Patents
Literature
248 results about "Ka band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Kₐ band (pronounced as either "kay-ay band" or "ka band") is a portion of the microwave part of the electromagnetic spectrum defined as frequencies in the range 26.5–40 gigahertz (GHz), i.e. wavelengths from slightly over one centimeter down to 7.5 millimeters. The band is called Kₐ, short for "K-above" because it is the upper part of the original NATO K band, which was split into three bands because of the presence of the atmospheric water vapor resonance peak at 22.24 GHz (1.35 cm), which made the center unusable for long range transmission. The 30/20 GHz band is used in communications satellite uplinks in either the 27.5 GHz and 31 GHz bands, and high-resolution, close-range targeting radars aboard military airplanes. Some frequencies in this radio band are used for vehicle speed detection by law enforcement. The Kepler Mission used this frequency range to downlink the scientific data collected by the space telescope.
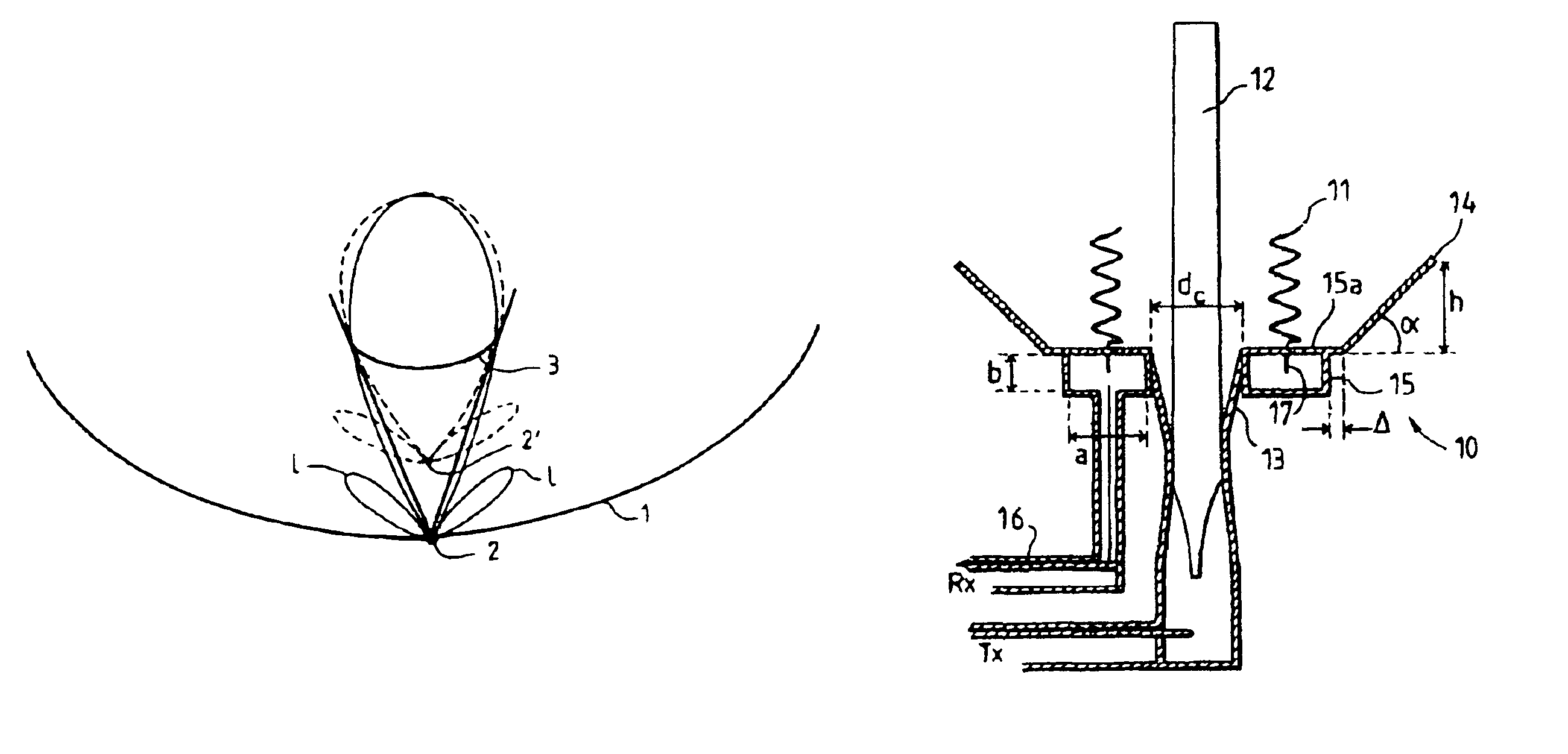
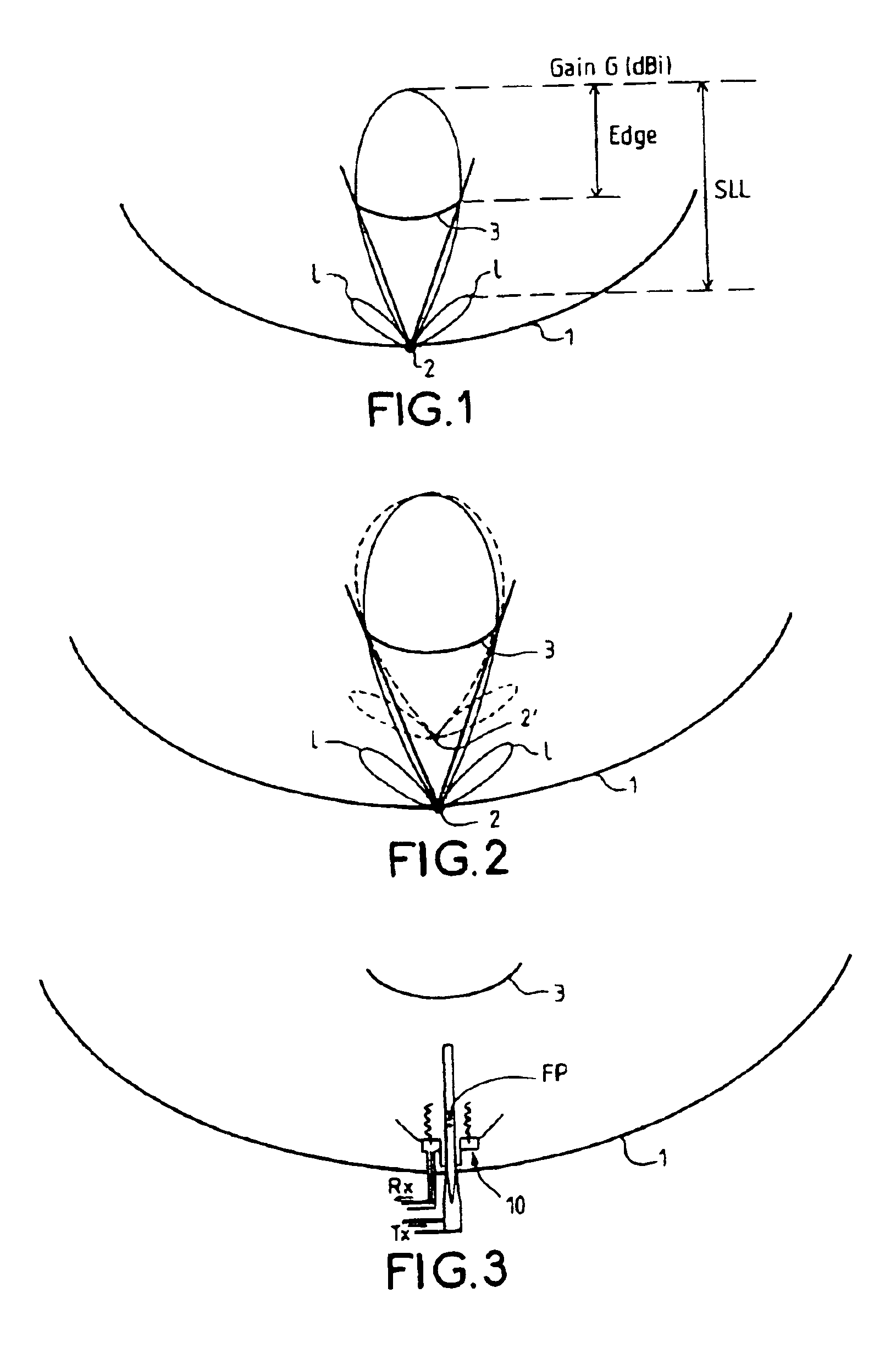
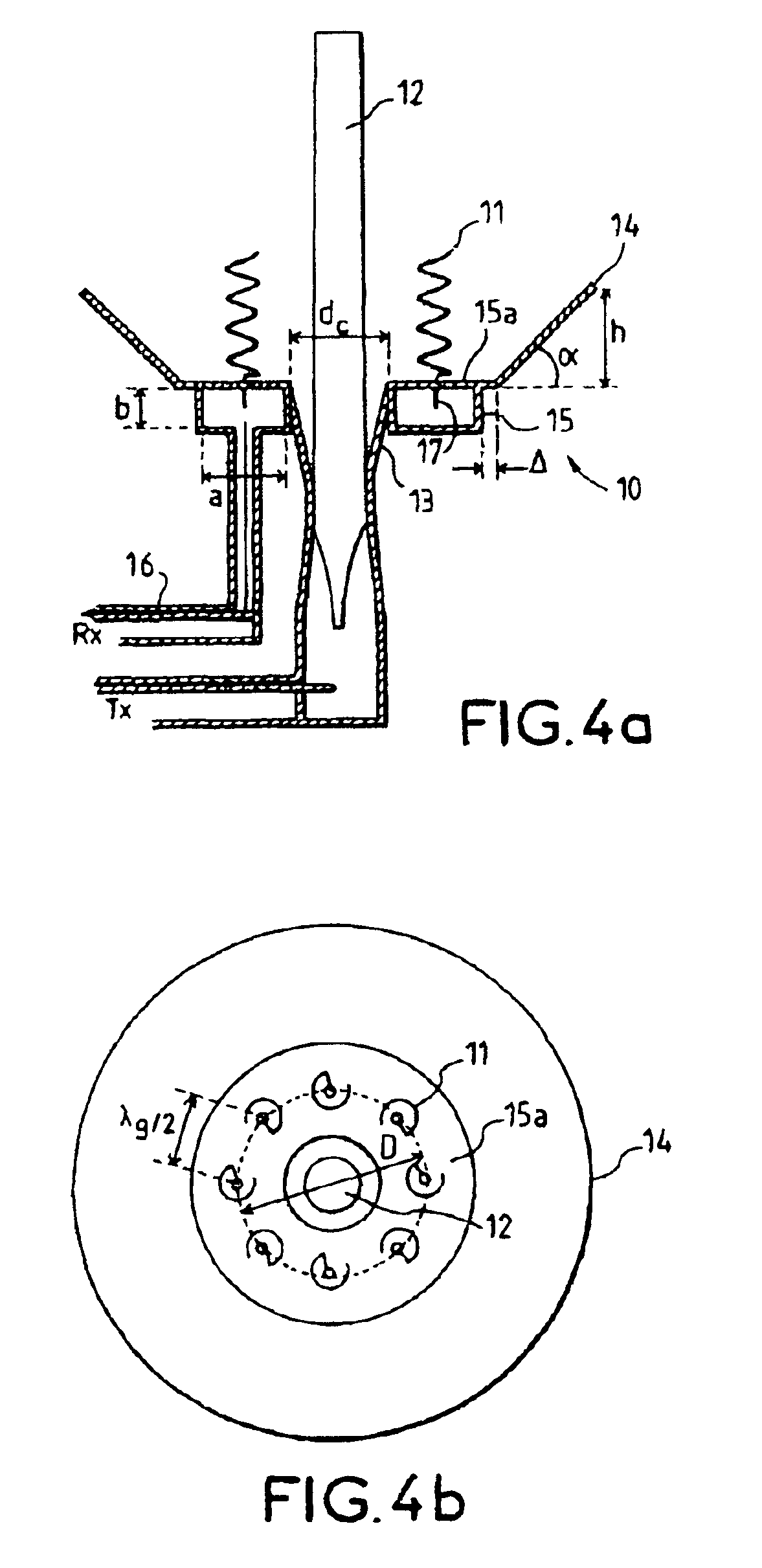
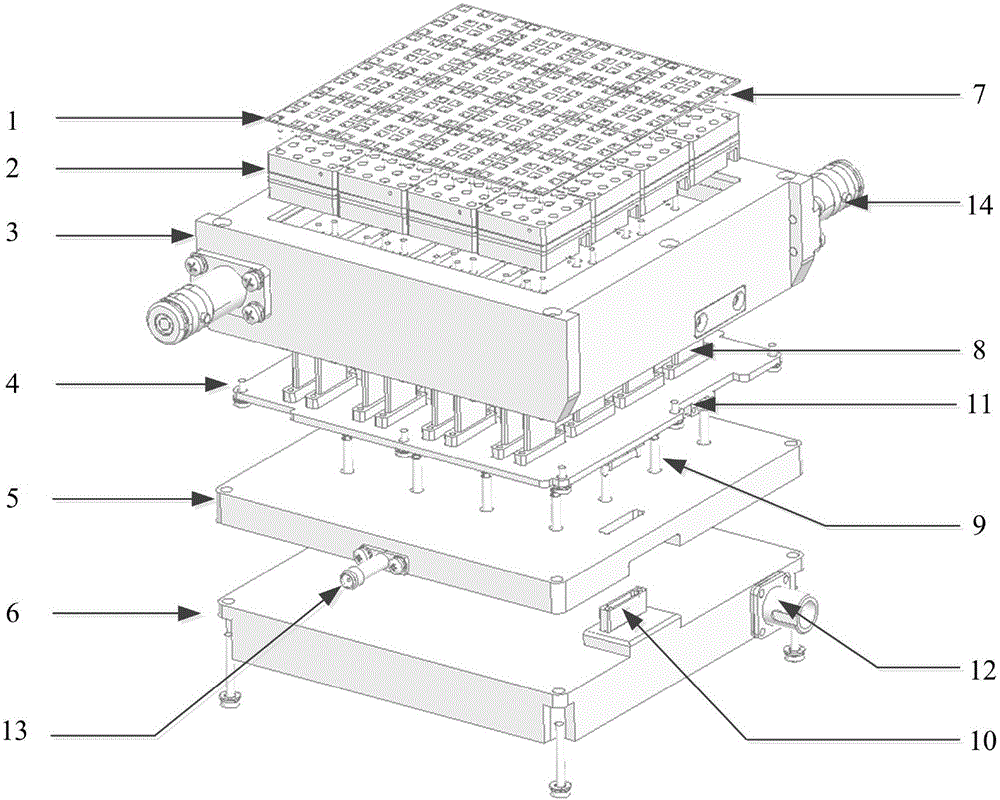
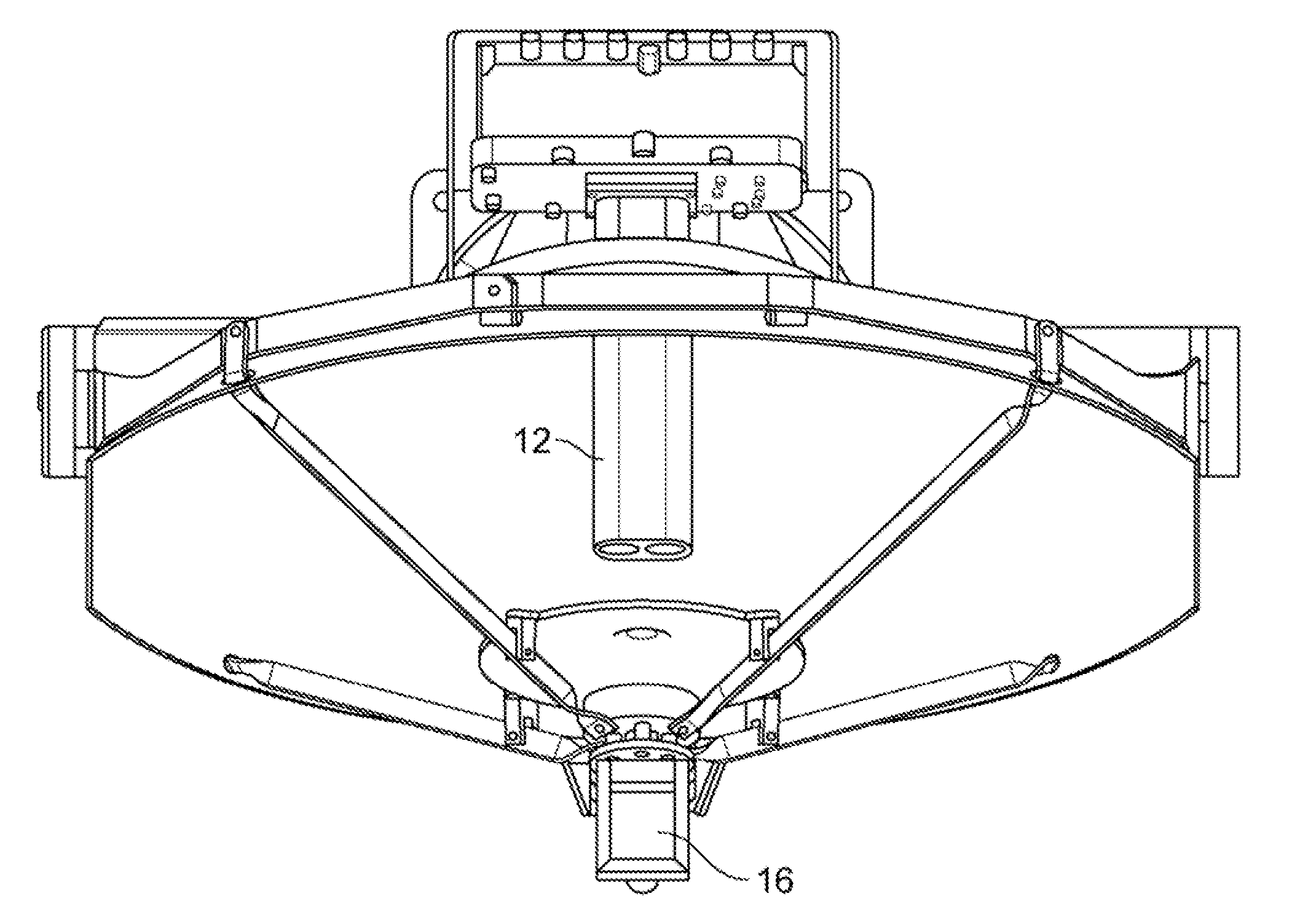
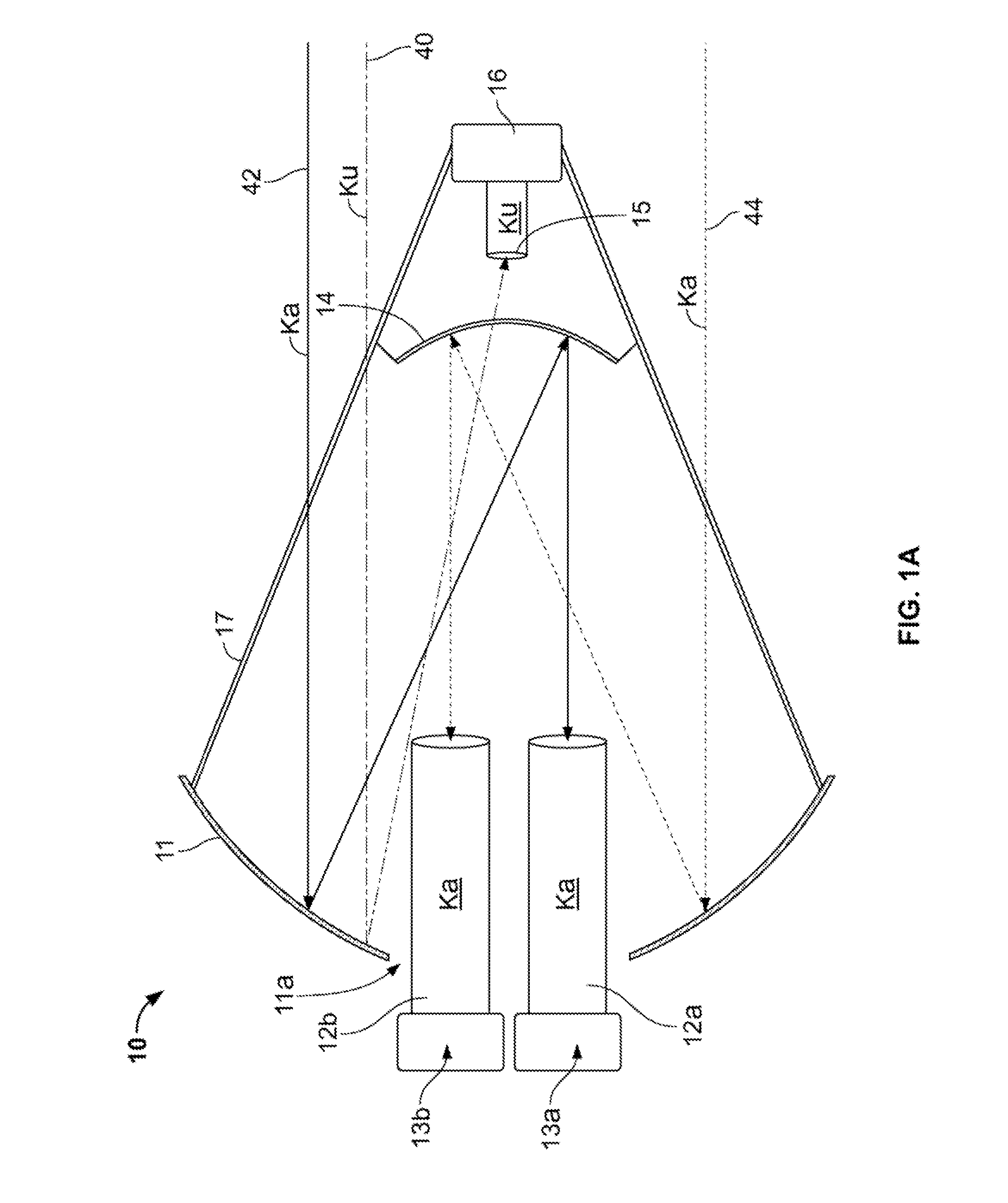
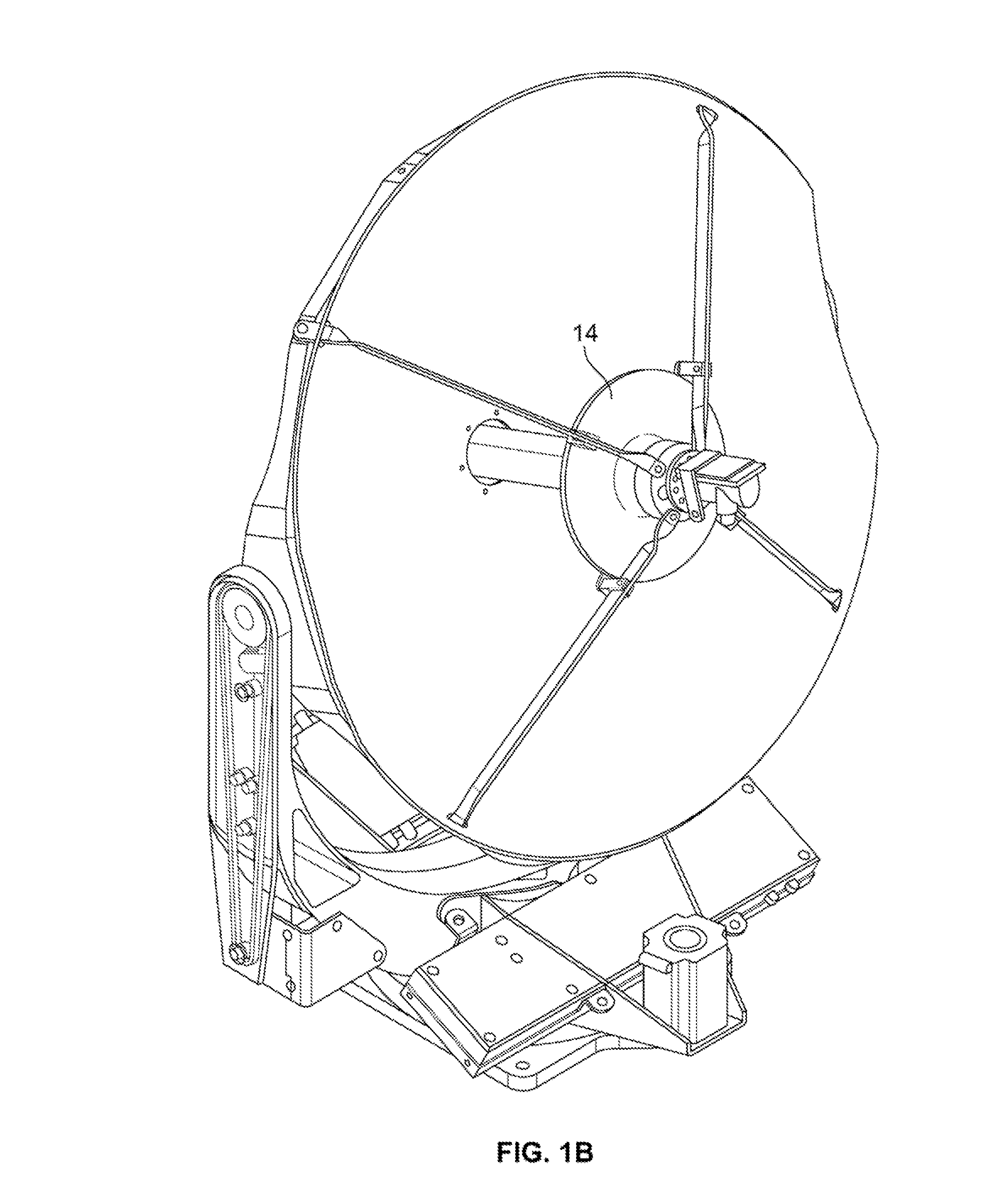
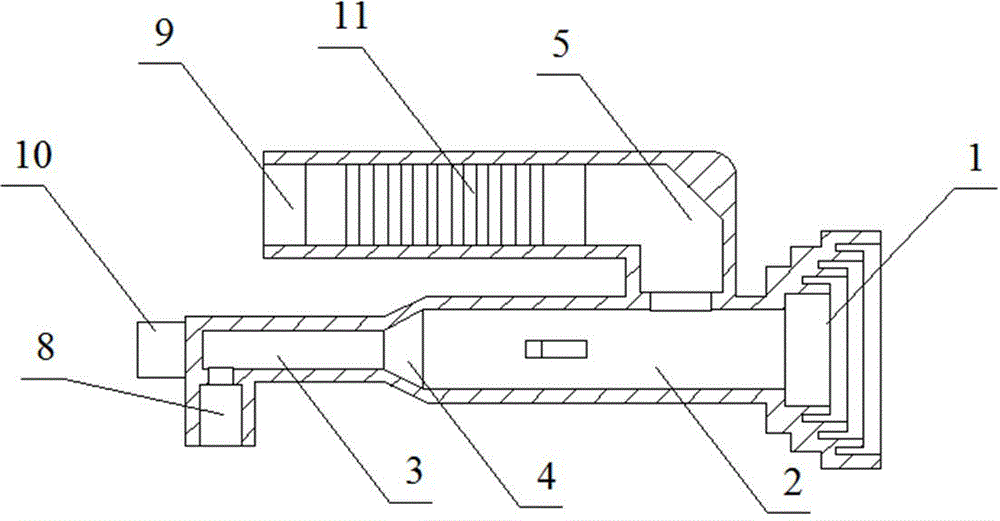
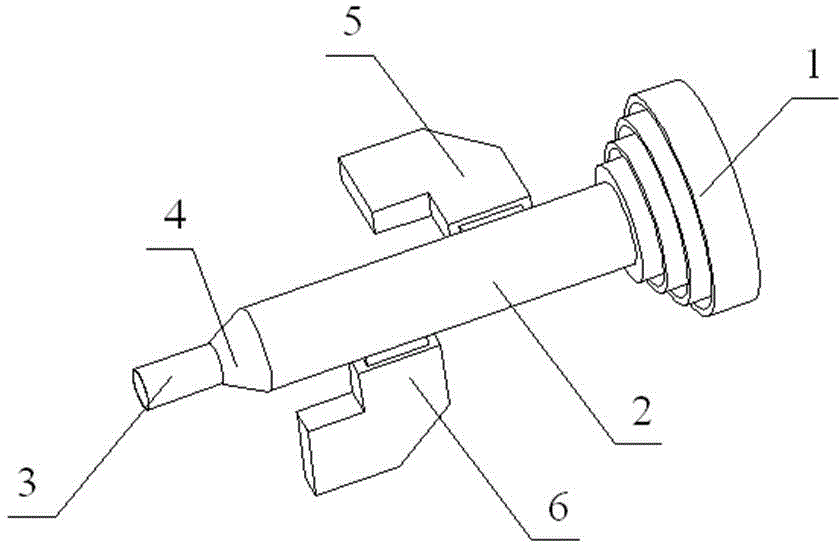
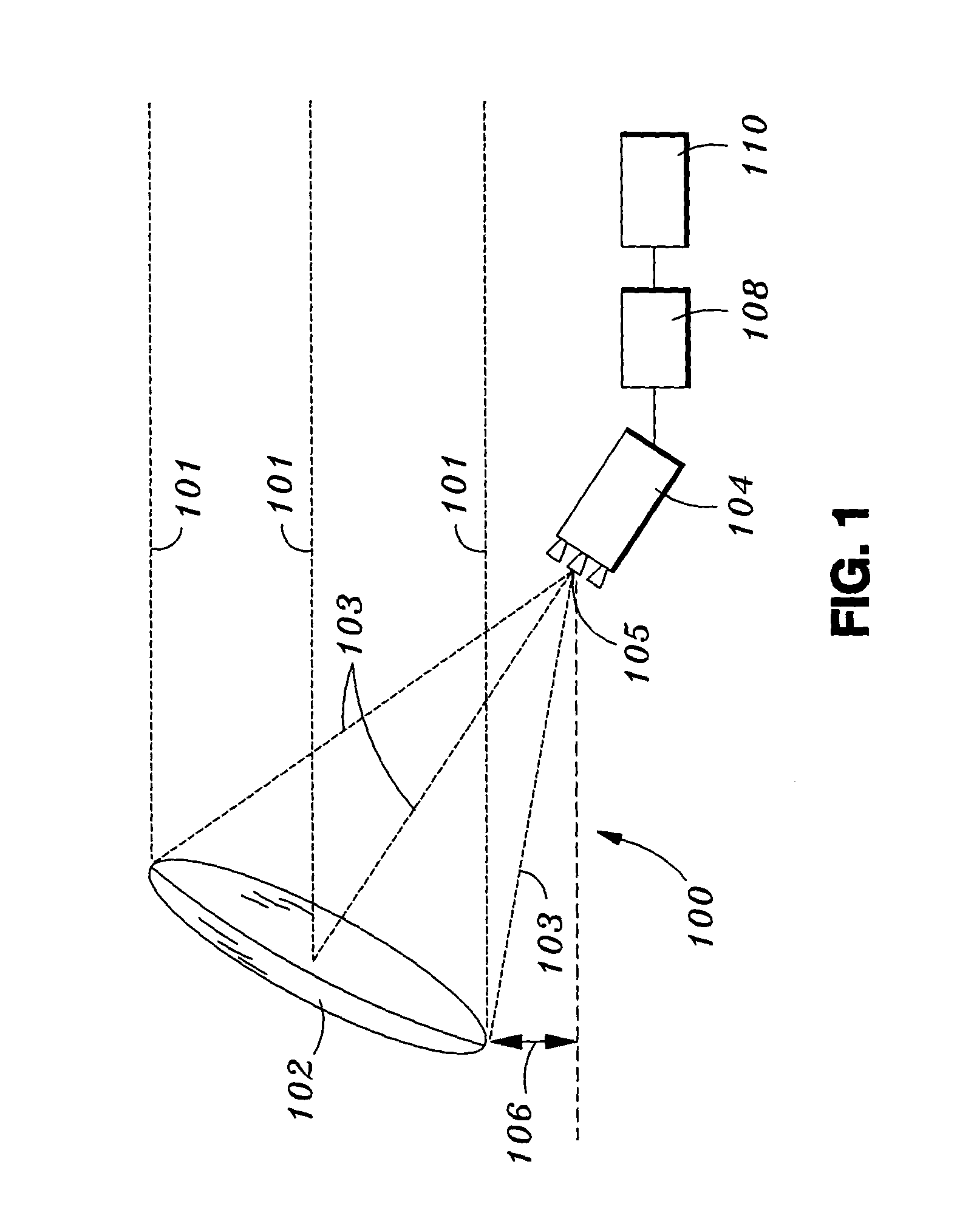
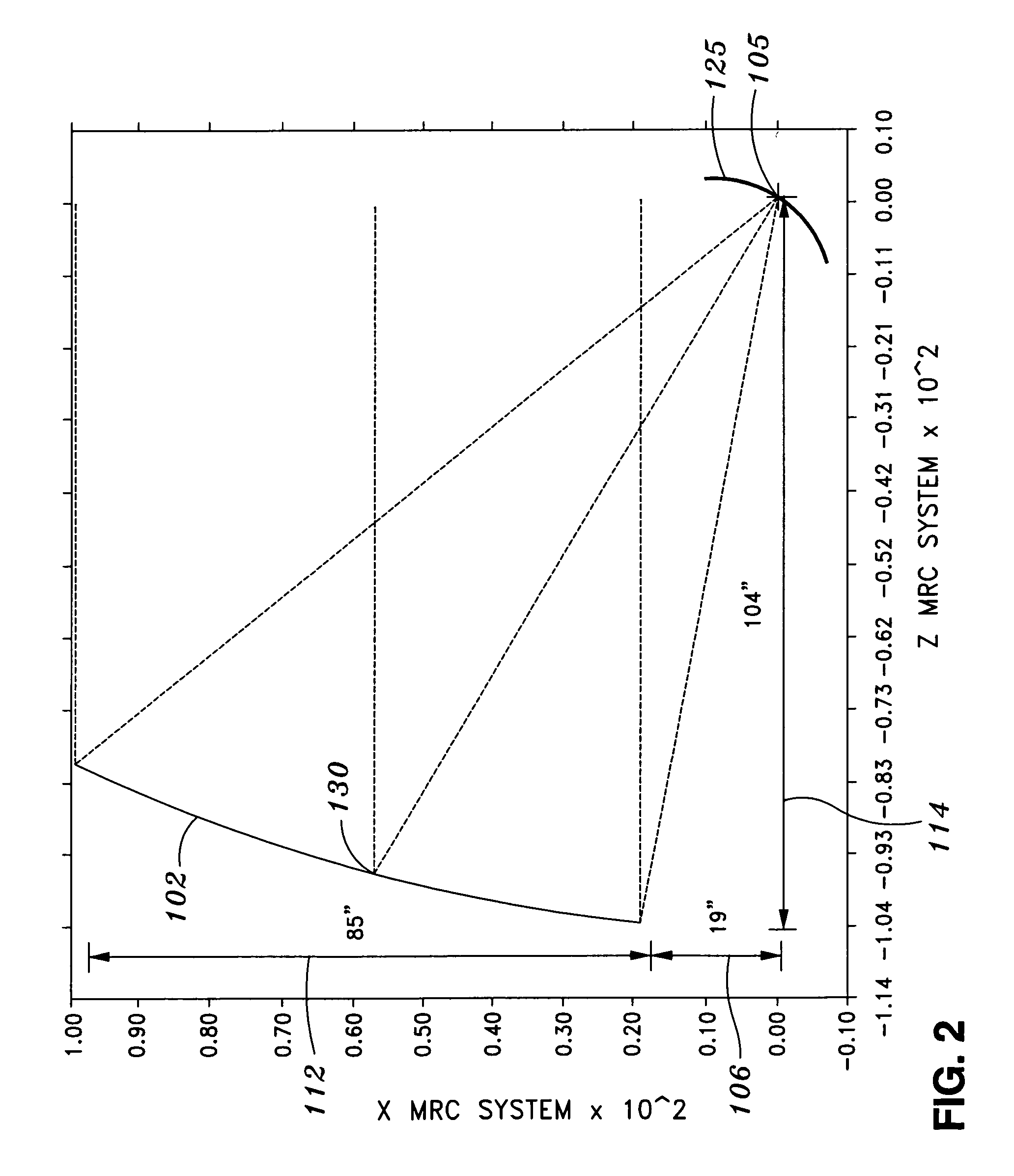
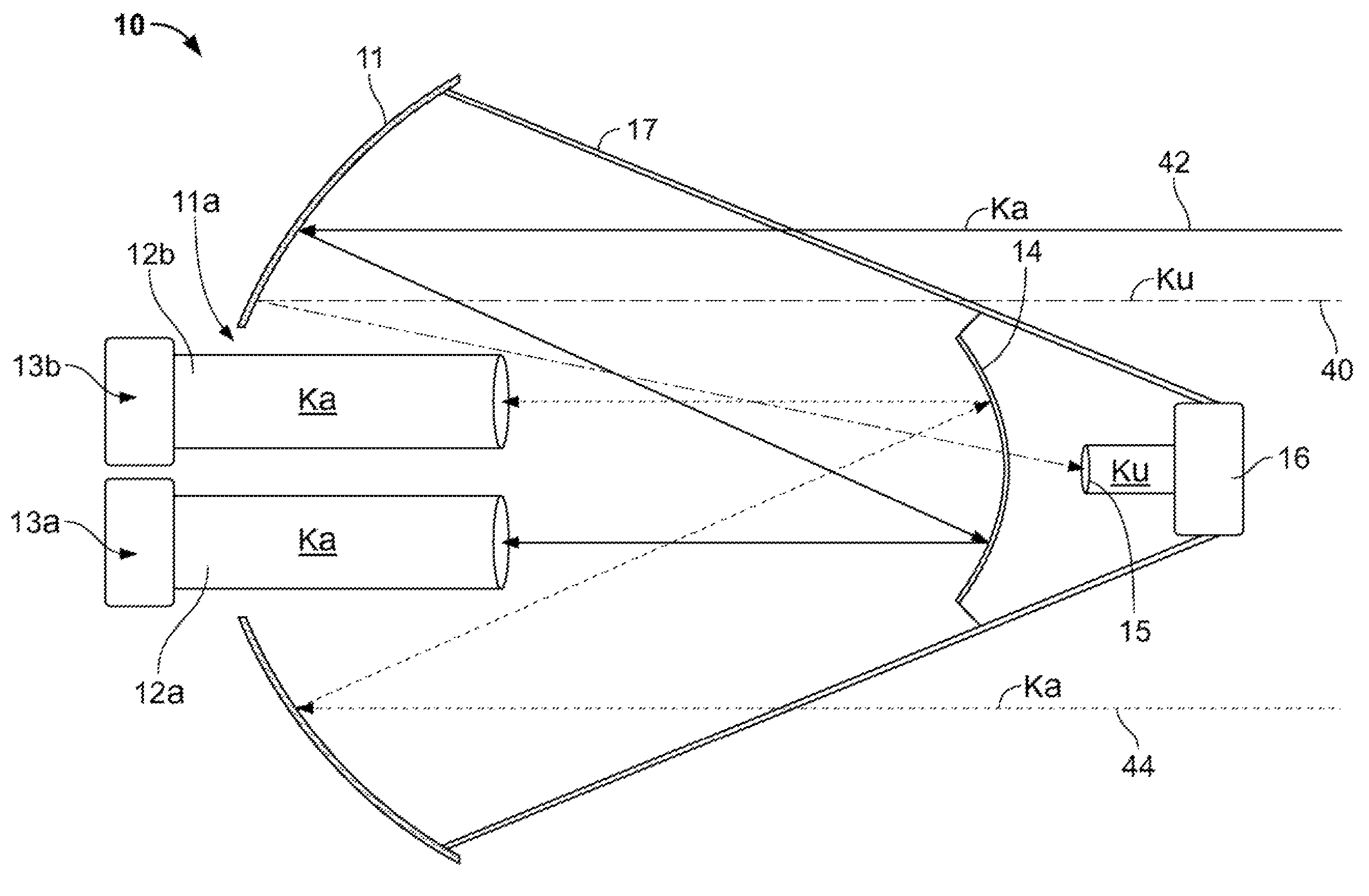
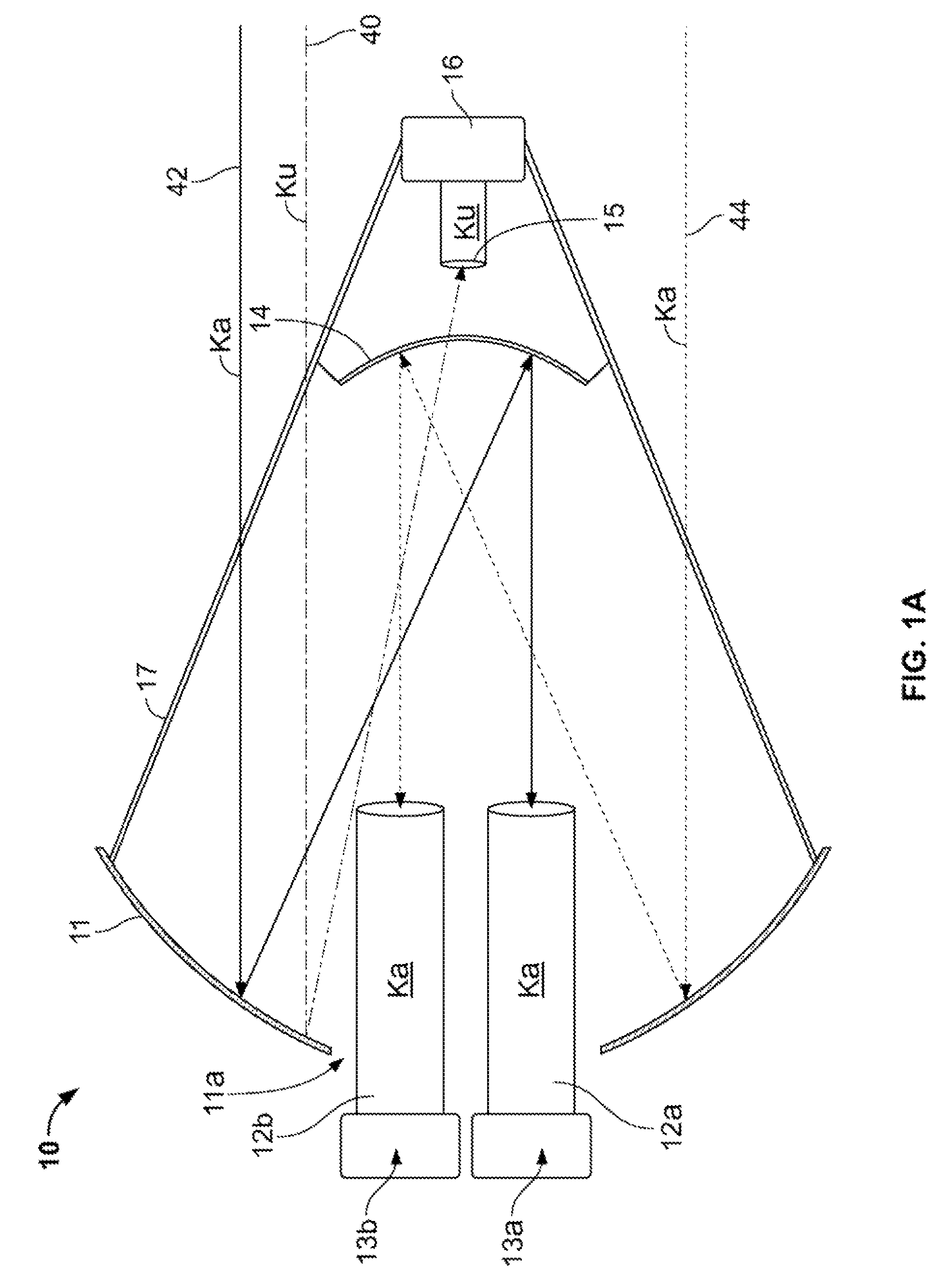
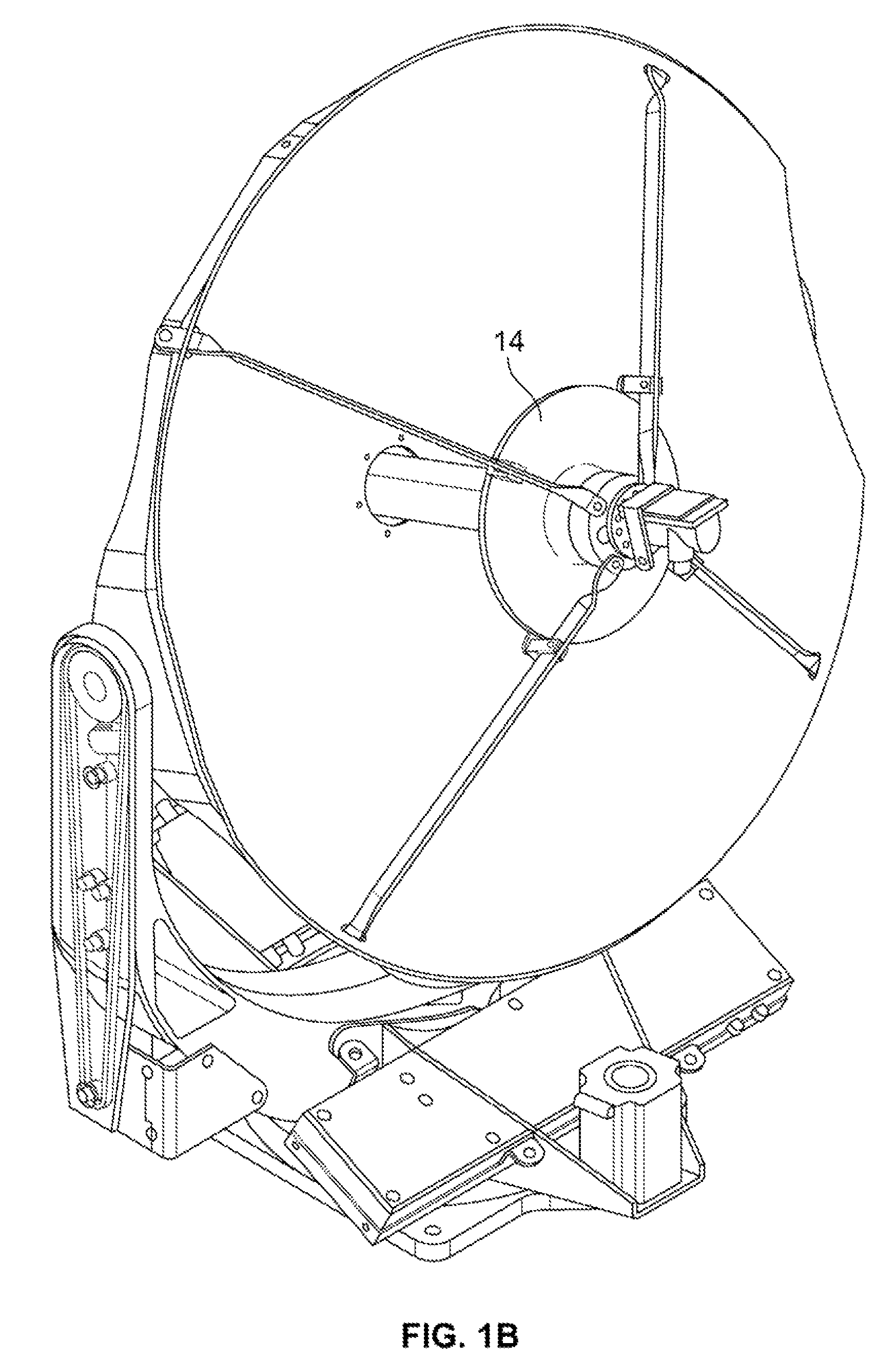
Transmission/reception sources of electromagnetic waves for multireflector antenna
InactiveUS6861998B2Reduce sidelobeReducing side lobe level SLLLogperiodic antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsElectromagnetic wave transmissionWaveguide
The present invention relates to an electromagnetic wave transmission / reception source for a multireflector antenna of the Cassegrain type comprising longitudinal-radiation means operating in a first frequency band and an array of n radiating elements of the travelling-wave type operating in a second frequency band with the n radiating elements arranged symmetrically around the longitudinal-radiation means, the array and the longitudinal-radiation means having an approximately common phase centre, the array of n radiating elements being excited by a waveguide of polygonal cross section. The invention applies especially in satellite communication systems operating in the C-, Ku- or Ka-bands.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
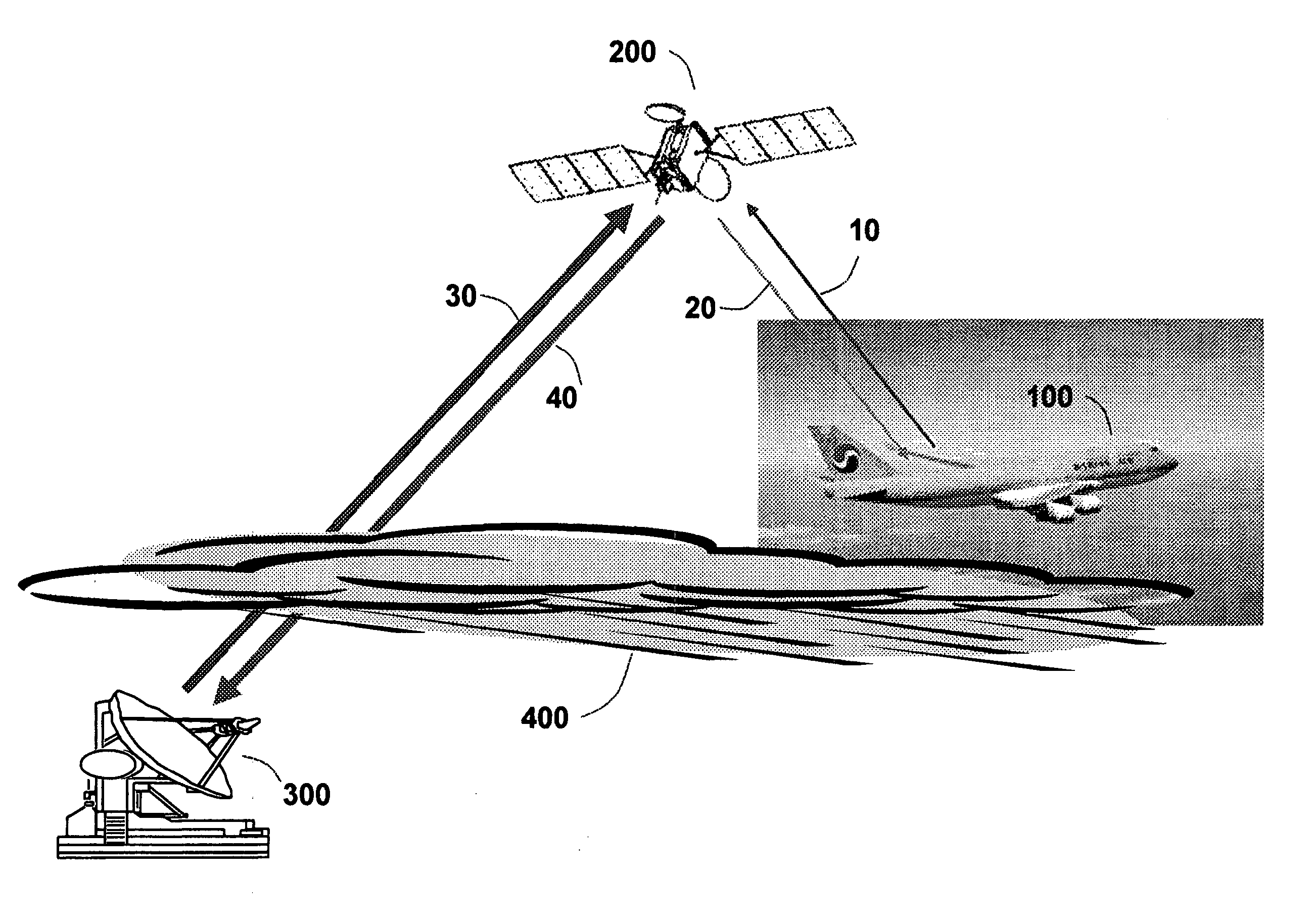
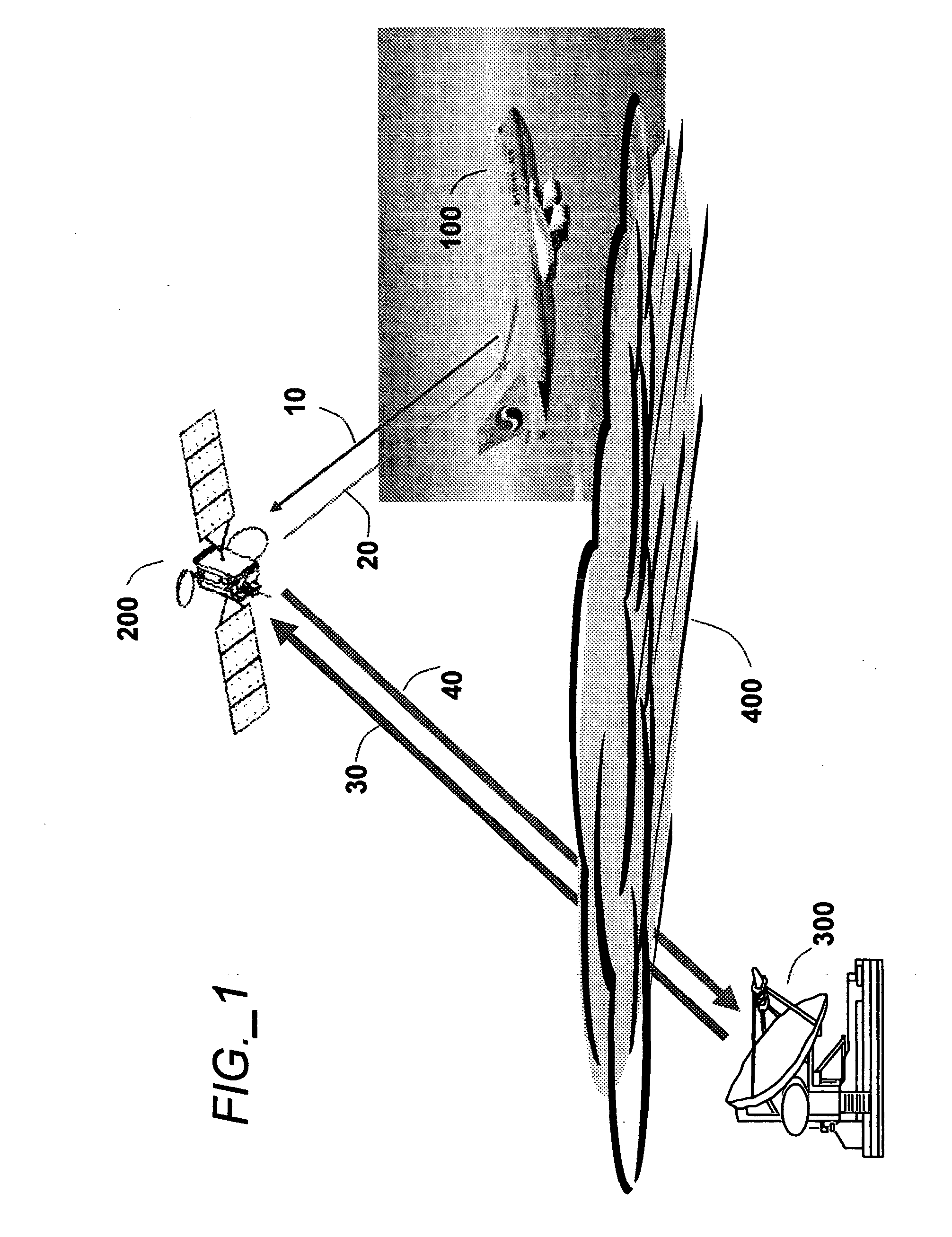
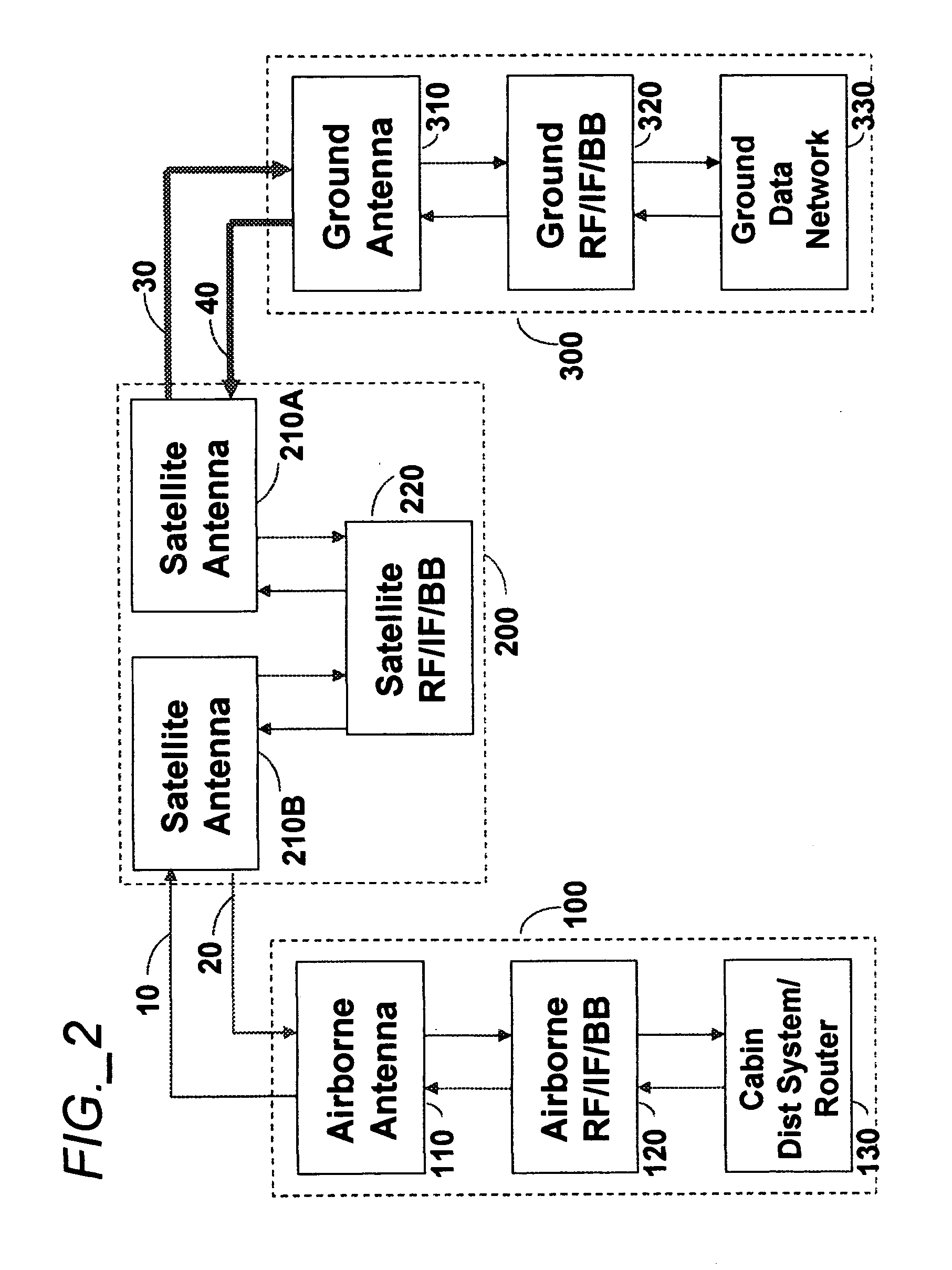
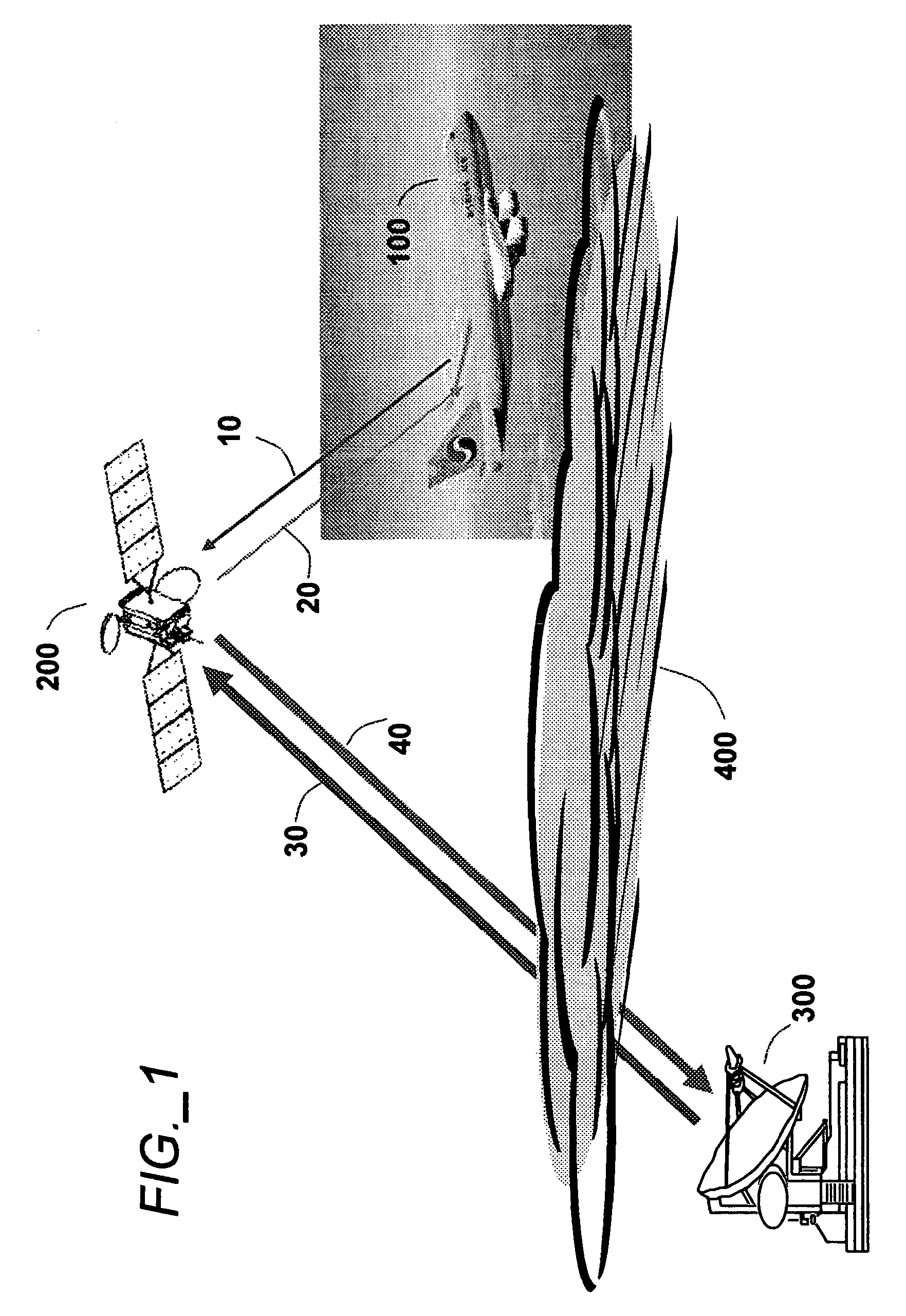
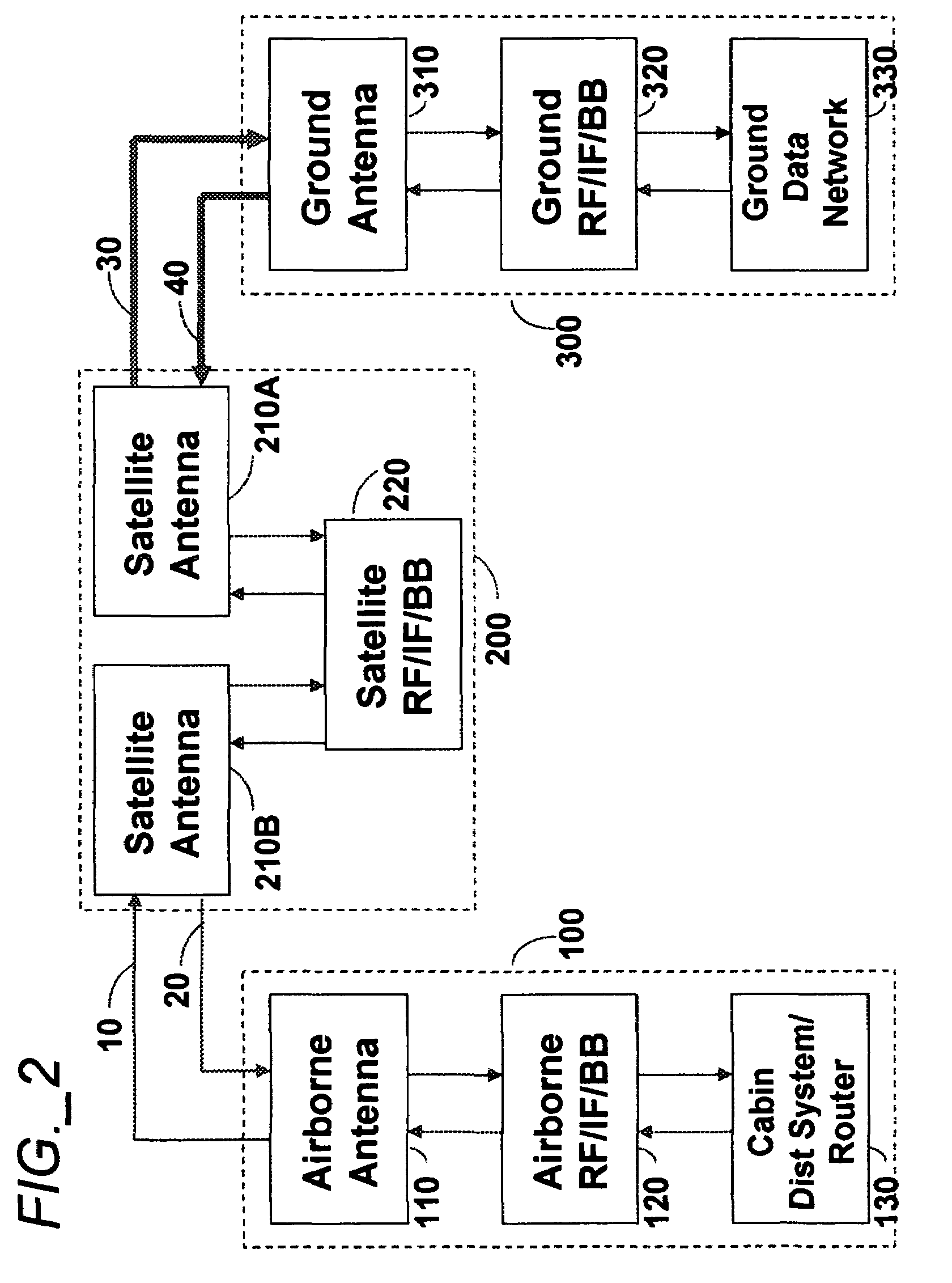
Aeronautical broadcast and communication system
ActiveUS20060040612A1Relatively large bandwidthMore bandwidthActive radio relay systemsWireless commuication servicesJet aeroplaneAviation
A method and system for a plurality of airplanes in flight to receive from and send to a plurality of ground stations broadcast and communication signals through a single or a plurality of geostationary satellites, wherein at least the mobile link between said airplanes and said satellite, uplink or downlink, uses the high frequency radio waves at 17 GHz or higher, such as Ka-band. The fixed link between said satellite and said ground stations may use any radio frequencies below the frequencies used to communicate between the satellite and the aircraft. The lower frequencies tend to be less susceptible to rain attenuation and hence suitable for closing the fixed broadcast and communication link. Frequencies such as C-band or Ku-band, or even Ka-band, are applied between satellite and ground such that the available link margin is sufficient to overcome rain attenuation at said ground stations. Said satellite carries a plurality of transponders that may include a plurality of frequency converters to enable the conversion between different frequencies. Said satellite generates a plurality of spot beams, shaped or unshaped, which collectively cover the flight routes of said airplanes, preferably the geodesic path between two highly populated regions.
Owner:NUBRON
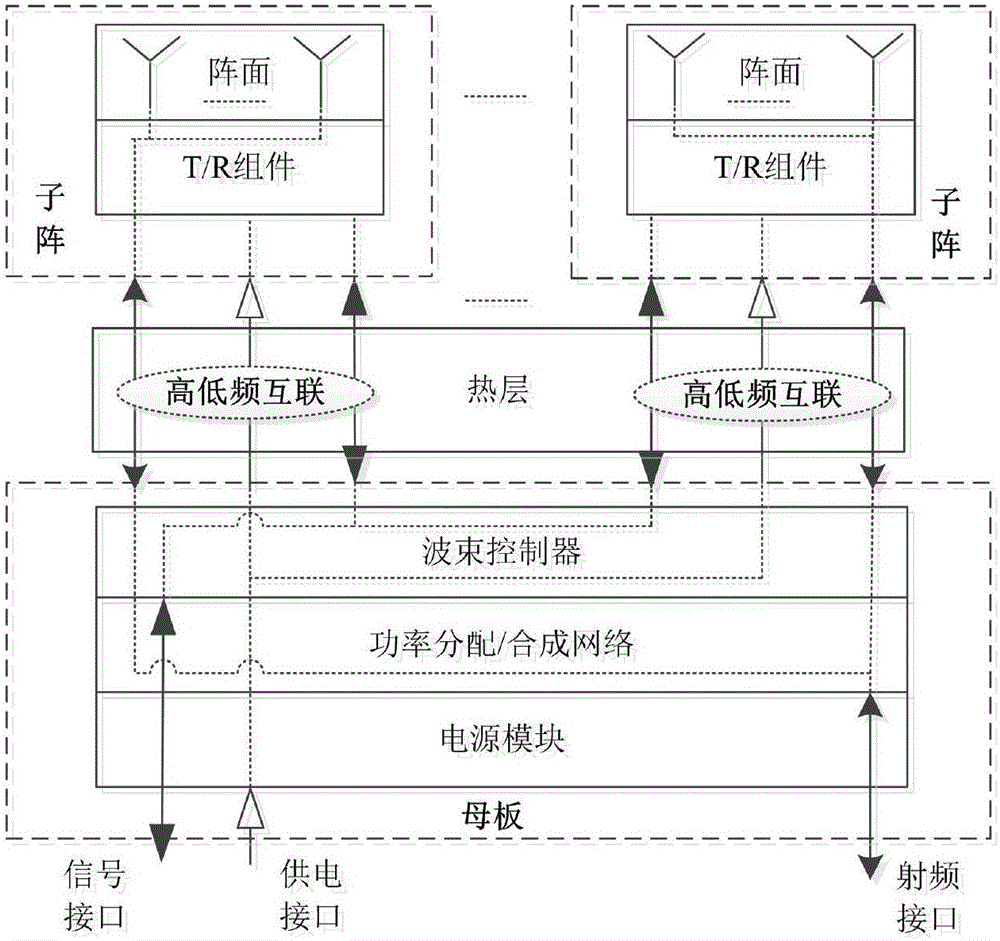
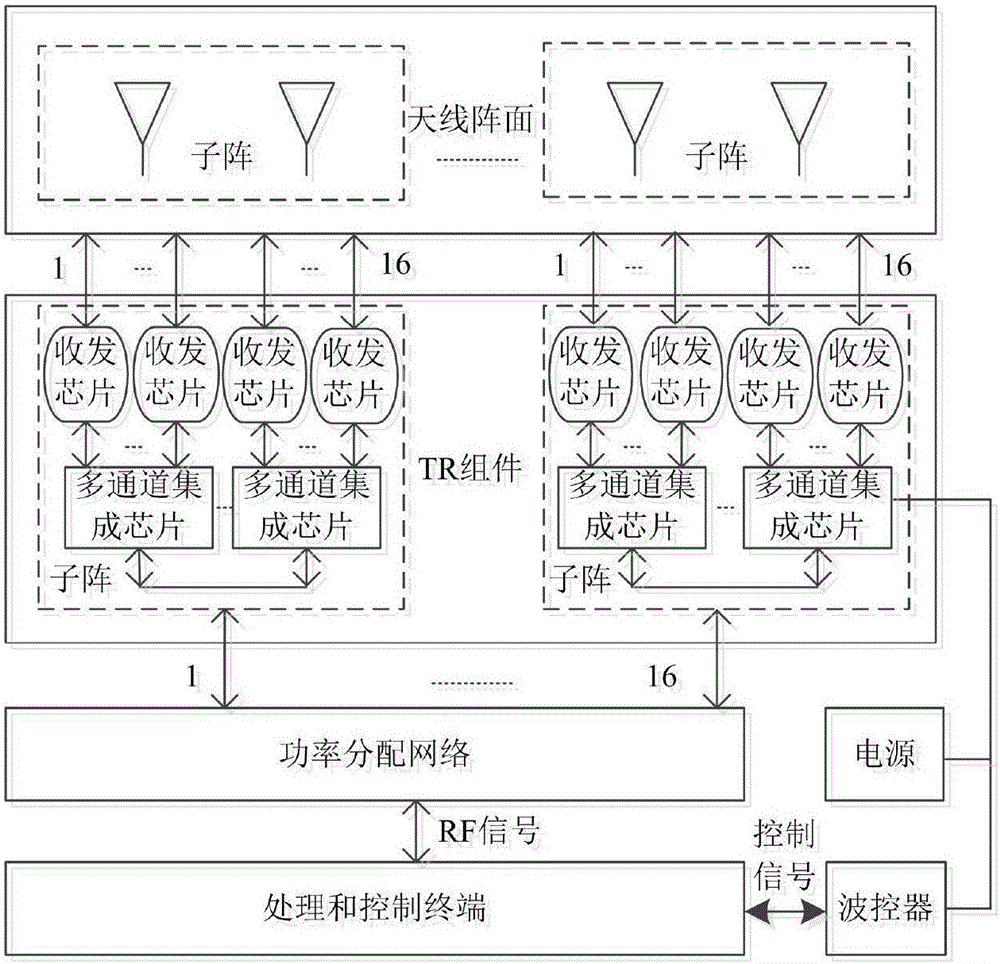
Ka-band tilt-structure active phased array antenna
InactiveCN105914476AHighly integratedImprove performanceAntenna arraysAntennas earthing switches associationArray elementActive phase
