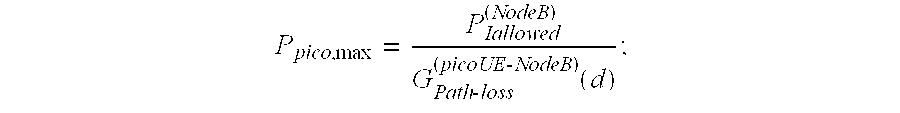Patents
Literature
1632 results about "Macrocell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
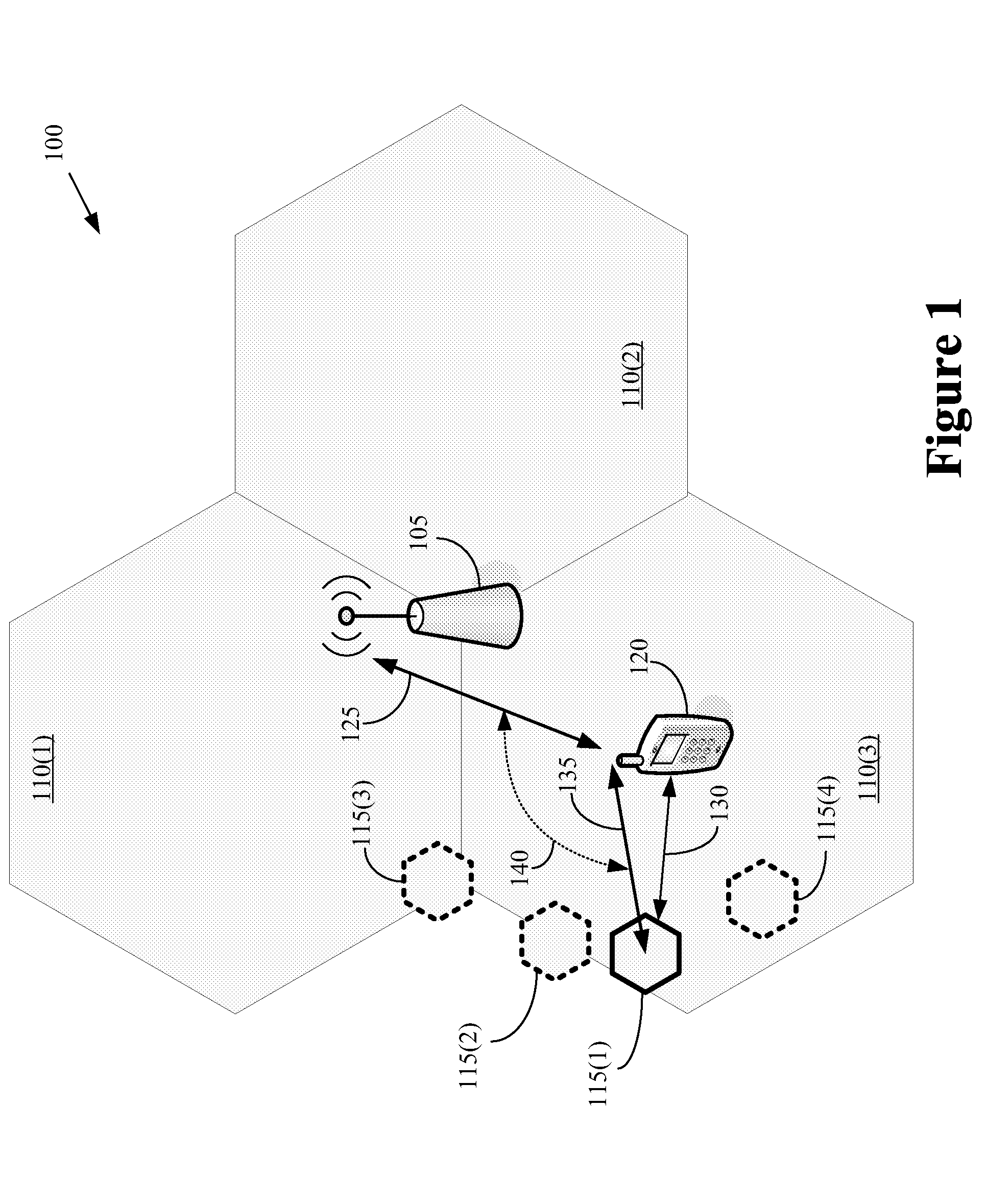
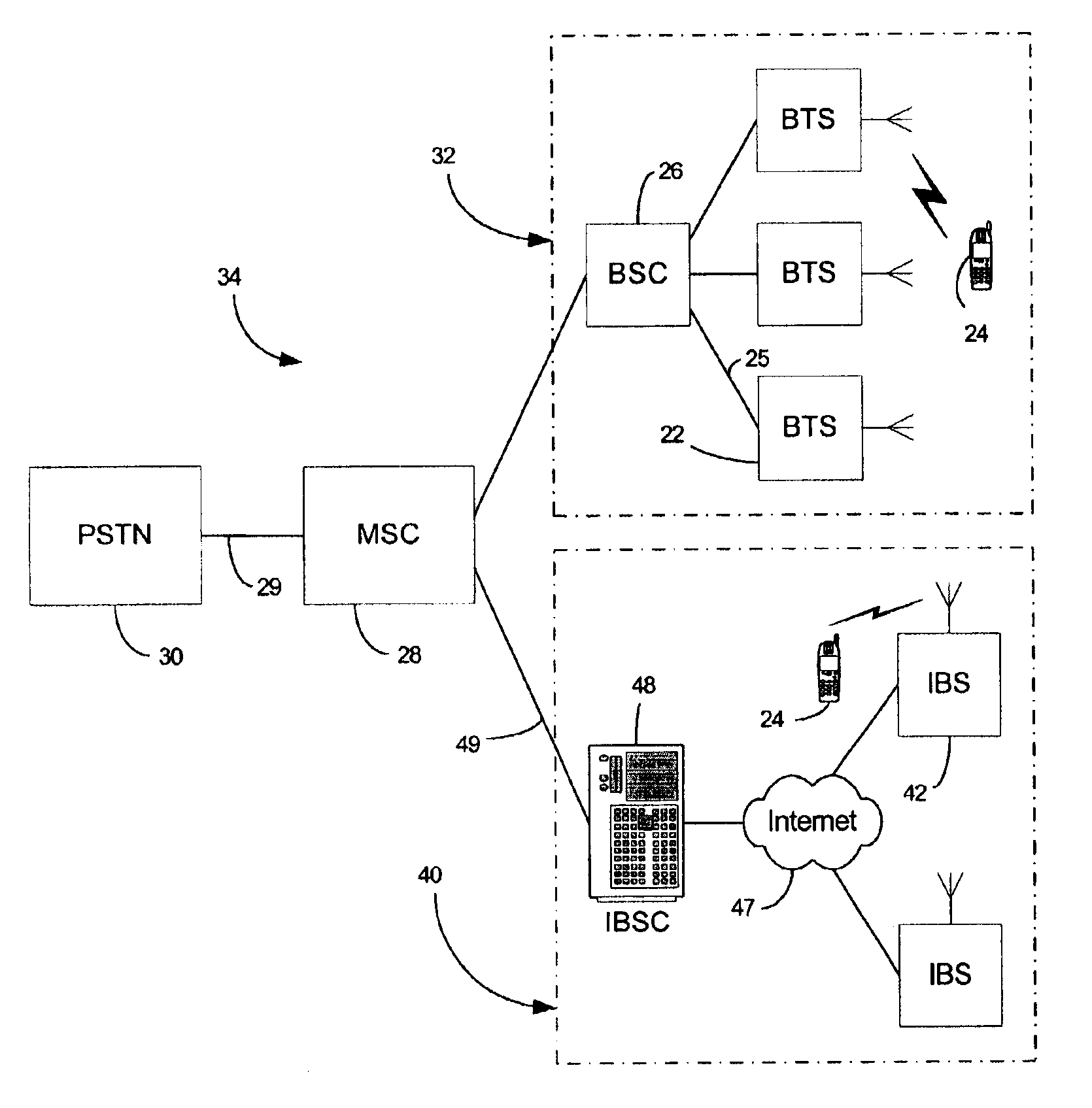
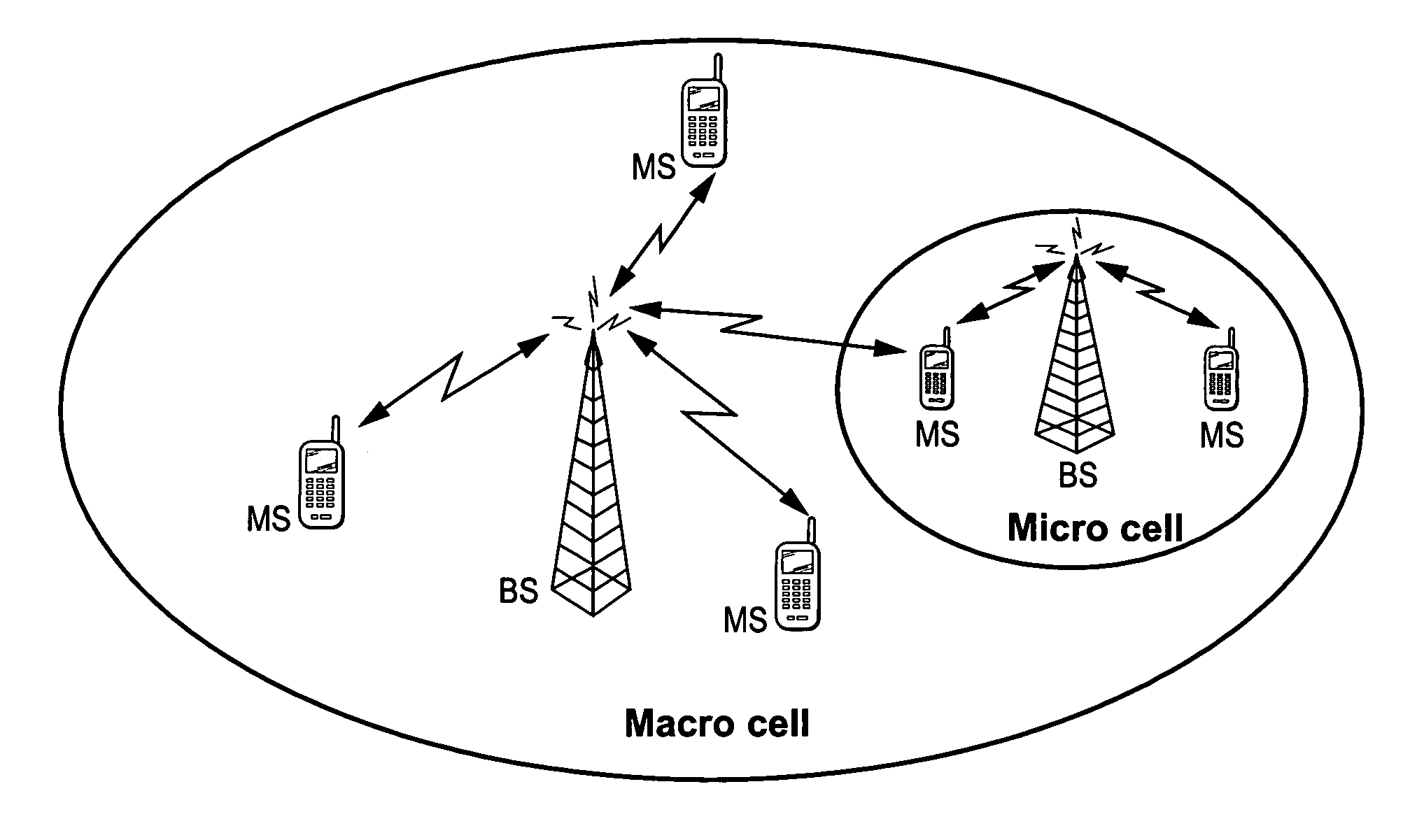
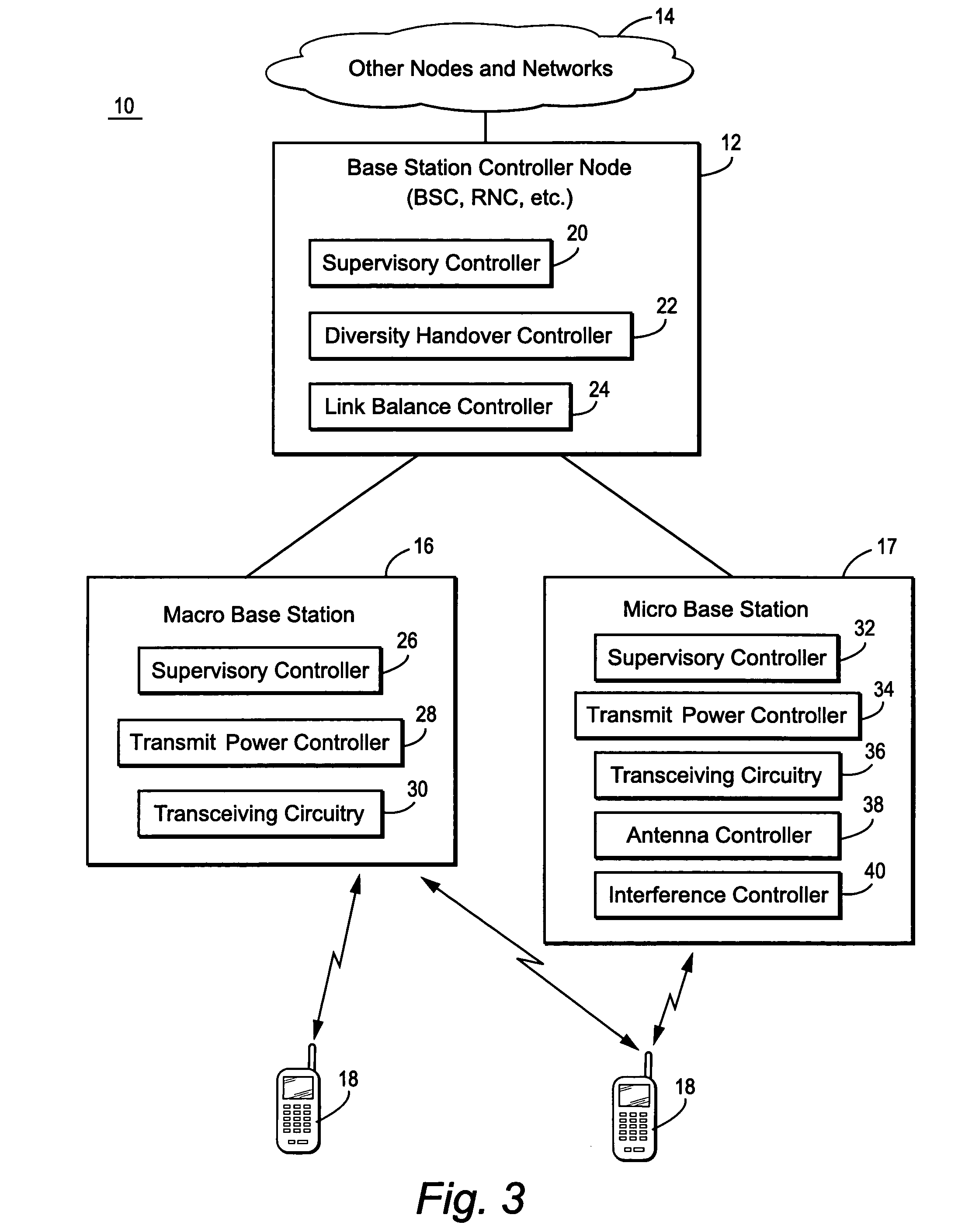
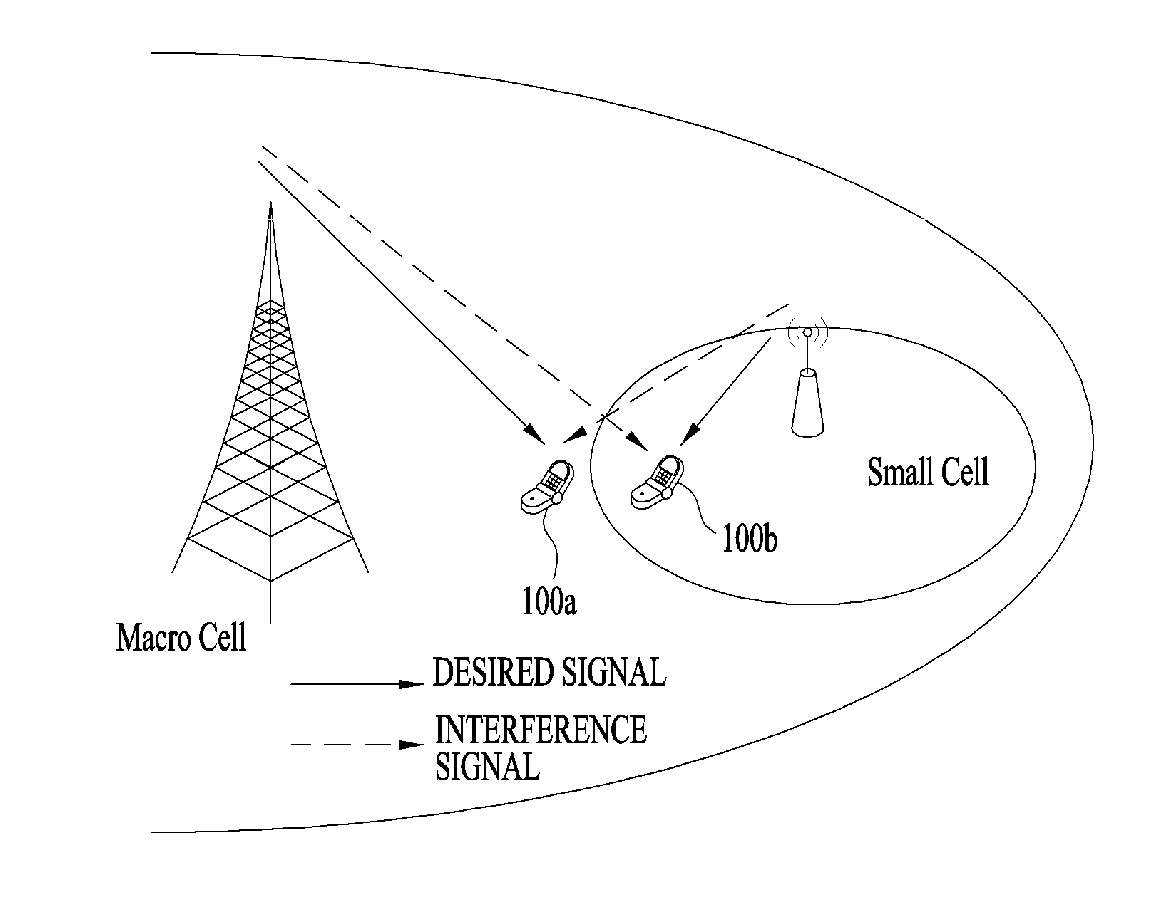
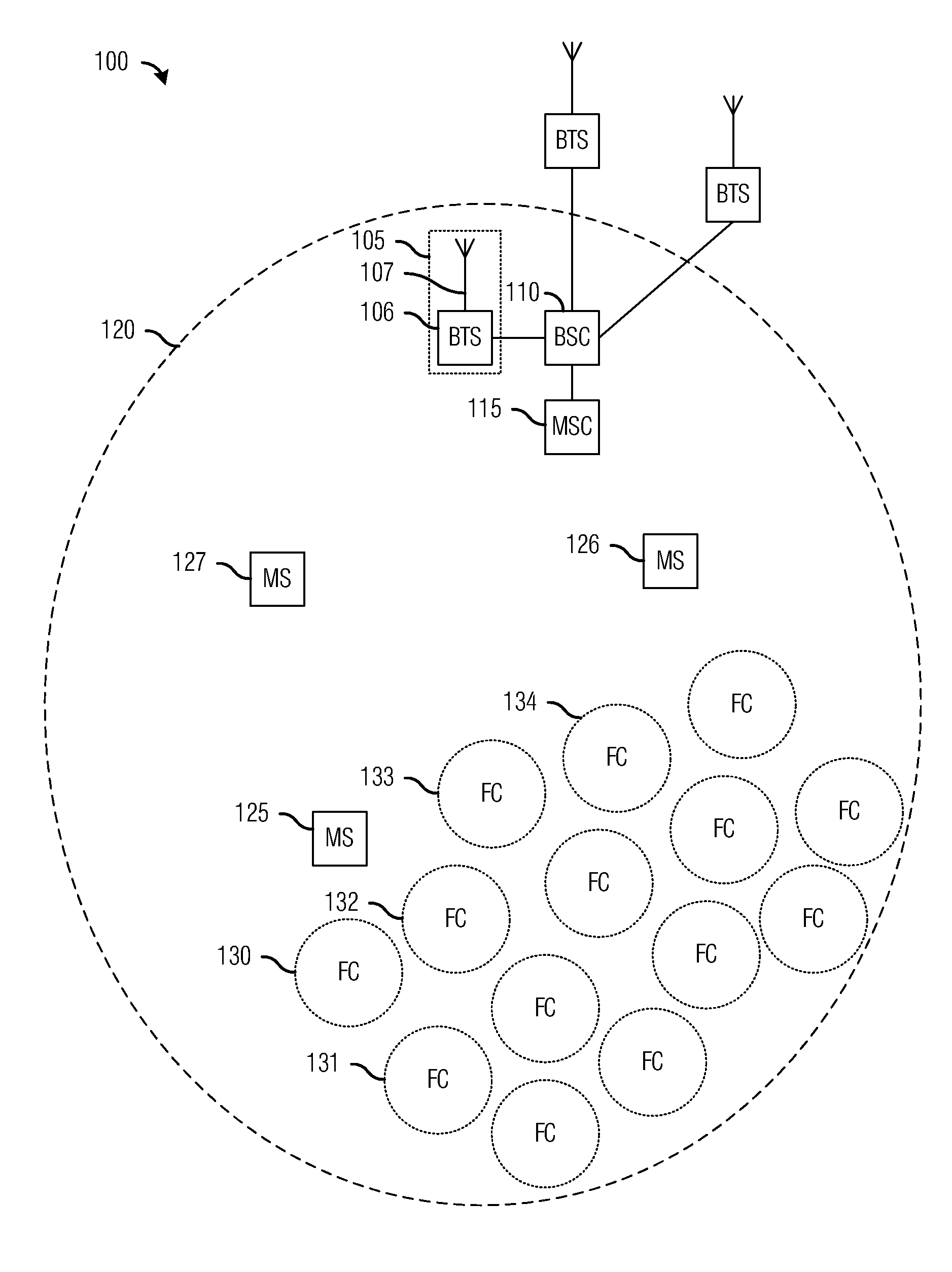
A macrocell or macrosite is a cell in a mobile phone network that provides radio coverage served by a high power cell site (tower, antenna or mast). Generally, macrocells provide coverage larger than microcell. The antennas for macrocells are mounted on ground-based masts, rooftops and other existing structures, at a height that provides a clear view over the surrounding buildings and terrain. Macrocell base stations have power outputs of typically tens of watts. Macrocell performance can be increased by increasing the efficiency of the transreciever.
