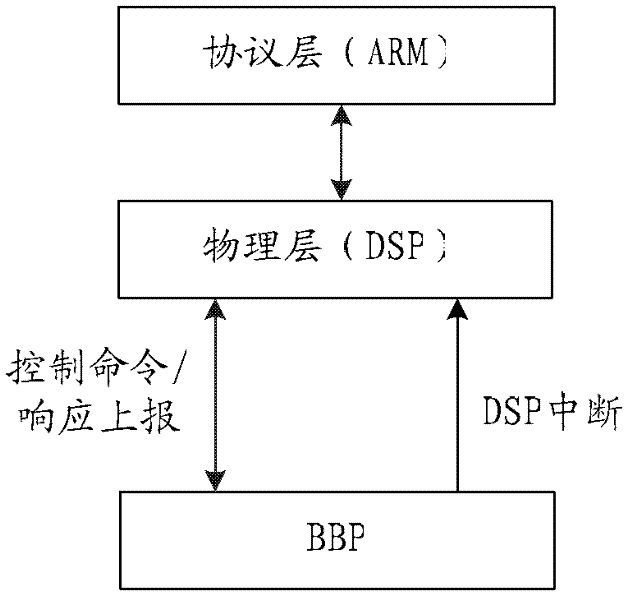
Patents
Literature
273 results about "Error vector magnitude" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
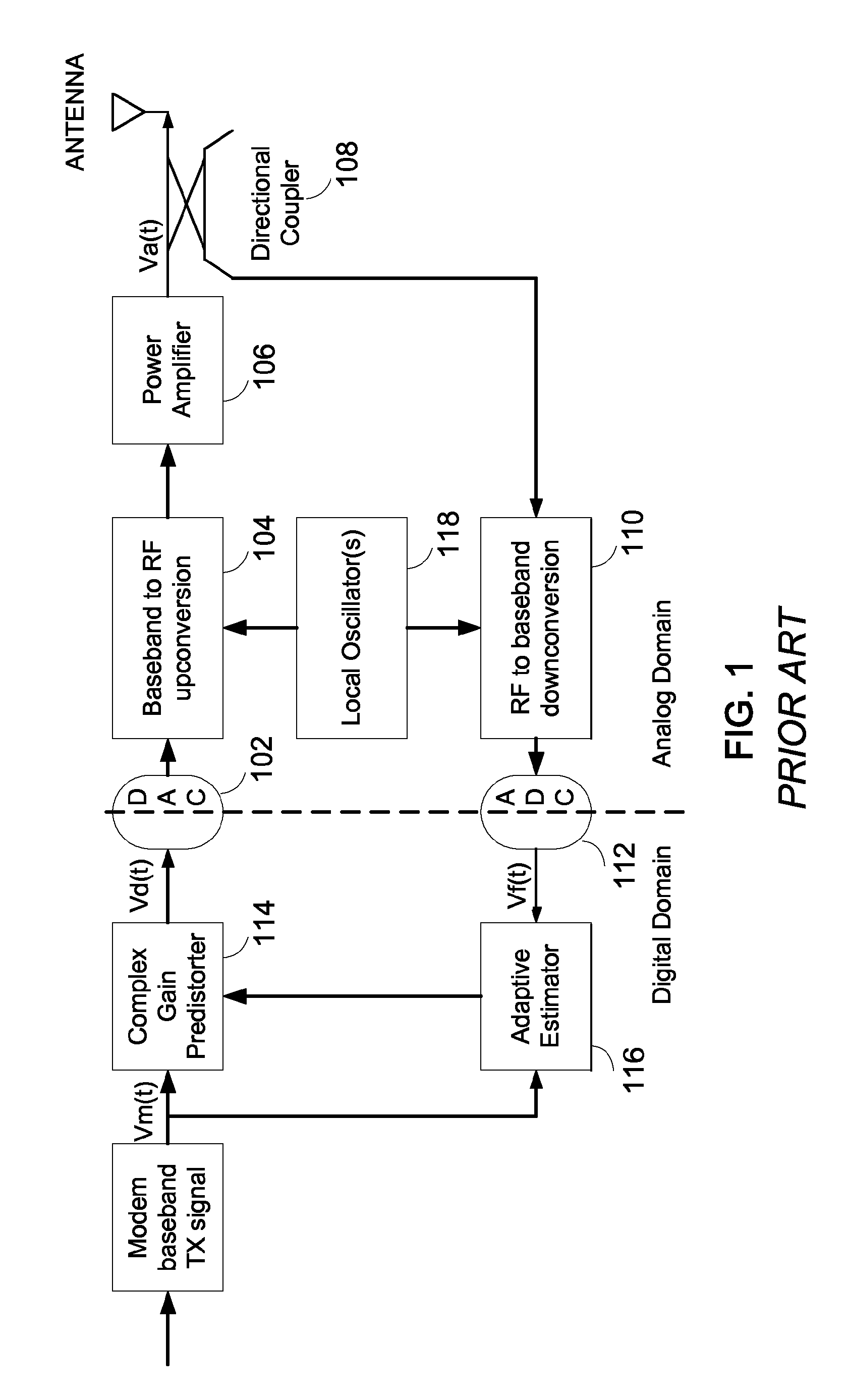
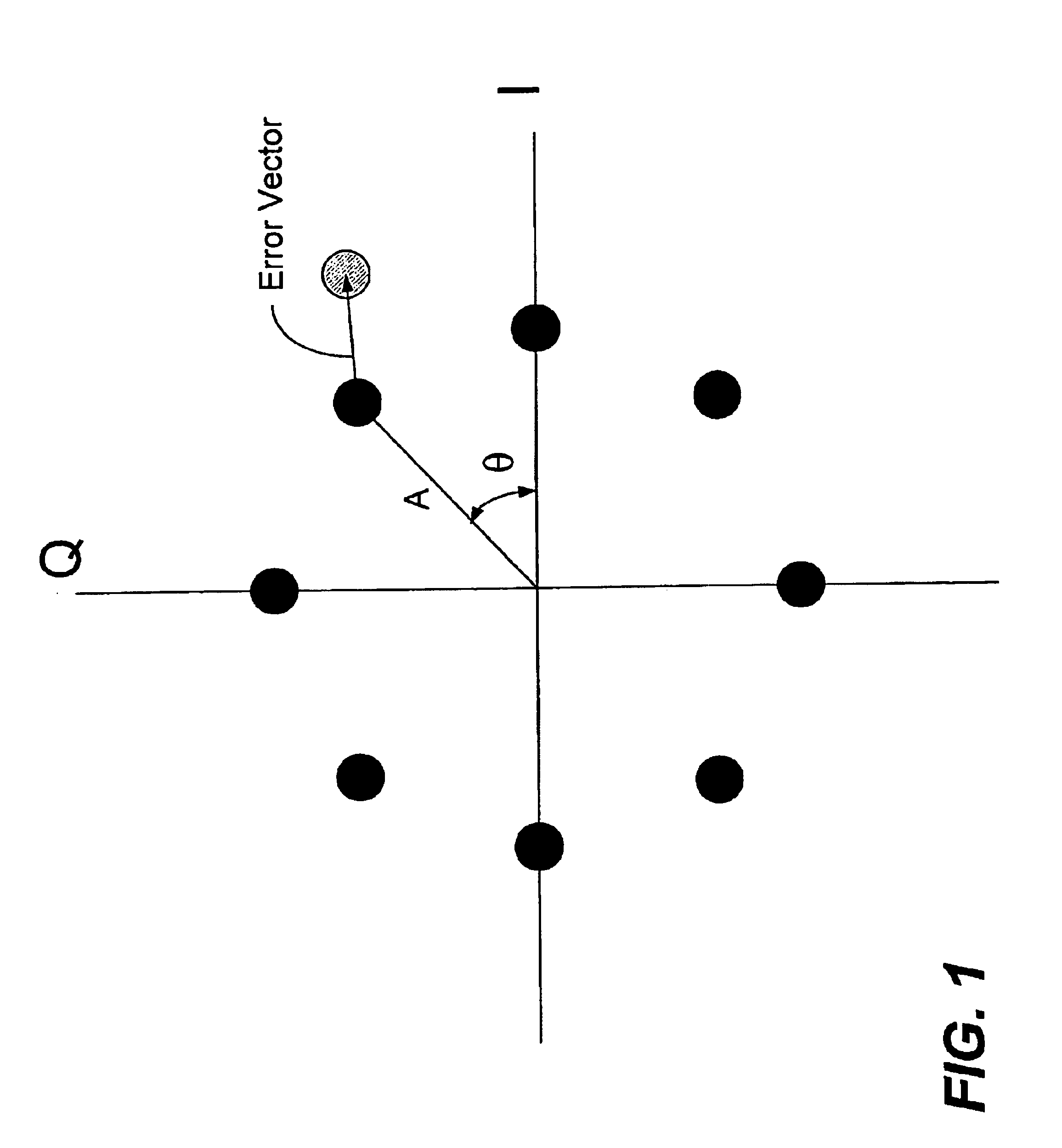
The error vector magnitude or EVM (sometimes also called relative constellation error or RCE) is a measure used to quantify the performance of a digital radio transmitter or receiver. A signal sent by an ideal transmitter or received by a receiver would have all constellation points precisely at the ideal locations, however various imperfections in the implementation (such as carrier leakage, low image rejection ratio, phase noise etc.) cause the actual constellation points to deviate from the ideal locations. Informally, EVM is a measure of how far the points are from the ideal locations.
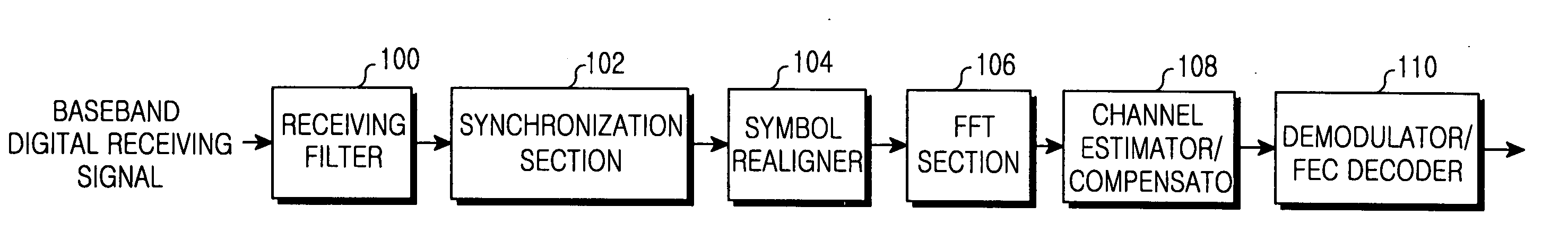
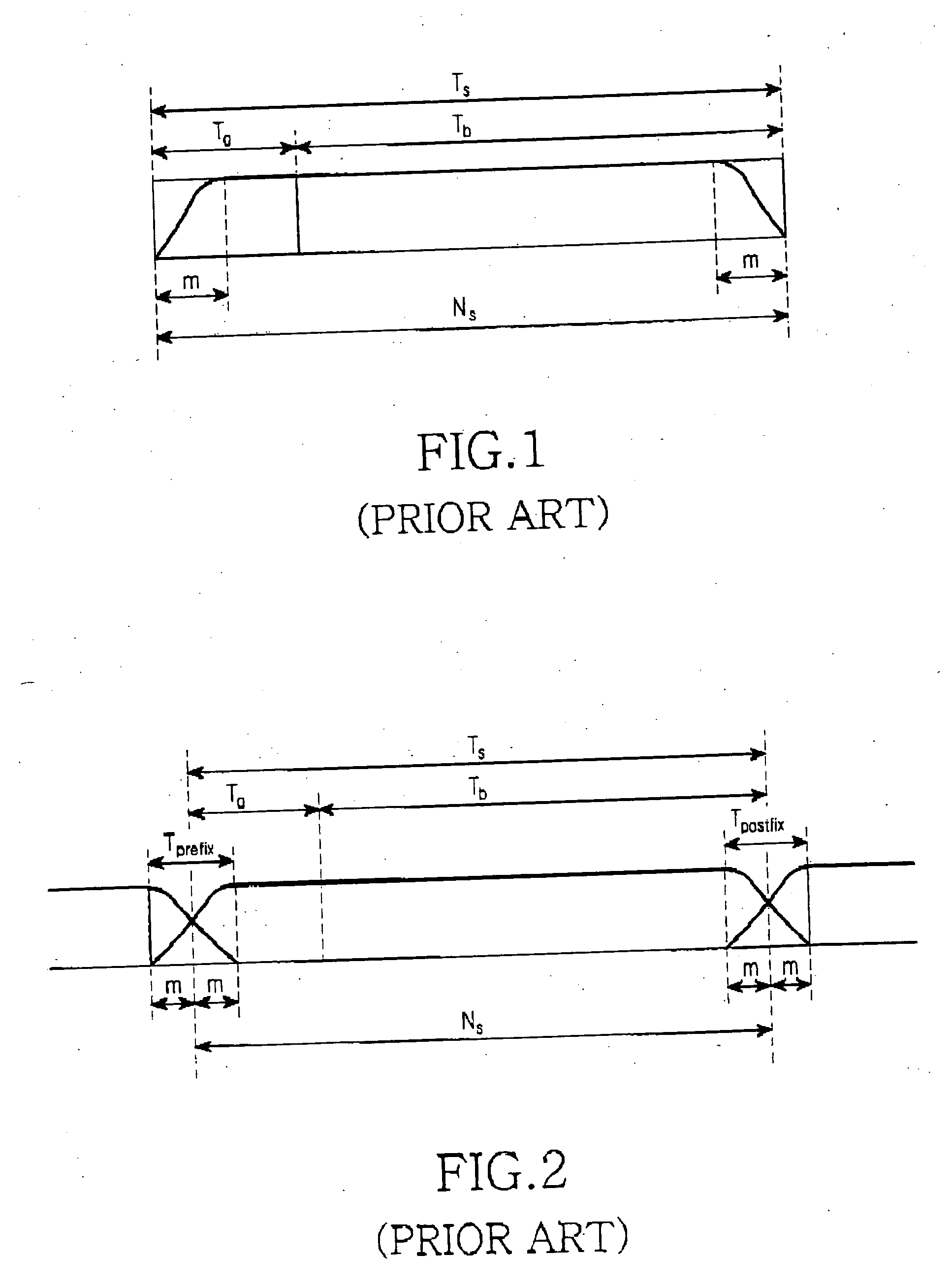
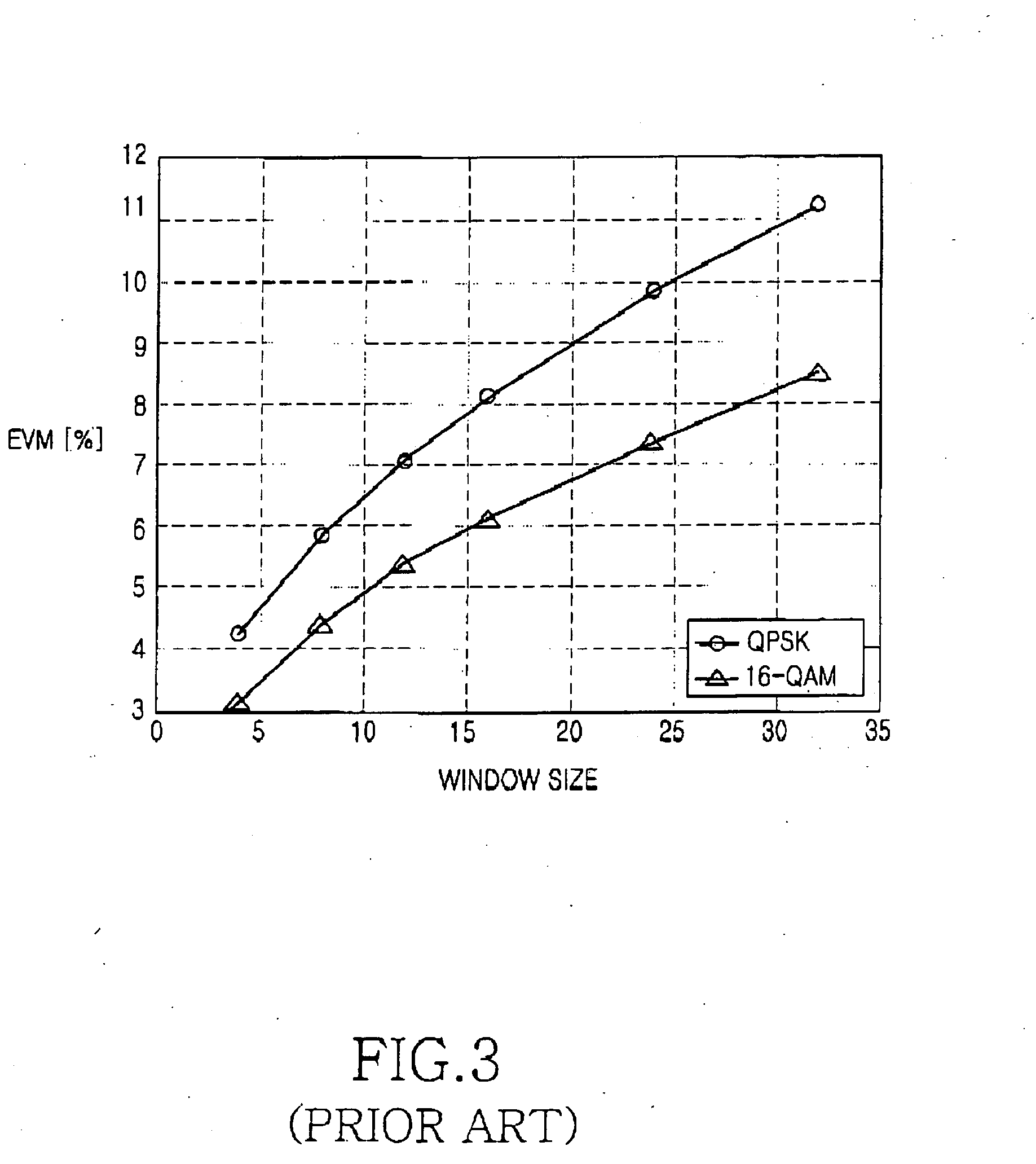
Apparatus and method for reducing an error vector magnitude in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing receiver
InactiveUS20060159006A1Degradation in error vector magnitudeSimple structureModulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexFast Fourier transformGuard interval
An apparatus and a method for reducing an error vector magnitude in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) receiver. The method includes the steps of inputting a receiving symbol including a guard interval and an effective symbol interval following the guard interval, in which a front portion of the guard interval and a rear portion of the effective symbol interval have windowing intervals corresponding to windowing of a transmitter, and replacing a signal of the rear windowing interval with a signal of an interval between the front windowing interval and the effective symbol interval, thereby outputting a signal of the effective symbol interval, which substitutes for a signal of the rear windowing interval, to a fast Fourier transform (FFT) section.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
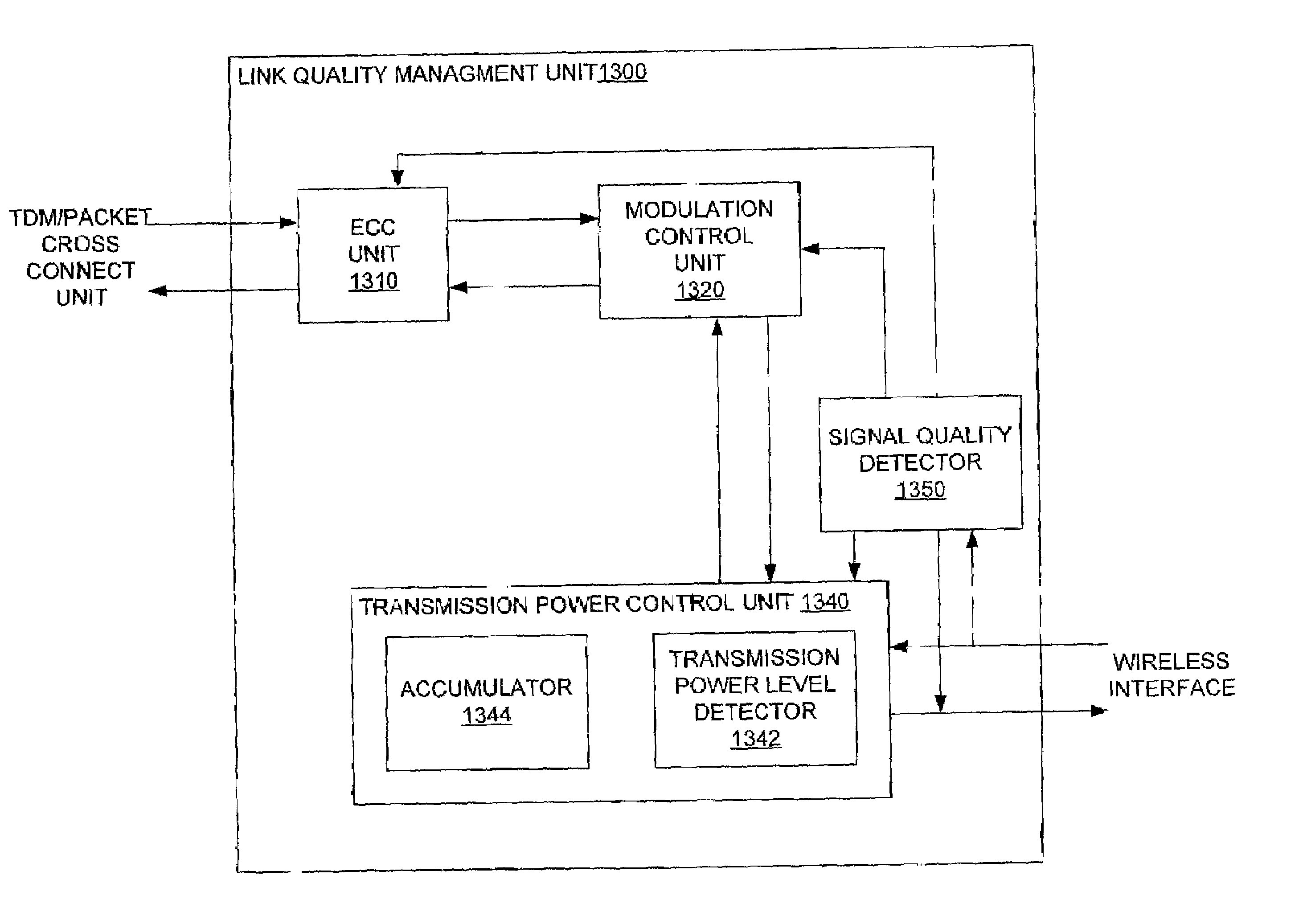
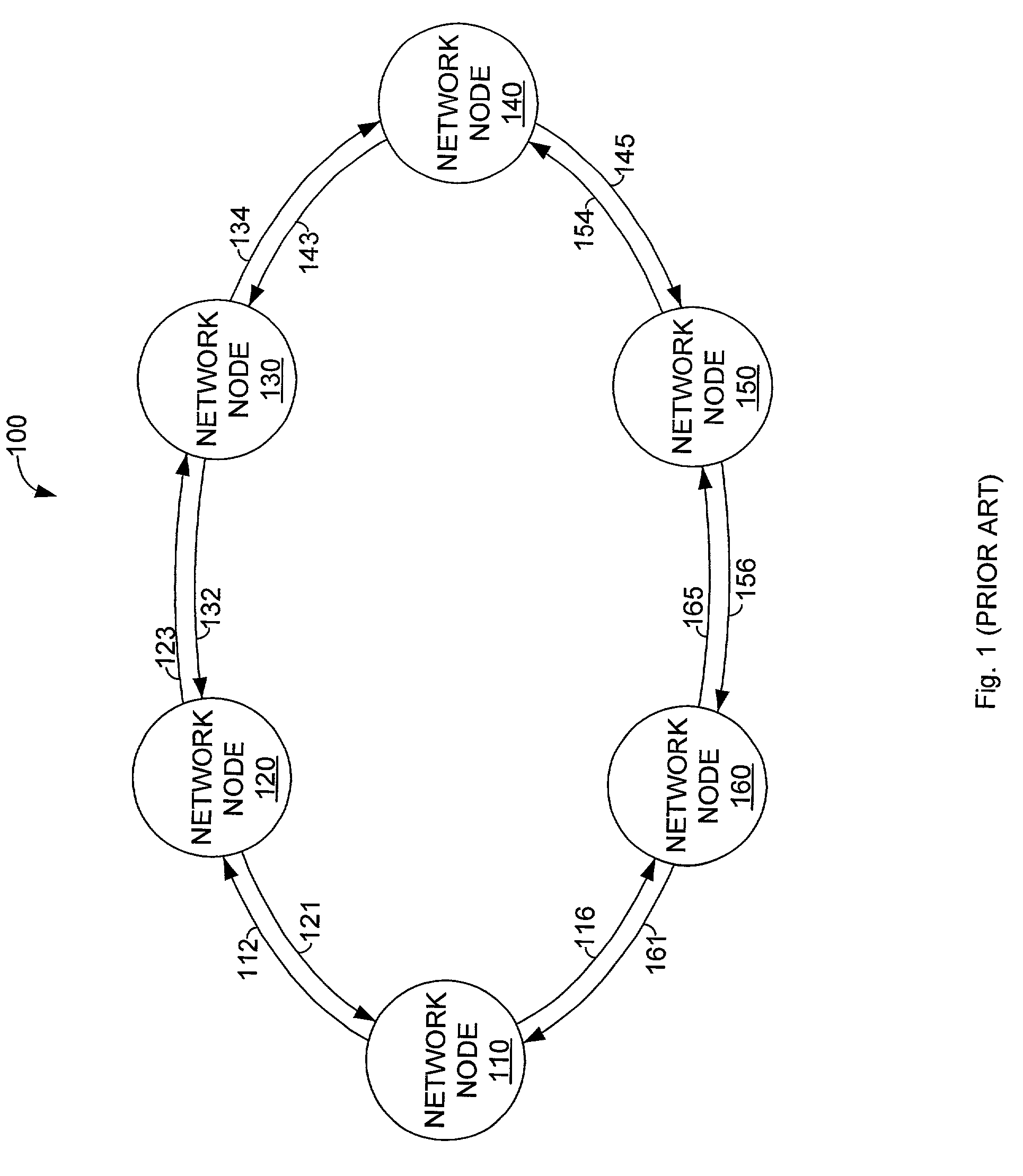
Adaptive link quality management for wireless medium
ActiveUS7165102B2Provide supportEasy to insertData switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Error vector magnitude
To provide the quality and reliability of a fiber optic link over a wireless link, network nodes in accordance with the present invention include a link quality management unit, which controls multiple transmission parameters of a wireless interface in response variable link conditions. For example, the link quality management unit of one embodiment of the present invention controls transmission power, modulation, and error correction. In general, a receiving network node provides feedback to a transmitting network node. Thus, in many embodiments of the present invention, the link quality management unit includes a signal quality detector, which measures a signal quality value, such as bit error rate, signal to noise ratio, or error vector magnitude. The measured signal quality is transmitted back to the transmitting node so that appropriate changes can be made to the transmission parameters.
