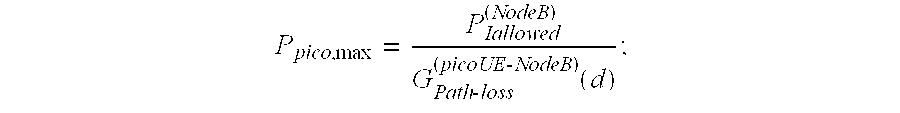Patents
Literature
525 results about "Picocell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
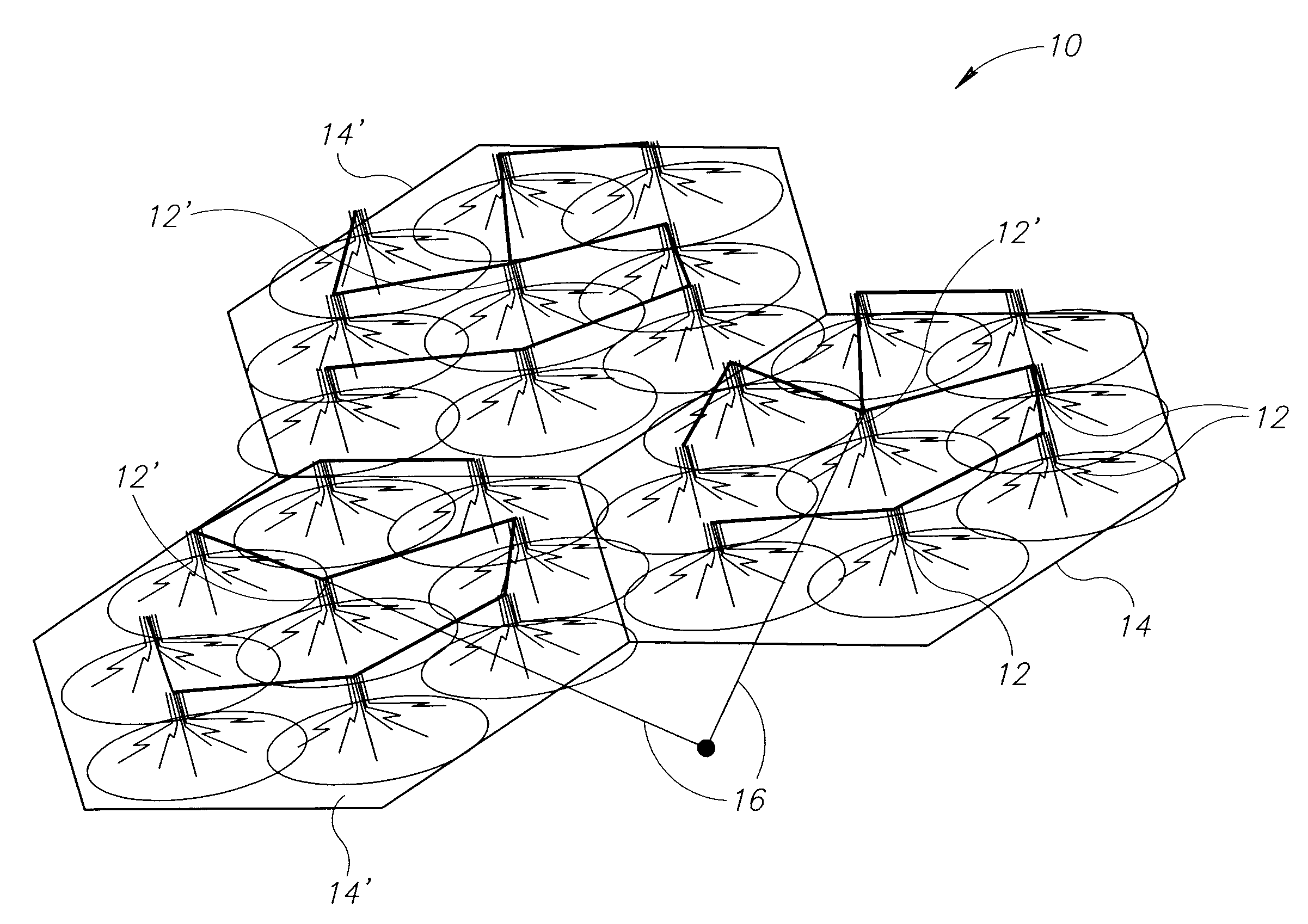
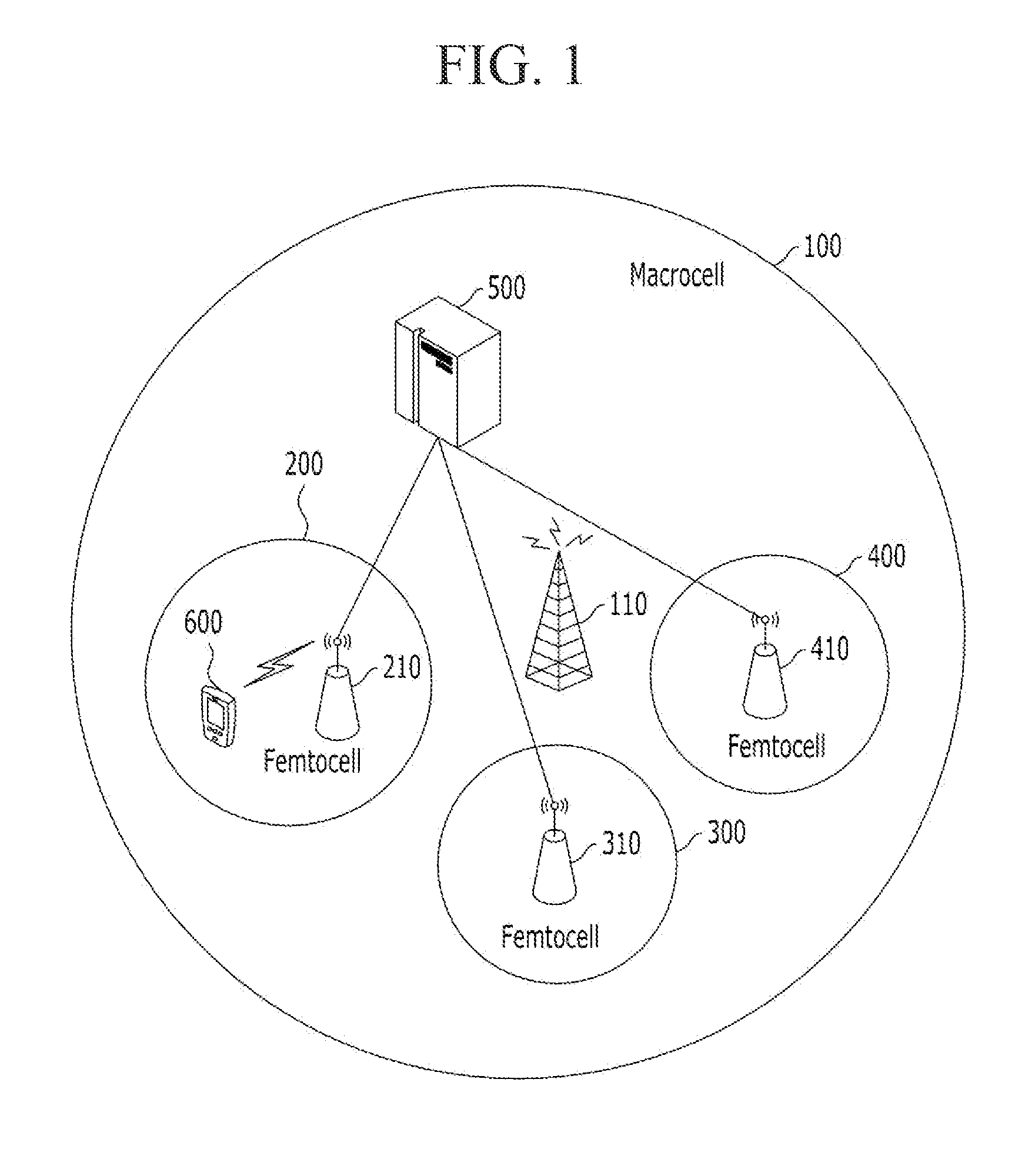
A picocell is a small cellular base station typically covering a small area, such as in-building (offices, shopping malls, train stations, stock exchanges, etc.), or more recently in-aircraft. In cellular networks, picocells are typically used to extend coverage to indoor areas where outdoor signals do not reach well, or to add network capacity in areas with very dense phone usage, such as train stations or stadiums. Picocells provide coverage and capacity in areas difficult or expensive to reach using the more traditional macrocell approach.
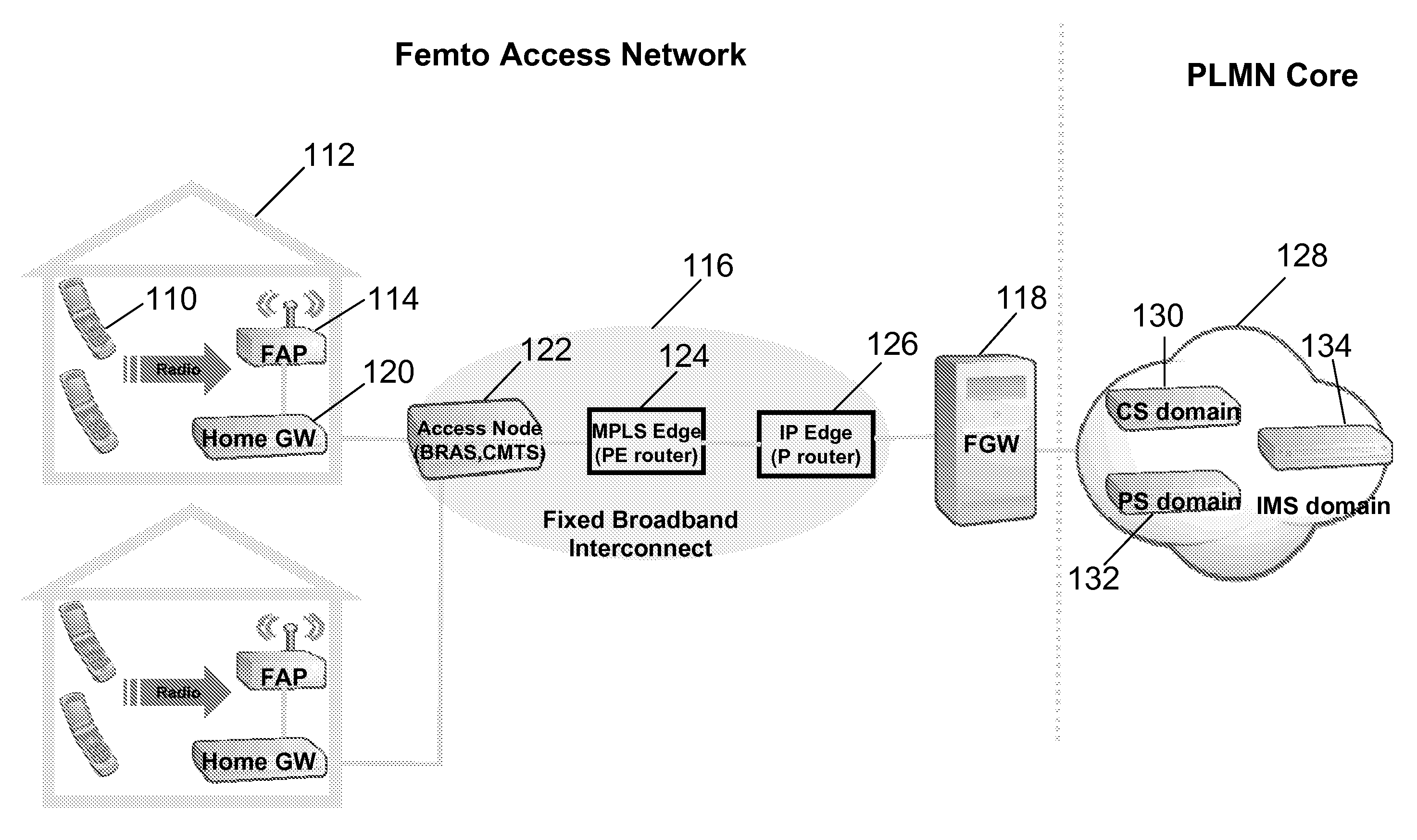
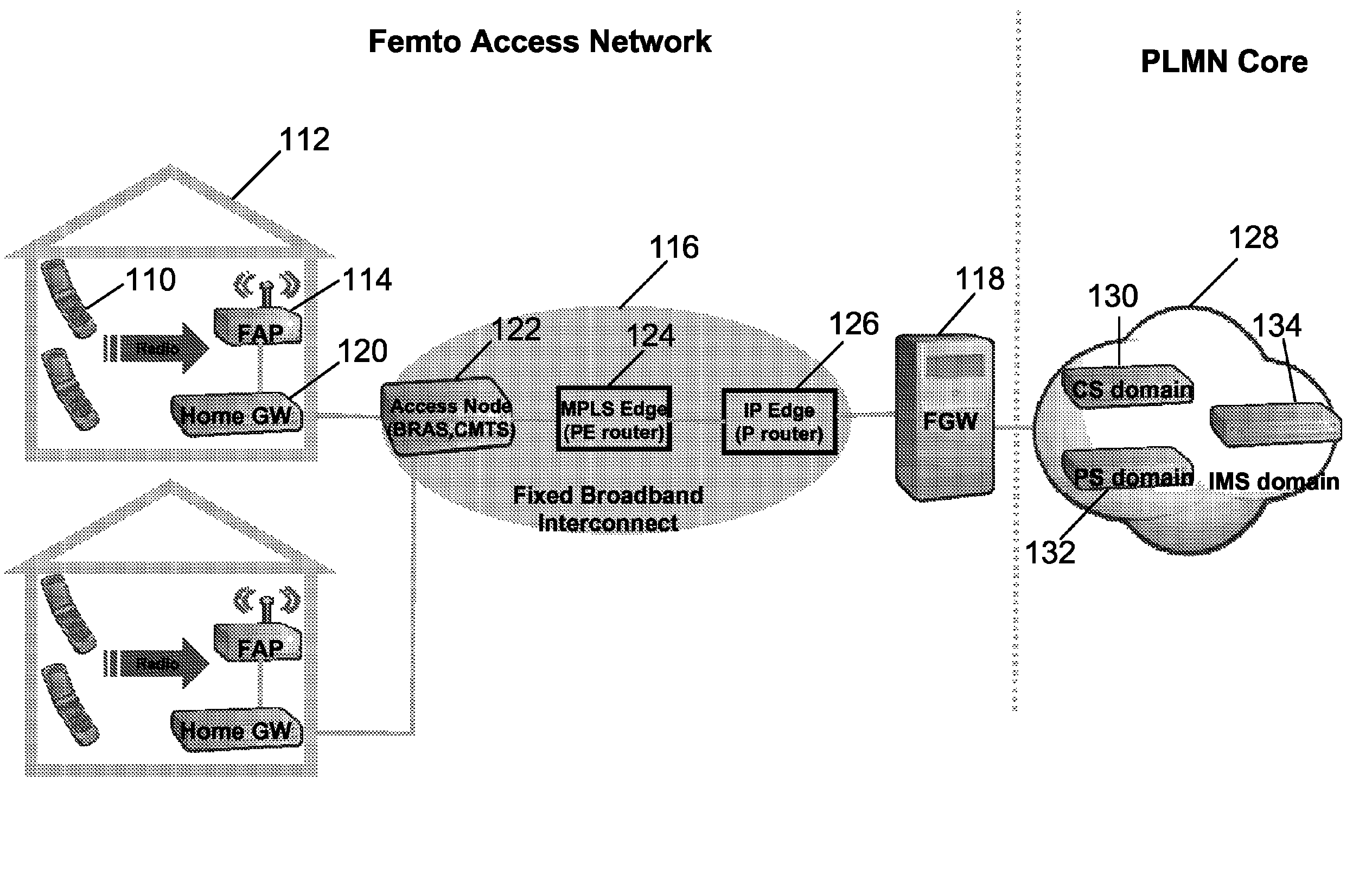
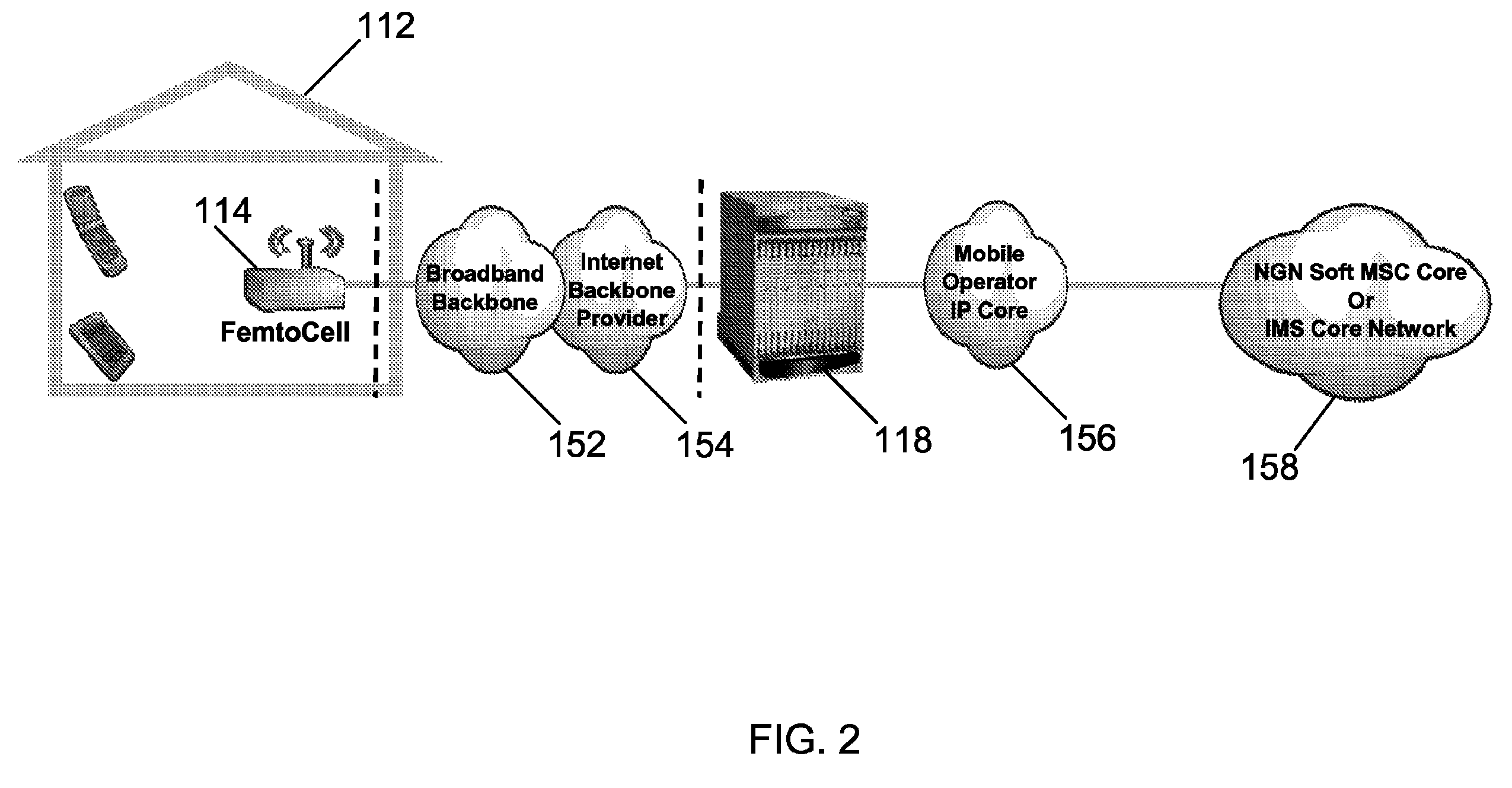
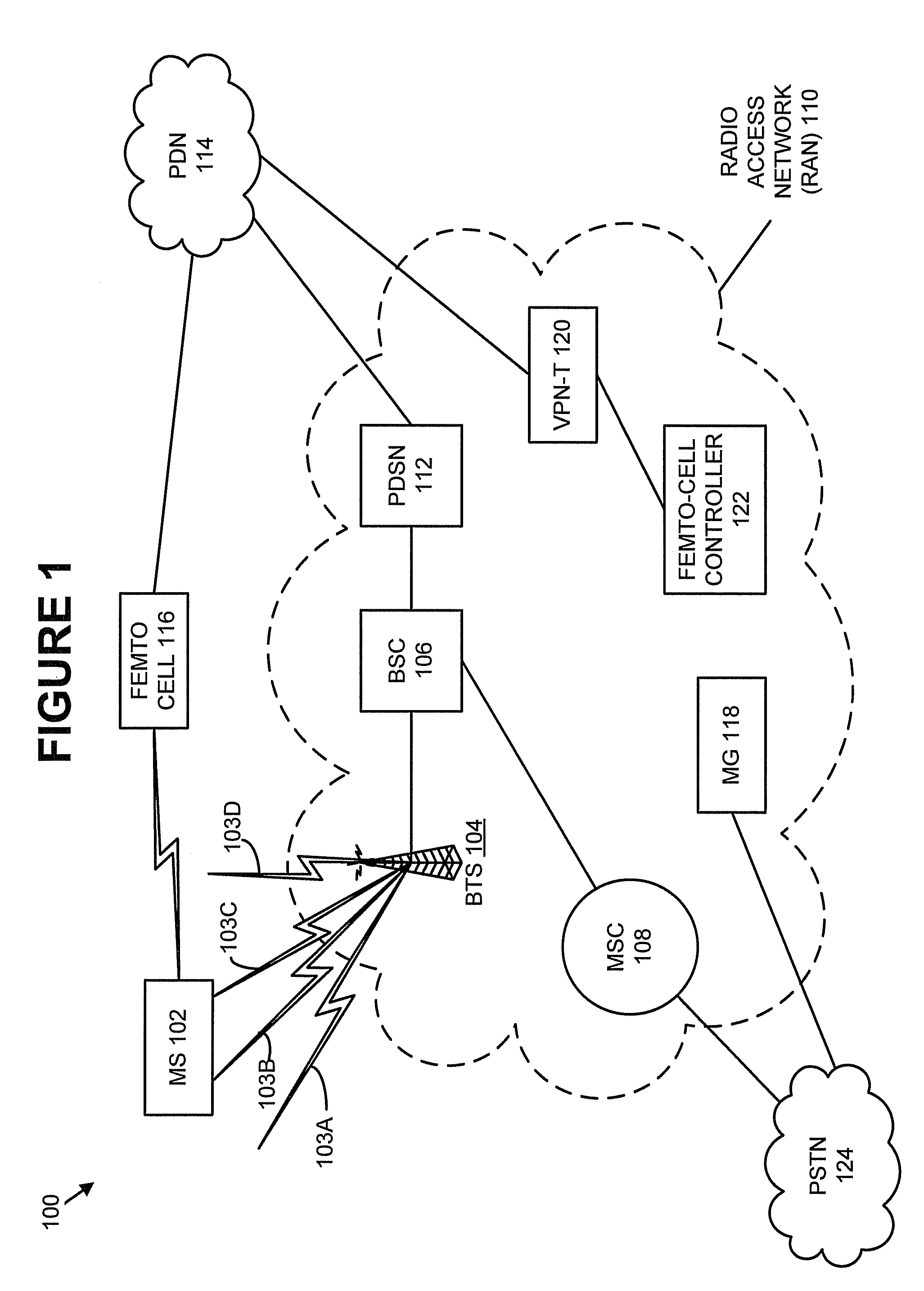
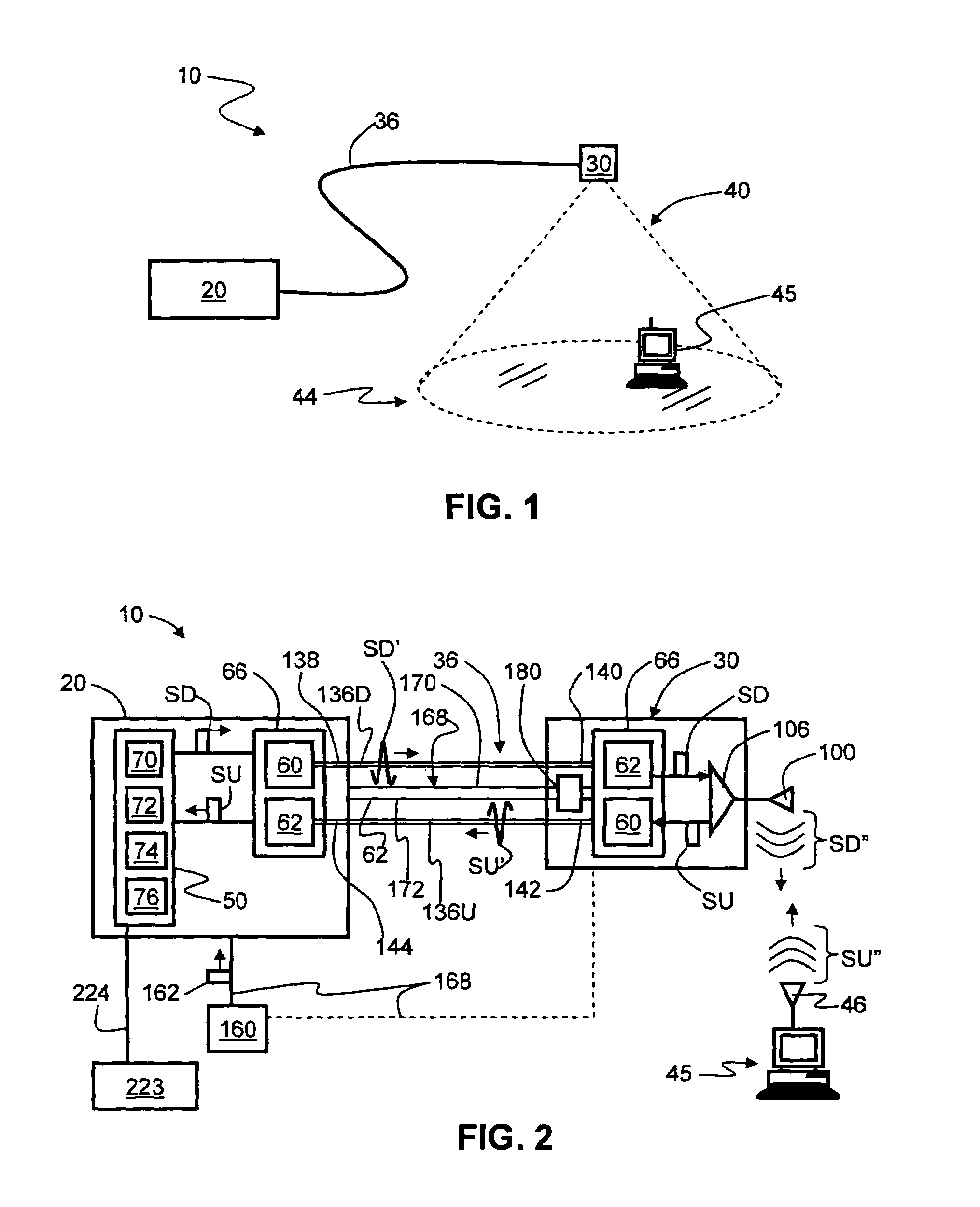
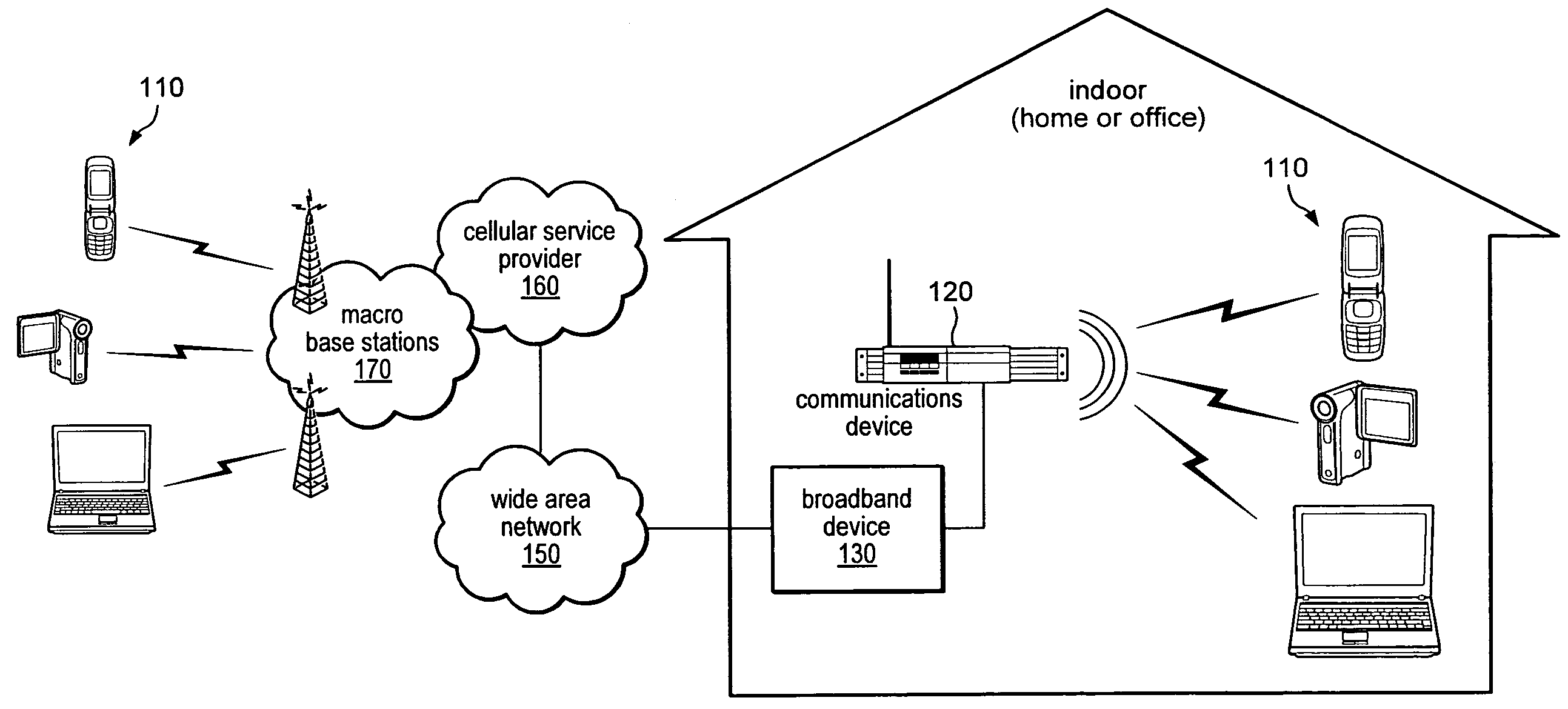
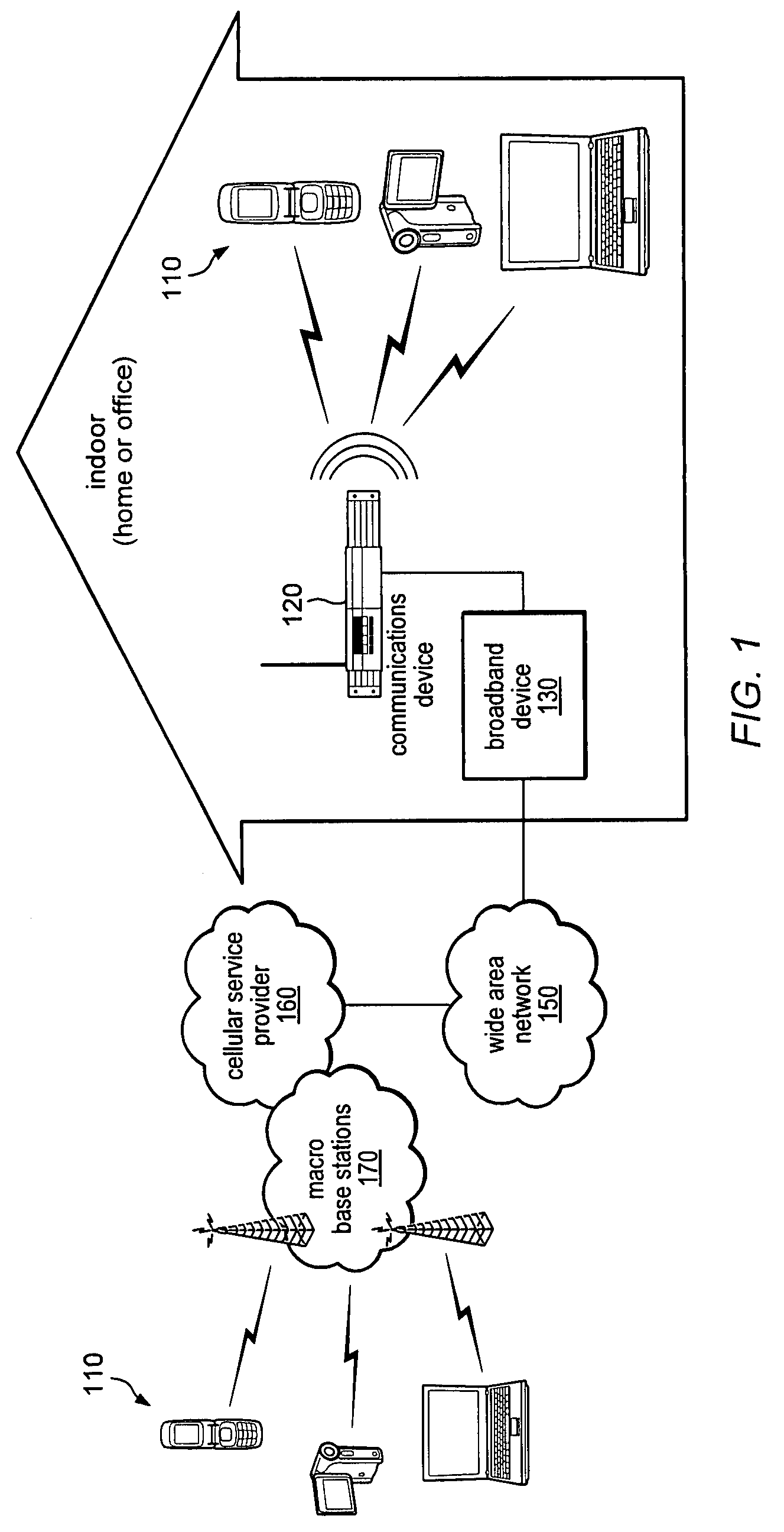
Interworking gateway for mobile nodes
Systems and methods are provided that allow inter-working between communication networks for the delivery of service to mobile nodes. A gateway is provided that communicates with a femto cell to extend service to an area that otherwise does not receive coverage from a service provider. The femto cell is a small scale base station used to provide coverage over a small area (such as a home or business), and connect to a home or enterprise network. The femto cell provides service for a mobile node and a gateway permits communication over a broadband network. The gateway integrates the mobile nodes connecting via a femto cell into the service provider's network. The gateway also allows provisioning of services and applications, control of service levels, and provides seamless handoffs to macro base stations and other types of access technologies such as Wi-Fi.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
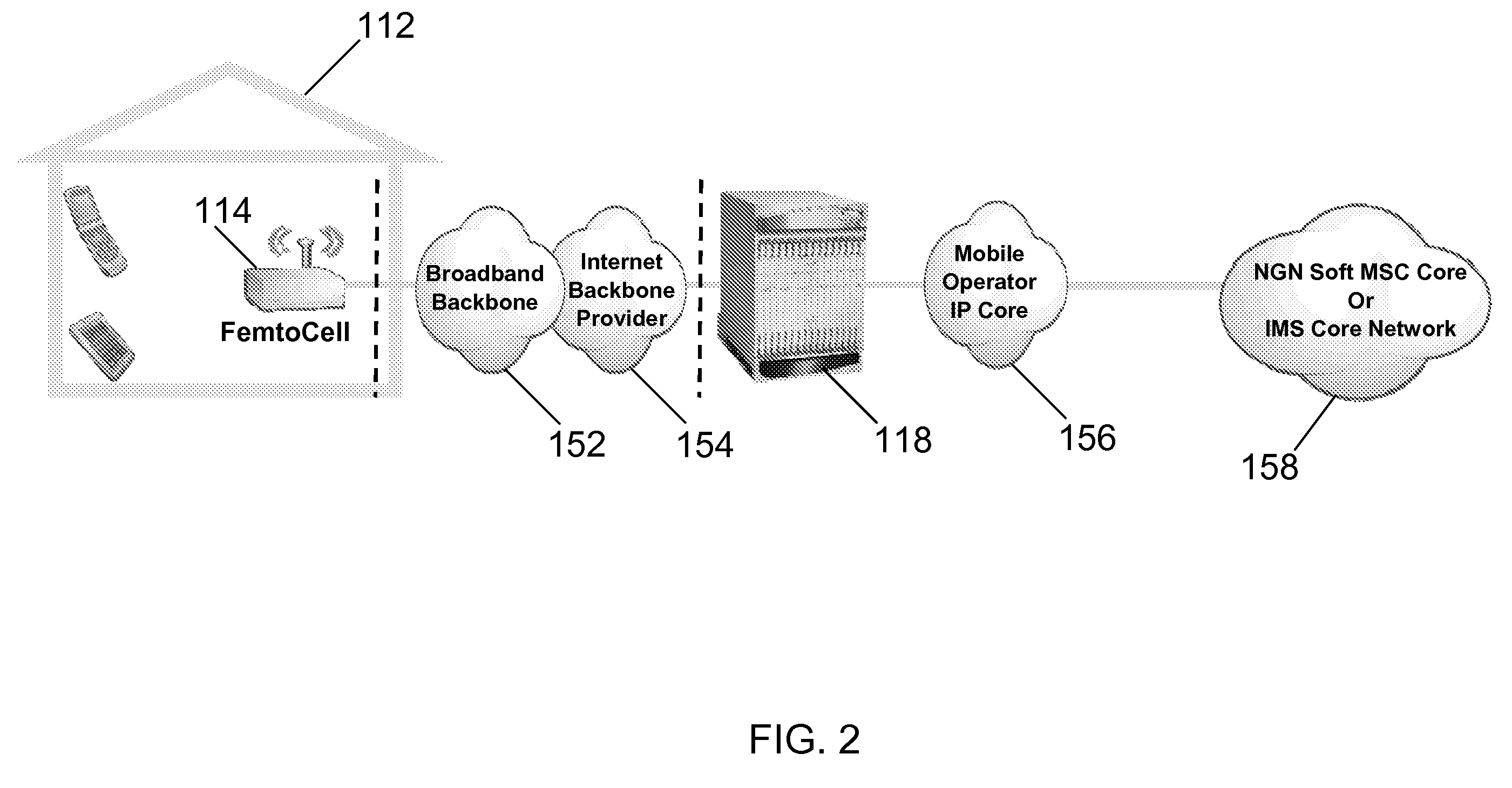
WiMAX ACCESS POINT NETWORK WITH BACKHAUL TECHNOLOGY
ActiveUS20080090575A1Low costLarge capacityPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementTransceiverModem device