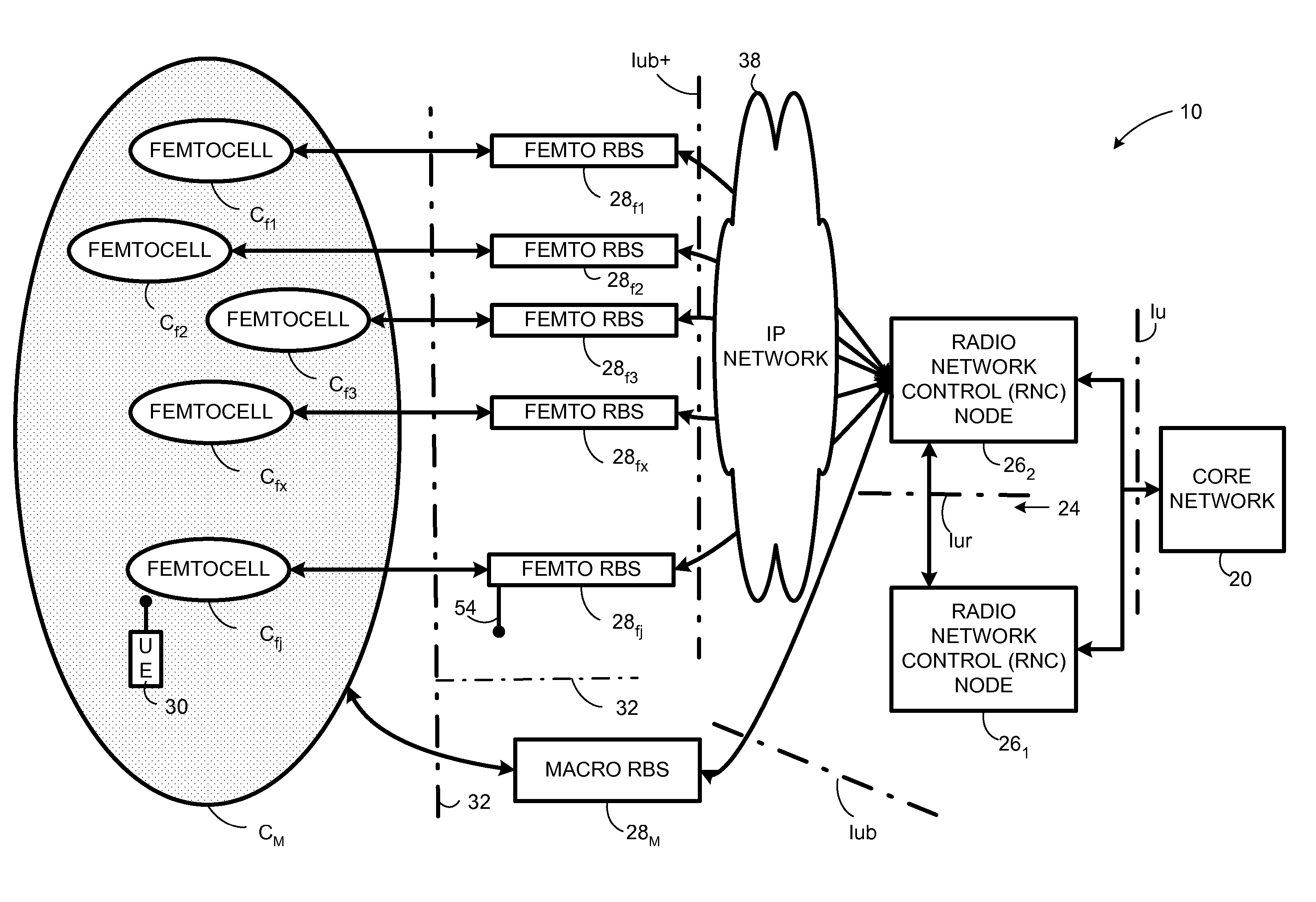
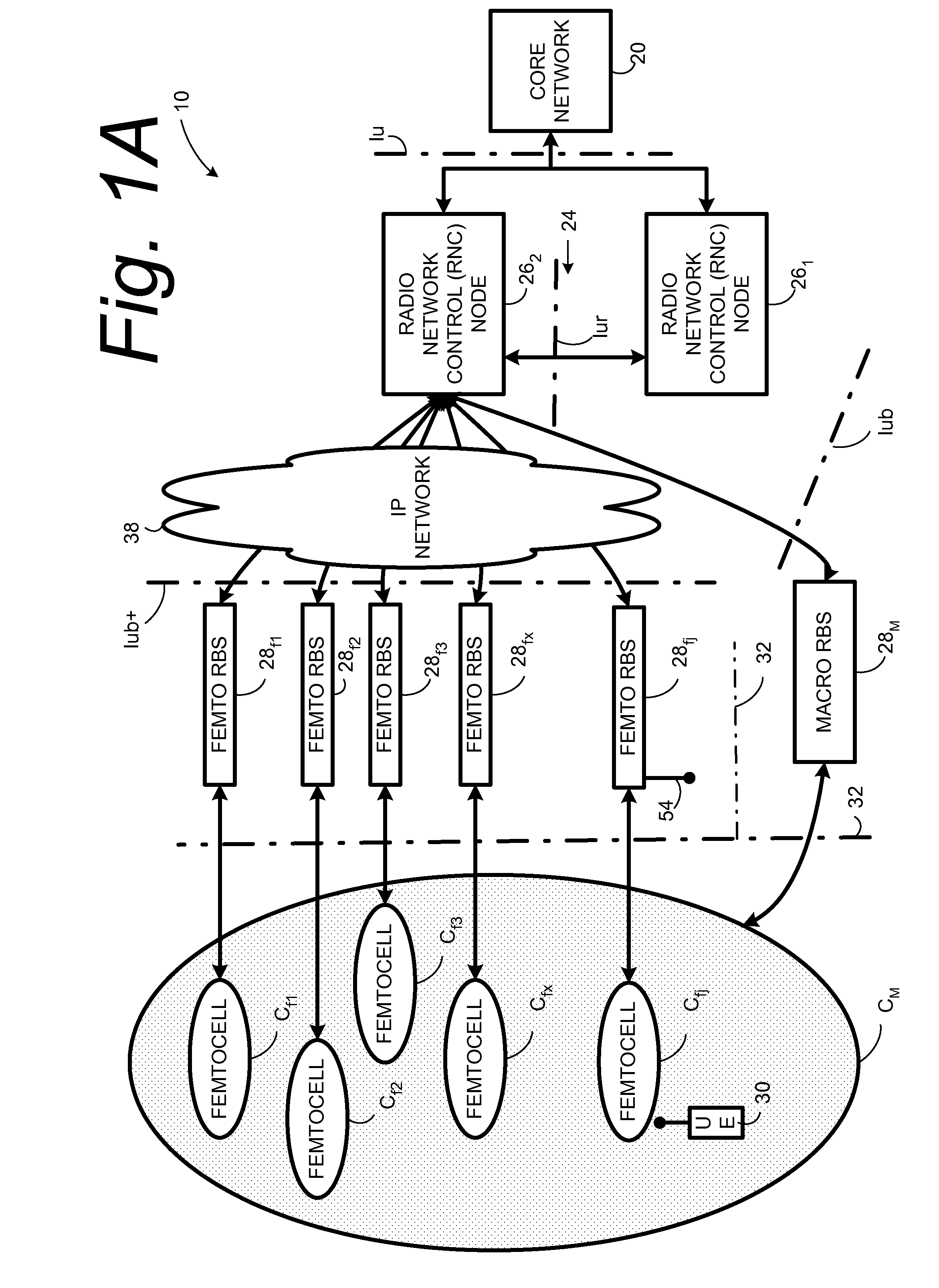
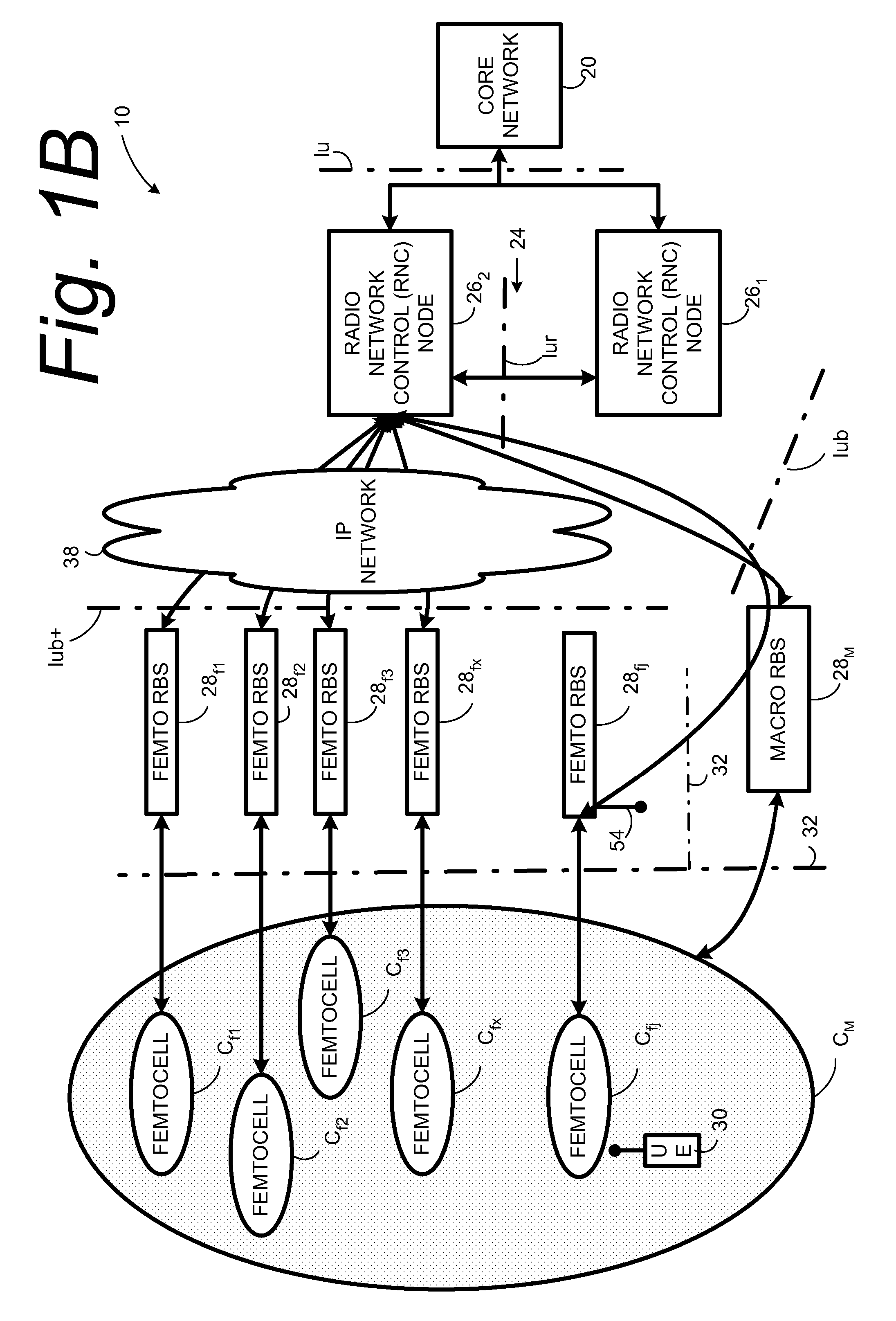
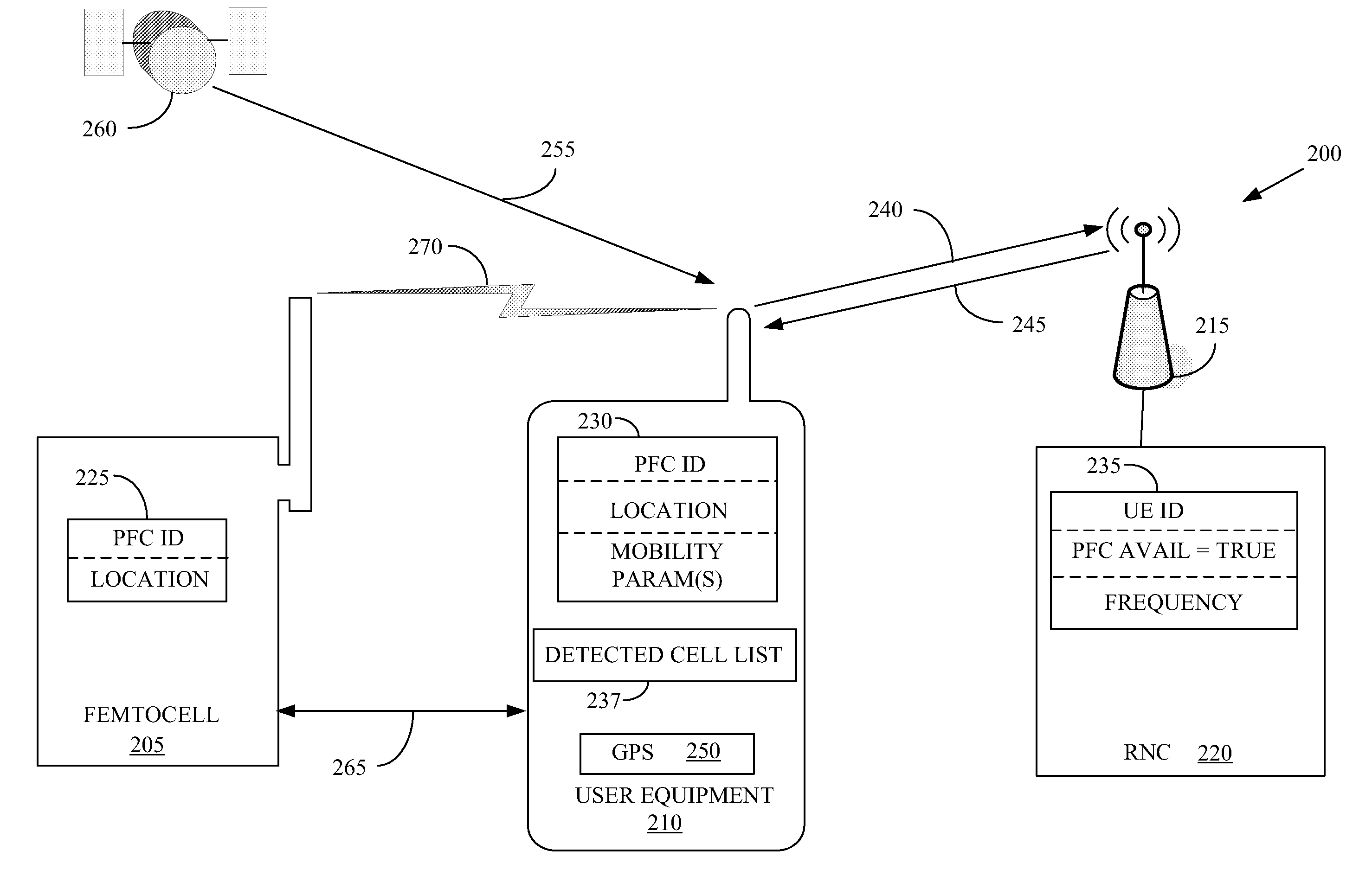
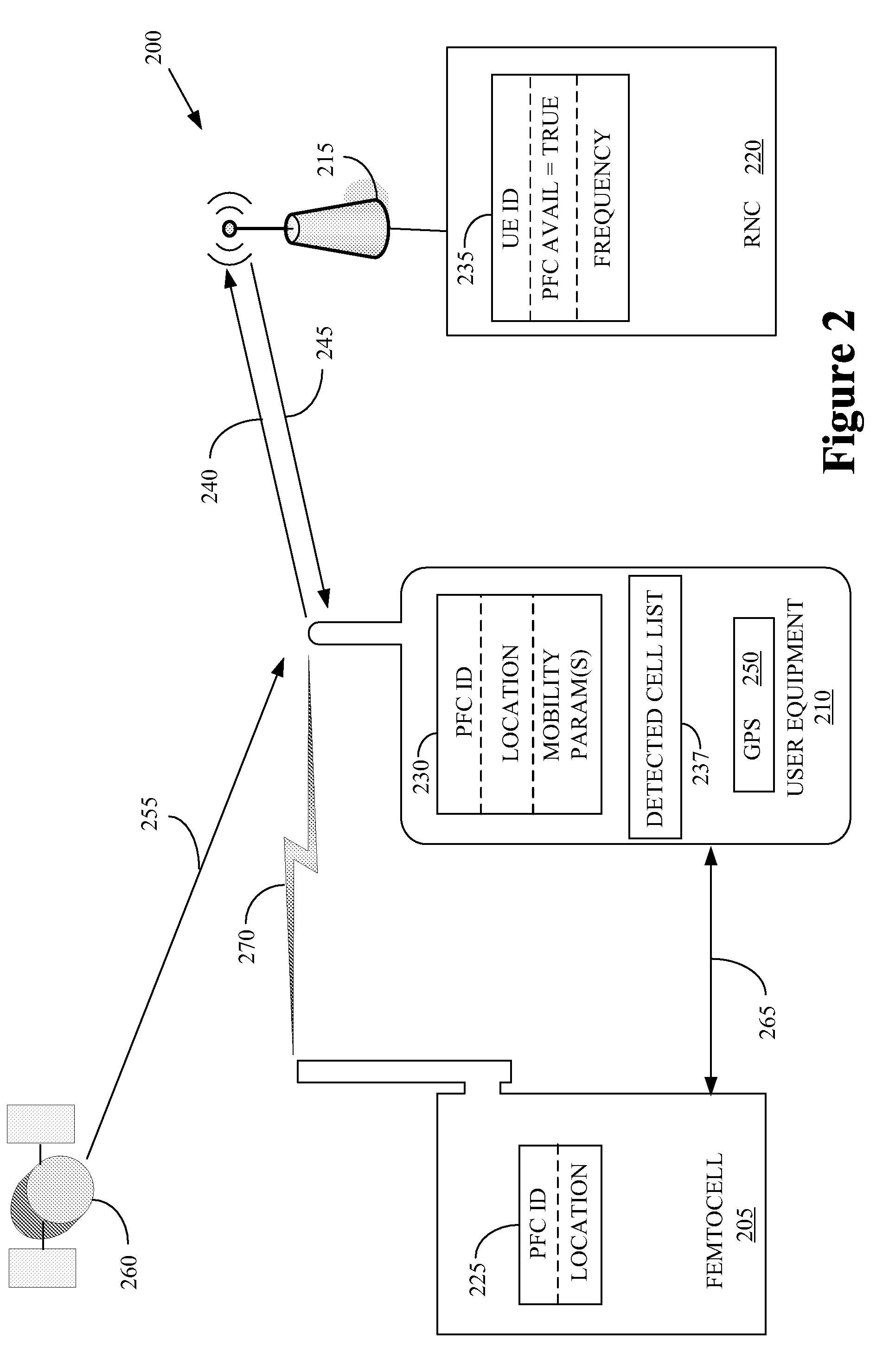
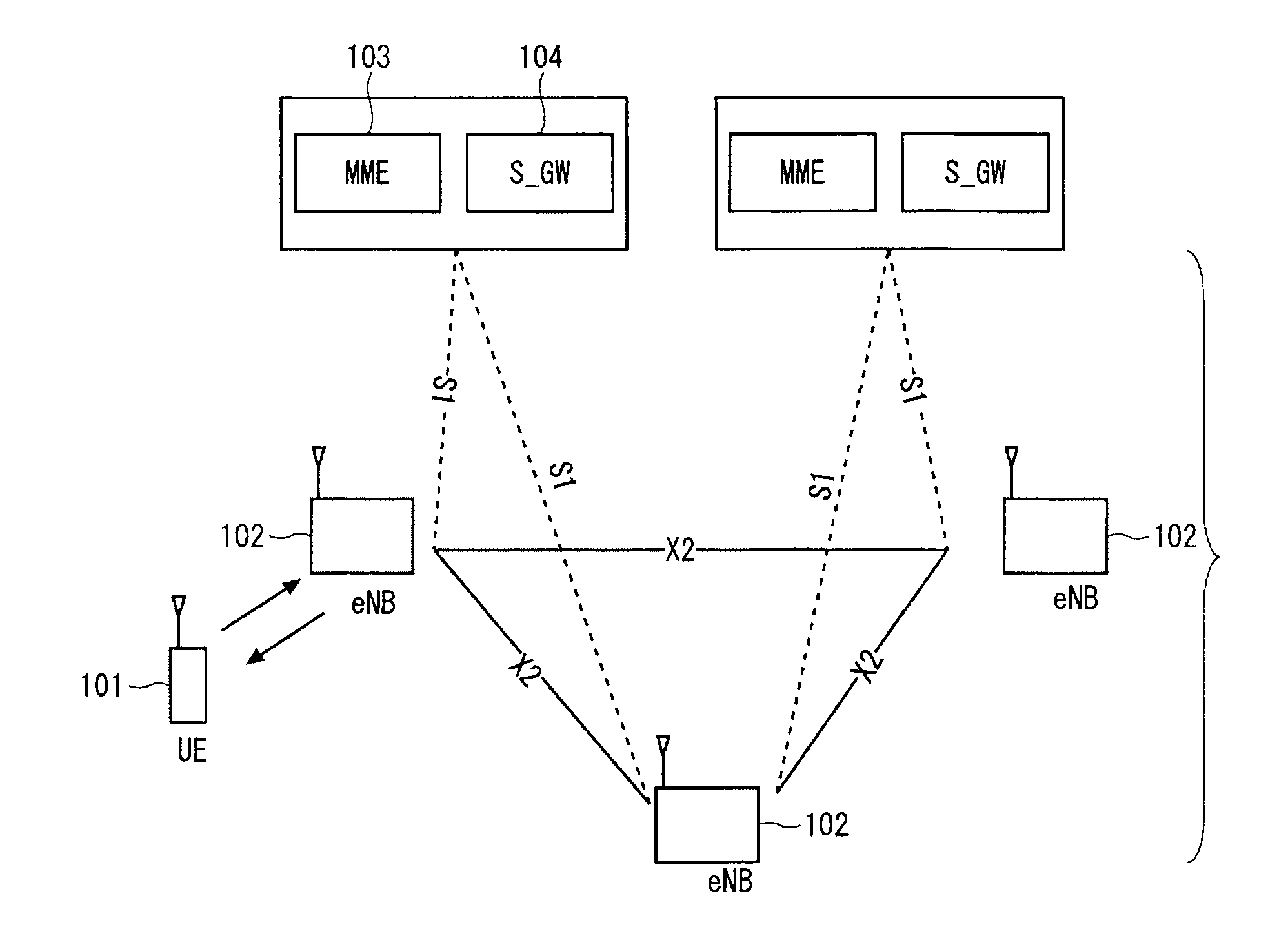
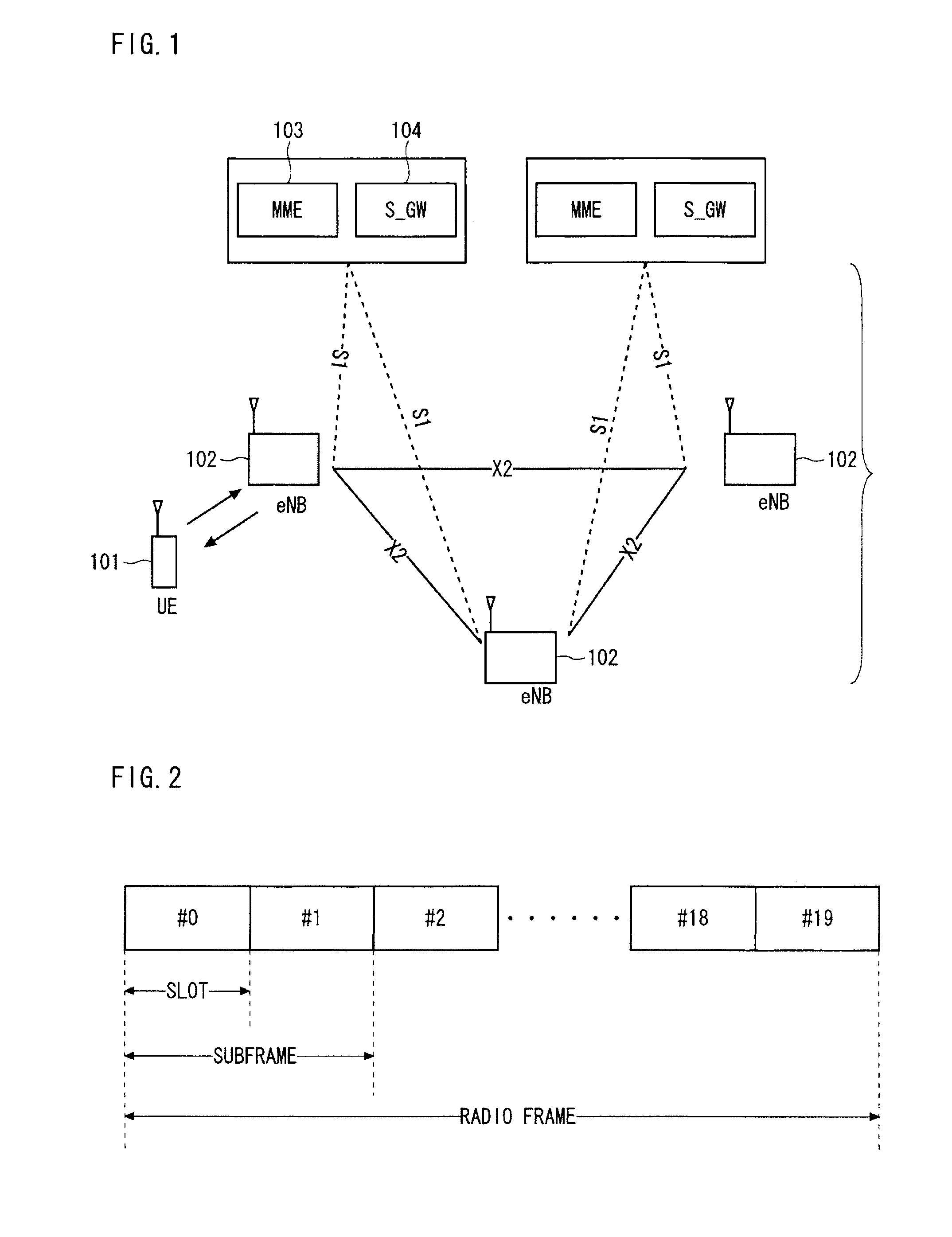
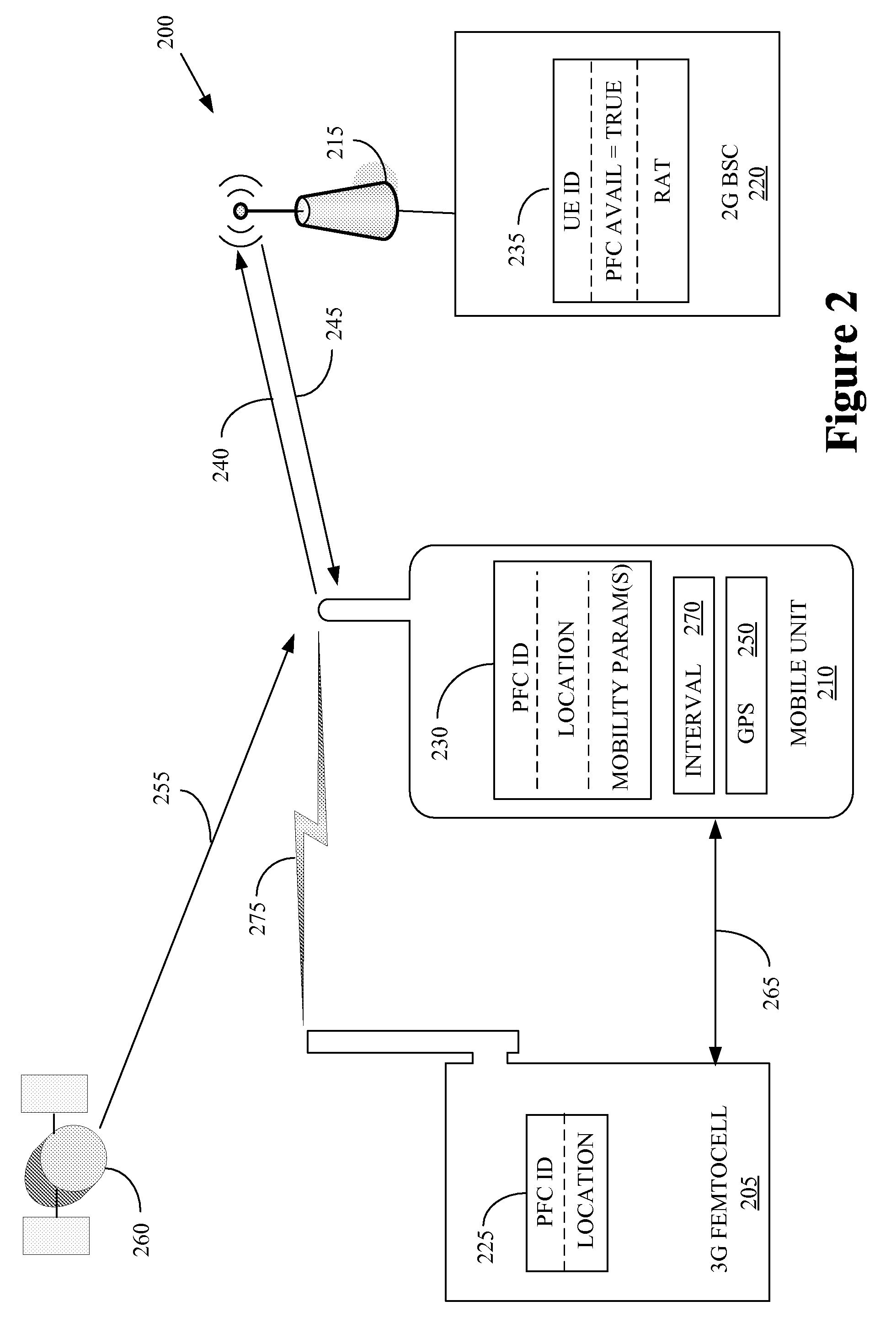
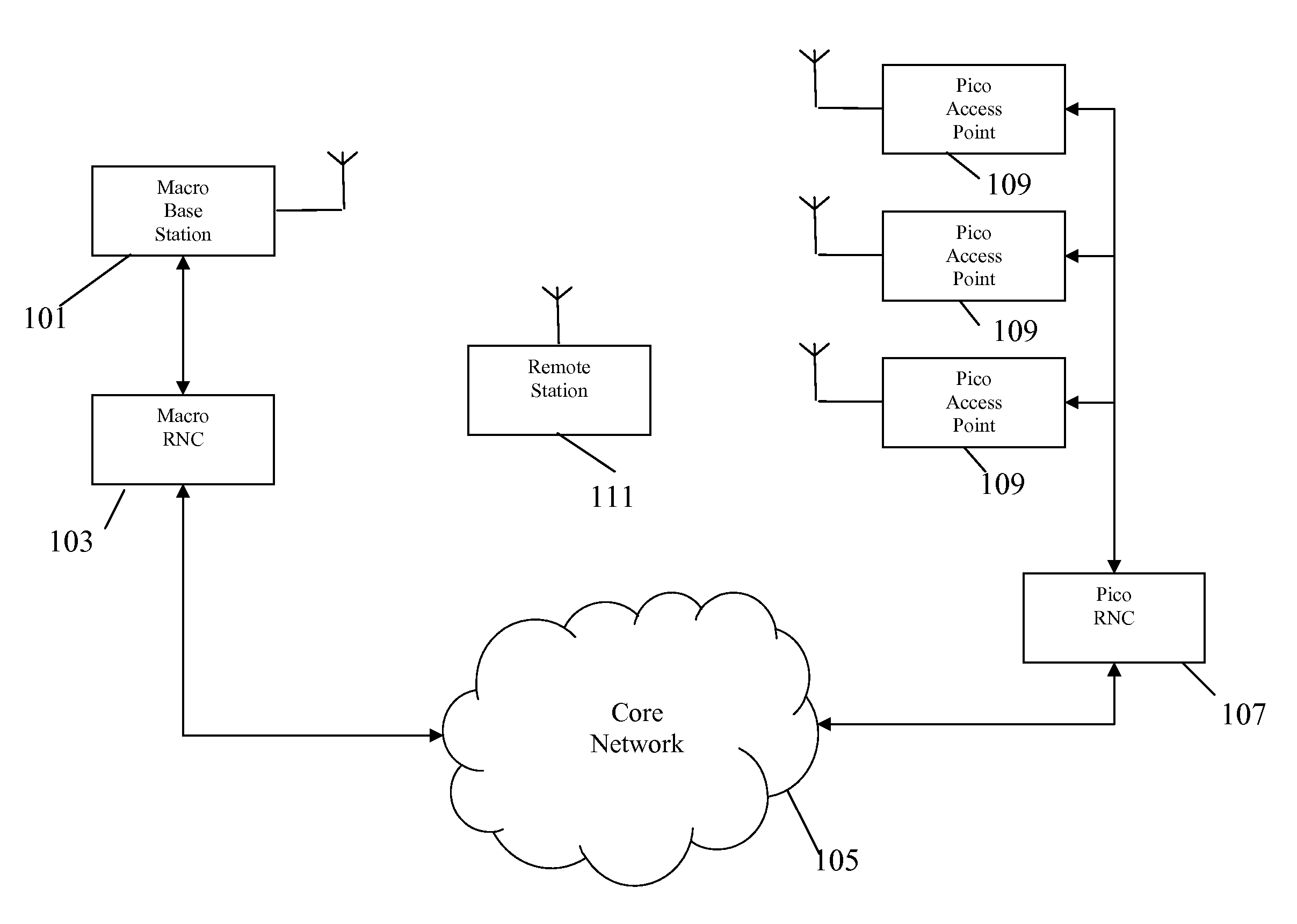
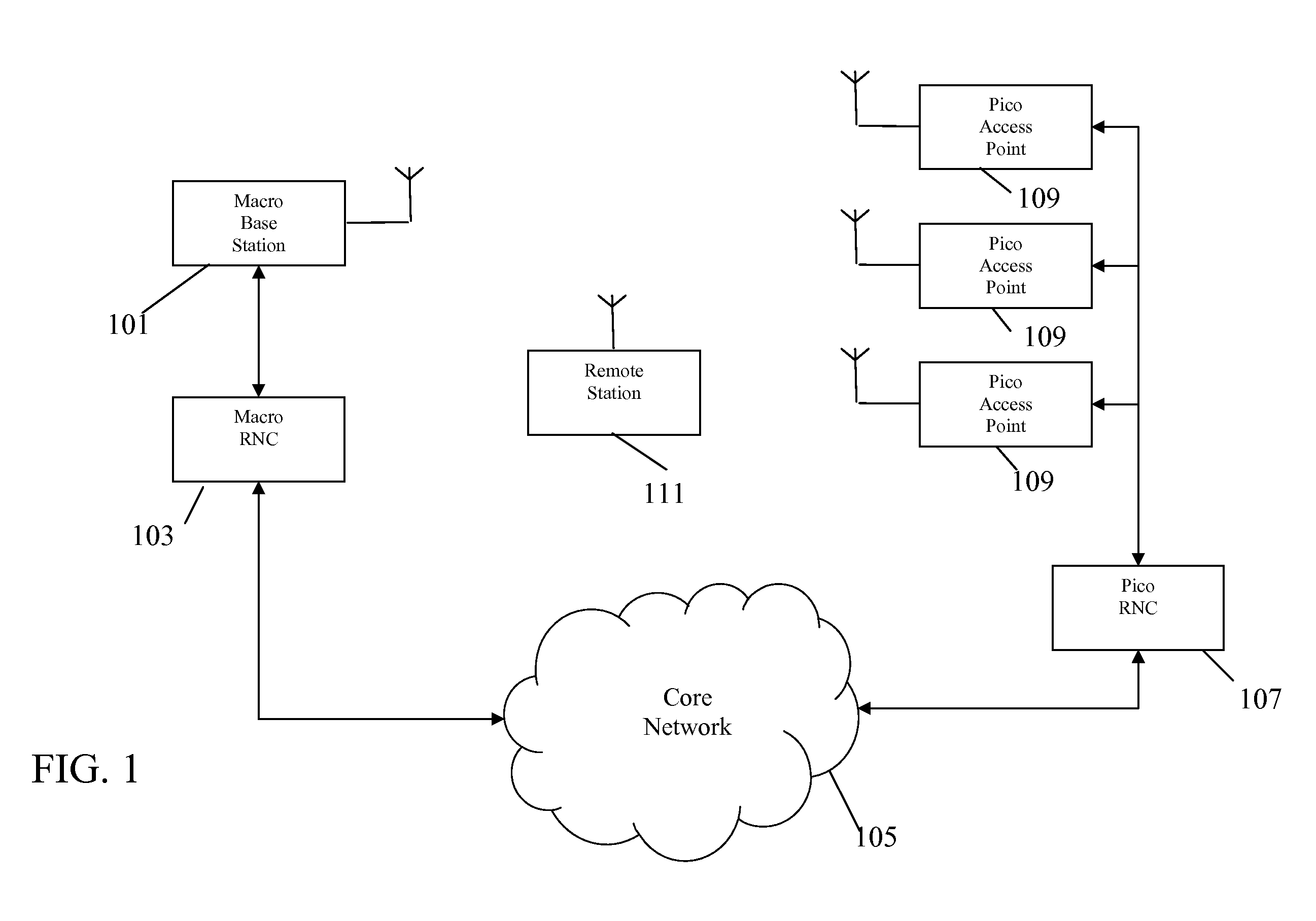
Automatic building of neighbor lists in mobile system
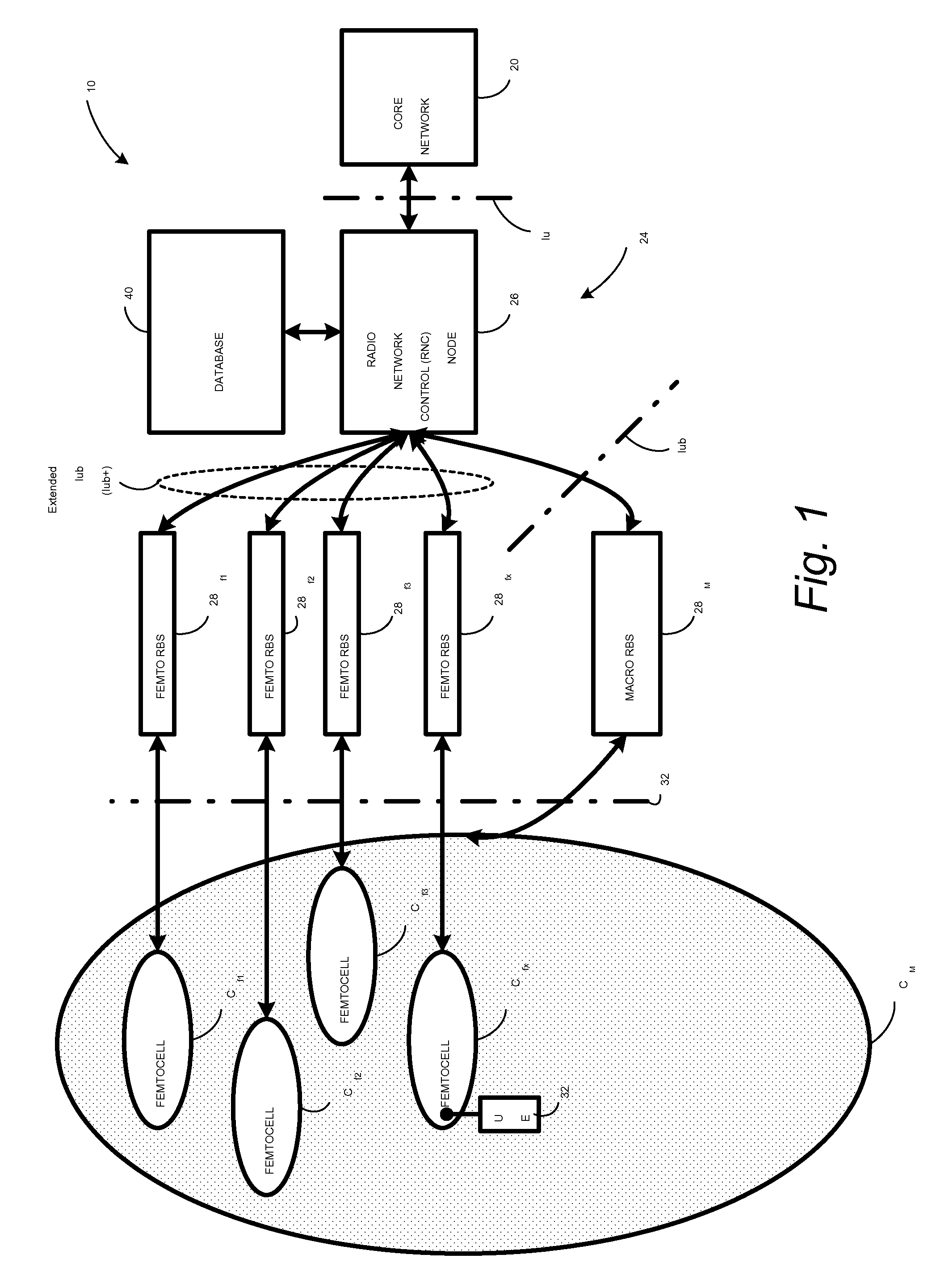
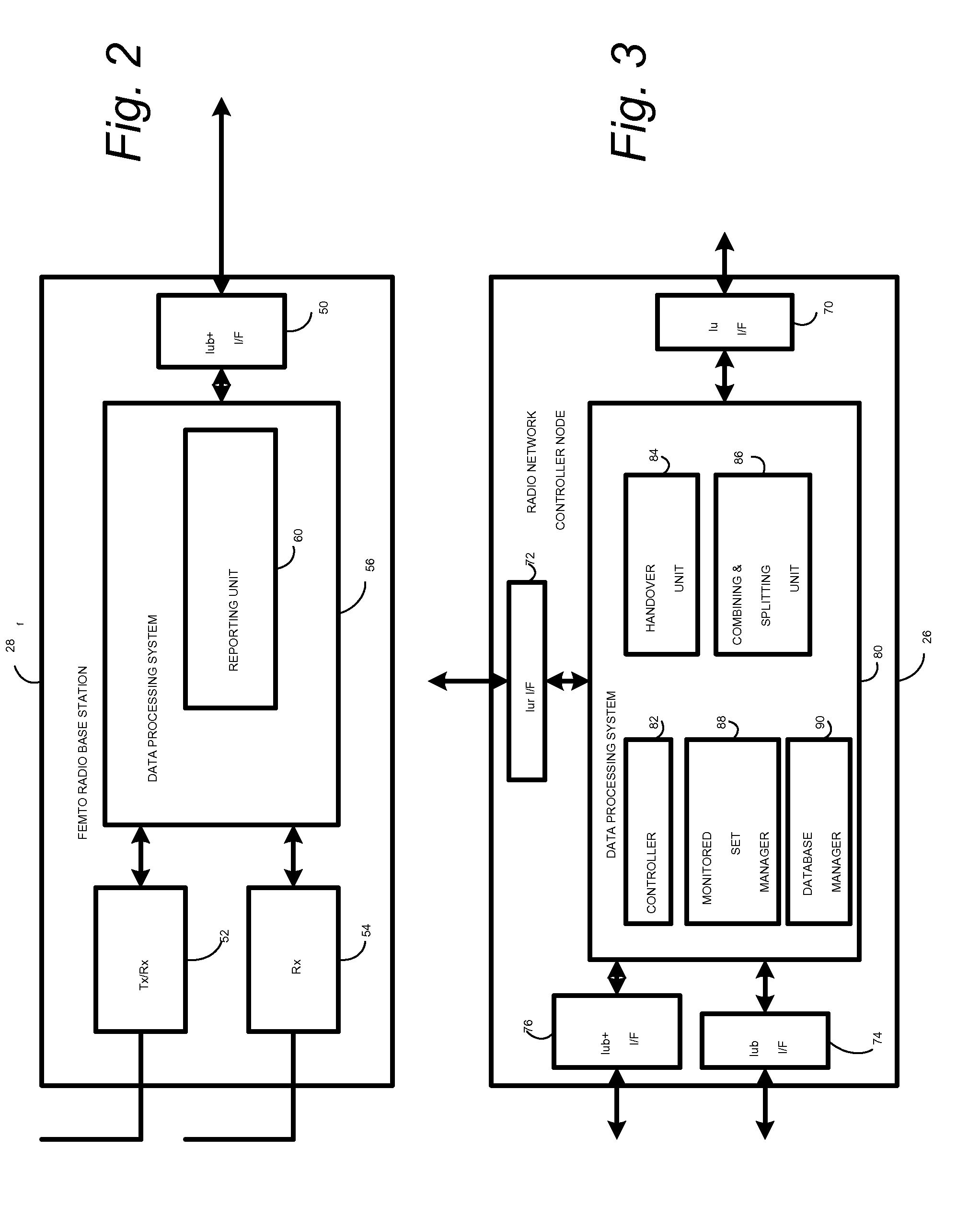
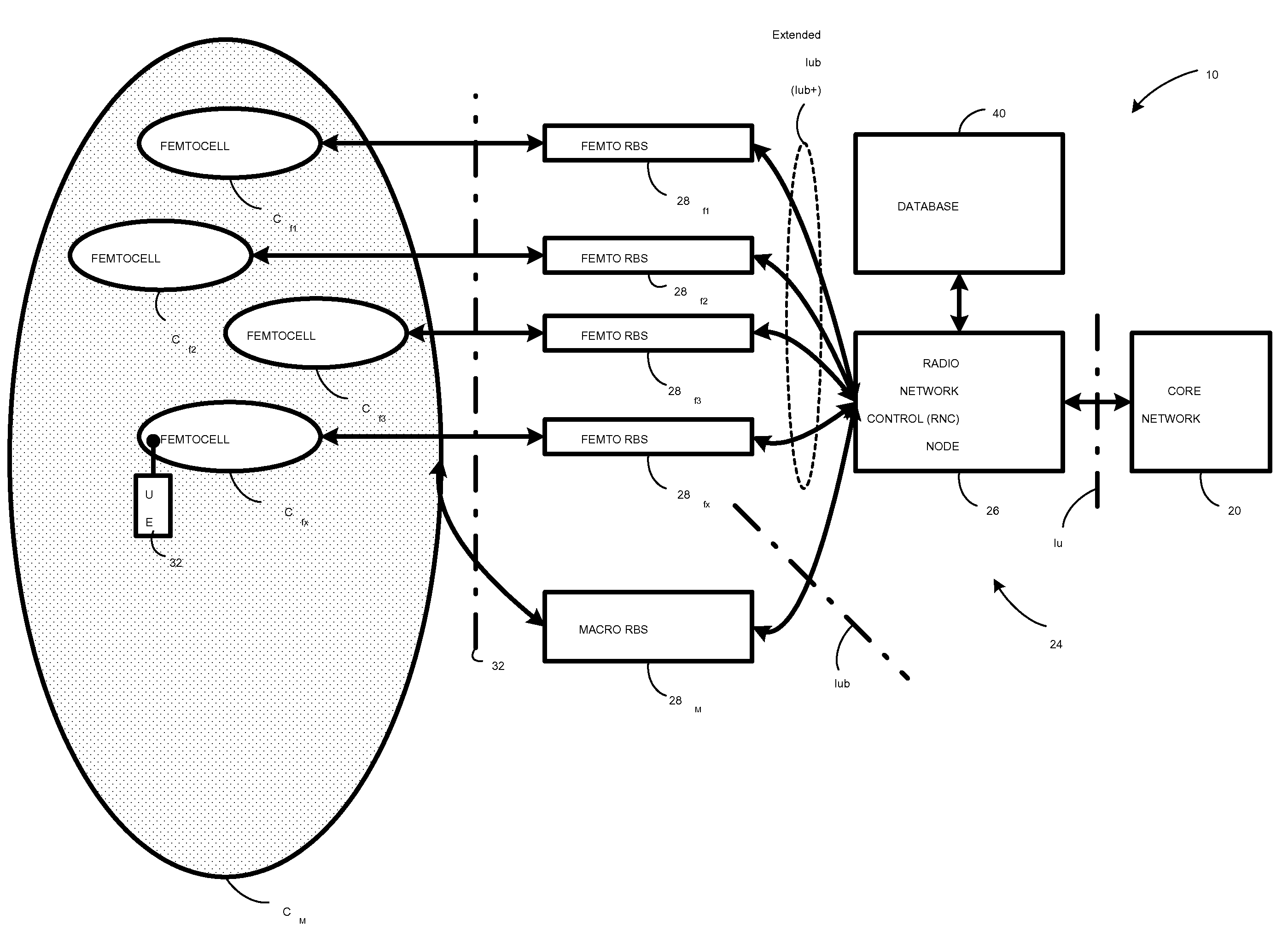
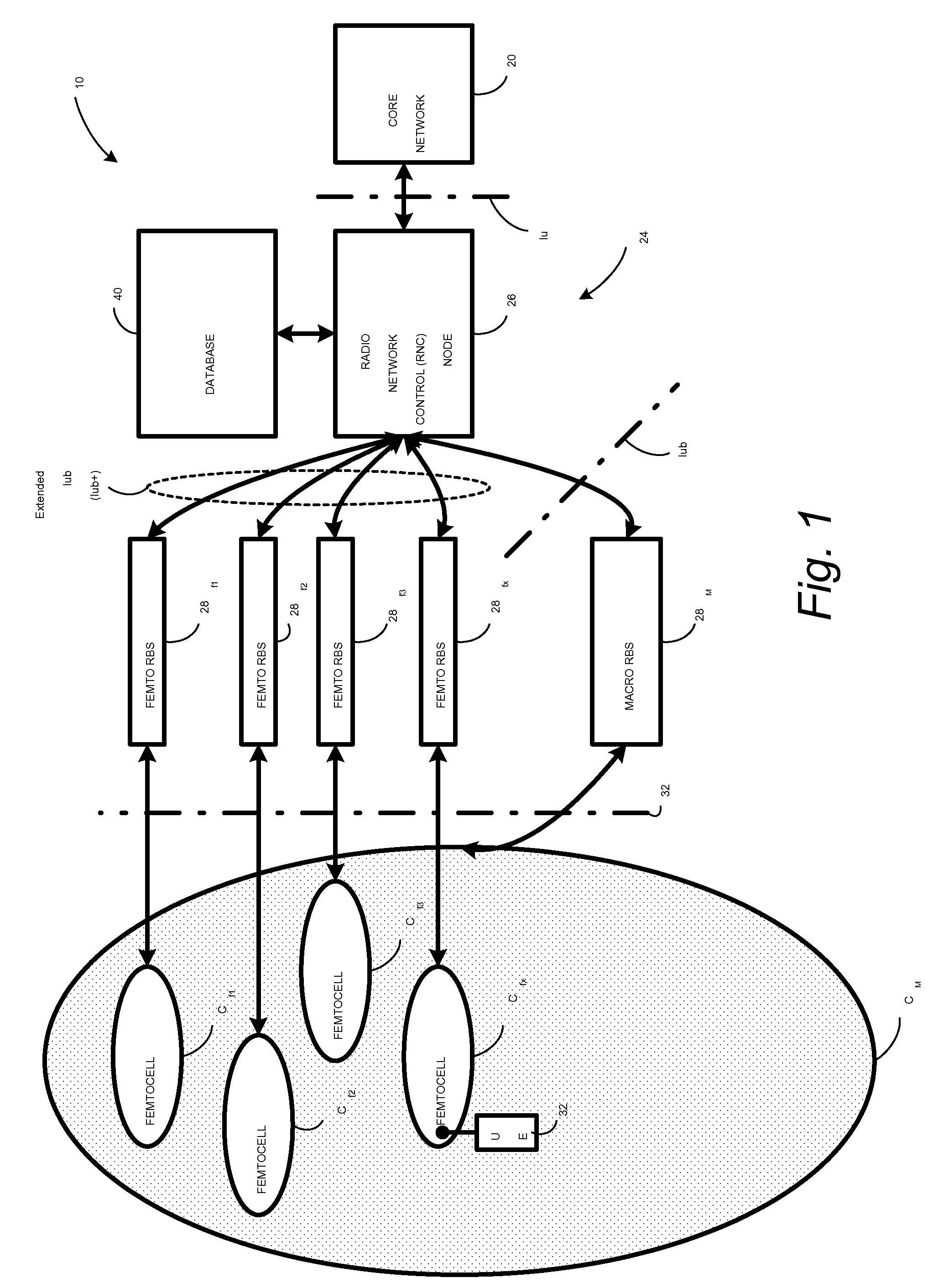
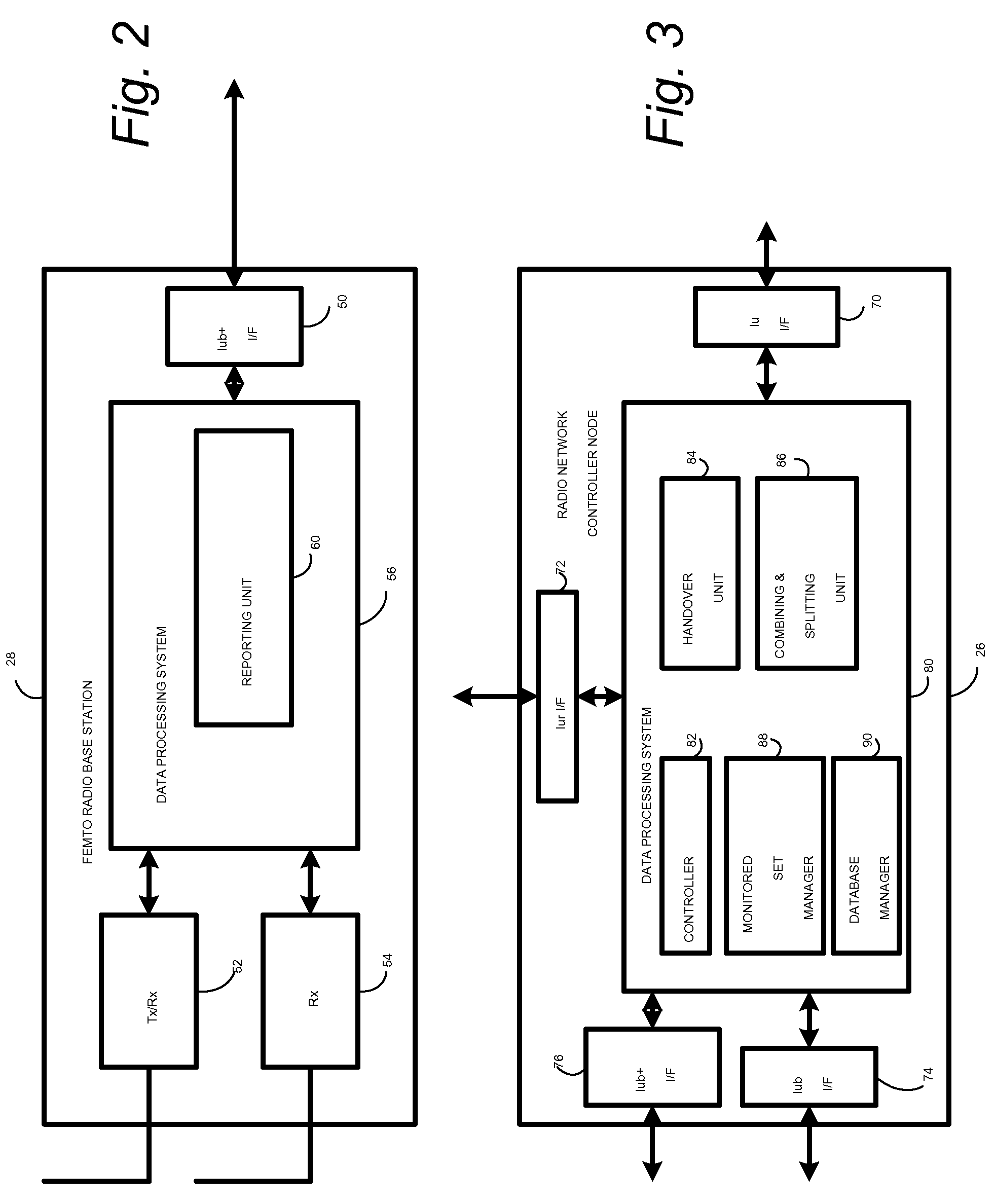
In a radio access network (24) a femto radio base station (28f) comprises a resident receiver (54) which acquires system information broadcast in a radio access network (24). At least part of the system information is used for building, at the femto radio base station (28f), a neighbor data structure (59) comprising information for neighboring cells. The neighbor data structure (59) is then used for building a neighbor list. The neighbor list is subsequently transmitted from the femto radio base station (28f) to a user equipment unit (30) served by the femto radio base station (28f). In some example embodiments and modes, the femto radio base station (28f) reports the neighbor data structure to a network node (26, 100) other than the femto radio base station. The other node (26, 100) uses the neighbor data structure for building the neighbor list at the other node. In some example embodiments and modes, acquisition of the system information comprises scanning a surrounding macro coverage area of the femto radio base station for obtaining cell identity information for detected cells. In other example embodiments and modes, the acquisition of the system information can additionally comprise camping on a macro cell and using / consulting at least one system information block in the camped-on macro cell is consulted / used for obtaining information about at least one neighboring cell.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