Owner:REDWAVE NETWORKS
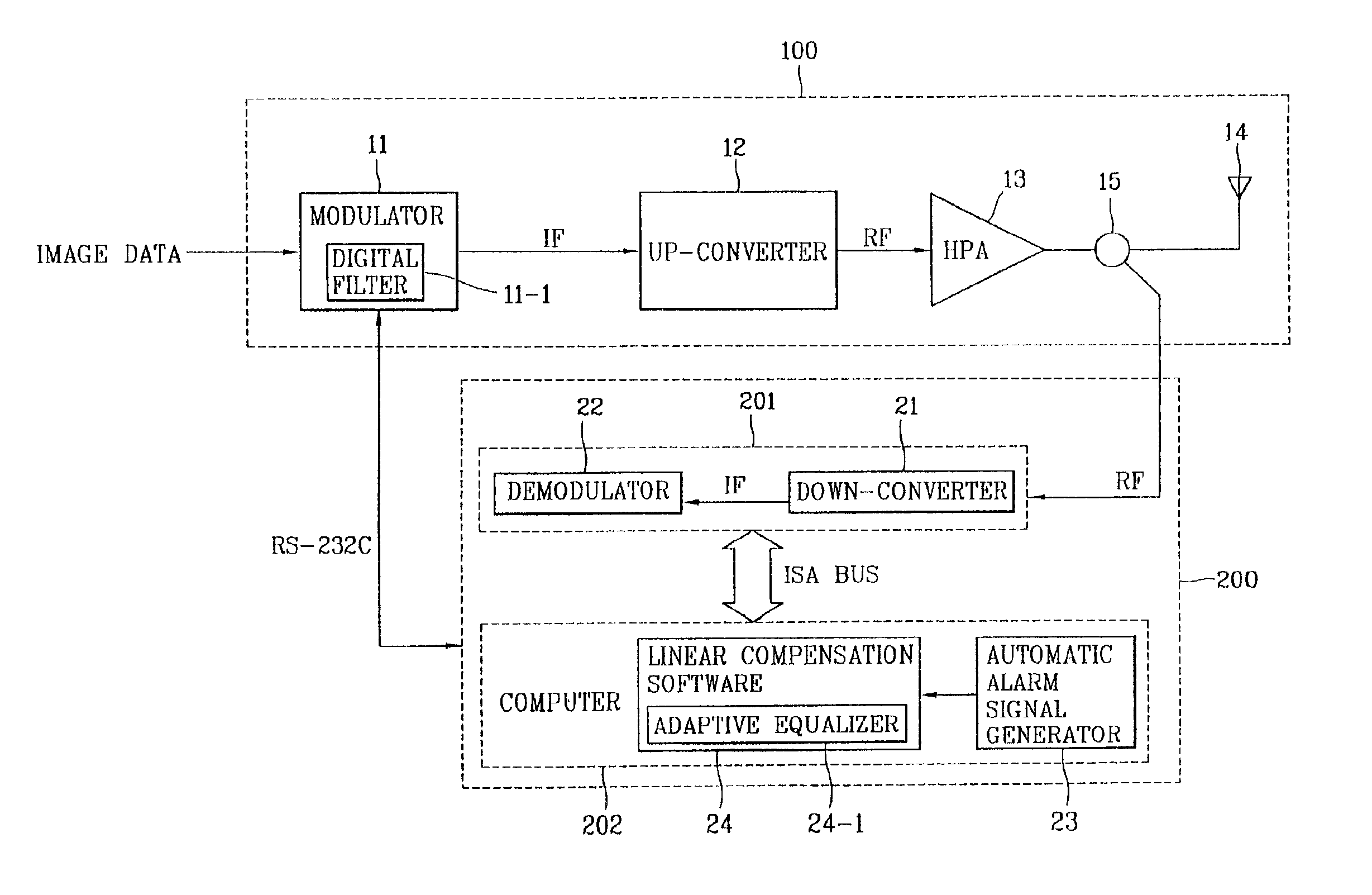
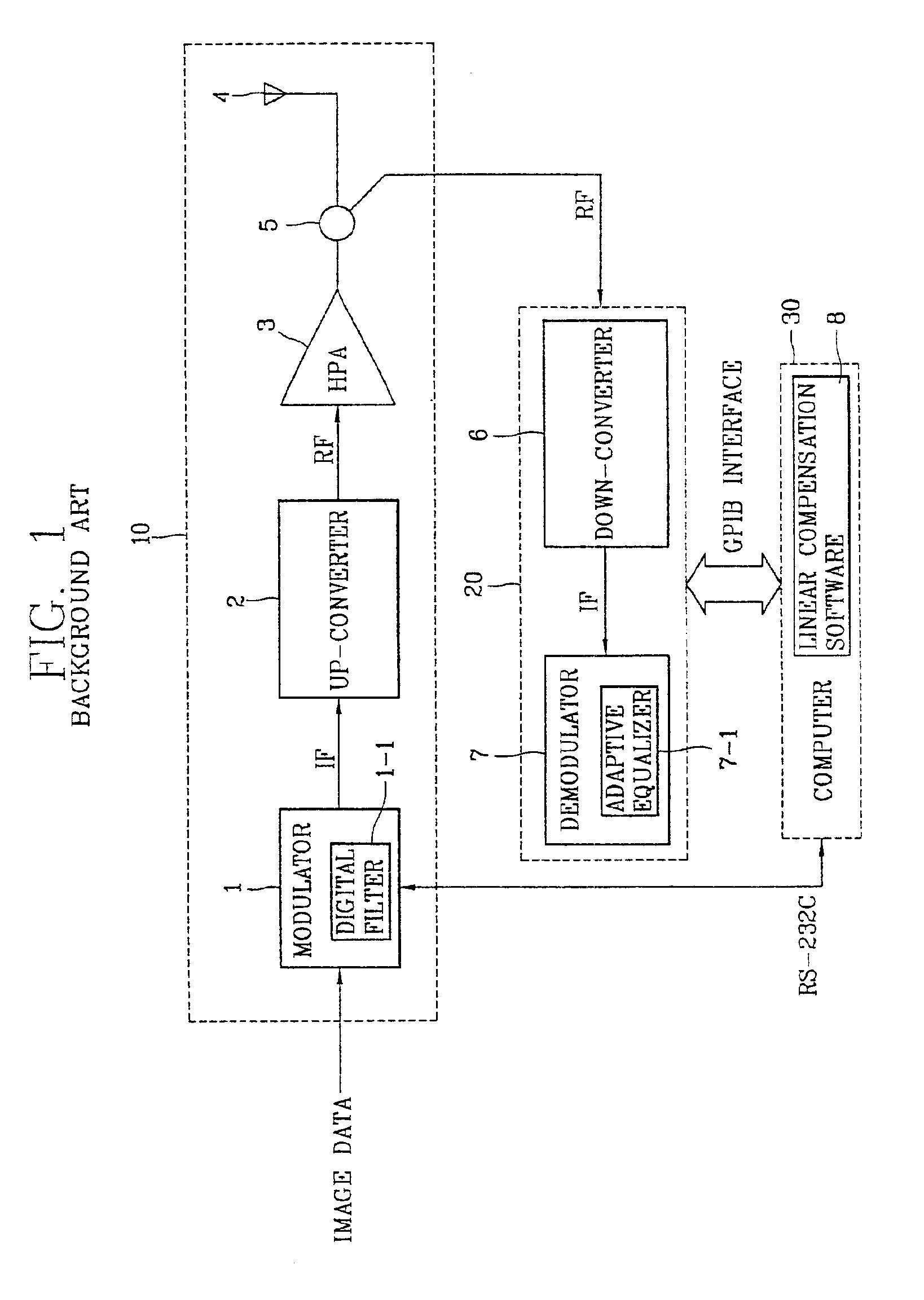
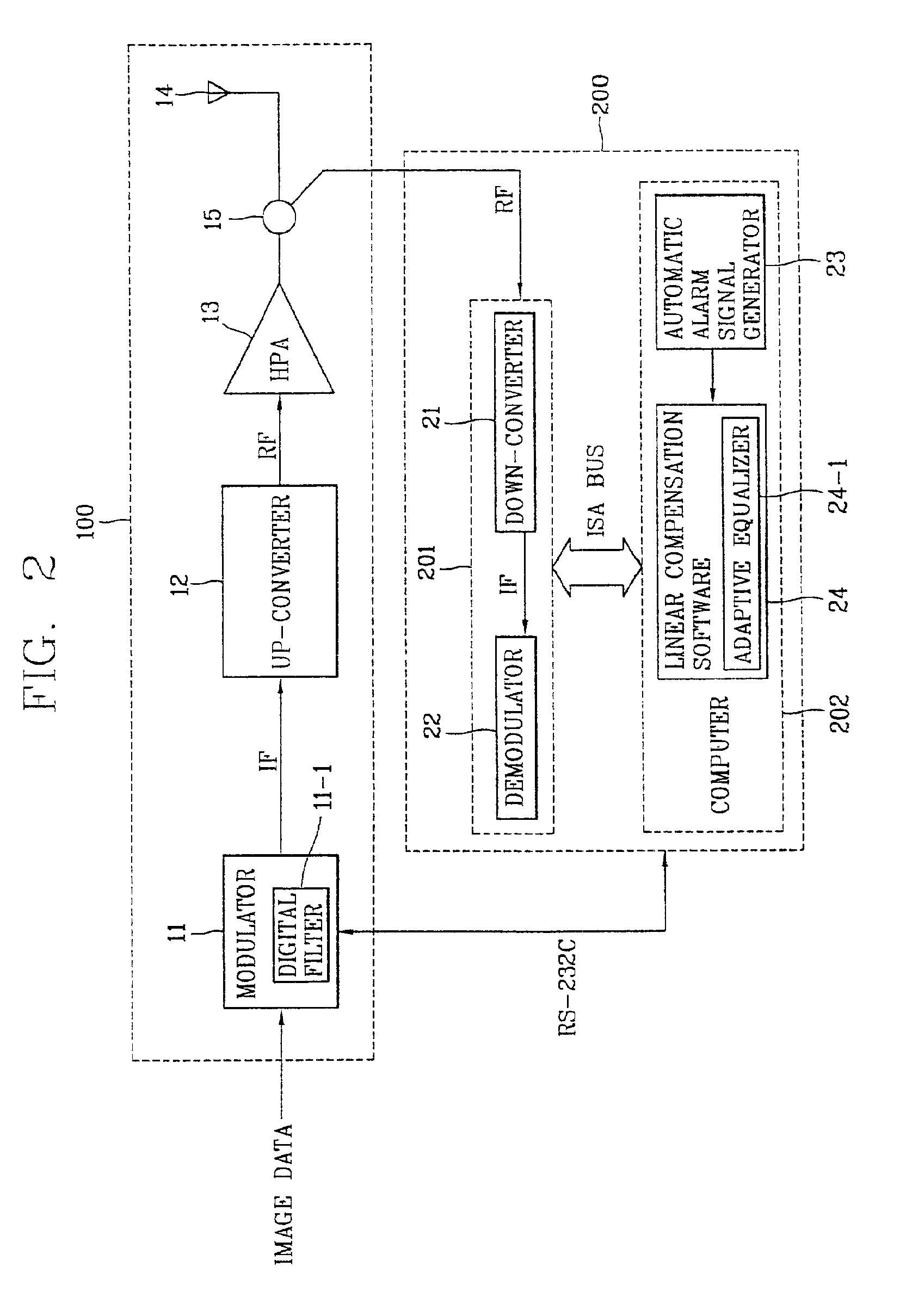
Linearization compensation system of digital TV relay apparatus and method thereof
InactiveUS6917389B2Effective compensationShorten the timeMultiple-port networksTelevision system detailsIntermediate frequencyEngineering
A linear compensation system of a digital TV relay or other apparatus preferably includes a transmitting unit configured to modulate a data to an intermediate frequency (IF) signal, up convert the IF signal to an RF signal, and amplify the RF signal to a predetermined level using a high power amplifier (HPA). The system also includes a linear compensation unit to preferably directly vary a step size of an adaptive equalizer according to whether a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) or an error vector magnitude (EVM) for an output signal of the HPA satisfies an advanced television systems committee (ATSC) or other standard. The linear compensation unit is thus configured to output an improved linear compensation coefficient to a modulator of the transmitting unit.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
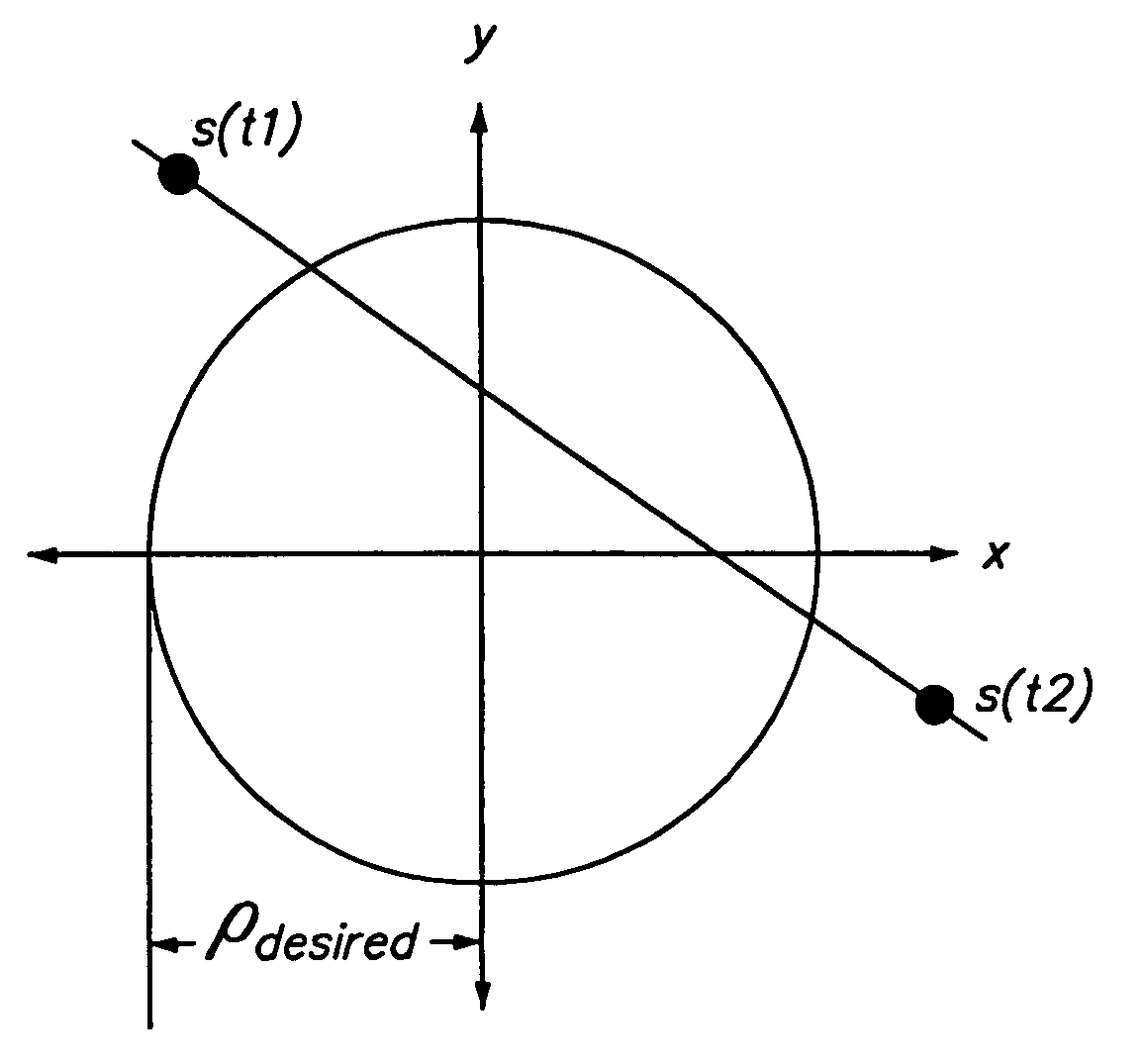
Reduction of average-to-minimum power ratio in communications signals
InactiveUS7054385B2Modulation with suppressed carrierAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSignal qualityError vector magnitude
This invention, generally speaking, modifies pulse amplitude modulated signals to reduce the ratio of average power to minimum power. The signal is modified in such a manner that the signal quality remains acceptable. The signal quality is described in terms of the Power Spectral Density (PSD) and the Error Vector Magnitude (EVM).
Owner:APPLE INC
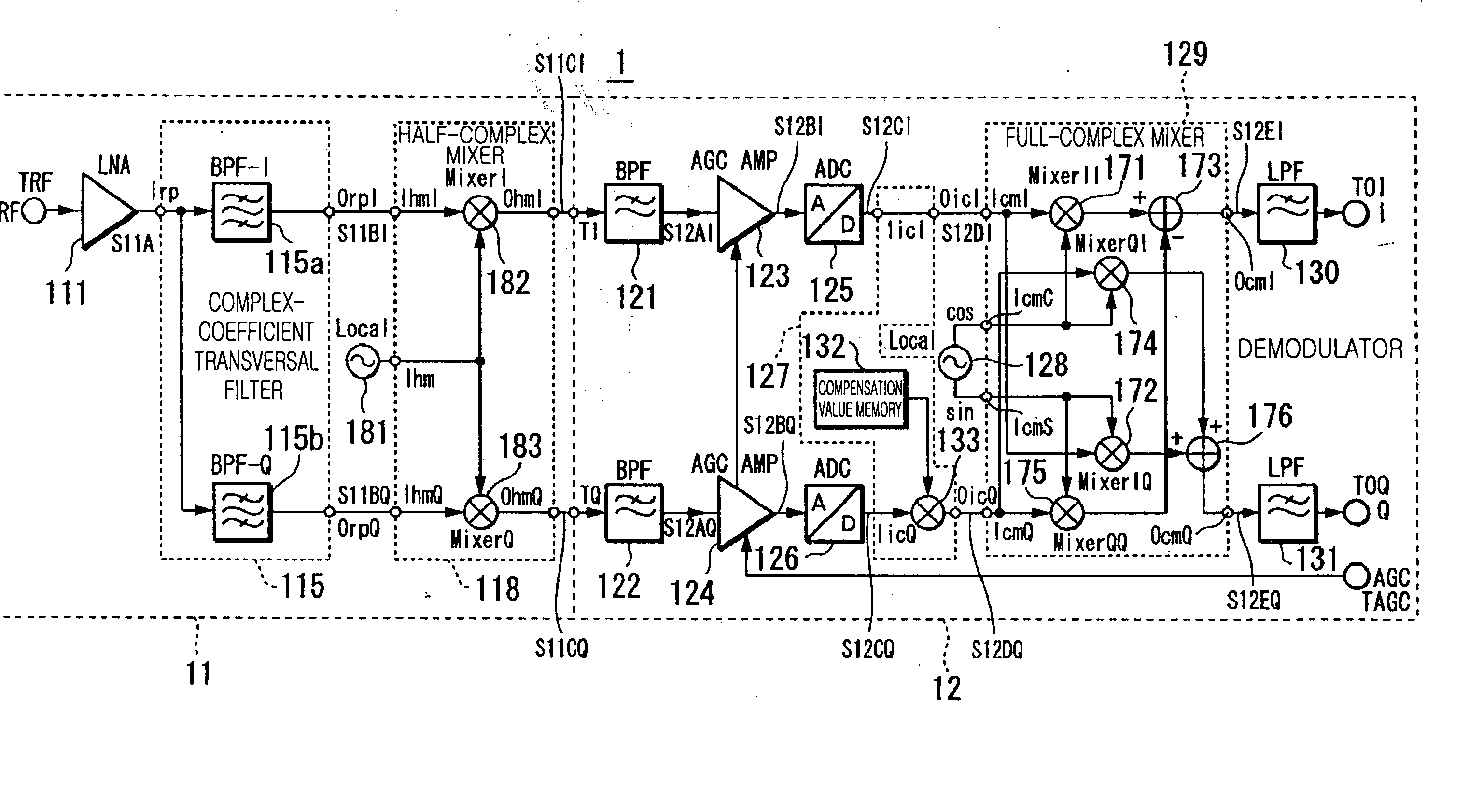
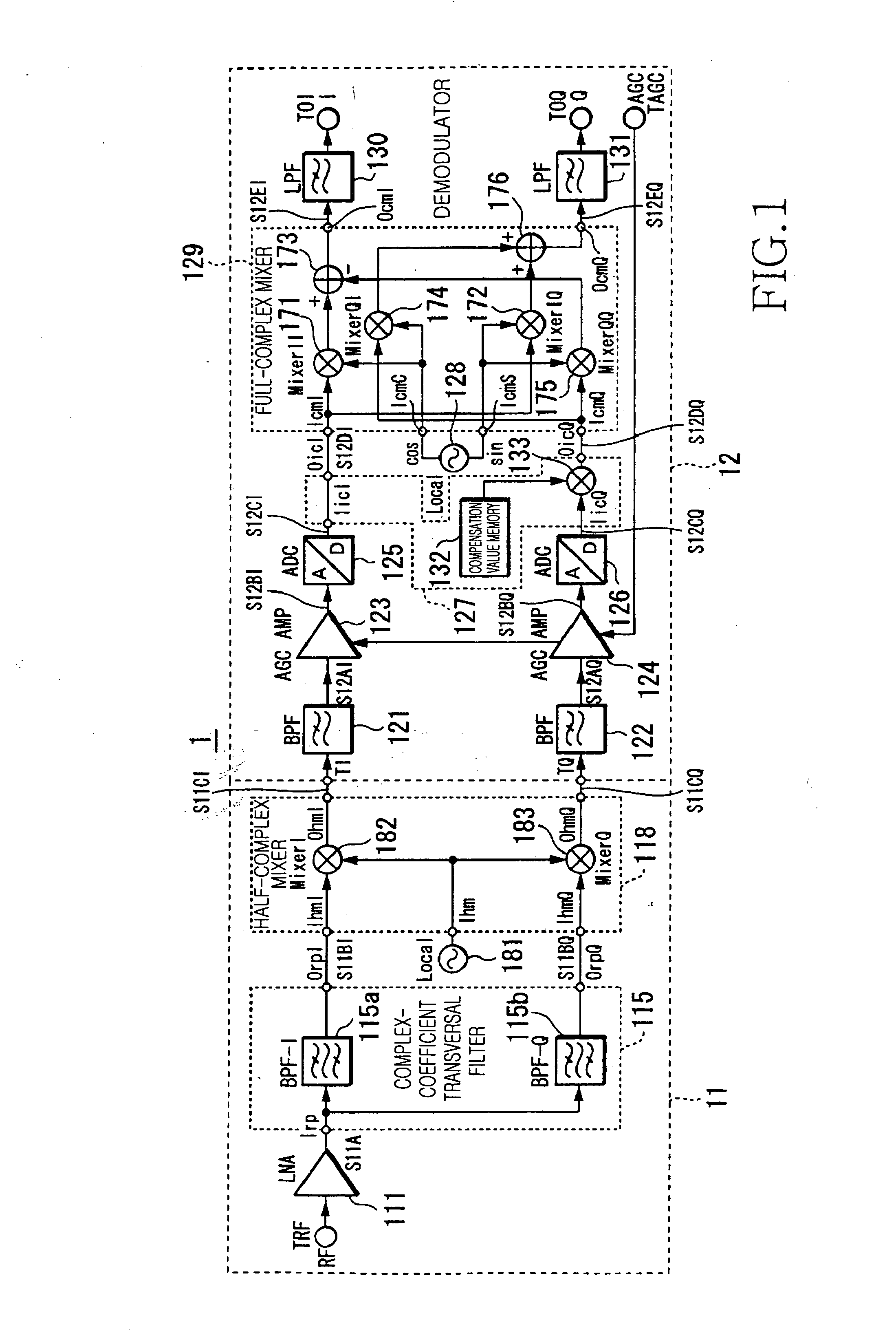
Downconverter and upconverter
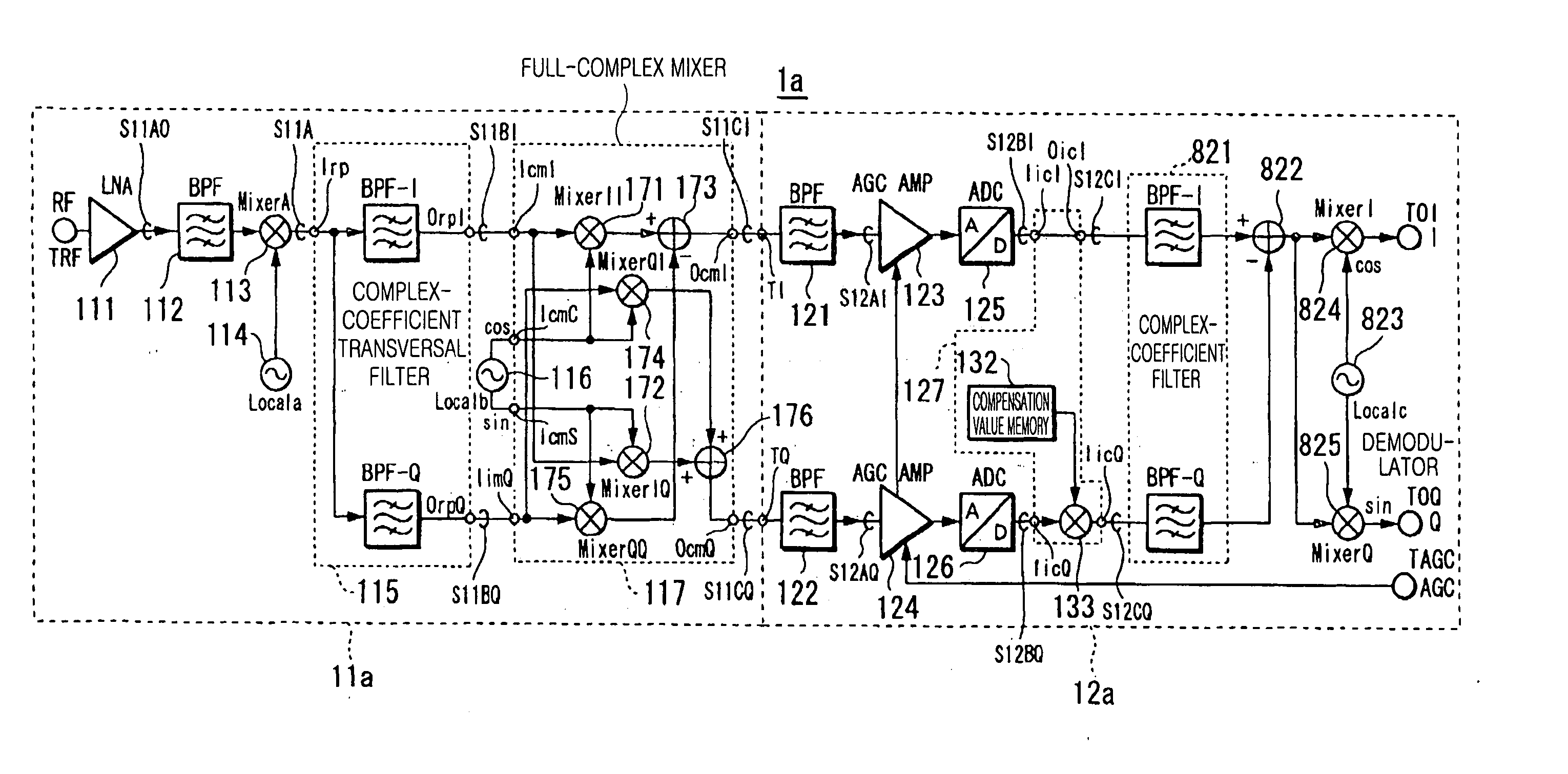
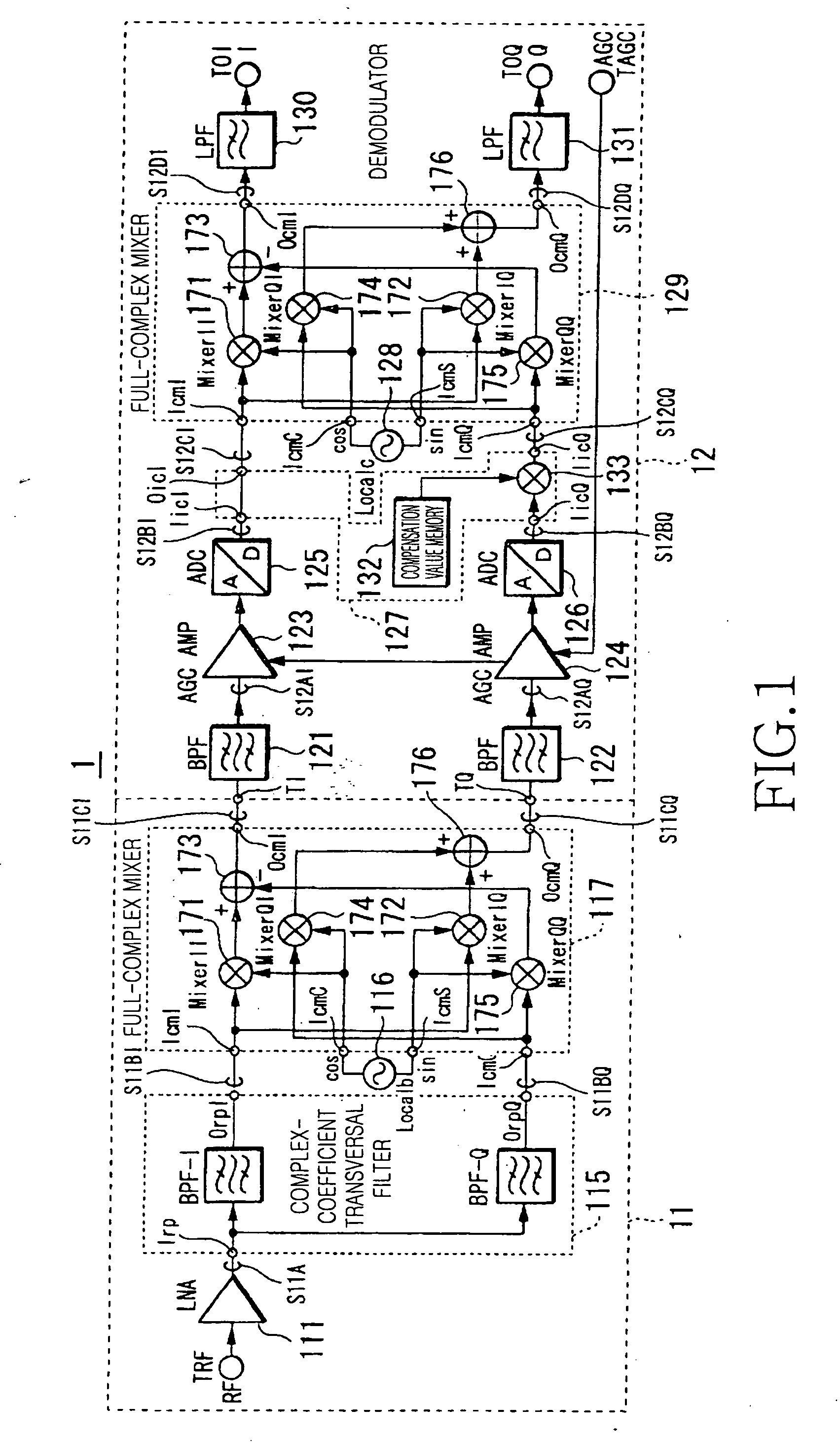
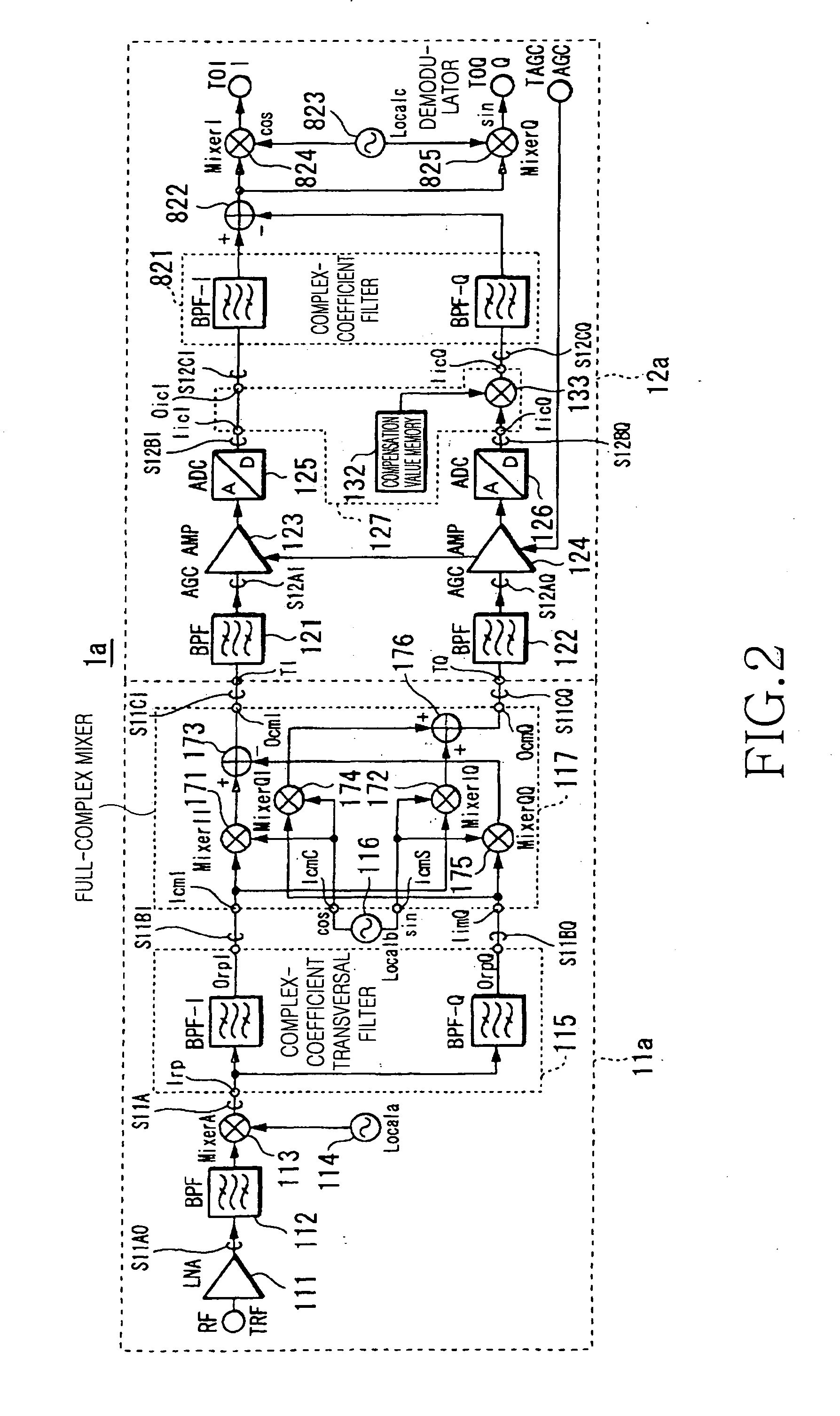
InactiveUS20060281429A1Reduce power consumptionSufficient image rejection ratioModulation transferenceTransmission noise suppressionFrequency changerIntermediate frequency
A downconverter and upconverter are provided which can obtain a satisfactory image rejection ratio in a low-Intermediate Frequency (IF) scheme while reducing power consumption, and can improve Error Vector Magnitude (EVM) in a zero-IF scheme. A complex-coefficient transversal filter rejects one side of a positive or negative frequency, and converts a Radio Frequency (RF) signal to a complex RF signal configured by real and imaginary parts. A local oscillator outputs a complex local signal in which a set frequency is set as a center frequency. A full-complex