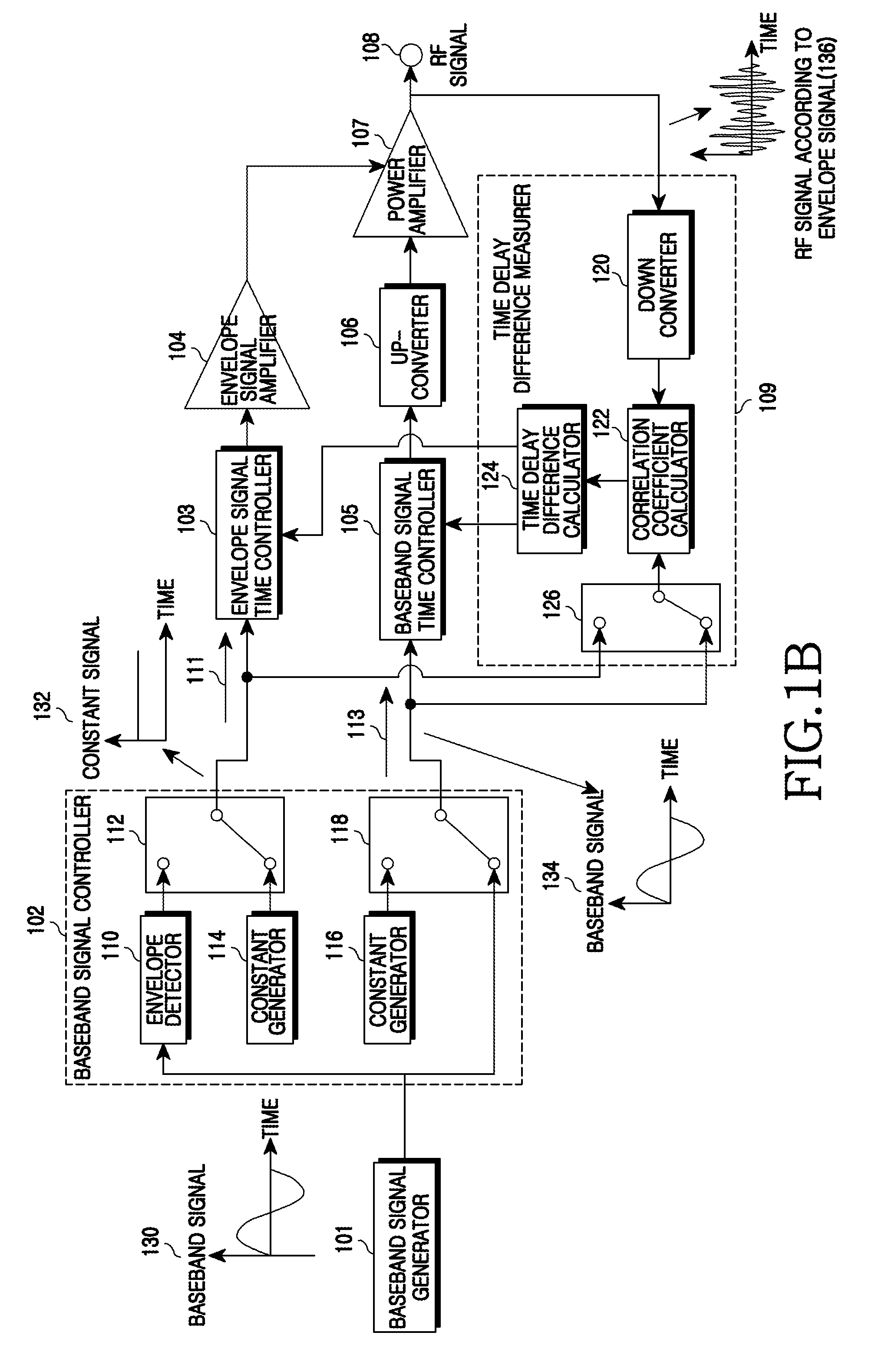
InactiveUS20090097591A1Modulated-carrier systemsPower amplifiersCorrelation coefficientCommunications system
An apparatus and a method for Envelope Tracking (ET) power amplification in a wireless communication system are provided. The apparatus includes a baseband signal controller for outputting an envelope signal in an envelope signal path and outputting a constant signal in a baseband signal path when measuring a time delay of the envelope signal path, and for outputting a constant signal in the envelope signal path and outputting a baseband signal in the baseband signal path when measuring a time delay of the baseband signal path, a time delay difference measurer for measuring a time delay of each path by calculating a correlation coefficient between the envelope signal path and the baseband signal path and a signal time controller for setting a time delay in a corresponding path using the time delay difference of each path and aligning times.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
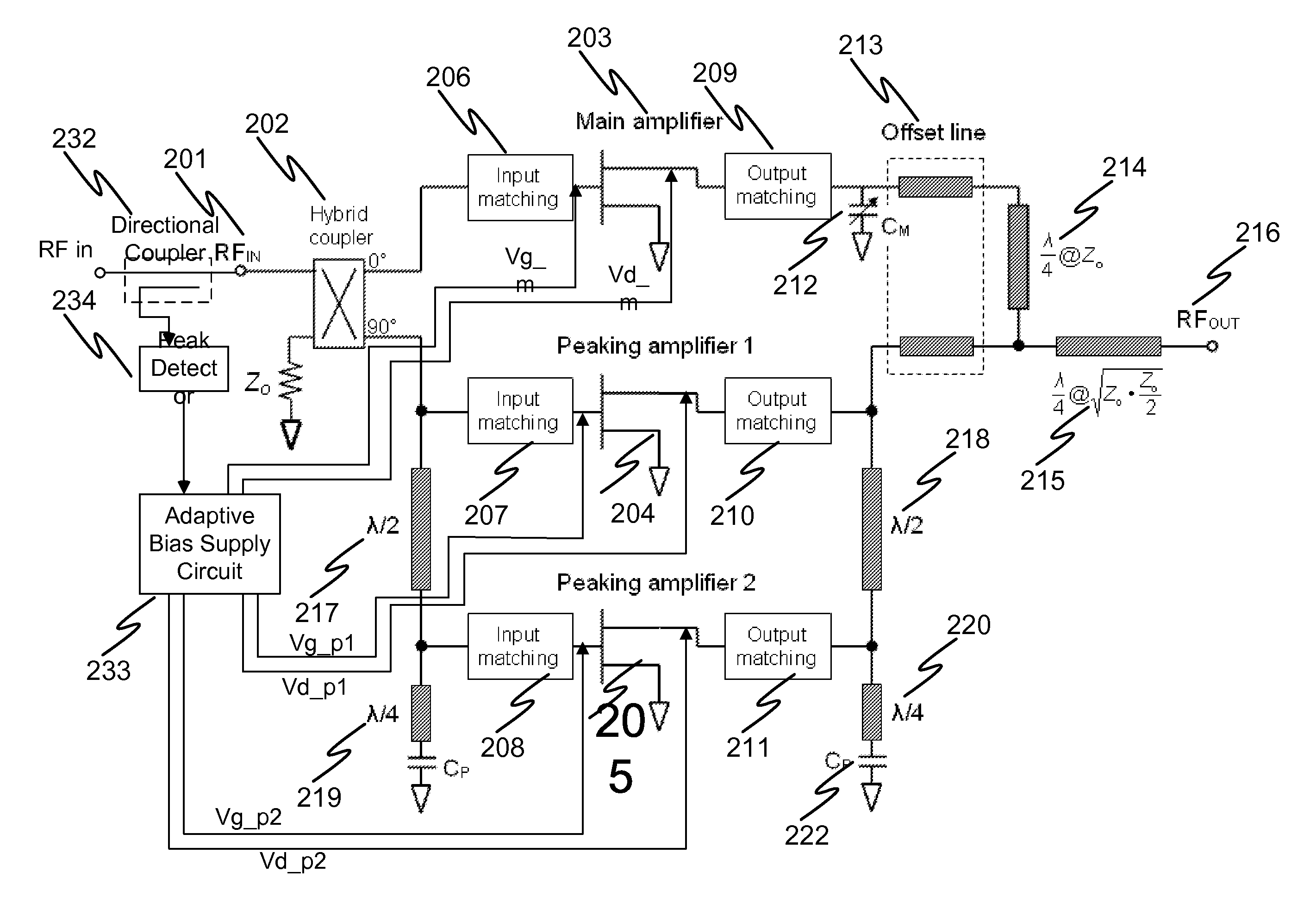
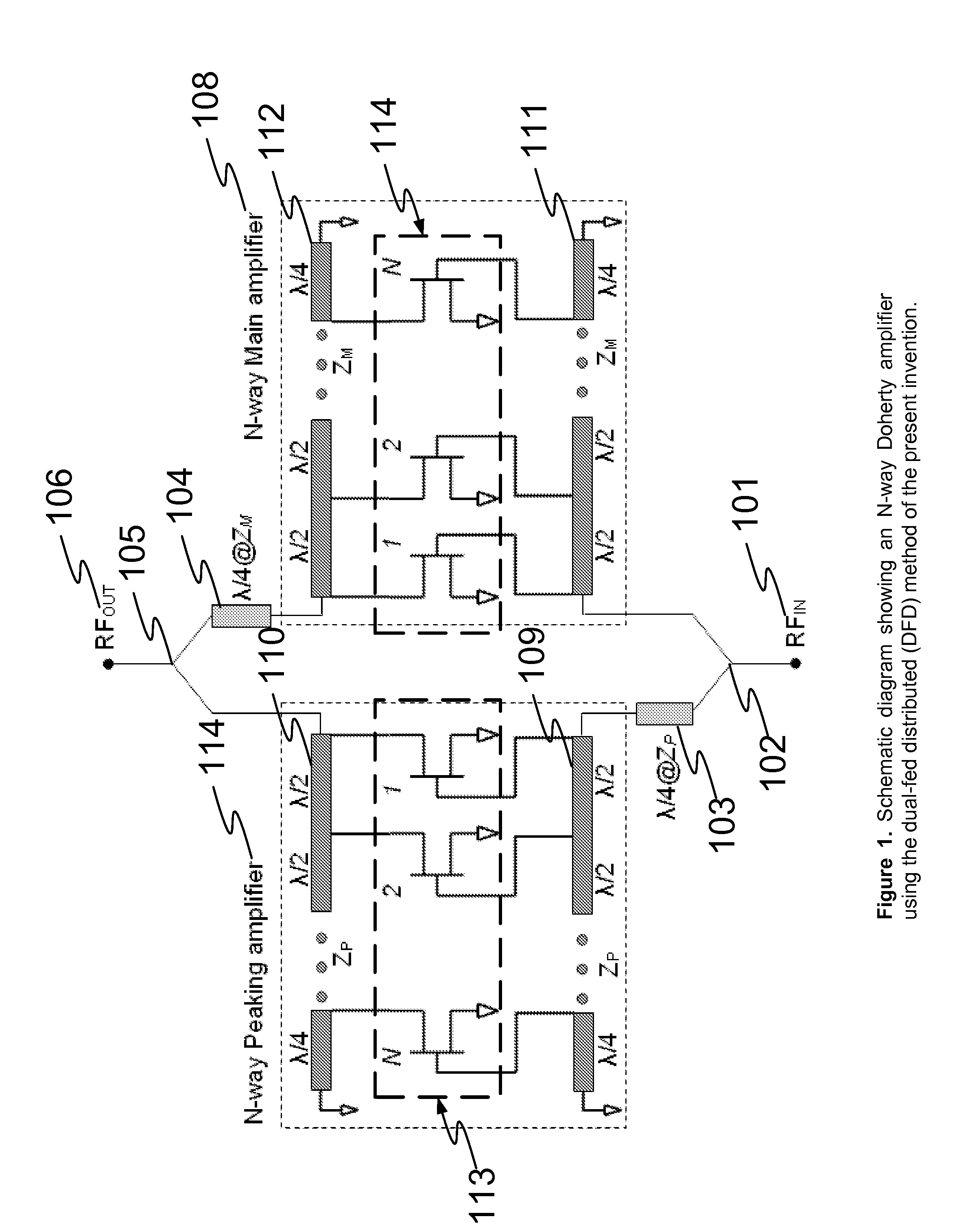
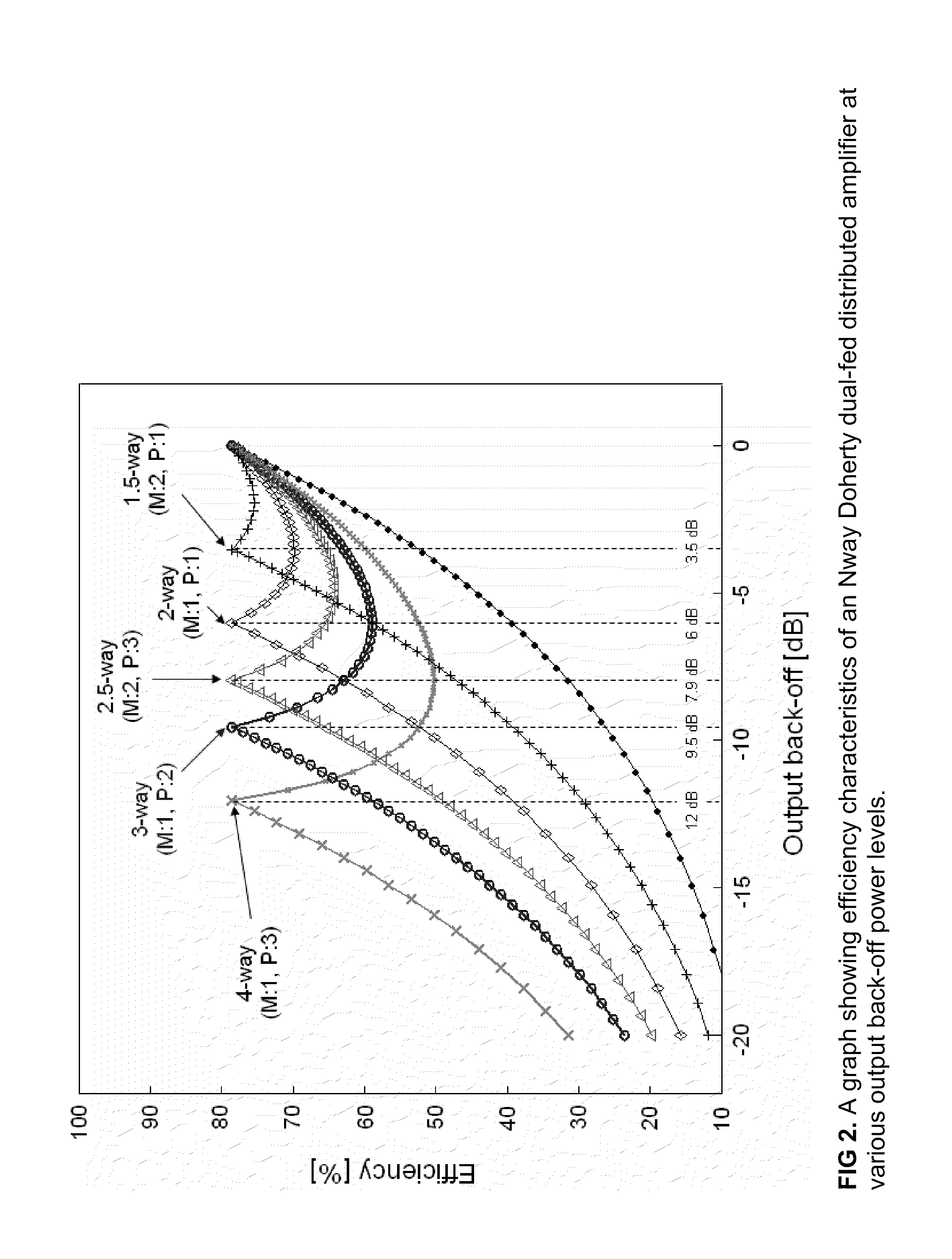
N-way Doherty distributed power amplifier with power tracking
ActiveUS8274332B2Improve performanceIncrease productionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsAdaptive biasMultiplexing
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
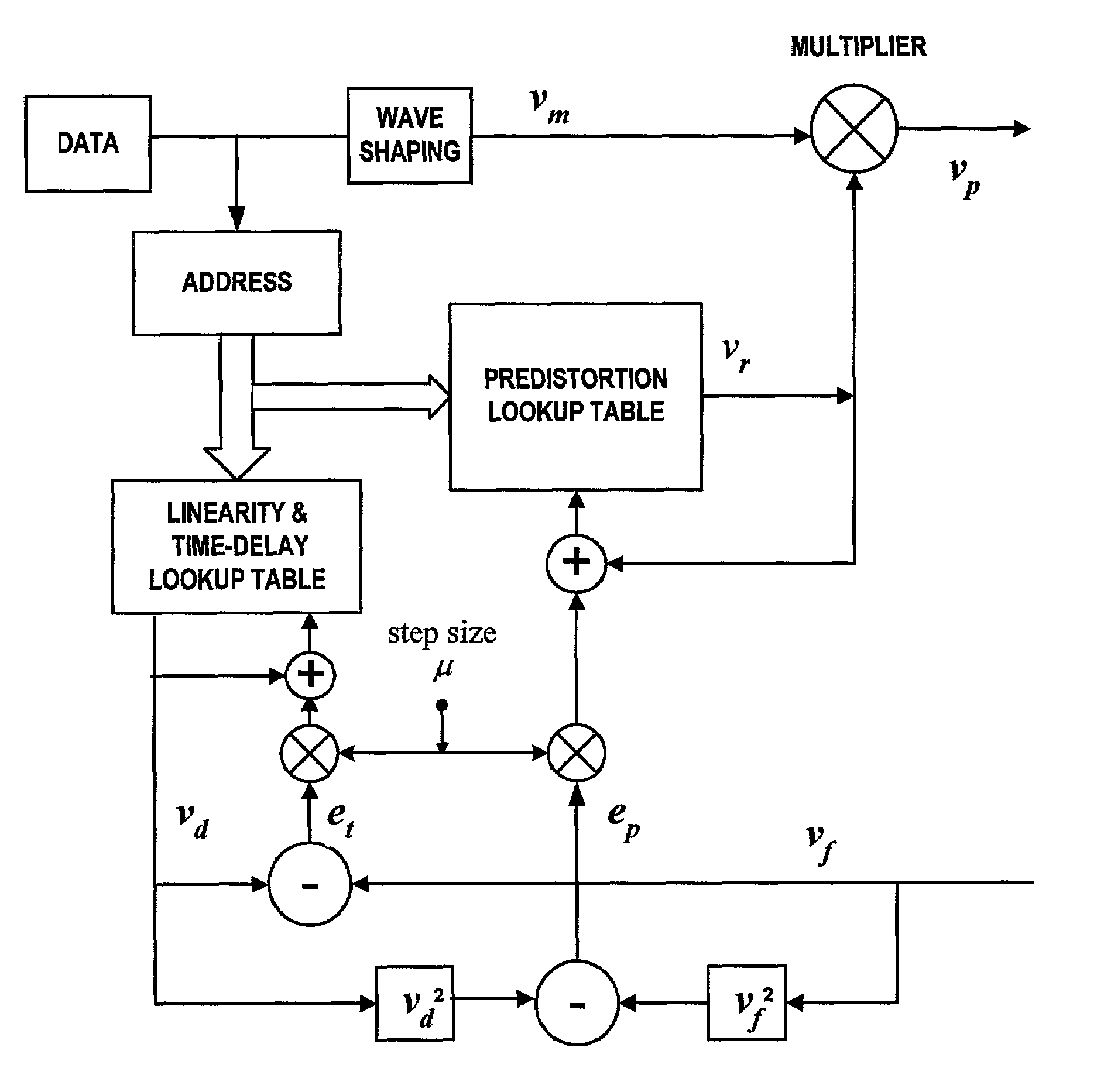
System and method for digital memorized predistortion for wireless communication
ActiveUS6985704B2Error preventionModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierWireless transmission