A WiMAX network and communication method, the network including a plurality of WiMAX nodes deployed in micro or pico cells for providing access service to a plurality of mobile subscribers, a plurality of these nodes being arranged in a cluster, one of the nodes in each cluster being a feeder node coupled to a core network, the modes in each cluster being couple for multi-hop transmission to the feeder node. According to a preferred embodiment, each node includes a transceiver with associated modem, an antenna arrangement coupled to the modem and arranged for multiple concurrent transmissions, and a MAC controller for controlling the transceiver, modem and antenna arrangement for providing both access and backhaul communication.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
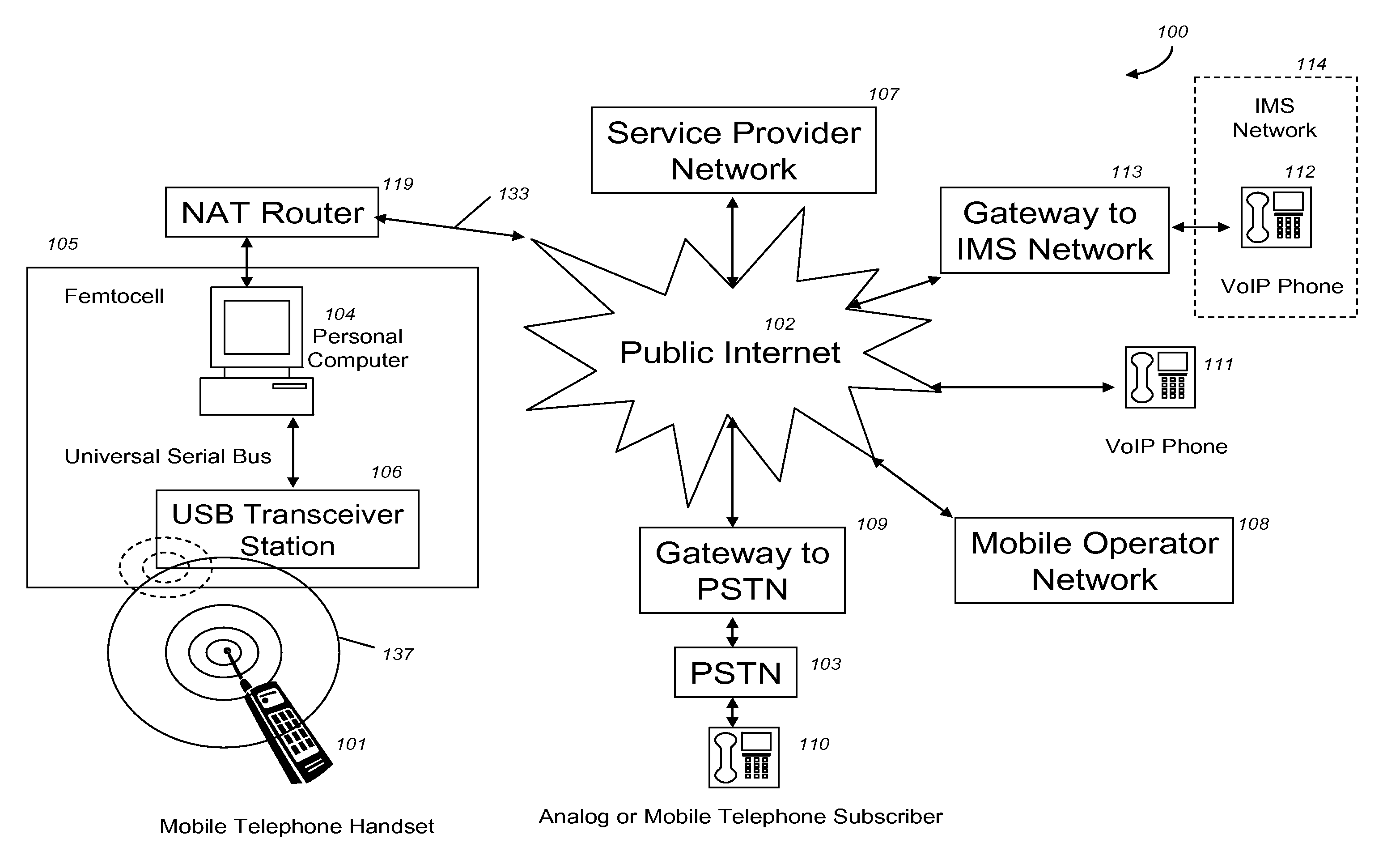
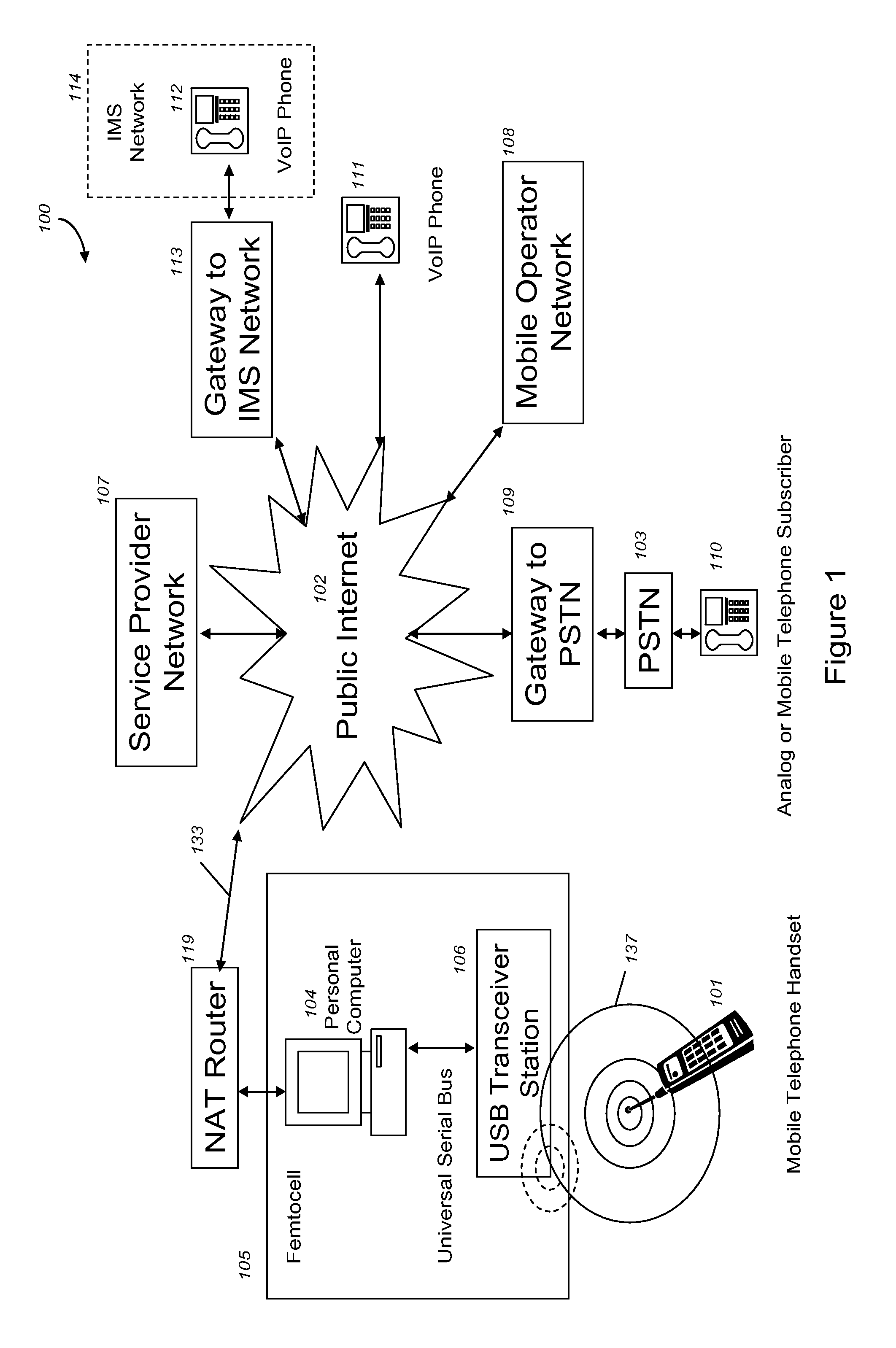
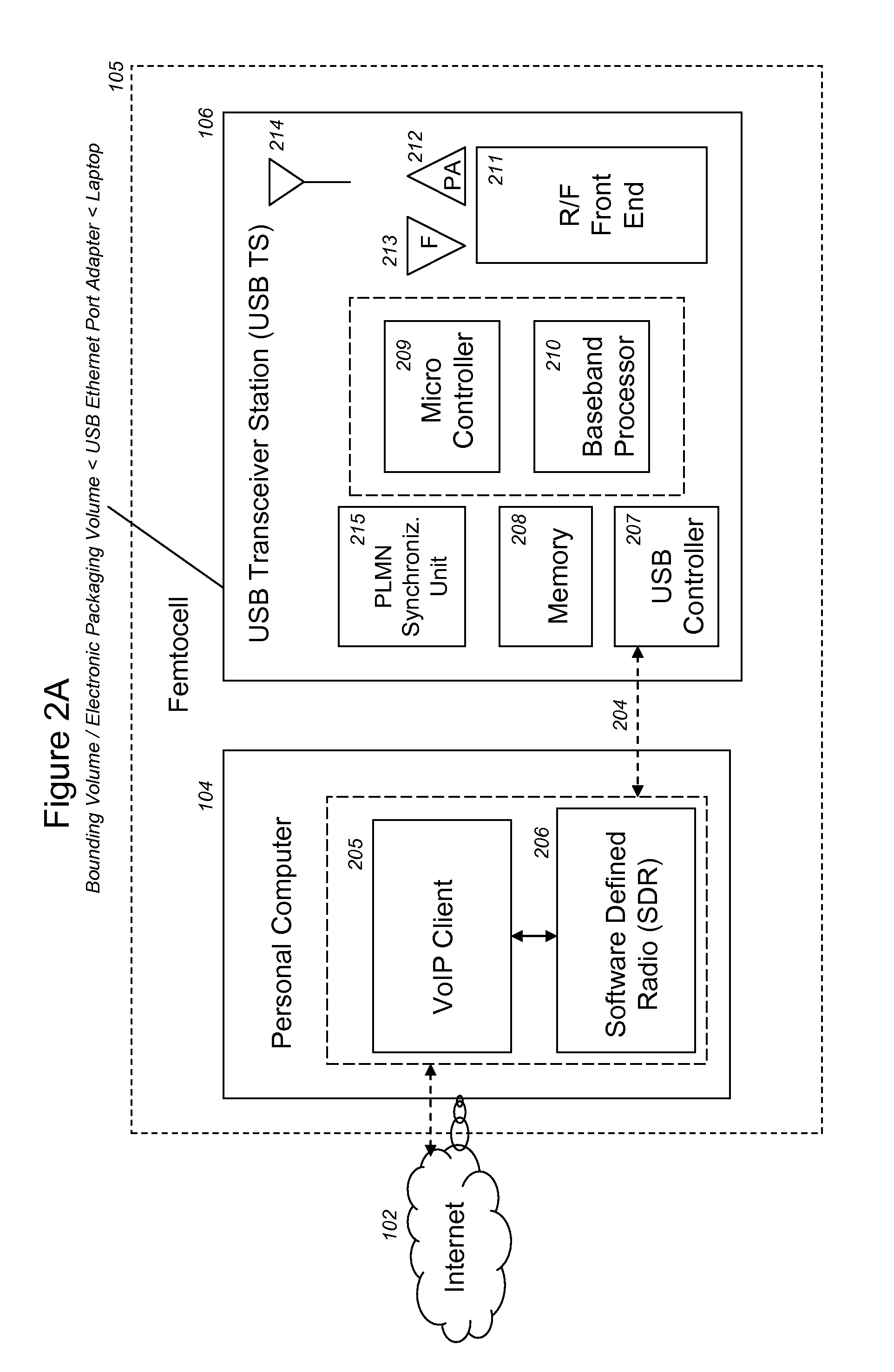
VoIP Enabled Femtocell with a USB Transceiver Station
InactiveUS20080244148A1High quality audioLow costNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentMicrocontrollerRF front end
Telephone calls between a mobile station (MS) and the mobile network or PSTN are routed through the Internet via VoIP using a femtocell, as opposed to the traditional macrocellular network. The femtocell can comprise a USB Transceiver Station that is connected to a personal computer through a universal serial bus port, which provides both power and a multi-megabit per second connection between the personal computer and the USB transceiver station. The USB transceiver station can comprise a microcontroller to manage signaling between the RF front end / baseband processor and the personal computer, as well as a precise timing mechanism to assist the synchronization of femtocell timing with the surrounding macrocellular network, if it is present. The USB transceiver station can have a compact form factor that that facilitates a high degree of portability by the subscriber, such as being readily attachable to their keychain.
Owner:SMALL CELL INNOVATIONS
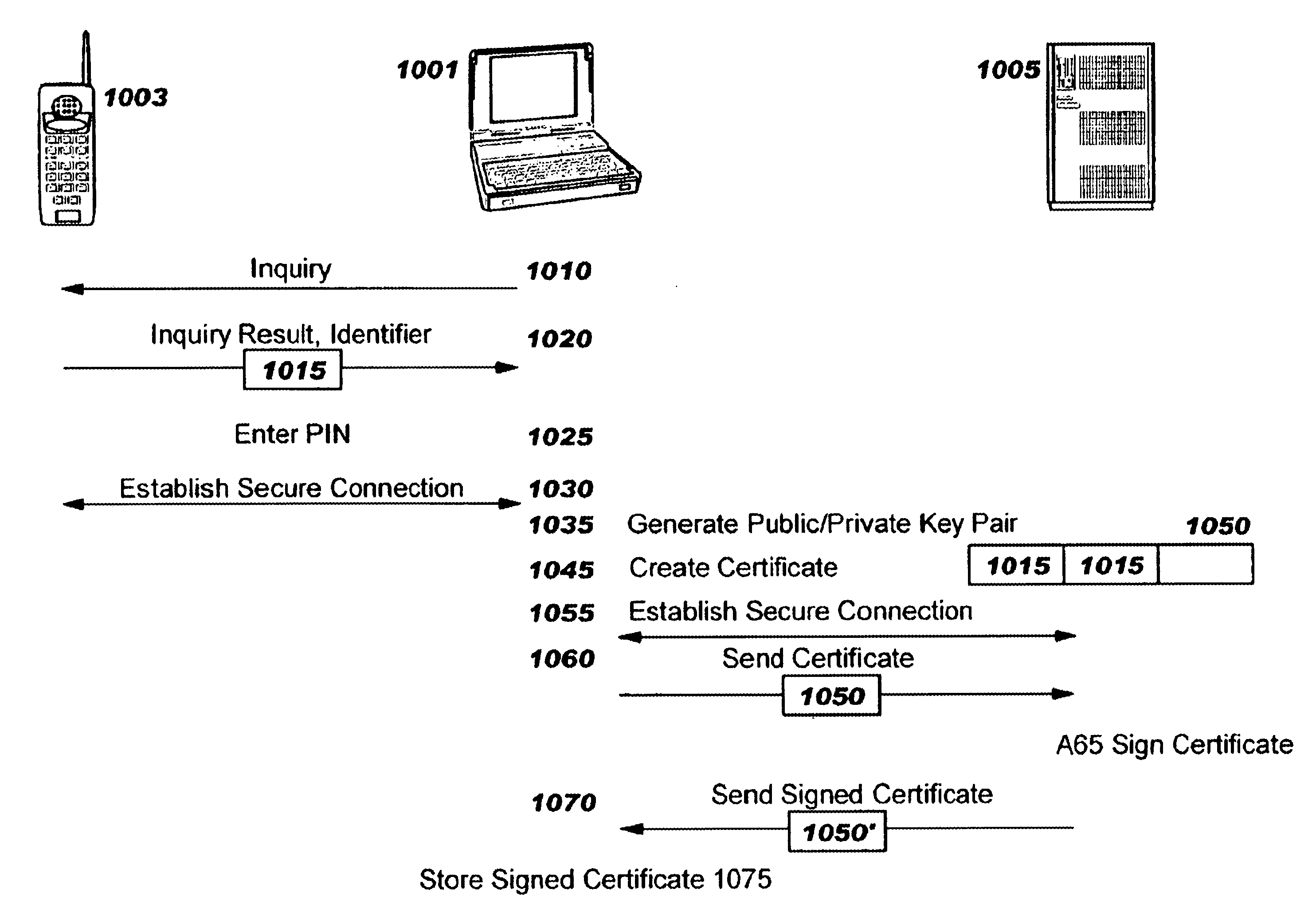
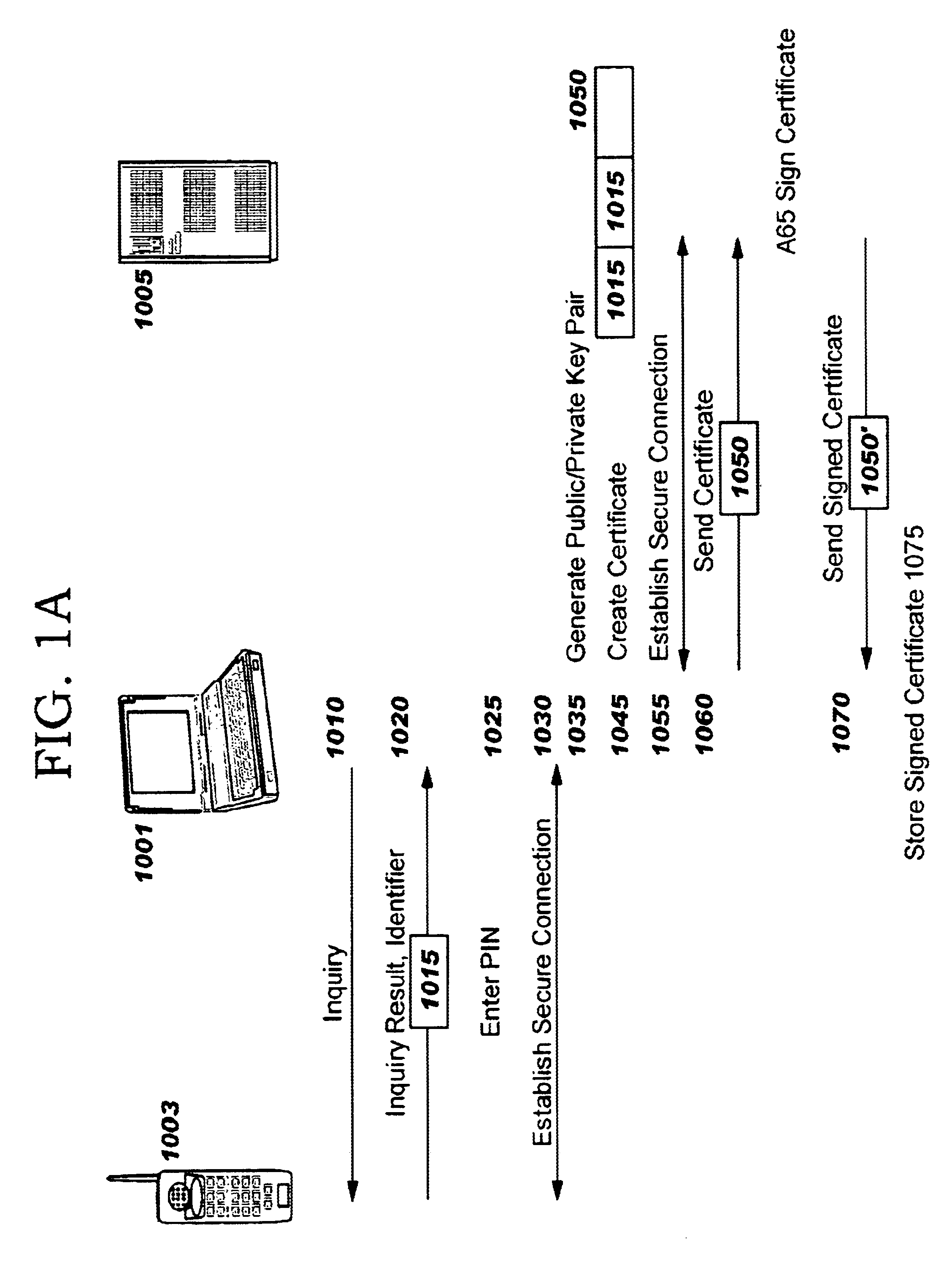
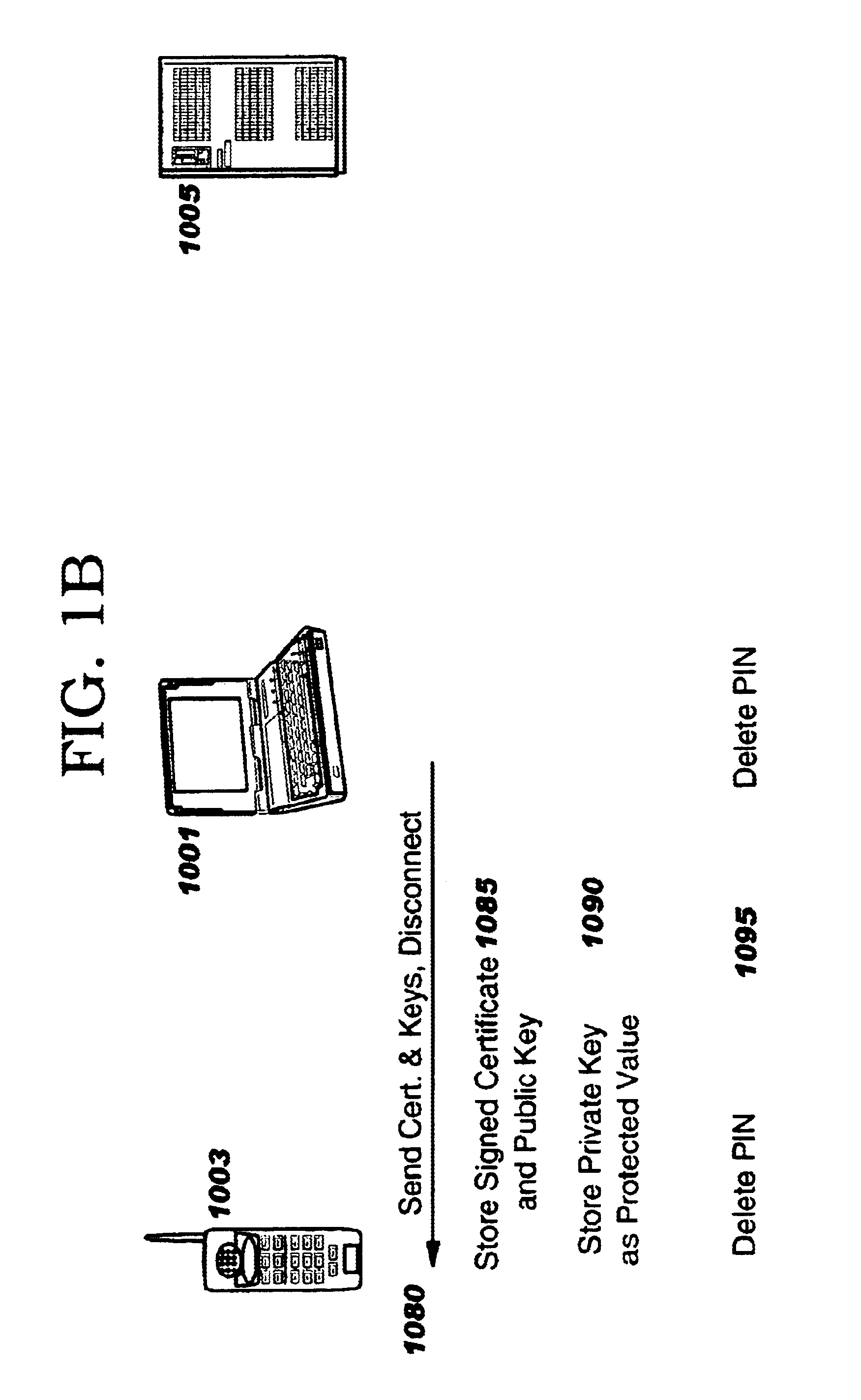
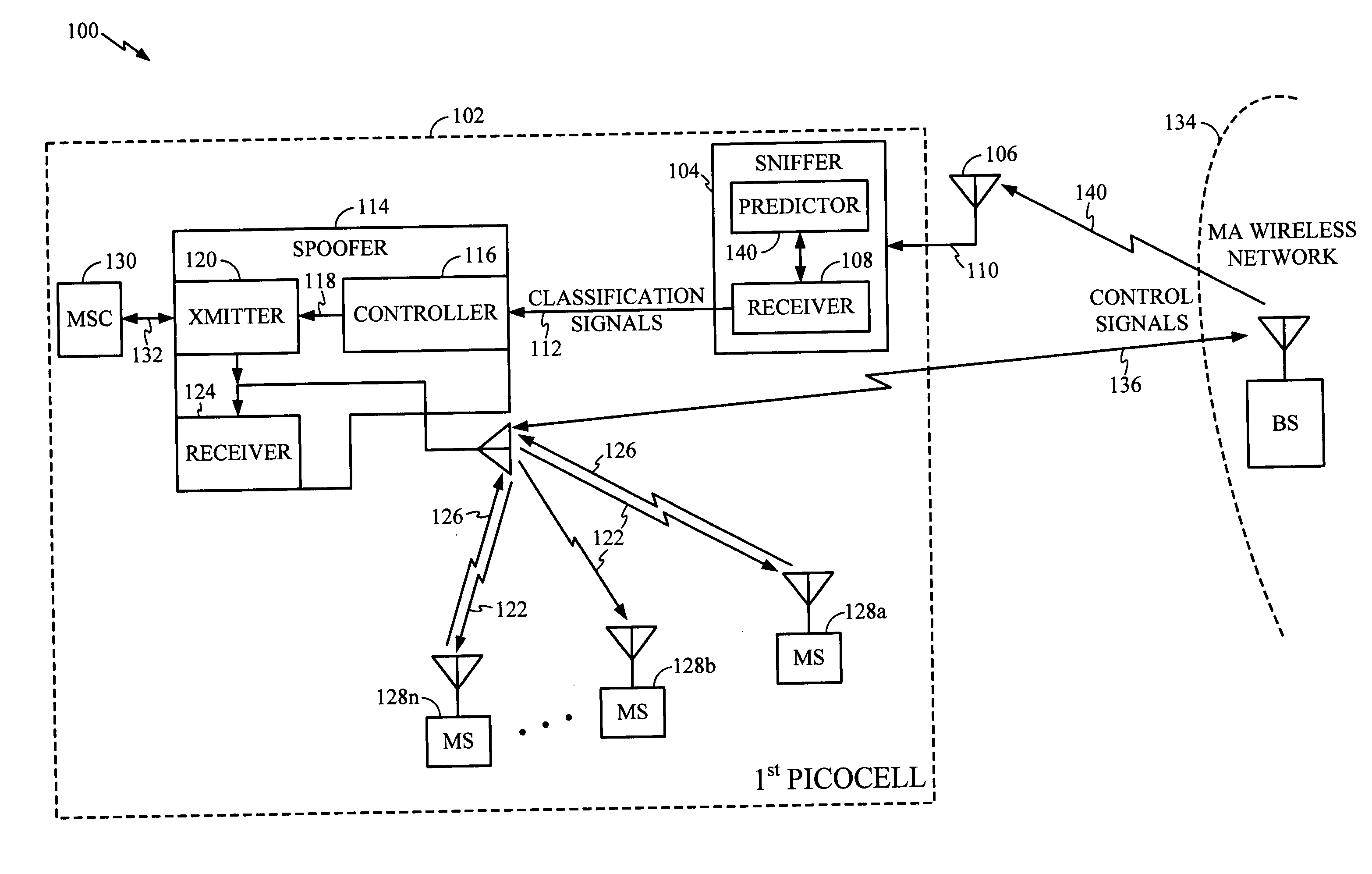
Method and apparatus for efficiently initializing secure communications among wireless devices
InactiveUS6886095B1Efficient administrationEliminating inflexibilityUser identity/authority verificationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSecure communicationRadio networks
A method and system for efficiently establishing secure communications between mobile devices in a radio network. The present invention utilizes public key cryptography and unique hardware identifiers to enable authorizations for access to wireless networks, such as picocells. The present invention prevents the mobile user from maintaining a plurality of secrets such as user identifier / password pairs, PINs, or encryption keys, for access to each device to which he might require access.