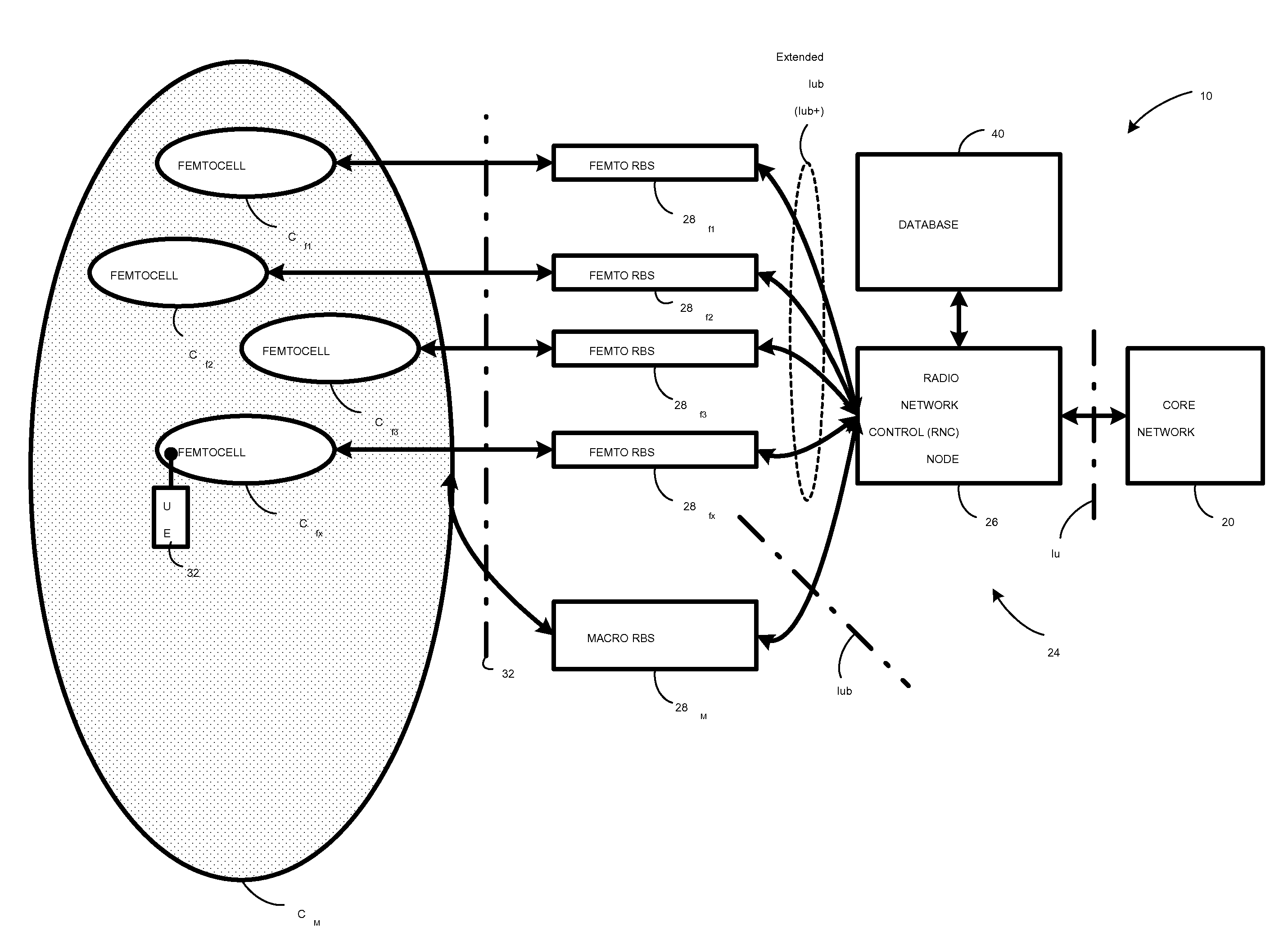
Dynamic Building of Monitored Set
A radio access network (24) comprises a radio network control node (26); a database (40); and a femto radio base station node (28f) serving a femtocell (Cf) of the radio access network. The femto radio base station node (28f) comprises a receiver (54) for receiving scanned cell information broadcast for one or more receivable cells of the radio access network, and a reporting unit (60). The reporting unit (60) provides the scanned cell information for the one or more receivable cells of the radio access network to the radio network control node (26). The radio network control node (60) is arranged, upon receipt of the scanned cell information, for providing configuration information to the femto radio base station node (for configuring the femto radio base station node) and for storing macro cell information for one or more receivable cells in the database (40). The macrocell information is stored in the database (40) in association with the femto radio base station node.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
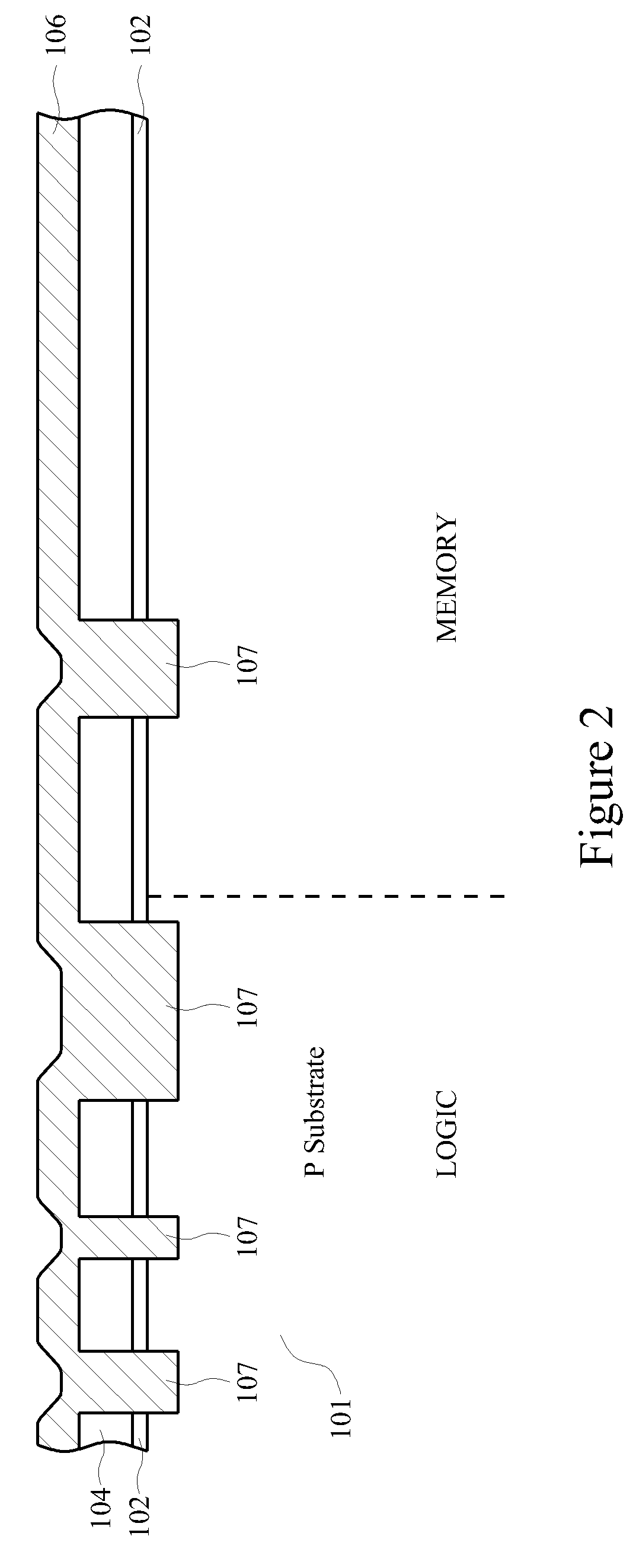
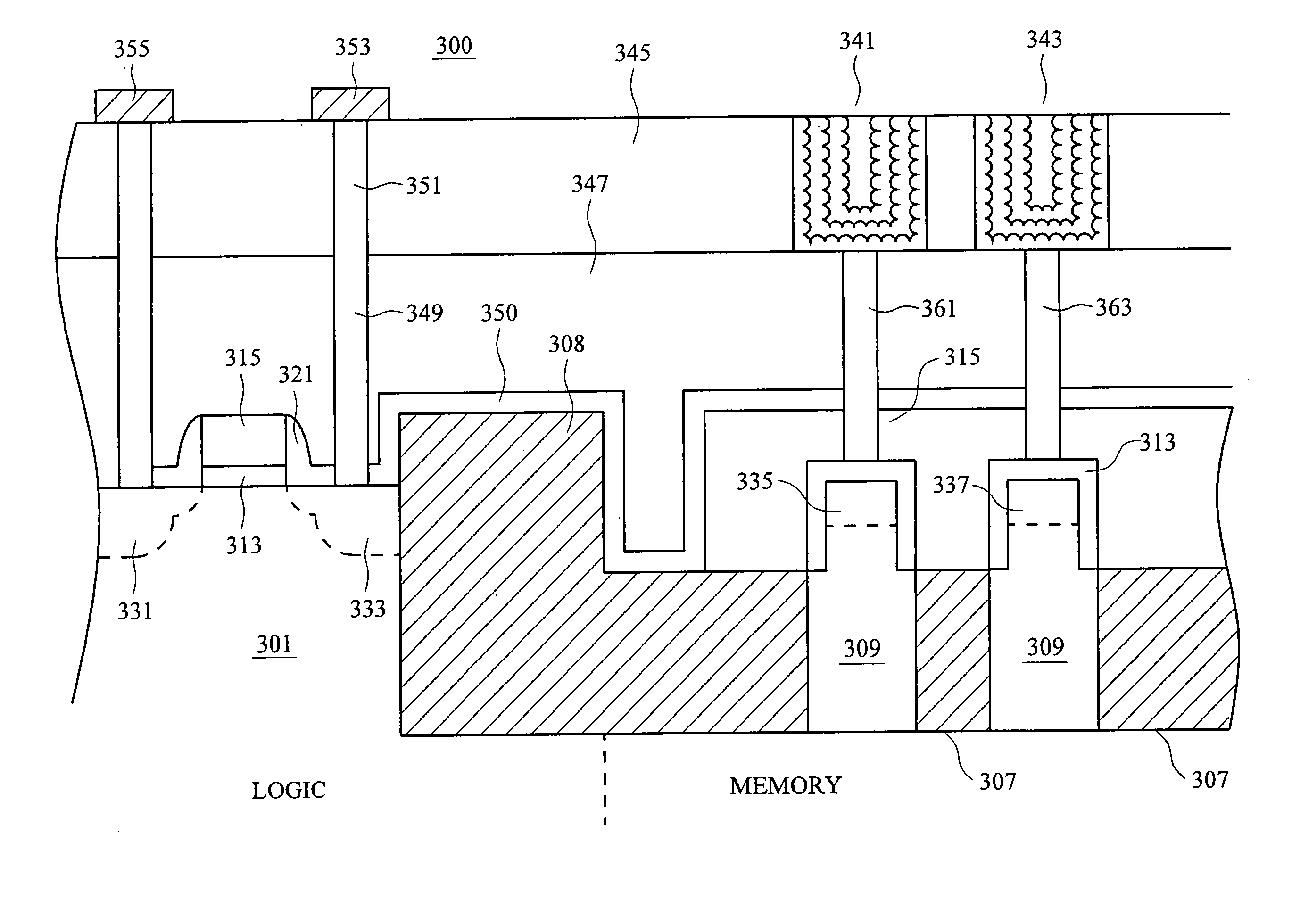
Method and structure for a 1T-RAM bit cell and macro
InactiveUS7425740B2Increase capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMetal-insulator-metalCapacitance
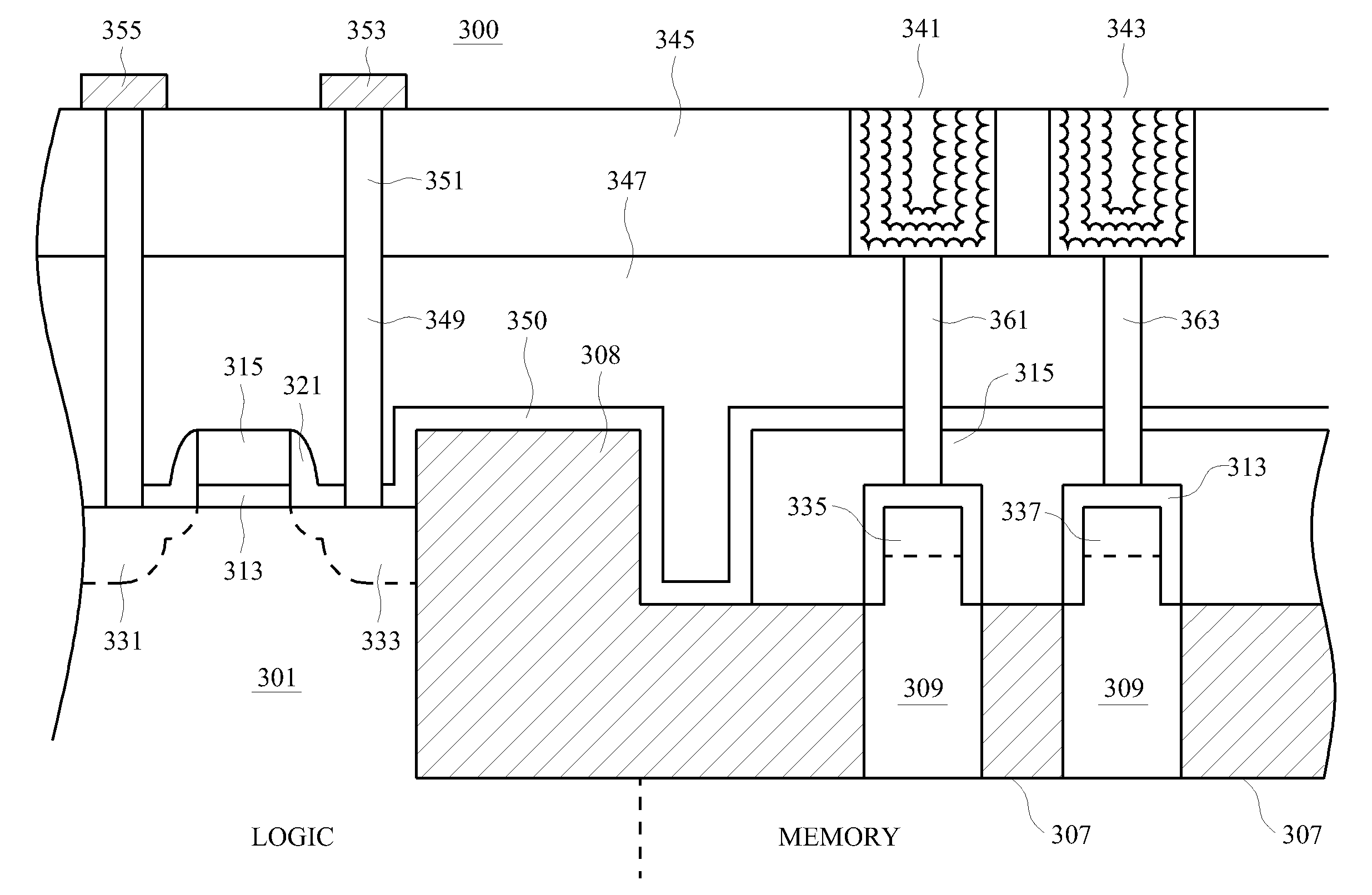
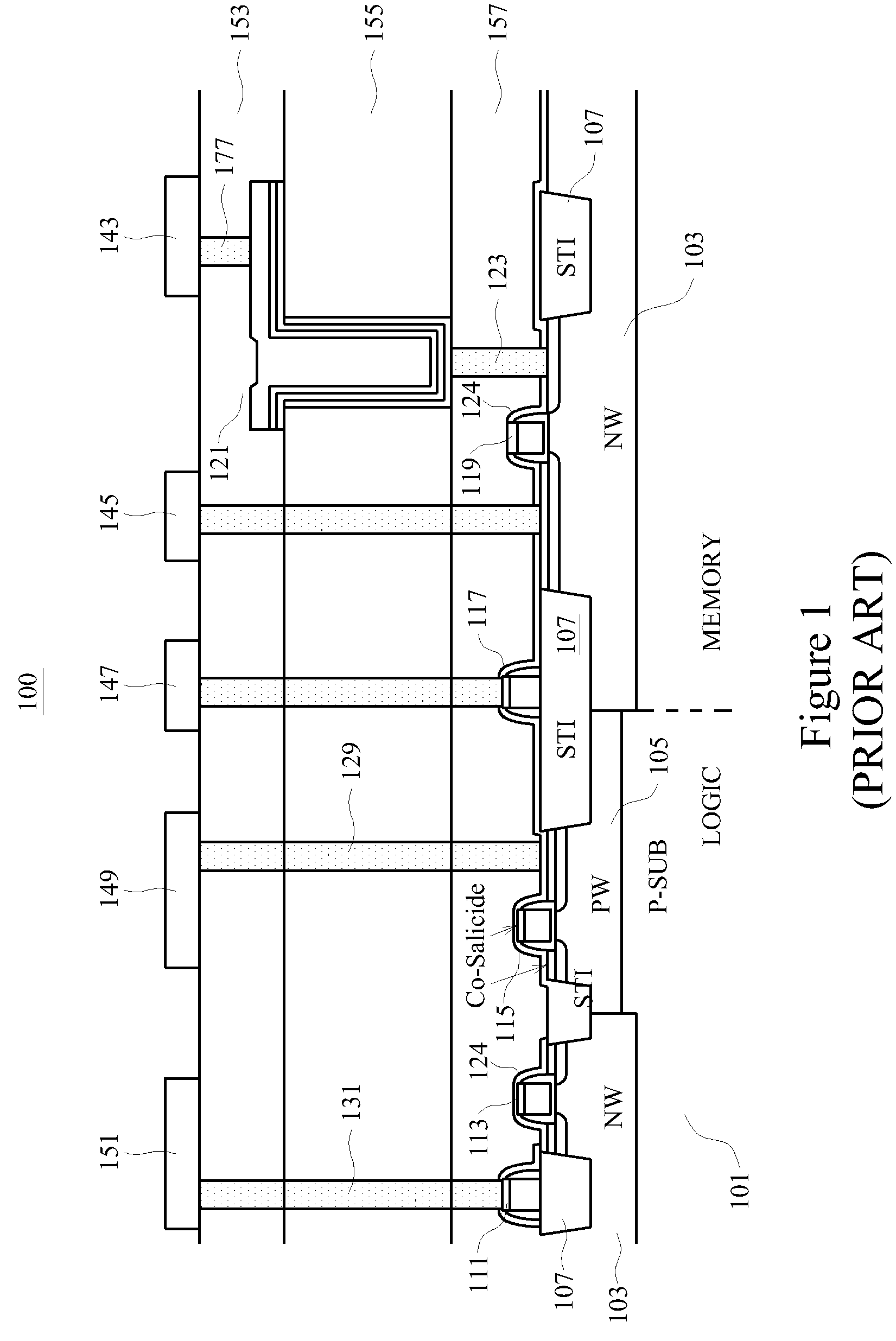
A one transistor (1T-RAM) bit cell and method for manufacture are provided. A metal-insulator-metal (MIM) capacitor structure and method of manufacturing it in an integrated process that includes a finFET transistor for the 1T-RAM bit cell is provided. In some embodiments, the finFET transistor and MIM capacitor are formed in a memory region and an asymmetric processing method is disclosed, which allows planar MOSFET transistors to be formed in another region of a single device. In some embodiments, the 1T-RAM cell and additional transistors may be combined to form a