Patents
Literature
539 results about "Waveguide grating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
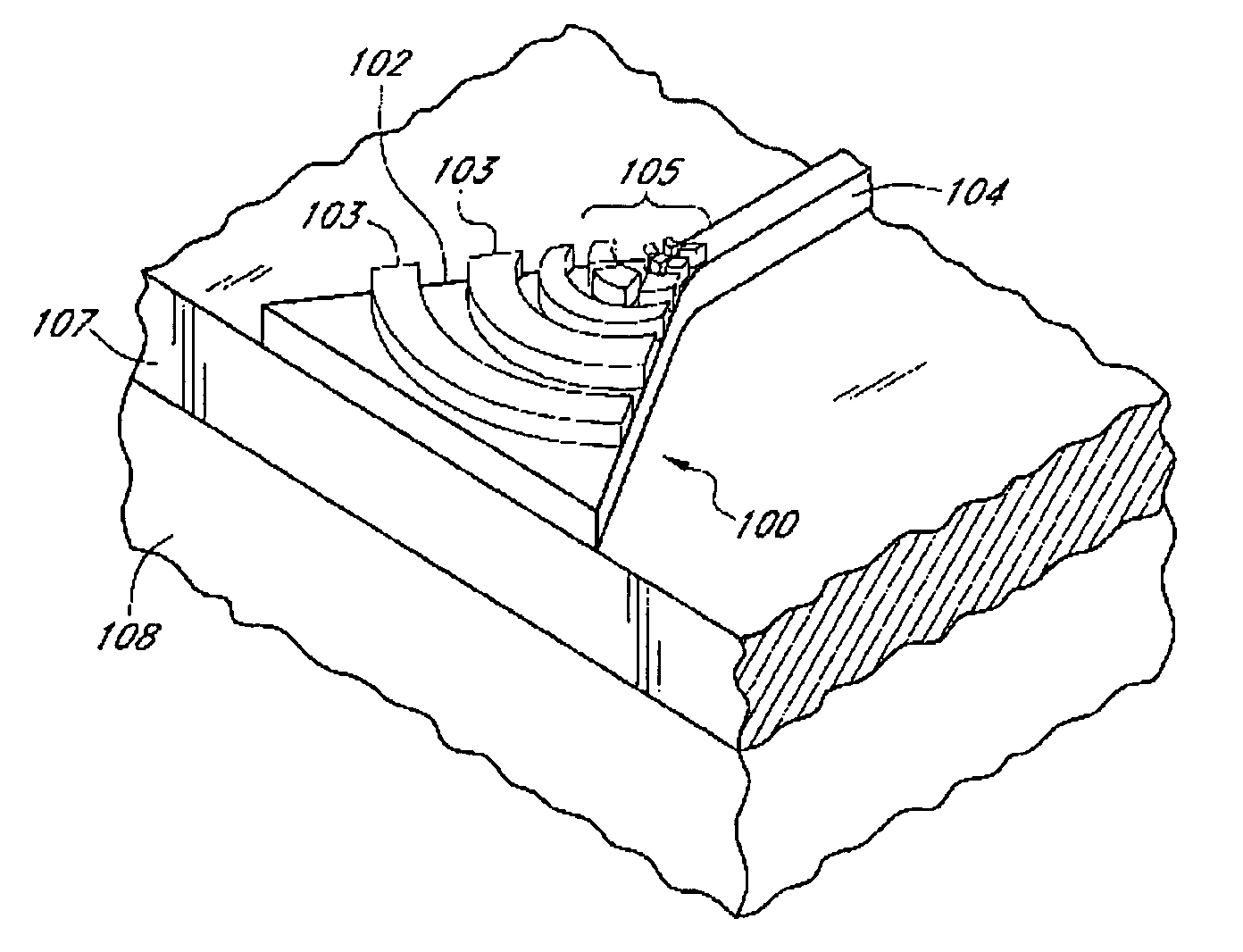
An arrayed waveguide grating is used in fiber optic transmission systems to permit a single optical fiber to carry multiple channels or communication bands. Fiber optic cables use very thin glass fibers to transmit light signals containing voice or data communications.
Methods for using resonant waveguide-grating filters and sensors
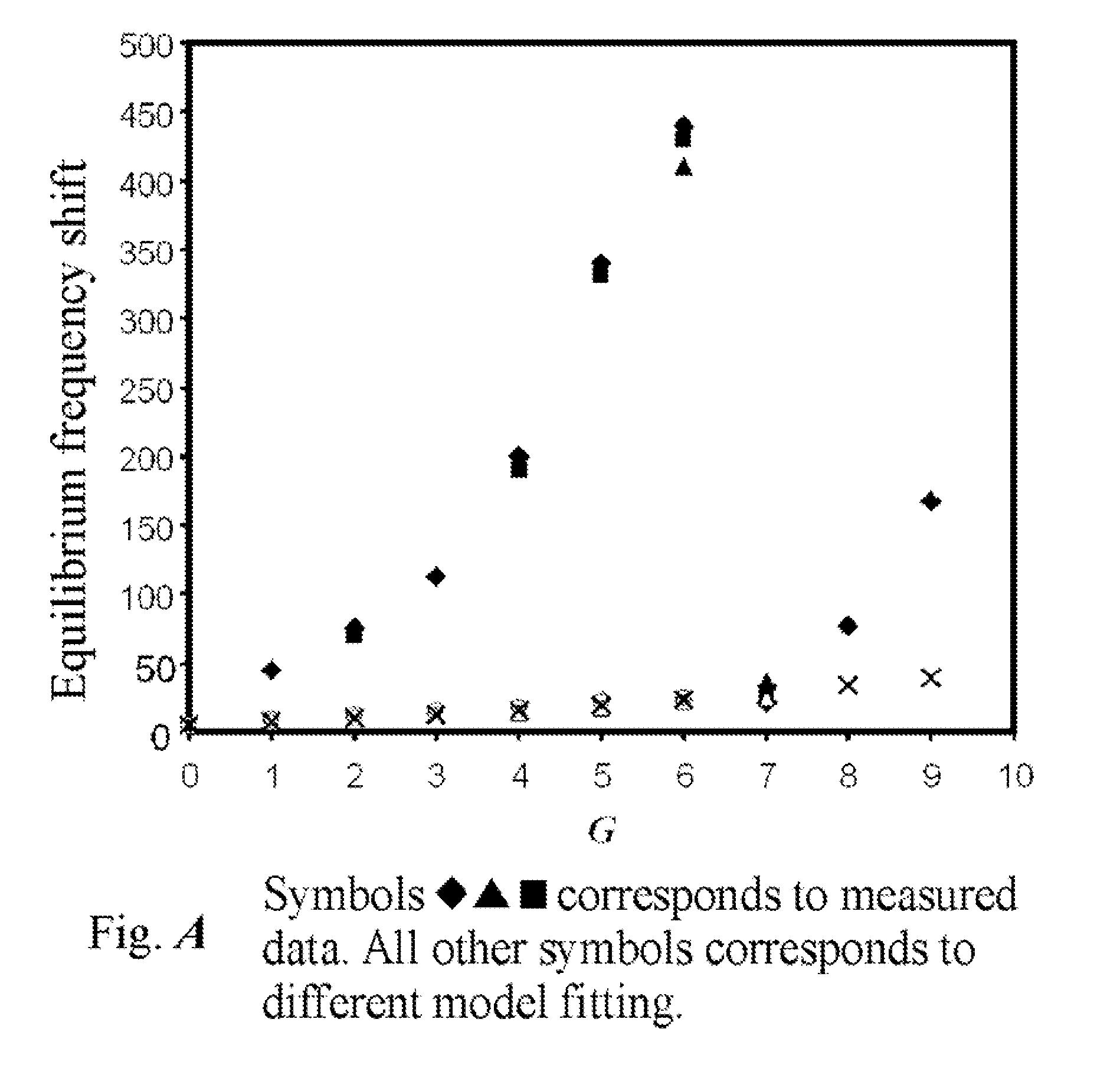
Methods of detecting one or more parameters of a medium are disclosed. The methods include providing a waveguide grating device, contacting the waveguide grating with a medium, propagating a signal having at least one signal attribute through the waveguide, and comparing the modified signal attribute to a known signal attribute to detect a parameter of the medium.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Resonant waveguide-grating filters and sensors and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS7167615B1Material analysis by optical meansCoupling light guidesPermittivitySpectral filtering
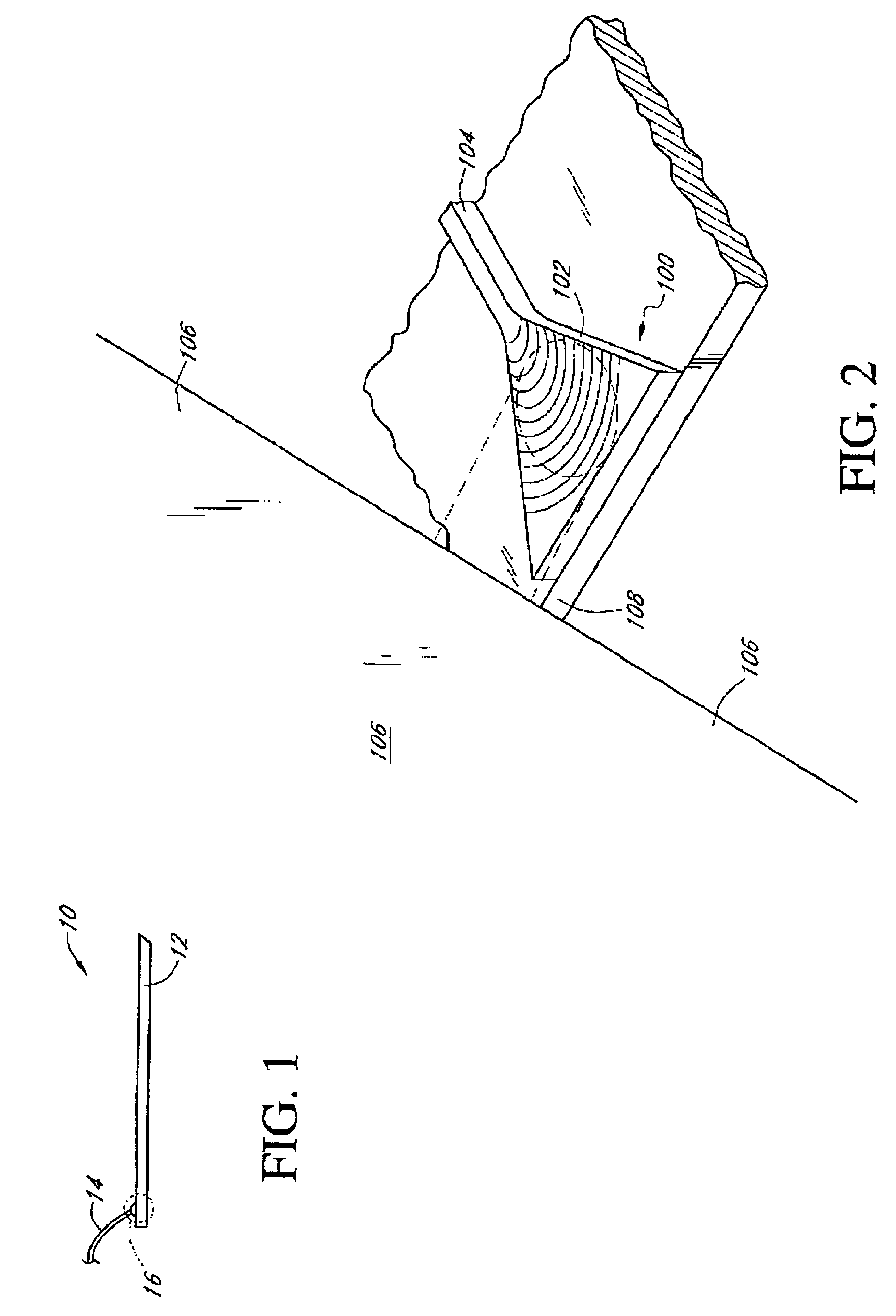
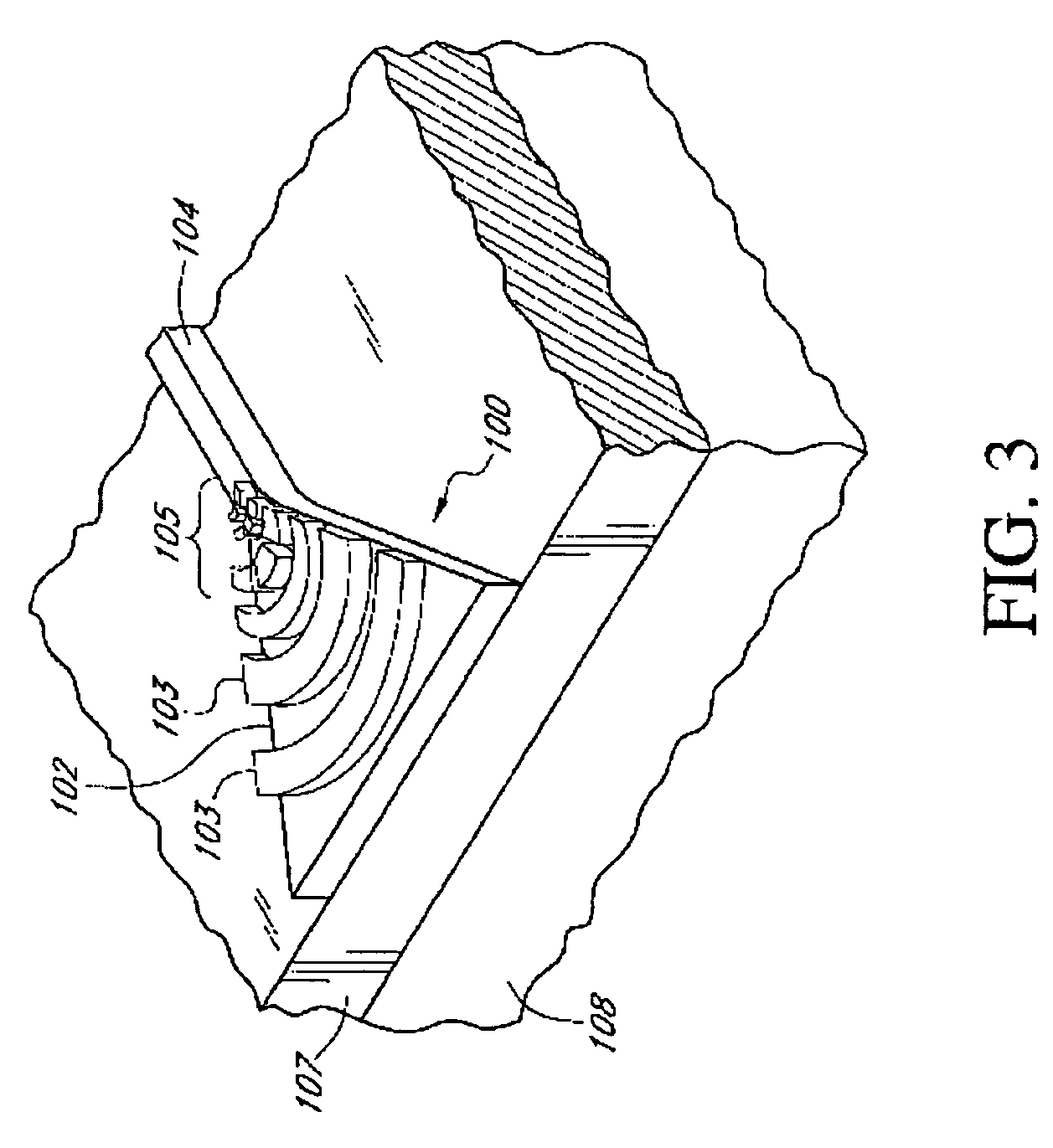
Waveguide grating devices. One includes at least one waveguide having an end, the end having an endface; and a waveguide grating fabricated on the endface, the waveguide grating having at least one waveguide layer and at least one grating layer. The waveguide layer is a separate waveguide from the waveguide on which the waveguide grating is fabricated. Systems for spectral filtering. One, which utilizes a guided-mode resonance effect in a waveguide, includes at least one waveguide having a proximal end and a distal end having an endface; and a waveguide grating fabricated on the end of the waveguide and having a plurality of variable parameters such as permittivity of the grating layer(s) and permittivity of the waveguide layer(s). Methods of forming waveguide grating devices, and methods of detecting one or more parameters of a medium using a waveguide grating device are also disclosed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Waveguide grating device
ActiveUS20160238772A1Complete understandingPlanar/plate-like light guidesCoupling light guidesWaveguide gratingDiffraction
An optical waveguide comprises at least two TIR surface and contains a grating. Input TIR light with a first angular range along a first propagation direction undergoes at least two diffractions at the grating. Each diffraction directs light into a unique TIR angular range along a second propagation direction.
Owner:DIGILENS +1
High Efficiency, Wavelength Stabilized Laser Diode Using AWG's And Architecture For Combining Same With Brightness Conservation
InactiveUS20070223552A1Efficient couplingBrightness and efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersLength waveSemiconductor
The invention relates to high power semiconductor lasers based on a laser diode array waveguide grating (DAWG) in which the wavelength is stabilized using an array waveguide grating (AWG) in an external cavity configuration. Another aspect of the present invention relates to techniques for efficiently coupling optical gain element arrays to an AWG. Another feature provides for the efficient and brightness-conserving combination of multiple high power DAWG lasers into a single output.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Coherent receiver having an interleave-chirped arrayed waveguide grating
ActiveUS20110038631A1Accurate representationPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWavelength demultiplexerComputational physics
An optical coherent detector that employs an interleave-chirped arrayed waveguide grating (AWG). The AWG has a periodic chirp pattern that enables the AWG to function as an optical 90-degree hybrid. If the AWG is implemented using a birefringent material, then the AWG can also function as a polarization demultiplexer. In one embodiment, the AWG is designed to simultaneously function as a wavelength demultiplexer, a polarization demultiplexer for each wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) signal component, and a 90-degree hybrid for each polarization-division-multiplexed component of each WDM signal component.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Waveguide grating device
ActiveUS9632226B2Complete understandingPlanar/plate-like light guidesDiffraction gratingsWaveguide gratingPhysics
An optical waveguide comprises at least two TIR surface and contains a grating. Input TIR light with a first angular range along a first propagation direction undergoes at least two diffractions at the grating. Each diffraction directs light into a unique TIR angular range along a second propagation direction.
