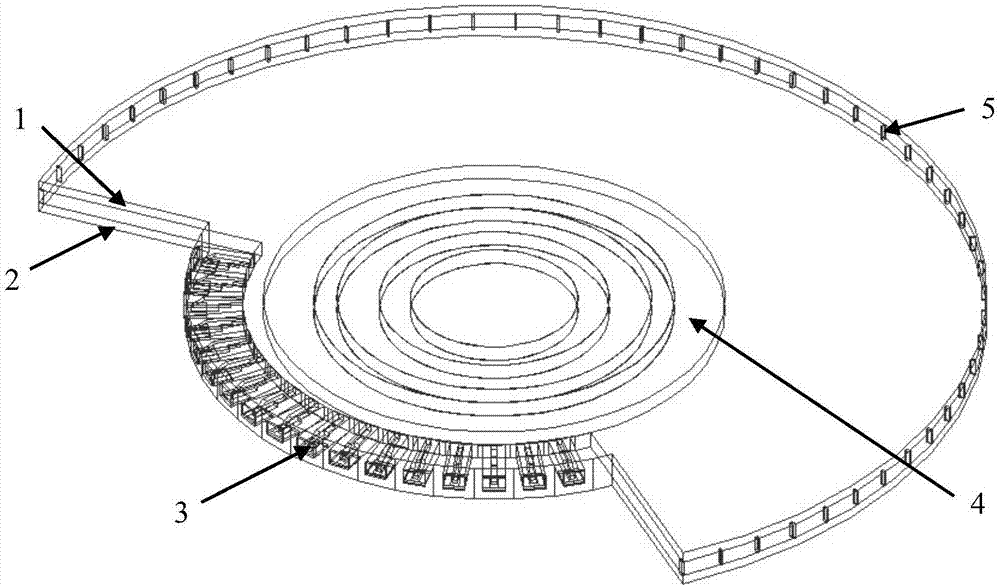
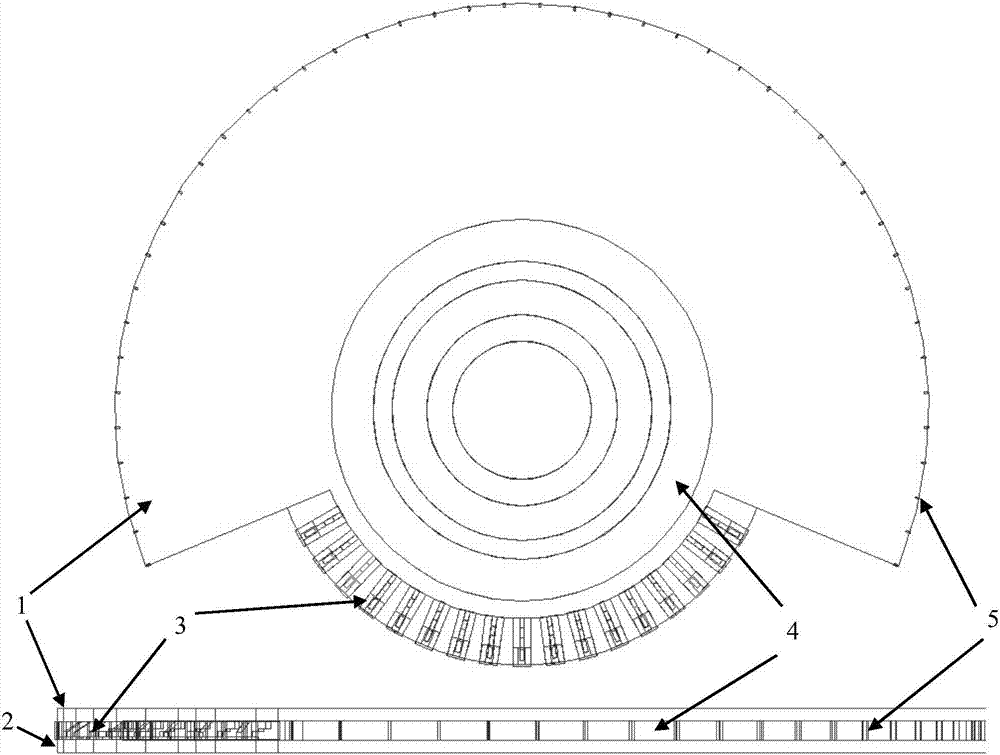
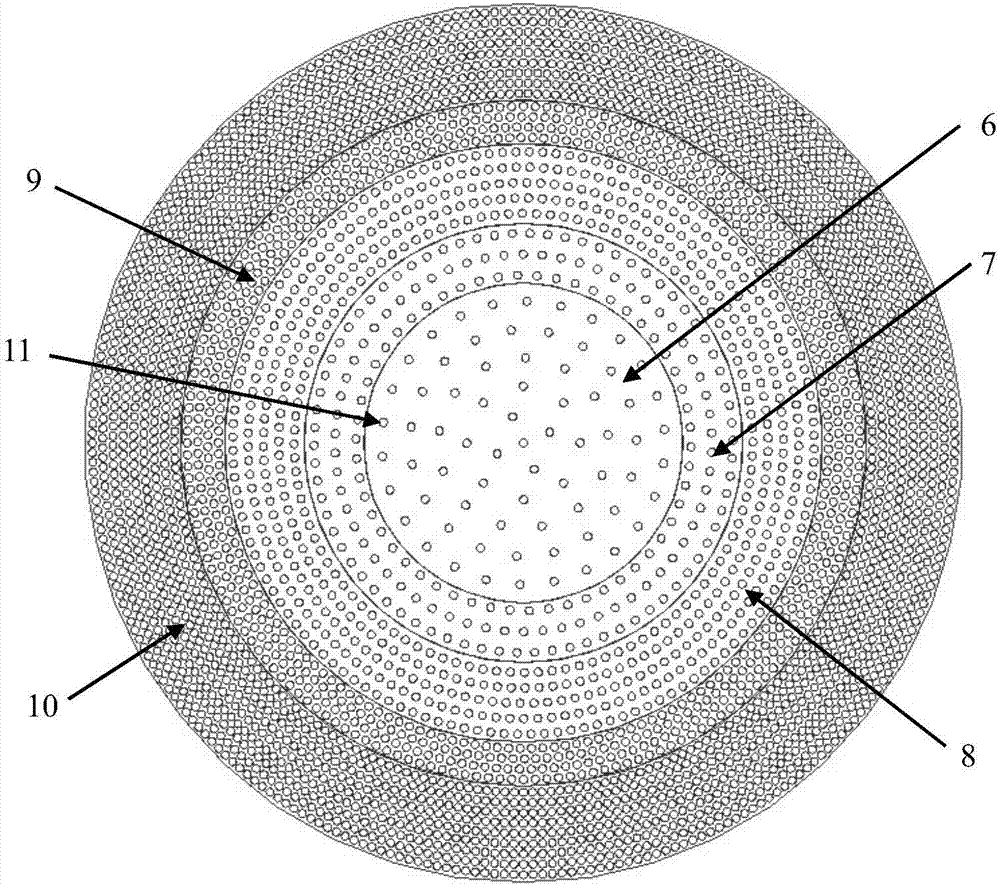
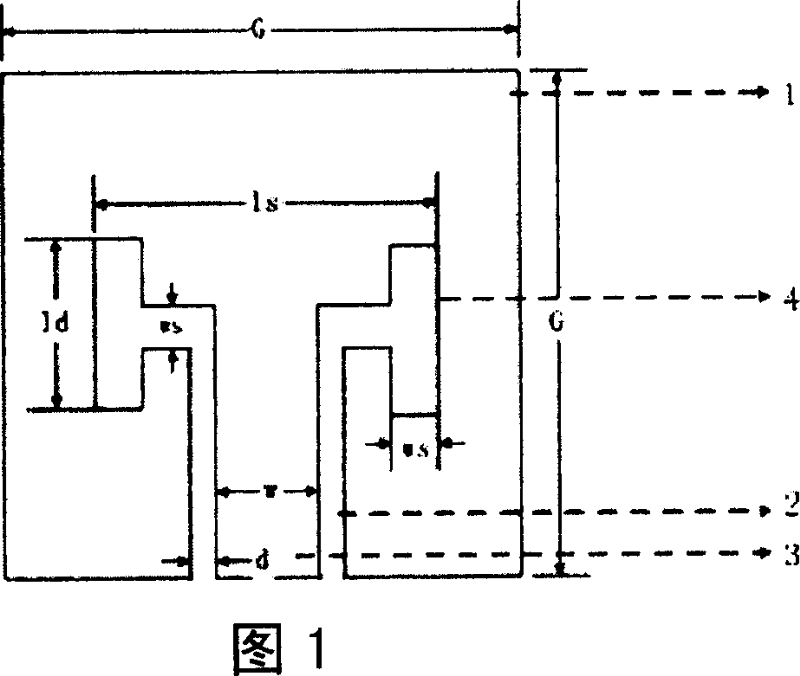
Patents
Literature
341results about "Waveguide mouths" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
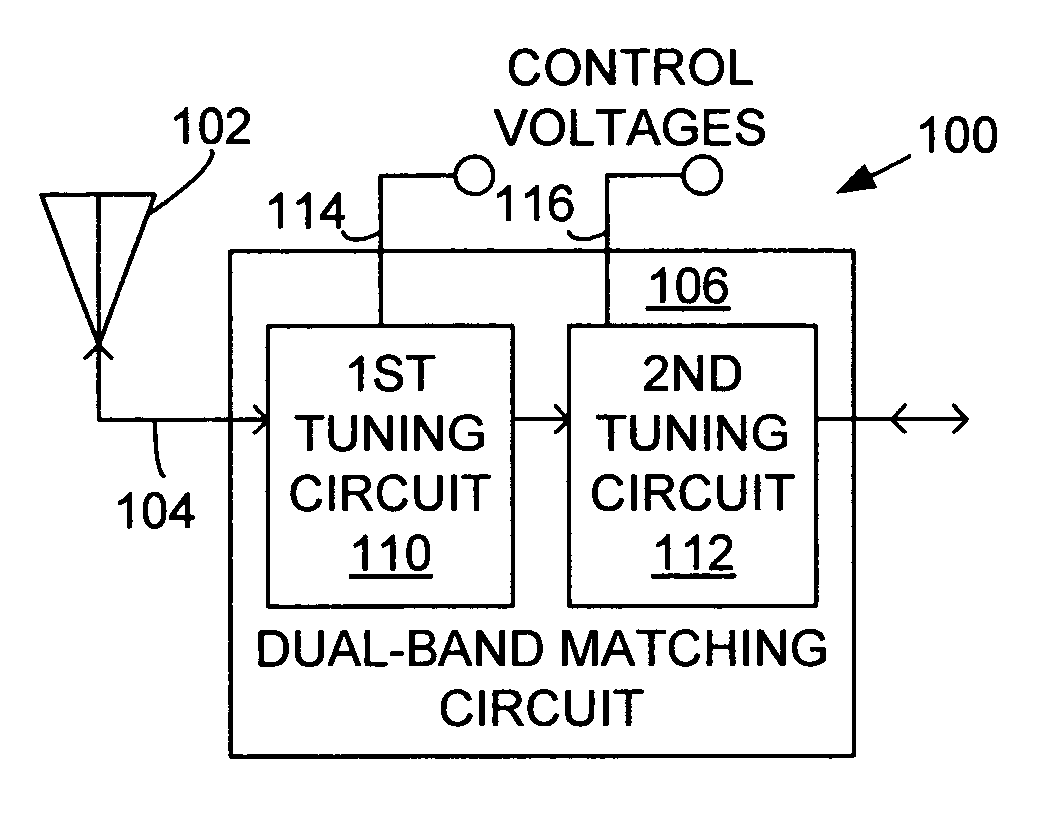
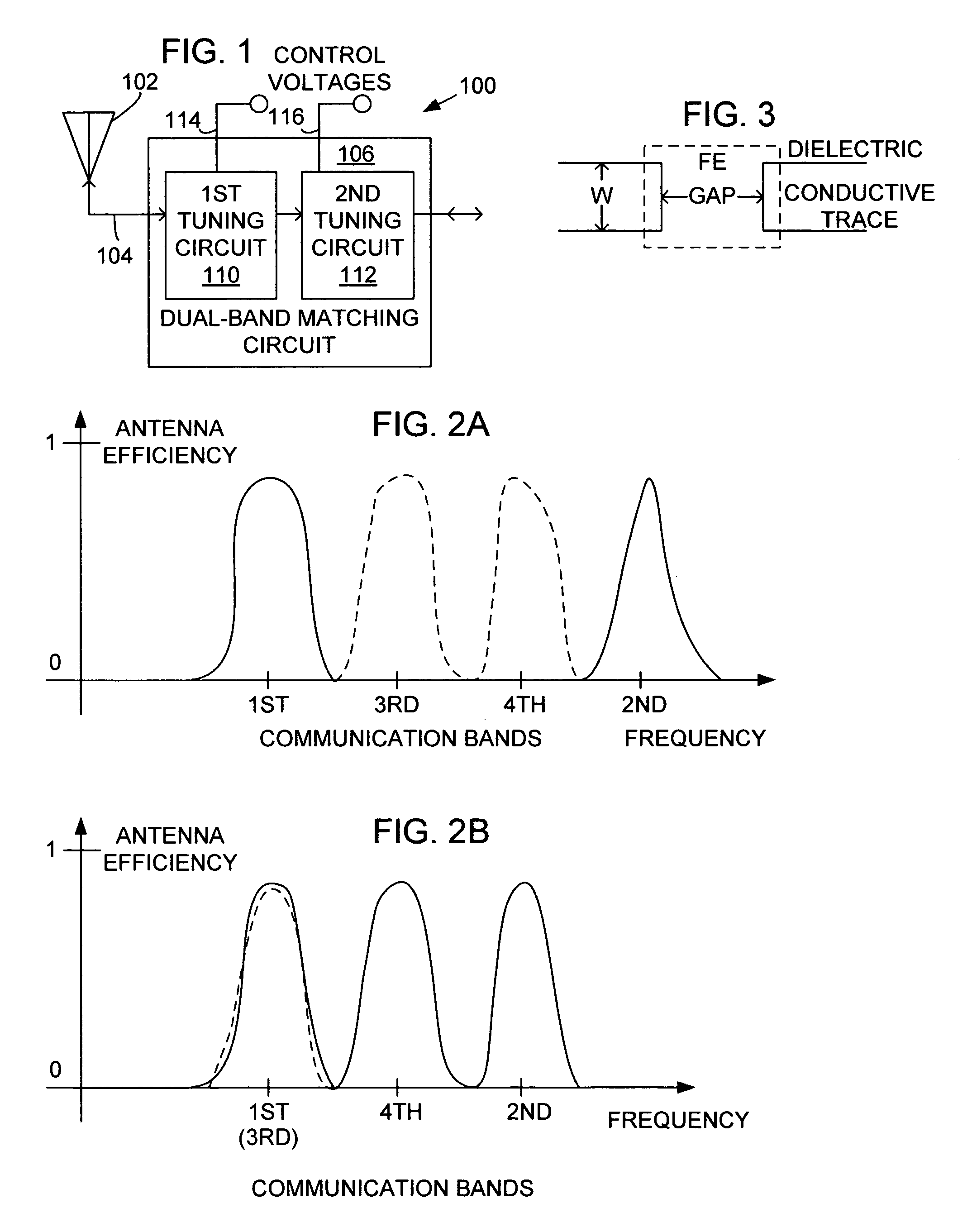
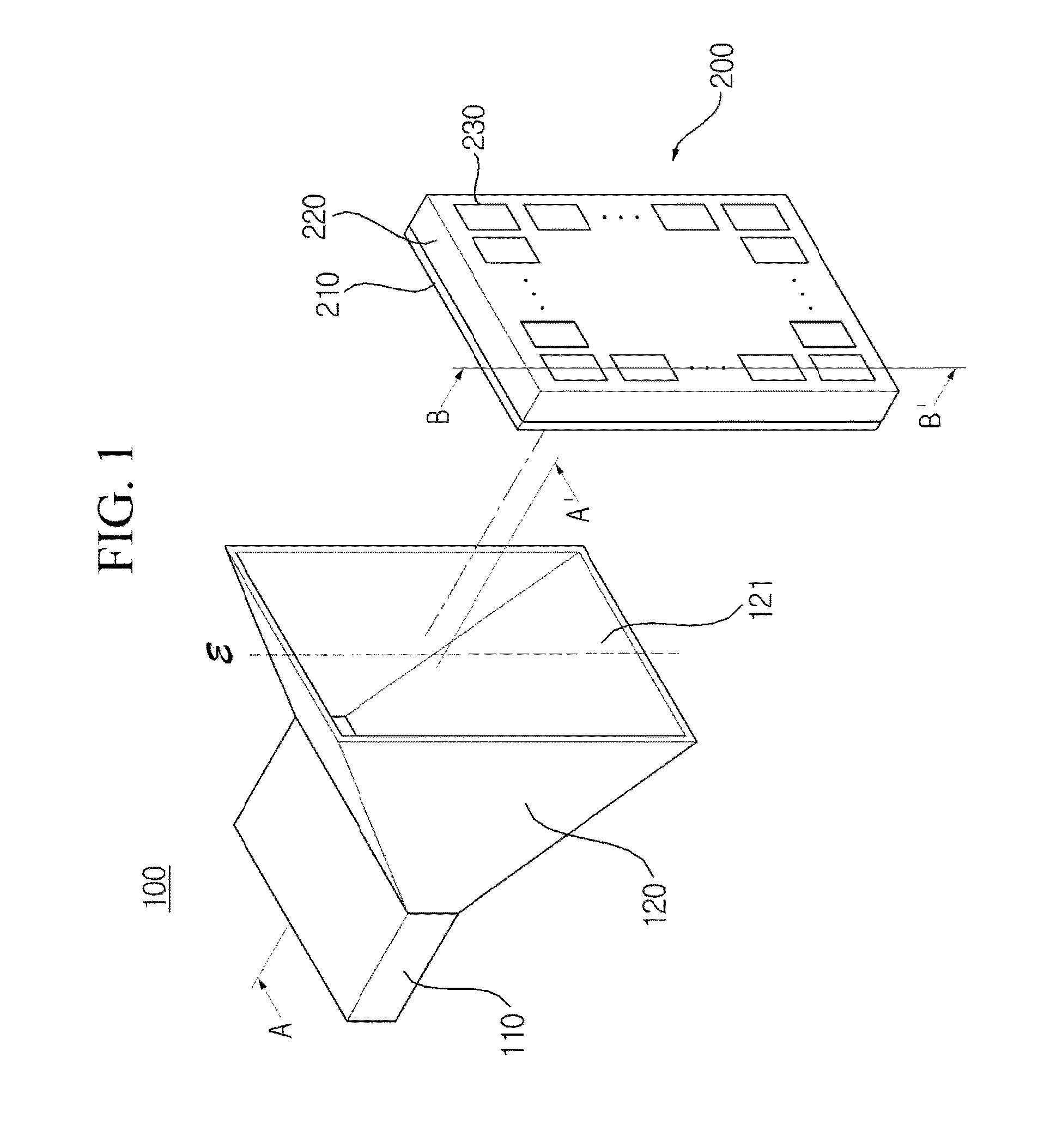
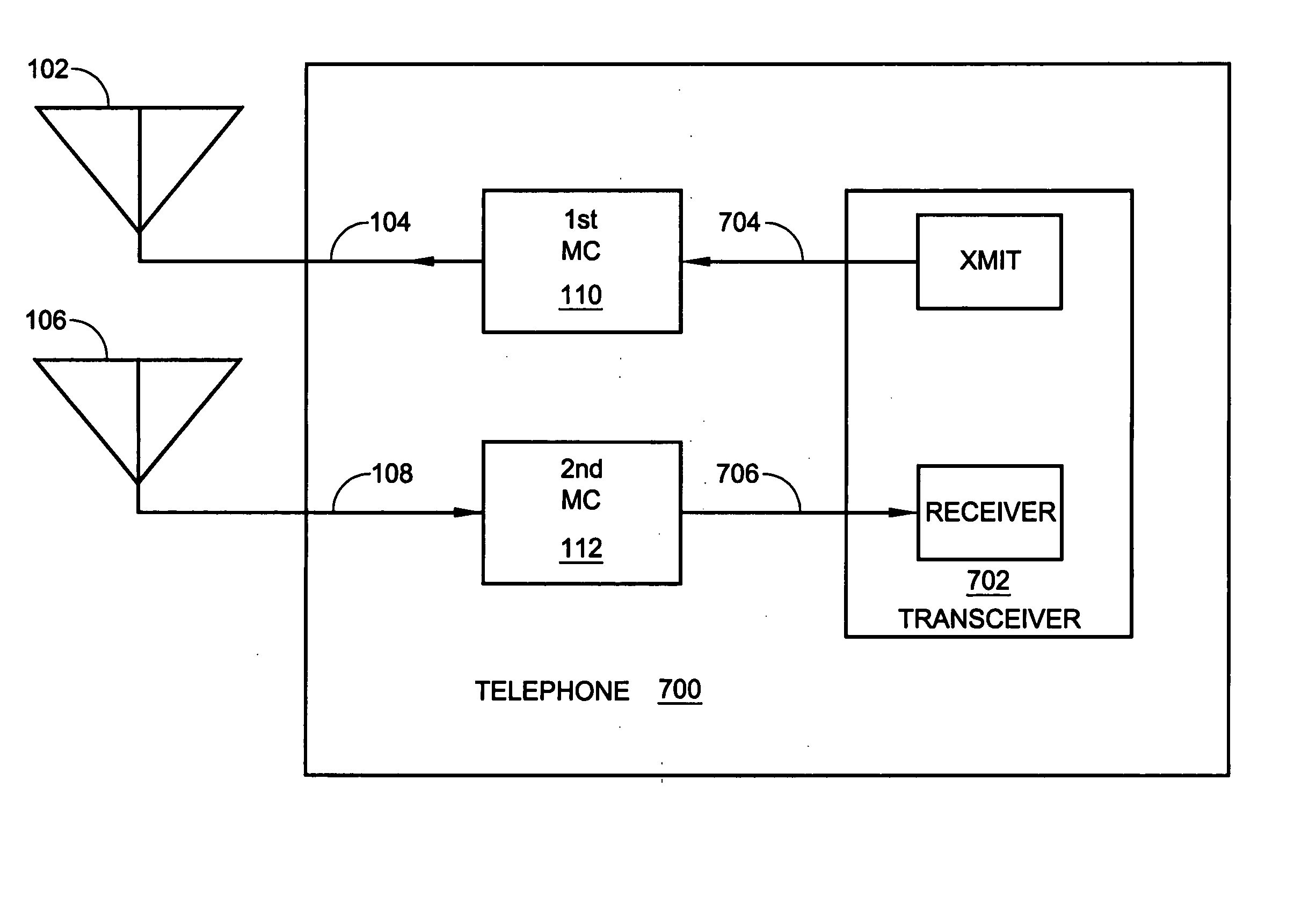
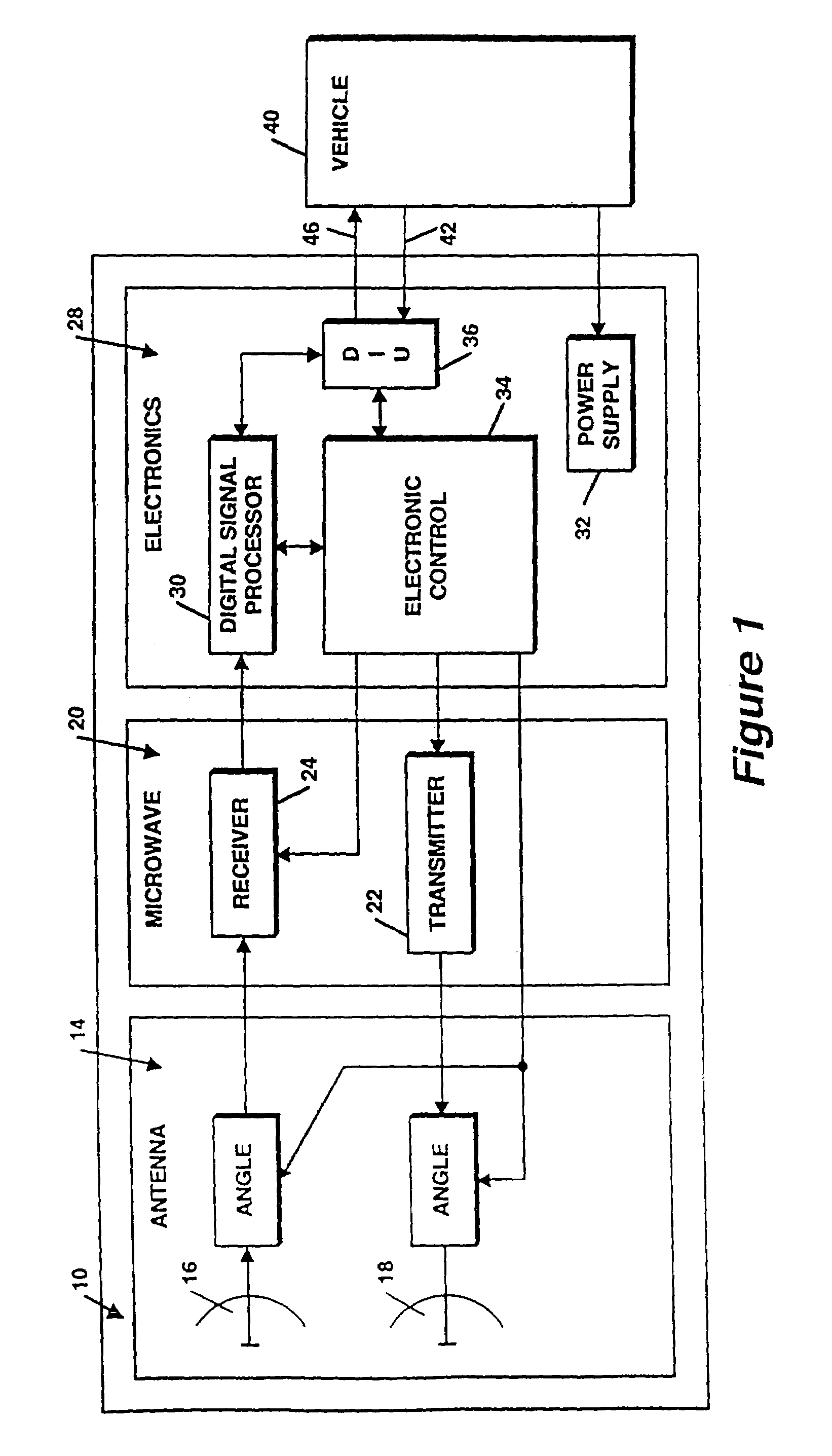
System and method for dual-band antenna matching
A dual-band antenna matching system and a method for dual-band impedance matching are provided. The method comprises: accepting a frequency-dependent impedance from an antenna; and, selectively supplying a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at either a first and a second communication band, or a third and a fourth communication band. More specifically, the method comprises: tuning a first tuning circuit to a first frequency; and, simultaneously tuning a second tuning circuit to a second frequency. In response, a conjugate match is supplied to the antenna in the first communication band in response to the first frequency. Simultaneously, the antenna is matched in the second communication band in response to the second frequency. When the first tuning circuit is tuned to a third frequency, and the second tuning circuit is tuned to a fourth frequency, then conjugate matches are supplied for the third and fourth communication bands, responsive to the third and fourth frequencies, respectively.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
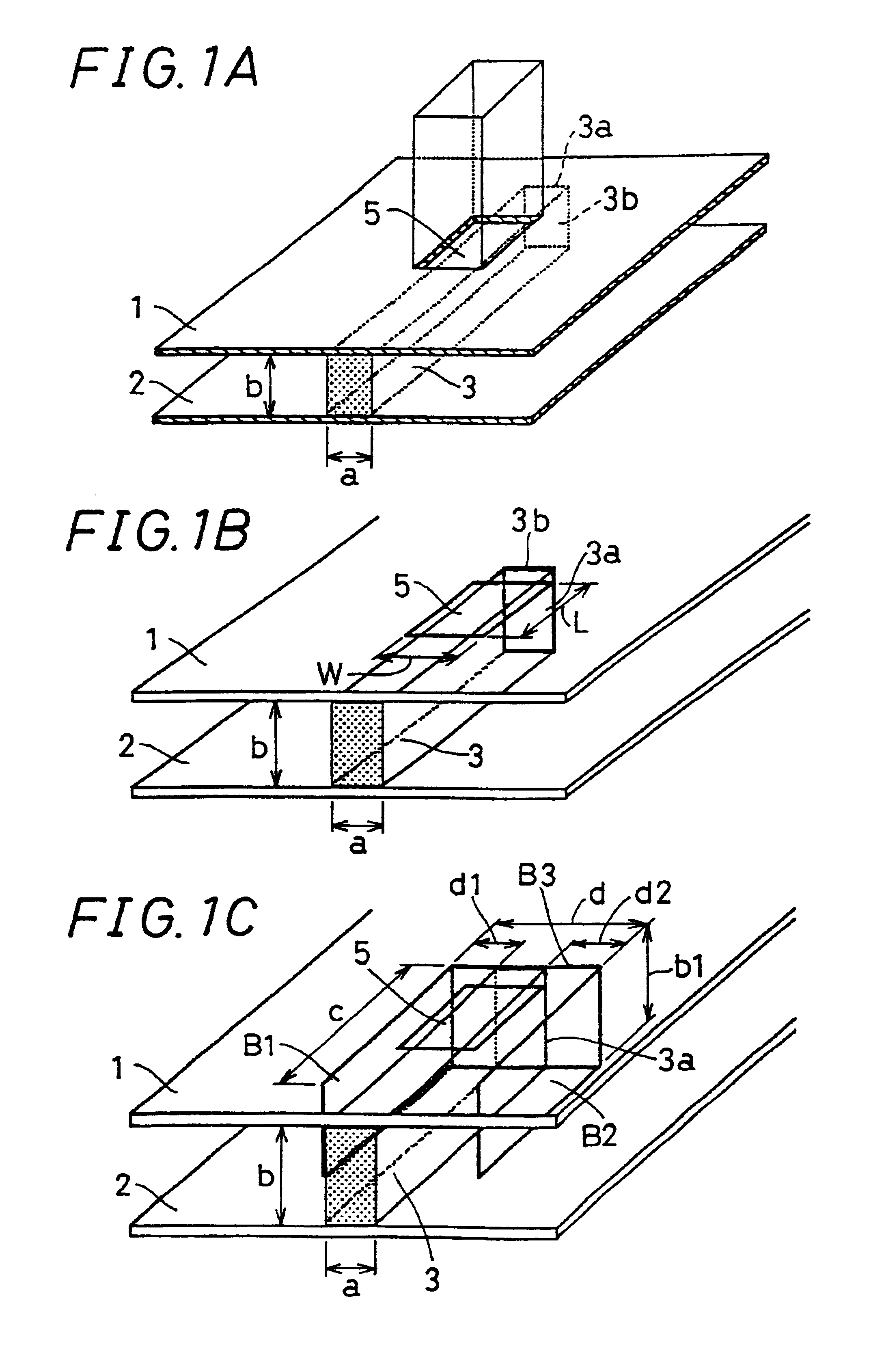
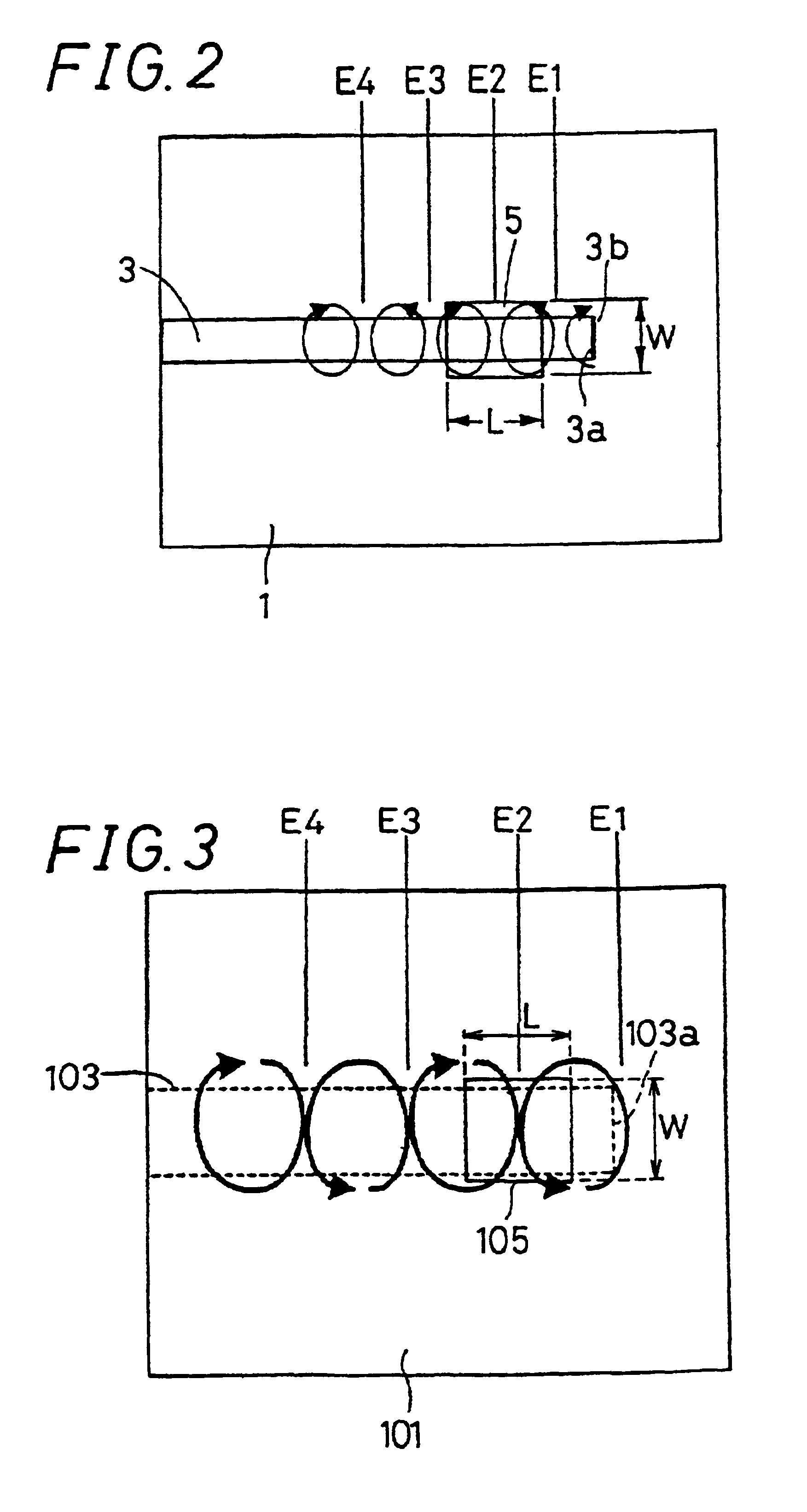
Structure for connecting non-radiative dielectric waveguide and metal waveguide, millimeter wave transmitting/receiving module and millimeter wave transmitter/receiver
