Patents
Literature
784 results about "Narrow beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
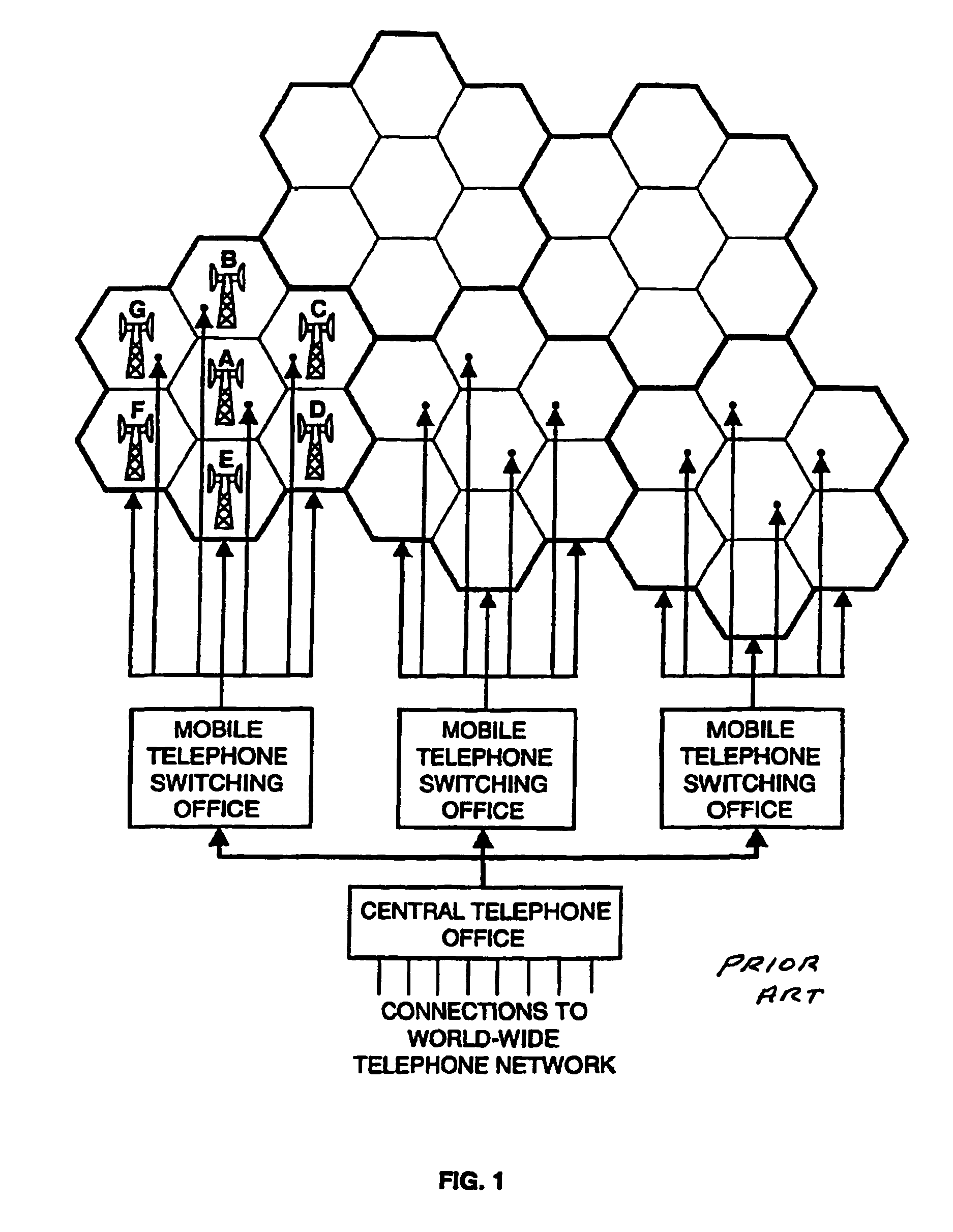
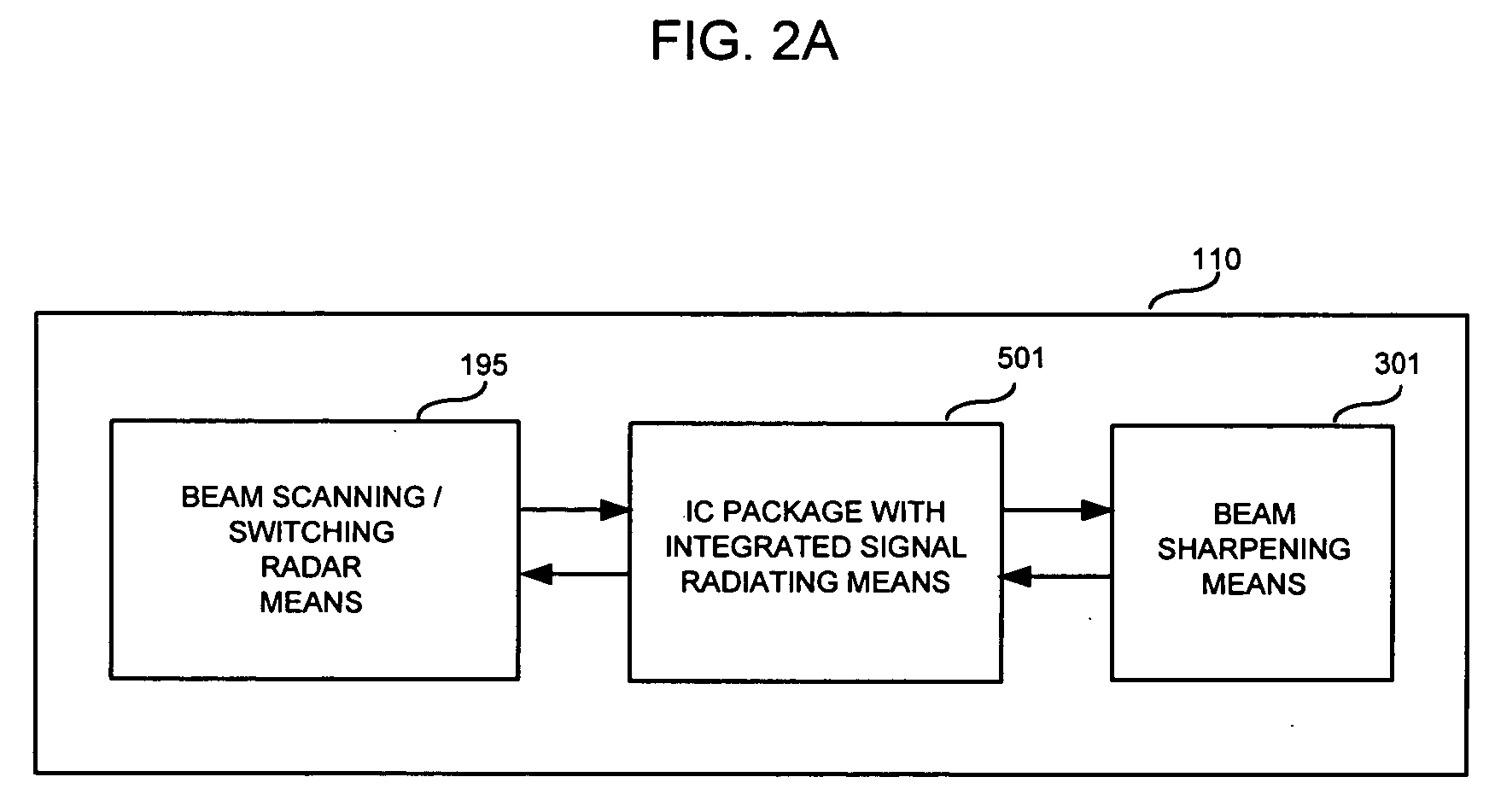
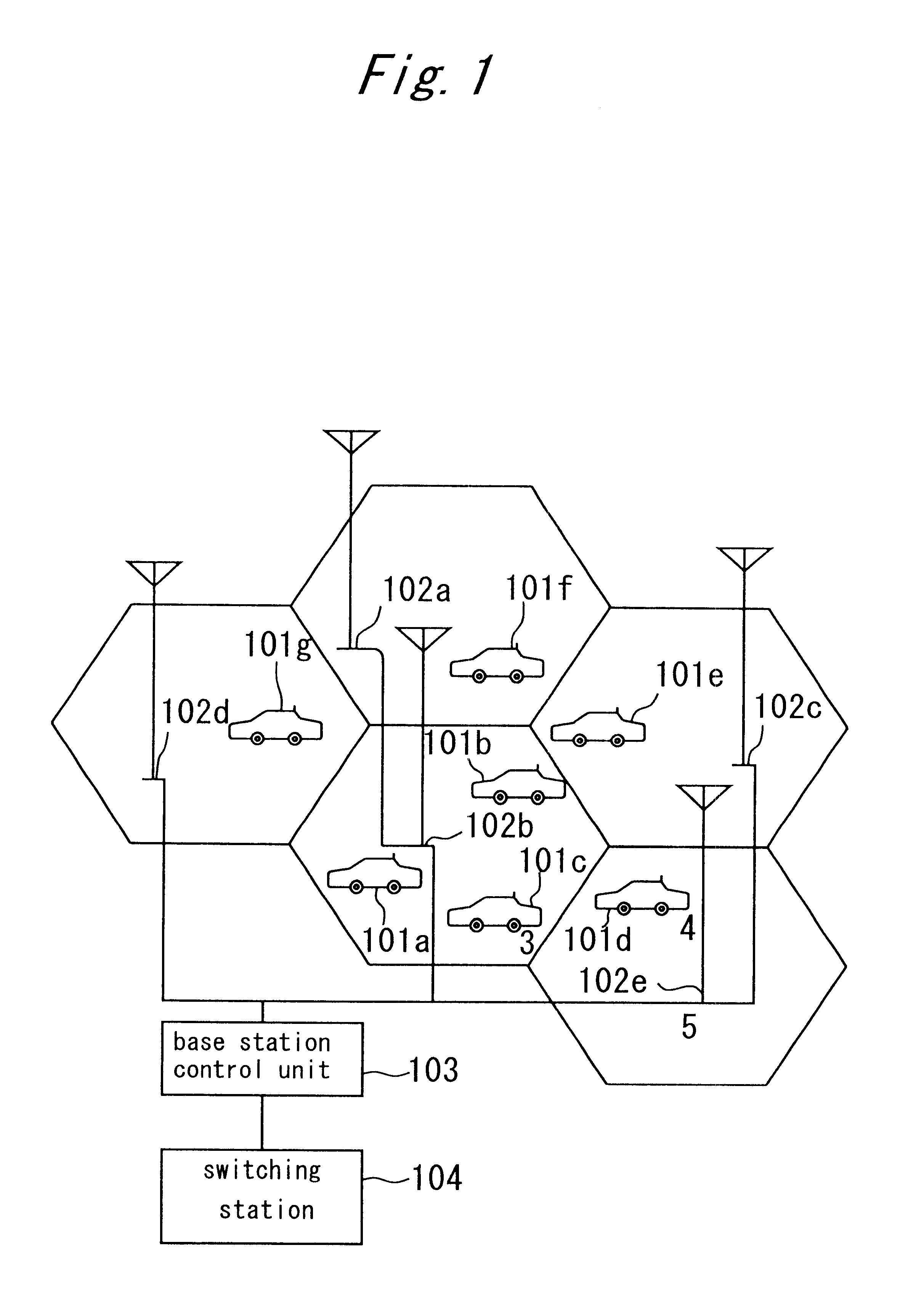
Cellular systems with distributed antennas
InactiveUS20090258652A1Efficient use ofIncrease data rateNetwork topologiesInformation formatWireless transceiverTransceiver
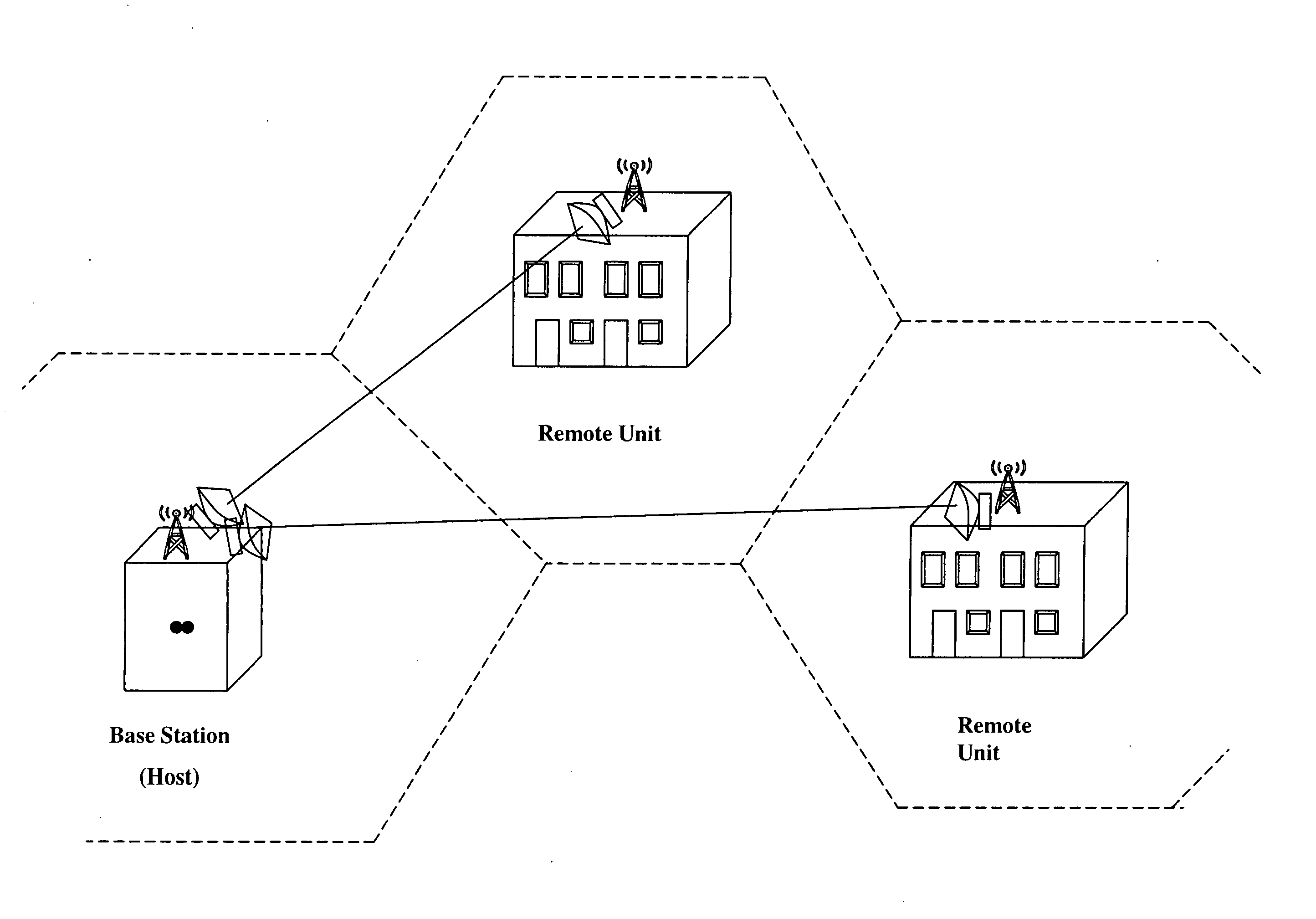
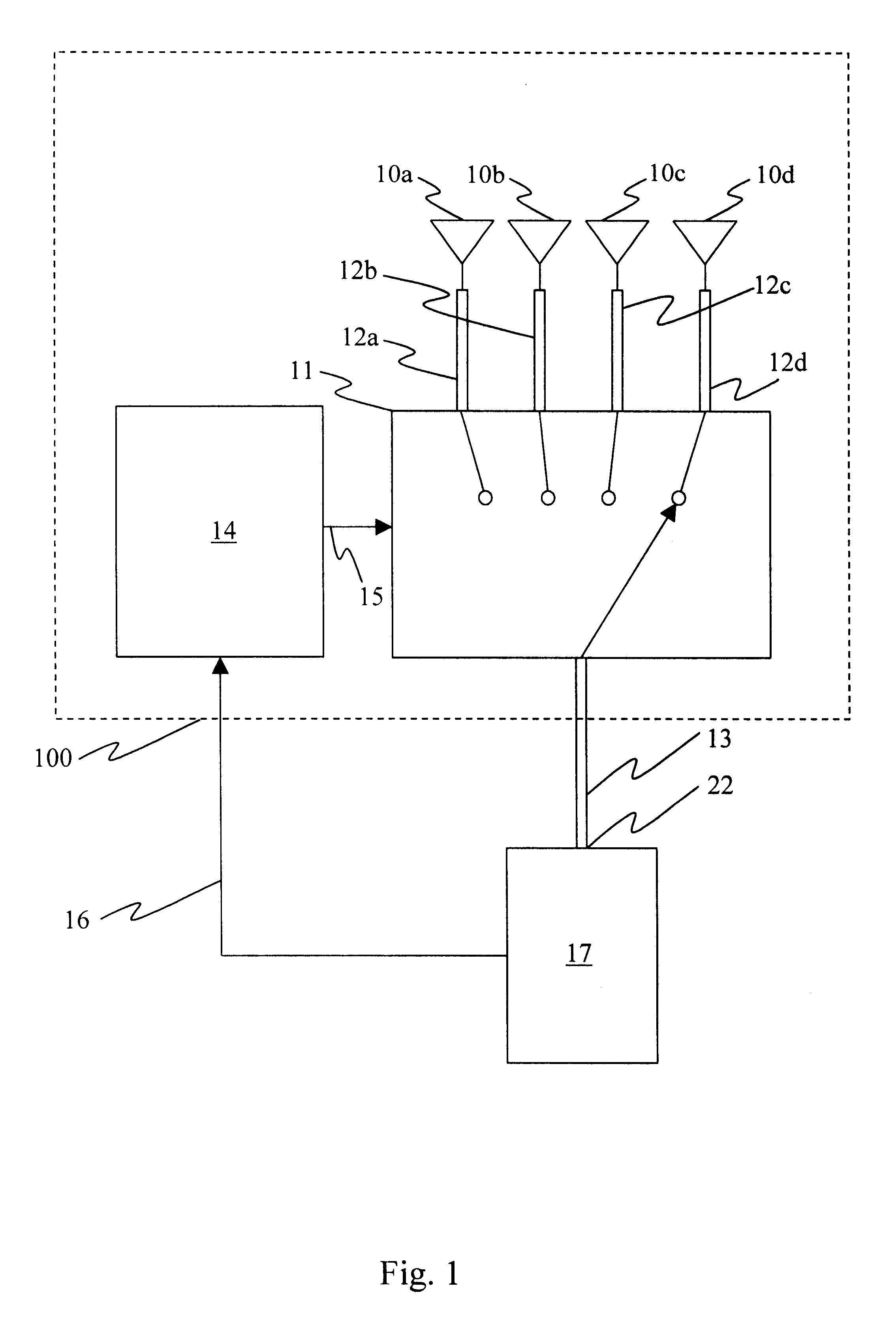
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations, each including at least transport management equipment and broadband equipment, at least one of which supports at least remote cellular station including RF equipment for communication with users of cellular devices. The system includes at lease one wireless narrow beam communication link operating at millimeter wave frequencies in excess of 60 GHz connecting a remote cellular station with a cellular base station equipped with broad band conversion electronic equipment and transport management equipment. In preferred embodiment the communication system includes a large number of remote cellular stations with each remote cellular station serving a separate communication cell. Each remote cellular station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a narrow beam millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another remote cellular station or a millimeter wave transceiver at a base station.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Subscriber based smart antenna
InactiveUS6229486B1Cost effectiveReduce distractionsSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsSystem capacitySignal quality
Owner:KRILE DAVID JAMES
Cellular systems with distributed antennas
InactiveUS8090379B2Efficient use ofLow frequency wireless internet access bandwidth isInformation formatNetwork topologiesWireless transceiverTransceiver
A communication system providing wireless communication among wireless users through a number of cellular base stations, each including at least transport management equipment and broadband equipment, at least one of which supports at least remote cellular station including RF equipment for communication with users of cellular devices. The system includes at lease one wireless narrow beam communication link operating at millimeter wave frequencies in excess of 60 GHz connecting a remote cellular station with a cellular base station equipped with broad band conversion electronic equipment and transport management equipment. In preferred embodiment the communication system includes a large number of remote cellular stations with each remote cellular station serving a separate communication cell. Each remote cellular station is equipped with a low frequency wireless transceiver for communicating with the wireless users within the cell at a radio frequency lower than 6 GHz and a narrow beam millimeter wave wireless transceiver operating at a millimeter wave frequency higher than 60 GHz for communicating with another millimeter wave transceiver at another remote cellular station or a millimeter wave transceiver at a base station.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
