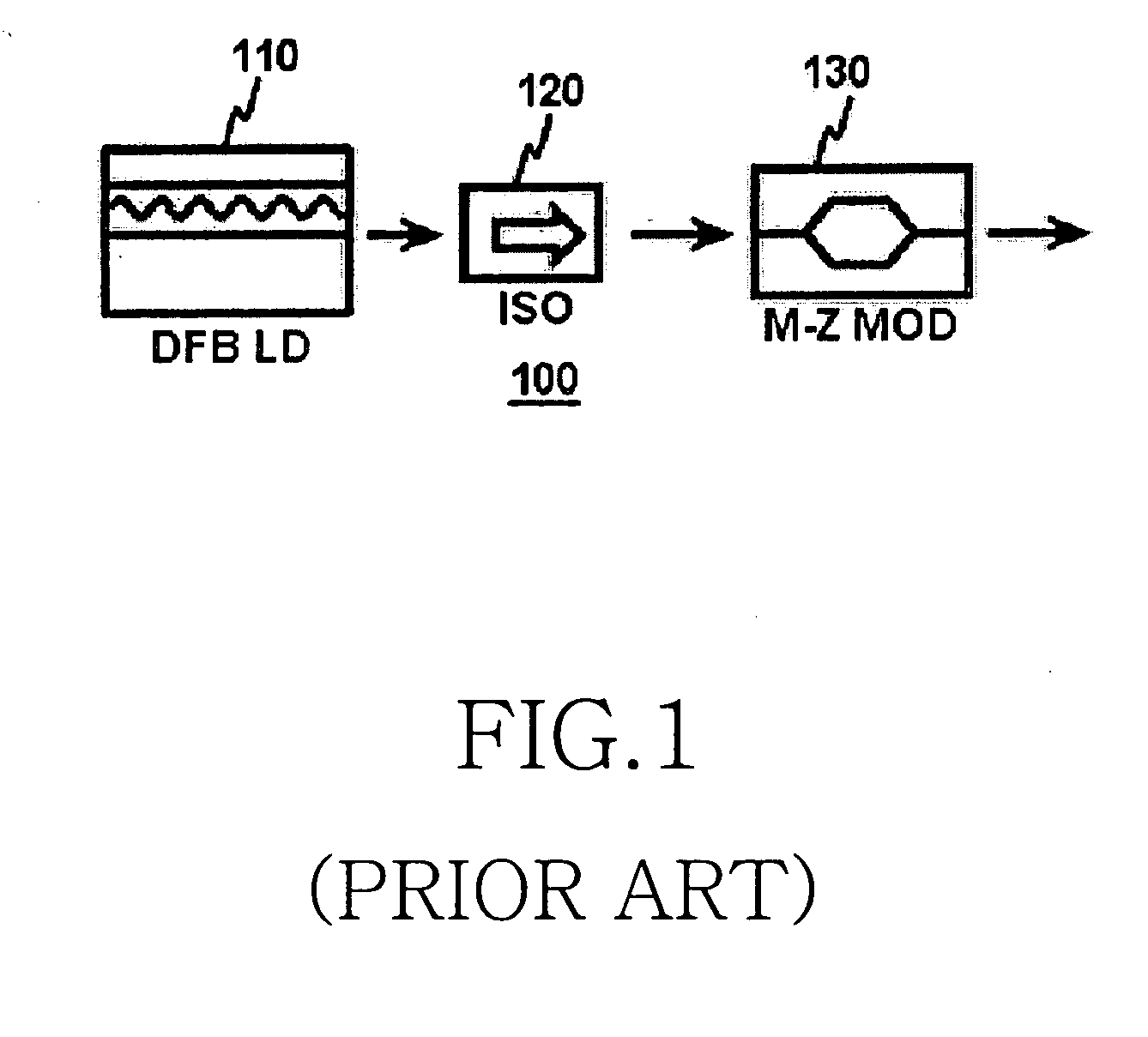
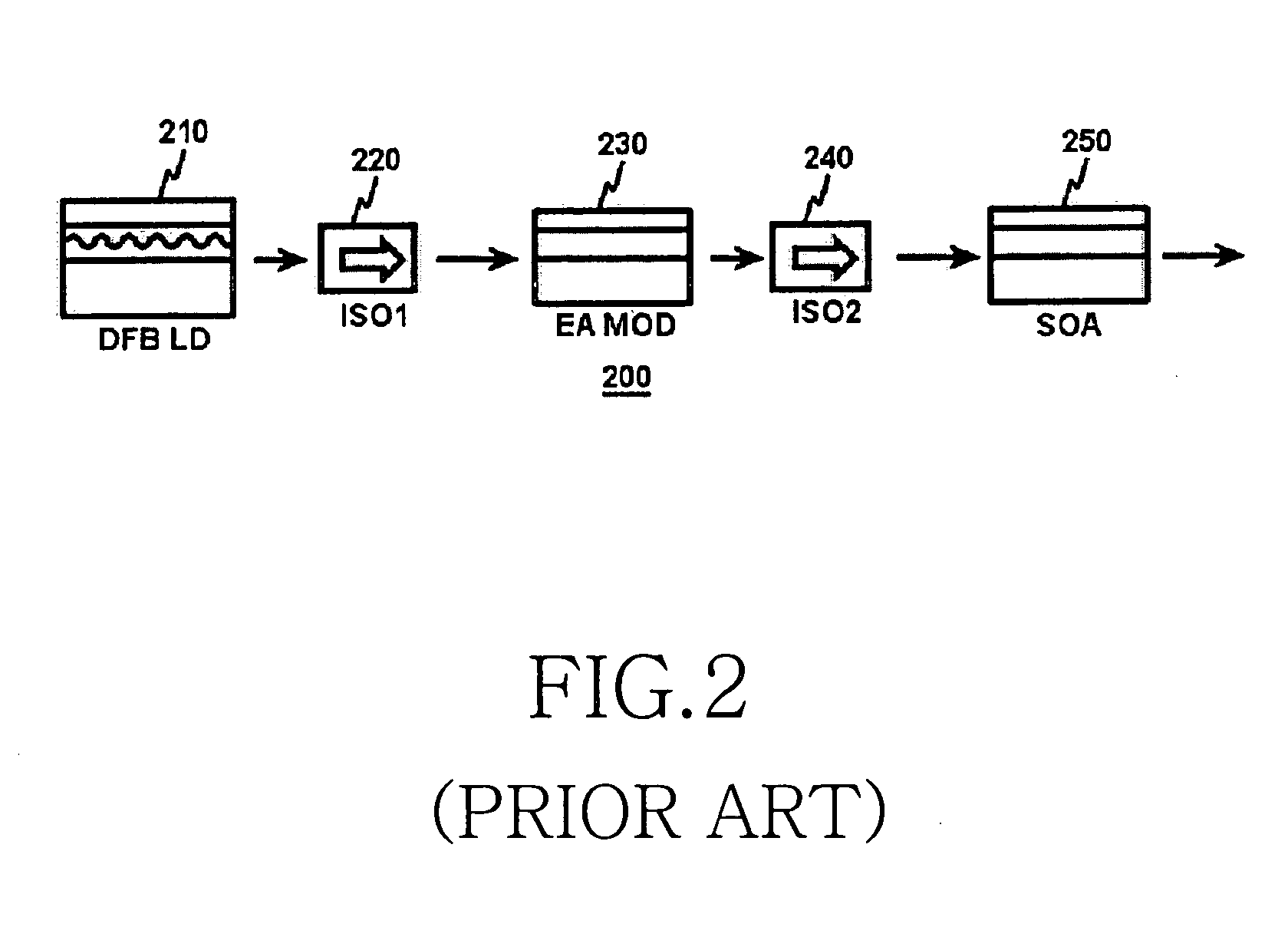
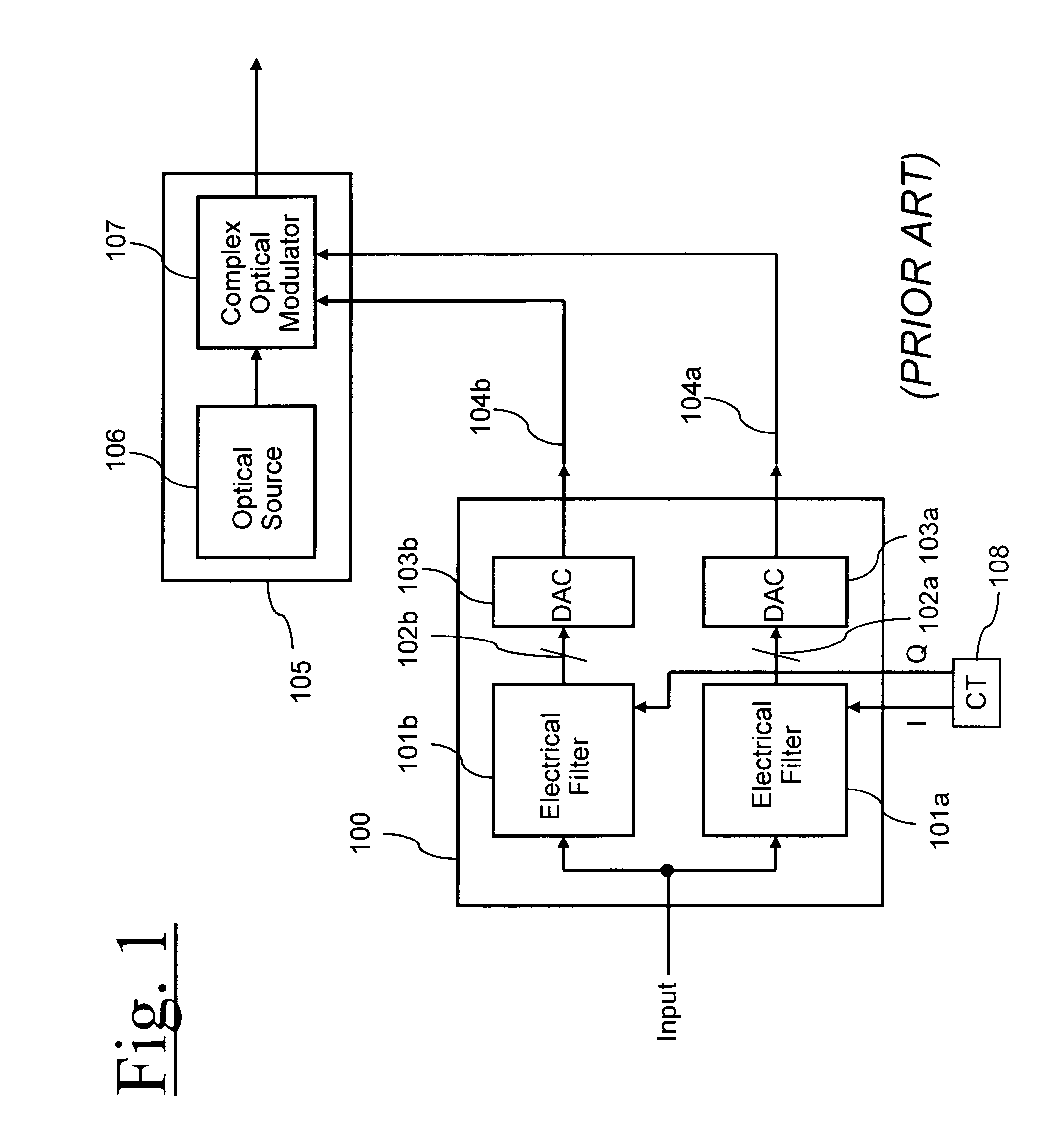
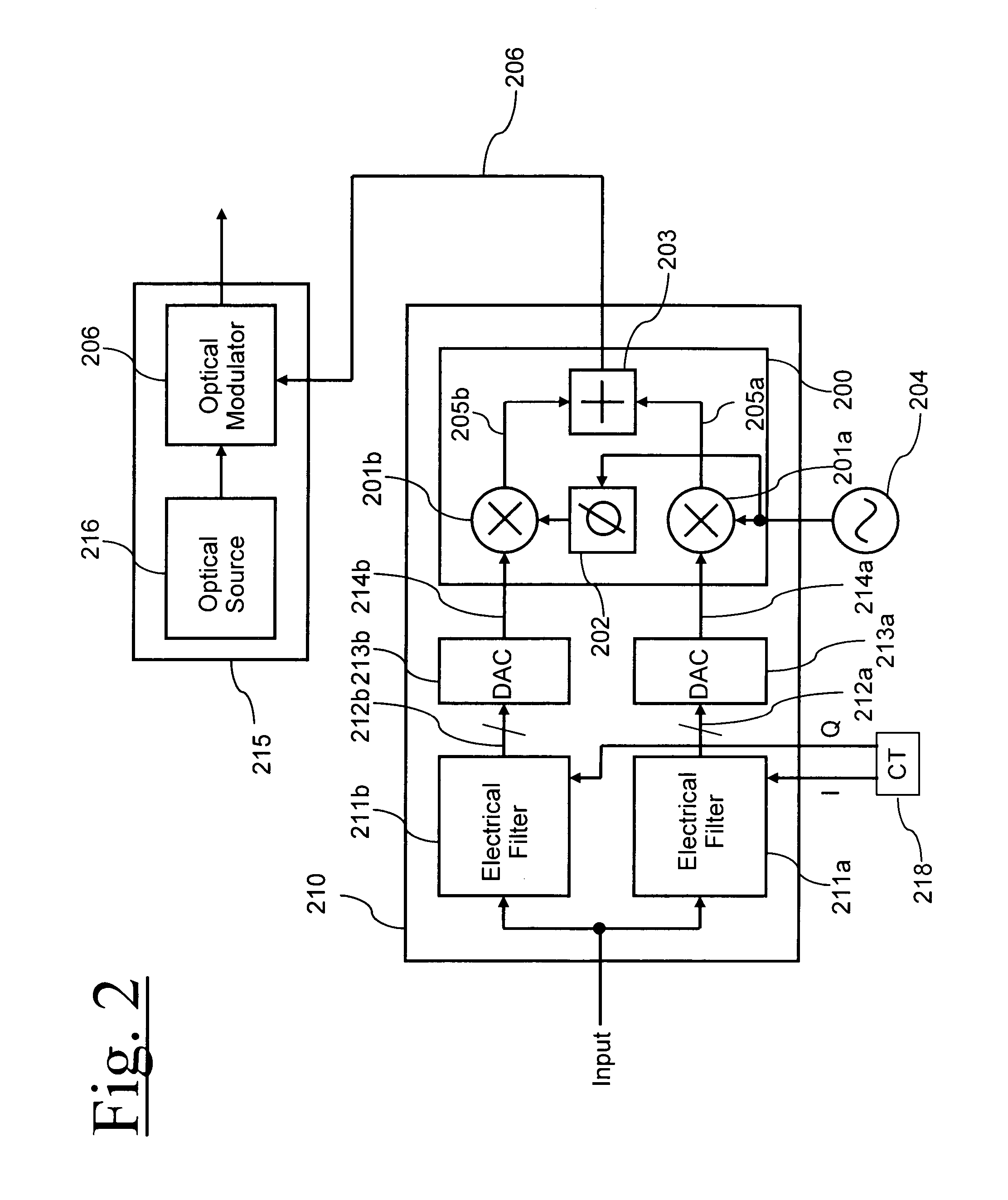
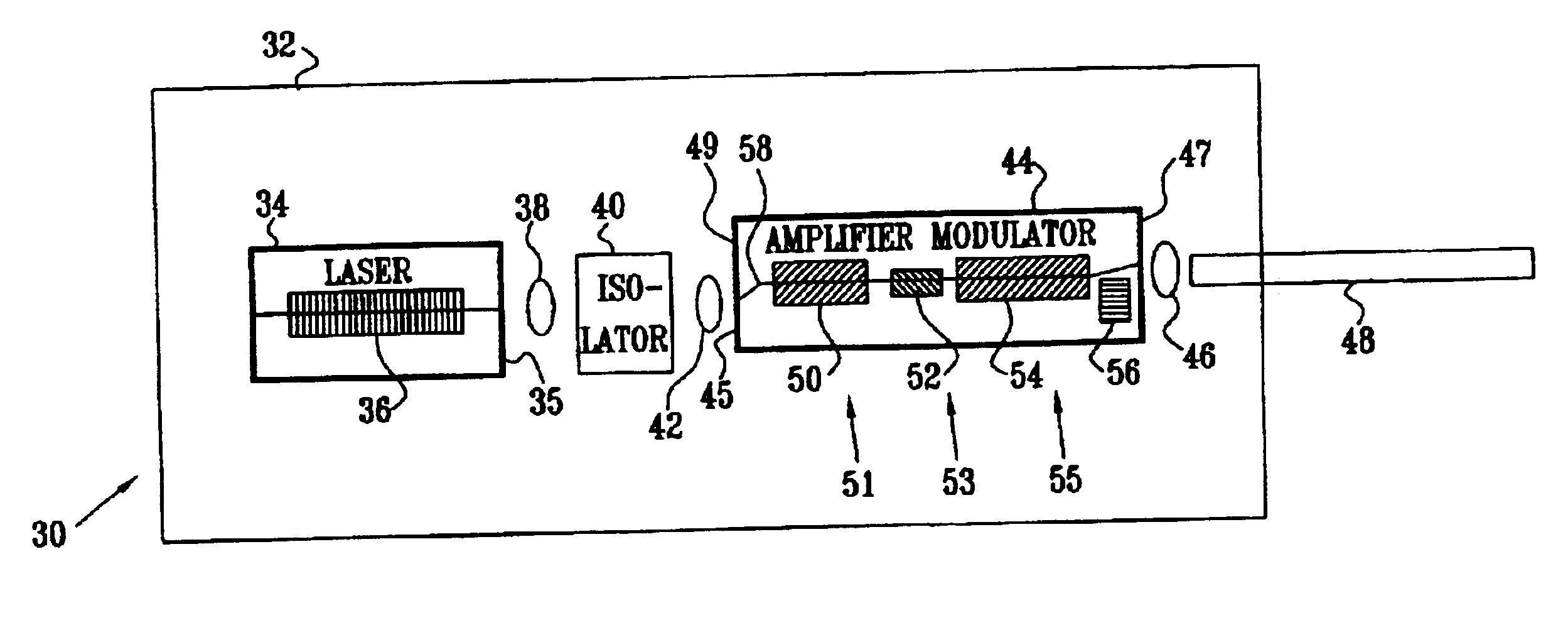
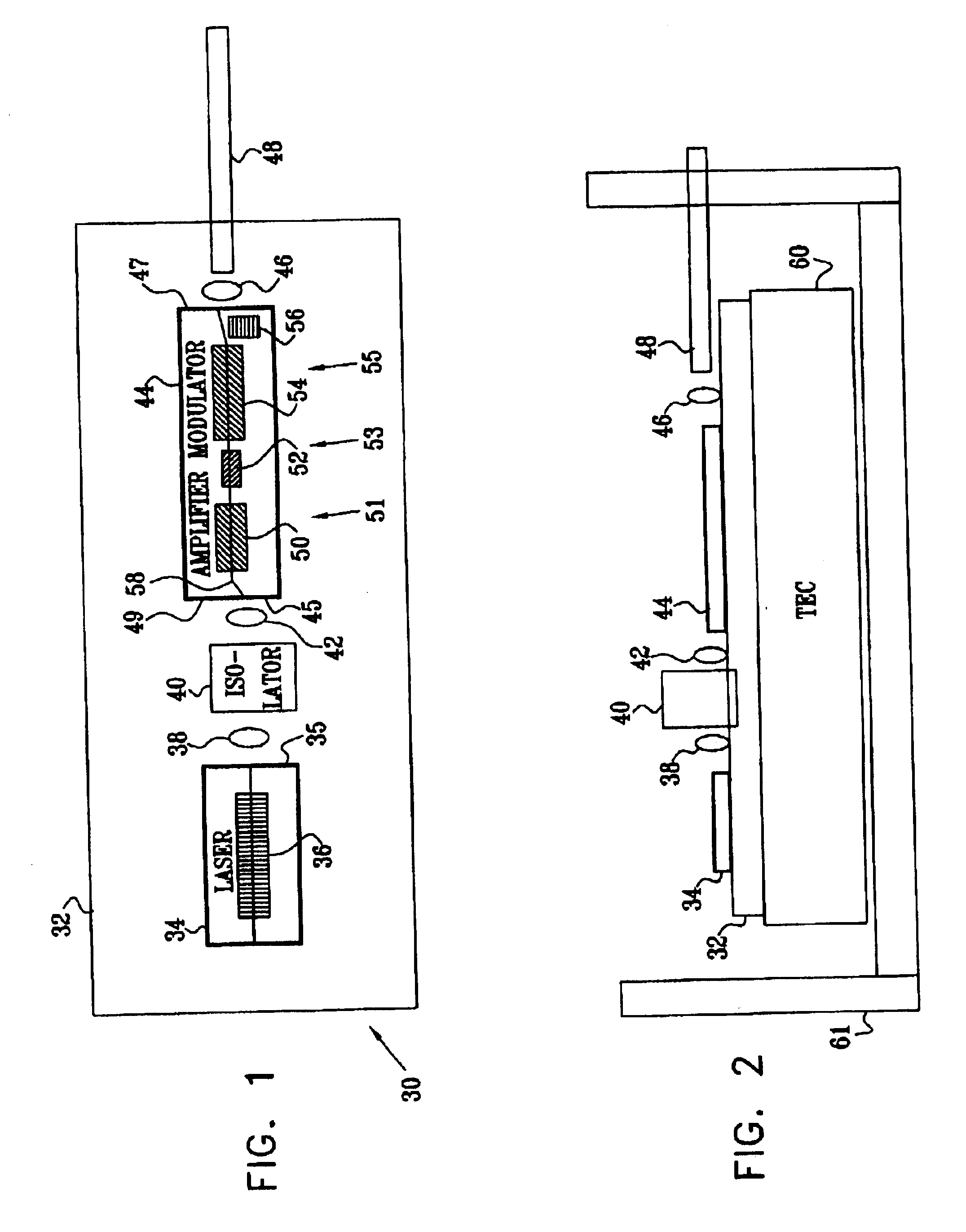
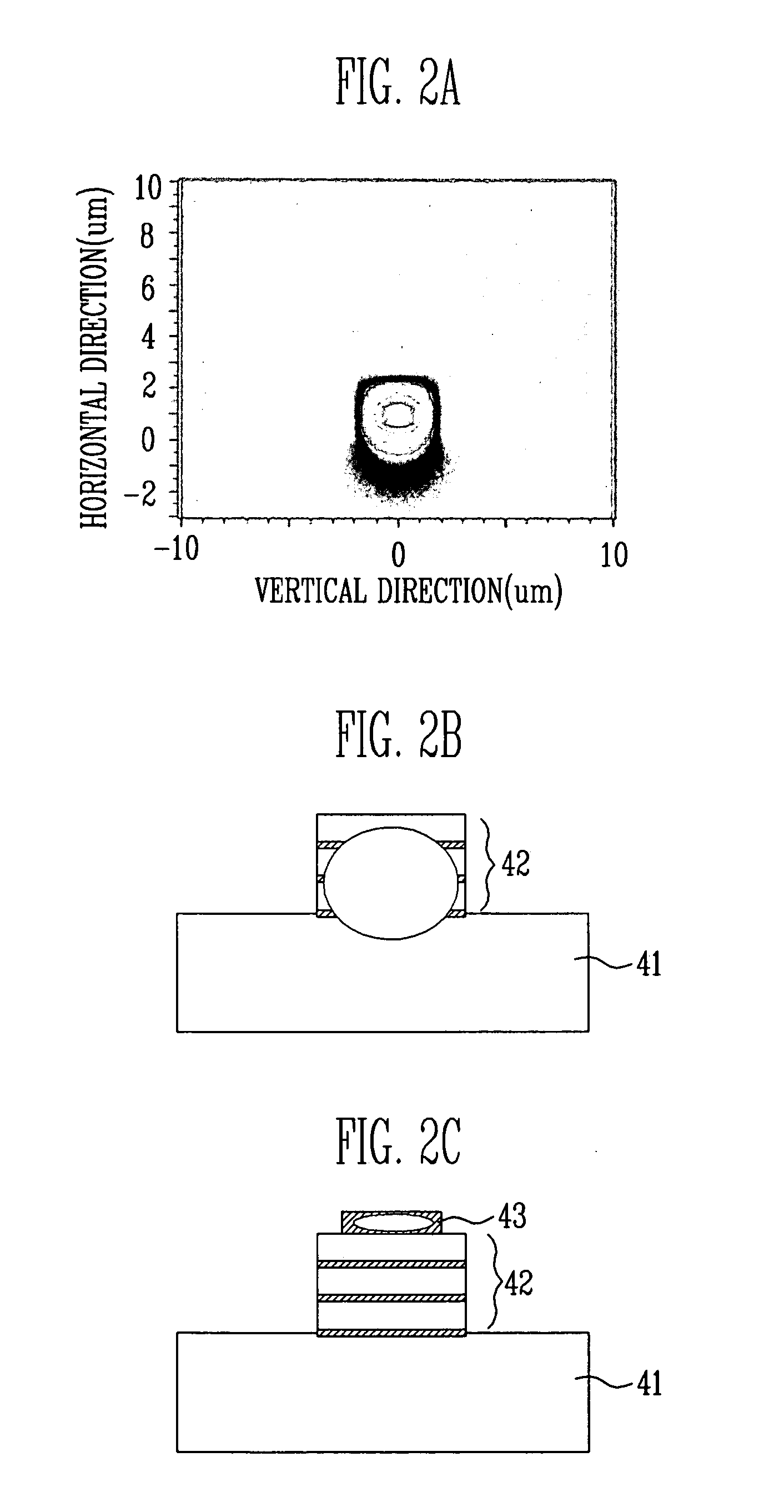
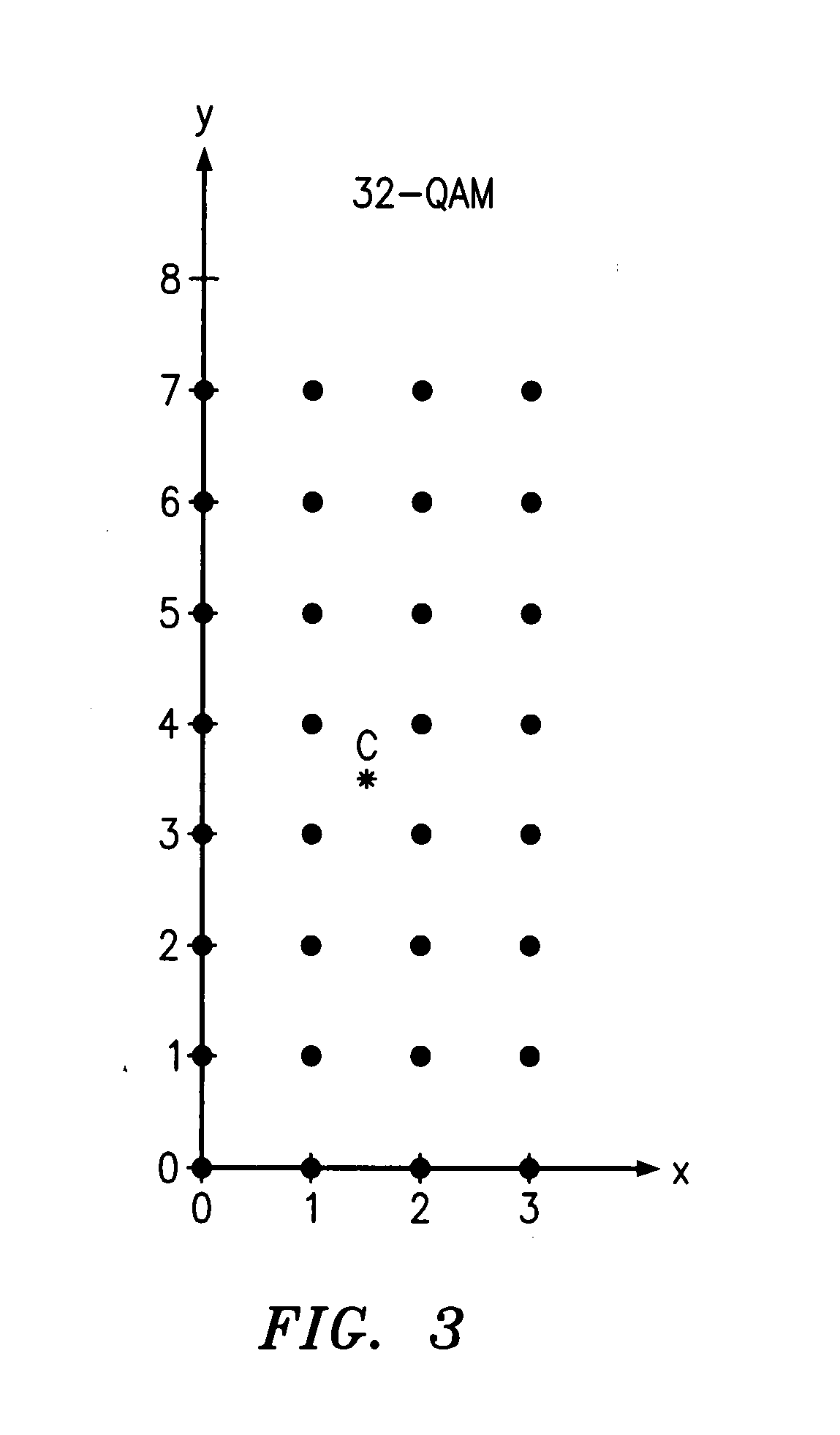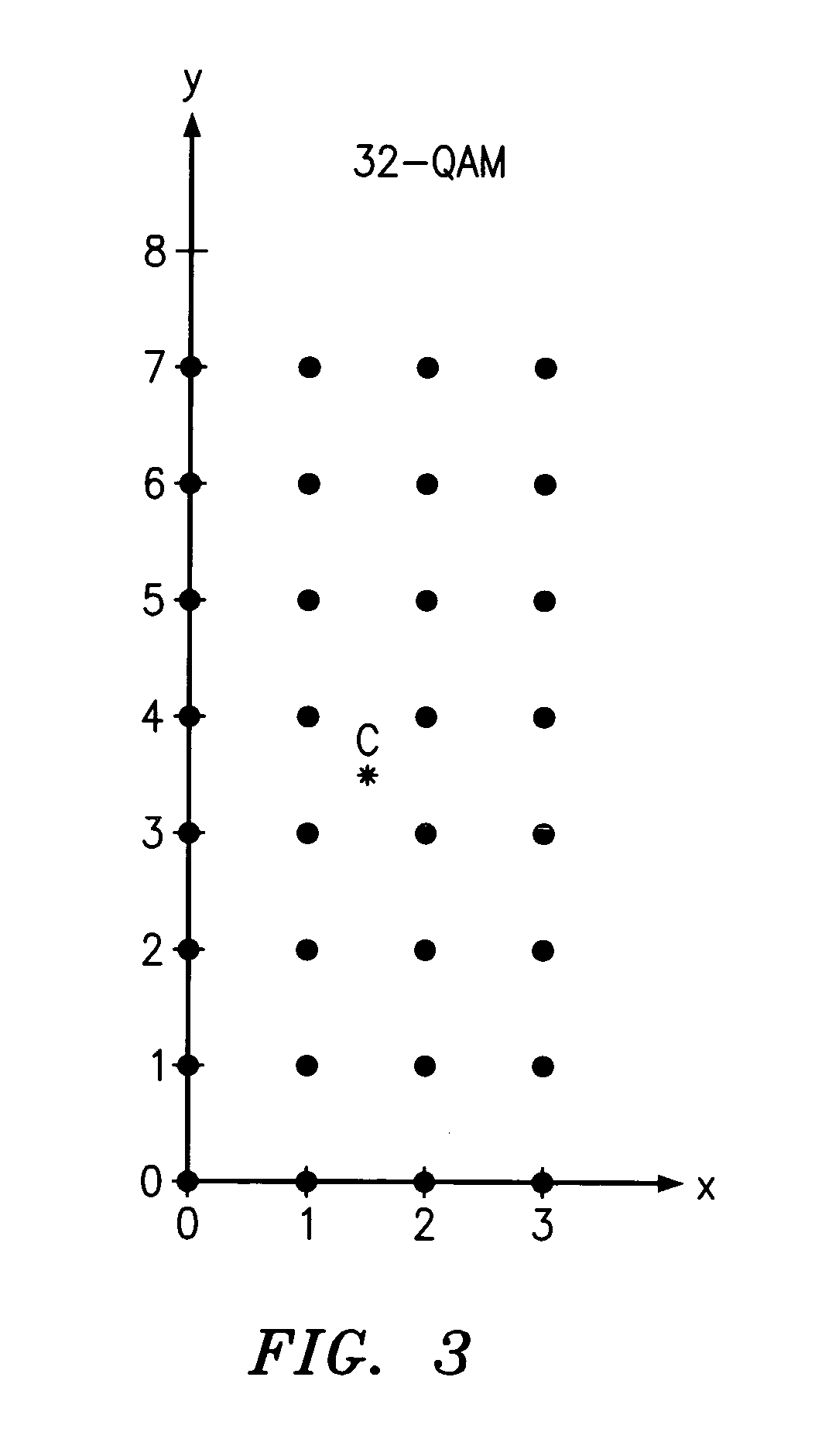Patents
Literature
253 results about "Electro-absorption modulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
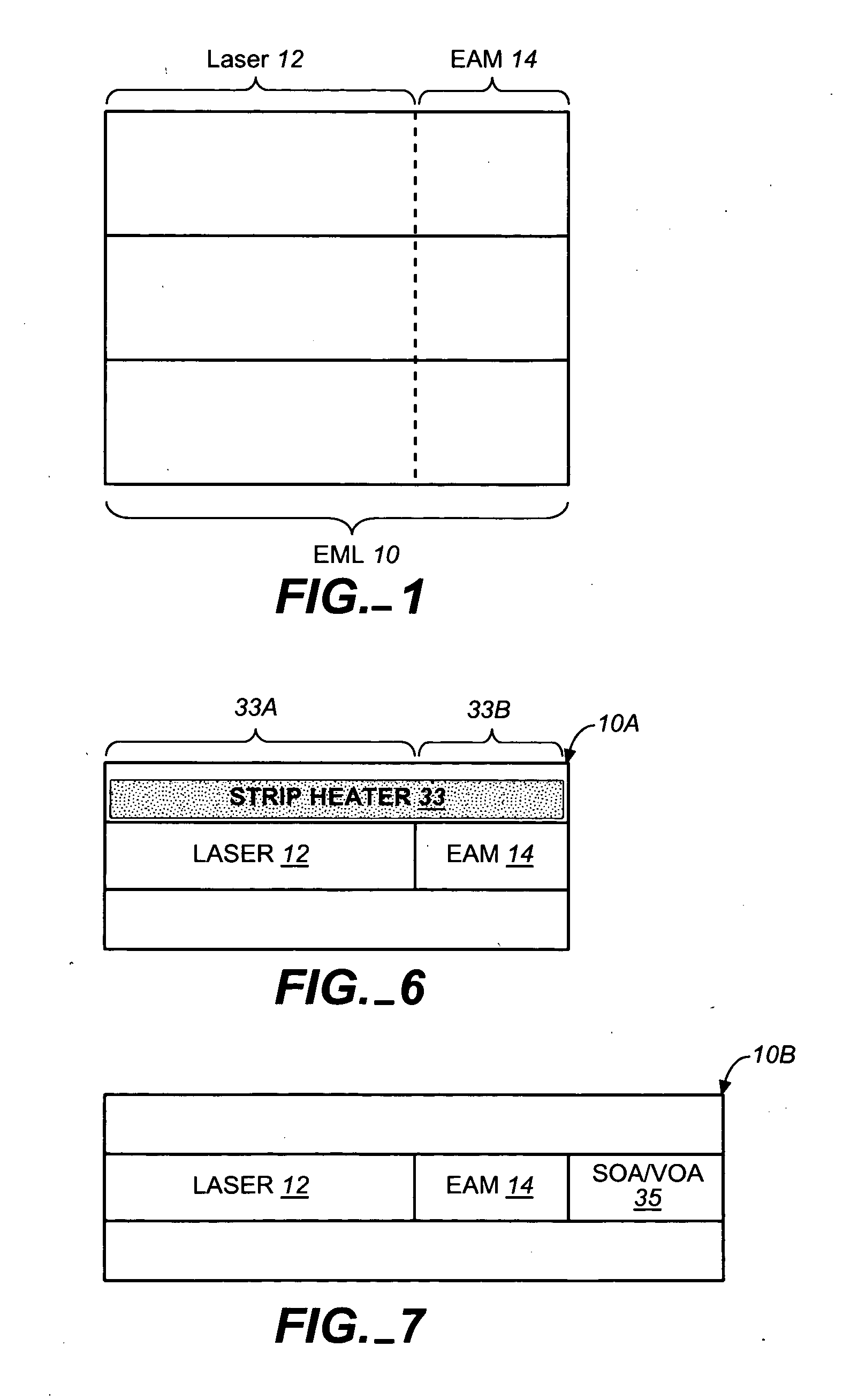
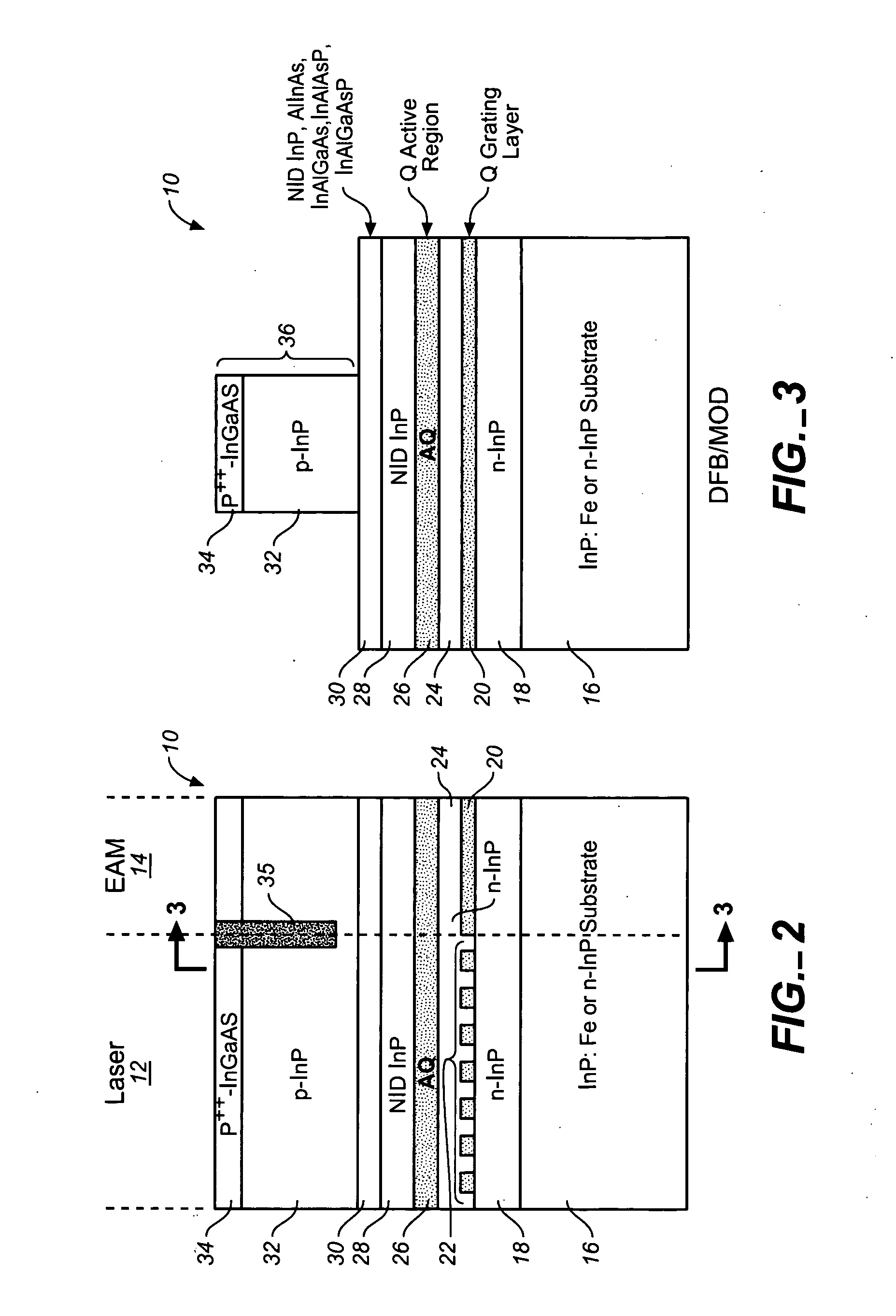
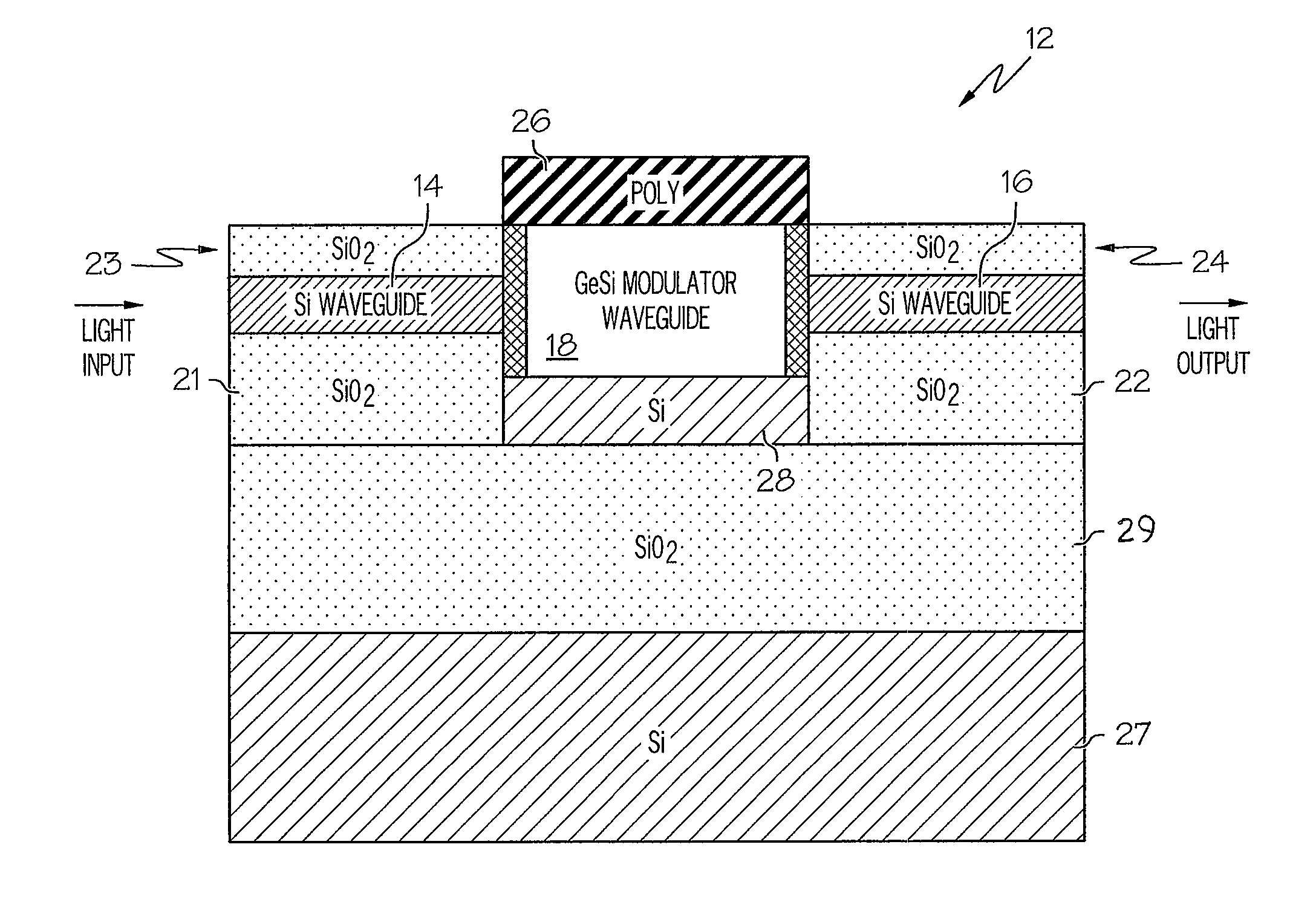
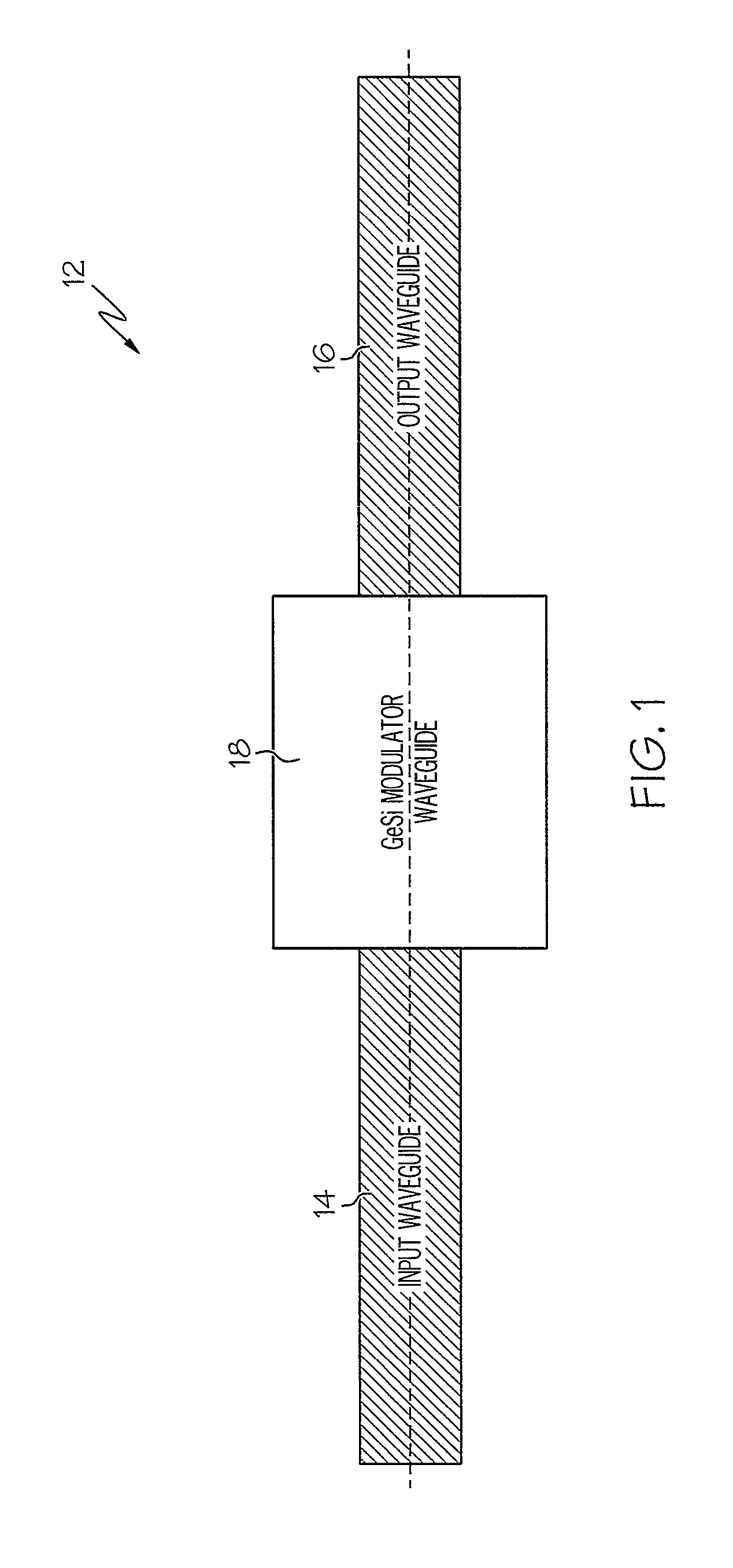
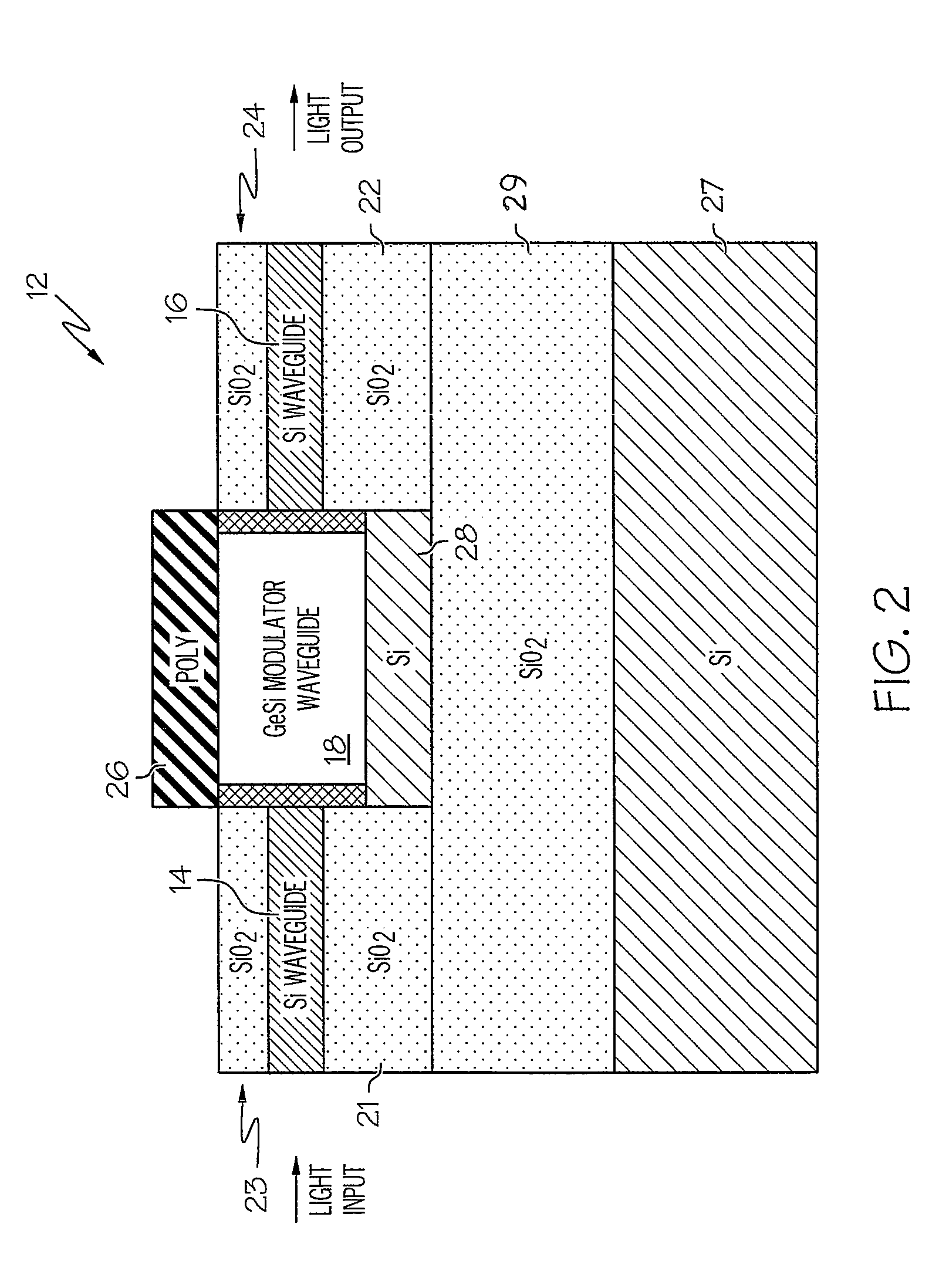
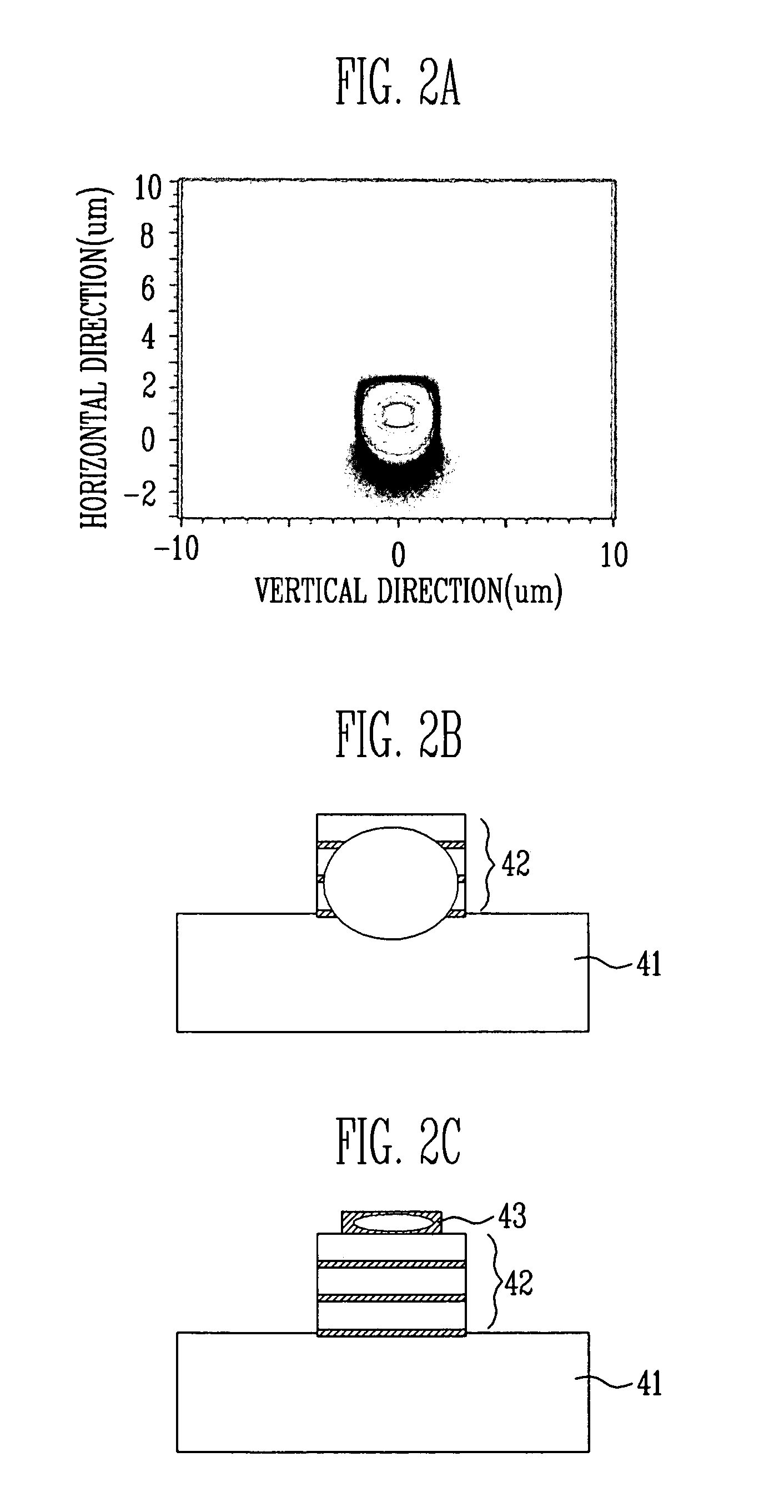
An electro-absorption modulator (EAM) is a semiconductor device which can be used for modulating the intensity of a laser beam via an electric voltage. Its principle of operation is based on the Franz-Keldysh effect, i.e., a change in the absorption spectrum caused by an applied electric field, which changes the bandgap energy (thus the photon energy of an absorption edge) but usually does not involve the excitation of carriers by the electric field.
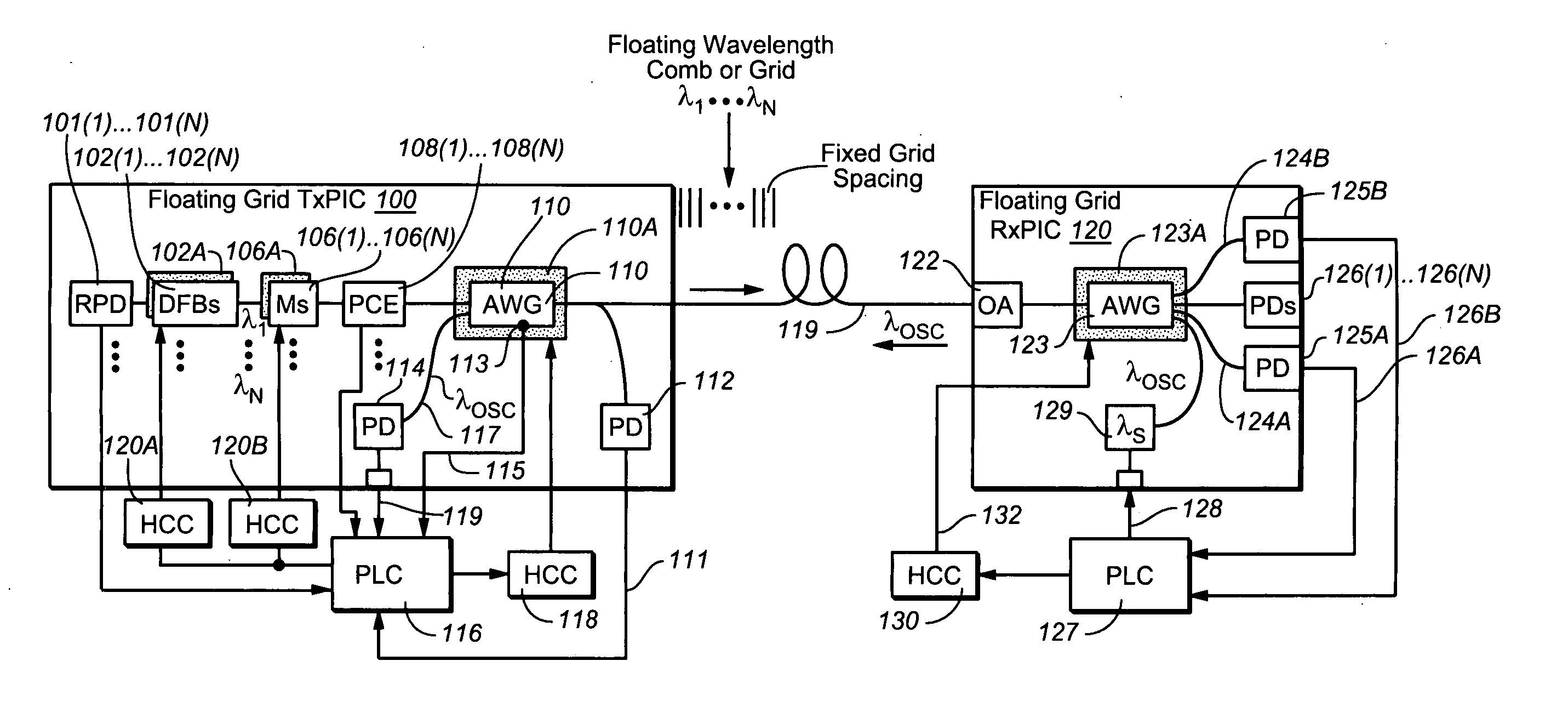
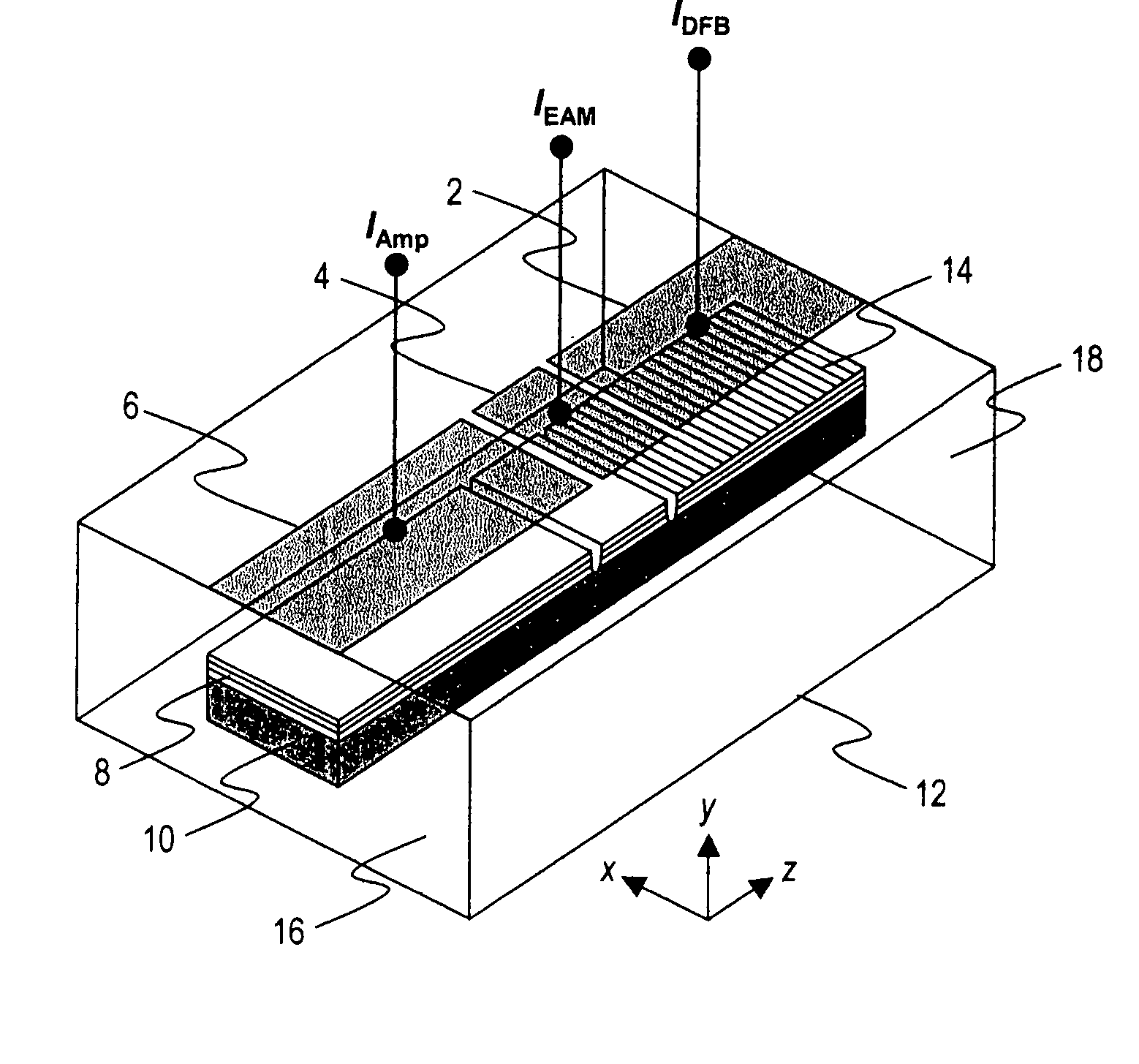
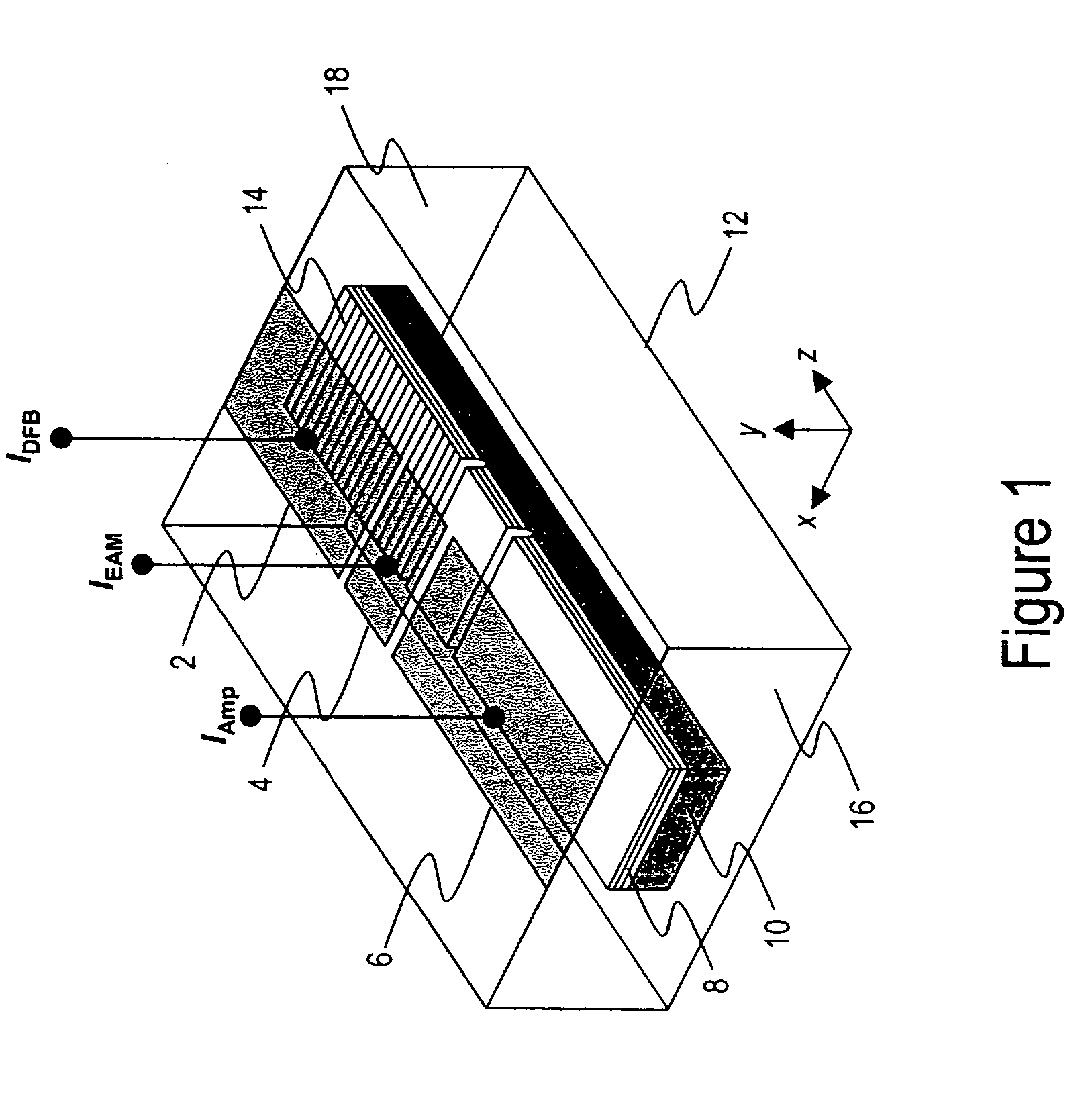
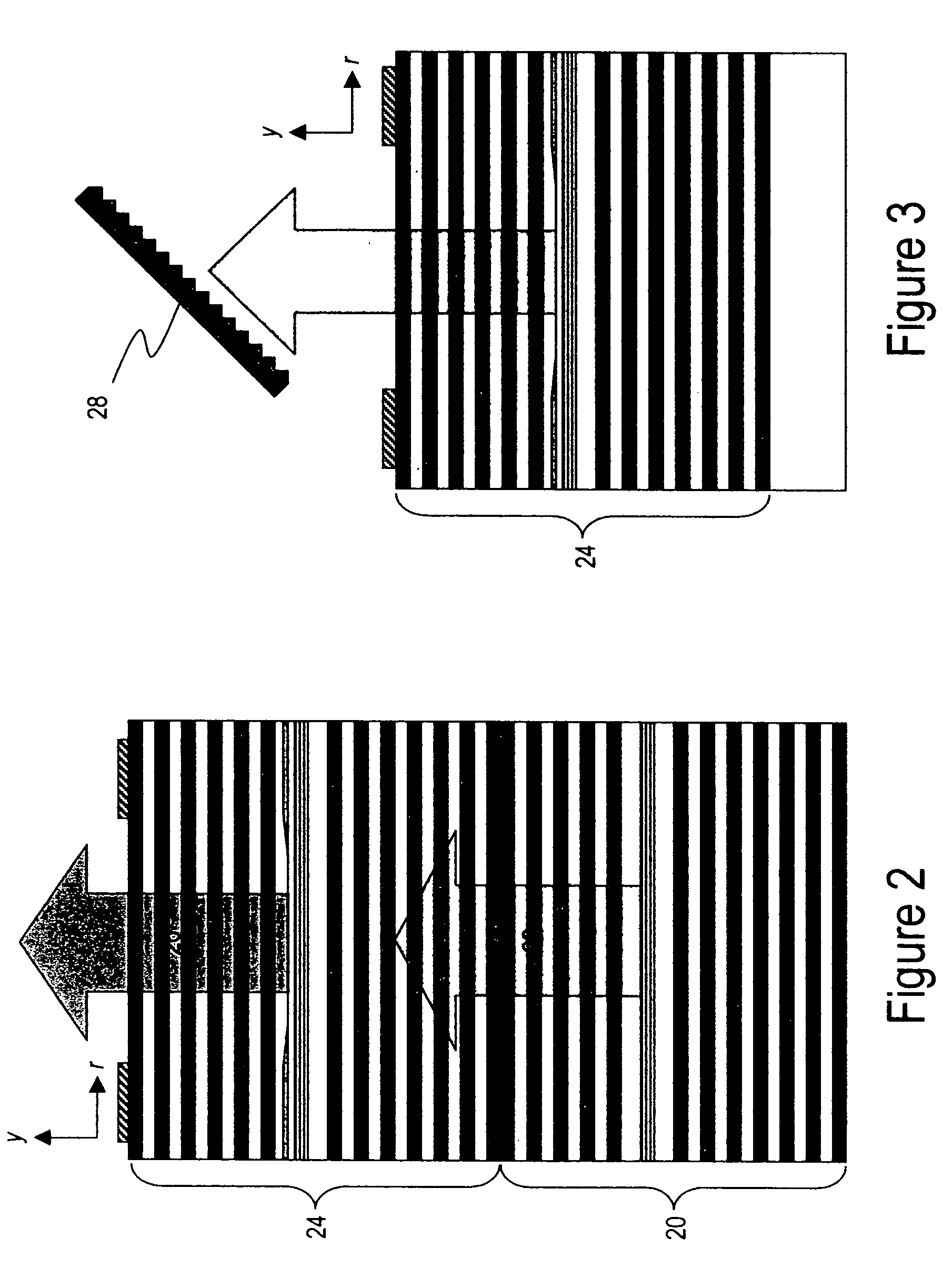
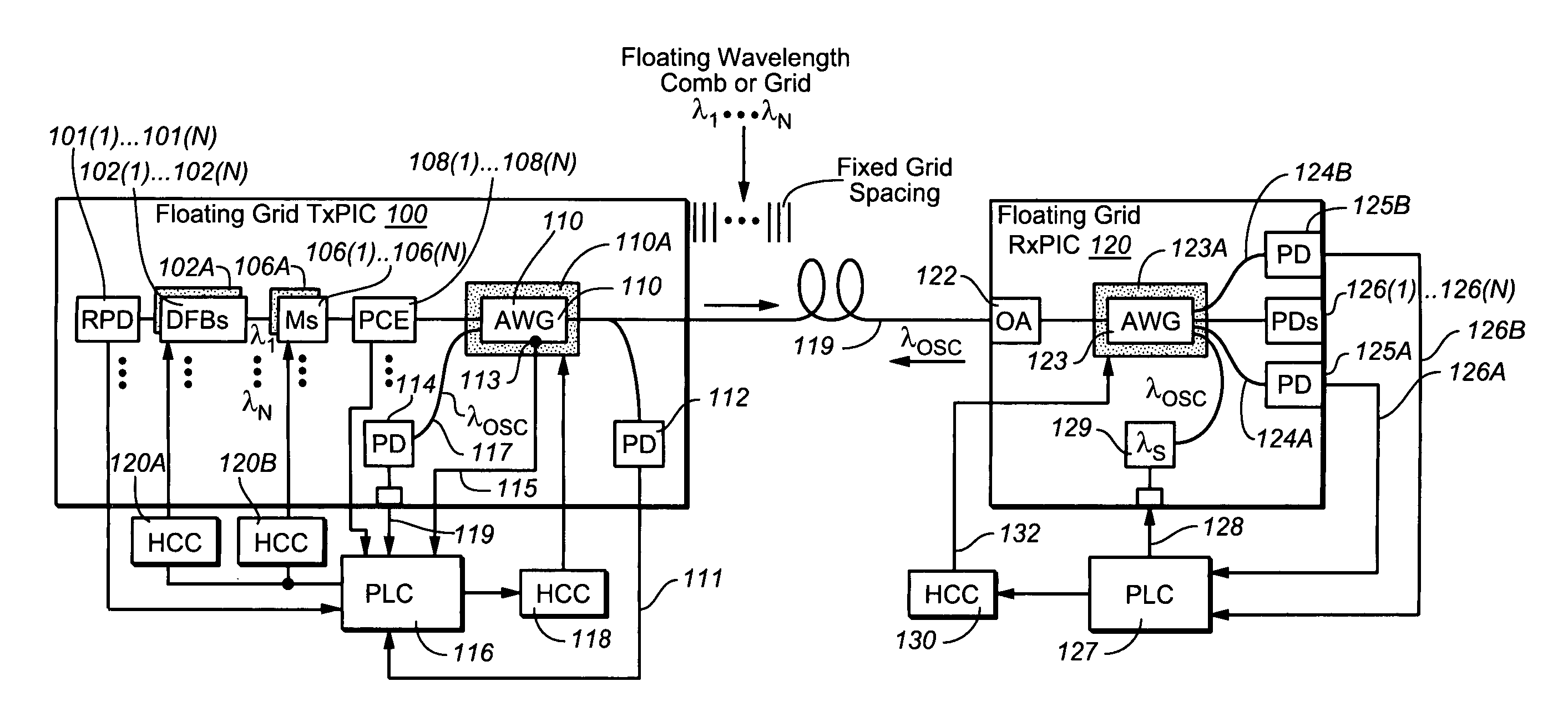
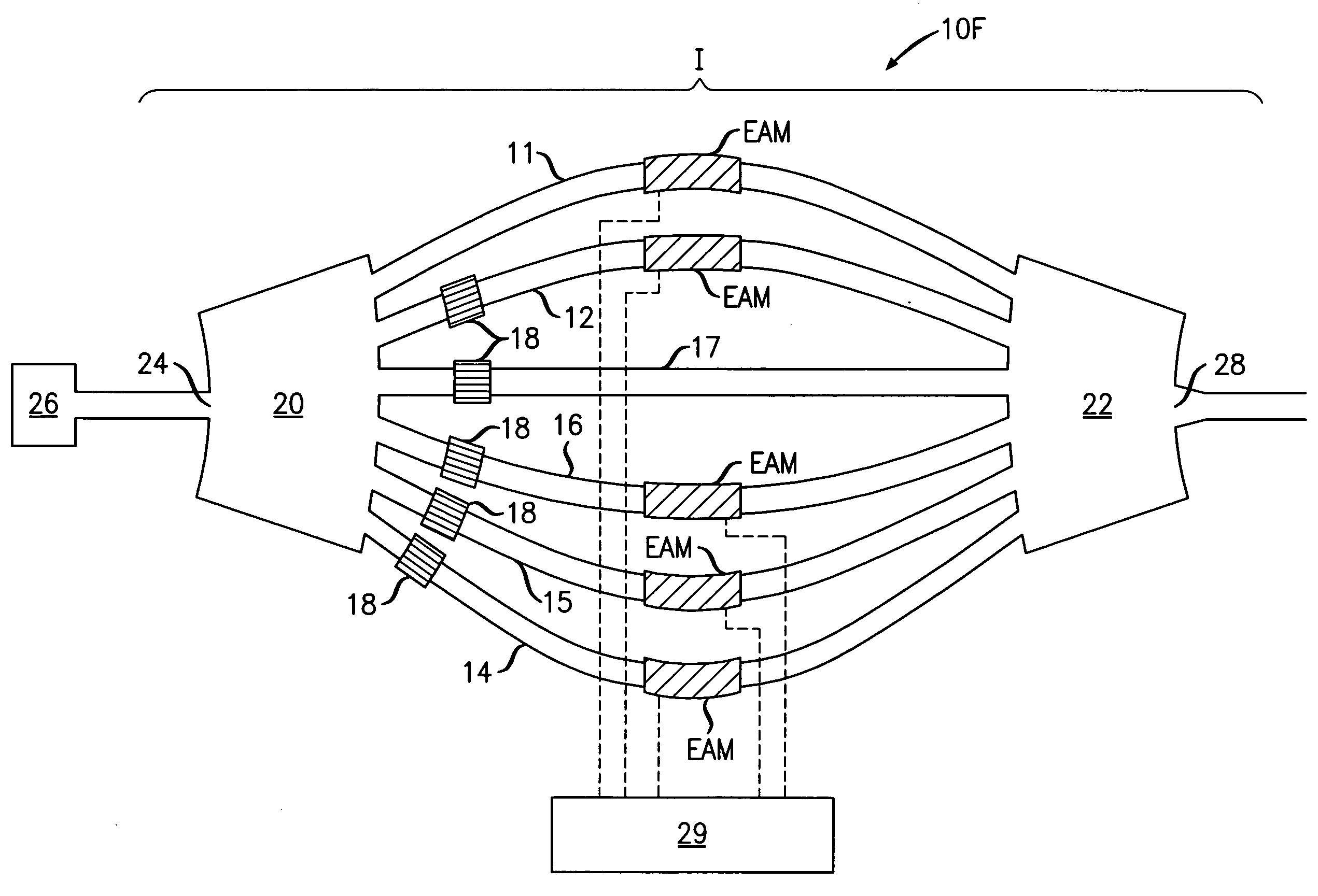
Coolerless photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for WDM transmission networks and PICs operable with a floating signal channel grid changing with temperature but with fixed channel spacing in the floating grid
