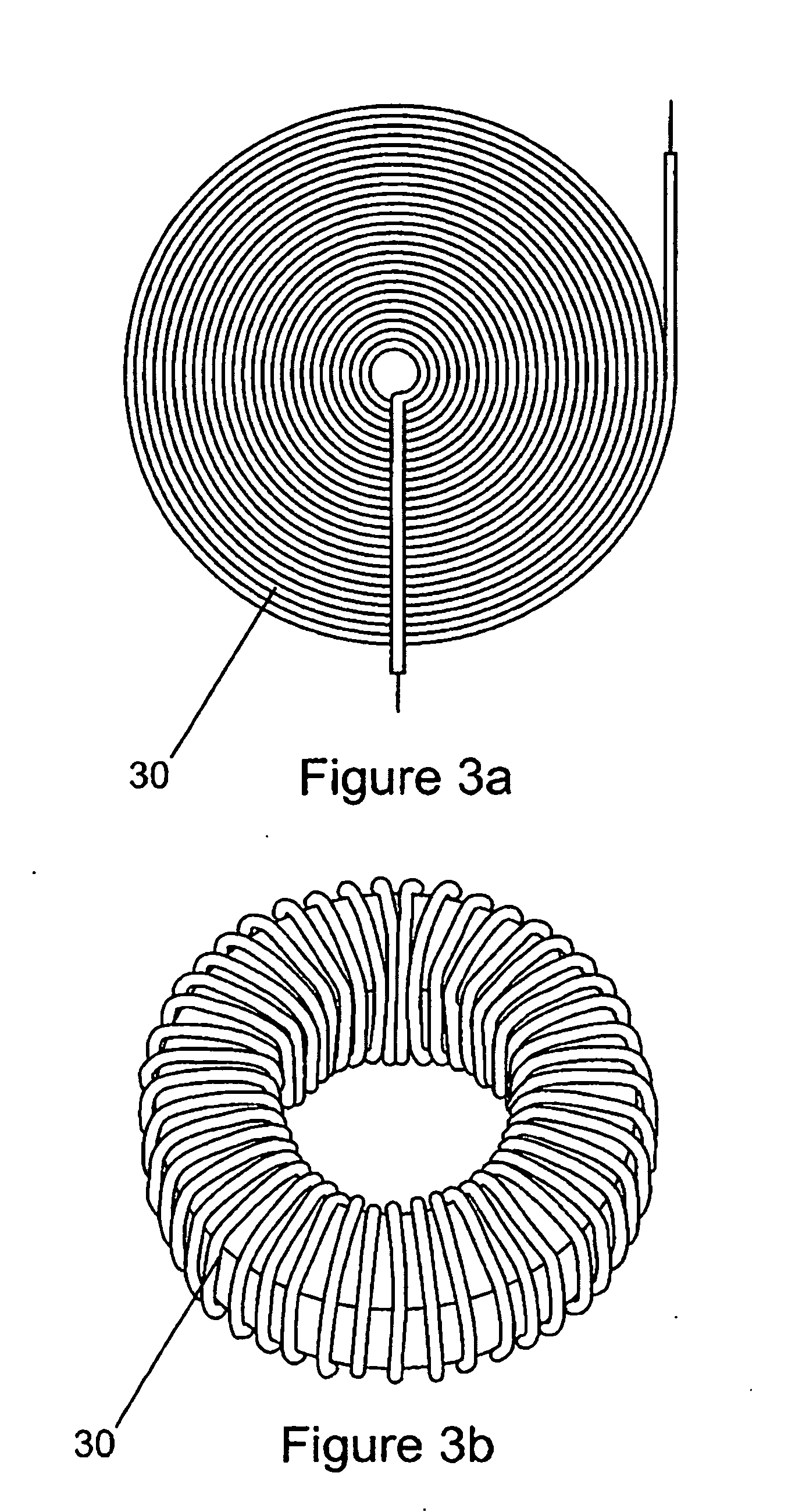
Patents
Literature
4775results about "Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
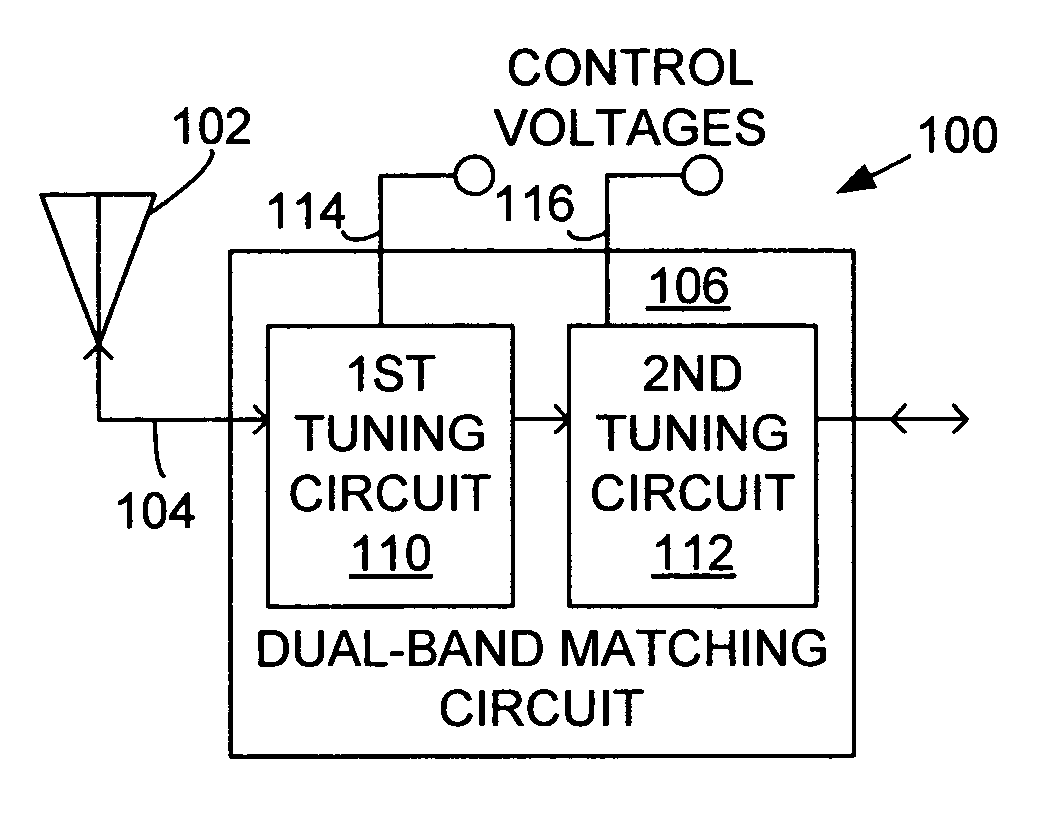
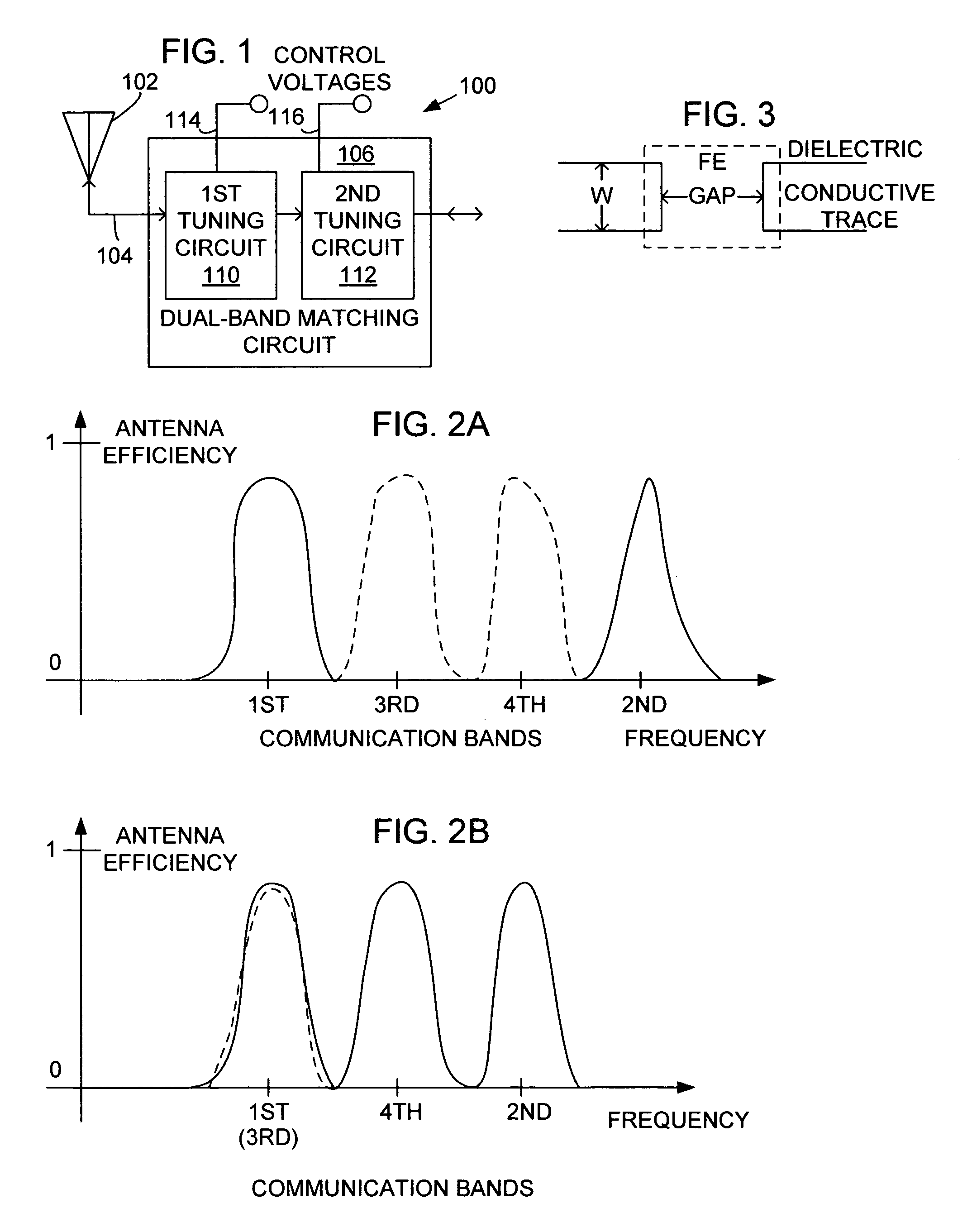
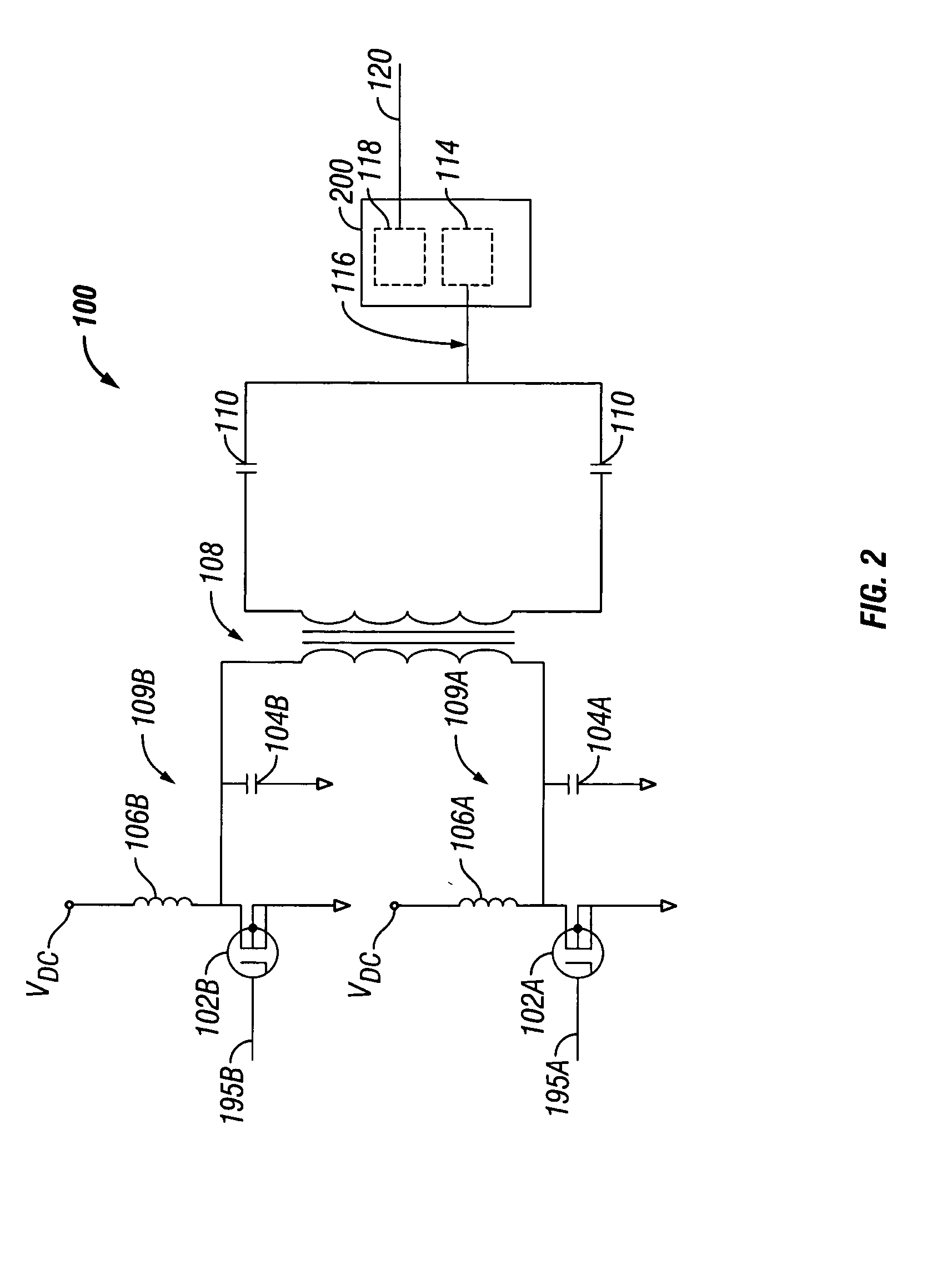
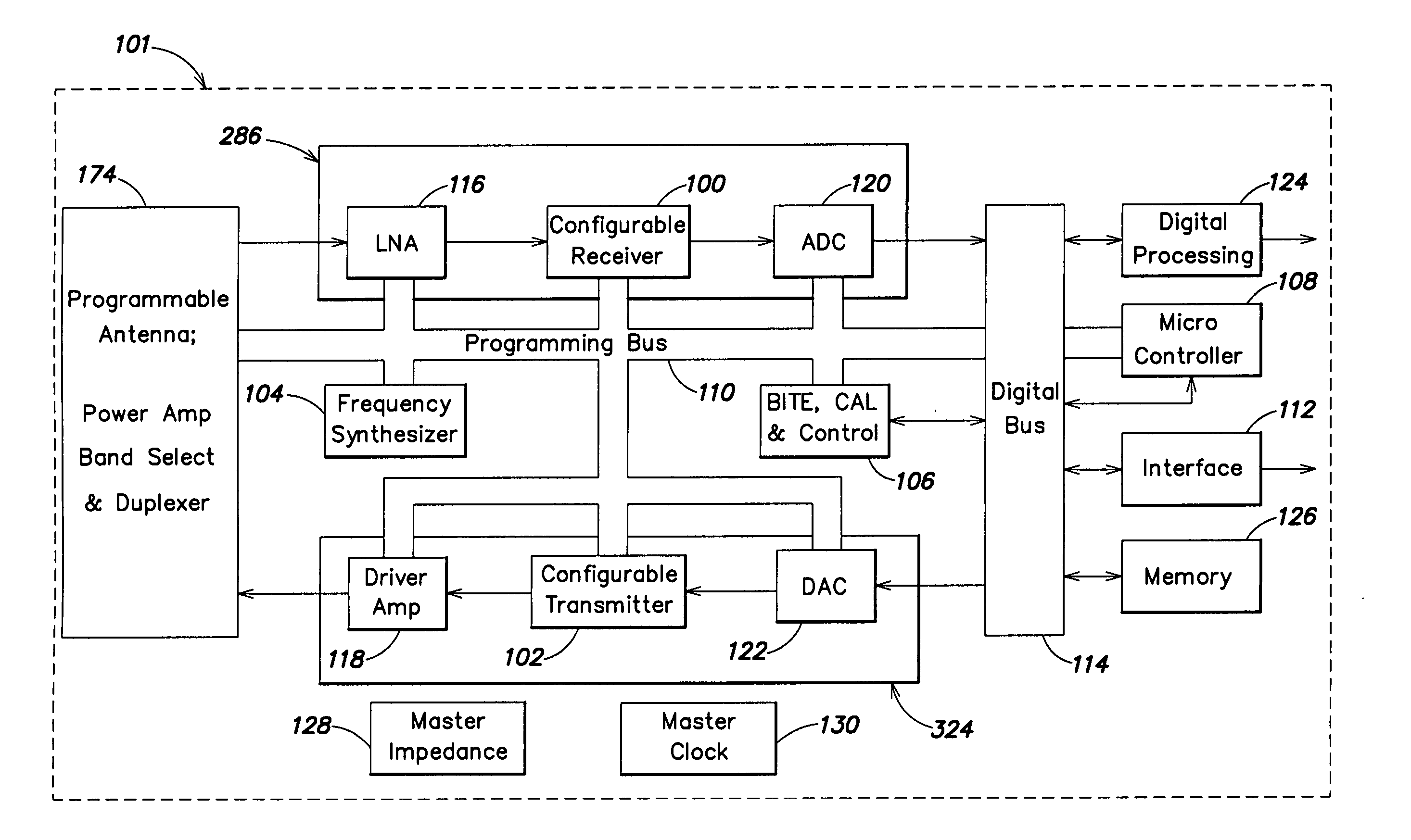
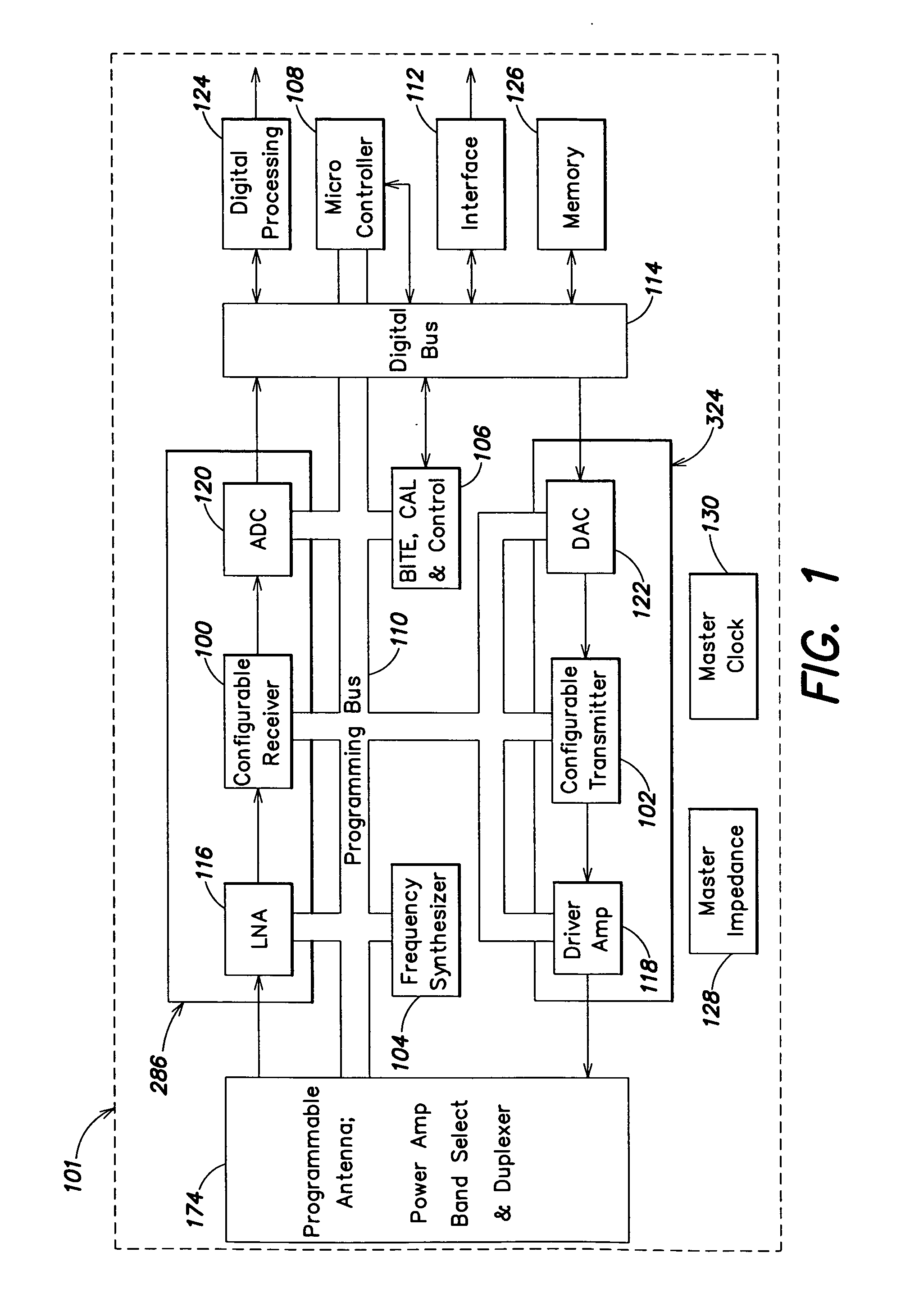
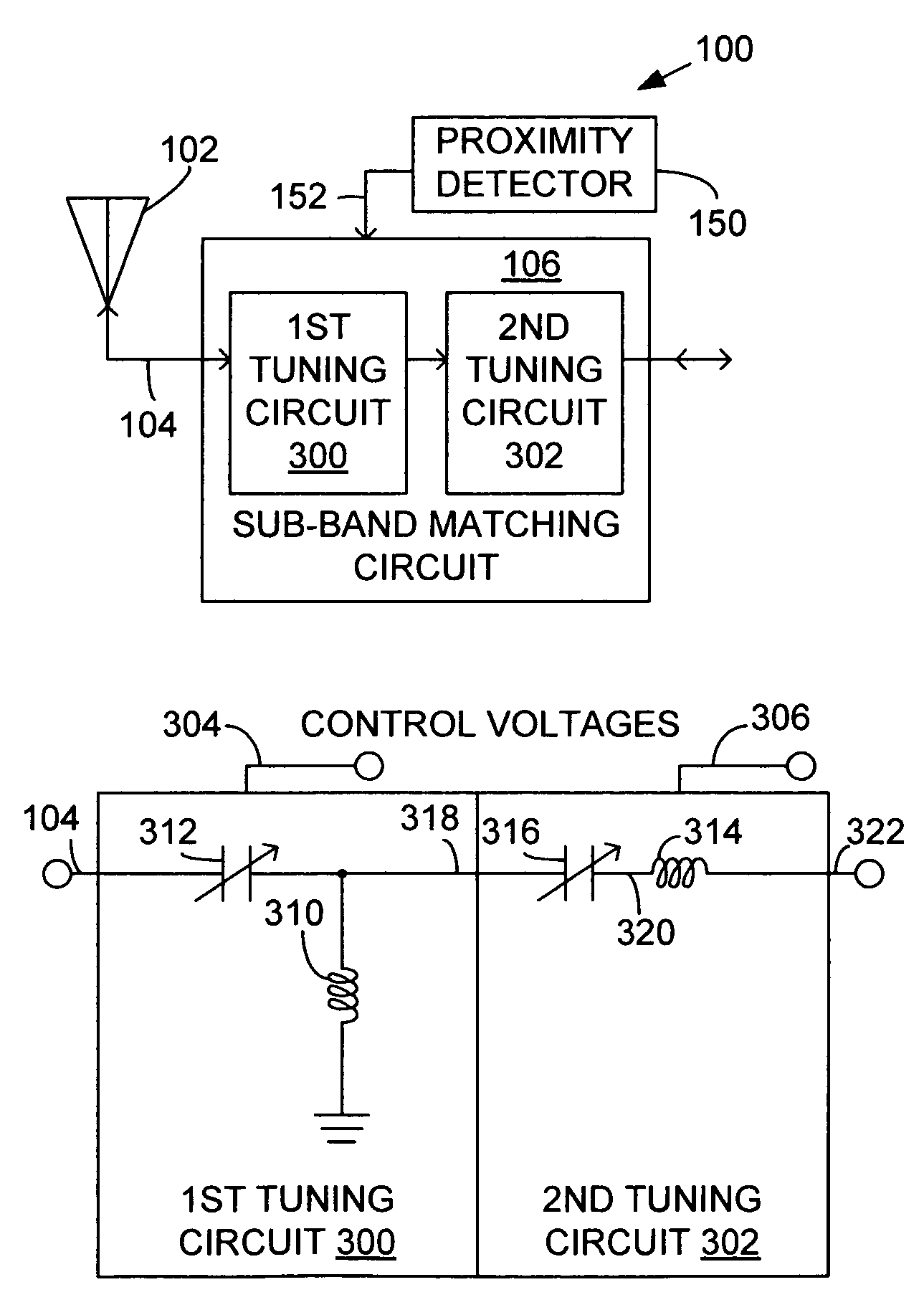
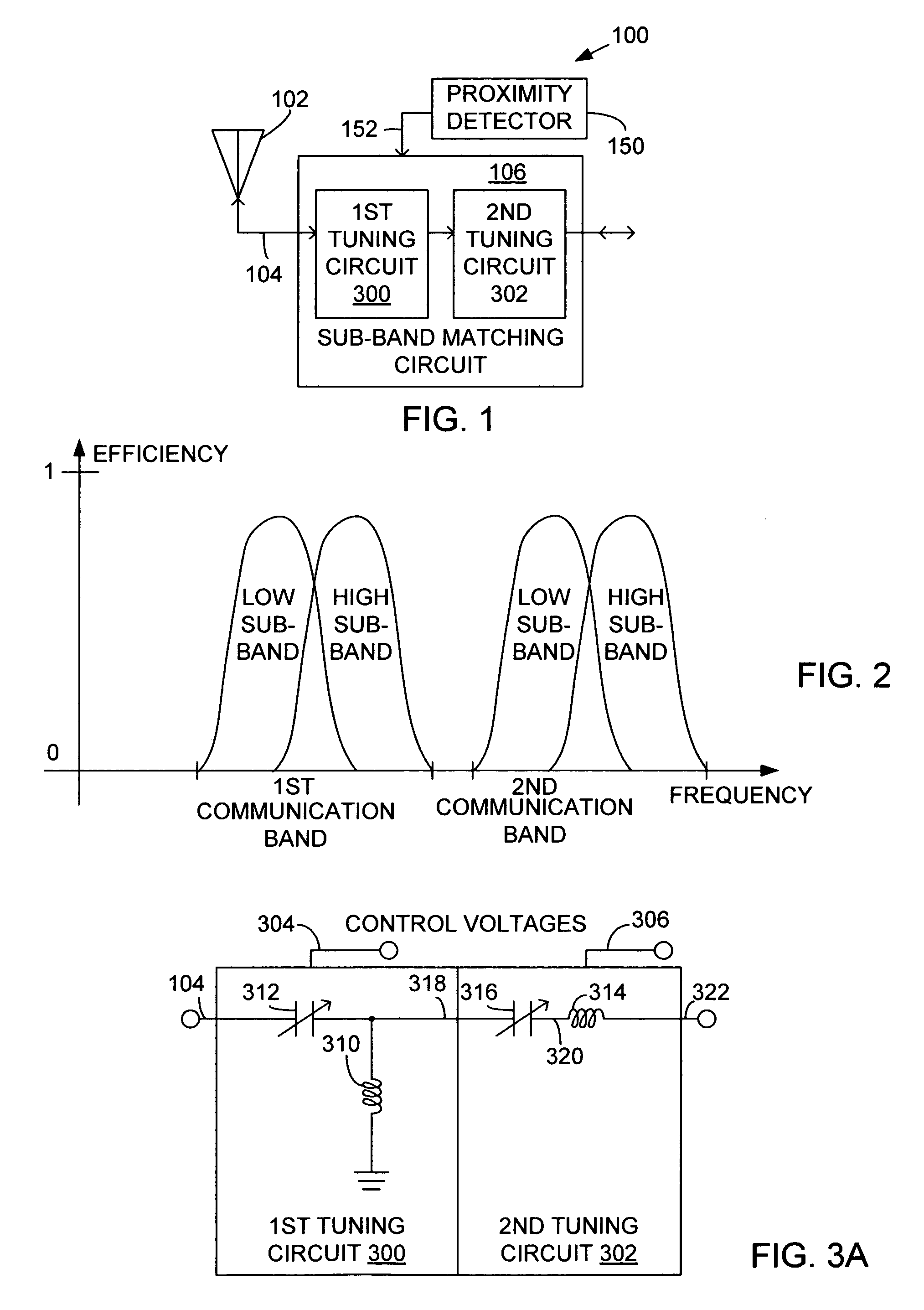
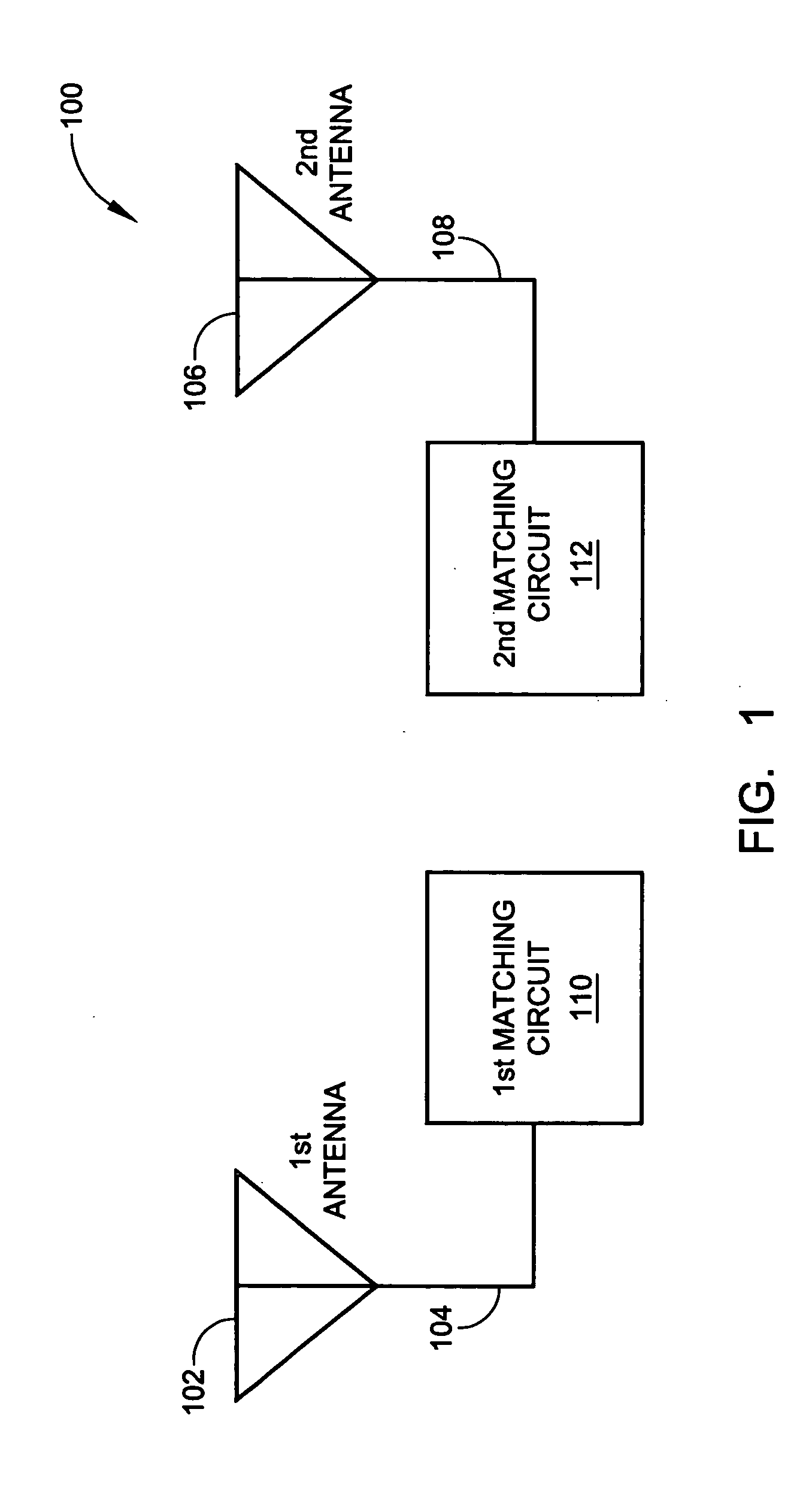
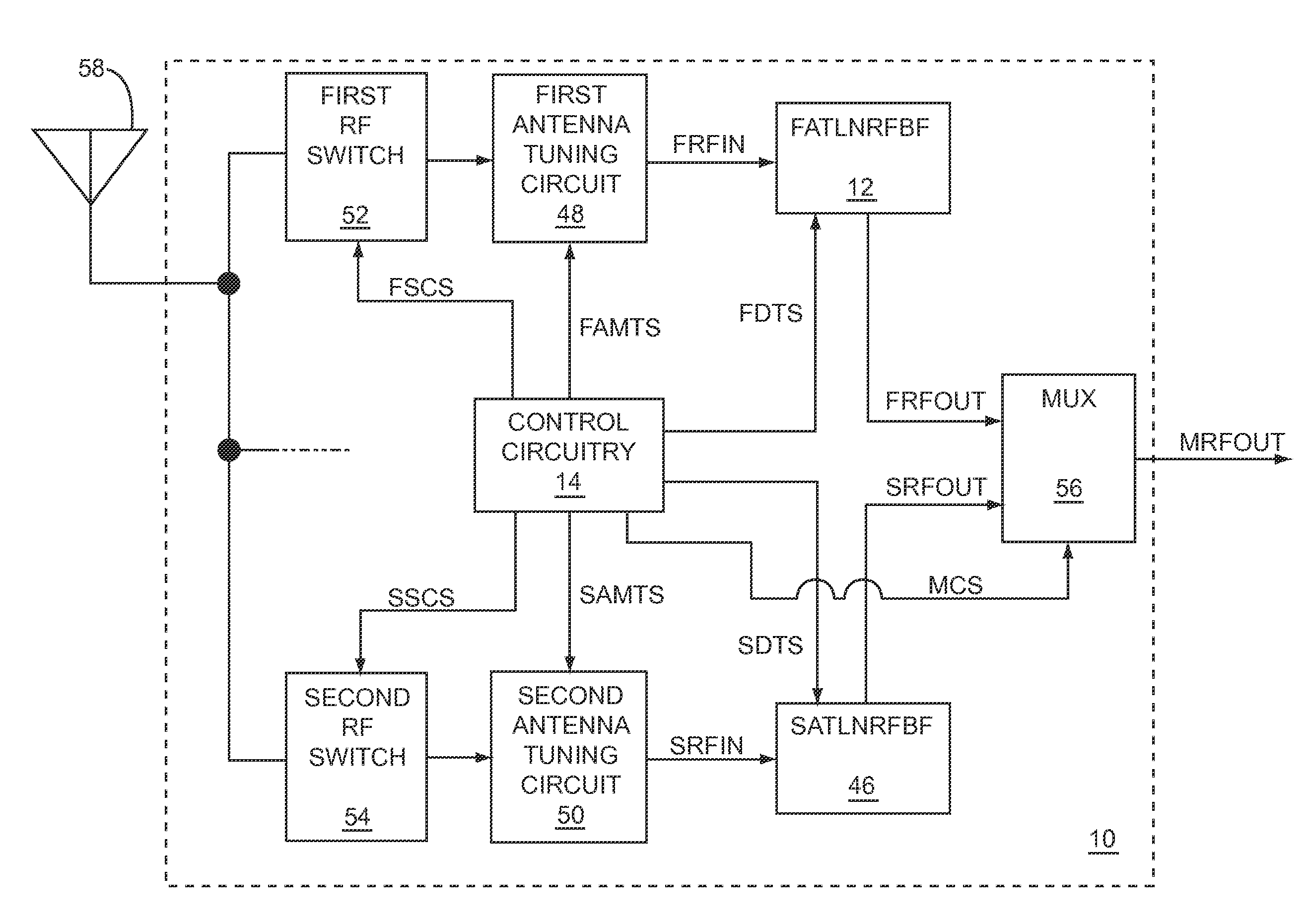
System and method for dual-band antenna matching
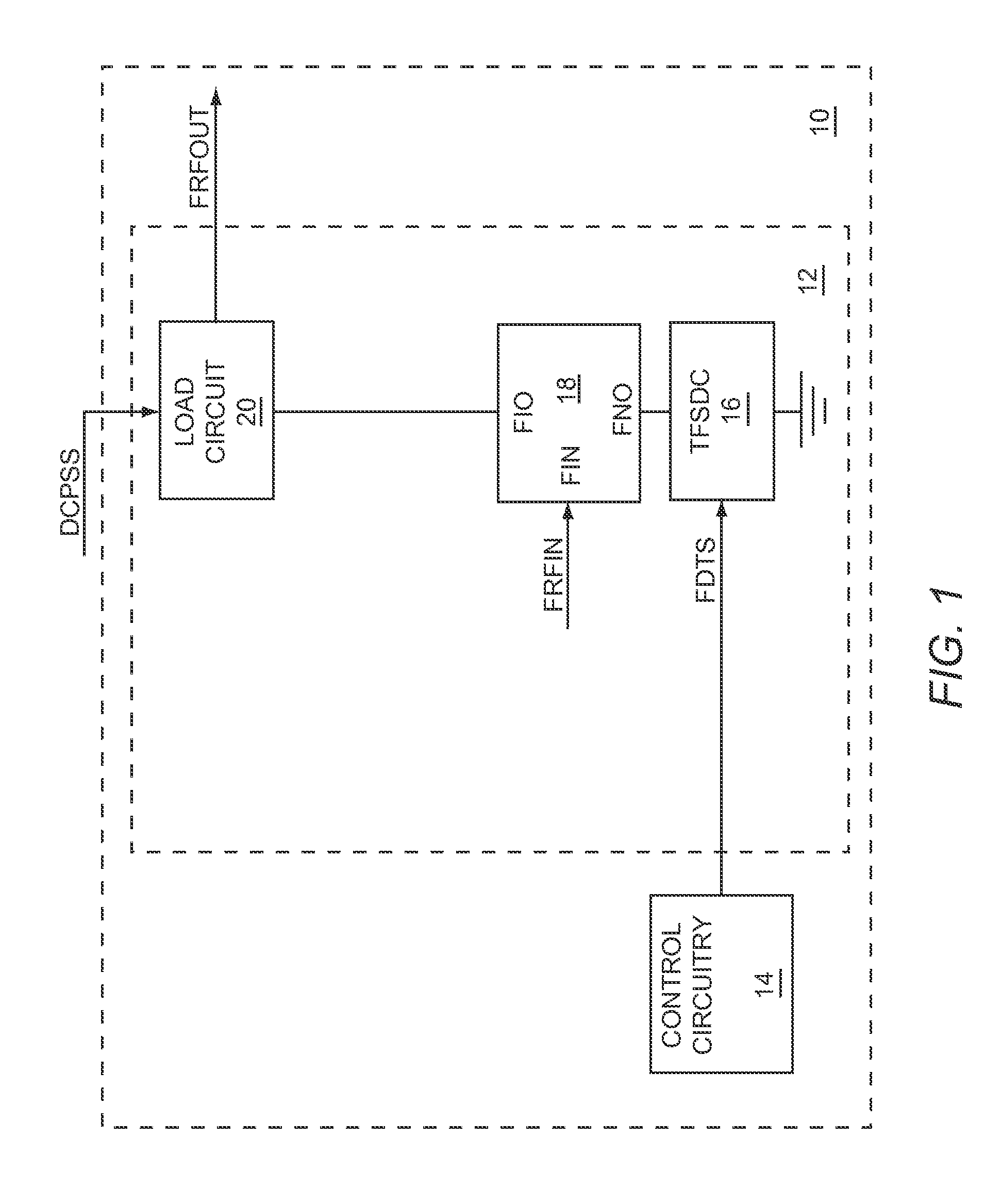
A dual-band antenna matching system and a method for dual-band impedance matching are provided. The method comprises: accepting a frequency-dependent impedance from an antenna; and, selectively supplying a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at either a first and a second communication band, or a third and a fourth communication band. More specifically, the method comprises: tuning a first tuning circuit to a first frequency; and, simultaneously tuning a second tuning circuit to a second frequency. In response, a conjugate match is supplied to the antenna in the first communication band in response to the first frequency. Simultaneously, the antenna is matched in the second communication band in response to the second frequency. When the first tuning circuit is tuned to a third frequency, and the second tuning circuit is tuned to a fourth frequency, then conjugate matches are supplied for the third and fourth communication bands, responsive to the third and fourth frequencies, respectively.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
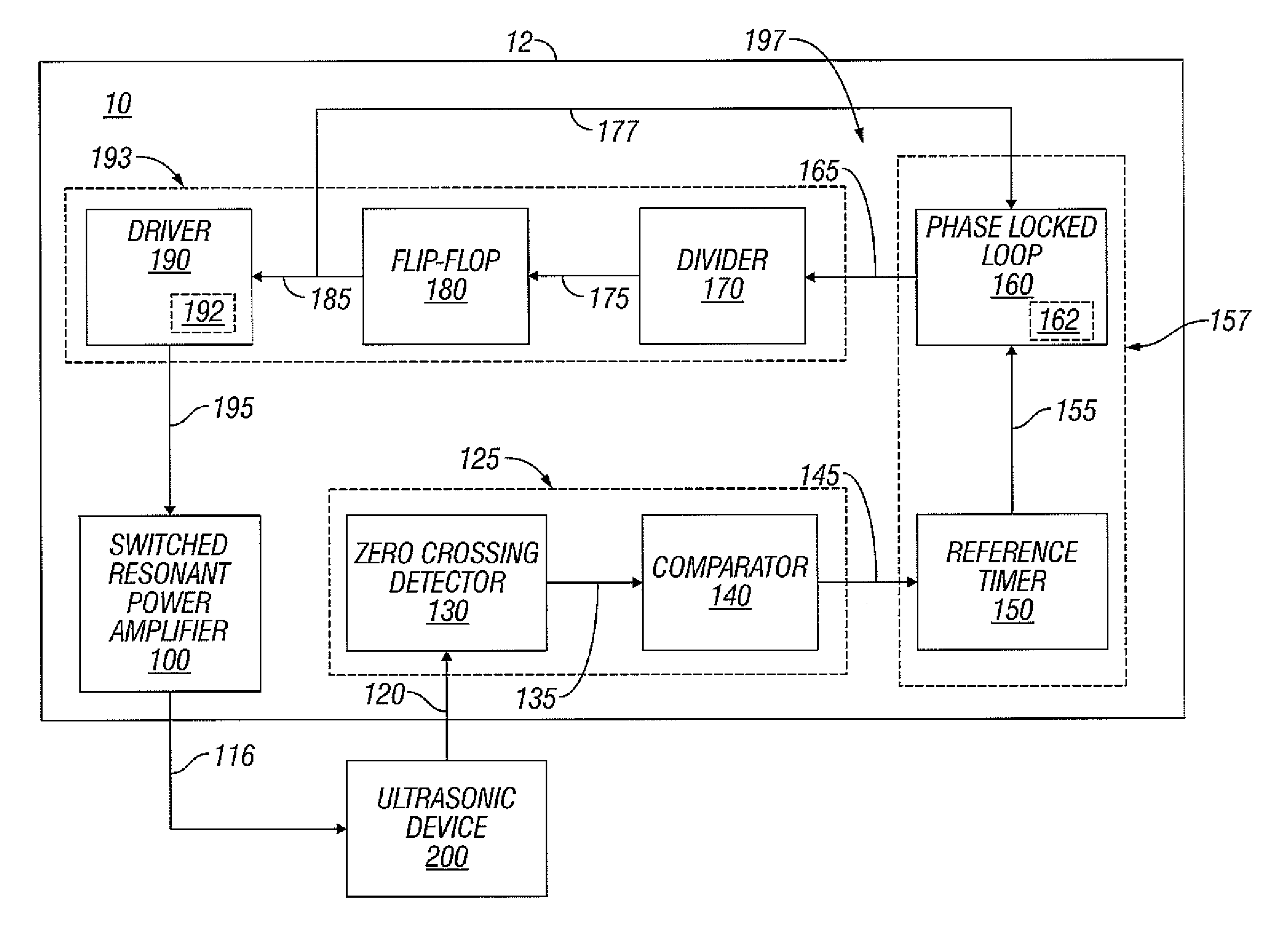
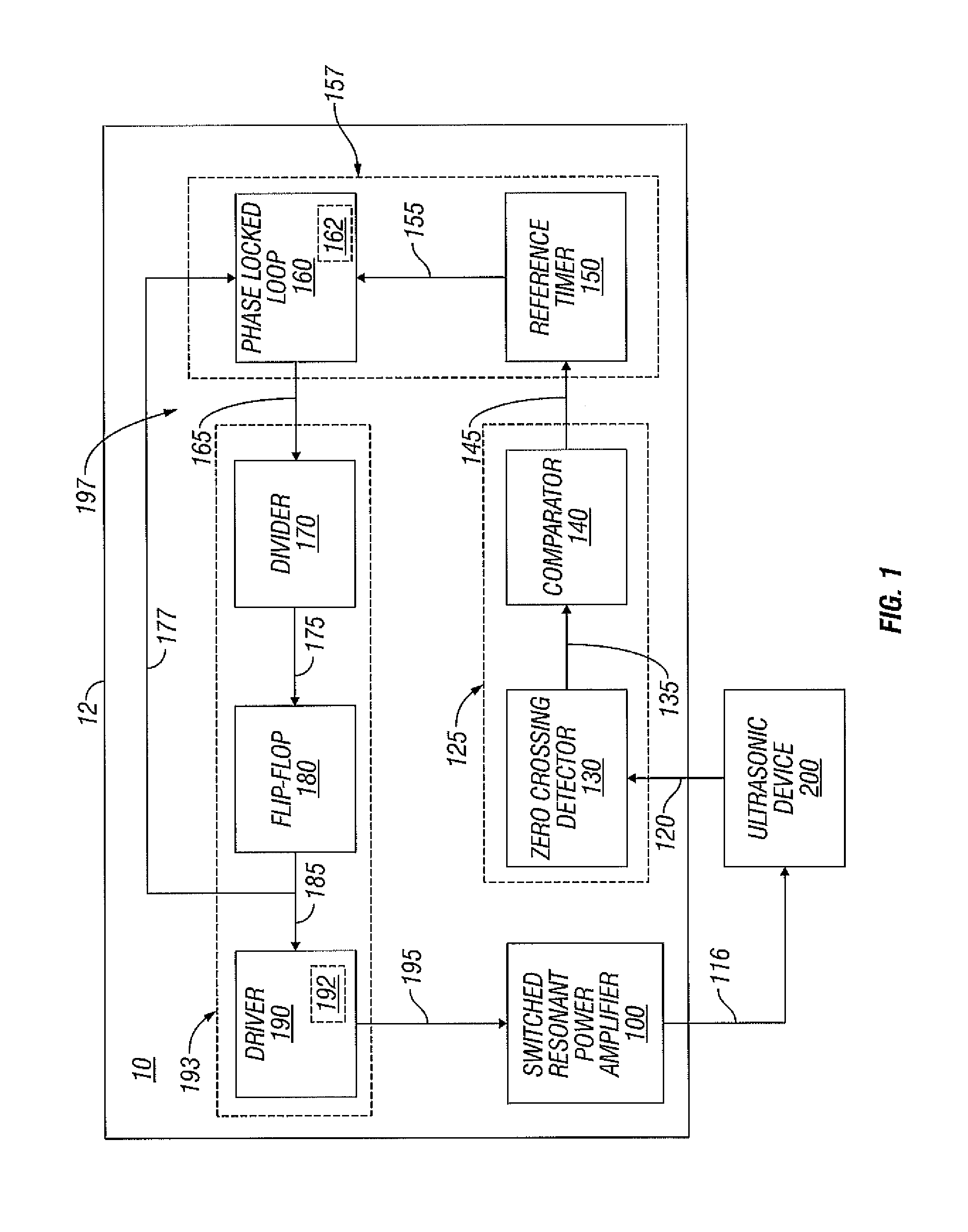
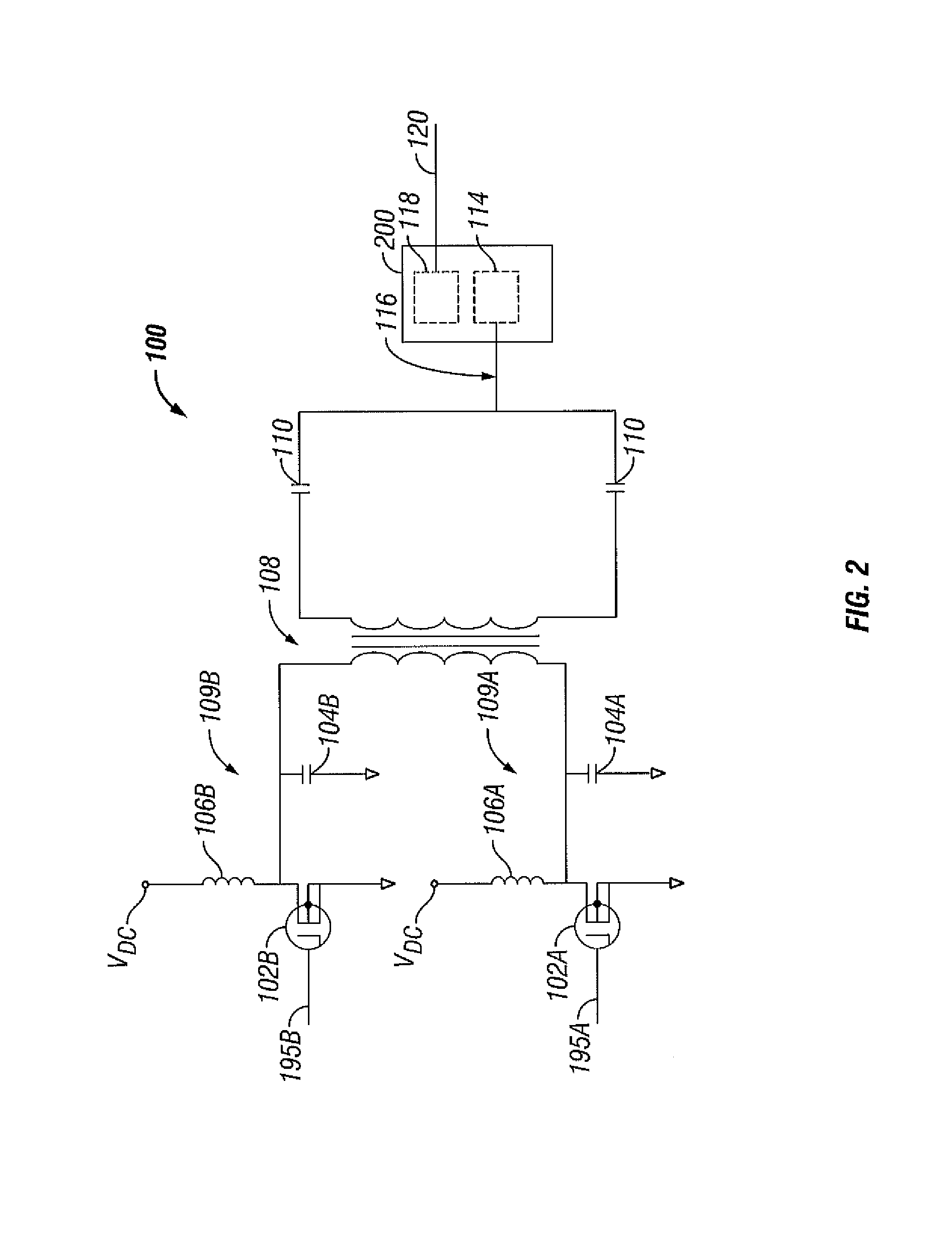
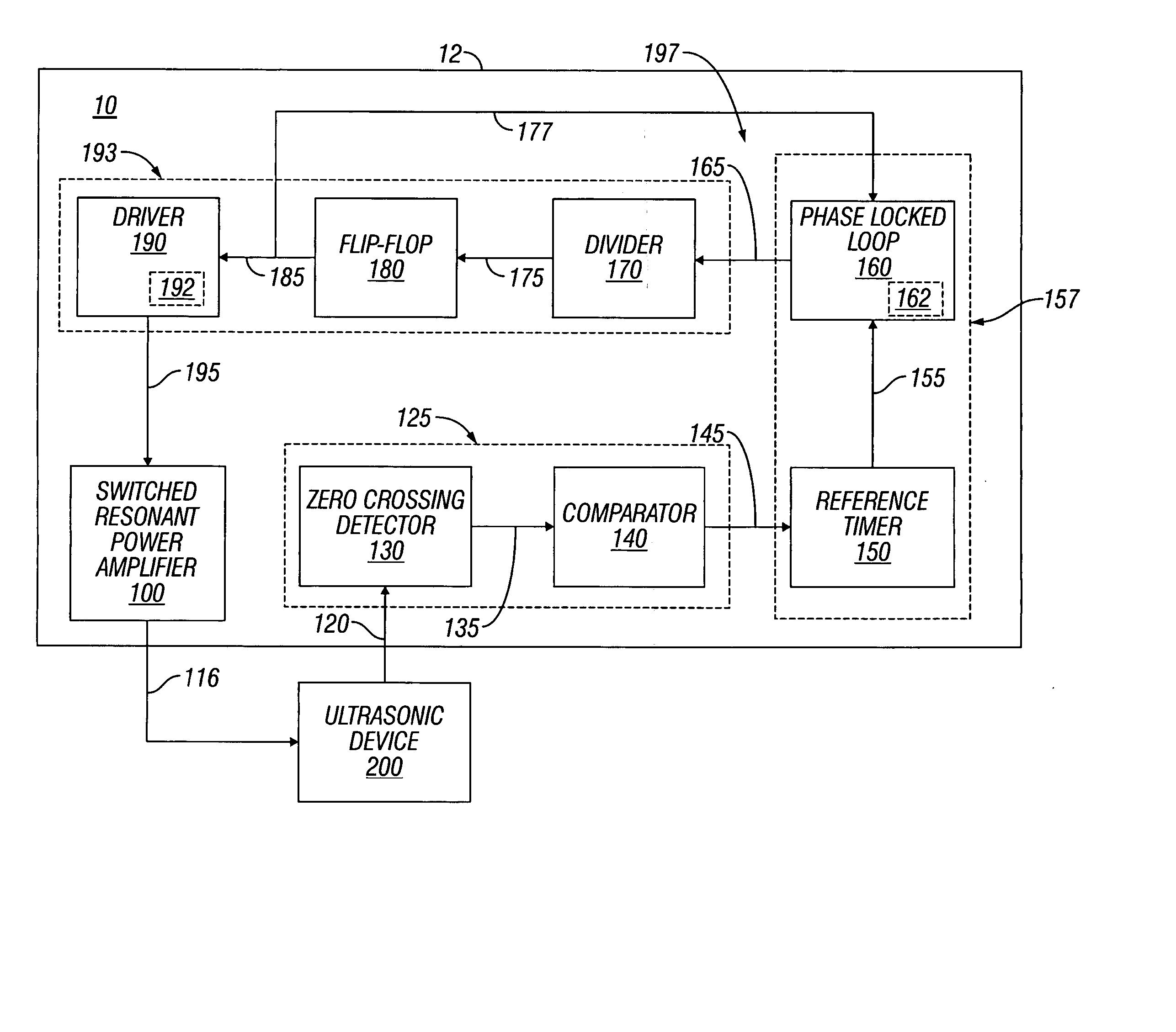
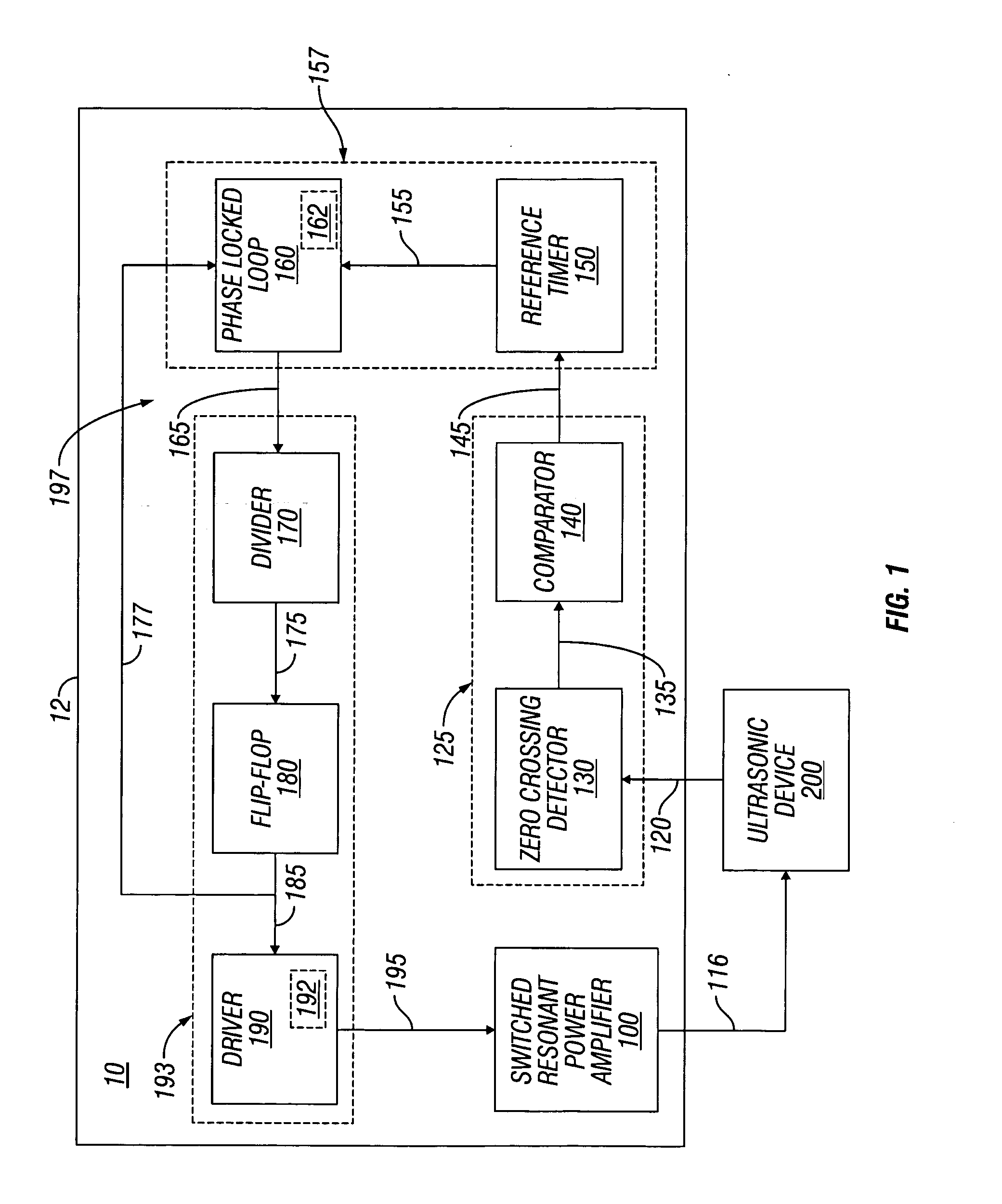
Switched resonant ultrasonic power amplifier system
ActiveUS7396336B2Operation efficiency can be improvedSmall footprintUltrasound therapyAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyHemt circuitsControl ultrasound
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Switched resonant ultrasonic power amplifier system
ActiveUS20050149151A1Reduce frequencyControl outputUltrasound therapyAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencySonificationAudio power amplifier
A switched resonant power amplifier system for ultrasonic transducers is disclosed. The system includes an amplifier that receives and processes a driver output signal for generating a drive signal that is provided to an ultrasonic device for controlling output of the ultrasonic device. An output control circuit receives and processes a signal related to a feedback signal generated by the ultrasonic device and a divider reference signal, and generates a compensated clock signal that is adjusted for at least one of phase and frequency differences between the received feedback signal and the divider reference signal. A compensated drive circuit receives and processes the compensated clock signal for generating the divider reference signal, and for generating the driver output signal.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
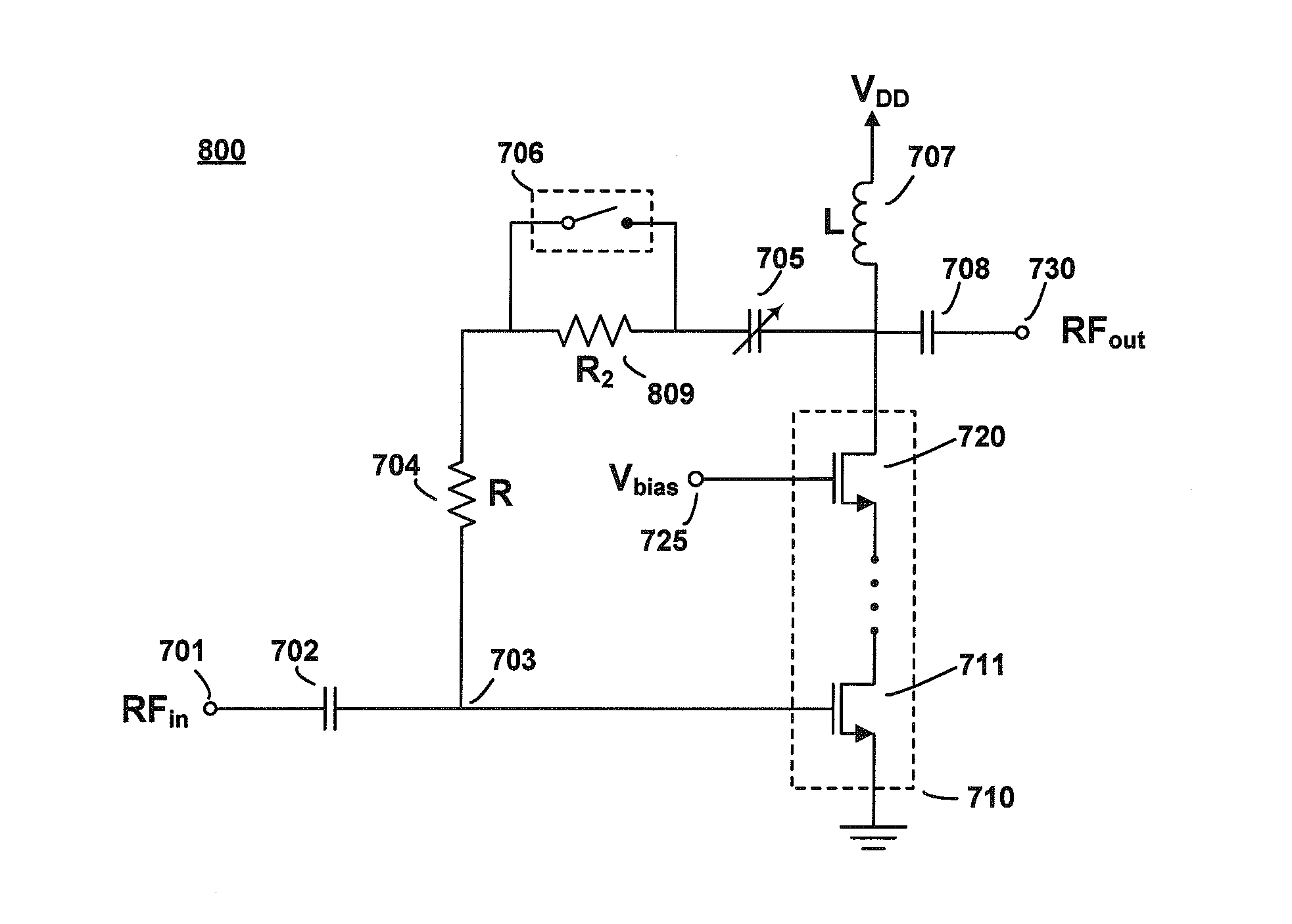
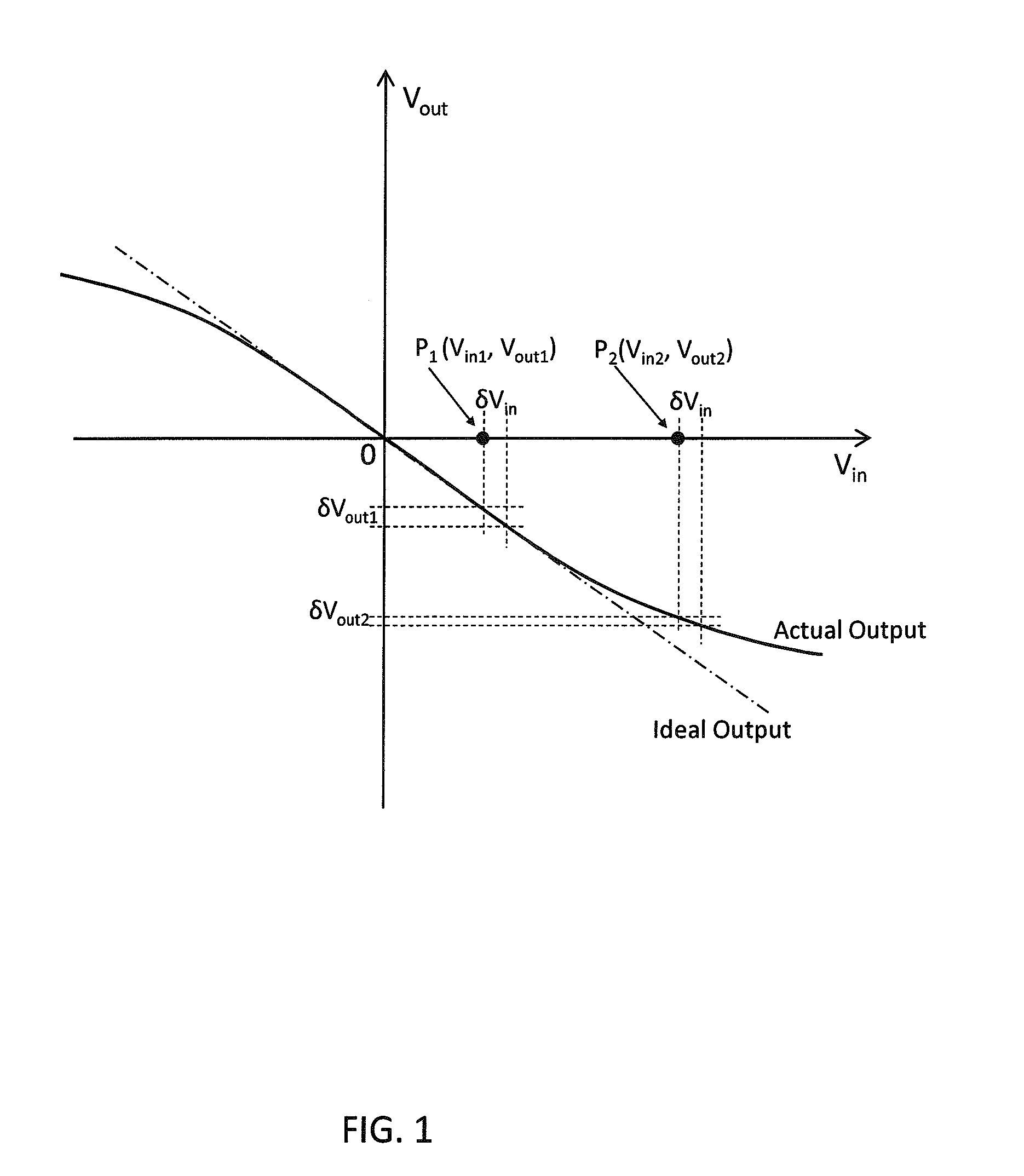