Owner:DIGILENS +1
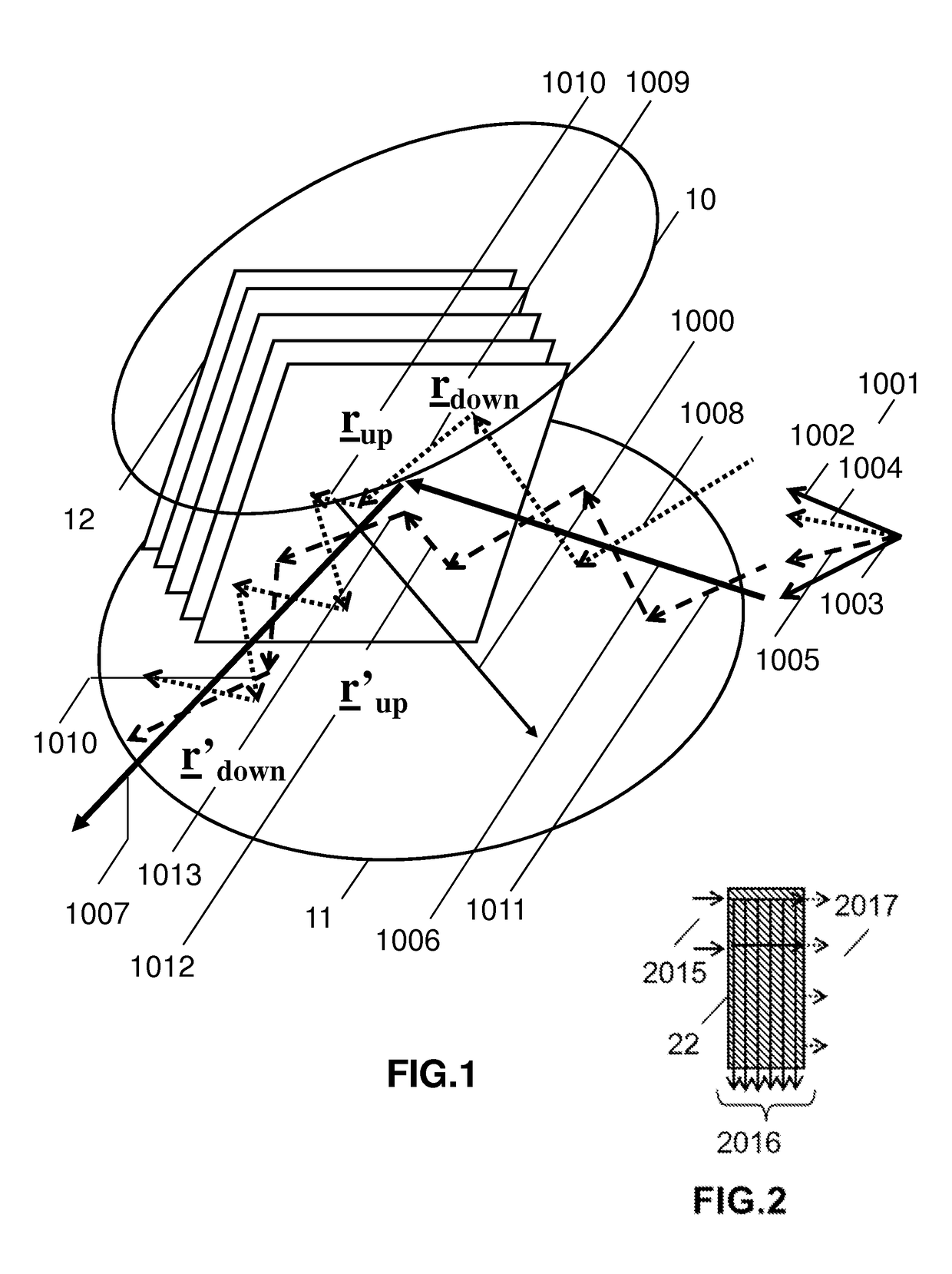
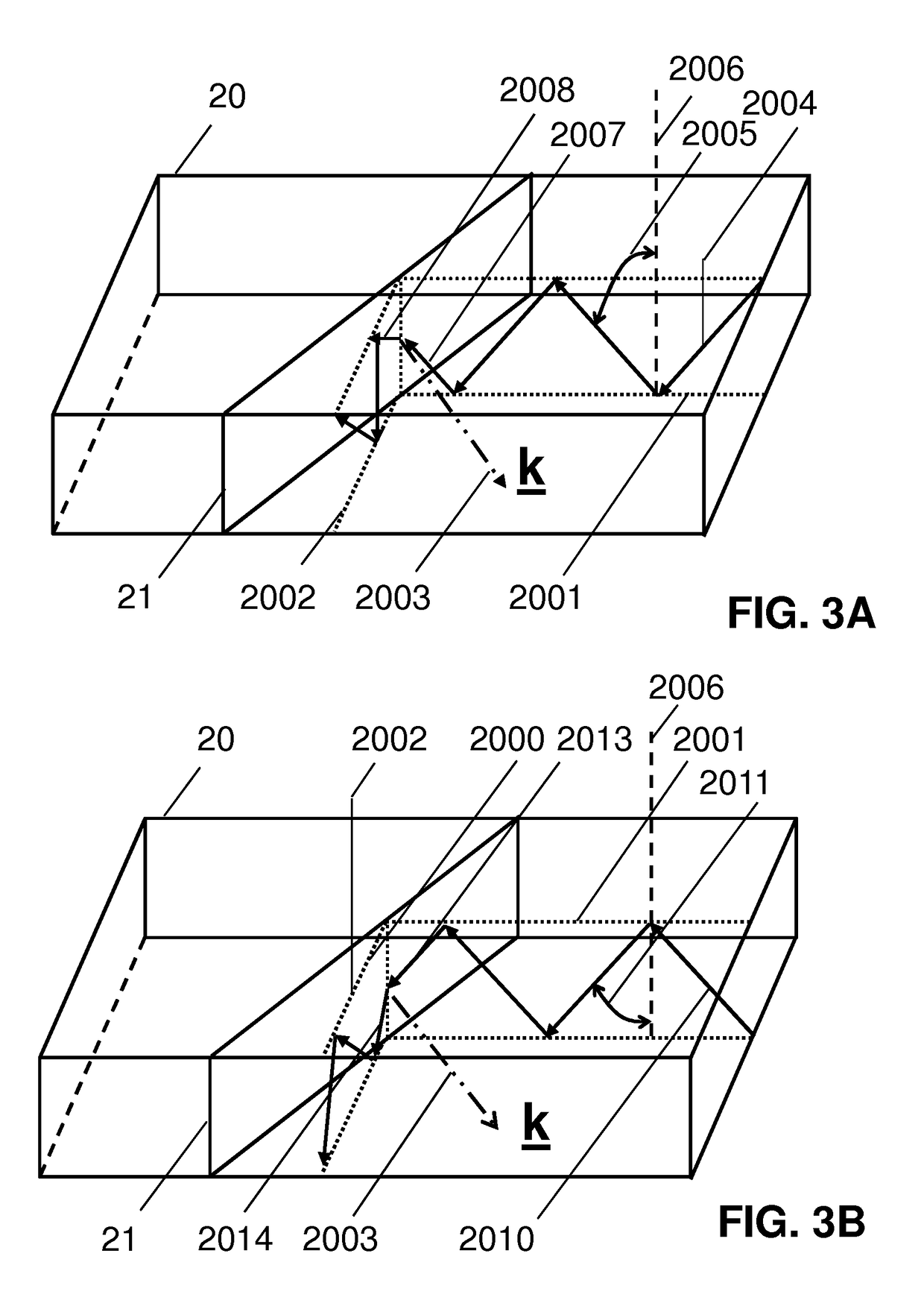
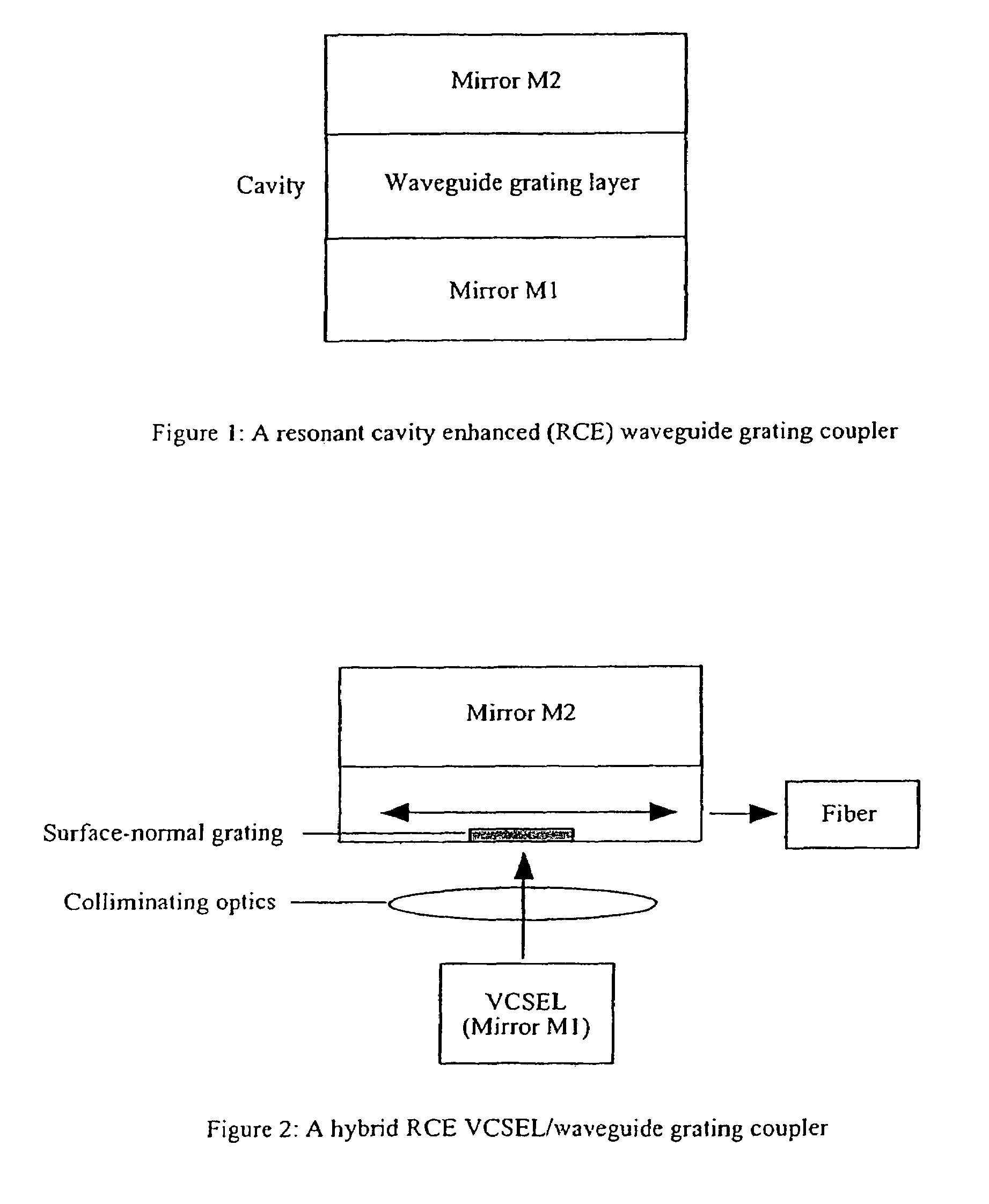
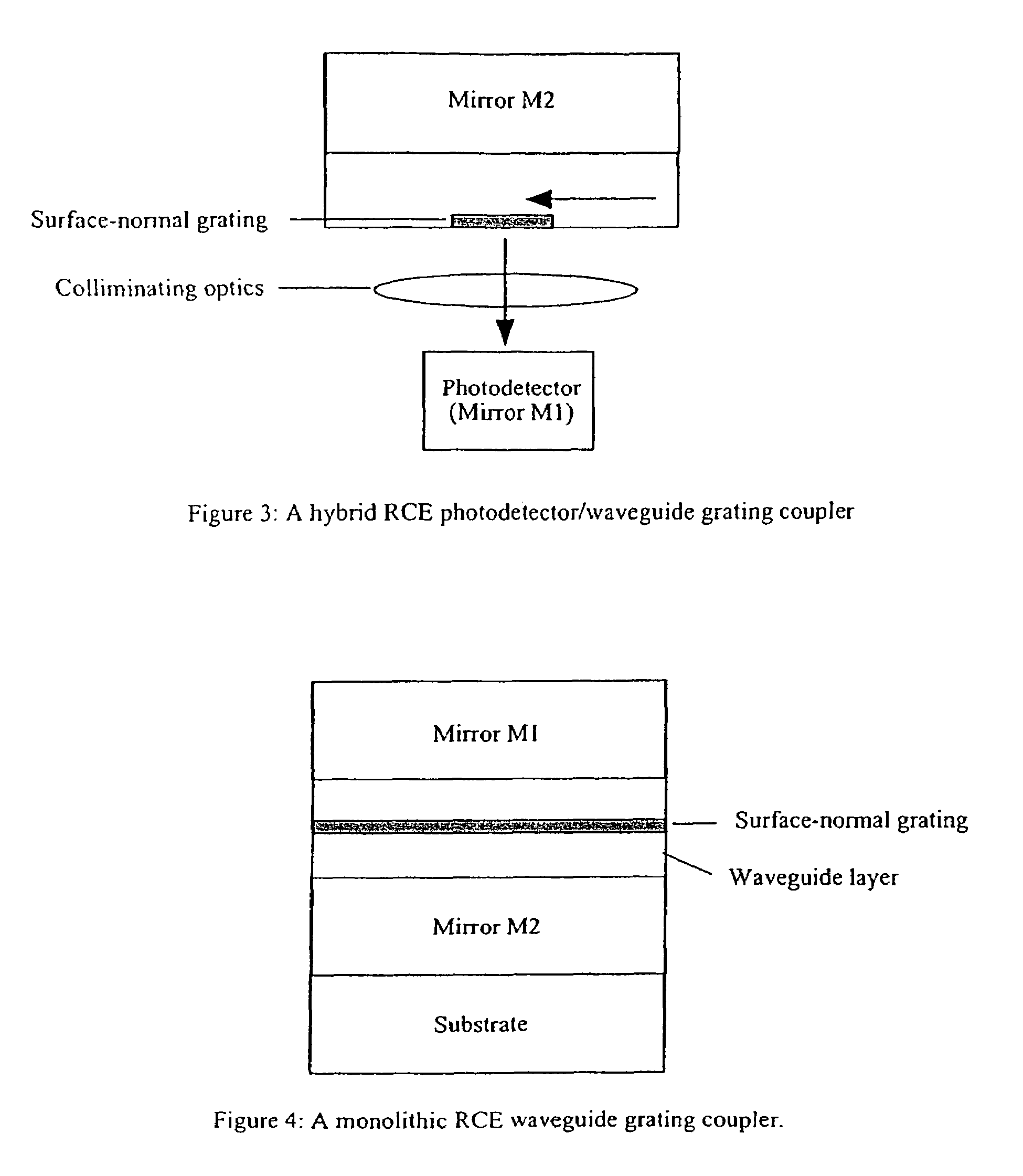
Polarization control using diffraction gratings in VCSEL waveguide grating couplers
InactiveUS7627018B1Convenient lightingIncrease heightOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersResonant cavityWaveguide grating
A VCSEL waveguide grating coupler is provided such that a first and second mirror are positioned to define a resonant cavity between them. The waveguide grating coupler further includes a waveguide having a first grating formed as a part of the waveguide to couple light of a first polarization mode into the waveguide. A second grating is formed on the waveguide grating coupler and is orthogonal to the first grating. The second grating is operative to enhance the light coupled to the waveguide by creating a loss difference between light of the first polarization mode and light of a second polarization mode, so that light of the first polarization mode lases preferentially within the VCSEL.
Owner:OC ACQUISITION CORP
Optical waveguide grating coupler
ActiveUS20040156590A1Improve efficiencyDiffraction gratingsCoupling light guidesCurve shapeOptical intensity
An optical waveguide grating coupler for coupling light between a planar waveguide and an optical element such as an optical fiber. The optical waveguide grating coupler includes a grating comprising a plurality of elongate scattering elements. The optical waveguide grating coupler is preferably flared, and in various embodiments has hyperbolically shaped sidewalls. The elongate scattering elements are preferably curved, and in some embodiments, the scattering elements have elliptically curved shapes. Preferably, the elongated scattering elements have grating widths selected to accommodate the desired optical intensity distribution.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Optical waveguide grating coupler
ActiveUS7245803B2Improve efficiencyDiffraction gratingsCoupling light guidesCurve shapeOptical intensity
An optical waveguide grating coupler for coupling light between a planar waveguide and an optical element such as an optical fiber. The optical waveguide grating coupler includes a grating comprising a plurality of elongate scattering elements. The optical waveguide grating coupler is preferably flared, and in various embodiments has hyperbolically shaped sidewalls. The elongate scattering elements are preferably curved, and in some embodiments, the scattering elements have elliptically curved shapes. Preferably, the elongated scattering elements have grating widths selected to accommodate the desired optical intensity distribution.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Optical communication network system
ActiveUS7298974B2Quickly reconfiguredOptimizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksNetworked systemFiber-optic communication
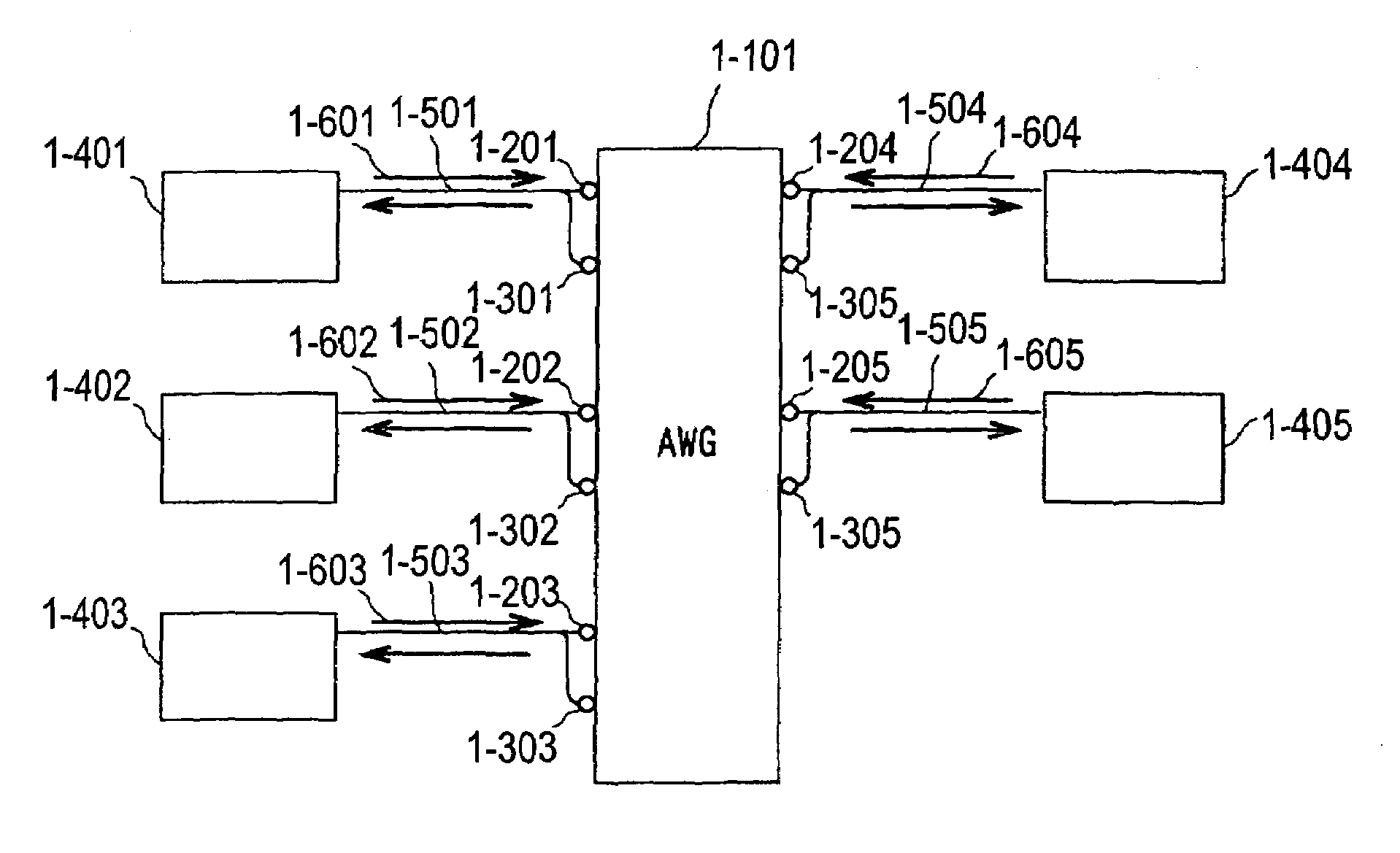
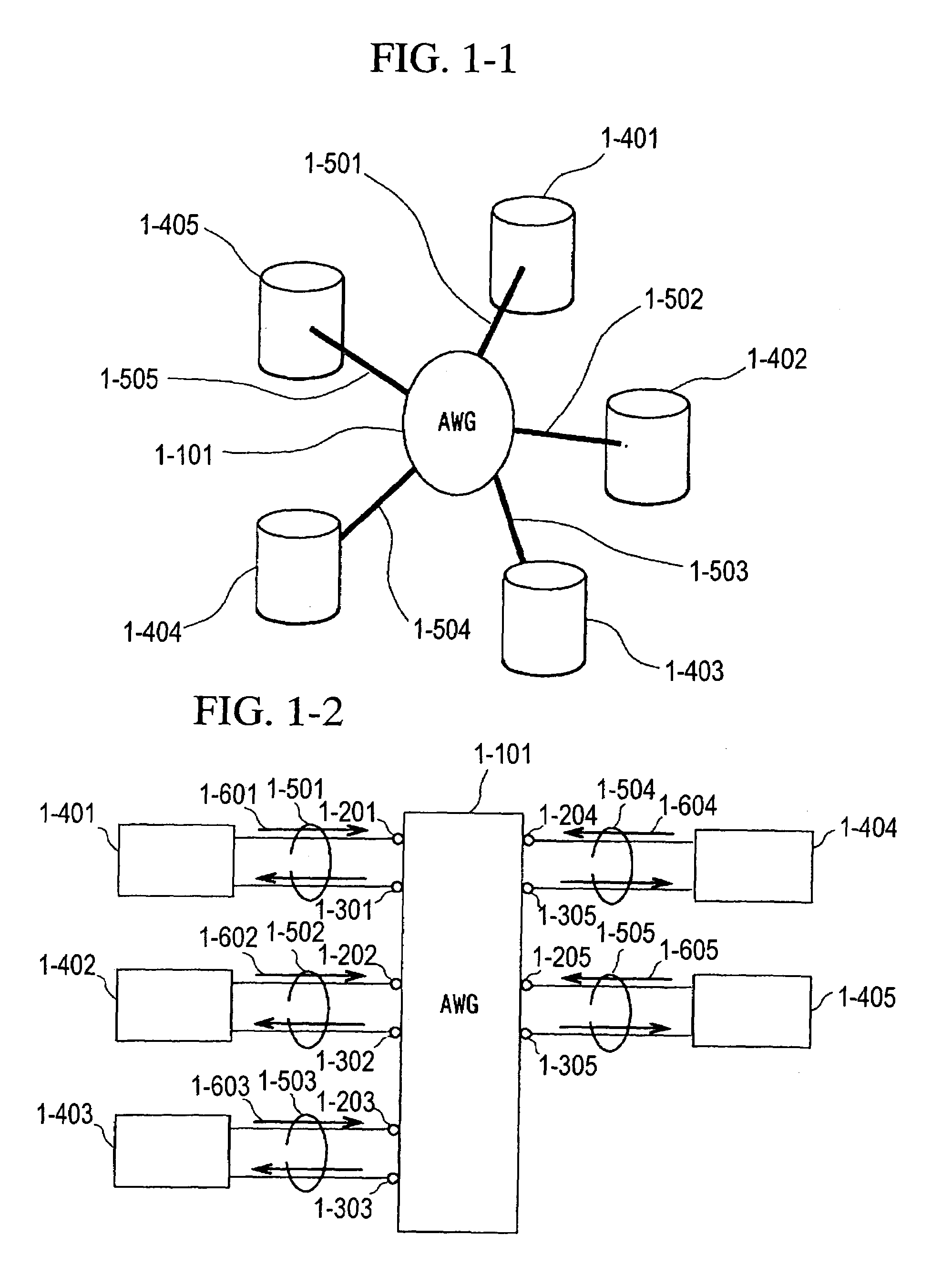
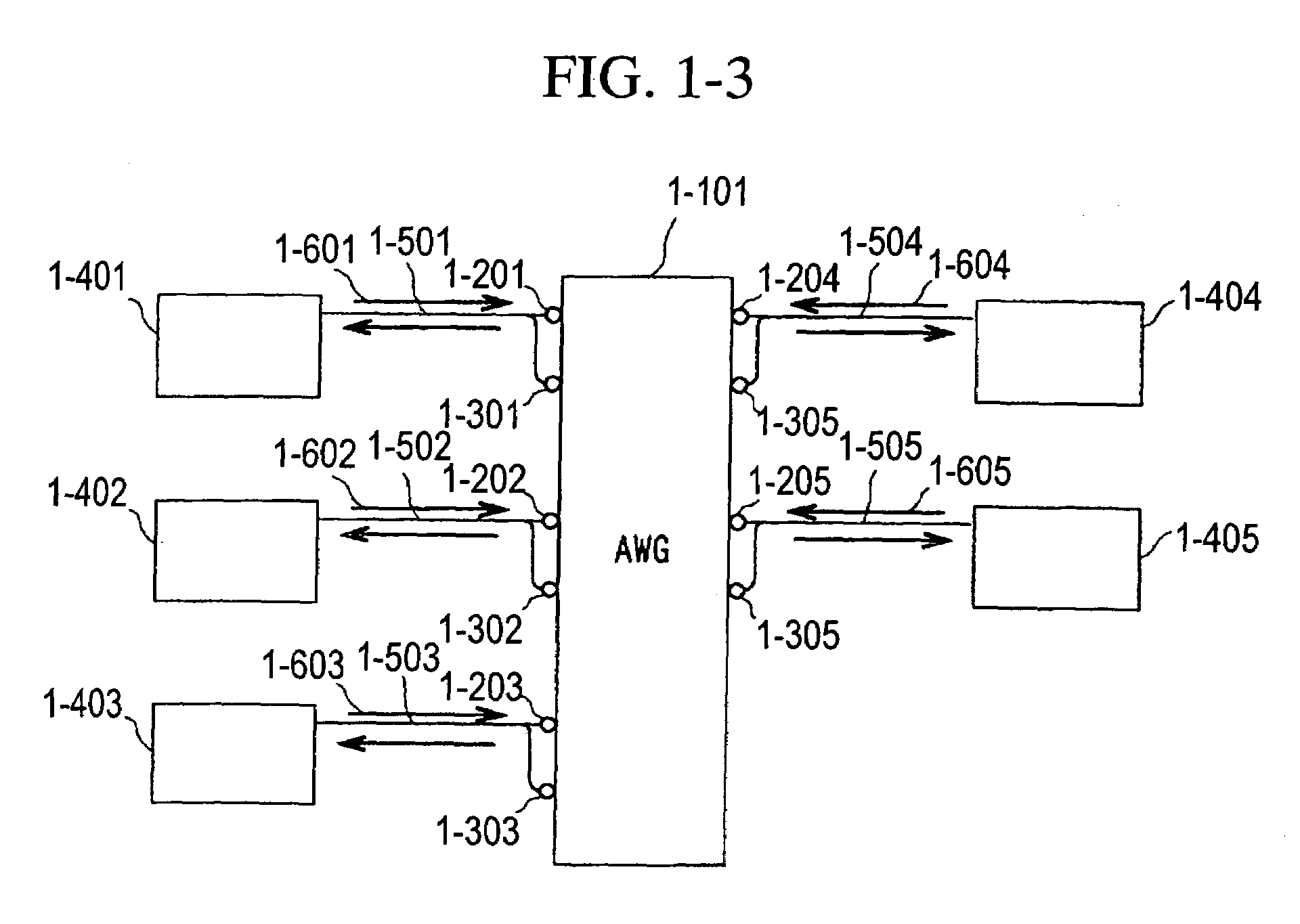