InactiveUS6868258B2Reduce lossImprove detection distanceWaveguide mouthsAntenna connectorsDielectricElectrical conductor
It is an object of the invention to provide a connection structure for connecting the dielectric strip of an NRD guide with a metal waveguide, in which the conversion loss (connection loss) for high-frequency signals is reduced, and in which the NRD guide as well as the millimeter wave integrated circuit in which the NRD guide is incorporated can be made smaller. A non-radiative dielectric waveguide is made by arranging a dielectric strip for propagating high-frequency signals between parallel planar conductors arranged at a spacing of not more than half the wavelength of a high-frequency signal, a conductive member being arranged at an end face of a terminal end of the dielectric strip. An aperture is formed in at least one of the parallel planar conductors at a location where the electrical field of an LSM mode stationary wave propagating along the dielectric strip becomes largest. An open terminal end of a metal waveguide is connected to this aperture.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
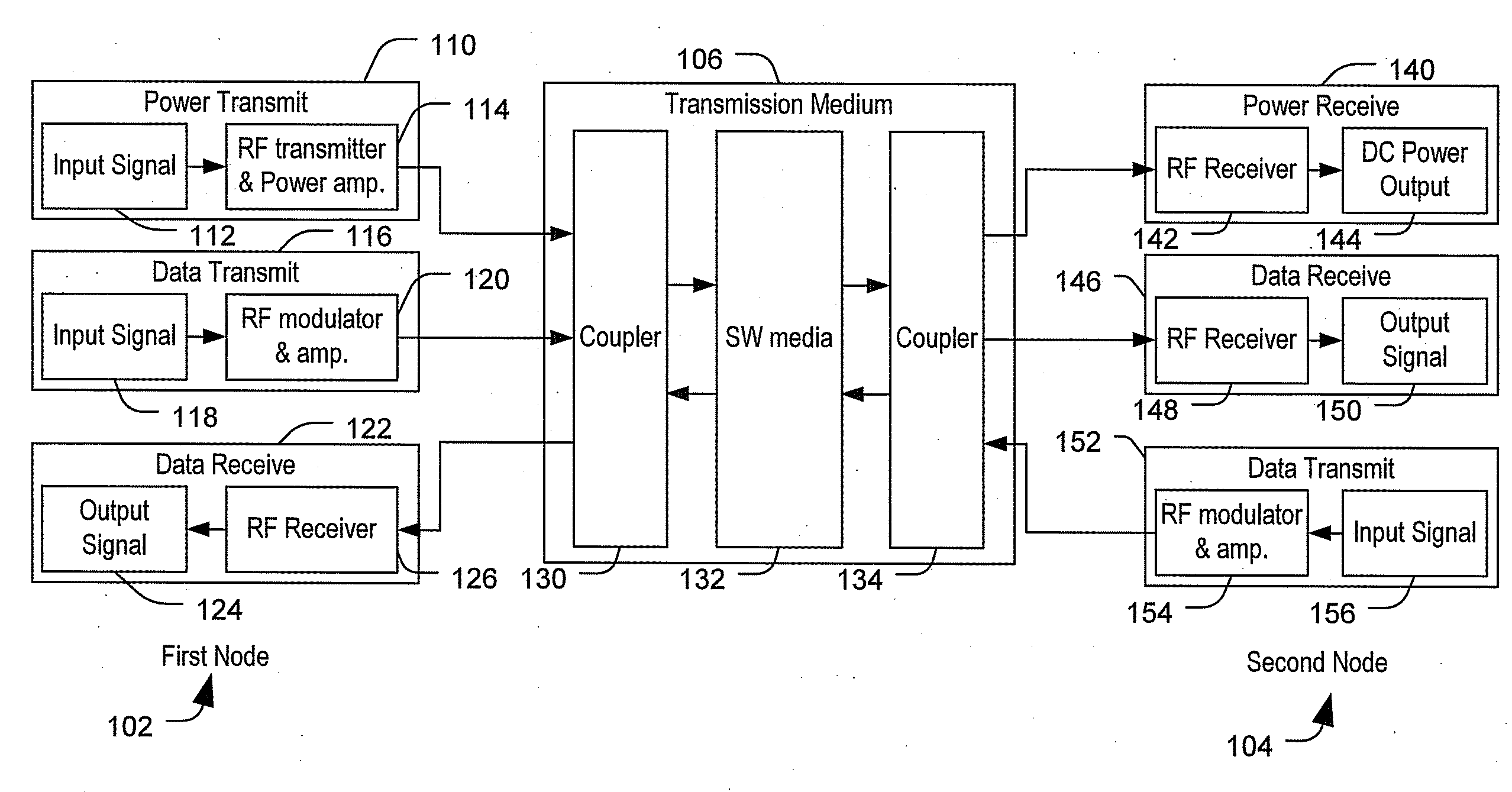
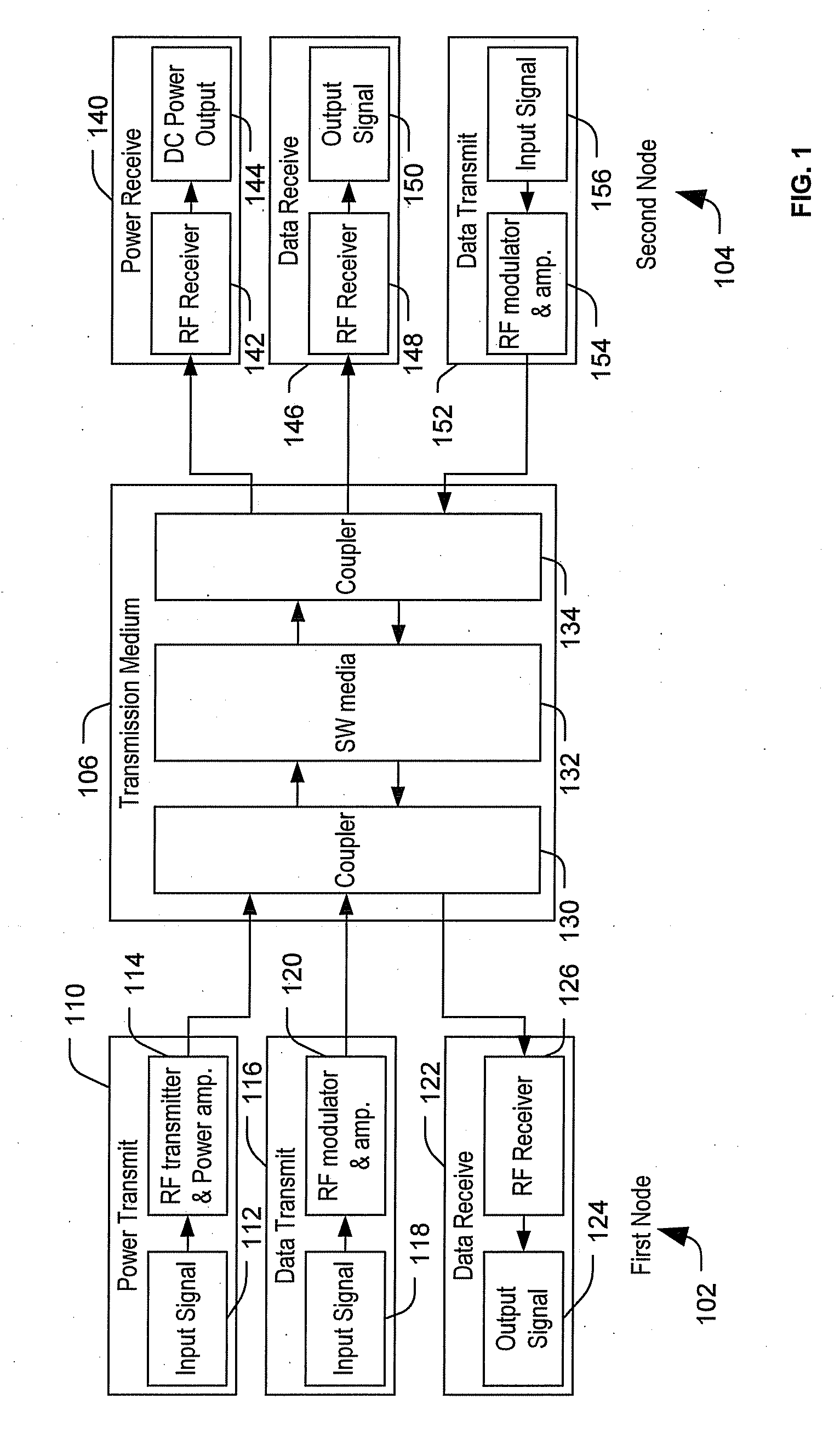
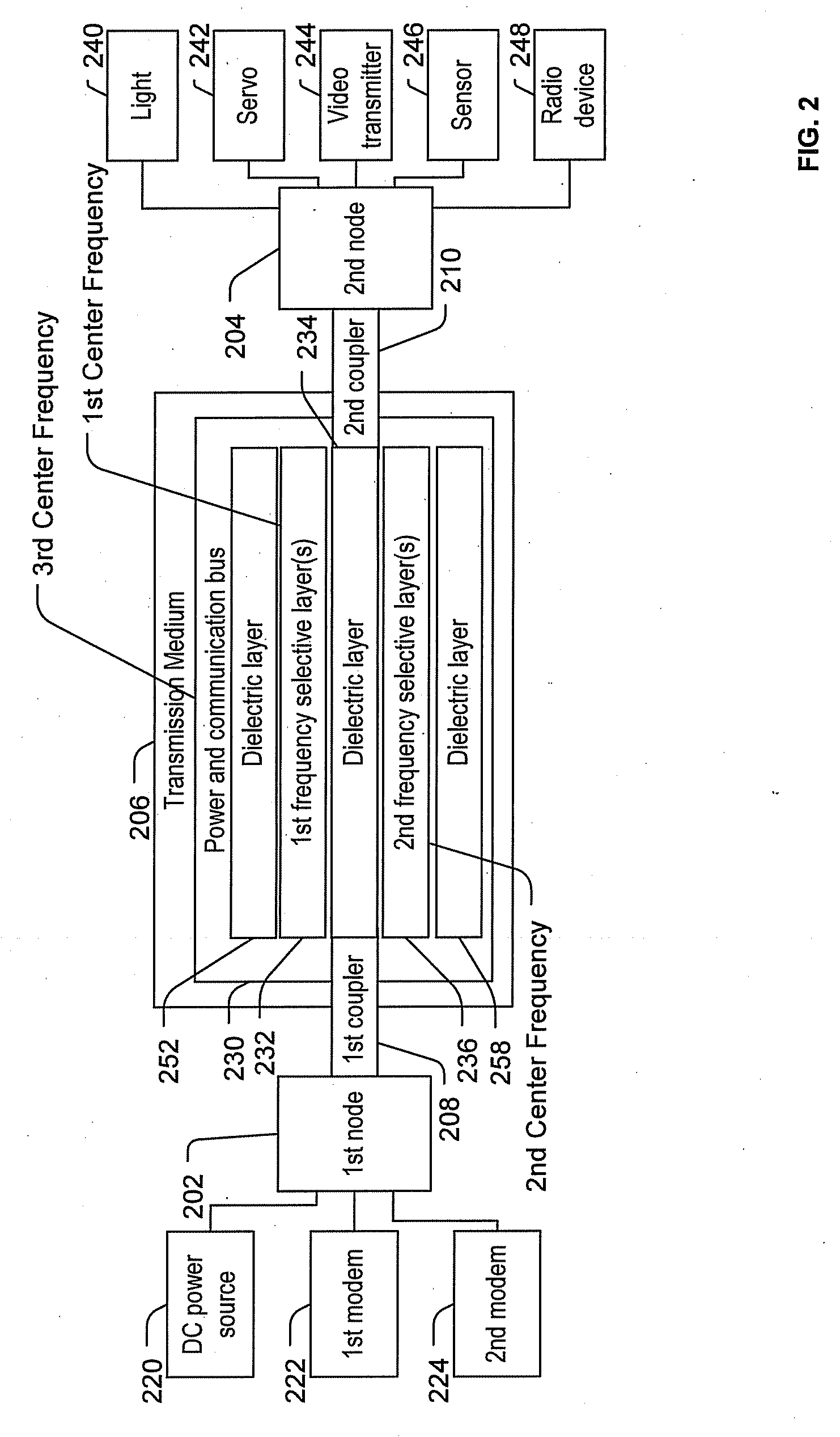
Transmitting power and data
ActiveUS20100214183A1Waveguide mouthsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesTransmitted powerDielectric layer
Apparatus, systems and methods to transmit power and data are provided. A particular apparatus to transmit power and data includes a transmission medium. The transmission medium includes at least one first frequency selective surface (FSS) layer, at least one second FSS layer, and a dielectric layer separating the at least one first FSS layer and the at least one second FSS layer. In a particular