Patents
Literature
1104 results about "Wave frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The frequency of a wave refers to how often the particles of the medium vibrate when a wave passes through the medium. Frequency is a part of our common, everyday language. ... The speed of an object refers to how fast an object is moving and is usually expressed as the distance traveled per time of travel. For a wave, the speed is the distance traveled by a given point on the wave (such as a crest) in a given period of time.
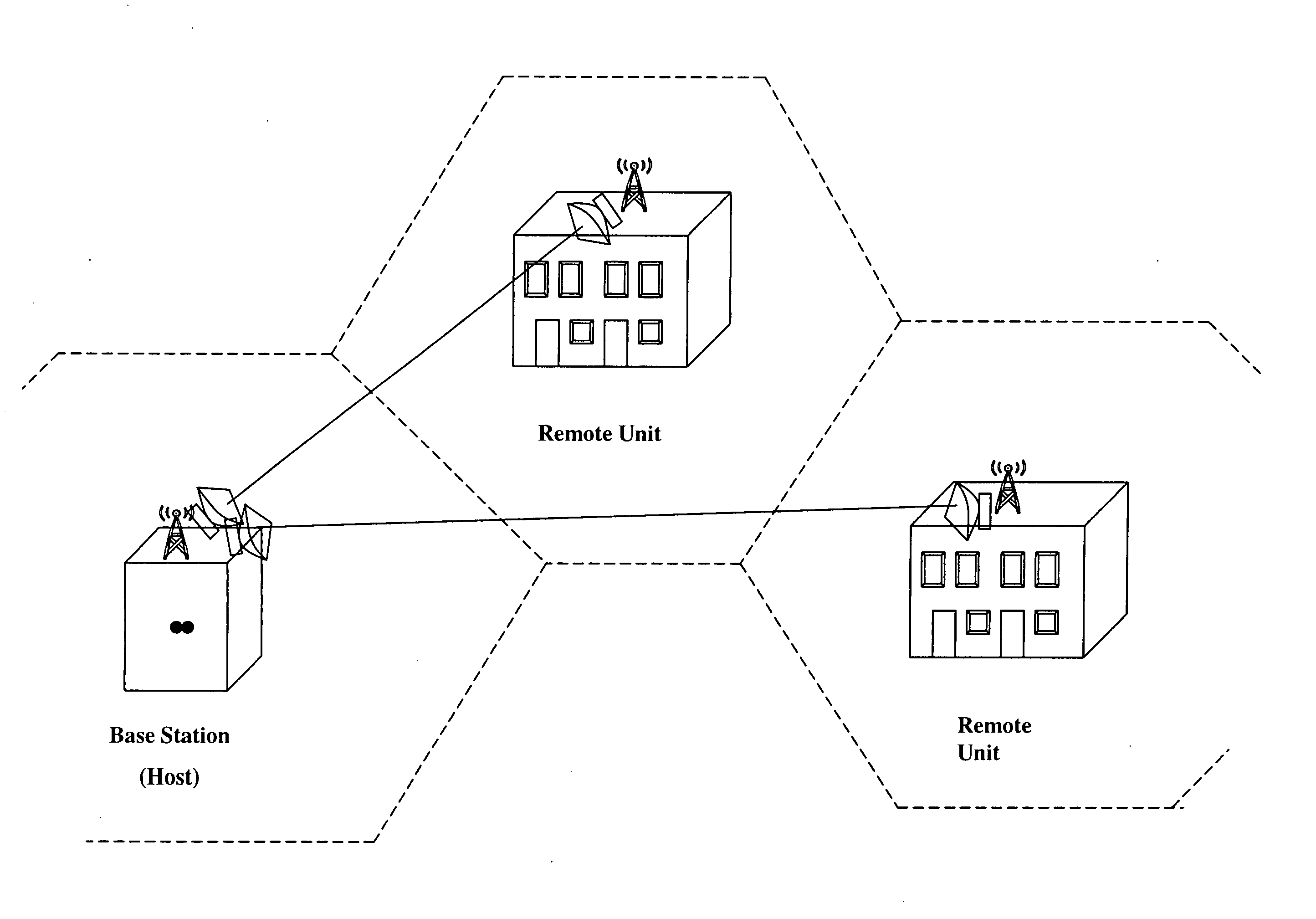
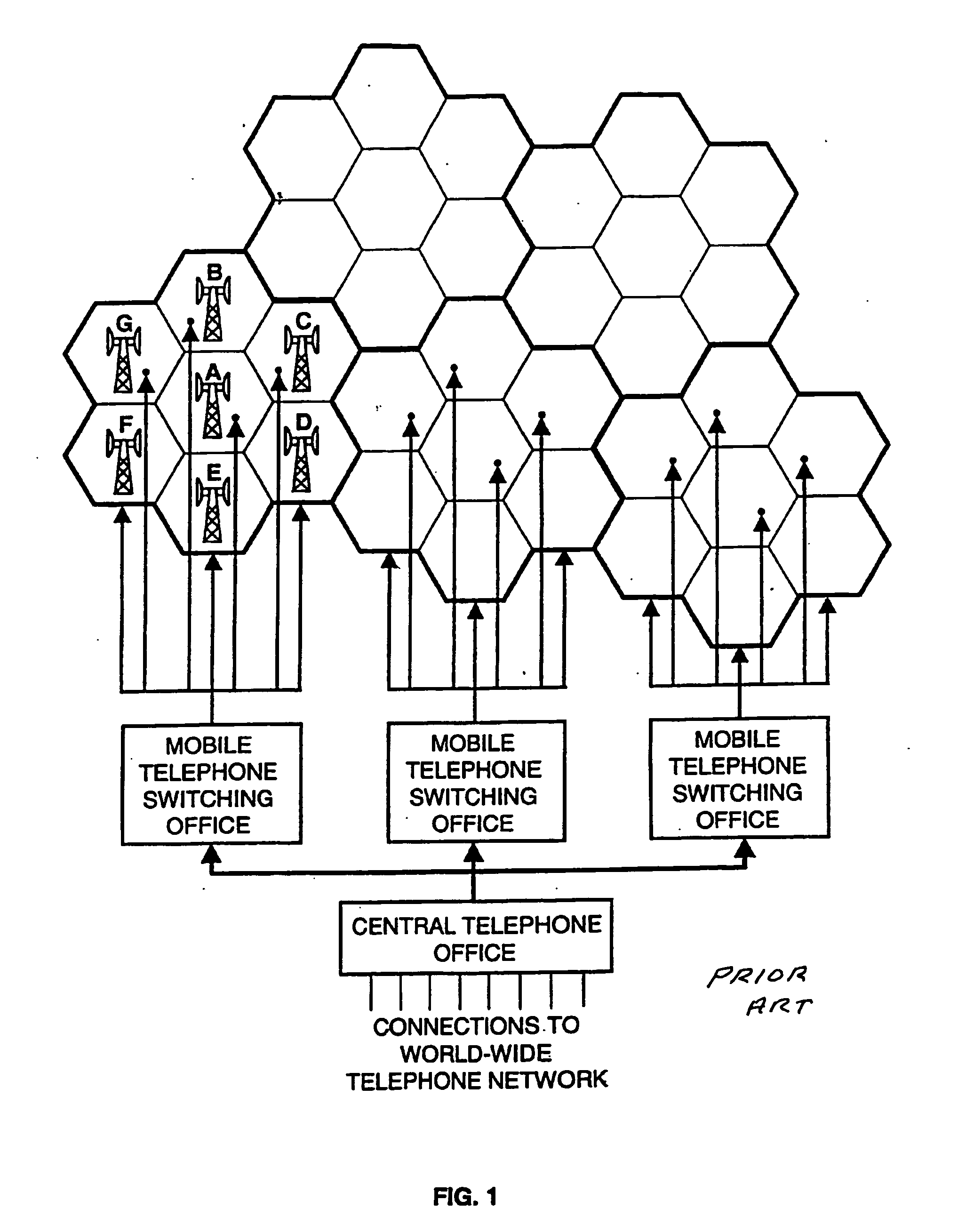
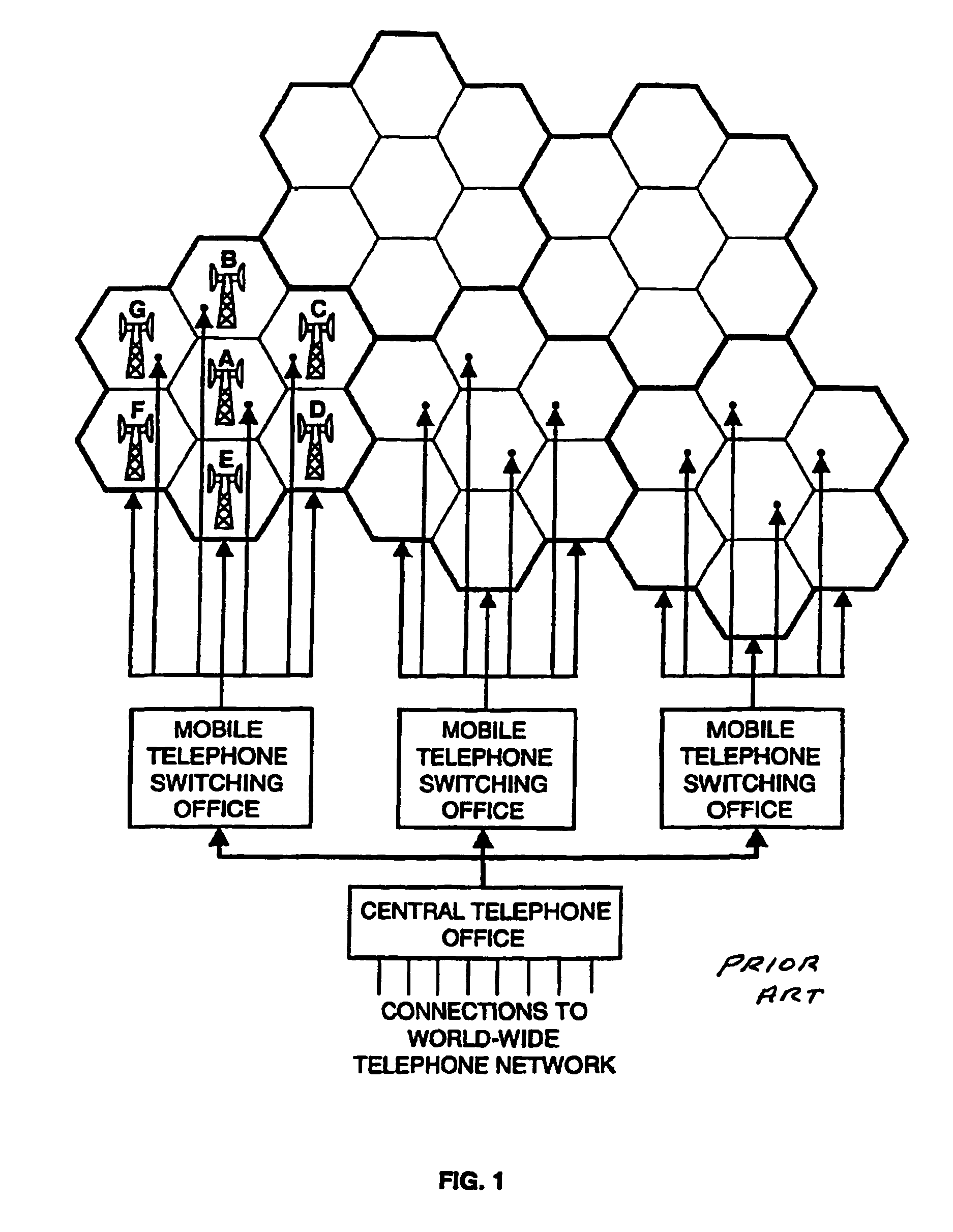
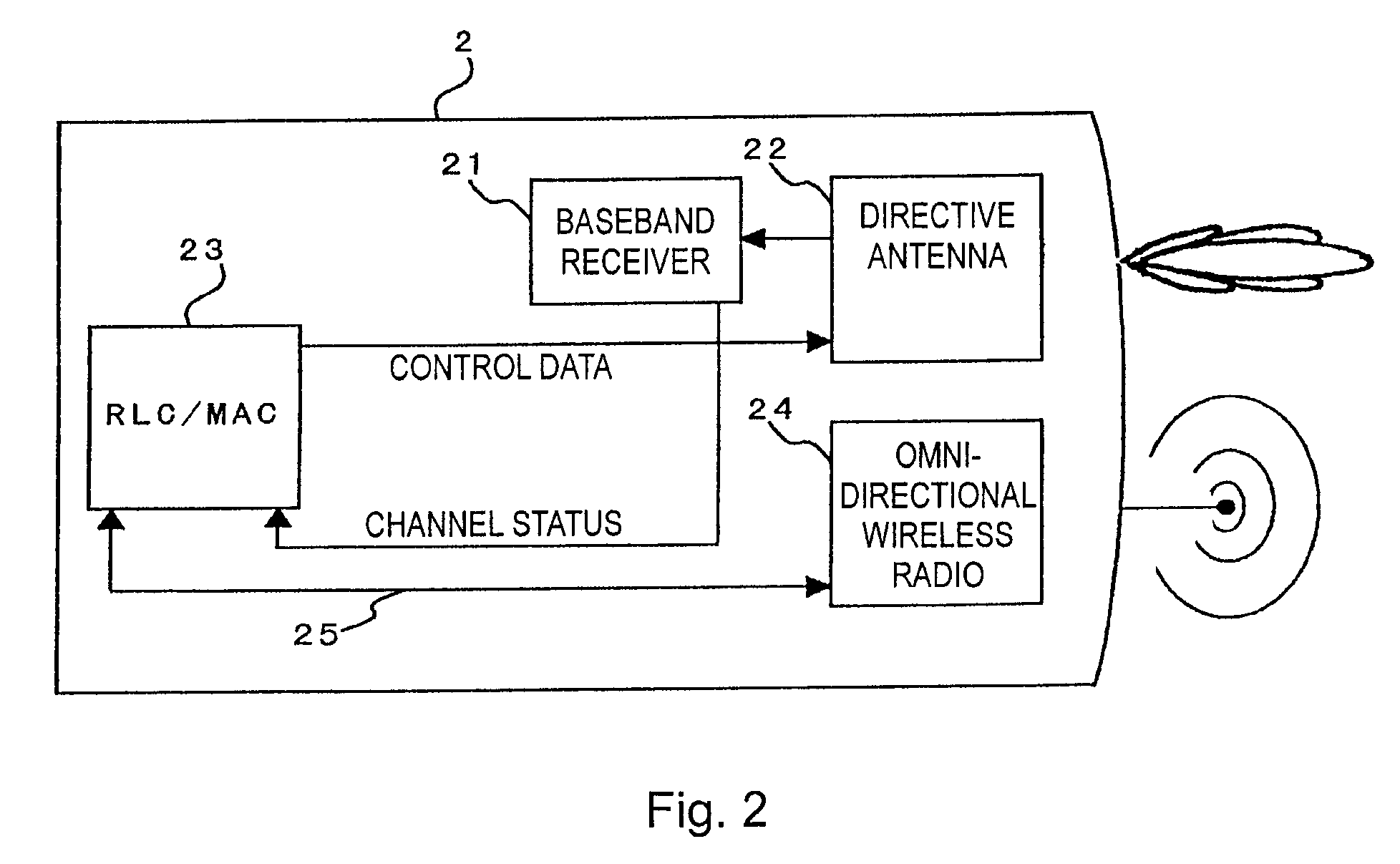
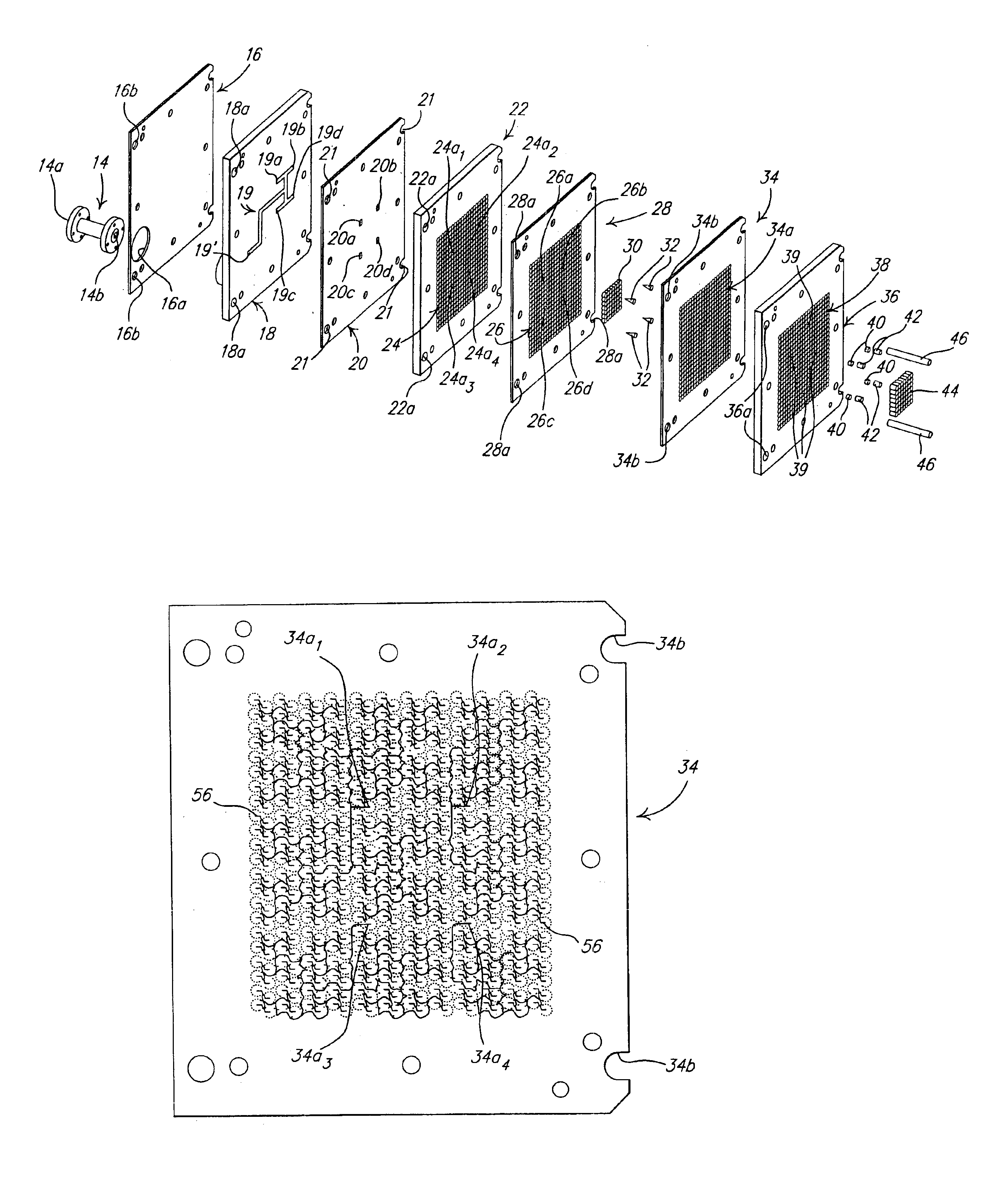
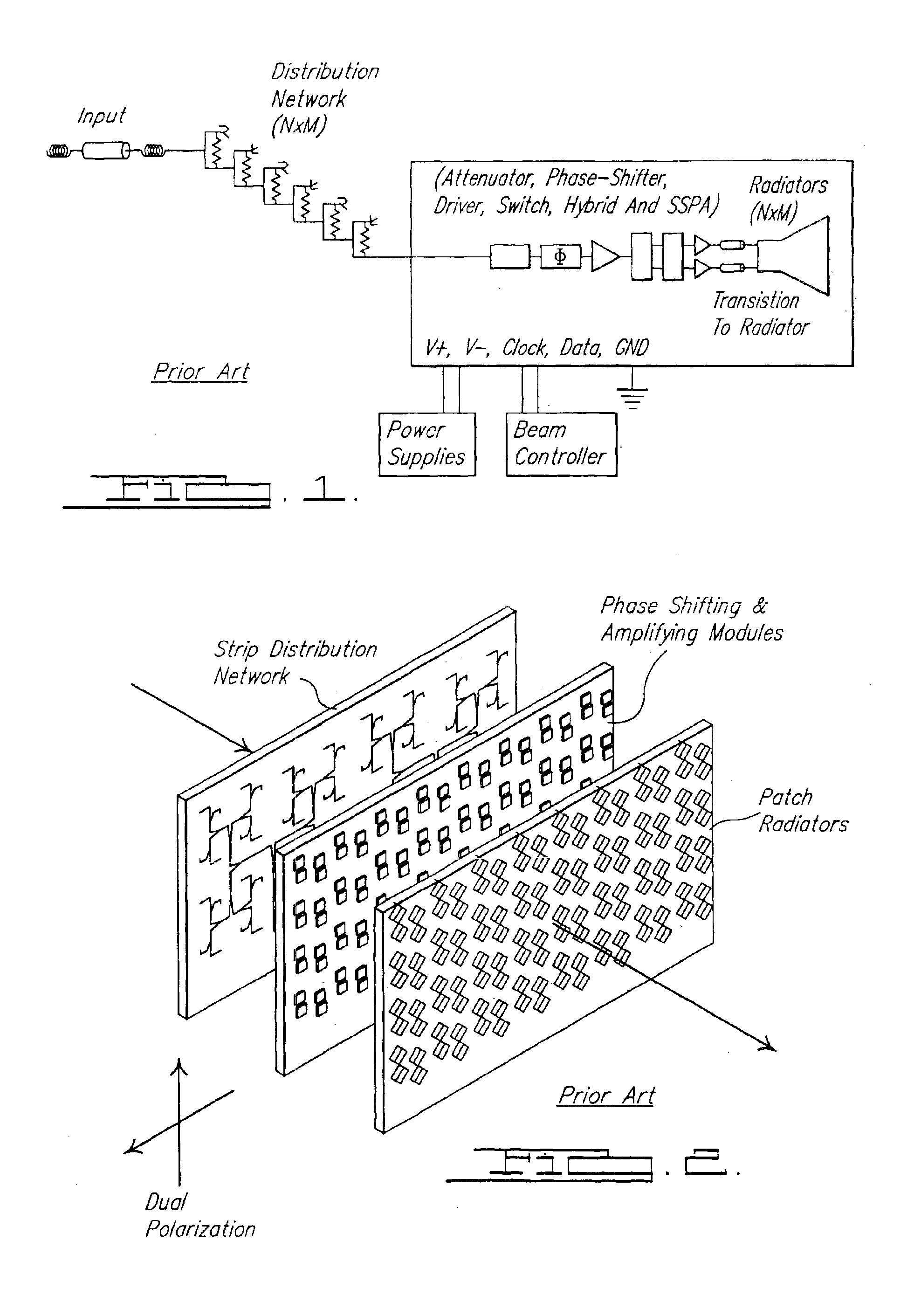
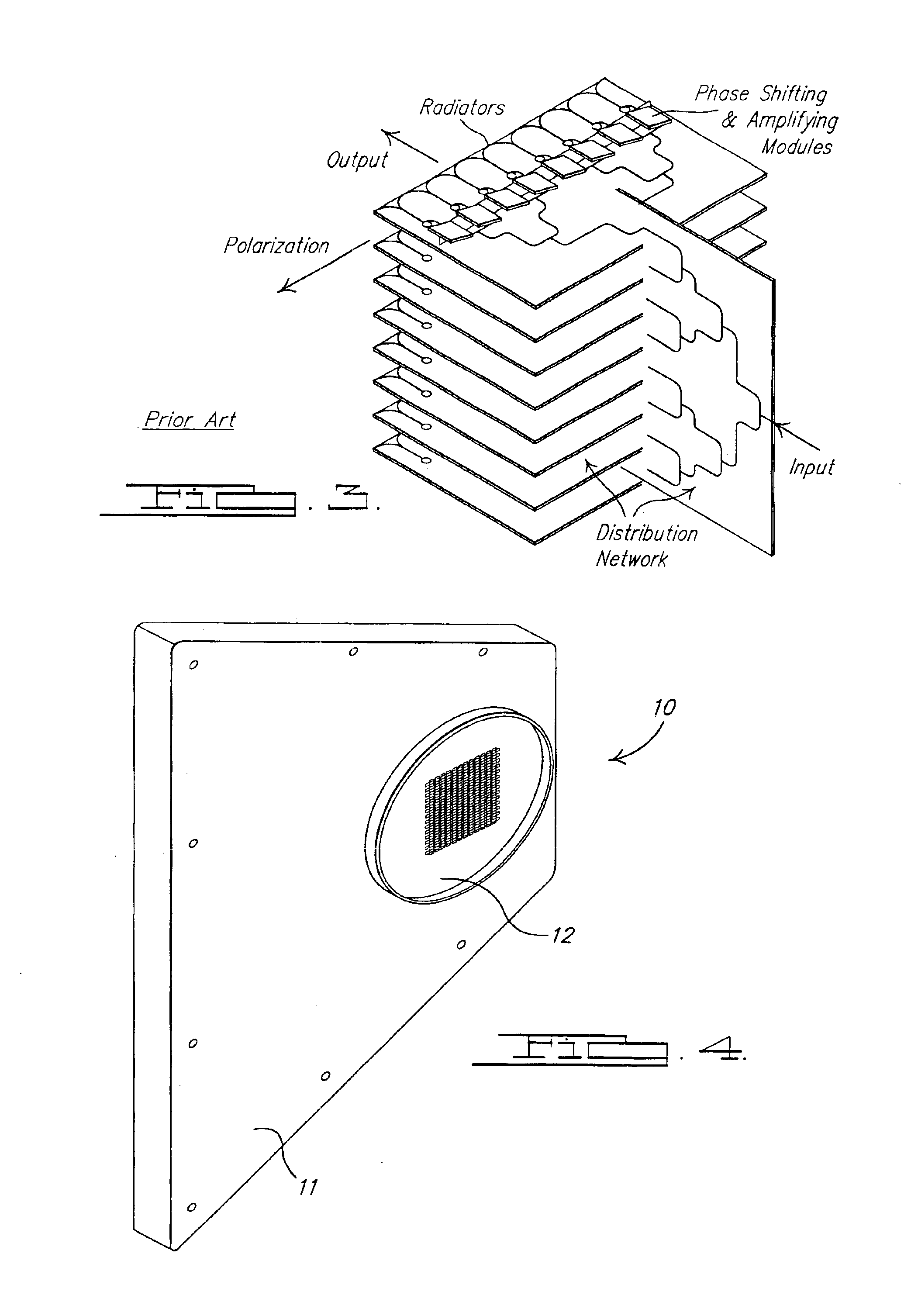
Cellular systems with distributed antennas
InactiveUS20090258652A1Efficient use ofIncrease data rateNetwork topologiesInformation formatWireless transceiverTransceiver
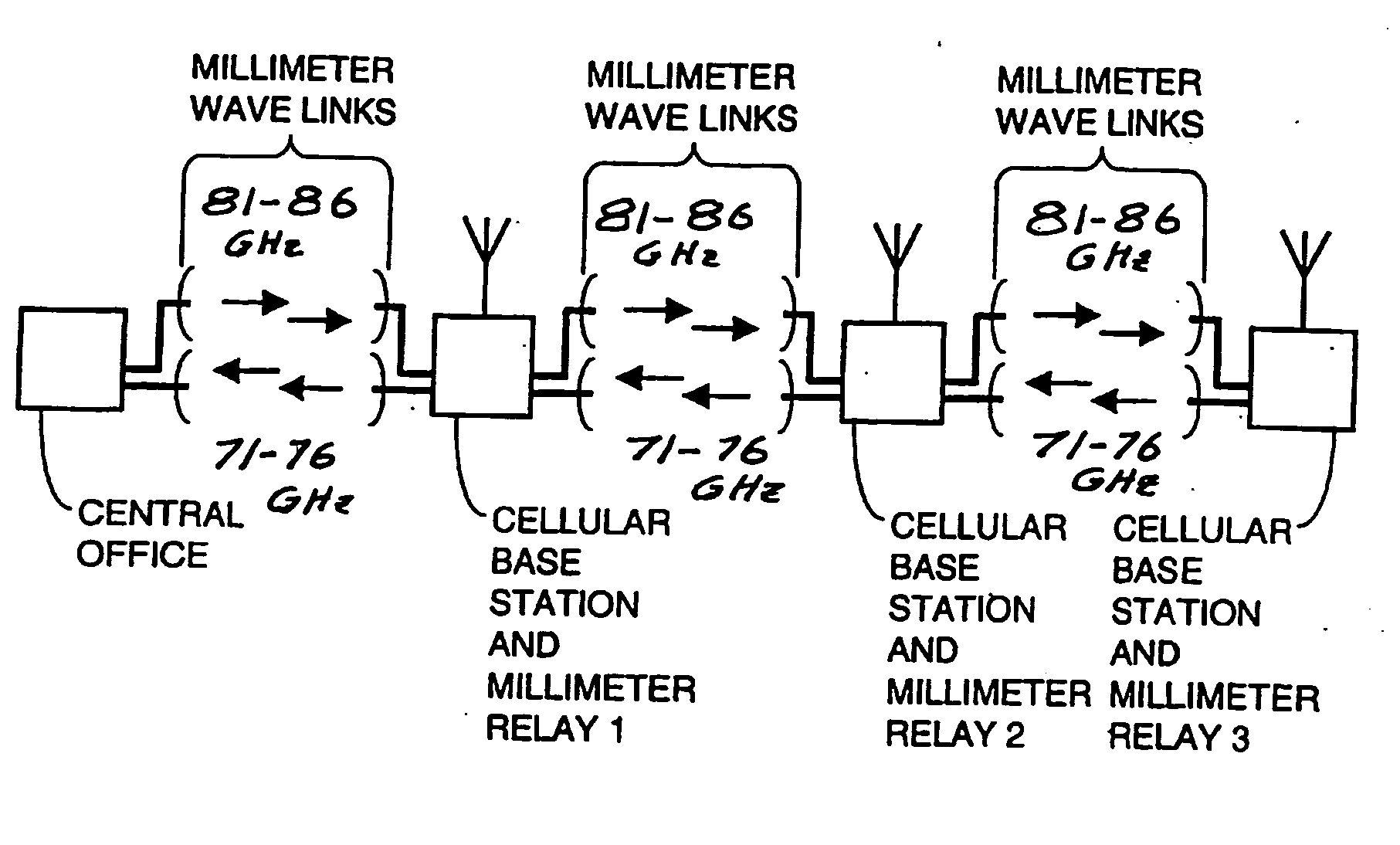
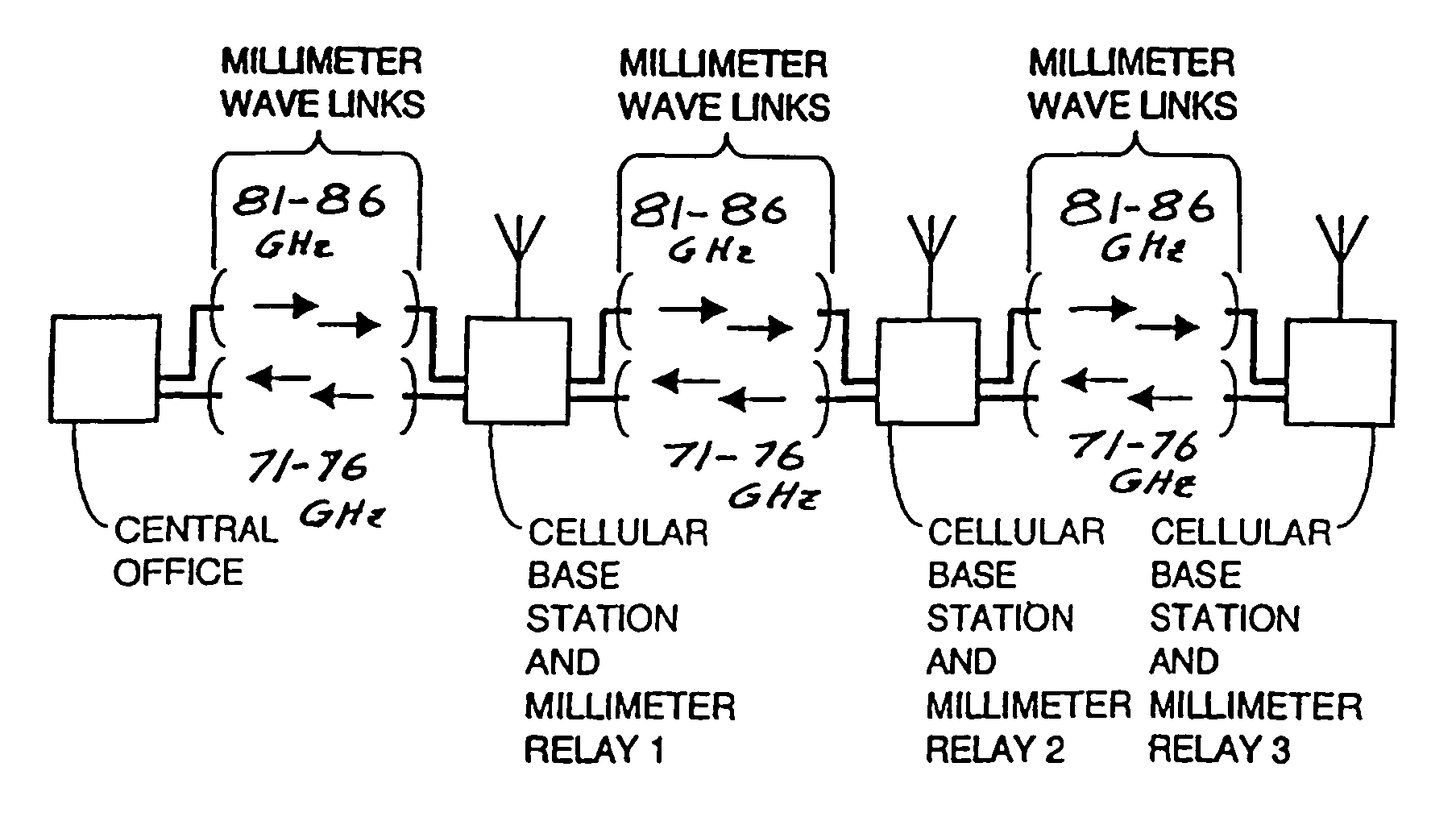
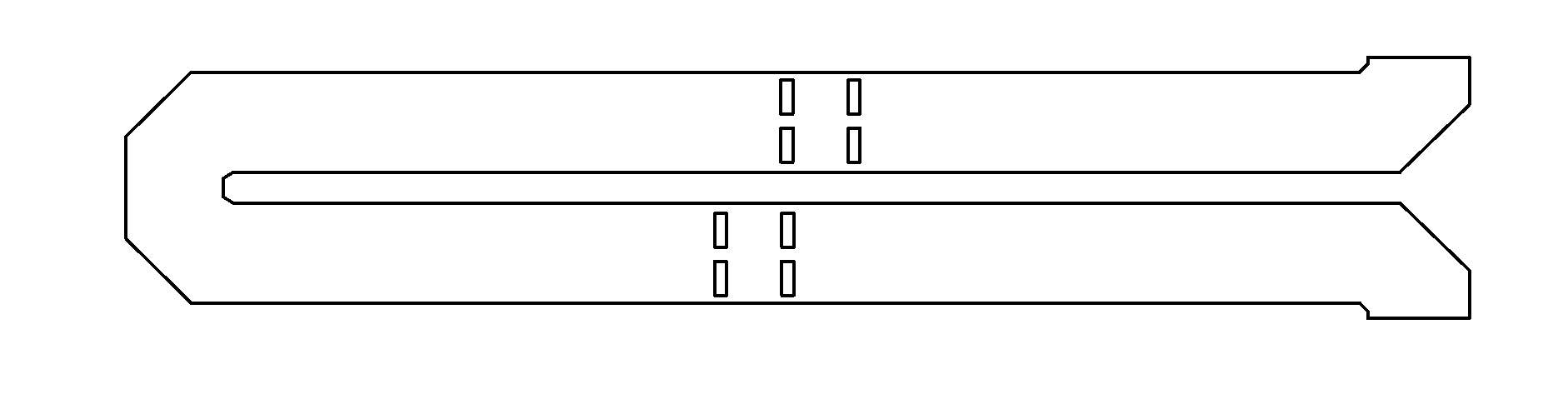
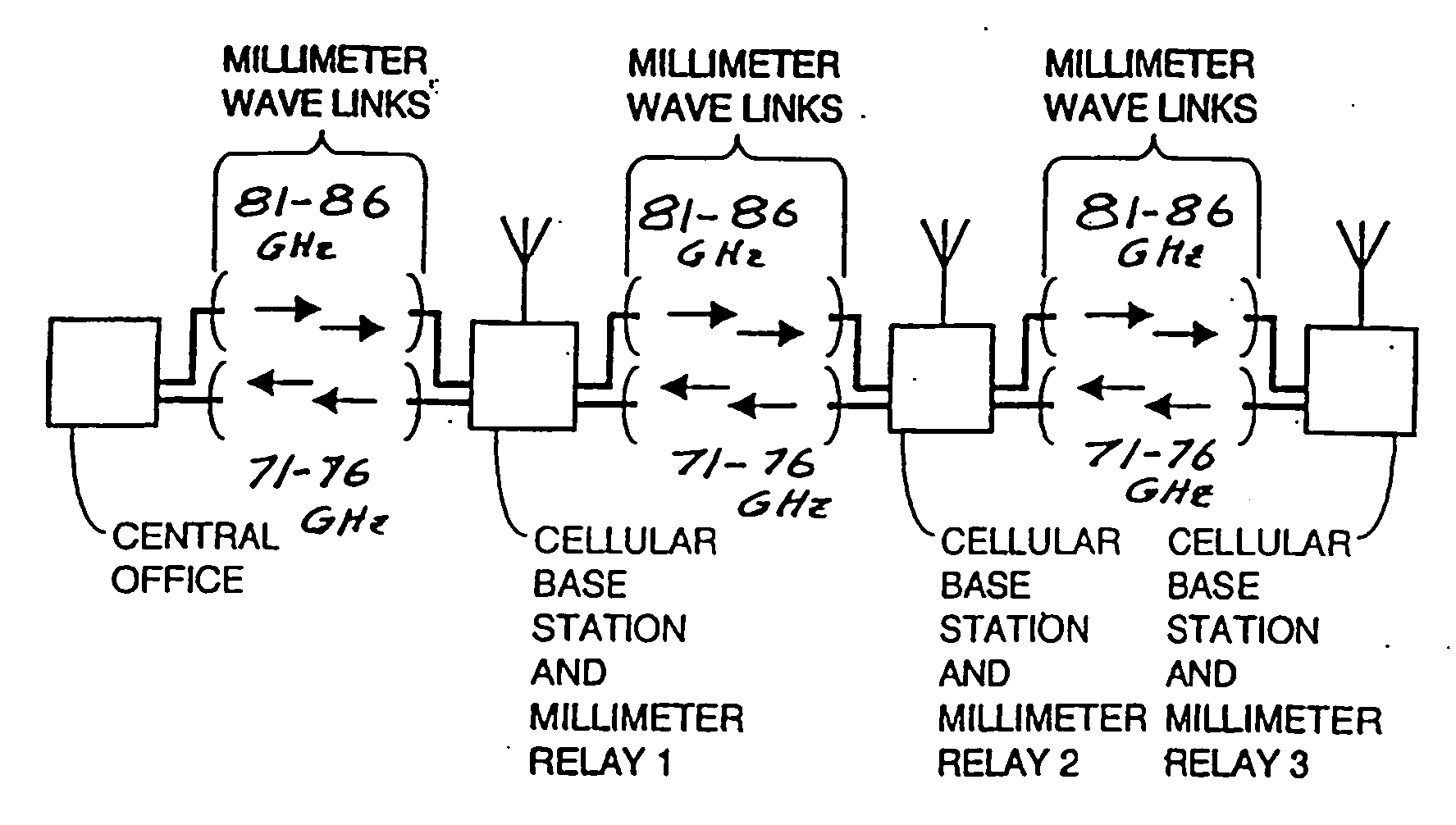
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations, each including at least transport management equipment and broadband equipment, at least one of which supports at least remote cellular station including RF equipment for communication with users of cellular devices. The system includes at lease one wireless narrow beam communication link operating at millimeter wave frequencies in excess of 60 GHz connecting a remote cellular station with a cellular base station equipped with broad band conversion electronic equipment and transport management equipment. In preferred embodiment the communication system includes a large number of remote cellular stations with each remote cellular station serving a separate communication cell. Each remote cellular station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a narrow beam millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another remote cellular station or a millimeter wave transceiver at a base station.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
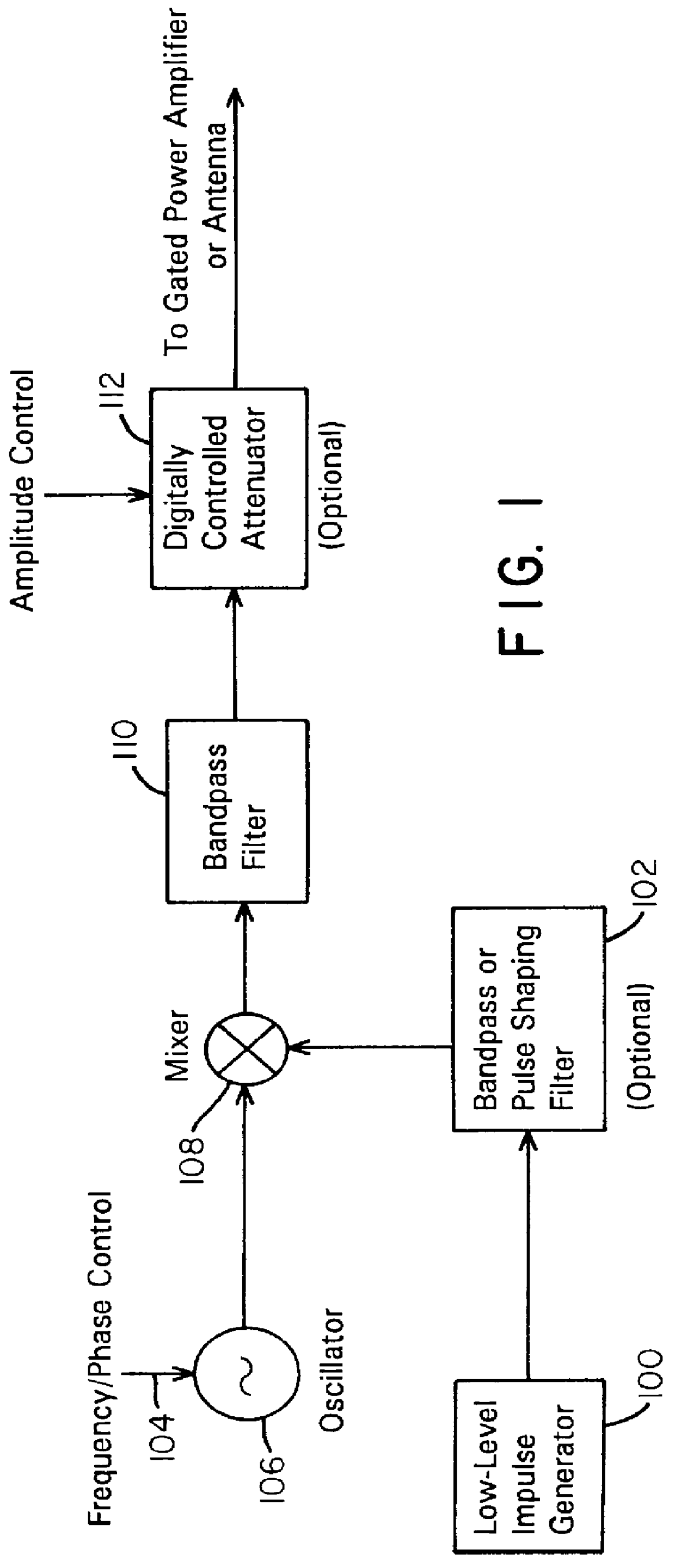
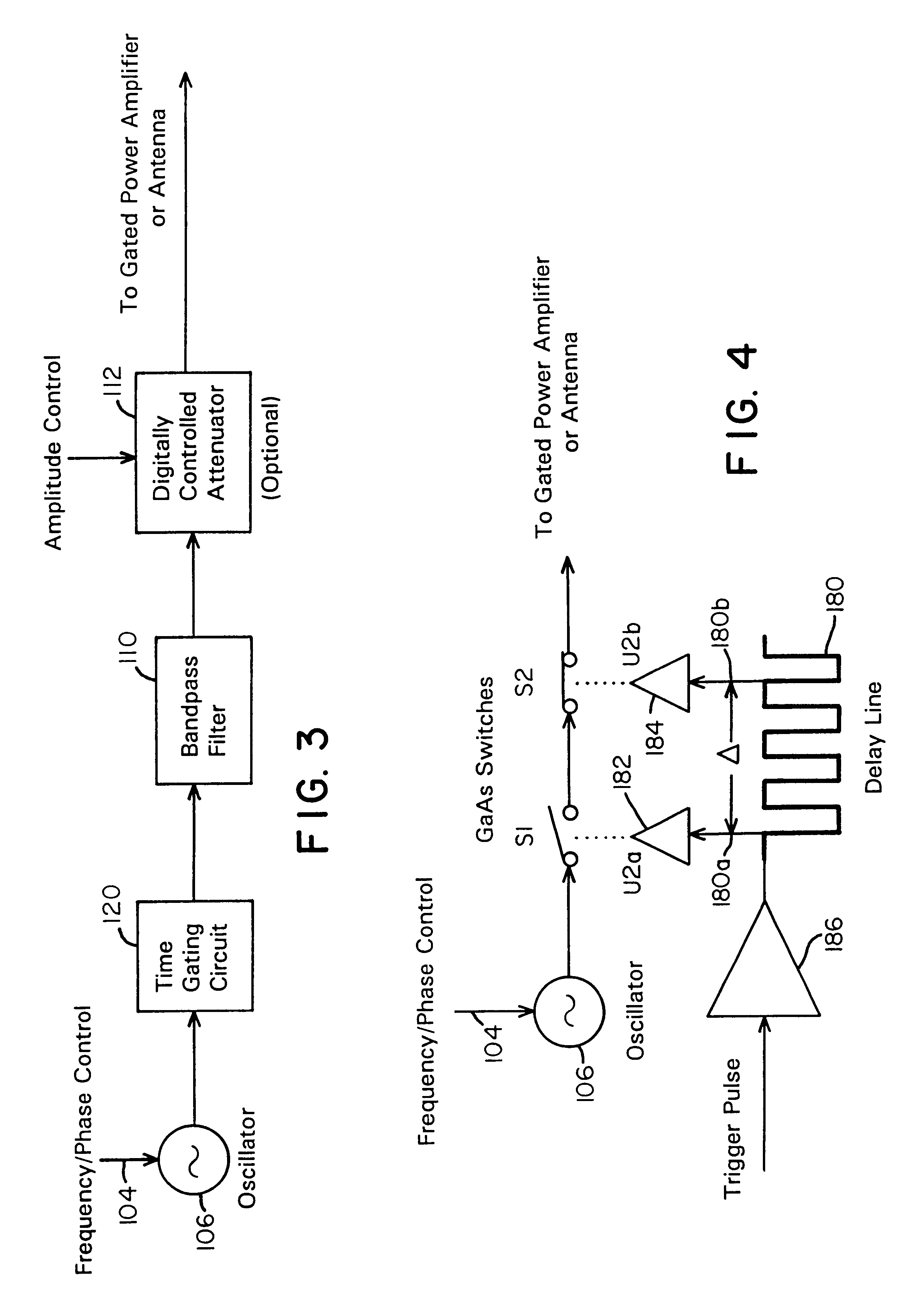
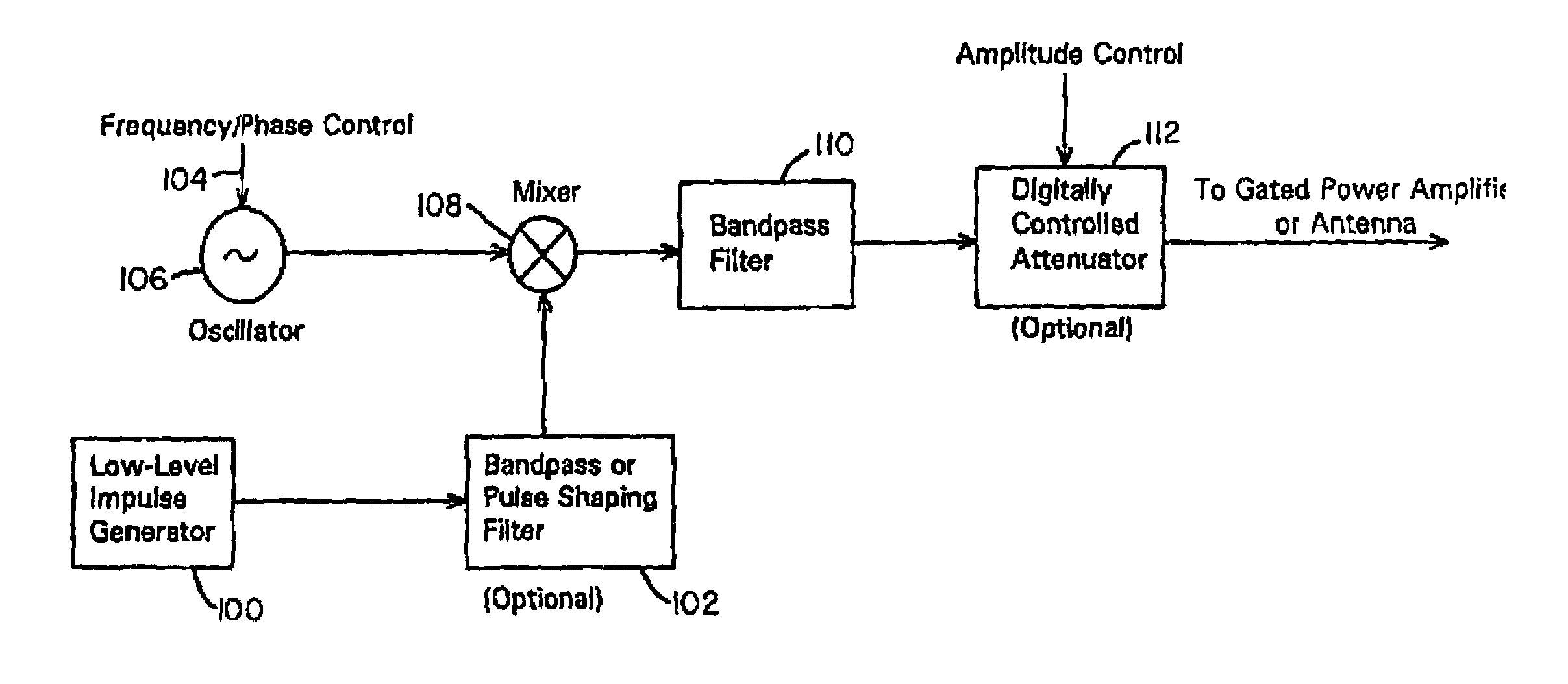
Waveform adaptive ultra-wideband transmitter
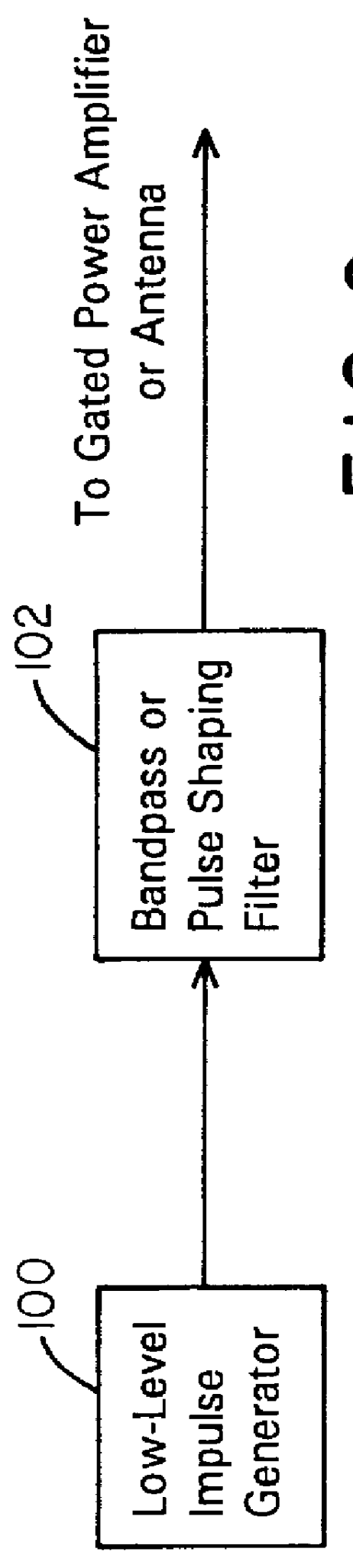
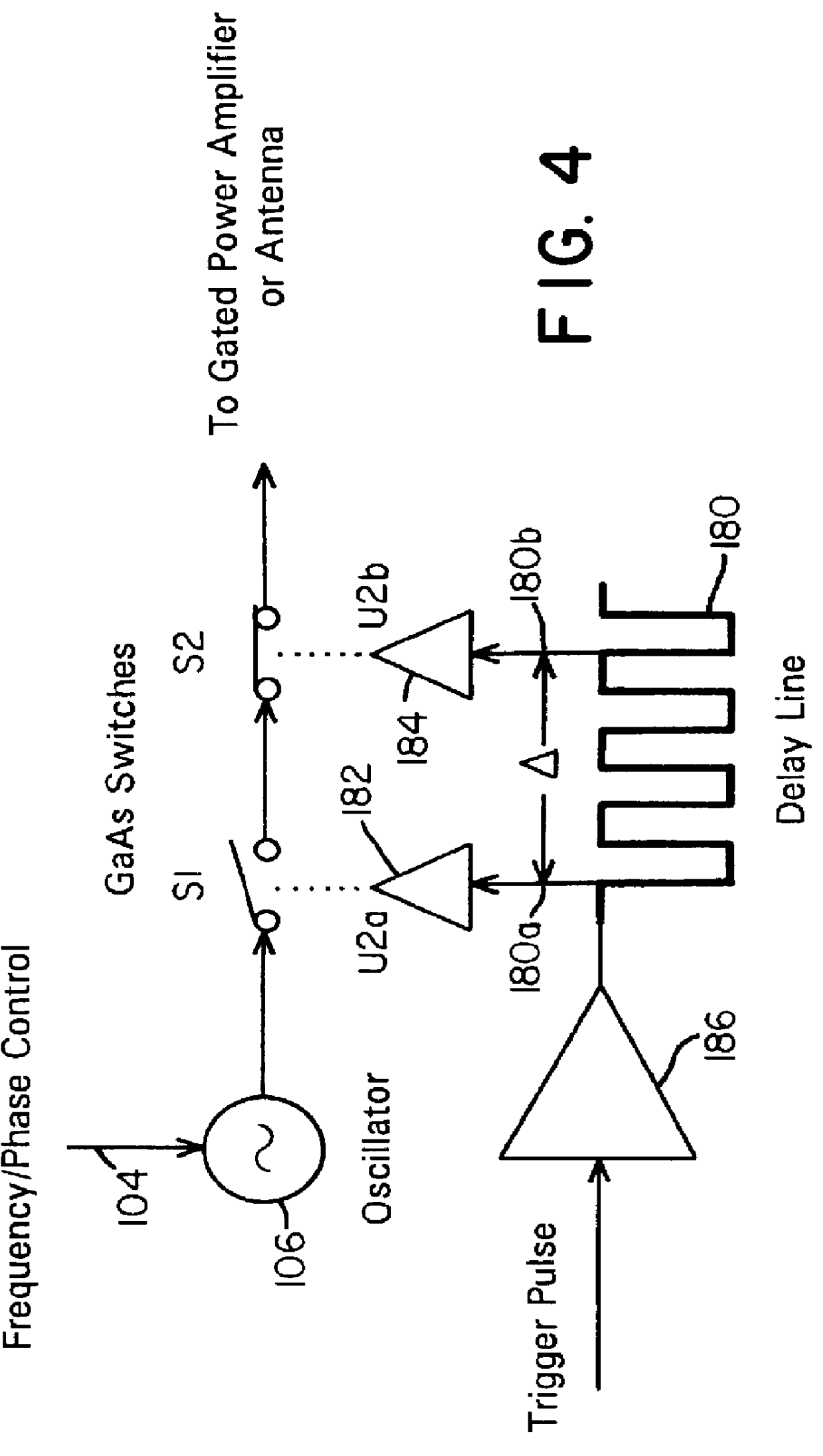
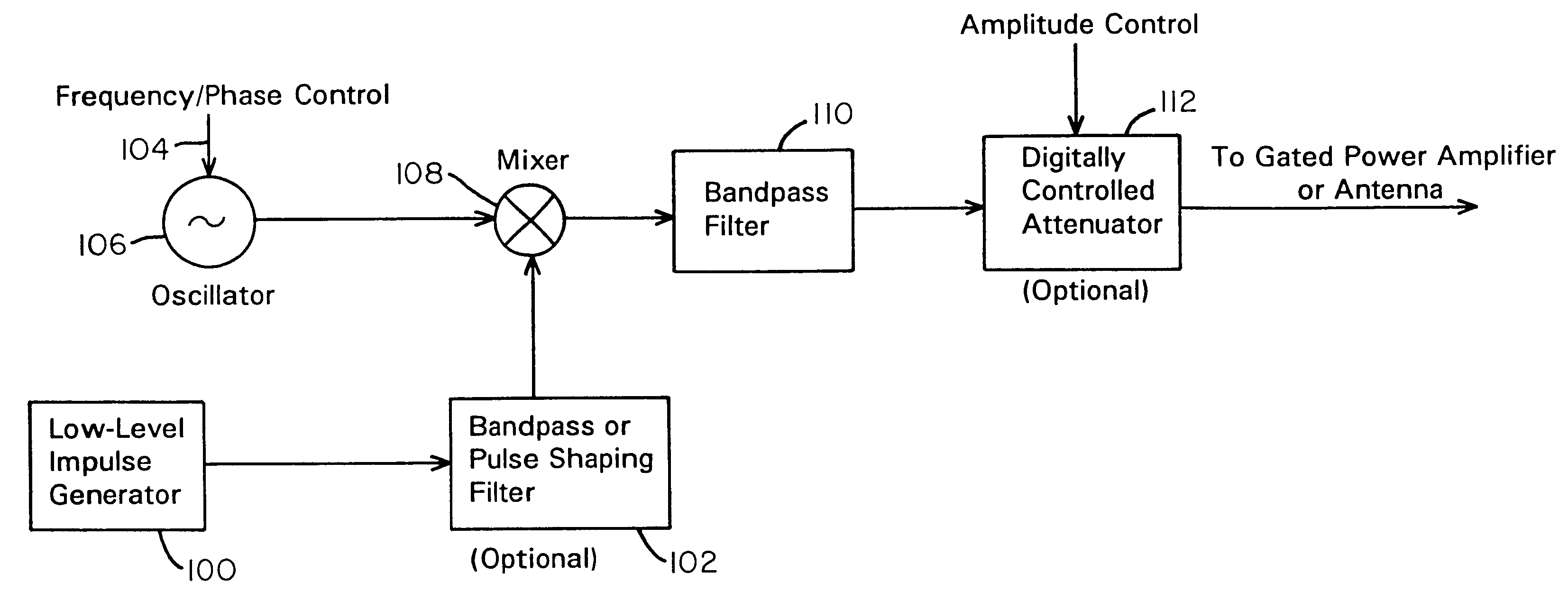
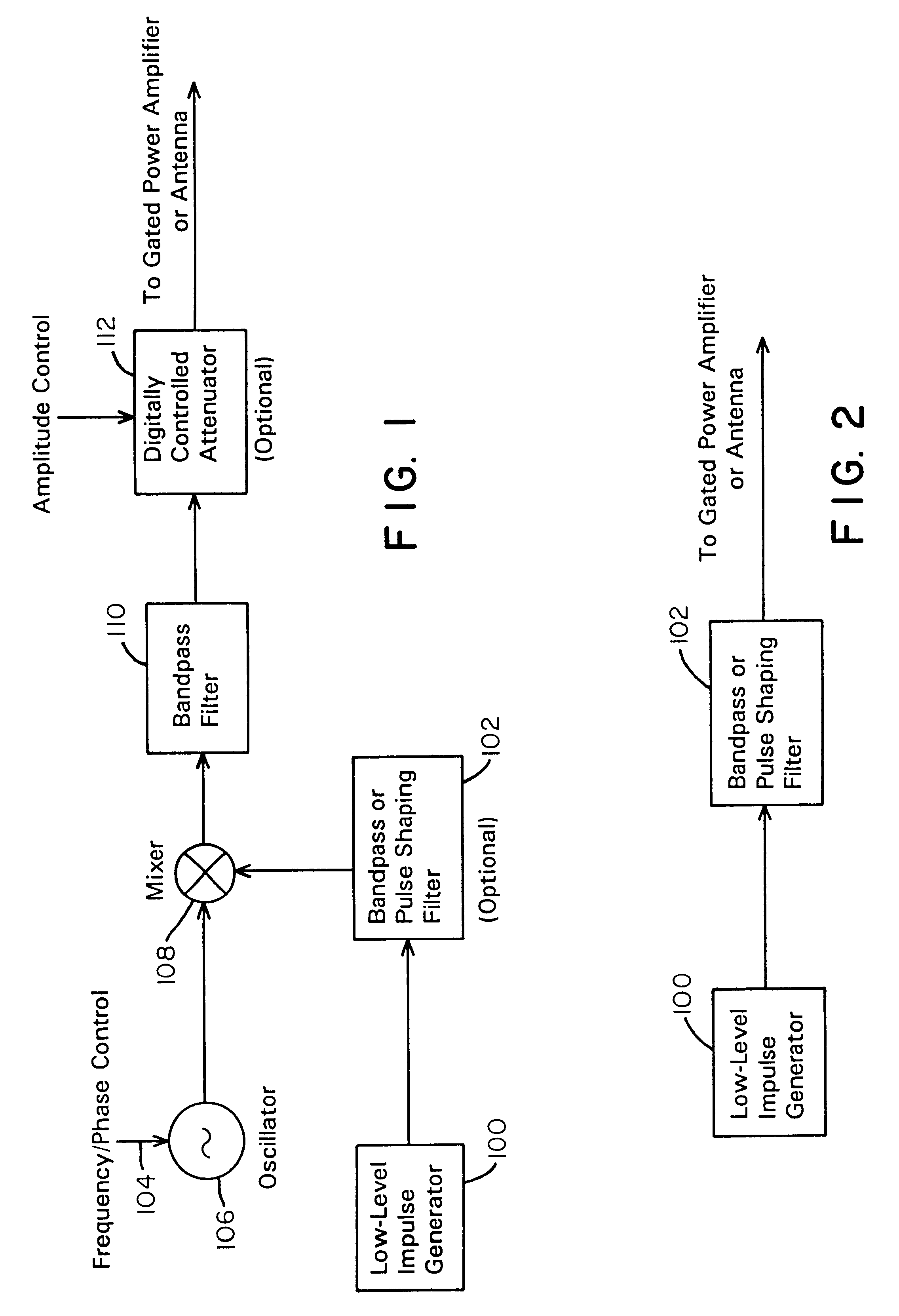
