Patents
Literature
4182results about "Radio relay systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
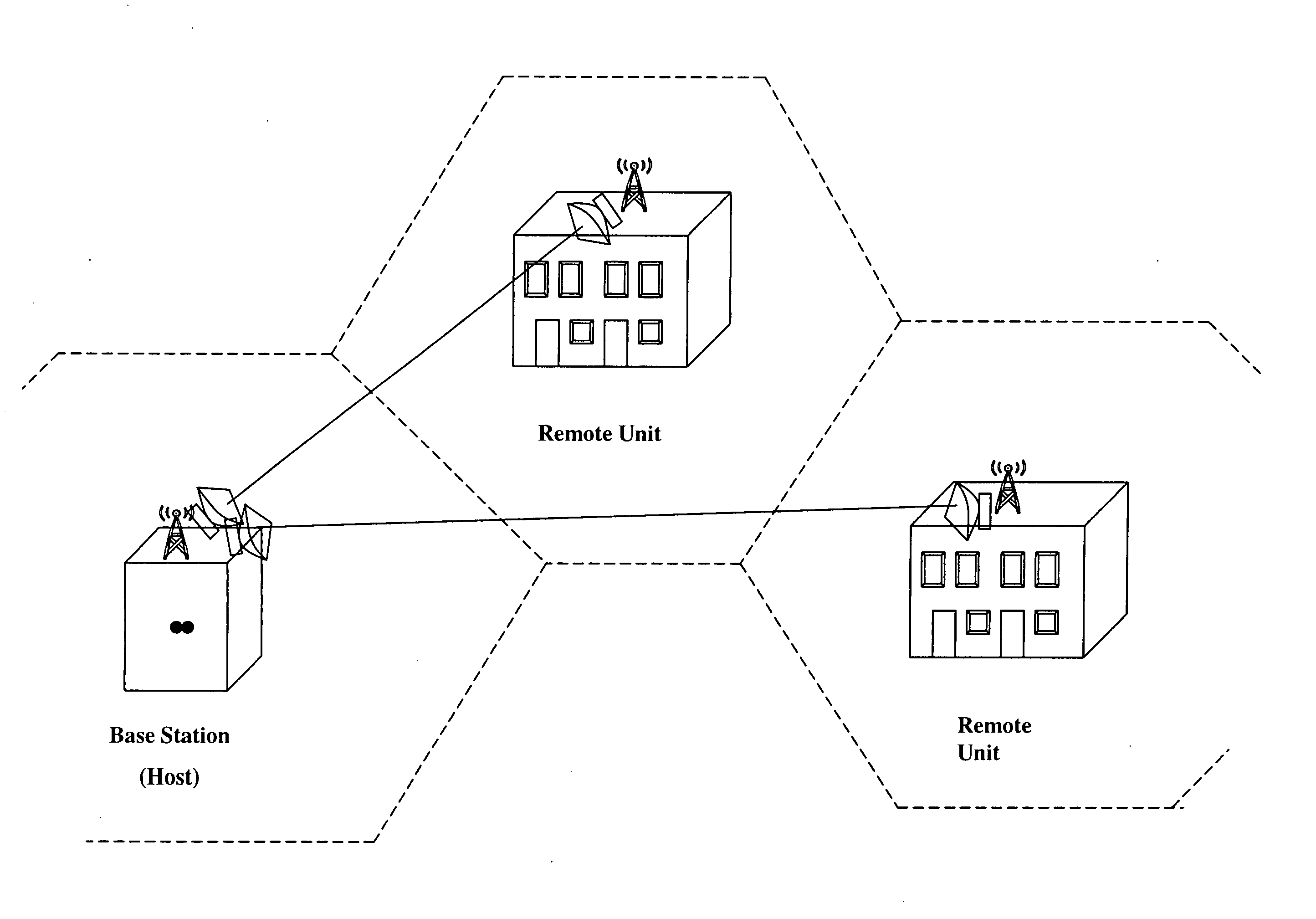
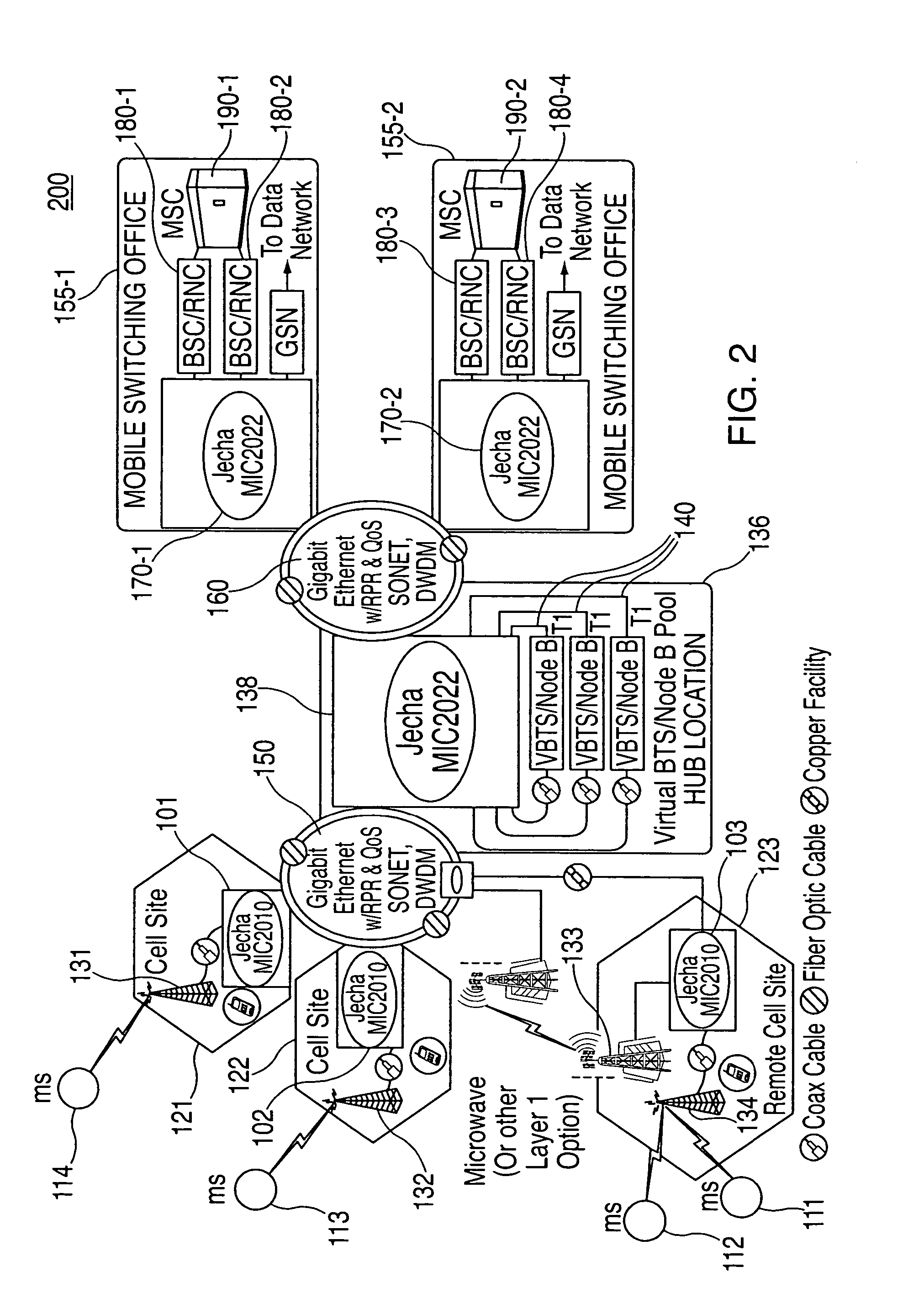
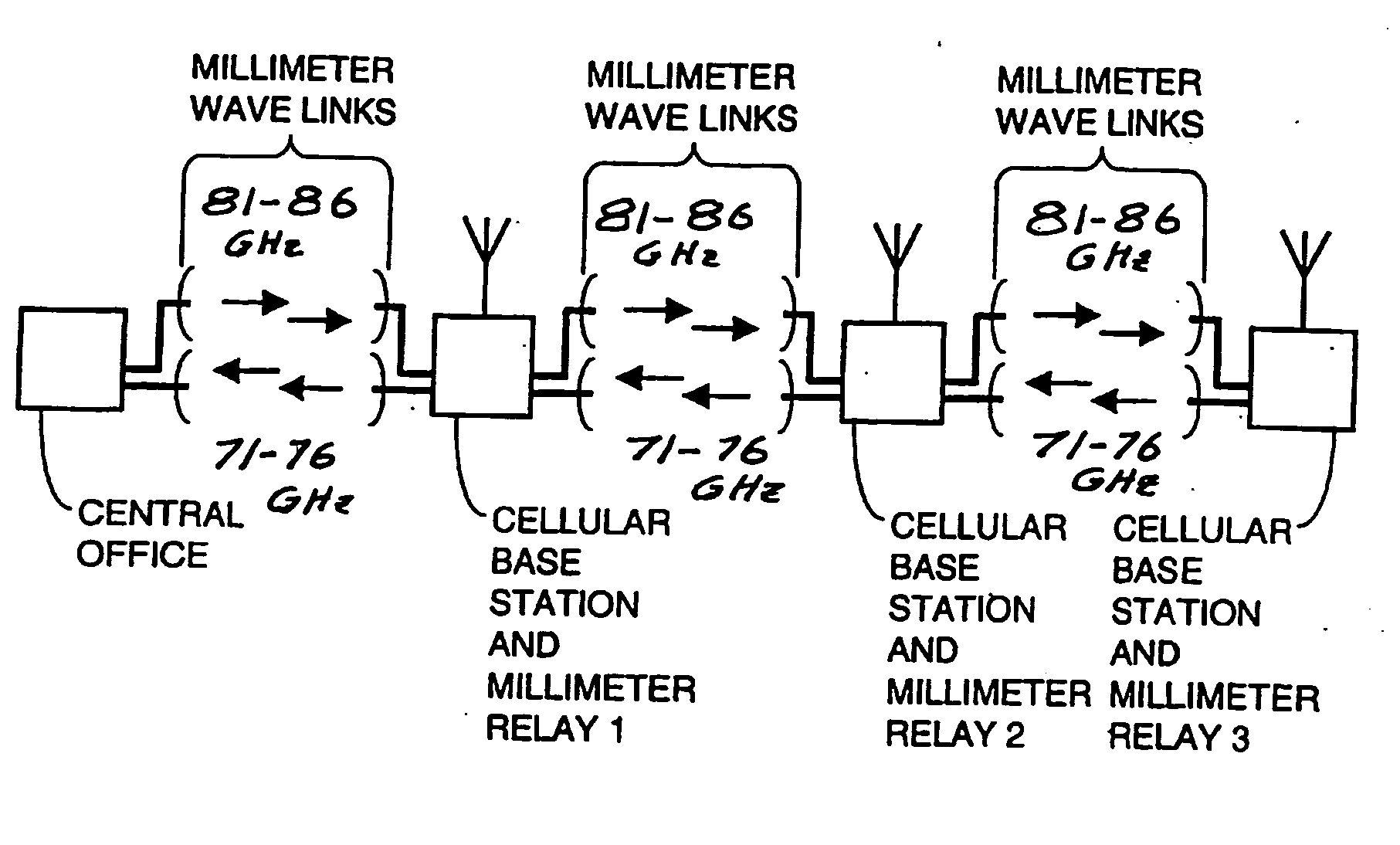
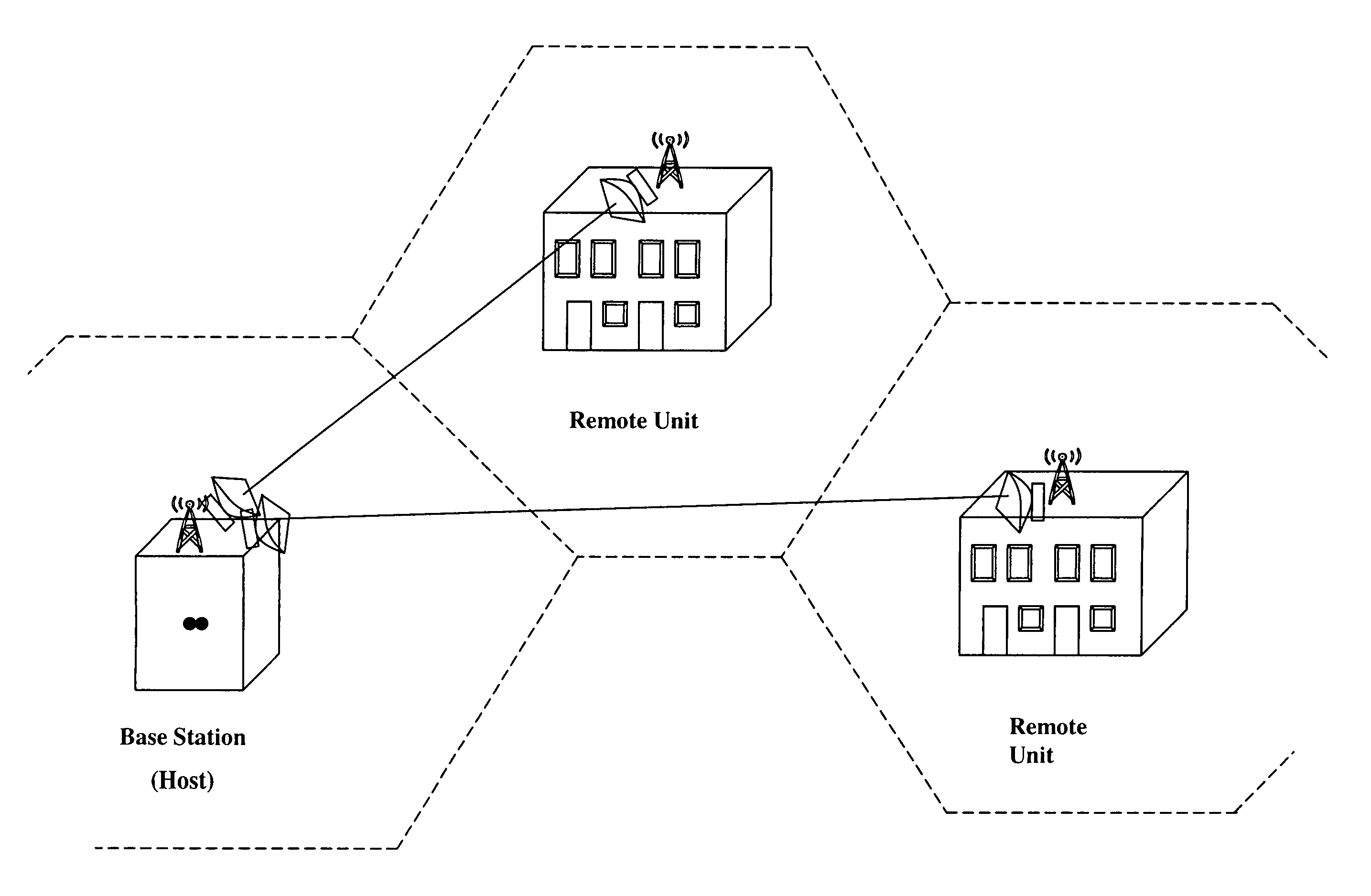
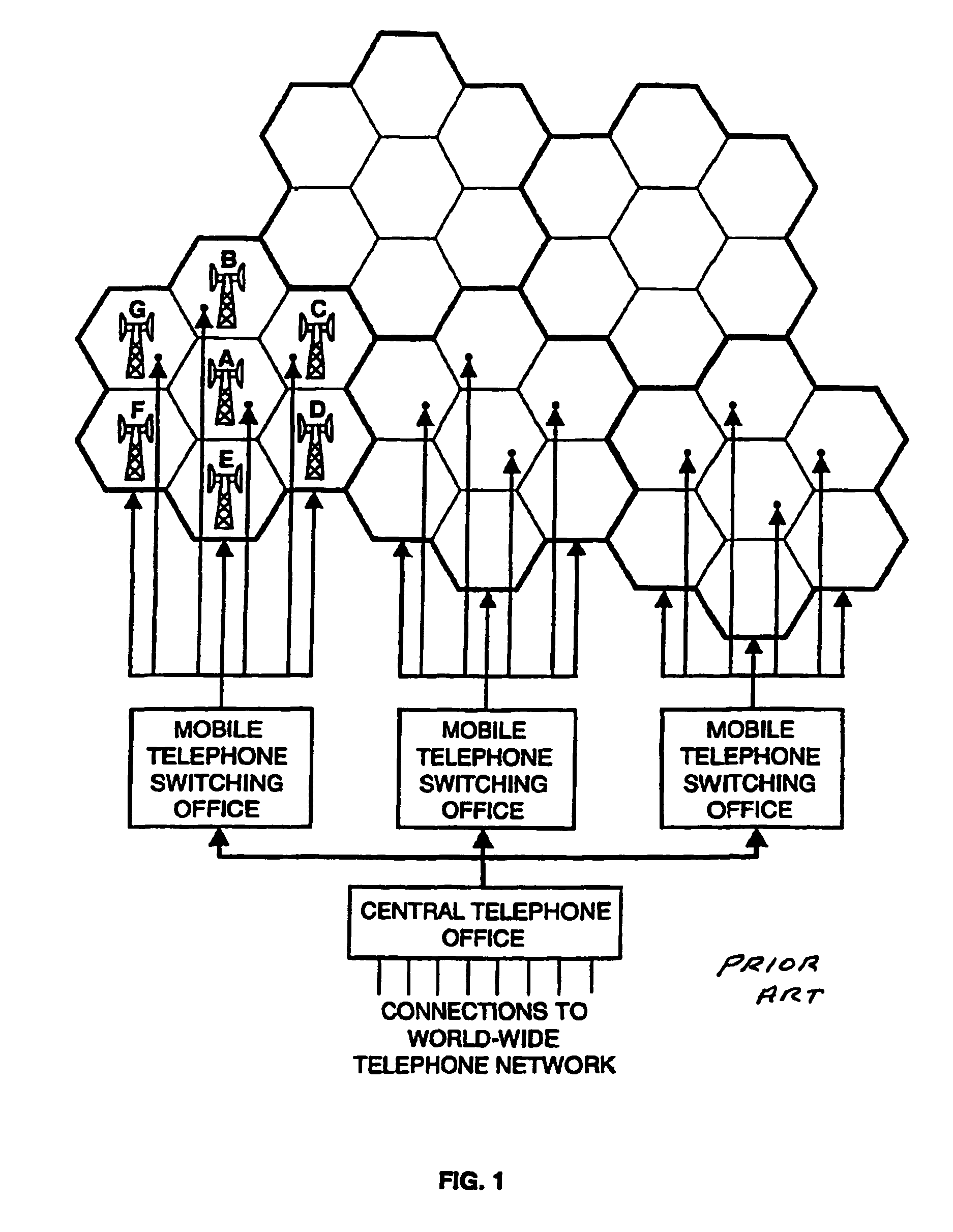
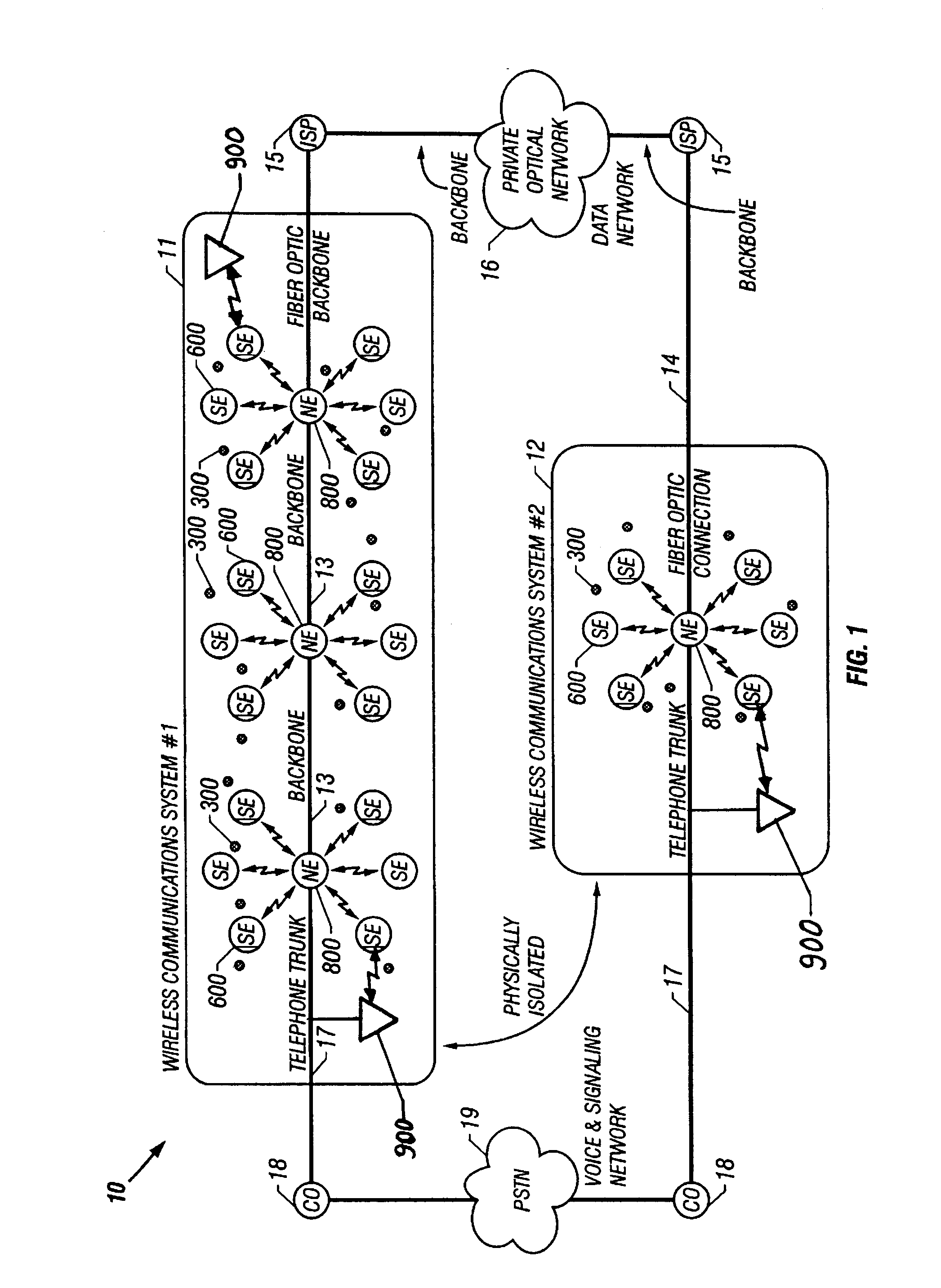
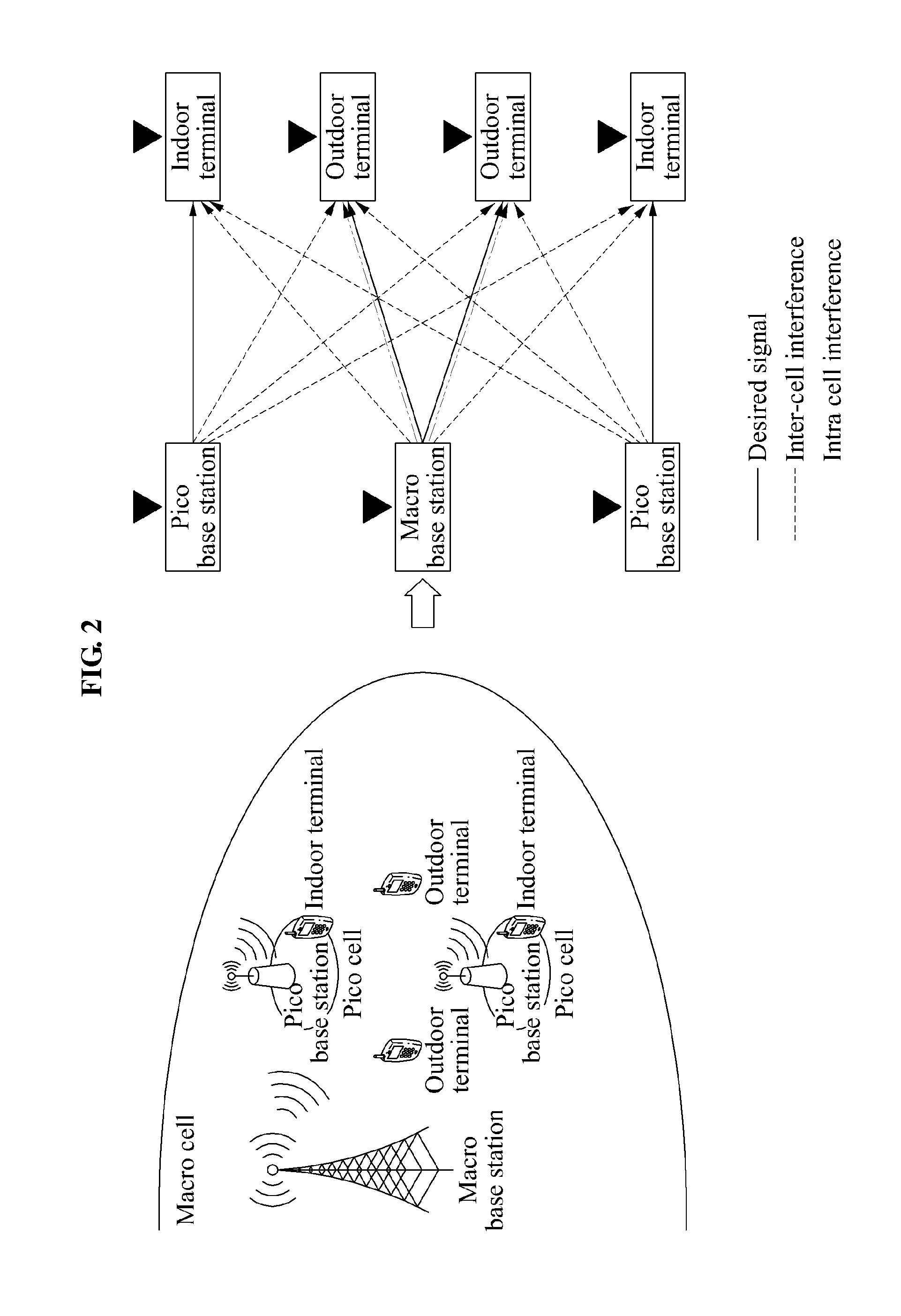
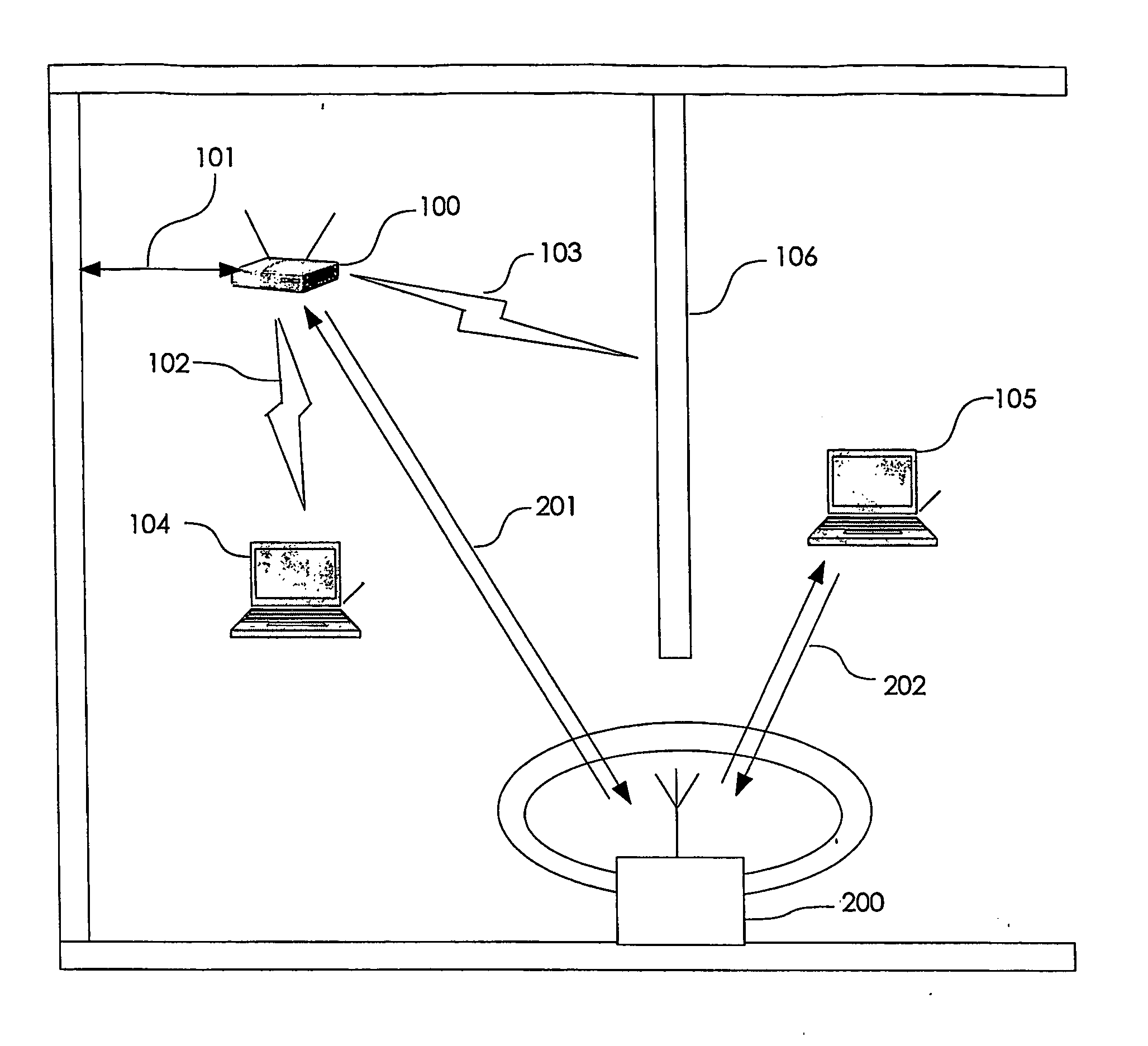
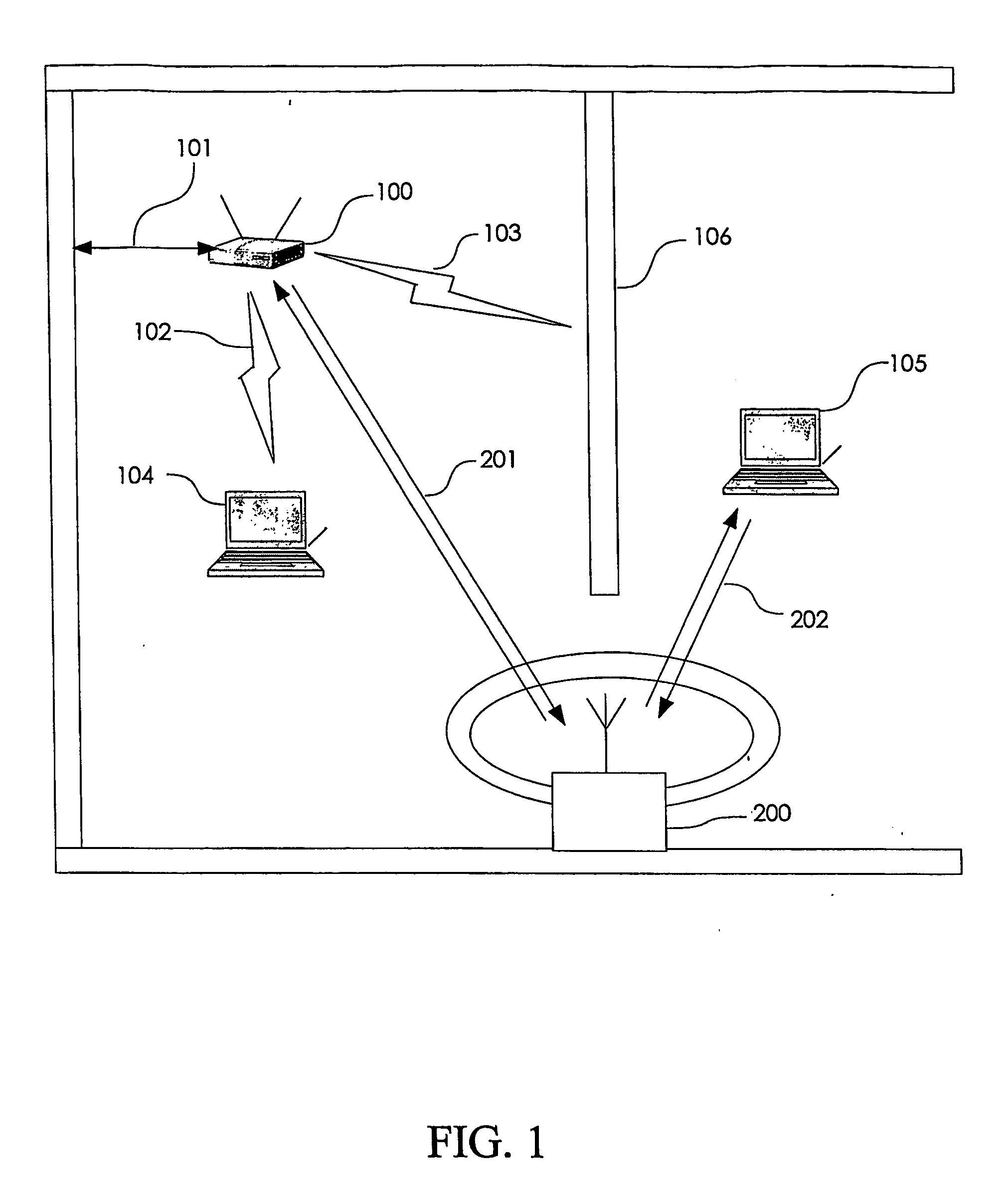
Cellular systems with distributed antennas
InactiveUS20090258652A1Efficient use ofIncrease data rateNetwork topologiesInformation formatWireless transceiverTransceiver
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations, each including at least transport management equipment and broadband equipment, at least one of which supports at least remote cellular station including RF equipment for communication with users of cellular devices. The system includes at lease one wireless narrow beam communication link operating at millimeter wave frequencies in excess of 60 GHz connecting a remote cellular station with a cellular base station equipped with broad band conversion electronic equipment and transport management equipment. In preferred embodiment the communication system includes a large number of remote cellular stations with each remote cellular station serving a separate communication cell. Each remote cellular station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a narrow beam millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another remote cellular station or a millimeter wave transceiver at a base station.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
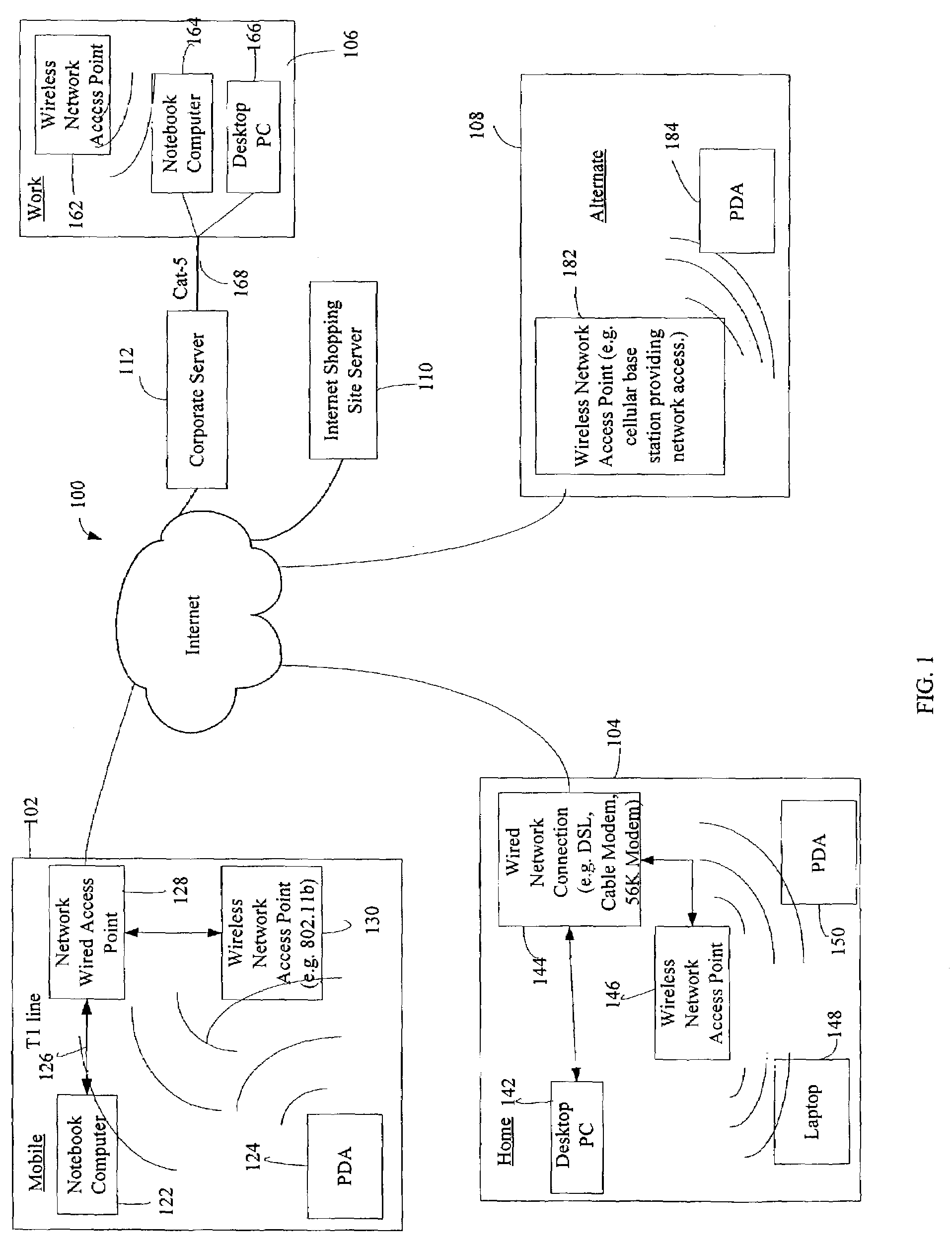
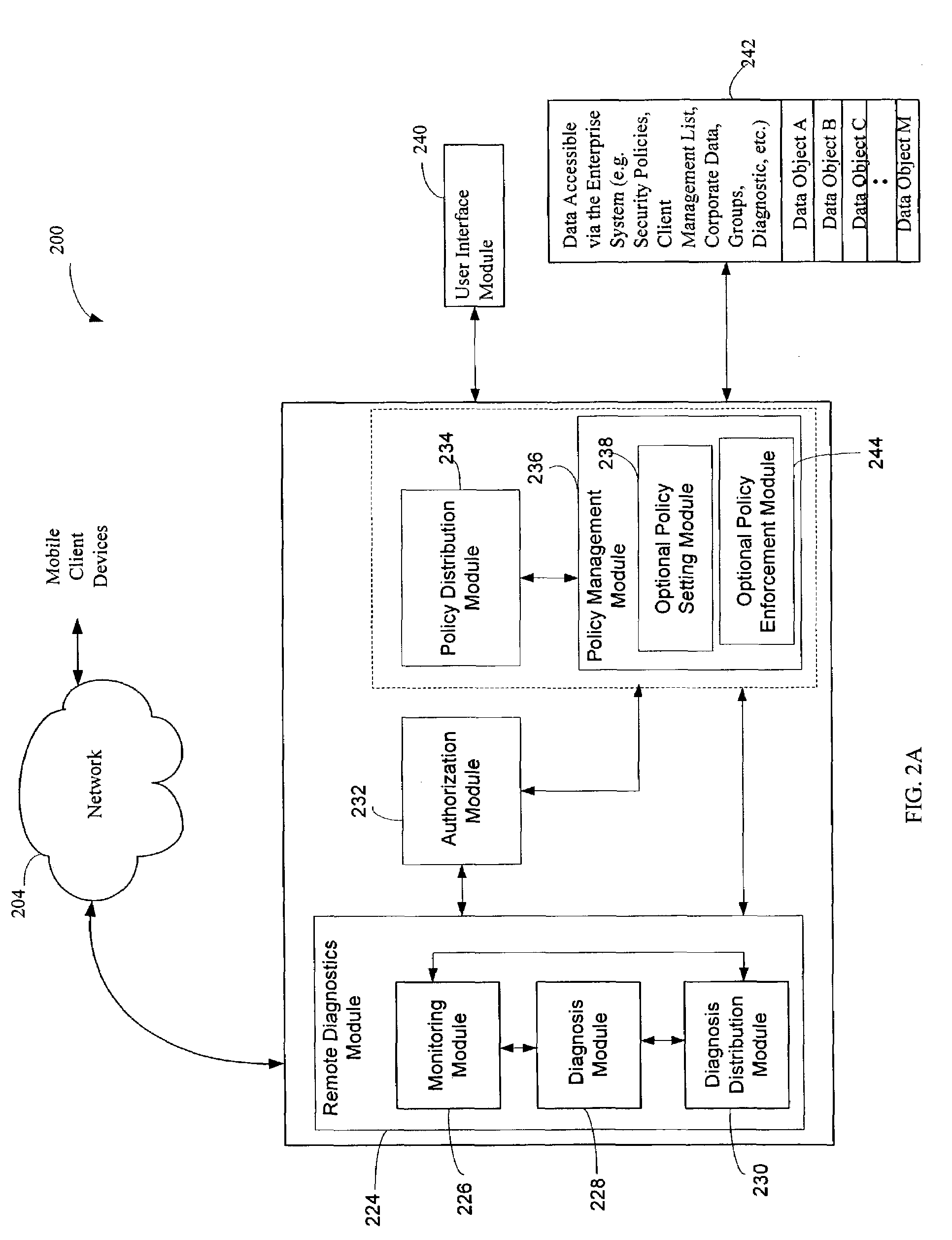
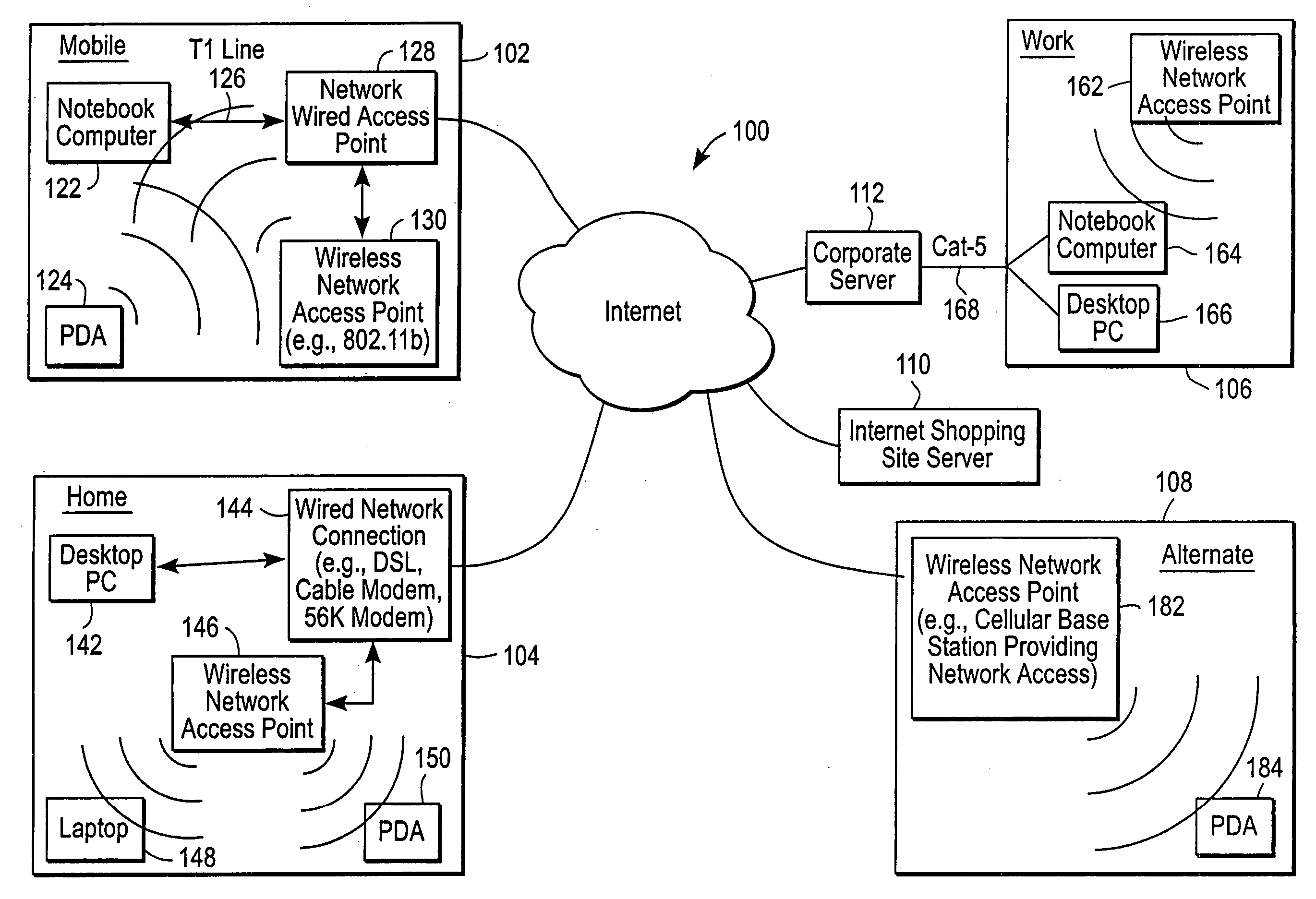
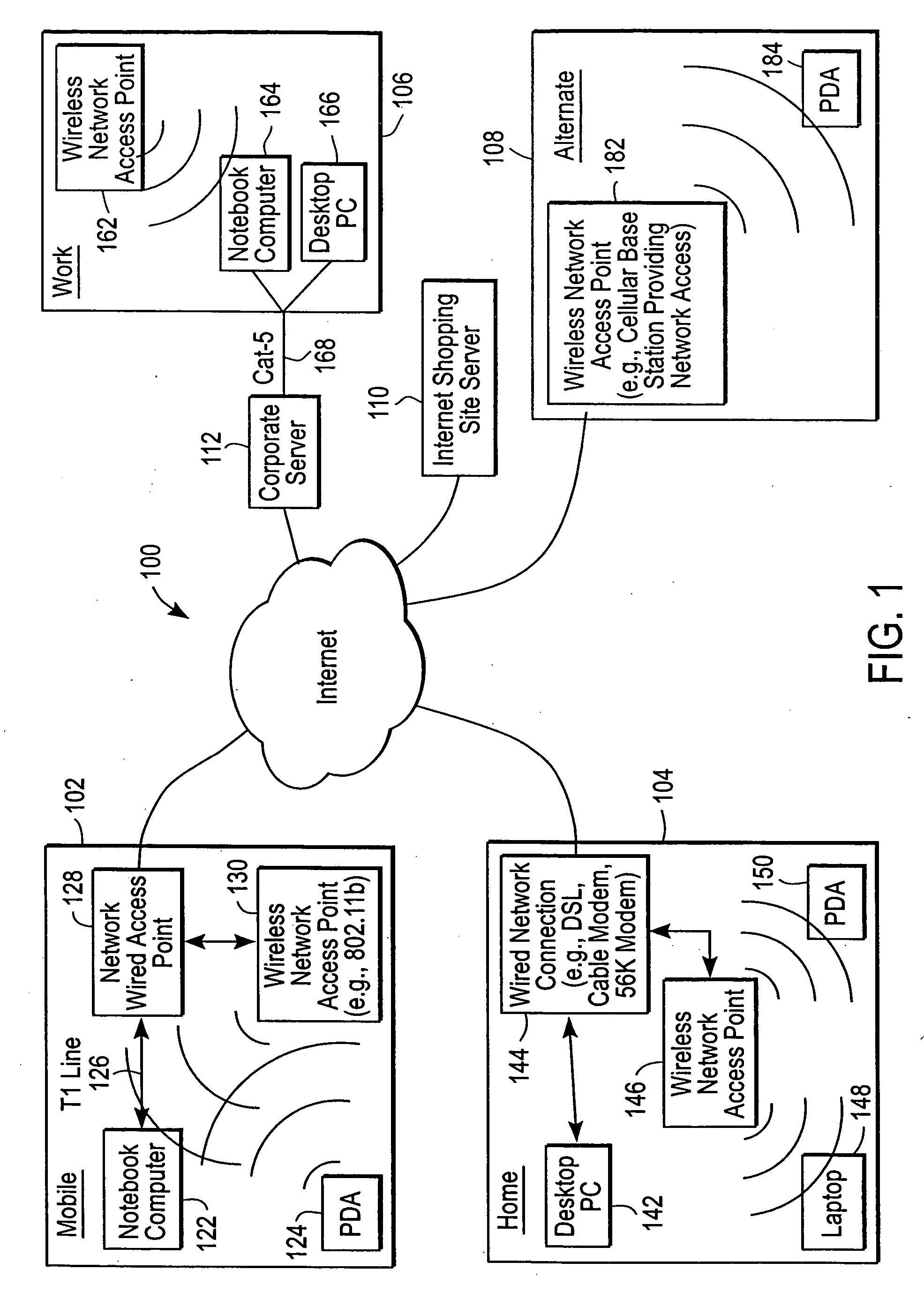
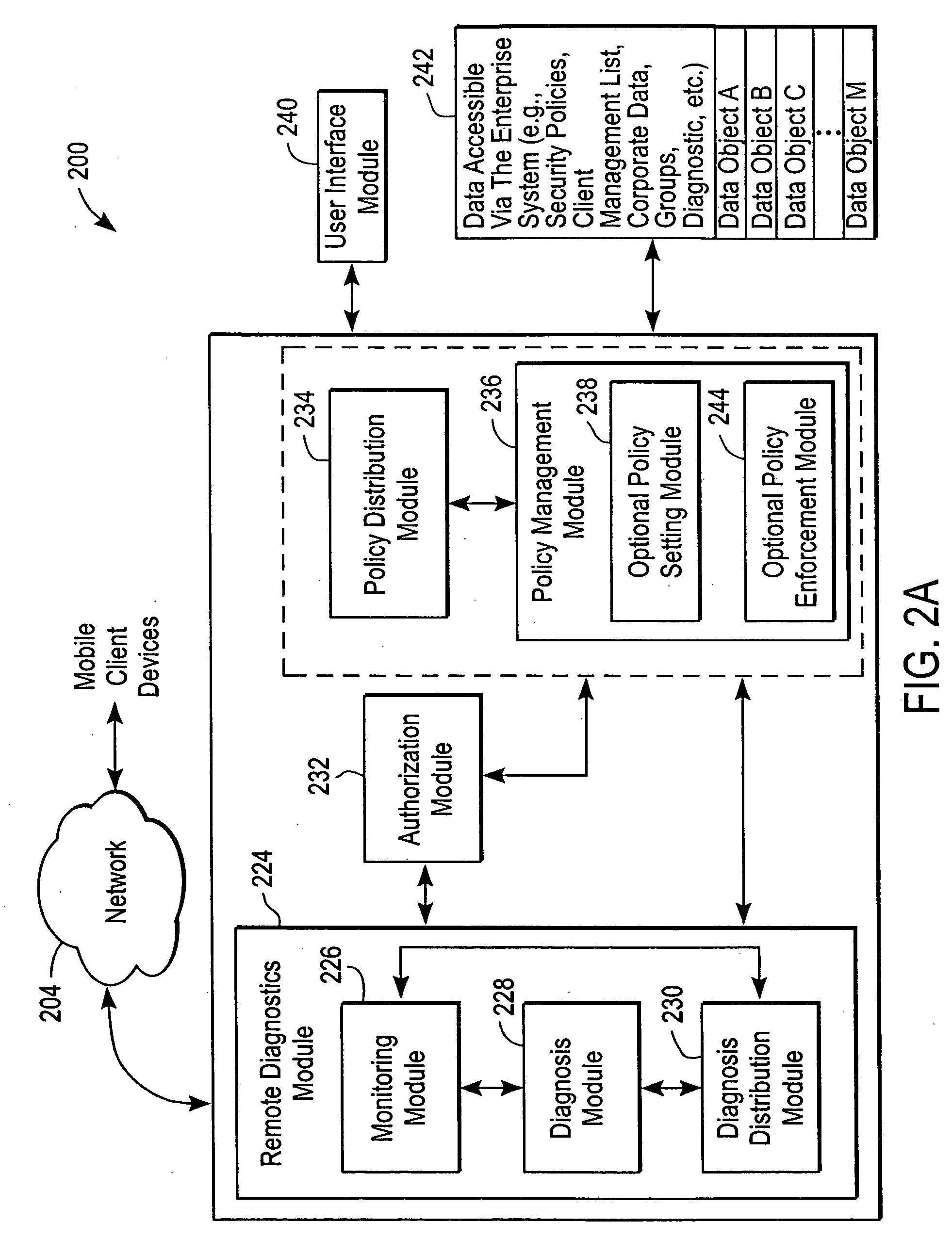
Administration of protection of data accessible by a mobile device
The administration of protection of data on a client mobile computing device by a server computer system such as within an enterprise network or on a separate mobile computing device is described. Security tools are described that provide different security policies to be enforced based on a location associated with a network environment in which a mobile device is operating. Methods for detecting the location of the mobile device are described. Additionally, the security tools may also provide for enforcing different policies based on security features. Examples of security features include the type of connection, wired or wireless, over which data is being transferred, the operation of anti-virus software, or the type of network adapter card. The different security policies provide enforcement mechanisms that may be tailored based upon the detected location and / or active security features associated with the mobile device. Examples of enforcement mechanisms are adaptive port blocking, file hiding and file encryption.
Owner:APPLE INC
Administration of protection of data accessible by a mobile device