embodiment, the apparatus also includes a first coupler coupled to the transmission medium to send a signal along the transmission medium and a second coupler coupled to the transmission medium. The second coupler may receive signals via the transmission medium, receive power via the transmission medium to power devices coupled to the second coupler, process and send data via the transmission medium, or any combination thereof.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
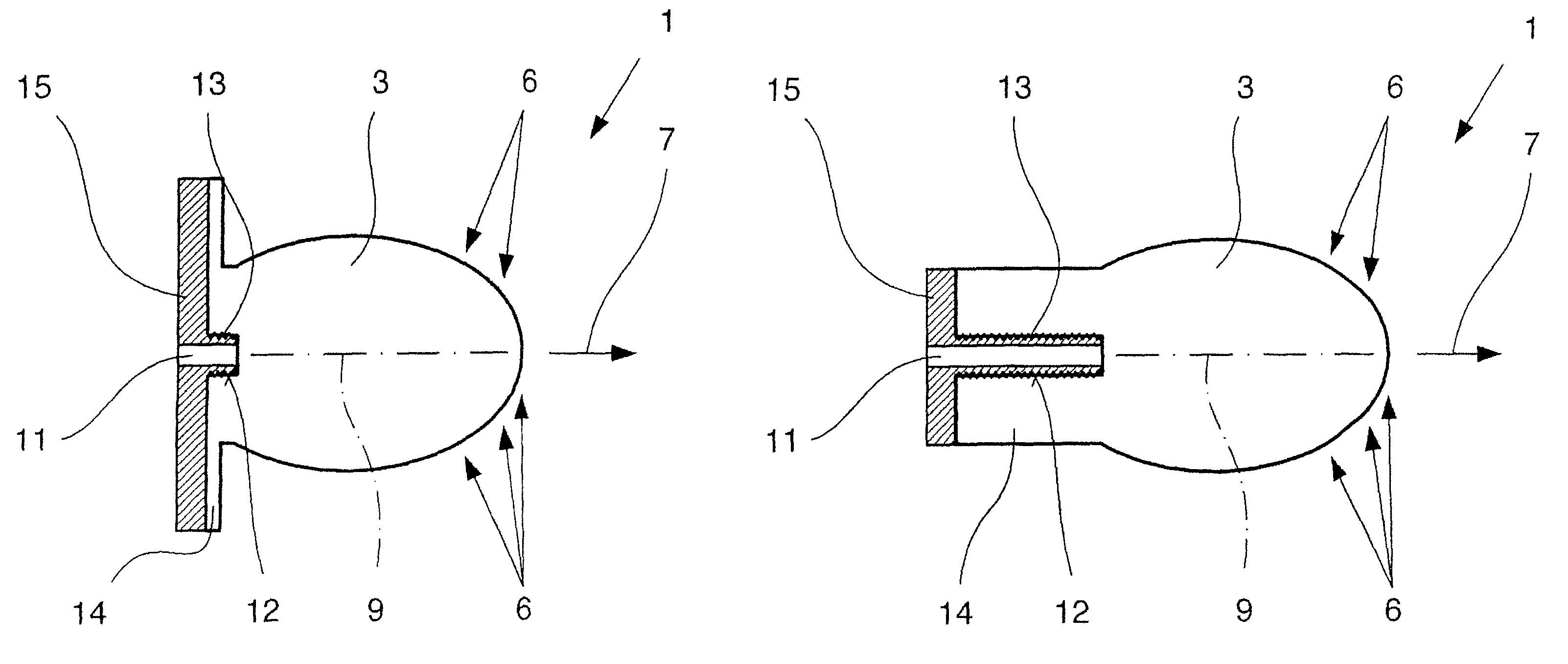
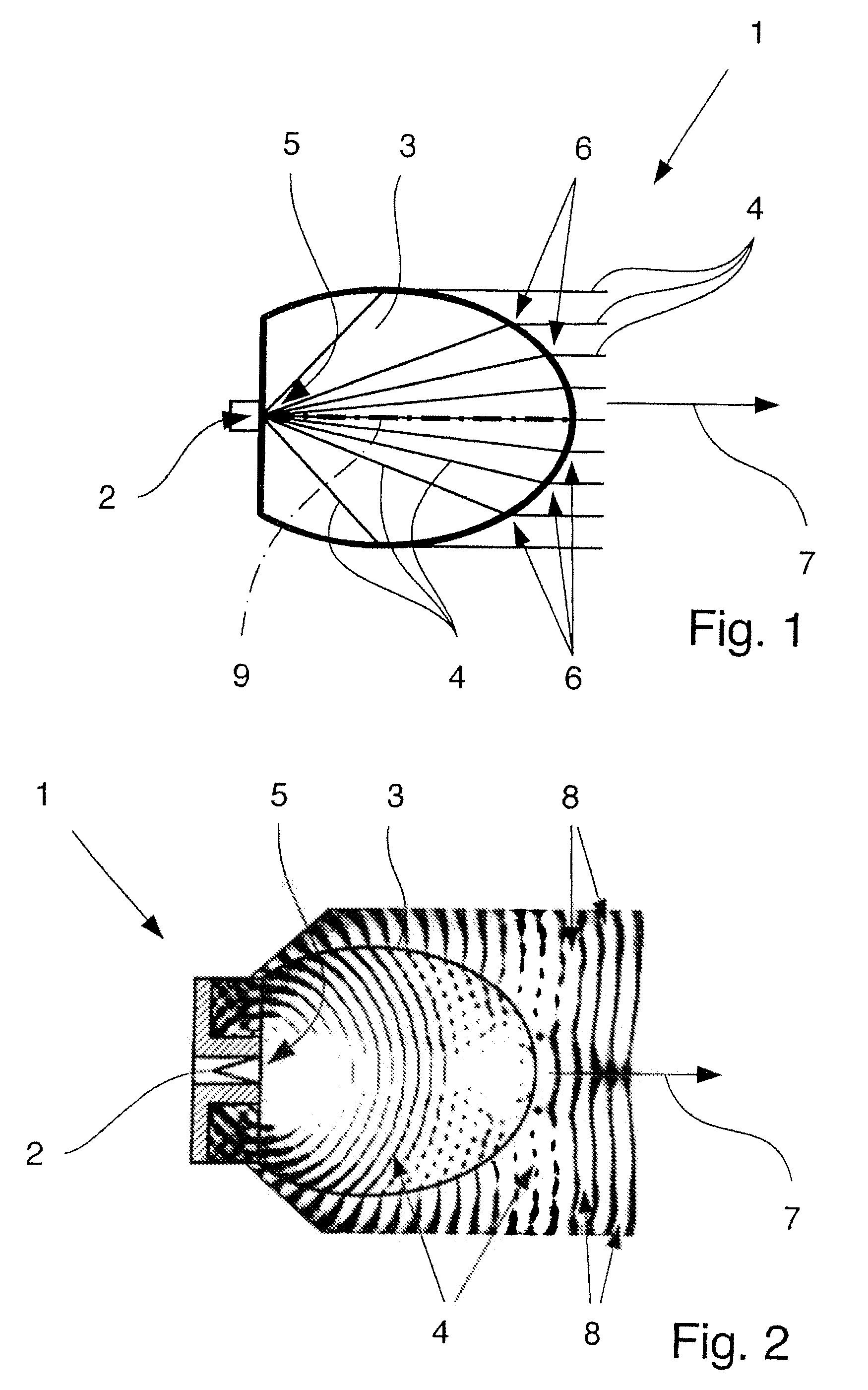
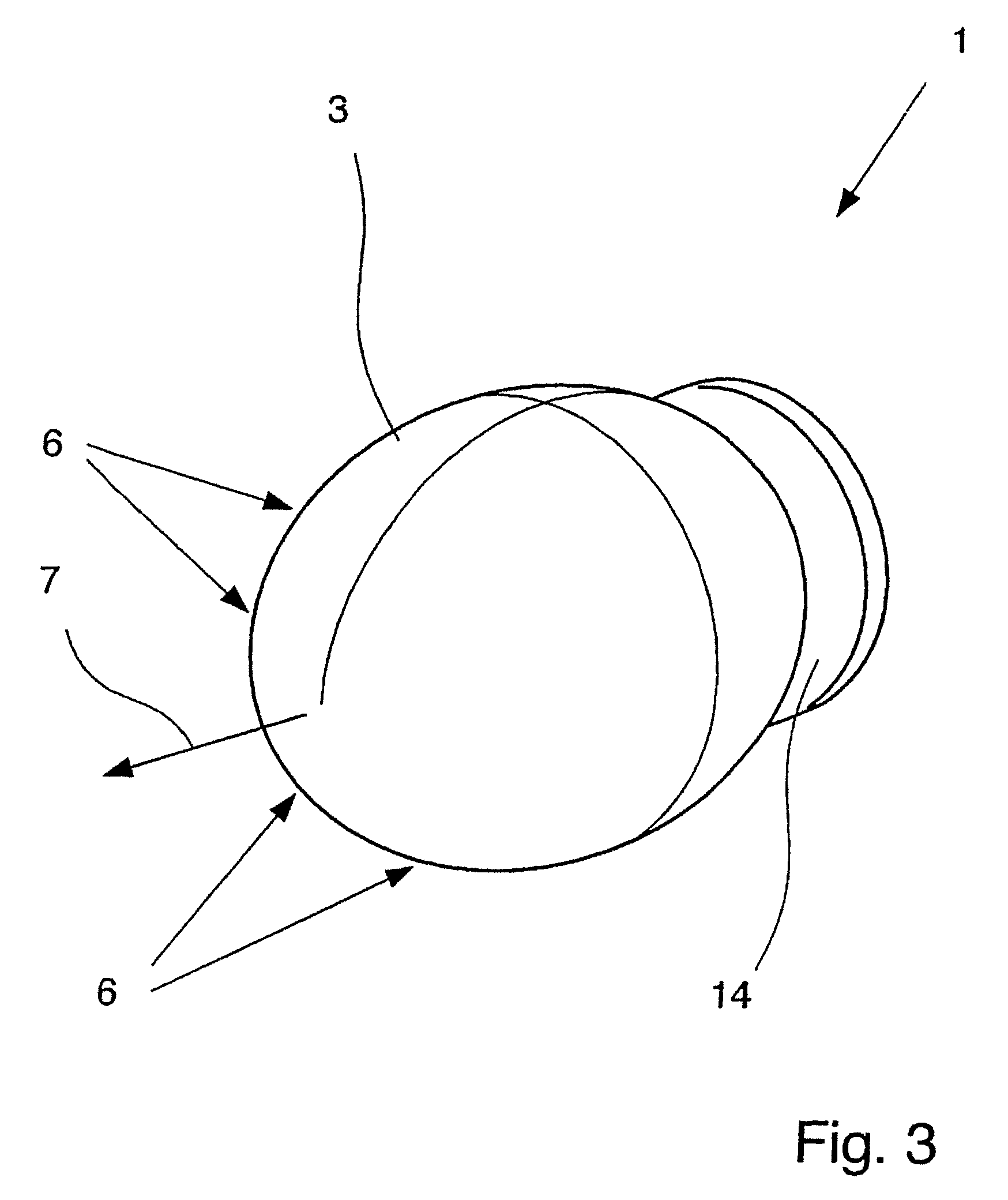
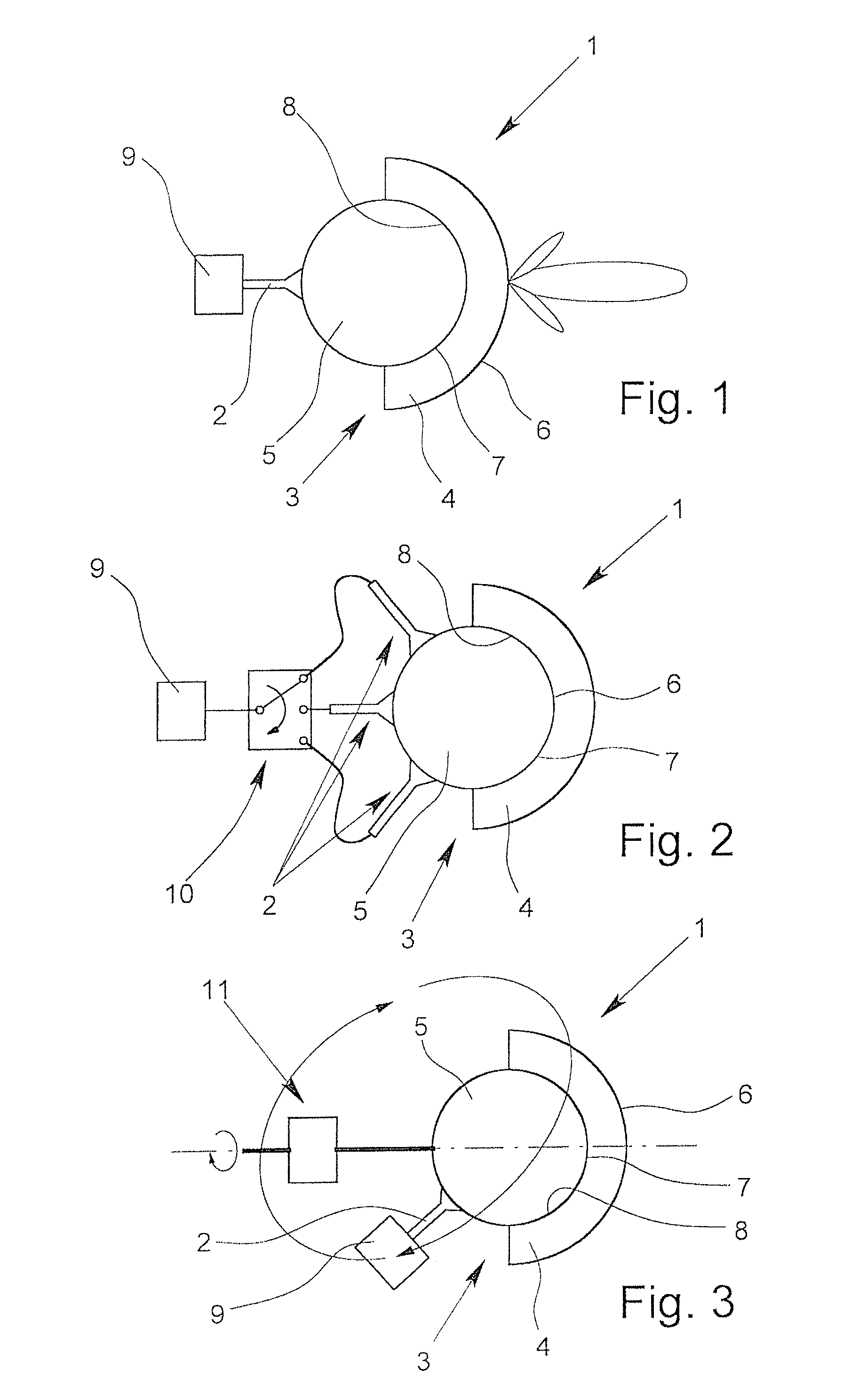
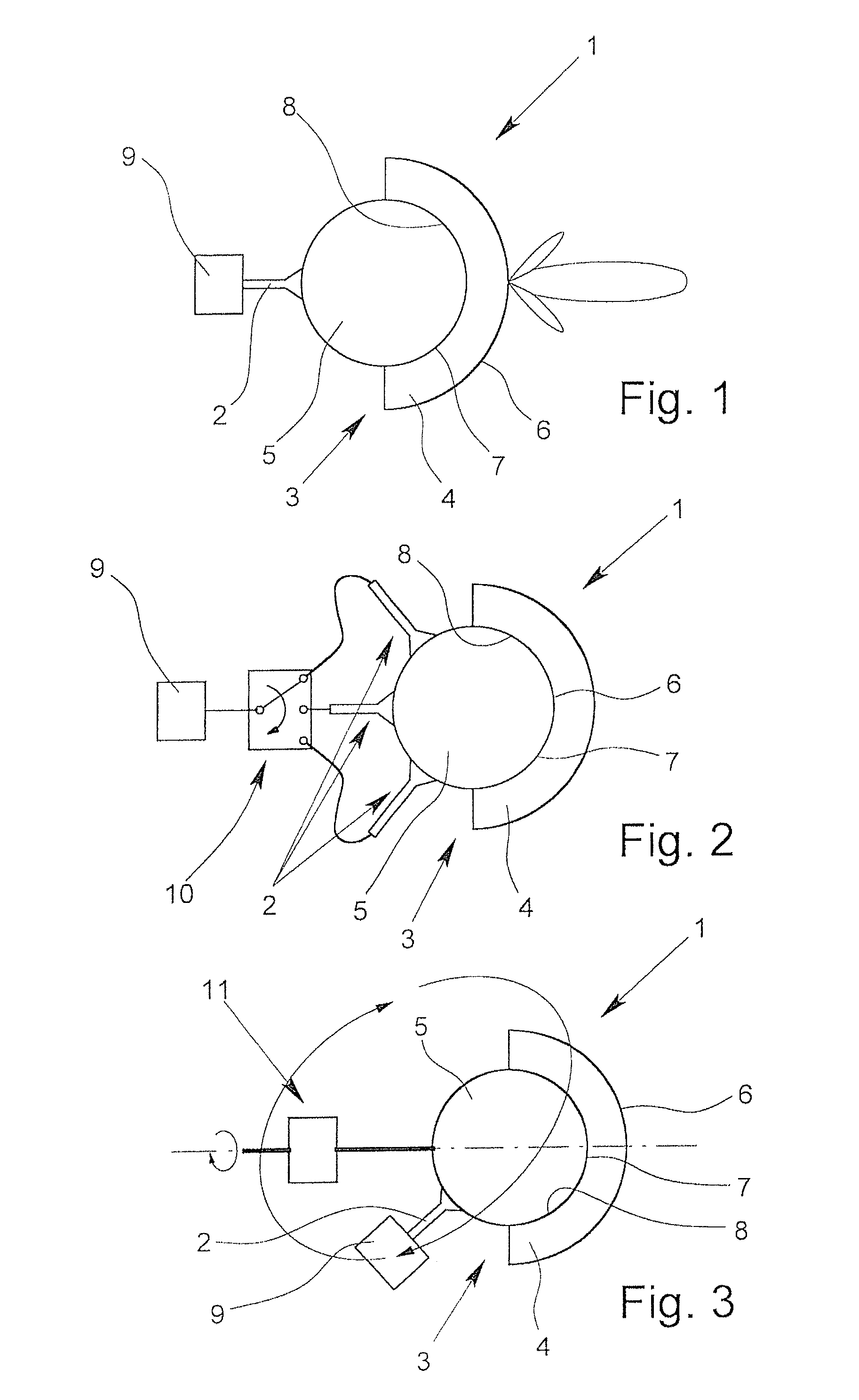
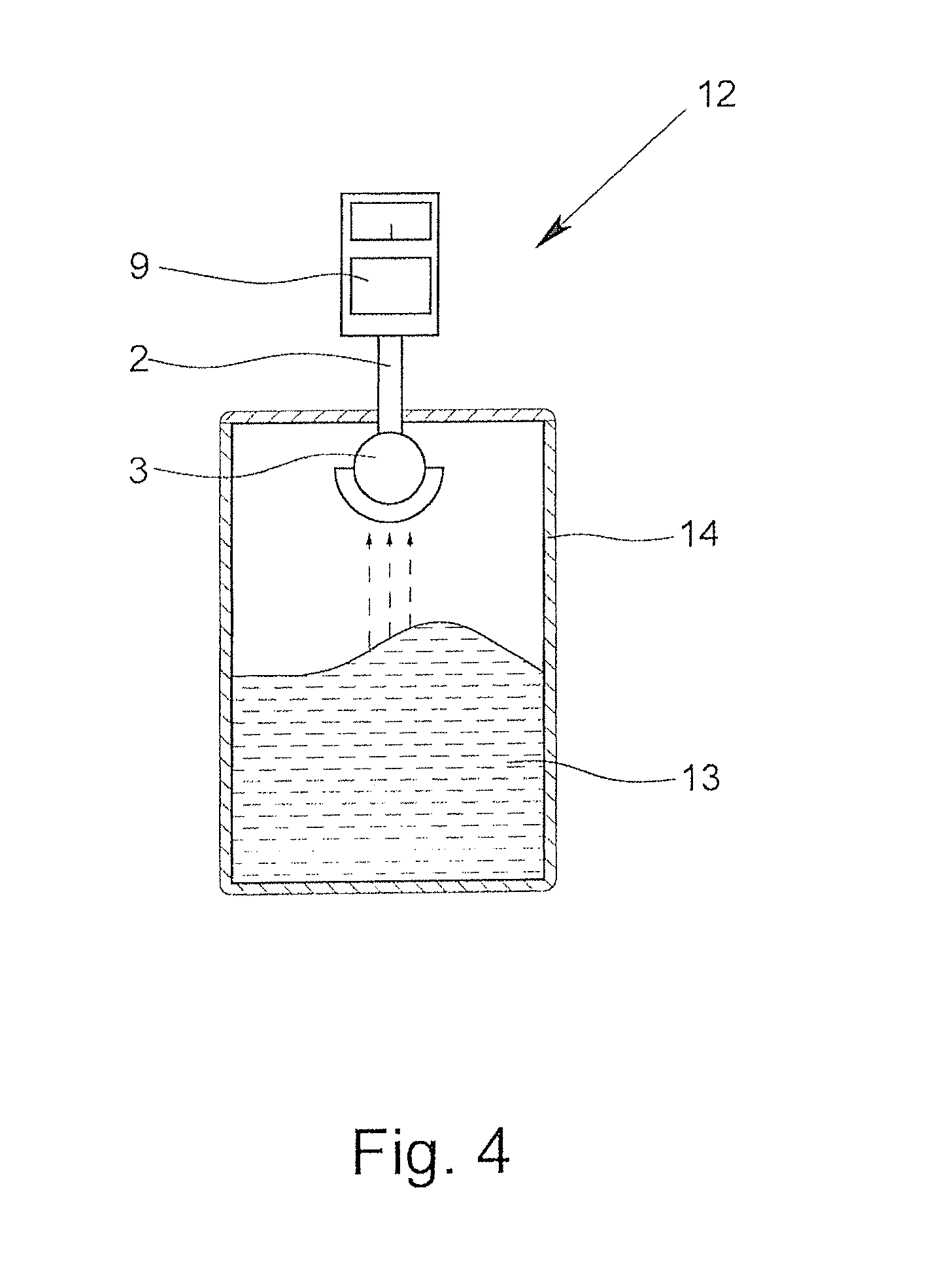
Dielectric antenna with an electromagnetic feed element and with an ellipsoidal lens made of a dielectric material
ActiveUS8917215B2Avoid disadvantagesEasy to packWaveguide mouthsDielectric antennasElectromagnetic radiation
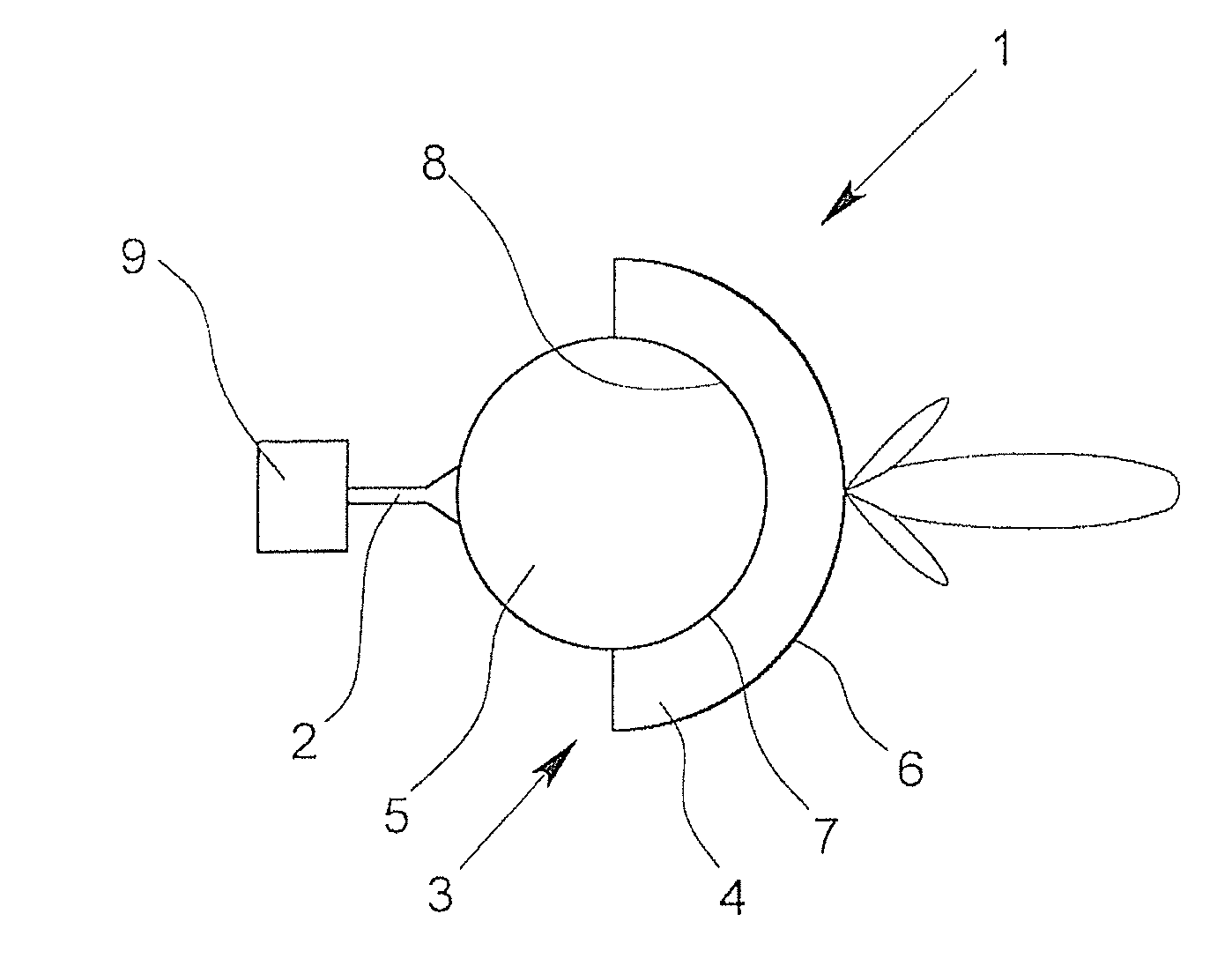
A dielectric antenna with an electromagnetic feed element (2) and with a lens (3) made of a dielectric material, the feed element (2) emitting electromagnetic radiation (4) and the lens (3) being supplied with electromagnetic radiation (4) in the feed region (5), the lens (3) relaying the electromagnetic radiation (4) and radiating it with the transmission region (6). To configure these dielectric antennas such that the disadvantages of the dielectric antennas known from the prior art are at least partially avoided, first of all, the lens (3) is shaped essentially ellipsoidally at least in the transmission region (6) and the lens (3) is arranged relative to the feed element (2) such that the electromagnetic radiation (4) emitted by the lens (3) in the direction of maximum radiation (7) of the antenna has an essentially planar phase front.