The invention provides a Ka-band tilt-structure active phased array antenna, so as to provide an active phased array antenna which is high in integration density and can improve maintainability and interchangeability. According to the technical scheme, one path of RF signals transmitted by a transmitting signal processing terminal are transmitted to a power distribution / synthesis network (5) via a signal interface and a radio frequency interface to be divided into M paths of signals; according to information of an azimuth angle and a pitch angle of the phased array antenna provided by the transmitting signal processing terminal in real time, a beam controller (4) calculates and obtains beam pointing of the phased array antenna in real time through an FPGA; the beam pointing of the phased array antenna is converted into phase data needed by each array element under control of the beam controller (4); the data are transmitted to tilt-type TR assembly sub array modules in N channels respectively via a high and low-frequency interconnected multi-core high and low-frequency socket, and under control of the beam controller, M*N paths of signals are transmitted to an antenna array, and thus signal transmission is completed, and synchronous electric control scanning of beams transmitted by the phased array antenna is realized.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Multi-Band Antenna System for Satellite Communications
The present invention provides an improved antenna system on moving platform that is in communication with multiple satellites for simultaneous reception and transmission of RF energy at multiple frequencies. The antenna is implemented as a multi-beam, multi-band antenna having a main reflector with multiple feed horns and a sub-reflector having a reflective surface defining an image focus for a Ka band frequency signal and a prime focus for a Ku band frequency signal.
Owner:KVH IND INC
Low profile active electronically scanned antenna (AESA) for ka-band radar systems
InactiveUS20050146479A1Space is requiredPrevent RF leakageRadiating element housingsAntenna arrays manufactureTransceiverRadar systems
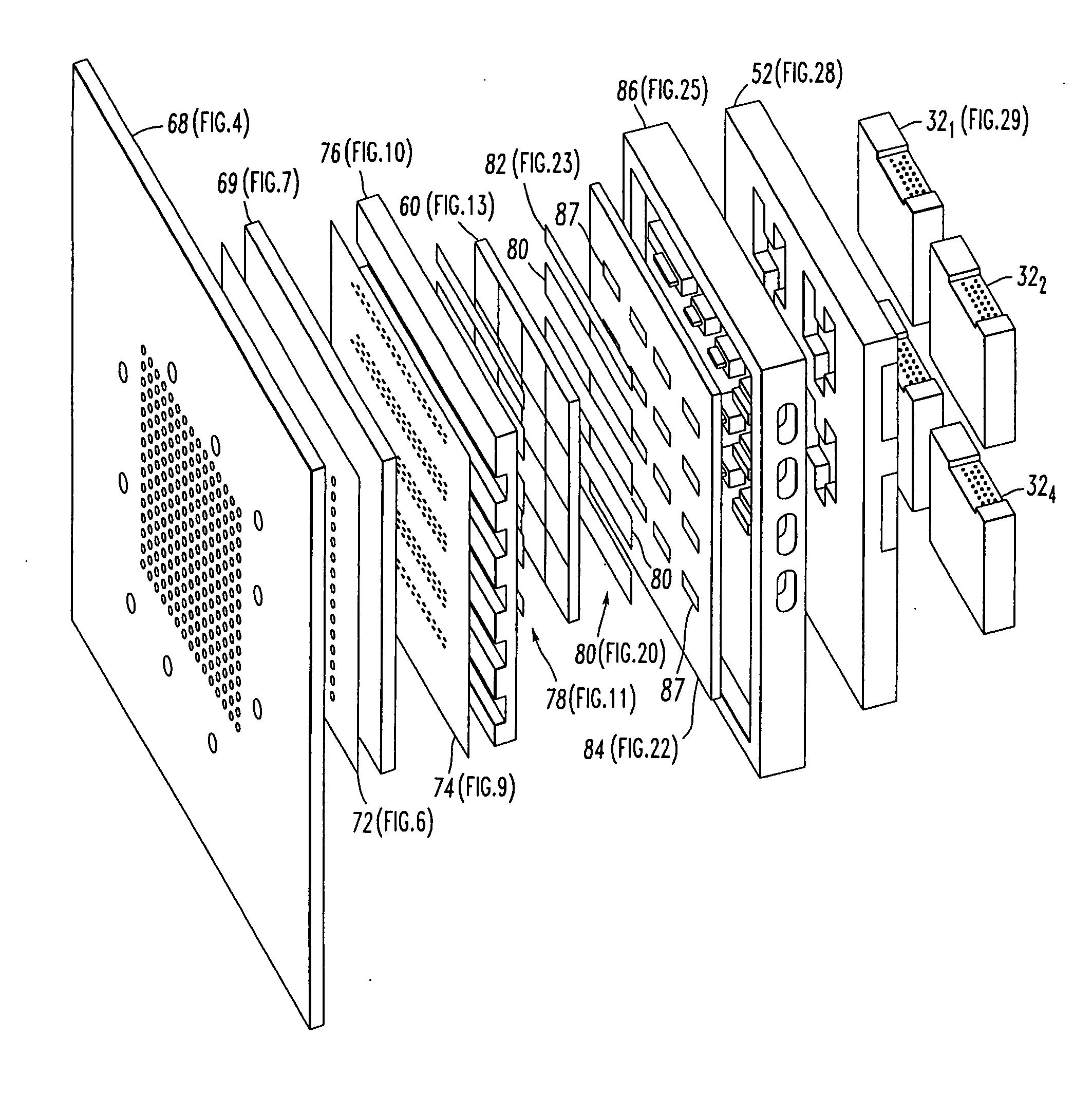
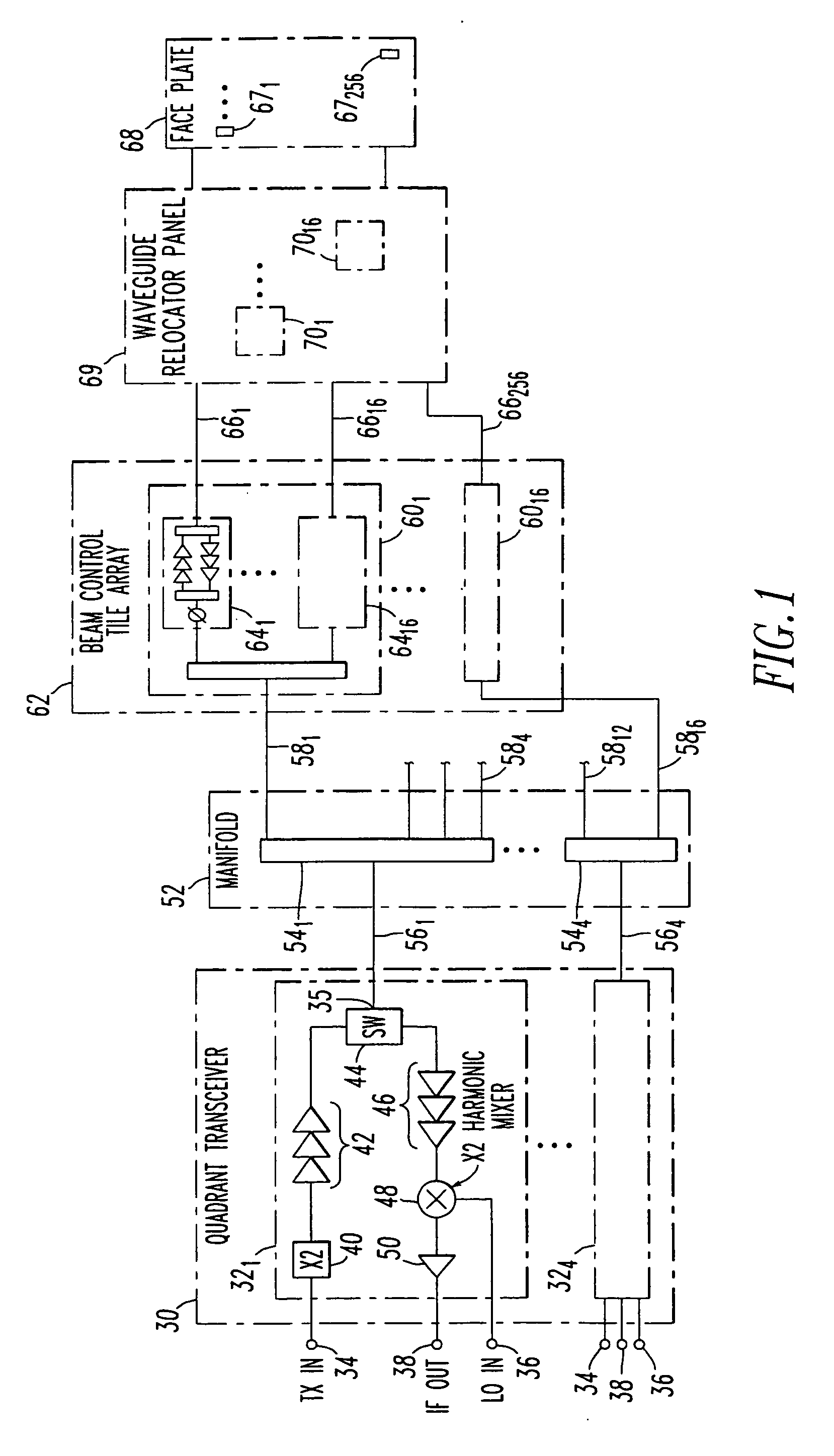
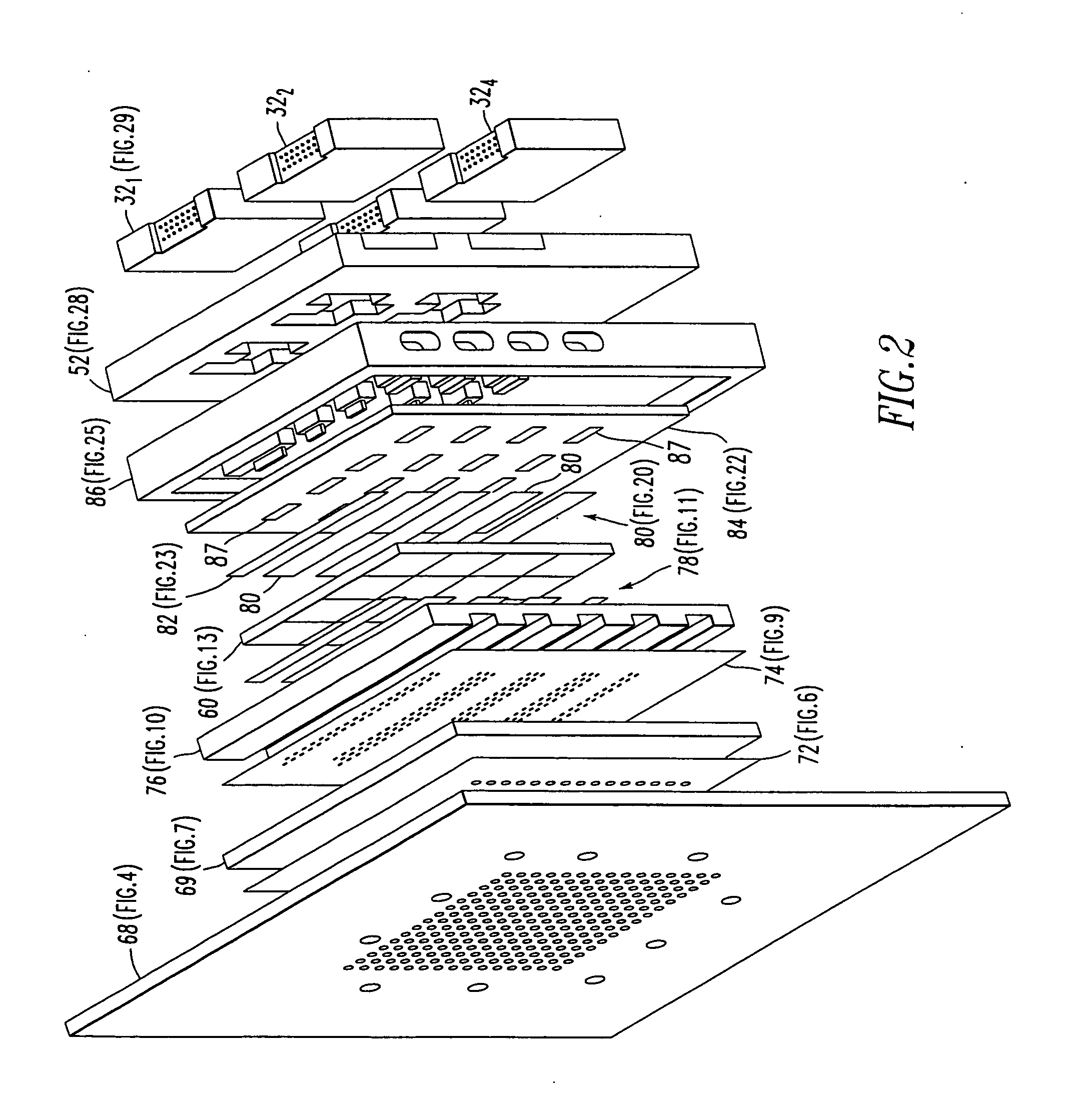
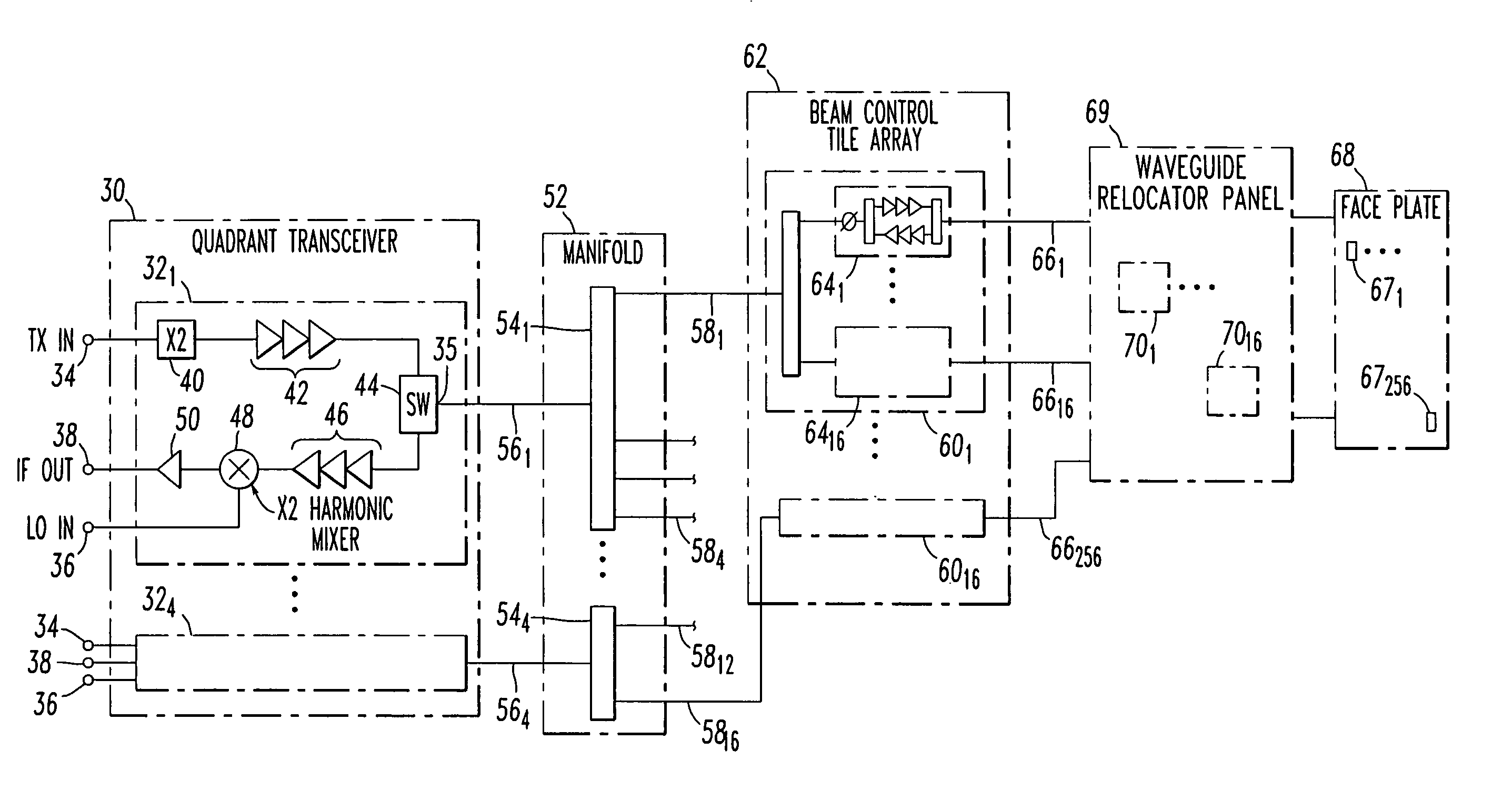
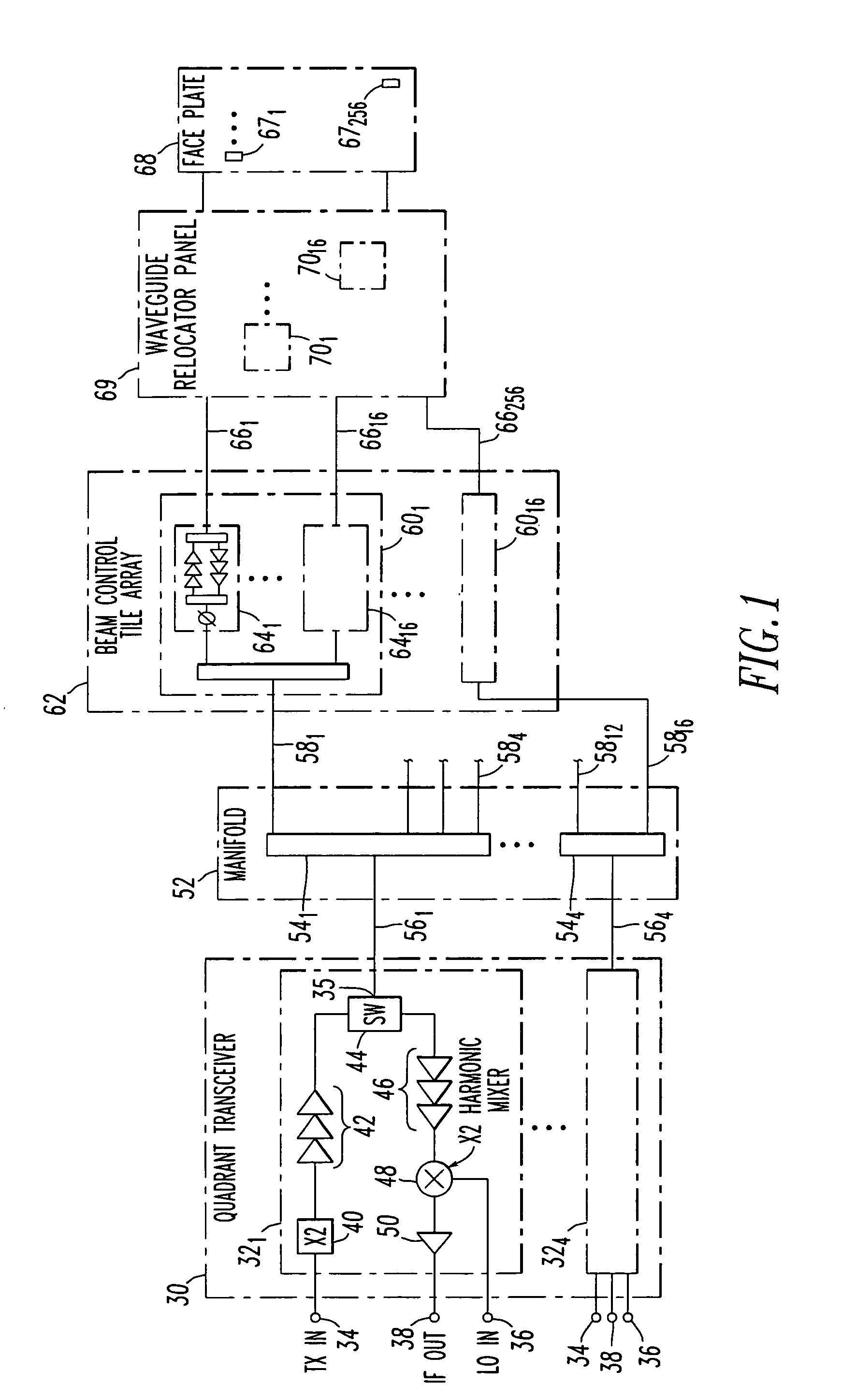
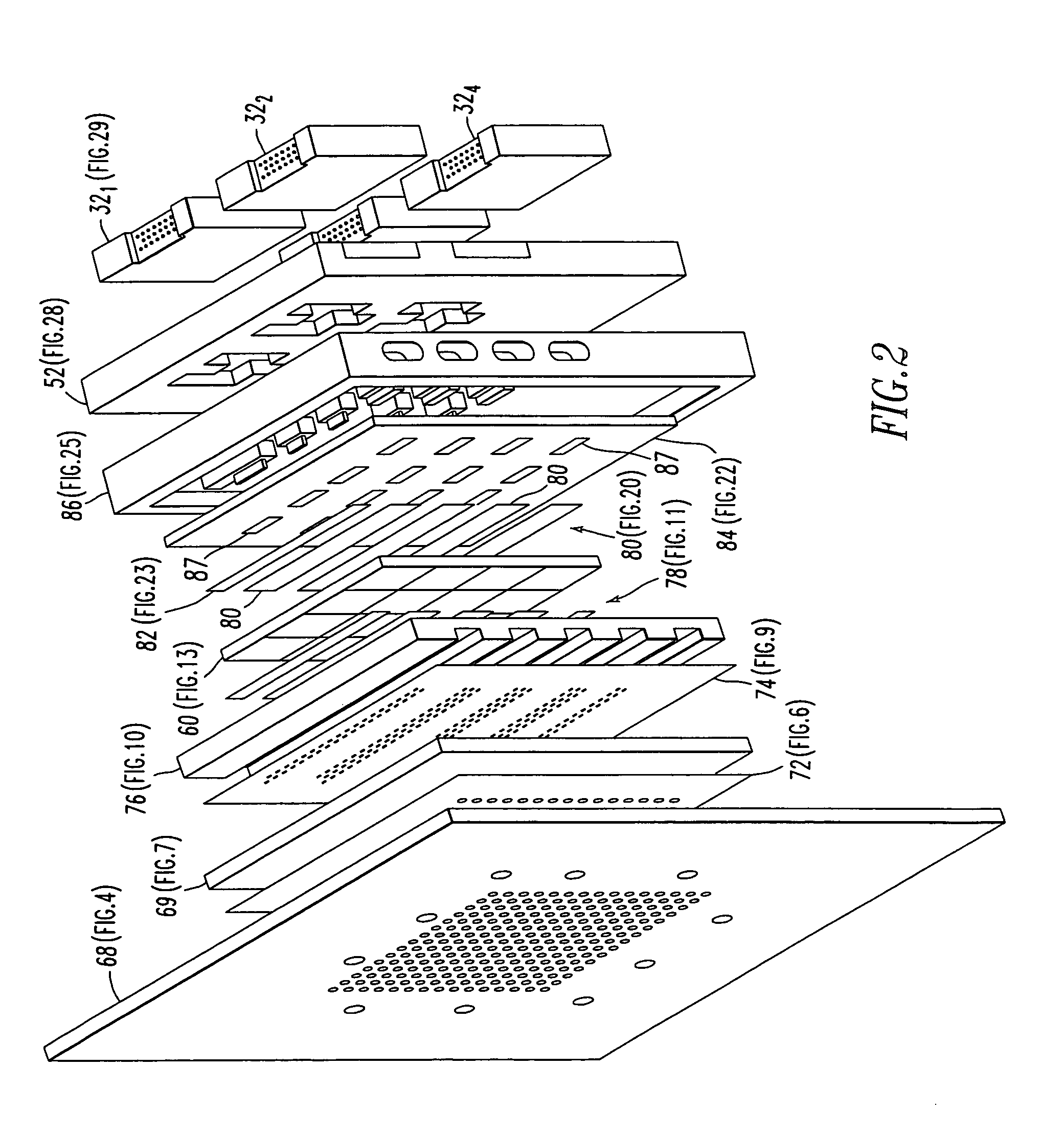
A vertically integrated Ka-band active electronically scanned antenna including, among other things, a transitioning RF waveguide relocator panel located behind a radiator faceplate and an array of beam control tiles respectively coupled to one of a plurality of transceiver modules via an RF manifold. Each of the beam control tiles includes a respective plurality of high power transmit / receive (T / R) cells as well as dielectric waveguides, RF stripline and coaxial transmission line elements. The waveguide relocator panel is preferably fabricated by a diffusion bonded copper laminate stack up with dielectric filling. The beam control tiles are preferably fabricated by the use of multiple layers of low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) material laminated together. The waveguide relocator panel and the beam control tiles are designed to route RF signals to and from a respective transceiver module of four transceiver modules and a quadrature array of antenna radiators matched to free space formed in the faceplate. Planar type metal spring gaskets are provided between the interfacing layers so as to provide and ensure interconnection between mutually facing waveguide ports and to prevent RF leakage from around the perimeter of the waveguide ports. Cooling of the various components is achieved by a pair of planar forced air heat sink members which are located on either side of the array of beam control tiles. DC power and control of the T / R cells is provided by a printed circuit wiring board assembly located adjacent to the array of beam controlled tiles with solderless DC connections being provided by an arrangement of “fuzz button” electrical connector elements.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Aeronautical broadcast and communication system
ActiveUS7505736B2Relatively large bandwidthMore bandwidthActive radio relay systemsBroadcast transmission systemsAviationJet aeroplane