mixer, connected to the complex-coefficient transversal filter and the local oscillator, perform a frequency conversion process by multiplying a complex signal output from the complex-coefficient transversal filter and the complex local signal output from the local oscillator, and outputs a complex signal of a frequency separated by the set frequency from a frequency of the RF signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
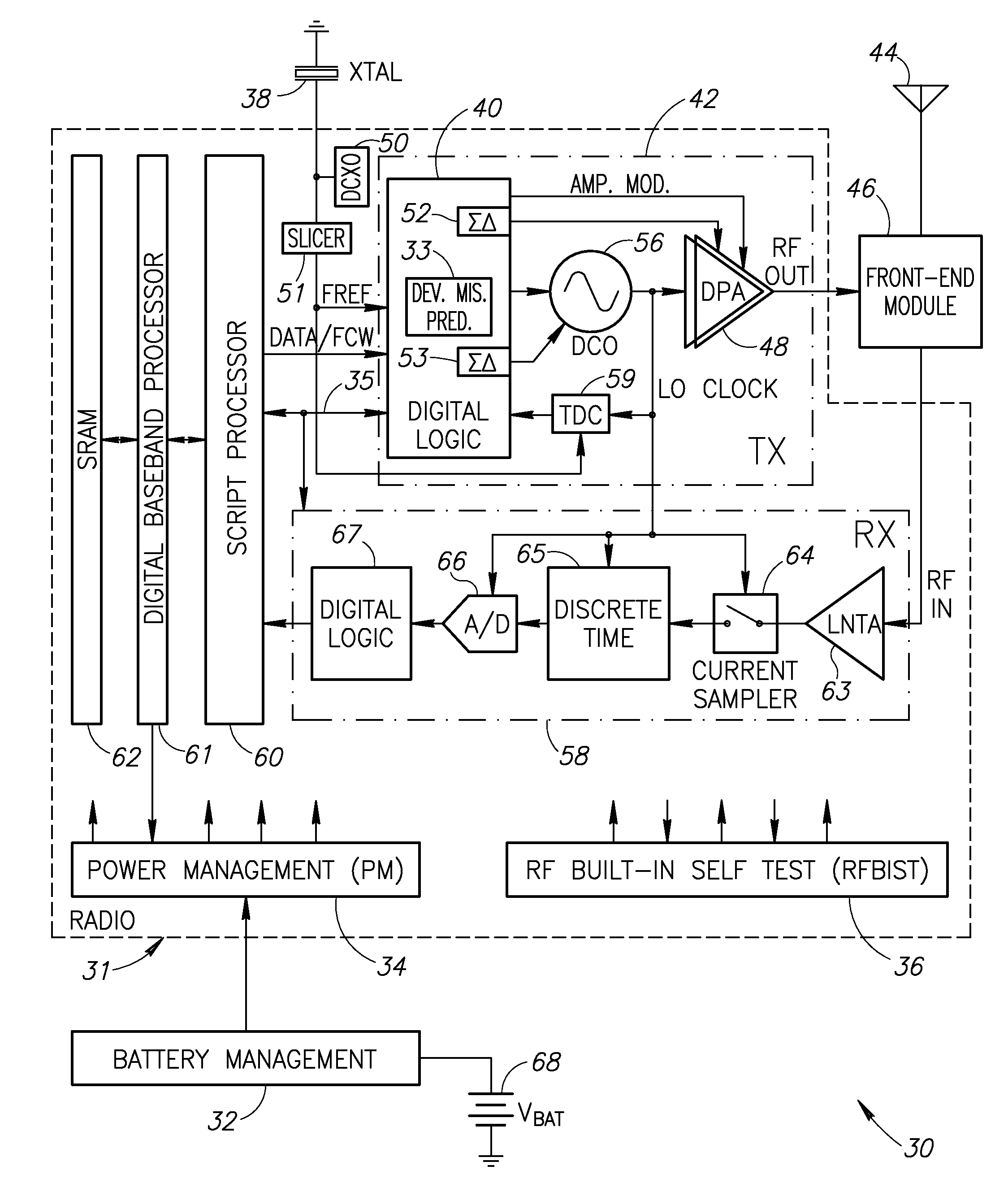
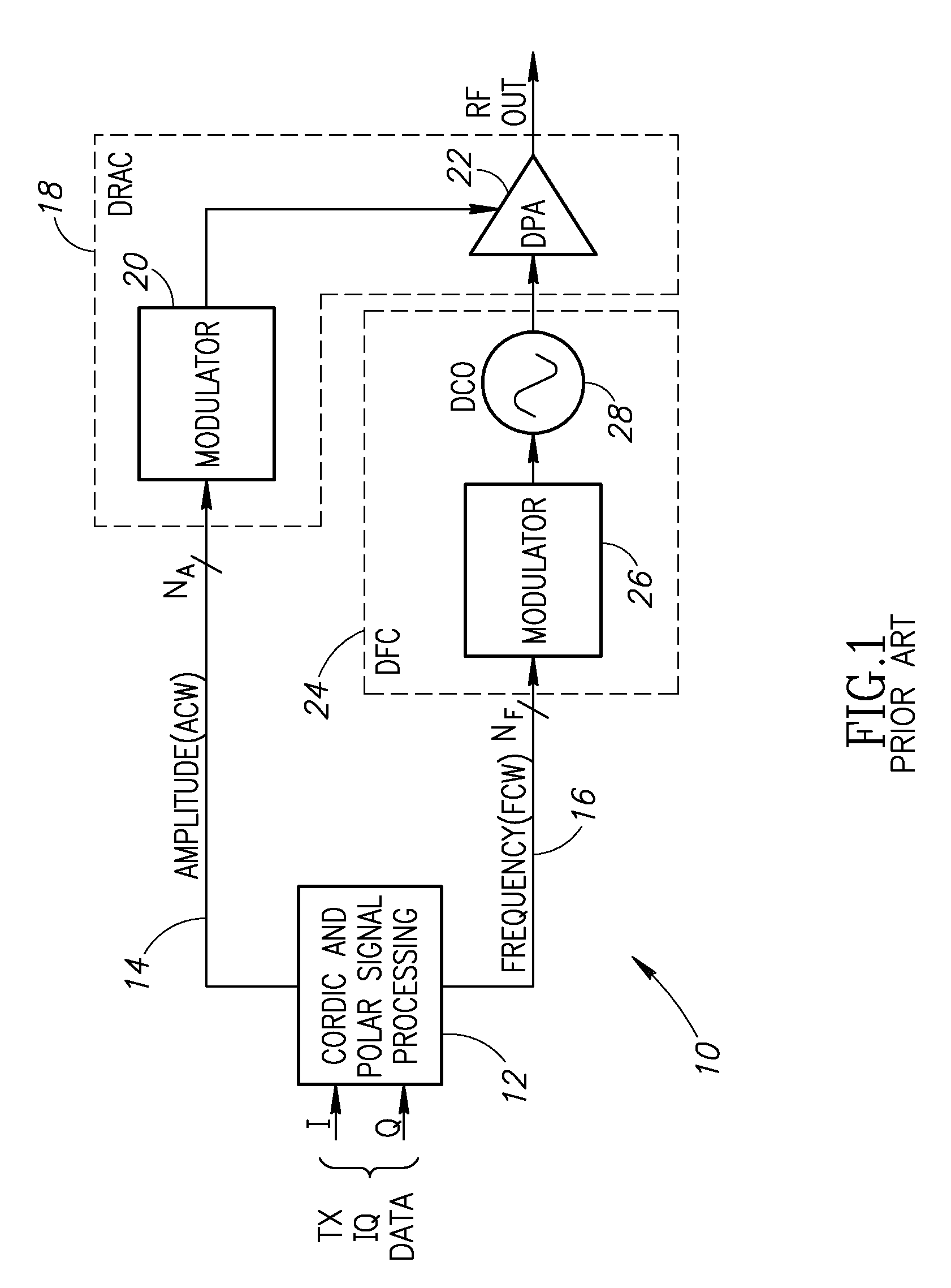
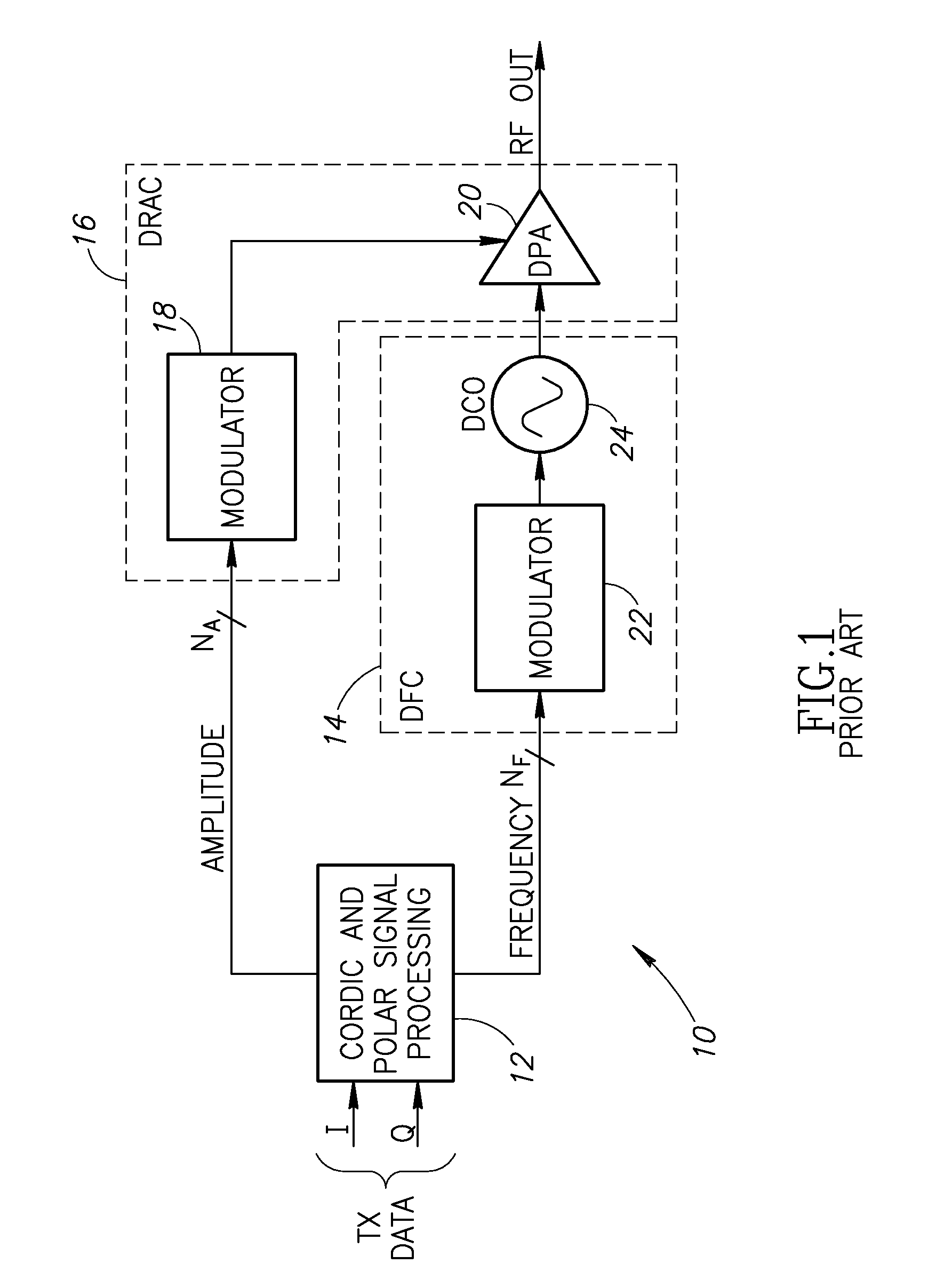
Predistortion mechanism for compensation of transistor size mismatch in a digital power amplifier
InactiveUS20100188148A1Minimal area requirementImprove performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationError vector magnitudeTransistor sizing
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of predistortion compensation of device (e.g., transistor) mismatch in a digital power amplifier (DPA). The device mismatch predistortion mechanism of the present invention addresses the problem of matching between two types of binary weighted transistors, whereby mismatched transistors cause degradation in wideband noise. The invention provides a digital predistortion mechanism which functions to pre-distort the mismatch ratio based on a data table calculated a priori enabling a polar transmitter to meet output spectrum and error vector magnitude (EVM) requirements of the particular modern wideband wireless standard, such as GSM, 3G WCDMA, etc.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
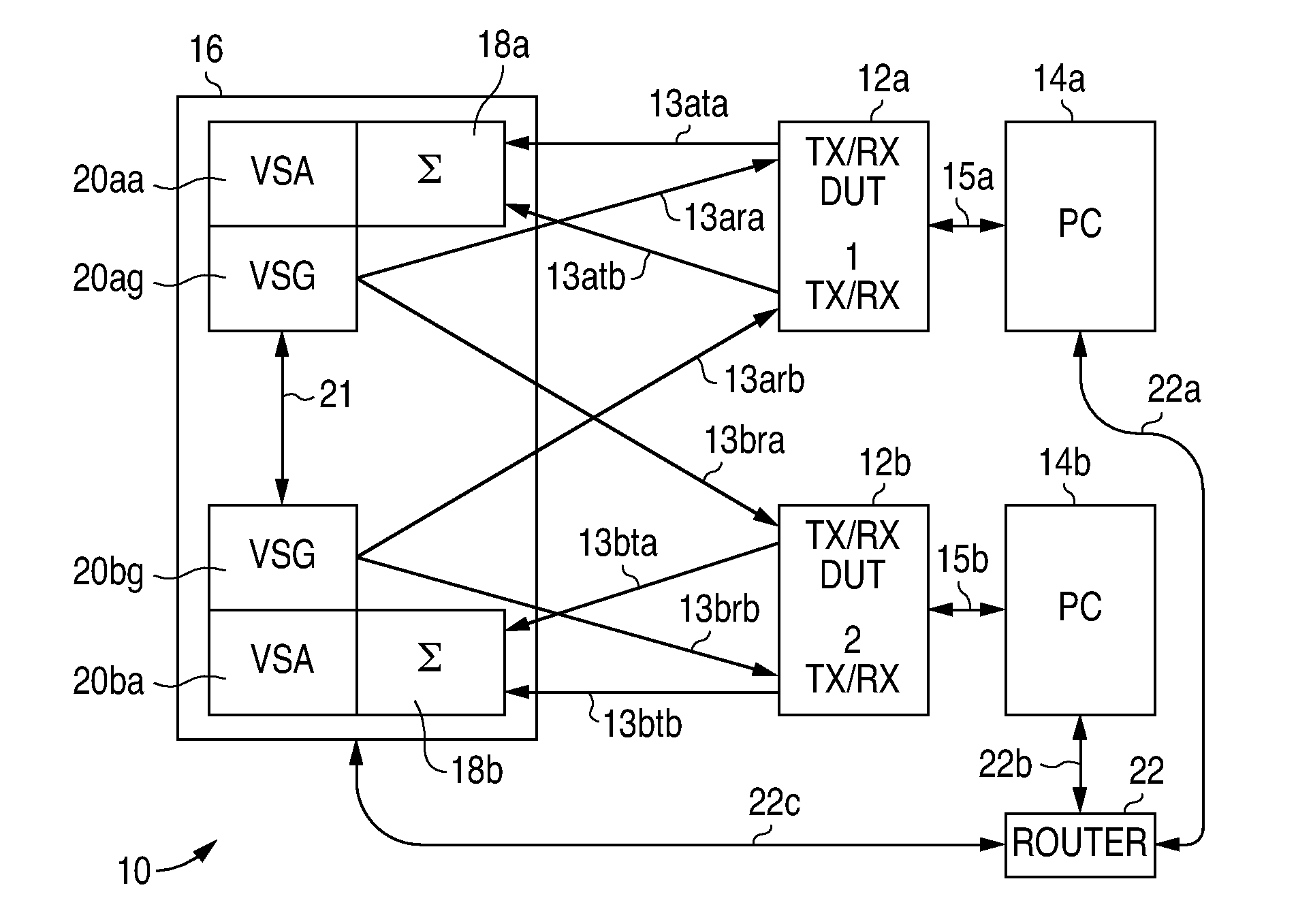
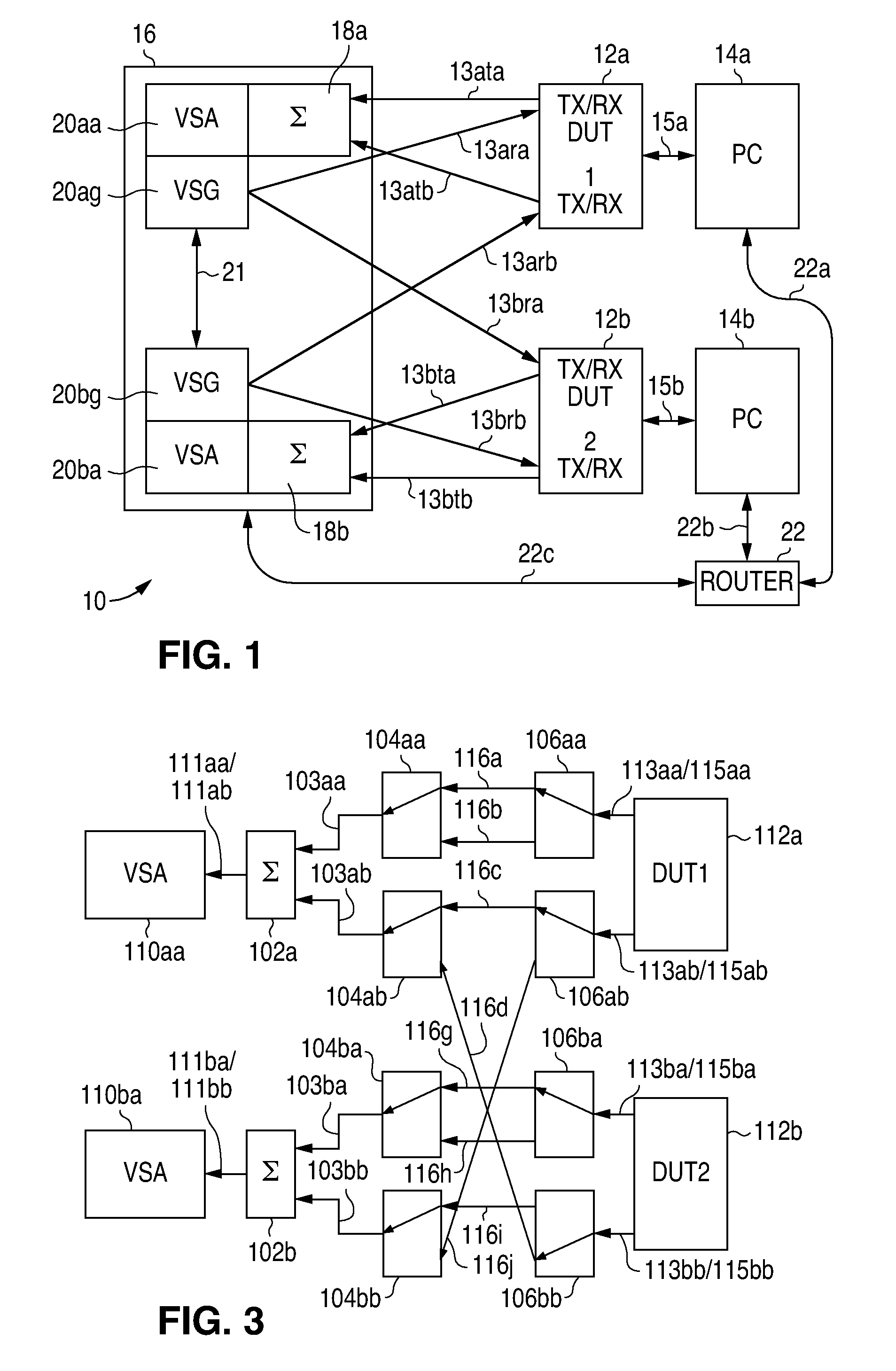
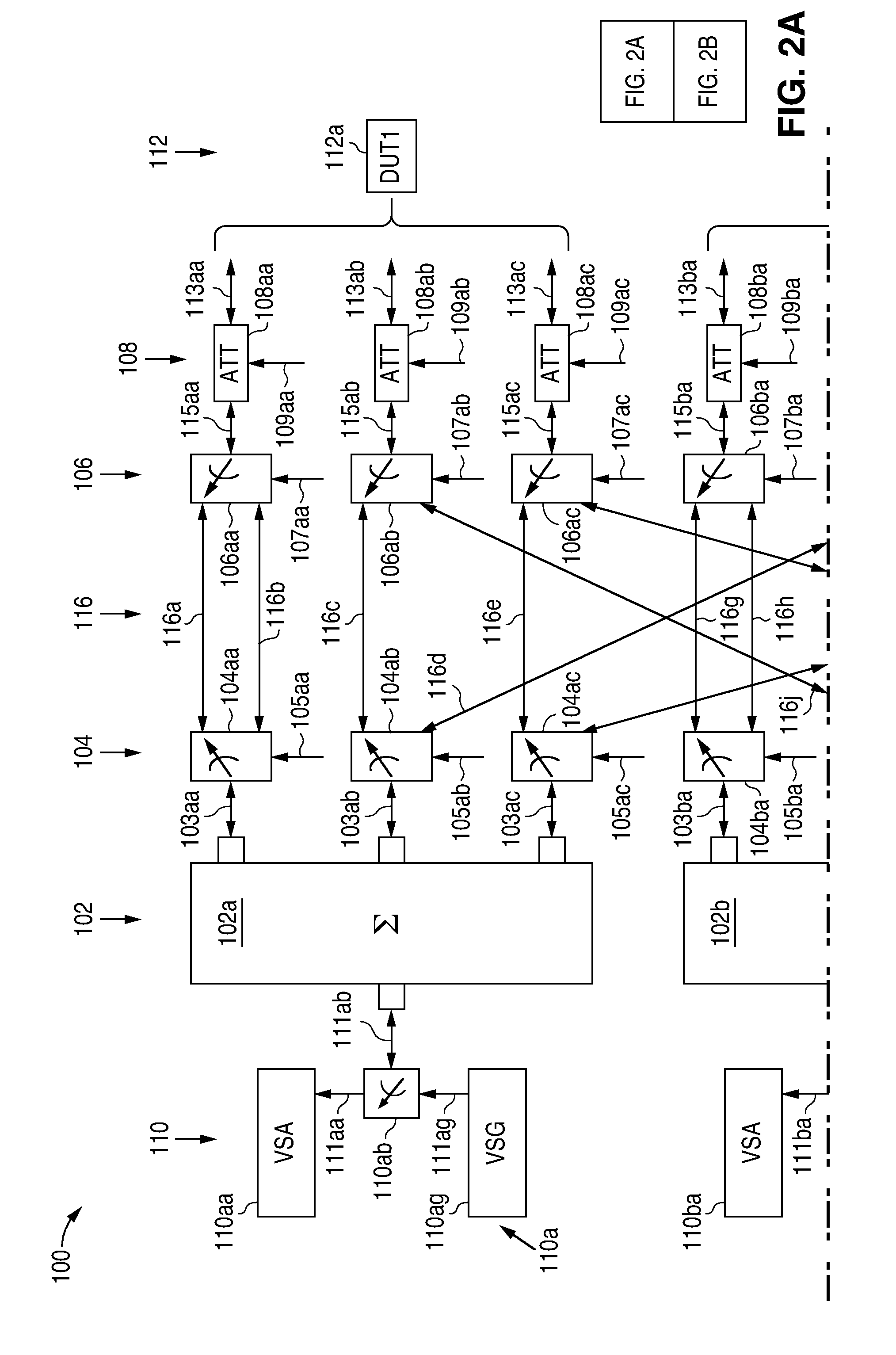
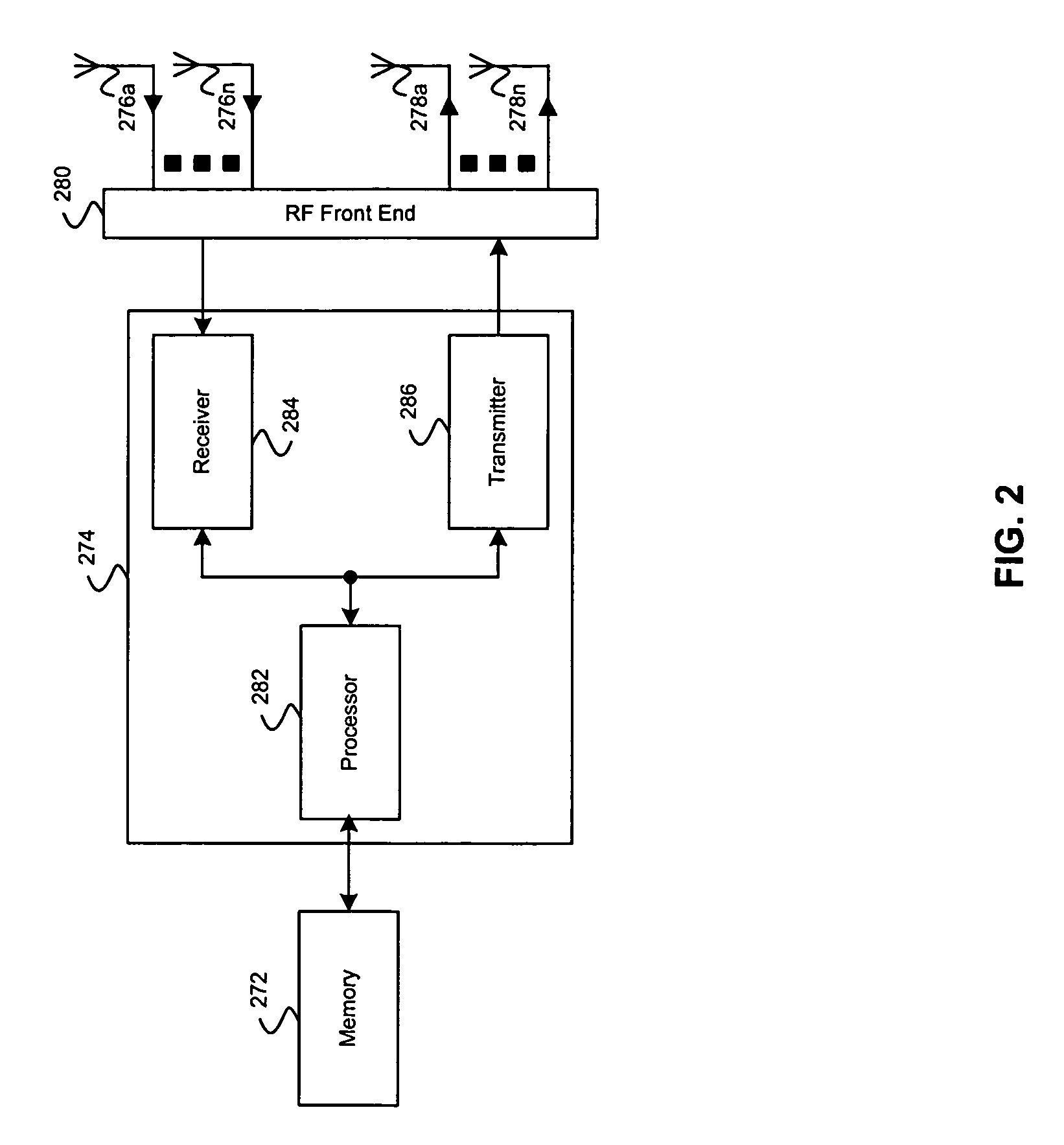
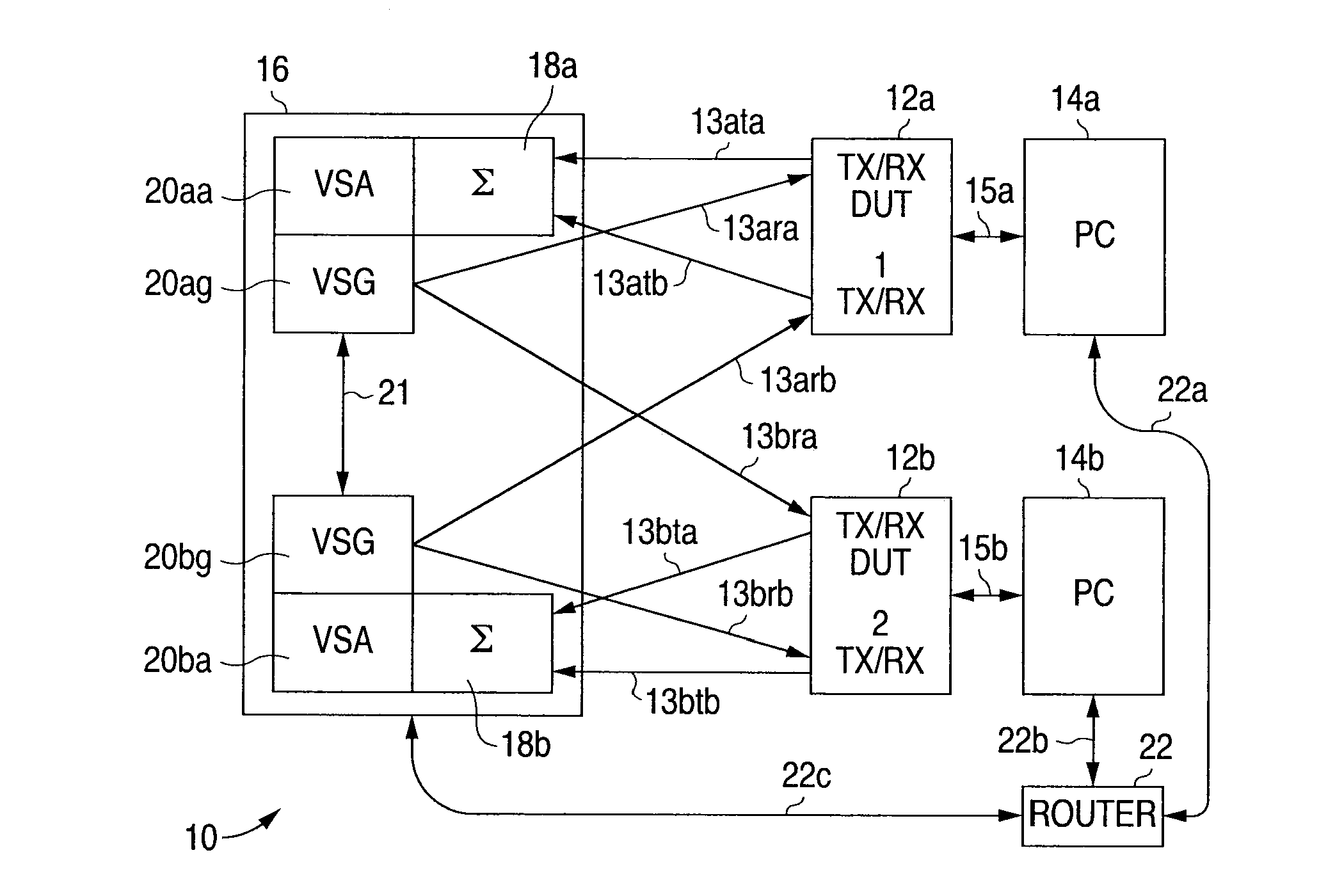
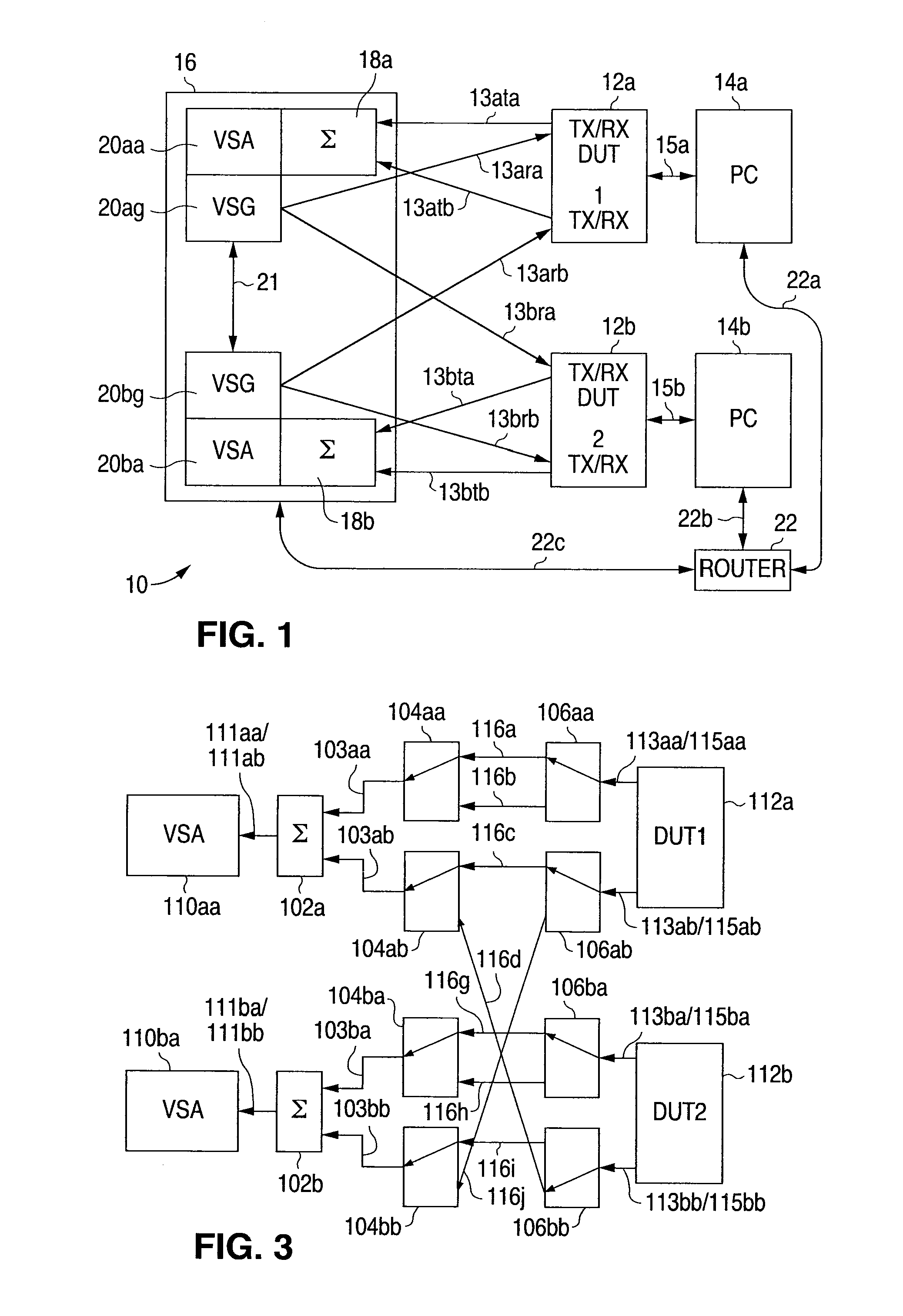
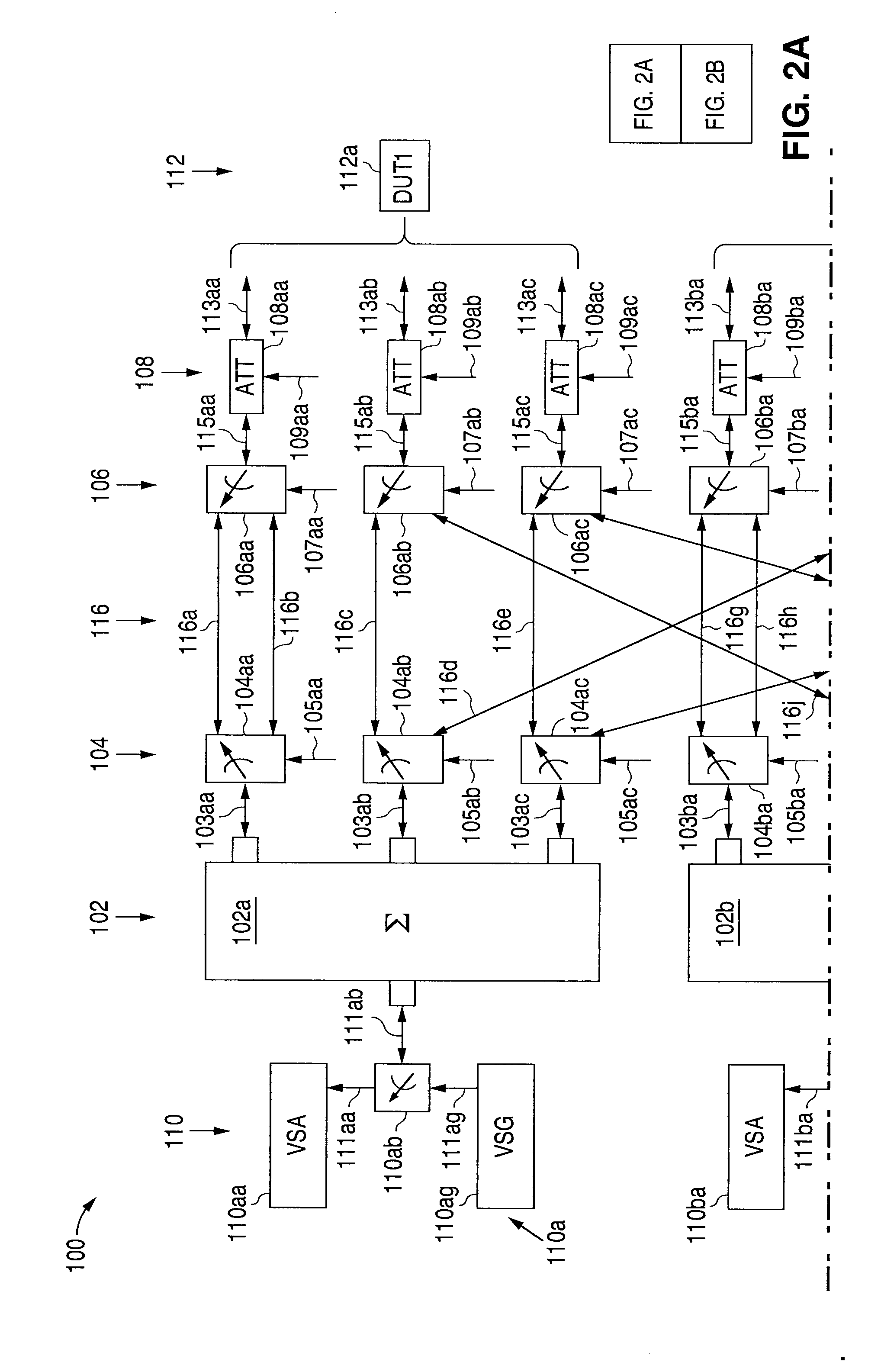
Digital Communications Test System for Multiple Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) Systems
ActiveUS20100123471A1Improve test throughputElectrical testingSecret communicationComputer hardwareError vector magnitude
A digital communications test system and method for testing a plurality of devices under test (DUTs) in which multiple sets of a single vector signal analyzer (VSA) and single vector signal generator (VSG) can be used together to perform error vector magnitude (EVM) measurements for one or more DUTs in parallel, including one or more of composite, switched and multiple input multiple output (MIMO) EVM measurements. This allows N pairs of a VSA and VSG to test N DUTs with N×N MIMO in substantially the sane time as a single VSA and VSG pair can test a single DUT, thereby allowing a substantial increase in testing throughput as compared to that possible with only a single VSA and VSG set.