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
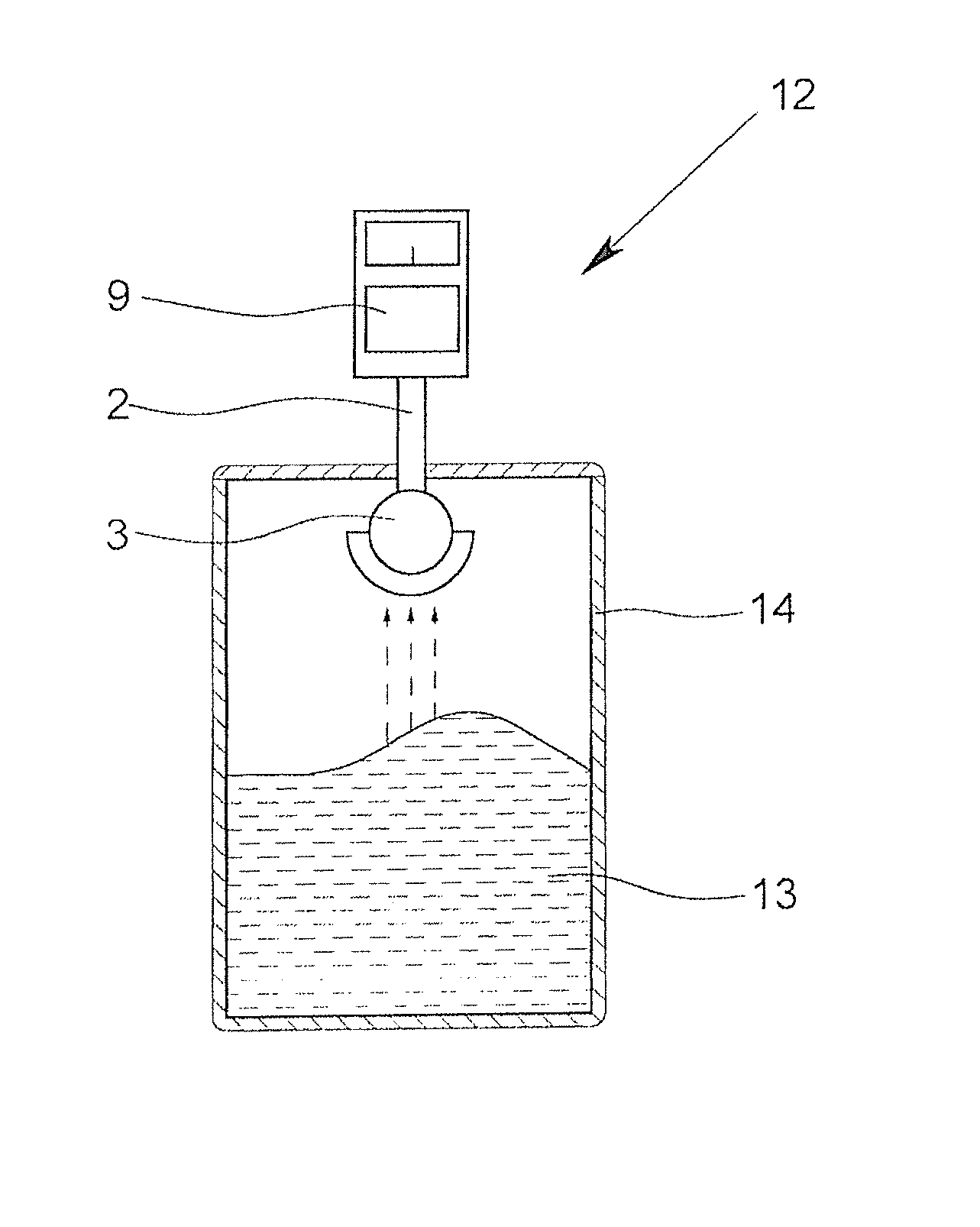
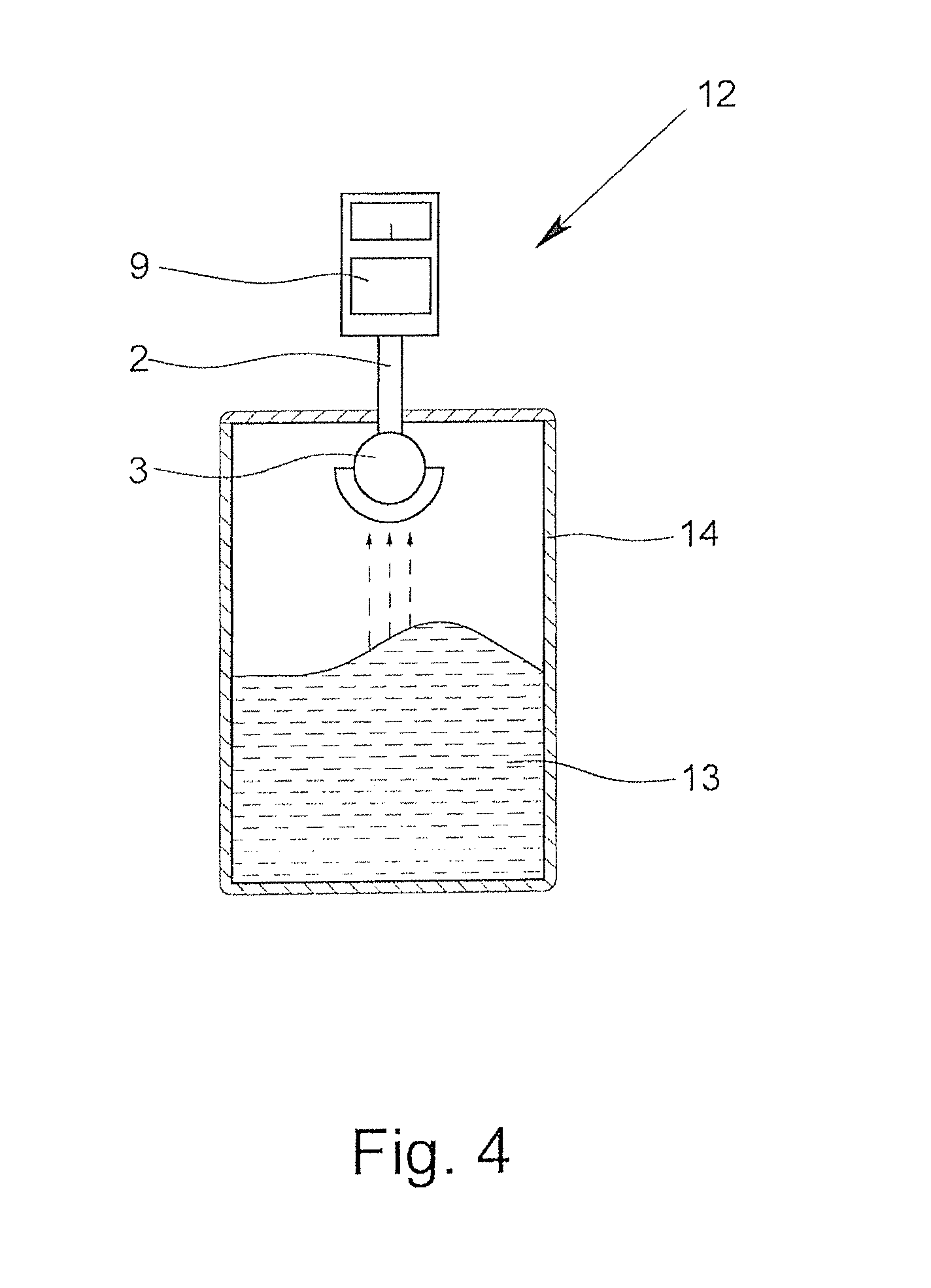
Dielectric antenna and fill level sensor using the radar principle
InactiveUS8881588B2Shorten the lengthReduce antenna sizeWaveguide hornsWaveguide mouthsDielectricRadar
A dielectric antenna (1) having at least one supply element (2) and at least one lens (3) formed of a dielectric material. The dielectric antenna makes it possible to measure the surface of a medium with an essentially consistent measuring accuracy in that the lens (3) has an outer component (4) and an inner component (5). The outer component (4) has a radiating surface (6) that is spherical and an inner surface (7) that is spherical, and the inner component (5) has a contact surface (8) that spherical. Furthermore, the antenna is usable as part of a fill level sensor operating on the radar principle.
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
Beam controller for aperture antenna, and aperture antenna therewith
The present invention relates to an aperture antenna capable of controlling a shape of a radiated beam without changing a structure of an aperture antenna by connecting a beam controller with a single aperture antenna. the aperture antenna including a beam controller according to the present invention includes: a waveguide; an aperture horn of which one end is connected to the waveguide and the other end is provided with an opening; and a beam controller including a feeding unit connected to the opening and provided with a plurality of slits, a dielectric layer connected to the feeding unit, and a plurality of patches connected to the dielectric layer to control a beam shape of a signal introduced into the feeding unit and radiated through the patches.
Owner:LIG NEX1 CO LTD
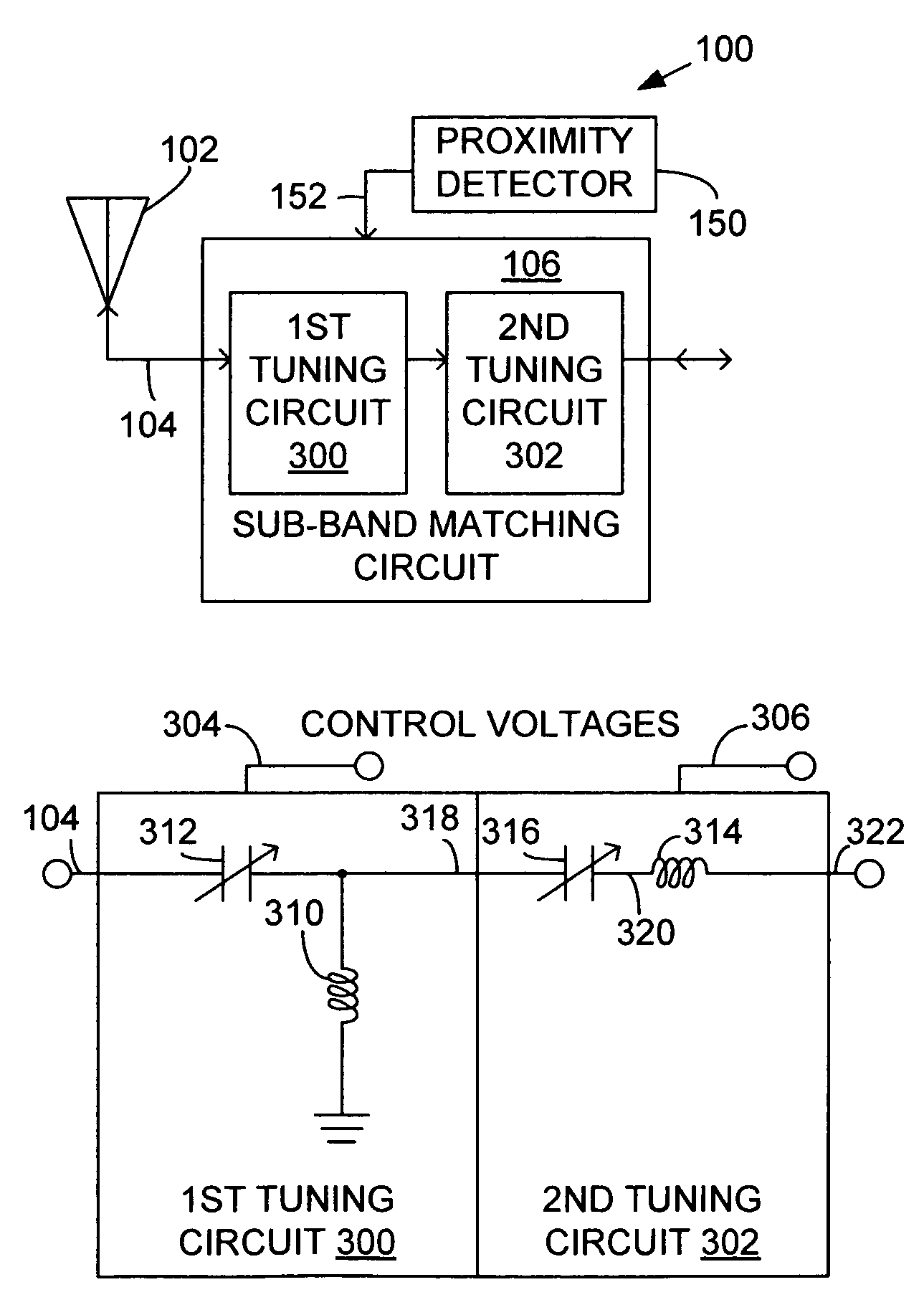
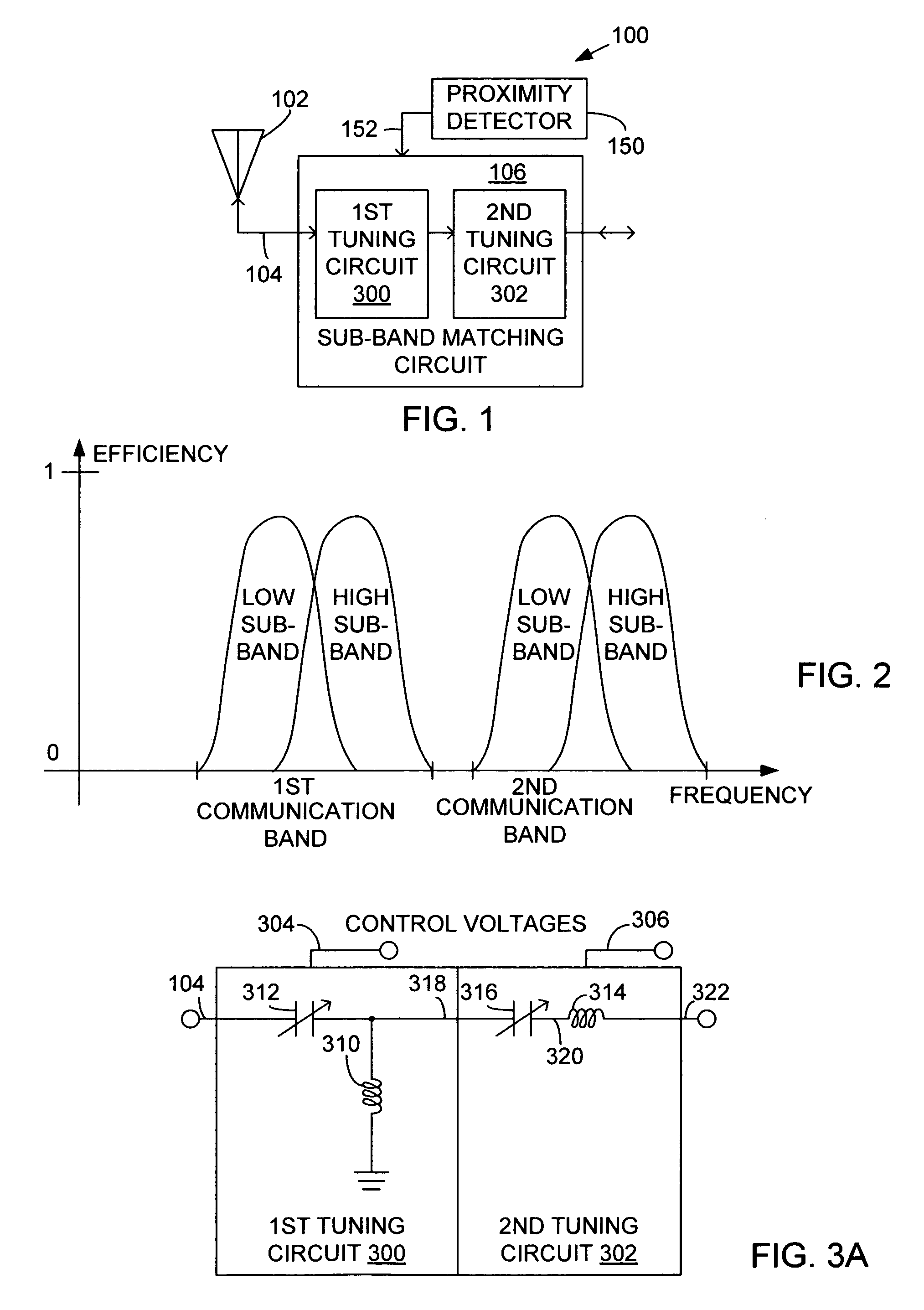
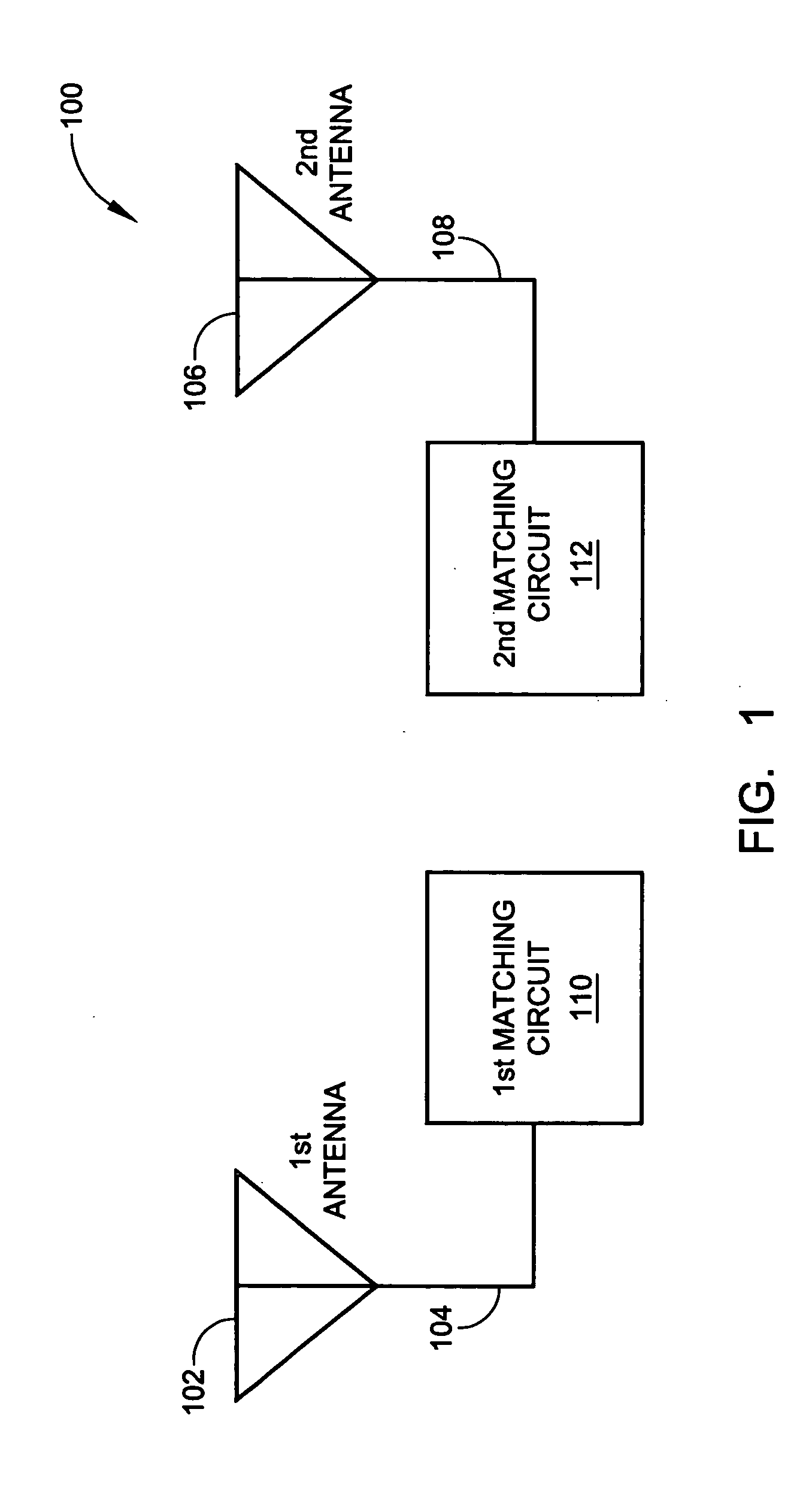
System and method for impedance matching an antenna to sub-bands in a communication band
InactiveUS7176845B2Improve efficiencyReduce noiseMultiple-port networksAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna impedanceMethod selection
A sub-band antenna matching method and an antenna matching system for selectively matching a communication bandwidth segment impedance have been provided. The method comprises: accepting a frequency-dependent impedance from an antenna; and, selectively supplying a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at a sub-band of a first communication band. In some aspects, the method selectively supplies a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at a sub-band of a second communication band. More specifically, the method comprises: tuning a first tuning circuit to a first frequency; simultaneously tuning a second tuning circuit to a second frequency to match the antenna at a low end of the first communication band. Likewise, the first tuning circuit is tuned to a third frequency and the second tuning circuit is tuned to a fourth frequency to match the antenna at a high end of the first communication band in response to the third and fourth frequencies.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
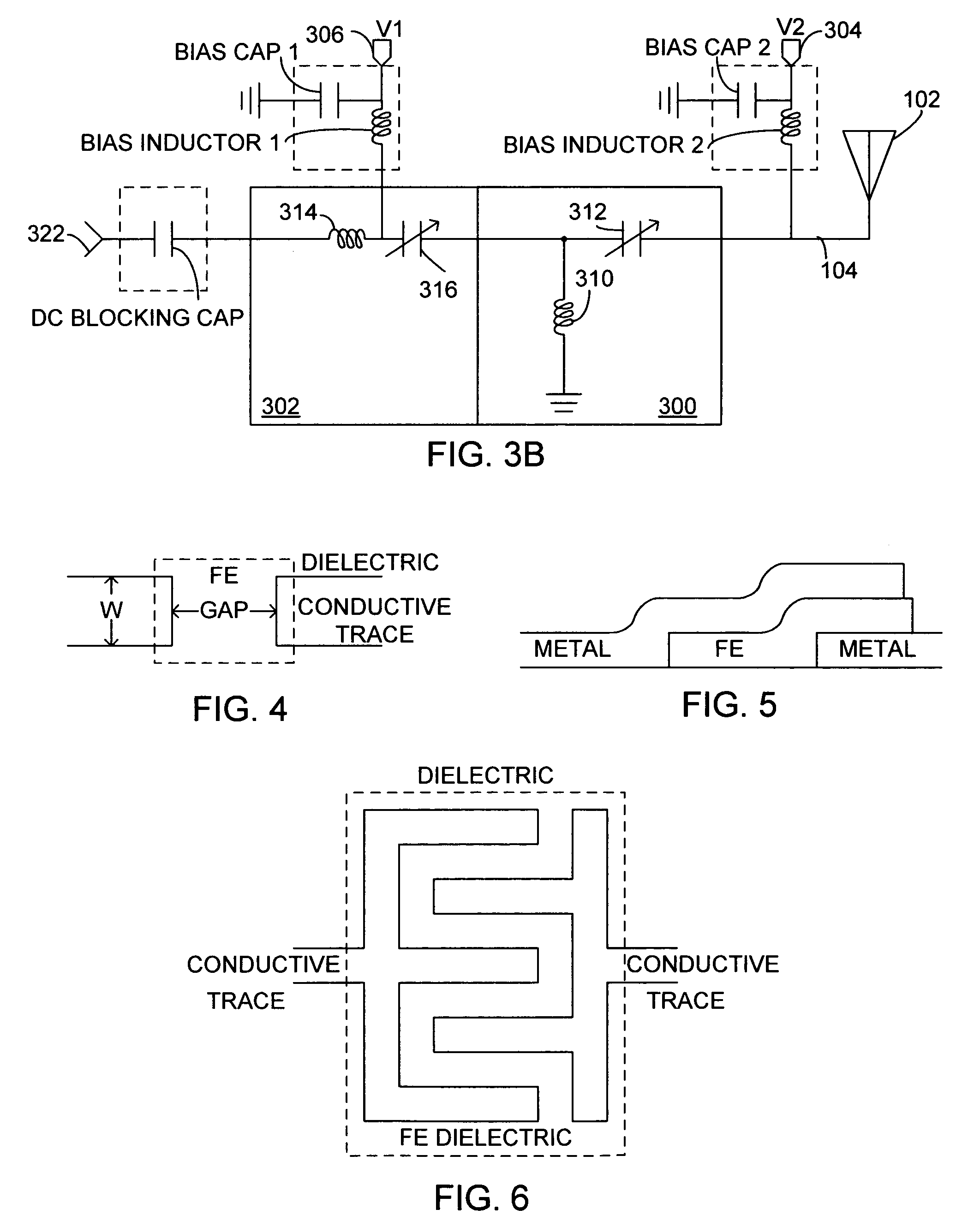
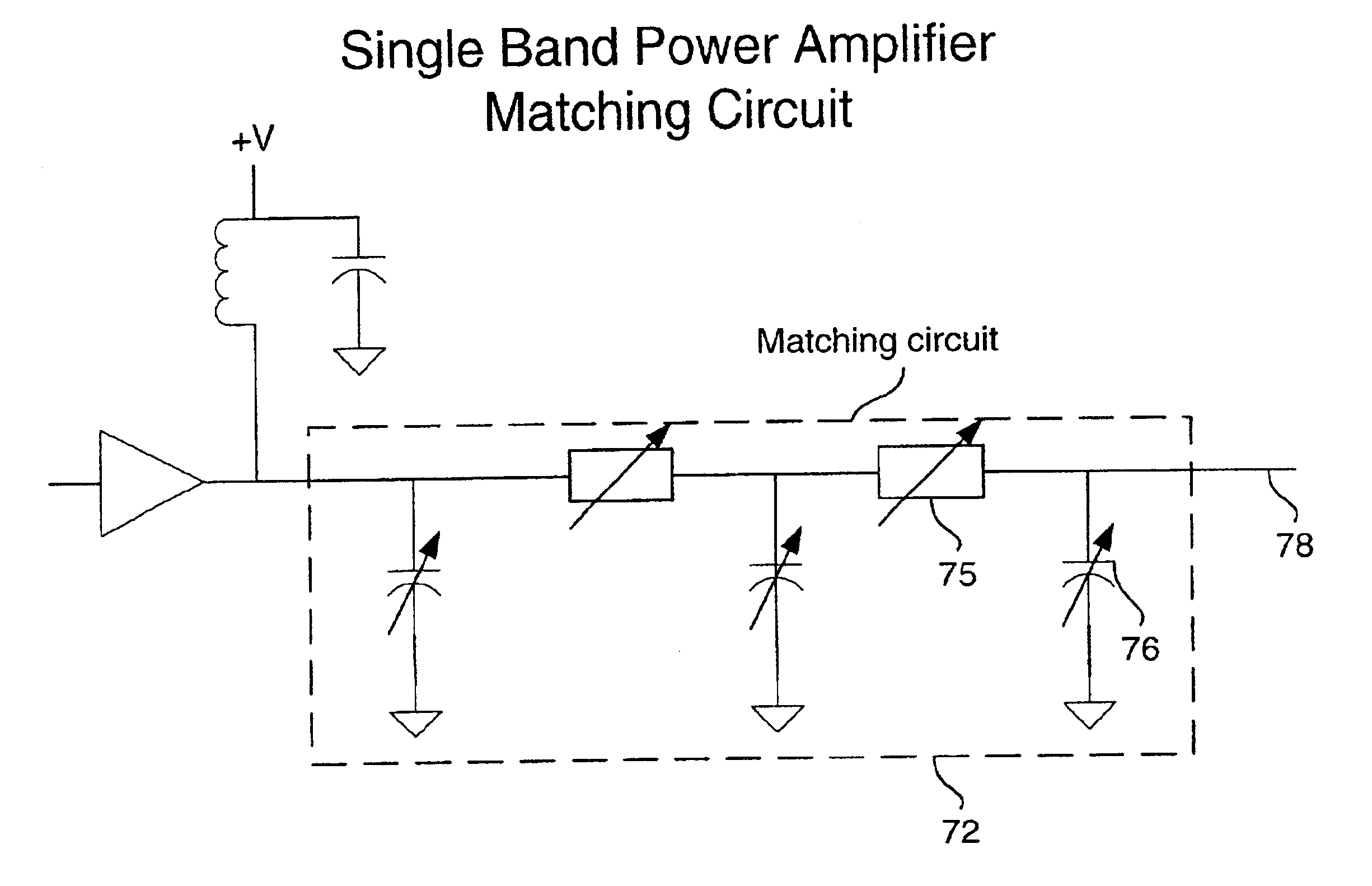
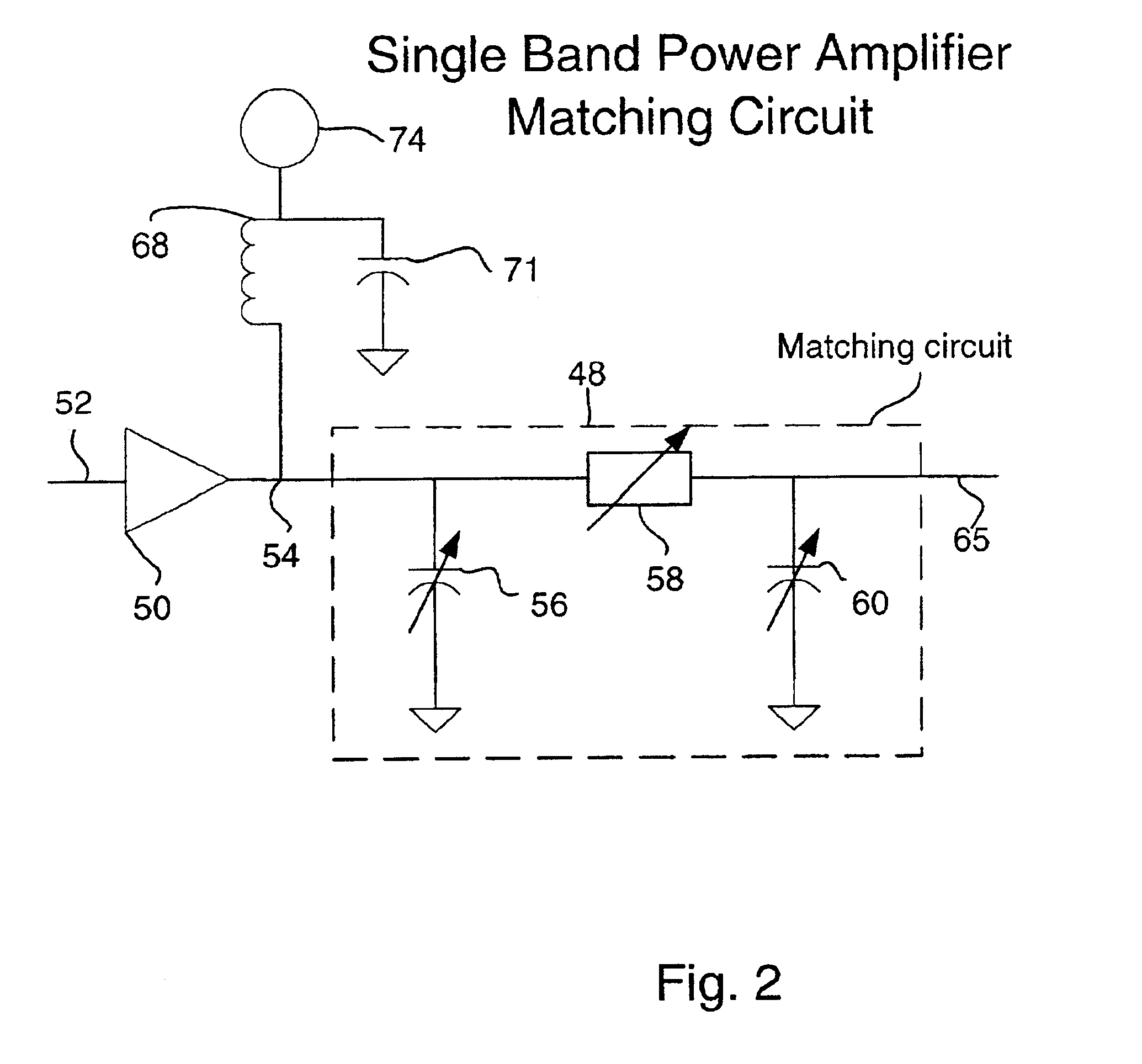
Tunable power amplifier matching circuit
InactiveUS6859104B2Reduce cost and size and power consumptionMultiple-port networksHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
A power amplifier matching circuit is provided. The matching circuit includes a ferro-electric tunable component. A control signal is applied to the tunable component, changing the component's impedance. This changes the impedance of the matching circuit.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Full-duplex antenna system and method
A system and method is provided for full-duplex antenna impedance matching. The method comprises: effectively resonating a first antenna at a frequency selectable first channel in a first frequency band; generating a first antenna impedance at the first channel frequency; effectively resonating a second antenna at a frequency selectable second channel in the first frequency band; generating a second antenna impedance at the second channel frequency; supplying a first conjugate impedance match at the first channel frequency; and, supplying a second conjugate impedance match at the second channel frequency. For example, the first antenna may be used for transmission, while the second antenna is used for received communications. The antennas effectively resonant in response to: supplying frequency selectable conjugate impedance matches to the antennas; generating frequency selectable antenna impedances; and / or selecting the frequency of antenna resonance.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Planar antenna and antenna system
InactiveUS7030827B2Easy to manufactureImprove assembly strengthWaveguide mouthsAntenna supports/mountingsPhysicsCylindrical waveguide
The present invention relates to a planar antenna (1) for excitation of the TE01-mode of an electromagnetic wave and adapted to be arranged in a waveguide tube (2). The planar antenna comprises a substrate (6) of dielectric material having a first surface (7) intended to face towards a filling good surface and a second surface (8) facing in an opposite direction. A first group (9) of a plurality of dipole arms (10) is arranged on the first surface (7) or the second surface (8) on a perimeter of a circle with a predetermined radius. A second group (11) of a plurality of dipole arms (12) is arranged on the first surface (7) or the second surface (8) on the perimeter of the circle with the predetermined radius. The dipole arms (10) of the first group (9) extend in a first direction and the dipole arms (12) of the second group (11) extend in a direction opposite the first direction. Furthermore, the present invention relates to an antenna system comprising a cylindrical waveguide tube (2) having a bottom plate (3) and a tube portion (4) and a planar antenna (1) as mentioned above.
