Patents
Literature
354 results about "Focal line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intravascular folded tubular endoprosthesis
InactiveUS20080132996A1Accurately determinePrecise positioningStentsBlood vesselsThree vesselsFocal line
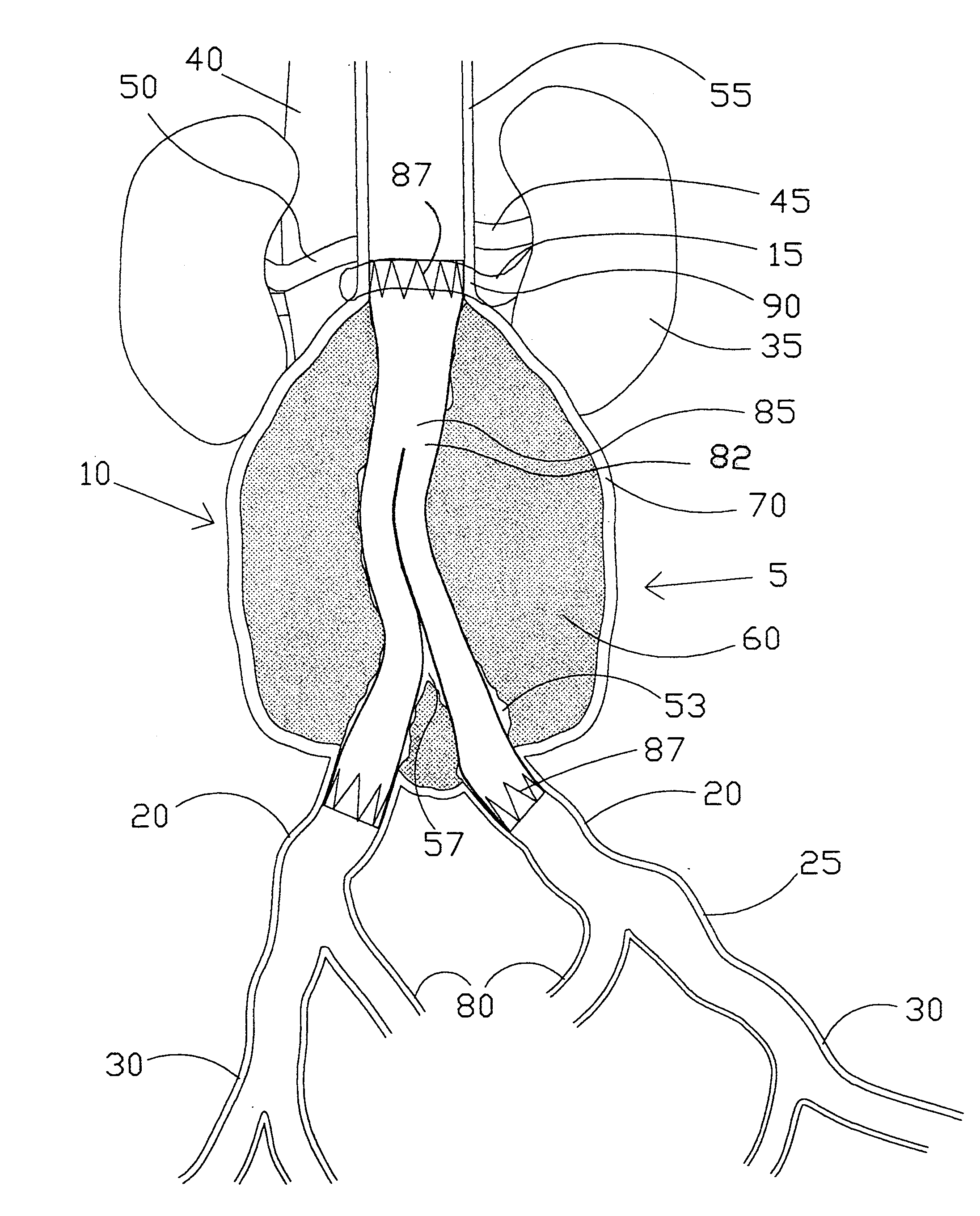
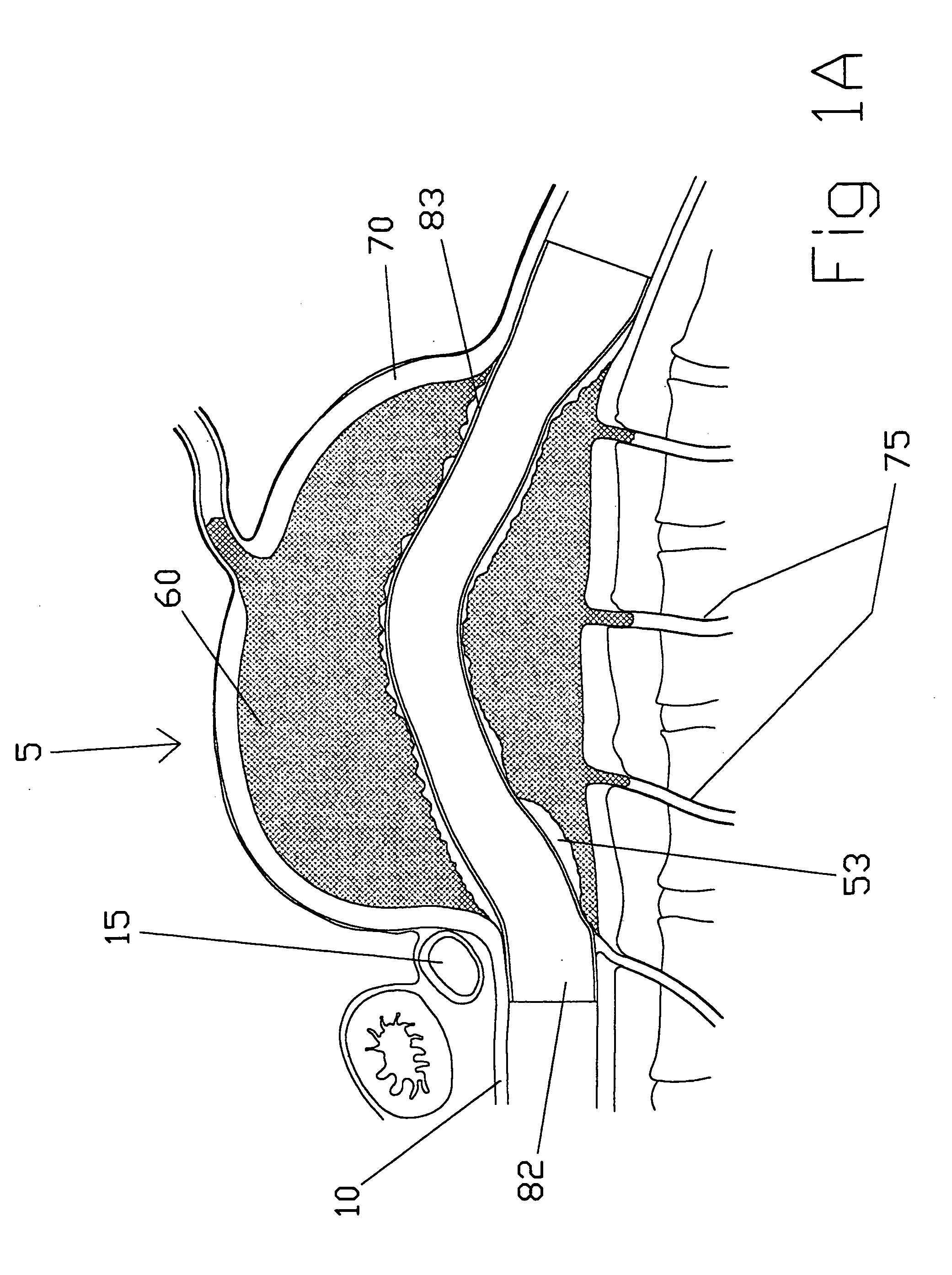
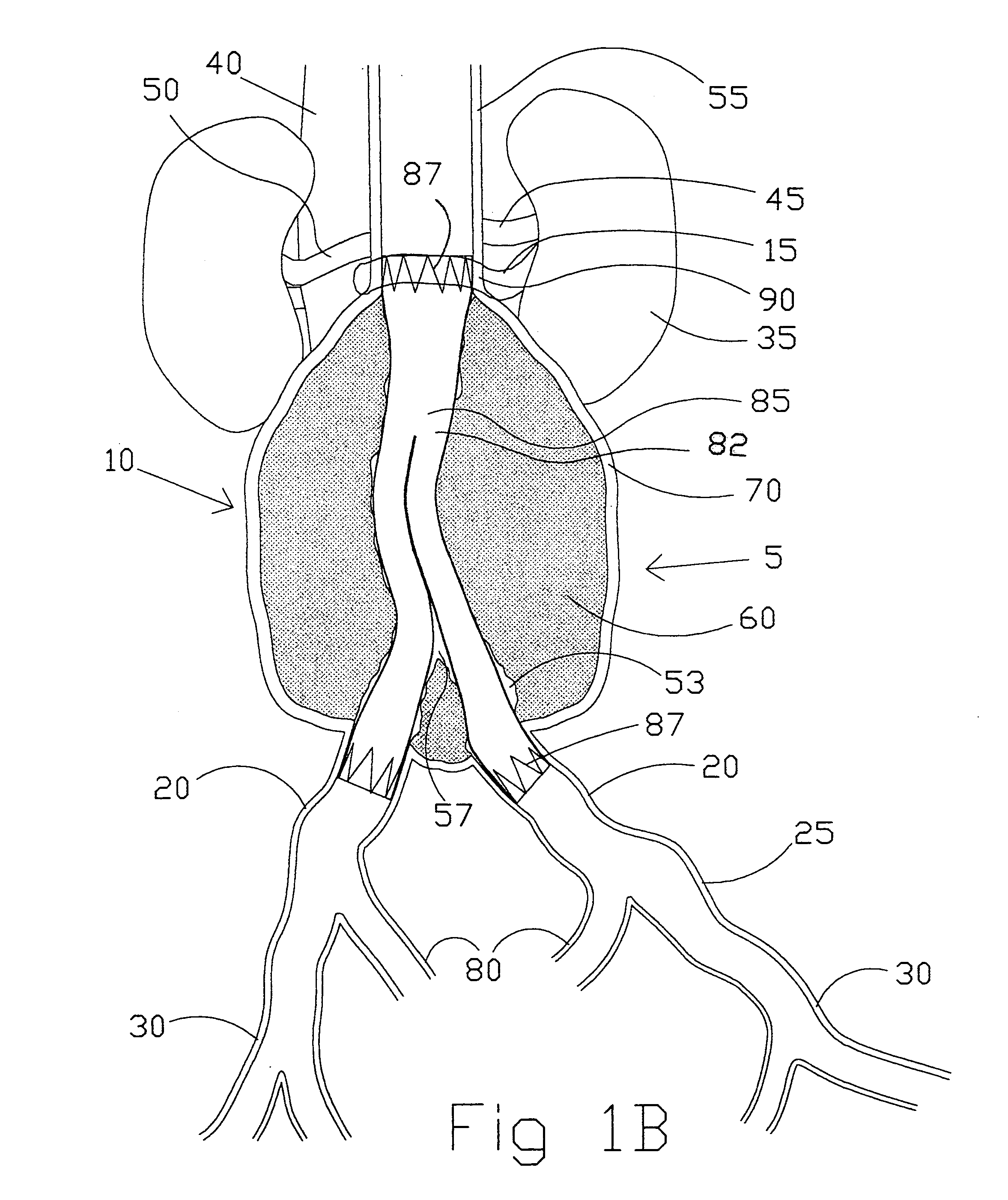
A bifurcated or straight intravascular folded tubular member is deliverable percutaneously or by small cutdown to the site of a vascular lesion. Its inserted state has a smaller nondeployed diameter and a shorter nondeployed length. The intravascular tubular member has a folded tubular section that is unfolded following insertion into the blood vessel. The length of the intravascular folded tubular member is sized in situ to the length of the vessel lesion without error associated with diagnostic estimation of lesion length. The folded tubular member is self-expandable or balloon-expandable to a larger deployed diameter following delivery to the lesion site. An attachment anchor can be positioned at the inlet or outlet ends of the intravascular folded tubular member to prevent leakage between the tubular member and the native vessel lumen and to prevent migration of the tubular member. The attachment anchor has a short axial length to provide a more focal line of attachment to the vessel wall. Such attachment is valuable in attaching to a short aortic neck in the treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysm. The attachment anchor can have barbs which are held in a protected conformation during insertion of the tubular member and are released upon deployment of the attachment anchor. The intravascular tubular member can be formed of woven multifilament polymeric strands with metallic strands interwoven along with them. Double weaving is incorporated to prevent leakage at crossover points.
Owner:DRASLER WILLIAM J +1
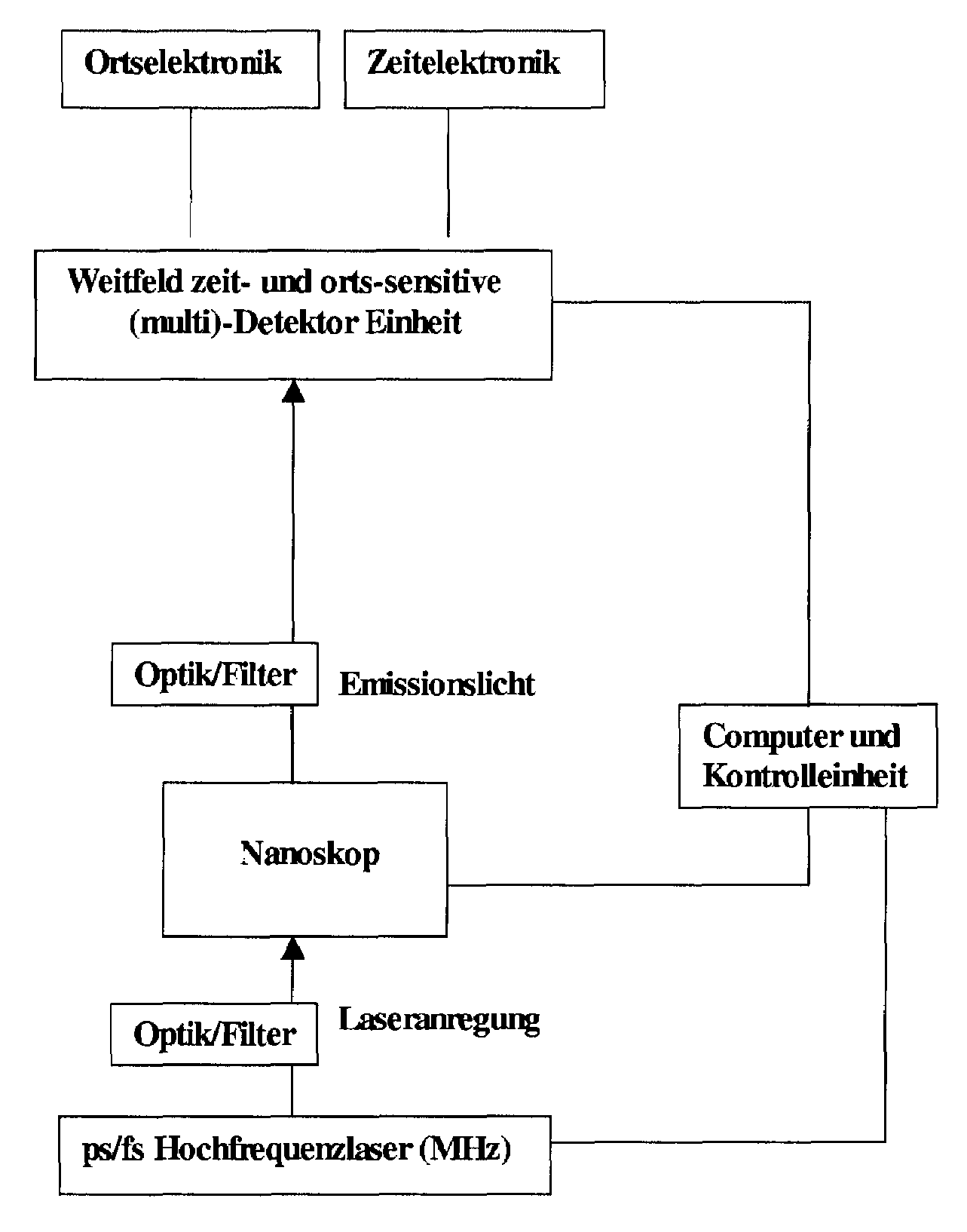
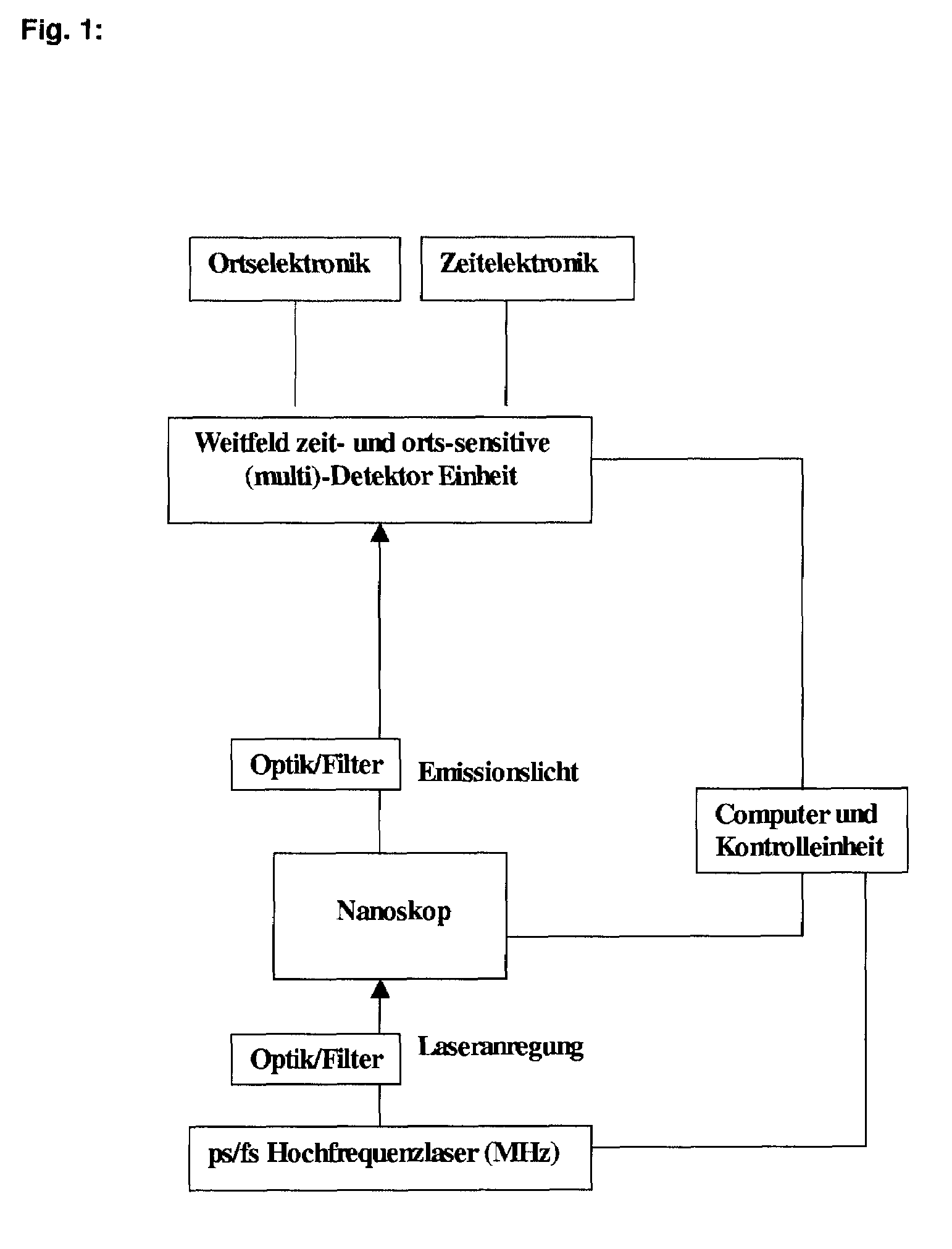
Method and microscope for high spatial resolution examination of samples
InactiveUS20070206278A1Prevent bleachingGood synchronizationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical propertyImage resolution
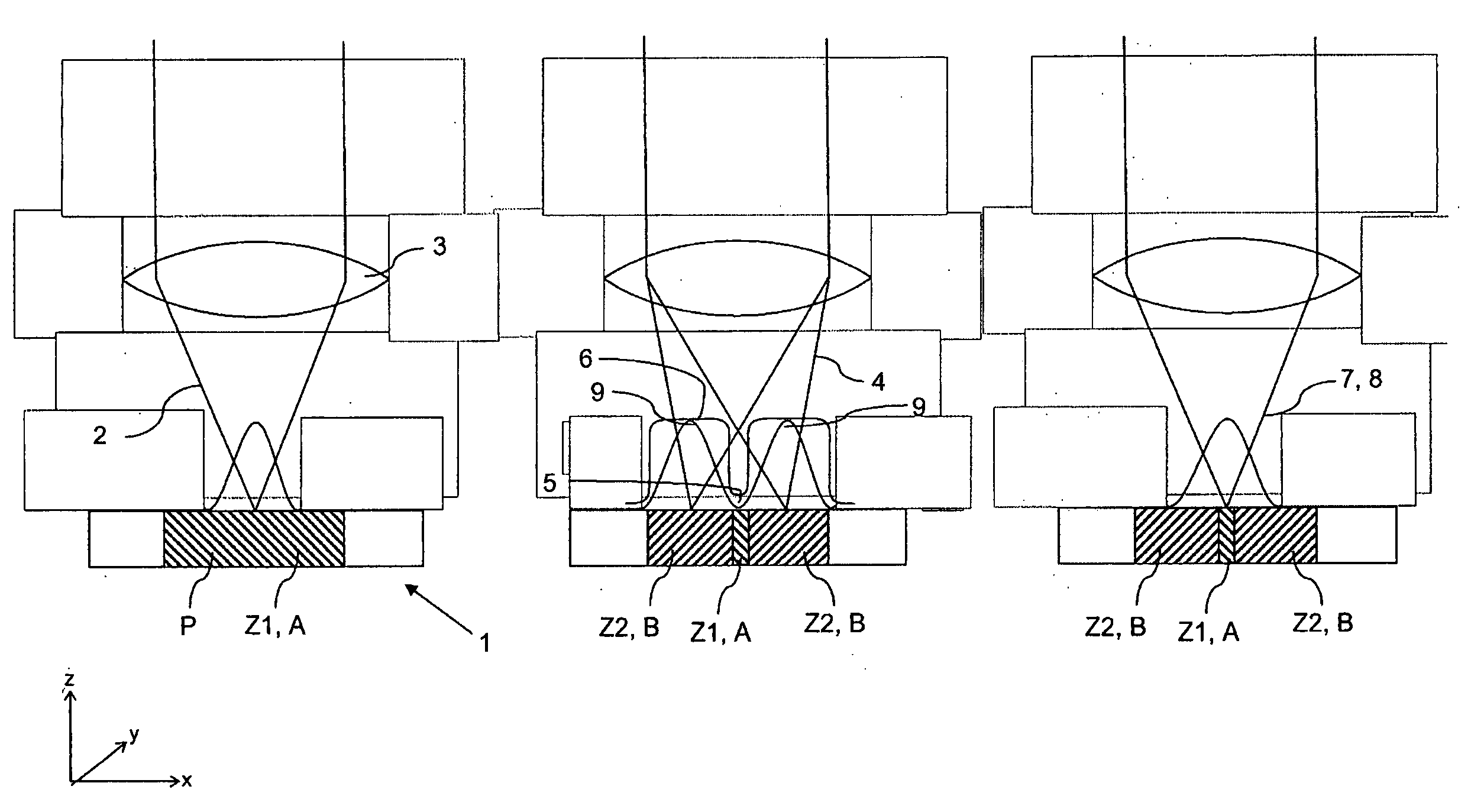
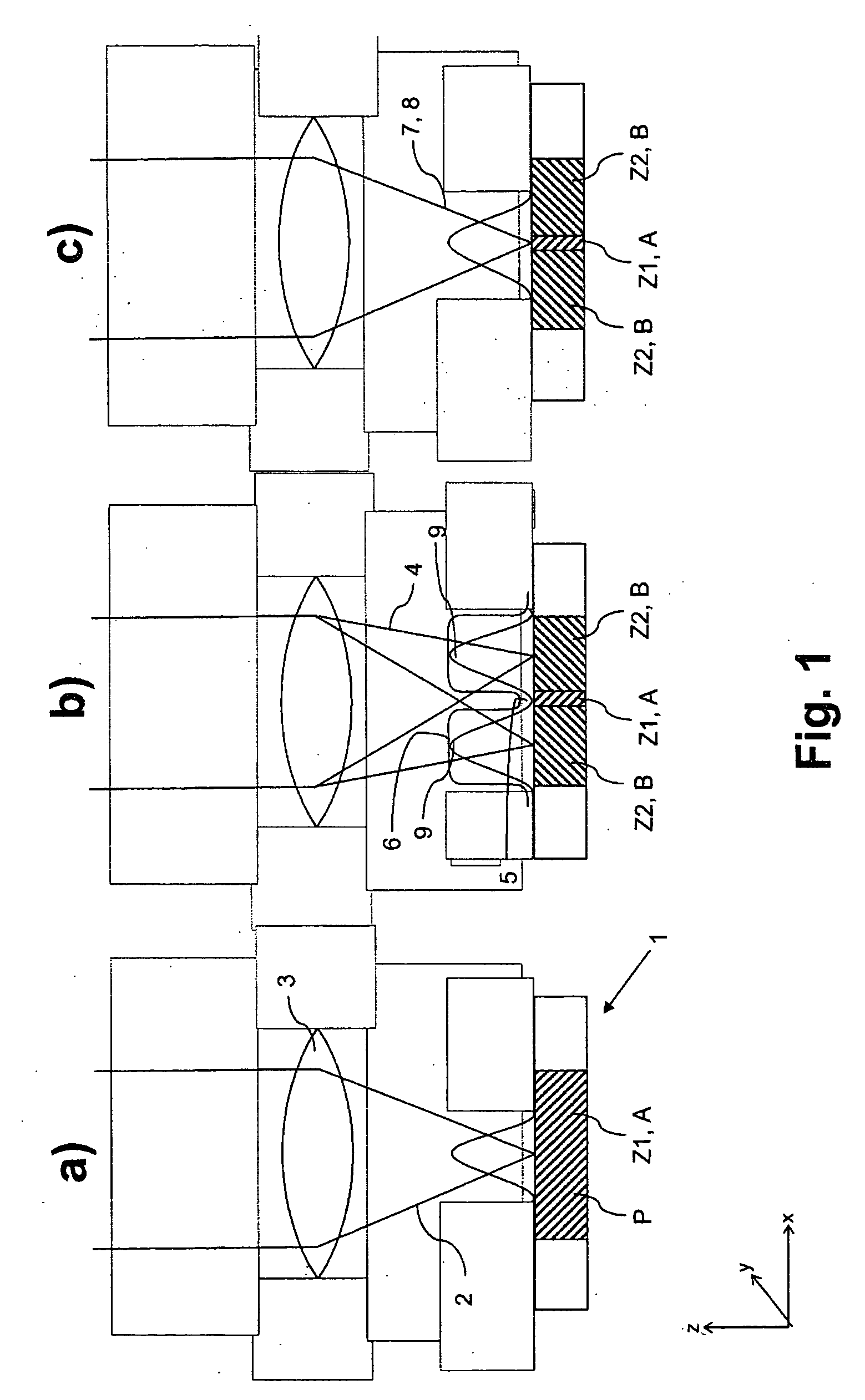
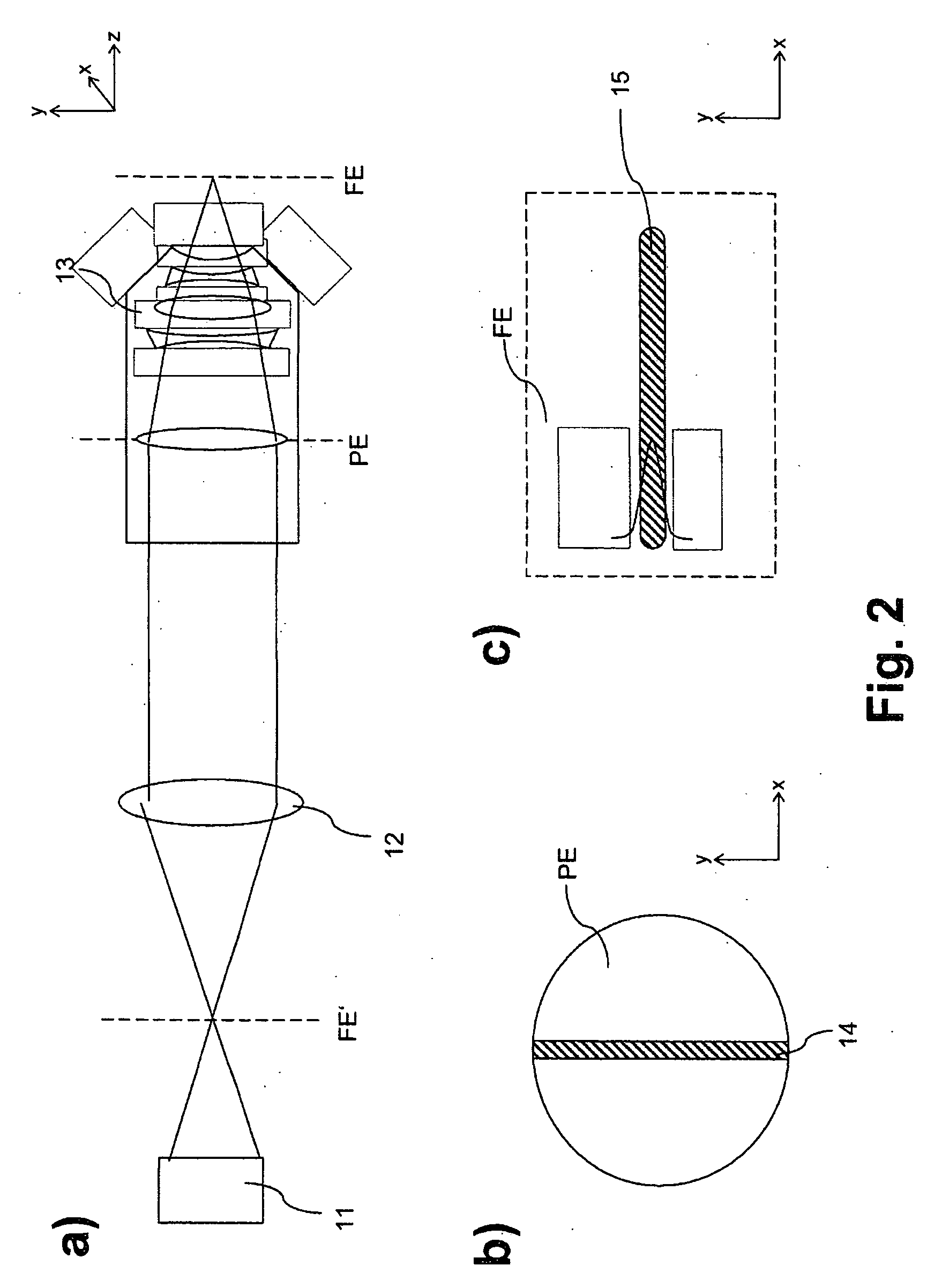
A method and a microscope, in particular a laser scanning fluorescence microscope, for high spatial resolution examination of samples, the sample (1) to be examined comprising a substance that can be repeatedly converted from a first state (Z1, A) into a second state (Z2, A), the first and the second states (Z1, A; Z2, B) differing from one another in at least one optical property, comprising the steps that the substance in a sample region (P) to be recorded is firstly brought into the first state (Z1, A), and that the second state (Z2, B) is induced by means of an optical signal (4), spatially delimited subregions being specifically excluded within the sample region (P) to be recorded, are defined in that the optical signal (4) is provided in the form of a focal line (10) with a cross-sectional profile having at least one intensity zero point (5) with laterally neighboring intensity maxima (9).