Owner:LITEPOINT
Method and system for minimizing effects of transmitter impairments in multiple input multiple output (MIMO) beamforming communication systems
ActiveUS20070201575A1Minimize impactDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationCommunications systemError vector magnitude
Owner:BELL NORTHERN RES LLC
Method of Determining True Error Vector Magnitude in a Wireless Lan
InactiveUS20090316589A1Measurement is faster and cheapNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCorrect operation testingPhase noiseError vector magnitude
Systematic transmit IQ phase and amplitude imbalances in the transmit chain of a wireless local area network (WLAN) cause a corresponding systematic shift in the roots of a constellation diagram. Additional random phase noise in the transmit chain will cause a further Gaussian distribution of points in the constellation diagram about the systematically shifted roots. This random distribution represents a true error vector magnitude (EVM). By transmitting a known training sequence through the transmit chain, which it is known will be shifted to all of the systematically shifted roots in the constellation diagram, the Gaussian spread around those shifted roots can be analysed to determine the true EVM.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
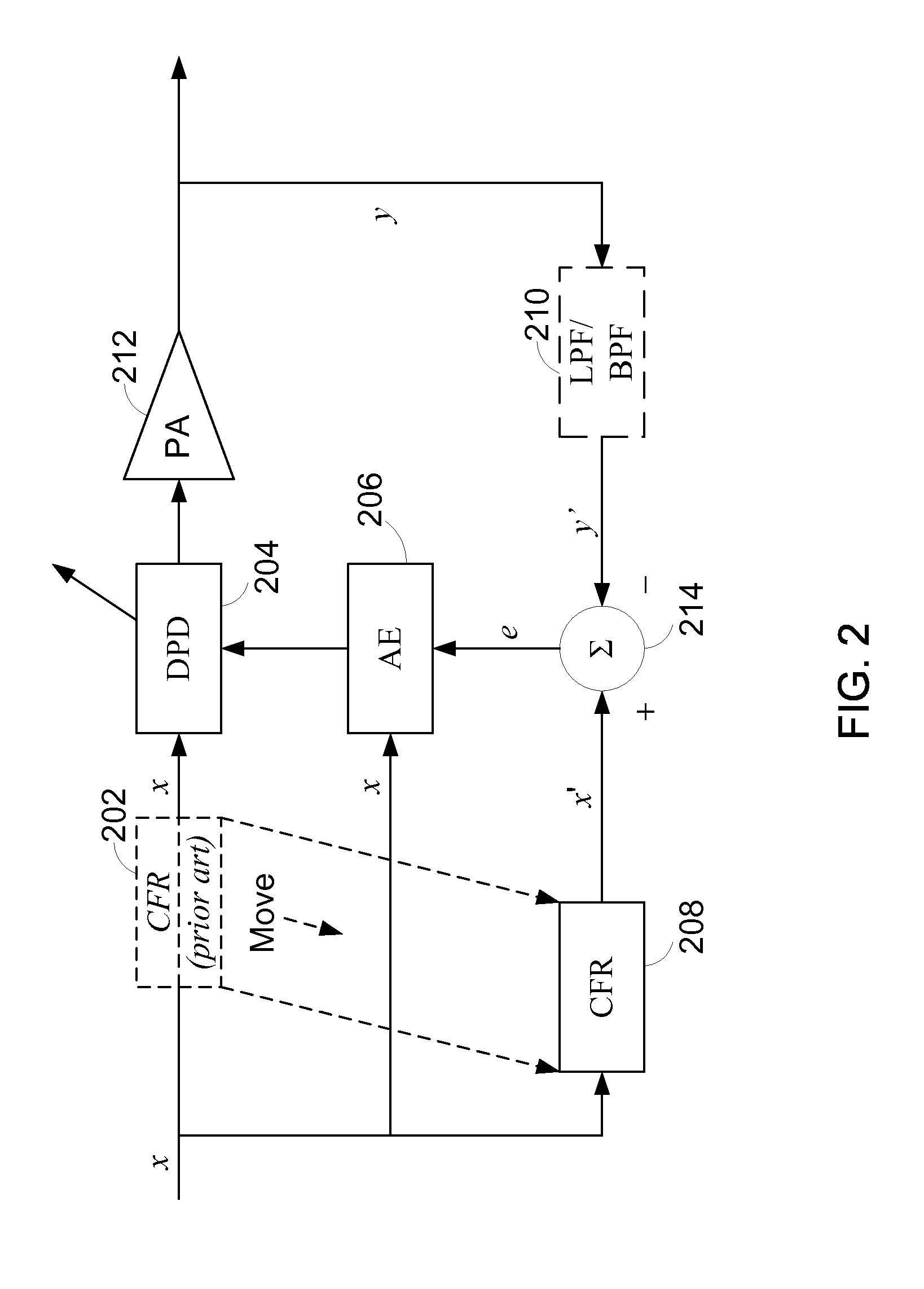
Predistortion with integral crest-factor reduction and reduced observation bandwidth
ActiveUS8446979B1Reduced observation bandwidthReduce processing requirementsResonant long antennasAmplifier with control circuitsAudio power amplifierError vector magnitude
Apparatus and methods configure digital predistortion linearizers for power amplification of bandlimited signals using non-linear amplifiers. The predistorter is configured to achieve both crest factor reduction (CFR) and predistortion for linearization. One embodiment advantageously reduces processing requirements conventionally associated with CFR by considering only the in-band component, that is, the information bearing component, of the desired signal to be reproduced for those cases in which the mitigation of in-band error vector magnitude (EVM) is preferred over the reduction of spurious out-of-band emissions.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
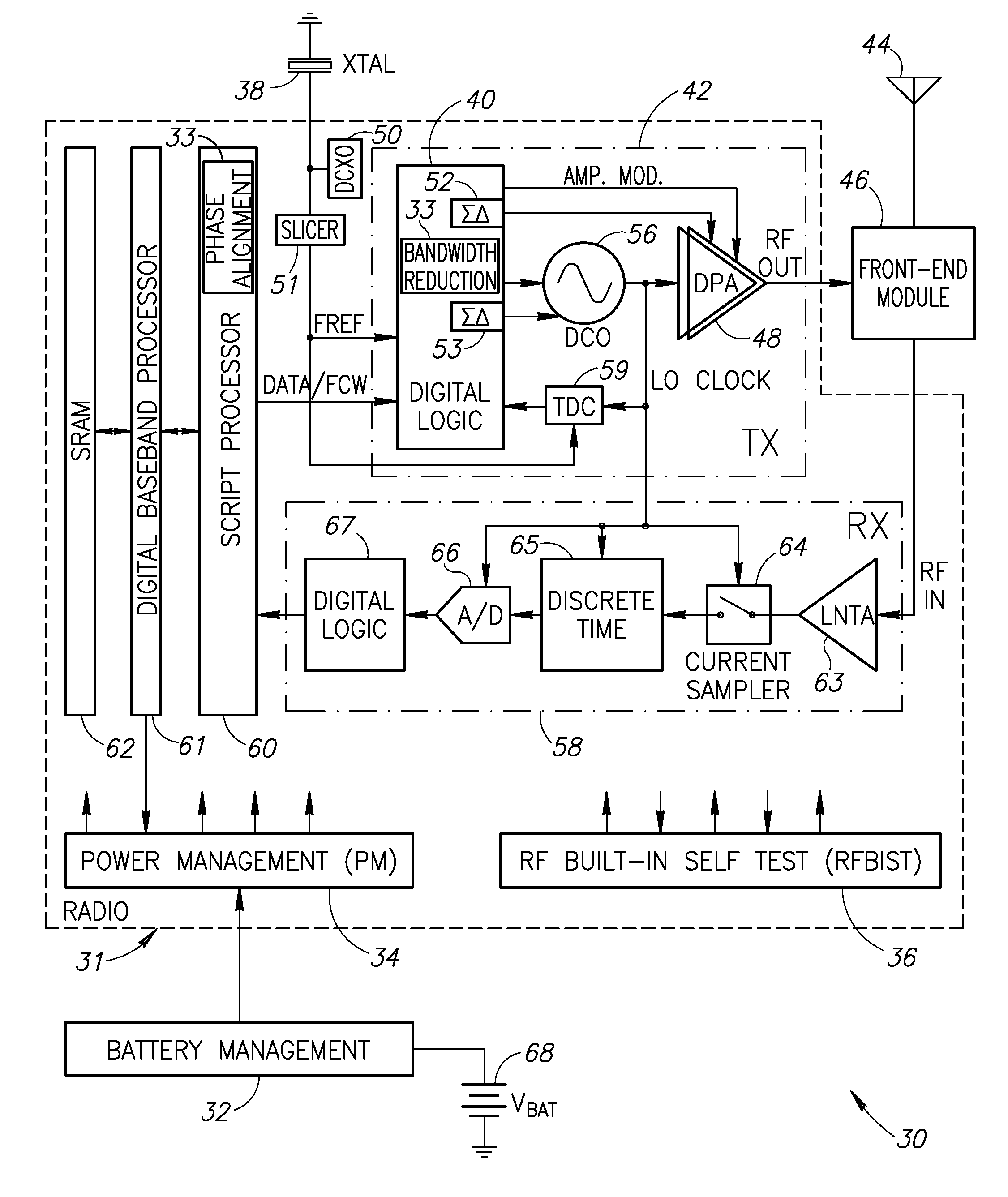
Bandwidth reduction mechanism for polar modulation
ActiveUS20090258612A1Reducing polar modulation bandwidthDegradation of modulation bandwidthSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationModulated-carrier systemsFrequency spectrumPhase bandwidth
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of reducing phase and amplitude modulation bandwidth in polar transmitters. The bandwidth reduction mechanism of the present invention effectively reduces the phase modulation bandwidth of the polar modulation performed in the transmitter by modifying the zero-crossing trajectories in the IQ domain. This significantly reduces the phase modulation bandwidth while still meeting the output spectrum and error vector magnitude (EVM) requirements of the particular modern wideband wireless standard, such as 3G WCDMA, etc. The mechanism detects a zero crossing or a near zero crossing within a predetermined threshold of the origin and an offset vector is generated that when added to the input TX IQ data, shifts the trajectory to avoid the origin thus reducing the resultant polar modulation amplitude and phase bandwidth.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Transmitting unit that reduces PAPR and method therefor
InactiveUS20110064162A1Modulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationCommunications systemCarrier signal
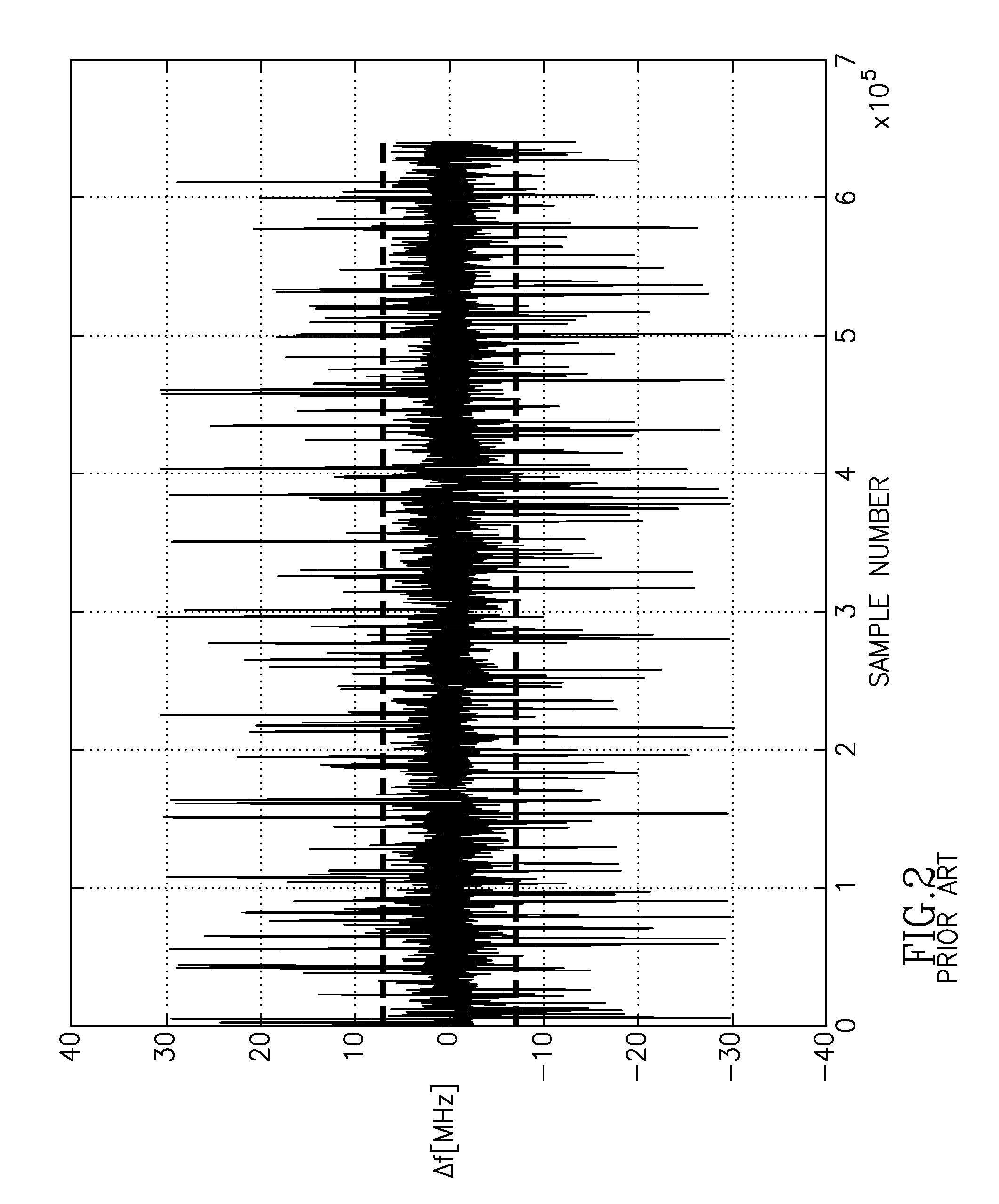
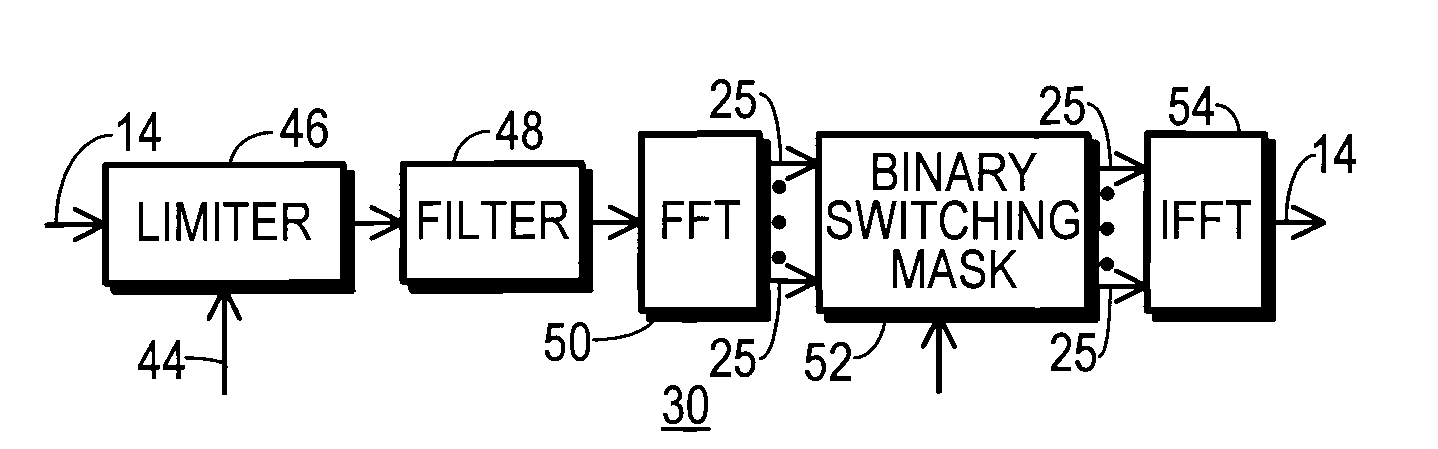
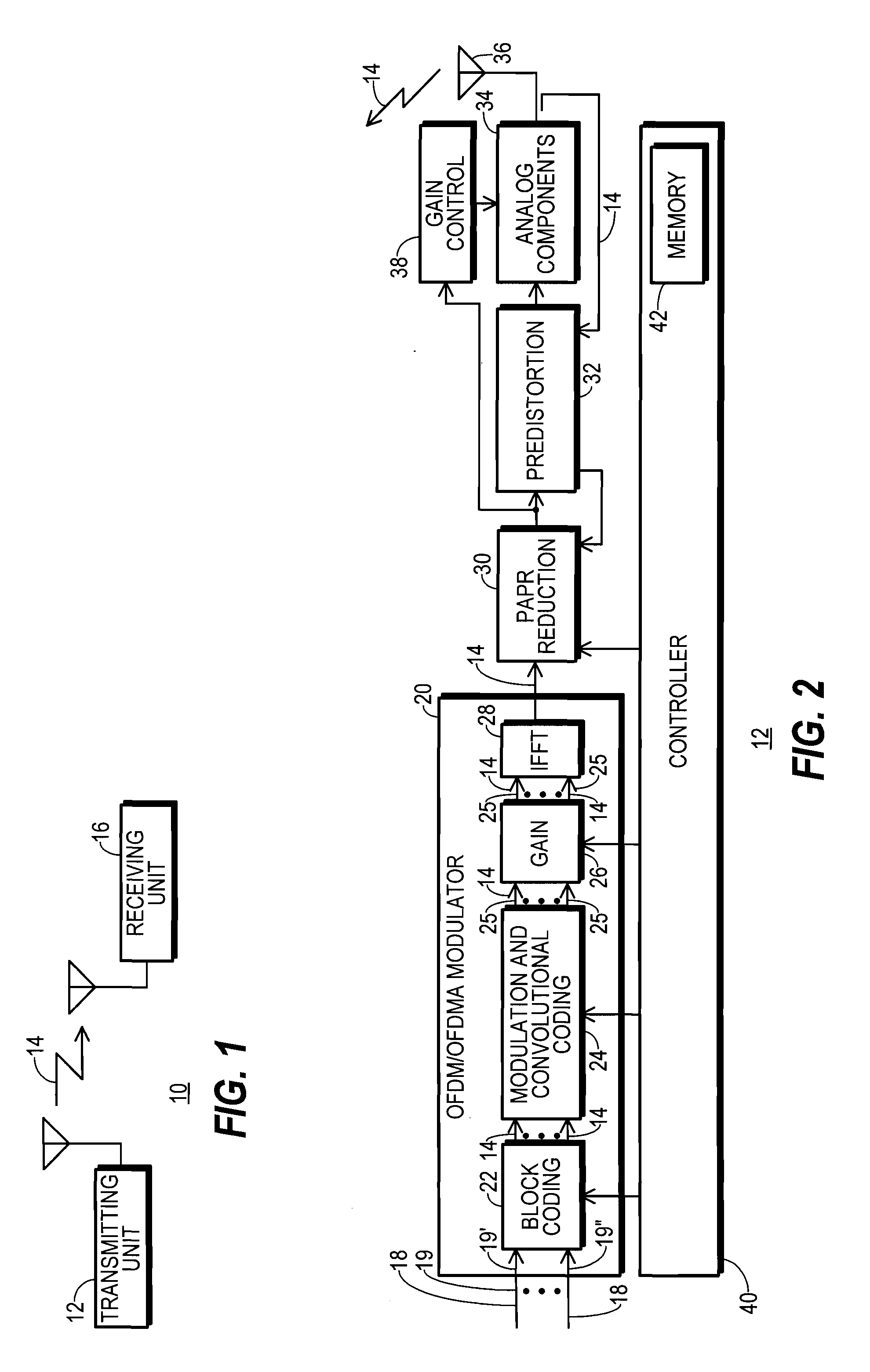
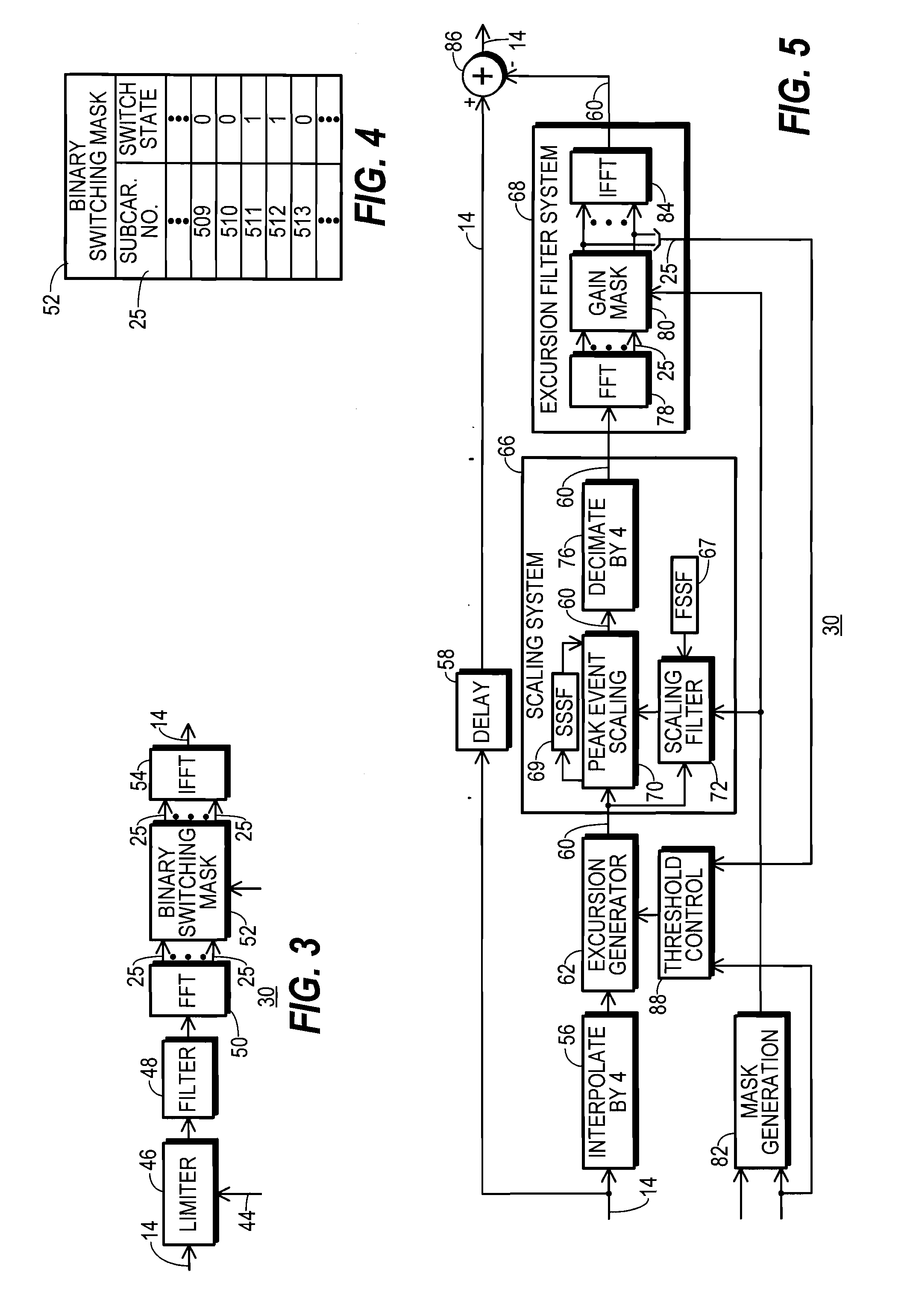
A communication system (10) includes a transmitting unit (12) with a peak to average power (PAPR) reduction section (30). The PAPR reduction section (30) modifies the PAPR reduction it effects in a communication signal (14) in accordance with two different error vector magnitude (EVM) constraints for each channel type (102), where a channel type (102) is a distinct combination of a modulation order and a coding rate. The EVM constraint followed for each subcarrier (25) in an OFDM or OFDMA application is selected in response to whether the subcarrier (25) conveys voice or non-voice data. The PAPR reduction section (30) may include a scaling filter (72). The scaling filter (72) is efficiently defined through the use of a predetermined sinc function (94) and a first stage scale factor (67) that is calculated in response to a weighted average of excursion signal subcarrier gains (150), where the weighting follows the distribution of channel types (102) through the subcarriers (25).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
