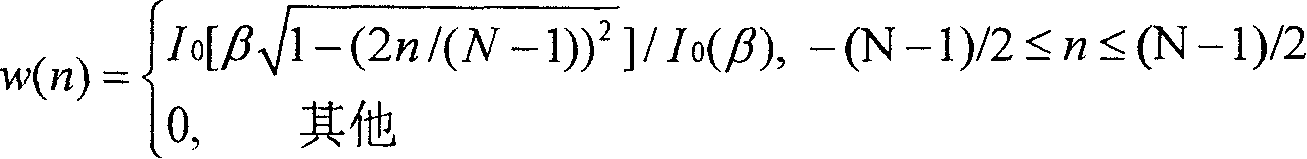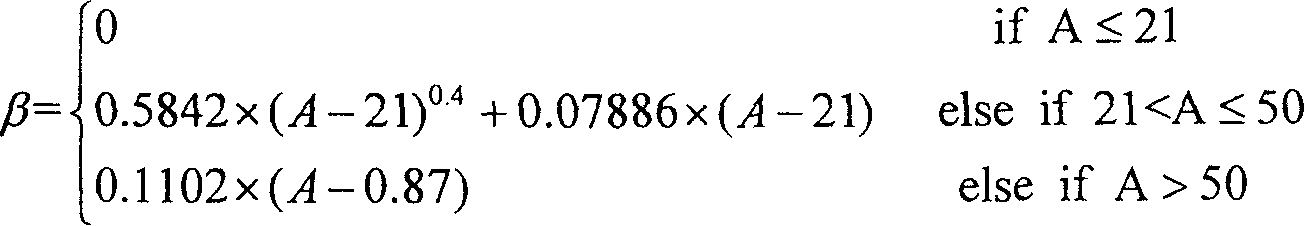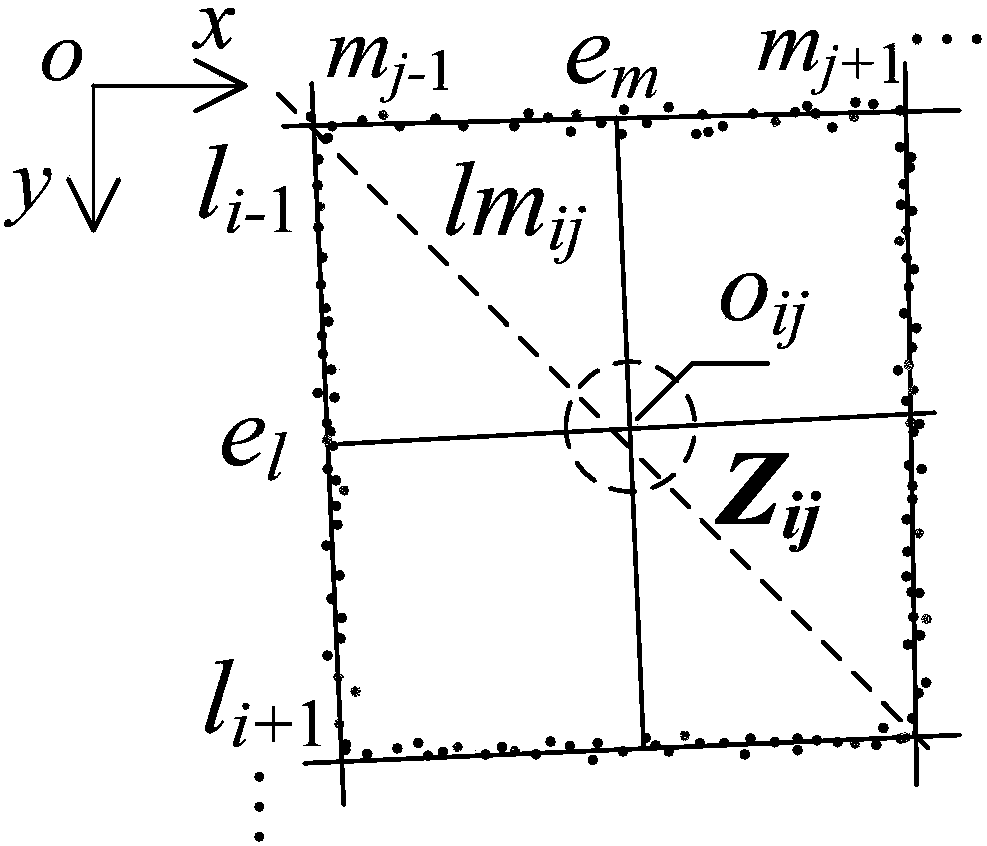Patents
Literature
75 results about "Sinc function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
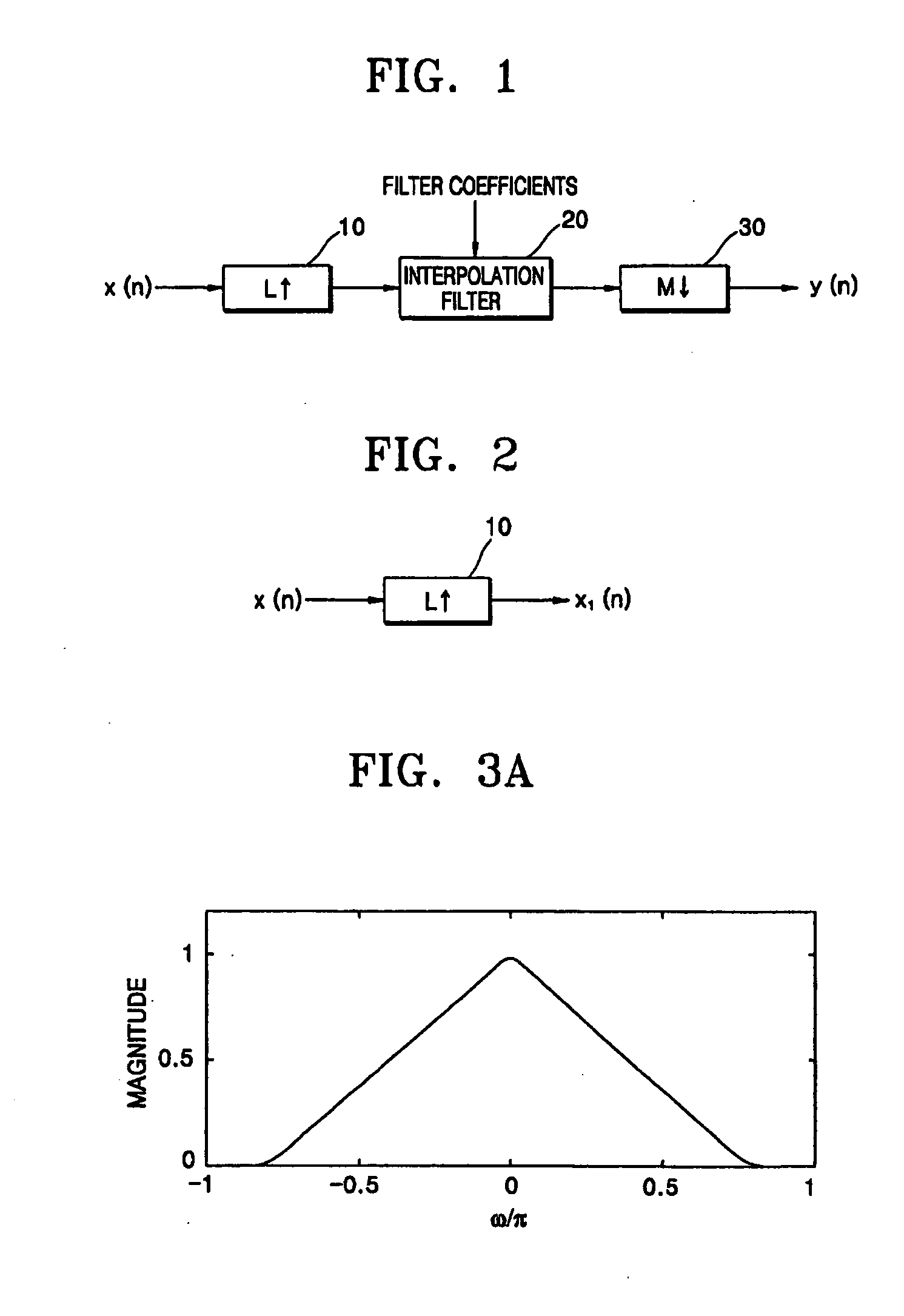
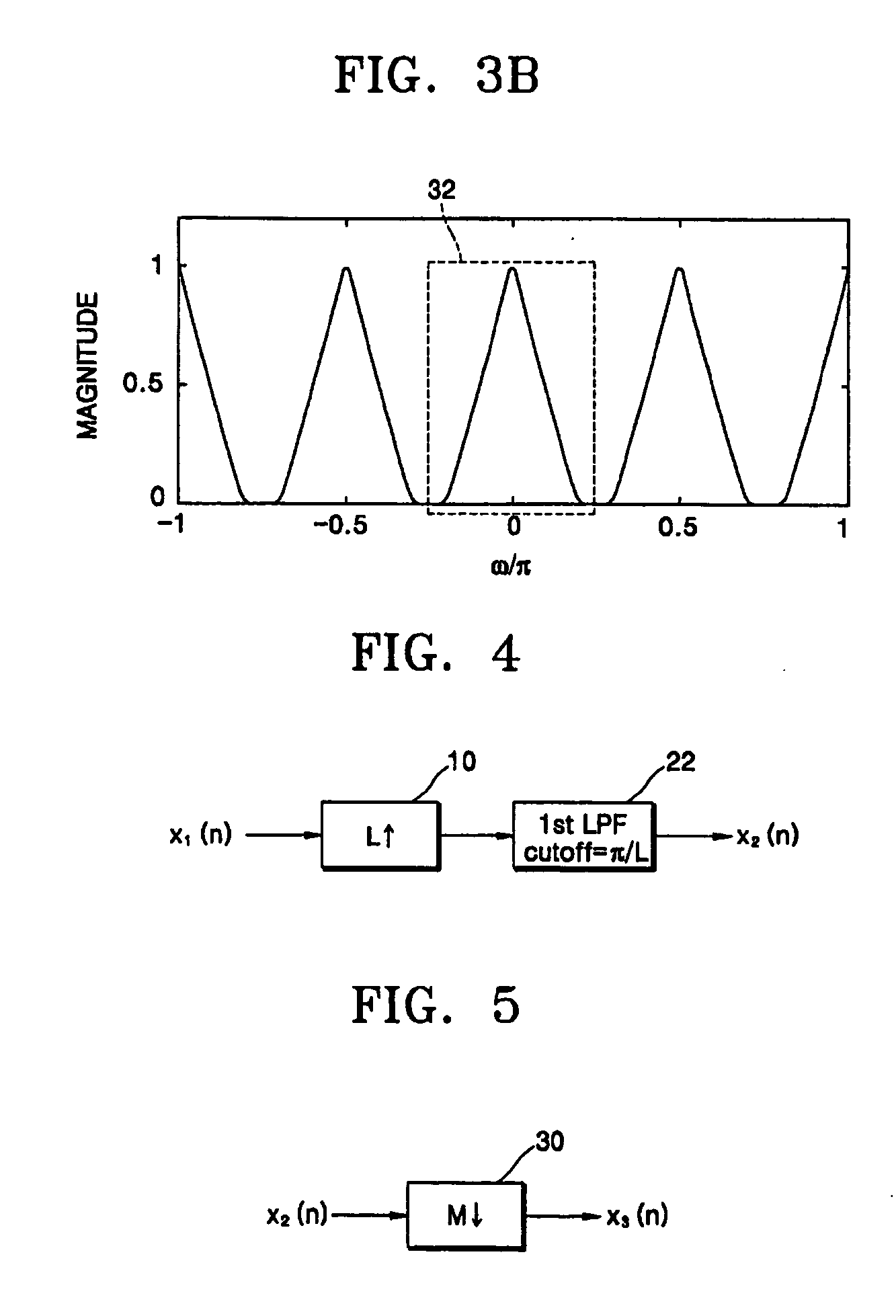
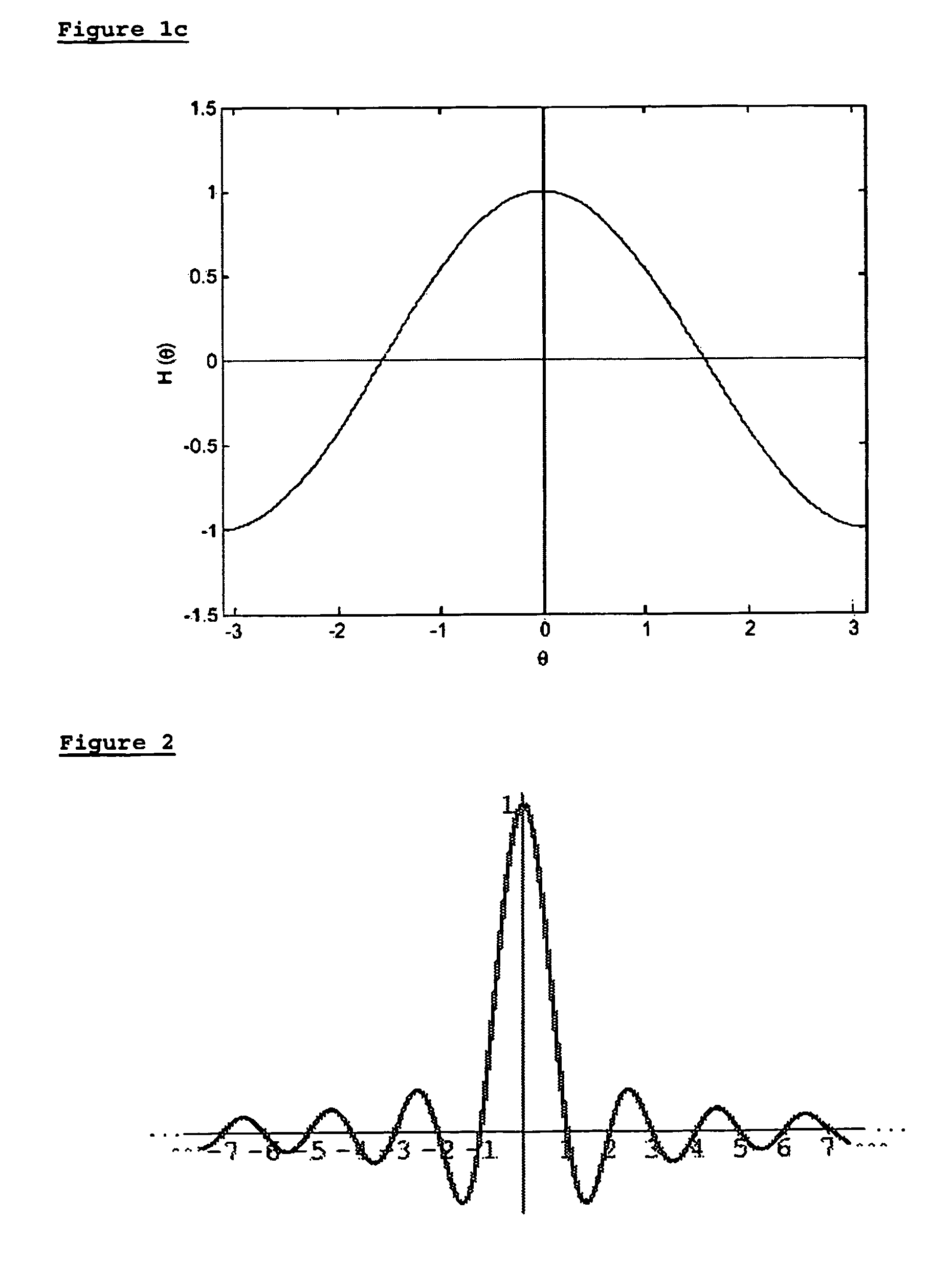
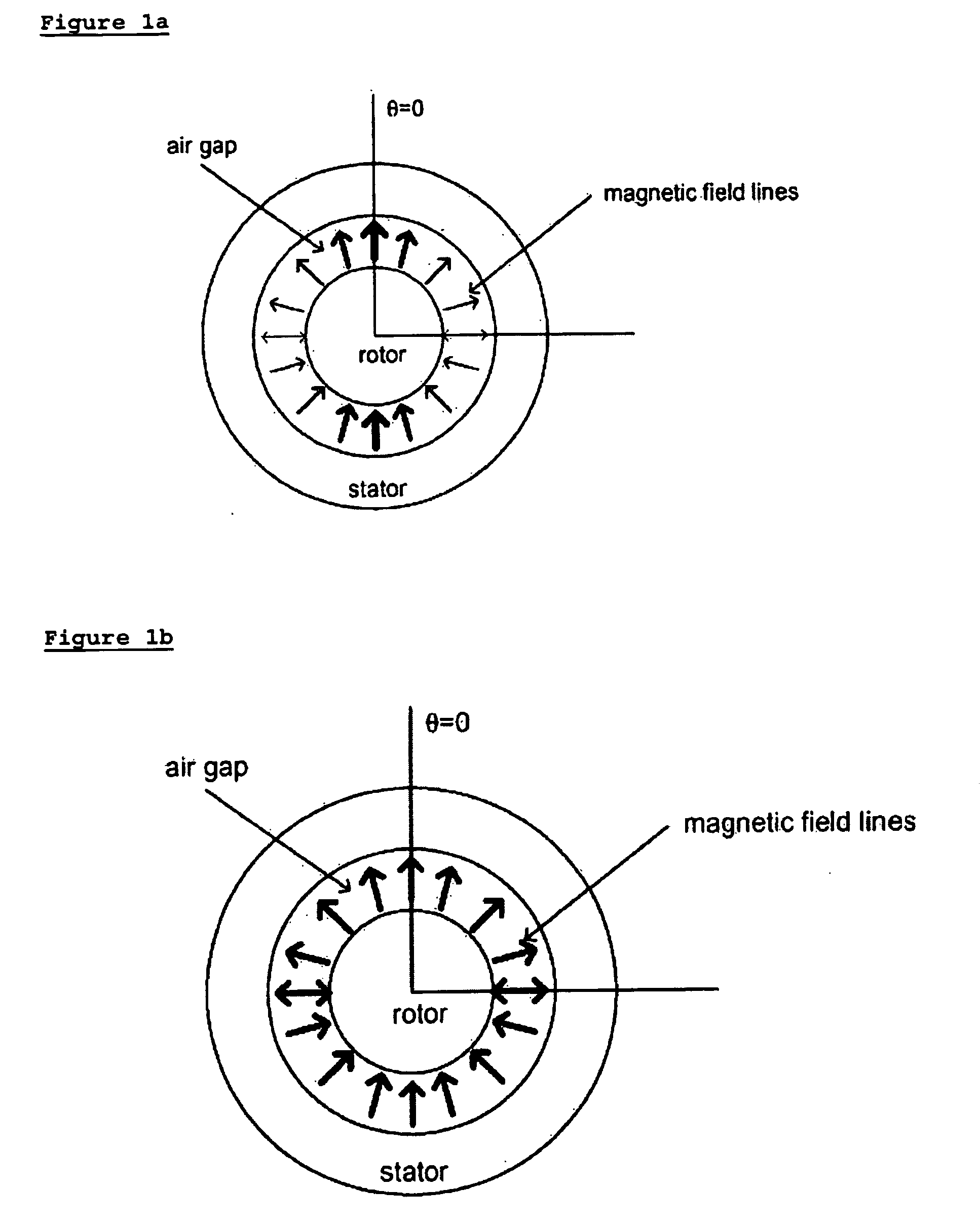
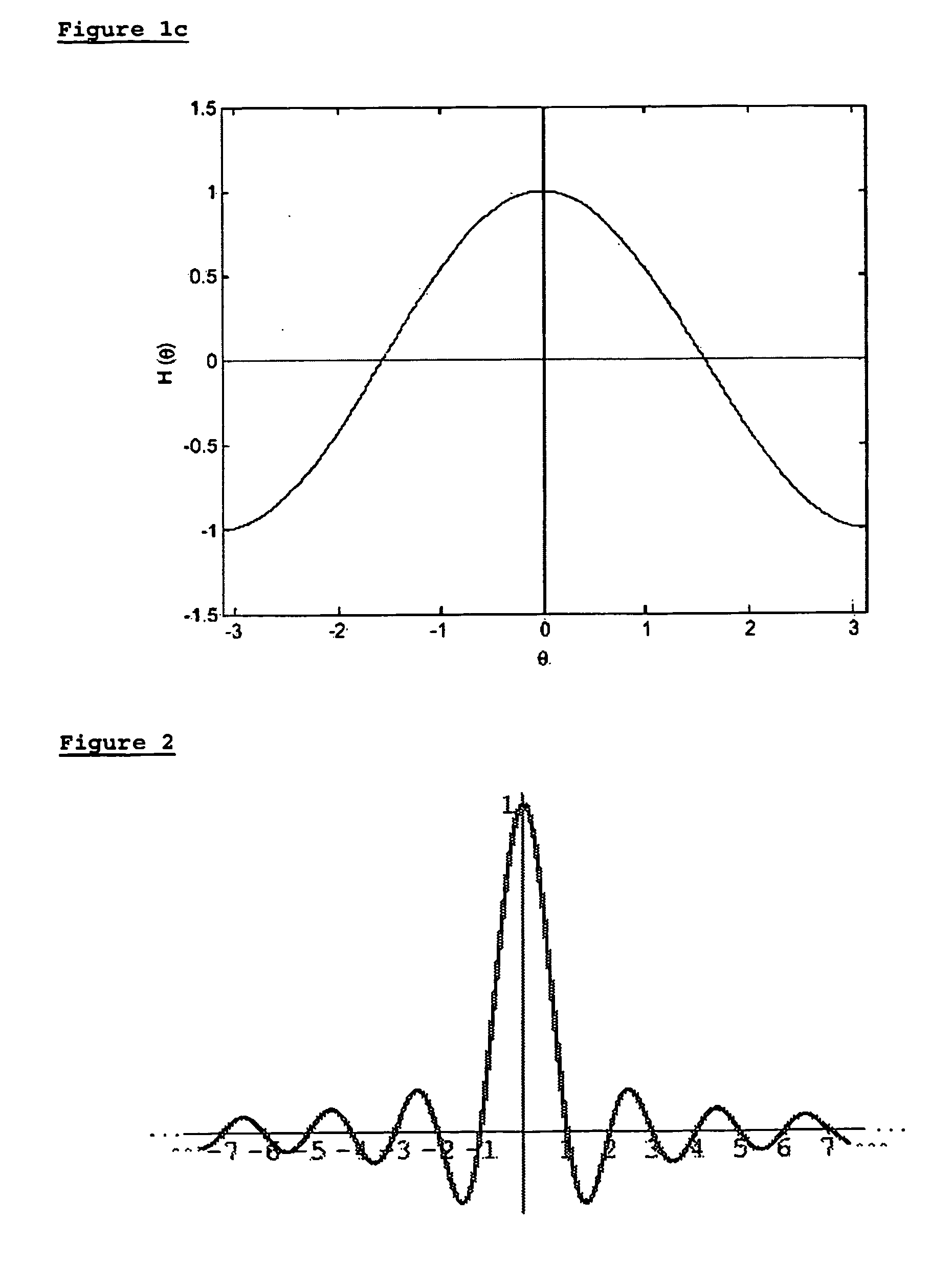
In mathematics, physics and engineering, the sinc function, denoted by sinc(x), has two slightly different definitions. In mathematics, the historical unnormalized sinc function is defined for x ≠ 0 by sinc(x)=sin(x)/x . In digital signal processing and information theory, the normalized sinc function is commonly defined for x ≠ 0 by sinc(x)=sin(πx)/πx . In either case, the value at x = 0 is defined to be the limiting value sinc(0):=limₓ→₀sin(ax)/ax=1 for all real a ≠ 0.