System and method for standoff detection of human carried explosives
ActiveUS6967612B1Low-cost and portableRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDisplay deviceCommunication link
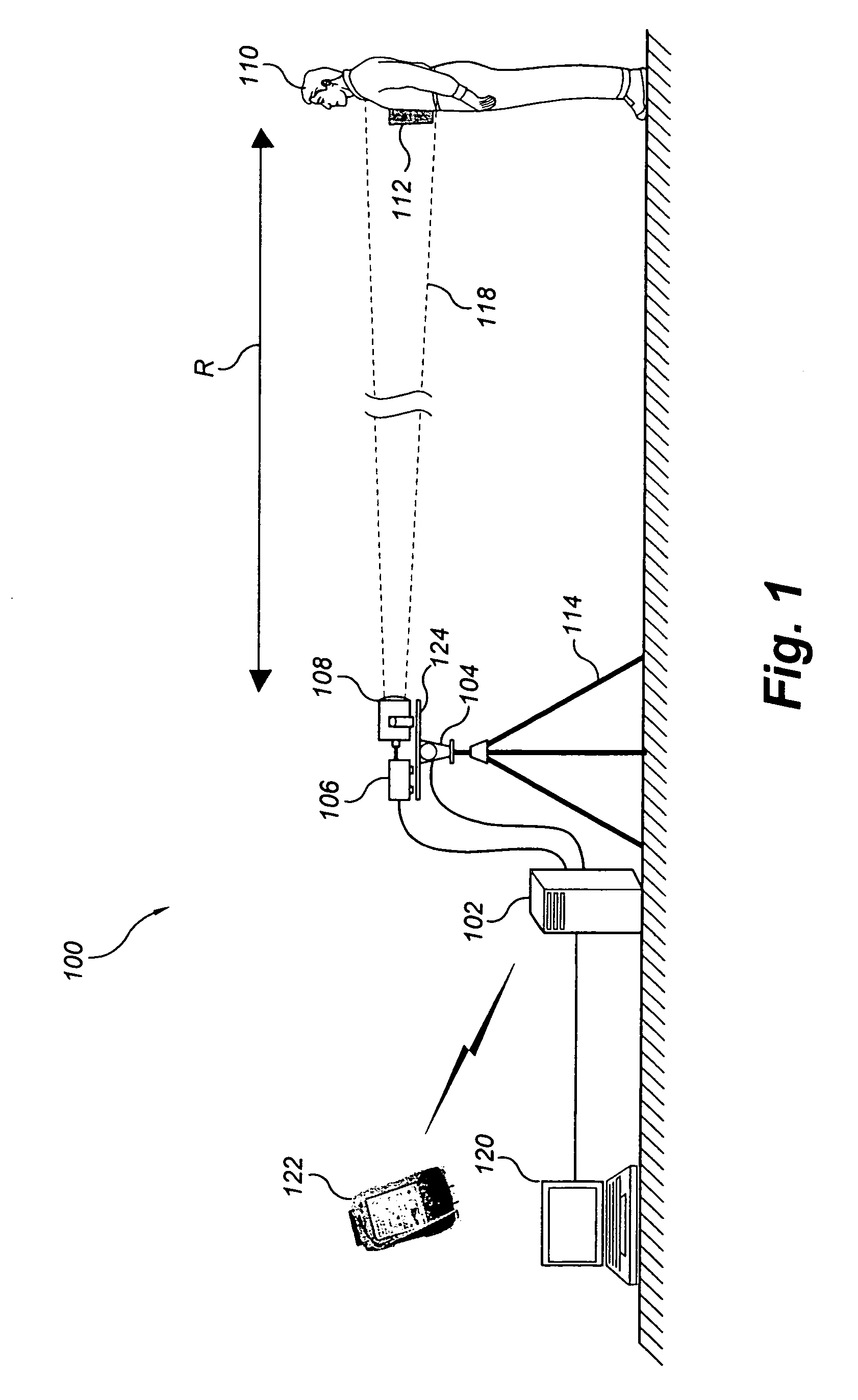
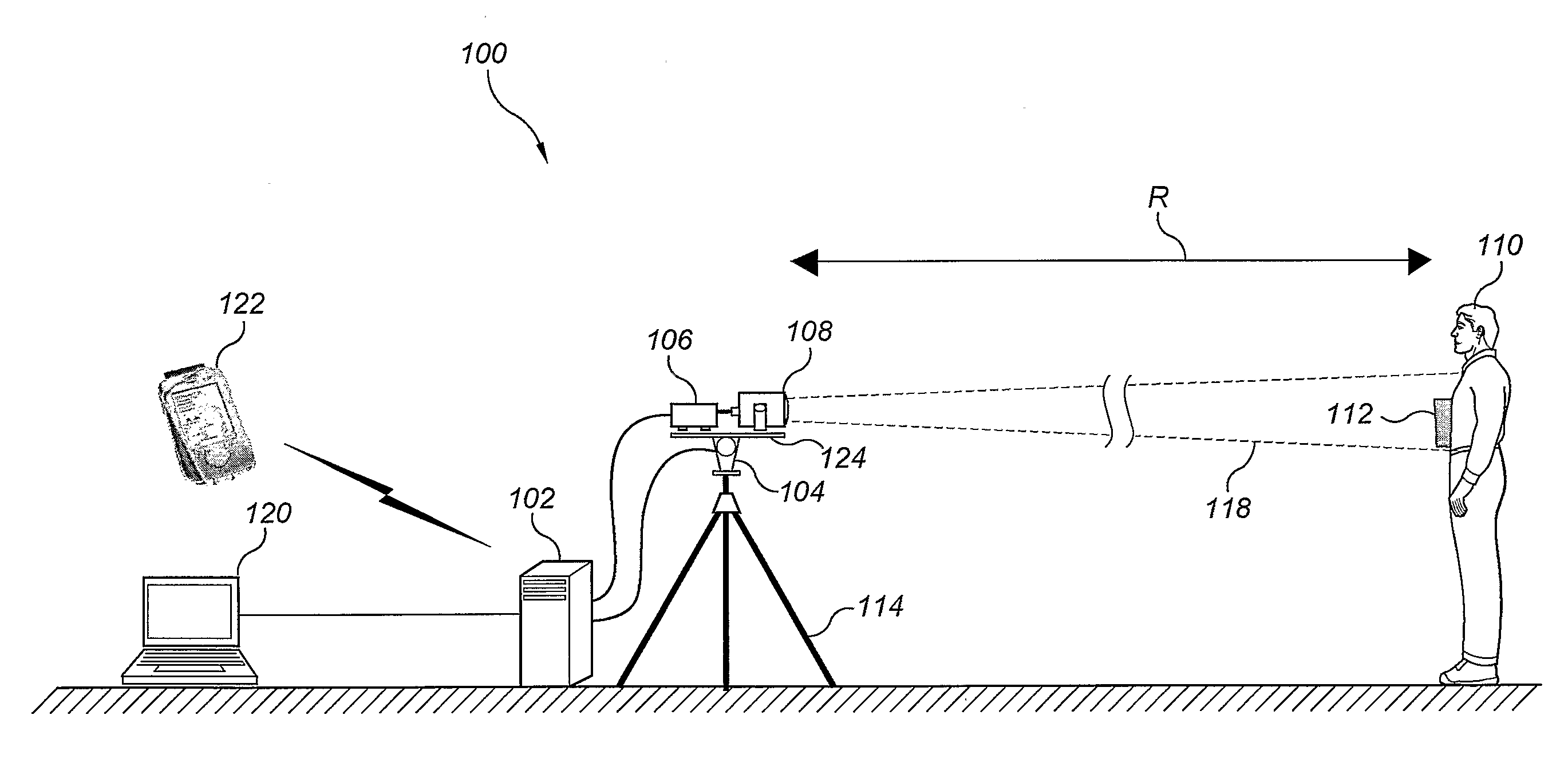
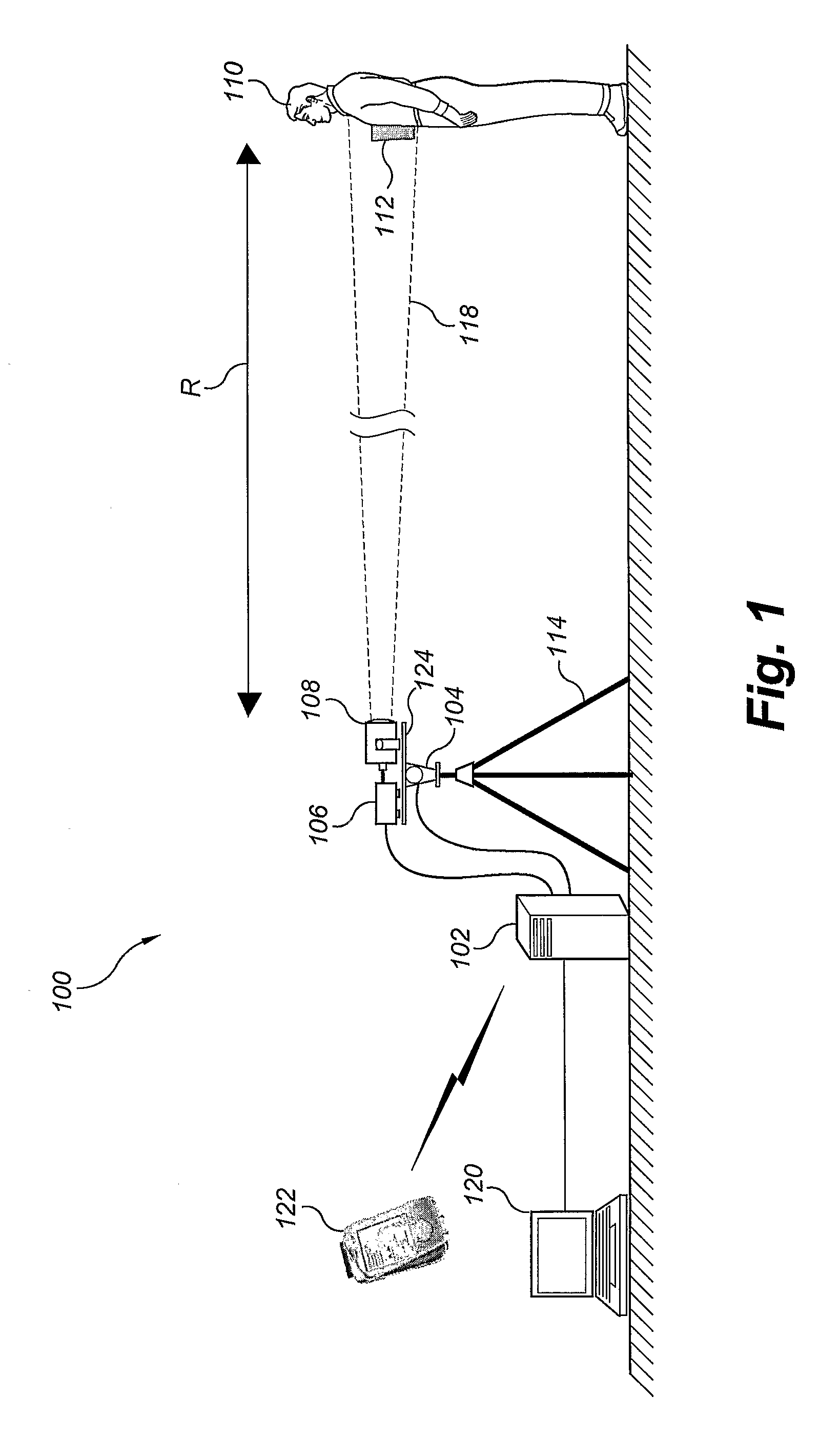
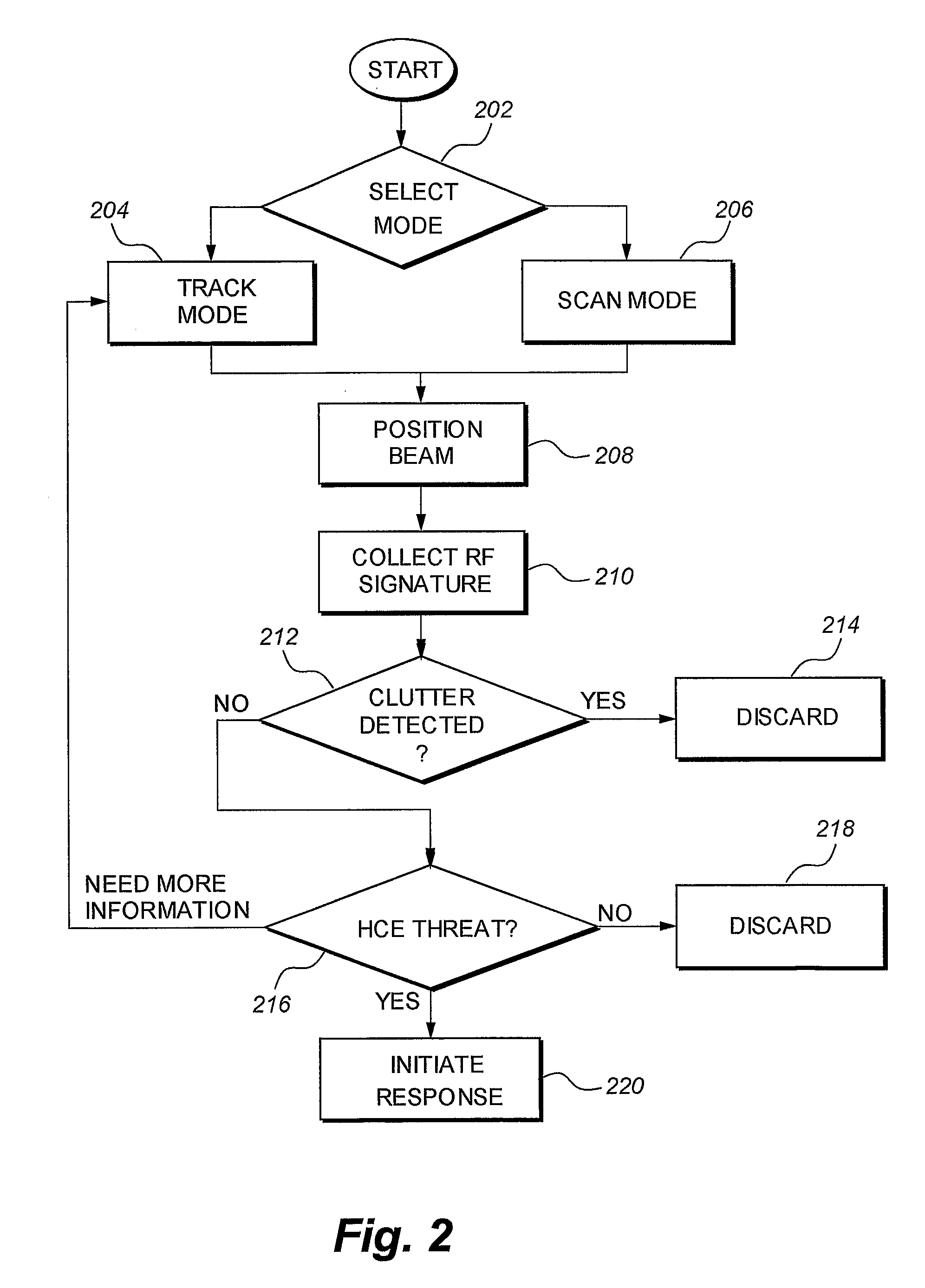
The system and method for standoff detection of human carried explosives (HCE) is a portable system that automatically detects HCE up to a range of 200 meters and within seconds alerts an operator to HCE threats. The system has radar only, or both radar and video sensors, a multi-sensor processor, an operator console, handheld displays, and a wideband wireless communications link. The processor receives radar and video feeds and automatically tracks and detects all humans in the field of view. Track data continuously cues the narrow beam radar to a subject of interest, the radar repeatedly interrogating cued objects, producing a multi-polarity radar range profile for each interrogation event. Range profiles and associated features are automatically fused over time until sufficient evidence is accrued to support a threat / non-threat declaration hypothesis. Once a determination is made, the system alerts operators through a handheld display and mitigates the threat if desired.
Owner:RAPISCAN LAB INC
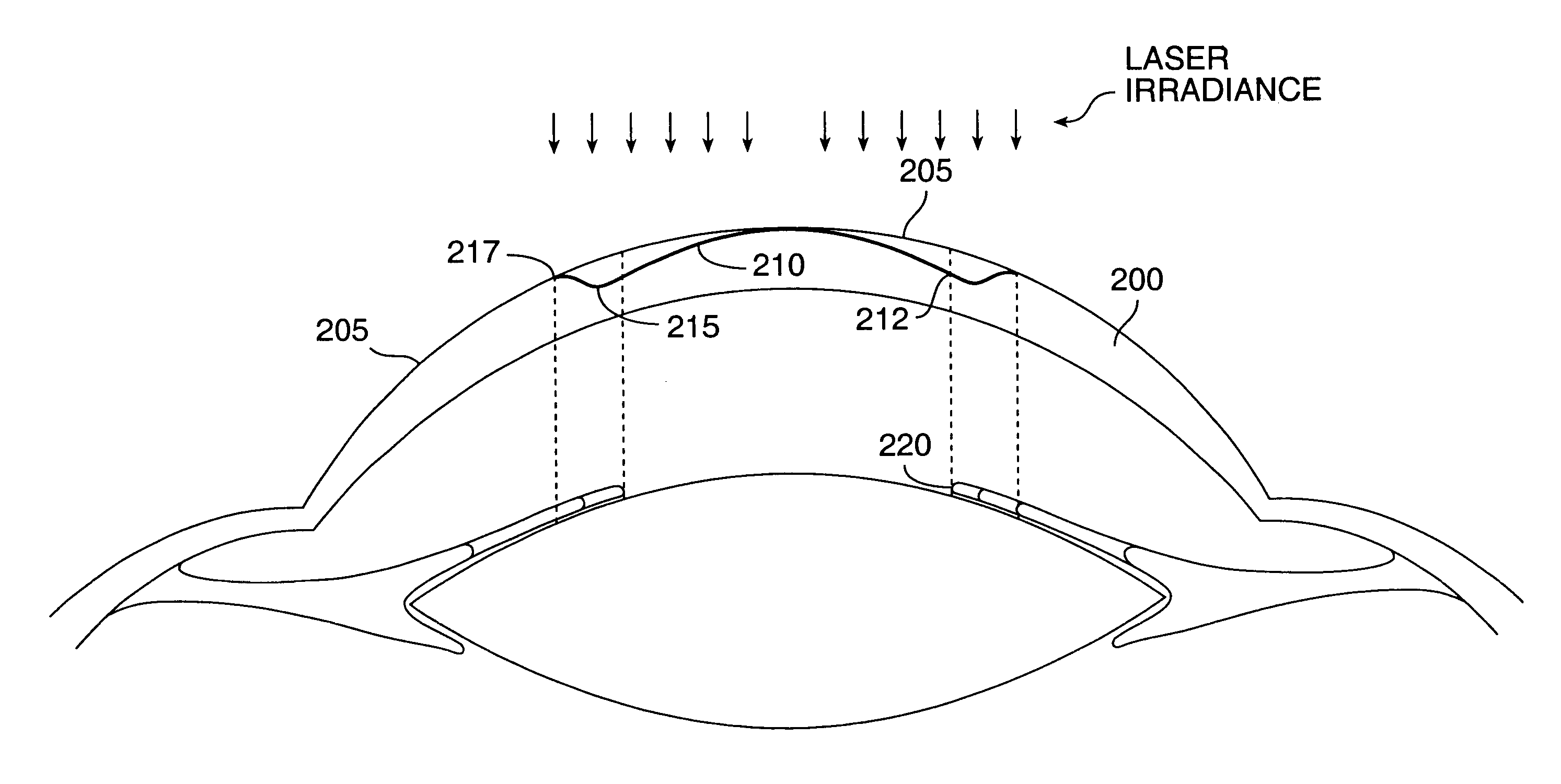
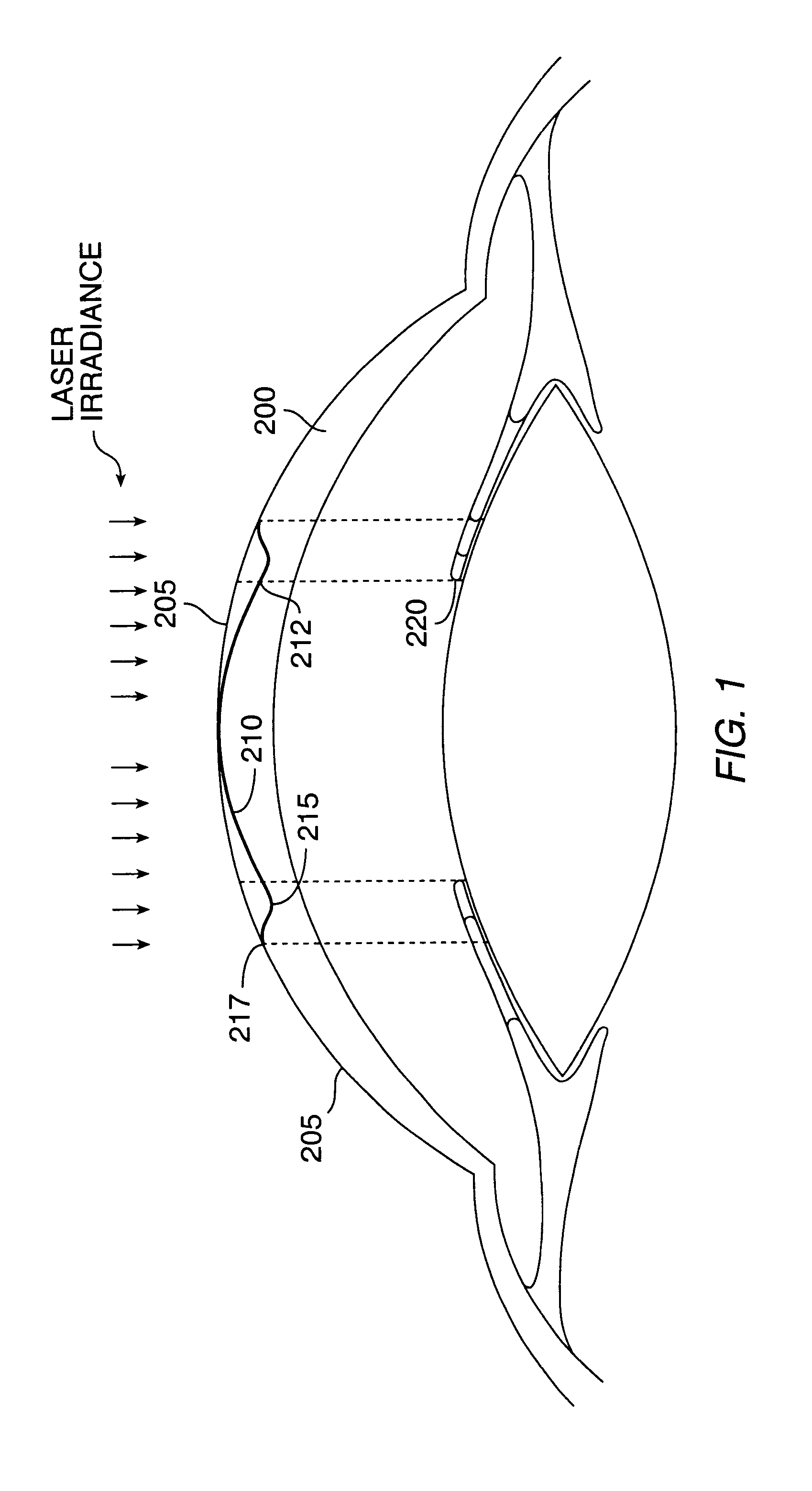
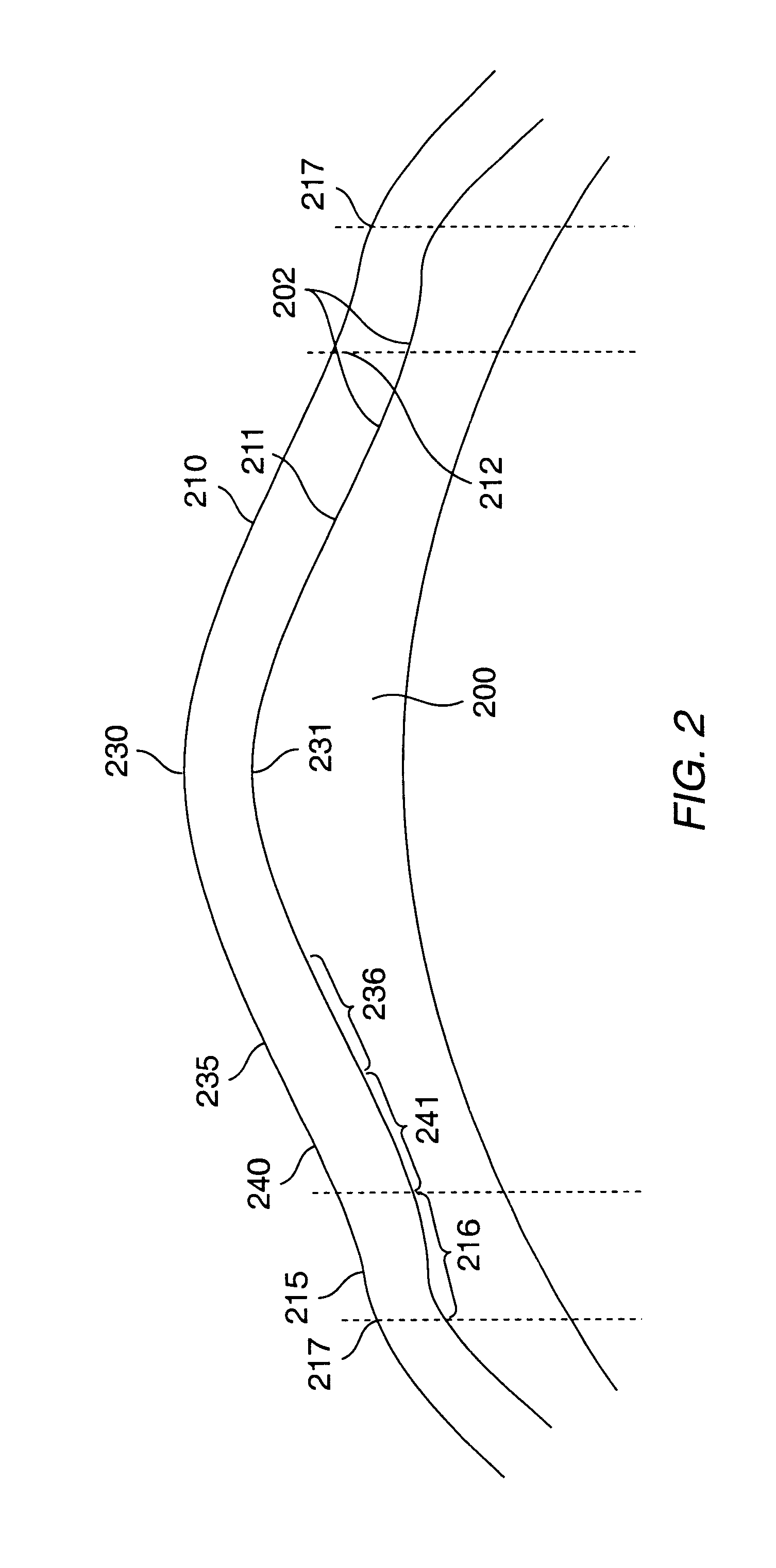
Method and systems for laser treatment of presbyopia using offset imaging
InactiveUS6280435B1Less attractiveReduce discontinuityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsWide areaHyperopic astigmatism
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Compact light-mixing LED light engine and white LED lamp with narrow beam and high cri using same
A directional lamp comprises a light source, a beam forming optical system configured to form light from the light source into a light beam, and a light mixing diffuser arranged to diffuse the light beam. The light source, beam forming optical system, and light mixing diffuser are secured together as a unitary lamp. The beam forming optical system includes: a collecting reflector having an entrance aperture receiving light from the light source and an exit aperture that is larger than the entrance aperture, and a lens disposed at the exit aperture of the collecting reflector, the light source being positioned along an optical axis of the beam forming optical system at a distance from the lens that is within plus or minus ten percent of a focal length of the lens.