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
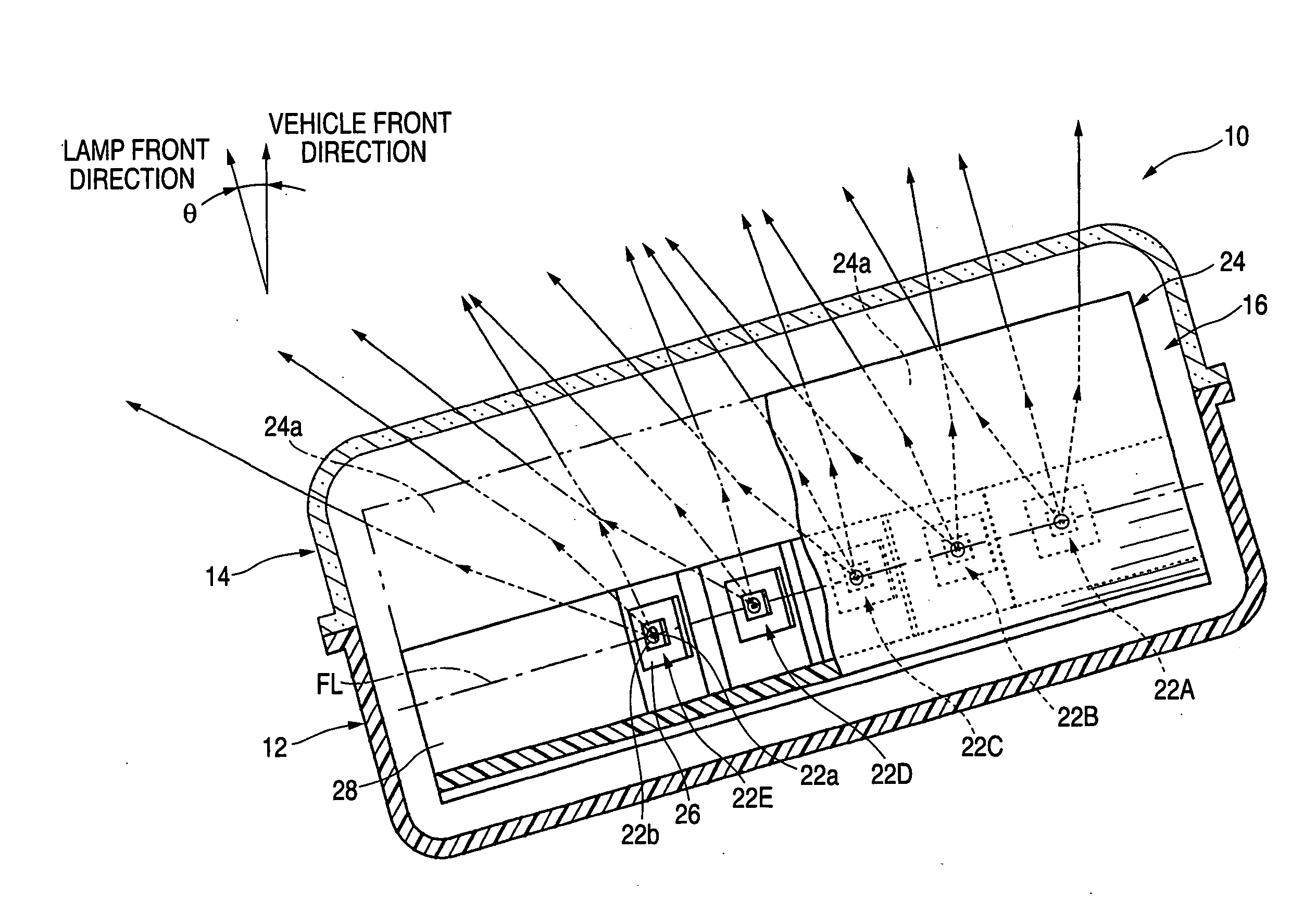
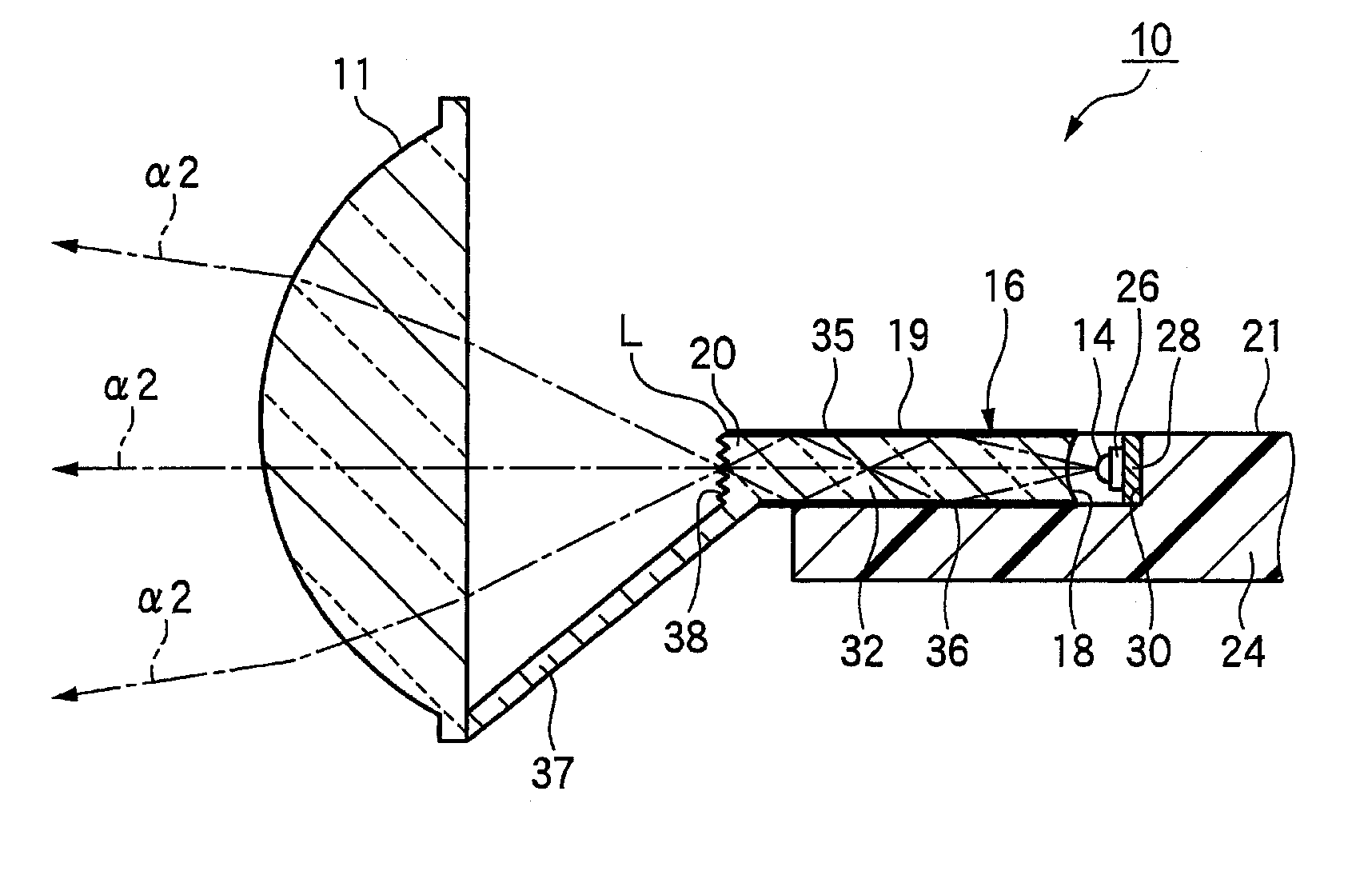
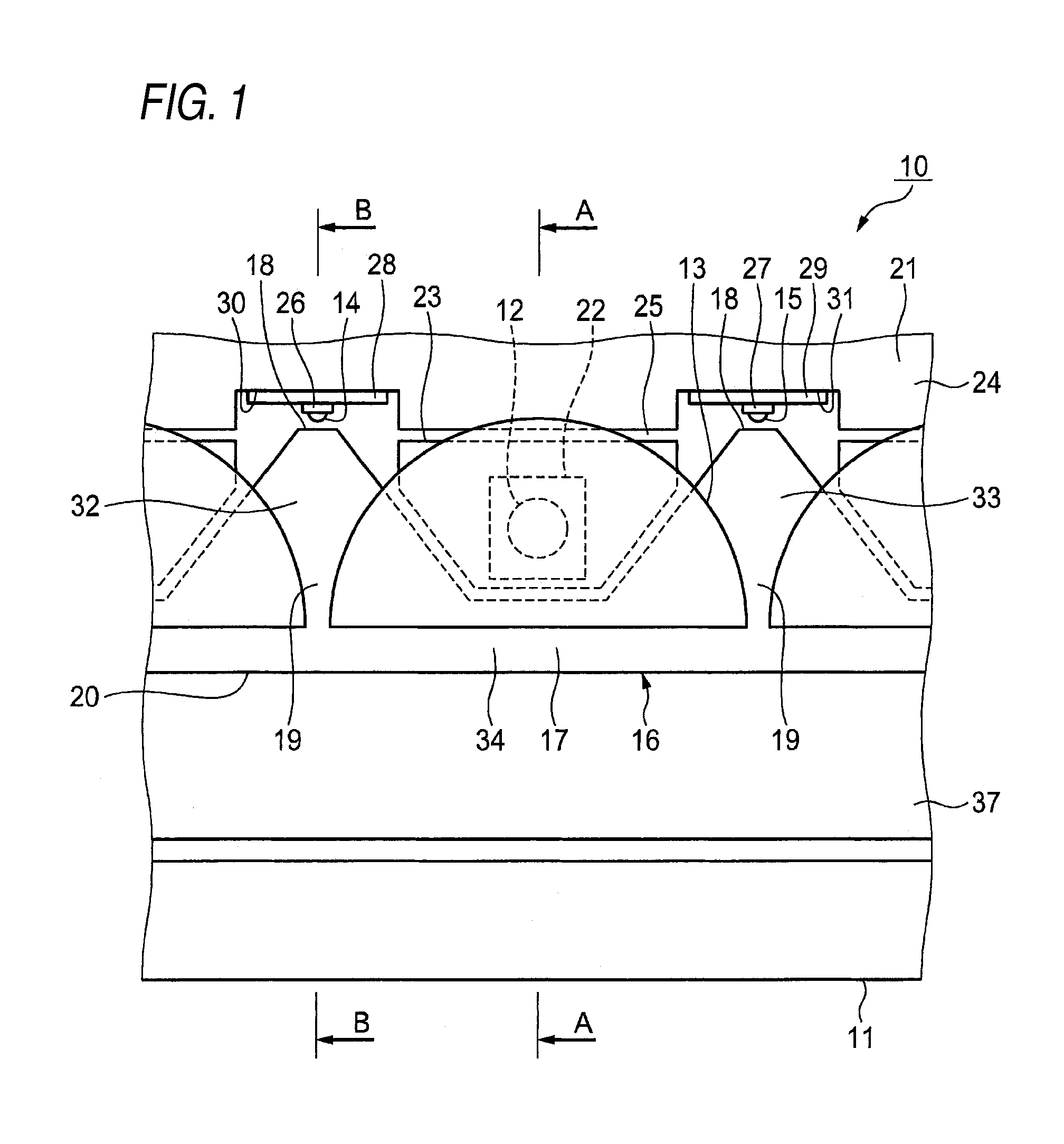
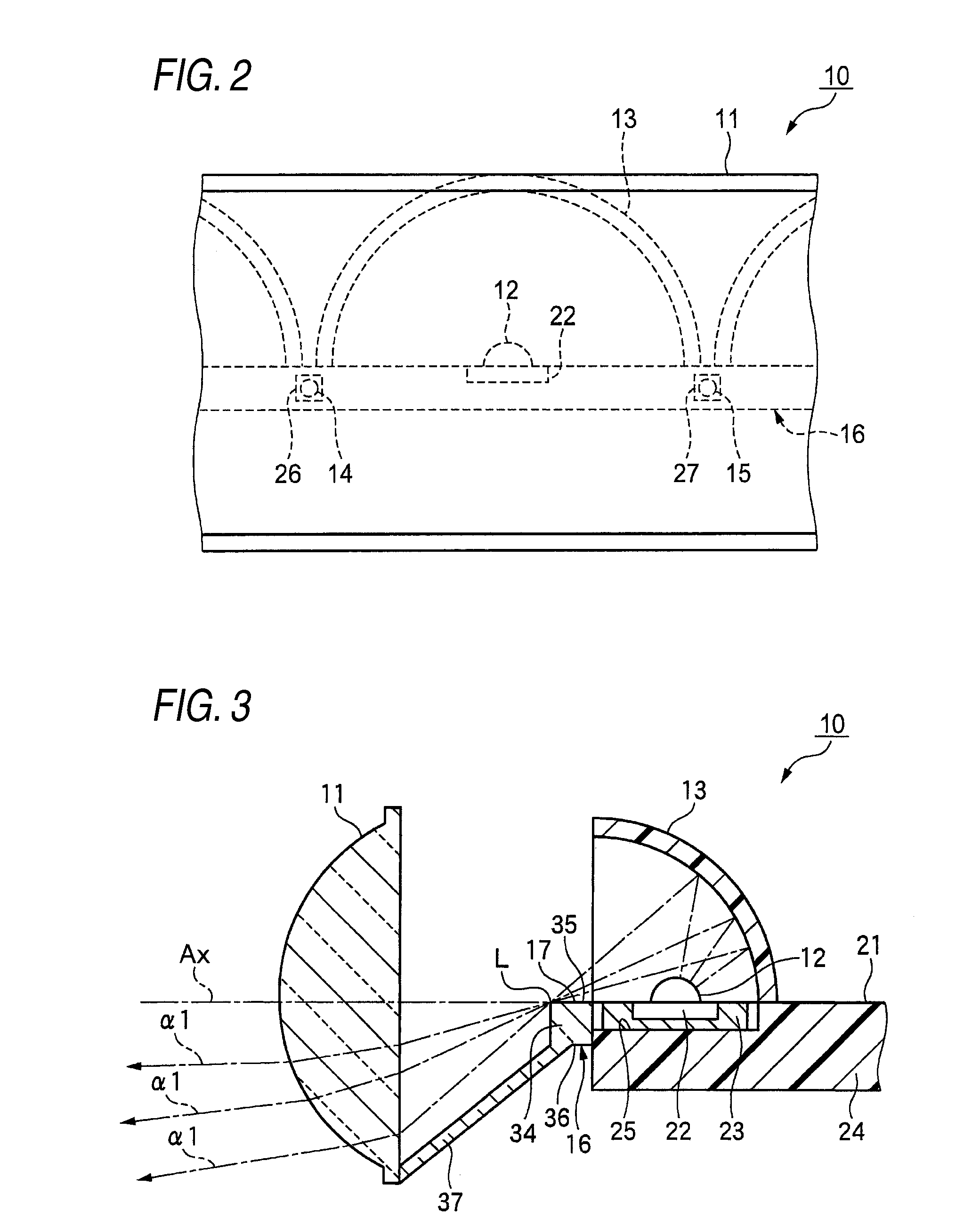
Vehicle lamp unit
InactiveUS20050180158A1Increase profitCompact configurationNon-electric lightingVehicle headlampsEngineeringExit surface
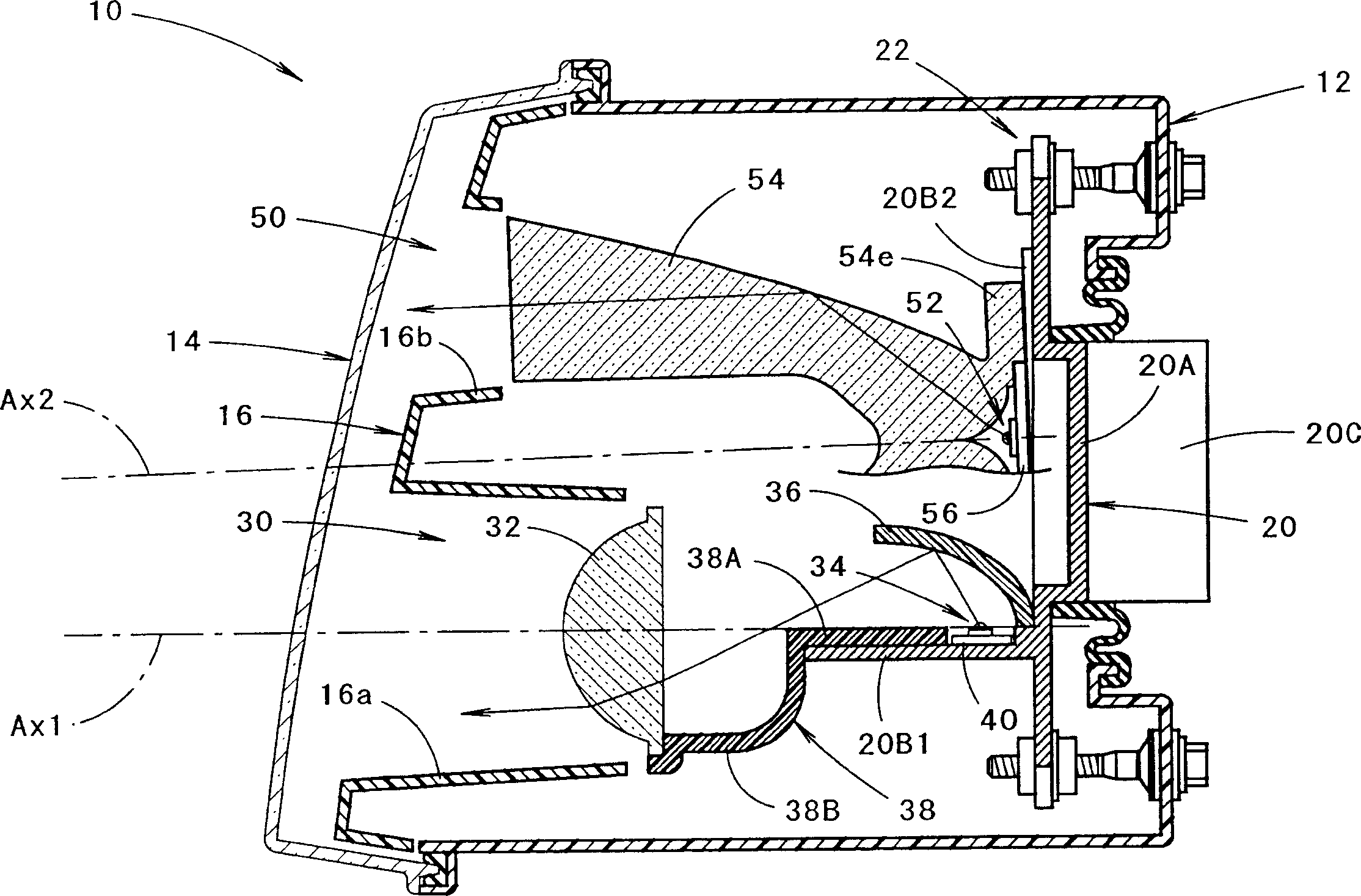
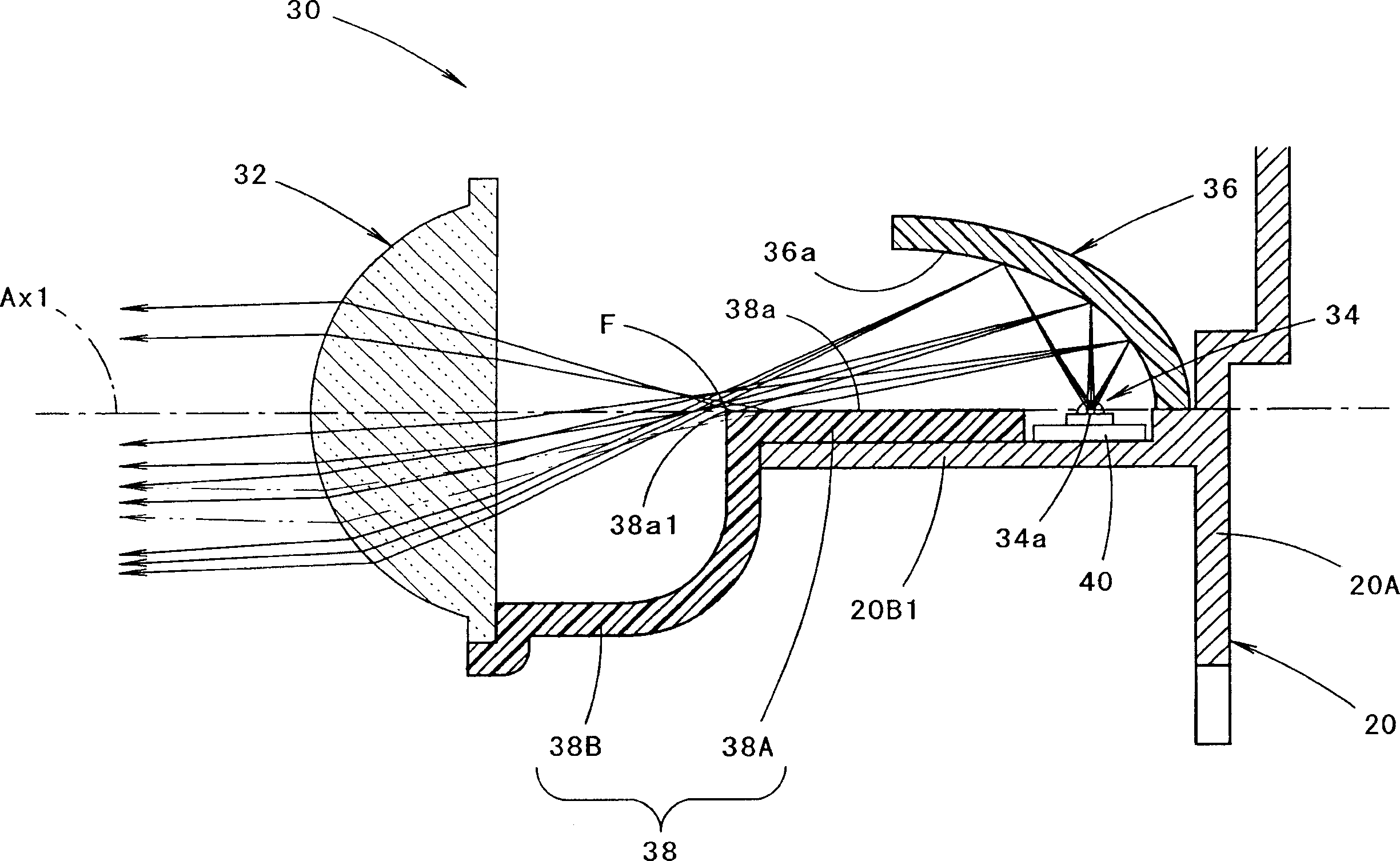
A pair of upper and lower incidence surfaces are formed on a rear face of a translucent member disposed to cover three light-emitting elements. On upper and lower sides of the incidence surfaces are formed a pair of reflection surfaces for causing light emitted by the light-emitting elements and having entered the translucent member to internally reflect forward. Each of the incidence surfaces is formed from a cylindrical convex-curved surface extending horizontally. Each of the reflection surfaces is formed from a parabolic cylindrical curved surface whose focal line passes through a virtual image point of each of the light-emitting elements formed by the corresponding incidence surfaces. By the above configuration, light emitted by the light-emitting elements is caused to internally reflect in such a manner as to diffuse in the horizontal direction, and not to diffuse in the vertical direction, thereby exiting forward from a pair of exit surfaces.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
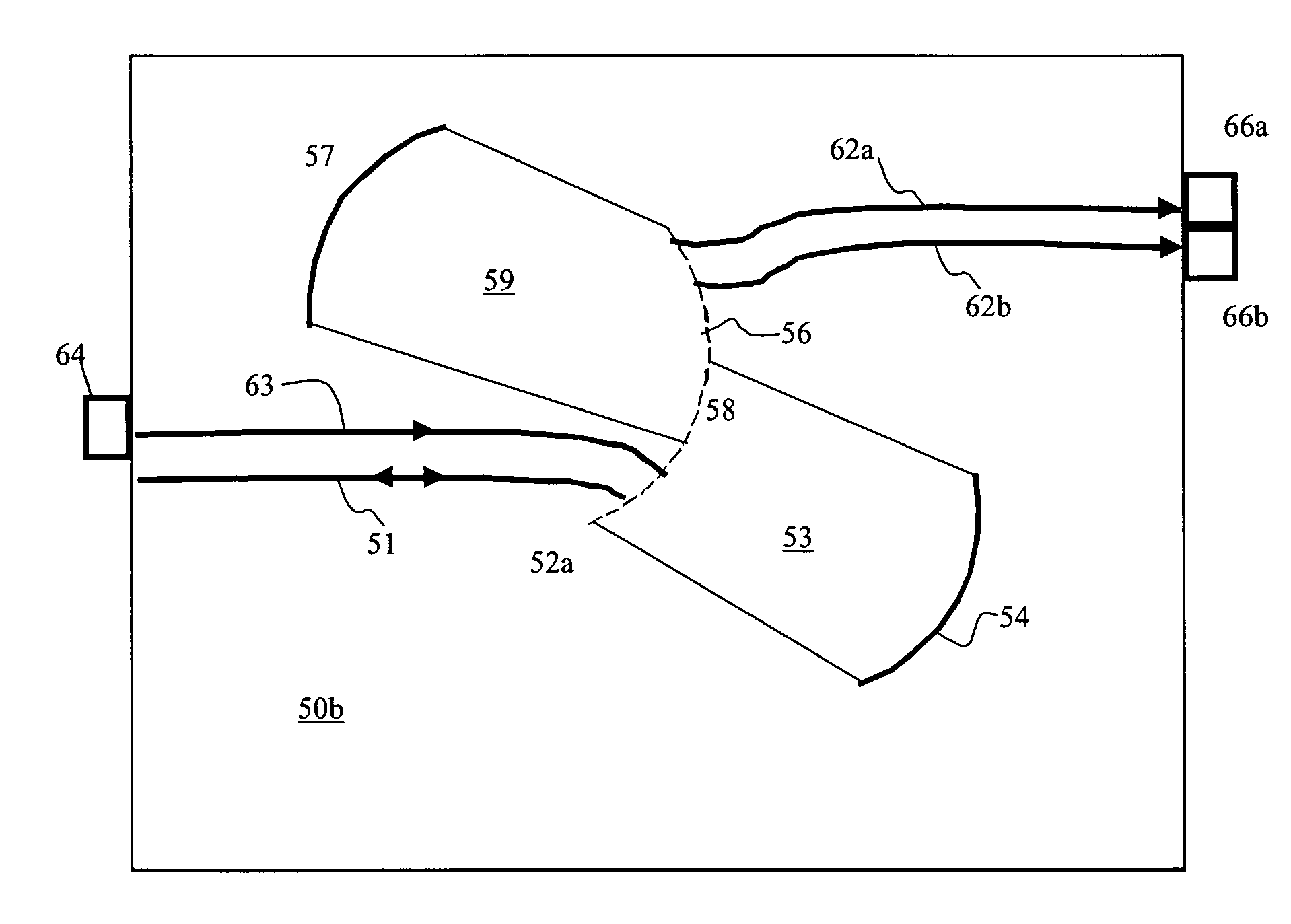
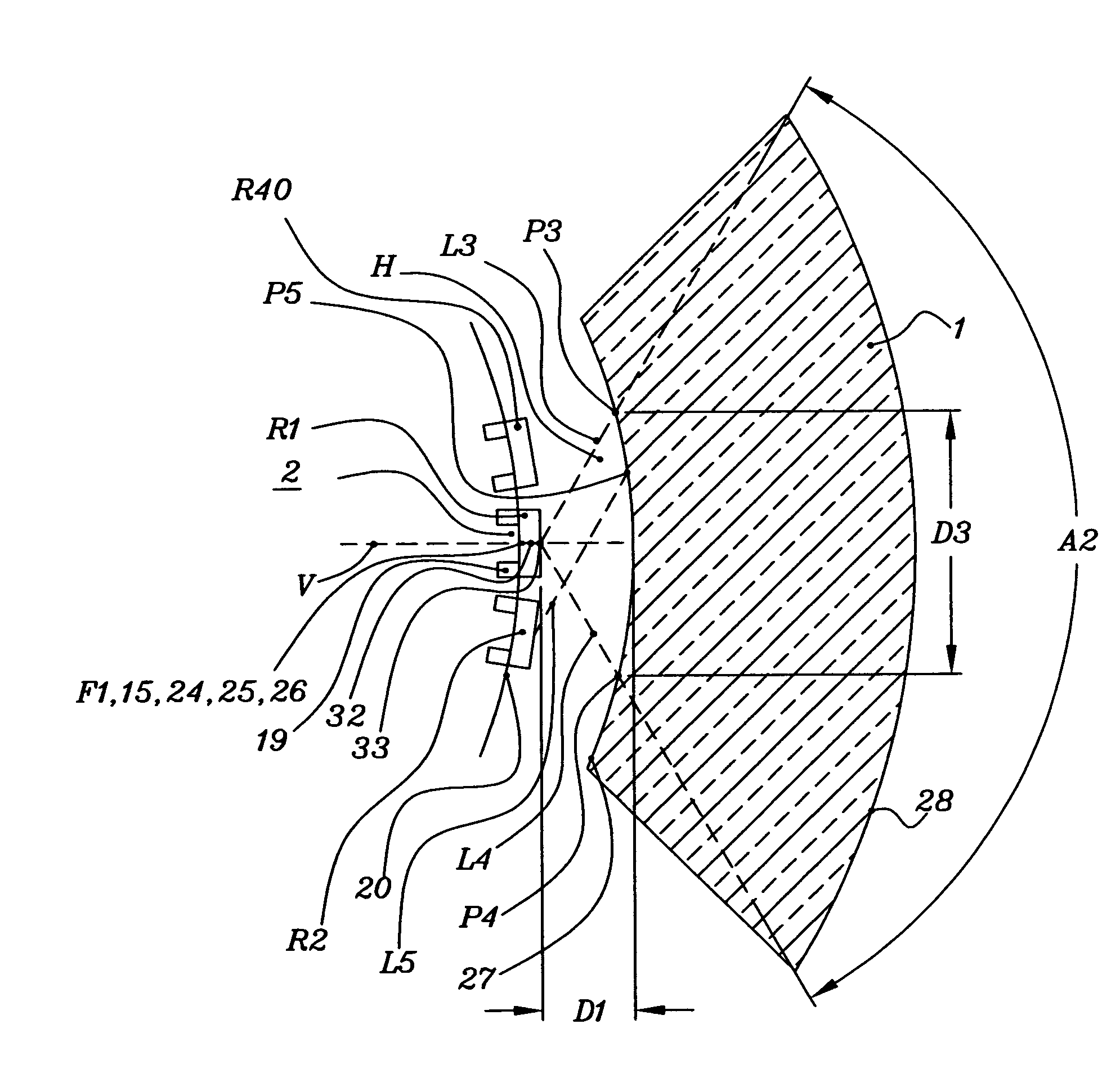
Very-low-profile cylindrical Luneberg lens antenna based on novel dielectric filling mode
The invention discloses a very-low-profile cylindrical Luneberg lens antenna based on a novel dielectric filling mode. The very-low-profile cylindrical Luneberg lens antenna comprises a cylindrical Luneberg lens, an arc feed source array (1) and an arc metallic reflection baffle plate (2), wherein the cylindrical Luneberg lens is arranged between an upper metal cover plate (3) and a lower metal cover plate (4), the arc feed source array (1) is arranged on a focal line of the cylindrical Luneberg lens, the arc metallic reflection baffle plate (2) is arranged on a non-radiation aperture of the cylindrical Luneberg lens, the cylindrical Luneberg lens comprises an upper filling dielectric piece (6) and a lower filling dielectric piece (5) which have different radii, n layers of through holes (21) and m layers of through holes (21) which have different distribution densities are respectively arranged on the upper filling dielectric piece (6) and the lower filling dielectric piece (5) from circle centers towards theoutside, m is larger than n, and the effective dielectric constants of the front n layers of two dielectric pieces are correspondingly the same. The very-low-profile cylindrical Luneberg lens antenna is simple to process, low profile and light weight are achieved, and the very-low-profile cylindrical Luneberg lens can be used for a multi-beam directional communication and beam scanning antenna better, particularly for millimeter-wave high frequency bands and application occasions requiring axial arraying.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
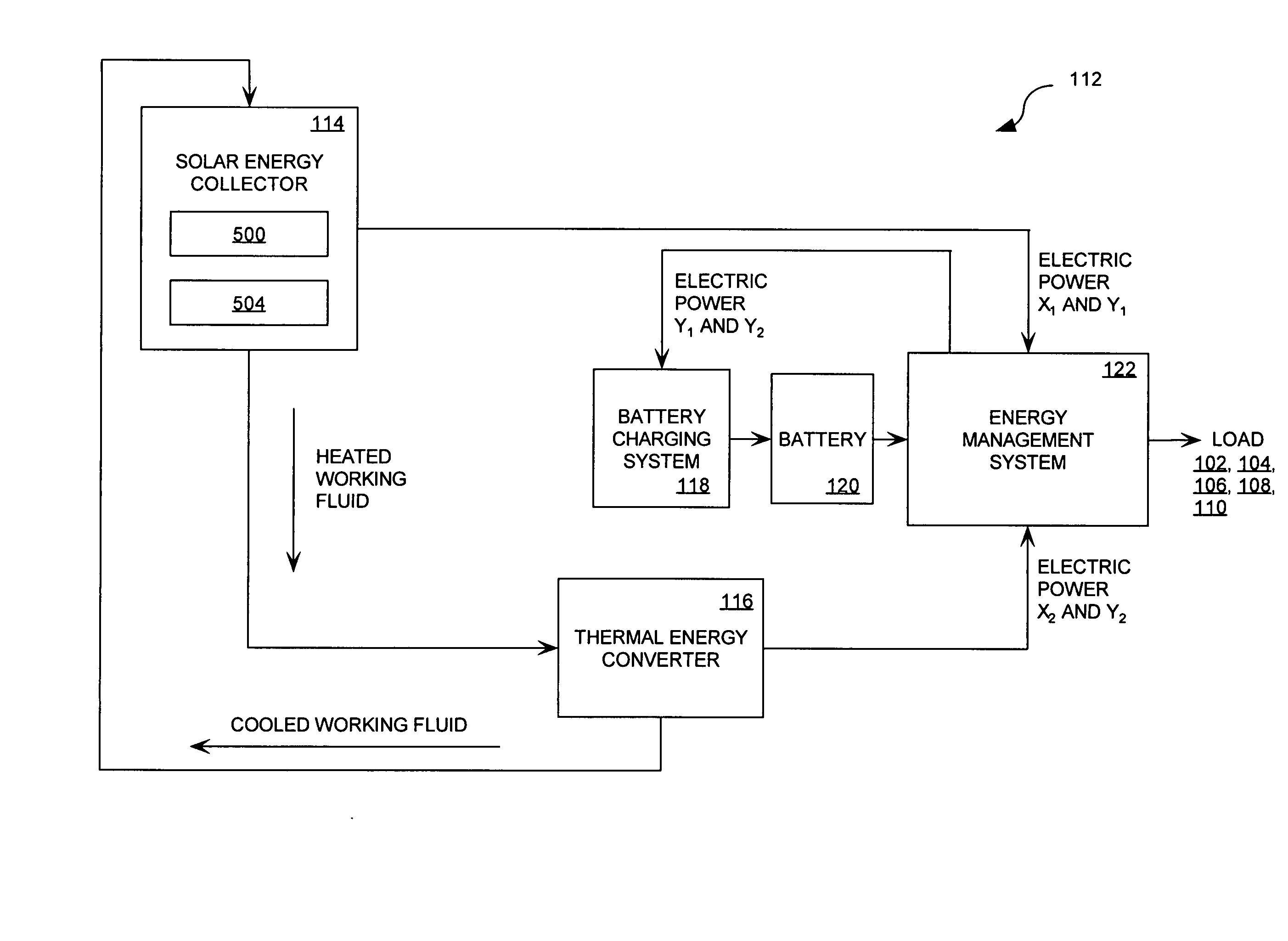
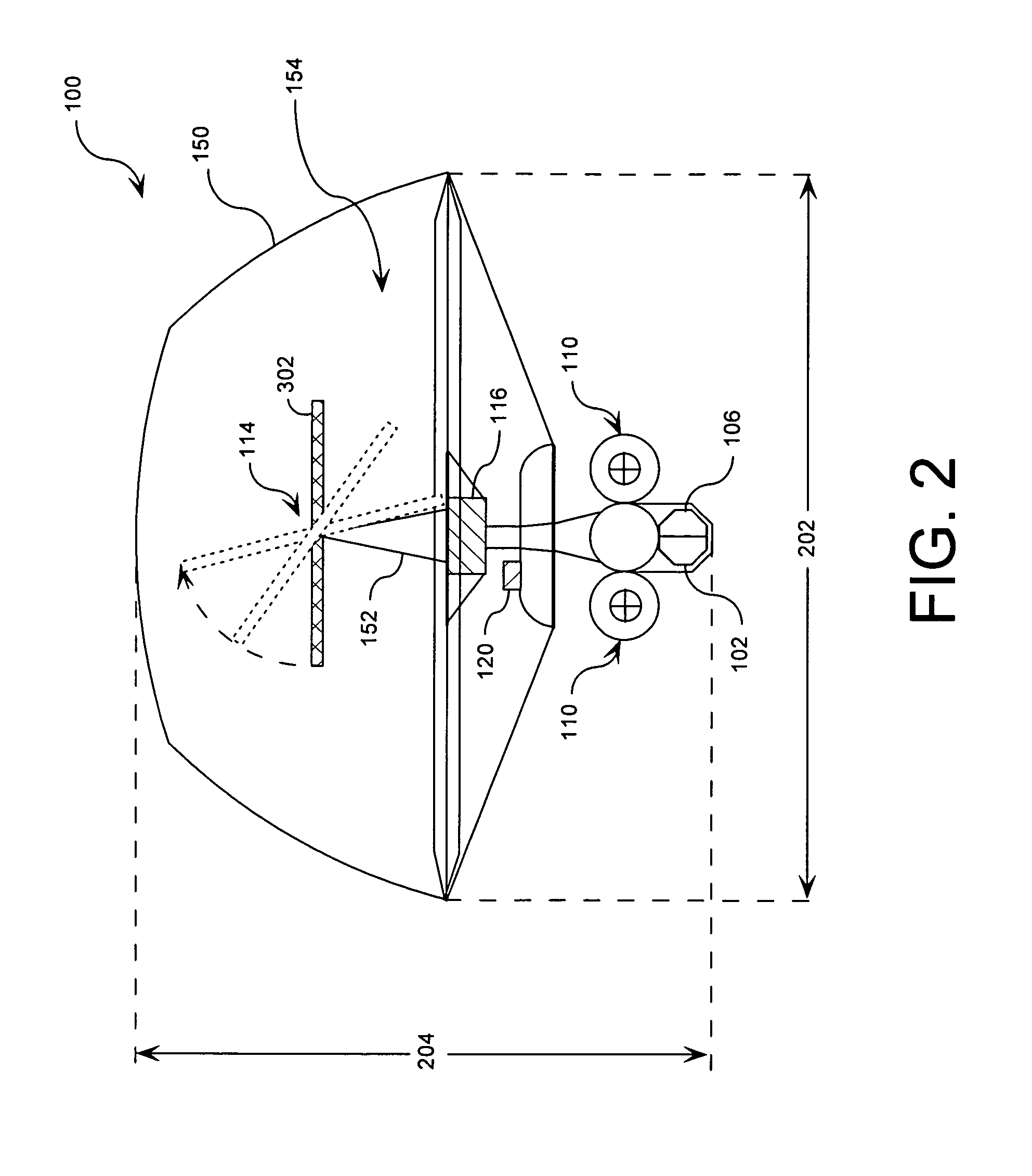