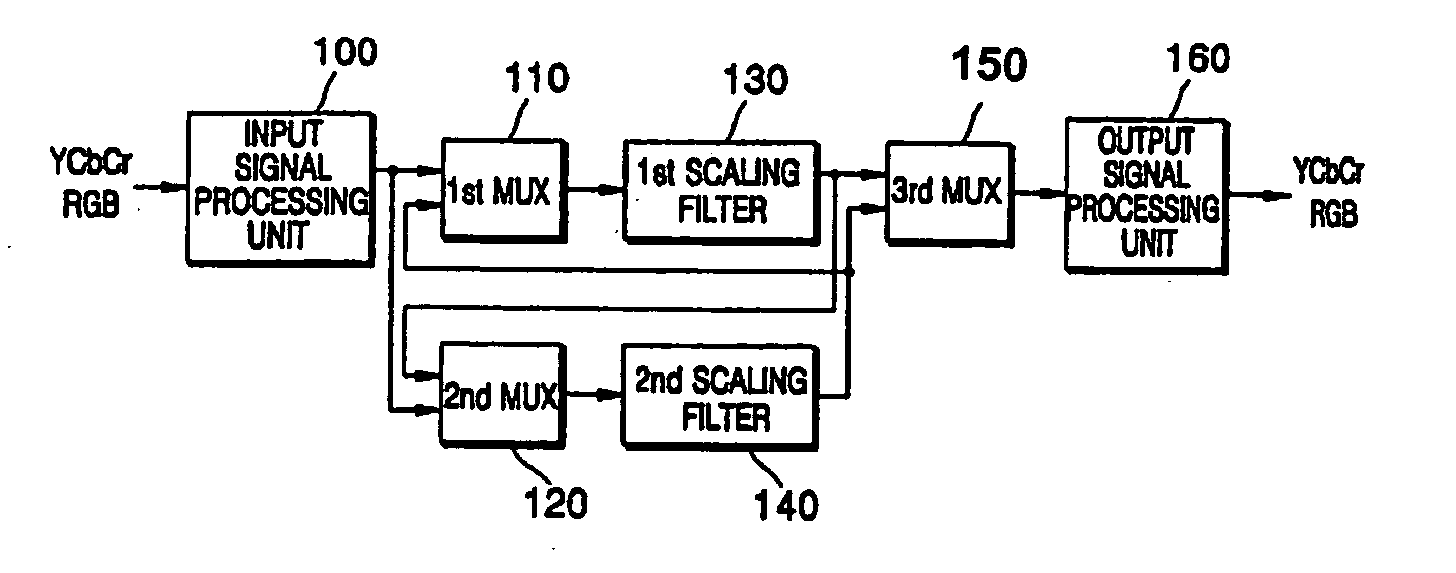
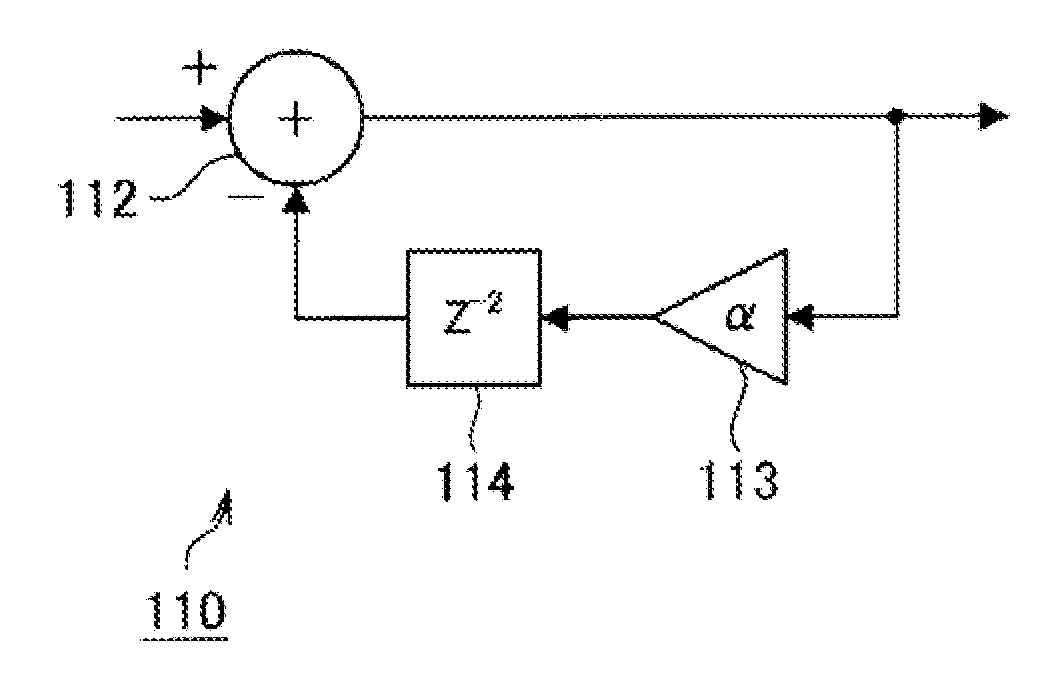
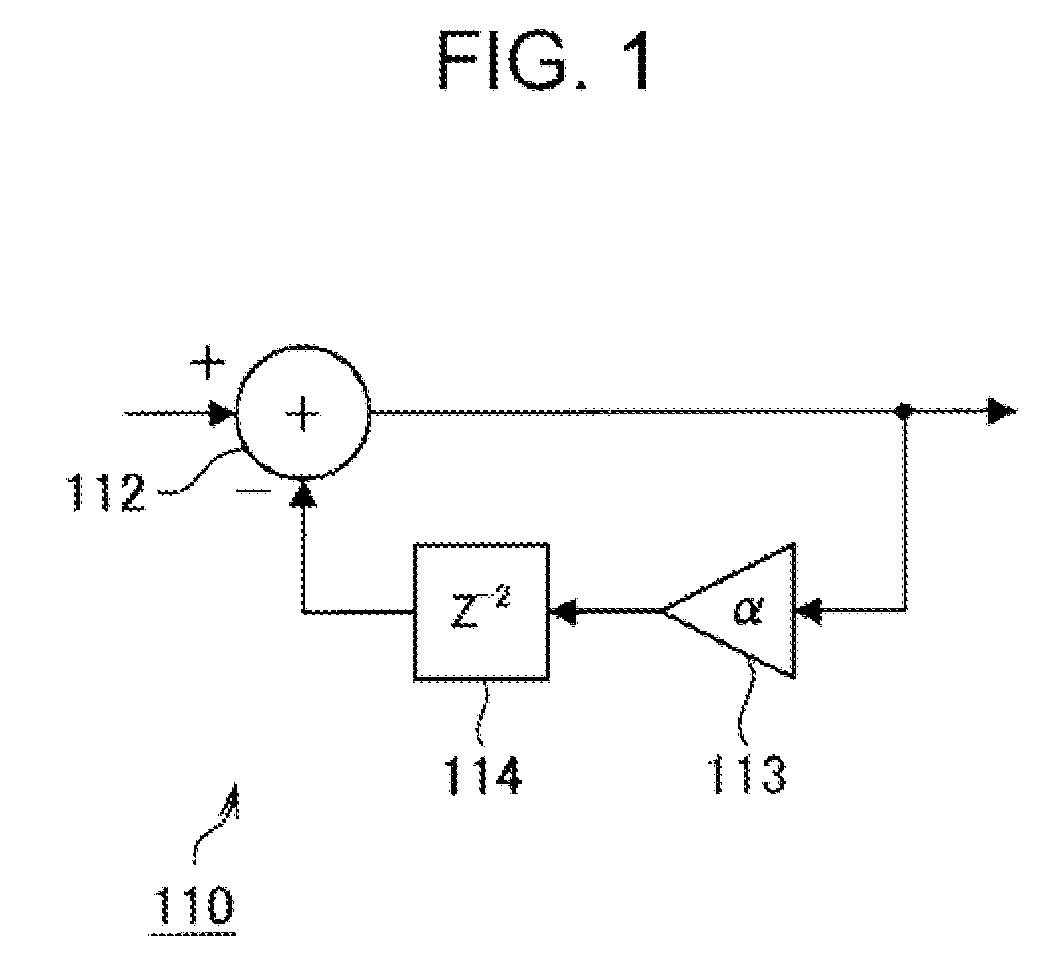
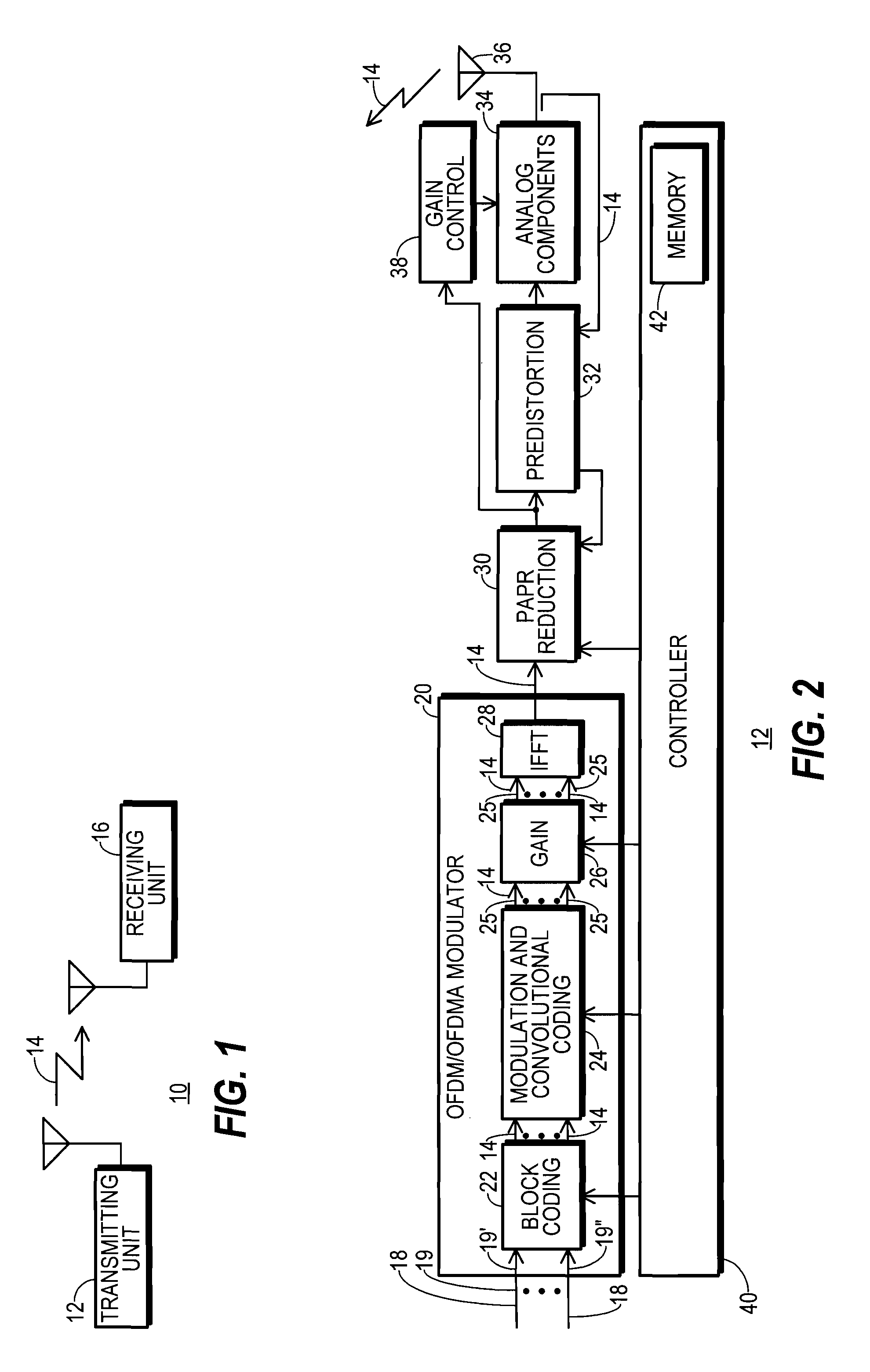
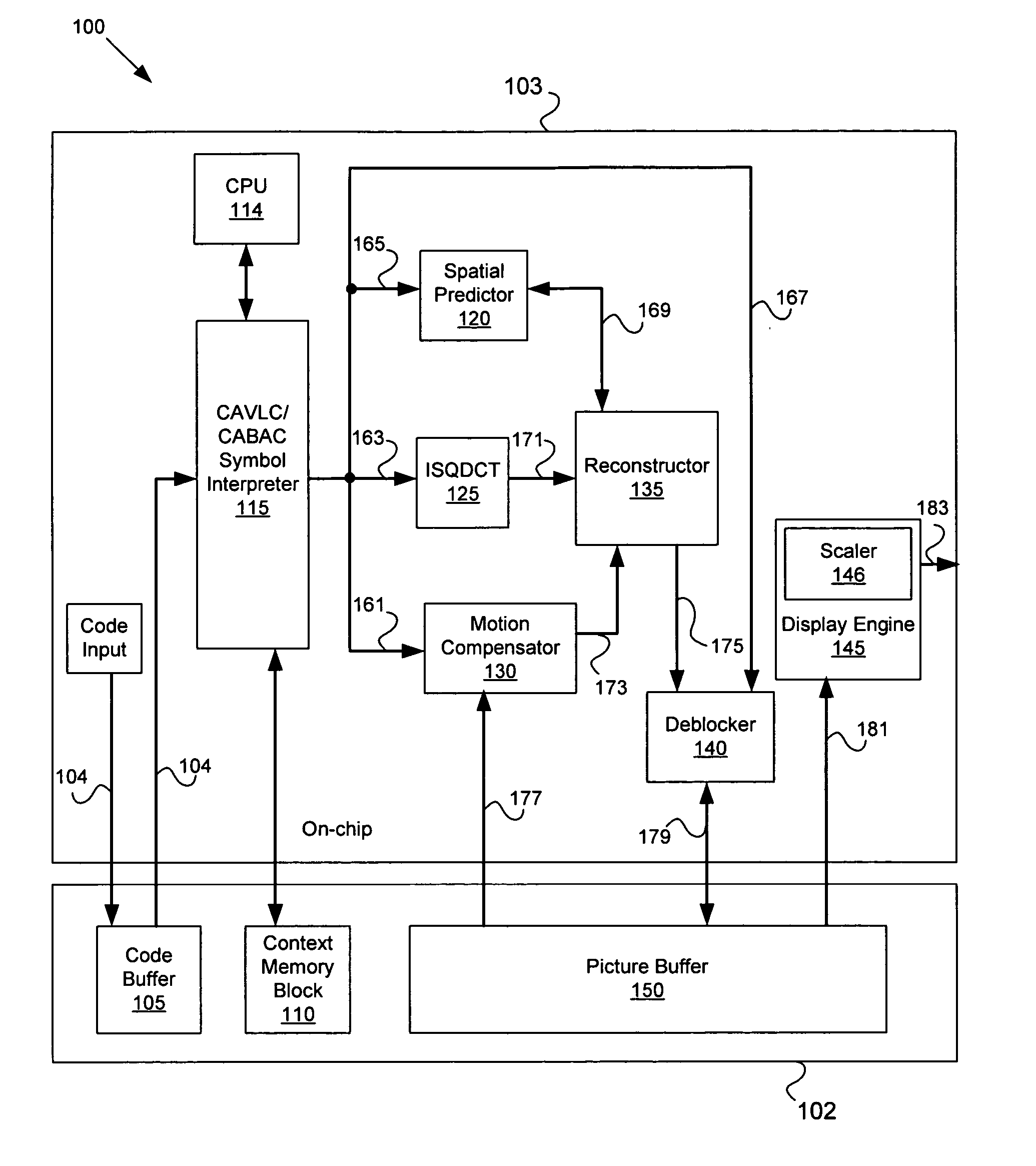
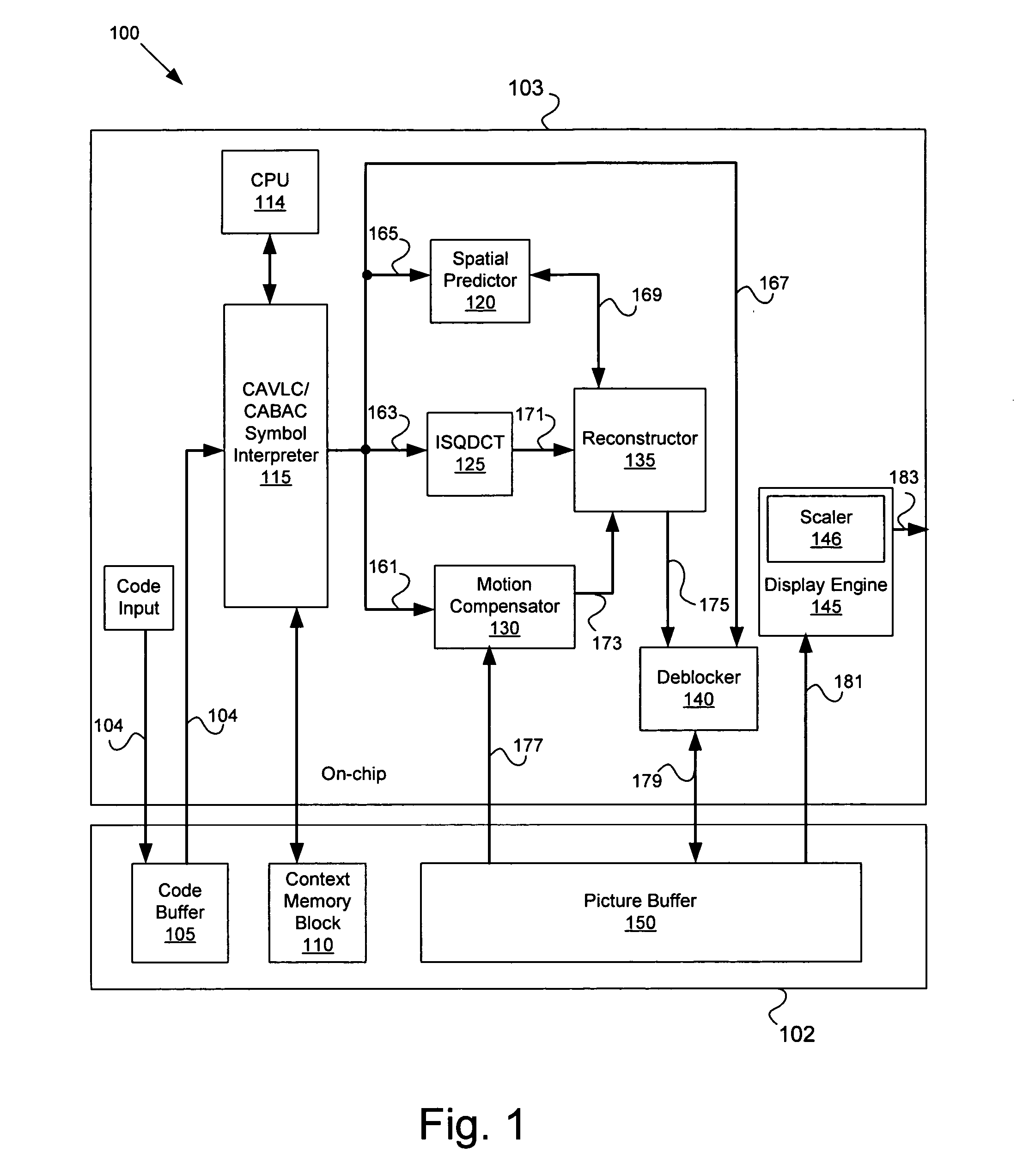
Method of converting resolution of video signals and apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20050134731A1Television system detailsGeometric image transformationImage resolutionGaussian function
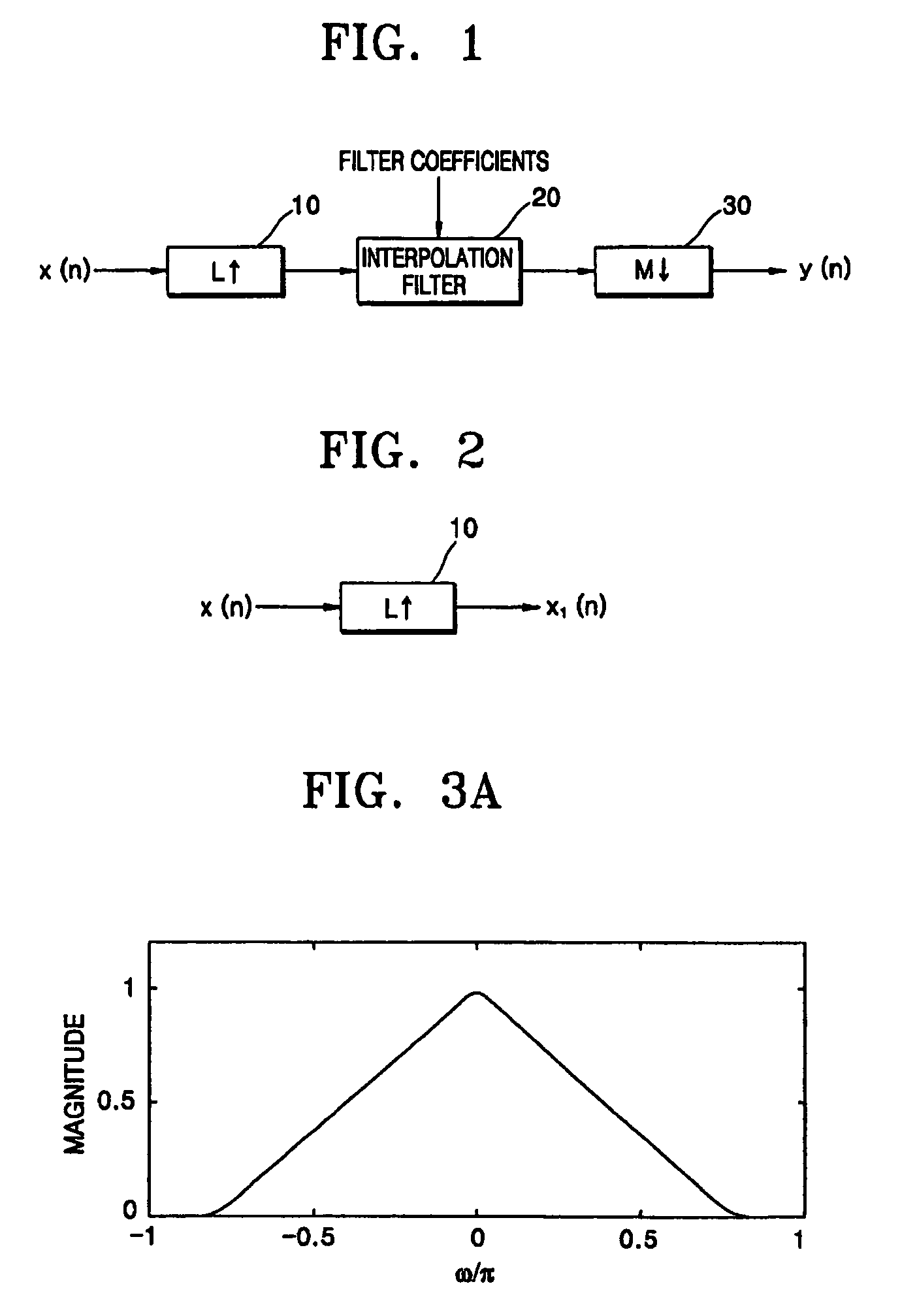
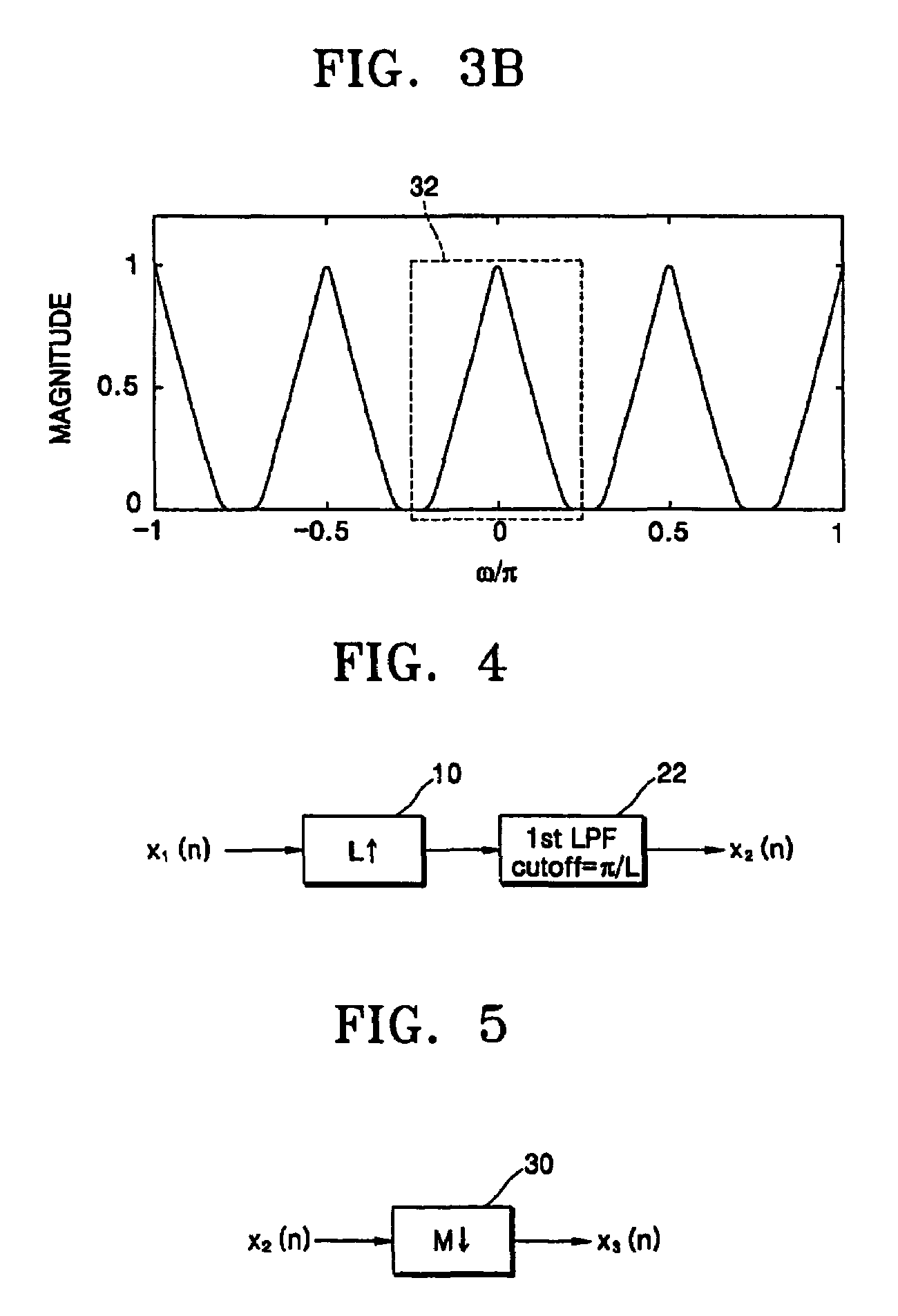
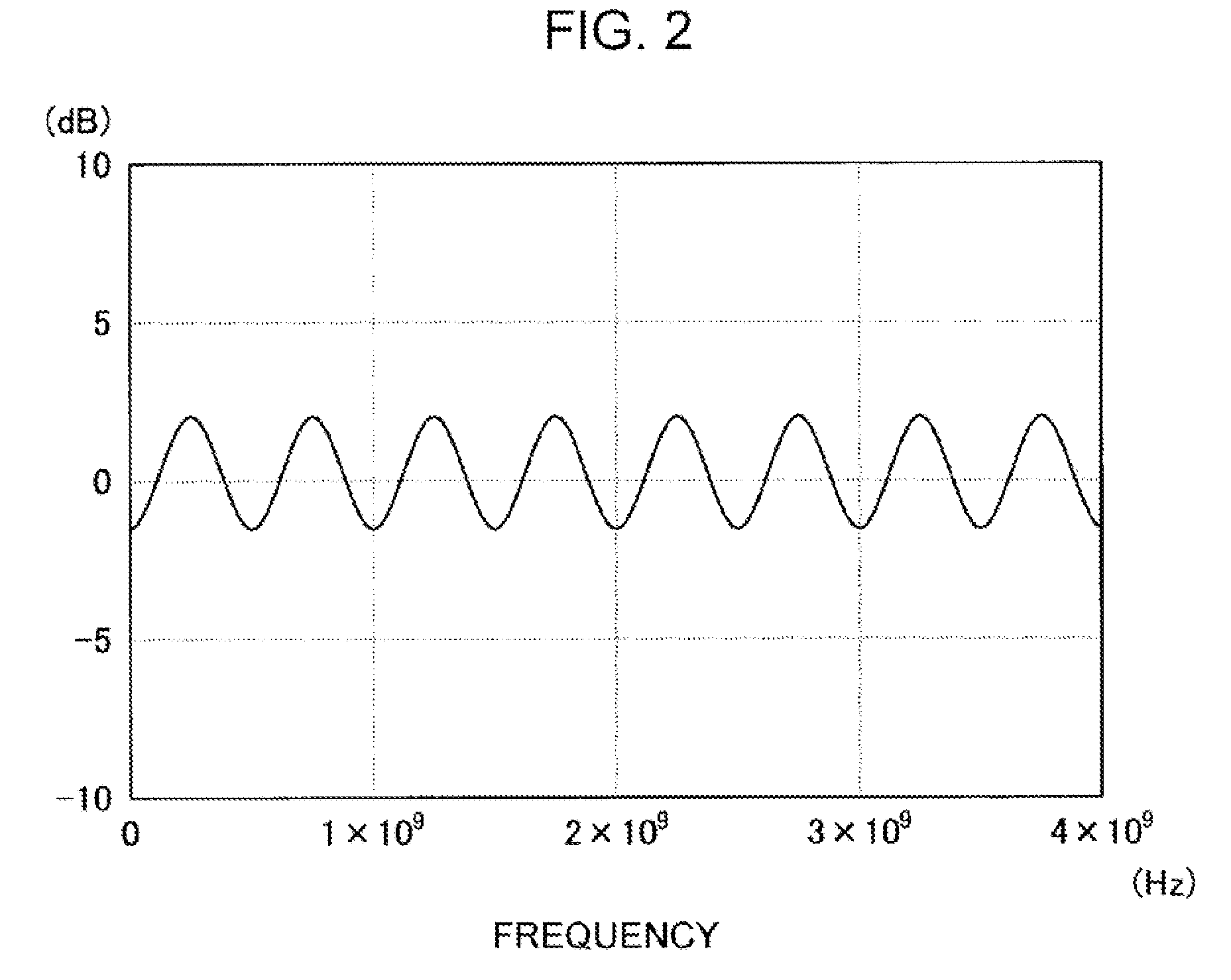
A method converts a resolution of video signals, the method including: calculating up-sampling and down-sampling ratios based on a resolution of an input video signal and a desired resolution of an output video signal; calculating a number of filter tabs by multiplying the up-sampling and down-sampling ratios by a number of side lobes; calculating first filter coefficients of a same number of the filter tabs by multiplying a window function by a sinc function; calculating final filter coefficients by subtracting a result of a multiplication of a Gaussian function by a window function from the first filter coefficients, and then normalizing the final filter coefficients; and performing filtering in vertical and horizontal directions based on the final filter coefficients by modifying a sampling rate of an input video signal depending on the up-sampling and down-sampling ratios, to obtain clear video images.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Pulse compression radar
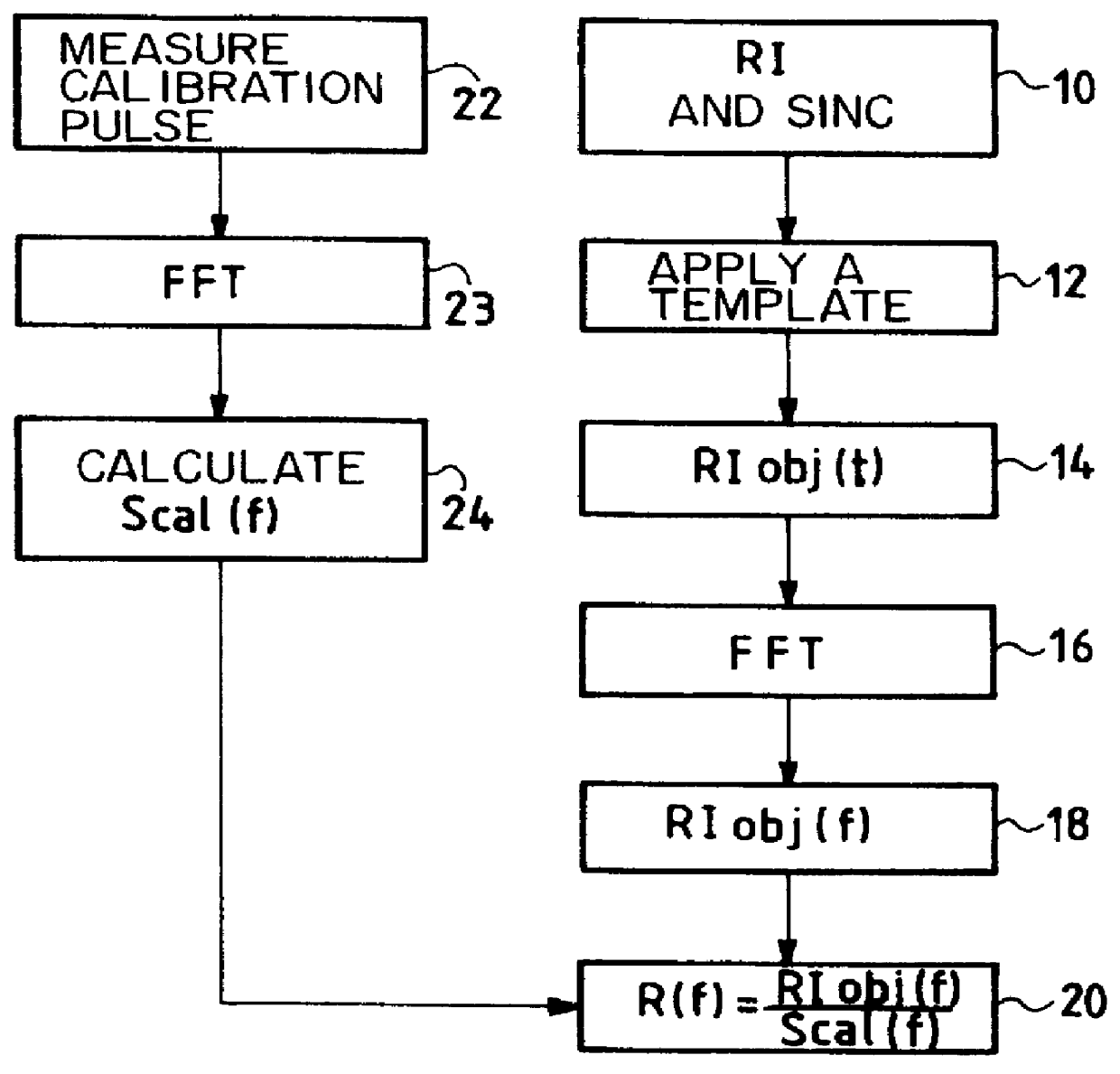
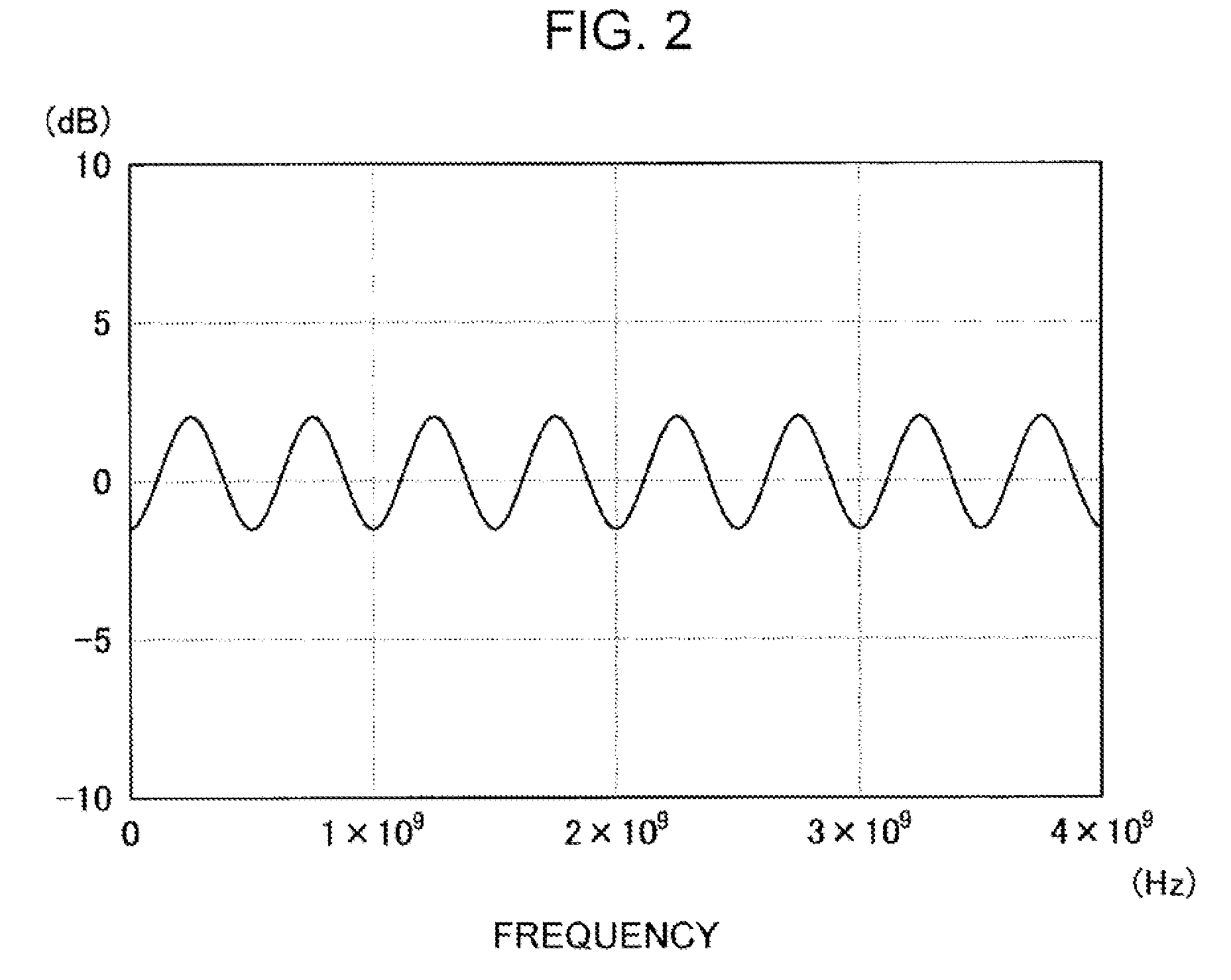
The invention concerns a method of synthesizing a replica used in the compression filter of pulse compression radar. The replica is calculated from the spectrum of a required impulse response. The required impulse response is preferably obtained from an analytical function, such as a sinc function or a weighted sinc function, and a template. It is preferable to use calibration signals of the instrument to calculate the replica. The invention also applies to synthetic aperture radar.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Transmitting unit that reduces PAPR and method therefor
InactiveUS20110064162A1Modulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationCommunications systemCarrier signal
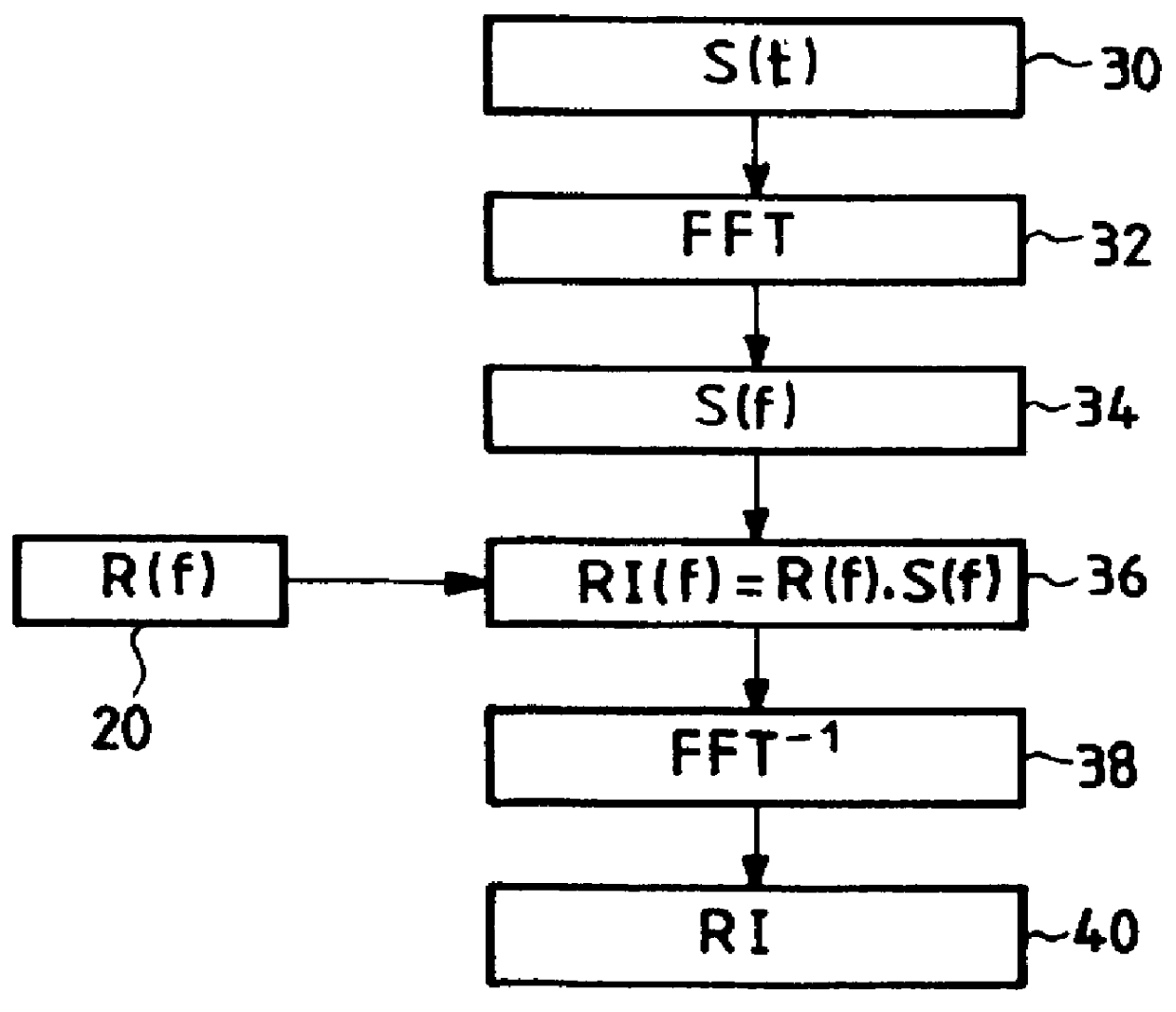
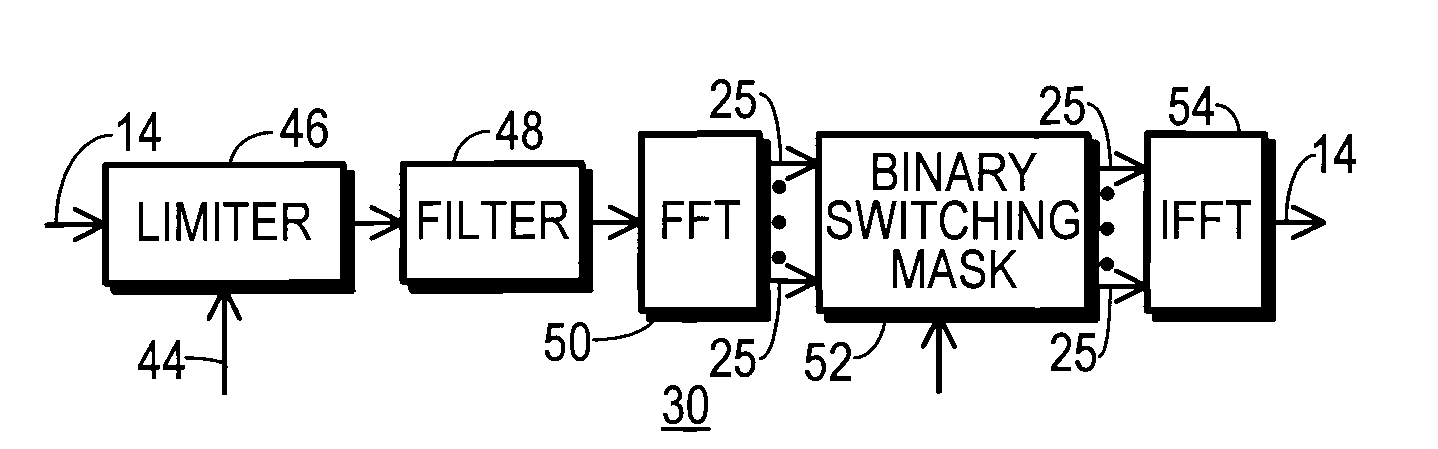
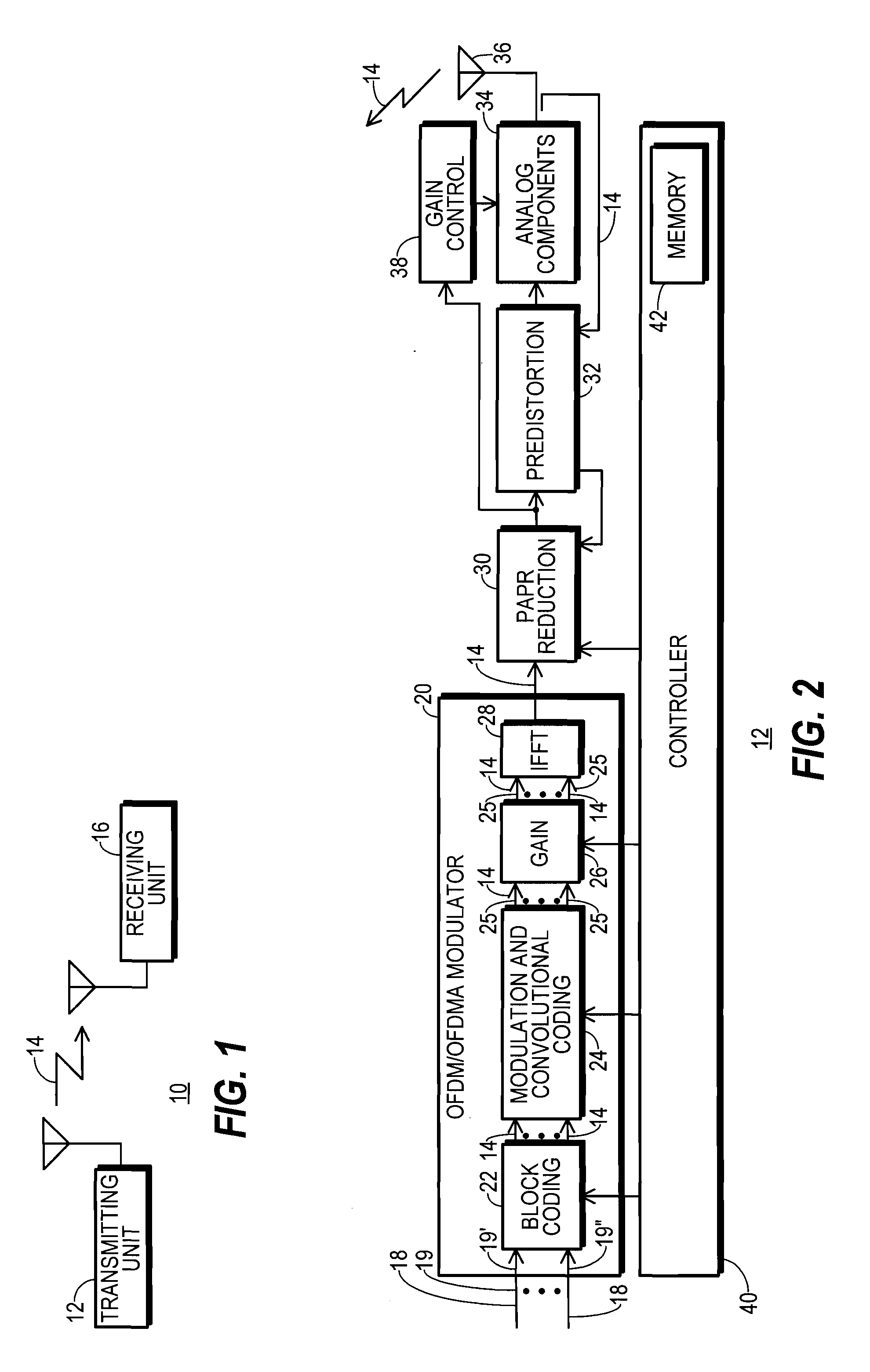
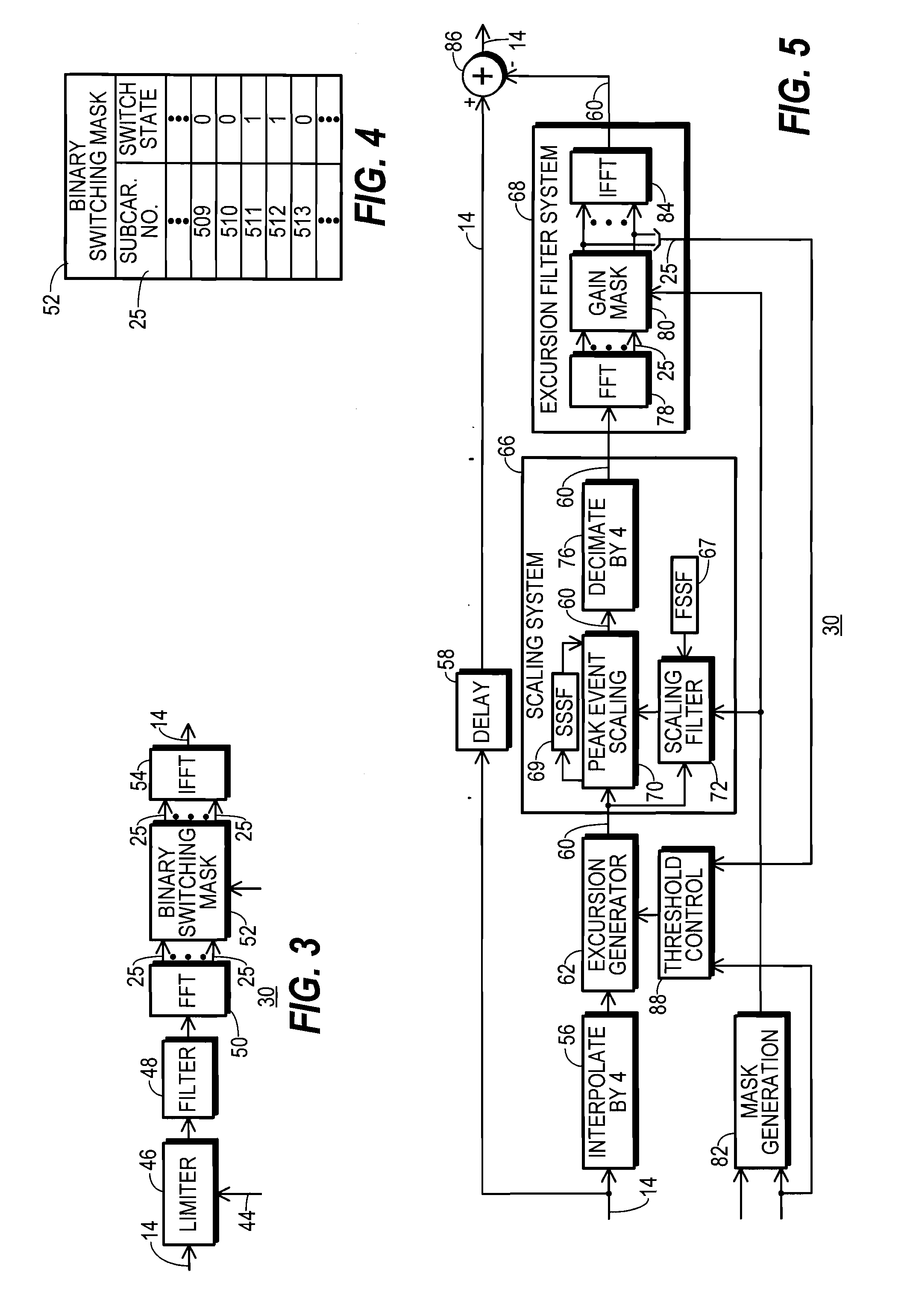
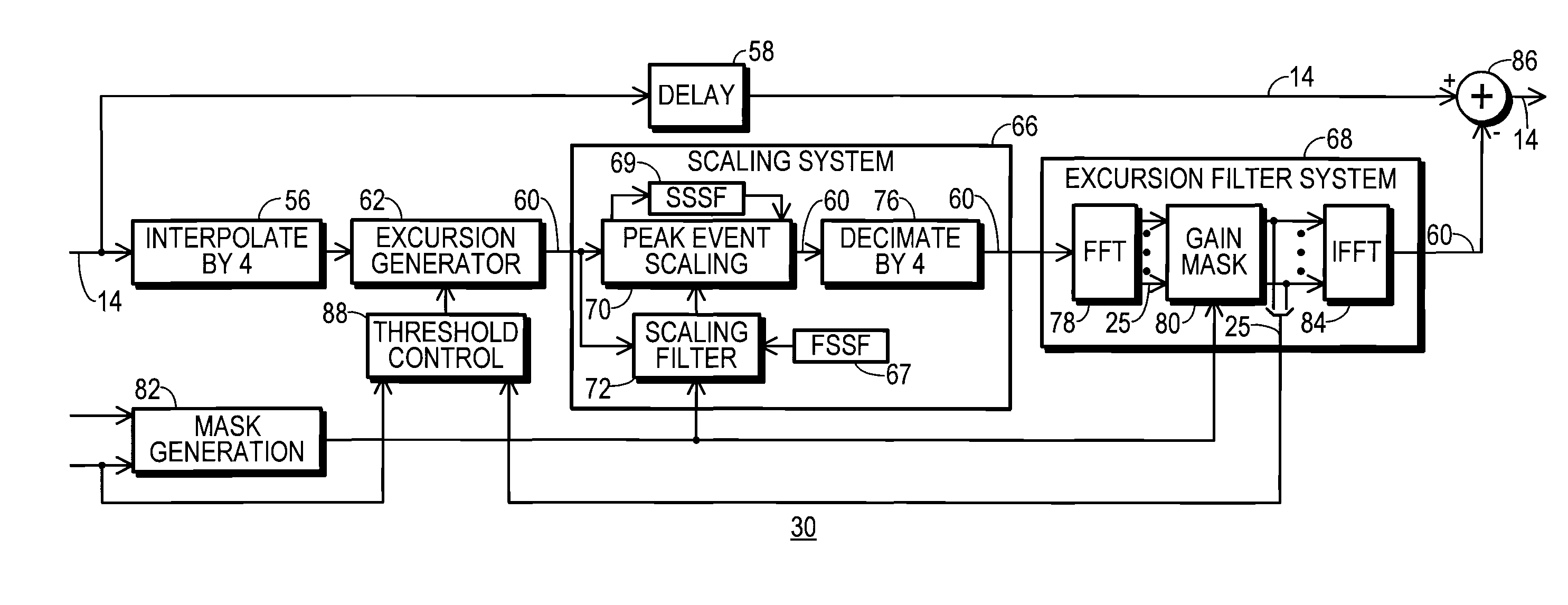
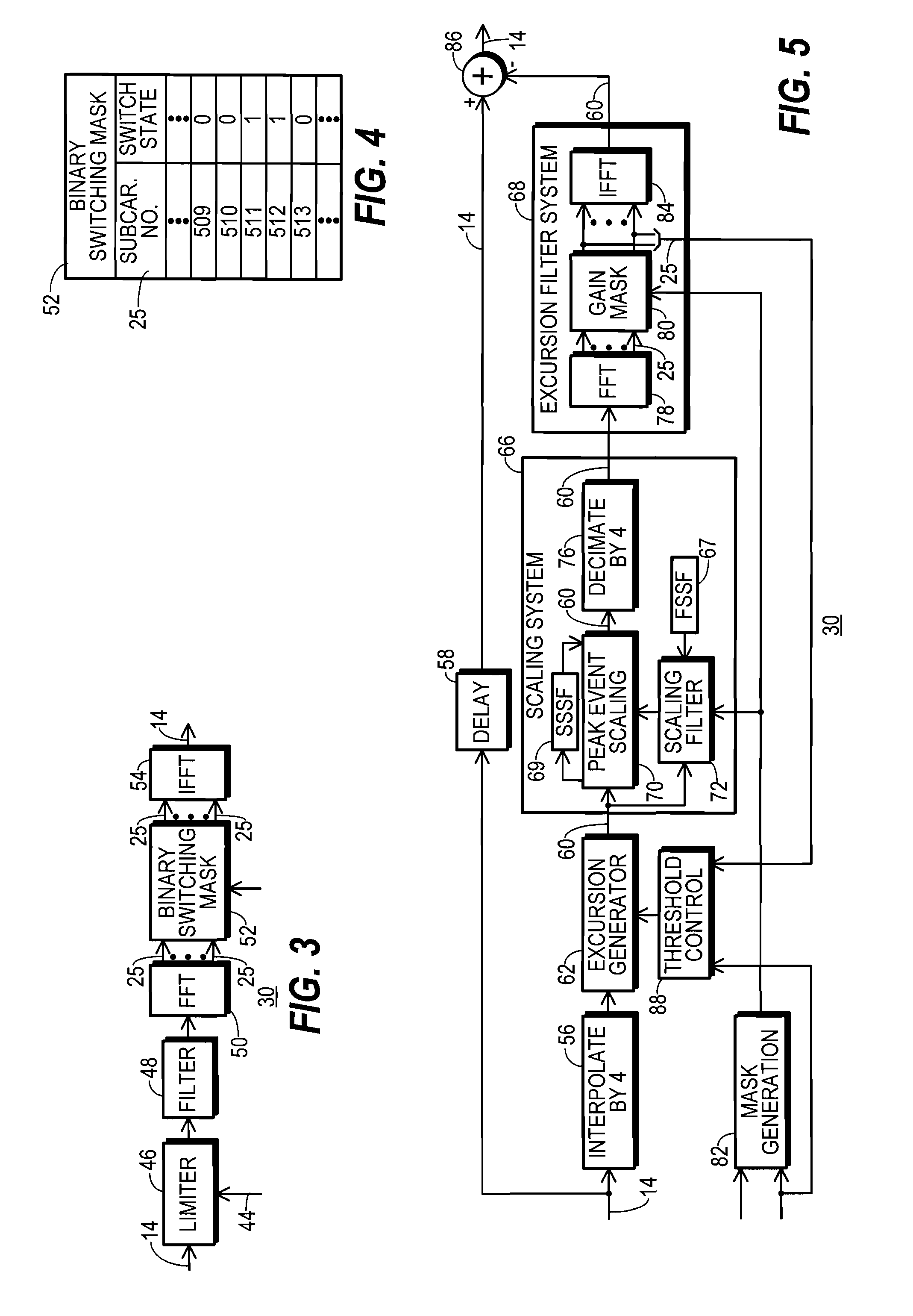
A communication system (10) includes a transmitting unit (12) with a peak to average power (PAPR) reduction section (30). The PAPR reduction section (30) modifies the PAPR reduction it effects in a communication signal (14) in accordance with two different error vector magnitude (EVM) constraints for each channel type (102), where a channel type (102) is a distinct combination of a modulation order and a coding rate. The EVM constraint followed for each subcarrier (25) in an OFDM or OFDMA application is selected in response to whether the subcarrier (25) conveys voice or non-voice data. The PAPR reduction section (30) may include a scaling filter (72). The scaling filter (72) is efficiently defined through the use of a predetermined sinc function (94) and a first stage scale factor (67) that is calculated in response to a weighted average of excursion signal subcarrier gains (150), where the weighting follows the distribution of channel types (102) through the subcarriers (25).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Method of converting resolution of video signals and apparatus using the same
ActiveUS7375767B2Television system detailsGeometric image transformationImage resolutionGaussian function