Owner:IBM CORP
Capacity Optimisation in a Cellular Wireless Network
ActiveUS20090046665A1Network topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSignal qualityInterference ratio
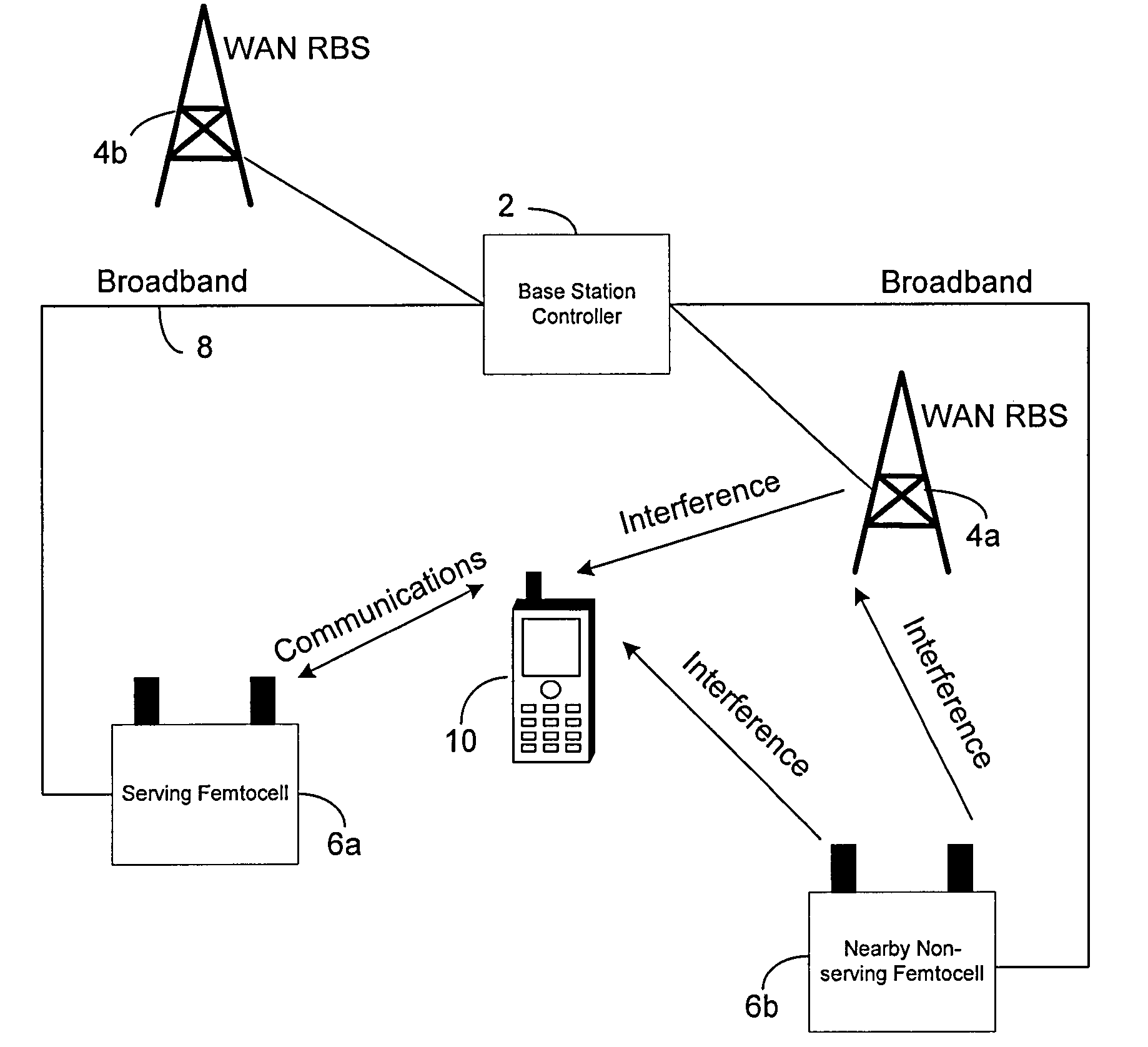
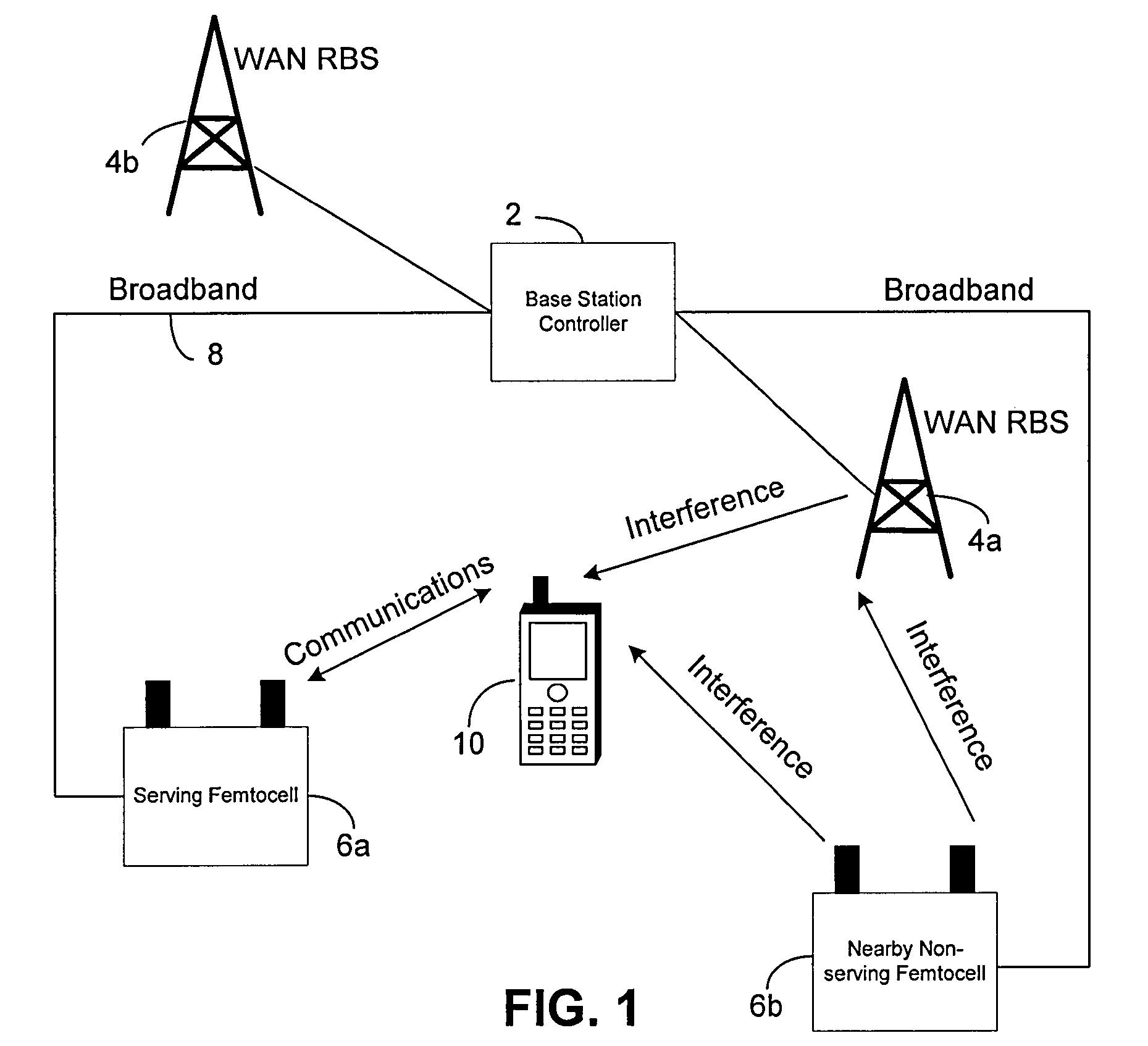
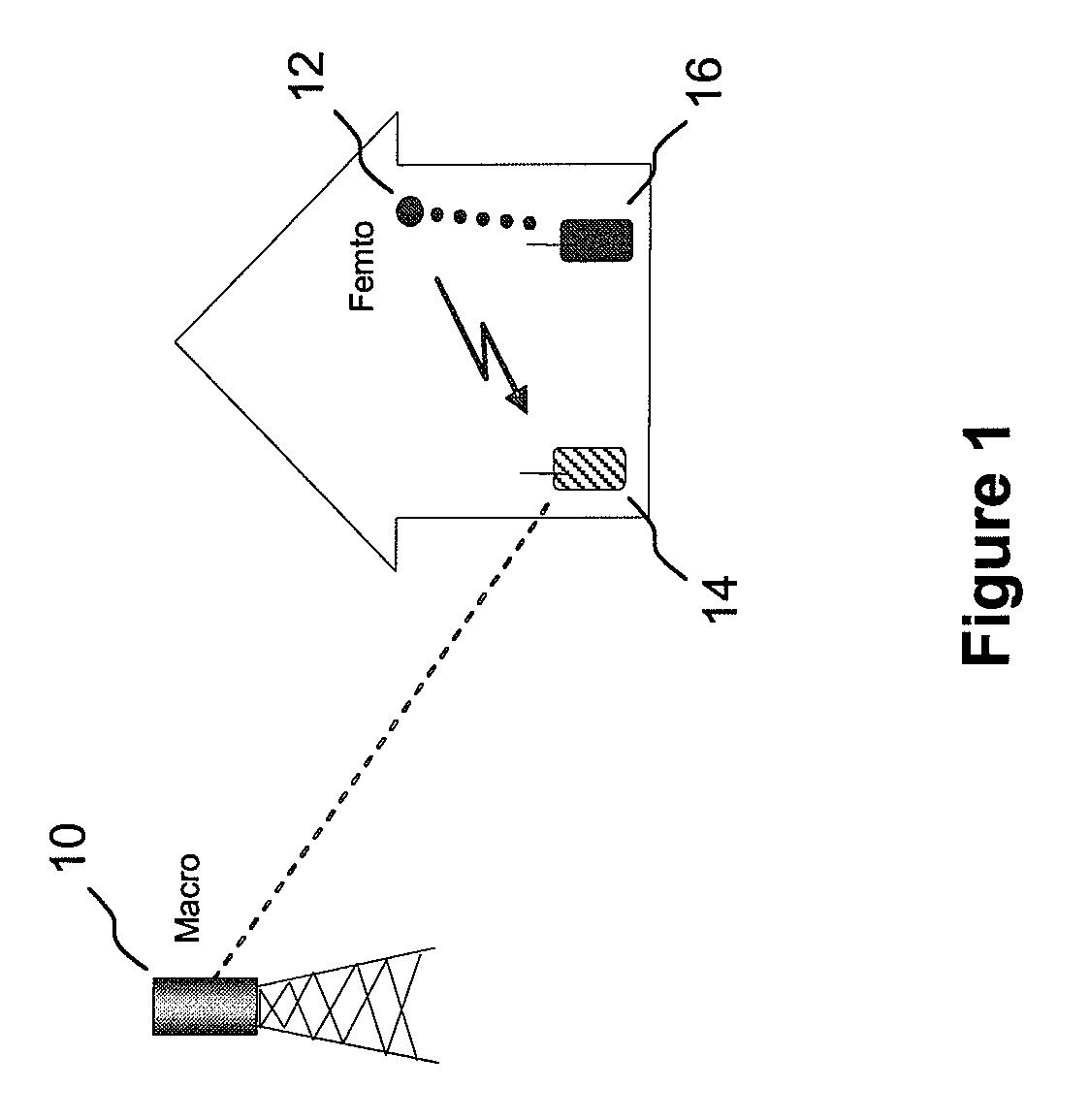
Embodiments of the invention relate to cellular wireless networks and are particularly suited to networks including different types of base stations. So-called femtocell base stations are typically deployed within a subscriber's premises and operate at low transmit power, providing a very limited area of wireless coverage. A femtocell is typically deployed within the area of wireless coverage of a conventional macrocell type of base station, and if handover from a macrocell is performed on the basis of the best signal to noise plus interference ratio, a connection is likely to be transferred to another macrocell rather than to a femtocell. However, in view of the low density of user equipments capable of transceiving with a femtocell, the femtocell could potentially provide a greater data rate to the user equipment terminal than is possible with a macrocell. A cellular wireless network according to an embodiment of the invention employs a method of handover algorithm that has dependence on both a measure of signal quality such as signal to noise plus interference ratio and on a measure of loading of the base station. The handover algorithm is thereby able to weight selection of a base station on the basis of data rate, and intelligently engineer handover to a femtocell.
Owner:APPLE INC
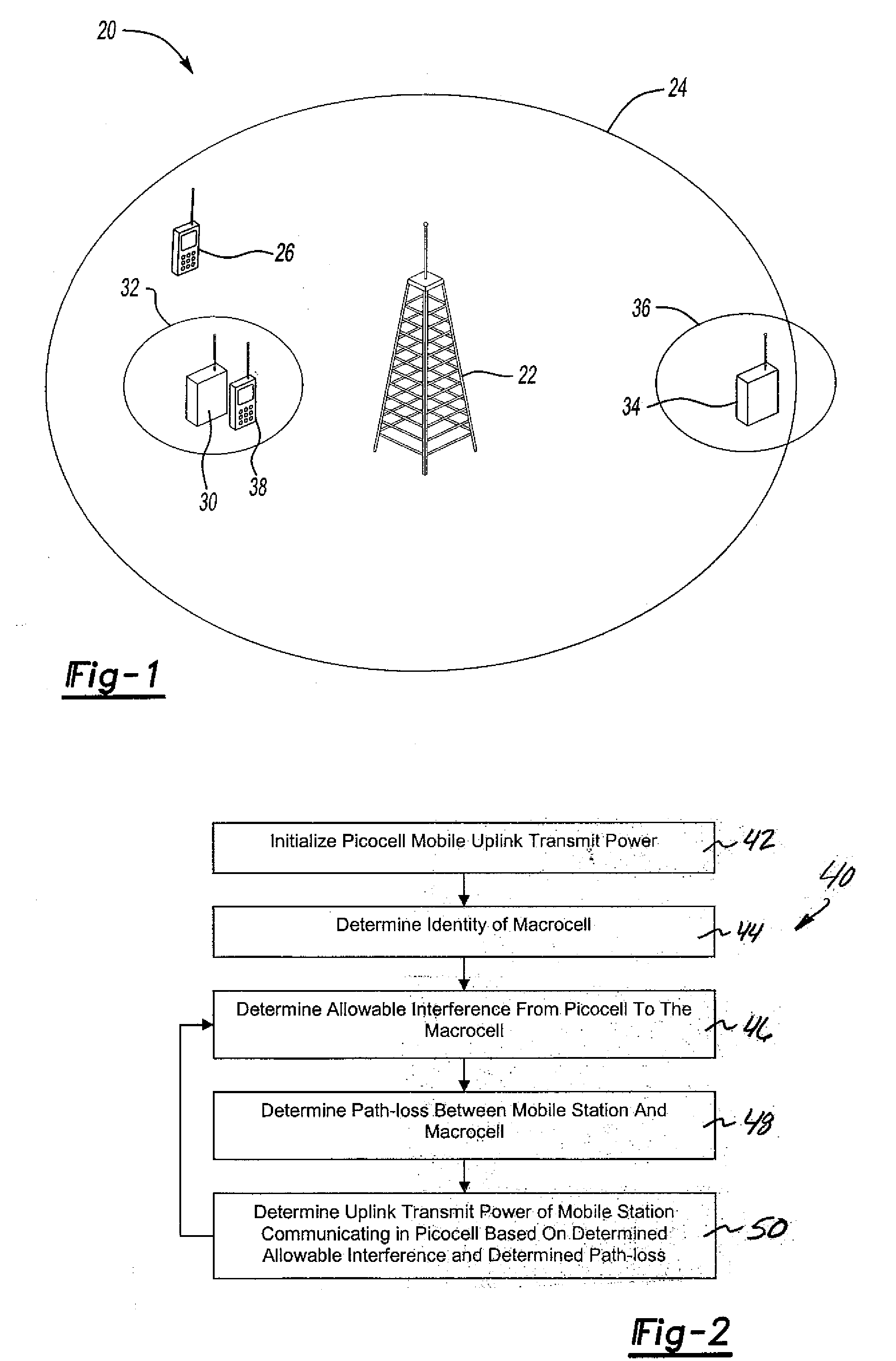
Controlling uplink power for picocell communications within a macrocell
InactiveUS20080146154A1Power managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsTransmitted power
A method of communicating in a picocell within a macrocell includes automatically setting an uplink transmit power of a mobile station to avoid uplink interference between the picocell and the macrocell. A disclosed example includes determining an allowable interference from the picocell to the macrocell. A path-loss between a mobile station and a macrocell is determined. An uplink transmit power of the mobile station for communicating in the picocell is determined based upon the determined allowable interference and the determined path-loss.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method and apparatus to manage femtocell traffic
Common techniques for processing cellular service uses a signal cellular tower, but these techniques are limited to the capacity of the single cellular tower. In contrast, a system employing an example embodiment of the invention increases ability to process cellular service by using an access point access network using resident wireless devices, referred to as a femtocell. A system supports communications of a resident and roaming device while employing the access point access network, based on database information, to support soft handoff between adjacent femtocells or from femtocell to cell tower and vice-versa. As a result, the system enables the resident and roaming devices to have seamless transitions between the cellular access network and the access point access network. Thus, the access point access network supplements cellular access networks and can provide cellular service regardless of the capacity of the cellular tower.