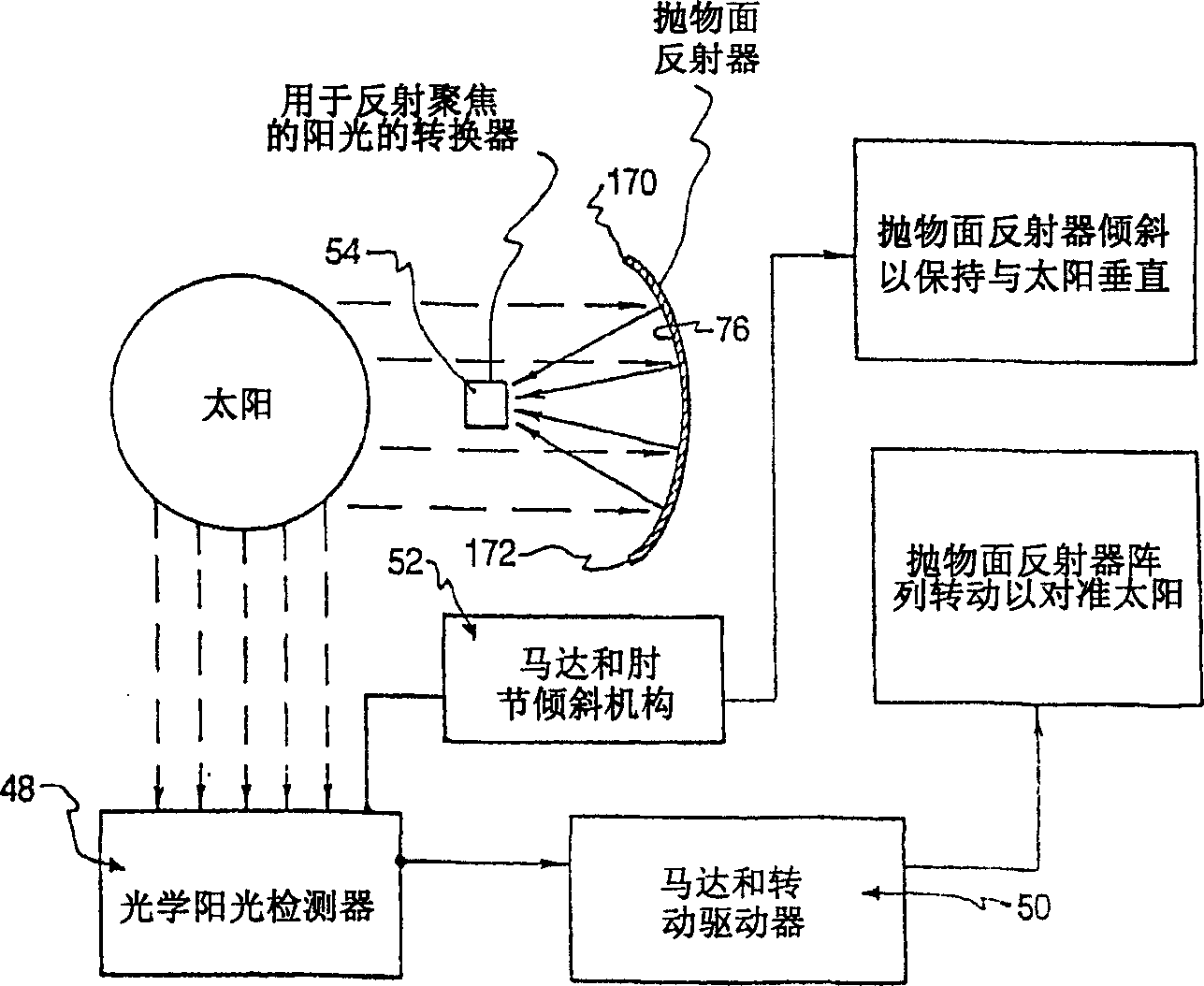
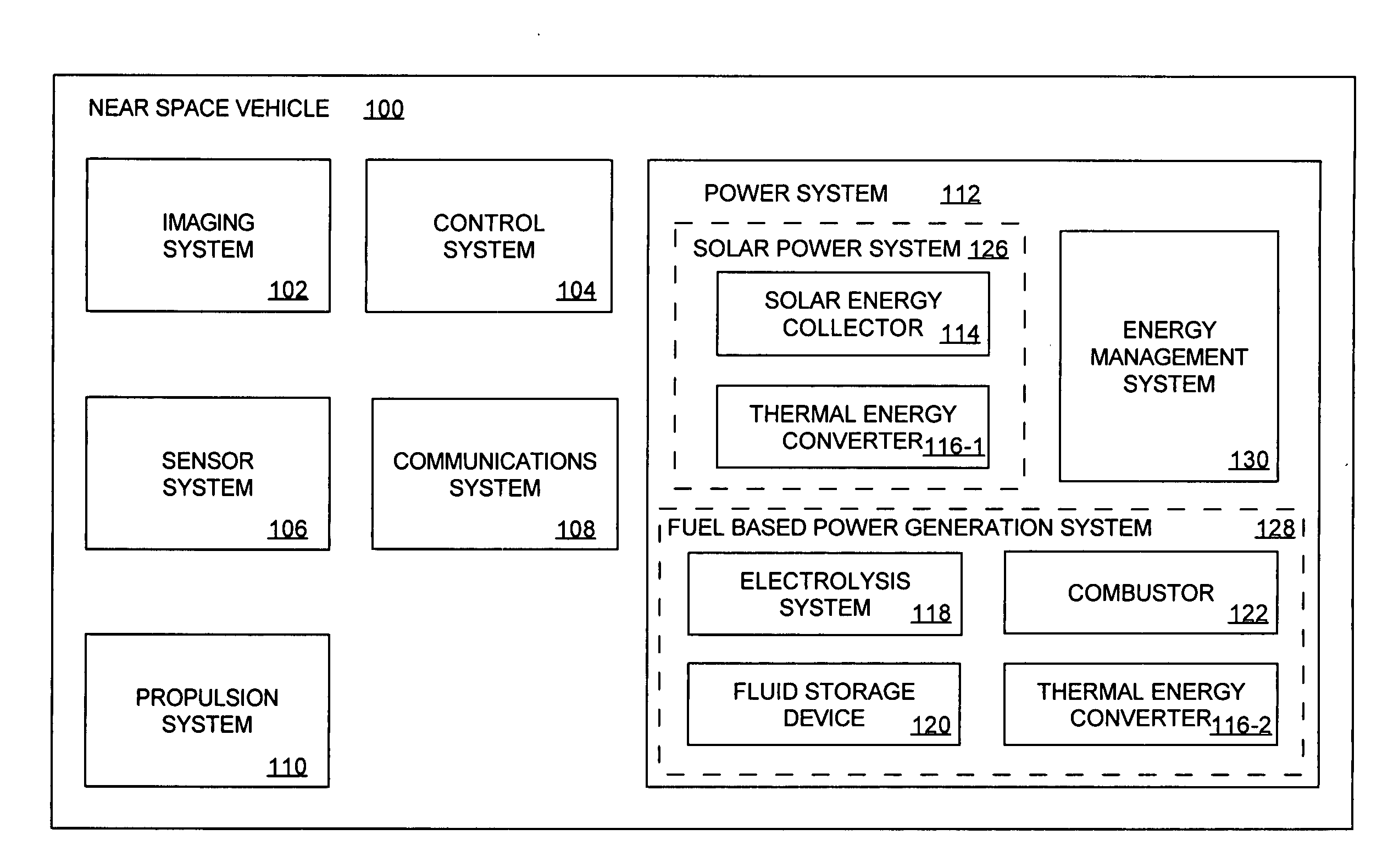
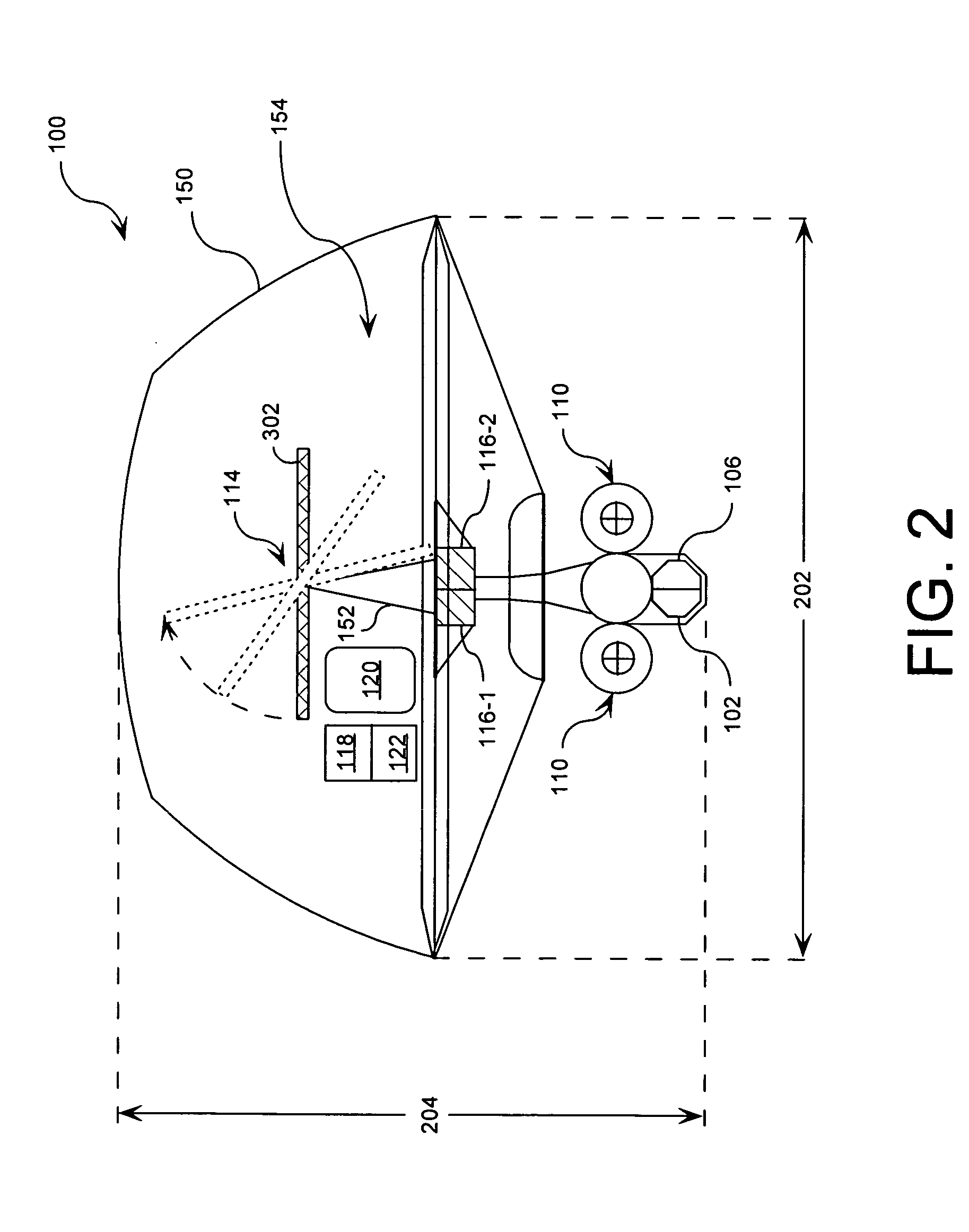
System for providing continuous electric power from solar energy
A system (112) for providing continuous electric power from solar energy is provided. The system includes a solar concentrator (302) formed of an optically reflective material having a curved surface that defines a focal center or a focal line toward which light incident on the curved surface is reflected. The system also includes a PV / thermal device (310) positioned substantially at the focal center or along the focal line. The PV / thermal device is comprised of a photovoltaic array (500) and a fluid cooling system for the photovoltaic array. The fluid cooling system includes a thermal energy collector (504). A battery charging system (118) is coupled to the photovoltaic array. The battery charging system includes a battery charging circuit. The battery charging system is programmed to selectively provide a charging current for the battery charging circuit during periods when the solar concentrator is exposed to solar radiation. The charging current can be selected so that a battery (120) charged by the battery charging circuit has power to continuously operate a load during periods when the solar concentrator is not exposed to solar radiation.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Lighting device for vehicle
For light irradiation transversely inclined with respect to the front of a vehicle lighting device that reflects light from a plurality of semiconductor light emitting devices toward the forward part of the lighting device via reflector, a structure is provided in which lights emitted from five semiconductor light emitting devices are reflected toward the forward part of a lighting device via reflector. A reflecting surface of the reflector is a parabolic cylindrical curved surface having a focal line extended horizontally. The five semiconductor light emitting devices are on the focal line at an interval. Each of the directions of the emitted lights is varied for each semiconductor light emitting device with respect to the focal line direction. Consequently, the light emitted from each of the semiconductor light emitting devices is not diffused vertically but only horizontally, thereby forming five oblong light distribution patterns in positions shifted from each other horizontally.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
Triple-band offset hybrid antenna using shaped reflector
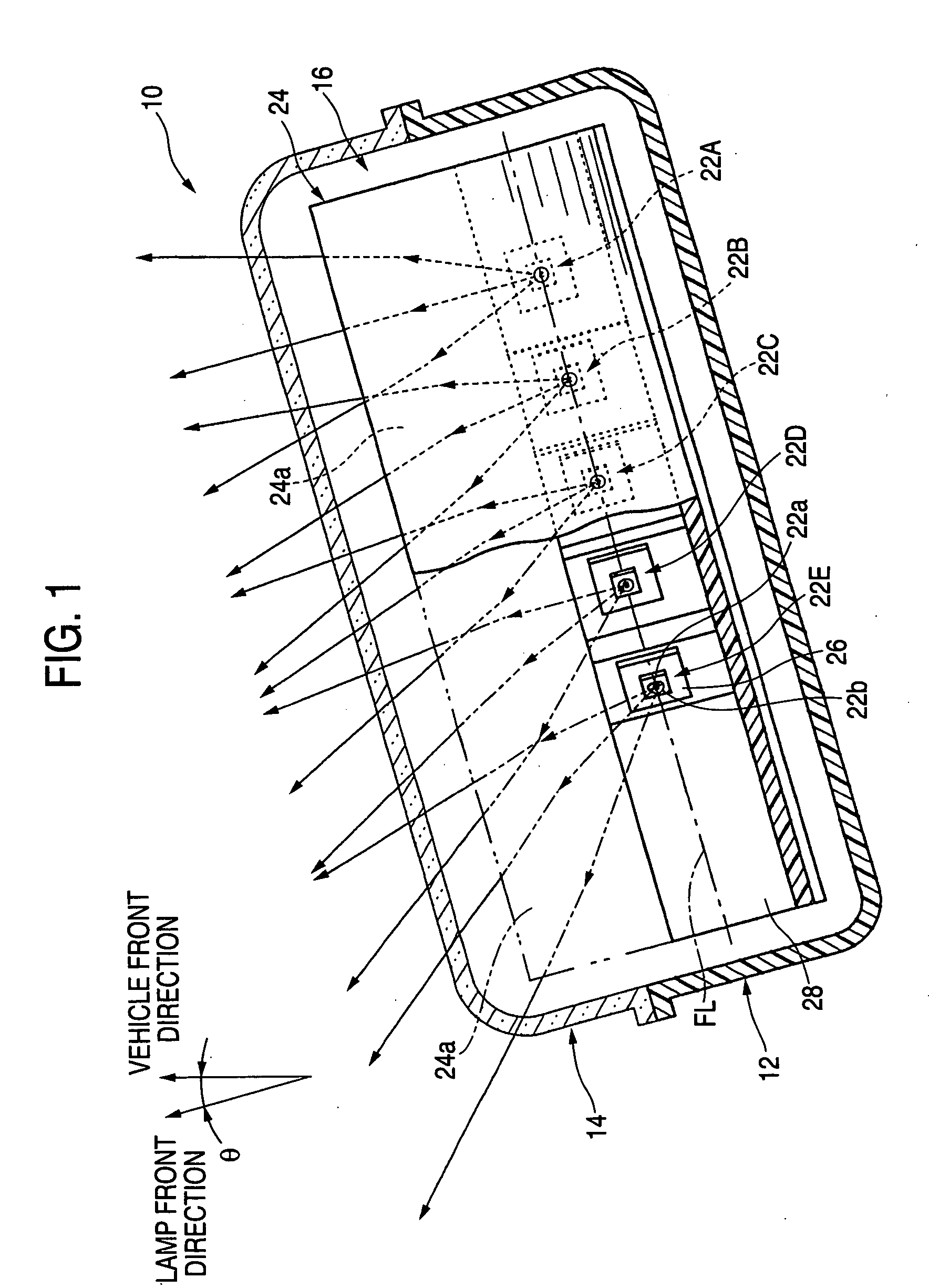
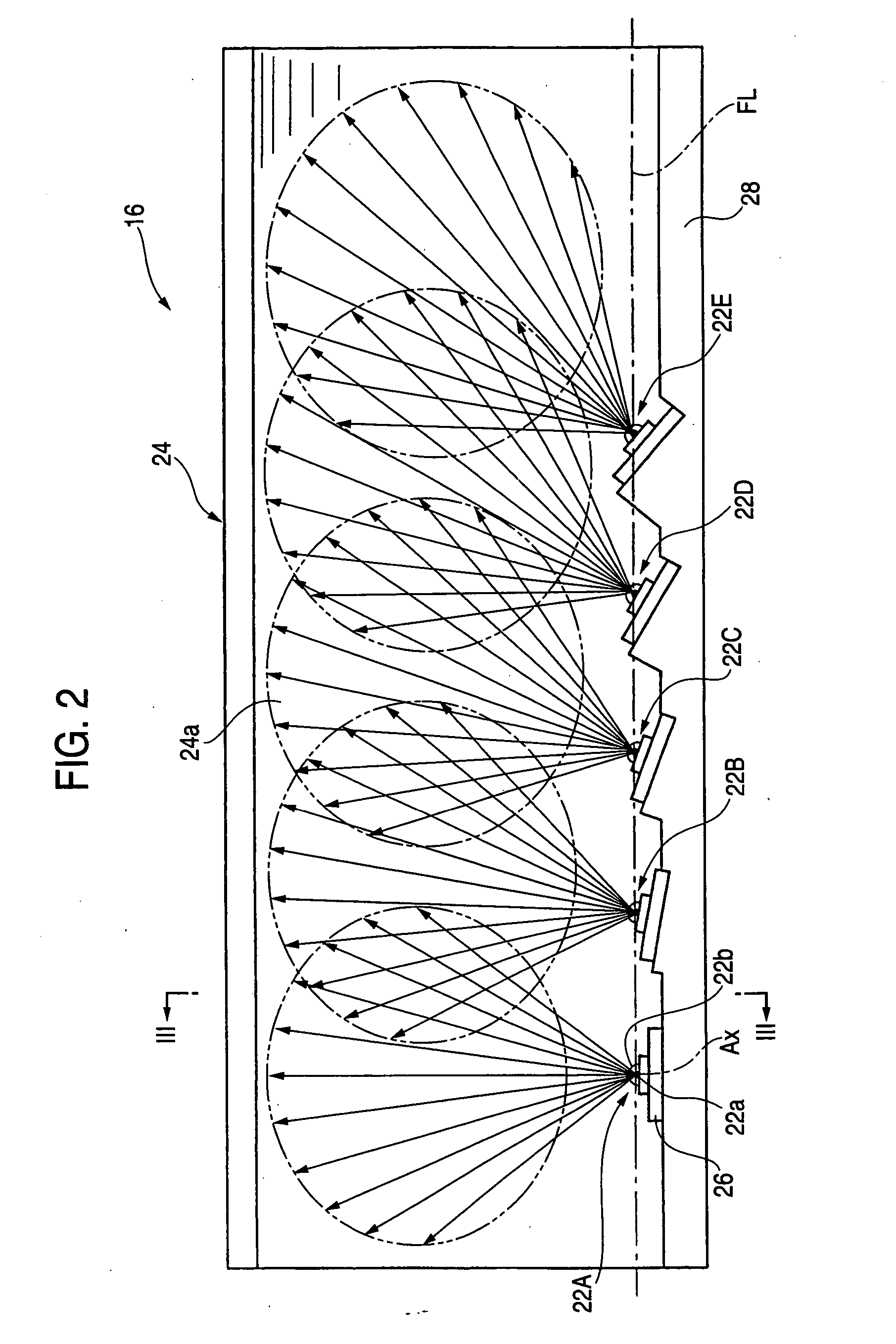
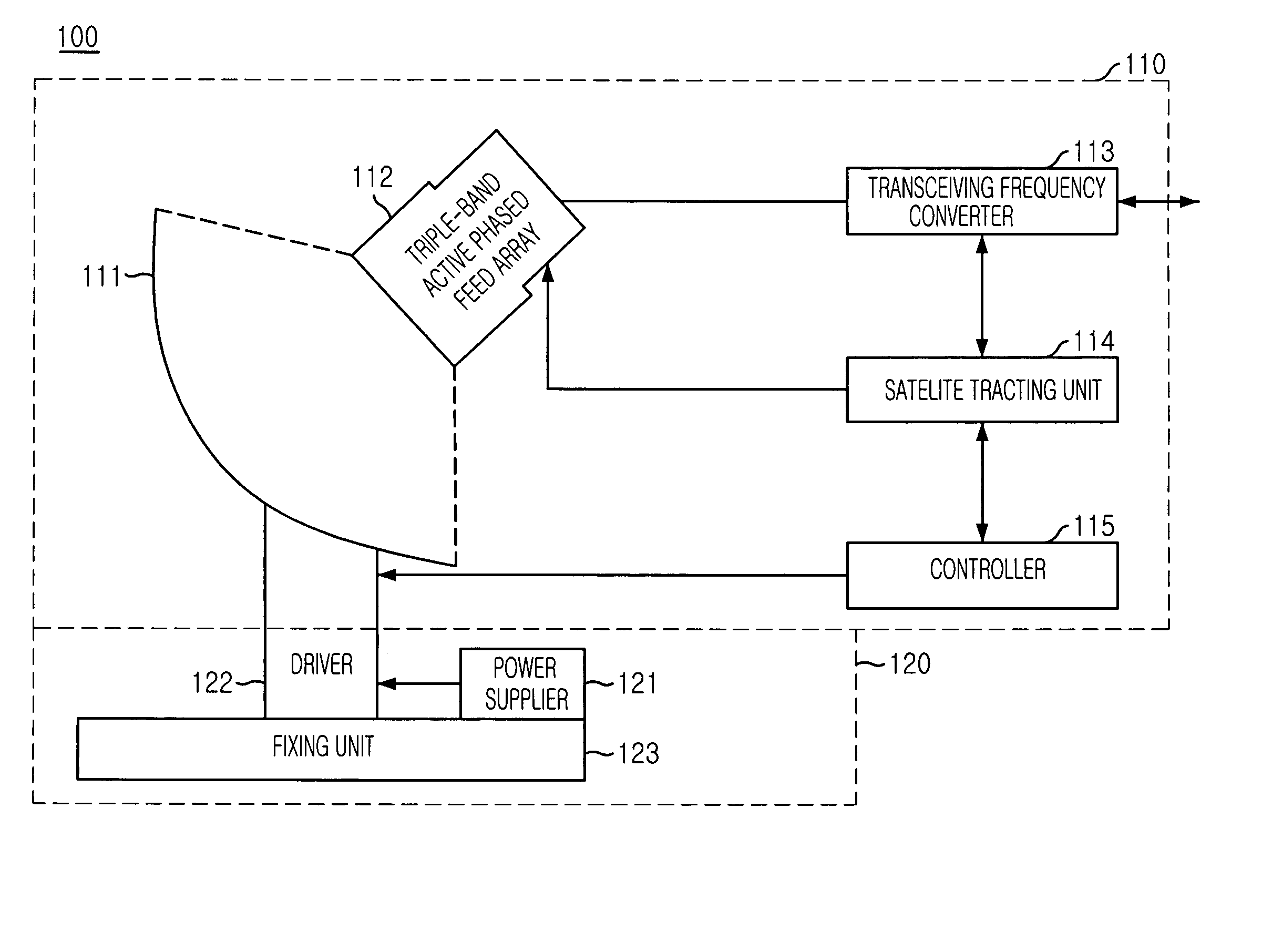
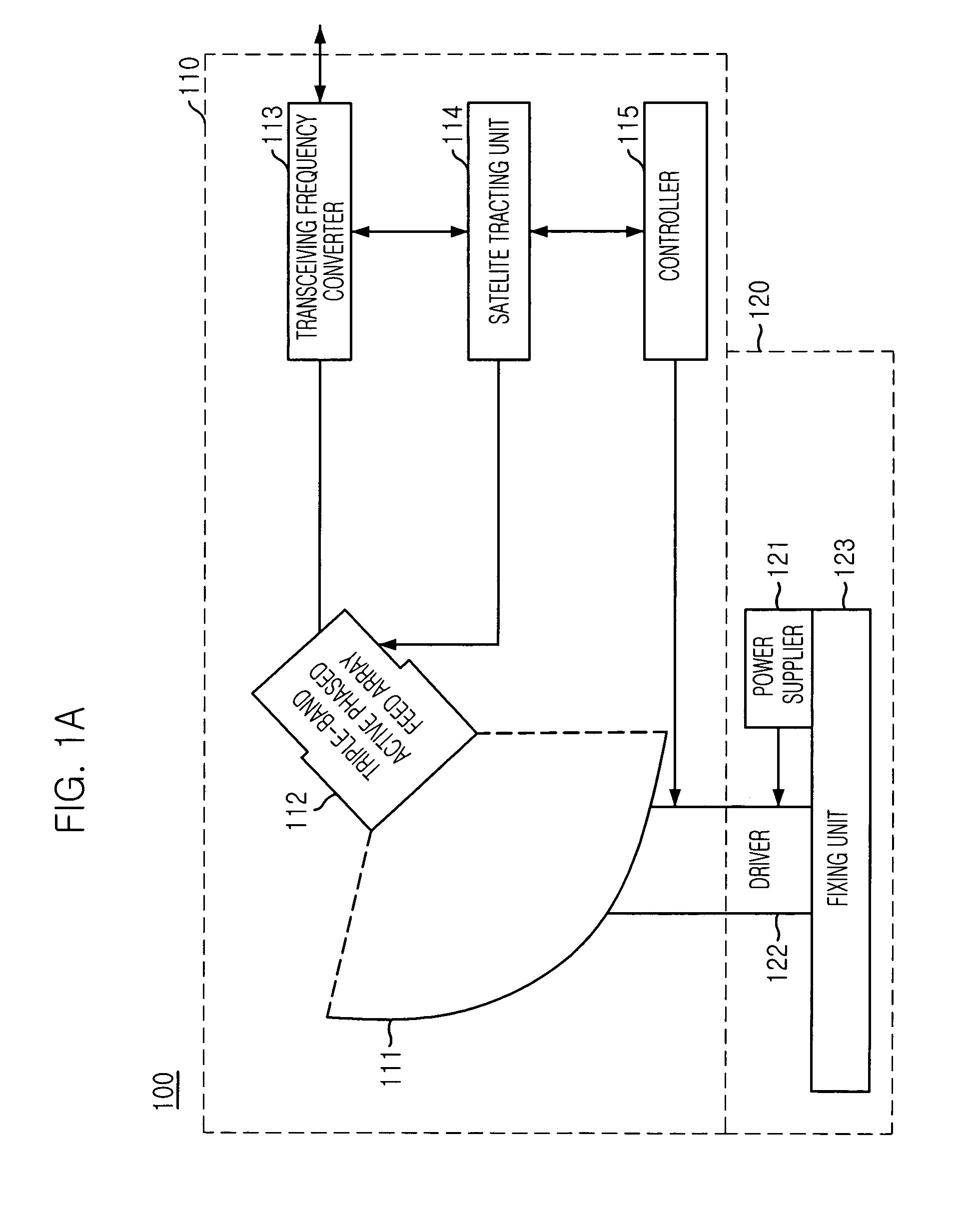
InactiveUS20050140563A1Reducing a blocking lossImprove efficiencyAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsSignal onRadio frequency signal
A triple-band offset hybrid antenna having a shaped reflector is disclosed. The triple-band offset hybrid antenna includes: a shaped reflector reflecting a K / Ku bands RF signals received from a satellite to focus an energy of the K / Ku band RF signals on a focal line and reflecting a Ka band RF transmitting signal; and a triple-band active phased feed array receiving the reflected K / Ku bands RF signals from the shaped reflector and radiating the Ka band RF transmitting signal to the shaped reflector, wherein the triple-active feed array including Ka / K bands feed array for transceiving Ka / K bands RF signal and a Ku band feed array for receiving a Ku band RF signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Vehicular lamp unit