A method converts a resolution of video signals, the method including: calculating up-sampling and down-sampling ratios based on a resolution of an input video signal and a desired resolution of an output video signal; calculating a number of filter tabs by multiplying the up-sampling and down-sampling ratios by a number of side lobes; calculating first filter coefficients of a same number of the filter tabs by multiplying a window function by a sinc function; calculating final filter coefficients by subtracting a result of a multiplication of a Gaussian function by a window function from the first filter coefficients, and then normalizing the final filter coefficients; and performing filtering in vertical and horizontal directions based on the final filter coefficients by modifying a sampling rate of an input video signal depending on the up-sampling and down-sampling ratios, to obtain clear video images.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Precompensation method for in-band group delay fluctuation of satellite navigation signal generating system
ActiveCN103281268AFlexible modificationImprove correction accuracyTransmission monitoringTransmitter/receiver shaping networksAudio power amplifierUnit impulse response
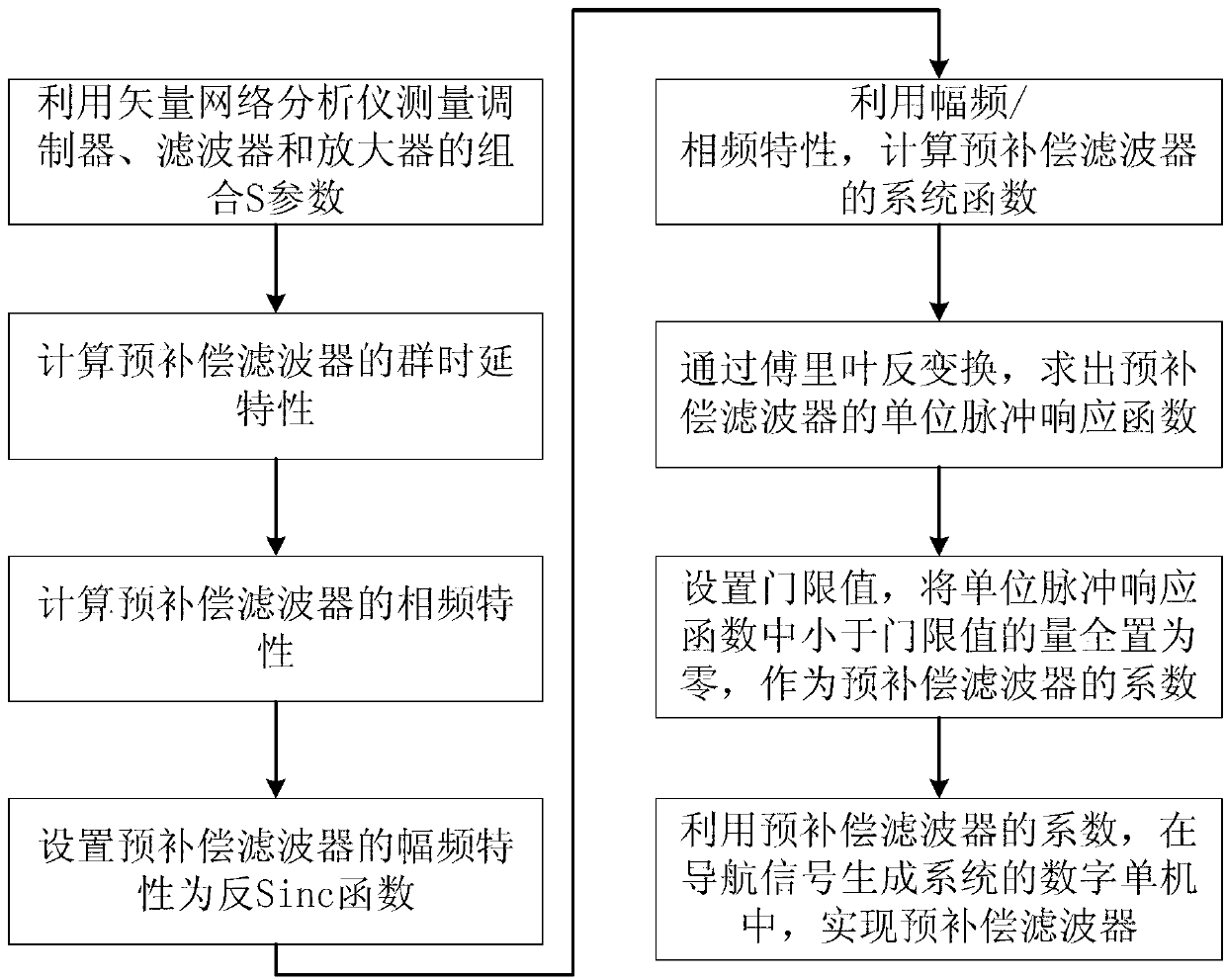
The invention relates to a precompensation method for in-band group delay fluctuation of a satellite navigation signal generating system, which comprises the following steps: (1) measuring a combined S parameter of a modulator, a filter and an amplifier in the satellite navigation signal generating system, and determining amplitude-frequency and group delay characteristic of the combination of the three devices; (2) counting the group delay characteristic of a precompensation filter according to the combined group delay characteristic; (3) obtaining the phase-frequency characteristic of the precompensation filter; (4) setting the phase-frequency characteristic of the precompensation filter to be an inverse Sinc function; (5) obtaining a system function of the precompensation filter according to the amplitude-frequency characteristic and phase-frequency characteristic of the precompensation filter; (6) obtaining a unit impulse response function of the precompensation filter; (7) setting a threshold value, and setting the quantity in the unit impulse response function, which is smaller than the threshold value, to be zero to be as a coefficient of the precompensation filter; and (8) realizing the precompensaiton filter in a digital standalone of the satellite navigation signal generating system by using the coefficient of the precompensation filter, so as to compensate the group delay fluctuation of the satellite navigation signal generating system.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Multi-antenna joint optimization clutter suppression method based on fractional time delay estimation
ActiveCN105527610AEasy to detectImprove the clutter rejection ratioWave based measurement systemsDecompositionTime delays
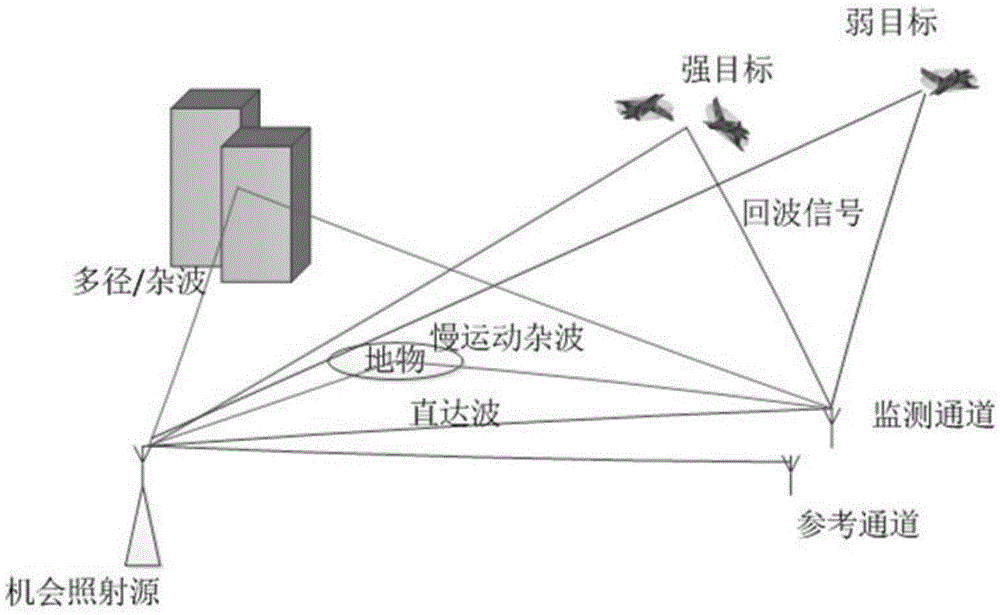
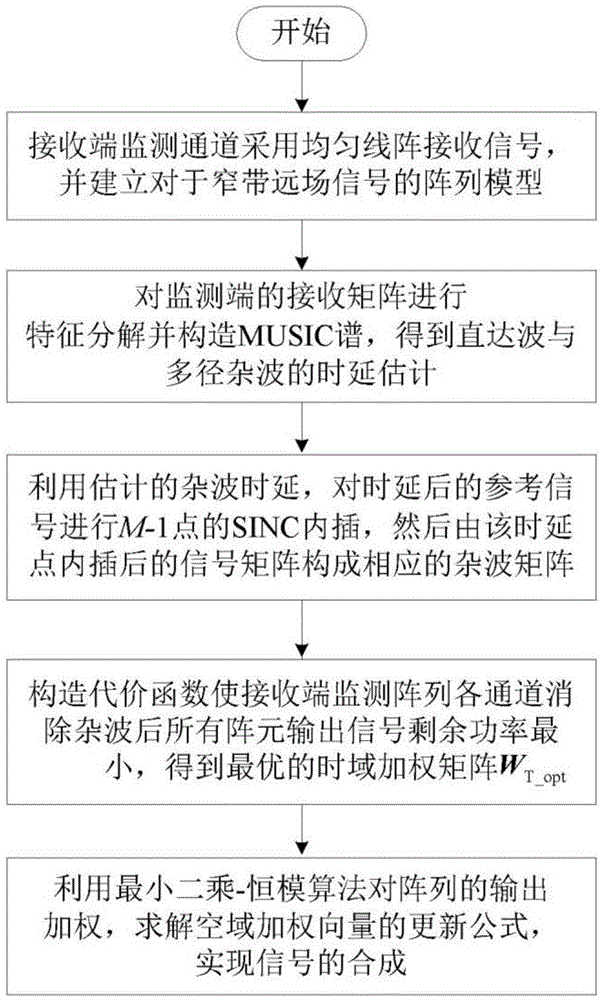
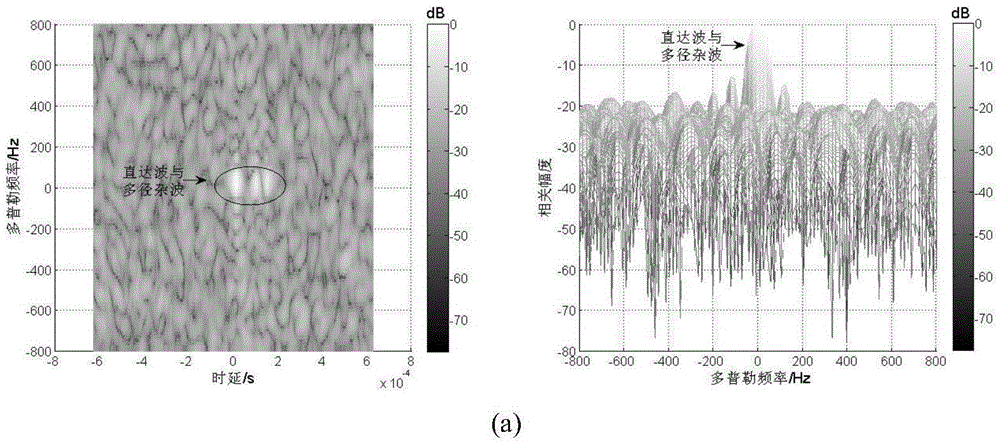
The present invention relates to a multi-antenna joint optimization clutter suppression method based on fractional time delay estimation. A receiving end monitoring channel receives a signal by using a uniform linear array, and a signal array model is established; the self-correlation matrix of an array model matrix is subjected to feature decomposition, a MUSIC spectrum is constructed, and the time delay estimation of a direct wave and a multipath clutter is obtained; the time delay signal after time delay is subjected to SINC function interpolation, and a corresponding clutter matrix is constructed; through constructing a cost function, an optimal time-domain weighting matrix WT_opt is obtained; the output of the array is weighted by using a least squares-constant modulus algorithm, a spatial weighting vector ws is solved, and the signal combination and output are carried out. According to the method, the time domain and spatial domain information of the signal are fully dug, the correlation of the signals in different array elements is monitored by using a receiving end, through the least squares-constant modulus algorithm, the noise and residual clutter outside a target echo coming direction are subjected to attenuation, the clutter rejection ratio of the output signal is raised, and the detection performance of a weak object can be improved at the same time.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