A fiber optic communication system includes a device of switching and setting wavelength of optical signals used in communication by network-node equipments, which sets the mapping of the wavelength of the optical signal used in communication by the network node equipments, and the input / output ports of an array waveguide grating (AWG), so as to construct a predetermined logical network topology by a plurality of network node equipments which are connected via optical fibers to the array waveguide grating that outputs optical signals inputted to optical input ports, to predetermined optical output ports in accordance with the wavelength thereof. As well as enabling a simple construction, it is easy to realize flexible network design, construction, and operation, and different network groups can also be easily connected to each other. Moreover, a fiber optic communication system having robust security and which can be stably operated even at the time of failure is realized at low cost.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Use of waveguide grating couplers in an optical mux/demux system
A group of waveguide grating couplers is disposed on a semiconductor substrate. The grating couplers are all within a spot illuminated on the substrate by a light from an optical fiber. The light propagating in the fiber is wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) and consists of several channels. Within the group of grating couplers, at least one grating coupler is designed to be tuned to each of the channels. The group of grating couplers demultiplexes the channels propagating in the fiber. A group of waveguide grating couplers can also be used to multiplex several channels of light into an optical fiber. Single mode and multimode fiber can be used to carry the multiplexed channels of light in an optical multiplexing and demultiplexing system.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission apparatus
InactiveUS6868200B2Cancellation effectHigh stability and precisionWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingTemperature control
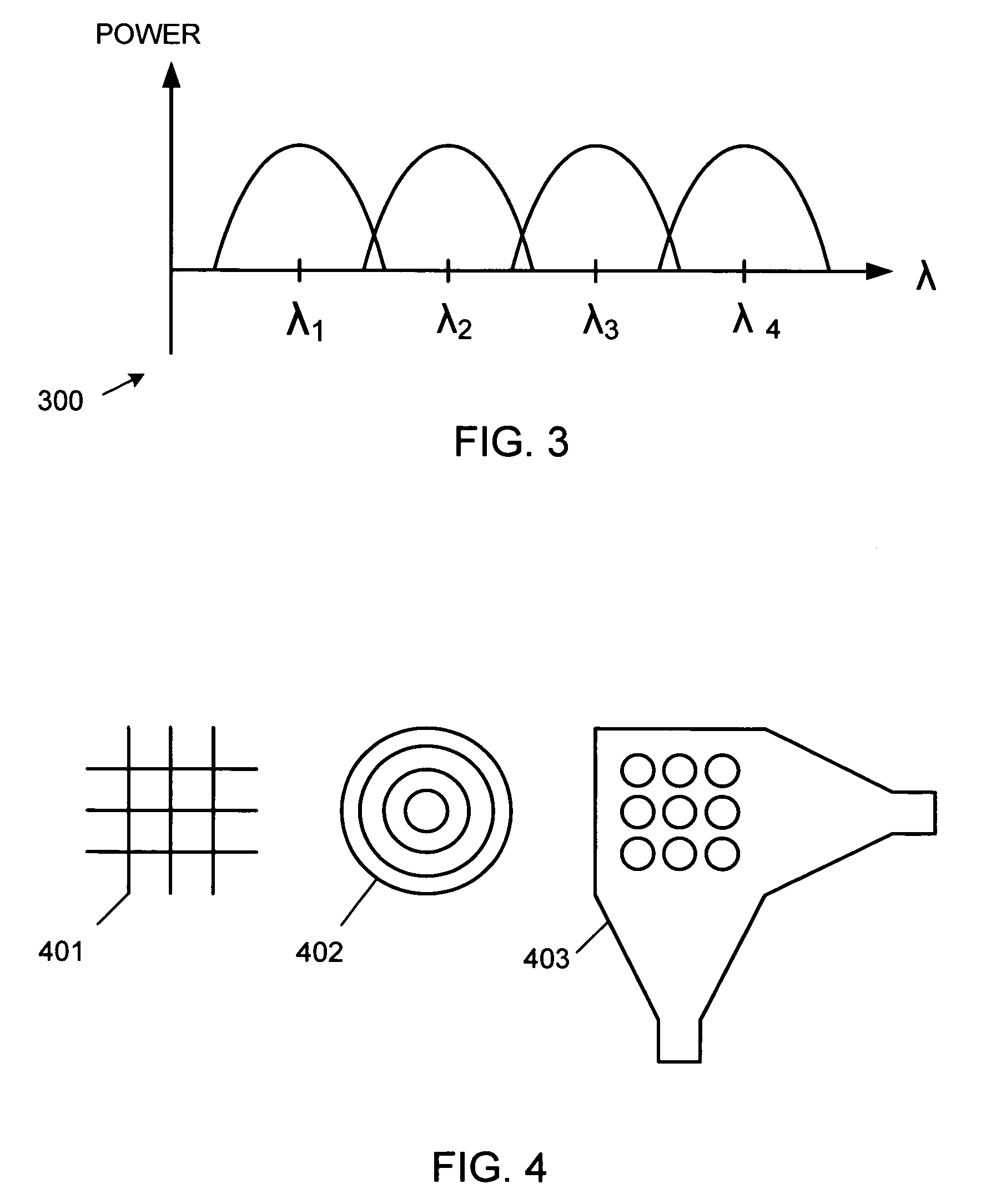
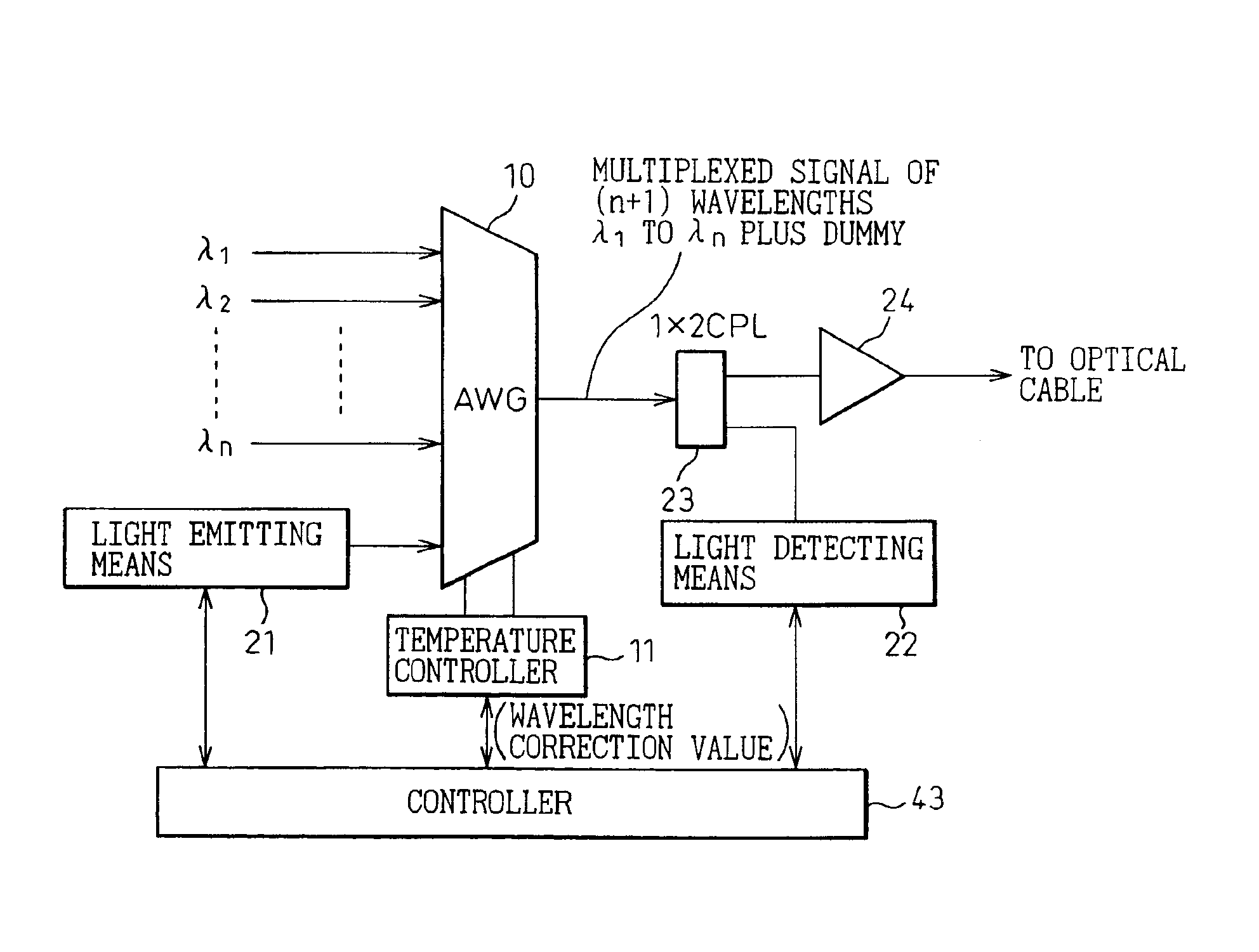
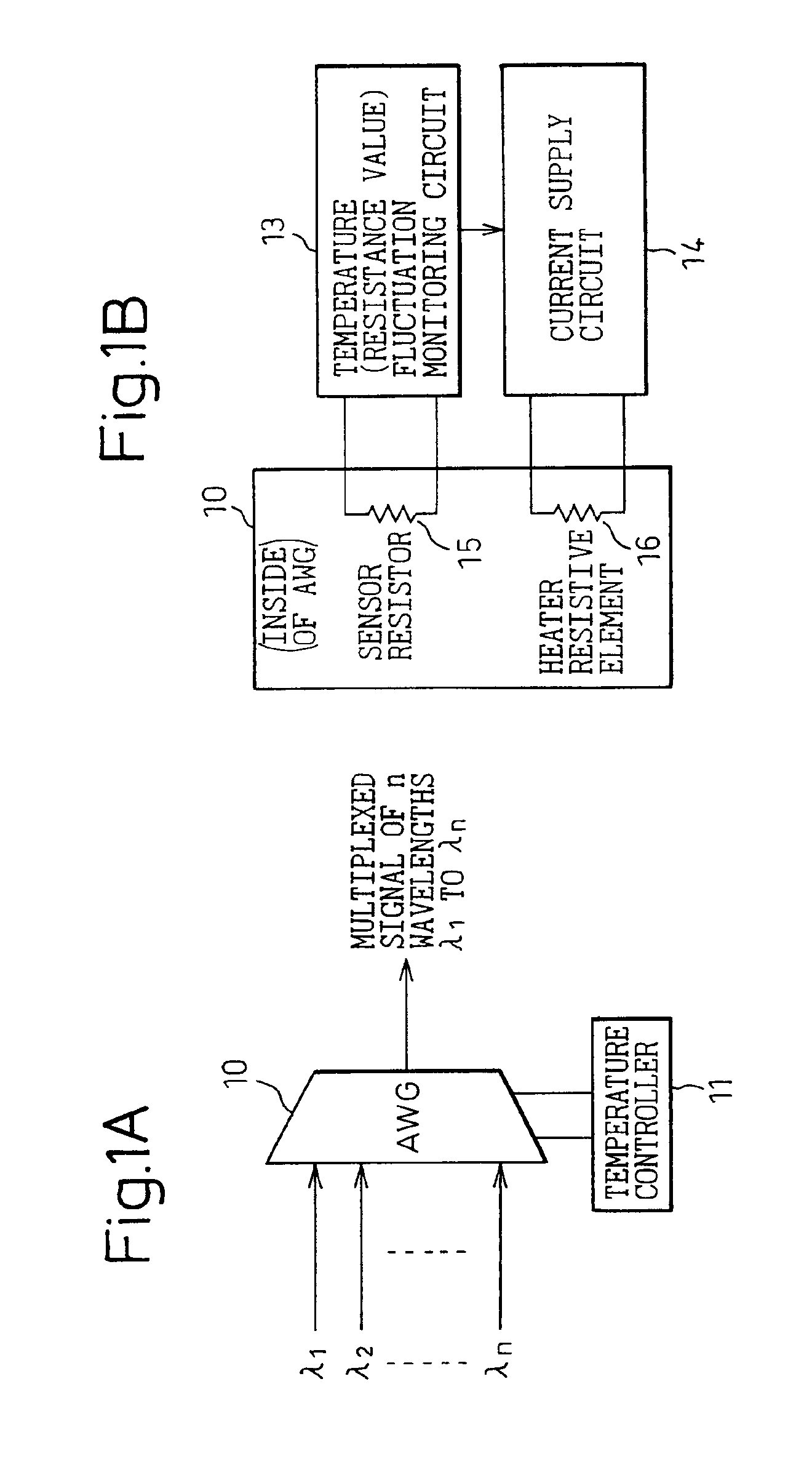
The present invention is directed to the provision of a wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission apparatus and, more particularly, to a wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission apparatus having high wavelength stability unaffected by the temperature characteristics, aging, etc. of an arrayed-waveguide grating (AWG) and its peripheral components. The wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission apparatus comprises: an arrayed-waveguide grating 10 having operating input / output ports and an input dummy port; a light emitting means 21 for generating a pilot signal to be input to the input dummy port; a light detecting means 22 for monitoring the pilot signal contained in a wavelength division multiplexed signal output from the operating output port; and a temperature control circuit 11 for controlling the temperature of the arrayed-waveguide grating in such a manner as to cancel the amount of wavelength fluctuation occurring in the arrayed-waveguide grating and detected by monitoring the pilot signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical performance monitor
ActiveUS7130505B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical performance monitoringPhotodiode
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Optical waveguide grating coupler with varying scatter cross sections