Owner:TELLABS VIENNA
System and Method for Co-Channel Interference Measurement and Managed Adaptive Resource Allocation for Wireless Backhaul
ActiveUS20120236731A1Reduce disadvantagesReduce co-channel interferenceError preventionTransmission systemsResource blockPublic resource
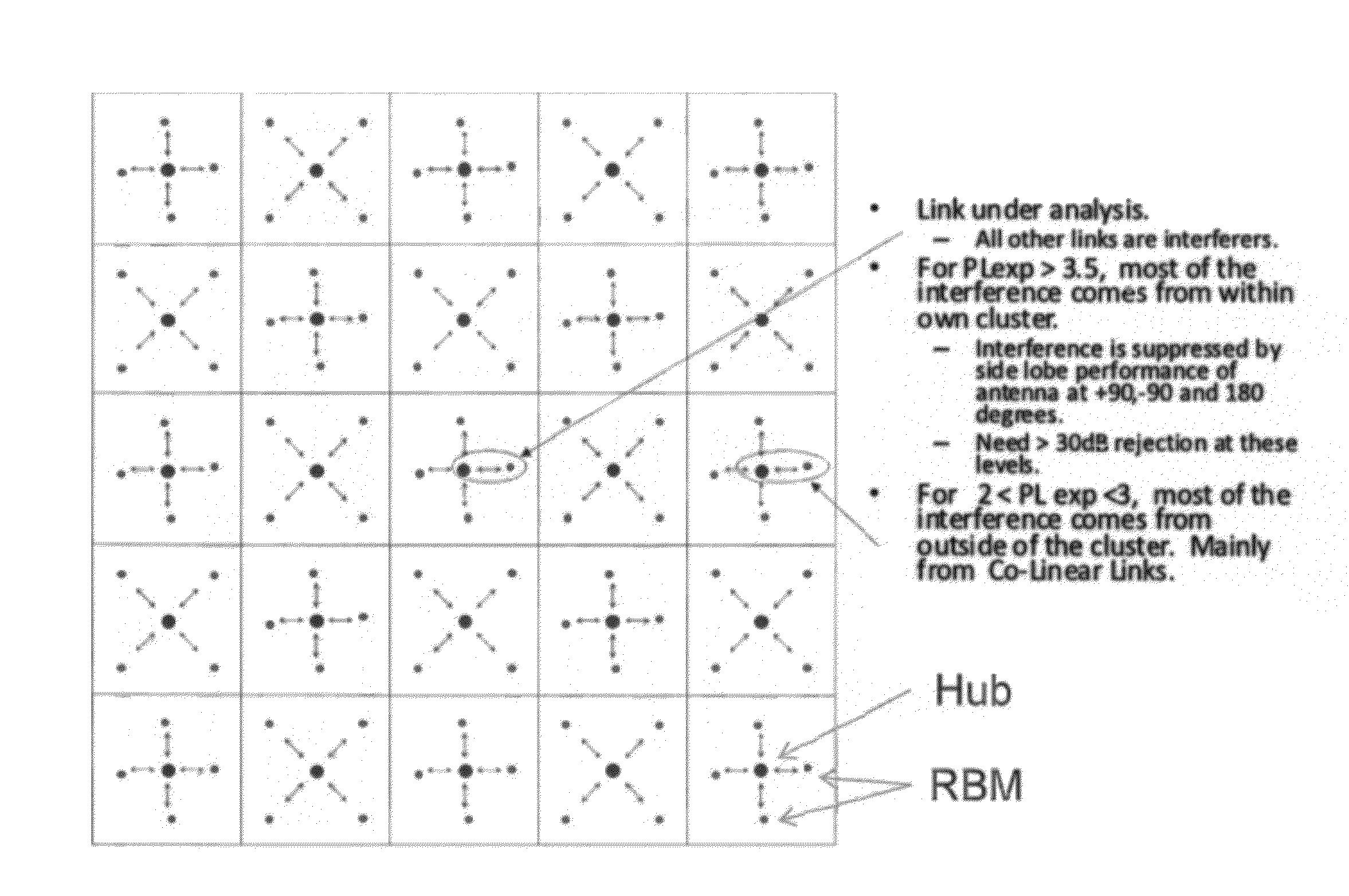
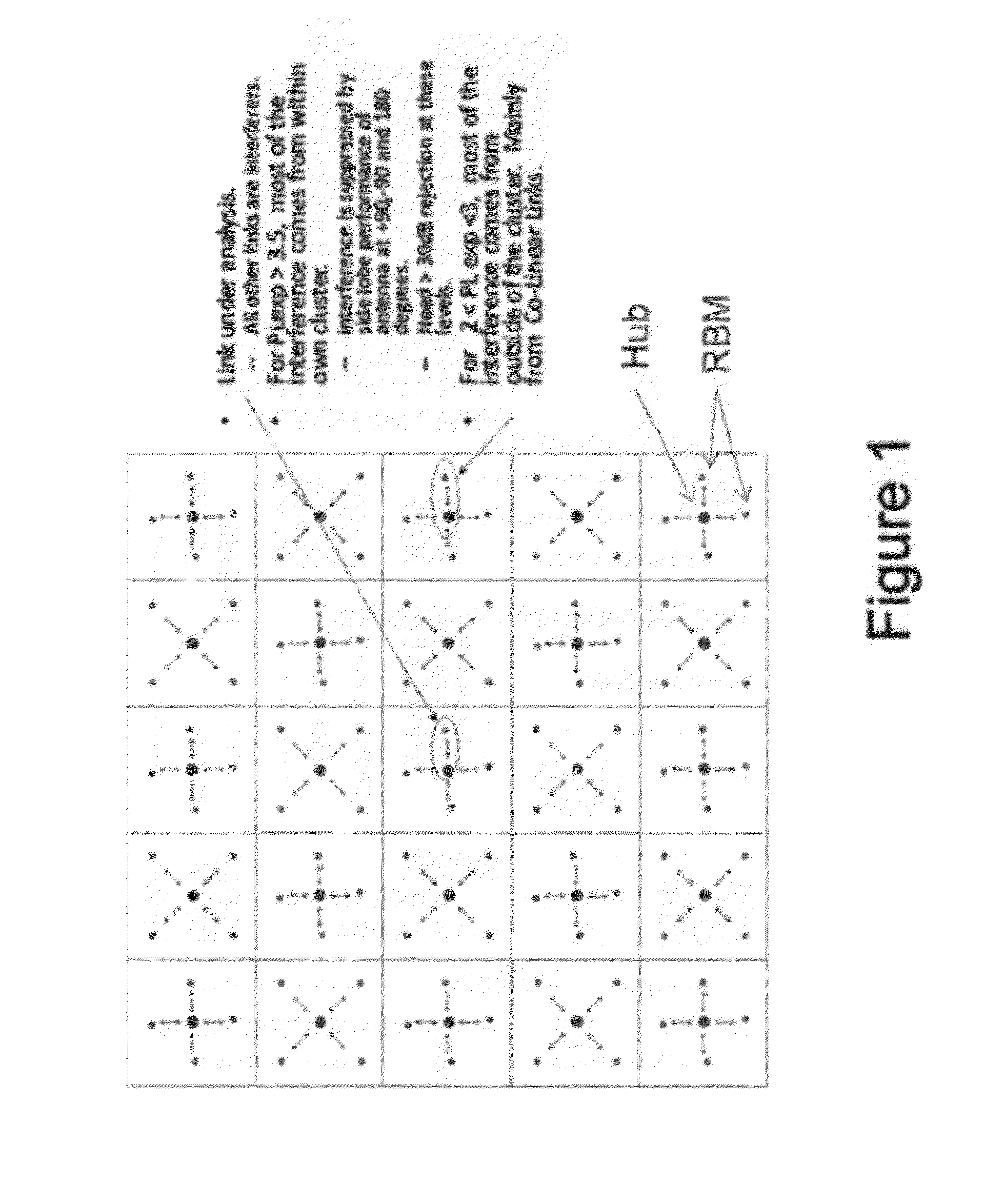
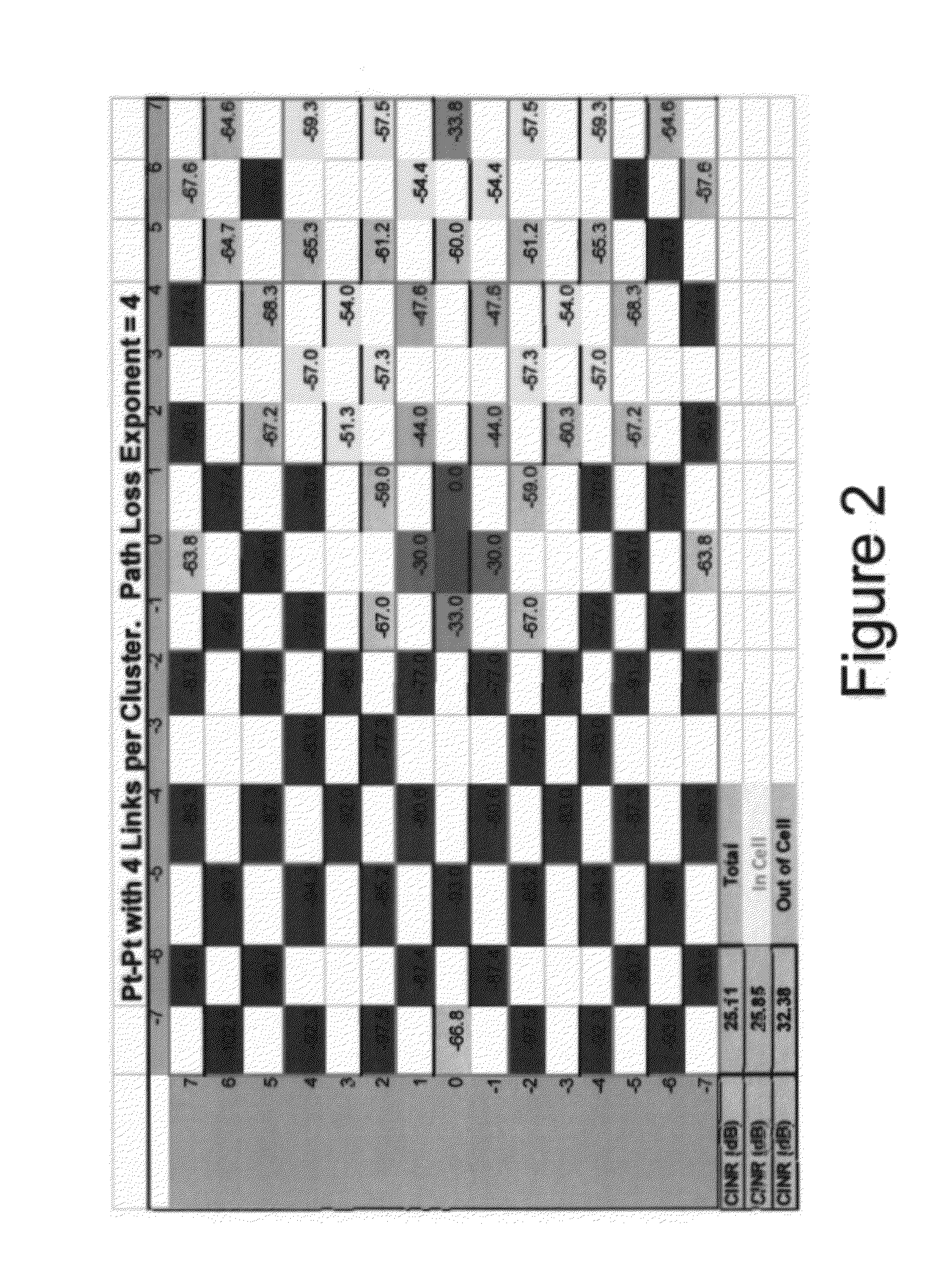
A system, method, and software are provided for measuring co-channel interference in a wireless network with particular application for management of resource allocation for Non Line of Sight (NLOS) wireless backhaul in MicroCell and PicoCell networks. Given the difficulty of predicting the mutual interference between multiple links, DownLink and UpLink co-channel interference are characterized between each Hub and each Remote Backhaul Module Unit periodically during active service. Beneficially, the co-channel interference metrics are used as the basis for intelligently and adaptively managing network resources to substantially reduce interference and increase the aggregate data capacity of the network e.g. by grouping of interfering and / or non-interfering links, and managing resource block allocations accordingly, i.e. assigning common resource blocks preferentially to weakly interfering links or groups of links and allocating different resource blocks or orthogonal channels to strongly interfering links or groups of links.
Owner:BLINQ NETWORKS
Interworking gateway for mobile nodes
Systems and methods are provided that allow inter-working between communication networks for the delivery of service to mobile nodes. A gateway is provided that communicates with a femto cell to extend service to an area that otherwise does not receive coverage from a service provider. The femto cell is a small scale base station used to provide coverage over a small area (such as a home or business), and connect to a home or enterprise network. The femto cell provides service for a mobile node and a gateway permits communication over a broadband network. The gateway integrates the mobile nodes connecting via a femto cell into the service provider's network. The gateway also allows provisioning of services and applications, control of service levels, and provides seamless handoffs to macro base stations and other types of access technologies such as Wi-Fi.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
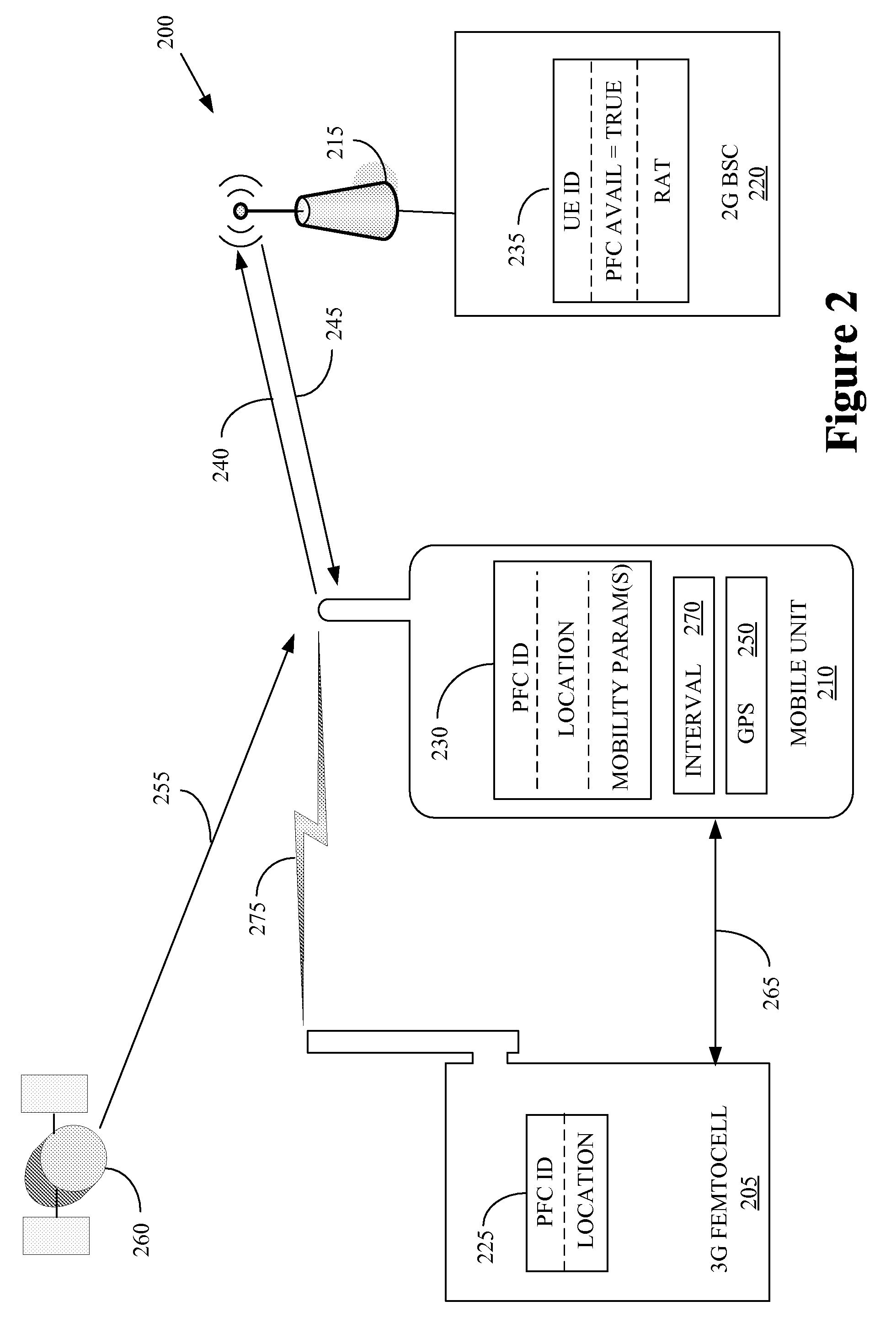
Methods and systems for temporarily modifying a macro-network neighbor list to enable a mobile station to hand off from a macro network to a femto cell
ActiveUS7929970B1Improve network efficiencyWaste of resourceNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsMobile station
Methods and systems are disclosed for temporarily modifying a macro-network neighbor list to enable a mobile station to hand off from a macro network to a femto cell. A method includes receiving a signal indicating that the mobile station detected coverage of a femto cell; after receiving the signal, adding the femto cell to the neighbor list, thereby enabling the mobile station to handoff to the femto cell; detecting that the mobile station completed handoff to the femto cell; and in response to detecting that the mobile station completed handoff to the femto cell, removing the femto cell from the neighbor list.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
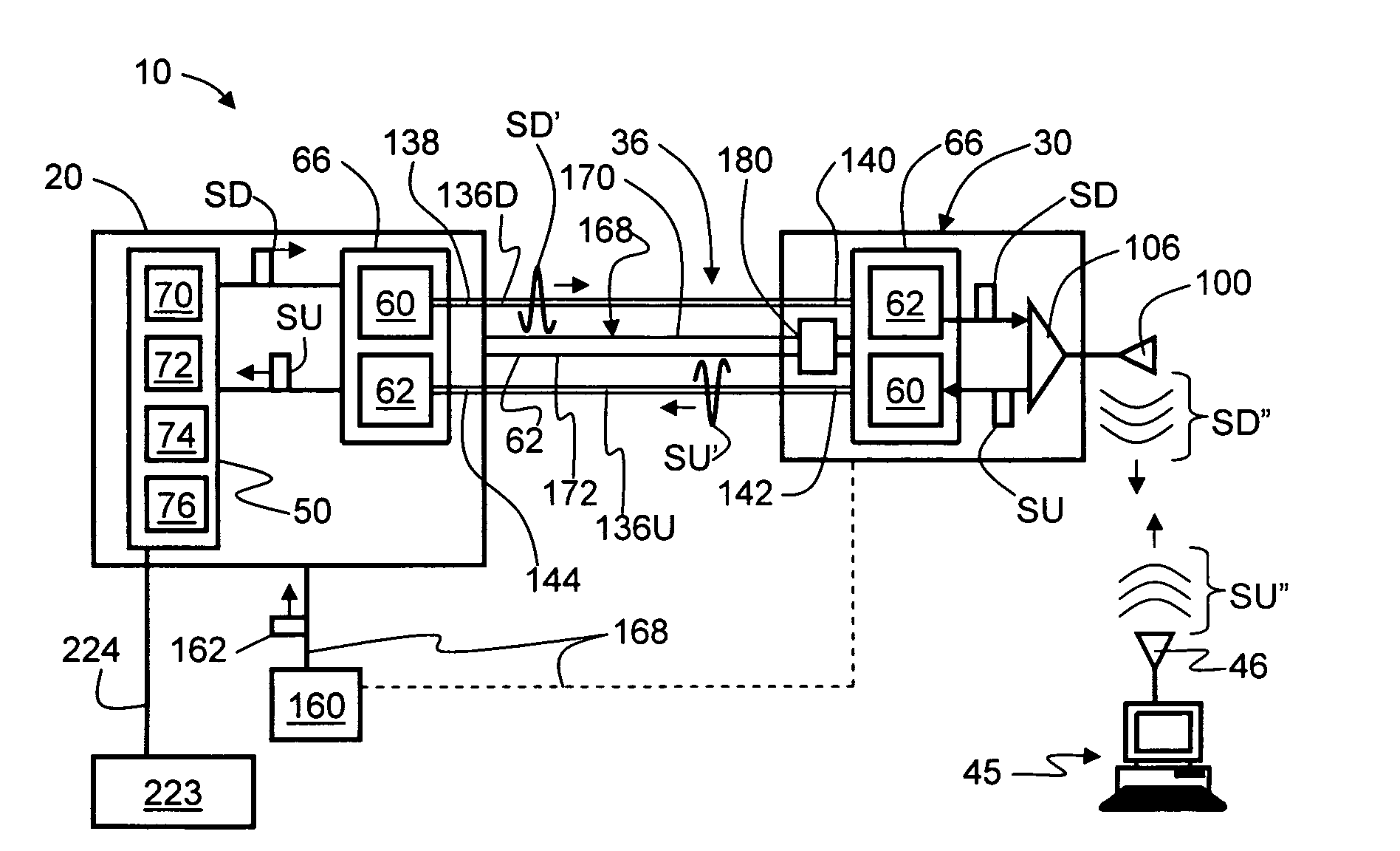
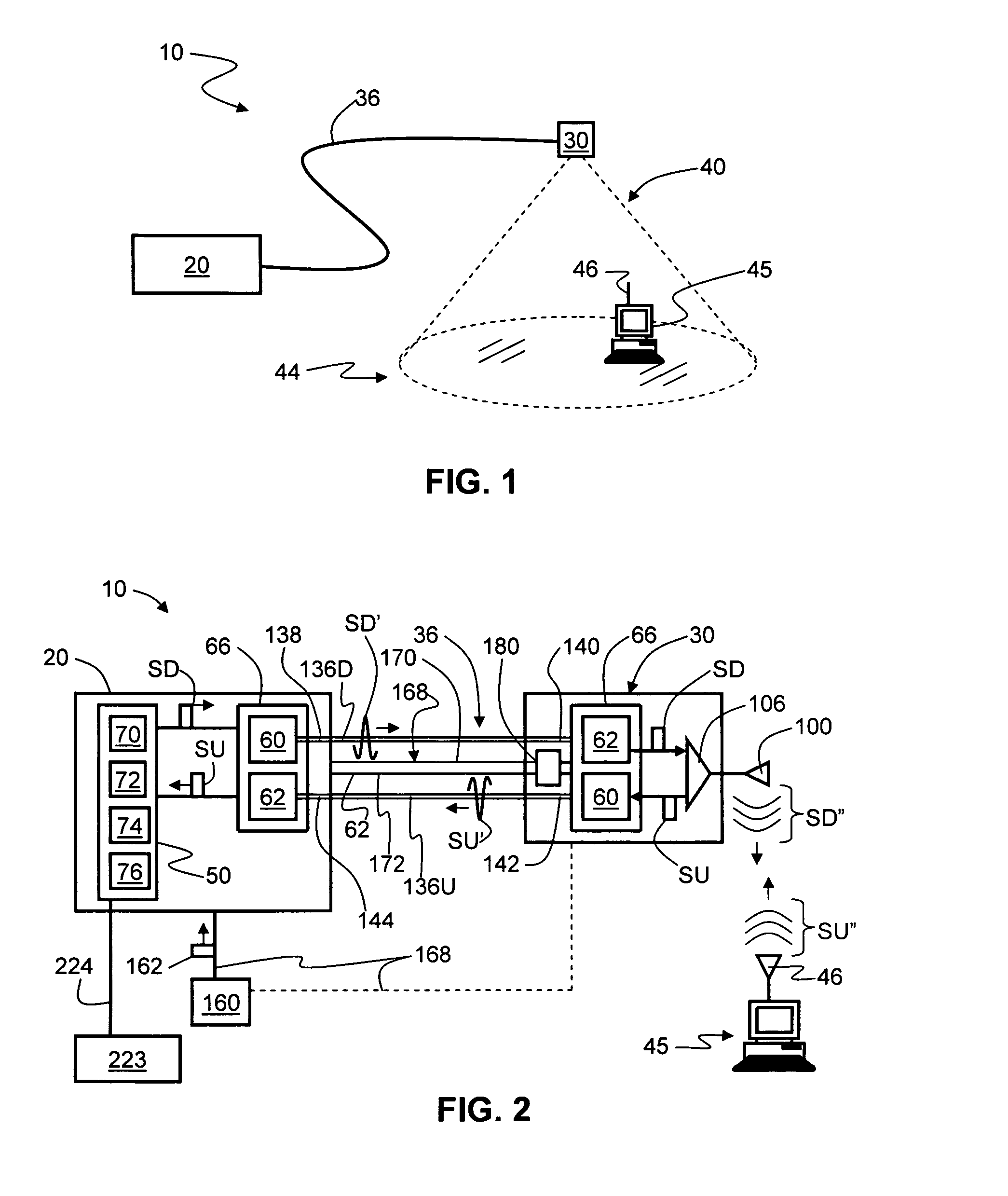
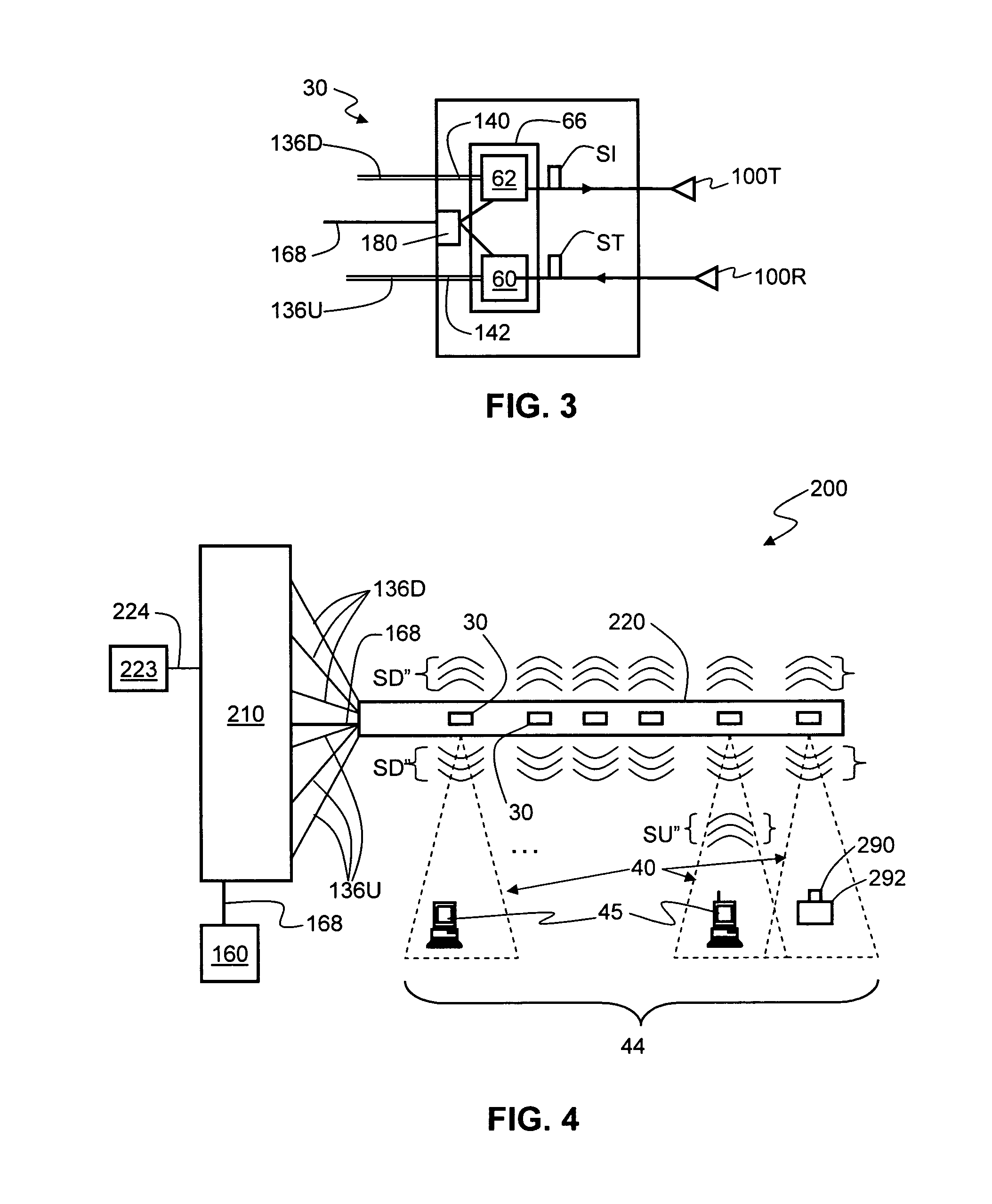
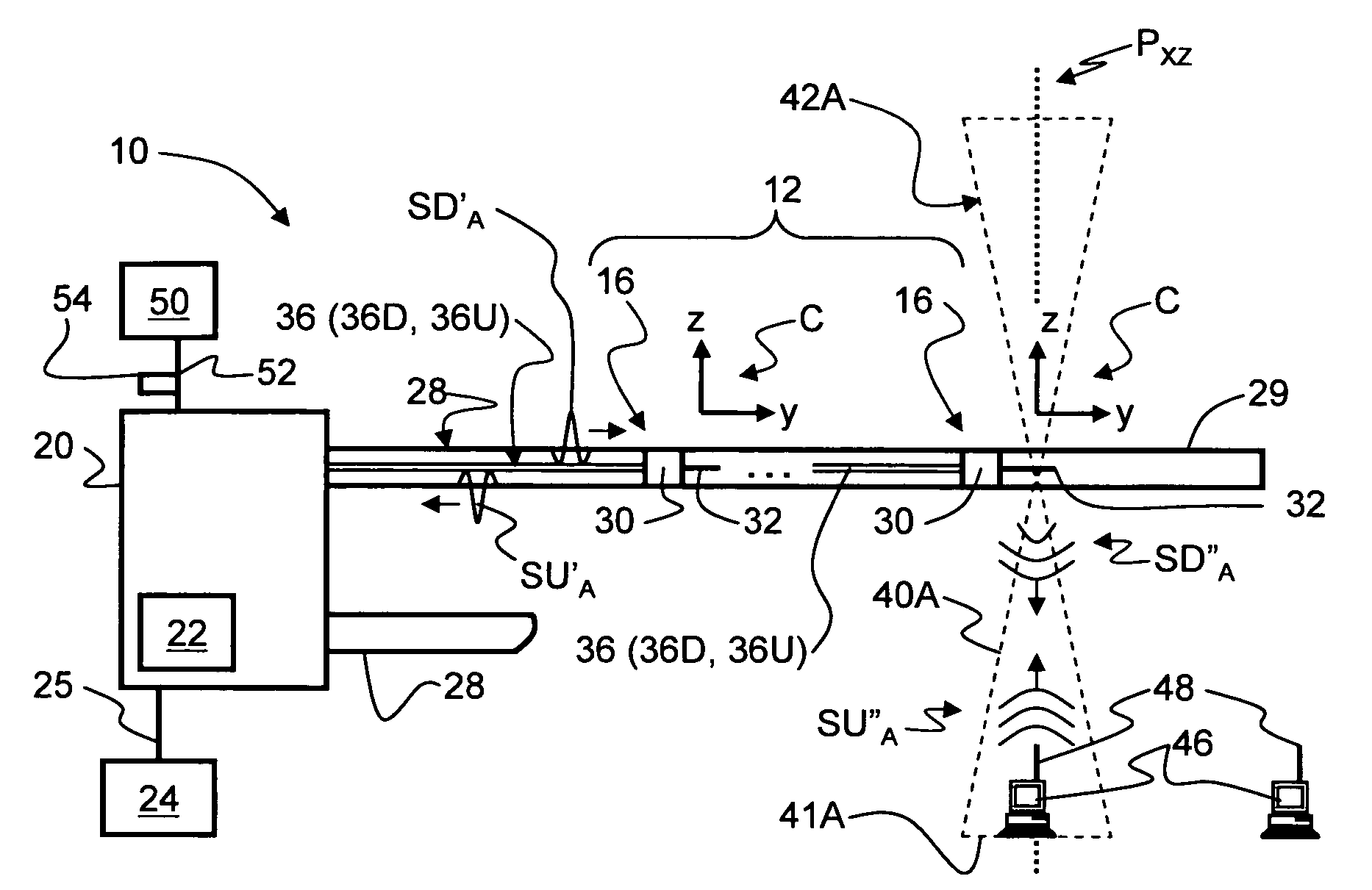
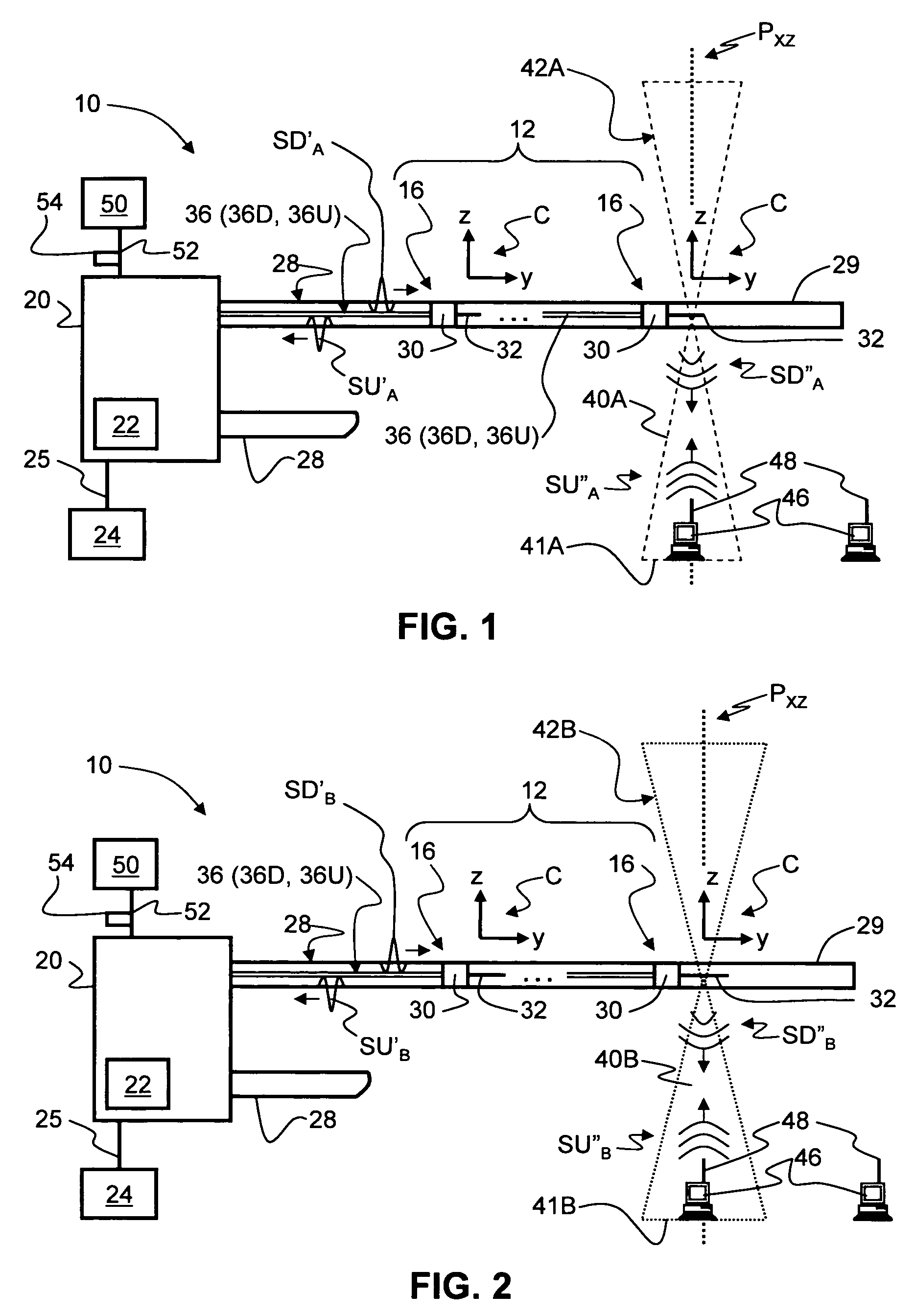
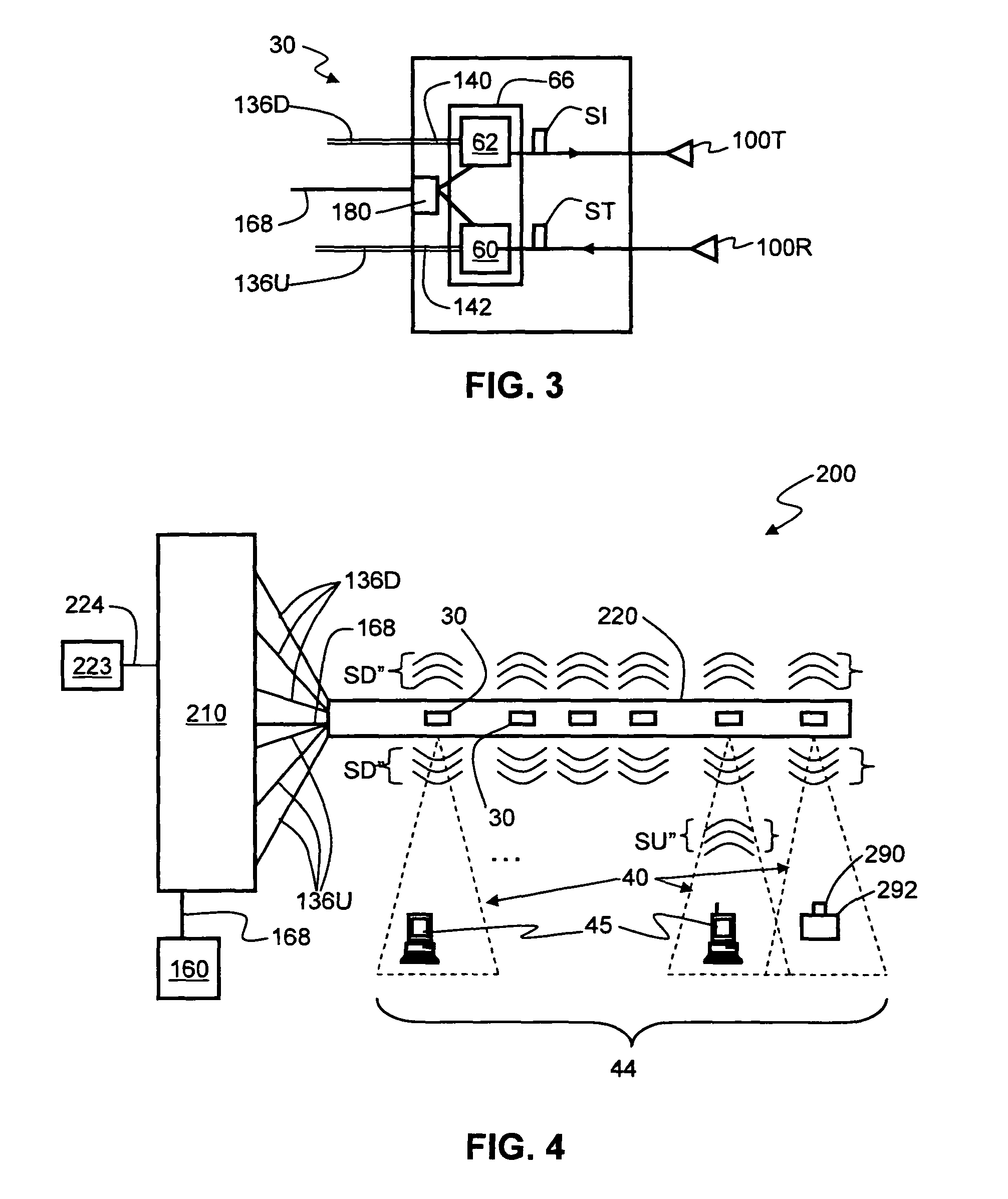
Radio-over-fiber (RoF) wireless picocellular system with combined picocells
A radio-over-fiber (RoF) wireless picocellular system adapted to form an array of substantially non-overlapping individual picocells by operating adjacent picocells at different frequencies is operated to form one or more combined picocells. The combined picocells are formed from two or more neighboring picocells by the central head-end station operating neighboring picocells at a common frequency. Communication between the central head-end station and a client device residing within a combined picocell is enhanced by the availability of two or more transponder antenna systems. Thus, enhanced communication techniques such as antenna diversity, phased-array antenna networks and multiple-input / multiple-output (MIMO) methods can be implemented to provide the system with enhanced performance capability. These techniques are preferably implemented at the central head-end station to avoid having to make substantial changes to the wireless picocellular system infrastructure.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Local network management of femtocells