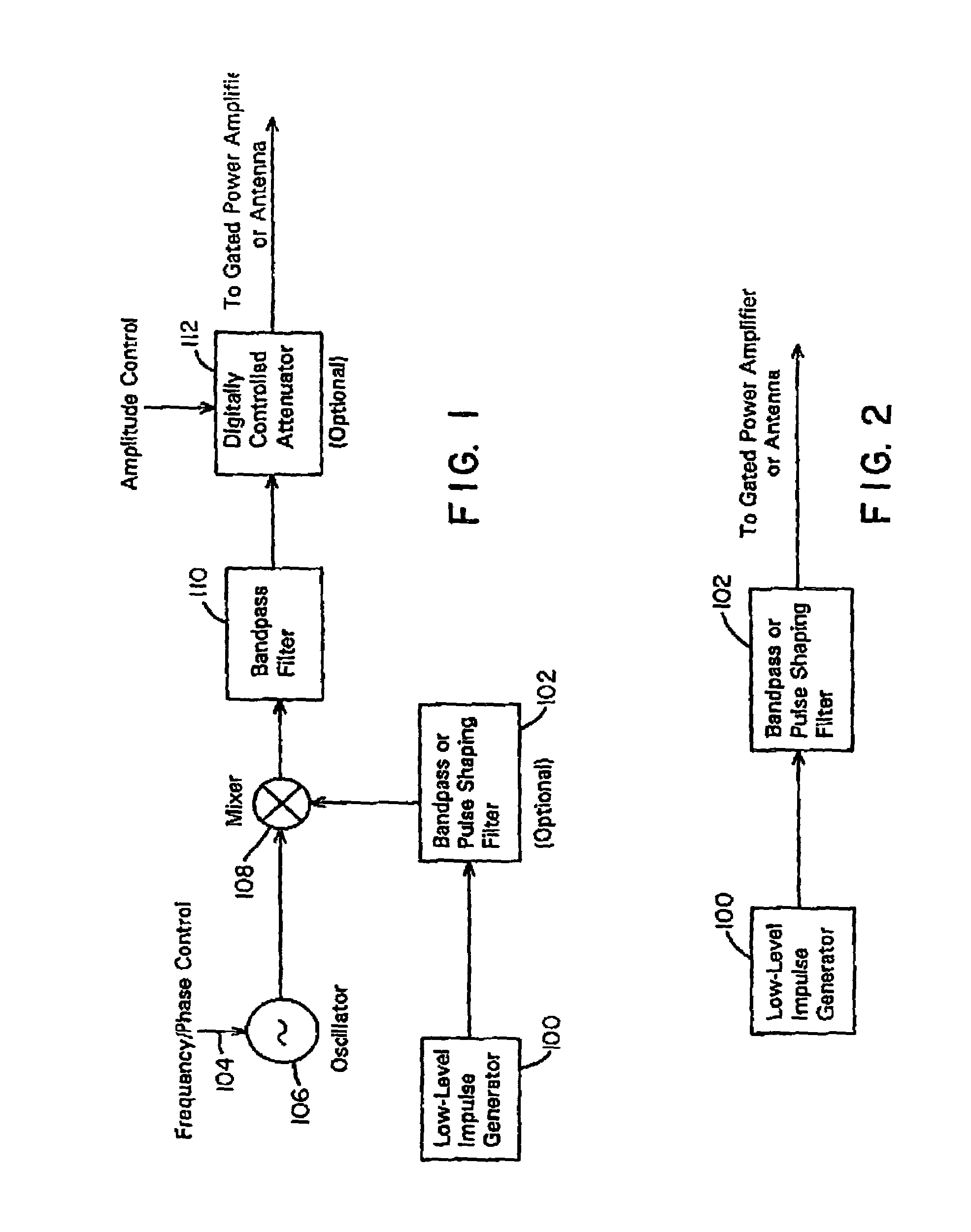
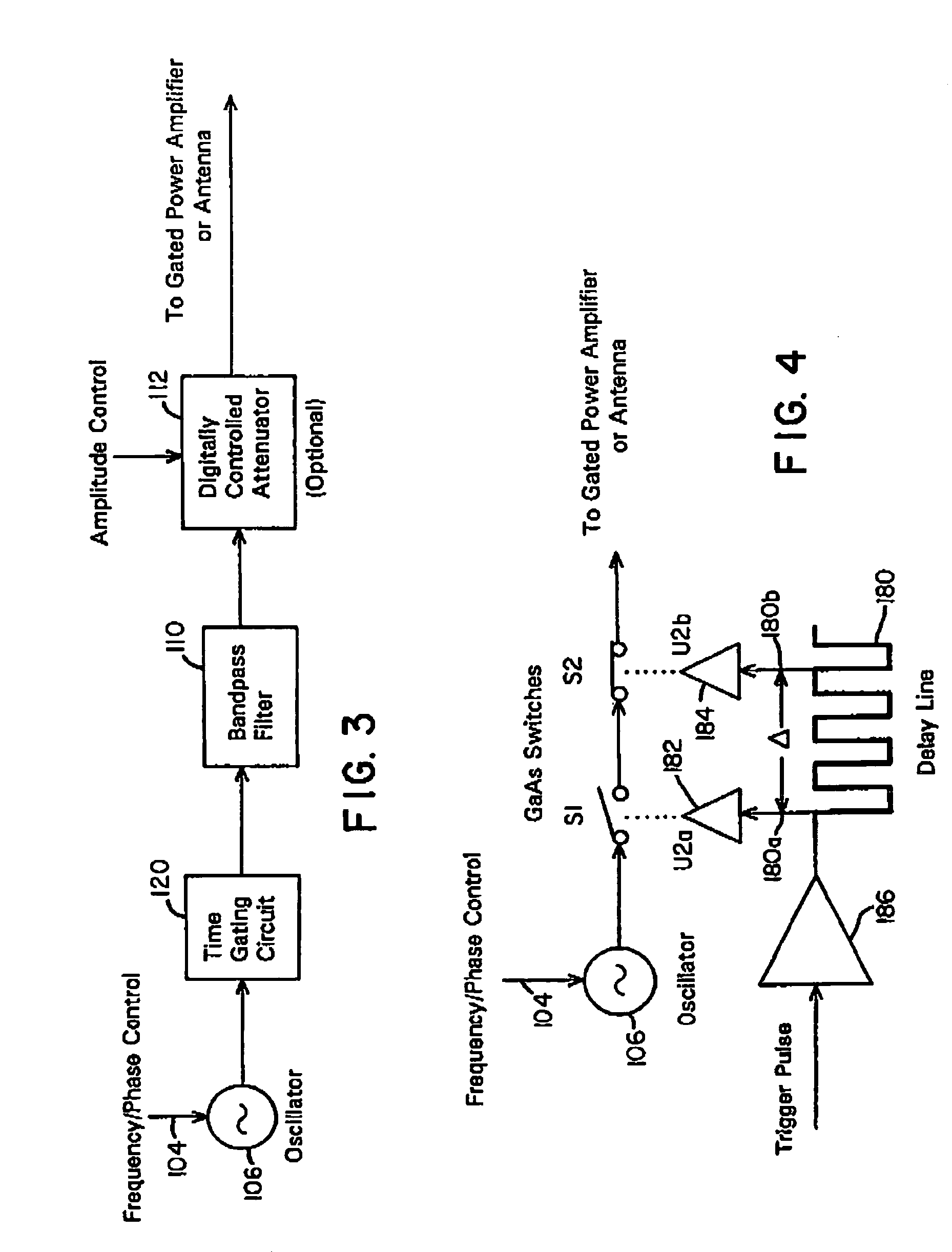
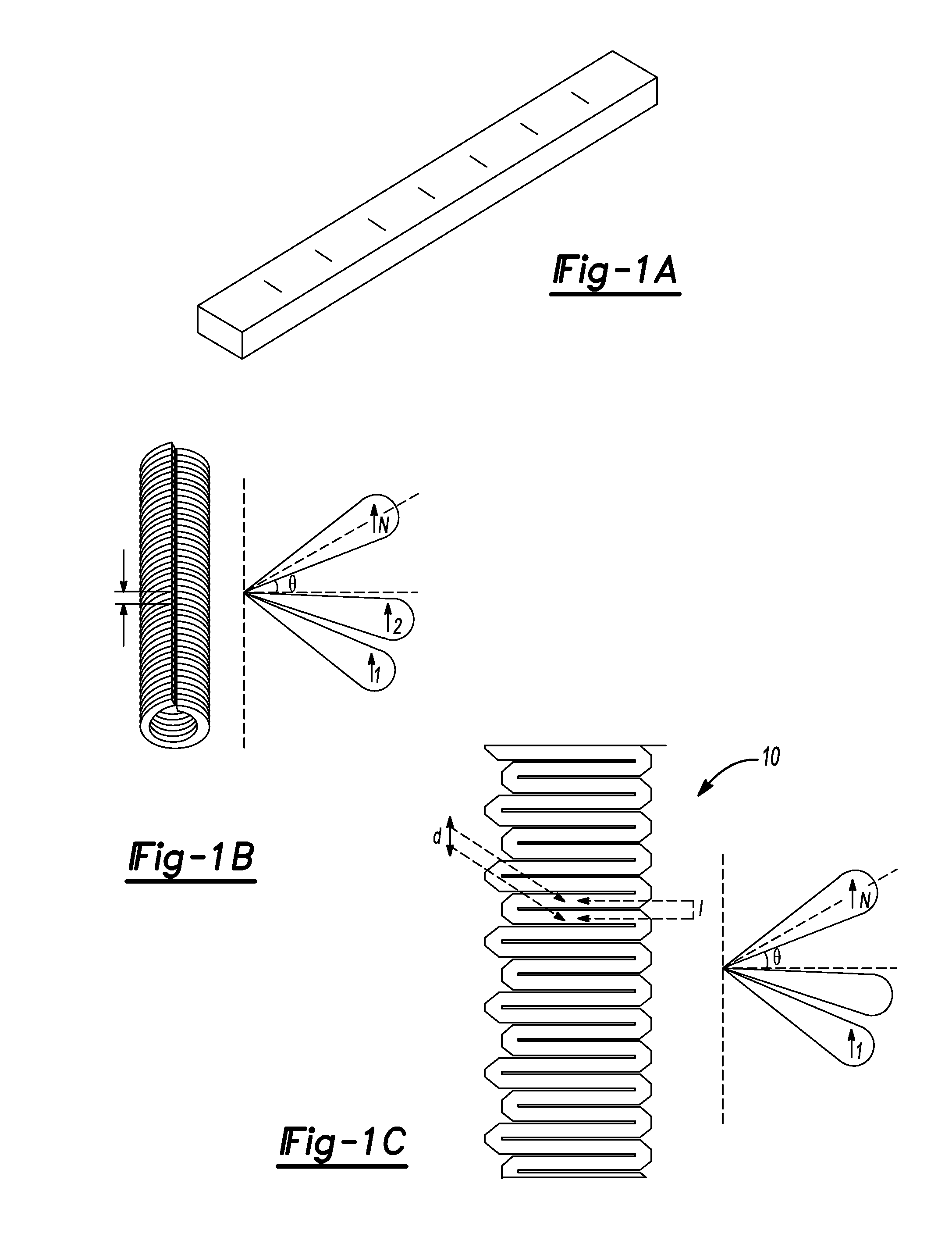
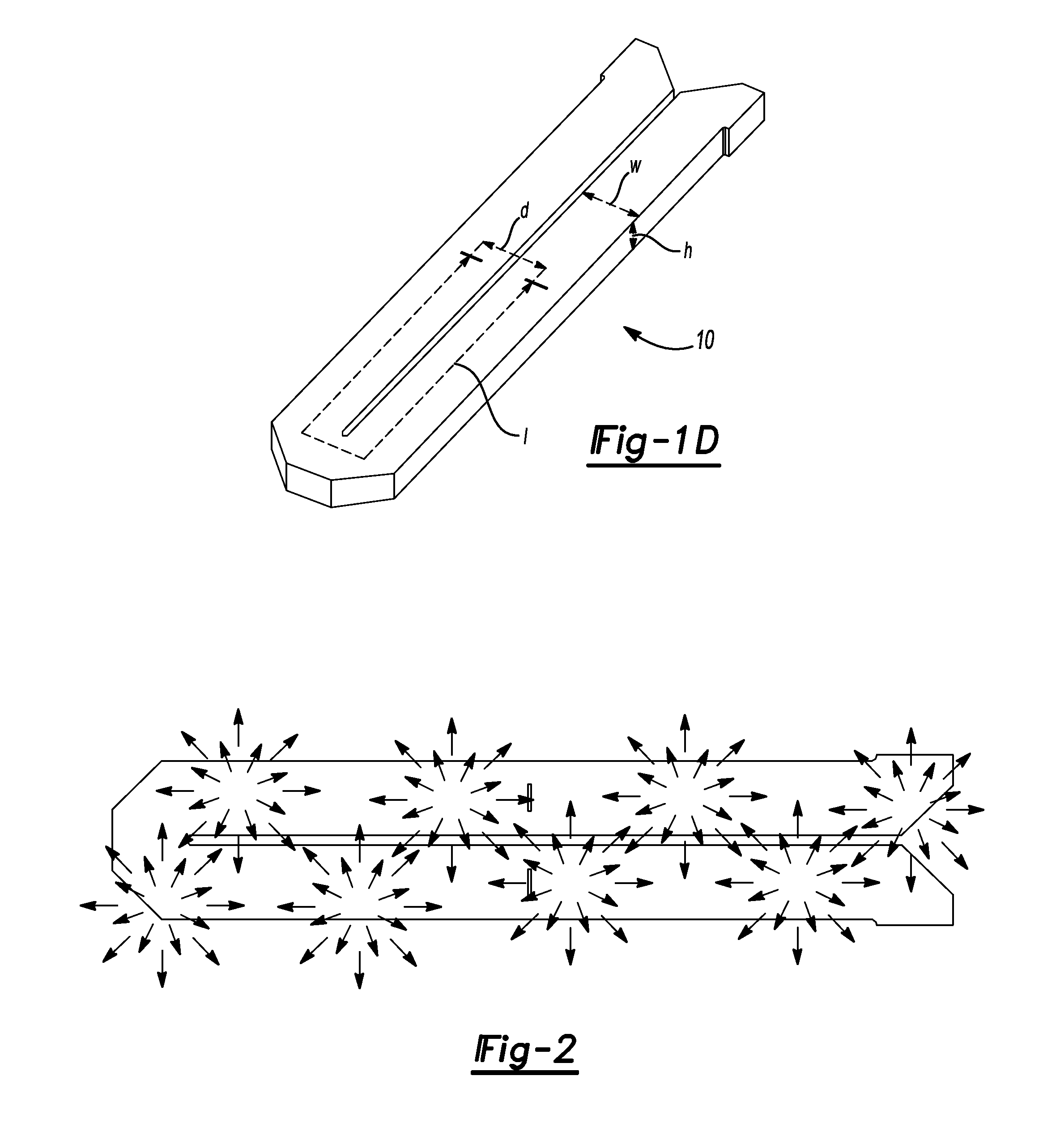
A waveform adaptive transmitter that conditions and / or modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Ultra wideband data transmission system and method
InactiveUS6690741B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAngle modulationBandpass filteringExtensibility
A data-modulated ultra wideband transmitter that modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Communication device and communication method using millimeter-wave frequency band
InactiveUS20140073337A1Interference minimizationAntenna arraysNetwork planningComputer hardwareManagement unit
There are provided a communication device using a millimeter-wave frequency band and a communication method using the millimeter-wave frequency band. The communication device includes a beam scheduling unit configured to schedule uplink and downlink beams corresponding to movement of a terminal, a core network interface unit configured to transmit data provided from the beam scheduling unit to a core network, and to provide data received from the core network to the beam scheduling unit, a mobility management unit configured to configure an uplink and downlink beam set based on inter-beam interference information provided from the beam scheduling unit, and an inter-base station interface unit configured to exchange a control message with another base station under control of the mobility management unit. Therefore, it is possible to efficiently build a cellular network using the millimeter-wave frequency band.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
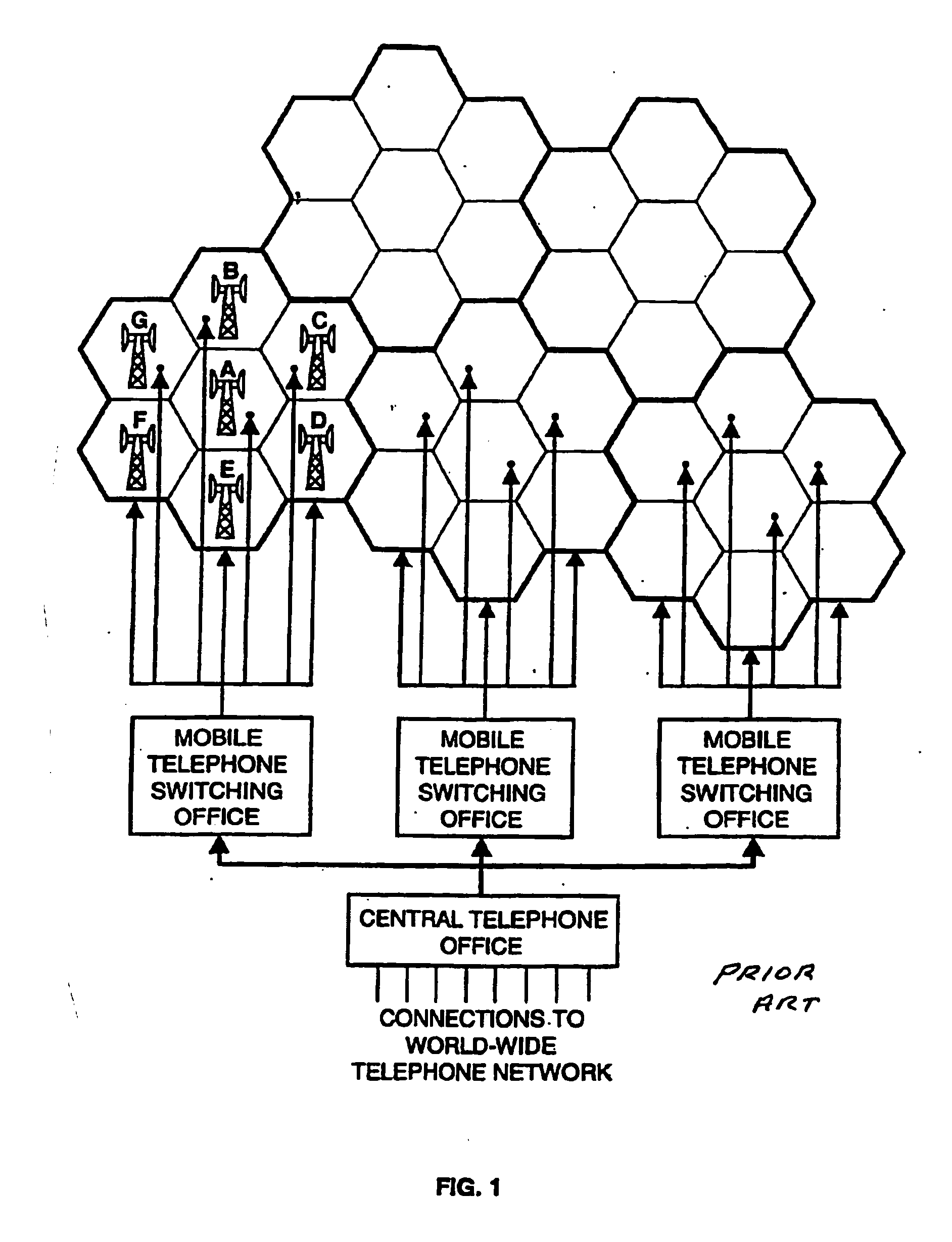
Wireless communication system
InactiveUS20060111047A1Efficient use ofLow frequency wireless internet access bandwidth isNetwork topologiesRepeater circuitsTransceiverWireless transceiver
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations. The system includes a connecting station with a millimeter wave wireless transceiver in communication with a fiber optic or high-speed cable communication network. The transceiver is adapted to communicate at millimeter wave frequencies higher than 60 GHz with another millimeter wave transceiver at one of the cellular base stations. Each of the base stations serves a separate communication cell. Each base station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another base stations