Owner:SAVANT TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for automotive radar sensor
InactiveUS20050225481A1Low costAdditional imaging capabilityAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSolid-state devicesEngineeringWaveguide
Methods and apparatus are presented which reduce the overall cost and increase the imaging capability for medium and long range automotive radar sensing applications through the combination of a high signal-to-noise ratio and wide dynamic range radar waveform and architecture, antenna arrangement, and a low cost packaging and interconnection method. In accordance with aspects of the present invention, one way a high signal-to-noise ratio and wide dynamic range imaging radar with reduced cost can be achieved is through the combination of a pulsed stepped-frequency-continuous-wave waveform and electrically beam-switched radar architecture, utilizing a planar package containing high-frequency integrated circuits as well as integrated high-frequency waveguide coupling ports, coupled to a multi-beam waveguide-fed twist-reflector narrow beam-width antenna. Other methods and apparatus are presented.
Owner:GHZ TR CORP
Beacon and associated components for a ranging system
A beacon for a ranging system includes an electronic scanned array (ESA) antenna and a transceiver. The ESA antenna is configured to emit a separate radio frequency (RF) phased-array narrow beam for each of a plurality of segments of an arc, and receive from an end user node a response signal based on at least one of the RF phased-array narrow beam. Each segment of the arc is scanned at a specified time interval. The transceiver is configured to transmit a pulsed signal via the RF phased-array narrow beam, and receive the response signal.
Owner:CORVUS TECH
Submersible multi-color LED illumination system
A submersible LED illumination system may include an array of LEDs, with a first portion of the LEDs capable of emitting white light and a second portion of the LEDs capable of emitting light of a single color. The system may further include a plurality of reflectors surrounding a corresponding one of the LEDs, where a first portion of the reflectors may be configured to provide a far field relatively narrow beam of illumination and a second portion of the reflectors may be configured to provide a near field relatively wide beam of illumination. A housing may enclose the array of LEDs and the reflectors. A transparent window may be disposed in the housing, an an optically clear material may be disposed between the LEDs, reflectors, and transparent window.
Owner:SEESCAN
Lighting systems for producing different beam patterns
InactiveUS20060039160A1Secure attachmentMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceWide beamBeam pattern
Various embodiments described herein include lighting systems that produce an optical beam. Moreover, in various embodiments, the beam may be altered to provide, for example, a narrow beam or a wide beam. One such lighting system includes a light source, a diffusing optical element, and a projection lens. The diffusing optical element is disposed between the light source and the projection lens and can be translated to provide zoom capability.