macro cell, multiple macro cells may form an integrated circuit. The MIM capacitors may include nanoparticles or nanostructures to increase the effective capacitance. The finFET transistors may be formed over an insulator. The MIM capacitors may be formed in interlevel insulator layers above the substrate. The process provided to manufacture the structure may advantageously use conventional photomasks.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
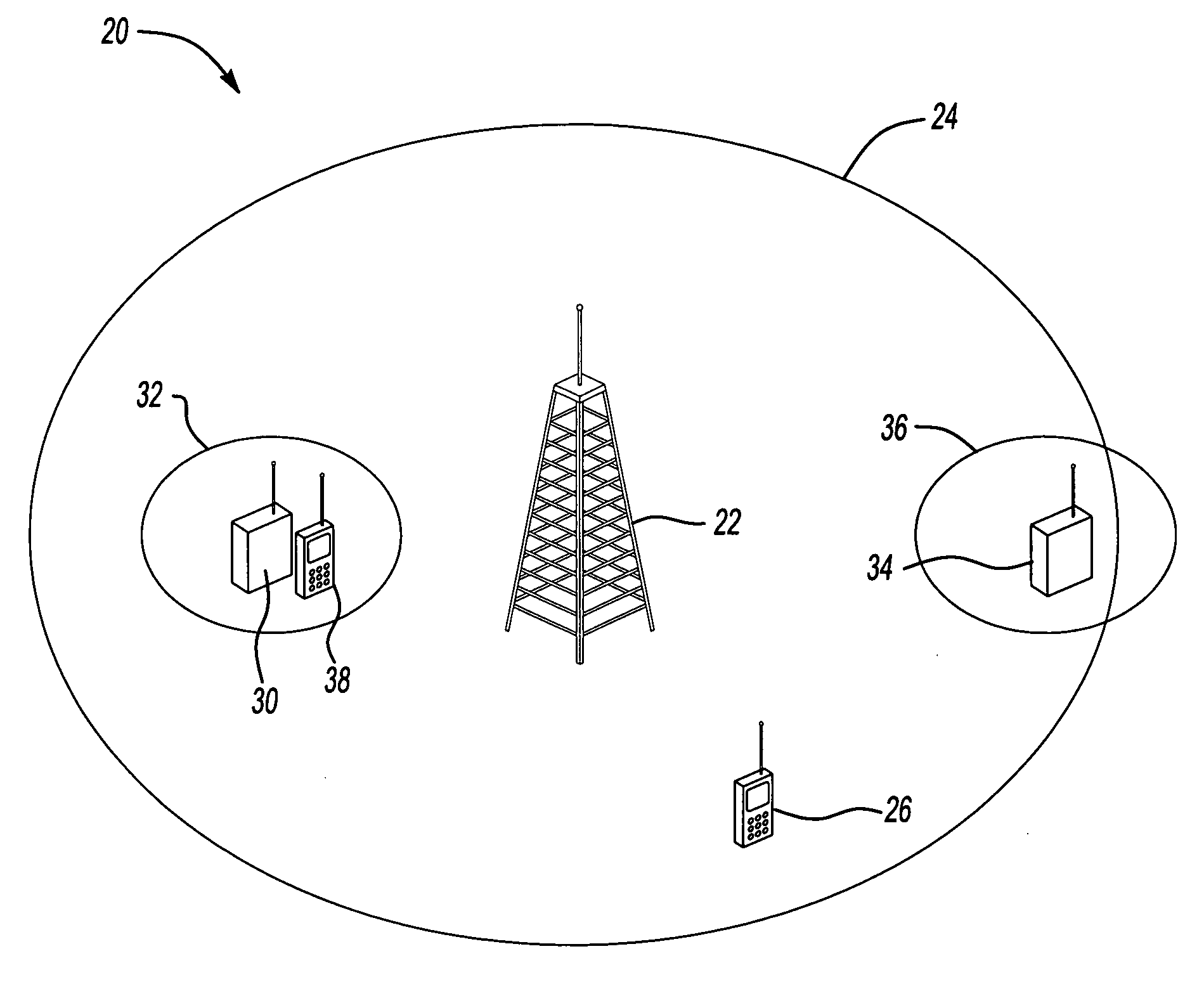
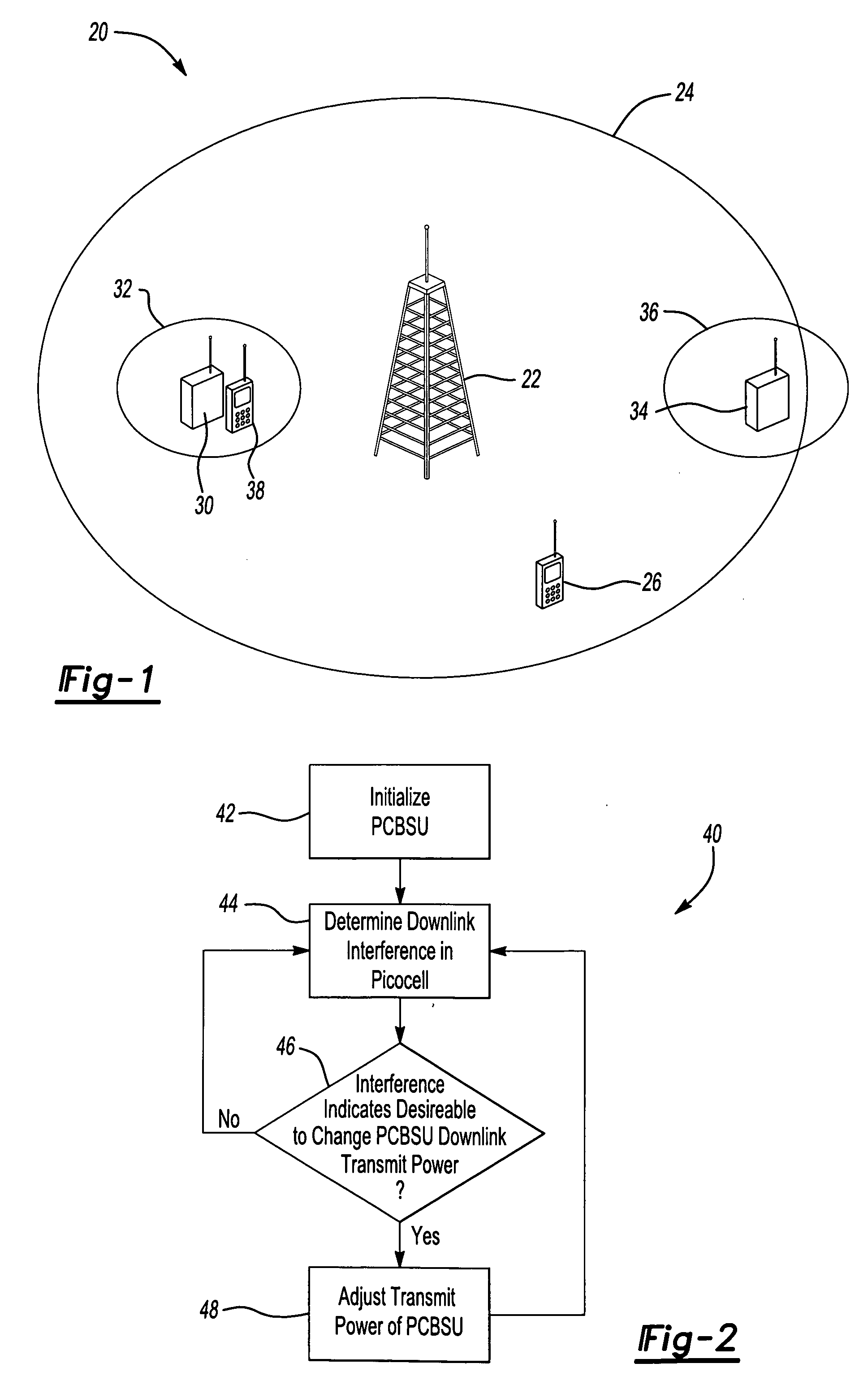
Wireless communication device with multiple external communication links
InactiveUS6842617B2Operational securityCollect revenuePower distribution line transmissionRepeater circuitsTelecommunications linkPopulation density
A decentralized asynchronous wireless communication system is disclosed for providing voice and data communication that allows flexibility of communication paths for local communication or for communication to external networks. The system makes use of communication docking bays that may communicate in a local mode with other communication docking bays or handsets within a same microcell via signal extenders. In an extended mode, a communication docking bay located in a first microcell of a first macrocell may communicate with a second communication docking bay or handset in a second microcell of the first macrocell via signal extenders and a network extender. In a remote mode, a communication docking bay located in a first microcell of a first macrocell may communicate with a second communication docking bay or handset in a second microcell of a second macrocell via signal extenders and network extenders. The communication docking bays also provide a communication path to a Public Switch Telephone Network and other communication medium. This feature provides an alternate means of connecting a mobile handset to a Public Switch Telephone Network without communicating through a network extender. The system is particularly suitable for operation in rural areas having a low population density.