or a millimeter wave transceiver at said at the connecting station. The base stations also are equipped with data transfer means for transferring data communicated through the low frequency transceiver to the millimeter wave wireless transceiver and for transferring data communicated through the millimeter wave wireless transceiver to the low frequency wireless transceiver. In preferred embodiments the system a part of a telephone system, an Internet system or a computer network.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Cellular systems with distributed antennas
InactiveUS8090379B2Efficient use ofLow frequency wireless internet access bandwidth isInformation formatNetwork topologiesWireless transceiverTransceiver
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations, each including at least transport management equipment and broadband equipment, at least one of which supports at least remote cellular station including RF equipment for communication with users of cellular devices. The system includes at lease one wireless narrow beam communication link operating at millimeter wave frequencies in excess of 60 GHz connecting a remote cellular station with a cellular base station equipped with broad band conversion electronic equipment and transport management equipment. In preferred embodiment the communication system includes a large number of remote cellular stations with each remote cellular station serving a separate communication cell. Each remote cellular station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a narrow beam millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another remote cellular station or a millimeter wave transceiver at a base station.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Out-of-band radio link protocol and network architecture for a wireless network composed of wireless terminals with millimetre wave frequency range radio units
ActiveUS20110053498A1Optimization rangeStable flowRadio relay systemsWireless communicationNetwork architectureDirectional antenna
The present invention relates to a wireless transmitter comprising a transmitter radio unit working a wireless transmitter comprising a transmitter radio unit working in the millimeter wave frequency band using a directional antenna and a bidirectional radio unit working in a frequency range different from said transmitter radio unit and using an omnidirectional antenna. The invention further relates to a wireless receiver and a wireless relay.