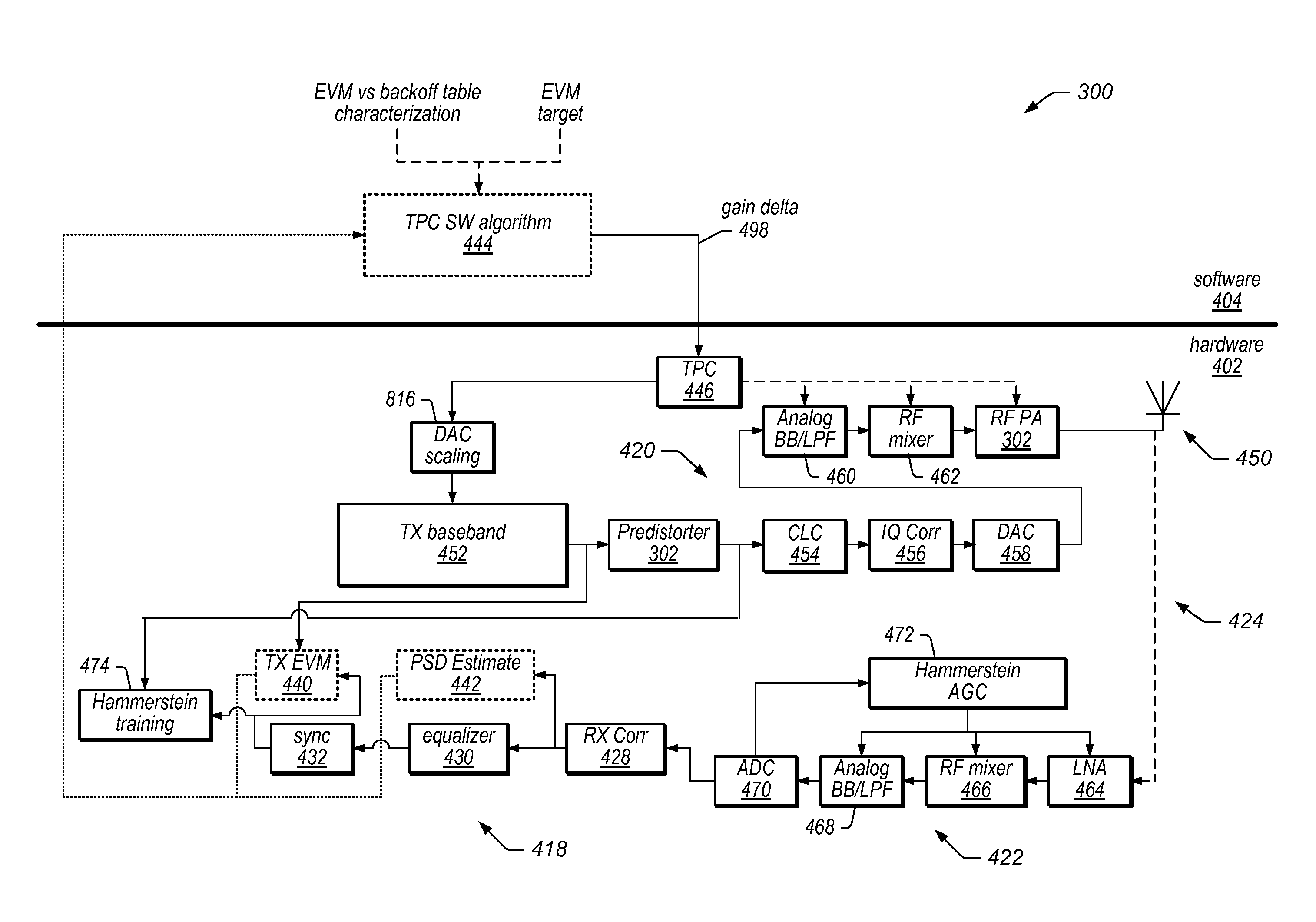
Transmit power control utilizing loopback error vector magnitude thresholds
InactiveUS8565343B1Reduce settingsReduce distortion problemsModulated-carrier systemsGain controlAudio power amplifierTransmitted power
A device and method for adjusting transmit power in a wireless communication device. The wireless communication device comprises a transmitter having a power amplifier, wherein the amplifier may introduce distortion into the transmit signal. The method may periodically determine an error vector magnitude (EVM) level in the transmitter of the wireless communication device. The EVM level may be determined based on differences between an ideal transmit signal without amplification, and an actual transmit signal with amplification. The method may then adjust one or more transmit gain settings of at least one gain stage of the wireless device based on the measured EVM level in the transmitter. In one embodiment, as the EVM increases, indicating that more distortion is being introduced, the method may reduce the gain settings of the gain stage(s) to reduce this distortion. If the EVM decreases, the method may increase the gain of the gain stage(s).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Downconverter and upconverter
InactiveUS20060256216A1Reduce power consumptionSufficient image rejection ratioTelevision system detailsModulated-carrier systemsFrequency changerIntermediate frequency
A downconverter and upconverter are provided which can obtain a sufficient image rejection ratio in a low-Intermediate Frequency (IF) scheme while reducing power consumption and can suppress Error Vector Magnitude (EVM)-related degradation in a zero-IF scheme. A complex-coefficient transversal filter rejects one side of a positive or negative frequency, and converts a Radio Frequency (RF) signal to a complex RF signal configured by real and imaginary parts. A local oscillator outputs a real local signal with a set frequency. A half-complex mixer, connected to the complex-coefficient transversal filter and the local oscillator, performs a frequency conversion process by multiplying the complex RF signal output from the complex-coefficient transversal filter and the real local signal output from the local oscillator, and outputs a complex signal of a frequency separated by the set frequency from a frequency of the RF signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
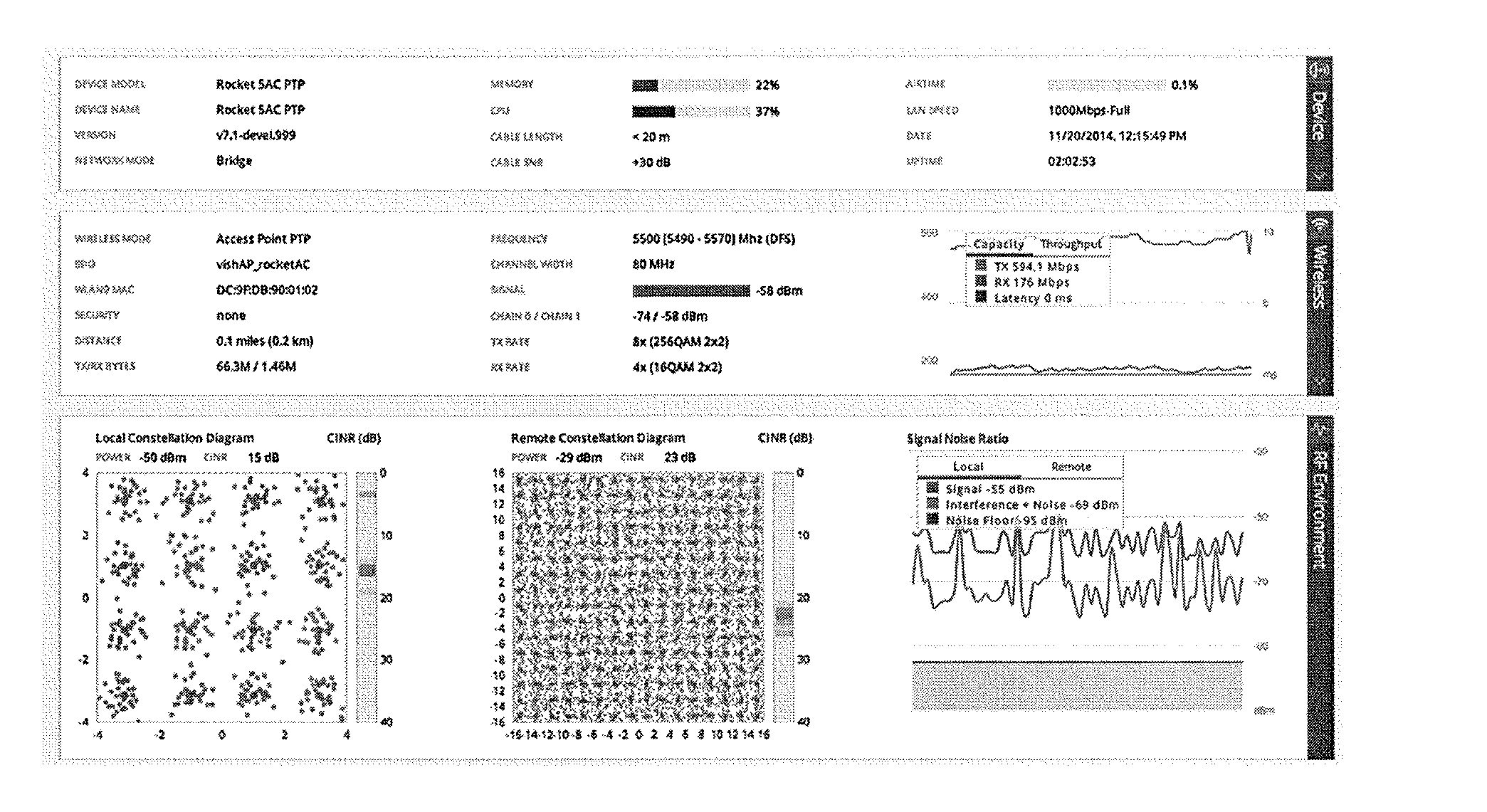
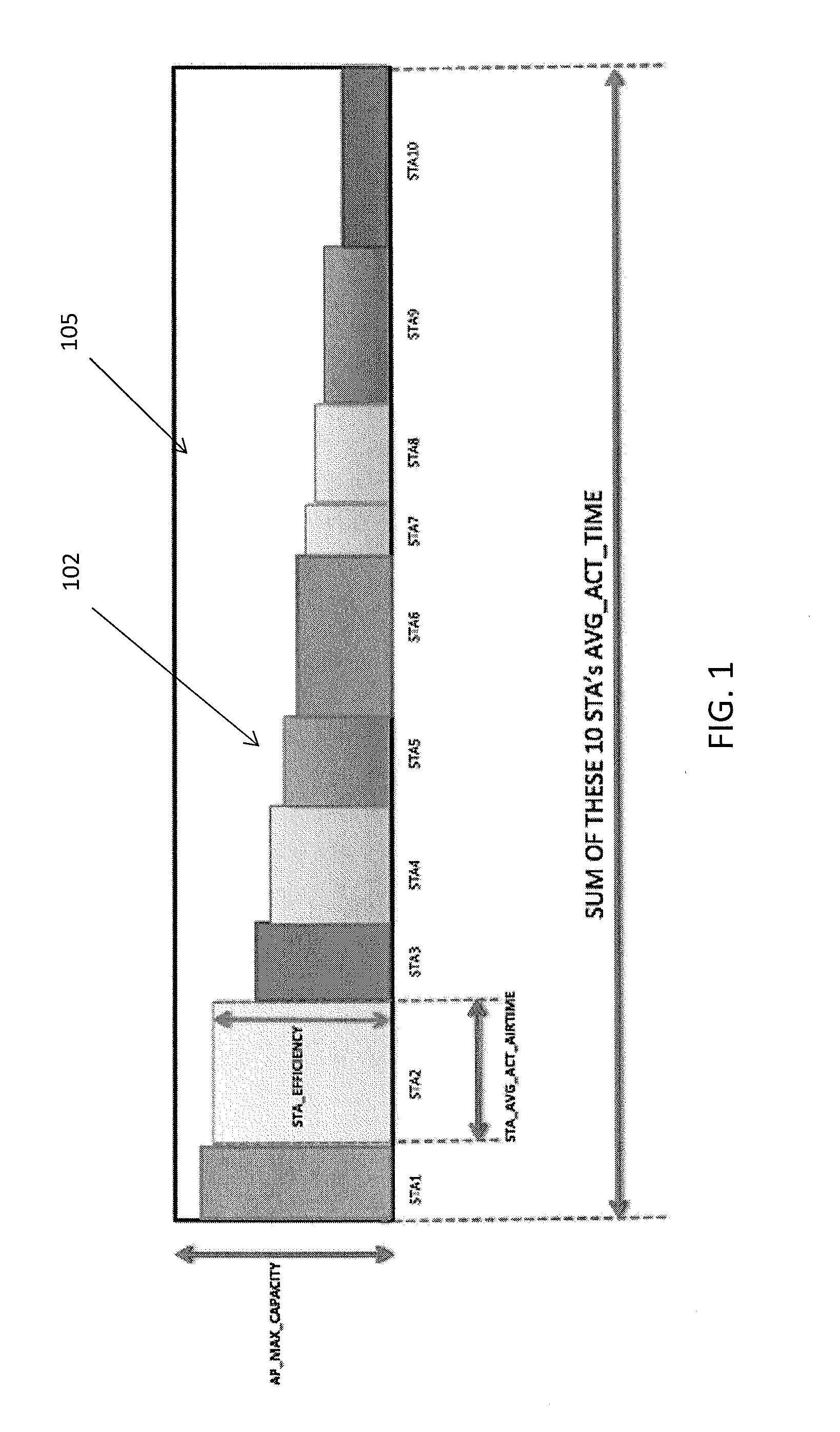
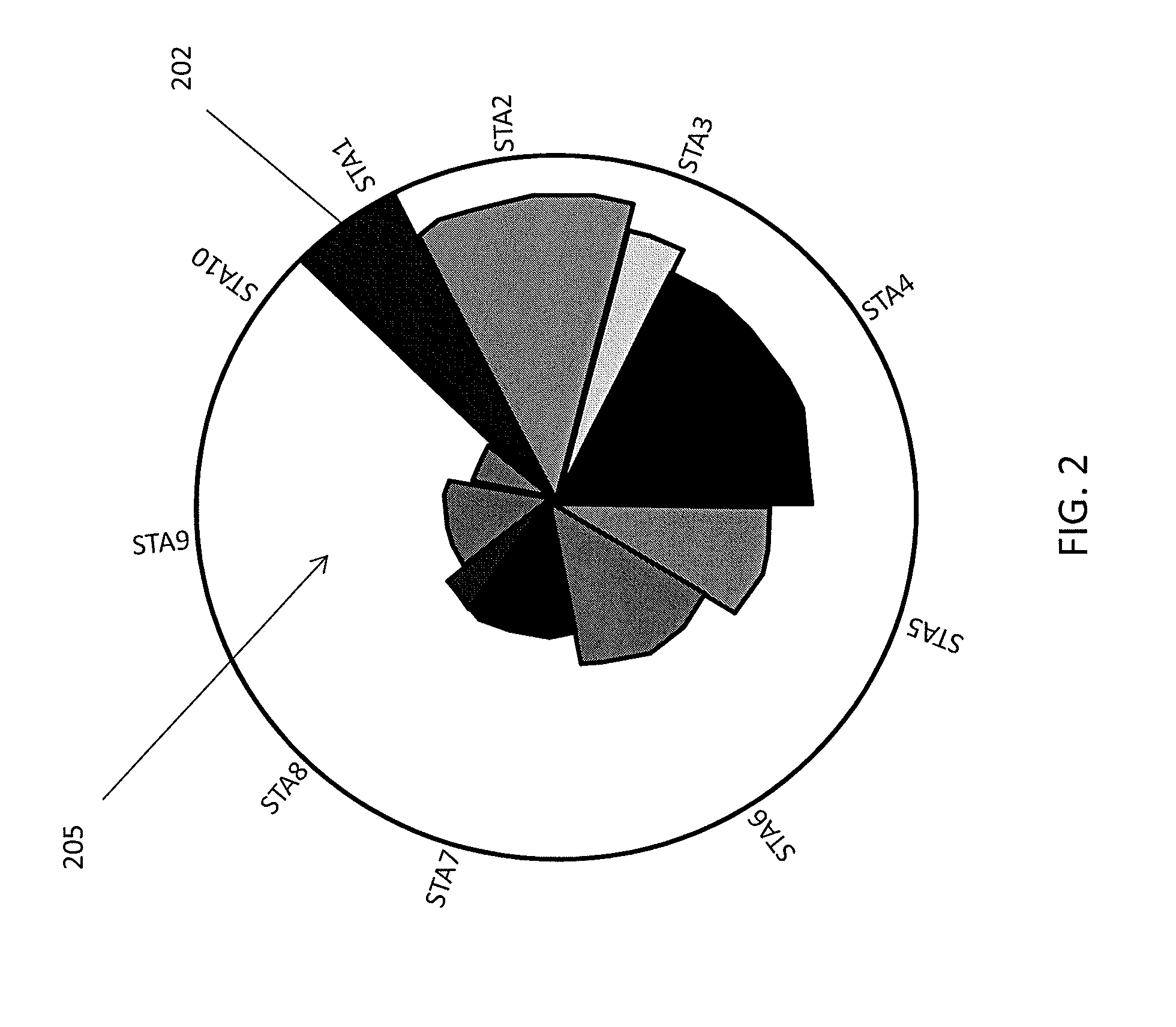
Methods and apparatuses for graphically indicating station efficiency and pseudo-dynamic error vector magnitude information for a network of wireless stations
ActiveUS20160066202A1Improve network performanceFast and efficientError preventionTransmission systemsGraphicsRadio equipment
Methods and apparatuses providing a visual metric of the efficiency of a network of devices communicating through a wireless access point (AP). These apparatuses and methods may also determine and display pseudo-dynamic error vector magnitude (EVM) information for a network of wireless stations, including displaying a pseudo-dynamic constellation diagrams using EVM information. These methods and apparatuses may transmit a plurality of sounding packets from each of one or more radio devices different modulation types (e.g., BPSK, QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM and 1024QAM), and receiving at least some of the sounding packets at a second radio device (e.g., an access point) and determining EVM information from the received sounding packets, and displaying (or providing for display) a constellation diagram including pseudo-dynamic EVM information that is a constrained approximation of actual EVM information.
Owner:UBIQUITI INC
Reduction of average-to-minimum power ratio in communications signals
InactiveUS20060227895A1Secret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSignal qualityError vector magnitude
This invention, generally speaking, modifies pulse amplitude modulated signals to reduce the ratio of average power to minimum power. The signal is modified in such a manner that the signal quality remains acceptable. The signal quality is described in terms of the Power Spectral Density (PSD) and the Error Vector Magnitude (EVM).
Owner:INTEL CORP
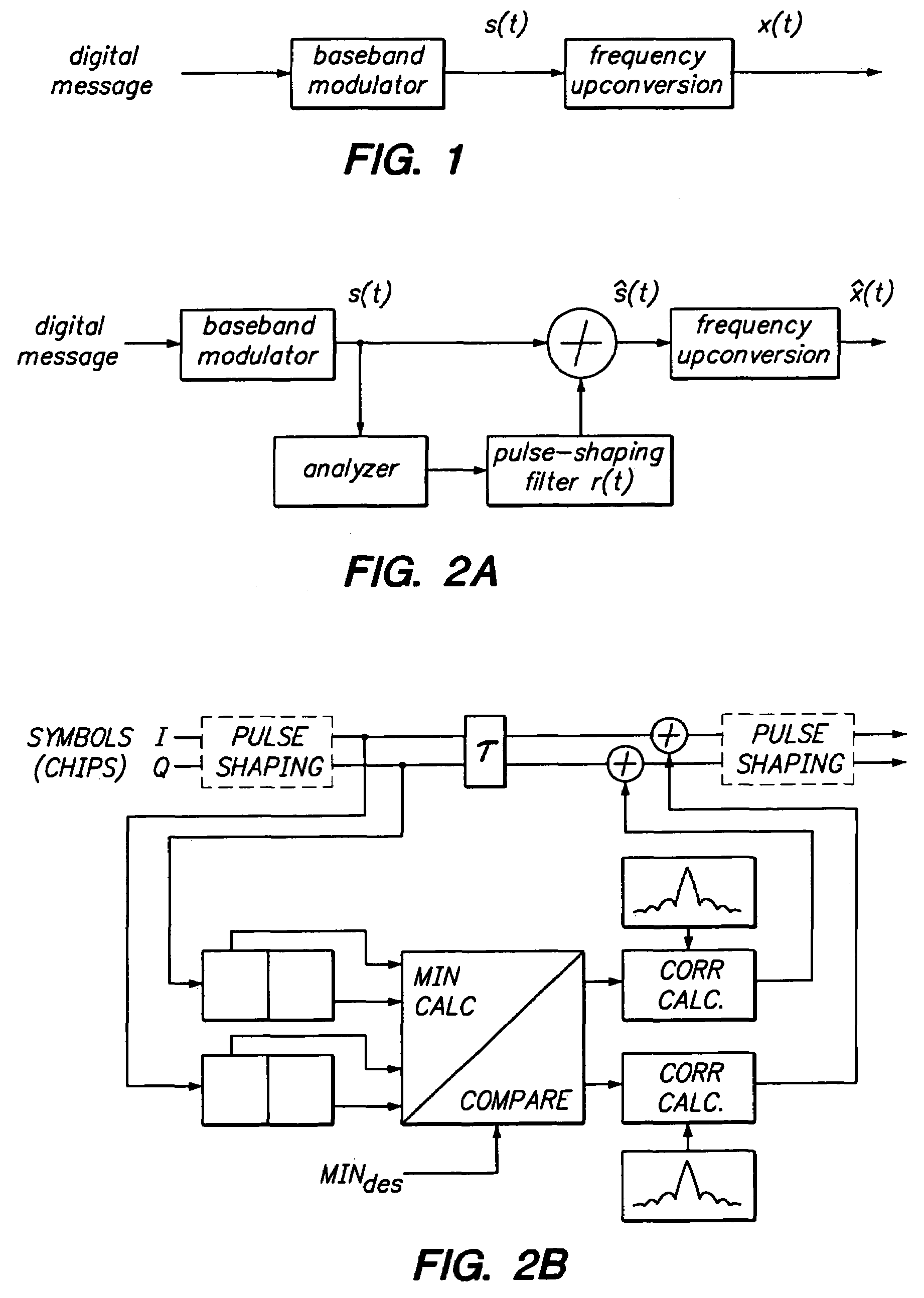
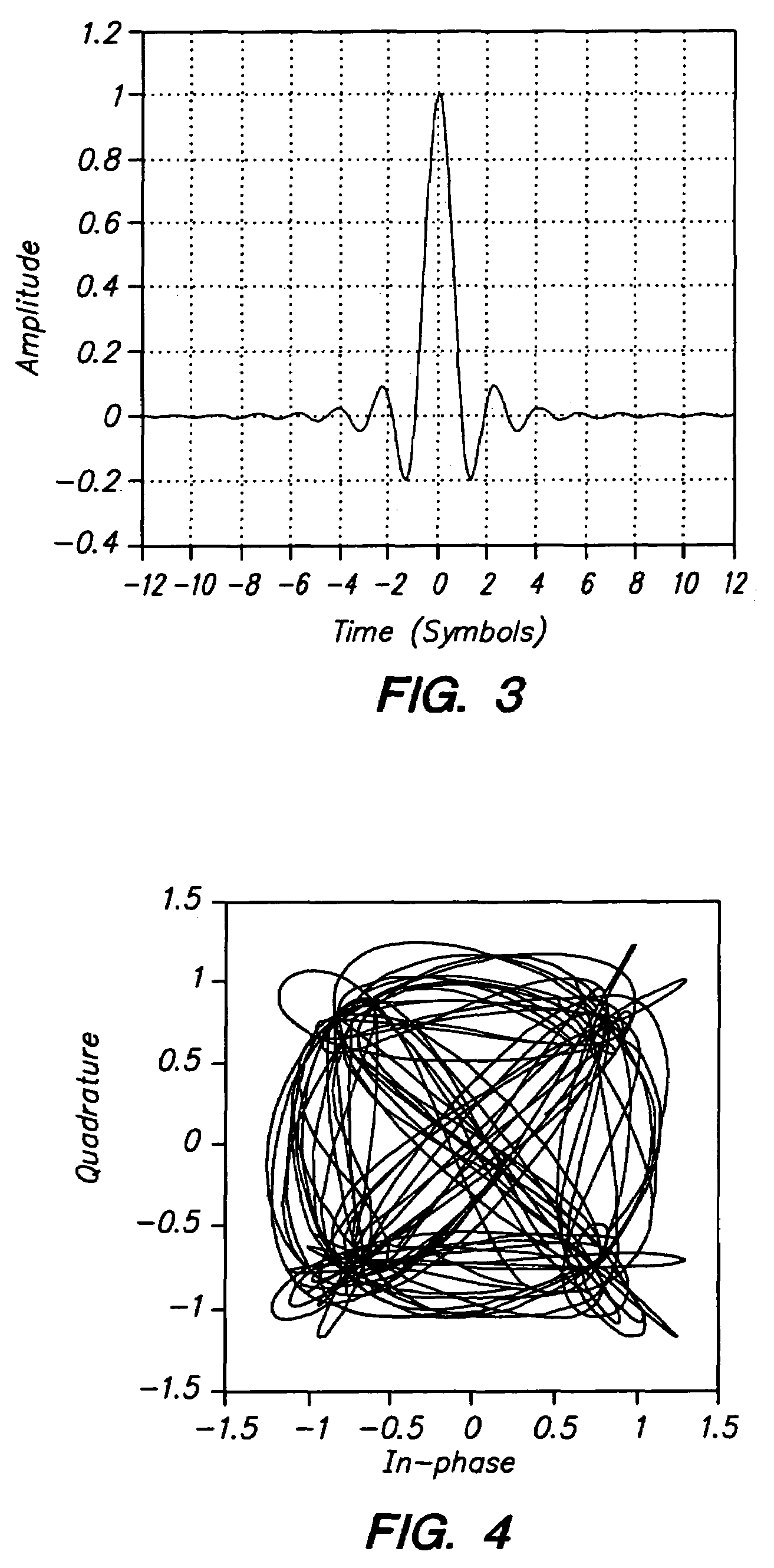