A method and system for a plurality of airplanes in flight to receive from and send to a plurality of ground stations broadcast and communication signals through a single or a plurality of geostationary satellites, wherein at least the mobile link between said airplanes and said satellite, uplink or downlink, uses the high frequency radio waves at 17 GHz or higher, such as Ka-band. The fixed link between said satellite and said ground stations may use any radio frequencies below the frequencies used to communicate between the satellite and the aircraft. The lower frequencies tend to be less susceptible to rain attenuation and hence suitable for closing the fixed broadcast and communication link. Frequencies such as C-band or Ku-band, or even Ka-band, are applied between satellite and ground such that the available link margin is sufficient to overcome rain attenuation at said ground stations. Said satellite carries a plurality of transponders that may include a plurality of frequency converters to enable the conversion between different frequencies. Said satellite generates a plurality of spot beams, shaped or unshaped, which collectively cover the flight routes of said airplanes, preferably the geodesic path between two highly populated regions.
Owner:NUBRON
Multi-beam and multi-band antenna system for communication satellites
An antenna system includes a reflector having a modified-paraboloid shape; and a multi-beam, multi-band feed array located at a focal point of the reflector so that the antenna system forms a multiple congruent beams that are contiguous. The system has a single reflector with non-frequency selective surface. The reflector is sized to produce a required beam size at K-band frequencies and is oversized at EHF-band frequencies. The synthesized reflector surface is moderately shaped and disproportionately broadens EHF-band and Ka-band beams compared to K-band beams. The synthesized reflector surface forms multiple beams each having a 0.5-degree diameter at K-band, Ka-band, and EHF band. The multi-beam, multi-band feed array includes a number of high-efficiency, multi-mode circular horns that operate in focused mode at K-band and defocused mode at Ka-band and EHF-band by employing “frequency-dependent” design for the horns.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Dual-band co-aperture flat array antenna
InactiveCN102394379ASolve occlusionCompact structureIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsLeaky-waveguide antennasGuidance systemFour quadrants
The invention discloses a dual-band co-aperture flat array antenna which is applied to multiband homing heads and intelligent ammunition guidance systems. The dual-band co-aperture flat array antenna comprises a single-ridge waveguide slot array surface, a substrate integrated waveguide slot array surface, single-ridge waveguide slot array feed networks and a substrate integrated waveguide slot array feed network. The single-ridge waveguide radiation slot array surface comprises a plurality of rows of parallel single-ridge waveguide radiation slot line arrays; a substrate integrated waveguide radiation slot array comprises a plurality of rows of parallel substrate integrated waveguide radiation slot line arrays; an antenna array surface is divided into four quadrants; the feed networks respectively feed array surfaces of the four quadrants so as to have the condition of realizing a single-pulse function; each quadrant has two sets of feed networks for respectively feeding the single-ridge waveguide slot line arrays and the substrate integrated waveguide slot line arrays; the single-ridge waveguide slot array surface works in an X-band; the substrate integrated waveguide slot array surface works in a Ka-band; arrays of two forms have a common aperture and do not mutually affect; and the problem of electromagnetic wave blocking caused by non-coplanar array surfaces is solved.
Owner:中国兵器工业第二〇六研究所
Low profile active electronically scanned antenna (AESA) for Ka-band radar systems
InactiveUS6975267B2Space is requiredRadiating element housingsAntenna arrays manufactureTransceiverRadar systems
A vertically integrated Ka-band active electronically scanned antenna including, among other things, a transitioning RF waveguide relocator panel located behind a radiator faceplate and an array of beam control tiles respectively coupled to one of a plurality of transceiver modules via an RF manifold. Each of the beam control tiles includes a respective plurality of high power transmit / receive (T / R) cells as well as dielectric waveguides, RF stripline and coaxial transmission line elements. The waveguide relocator panel is preferably fabricated by a diffusion bonded copper laminate stack up with dielectric filling. The beam control tiles are preferably fabricated by the use of multiple layers of low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) material laminated together. The waveguide relocator panel and the beam control tiles are designed to route RF signals to and from a respective transceiver module of four