ActiveUS20070279924A1Increase awarenessIncrease speedLight source combinationsLighting support devicesOptical axisEffect light
The reflection surface of a reflector is formed by a parabolic cylindrical plane extending in the horizontal direction orthogonal to an optical axis. A light emitting element is configured to have five light emitting chips arranged in a T-shape and these light emitting chips are lighted in two lighting modes. In the first lighting mode, a special light emitting chip and a pair of the left and right side special light emitting chips which front end edges are aligned on the focal line of the parabolic cylindrical plane are lighted simultaneously, whereby a light distribution pattern having a narrow vertical width and a prolong shape is formed. In the second lighting mode, a special light emitting chip located at the center portion and two general light emitting chips disposed in series on the backward side thereof are lighted simultaneously, whereby a light distribution pattern having a large vertical width and a prolong shape is formed.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
Lighting device for vehicle
InactiveUS20100053987A1Small sizeOptimizationNon-electric lightingVehicle headlampsOptical axisLight guide
A lighting device for a vehicle is provided. The lighting device includes a projection lens disposed on an optical axis and having a focal line, a first light emitting device disposed on a rear side of the focal line, a reflector which reflects light toward the focal line; a shade which shields a part of the light; a second light emitting device disposed on a rear side of the first light emitting device; and a light guide. The light guide includes an incident portion into which light emitted from the second light emitting device is introduced, a light guiding portion which guides the light, a shielding portion which forms a part of the shade, and an emitting portion coupled to the shielding portion and disposed on the focal line or in a vicinity of the focal line. The emitting portion emits the light guided by the light guiding portion.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
Double diffraction grating planar lightwave circuit
InactiveUS7068885B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesWaveguideWavelength range
The invention relates to a planar lightwave circuit including a pair of opposed concave reflective diffraction gratings sharing the same focal line, which separates first and second slab waveguide regions. The ends of input and output waveguides are positioned along the focal line for launching and receiving light directed by one or both of the diffraction gratings. The invention enables light within in a certain wavelength range to be launched from an input waveguide, directed by a single diffraction grating, and output waveguides, all within a single slab waveguide region, while light within another wavelength range will be directed from one diffraction grating to another for output waveguides in a different slab waveguide region.