ActiveUS20050055578A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsAnti virusEnterprise networking
The protection of data on a client mobile computing device by a server computer system such as within an enterprise network or on a separate mobile computing device is described. Security tools are described that provide different security policies to be enforced based on a location associated with a network environment in which a mobile device is operating. Methods for detecting the location of the mobile device are described. Additionally, the security tools may also provide for enforcing different policies based on security features. Examples of security features include the type of connection, wired or wireless, over which data is being transferred, the operation of anti-virus software, or the type of network adapter card. The different security policies provide enforcement mechanisms that may be tailored based upon the detected location and / or active security features associated with the mobile device. Examples of enforcement mechanisms are adaptive port blocking, file hiding and file encryption.
Owner:APPLE INC
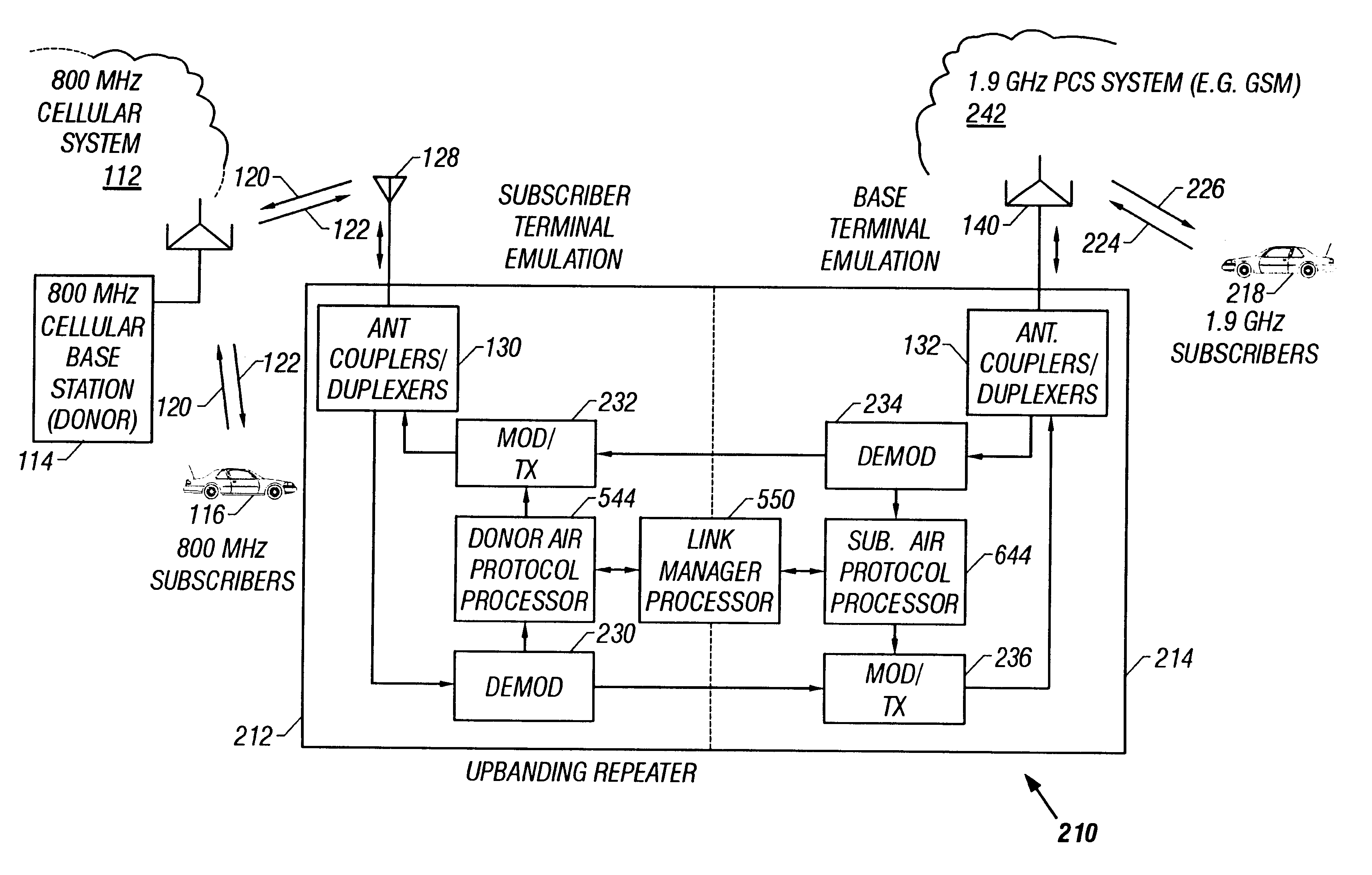
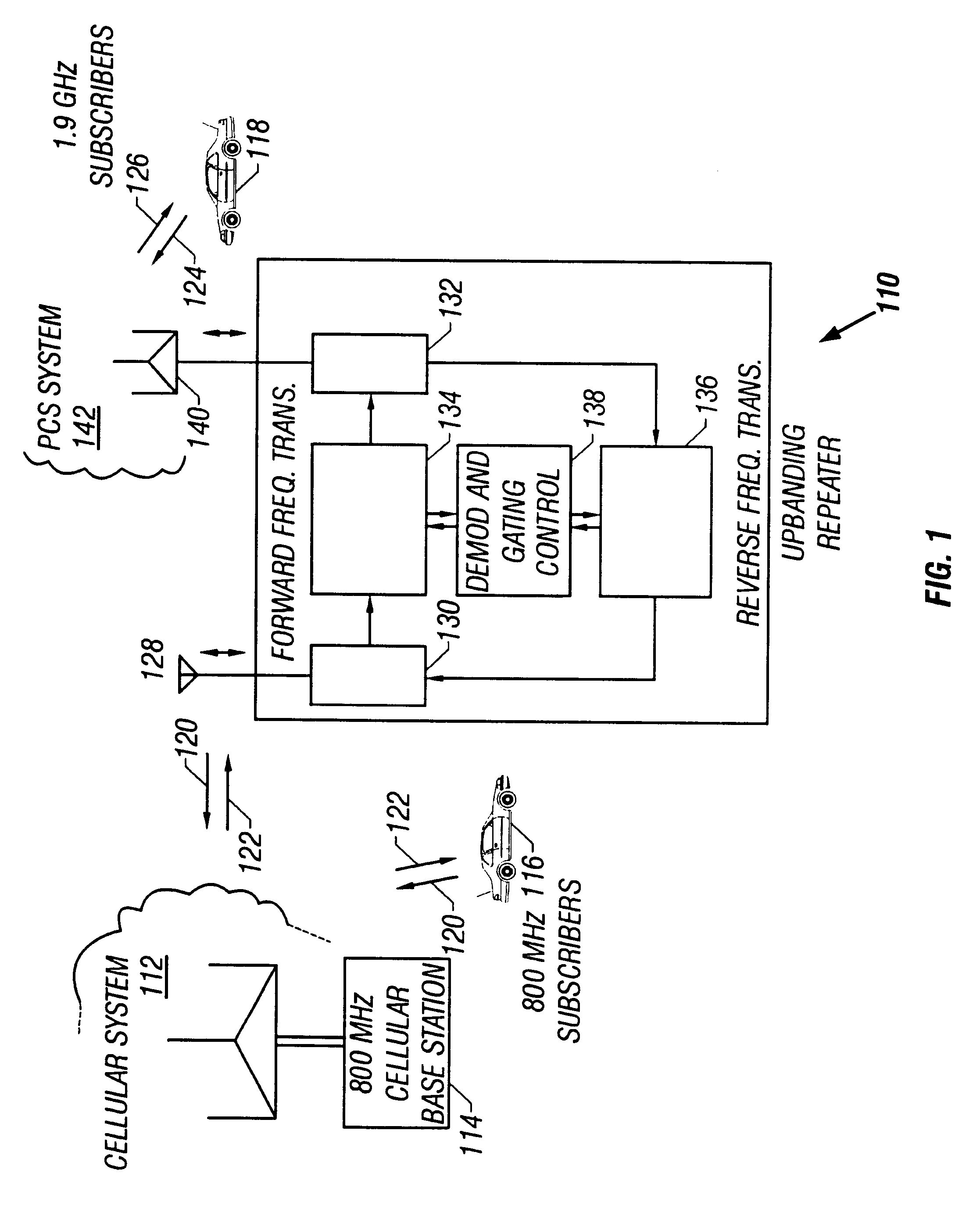
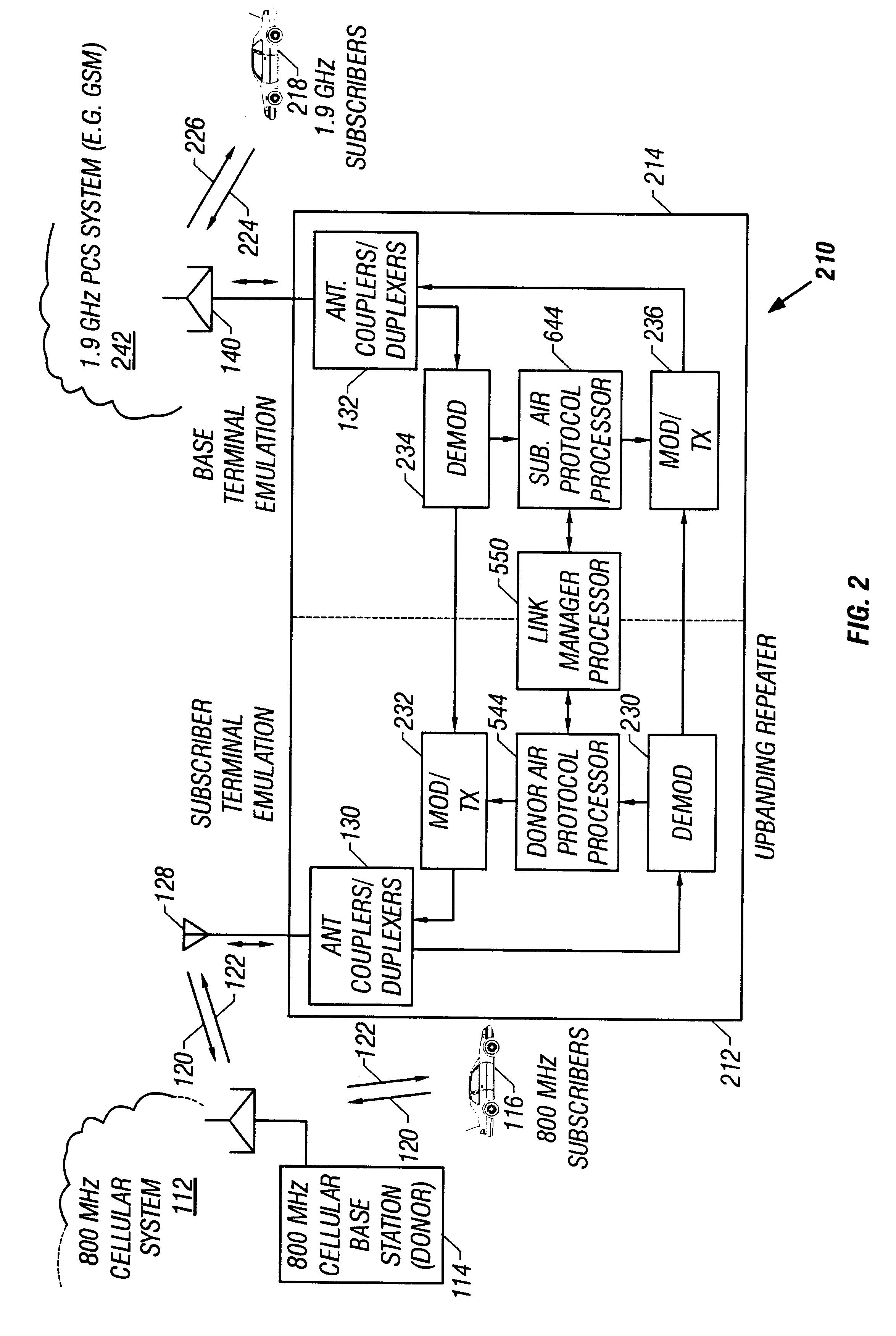
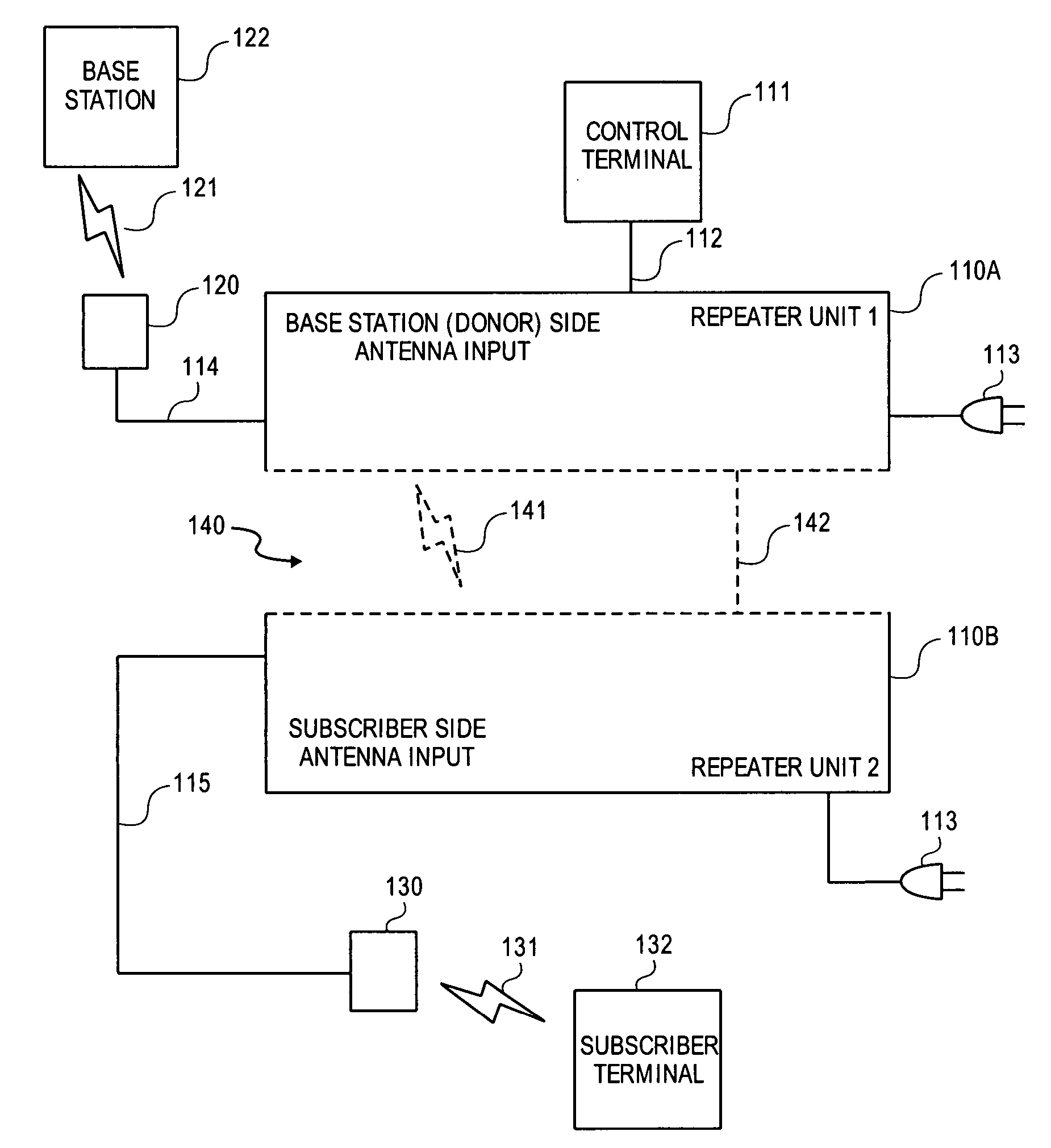
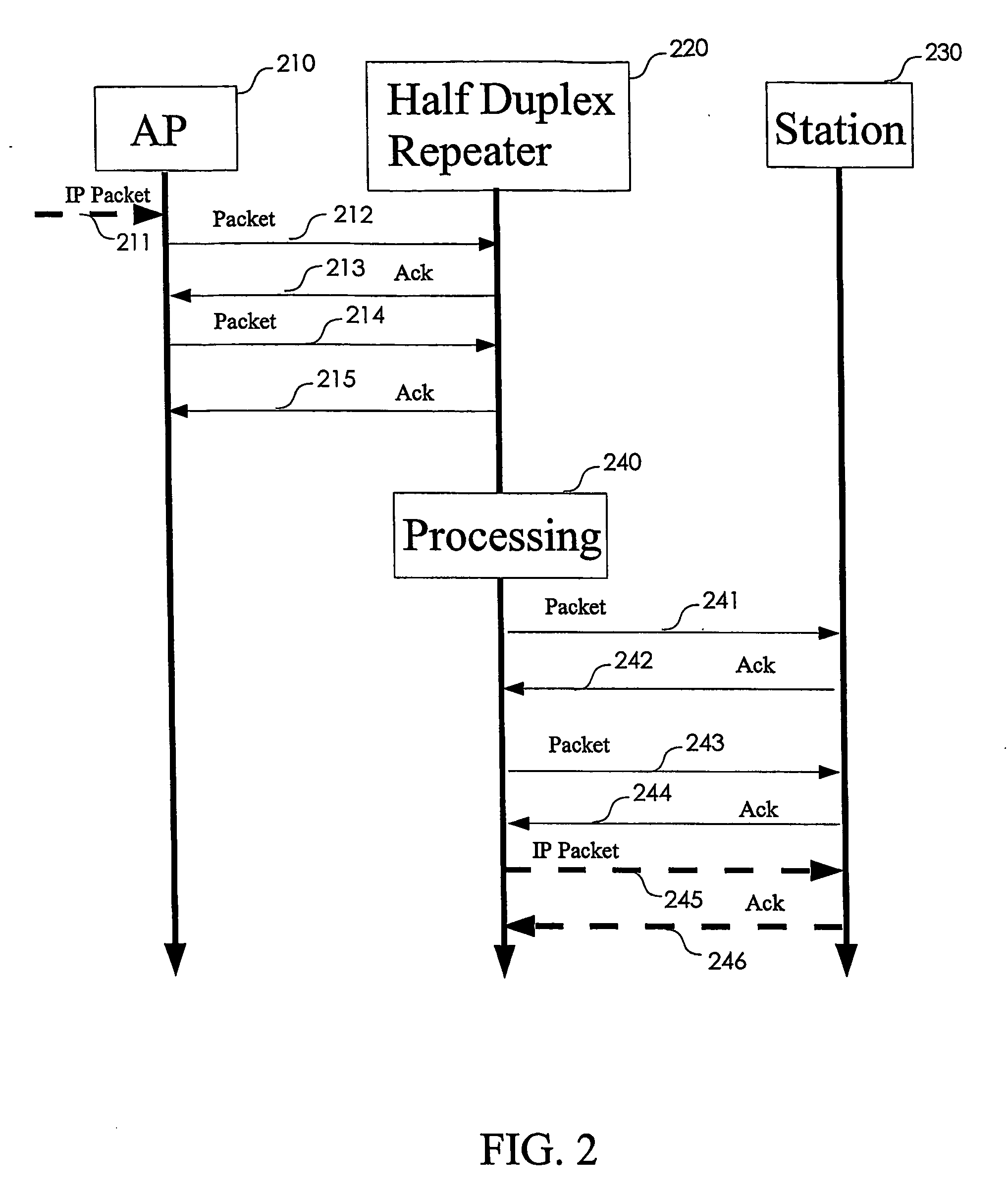
Band-changing repeater with protocol or format conversion
InactiveUS6404775B1Facilitate communicationInterference minimizationFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemOperating frequency
A repeater allows terminals of a first communications system, employing a first air protocol or radio interface, to communicate with terminals of a second communications system, employing a second air protocol or radio interface different from the first. Where the first and second air protocols differ only in operating frequency, but are otherwise compatible, the repeater may linearly translate signals from the first operating frequency to the second operating frequency, and vice versa, without demodulating and remodulating the signals. Where the air protocols differ in other ways, the repeater receives and demodulates signals from the first system, converts the signals to a common format, and remodulates and retransmits the signals according to the second air protocol (and vice versa), in the same frequency bands or in different frequency bands. The repeater translates control and signalling information transmitted in compliance with one air protocol to a format which complies with the other air protocol and has the same or equivalent effect. For each of the two communications system, the repeater emulates the functions of a terminal in that communications system, so that corresponding terminals in that system may communicate transparently with the repeater. The repeater provides a connection between the two emulated terminals, thereby allowing a terminal of the first system to use the repeater to communicate with an otherwise incompatible terminal of the second system.