Owner:OPTICAL RES ASSOCS
Methods, systems and devices for three dimensional input and control methods and systems based thereon
Owner:TITAN MEDICAL INC
Military UHF and commercial Geo-mobile system combination for radio signal relay
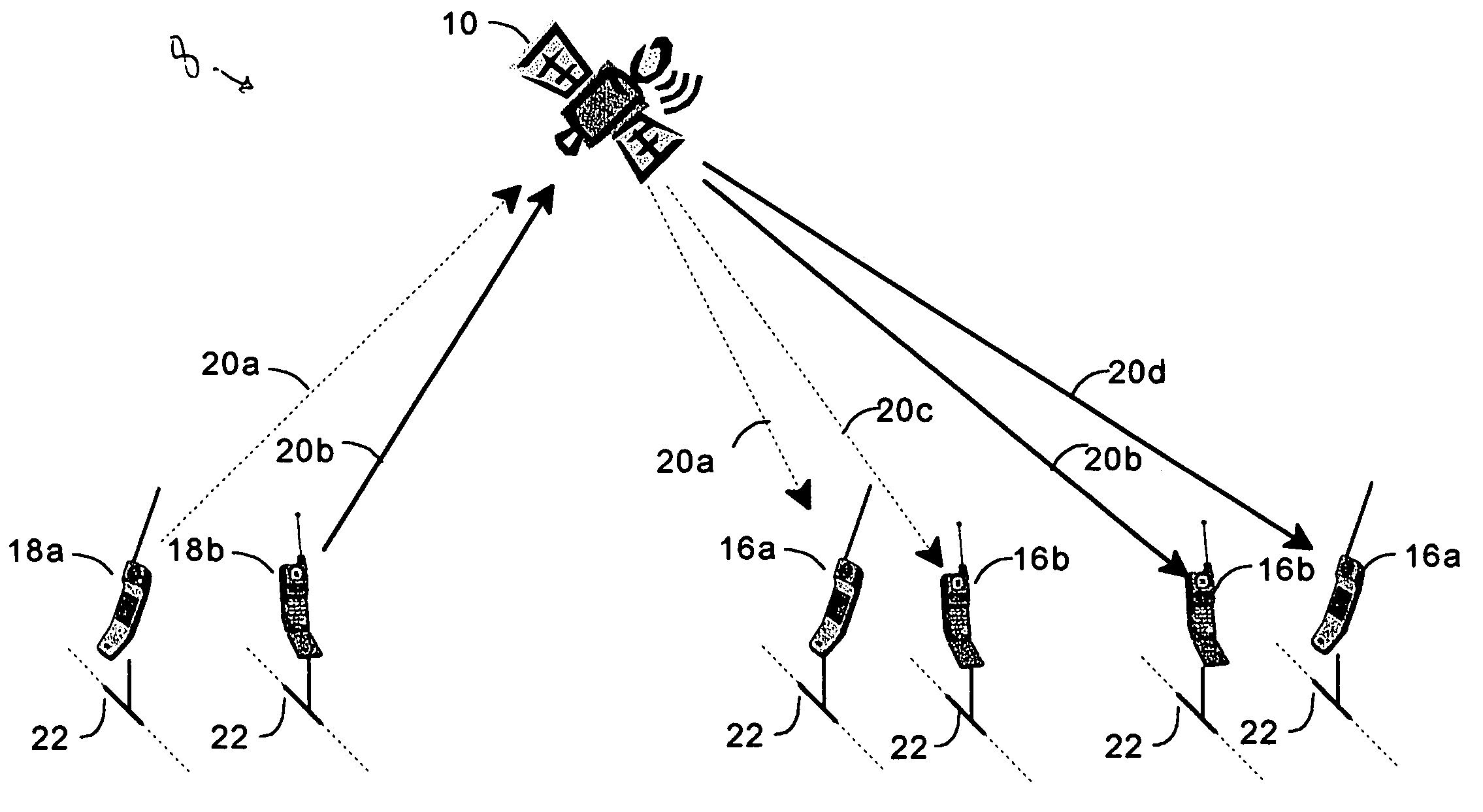
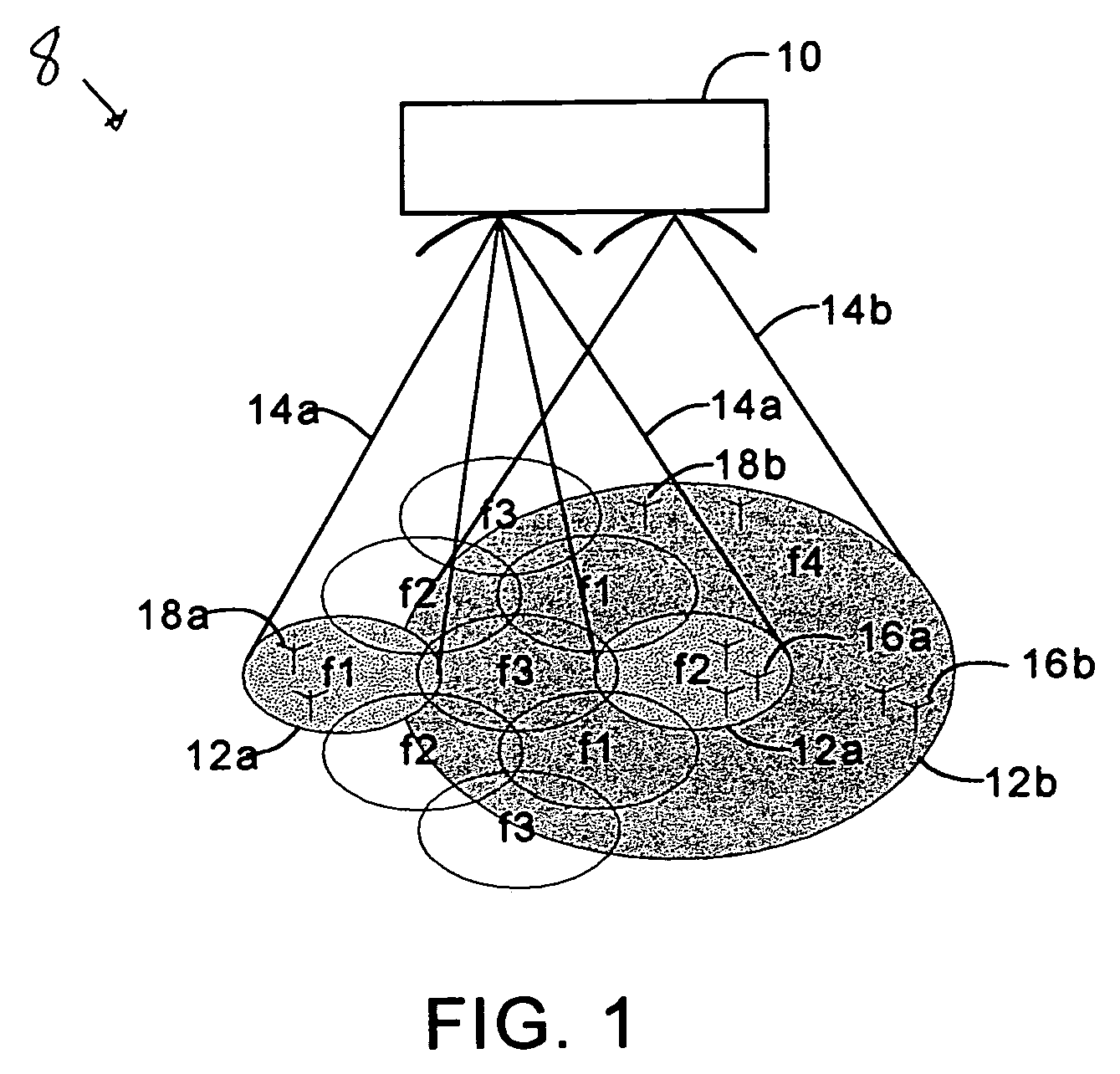
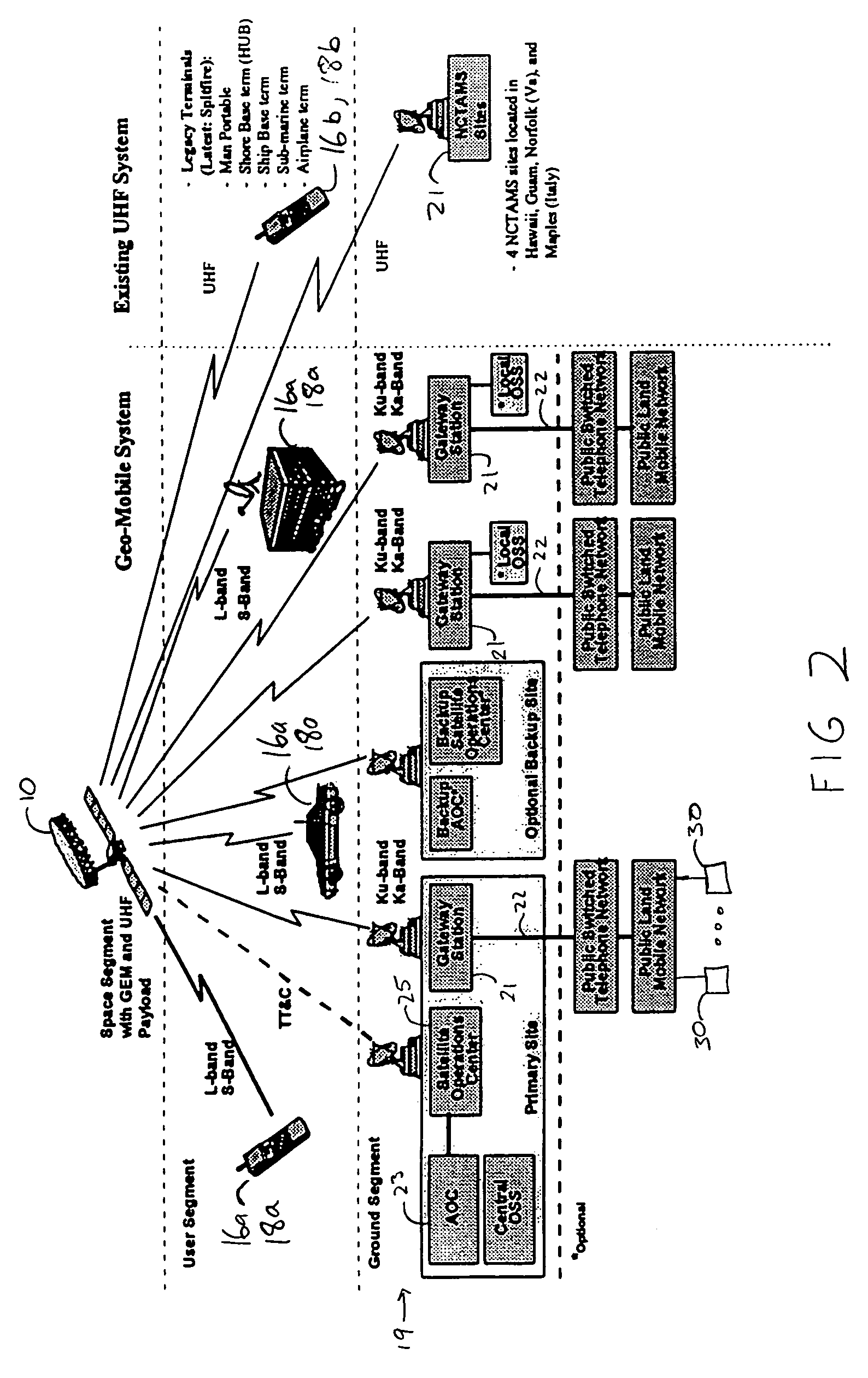
InactiveUS7366463B1Frequency-division multiplex detailsBroadcast transmission systemsCommunications systemSignal on
A radio signal relay device such as satellite is used to cover several relatively small geographical regions with relatively narrow beams as well as a relatively large geographical region with a single beam. This relatively wide beam permits legacy equipment to be used. A transmitting device in a beam transmits a signal to the relay device, which in turn retransmits the signal to a receiving device. The transmitting devices, relay device, and receiving devices synchronize communication by using a particular mode of communication which includes a band of carrier frequencies and a protocol. In addition to communicating like mode signals from a transmitter to a receiver, the relay device may be used in a dual mode communication system to translate signals from the one mode to another. A translator may direct a transmitter to modulate a signal on a different carrier frequency, convert one protocol into another protocol, or both.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
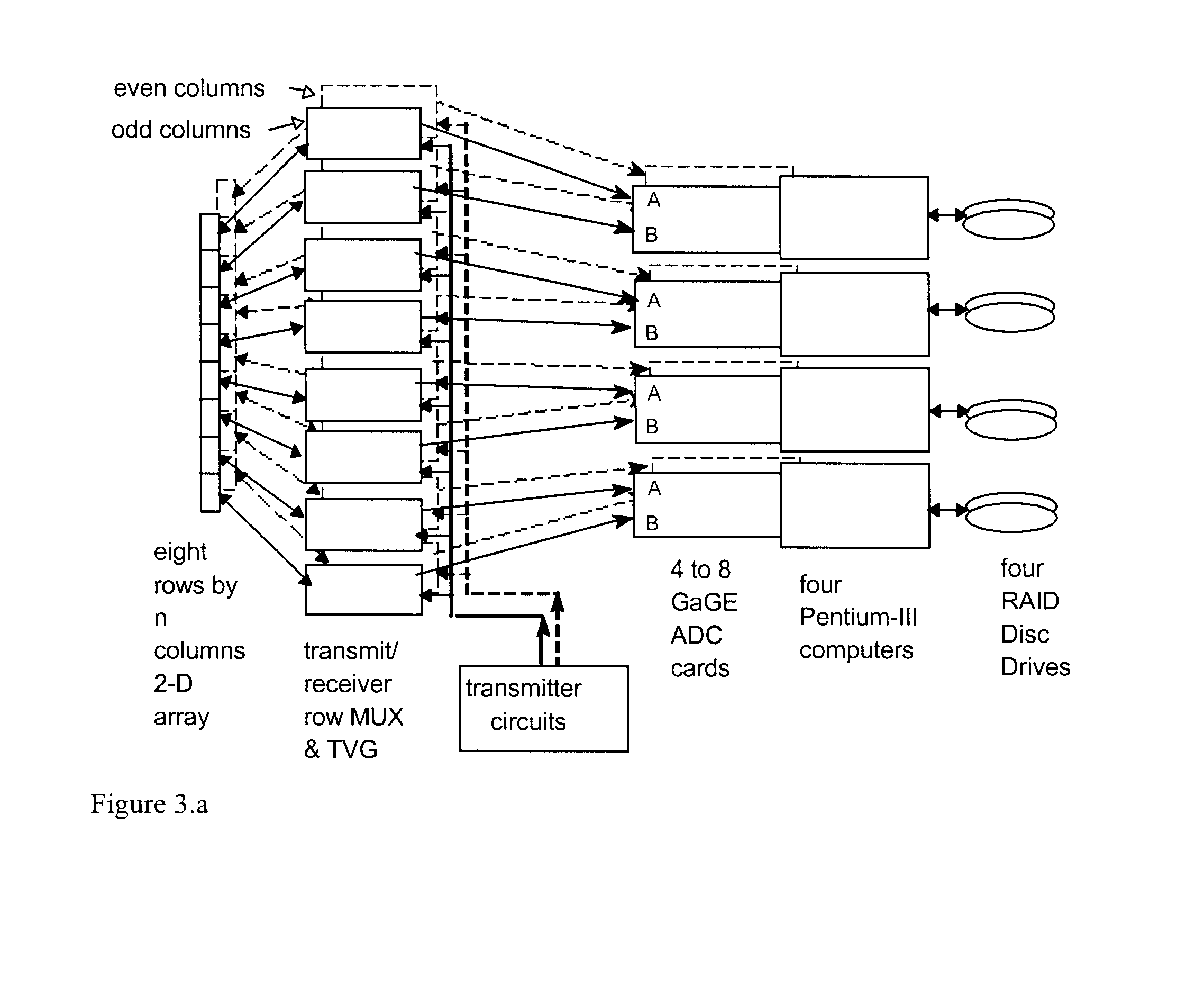
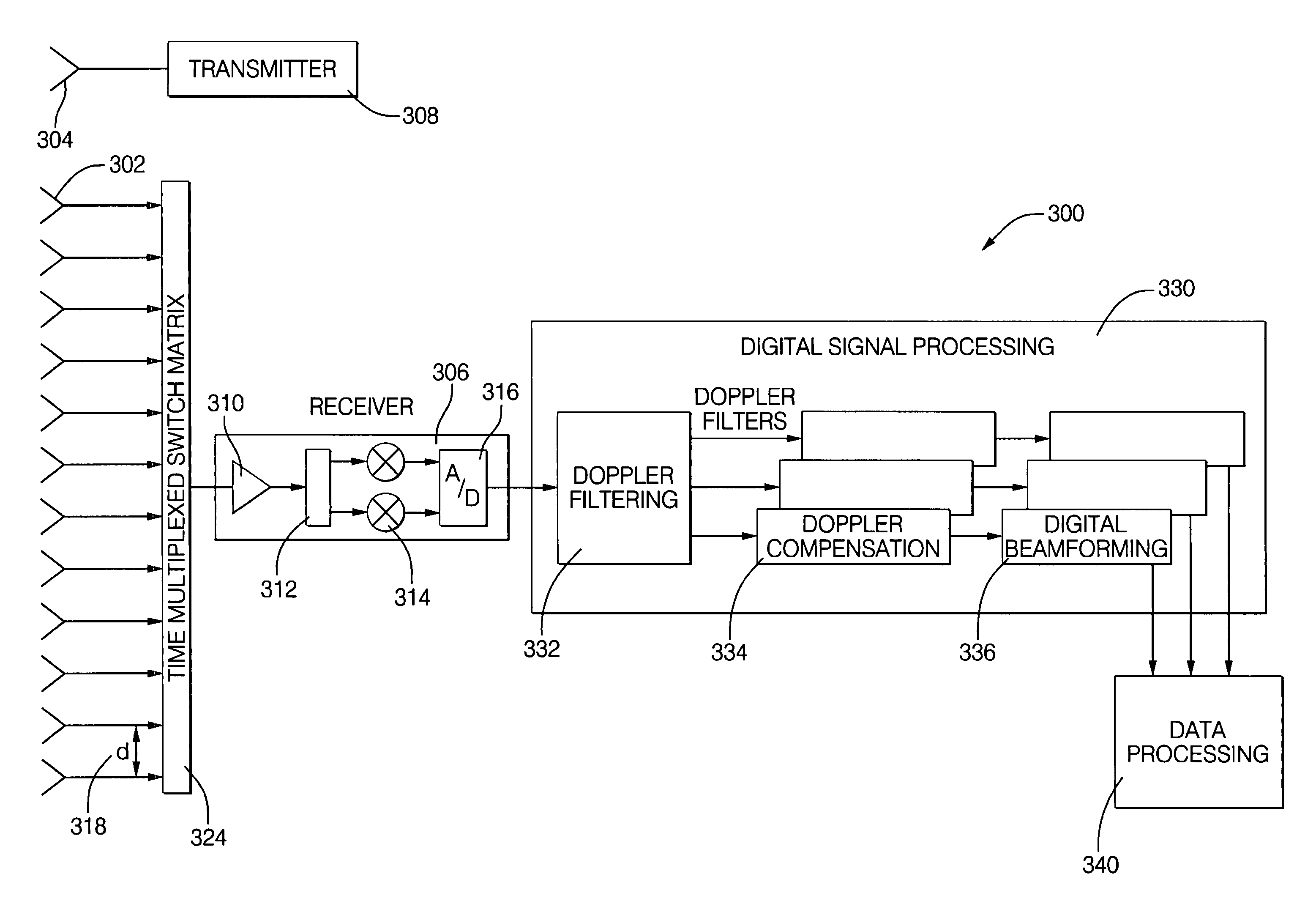
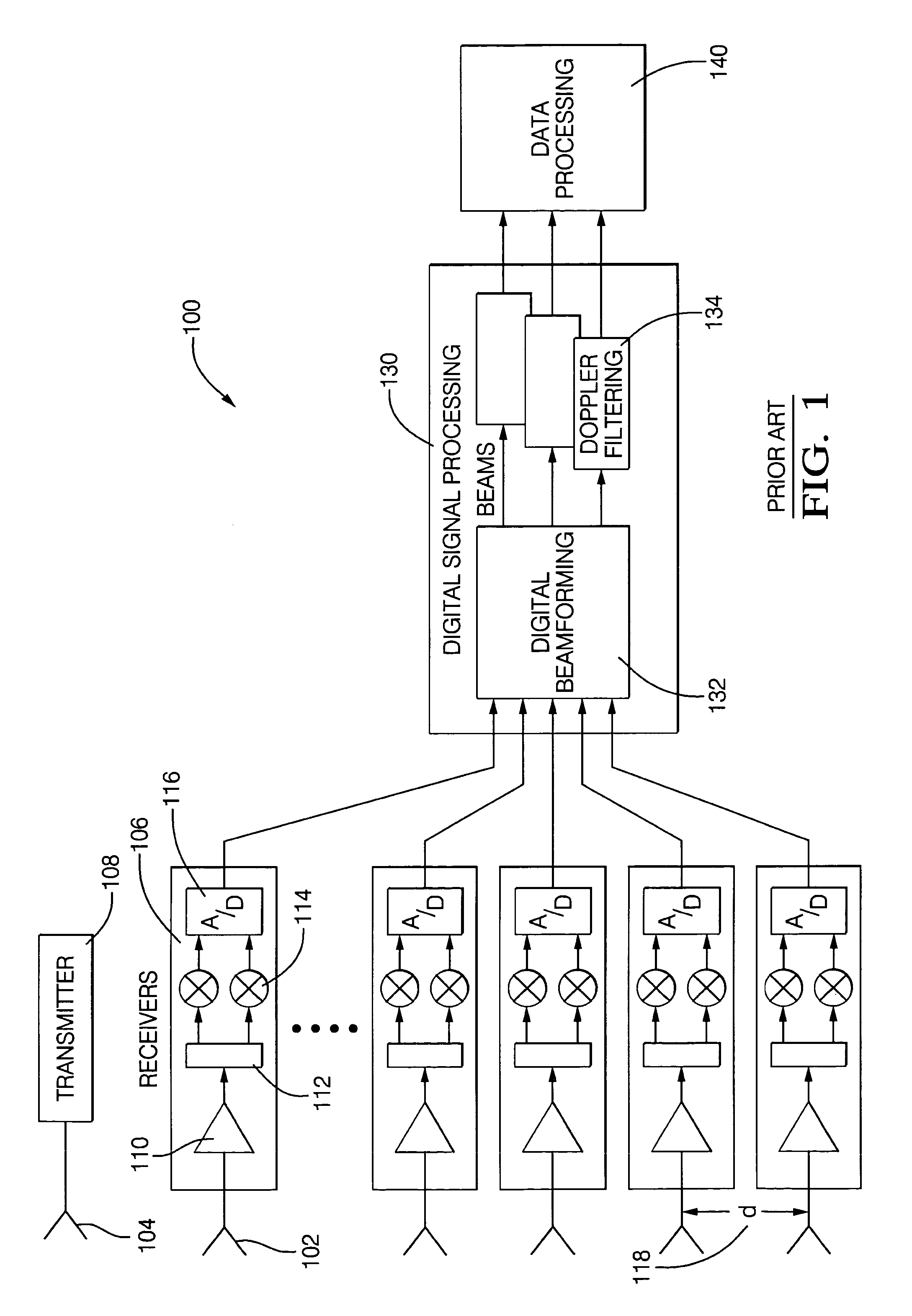
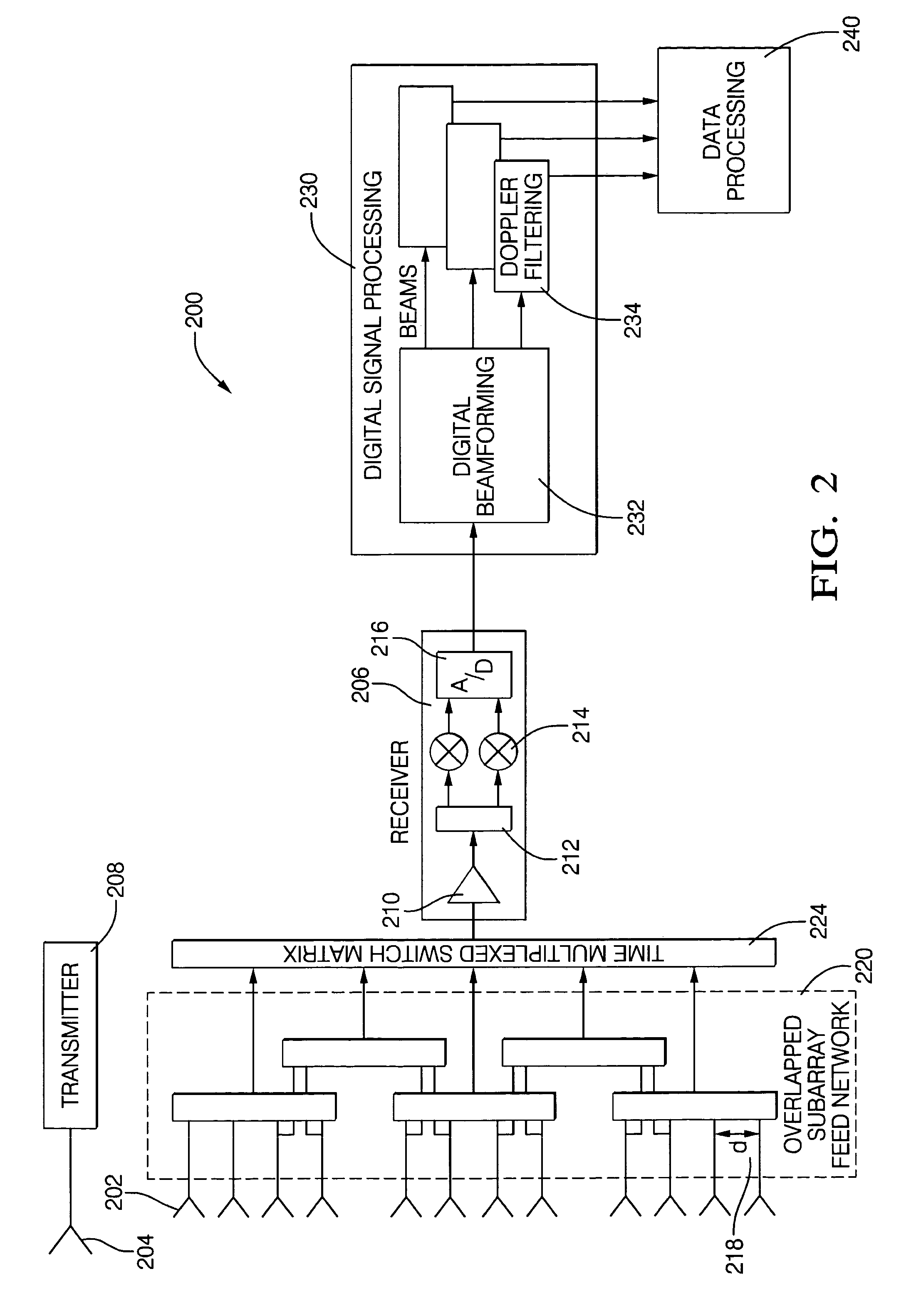
Digital beamforming for an electronically scanned radar system
ActiveUS20070001897A1Improve performanceLow costParticular array feeding systemsRadio transmissionRadar systemsGrating lobe
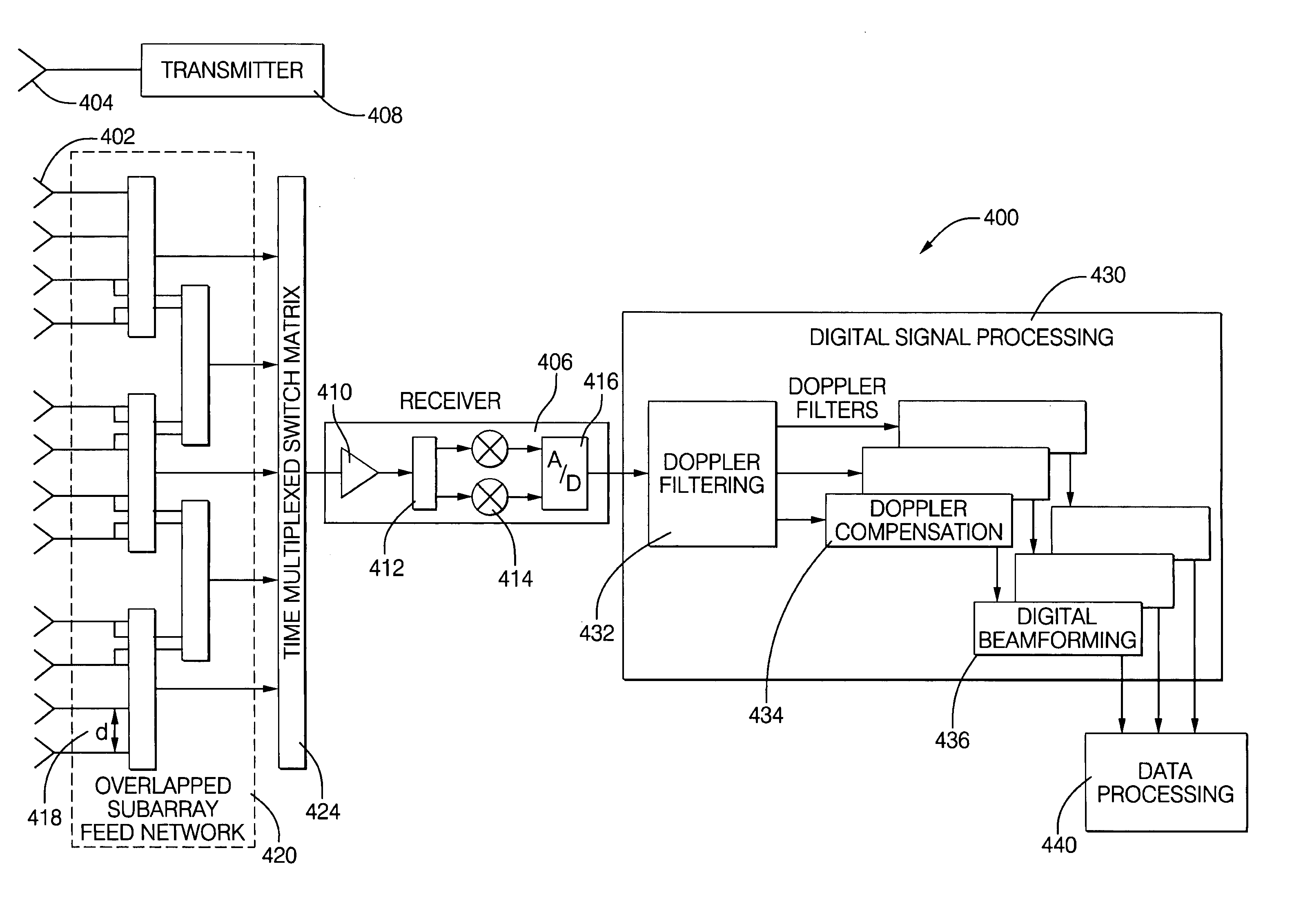
Digital beamforming is provided for use with electronically scanned radar. In an aspect, the present invention provides enhanced sensitivity, wide angle or field of view (FOV) coverage with narrow beams, minimized number of receivers, reduced sidelobes, eliminated grating lobes and beam compensation for target motion. In an aspect, the present invention employs a uniform overlapped subarray feed network, a time multiplexed switch matrix, and a restructured digital signal processor. Antenna channels share a receiver, rather than maintain a dedicated receiver for each antenna element, as in conventional systems. In an aspect, Doppler / frequency filtering is performed on each antenna element or subarray output prior to digital beamforming. Further, Doppler compensation is employed following Doppler / frequency filtering, followed by digital beamforming.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
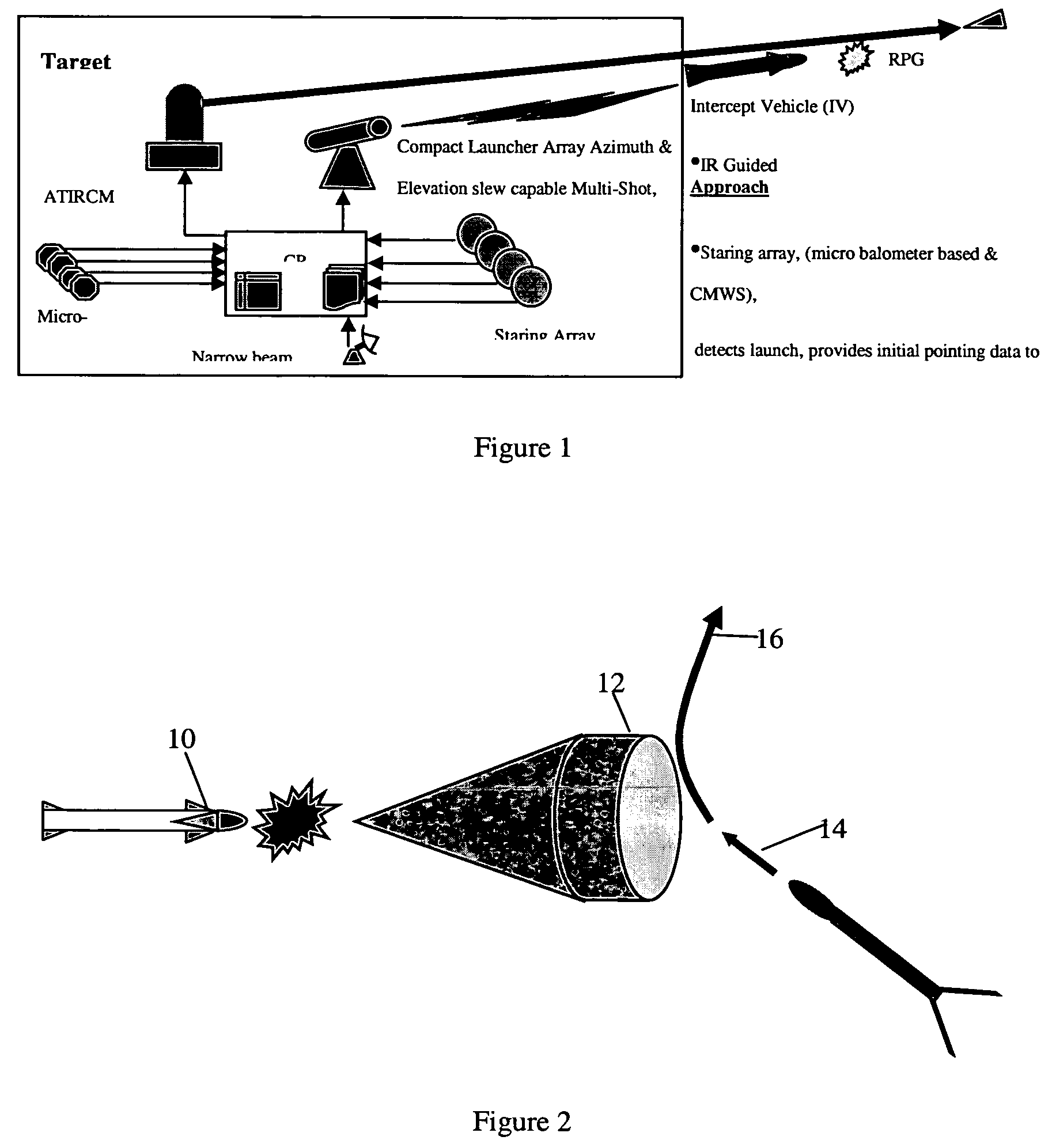