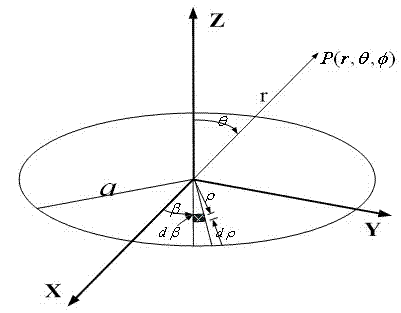
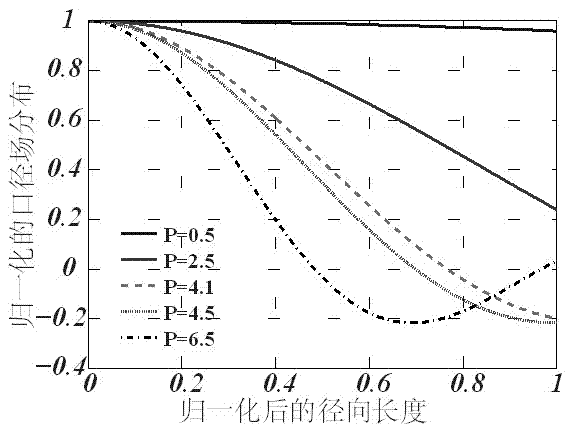
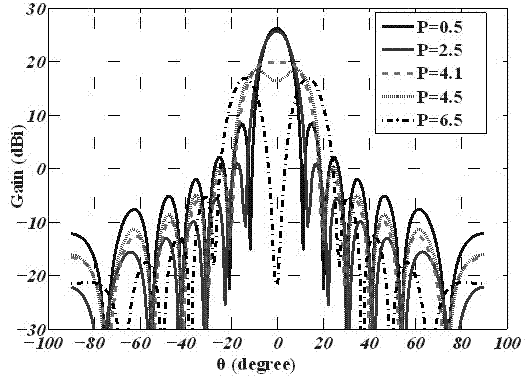
Method for designing array antenna with circular aperture field distribution based on Sinc function
The invention discloses a method for designing an array antenna with circular aperture field distribution based on a Sinc function. An antenna array is distributed on a circular aperture, and aperture fields are distributed on a concentric circle array composed of more than two concentric circles. Antenna units are arranged on each concentric circle, the number of the antenna units on the same concentric circle is at least 4 and is an even number, and the antenna units are uniformly distributed in a central symmetry mode. The aperture field distribution is regulated through a parameter weighting method based on the Sinc function, and the continuous aperture field distribution shaped with wave beams of different kinds is obtained. The radius and the excitation of each concentric circle in the concentric circle array corresponding to the wave beams of different kinds are obtained by calculating through a discrete method. The method avoids a complex and unordered multidimensional optimization process, and a realization method of deterministic and fast array antenna layout and excitation parameters is obtained. The method can be widely applied to analysis and design of array antennas such as phased array radar and navigational satellite, and the fast shaping of wave beams under different occasions is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
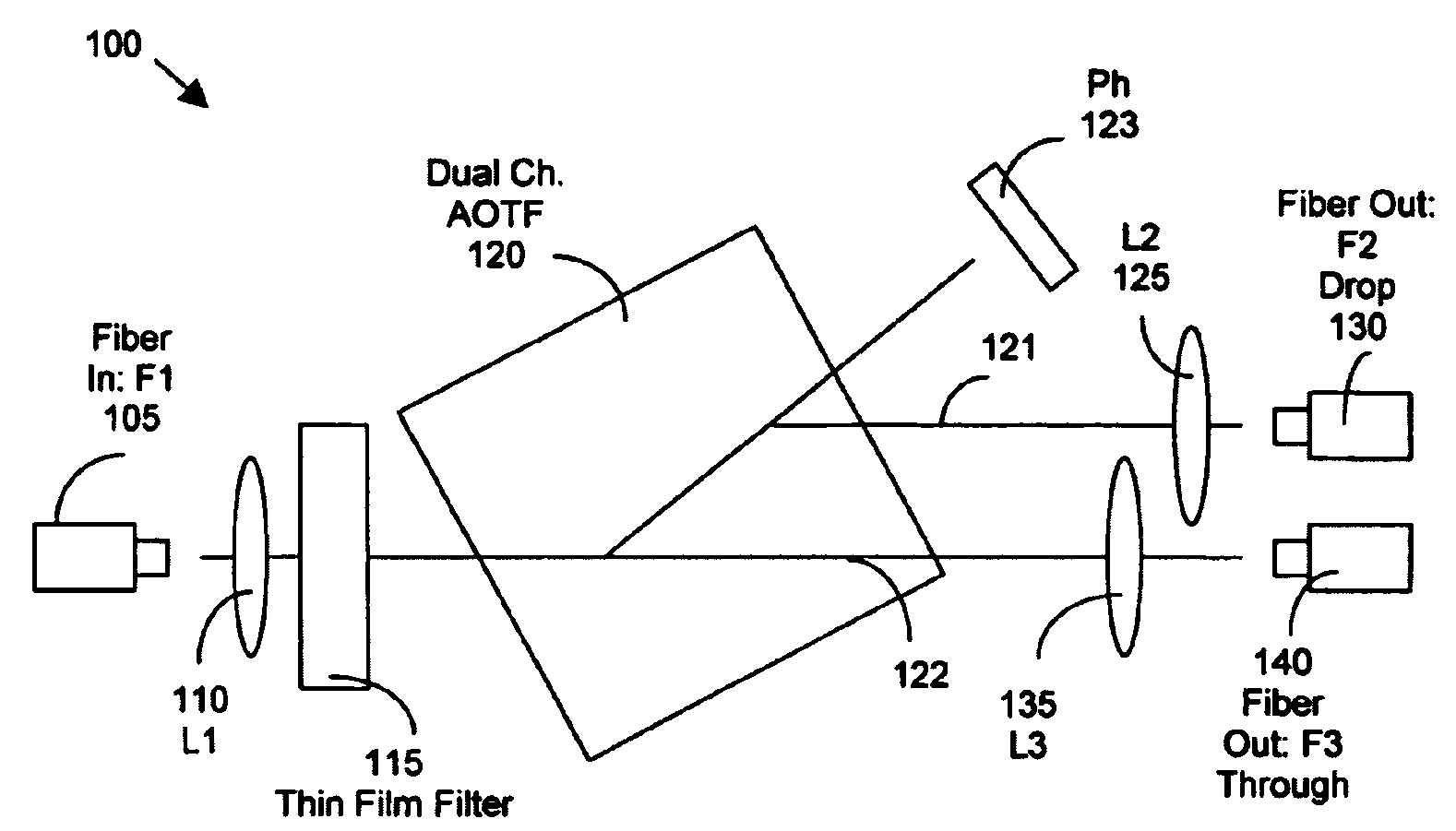
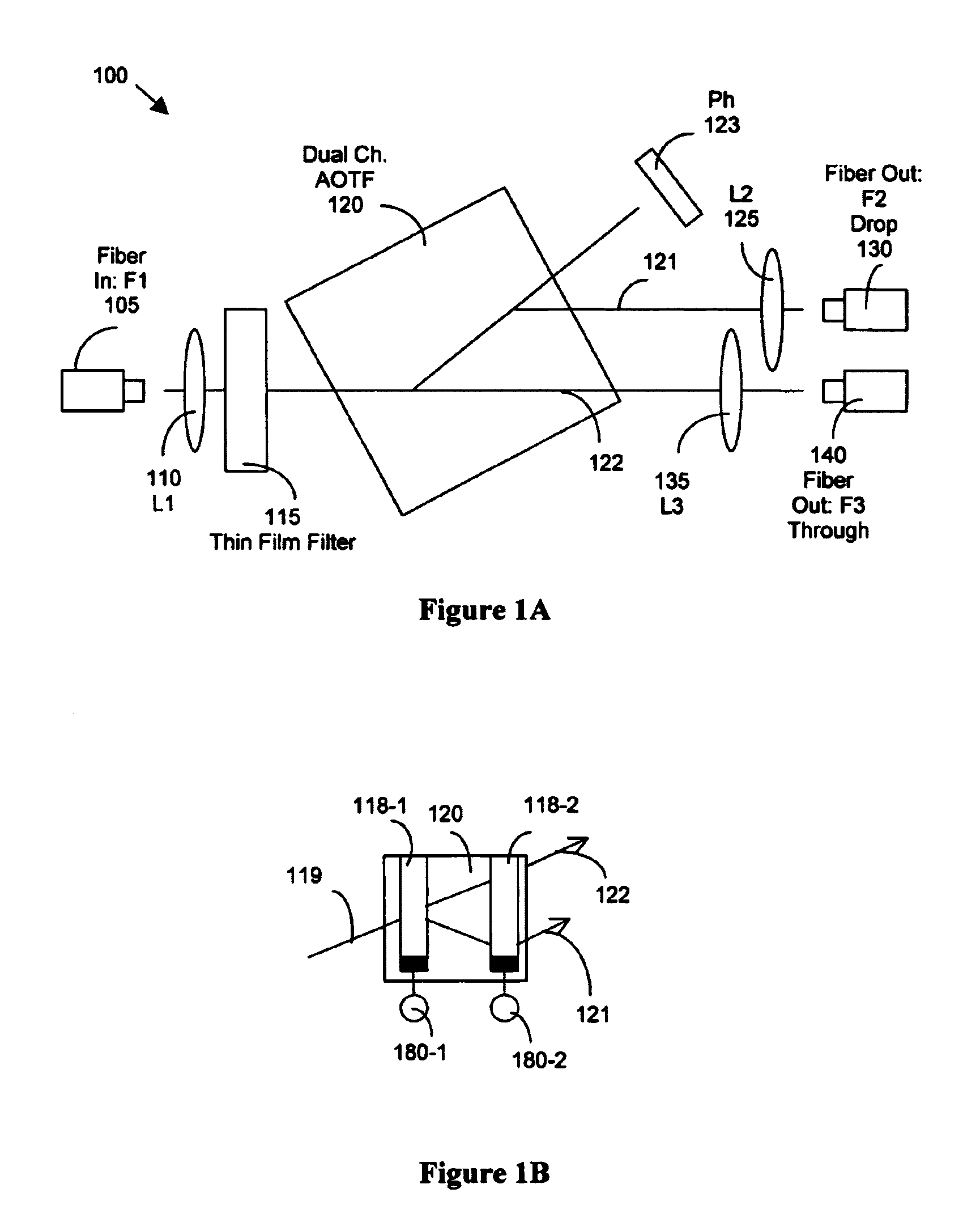
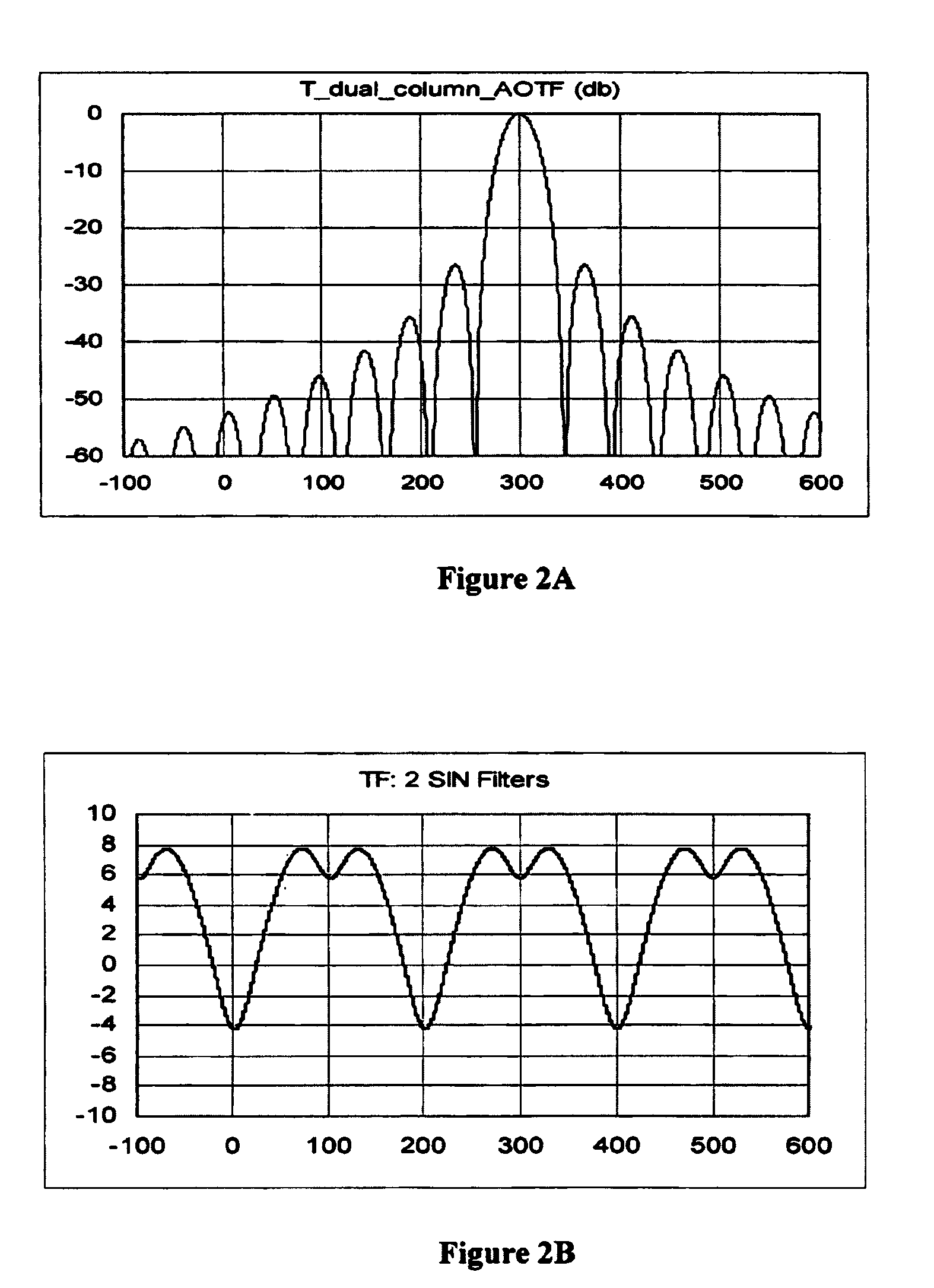
Tuning a narrow band filter for telecommunication applications with an acoustic optical tunable filter
InactiveUS7057799B2Suitable for implementationGuaranteed uptimeLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionSquare waveformAcoustic wave
An optical tunable filter that includes a thin-film filter for band-passing at least two bands of wavelengths. The tunable filter further includes a tunable band-passing device tunable over the at least two bands for tuning to a tunable pass-band spectrally overlapped with one of the at least two bands. The tunable band-passing device further includes an Acousto-optical cell tunable with acoustic wave signals. The thin-film filter cooperating with the tunable band-pass device for generating a tunable output waveform that has substantially a square waveform spectrally corresponding to the at least two bands. The thin-film filter further cooperates with the tunable band-pass device for generating a tunable output waveform having substantially a square waveform over a spectral range of a C-band, an L-band and an S-band. The tunable band-pass device band-passes a tunable substantially Sinc-function-like waveform and the thin film filter band-passing a substantially square waveform with a center attenuated dip for compensating the tunable substantially Sinc-function waveform.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
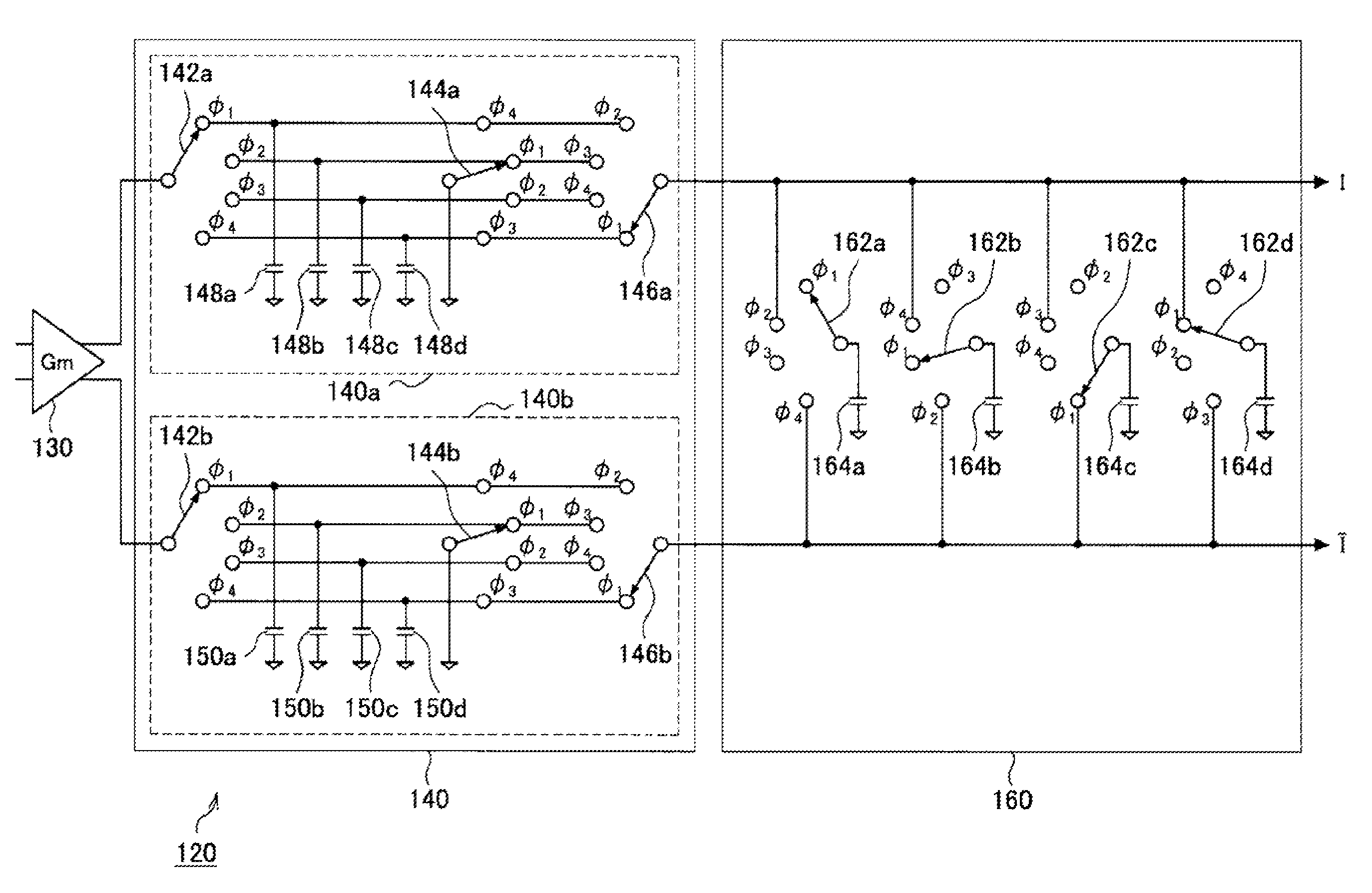
Charge Domain Filter Device
InactiveUS20080088389A1Reduce power consumptionMultiple-port networksTransversal filtersBandpass filteringSinc filter
A charge domain filter device includes a SINC filter with a frequency characteristic expressed by a SINC function, and a bandpass filter connected to an output end of the SINC filter and having a frequency characteristic with a particular center frequency.