transceiver modules and a quadrature array of antenna radiators matched to free space formed in the faceplate. Planar type metal spring gaskets are provided between the interfacing layers so as to provide and ensure interconnection between mutually facing waveguide ports and to prevent RF leakage from around the perimeter of the waveguide ports. Cooling of the various components is achieved by a pair of planar forced air heat sink members which are located on either side of the array of beam control tiles. DC power and control of the T / R cells is provided by a printed circuit wiring board assembly located adjacent to the array of beam controlled tiles with solderless DC connections being provided by an arrangement of “fuzz button” electrical connector elements.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
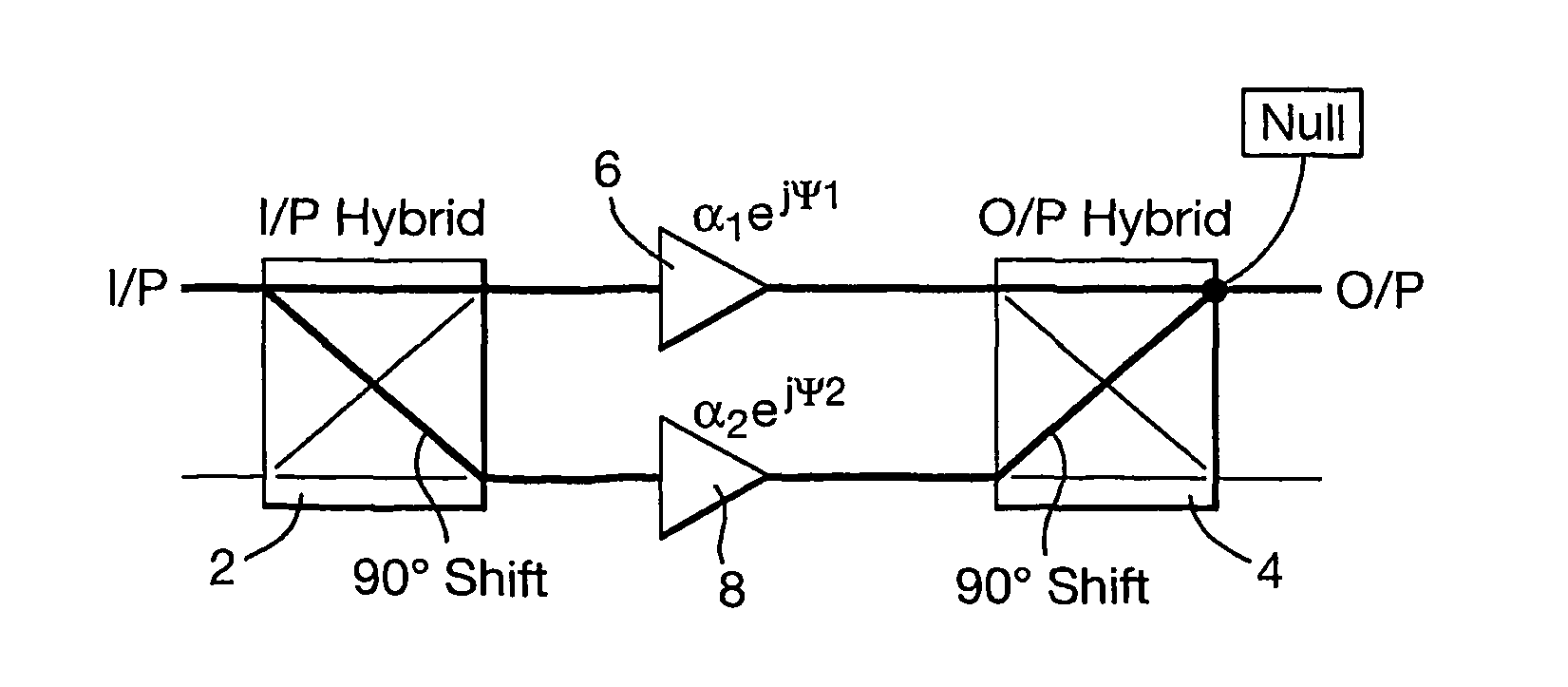
Multiport amplifiers in communications satellites
ActiveUS20100156528A1Improve relationshipSuitable for operationResonant long antennasAmplifier with control circuitsAudio power amplifierEngineering
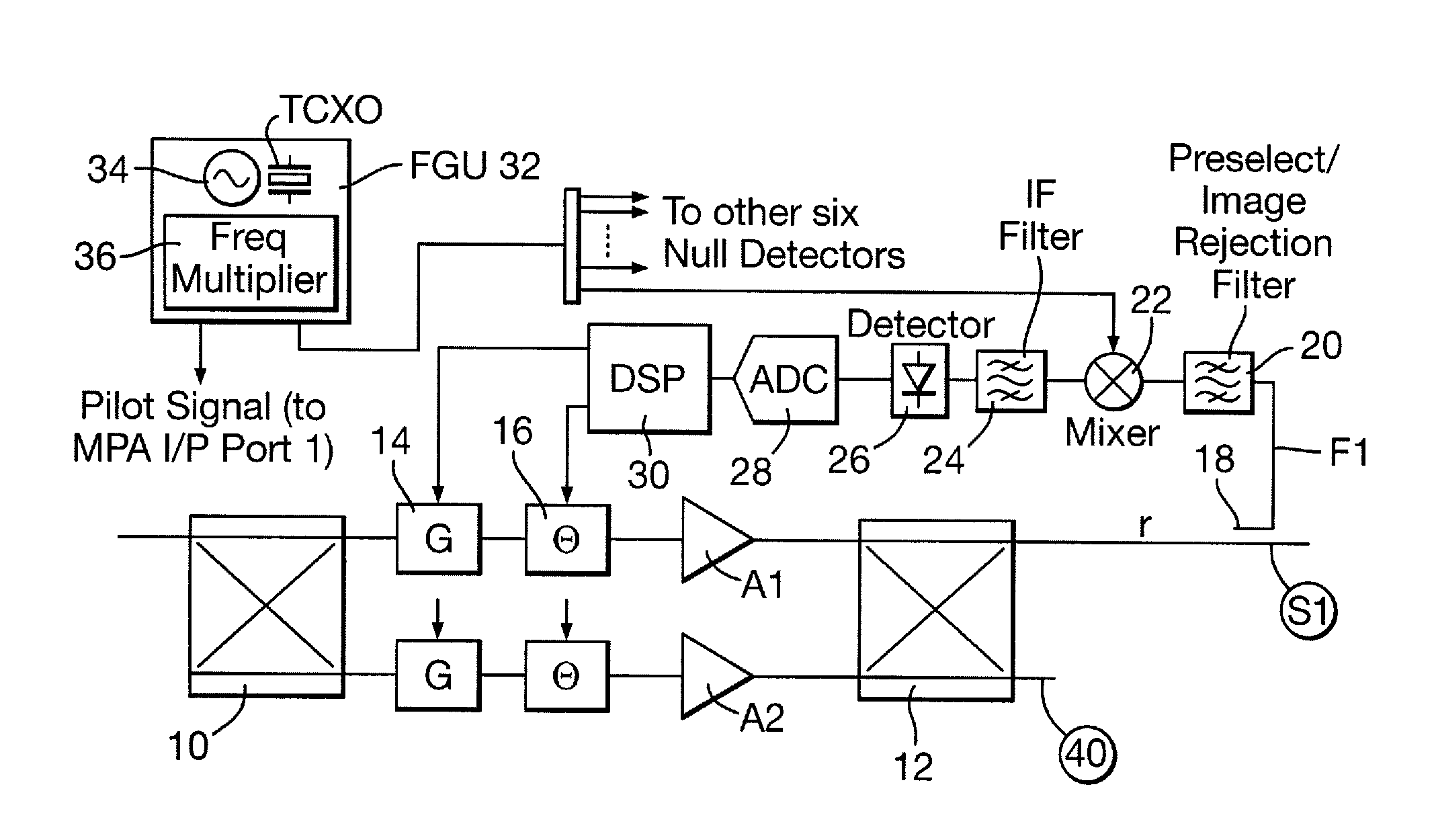
Feedback loops are used within a Multiport Amplifier (MPA) of a communications satellite to maintain phase and amplitude tracking and hence isolation and combining performance. at Ku and Ka-bands, for which there is increasing interest in MPA applications, and where wavelengths are short and maintenance of phase / amplitude tracking becomes highly challenging. Feedback loops are located at strategic points within the MPA Output Network (ONET) to detect tracking errors and provide compensation. Errors are detected through power measurements at “null points”, with zero power corresponding to accurate tracking. The feedback loops adjust the MPA phase / gains such that the levels at these points are maintained at zero. The scheme operates with a pilot signal for measurement of nulls, injected at one of the MPA inputs.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
Four-band multi-polarization co-aperture feed source
ActiveCN102938497AImprove compactnessReduce volumeWaveguide hornsRadiating elements structural formsCircularly polarized antennaResonance
The invention relates to a four-band multi-polarization co-aperture feed source. The four-band multi-polarization co-aperture feed source is formed by combining a double linear polarization antenna of a Ku band and a double circular polarization antenna of a Ka band and comprises a conical horn, a Ku circular waveguide, a tuning screw, a Ku flange, a horizontal polarization power divider, a first flange, a vertical polarization power divider, a medium rod, a circular waveguide feed window, a stop screw, a transition section and a double circular polarization antenna. The antenna of the Ku band uses four ports for symmetrical feeding to improve the symmetrical characteristic of a directional diagram, a transmission waveguide of an electromagnetic field of the Ku band is used as the transition section of the electromagnetic field of the Ka band, and the resonance medium rod is embedded into the waveguide of the Ku band for transmitting electromagnetic waves of the Ka band so that compactness of the antenna is greatly improved. By means of dielectric waveguides and conical horn nesting technologies, the purposes of achieving antenna beam conformity and sharing one phase center are achieved, uniformities of directional diagrams and uniformities of the phase centers in four working bands are guaranteed, isolation among bands is increased, and the compactness of the antenna is improved.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF TELEMETRY +1
Method and apparatus for automatically adjusting Ka waveband mobile satellite communications antenna attitude
InactiveCN101494318AEliminate the effect of pointing accuracySmall transient pointing deviationAntennasIn vehicleEngineering
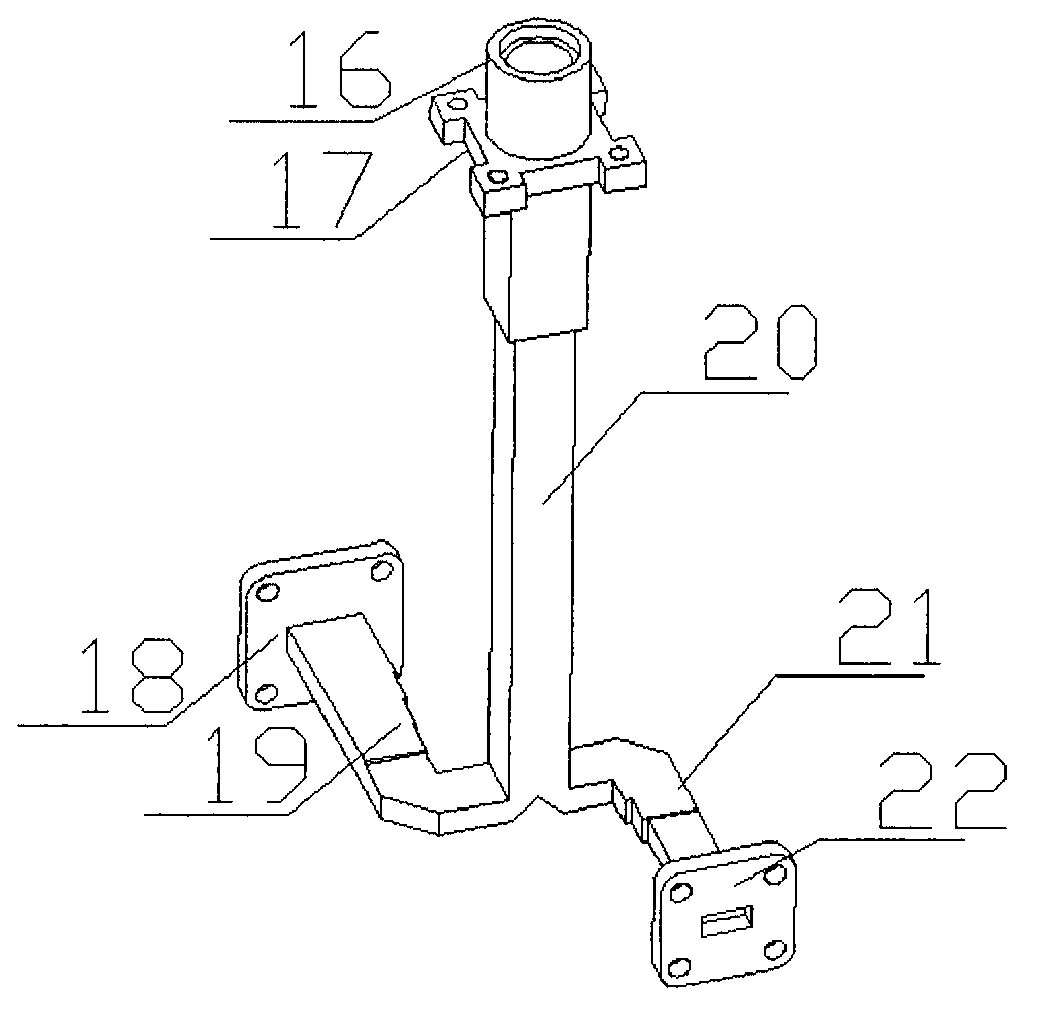
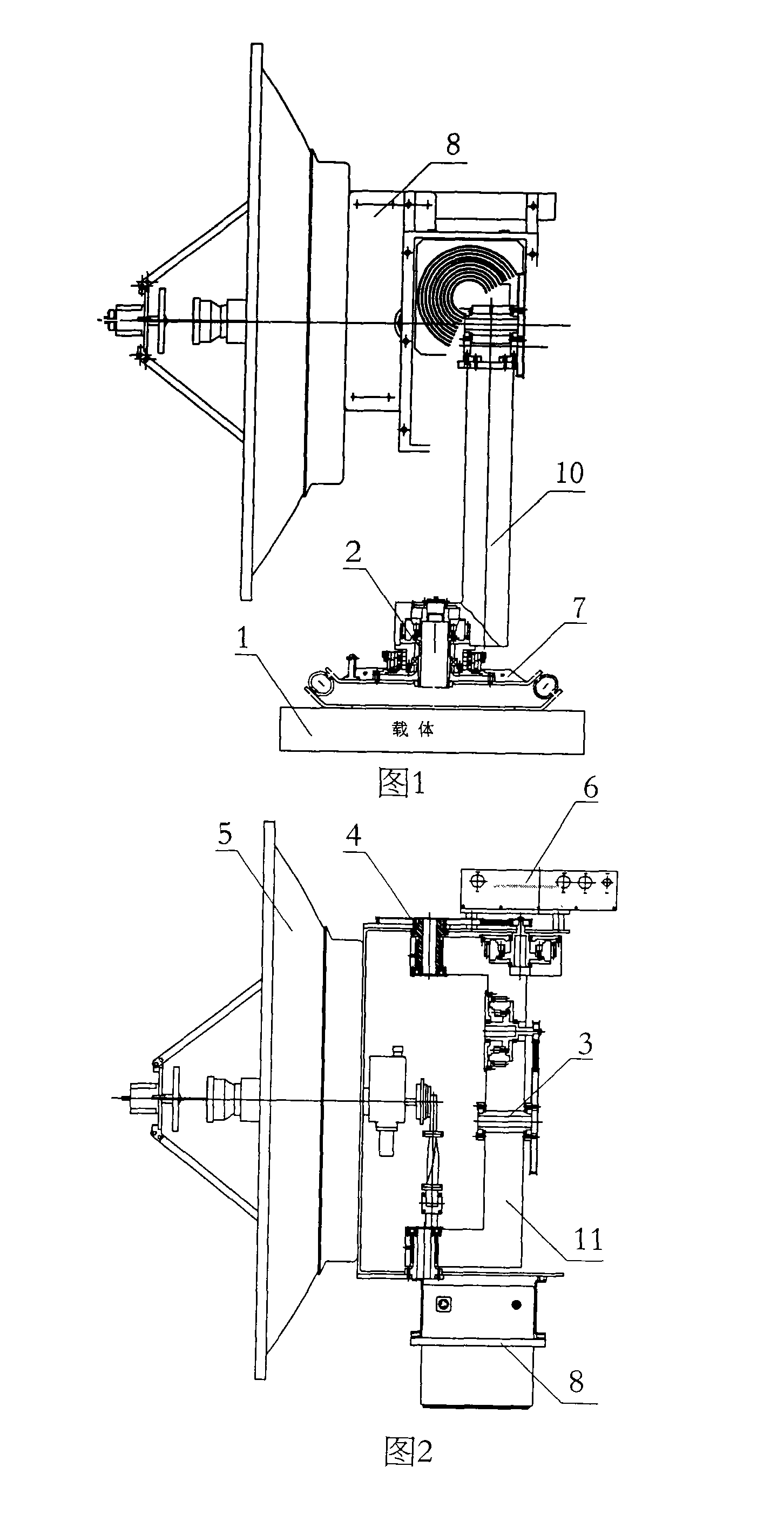
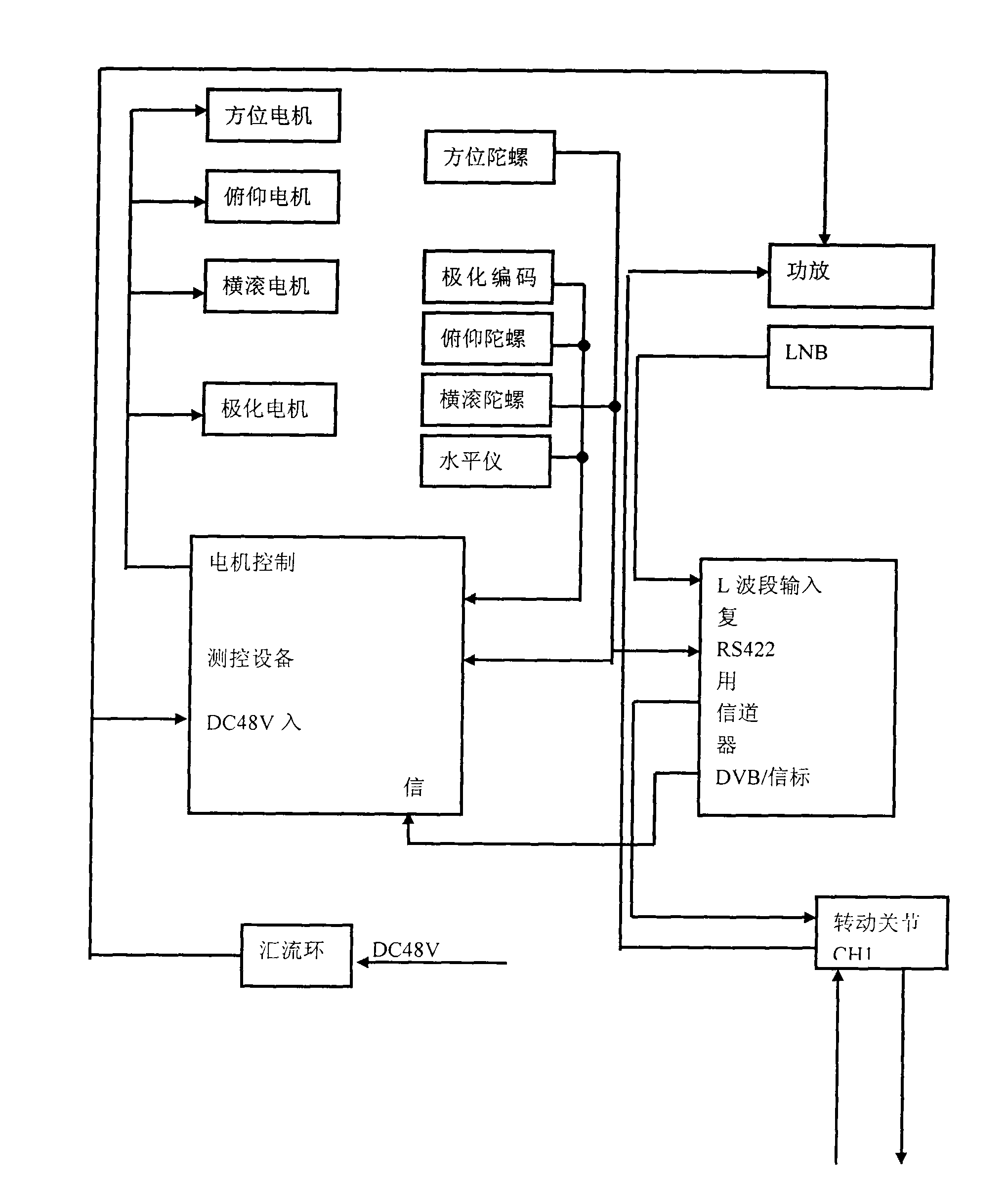
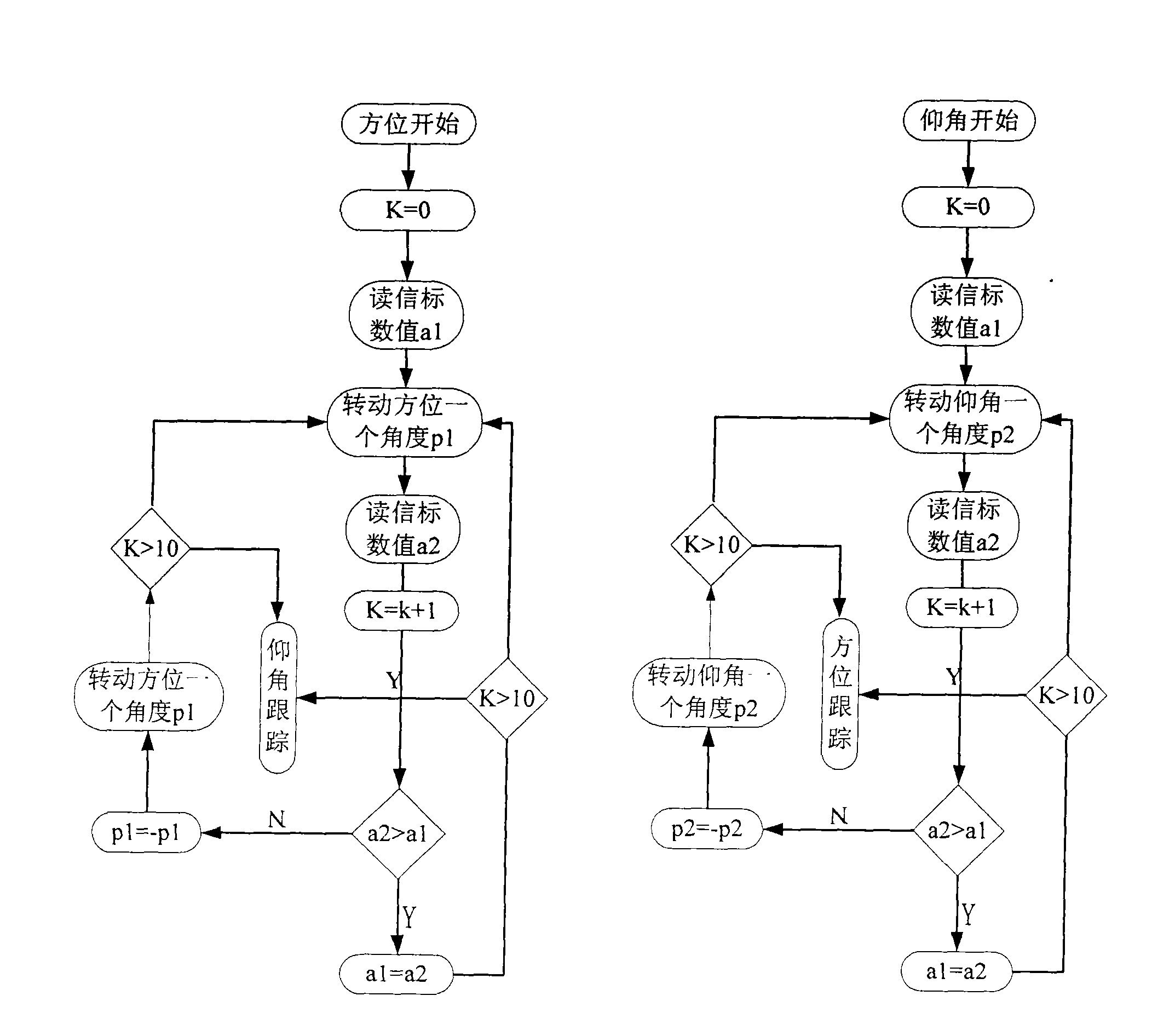