ActiveUS7260293B1Reduce scatter cross-sectionCoupling light guidesScattering cross-sectionCurve shape
Various configurations of elongate scattering elements in an optical waveguide grating coupler for coupling light between a planar waveguide and an optical element such as an optical fiber, where the light may have a Gaussian intensity distribution. The elongate scattering elements are preferably curved, and in some embodiments, the scattering elements have elliptically curved shape. One or more of the elongate scattering elements may be segmented into various geometrical shapes, such as rectangular, square, circular and elliptical. The elongate scattering elements have at least one characteristic selected from the group consisting of grating width, height, spacing, depth and index of refraction forming the elongate scattering elements, where the magnitude of the at least one characteristic varies irregularly with position along the guiding portion of the optical waveguide grating coupler.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
WDM PON with distribution via cyclic array waveguide grating
InactiveUS20100266283A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberLength wave
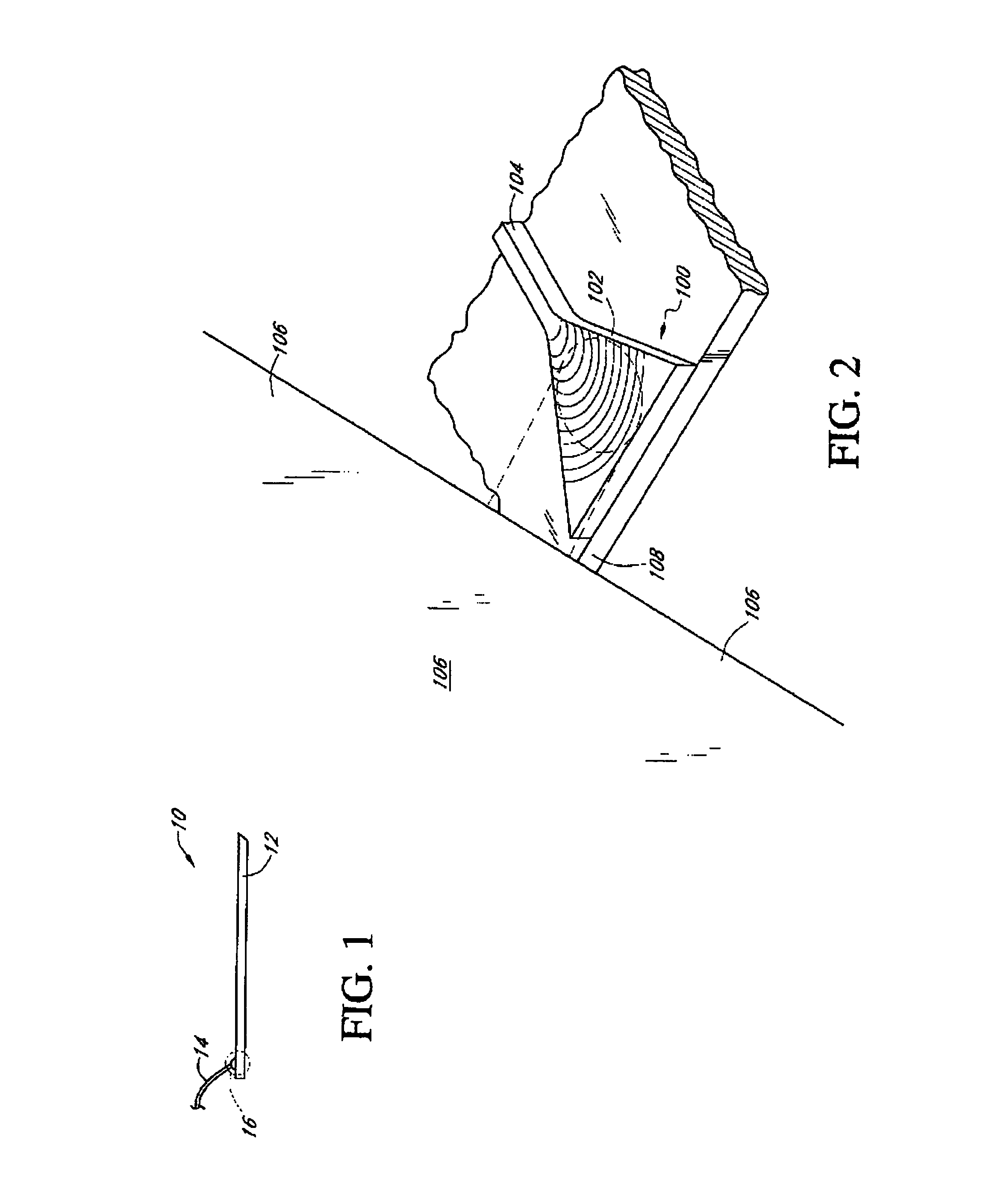
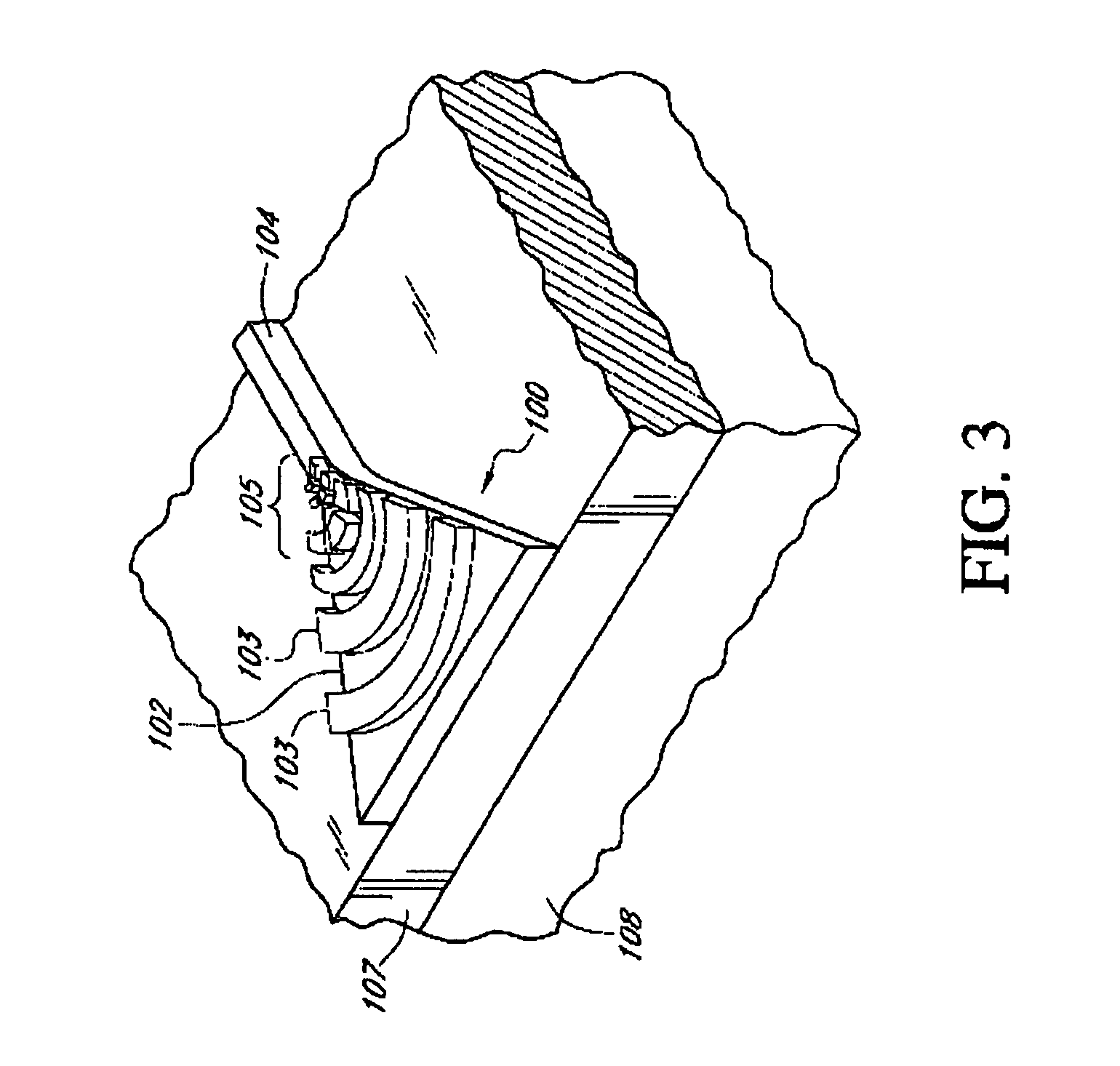
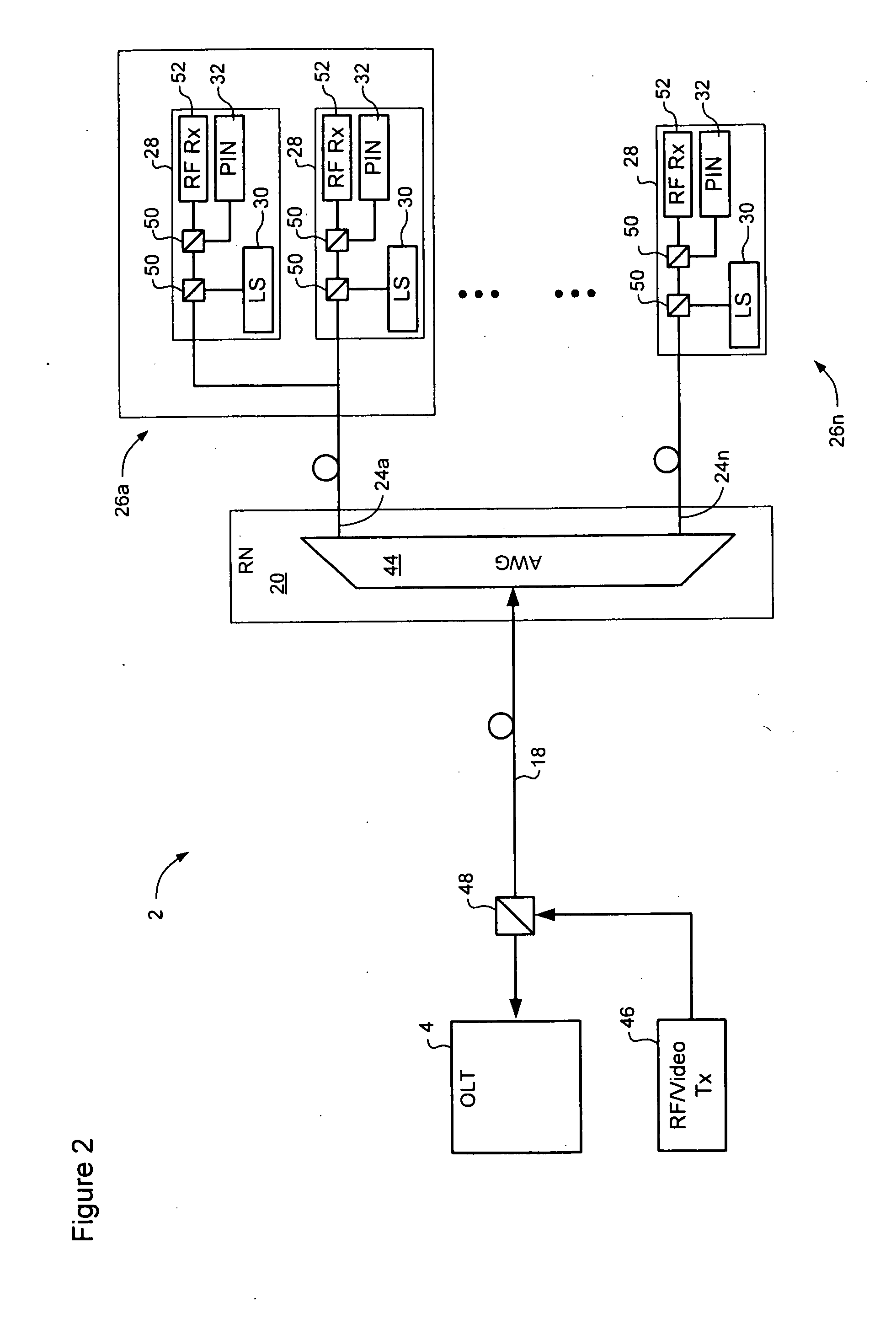
In a Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network (WDM-PON) including, a system for distributing uplink, downlink and RF / Video broadcast signalling. An Array Waveguide Grating (AWG) couples respective wavelength channels between a trunk fibre of the WDM-PON and a plurality of branch fibers of the WDM-PON. The AWG has a predetermined free spectral range and implements a channel plan comprising at least three spectral segments, each segment having a width equal to the free spectral range of the AWG. An Optical Line Terminal of the WDM-PON receives wavelength division multiplexed uplink signals within a first one of the spectral segments, and transmits wavelength division multiplexed downlink signals within a second one of the spectral segments. Respective channel plans within the first and second spectral segments are identical. An RF / Video broadcast transmitter generates an RF / Video broadcast signal within a third one of the spectral segments.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
Photonic waveguide structures for chip-scale photonic integrated circuits
InactiveUS7389029B2Avoiding direct dopingEasy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexElectro-optical sensor
Owner:APPLIED RES & PHOTONICS
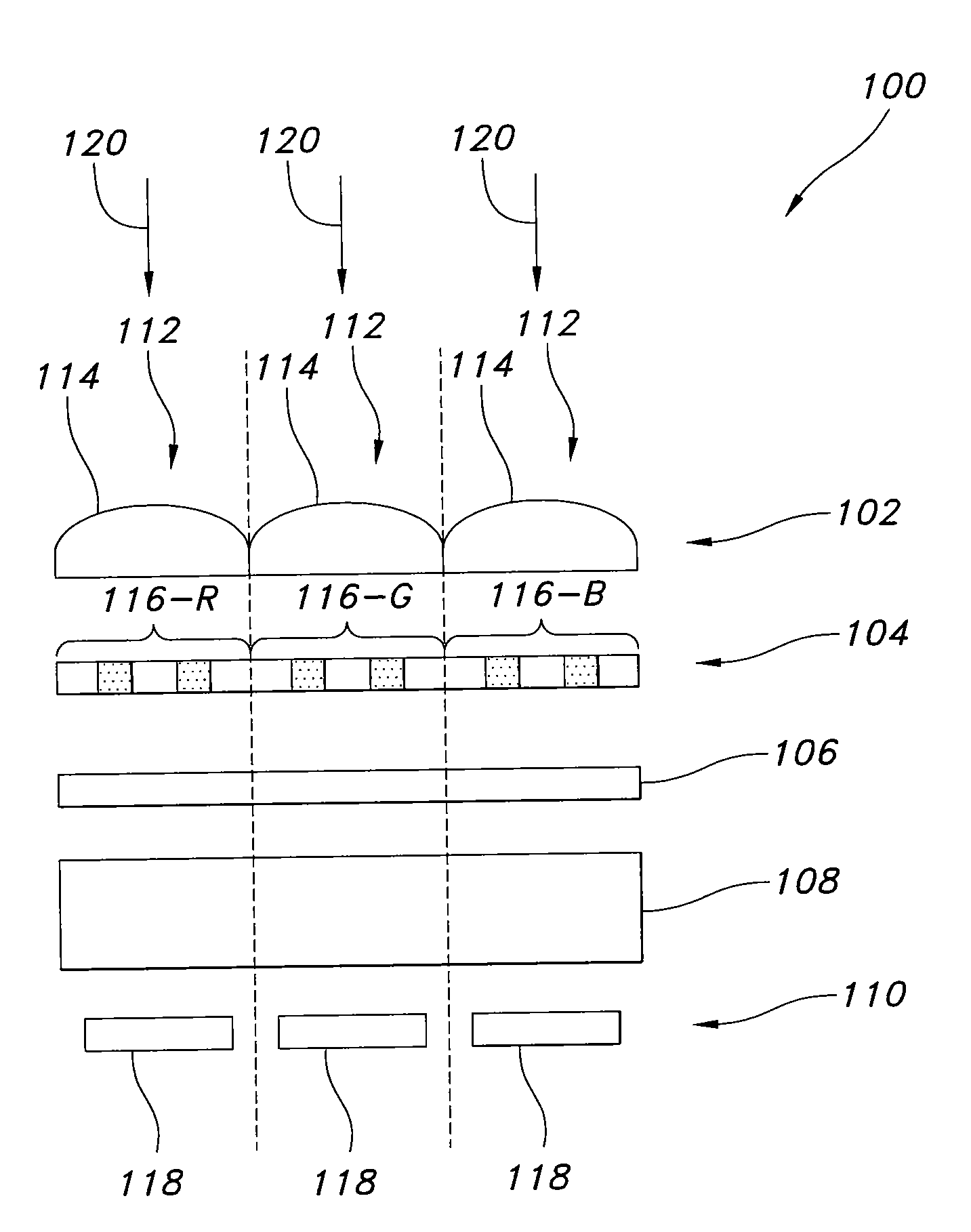
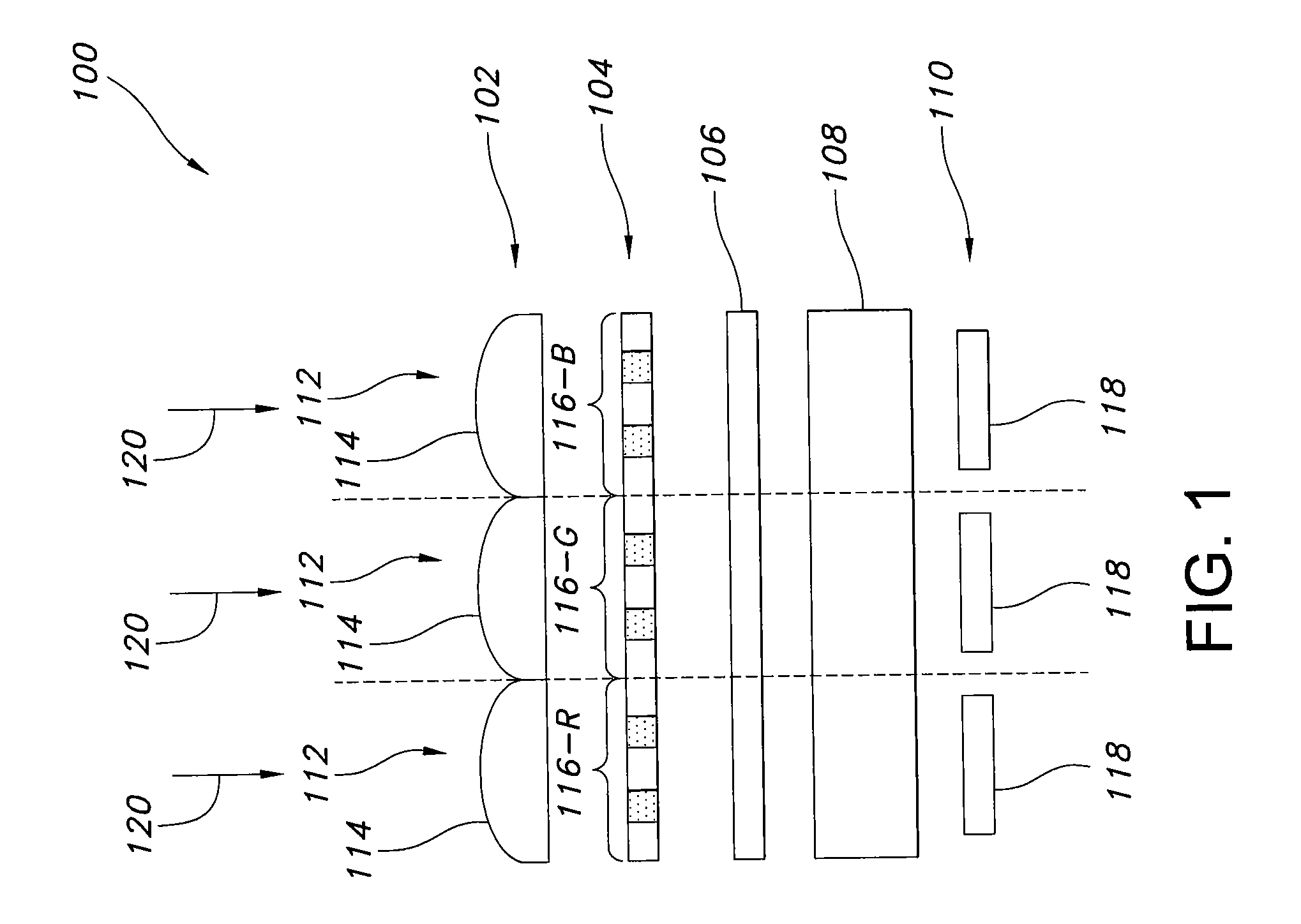
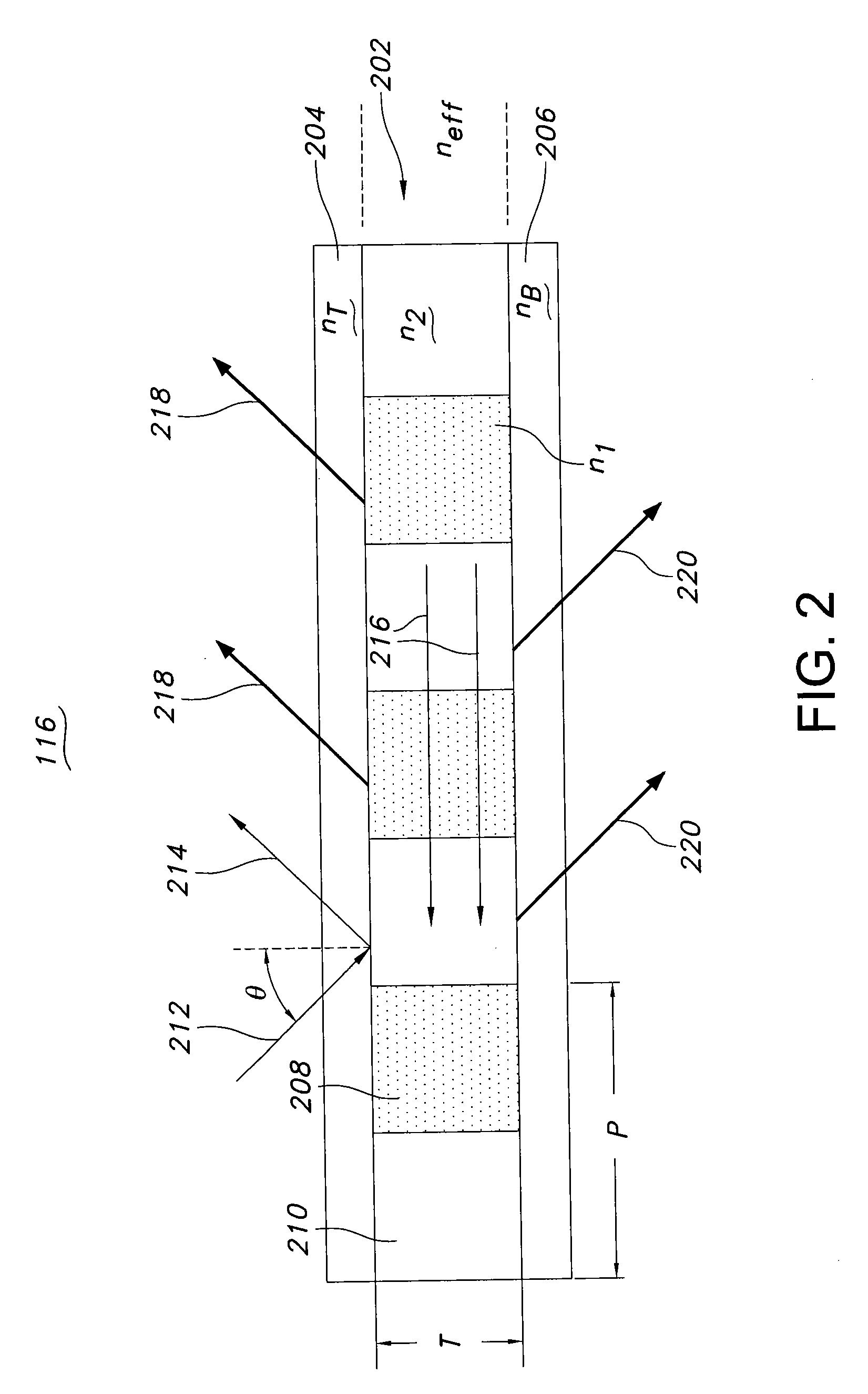
Guided-mode-resonance transmission color filters for color generation in CMOS image sensors
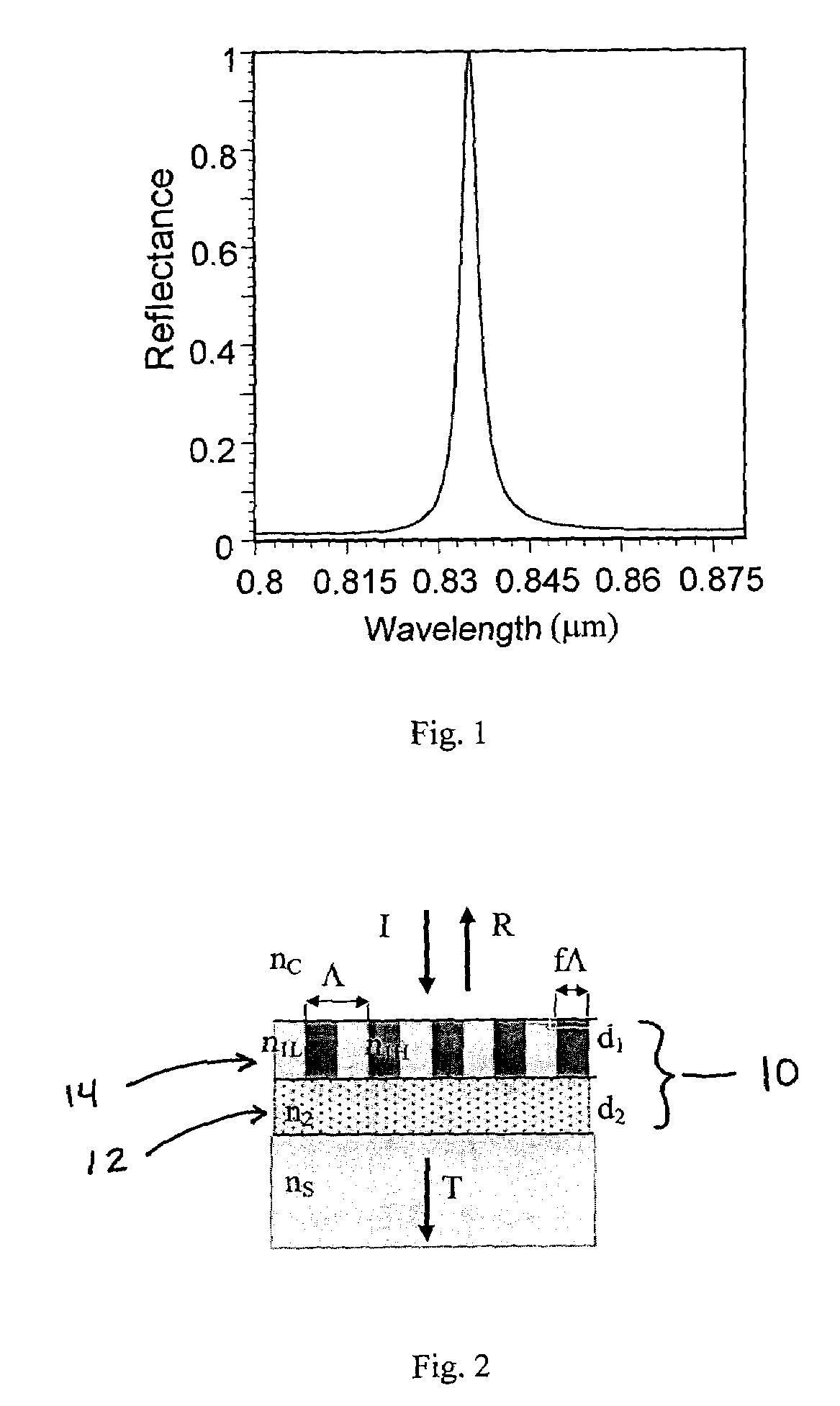
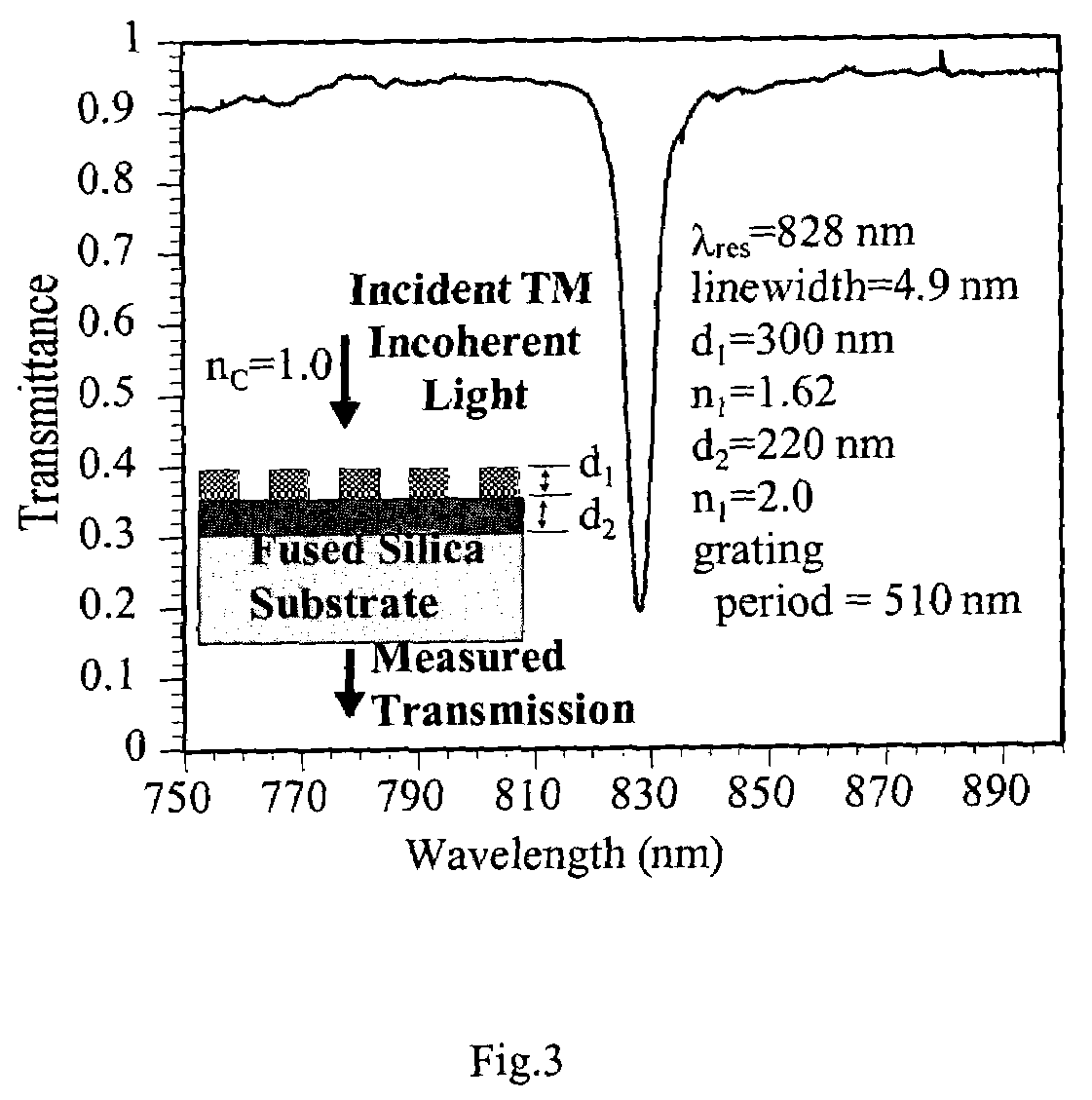
Imager pixel arrays and methods for forming imager pixel arrays. An image sensor pixel includes a photosensor and a waveguide grating resonance filter formed over the photosensor. The waveguide grating resonance filter is configured to pass light to the photosensor in a wavelength band and to block light outside of the wavelength band. The waveguide grating resonance filter includes a grating material having a first refractive index and arranged in a grating pattern with a grating pitch, and has an effective refractive index that is a function of the first refractive index. A combination of the grating pitch and the effective refractive index is selected to correspond to the wavelength band.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