Owner:SONY CORP
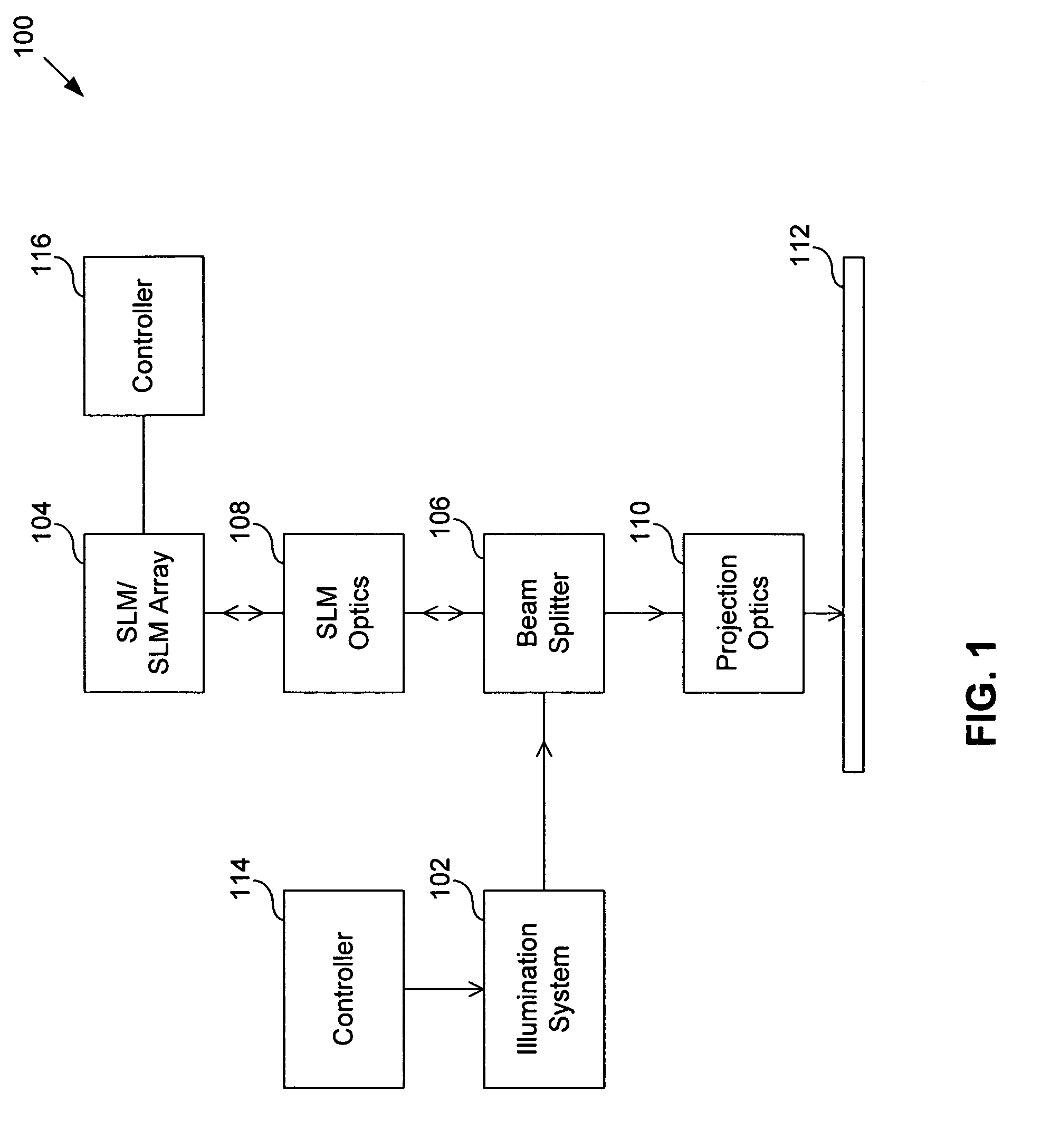
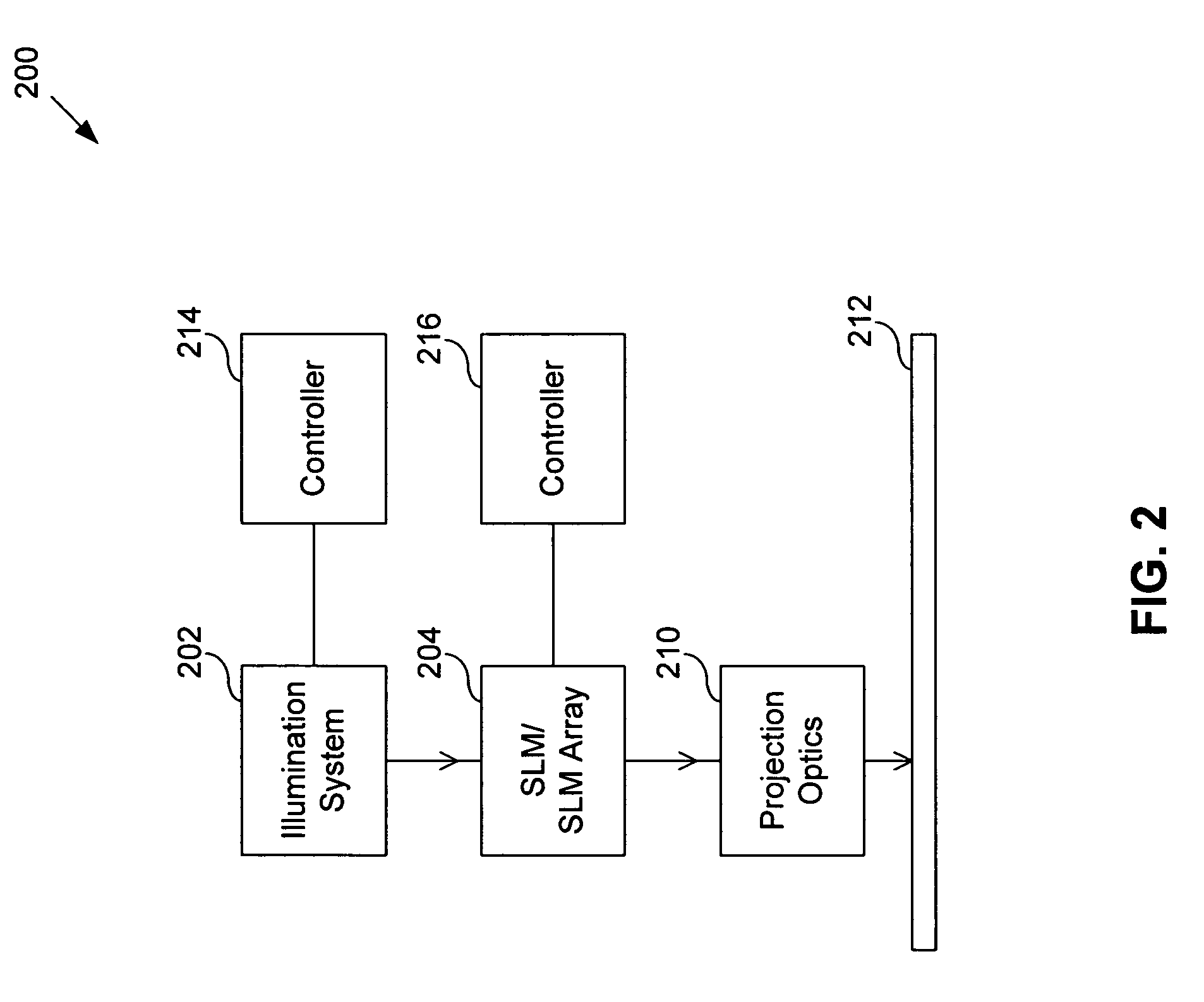
System and method for calculating aerial image of a spatial light modulator
ActiveUS6963434B1Optical radiation measurementColor television detailsSpatial light modulatorAerial photography
A method of calculating an aerial image of a spatial light modulator array includes calculating a pixel interference matrix that represents pair wise interference between pixels of the spatial light modulator array; calculating effective graytones corresponding to modulation states of the pixels; and calculating the aerial image based on the pixel interference matrix and the effective graytones. The graytones depend only on the modulation states of the pixels. The pixel interference matrix depends only on position variables. The position variables are position in an image plane and position in a plane of a source of electromagnetic radiation. The pixel interference matrix can be a matrix of functions. The pixel interference matrix can be a four dimensional matrix. The effective graytones are approximated using sinc functions, or using polynomial functions.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Charge domain filter device
InactiveUS7636012B2Reduce power consumptionMultiple-port networksTransversal filtersBandpass filteringSinc filter
A charge domain filter device includes a SINC filter with a frequency characteristic expressed by a SINC function, and a bandpass filter connected to an output end of the SINC filter and having a frequency characteristic with a particular center frequency.
Owner:SONY CORP
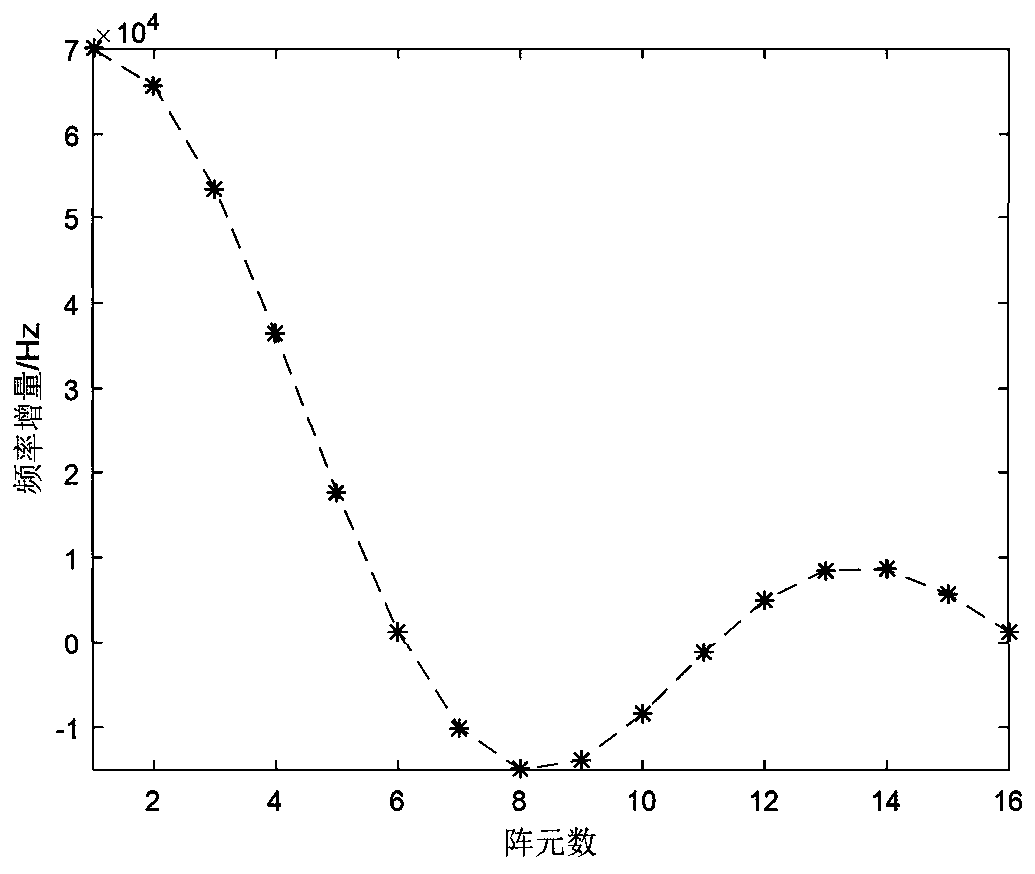
Target parameter estimation method based on FDA-MIMO radar
ActiveCN109901149AImprove estimation performanceSolve the coupling problemRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCouplingEstimation methods
The invention belongs to the radar signal processing technology field and discloses a target parameter estimation method based on an FDA-MIMO radar. The method comprises the following steps of designing a frequency increment resulting in wave beam coupling and an array element spacing, breaking linearly increasing synchronization between the two, achieving a decoupling effect, and providing a condition for unique estimation of a target distance angle; and through designing, making the frequency increment of each array element satisfy a sinc function increasing relation, and then carrying outangle and distance estimation to obtain an accurate target angle and distance information. By using the method of the invention, coupling of an emission wave beam at a distance-angle can be solved. When the distances and the angles of multiple targets are different, the distance and the angle of the target is well estimated to avoid occurrence of false targets, and estimation performance of the radar is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
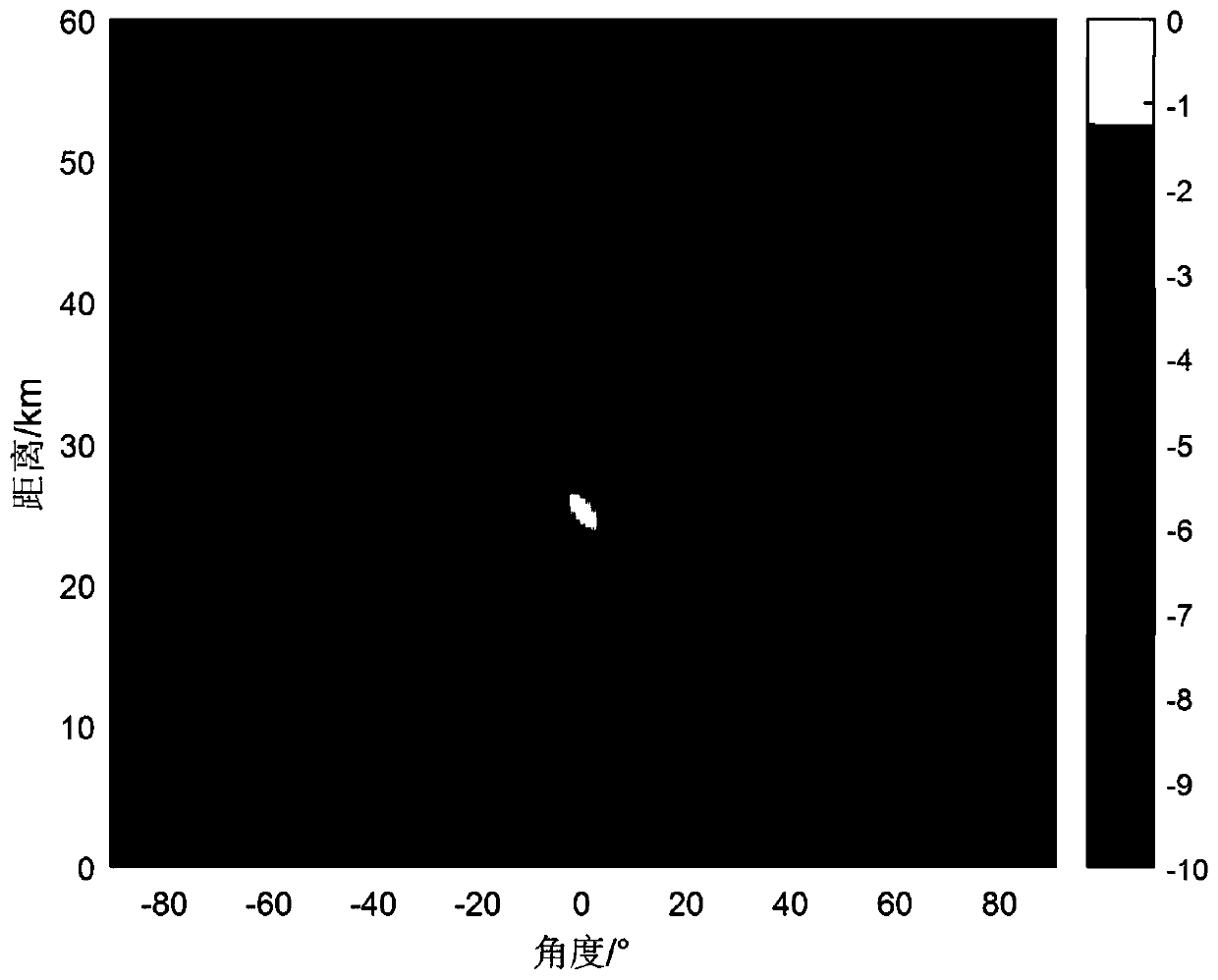
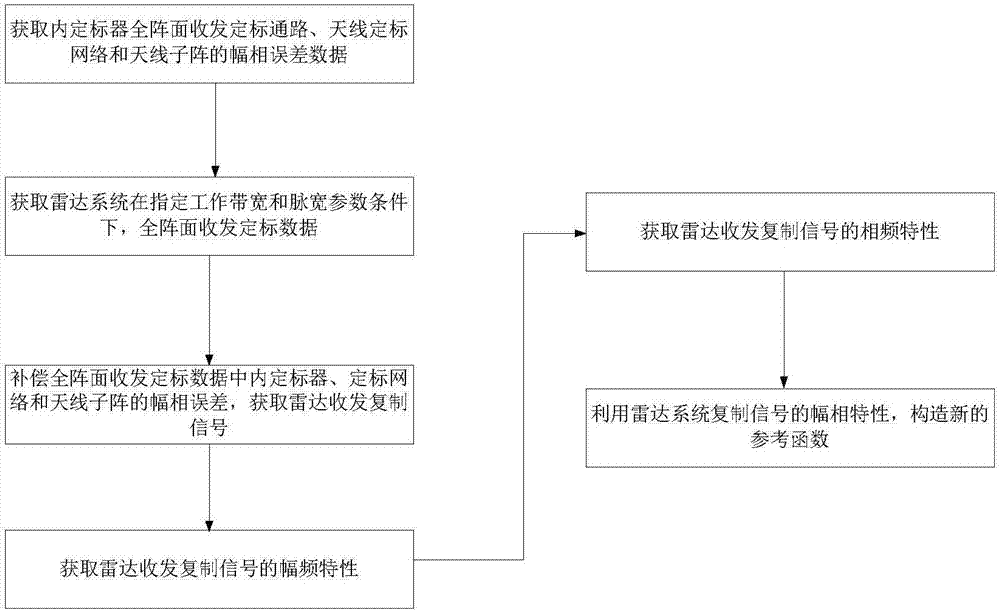
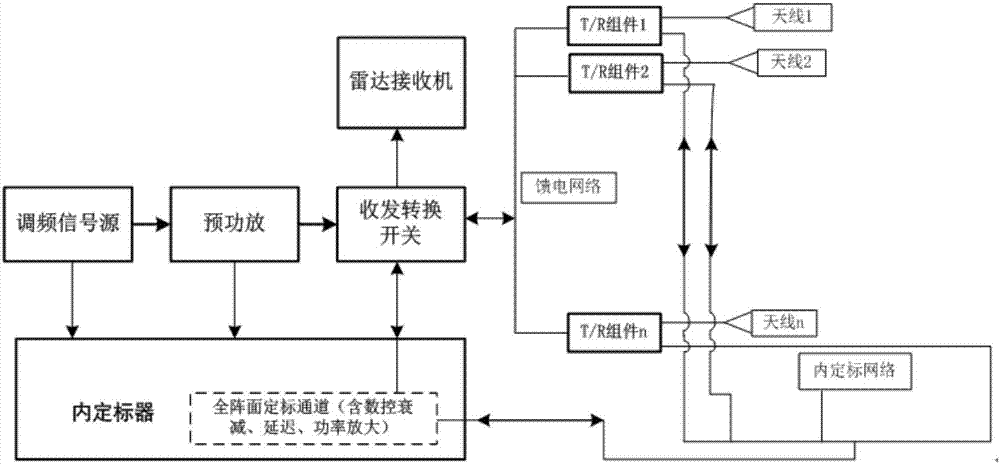
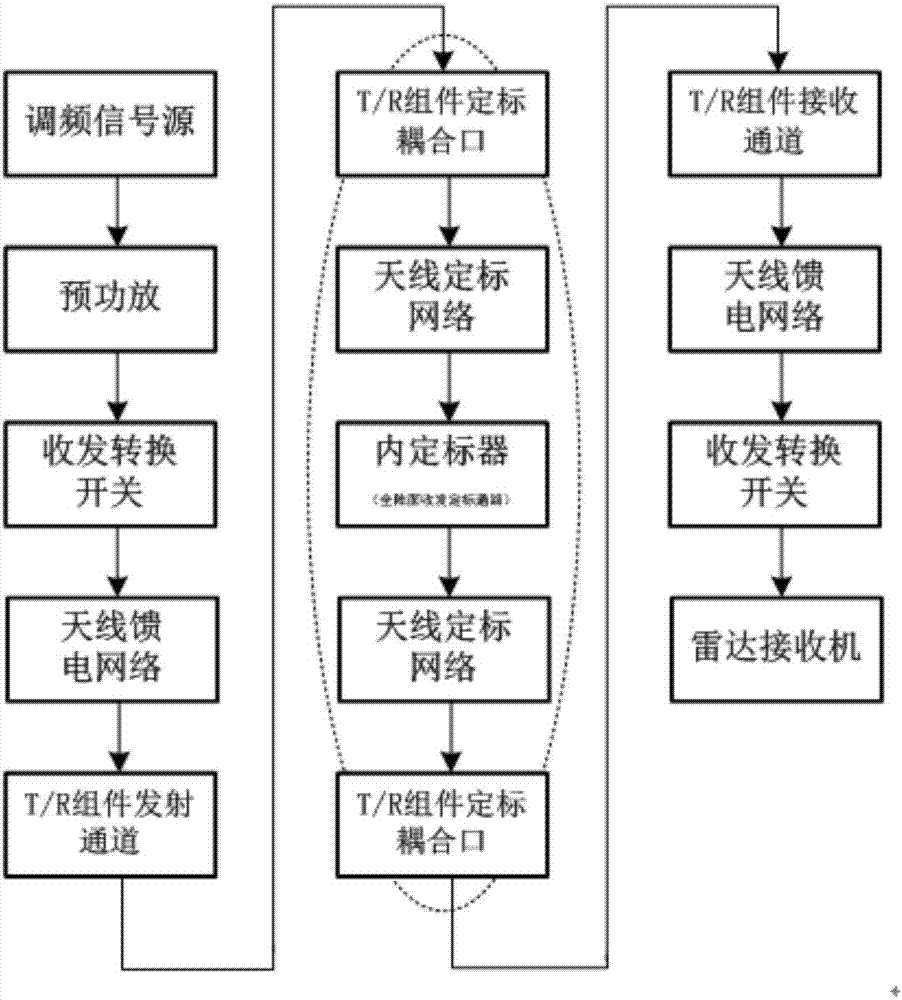
Spaceborne synthetic aperture radar reference function acquiring method based on internal scaling data
ActiveCN107271994AImprove matchHigh imaging performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsMicrowave
The invention provides a spaceborne synthetic aperture radar reference function acquiring method based on internal scaling data. The method comprises the following steps of 1, acquiring amplitude phase error data of an internal scaler full-array-plane received-and-transmitted scaling pathway, an antenna scaling network and an antenna sub-array; 2, acquiring full-array-plane received-and-transmitted scaling data of a radar system on the condition of a preset working bandwidth and pulse width parameter; and 3, compensating amplitude phase error of the internal scaler, the scaling network and the antenna sub-array in the full-array-plane received-and-transmitted scaling data and the like. According to the method of the invention, on the condition of relatively high characteristic consistency between a radar received-and-transmitted copying signal and an actual received-and-transmitted signal, a reference function is used for performing coupling processing, thereby obtaining an effect which is approximate to a standard sinc function, and realizing most powerful supplementing and improvement to predistortion processing of the radar system. The spaceborne synthetic aperture radar reference function acquiring method is suitable for subsequent all radar microwave loads with a full-array-plane received-and-transmitted scaling mode and settles a problem of relatively high influence of radar system amplitude phase error to an imaging performances. Furthermore the method has a remarkable effect for improving imaging performance of the radar system.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
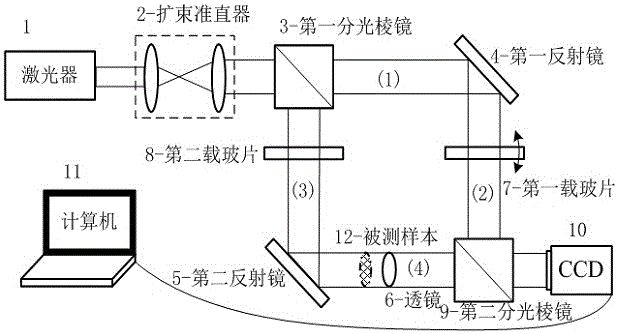
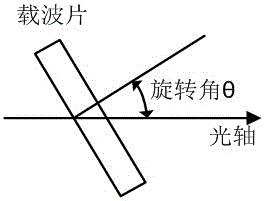
System and method of utilizing two-step phase-shifting coaxial holographic technology to realize 90 DEG phase shift and calibration
The invention relates to a system and method of utilizing the two-step phase-shifting coaxial holographic technology to realize 90 DEG phase shift and calibration. The method comprises: establishing a mach-zehnder double beam plane quasi coaxial holographic optical path system, and separately adding a standard glass slide into an object optical path and a reference light path; adding a condensing lens into the object optical path to converge with the plane of the reference light path to form spherical interference fringes; the spherical interference fringes being distributed in a Sinc function, fine tuning a rotating platform to allow the center of a Sinc function distribution curve to be a maximum value; continuing fine tuning the rotating platform, allowing the center of a sampled Sinc function distribution curve to be a minimum value; and removing the condensing lens in the object optical path, placing a tested sample, and marking according to twice scale values of the rotating platform so as to collect two holograms with 90 DEG phase shift. The recording device referred in the method has the characteristics of less optical elements, simple structure, convenient operation, high adjusting precision, and low cost, and can realize 90 DEG phase shift and calibration in the two-step phase-shifting coaxial holographic technology.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Transmitting unit that reduces PAPR and method therefor
InactiveUS8824574B2Secret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemCarrier signal
A communication system includes a transmitting unit with a peak to average power (PAPR) reduction section. The PAPR reduction section modifies the PAPR reduction it effects in a communication signal in accordance with two different error vector magnitude (EVM) constraints for each channel type, where a channel type is a distinct combination of a modulation order and a coding rate. The EVM constraint followed for each subcarrier in an OFDM or OFDMA application is selected in response to whether the subcarrier conveys voice or non-voice data. The PAPR reduction section may include a scaling filter. The scaling filter is efficiently defined through the use of a predetermined sinc function and a first stage scale factor that is calculated in response to a weighted average of excursion signal subcarrier gains, where the weighting follows the distribution of channel types through the subcarriers.