The invention discloses a method for automatically adjusting the posture of a Ka wave-band mobile satellite communication antenna and a device, wherein, three axes-an azimuth axis, a wobble shaft, and a pitch axis which drive the antenna to rotate are firstly arranged on a pedestal of the antenna in a space orthogonal mode to realize angular motion isolation of the three space orthogonal axes; then an antenna component is respectively configured with the azimuth axis, the wobble shaft, and the pitch axis as a center to lead an overall centroid of the antenna component installed on the pitch axis to fall on the pitch axis, the overall centroid of the antenna component installed on two sides of the axes of the wobble axis to fall on the wobble axis, and the overall centroid of the antenna component on the azimuth axis to fall on the azimuth axis; finally based on the antenna as a detecting standard of the antenna pointing deviation, pointing deviation caused by drifting of a sensor is eliminated by tracking a beckon signal of a satellite and alternately driving an intersection angle of the azimuth axis and / or the pitch axis, thus ensuring the antenna in an optimal receiving state. The method for automatically adjusting the posture of Ka wave-band mobile satellite communication antenna and the device have the advantages of high precision, simple structure, small volume, and low cost, can be widely applied to emergency communication, rescue and relief work, and also can be used for commercial purpose in vehicles, ships, trains, and the like.
Owner:NANJING PANDA ELECTRONICS +3
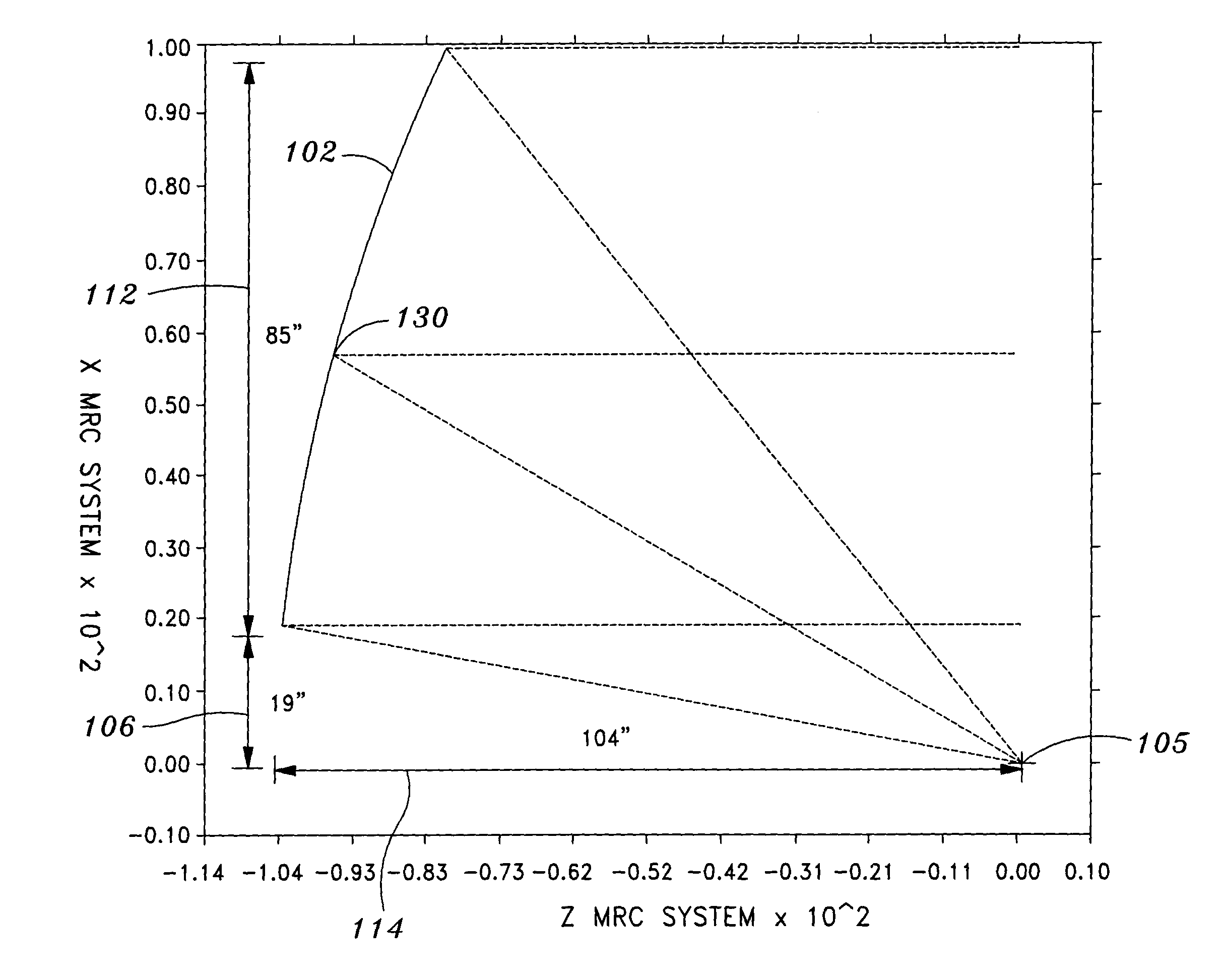
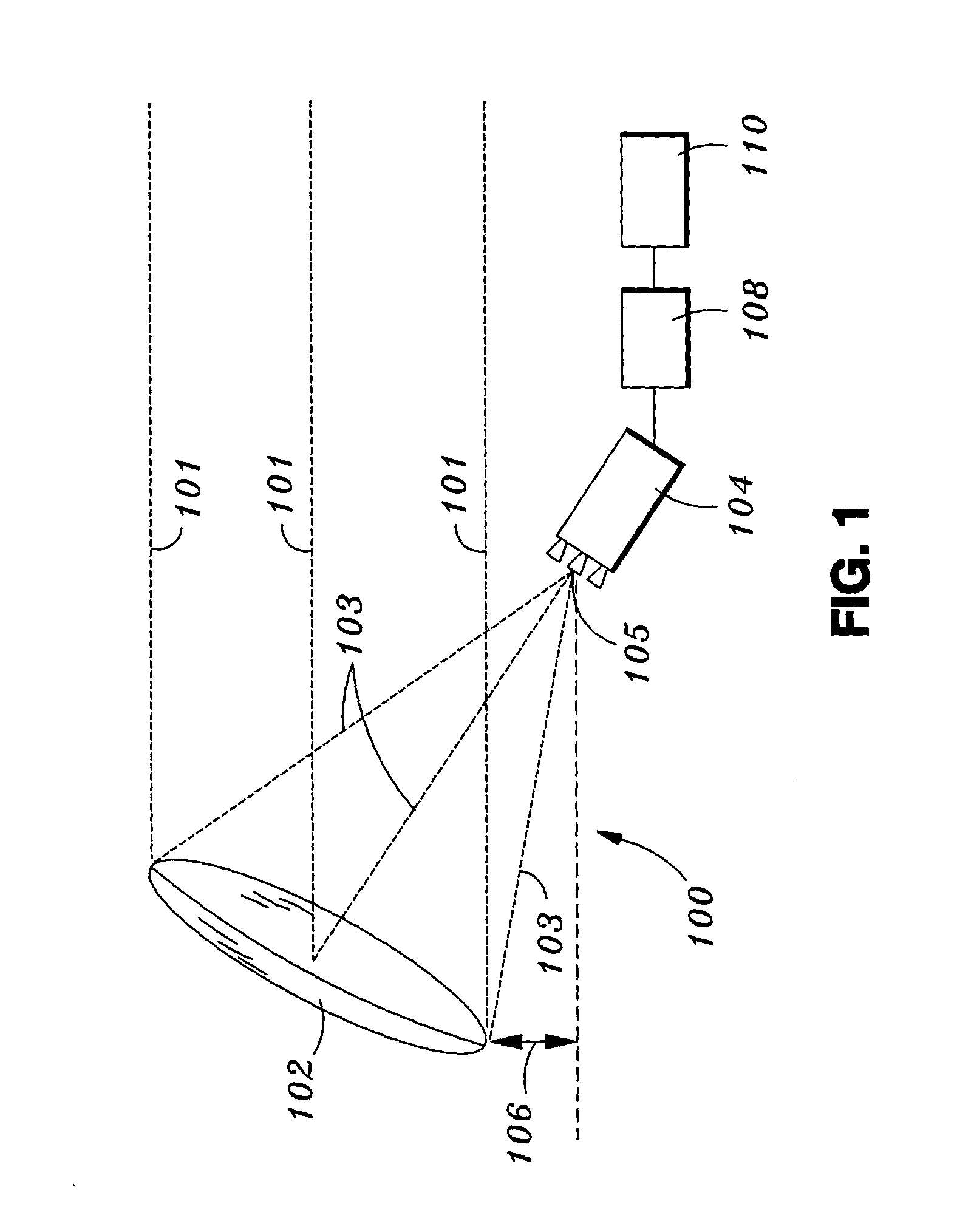
Triple-band offset hybrid antenna using shaped reflector
InactiveUS20050140563A1Reducing a blocking lossImprove efficiencyAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsSignal onRadio frequency signal
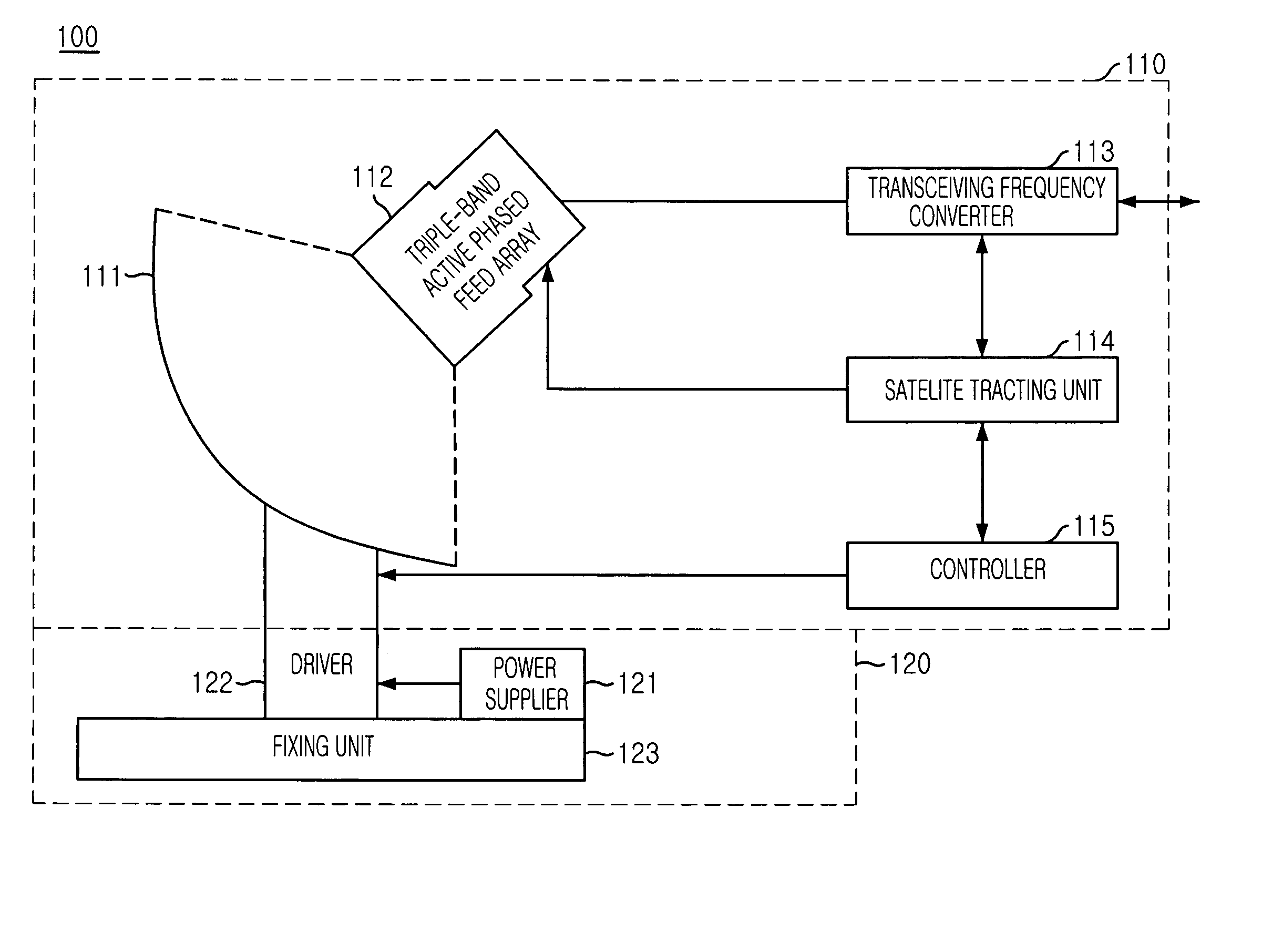
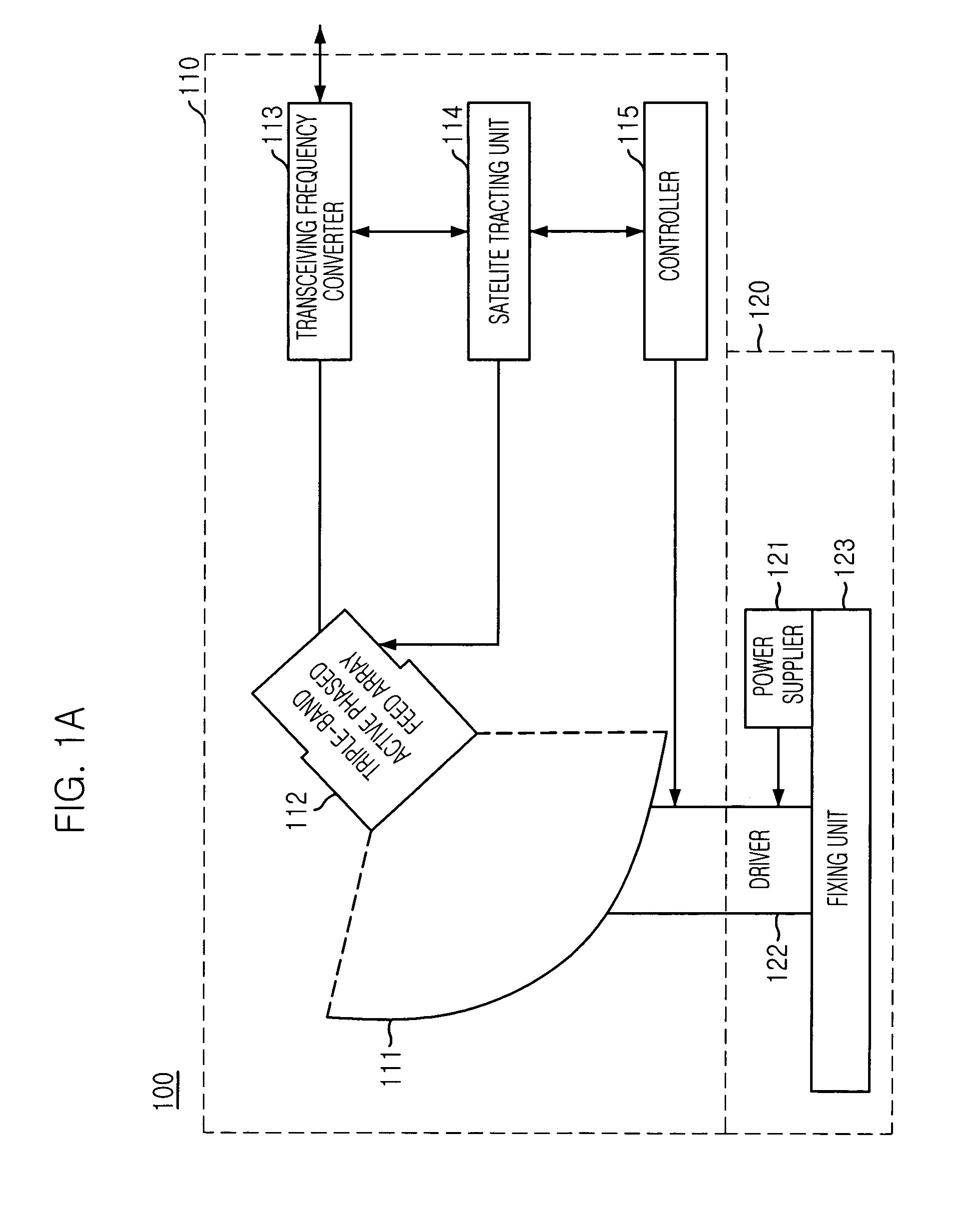
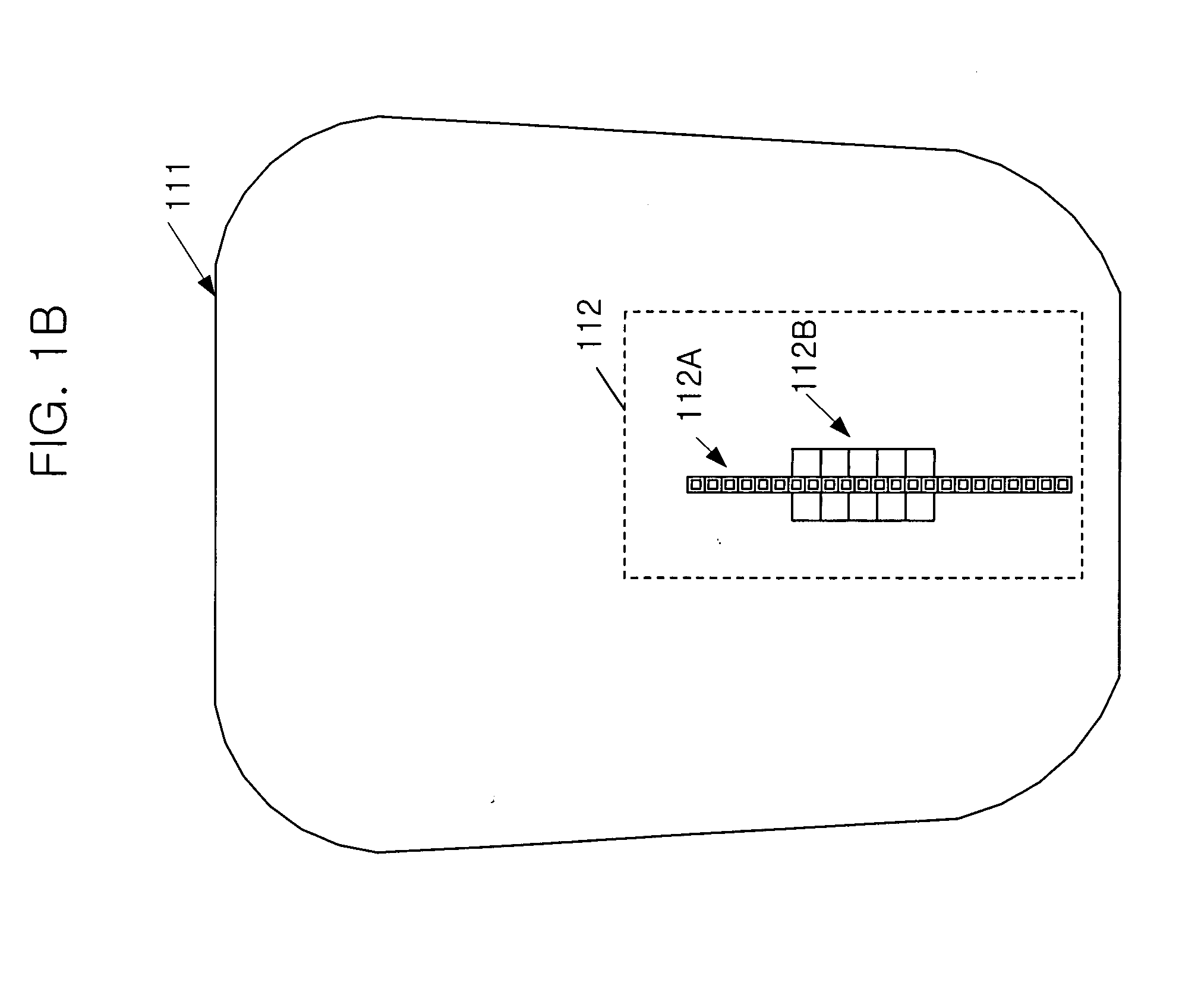
A triple-band offset hybrid antenna having a shaped reflector is disclosed. The triple-band offset hybrid antenna includes: a shaped reflector reflecting a K / Ku bands RF signals received from a satellite to focus an energy of the K / Ku band RF signals on a focal line and reflecting a Ka band RF transmitting signal; and a triple-band active phased feed array receiving the reflected K / Ku bands RF signals from the shaped reflector and radiating the Ka band RF transmitting signal to the shaped reflector, wherein the triple-active feed array including Ka / K bands feed array for transceiving Ka / K bands RF signal and a Ku band feed array for receiving a Ku band RF signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Low section compact dual-band dual-polarization common aperture microstrip antenna
InactiveCN103606745AMature processing technologyEnsure consistencyAntenna earthingsPolarised antenna unit combinationsGround plateKu band
The invention provides a low section compact dual-band dual-polarization common aperture microstrip antenna which is formed by two layers of double-face copper clad microwave dielectric plates. The needed double-frequency antenna array and Ku band antenna feed network are formed on the upper surface of the upper layer dielectric plate through etching process, and an L type coupling slot is arranged on a grounded plate at the lower surface of the upper layer dielectric plate. A Ka band antenna feed network is at the lower layer of the lower layer dielectric plate, and the antenna is subjected to coupled feeding through the slot. Two frequencies of the antenna coverage are a Ka band and a Ku band. According to the antenna, through the reasonable array layout, a Ka band antenna and a Ku band antenna are in coplanar nested placement in a same aperture, the structure is compact, the feed network of the antenna is hierarchically designed, and the wiring space is relatively abundant. The antenna can be applied to a satellite communication terminal of Ku and Ka bands.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
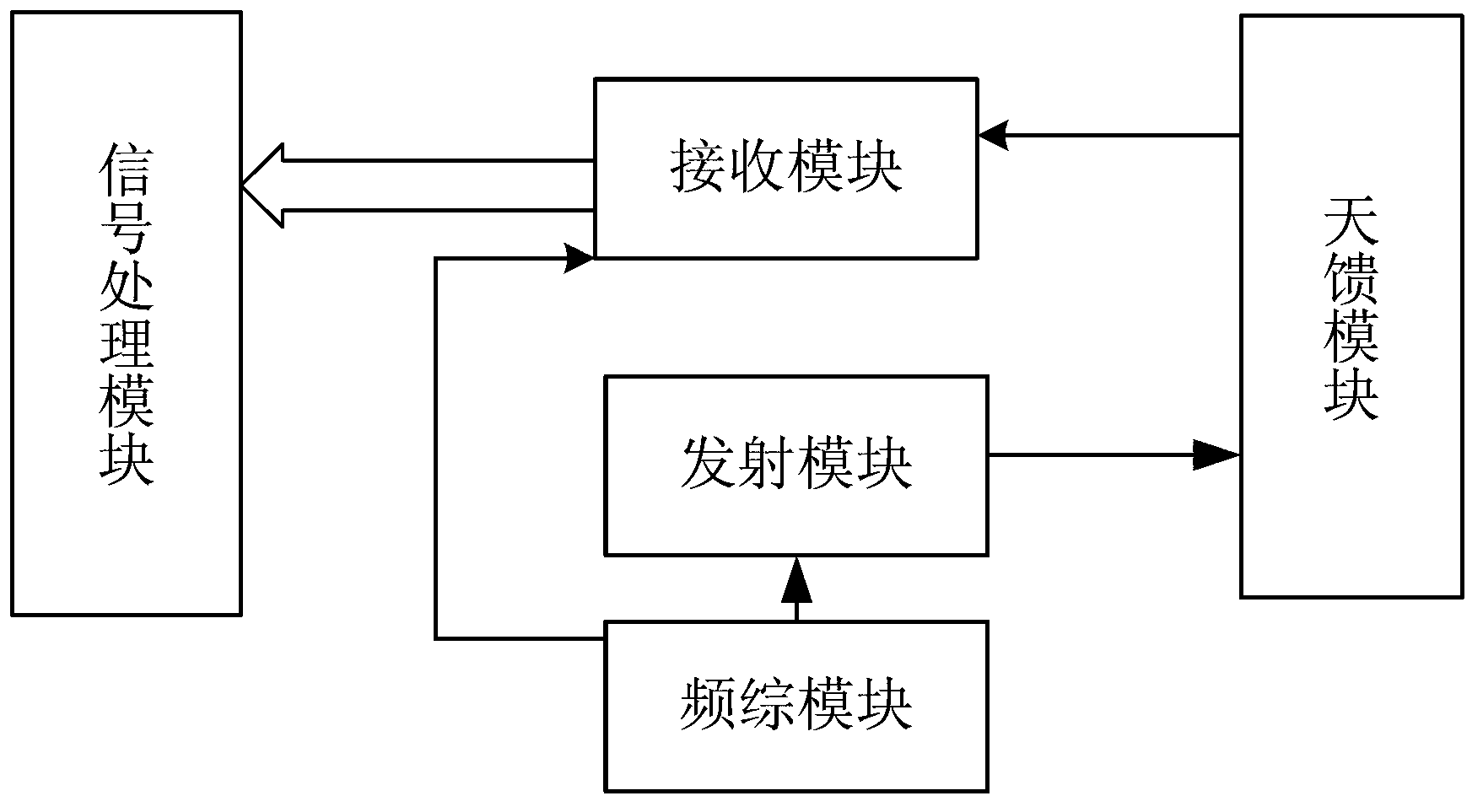
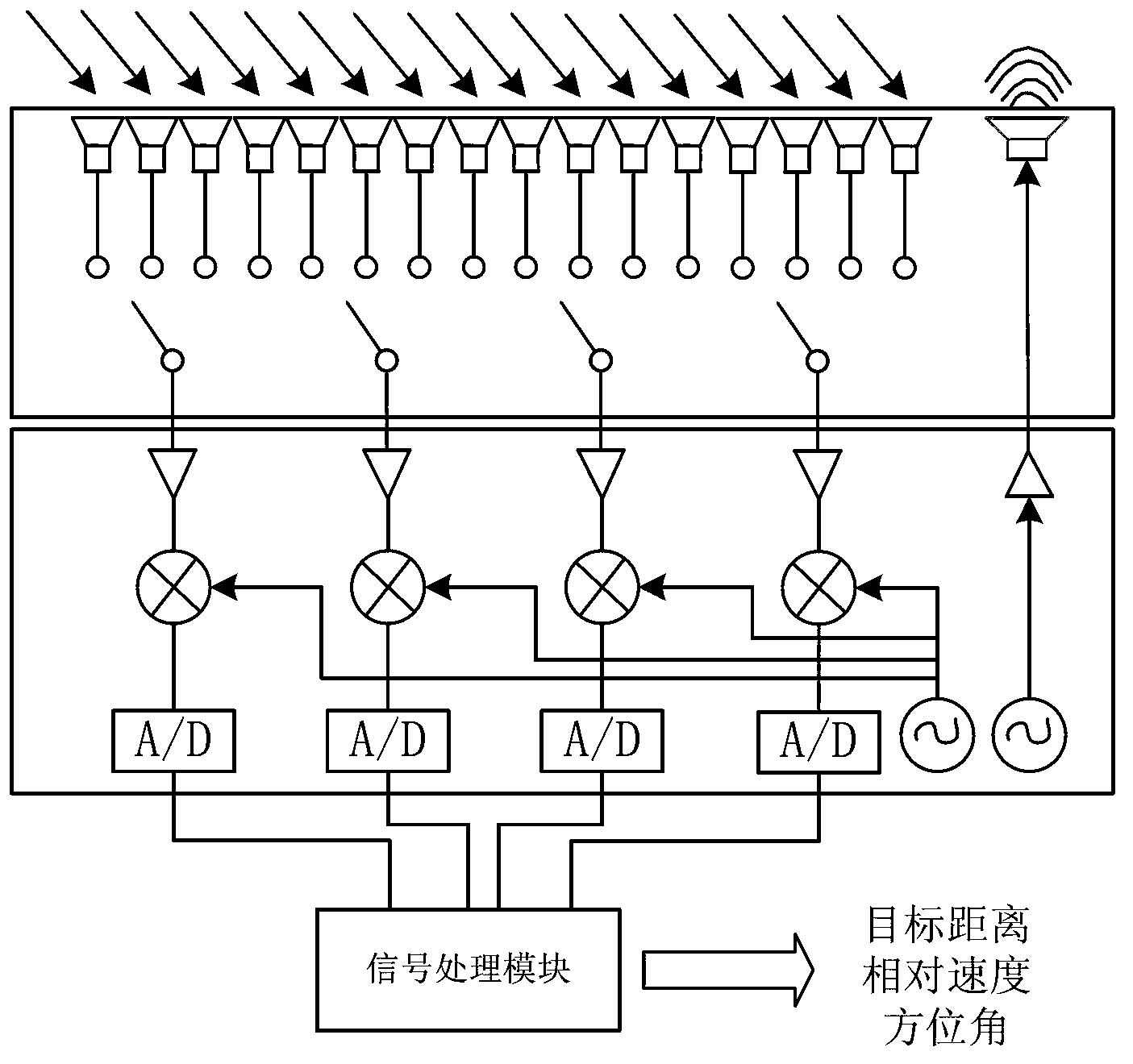
Vehicular millimeter-wave train collision avoidance radar system
ActiveCN103235310ATo achieve the purpose of collision avoidanceImprove anti-interference abilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLocal oscillator signalRadar systems
The invention provides a vehicular millimeter-wave train collision avoidance radar system which comprises a frequency synthesizer module, a transmitting module, a receiving module, an antenna feeder module, and a signal processing module. The frequency synthesizer module is used for generating X-band transmitting excitation signals and X-band receiving local oscillator signals. The transmitting module is used for doubling the frequency of the X-band transmitting excitation signals to Ka band. The antenna feeder module comprises a transmitting antenna, Kn receiving antennas and n single-pole K-throw switches. Each two adjacent K receiving antennas are connected with the receiving module through one single-pole K-throw switch. The receiving module comprises n receivers. Each receiver is connected with one single-pole K-throw switch in the antenna feeder module. The signal processing module is used for processing the received signals to obtain the distance, speed and angular information of a target, and transmitting the information to a train central control system. The train central control system issues stop commands to trains. The vehicular millimeter-wave train collision avoidance radar system is installed on the train and is capable of accurately detecting obstacles in front of the train to well functionally avoid train collision.