InactiveUS20090253421A1Minimize the possibilityInterference minimizationSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork managementFemtocell
A system and method of minimizing signal interference within a wireless network is provided, wherein the wireless network includes a controller communicatively coupled to at least one femtocell, and the femtocell is operative to wirelessly transmit and receive data. A portable electronic device is used to collect signal environment data, and the collected signal environment data is analyzed. Based on the analyzed signal environment data, the at least one femtocell is commanded to alter at least one signal transmission characteristic.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
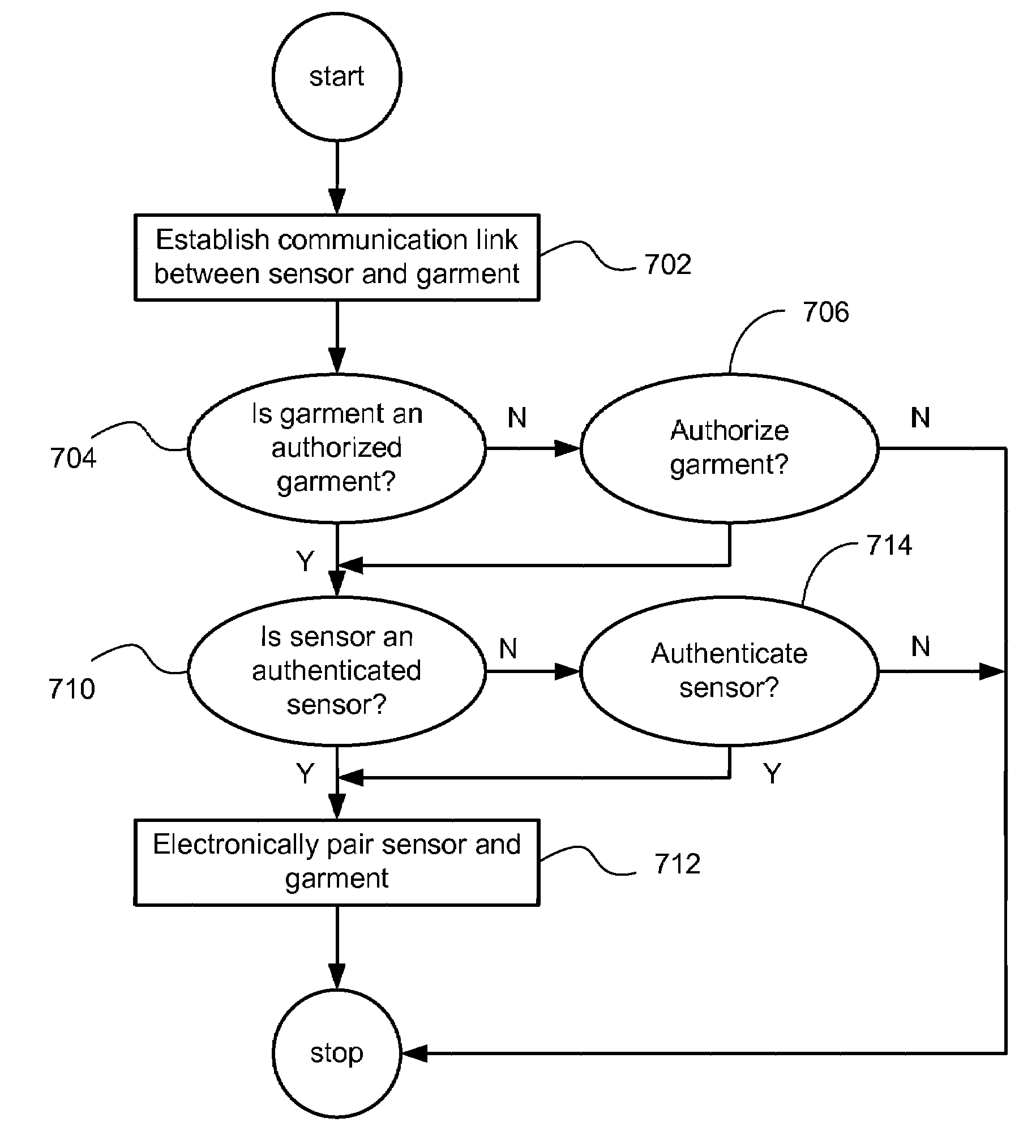
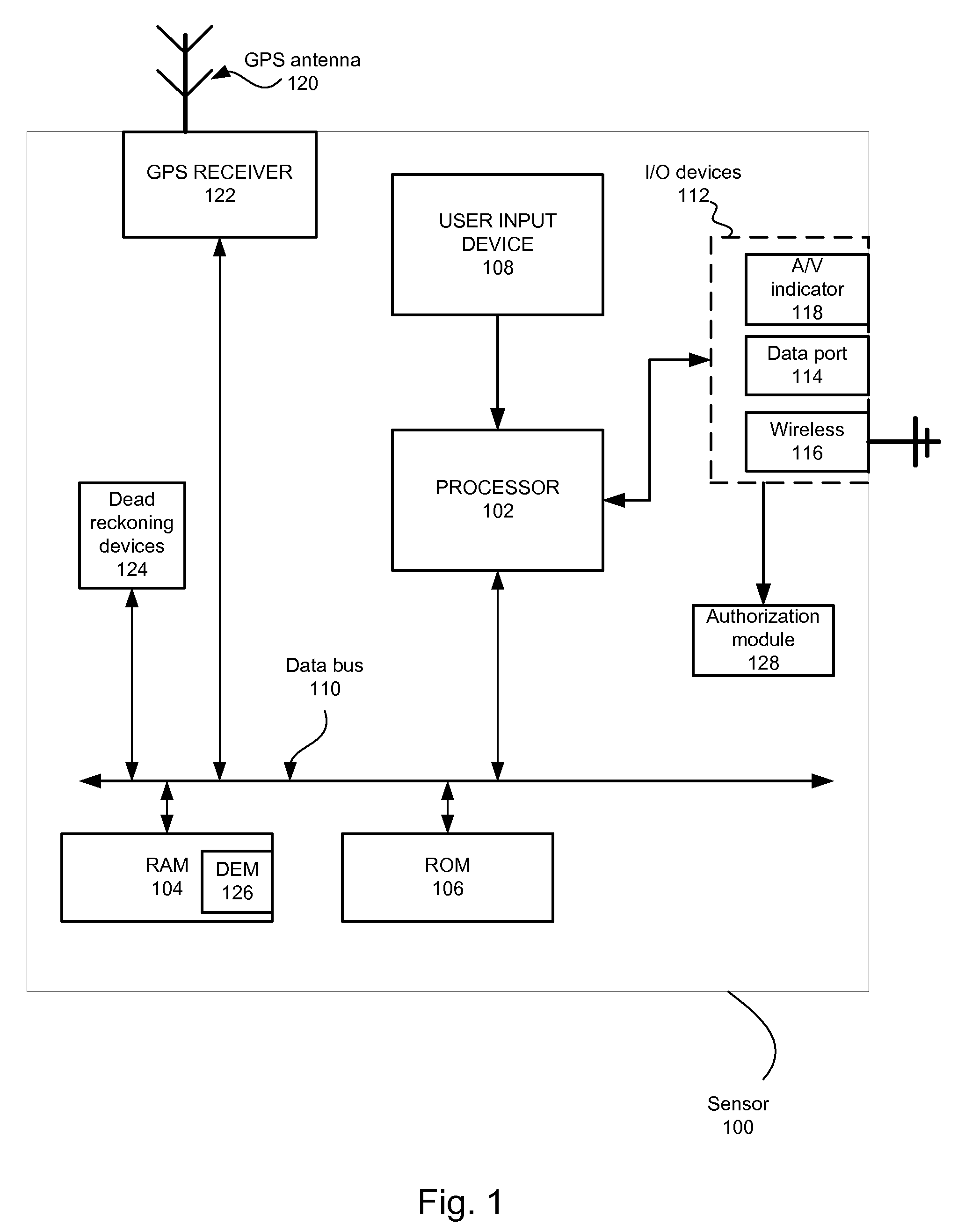
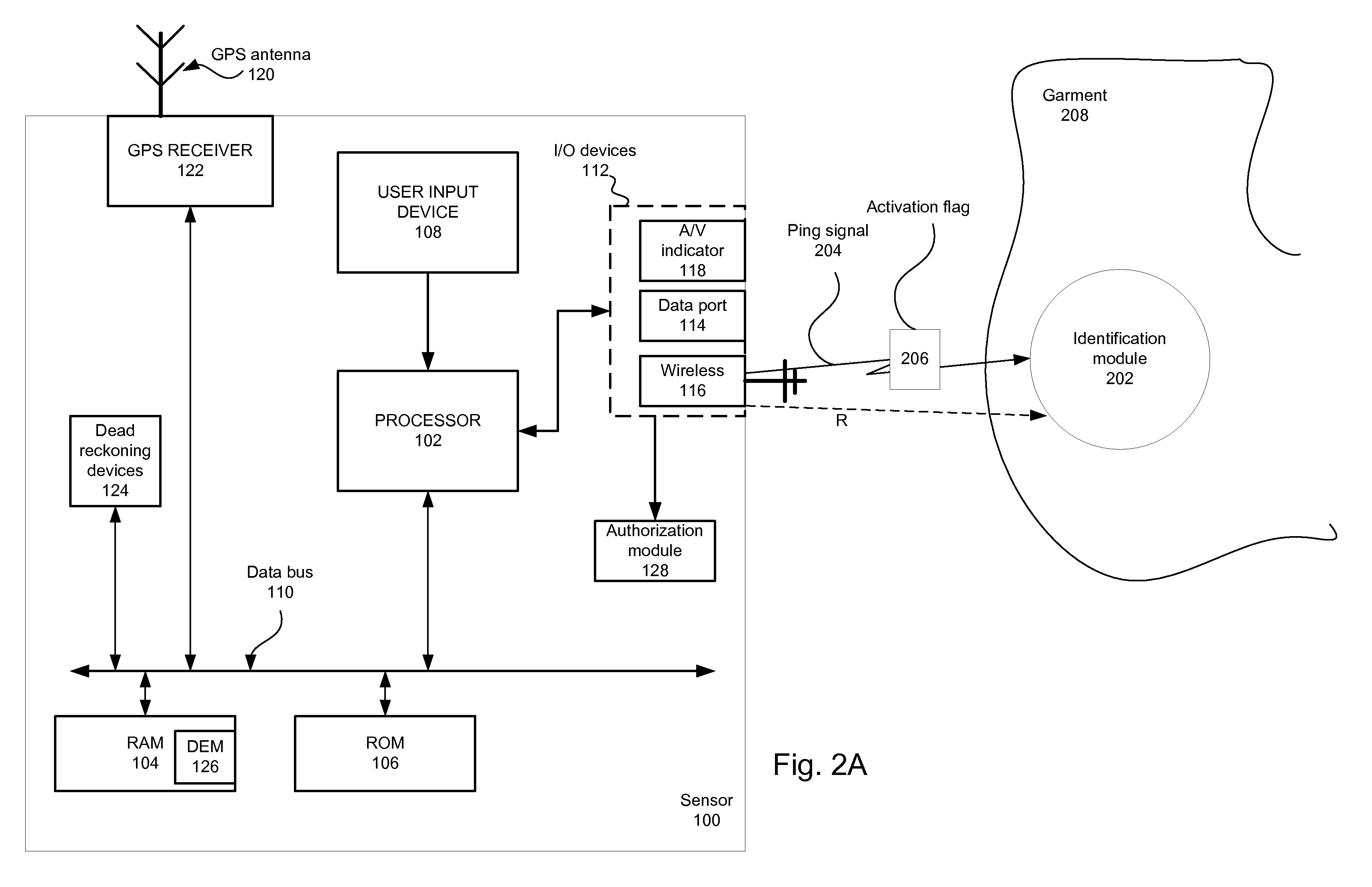
Smart garment
InactiveUS20080218310A1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsExternal dataEngineering
A sensor authenticated to a garment transfers information, either wirelessly or wired, to an external data processing device. Such information includes location information, physiometric data of the individual wearing the garment, garment performance and wear data (when the garment is an athletic shoe, for example). The external data processing device can be portable digital media players that are, in turn, in wireless communication with a server computer or other wireless devices.
Owner:APPLE INC
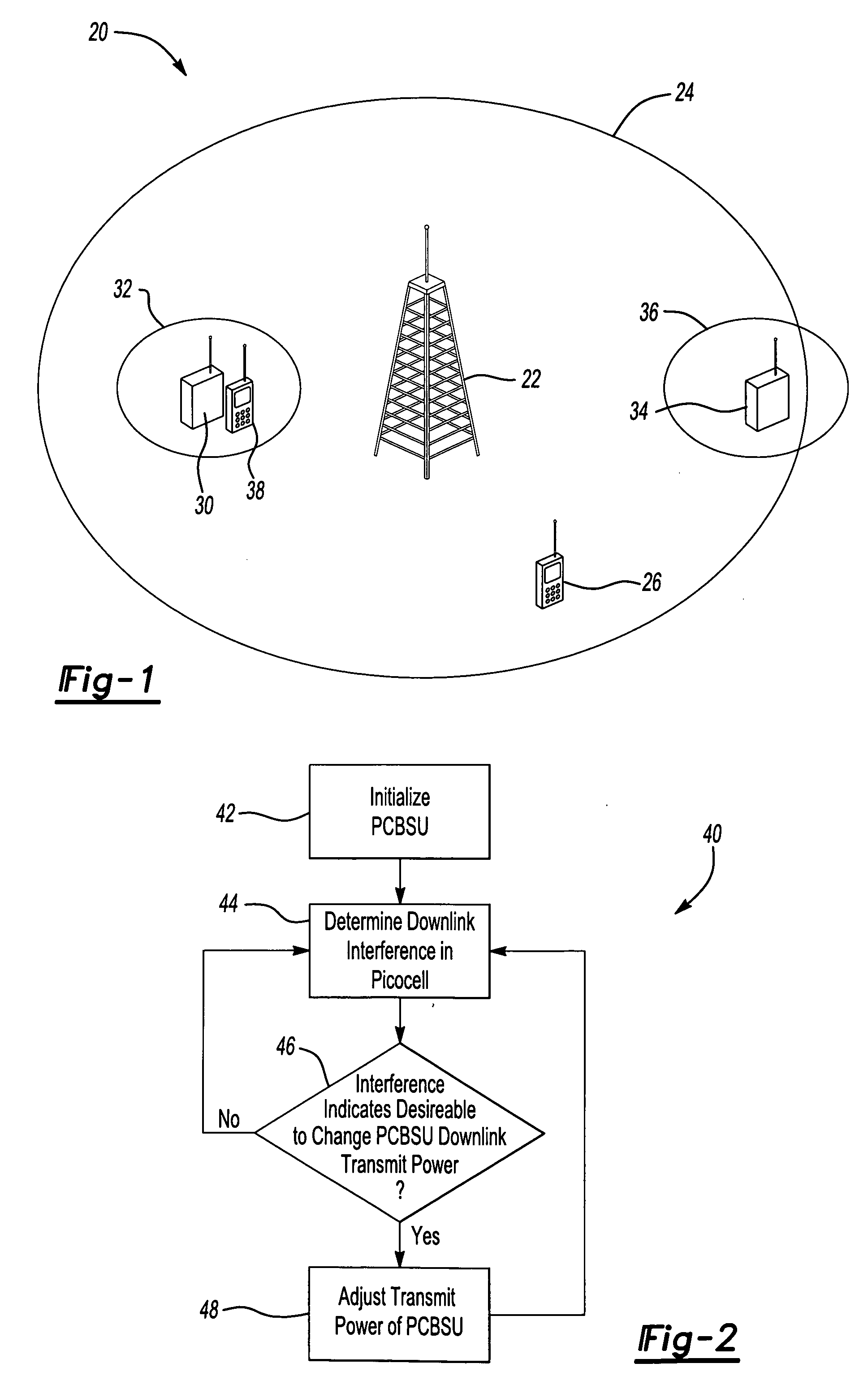
Controlling transmit power of picocell base units
ActiveUS20070270151A1Power managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemTransmitted power
A transmit power control technique within a wireless communication system includes adjusting a transmit power used by a picocell base station unit based upon a position of the picocell within a macrocell. When a picocell base station unit is located relatively close to a macrocell base station or center of the macrocell, the transmit power of the picocell base station unit is increased to avoid downlink interference from the macrocell base station for mobile stations communicating within the picocell. When a picocell base station unit is located relatively close to an edge of a macrocell, the transmit power of the picocell base station is decreased to avoid interference caused by the picocell base station unit for mobile stations communicating within the macrocell in the vicinity of the picocell. In a disclosed example determined downlink interference levels provide an indication of the position of the picocell within the macrocell and provide an indication of how to automatically adjust the transmit power of the picocell base station unit.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
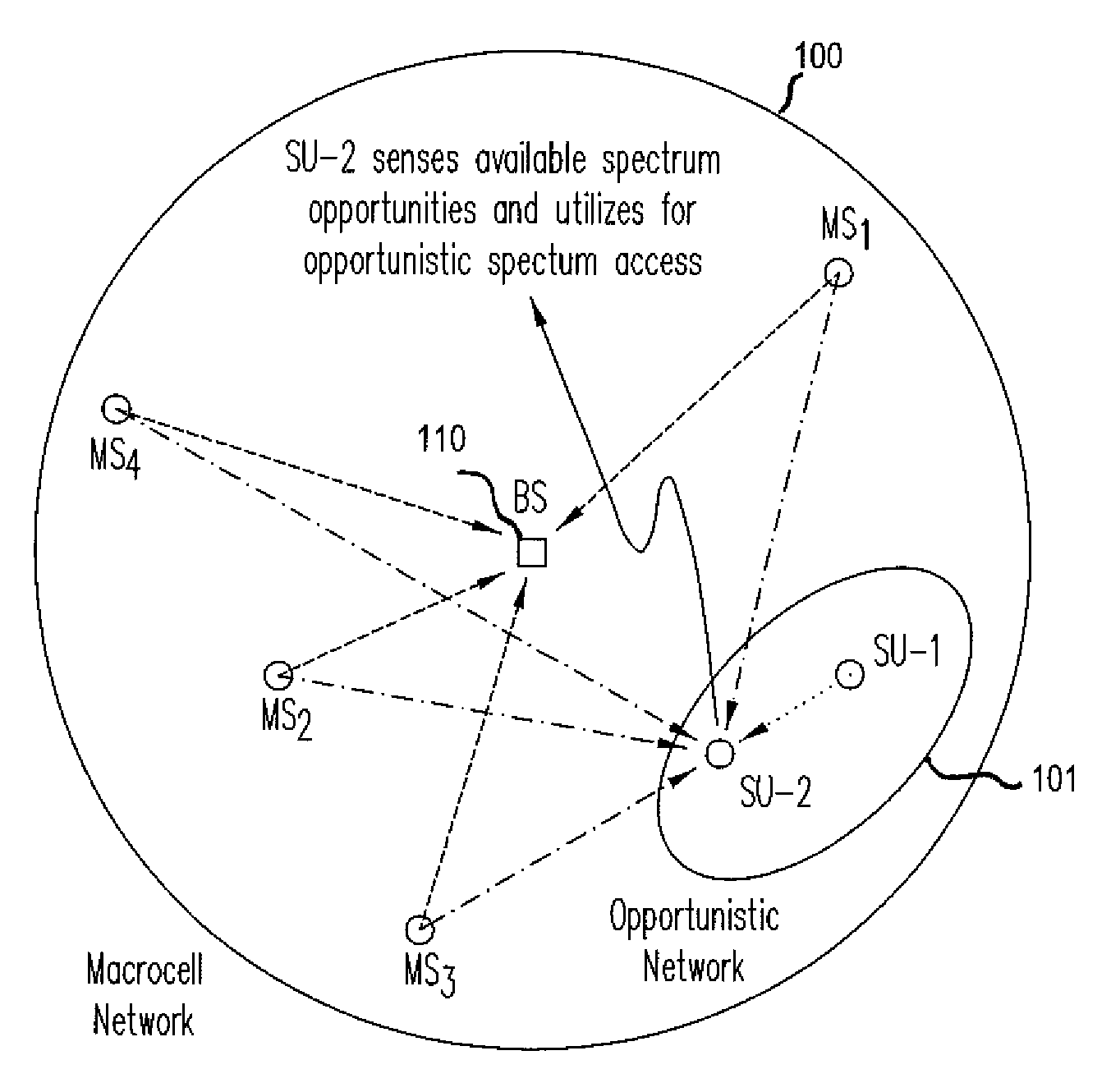
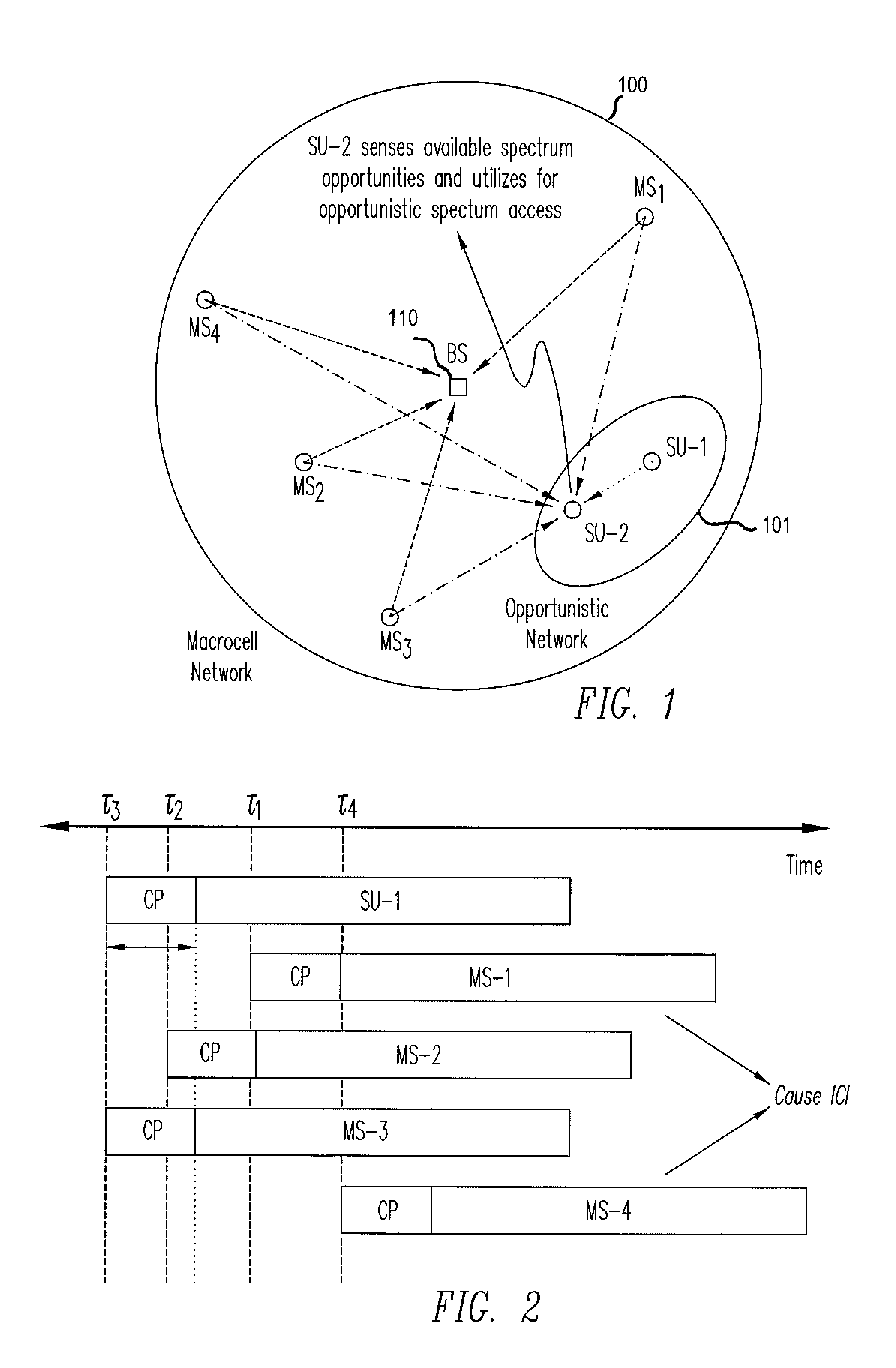
Method for interference-minimizing resource block-size selection at a macrocell, a microcell and a femtocell
A method for minimizing interference is applicable to a primary network whether or not spectrum resources are assigned to its users using a block-wise subcarrier assignment scheme or a randomized allocation scheme. The identified unused spectrum resources that are to be assigned to the users of the opportunistic network exclude un-used subcarriers adjacent to subcarriers used by the users of the primary network to avoid interference. The opportunistic network may assign the identified unused spectrum resources using a scheme that selects a block size for an adaptive modulation and coding scheme or for avoidance of waste of spectrum resources.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Redundant transponder array for a radio-over-fiber optical fiber cable
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
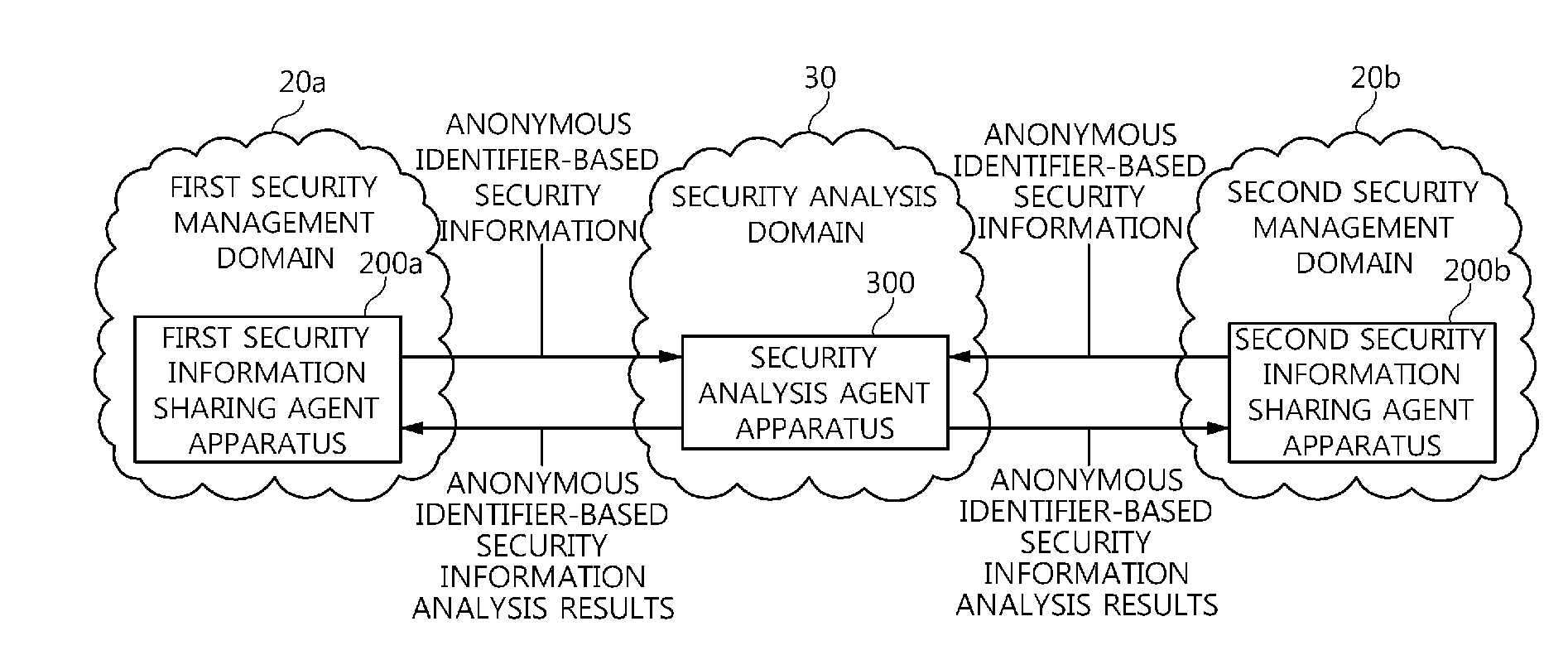
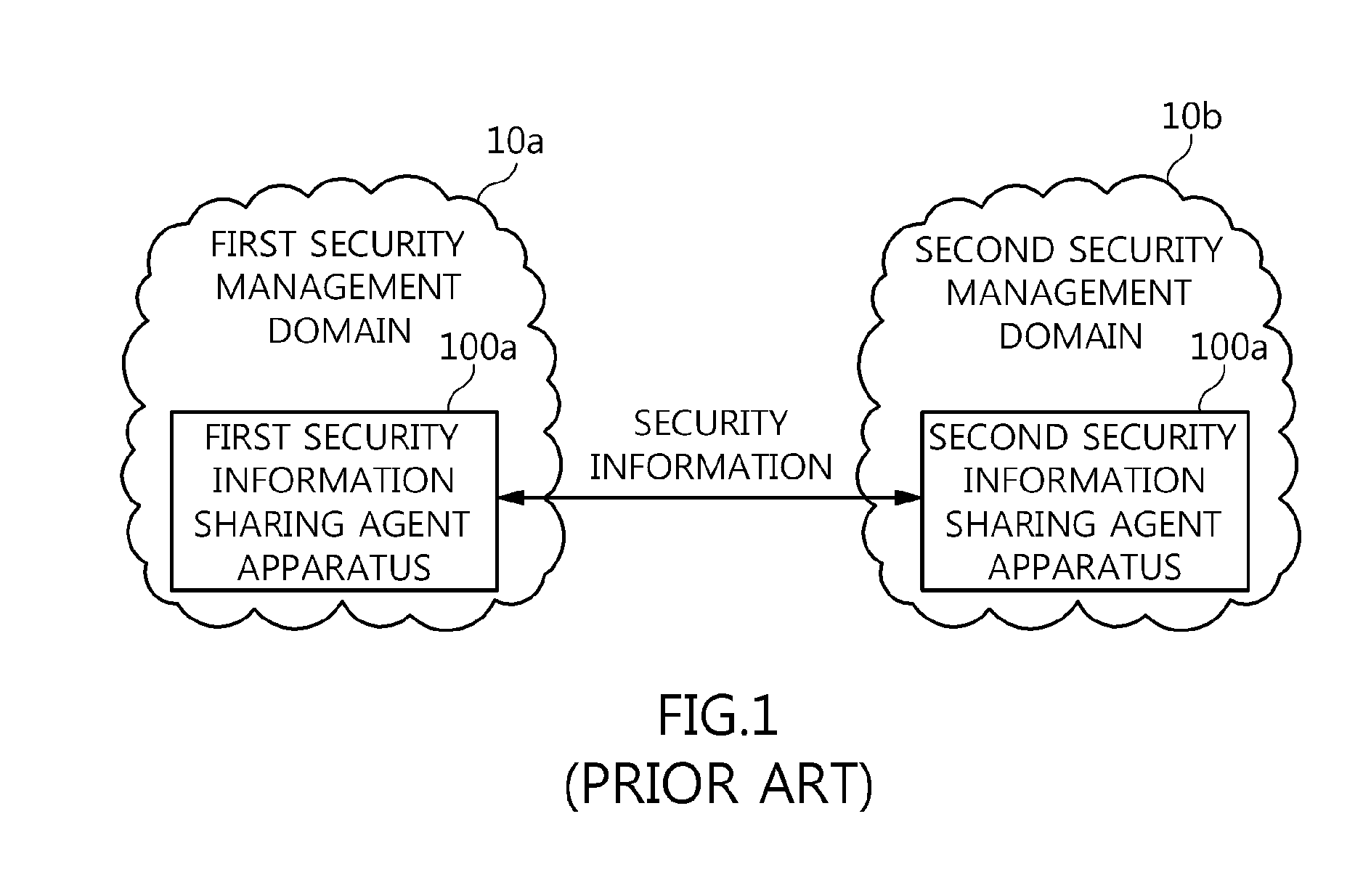
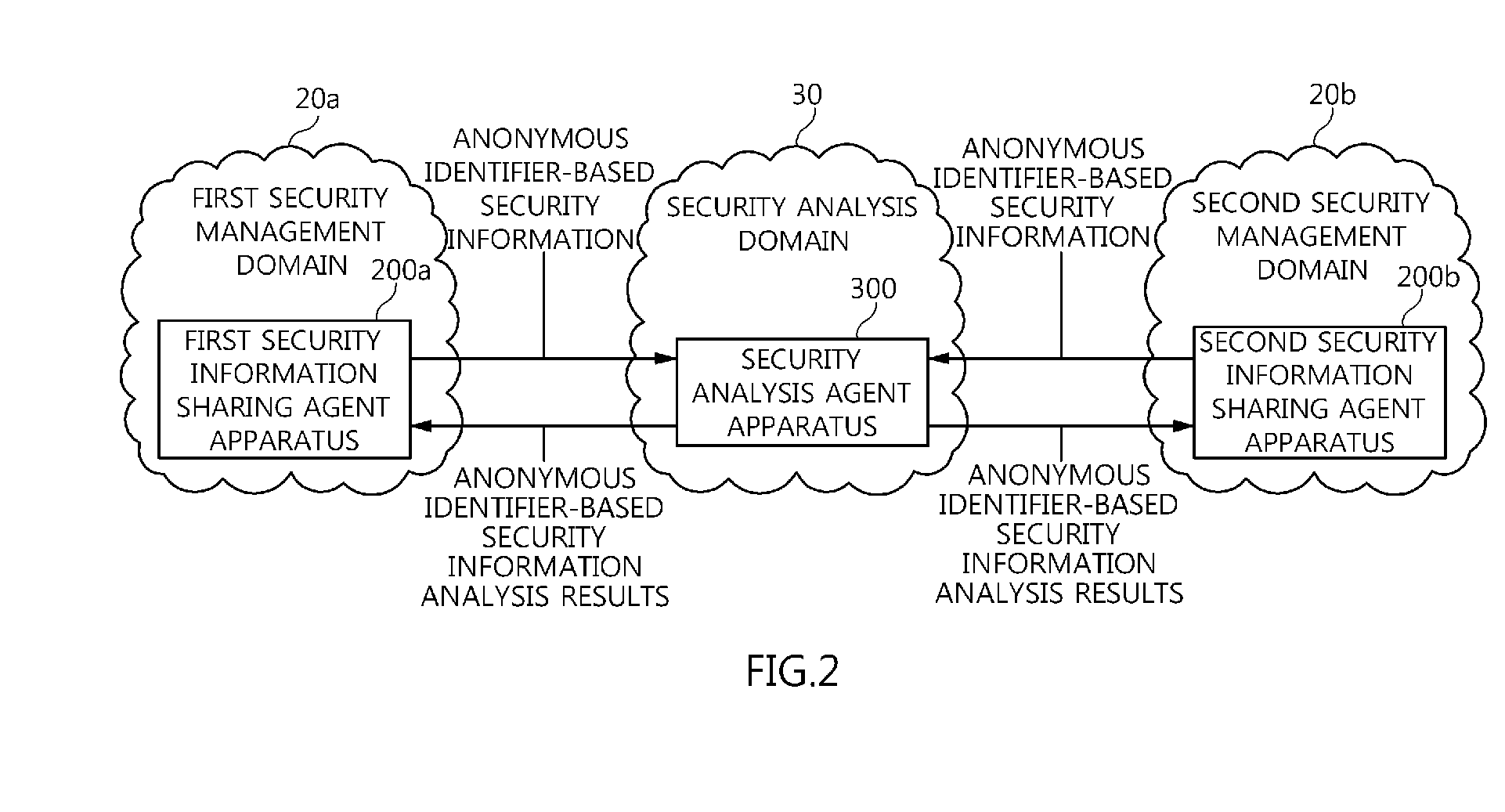
Agent apparatus and method for sharing anonymous identifier-based security information among security management domains
ActiveUS20130139268A1Prevent leakageProtection of personal informationDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCommunication unitPicocell
The present invention relates to an agent apparatus and method for sharing anonymous identifier-based security information among security management domains. A plurality of security information sharing agent apparatuses respectively located in a plurality of security management domains and configured to collect security information and transmit collected security information to outside of the security management domains. Each security information sharing agent apparatus includes an identifier conversion unit for converting real name identifier-based security information into anonymous identifier-based security information by converting a real name identifier included in the security information into an anonymous identifier, and a security information communication unit for transmitting the anonymous identifier-based security information obtained by the identifier conversion unit to outside of a corresponding security management domain so that security information is shared among the plurality of security management domains.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