An embodiment of the invention is a system for signal processing in preparation for wireless transmission, the wireless transmission being from a portable wireless communication device and including use of a power amplifier having nonlinear characteristics. The system includes memory for storing digitally-indexed information. The digitally-indexed information models nonlinear characteristics of the power amplifier, and the digitally-indexed information is stored prior to processing of a first signal that reflects information to be communicated. The system further includes first logic, configured to accept the first signal and to retrieve, based on the first signal, a portion of the digitally-indexed information stored in the memory, and second logic, configured to generate a second signal based on the portion of the digitally-accessed information and on the first signal. The second signal pre-compensates for the nonlinear characteristics of the power amplifier, and the second signal is for wireless transmission based on the second signal.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
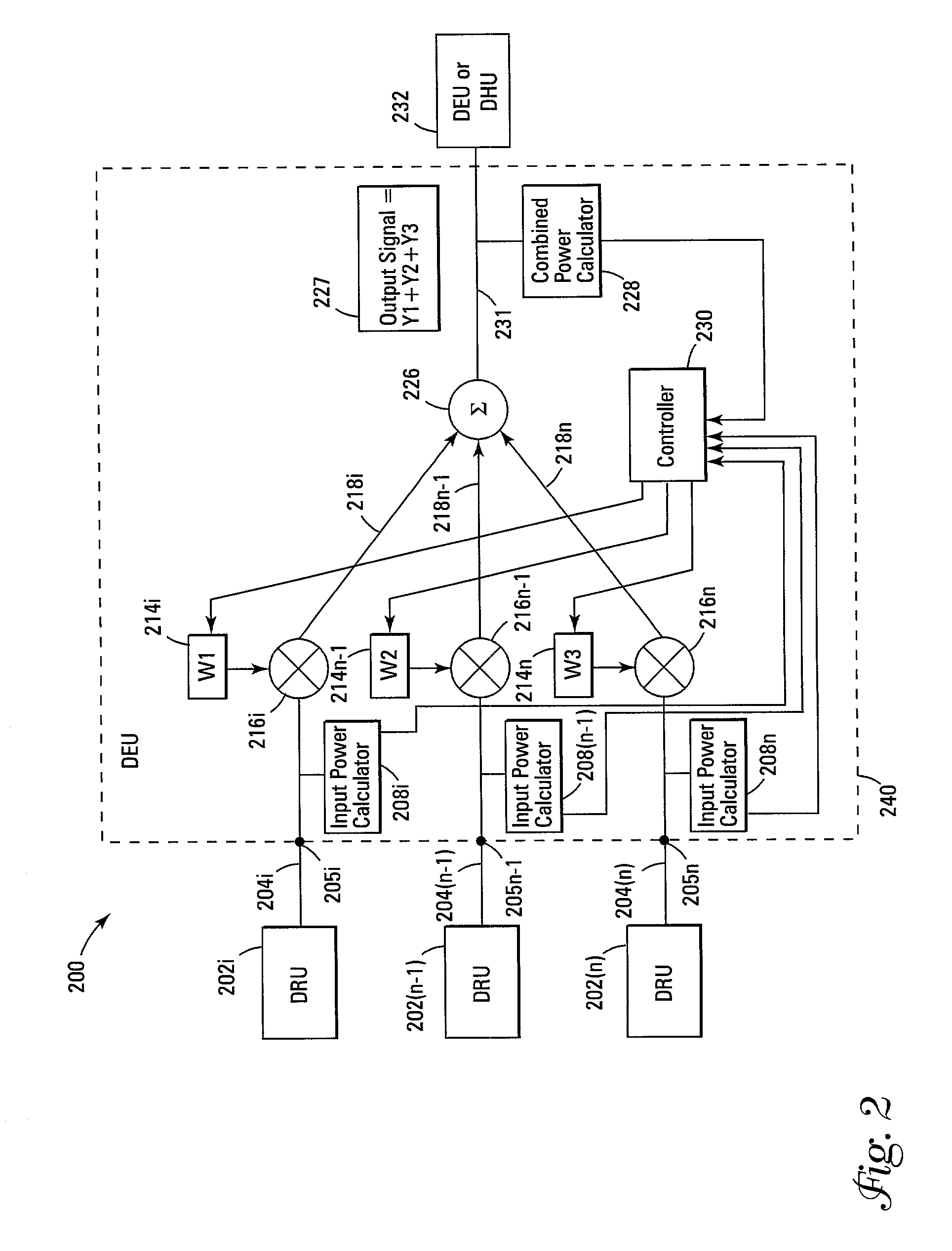
Distributed automatic gain control system
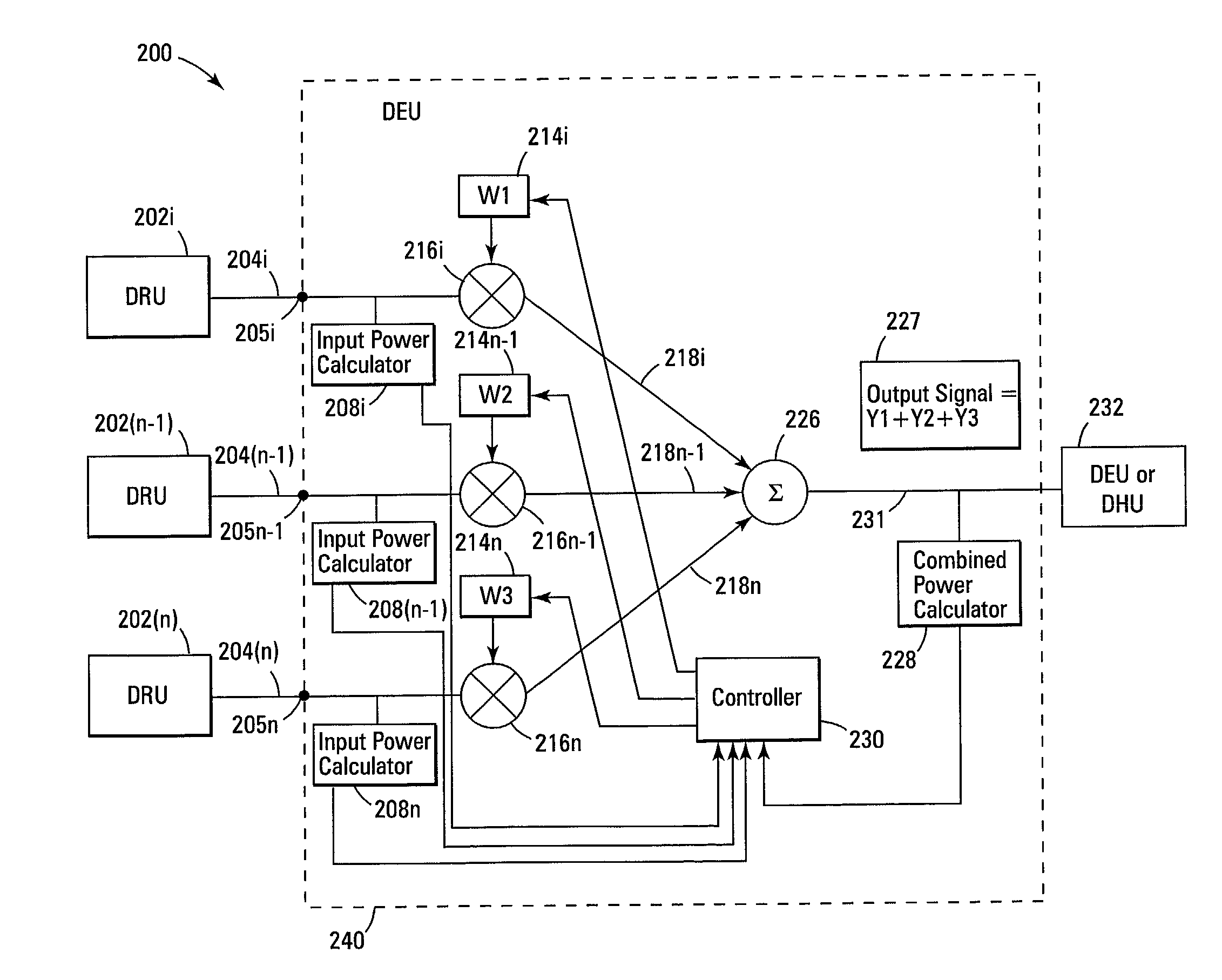
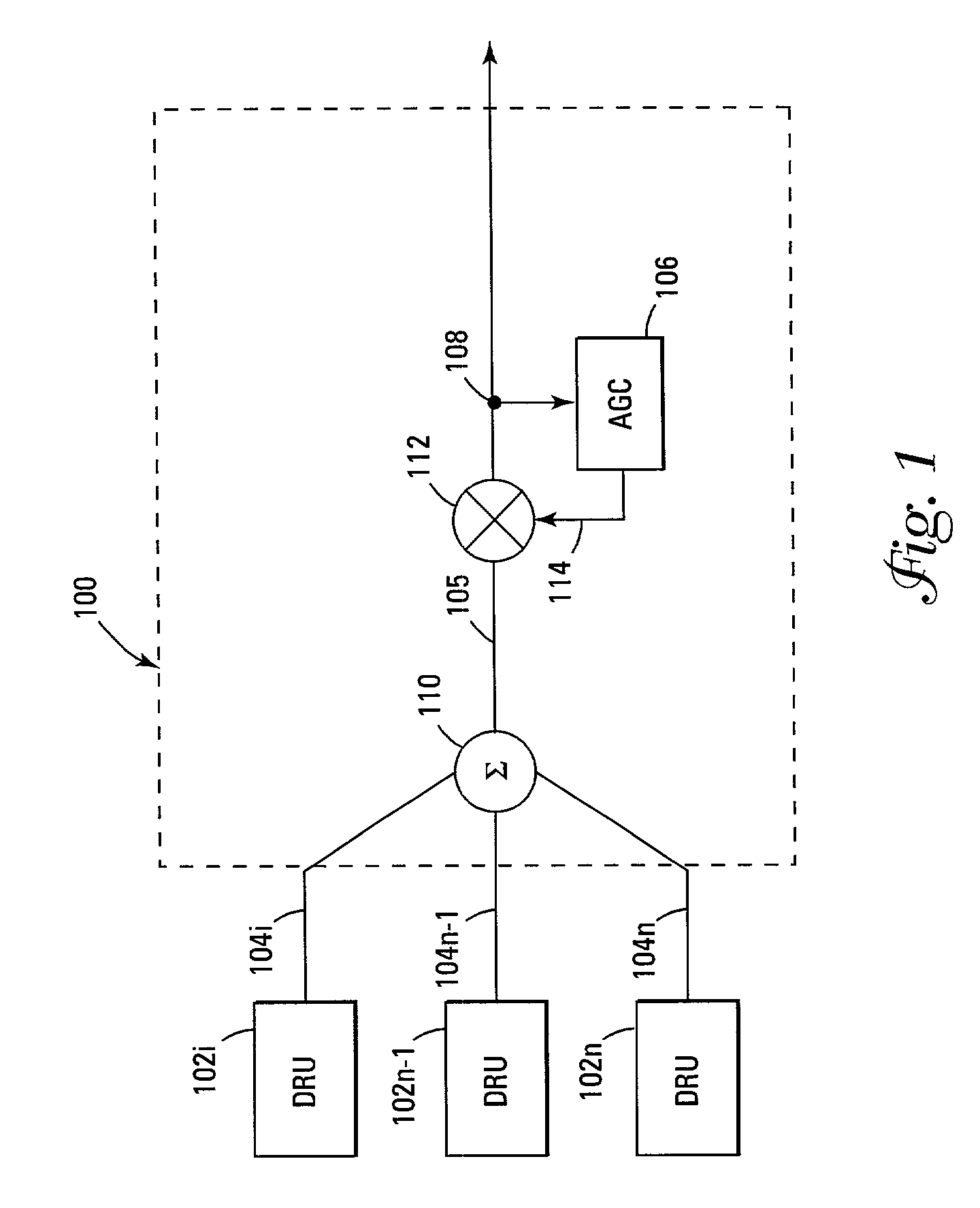
A wireless distribution system includes a number of remote units distributed in a coverage area to receive wireless signals and to provide the signals through the distribution system to input ports of a node where the signals are combined, a number of input power monitors operatively connected to one or more of the input ports to determine power levels of signals received at the input ports, variable gain controllers to control signals received at some or all of the input ports, a node to combine a plurality of signals from the plurality of input ports, and a controller to provide control signals to control one or more of the variable gain controllers.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
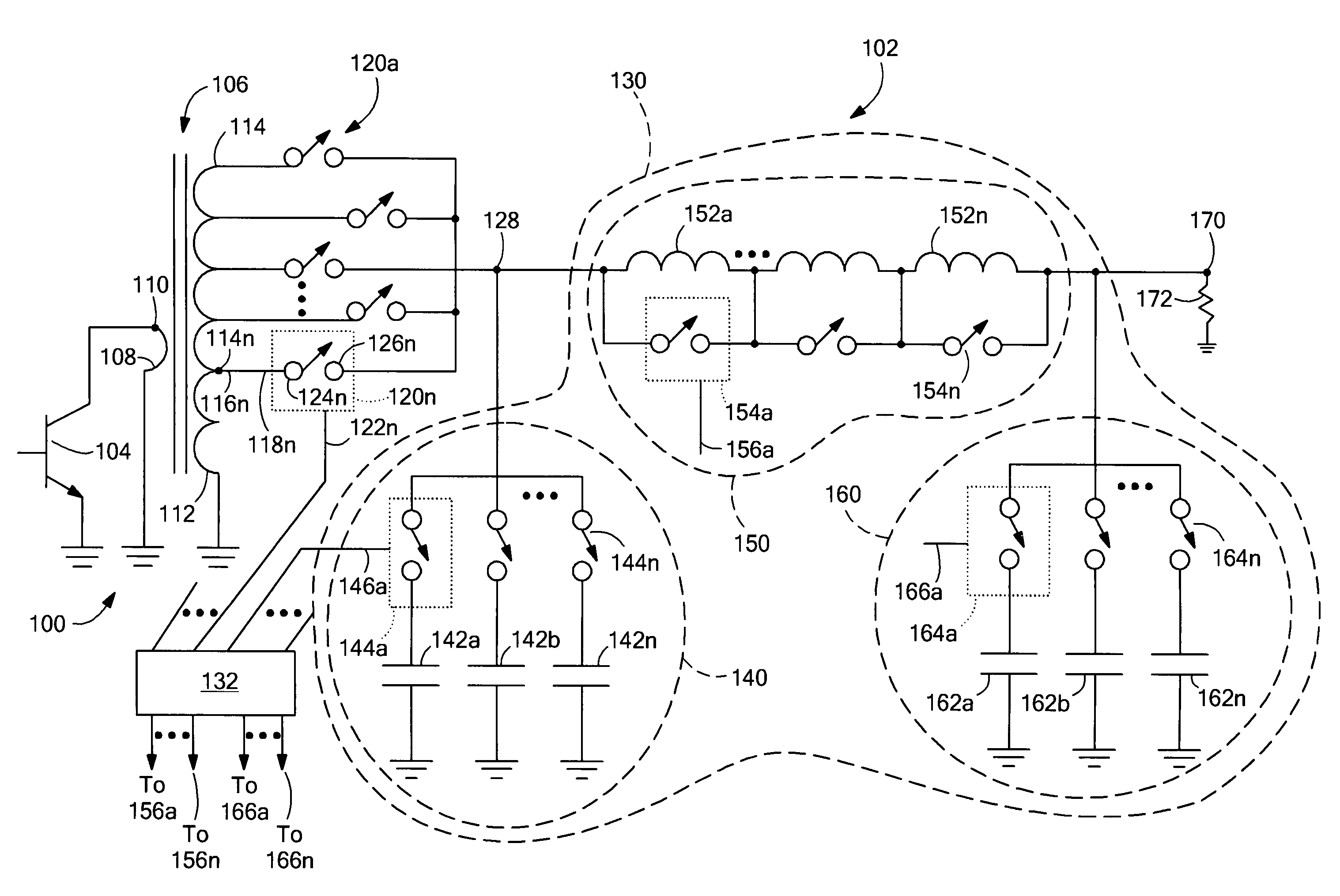
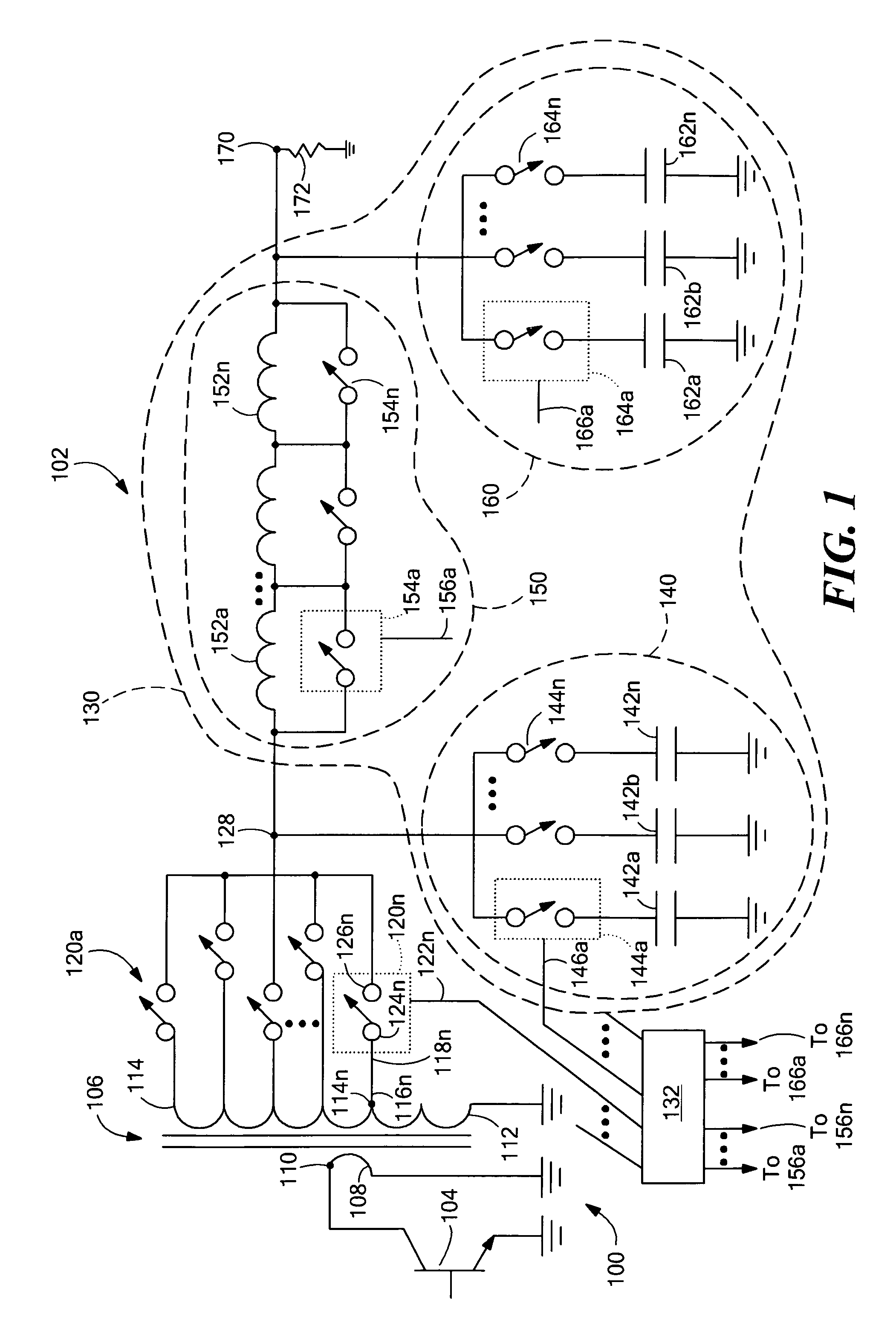