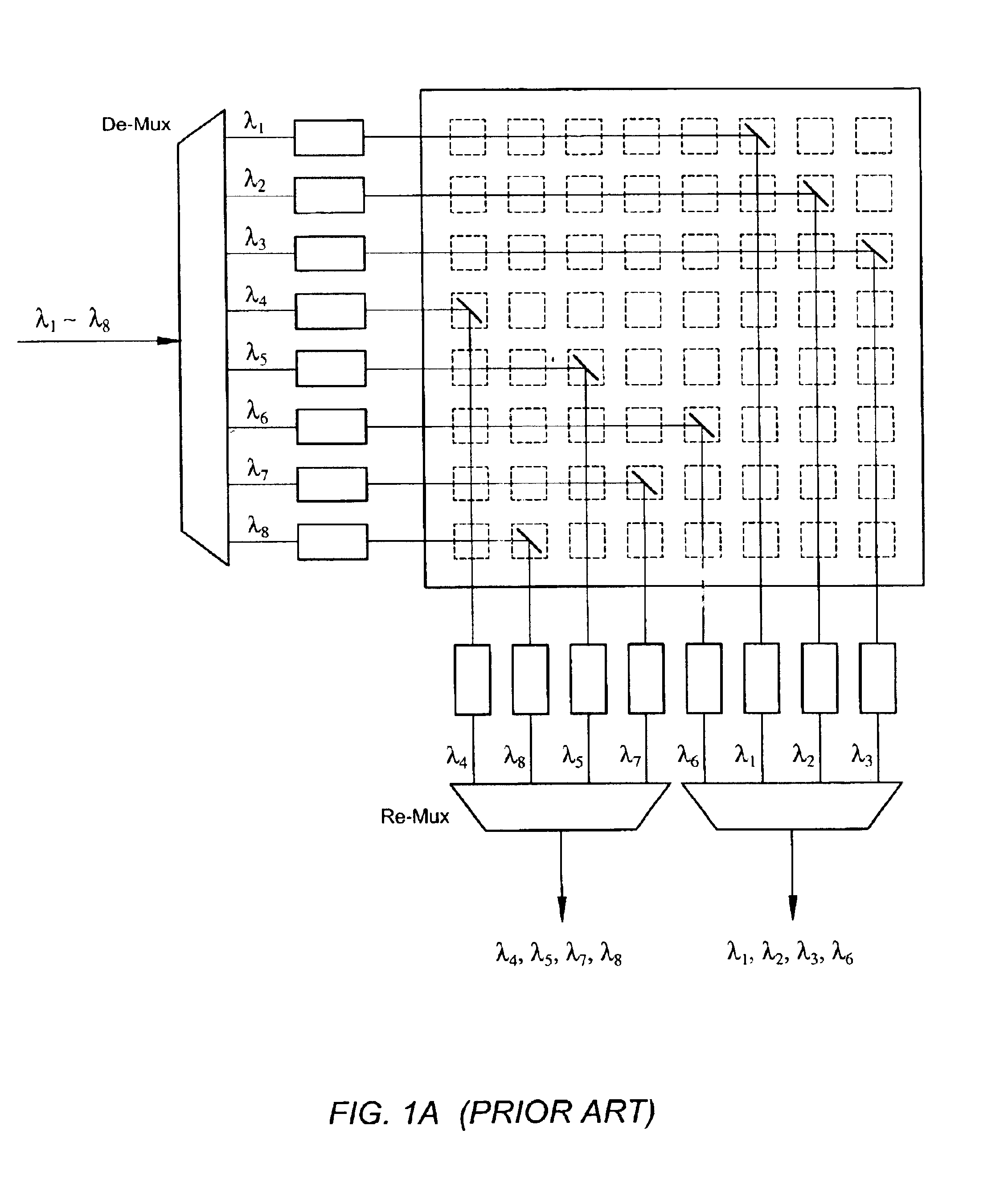
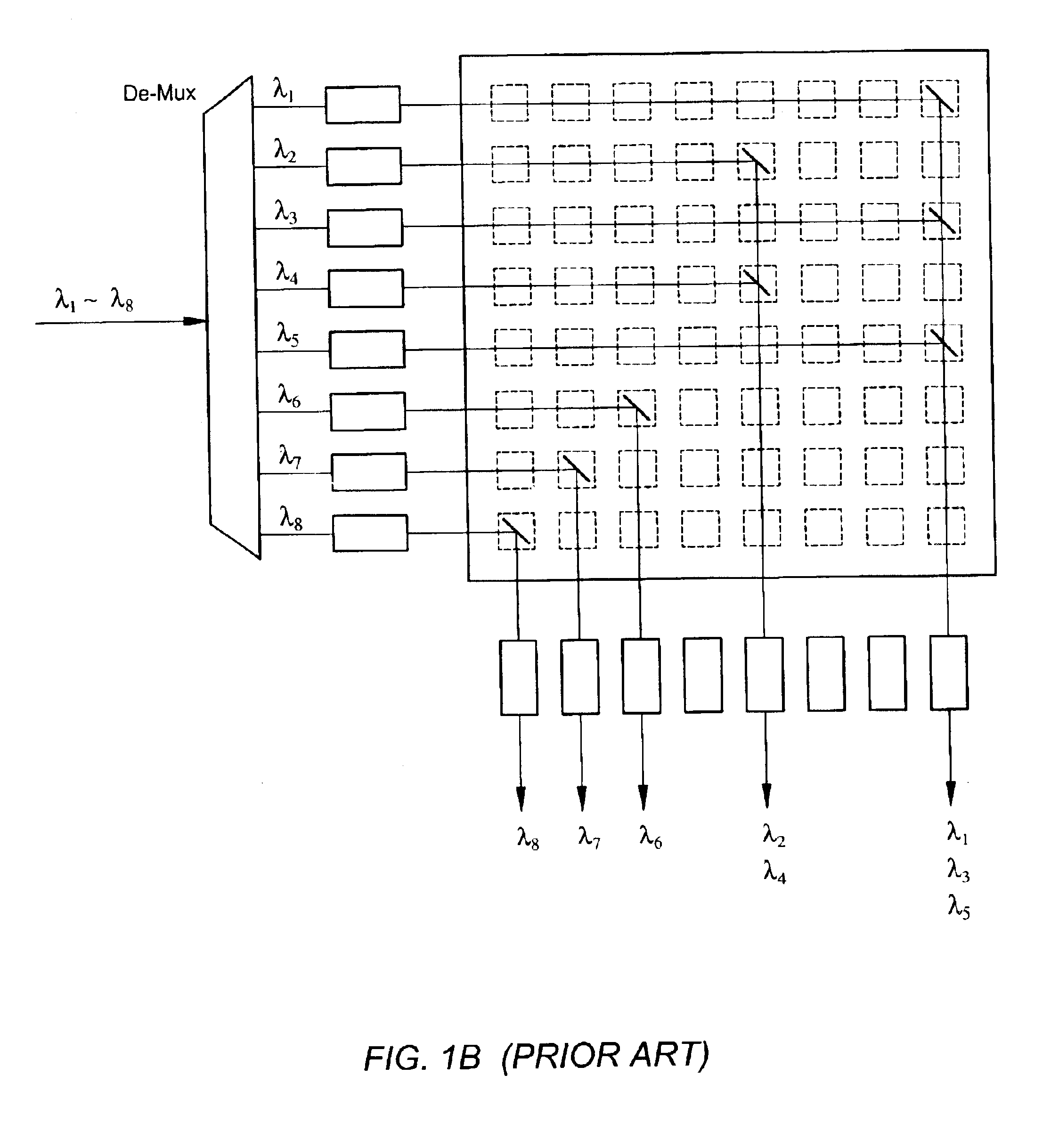
Waveguide grating-based wavelength selective switch actuated by micro-electromechanical system
InactiveUS6842563B2Easy to manufactureHigh strengthMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingMicrowave
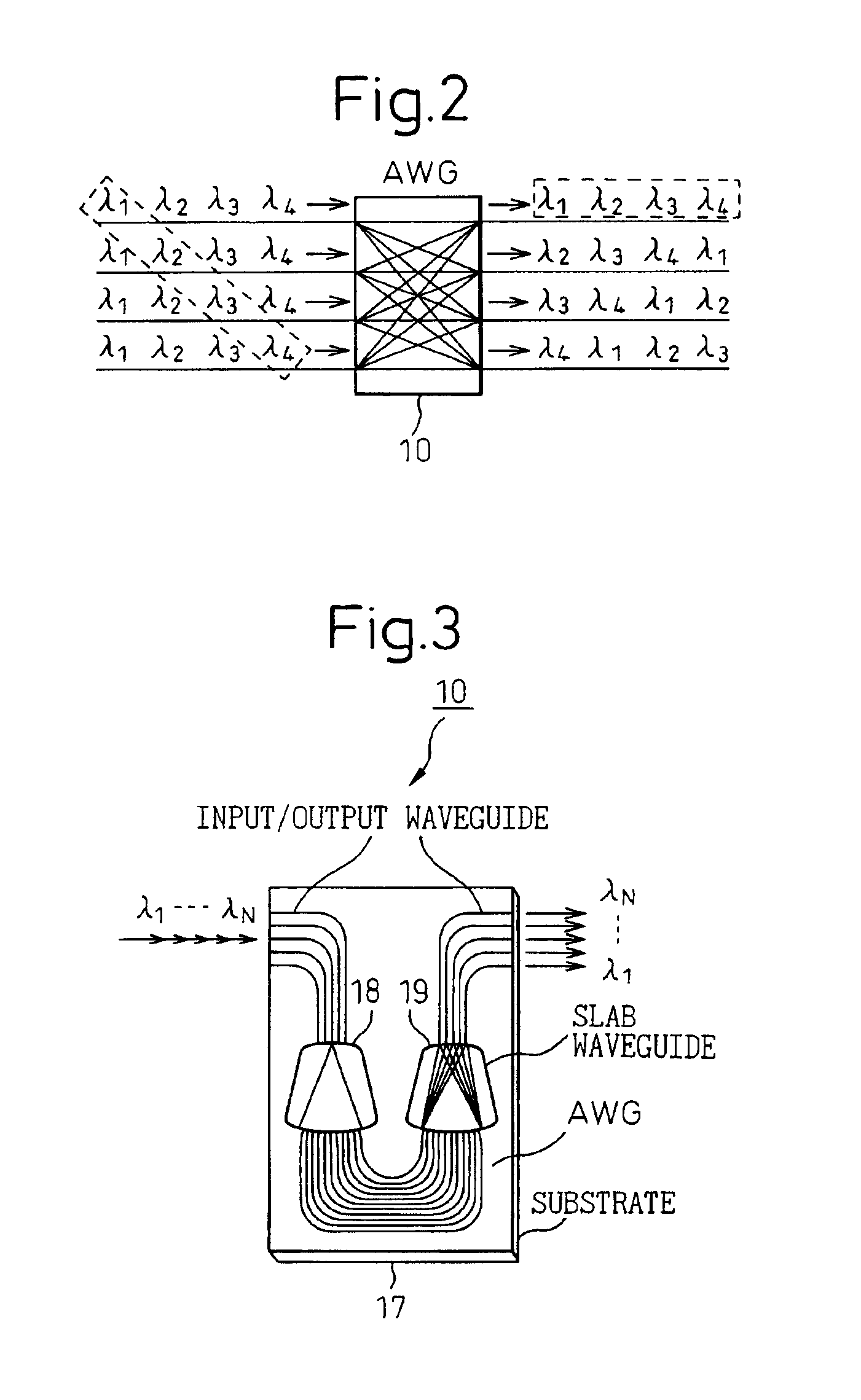
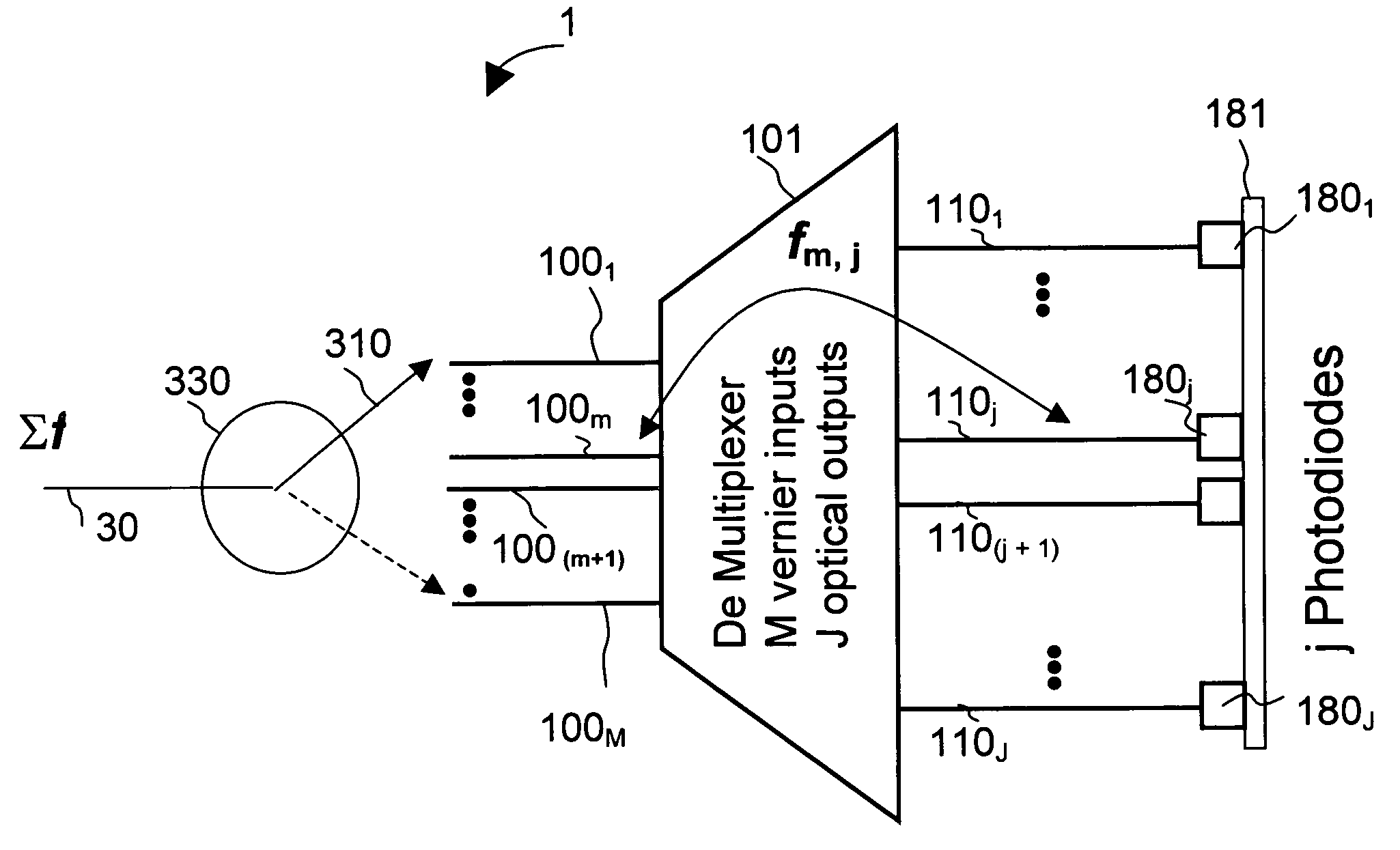
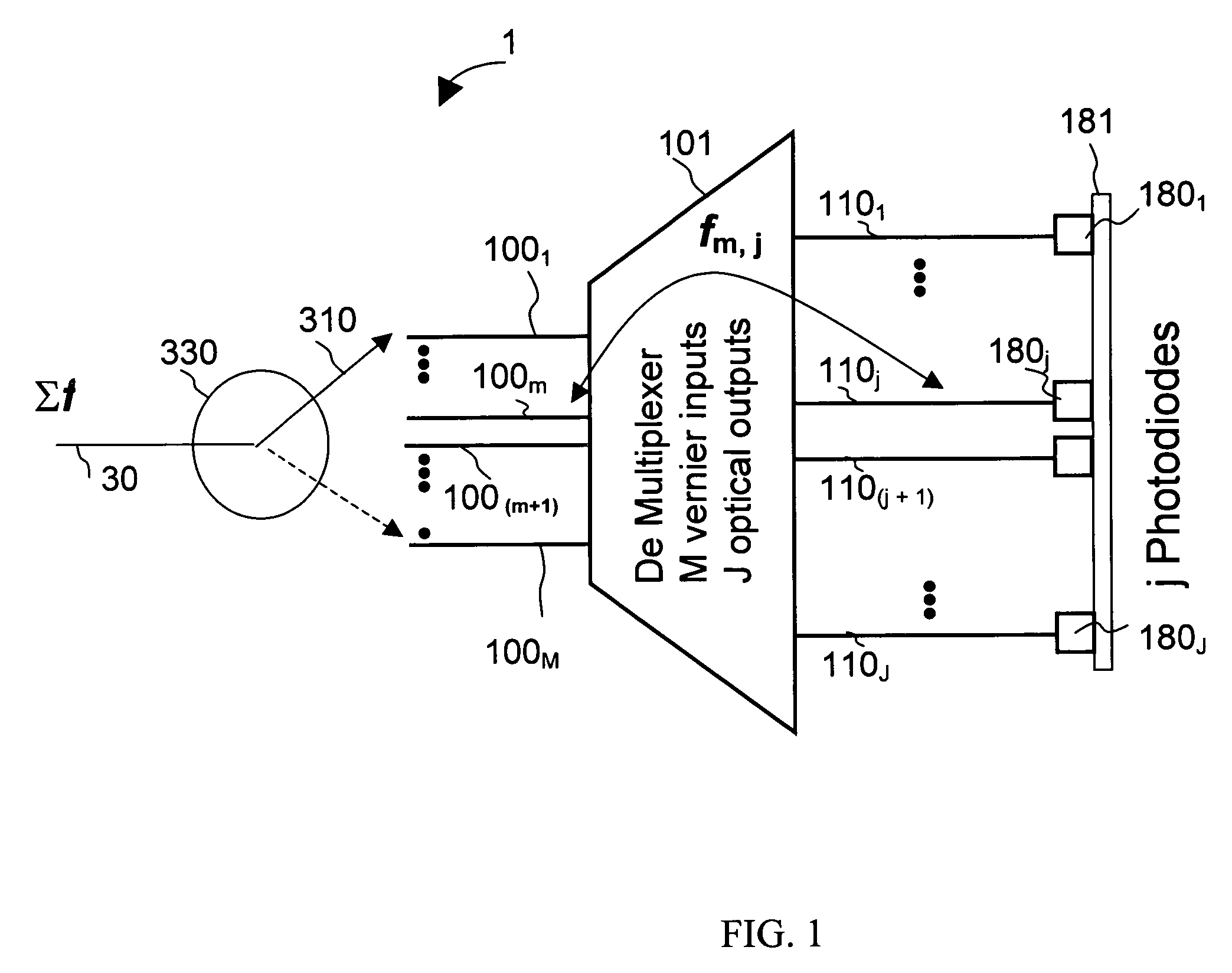
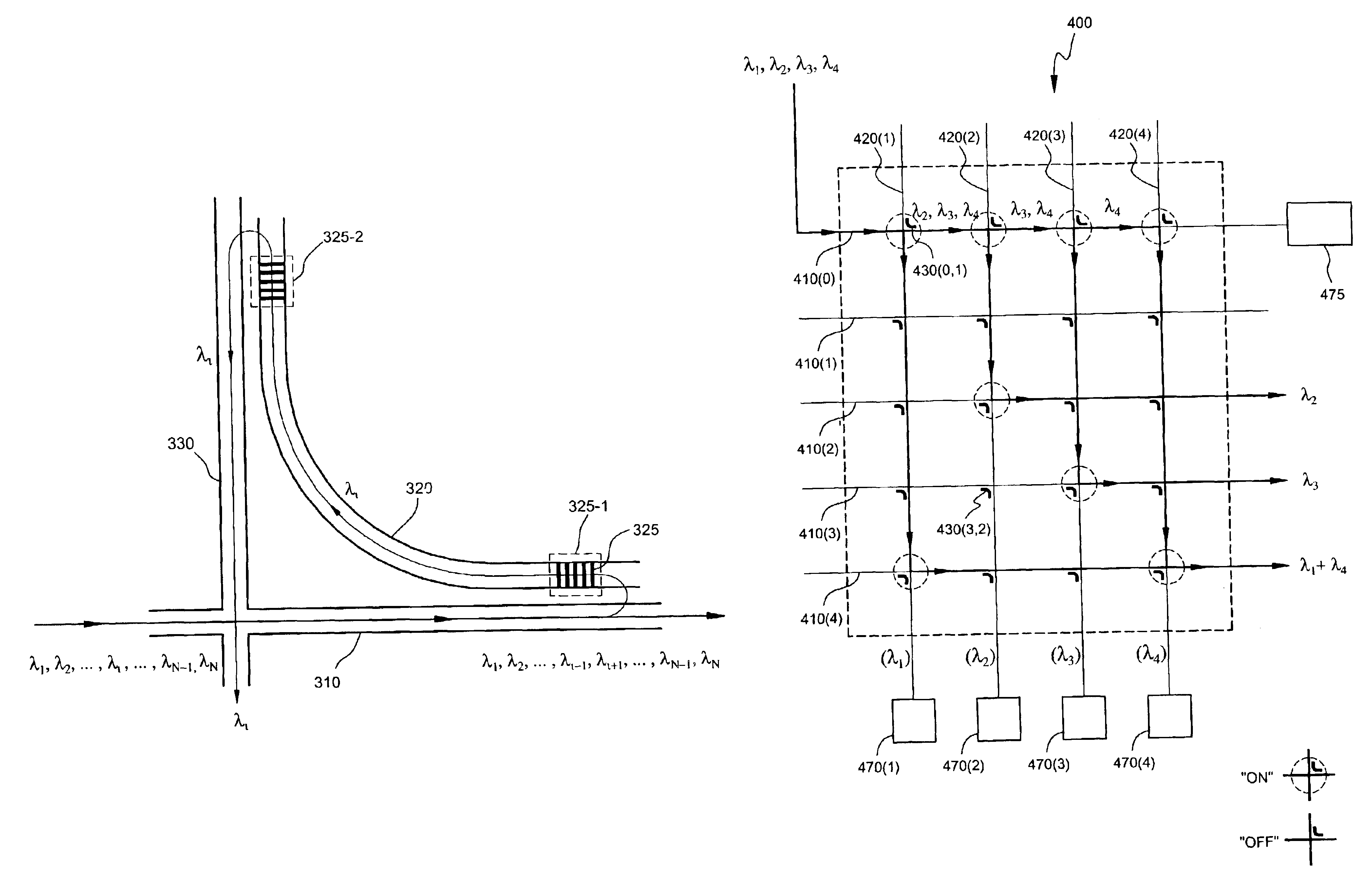
The present invention is a wavelength-selective optical switching system. The switching system includes an input waveguide designated as waveguide WG(0) for receiving a multiplexed optical signal comprising optical signals transmitted over a plurality of wavelength channels represented by λ1, λ2, λ3, , λN, where N is a positive integer wherein the input waveguide extending over a first direction. The switching system further includes a two dimensional waveguide array comprising a plurality of first direction waveguides WG(i), i=1, 2, 3, , M extending over the first direction substantially parallel to the input waveguide WG(0) where M is a positive integer and a plurality of second direction waveguides WG′(j), j=1, 2, 3, N, extending over a second direction substantially perpendicular to the first direction and intersecting with the input waveguide and each of the first direction waveguide WG(i), i=0, 1, 2, 3, ,M, thus forming (M+1)×N intersections. The switching system further includes a plurality of wavelength selective grating-based switches SW(i, j) where i=0, 1, 2, 3, , M and j=1, 2, 3, , N, each disposed on one of the (M+1)×N intersections for selectively transmitting an optical signal of wavelength λj into a waveguide WG′(j) and for selectively transmitting an optical signal of a predefined combination of wavelengths into at least one of the waveguide WG(i) for i=1, 2, 3, M.
Owner:OPLUN
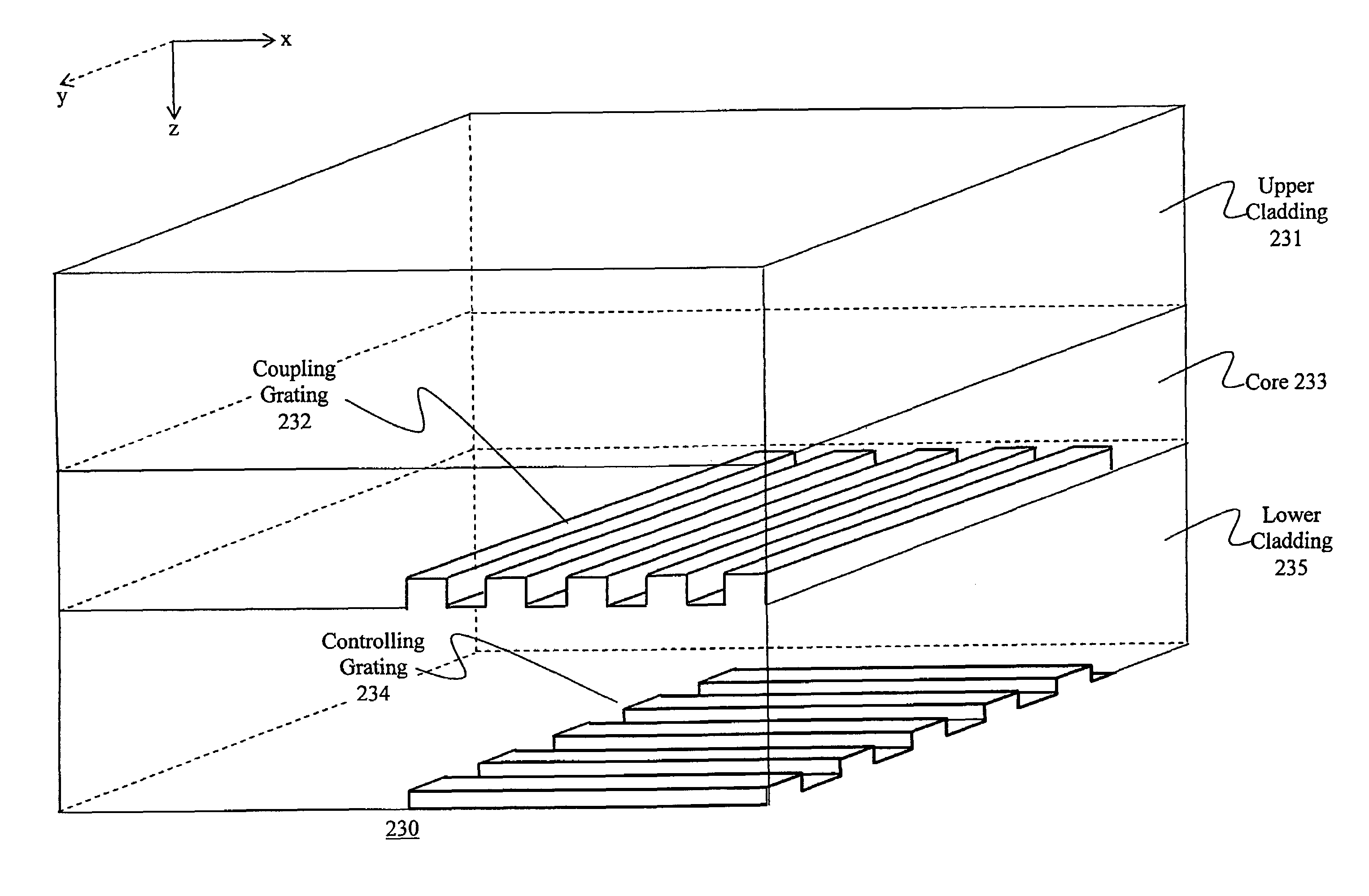
Integrated Photonics Waveguide Grating Coupler
A photonic integrated device comprises a waveguide embedded in a photonic substrate. The waveguide has a waveguide radiation exit surface and the waveguide is optically connected to a two dimensional grating. The photonic integrated device also comprises a two dimensional grating having a plurality of curved elongate scattering elements. The two dimensional grating is adapted for diffracting radiation received from the waveguide toward a direction out of the photonic substrate and the curved elongate scattering elements are oriented with respect to the waveguide such that, for points of the scattering elements which can be irradiated by radiations stemming from the waveguide, normal lines to at least the curved elongate scattering element closest to the waveguide radiation exit surface do not substantially intersect with the waveguide radiation exit surface of the waveguide.
Owner:UNIV GENT +1
Fabrication of waveguides and bragg gratings with uv-irradiation
InactiveUS20060127024A1Highly accurate repositioningAdded fabricationGlass making apparatusCoupling light guidesLight spotRefractive index