Owner:SONY CORP
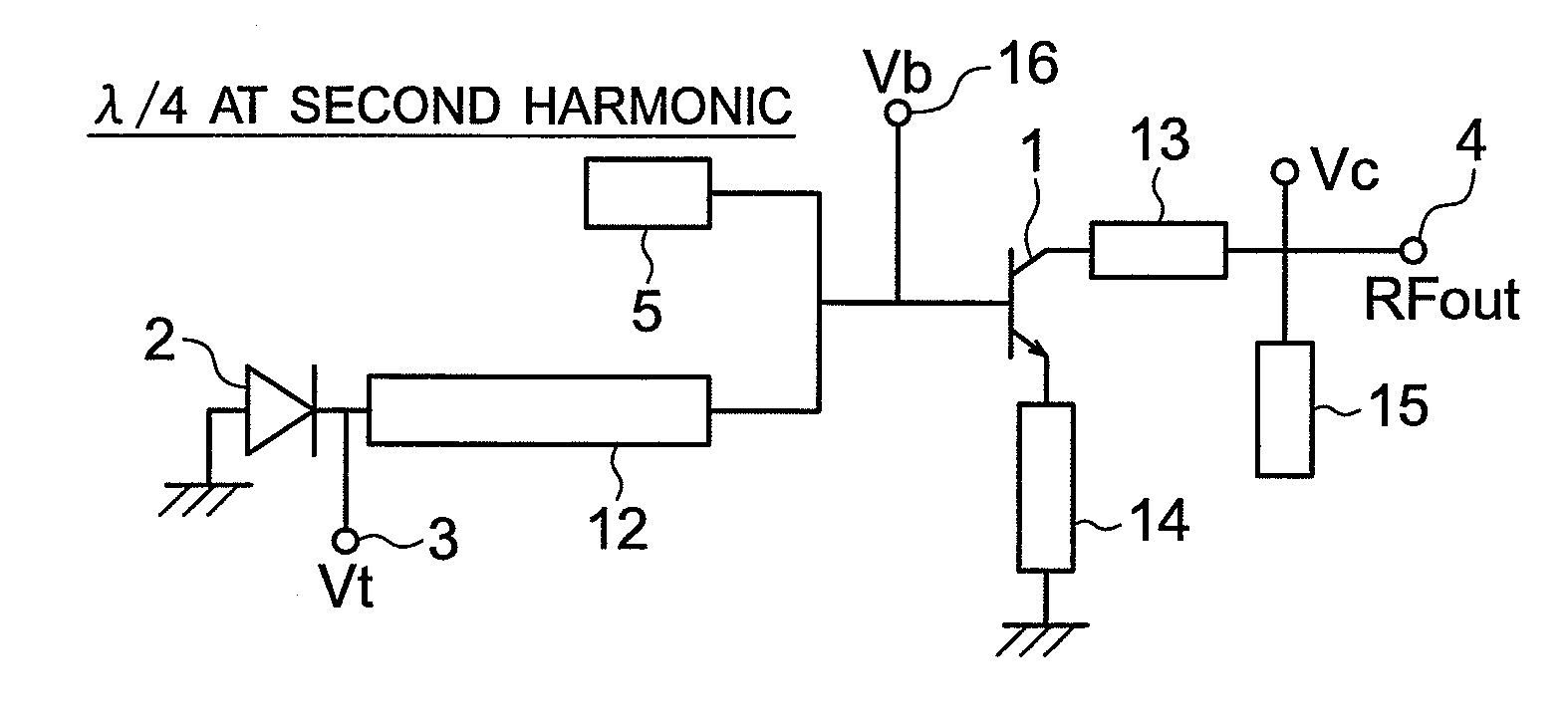
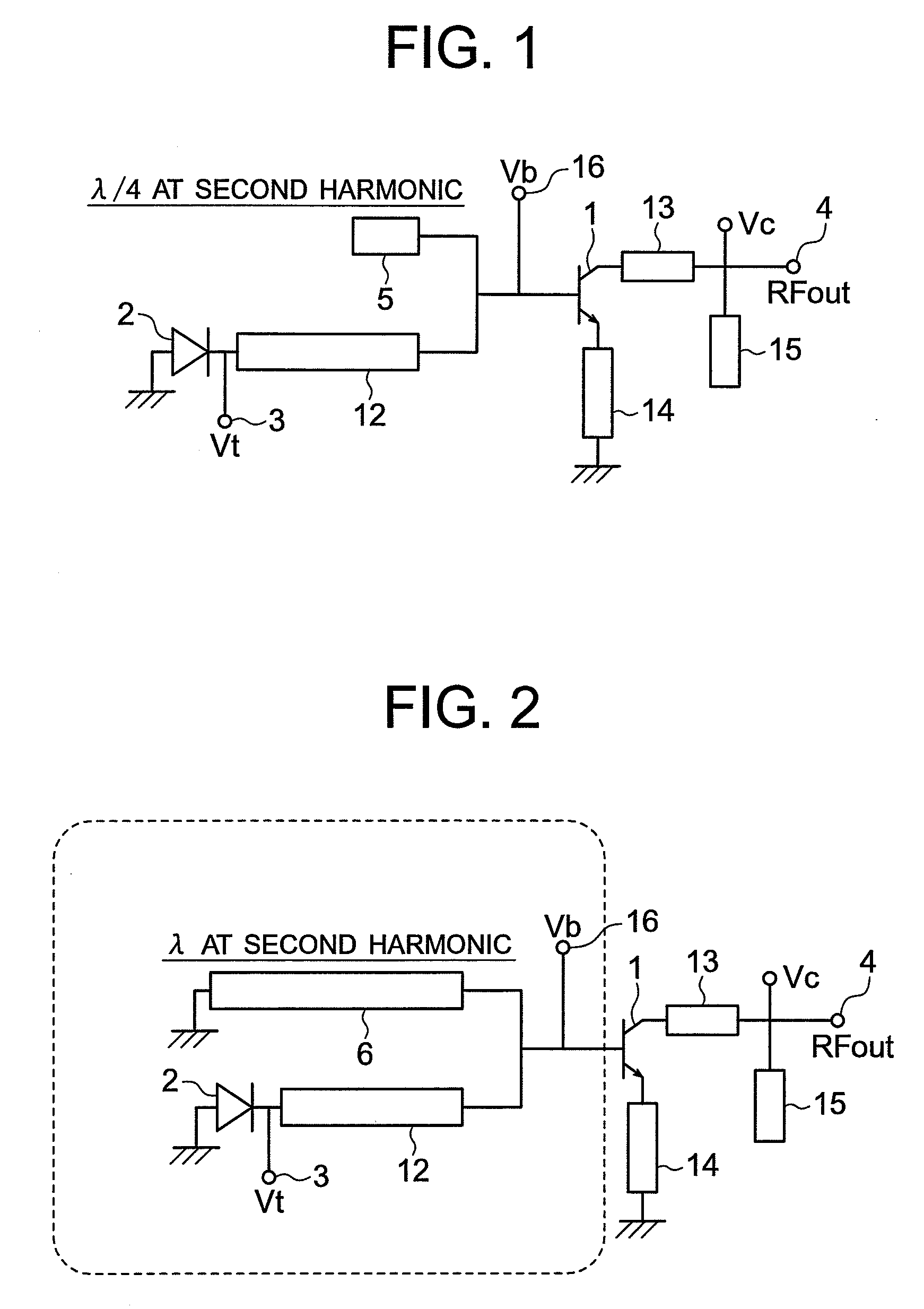
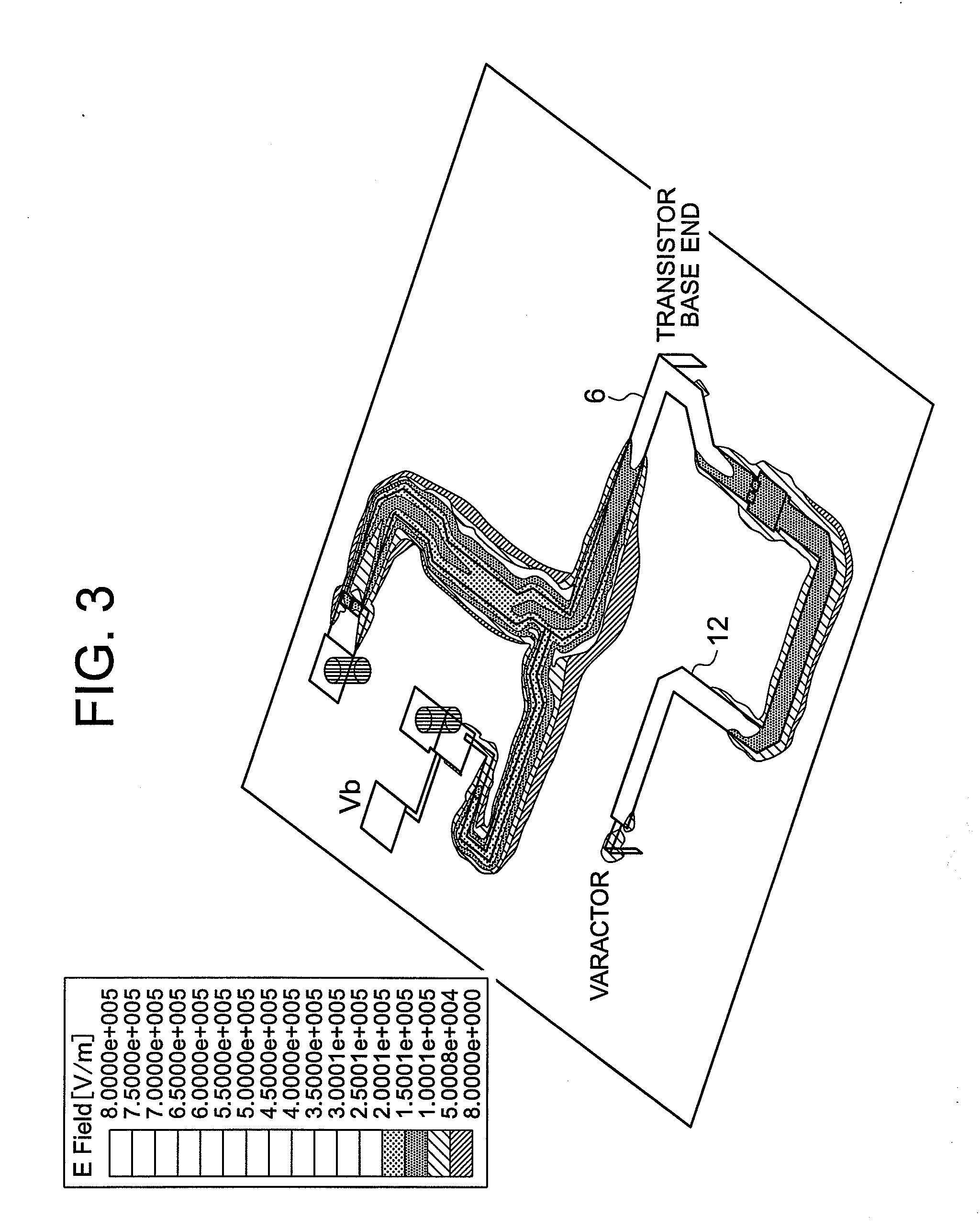
Voltage controlled oscillator, mmic, and high frequency wireless device
InactiveUS20100052799A1Low phase noise characteristicReduce noisePulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsPhase noiseHarmonic
A voltage controlled oscillator having low phase noise and including: a variable resonator including a varactor and a control voltage terminal; and an open-end stub connected in parallel to the variable resonator, the open-end stub having a length shorter than or equal to an odd multiple of one quarter of a wavelength of a harmonic signal plus one sixteenth of the wavelength of the harmonic signal, and longer than or equal to an odd multiple of one quarter of the wavelength of the harmonic signal minus one sixteenth of the wavelength of the harmonic signal. In this structure, a high Q value is realized for a fundamental wave frequency. Fluctuation in a control voltage due to a harmonic signal is controlled.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Electromagnetic wave frequency filter
InactiveUS7321707B2Simple designEfficient extractionNanoopticsCoupling light guidesPhase shiftedFrequency matching
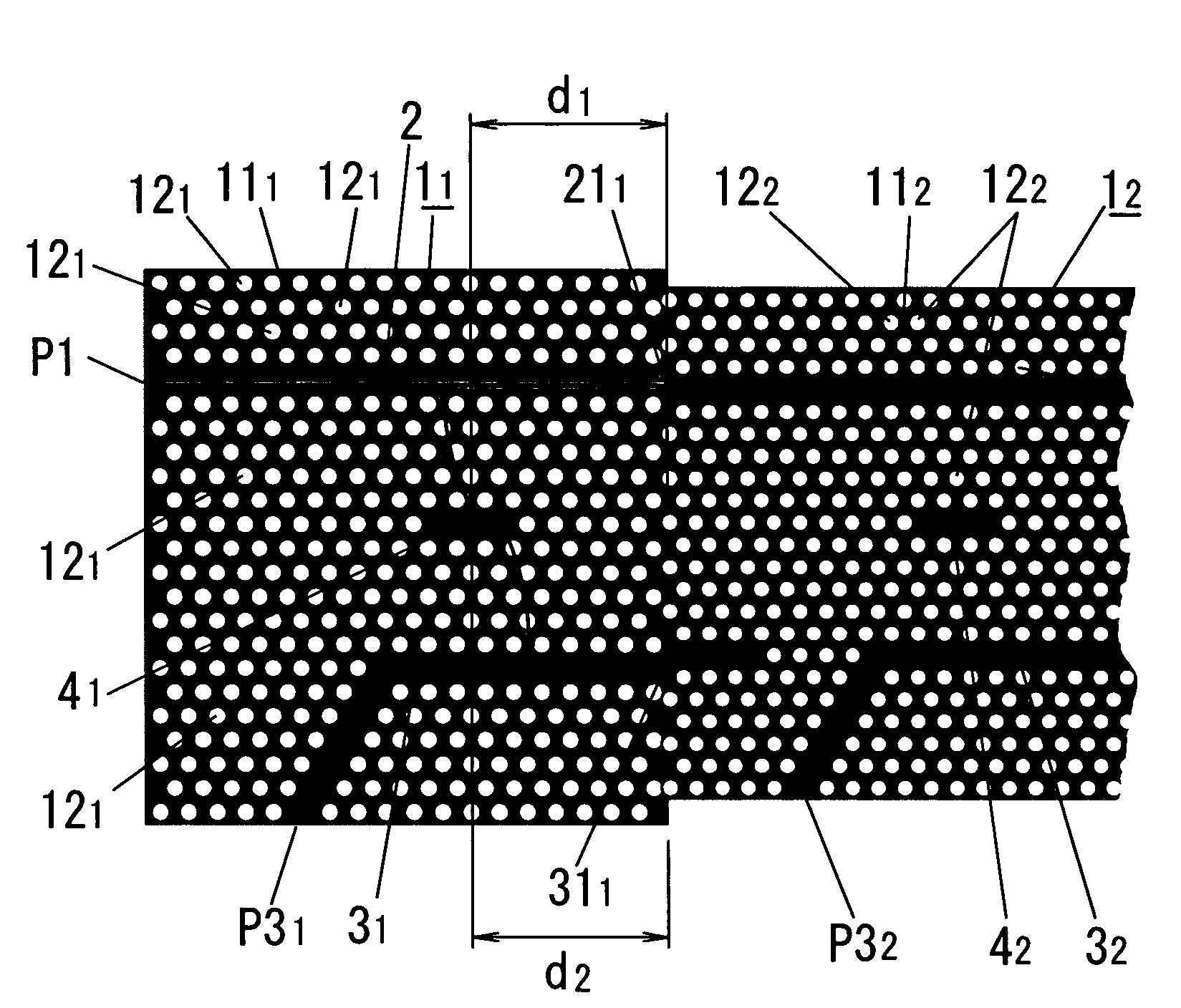
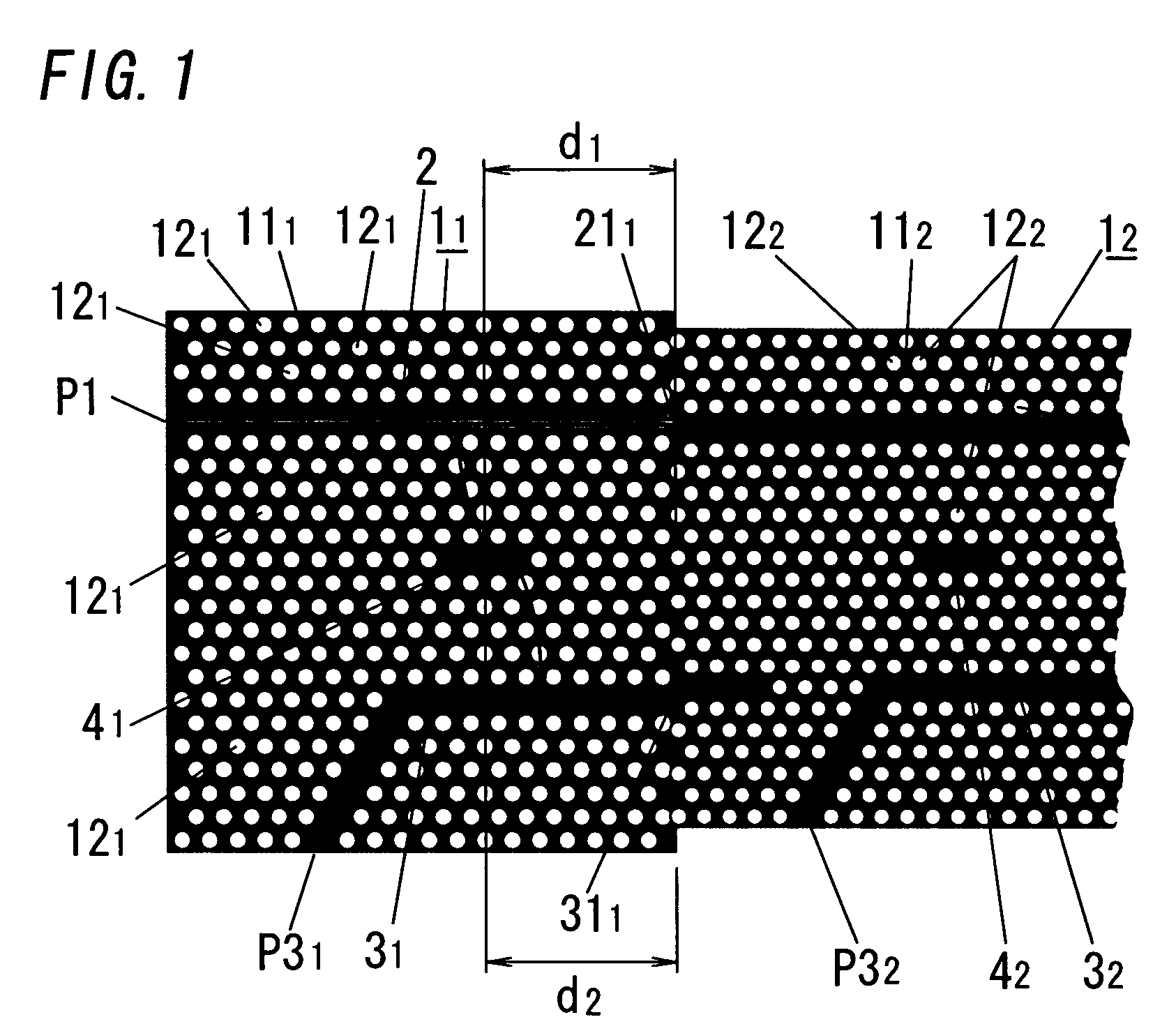
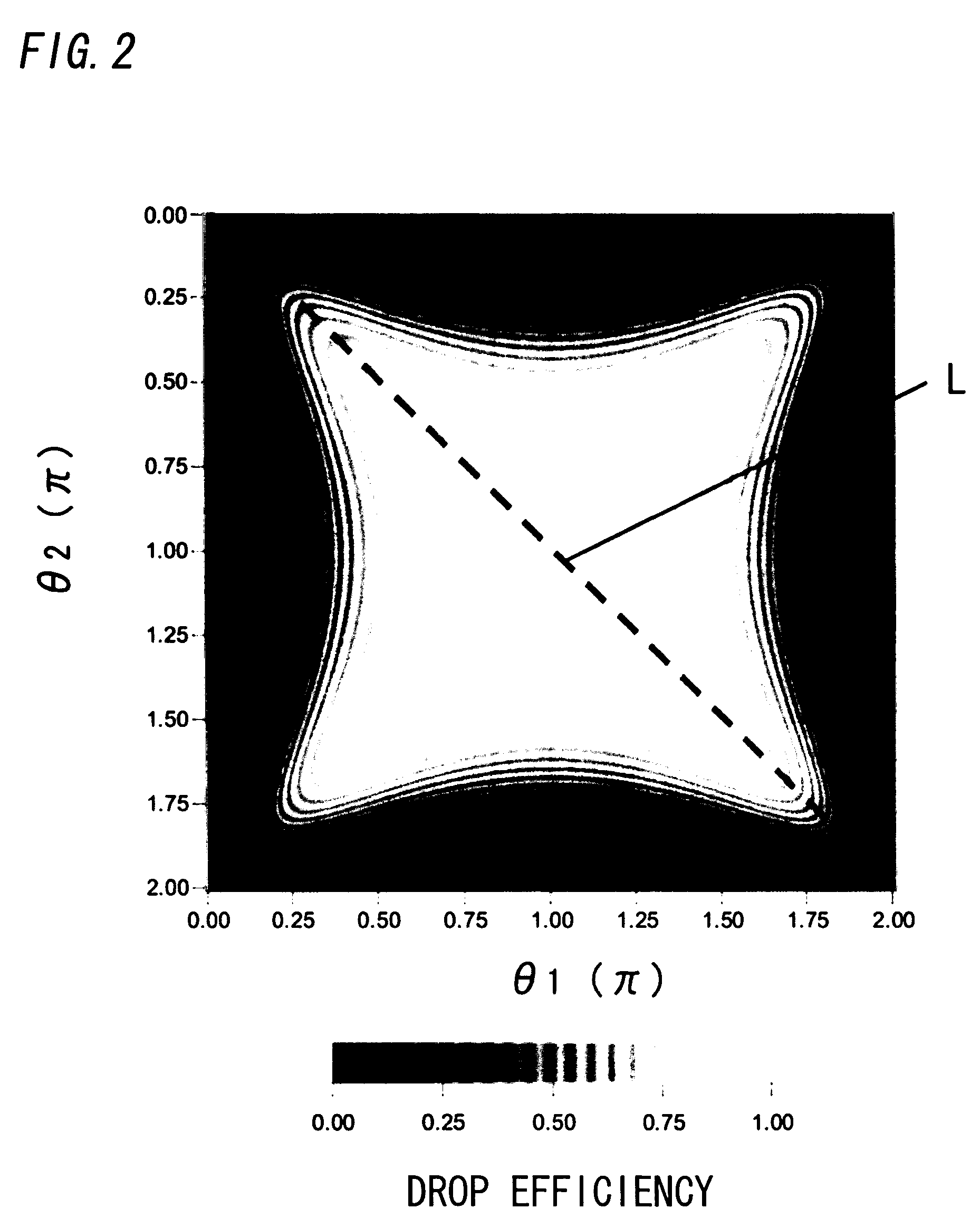
In this electromagnetic wave frequency filter, an electromagnetic wave of a predetermined frequency matching a resonant frequency of a resonator 41 is transmitted from an input waveguide 2 to an output waveguide 3 through the resonator 41, and is outputted from a drop port P31. This filter has an input-waveguide-side reflector 211 and an output-waveguide-side reflector 311, which reflect the electromagnetic wave of the predetermined frequency. The electromagnetic wave frequency filter satisfies the following relation:Qinb / (1−cos θ1)<<Qv,Qinb / (1−cos θ1)=Qinr / (1−cos θ2),θ1, θ2≠2Nπ(N=0, 1, . . . ),where θ1 is a phase shift amount of the electromagnetic wave reflected by the input-waveguide-side reflector 211, θ2 is a phase shift amount of the electromagnetic wave reflected by the output-waveguide-side reflector 311, Qinb is a Q-factor between the resonator 41 and the input waveguide 2, Qinr is a Q-factor between the resonator 41 and the output waveguide 31, and Qv is a Q-factor between the resonator 41 and free space.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Wireless millimeter wave communication system with mobile base station
InactiveUS7912506B2Efficient use ofLow frequency wireless internet access bandwidth isNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentTruck-trailerMillimeter wave communication systems
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations. At least one of the base stations is a mobile base station in which low and high speed wireless transceivers are mounted on a temporarily stationary mobile vehicle such as a truck trailer or a truck. The system includes at least one connecting station with a millimeter wave wireless transceiver in communication with a fiber optic or high-speed cable communication network. The transceiver is adapted to communicate at millimeter wave frequencies higher than 60 GHz with another millimeter wave transceiver at one of the cellular base stations. Each of the base stations serves a separate communication cell. Each base station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another base station or a millimeter wave transceiver at said at the connecting station. The base stations are also equipped with data transfer means for transferring data communicated through the low frequency wireless transceiver to the millimeter wave wireless transceiver and for transferring data communicated through the millimeter wave wireless transceiver to the low frequency wireless transceiver. In preferred embodiments the system is a part of a telephone system, an Internet system or a computer network.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
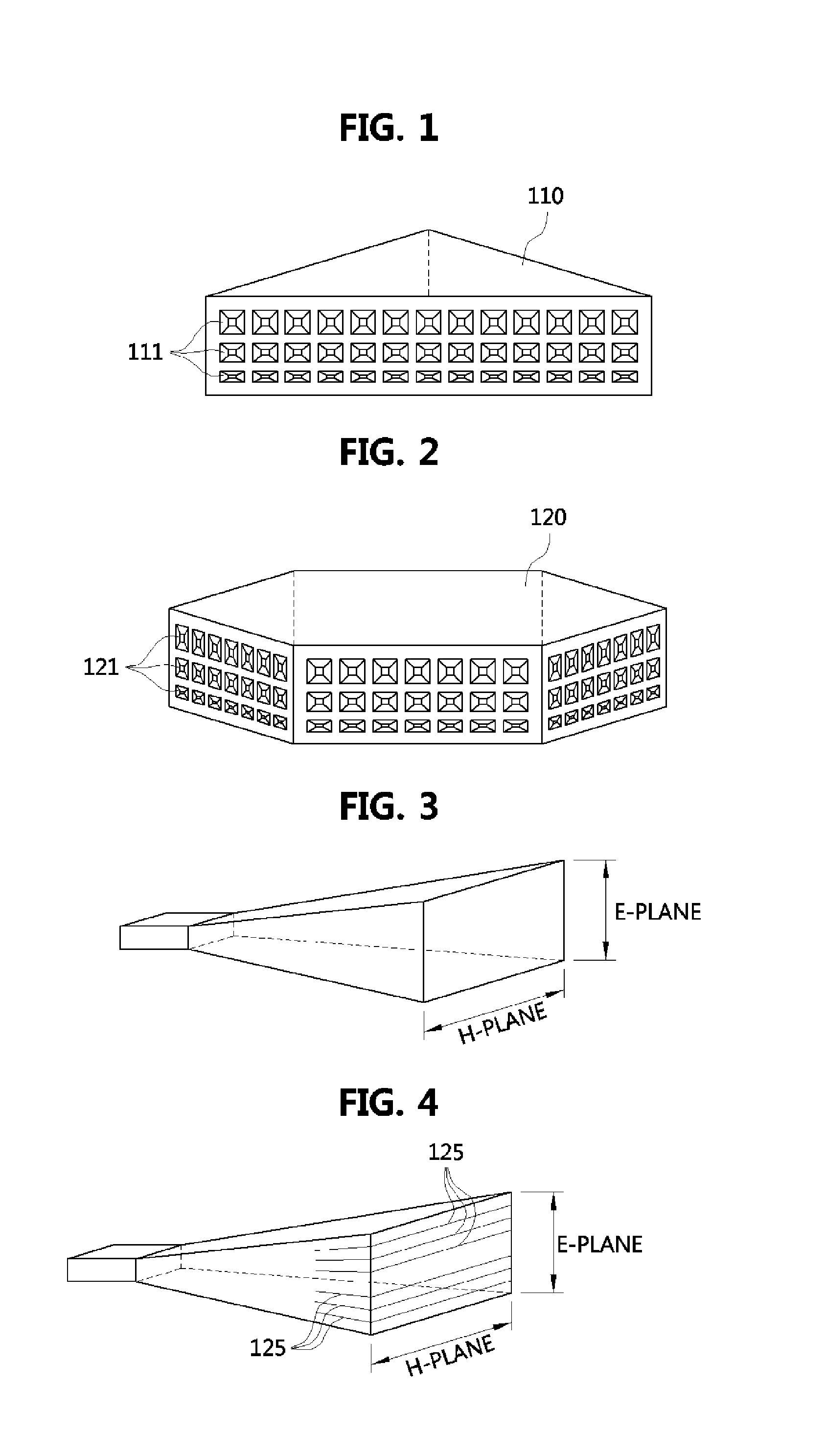
Antenna Array Feed Line Structures For Millimeter Wave Applications
ActiveUS20090009399A1Easy to operateParticular array feeding systemsSimultaneous aerial operationsDielectric substrateCoplanar waveguide
Improved feed line networks for antenna arrays operating at millimeter wave frequencies are provided for constructing planar antenna arrays printed on the surface of a dielectric substrate. A planar antenna array includes an array of planar radiator elements interconnected through a feed line network of planar coplanar transmission lines that enable high-efficiency operation, at millimeter wave operating frequencies. For example, a feed network may be formed with a network of coplanar strip line transmission lines including one or more coplanar strip line (CPS) and one or more coplanar waveguide (CPW) transmission line, which are interconnected using balun structures, to enable high efficiency operation at millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
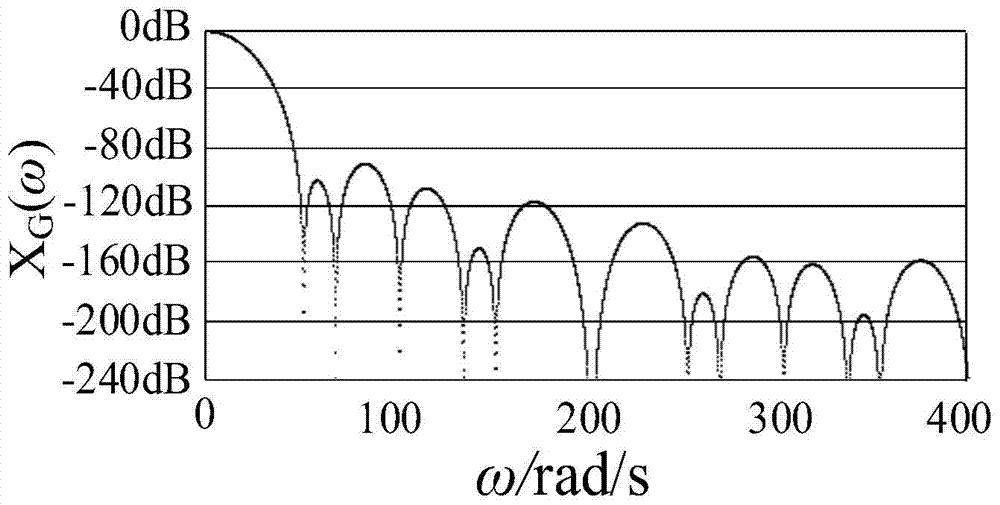
Harmonic amplitude measurement method and system of power signal
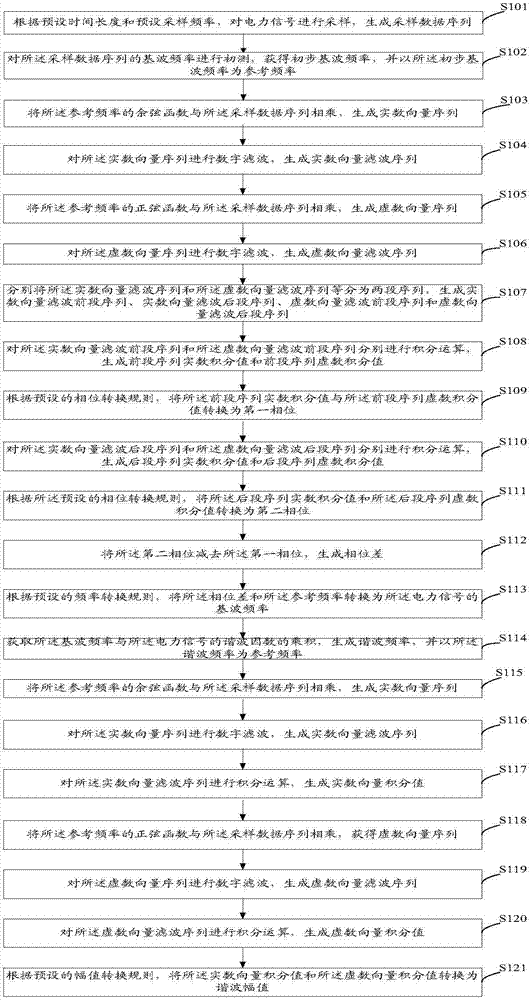
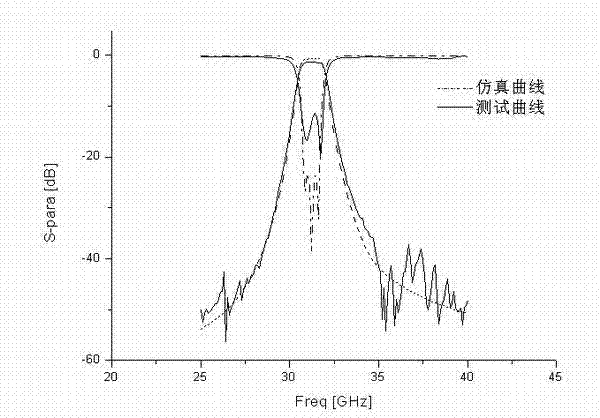
ActiveCN104502706AHigh precisionSuppression of aliasing interference componentsFrequency analysisPhase differenceHarmonic
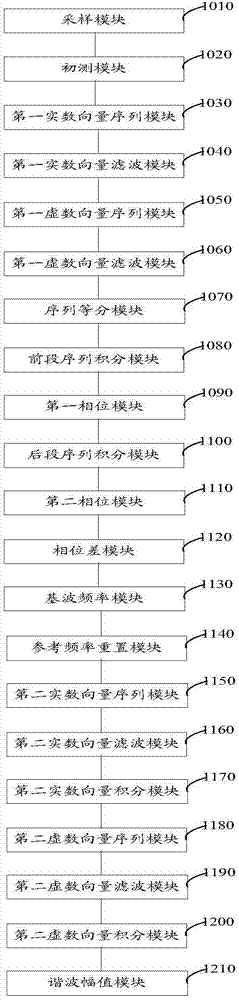
The invention discloses a harmonic amplitude measurement method and system of a power signal. The method comprises the following steps: performing digital filtering on an imaginary vector sequence and a real vector sequence to generate an imaginary vector filter sequence and a real vector filter sequence; equally dividing the real vector filter sequence and the imaginary vector filter sequence into two sections of sequences to generate a real vector filter front-section sequence, a real vector filter rear-section sequence, an imaginary vector filter front-section sequence and an imaginary vector filter rear-section sequence respectively; integrating the real vector filter front-section sequence, the imaginary vector filter front-section sequence, the real vector filter rear-section sequence and the imaginary vector filter rear-section sequence in sequence to solve phase and phase difference; converting the phase difference and reference frequency into fundamental wave frequency of the power signal. The product of the fundamental wave frequency and a harmonic factor is used as the reference frequency to perform harmonic wave amplitude measurement. By implementing the method and the system, mixed frequency interference elements in the imaginary vector sequences and the real vector sequences can be inhibited to generate the harmonic wave amplitude with high precision.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Millimeter wave surface imaging radar system
InactiveUS20110199254A1Ample scan coverageReliable and effective FOD detectionAntenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar imagingMillimetre wave
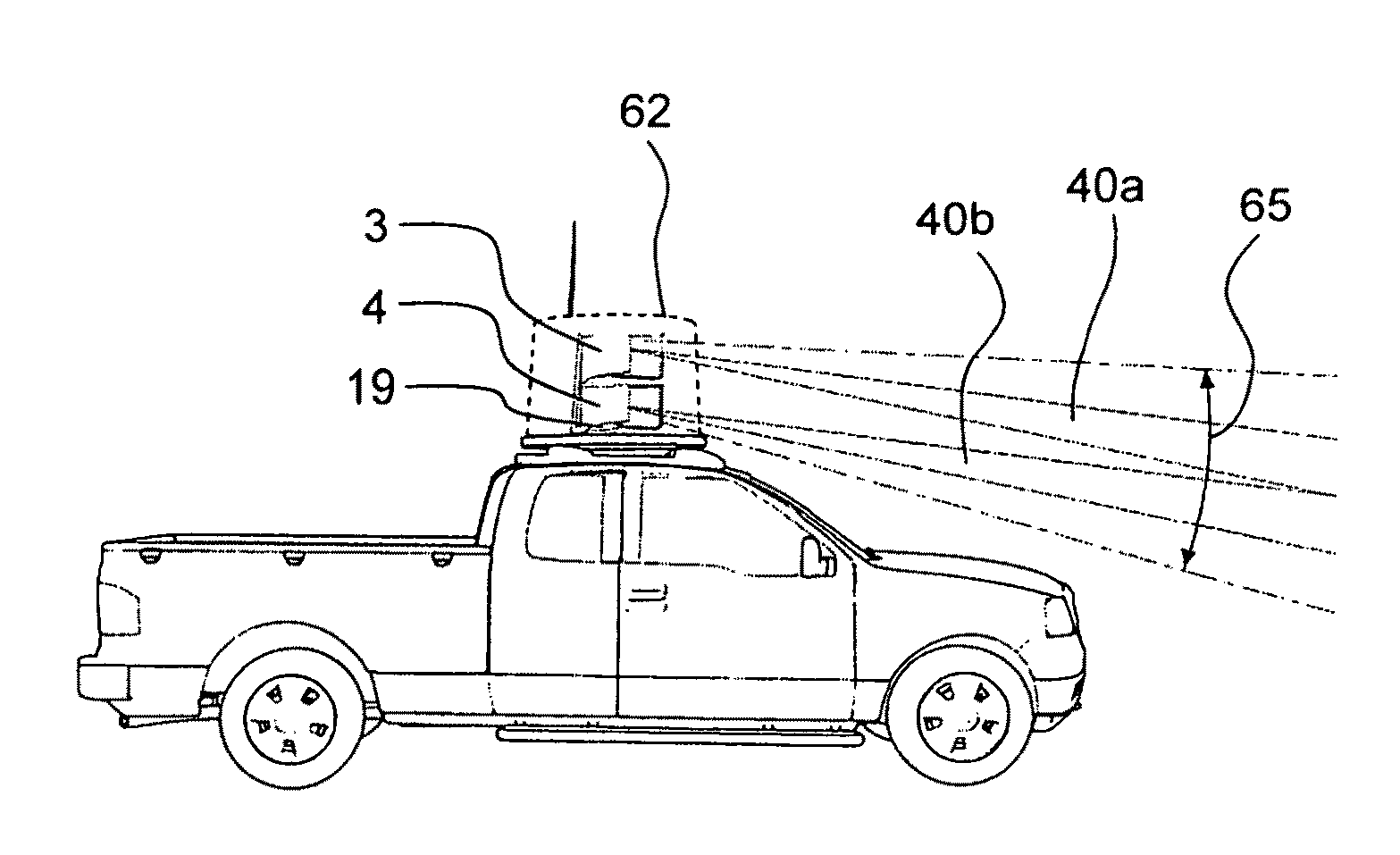
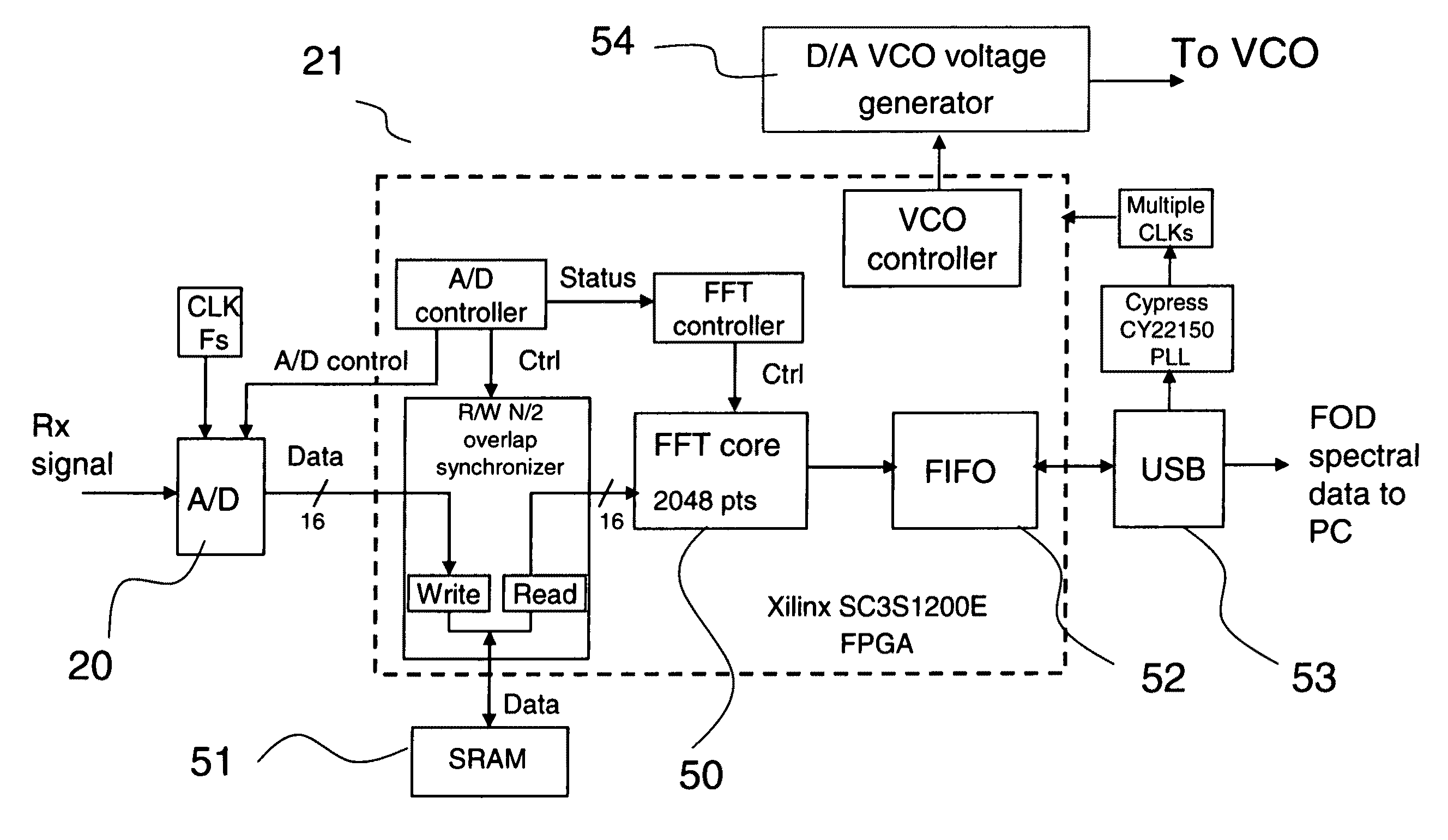
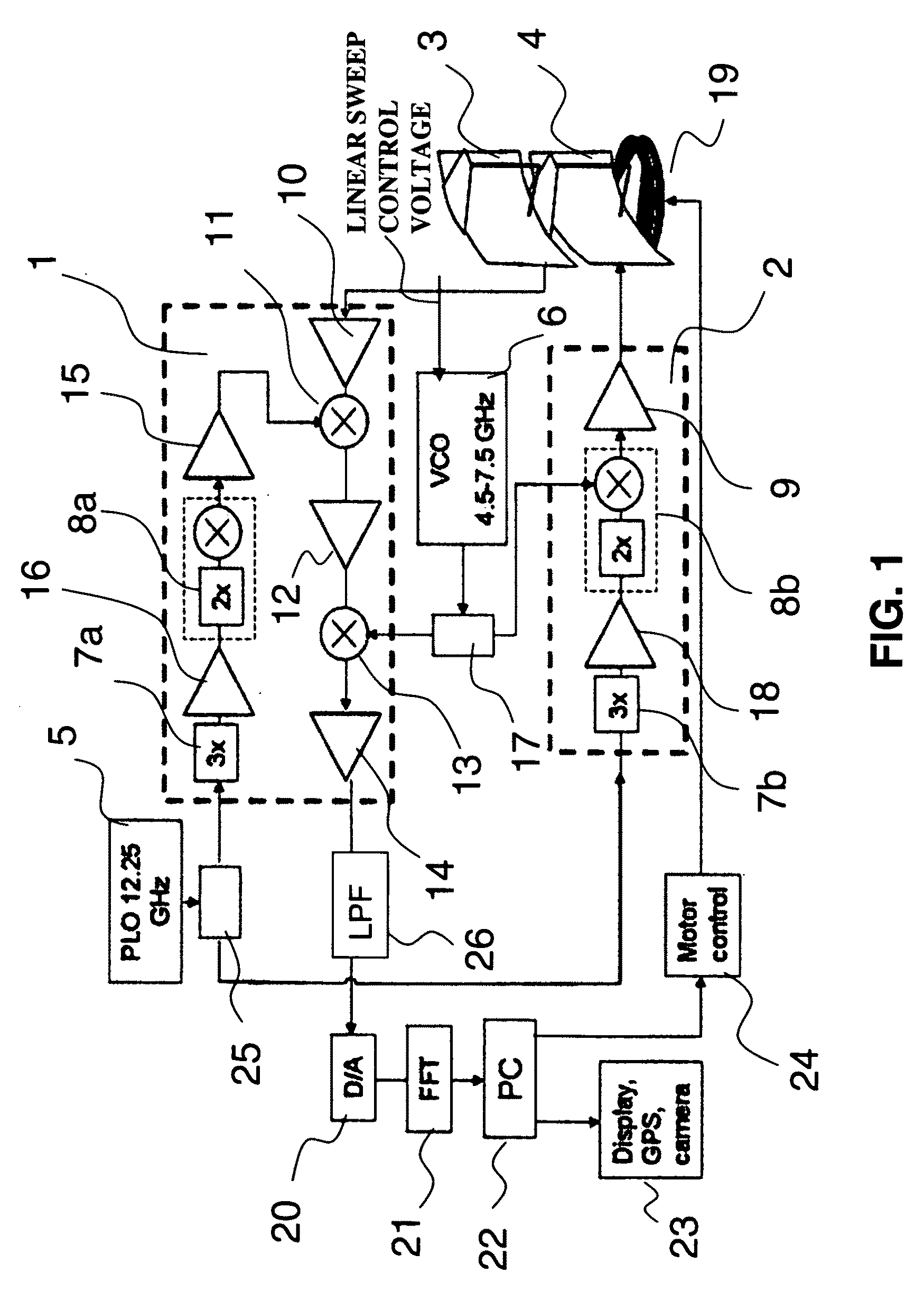