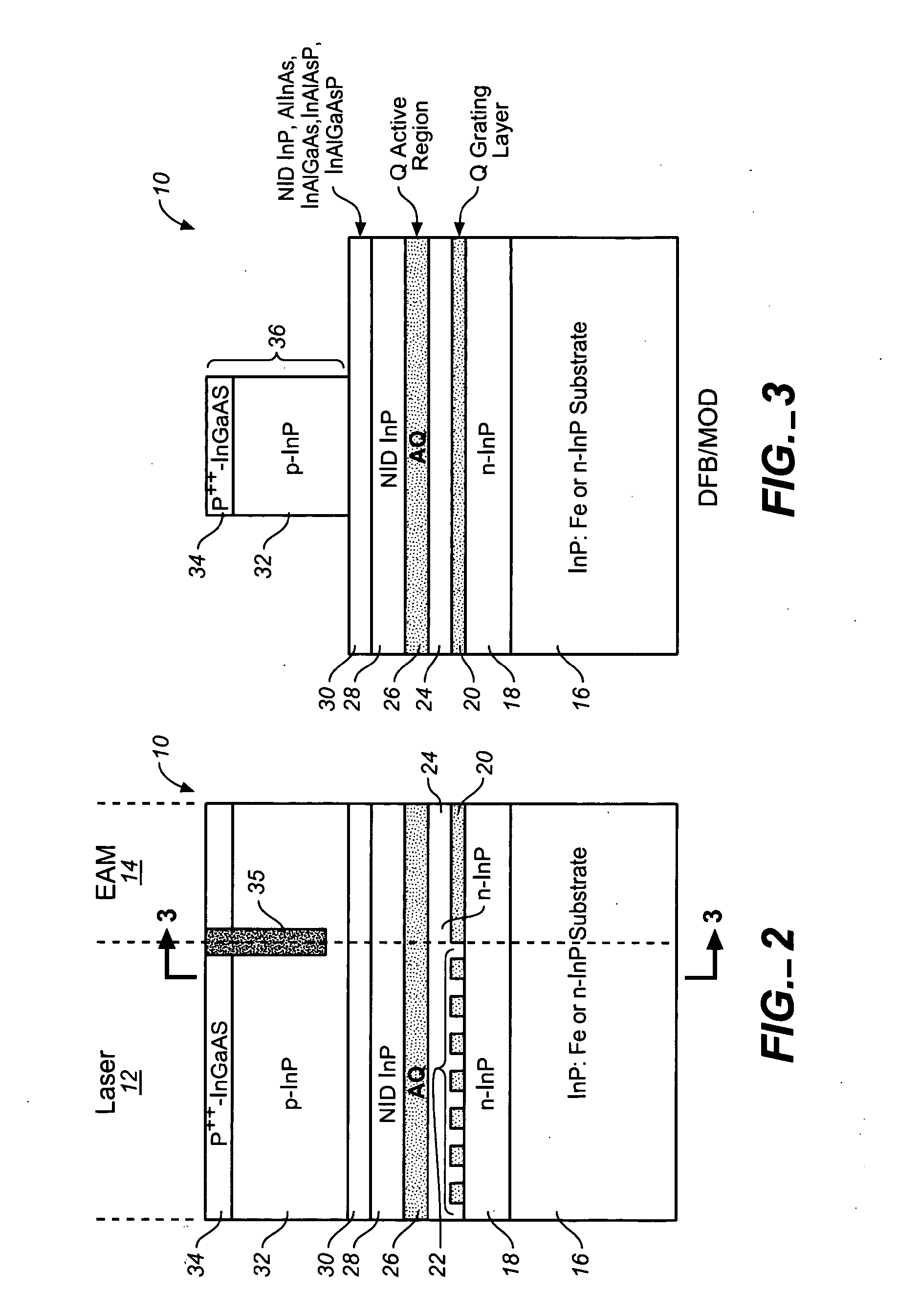
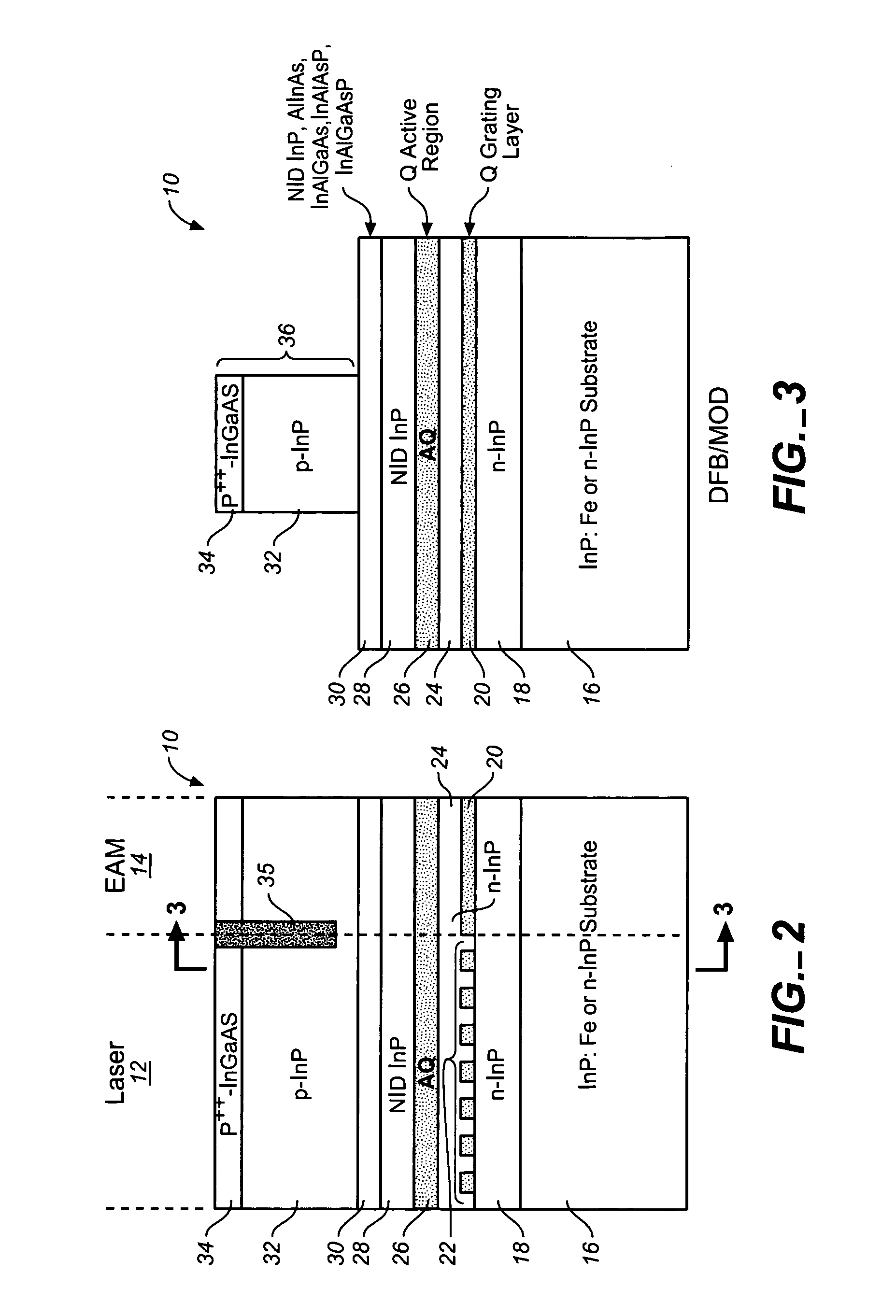
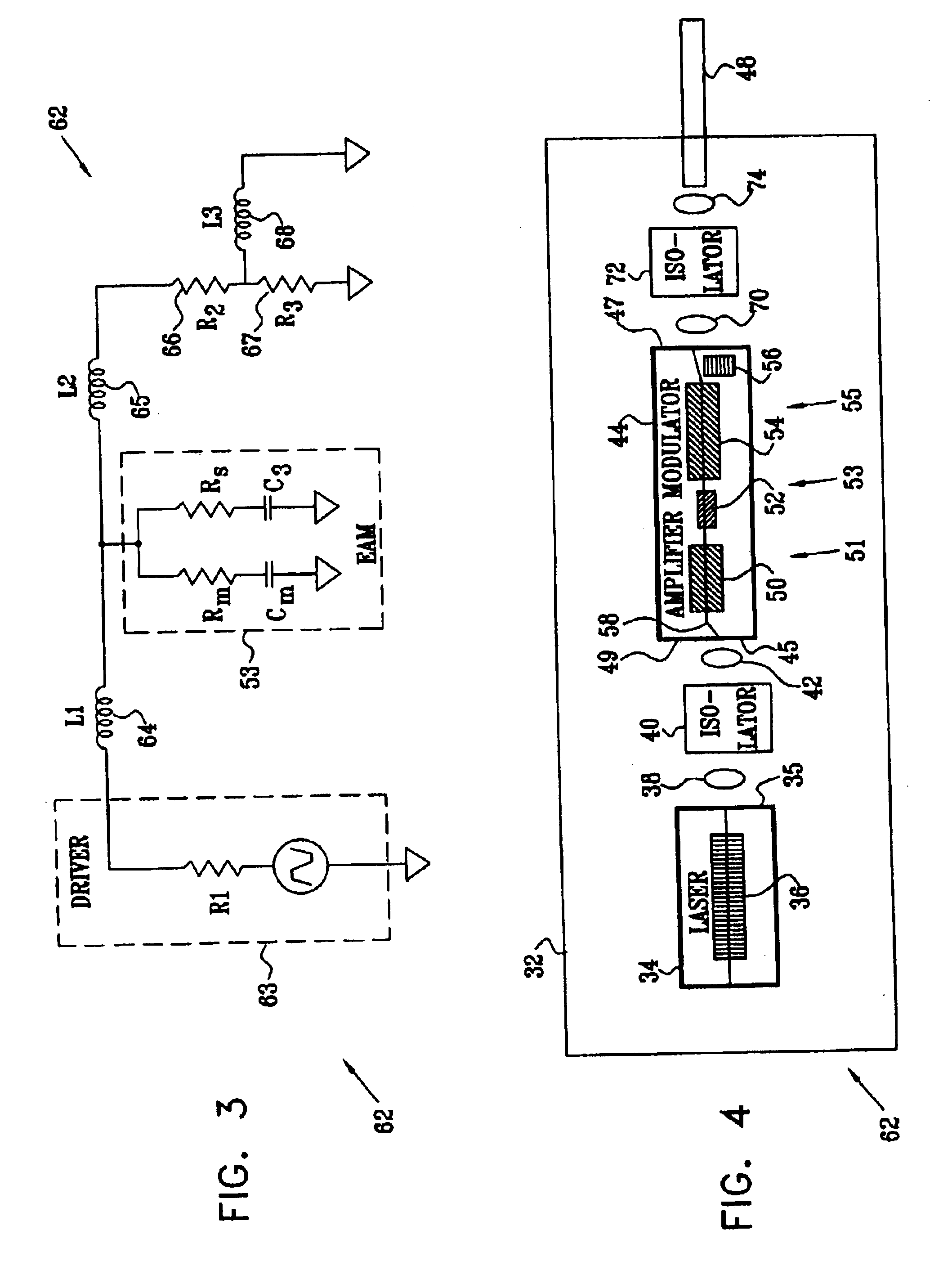
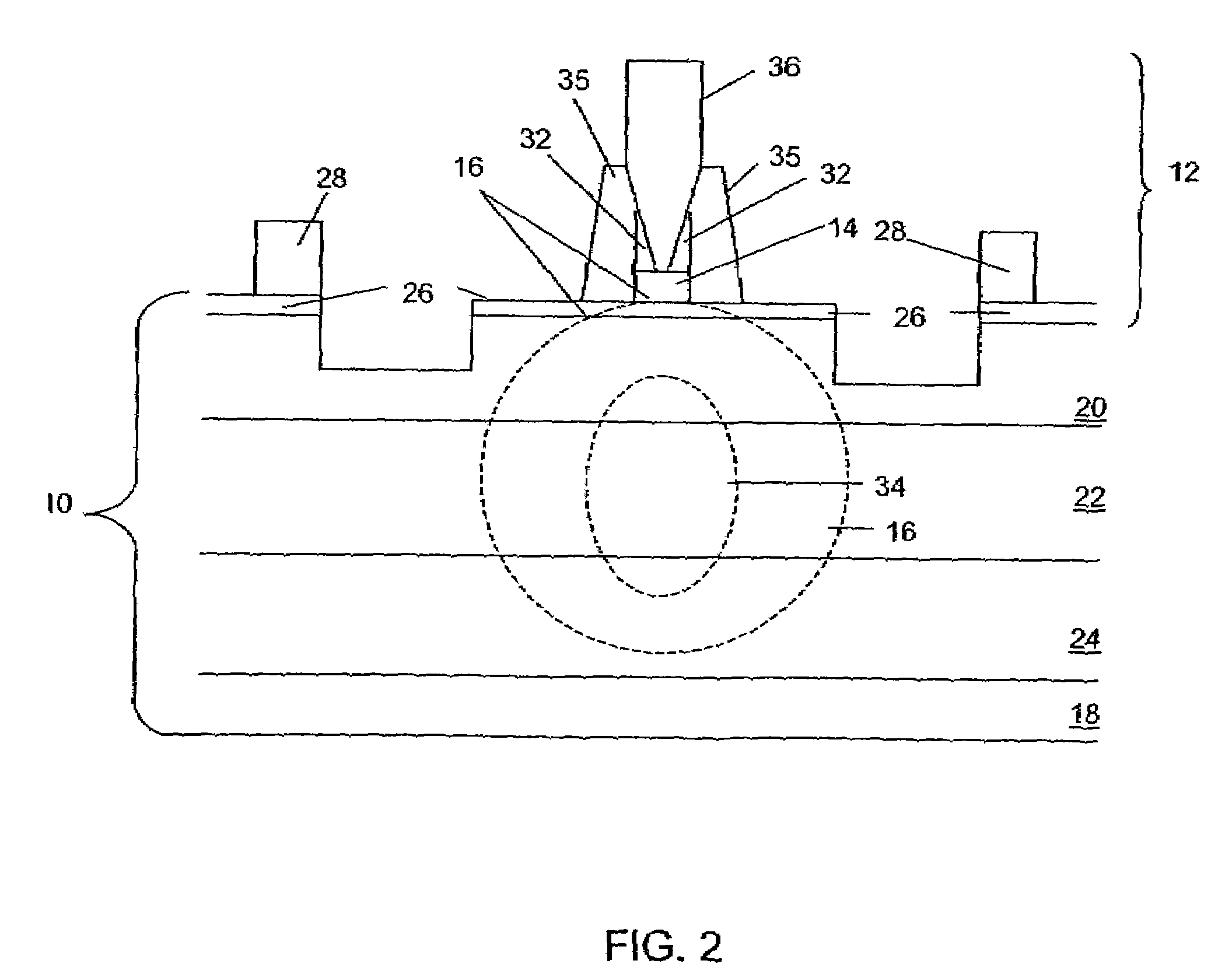
ActiveUS20050249509A1Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedEasy to controlLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorHermetic packaging
A coolerless photonic integrated circuit (PIC), such as a semiconductor electro-absorption modulator / laser (EML) or a coolerless optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC), may be operated over a wide temperature range at temperatures higher then room temperature without the need for ambient cooling or hermetic packaging. Since there is large scale integration of N optical transmission signal WDM channels on a TxPIC chip, a new DWDM system approach with novel sensing schemes and adaptive algorithms provides intelligent control of the PIC to optimize its performance and to allow optical transmitter and receiver modules in DWDM systems to operate uncooled. Moreover, the wavelength grid of the on-chip channel laser sources may thermally float within a WDM wavelength band where the individual emission wavelengths of the laser sources are not fixed to wavelength peaks along a standardized wavelength grid but rather may move about with changes in ambient temperature. However, control is maintained such that the channel spectral spacing between channels across multiple signal channels, whether such spacing is periodic or aperiodic, between adjacent laser sources in the thermally floating wavelength grid are maintained in a fixed relationship. Means are then