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
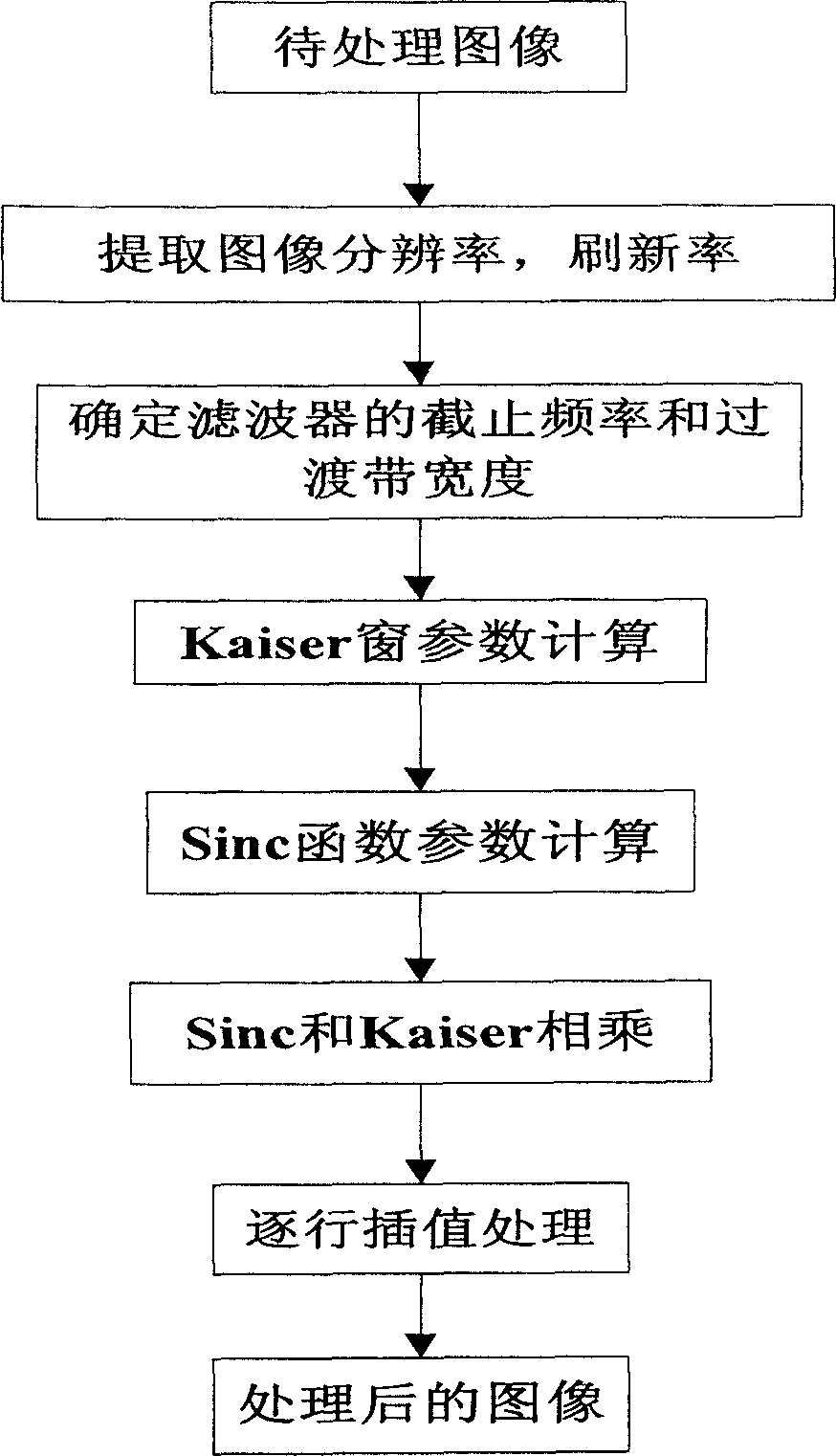
Window added interpolation method for Sinc function in image scaling device
An interpolation selecting method of image pantograph includes using a weighting sequence to make amplitude be attenuated slowly to be zero near two ends of filter, naming this weighting sequence as window, calculating out cut-off frequency and transition bandwidth of filter according to image character of image to be contracted and enlarged then calculating out beta parameter of Kaiser window and length parameter N of window as well as parameter of Sinc function.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
High phase order electrical rotating machine with distributed windings
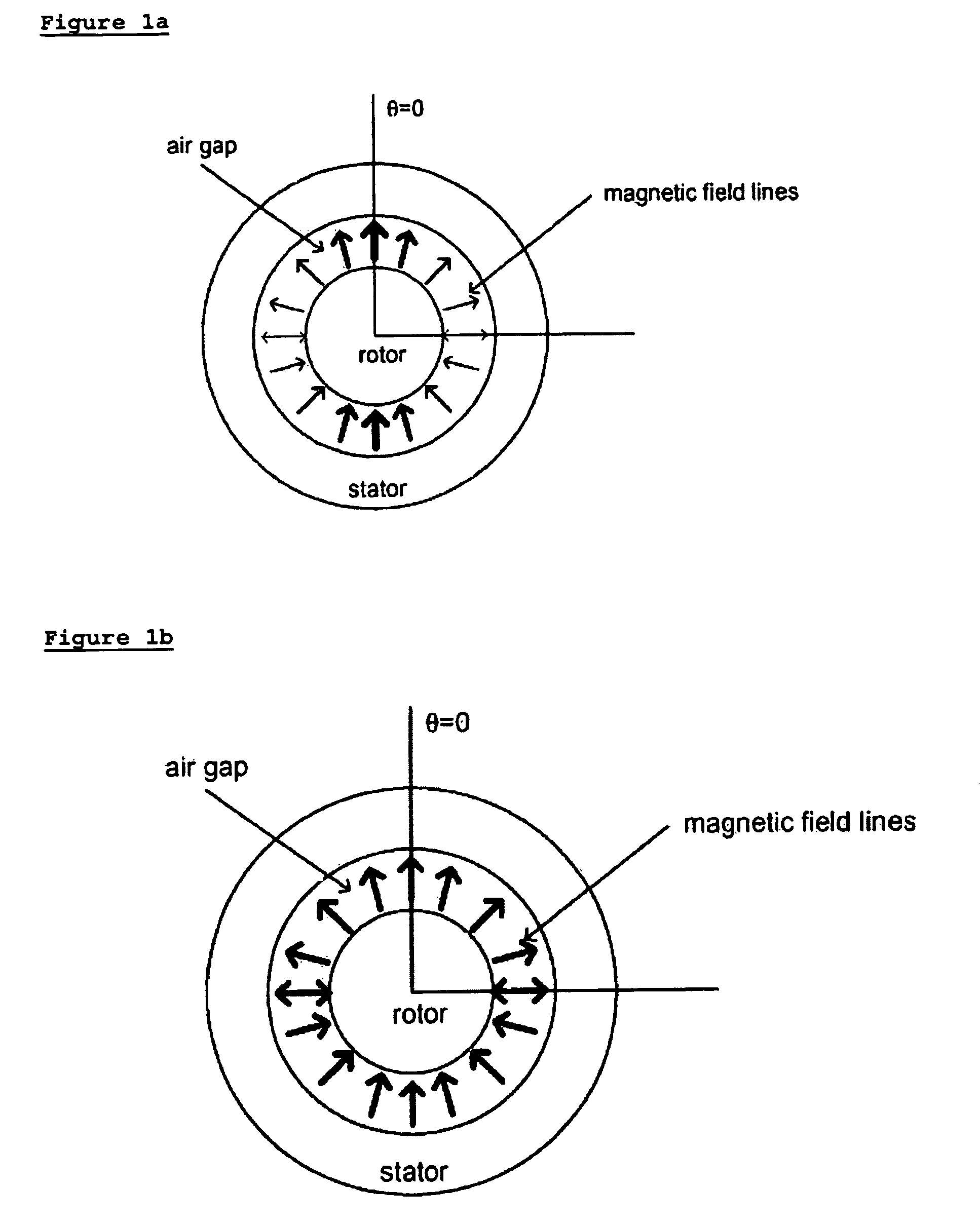
InactiveUS7075265B2Change the impedance of the machineProduced economicallySingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlElectric machineThird harmonic
A rotating induction machine, containing five or more different phases, having windings distributed according to a sinc function with a cutoff frequency allowing low-order spatial harmonics but preventing higher order spatial harmonics from flowing. In a preferred embodiment, the machine is connected to drive means capable of injecting third harmonic into the machine. In a further preferred embodiment, the windings are connected to the drive means with a mesh connection and the machine has five phases.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
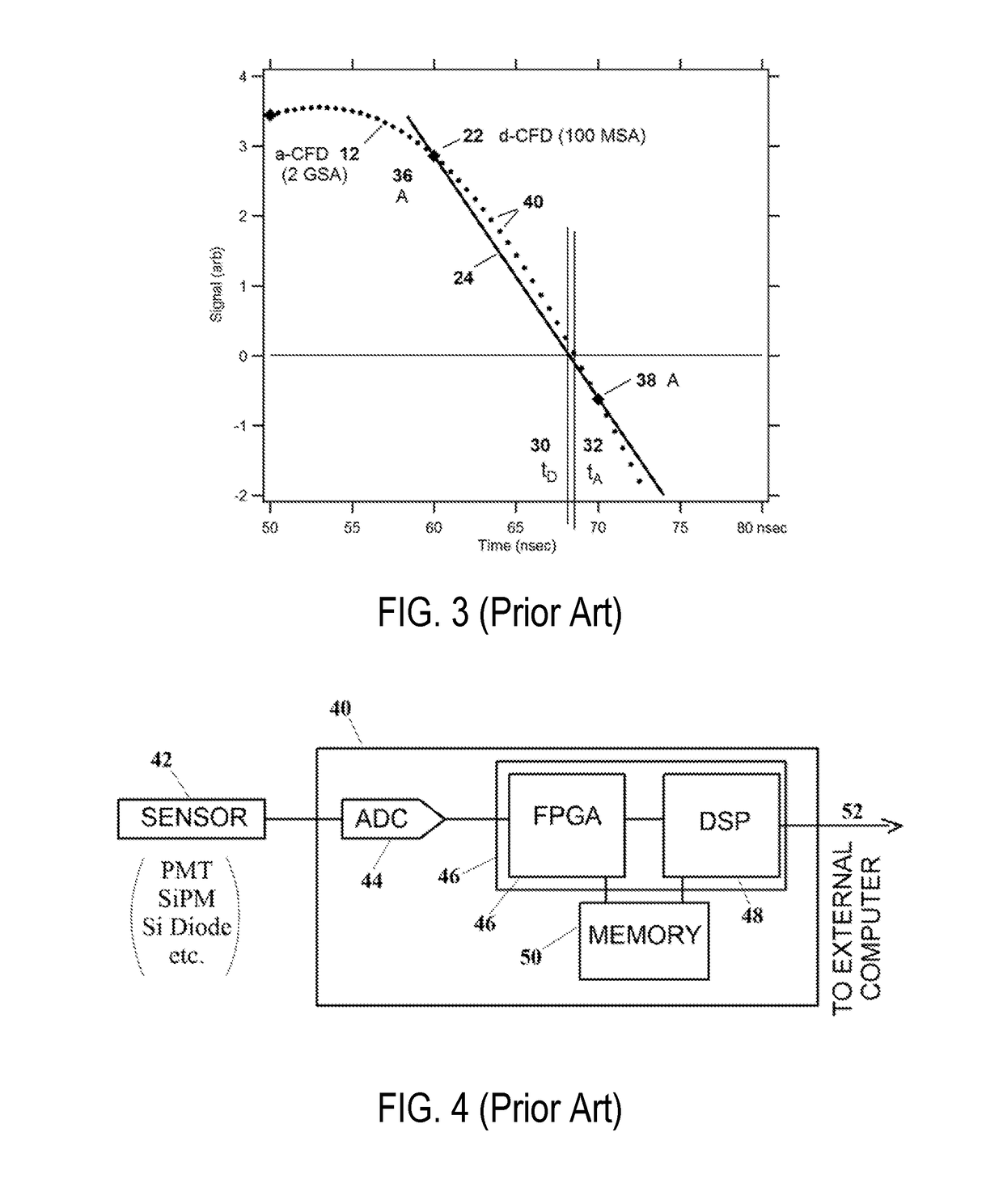
Interpolation Measurement of the Arrival Time and/or Amplitude of a Digitized Electronic Pulse
ActiveUS20180113203A1Wave based measurement systemsElectric unknown time interval measurementImage resolutionGaussian function
A digital processing technique for measuring the time of arrival of a digitized electronic signal pulse for in-line implementation in a field programmable gate array or digital signal processor. For each detected pulse, an interpolation method is used to estimate its maximum M, M is multiplied by a fraction f, and a second interpolation method is used to estimate the time when the pulse reaches the value f·M, which is then taken as the pulse's time of arrival. Various interpolation methods may be used. A particularly accurate method employs convolution of the pulse data by a kernel that is the product of the sinc function and a Gaussian. Detector physics limited time resolutions of 2-5% of the sampling interval are demonstrated. Estimating M is useful in its own right for determining pulse amplitudes, for example as a measure of the energies of photons absorbed in a detector.
Owner:XIA
System and method for automatic filter generation using sampled sinc function with windowed smoothing
InactiveUS20050259753A1Geometric image transformationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSinc functionOn the fly
Methods and systems for processing a plurality of pixels, in a video system, are disclosed. Aspects of the method may comprise acquiring scaling factors associated with a plurality of output pixels and generating filter coefficients during the generation of the output pixels. The filter coefficients may be utilized to filter a plurality of pixels to produce the plurality of output pixels. The filter coefficient may be generated on the fly utilizing a windowed sinc function corresponding to the scaling factors. The sinc function may be sampled according to the needed number of filter taps to determine the filter coefficients.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
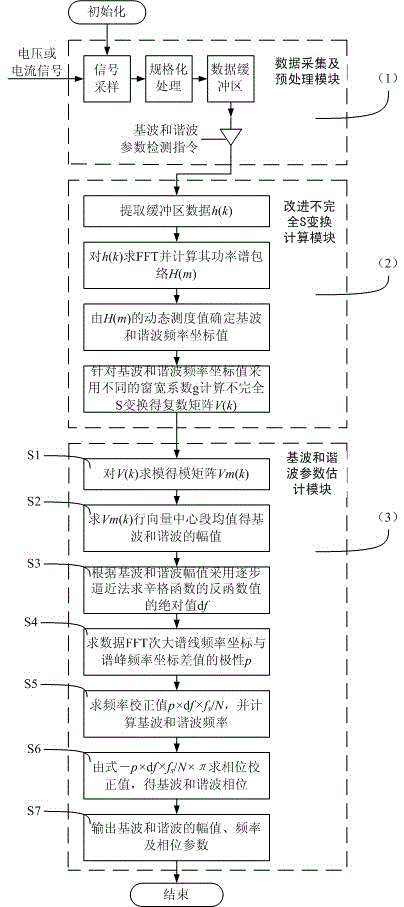
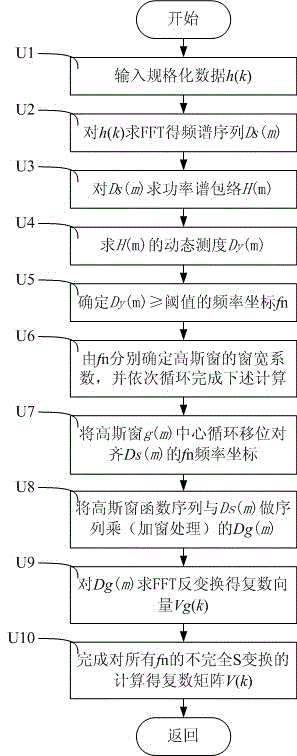
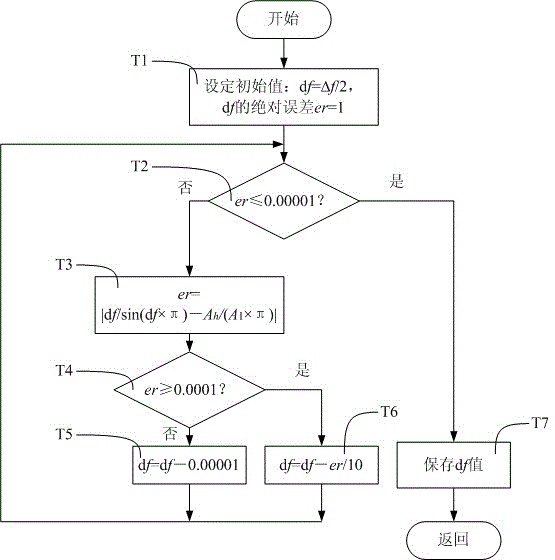
Fundamental wave and harmonic wave parameter estimation method based on incomplete improved S transformation
ActiveCN105652085AIncrease overheadGuaranteed real-timeSpectral/fourier analysisPhase correctionFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a fundamental wave and harmonic wave parameter estimation method based on incomplete improved S transformation. According to the method, a data collecting and preprocessing module (1), an incomplete improved S transformation computing module (2) and a fundamental wave and harmonic wave parameter estimation module (3) are included. The data collecting and preprocessing module (1) conducts standardized processing on collected data; the incomplete improved S transformation computing module (2) conducts incomplete improved S transformation computing on standardized data; the fundamental wave and harmonic wave parameter estimation module (3) obtains fundamental wave and harmonic wave amplitudes through a row amplitude vector center section mean of the incomplete improved S transformation at first, and then obtains the frequency and phase correction values of fundamental waves and harmonic waves according to the amplitudes by adopting inverse function values of a sinc function and polarities of spectrum peak frequency coordinate difference values and secondary maximum spectrum lines of fundamental waves and harmonic waves corresponding to spectra, and then the frequencies and phases of the fundamental waves and the harmonic waves are obtained. The method provides a real-time and precise means for detecting fundamental wave and harmonic wave parameters of an electric system.
Owner:河北辰恒电力工程有限公司
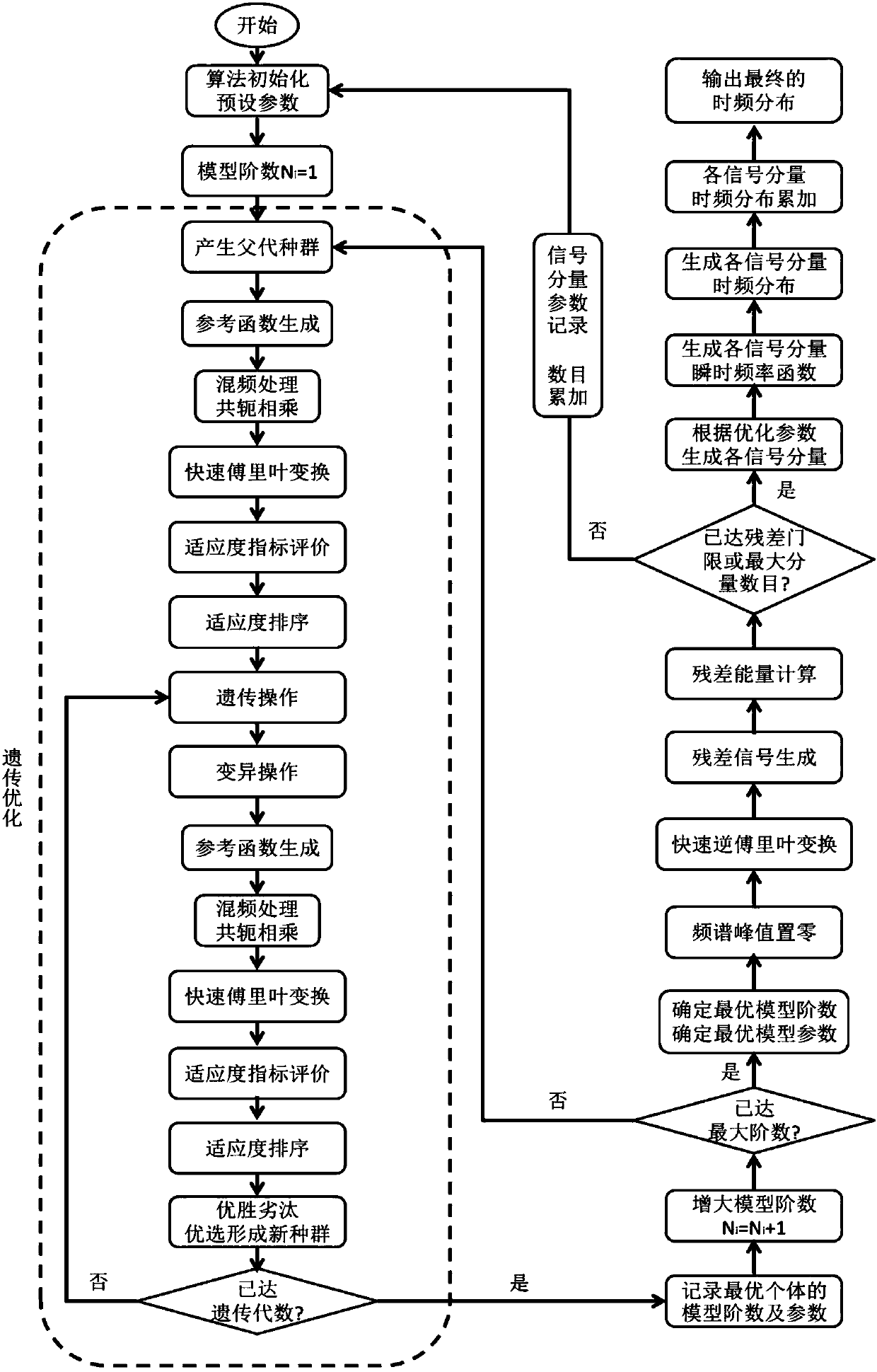
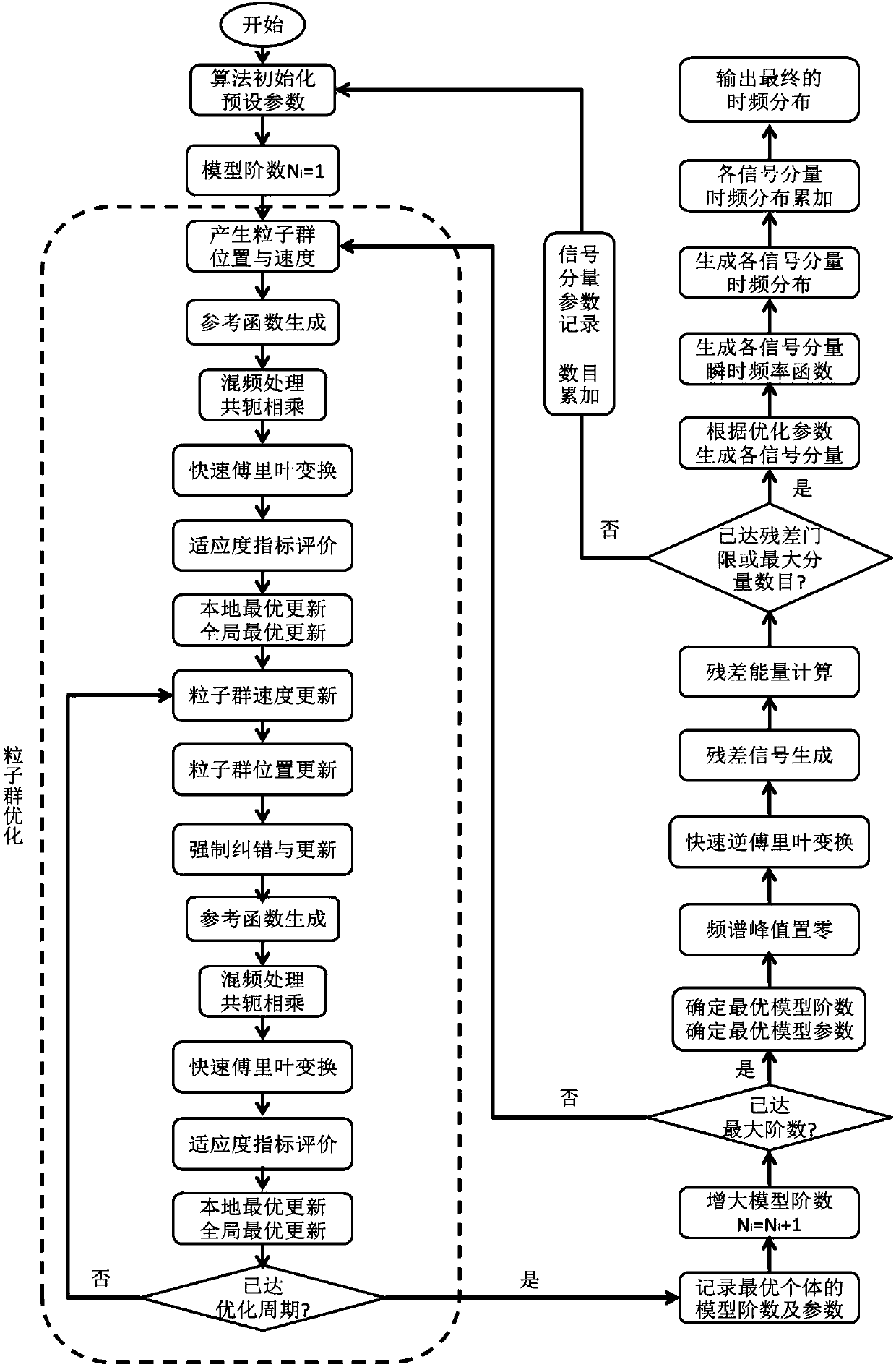
Polynomial phase signal adaptive time frequency transformation method based on genetic optimization
ActiveCN107729289AOvercome the defect of cross term in non-single componentOvercome the defect of cross termCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsDecompositionTime frequency decomposition