A short range millimeter wave surface imaging radar system. The system includes electronics adapted to produce millimeter wave radiation scanned over a frequency range of a few gigahertz. The scanned millimeter wave radiation is broadcast through a frequency scanned transmit antenna to produce a narrow transmit beam in a first scanned direction (such as the vertical direction) corresponding to the scanned millimeter wave frequencies. The transmit antenna is scanned to transmit beam in a second direction perpendicular to the first scanned direction (such as the horizontal or the azimuthal direction) so as to define a two-dimensional field of view. Reflected millimeter wave radiation is collected in a receive frequency scanned antenna co-located (or approximately co-located) with the transmit antenna and adapted to produce a narrow receive beam approximately co-directed in the same directions as the transmitted beam in approximately the same field of view. Computer processor equipment compares the intensity of the receive millimeter radar signals for a pre-determined set of ranges and known directions of the transmit and receive beams as a function of time to produce a radar image of at least a desired portion of the field of view. In preferred embodiment the invention is mounted on a truck and adapted as a FOD finder system to detect and locate FOD on airport surfaces.
Owner:TREX AVIATION
Sub-lethal, wireless projectile and accessories
InactiveUS6880466B2Increase energy levelReduce power levelAmmunition projectilesElectric shock equipmentsSTUNElectric discharge
The invention is a circuit capable of being positioned in a variety of wireless projectile and of delivering a series of pulsed electric discharges in two wave frequencies so as to stun and disable a target individual. The projectiles are adapted to be discharged from a different types of devices and powered by explosive, pneumatic, or manual means. At least one mode includes the ability to deliver a stunning physical blow in addition to the electric shock. The device is sub-lethal, but totally disabling in effects on a target individual.
Owner:CSA ENERGY
Millimeter wave imaging system
InactiveUS6937182B2Geological detection using milimetre wavesRadio transmissionMillimetre waveAntenna element
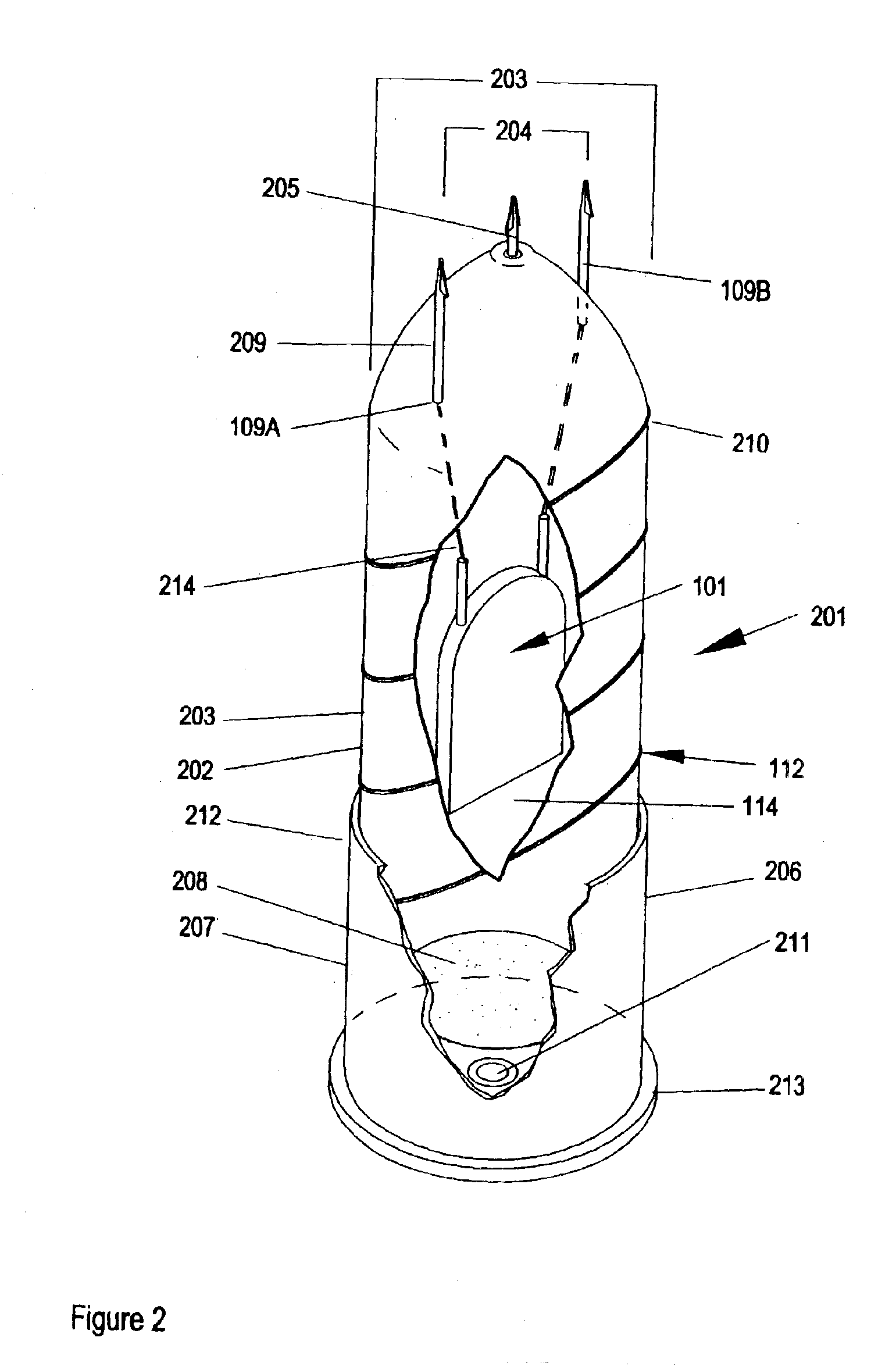
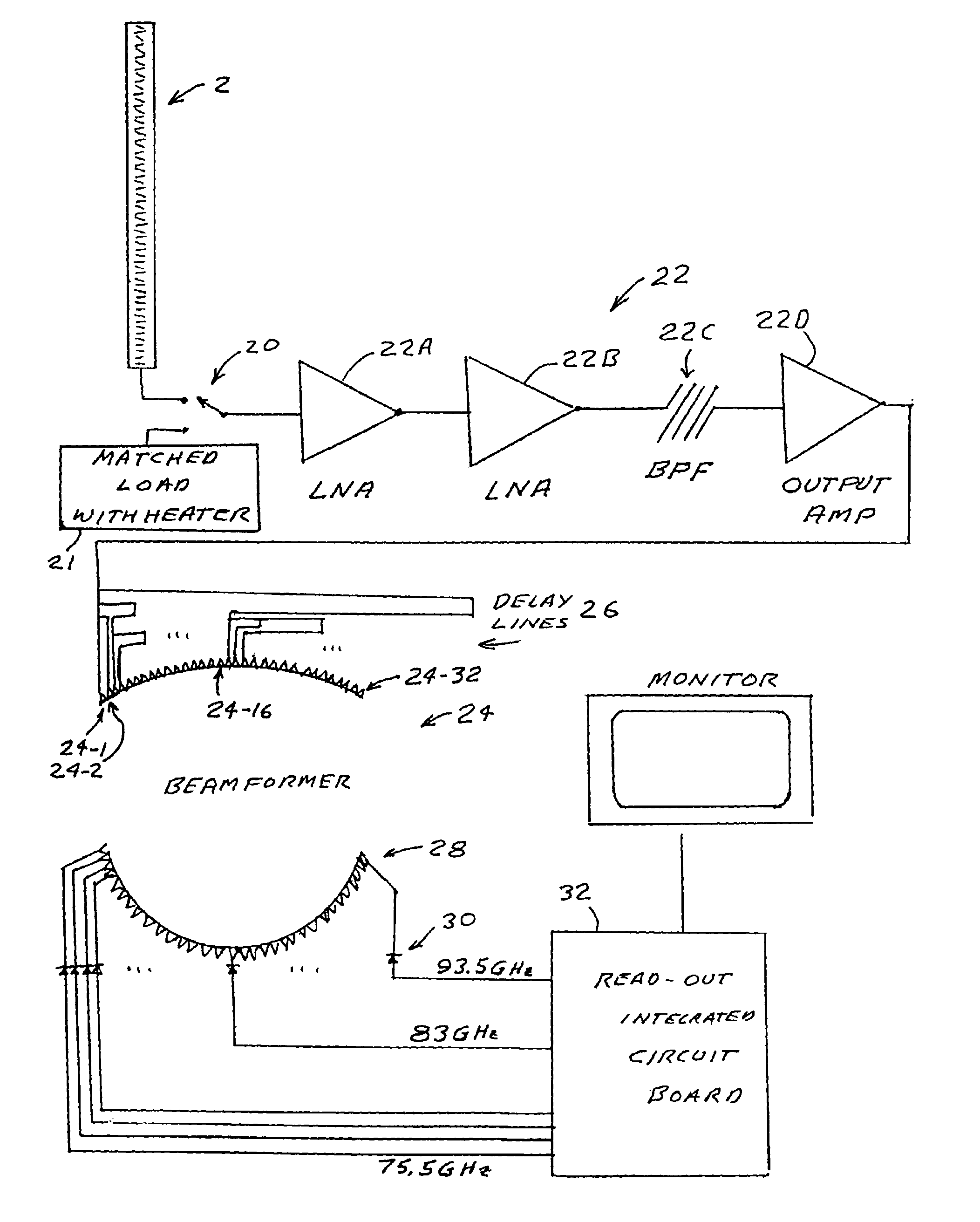
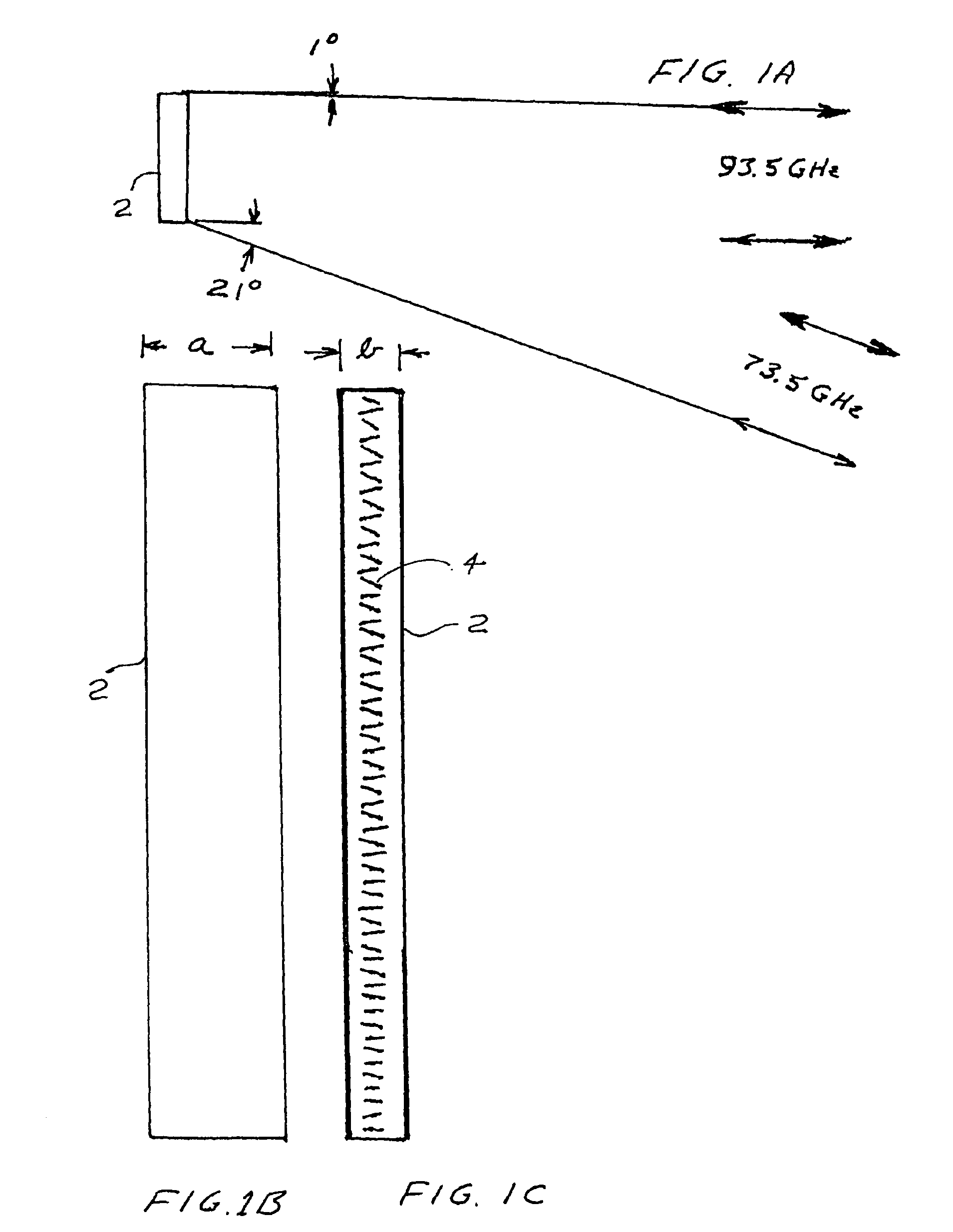
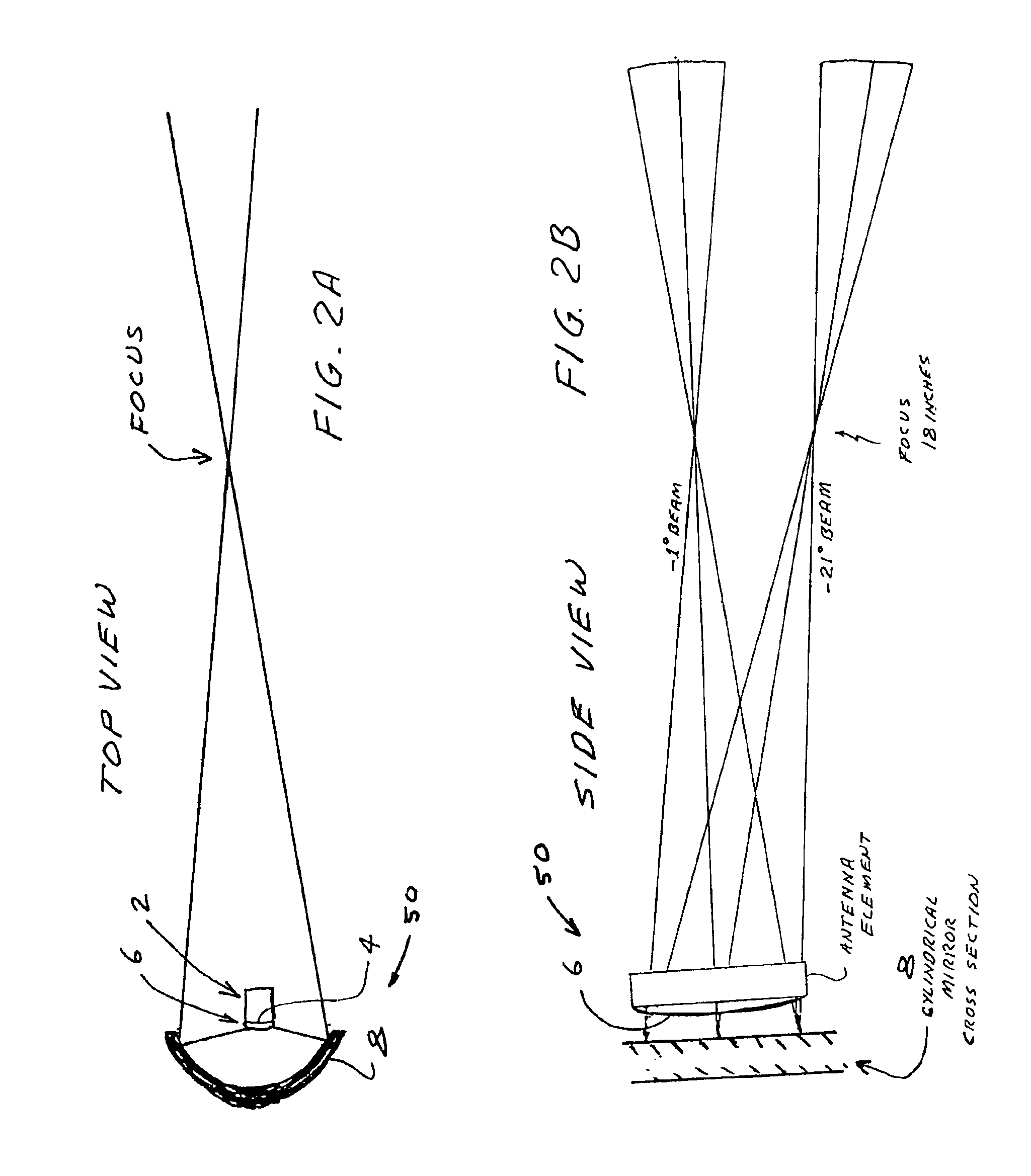
A millimeter wave imaging system that includes at least one millimeter wave frequency scanning antenna for collecting frequency dependent beams of millimeter wave radiation from a narrow one-dimensional field of view. The collected radiation is amplified at the collected frequencies and the amplified signals are separated into frequency dependent bins with a tapped-delay beam-former. These bins are then sampled to produce a one-dimensional image of the antenna field of view. A two dimensional image of a target may be obtained by moving the target across the field of view of the scanning antenna. In a preferred embodiment the antenna is only 4.5 inches in length and constructed from WR-10 waveguide with inclined slots cut in one of the narrow walls at 79 mil spacings. This geometry creates a frequency-scanned antenna spanning a 20 degree vertical field of view over a 75.5-93.5 GHz operational band of the sensor, starting at approximately 1 degree below horizontal at 93.5 GHz and ranging to approximately 21 degrees below horizontal at 75.5 GHz. In this embodiment 64 of these antenna elements are arranged in four stacks of 16 antennas focused at about 18 inches to construct a portal contraband screener.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISE
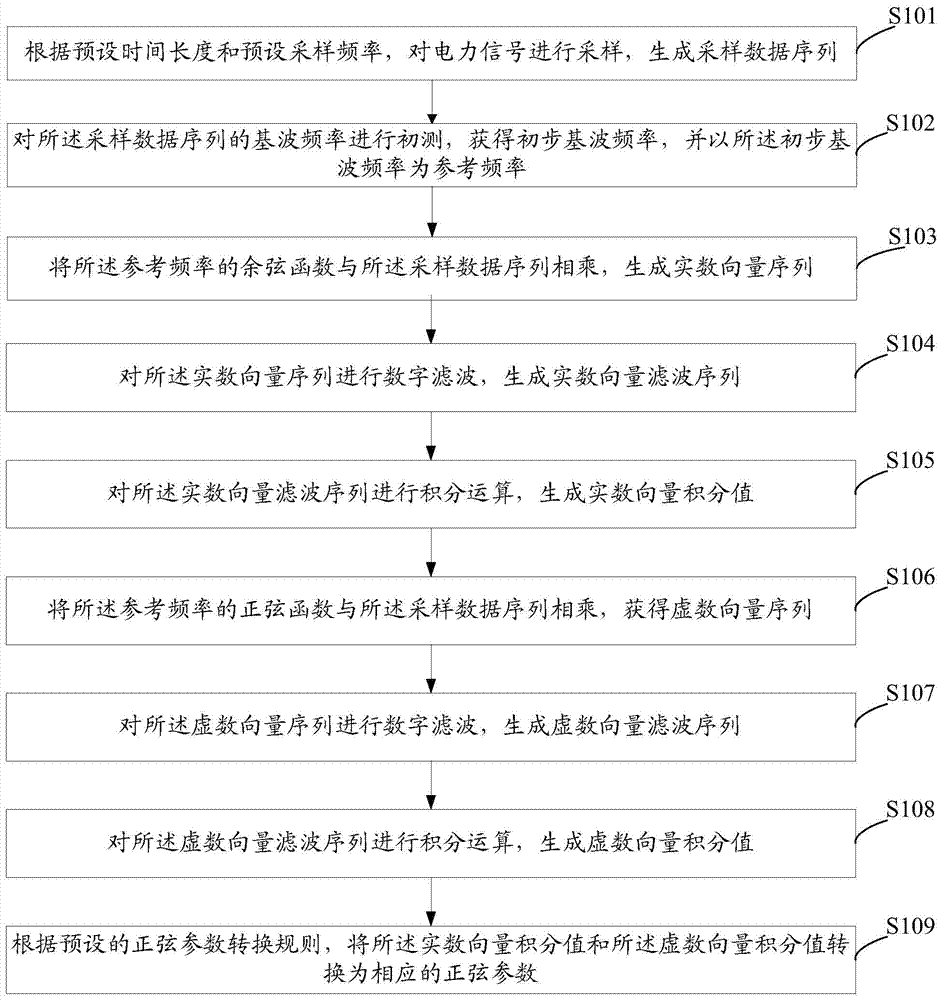
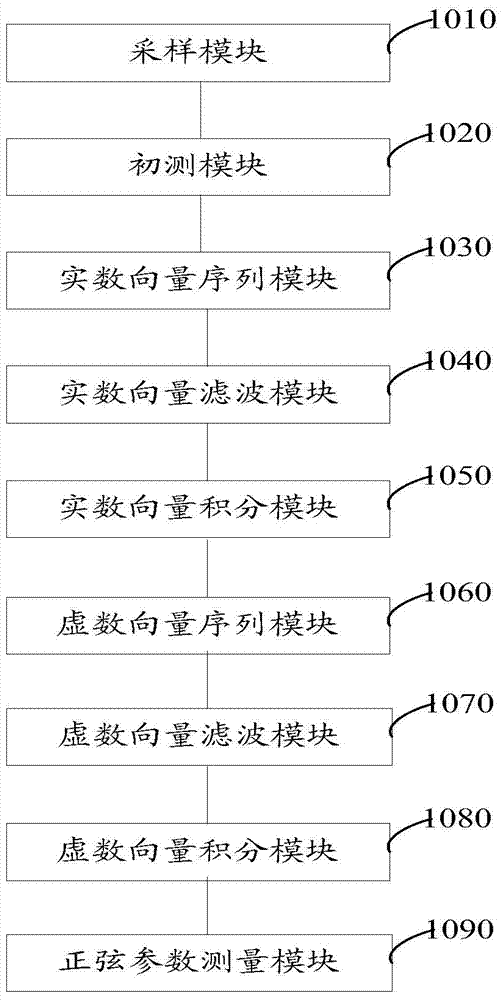
Sinusoidal parameter measurement method and system of power signal
ActiveCN104502700AHigh precisionSuppression of aliasing interference componentsFrequency measurement arrangementDigital filterData sequences
The invention discloses a sinusoidal parameter measurement method and system of a power signal. The method comprises the following steps: performing preliminary measurement on fundamental wave frequency of a sampling data sequence to acquire preliminary fundamental wave frequency and multiplying a cosine function and a sine function of the preliminary fundamental wave frequency serving as the reference frequency by the sampling data sequence respectively to generate a real vector sequence and an imaginary vector sequence; performing digital filtering on the real vector sequence and the imaginary vector sequence to generate a real vector filter sequence and an imaginary vector filter sequence, and further integrating to generate a real vector integral value and an imaginary vector integral value; converting the real vector integral value and the imaginary vector integral value into corresponding sinusoidal parameters according to a preset sinusoidal parameter conversion rule. By implementing the method and the system, mixed frequency interference elements in the real vector sequence and the imaginary vector sequence can be inhibited to generate high-precision real vector and imaginary vector sequence integral values so as to finally obtain the sinusoidal parameters with higher precision.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Ultra-wideband receiver and transmitter
InactiveUS7209523B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsPulse demodulatorExtensibilityBandpass filtering
A waveform-adaptive ultra-wideband (UWB) transmitter and noise-tracking UWB receiver for use in communications, object detection and radar applications. In one embodiment, the output of an oscillator is gated by a low-level impulse generator either directly or through an optional filter. In a special case of that embodiment wherein the oscillator is zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, the low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The low-level impulse signal can be generated digitally. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry data, or may be used in object detection or ranging applications. The power amplifier may be gated to provide a power-efficient UWB transmitter. The UWB transmitter exhibits well defined and controllable spectral characteristics. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Mobile millimeter wave imaging radar system
InactiveUS20090135051A1Ample scan coverageEffective and reliable detectionAntenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsRadar imaging
A short range millimeter wave imaging radar system. The system includes electronics adapted to produce millimeter wave radiation scanned over a frequency range of a few gigahertz. The scanned millimeter wave radiation is broadcast through a frequency scanned transmit antenna to produce a narrow transmit beam in a first scanned direction (such as the vertical direction) corresponding to the scanned millimeter wave frequencies. The transmit antenna is scanned to transmit beam in a second direction perpendicular to the first scanned direction (such as the horizontal or the azimuthal direction) so as to define a two-dimensional field of view. Reflected millimeter wave radiation is collected in a receive frequency scanned antenna co-located (or approximately co-located) with the transmit antenna and adapted to produce a narrow receive beam approximately co-directed in the same directions as the transmitted beam in approximately the same field of view. Computer processor equipment compares the intensity of the receive millimeter radar signals for a pre-determined set of ranges and known directions of the transmit and receive beams as a function of time to produce a radar image of at least a desired portion of the field of view. In preferred embodiment the invention is mounted on a truck and adapted as a FOD finder system to detect and locate FOD on airport surfaces.