Owner:WAHOO COMM CORP
Method and apparatus to allow hand-off from a macrocell to a femtocell
InactiveUS20080305801A1Facilitates session controlBandwidth adjustableTransmission systemsNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsMobile station
A method for hand-off of a CDMA access mobile from a macrocell to a femtocell is disclosed. The method includes tracking each femtocell which mobile stations have allowed access incorporating a mobile station identification for each of the mobile stations. The method continues with storing the mobile station identification for each femtocell. This may occur in a database or similar structure. The message continues on with requesting a hand-off from the macrocell to the femtocell via PN offset and the method concludes with querying all femtocells that have that PN offset that are within range of the macrocell's neighbor list. If only one femtocell fits that criteria the method is done. If more than one femtocell fits that criteria, a priority list may be set up based at least in part on the number of times and / or frequency that the mobile station has been allowed access on the femtocell. The method could include allocating resources for all high priority femtocells and cleaning up resources for the femtocells that do not send a hand-off complete message.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
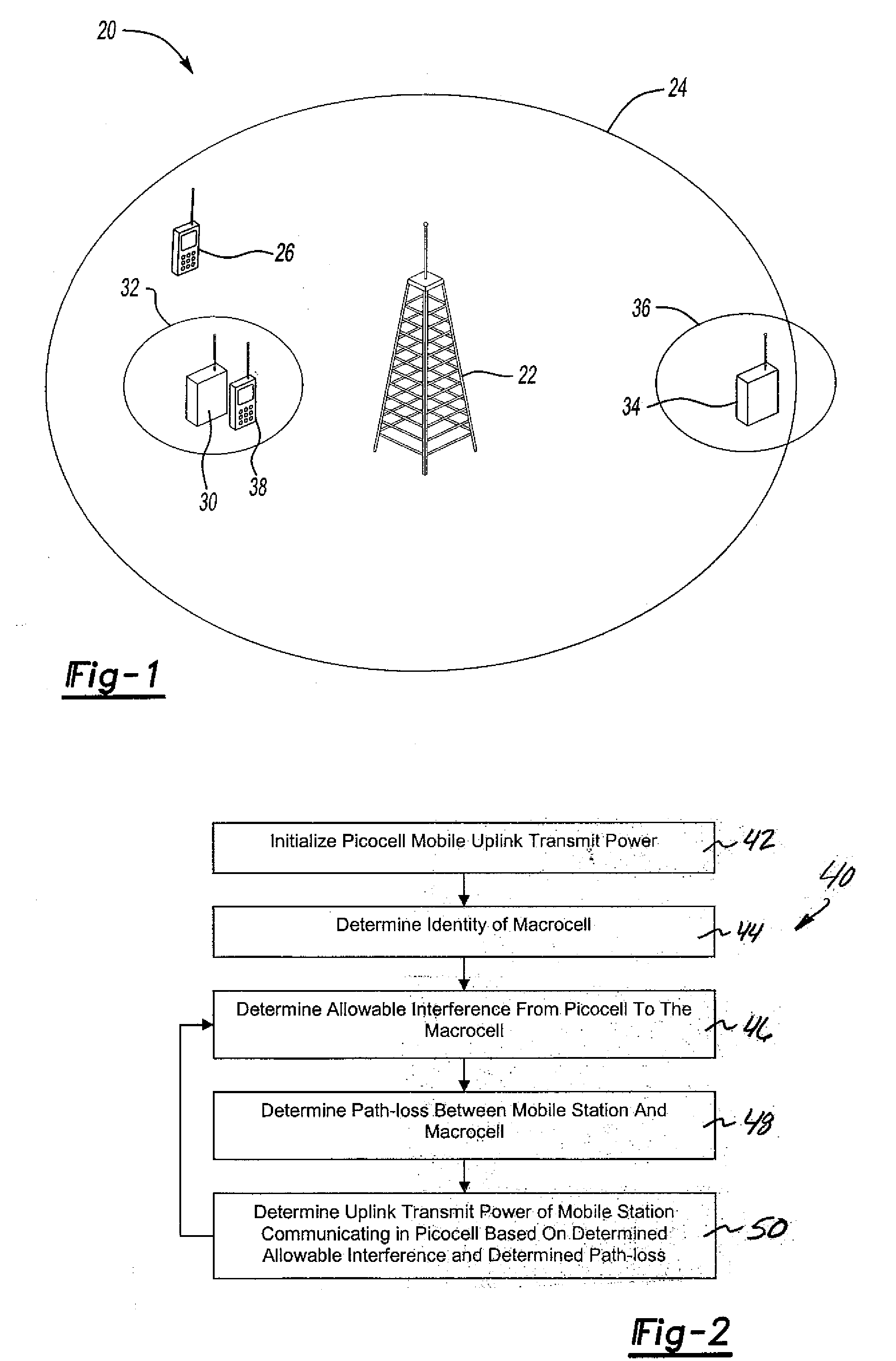
Controlling uplink power for picocell communications within a macrocell
InactiveUS20080146154A1Power managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsTransmitted power
A method of communicating in a picocell within a macrocell includes automatically setting an uplink transmit power of a mobile station to avoid uplink interference between the picocell and the macrocell. A disclosed example includes determining an allowable interference from the picocell to the macrocell. A path-loss between a mobile station and a macrocell is determined. An uplink transmit power of the mobile station for communicating in the picocell is determined based upon the determined allowable interference and the determined path-loss.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
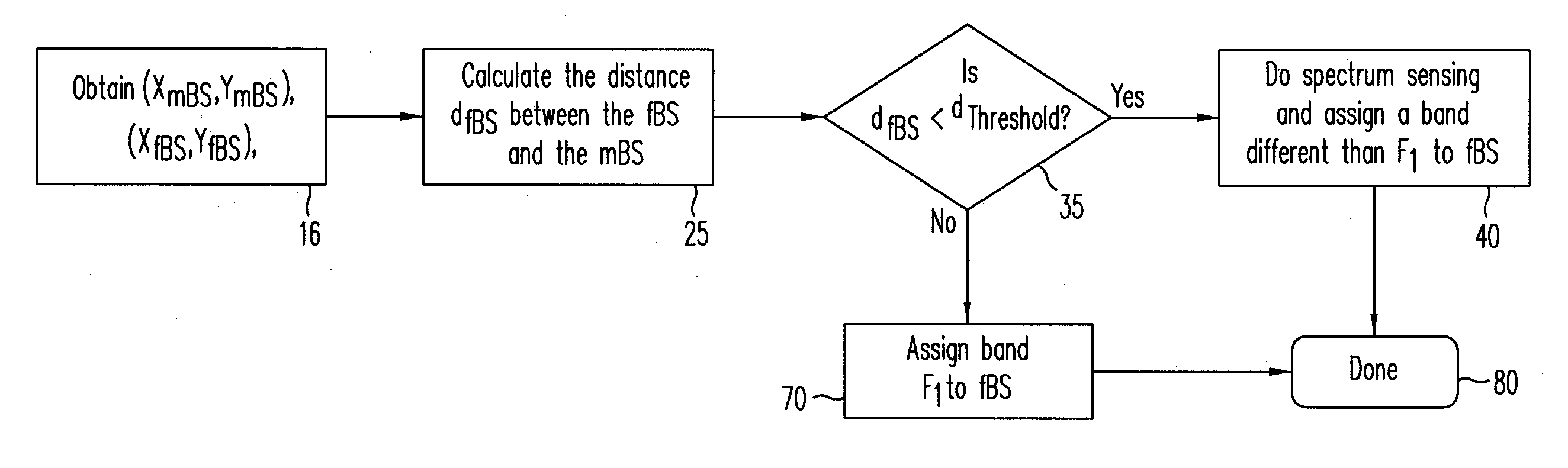
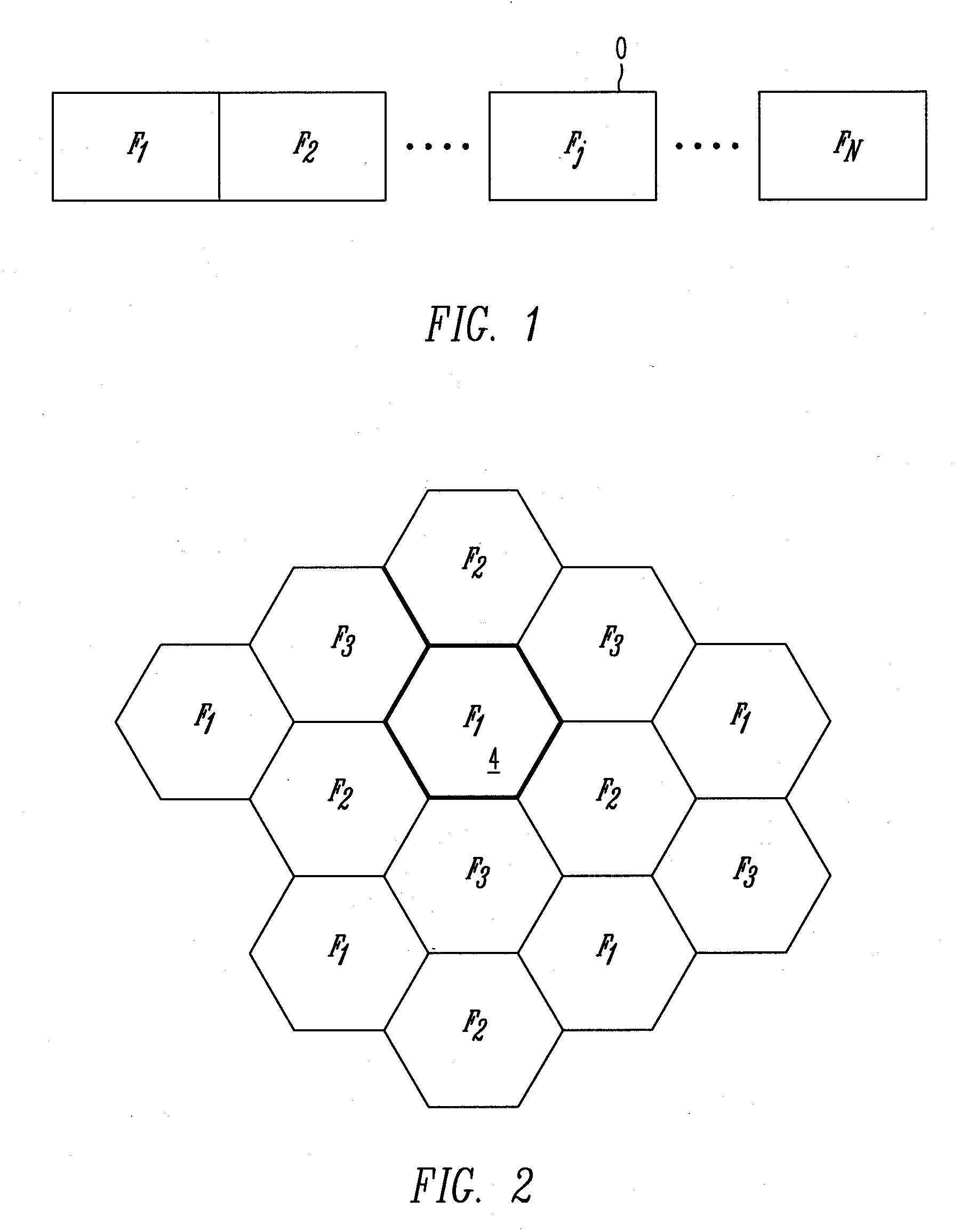
Femtocell Channel Assignment and Power Control for Improved Femtocell Coverage and Efficient Cell Search
ActiveUS20090291690A1Increase efficiency and coverageEfficient managementPower managementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
A method and a communication system including femtocells within a macrocell efficiently manage interference between the different femtocells, and between each femtocell and a macrocell. An efficient frequency assignment scheme for the femtocells minimizes interference between a femtocell and a macrocell and among different femtocells using a spectrum-sensing technique carried out by the femtocells. The frequency assignment scheme selects a suitable channel from a set of candidate channels and ensures that the femtocell has an acceptable coverage area even when it is close to the macrocell base station (BS). The frequency assignment scheme favors a co-channel implementation to take advantage of the hand-off and cell search characteristics of the co-channel implementation. In one embodiment, a joint power control and frequency band assignment technique is used, which partitions the coverage area of the macrocell into an inner region, a power control region, and an outer region. Depending on a femtocell's location, it is assigned a certain power level and a frequency band. Power control may be used within the power-control region while, in the other regions, a fixed transmission power may be used.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Wireless communication system and handover method therein
InactiveUS20100093358A1Avoiding a shortage of Primary Scrambling Codes (PCSs)Increase probabilityNetwork topologiesOrthogonal multiplexCommunications systemMacro base stations
A wireless communication system and handover method for the wireless communication system are provided. A handover method for a wireless communication system including a plurality of femto cells and at least one macro cell within which the femto cells are disposed includes determining, at a Radio Network Controller (RNC), a handover of a terminal to a femto base station based on a measurement report of the terminal and preset handover parameters, sending a radio link setup request message to a femto base station gateway, the radio link setup request message including a uplink scrambling code and an International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) of the terminal and a Logical Cell Identifier (LCID) of femto base stations reusing frequency of a macro base station, searching, at the femto base station gateway, for femto base stations of which LCIDs match the LCID contained in the radio link setup request message, and performing, when only one LCID-matched femto base station is discovered, the handover of the terminal to the LCID-matched femto base station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
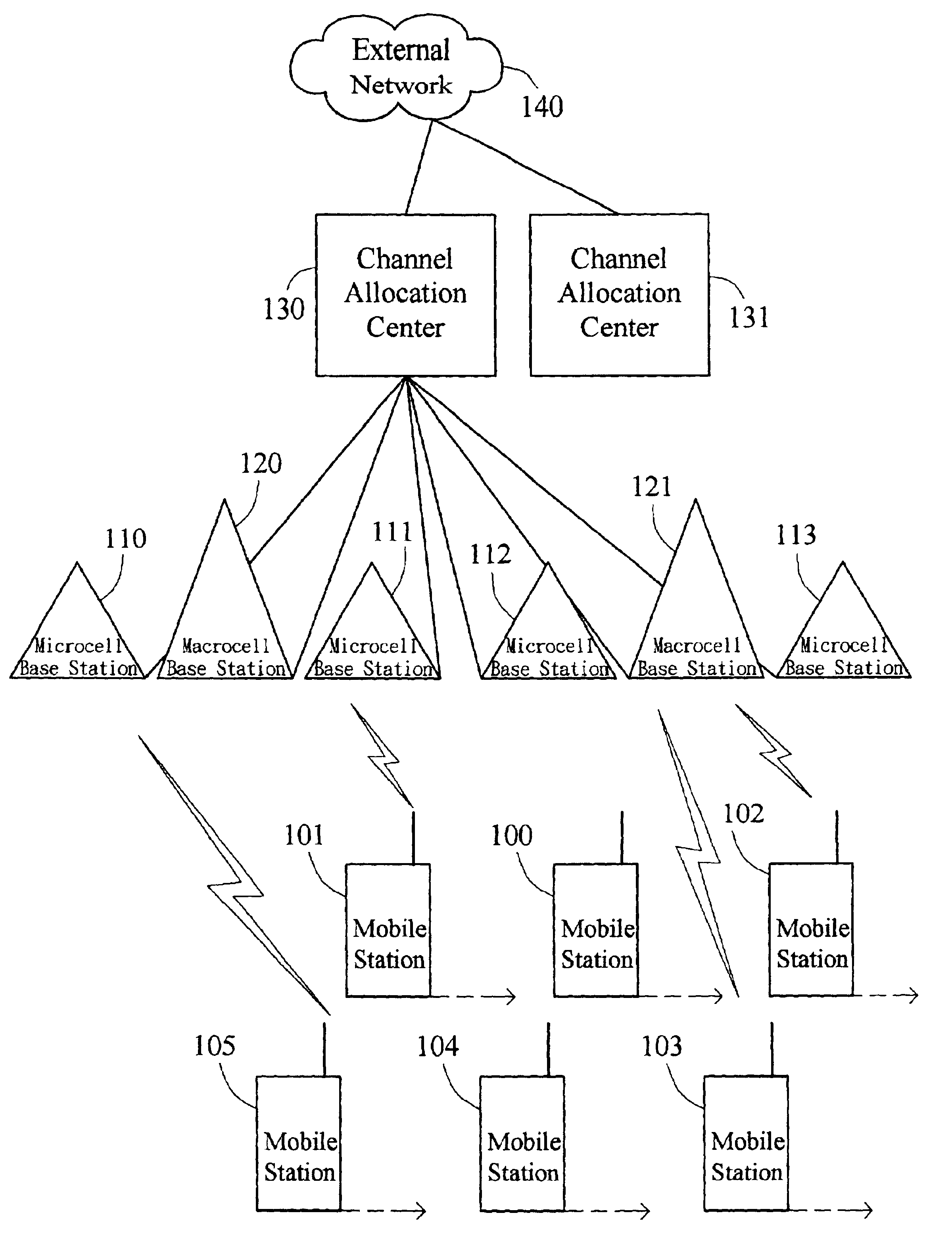
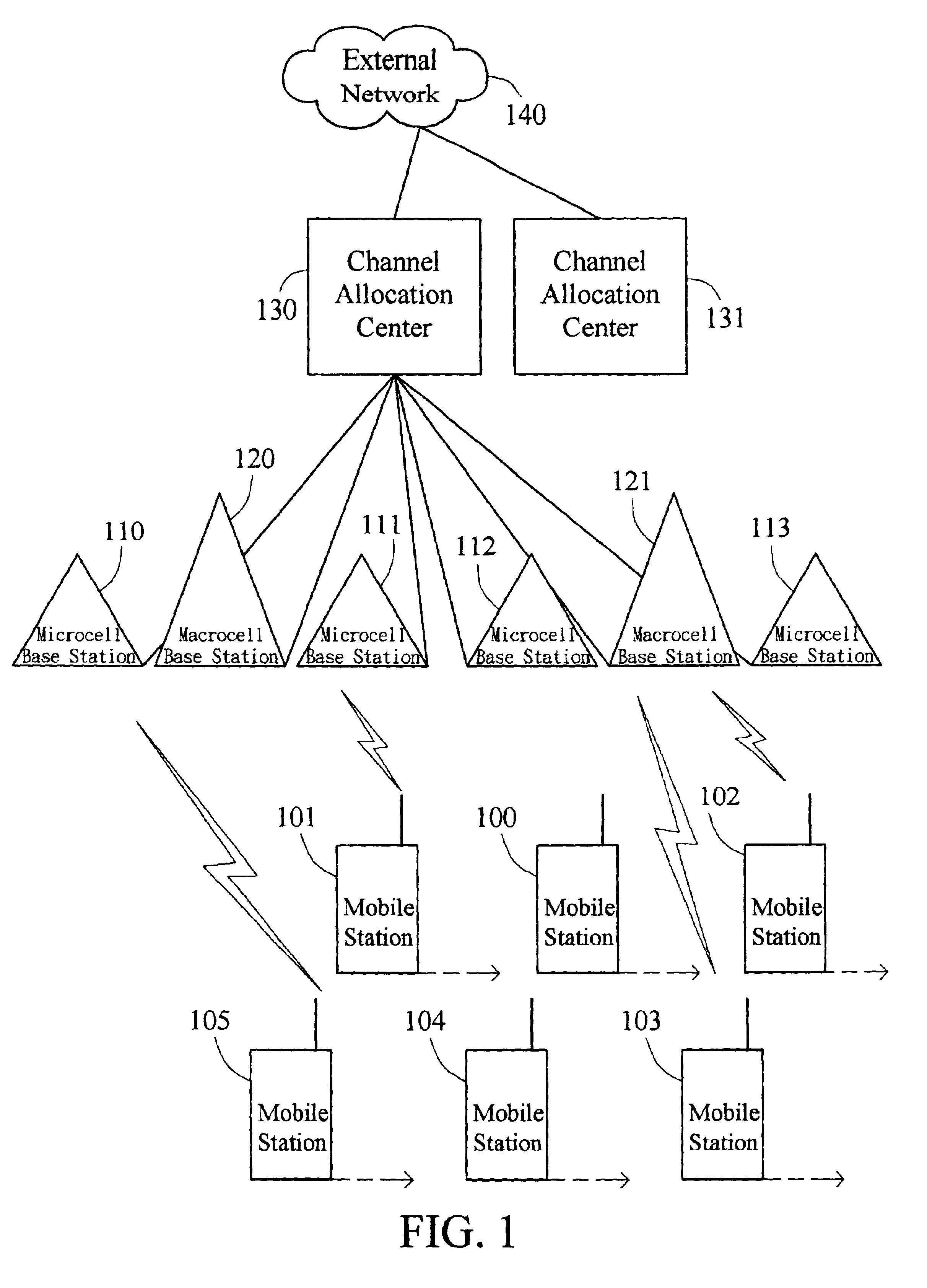
System and method for channel allocation in a multi-band wireless network
InactiveUS6954645B2Improve user satisfactionImproves the call blockingConnection managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMulti bandRadio channel
Disclosed is a system and method for channel allocation in a multi-band wireless network. The system includes microcell base stations, at least one macrocell base station, a mobile station, and a channel allocation center. When the mobile station makes / receives a call or executes a handover, the channel allocation center uses repacking on demand (RoD) scheme to allocate a radio channel of either a macrocell base station or a microcell base station to the mobile station. RoD has the following steps. First, a microcell channel is trying to be allocated if available. If no microcell channel is available, a macrocell channel is then trying to be allocated. Third, if no macrocell channel is available, repacking is performed to execute a handover of another mobile station's call from the macrocell to another microcell, and to allocate a reclaimed macrocell channel to the mobile station. Otherwise, no repacking call is available and the mobile station is blocked or forced terminated. By the invention, call blocking probability and call handover rate of the mobile stations in the multi-band wireless network can be reduced, and thus users' satisfaction can be enhanced.
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
Location-based handovers from a macrocell to a femtocell using event-triggered measurement reporting
The present invention provides a method for implementation in user equipment that is configured to communicate with a wireless communication system that comprises one or more macro-cells and one or more femtocells. The method includes comparing, at the user equipment, a location of the user equipment and a location of one or more femtocells. The method also includes transmitting, from the user equipment to the macrocell(s), a first measurement report, with a location-based event, when the comparison indicates that the user equipment is within a selected range of the femtocell(s).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Cellular communication system, method for inter-cell handover of terminal and macro base station