Owner:北京理工雷科电子信息技术有限公司
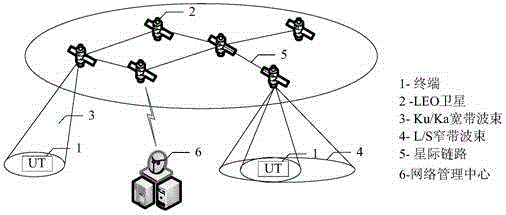
Mobile communication system and method based on low-orbit satellite constellation network
InactiveCN106253964AReduce transmission delayExpand coverageRadio transmissionHigh bandwidthMobile communication systems
The invention provides a mobile communication system based on a low-orbit satellite constellation network, which comprises at least one low-orbit satellite, and is characterized in that the low-orbit satellites provide L / S-band based narrowband communication and Ku / Ka-band / laser based broadband communication for users; and the system further provides inter-satellite link transmission among the plurality of low-orbit satellites when user terminals are located at different satellites. The invention further provides a corresponding communication method. According to the invention, broadband data services can be provided for the users by combining the characteristics of large coverage area of an L / S-band and high bandwidth of a Ku / Ka-band / laser.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
Dual-band and dual-polarization millimeter wave feed source
ActiveCN104979638ASimple structureBreak through the technical problem of dual-frequency dual-polarization millimeter-wave feedWaveguide hornsSimultaneous aerial operationsLow-pass filterDual mode
The invention provides a dual-band and dual-polarization millimeter wave feed source which comprises a radiation end, a Ka-band orthogonal mode coupling and a W-band orthogonal mode coupling. The radiation end and the couplings use a waveguide structure. Dual bands and dual polarization are realized through single caliber. A high band is located in the middle. Low bands carry out feeding from sides. A high-band dual-mode feed source is connected with an external orthogonal mode coupling. The low bands carry out feeding from a circular waveguide segment with increasing diameter. The dual-polarization feed source has a simple main structure, and breaks through the technical problems of the dual-band and dual-polarization millimeter wave feed source. In order to prevent crosstalk and improve the feed source performance, a filter is added on an output rectangular waveguide segment of a low-band orthogonal mode coupling. The filter is a low-pass filter which has low-band passband and high-band stop-band. Two kinds of polarization exit waveguide of two bands are respectively located in four directions of a major radiation waveguide axis, are in pairwise orthogonal, are staggered up and down, are not located in the same level, and are easily connected with rear end waveguide.
Owner:ANHUI SUN CREATE ELECTRONICS
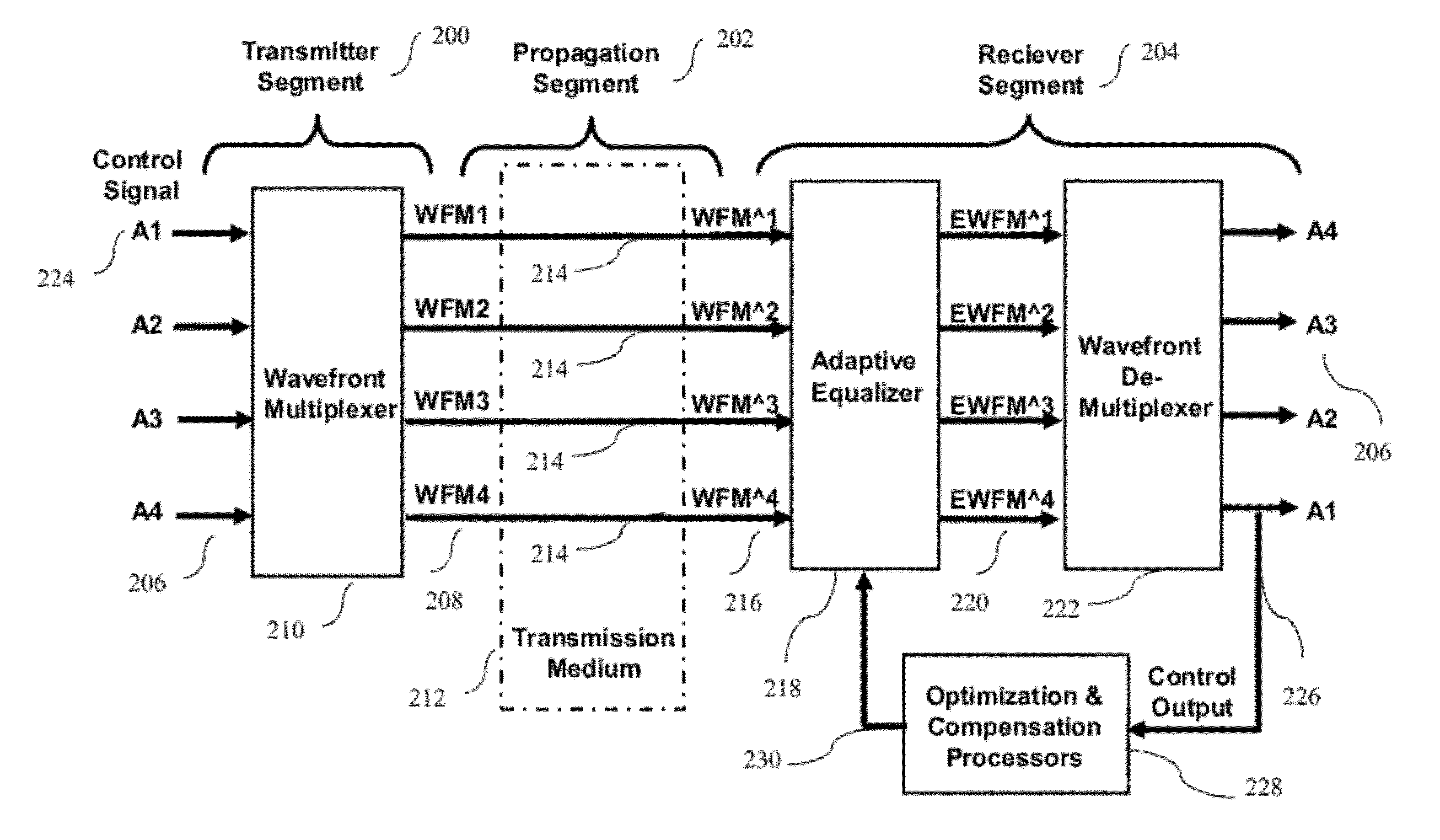
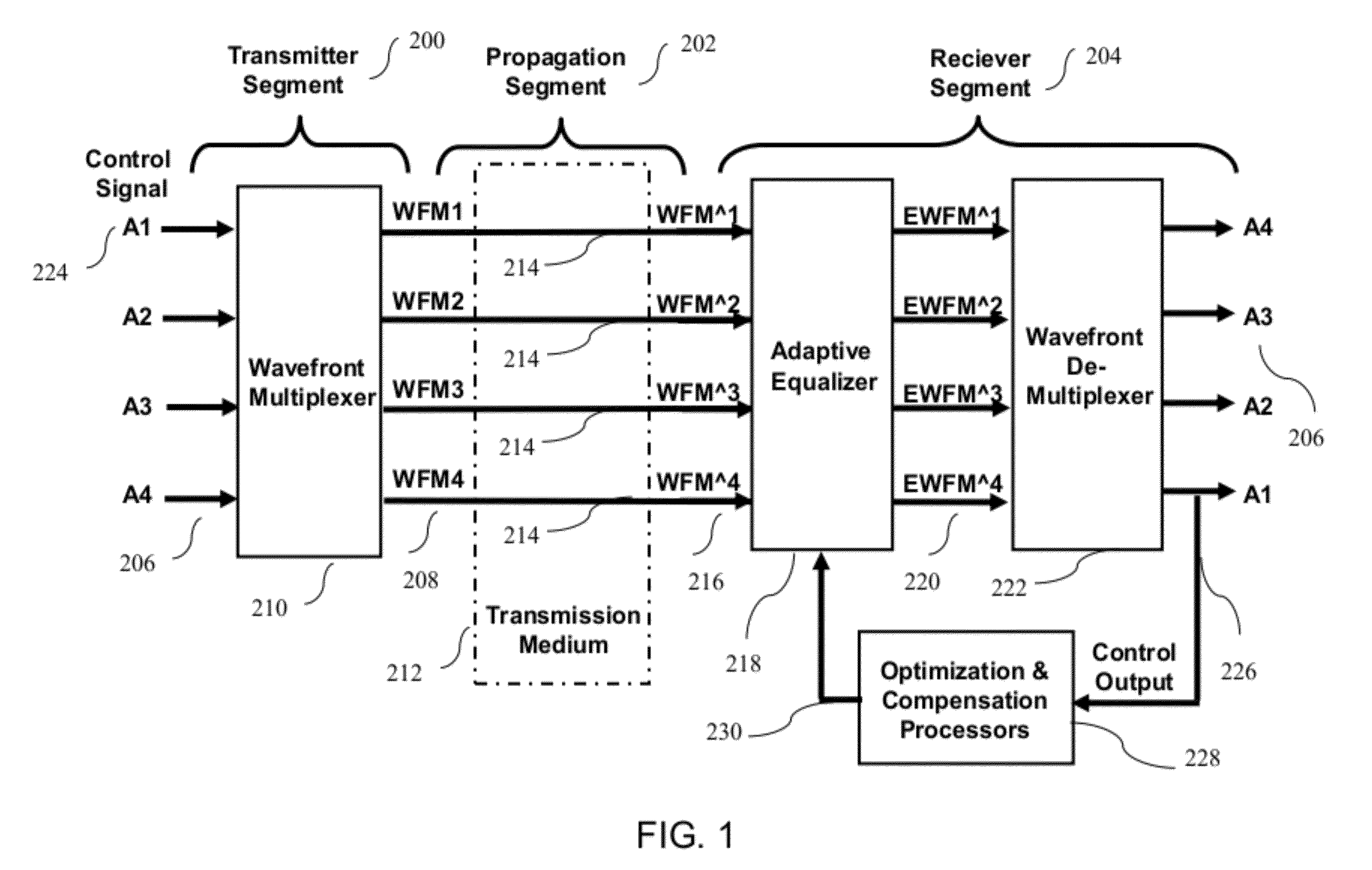
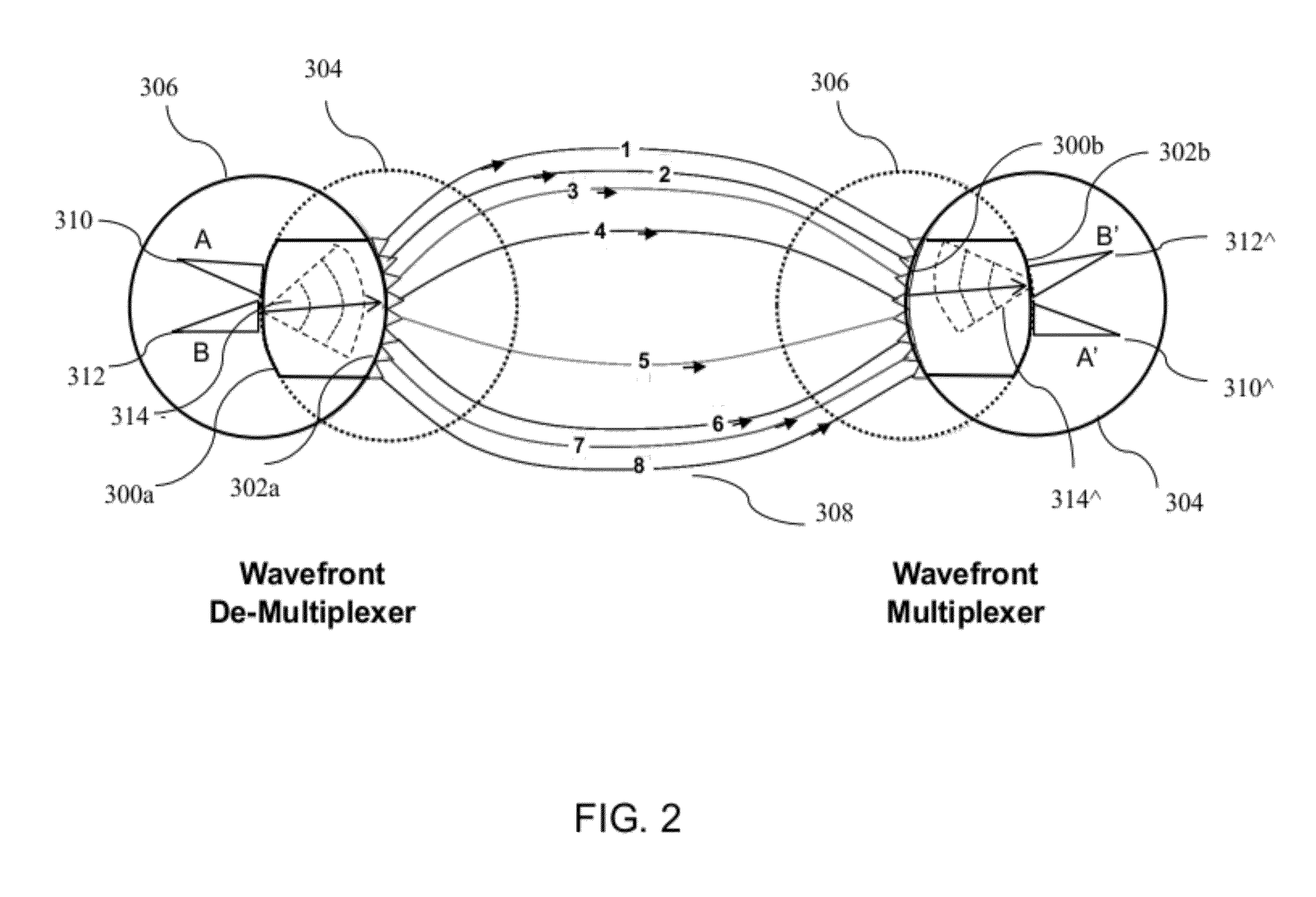
Coherent Power Combining via Wavefront Multiplexing on Deep Space Spacecraft
InactiveUS20120140780A1Increase power levelFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division optical multiplex systemsData streamTransmitted power
A communication system and method for a deep space spacecraft receiver to perform post-processing to dynamically combine received signal power coherently for pre-processed signal streams radiated non-coherently from a distributed, multiple element, Ka-band transmitting array via multiple concurrent propagation paths. Mutually orthogonal data and pilot signals travel though the multiple propagation paths. A pre-processor utilizing wavefront multiplexing restructures signal streams on the ground into multi-channel wavefrom structures along with injections of pilot signals for diagnostic and probing purposes. These restructured, or “wavefront multiplexed” (WFM) signals are transmitted through propagation channels to a receiver on the spacecraft, wherein adaptive equalization and wavefront de-multiplexing coherently separates the mixtures of received WFM signals. Transmitting power can be dynamically allocated for the multiple concurrent data streams, radiated to different spacecraft within the same field of view according to continuously changing demand by changing the relative input power ratios of the WFM signal mixtures.