Mems-tuned high power, high efficiency, wide bandwidth power amplifier
InactiveUS6992543B2High output power levelAdvantage in sizeMultiple-port networksAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesTransformerControl signal
A circuit for matching the impedance of an output load to an active device includes a transformer including a first winding having a terminal for coupling to the output of the active device and a second winding electromagnetically coupled to the first winding, and a plurality of taps, each of the plurality of taps having a first end coupled to a position on the second winding corresponding to a ratio of the second winding to first winding differing from other ones of the plurality of taps, and a second end. The matching circuit further includes a plurality of MEMS switches each having a control input for receiving a corresponding control signal, a first terminal coupled to the second end of a corresponding one of the plurality of taps, and a switched output selectively coupled to a matching junction in response to the corresponding control signal.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
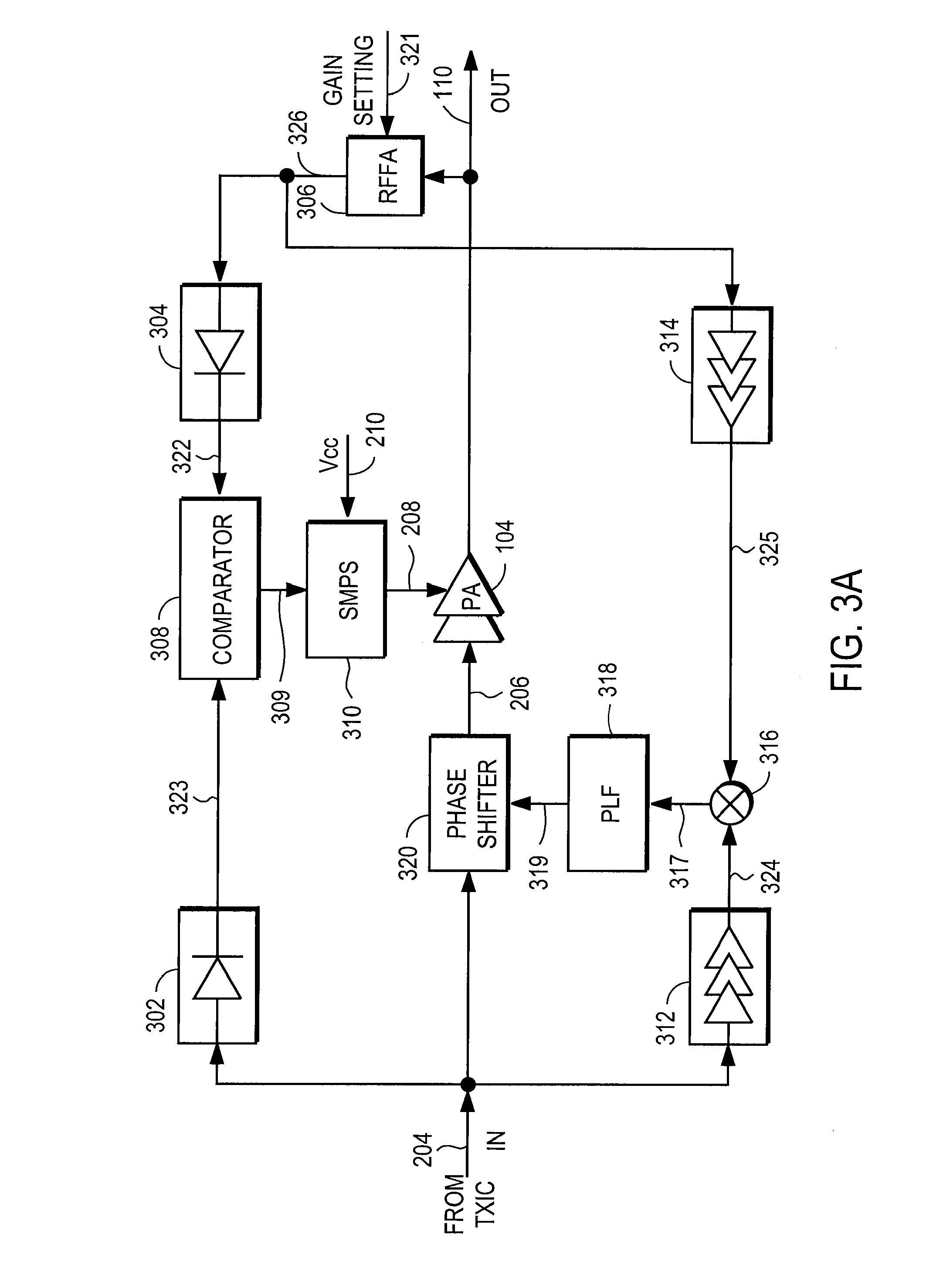
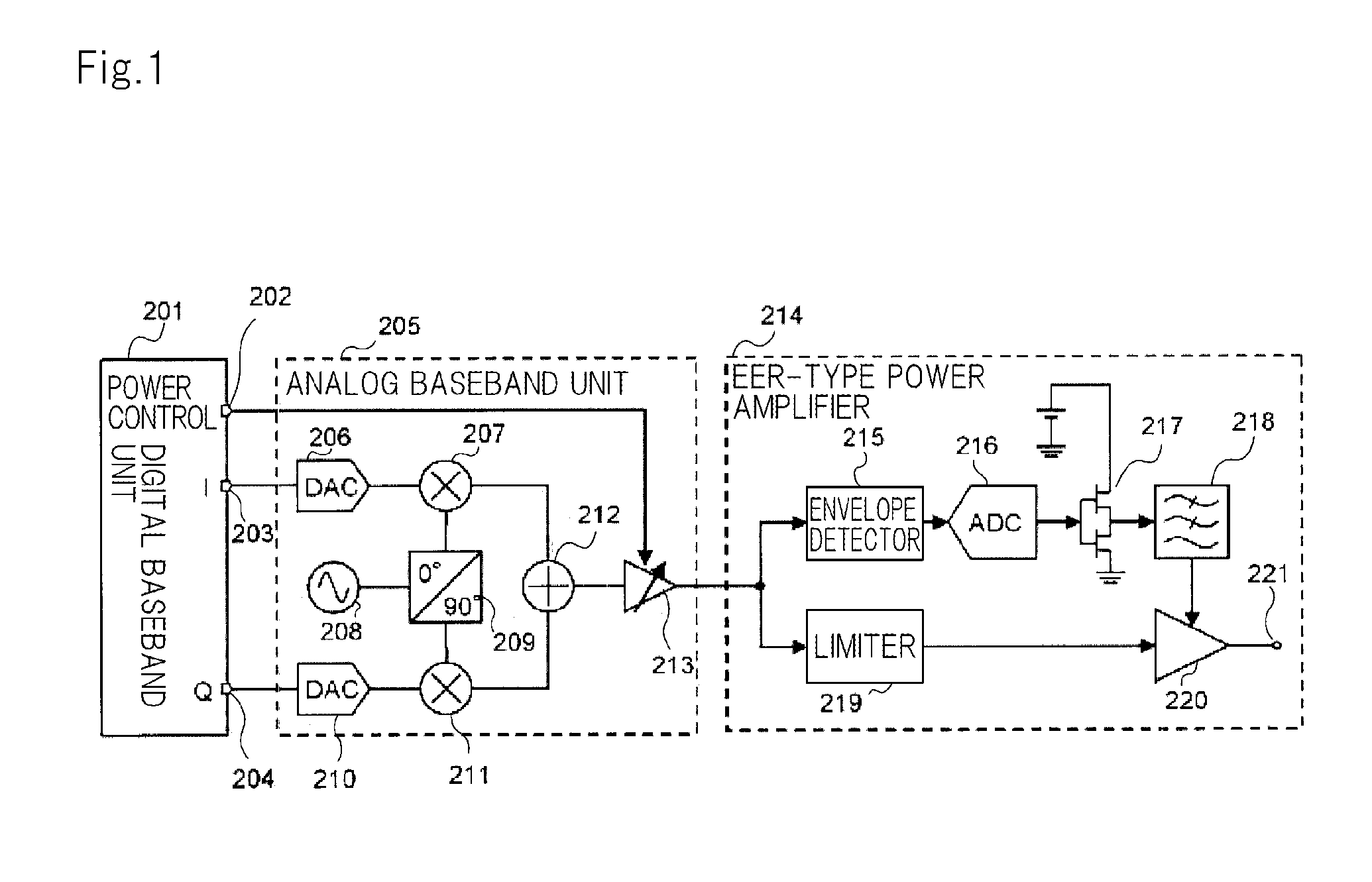
High efficiency amplification
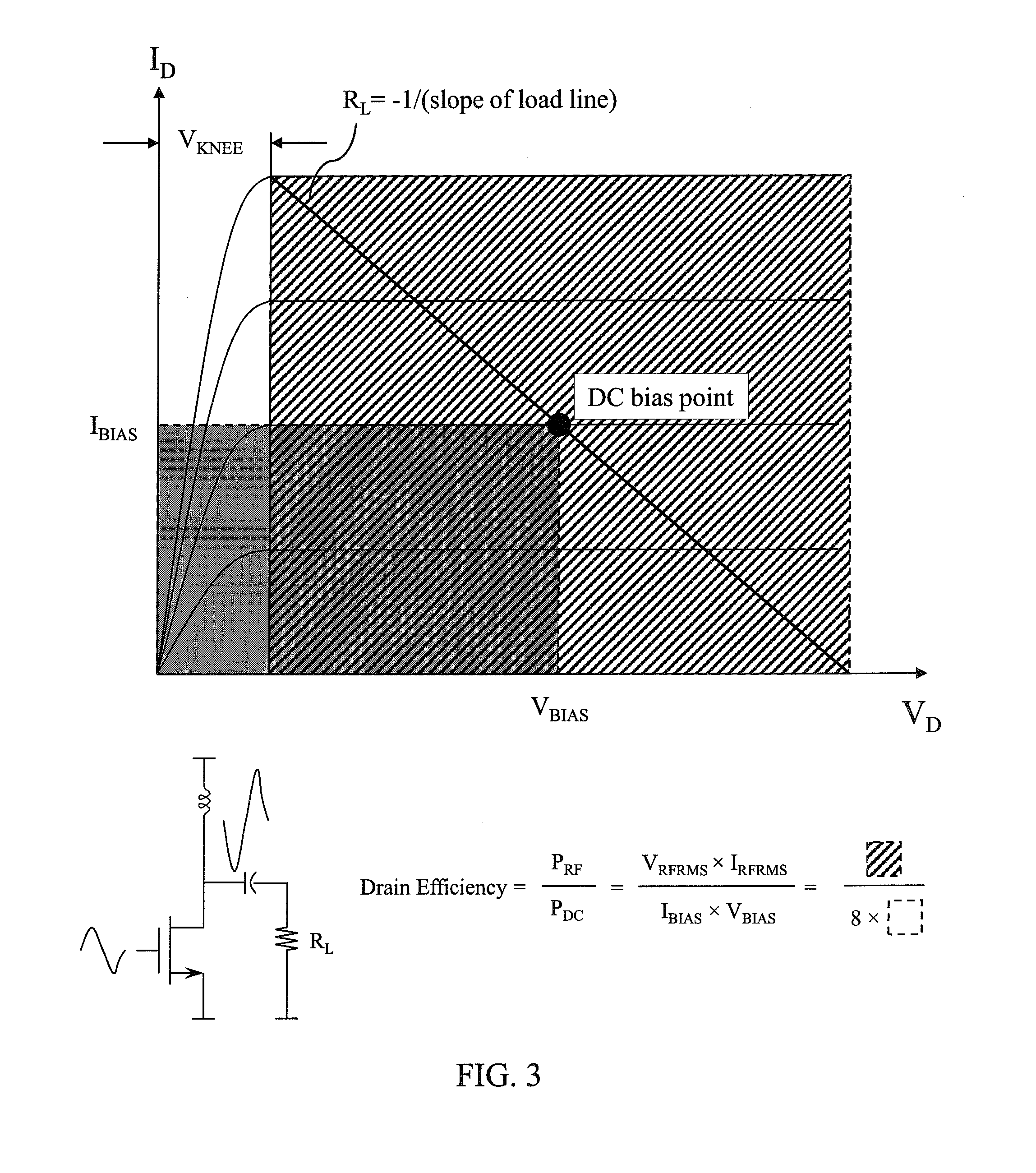
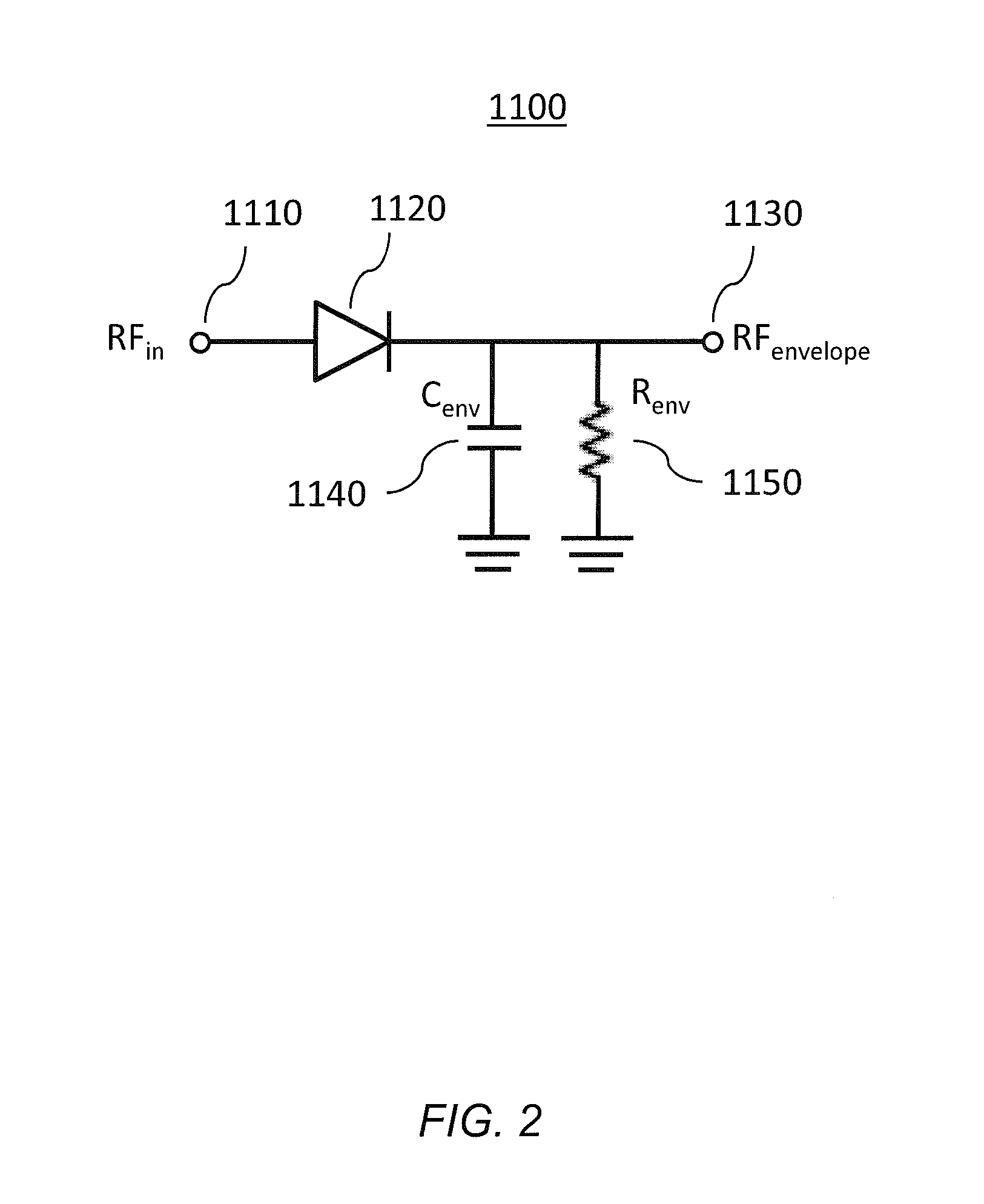
InactiveUS7482869B2Fast corrective loopWide bandwidthHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierSignal envelope
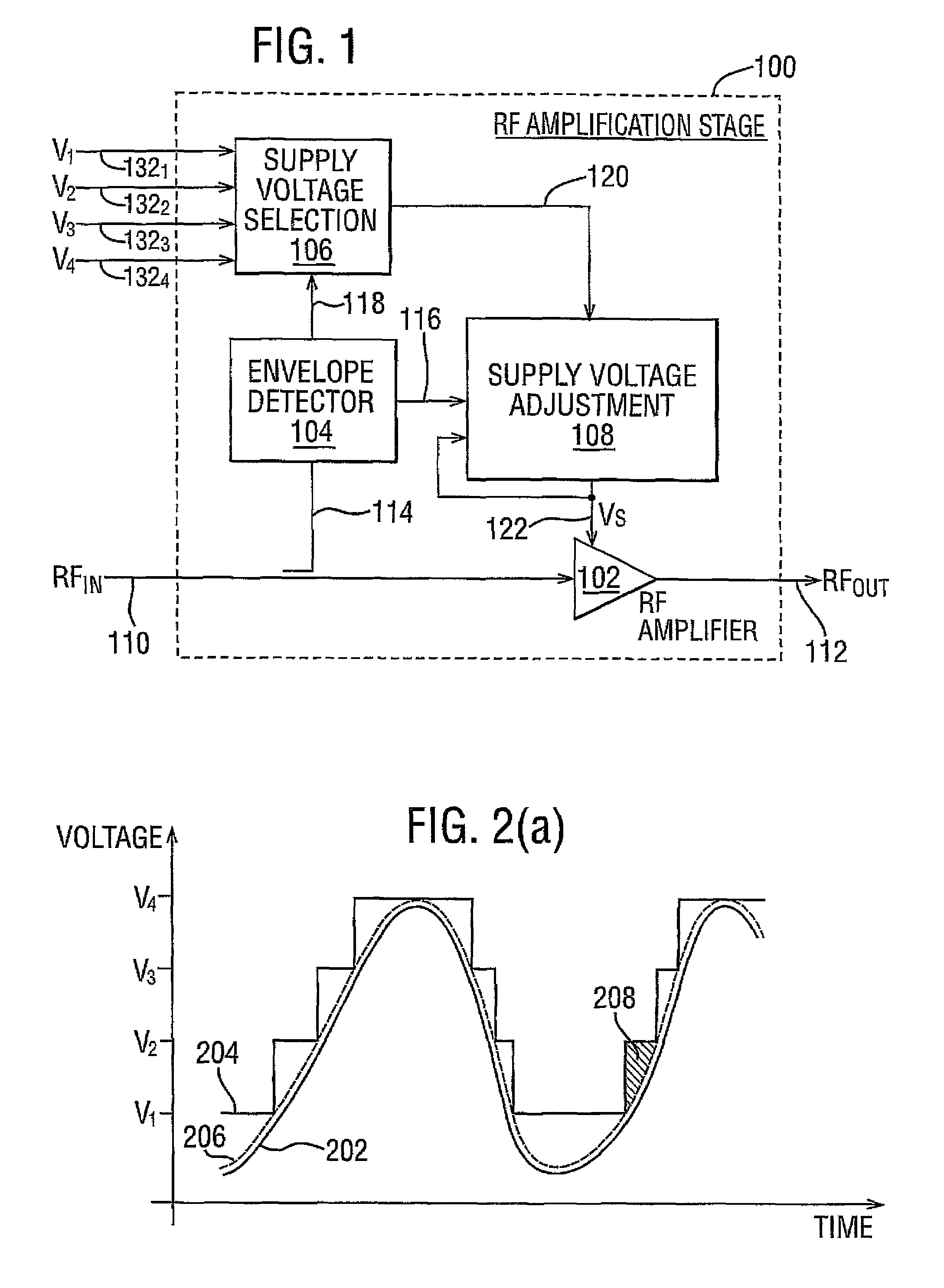
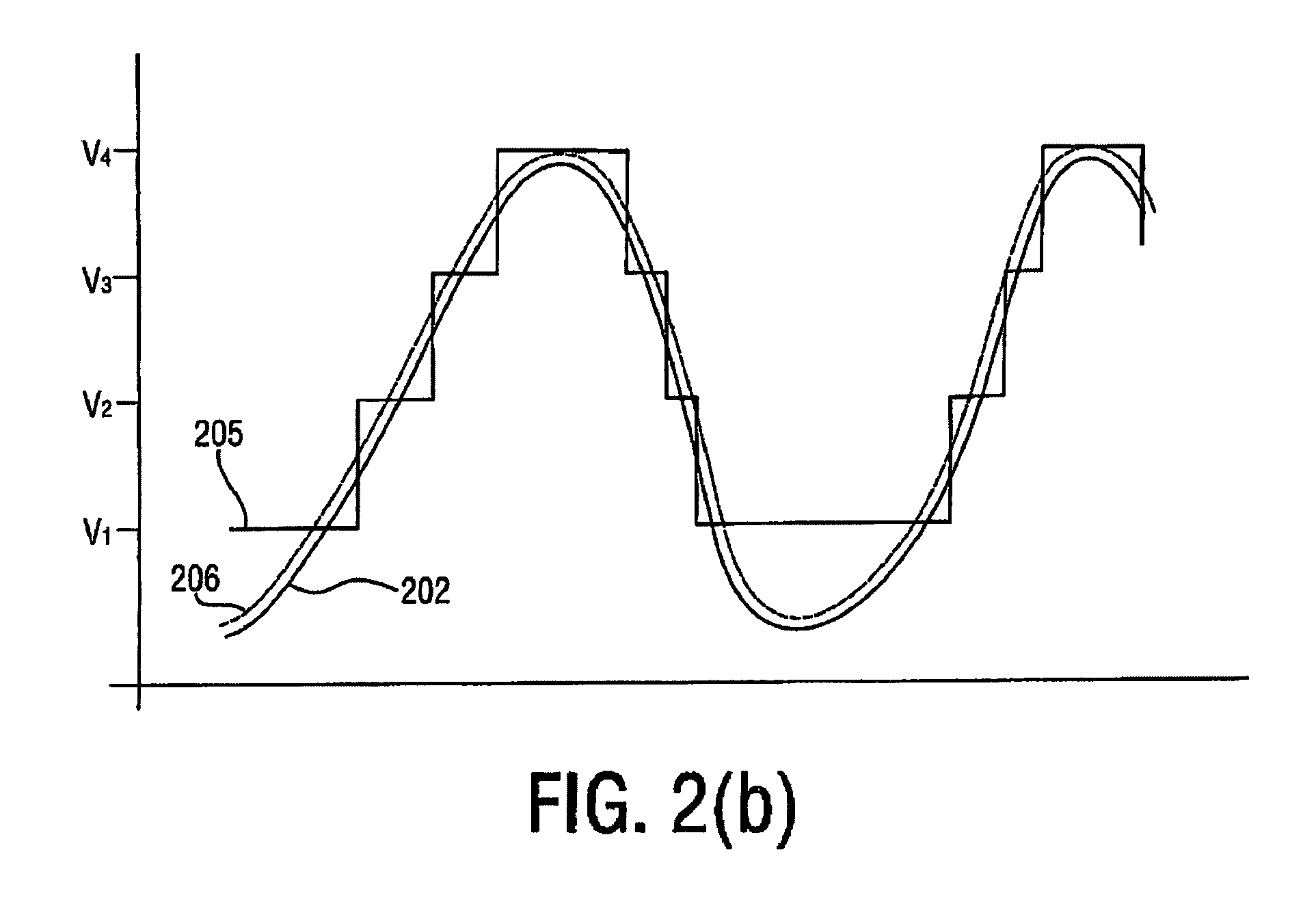
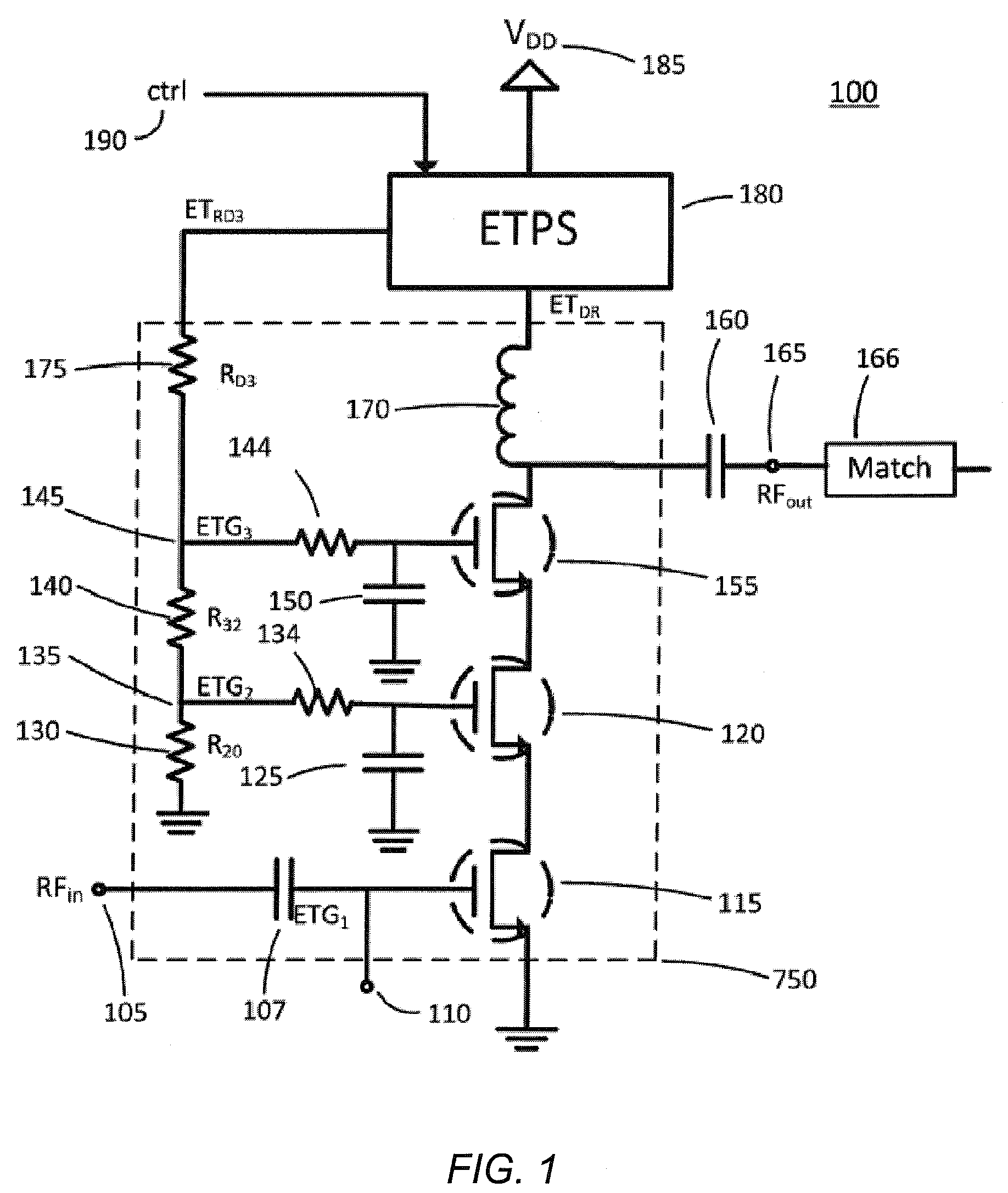
A radio frequency amplification stage including an amplifier for receiving an input signal to be amplified and a power supply voltage; and a power supply voltage stage for supplying said power supply voltage, including a circuit for providing a reference signal representing the envelope of the input signal; a