Owner:TREX AVIATION
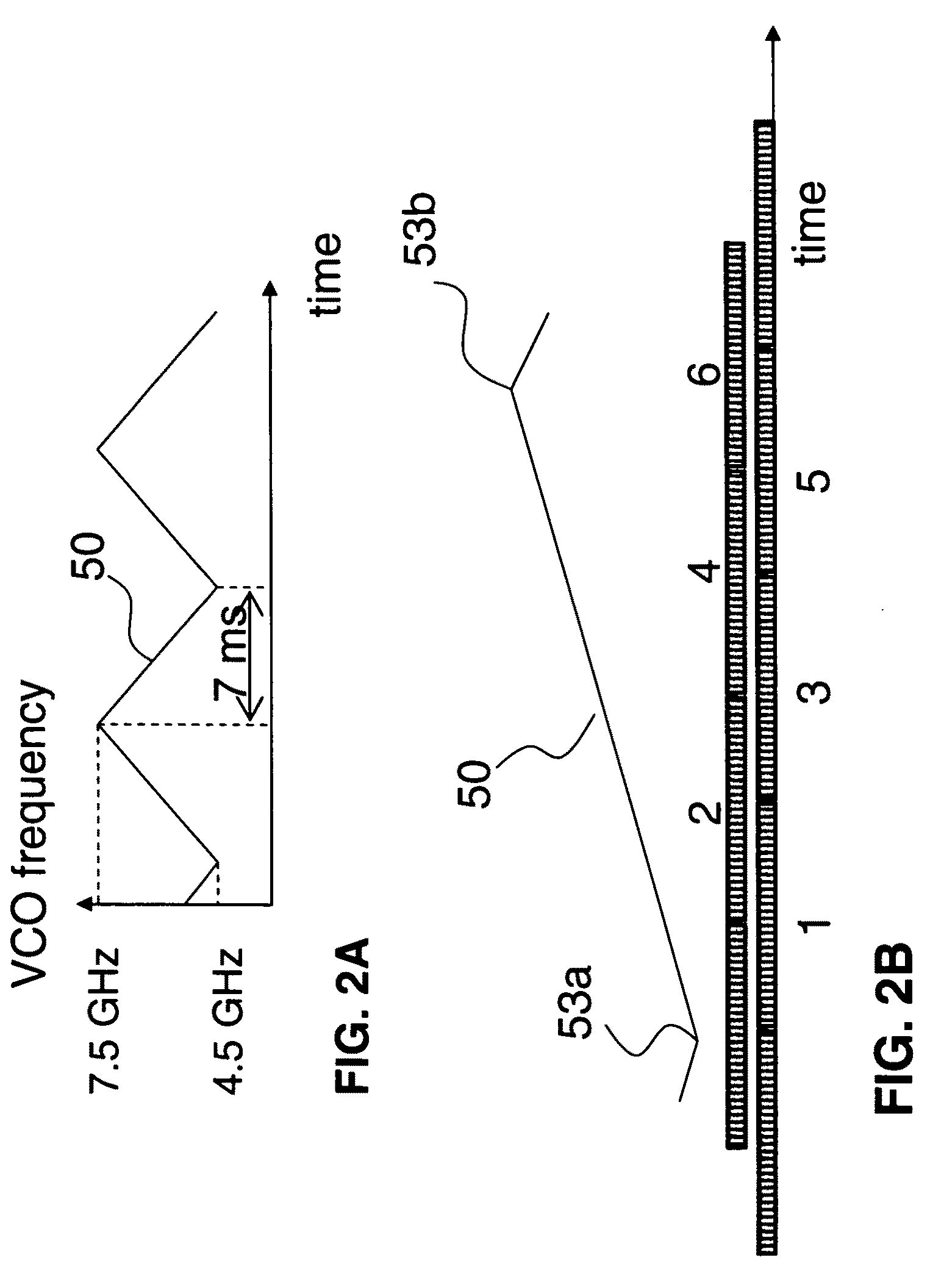
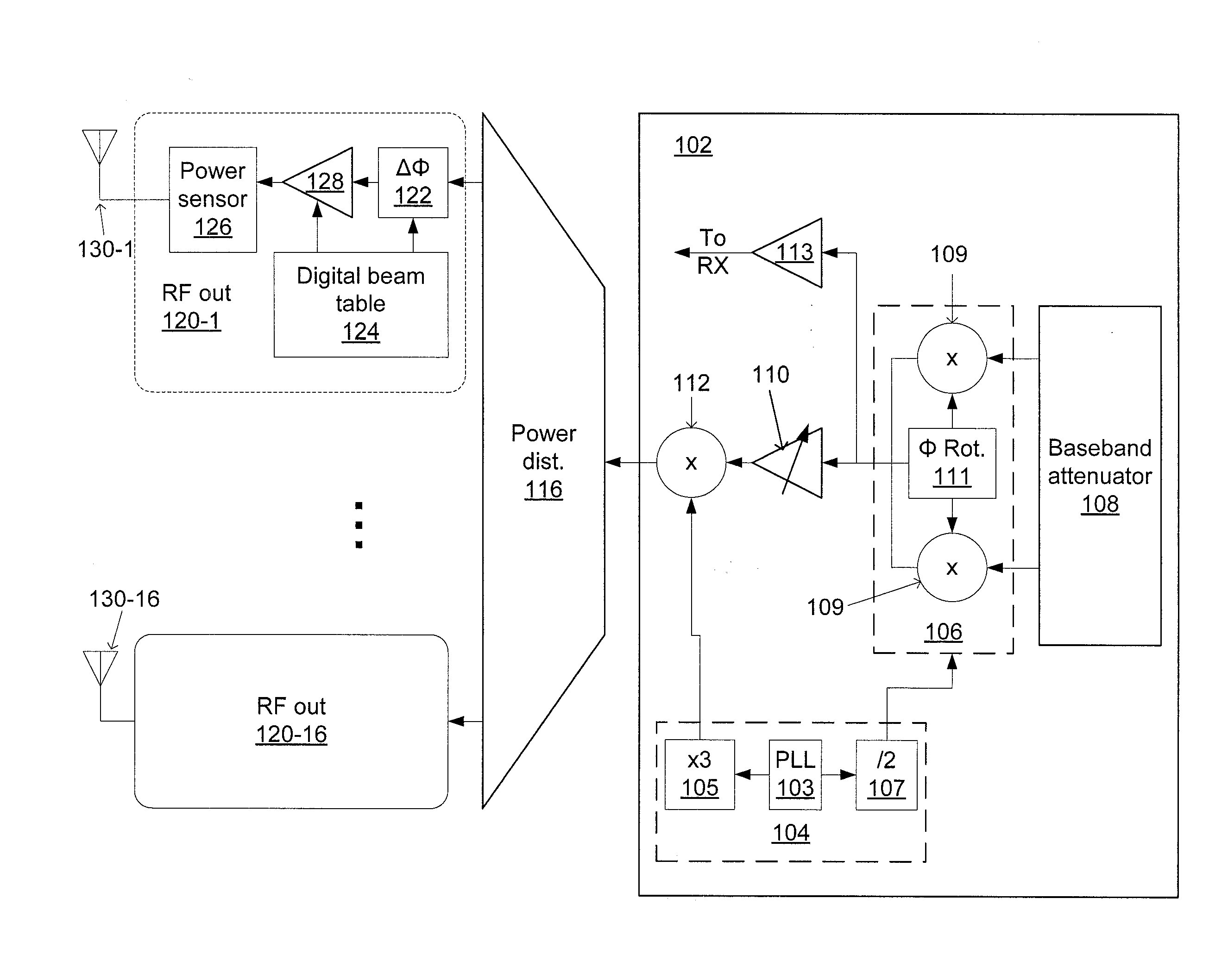
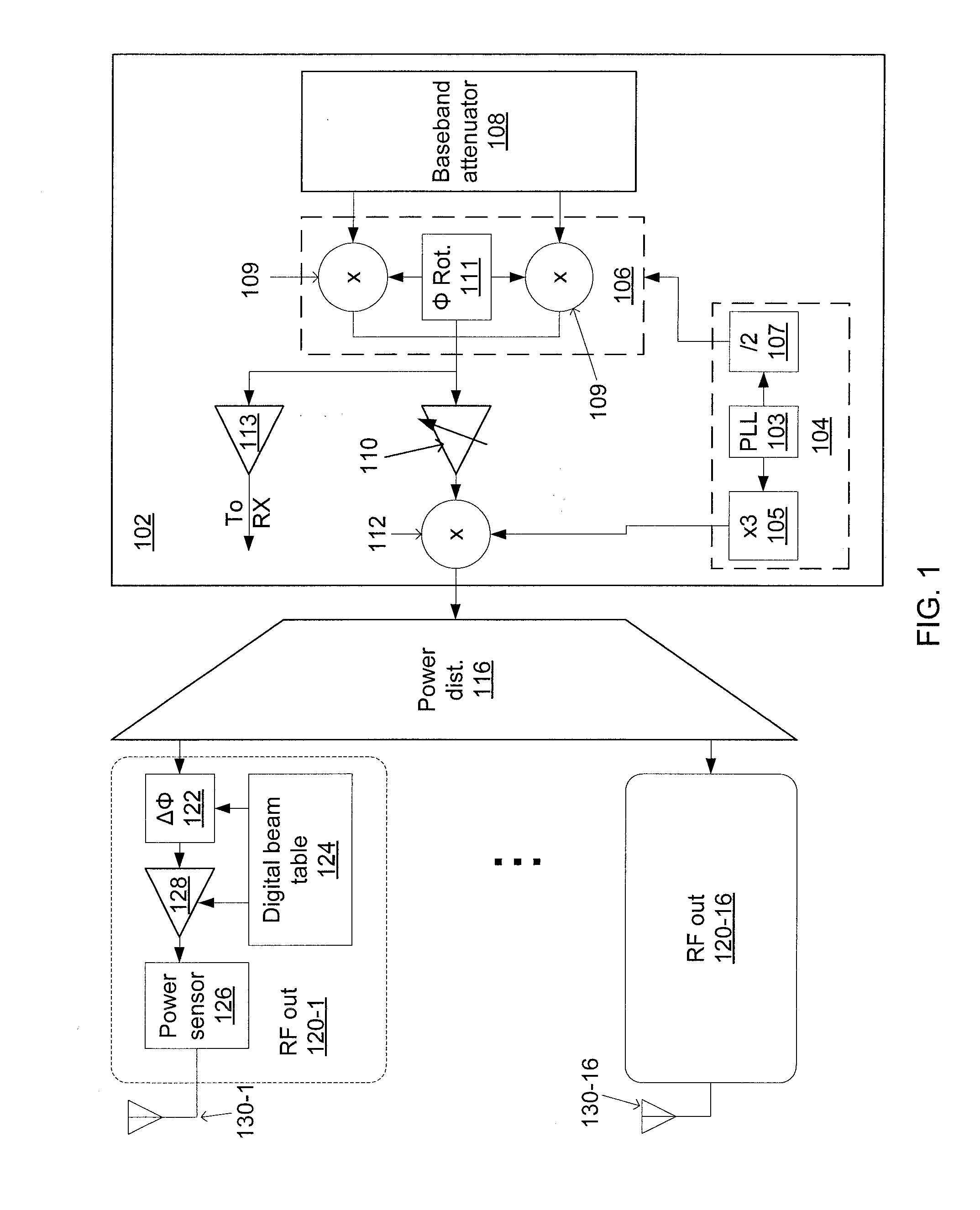
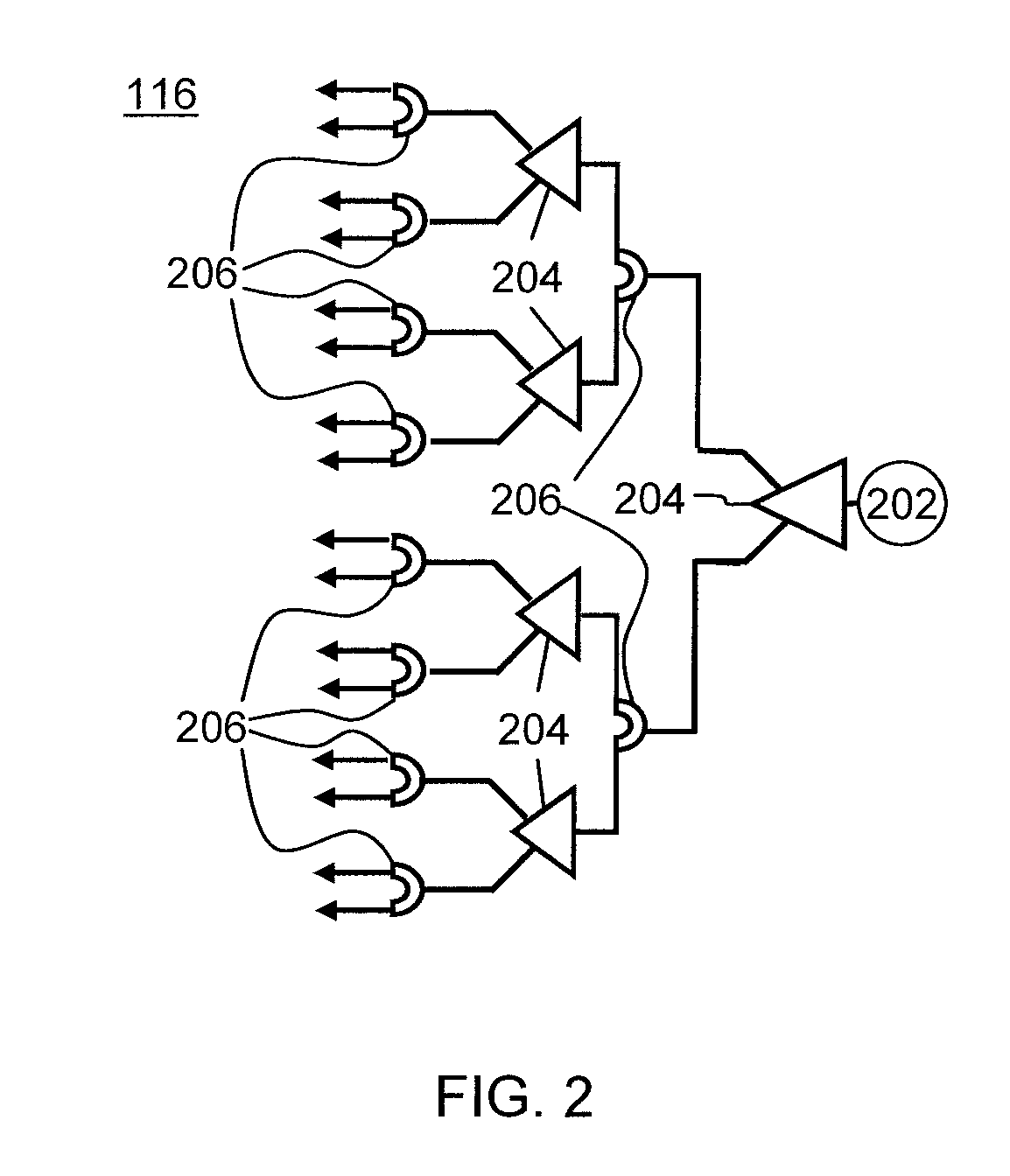
Phased-array transceiver for millimeter-wave frequencies
ActiveUS20110063169A1Wide power consumptionWide signal dynamic rangeAntennasTransceiverMillimetre wave
A phased-array transmitter and receiver that may be effectively implemented on a silicon substrate. The transmitter distributes to front-ends, and the receiver combines signals from front-ends, using a power distribution / combination tree that employs both passive and active elements. By monitoring the power inputs and outputs, a digital control is able to rapidly provide phase and gain correction information to the front-ends. Such a transmitter / receiver includes a plurality of radio frequency (RF) front-ends and a power splitting / combining network that includes active and passive components configured to distribute signals to / from the front-ends.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Method and apparatus for forming millimeter wave phased array antenna
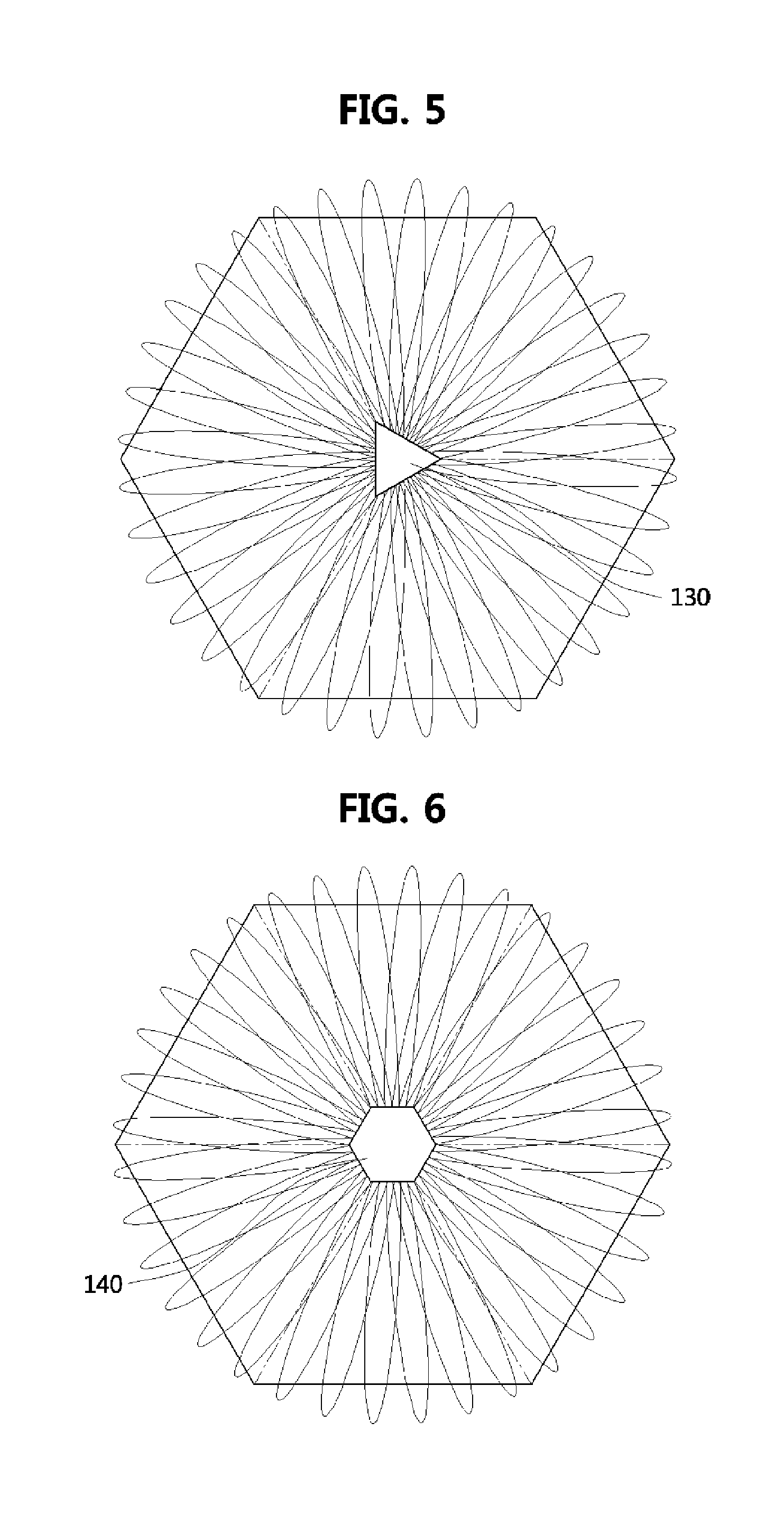
InactiveUS6900765B2Small reduction in efficiency of systemSimplify complexitySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsBeam hoppingNetwork Communication Protocols
A phased array antenna system having a corporate waveguide distribution network stripline printed circuit board. The stripline printed circuit board receives electromagnetic (EM) wave energy from a 1×4 waveguide distribution network input plate and distributes the EM wave energy to 524 radiating elements. The stripline circuit board enables extremely tight spacing of independent antenna radiating elements that would not be possible with a rectangular air filled waveguide. The antenna system enables operation at millimeter wave frequencies, and particularly at 44 GHz, and without requiring the use of a plurality of look-up tables for various phase and amplitude delays, that would otherwise be required with a rectangular, air-filled waveguide distribution structure. The antenna system can be used at millimeter wave frequencies, and in connection with the MILSTAR communications protocol, without the requirement of knowing, in advance, the next beam hopping frequency employed by the MILSTAR protocol.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
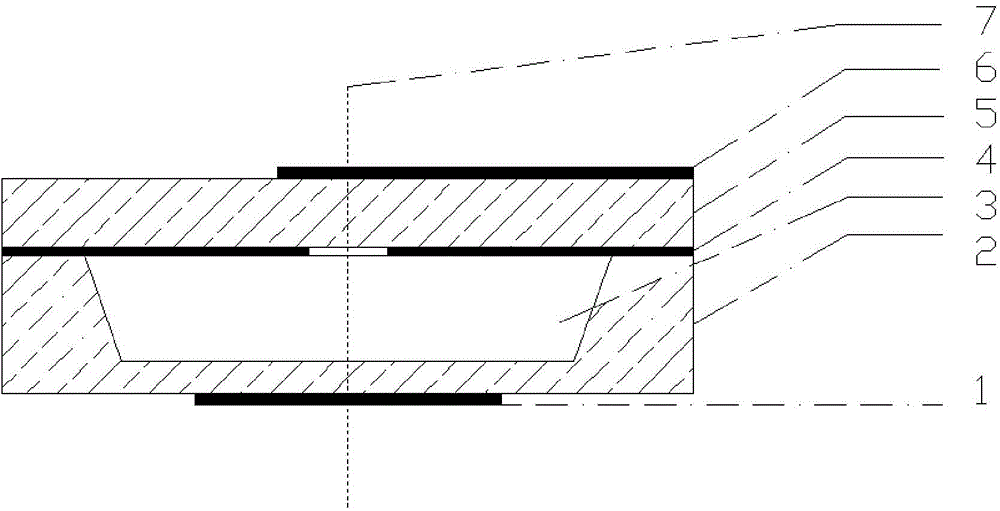
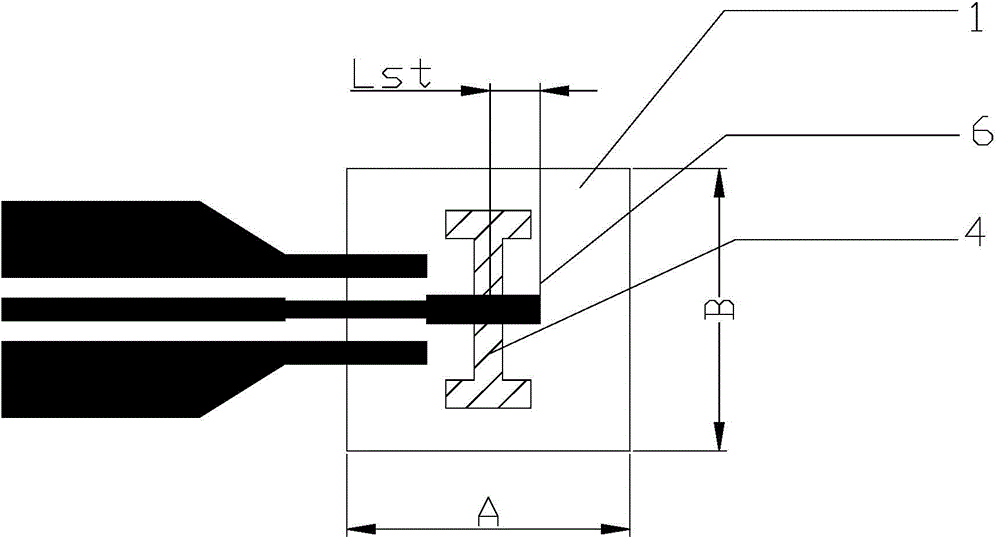
Silicon-based multi-layer cavity filter
ActiveCN102361113AHigh Q valueReduce radiation lossWaveguide type devicesResonant cavitySystem integration
The invention discloses a silicon-based multi-layer cavity filter, which is formed by superposing more than two medium layers up and down, wherein a through hole is formed in each medium layer; an internal wall metal layer which is formed by using a silicon micro-machining technology is arranged on an internal wall of the through hole; an intermediate metal layer which is formed by using the silicon micro-machining technology is arranged between the two adjacent medium layers; an inter-stage coupling window is arranged on the intermediate metal layer; an upper surface of a top medium layer and a lower surface of a bottom medium layer are respectively provided with a surface metal layer which is formed by using the silicon micro-machining technology; a metal layer which is contacted with the upper and lower surfaces of each medium layer and an internal wall metal layer form a resonant cavity; and an input tap lead is arranged on one resonant cavity, and an output tap lead is arranged on another resonant cavity. The silicon-based multi-layer cavity filter is small in size, has a shielding function, can meet the accuracy requirement of microwave / millimeter wave frequency band, and is free from encapsulation, good in device consistency, compatible with an integrated circuit process, easy to implement system integration and convenient to assemble and debug.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
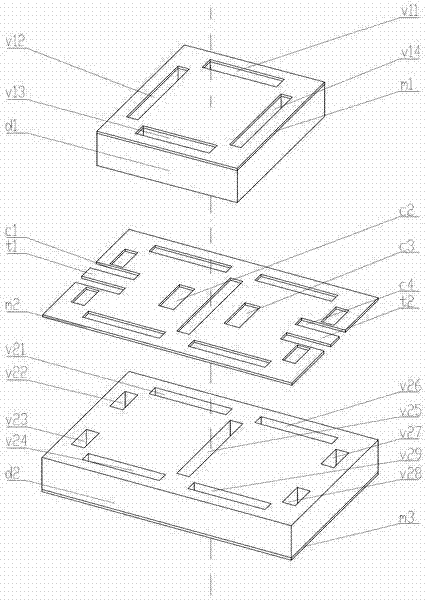
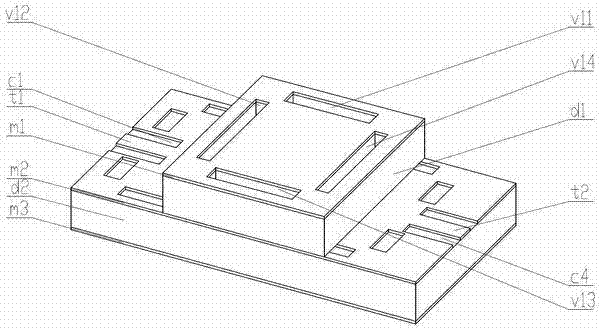
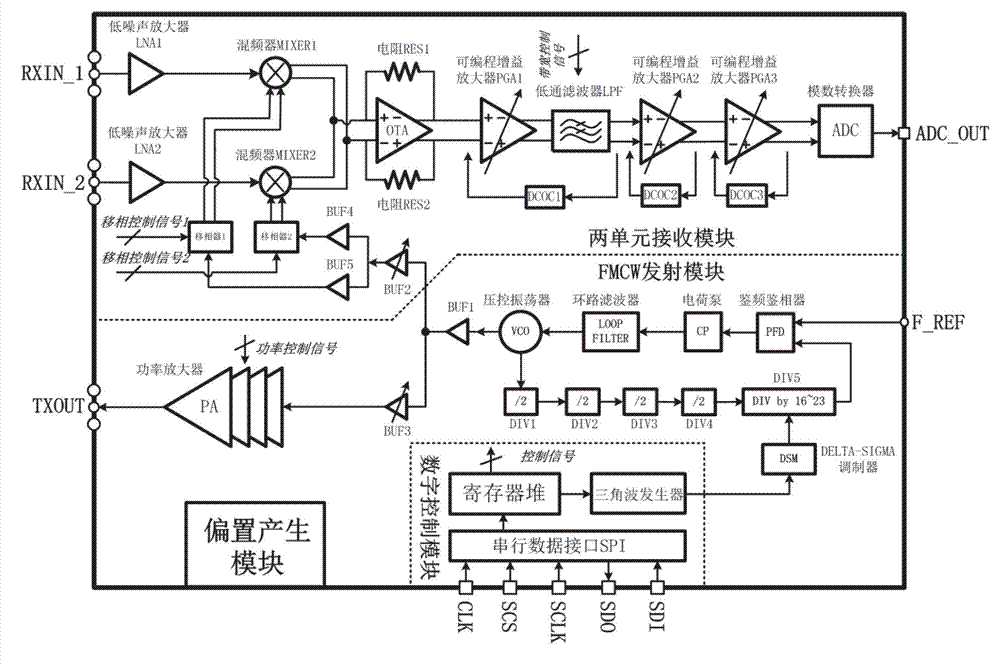
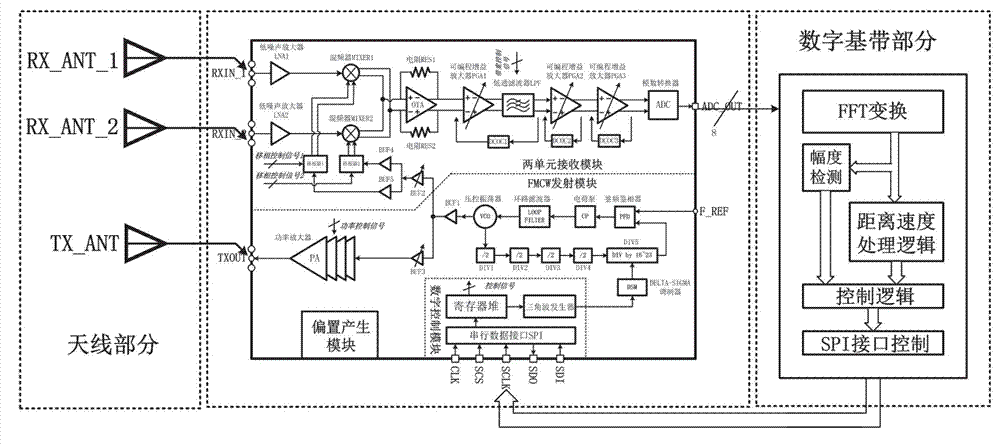
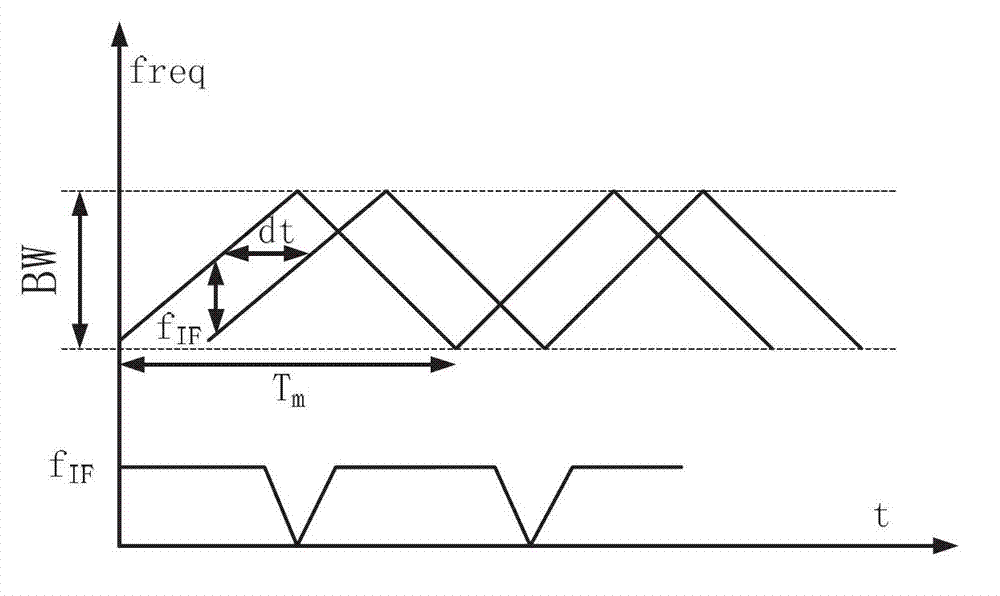
Millimeter wave frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) two-unit phased array distance and velocity measurement monolithic radar transceiver
The invention provides a millimeter wave frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) two-unit phased array distance and velocity measurement monolithic radar transceiver and belongs to the field of distance and velocity measurement radar transceivers. The millimeter wave FMCW two-unit phased array distance and velocity measurement monolithic radar transceiver is characterized by being formed by a FMCW transmitting module, a two-unit receiving module, a digital control module and a polarization generating module. The FMCW transmitting module is used for generating FMCW continuous-wave modulated signals, the continuous-wave modulated signals are sent out through an antenna after being amplified, the two-unit receiving module is used for processing signals reflected back from a target, the digital control module is used for controlling configurable amount in a system, sweep frequency cycle of FMCW modulation signals, sweep frequency bandwidth, signal transmitting power, gain of a receiving branch, bandwidth of a five-order Butterworth low-pass filter and phase shift value of a phase shifter can be configured, and the millimeter wave FMCW two-unit phased array distance and velocity measurement monolithic radar transceiver can be applied to detection of targets at close distance, far distance and different angles.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