Owner:ENABLENCE
Linear solar energy collection system
InactiveUS20100051015A1Improves solar field efficiencyReduce stepsSolar heating energySolar heat devicesCollection systemEngineering
A modular linear solar energy collection system comprises one or more reflector units each having a light-weight generally planar aluminum frame that mounts a number of solar panels in a fixed position at angles which progressively increase from the frame centerline outwardly to its perimeter so as to collectively form a surface having a shape approximating that of a parabola. The focal line of such parabola is coincident with a secondary reflector which receives sunlight incident on the solar panels and reflects such light onto a receiver tube mounted in a fixed position concentric to the centerline of the frame. The frame is connected to a drive mechanism operative to pivot the frame and solar panels in order to track the position of the sun during the course of a day.
Owner:ARXIEL CLEAN TECH
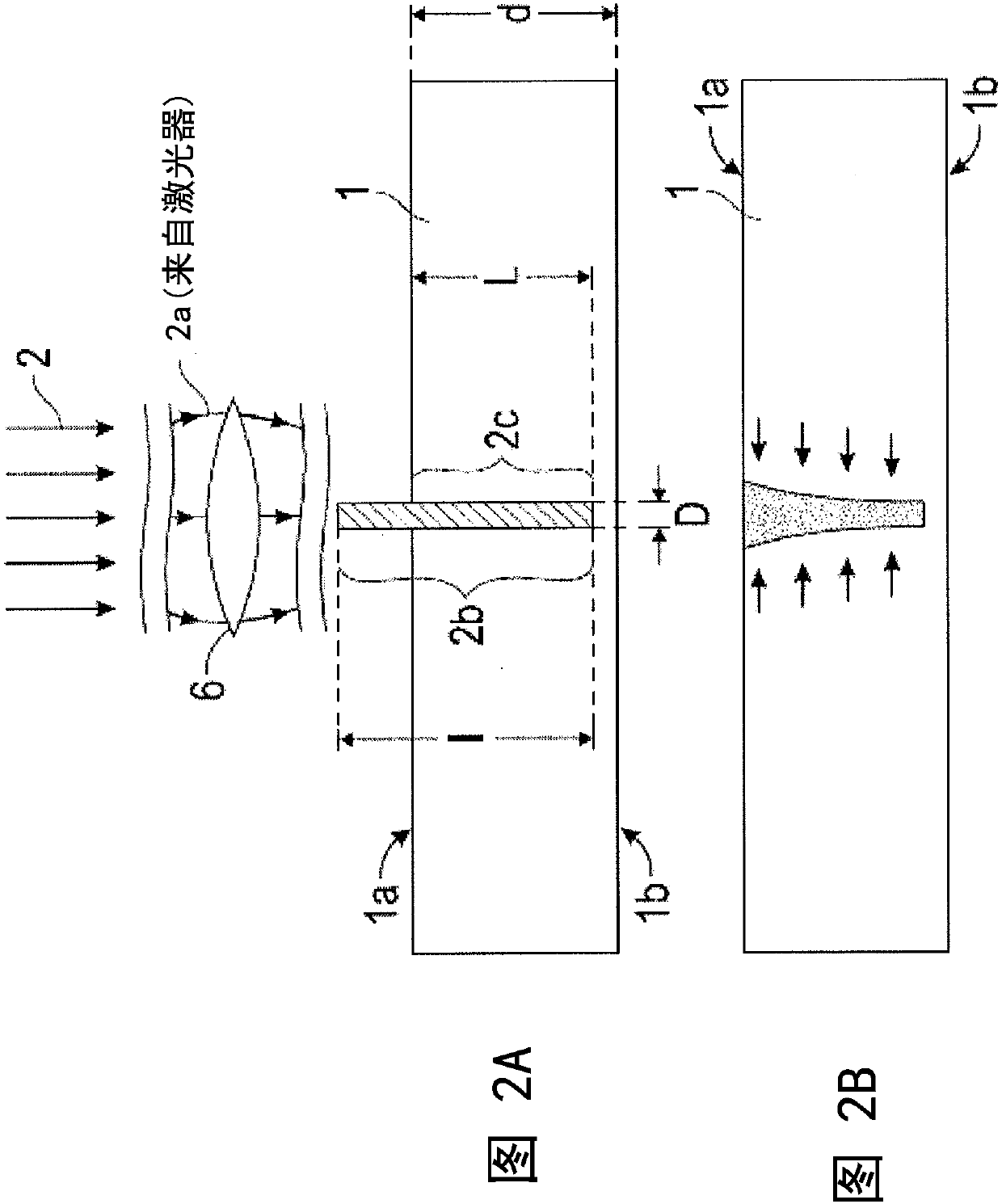
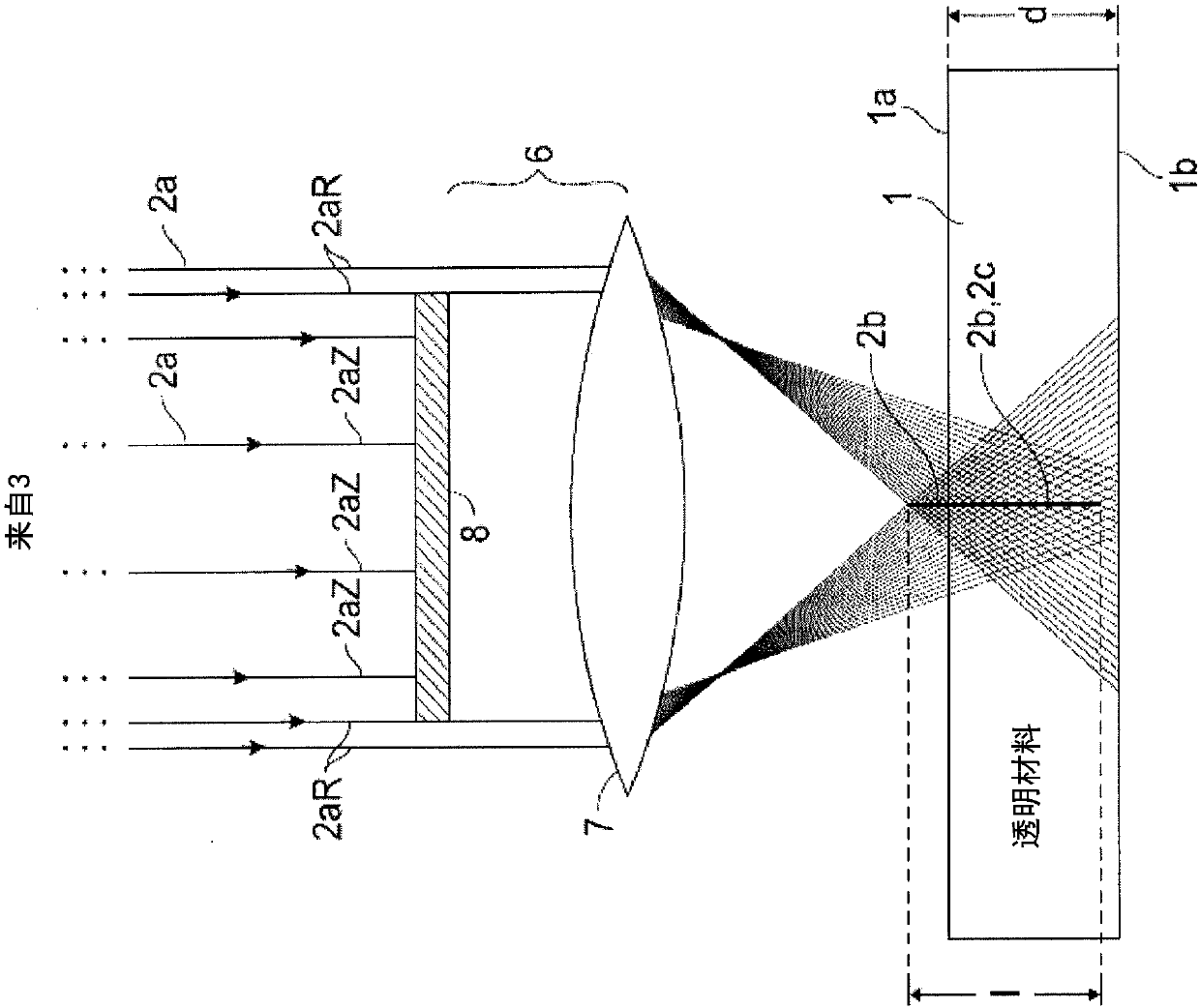
System for and method of processing transparent materials by using laser beam focal lines adjustable in length and diameter
A system for and a method of processing a transparent material, such as glass, by using an adjustable laser beam line focus are disclosed. The system for processing the transparent material includes a laser source operable to emit a pulsed laser beam, and an optical assembly (6') disposed within an optical path of the pulsed laser beam. The optical assembly (6') is configured to transform the pulsed laser beam into a laser beam focal line having an adjustable length and an adjustable diameter. At least a portion of the laser beam focal line is operable to be positioned within a bulk of the transparent material such that the laser beam focal line produces a material modification along the laser beam focal line. Method of laser processing a transparent material by adjusting at least one of the length of the laser beam focal line and the diameter of the laser beam focal line is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Three dimensional radar antenna method and apparatus
InactiveUS8558734B1Low costIndividually energised antenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionThin metalRadar
A ground based avian radar receive antenna is implemented using a vertically oriented offset parabolic cylindrical antenna. The desired azimuth beamwidth is determined by the width of the parabolic cylinder reflector surface and the desired elevation beamwidth by the height of the parabolic cylinder reflector surface. A vertical array of antenna elements is mounted along the vertical focal line to provide electronic scanning in elevation. Low sidelobe levels are obtained using tapered antenna element illumination. Low cost modular construction with high reflector accuracy is obtained by attaching a thin metal reflector to thin ribs machined or stamped in the shape of the parabolic cylinder reflector surface. The antenna is enclosed in a radome and mechanically rotated 360 degrees in azimuth.