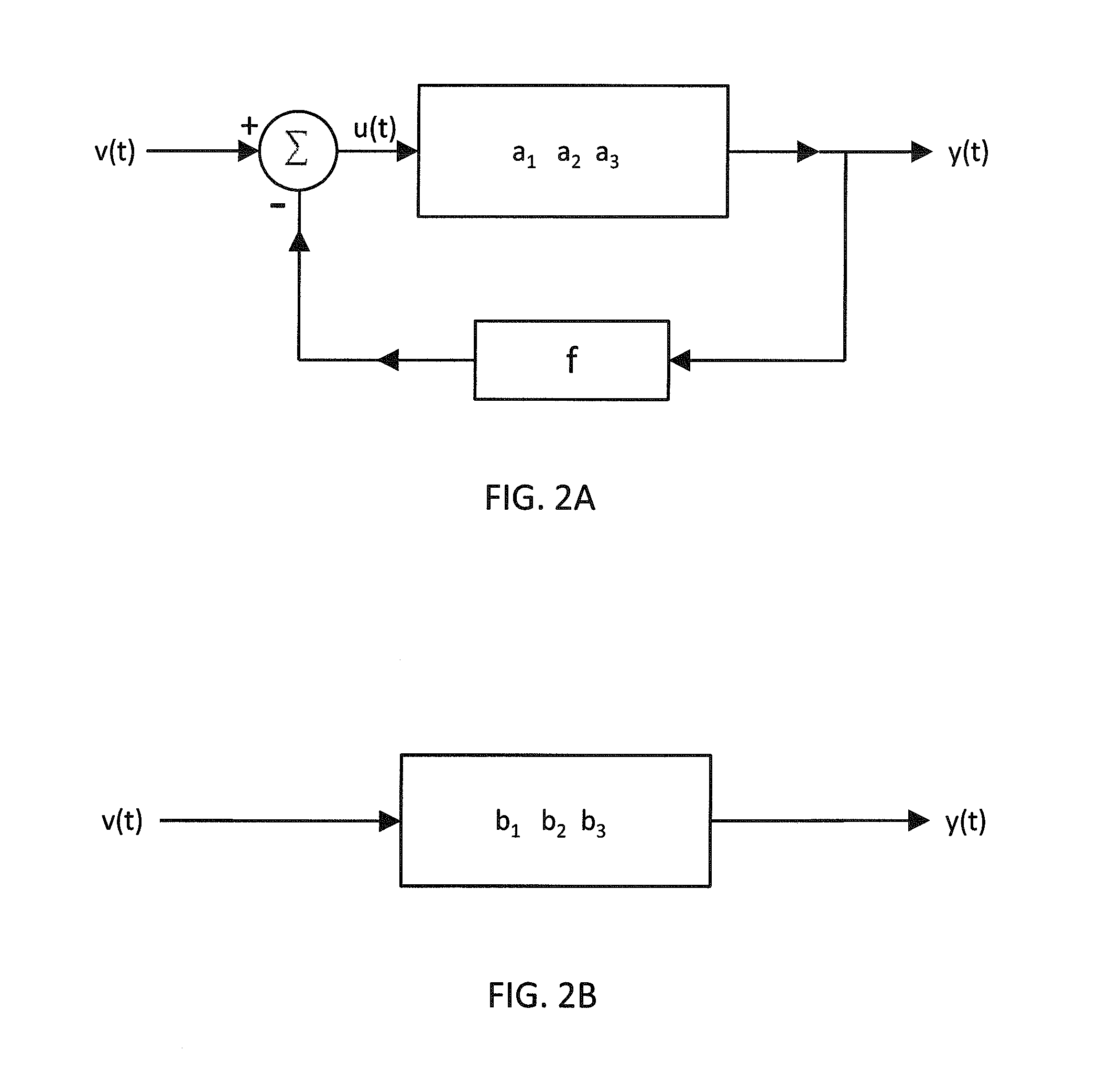
Amplifier with Variable Feedback Impedance
ActiveUS20150091650A1Reducing effect of variableMaintaining the characteristic output voltage range of the RF amplifierAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesRF amplifierVoltage amplitudeAudio power amplifier
A variable feedback impedance is presented capable of providing high linearity (e.g. as represented by 1P2 and 1P3) and high linear range (e.g. as represented by P1dB) when used in a feedback path of an RF amplifier in the presence of high voltage amplitudes.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Programmable radio transceiver
ActiveUS20060030277A1Prevent leakageLow noise amplifierSolid-state devicesAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesExtensibilityTransceiver
A fully integrated, programmable mixed-signal transceiver comprising a radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) which is frequency and protocol agnostic with digital inputs and outputs, the transceiver being programmable and configurable for multiple radio frequency bands and standards and being capable of connecting to many networks and service providers. The RFIC does not use spiral inductors and instead includes transmission line inductors allowing for improved scalability. Components of the transceiver are programmable to allow the transceiver to switch between different frequency bands of operating. Frequency switching can be accomplished though the content of digital registers coupled to the components.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
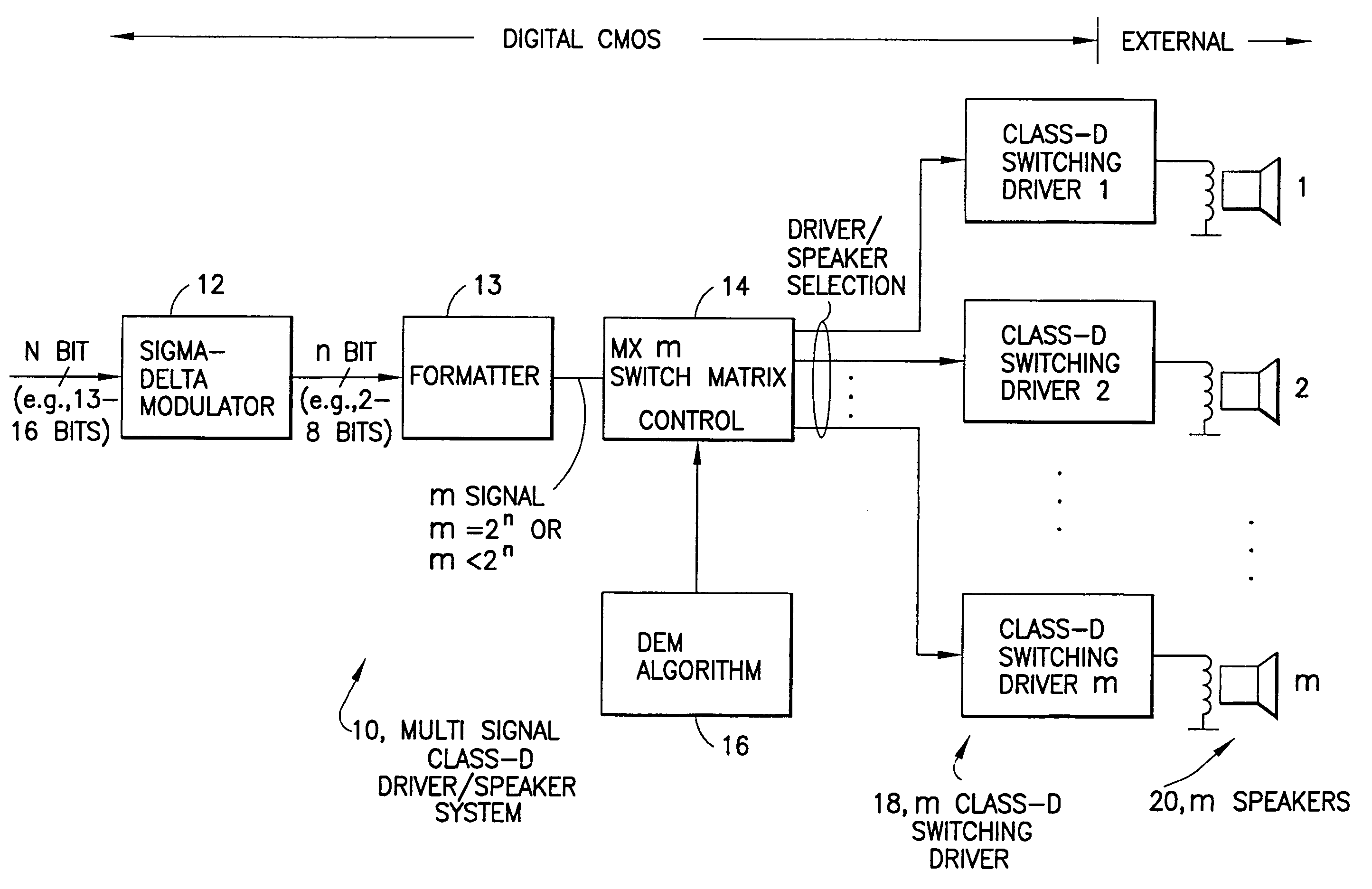
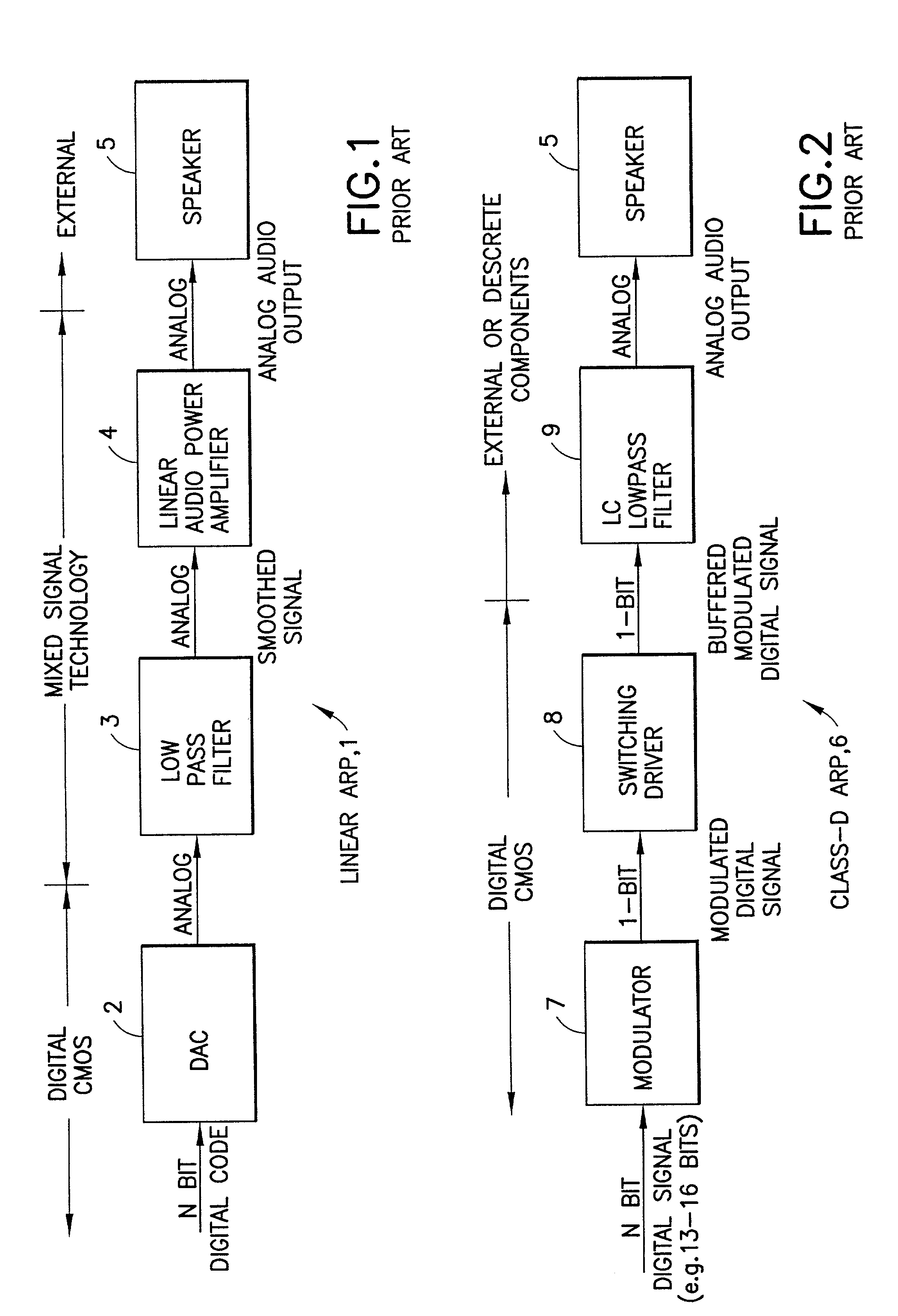
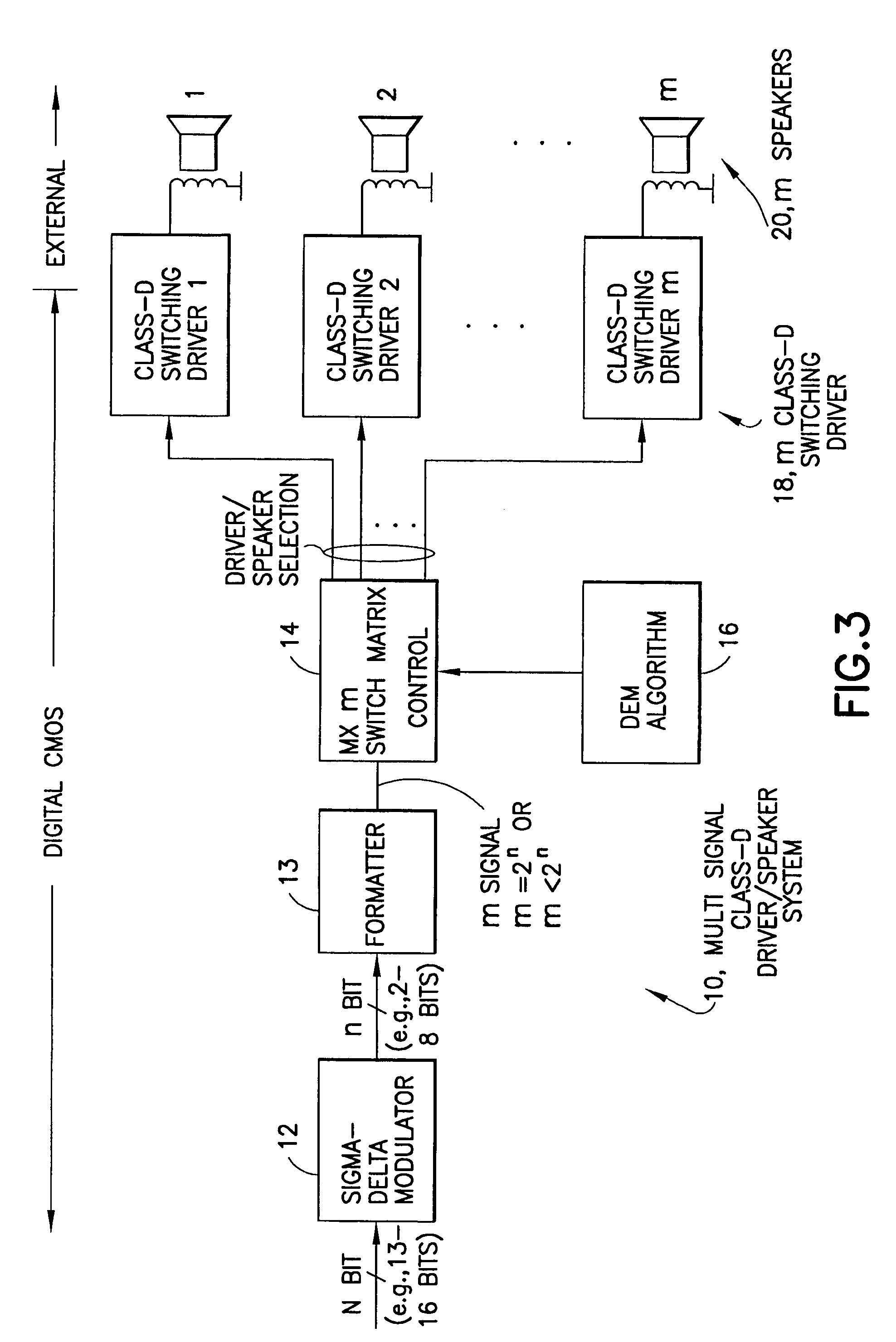
Method and apparatus for implementing a class D driver and speaker system
InactiveUS7058463B1Spread distortionDigitally weighted transducing elementsAnalogue conversionImage resolutionWide band
An audio path is constructed to include a multi-bit sigma-delta converter for converting an N-bit digital input to an n-bit output representing an over-sampled, lower resolution n-bit version of the N-bit digital input; a formatter for converting the n-bit output to an m signal output (e.g., as a thermometer code, a SDM format or a PWM format); an m-by-m switching matric for receiving the m output signals and for reordering the m output signals, m class-D drivers individual ones of which are driven by one of the reordered m output signals for driving one of m speakers; and a dynamic element matching (DEM) block coupled to the switching matric for controlling the reordering of the m output signals driving the m class-D drivers for spreading the distortion due at least to driver-speaker pair mismatch to wide band noise. The DEM may operate to generate white noise, or it may generate shaped (colored) noise.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
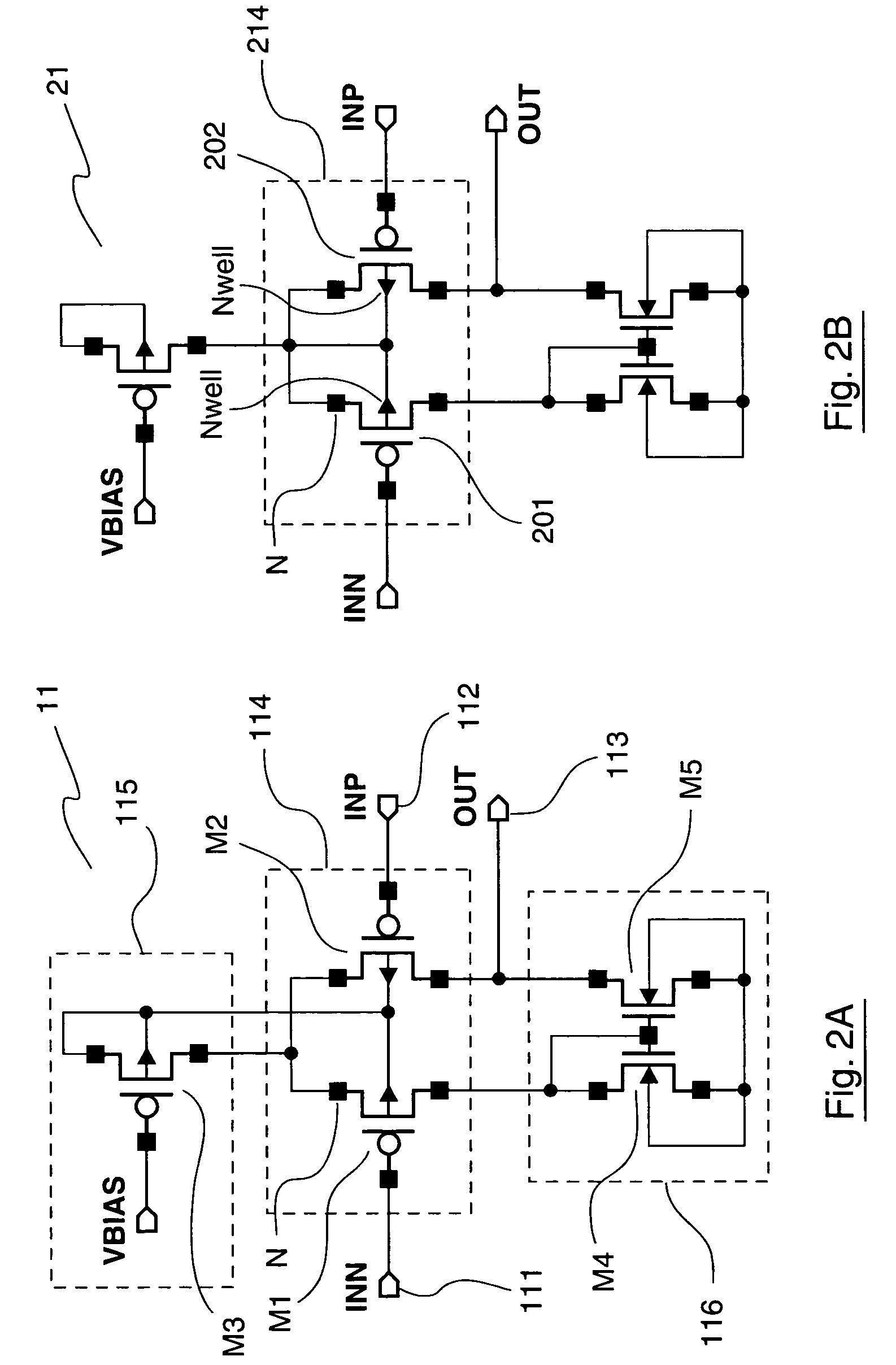
Electronic circuit including at least one first and one second differential pair with the transistors sharing one and the same well
ActiveUS20060158270A1Reduce capacitanceReduce surfaceSolid-state devicesAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesEngineeringTransistor
The disclosure relates to an electronic circuit including at least one first and one second differential pair each including a plurality of transistors. All the transistors of said first and second differential pair are included in a single well.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
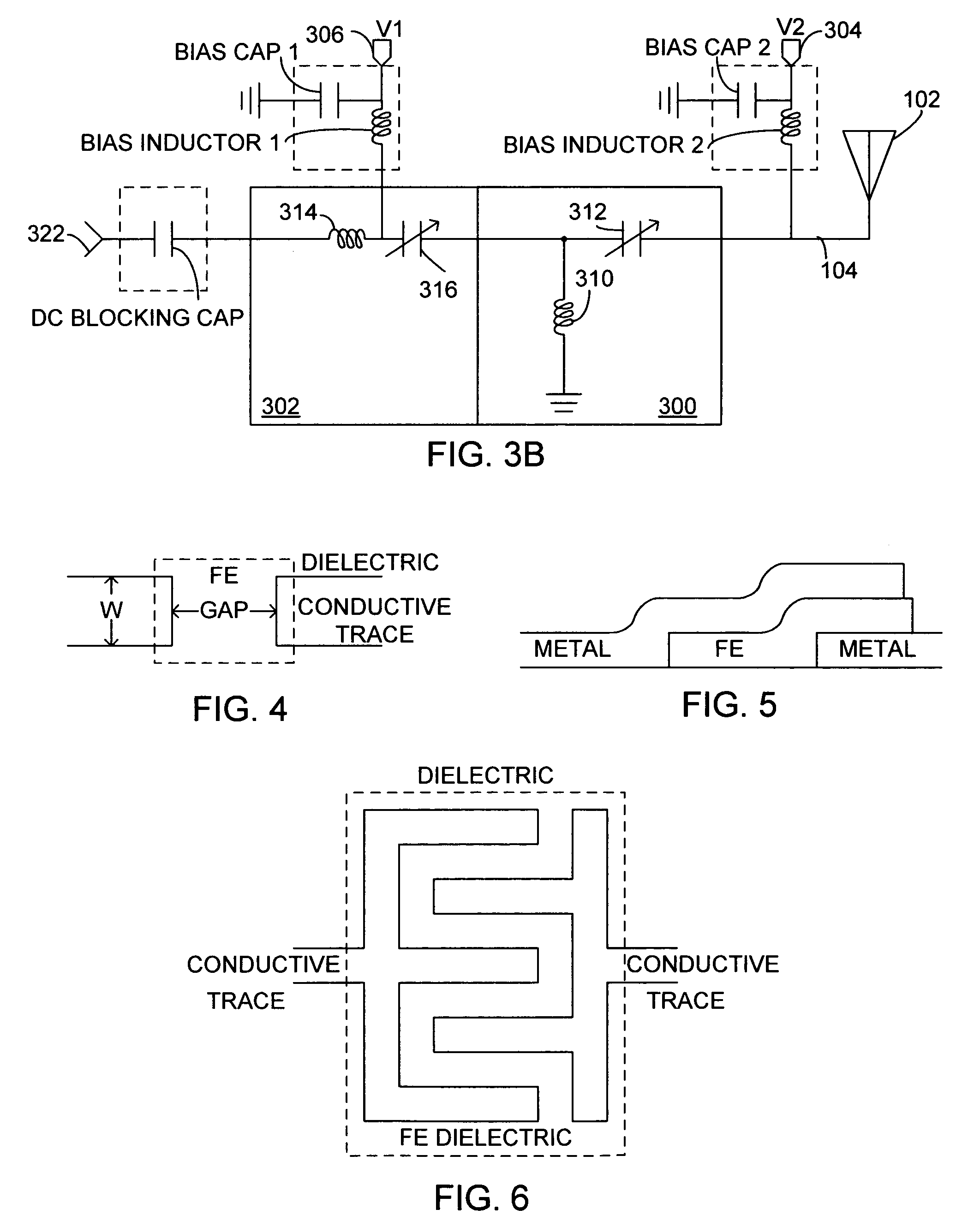
System and method for impedance matching an antenna to sub-bands in a communication band
InactiveUS7176845B2Improve efficiencyReduce noiseMultiple-port networksAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna impedanceMethod selection
A sub-band antenna matching method and an antenna matching system for selectively matching a communication bandwidth segment impedance have been provided. The method comprises: accepting a frequency-dependent impedance from an antenna; and, selectively supplying a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at a sub-band of a first communication band. In some aspects, the method selectively supplies a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at a sub-band of a second communication band. More specifically, the method comprises: tuning a first tuning circuit to a first frequency; simultaneously tuning a second tuning circuit to a second frequency to match the antenna at a low end of the first communication band. Likewise, the first tuning circuit is tuned to a third frequency and the second tuning circuit is tuned to a fourth frequency to match the antenna at a high end of the first communication band in response to the third and fourth frequencies.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
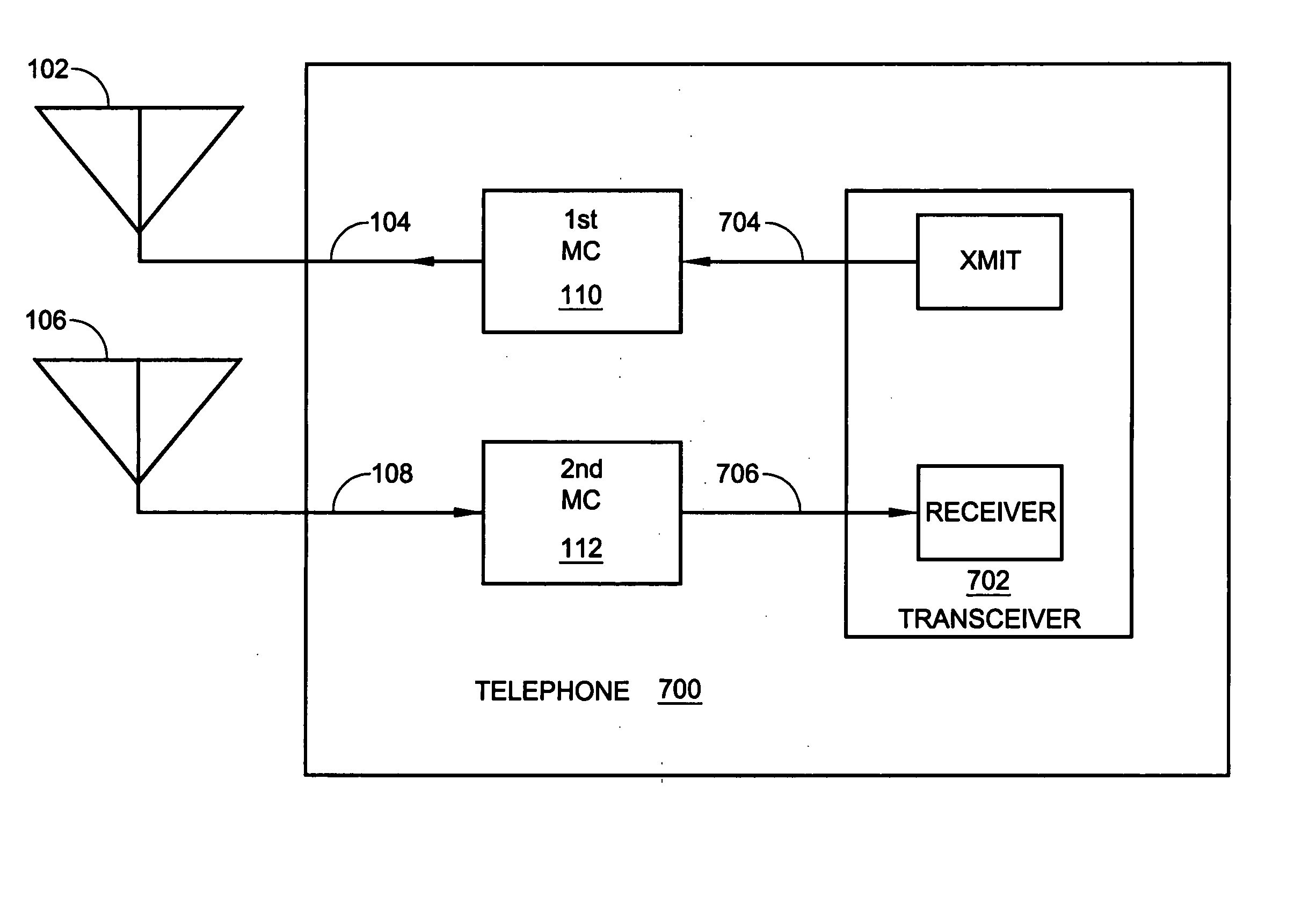
Full-duplex antenna system and method
A system and method is provided for full-duplex antenna impedance matching. The method comprises: effectively resonating a first antenna at a frequency selectable first channel in a first frequency band; generating a first antenna impedance at the first channel frequency; effectively resonating a second antenna at a frequency selectable second channel in the first frequency band; generating a second antenna impedance at the second channel frequency; supplying a first conjugate impedance match at the first channel frequency; and, supplying a second conjugate impedance match at the second channel frequency. For example, the first antenna may be used for transmission, while the second antenna is used for received communications. The antennas effectively resonant in response to: supplying frequency selectable conjugate impedance matches to the antennas; generating frequency selectable antenna impedances; and / or selecting the frequency of antenna resonance.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
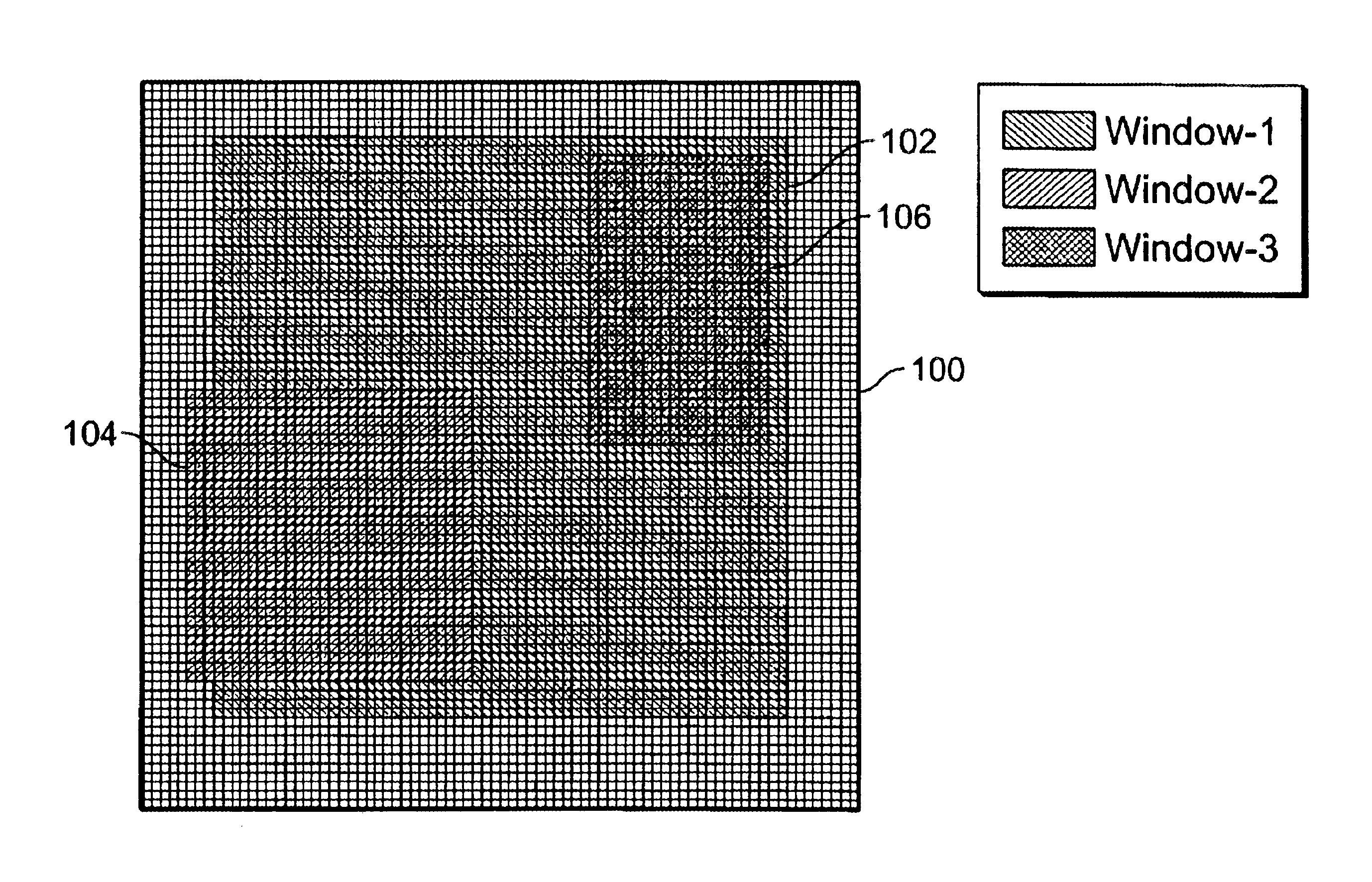
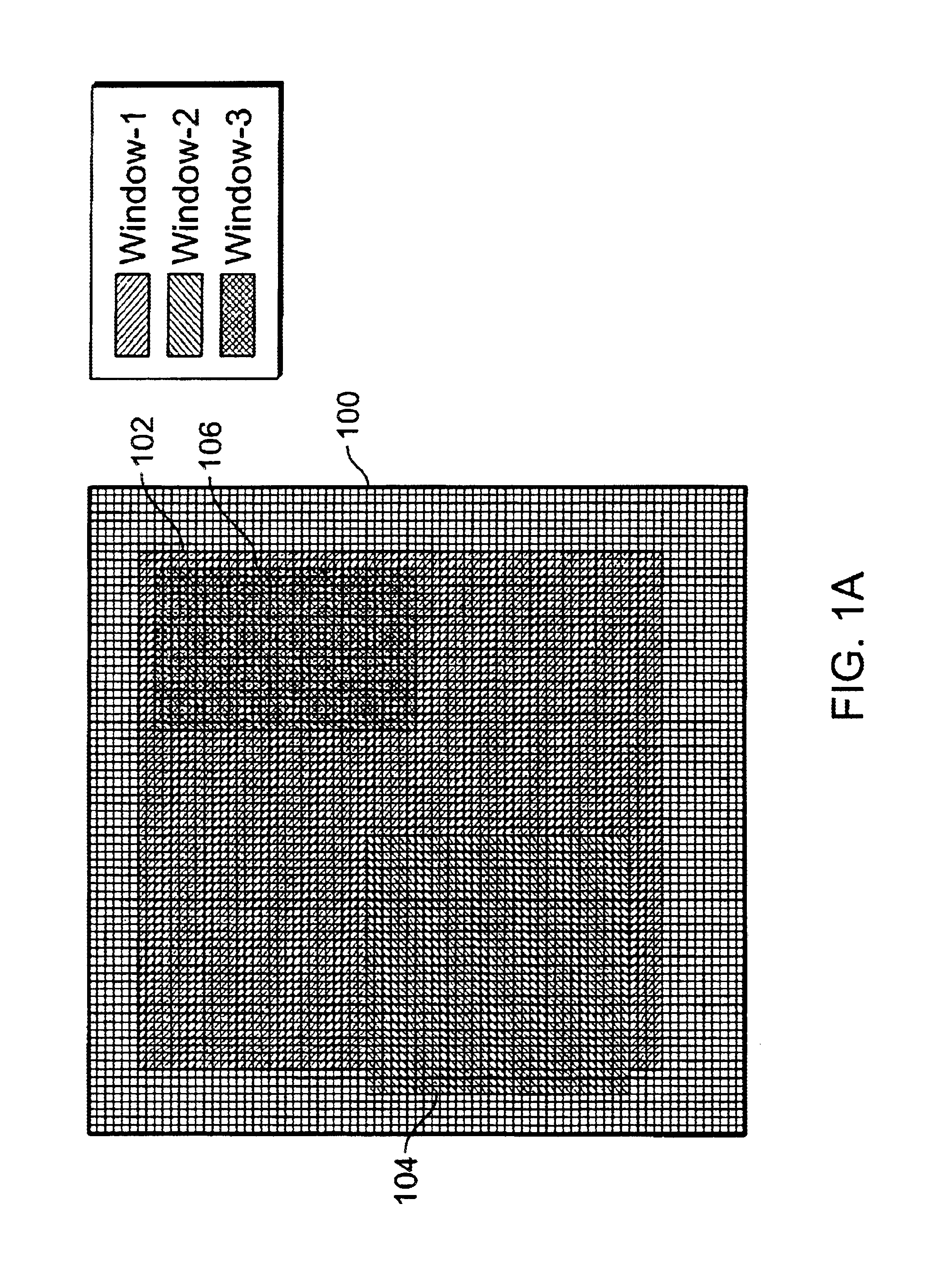
Dynamically re-configurable CMOS imagers for an active vision system
InactiveUS6839452B1Television system scanning detailsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCMOSImage resolution
A vision system is disclosed. The system includes a pixel array, at least one multi-resolution window operation circuit, and a pixel averaging circuit. The pixel array has an array of pixels configured to receive light signals from an image having at least one tracking target. The multi-resolution window operation circuits are configured to process the image. Each of the multi-resolution window operation circuits processes each tracking target within a particular multi-resolution window. The pixel averaging circuit is configured to sample and average pixels within the particular multi-resolution window.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