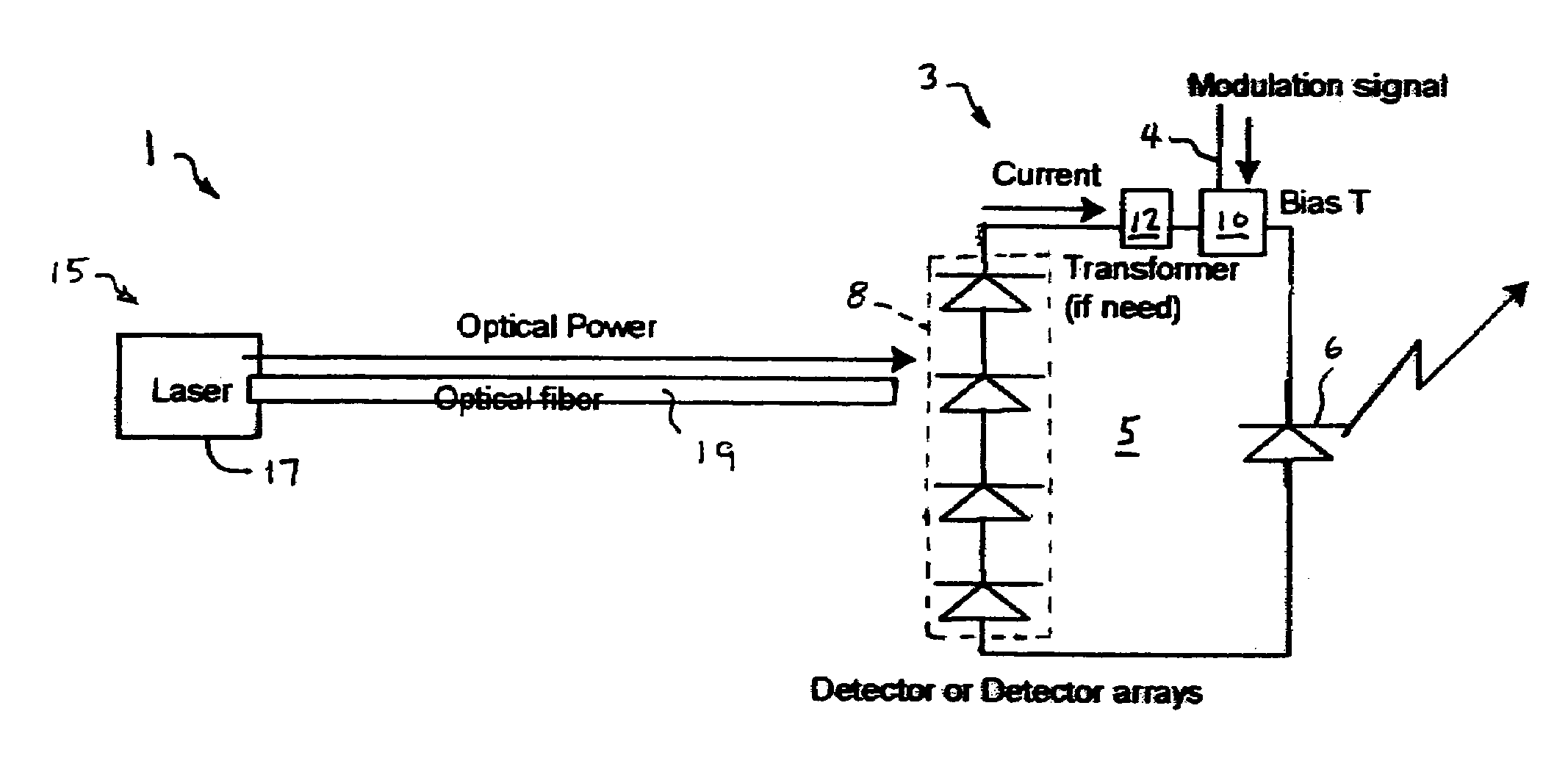
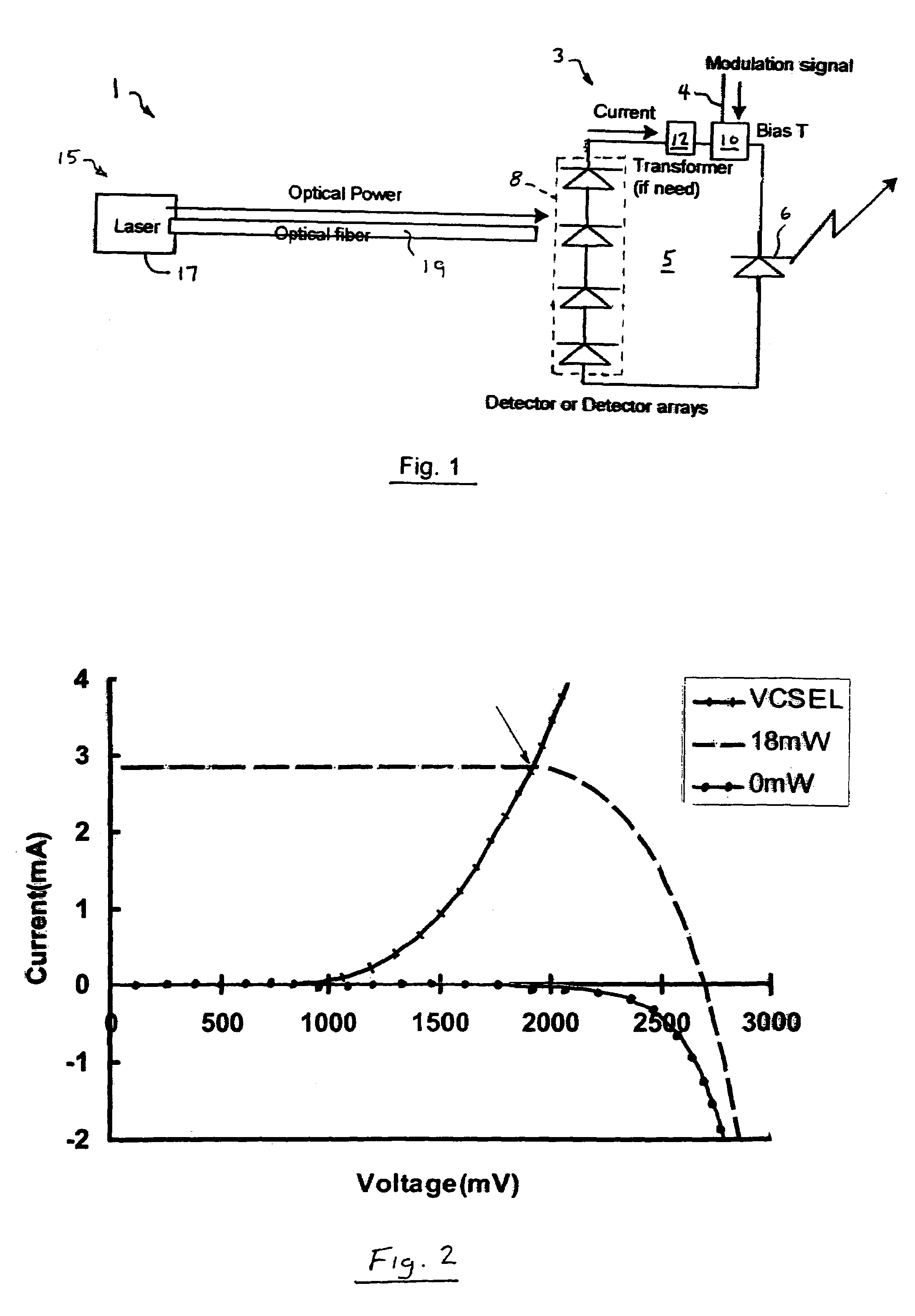
System and method for optically powering a remote network component
ActiveUS7388892B2Low costEasy to operateLaser detailsElectromagnetic transceiversFiberVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
Both a system and method for optically powering a network component, such as the transponder of a picocell, is provided. The system includes a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) for processing an input signal, a remotely-located optical power source, and an optical fiber for conducting optical power from the source to the VCSEL. The VCSEL may be electrically biased from current generated by an optical-electro converter coupled to the fiber, or directly optically biased from light from the optical power source. A bias tee is connected between an input signal and an input of the VCSEL such that the VCSEL generates a modulated optical signal. The system may be the transponder of a picocell system where the VCSEL generates an optical uplink signal conducted to a head-end circuit via the same or a separate optical fiber.
Owner:CORNING INC
Wireless picocellular RFID systems and methods
InactiveUS20070257796A1Near-field in RFIDElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingElectronic taggingLocation tracking
The wireless radio-frequency identification (RFID) picocellular system includes a central control station optically coupled to one or more electrical-optical (E-O) access point devices that generate the individual picocells. The central control station includes service units that provide conventional wireless cellular services, and further includes one or more RFID reader units. The E-O access point devices are adapted to receive electromagnetic RFID tag signals from RFID tags within the associated picocell and transmit optical RFID tag signals to the central control station, which converts the optical RFID tag signals to electrical RFID tag signals, which are then received by the one or more RFID reader units. The system allows for large numbers of RFID tags in the picocellular coverage area to be quickly read and the information stored. The relatively small size of picocells allows for high-precision locating and position tracking of items without the need for manually scanning RFID tags with an RFID reader.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
System and method for providing an adapter for re-use of legacy dimms in a fully buffered memory environment
A system and method for providing an adapter for re-use of legacy DIMMS in a fully buffered memory environment. The system includes a memory adapter card having two rows of contacts along a leading edge of a length of the card. The rows of contacts are adapted to be inserted into a socket that is connected to a daisy chain high-speed memory bus via a packetized multi-transfer interface. The memory adapter card also includes a socket installed on the trailing edge of the card. In addition, the memory adapter card includes a hub device for converting the packetized multi-transfer interface into a parallel interface having timings and interface levels that are operable with a memory module having a parallel interface that is inserted into the socket. In addition, the hub device converts the packetized multi-transfer interface into a parallel interface having timings and interface levels that are operable with a memory module having a parallel interface that is inserted into the socket. The hub device also converts the parallel interface into the packetized multi-transfer interface.
Owner:IBM CORP
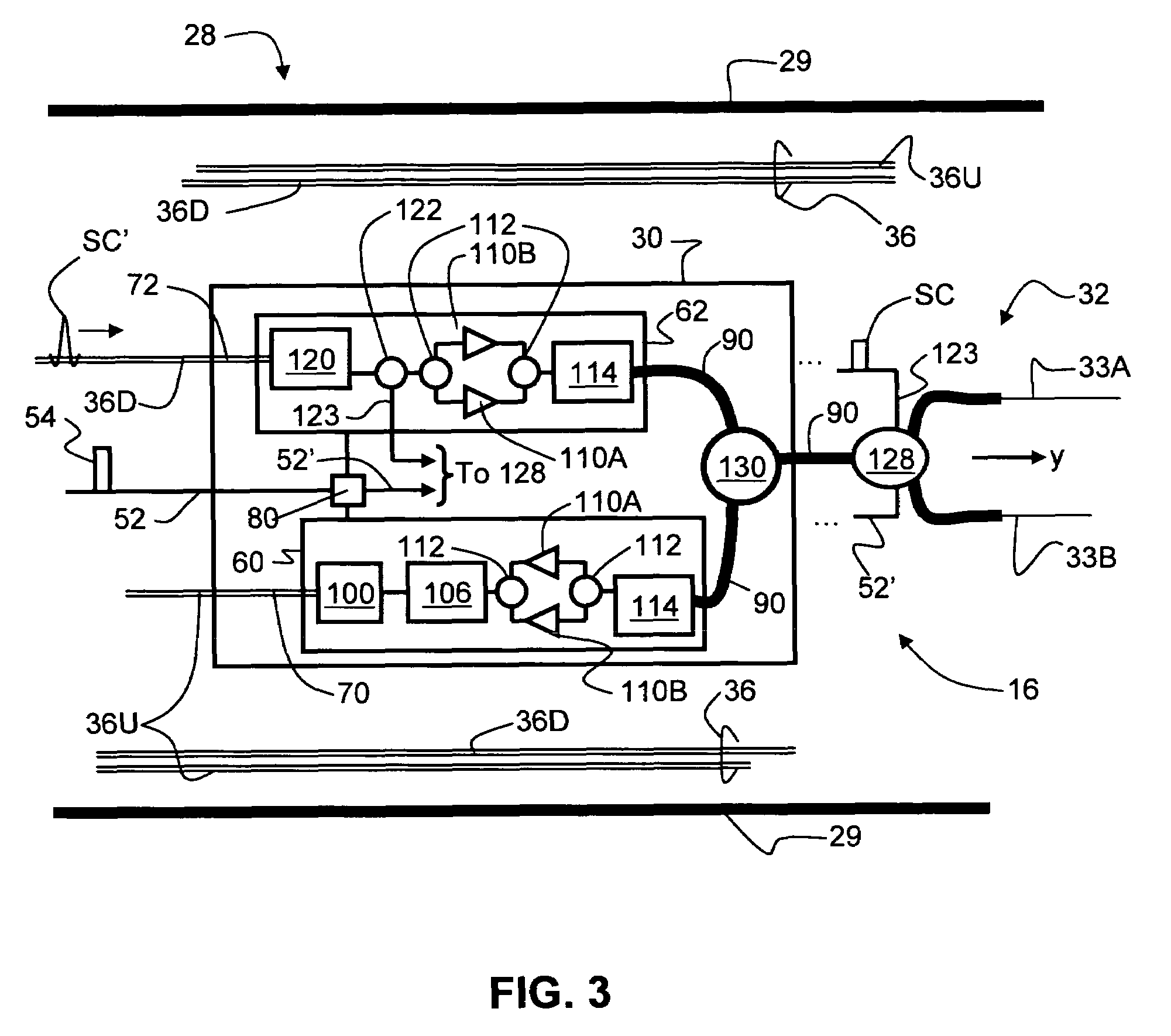
Radio-over-fiber (RoF) optical fiber cable system with transponder diversity and RoF wireless picocellular system using same
InactiveUS7787823B2Radio transmissionElectromagnetic transmissionRadio over fiberAntenna polarization
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
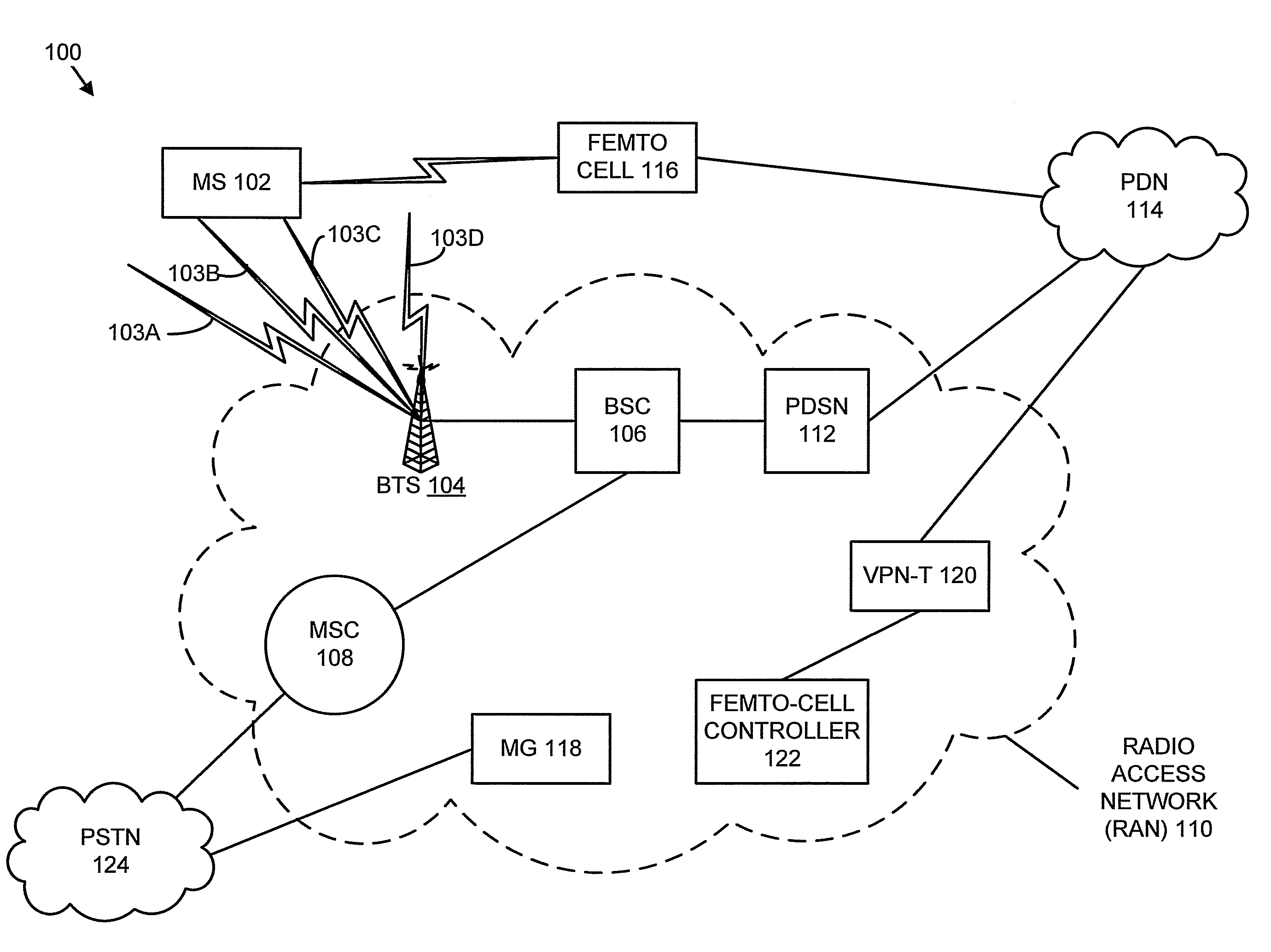
Location-based, event triggered inter-radio access technology handovers from a CDMA macrocell to a wcdma femtocell
ActiveUS20100124931A1Well formedAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesRadio access technologyCommunications system
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
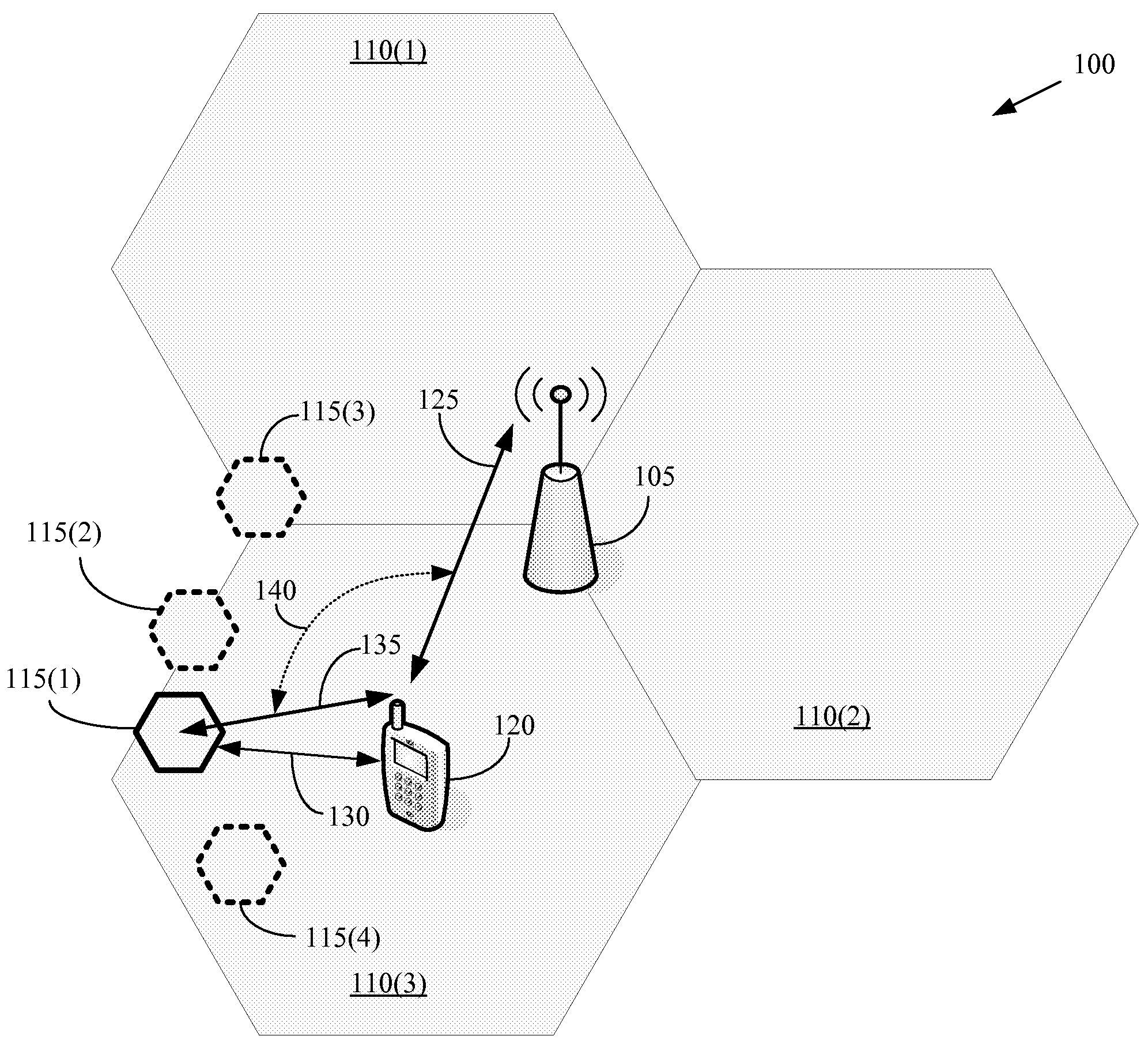
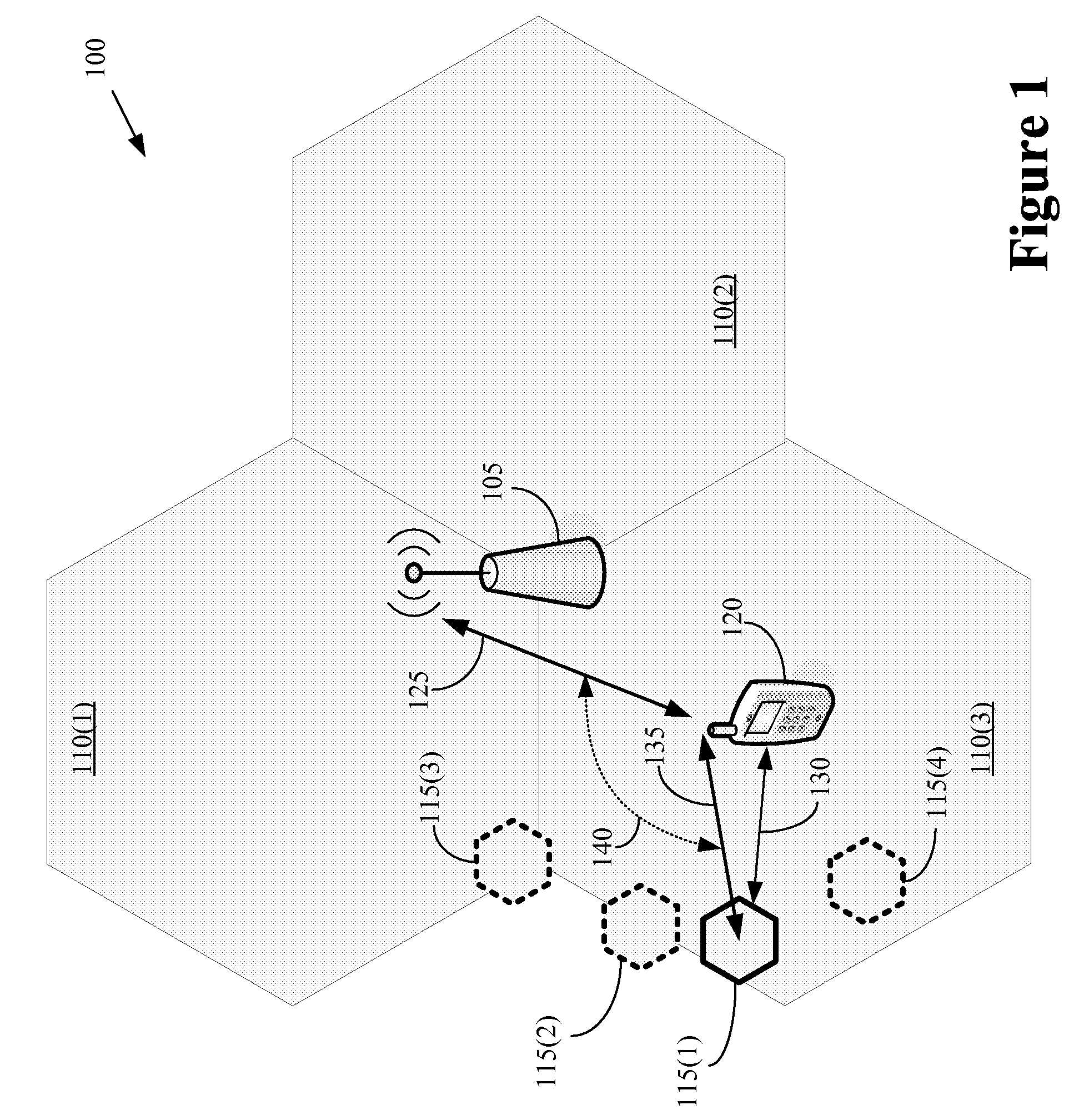
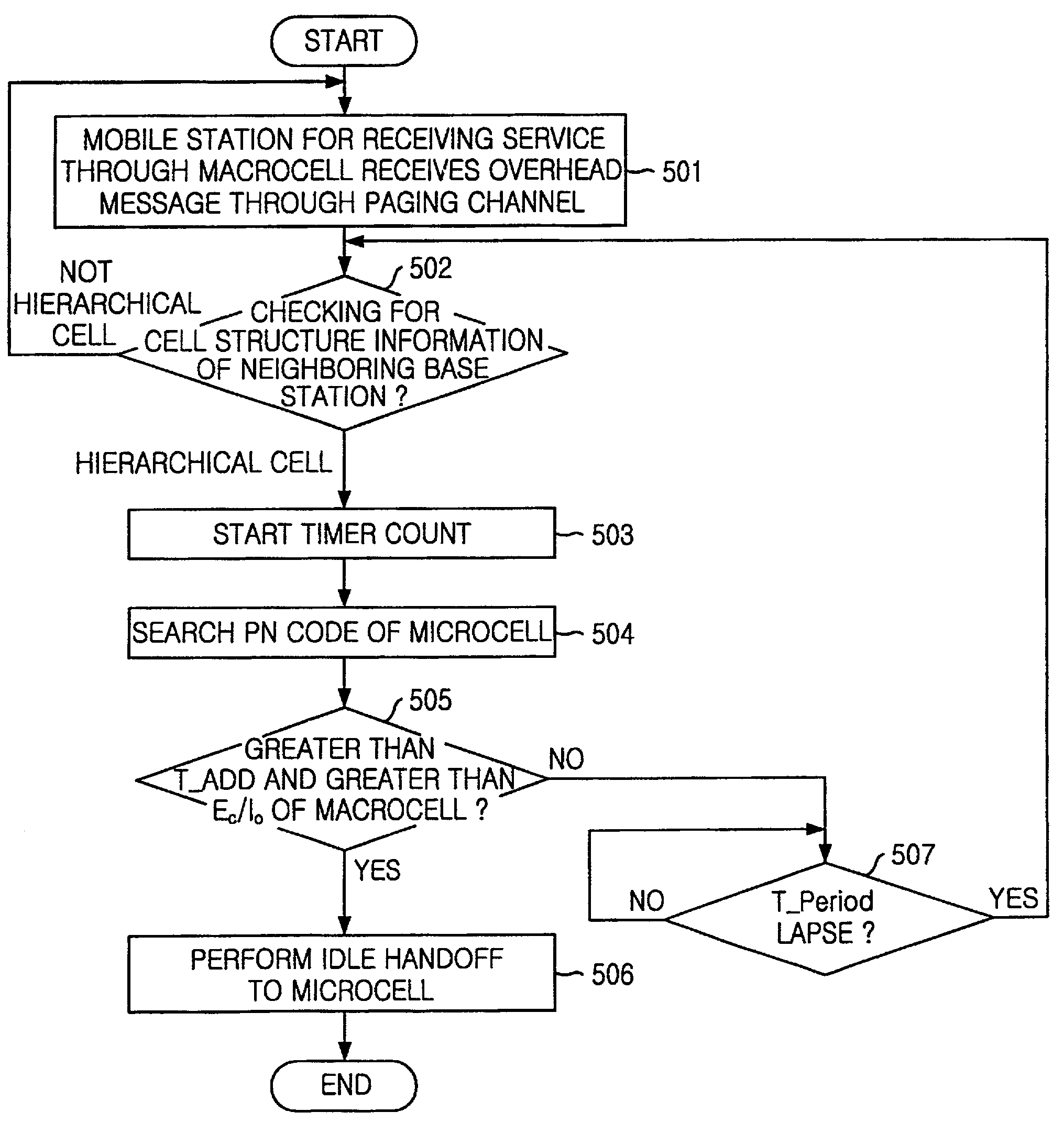
Method for carrying out handoff between macrocell and microcell in hierarchical cell structure