provided at an optical receiver to discover and lock onto floating wavelength grid of transmitted WDM signals and thereafter demultiplex the transmitted WDM signals for OE conversion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Semiconductor photonic nano communication link apparatus
InactiveUS7603016B1Eliminate needNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersElectro-absorption modulatorPhotonics
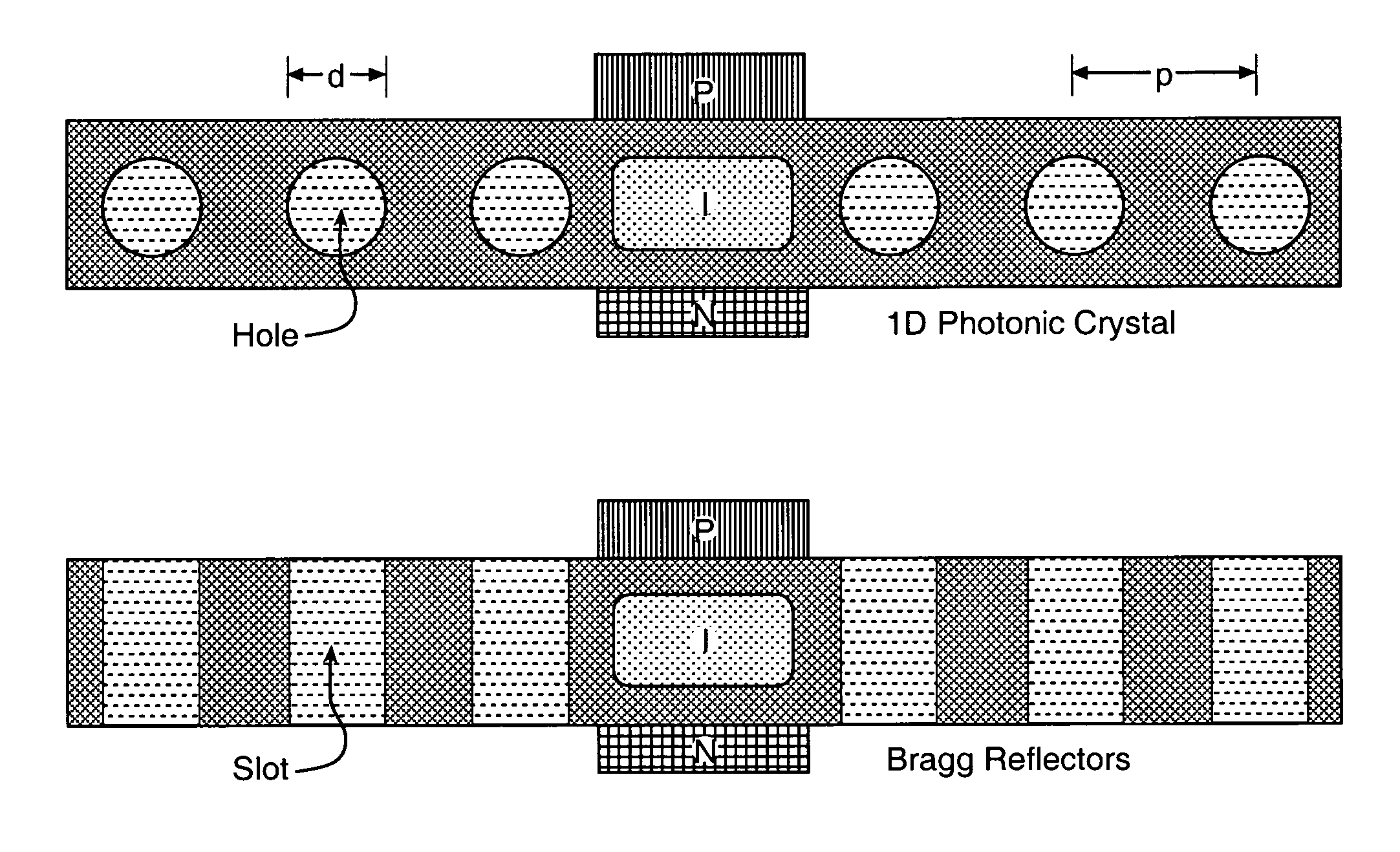
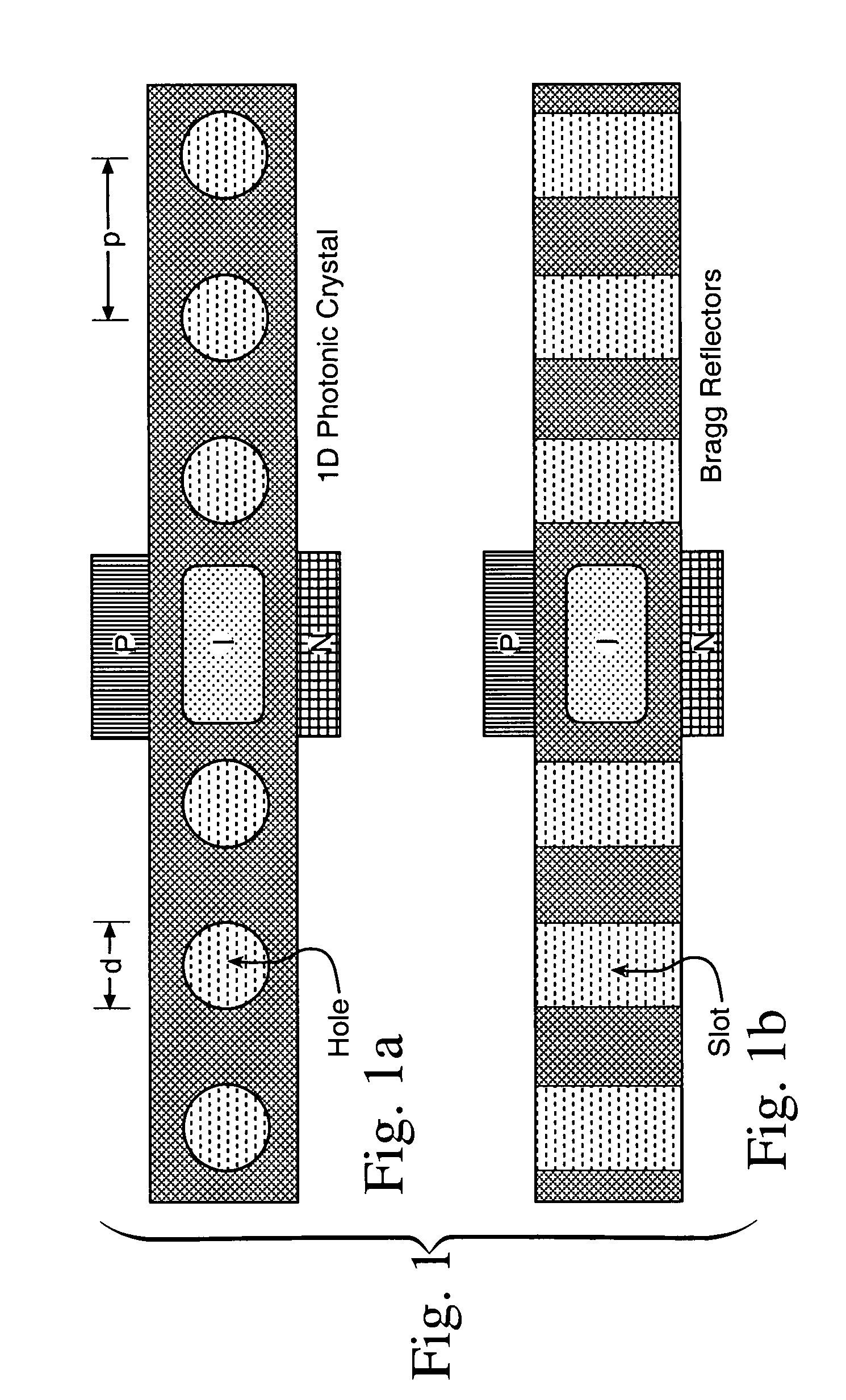
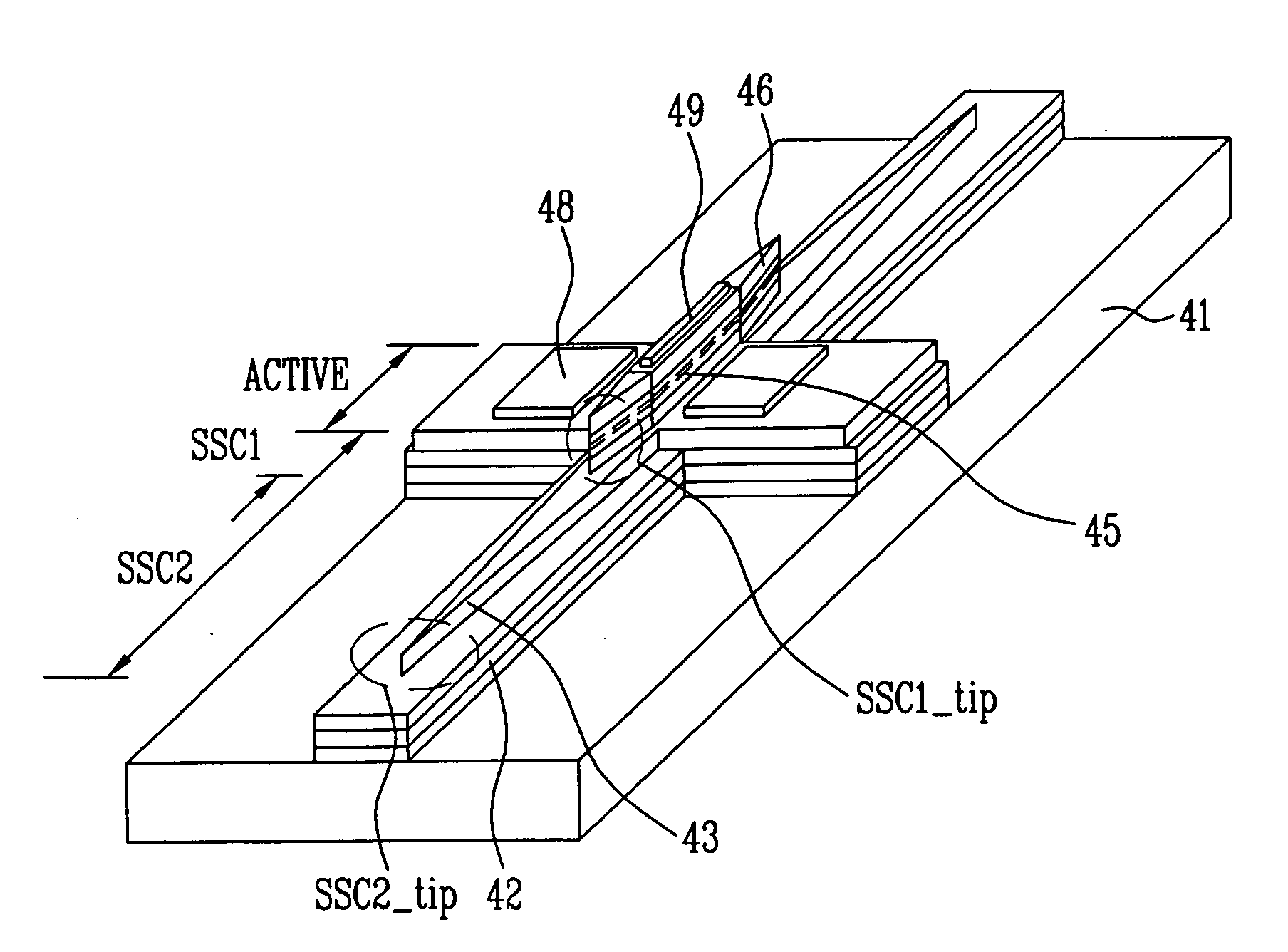
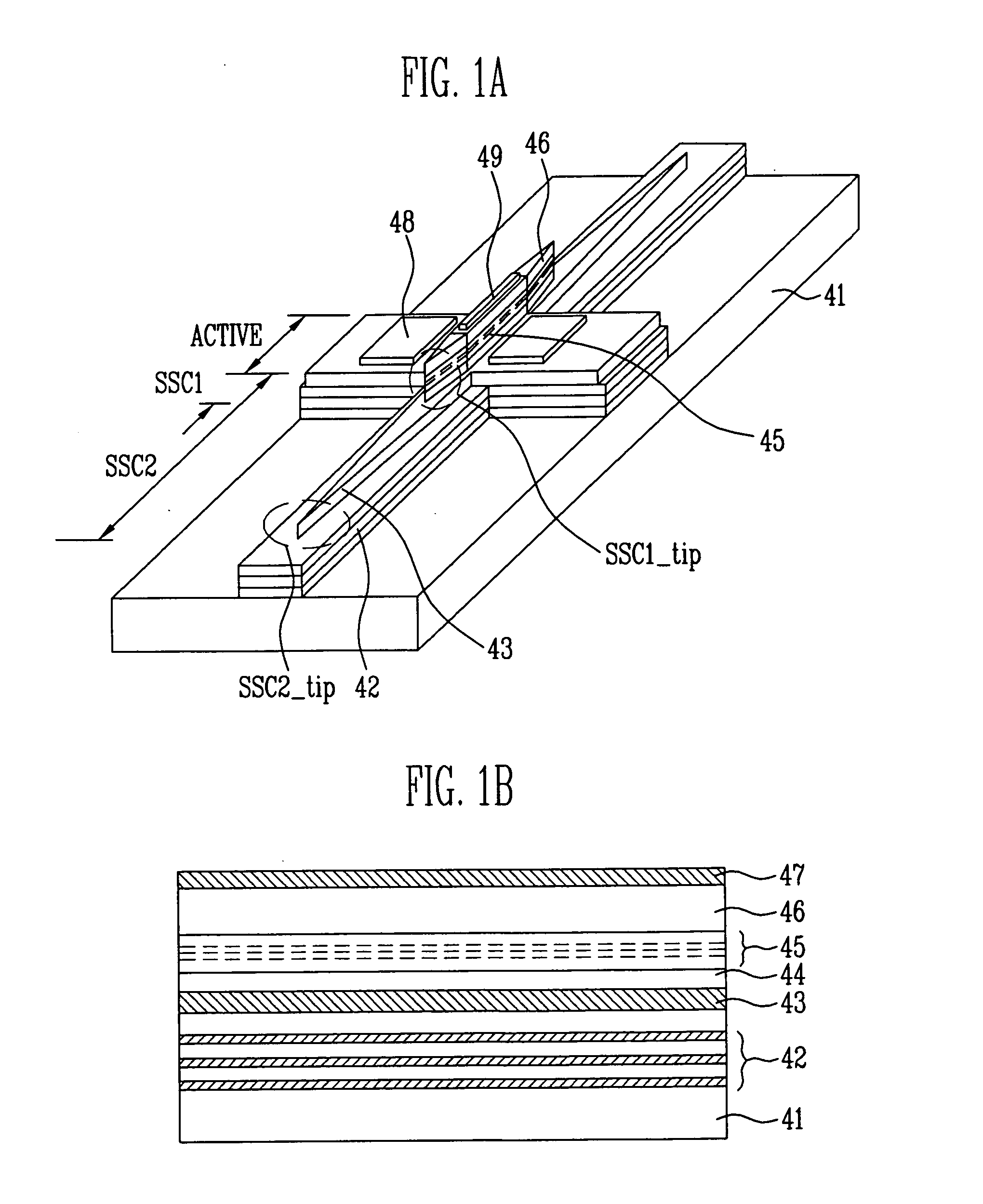
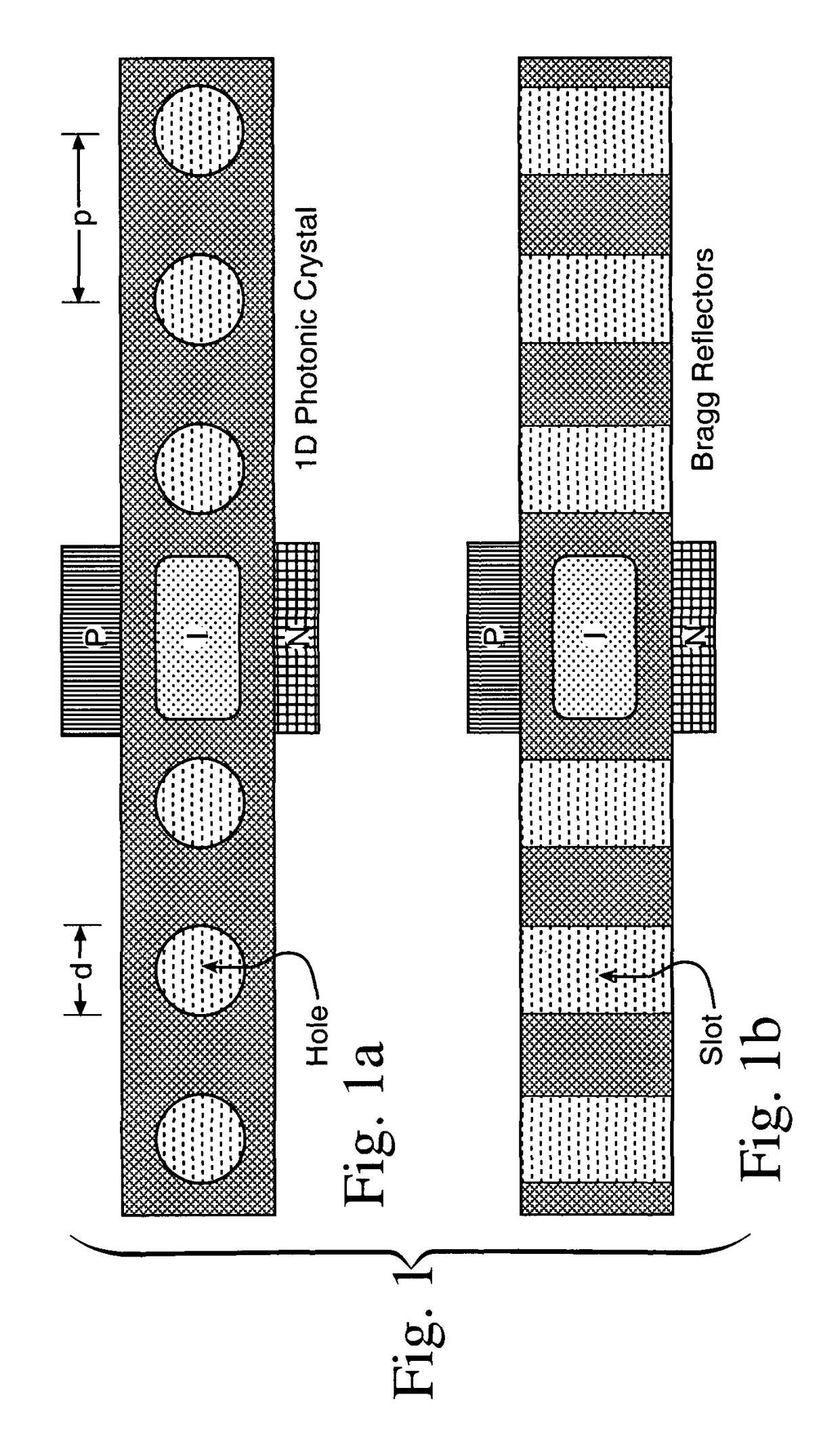
A CMOS compatible ten-gigabit-per-second region nano-waveguide included photonic communication link apparatus of low energy use per transmitted bit. An embodiment of the link includes an electrically pumped laser, an electro absorption modulator and a photodetector for the 1.5 to 2.0 micrometer infrared spectral region; omission of the separate electro absorption modulator is additionally disclosed. Each of these three nano-scale elements preferably includes active semiconductor crystal material situated in a preferably Silicon resonator within a nano-strip waveguide. The resonator is defined by dispersed resonator mirrors having tapered separation distance one dimensional photonic crystal lattice apertures of oxide holes or slots. Each of the three devices may be a semiconductor heterodiode pumped or controlled by laterally disposed wings enclosing the resonator to form a lateral PIN heterodiode for current injection or high E-field generation depending on bias and composition conditions selected.