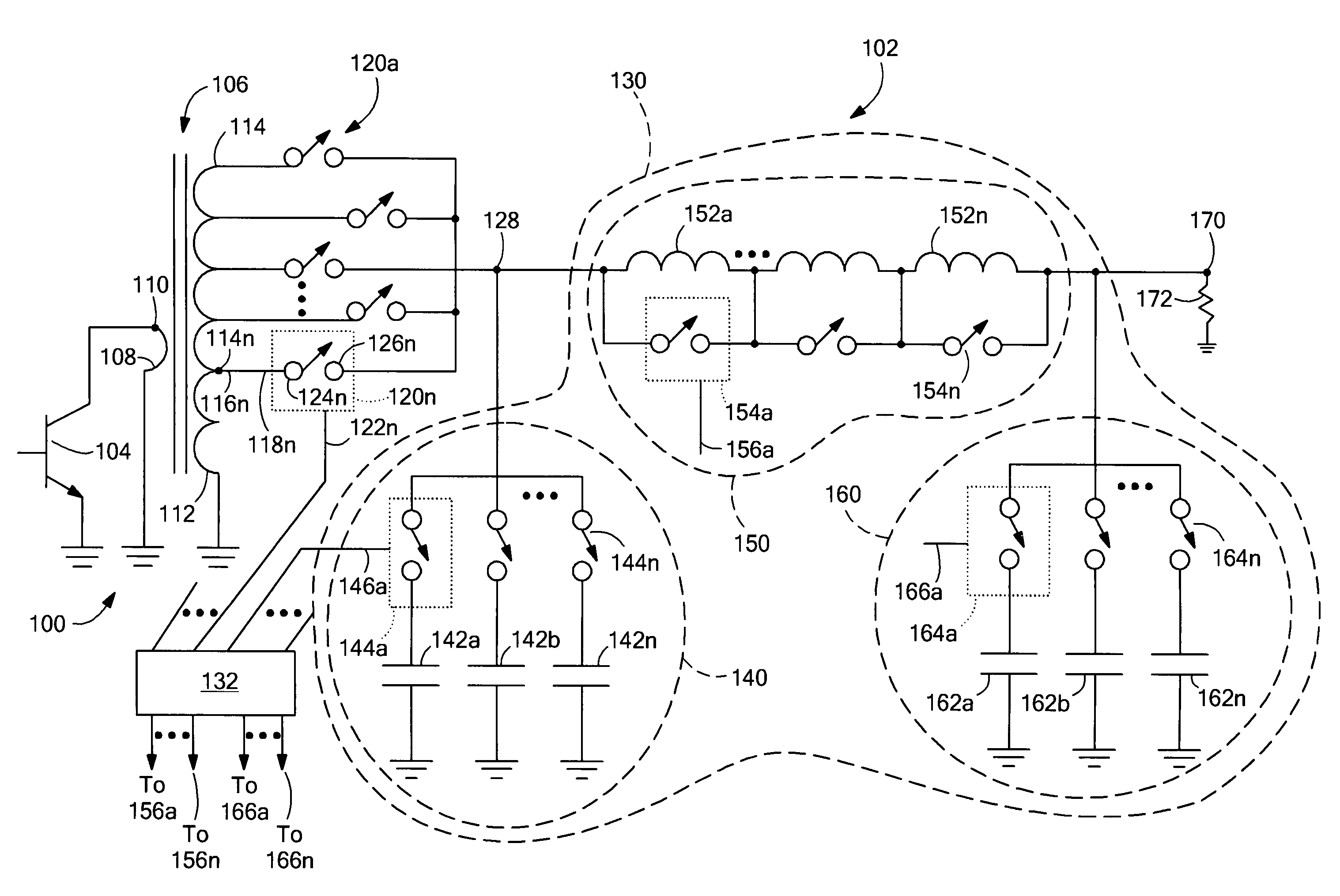
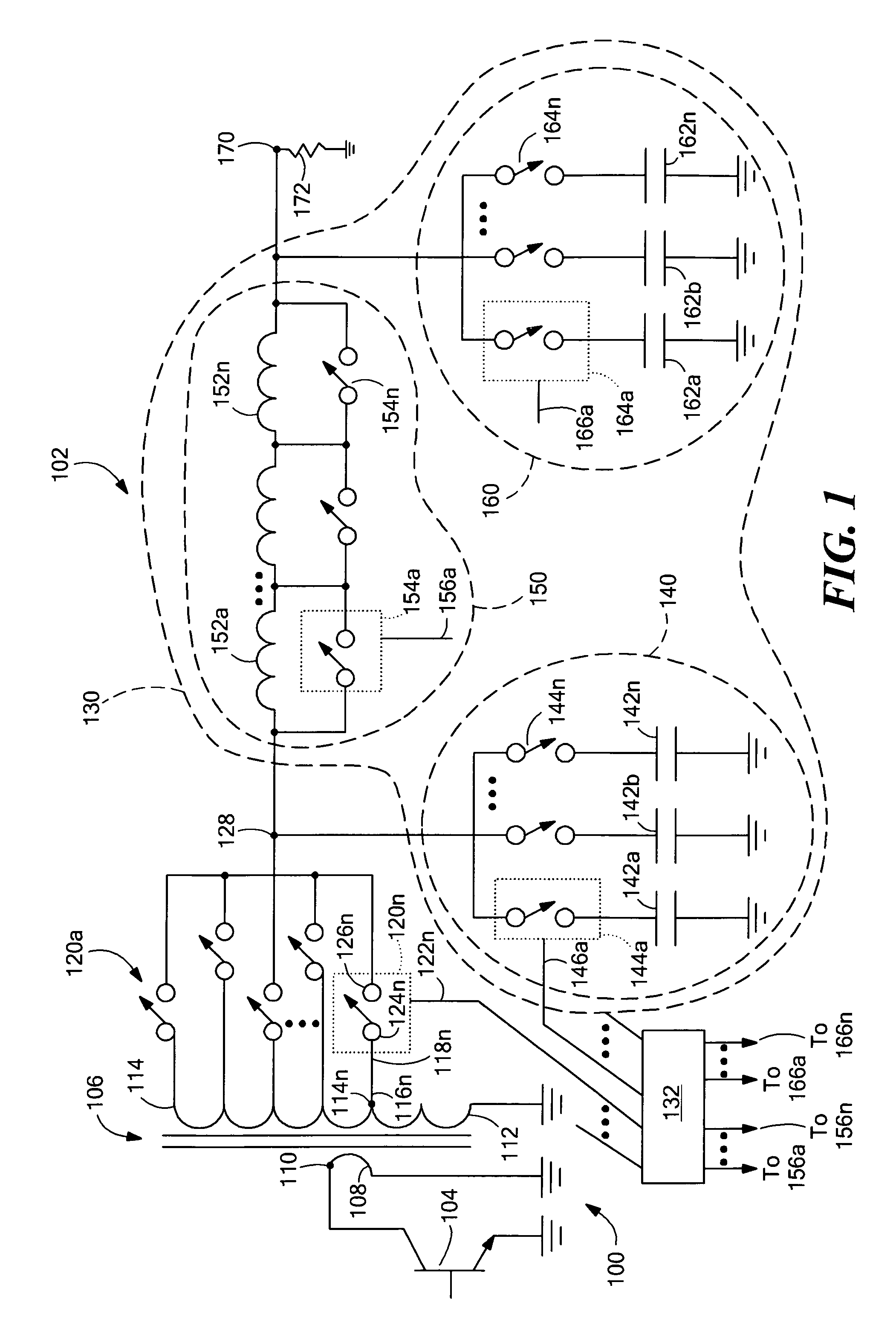
Mems-tuned high power, high efficiency, wide bandwidth power amplifier
InactiveUS6992543B2High output power levelAdvantage in sizeMultiple-port networksAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesTransformerControl signal
A circuit for matching the impedance of an output load to an active device includes a transformer including a first winding having a terminal for coupling to the output of the active device and a second winding electromagnetically coupled to the first winding, and a plurality of taps, each of the plurality of taps having a first end coupled to a position on the second winding corresponding to a ratio of the second winding to first winding differing from other ones of the plurality of taps, and a second end. The matching circuit further includes a plurality of MEMS switches each having a control input for receiving a corresponding control signal, a first terminal coupled to the second end of a corresponding one of the plurality of taps, and a switched output selectively coupled to a matching junction in response to the corresponding control signal.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
High frequency power amplifier and wireless communication module
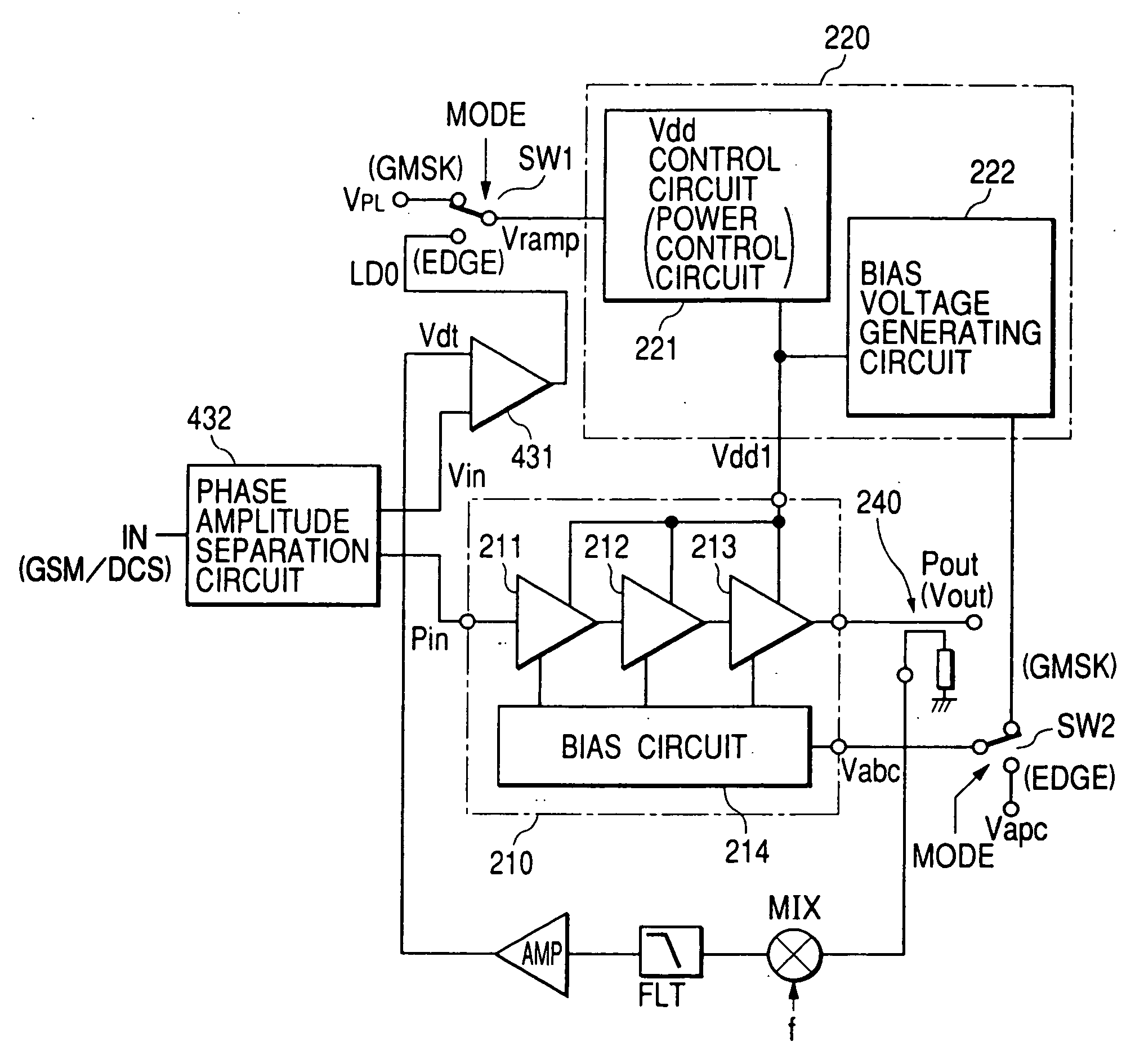
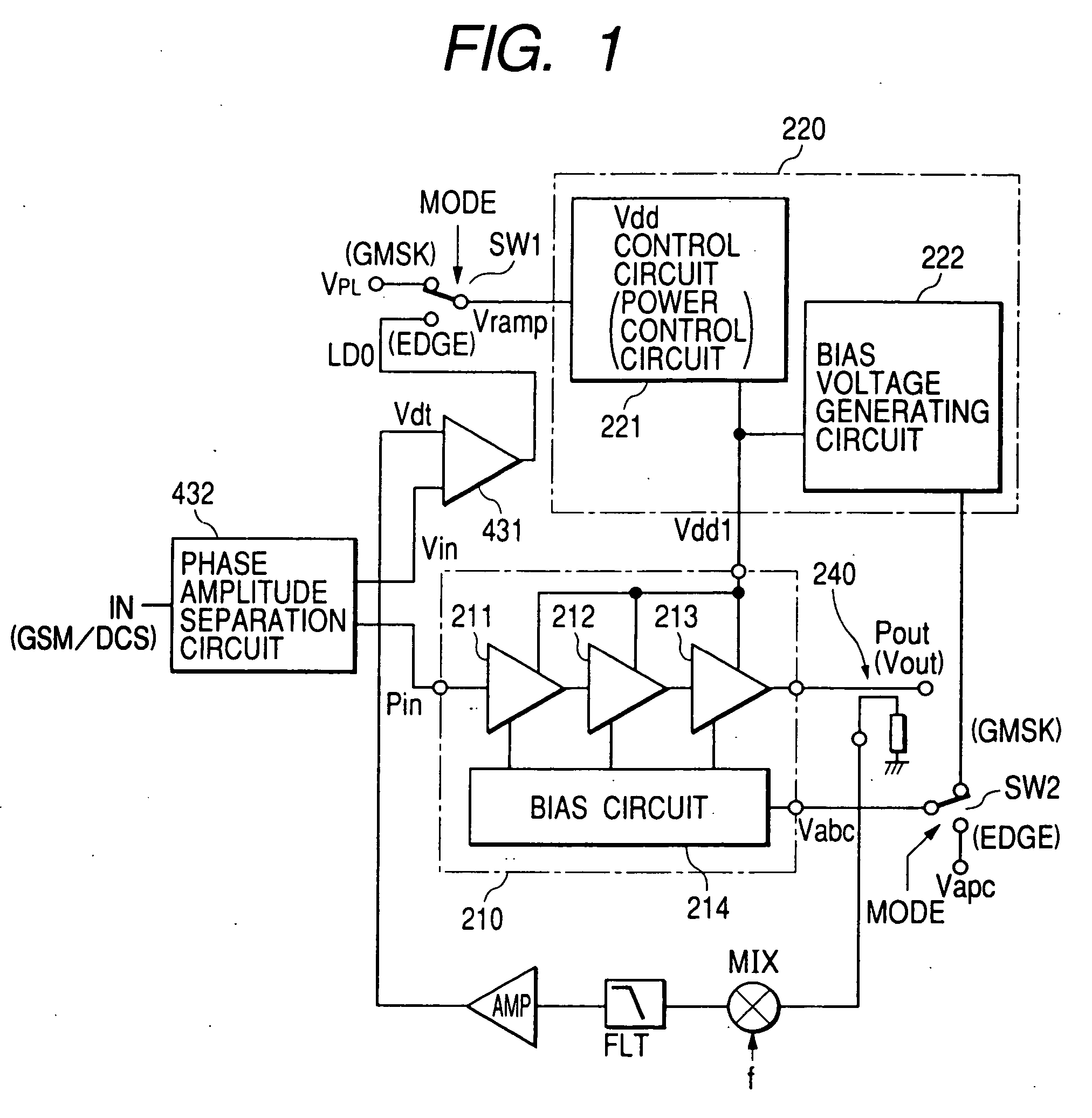
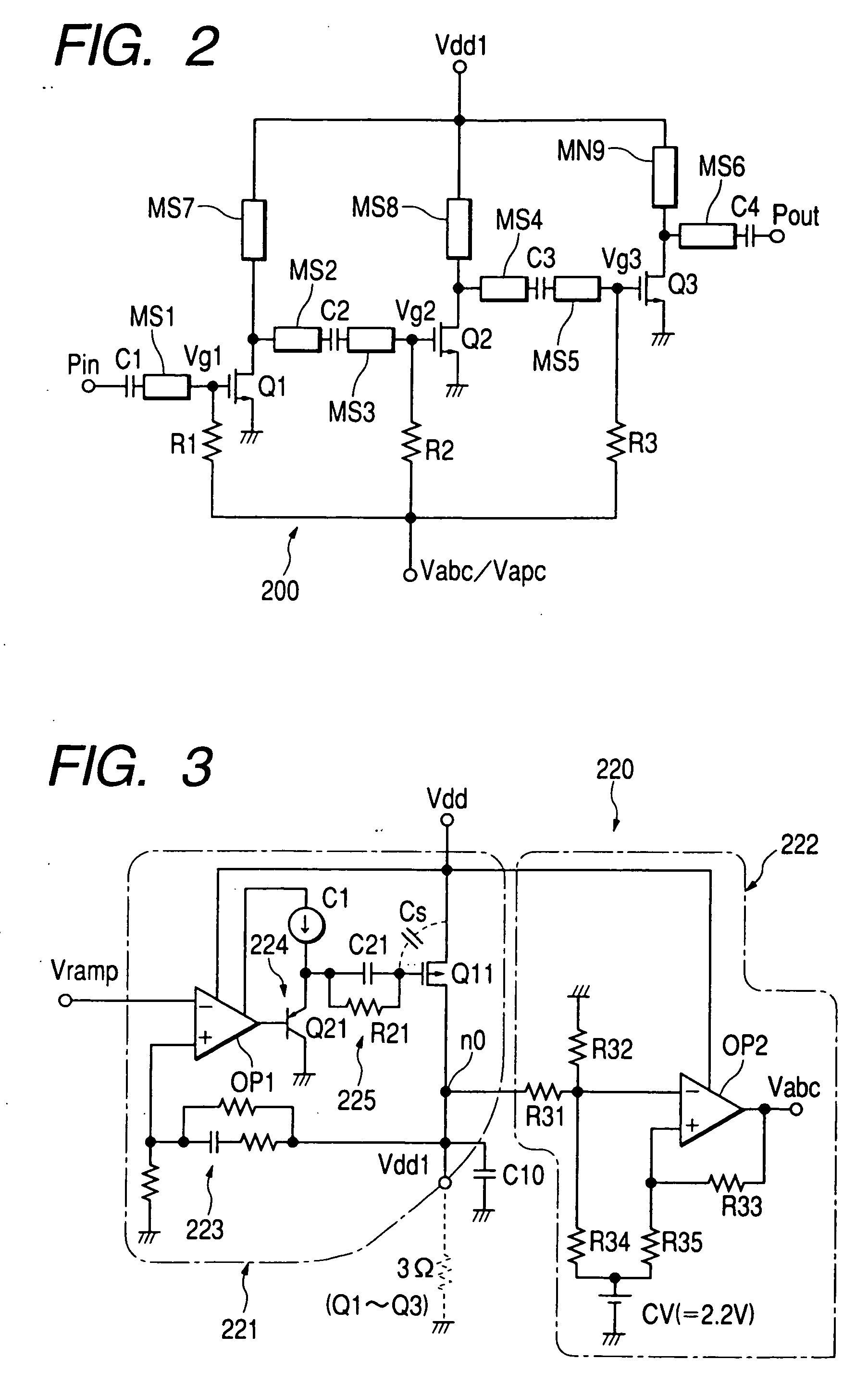
InactiveUS20050200407A1Reduce circuit sizeReduce the packing densityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierHigh frequency power
The present invention provides a high frequency power amplifier of an open-loop type, which outputs a signal having a level corresponding to an output level required under control of a power supply voltage for each output power FET, based on a control signal for the output level. The high frequency power amplifier is provided with a bias voltage generating circuit which generates a gate bias voltage of each output power FET according to an output voltage of a power control circuit for controlling the power supply voltage for the output power FET, based on the control signal for the output level.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
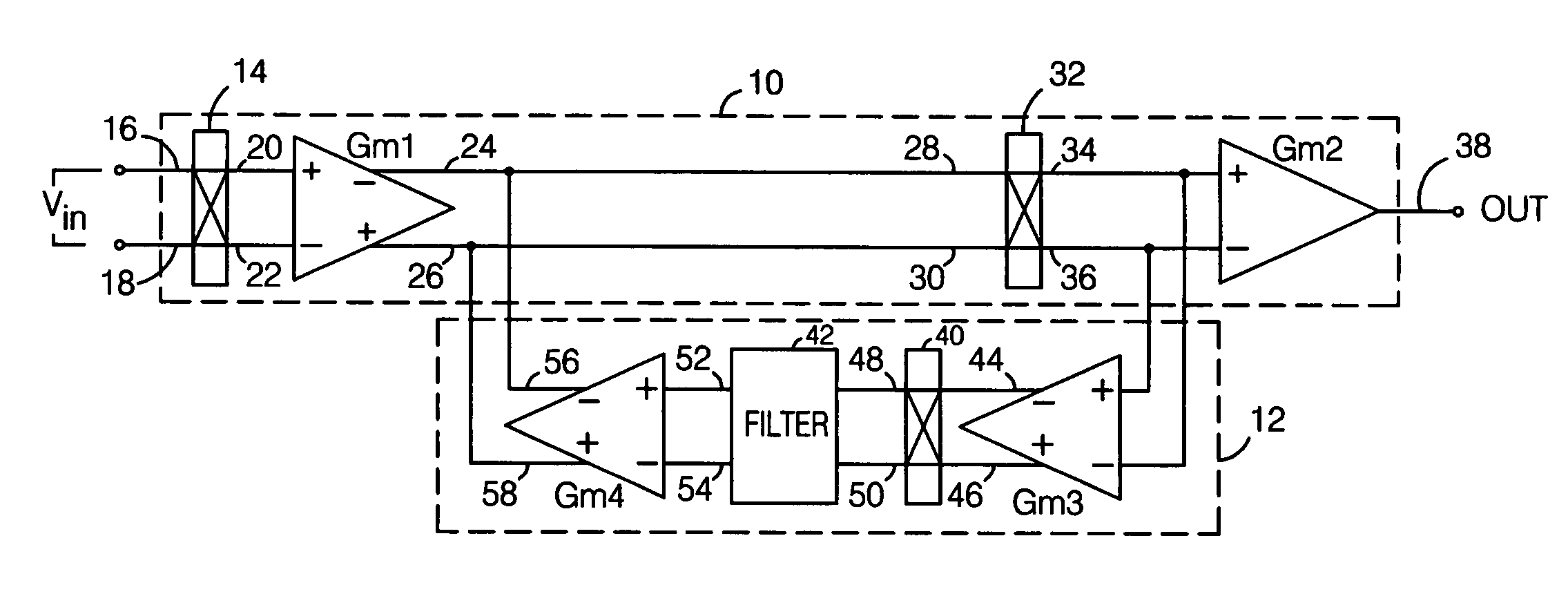
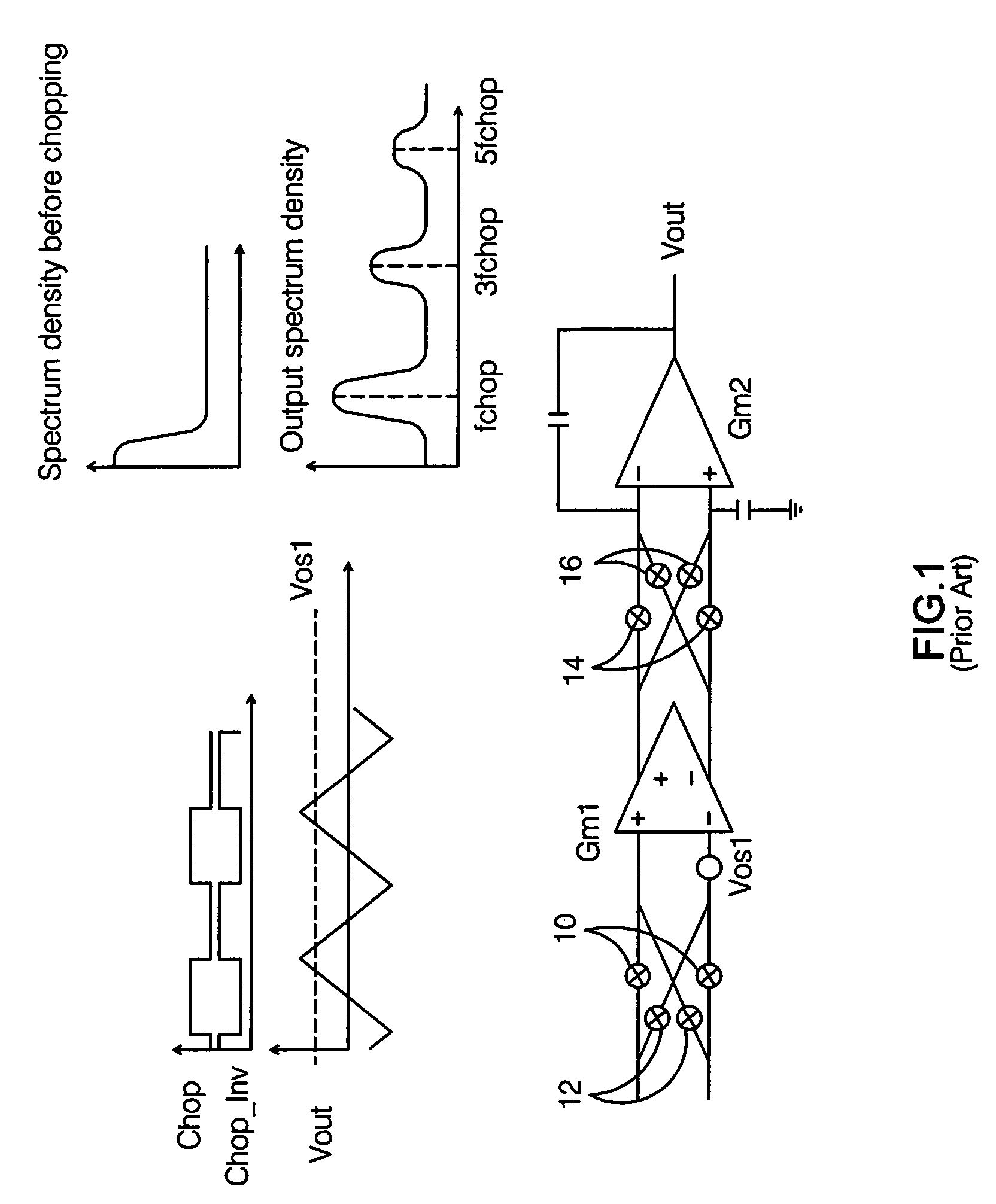
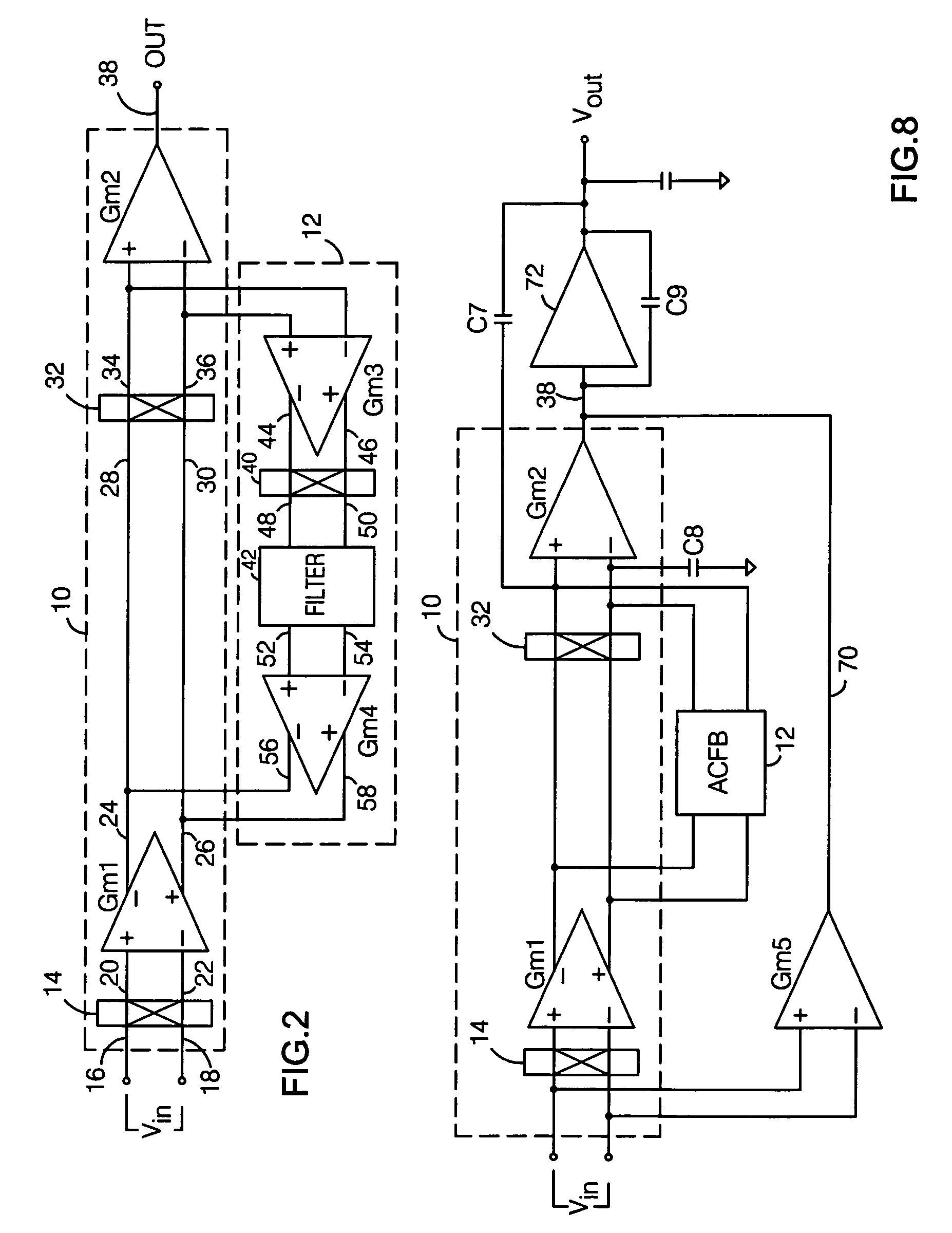
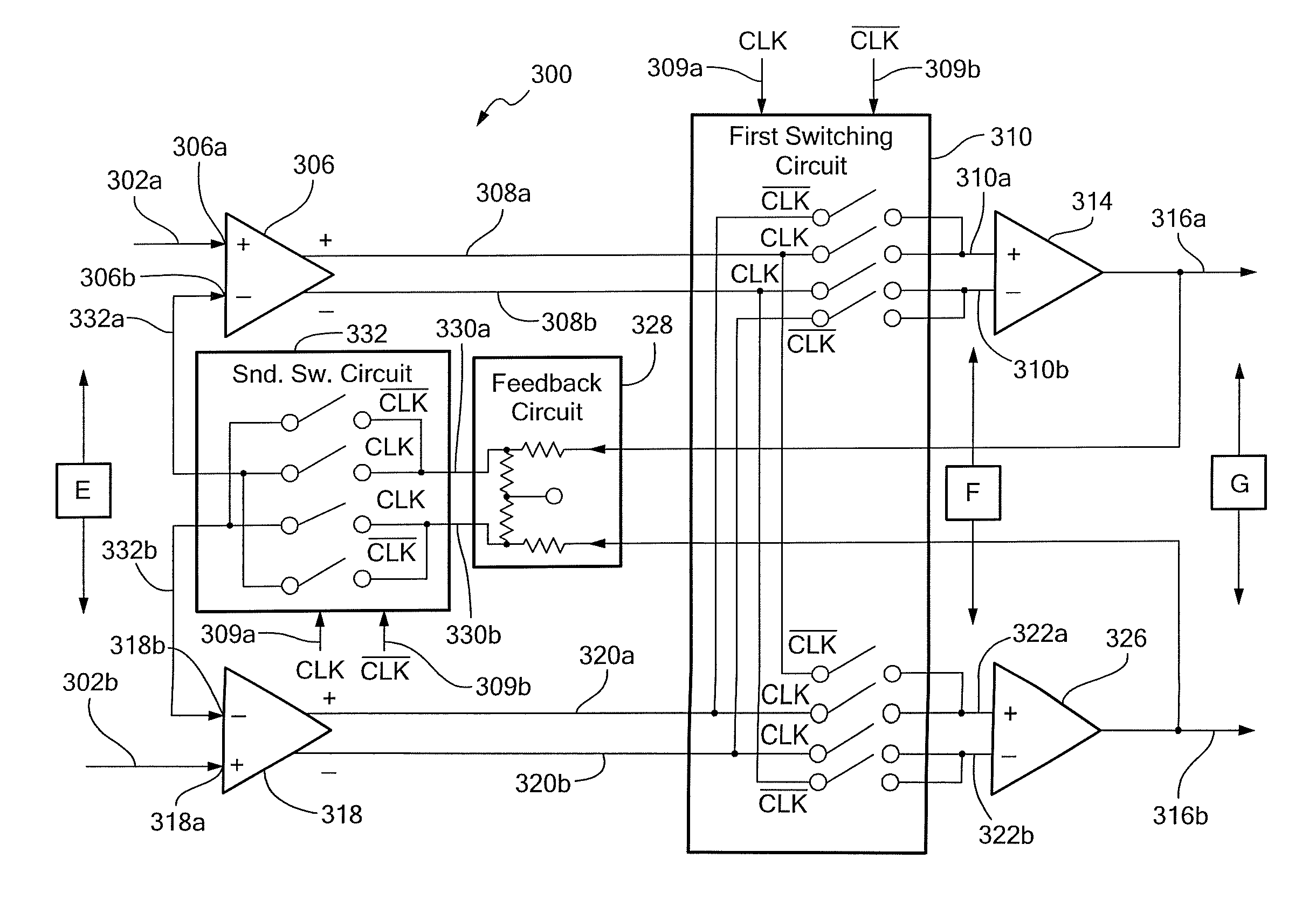
Auto-correction feedback loop for offset and ripple suppression in a chopper-stabilized amplifier
ActiveUS7764118B2Suppress both input offset voltage effects and offset voltage-inducedReduce componentsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierEngineering
A chopper-stabilized amplifier includes a main signal path having first and second chopping circuits at the inputs and outputs of a transconductance amplifier, and an auto-correction feedback loop. The feedback loop includes a transconductance amplifier connected to amplify the chopped output from the main signal path, a third chopping circuit which chops the amplified output, a filter which filters the chopped output to substantially reduce any offset voltage-induced AC component present in the signal being filtered, and a transconductance amplifier which receives the filtered output and produces an output which is coupled back into the main signal path. When properly arranged, the auto-correction feedback loop operates to suppress transconductance amplifier-related offset voltages and offset voltage-induced ripple that might otherwise be present in the amplifier's output.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
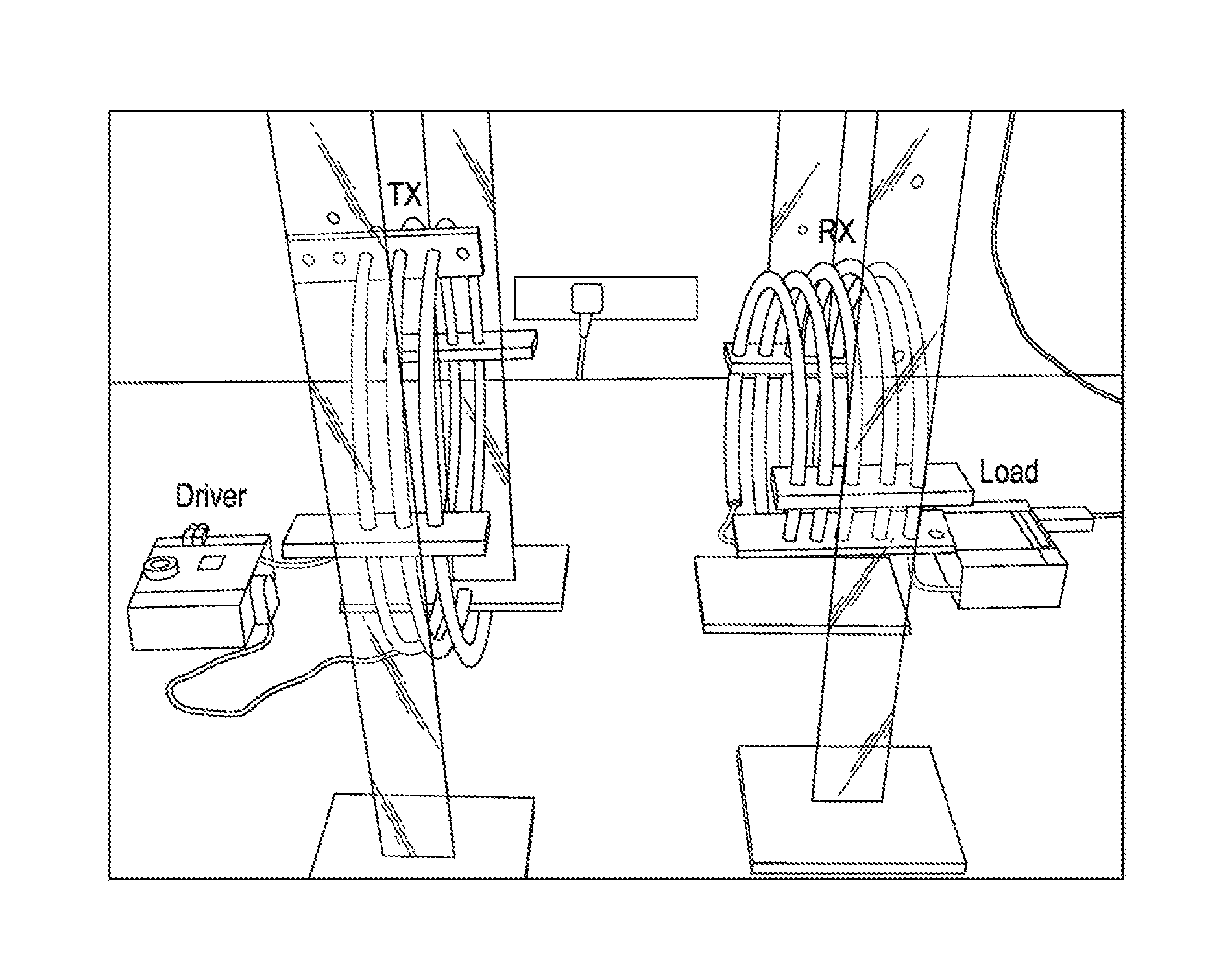
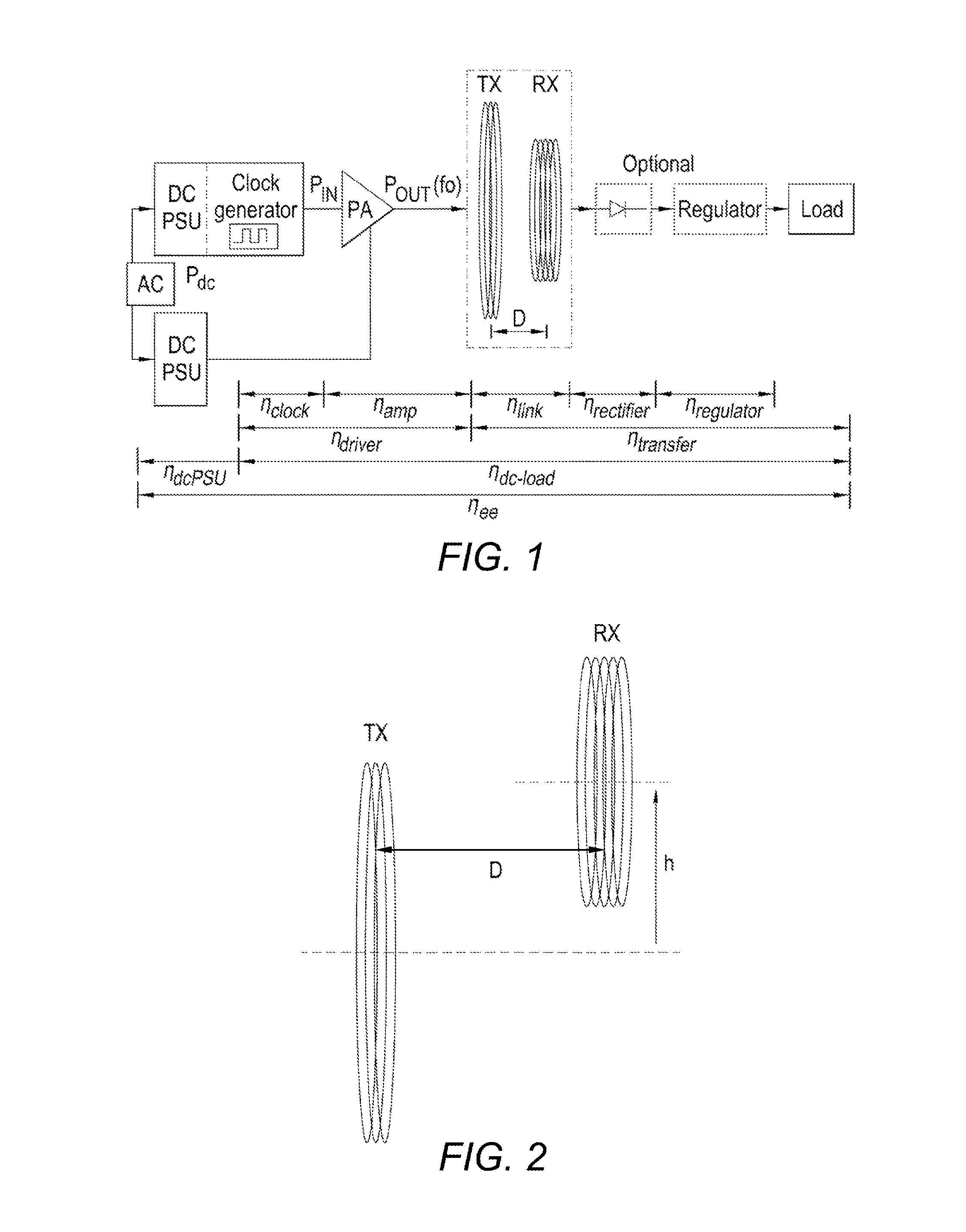
Inductive Power Transfer System
An inductive power transfer system comprises a transmitter coil TX and a receiver coil RX spaced from the transmitter coil. A transmitter circuit comprises the transmitter coil and is in the form of a Class E amplifier with a first inductor Uchoke and a transistor in series between the terminals of a power supply, a first transmitter capacitor Cpar in parallel with the transistor between the first inductor and a power supply terminal, a primary tank circuit in parallel with the first transmitter capacitor, the primary tank circuit comprising the transmitter coil and a second transmitter capacitor Cres arranged in parallel with the transmitter coil, and a third transmitter capacitor Cser in series with the first inductor between the first transmitter capacitor and the primary tank circuit. The transistor is arranged to switch at a first frequency ωd and the capacitance of the second transmitter capacitor is selected such that the resonant frequency ωOTX of the primary tank circuit is greater than the first frequency. The receiver circuit comprises a Class E rectifier having a first receiver capacitor CL arranged in parallel with a load RL and a secondary tank circuit in parallel with the first receiver capacitor. The secondary tank circuit comprises the receiver coil and a second receiver capacitor Cres arranged in parallel or series with the receiver coil. A first diode Dr2 is provided between the secondary tank circuit and the first receiver capacitor. The capacitance of the second receiver capacitor is selected such that the resonant frequency ωoRX of the secondary tank circuit differs from the first frequency, so that the secondary tank circuit operates in semi-resonance and maintains some reactive impedance. The transmitter circuit is configured to vary the first frequency, in order to achieve a desired impedance of the primary tank circuit.
Owner:FREEVOLT TECH LTD
Low-noise active-pixel sensor for imaging arrays with high speed row reset
InactiveUS6532040B1Reduce noiseEasy to manufactureTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorLow noise
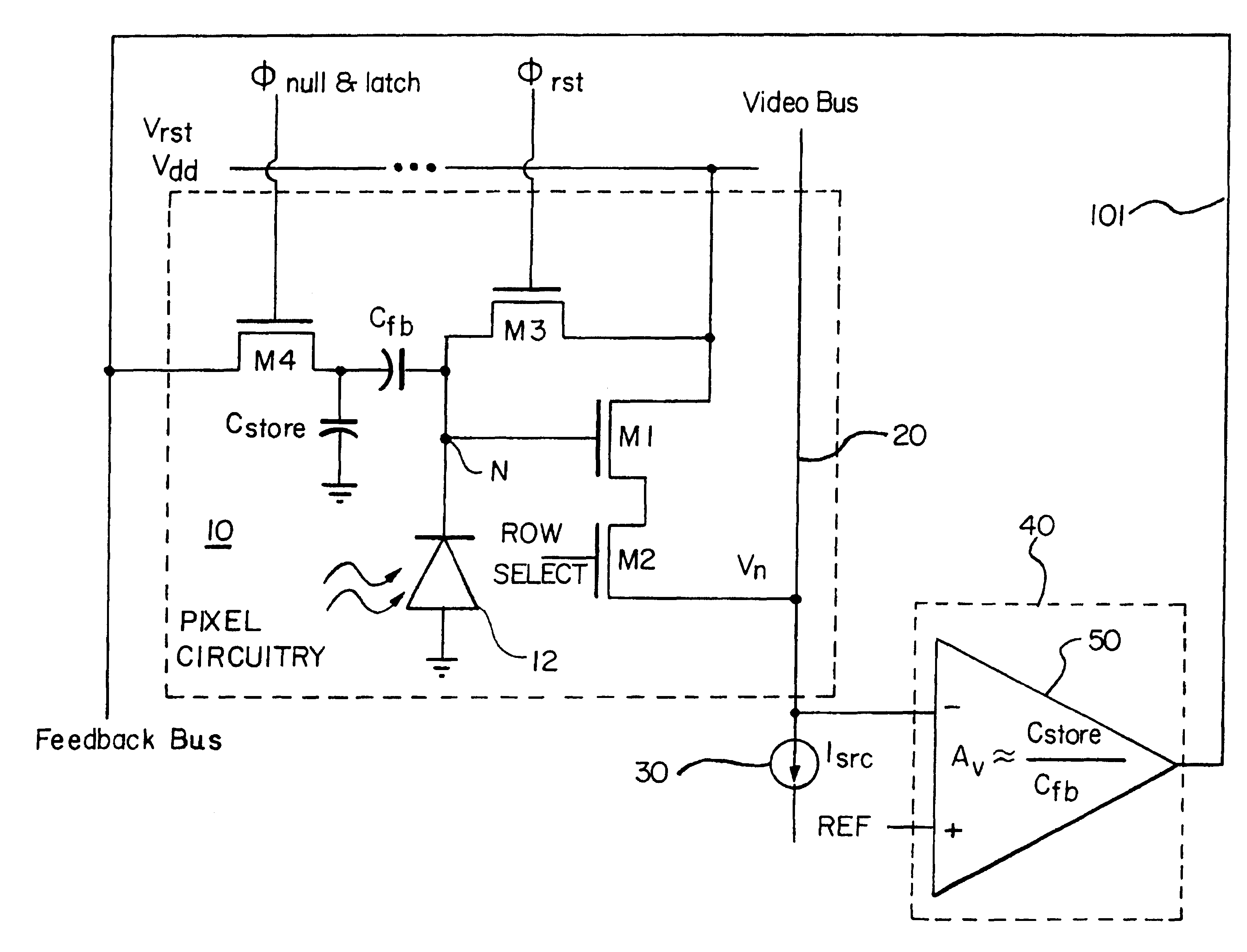
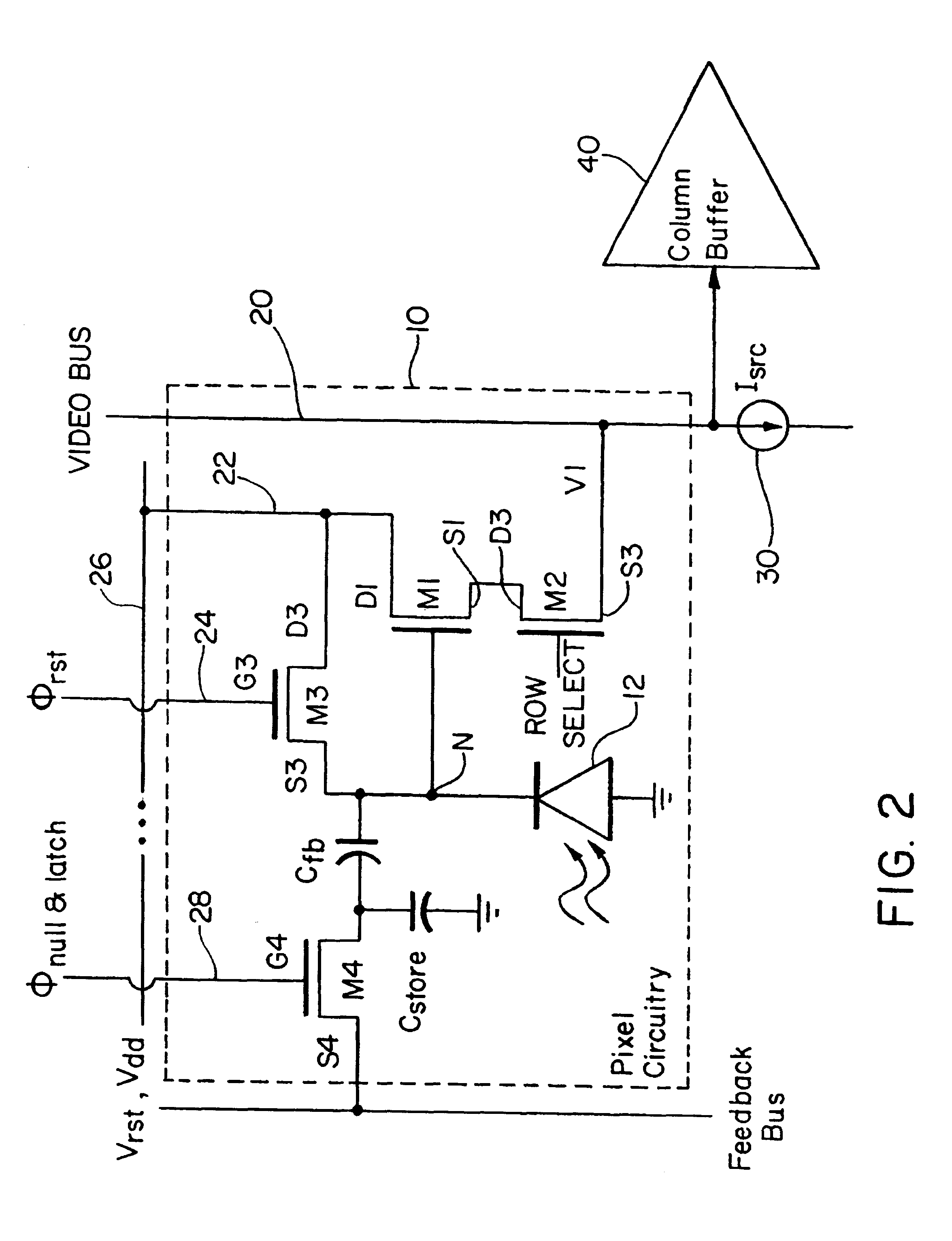
An imager pixel including a photodetector, a first MOS transistor functioning as the driver of a source follower amplifier during signal readout, a second MOS transistor serving as a pixel readout transistor, a third MOS transistor serving as a photodetector reset transistor, and a reset noise cancellation circuit including a fourth MOS transistor, first and second capacitances, and an amplifier having a gain which is the inverse of the ratio of the first to the second capacitance.