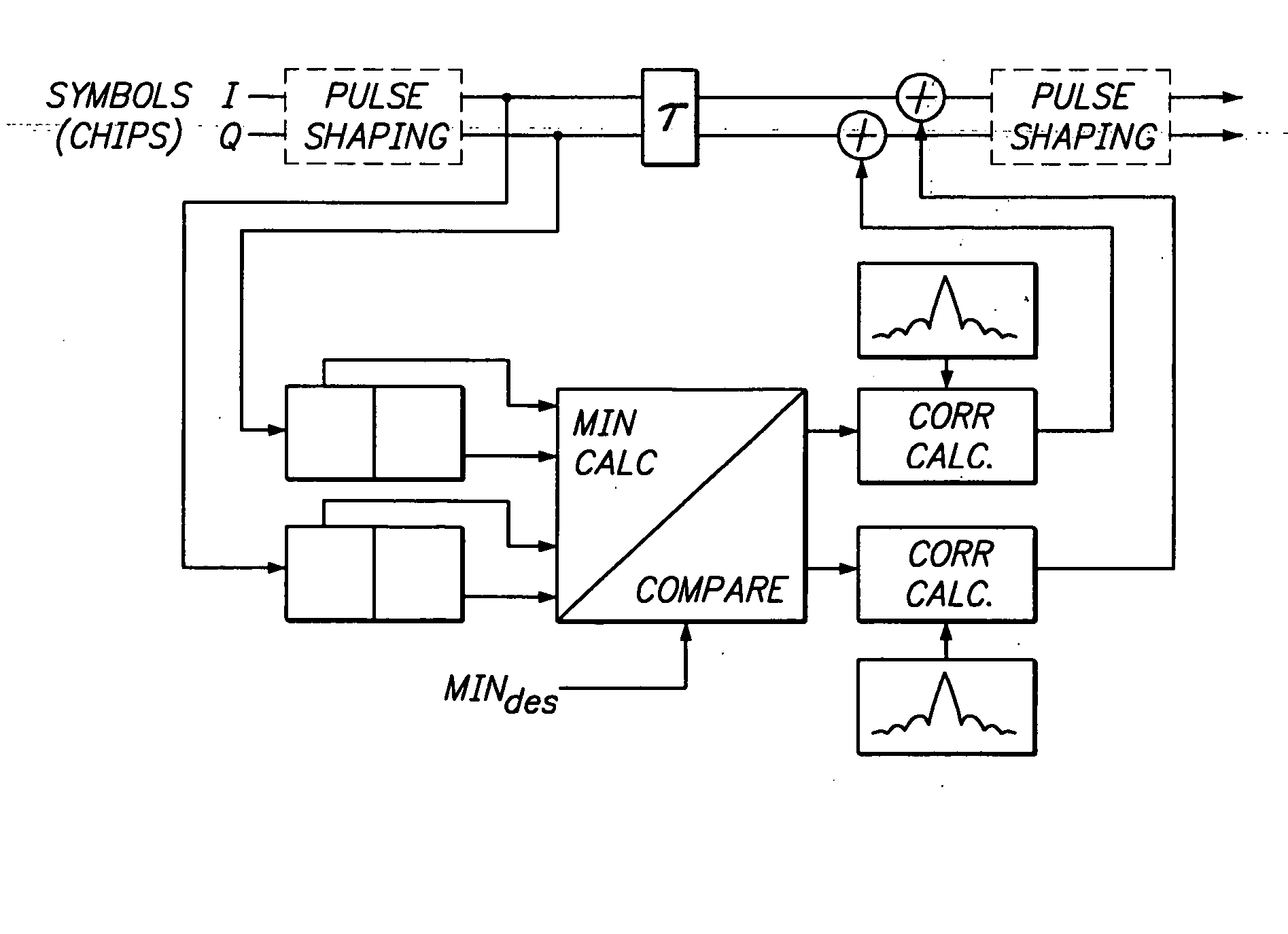
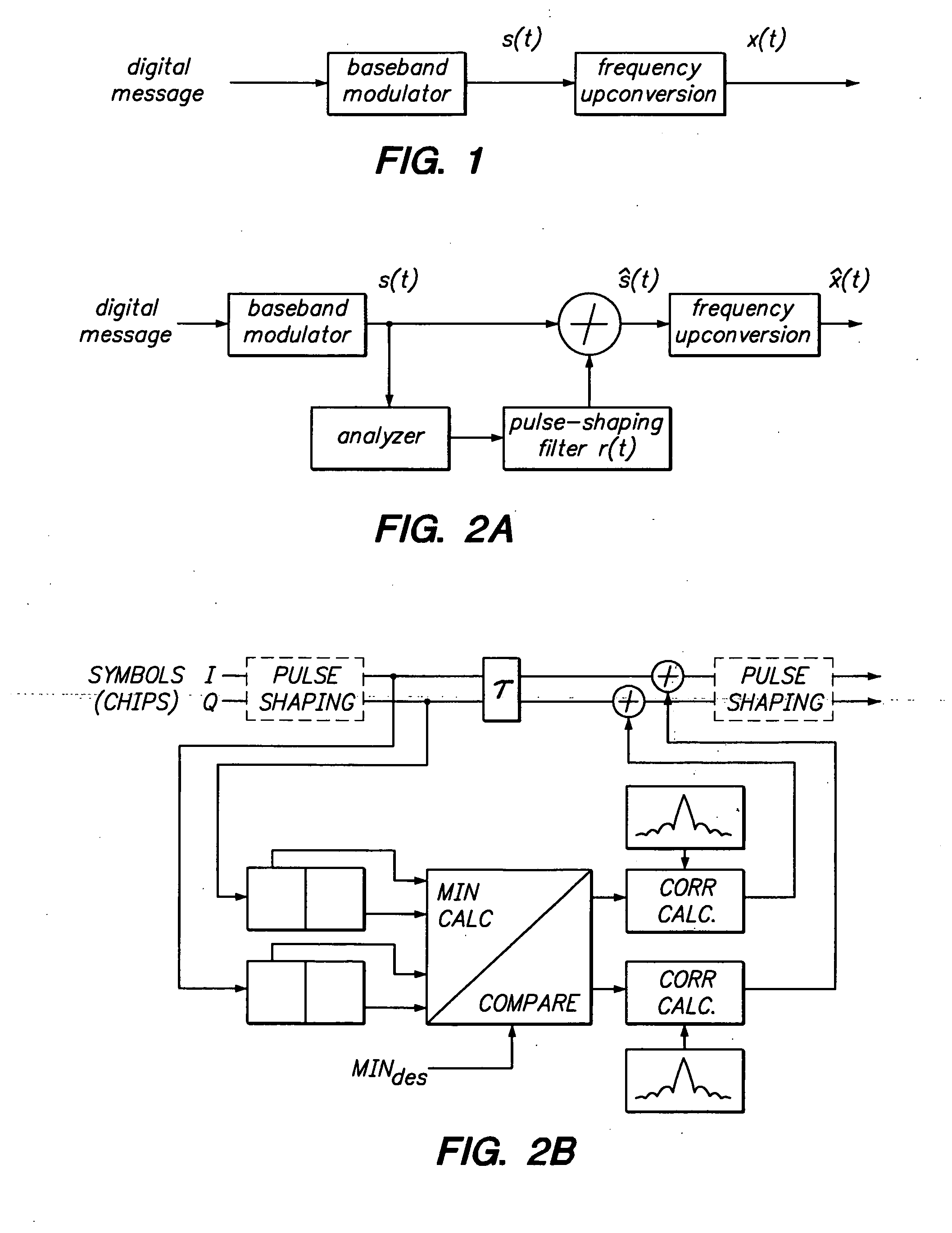
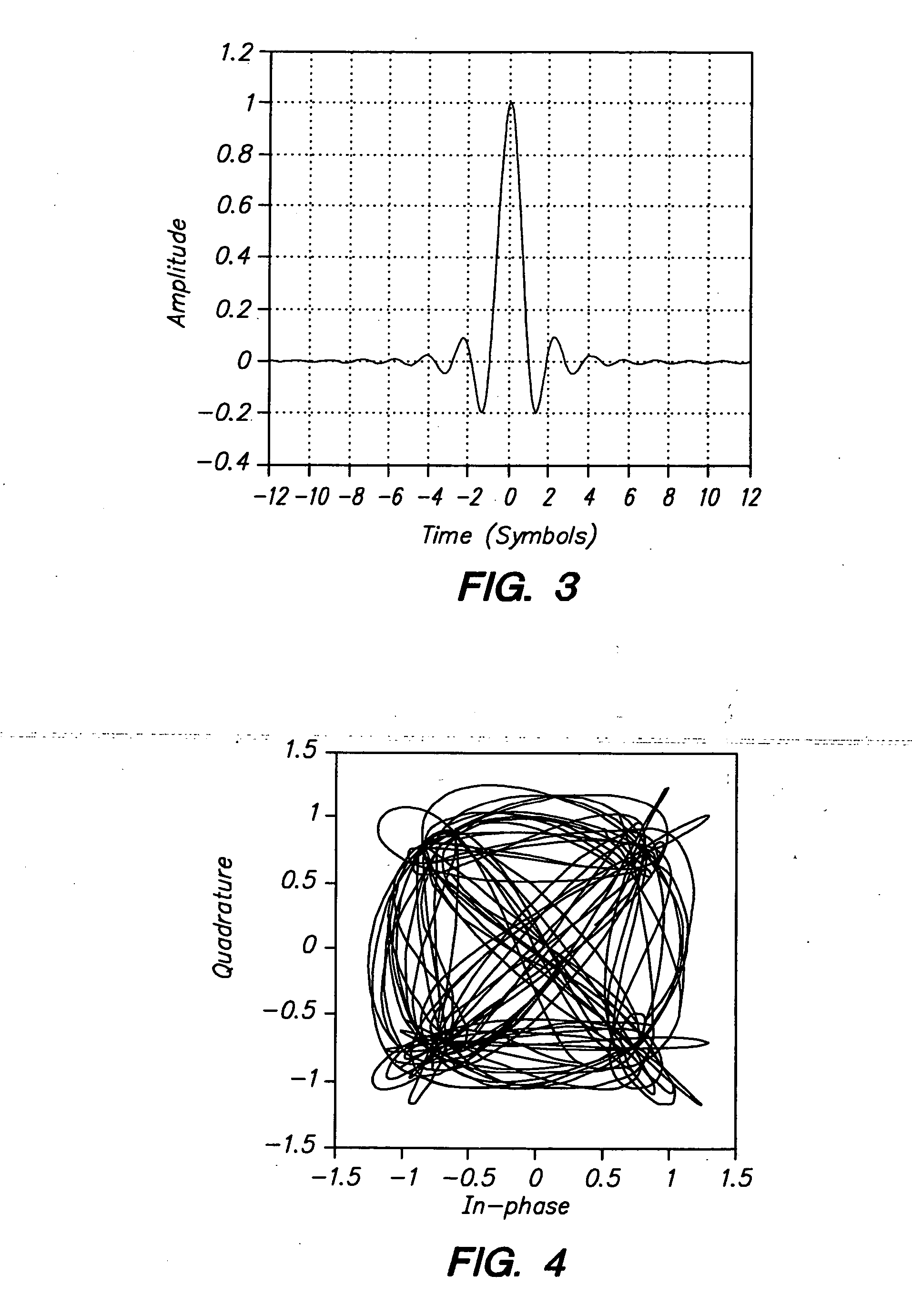
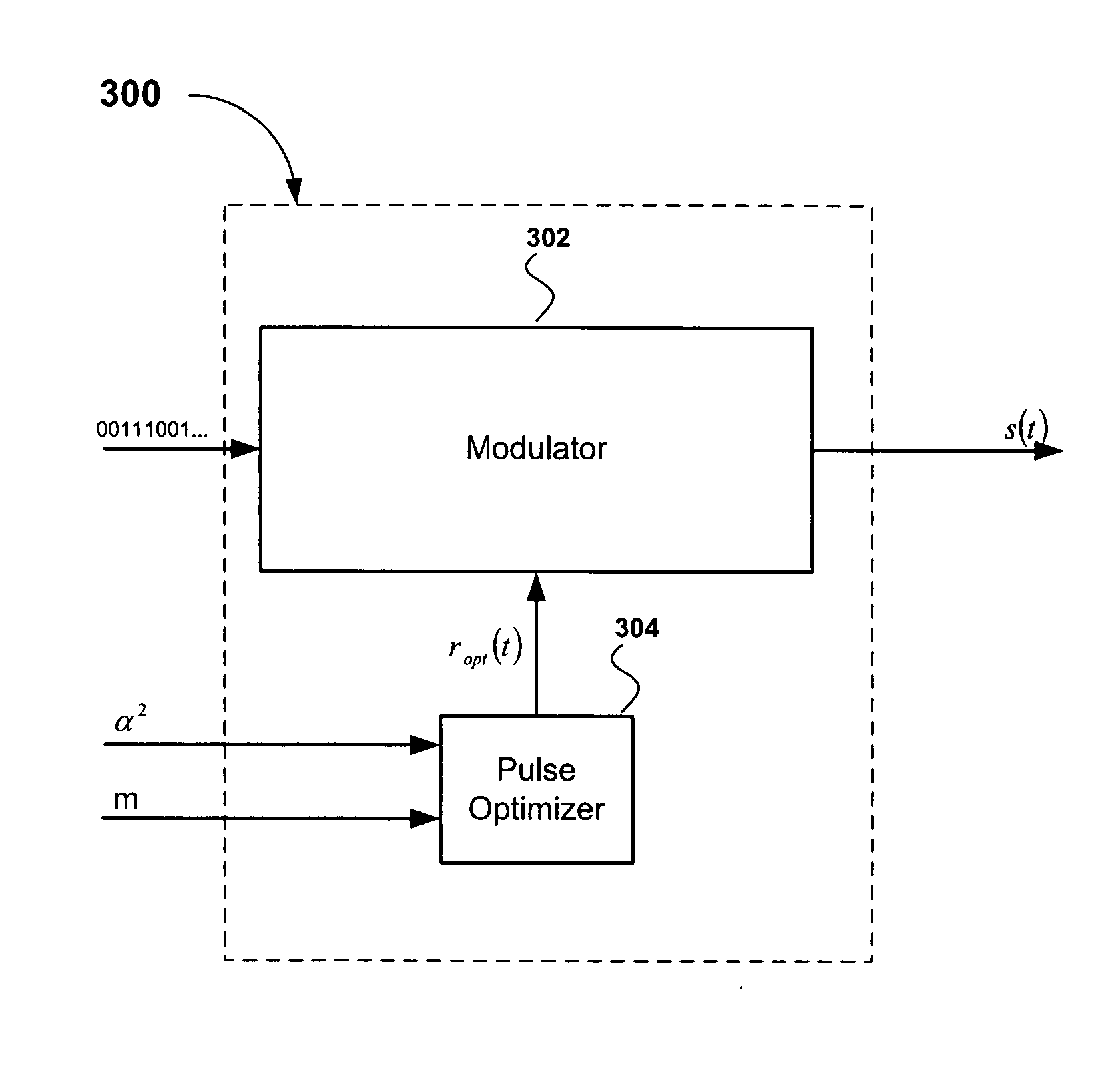
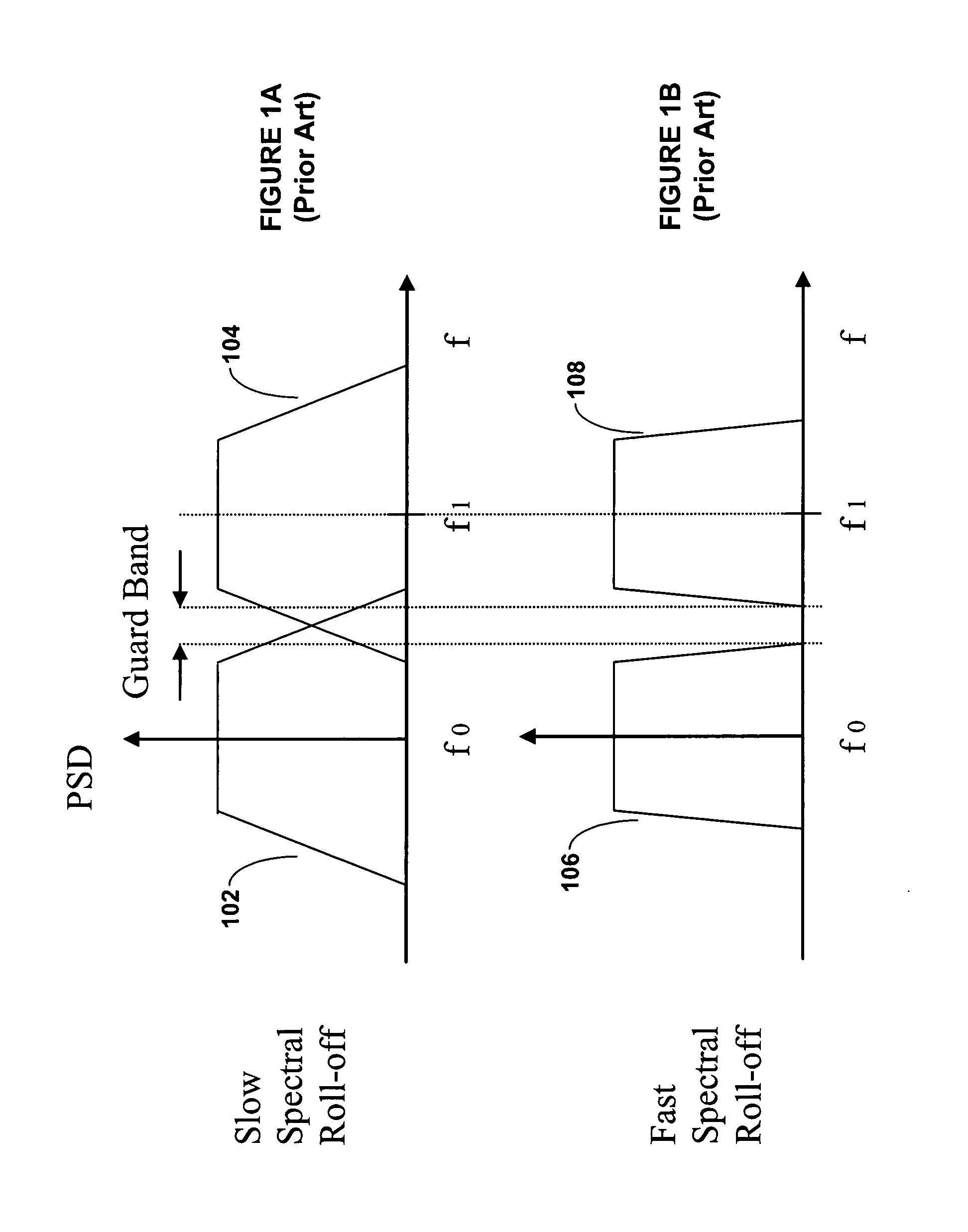
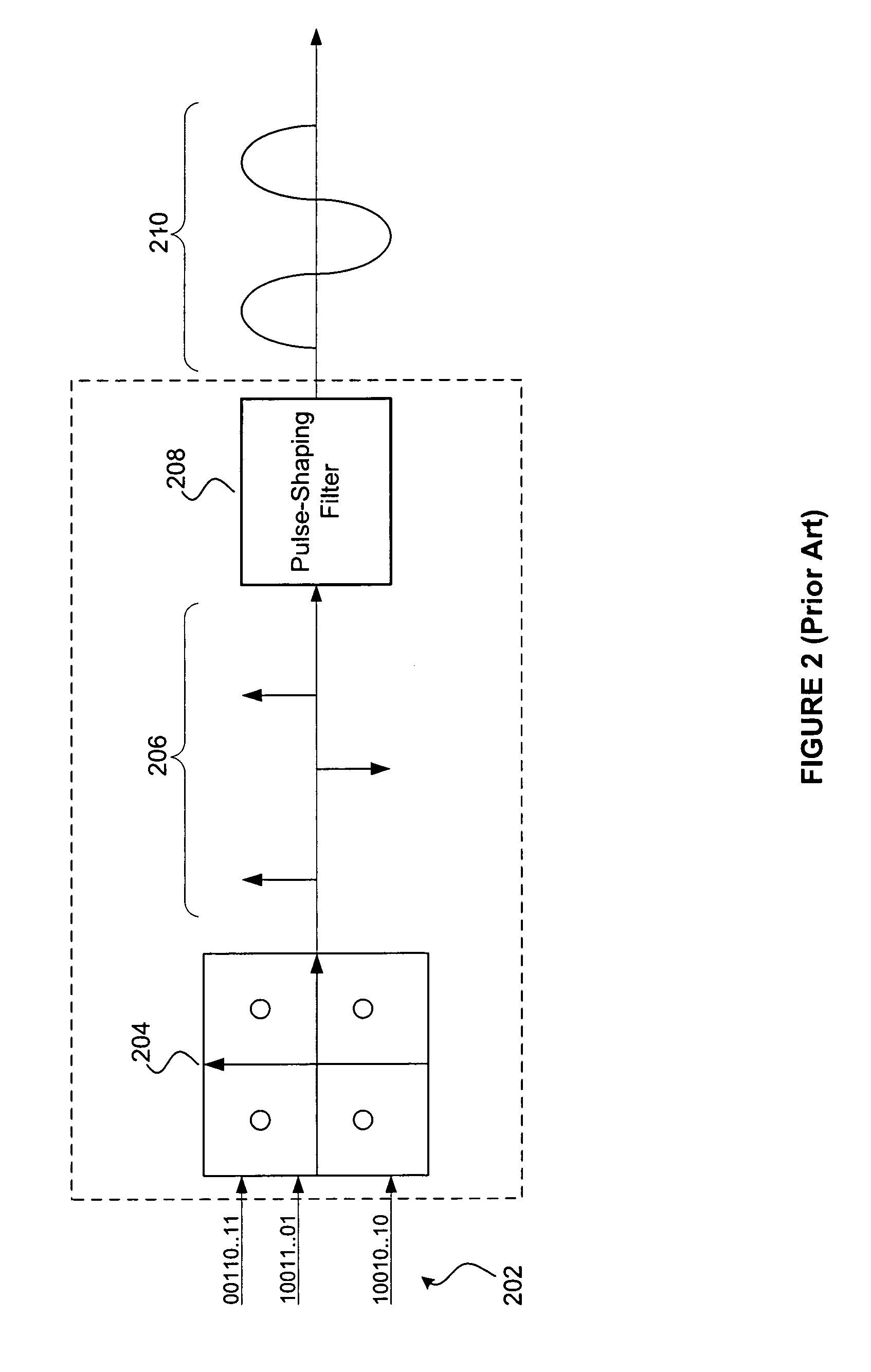
Method and Apparatus for Pulse Optimization for Hardware Implementation
InactiveUS20080187072A1Increased level of distortionAvoid it happening againSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsChannel powerSignal quality
Methods and apparatus for optimizing pulses provided by a pulse-shaping filter implemented in hardware. Pulses are optimized and generated by the pulse-shaping filter that are of finite length and meet one or more signal quality criteria, e.g., error vector magnitude (EVM) and / or adjacent channel leakage ratio (ACLR). According to one exemplary embodiment, a first finite length constraint is identified and a second out-of-band power criterion is identified. An error function is defined which measures the distortion of the generated signal relative to a reference pulse modeled after an ‘ideal’ pulse. The error function is minimized to determine optimized pulses, which when used to pulse-shape a communications signal, do not substantially increase in-channel distortion of said communications signal. To avoid the generation of excessive out-of-channel power, minimization is performed subject to a predetermined maximum allowable out-of-channel power condition.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
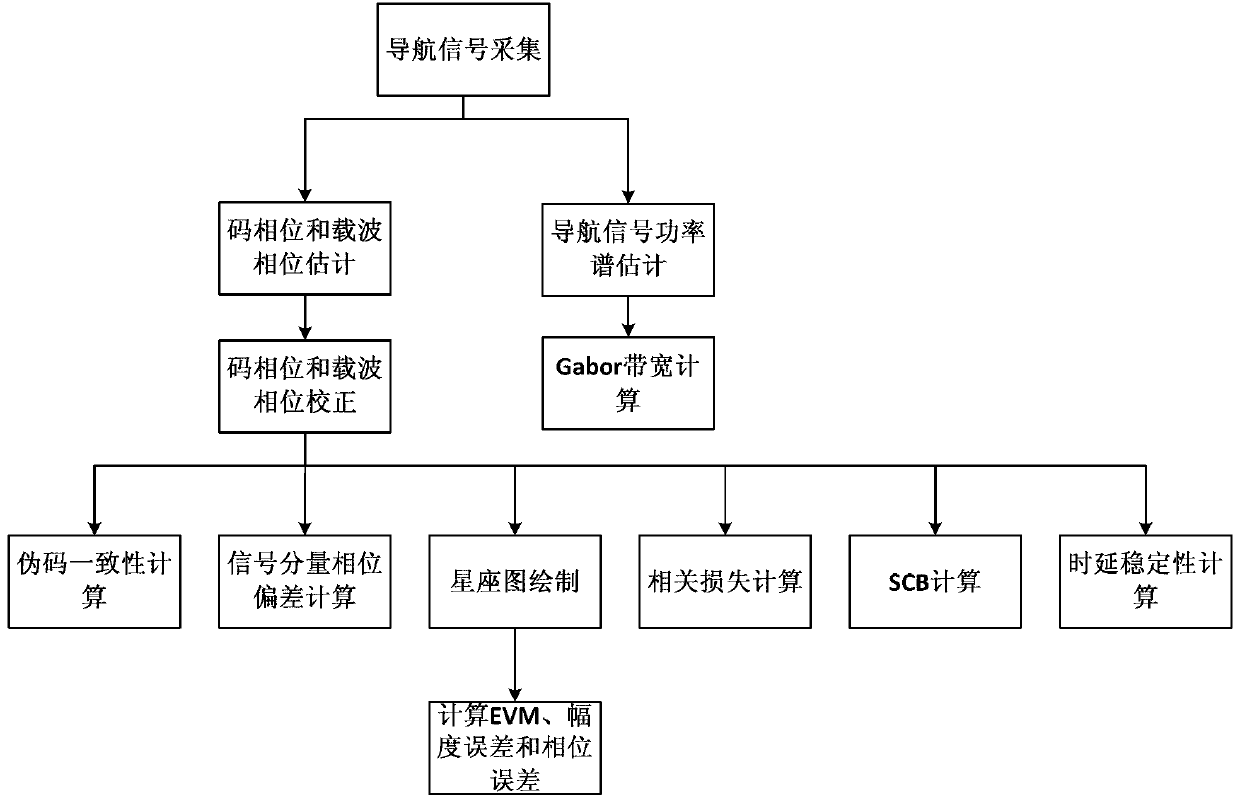
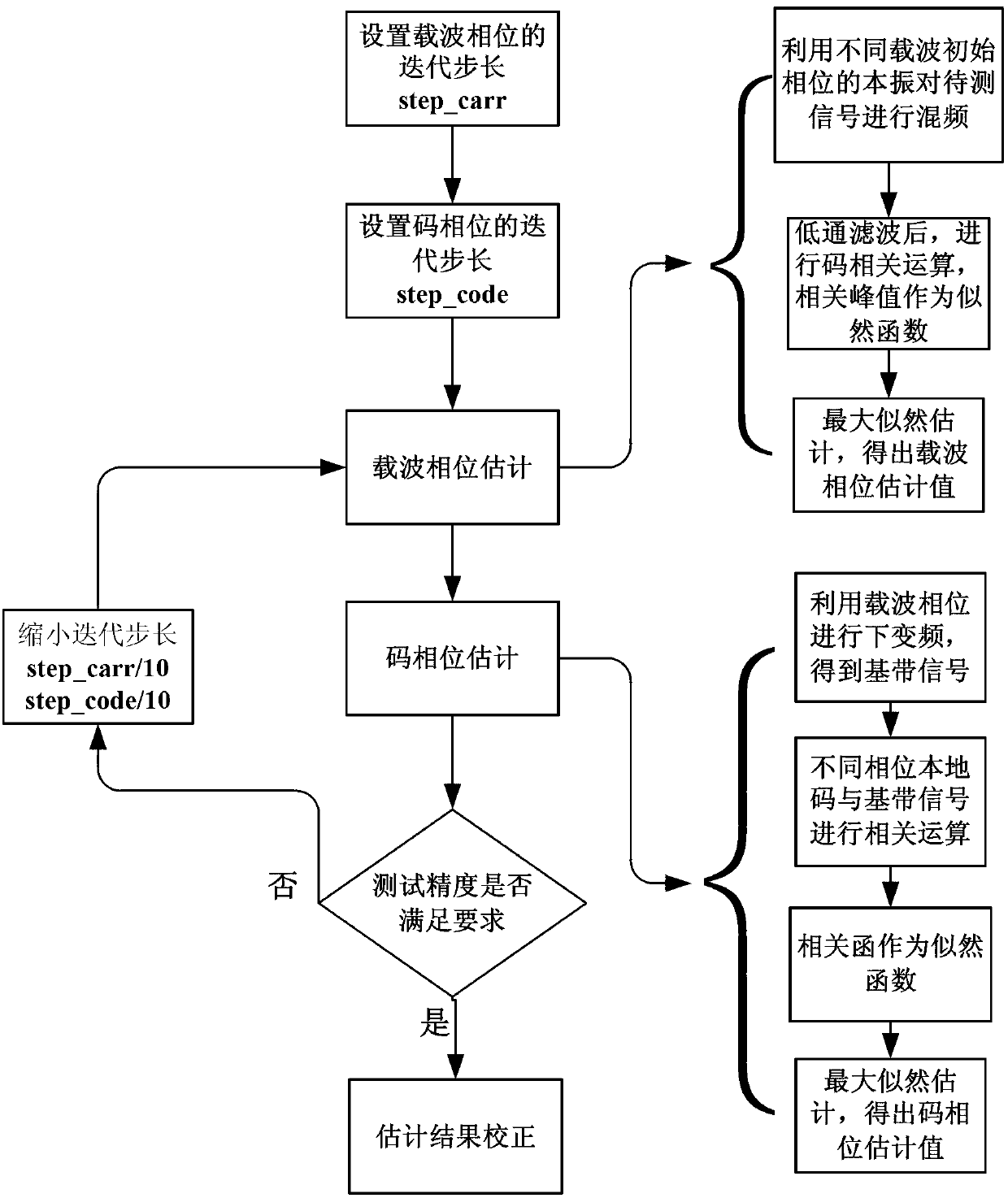
Method for determining satellite navigation signal quality evaluation parameters
ActiveCN103278825AMeeting the Needs of Payload TestingWide coverage of indicatorsSatellite radio beaconingSignal qualityPhase deviation
The invention provides a method for determining satellite navigation signal quality evaluation parameters. The satellite navigation signal quality evaluation parameters comprise Gabor bandwidth, error vector magnitude (EVM), amplitude error, phase error, pseudo-code consistency, phase deviation, phase loss, S curve offset and delay stability. By changing an ideal pseudo-code generating mode, common spread spectrum signals such as binary phase shift keying (BPSK) and quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK) can be evaluated, various special navigation signals such as binary offset carrier (BOC), alternate binary offset carrier (AltBoc), time division alternate binary offset carrier (Td-AltBoc) and time multiplexed binary offset carrier (TMBOC) can be evaluated; and by the high-precision evaluation of pseudo-code phase and carrier phase, each evaluation item of the navigation signals can be highly precisely evaluated, and the requirement on navigation satellite effective load testing can be met.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
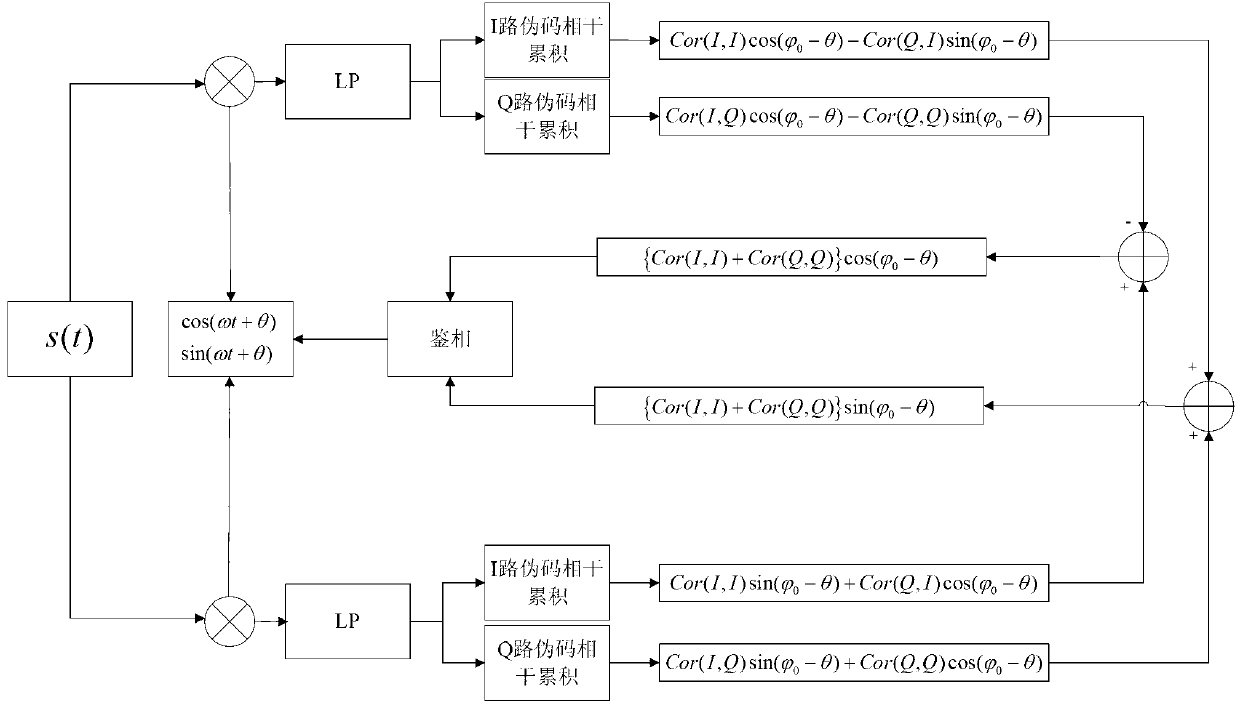
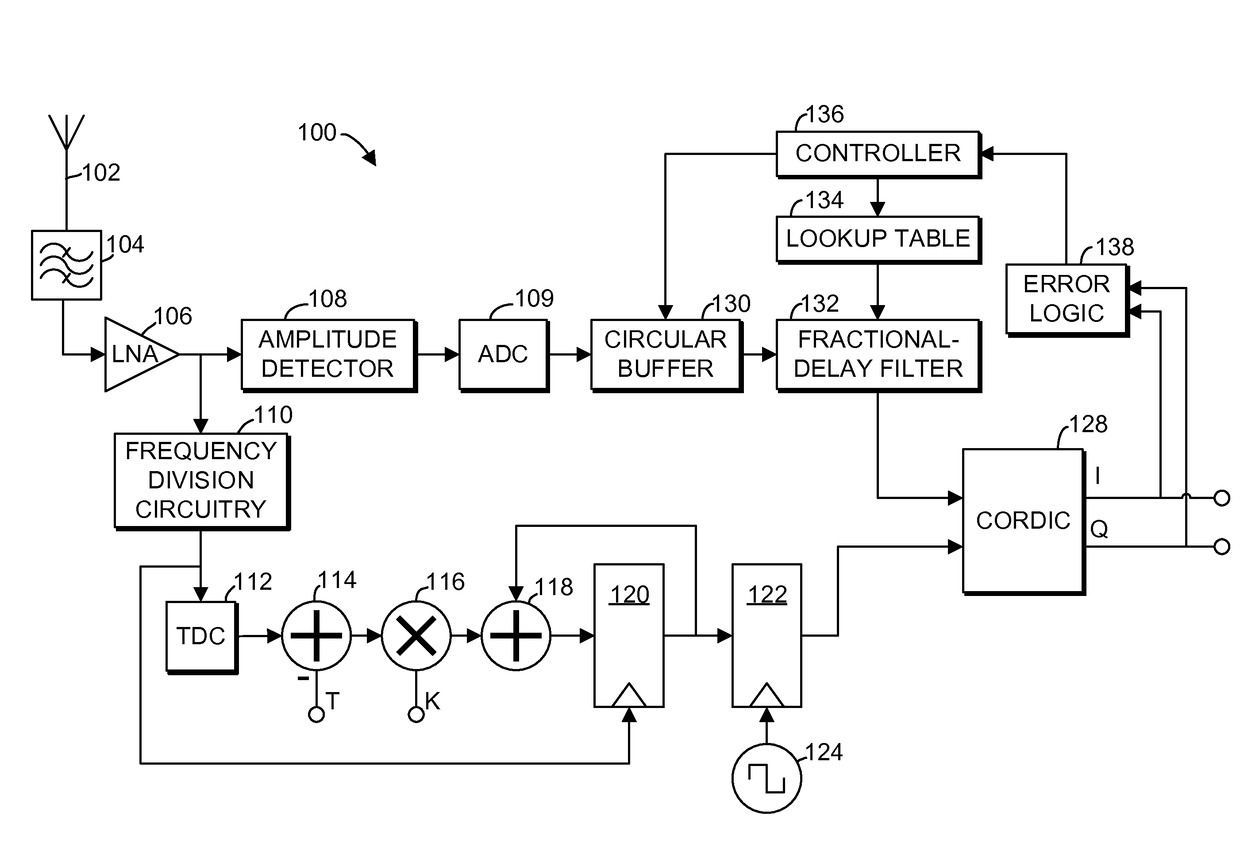
Method and apparatus for polar receiver with phase-amplitude alignment
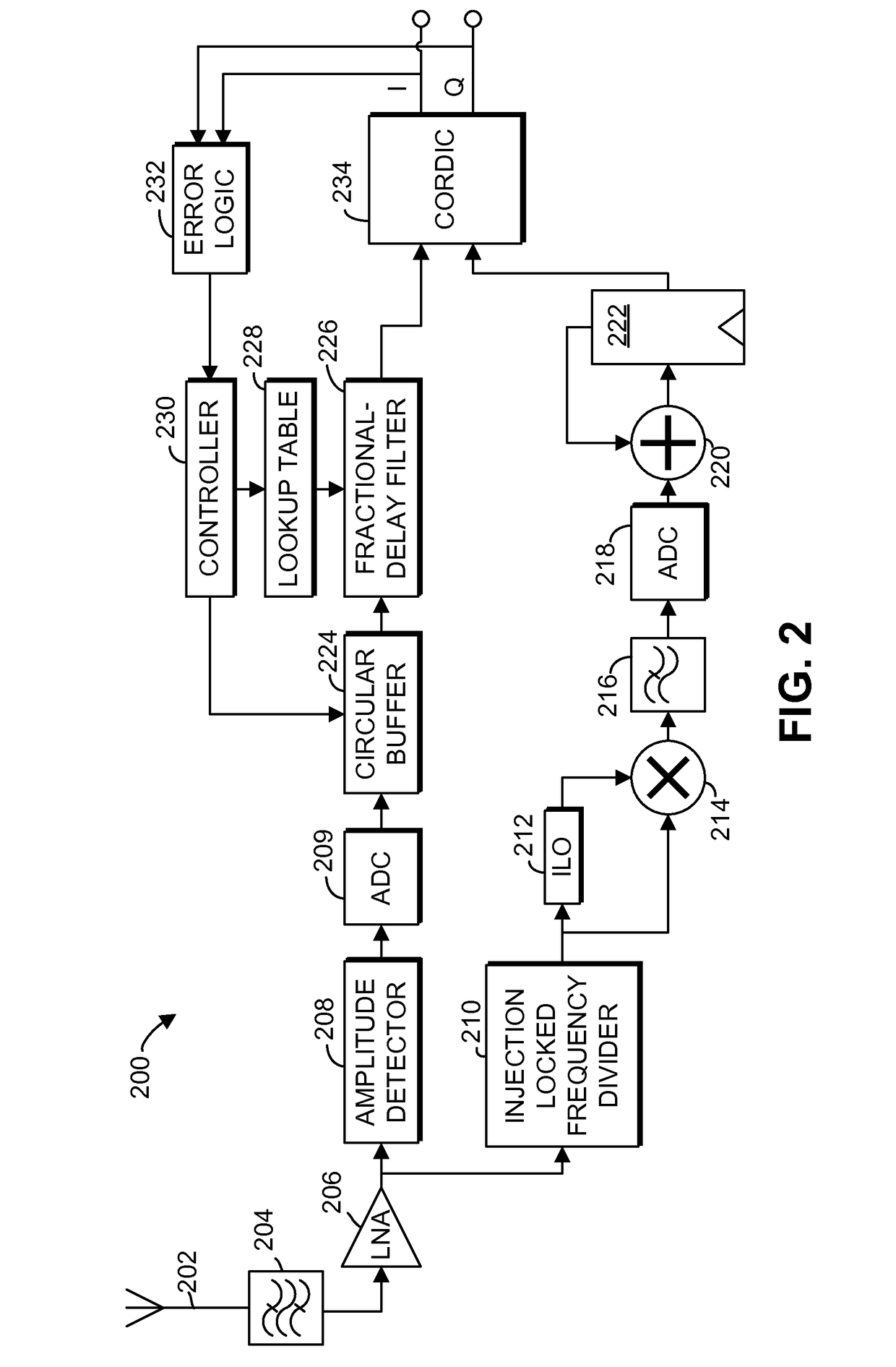
Systems and methods are provided for aligning amplitude and phase signals in a polar receiver. A receiver generates digital amplitude and phase signals representing the amplitude and phase of a modulated input signal. At least one of the digital signals is filtered using a fractional delay filter with a variable delay. The delay of the fractional delay filter is adjusted to align the amplitude and phase signals. In some embodiments, an error vector magnitude is determined by comparing in-phase and quadrature values of the signal with values corresponding to a constellation point, and the delay is adjusted based on the error vector magnitude. The fractional delay filter may be a finite impulse response filter with coefficients stored in a lookup table that correspond to different delays.
Owner:INNOPHASE
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing error vector magnitude calibration based on separate multi-tone measurement
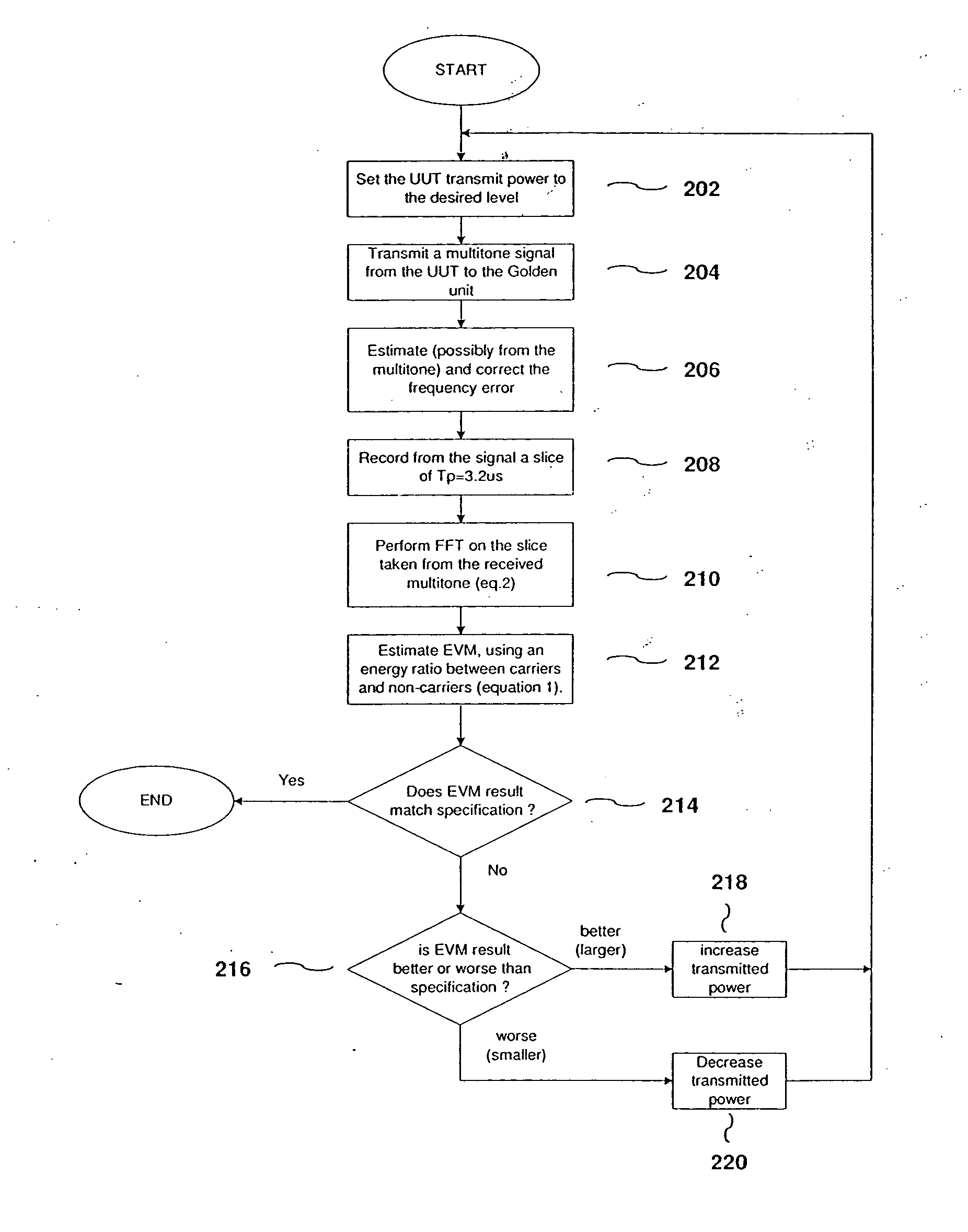
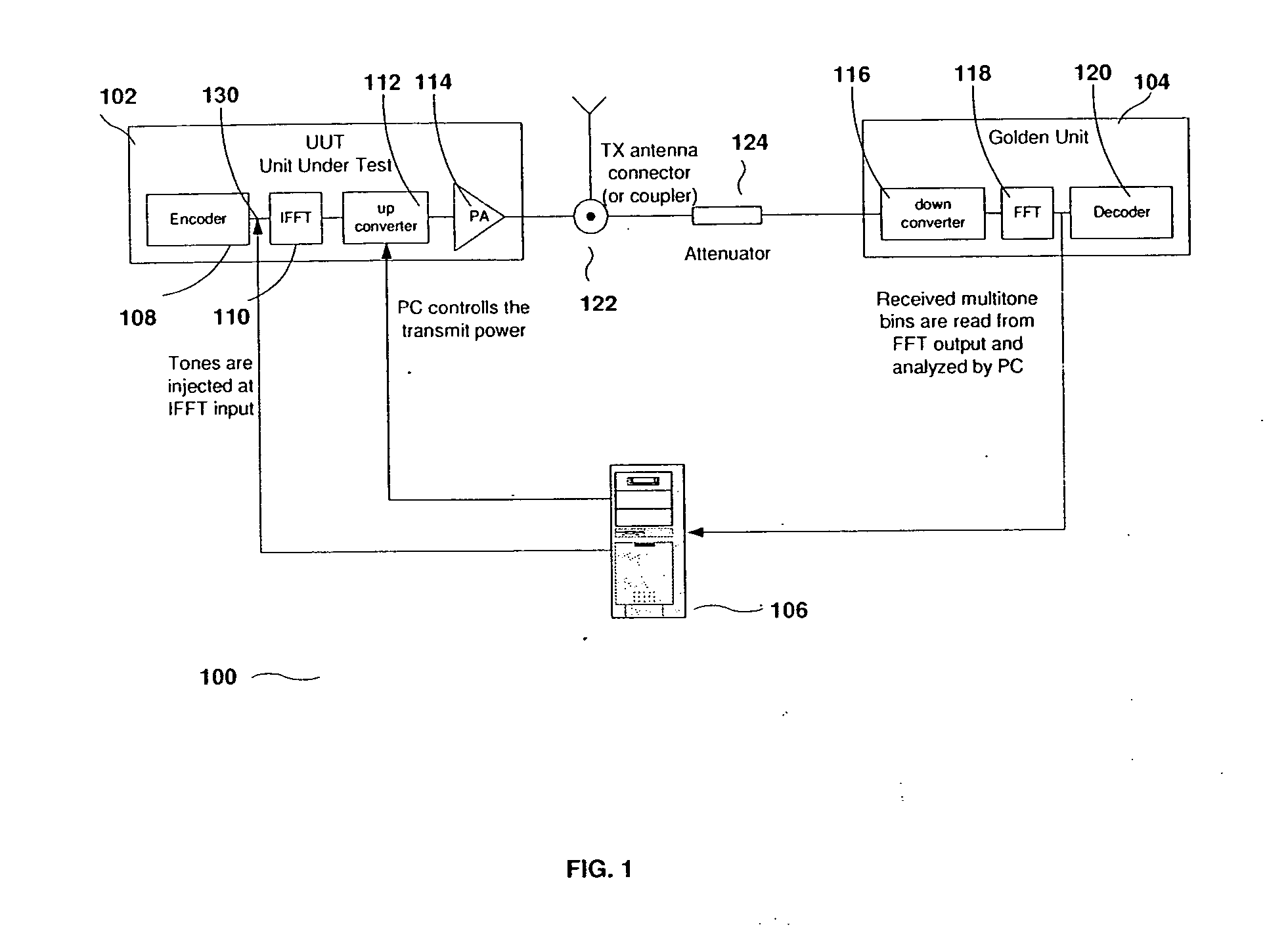
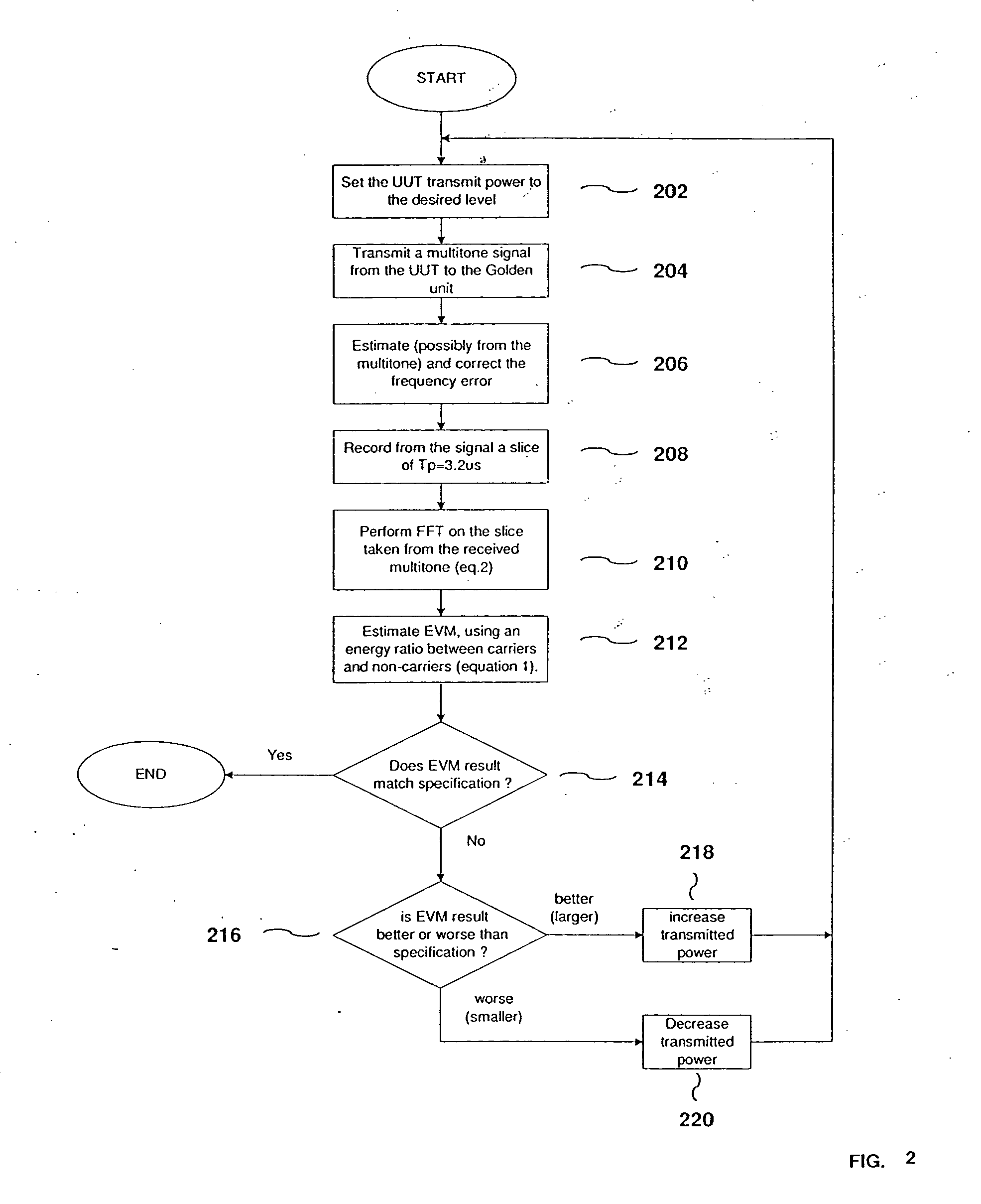
InactiveUS20050052990A1Measure quickly and accuratelyCorrect operation testingMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalError vector magnitude
A method for estimating the error vector magnitude (EVM) of an OFDM signal comprises the steps of obtaining a multi-tone EVM of a separate multi-tone signal, and using the multi-tone EVM to estimate the OFDM EVM. The multi-tone signal is designed to have carriers that occupy a small fraction of OFDM bins, and its EVM is estimated from the ratio of sums of full bin energies and empty bin energies.