InactiveCN102348244AReduce negative impactAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesMacro base stationsMicro cell
The invention discloses a cellular communication system, a method for the inter-cell handover of a terminal and a macro base station. The cellular communication system comprises the macro base station and at least one micro base station within the coverage of the macro base station. The macro base station is used for establishing a control channel for the terminal of the micro base station, performing accessing management operations on the micro base stations within the coverage, receiving a handover request of the terminal and realizing the handover of the terminal to another micro base station within the coverage. The micro base station is used for establishing a data channel for an accessing terminal to perform data transmission with the terminal. By the system, the method and the macro base station, a user control plane and a data plane under a micro cell can be separated, so that the resources of the micro base station can be better used for data communication. Therefore, negative impact on the system can be reduced in a macro cell-micro cell coexisting networking way.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
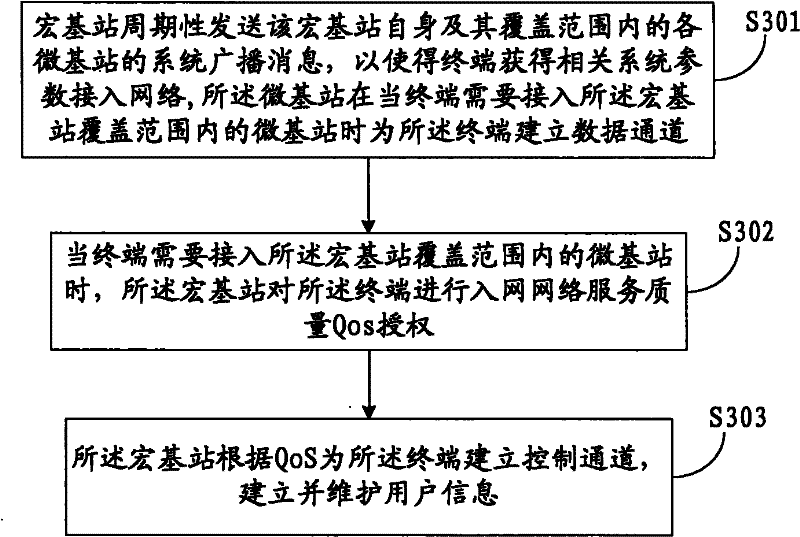
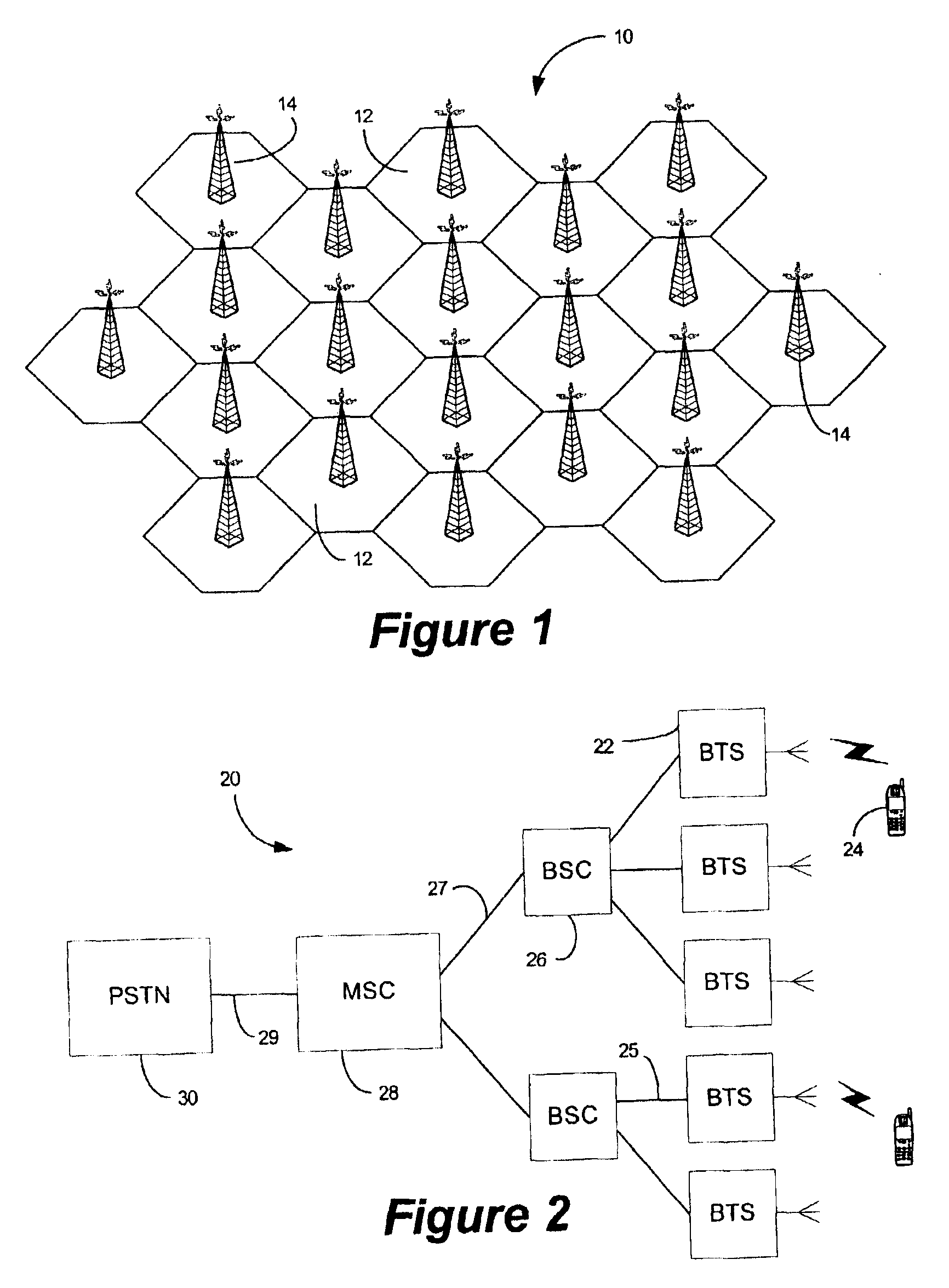
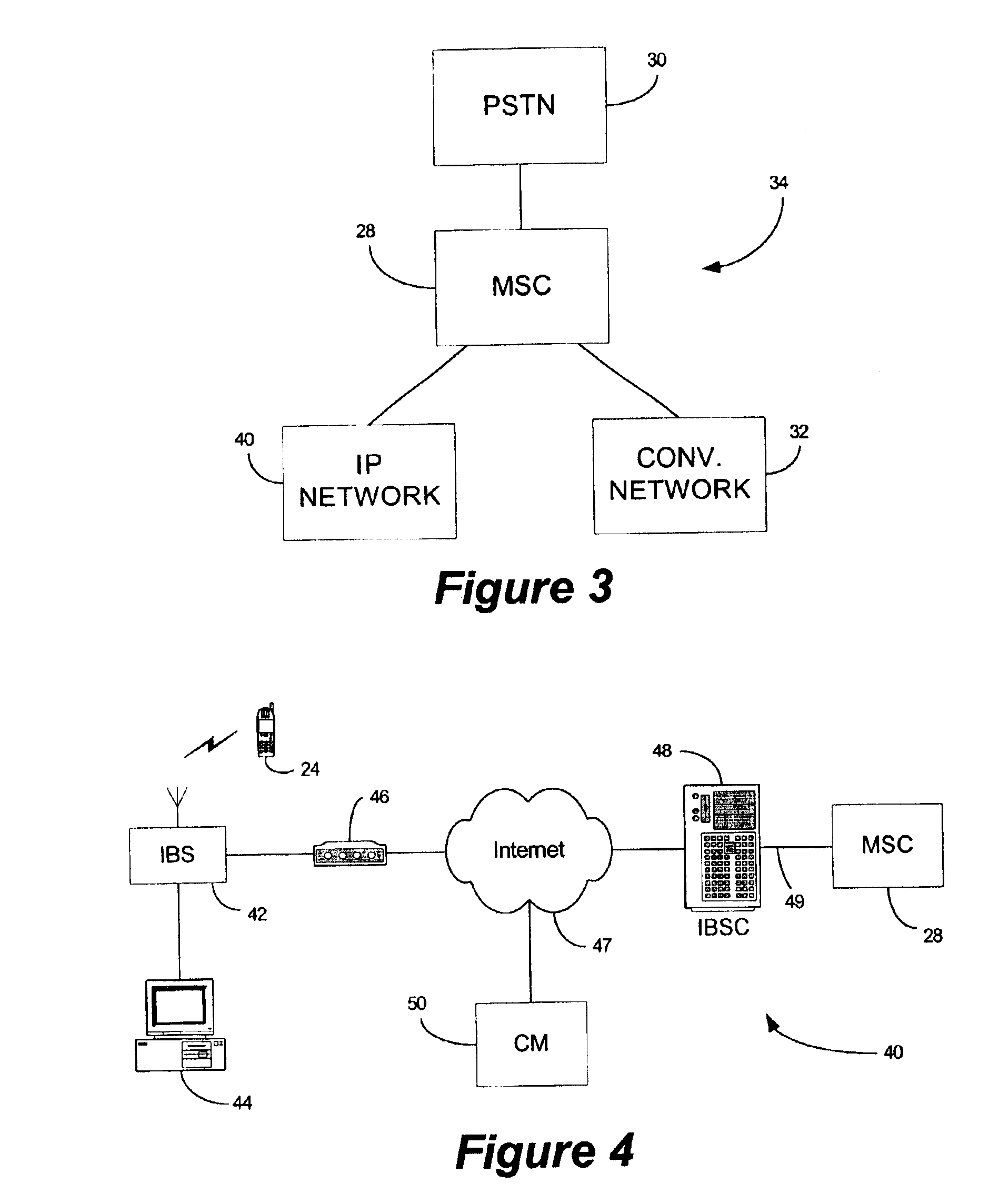
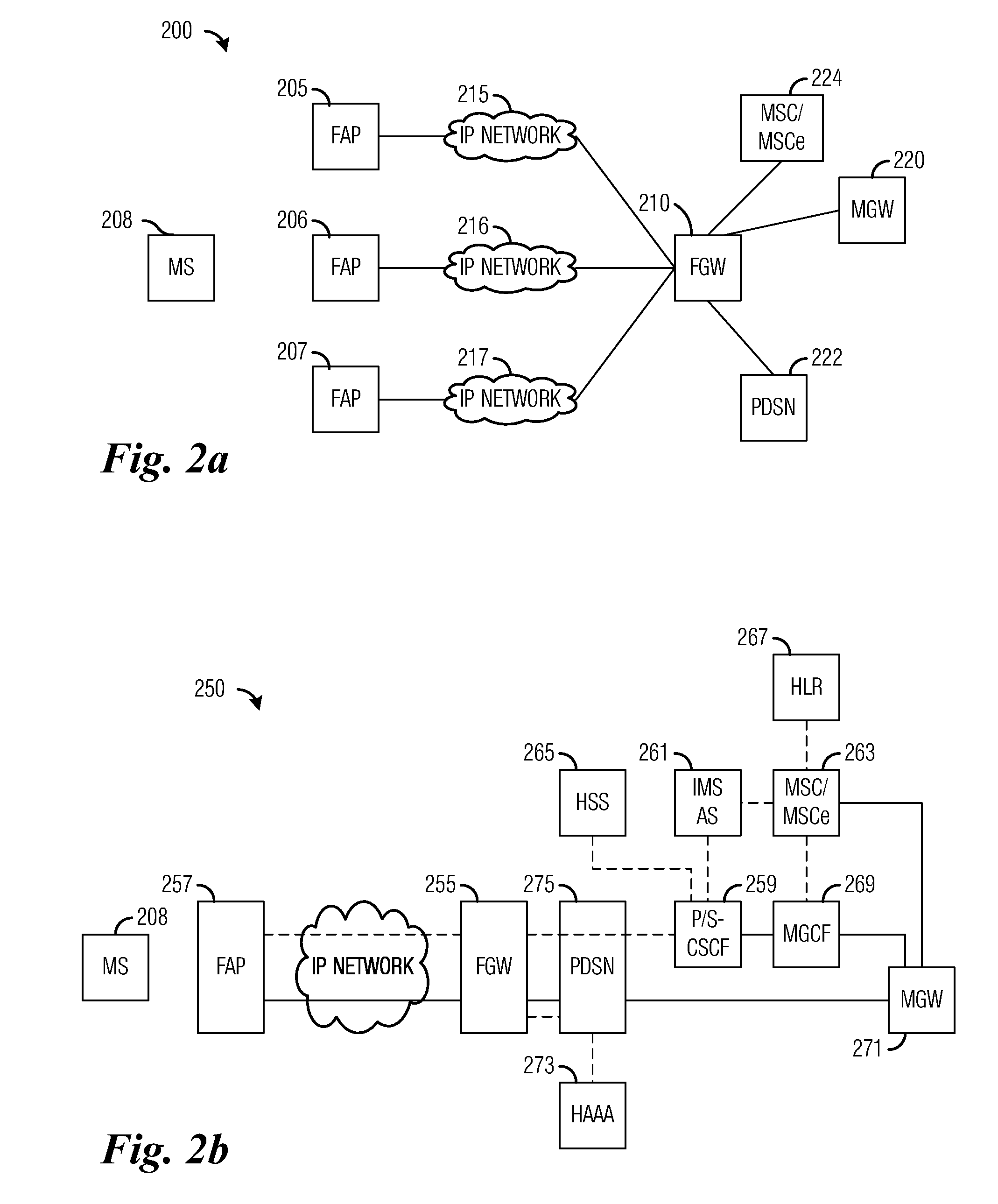
Internet base station
InactiveUS7117015B2Improve traffic capacityMinimal costNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless trafficMobile station
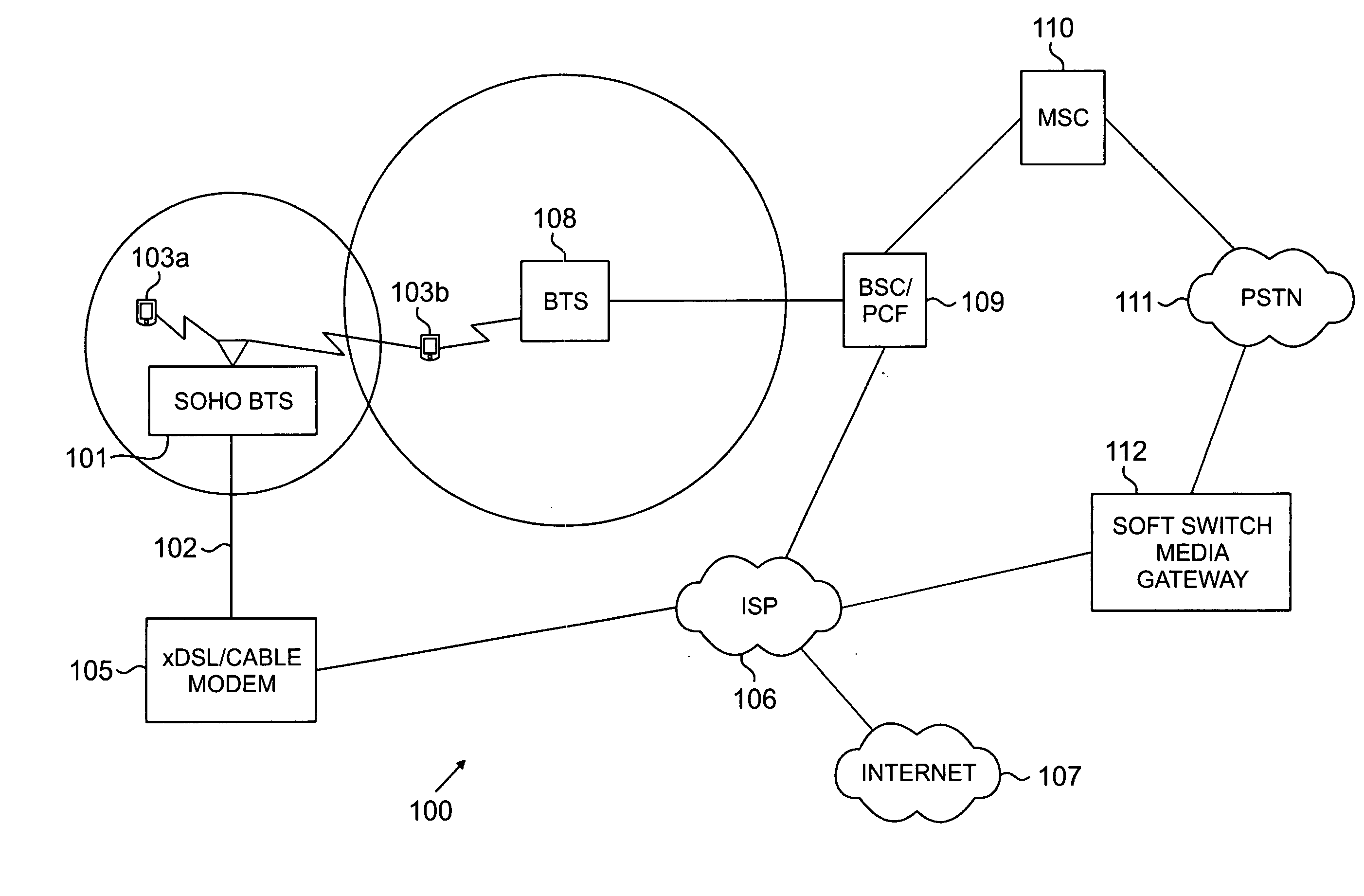
A portable, low power base station is configured to convey wireless traffic between a mobile station and a conventional wireless network via the Internet. The base station is configured to connect to the Internet at a user-selected location and establishes a small area of wireless coverage within a greater macrocell network. The user sets the operating parameters of the base station.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Dynamic building of monitored set
A radio access network (24) comprises a radio network control node (26); a database (40); and a femto radio base station node (28f) serving a femtocell (Cf) of the radio access network. The femto radio base station node (28f) comprises a receiver (54) for receiving scanned cell information broadcast for one or more receivable cells of the radio access network, and a reporting unit (60). The reporting unit (60) provides the scanned cell information for the one or more receivable cells of the radio access network to the radio network control node (26). The radio network control node (60) is arranged, upon receipt of the scanned cell information, for providing configuration information to the femto radio base station node (for configuring the femto radio base station node) and for storing macro cell information for one or more receivable cells in the database (40). The macrocell information is stored in the database (40) in association with the femto radio base station node.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method to locate femto cells with passive assistance from a macro cellular wireless network
ActiveUS20090098873A1Eliminate disadvantagesEnergy efficient ICTAssess restrictionFemto-Mobile station
A system, method and computer product for a mobile station to locate a femto cell, the method comprising: (a) storing in a database information to locate at least one femto cell; (b) receiving, from at least one macro cell, location information of the UE; (c) searching within the database to determine if the UE is in a general proximity of at least one femto cell; (d) if so, accessing the femto cell using the database information corresponding to the femto cell.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for directing traffic between overlying macrocells and microcells
The present invention provides embodiments of methods for directing traffic between cells of different sizes. One embodiment of the method includes determining, at a mobile unit, whether to hand off from a source cell to a target cell based on information indicating sizes of coverage areas of the source cell and the target cell.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
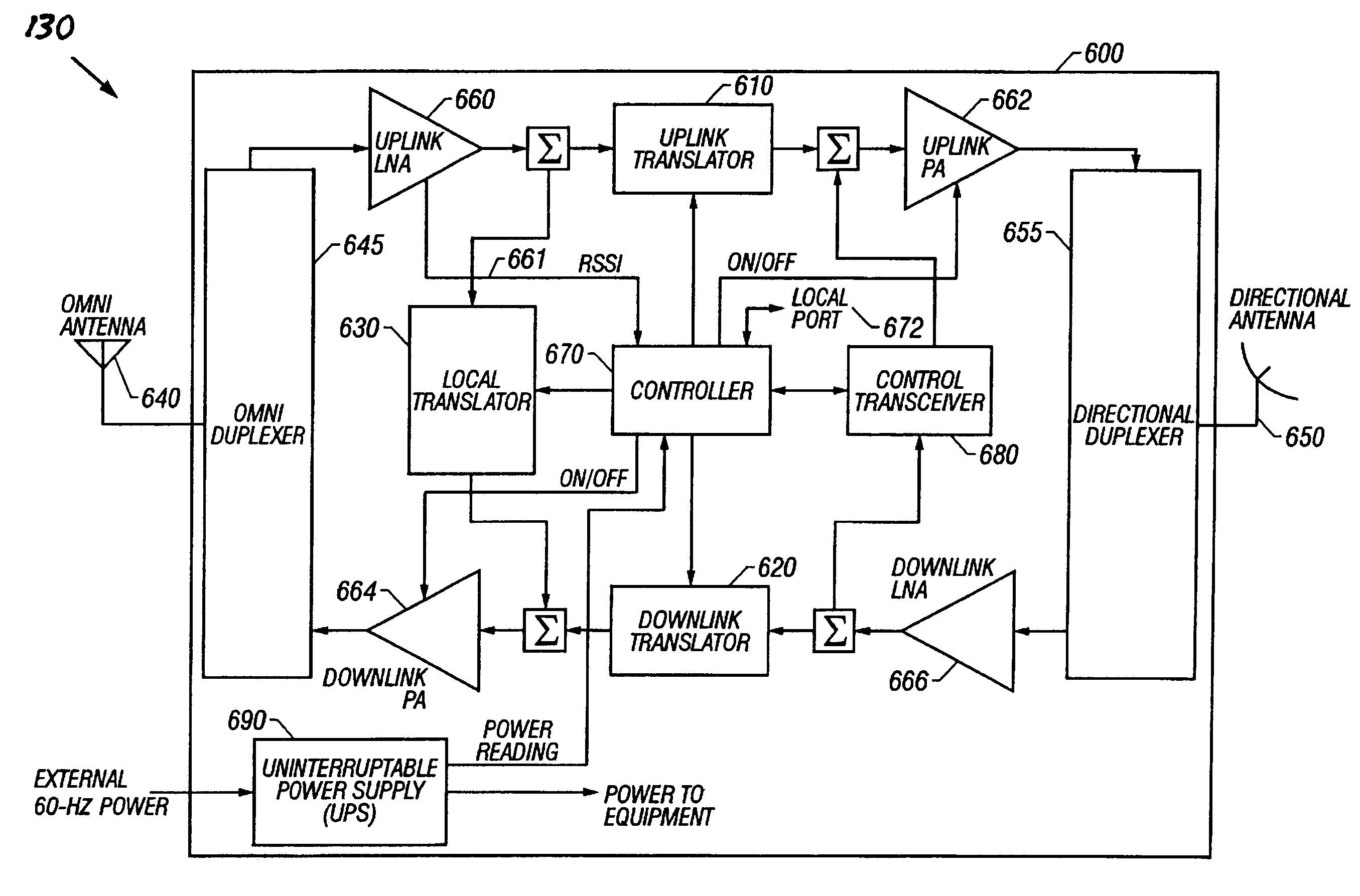
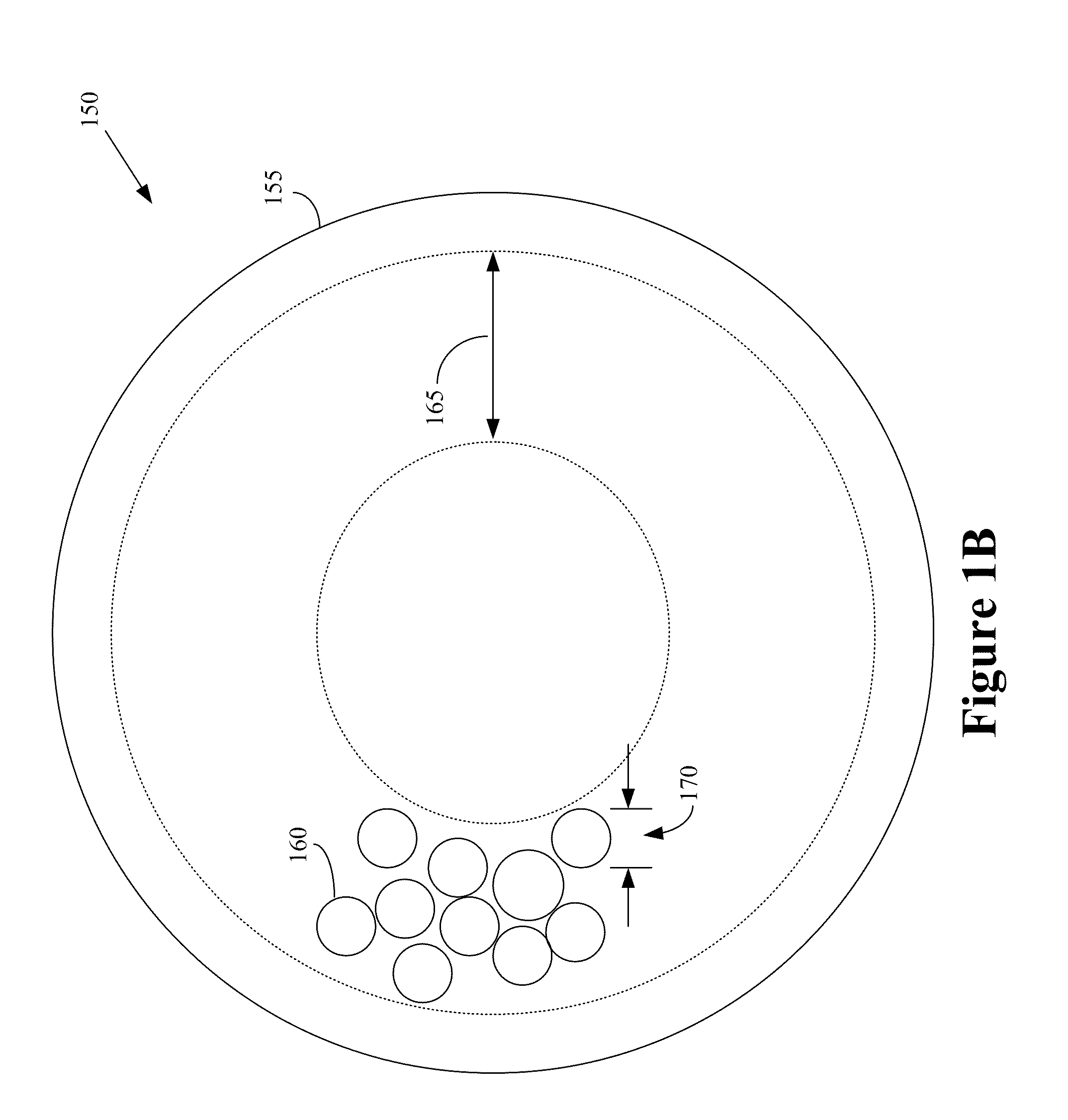
Controlling transmit power of picocell base units
ActiveUS20070270151A1Power managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemTransmitted power
A transmit power control technique within a wireless communication system includes adjusting a transmit power used by a picocell base station unit based upon a position of the picocell within a macrocell. When a picocell base station unit is located relatively close to a macrocell base station or center of the macrocell, the transmit power of the picocell base station unit is increased to avoid downlink interference from the macrocell base station for mobile stations communicating within the picocell. When a picocell base station unit is located relatively close to an edge of a macrocell, the transmit power of the picocell base station is decreased to avoid interference caused by the picocell base station unit for mobile stations communicating within the macrocell in the vicinity of the picocell. In a disclosed example determined downlink interference levels provide an indication of the position of the picocell within the macrocell and provide an indication of how to automatically adjust the transmit power of the picocell base station unit.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
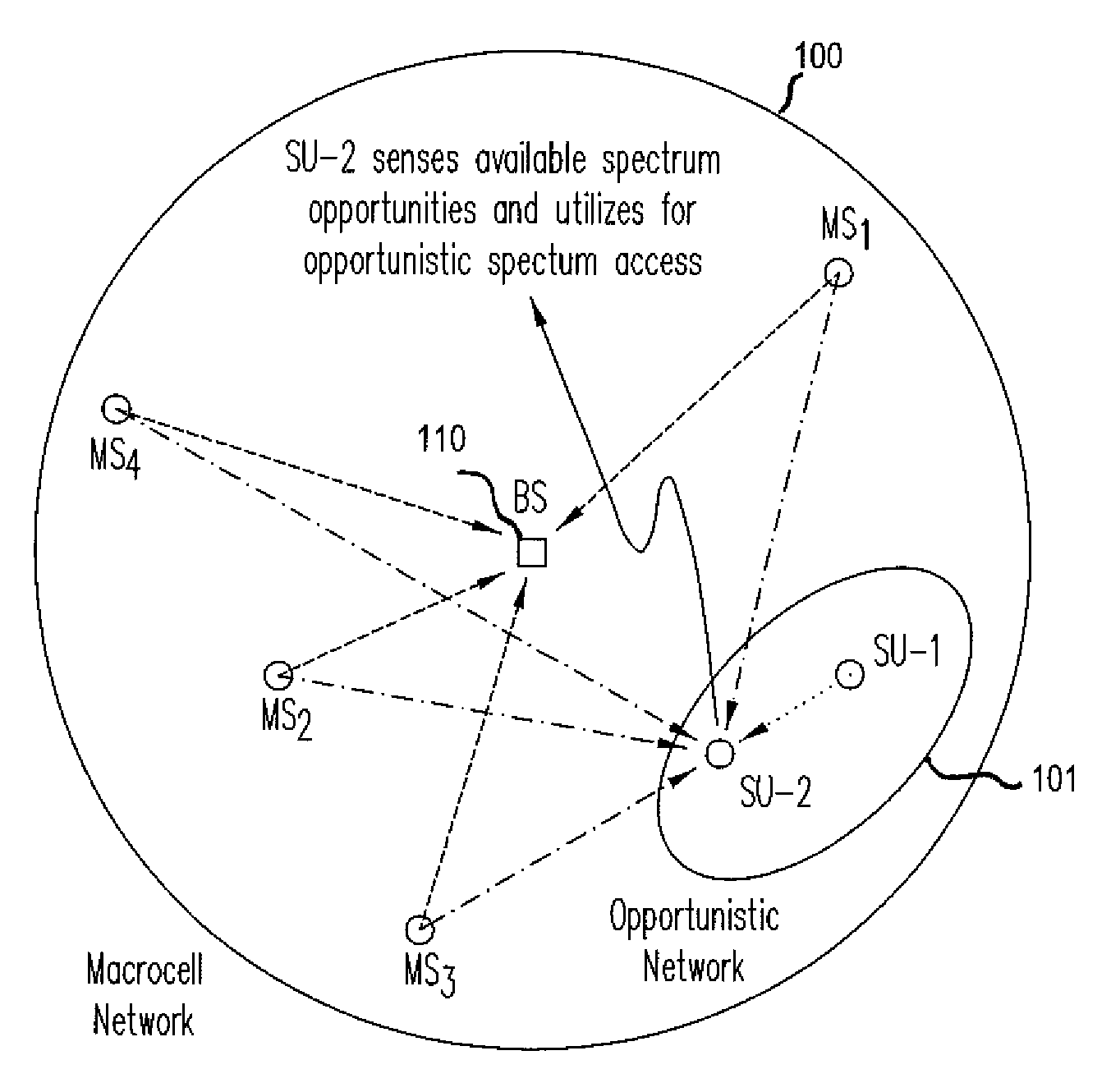
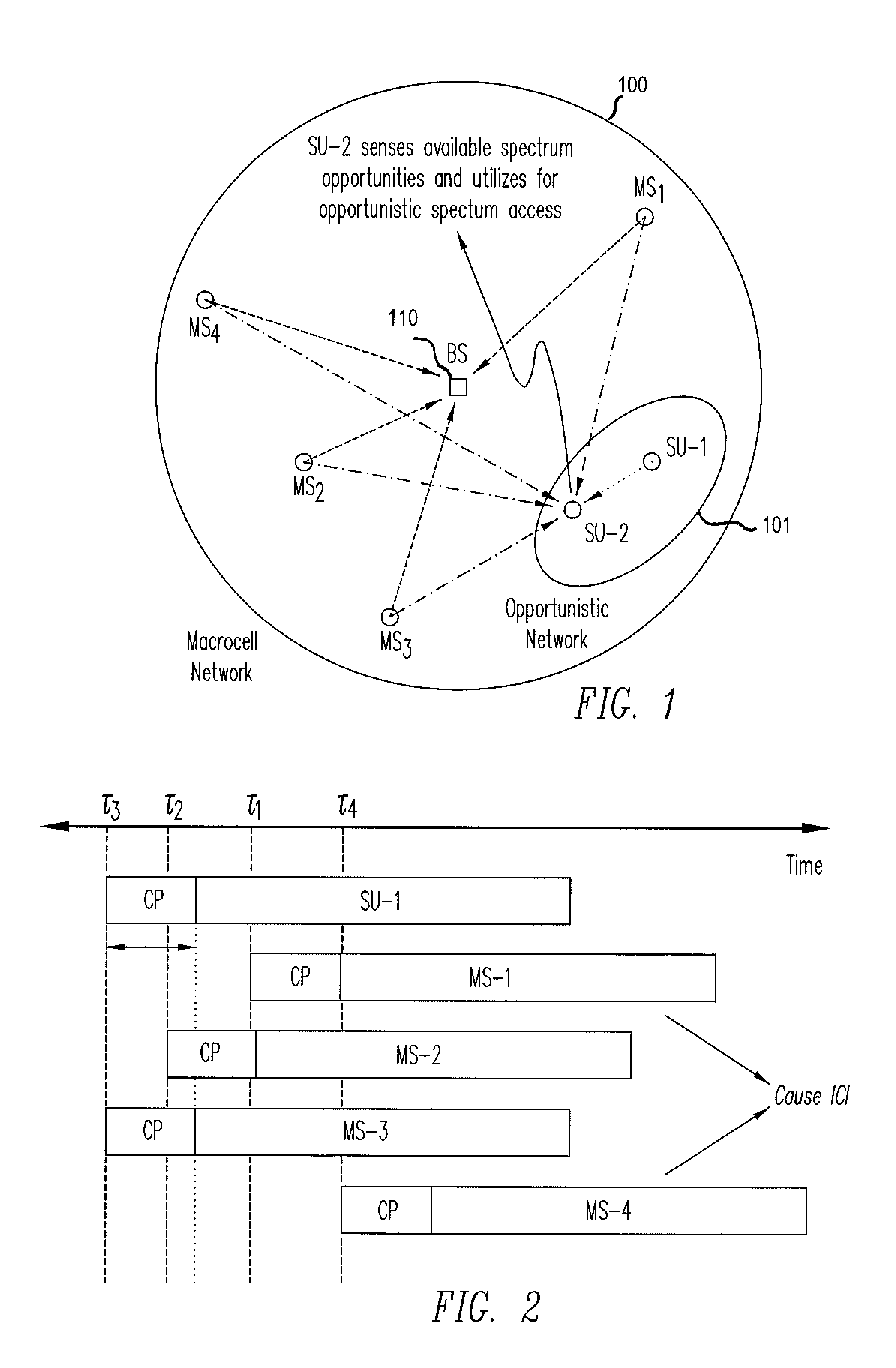
Method for interference-minimizing resource block-size selection at a macrocell, a microcell and a femtocell
A method for minimizing interference is applicable to a primary network whether or not spectrum resources are assigned to its users using a block-wise subcarrier assignment scheme or a randomized allocation scheme. The identified unused spectrum resources that are to be assigned to the users of the opportunistic network exclude un-used subcarriers adjacent to subcarriers used by the users of the primary network to avoid interference. The opportunistic network may assign the identified unused spectrum resources using a scheme that selects a block size for an adaptive modulation and coding scheme or for avoidance of waste of spectrum resources.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
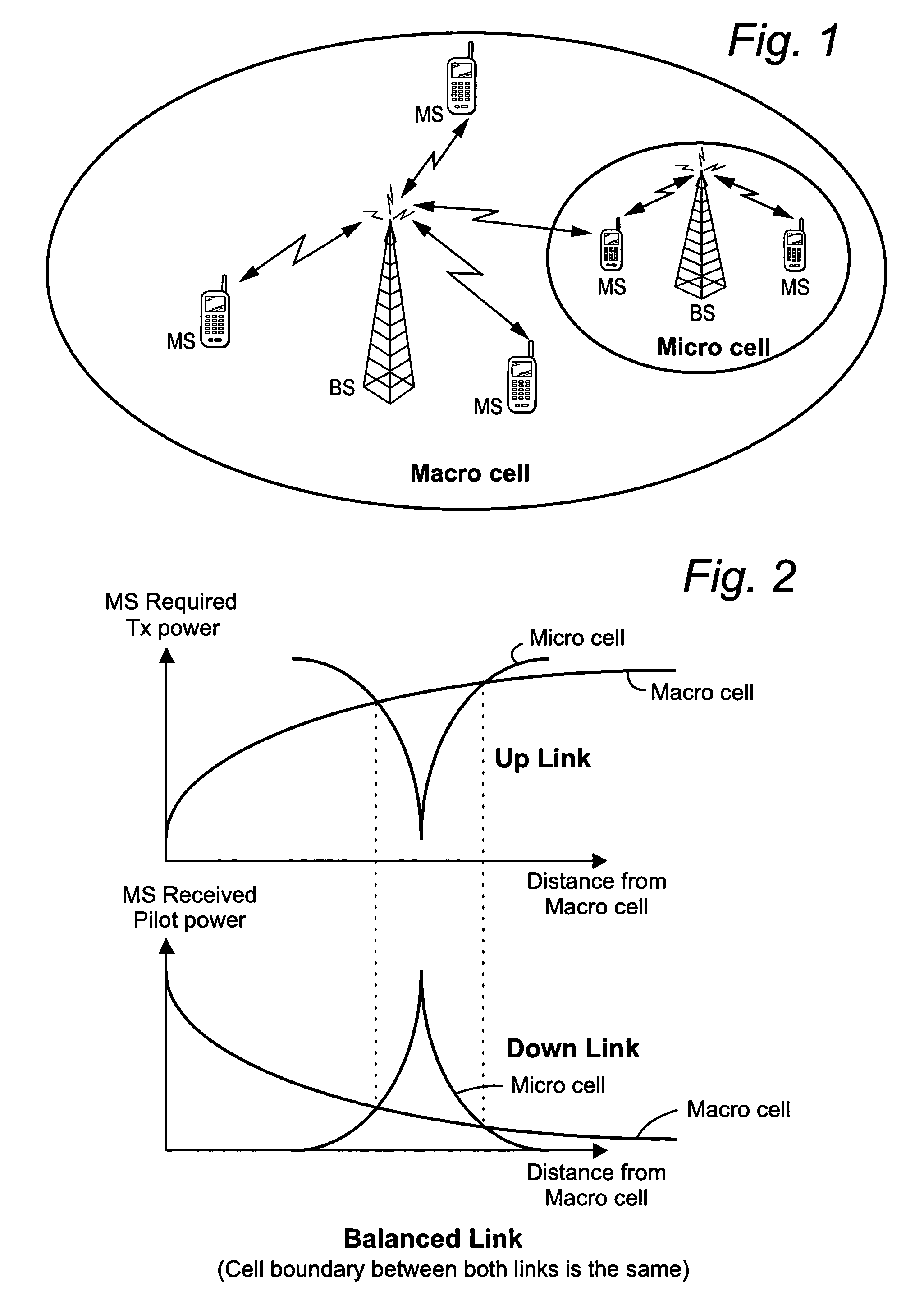
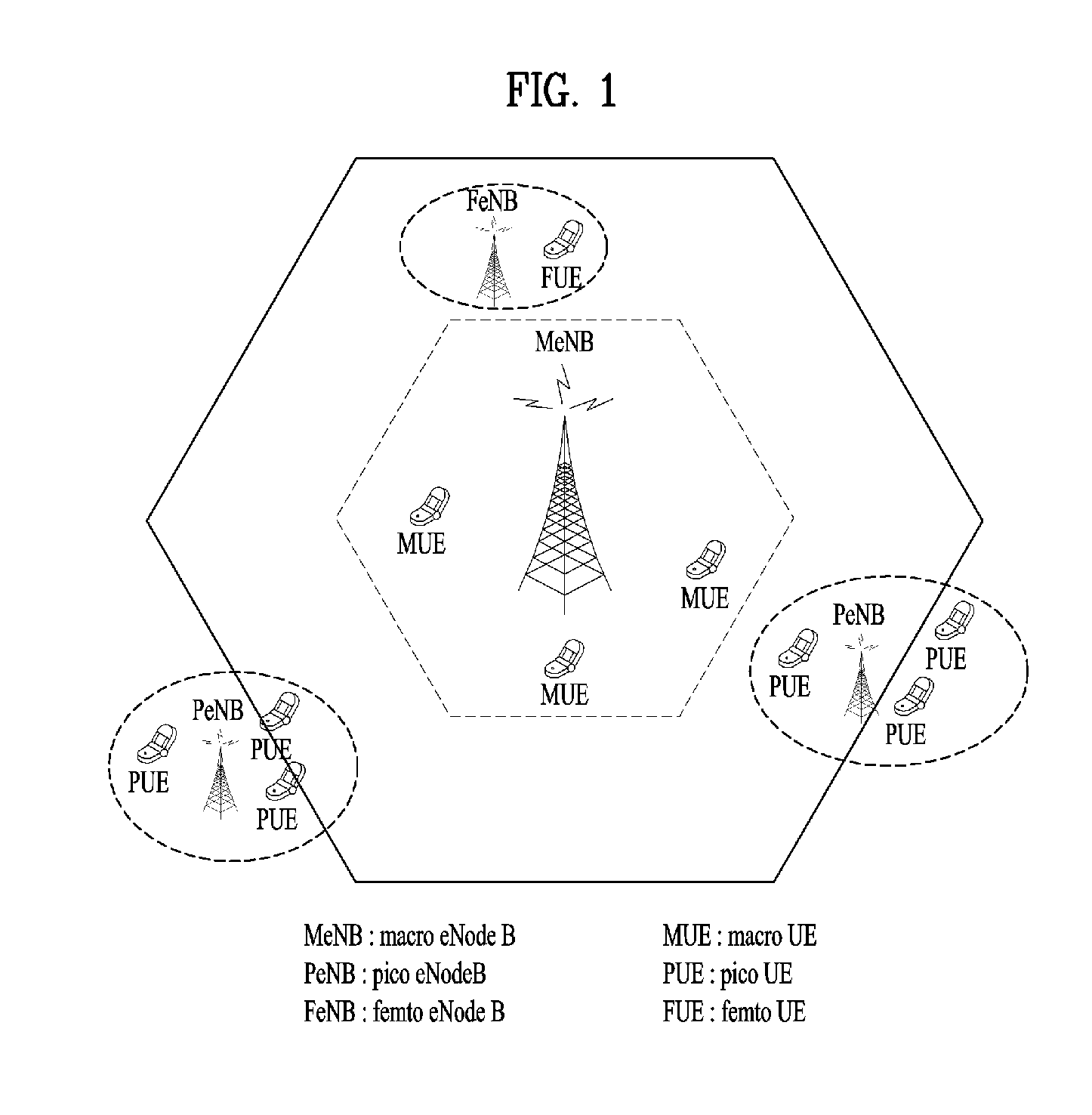
Mobile communications in a hierarchical cell structure
InactiveUS7142861B2Long talk timeIncrease capacityCode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio networksCommunications system