Owner:PIESINGER GREGORY HUBERT
Millimeter-wave fan beam cylindrical Luneberg lens antenna based on metal perturbation structure
ActiveCN107275788AEasy to processAchieve wideningWaveguide mouthsIndividually energised antenna arraysMicrowave substrateWide beam
The invention discloses a millimeter-wave fan beam cylindrical Luneberg lens antenna based on a metal perturbation structure. The antenna achieves a pitch beam width reaching 104 degree and azimuth plane + / - 60 degree scanning. The antenna comprises a cylindrical Luneberg lens located between an upper metal flat plate (1) and a lower metal flat plate (2); an arc feed source array (3) located on the focal line of the cylindrical Luneberg lens; and the metal perturbation structure (5) arranged on the radiating aperture of the lens circumferentially. The cylindrical Luneberg lens comprises a cylindrical filling dielectric sheet (4). The filling dielectric sheet uses a low-loss microwave substrate as a substrate material and is divided into five layers according to a concentric circle structure from inside to outside. Respective layers have through-holes with different densities. The through-holes are filled with air. The antenna is light in weight and easy to process, greatly increases the pitch surface beam width, realizes a wide beam scanning range in the horizontal plane so as to be better applied to a multi-beam directional communication and beam scanning antenna, especially the millimeter wave high-frequency band and applications requiring axial grouping.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Conversion of solar energy
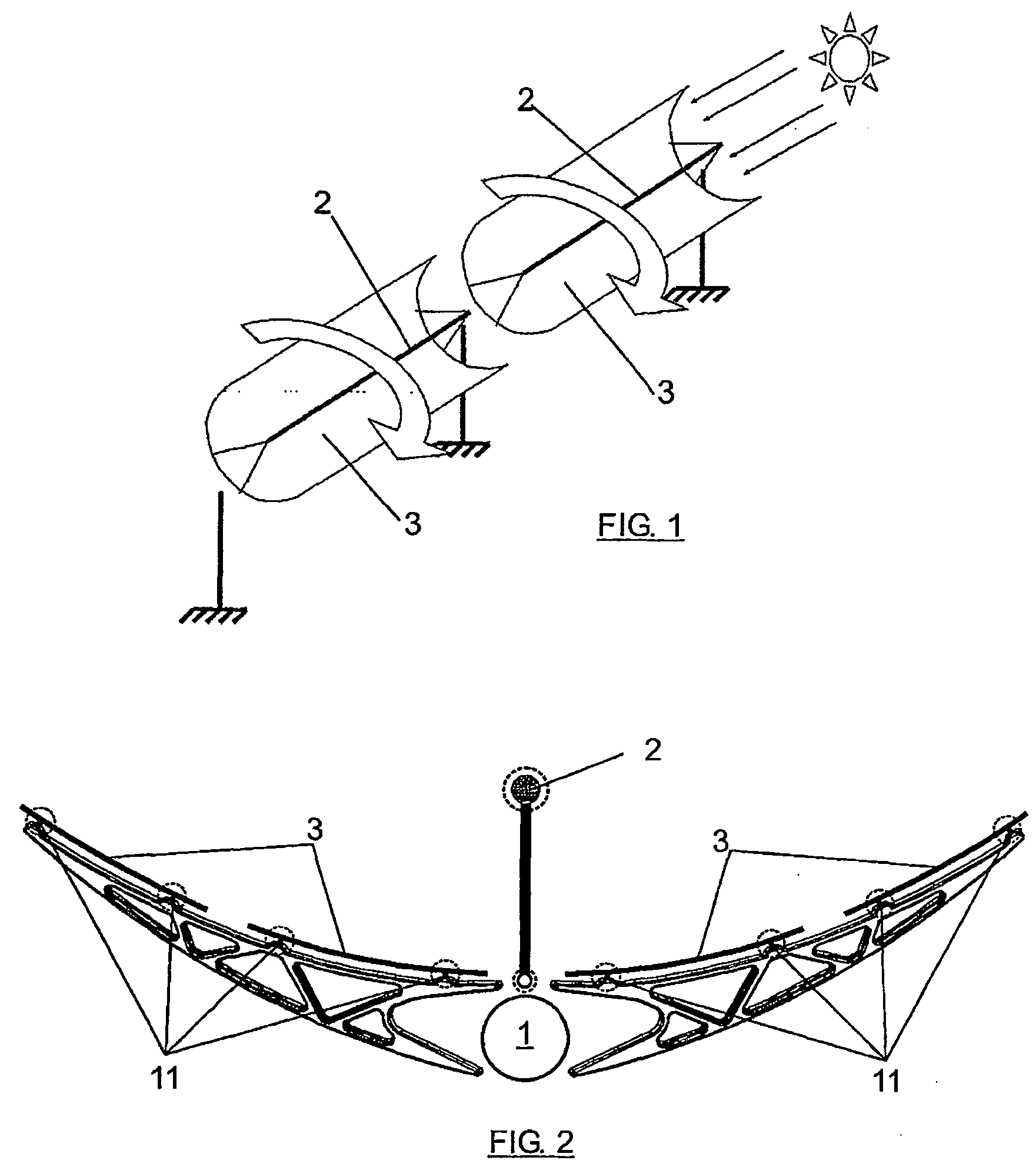
An array of elongated concave parabolic trough-shaped reflectors is disclosed. The orientation of the array is biaxially kept essentially perpendicular to rays of the sun by an optical control such that sunlight is reflected and concentrated along a focal line of each elongated reflector by which (a) water in a tube disposed at the focal line is heated by reflected line focused sunlight impinged thereon and / or (b) line focused reflected sunlight is optically transformed into point focused reflected sunlight using Fresnel lenses from which electricity is generated using solar cells upon which the point focused reflected sunlight is impinged.
Owner:THE SUN TRUST L L C
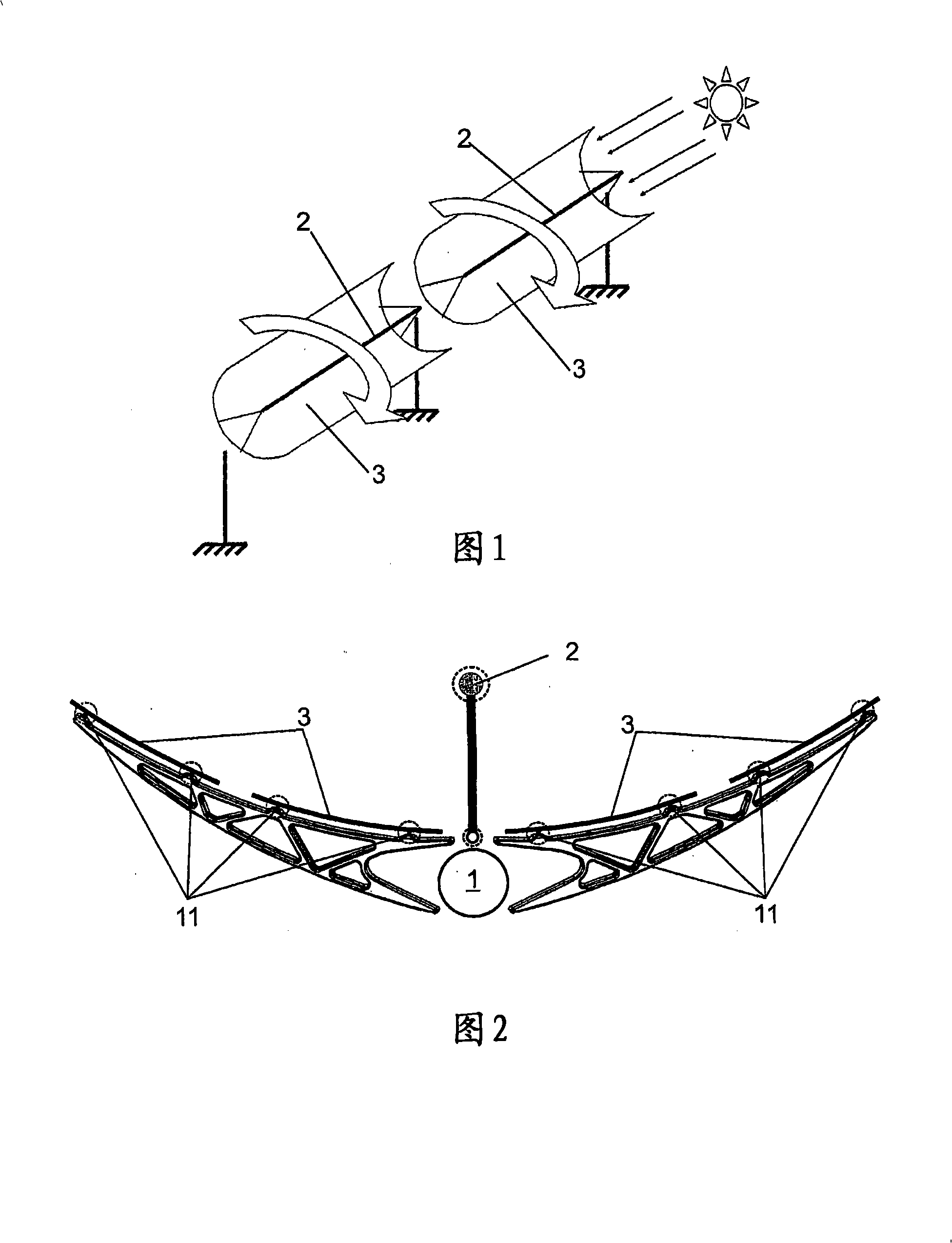
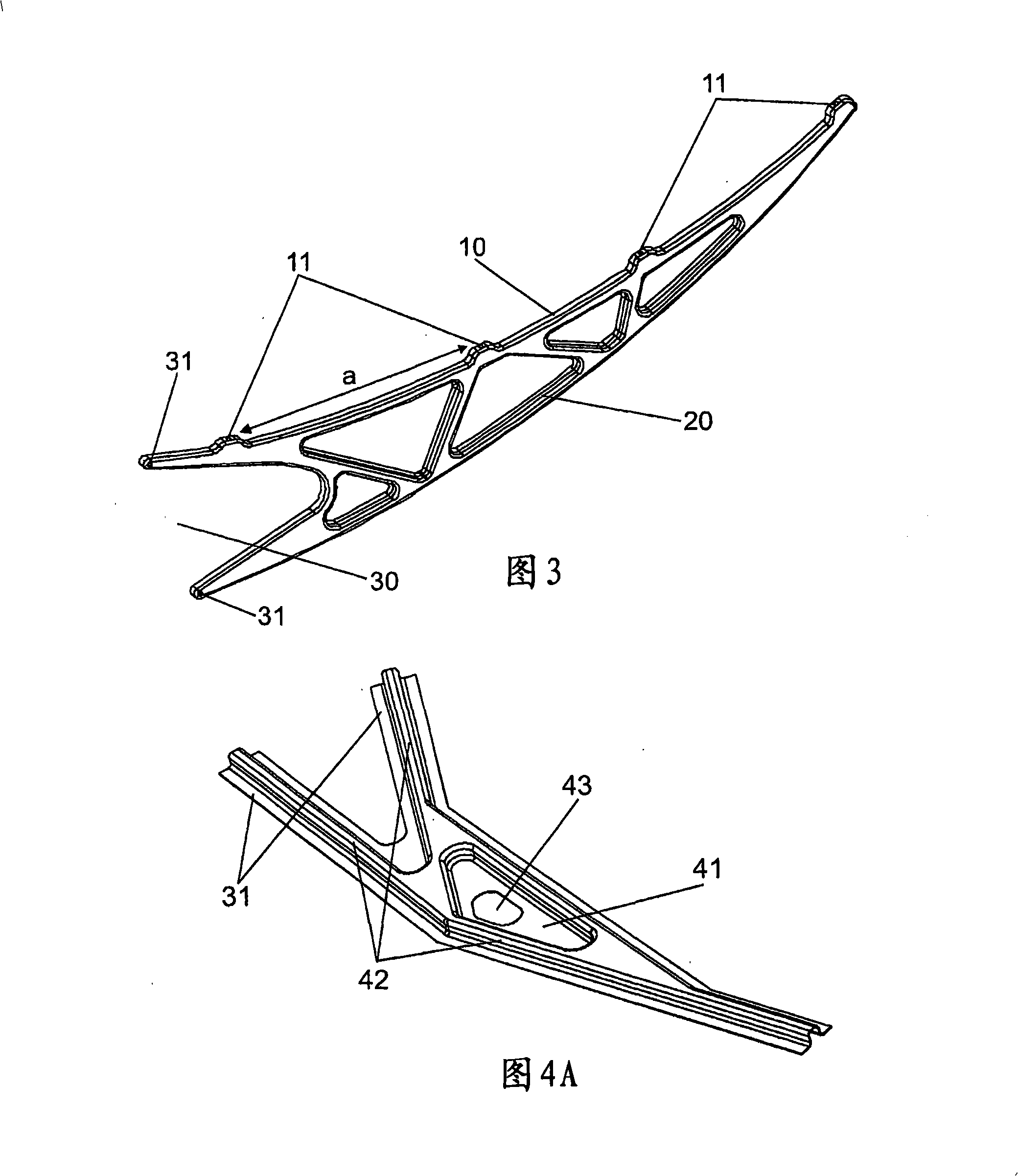
Support arm, cylindrical-parabolic solar collector support and method of producing said arm
InactiveCN101305247AImprove automationLow costArched girdersSolar heating energyCarrying capacityEngineering
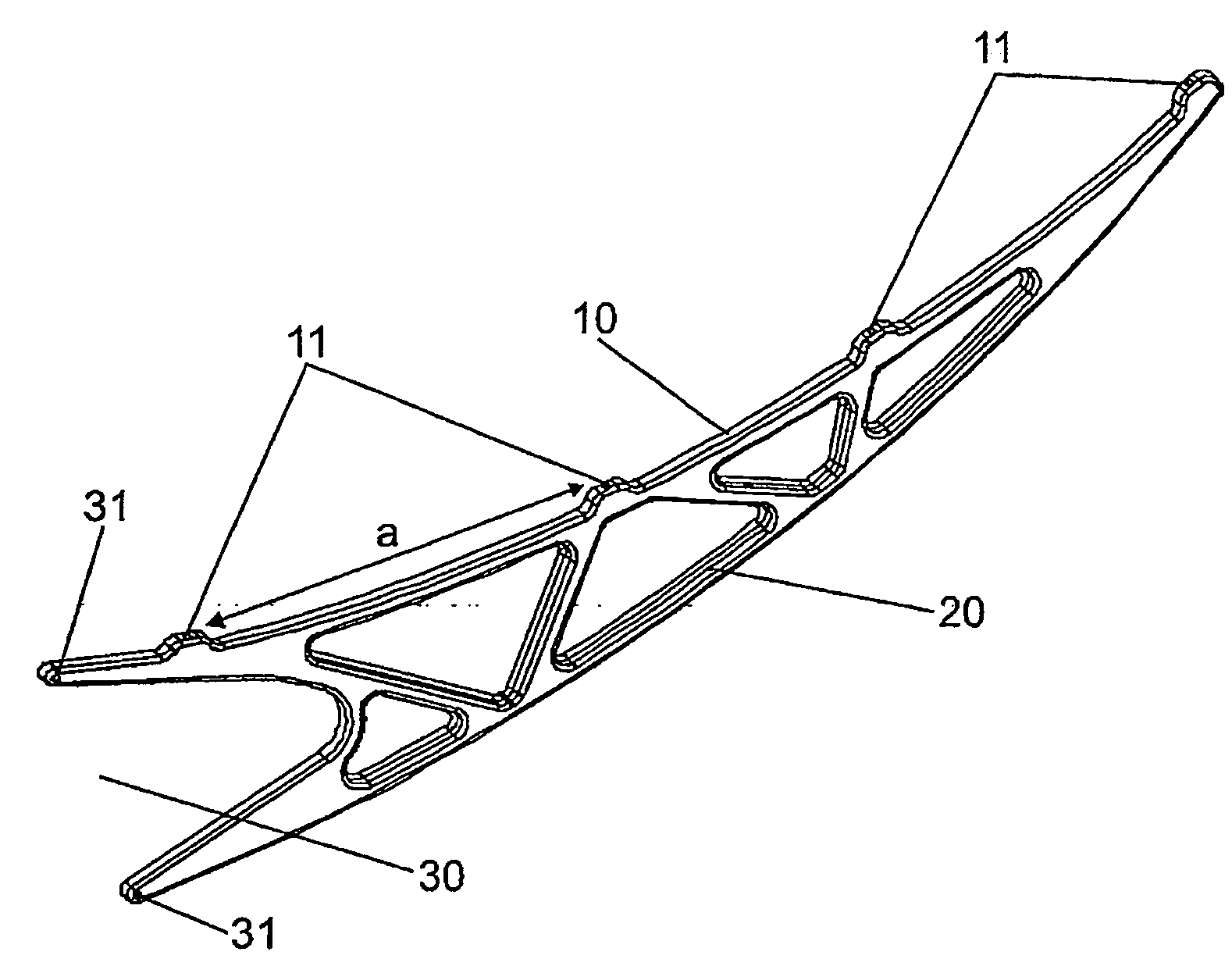
The invention relates to a support arm for a cylindrical-parabolic collector, which is intended to be coupled to a central body (1) of the collector in the form of a bracket in a direction that is essentially perpendicular to a focal line (2) of the collector. The inventive arm takes the form of a wedge comprising: a first side (10) which is equipped with support devices (11) for supporting at least one mirror (3), a second side (20), and a third side (30) which is equipped with support devices (31) such that the arm is supported by the central body (1). The arm is formed by at least one press-formed plate such as to produce a resistant structure that provides stiffness and a carrying capacity by means of a plurality of ribs (42) which form a lattice comprising a plurality of laminar segments (41) between said ribs.
Owner:SENER ING Y SISTEMAS
Cavity-type solar collector
InactiveCN101655286AImprove heat collection efficiencyReduce wind resistanceSolar heating energySolar heat devicesInsulation layerCollector device
The invention relates to a cavity-type solar collector, in particular to a solar collector suitable for focusing with a trough-type paraboloid. The cavity-type solar collector comprises a paraboloid 1, a parabolic bracket 2, a supporting frame 3, a hub disk 4, a collector bracket 5, a collector connection plate 6, a collector heat insulation layer 7, a collector outer cavity 8, a collector inner cavity 9, a collector light incidence port 10 and the like. The paraboloid 1 is a trough-type paraboloid of which the surface is plated with a reflective membrane; the collector inner cavity 9 and thecollector outer cavity 8 are tubular and the cross sections thereof are open ellipses, open polygons or combinations of the open ellipses and the open polygons; the collector inner cavity 9 and the collector outer cavity 8 form an annular space; the surface of the collector inner cavity 9 is blackened; and the collector light incidence port 10 is positioned on a focal line of the paraboloid 1. Thecavity-type solar collector has the advantages that: when the cavity-type solar collector is used, focused sunlight enters into the collector inner cavity through the collector light incidence port and is reflected many times in the collector inner cavity to allow the solar energy to be adsorbed repeatedly by the collector inner cavity, so the heat collecting efficiency of the solar energy is improved.