Owner:ENVARA
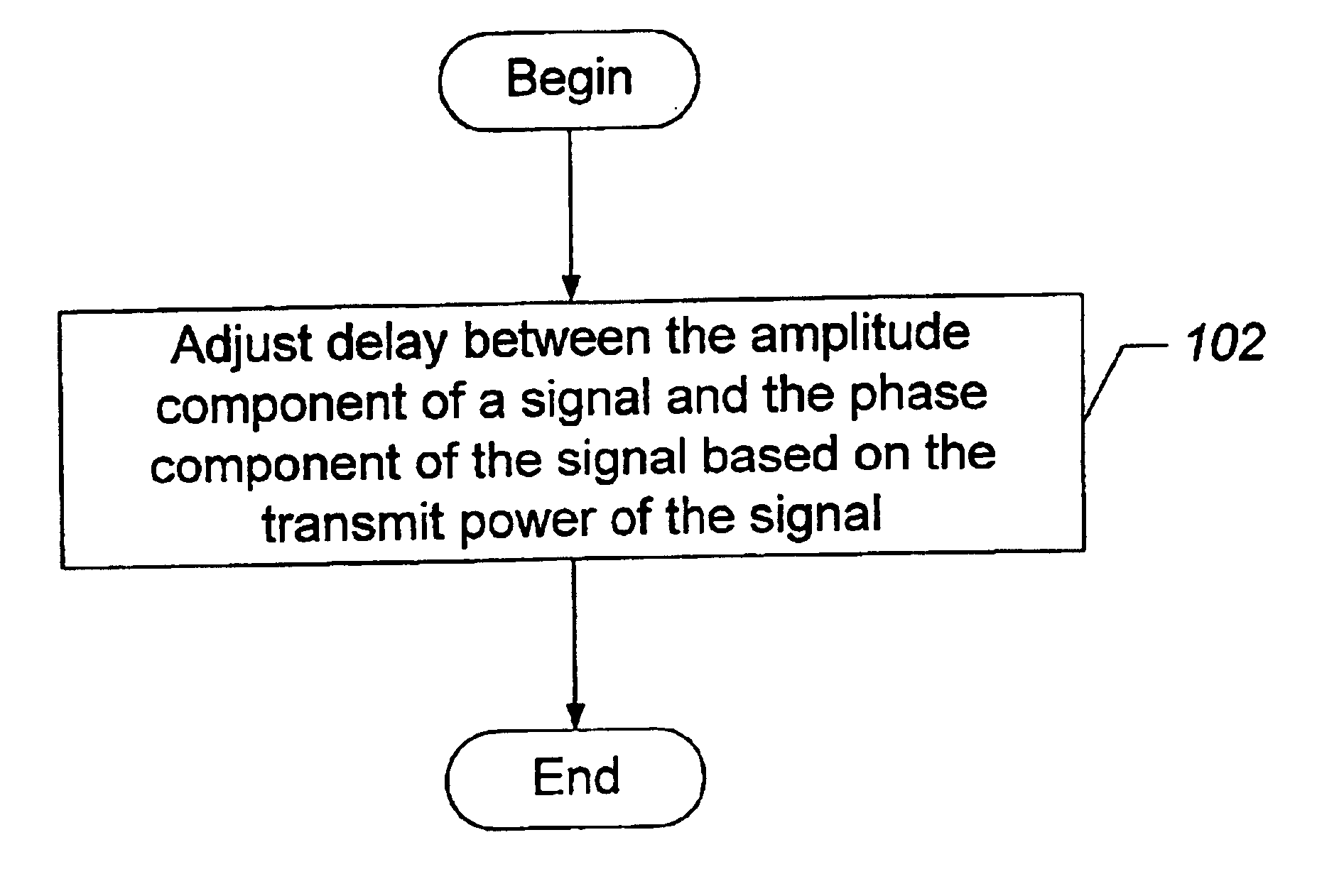
Methods, transmitters, and computer program products for transmitting a signal by adjusting a delay between an amplitude component of the signal and a phase component of the signal based on the transmission power
InactiveUS6909757B2Correction can not be performedResonant long antennasCarrier regulationAdjacent channel power ratioError vector magnitude
Embodiments of methods, transmitters, and computer program products are provided for transmitting a signal by adjusting a delay between an amplitude component of the signal and a phase component of the signal based on the transmission power. Error vector magnitude and adjacent channel power ratio are two common criteria used in evaluating transmitter performance. By adjusting the delay between the amplitude component of the transmitted signal and the phase component of the transmitted signal, the error vector magnitude and / or the adjacent channel power ratio may be reduced. The particular delay value that provides the best error vector magnitude performance and / or adjacent channel power ratio performance may differ based on the transmission power level. Therefore, the delay value is adjusted based on the transmission power.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
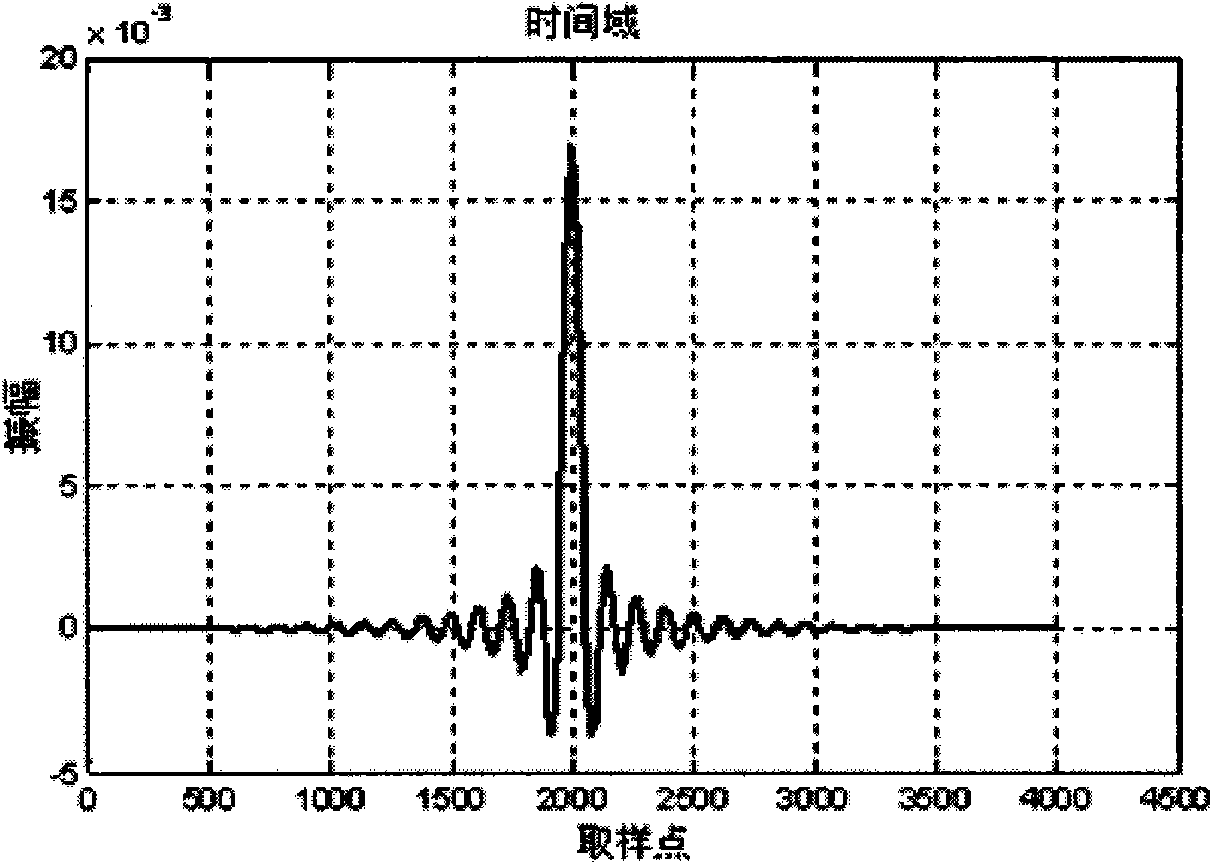
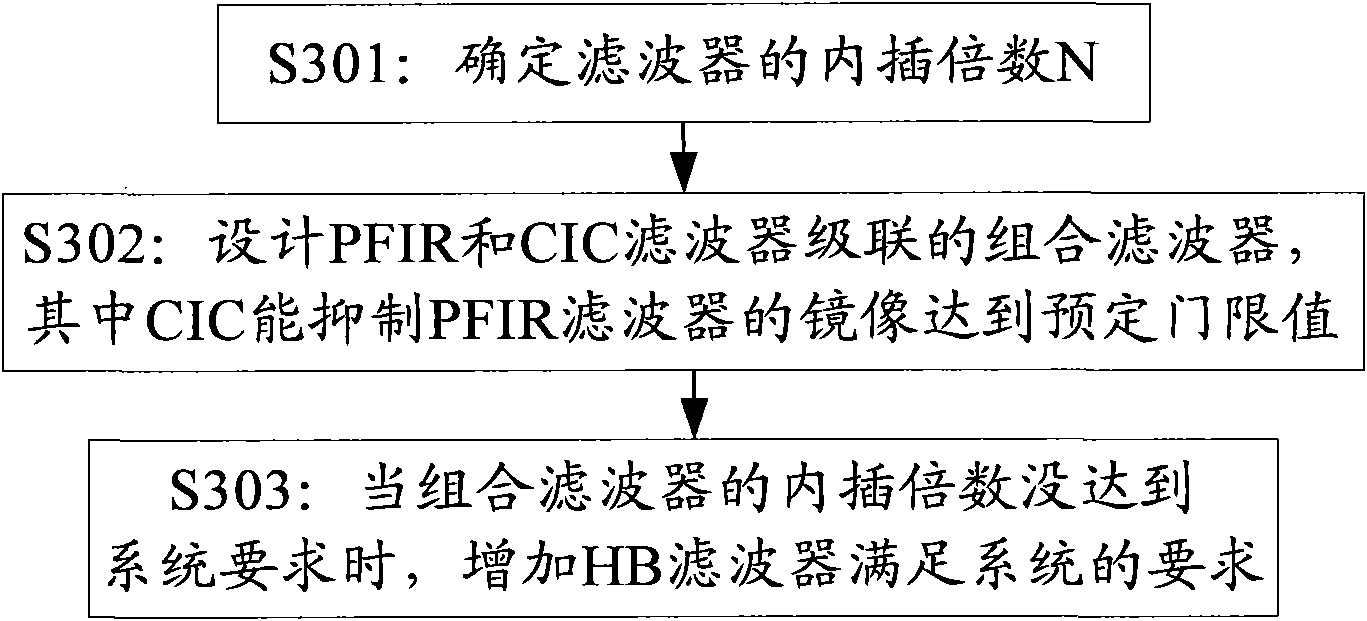
Design method and design device for cascade filter
ActiveCN102098025ASmall distortionGood band-limiting characteristicsDigital technique networkFinite impulse responseAdjacent channel power ratio
The embodiment of the invention provides a design method for a cascade filter, which comprises the following steps of: determining the interpolation times N of the filter; calculating the filter coefficient of a programmable finite impulse response (PFIR) filter, and obtaining a design scheme of a cascade combined filter of PFIR and cascaded integrator comb (CIC) filters; and when the interpolation times of the cascade combined filter of the PFIR and CIC filters does not reach the predetermined times, designing a half band (HB) filter, so that the filter performance of the cascade combined filter of the PFIR and CIC filters and the HB filter meets the interpolation times requirement of a system, and the design of the PFIR filter is realized by adopting a multistage design scheme. According to the embodiment provided by the invention, by adopting the design device for the multistage filter, the order of the designed filter is in a realizable range of the FPGA, and the indexes such as interpolation times of signals, error vector magnitude (EVM), adjacent channel power ratio (ACPR) and the like can meet the protocol requirement. Moreover, according to the technical scheme provided bythe invention, the resource consumption of the filter is also lower than that of the design method for the traditional filter, and the use of FPGA hardware resources can be effectively reduced.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Method and system for minimizing effects of transmitter impairments in multiple input multiple output (MIMO) beamforming communication systems
ActiveUS7664200B2Diversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationCommunications systemError vector magnitude
Aspects of a method and system for minimizing effects of transmitter impairments in multiple input multiple output (MIMO) beamforming communication systems are presented. In one aspect of a system for minimizing effects of transmitter impairments, a MIMO transmitter may enable nulling of transmitter-induced noise by adjusting at least a portion of a plurality of signals transmitted based on a transmitter error vector magnitude (EVM). The transmitter may enable transmission of the plurality of signals subsequent to the nulling. In another aspect of a system for minimizing effects of transmitter impairments a MIMO receiver may enable nulling of transmitter-induced noise contained in a plurality of received signals based on a transmitter EVM. Each of the plurality of received signals may include information contained in a plurality of spatial streams. The receiver may enable detecting estimated values for the information contained in the plurality of spatial streams based on the nulling.
Owner:BELL NORTHERN RES LLC
Digital communications test system for multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) systems
ActiveUS20110096821A1Improve test throughputSecret communicationTransmission monitoringComputer hardwareError vector magnitude
Owner:LITEPOINT CORP
Method and apparatus for automated correlation of digital modulation impairment
InactiveUS7016401B1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Image resolution
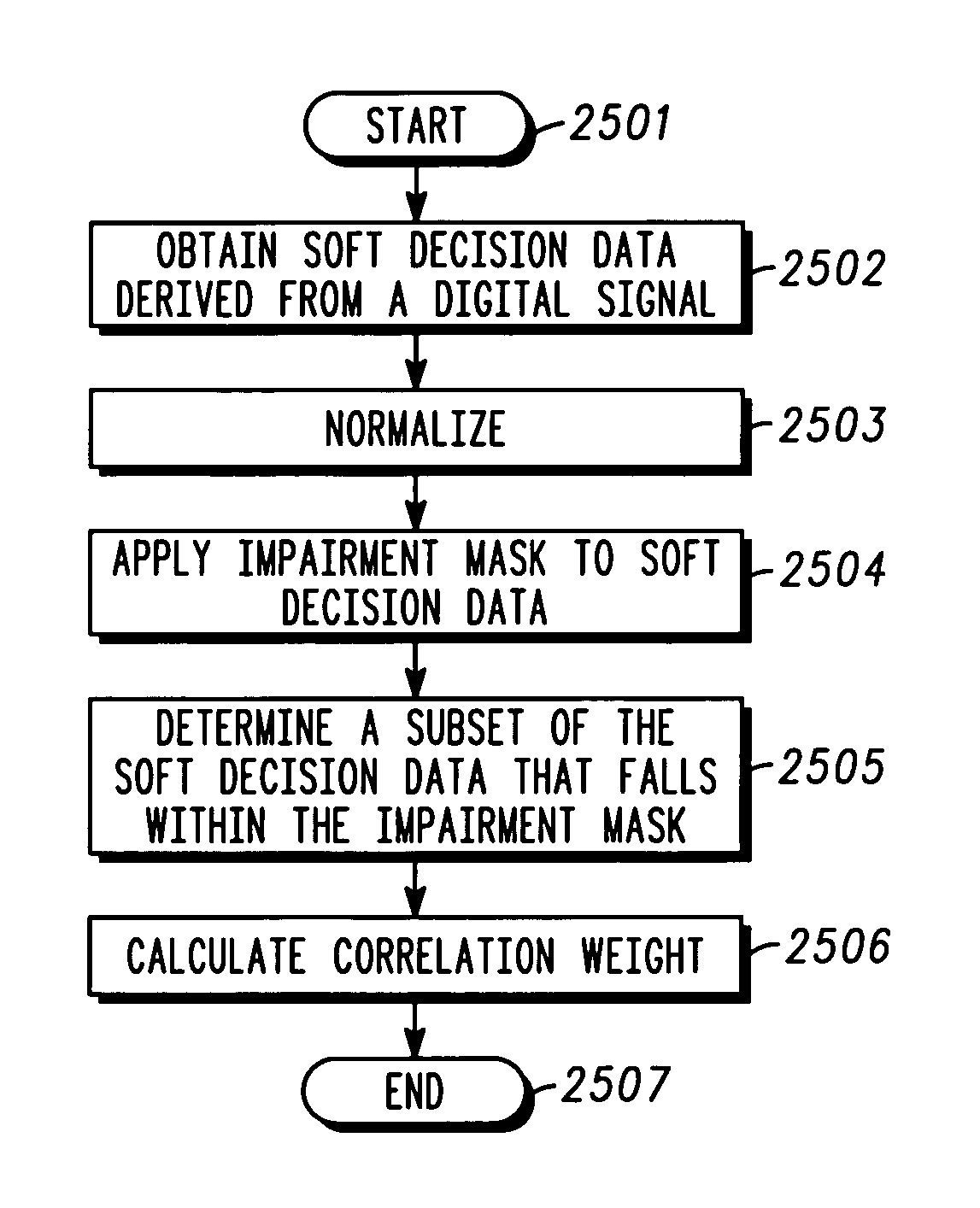
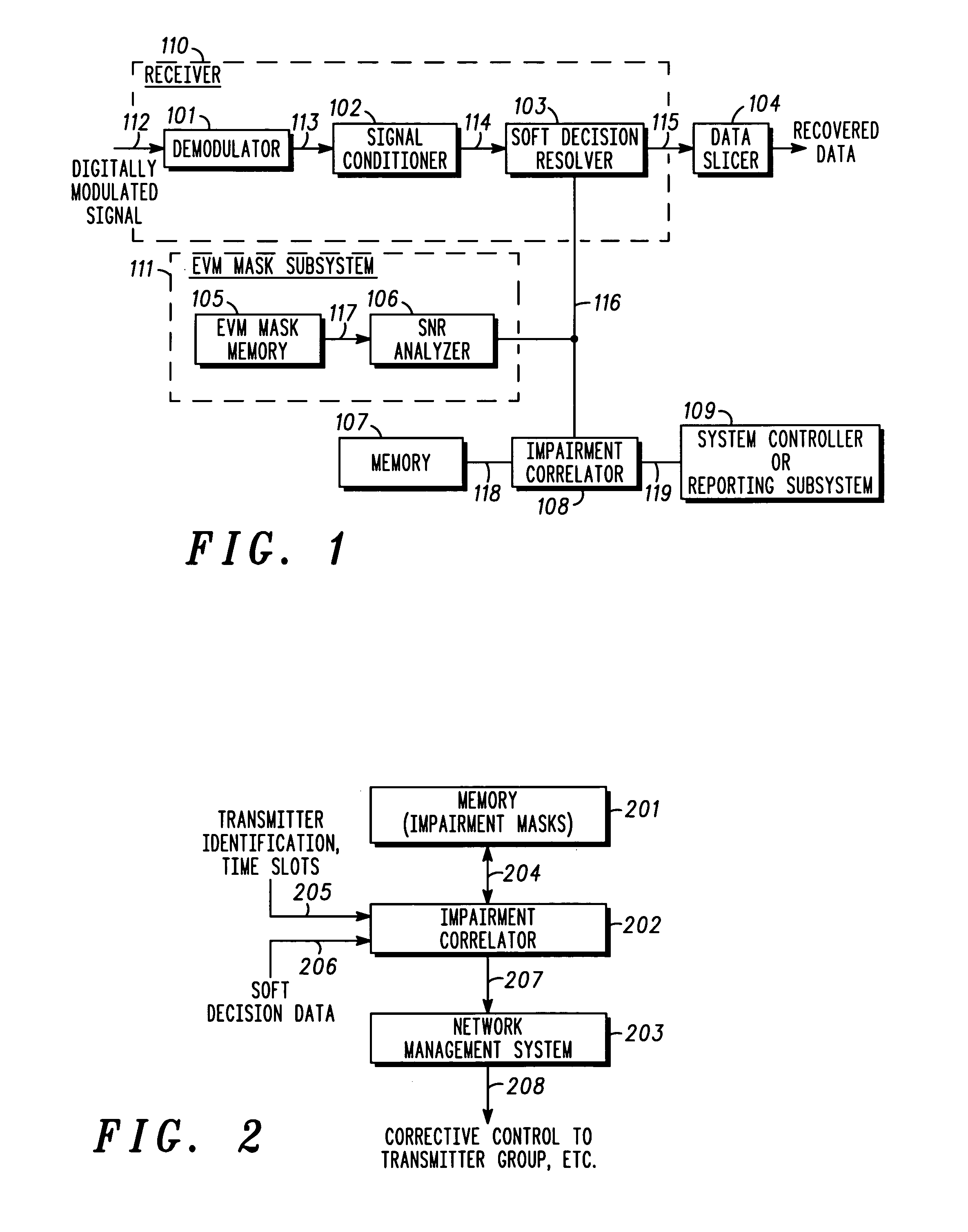
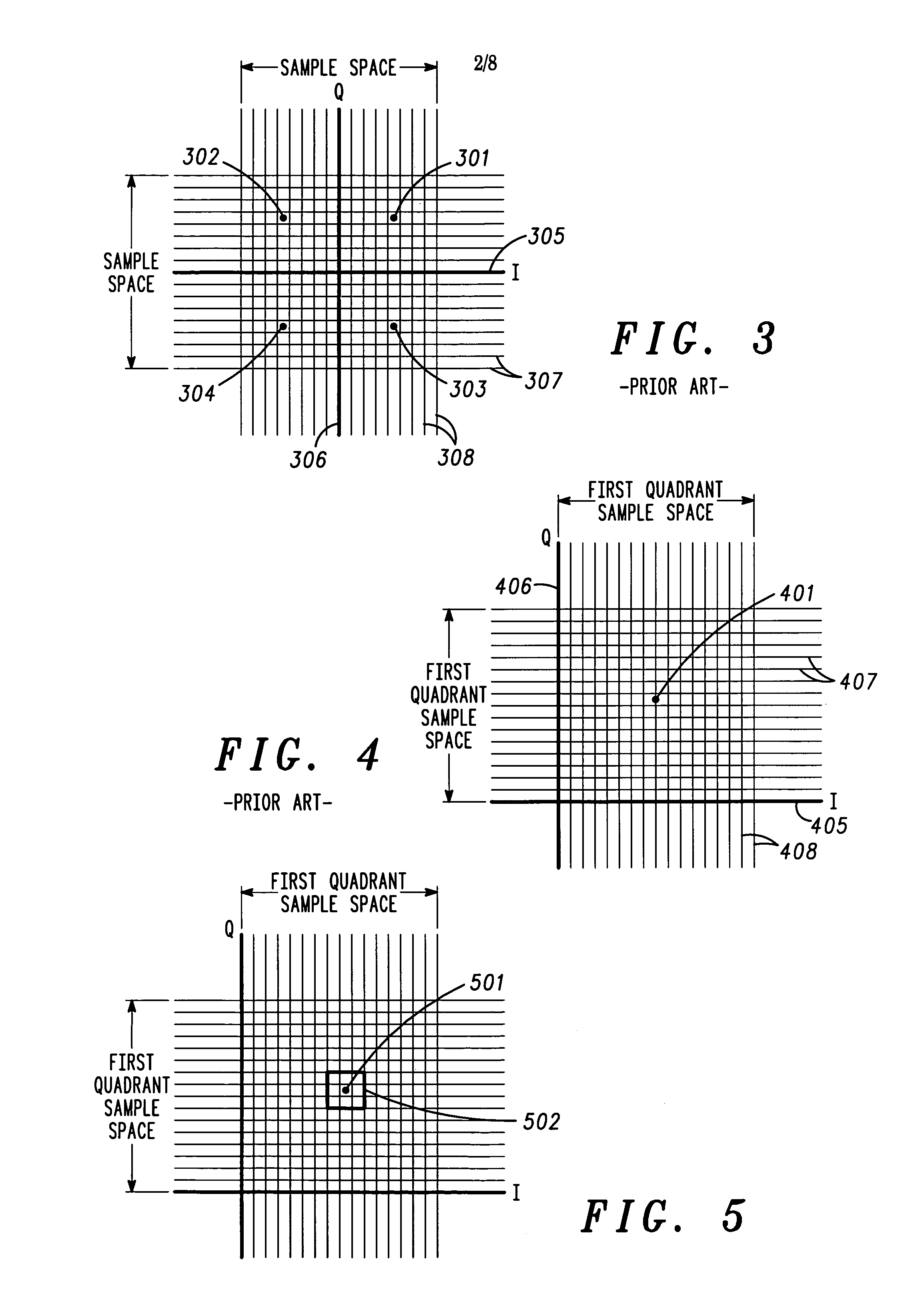
A method and apparatus for automated correlation of digital modulation impairment is described. The technique obtains soft decision data (116, 2502) and extracts signal space location information of sufficient resolution to distinguish different types of impairment to a digitally modulated signal. The technique applies an error vector magnitude mask (117, 502) and determines the signal-to-noise ratio of the digitally modulated signal. The technique applies impairment masks (118, 2504) and provides a characterization (119) of impairment affecting the digitally modulated signal (112). The technique determines a subset of the soft decision data (116, 2502) that falls within the impairment masks (118, 2505) and calculates correlation weights (2506). The technique may be used to identify, isolate, and classify different types of impairment. Given sufficient data collection, sources of impairments may be determined precisely.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
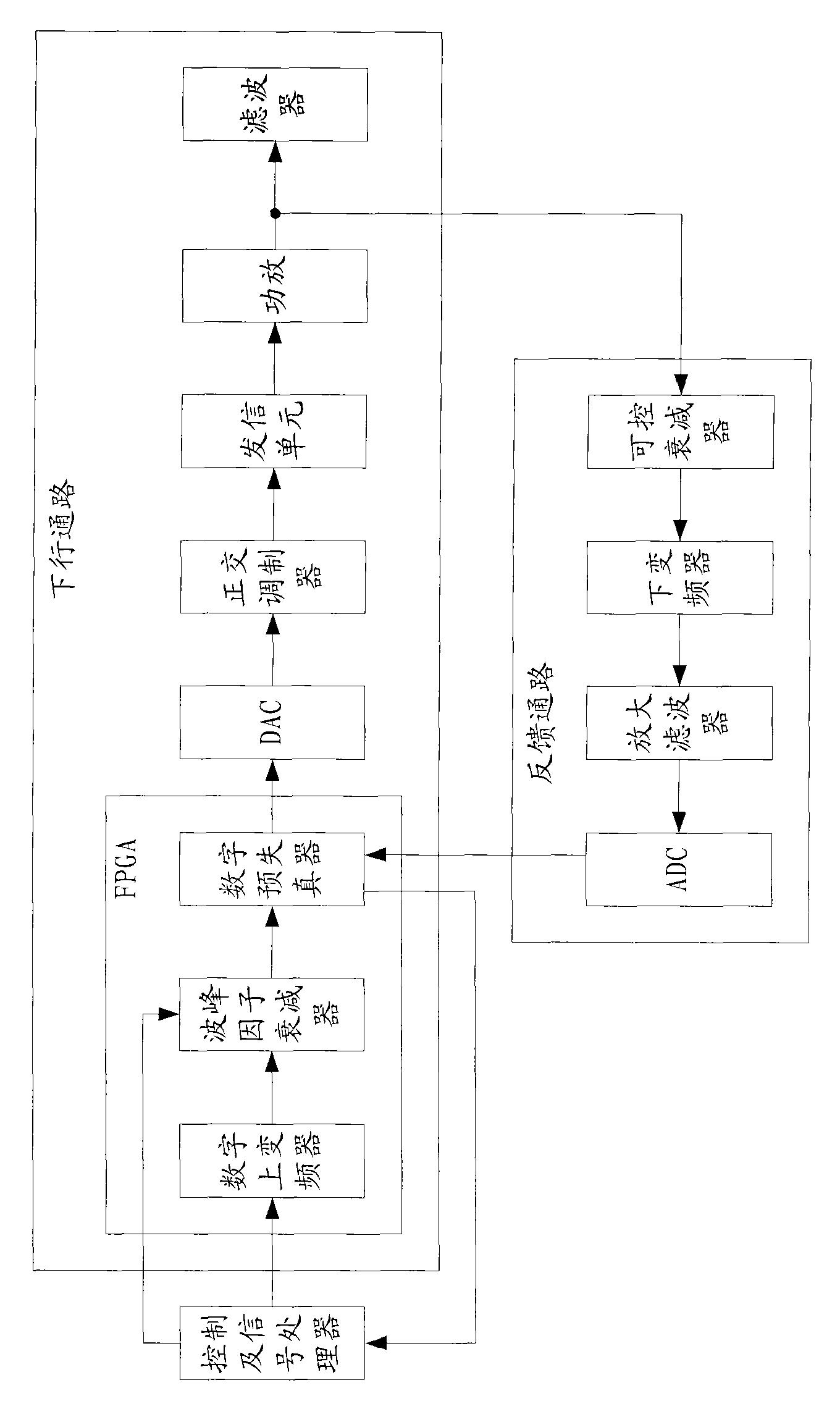
Method for adaptively adjusting CFR threshold and radio frequency zooming system
ActiveCN101562478ADetect and warn of corruptionGood amplifier performancePower managementRadio transmission for post communicationTD-SCDMAError vector magnitude
The invention is suitable for the field of TD-SCDMA communication, and provides a method for adaptively adjusting CFR threshold and a radio frequency zooming system. The method comprises the following steps that: A, capturing a downlink time slot signal from signals fed back to digital pre-distortion (DPD) from power amplification; B, analyzing and calculating an output index of the power amplification from the time slot signal, wherein the index at least comprises an error vector magnitude (EVM); and C, judging whether the index meets the preset standard, and if so, returning and carrying out the step A, otherwise, according to the preset stepping, adjusting the CFR threshold and returning to carry out the step A. The method can detect the index of the PA output signal in real time by utilizing a feedback loop of the DPD, and adaptively adjusts the CFR threshold according to the index to achieve the optimization of the power amplification performance.