Owner:ALLEN TELECOM LLC
Enhanced physical layer repeater for operation in WiMAX systems
A method and repeater are described for repeating using a time division duplex (TDD) radio protocol. A signal is transmitted from a first station to a second station using a downlink and an uplink. The signal can be detected on the uplink or the downlink. The repeater can synchronize to time intervals associated with the detected signal that are measured during an observation period. The signal can be retransmitted from the second station to the first station if the signal is detected on the uplink and re-transmitted from the first station to the second station if the signal is detected on the downlink. A gain value associated with the downlink can be used to establish a gain value associated with the uplink.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Monitoring and tracking of assets by utilizing wireless communications
InactiveUS6972682B2Minimal requirementFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital data processing detailsCommunications systemComputer science
Systems, devices, methods, and programs disclosed herein provide a solution for monitoring and tracking assets by utilizing wireless communications. A representative system for monitoring assets includes a remote monitoring station (RMS) and a network of identification (ID) tags. Each ID tag is coupled to an asset and is configured to wirelessly communicate with other ID tags in the network within a predetermined proximity. Each tag is also configured to relay communications from other ID tags so that a communication path is established between the RMS and any ID tag in the network, either directly or via other ID tags.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
System and method for optimizing network capacity in a cellular wireless network
InactiveUS20050007993A1Easy to adaptNetwork traffic/resource managementPower distribution line transmissionQuality of serviceFiber
Owner:CHAMBERS MAHDI +1
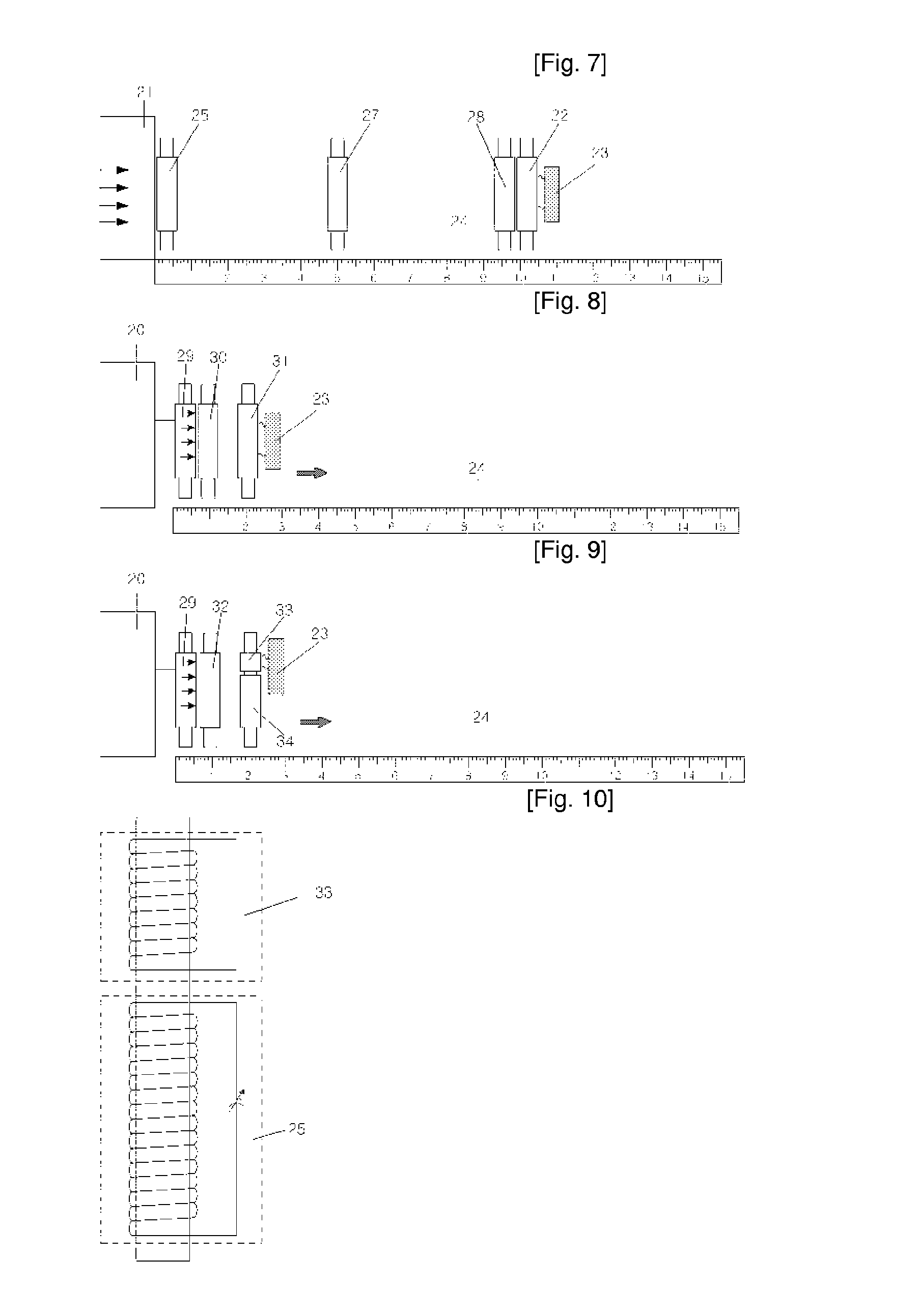
Amplification Relay Device of Electromagnetic Wave and a Radio Electric Power Conversion Apparatus Using the Above Device
ActiveUS20080266748A1Improve throughputMultiple-port networksNear-field transmissionElectric power transmissionImpedance matching
The present invention provides an amplifying repeater, which is constructed in such a manner that a ferrite core is inserted into a coil with a pre-determined number of winds to increase an induced electromotive force caused by an increase in flux linkage using a time-varying magnetic field of electromagnetic waves at a position distant from various electromagnetic wave generating sources by a predetermined distance and the induction coil and a variable condenser for inducing resonance are connected to each other to increase current while reducing a resistant component existing in the induction coil to intensify and amplify the magnetic field of electromagnetic waves. Furthermore, the present invention provides a wireless power conversion charging device using the magnetic field of electromagnetic waves, which is located between an electromagnetic wave generating source transmitter and a receiving coil or attached to the transmitter and receiving coil. The wireless power conversion charging device includes a rectifying diode for rectifying an electromotive force induced in a construction in which a resonance and impedance matching variable condenser is connected to a coil in series or in parallel in order to transmit maximum induced power to a charging battery that is a load using electromagnetic waves amplified by the amplifying repeater, and a smoothing condenser for smoothing the rectified voltage. Accordingly, charging power required for various small power electronic devices can be provided and power can be supplied to various loads.
Owner:JC PROTEK +1
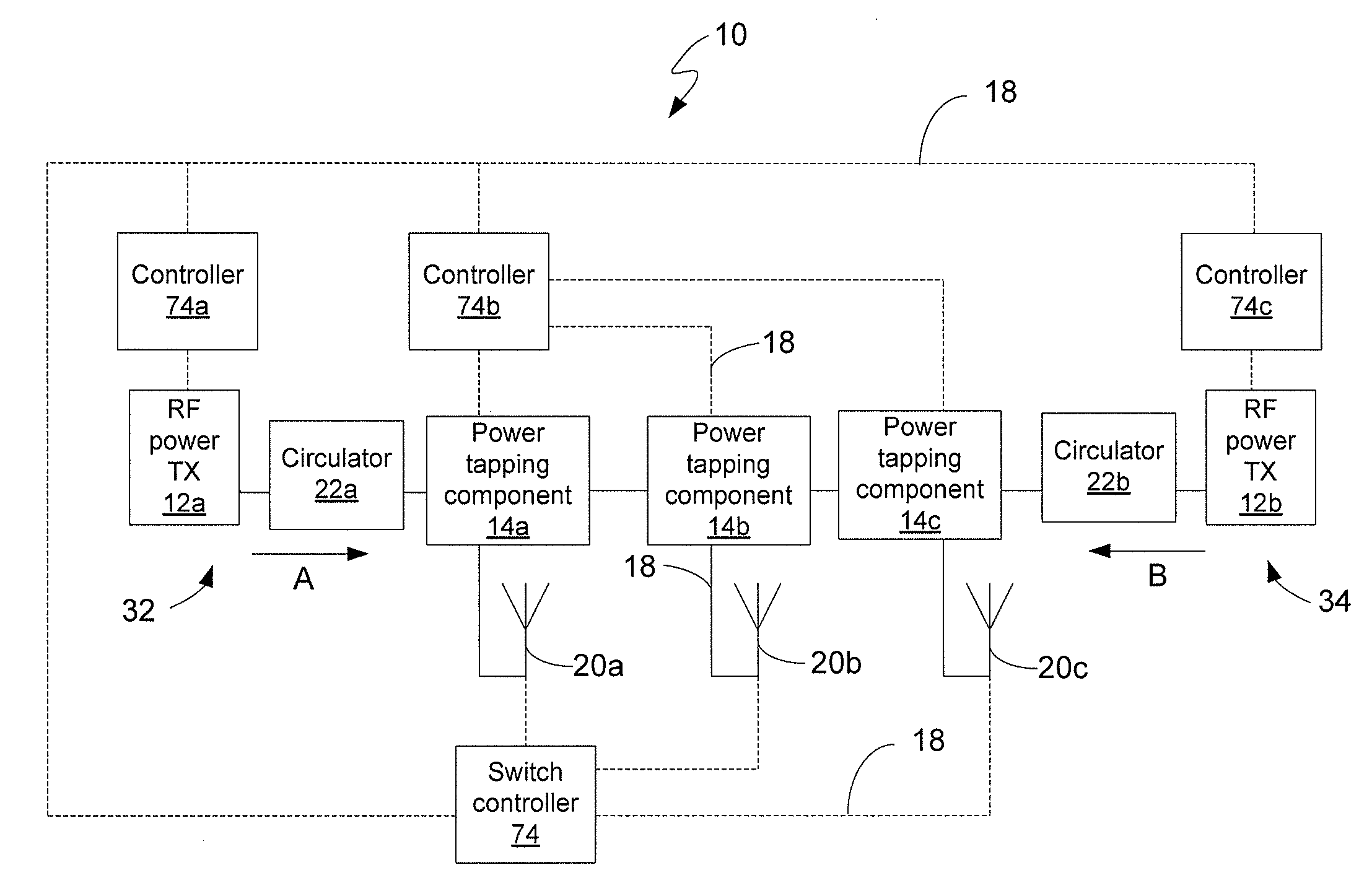
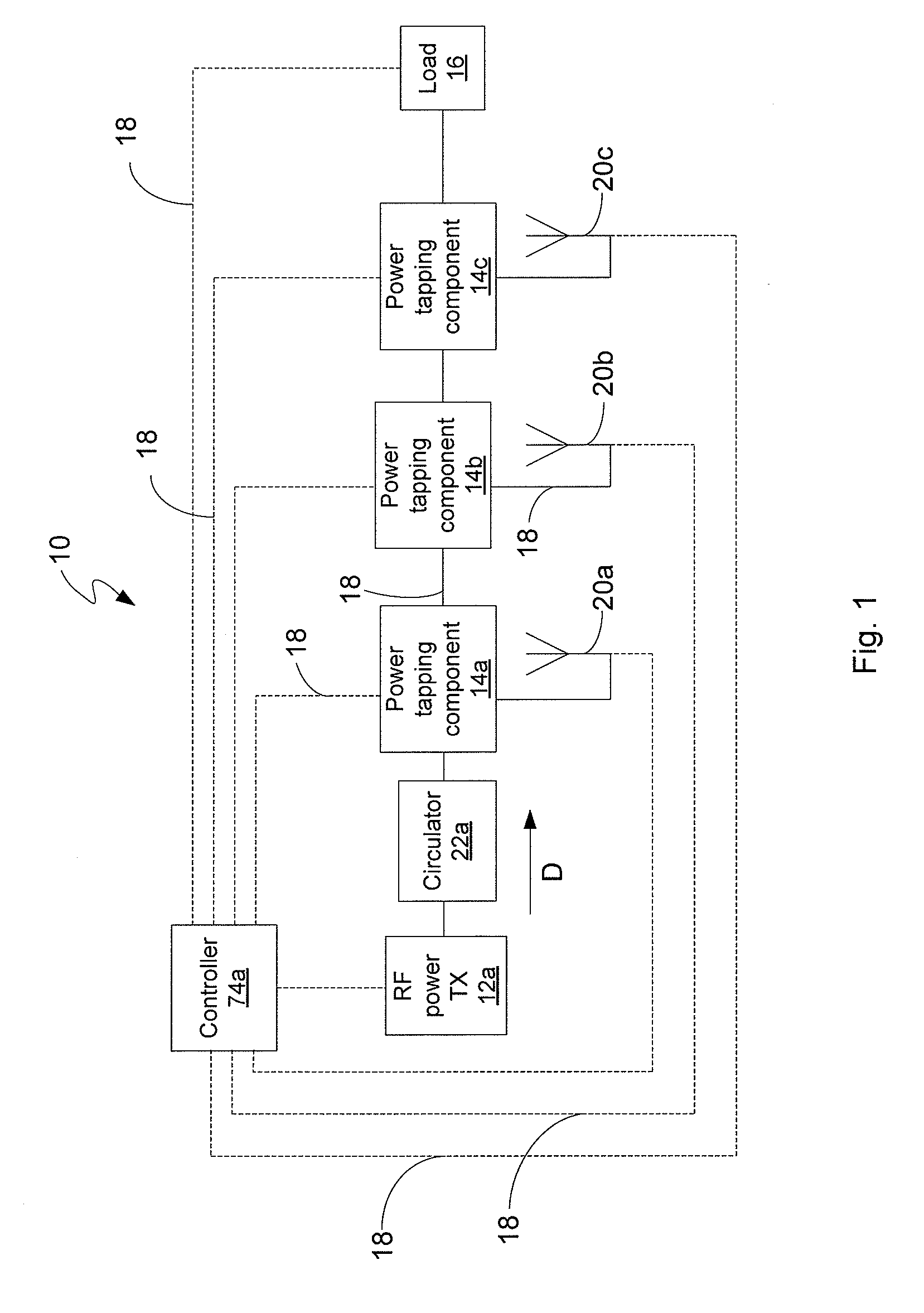
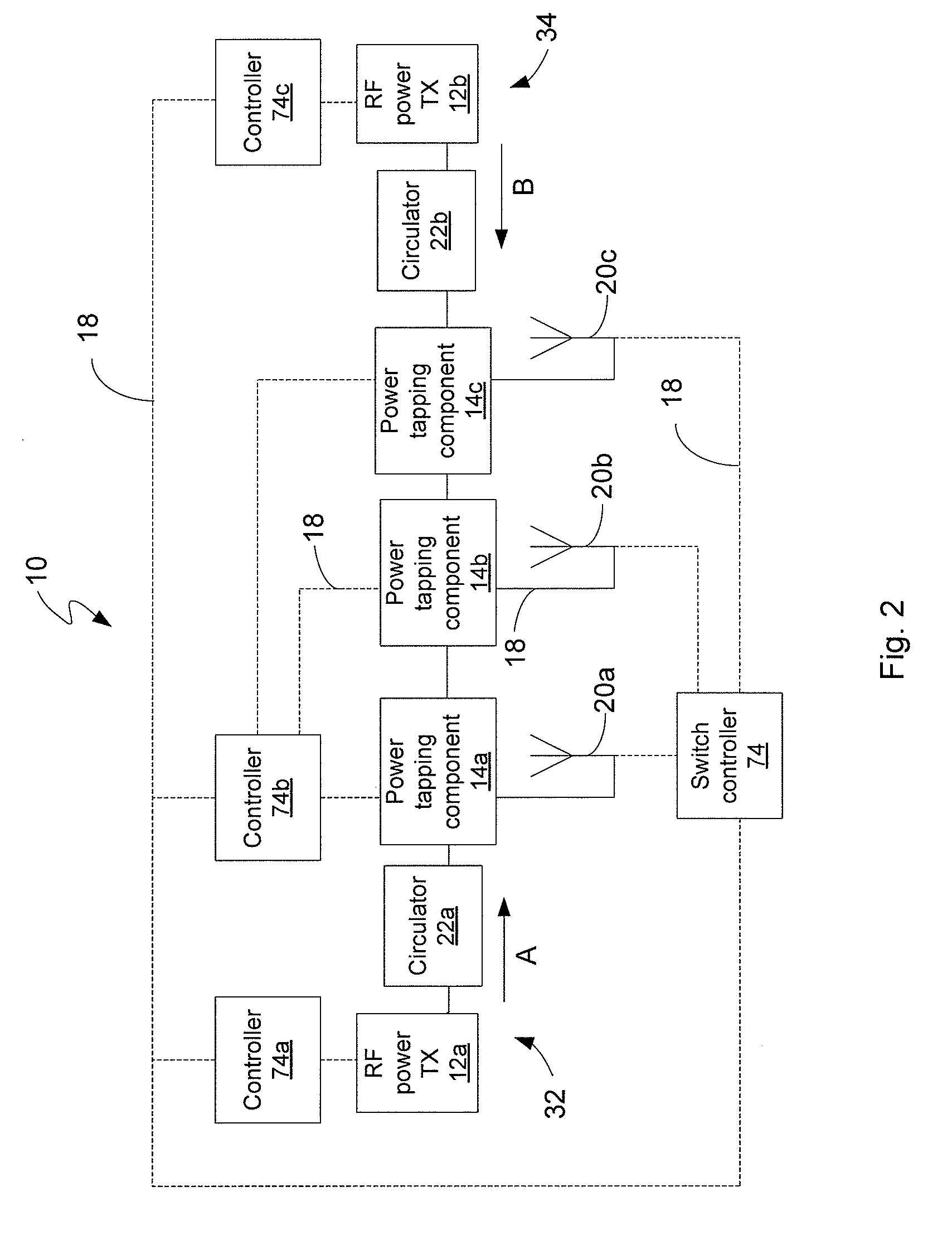
RF power transmission network and method
ActiveUS7639994B2Improve scalabilityIncrease the lengthResonant long antennasRepeater circuitsElectric powerRadio frequency power transmission
Disclosed is an RF power transmission network. The network includes at least one RF power transmitter, at least one power tapping component, and at least one load. The at least one RF power transmitter, the at least one power tapping component, and the at least one load are connected in series. The RF power transmitter sends power through the network. The power is radiated from the network to be received by a device to be charged, re-charged, or directly powered by the power.
Owner:POWERCAST
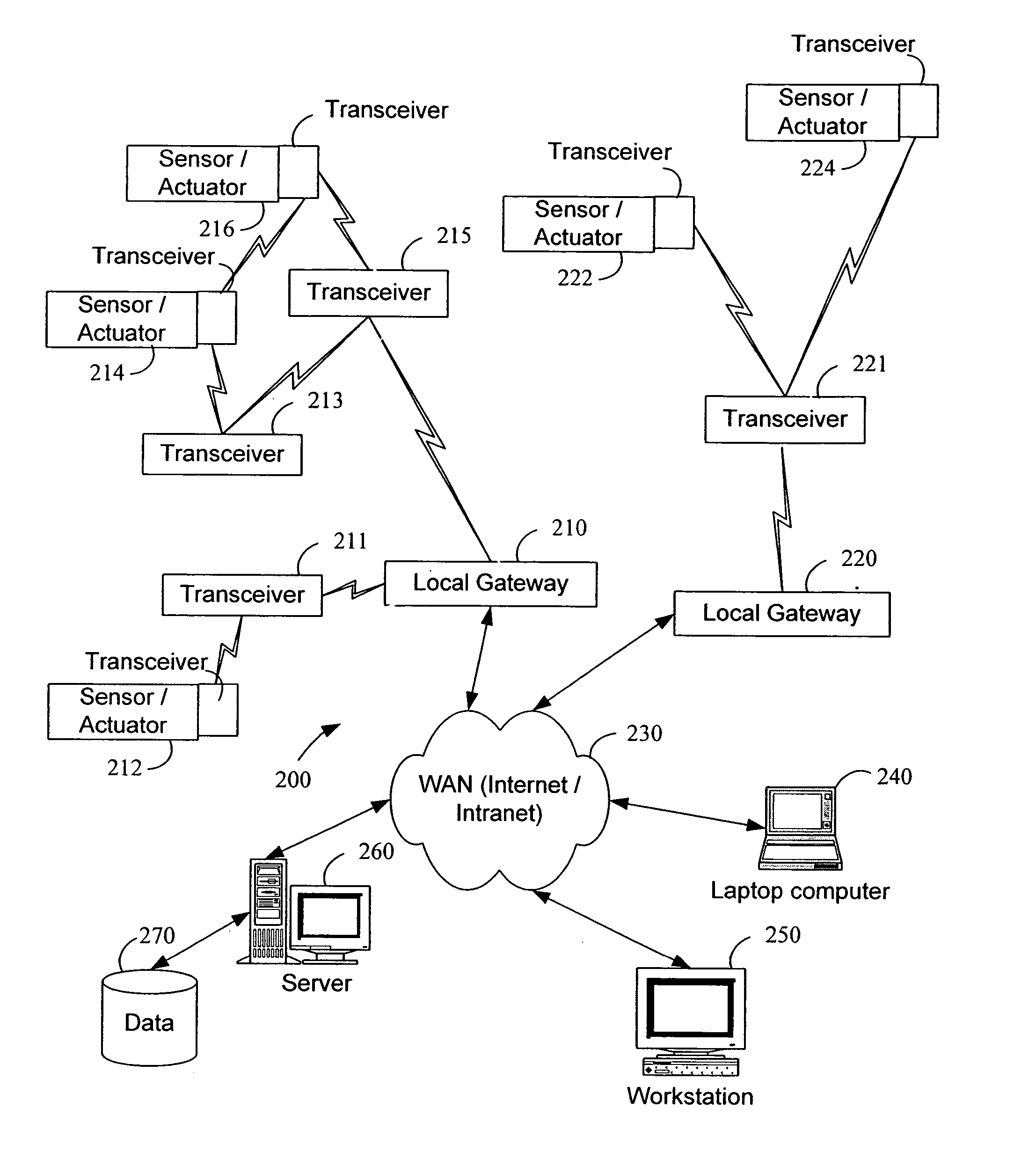
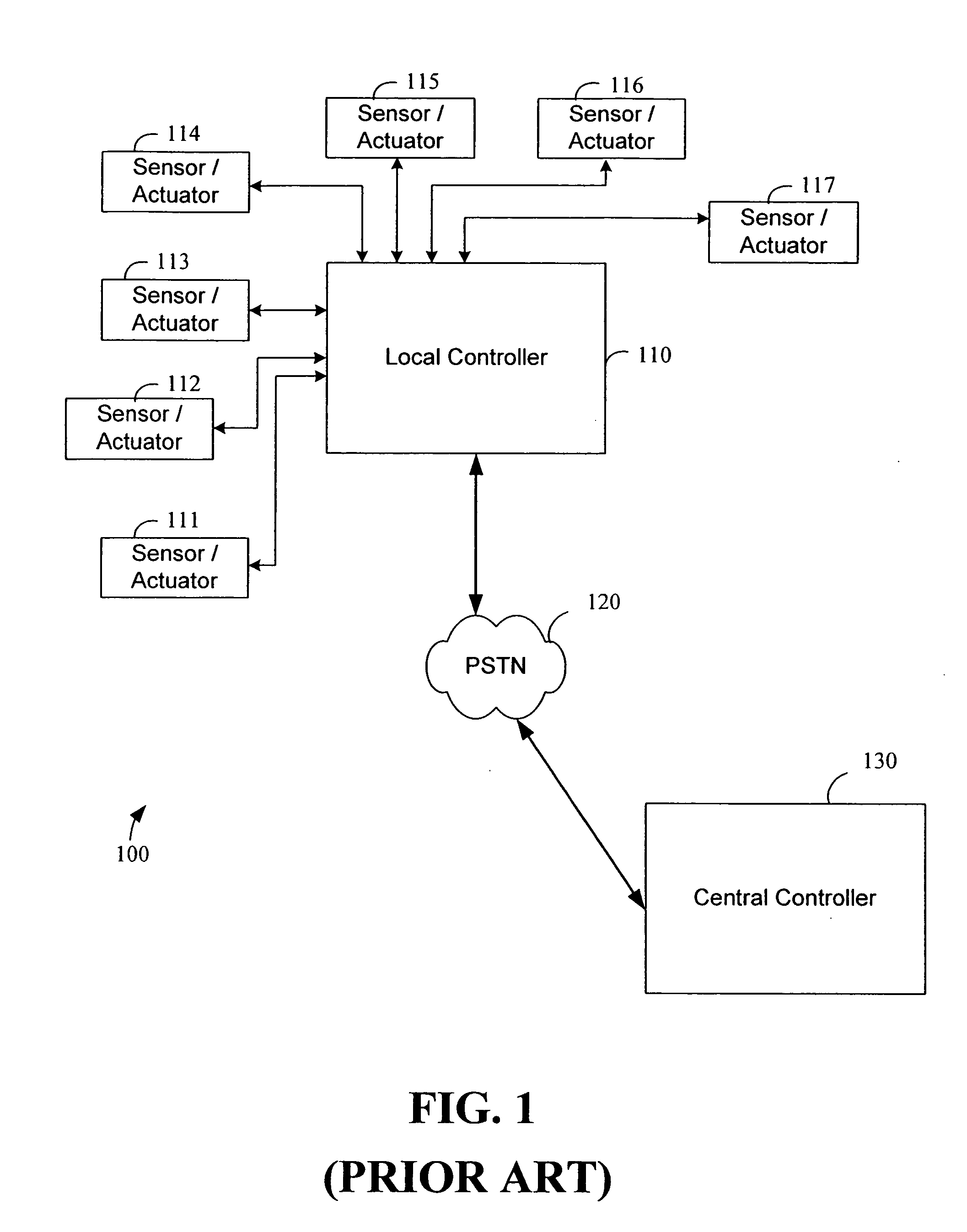
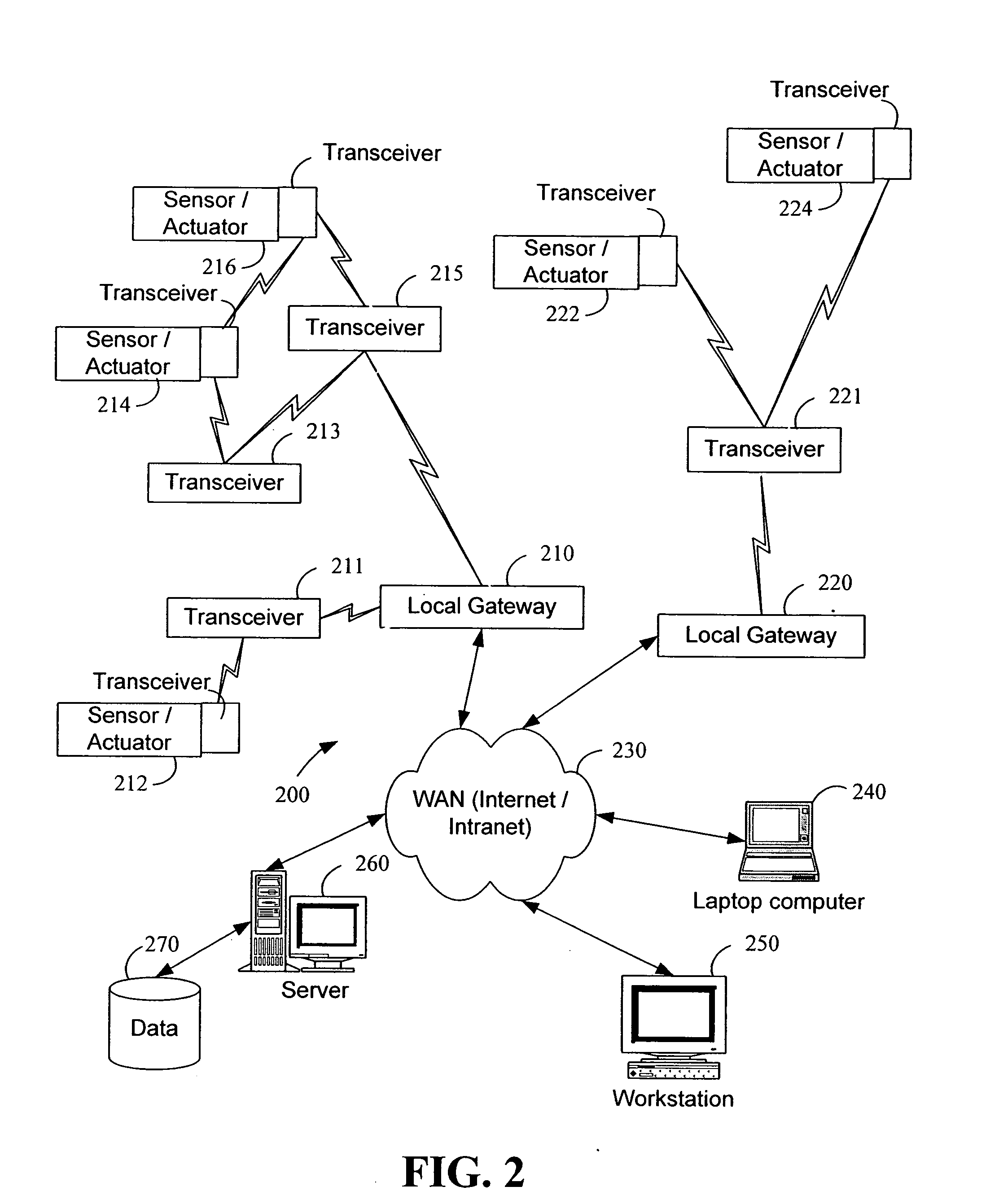
System and method for monitoring and controlling remote devices
InactiveUS20060181406A1Closed feedback loopIntegrated inexpensivelyFrequency-division multiplex detailsRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTransceiverControl signal
The present invention is generally directed to a system for monitoring a variety of environmental and / or other conditions within a defined remotely located region. In accordance with one aspect of the invention, a system is configured to monitor utility meters in a defined area. The system is implemented by using a plurality of wireless transmitters, wherein each wireless transmitter is integrated into a sensor adapted to monitor a particular data input. The system also includes a plurality of transceivers that are dispersed throughout the region at defined locations. The system uses a local gateway to translate and transfer information from the transmitters to a dedicated computer on a network. The dedicated computer, collects, compiles, and stores the data for retrieval upon client demand across the network. The computer further includes means for evaluating the received information and identifying an appropriate control signal, the system further including means for applying the control signal at a designated actuator.