Owner:US SEC THE AIR FORCE THE
Hybrid silicon laser-quantum well intermixing wafer bonded integration platform for advanced photonic circuits with electroabsorption modulators
ActiveUS20090245298A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical resonator shape and constructionElectro-absorption modulatorWafer bonding
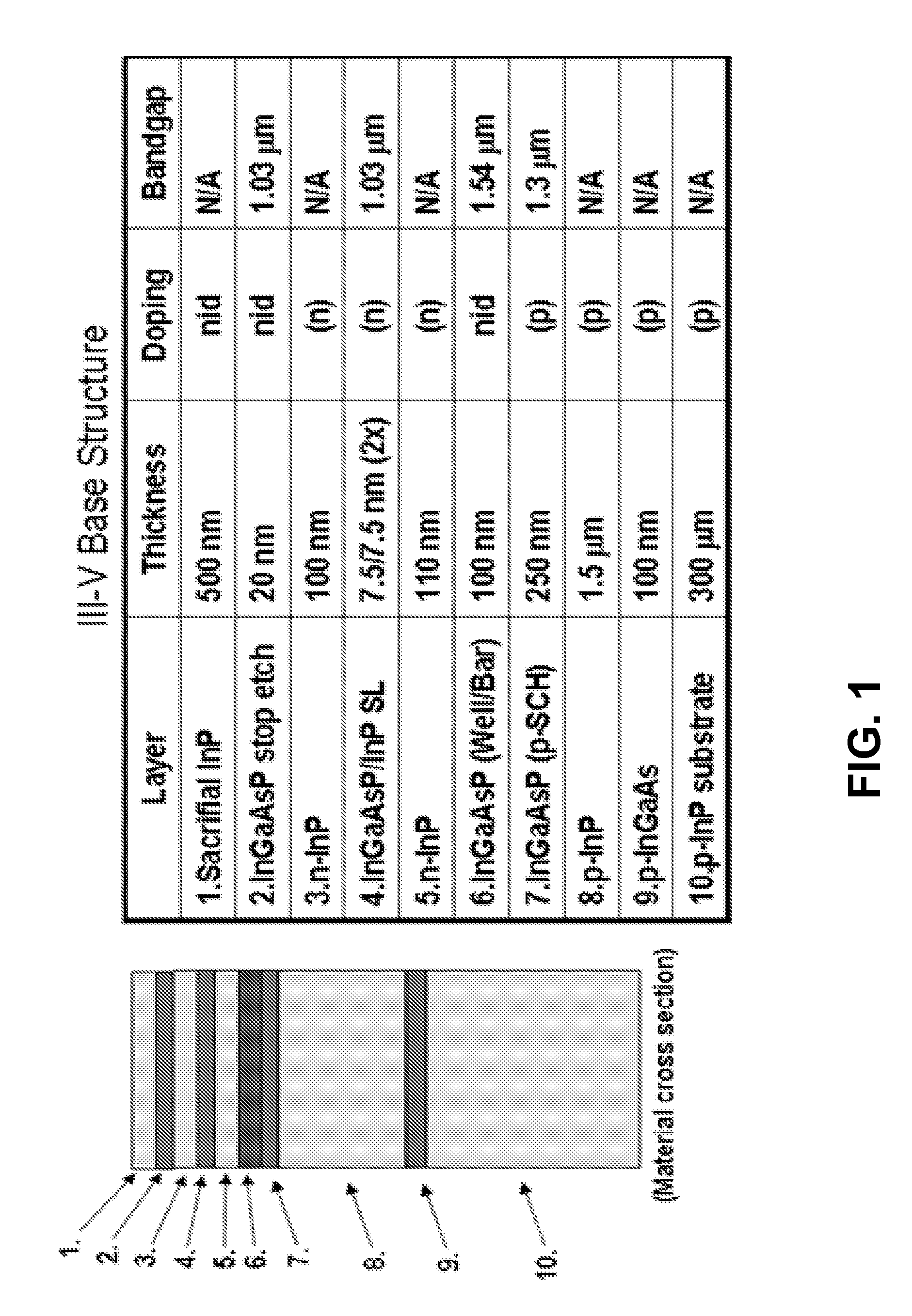
Photonic integrated circuits on silicon are disclosed. By bonding a wafer of compound semiconductor material as an active region to silicon and removing the substrate, the lasers, amplifiers, modulators, and other devices can be processed using standard photolithographic techniques on the silicon substrate. A silicon laser intermixed integrated device in accordance with one or more embodiments of the present invention comprises a silicon-on-insulator substrate, comprising at least one waveguide in a top surface, and a compound semiconductor substrate comprising a gain layer, the compound semiconductor substrate being subjected to a quantum well intermixing process, wherein the upper surface of the compound semiconductor substrate is bonded to the top surface of the silicon-on-insulator substrate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
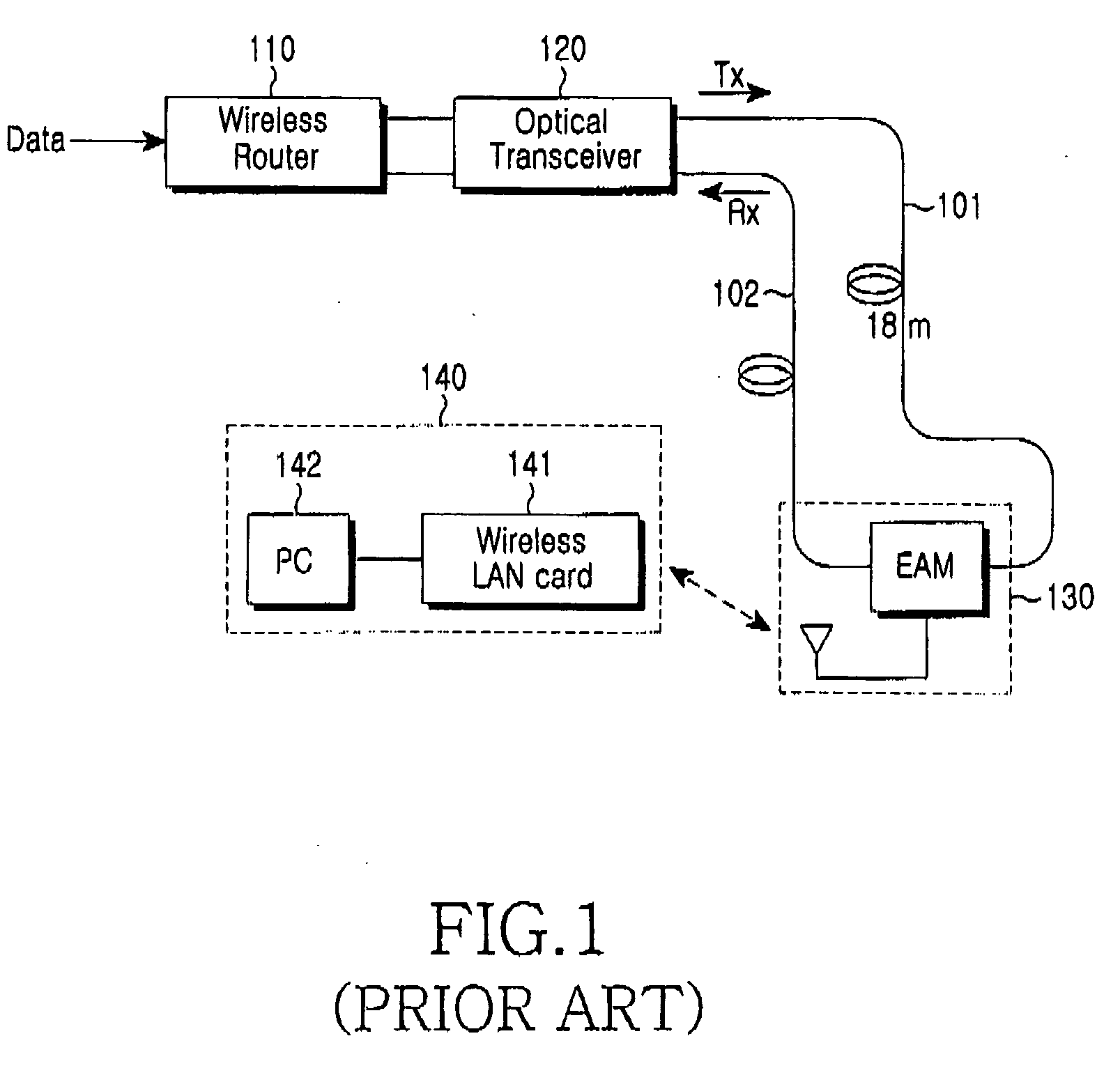
Wireless remote access base station and pico-cell system using the same
InactiveUS20070058978A1Compensation lossInformation formatContent conversionElectro-absorption modulatorAudio power amplifier
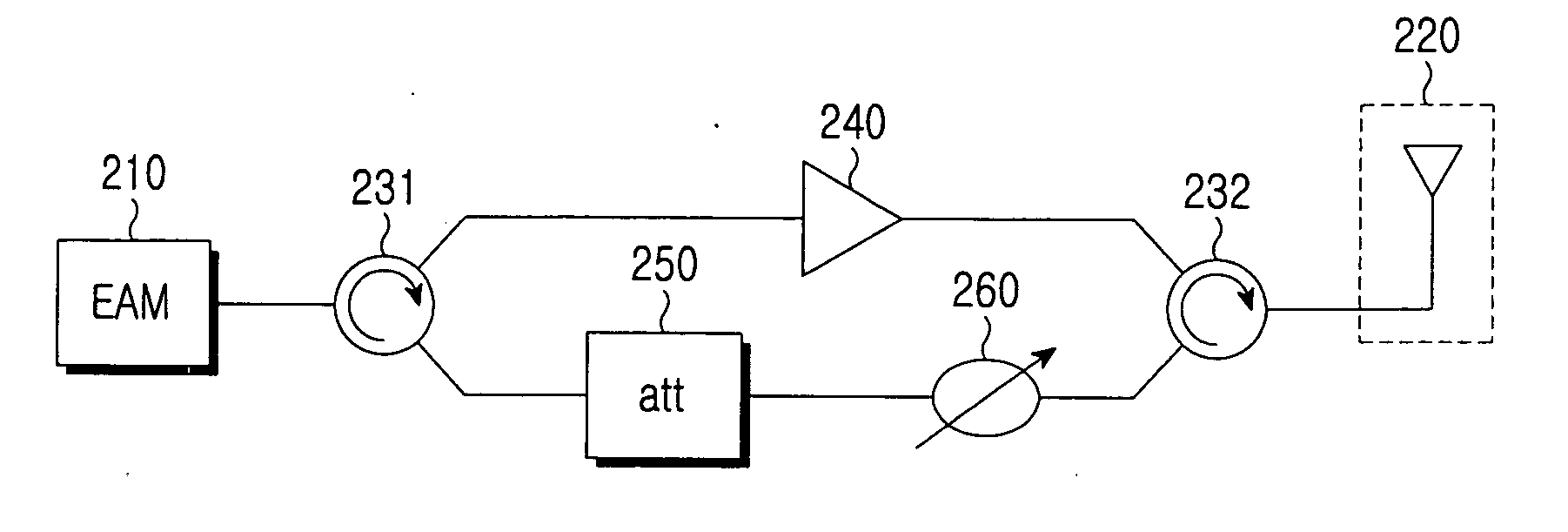
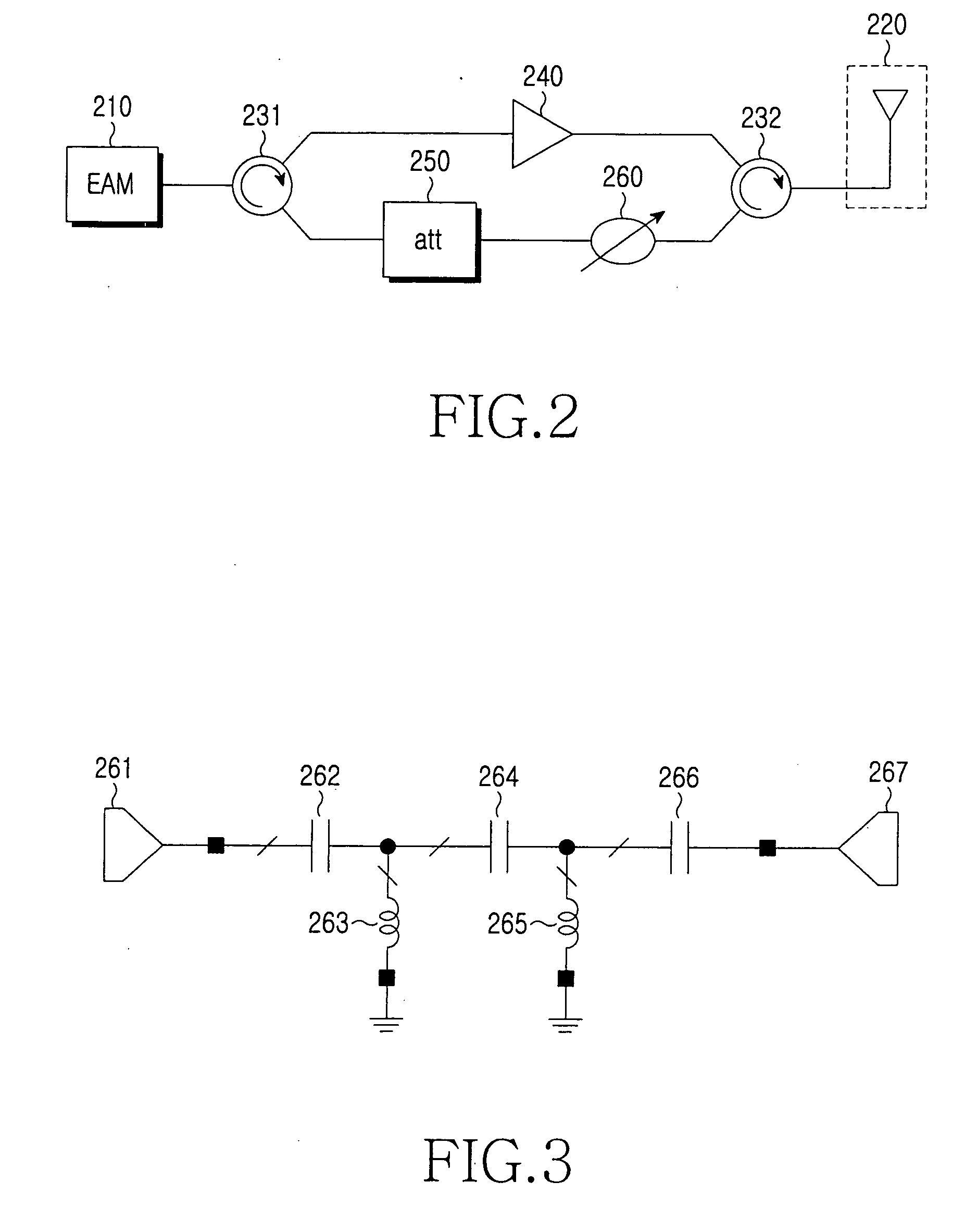
A wireless remote access base station for converting a downstream optical signal to a downstream radio frequency (RF) signal, transmitting the converted downstream RF signal wirelessly, converting a received upstream RF signal to an upstream optical signal, and transmitting the upstream optical signal is provided. The remote base station includes: an electro-absorption modulator (EAM) for converting a downstream optical signal to a downstream RF signal and an upstream RF signal to an upstream optical signal; an antenna for transmitting the downstream RF signal wirelessly and outputting the upstream RF signal received wirelessly to the EAM; and an amplifier, which is located between the EAM and the antenna, amplifies the downstream RF signal and outputs the amplified downstream RF signal to the antenna.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Planar waveguide surface emitting laser and photonic integrated circuit
InactiveUS20040105476A1Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionElectro-absorption modulatorPhotovoltaic detectors
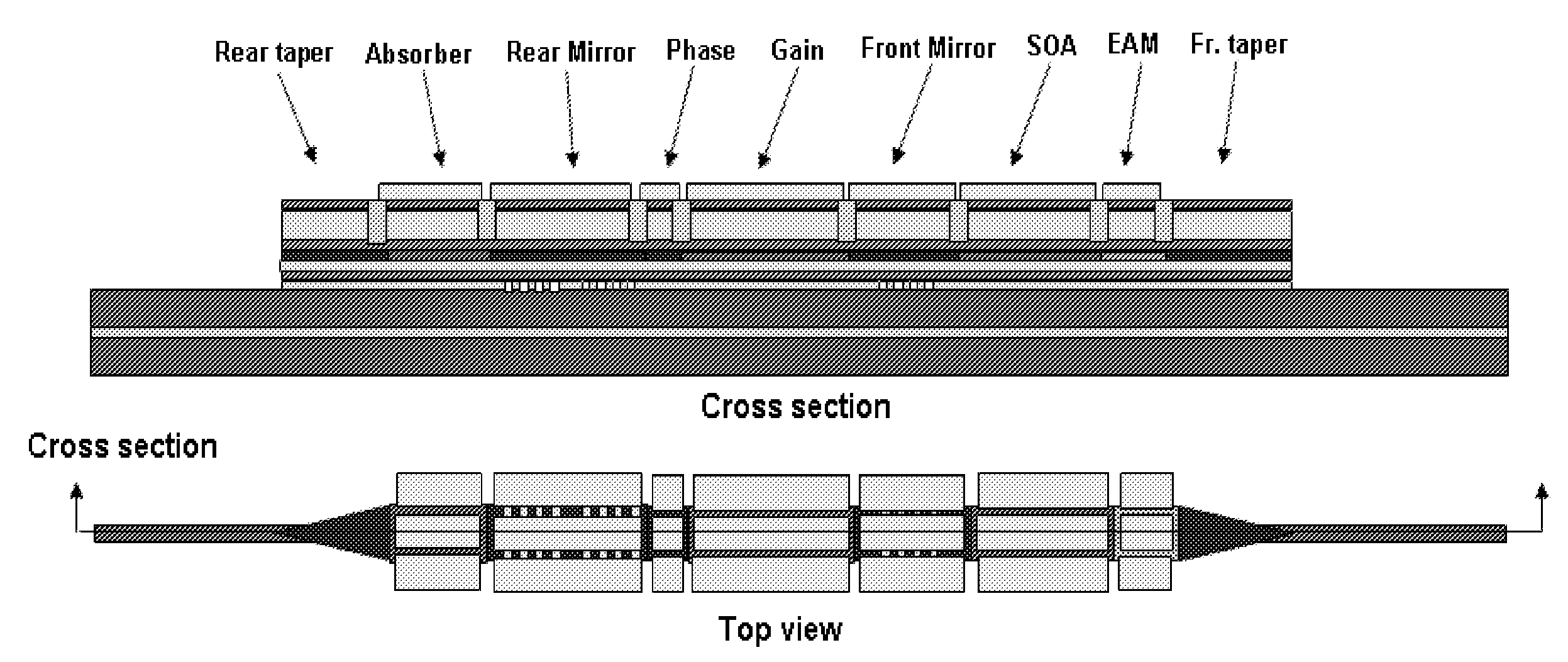
The present invention is a planar waveguide surface emitting laser (PWSEL) and photonic integrated circuit (PIC) technology. The PWVCL can stand alone or it can be integrated with a variety of optical devices, such as tuners, electro-optic or electro-absorption modulators (EOM or EAM), optical amplifiers (OA), waveguide or traveling wave photo detectors (WPD or TWPD), narrow or broadband filters, active or passive waveguides, and waveguide splitters or couplers to form photonic integrated circuits. Most or all of the components share the same transverse waveguide. A lateral index step or other suitable technique completes the waveguide so that light is guided in the longitudinal direction. Optical taps (reduced reflectivity mirrors) allow for surface emission of the light.