Owner:成都芯通软件有限公司
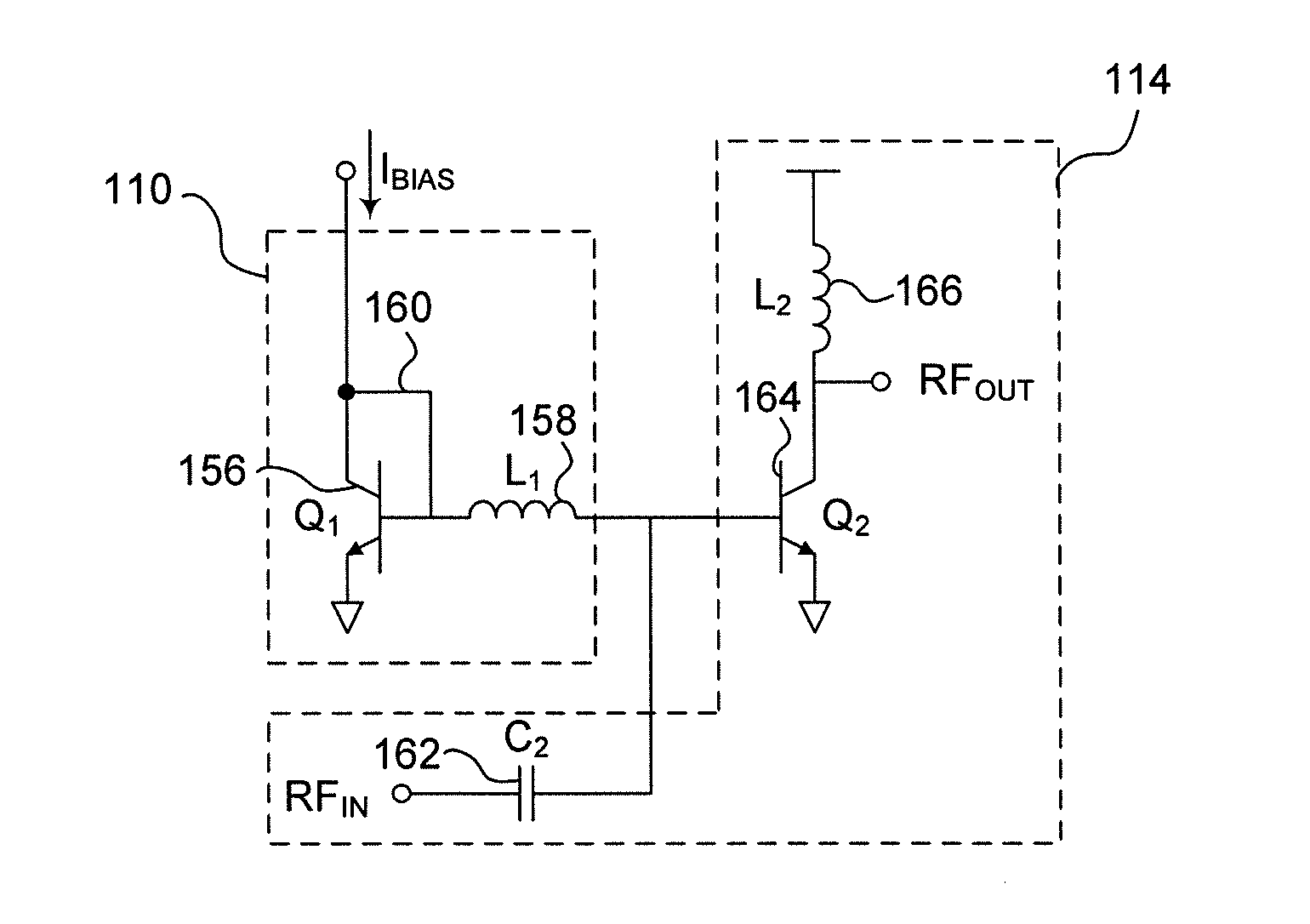
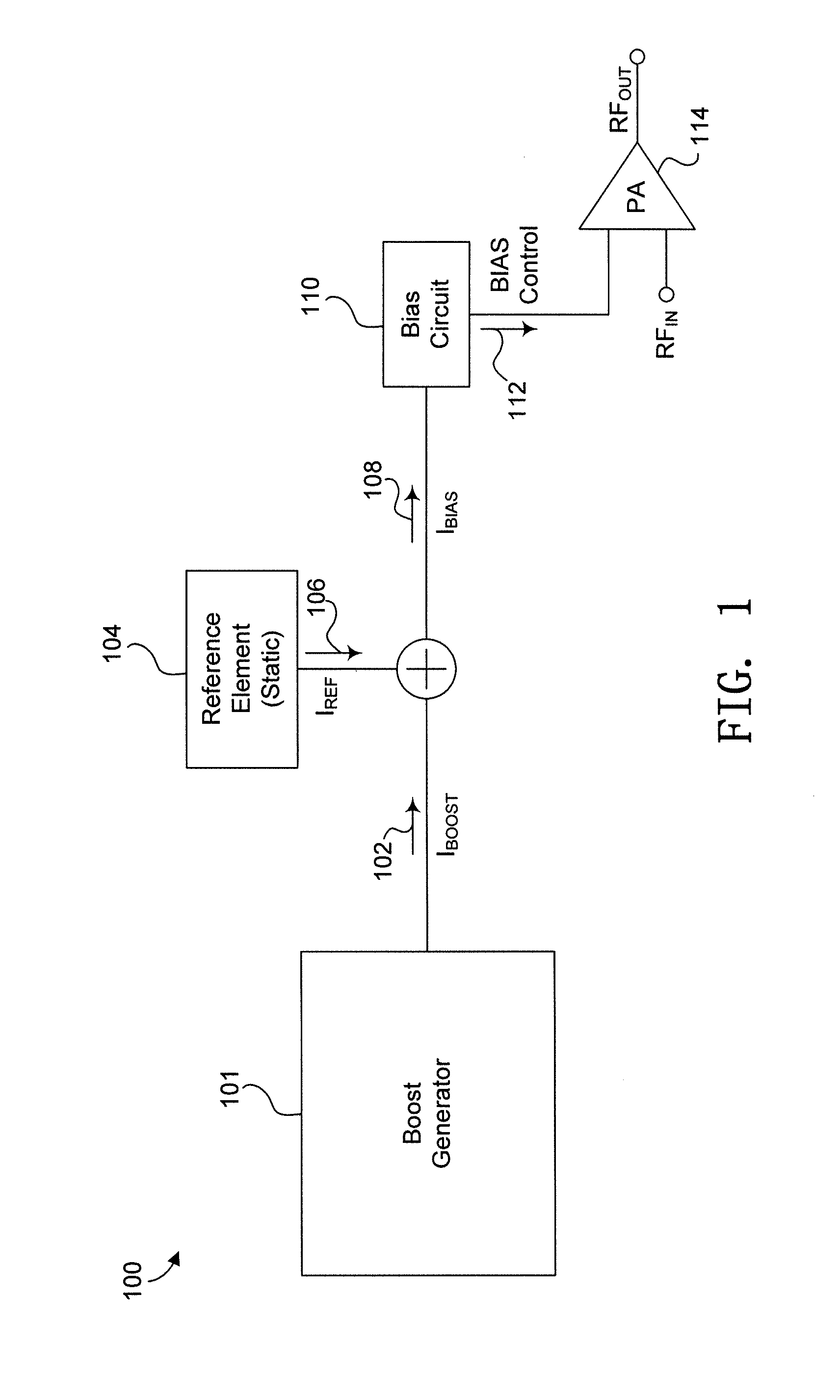
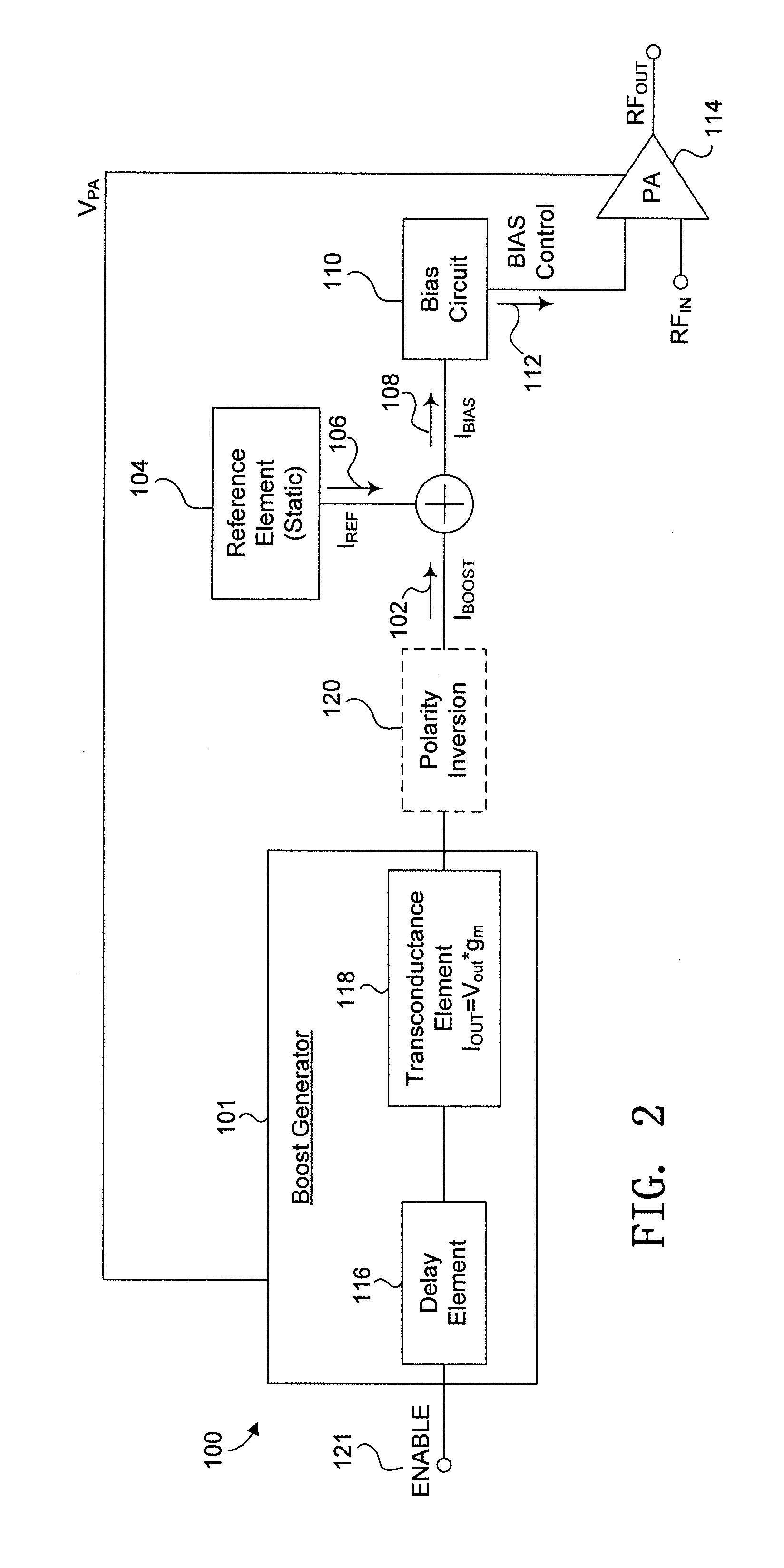
Integrated start-up bias boost for dynamic error vector magnitude enhancement
Devices and methods for correcting for start-up transients in integrated power amplifiers are disclosed. A delay element is arranged to produce a delay waveform signal that is responsive to an input voltage signal. A transconductance element has an input that receives the delay waveform signal and is arranged to provide an output boost current that is based on the delay waveform signal and a gain of the transconductance element. A reference element provides an output bias current that is responsive to a static reference current and the boost current. A bias element has an input that receives the bias current and is arranged to provide a bias control output. A power amplifier is responsive to the bias control output and is arranged to provide an amplified power output. In some examples, the boost current is adjusted based on a supply voltage and an input power of the power amplifier.
Owner:MICROSEMI
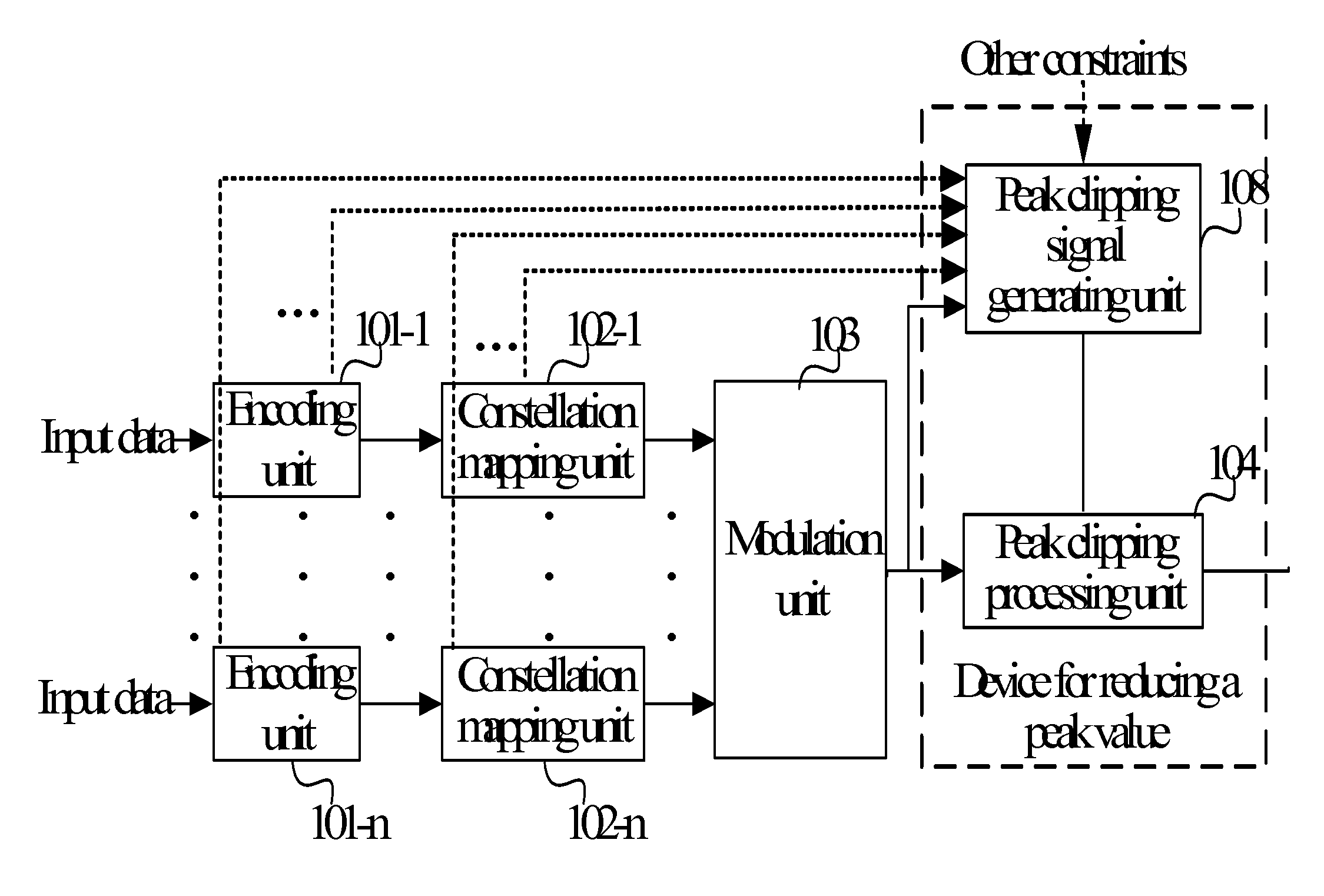
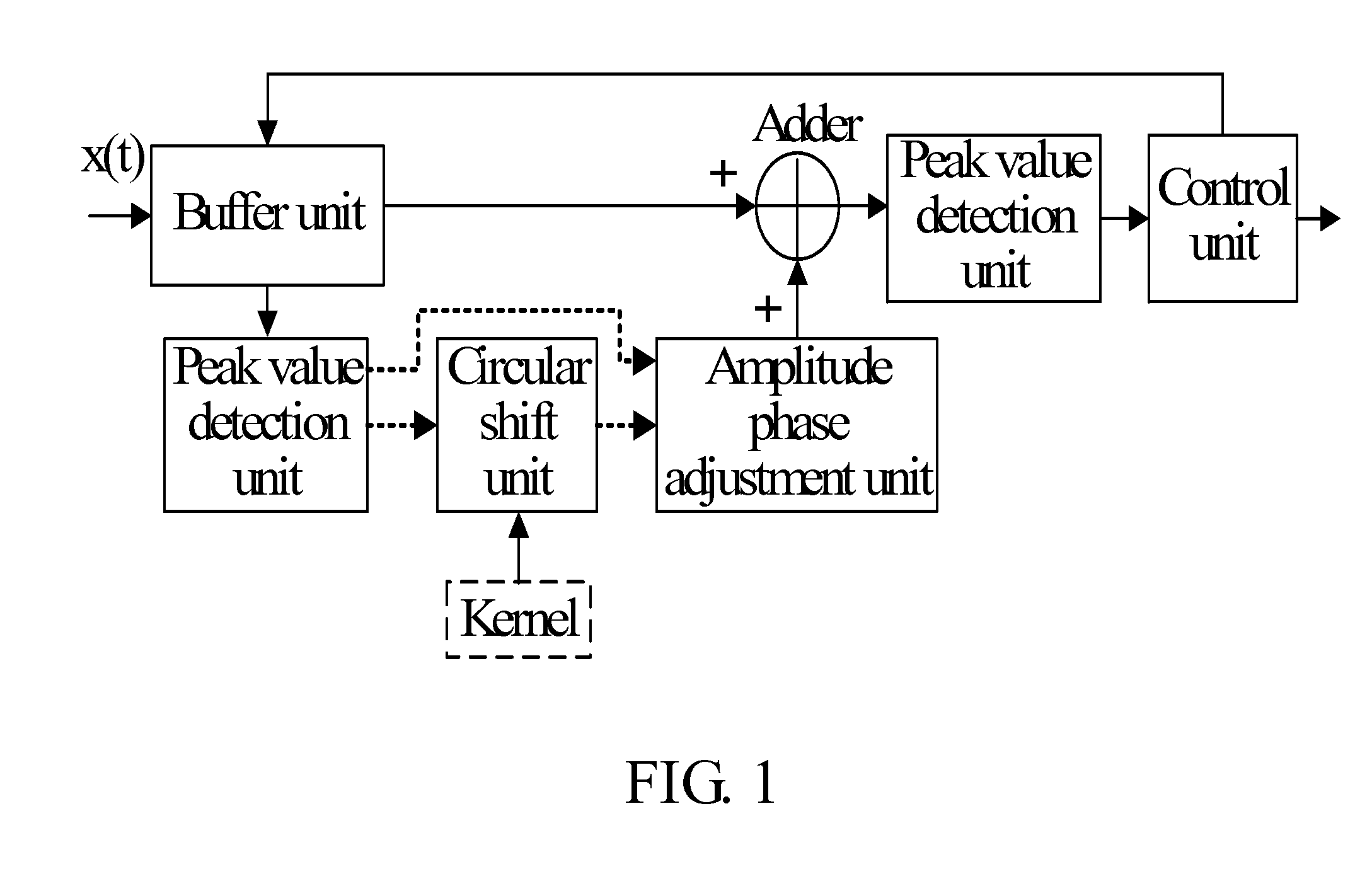
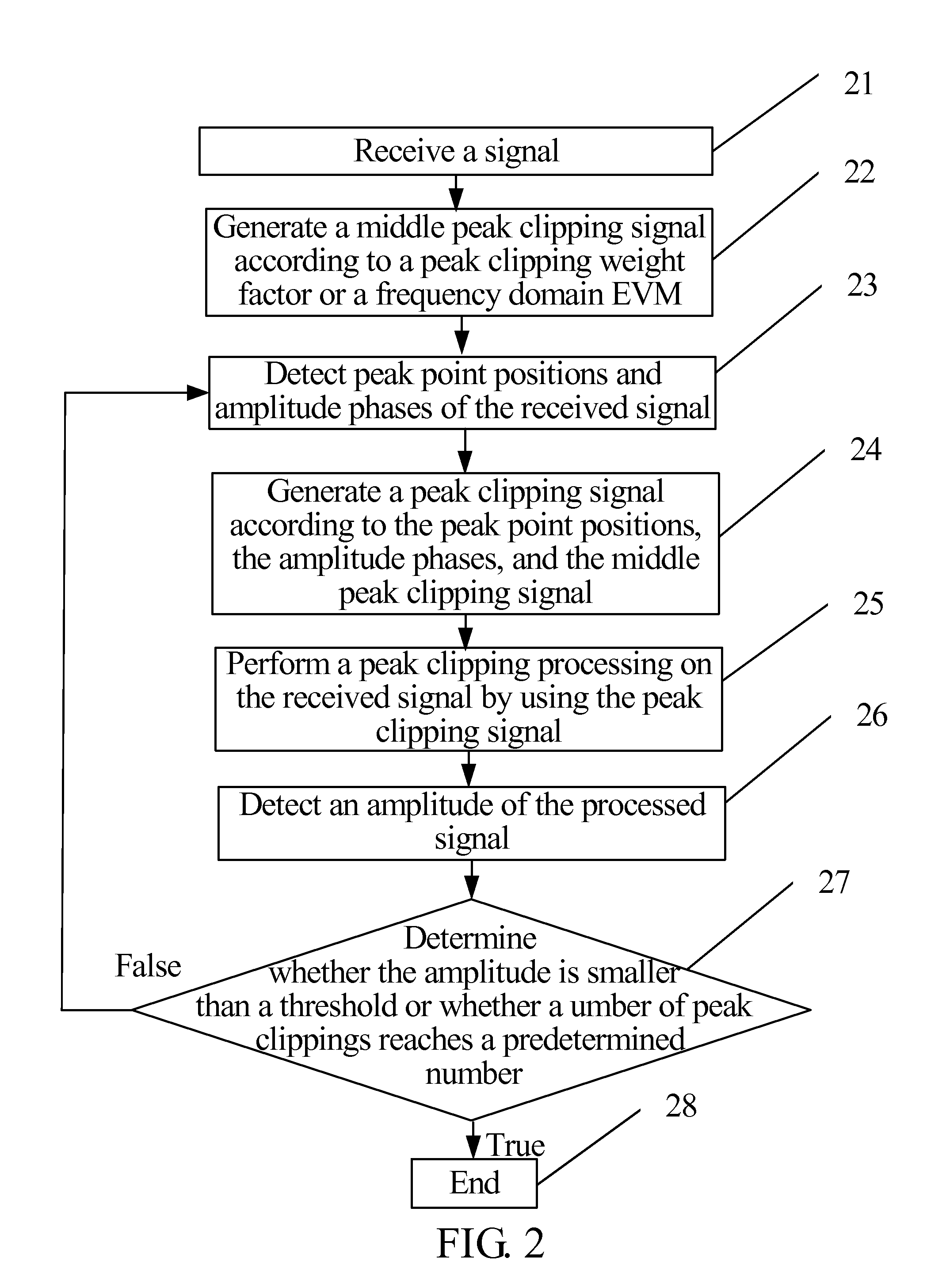
Method and device for reducing signal peak value and transmitting device
InactiveUS20100020895A1Improve system performanceImprove anti-interference abilityModulated-carrier systemsPulse demodulatorCarrier signalError vector magnitude
A method and a device for reducing a signal peak value are adapted to solve a problem that overall performance of a system is significantly degraded caused by allocating a same weight to each sub-carrier so as to averagely distribute a peak clipping noise to each sub-carrier. The method includes: receiving a signal (21); and performing a peak clipping processing on the received signal by using a peak clipping signal (25). The peak clipping signal is formed according to a peak clipping weight factor and the received signal, or according to a frequency domain error vector magnitude (EVM) and the received signal. In the method, a weight of each sub-carrier is set according to the peak clipping weight factor or the frequency domain EVM during the peak clipping processing, thereby improving the overall performance of the system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Receiver and image suppression method thereof
ActiveCN102594381AError Vector Magnitude BoostBoost in-band spursTransmissionIntermediate frequencyRadio frequency signal
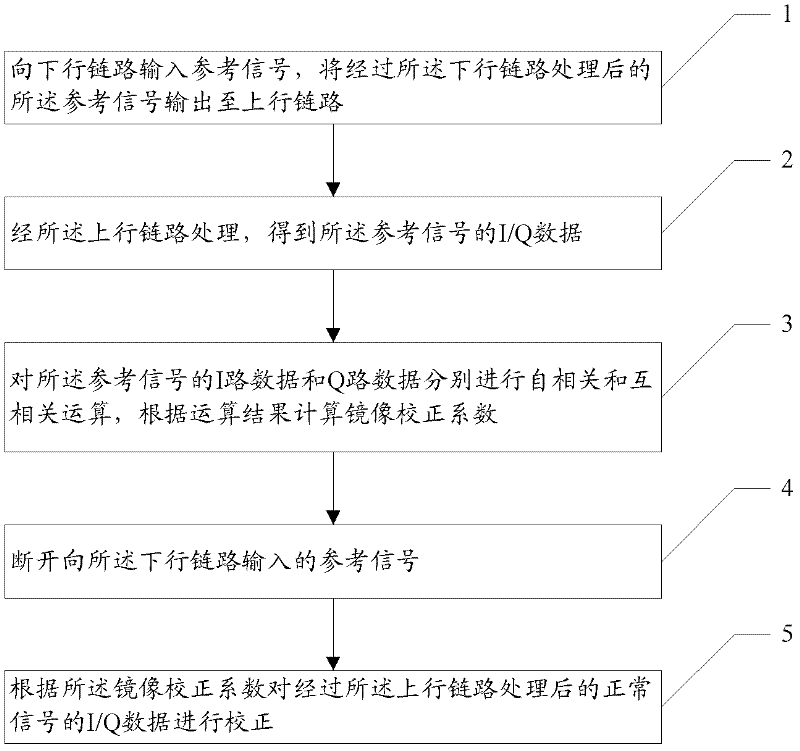
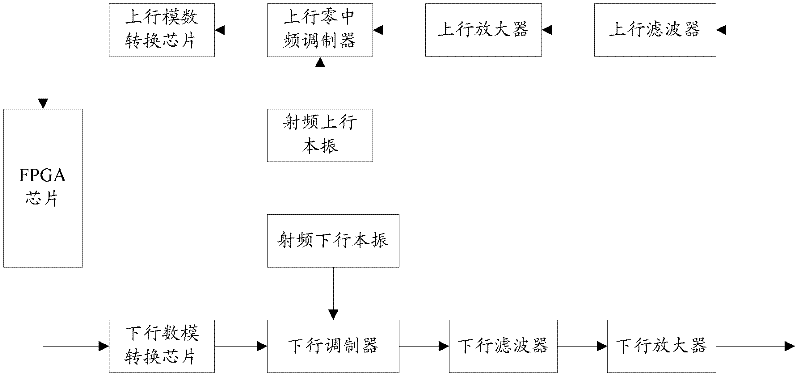
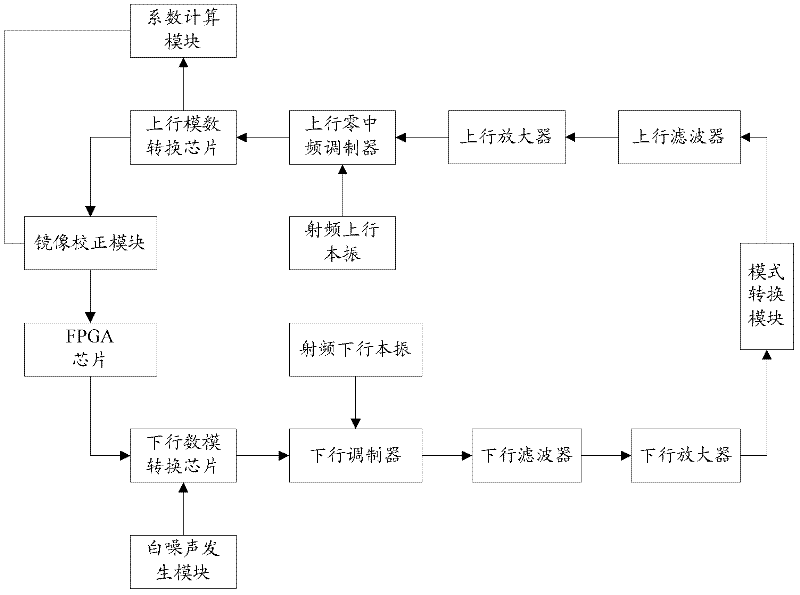
The embodiment of the invention discloses a receiver and an image suppression method thereof; after the receiver is electrified, a reference signal is input into a down link; the reference signal is processed by the down link and then is processed by an up link, and in-phase / quadrature (I / Q) data is obtained; the autocorrelation, the cross-correlation, the summing and averaging and an image correction coefficient of the obtained I / Q data are sequentially calculated, and the image correction coefficient is obtained; and the reference signal is finally cut off. Consequently, when in normal communication, after a radio frequency signal is processed by the up link, an image can be corrected according to the image correction coefficient. The method is particularly applicable to a homodyne receiver; the reference signal is preferred to be a white noise signal; and after primary image correction of an uplink homodyne modulator, the radio frequency signal carries out secondary image correction according to the image correction coefficient. Finally, the image can be corrected to -70dbm, and the error vector amplitude, in-band stray, sensitivity and other indicators of a system are improved.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
Digital signal error vector magnitude testing method, digital signal error vector magnitude testing device and digital signal error vector magnitude testing system
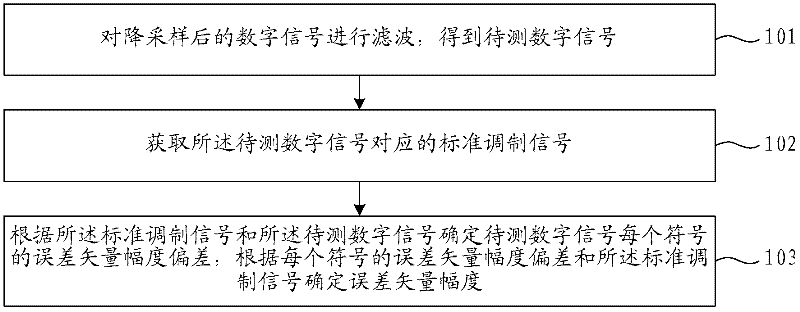
InactiveCN102377499AImprove the efficiency of obtaining EVMTransmission monitoringError vector magnitudeComputer science
The invention discloses a digital signal error vector magnitude testing method, a digital signal error vector magnitude testing device and a digital signal error vector magnitude testing system, wherein the digital signal error vector magnitude testing method includes the following steps: filtering down-sampled digital signals to obtain digital signals to be tested; obtaining standard modulation signals corresponding to the digital signals to be tested; according to the standard modulation signals and the digital signals to be tested, determining the error vector magnitude deviation of each symbol of the digital signals to be tested, and according to the error vector magnitude deviation of each symbol and the standard modulation signals, determining error vector magnitude. Since the embodiment of the invention integrates the test and calculation of error vector magnitude, the efficiency of obtaining error vector magnitude can be increased.
Owner:HISILICON TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com