Owner:SIPCO
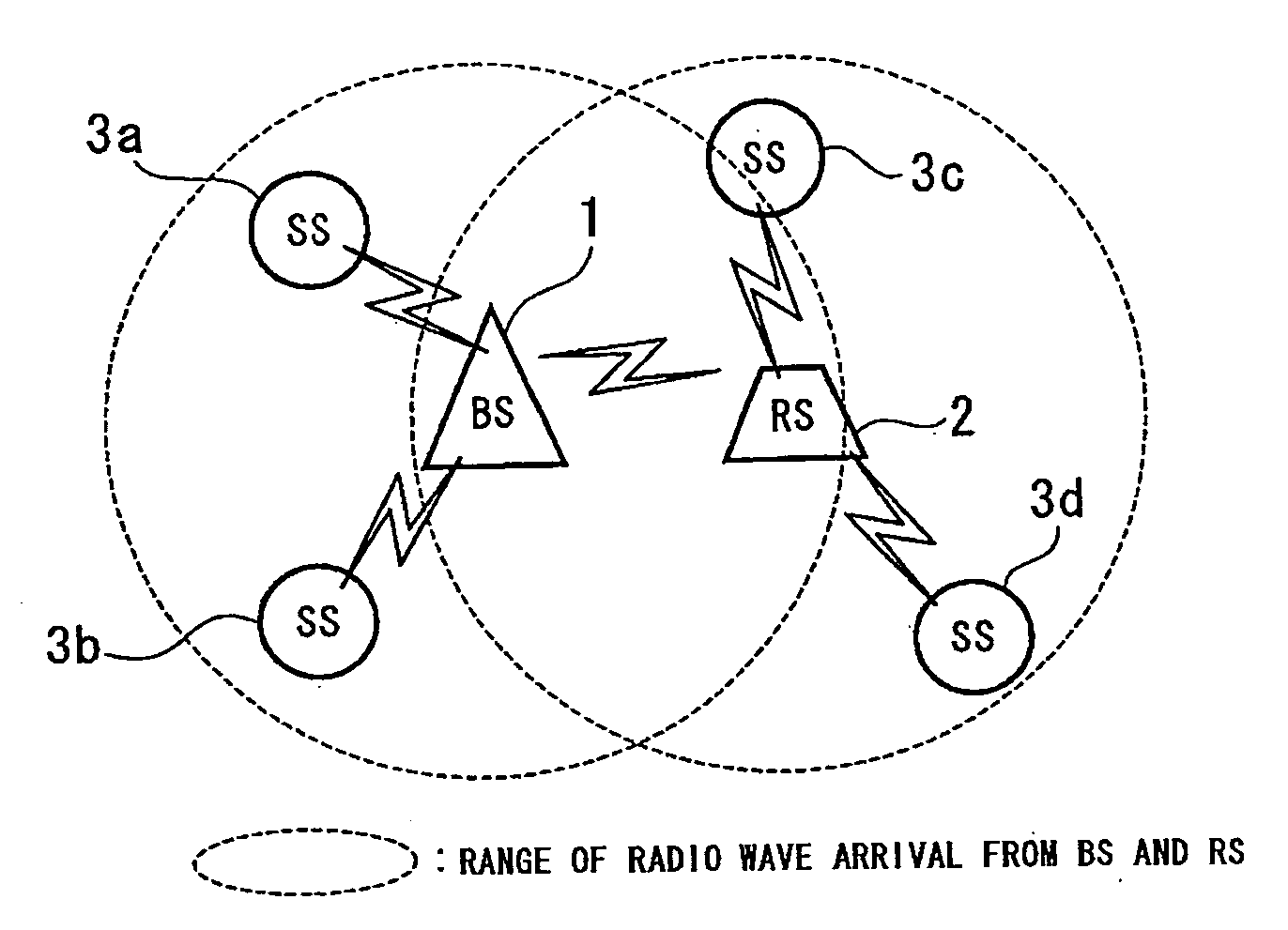
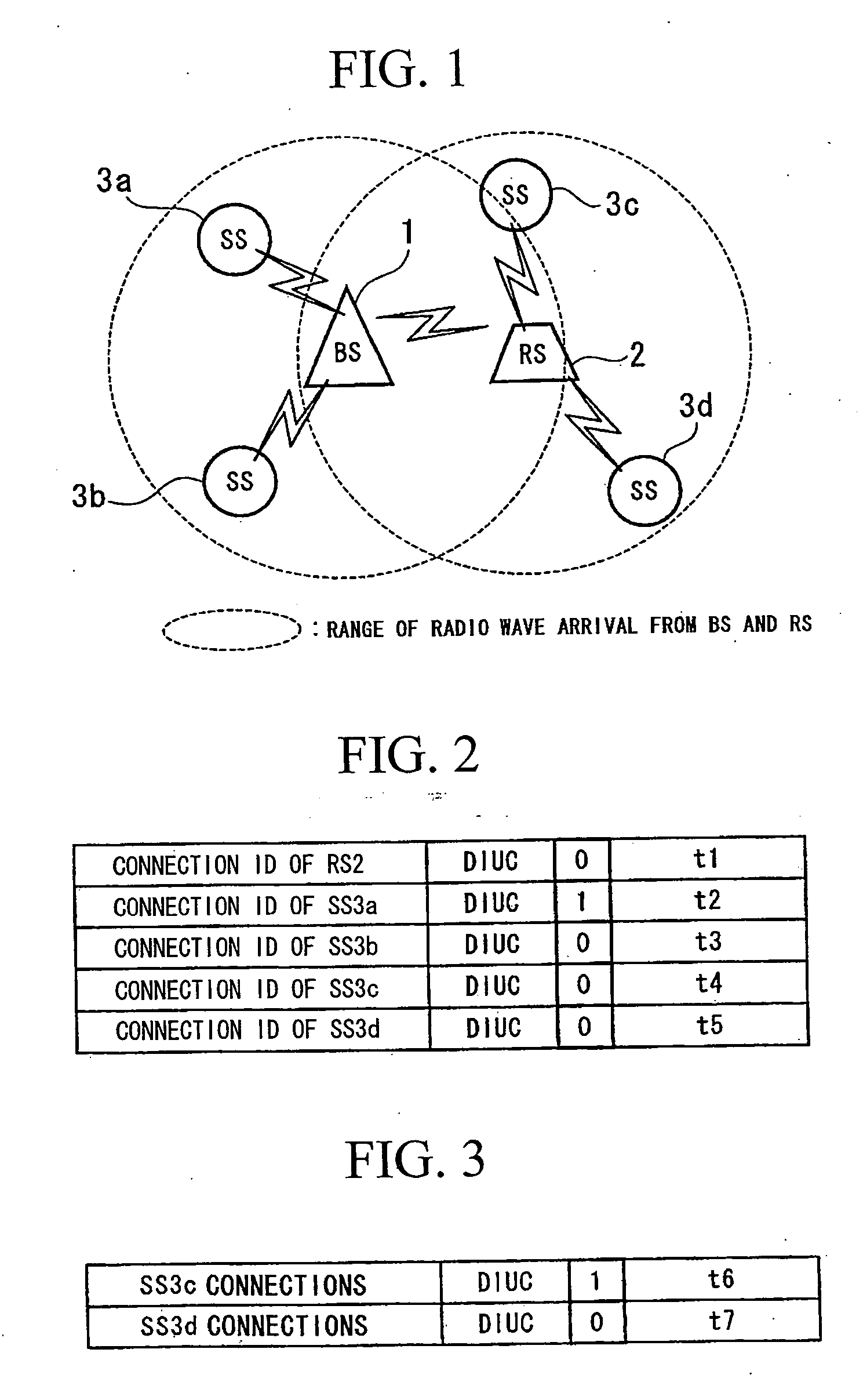
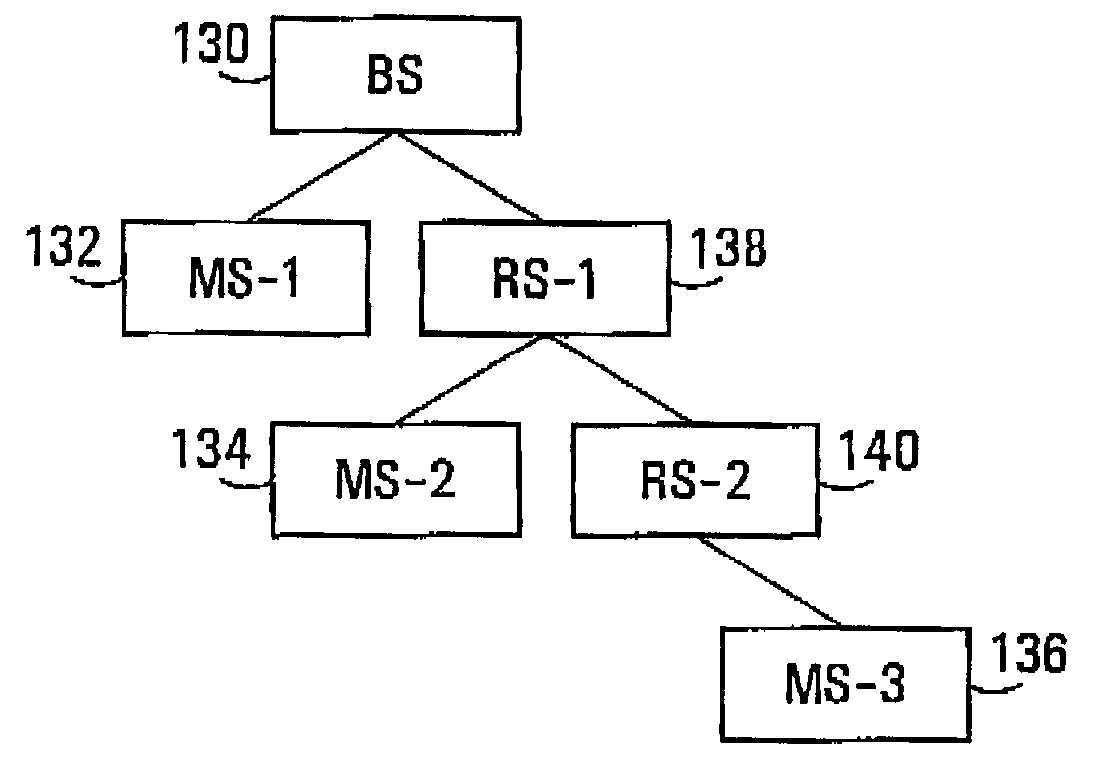
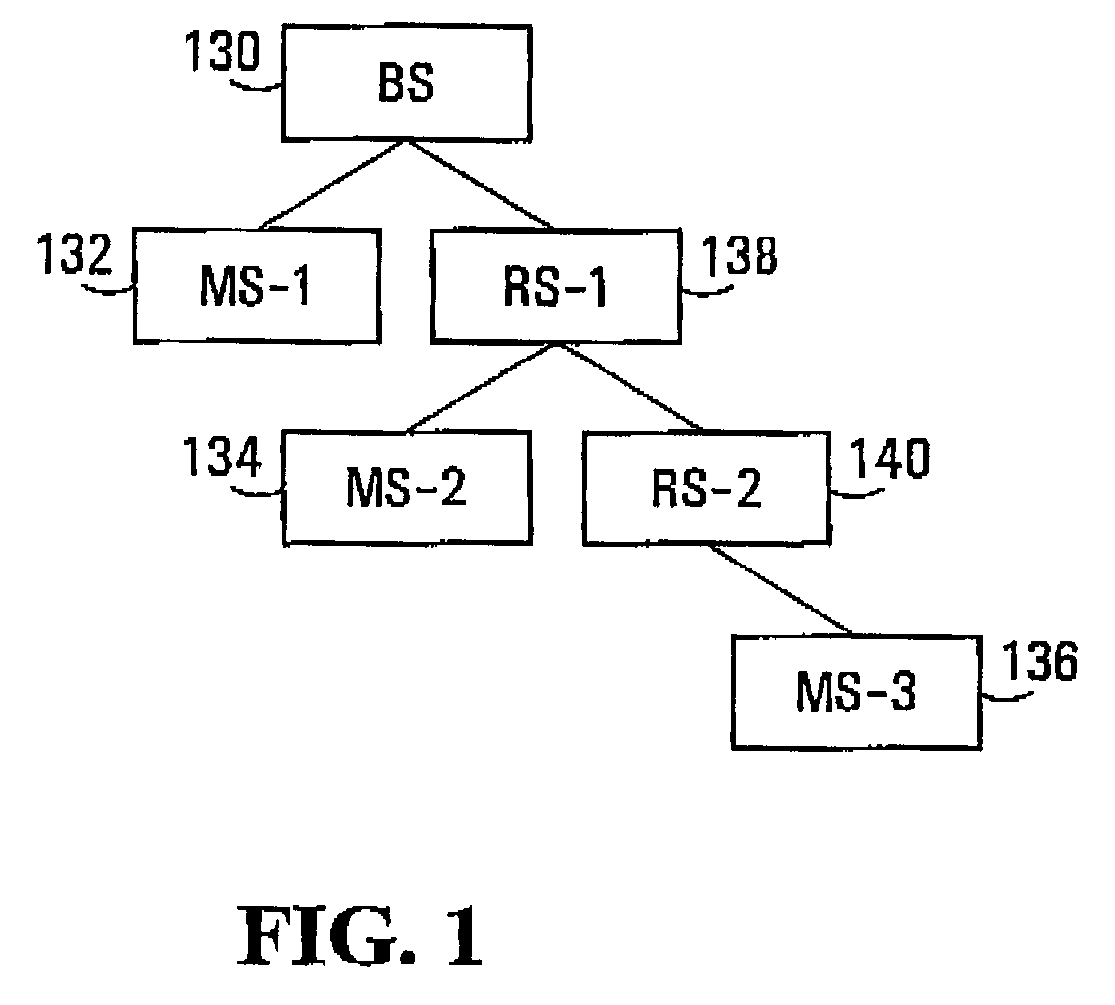
Wireless communication system, relay station device and base station device
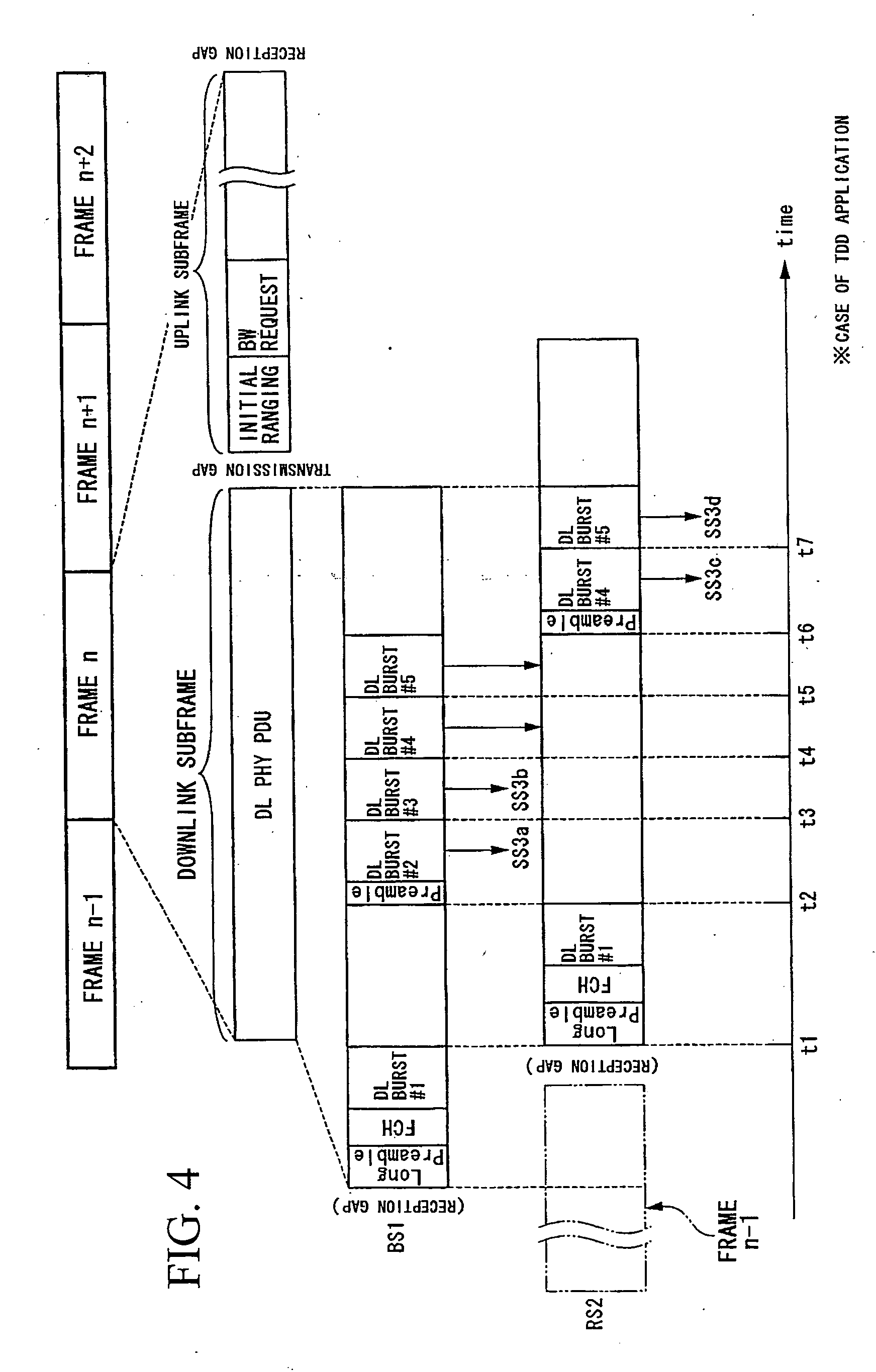
InactiveUS20060046643A1Repeater circuitsRadio relay systemsCommunications systemInformation transmission
A wireless communication system, relay station device, and base station device reduce dead zones in which communication with the base station device is not possible, and enable expansion of service areas. The BS transmits to the RS burst packets and MAP messages including information providing notification of the timing of information transmission and reception. The RS receives the MAP messages and burst packets. The RS stores, in the Preamble Present bits in MAP messages, information providing notification of the preamble transmission timing to control synchronization of reception by the SSs, and transmits the MAP messages to the SSs. The RS transmits burst packets to which preambles are appended to the SSs.
Owner:KDDI CORP
Analogue regenerative transponders including regenerative transponder systems
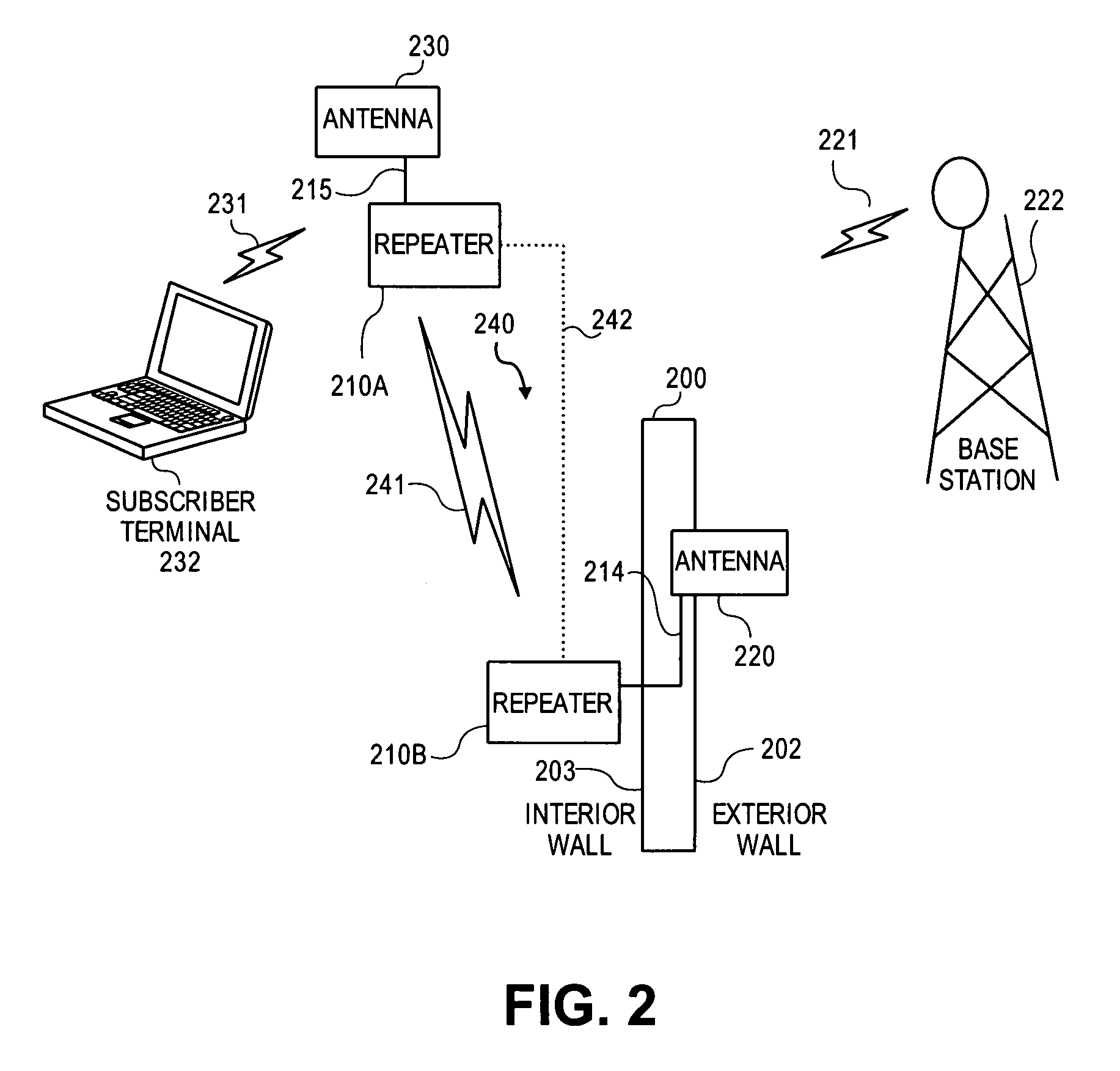
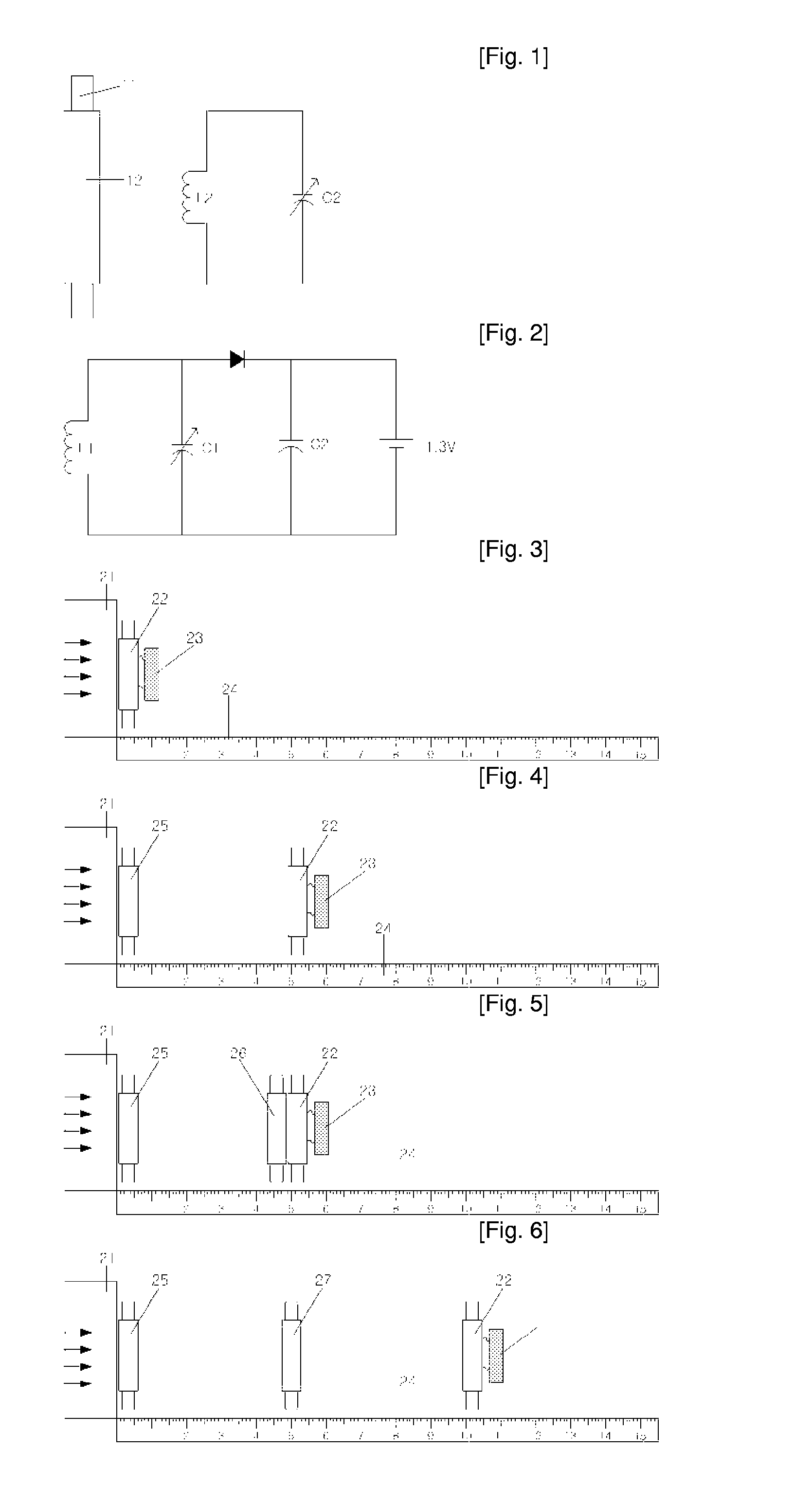
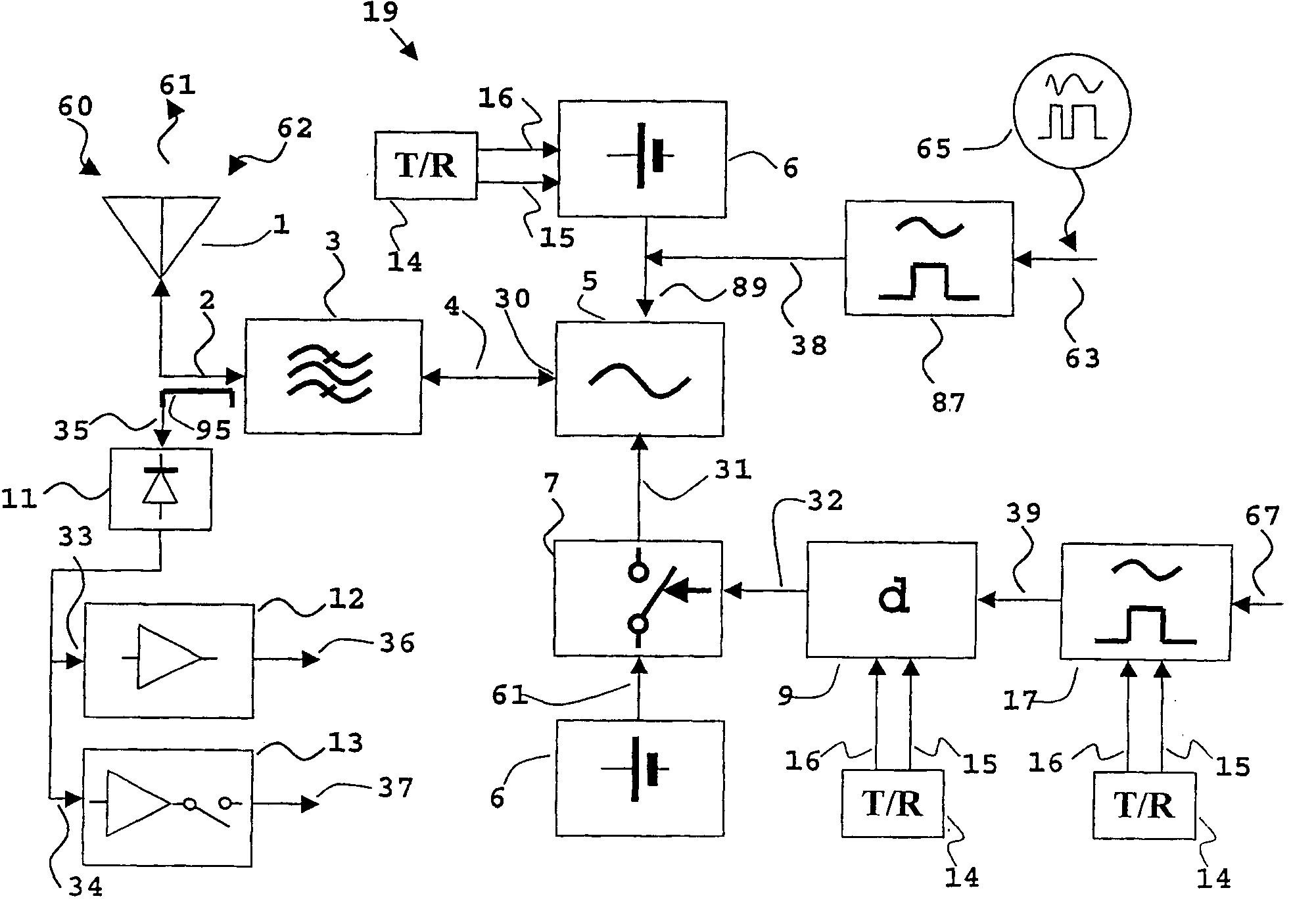
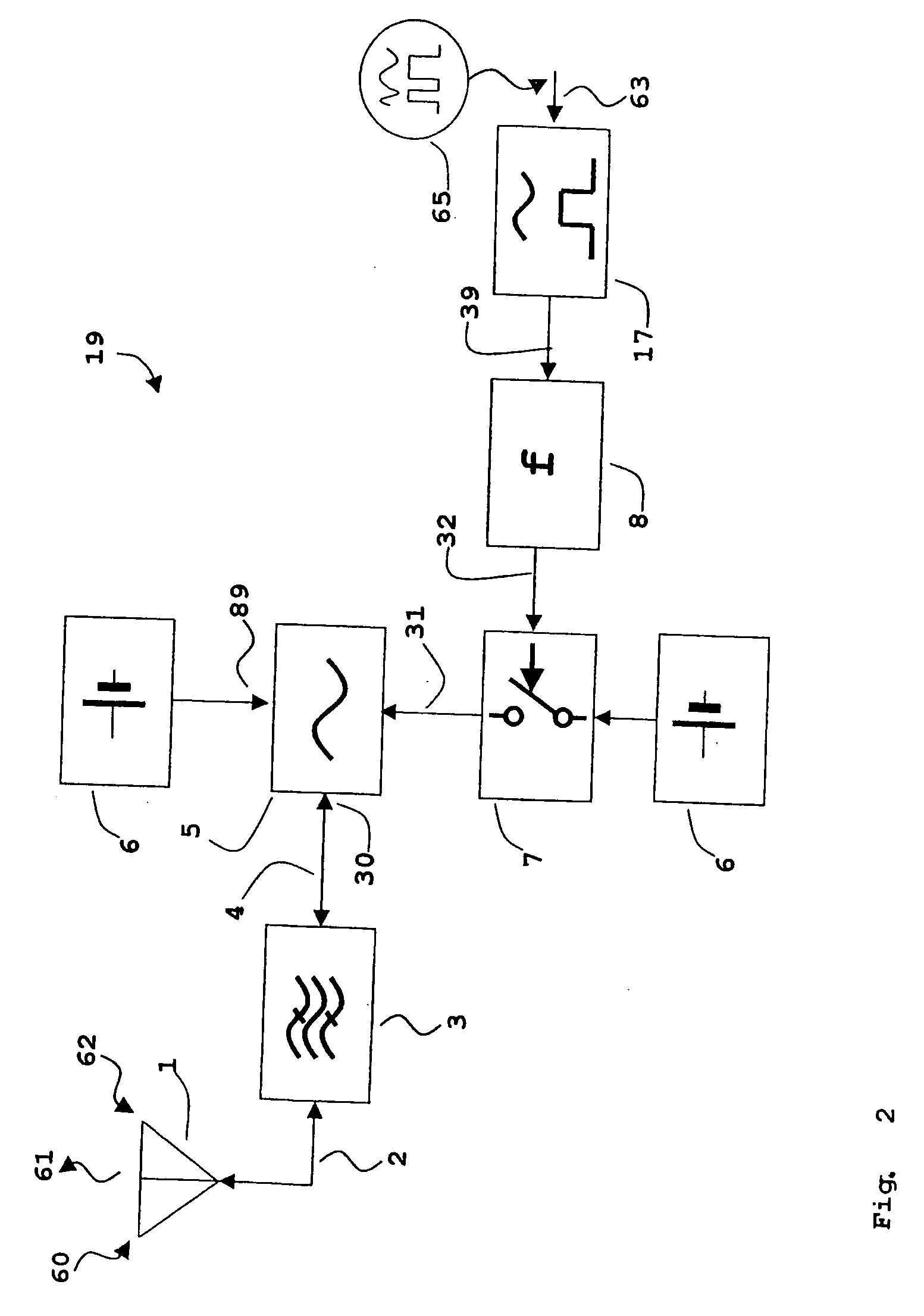
InactiveUS20050068223A1Expand coverageExtend radio coverageRadio relay systemsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringPositioning system
In a transponder (19) for amplification of a received signal (60) into an antenna (1), to a signal (61) for retransmission, and where the retransmitted signal (61) possibly may have information superimposed, a quenched oscillator (5) is incorporated as amplifying element. The oscillator (5) is preferably of superregenerative type and exhibits negative resistance (30) for the received signal (60). Transponders according to the present invention may be introduced as system elements in a wireless or wire based network to work as intelligent or unintelligent connections in the network. The transponders can also be used in positioning systems.