Owner:WASSERBAUER JOHN G
Method for Fabricating Butt-Coupled Electro-Absorptive Modulators
InactiveUS20100330727A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsEtchingElectro-absorption modulator
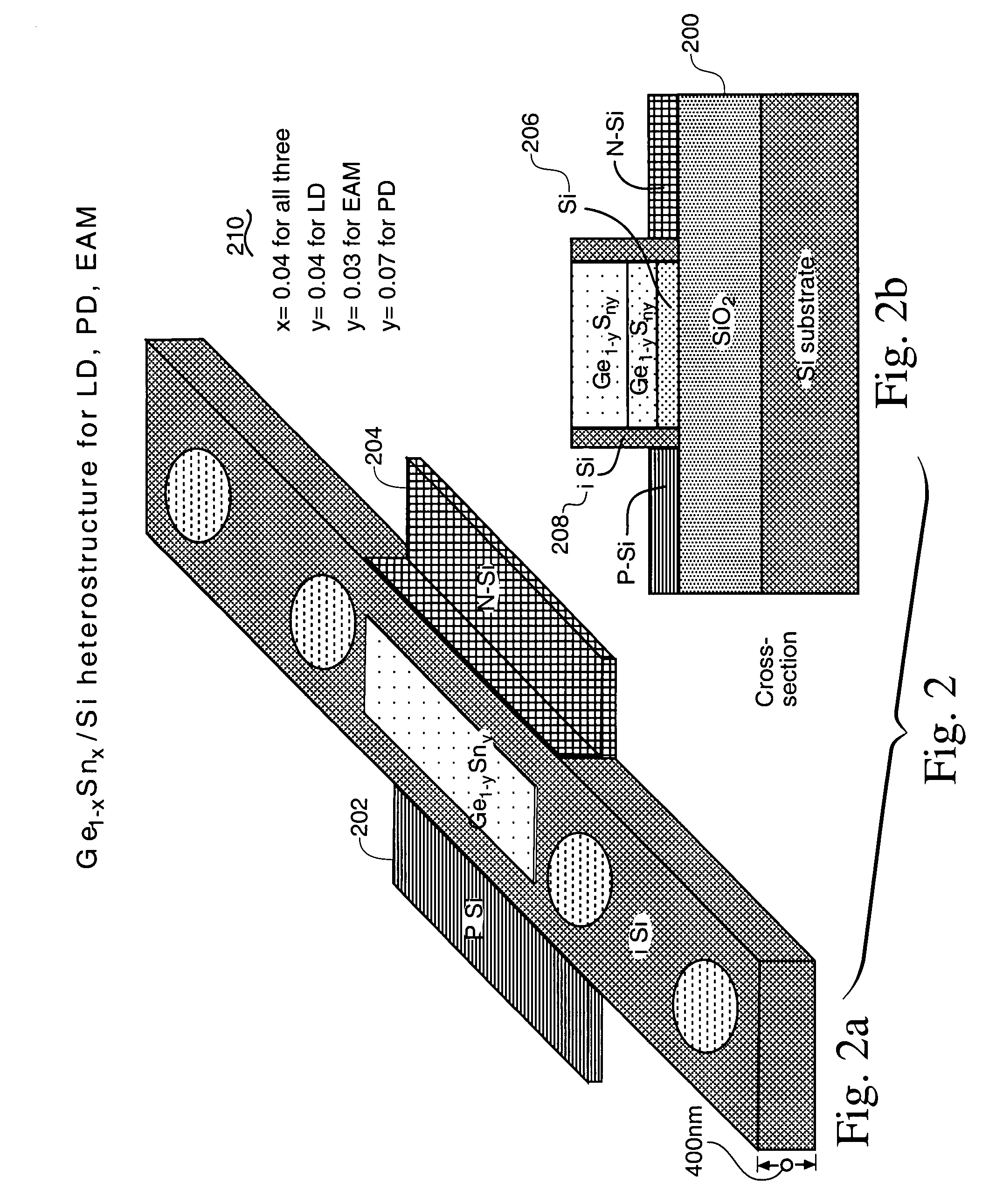
A method for fabricating butt-coupled electro-absorptive modulators is disclosed. A butt-coupled electro-absorptive modulator with minimal dislocations in the electro-absorptive material is produced by adding a dielectric spacer for lining the coupling region before epitaxially growing the SiGe or other electro-absorptive material. It has been determined that during the SiGe growth, the current process has exposed single crystal silicon at the bottom of the hole and exposed amorphous silicon on the sides. SiGe growth on the amorphous silicon is expected to have more dislocations than single crystal silicon. There should also be dislocations or fissures where the SiGe growth from the each nucleation source finally join. Thus, a dielectric sidewall can protect an exposed waveguide face from any etching from an aggressive surface preparation prior to epi growth.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
COOLERLESS PHOTONIC INTEGRATED CIRCUITS (PICs) FOR WDM TRANSMISSION NETWORKS AND PICs OPERABLE WITH A FLOATING SIGNAL CHANNEL GRID CHANGING WITH TEMPERATURE BUT WITH FIXED CHANNEL SPACING IN THE FLOATING GRID
ActiveUS20100166424A1Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorPeak value
A coolerless photonic integrated circuit (PIC), such as a semiconductor electro-absorption modulator / laser (EML) or a coolerless optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC), may be operated over a wide temperature range at temperatures higher then room temperature without the need for ambient cooling or hermetic packaging. Since there is large scale integration of N optical transmission signal WDM channels on a TxPIC chip, a new DWDM system approach with novel sensing schemes and adaptive algorithms provides intelligent control of the PIC to optimize its performance and to allow optical transmitter and receiver modules in DWDM systems to operate uncooled. Moreover, the wavelength grid of the on-chip channel laser sources may thermally float within a WDM wavelength band where the individual emission wavelengths of the laser sources are not fixed to wavelength peaks along a standardized wavelength grid but rather may move about with changes in ambient temperature. However, control is maintained such that the channel spectral spacing between channels across multiple signal channels, whether such spacing is periodic or aperiodic, between adjacent laser sources in the thermally floating wavelength grid are maintained in a fixed relationship. Means are then provided at an optical receiver to discover and lock onto floating wavelength grid of transmitted WDM signals and thereafter demultiplex the transmitted WDM signals for OE conversion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Coolerless photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for WDM transmission networks and PICs operable with a floating signal channel grid changing with temperature but with fixed channel spacing in the floating grid
ActiveUS7636522B2Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorPeak value
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Q-modulated semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20060088066A1Effective refractive indexLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionElectro-absorption modulatorDistributed Bragg reflector
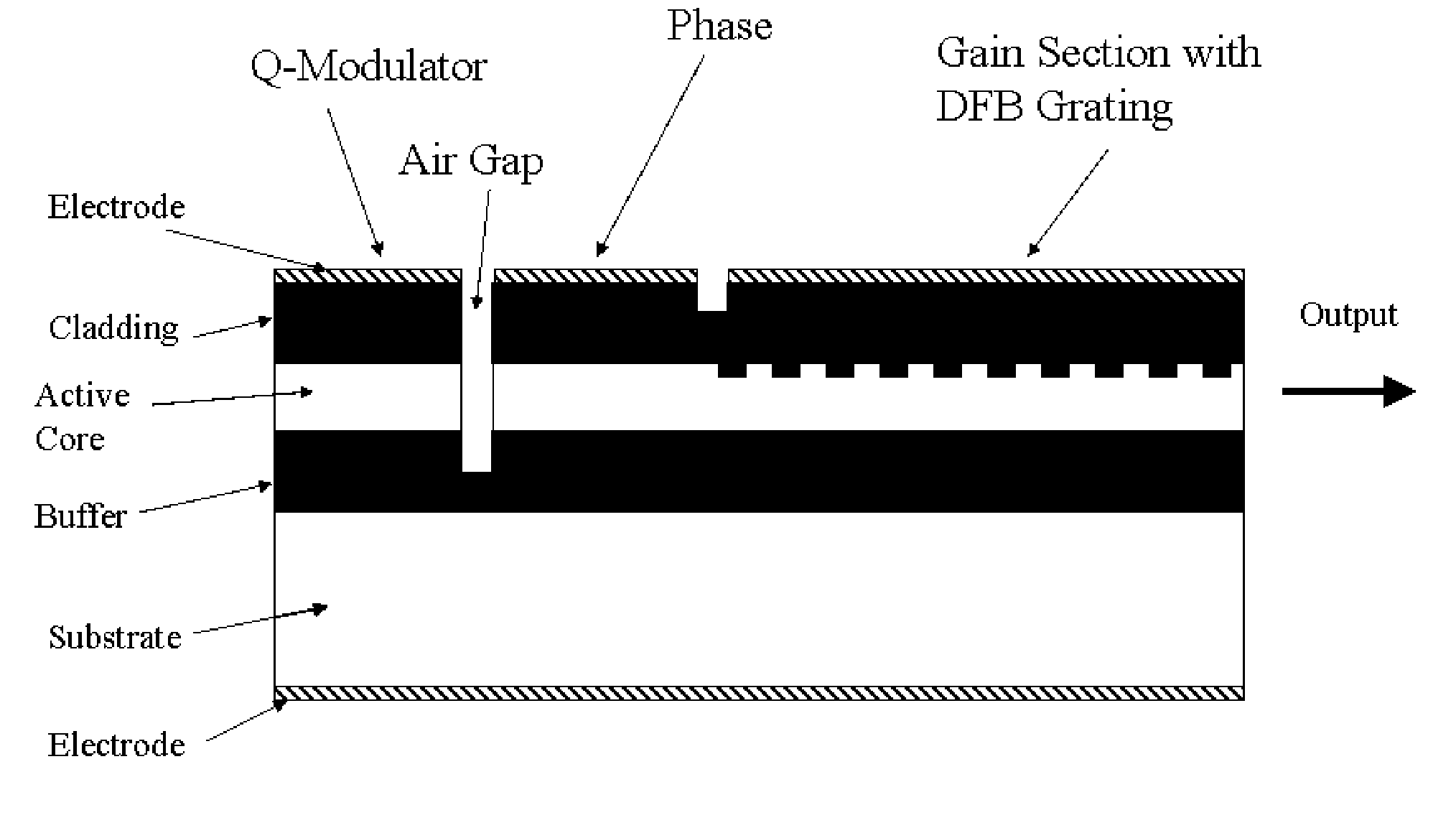
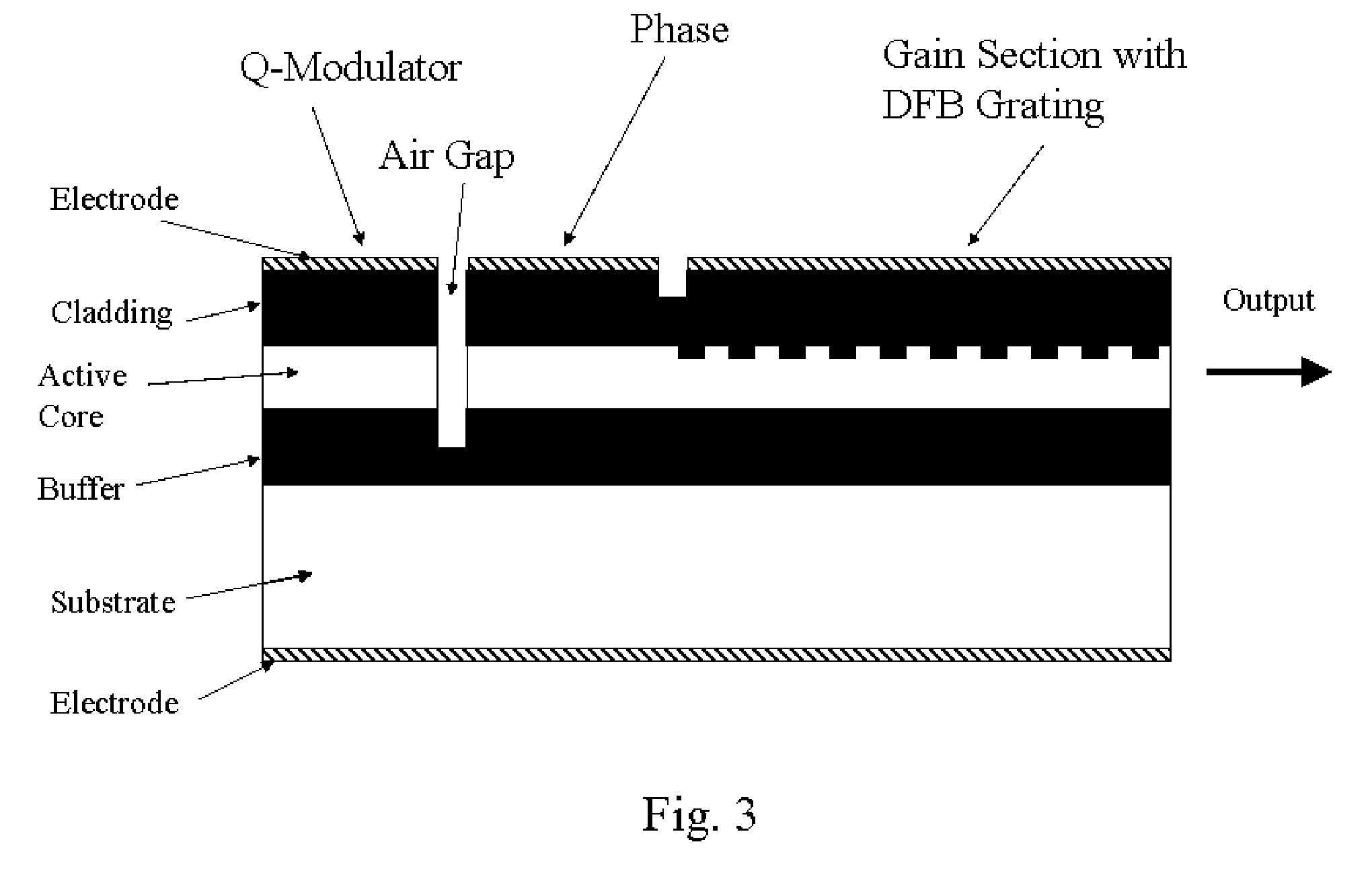
A Q-modulated semiconductor laser comprises an optical gain section and an electro-absorptive modulator section, separated by a vertically etched air gap acting as a partially reflecting mirror. The modulator section is placed inside an anti-resonant Fabry-Perot cavity and acts as the rear reflector of the laser. The change of the absorption coefficient in the modulator section results in a change in the Q-factor of the laser, and consequently the lasing threshold and output power. Different embodiments are disclosed, which involve a distributed feedback (DFB) laser, a Fabry-Perot laser, a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) laser, or a wavelength switchable multi-cavity laser. The integrated Q-modulated laser has advantages of high speed, high extinction ratio, low wavelength chirp and low cost.
Owner:LIGHTIP TECH
Semiconductor monolithic integrated optical transmitter
InactiveUS20050006654A1Minimizing distortion of lightIncrease powerLaser detailsSolid-state devicesGratingElectro-absorption modulator
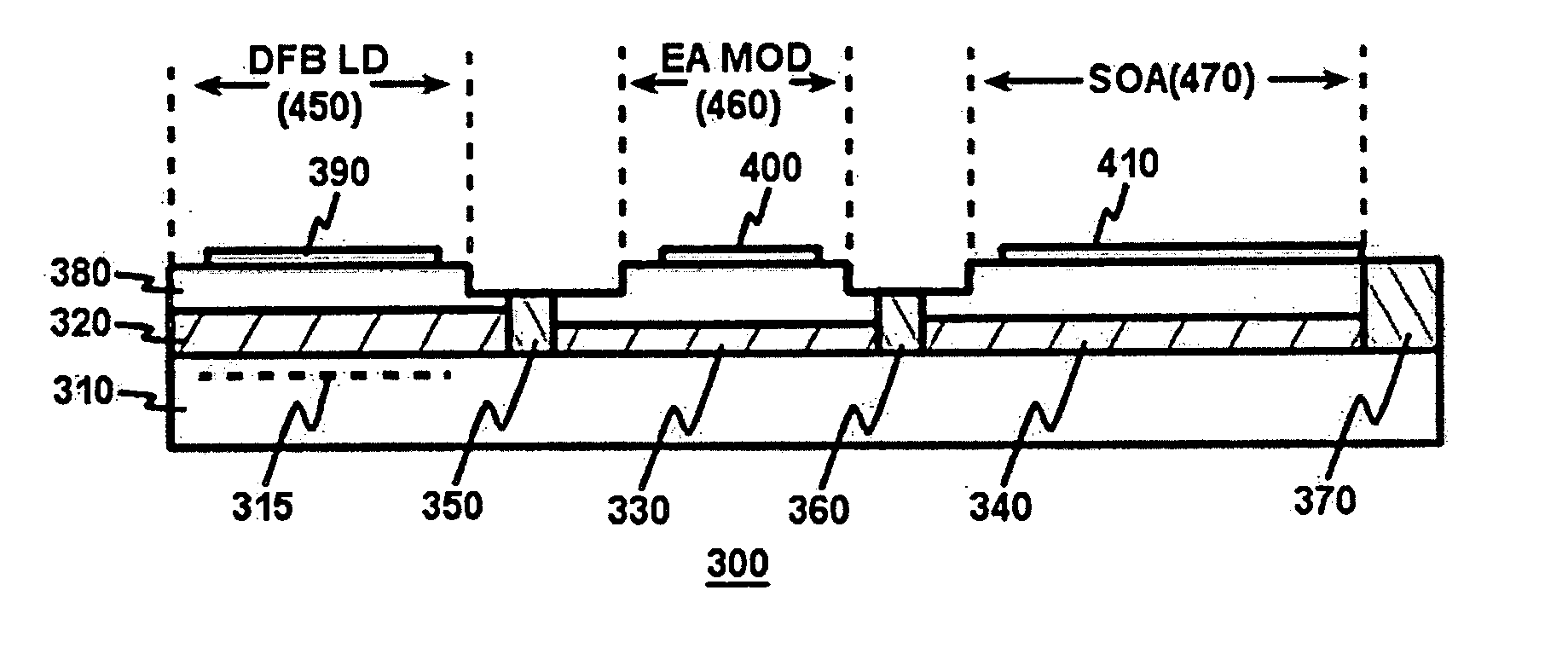
A semiconductor monolithic integrated optical transmitter including a plurality of active layers formed on a semiconductor substrate is disclosed, which comprises: a distributed feedback laser diode including a grating for reflecting light with a predetermined wavelength and a first active layer for oscillating received light from the grating; an electro-absorption modulator including a second active layer for receiving light from the first active layer, wherein the received light intensity is modulated through a change of absorbency in accordance with an applied voltage; an optical amplifier including a third active layer for amplifying received light from the second active layer; a first optical attenuator between the first active layer and the second active layer; and a second optical attenuator between the second active layer and the third active layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Refrigeration-type coaxial packaging light-emitting tube core
InactiveCN102650718AHigh speed modulation feedSignal distortion is smallLaser detailsCoupling light guidesCapacitanceElectro-absorption modulator
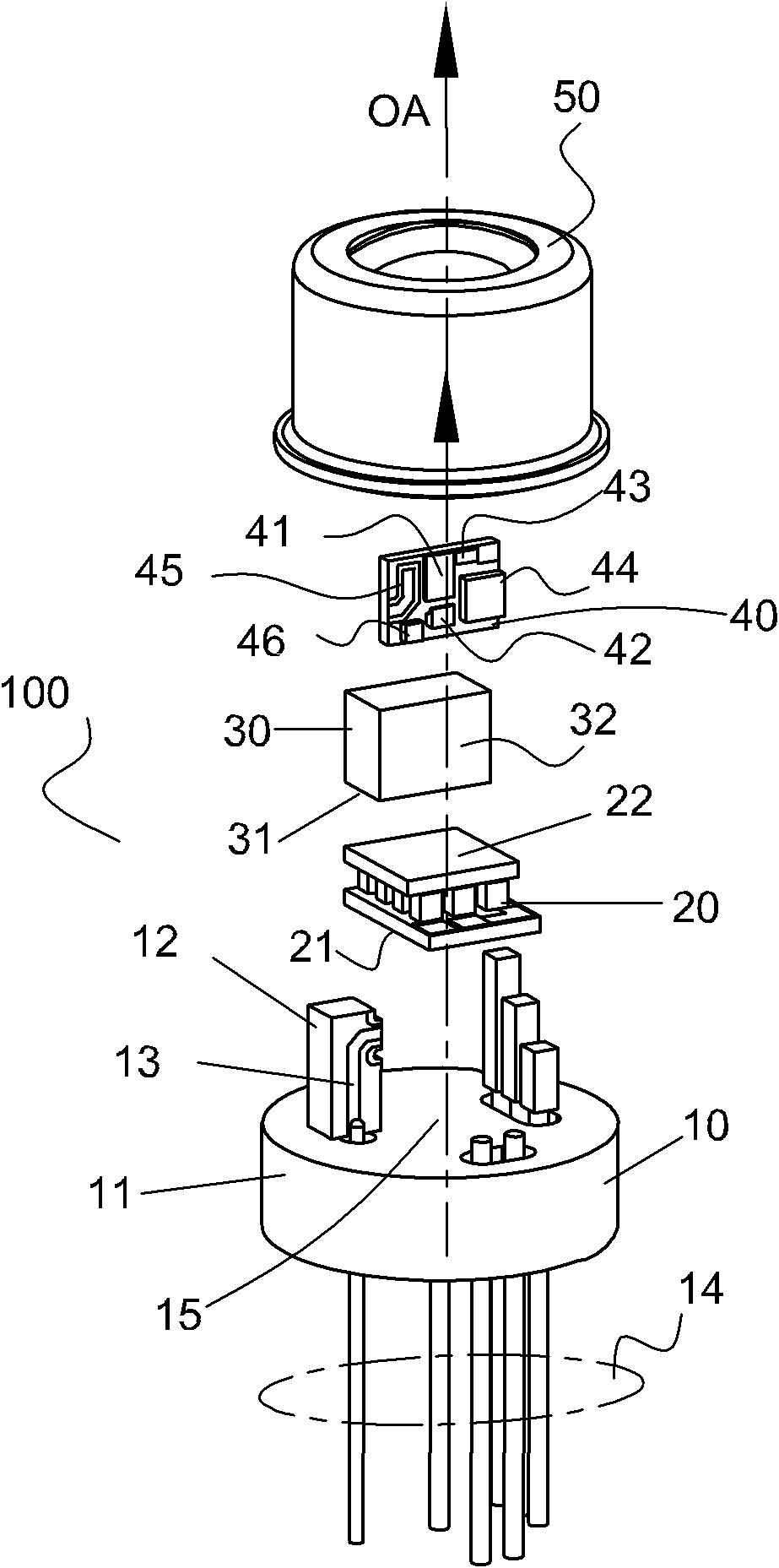
The invention provides a refrigeration-type coaxial packaging light-emitting tube core, which comprises a transistor outline (TO) tube shell, a refrigerator, a heat sink, a laser carrier and a sealing tube cap, wherein the TO tube shell comprises a tube shell base. At least seven pins are arranged around the tube shell base; the pins comprise a radio frequency (RF) signal pin, and the laser carrier with a microstrip line is arranged on the RF signal pin; the radiating surface of the refrigerator and the surface of the tube shell base are fixed in the manner of sticking; the refrigeration surface of the refrigerator and the surface of the heat sink are fixed in the manner of sticking; the heat sink and the surface of the laser carrier with a matched resistor and the microstrip line are fixed in the manner of sticking; an electric absorption modulation laser chip, a backlight detector, a thermistor and a power filter capacitor are fixedly arranged on the surface of the laser carrier in the manner of sticking; one end of the microstrip line of the laser carrier is connected with the anode of an electric absorption modulator; and the other end of the microstrip line of the laser carrier is connected with a microstrip line on the RF signal pin through a conductor wire. When installation is performed, the emitted light outlet optical axis of the laser chip and the optical axis (OA) of the central axis of the TO tube shell are coaxial. Optical steering elements are not needed, the process is simple, and the signal distortion can be reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEOPHOTONICS TECH
Low-cost tunable DFB semiconductor laser device of integrated modulator and manufacturing method
ActiveCN103956652APackage structure design is simpleReduce complexityLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectricityElectro-absorption modulator