A method of simultaneously defining a waveguide and grating in a sample of photosensitive material comprises providing a sample of material (24) having a region which is photosensitive to light of a specific wavelength, generating a spot of light (22) at the specific wavelength, the spot having a periodic intensity pattern of high and low intensity fringes, and a width which is related to the width of the channel, positioning the spot within the photosensitive region and causing relative movement between the sample and the light spot along the desired path of the waveguide / grating define a channel of altered refractive index by exposing parts of the photosensitive region to the light spot. Modulation of the light spot to produce multiple exposures produces a grating, while continuous exposure results in a uniform waveguide. These structures can be written in straight lines or around curves, and can be accurately overwritten, so that complex optical devices can be produced in a single fabrication step.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Packaging method for high-efficiency vertical coupling interconnection of optical fiber and optical waveguide chip
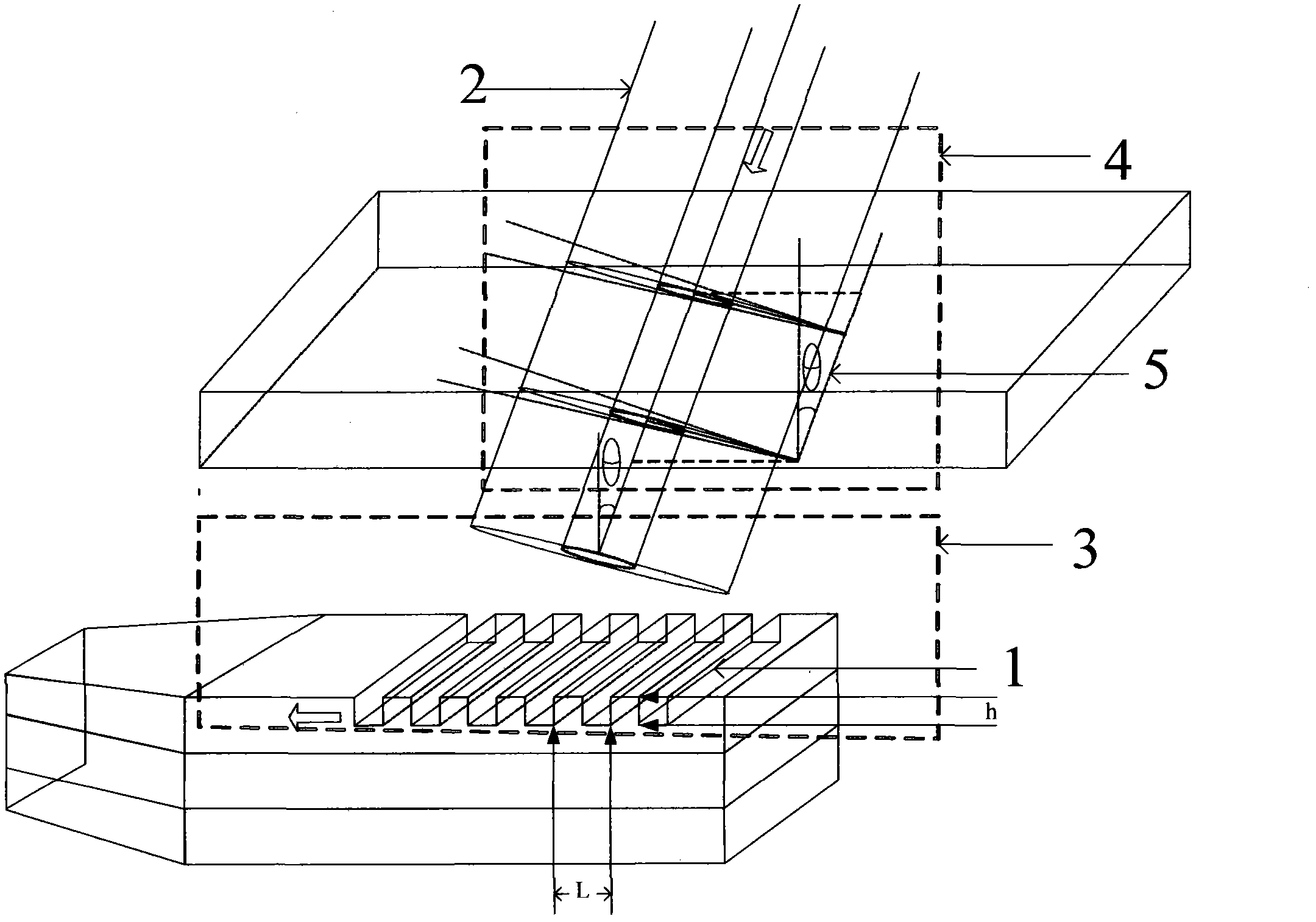
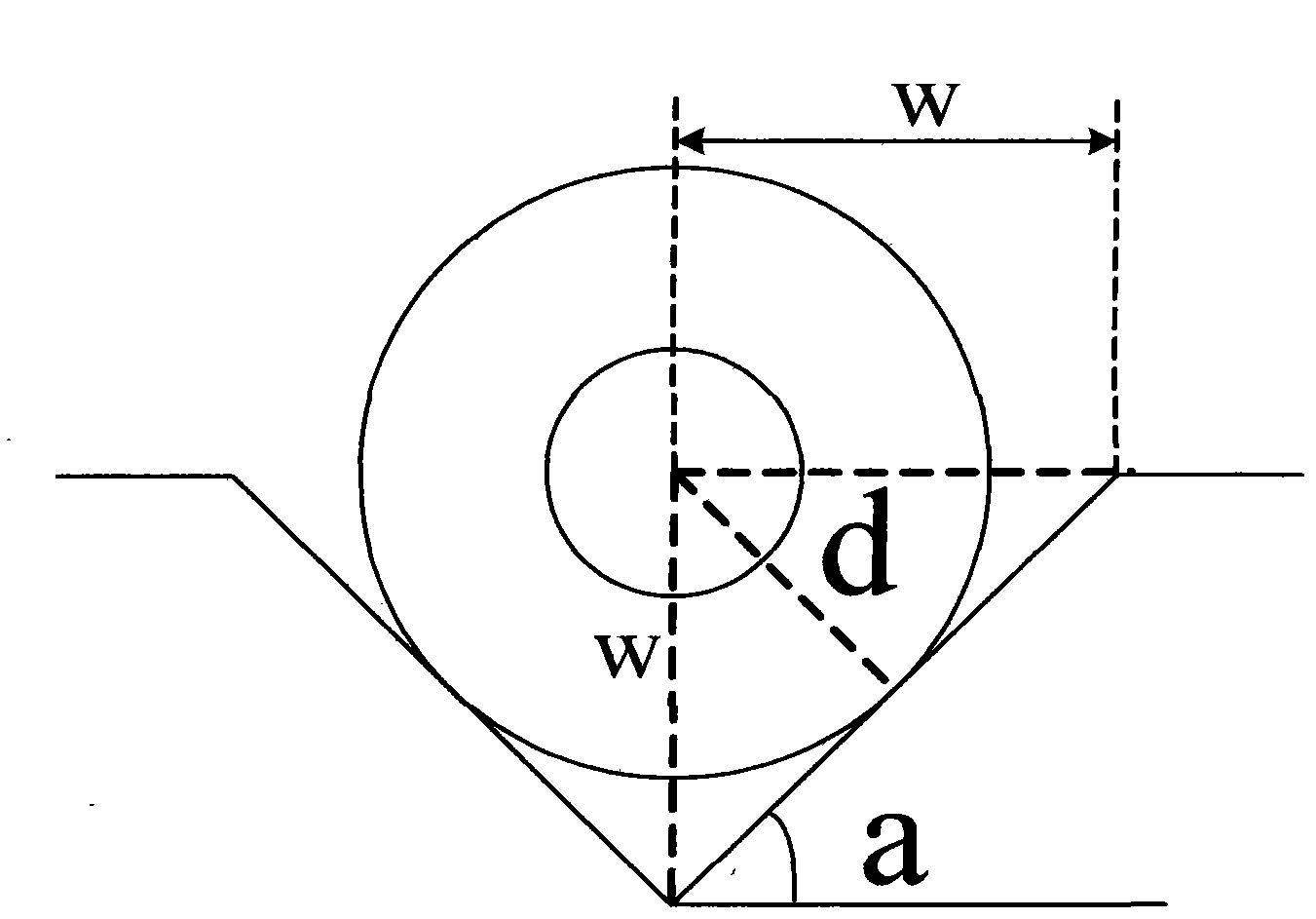
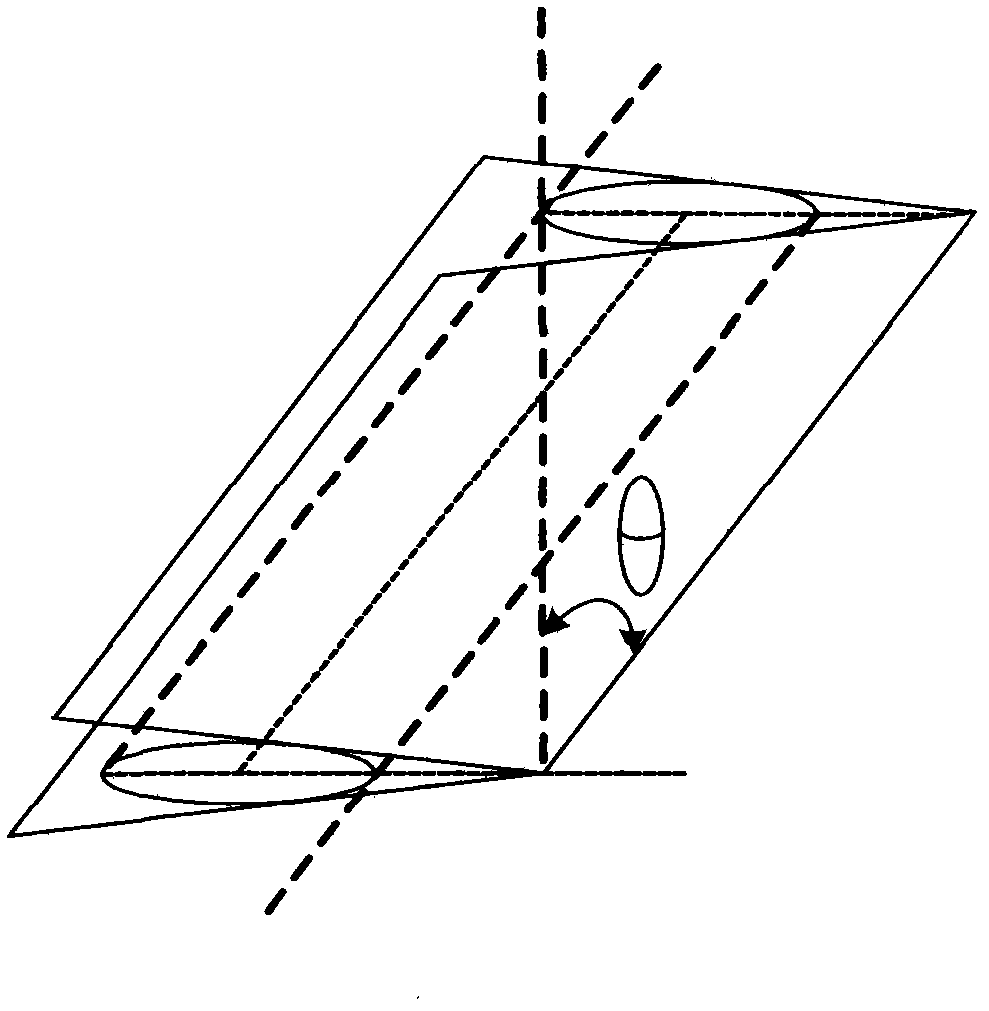
The invention discloses a packaging method for high-efficiency vertical coupling interconnection of optical fiber and optical waveguide chip which comprises the following steps of: preparing a silica-based nano waveguide grating and scanning the silica-based nano waveguide grating by applying a scanning electron microscope; preparing a curing packaging material with a low refractive index; preparing a monomode optical fiber; coating an optical anti-reflection film on the surface of the silica-based nano waveguide grating; regulating the position between the monomode optical fiber and the silica-based nano waveguide grating; dispensing an adhesive at the coupling ends of the monomode optical fiber and the silica-based nano waveguide grating; exposing and curing an inner packaged body subjected to adhesive dispensing; preparing a V-shaped optical fiber positioning groove; placing the monomode optical fiber in the V-shaped optical fiber positioning groove; carrying out curing packaging on the monomode optical fiber; exposing and curing the V-shaped optical fiber positioning groove subjected to adhesive dispensing; and testing the finally packaged structure. The invention overcomes the defects of instability and the like of a nano waveguide and grating vertical coupling system on the existing optical integrated chip. The packaged structure provided by the invention has simple structure and high stability, resists external interference and is easy for array integration.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
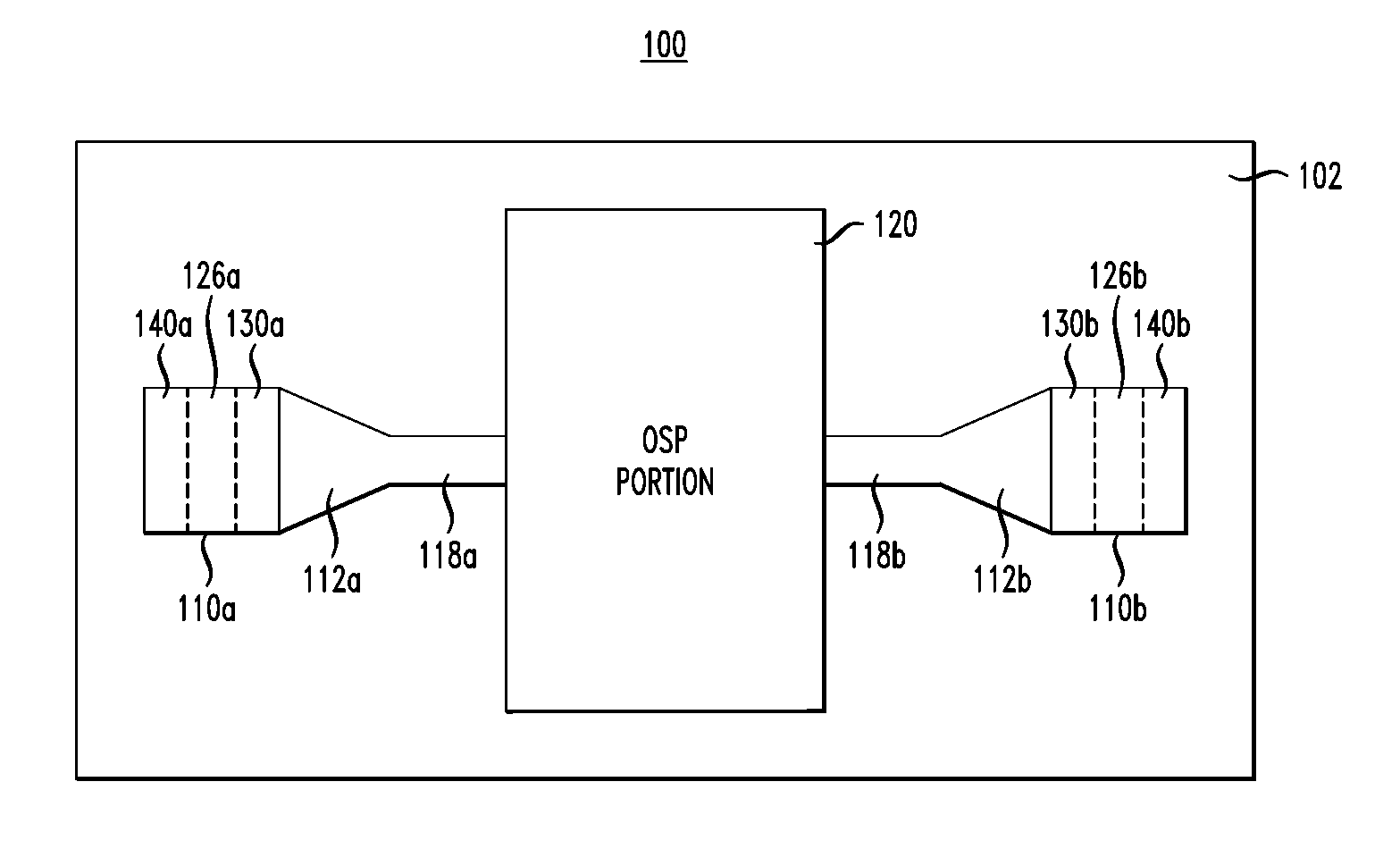
Photonic integrated circuit having a waveguide-grating coupler
ActiveUS20110150386A1Easy to integrateHigh Refractive Index ContrastOptical articlesNanoopticsRefractive indexEngineering