A method for carrying out an idle handoff from a macrocell to a microcell (picocell) in a hierarchical cell structure includes the steps of: a) allocating different frequency assignments (FA) to the macrocell and the microcell in a same service band, to construct the hierarchical cell structure; b) transmitting cell structure information of neighboring base stations and pseudo noise (PN) code from base station to mobile station; c) checking whether the mobile station is in the hierarchical cell by using the cell structure information of neighboring base station; and d) checking whether a value of the pseudo noise (PN) code is greater than T_ADD and greater than Ec / Io of the macrocell by periodically searching the pseudo noise (PN) code of the microcell, to carry out an idle handoff to the microcell, wherein the T_ADD represents a value of base station pilot strength required for the base station of neighboring set to be included in a candidate set, the Ec represents an pilot energy accumulated during one pseudo noise (PN) chip period, and the Io represents a total power spectrum density within a reception bandwidth.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
Radio-over-fiber (RoF) optical fiber cable system with transponder diversity and RoF wireless picocellular system using same
InactiveUS20080070502A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionRadio over fiberAntenna polarization
A radio-over-fiber (RoF) optical fiber cable system with transponder diversity for a RoF wireless picocellular system that includes at least one optical fiber cable. The at least one optical fiber cable supports one or more groups of two or more transponders, wherein the transponders in a given group are arranged to form substantially co-located picocells. The transponders in each transponder group may also have one of two orthogonal antenna polarizations. A diversity combiner optically coupled to each transponder determines respective signal strengths from each transponder in each transponder group. The transponder with the greatest signal strength in a given transponder group is selected to form the picocell for the given group. This allows for the optical fiber cable system to adjust to changes in the signal strength of each picocell, such as caused by a transponder obstruction or failure.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
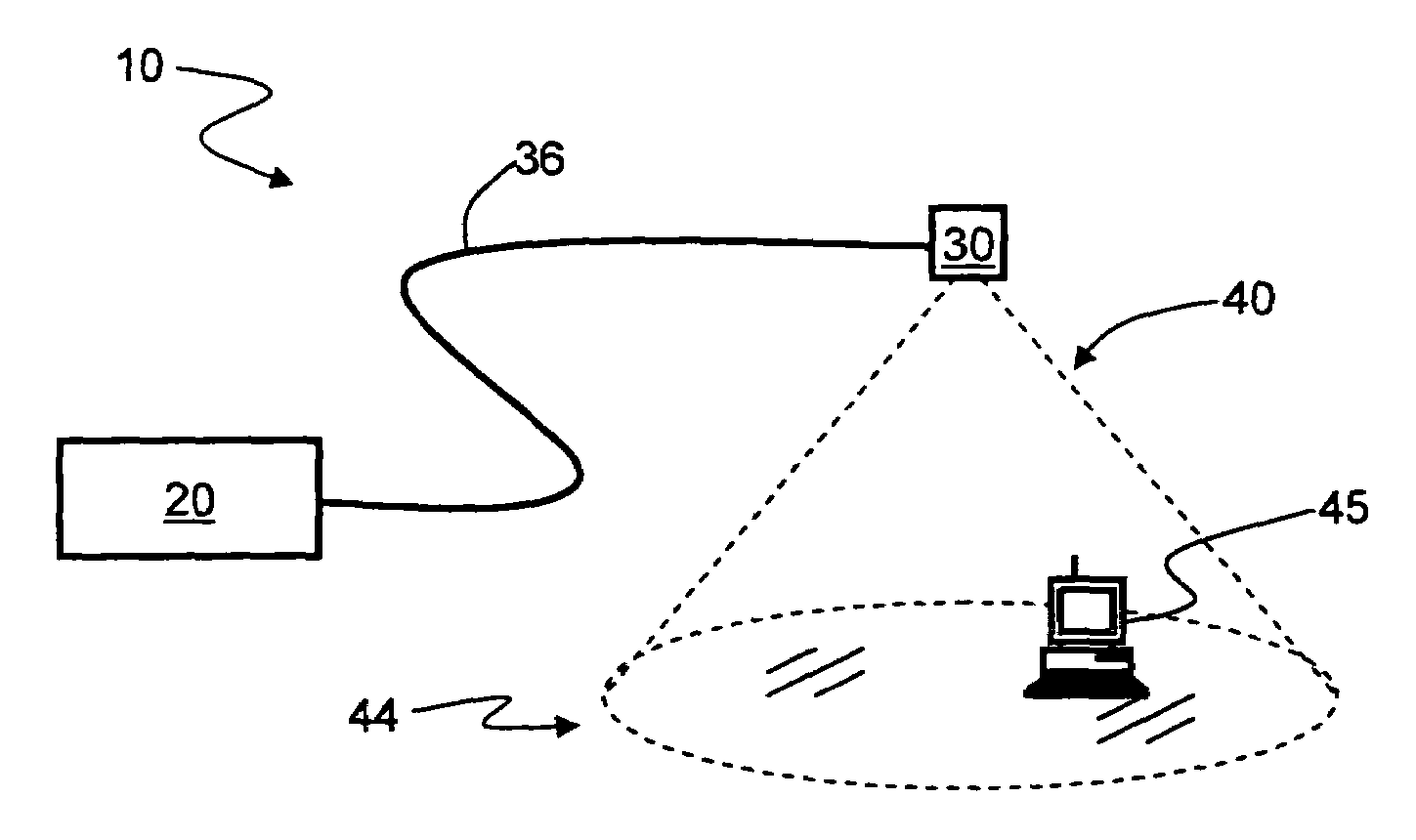
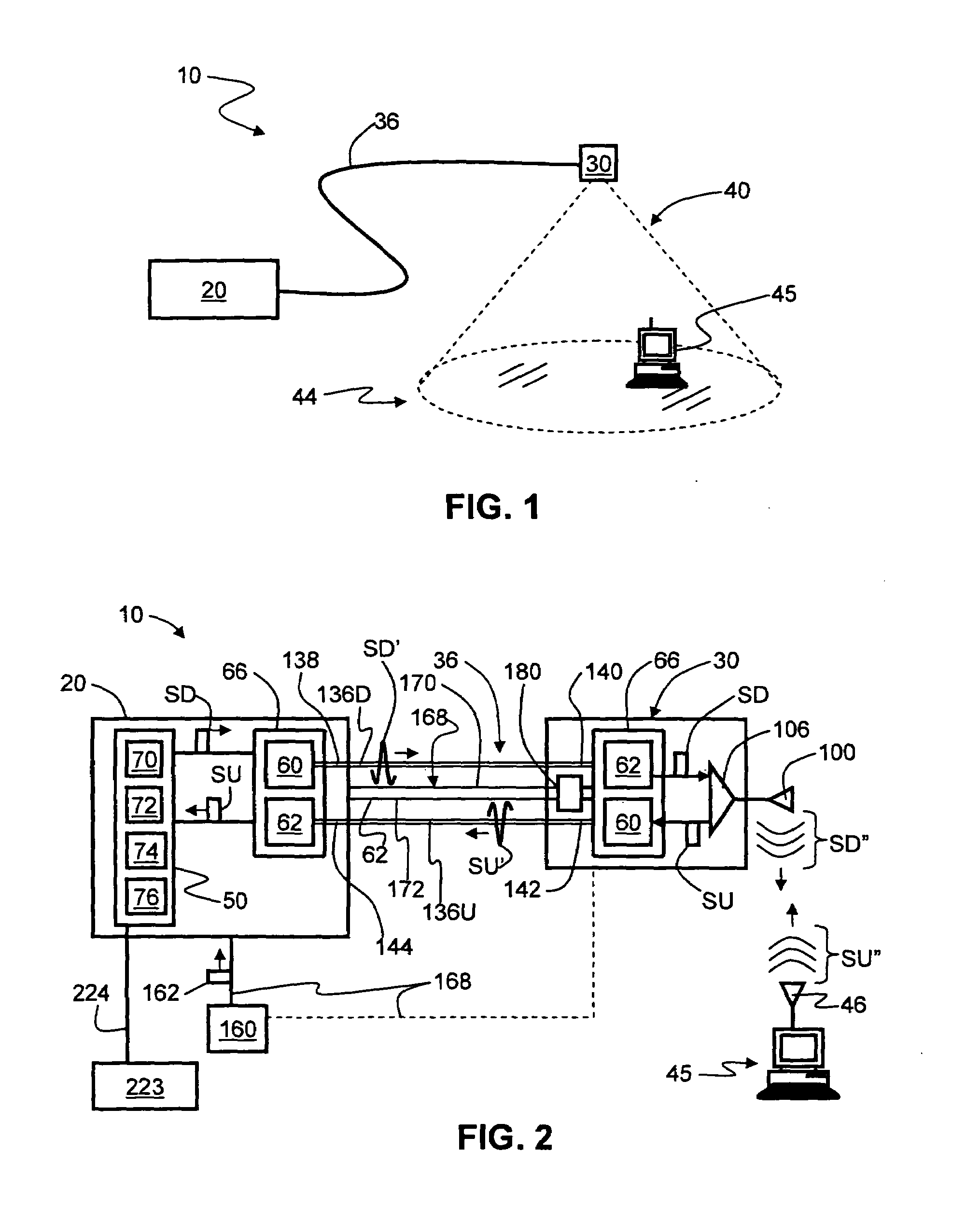
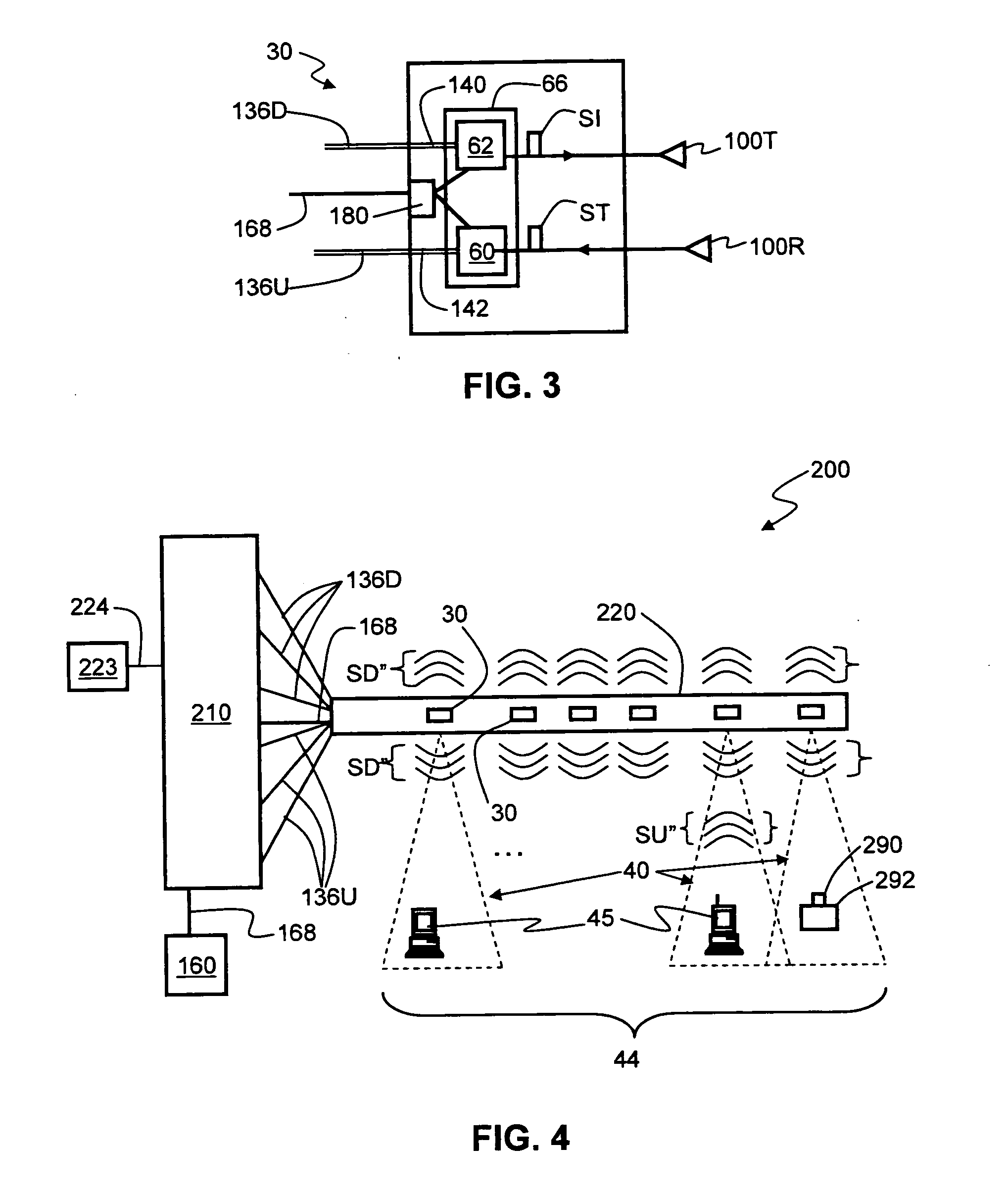
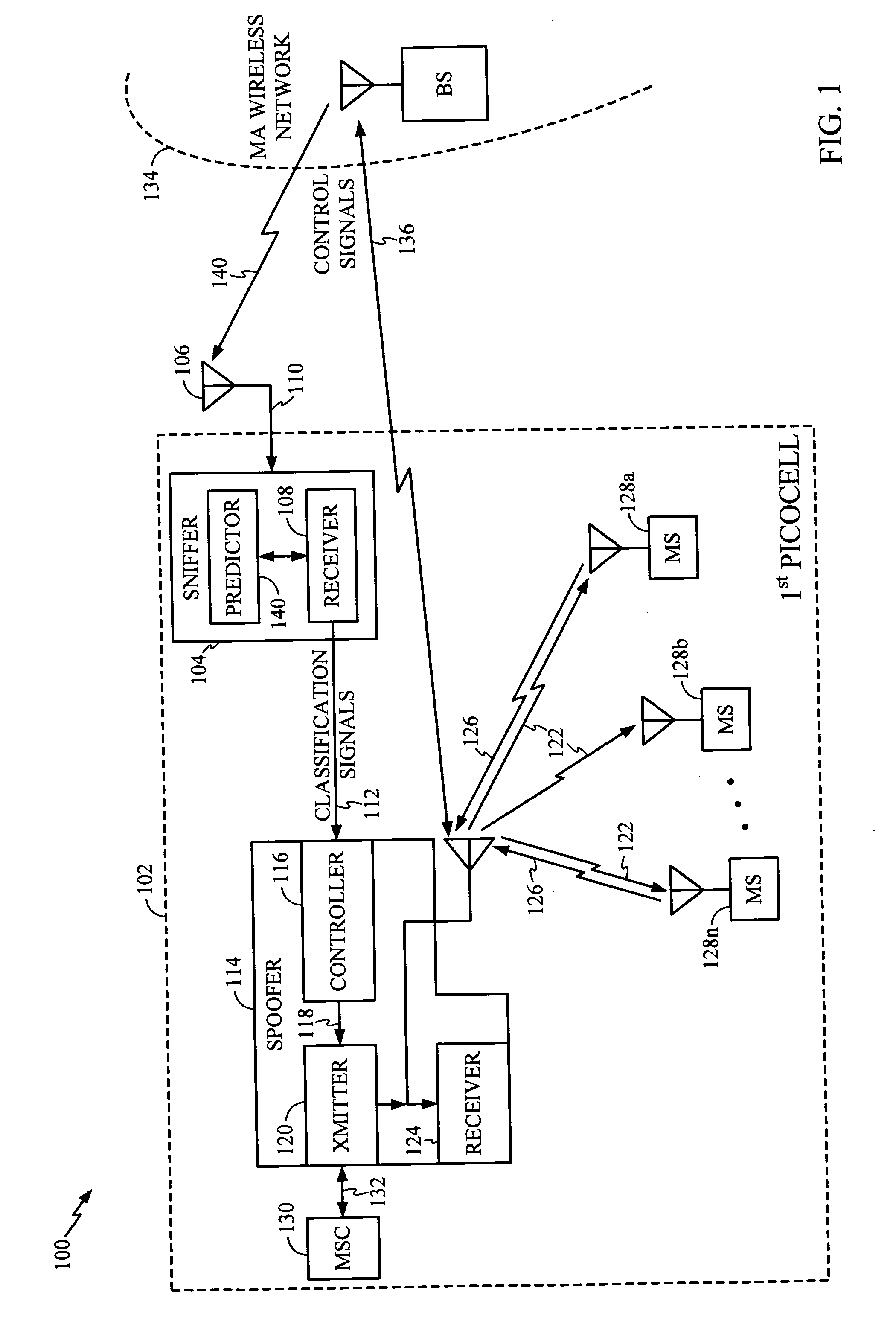
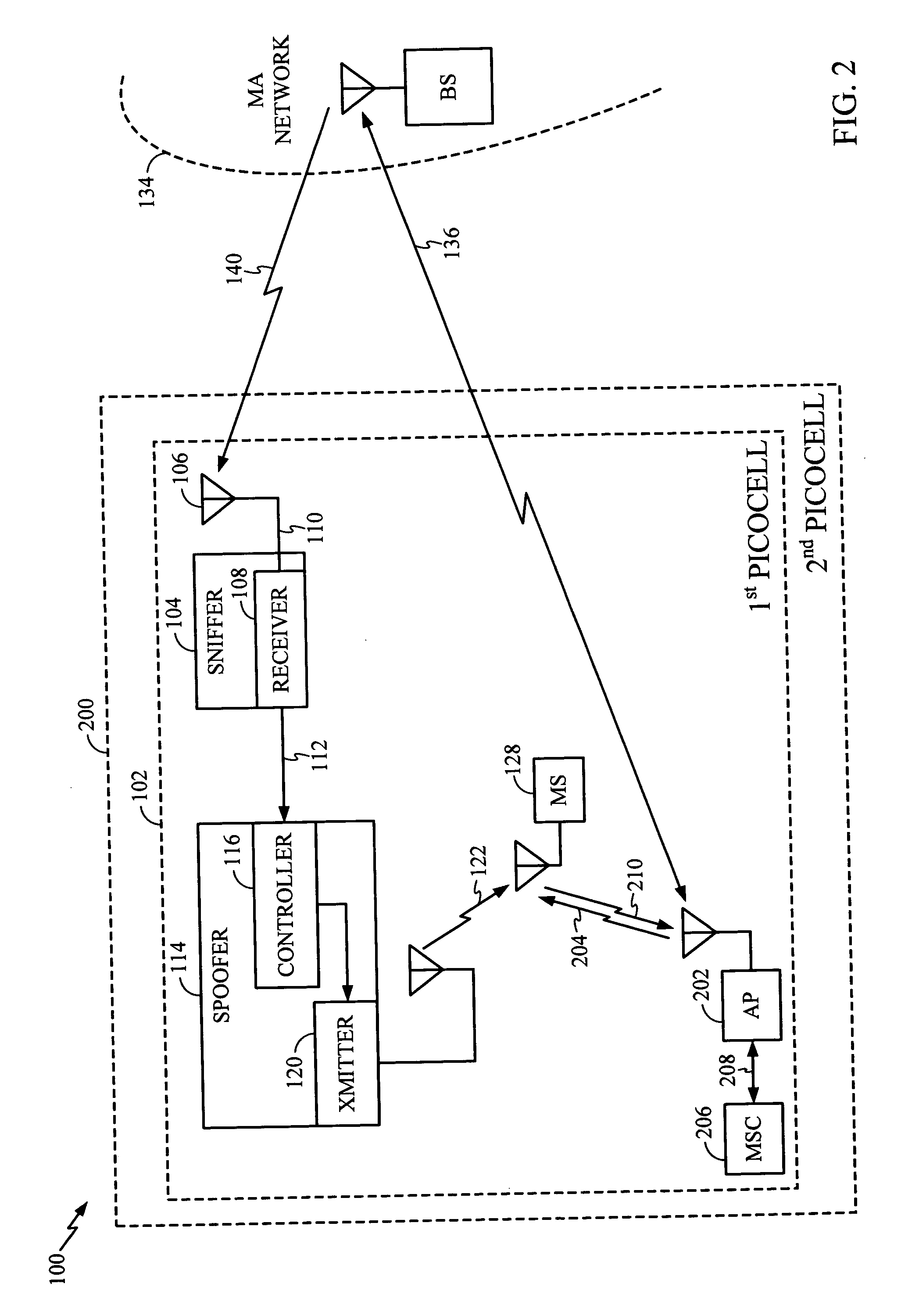
System and method for creating a wireless picocell
ActiveUS20060217121A1Assess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsMobile station
A system and method are provided for creating a picocell service alternate to a wireless network service. The method comprises: detecting a multiple access (MA) wireless communications network, such as a terrestrial or satellite network; and, generating a first picocell in a response to detecting the MA wireless network. Typically, the method comprises receiving requests for picocell service from mobile stations, in response to generating the first picocell. In one aspect, the service requests made by the mobile stations are denied. In another aspect, the method further comprises: establishing a first picocell MSC; and, providing network services to mobile stations via the first picocell, in response to the requests for picocell service. For example, the first picocell MSC may provide the same network services that are provided by a conventional terrestrial network, for example. Alternately, the method establishes an alternative wireless network (a second picocell) to provide services.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
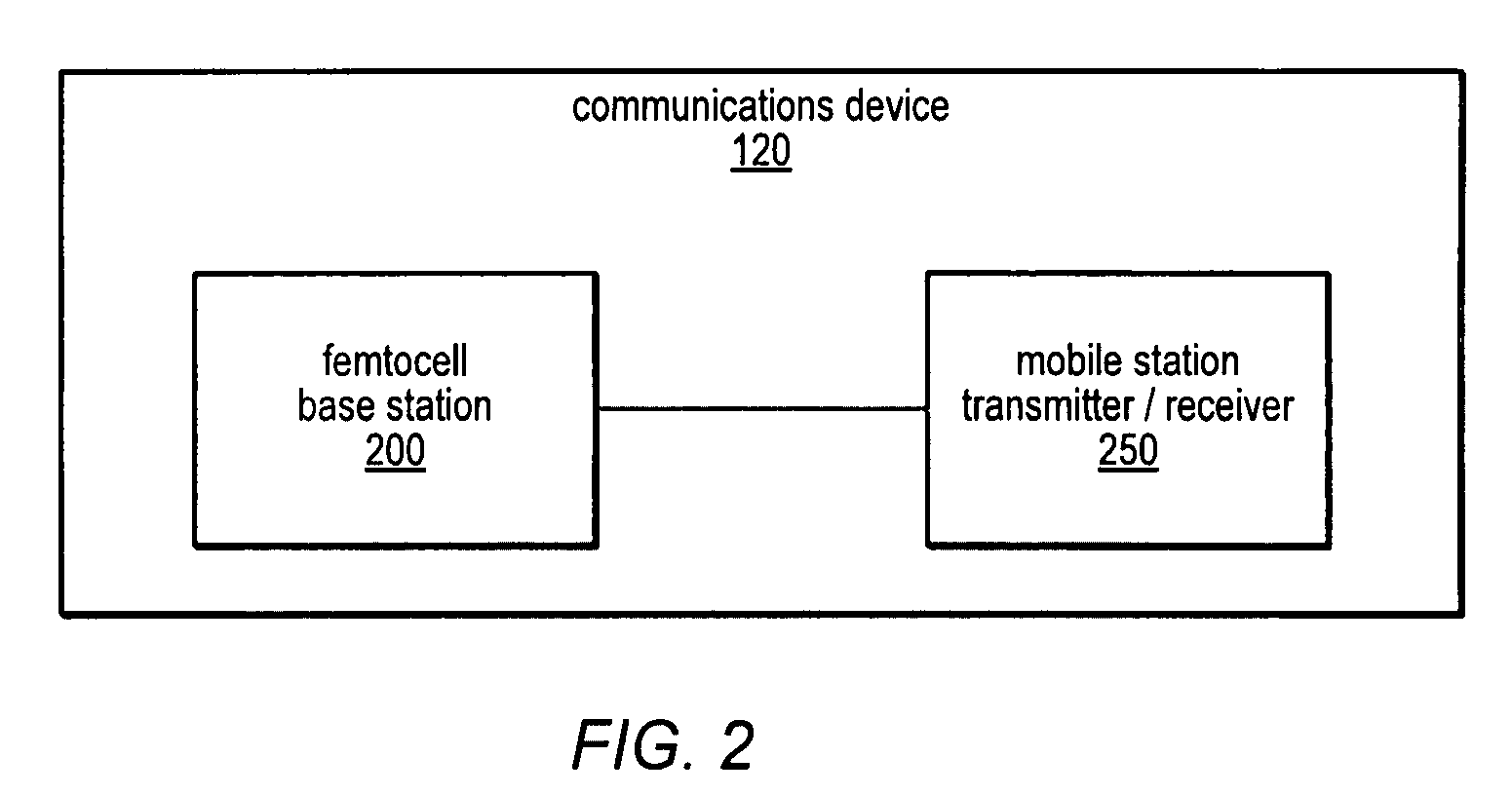
Femtocell base station with mobile station capability
ActiveUS20090082010A1Improving cellular receptionNetwork topologiesInformation formatMobile stationRadio frequency
A communication device that includes a femtocell base station and a mobile station transmitter / receiver. The femtocell base station may provide bidirectional internet protocol (IP) communication for one or mobile devices to a cellular network. The femtocell base station may be operable to communicate with the cellular network using a wide area network. The mobile station transmitter / receiver may be coupled to the femtocell base station (in a same housing). The mobile station transmitter / receiver may be operable to perform radio frequency (RF) wireless communication with the cellular network, e.g., to detect and / or report environmental parameters, performing testing (e.g., loopback testing), and / or provide communication for the one or more mobile devices (e.g., when the wide area network is down), among others.