The invention provides a polynomial phase signal adaptive time frequency transformation method based on genetic optimization. Time frequency decomposition of polynomial phase signals can be finished,every signal component obtained by decomposition only corresponds to a single component of a frequency point at any time, then values are obtained by the various signal components and instantaneous frequency at any time, signal frequency distribution corresponding to the corresponding time is directly calculated and generated by only retaining a main lobe responded Sinc function, the shortcoming that cross terms exist due to the fact that one time corresponds to non-single components of a plurality of frequency points in the traditional time frequency transformation is overcome, and thus, timefrequency distribution which does not have any cross term interference and has excellent time frequency combined resolution is output finally. The polynomial phase signal adaptive time frequency transformation method based on genetic optimization is simple in principle and convenient to operate; adverse impact of cross term interference of a classic time frequency analysis method and loss of timefrequency combined resolution can be overcome effectively, and the quality and benefit of non-stable polynomial phase signal time frequency analysis can be improved effectively.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
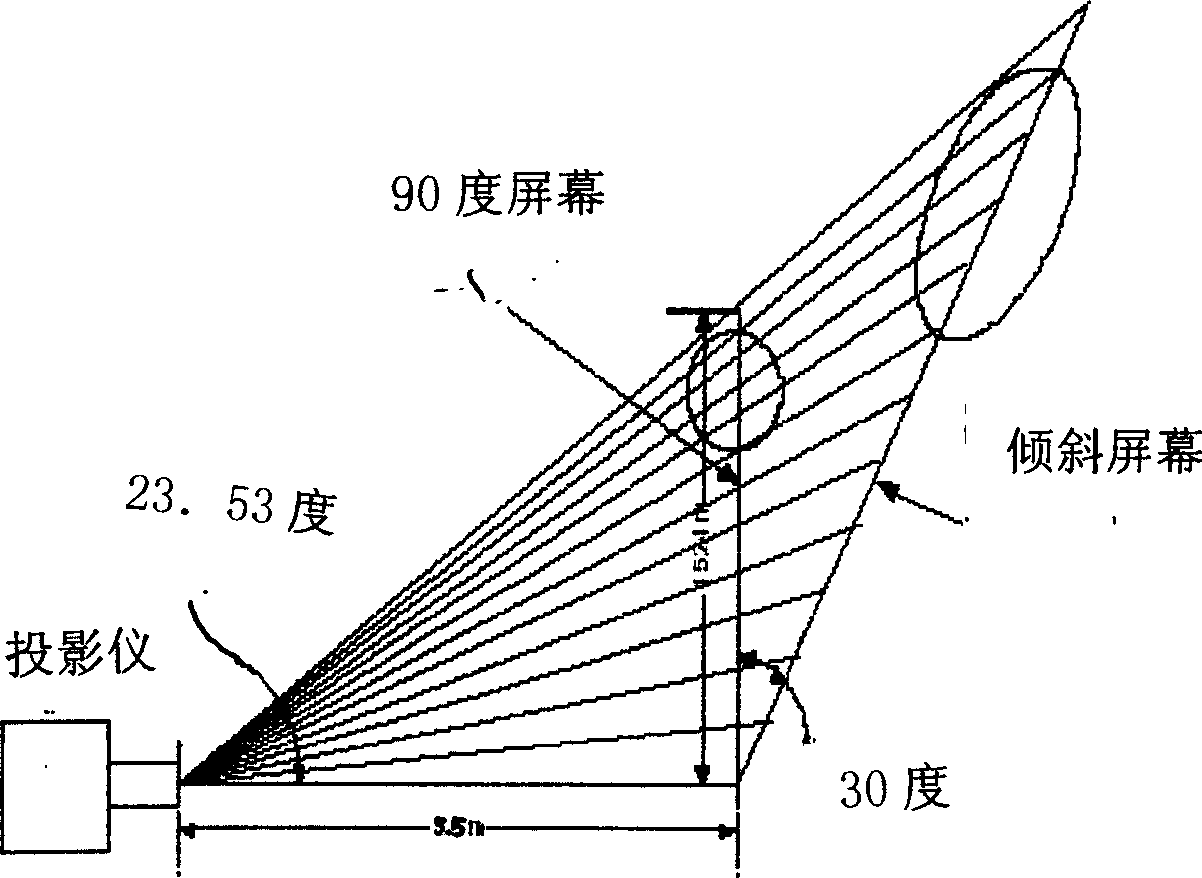
Trapezoidal correcting system for projector
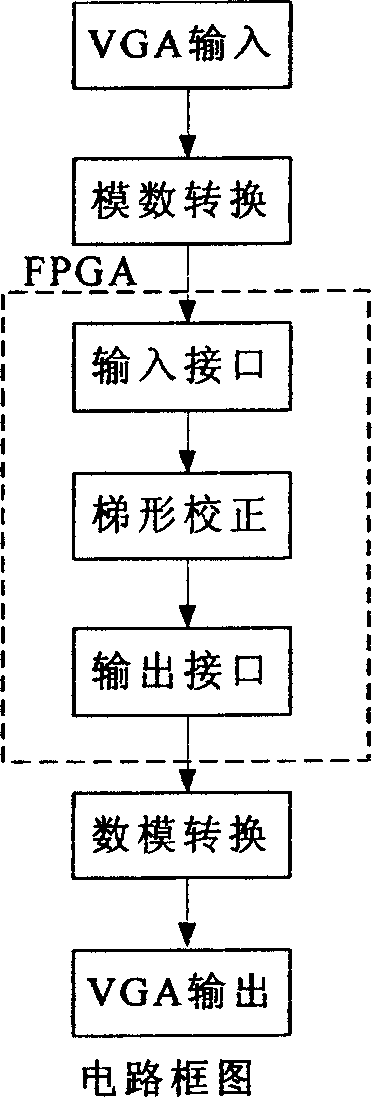
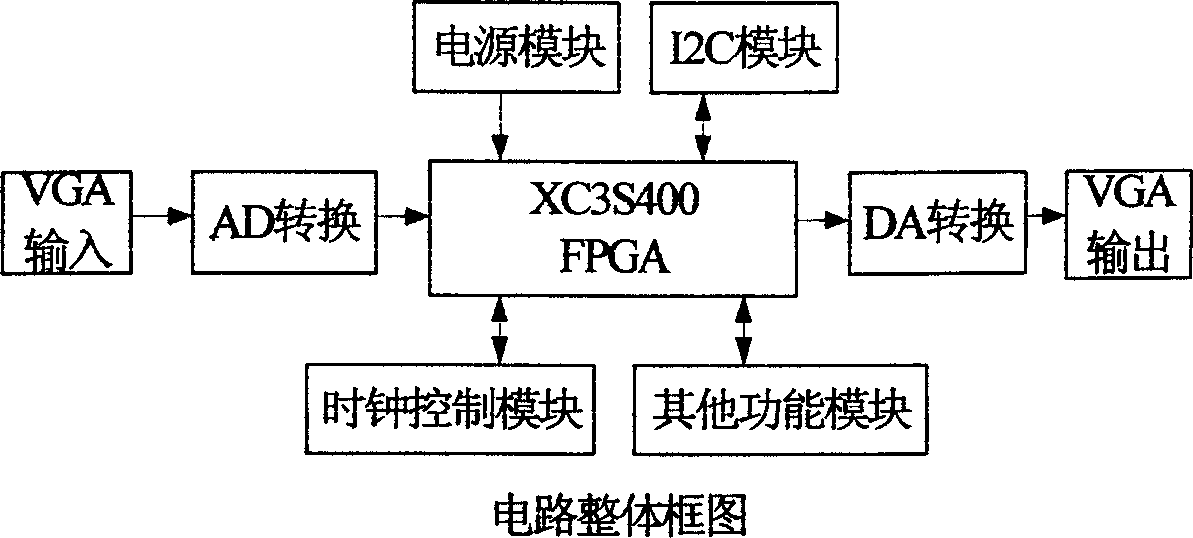
InactiveCN1862363ACorrect image distortion issuesImprove the display effectTelevision system detailsProjectorsFiltrationCorrection technique
The present invention relates to a projector trapezium correction system. On the output end of picture current of projector the invented projector trapezium correction system can be adopted to make image processing. Said processing method includes the following steps: firstly, making the picture current be passed through A / D converter circuit to obtain digital signal, after having been processed making the digital signal be passed through D / A converter circuit to obtain analog signal and output it; using FPGA chip as image processing core chip, the FPGA chip is connected with data and control port of microprocessor, utilizing microprocessor to control FPGA to execute operation, said microprocessor has memory, clock and power supply module, image processing software is used for processing video signal, in which pretreatment adopts Kaiser window and Sinc function filter to make filtration, the correction adopts line interpolation algorithm and ZEROPAD edge sawtooth correction technique and signal communication between chips adopts I2C bus connection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
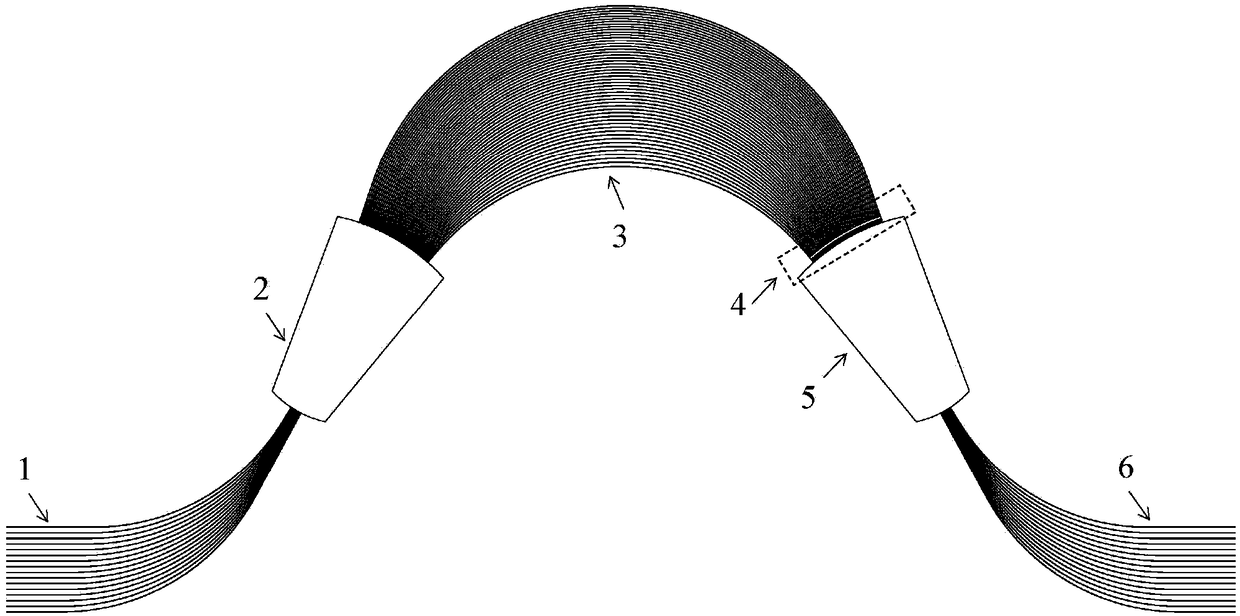
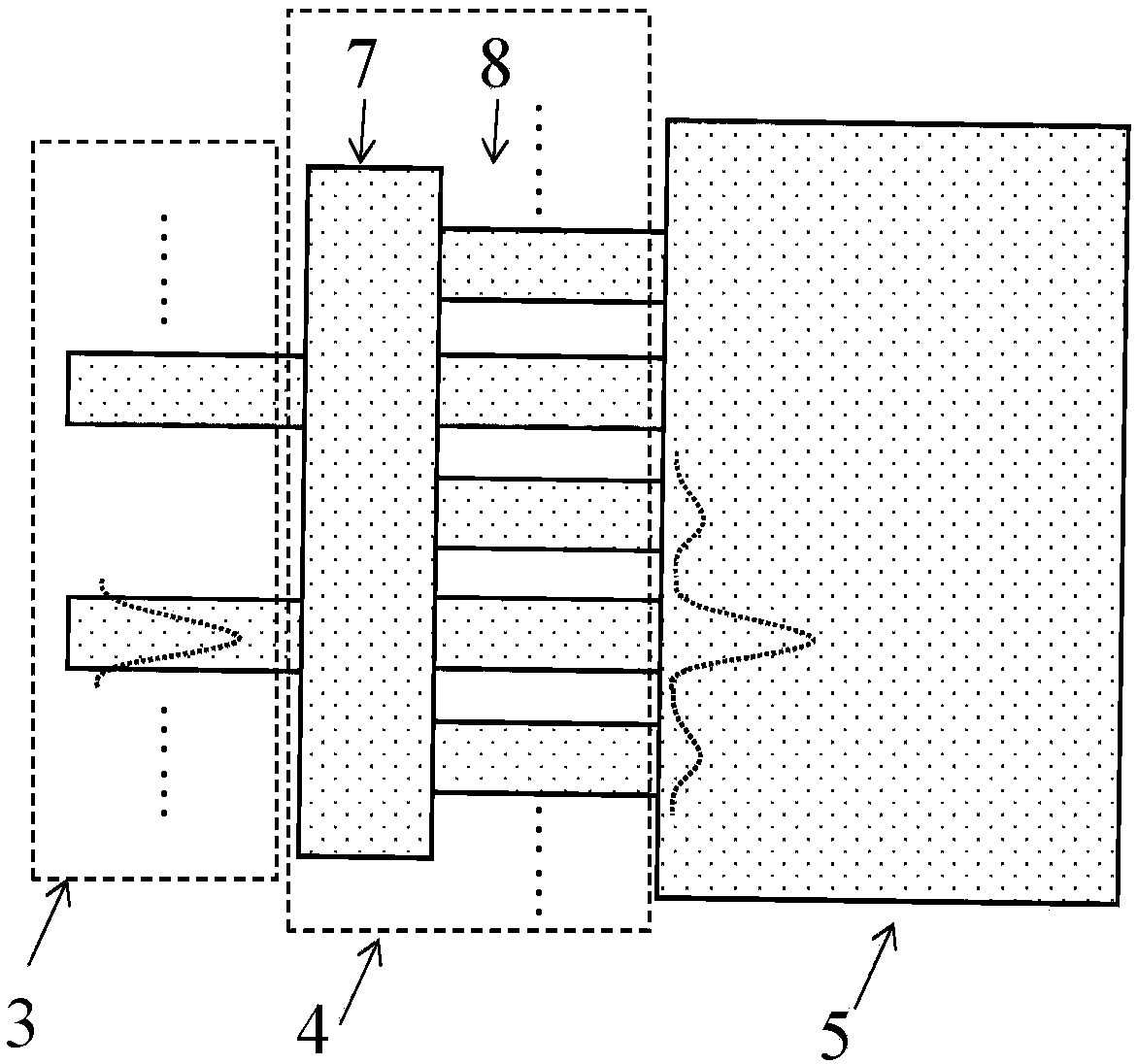
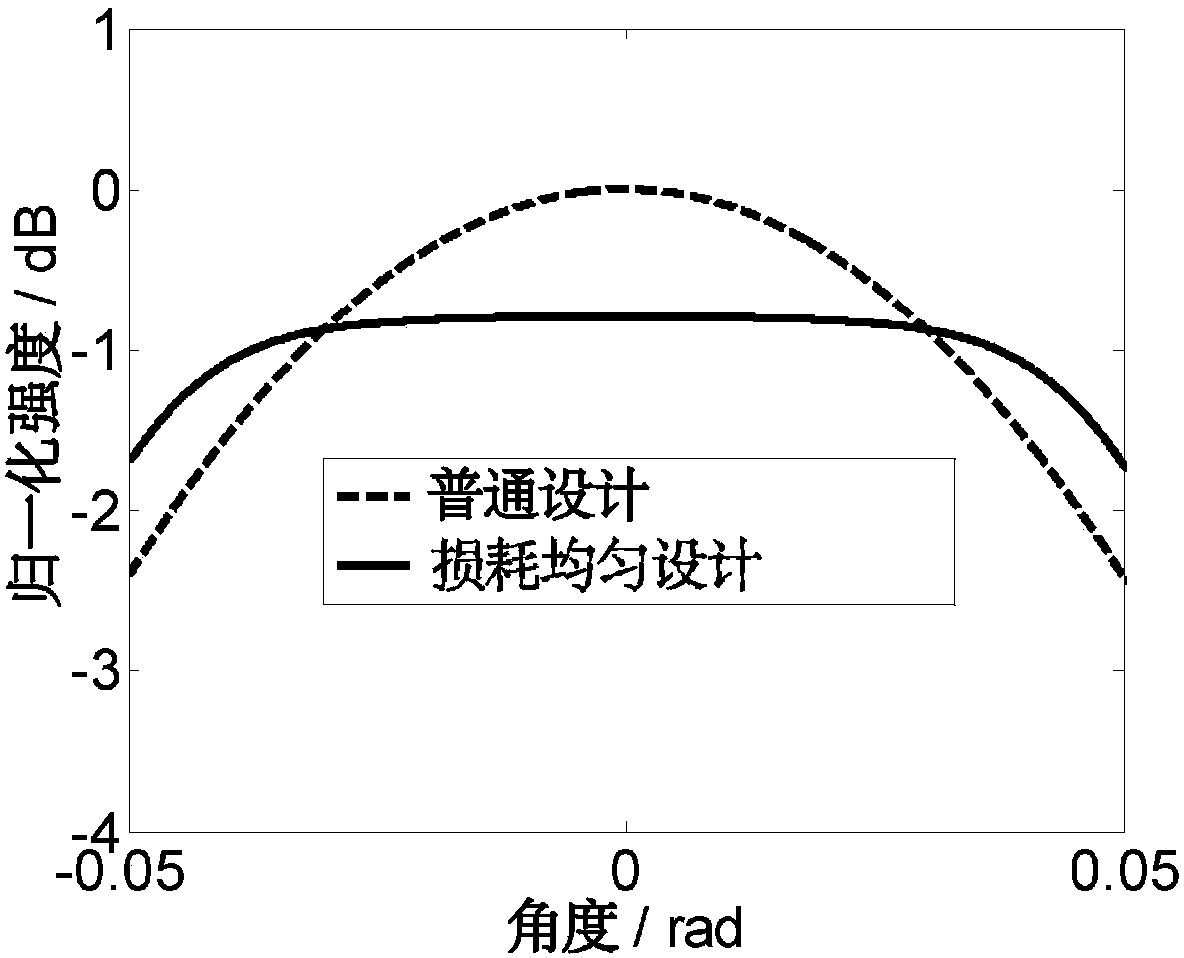
Array waveguide grating router with uniform loss
ActiveCN108469651AUniform lossSmall sizeOptical waveguide light guideHigh level techniquesGratingWaveguide
The invention discloses an arrayed waveguide grating router with uniform loss. Light is input from input waveguide to an input star coupler. Due to the Kirchhoff diffraction phenomenon, the optical field is expanded in the input star coupler and is received by the array waveguide. Then the received light of the array waveguide passes through the Sinc function coupling zone and forms focused imaging in an output star coupler. The Sinc function coupling region transforms the Gaussian optical field transmitted by the array waveguide into the Sinc function type optical field, so that the rectangular optical field is output from the output star coupler to achieve the function of uniform loss of the arrayed waveguide grating router. The arrayed waveguide grating router solves the problem of non-uniformity of loss inherent in the arrayed waveguide grating router. It has the advantages of large volume difference, low cost, small serial interference and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
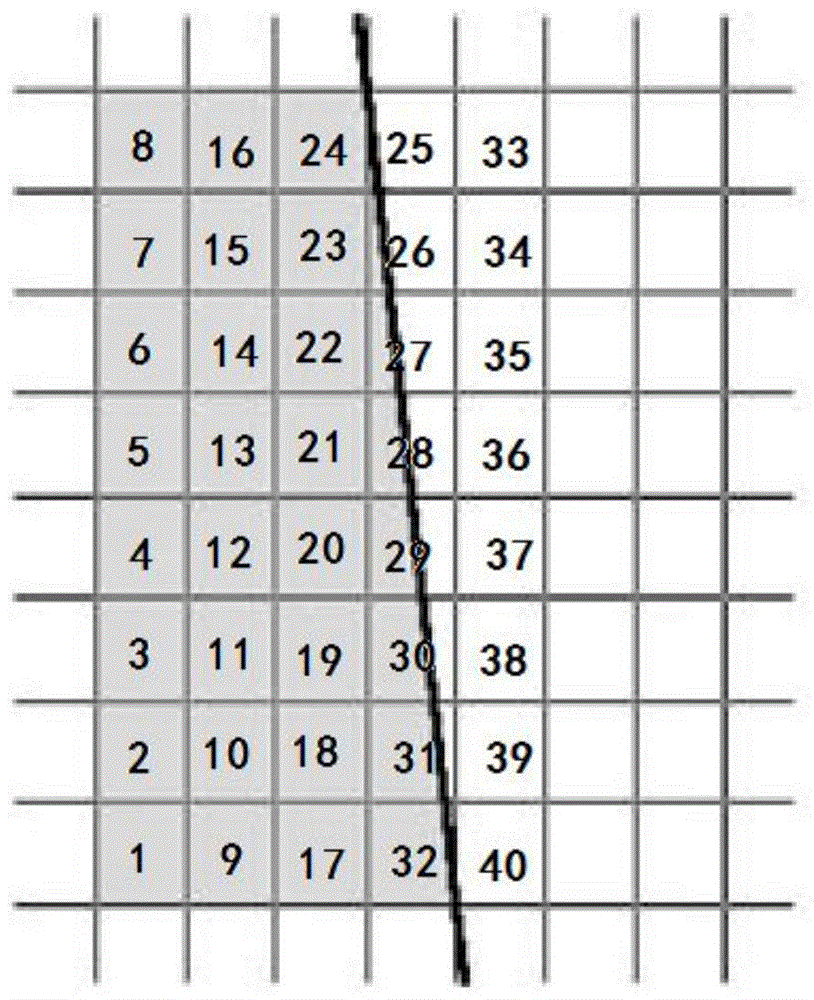
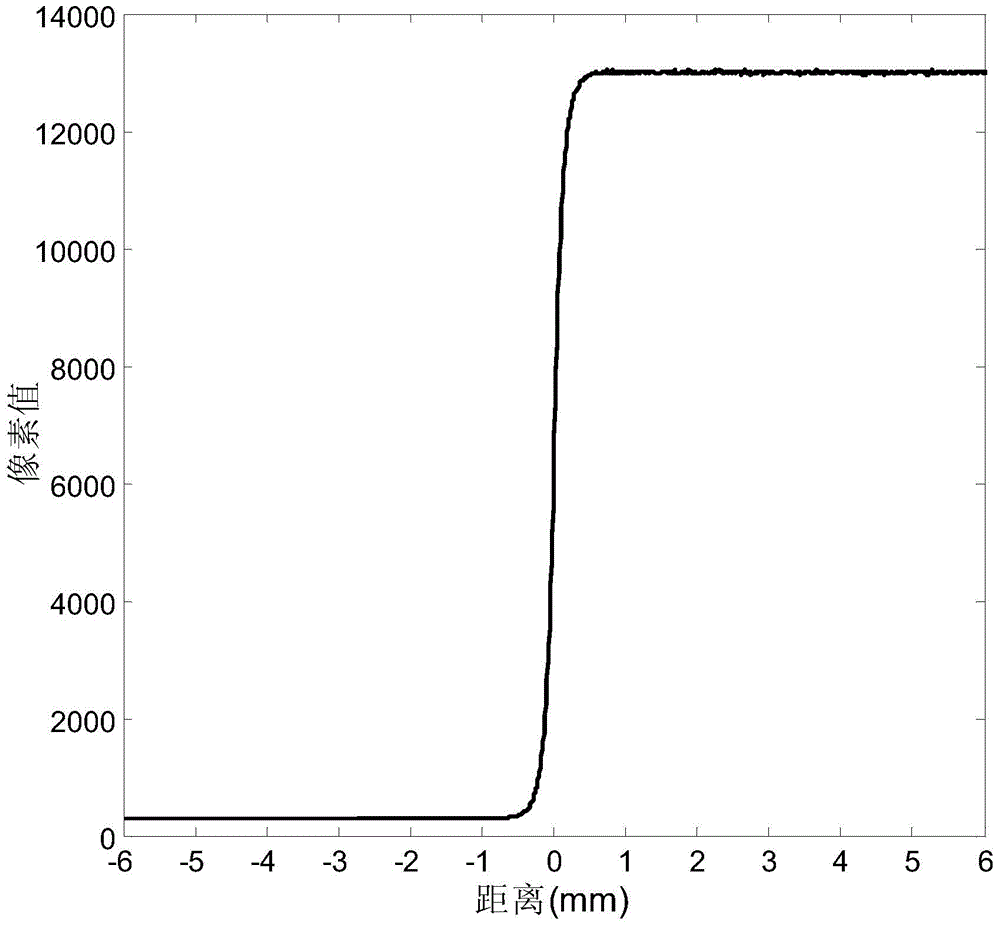
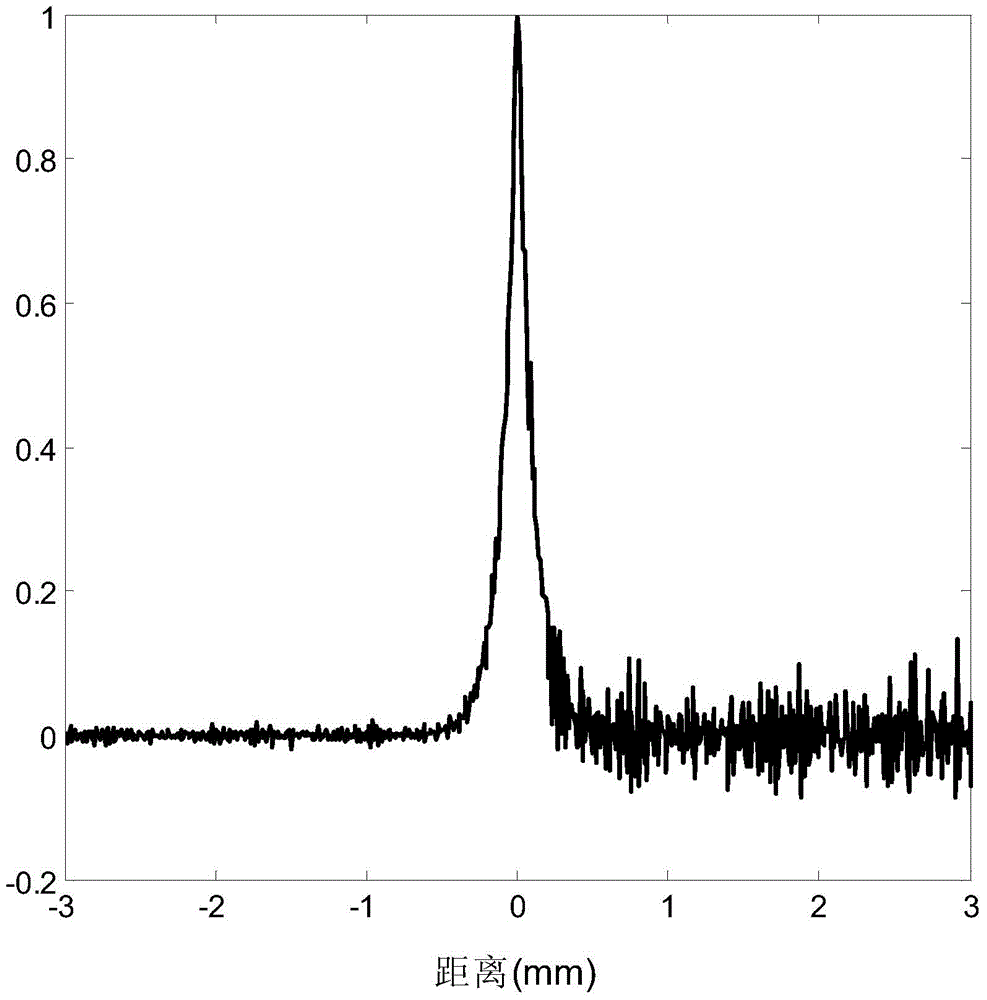
Resolution performance evaluation method for digital X-ray imaging system
InactiveCN104083177AHigh measurement accuracyEfficiently assess performanceRadiation diagnosticsX-rayCurve fitting
The invention provides a resolution performance evaluation method for a digital X-ray imaging system. The method comprises the steps that (1) a plurality of incision images are continuously collected; (2) superposition averaging is performed on the collected incision images, afterwards, incision boundary detection is performed on the averaged incision images, and an incision boundary straight line is obtained through line fitting; (3) an incision tilt angle is obtained, and an oversampling ESF curve is constructed; (4) the oversampling ESF curve is de-noised by the adoption of a monotonic curve fitting method; (5) a suitable translation distance is selected, a real ESF curve and a difference curve of a translation distance result of the real ESF curve are constructed, and Fourier transform is performed on the real ESF curve and the difference curve to obtain sinc functions; (6) suitable translation is performed on an actual oversampling ESF curve, and then subtraction is performed between the actual oversampling ESF curve and the original oversampling ESF curve to obtain a symmetrical oversampling curve; (7) a system modulation transfer function is solved through a deterioration model formula under a frequency domain. According to the resolution performance evaluation method, compared with a traditional incision measuring method, a more accurate MTF curve can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
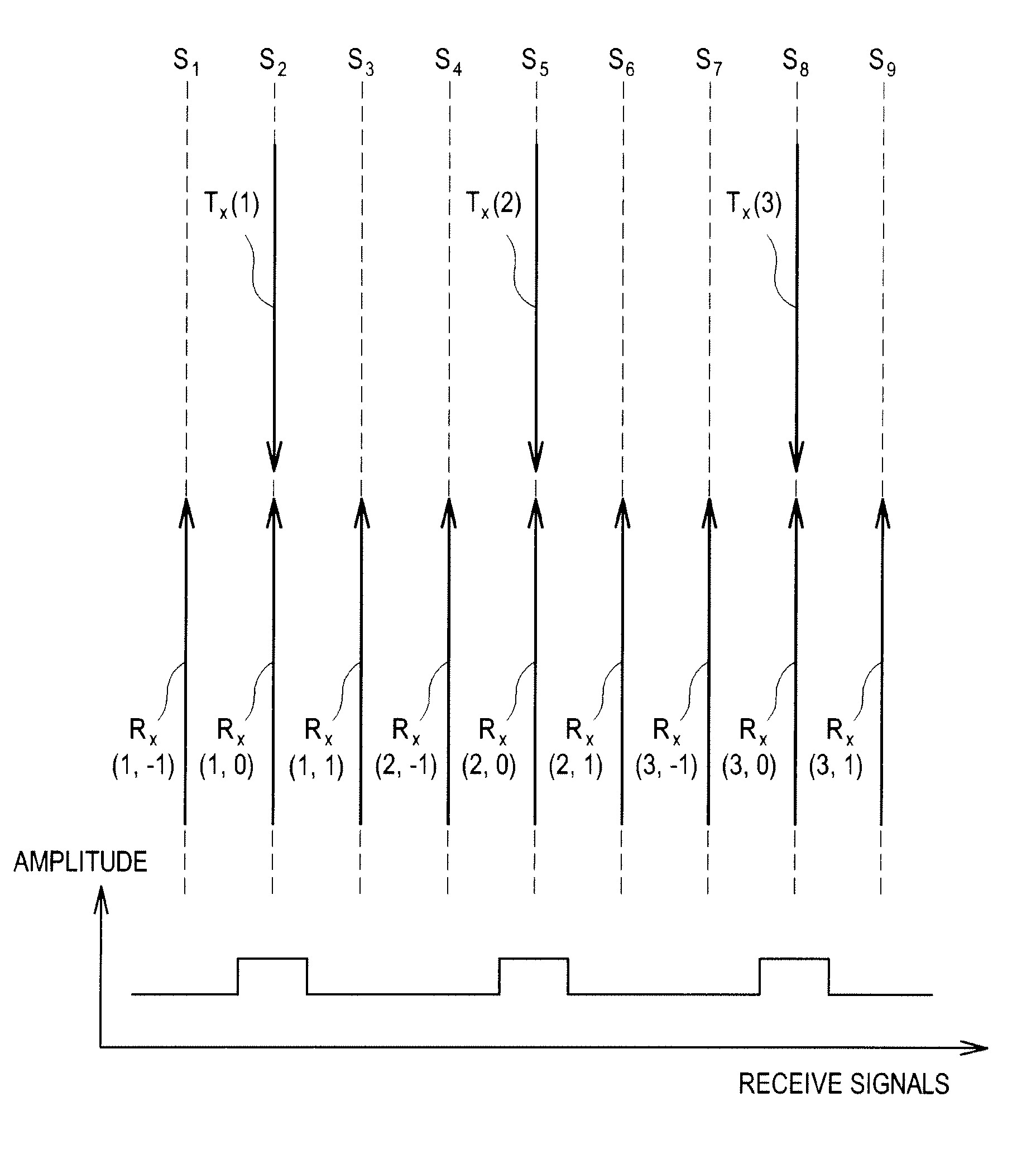
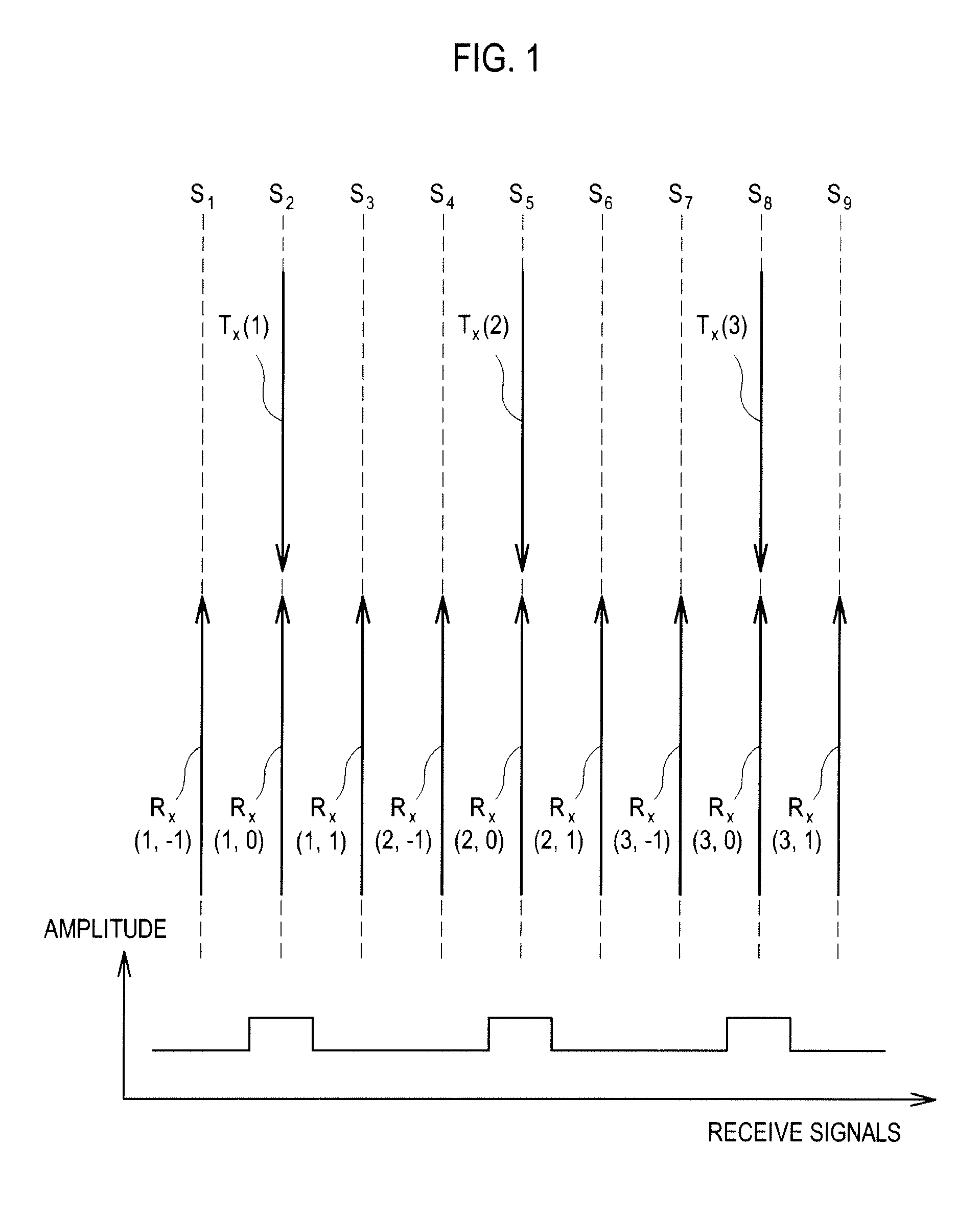
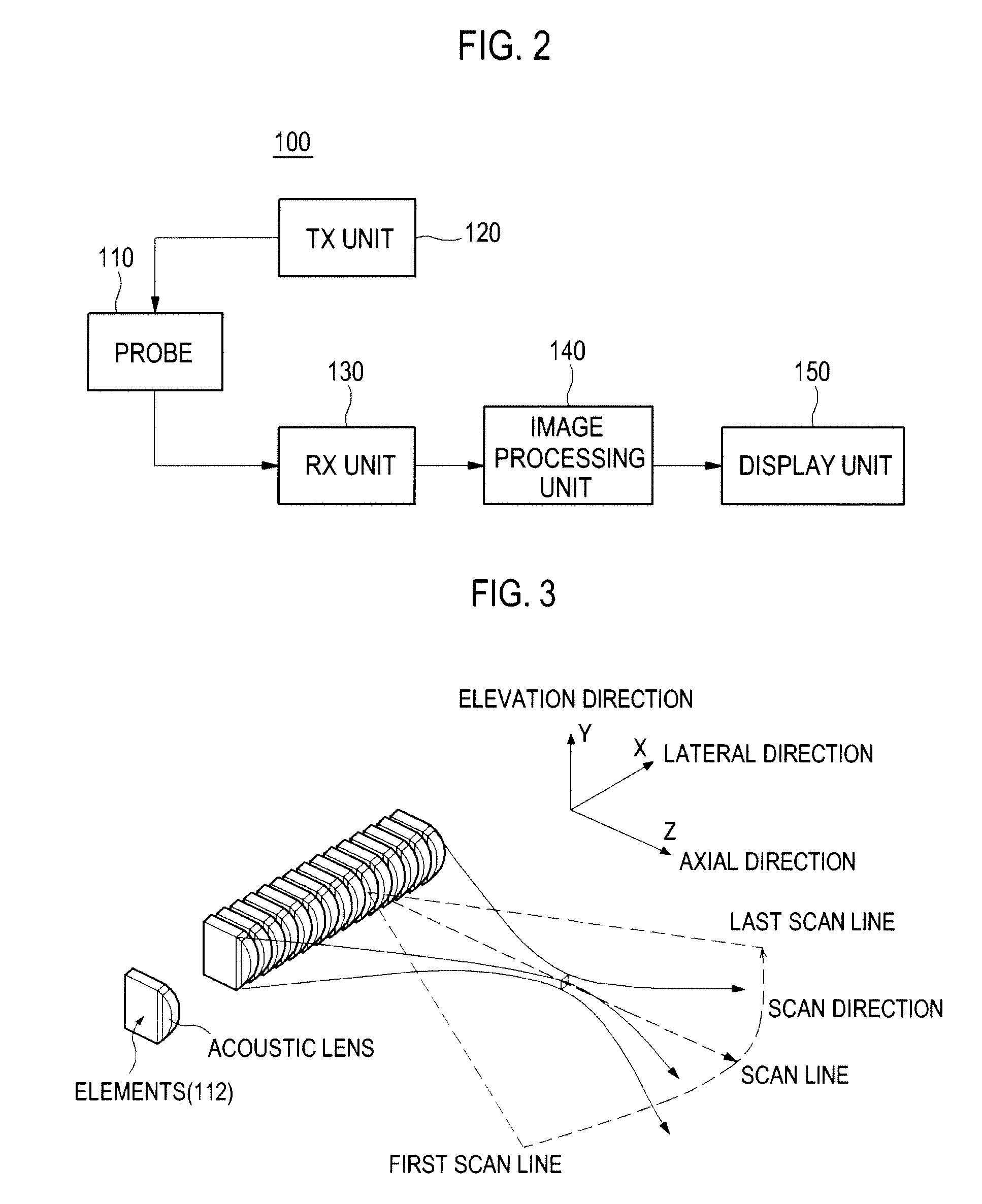
Transmit Apodization Using A Sinc Function In An Ultrasound System
ActiveUS20090137903A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMultiple-port networksSonificationScan line
The present invention relates to transmit apodization using a sinc function in an ultrasound system. The ultrasound system includes: a transmission unit operable to generate transmit pulse signals with transmit apodization applied by using a sinc function; a probe operable to generate ultrasound signals based on the transmit pulse signals to thereby form a transmit beam and transmit the transmit beam along a predetermined scan line among a plurality of scan lines in a target object, the probe being further operable to receive ultrasound echoes reflected from the target object; and a reception unit operable to form receive signals corresponding to a plurality of scan lines based on the ultrasound echoes.