Owner:刘玉山 +2
Sectional type groove type solar energy condenser
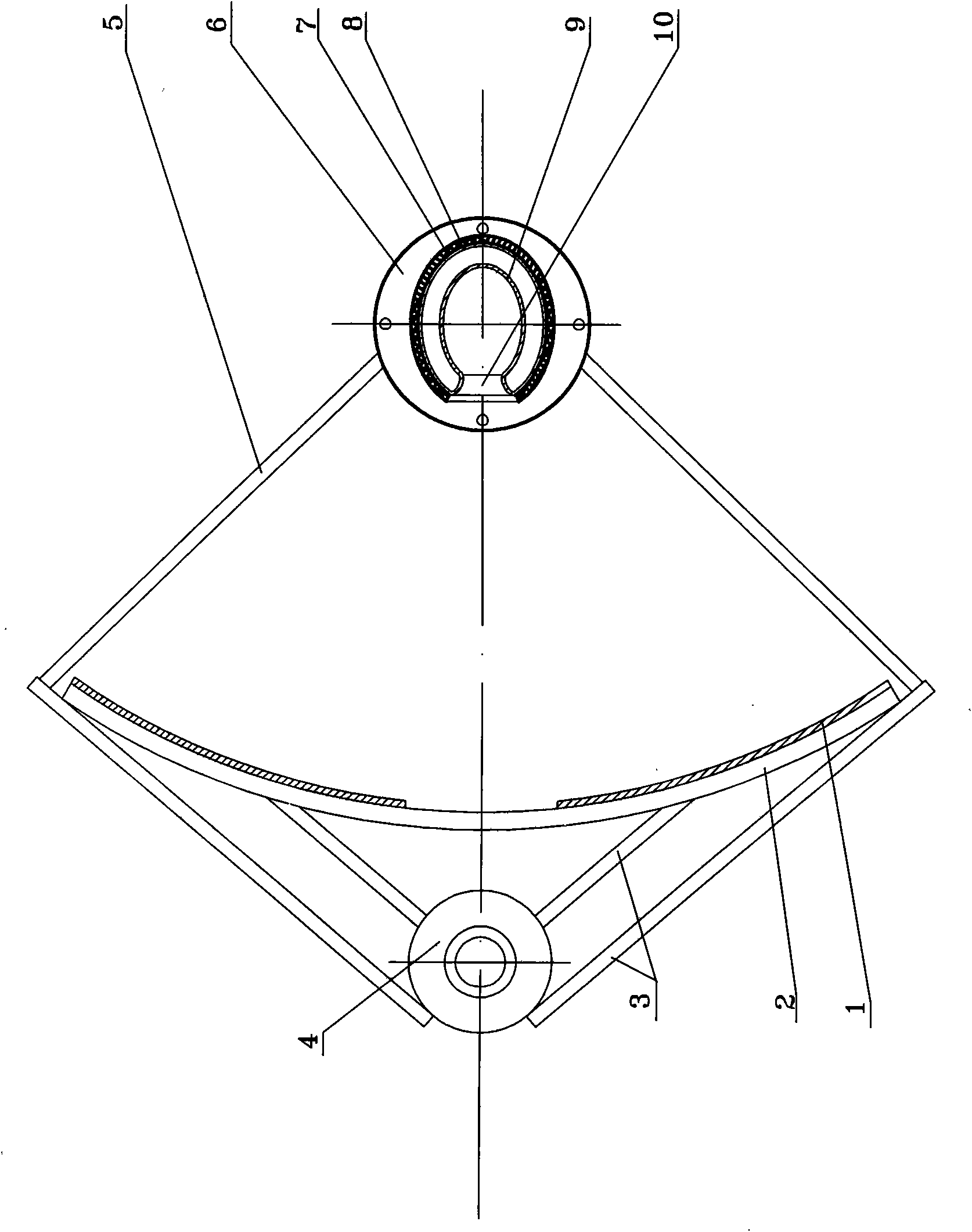
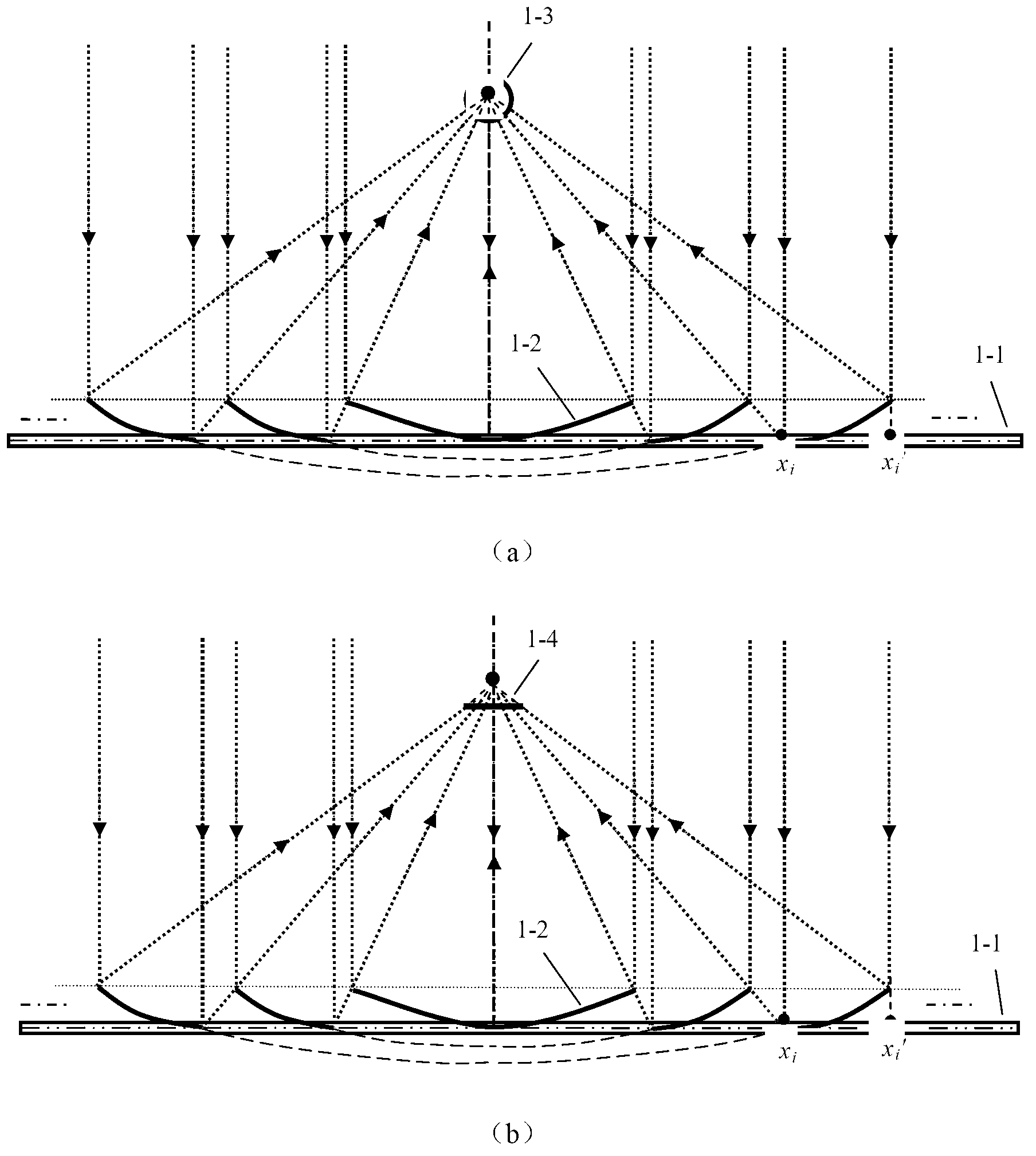
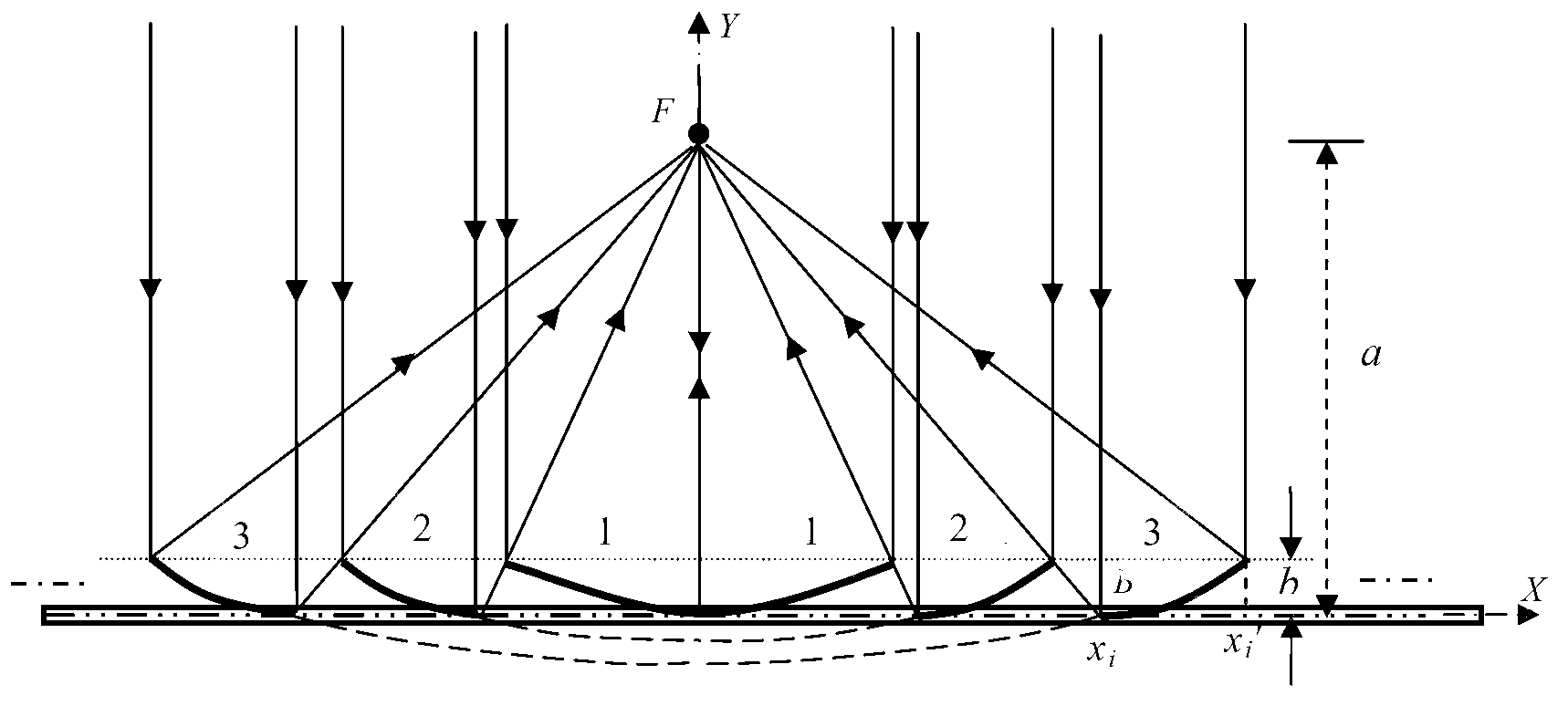
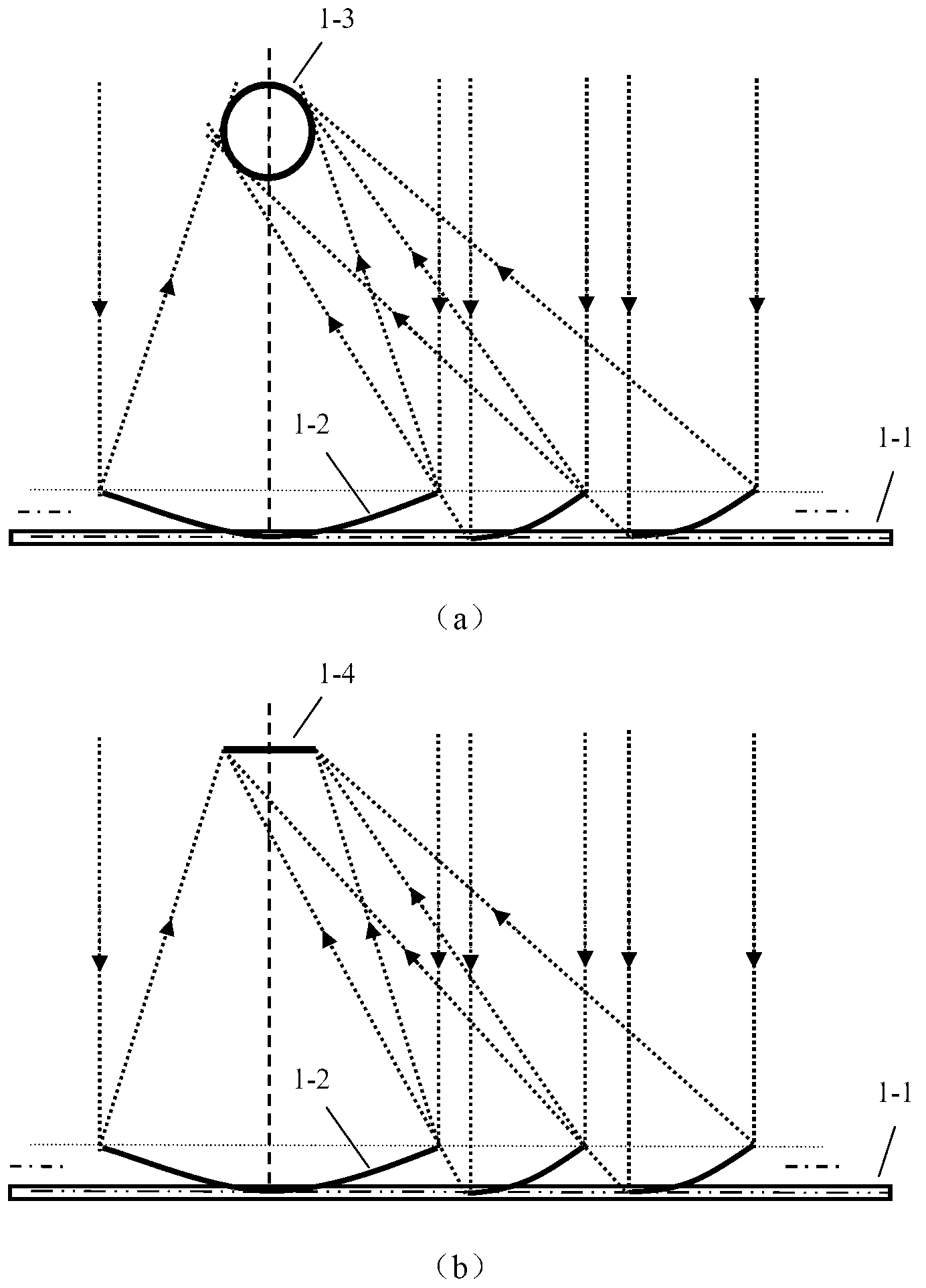
InactiveCN102798968AIncrease the concentration ratioHigh collector temperatureSolar heating energySolar heat devicesEngineeringFocal line
The invention discloses a sectional type groove type solar energy condenser which comprises a flat frame (1-1), parabolic reflectors (1-2), a cylindrical condensation receiver (1-3) or flat condensation receiver (1-4), wherein a plurality of parabolic reflectors (1-2) are sequentially arranged on the flat frame (1-1). The position, curvatures and opening widths of the parabolic reflectors (1-2) change with a focal line; in order to achieve the optical condensation effect, effective light rays reflected by the parabolic reflectors (1-2) all fall in an effective area of the cylindrical condensation receiver (1-3) or flat condensation receiver (1-4), light rays reflected by one reflection mirror surface behind exactly pass through the edge of the previous reflection mirror surface, the space of the flat frame (1-1) is maximally utilized and the light rays can not be shielded; and the flat frame (1-1) is fixed on a solar tracking frame. According to the sectional type groove type solar energy condenser, the pressure resistance against the wind is increased, the condensation ratio is increased within a limited area range, higher heat collection temperature is obtained and the industrial application is facilitated.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System for providing continuous electric power from solar energy
A system (112) for generating electric power from solar energy is provided. The system is comprised of a solar concentrator (302) formed of an optically reflective material having a curved surface. The curved surface defines a focal center or a focal line toward which light incident on the curved surface is reflected. A thermal energy collector (310) is positioned substantially at the focal center or along the focal line. A thermal energy converter (116-1) is operatively coupled to the thermal energy collector. The thermal energy converter is configured for converting thermal energy collected by the thermal energy collector to electric power. A fuel based power generation system (128) is also provided. The fuel based power generation system is operatively connected to the thermal energy converter. The thermal energy converter provides electric power to the fuel based power generation system for generating a fuel and an oxidizer when the thermal energy collector is exposed to solar radiation.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Concentrating solar power with glasshouses
Owner:GLASSPOINT SOLAR
Surface plasma resonance sensor
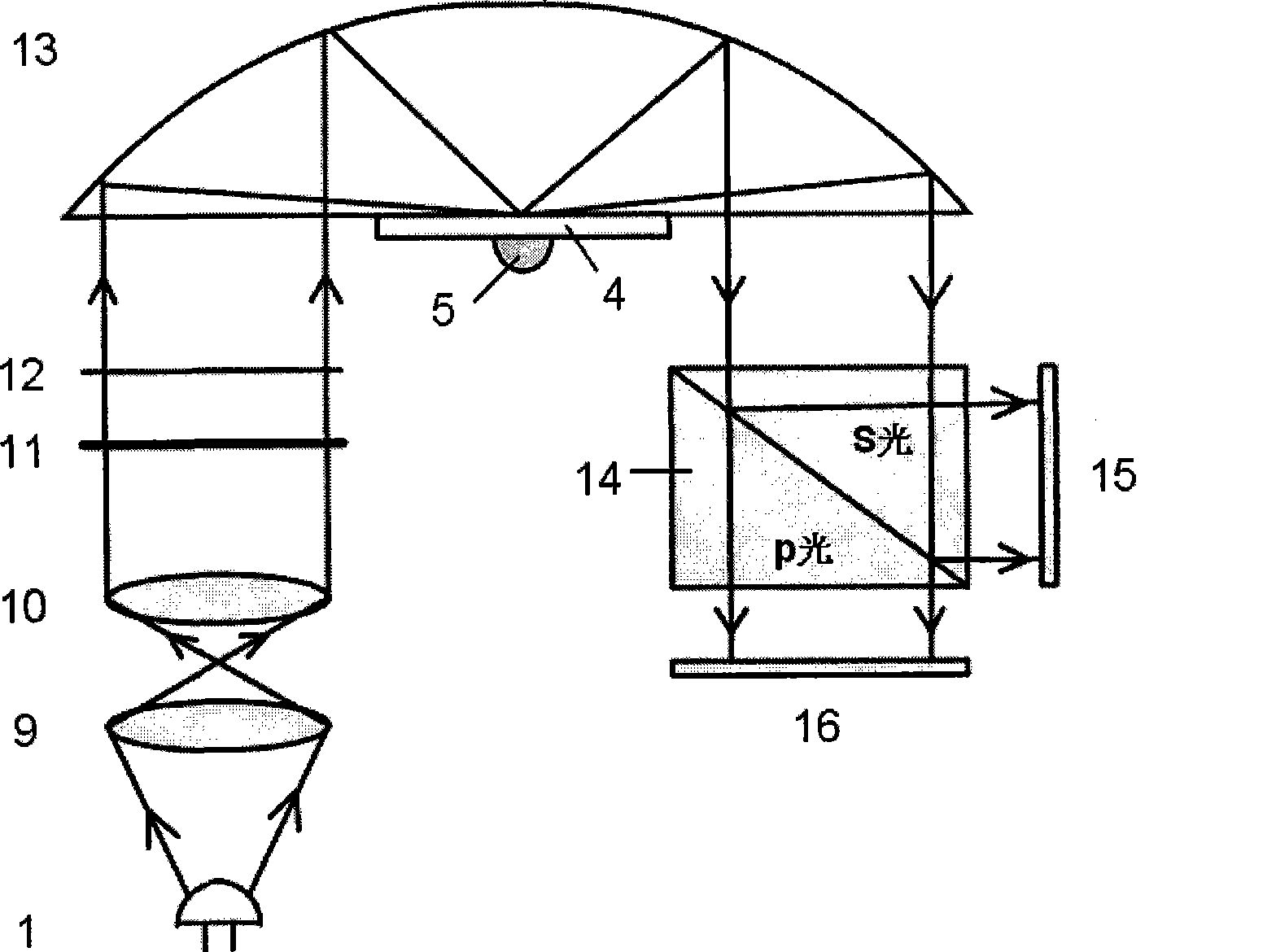
InactiveCN101477044AImprove detection stabilityEliminate the effects ofPrismsPhase-affecting property measurementsOptical reflectionPrism
The invention discloses a surface plasma resonance sensor coupled with a parabolic cylindrical reflection prism, which comprises an optical transmitter module, an optical receiver module, and an optical reflection module used for receiving rays emitted by the optical transmitter module and reflecting the rays to the optical receiver module. The optical transmitter module is orderly provided with a light source, a beam expanding lens, a collimating mirror, a filter, and a rectangular diaphragm in the direction of the rays; the optical reflection module consists of the parabolic cylindrical reflection prism and a metal film positioned at the position of a focal line of the parabolic cylindrical reflection prism; and the optical receiver module consists of a polarization splitting prism used for receiving the rays emitted by the light reflection module, a first CCD array used for receiving s light emitted by the polarization splitting prism, and a second CCD array used for receiving p light emitted by the polarization splitting prism. The surface plasma resonance sensor has simple and compact structure, accurate light beam convergence, and simple and convenient production and debugging, and effectively improves the detection stability of the surface plasma resonance sensors with angular modulation.