A photonic integrated circuit (PIC) having a waveguide-grating coupler with two evanescently coupled waveguides. The first waveguide is fabricated using materials suitable for manufacturing active optical elements in the PIC. The second waveguide is fabricated using materials capable of providing a relatively high index-of-refraction contrast for the constituent waveguide grating. The waveguide-grating coupler is compatible with the III-V semiconductor technology while being relatively easy to fabricate on an industrial scale.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Hitless variable-reflective tunable optical filter
InactiveUS20050147348A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingData stream
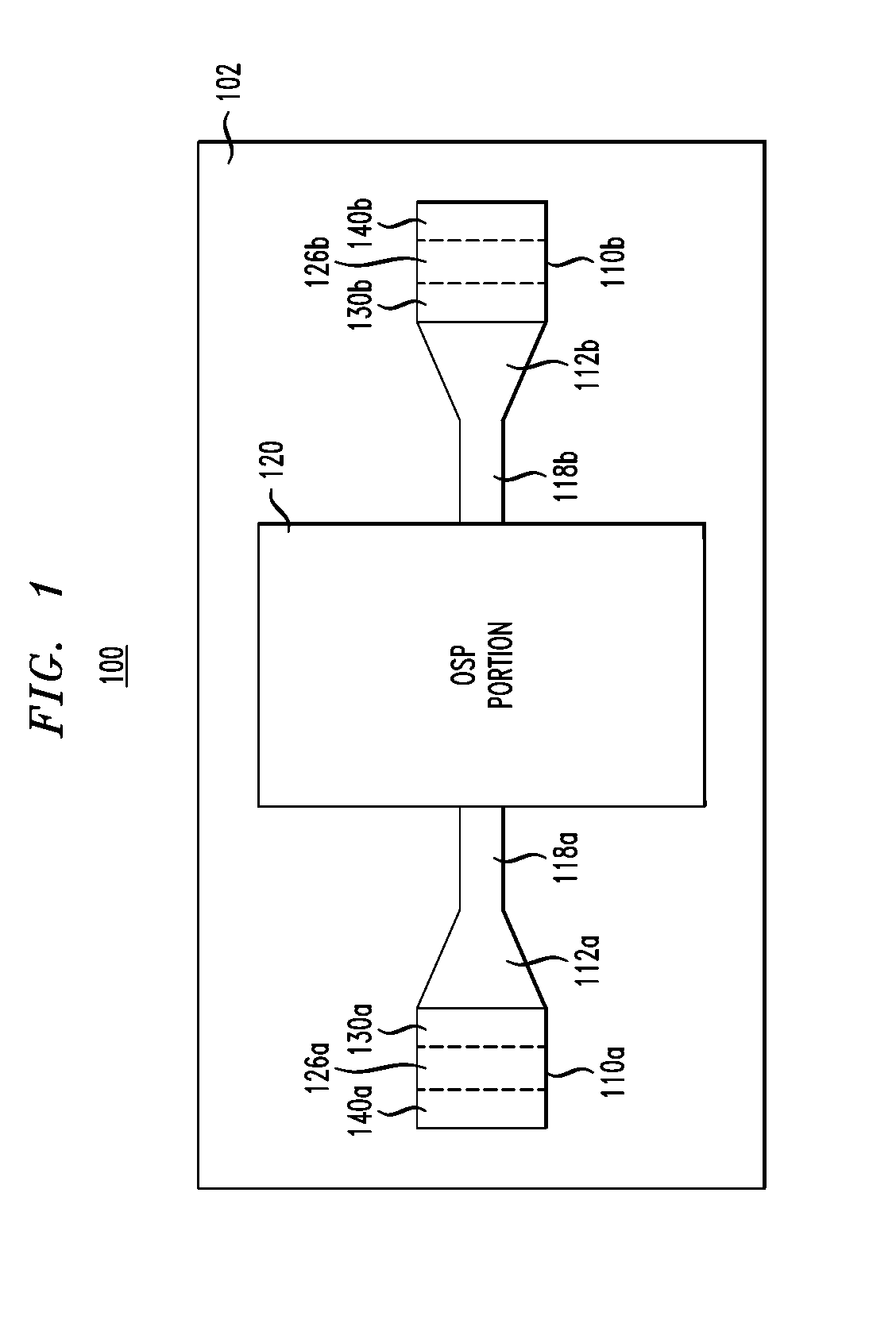
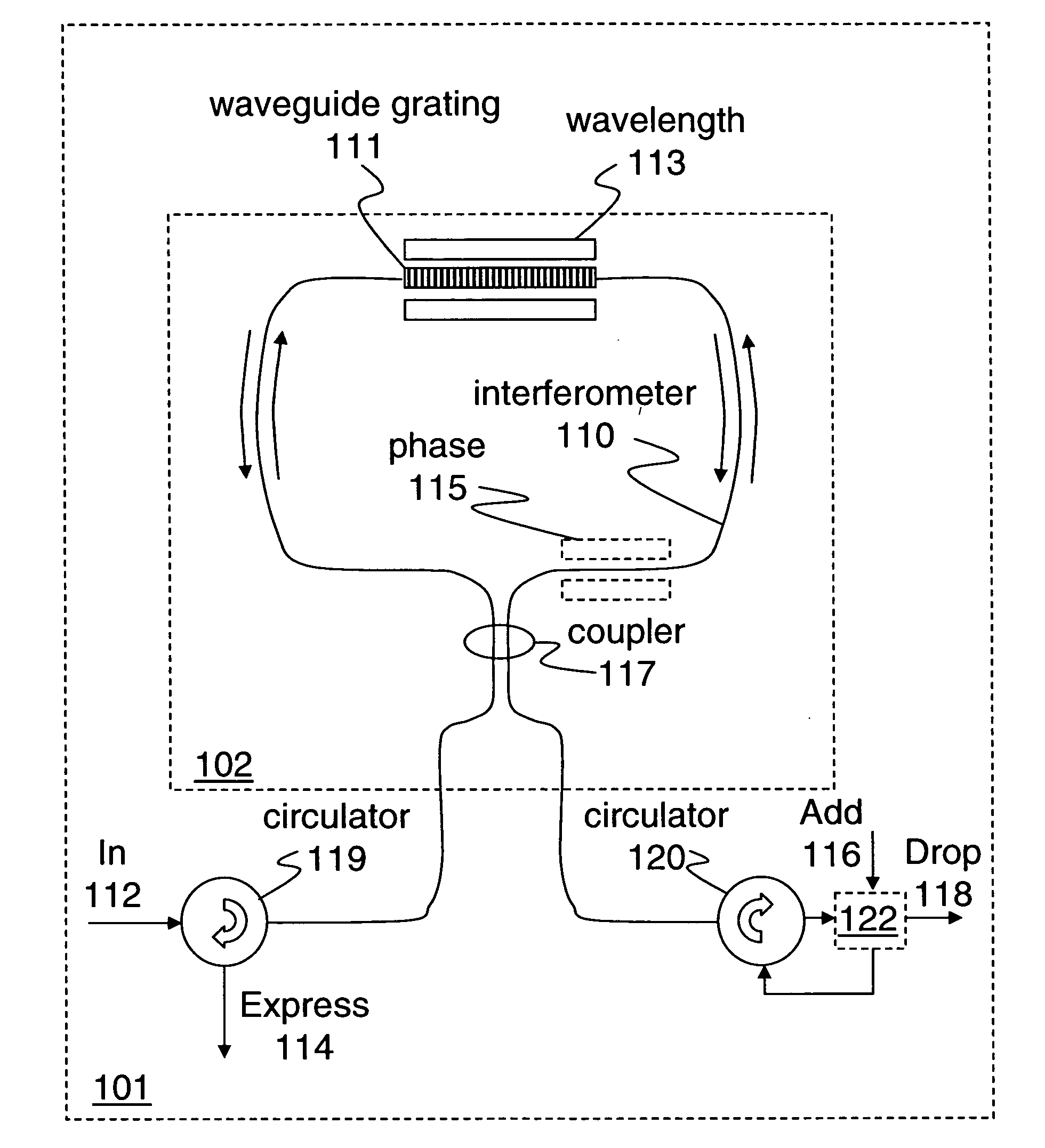
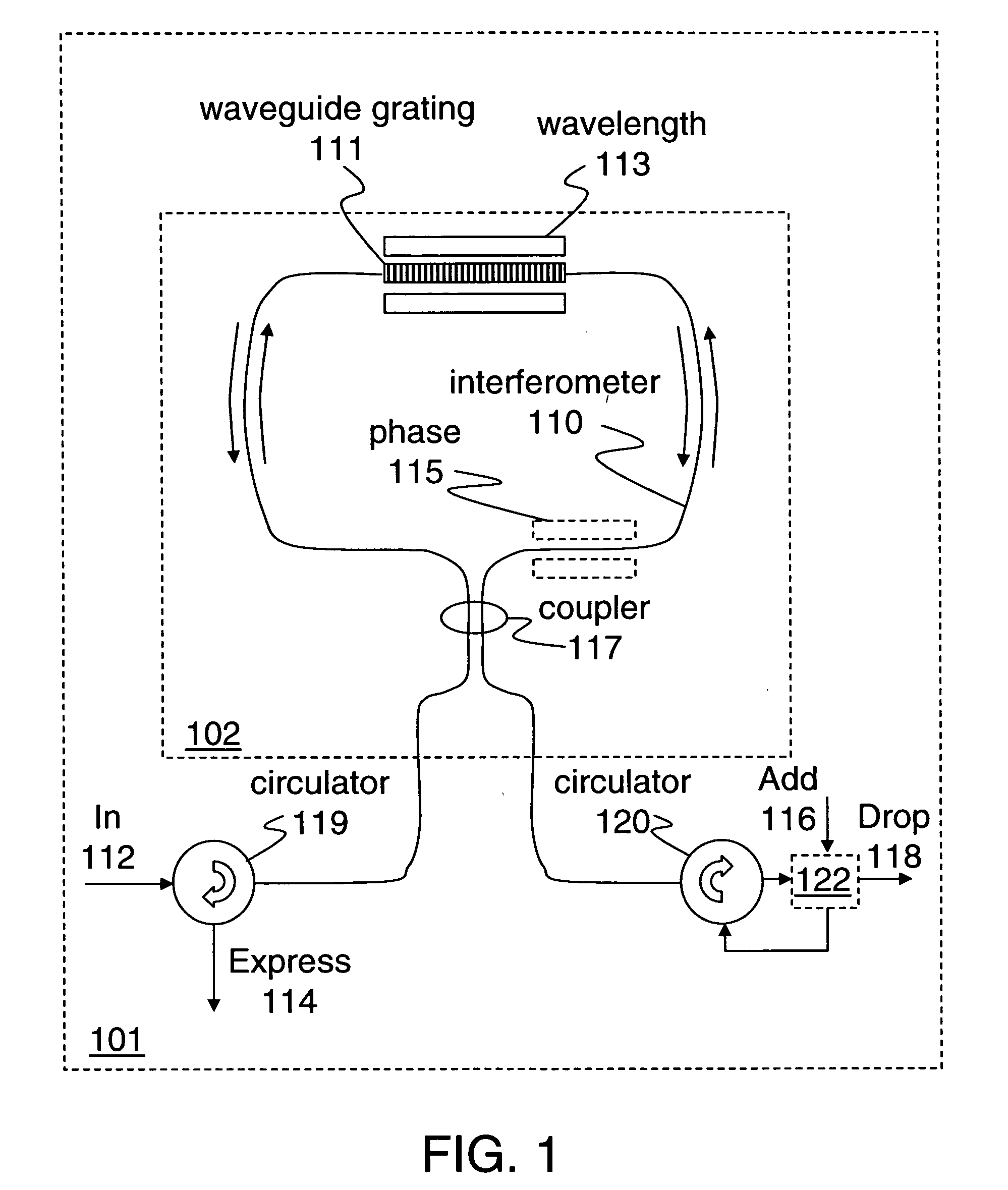
A variable-reflective tunable optical filter includes an interferometer adapted to control the powers of added or dropped signals and an optical waveguide grating to select the wavelength channels of the added or dropped signals. The waveguide grating is tunable to filter a dropped signal from an input data stream and filter an added signal into an output data stream. While a reflection band of the waveguide grating is being adjusted to tune a wavelength channel, the phase of at least one leg of the interferometer may be adjusted to direct signals of any wavelength channel selected by said waveguide from the input data stream to the output data stream, thereby providing hitless optical add-drop multiplexing.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Arrayed waveguide grating type optical multiplexer and demultiplexer
InactiveUS20120195553A1Reduce gapMinimizing size of whole arrayCoupling light guidesMultiplexerLength wave
An arrayed waveguide grating type optical multiplexer and demultiplexer which reduces a package size although plural arrayed waveguide gratings are included, is provided, comprising plural arrayed waveguide gratings which are provided in parallel to one another on a substrate and each of which has a first waveguide, a first slab waveguide, an arrayed waveguide, a second slab waveguide, and a second waveguide, and also includes a waveguide chip divided into a first and second separated waveguide chip in the first or second slab waveguide in each of the arrayed waveguide gratings and a compensation member compensating a temperature dependent shift of a light transmission center wavelength in the arrayed waveguide grating by relatively moving the first and second waveguide chip when expanded or contracted according to a temperature change. The waveguide chip has a shape bending along a bending direction of the arrayed waveguide.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Optical waveguide grating and method and mask for forming same
An optical waveguide grating is formed in an optical waveguide core and / or in an optical waveguide cladding where an electric filed of light propagating in the core is spreading by implanting accelerated ions through a mask to the optical waveguide. The mask has enough thickness to prevent the ions irradiated to the masked parts from reaching the portion where the grating is formed. The acceleration energy of the ions is chosen to make the lateral straggling of the implanted ions in the optical waveguide less than three fourths of the period of the grating, or the acceleration energy is chosen to make all or a part of the implanted ions pass through the portion where the grating is formed.