The invention discloses a low-cost tunable DFB semiconductor laser device of an integrated modulator. The tunable DFB semiconductor laser device is manufactured with the reconstruction-equivalent chirped technology, multiple DFB semiconductor laser devices share one modulator, and the tunable wavelength range can be expanded by increasing the number of laser devices or adopting the active and passive integration method. The integrated modulator is an semiconductor optical amplifier modulator (SOA), or an electric absorption modulator (EAM), or a Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM) and can be realized by means of the quantum well intermixing technology (QWI), the Butt-joint growth technology or the selective area growth technology (SAG), and quantum well materials are based on the InP / InGaAsP or InP / AlGaInAs material system. Due to the fact that only one radio frequency port is needed for modulation at least, cost can be reduced by simplifying package design, and practicality and usability are improved greatly.
Owner:南京华飞光电科技有限公司
Method of tuning wavelength tunable electro-absorption modulators
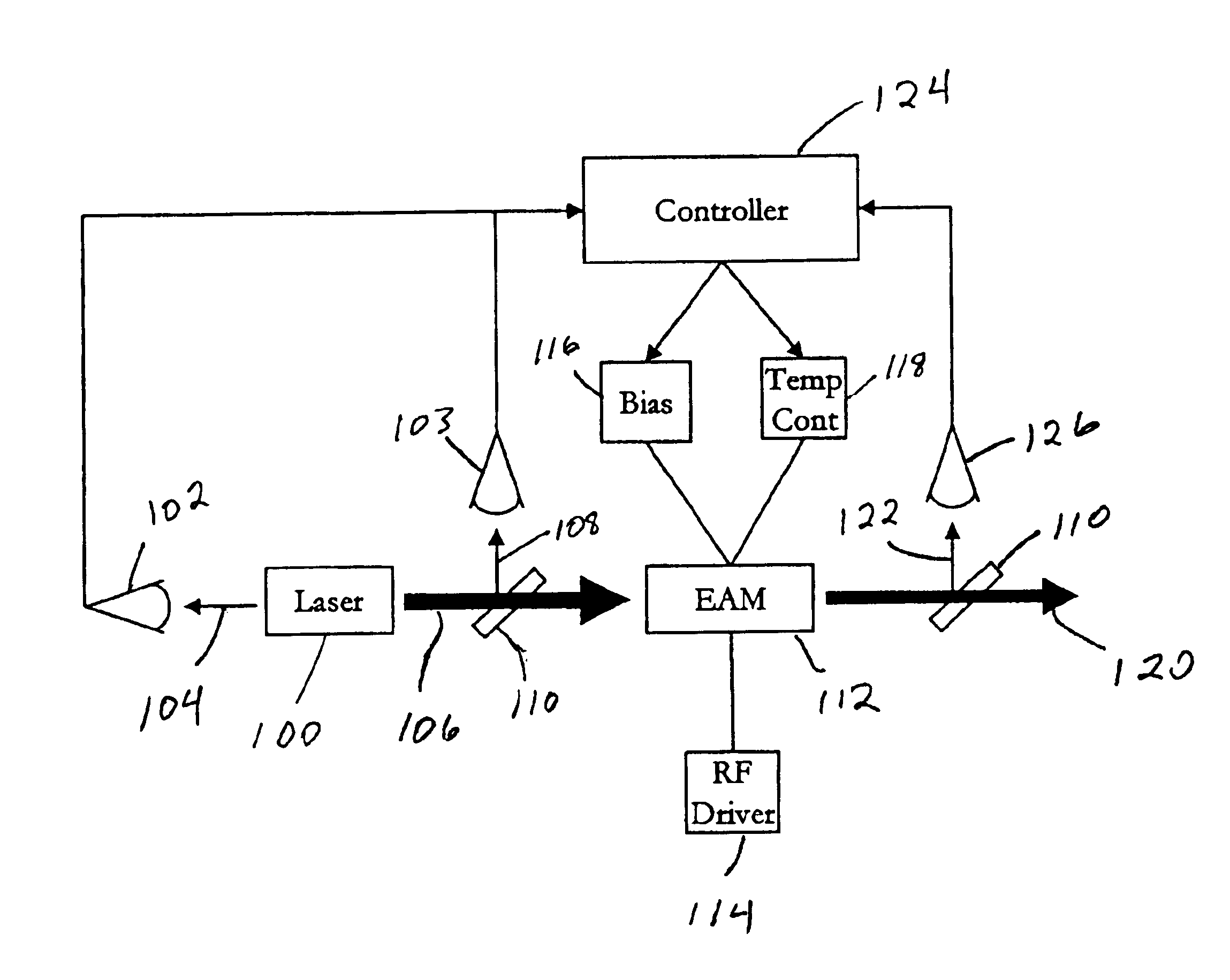
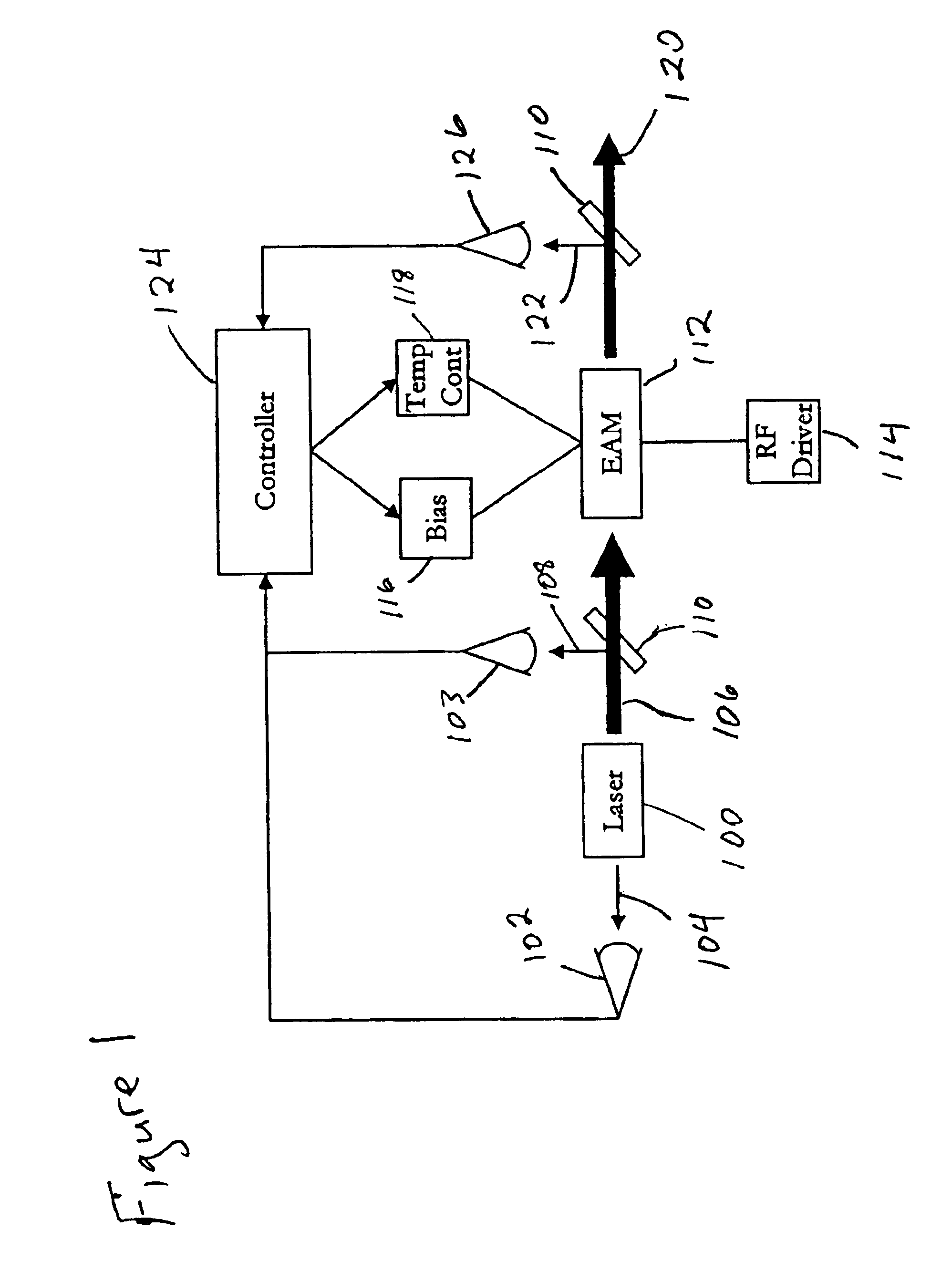
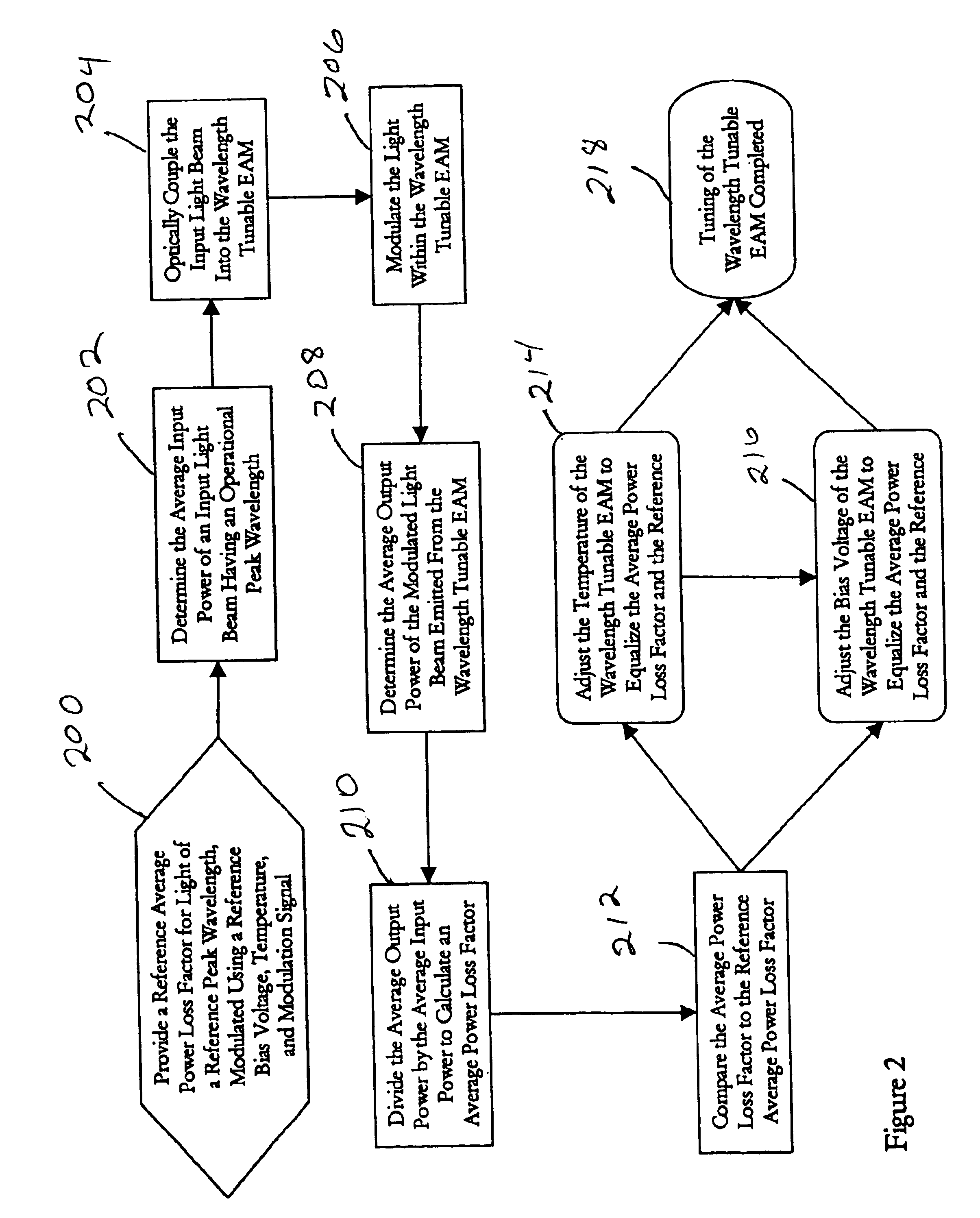
A method of tuning an electroabsorption modulator (EAM). A reference average power loss factor for light having a reference peak wavelength that is modulated by the EAM is provided. This loss factor is based on operation of the EAM using a reference bias voltage, a reference temperature, and a reference modulation signal which has a predetermined duty cycle. Input light is coupled into the EAM and modulated using a modulation signal which has the same duty cycle as the reference modulation signal. The input power of the input light and the average output power of light emitted from the EAM are measured. These input and average output powers are used to generate an average power loss factor. The average power loss factor is compared to the reference average power loss factor and the bias voltage and / or the temperature of the EAM are adjusted to reduce differences between these loss factors.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
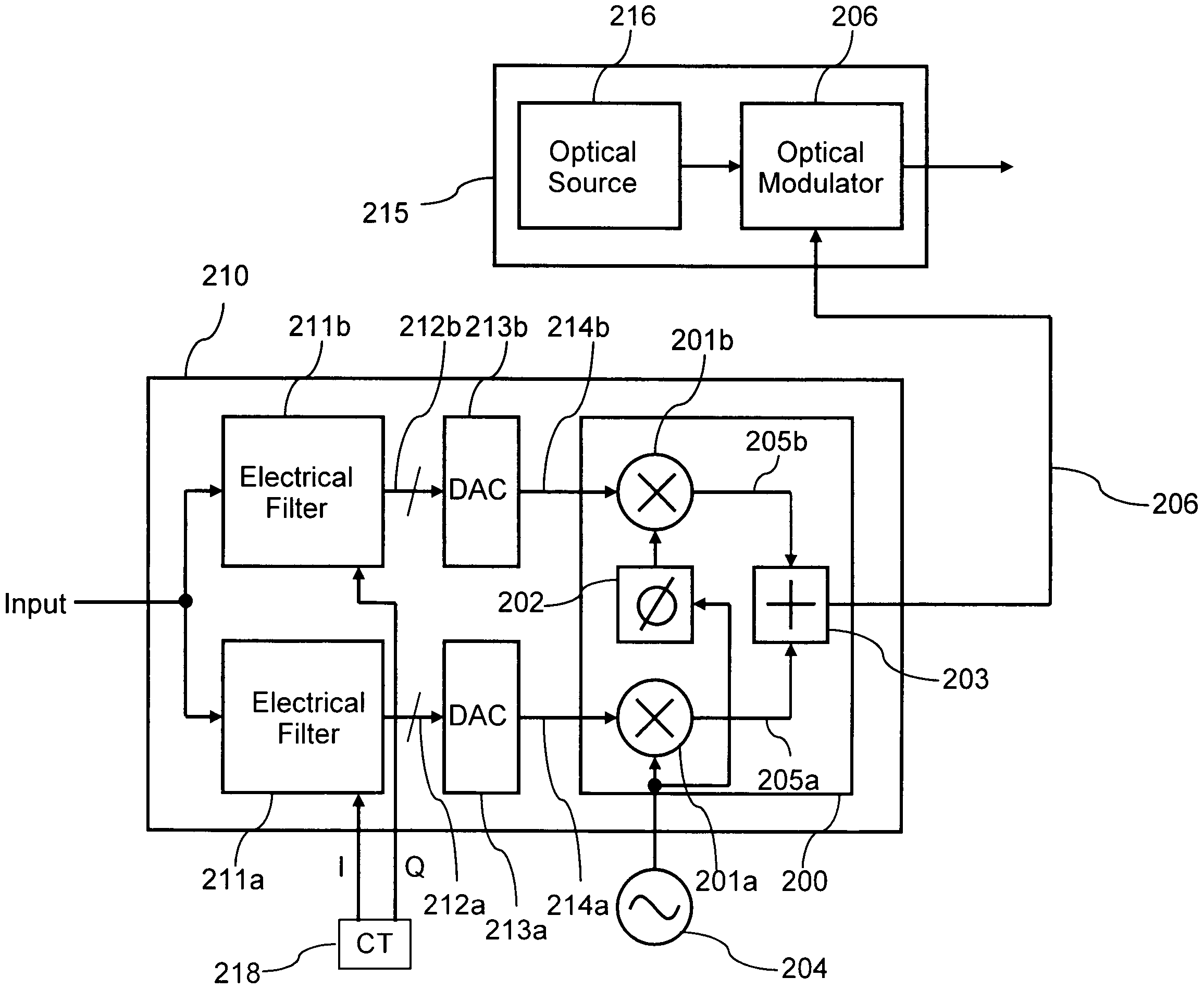
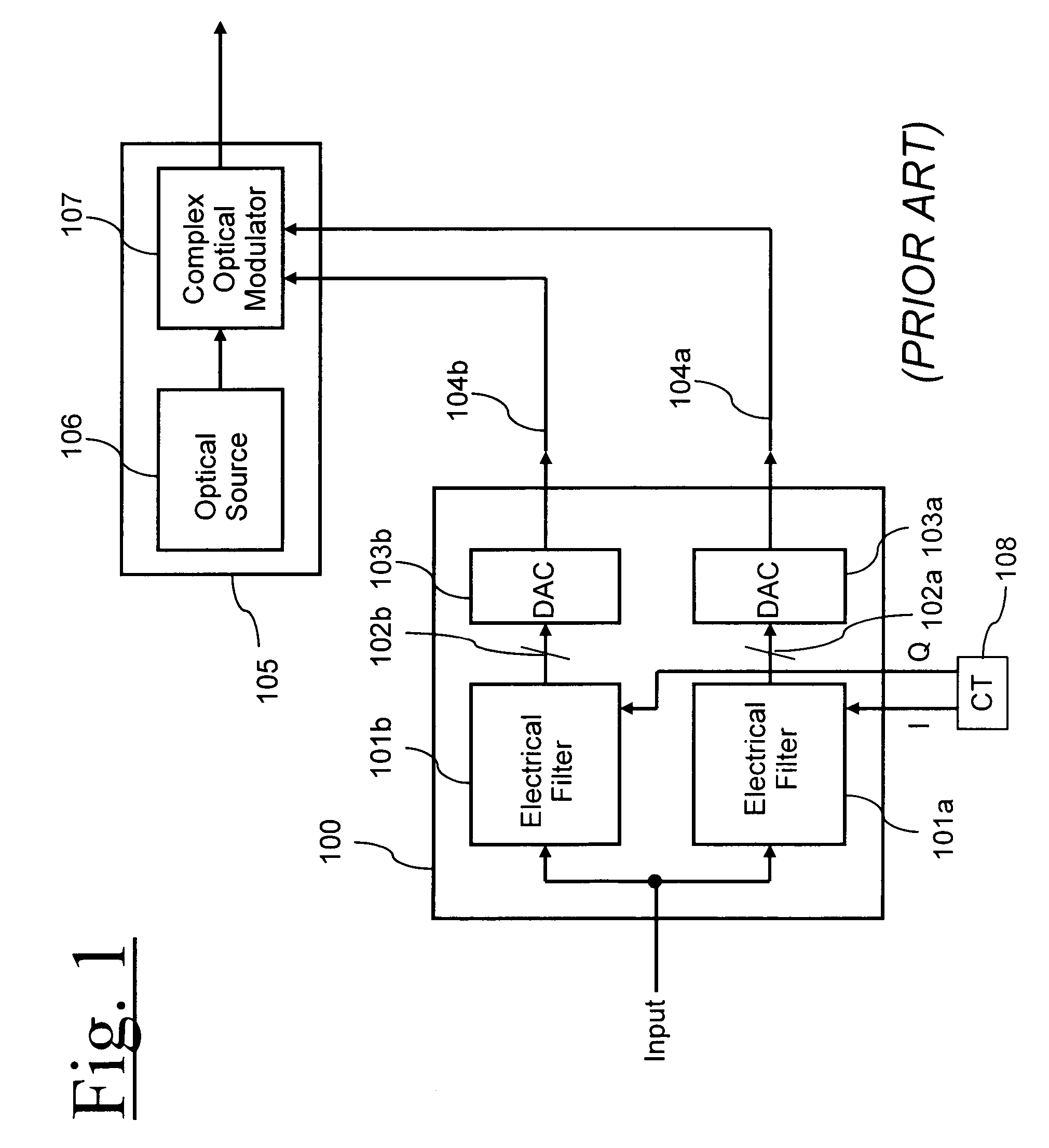
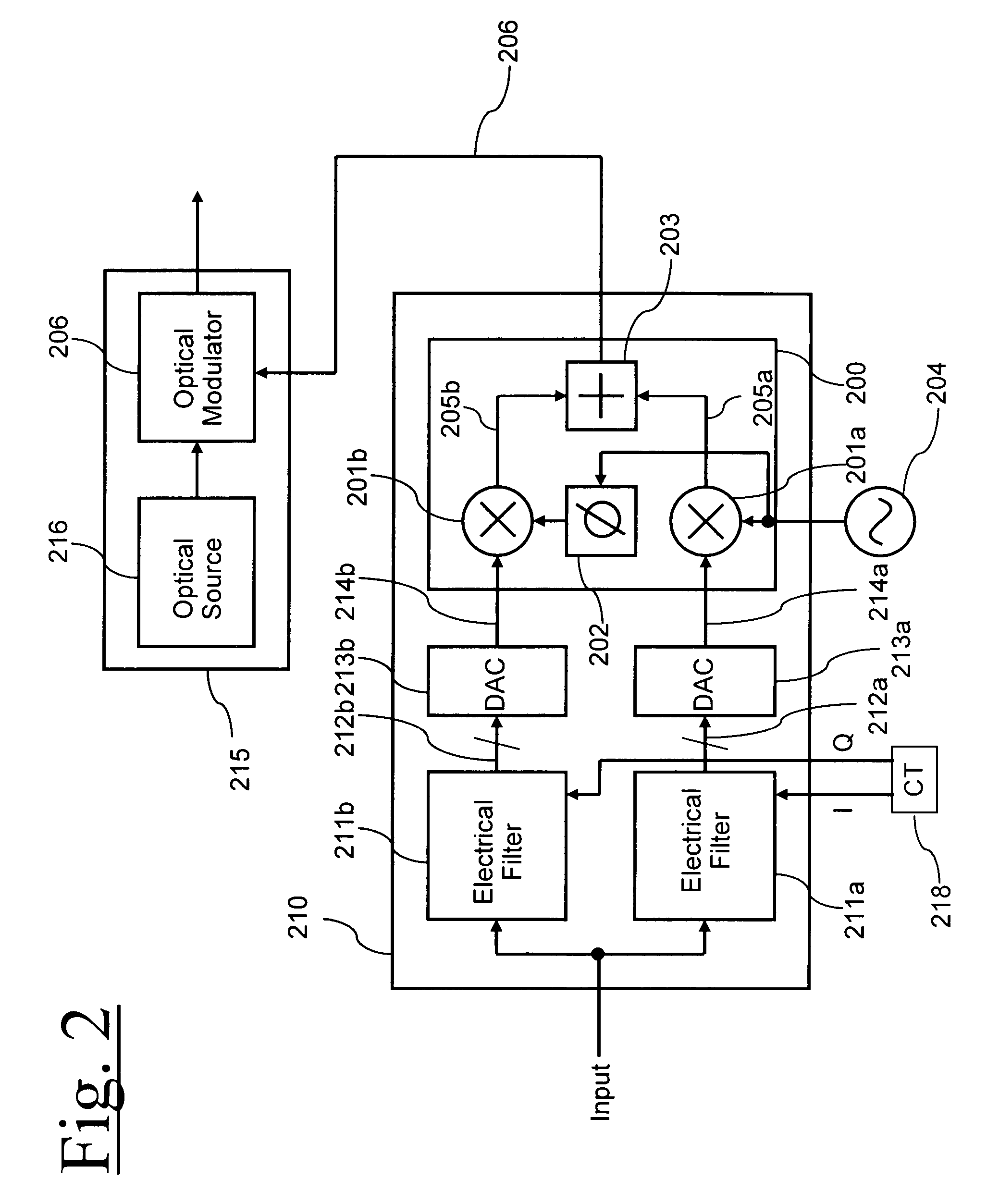
Electrical compensation of optical impairments
ActiveUS20070140703A1Mitigation of impairmentLow costElectromagnetic transmittersOptical transmissionElectro-absorption modulatorLocal oscillator
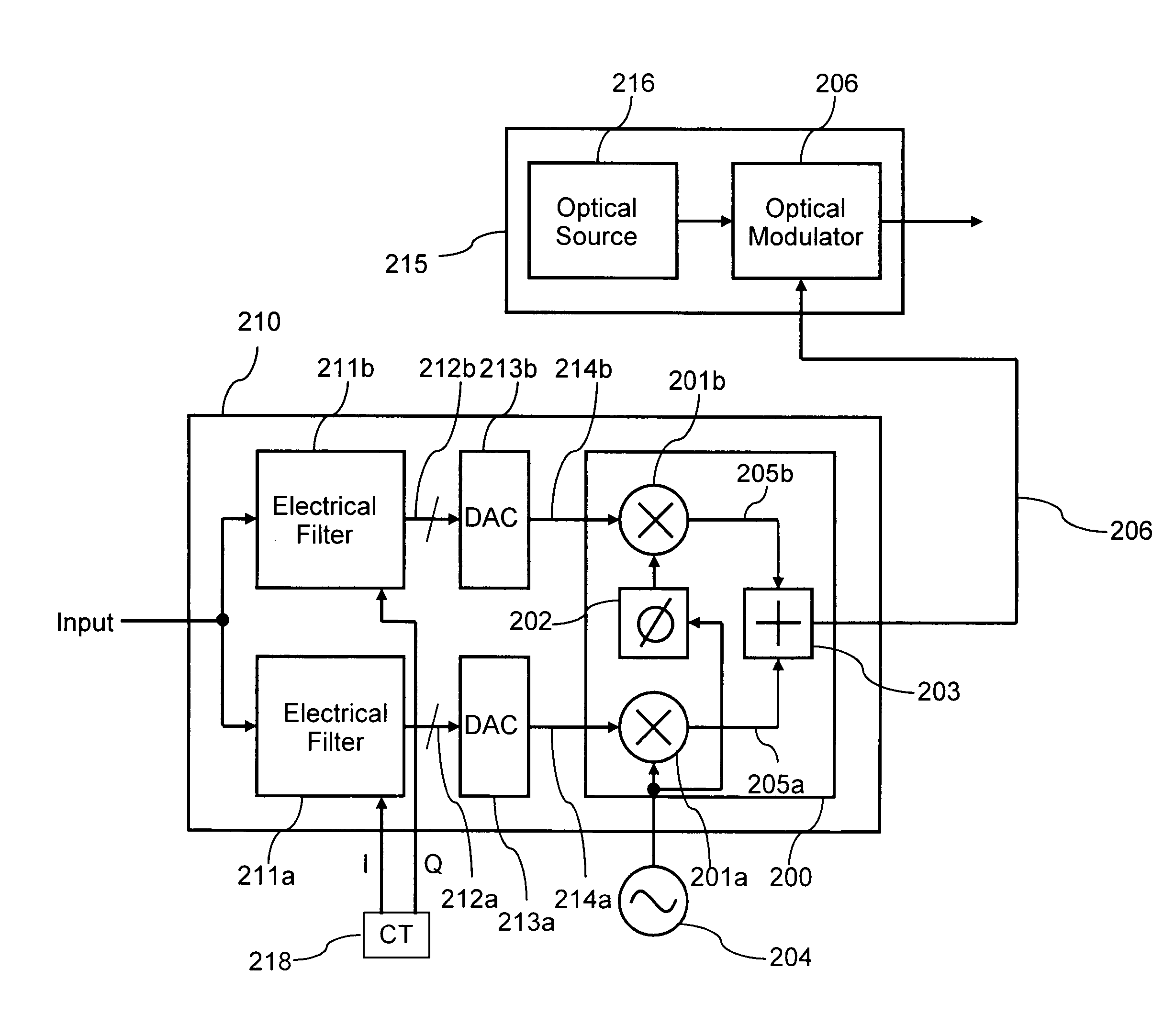
Optical impairments such as dispersion and fibre nonlinearity are compensated by generating a pre-distorted electrical signal at the transmitter. This signal is modulated onto a carrier signal, so that it is upconverted in frequency. This up converted signal is then used to modulate an optical source. Generally the optical signal will have two sidebands, one of which has the correctly pre-distorted information and the other which is unwanted. Information in the unwanted optical sideband is either filtered optically or electrically. In the preferred embodiments, the transmitter uses a tunable semiconductor laser with an integrated electroabsorption modulator to modulate the light. The preferred receiver is a coherent receiver with a tunable local oscillator laser. The receiver uses an electrical filter to remove the information in the unwanted sideband.
Owner:CIENA
Hybrid optical transmitter with electroabsorption modulator and semiconductor optical amplifier
InactiveUS6862136B2Increase transmit powerImprove signal qualityLaser detailsLaser output parameters controlOptical radiationElectro-absorption modulator
An optical radiation amplifier, including an input port which receives the optical radiation and a first semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA), which is coupled to receive the optical radiation from the input port and is adapted to amplify the optical radiation to produce amplified optical radiation in response to a first current injected into the first SOA. The amplifier also includes an electro-absorption modulator (EAM), which is coupled to receive the amplified optical radiation and is adapted to modulate the amplified optical radiation in response to a modulation voltage applied to the EAM so as to produce modulated radiation. There is a second SOA, which is coupled to receive the modulated radiation and is adapted to amplify the modulated radiation in response to a second current injected into the second SOA.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Electrical compensation of optical impairments
ActiveUS7330667B2Mitigation of impairmentLow costElectromagnetic transmittersOptical transmissionElectro-absorption modulatorLocal oscillator
Optical impairments such as dispersion and fibre nonlinearity are compensated by generating a pre-distorted electrical signal at the transmitter. This signal is modulated onto a carrier signal, so that it is upconverted in frequency. This up converted signal is then used to modulate an optical source. Generally the optical signal will have two sidebands, one of which has the correctly pre-distorted information and the other which is unwanted. Information in the unwanted optical sideband is either filtered optically or electrically. In the preferred embodiments, the transmitter uses a tunable semiconductor laser with an integrated electroabsorption modulator to modulate the light. The preferred receiver is a coherent receiver with a tunable local oscillator laser. The receiver uses an electrical filter to remove the information in the unwanted sideband.
Owner:CIENA
Method for fabricating butt-coupled electro-absorptive modulators
InactiveUS8871554B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsEtchingElectro-absorption modulator
A method for fabricating butt-coupled electro-absorptive modulators is disclosed. A butt-coupled electro-absorptive modulator with minimal dislocations in the electro-absorptive material is produced by adding a dielectric spacer for lining the coupling region before epitaxially growing the SiGe or other electro-absorptive material. It has been determined that during the SiGe growth, the current process has exposed single crystal silicon at the bottom of the hole and exposed amorphous silicon on the sides. SiGe growth on the amorphous silicon is expected to have more dislocations than single crystal silicon. There should also be dislocations or fissures where the SiGe growth from the each nucleation source finally join. Thus, a dielectric sidewall can protect an exposed waveguide face from any etching from an aggressive surface preparation prior to epi growth.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Distributed feedback semiconductor laser and electric absorption modulator integrated light source and mfg. method
InactiveCN1452284AHigh modulation ratePromote absorptionLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersCommunications systemGrating
A distributed feedback (DFB) laser-electric absorption modulator (EAM) integrated light source is characterized by that the DFB laser has the raster structure formed by periodically arranged active layer material and said integrated light source has the active layer material with epitaxial quantum trap structure. Its preparing process is also disclosed. Its advantage is optimized performance of both units.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
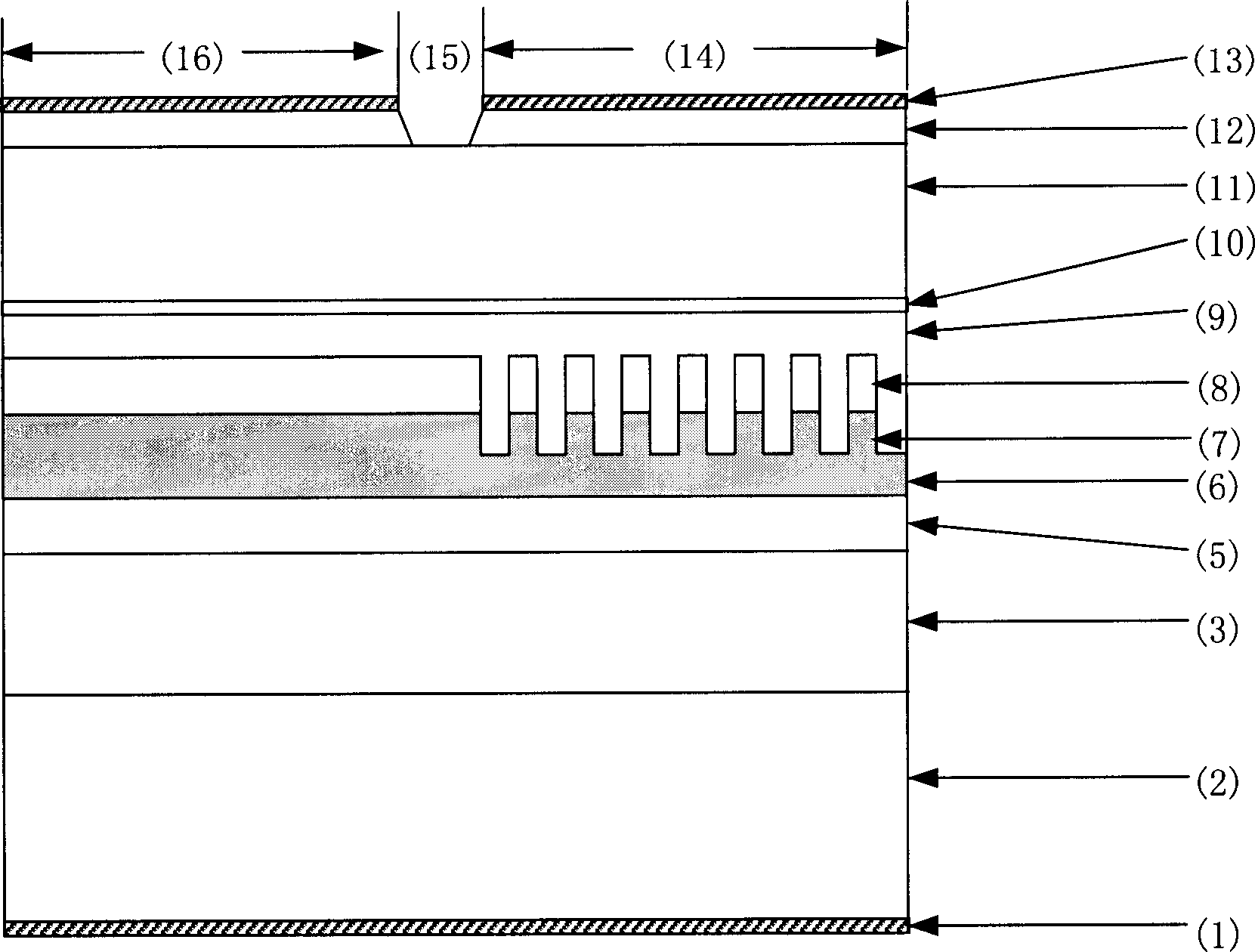
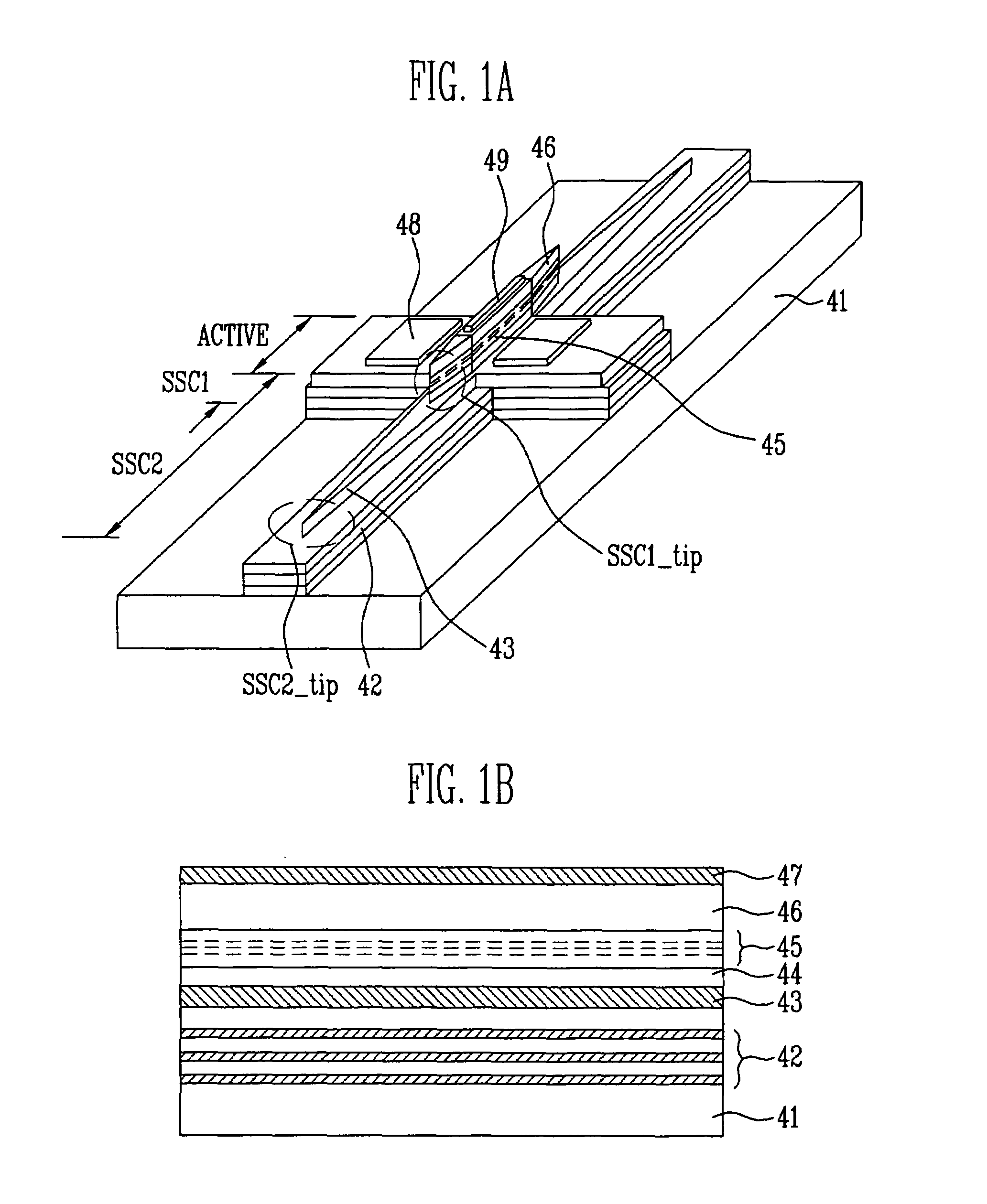
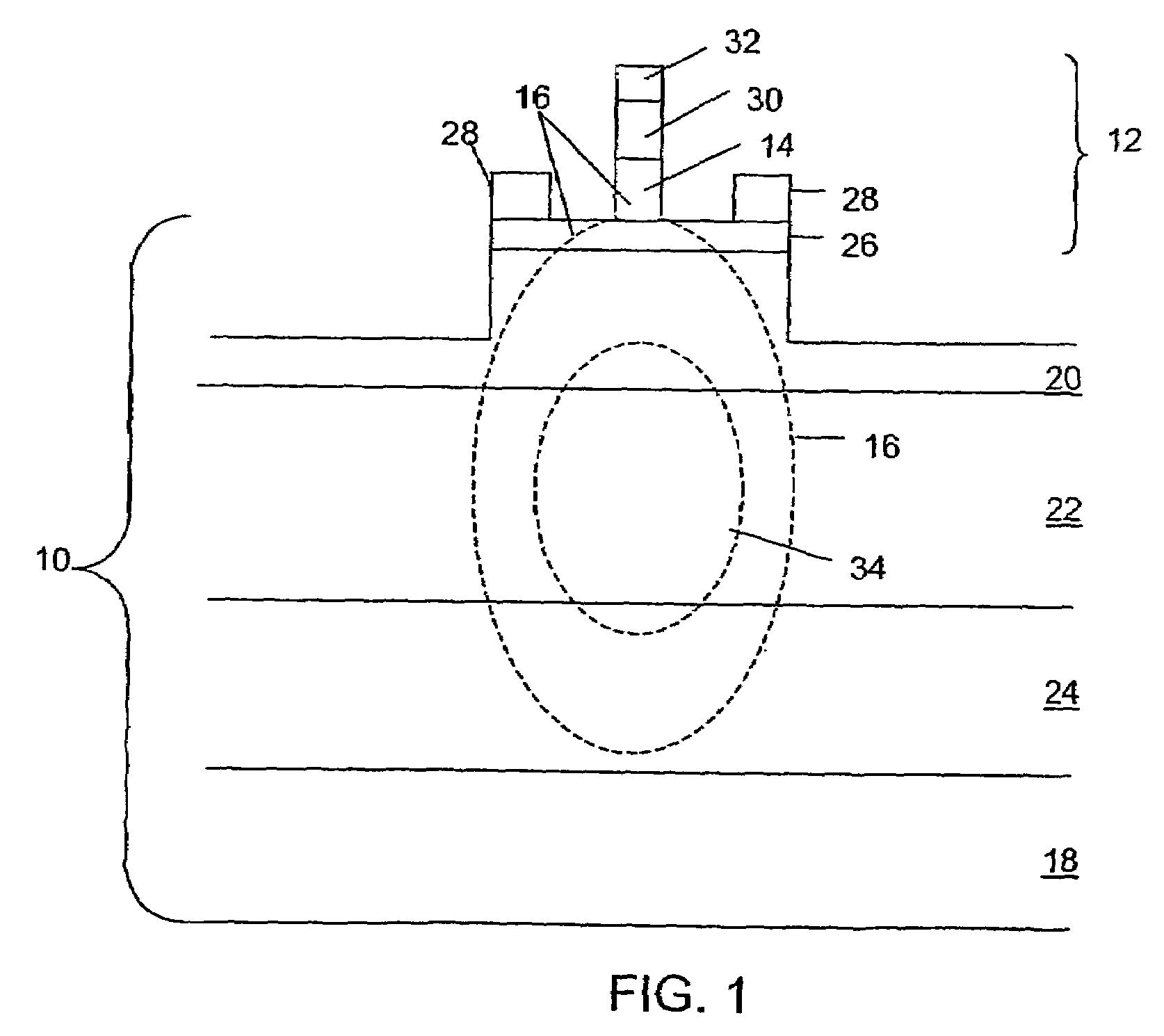
Electroabsorption modulator and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060126987A1Low optical coupling lossHigh input optical powerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsElectro-absorption modulatorOptical power
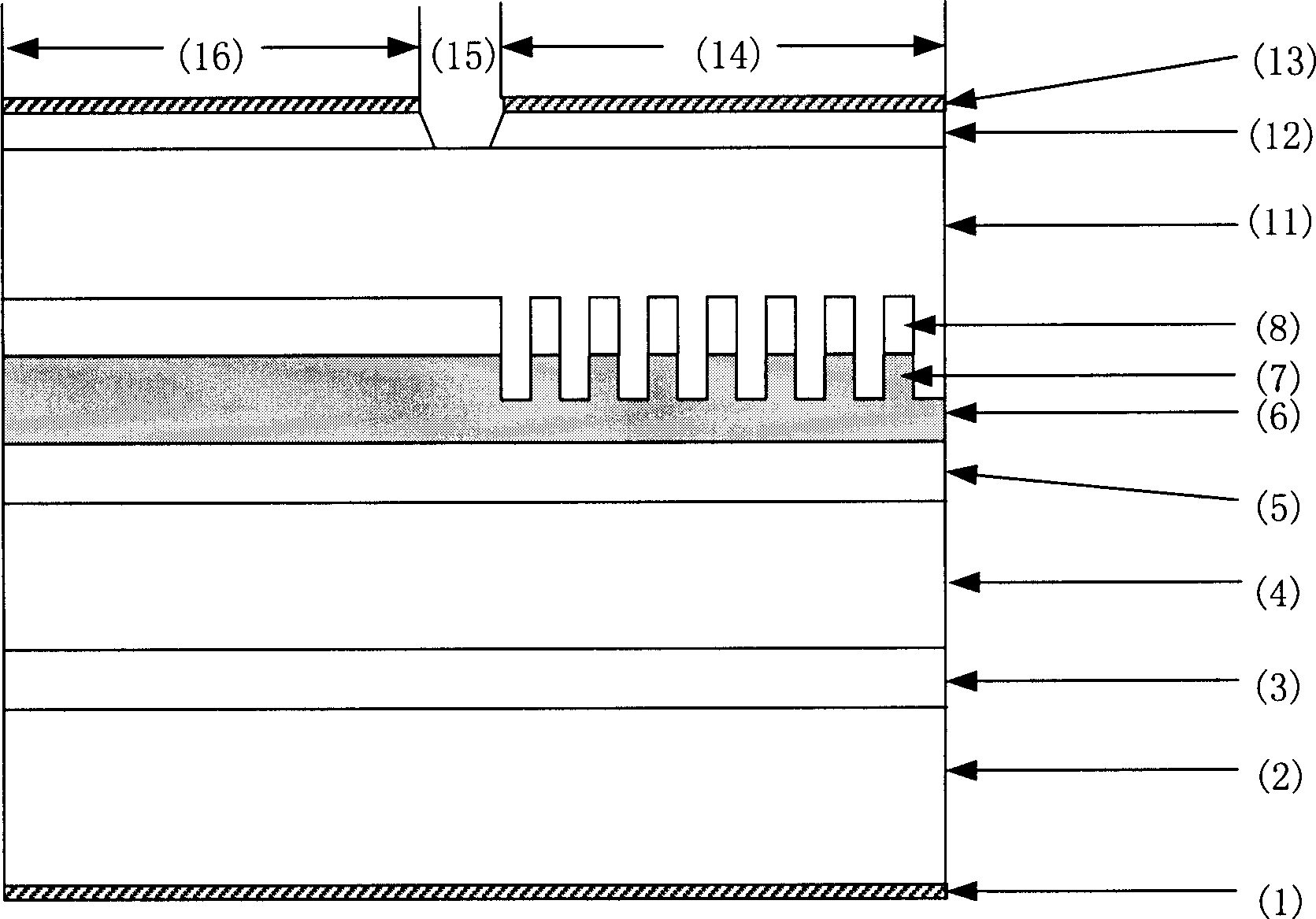
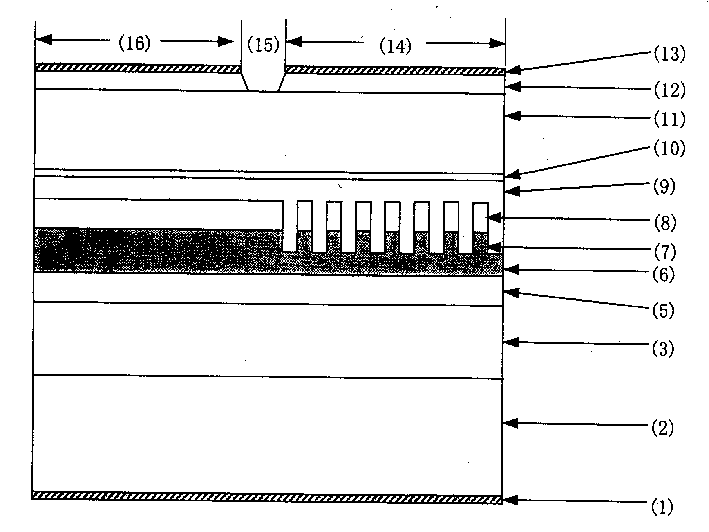
Provided is a double waveguide electroabsorption modulator, in which two spot size converters are integrated between first and second optical waveguides, thereby reducing an insertion loss between an optical fiber and an optical modulator while favorably operating even in high input optical power. Therefore, the electroabsorption modulator can stably operate in higher input optical power while reducing an optical coupling loss and an optical confinement factor (OCF).