circuit for selecting one of a plurality of supply voltage levels in dependence on the reference signal; and a circuit for generating an adjusted selected power supply voltage, including an ac amplifier for amplifying a difference between the reference signal and one of the selected supply voltage level or the adjusted selected supply voltage level, and a summer for summing the amplified difference with the selected supply voltage to thereby generate the adjusted supply voltage.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
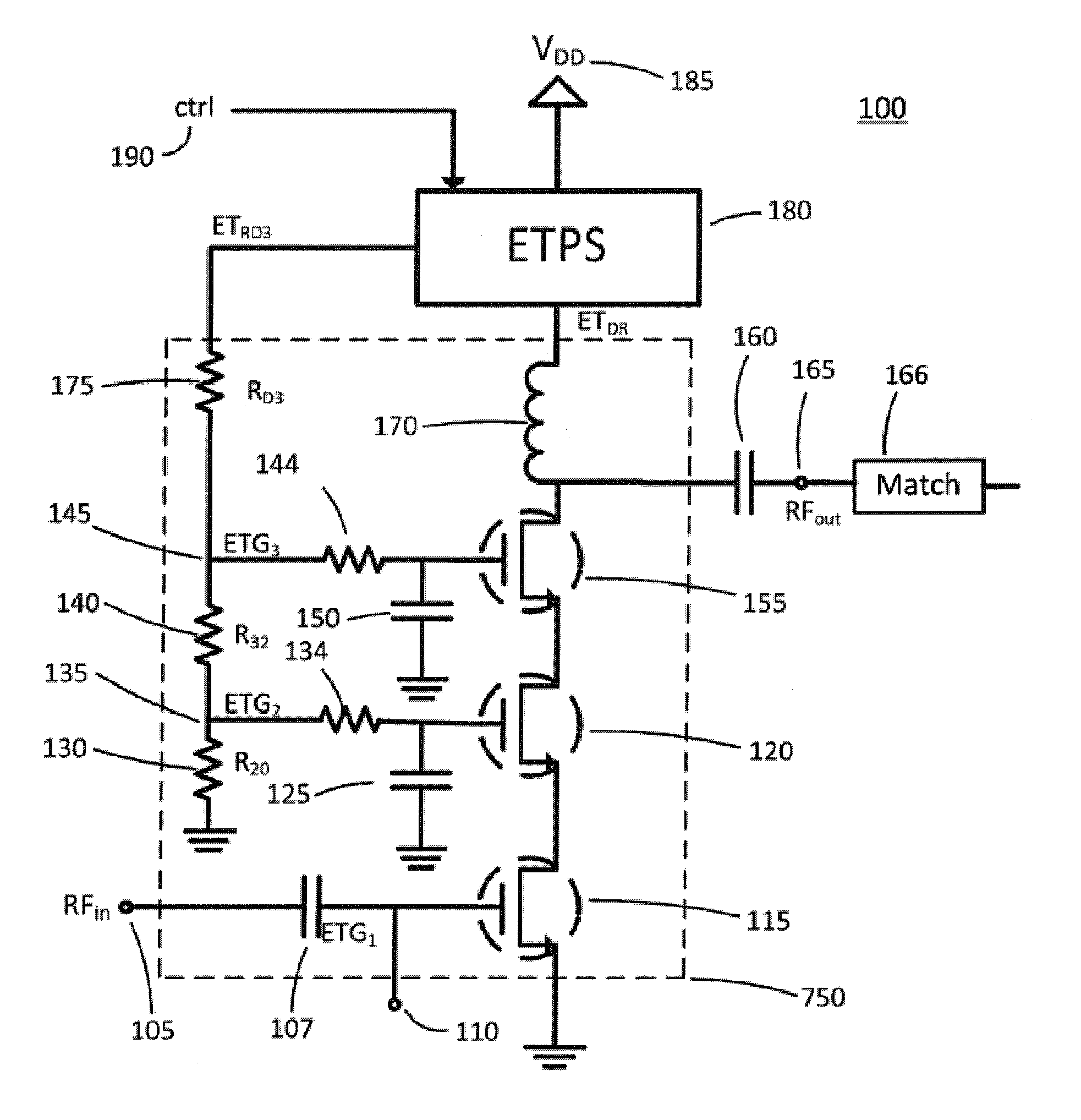
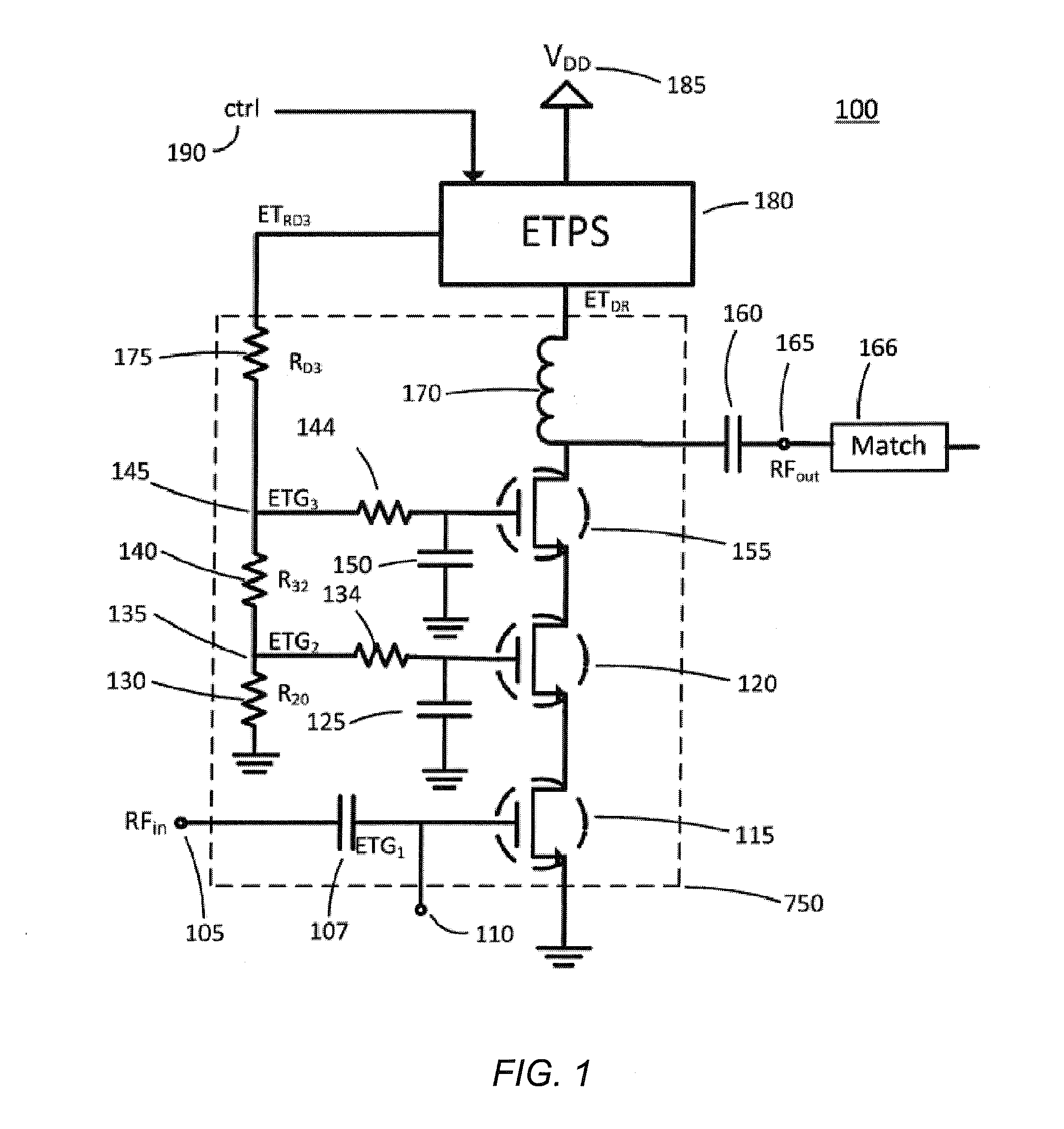
Scalable Periphery Tunable Matching Power Amplifier
A scalable periphery tunable matching power amplifier is presented. Varying power levels can be accommodated by selectively activating or deactivating unit cells of which the scalable periphery tunable matching power amplifier is comprised. Tunable matching allows individual unit cells to see a constant output impedance, reducing need for transforming a low impedance up to a system impedance and attendant power loss. The scalable periphery tunable matching power amplifier can also be tuned for different operating conditions such as different frequencies of operation or different modes.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
RF transmitter with variably biased RF power amplifier and method therefor
InactiveUS20070281635A1More powerSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasPeak valueWide band
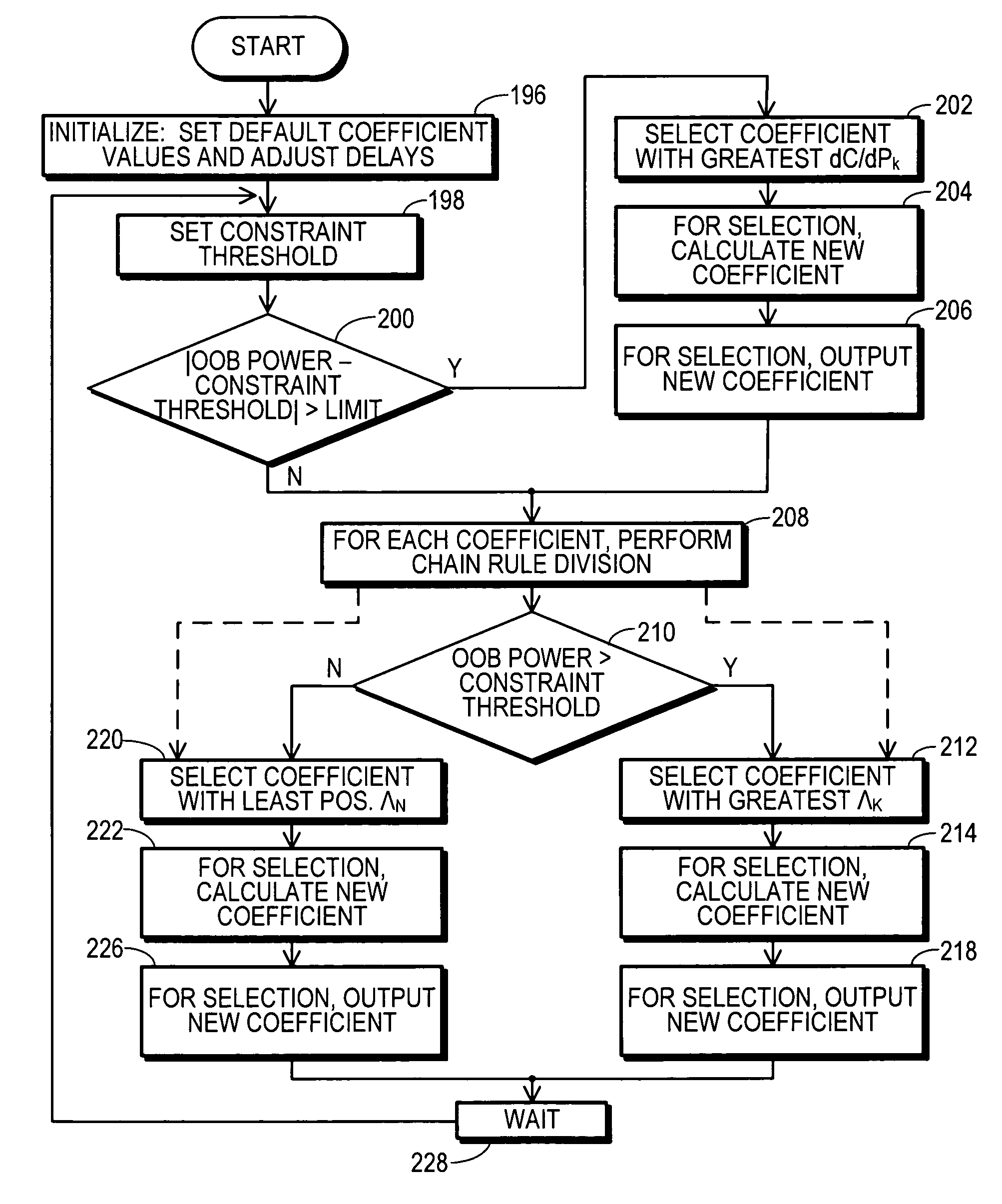
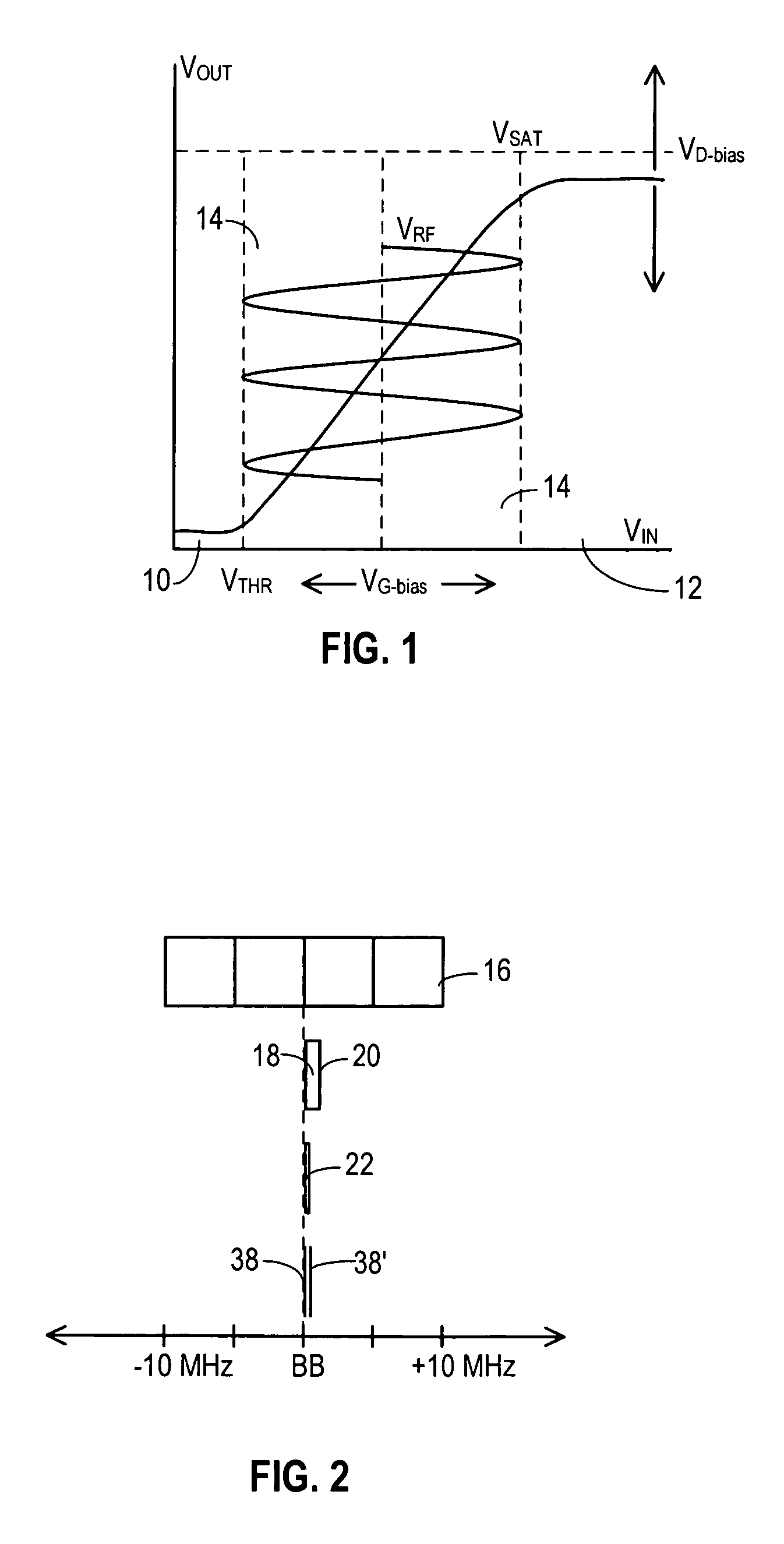
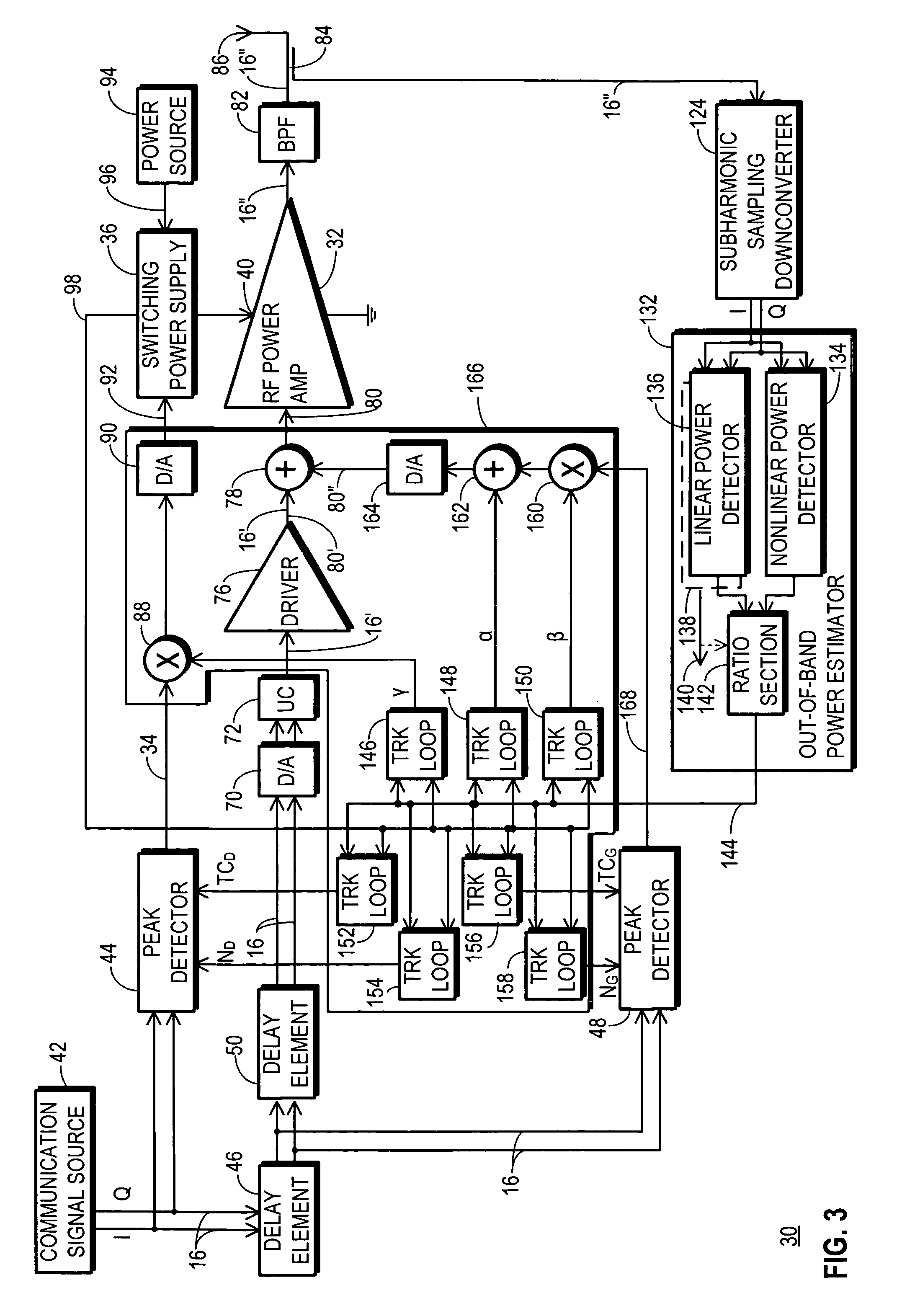
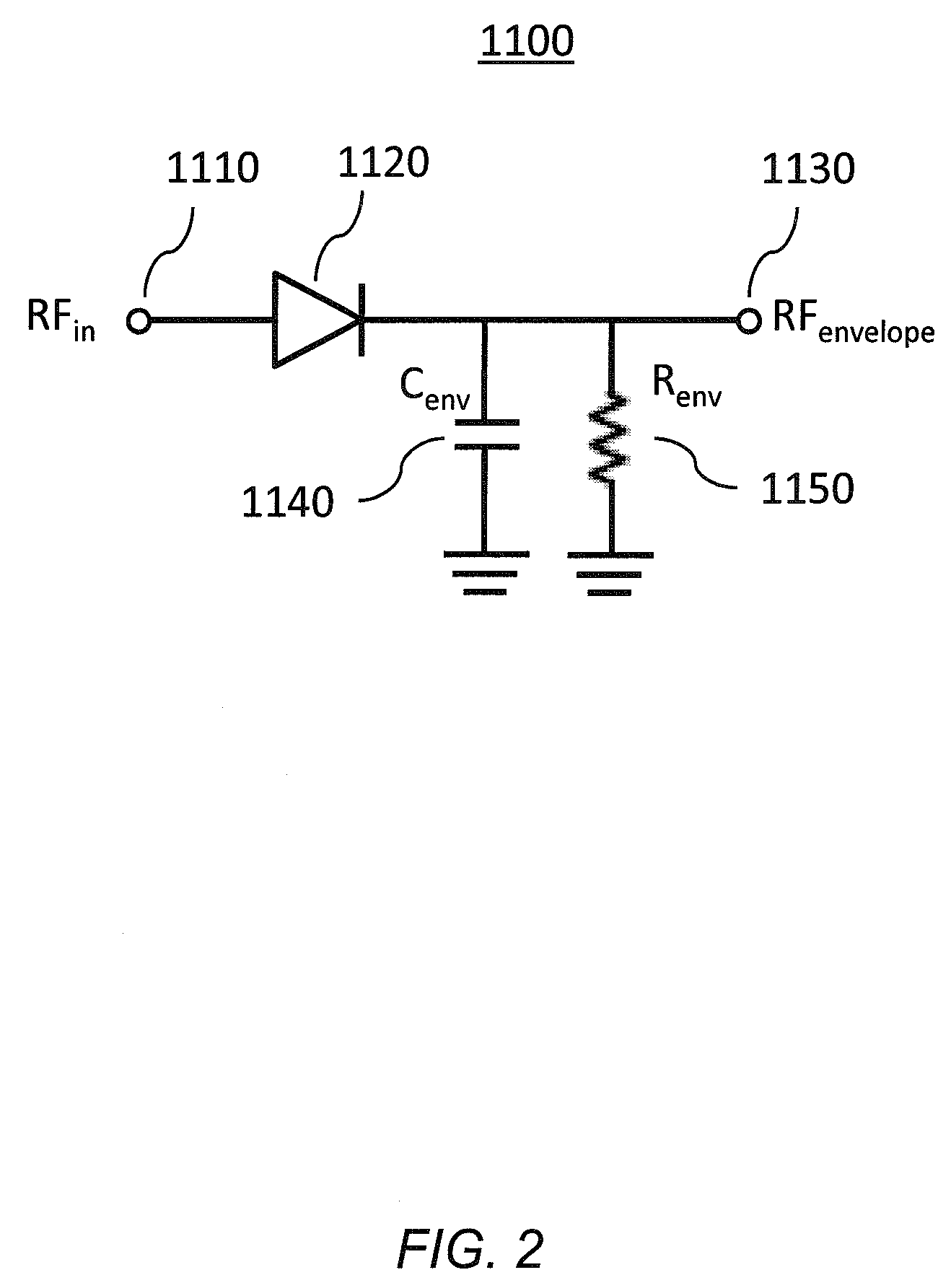