Owner:APPLE INC
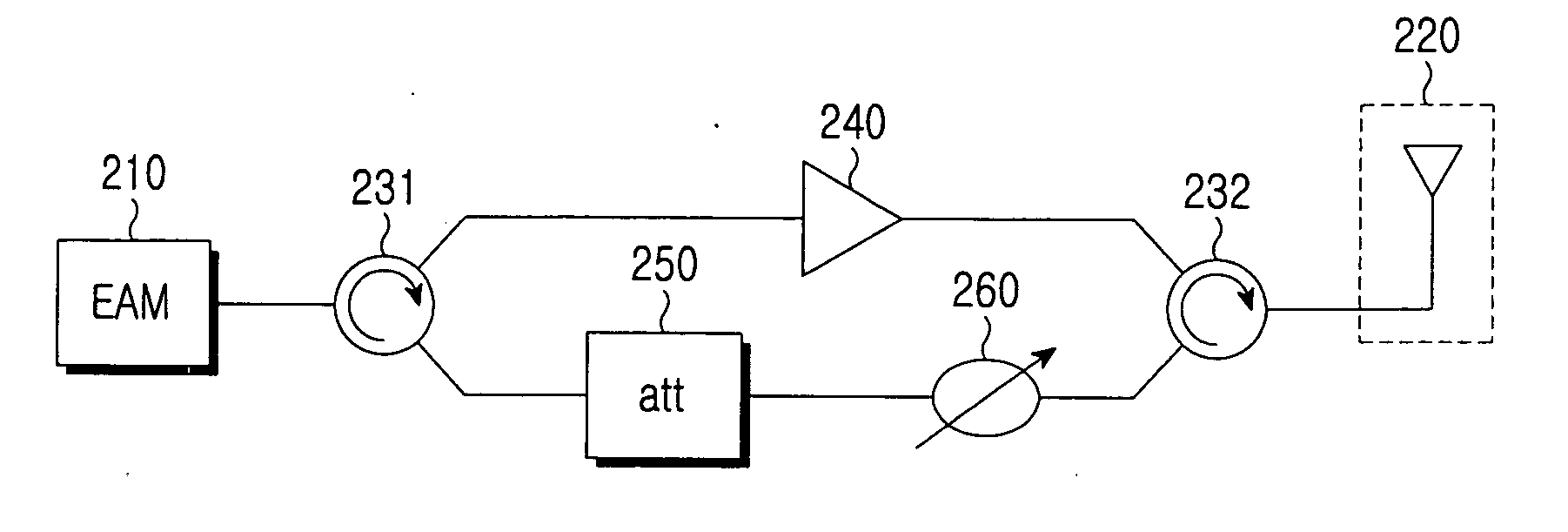
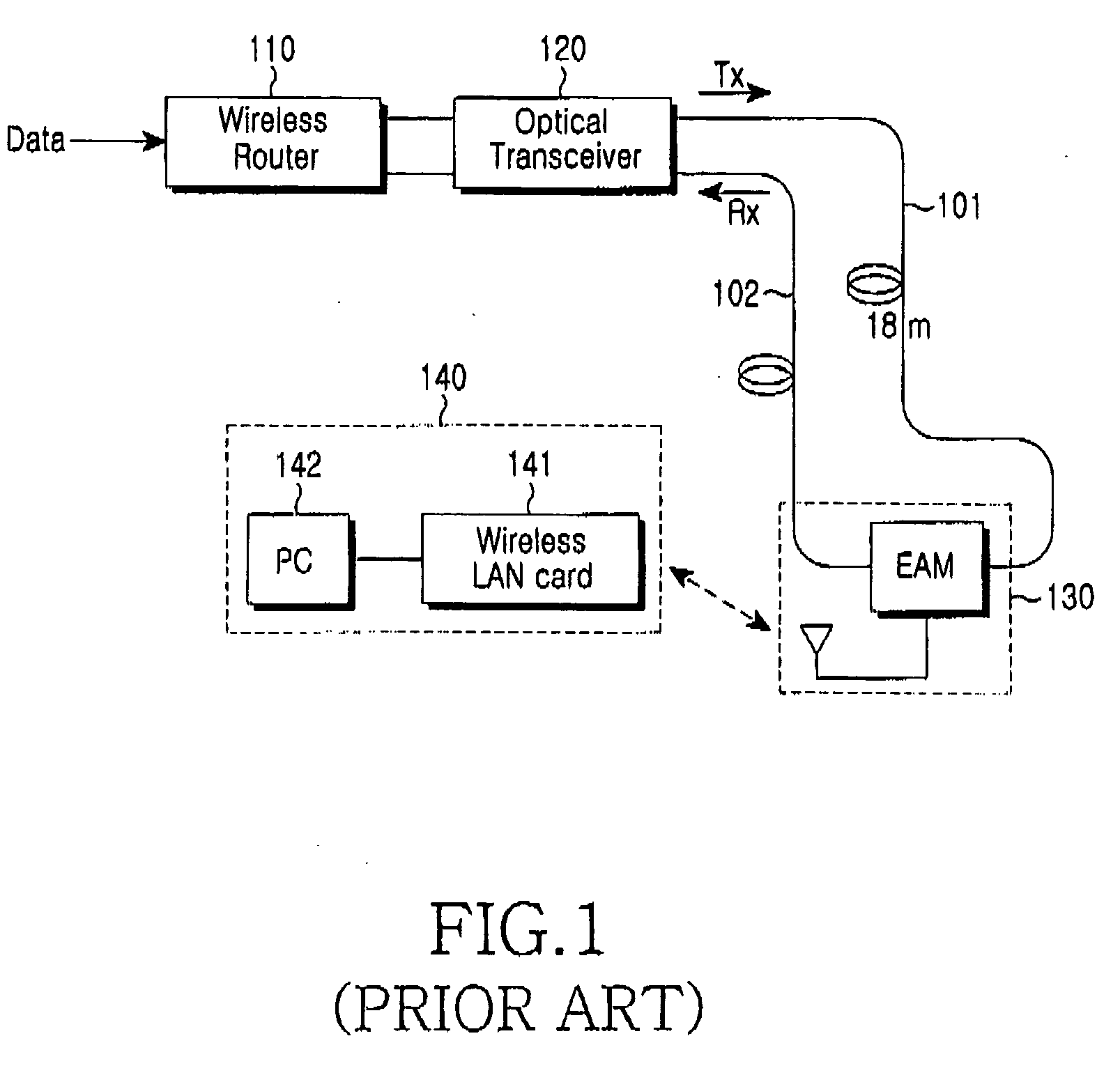
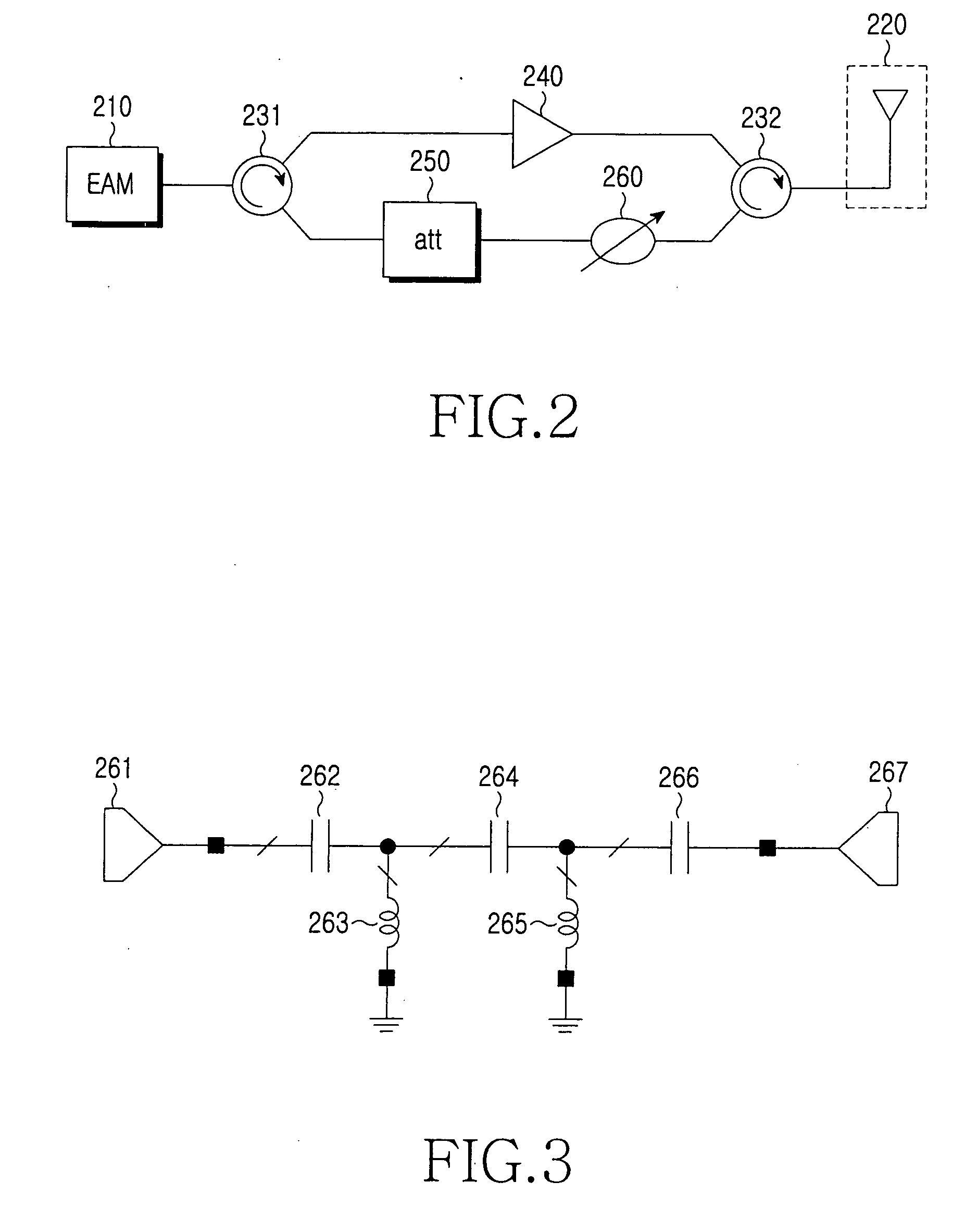
Wireless remote access base station and pico-cell system using the same
InactiveUS20070058978A1Compensation lossInformation formatContent conversionElectro-absorption modulatorAudio power amplifier
A wireless remote access base station for converting a downstream optical signal to a downstream radio frequency (RF) signal, transmitting the converted downstream RF signal wirelessly, converting a received upstream RF signal to an upstream optical signal, and transmitting the upstream optical signal is provided. The remote base station includes: an electro-absorption modulator (EAM) for converting a downstream optical signal to a downstream RF signal and an upstream RF signal to an upstream optical signal; an antenna for transmitting the downstream RF signal wirelessly and outputting the upstream RF signal received wirelessly to the EAM; and an amplifier, which is located between the EAM and the antenna, amplifies the downstream RF signal and outputs the amplified downstream RF signal to the antenna.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
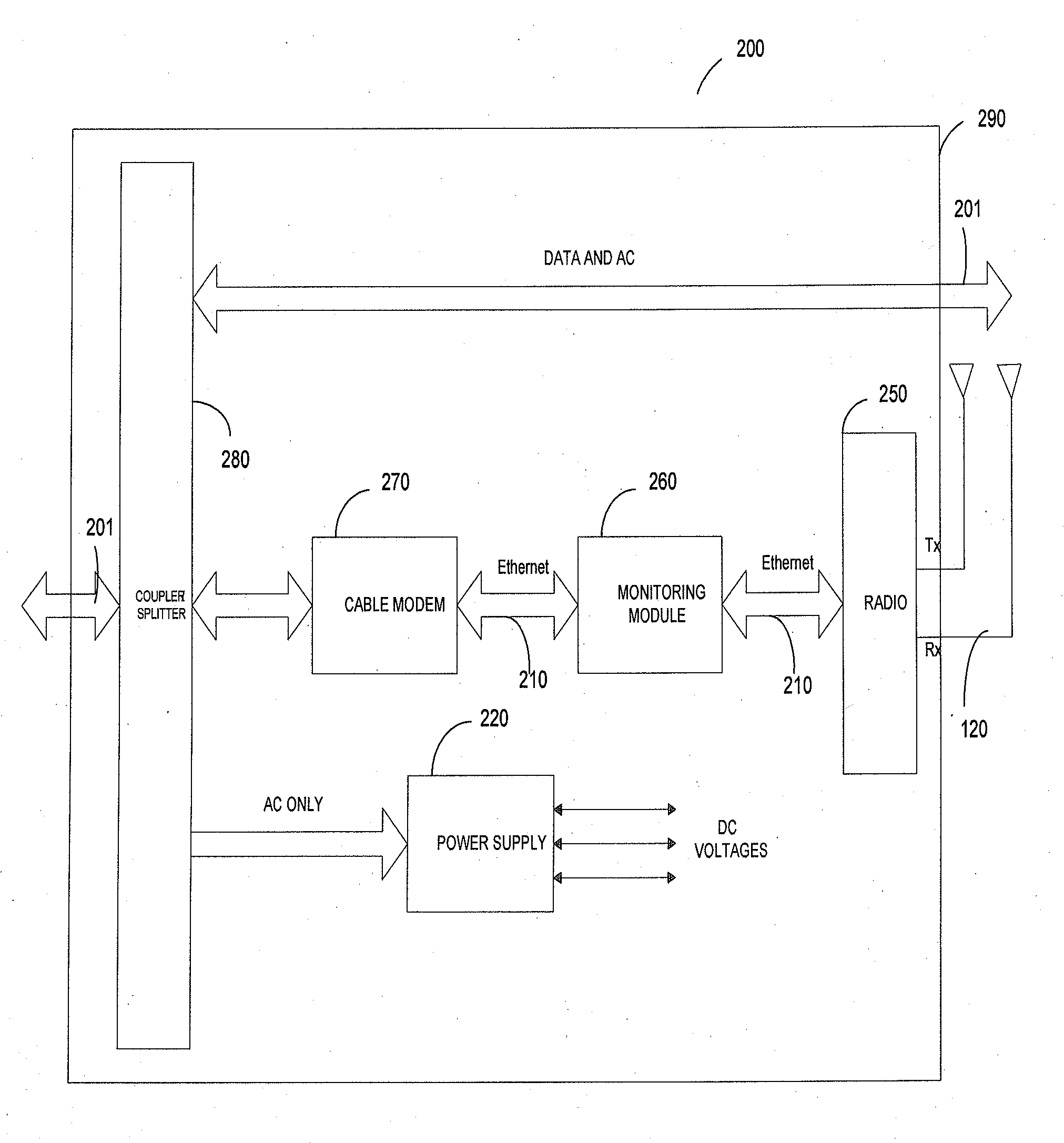
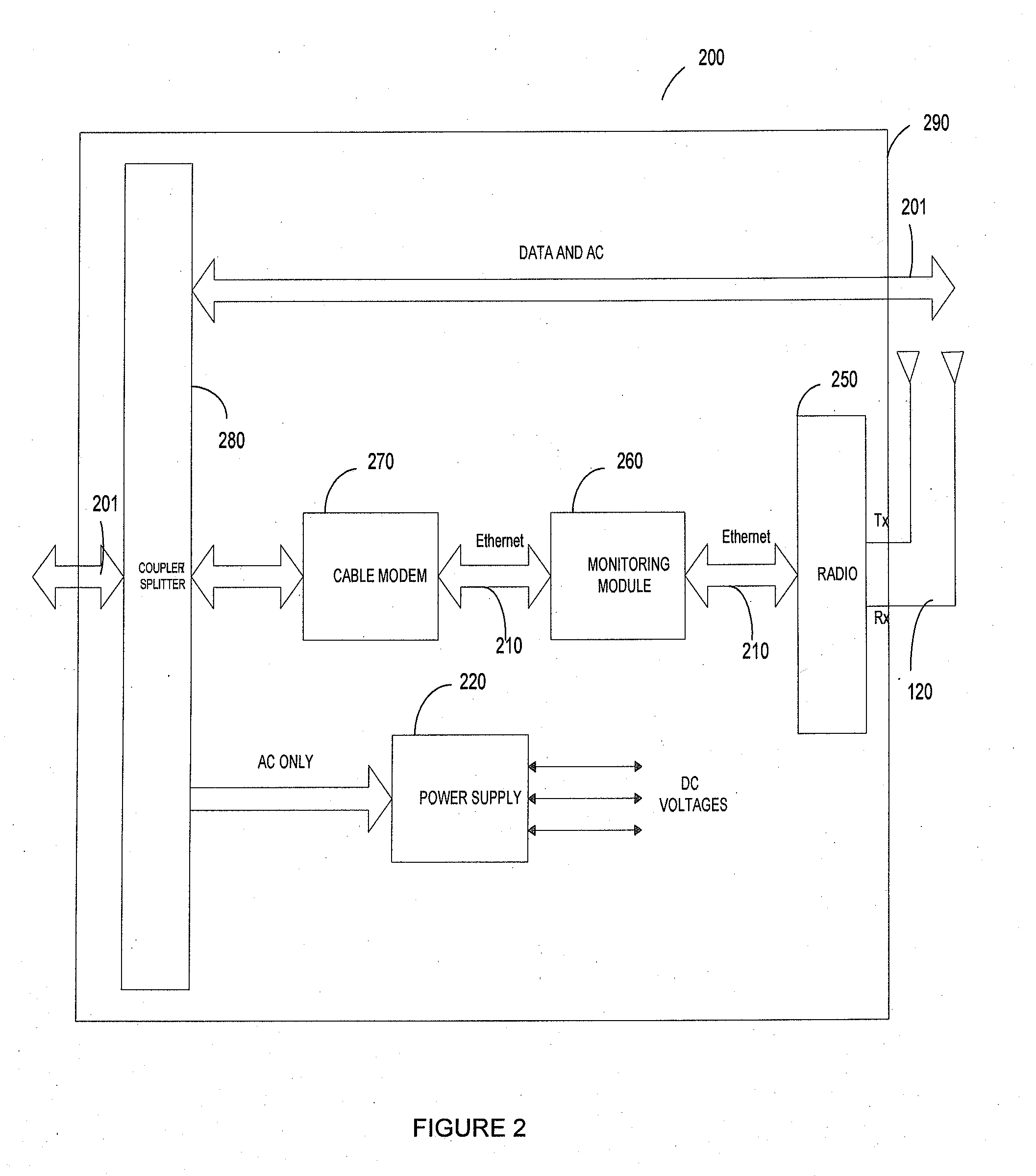
Messenger strand mounted pico-cell radio
InactiveUS20090304055A1Increase user capacityExtend wireless coverageSubstation equipmentHigh level techniquesTerrainTransceiver
A messenger strand mounted low-power pico-cell radio, having its own environmentally controlled box, mounted on utility messenger strands, connects to the cable using the Internet protocol (IP) for back-haul, and has in-band monitor and control capability. These pico-cell radios also receive power through the same cable connection. The configuration control and monitoring is by independent discretely-managed internal mechanisms that can be remotely addressed. These internal mechanisms include the modem for backhaul, wireless radio transceiver(s), and the system management device for operation, administration, maintenance, and control. Such pico-cell radios help to provide wireless connectivity and coverage efficiently by reducing dark spots in wireless coverage. Distributing these radios in reasonable, close proximity enables wireless coverage in difficult terrains, where current high power systems fail. The radios disclosed herein eliminate the need and cost for additional power lines and IP connection lines, and are therefore easy to install and maintain.
Owner:PUBLIC WIRELESS
Radio Resource Allocation for Cellular Wireless Networks
ActiveUS20090040972A1Strong signalKeep in touchNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumTransmitted power
Embodiments of the invention relate to cellular wireless networks and are particularly suited to networks including different types of base stations. So-called femtocell types of base stations are typically deployed within a subscriber's premises and operate at low transmit power, providing a very limited area of wireless coverage. A femtocell is typically deployed within the area of wireless coverage of a conventional macrocell, occupying the same frequency spectrum and timeslots as the macrocell. A problem can be presented to a user equipment terminal that is close to the femtocell but unable to gain access to it, because the transmissions from the femtocell may appear as interference to the user equipment terminal, preventing it from accessing the macrocell which it could otherwise access. A cellular wireless network according to an embodiment of the invention employs a method of allocating radio resource to femtocells so that the transmissions from femtocells do not occupy the same radio resource blocks as those used by the macrocell for signalling; embodiments of the invention thereby prevent interference associated with signalling to cause a connection to be lost, or prevent a connection being set up.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Controlling femtocell operation bandwidth based on interference to macrocell
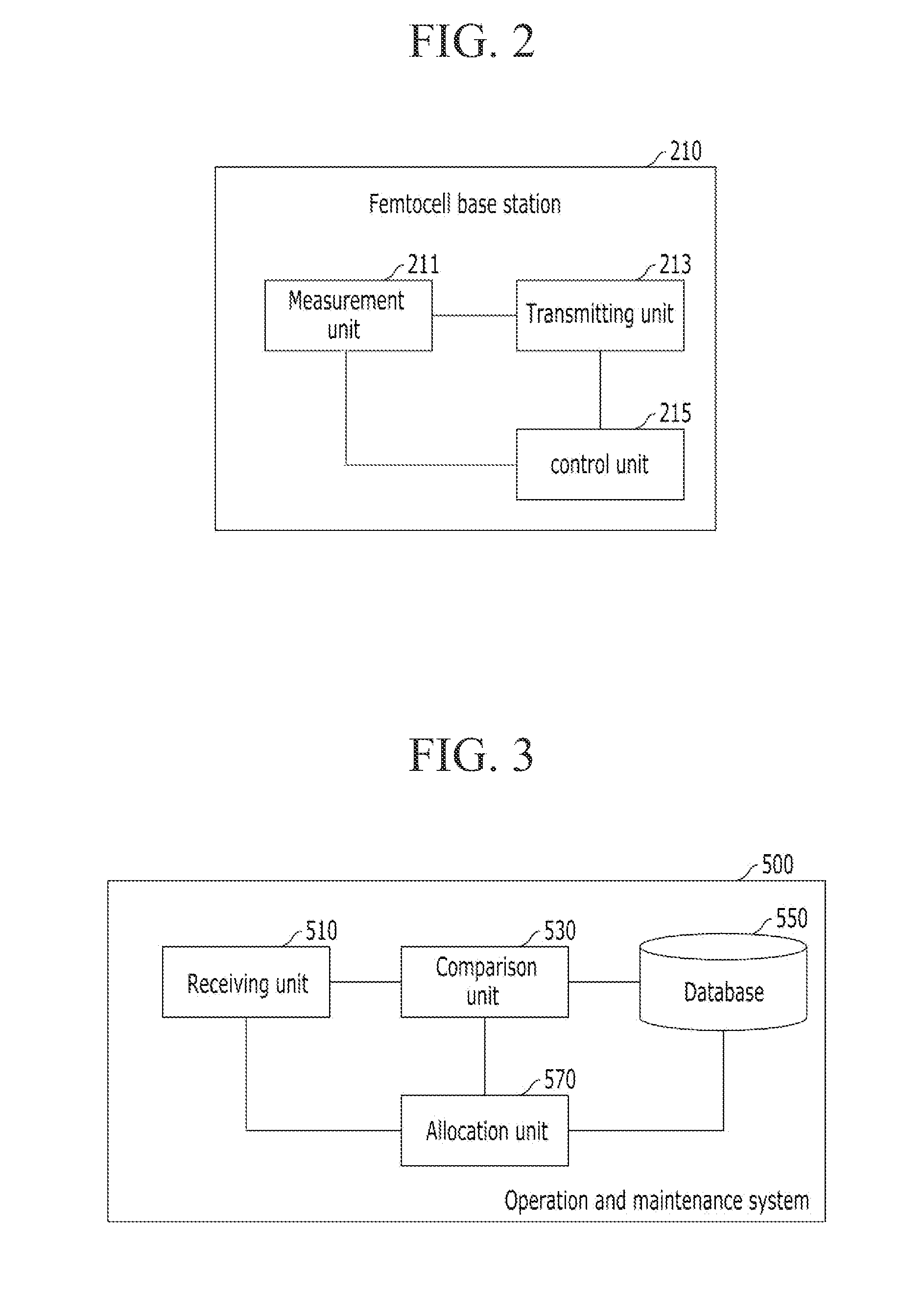
ActiveUS20120264445A1Interference minimizationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesPicocellControl unit
The disclosure is related to controlling an operation bandwidth for a femtocell based on femtocell interference to a macrocell in order to minimize femtocell interference. A femtocell base station may include a measurement unit, a transmitting unit, and a control unit. The measurement unit may be configured to measure an interference amount of a macrocell adjacent to the femtocell base station. The transmitting unit may be configured to transmit the measured interference amount to a system. The control unit may be configured to i) accept an allocated operation bandwidth by the system and ii) control transmission and reception of signals with the allocated operation bandwidth. The operation bandwidth may be adjustable by the system based on the measured interference amount.
Owner:VALUE INNOVATION PARTNERS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com