Owner:SAMSUNG MEDISON
Polynomial phase signal time-frequency transform method based on particle swarm optimization
ActiveCN107729288AOvercome the defect of cross term in non-single componentOvercome the defect of cross termArtificial lifeComplex mathematical operationsDecompositionMultiple frequency
The invention provides a polynomial phase signal time-frequency transform method based on particle swarm optimization which is capable of performing time-frequency decomposition on polynomial phase signals; each signal component acquired from the decomposition is a single component corresponding to only one frequency point at any moment; the signal components and instantaneous frequency values ofall moments are subjected to direct calculation by reserving only main-lobe-responsive Sinc function so as to generate a signal frequency distribution of each corresponding moment; the defect is overcome that non-single components with one moment corresponding to multiple frequency points in traditional time-frequency transform have cross components; a time-frequency distribution with no cross-component interference and good time-frequency joint resolution is finally output. The polynomial phase signal time-frequency transform method based on particle swarm optimization has the advantages thatthe principle is simple, operating is convenient, the adverse influence of cross-component disturbances from the conventional time-frequency analysis methods and the loss of time-frequency joint resolution can be effectively overcome, and the quality and benefit of nonstationary polynomial phase signal time-frequency analysis can be effectively improved.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
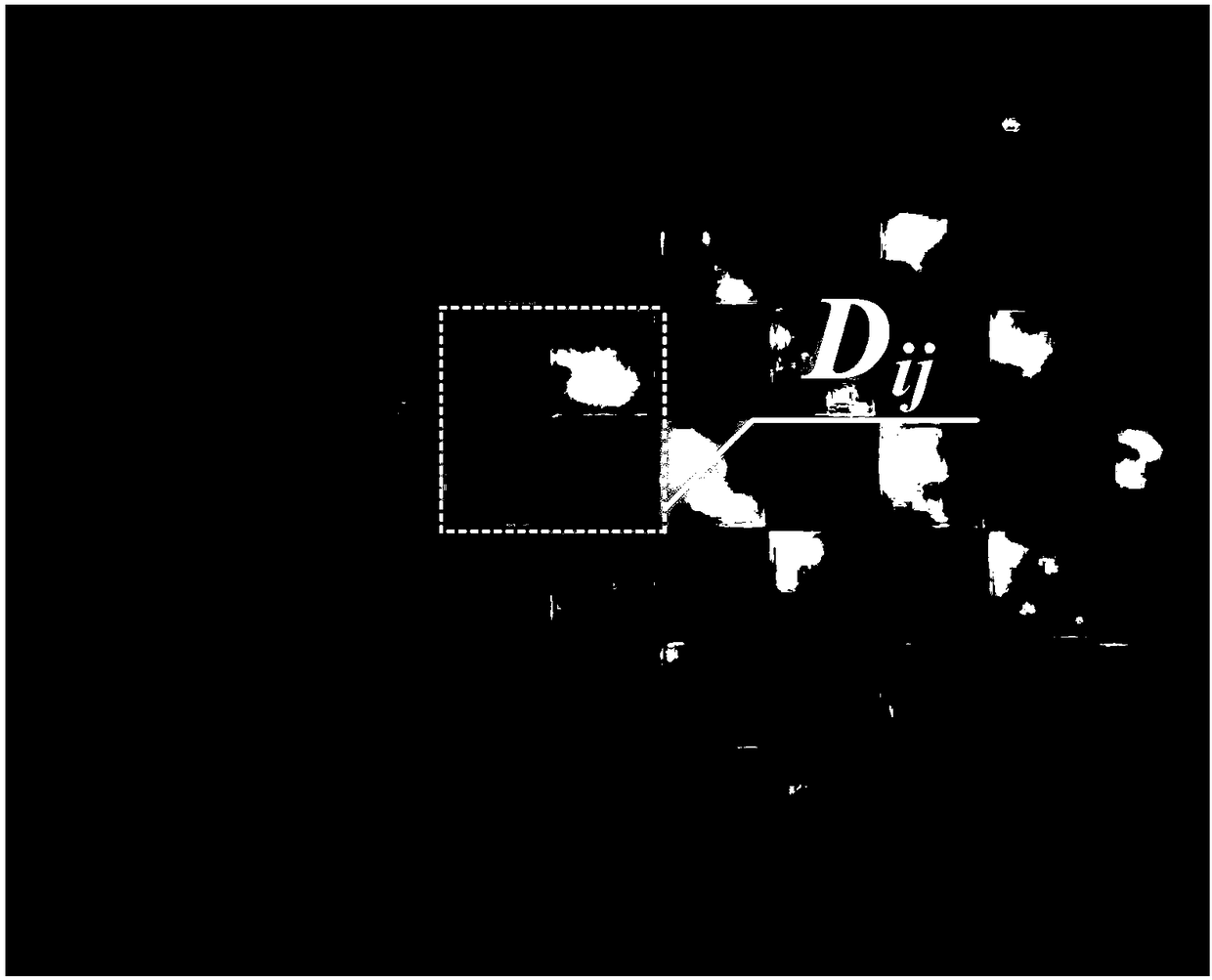
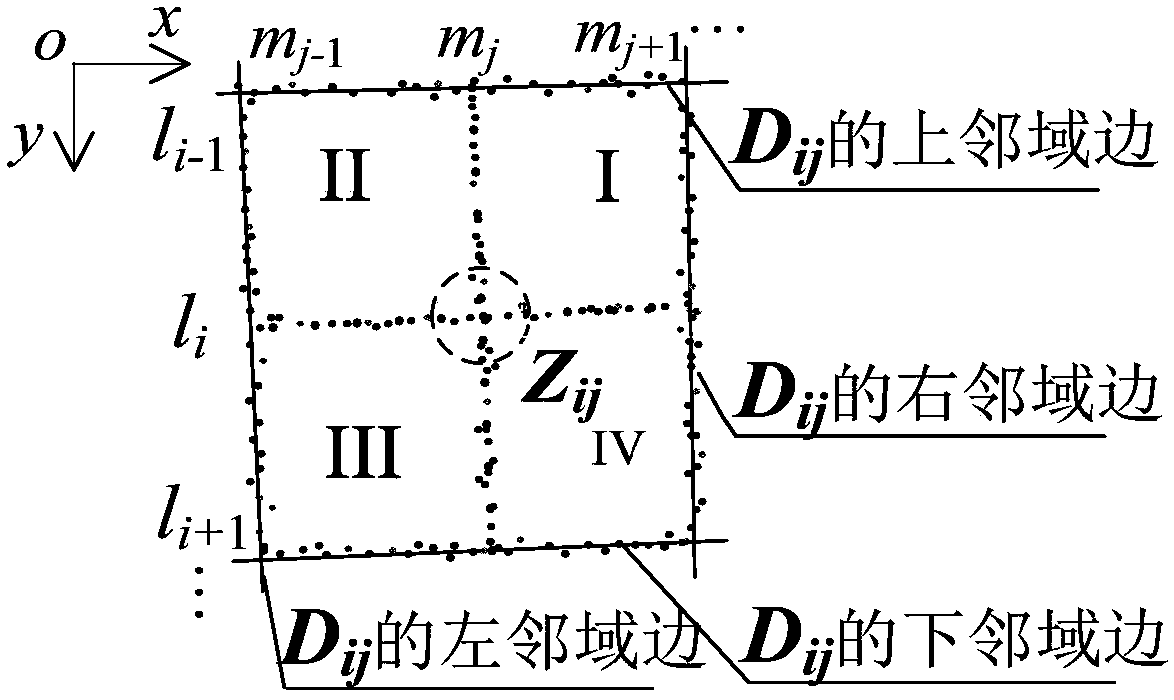
Sub-pixel level corner detection method and system
The invention discloses a sub-pixel level corner detection method and a system. The method comprises: providing a calibration plate, and acquiring an image of the calibration plate; preprocessing theimage to obtain a first image; performing edge extraction in any four neighborhood D<ij> of the first image, and fitting four neighborhood edges in the four neighborhood D<ij> to obtain a linear equation of the four neighborhood edges; obtaining coordinates of an equidistant point O<ij> in the four neighborhood D<ij> according to the linear equation of the four neighborhood edges; obtaining a direction of the diagonal of the four neighborhood according to the linear equation of the four neighborhood edges in the four neighborhood D<ij>, wherein the diagonal is one of the two diagonals of the four neighborhood D<ij> with a lower average gray-scale value; using a SINC function gray-scale distribution to constrain a corner position to obtain a sub-pixel level corner within a domain segment ina four-neighborhood diagonal direction over the equidistant point O<ij> in the four neighborhood Dij. The sub-pixel level corner detection method reduces the influence of noise on the image acquisition of the calibration plate, and effectively improves the accuracy and the precision of sub-pixel corner detection.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
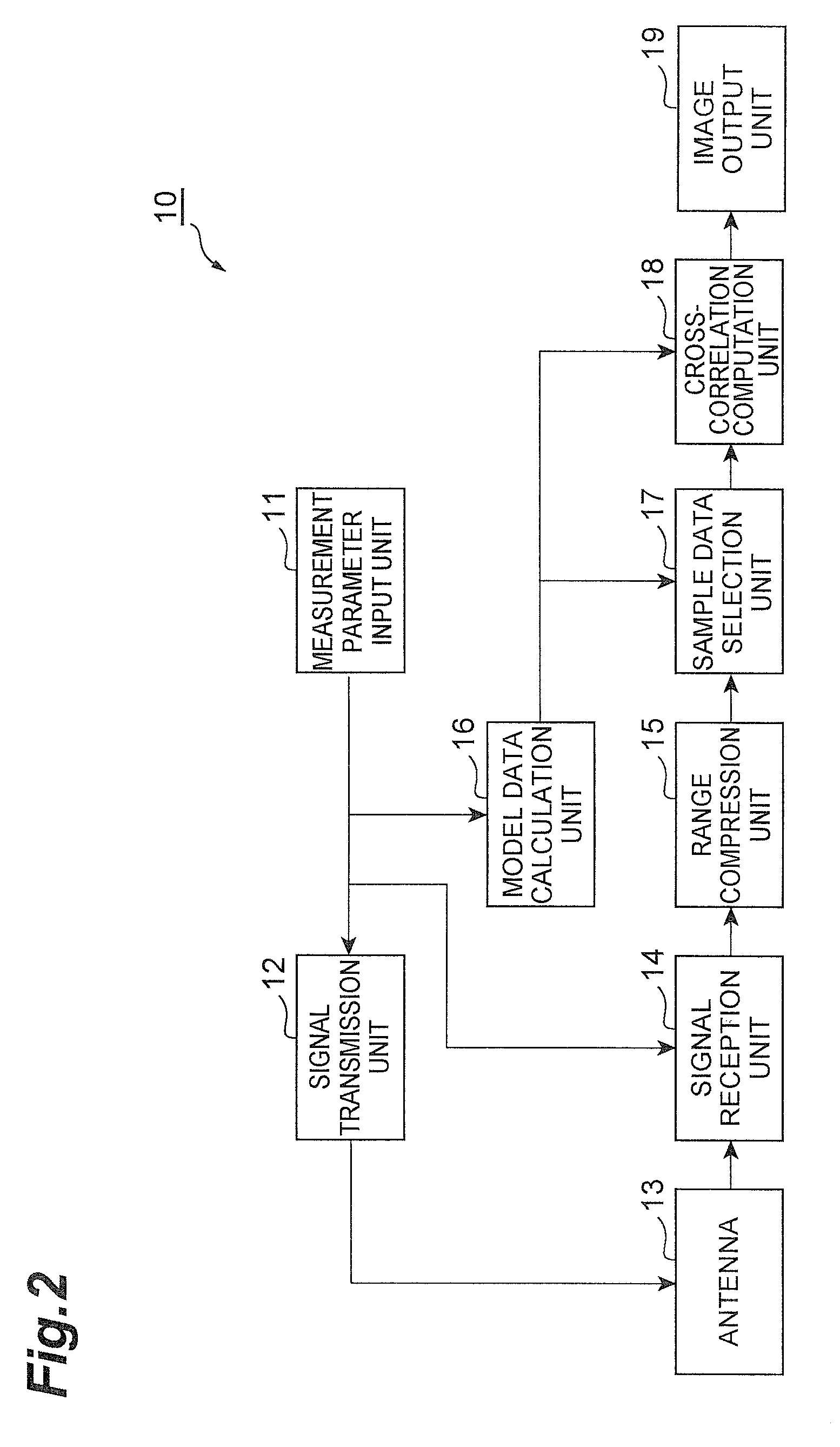
Synthetic aperture processing system and synthetc aperture processing method
InactiveUS20110032142A1Improve accuracyReduce the amount of calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAcoustic wave reradiationData segmentReflected waves
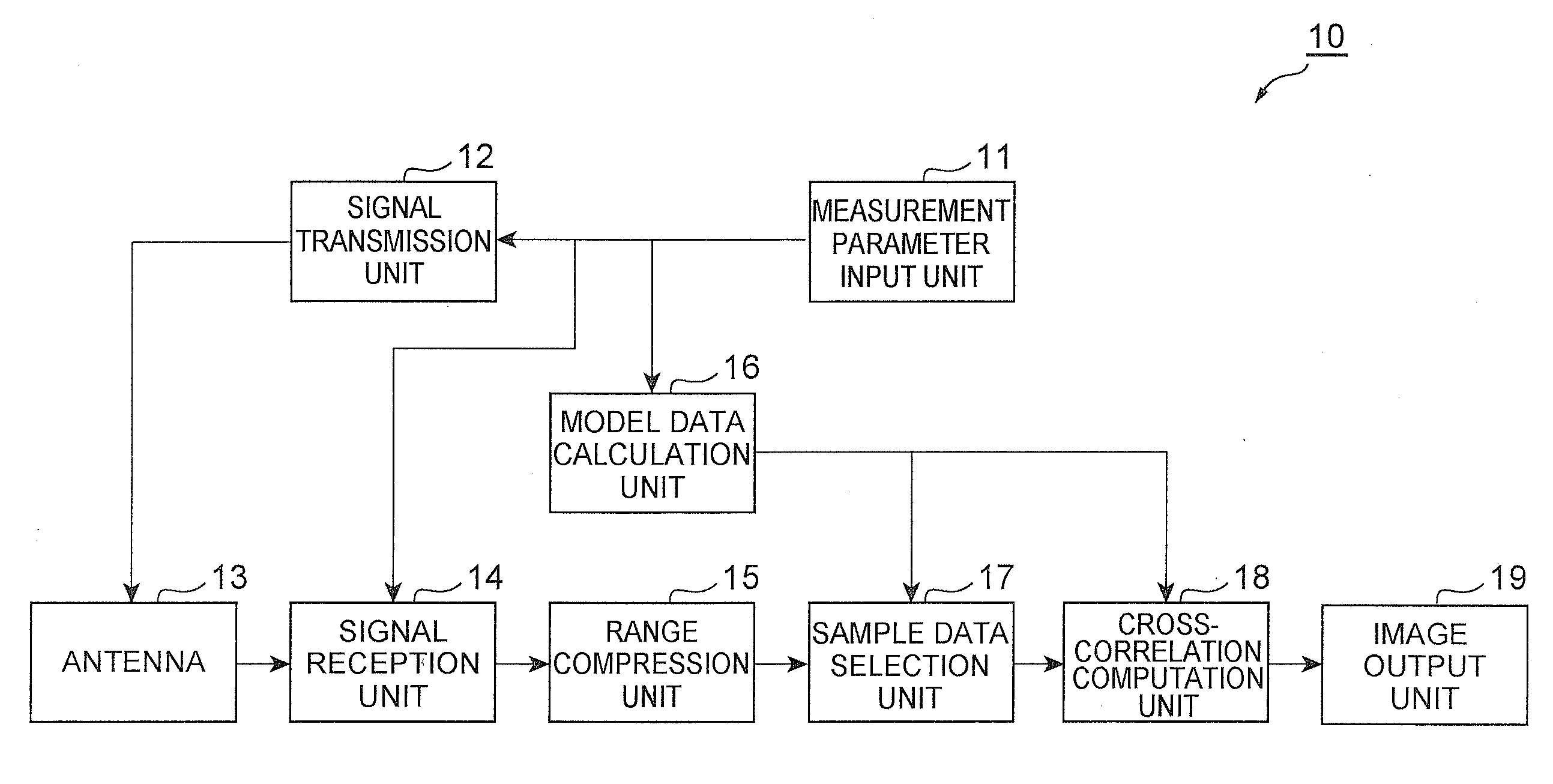
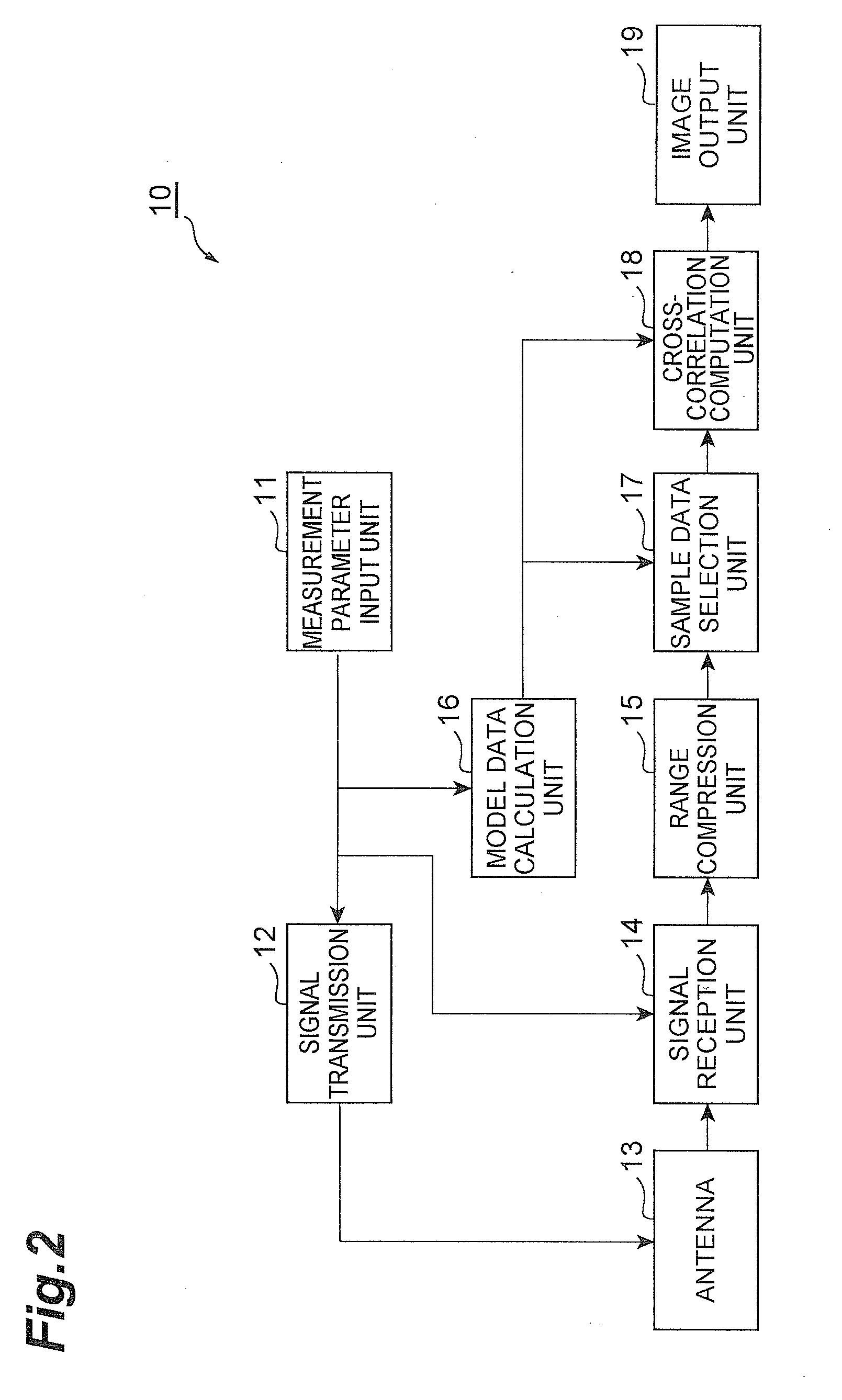
A synthetic aperture processing system 10 includes a signal transmission unit 12 for generating a plurality of chirp waves and radiating the plurality of chirp waves to an irradiation region from a plurality of measuring sites, a signal reception unit 14 for receiving a plurality of reflected waves caused by the plurality of chirp waves radiated from the signal transmission unit 12, a range compression unit 15 for range-compressing each of the reflected waves received by the signal reception unit 14 and generating reception data consisting of a plurality of sinc functions, a cross-correlation computation unit 18 for, based on a plurality of model data segments consisting of a plurality of sinc functions obtained by range-compression of ideal reception waves caused by the reflection of the frequency-modulated waves at a plurality of predetermined sites in the irradiation region and the reception data generated by the range compression unit 15, calculating correlation values representing a degree of correlation between each of the model data segments and the reception data, and image output unit 19 for outputting the correlation values calculated by cross-correlation computation unit 18.
Owner:JAPAN AGENCY FOR MARINE-EARTH SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
High phase order electrical rotating machine with distributed windings
InactiveUS20050218863A1Produced economicallyChange the impedance of the machineSingle-phase induction motor startersDC motor speed/torque controlElectric machineThird harmonic
A rotating induction machine, containing five or more different phases, having windings distributed according to a sinc function with a cutoff frequency allowing low-order spatial harmonics but preventing higher order spatial harnomics from flowing. In a preferred embodiment, the machine is connected to drive means capable of injecting third harmonic into the machine. In a further preferred embodiment, the windings are connected to the drive means with a mesh connection and the machine has five phases.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Synthetic aperture processing system and synthetc aperture processing method
InactiveUS8421669B2Improve accuracyReduce the amount of calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAcoustic wave reradiationData segmentReflected waves
A synthetic aperture processing system that includes a signal transmission unit for generating and radiating a plurality of chirp waves to an irradiation region from measuring sites, a signal reception unit for receiving a plurality of reflected waves caused by the plurality of chirp waves, a range compression unit for range-compressing each of the reflected waves and generating reception data consisting of sinc functions, a cross-correlation computation unit for, based on a plurality of model data segments, calculating correlation values representing a degree of correlation between each of the model data segments and the reception data, and image output unit for outputting the correlation values calculated by cross-correlation computation unit.
Owner:JAPAN AGENCY FOR MARINE-EARTH SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com