An RF transmitter (30) includes an RF power amplifier (32) for which the power input bias voltage (40) and signal input bias voltage (80) are controlled within feedback loops. A peak detector (44) generates a lowered-spectrum, peak-tracking signal (34) that follows the largest amplitude peaks of a wide bandwidth communication signal (16) but exhibits a lower bandwidth. This signal (34) is scaled in response to the operation of a drain bias tracking loop (146) then used to control a switching power supply (36) that generates the power input bias voltage. The tracking loop (146) is responsive to out-of-band power detected in a portion of the amplified RF communication signal (16″). A ratio of out-of-band power (128) to in-band power (126) is manipulated in the tracking loop (146) so that the power input bias voltage is modulated in a way that holds the out-of-band power at a desired predetermined level.
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
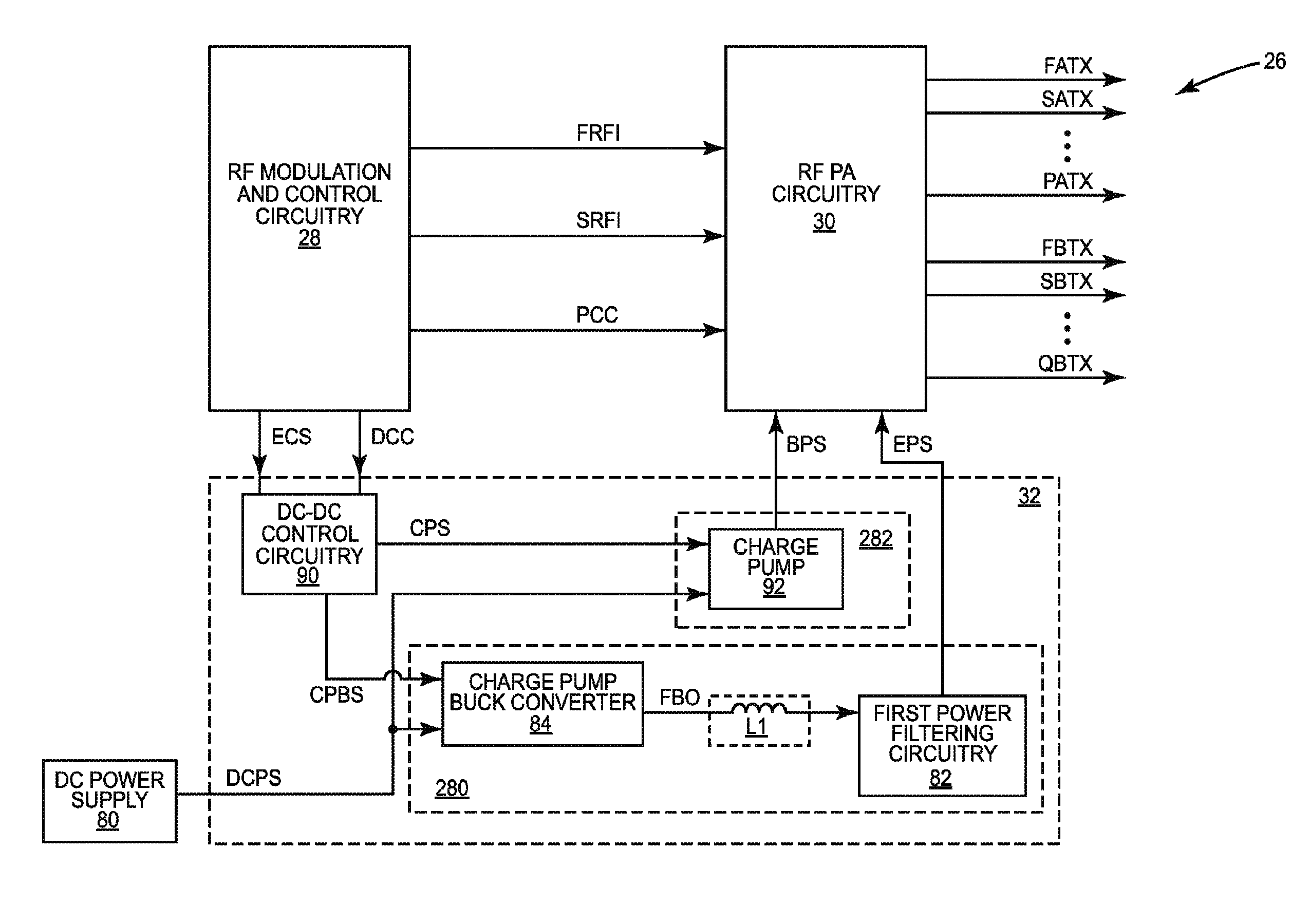
Pa envelope power supply undershoot compensation
ActiveUS20120299647A1Prevent undershootHigh frequency amplifiersGated amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
A power amplifier (PA) envelope power supply, which provides an envelope power supply signal to radio frequency (RF) PA circuitry, and a process to prevent undershoot of the PA envelope power supply is disclosed. The process includes determining if an envelope control signal to the PA envelope power supply has a step change from a high magnitude to a low magnitude that exceeds a step change limit. Such a step change may cause undershoot of the PA envelope power supply. As such, if the step change exceeds the step change limit, the envelope control signal is modified to use an intermediate magnitude for period of time. Otherwise, if the step change does not exceed the step change limit, the envelope control signal is not modified.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Digital Hybrid Mode Power Amplifier System