Owner:VAVIK GEIR MONSEN
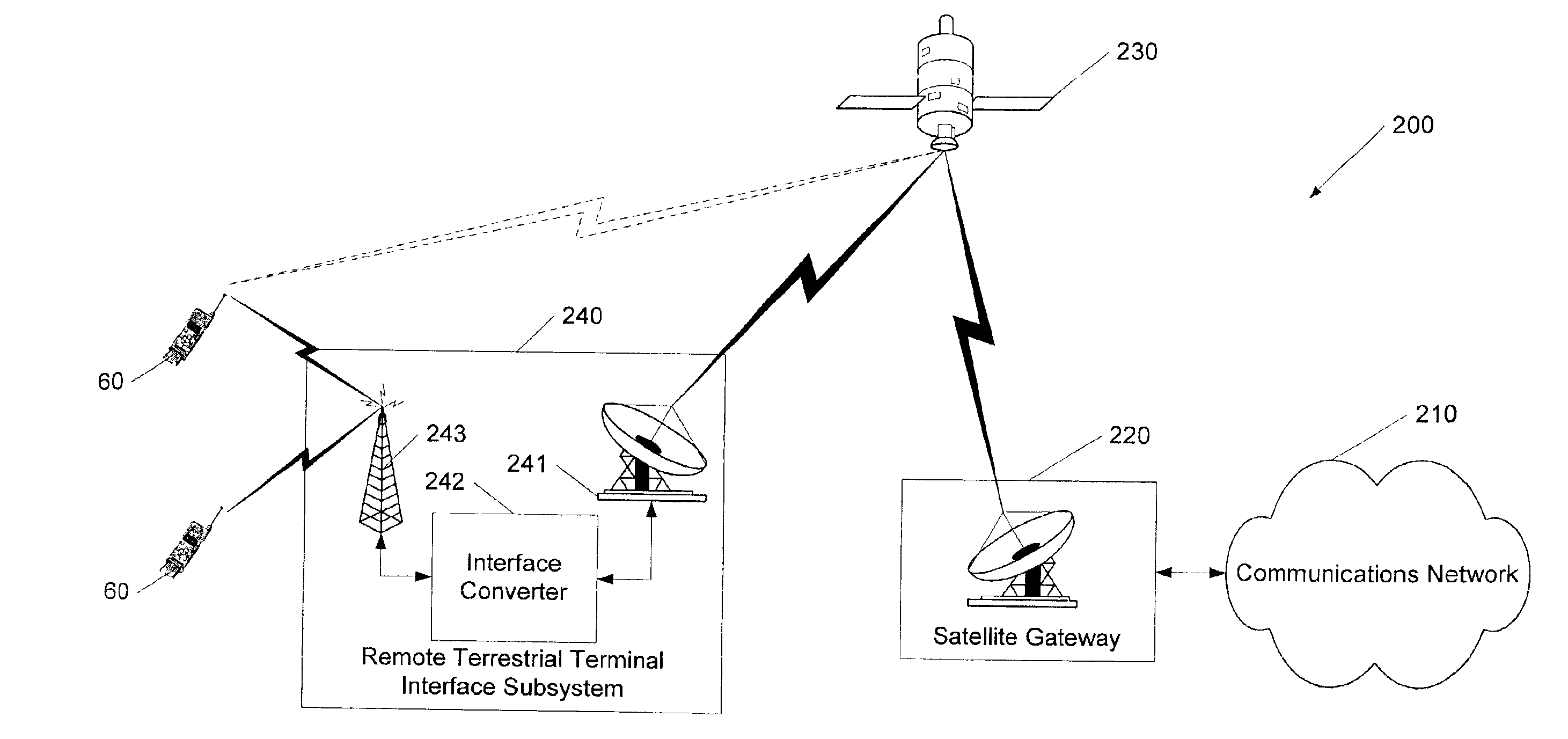
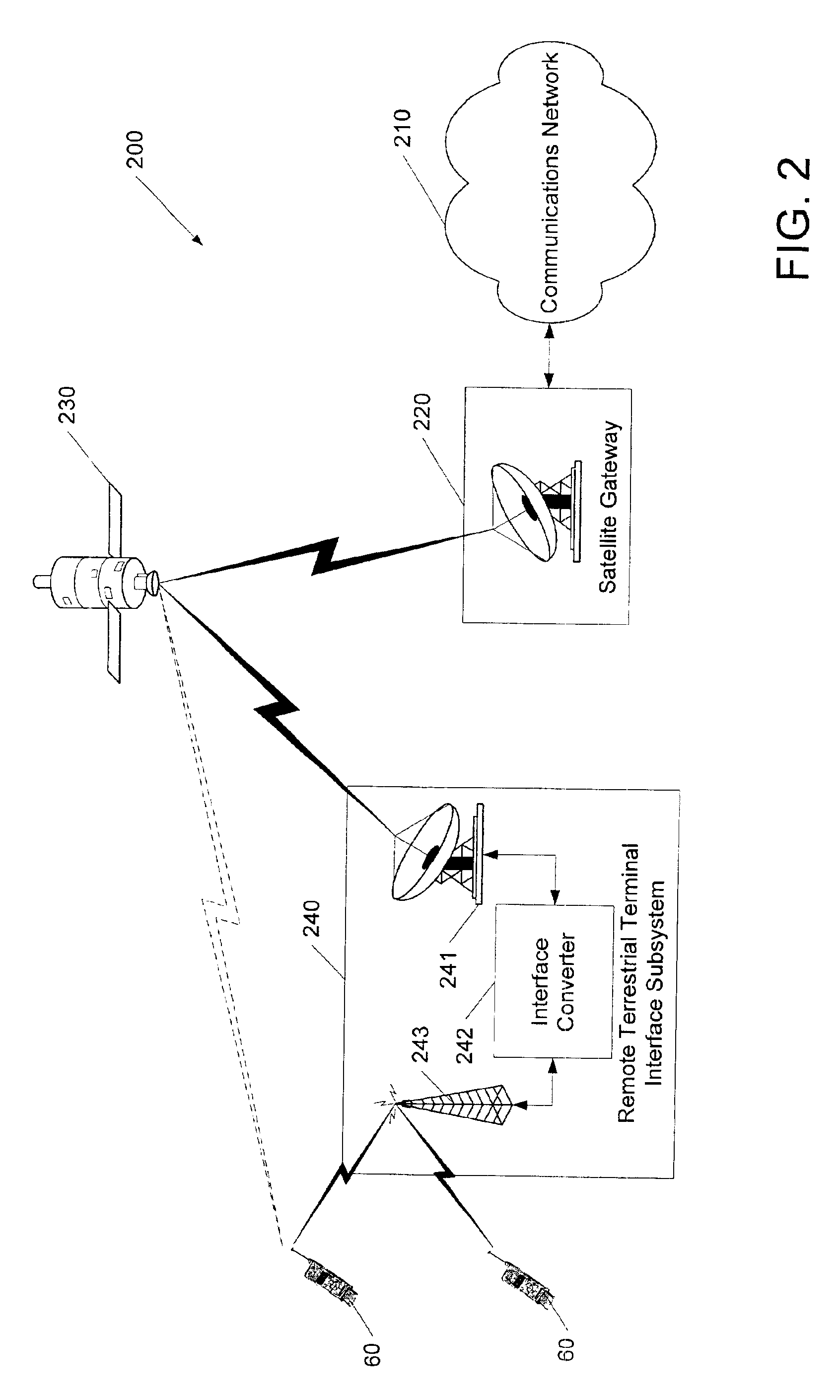
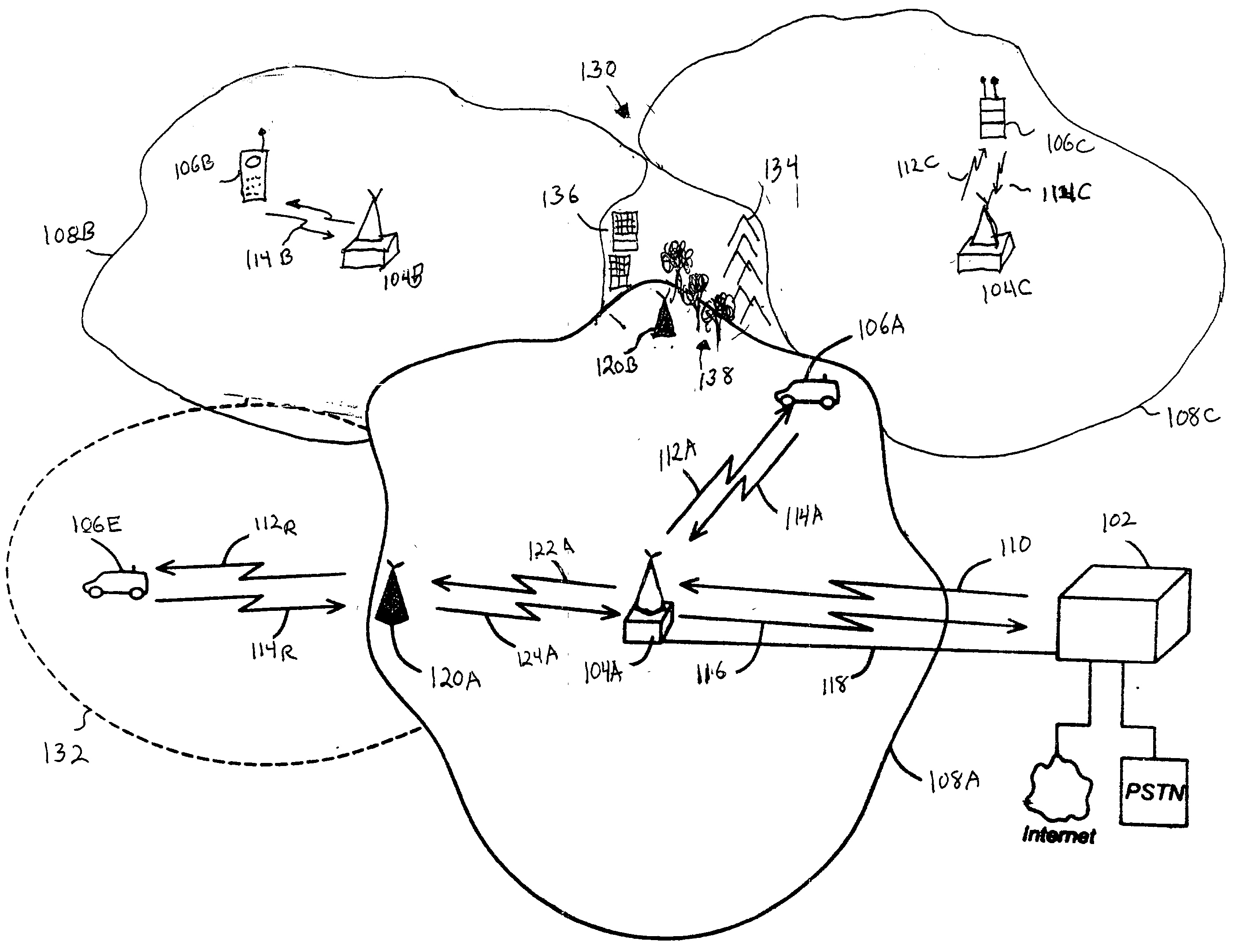
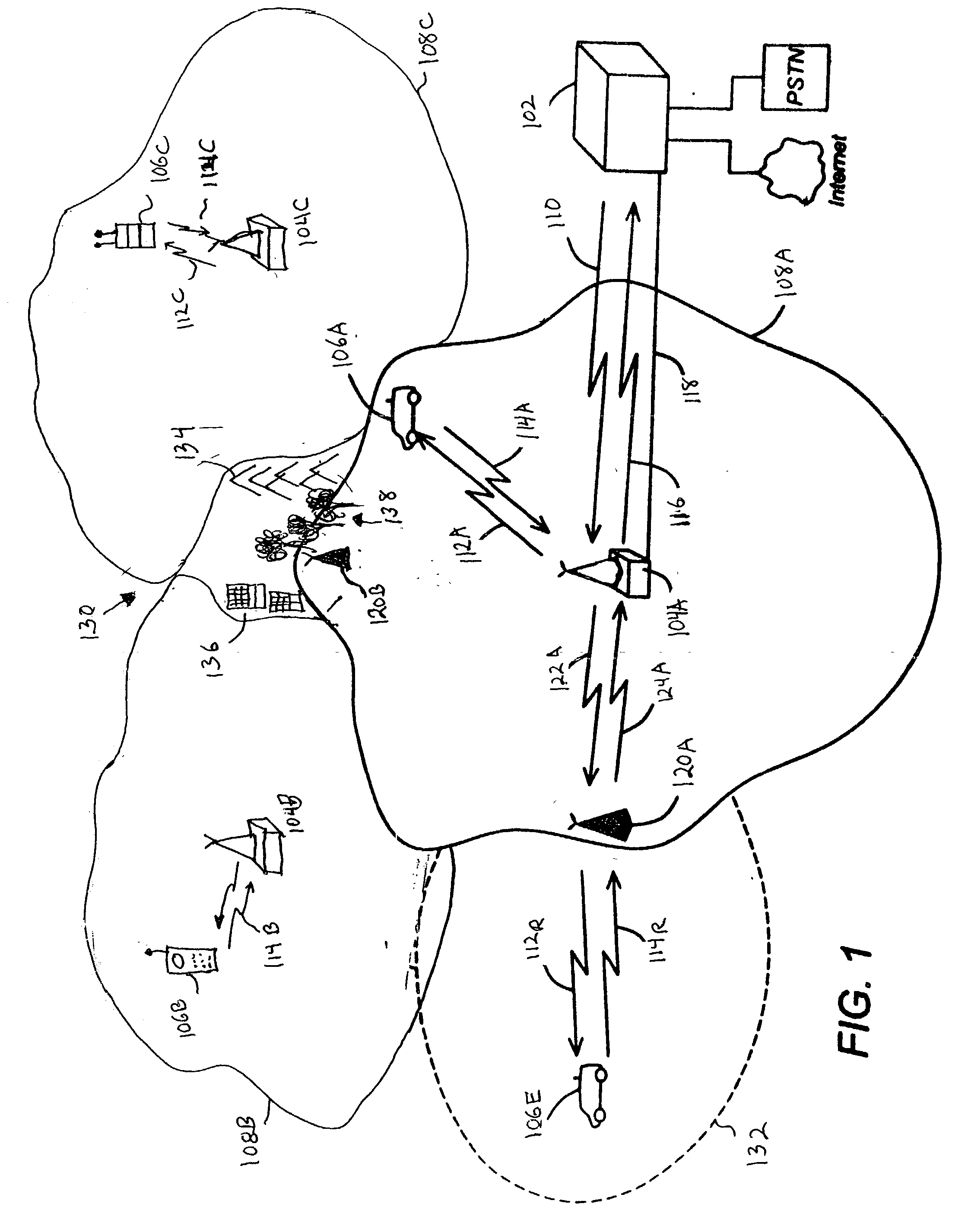
Wireless communications systems and methods using satellite-linked remote terminal interface subsystems
InactiveUS6856787B2Wireless commuication servicesRadio relay systemsCommunications systemCommunications satellite
A satellite gateway is coupled to a communications network and is operative to communicate with a communications satellite. A terrestrial terminal interface subsystem is operative to communicate with the satellite gateway via the communications satellite using a first radio interface and to communicate with terminals over a geographic area using a second radio interface. The communications network may be a wireless communications network, and the satellite gateway is configured to communicate with a base station controller of the wireless communications network, such that the terrestrial terminal interface subsystem may provide one or more satellite-linked terrestrial base stations.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Method and system for wireless communication networks using cooperative relaying
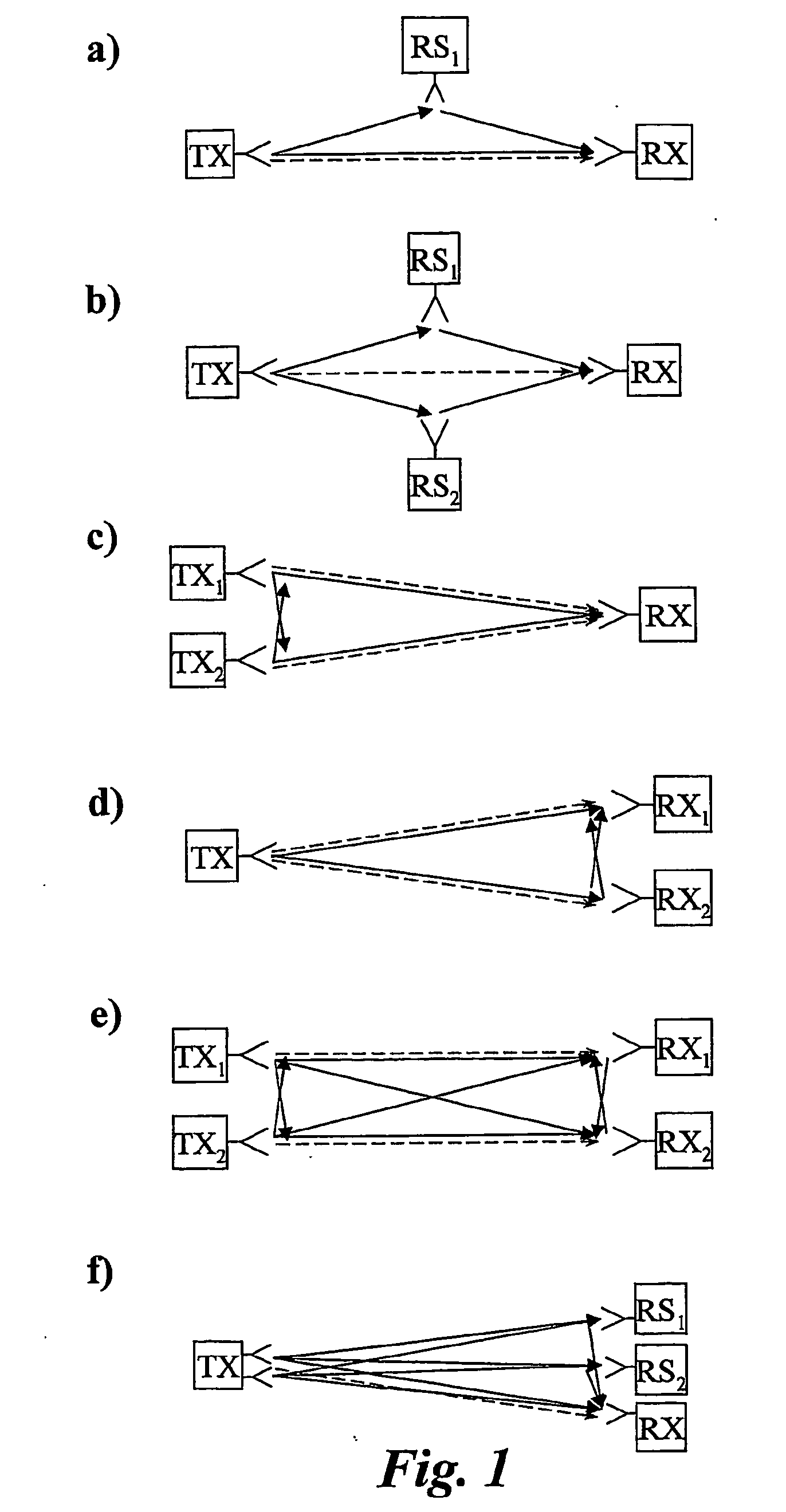
ActiveUS20070160014A1Easy to implementEliminate needSite diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemControl signal
The present invention relates to relay supported wireless communication to enhance communication performance. In the wireless communication system according to the invention neighboring relay stations are arranged with substantially overlapping coverage. In the method according to the invention mobile stations makes soft association to relay stations. The mobile stations feed back the selection of relay stations and channel quality measures to the base station. The base station adapts the transmission to the relay stations based on each mobile stations reported soft associations and channel quality measures. In this way the control signaling to and from the relay stations can be very limited.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
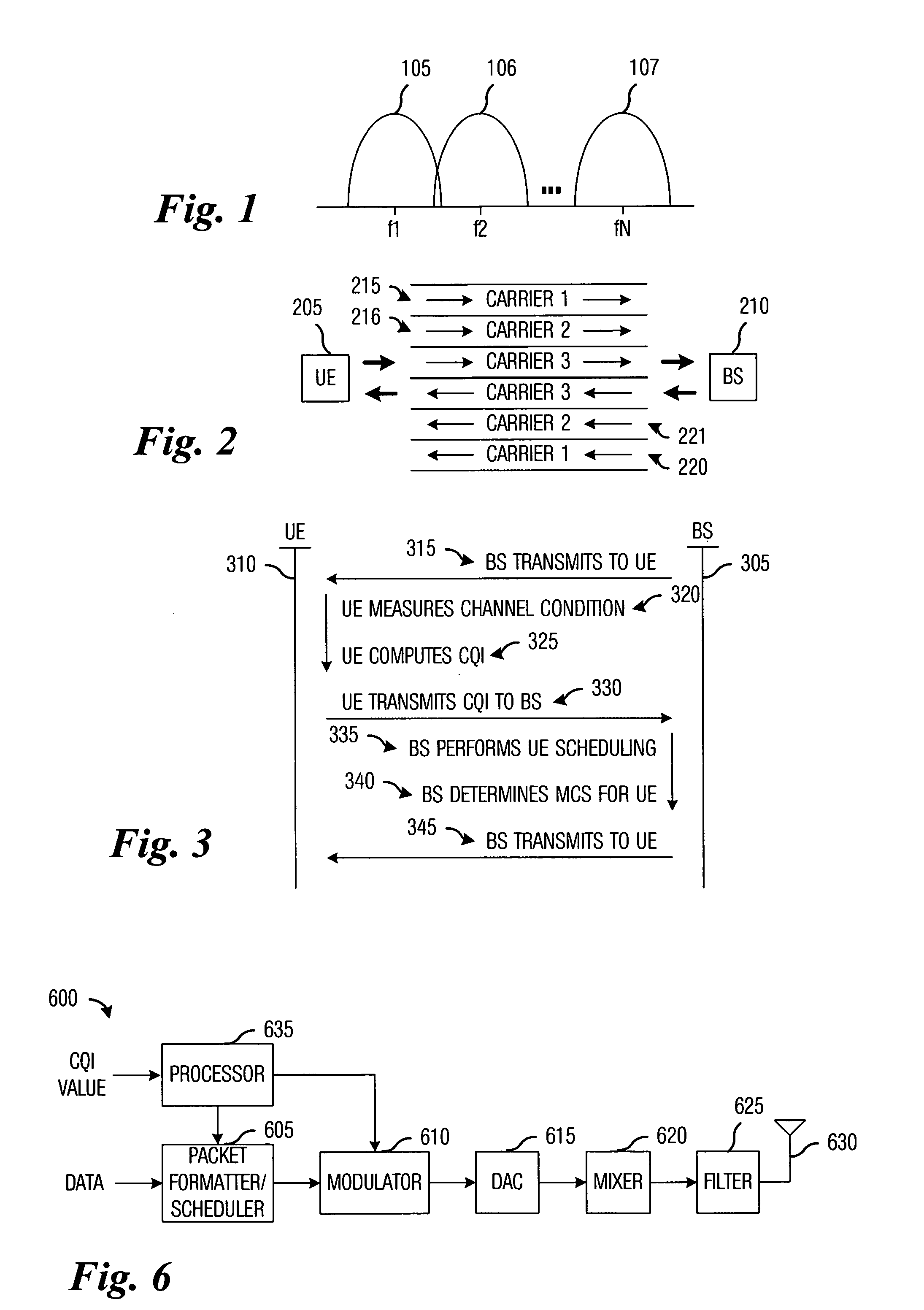
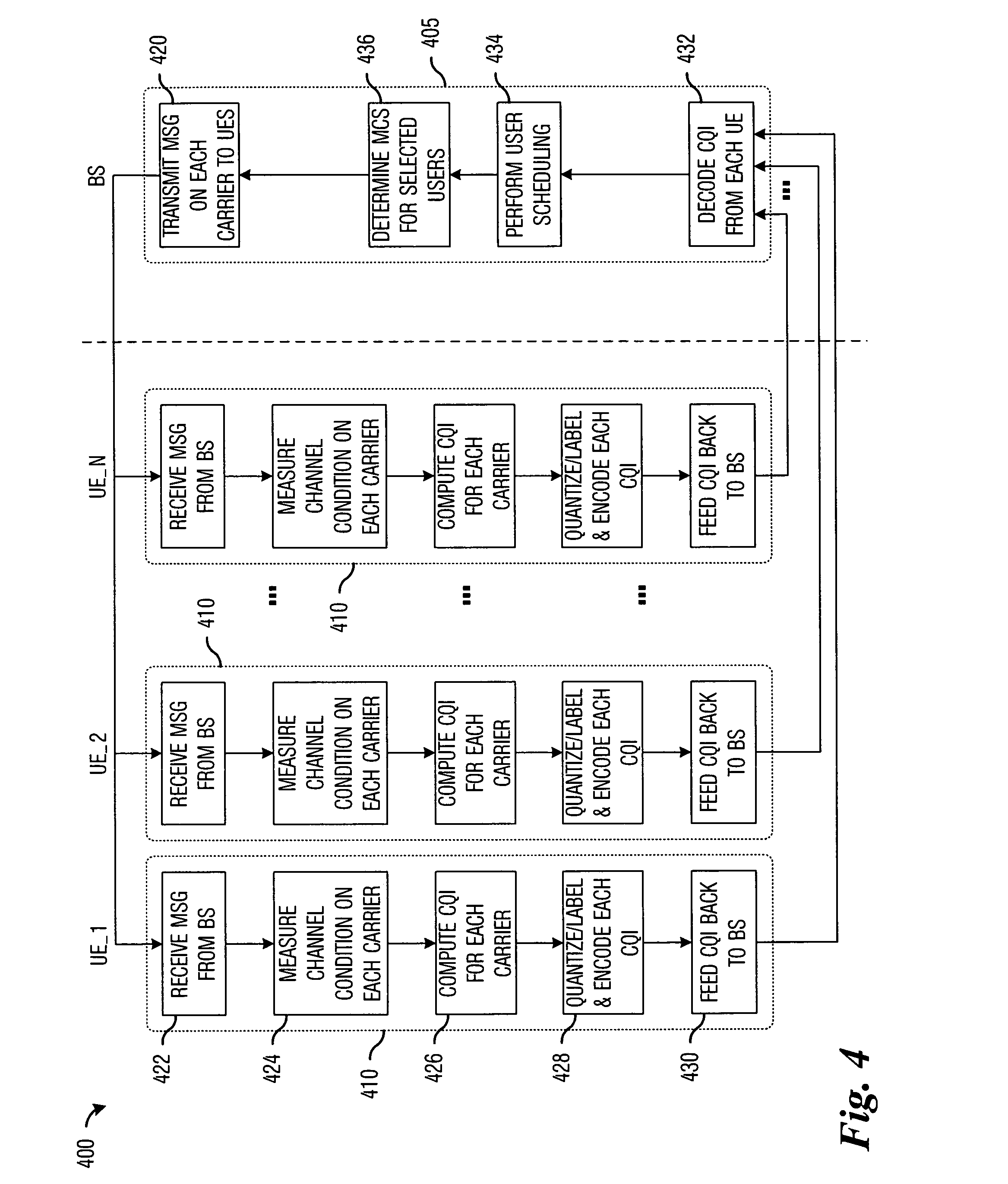
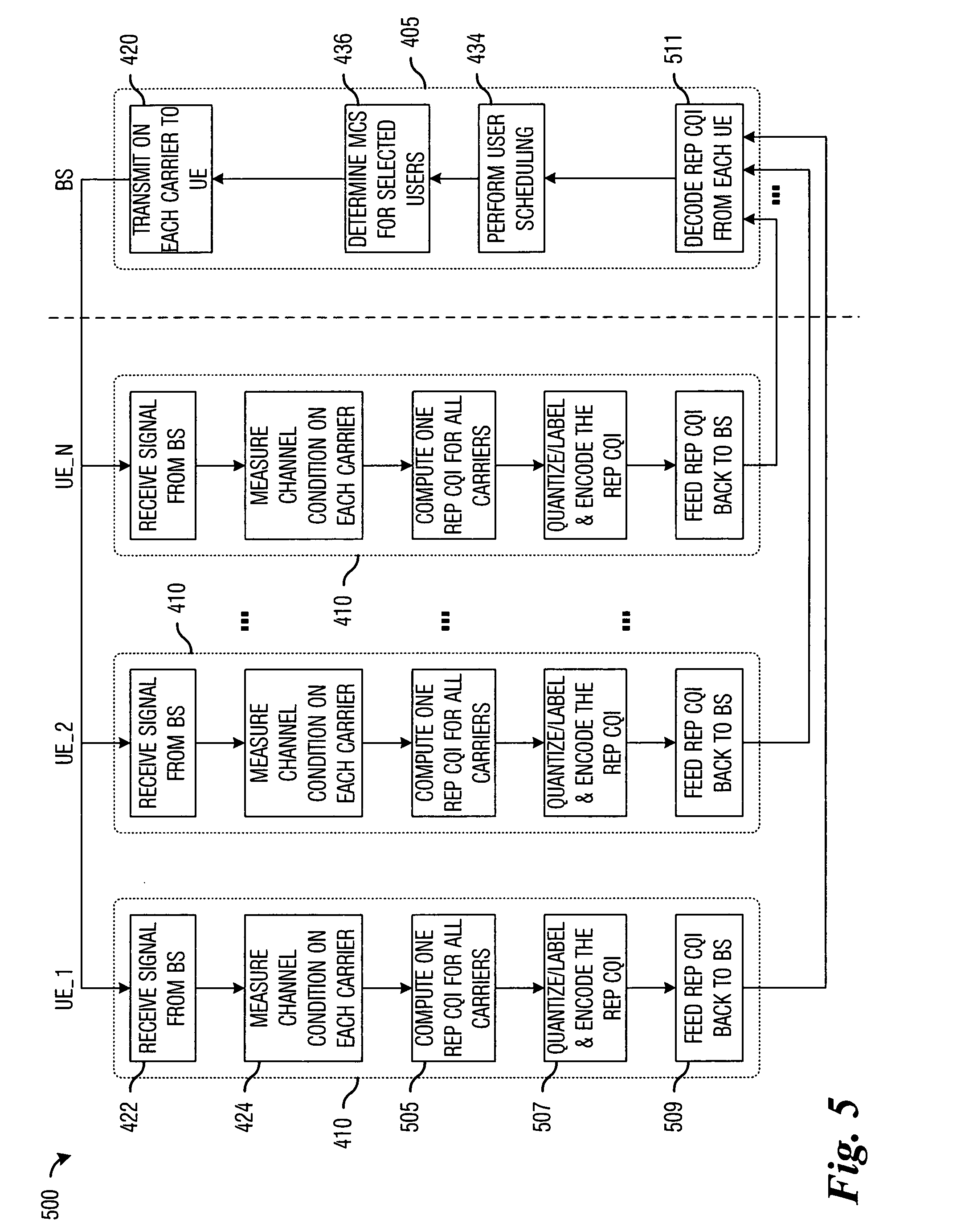
Method for channel quality indicator computation and feedback in a multi-carrier communications system
InactiveUS20050207367A1Improve retransmission performanceAccurate estimateFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemCarrier signal
Method for computing and transmitting channel quality information in a multi-carrier communications system. A preferred embodiment comprises receiving a transmission from a transmitter, wherein the transmission occurs over a plurality of carriers, measuring a channel condition for each carrier in a plurality of carriers, computing a channel quality indicator based upon the measured channel condition, and providing the channel quality indicator to the transmitter. The channel quality indicator can be used at the transmitter to schedule transmissions to various users in the multi-carrier communications system to maximize utilization of the carriers as well as overall network performance.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
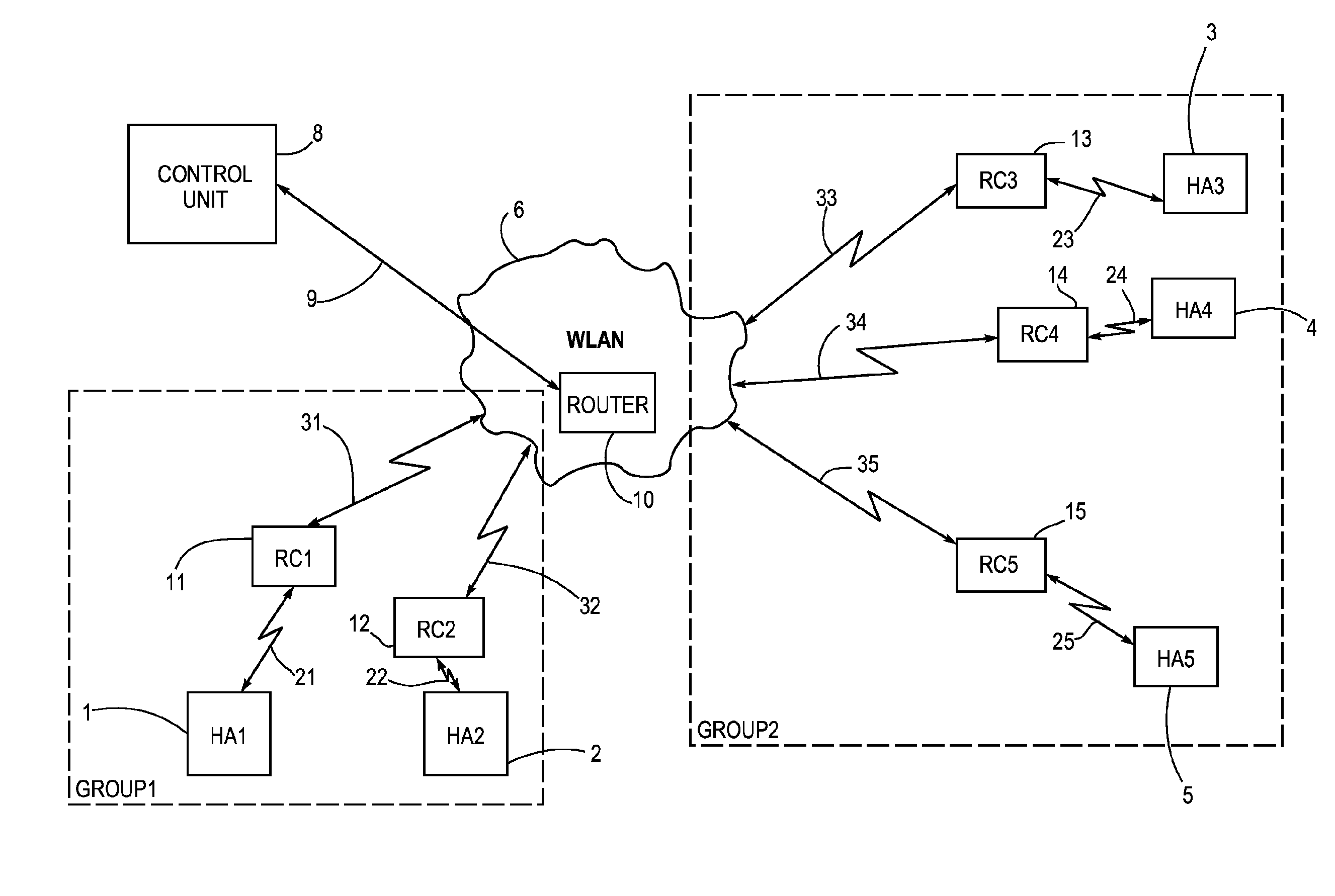
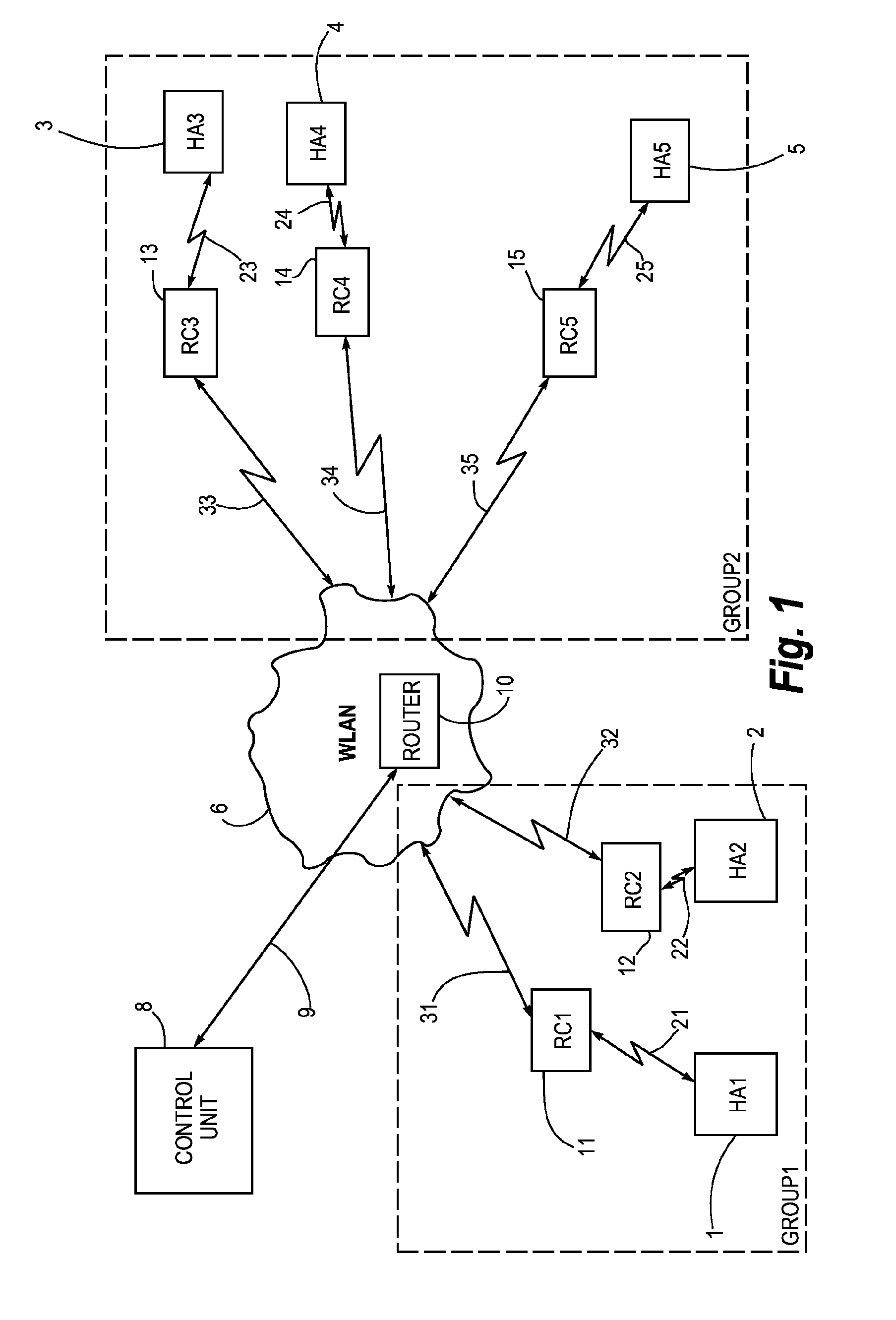
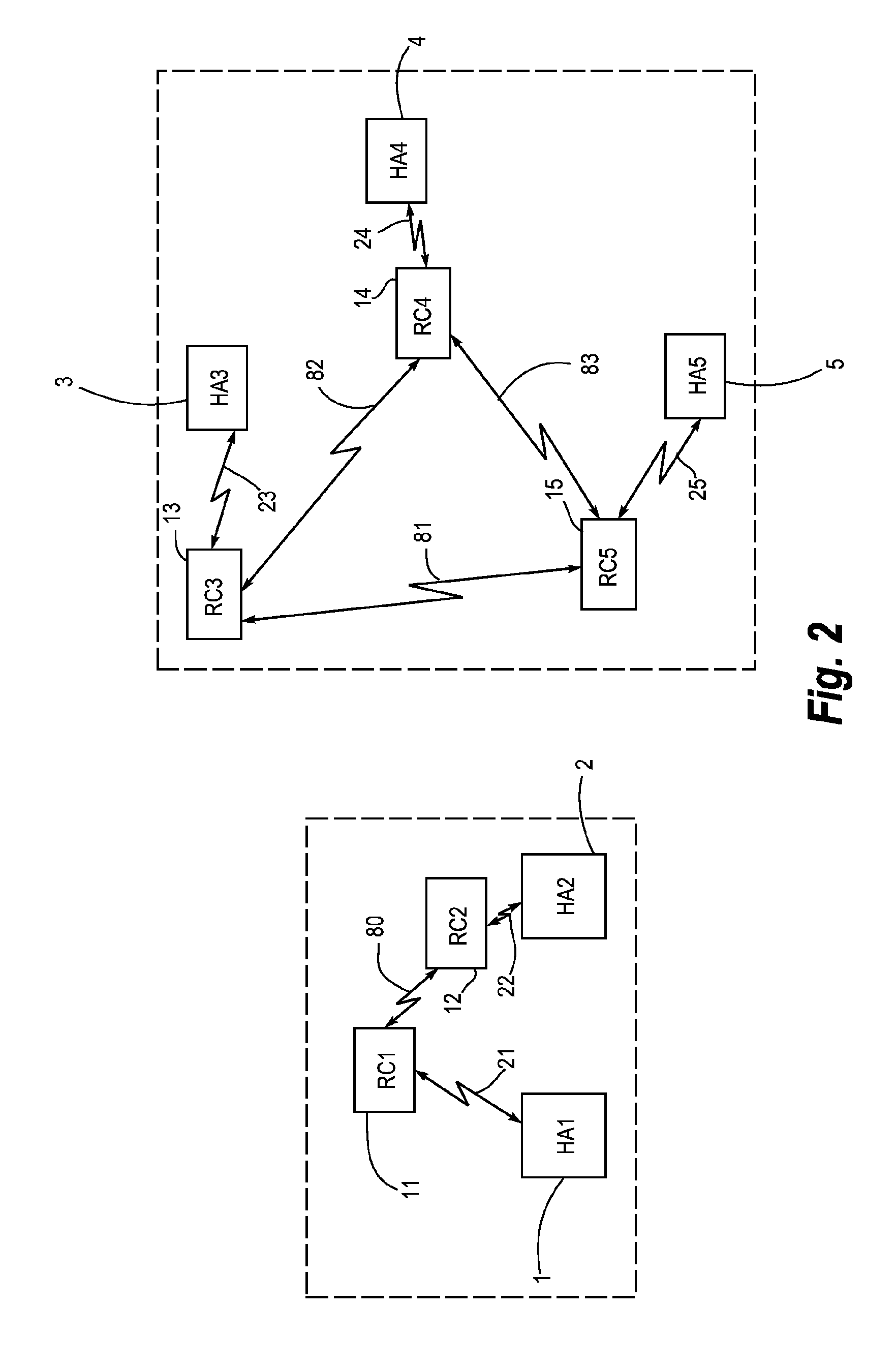
Hearing aid system for establishing a conversation group
ActiveUS20100086152A1Small sizePower transmissionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexEngineeringHearing aid
A hearing aid system adapted for establishing a conversation group with other hearing aid systems used by different users, comprises a hearing aid (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) with an associated relay device (11, 12, 13, 14, 15). The relay device is (11, 12, 13, 14, 15) adapted for wireless communication (21, 22, 23, 24, 25) with said hearing aid and for wireless communication (31, 32, 33, 34, 35) with a second hearing aid system. The relay device (11, 12, 13, 14, 15) is also adapted for receiving and displaying information about said second hearing aid systems being available for participation in said conversation group, and it comprises means for selection of said other hearing aid systems for inclusion into the conversation group. The invention further provides a method for establishing a conversation group among hearing aid users.