Owner:VEGA GRIESHABER GMBH & CO
Horn Antenna with Integrated Impedance Matching Network for Improved Operating Frequency Range
ActiveUS20100033391A1Reduce Impedance MismatchReduce mismatchWaveguide hornsWaveguide mouthsCapacitanceHorn antenna
A dual- or quad-ridged horn antenna with an embedded impedance matching network is provided herein. According to one embodiment, the horn antenna may include at least one pair of ridges arranged opposite one another for guiding an electromagnetic wave there between. A transmission line is coupled to a first one of the ridges for supplying power to, or receiving a signal from, a feed region of the horn antenna. To reduce impedance mismatches between the transmission line and the ridges, an impedance matching network is embedded within a second one of the ridges at the feed point. The impedance matching network reduces impedance mismatch and extends the operational frequency range of the horn antenna by providing a sufficient amount of series capacitance between the transmission line and the ridges at the feed region. As set forth herein, the impedance matching network is preferably implemented as an open-circuit transmission line stub or capacitive stub.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Radar detection method and apparatus
Owner:VALEO RADAR SYST
Dielectric antenna and fill level sensor using the radar principle
InactiveUS20130220011A1Shorten the lengthReduce antenna sizeWaveguide hornsWaveguide mouthsDielectricRadar
A dielectric antenna (1) having at least one supply element (2) and at least one lens (3) formed of a dielectric material. The dielectric antenna makes it possible to measure the surface of a medium with an essentially consistent measuring accuracy in that the lens (3) has an outer component (4) and an inner component (5). The outer component (4) has a radiating surface (6) that is spherical and an inner surface (7) that is spherical, and the inner component (5) has a contact surface (8) that spherical. Furthermore, the antenna is usable as part of a fill level sensor operating on the radar principle.
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
Circularly Polarized Antenna and Radar Device Using the Same
InactiveUS20080231541A1Avoid it happening againDesired characteristicWaveguide mouthsSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrical conductorAntenna gain
A circularly polarized antenna has a dielectric substrate, a ground conductor which is piled up one surface side of the dielectric substrate, a circularly polarized type of antenna element formed on an opposite surface of the dielectric substrate, a plurality of metal posts whose respective one end sides are connected to the ground conductor and penetrate the dielectric substrate along a thickness direction thereof, and whose respective other sides extend up to the opposite surface of the dielectric substrate, the plurality of metal posts configuring a cavity by being provided at predetermined intervals so as to surround the antenna element, and a conducting rim which short-circuits the respective other end sides of the plurality of metal posts along an array direction thereof, and is provided so as to extend by a predetermined distance in a direction of the antenna element at the side of the opposite surface of the dielectric substrate. With the circularly polarized antenna, a radiation characteristic of the antenna can be made to be a desired characteristic by preventing a surface wave from being generated by means of the cavity and the conducting rim, and a frequency characteristic of the antenna gain can be made to have a sharp notch within the RR prohibited band by utilizing a resonance of the cavity. Accordingly, the circularly polarized antenna is effective for reducing radio interference with the EESS or radio astronomical services.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP +1
Radar detection method and apparatus
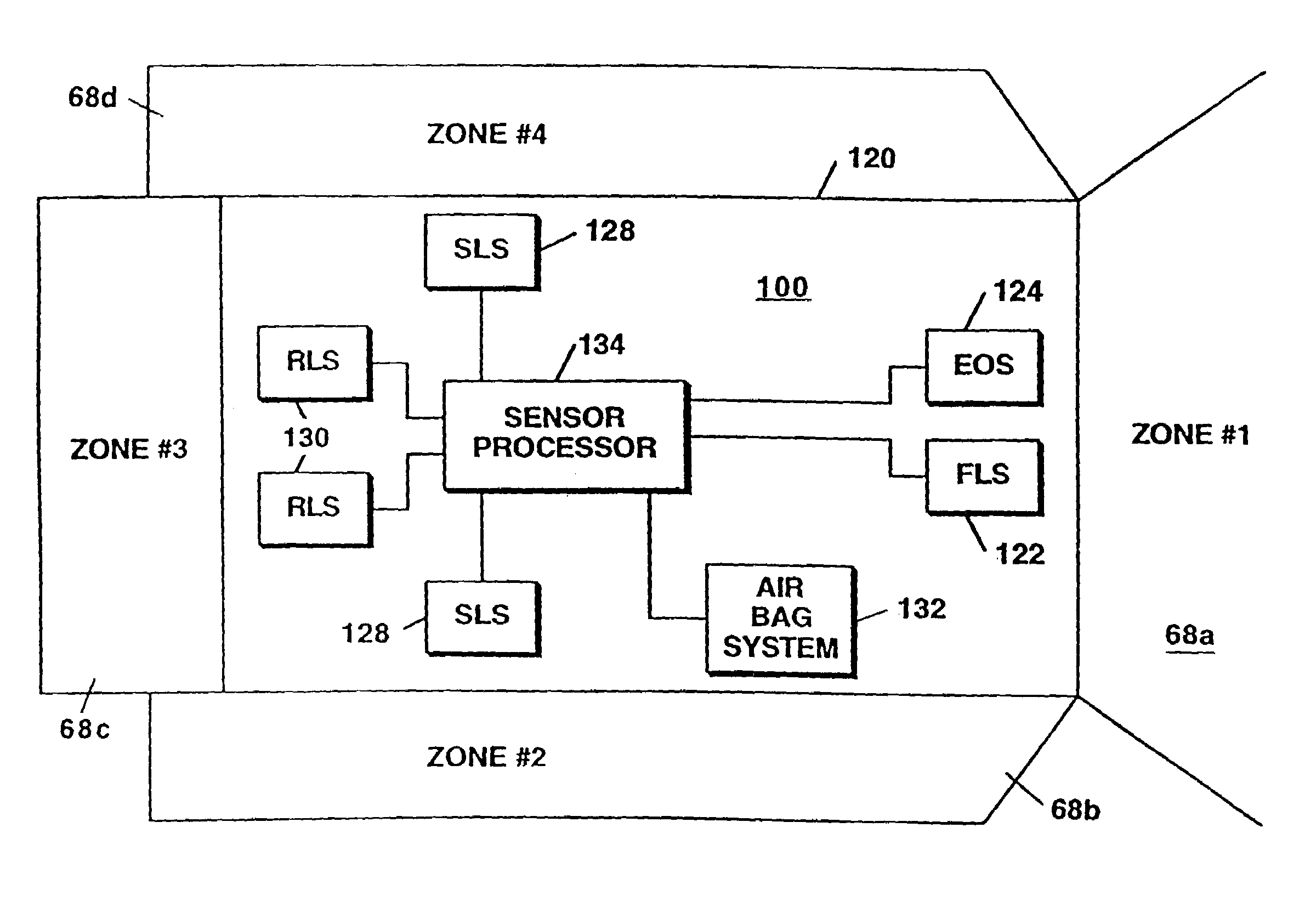
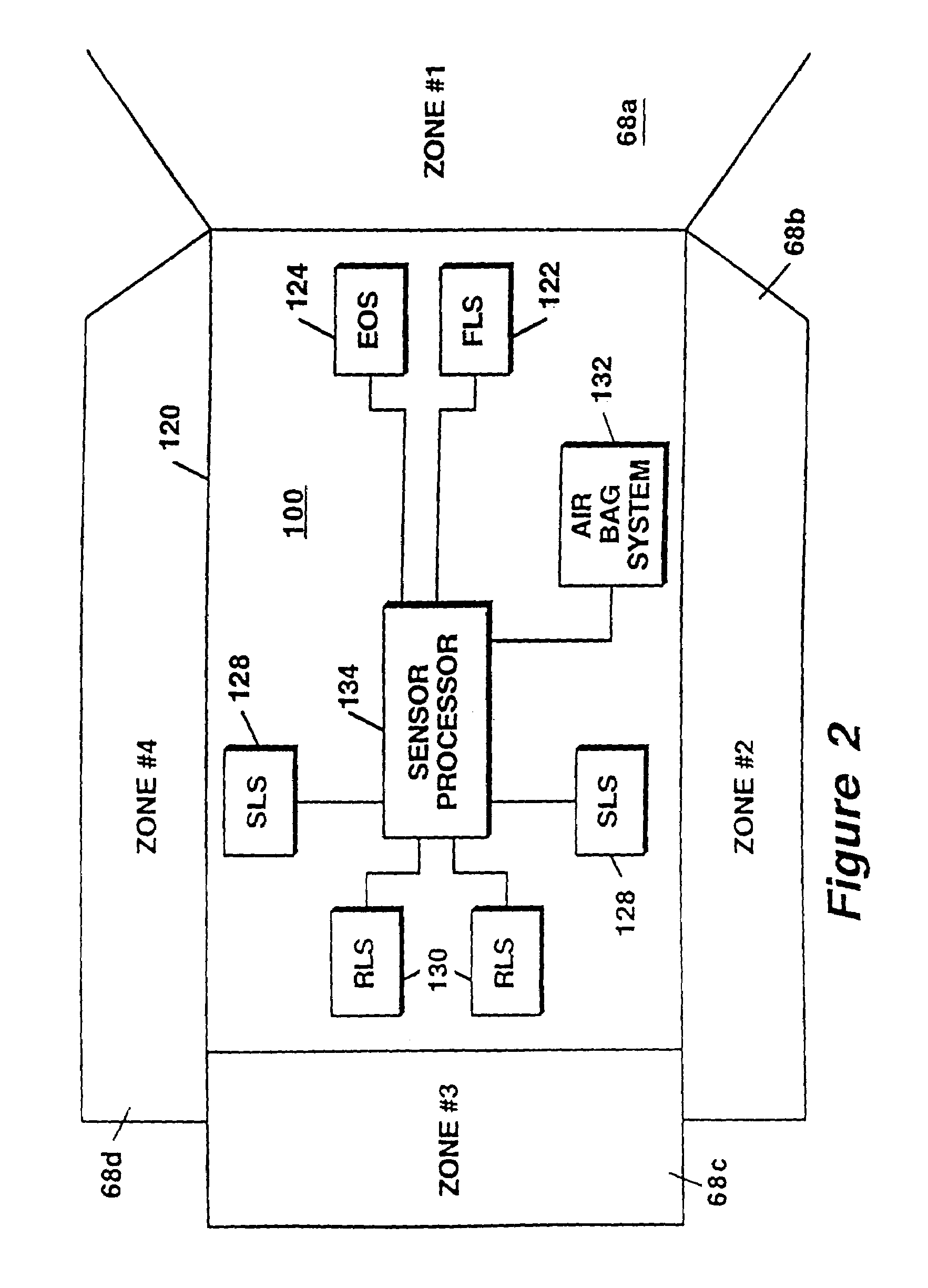
InactiveUS6864831B2Increase probabilityImprove accuracyMultiple-port networksVehicle fittingsRadar detectionRadar beam
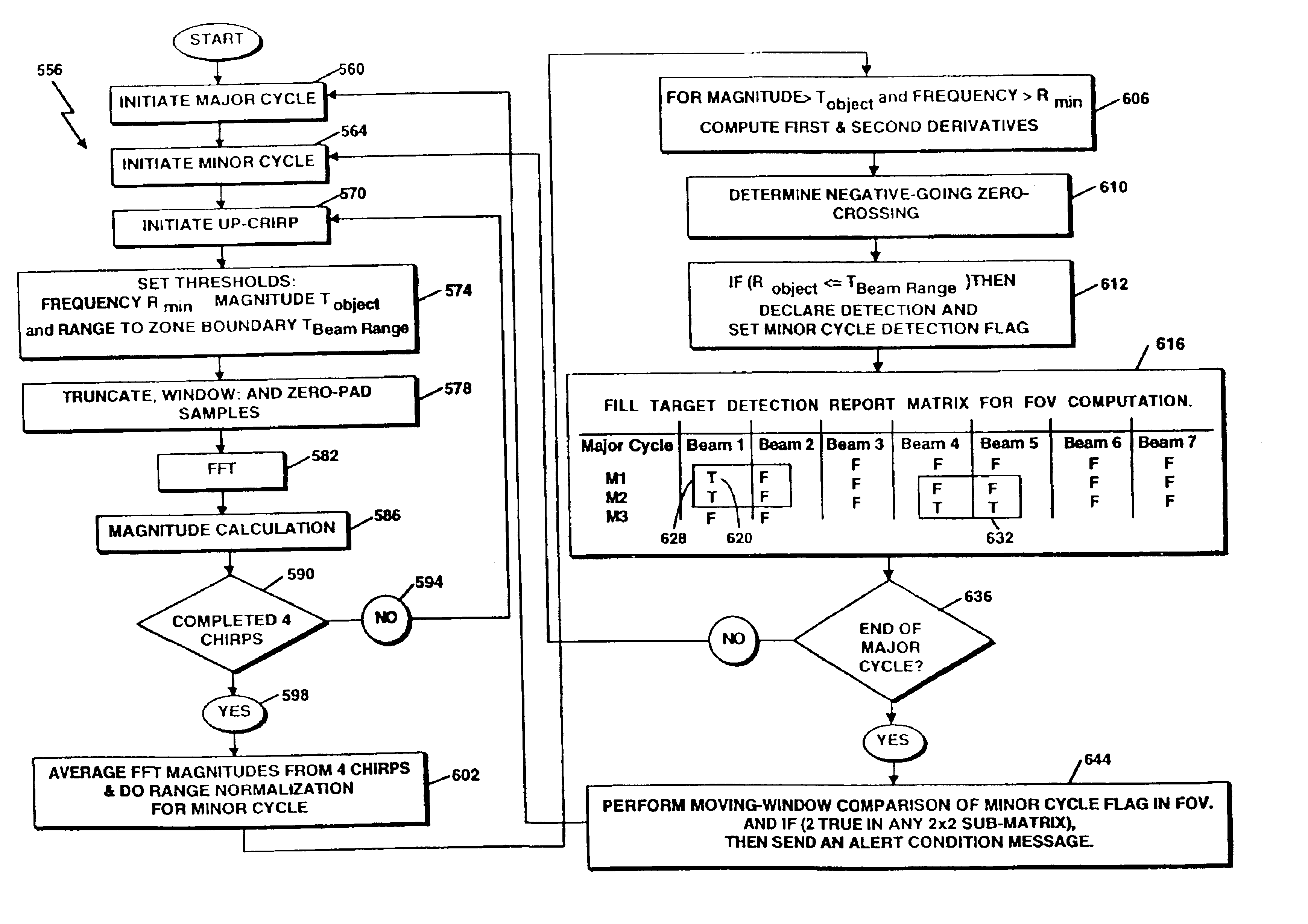
A radar detection process includes computing a derivative of an FFT output signal to detect an object within a specified detection zone. In one embodiment, a zero crossing in the second derivative of the FFT output signal indicates the presence of an object. The range of the object is determined as a function of the frequency at which the zero crossing occurs. Also described is a detection table containing indicators of the presence or absence of an object within a respective radar beam and processing cycle. At least two such indicators are combined in order to detect the presence of an object within the detection zone.