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
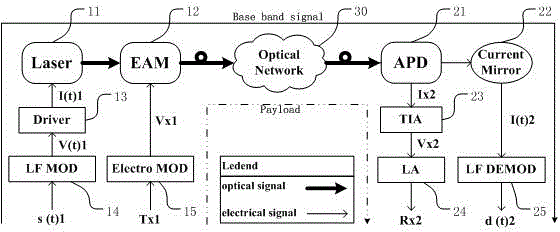
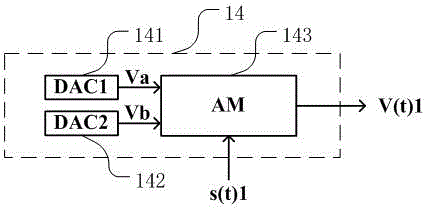
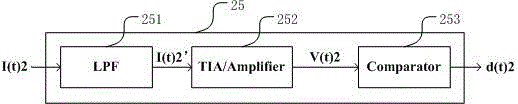
Optical module of in-band pass through monitoring signal based on amplitude modulation
ActiveCN104980225AResource SharingIncrease flexibilityElectromagnetic transceiversElectro-absorption modulatorTransconductance
The present invention discloses an optical module of an in-band pass through monitoring signal based on amplitude modulation, belonging to the field of communication technology. The optical module comprises a low speed baseband amplitude modulation circuit, a laser driving circuit, a laser, an electro-absorption signal modulation circuit, an electro-absorption modulator, an avalanche photodiode, a transconductance amplifier, an amplitude limiting amplifier, a mirror current circuit, and a low-frequency demodulation circuit. Compared with a conventional optical module, according to the optical module of the invention, a monitoring signal is loaded to the envelope of a bearing service signal through amplitude modulation and shares cable and channel resources with a bearing service signal, the channel resource is saved, the monitoring signal of the pass through is unrelated to a bearing service signal protocol, and the use flexibility is high. Since a low speed baseband signal amplitude modulation and demodulation unit is integrated in the optical module, the additional adding of an optical function unit is not needed, the pass through of the monitoring signal can be realized, and the optical module is a most cost-effective solution for an application scene with the need of monitoring signal transmission.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
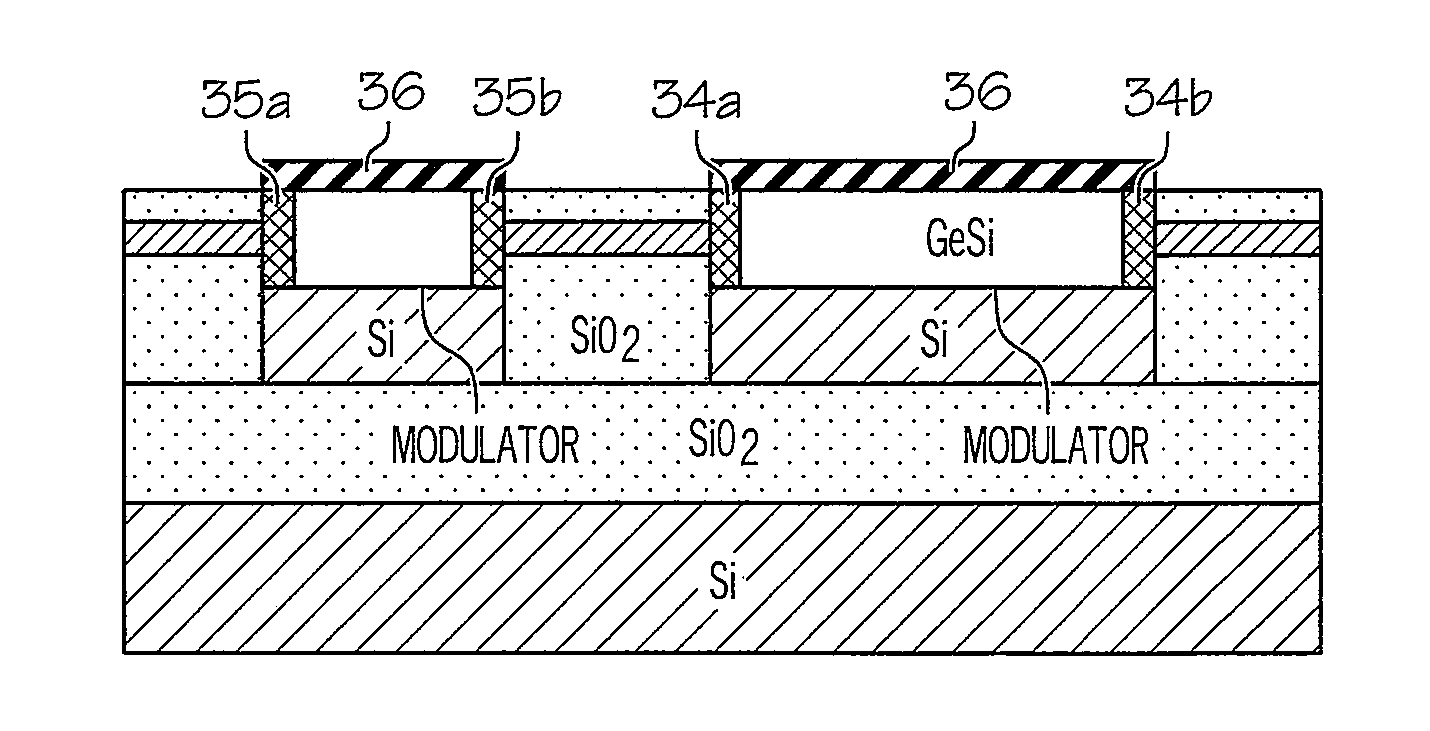
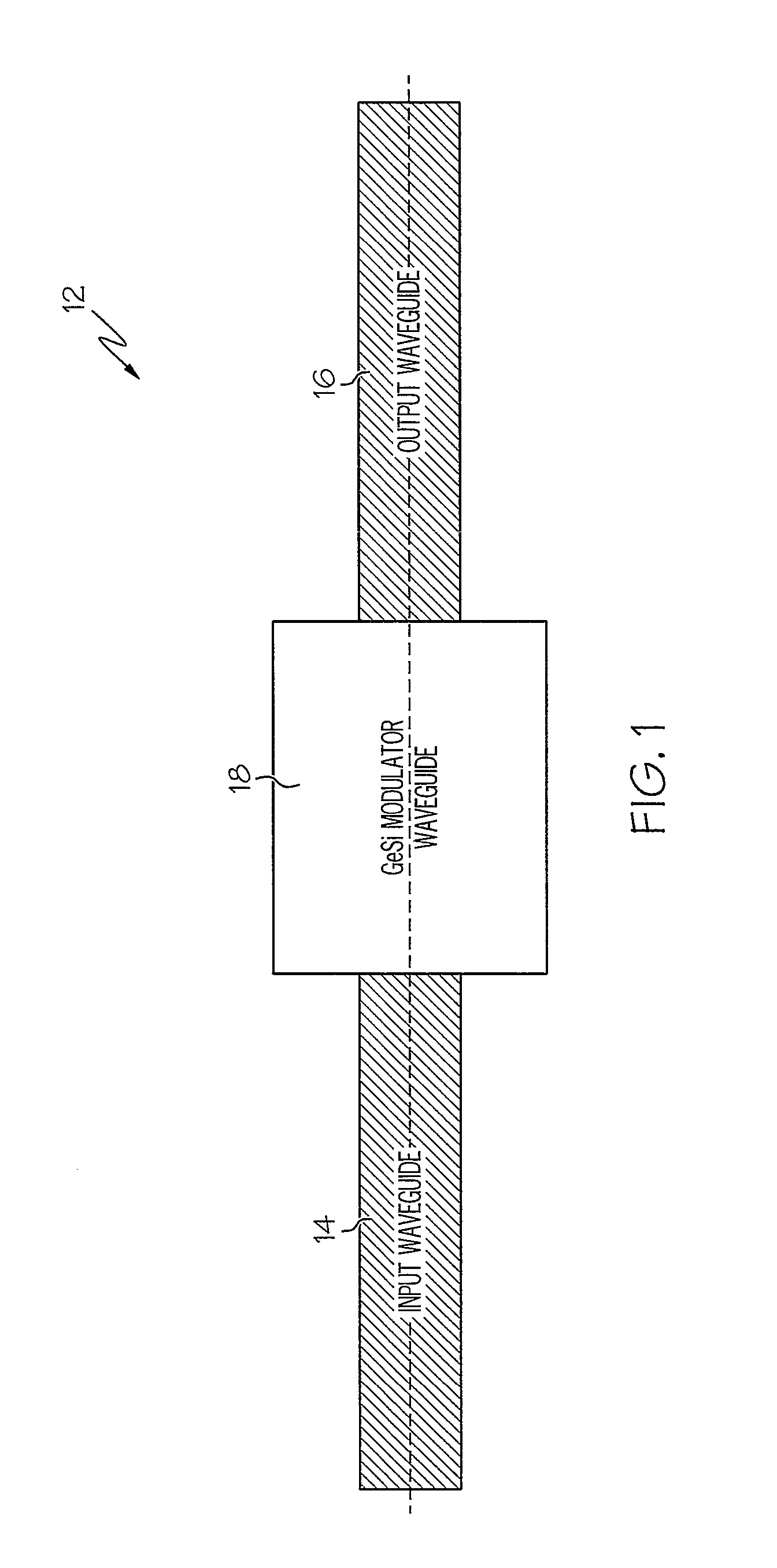
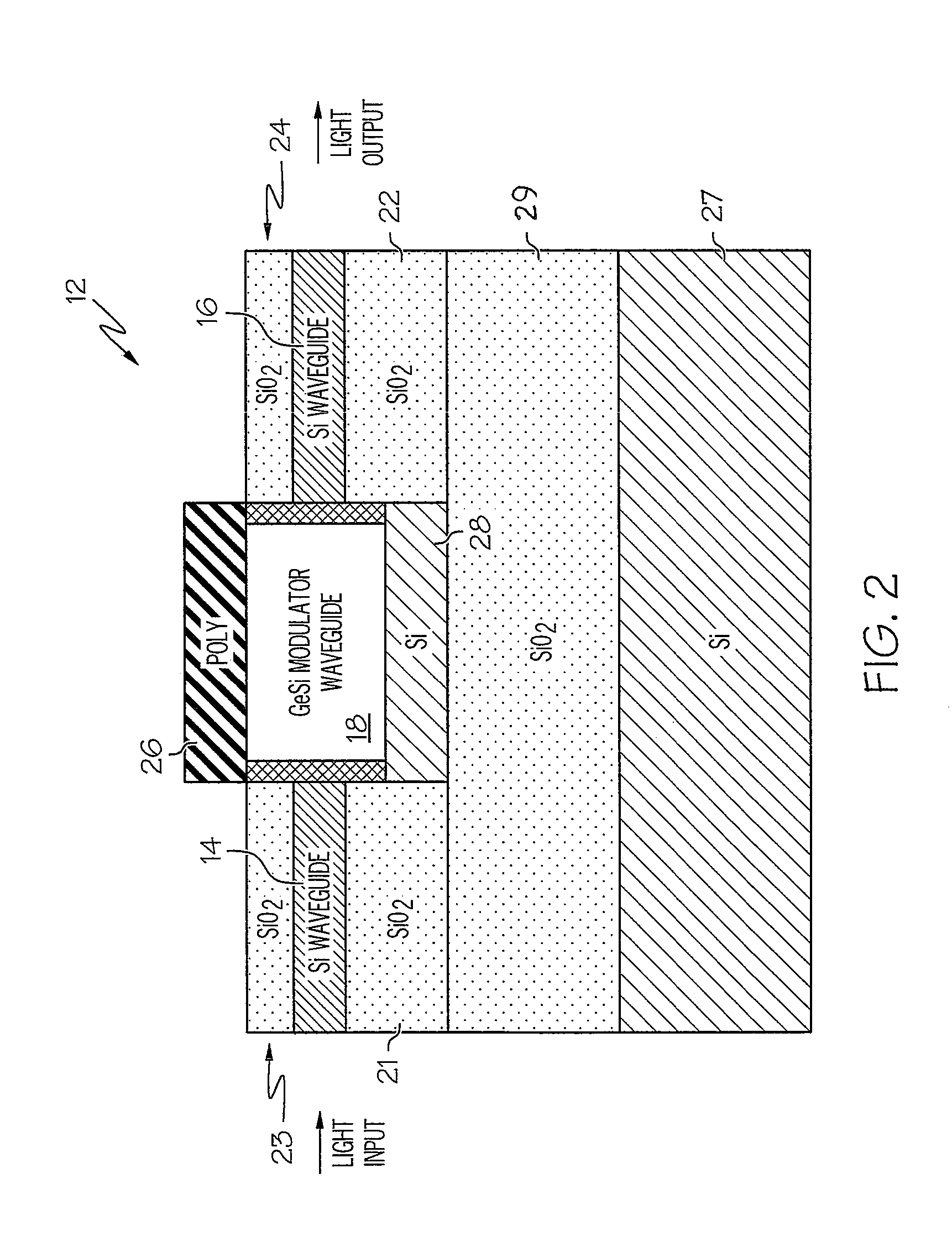
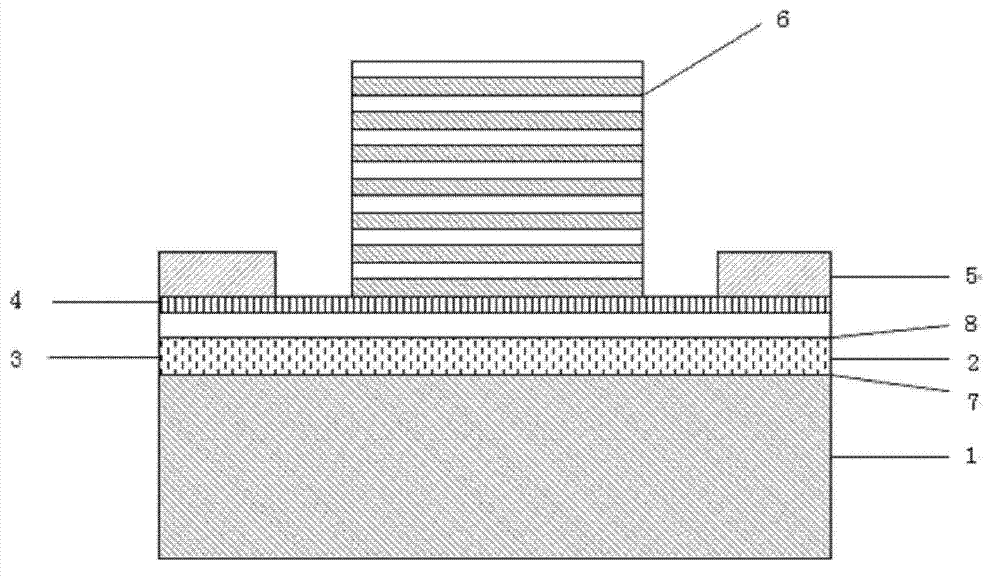
Integrated electro-absorption modulator
ActiveUS9142698B1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityElectro-absorption modulator
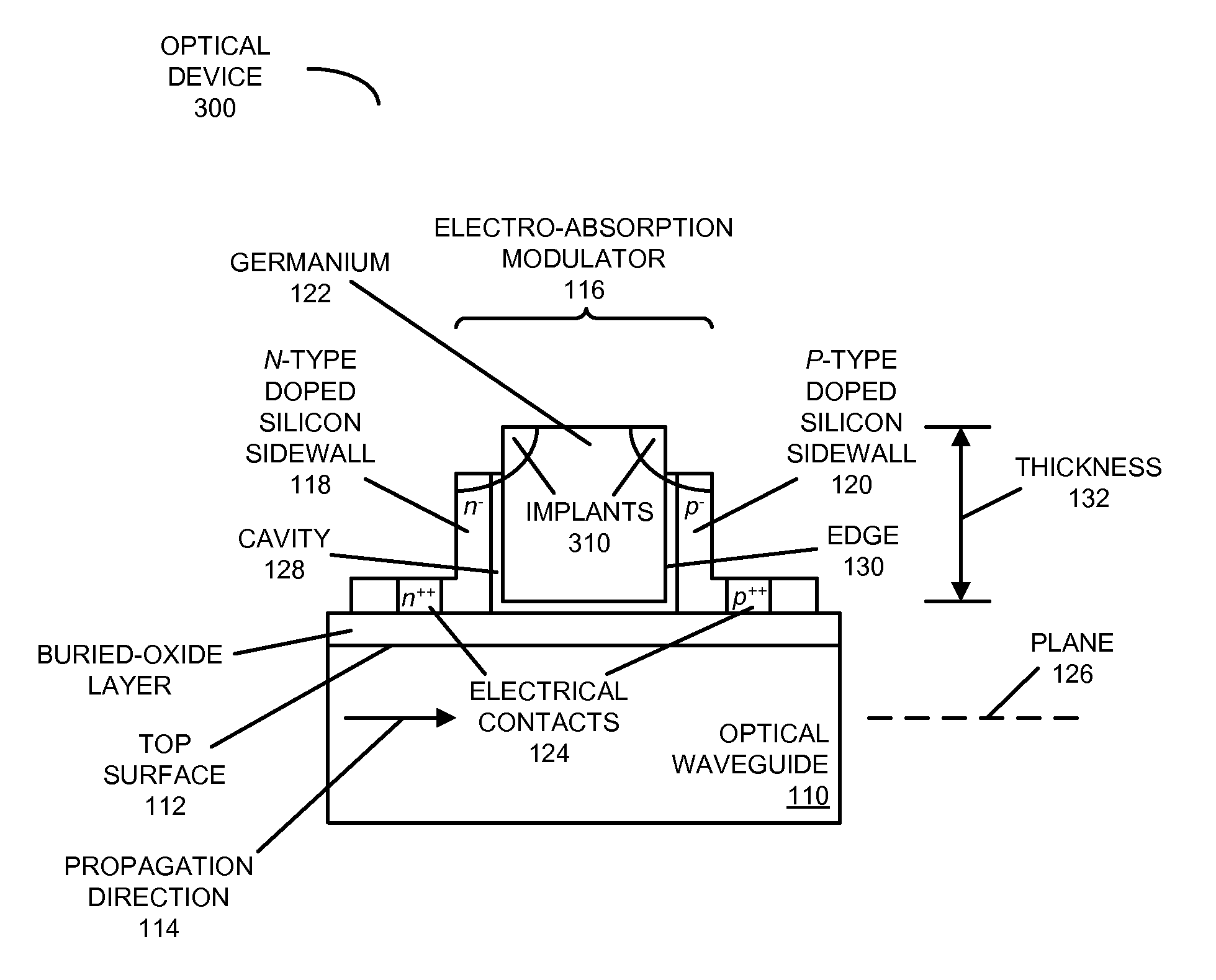
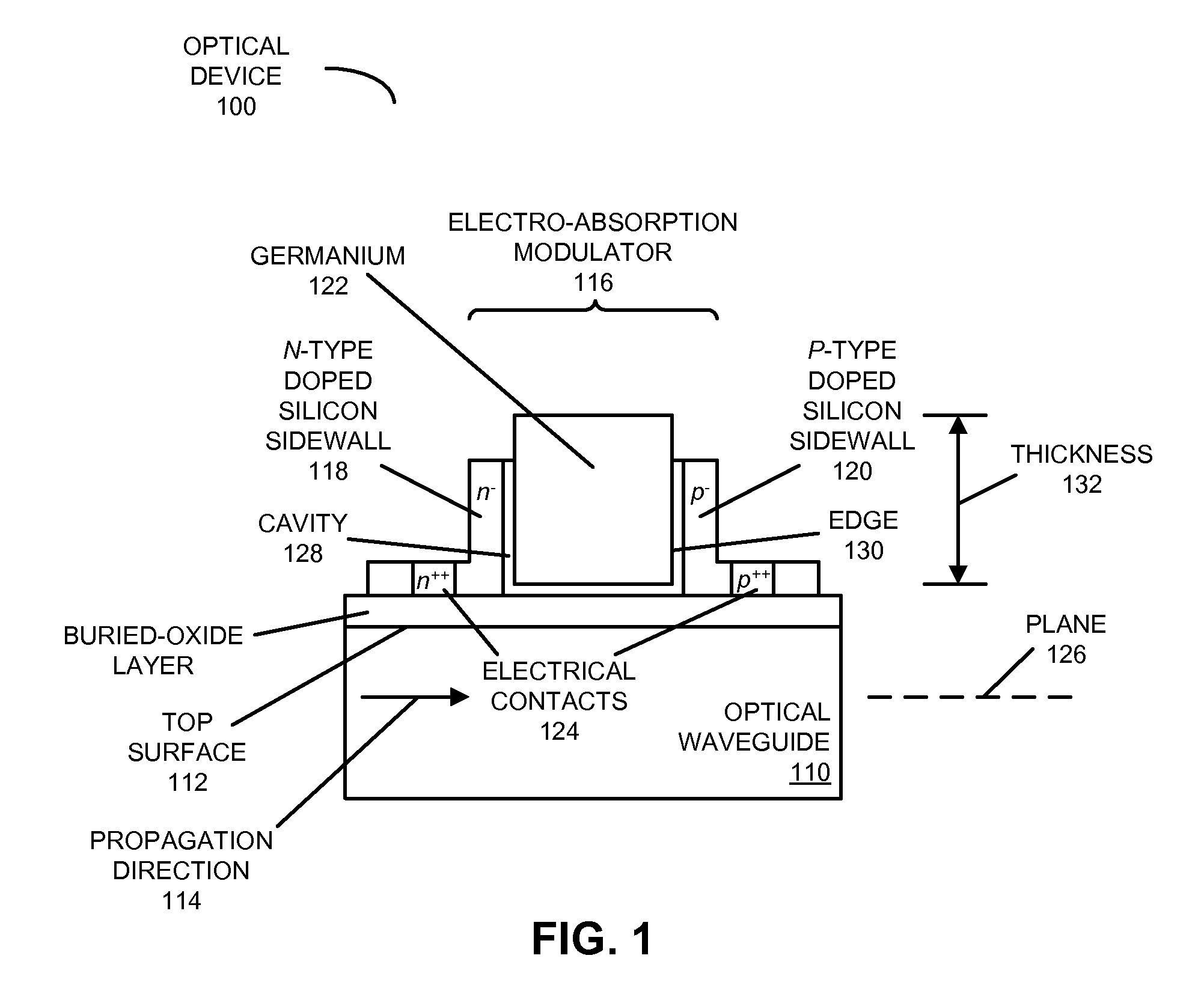
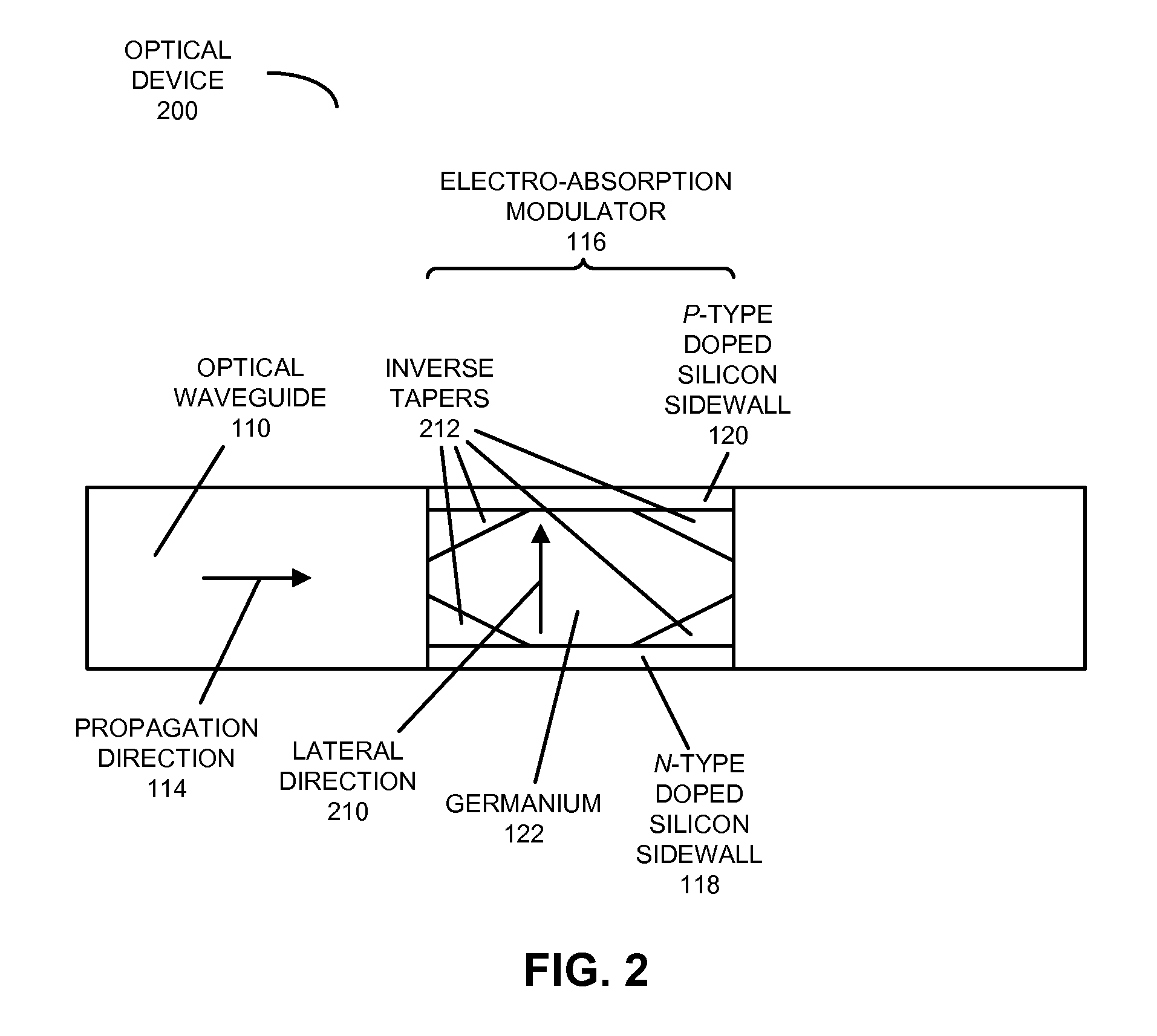
An integrated optical device includes an electro-absorption modulator disposed on a top surface of an optical waveguide. The electro-absorption modulator includes germanium disposed in a cavity between an n-type doped silicon sidewall and a p-type doped silicon sidewall. By applying a voltage between the n-type doped silicon sidewall and the p-type doped silicon sidewall, an electric field can be generated in a plane of the optical waveguide, but perpendicular to a propagation direction of the optical signal. This electric field shifts a band gap of the germanium, thereby modulating the optical signal.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
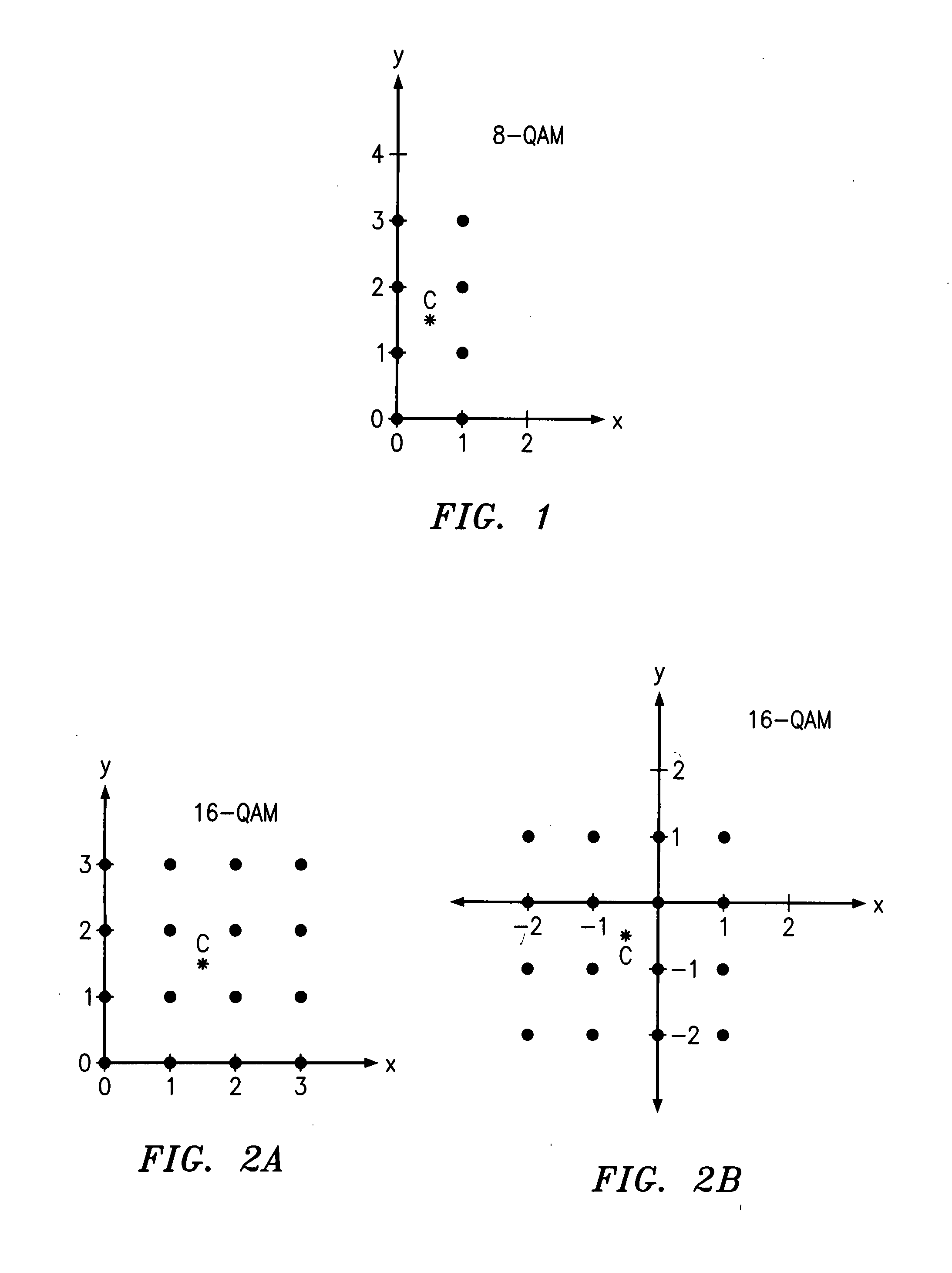
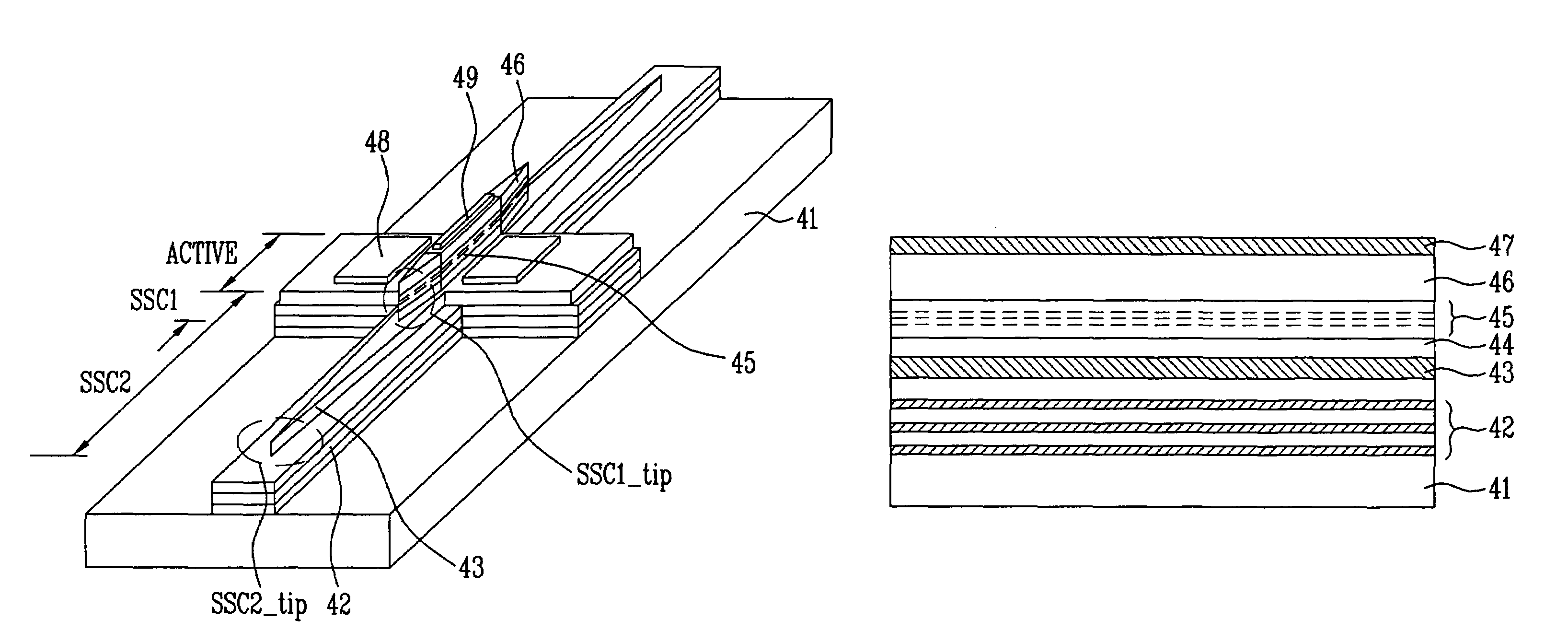
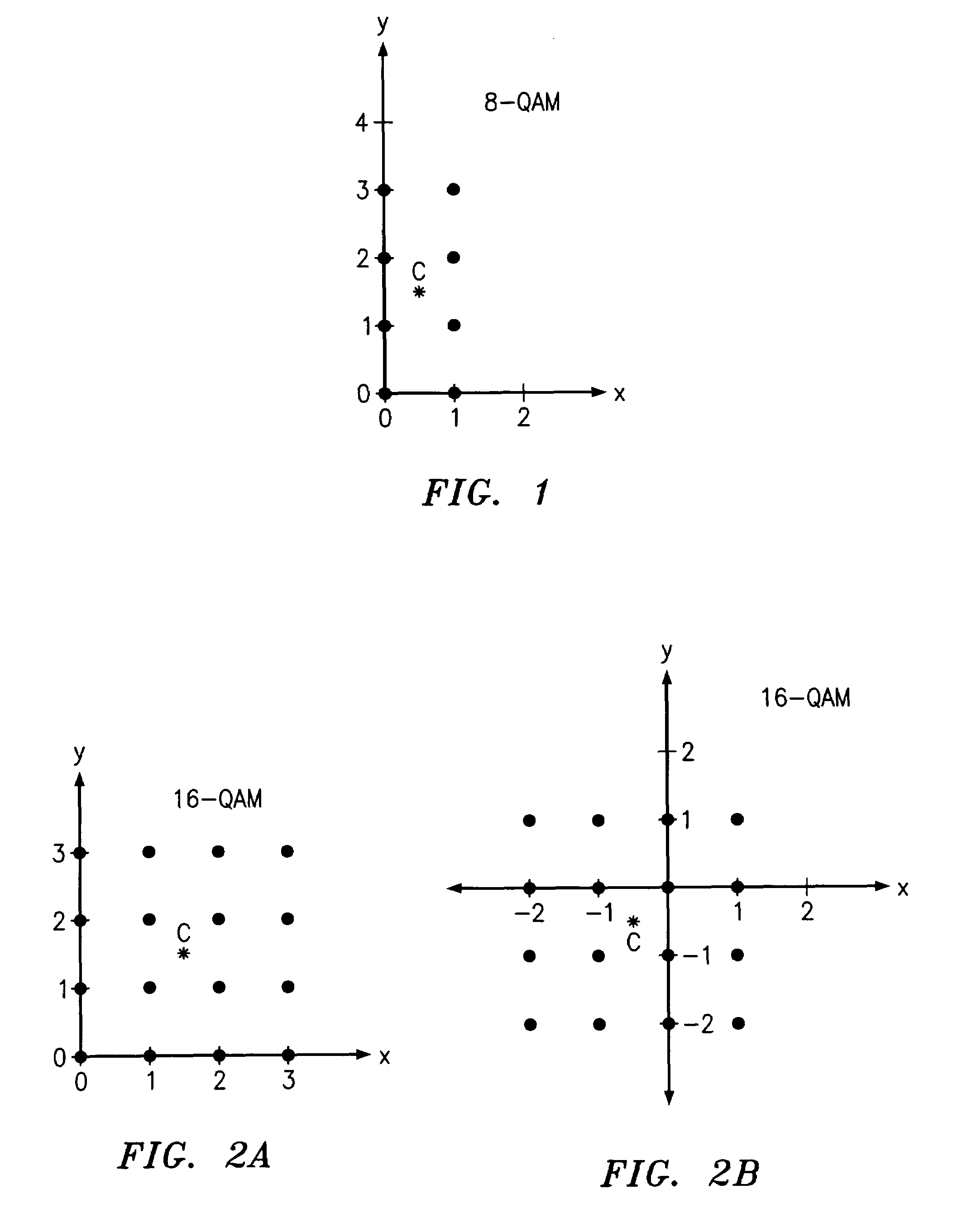
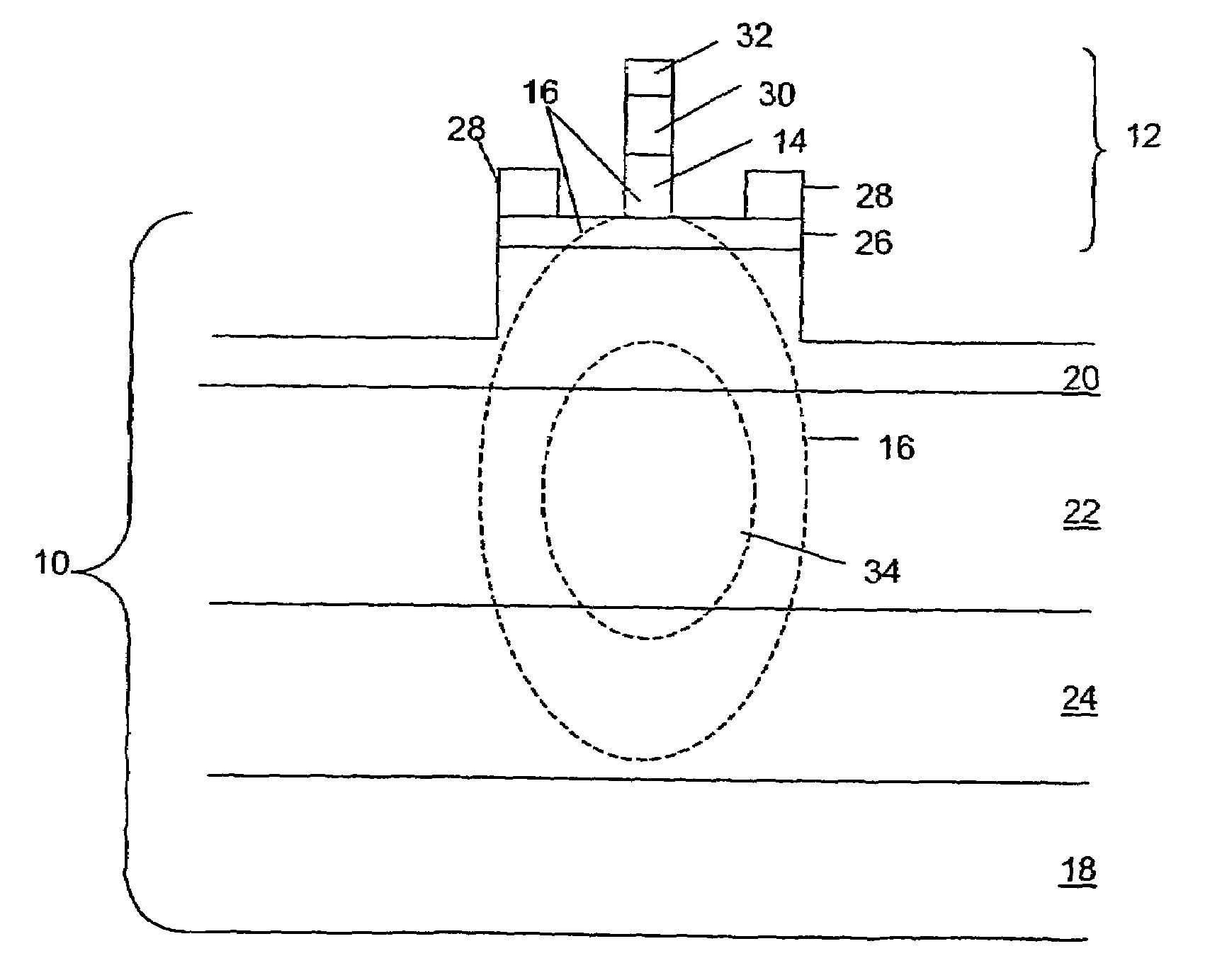
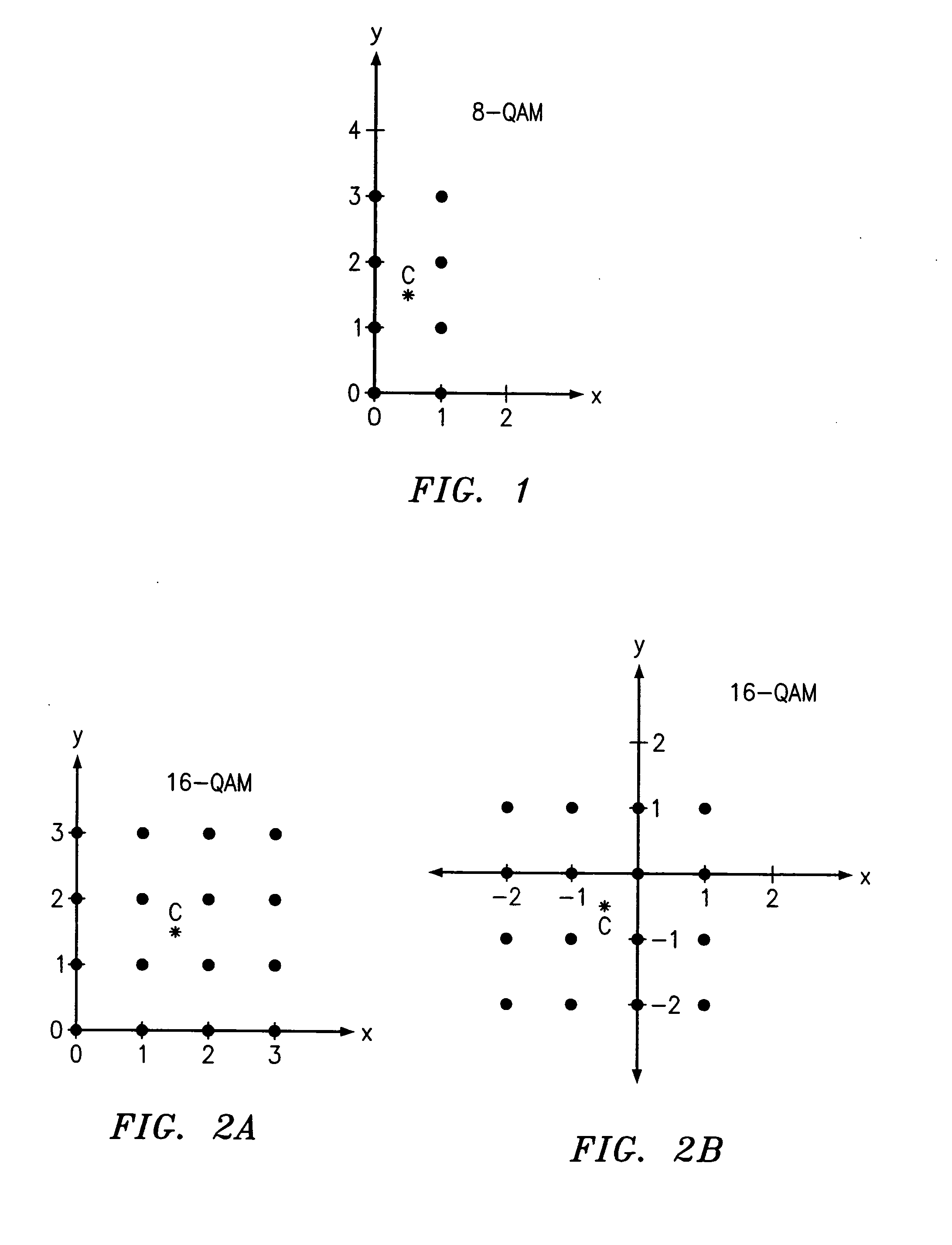
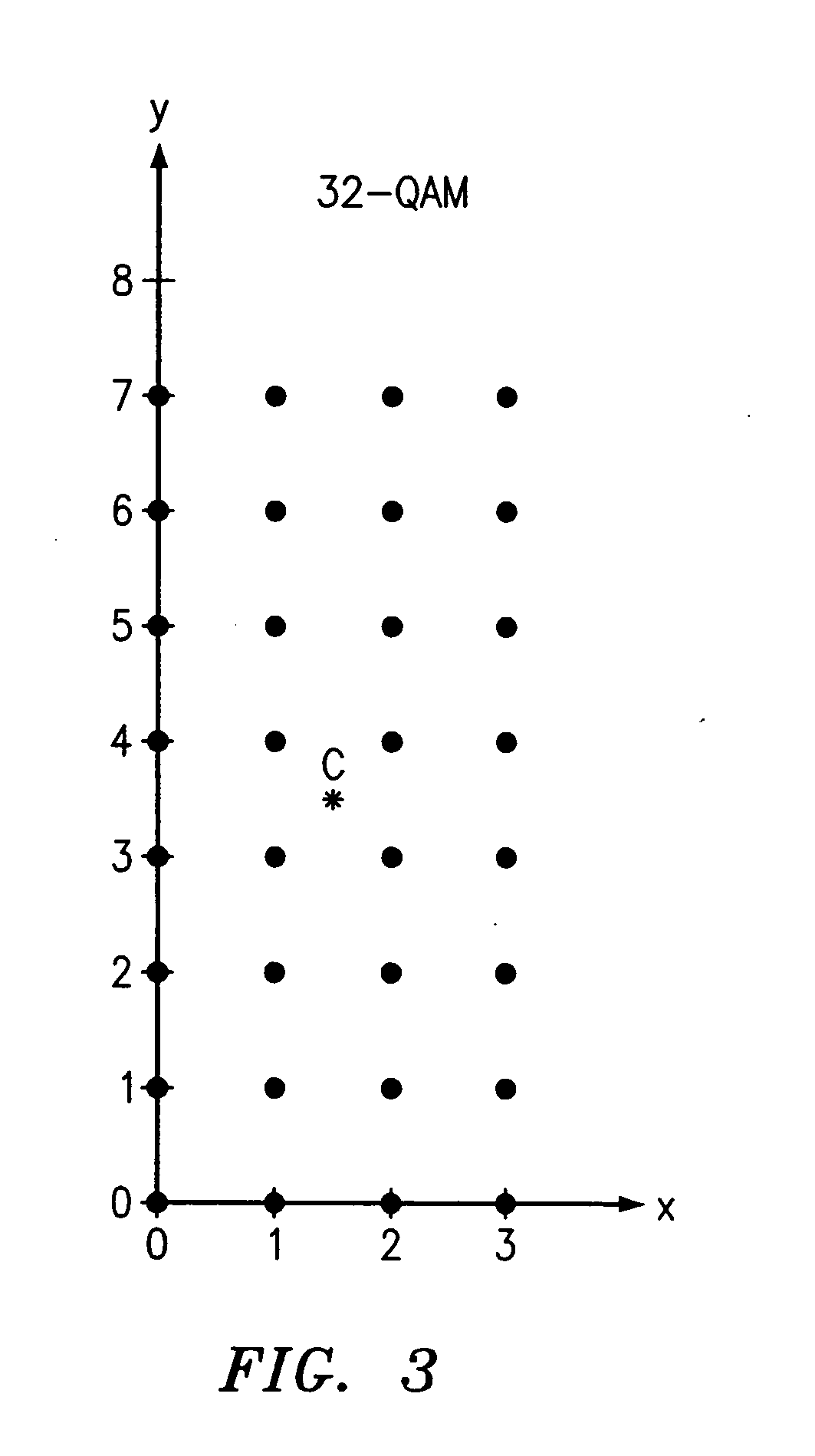
QAM optical modulators
ActiveUS20090169148A1Electromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsElectro-absorption modulatorMaximum amplitude
An exemplary optical modulator includes an interferometer. The interferometer includes an input optical coupler, an output optical coupler, and two or more controllable optical waveguides. Each controllable optical waveguide connects the input optical coupler to the output optical coupler and has an electro-absorption modulator along a segment thereof. Two of the controllable optical waveguides are connected to transmit to an output of the output optical coupler light of substantially different maximum amplitude.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Electroabsorption modulator and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7359588B2Low optical coupling lossIncrease powerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsElectro-absorption modulatorOptical power
Provided is a double waveguide electroabsorption modulator, in which two spot size converters are integrated between first and second optical waveguides, thereby reducing an insertion loss between an optical fiber and an optical modulator while favorably operating even in high input optical power. Therefore, the electroabsorption modulator can stably operate in higher input optical power while reducing an optical coupling loss and an optical confinement factor (OCF).