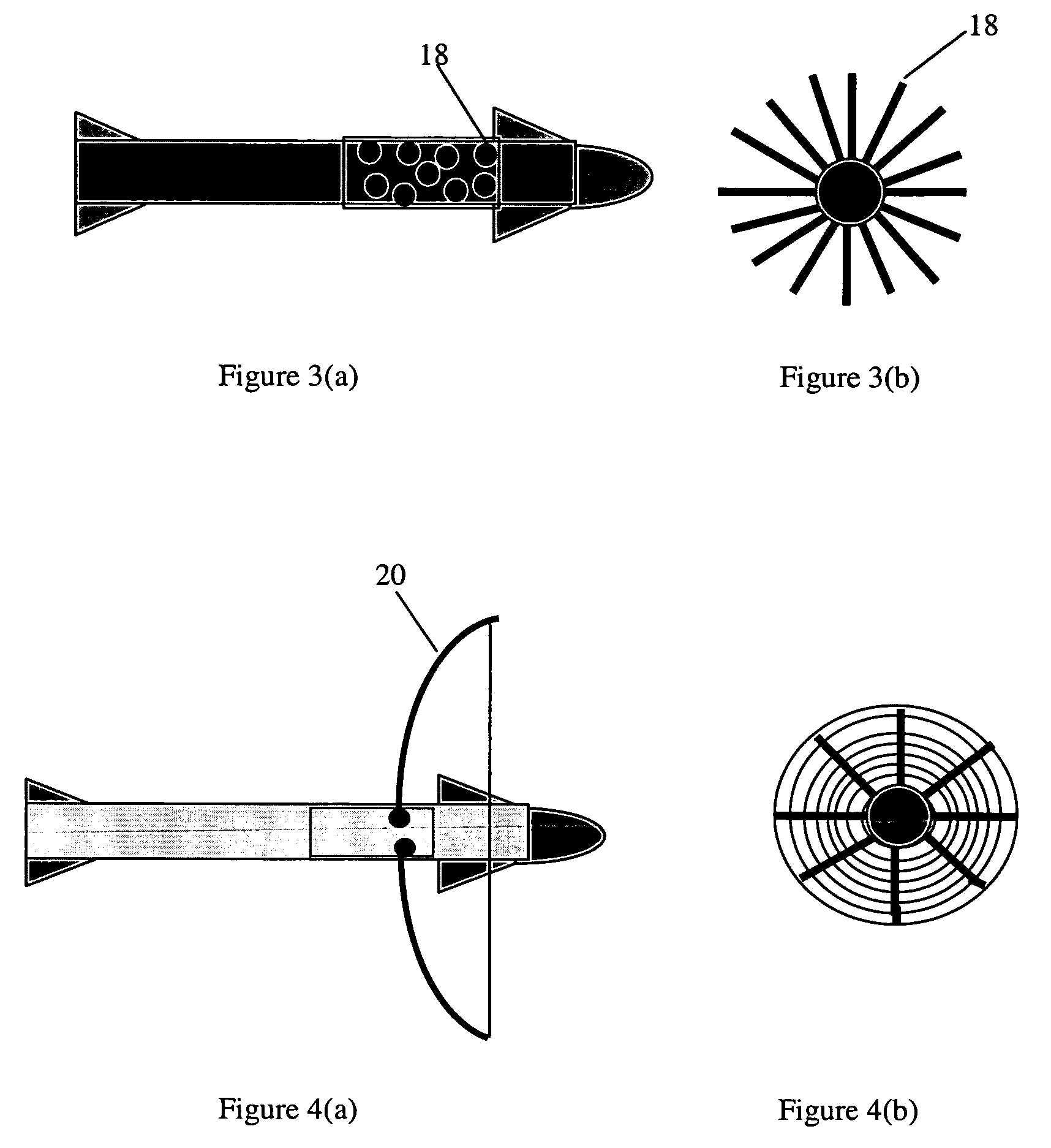
System for interception and defeat of rocket propelled grenades and method of use
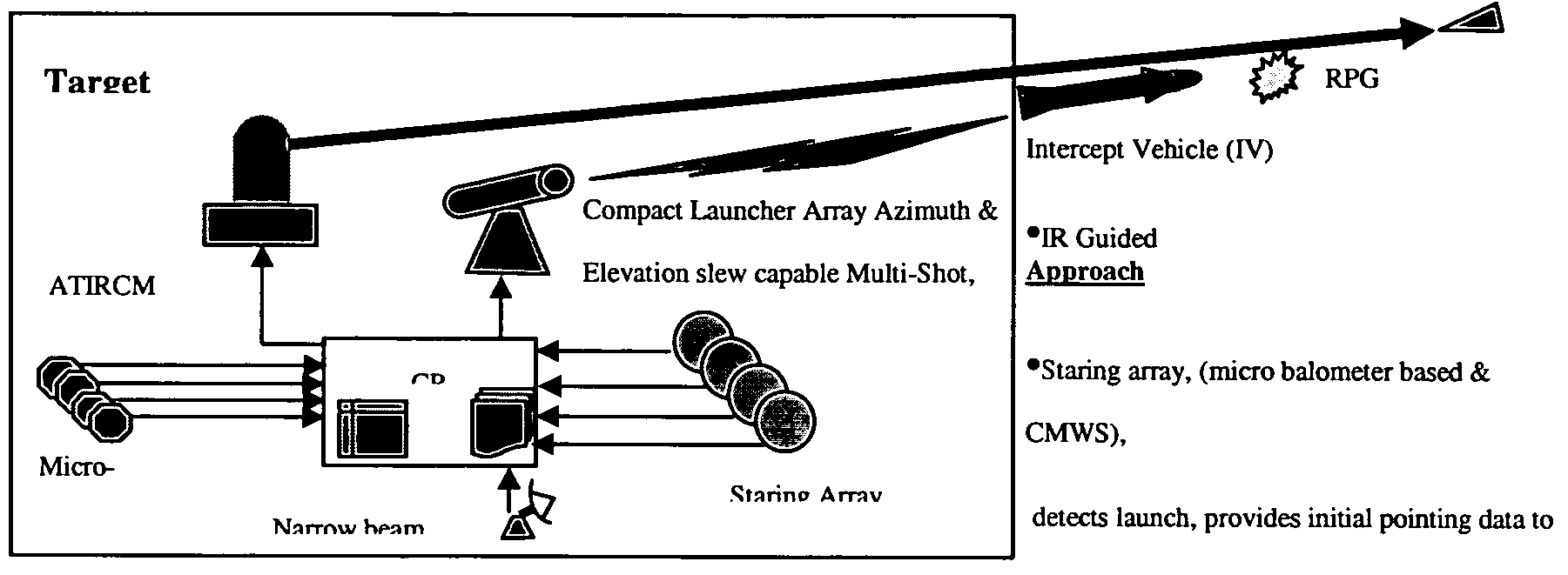
A method for intercepting and a defeating rocket propelled grenade (RPG) which includes the steps of detecting a thermal signature from a launch of the RPG; and cueing a narrow beam radar which locates the RPG and develops a ballistic solution and target intercept point for intercepting the PPG with an intercept vehicle.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
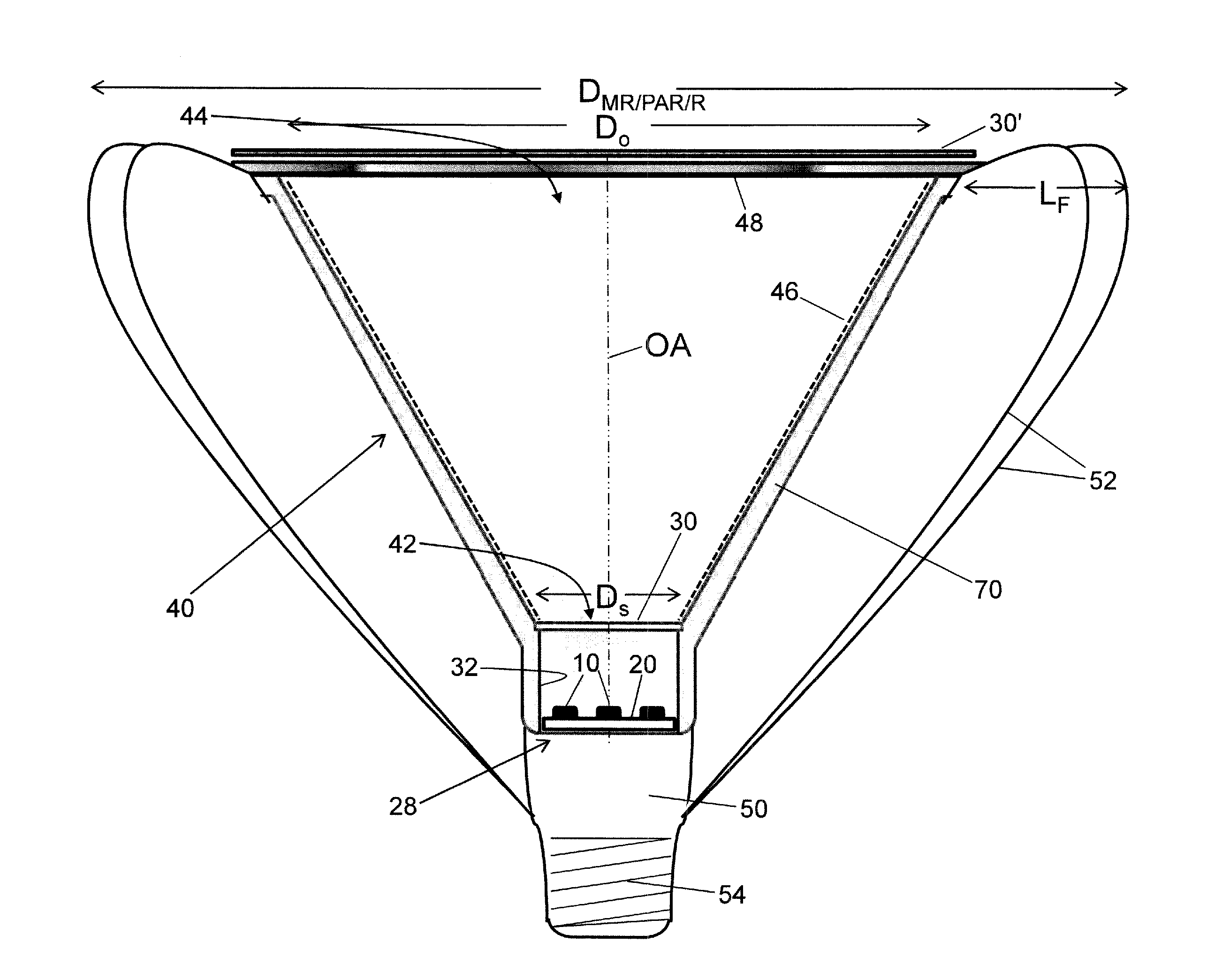
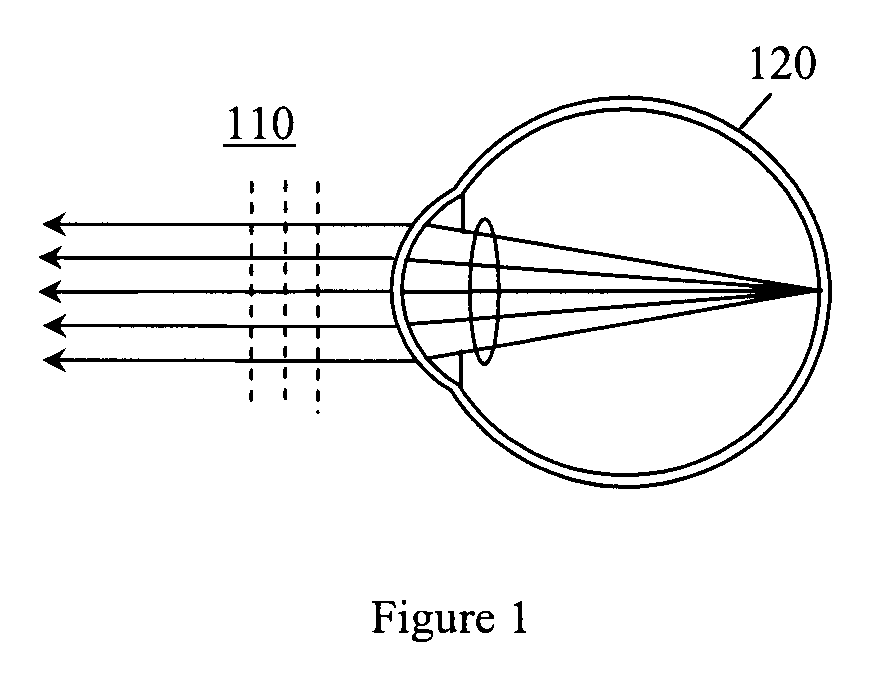
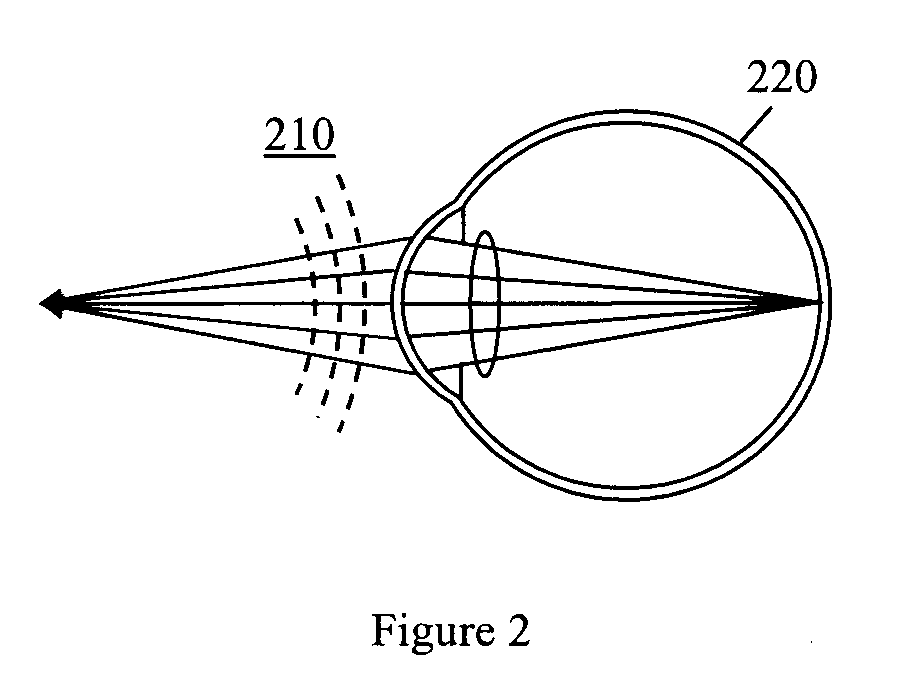
Optimizing vision correction procedures
InactiveUS20100110379A1Easy to measureOut noiseOptical measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringWavefront sensorCylindroma
In one embodiment, an apparatus for optimizing vision correction procedures comprising: a narrow beam of light directed to a patient's retina; a dynamic defocus and compensation offsetting device configured to offset the defocus of a wavefront from an eye, a wavefront sensor configured to measure the local tilt of a number of subwavefronts sampled around an annular ring (the diameter of which can be dynamically changed) over the wavefront with the defocus offset; and a display device configured to display a two dimensional (2D) data points pattern in real time with each data point location representing a corresponding local tilt of the sampled subwavefronts. A proper defocus offset, not passive compensation, can reveal the predominant feature(s) of other wavefront aberration component(s), thus enabling a refractive surgeon to fine tune the vision correction procedure and minimize the remaining wavefront aberration(s) in real time. Meanwhile, by sampling the wavefront around annular rings and displaying the local tilt of the sampled subwavefronts on a monitor in the form of a 2D data points pattern, a refractive ophthalmic surgeon can easily correlate the measurement result to the two major refractive errors, namely spherical and cylinder refractive errors, including the axis of astigmatism.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
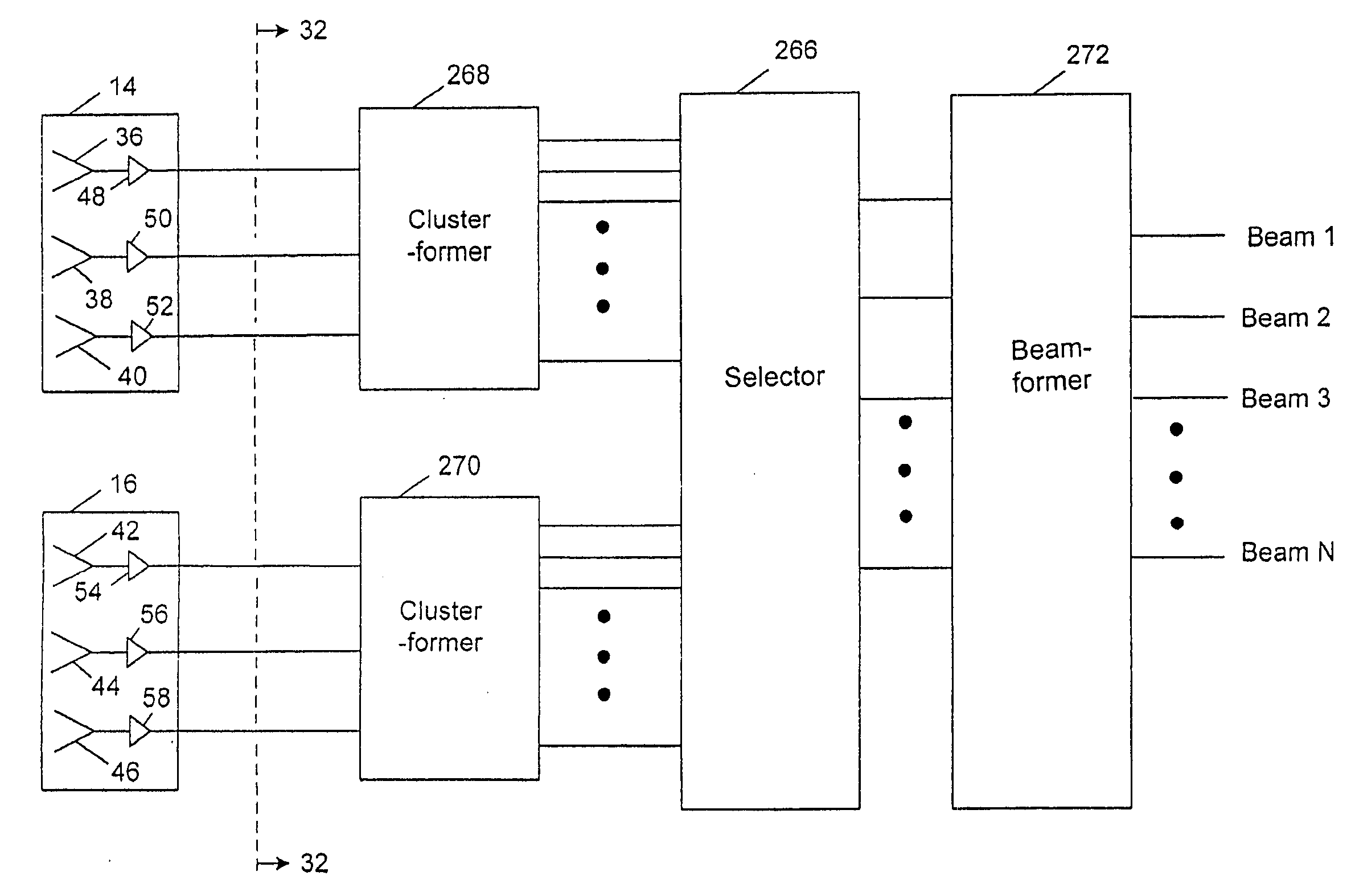
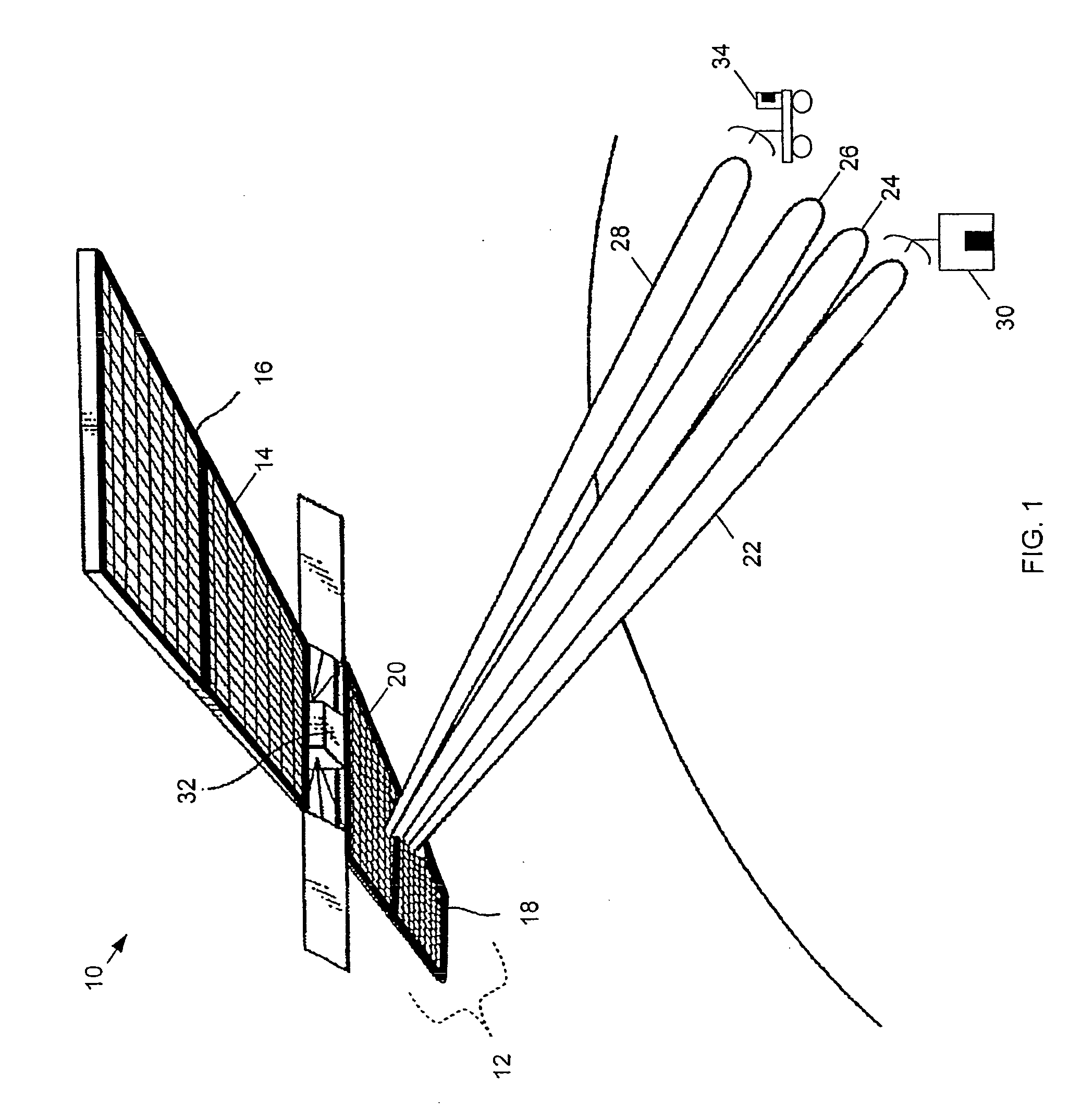
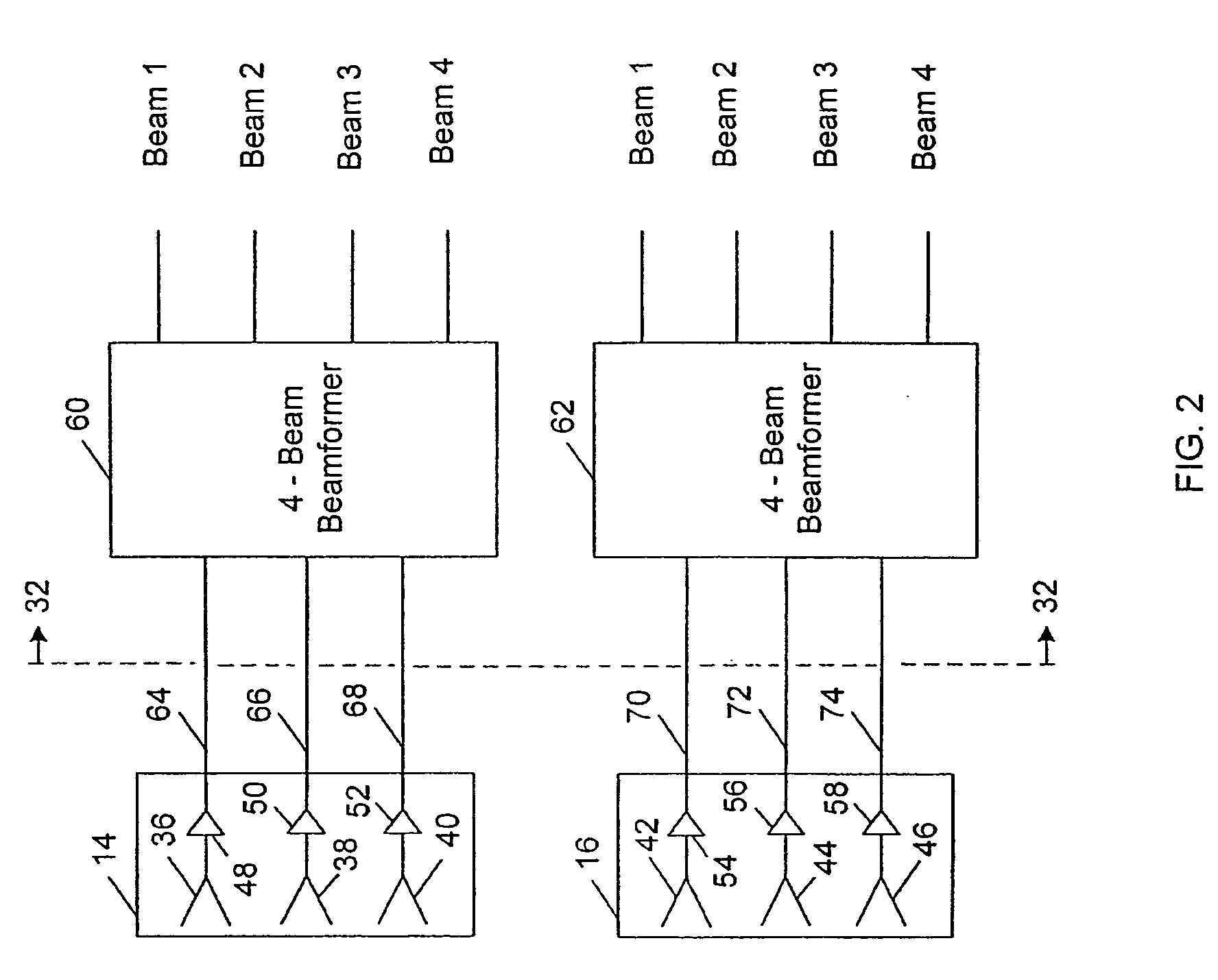
Shared phased array cluster beamformer
A shared beamformer flexibly allocates beams among clusters of beams produced by phased array antenna apertures that are deployed on a satellite (or other type of platform). By sharing the beamformer among the beam clusters, if one beam cluster is not providing useful coverage, the beams may be reallocated to one or more other beam clusters that are providing useful coverage. To share the beamformer among the beam clusters, a selector network is used to select which particular beam cluster (or clusters) is used for producing one or more narrow beams that are constrained to the coverage area of the beam cluster (or clusters).