Owner:VALEO RADAR SYST
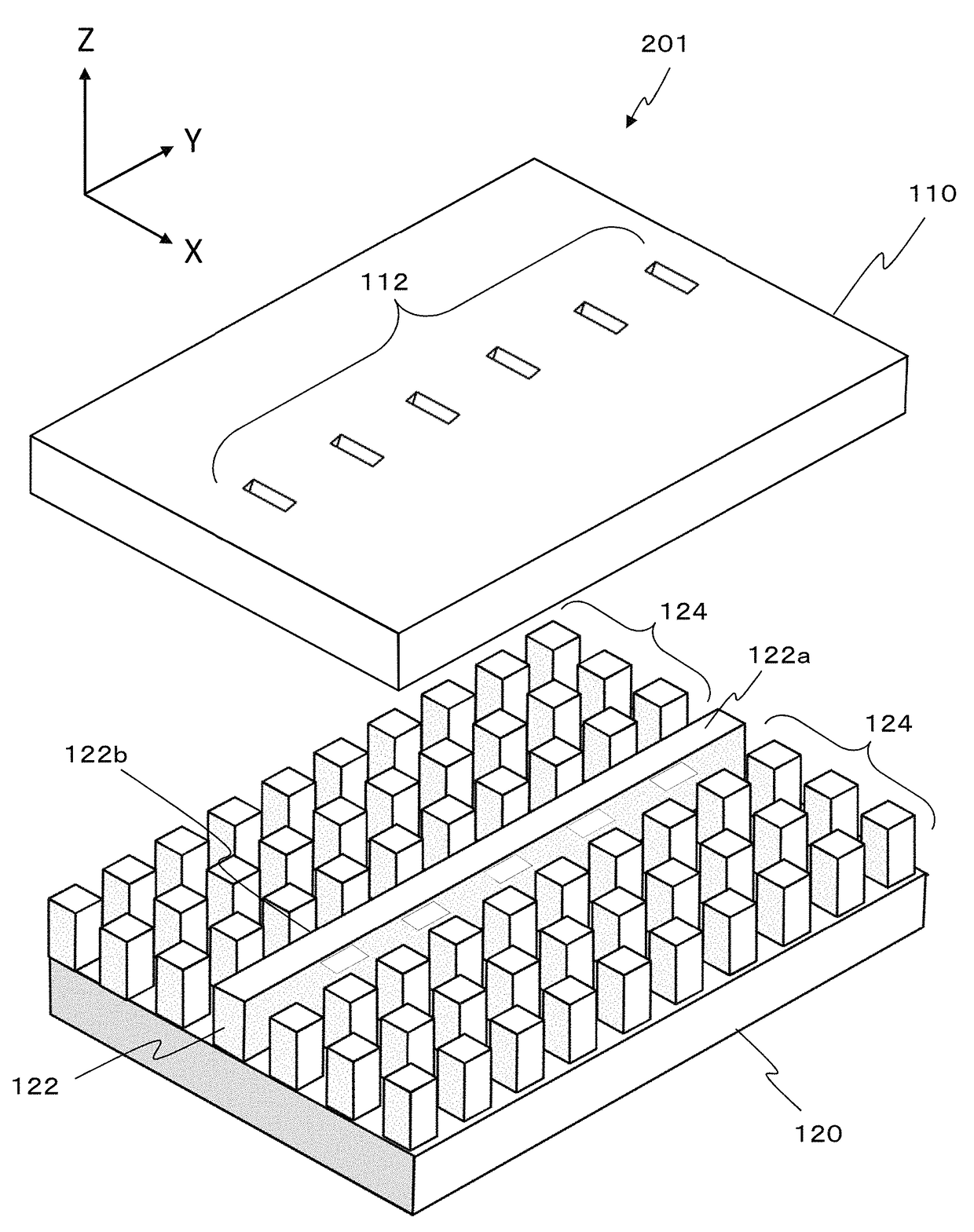
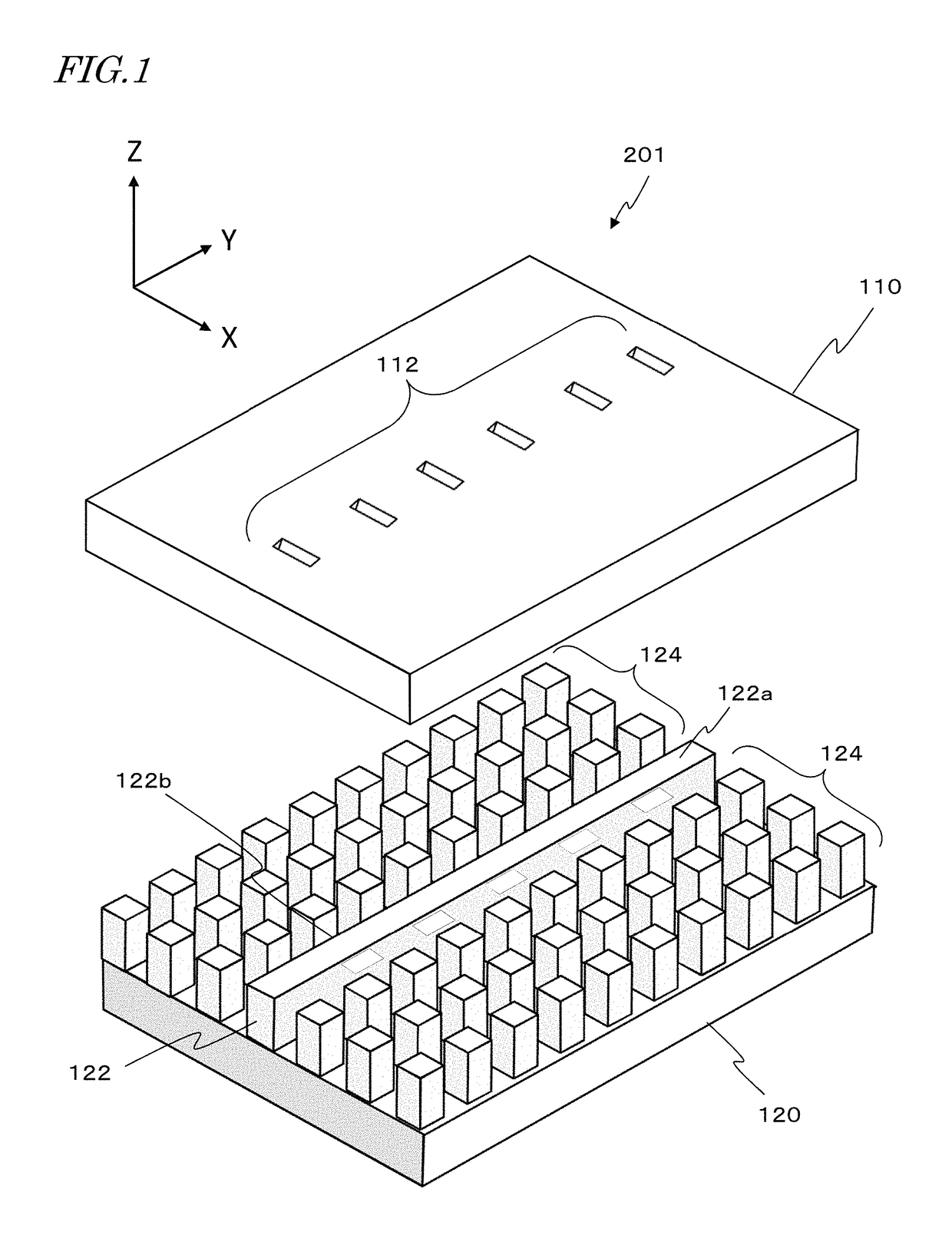
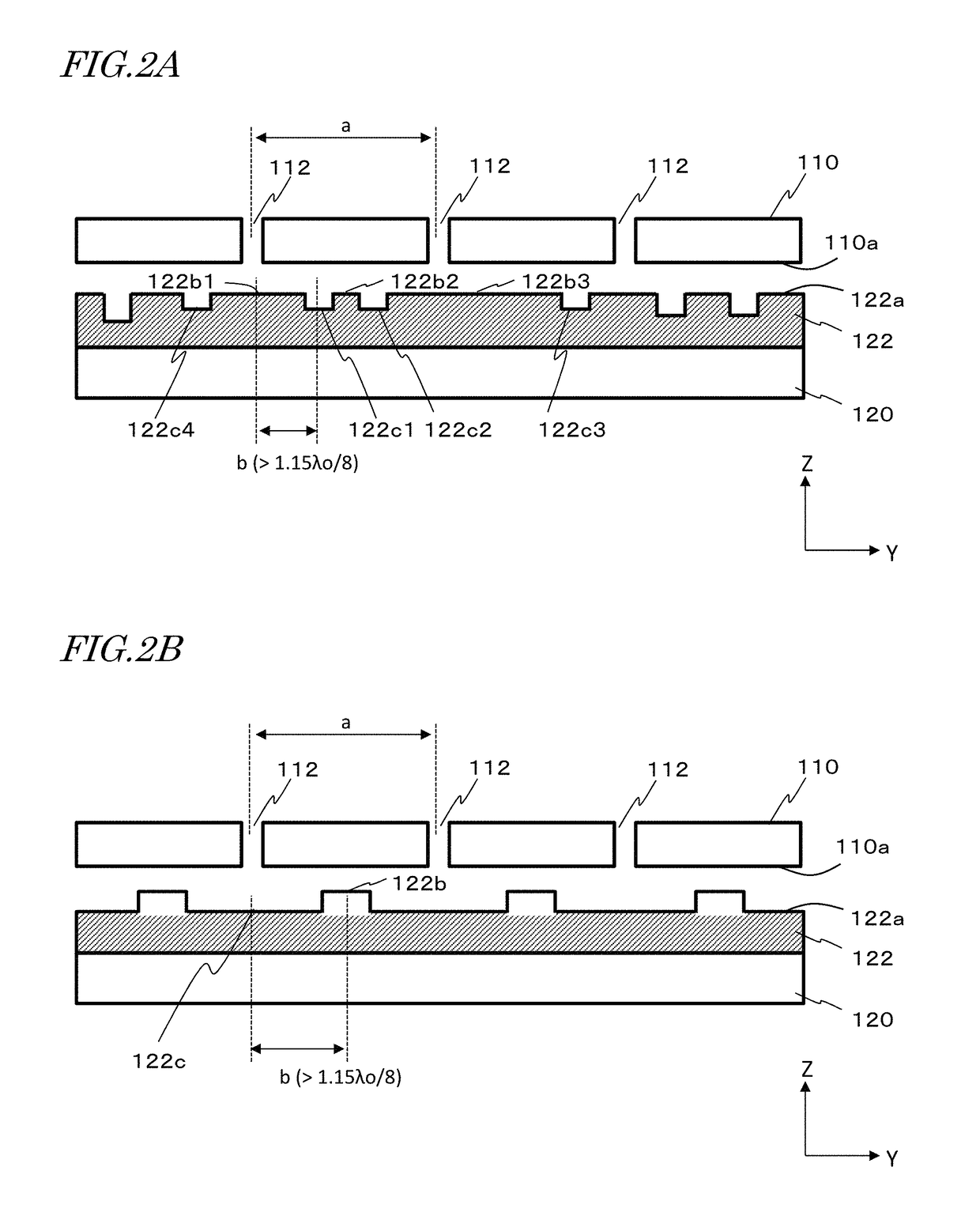
Slot array antenna
A slot array antenna includes: an electrically conductive member having an electrically conductive surface and slots therein, the slots being arrayed in a first direction which extends along the conductive surface; a waveguide member having an electrically conductive waveguide face which opposes the slots and extends along the first direction; and an artificial magnetic conductor extending on both sides of the waveguide member. At least one of the conductive member and the waveguide member includes dents on the conductive surface and / or the waveguide face, the dents each serving to broaden a spacing between the conductive surface and the waveguide face relative to any adjacent site. The dents include a first, second, and third dents which are adjacent to one another and consecutively follow along the first direction. A distance between centers of the first and second dents is different from a distance between centers of the second and third dents.
Owner:NIDEC CORP +1
Radio frequency coupling structure
A radio frequency coupling structure is arranged to couple a radio frequency signal between a first side of the radio frequency coupling structure to a second side of the radio frequency coupling structure opposite to the first side. The radio frequency coupling structure comprises a dielectric layer, a first electrically conductive layer comprising a first transition structure, a second electrically conductive layer comprising a second transition structure, and an integrated waveguide structure formed by an array of electrically conductive vias extending through the dielectric layer from the first to the second electrically conductive layer to enclose a portion of the dielectric layer. The portion is arranged to guide the radio frequency signal between the first transition structure and the second transition structure.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Waveguide flat array antenna
InactiveCN102064380AAvoid complex welding processesExpand standing wave bandwidthWaveguide mouthsAntenna arraysElectricityWaveguide
The invention provides a waveguide flat array antenna, which has the characteristics of broadband and high-efficiency feed. Rectangular open waveguides 11 are used as radiation units; four rectangular open waveguides in one group form a sub array, and are arranged in a 2*2 rectangle and supplied with broadband equal-amplitude in-phase feed by a rectangular cavity 21; and in order to ensure efficient transmission of electromagnetic wave, the joint of each rectangular open waveguide 11 and the rectangular cavity 21 is provided with matched steps 13 and 23. The center of the rectangular cavity 21 is provided with a rectangular window 22 which is connected with a feed network of the next layer. In order to ensure smooth signals, a rectangular matching block 42 is arranged at the feed network corner connected with each rectangular window 22. The feed network consists of multistage parallel E-T so as to ensure that the antenna has enough bandwidth. The transceiving capacity of circularly polarized wave is realized by arranging a circularly polarized cover. Compared with the conventional flat antenna, the waveguide flat array antenna has broader bandwidth and higher feed efficiency.
Owner:李峰
Radar level gauging system
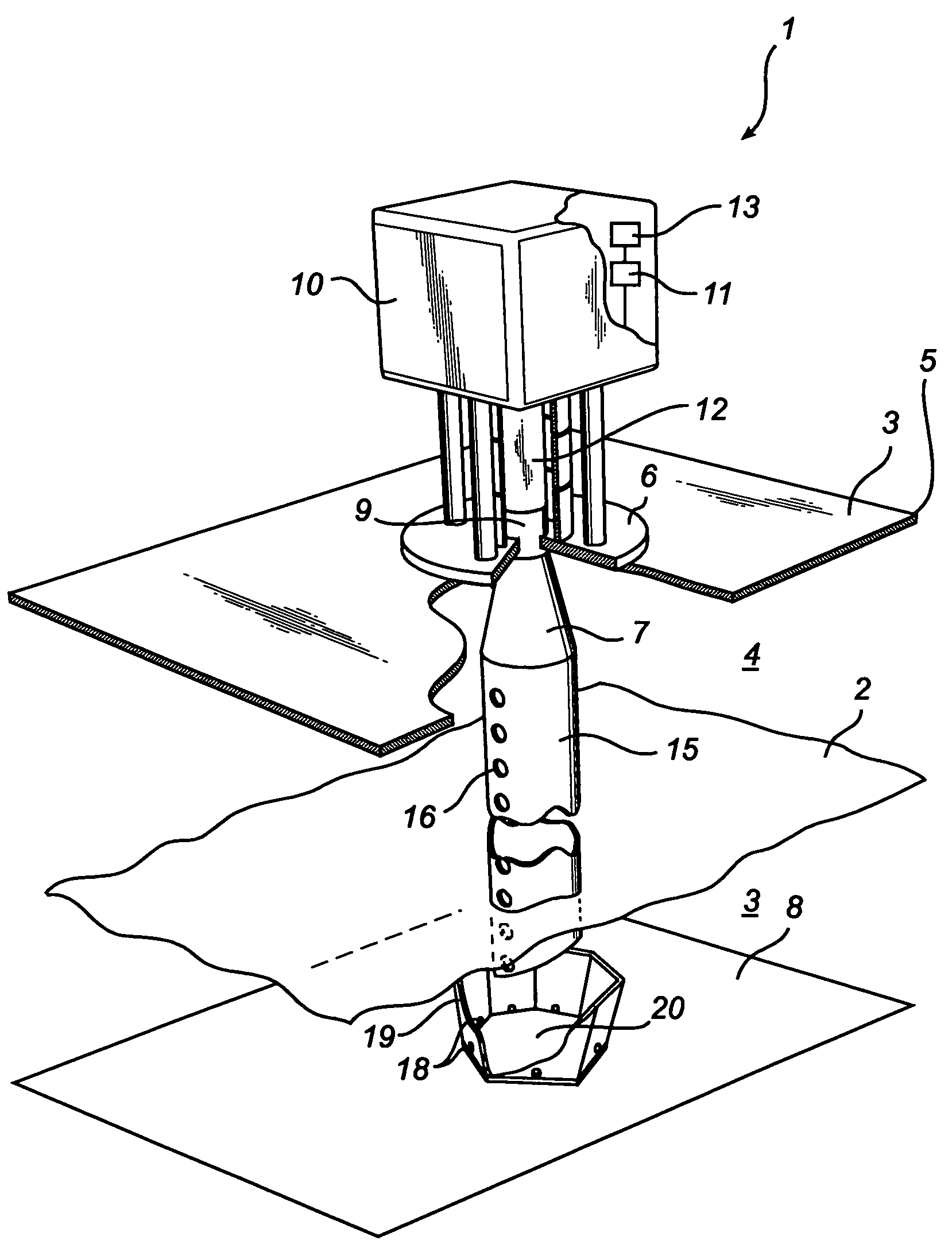
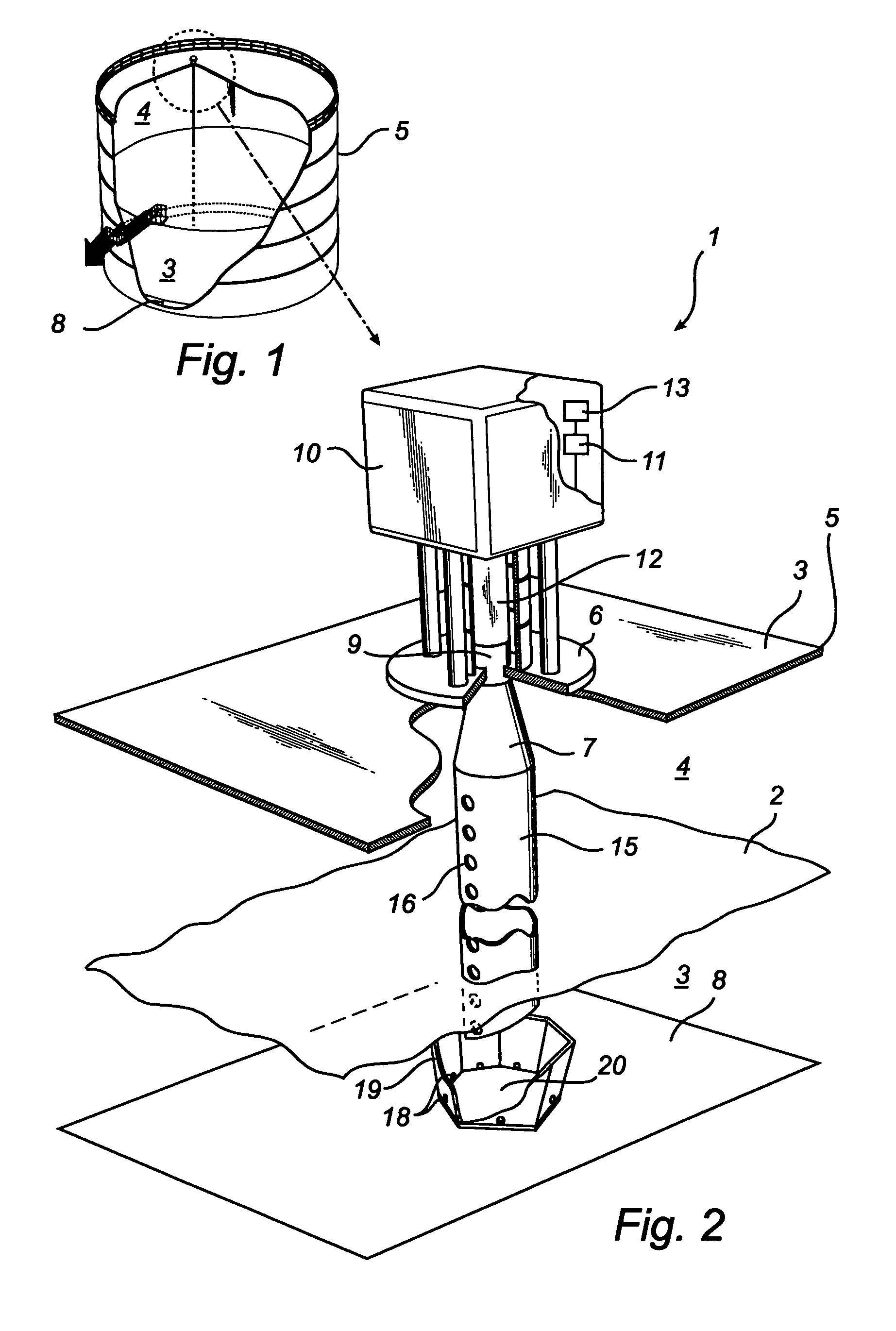
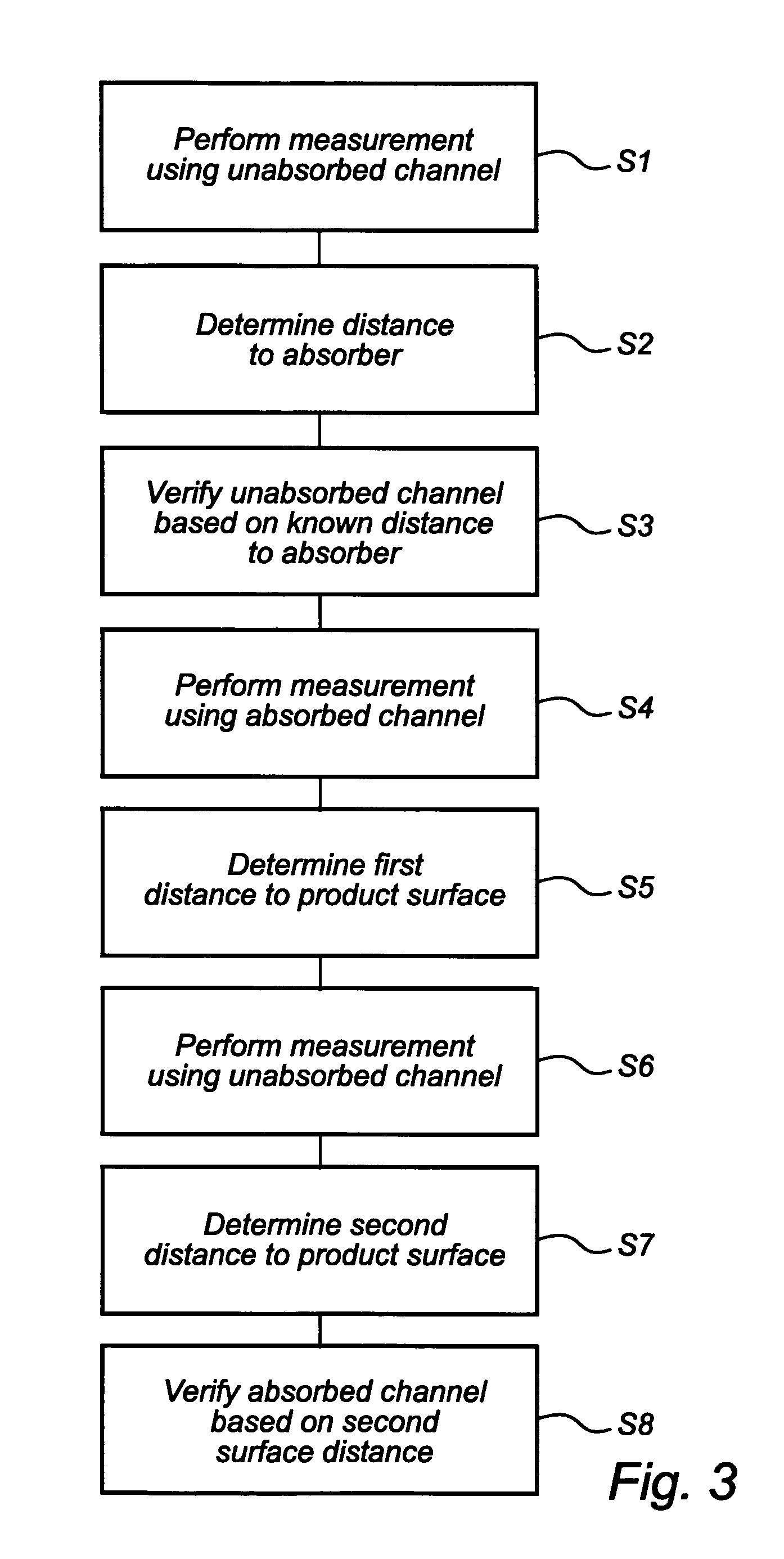
InactiveUS20070236385A1Leveling precisionAccurate level measurementWaveguide mouthsLevel indicatorsRadarAbsorbed energy
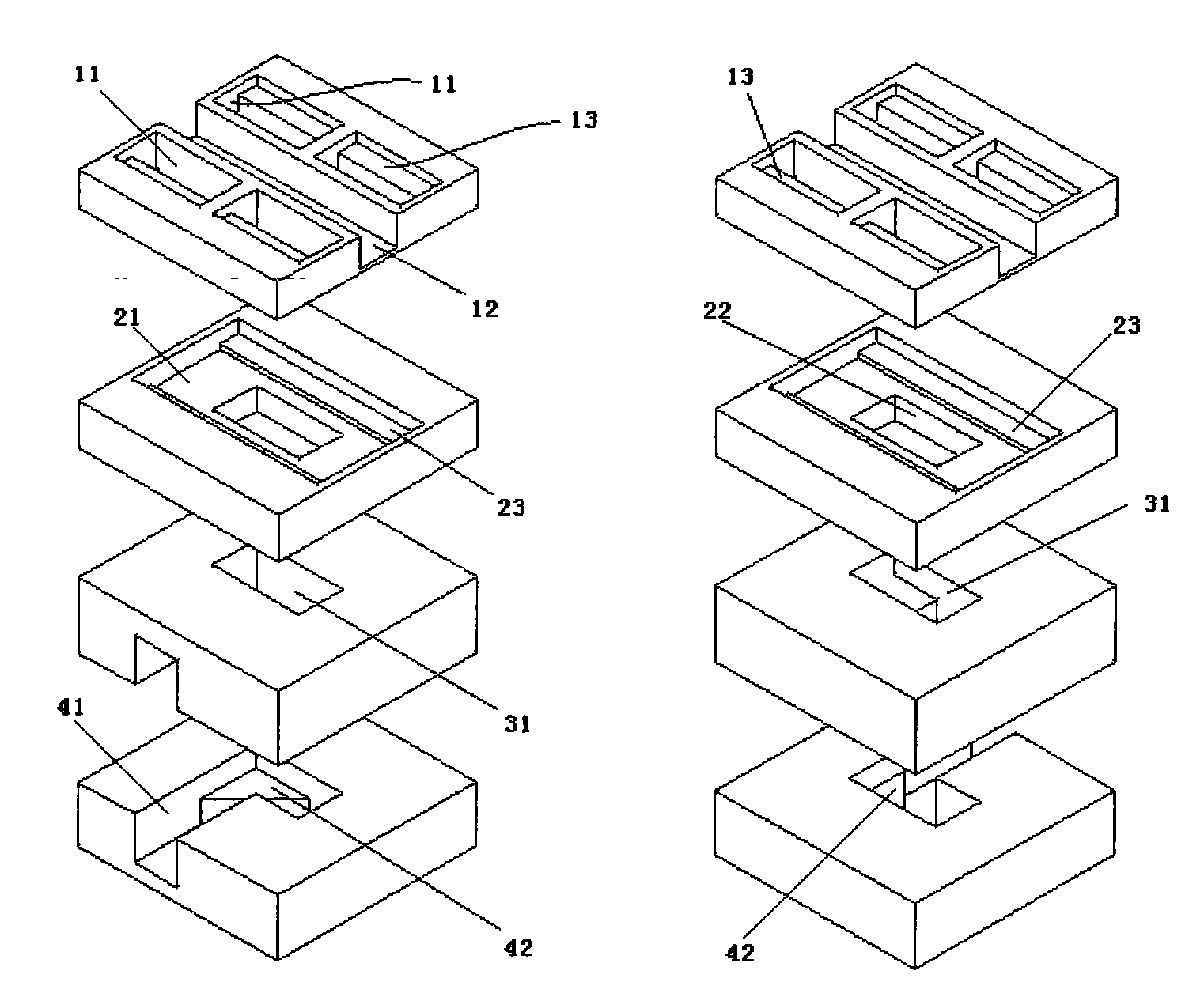
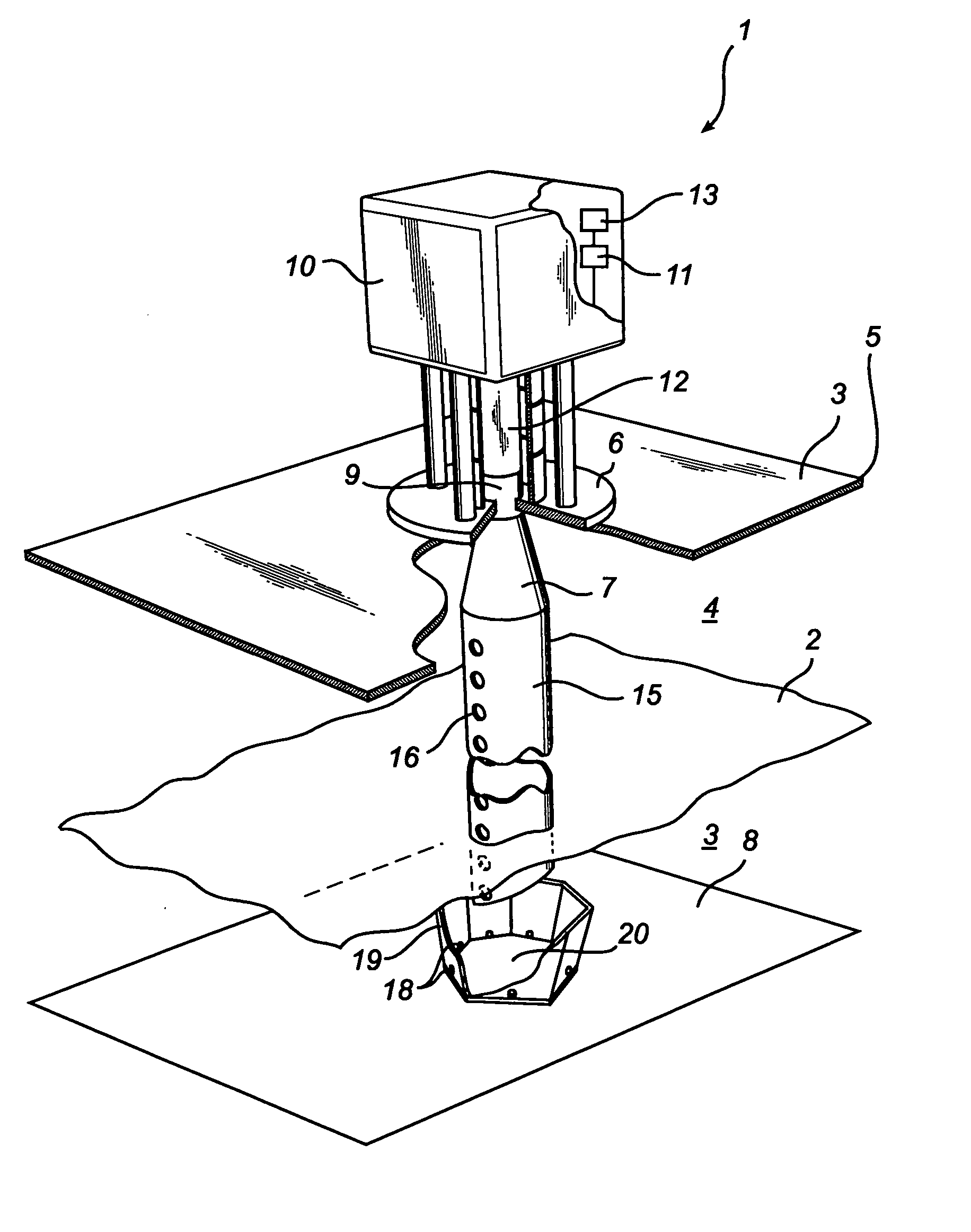
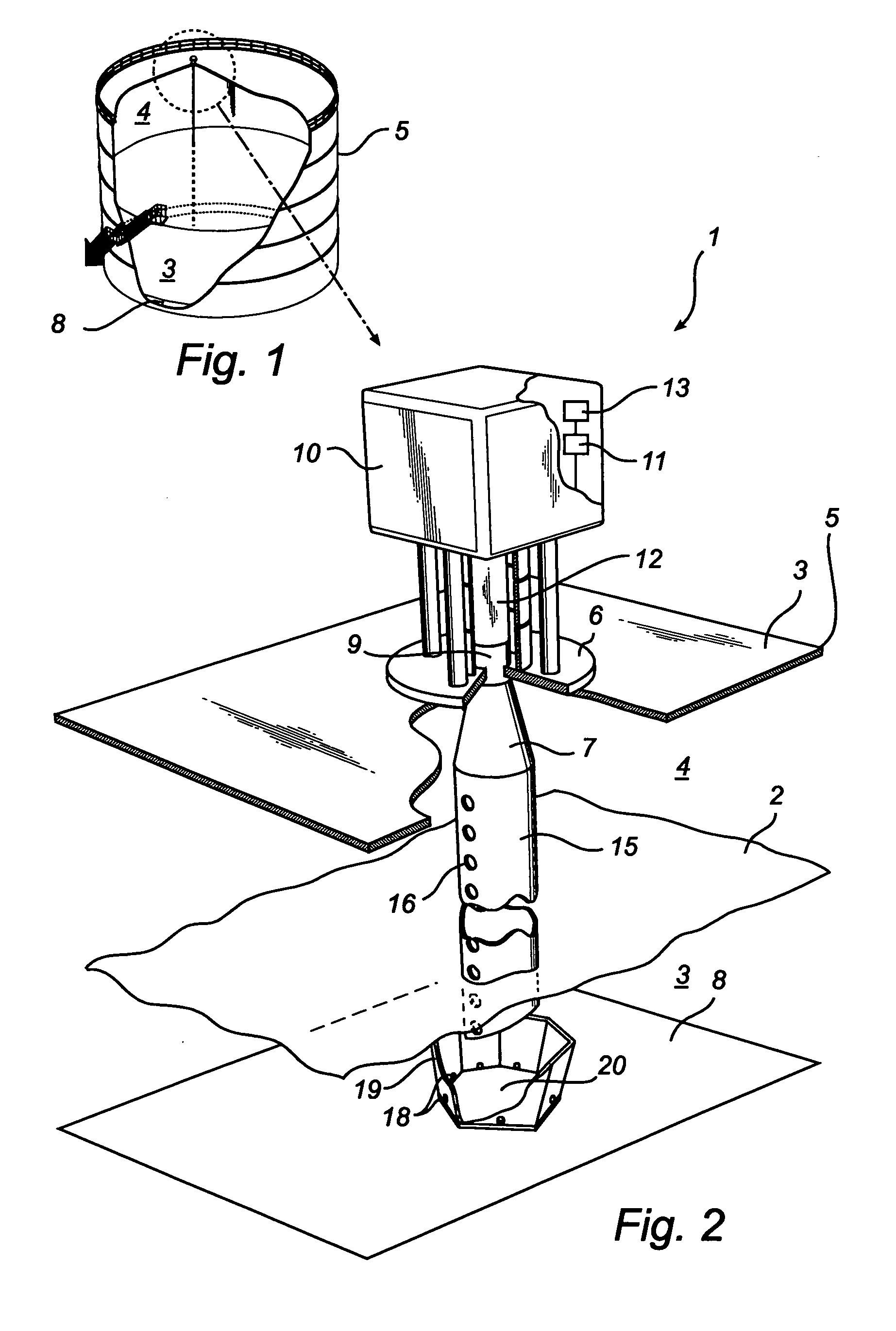
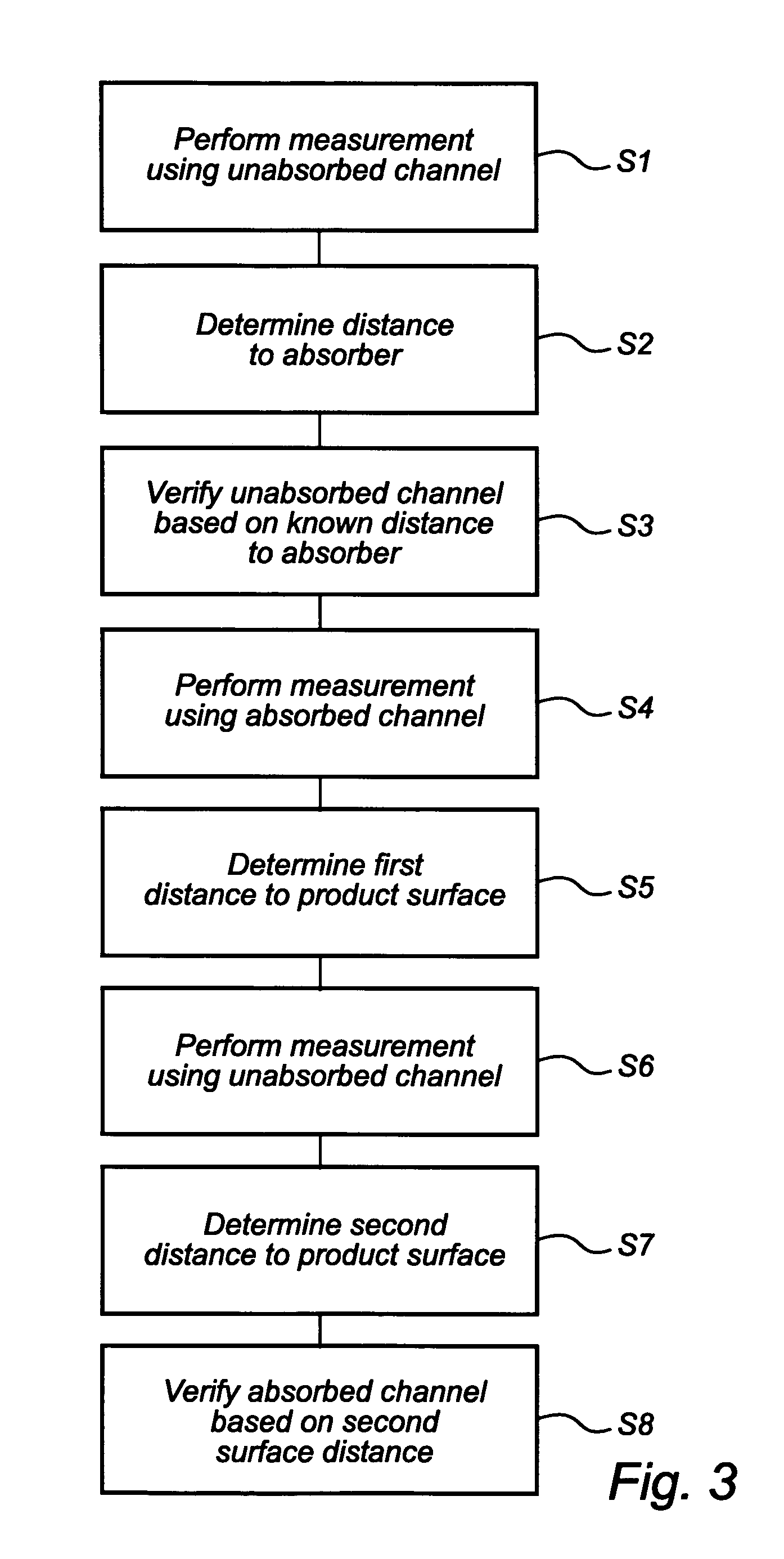
A radar level gauging system comprising a microwave unit for transmitting and receiving first microwaves having a first and second distinguishable characteristics, a microwave absorber adapted to be arranged in a bottom region of the tank and adapted to absorb electromagnetic energy of microwaves having one of the first and second characteristics, and processing circuitry adapted to determine the product level based on a relationship between transmitted and received microwaves. The system thus emits microwaves in two channels, and the absorber is arranged to absorb energy in only one of the channels. Using the absorbed channel, it is possible to obtain a measurement with very limited interference from the bottom, which thus will be accurate also for levels close to the bottom. Using the unabsorbed channel, it is possible to obtain a reference measurement of the distance to the reflecting part of the absorber, thus enabling verification of the of the system.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Slot array antenna
A slot array antenna includes: an electrically conductive member having an electrically conductive surface and slots therein, the slots being arrayed in a first direction which extends along the conductive surface; a waveguide member having an electrically conductive waveguide face which opposes the slots and extends along the first direction; and an artificial magnetic conductor extending on both sides of the waveguide member. At least one of the conductive member and the waveguide member includes dents on the conductive surface and / or the waveguide face, the dents each serving to broaden a spacing between the conductive surface and the waveguide face relative to any adjacent site. The dents include a first, second, and third dents which are adjacent to one another and consecutively follow along the first direction. A distance between centers of the first and second dents is different from a distance between centers of the second and third dents.
Owner:NIDEC CORP +1
Dielectric loaded antenna apparatus with inclined radiation surface and array antenna apparatus including the dielectric loaded antenna apparatus