InactiveUS20080265996A1High performance and cost-effectiveImprove linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersPeak valueMulti carrier
A RF-digital hybrid mode power amplifier system for achieving high efficiency and high linearity in wideband communication systems is disclosed. The present invention is based on the method of adaptive digital predistortion to linearize a power amplifier in the RF domain. The power amplifier characteristics such as variation of linearity and asymmetric distortion of the amplifier output signal are monitored by the narrowband feedback path and controlled by the adaptation algorithm in a digital module. Therefore, the present invention could compensate the nonlinearities as well as memory effects of the power amplifier systems and also improve performances, in terms of power added efficiency, adjacent channel leakage ratio and peak-to-average power ratio. The present disclosure enables a power amplifier system to be field reconfigurable and support multi-modulation schemes (modulation agnostic), multi-carriers and multi-channels. As a result, the digital hybrid mode power amplifier system is particularly suitable for wireless transmission systems, such as base-stations, repeaters, and indoor signal coverage systems, where baseband I-Q signal information is not readily available.
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
Optimization Methods for Amplifier with Variable Supply Power
ActiveUS20140184334A1Affecting responseAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierLinear region
Optimization methods via various circuital arrangements for amplifier with variable supply power are presented. In one embodiment, a switch can be controlled to include or exclude a feedback network in a feedback path to the amplifier to adjust a response of the amplifier dependent on a region of operation of the amplifier arrangement (e.g. linear region or compression region).