Owner:RE SECURED NETWORKS LLC +2
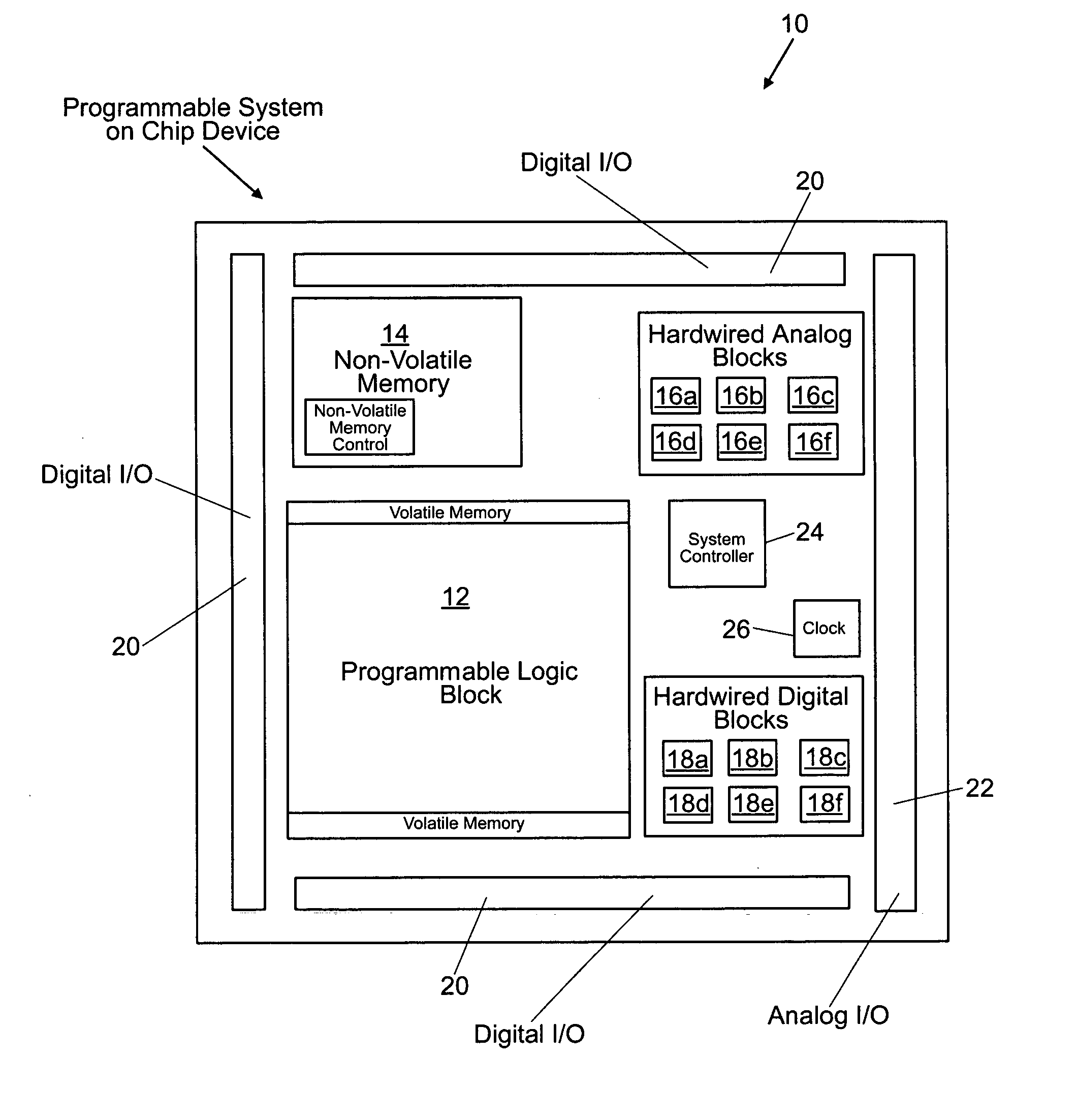
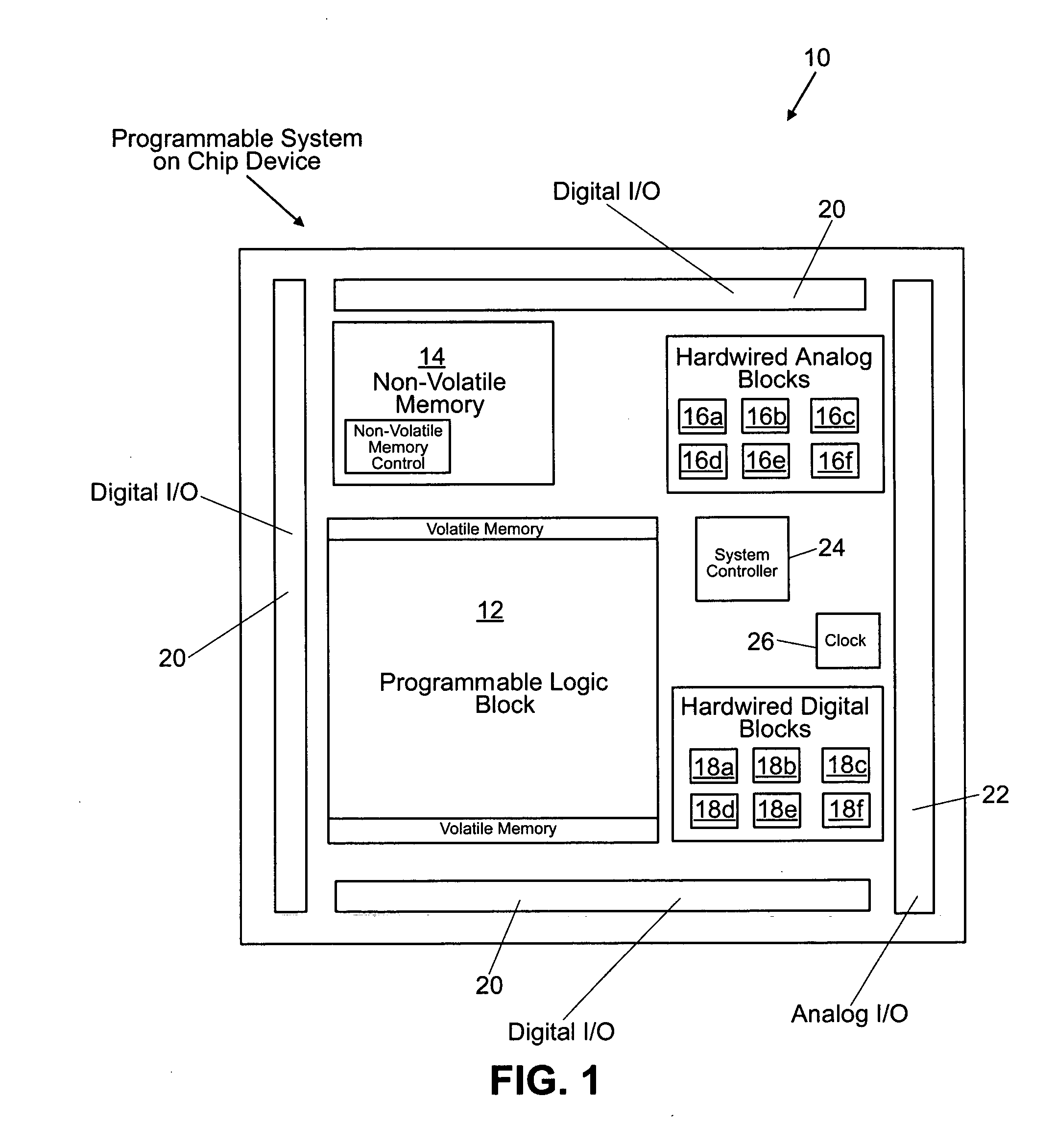
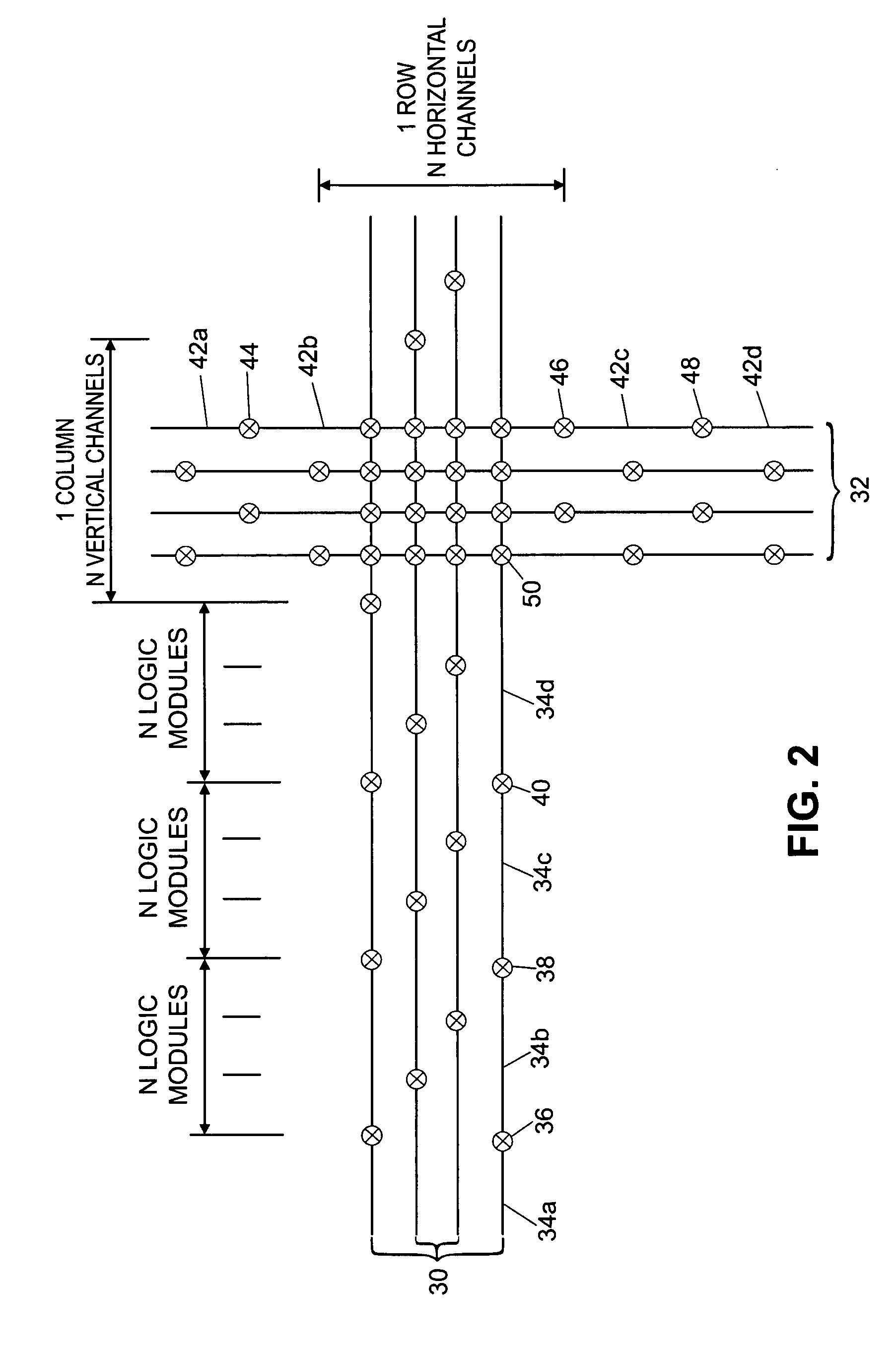
Programmable system on a chip
ActiveUS20050237083A1Thermometers using electric/magnetic elementsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
A programmable system-on-a-chip integrated circuit device comprises a programmable logic block, a non-volatile memory block, an analog sub-system, an analog input / output circuit block, and a digital input / output circuit block. A programmable interconnect architecture includes programmable elements and interconnect conductors. Ones of the programmable elements are coupled to the programmable logic block, the non-volatile memory block, the analog sub-system, the analog input / output circuit block, the digital input / output circuit block, and to the interconnect conductors, such that inputs and outputs of the programmable logic block, the non-volatile memory block, the analog sub-system, the analog input / output circuit block, and the digital input / output circuit block can be programmably coupled to one another.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
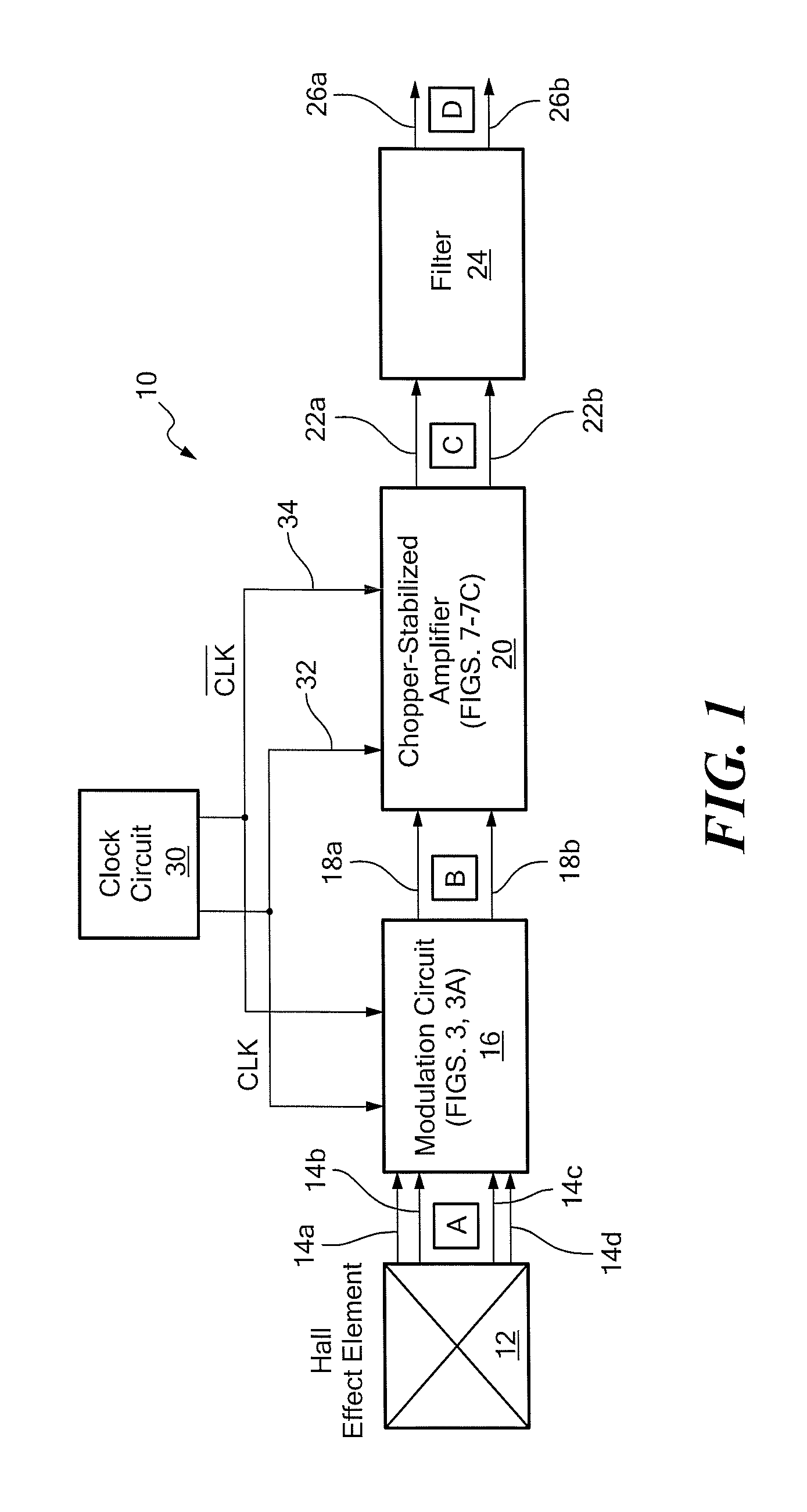
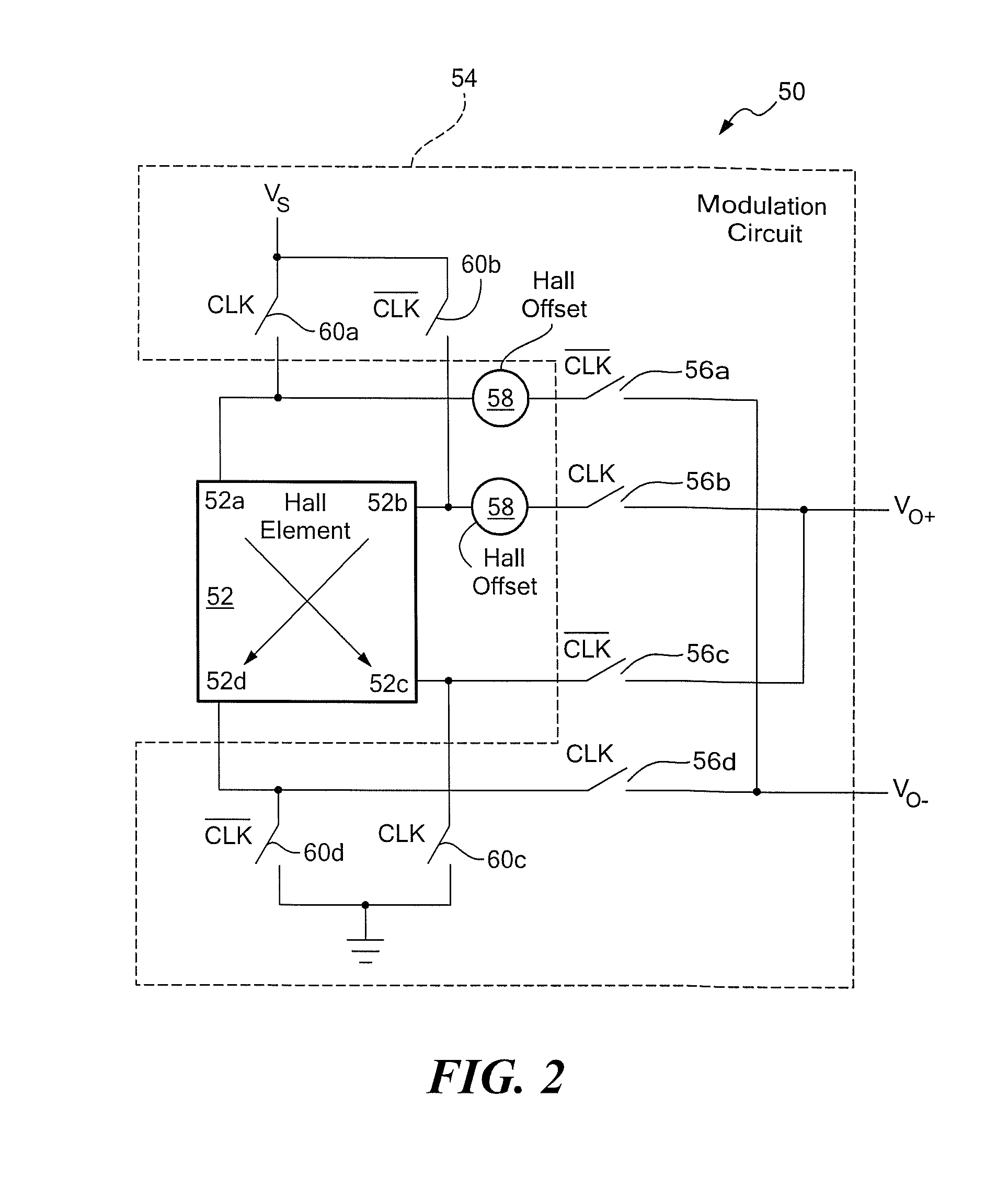
Chopper-stabilized amplifier and magnetic field sensor
ActiveUS7605647B1Reduced offset componentIncrease the switching frequencyGalvano-magnetic amplifiersMagnetic measurementsAudio power amplifierLow-pass filter
A chopper-stabilized amplifier has switching networks arranged to support a high frequency clocking signal and to provide a high common mode rejection and a high rejection of an offset component of an input signal. A magnetic field sensor includes a Hall effect element coupled to a modulation circuit. The modulation circuit provides a signal to the chopper-stabilized amplifier. The chopper-stabilized amplifier provides an output signal to a low pass filter, which provides an output signal from the magnetic field sensor.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Wireless electric field power transmission system and method
ActiveUS20130147427A1Prevent electromagnetic field (EMF) leakageIncrease the electric field strengthNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemElectrical conductorTransfer system
A wireless electric field power transmission system comprises: a transmitter comprising a transmitter antenna, the transmitter antenna comprising at least two conductors defining a volume therebetween; and at least one receiver, wherein the transmitter antenna transfers power wirelessly via electric field coupling when the at least one receiver is within the volume.
Owner:SOLACE POWER INC
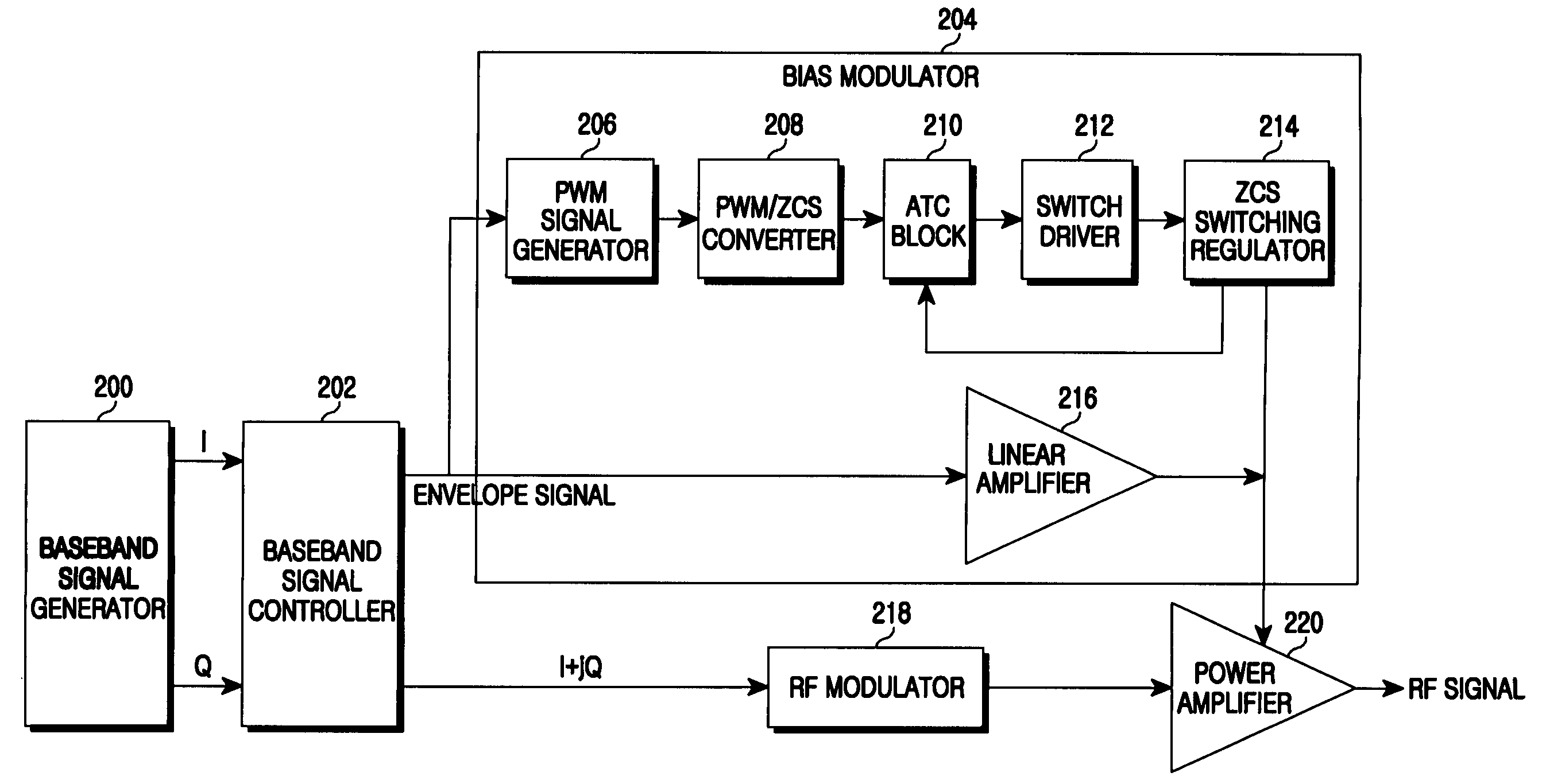
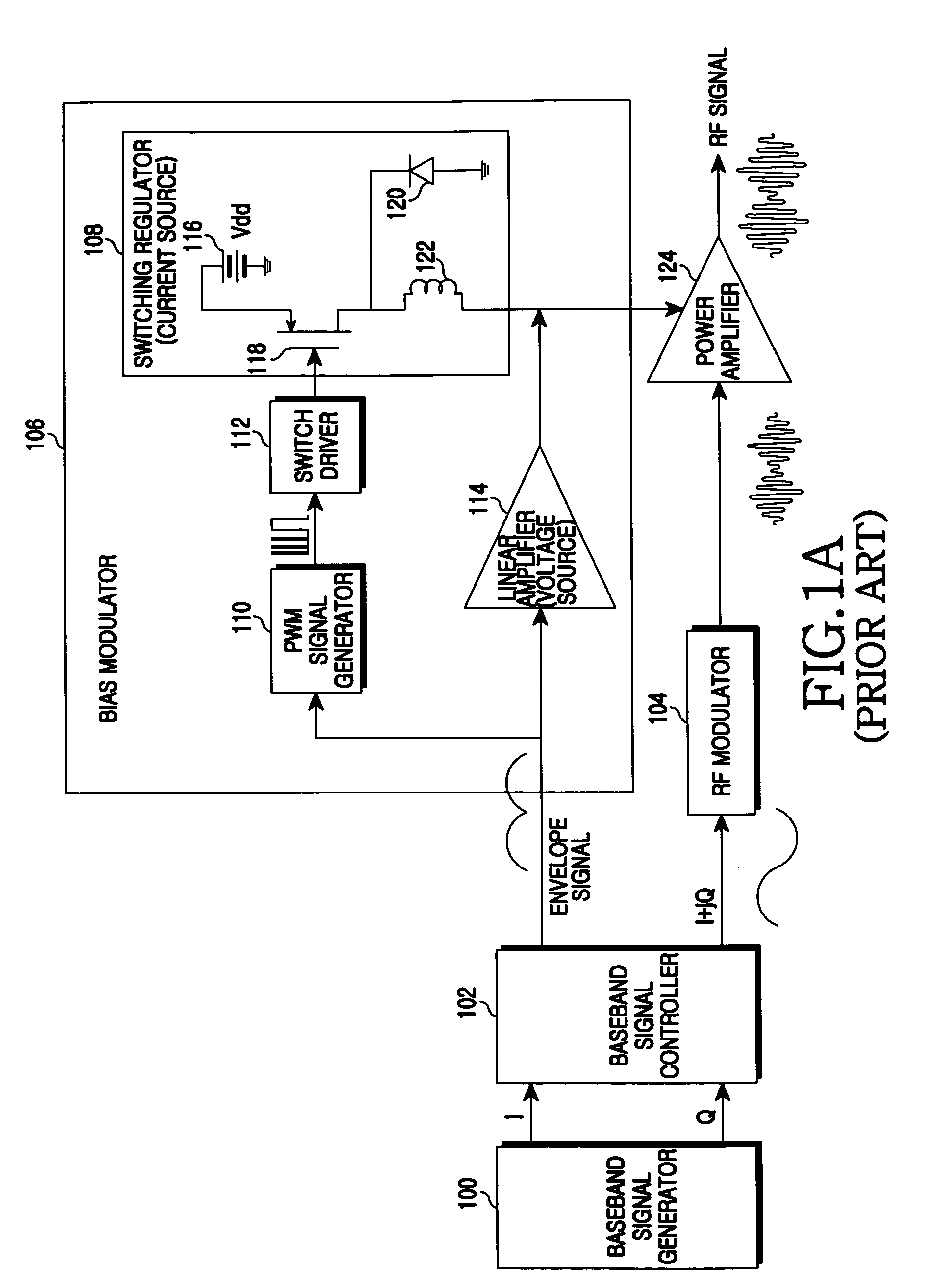
Apparatus and method for bias modulator using zero current switching
ActiveUS20090218995A1Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAngle modulationControl signalEngineering
An apparatus and a method for a bias modulator using a Zero Current Switching (ZCS) are provided. The bias modulator includes a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal generator for converting an input envelope signal to a PWM signal; a PWM / ZCS converter for calculating the number of ZCS control signals to be provided within an on-time duration of the PWM signal and generating at least one ZCS control signal according to the number of the ZCS control signals; and a ZCS switching regulator for generating a bias current according to the ZCS control signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Using degeneration in an active tunable low-noise radio frequency bandpass filter
ActiveUS8314653B1Easy to FeedbackReduce gainSwitched capacitor networksAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesLow noiseBandpass filtering
The present disclosure relates to a first active tunable low-noise RF bandpass filter that includes at least a first transistor element and a tunable frequency selective degeneration circuit coupled to a first non-inverting output of the first transistor element. The first active tunable low-noise RF bandpass filter combines low noise amplifier (LNA) and tunable bandpass filter functionalities into a single active RF bandpass filter. The tunable frequency selective degeneration circuit uses degeneration at frequencies outside of a passband of the active RF bandpass filter to increase feedback, thereby decreasing gain of the active RF bandpass filter. By decreasing the gain, linearity of the active RF bandpass filter may be improved in the presence of strong interfering RF signals, thereby enabling elimination of passive bandpass filter elements, such as surface acoustic wave (SAW) and bulk acoustic wave (BAW) filters, without degrading reception of in-band RF signals.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Portable multi-device power supply, battery charger, and docking system
ActiveUS8107243B2Gain controlAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesPower flowElectrical battery
Owner:CALLPOD
RF power transmission, modulation, and amplification, including embodiments for generating vector modulation control signals
ActiveUS7620129B2Amplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyControl signalFrequency characteristic
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
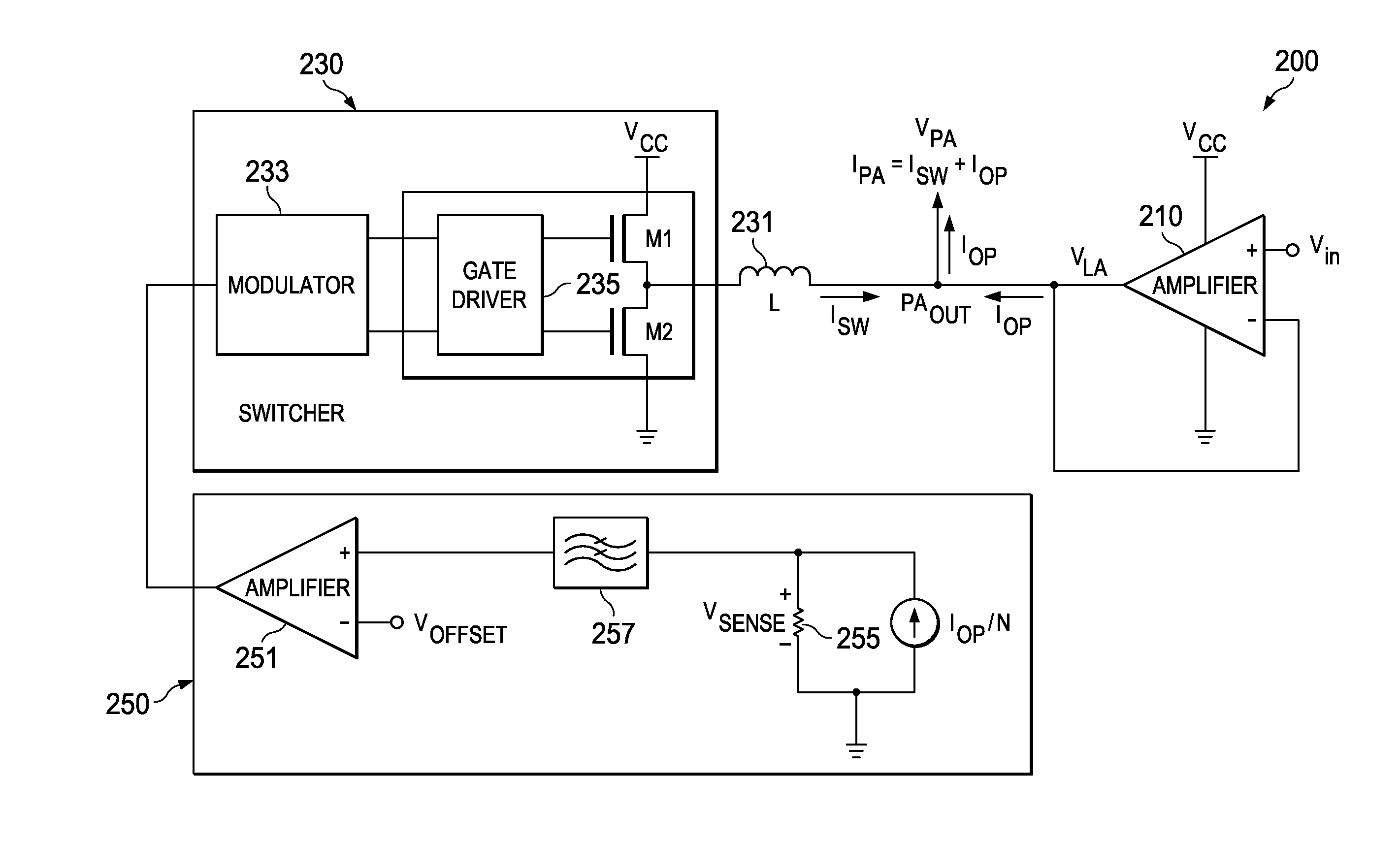
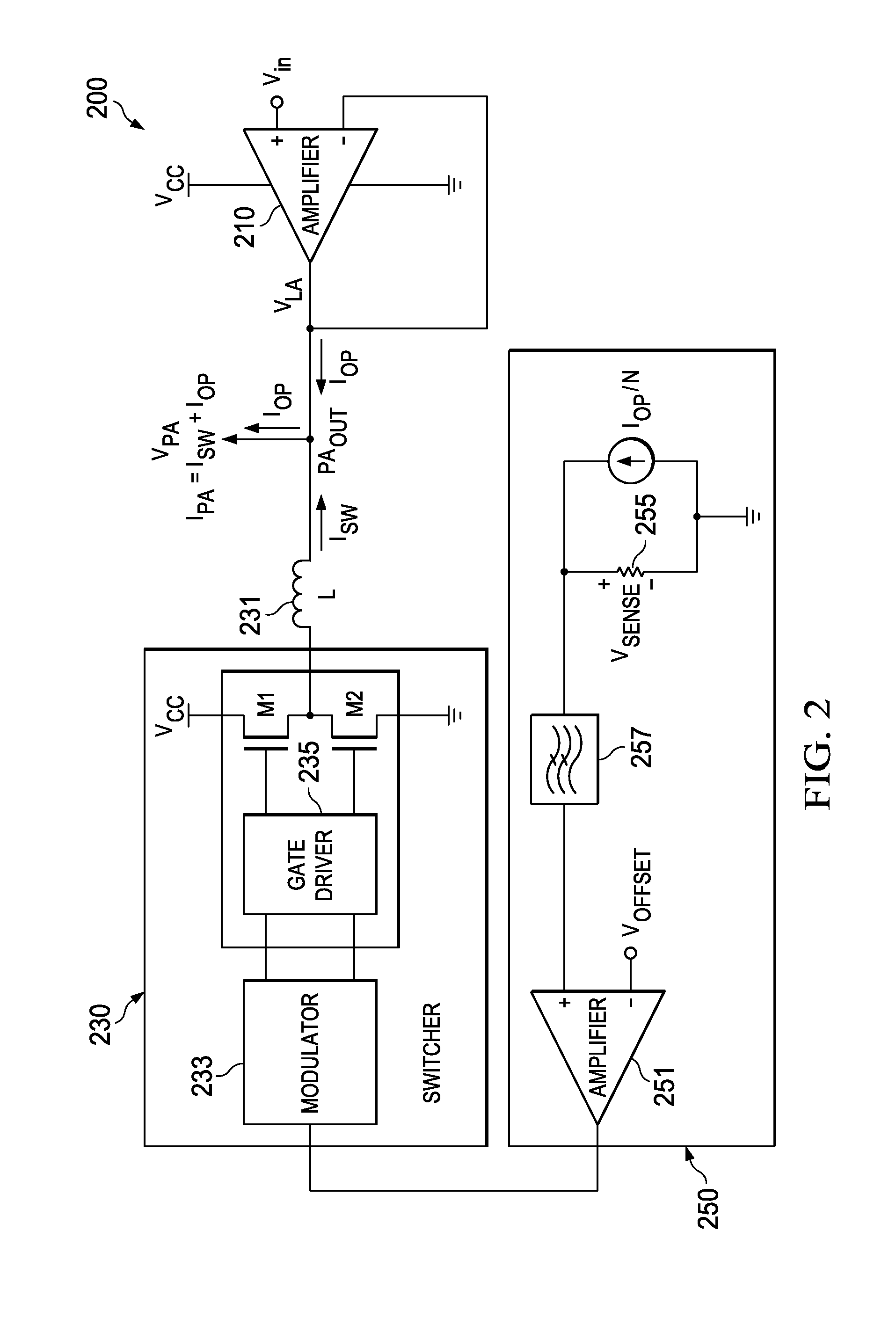
Parallel arranged linear amplifier and dc-dc converter
InactiveUS20100045247A1Enhanced inhibitory effectNot control loop stabilityAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric variable regulationDc dc converterAudio power amplifier
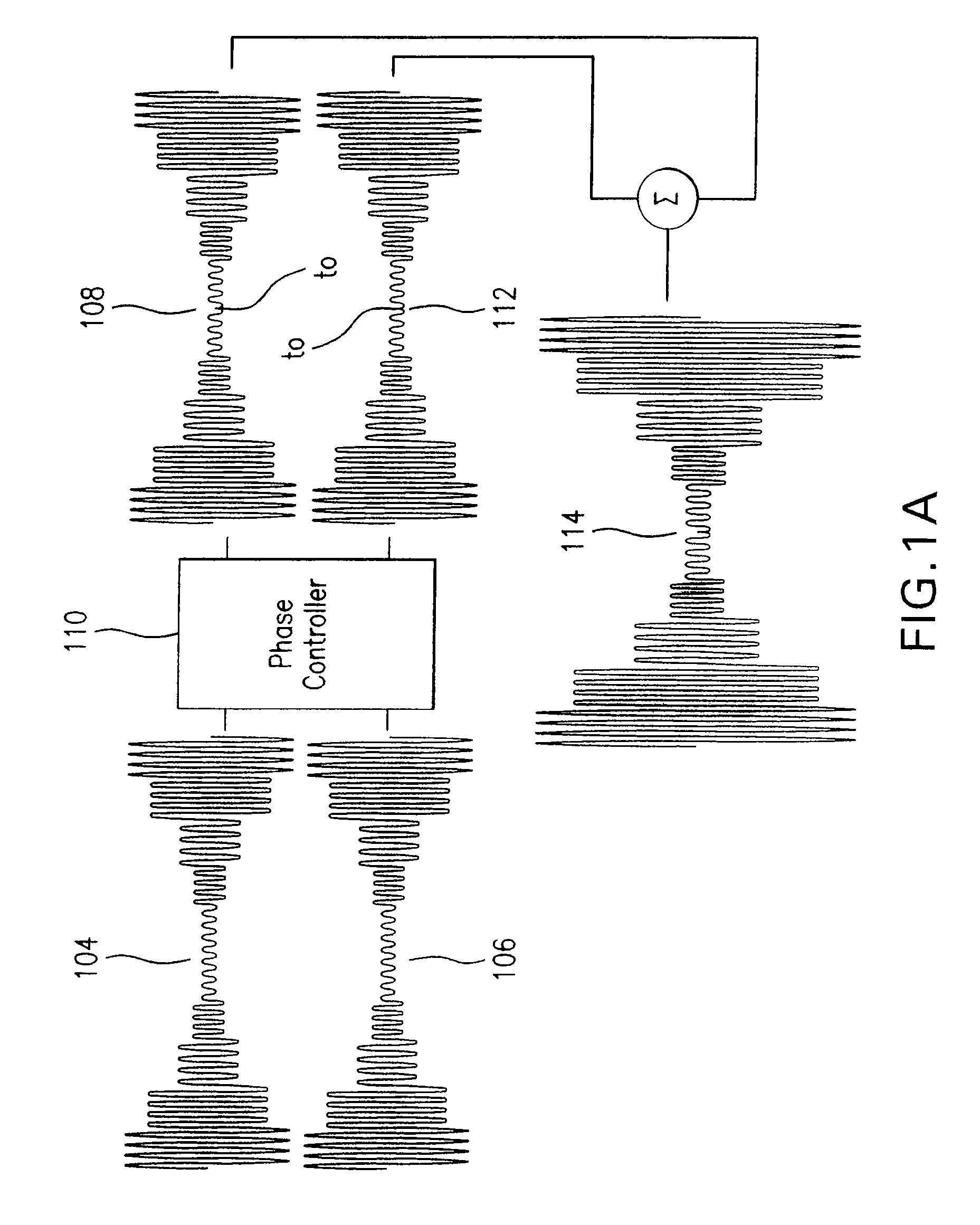