ActiveUS7088290B2Not be restrictWide coverageWaveguide mouthsSimultaneous aerial operationsDielectricEllipse
A dielectric loaded antenna apparatus has a column-shaped loaded dielectric which is loaded on an end portion of a feeding line of the dielectric loaded antenna apparatus. The loaded dielectric has an inclined radiation surface which is inclined from a surface perpendicular to an axial direction of the loaded dielectric. A cross section of the loaded dielectric perpendicular to the axial direction of the loaded dielectric has a shape of one of a circle, ellipse and polygon. The feeding line is a waveguide which includes a radiation waveguide and a feeding waveguide. The radiation waveguide has an axis parallel to the axial direction of the loaded dielectric and includes an opening for feeding an electromagnetic wave to the loaded dielectric. The feeding waveguide feeds the electromagnetic wave to the radiation waveguide.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Broadband circularly-polarized panel array antenna
ActiveCN104953256ANo increase in heightLow profileWaveguide mouthsAntenna arraysCircularly polarized antennaCoupling
The invention belongs to the technical field of design and manufacture of millimeter-wave circularly-polarized antennas, aims to solve the problem of difficulty in integration of broadband, high efficiency and arraying of existing millimeter-wave circularly-polarized antennas, and provides a broadband circularly-polarized panel array antenna. The broadband circularly-polarized panel array antenna has the advantages that a novel 90-degree phase delay line is used for feed of a cross recess, four parasitic patches added above the cross recess are used for improving antenna unit gain and 3dB axial ratio bandwidth, and the designed 90-degree phase delay line has three independent branches which are used for phase delay, amplitude compensation and matching adjustment respectively; a group of short-circuit metal holes are designed beside a strip line to effectively inhibit spreading of a TEM (transverse electromagnetic) mode outside a feed network area, unit cross coupling is reduced greatly, and arraying performance is guaranteed; the antenna made of a multilayer PCB (printed circuit board) has the advantage of low cost and is applicable to millimeter-wave large-scale circularly-polarized arraying, and the problem of difficulty in integration of circularly-polarized antenna efficiency and the axial ratio bandwidth on millimeter-wave frequency bands is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Antenna element-waveguide converter and radio communication device using the same
InactiveUS20110234466A1Improve reliabilityWithout complicating manufacturing processWaveguide hornsWaveguide mouthsEngineeringAntenna substrate
An antenna element-waveguide converter includes an antenna substrate having, on one surface, an antenna element and rectangular metal plates arranged in a plurality of rows to surround this antenna element, and a waveguide having, at one end, an opening opposed to the one surface of the antenna substrate. Surfaces of the rectangular metal plates and the opening of the waveguide are arranged with a predetermined gap left therebetween in a direction perpendicular to the one surface of the antenna substrate. Thus arranging the antenna substrate and the waveguide avoids a stress due to assembly variations, which can achieve favorable antenna characteristics.
Owner:SHARP KK
Radar level gauging system
InactiveUS7532155B2Accurate level measurementAvoid reflectionsWaveguide mouthsMachines/enginesRadarAbsorbed energy
A radar level gauging system comprising a microwave unit for transmitting and receiving first microwaves having a first and second distinguishable characteristics, a microwave absorber adapted to be arranged in a bottom region of the tank and adapted to absorb electromagnetic energy of microwaves having one of the first and second characteristics, and processing circuitry adapted to determine the product level based on a relationship between transmitted and received microwaves.The system thus emits microwaves in two channels, and the absorber is arranged to absorb energy in only one of the channels. Using the absorbed channel, it is possible to obtain a measurement with very limited interference from the bottom, which thus will be accurate also for levels close to the bottom. Using the unabsorbed channel, it is possible to obtain a reference measurement of the distance to the reflecting part of the absorber, thus enabling verification of the of the system.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Technique for changing a range gate and radar coverage
InactiveUS6977609B2Increase probabilityImprove accuracyMultiple-port networksVehicle fittingsRadar detectionRange gate
A radar detection process includes computing a derivative of an FFT output signal to detect an object within a specified detection zone. In one embodiment, a zero crossing in the second derivative of the FFT output signal indicates the presence of an object. The range of the object is determined as a function of the frequency at which the zero crossing occurs. Also described is a detection table containing indicators of the presence or absence of an object within a respective radar beam and processing cycle. At least two such indicators are combined in order to detect the presence of an object within the detection zone and with changing range gates in each of the antenna beams the coverage of the detection zone can be varied.
Owner:VALEO RADAR SYST
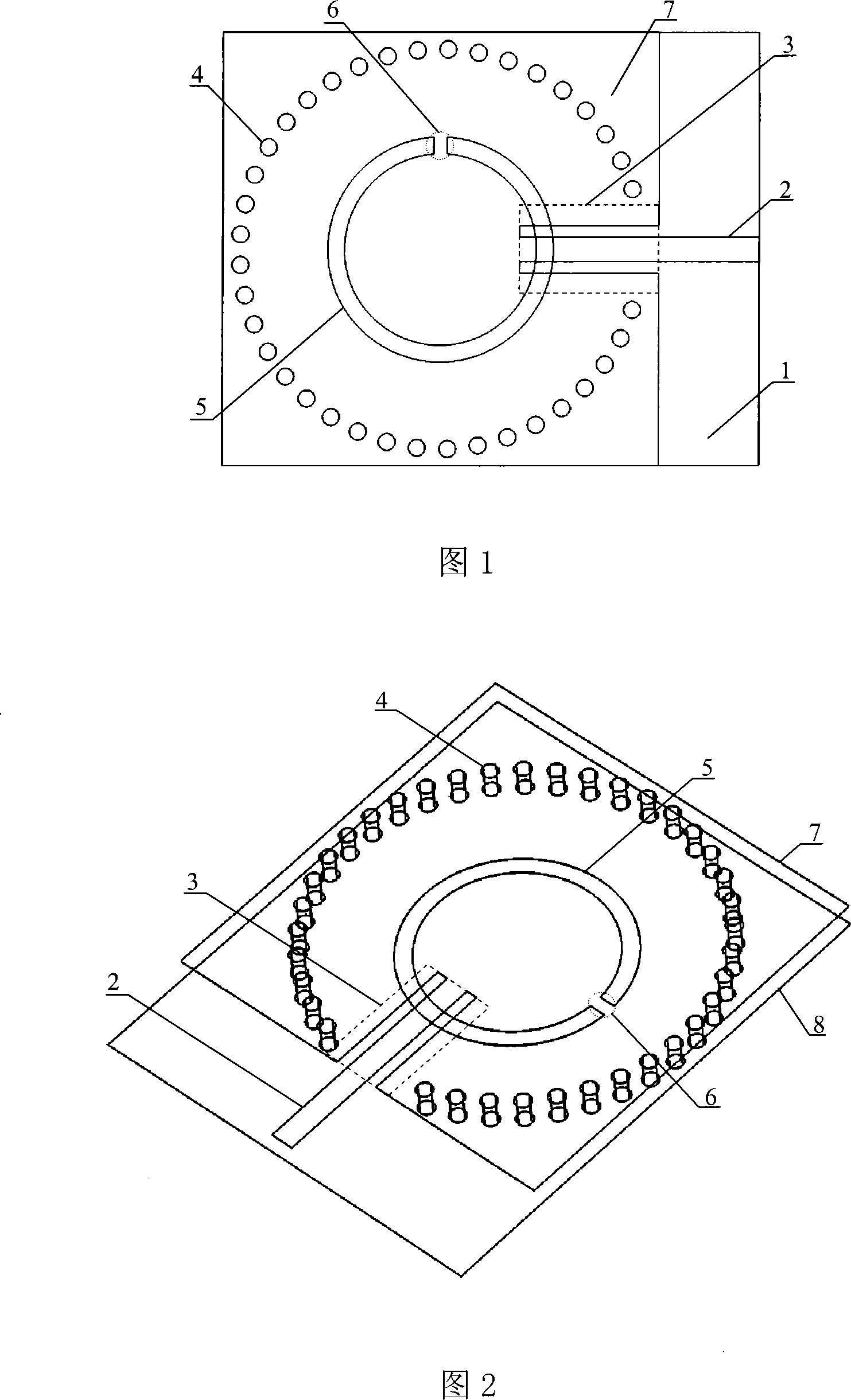
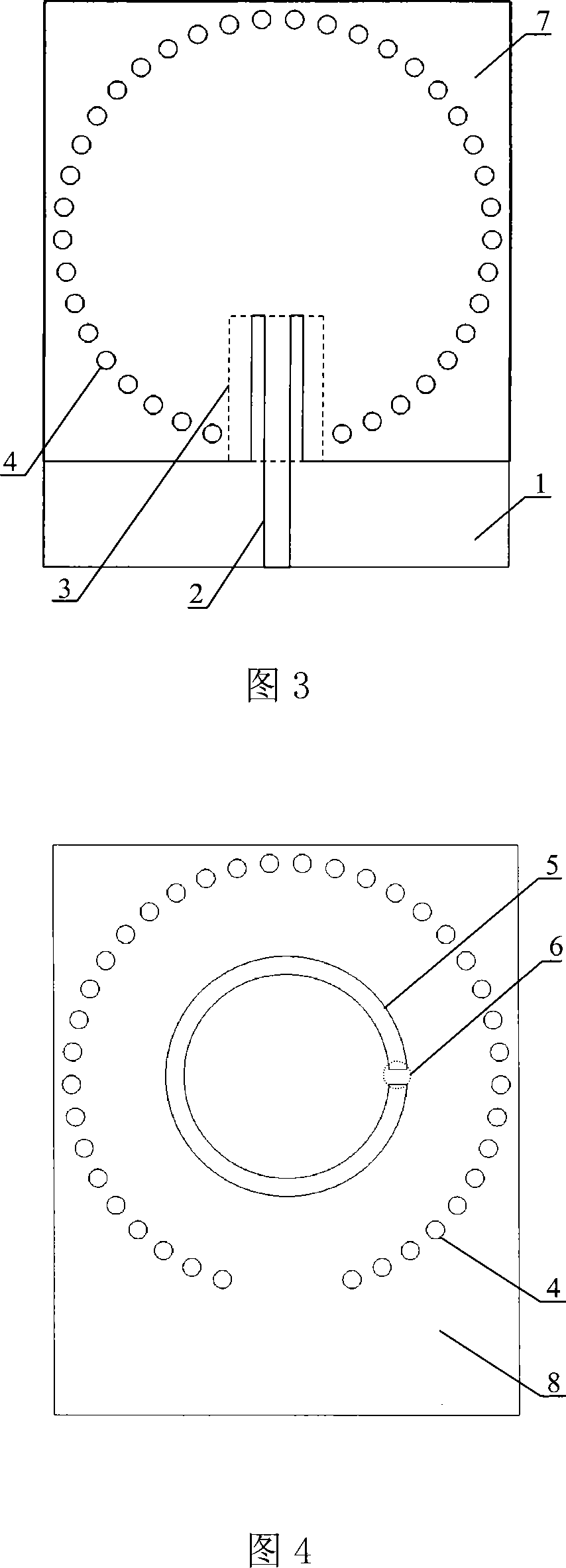
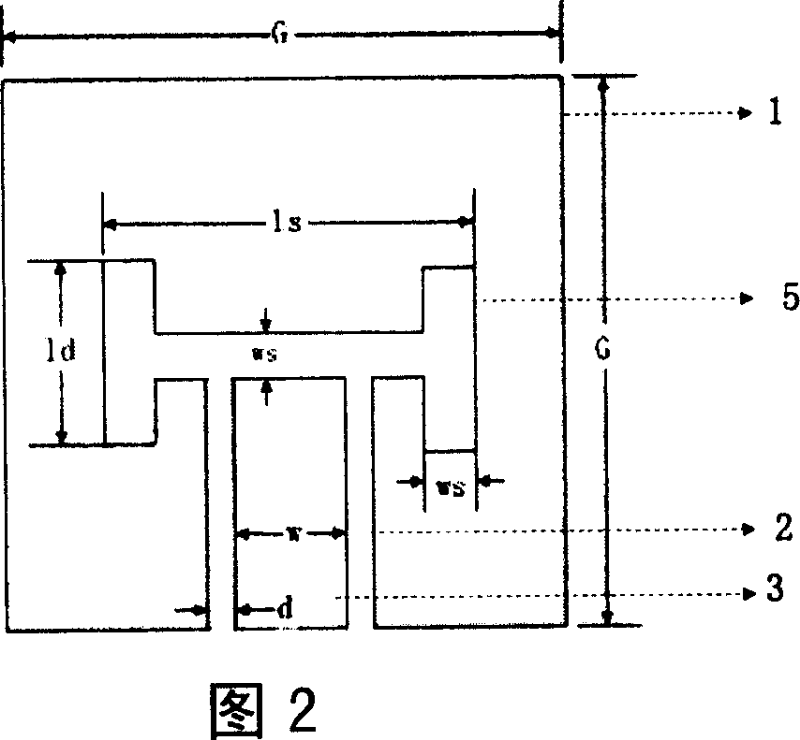
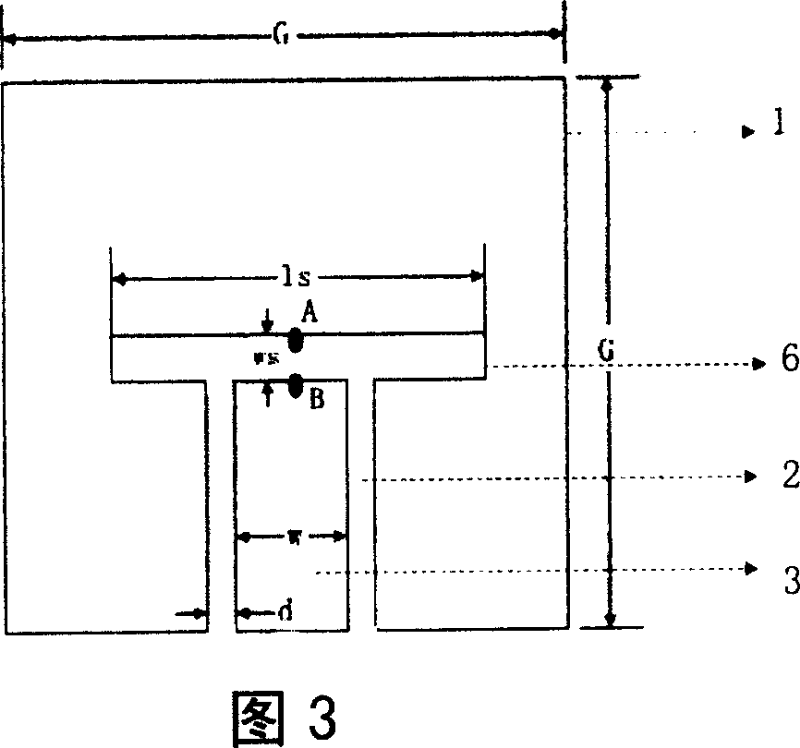
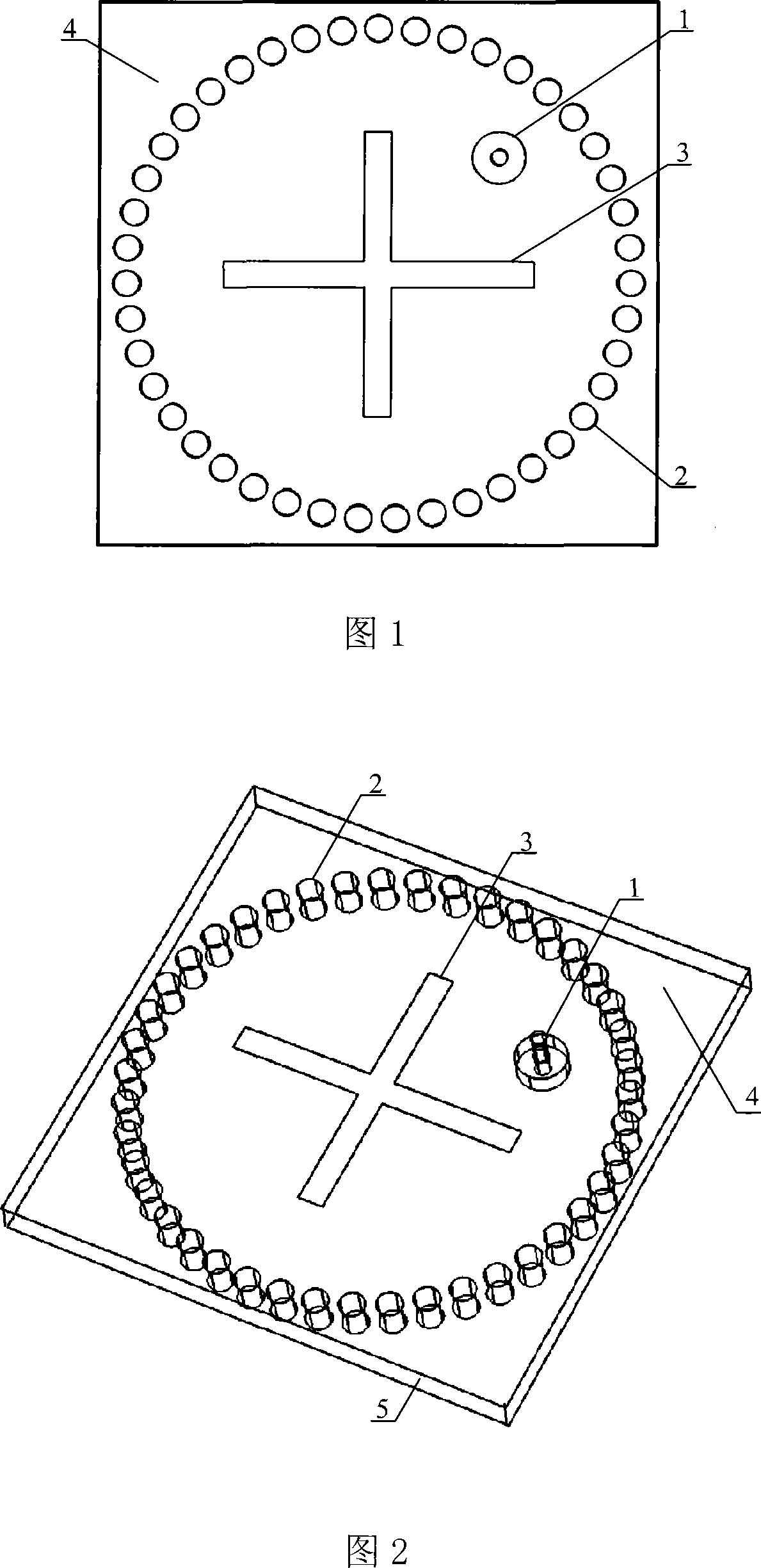
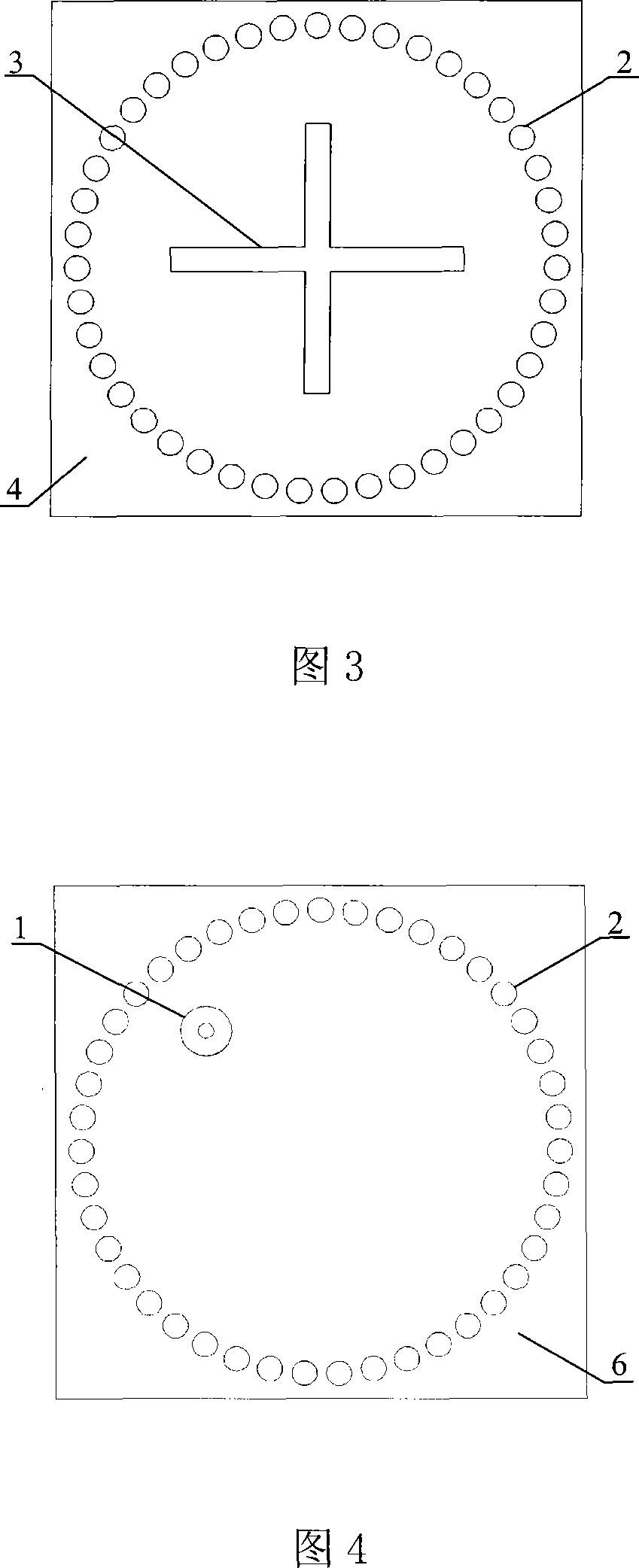
Low profile rear cavity ring gap one-point short circuit round polarization antenna