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
System and Method For Standoff Detection of Human Carried Explosives
ActiveUS20080129581A1Special data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionVideo sensorsRadar
The system and method for standoff detection of human carried explosives (HCE) automatically detects HCE (112) up to a range of (200) meters and within seconds alerts an operator to HCE (112) threats. The system (100) has radar only, or both radar and video sensors, a multi-sensor processor (102), an operator console (120), handheld displays (122), and a wideband wireless communications link. The processor (102) receives radar and video feeds and automatically tracks and detects all humans (110) in the field of view. Track data continuously cues the narrow beam radar (118) to a subject of interest (110), (112) the radar (106), (108) repeatedly interrogating cued objects (110), (112), producing a multi-polarity radar range profile for each interrogation event. Range profiles and associated features are automatically fused over time until sufficient evidence is accrued to support a threat / non-threat declaration hypothesis. Once a determination is made, the system (100) alerts operators through a handheld display (122) and mitigates the threat if desired.
Owner:RAPISCAN LAB INC
Underwater Vehicle With Sonar Array
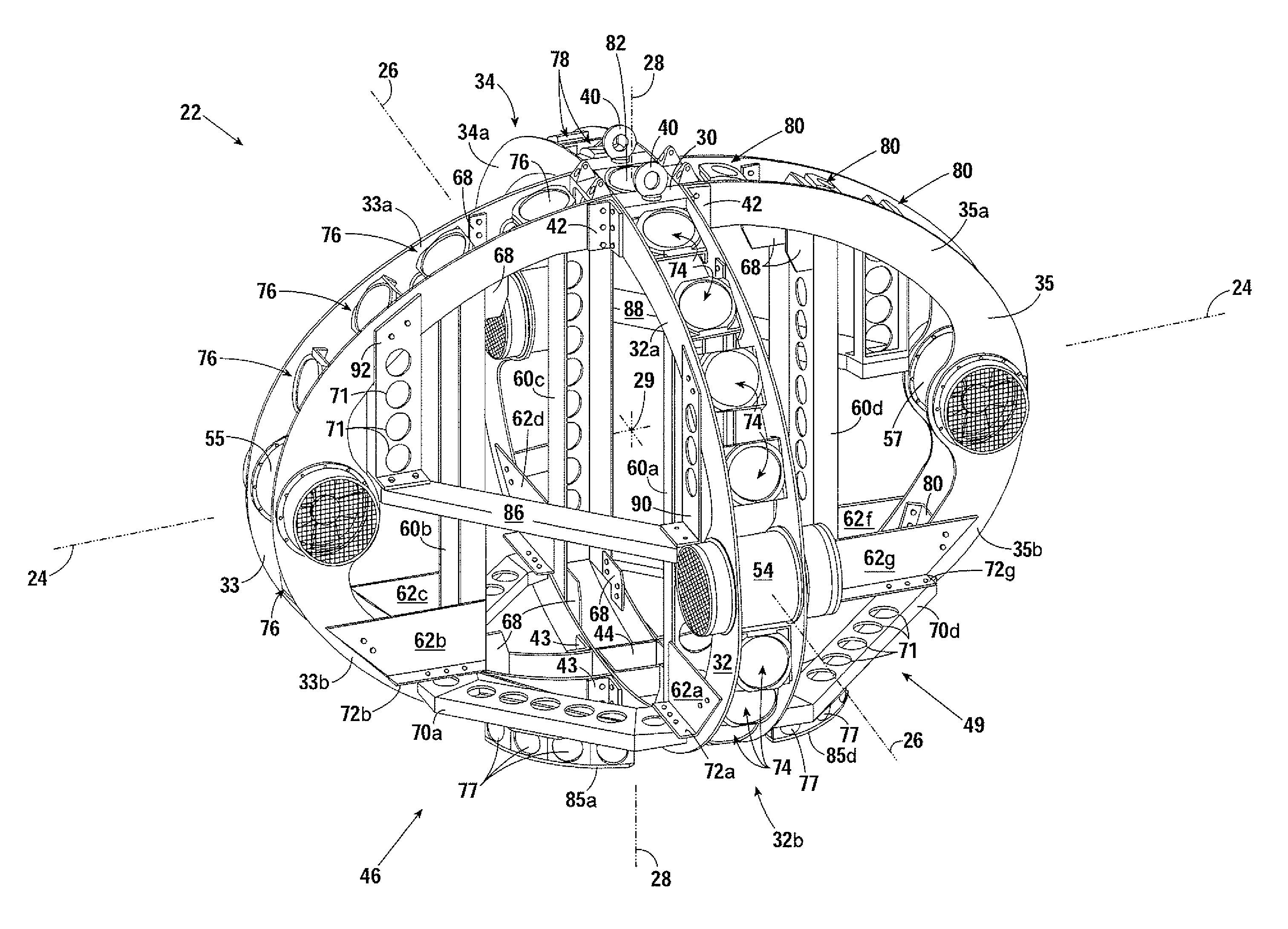
ActiveUS20090031940A1Sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionUnderwater vesselsTransducerShells of revolution
An underwater vehicle including an axi-symmetric framing system rotatable about a centerline to define a shell of revolution having a uniformly-convex outer boundary. A narrow-beam sonar array is mounted on the axi-symmetric framing system, and includes a multitude of simultaneously-fireable and / or asynchronously-fireable transducers distributed substantially evenly over a 4π-steradian viewing angle. The present invention provides the necessary configuration for a vehicle wherein an internal algorithm can compare a “new” geometry to an “old” geometry collected earlier to construct a best fit of the new world map with the old world map and locate the vehicle within the context of the new world map. This then provides a completely independent mechanism for correction of the gradual drift in x and y that is not dependent on any form of external navigation aid.
Owner:STONE AEROSPACE INC
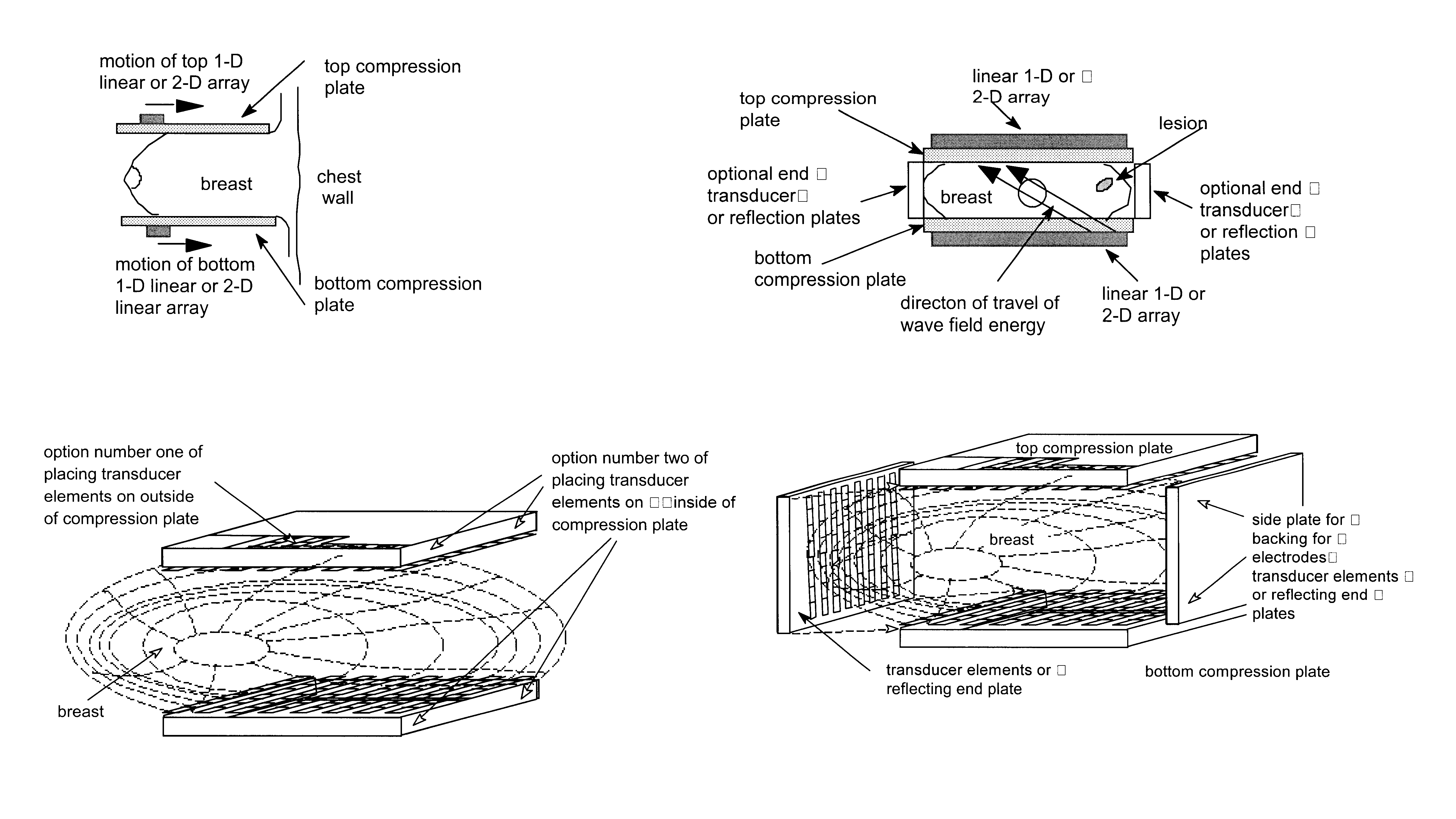
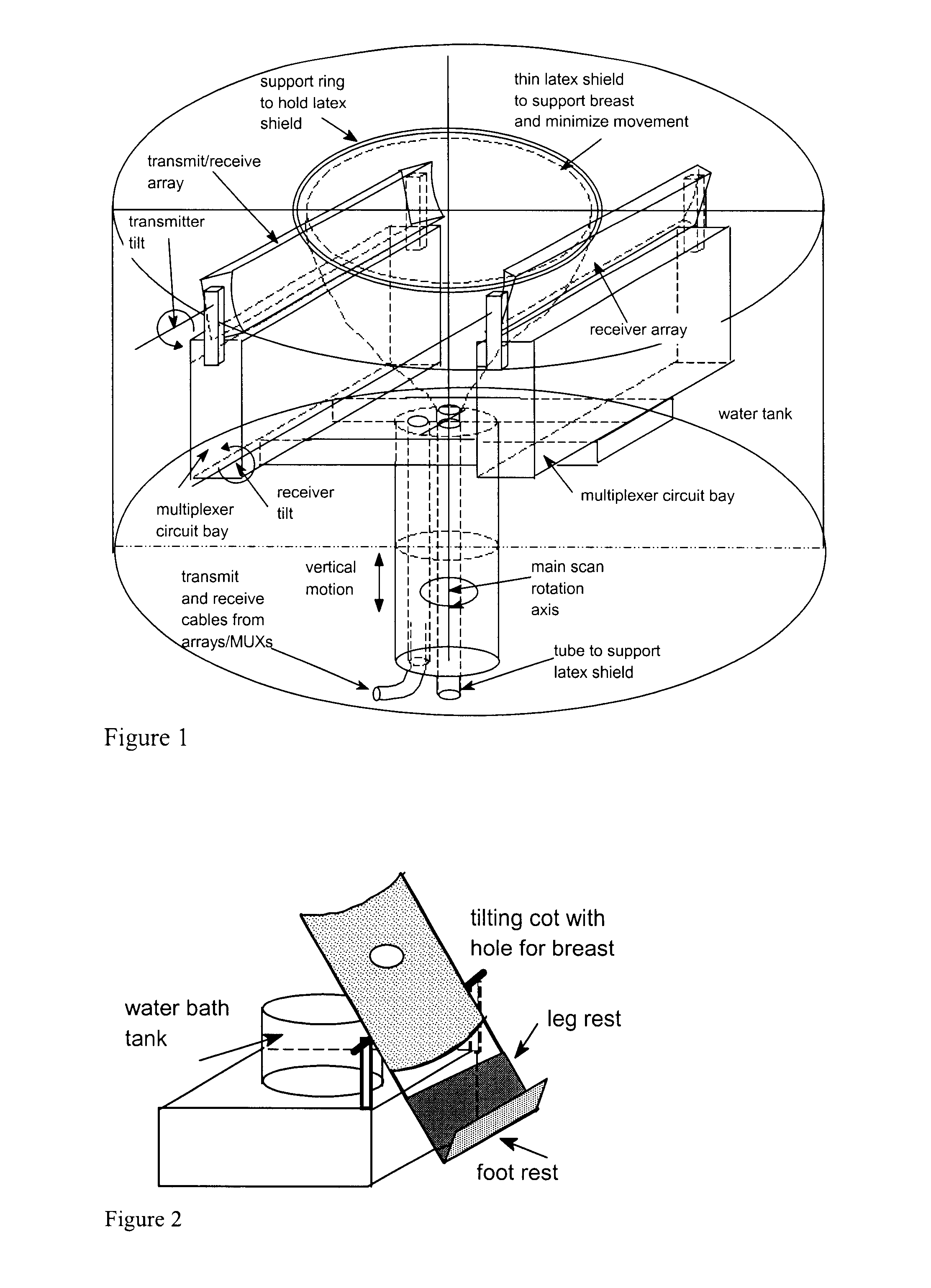
Apparatus and method for imaging objects with wavefields
This invention describes a method for increasing the speed of the parabolic marching method by about a factor of 256. Firstly, to form true 3-D images or 3-D assembled from 2-D slices. Secondly, the frequency of operation can be increased to 5 MHz to match the operating frequency of reflection tomography. This allow the improved imaging of speed of sound which in turn is used to correct errors in focusing delays in reflection tomography imaging. This allows reflection tomography to reach or closely approach its theoretical spatial resolution of ½ to ¾ wave lengths. A third benefit of increasing the operating frequency of inverse scattering to 5 MHz is the improved out of topographic plane spatial resolution. This improves the ability to detect small lesions. It also allow the use of small transducers and narrower beams so that slices can be made closer to the chest wall.