Owner:CHANG DONALD C D
Ultra-wideband millimeter-wave linearly-polarized waveguide aperture array antenna
InactiveCN103811877ASmall sizeSmall standing waveAntenna arraysSlot antennasUltra-widebandRadar systems
The invention relates to an ultra-wideband millimeter-wave linearly-polarized waveguide aperture array antenna, belonging to the technical field of microwave detection. In the waveguide aperture array antenna, a multi-power-dividing feed network is combined with a waveguide aperture radiation array, and an antenna is simulated and designed by applying the thought of integral design of an antenna feeder system. By changing the amplitude of each port of an HT power divider network, the characteristics of low standing wave, high grain, low minor lobe and wide wave beam are realized, an ultra-large frequency bandwidth is realized, and the ratio of the frequency bandwidth to the central frequency is up to 6.6 percent. On the aspect of structure, the entire antenna comprises a bottom plate, a feed network and a radiation portion, thereby greatly reducing the workload of simulation and machining, reducing the processing error to the maximum extend, reducing the size and weight of the antenna, and achieving adaptation to various occasions and experiments. The antenna is capable of receiving / transmitting signals at the same time, is suitable for Ka waveband communication and detection, and is suitable to be applied to communication systems, navigation systems and radar systems of various fixed and movable platforms.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Multiport amplifiers in communications satellites
ActiveUS8103225B2Improve relationshipSuitable for operationResonant long antennasAmplifier with control circuitsAudio power amplifierEngineering
Feedback loops are used within a Multiport Amplifier (MPA) of a communications satellite to maintain phase and amplitude tracking and hence isolation and combining performance. at Ku and Ka-bands, for which there is increasing interest in MPA applications, and where wavelengths are short and maintenance of phase / amplitude tracking becomes highly challenging. Feedback loops are located at strategic points within the MPA Output Network (ONET) to detect tracking errors and provide compensation. Errors are detected through power measurements at “null points”, with zero power corresponding to accurate tracking. The feedback loops adjust the MPA phase / gains such that the levels at these points are maintained at zero. The scheme operates with a pilot signal for measurement of nulls, injected at one of the MPA inputs.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
Multi-beam and multi-band antenna system for communication satellites
An antenna system includes a reflector having a modified-paraboloid shape; and a multi-beam, multi-band feed array located at a focal point of the reflector so that the antenna system forms a multiple congruent beams that are contiguous. The system has a single reflector with non-frequency selective surface. The reflector is sized to produce a required beam size at K-band frequencies and is oversized at EHF-band frequencies. The synthesized reflector surface is moderately shaped and disproportionately broadens EHF-band and Ka-band beams compared to K-band beams. The synthesized reflector surface forms multiple beams each having a 0.5-degree diameter at K-band, Ka-band, and EHF band. The multi-beam, multi-band feed array includes a number of high-efficiency, multi-mode circular horns that operate in focused mode at K-band and defocused mode at Ka-band and EHF-band by employing “frequency-dependent” design for the horns.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
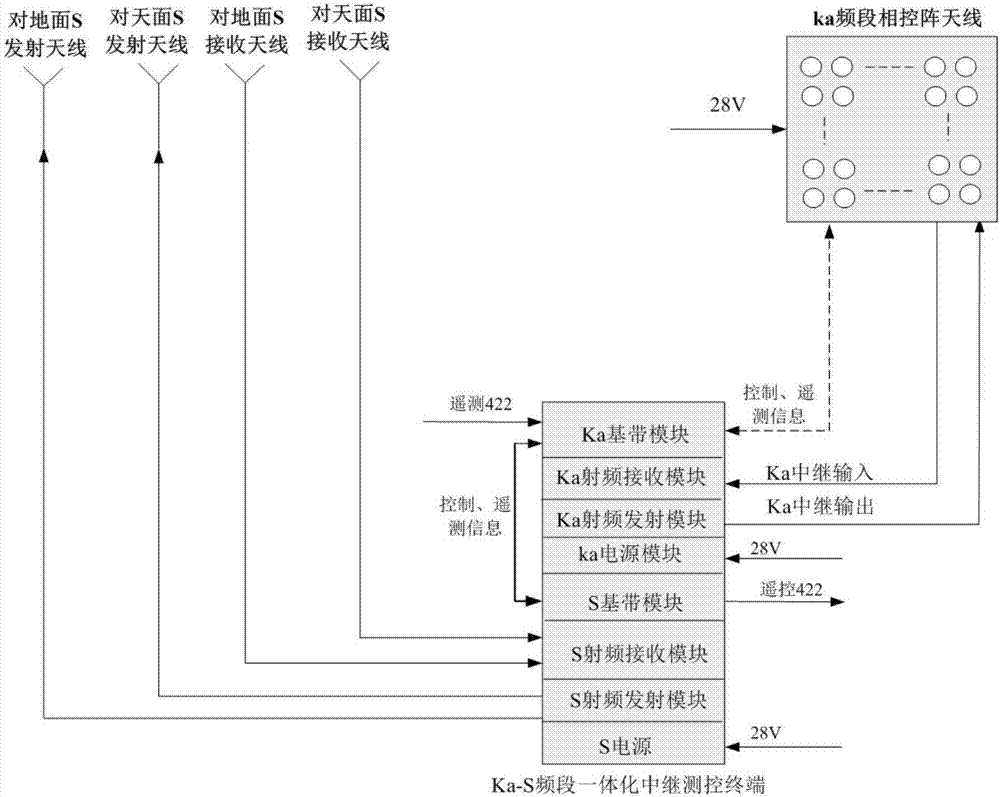
Measurement and control method based on Ka-S-band relay integrated measurement and control system
ActiveCN107332605AImprove efficiencyImprove reliabilitySpatial transmit diversityTelecommunications linkSky
The invention provides a measurement and control method based on a Ka-S-band relay integrated measurement and control system. The method comprises two communication links: S-band relay measurement and control and Ka-band relay measurement and control. An integrated association design technology is employed in the two kinds of band relay. Wide beam antennas are employed in the S-band relay measurement and control communication link and to-sky and to-ground array transmitting / receiving is realized, thereby realizing wide beam coverage. Phased array antennas are employed in the Ka-band relay measurement and control communication link, the Ka relay link can be rapidly tracked and held under the condition that platform postures are continuously changed, and to-sky and to-ground array transmitting / receiving is realized, thereby realizing wide beam coverage. According to the method, the problem that the communication rate is relatively low when the S-band relay measurement and control is employed independently, a real-time coverage range is small when the Ka-band relay measurement and control is employed independently, and the efficiency is relatively low when the two forms of relay measurement and control is not related, in aircraft relay measurement and control is solved.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS TECH
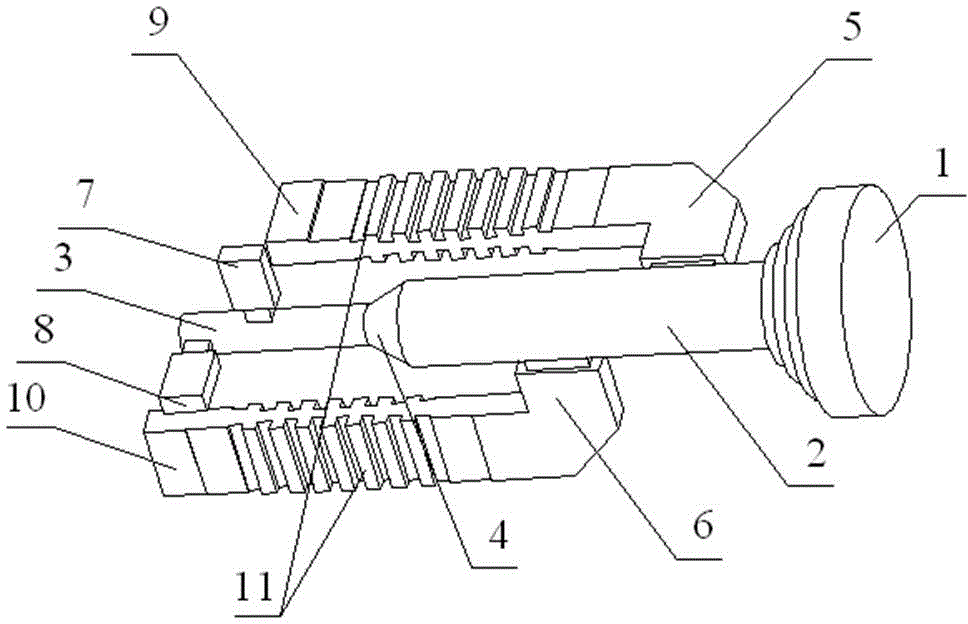
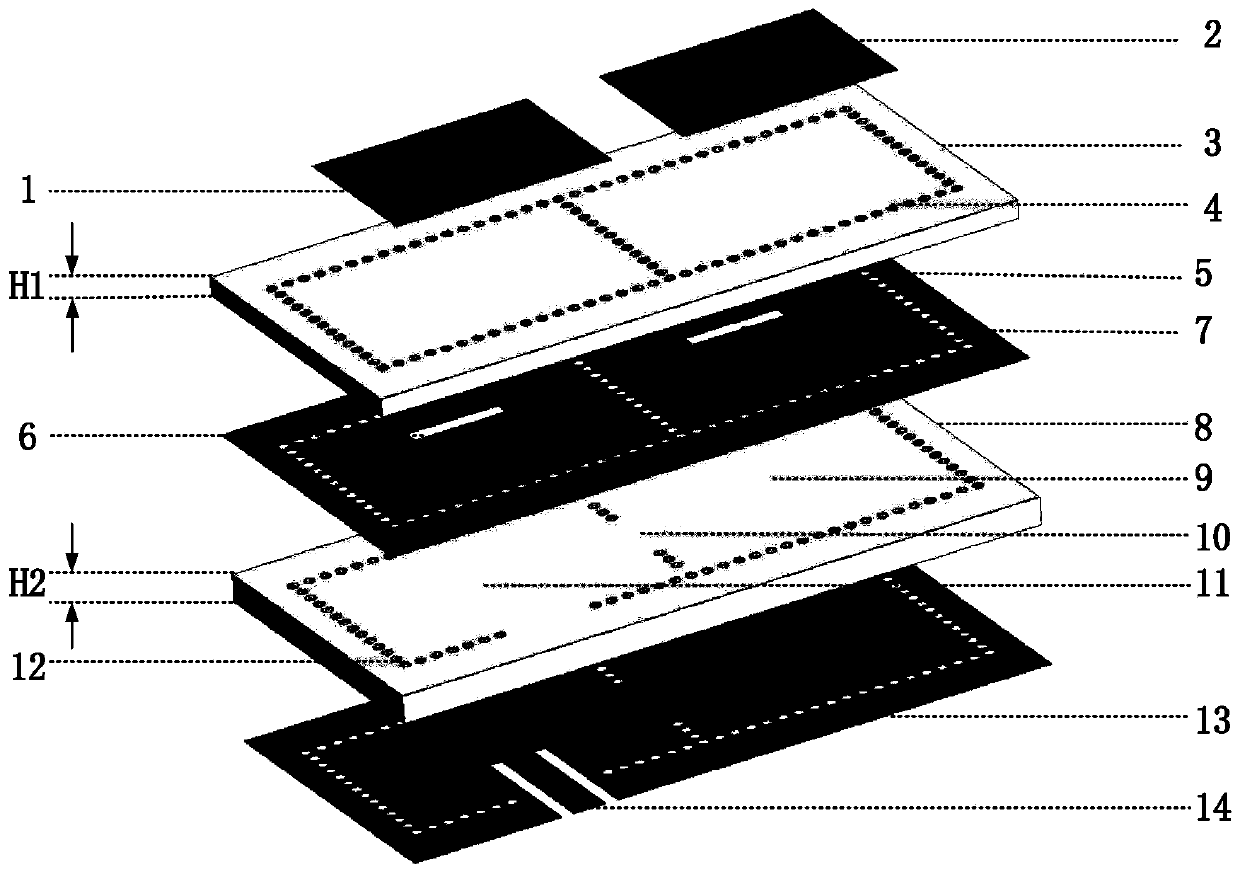
Ka-band miniaturized filter antenna based on SIW structure
ActiveCN110544822AAvoid lossHigh gainRadiating elements structural formsWaveguide type devicesResonant cavityMiniaturization
The invention proposes a Ka-band miniaturized filter antenna based on a substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) structure to mainly solve the problem that a conventional filter antenna is too large in size and difficult to integrate. The Ka-band miniaturized filter antenna includes two metal layers, two dielectric layers and a microstrip radiation unit. A first metal layer (13) is provided with a coplanar waveguide (14). A first dielectric layer (8) is located between the first metal layer (13) and a second metal layer (5), and is provided with periodic metalized through holes (12) on its periphery and center to form two resonant cavities (9, 11). An inductive window (8) is arranged between the two resonant cavities for coupling the two resonant cavities. The second metal layer is provided with two rectangular windows (6, 7). A first radiation unit (1) is disposed on the upper left of the second dielectric layer (3), and a second radiation unit (2) is disposed on the upper right of the second dielectric layer (3). The two radiation units form a radiation array. The Ka-band miniaturized filter antenna has good frequency selectivity and high gain, is easy to integrate, and suitable forKa-band wireless communication.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
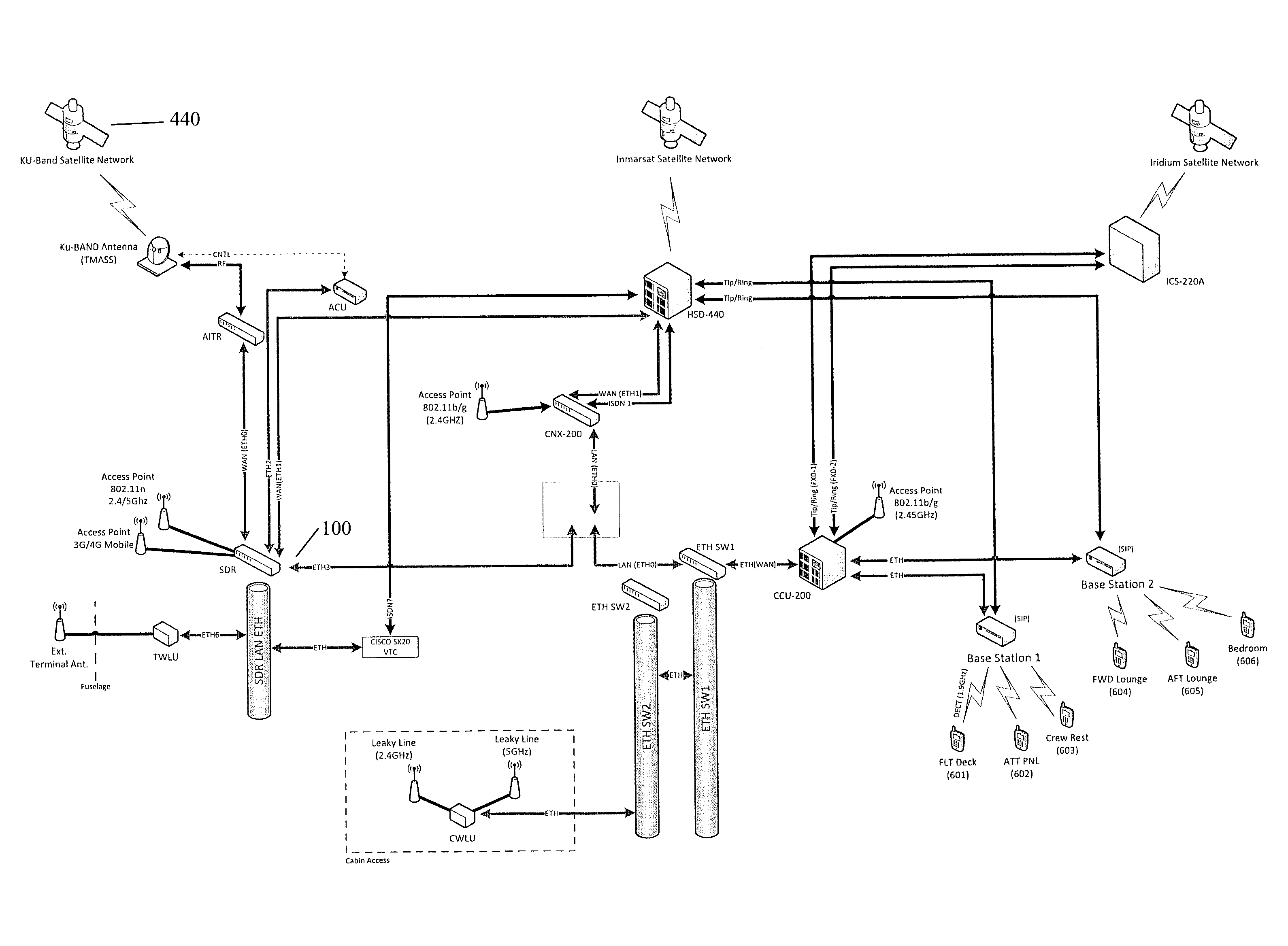
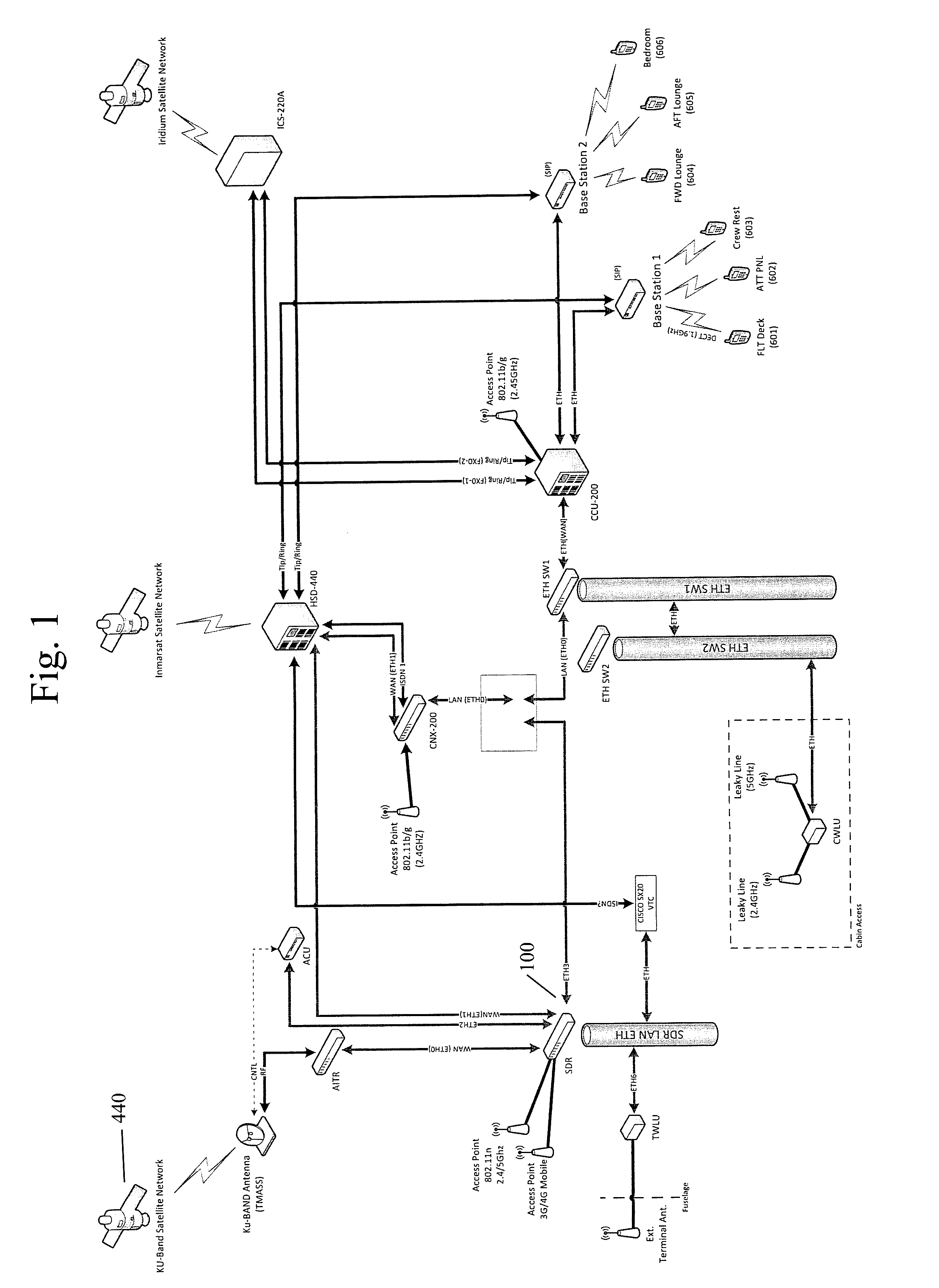
Router for aircraft communications with simultaneous satellite connections
ActiveUS9553658B1Prevents all available bandwidthIncrease speedRadio transmissionMobile appsOn board
Methods, devices, routers and systems for a satellite-ready Satcom Direct router with simultaneous use of Inmarsat, SwiftBroadband, Swift 64, Ku-Band and Ka-Band satellite connections with intelligent traffic control, along with Wi-Fi access and 3G / 4G cellular network connectivity. The router is compatible with existing Wi-Fi access points and is backward-compatible with 802.11b / g. Up to four or more simultaneous wireless networks can be supported, allowing multiple systems to operate on aircraft without additional wireless access points and providing 3G / 4G network connectivity when the aircraft is on the ground. A downloadable Satcom Direct router mobile App provides on-board cabin services including one or more of moving maps, flight tracker and command and control of satellite links.
Owner:SATCOM DIRECT
Ku/Ka dual-band transmitting-receiving community antenna feed source assembly
ActiveCN105896088AReal-time polarization adjustmentCompact structureWaveguide hornsSimultaneous aerial operationsFull waveDual mode
The invention discloses a Ku / Ka dual-band transmitting-receiving community antenna feed source assembly, which comprises a Ku / Ka waveband antenna feed assembly and a polarization adjusting mechanism, wherein the Ku / Ka waveband antenna feed assembly comprises a Ku waveband transmitting and receiving assembly and a Ka waveband transmitting and receiving assembly; and the polarization adjusting mechanism comprises a driving motor assembly, a transmission gear, a Ka rotation joint, a Ku transmission rotation joint and a Ku receiving rotation joint, and the driving motor assembly drives the Ka rotation joint, the Ku transmission rotation joint and the Ku receiving rotation joint to adjust a polarization angle through transmission of the transmission gear. The Ku / Ka dual modes share one feed source horn, a dielectric rod is cancelled, a full-waveguide mode is adopted, the structure is compact, the utilization rate is high, Ka circular polarization switching is facilitated, good Ku / Ka wave frequency band isolation is provided, and good polarization separation, polarization isolation, radiation features, a standing-wave ratio and gains are realized in the frequency band; and Ku line polarization adjustment can be carried out in real time, and automatic satellite aiming is realized.
Owner:HUNAN AEROSPACE HUNAYU COMM TECH CO LTD
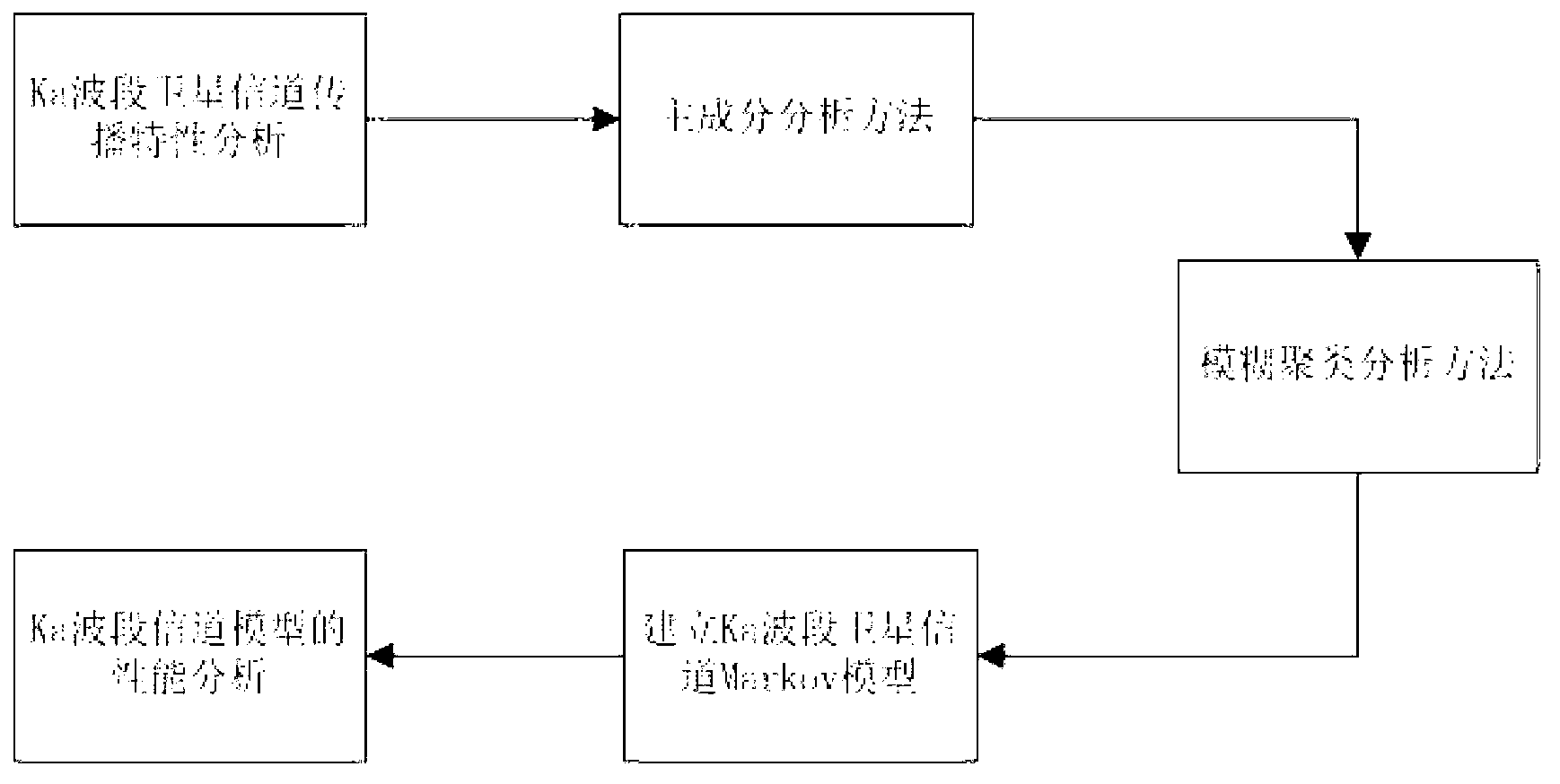
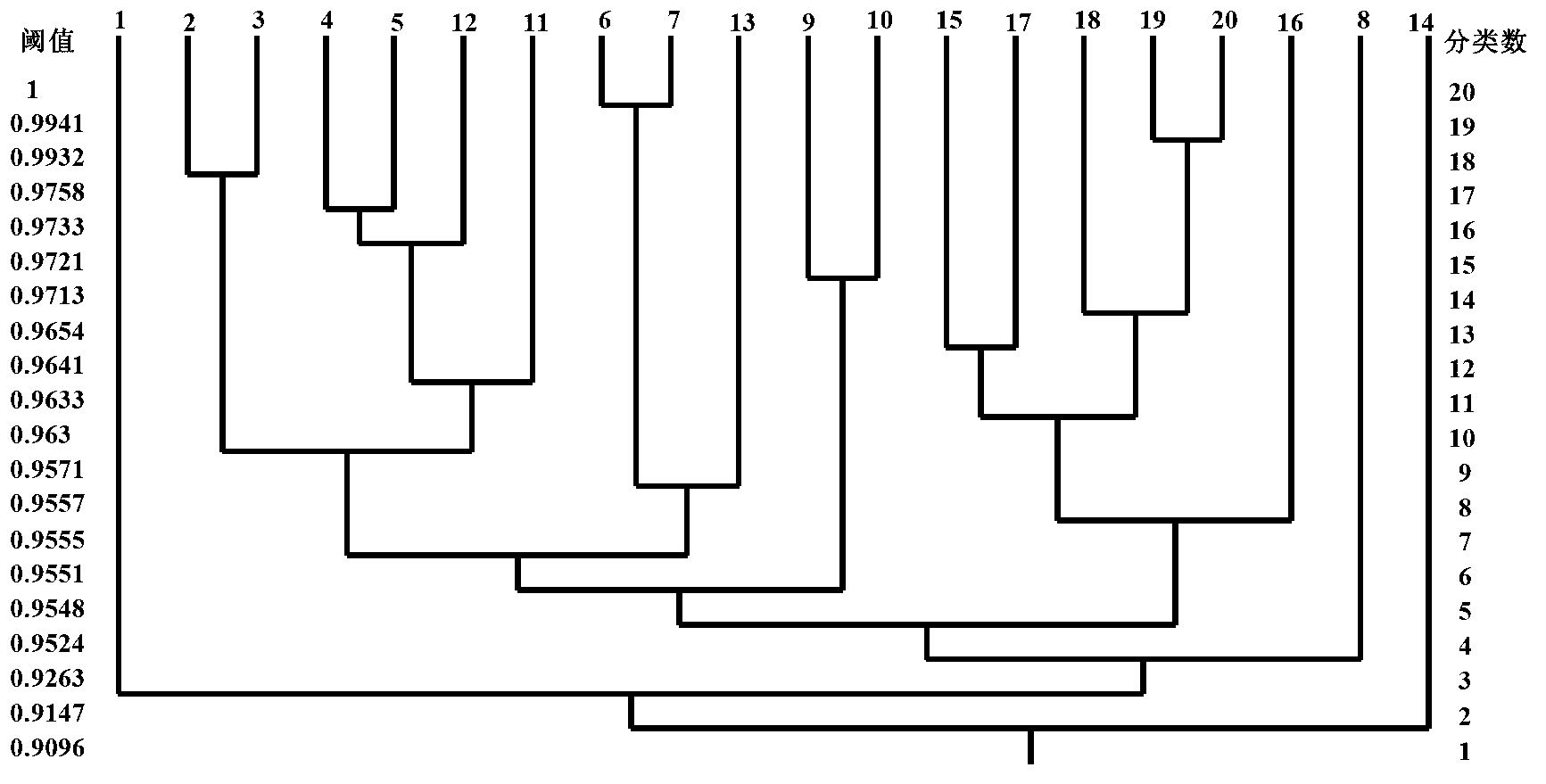
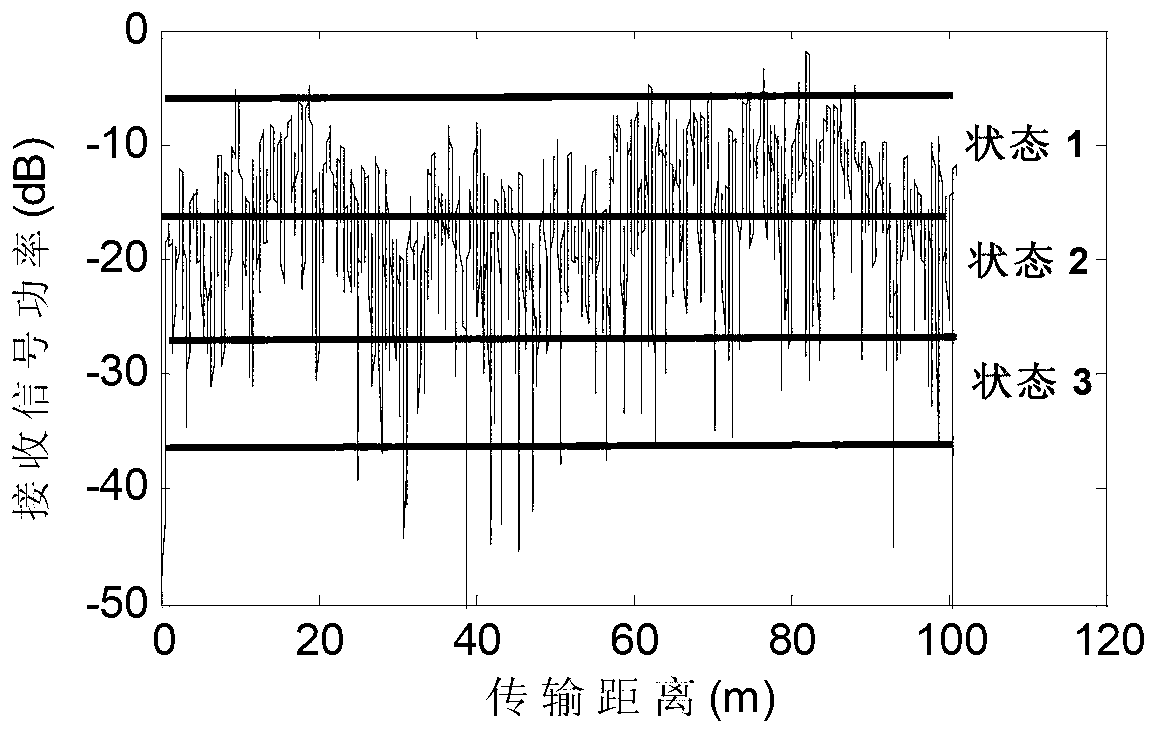
Ka-band satellite channel modeling method integrated with meteorological factors
InactiveCN103188011AVerify accuracyVerify validityNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionFuzzy clustering analysisPrincipal component analysis
The invention provides a Ka-band satellite channel modeling method integrated with meteorological factors and aims at solving the problems that data classification is lack of theoretical basis and simulation data are difficult to obtain in a traditional Ka-band satellite channel modeling process. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, analyzing the propagation characteristic of a Ka-band satellite channel and the influences of multipath propagation, rainfall, atmospheric absorption, atmospheric scintillation and other factors to satellite channel modeling; and secondly, establishing a multistate Markov model of the Ka-band satellite channel by using a principal component analysis and fuzzy clustering analysis method. Through comparing the electrical level crossing-over rate and the average decay time of the established model with the electrical level crossing-over rate and the average decay time of a former model, the accuracy and the effectiveness of the channel model are checked, the theoretical basis is provided for resisting the rain attenuation of the Ka-band satellite channel, and meanwhile, Ka-band satellite channel modeling method has great practical significance in technical research on the aspects of signal modulation, coding mode and power control of Ka-band satellite communication.