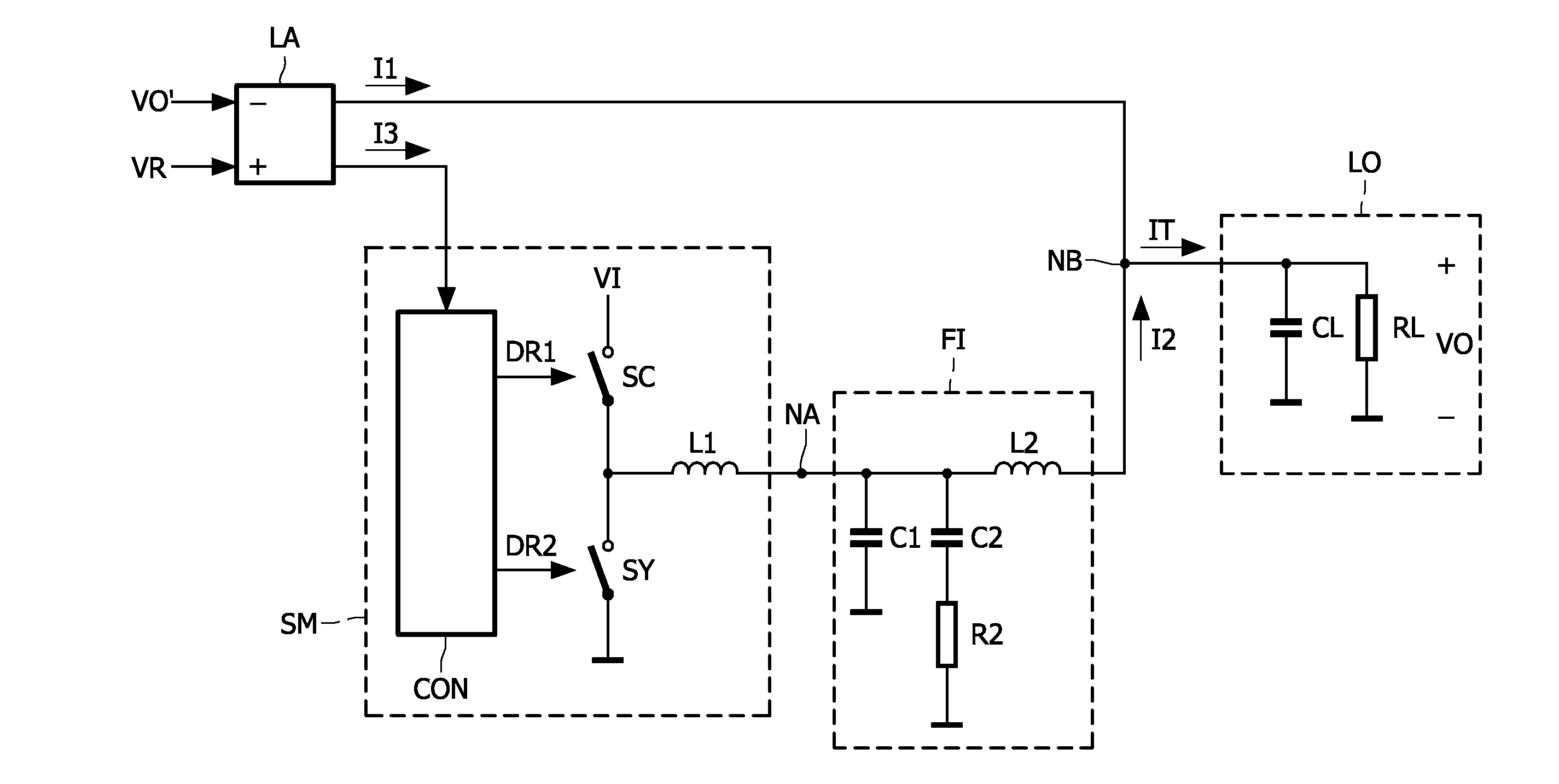
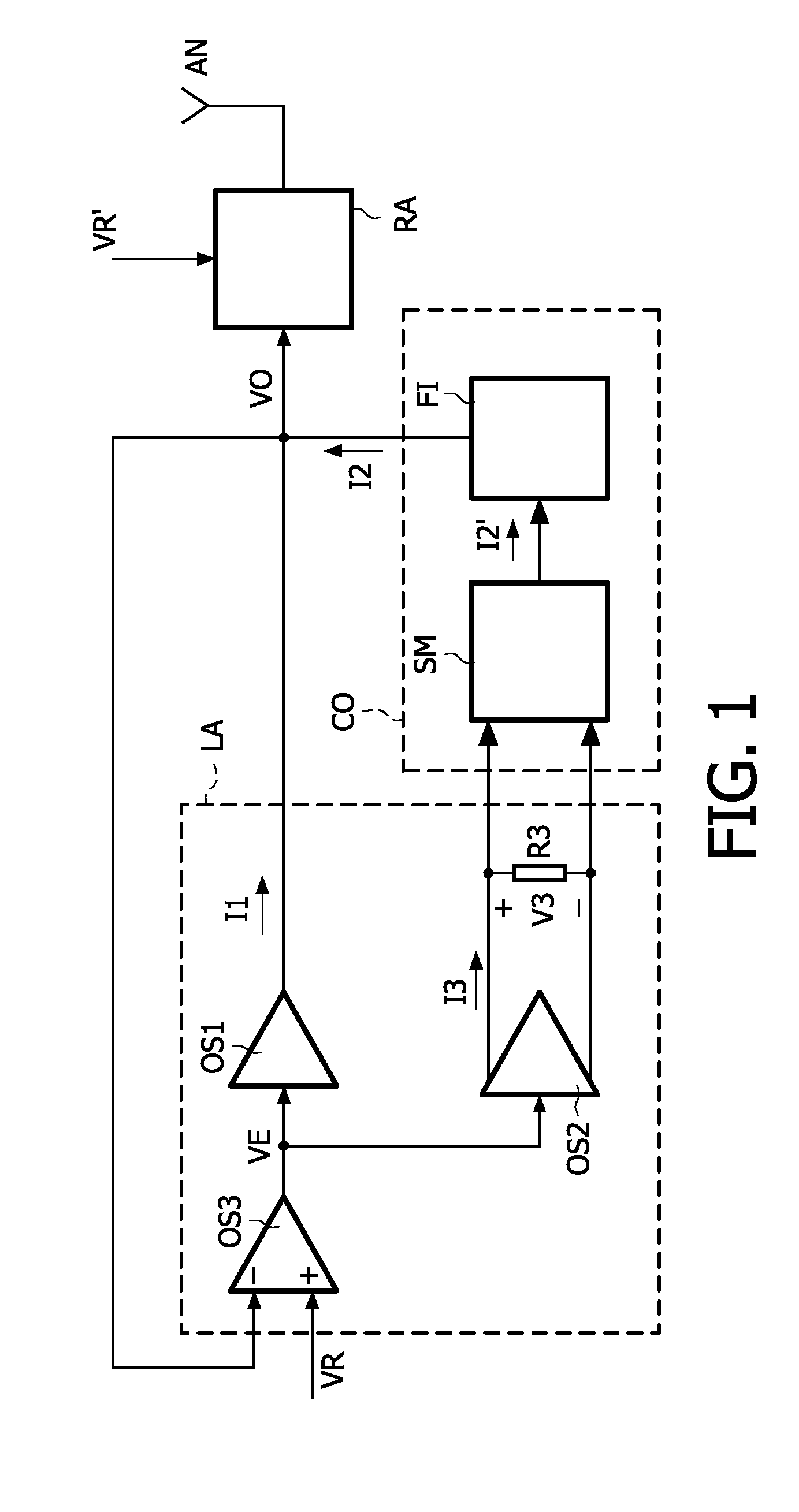
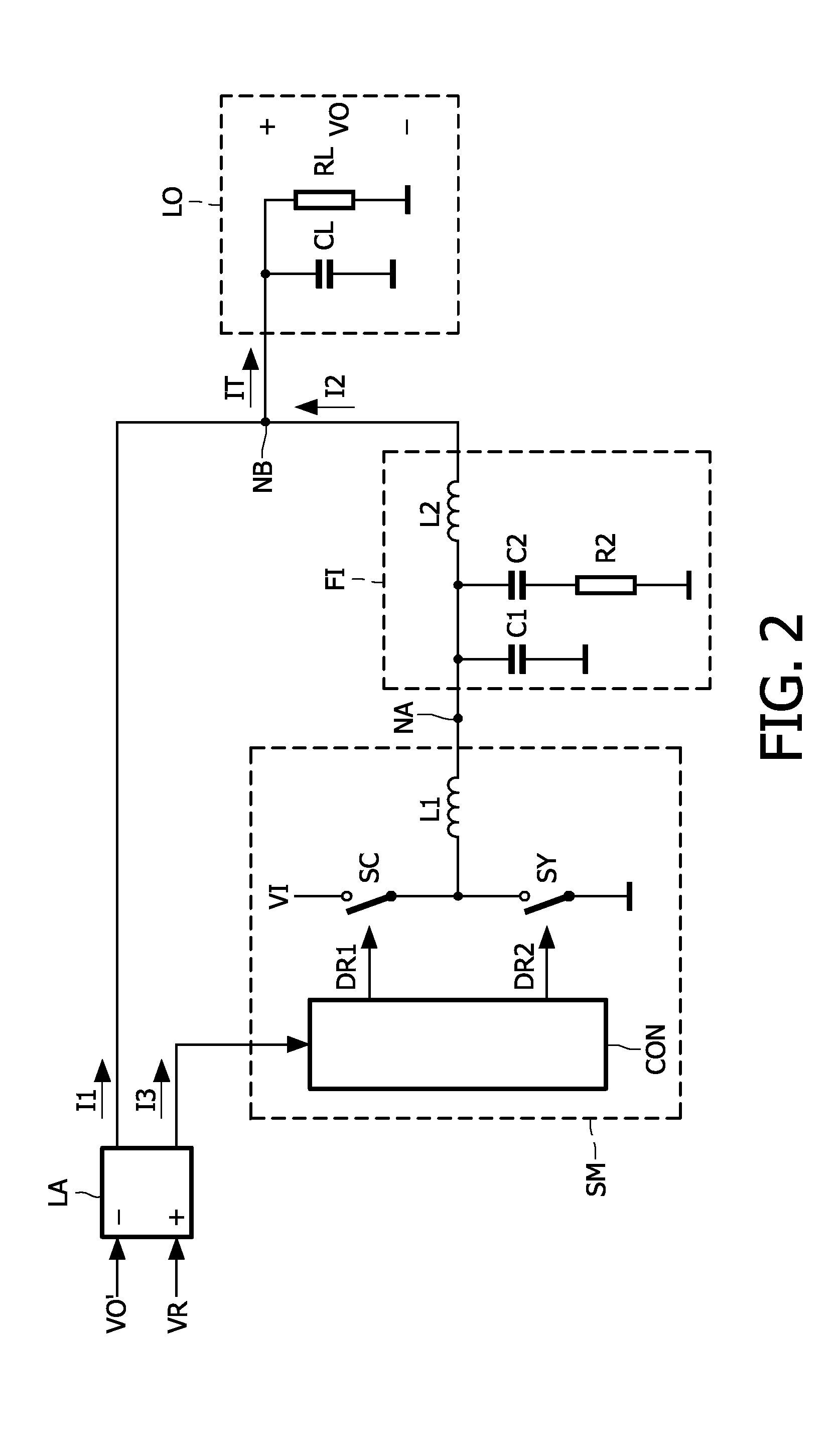
A power supply system comprises a parallel arrangement of a linear amplifier (LA) and a DC-DC converter (CO). The linear amplifier (LA) has an amplifier output to supply a first current (II) to the load (LO). The DC-DC converter (CO) comprises: a converter output for supplying a second current (12) to the load (LO), a first inductor (L1), and a switch (SC) coupled to the first inductor (L1) for generating a current in the first inductor (L1), and a low-pass filter (FI) arranged between the first inductor (L1) and the load (LO). The low pass filter (FI) comprises a first capacitor (C1; CA) which has a first terminal coupled to the switch (SC) an a second terminal coupled to a reference voltage level (GND), and a second inductor (L2; LC) which has a first terminal coupled to the first inductor (L1) and a second terminal coupled to the load (LO). The low-pass filter further comprises, either: (i) a series arrangement of a second capacitor (C2) and a damping resistor (R2), which series arrangement is arranged in parallel with the first capacitor (C1), or (ii) a parallel arrangement of a third capacitor (CB) and a damping resistor (RB) arranged in series with the first capacitor (CA), or (iii) a series arrangement of a third inductor (L3) and a damping resistor (R3), which series arrangement is arranged in parallel with the second inductor (L2), or (iv) a parallel arrangement of a fourth inductor (LD) and a damping resistor (RD), which parallel arrangement is arranged in series with the second inductor (LC).
Owner:NXP BV
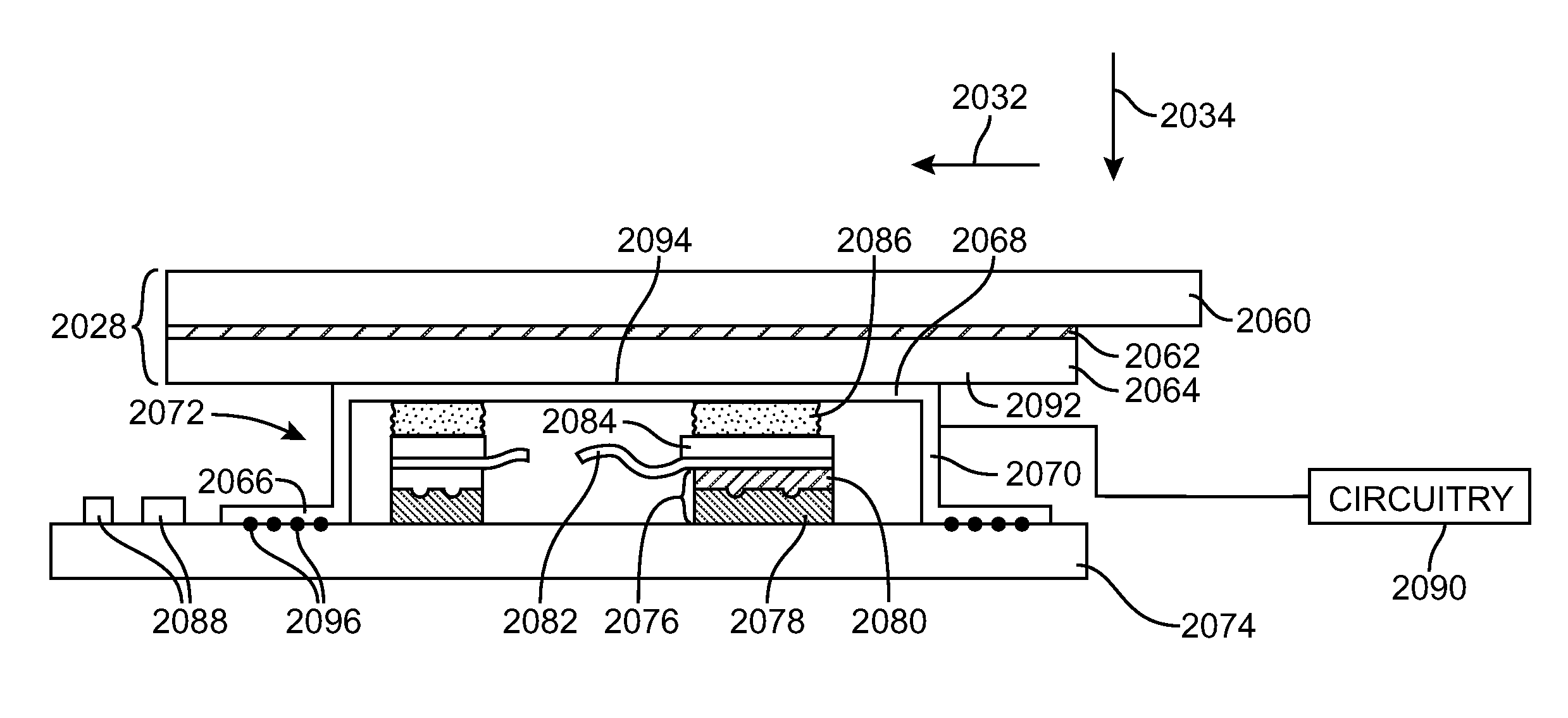
Electronic subassemblies for electronic devices
InactiveUS20110255850A1Improve device aestheticImprove device aestheticsCoupling device connectionsFinal product manufactureEngineeringHeat sink
Electronic devices may be provided that include mechanical and electronic components. Connectors may be used to interconnect printed circuits and devices mounted to printed circuits. Printed circuits may include rigid printed circuit boards and flexible printed circuit boards. Heat sinks and other thermally conductive structures may be used to remove excess component heat. Structures may also be provided in an electronic device to detect moisture. Integrated circuits and other circuitry may be mounted on a printed circuit board under a radio-frequency shielding can.
Owner:APPLE INC
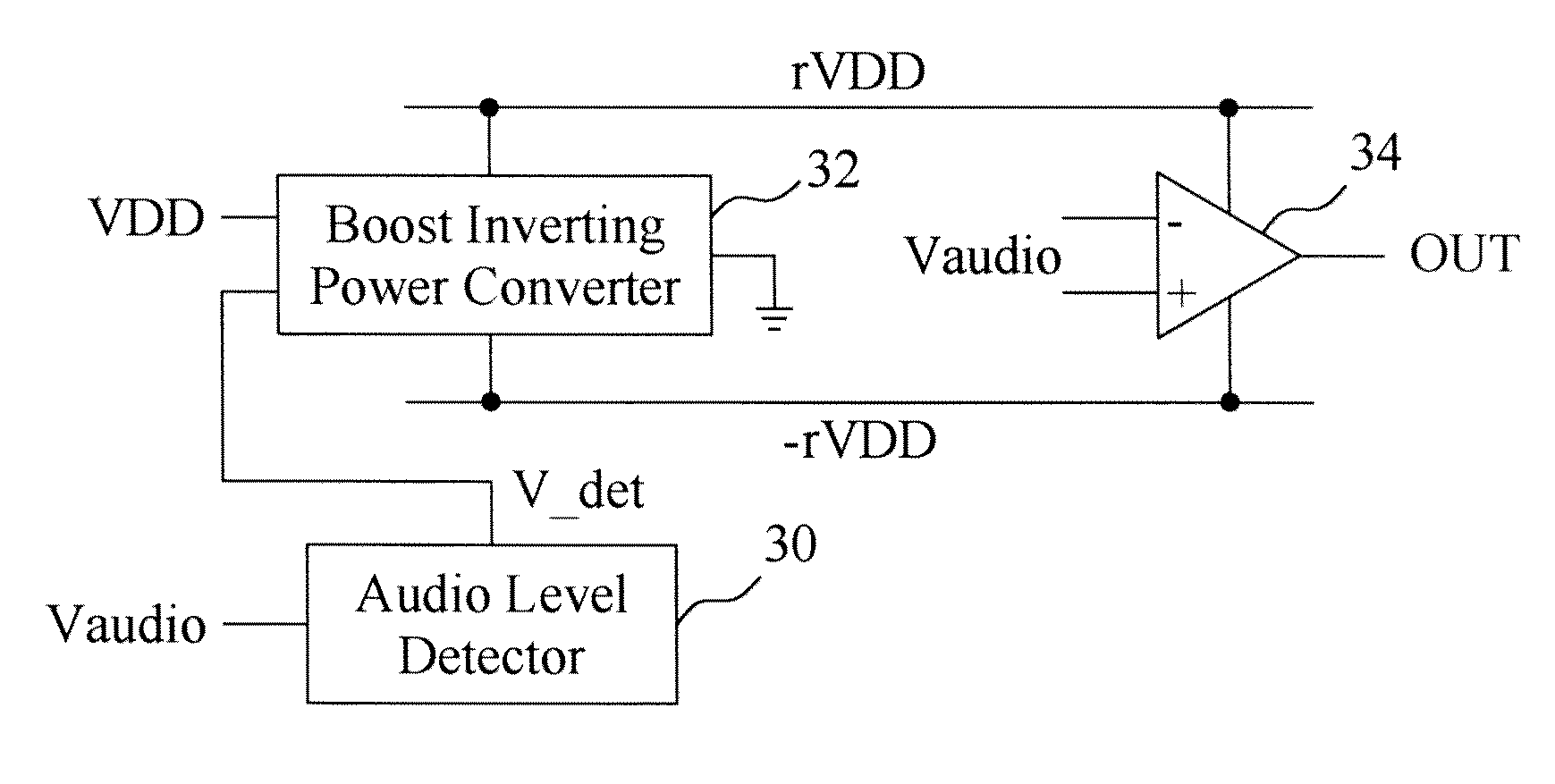
Highly efficient class-g amplifier and control method thereof
InactiveUS20110084760A1Improve efficiencyLow costNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlAudio power amplifierNegative power
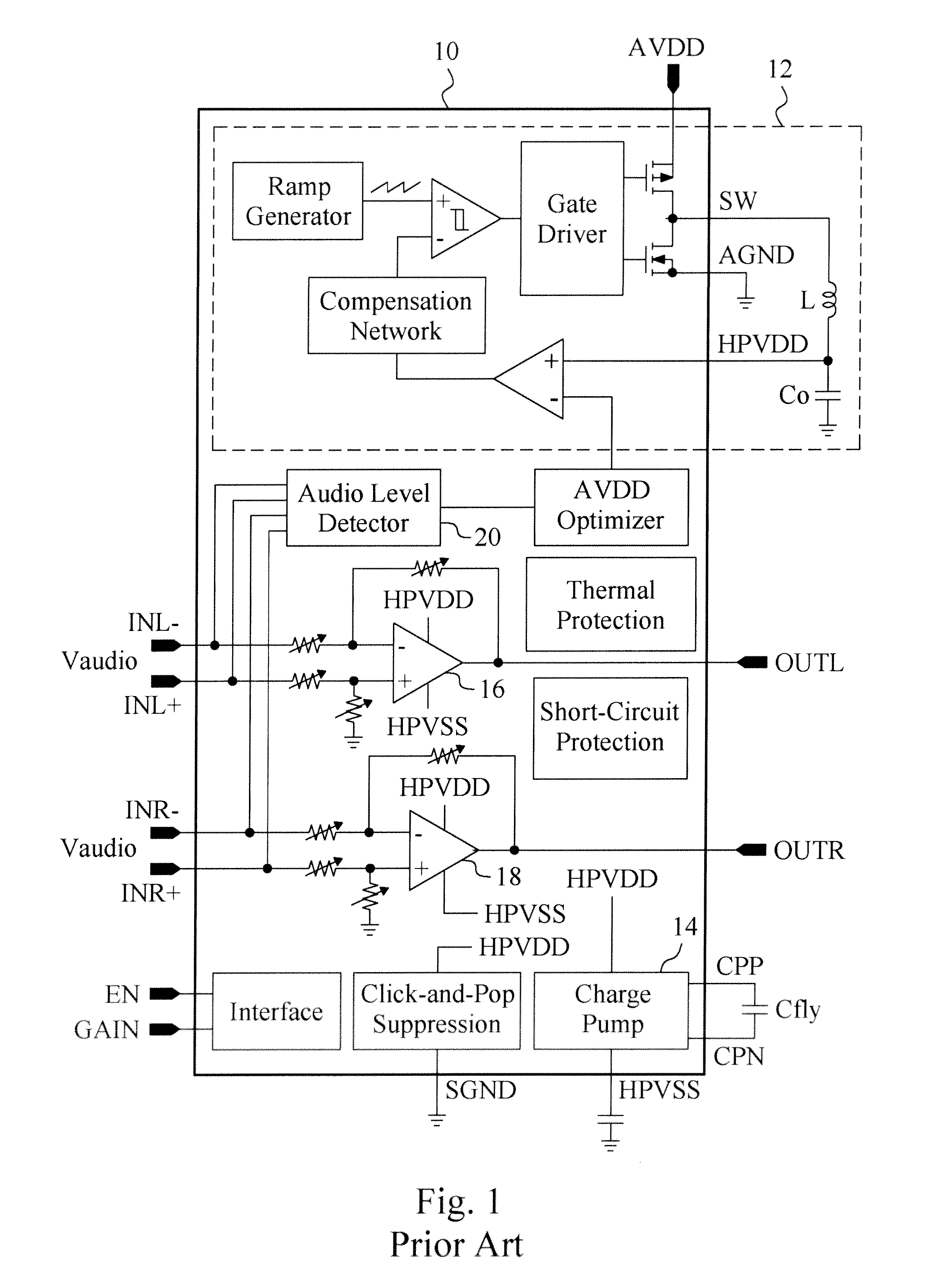
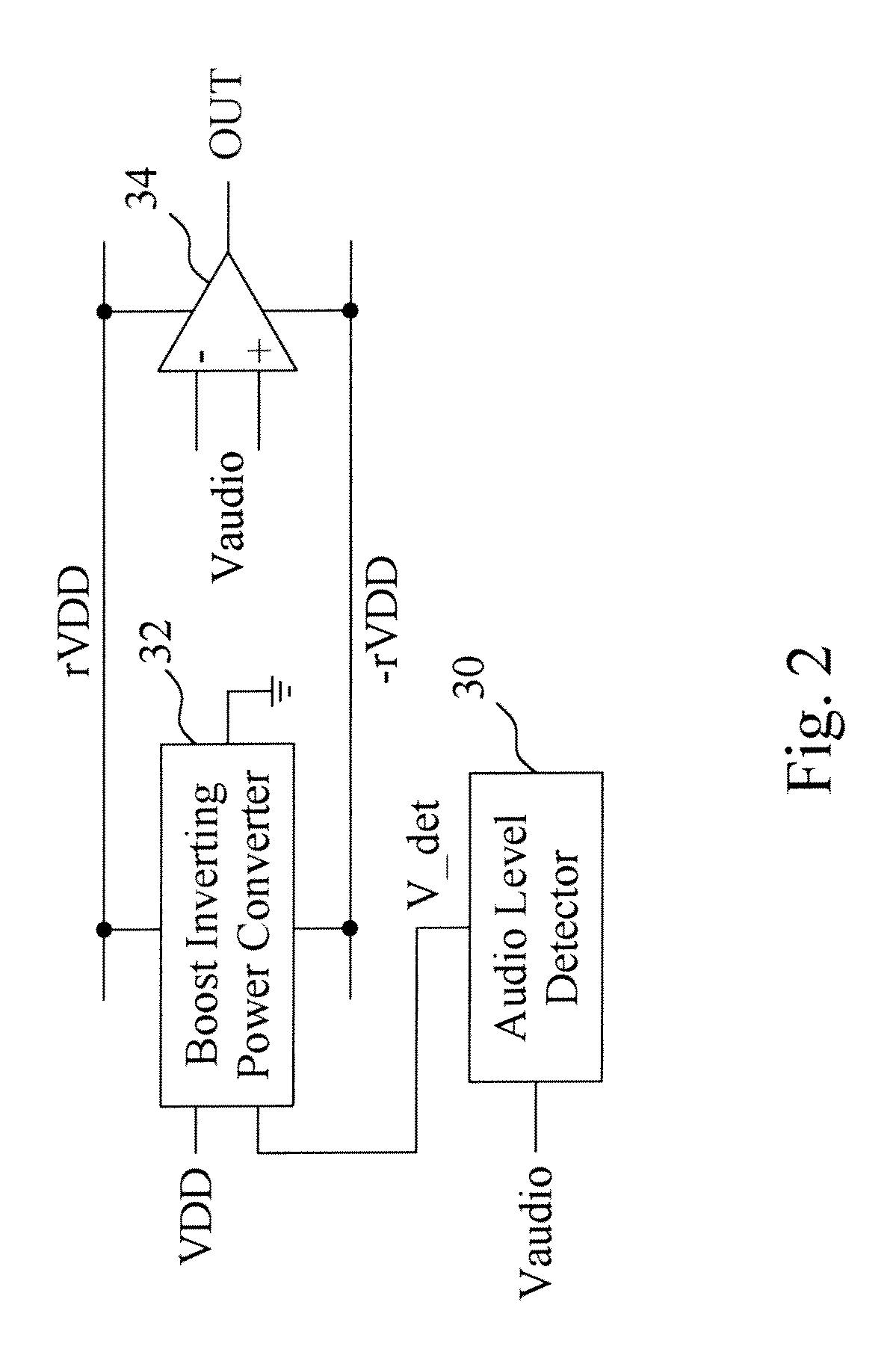
A highly efficient class-G amplifier includes an amplifier circuit coupled between a positive power rail and a negative power rail to amplify an audio input signal of the class-G amplifier, and a boost inverting power converter to convert a supply voltage to a positive rail voltage and a negative rail voltage on the positive and negative power rails. The boost inverting power converter includes a boost inverting power stage coupled to the positive and negative power rails, and a controller to switch the boost inverting power stage between a boost mode and an inverting mode. An audio level detector detects the audio input signal for the controller to adjust the positive and negative rail voltages. The class-G amplifier has higher efficiency and requires lower cost because it does not need a charge pump.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Wireless radio frequency signal transceiving system
ActiveUS20100202499A1Modulation transferenceDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAudio power amplifierRadio frequency signal
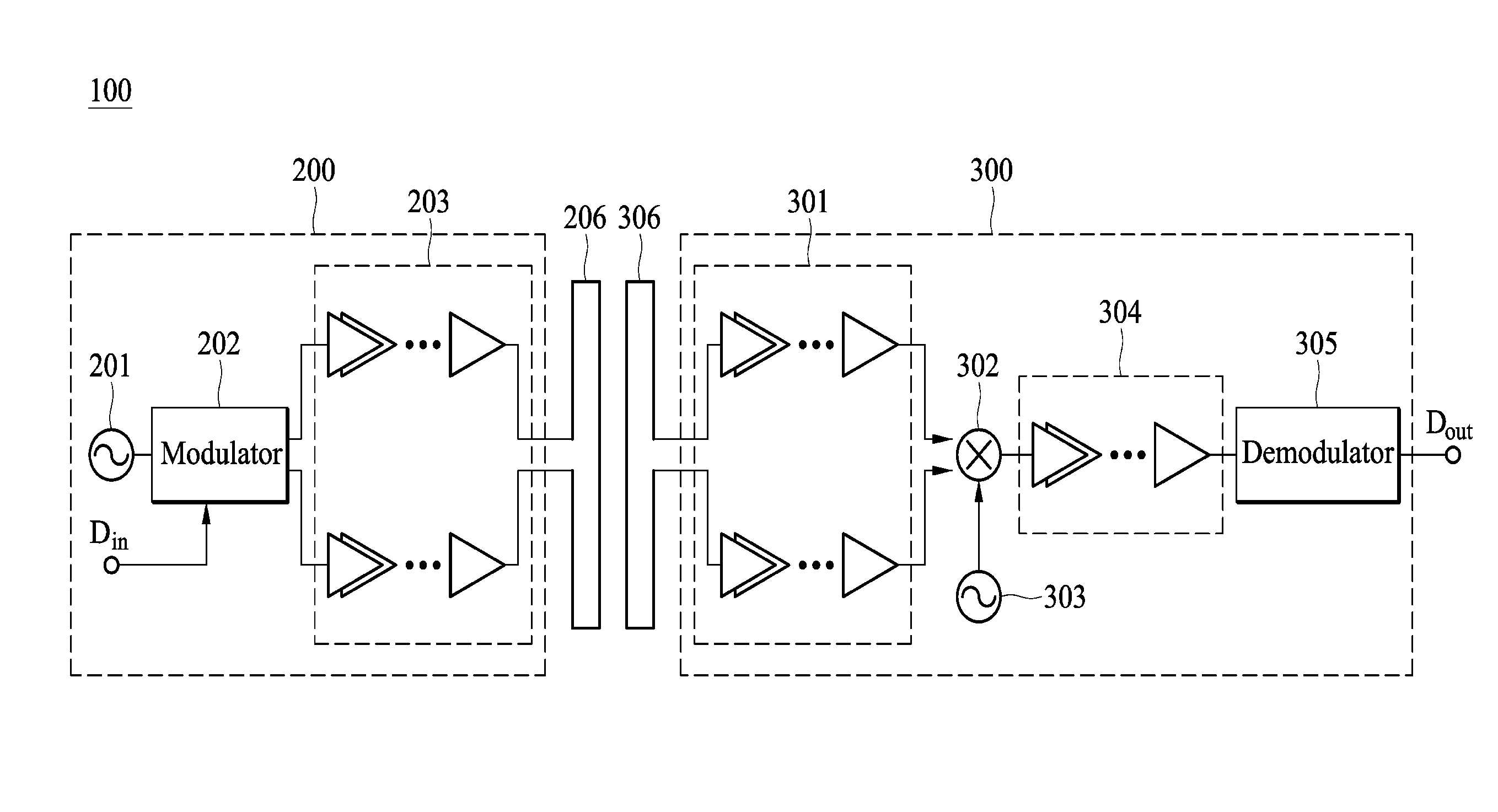
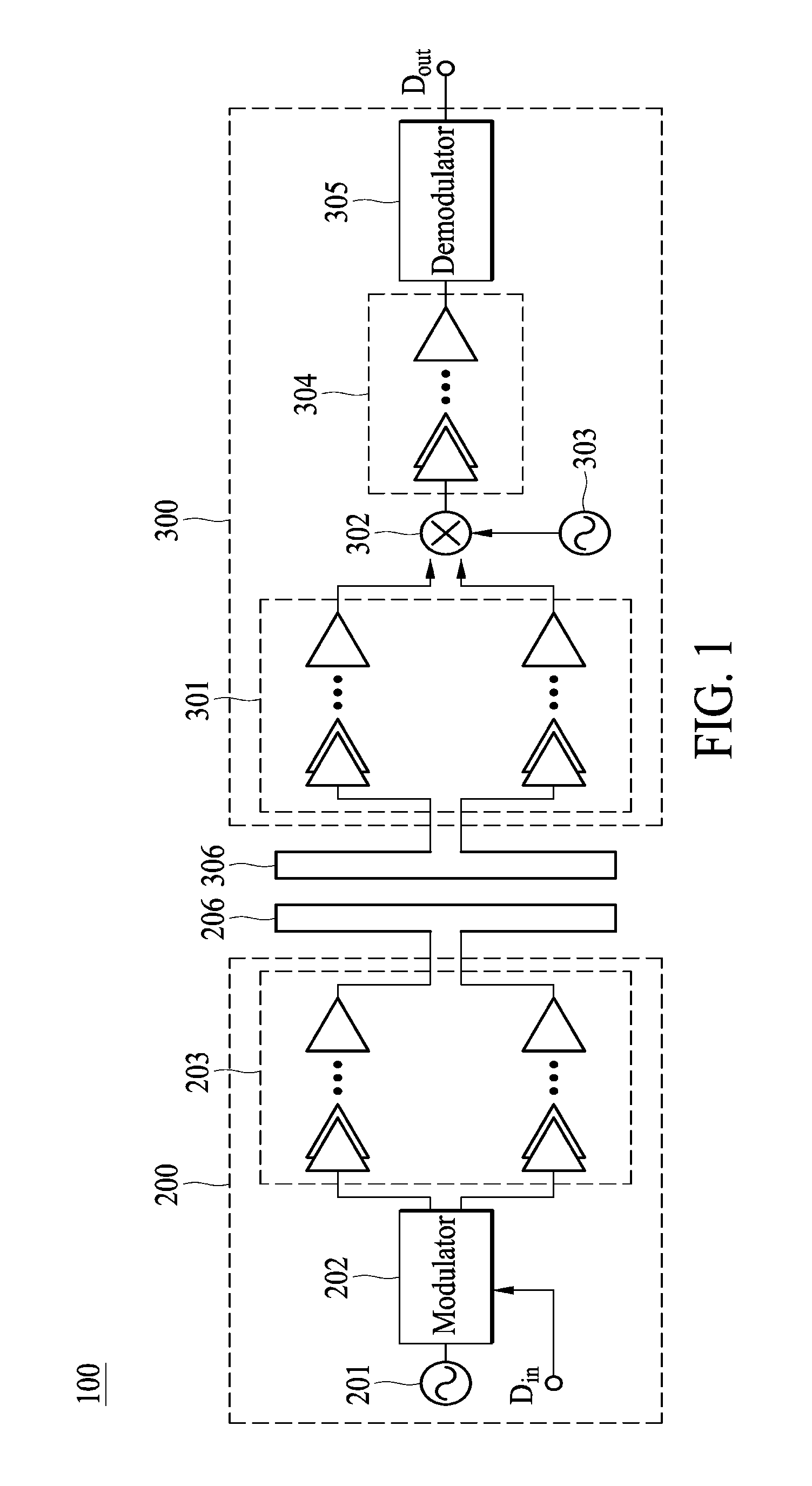
A differential radio frequency signal transmitter is provided. The differential radio frequency signal transmitter includes an oscillator, a modulator and an amplifier module. The oscillator generates a pair of differential oscillation signals. The modulator generates a pair of differential modulated signals according to an input signal and the pair of differential oscillation signals. The input signal is a digital signal. When the input signal is at a first state, the modulator outputs the pair of differential oscillation signals as the pair of differential modulated signals, and when the input signal is at a second state, the modulator outputs a constant voltage signal as the pair of differential modulated signals. The amplifier module receives and amplifies the pair of differential modulated signals and generates a pair of differential radio frequency signals, accordingly.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Portable multi-device power supply, battery charger, and docking system
A multiple electronic device power supply, battery charger, and USB docking system has a plurality of power ports for charging / powering electronic devices and a plurality of USB ports for coupling peripheral devices to a computer or large electronic device. Electronic devices which may be charged using the present invention can require current from less than 500 mA to approximately 6 A. Voltage setting resistors in specialized adapters serve to set the voltage needed for individual devices in order to manage current and voltage distribution throughout the present invention, particularly when large and mid-sized electronic devices are connected to the present multiple device charger and docking system. Default settings set the voltage output at 24 volts if not otherwise directed.