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
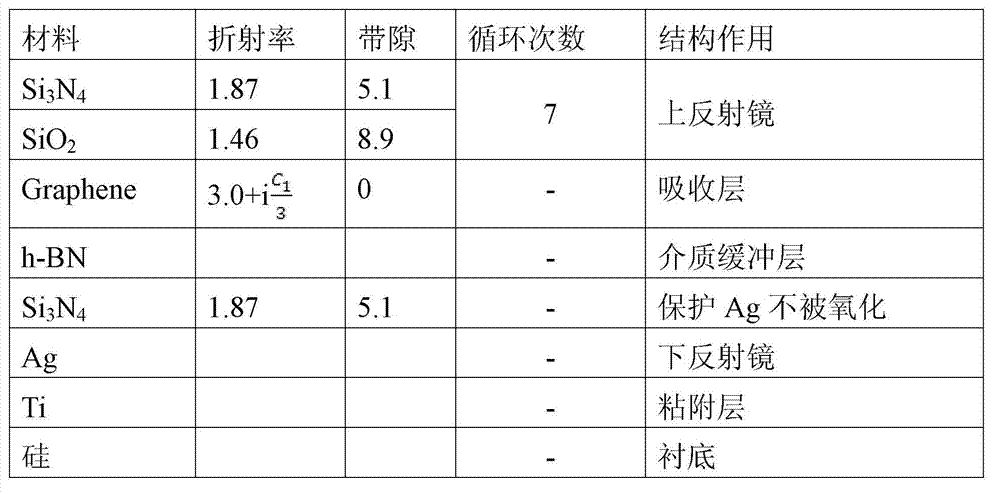
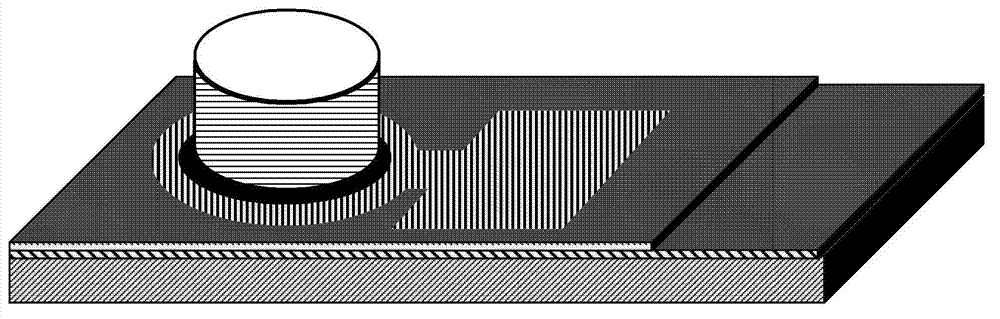
Resonant cavity enhanced grapheme electric absorption modulator
ActiveCN103091870AIncreased freedom in spectral designEasy to integrateNon-linear opticsElectro-absorption modulatorLight modulation
The invention discloses a resonant cavity enhanced grapheme electric absorption modulator which is manufactured on an underlay. The resonant cavity enhanced grapheme electric absorption modulator comprises a lower reflector formed on the underlay, a medium buffering layer formed on the lower reflector, a single layer grapheme thin membrane formed on the medium buffering layer, an upper reflector formed on a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) structure of the single layer grapheme thin membrane, and a metal positive electrode formed on the single layer grapheme thin membrane and arranged on the periphery of the upper reflector in a surrounding mode. Due to the fact that light lights on a component in a perpendicular mode, the resonant cavity enhanced grapheme electric absorption modulator is capable of adjusting level of Fermi level in grapheme by exerting gate bias on the component, and thus whether the grapheme absorbs the light is controlled, and the purpose of light modulation is achieved. The resonant cavity enhanced grapheme electric absorption modulator has the advantages of being capable of being large in degree of freedom of design of size and spectrum modulation range, low in consumption, low in insertion loss, free from polarization state requirements to light signals, and prone to silicon substrate integration.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for improving radio over fiber link performance
InactiveCN102611504ASuppression of second-order nonlinear distortionDistortion/dispersion eliminationRadio-over-fibreNonlinear distortionRadio over fiber
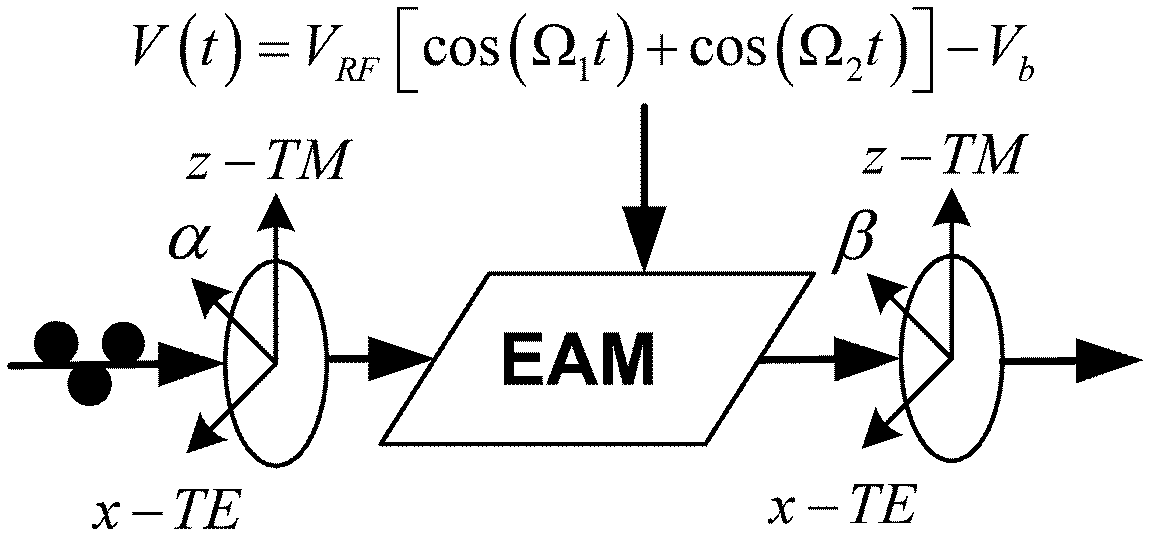
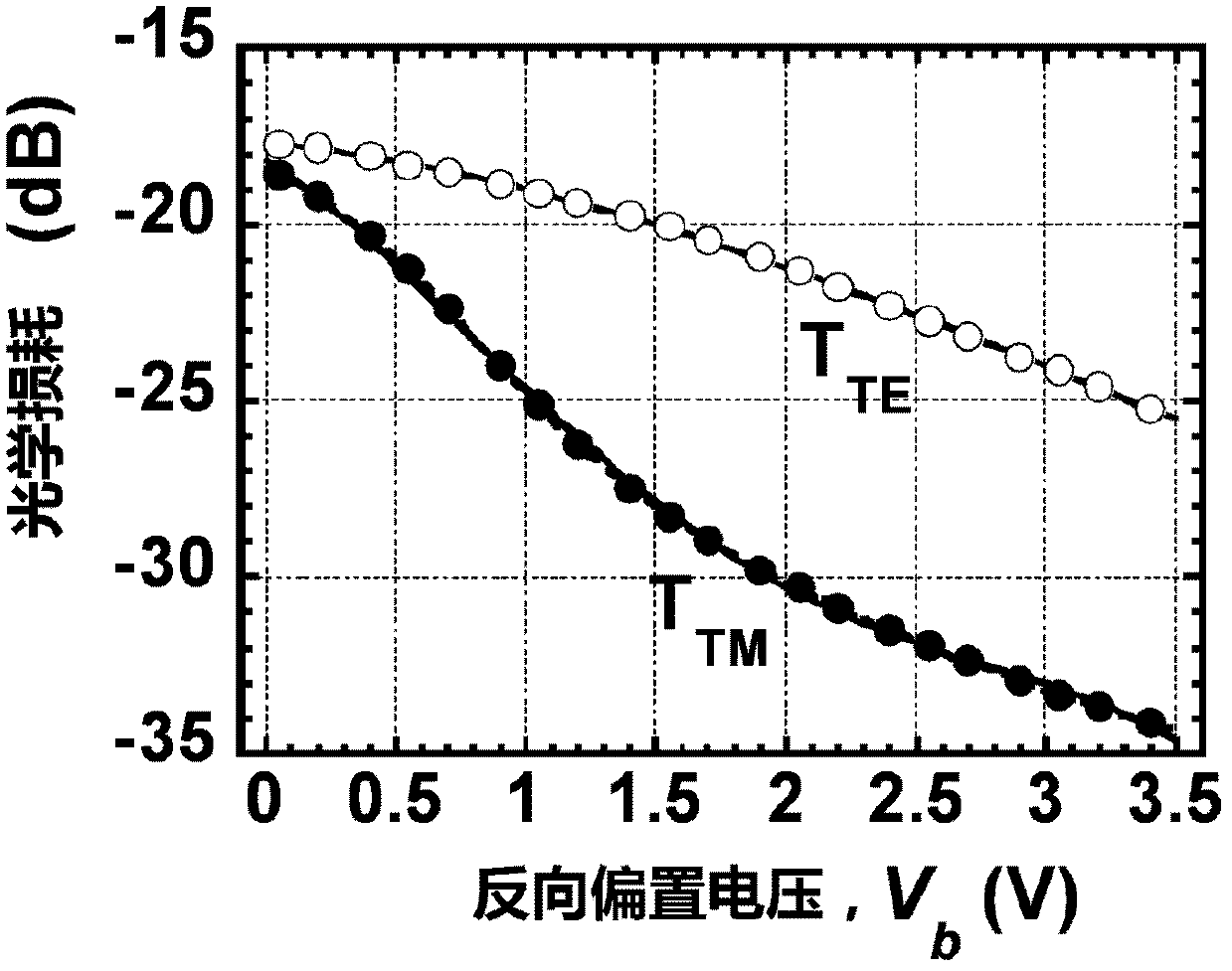
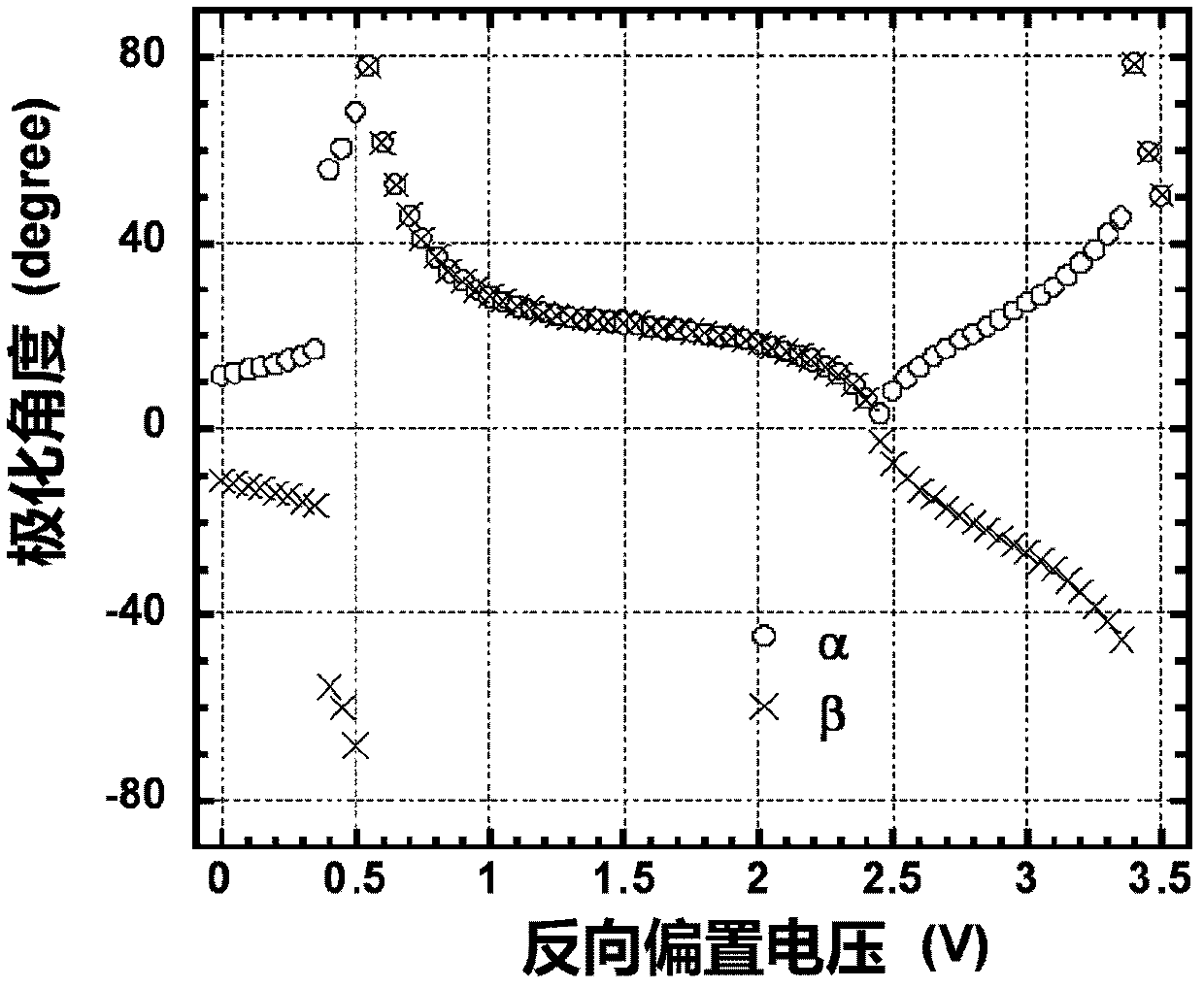
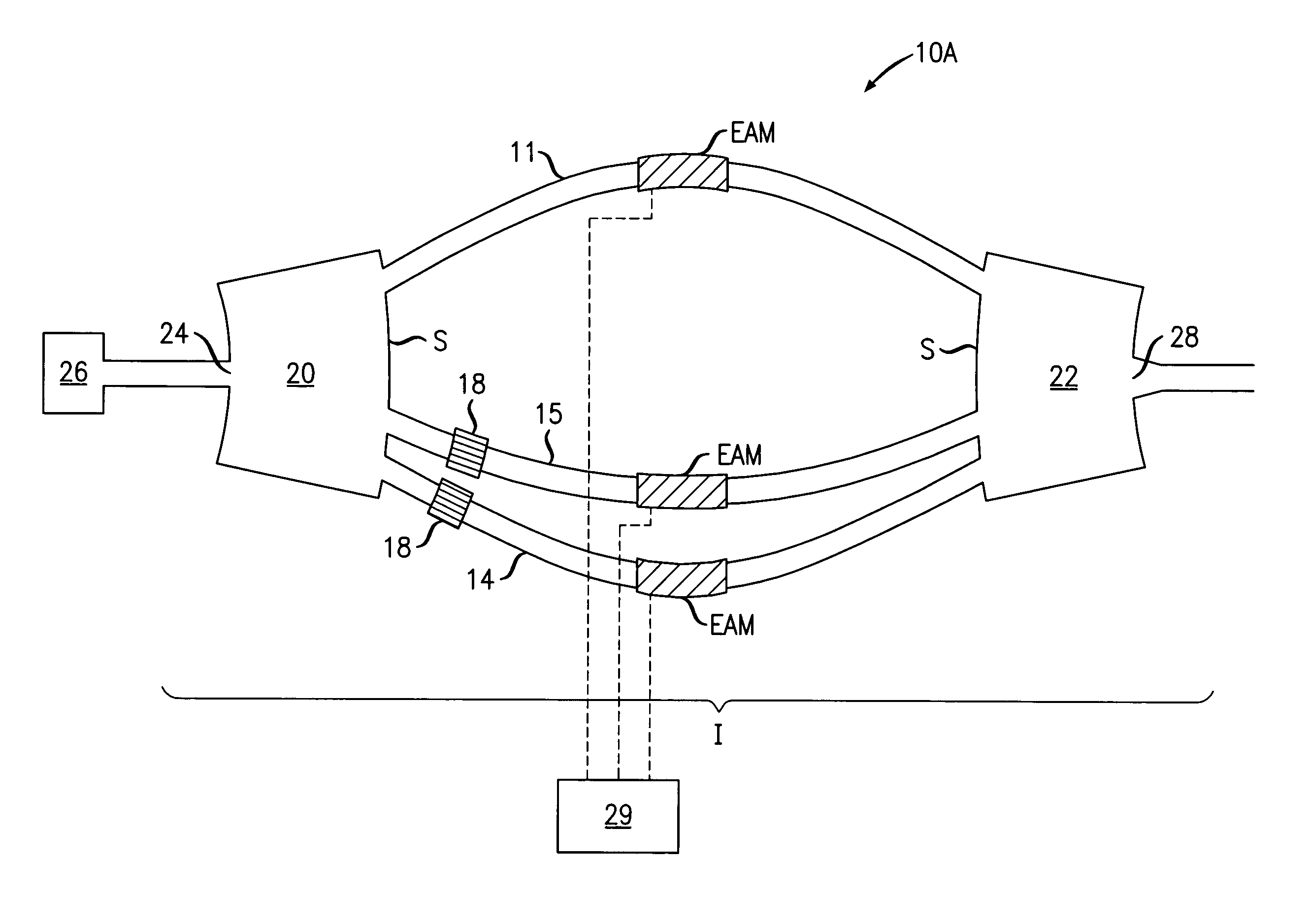
The invention relates to a method for improving radio over fiber (RoF) link performance, which belongs to the technical field of electronics. According to the method, the RoF link performance is improved by a mixed-polarization electro-absorption modulator (EAM) or a mixed-polarization Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM). The improvement is as follows: the mixed-polarization EAM or the mixed-polarization MZM is composed of a linear polarizer with an angle of alpha, an EAM or MZM and a second linear polarizer with an angle of beta; the two linear polarizers are respectively placed at the front end and the rear end of the EAM or the MZM; and the values of the alpha and the beta are related with the characteristics of the modulators. The method has the following advantages: (1) third-order non-linear and second-order non-linear distortions can be inhibited, and the SFDR (spurious-free dynamic range) is improved by more than about 12dB for a 20km optical fiber transmission RoF system using the mixed-polarization EAM and is improved by about 12dB for the 20km fiber transmission RoF system using the mixed-polarization MZM; and (2) through an OFDM UWB (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing ultra wide band) signal test, the EVM (error vector magnitude) is improved by 3dB by using the mixed-polarization EAM and is improved by 8.7dB by using the mixed-polarization MZM.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
QAM optical modulators
ActiveUS7636501B2Electromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsElectro-absorption modulatorMaximum amplitude
An exemplary optical modulator includes an interferometer. The interferometer includes an input optical coupler, an output optical coupler, and two or more controllable optical waveguides. Each controllable optical waveguide connects the input optical coupler to the output optical coupler and has an electro-absorption modulator along a segment thereof. Two of the controllable optical waveguides are connected to transmit to an output of the output optical coupler light of substantially different maximum amplitude.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Bias circuit of electroabsorption modulated laser
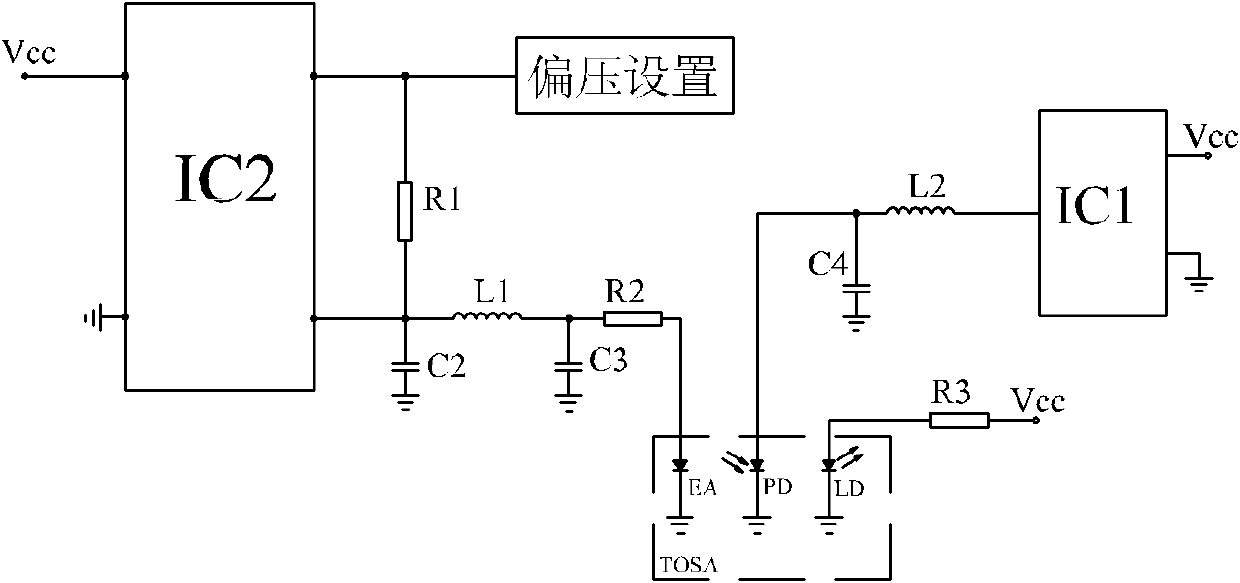
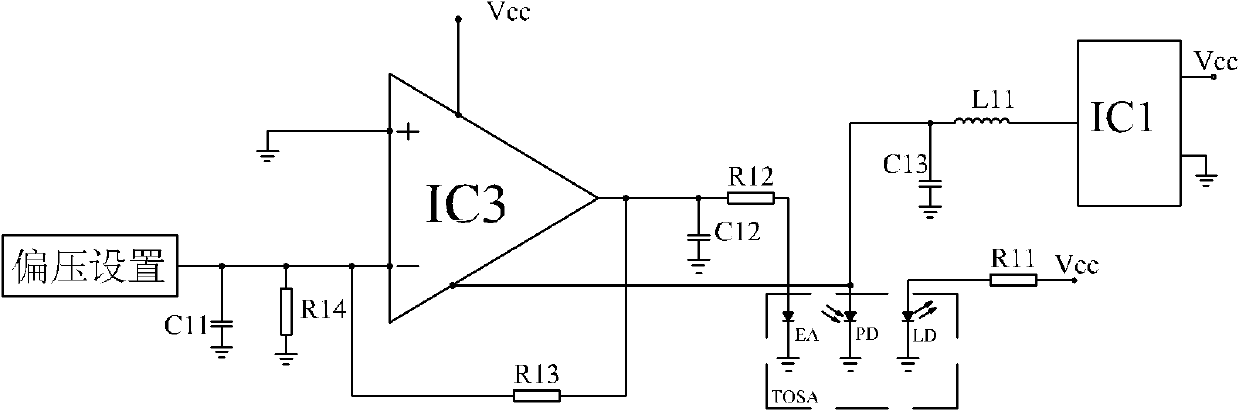
ActiveCN102571003AImprove work performanceLow costLaser constructional detailsDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceElectro-absorption modulator
The invention provides a bias circuit of an electroabsorption modulated circuit. The bias circuit comprises a light emitting assembly TOSA (Transmitter Optical Sub Assembly), a conversion charge pump with nonadjustable output voltage or a switch tube chip, an operation amplifier, and a feedback resistor, wherein the light emitting assembly TOSA is composed of an electroabsorption modulator EA, a semiconductor laser LD and a monitor diode PD, which have a common grounded cathode; the anode of the semiconductor laser LD is connected with a power supply Vcc through a first current limiting resistor; the conversion charge pump or the switch tube chip has a positive power pin connected with the power supply Vcc, a grounded negative power pin, and an output pin connected with one end of a first inductor; the other end of the inductor is connected with the anode of the monitor diode PD and with one end of a third filter capacitor; the other end of the capacitor is grounded; the operation amplifier has a positive power pin connected with the power supply Vcc, a negative power pin connected with the anode of the monitor diode PD, a grounded positive input pin, a negative input pin connected with an external bias unit through a loop resistor, and an output pin connected with the anode of the electroabsorption modulator EA; and the feedback resistor is connected between the negative input pin and the output pin of the operation amplifier.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEOPHOTONICS TECH
Semiconductor photonoic nano communication link method
InactiveUS7907848B1Improved photonic modulationPromote absorptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFibre transmissionElectro-absorption modulatorSignal on
An optical signal low energy method for coupling electrical signals on-chip between component circuits of for example a CMOS circuit array. The described coupling method employs infrared signals communicated along a nano-scale resonant semiconductor waveguide between for example PIN diode signal transducers. The coupling may employ an electrically pumped laser, an electro absorption modulator and a photodetector all for typically the 1.5 to 2.0 micrometer spectral region with each formed using for example PIN heterodiode semiconductor devices. Each of these three devices includes active semiconductor crystal material situated in a resonator within a strip waveguide. The resonator is defined by two fabricated mirrors having a tapered location one dimensional photonic crystal lattice of oxide hole or slot apertures. Each semiconductor device is for example a heterodiode pumped or controlled by laterally disposed wings enclosing the resonator to form a lateral PIN structure for current injection or high E-field generation. CMOS compatible ten gigabit per second signals of low energy use per transmitted bit are achieved.
Owner:AIR FORCE US SEC THE THE
QAM optical modulators
InactiveUS20100111466A1Electromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsElectro-absorption modulatorMaximum amplitude
An exemplary optical modulator includes an interferometer. The interferometer includes an input optical coupler, an output optical coupler, and two or more controllable optical waveguides. Each controllable optical waveguide connects the input optical coupler to the output optical coupler and has an electro-absorption modulator along a segment thereof. Two of the controllable optical waveguides are connected to transmit to an output of the output optical coupler light of substantially different maximum amplitude.
Owner:RPX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com