InactiveCN101170213AReduce volumeReduce manufacturing costWaveguide mouthsRadiating elements structural formsCircularly polarized antennaDielectric substrate
The invention relates to a one-point short-circuit circularly polarized antenna with a low-profile cavity-backed annular slot. The existing cavity-backed circularly polarized antenna based on one-point short-circuit of the annular slot has complex structure, large volume, inability to planar integration, and high cost. In the present invention, a metal layer is plated on both sides of the dielectric substrate, and the upper metal layer is etched with a microstrip line for power feeding and a common ground coplanar waveguide transmission line, and the middle metal strip of the coplanar waveguide transmission line extends outwards as a microstrip line . Through the upper metal layer, the dielectric substrate and the lower metal layer, a plurality of metallized through holes arranged in a circle are opened to form a cavity, and the coplanar waveguide transmission line extends into the cavity. The lower metal layer is etched with a circular radiation slit with a short circuit in the area corresponding to the cavity. Compared with the conventional cavity-backed circularly polarized antenna composed of a metal cavity, the present invention is manufactured by common PCB technology, has low manufacturing cost, can be seamlessly integrated with a microstrip circuit, and improves system integration.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Dielectric waveguide antenna
ActiveUS8692731B2Reduce reflectionWaveguide mouthsRadiating elements structural formsImpedance matchingDielectric waveguides
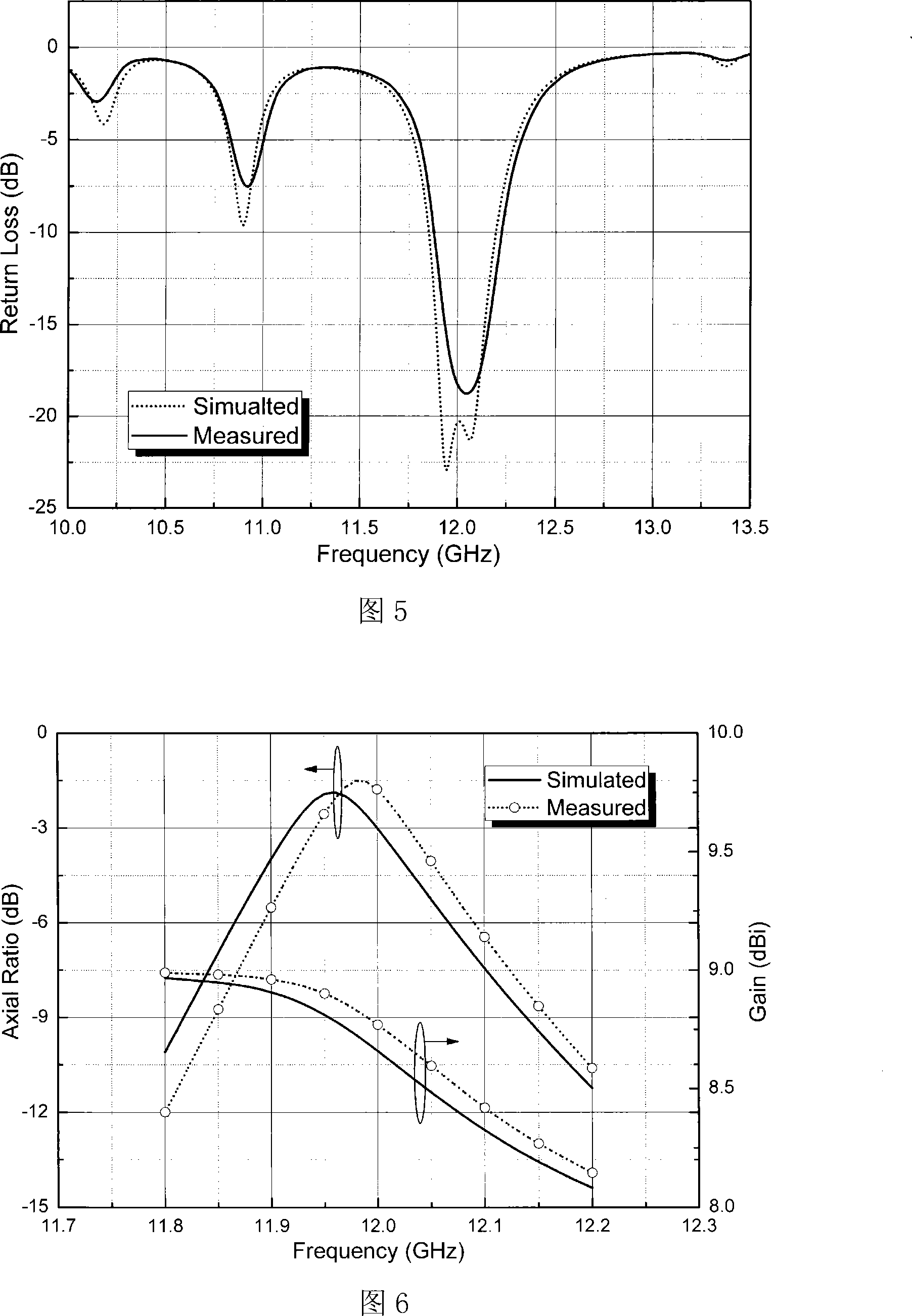
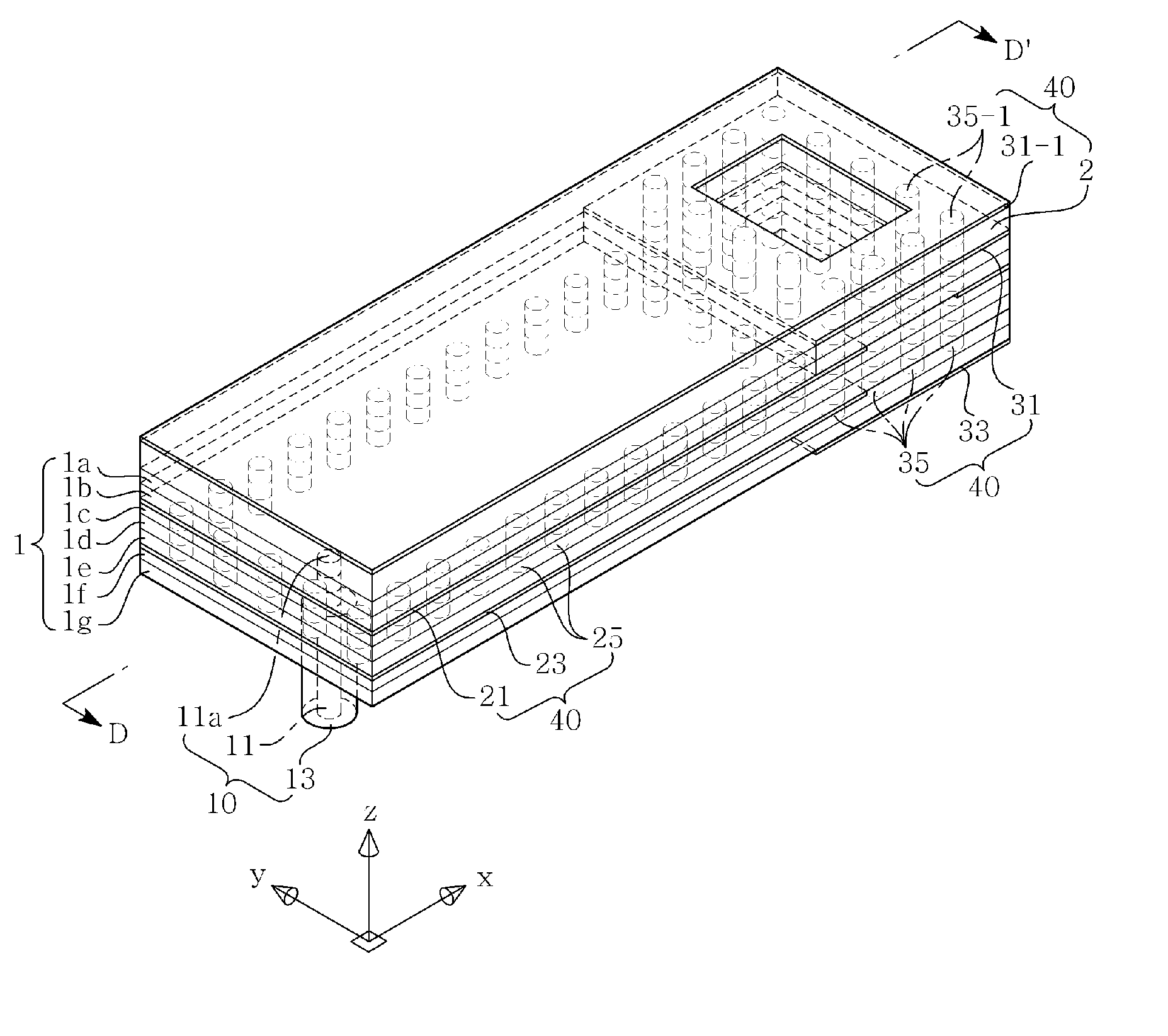
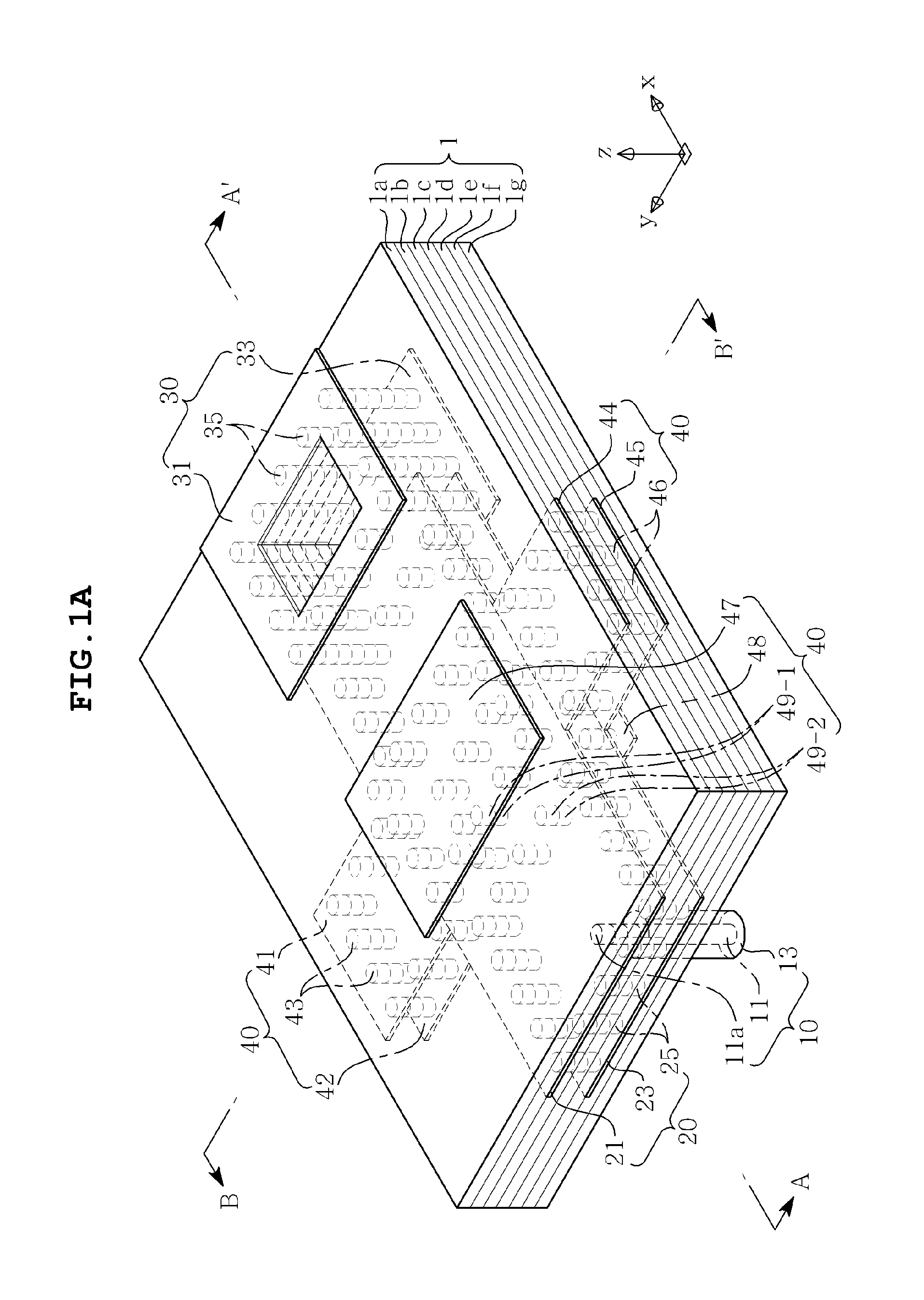
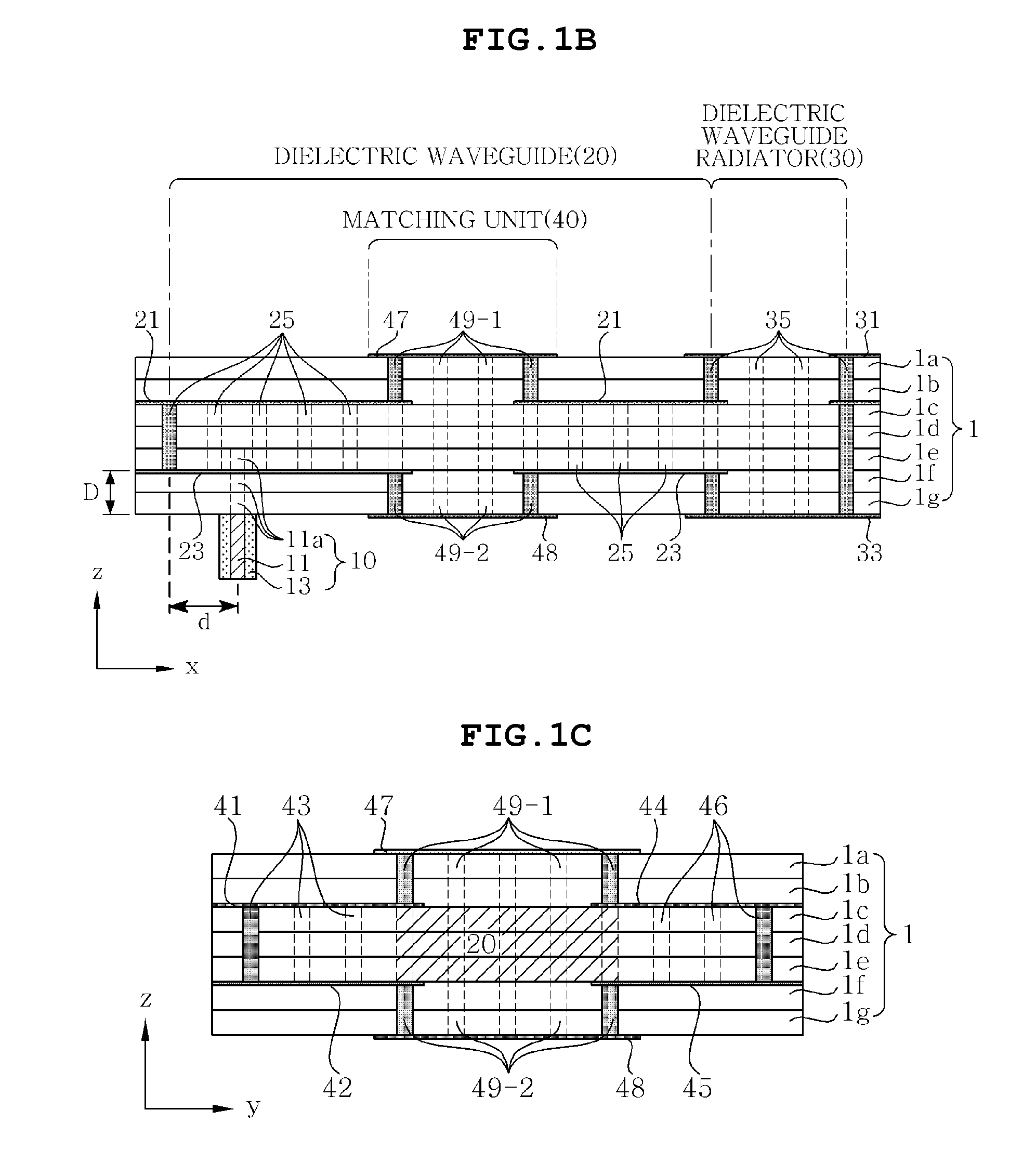
Disclosed herein is a dielectric waveguide antenna including: a dielectric waveguide transmitting a signal applied from a power feeder; a dielectric waveguide radiator radiating the signal transmitted from the dielectric waveguide to the air through a first aperture; and a matching unit formed in a portion of the dielectric waveguide and controlling a serial reactance and a parallel reactance to thereby perform impedance matching between the dielectric waveguide radiator and the air, in order to reduce reflection generated in the first aperture during the radiation of the signal through the first aperture. Reflection in the aperture is reduced through the matching unit having various structures, thereby making it possible to improve characteristics of the dielectric waveguide antenna.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
Millimeter-wave fan beam cylindrical Luneberg lens antenna based on metal perturbation structure
ActiveCN107275788AEasy to processAchieve wideningWaveguide mouthsIndividually energised antenna arraysMicrowave substrateWide beam
The invention discloses a millimeter-wave fan beam cylindrical Luneberg lens antenna based on a metal perturbation structure. The antenna achieves a pitch beam width reaching 104 degree and azimuth plane + / - 60 degree scanning. The antenna comprises a cylindrical Luneberg lens located between an upper metal flat plate (1) and a lower metal flat plate (2); an arc feed source array (3) located on the focal line of the cylindrical Luneberg lens; and the metal perturbation structure (5) arranged on the radiating aperture of the lens circumferentially. The cylindrical Luneberg lens comprises a cylindrical filling dielectric sheet (4). The filling dielectric sheet uses a low-loss microwave substrate as a substrate material and is divided into five layers according to a concentric circle structure from inside to outside. Respective layers have through-holes with different densities. The through-holes are filled with air. The antenna is light in weight and easy to process, greatly increases the pitch surface beam width, realizes a wide beam scanning range in the horizontal plane so as to be better applied to a multi-beam directional communication and beam scanning antenna, especially the millimeter wave high-frequency band and applications requiring axial grouping.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Variable frequency coupling feeder apparatus for wide-band microstrip aerial
InactiveCN101038983AImprove polarization characteristicsHigh bandwidthWaveguide mouthsRadiating elements structural formsFrequency conversionCoplanar waveguide
The invention relates to a frequency variable coupling feeding device used in boardband microstrip antenna which includes coplanar waveguide and coupling slit thereon, and a varicap device whose two pins are fixed to two sides of the center of the coupling slit of the coplanar waveguide. Feeding manner is changed by regulating the varicap device, and the provided device can switch frequency resonant points of the antenna in a very wide band thereby realizing frequency conversion when feeding for the antenna; in the state of fixed antenna dimension and fixed shape of the coupling slit, the invention can improve the antenna performance such as better bandwidth and plus only by regulating the varicap device. The invention provided device is fit for the broadband or multi-frequency wireless communication field.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
One point coaxial feed low profile back-cavity circularly polarized antenna
InactiveCN101179149AReduce volumeLow profileWaveguide mouthsRadiating elements structural formsCoaxial probeCircularly polarized antenna
Owner:舟山乐讯智能科技有限公司
Popular searches
Discontinuous tuning by electric means Substation equipment Capacitor with voltage varied dielectric Antennas earthing switches association Oscillations generators Amplifier input/output impedence modification Leaky-waveguide antennas Dielectric property measurements Pulse automatic control Generator stabilization
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com