Owner:WIDEX AS
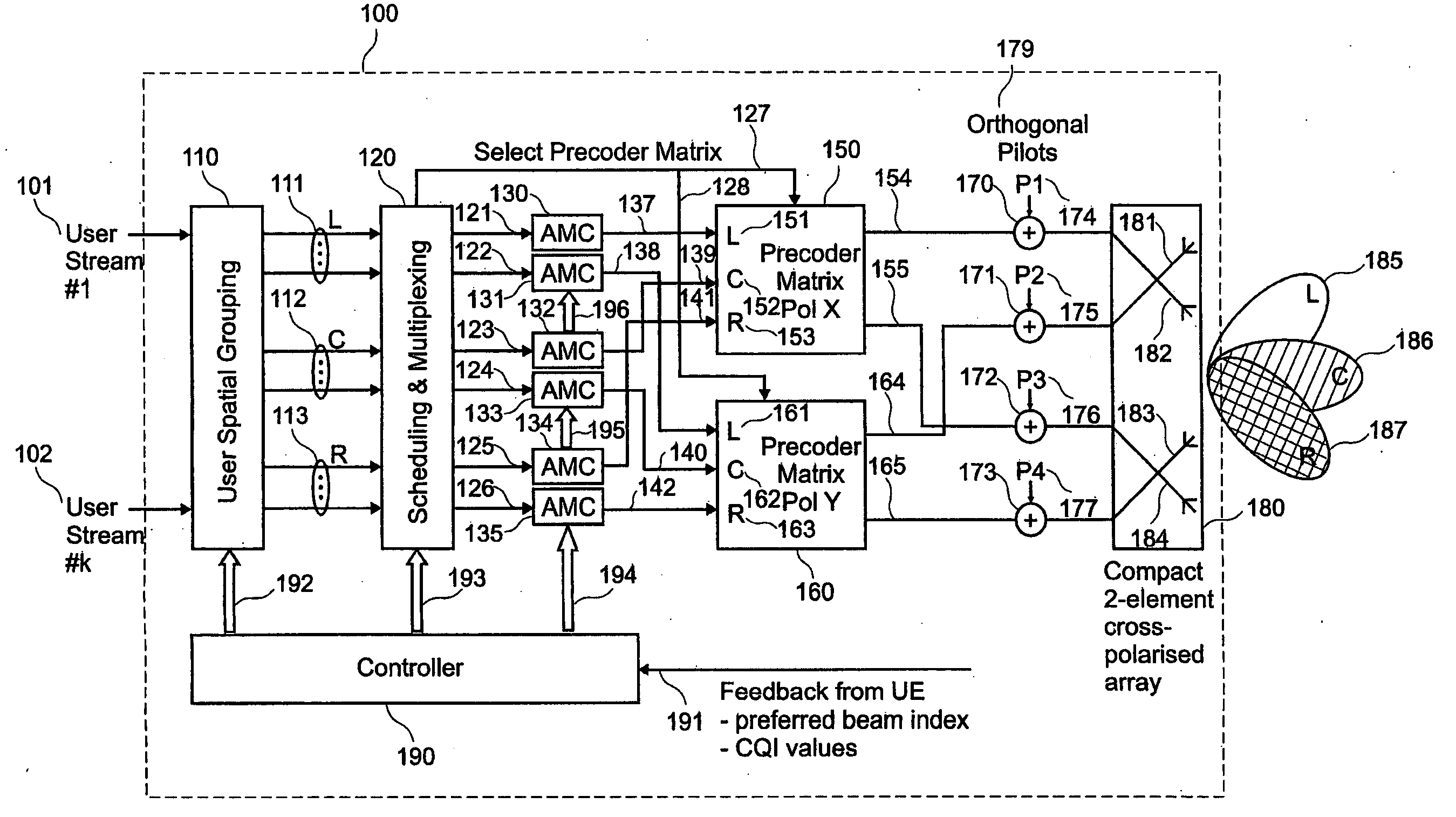
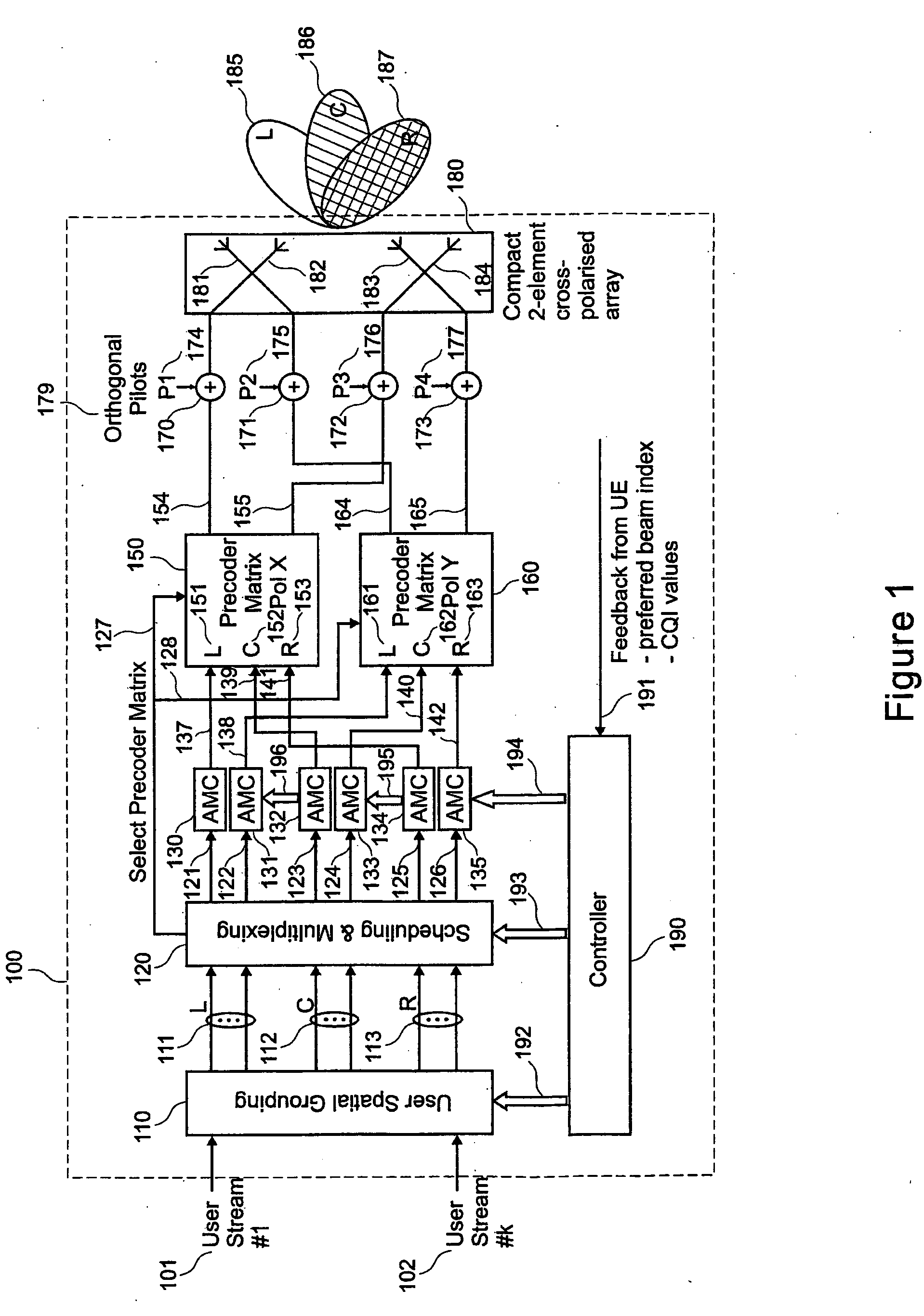
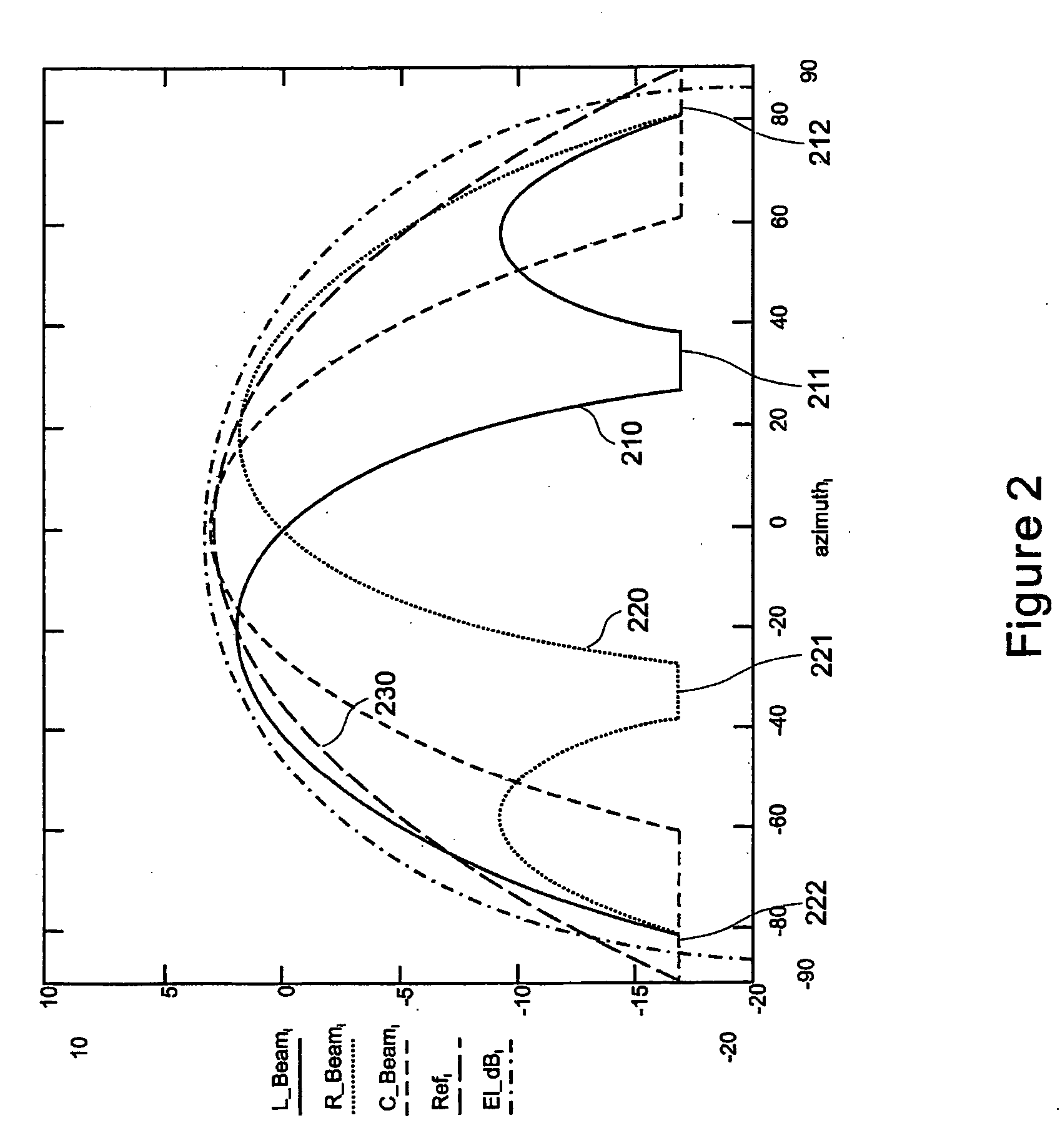
Pre-coded diversity forward channel transmission system for wireless communications systems supporting multiple MIMO transmission modes
InactiveUS20070099578A1Polarisation/directional diversityTransmission noise suppressionPolarization diversityMimo transmission
A wireless communications system supporting multiple MIMO transmission modes supporting both diversity and directional transmissions under a plurality of different transmission modes comprises a plurality of transmit and receive antenna elements where the transmit antenna elements are arranged to provide polarization diversity. The transmitting station derives actual knowledge of the forward channel by feeding back certain information such as a preferred beam index and a channel quality indicator figure of merit for that beam from the receiving station to the transmitting station along a reverse channel. The receiving station knows the beam weights used by the transmitting station. The transmitting station applies the fed back information to transmit user data intended for the receiving station in the optimal fashion, such as along the preferred beam and at a time when forward channel conditions are satisfactory. The system provides robust single or multiple stream diversity transmission, together with the option of single user or multi-user beamforming to allow on-the-fly trade-offs between coverage gain and capacity in a wireless telecommunications system.
Owner:TENXC WIRELESS
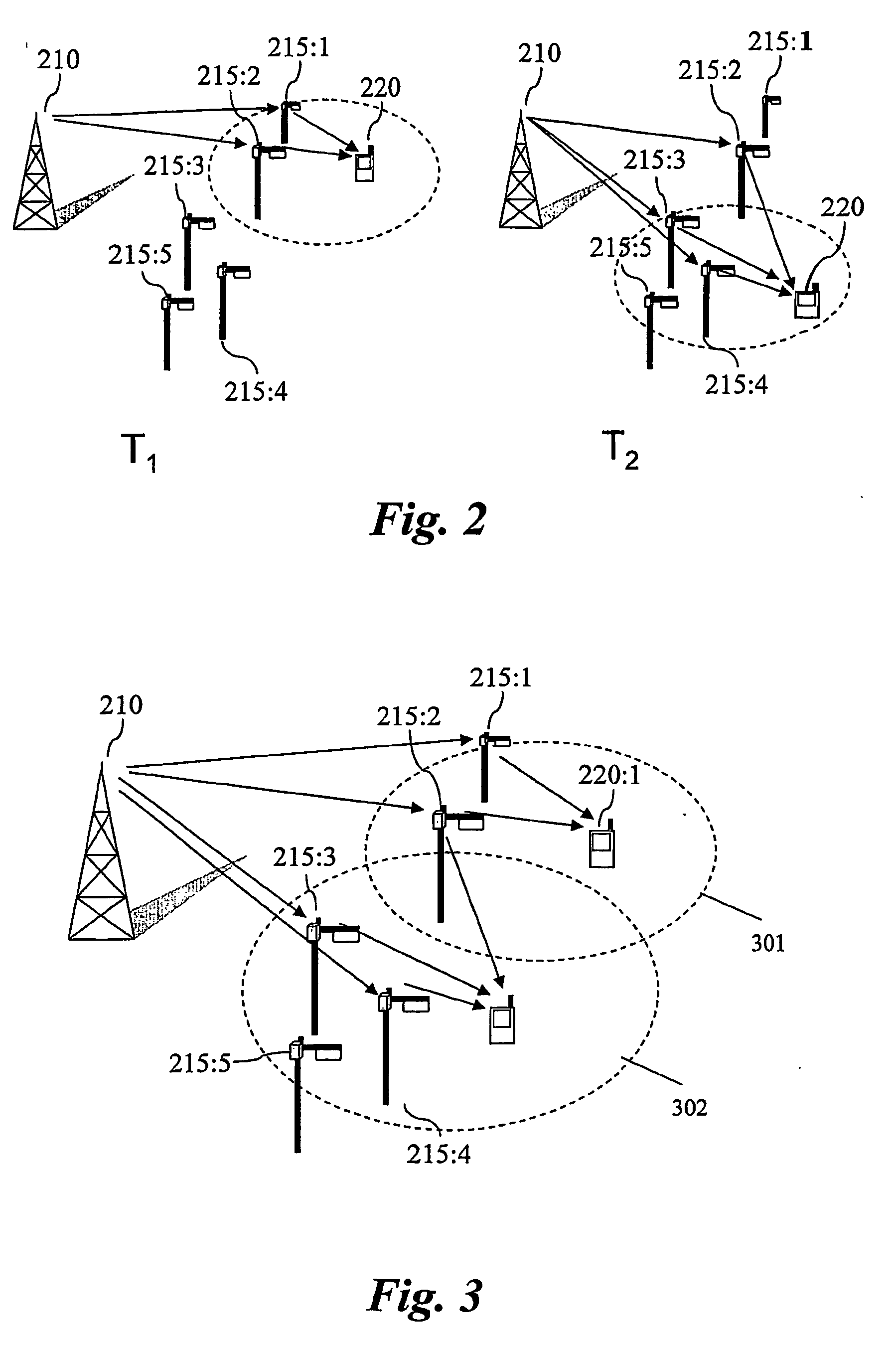
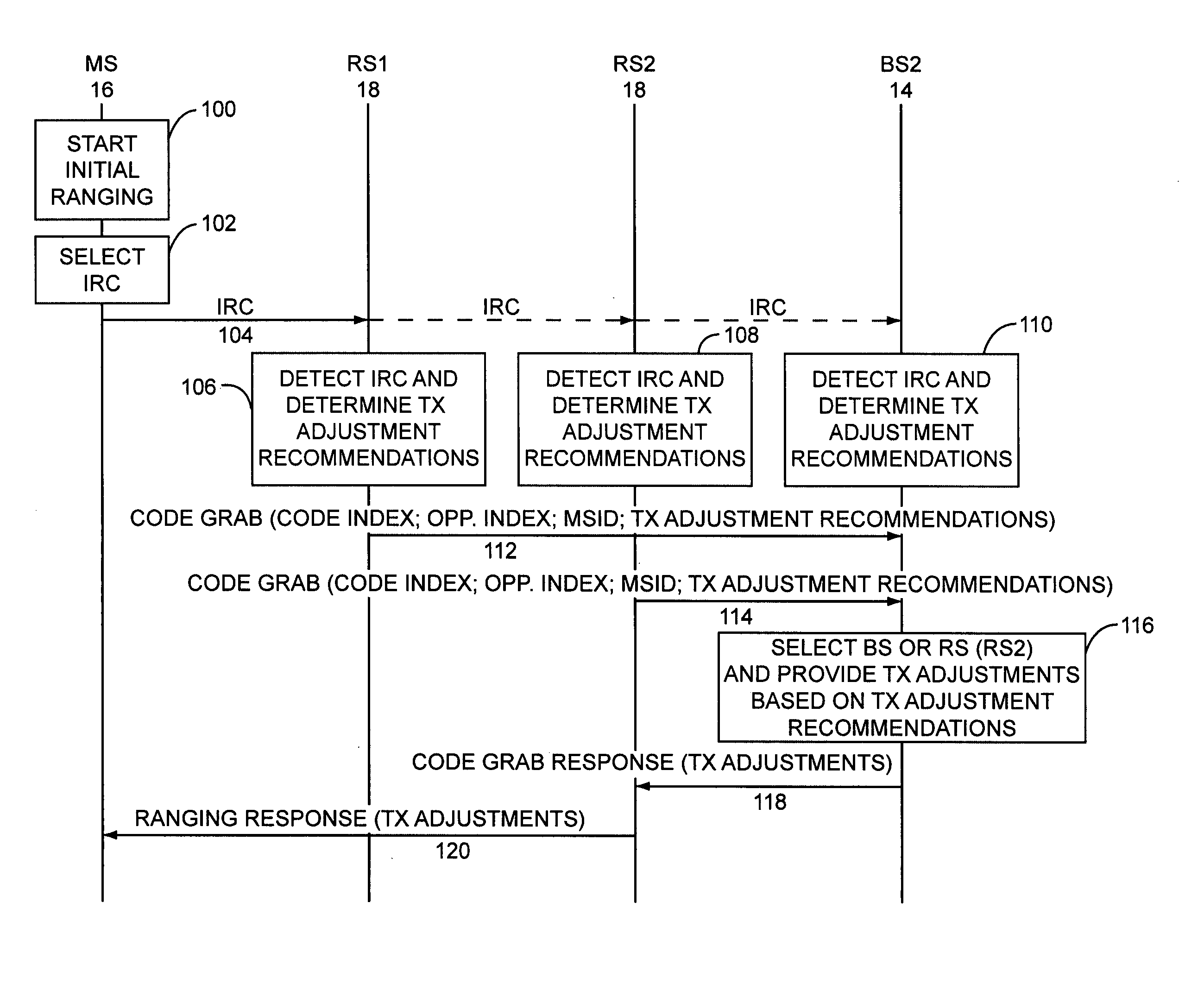
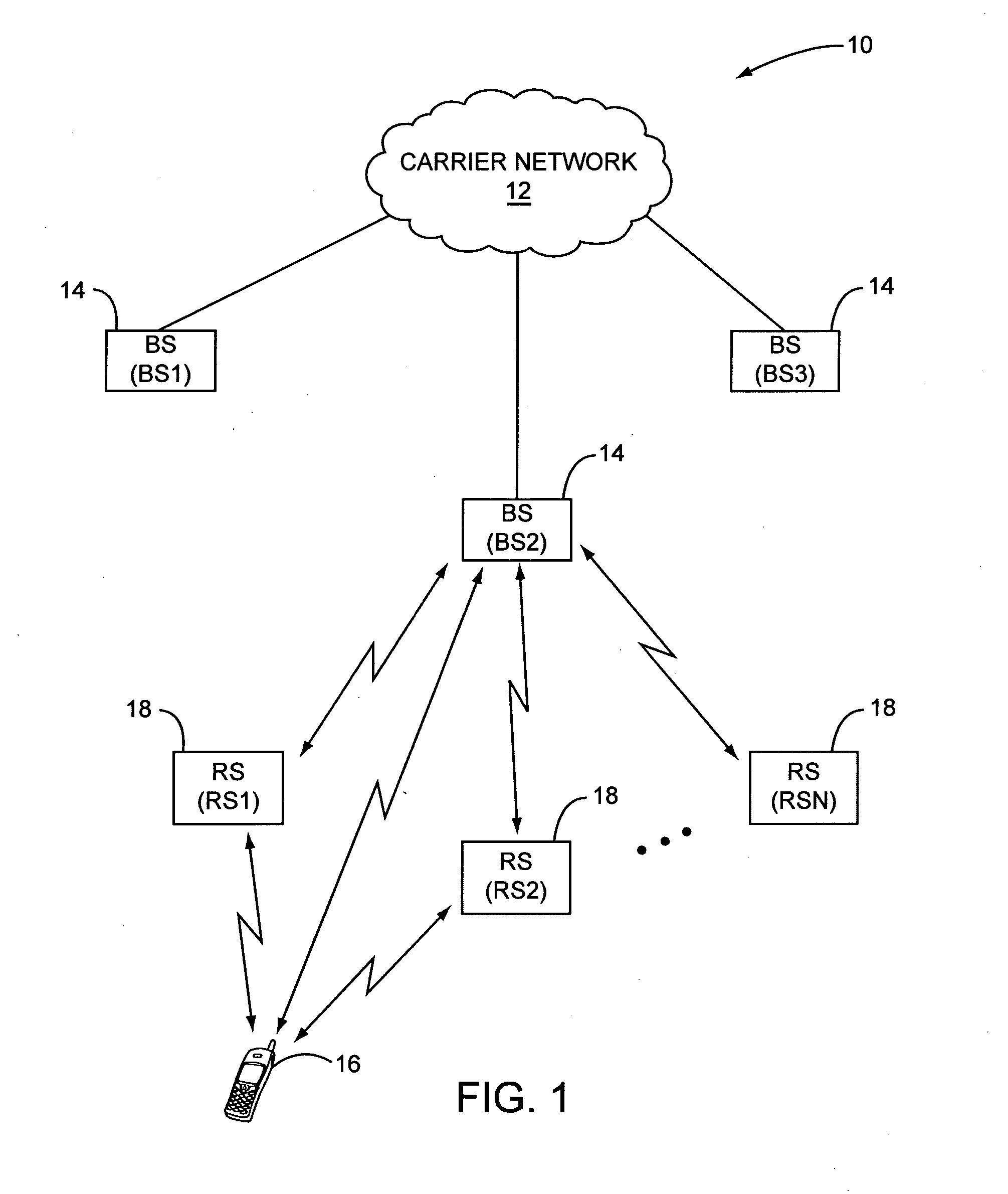
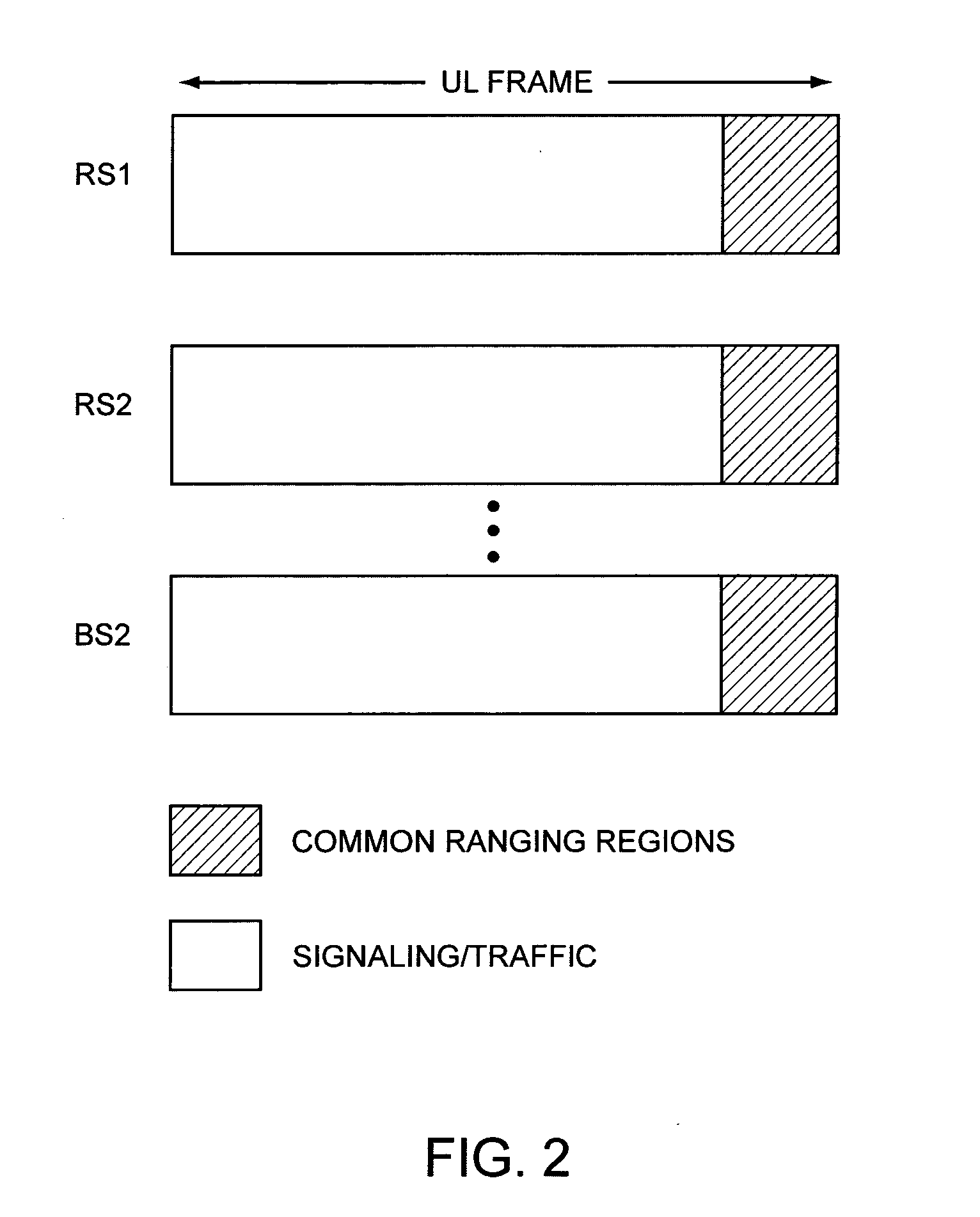
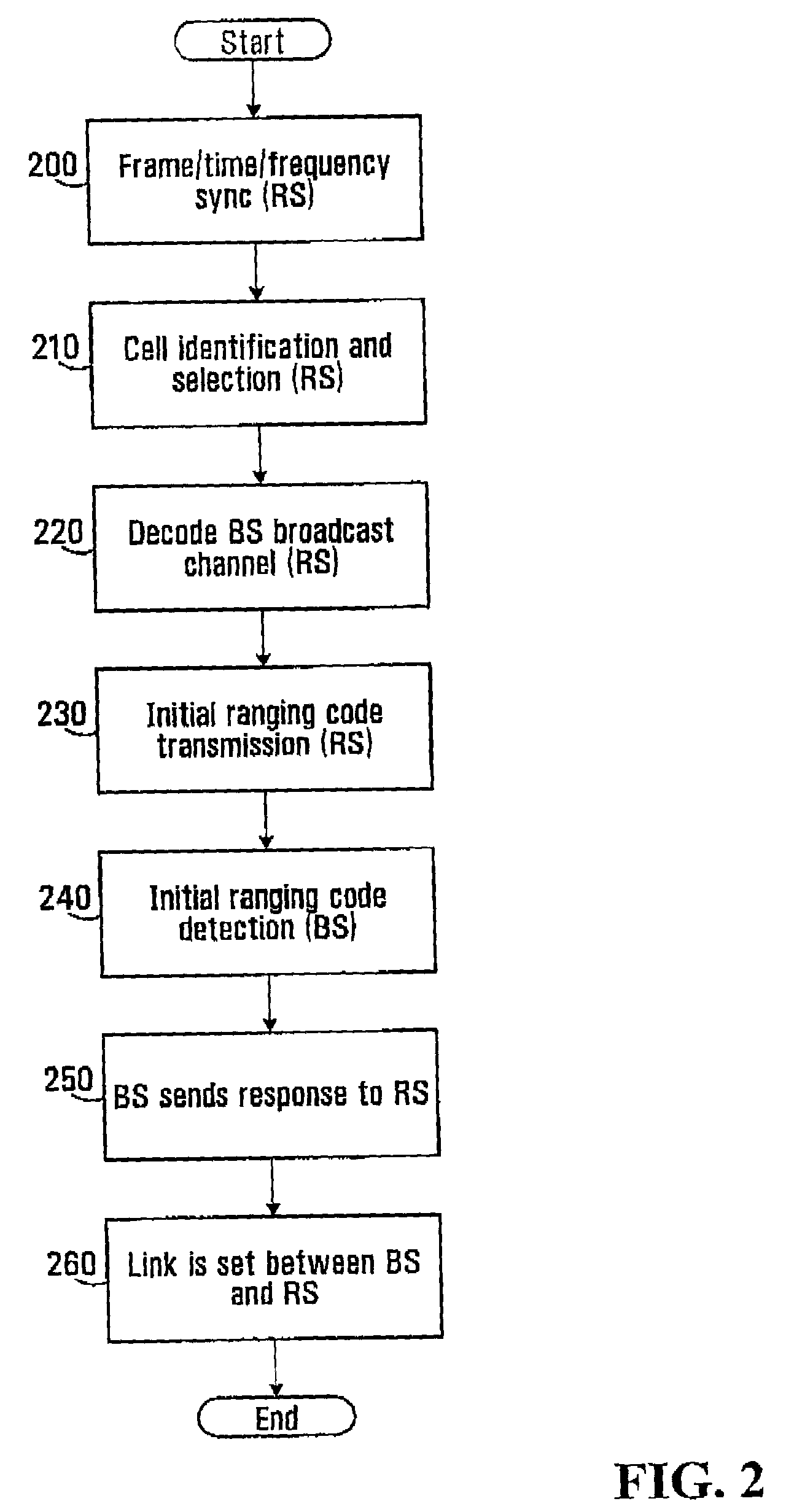
Ranging regions for wireless communication relay stations
ActiveUS20090073916A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexMobile stationRange function
One embodiment of the present invention provides a unique ranging technique in wireless communication environments that employ relay stations associated with a base station. Each relay station, and optionally the base station itself, can be allocated a unique ranging region having unique ranging resources that may be used by a mobile station to initiate a ranging function with the corresponding relay station or base station.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Wireless communication system
InactiveUS20060111047A1Efficient use ofLow frequency wireless internet access bandwidth isNetwork topologiesRepeater circuitsTransceiverWireless transceiver
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations. The system includes a connecting station with a millimeter wave wireless transceiver in communication with a fiber optic or high-speed cable communication network. The transceiver is adapted to communicate at millimeter wave frequencies higher than 60 GHz with another millimeter wave transceiver at one of the cellular base stations. Each of the base stations serves a separate communication cell. Each base station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another base stations or a millimeter wave transceiver at said at the connecting station. The base stations also are equipped with data transfer means for transferring data communicated through the low frequency transceiver to the millimeter wave wireless transceiver and for transferring data communicated through the millimeter wave wireless transceiver to the low frequency wireless transceiver. In preferred embodiments the system a part of a telephone system, an Internet system or a computer network.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
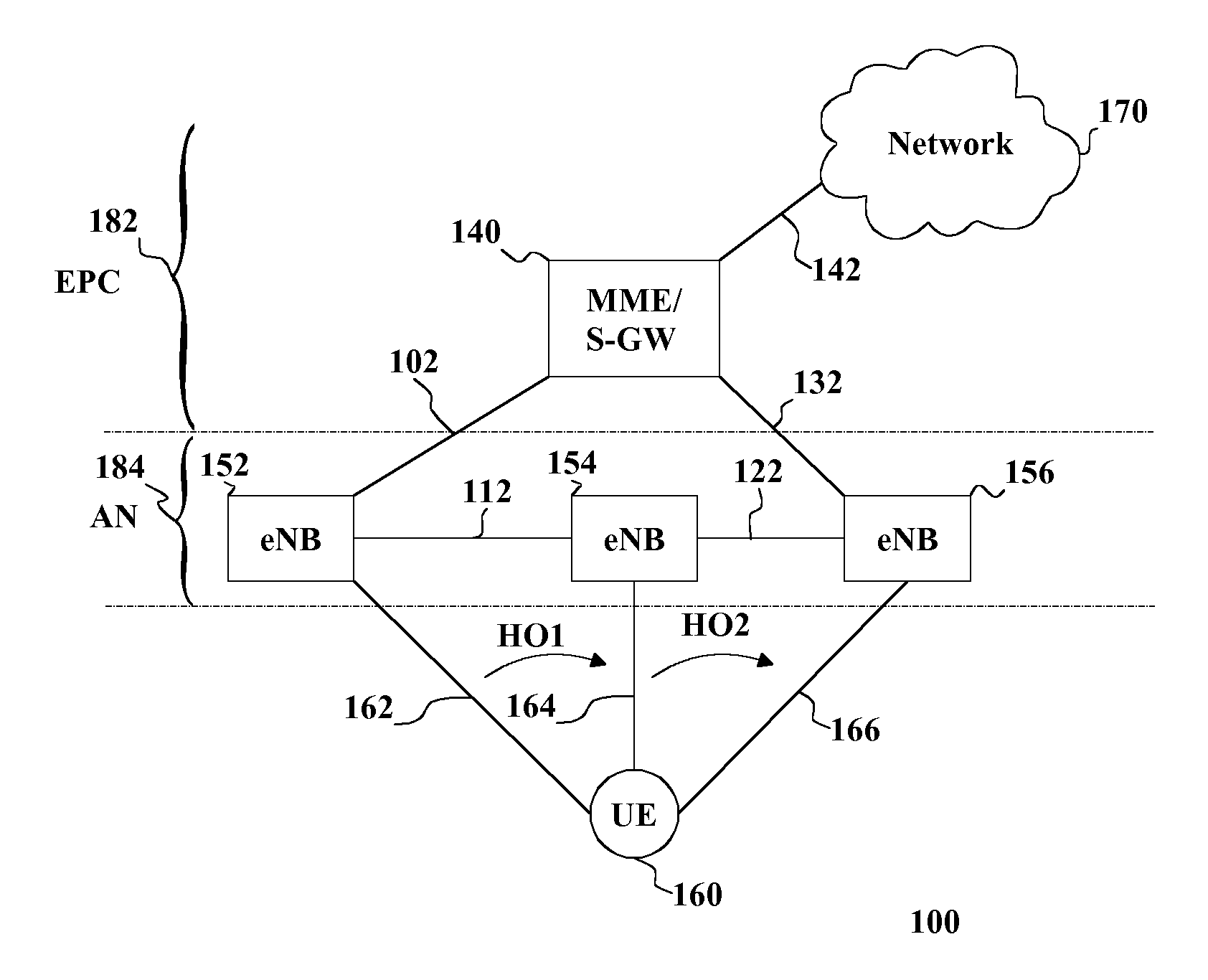
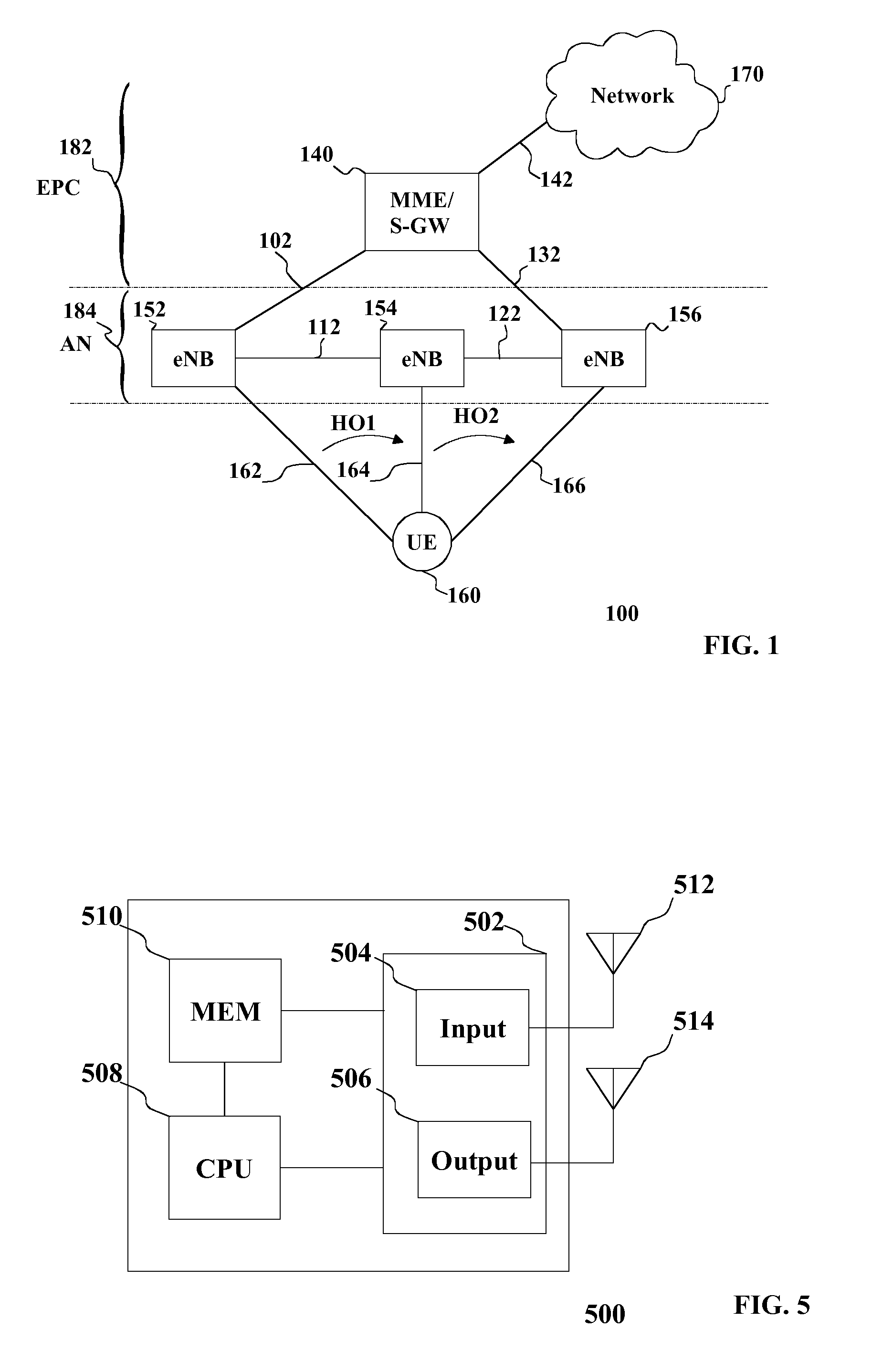
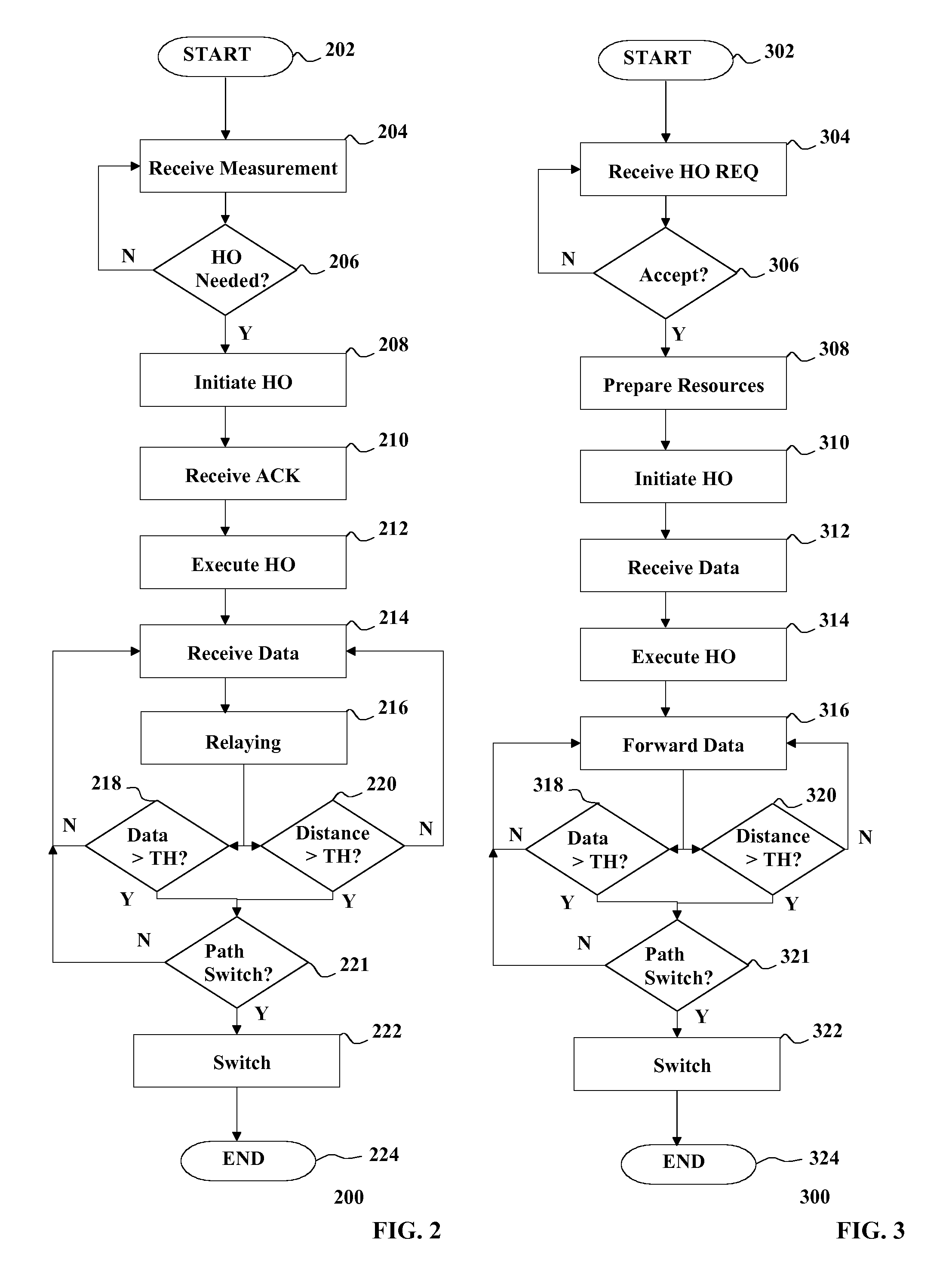
Handover of Connection of User Equipment
InactiveUS20130201904A1Increase profitLess capacityFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexAccess networkHandover
There is provided initiating a handover of a connection of user equipment, the connection including a path from an access network to a core network and switching the path to the core network on the basis of data received on the connection exceeding a threshold.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Zones for wireless networks with relays
ActiveUS20090303918A1Easy to detectAvoid collisionFrequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsDistribution methodMobile station