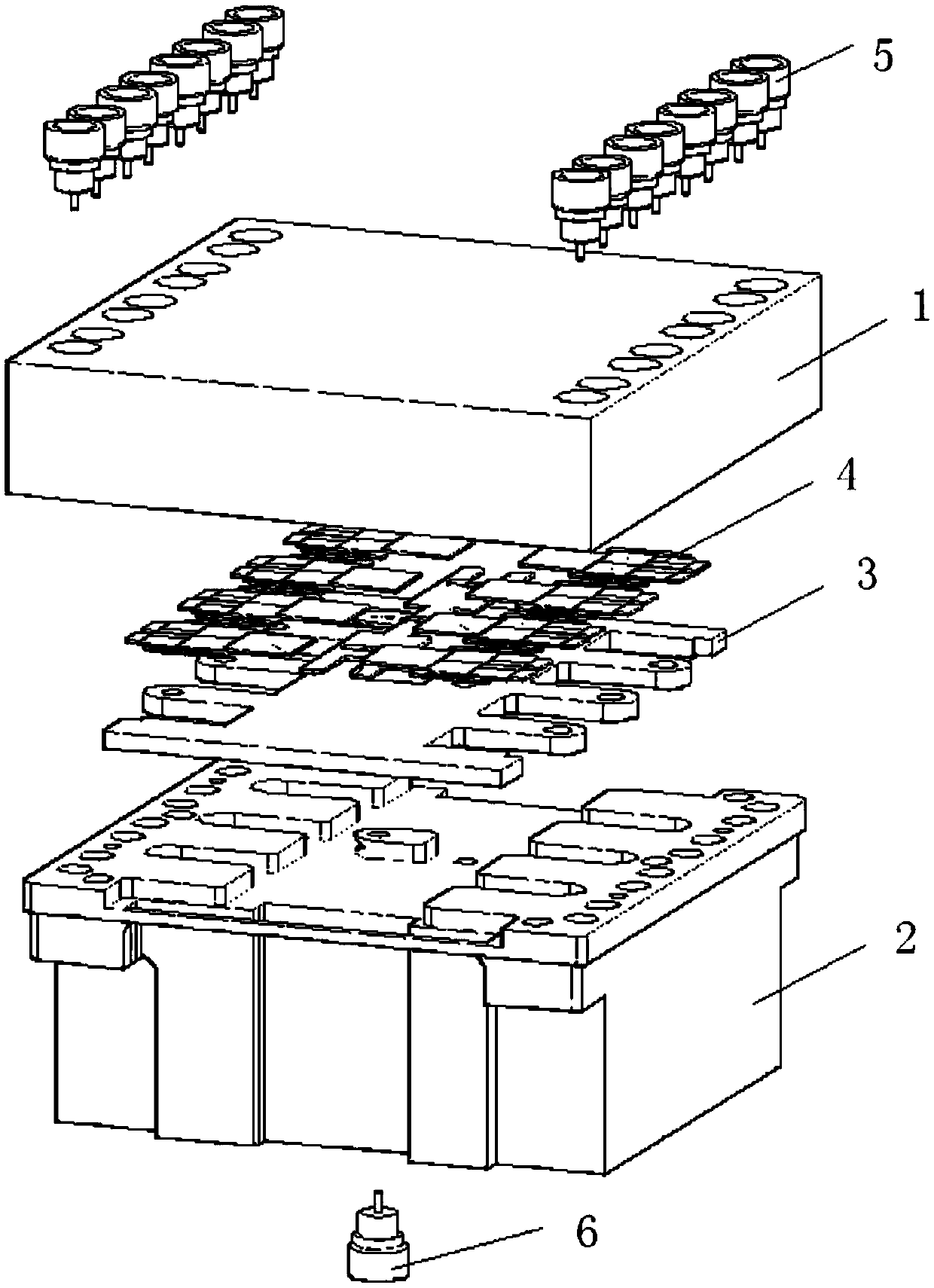
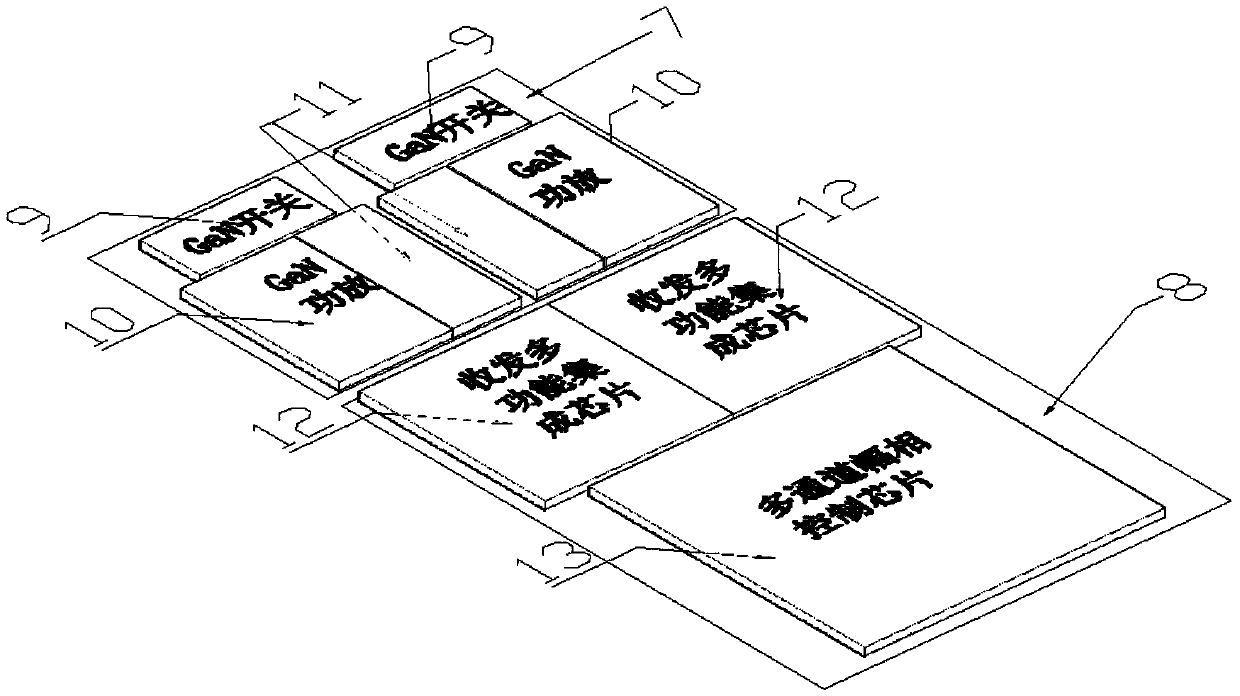
Millimeter wave tile-type phased-array antenna TR module
ActiveCN105514566AReduce thermal resistanceShort cooling pathAntenna supports/mountingsModular arraysHigh densityRadio frequency signal
The invention relates to a millimeter wave tile-type phased-array antenna TR module, and the invention aims at providing a TR module realization scheme with advantages of high reliability, low cost and high density integration for a millimeter wave frequency range high-power active phased-array antenna (APAA). The millimeter wave tile-type phased-array antenna TR module can be realized by the following scheme: a radio-frequency signal is fed from a radio-frequency vertical interconnection interface of a common port of the lower cavity bottom of the TR module, after the radio-frequency signal is performed the power distribution through a power divider mounting on the surface of a multi-layer circuit board and the like, the radio-frequency signal is fed in a multichannel amplitude-phase control chip connected with every transmit-receive channel, after the radio-frequency signal is performed the second power distribution by the multichannel amplitude-phase control chip, the amplitude-phase information of each channel radio-frequency signal is adjusted according to the state of the external control code and is outputted to a TR multi-function chip, the signal is amplified and outputted to the final power amplifier until saturation, the signal is outputted to a power switch, the emission access is gated, and the signal is transmitted to antenna radio-frequency vertical interconnection interfaces arranged on two ends of the cavity on the TR module; when the TR module receives a work, the radio-frequency signal passes through the TR module in a reverse direction.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Micromachined millimeter-wave frequency scanning array
ActiveUS20150263429A1Available bandwidthIncrease rangeRadiating elements structural formsLinear waveguide fed arraysPatch arrayFrequency multiplier
A frequency scanning traveling wave antenna array is presented for Y-band application. This antenna is a fast wave leaky structure based on rectangular waveguides in which slots cut on the broad wall of the waveguide serve as radiating elements. A series of aperture-coupled patch arrays are fed by these slots. This antenna offers 2° and 30° beam widths in azimuth and elevation direction, respectively, and is capable of ±25° beam scanning with frequency around the broadside direction. The waveguide can be fed through a membrane-supported cavity-backed CPW which is the output of a frequency multiplier providing 230˜245 GHz FMCW signal. This structure can be planar and compatible with micromachining application and can be fabricated using DRIE of silicon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Wireless millimeter wave communication system with mobile base station
InactiveUS20060264210A1Efficient use ofHigh data rate communicationNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentTruck-trailerMillimeter wave communication systems
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations. At least one of the base stations is a mobile base station in which low and high speed wireless transceivers are mounted on a temporarily stationary mobile vehicle such as a truck trailer or a truck. The system includes at least one connecting station with a millimeter wave wireless transceiver in communication with a fiber optic or high-speed cable communication network. The transceiver is adapted to communicate at millimeter wave frequencies higher than 60 GHz with another millimeter wave transceiver at one of the cellular base stations. Each of the base stations serves a separate communication cell. Each base station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another base station or a millimeter wave transceiver at said at the connecting station. The base stations are also equipped with data transfer means for transferring data communicated through the low frequency wireless transceiver to the millimeter wave wireless transceiver and for transferring data communicated through the millimeter wave wireless transceiver to the low frequency wireless transceiver. In preferred embodiments the system is a part of a telephone system, an Internet system or a computer network.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
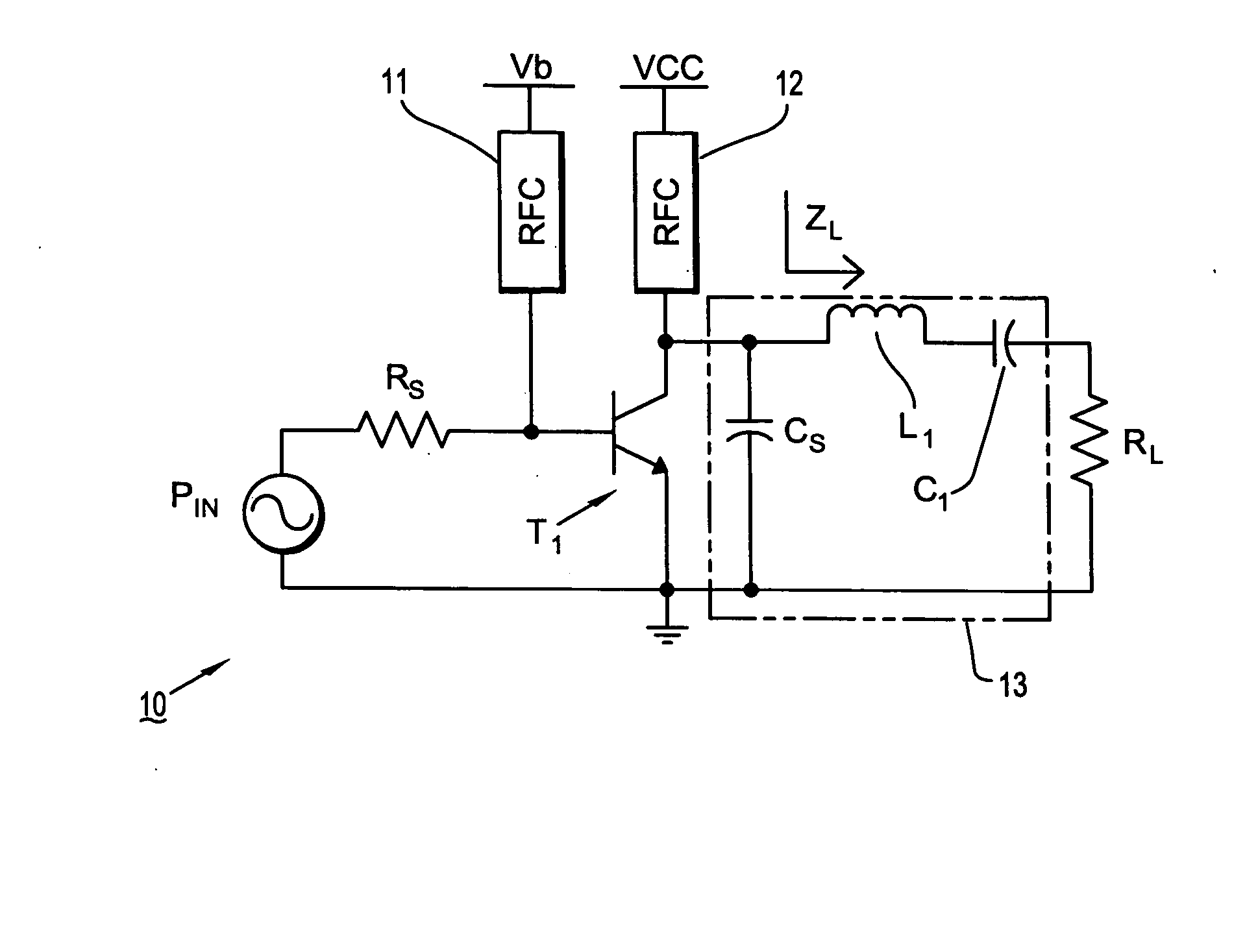
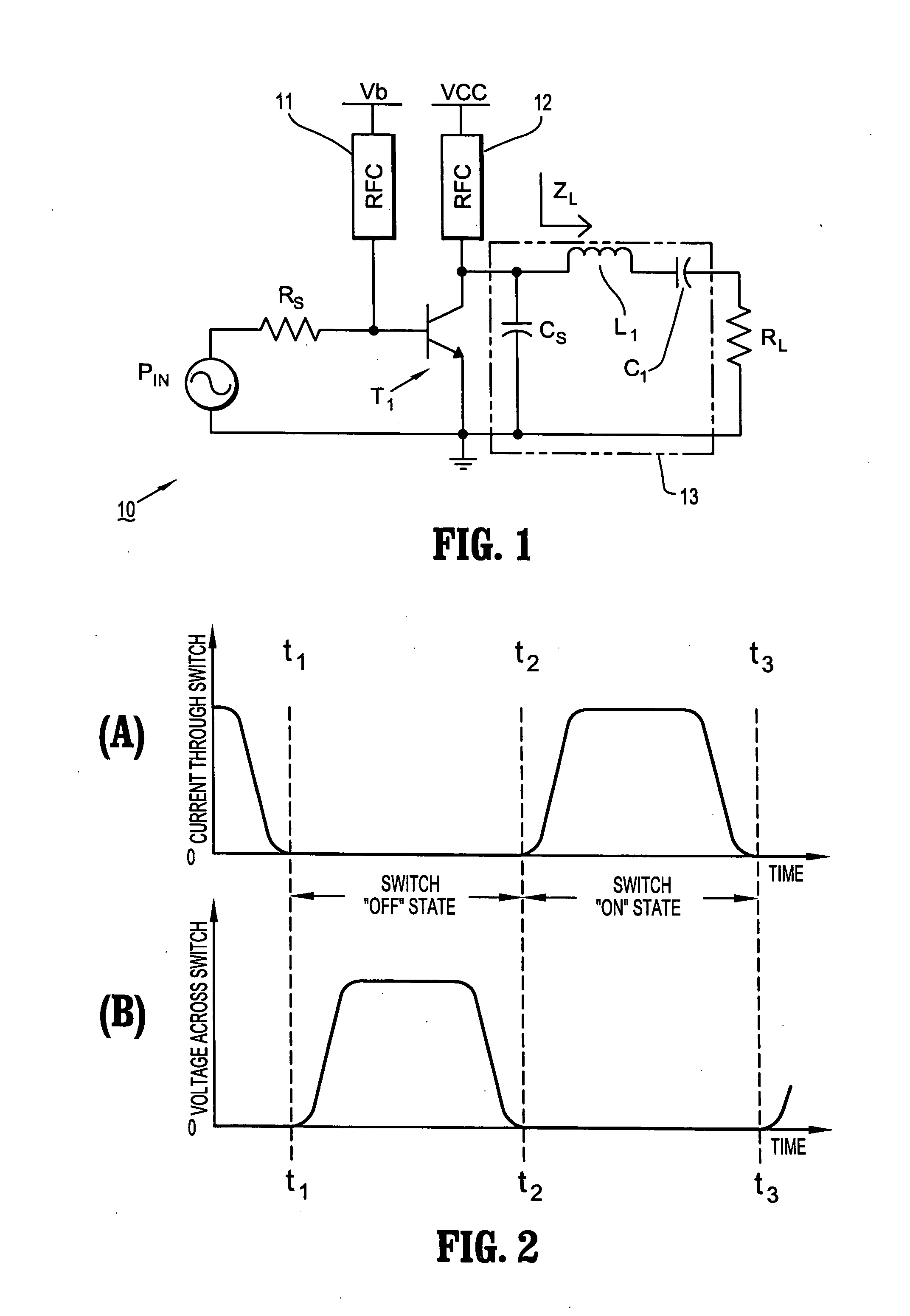
Circuits and methods for implementing power amplifiers for millimeter wave applications
ActiveUS20060261890A1Improve driving conditionsPower added efficiencyRF amplifierAmplifiers with semiconductor devices onlyAudio power amplifierEngineering
Circuits and methods are provided for implementing highly efficient switch-mode power amplifiers using BJTs (bipolar junction transistors) as active switching devices at millimeter-wave frequencies. More specifically, circuits and methods are provided for driving power amplifiers with BJT switching devices to achieve highly efficient switch-mode (e.g., Class E) operation at millimeter wave frequencies (e.g., 60 GHz).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Almost perfect absorbing structure for wide wave band