Owner:PSEMI CORP
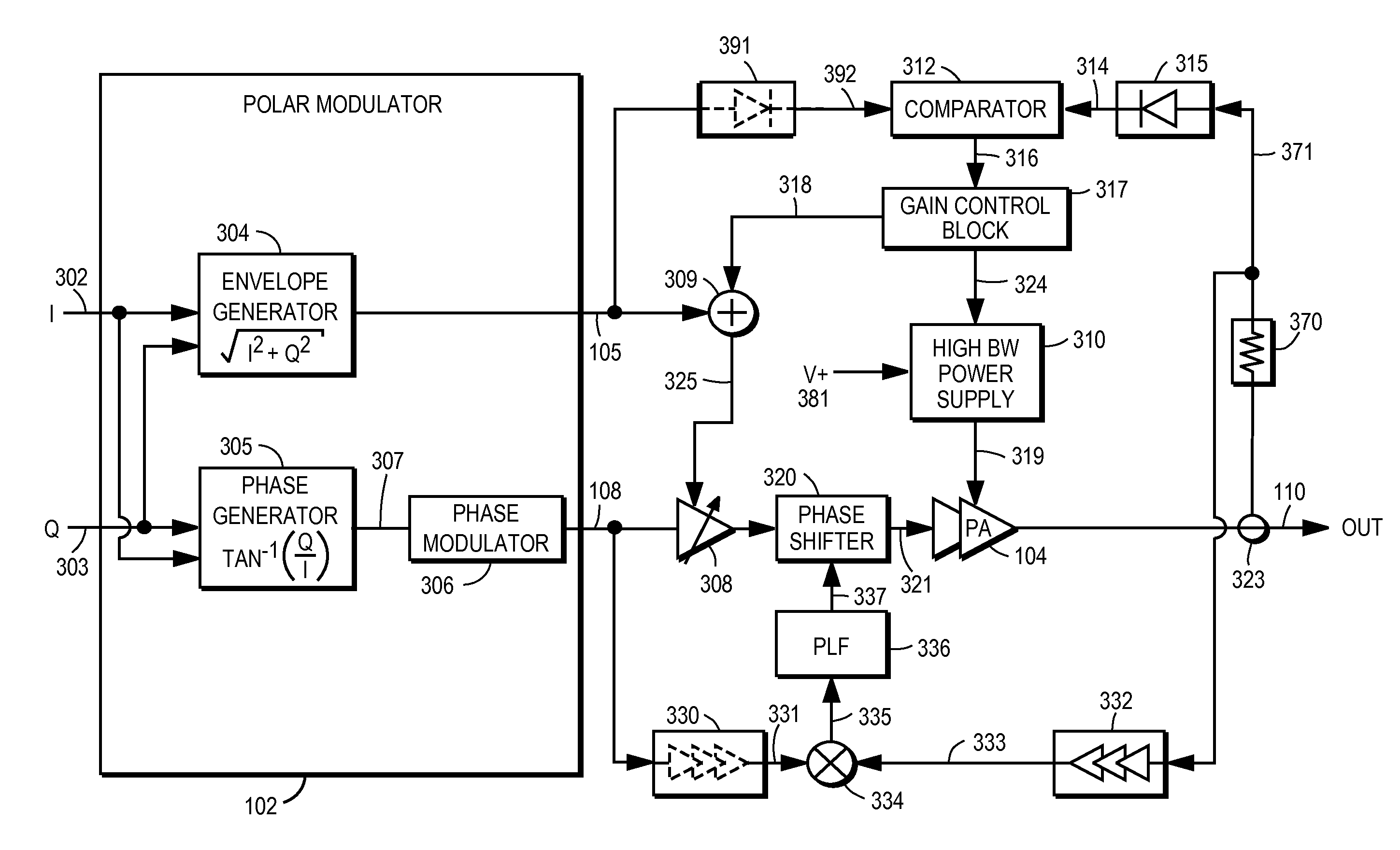
Power amplifier controller with polar transmitter
ActiveUS7783269B2Reduce glitchesImprove power efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierEngineering
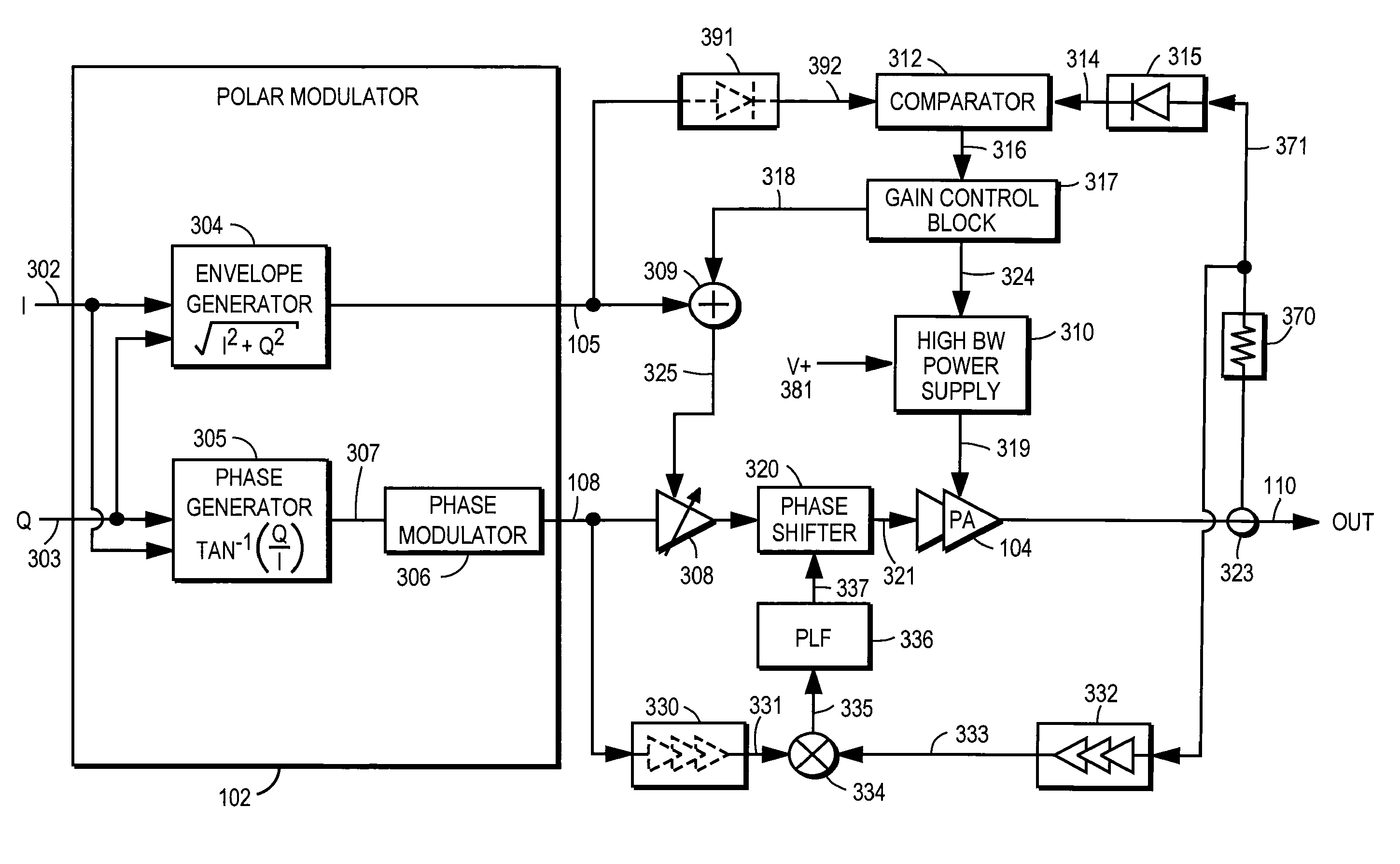
A power amplifier controller controls a power amplifier and is coupled to a polar modulator. The polar modulator generates an amplitude component and a phase-modulated component of the desired RF modulated signal, and outputs to the power amplifier controller. The power amplifier controller regenerates a combined phase and amplitude modulated RF signal to generate an input signal to a power amplifier by adjusting the gain of a VGA based on the amplitude component of the desired RF modulated signal. Concurrently, the power amplifier controller both controls an adjusted supply voltage to the PA and adjusts the gain of the VGA based upon an amplitude correction signal or amplitude error signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Optimization methods for amplifier with variable supply power
ActiveUS9219445B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlLinear regionAudio power amplifier
Owner:PSEMI CORP
RF Power Amplifier Controller Circuit Including Calibrated Phase Control Loop
ActiveUS20070184794A1Reduce phase distortionNarrow bandwidthResonant long antennasPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierPhase difference
An RF power amplifier system comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal. The phase control loop may comprise one or more variable phase delays introducing a relative phase delay to allow the phase differences between the input and output signals of the PA circuit to be within a range compatible with a phase comparator generating the phase error signal, and a low frequency blocking module that removes the larger extent, lower frequency components of the phase error signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
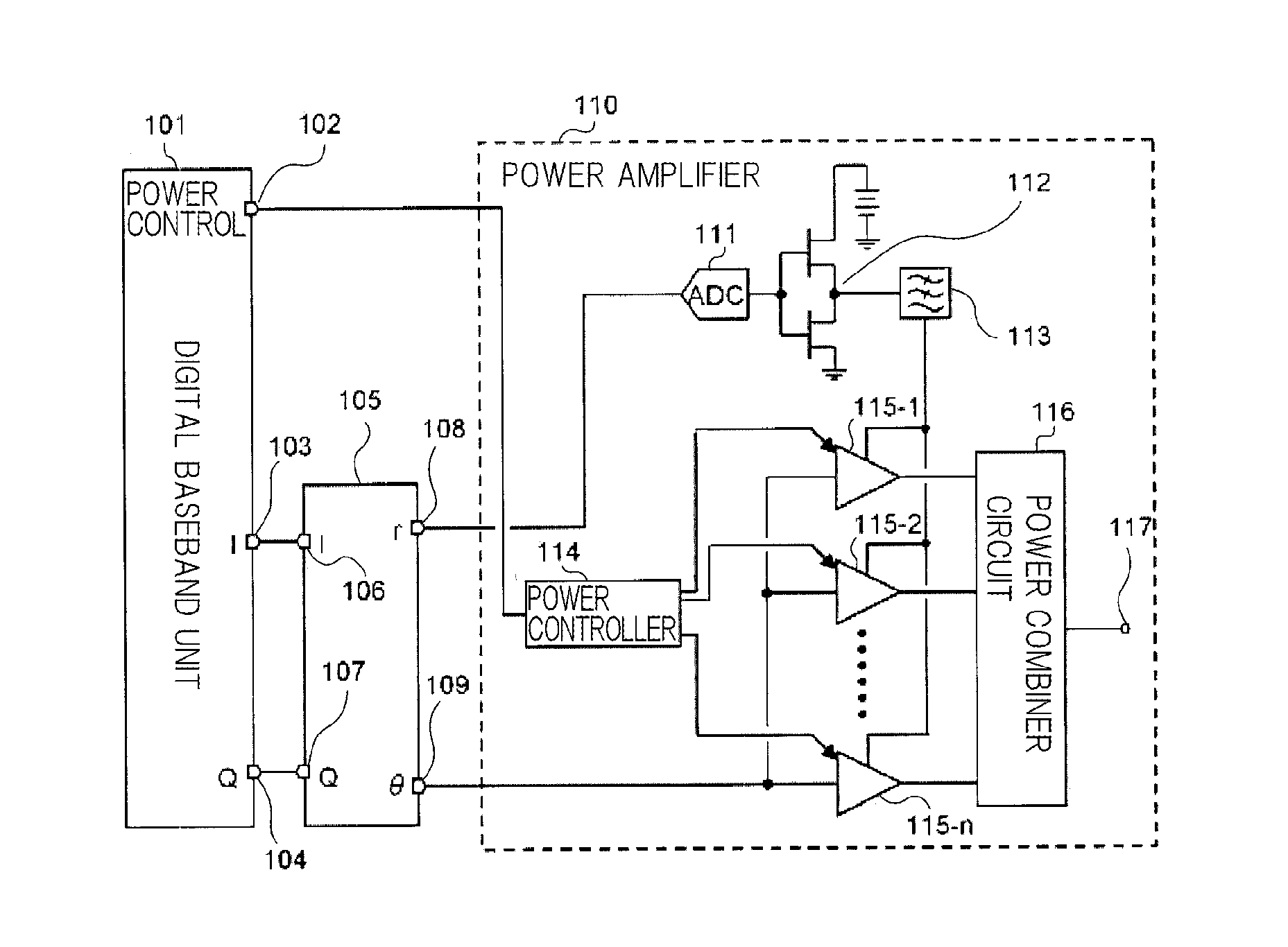
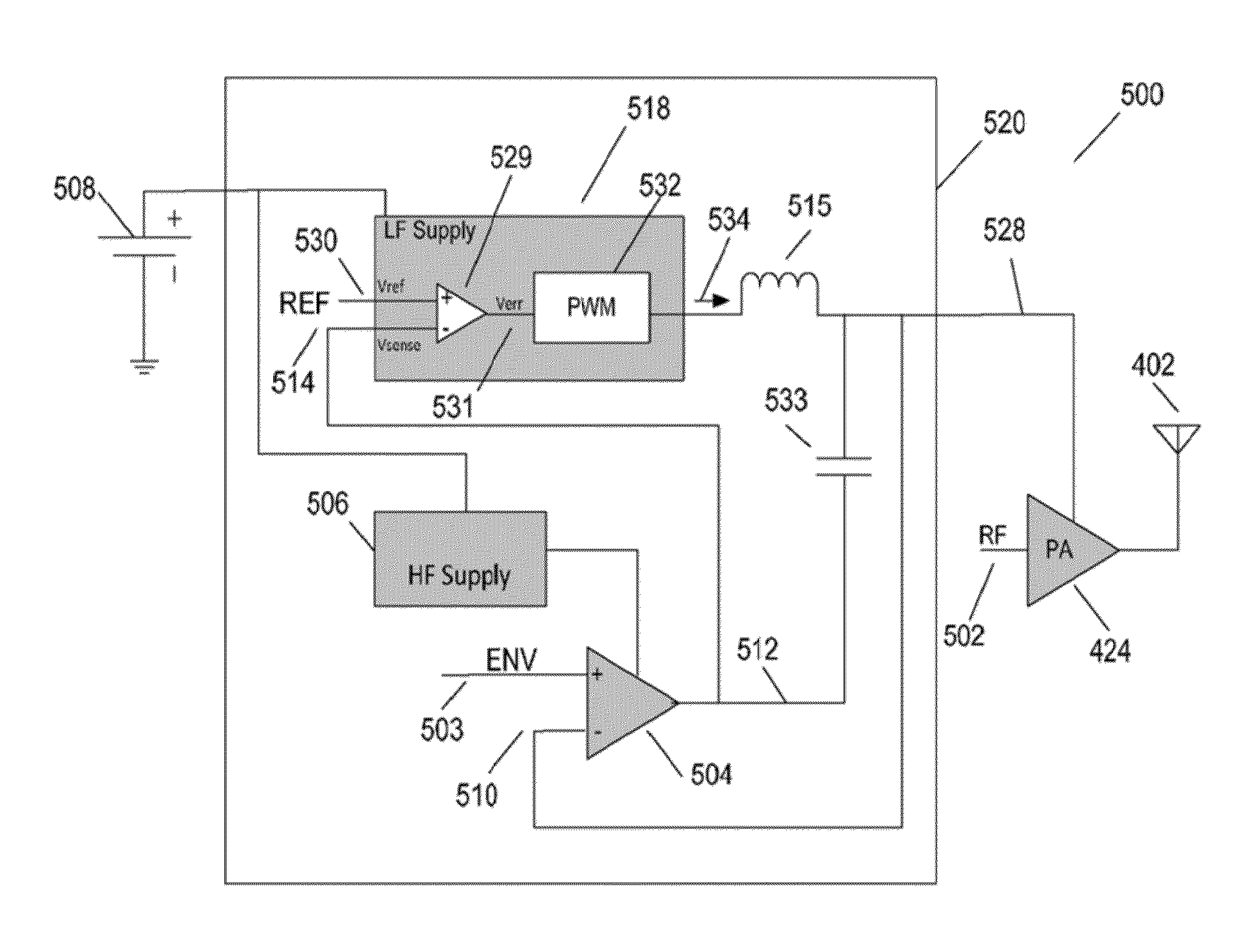
Power amplifier and radio wave transmitter having the same
ActiveUS20100266066A1Eliminate high frequency noiseNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsPower controllerHigh frequency power
A power amplifier (10) comprises: an A / D converter (11) for converting, to a time discrete signal, an envelope signal included in a high-frequency modulated signal and including only an amplitude modulated component of the high-frequency modulated signal; a switching amplifier (12) for amplifying the output signal of the A / D converter (11); a low-pass filter (13) for removing high frequency noise from the output signal of the switching amplifier (12); a plurality of high-frequency power amplifiers (15-1 to 15-n) for receiving the output signal of the low-pass filter (13) as a power supply and for amplifying a carrier signal included in the high-frequency modulated signal; and a power controller (14) for adjusting the average power of the output signal of the power amplifier (10) by controlling the total gains of the plurality of high-frequency power amplifiers (15-1 to 15-n).