Owner:TECHNISCAN
Digital beamforming for an electronically scanned radar system
ActiveUS7474262B2Improve performanceLow costParticular array feeding systemsRadio transmissionRadar systemsEngineering
Digital beamforming is provided for use with electronically scanned radar. In an aspect, the present invention provides enhanced sensitivity, wide angle or field of view (FOV) coverage with narrow beams, minimized number of receivers, reduced sidelobes, eliminated grating lobes and beam compensation for target motion. In an aspect, the present invention employs a uniform overlapped subarray feed network, a time multiplexed switch matrix, and a restructured digital signal processor. Antenna channels share a receiver, rather than maintain a dedicated receiver for each antenna element, as in conventional systems. In an aspect, Doppler / frequency filtering is performed on each antenna element or subarray output prior to digital beamforming. Further, Doppler compensation is employed following Doppler / frequency filtering, followed by digital beamforming.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Directed LED Light With Reflector
A high intensity light is disclosed. A first circular lighting array having a plurality of reflectors and light emitting diodes is provided. A second circular lighting array is mounted on the first circular lighting array. The second circular lighting array has a second plurality of reflectors and light emitting diodes. Each reflector includes a tulip-shaped reflective surface having a symmetrical vertical cross section and a different symmetrical horizontal cross section. The reflective surface creates a uniform beam reflecting from a corresponding LED at horizontal angles relative to the reflective surface and a narrow beam in vertical angles relative to the reflective surface.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH LED SOLUTIONS
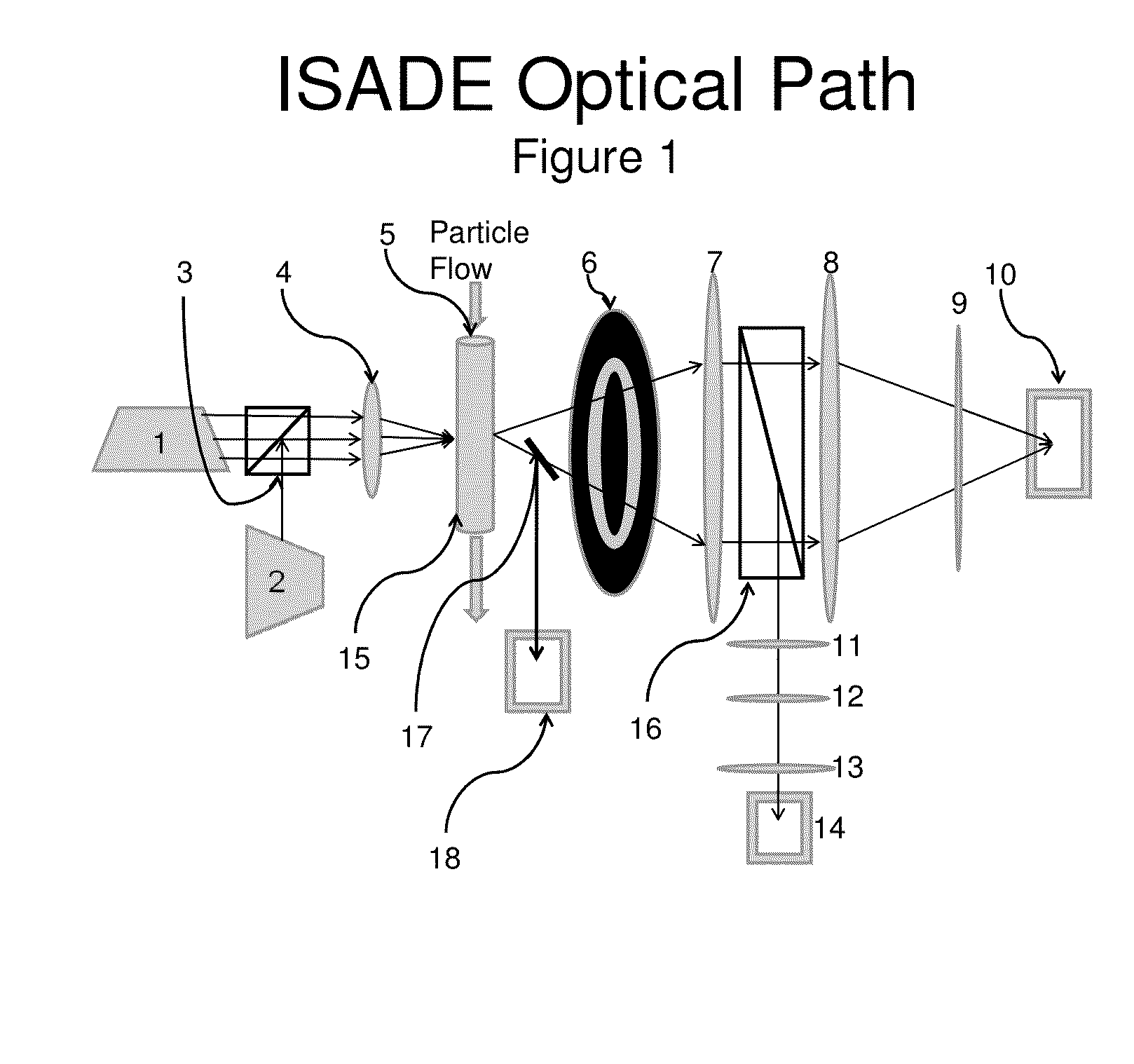
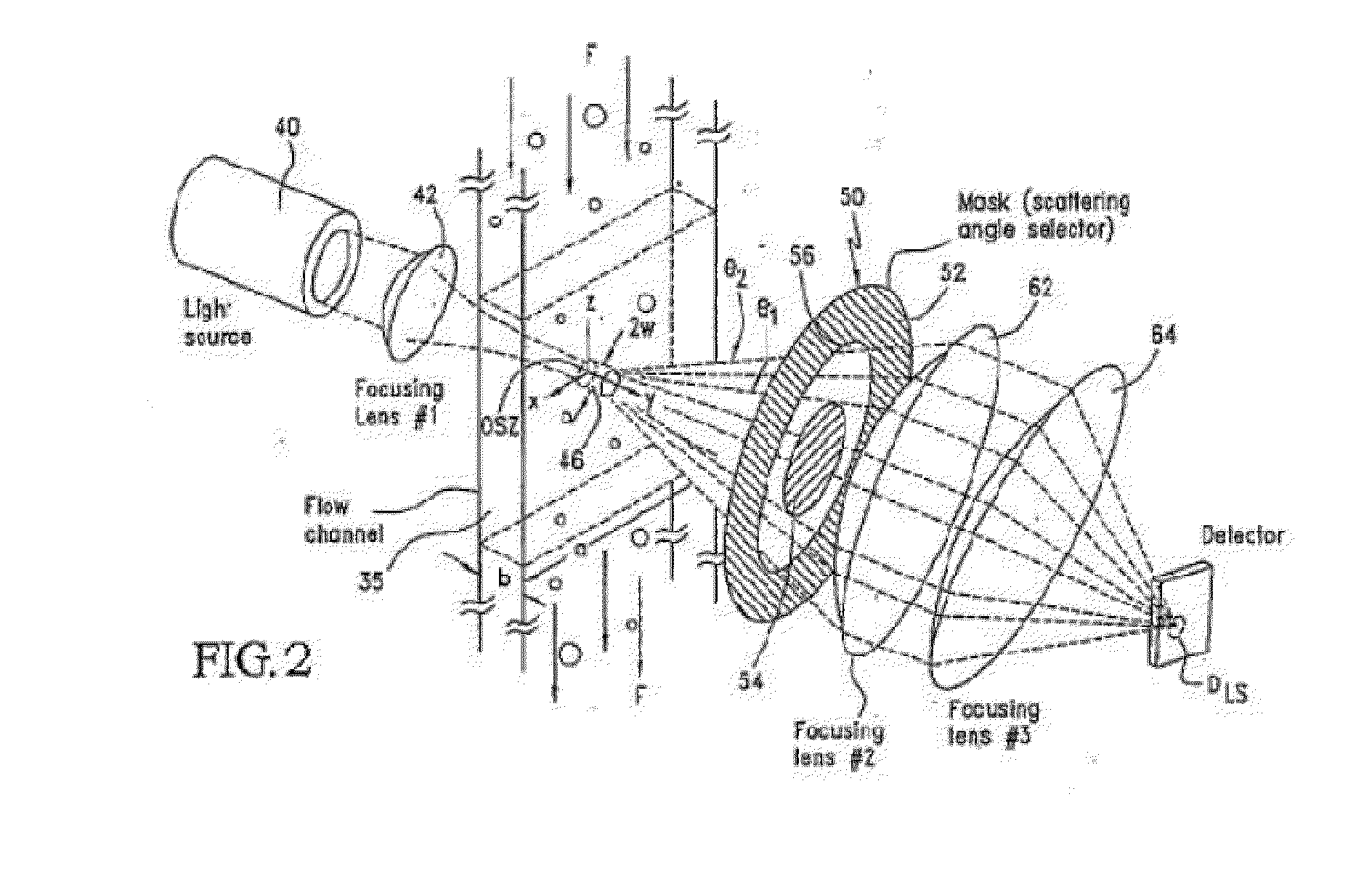
Instrument and method for optical particle sensing
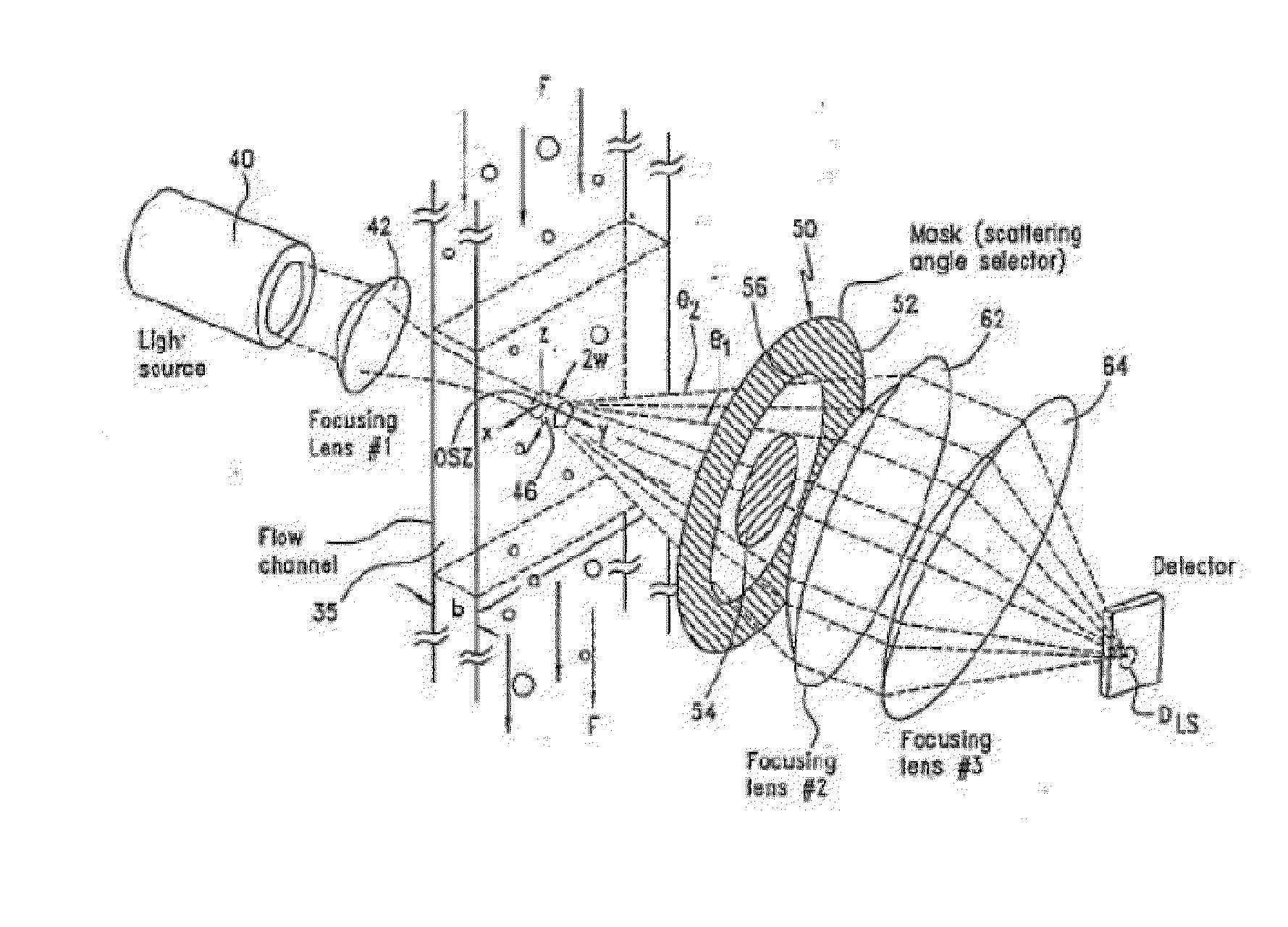
ActiveUS20140234865A1Narrow size distributionConsistent amountCompound screeningApoptosis detectionFlow cellFluorescence
Devices for detecting particle sizes and distributions using focused light scattering techniques, by passing a sample through a focused beam of light, are disclosed. In one embodiment, the devices include one or more lasers, whose light is focused into a narrow beam and into a flow cell, and dispersions are passed through the flow cell using hydrodynamic sample injection. In another embodiment, a plurality of lasers is used, optionally with hydrodynamic sample injection. Particles pass through and scatter the light. The scattered light is then detected using scatter and extinction detectors, and, optionally, fluorescence detectors, and the number and size of the particles is determined. Particles in the size range of 0.1 to 10 μm can be measured. Using the device, significantly smaller particles can be detected than if techniques such as EQELS, flow cytometry, and other conventional devices for measuring biological particles.
Owner:INVITROX
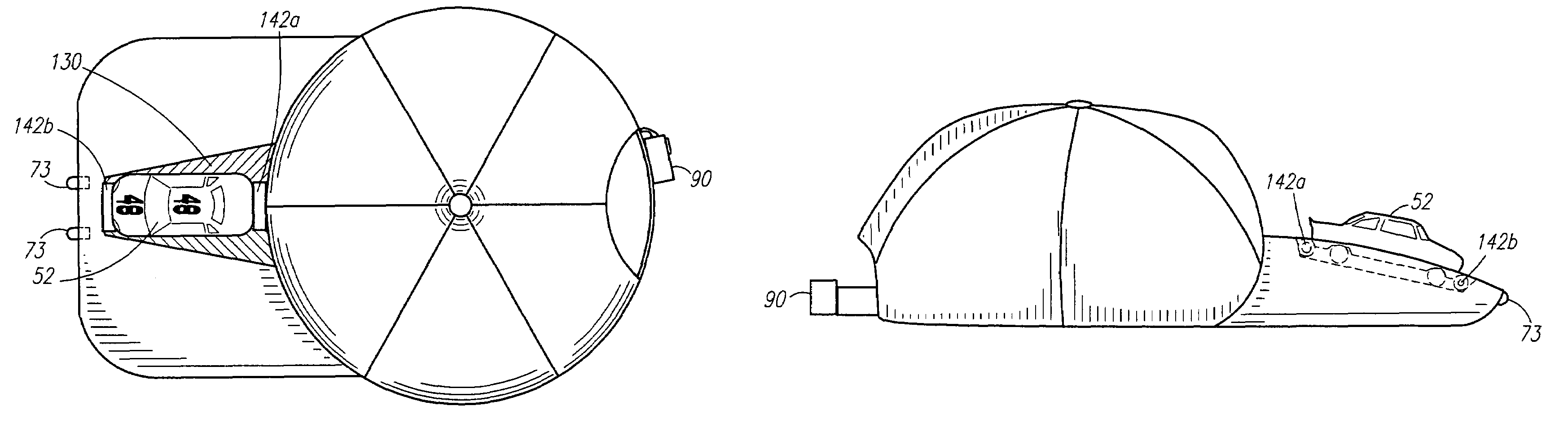
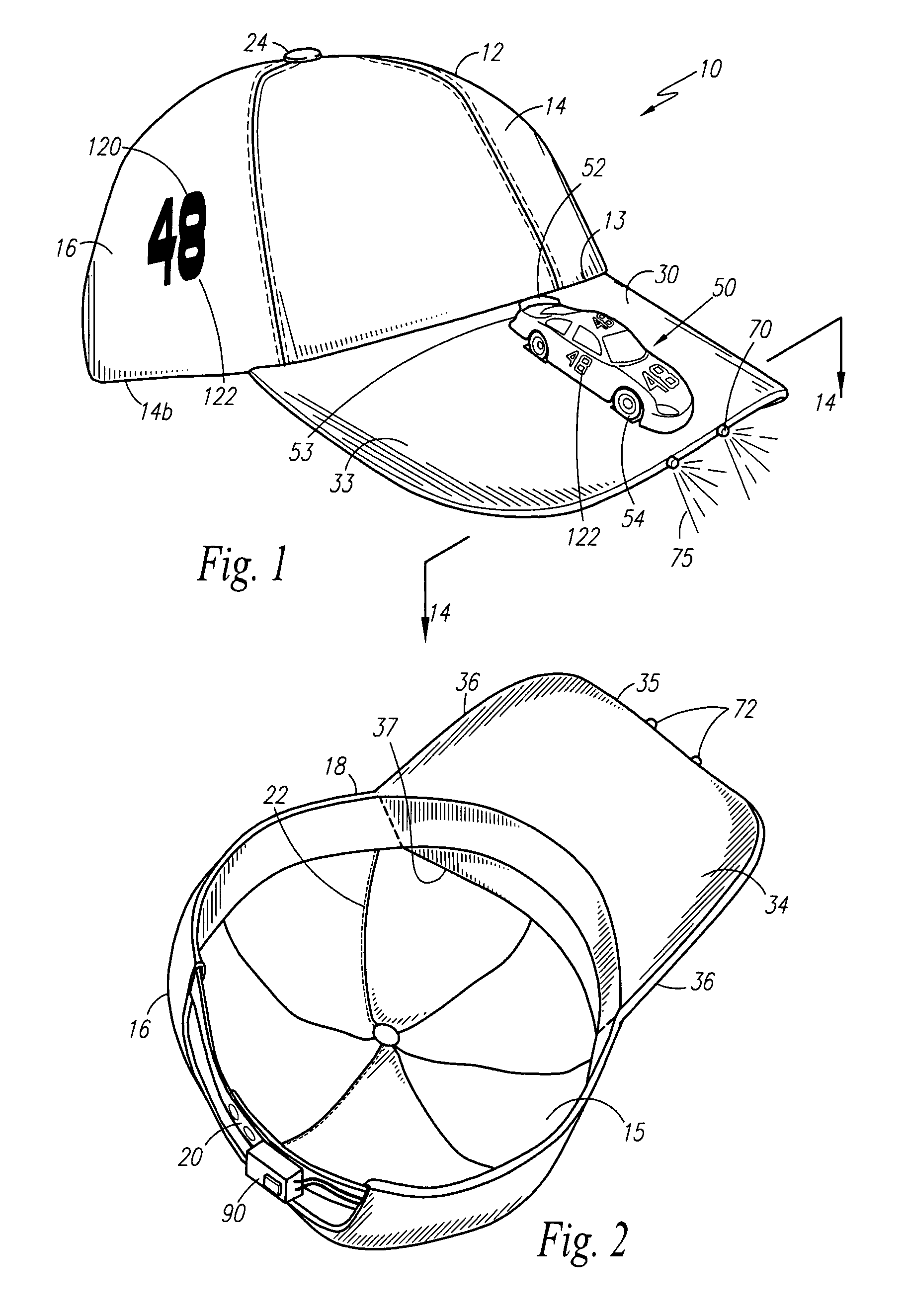
Headgear for attaching a toy
A headgear apparatus in the design of a baseball style cap is provided having an attachment means adapted to removably hold a toy miniature car atop the brim thereof. The apparatus includes a light source for directing narrow beams of light forwardly from the forward peripheral edge of the brim of the headgear.
Owner:FULTON BRIAN K
Method and apparatus for multi-user scheduling for interference avoidance in adaptive beamforming systems
InactiveUS20080267063A1Improve performanceIncrease data rateSite diversityError preventionSequence designTelecommunications
A method and apparatus of imparting coverage gain to cell-edge or cusp mobile subscribers without resort to diluted frequency reuse factors is disclosed. Each base station adopts a priori a beam illumination sequence designed to minimize or obviate the likelihood of beam clashes in a narrow beam adaptive beamforming system. Such sequences may be optimized to impact primarily cell-edge subscribers or subscribers within cusp areas of adjoining beams or sectors. The inventive protocols may be applicable to fixed multibeam systems as well as individual steered beam and spatial null generation antenna systems.
Owner:TENXC WIRELESS
Miniature mass spectrometer system
ActiveUS20120138790A1Small sizeReduce weightMiniaturised spectrometersIsotope separationIon beamMass analyzer
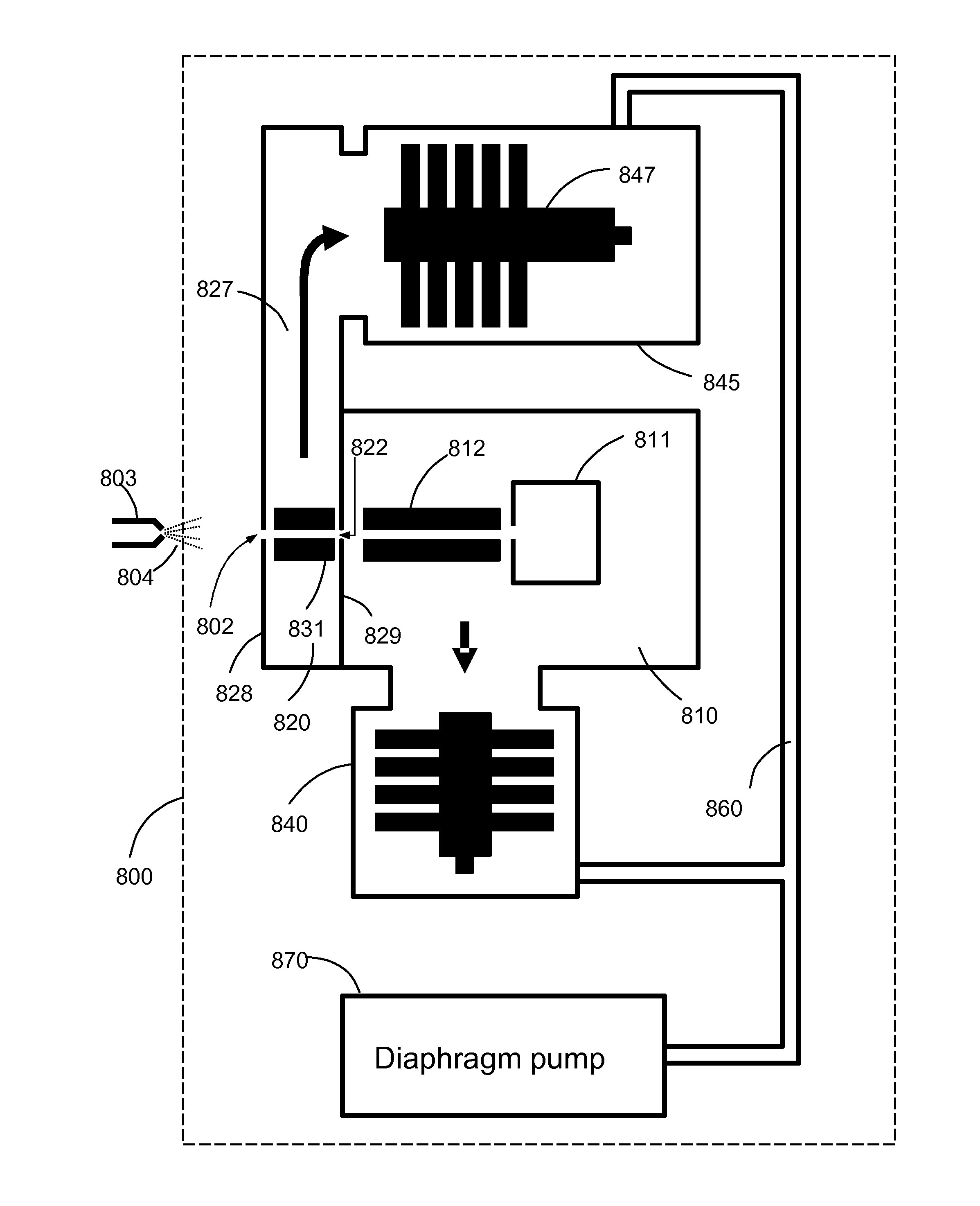
A miniature mass spectrometer that may be coupled to an atmospheric pressure ionisation source is described. Ions pass through a small orifice from a region at atmospheric pressure or low vacuum, and undergo efficient collisional cooling as they transit a very short, differentially pumped ion guide. A narrow beam of low energy ions is passed through a small aperture and into a separate chamber containing the mass analyser.