InactiveCN101740722AEnhance electromagnetic wave absorption efficiencyImplement extensionsFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesSurface plasmonMetallic materials
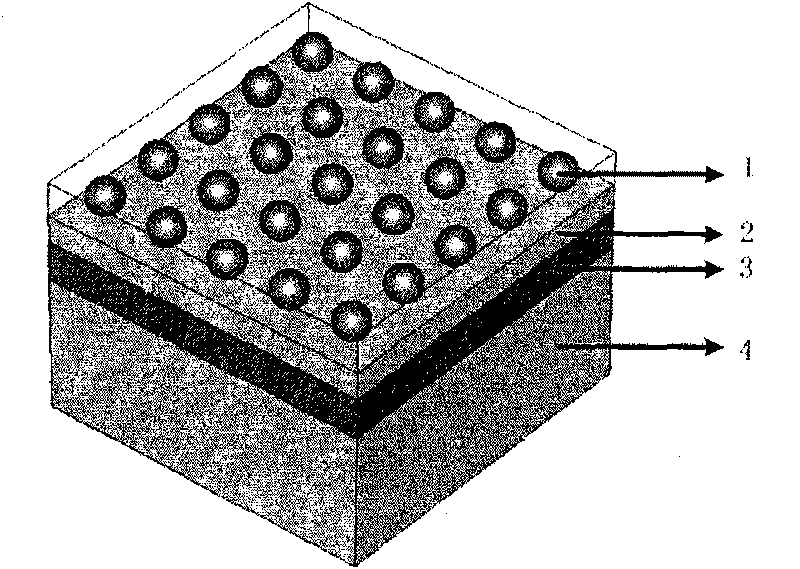
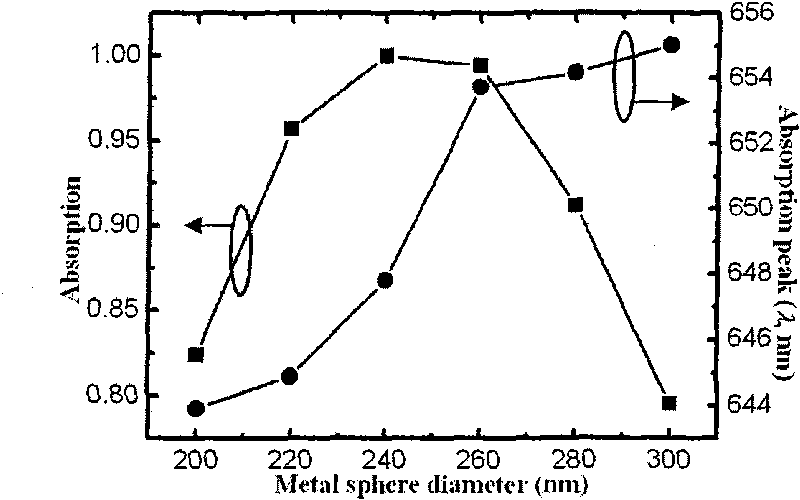
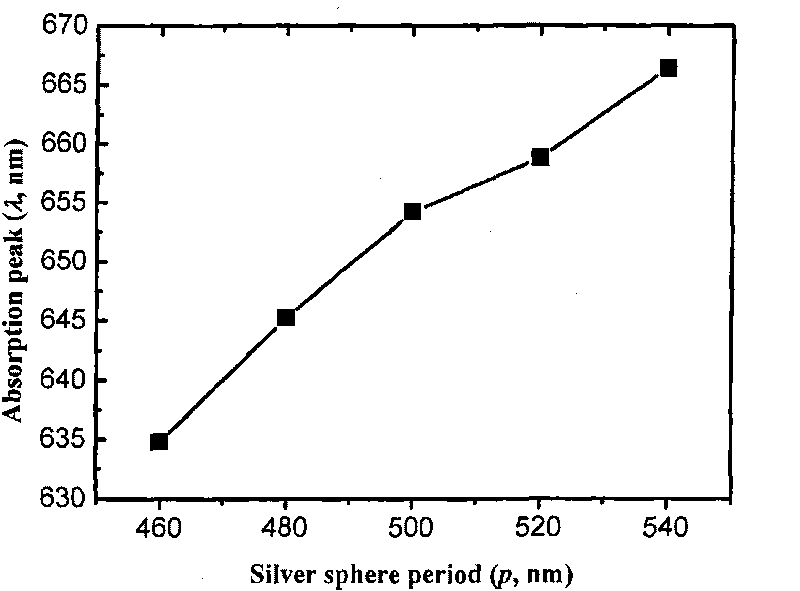
The invention relates to an almost perfect absorbing structure for wide wave band, which comprises the following steps: (1) determining absorbing material and metal material according to the incoming wave frequency band; (2) manufacturing structure of apparatus; (3) determining the range of diameter d of metal spherical particles according to the local effect of plasma on the surface of the metalspherical particles; (4) determining the distribution and range of period p according to the electromagnetic resonation effect among metal spherical particles-medium-metal film; and (5) optimizing particle diameter d and distribution period p to realize expansion of the bandwidth of the entire apparatus. The invention realizes almost perfect absorbing function on wide wave band within visible light range.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
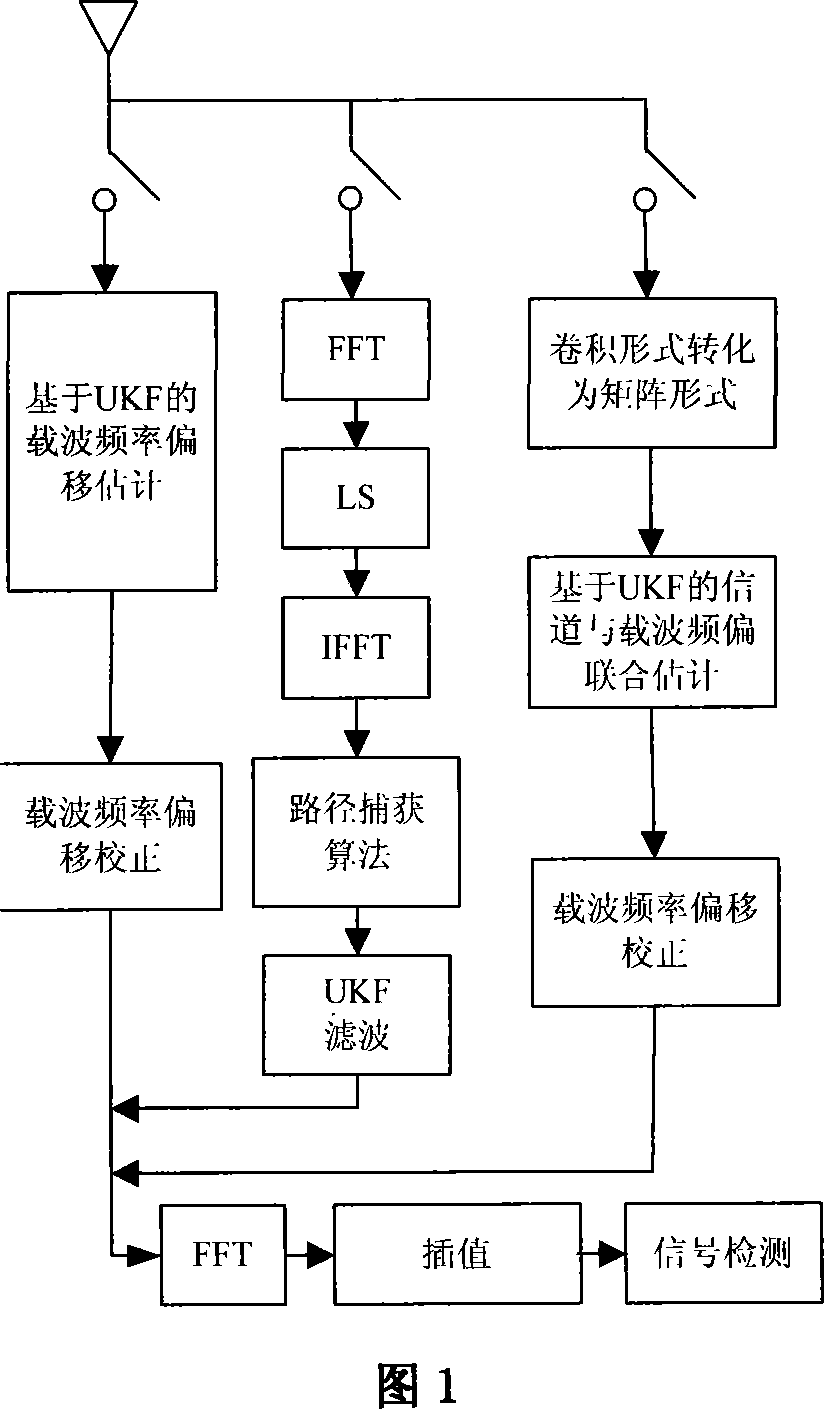
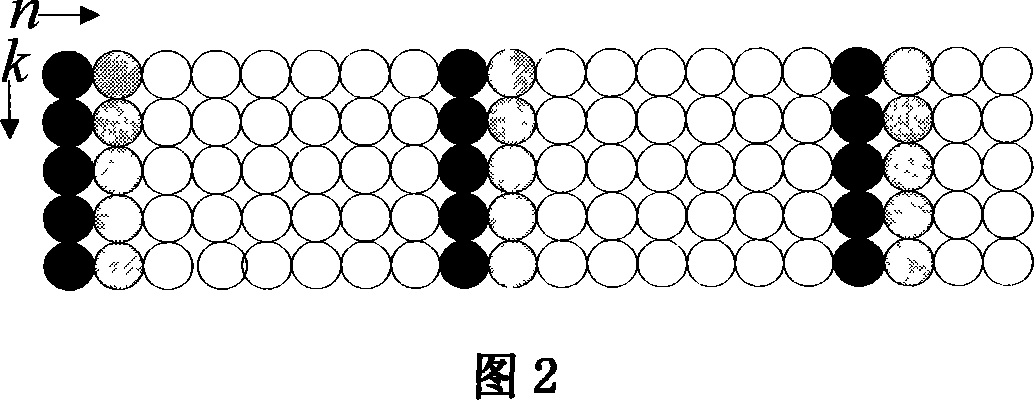
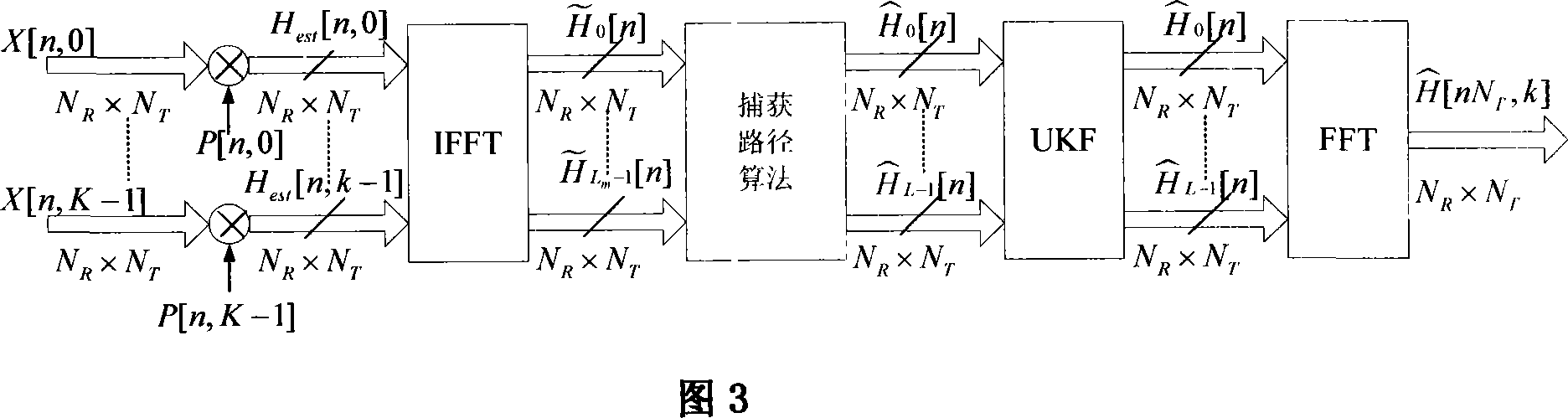
UKF-based channel and carrier frequency deviation estimating method in the OFDM system
InactiveCN101056302AReduce computational complexityImprove estimation accuracyBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier frequency offsetCarrier signal
An UKF based channel and carrier wave frequency shift estimation method in OFDM system is applied in the technique field of wireless transmission. Said channel estimation method starts from a frequency domain, to get cursory estimated values at pilot channels firstly by using a LS method, and then to get accurate estimated values by utilizing path capturing method and UKF method in time domain. According to the UKF based carrier wave frequency shift estimation method in OFDM system in accordance with the present invention, wave frequency shift is estimated in time domain through UKF filtering method, and then ICI is eliminated through carrier wave frequency shift correction. Aiming at OFDM system in which disturbances between sub-carriers exist and which passes through time-varying wireless channel, the present invention further provides an UKF based channel and carrier wave frequency combination estimation method which is capable of eliminating ICI and improving veracity of channel estimation and exhibits excellent astringency and robustness by utilizing specific pilot frequency structure and convolutional change forms of a matrix.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
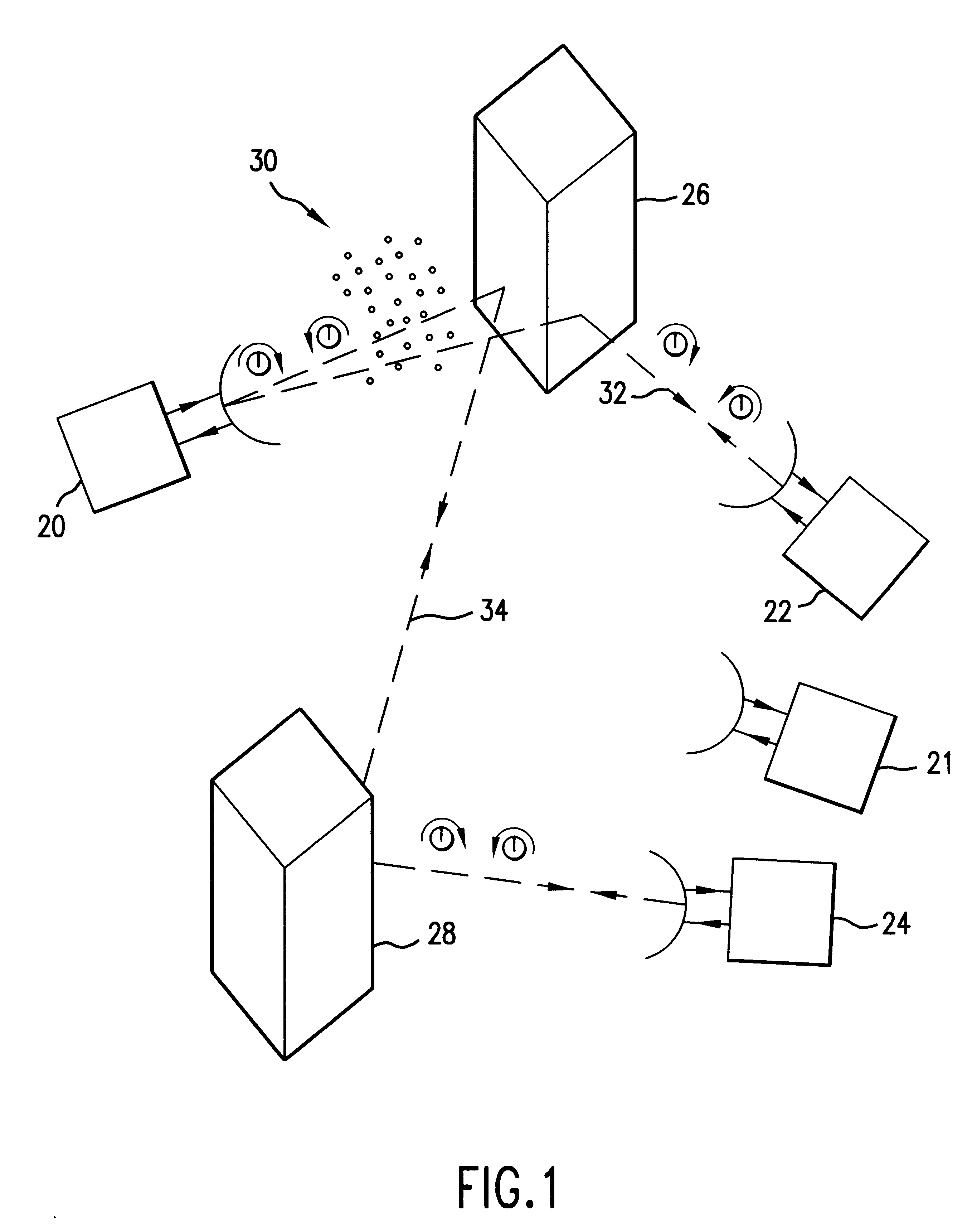
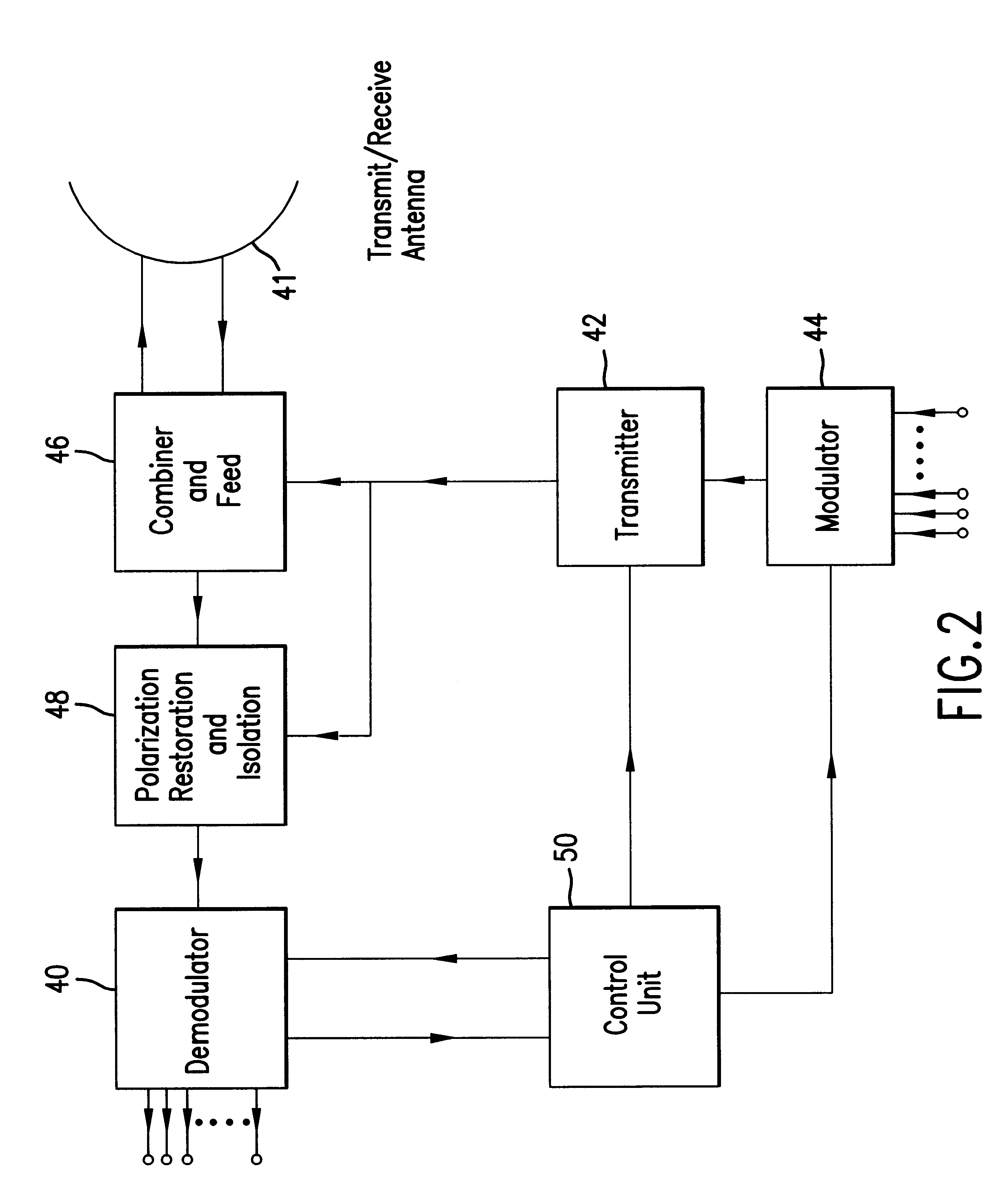
Multi-function interactive communications system with circularly/elliptically polarized signal transmission and reception
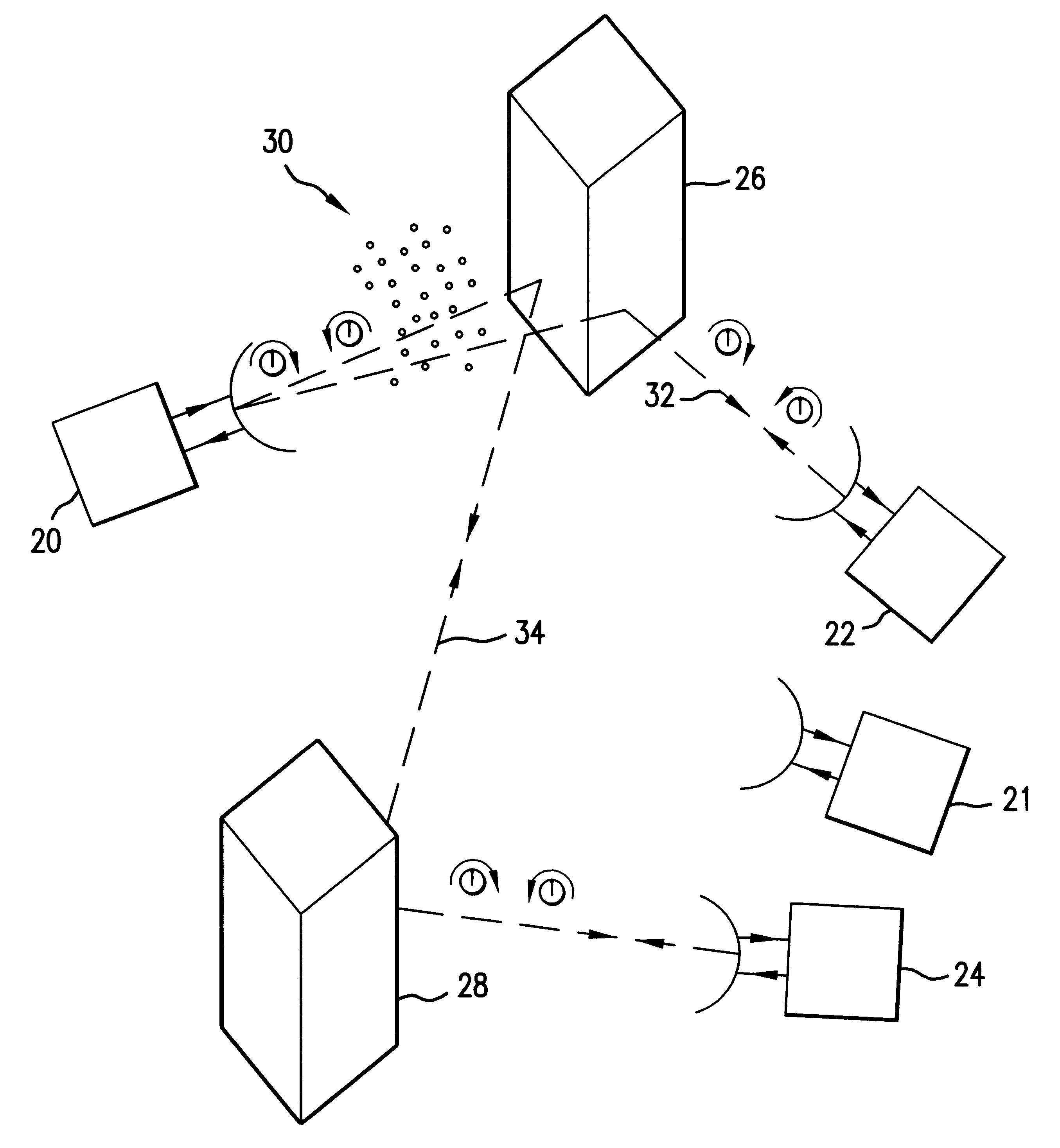
InactiveUS6233435B1Increase channel capacityNegligible effectPolarisation/directional diversityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPolarization diversityTransceiver
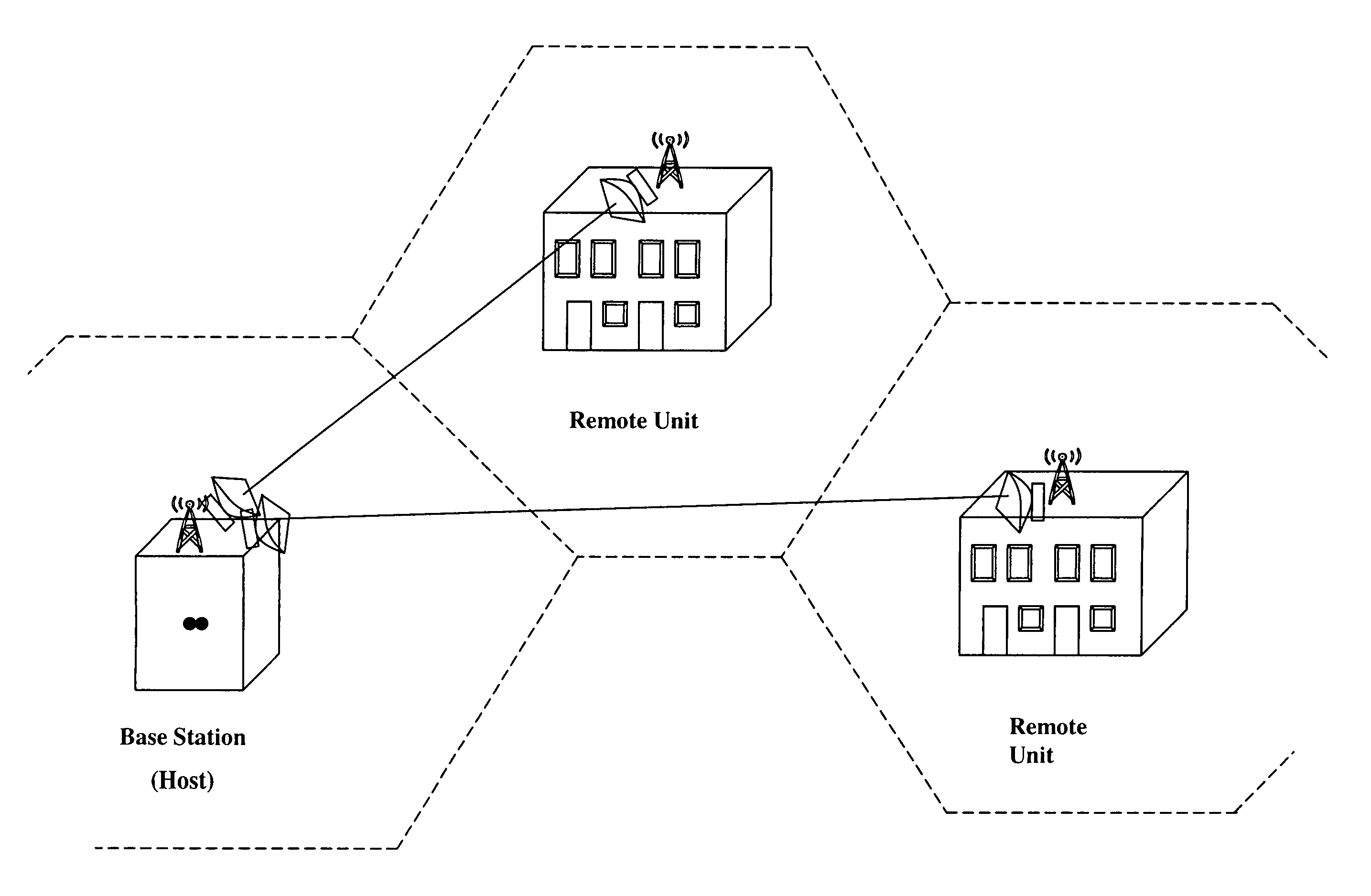
A communications system that uses electromagnetic waves. The communications system preferably operates in the millimeter-wave frequencies, and provides relatively high signal restoration and isolation. The communications system can use polarization diversity to increase the capacity of a channel. Isolation and restoration features in the transceivers eliminate or reduce the effects of precipitation and / or reflection and diffraction from objects, and thus is well-suited for an urban environment.The transceiver will select the proper antenna and signal path for optimal information throughput as the conditions in the propagation medium of the network vary.
Owner:TELECOMM EQUIP
Vertical coupled feeding structure applied to millimeter-wave microstrip antenna
InactiveCN104577316ALower effective dielectric constantWorking frequency bandwidthRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsMicrostrip patch antennaCoplanar waveguide
The invention relates to a vertical coupled structure applied to a millimeter-wave microstrip antenna. The vertical coupled structure comprises microstrip patch antennae, a bottom-layer medium chip substrate, a substrate cavity forming structure, a grounding plate with a gap, a top-layer chip substrate and a coplanar waveguide adapter microstrip feeder line. The microstrip patch antennae are arranged on the bottom sides of the bottom-layer medium chip substrate and the top-layer chip substrate. The substrate cavity forming structure is formed by forming a cavity in the bottom-layer medium chip substrate. The coupling caliber of the gap is located between a bottom-layer medium chip and a top-layer chip. The coplanar waveguide adapter microstrip feeder line is arranged on the upper surface of the top-layer chip substrate. The interlayer vertical interconnection problem of the antenna and a radio-frequency circuit when working frequency is within a millimeter-wave frequency range can be solved by means of the vertical coupled structure. The vertical coupled structure has the advantages of being free of weld points and parasitic radiation and capable of obtaining an even radiation pattern, overcoming the adverse influence brought by a traditional single feed mode and design limitations and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com