A hierarchical cell structure (HCS) cellular communications system includes a macro cell encompassing a smaller micro cell that employ the same frequency band. The macro cell includes a macro cell base station, and the micro cell includes a micro cell base station. An uplink communication cell boundary between the macro cell and the micro cell is established, and a downlink communication cell boundary between the macro cell and the micro cell is established. A radio network controller determines whether a condition exists in the HCS system which indicates that the uplink and downlink micro cell boundaries should be unbalanced. If the condition is met or exists, the power and / or antenna beam tilt of a downlink transmission from the micro cell base station is reduced to unbalance the uplink and downlink micro cell boundaries. Alternatively, the radio network controller may employ an offset value to mathematically reduce mobile detected pilot power levels associated with the micro base station.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Mobile communication system
InactiveUS20110280223A1Reduce distractionsNetwork topologiesBroadcast service distributionControl signalMobile communication systems
There is a problem that when a closed subscriber group (CSG) cell (1303) available to subscribers is installed in a macro cell area (1301), communication cannot be performed due to the interference between a macro cell (1302) and the CSG cell (1303) in an area (1304) thereof. The CSG cell (1303) that is provided in the CSG cell area (1304) and transmits a downlink synchronization signal using a radio frame assigns control signals to a first subframe and a second subframe among a plurality of subframes constituting the radio frame, and the macro cell (1302) that is provided in the macro cell area (1301) and transmits a downlink synchronization signal using the radio frame assigns control signals to a third subframe and a fourth subframe, which are shifted from the first subframe and the second subframe by a predetermined number of subframes, respectively, among the plurality of subframes constituting the radio wave, the CSG cell (1303) and the macro cell (1302) being configured to perform transmission in synchronization with each other.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and device for discovering micro cell
ActiveCN102883408AEffective energy savingEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemMicro cell
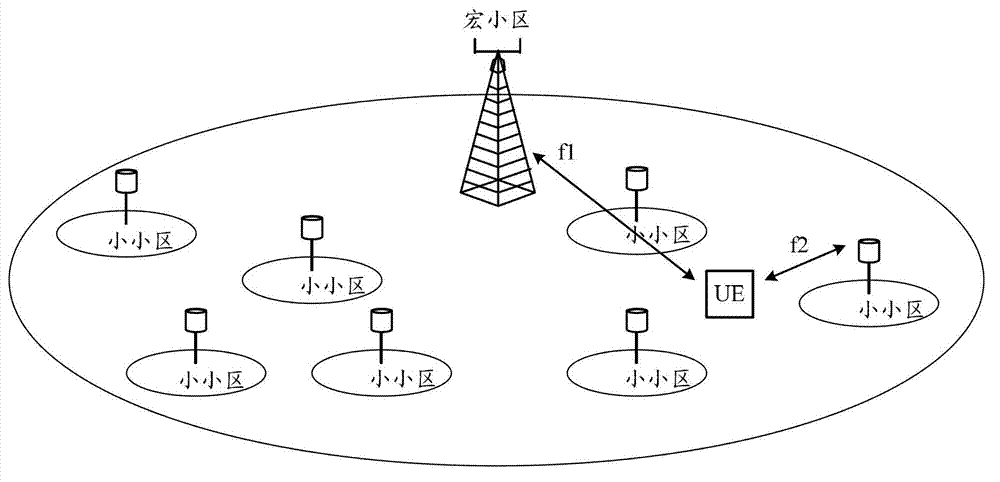
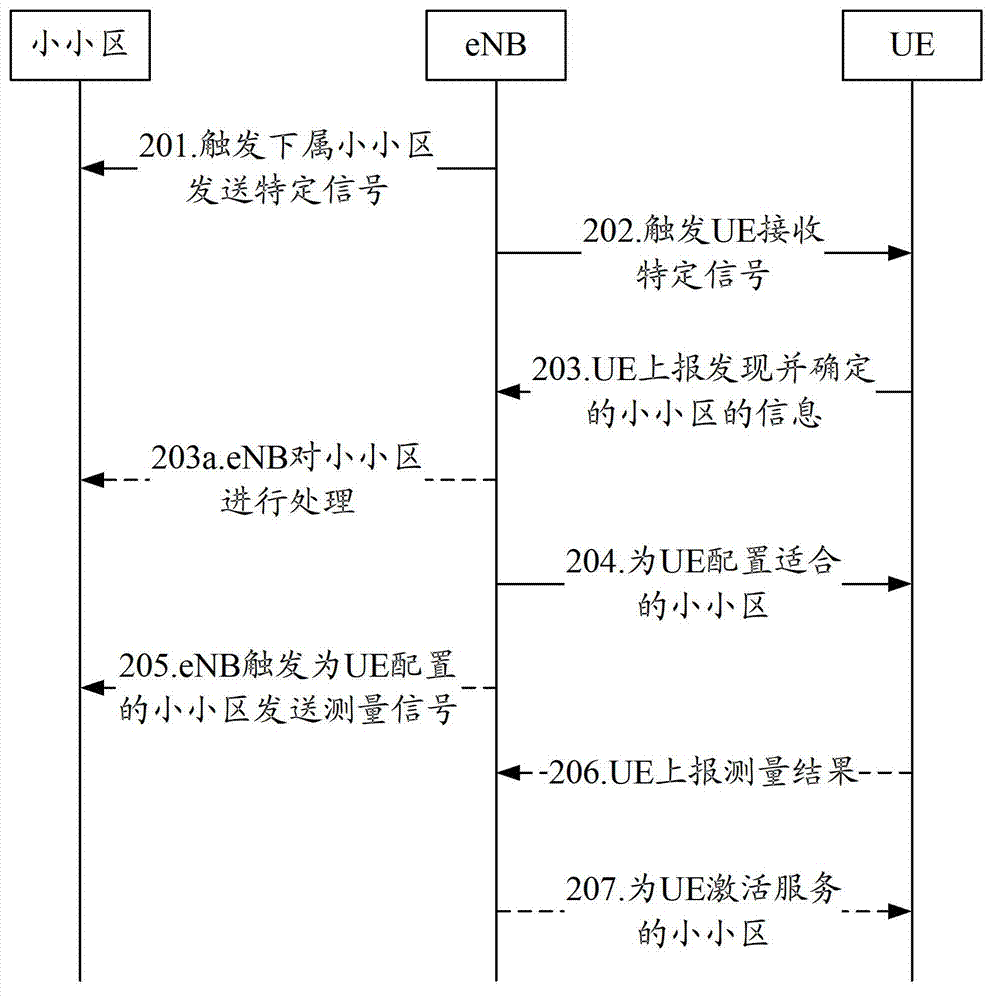
The invention discloses a method and a device for discovering a micro cell. The method comprises the following steps that: a base station of a macro cell triggers micro cells in a nonactivated state to send specific signals and triggers user equipment (UE) to receive the specific signals sent by the micro cells; the base station receives information of the micro cells which are discovered and determined to be reported by the UE according to the received specific signals; and the base station selects part of or all of the micro cells from the micro cells determined by the UE and configures part or all of the micro cells into quasi service micro cells of the UE. By the method and the device, the effect that in a wireless communication system heterogeneous network, the UE in the macro cell can discover the micro cells in the macro cell and a network side can select the suitable micro cells for the UE to provide services; and both the network side and the UE can be ensured to be effective and energy-saving by the mechanism disclosed by the invention.
Owner:ZTE CORP
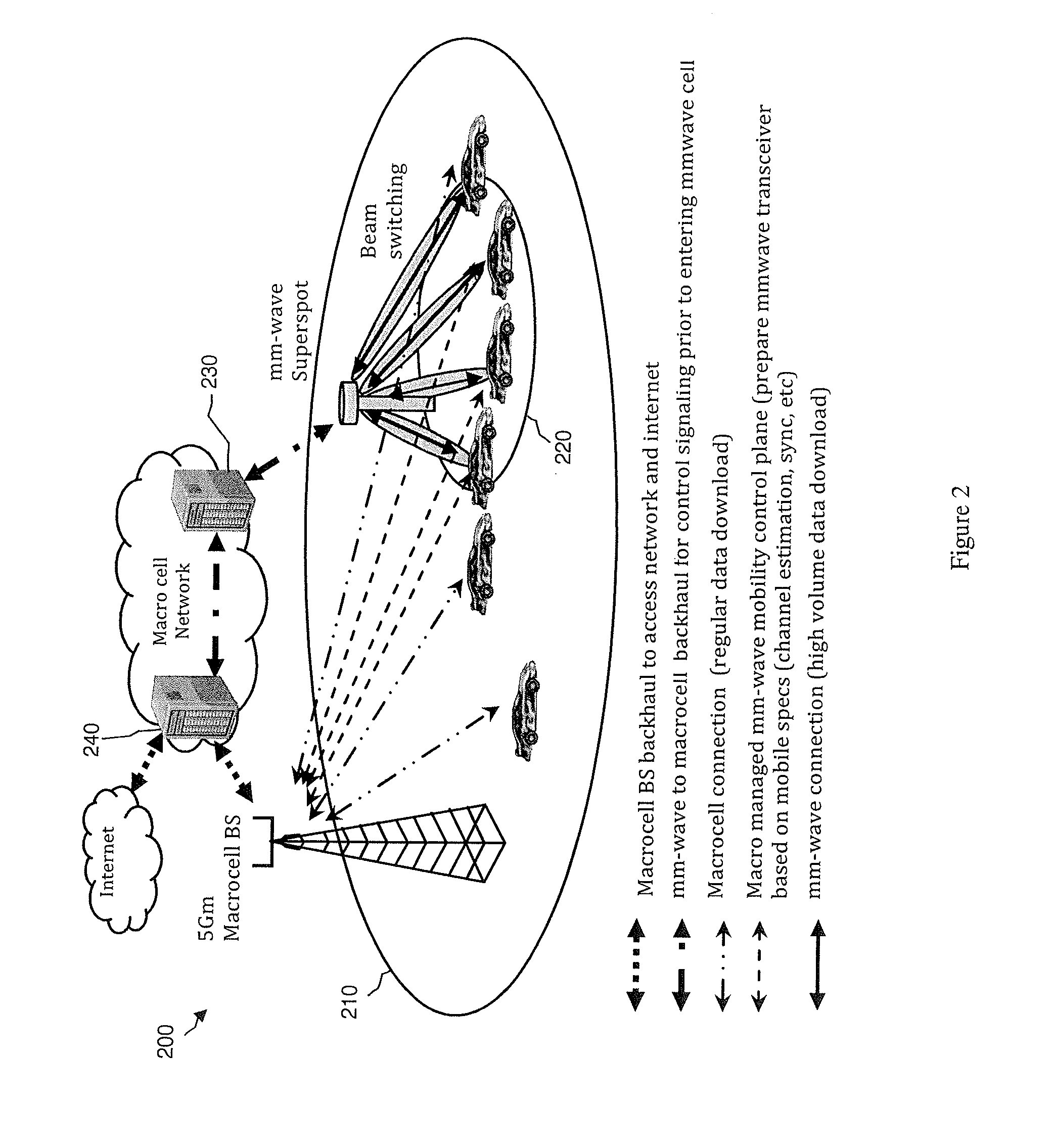
Macrocell Enabled MM-Wave Superspot for Mobility
InactiveUS20150092676A1Increase speedInformation formatConnection managementSignal qualityMillimetre wave
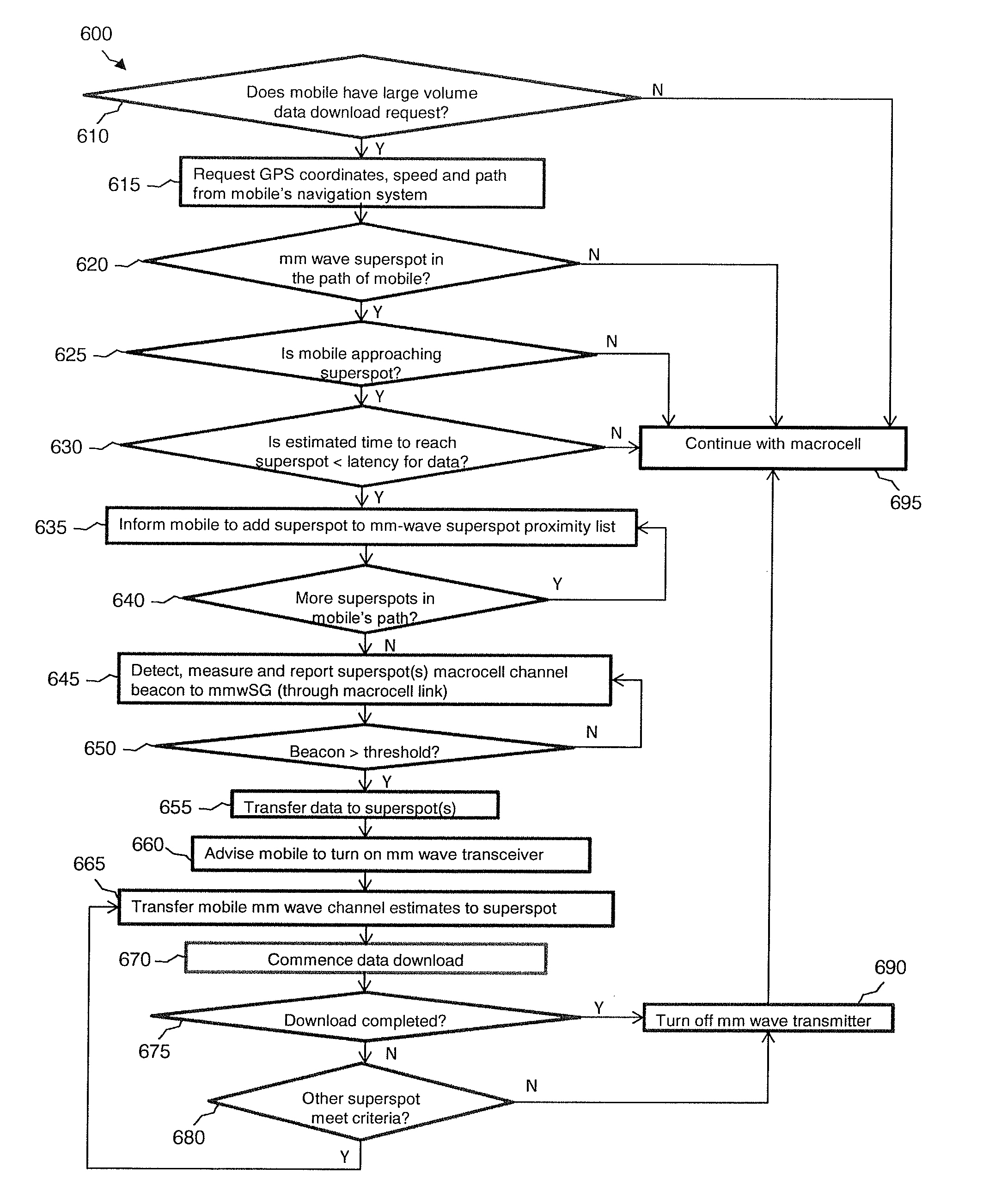
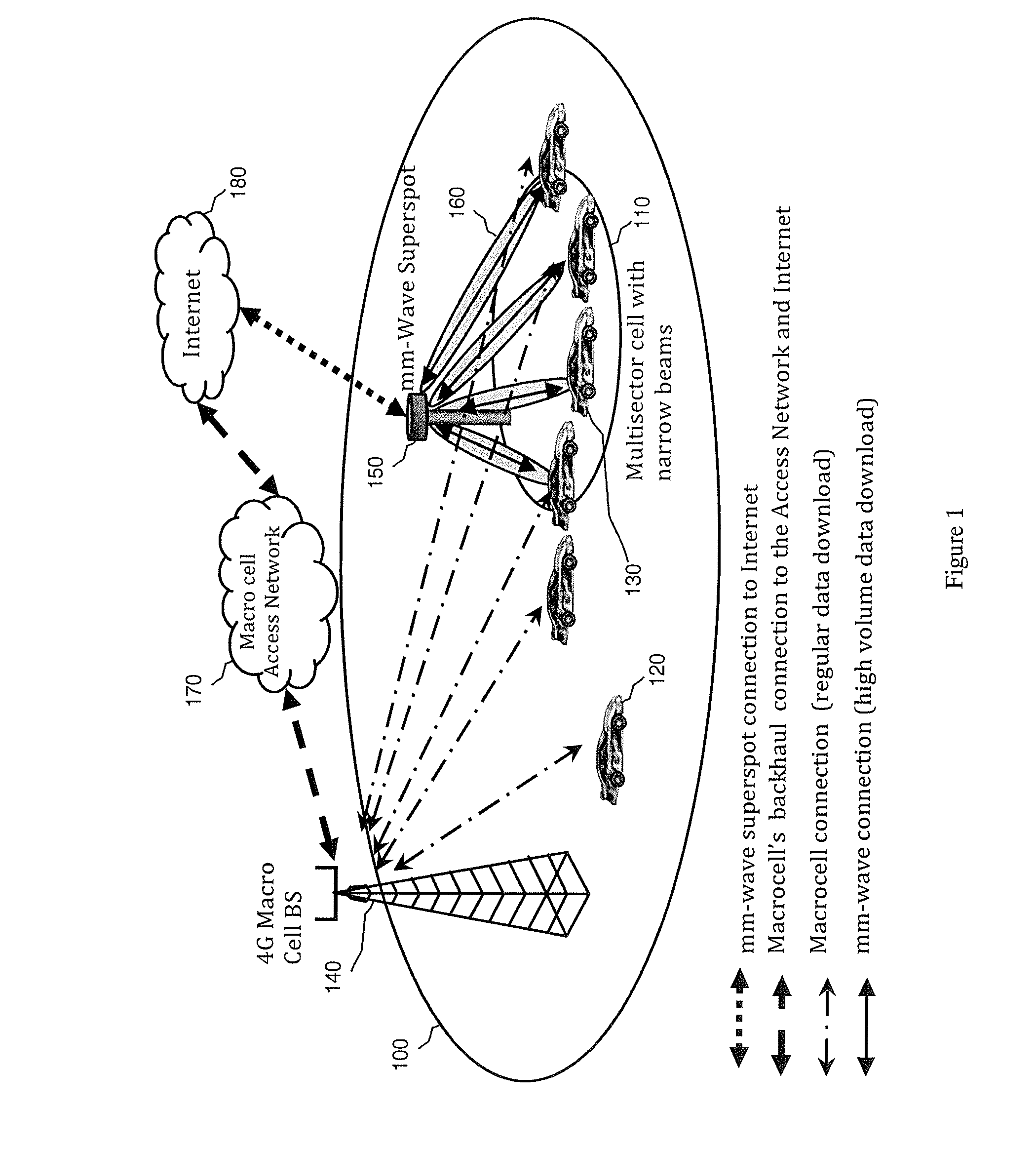
A system and method may use mm-wave superspots to download high volumes of data to a moving or stationary mobile device traveling along a travel route that the moving mobile device is traveling. A macrocell in communication with the mobile device may predict the route that the mobile device is traveling, such as via GPS location, moving speed and direction, map information, etc. Alternatively, the route being taken may be determined by wireless communication, such as between the mobile device and a macrocell and / or superspot. The macrocell and / or superspot may determine whether (1) there are any mm-wave superspots along the predicted or known route that the mobile device is taking; (2) there is any data that is requested or remaining to download to the moving mobile device; and / or (3) the received signal quality, channel conditions, and / or macrocell traffic to the mobile device are favorable for superspot downloading.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Location-based, event triggered inter-radio access technology handovers from a CDMA macrocell to a wcdma femtocell
ActiveUS20100124931A1Well formedAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesRadio access technologyCommunications system
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
Method for carrying out handoff between macrocell and microcell in hierarchical cell structure
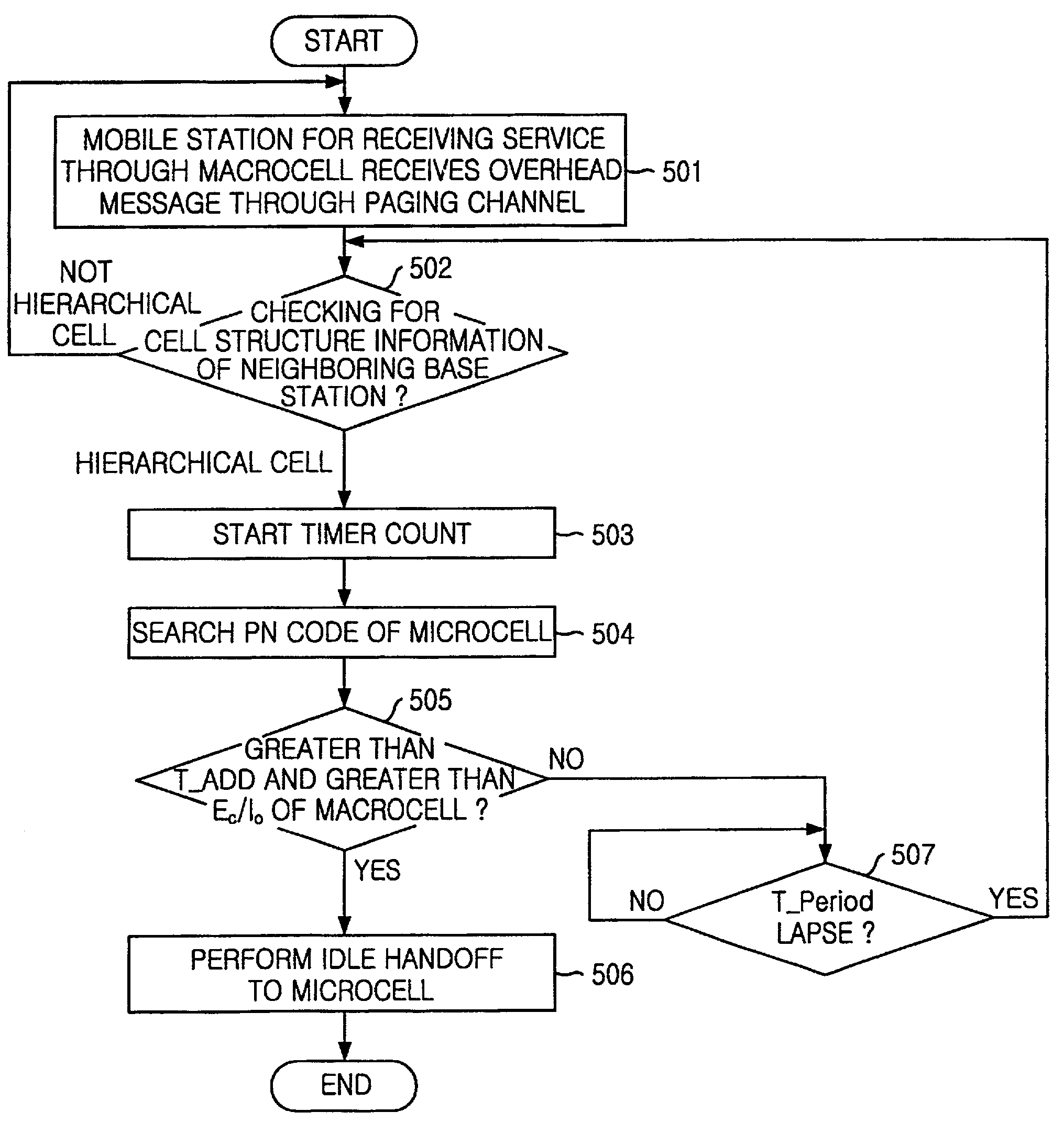
A method for carrying out an idle handoff from a macrocell to a microcell (picocell) in a hierarchical cell structure includes the steps of: a) allocating different frequency assignments (FA) to the macrocell and the microcell in a same service band, to construct the hierarchical cell structure; b) transmitting cell structure information of neighboring base stations and pseudo noise (PN) code from base station to mobile station; c) checking whether the mobile station is in the hierarchical cell by using the cell structure information of neighboring base station; and d) checking whether a value of the pseudo noise (PN) code is greater than T_ADD and greater than Ec / Io of the macrocell by periodically searching the pseudo noise (PN) code of the microcell, to carry out an idle handoff to the microcell, wherein the T_ADD represents a value of base station pilot strength required for the base station of neighboring set to be included in a candidate set, the Ec represents an pilot energy accumulated during one pseudo noise (PN) chip period, and the Io represents a total power spectrum density within a reception bandwidth.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
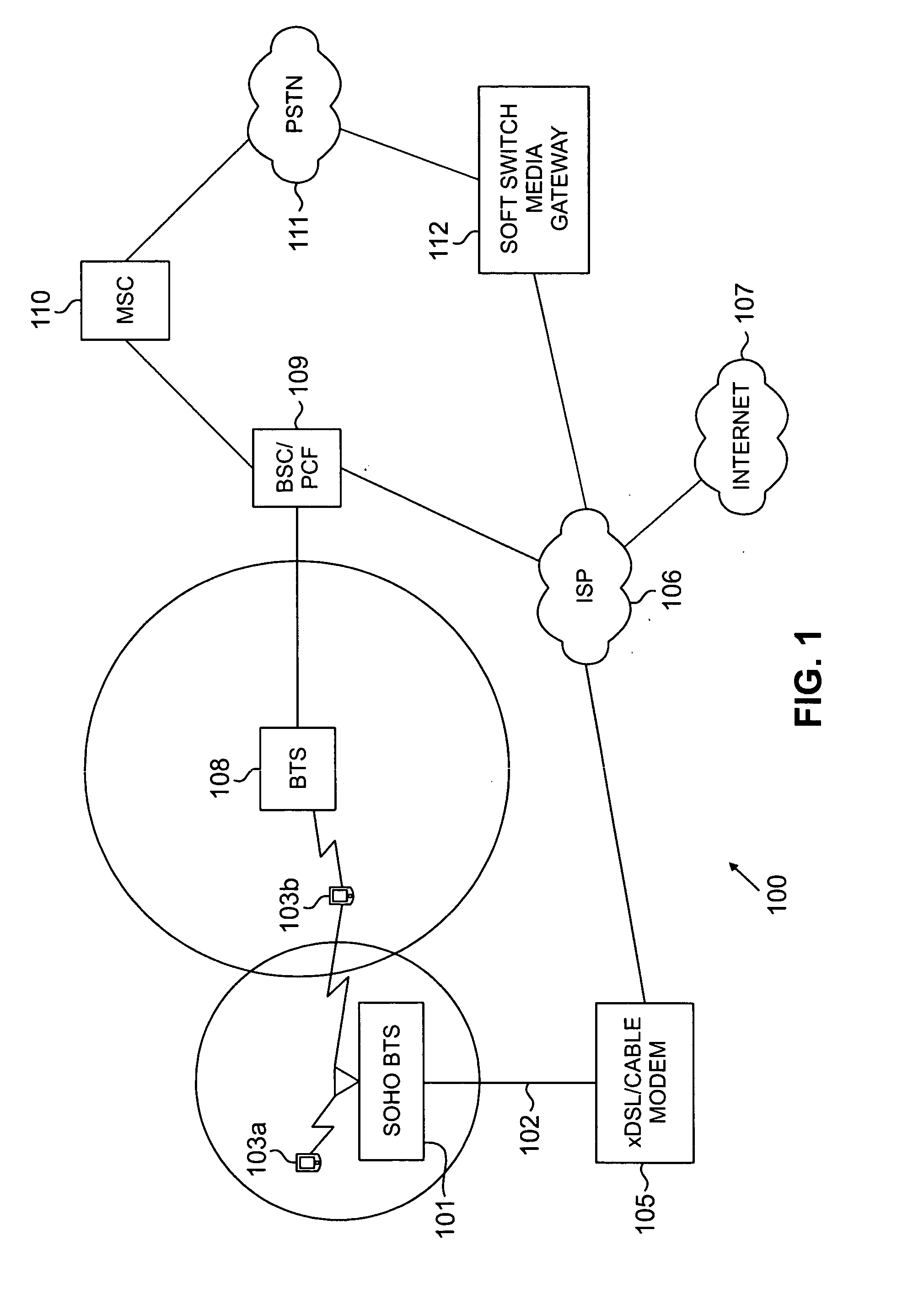
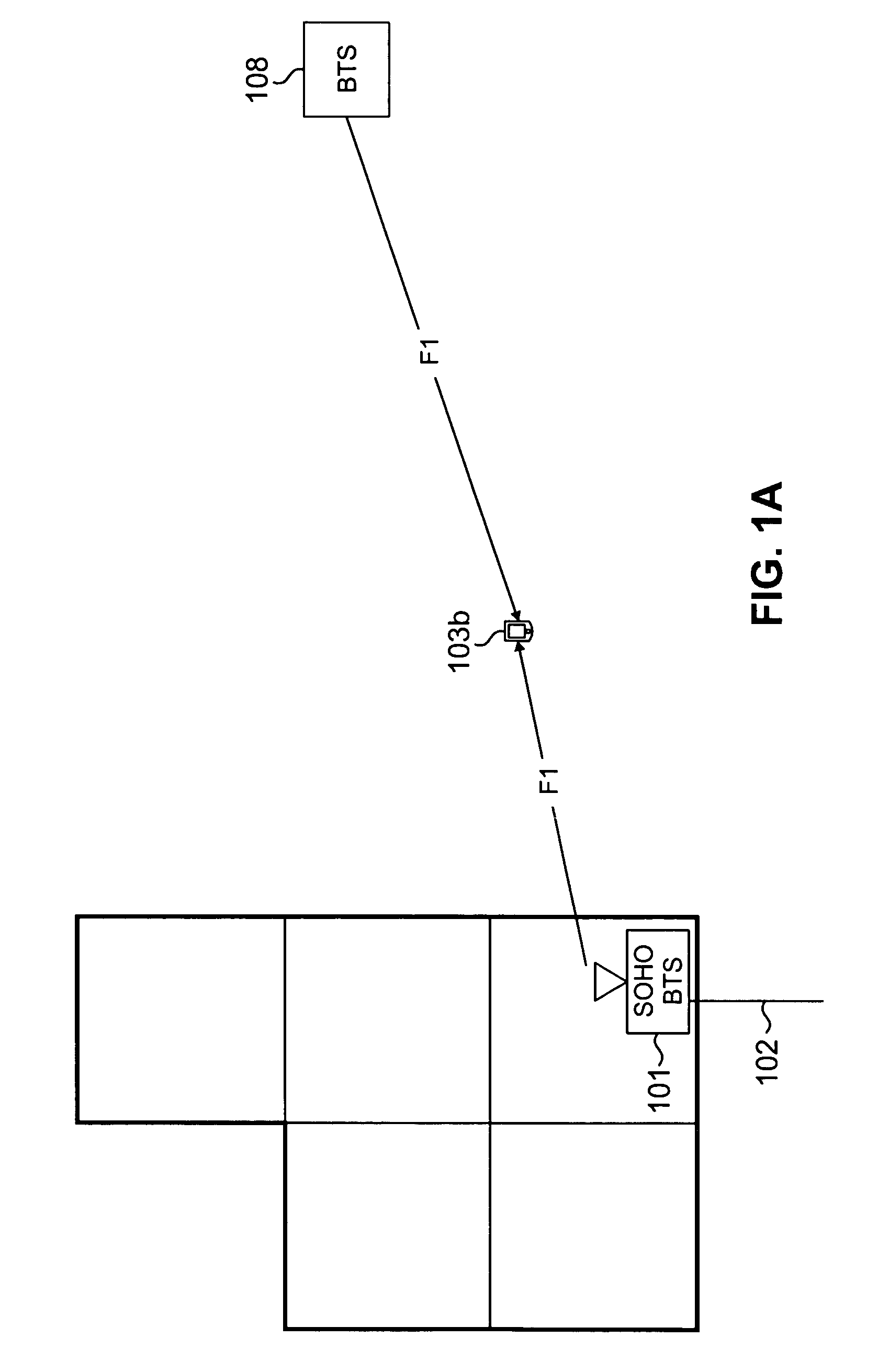
System and method for providing SOHO BTS coverage based on angle of arrival of mobile station signals
InactiveUS20080026763A1Optimizes RF coverageControl interferenceEnergy efficient ICTRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsFrequency spectrumTransmitted power