Owner:MICROSAIC SYST
Reconfigurable micro-mesh communication system
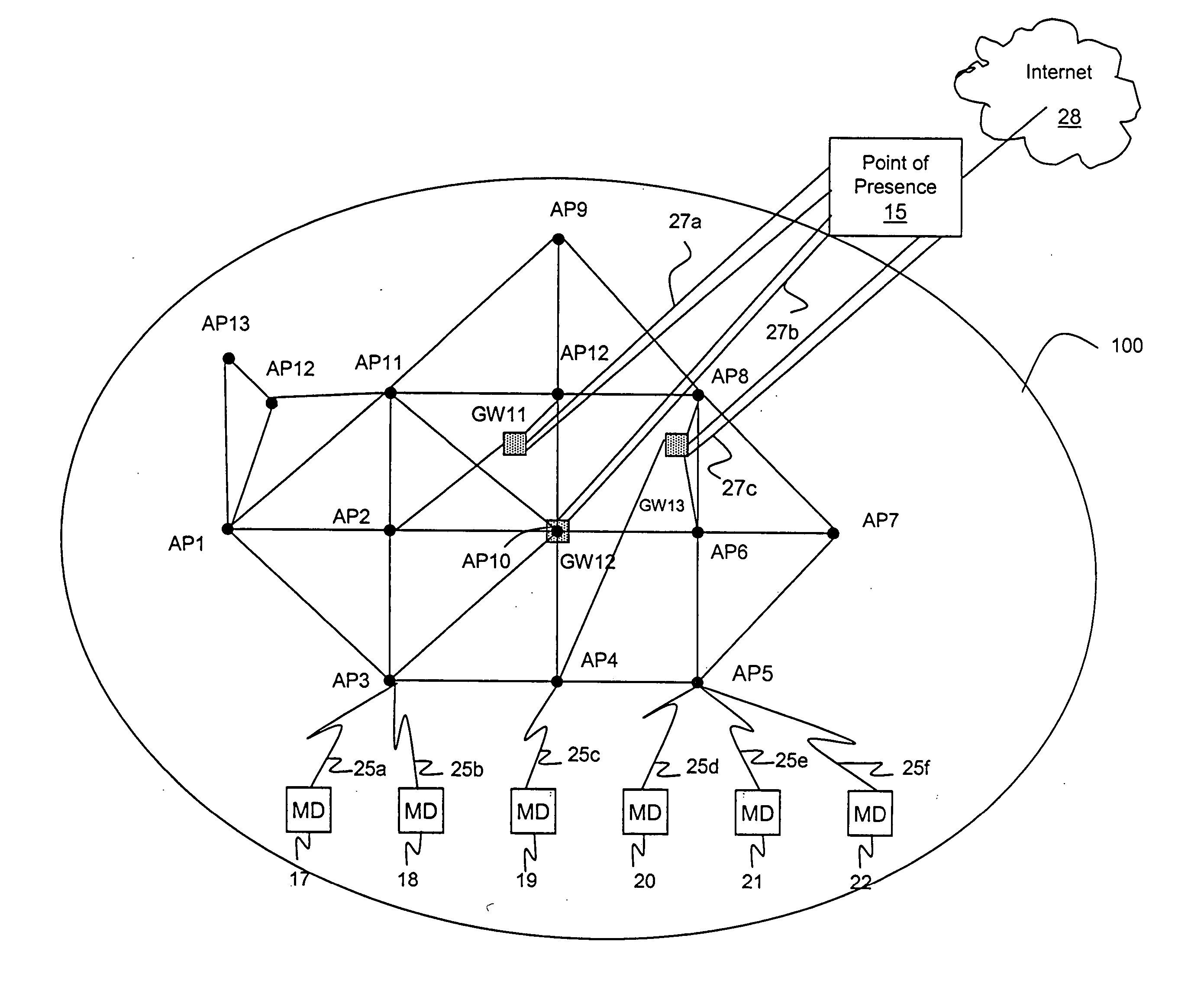
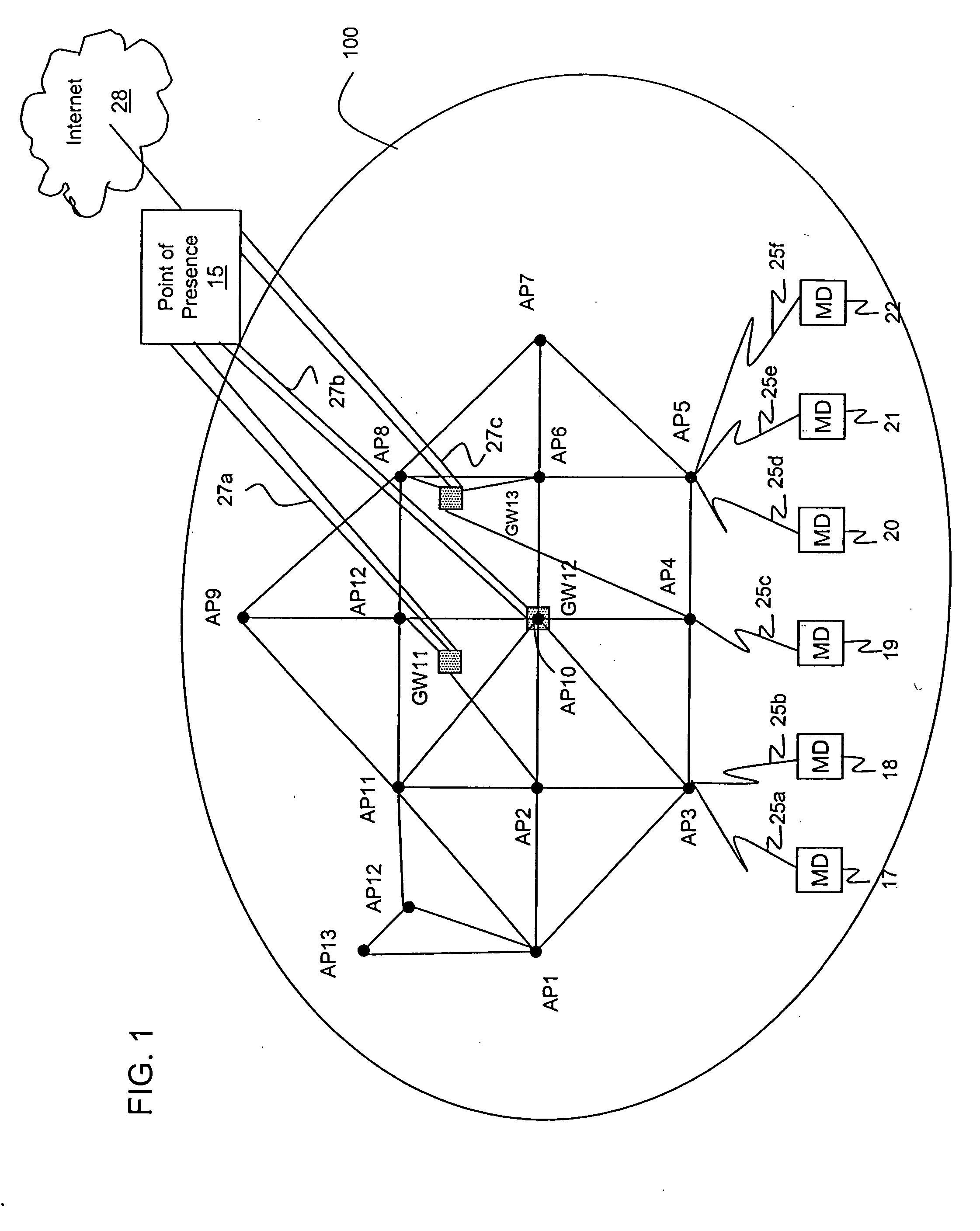
InactiveUS20050272430A1Network topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemPoint of presence
Wide area wireless networks with high network throughput and low provisioning and maintenance costs. The wireless networks comprise a distributed reconfigurable micro-mesh cluster having direct wireless link capability. Multiple channels operating at different frequencies can be used per direct wireless link. To further reduce the provisioning and maintenance costs, narrow beam antennas are used at the point of presence. To expand the wide area wireless networks into the home market, adjustable antennas are installed at homes.
Owner:AIIRMESH COMM
Ion transport device and modes of operation thereof
ActiveUS7781728B2Reduce streamingElectrostatic separatorsParticle separator tubesVoltage amplitudeLight beam
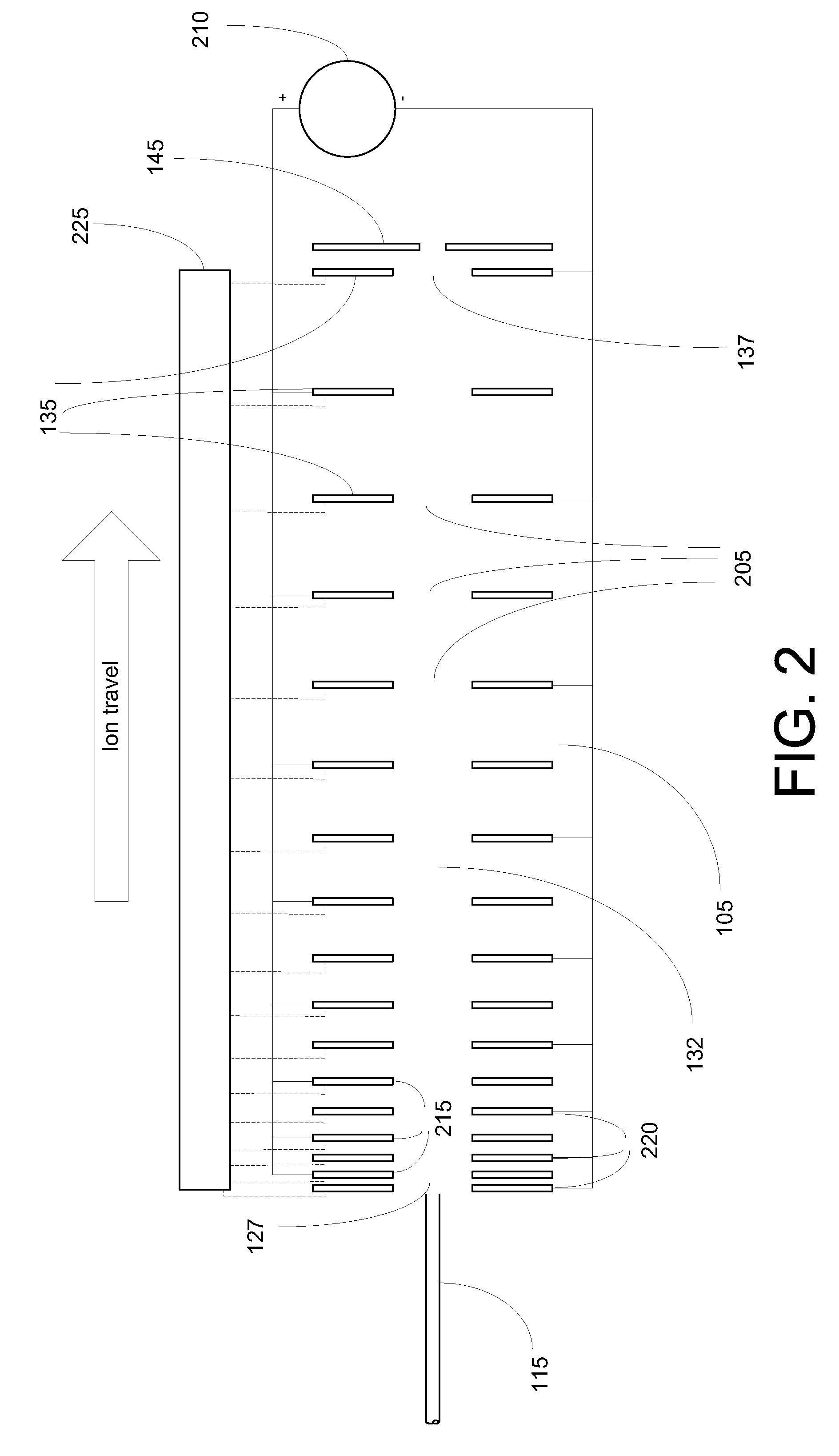
A device for transporting and focusing ions in a low vacuum or atmospheric-pressure region of a mass spectrometer is constructed from a plurality of longitudinally spaced apart electrodes to which oscillatory (e.g., radio-frequency) voltages are applied. In order to create a tapered field that focuses ions to a narrow beam near the device exit, the inter-electrode spacing or the oscillatory voltage amplitude is increased in the direction of ion travel.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Edge-illuminated panels with shaped-edge diffuser
InactiveUS20080186737A1Easy to operateMinimal maintenanceMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight beamEngineering
An edge-illuminated panel with a shaped edge diffuser is provided. The panel includes a panel frame having at least one illuminated frame member coupled to the shaped edged diffuser. The diffuser includes a diffusion layer having a shaped illuminated edge. The panel frame includes at least one wide-angled light source located substantially within the at least one illuminated frame member. The wide-angled light source, e.g., a light emitting diode, illuminates the shaped illuminated edge of the diffusion layer with a substantially wide-angled beam of light. The shaped illuminated edge then transforms the substantially wide-angled beam of light into a substantially narrow beam of light capable of penetrating the diffusion layer. In some embodiments, the shaped illuminated edge of the diffusion layer includes a curved portion. In other embodiments, the shaped illuminated edge includes two or more curved and / or substantially flat portions
Owner:ILLUMINER
Laser annealing apparatus and annealing method of semiconductor thin film
InactiveUS20050169330A1Improve mobilityKeep energy smallTransistorPolycrystalline material growthBand shapeLight beam
When a laser bean temporally modulated in amplitude by a modulator is shaped into a long and narrow beam by a beam shaper, the scanning-direction size of the long and narrow beam shaped by the beam shaper is selected to be in a range of from 2 to 10 microns, preferably in a range of from 2 to 4 microns and the scanning speed of the beam is selected to be in a range of from 300 to 1000 mm / s, preferably in a range of from 500 to 1000 m / s. As a result, damage of the silicon thin film can be suppressed while energy utilizing efficiency of the laser beam can be improved. Accordingly, laterally grown crystals (belt-like crystals) improved in throughput can be obtained on a required region of a substrate scanned and irradiated with the laser beam.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS
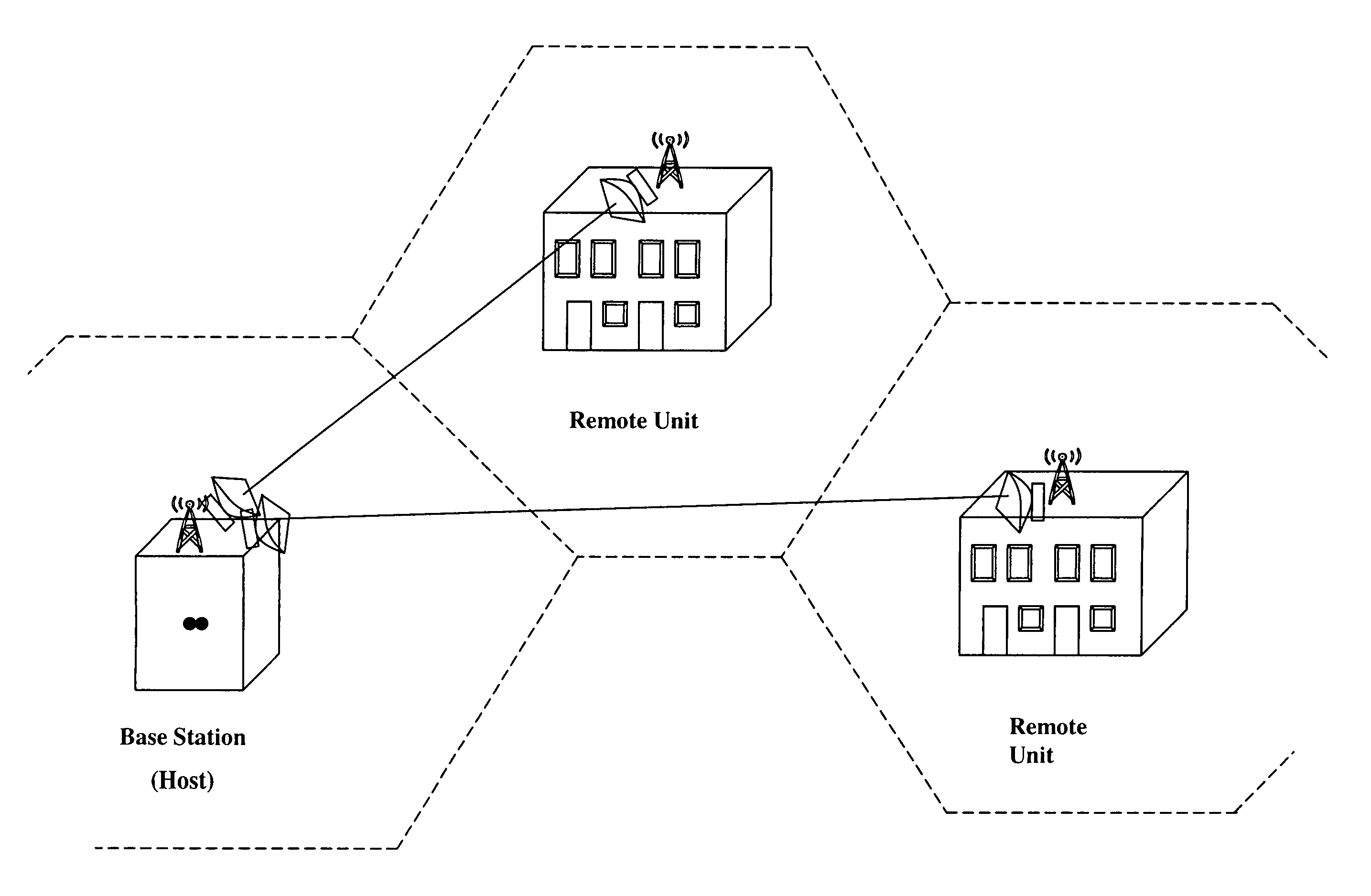
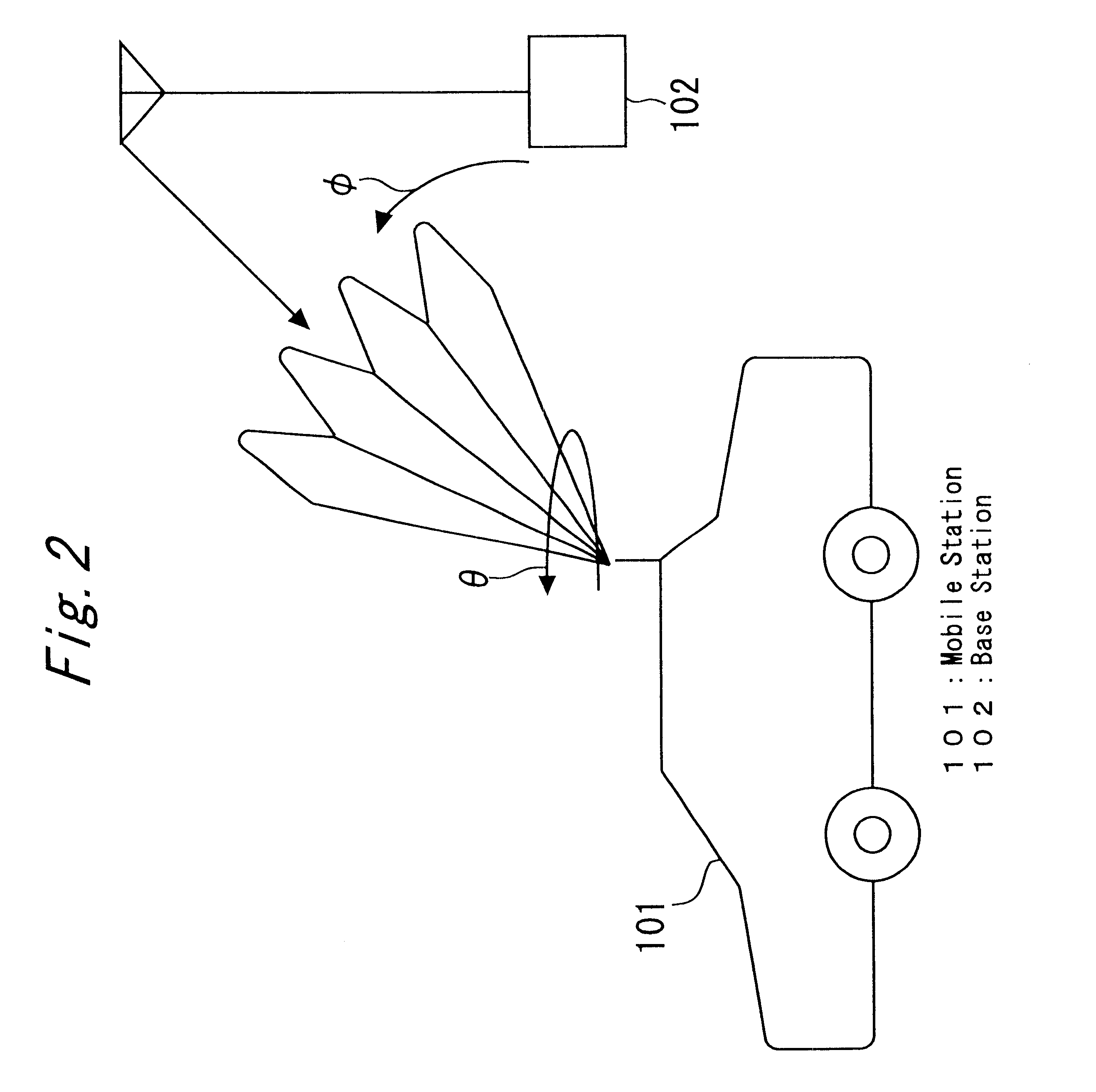
Mobile radio communication system
InactiveUS6370377B1Reduce tracking timeActive radio relay systemsSubstation equipmentOmnidirectional antennaCommunications system
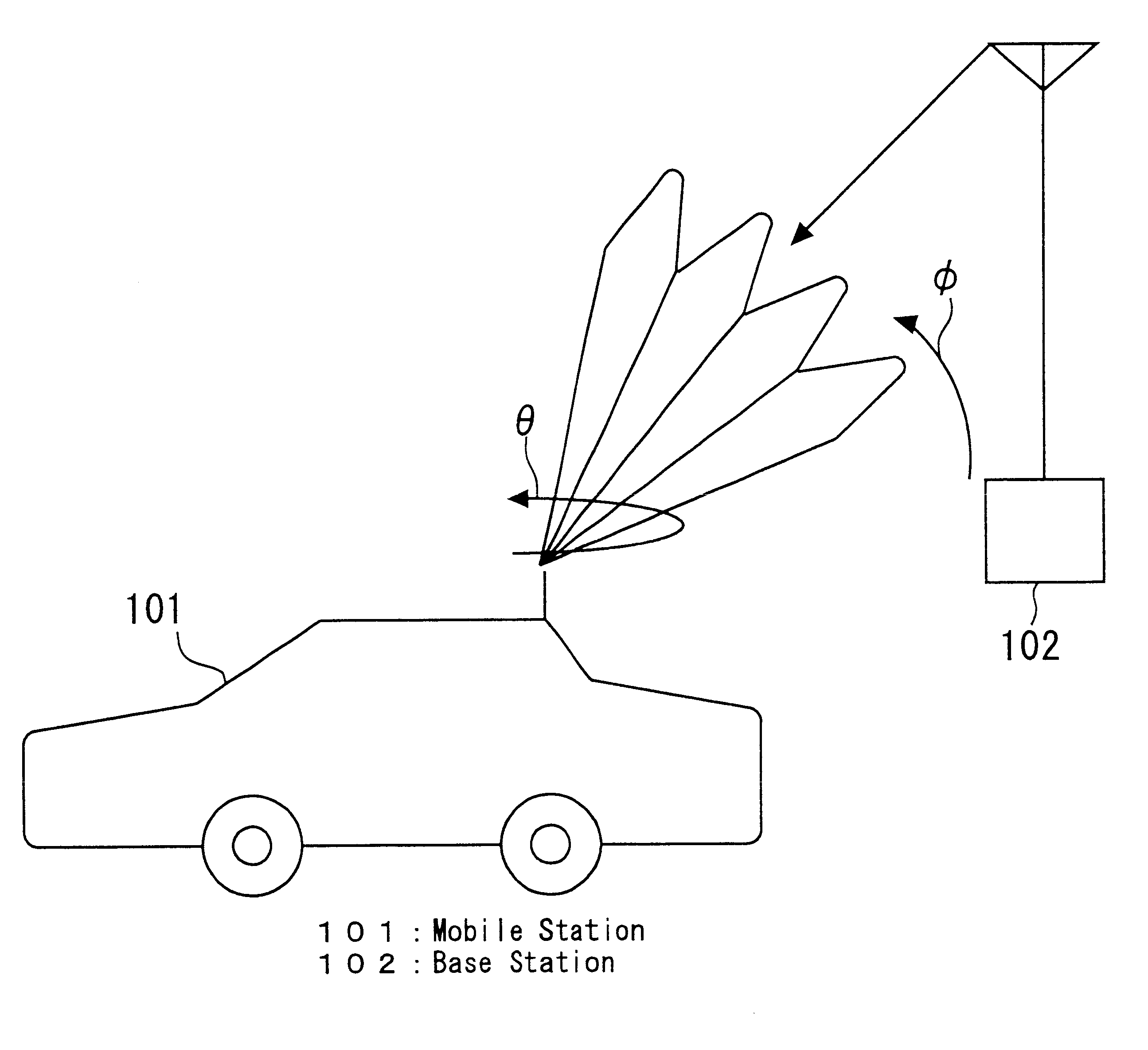
A mobile radio communication system which does not need an omnidirectional channel for both a base station and a mobile station to track each other and uses only a narrow beam channel and can reduce a tracking time than before for an adjacent base station and a mobile station to search each other while a visiting area base station and the mobile station are communicating in the overlapped area. The base station and the mobile station comprise a unit for transmitting and receiving in forward or reverse channel, in different frequency, in different tracking channel using a narrow beam. Both the mobile station and the visiting area base station search the location each other, and after searched, they assign the frequency and the beam used in the tracking channel. At the same time, by comprising a searching slot in an information channel to search an adjacent base station while communicating with the visiting area base station, a tracking of other adjacent base station can be performed.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com