Owner:紫光陕数大数据有限公司
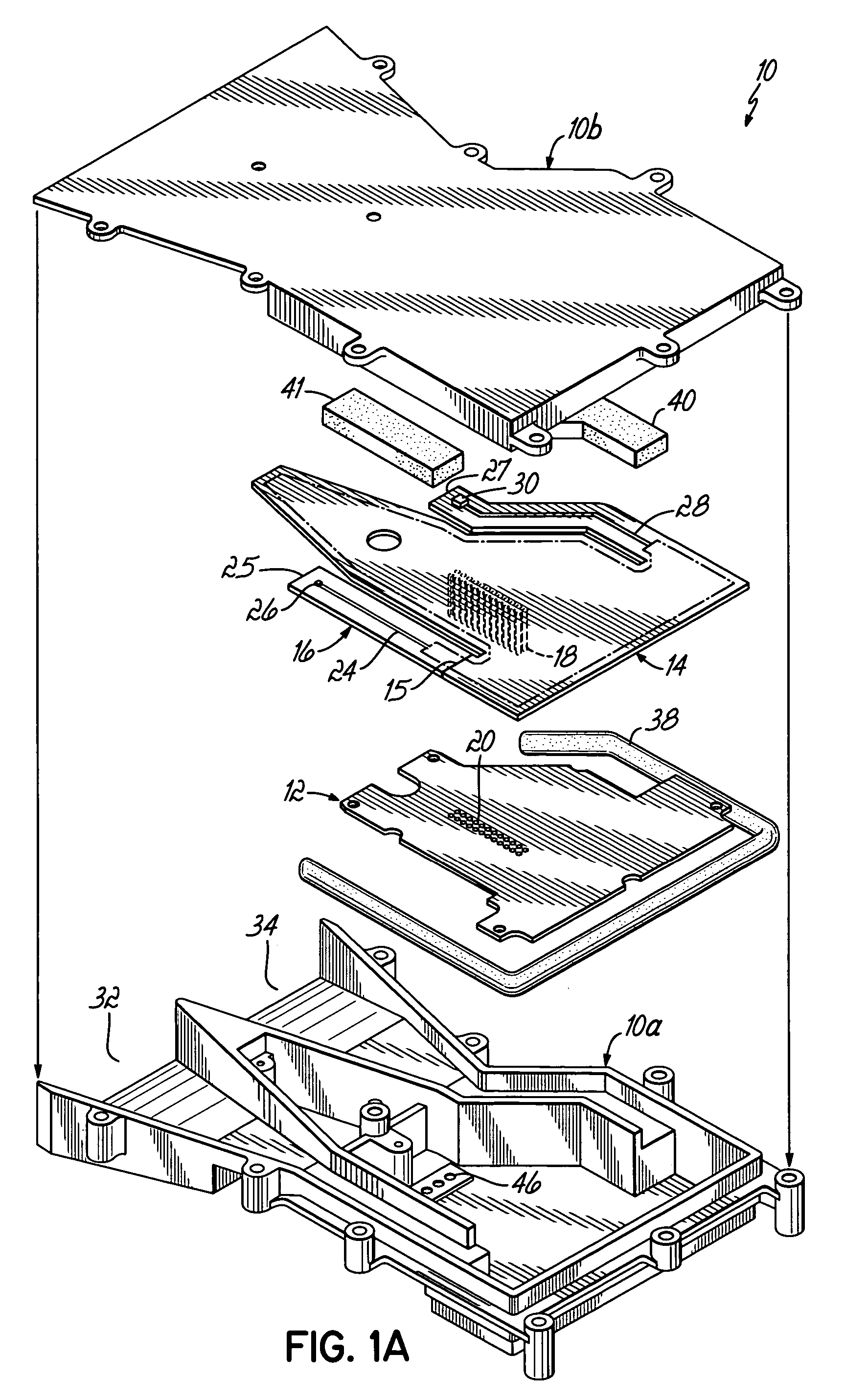
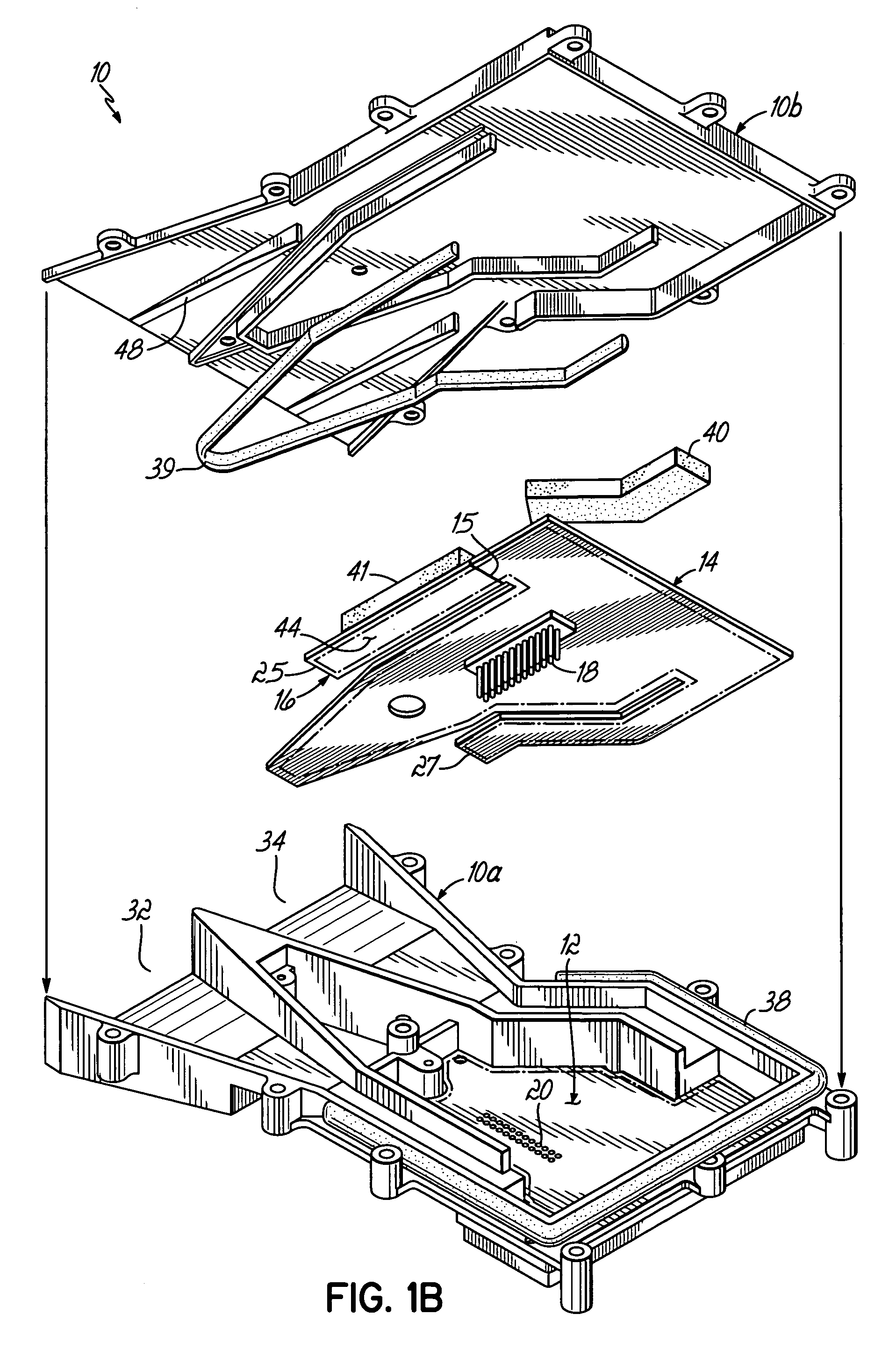
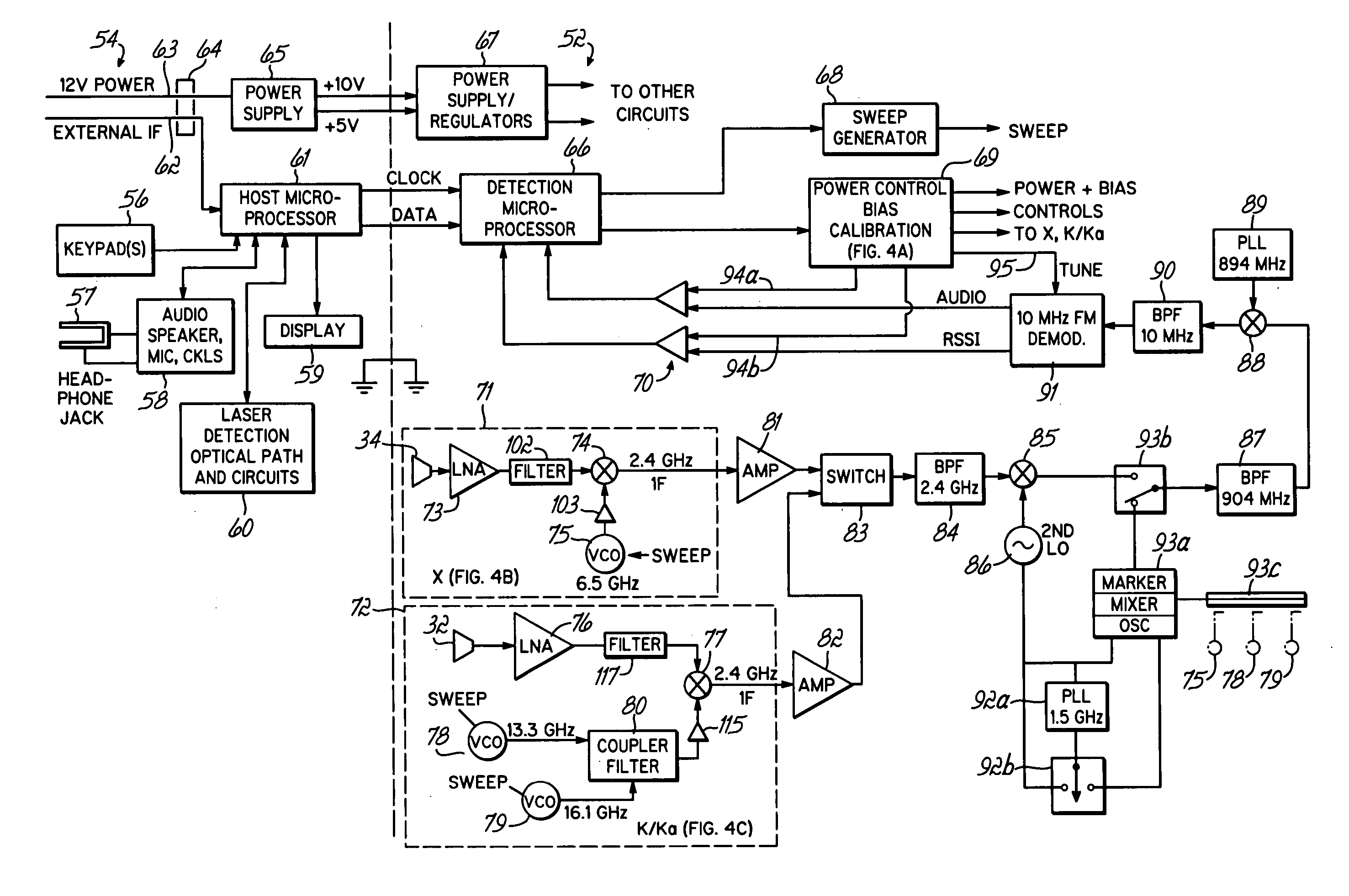
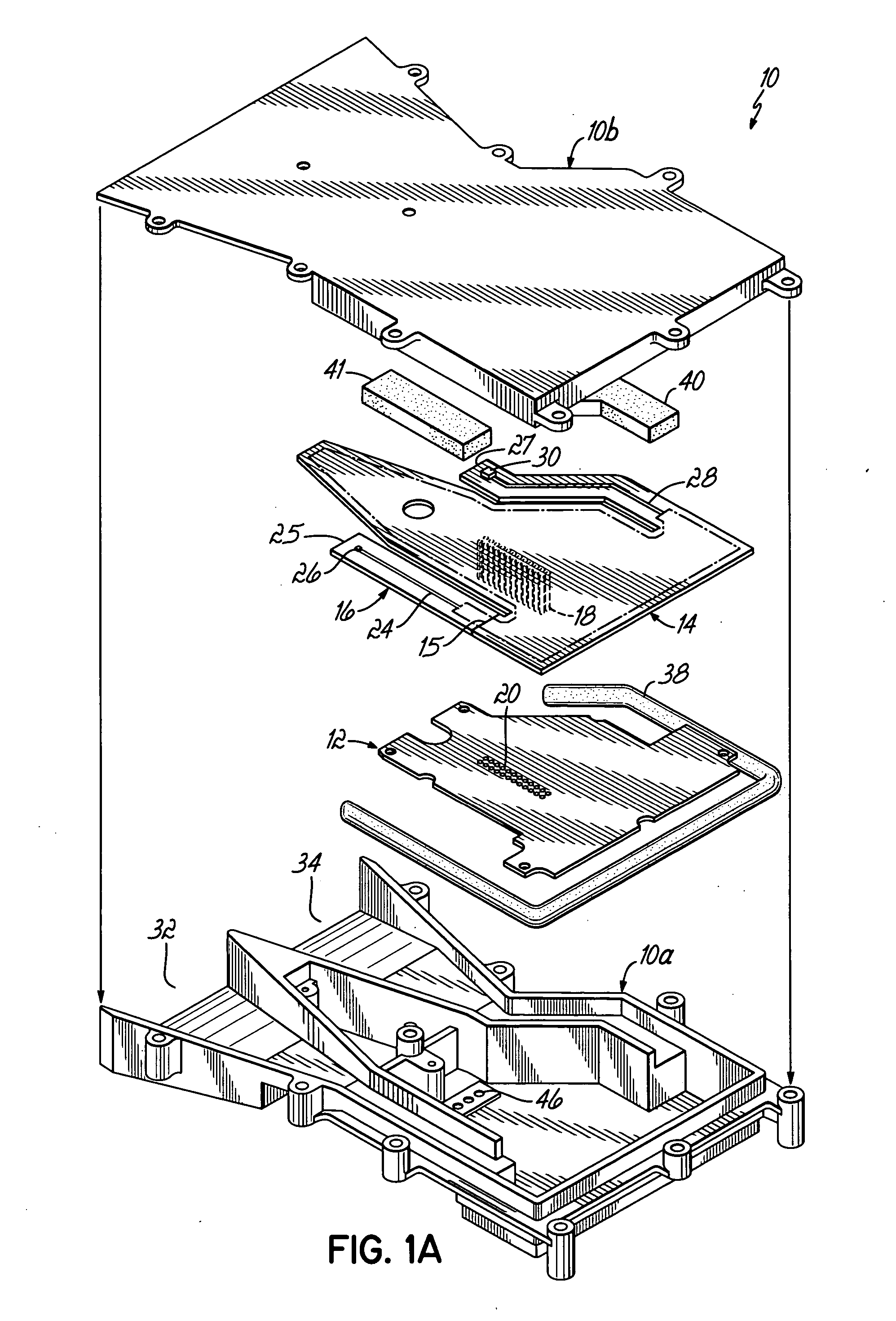
Radar detector with reduced emissions
ActiveUS7388537B2Reduce radiationReduce complexityCommunication jammingTransmissionLow noiseAudio power amplifier
A radar detector includes features to reduce emissions such as those typically generated by the detector's local oscillator. Two low noise amplifiers (LNA's), operating in X band and a combined K / Ka band, respectively amplify X and K / Ka band signals from separate antennae, and deliver those signals over separate, elongated and narrow signal paths to X and K / Ka mixers, where those signals are mixed with local oscillator (LO) signals to produce IF for detection. The elongated, narrow signal paths from the antennae to the mixers reduce LO emissions, and those emissions are further reduced by incorporating radar absorbers between the circuit board and detector case along the antenna-mixer path, including radar absorptive paint on the circuit board itself along this path, and sealing the case with a conductive sealing gasket.
Owner:ESCORT INC
Radar detector with reduced emissions
ActiveUS20080007444A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce radiationCommunication jammingTransmissionLow noiseAudio power amplifier
A radar detector includes features to reduce emissions such as those typically generated by the detector's local oscillator. Two low noise amplifiers (LNA's), operating in X band and a combined K / Ka band, respectively amplify X and K / Ka band signals from separate antennae, and deliver those signals over separate, elongated and narrow signal paths to X and K / Ka mixers, where those signals are mixed with local oscillator (LO) signals to produce IF for detection. The elongated, narrow signal paths from the antennae to the mixers reduce LO emissions, and those emissions are further reduced by incorporating radar absorbers between the circuit board and detector case along the antenna-mixer path, including radar absorptive paint on the circuit board itself along this path, and sealing the case with a conductive sealing gasket.
Owner:ESCORT INC
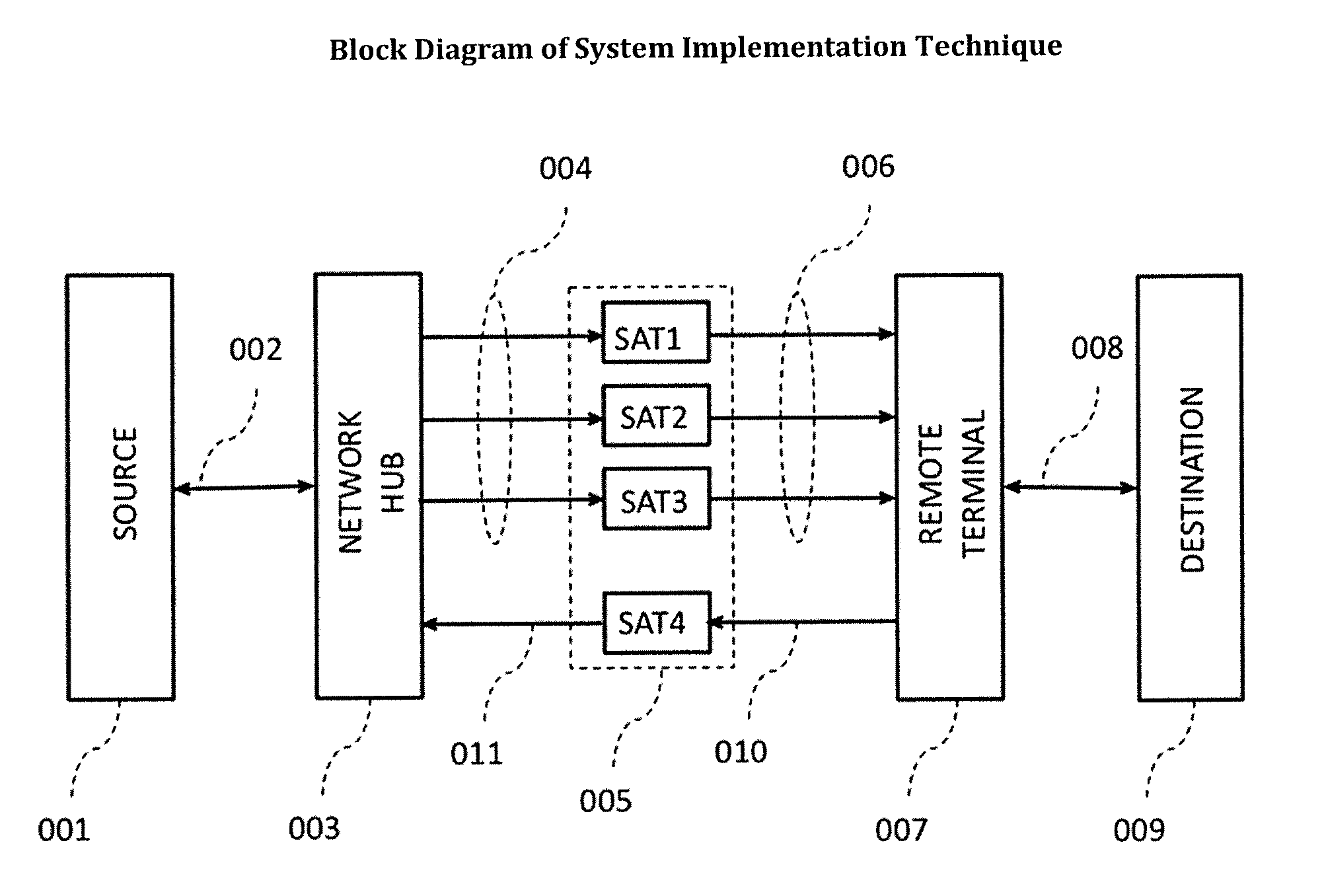
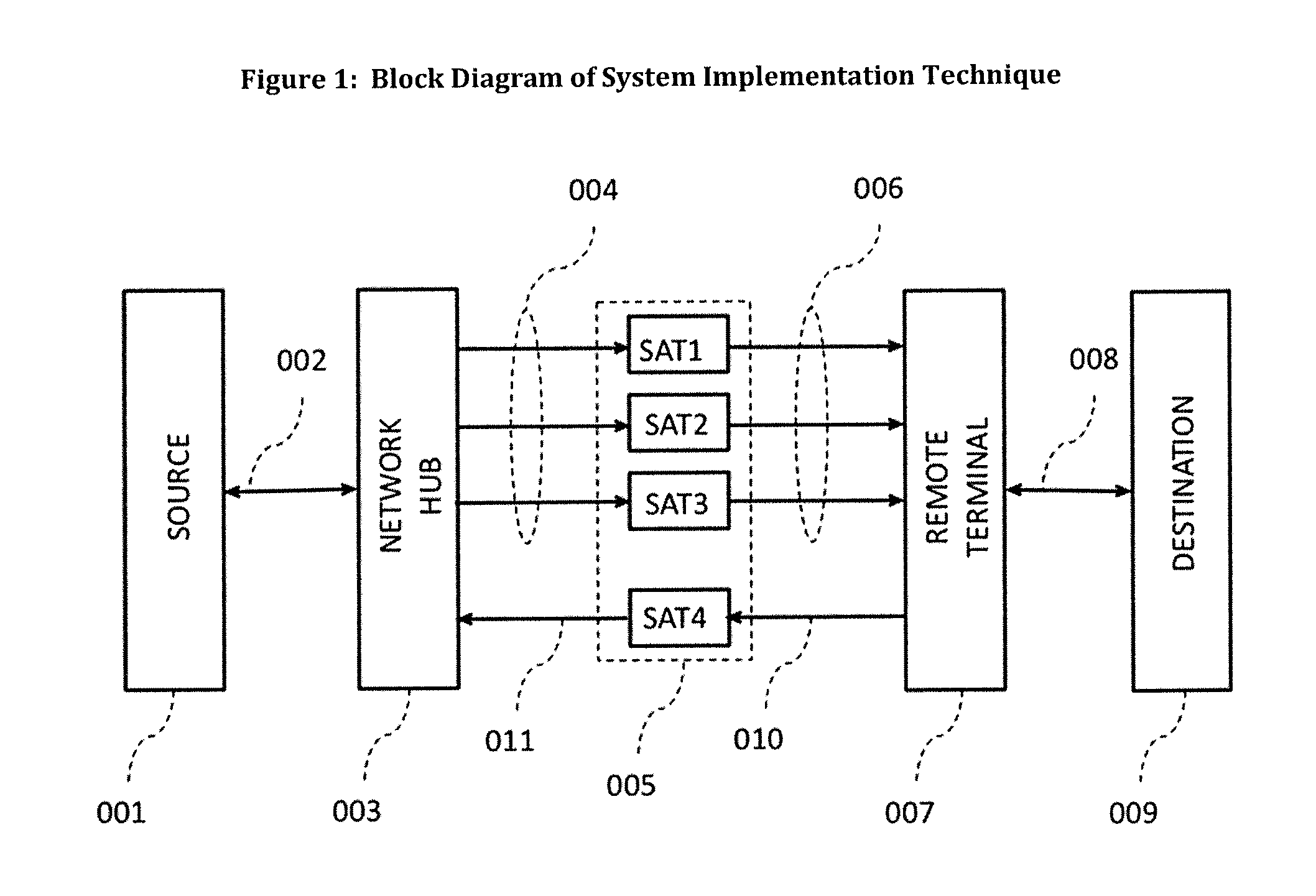
Process of spectrum diversity of satellite link for data and internet applications using single antenna and router
ActiveUS20130295841A1Maximize throughputImprove data throughputSimultaneous aerial operationsNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency spectrumThe Internet
A satellite communication system between a source and a destination over multiple satellite communications paths including first identifying the link performance established in multiple spectrums, performing a link comparison among the multiple spectrums (for example C-, Ku-, or Ka-Band) in order to determine a spectrum link that provides the highest throughput within an acceptable reliability criteria, and switching among the multiple spectrum links to provide that determined spectrum link between the source and the destination.
Owner:ABS GLOBAL LTD
Multi-band antenna system for satellite communications
Owner:KVH IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com