Beamforming techniques to limit radiated power where there is the potential for interference with macro-cellular coverage or with adjacent mobile stations. Smart antenna beamforming techniques (including the use of angle of arrival information) are combined with access probe information to determine the direction for radiated power and the level of the needed transmitted power as well for the small office or home (SOHO) environment. The placement of RF power in the SOHO specific to where it is needed, minimizes radiating power in directions where it will cause interference with macrocell coverage. In addition, the beamforming techniques provide a base transceiver station with an economical method to quickly solve coverage issues internal to a SOHO, without introducing interference external to this coverage environment. In addition, there specific placement of the RF power where it is needed provides an increase in spectral efficiency of a deployed network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of configuring dual connectivity to ue in heterogeneous cell deployment
InactiveUS20140335869A1Reduce distractionsReduce signalingConnection managementSubstation equipmentTelecommunicationsSmall cell
A method and a macro cell eN B are disclosed. The method includes receiving a measurement report message of the small cell from the UE connected to the macro cell, determining to configure dual connectivity with the macro cell and the small cell to the UE based on a measured value contained in the measurement report message, transmitting a dual connectivity request message for requesting connection with the UE to the small cell, receiving a dual connectivity response message indicating that the small cell is connected to the UE to determine to allocate a resource to the UE, from the small cell, and transmitting an RRC configuration message for requesting addition of connection with the small cell, to the UE.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and structure for a 1T-RAM bit cell and macro
InactiveUS20070080387A1Function increaseIncrease capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMetal-insulator-metalMOSFET
A one transistor (1T-RAM) bit cell and method for manufacture are provided. A metal-insulator-metal (MIM) capacitor structure and method of manufacturing it in an integrated process that includes a finFET transistor for the 1T-RAM bit cell is provided. In some embodiments, the finFET transistor and MIM capacitor are formed in a memory region and an asymmetric processing method is disclosed, which allows planar MOSFET transistors to be formed in another region of a single device. In some embodiments, the 1T-RAM cell and additional transistors may be combined to form a macro cell, multiple macro cells may form an integrated circuit. The MIM capacitors may include nanoparticles or nanostructures to increase the effective capacitance. The finFET transistors may be formed over an insulator. The MIM capacitors may be formed in interlevel insulator layers above the substrate. The process provided to manufacture the structure may advantageously use conventional photomasks.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
System and Method for Providing Connection Handoffs in Wireless Networks
InactiveUS20090219888A1Overcome size limitationsIncrease resourcesBroadcast service distributionWireless commuication servicesTelecommunicationsMacrocell
System and method for providing connection handoffs from macrocell to femtocell in wireless networks. A method comprises determining a group identifier from a received pseudorandom number sequence, determining a list of access points from a plurality of access points, wherein the access points in the list of access points are all identified by a group identifier, transmitting a request for detecting an identifier of the communications device to each access point in the list of access points, receiving a positive acknowledgement from a locating access point in the list of access points, and locating the communications device in a coverage area of the locating access point. The acknowledgement indicates that the locating access point successfully detected the identifier.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
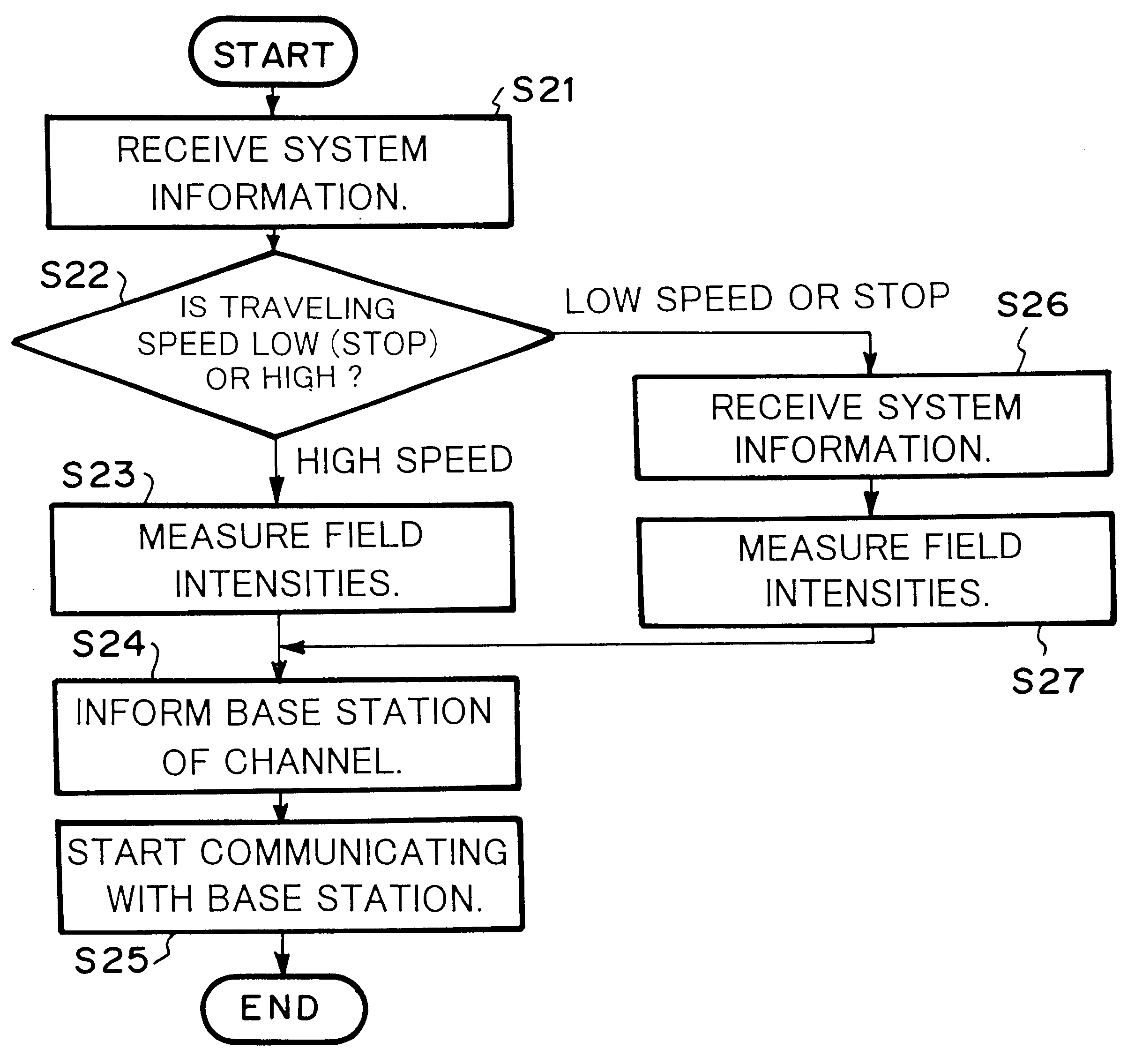
Mobile radio communication system with macro and micro cell handoff based on mobile determined crossing rates and fading rates
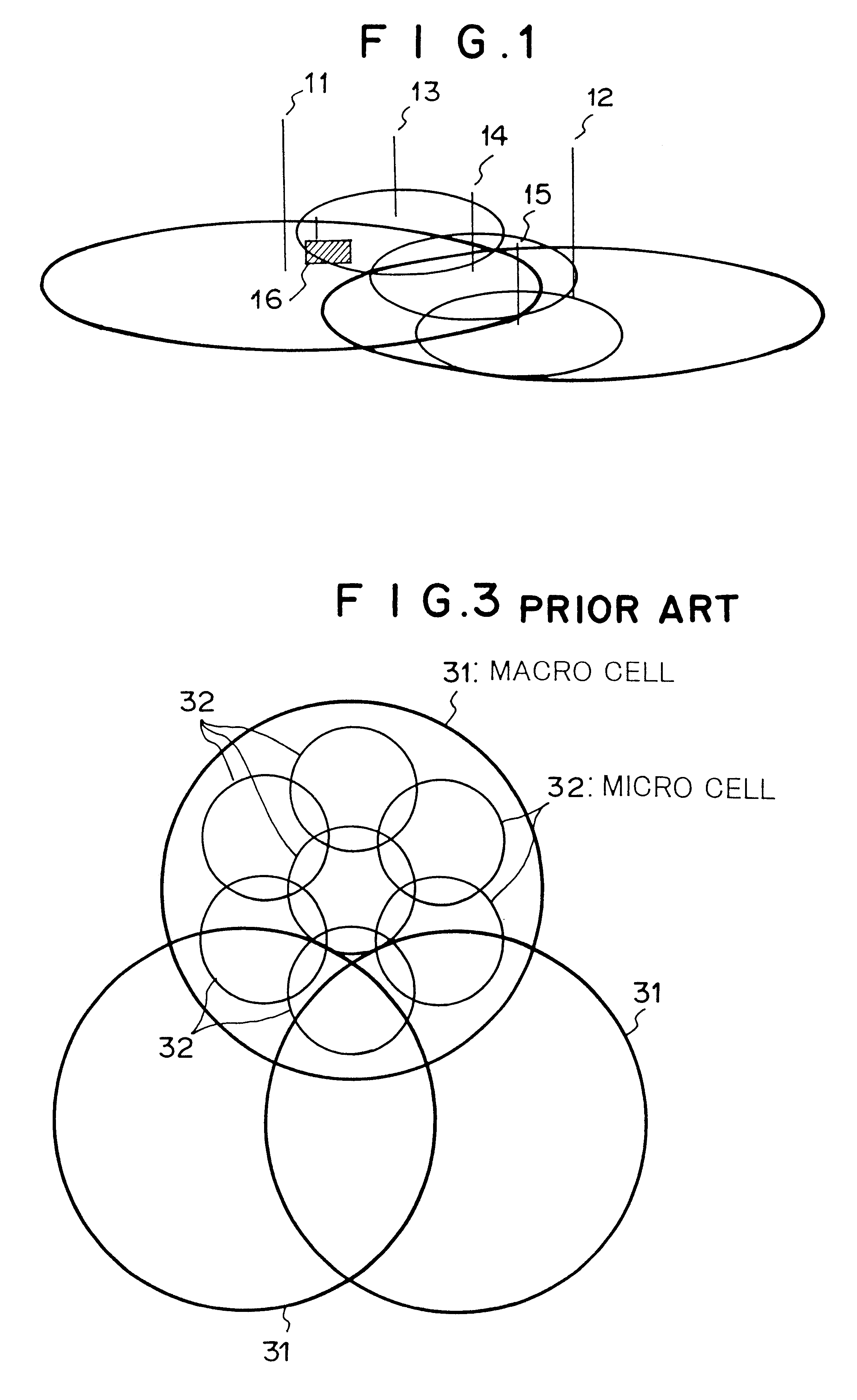
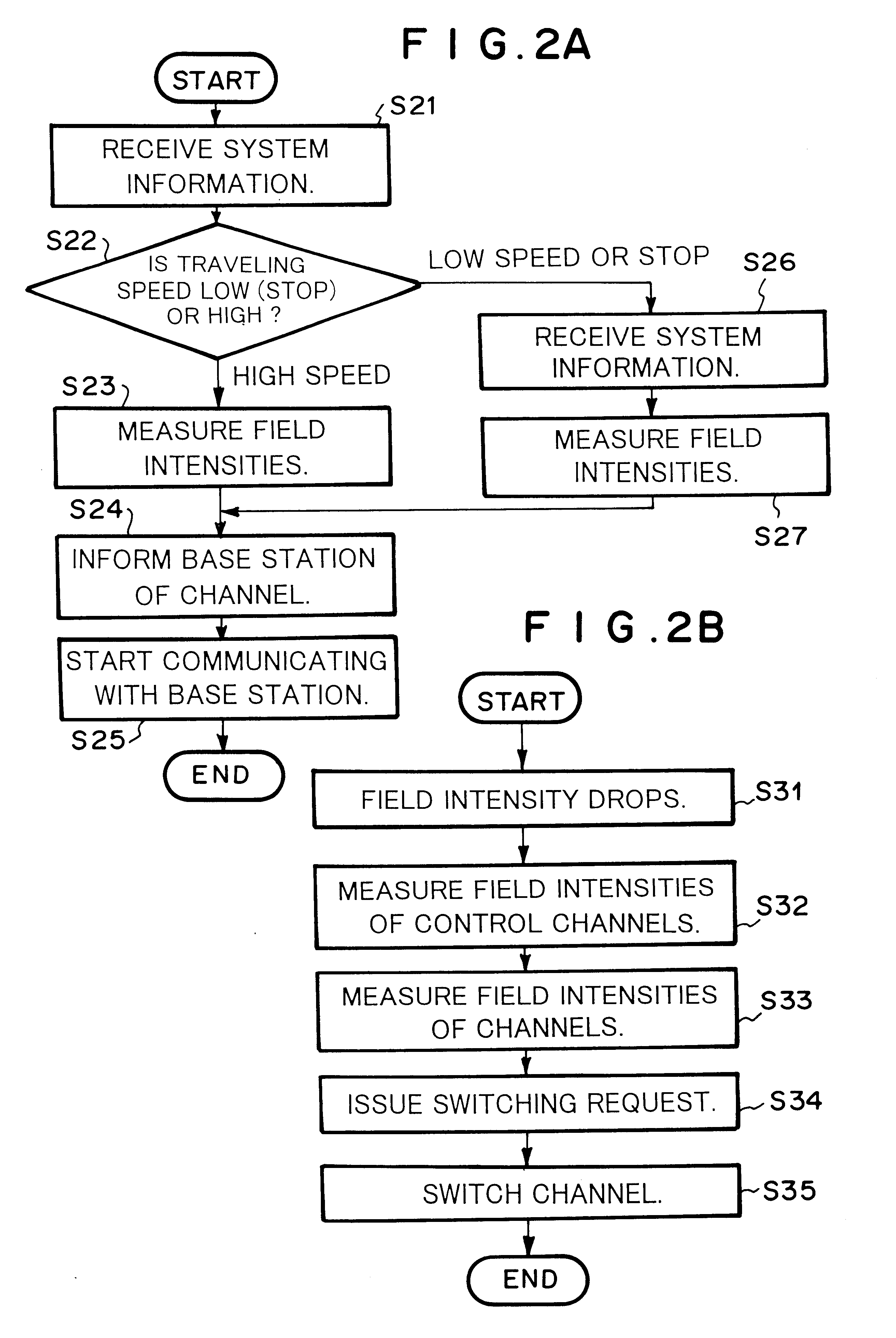
A radio base station broadcasts system information through a control channel. Each mobile station receives system information (at step S21) and determines the moving speed thereof (at step S22). When the mobile station is moving at high speed, the mobile station measures the field intensities of available channels on which the mobile station can communicate with a macro cell radio base station (at step S23 or S27). When the mobile station is moving at low speed, the mobile station measures the field intensities of available channels on which the mobile station can communicate with a micro cell radio base station (at step S27 or S23). However, when the radio base station to which the mobile station is moving is different from the radio base station from which the mobile station has received the control channel at first, the mobile station receives new system information from the relevant base station at step S26. The mobile station selects a channel corresponding to the measured result and starts communicating with the new radio base station (at steps S24 and S25).
Owner:NEC CORP
Handover in a cellular communication system
InactiveUS20080101301A1Easy to implementImprove performanceRadio transmissionWireless communicationCellular communication systemsMacrocell
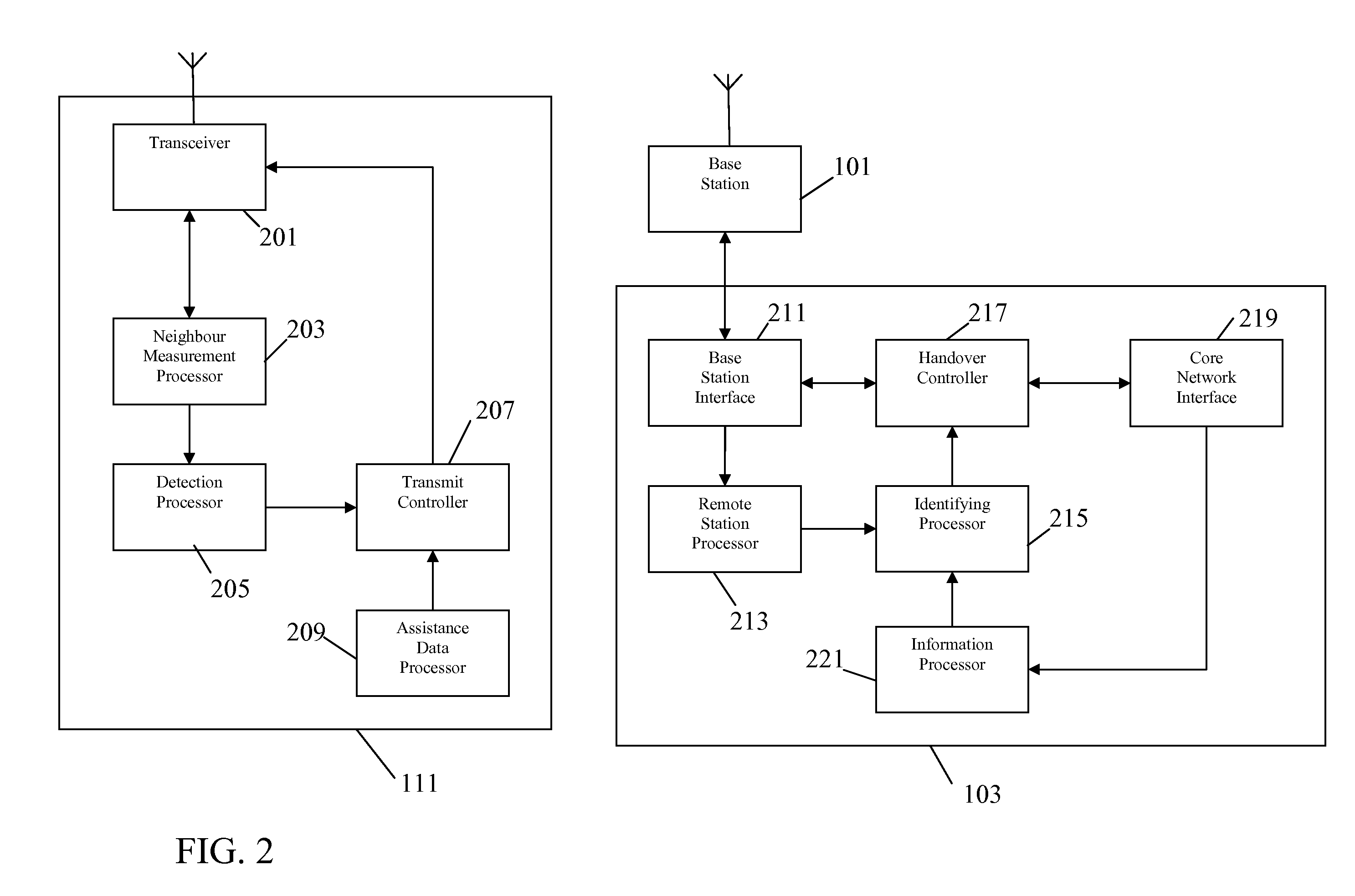
A cellular communication system includes base stations supporting macro cells and with unique cell scrambling codes within a region. The system further includes access points supporting underlay cells and with shared cell scrambling codes within the region. One or more of the access points or base stations comprise transmit means for transmitting an indication of at least a first shared scrambling code to a remote station. The shared scrambling code is shared by a plurality of access points. The remote station is arranged to receive the first shared scrambling code and to determine if a first signal using the first shared scrambling code is received. If the first signal is detected, a handover controller initiates a handover of the remote station to at least a first access point of the plurality of access points sharing the first shared scrambling code.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Radio-Access Method for Mobile-Radio Networks, Related Networks and Computer Program Product
InactiveUS20090252139A1Increase flexibilityRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesRadio coverageRadio networks
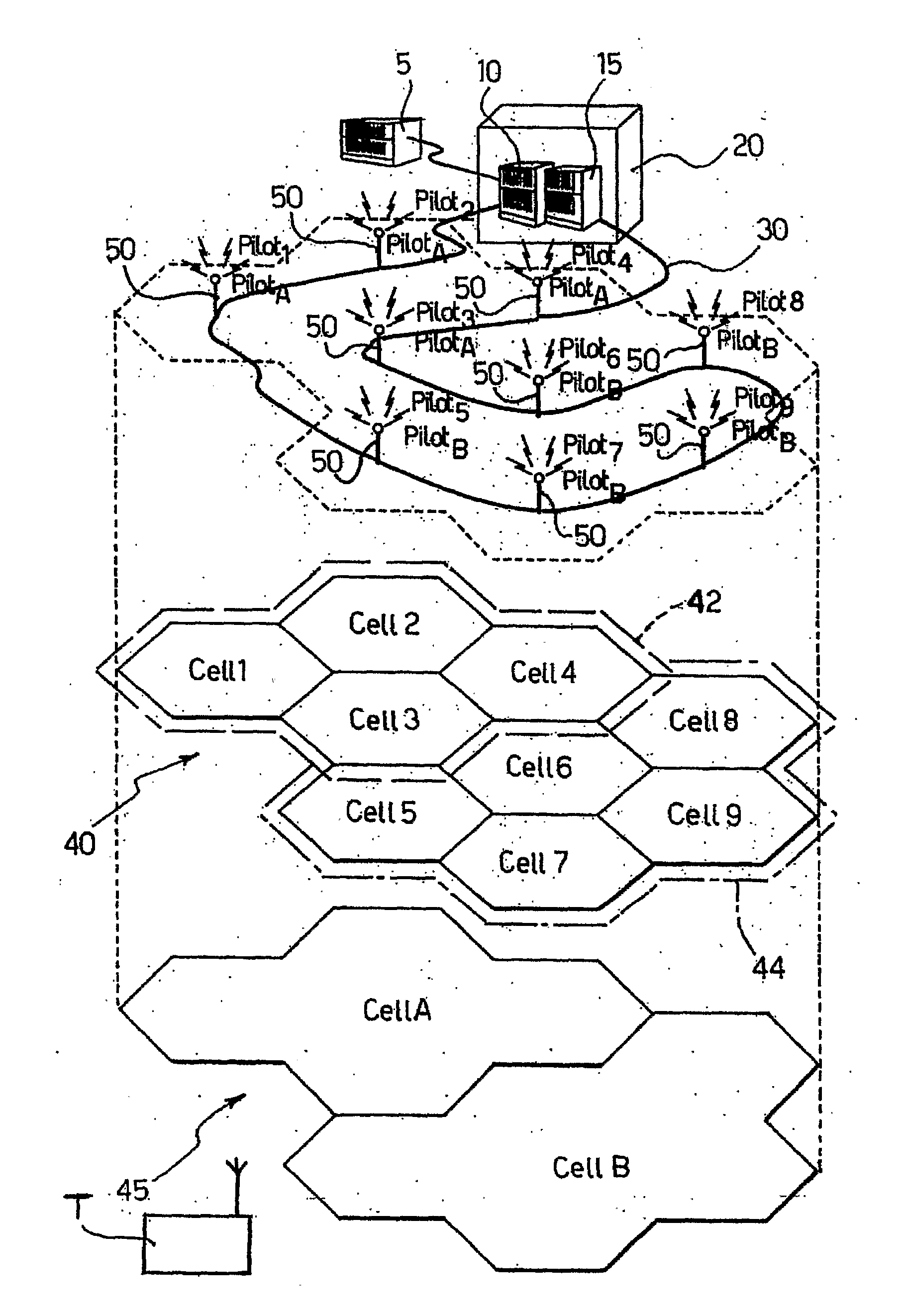
A mobile-radio network includes radio base stations providing radio coverage to the users of the network via antenna elements, wherein the antenna elements are equipped with at least one first communication channel and at least one second communication channel. The first communication channel provides a first layer of individual microcell radio coverage for the antenna elements. The second communication channel is made common to groups of the antenna elements and provides a second layer of virtual macrocell radio coverage, wherein the coverage of each virtual macrocell aggregates the microcell radio coverages of the antenna elements included in the respective group.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com