Owner:CALLPOD
Data recovery system for source synchronous data channels
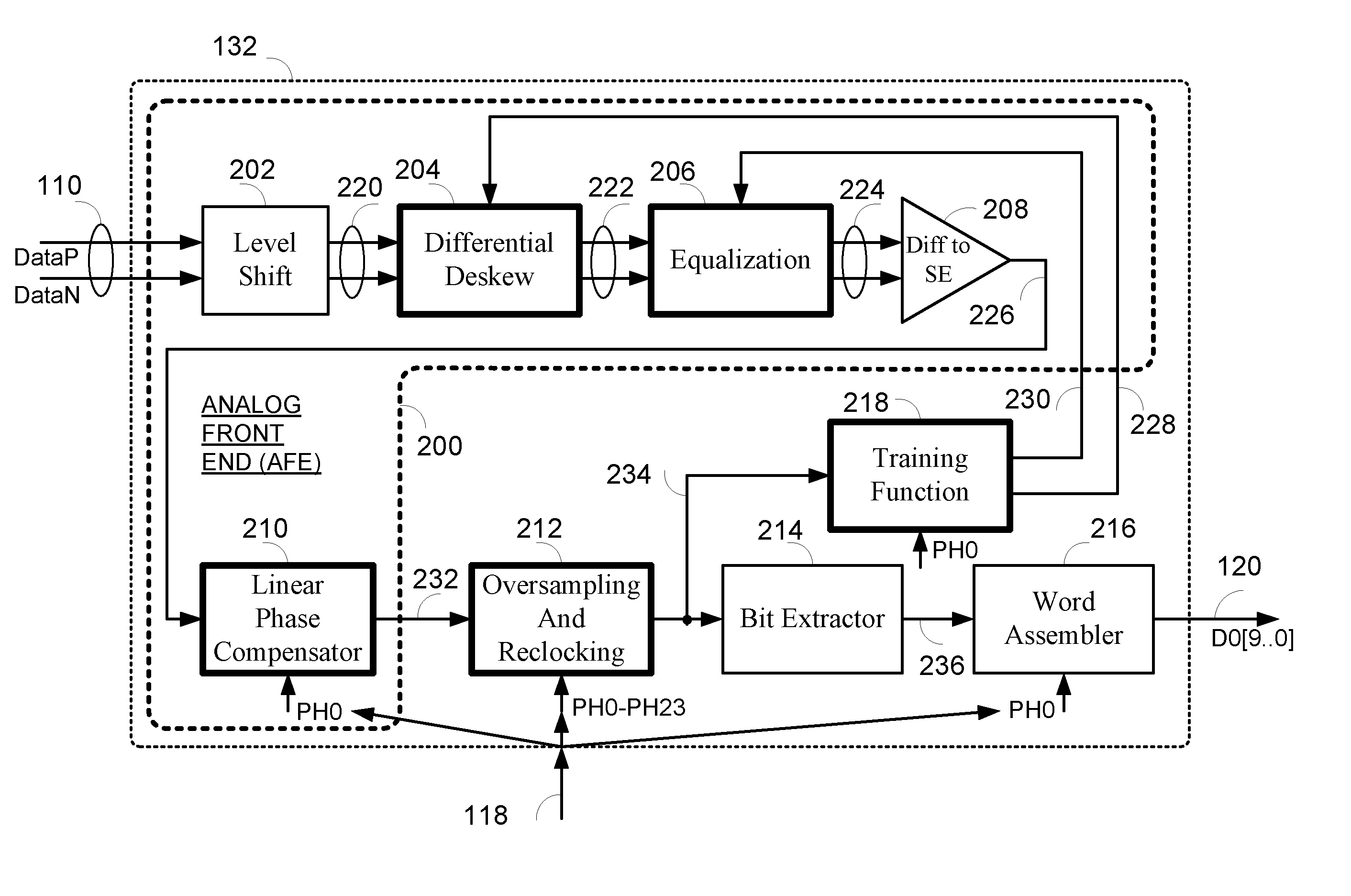
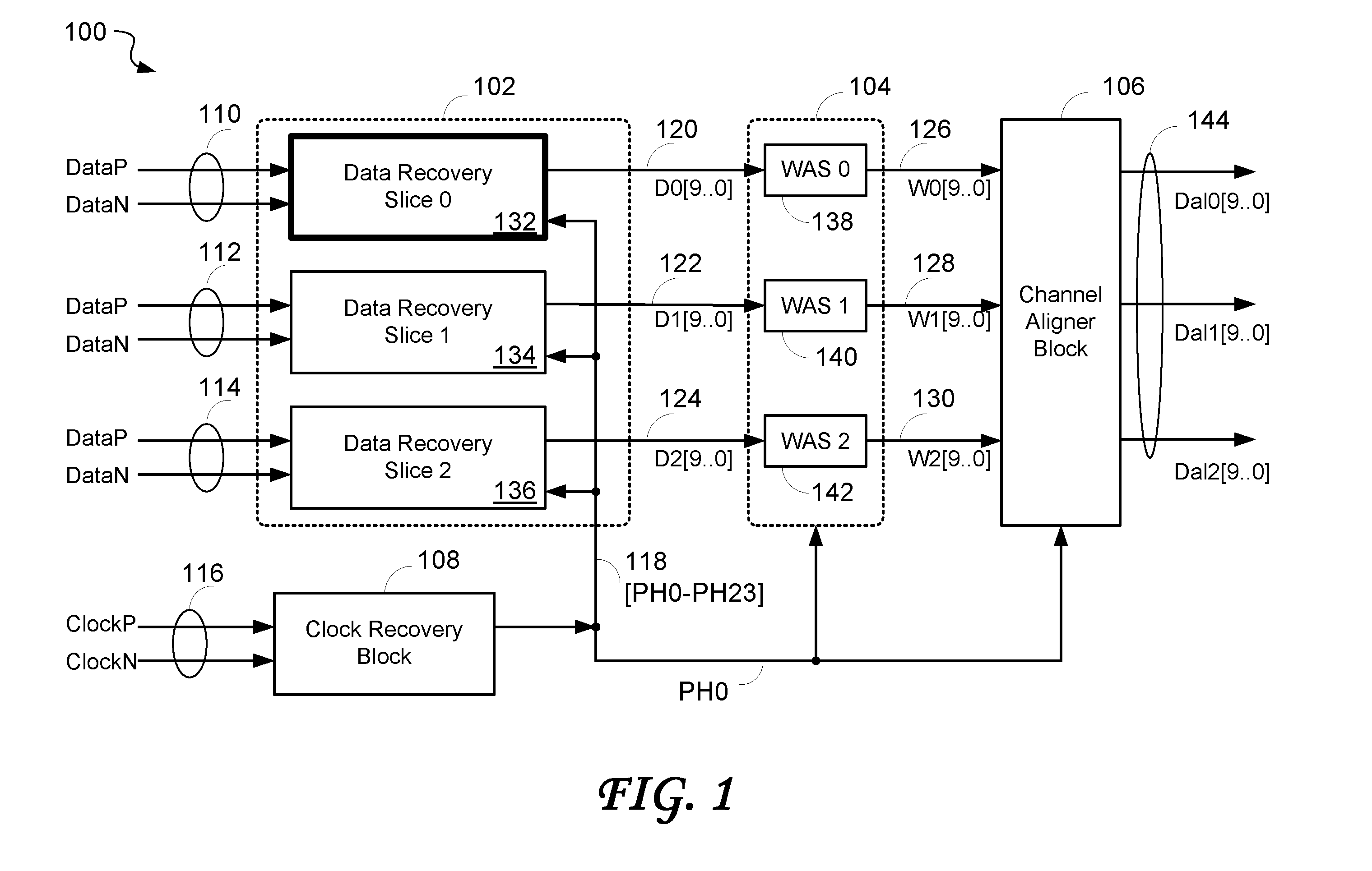
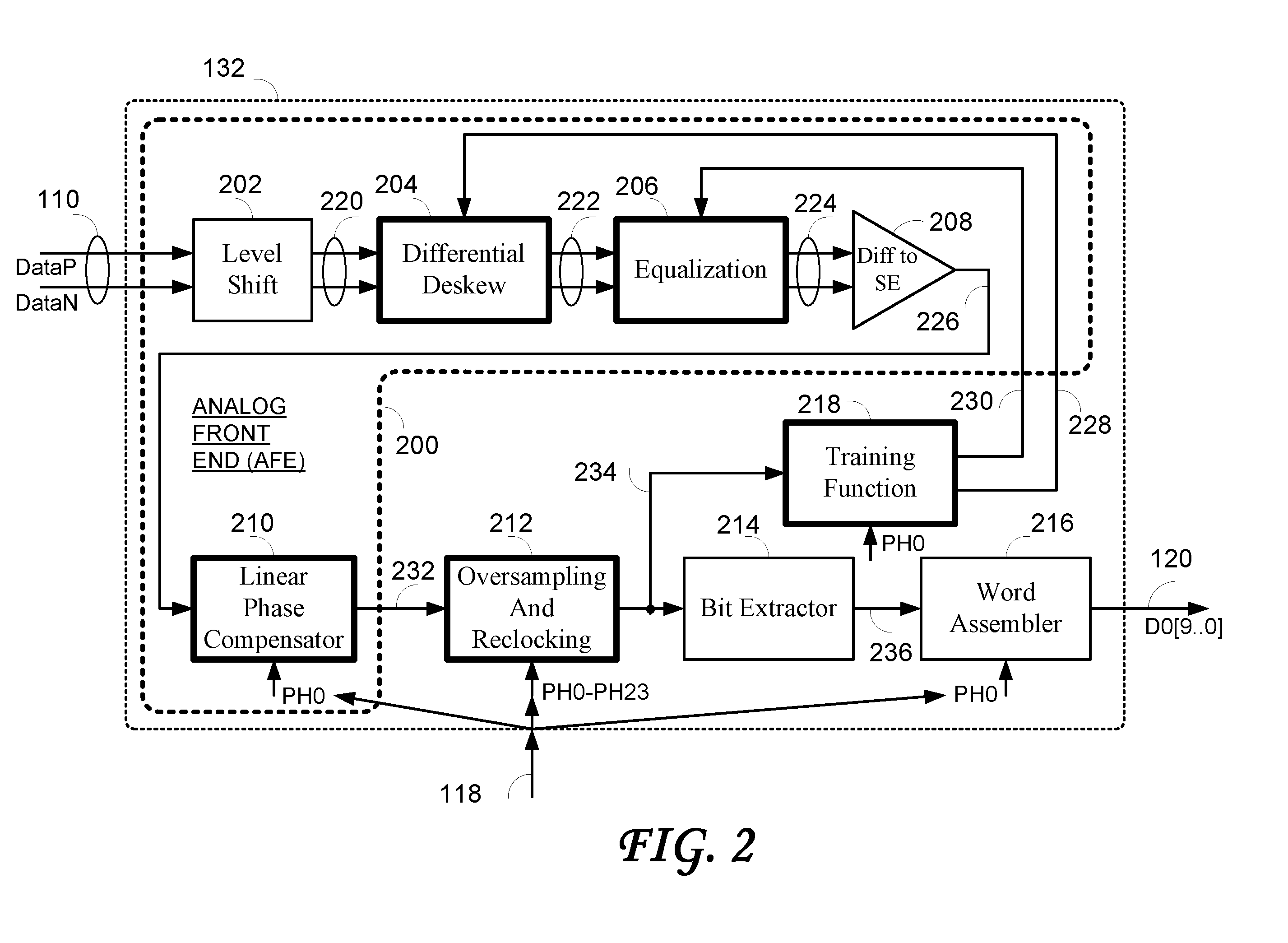
ActiveUS20070164802A1Easy Data RecoveryReduce distortion problemsModulated-carrier systemsPulse demodulator24-bitAnalog signal
A high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI) receiver recovers high speed encoded data which are transmitted differentially over data channels of a lossy cable, along with a clock. Inter symbol interference, high-frequency loss, skew between the clock and data channels, and differential skew within a differential signal are compensated by analog circuits which are automatically tuned for best performance by observing the quality of the recovered analog signal. Oversampling is used to provide a 24-bit digital representation of the analog signal for determining the quality of the signal. A corresponding method of deskewing a differential signal and a system and circuit therefor are also provided.
Owner:REDMERE TECH
Switched mode assisted linear regulator with seamless transition between power tracking configurations
ActiveUS20150188432A1Selectively configuring the power supplyMaximize currentEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionLinear regulatorCapacitance
A Switch Node Assisted Linear architecture, including a linear amplifier in parallel with a switched converter, is configurable in two tracking modes: (a) a SMAL regulator in which the amplifier sets toad voltage with an envelope tracking bandwidth, and the switched converter is configured for current assist, and (b) a Switched Mode Power Supply configuration in which the amplifier is switch-decoupled, and the switcher circuit is switched configured with an output capacitor, operable as an SMPS providing load voltage with an adaptive tracking bandwidth that is less than the envelope tracking bandwidth. Staged switching effects substantially seamless transitions between tracking modes, with the amplifier holding the load voltage at a substantially constant envelope tracking voltage (CVET): (a) for ET-AT transitions, the CVET mode enables pre-charging the output capacitor to a target AT voltage, prior to switch-decoupling the amplifier; and (b) for AT-ET transitions, CVET mode enables discharging the output capacitor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
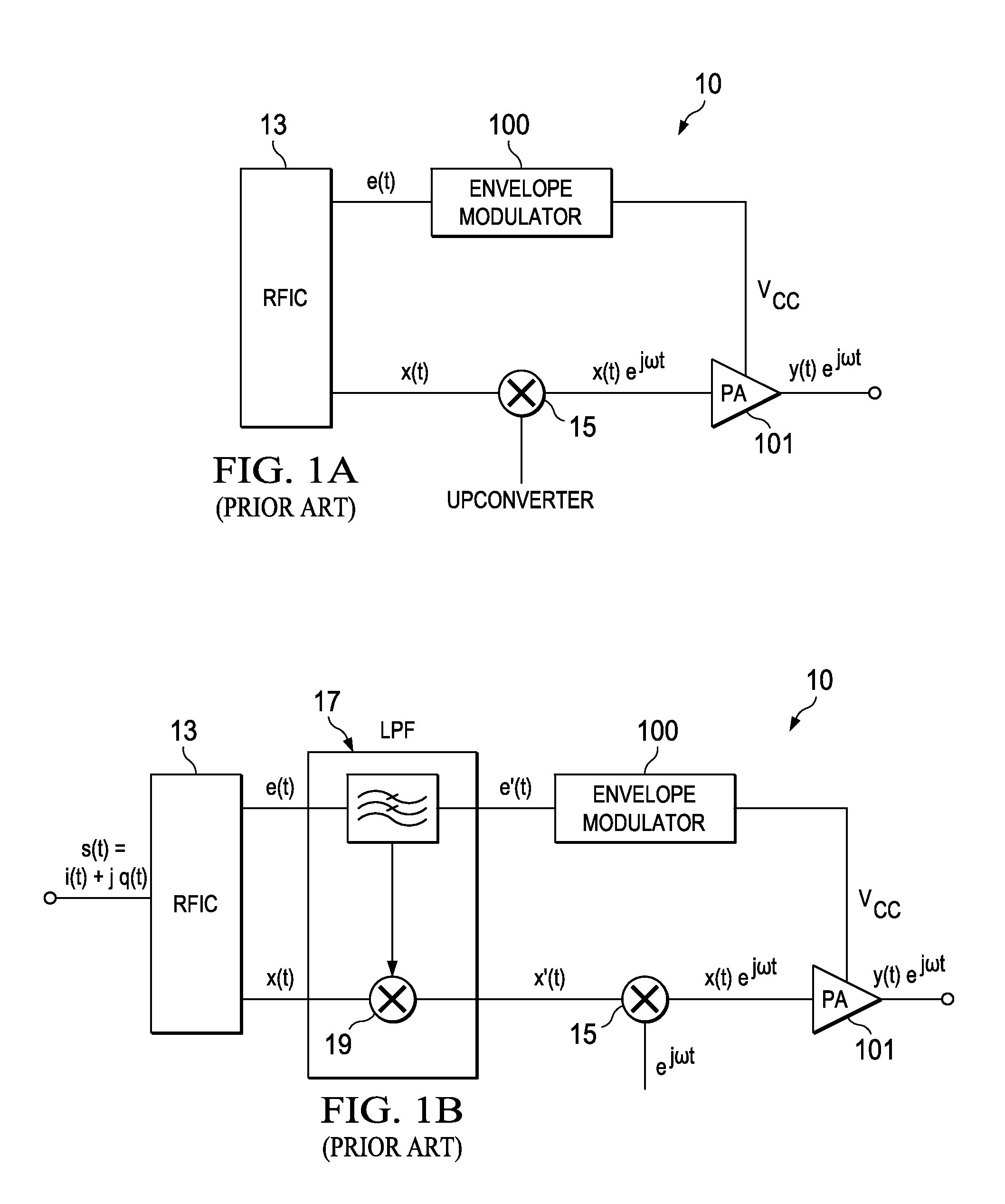
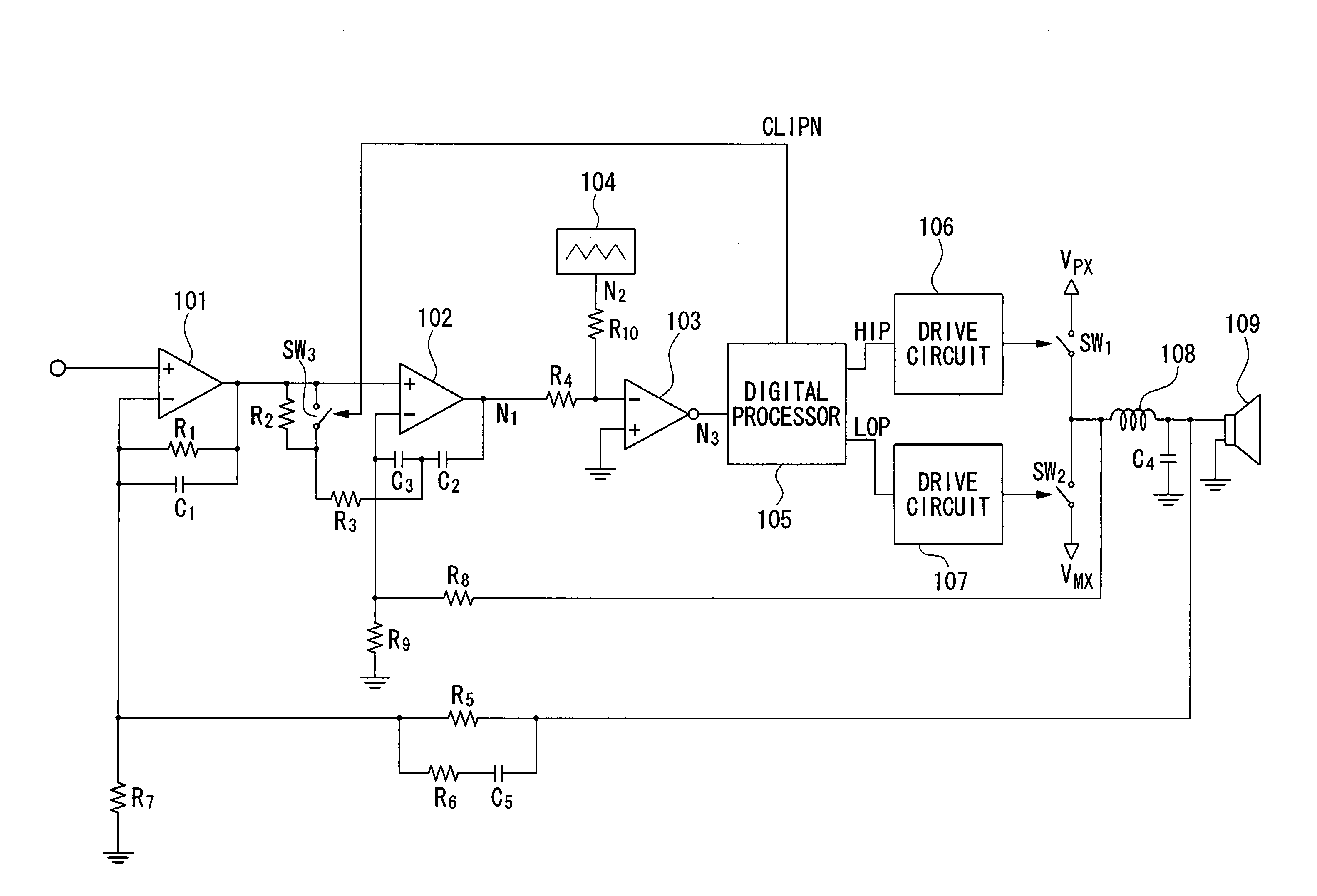
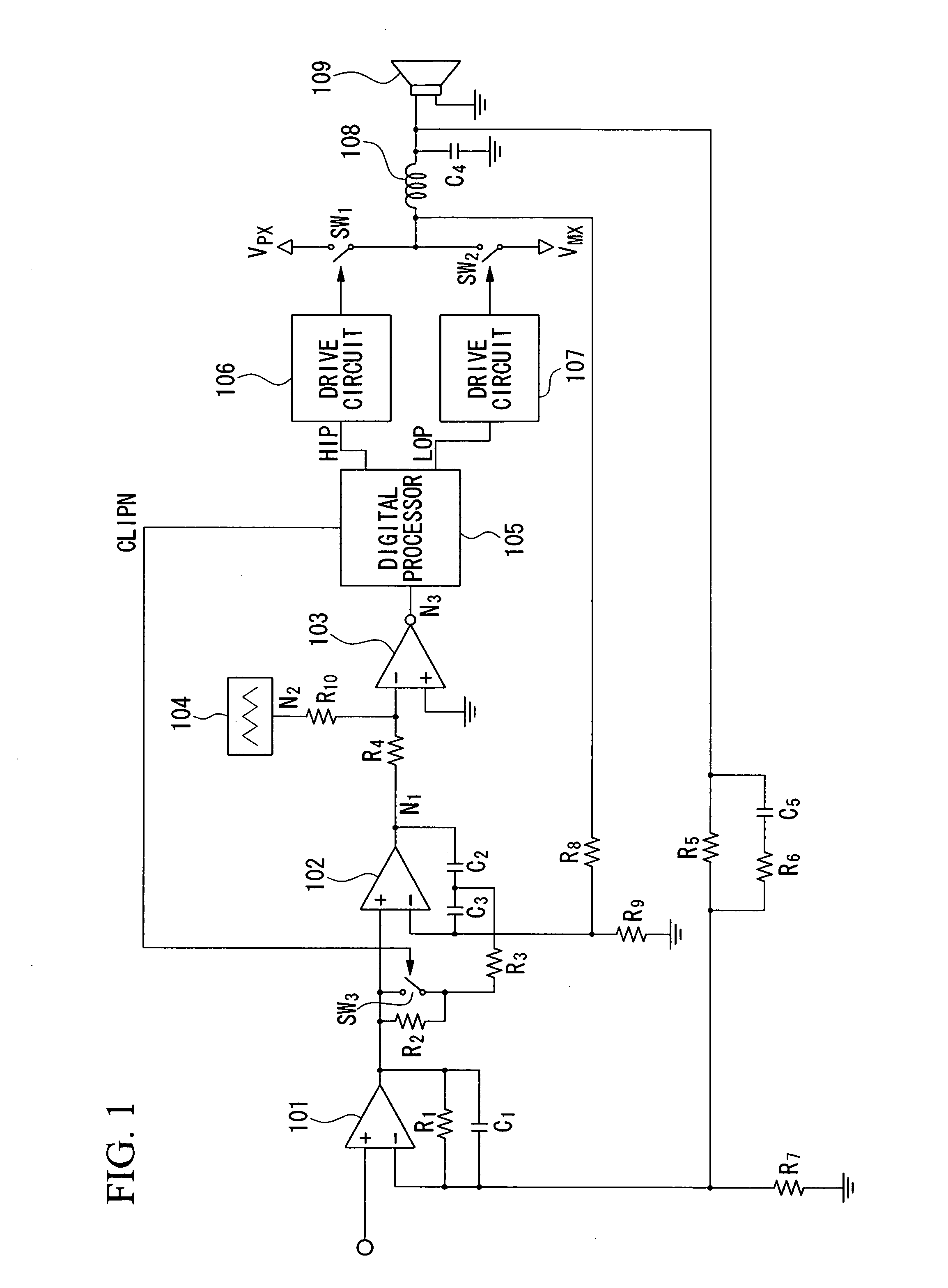
Pulse-width modulation amplifier and suppression of clipping therefor
ActiveUS20060008095A1Avoid excessive currentPower use efficiency decreaseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlLeading edgeAudio power amplifier
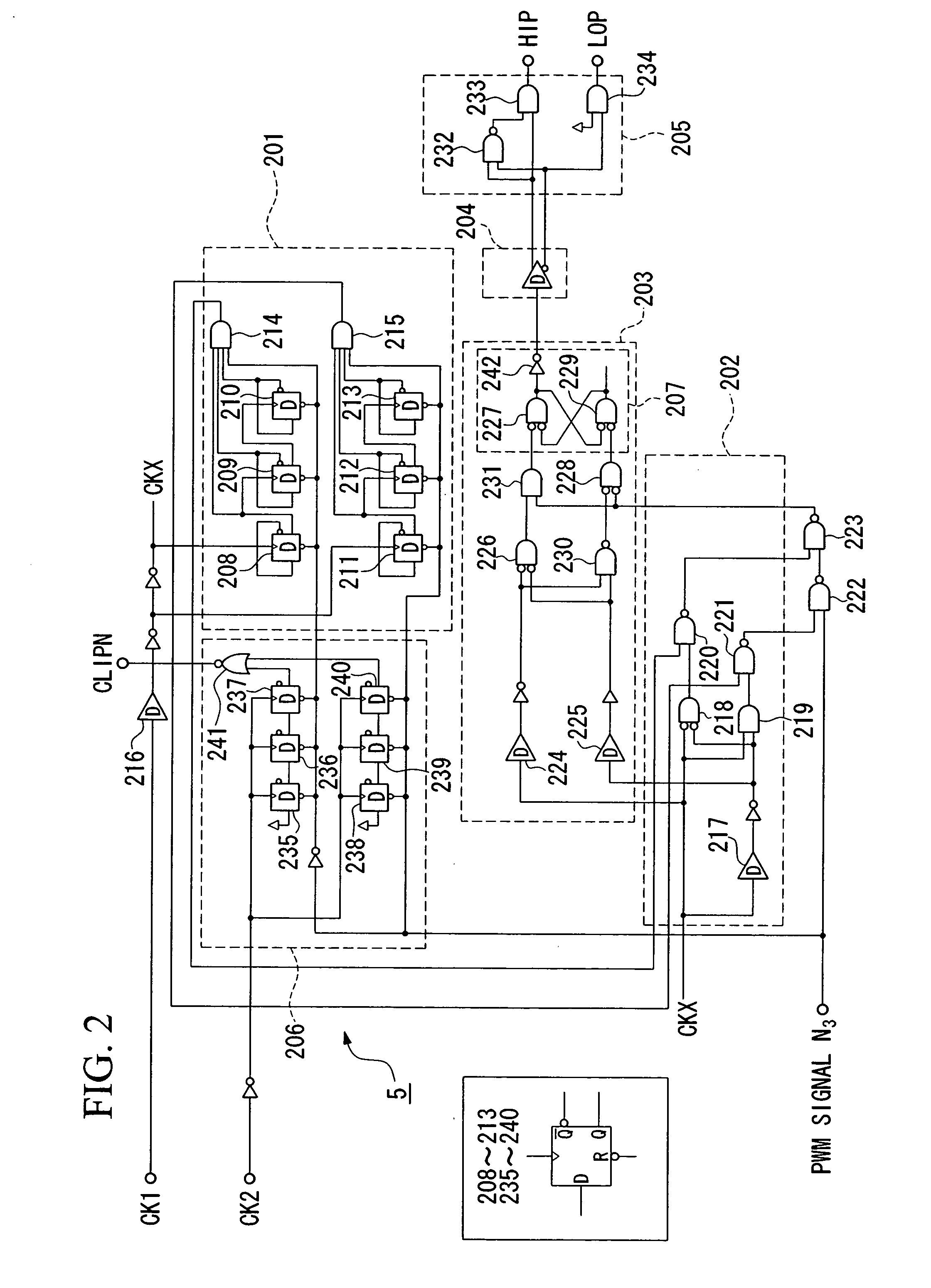
A pulse-width modulation (PWM) amplifier is adapted to a class-D amplifier in which an analog input signal is subjected to integration, pulse-width modulation, and switched amplification, wherein a glitch elimination circuit eliminates noise from a pulse-width modulated signal, from which a high pulse signal and a low pulse signal are isolated such that each pulse is delayed by a dead time at the leading-edge timing thereof. When both of them are simultaneously set to a high level, one of them is reduced in level. In response to the occurrence of clipping, an integration constant applied to an operational amplifier is automatically changed from a primary integration constant to a secondary integration constant. When the clipped state is sustained for a prescribed time, an inversion pulse is compulsorily introduced into the pulse-width modulated signal.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Popular searches
Discontinuous tuning by electric means Substation equipment Capacitor with voltage varied dielectric Antennas earthing switches association Oscillations generators Amplifier input/output impedence modification Leaky-waveguide antennas Waveguide horns Dielectric property measurements Waveguide mouths
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com