Owner:NEC CORP
Balanced high-frequency device and balance-characteristics improving method and balanced high-frequency circuit using the same
InactiveUS6900705B2Reduce componentsImpedence matching networksMultiple-port networksHemt circuitsEngineering
Owner:SKYWORKS PANASONIC FILTER SOLUTIONS JAPAN
Remote radio head unit system with wideband power amplifier and method
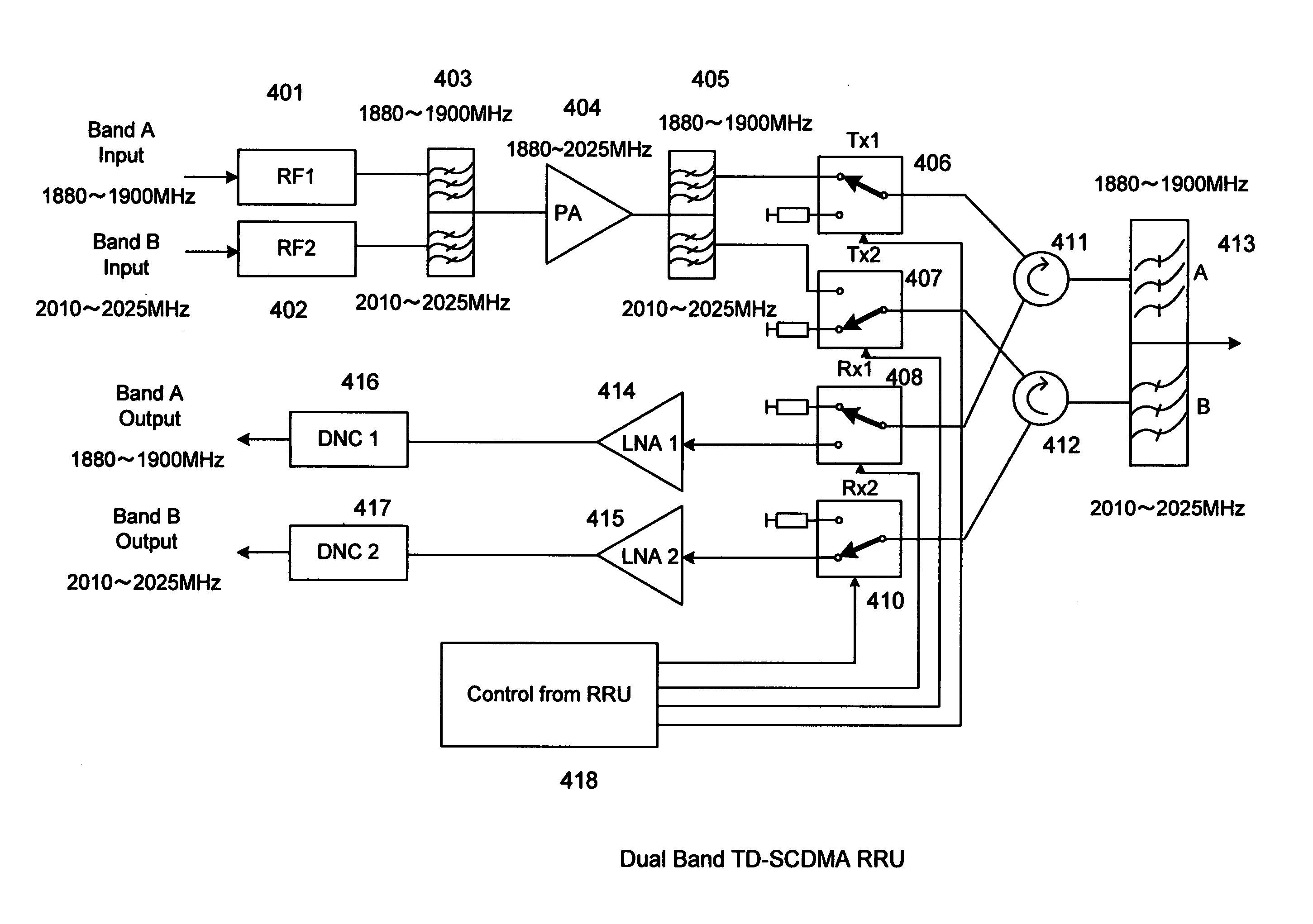
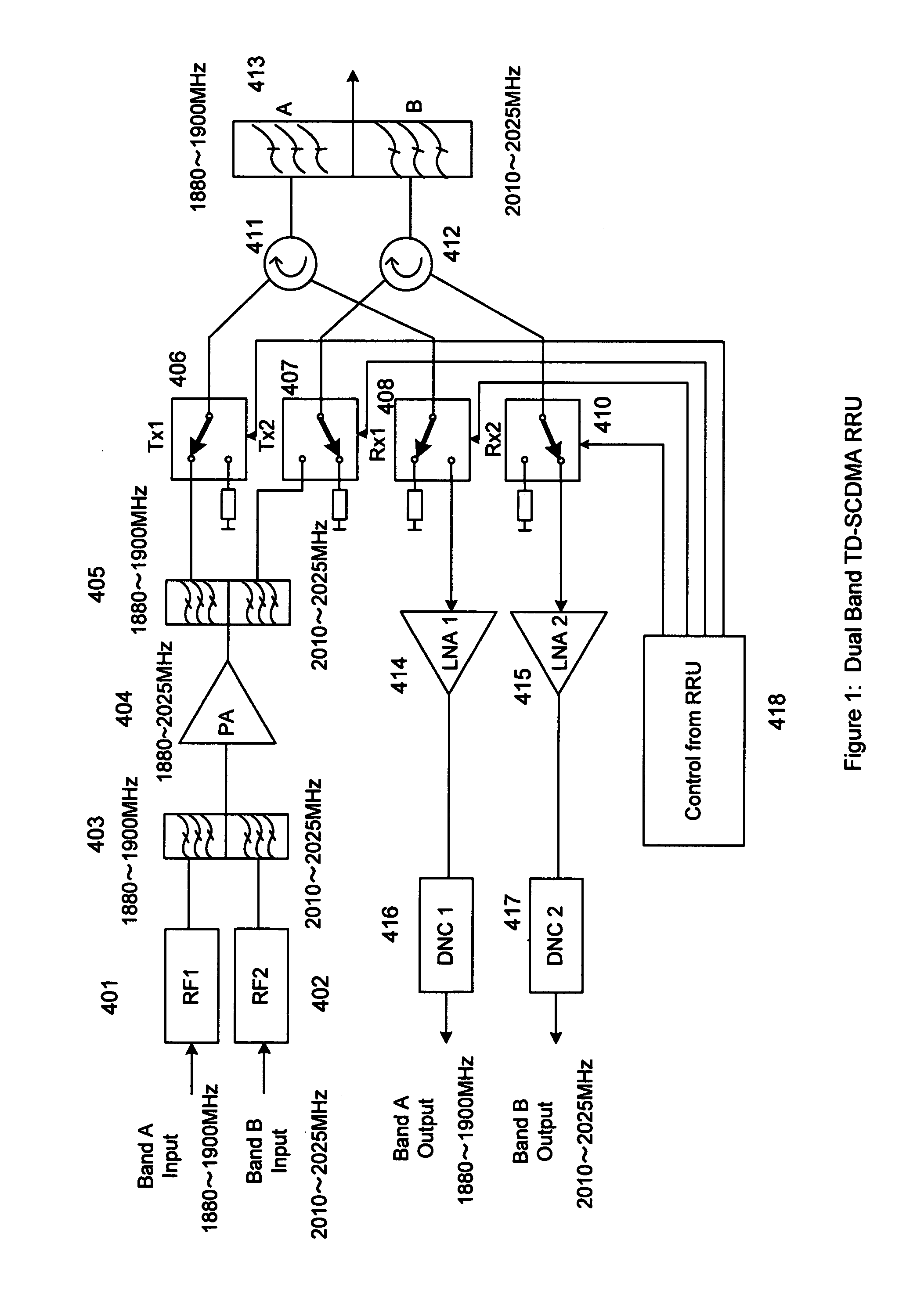
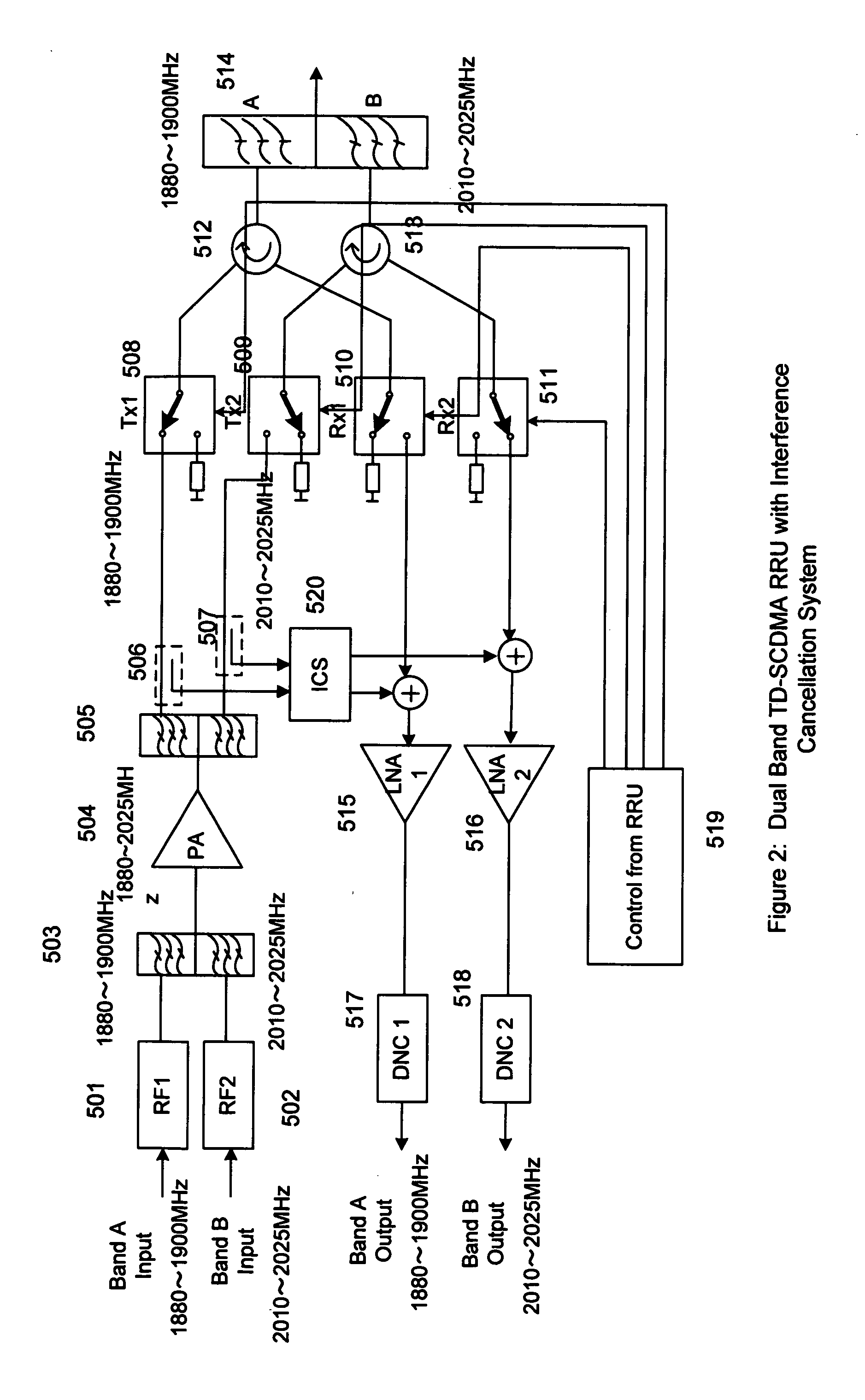
ActiveUS20110158081A1Improve performanceCost is economizedAmplifiers with memory effect compensationAmplifier with control circuitsMulti bandAudio power amplifier
A remote radio head unit (RRU) system for multiple operating frequency bands, multi-channels, driven by a single or more wide band power amplifiers. More specifically, the present invention enables multiple-bands RRU to use fewer power amplifers in order to reduce size and cost of the multi-band RRU. The present invention is based on the method of using duplexers and / or interference cancellation system technique to increase the isolation between the transmitter signal and receiver signal of the RRU.
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
Direct current (DC)-dc converter having a multi-stage output filter
ActiveUS20130271221A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceDc dc converter
A direct current (DC)-DC converter that includes a first switching converter and a multi-stage filter is disclosed. The multi-stage filter includes at least a first inductance (L) capacitance (C) filter and a second LC filter coupled in series between the first switching converter and a DC-DC converter output. The first LC filter has a first LC time constant and the second LC filter has a second LC time constant, which is less than the first LC time constant. The first switching converter and the multi-stage filter form a feedback loop, which is used to regulate the first switching power supply output signal based on the setpoint. The first LC filter includes a first capacitive element having a first self-resonant frequency, which is about equal to a first notch frequency of the multi-stage filter.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Dynamic stability, gain, efficiency and impedance control in a linear/non-linear CMOS power amplifier
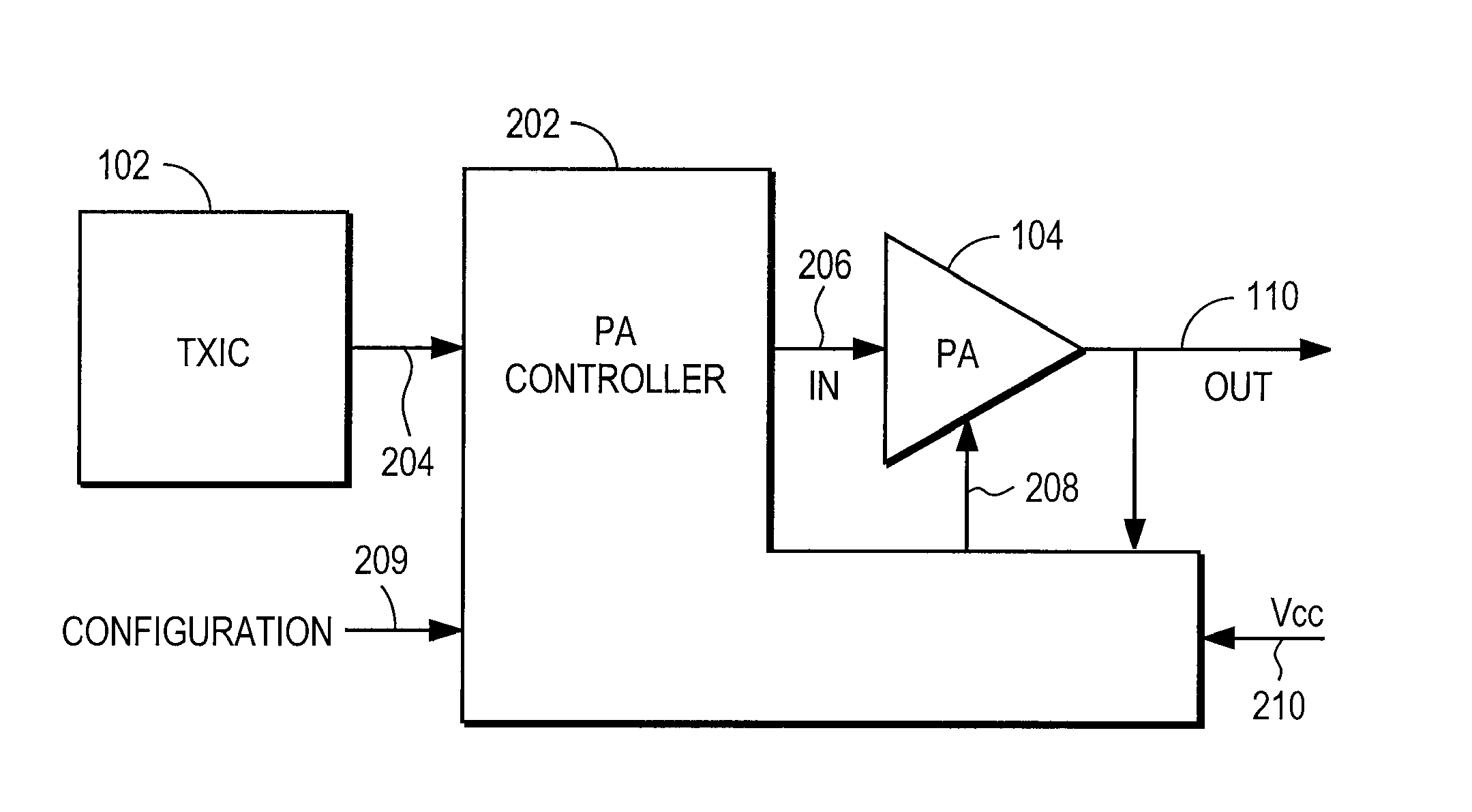
A power amplifier (PA) provides dynamic stability and gain control for linear and non-linear operation. The PA operates with a baseband processor and a transmitter, in which the PA receives a signal from the transmitter for power amplification prior to transmission of the signal. The PA is configured to select between the linear mode of operation and the non-linear mode of operation, in which device scaling within the PA is achieved by changing a device sizing of at least one stage of the PA. Further to changing the device size, the PA changes biasing resistance and impedance of a matching network in response to the changing of the device size to control power output and stability for the PA.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Control Systems and Methods for Power Amplifiers Operating in Envelope Tracking Mode
ActiveUS20140184337A1Improve stabilityReduce oscillationPower amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierControl system
Control systems and methods for power amplifiers operating in envelope tracking mode are presented. A set of corresponding functions and modules are described and various possible system configurations using such functions and modules are presented.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Power Amplifier Controller With Polar Transmitter
ActiveUS20100311365A1Reduce phase distortionMinimize the differenceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierEngineering
A power amplifier controller controls a power amplifier and is coupled to a polar modulator. The polar modulator generates an amplitude component and a phase-modulated component of the desired RF modulated signal, and outputs to the power amplifier controller. The power amplifier controller regenerates a combined phase and amplitude modulated RF signal to generate an input signal to a power amplifier by adjusting the gain of a VGA based on the amplitude component of the desired RF modulated signal. Concurrently, the power amplifier controller both controls an adjusted supply voltage to the PA and adjusts the gain of the VGA based upon an amplitude correction signal or amplitude error signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Integrated circuit wireless communication unit and method for providing a power supply
ActiveUS20140361837A1Power amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyCommunication unitAudio power amplifier
An integrated circuit comprises a radio frequency (RF) power amplifier (PA) output stage; at least one amplifier stage prior to the RF PA output stage; a linear amplifier comprising a voltage feedback wherein the linear amplifier is operably coupled to a low frequency supply module such that the linear amplifier and low frequency supply module provide a combined first power supply to the RF PA output stage; and a switched mode power supply module arranged to provide a second power supply to the linear amplifier and to the at least one amplifier stage prior to the RF PA output stage.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com