Methods and systems are provided for use with wireless networks having once or more cell in which each cell includes a base station (BS), at least one relay station (RS) and at least one mobile station (MS). The at least one relay station can be used as an intermediate station for providing communication between the BS and MS. Methods are provided for an RS to initially access the network, access of the RS by MSs initially accessing the network, methods of allocating OFDM resources for communicating between the BS, RS and / or MS for example dividing transmission resources into uplink and downlink transmissions, and methods of inserting pilot symbols into transmission resources used by the RS. In some embodiments on the invention, the methods are consistent and / or can be used in conjunction with existing standards such as 802.16e.
Owner:APPLE INC
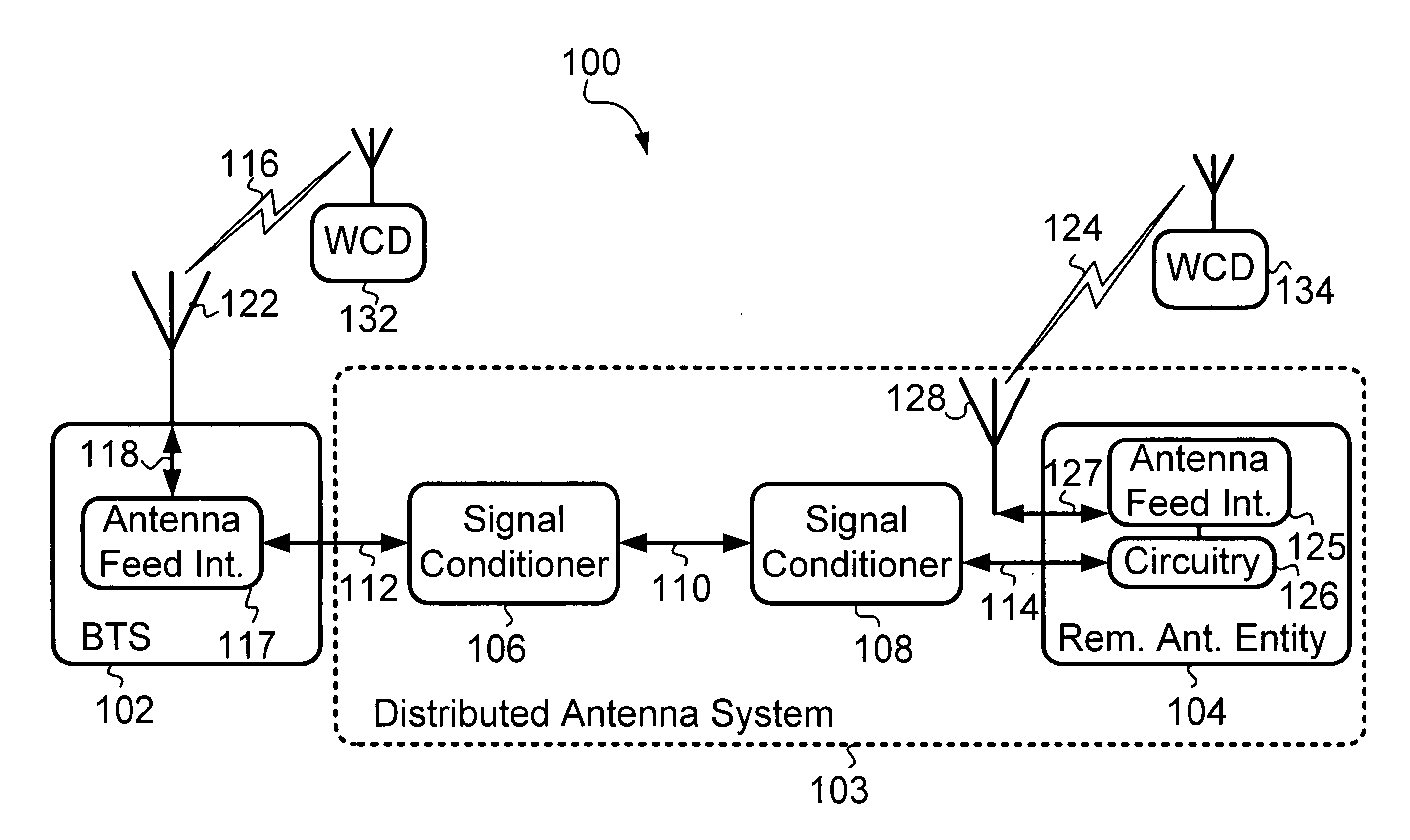
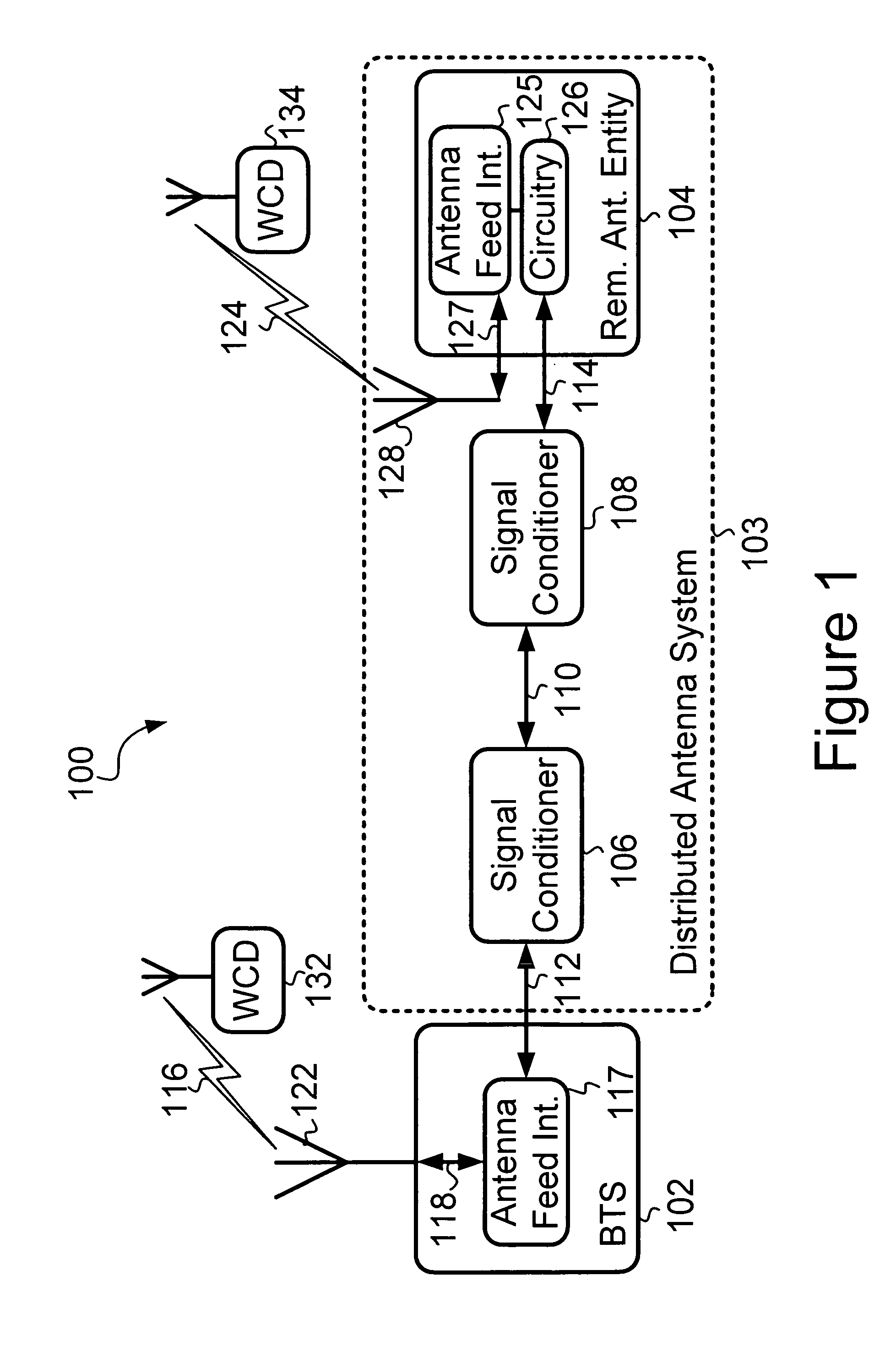
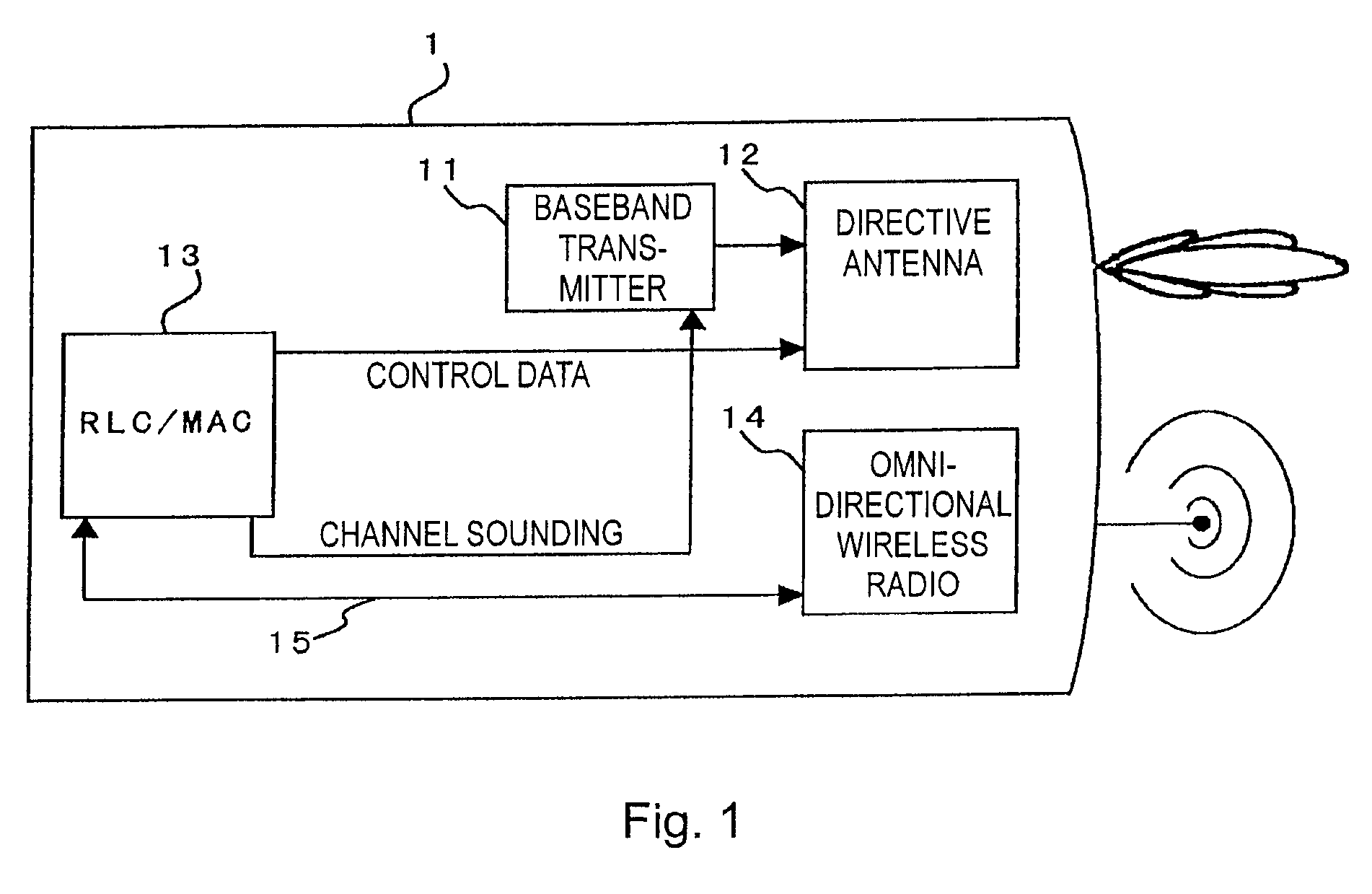
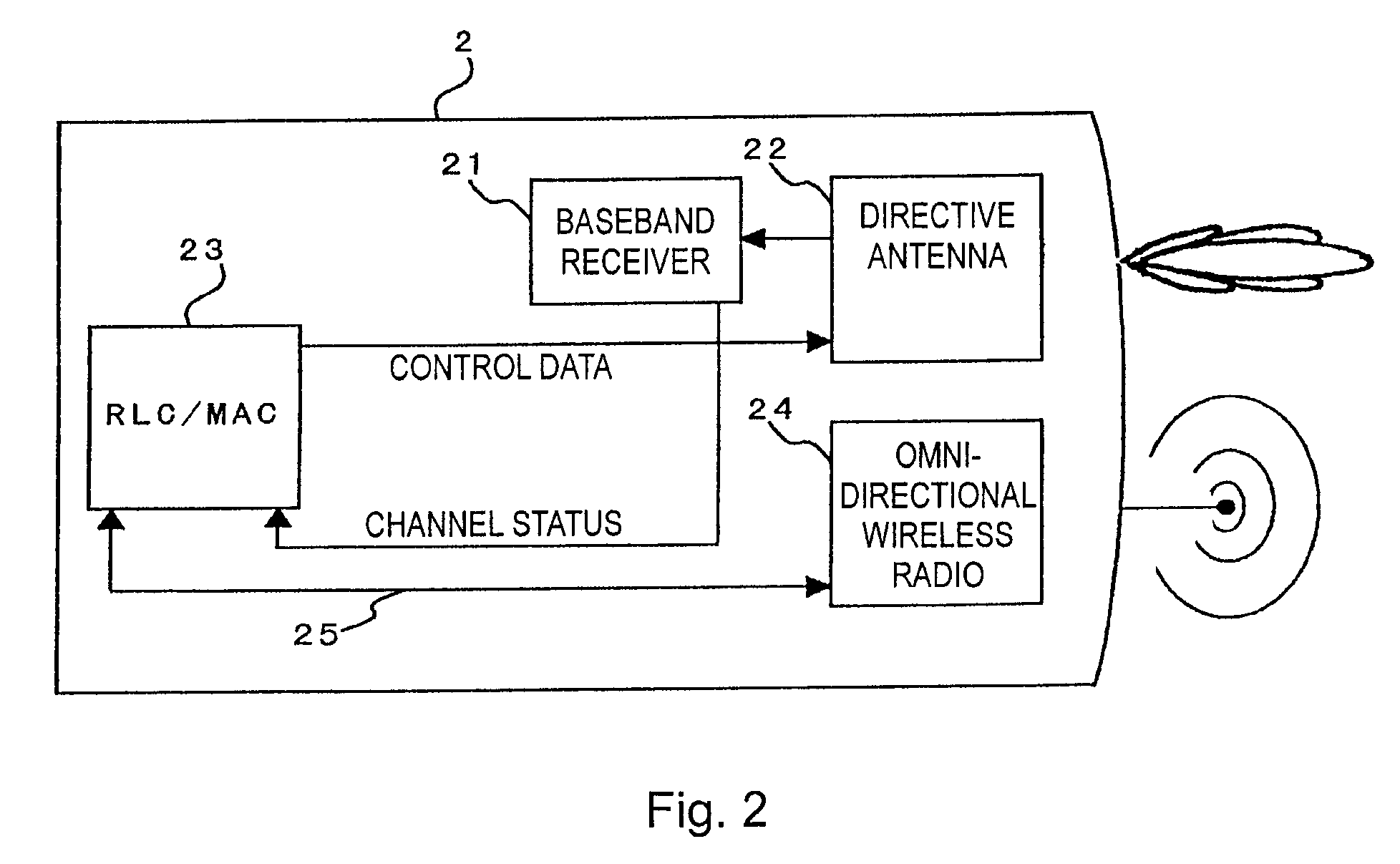
Cellular systems with distributed antennas
InactiveUS8090379B2Efficient use ofLow frequency wireless internet access bandwidth isInformation formatNetwork topologiesWireless transceiverTransceiver
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations, each including at least transport management equipment and broadband equipment, at least one of which supports at least remote cellular station including RF equipment for communication with users of cellular devices. The system includes at lease one wireless narrow beam communication link operating at millimeter wave frequencies in excess of 60 GHz connecting a remote cellular station with a cellular base station equipped with broad band conversion electronic equipment and transport management equipment. In preferred embodiment the communication system includes a large number of remote cellular stations with each remote cellular station serving a separate communication cell. Each remote cellular station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a narrow beam millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another remote cellular station or a millimeter wave transceiver at a base station.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
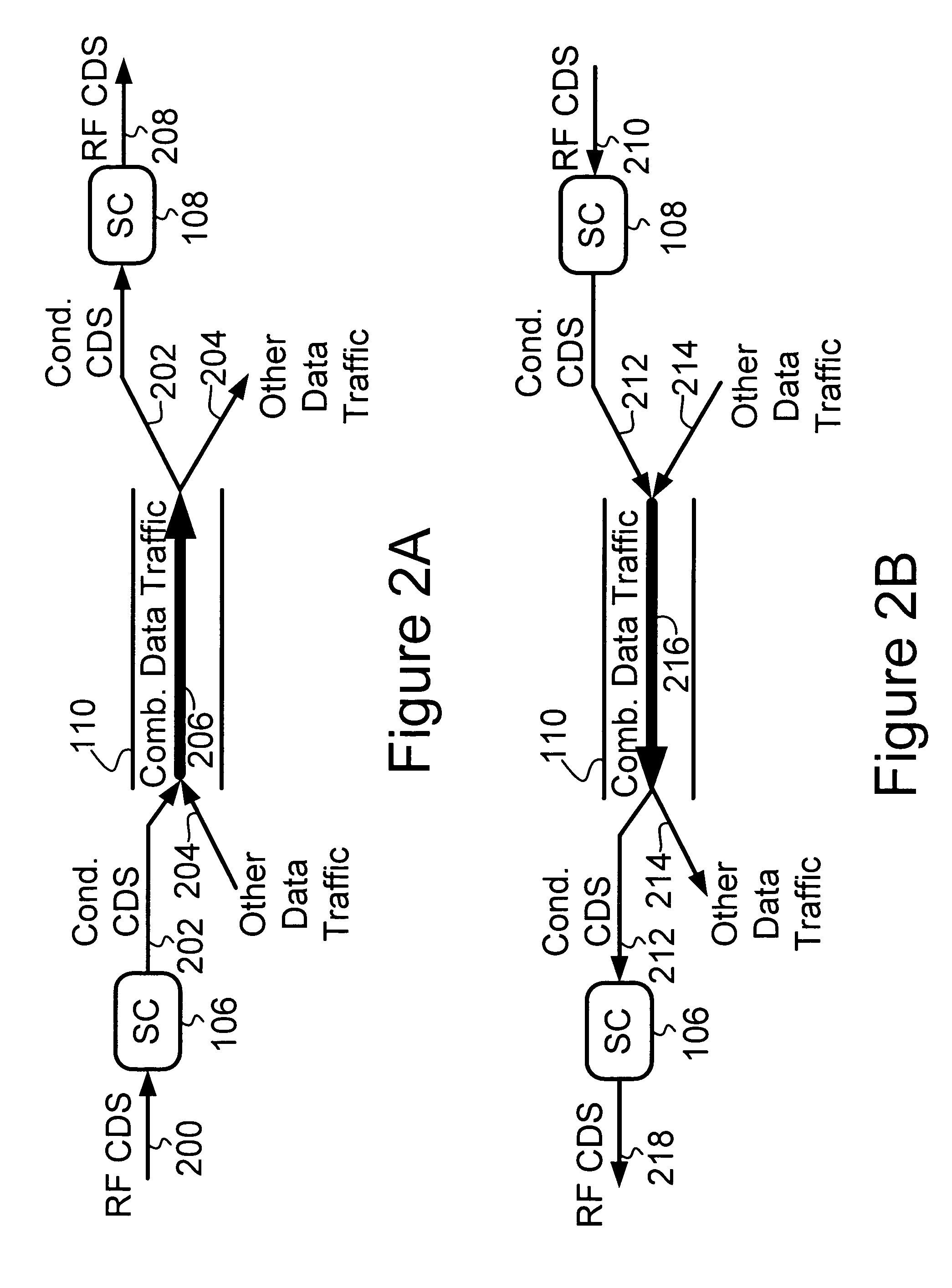
Signal conditioner and method for communicating over a shared transport medium a combined digital signal for wireless service
ActiveUS7634250B1Less bandwidthEasy to usePower distribution line transmissionRepeater circuitsTransport mediumEngineering
A signal conditioner (SC) and method for performing communications via a shared transport medium between a base transceiver station (BTS) and a remote antenna entity (RAE). A first SC is connected to the BTS and a second SC is connected to the RAE. Each SC interfaces to the transport medium. The first SC receives an RF signal representing a combined digital signal (CDS) from the BTS. The first SC recovers and conditions the CDS, and then transmits the conditioned CDS to the second SC via the transport medium. The second SC receives the conditioned CDS, recovers the CDS, produces an RF signal representing the CDS, and transmits this RF signal to the RAE. The RAE sends this RF signal to an antenna of the RAE for transmission of this RF signal via the antenna. First SC and second SC also facilitate communication of a CDS from RAE to BTS.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
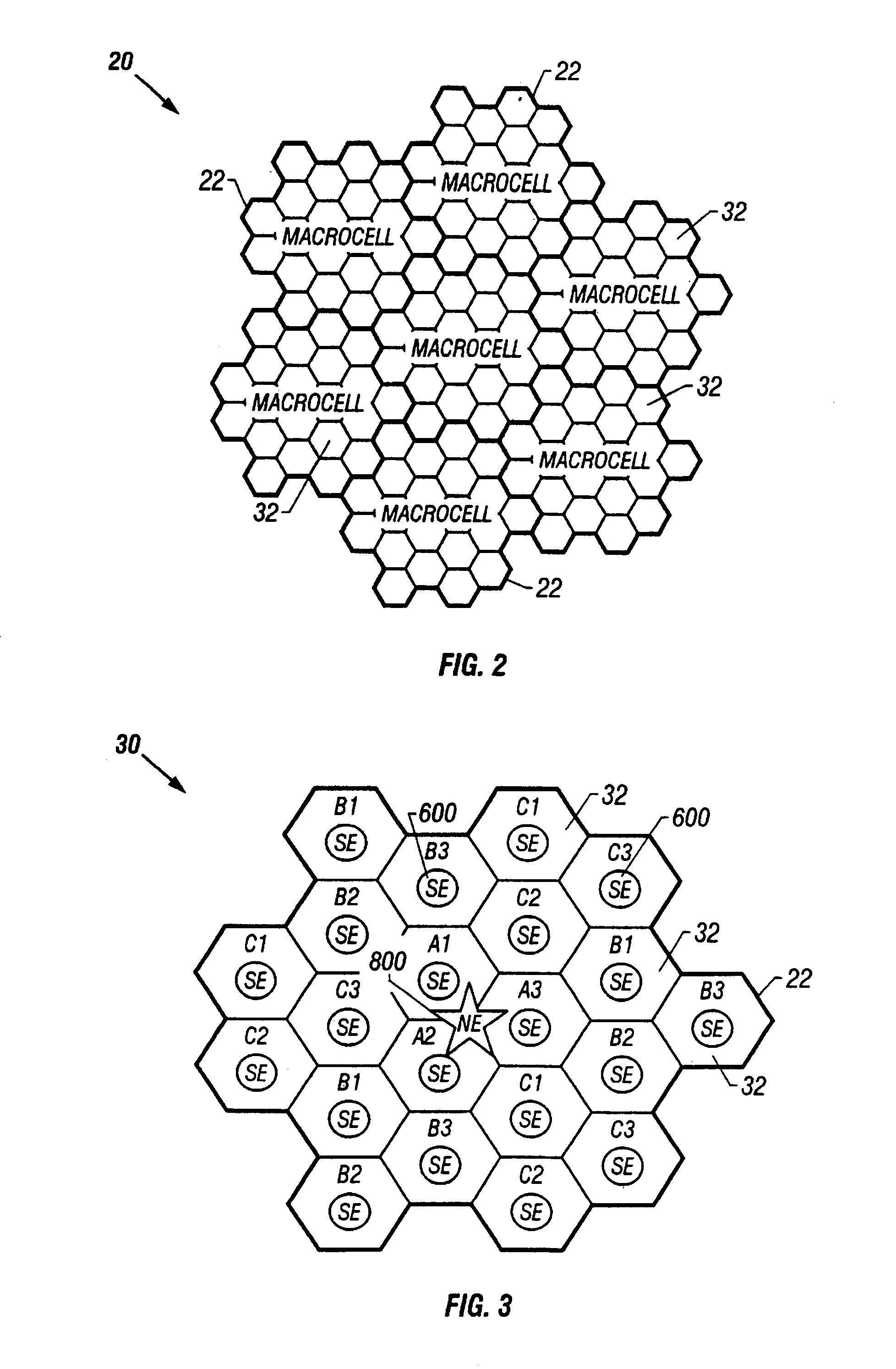
Wireless communication device with multiple external communication links
InactiveUS6842617B2Operational securityCollect revenuePower distribution line transmissionRepeater circuitsTelecommunications linkPopulation density
A decentralized asynchronous wireless communication system is disclosed for providing voice and data communication that allows flexibility of communication paths for local communication or for communication to external networks. The system makes use of communication docking bays that may communicate in a local mode with other communication docking bays or handsets within a same microcell via signal extenders. In an extended mode, a communication docking bay located in a first microcell of a first macrocell may communicate with a second communication docking bay or handset in a second microcell of the first macrocell via signal extenders and a network extender. In a remote mode, a communication docking bay located in a first microcell of a first macrocell may communicate with a second communication docking bay or handset in a second microcell of a second macrocell via signal extenders and network extenders. The communication docking bays also provide a communication path to a Public Switch Telephone Network and other communication medium. This feature provides an alternate means of connecting a mobile handset to a Public Switch Telephone Network without communicating through a network extender. The system is particularly suitable for operation in rural areas having a low population density.