Owner:浙江诺迦生物科技有限公司
Acoustic module and control system for handheld ultrasound device
ActiveUS20170043189A1Uniformity in acoustic outputImprove overall acoustic uniformityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyOperating pointAcoustic energy
An acoustic module with a transducer and a solid waveguide. The transducer and waveguide may be curved to focus the acoustic energy along a focal line. The transducer, the top surface of the waveguide and the bottom surface of the waveguide may extend along coaxial curves. The waveguide may include a recess closely receiving the transducer. The waveguide may include an integral skirt that provides a thermal mass. The acoustic module may include a space to accommodate thermal management options. For example, the acoustic module may include a heatsink, an active ventilation system and / or a phase change material. The ultrasound device may include a controller configured to perform a uniformity scan sweep during supply of operating power to the transducer. The uniformity scan sweep can extend through a frequency range that includes the operating point of the acoustic module and does not exceed an acceptable efficiency loss.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Method and microscope for high spatial resolution examination of samples
InactiveUS7679741B2Quick scanCost effectiveRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical propertyImage resolution
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Vehicle lamp unit
InactiveCN1654880AImprove beam utilizationIncrease brightnessVehicle headlampsPoint-like light sourceLight beamEngineering
A pair of upper and lower incidence surfaces are formed on a rear face of a translucent member disposed to cover three light-emitting elements. On upper and lower sides of the incidence surfaces are formed a pair of reflection surfaces for causing light emitted by the light-emitting elements and having entered the translucent member to internally reflect forward. Each of the incidence surfaces is formed from a cylindrical convex-curved surface extending horizontally. Each of the reflection surfaces is formed from a parabolic cylindrical curved surface whose focal line passes through a virtual image point of each of the light-emitting elements formed by the corresponding incidence surfaces. By the above configuration, light emitted by the light-emitting elements is caused to internally reflect in such a manner as to diffuse in the horizontal direction, and not to diffuse in the vertical direction, thereby exiting forward from a pair of exit surfaces.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
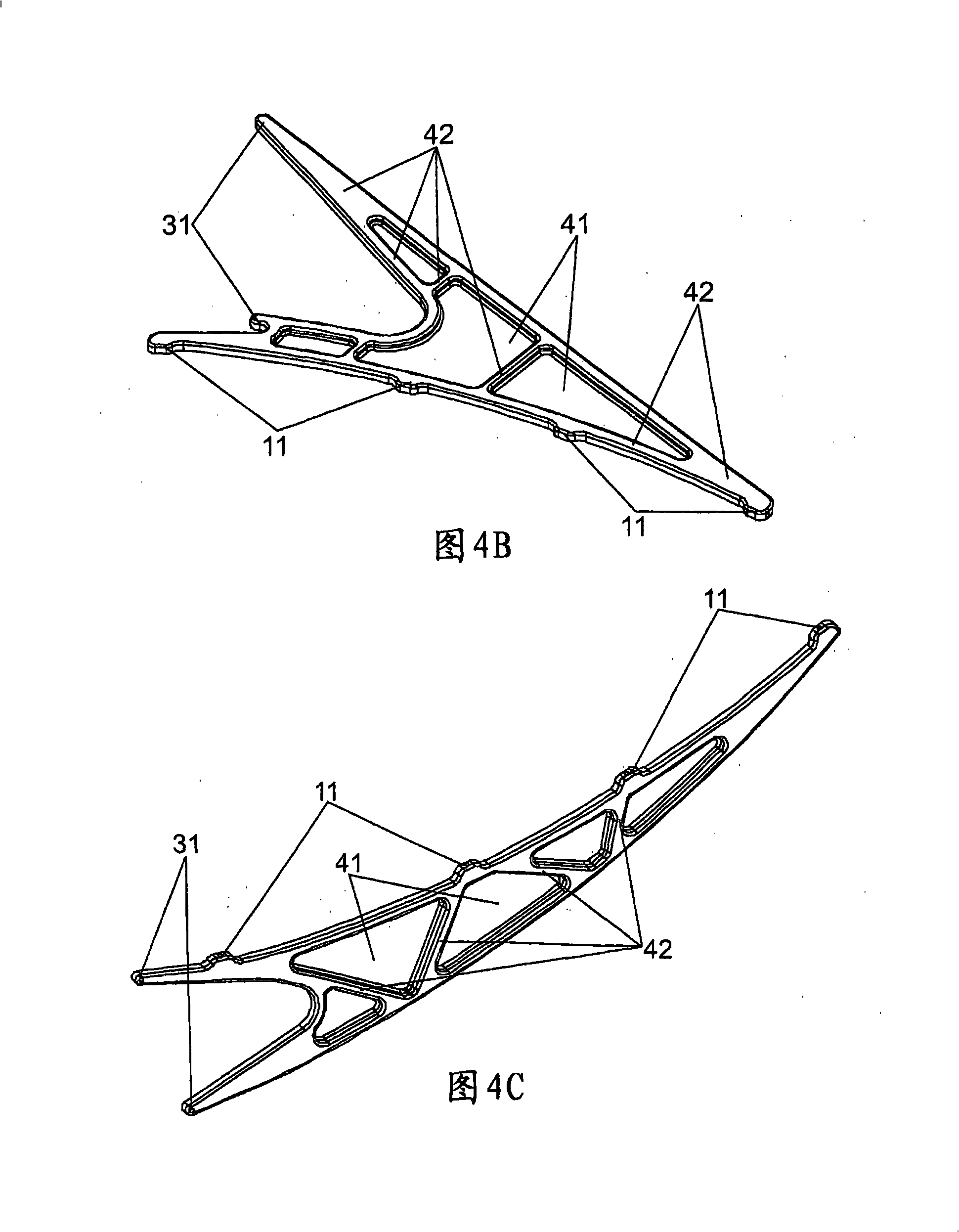
Support arm, cylindrical-parabolic solar collector support and method of producing the arm
ActiveUS20090194657A1Provide capacityProvide stiffnessSolar heating energySolar heat devicesCarrying capacityEngineering
The invention relates to a support arm for a cylindrical-parabolic collector, which is intended to be coupled to a central body (1) of the collector in the form of a bracket in a direction that is substantially perpendicular to a focal line (2) of the collector. The inventive arm takes the form of a wedge comprising: a first side (10) which is provided with support devices (11) for supporting at least one mirror (3), a second side (20), and a third side (30) which is provided with support devices (31) such that the arm is supported by the central body (1). The arm is formed by at least one press-formed plate such as to obtain a resistant structure that provides stiffness and a carrying capacity by means of a plurality of ribs (42) which form a lattice comprising a plurality of laminar segments (41) between said ribs.
Owner:SENER ING Y SISTEMAS
Light for an Aircraft
InactiveUS20130077332A1Convenient lightingHigh imagingLight source combinationsPoint-like light sourceLight-emitting diodeAirplane
A light for an aircraft comprises a holder for carrying a first group of light emitting diodes arranged along a curvilinear line and a first reflector having an elliptic reflective partial surface defining a plurality of focal points forming a first curvilinear focal line coinciding with the light emitting sites of the first group of light emitting diodes and second focal point or curvilinear focal line. The light further includes a second optical unit comprising a single further focal point or curvilinear focal line that coincides with the second focal point or focal line of the first reflector. The light further includes a second group of light emitting diodes displaced axially with respect to the first light emitting diodes, which emit light that bypasses the second focal point or focal line of the first reflector of the first optical unit.
Owner:GOODRICH LIGHTING SYST
Broad beam light
A high efficiency, broad beam lighting device 30 having a converging lens 1 having a curved focal line 26. A source of light comprising a plurality 9 of ceramic LED lamps disposed in an equiangular array having their apparent emission line between minimum divergence curved line 37 and interior surface 27 of converging lens 1 on broad beam curved line 39 such that each LED has its emitted light concentrated by lens 1 into an elongated light beam comprising a central zone substantially surrounded by a peripheral zone. Converging lens 1 further concentrates the light emitted by plurality 9 of LED lamps into a composite elongated light beam having a broad vertical beam spread and concurrently increasing the intensity at the location of the central zone of the elongated light beam of each LED by adding to that central zone location light from the elongated light beam of at least one adjacent LED.
Owner:MCDERMOTT MARY JANE
Automatic-tracking double paraboloids light-concentrating, power-generating and heating system
InactiveCN102082195AReduce external distractionsReduce manual maintenance workloadPhotovoltaic supportsMirrorsParaboloidHeating system
The invention discloses an automatic-tracking double paraboloids light-concentrating, power-generating and heating system, which comprises a big parabolic reflecting surface and a small parabolic reflecting surface. The concave surfaces of the two paraboloids are opposite to each other, and the normal axes are on a same straight line with focal points or focal lines superposed with each other. An infrared filter plate is arranged on or adjacent to the focal points of the two paraboloids; a photovoltaic electroplate is fixed on the bottom of the concave surface of the big parabolic reflecting surface; the photovoltaic electroplate is connected with a metal heat-conductive sheet; a cooling metal slim tube is attached to the metal heat-conductive sheet; the photovoltaic electroplate is connected with the rotating shafts of transverse direction and longitudinal direction via a mechanical supporting mechanism. A look-down detector is arranged in front of the small parabolic reflecting surface, and the spherical axis of the detector is parallel to the axis of the paraboloid; the look-down detector is connected with a controller which is connected with an actuating motor for controlling the rotation of transverse rotating shaft and the longitudinal rotating shaft. The system is reasonable in structure, solves the problems of much interference, low precision and poor stability of the existing sunlight tracking system, reduces detection error and improves tracking precision and stability.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Radiation measuring device of light-gathering heat collection pipe and scanning analysis method thereof
InactiveCN101871811AEasy to controlFine Circumferential ScanningSpectrum investigationSolar heat devicesMeasurement deviceRadiometer
The invention belongs to the field of solar heat collection, in particular relates to a radiation measuring device of light-gathering heat collection pipe and a scanning analysis method thereof. The radiation measuring device of light-gathering heat collection pipe comprises a heat collection pipe sleeve, an axial scanning driver, wherein a circumferential scanner and a spectral radiometer, the device is fixed on the heat collection pipe to be measured to form a heat collection pipe assembly, the heat collection pipe assembly is arranged on the focal line of a parabolic groove face reflector, the axial scanning driver realizes the axial movement of the circumferential scanner, the circumferential scanner realizes the circumferential scanning movement of optical fiber, and the optical fiber transmits the received radiation energy to the spectral radiometer, so that fine measurement of radiation energy flow at the surface of the heat collection pope is realized; the scanning analysis method uses optical fiber to collect and transmit the focus radiation energy at the wall surface of the heat collection pipe point by point, uses the spectral radiometer to measure the optical parameters, and optically detects the parameters of the radiation energy flow at the wall surface of the heat collection pipe including light intensity, optical power spectral density, color temperature, and the like. The invention is applied to solar thermal power generation requiring high power condensation.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
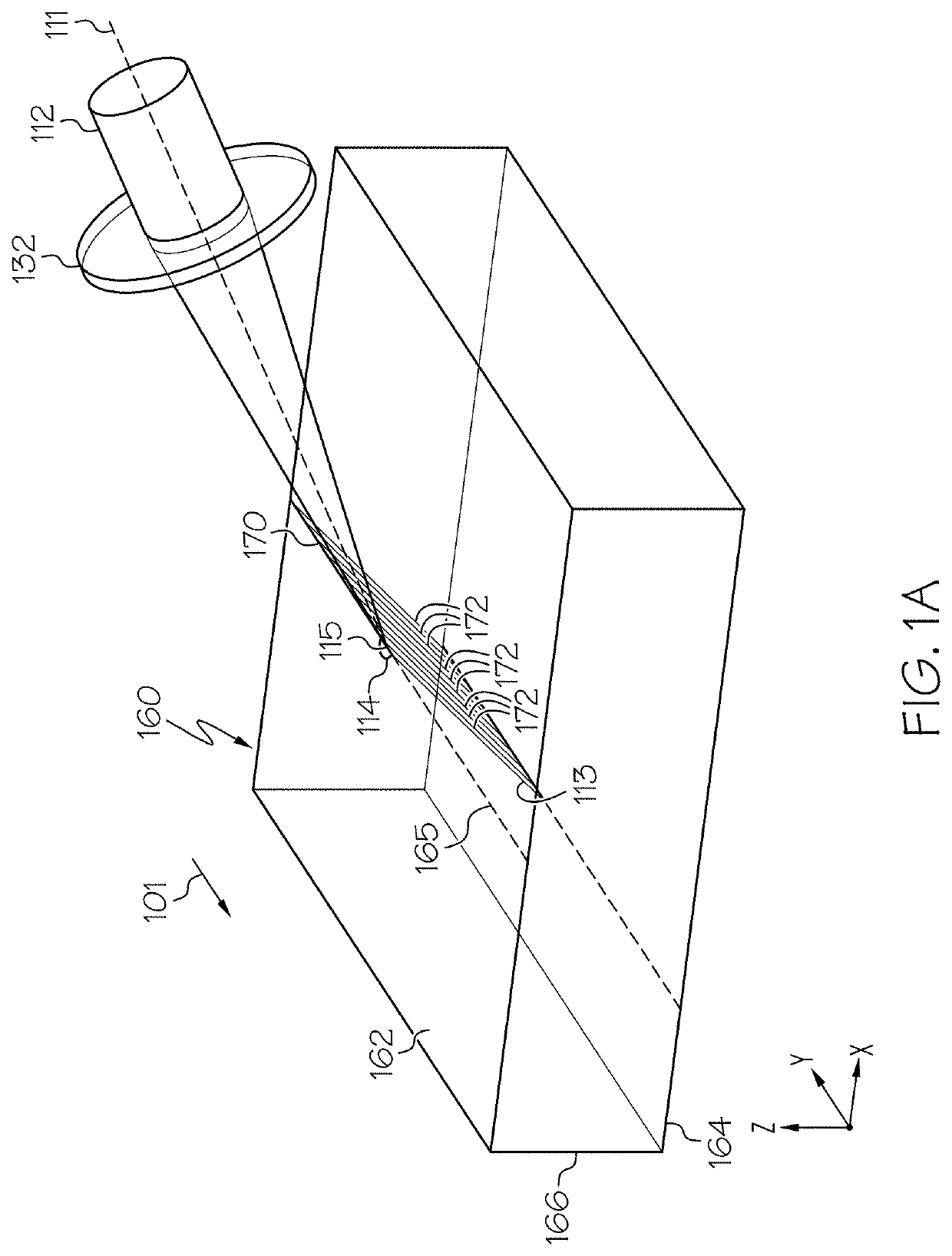
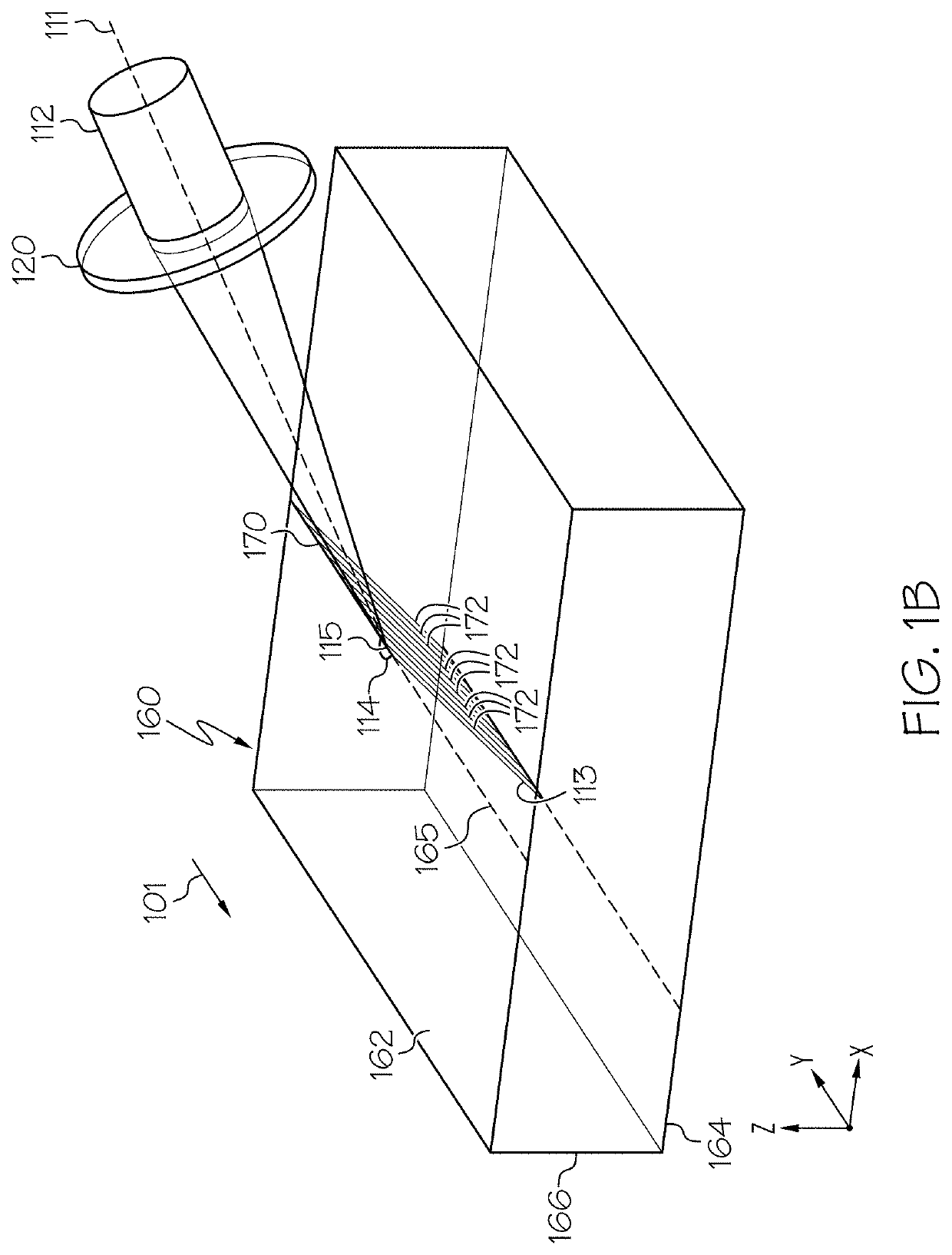
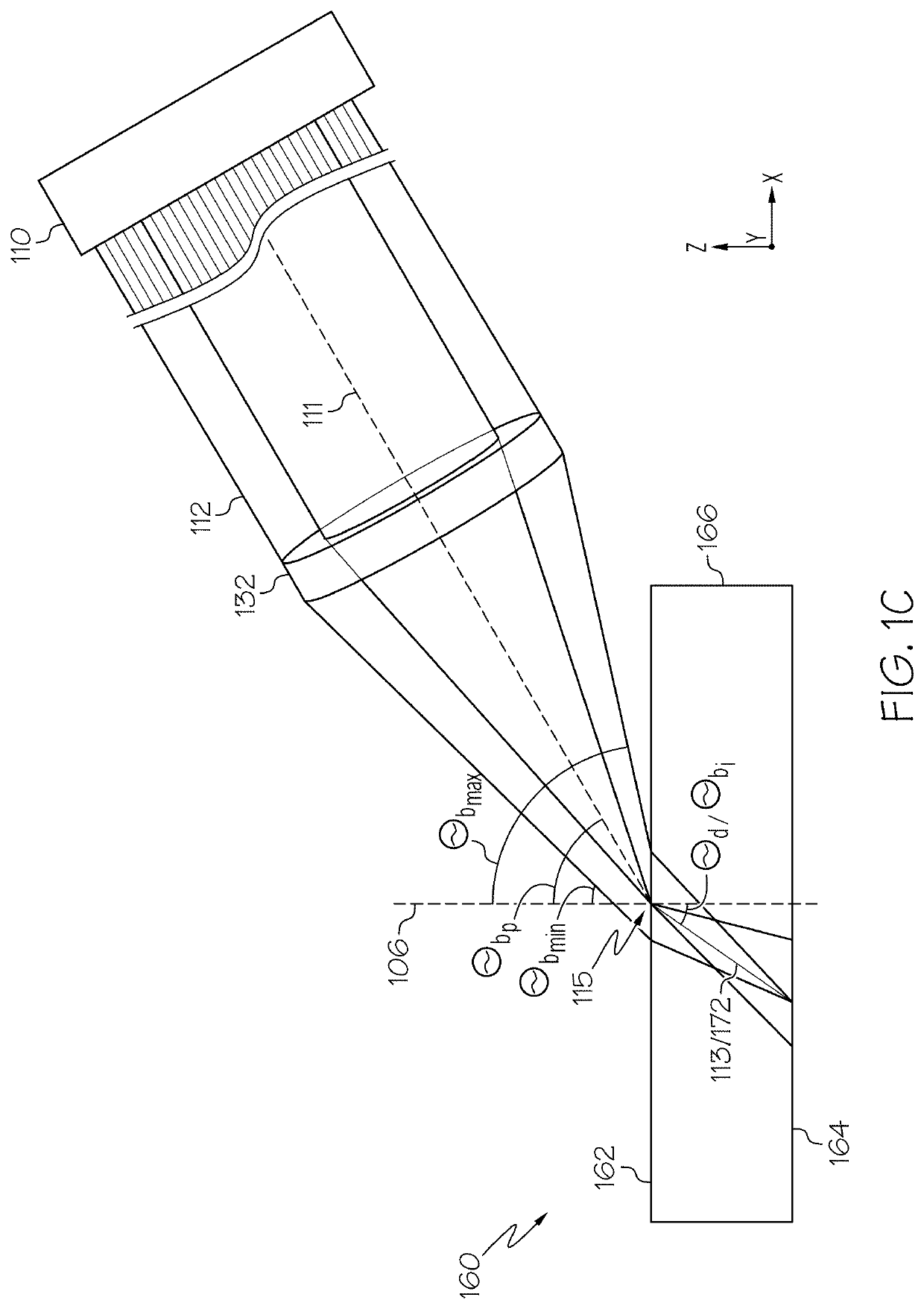
Phase-modified quasi-non-diffracting laser beams for high angle laser processing of transparent workpieces
ActiveUS20200361037A1Glass severing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesBeam angleLaser processing
A method for processing a transparent workpiece that includes directing a laser beam the transparent workpiece. The laser beam incident to the impingement surface has an oblong angular spectrum and portion of the laser beam directed into the transparent workpiece is a laser beam focal line and generates an induced absorption to produce a defect within the transparent workpiece. The laser beam focal line includes a wavelength λ, a spot size wo, a Rayleigh range ZR that is greater thanFDπwo2λ,where FD is a dimensionless divergence factor comprising a value of 10 or greater, and an internal beam angle of greater than 10° relative to a plane orthogonal to an impingement surface at an impingement location, such that the defect has a defect angle within the transparent workpiece of greater than 10° relative to a plane orthogonal to the impingement surface at the impingement location.
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com