Owner:WAHOO COMM CORP
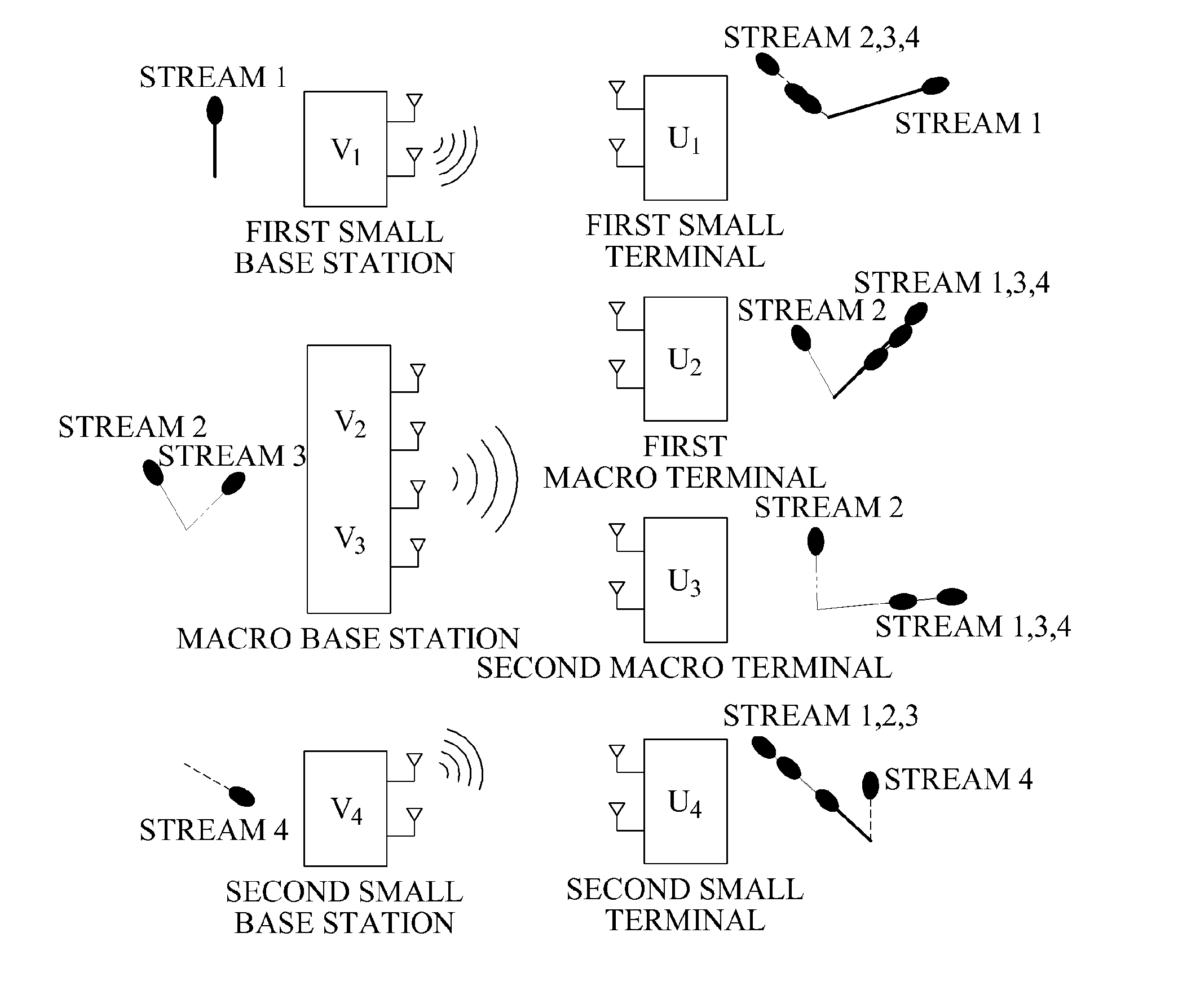
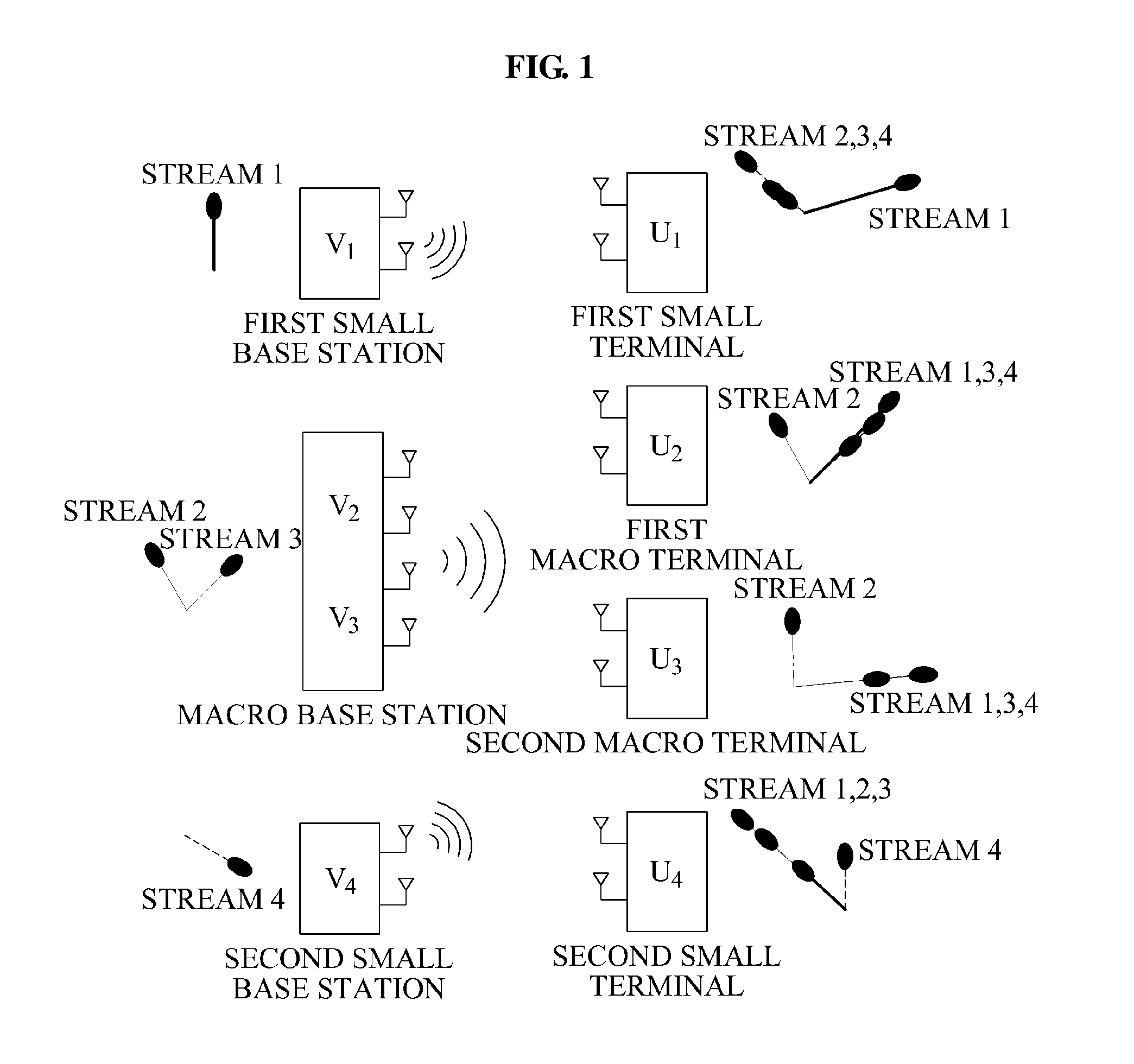
Method and apparatus for determining downlink beamforming vectors in hierarchical cell communication system
InactiveUS20120077485A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionDownlink beamformingCommunications system
Provided is a method and apparatus for determining a downlink beamforming vector in a hierarchical cell communication system. Small base stations may determine transmit beamforming vectors of the small base stations so that interference from the small base stations may be reduced in a macro terminal. A macro terminal and small terminals may determine receive beamforming vectors based on the transmit beamforming vectors of the small base stations. A macro base station may determine a transmit beamforming vector based on effective channels to terminals using the receive beamforming vectors of the terminals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
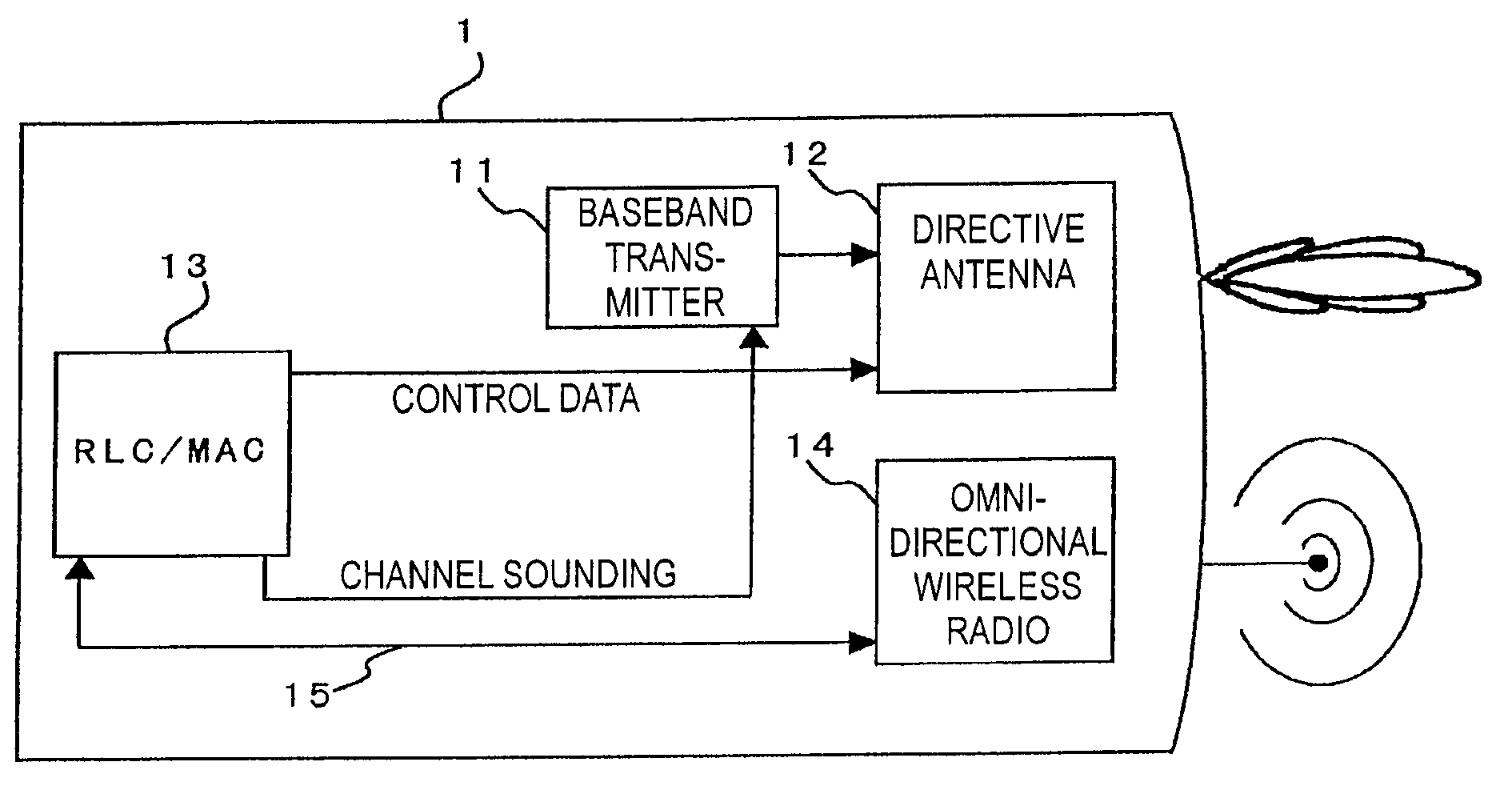
Out-of-band radio link protocol and network architecture for a wireless network composed of wireless terminals with millimetre wave frequency range radio units
ActiveUS20110053498A1Optimization rangeStable flowRadio relay systemsWireless communicationNetwork architectureDirectional antenna
The present invention relates to a wireless transmitter comprising a transmitter radio unit working a wireless transmitter comprising a transmitter radio unit working in the millimeter wave frequency band using a directional antenna and a bidirectional radio unit working in a frequency range different from said transmitter radio unit and using an omnidirectional antenna. The invention further relates to a wireless receiver and a wireless relay.
Owner:SONY CORP
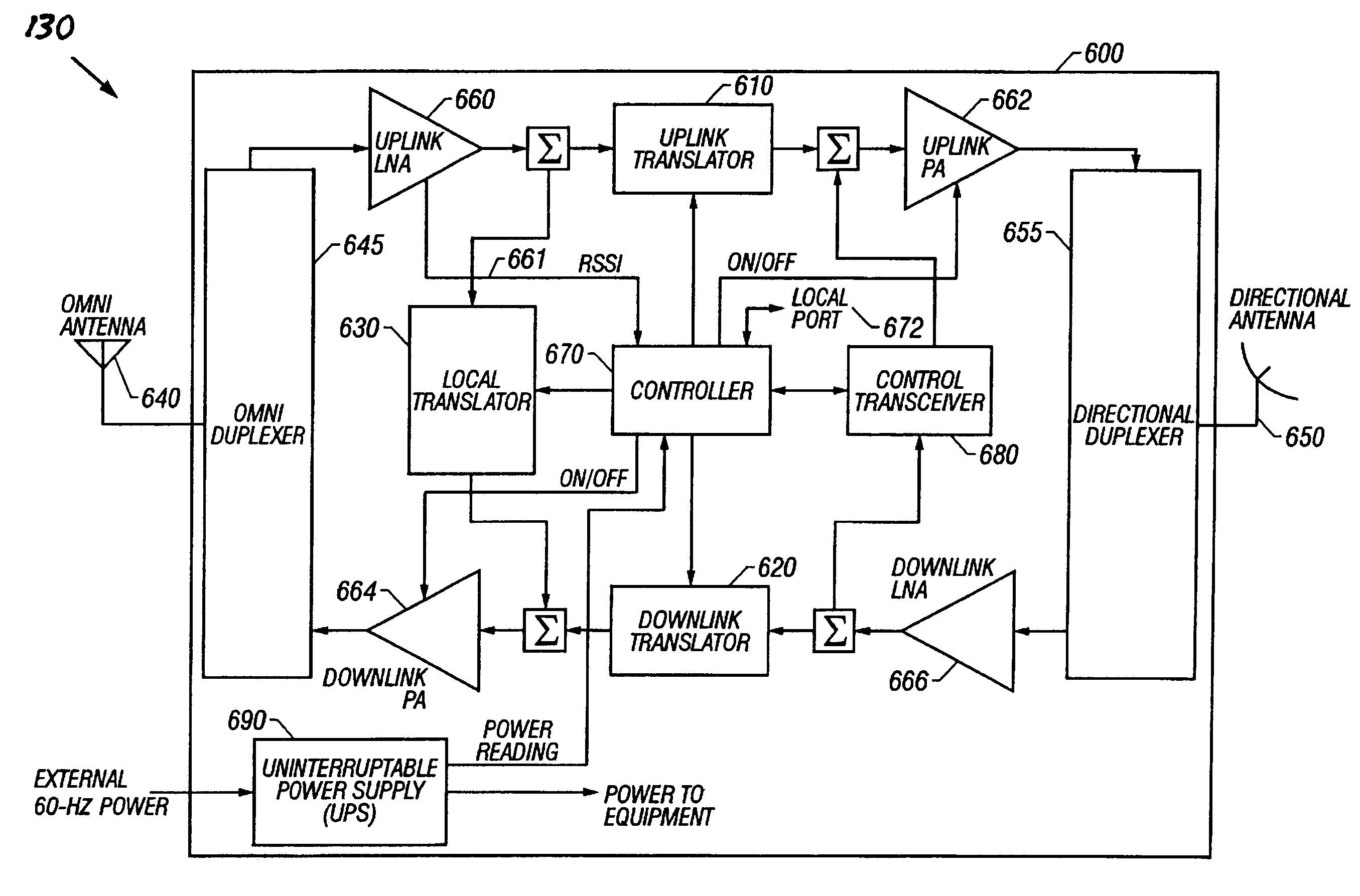
Reverse link power controlled repeater
InactiveUS20030123401A1Power managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemEngineering
The invention provides a mechanism for automatically setting reverse link gain or power for a repeater (120) used in a communication system (100) through the use of the reverse link power control of a built-in wireless communications device. By embedding a wireless communication device (430, 630, 700) inside the repeater and injecting reverse link signals of the embedded device into the reverse link of the repeater (124A, 124B), the gain of the repeater is maintained relatively constant. The embedded WCD can also be activated on a periodic basis to make calls and utilize reverse link power-control to calibrate or re-calibrate the gain of the repeater, making it a power-controlled repeater.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for automatic control of rf level of a repeater
A method and apparatus for controlling an output power level of a radio frequency (RF) repeater (100 or 200). A system includes a receiver to receive a signal, a filtering unit configured to pass frequency components at or around a frequency band of a predetermined communication channel, an attenuator (124 or 142) to produce an attenuated signal by attenuating a parameter of the signal, a power amplifier (150) to adjust the output power level of repeater to a desired level by adjusting the gain of one or more components of the system, and a microprocessor (170) to receive an input responsive to the output power level of the repeater and, in response to the input, to transfer control signals to the receiver and the attenuator. The method includes sampling traffic load characteristics during operation of a network and adjusting a gain of one or more components of the repeater based on the traffic load characteristics.
Owner:AXELL WIRELESS
Wireless network repeater
InactiveUS20060098592A1OptimizationQuickly reconfiguredSite diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemRepeater
A frequency translating repeater (250) for use in a time division duplex radio protocol communications system includes a processor (260), a bus (261), a memory (262), an RF section (264), and an integrated station device (264). An access point (210) is detected based on information transmitted frequency channels using a protocol. Detection is initiated automatically during a power-on sequence or by activating an input device such as a button. Frequency channels are scanned for a beacon signal and an access point chosen as a preferred access point based on a metric such as power level.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
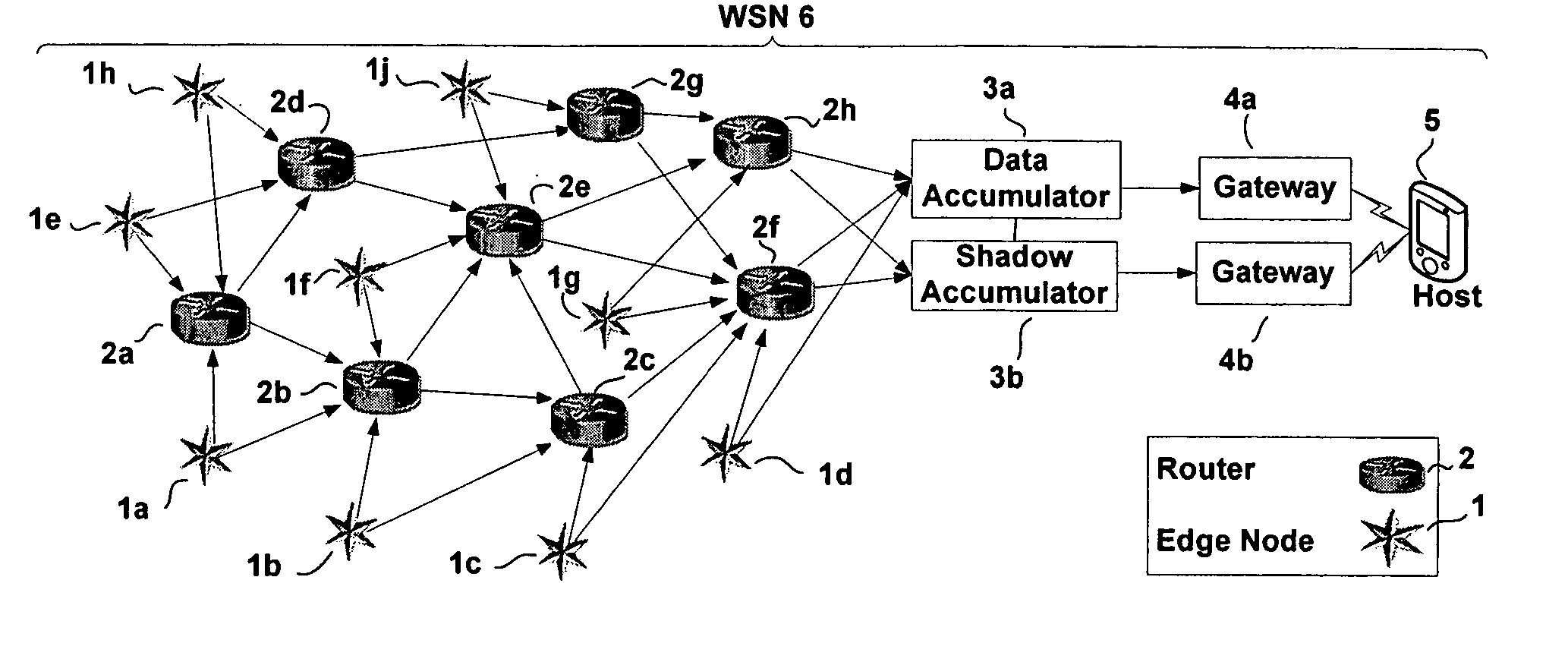
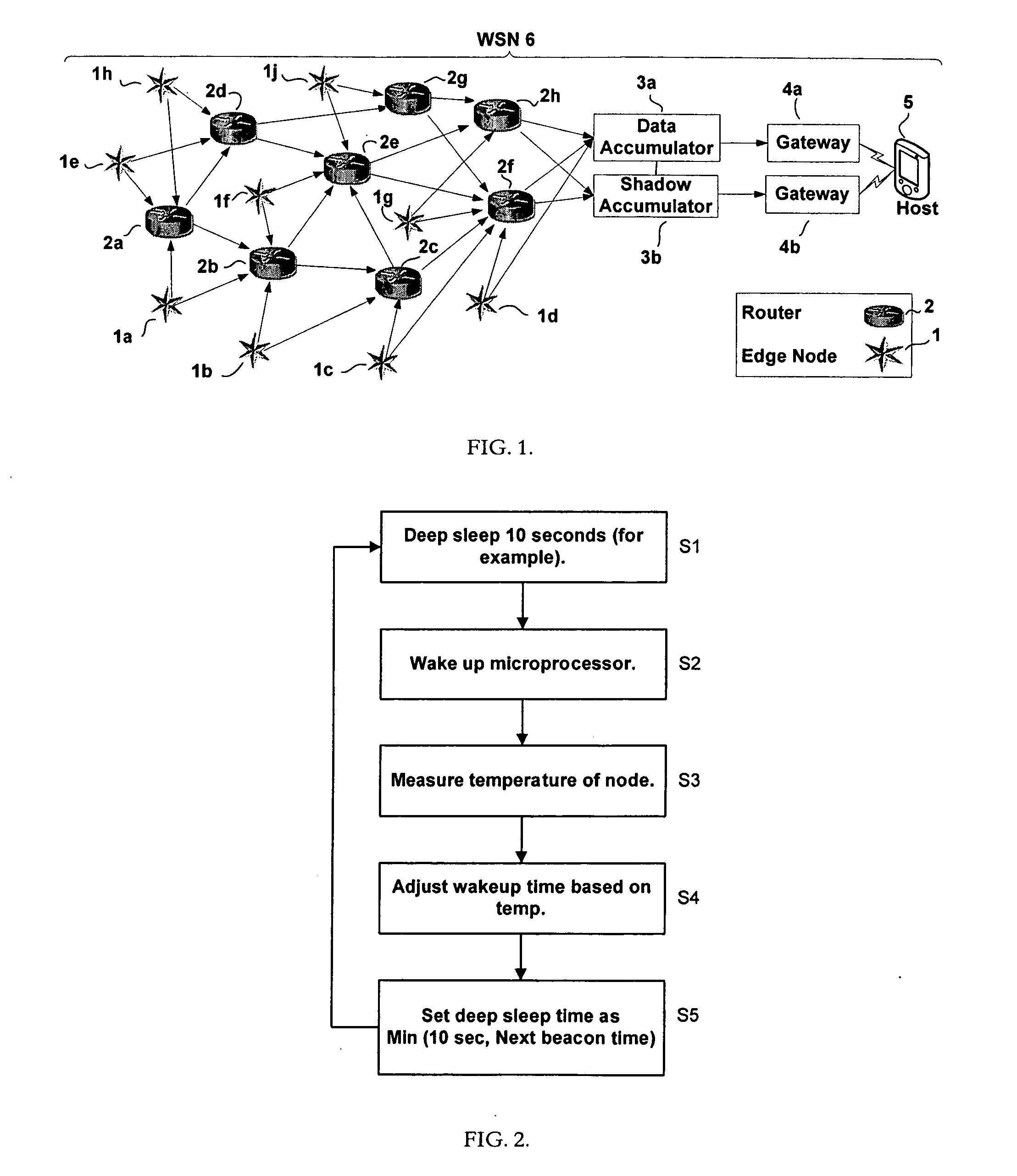
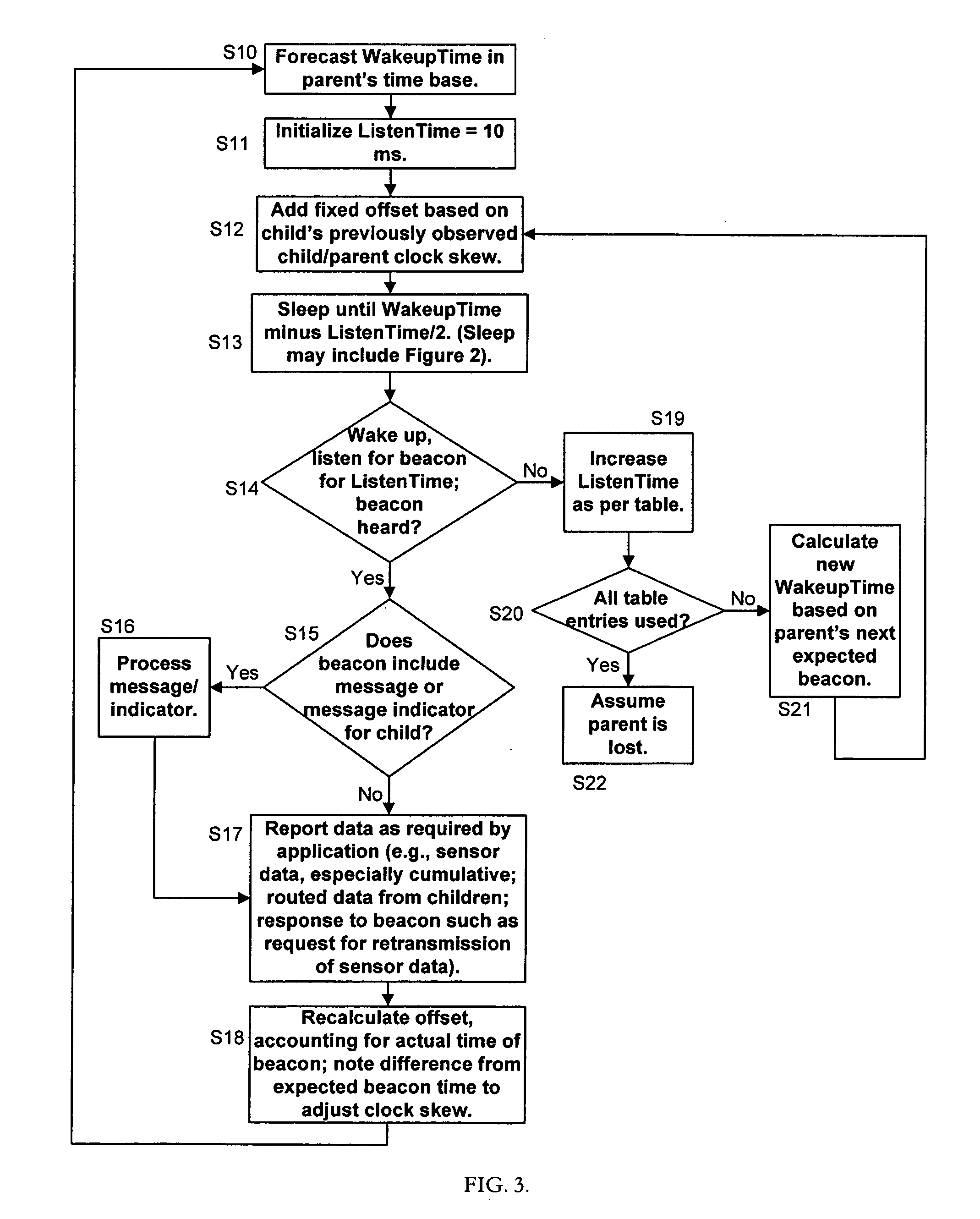
Method for reporting and accumulating data in a wireless communication network
ActiveUS20060187866A1Affect operationAffect abilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime managementEdge node
A method and apparatus for coordinating communication in a wireless sensor network may include a plurality of nodes, such as routers, edge nodes, data accumulators and / or gateways. Time management functions, such as determining an elapsed time, may be controlled based on a detected temperature, e.g., a temperature detected at a node, and / or based on a detected clock skew between two or more clocks in two or more different devices. Accurate time management may allow for devices to more accurately coordinate communication instances, e.g., communication that occurs at periodic wake up times. A cluster head, such as a data accumulator, may be associated with a network after its initial formation and cause nodes in the network to alter their hierarchy in the network, thereby making the cluster headaccumulator a parent to nodes in the network. Nodes having a relatively lower hop count may have a higher battery capacity than nodes having a higher hop count.
Owner:YOKOGAWA USA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com