Owner:WASEDA UNIV
Waveguide grating structure and optical measurement arrangement
InactiveUS20100026323A1High measurement accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorResistance/reactance/impedenceLight beamOptical measurements
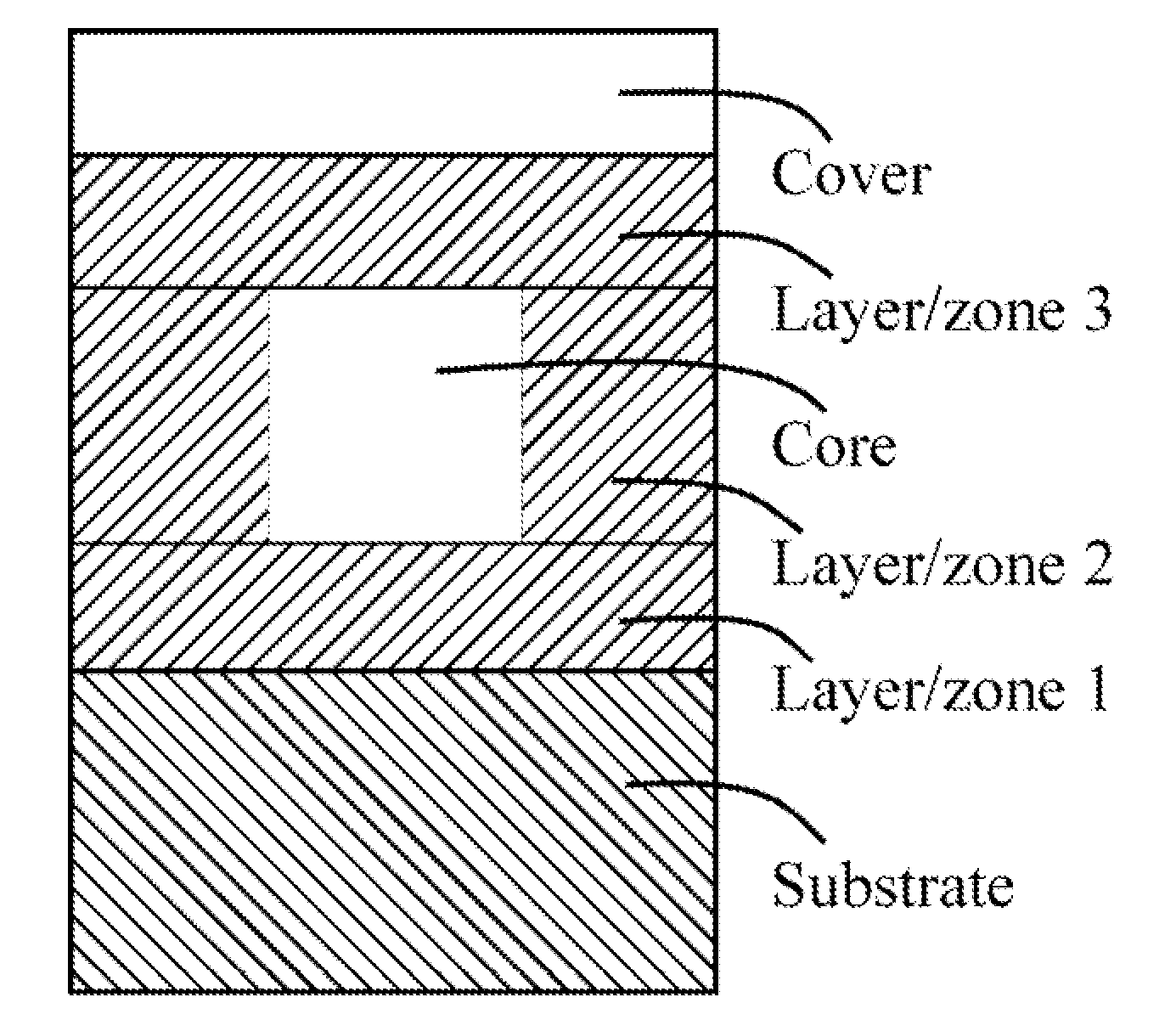
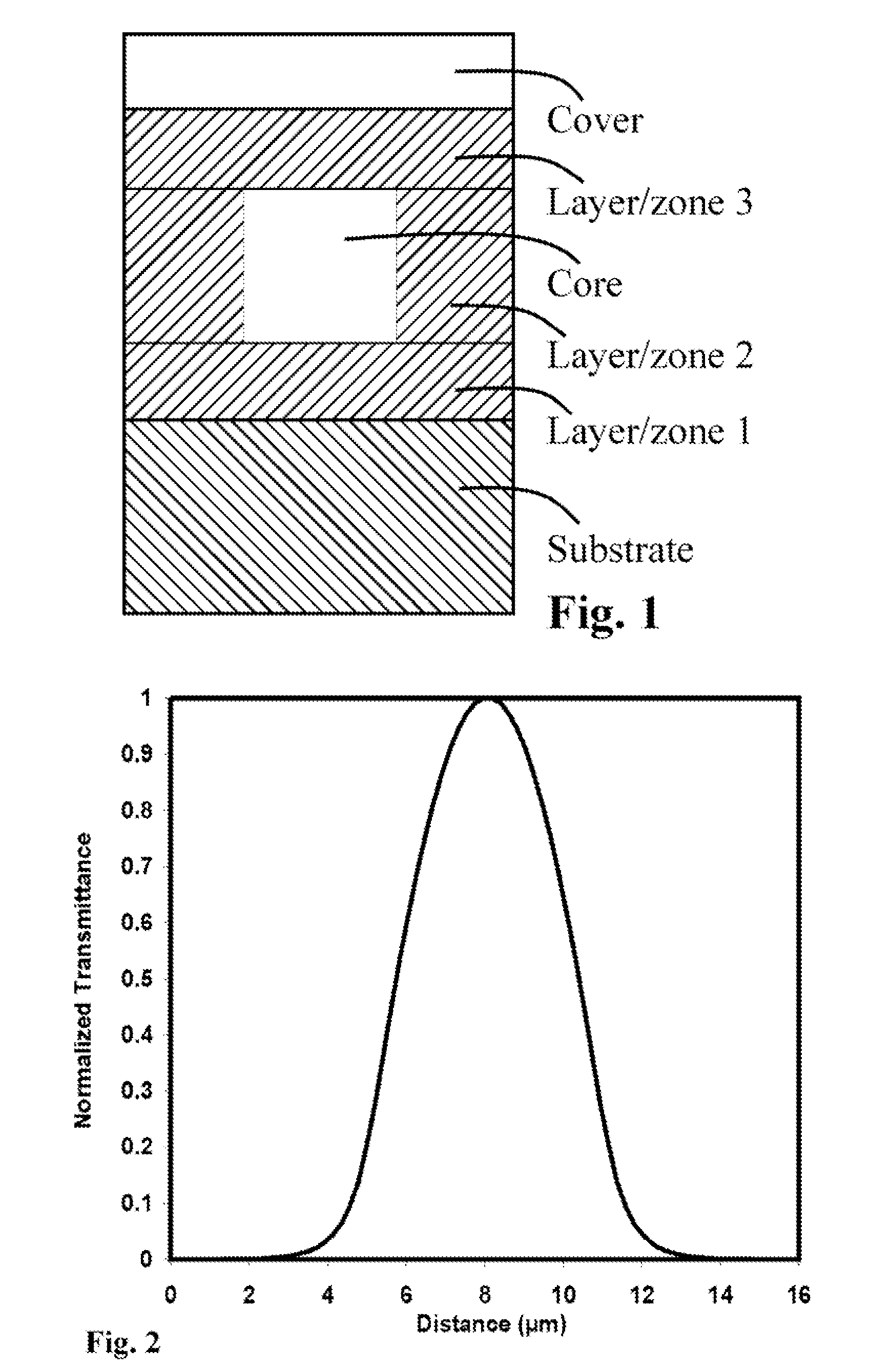
The present invention describes (bio)chemo-functional waveguide grating structures consisting of at least one (bio)chemo-functional waveguide grating structure unit or at least one (bio)chemo-functional sensor location with beam guidance permitting light beam separation, as well as detection methods for parallel analysis which are marking-free or based on marking.
Owner:ARTIFICIAL SENSING INSTR ASI
Highly efficient focusing waveguide grating coupler using leaky mode
InactiveUS20050008294A1Coupling efficiency is highReduce dependenceCoupling light guidesFresnel lensManufacturing technology
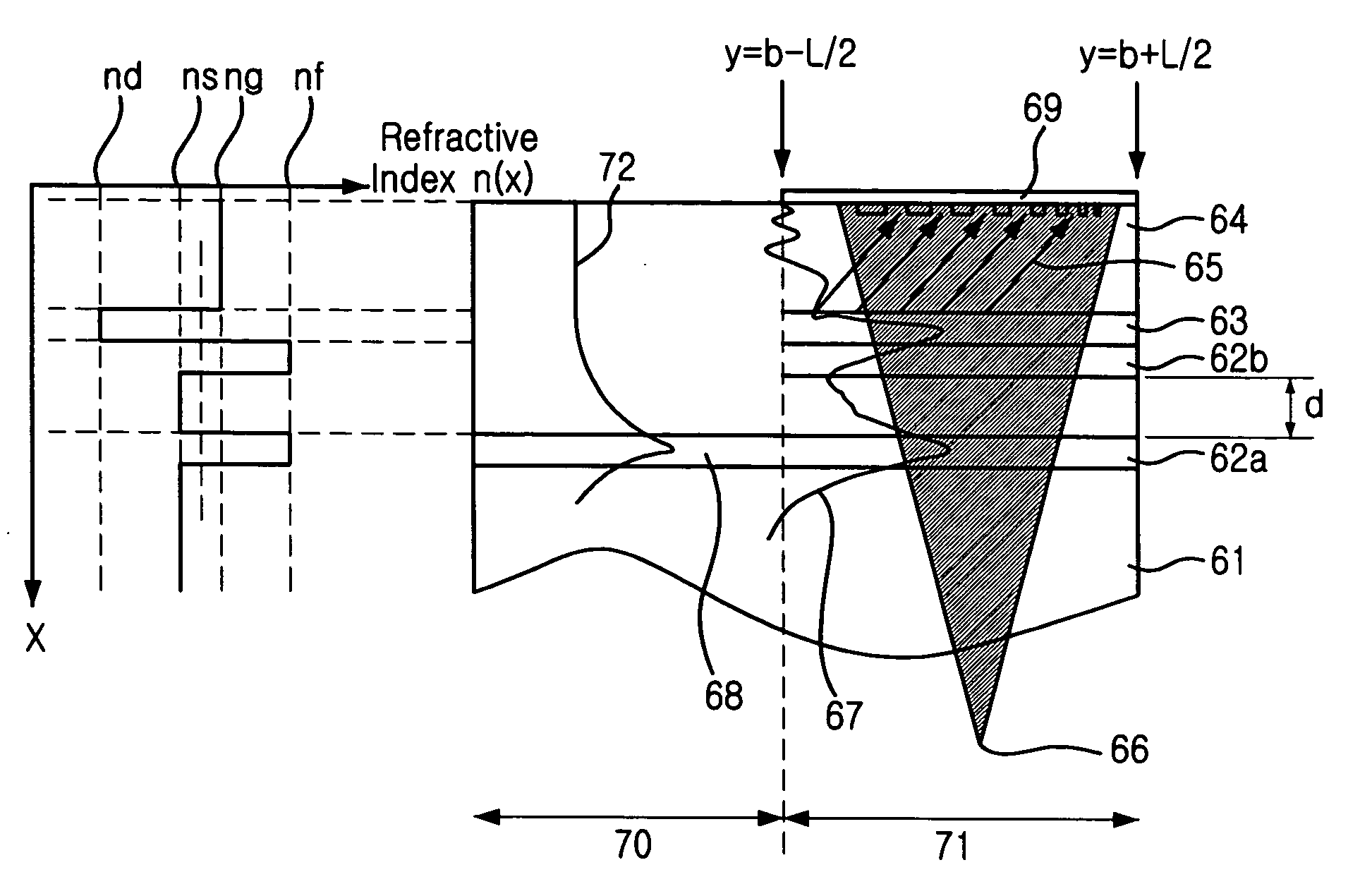
Provided is a focusing waveguide grating coupler using a leaky mode which can form single output beam while relieving the dependency on manufacturing processes. The focusing waveguide grating coupler of the present research includes: a substrate having a first refraction index n1; a first core layer having a second refraction index n2, the first core layer being formed on the substrate; a second core layer having a third refraction index n3, the second core layer being formed on the first core layer apart from the first core layer with a space d in between; a first cladding layer having a fourth refraction index n4, the first cladding layer being formed on the second core layer; a second cladding layer having a fifth refraction index n5, the second cladding layer being formed on the first cladding layer and inserted between the first core layer and the second core layer; and a Fresnel lens positioned on the second cladding layer, wherein the refractive indexes satisfy conditions of n5>(n2, n3)>n1 and n5>n4; and light inputted through the first and second core layers to the Fresnel lens as radiated leaky beam by a leaky mode formed according to the conditions, and the leaky beam forms an optical focus by performing single directional coupling.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Multi-band arrayed waveguide grating
An arrayed waveguide grating router (AWGR) comprises sets of output waveguides for a number of bands. Angular separation of adjacent output waveguides is relatively small for adjacent output waveguides. within a band and significantly larger for adjacent output waveguides belonging to different bands. In specific embodiments the output waveguides are arranged into at least two bands, each band comprising at least two adjacent waveguides. Each band is used in conjunction with an input waveguide specific to the particular band. AWGRs according to the invention may be made so that the passbands from a plurality of output waveguides fall on a wavelength grid or a frequency grid. Dummy waveguides may be included for ease of fabrication.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS CORP
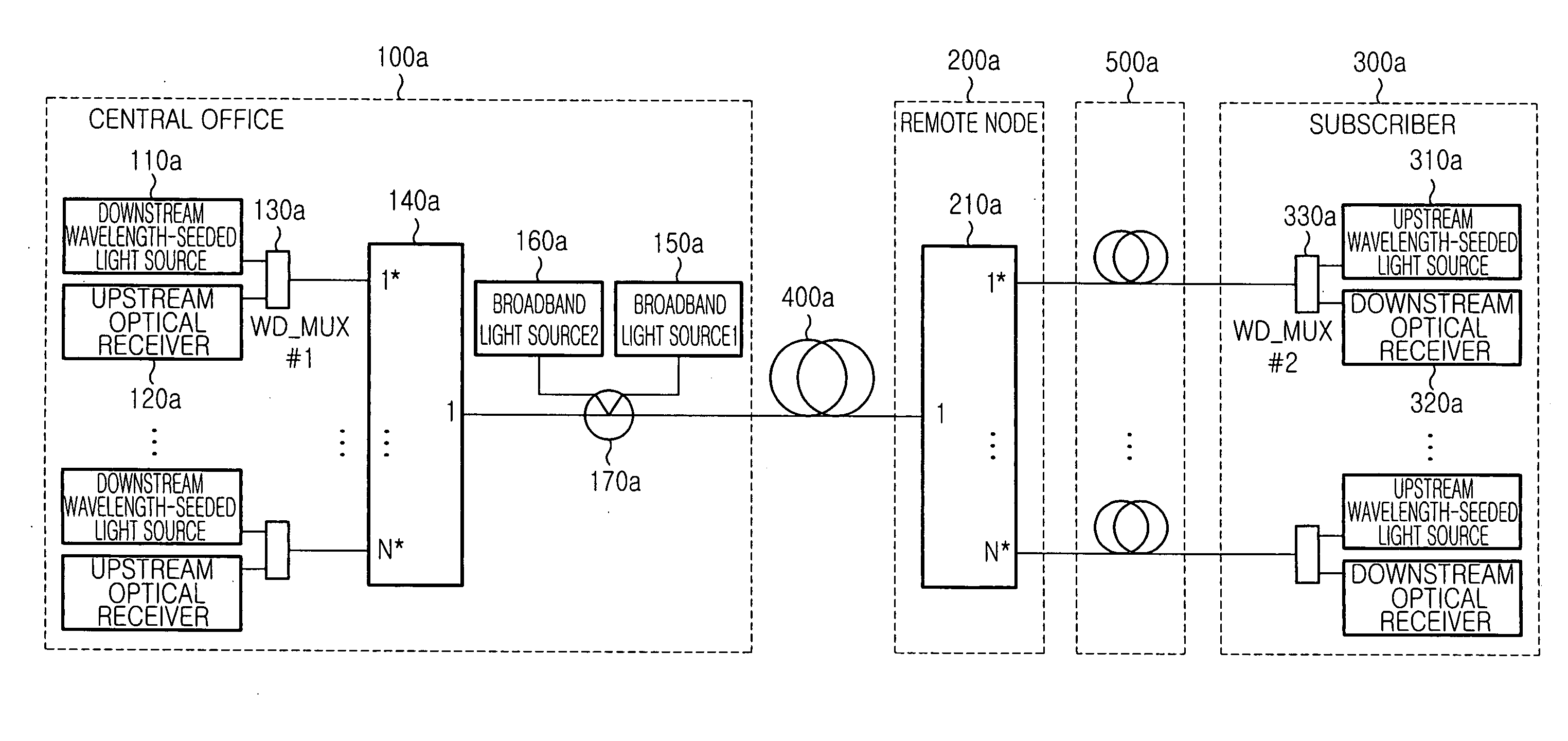
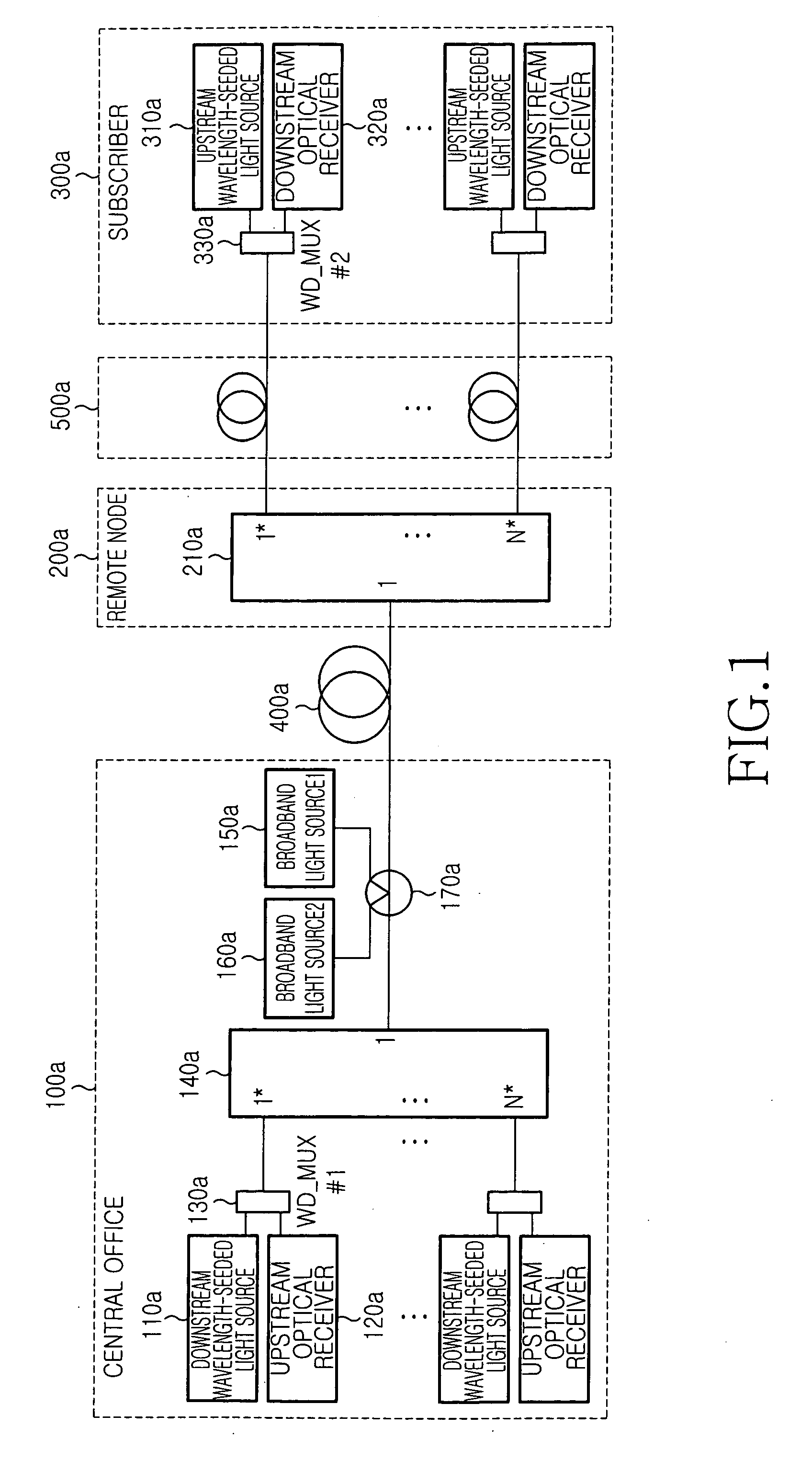
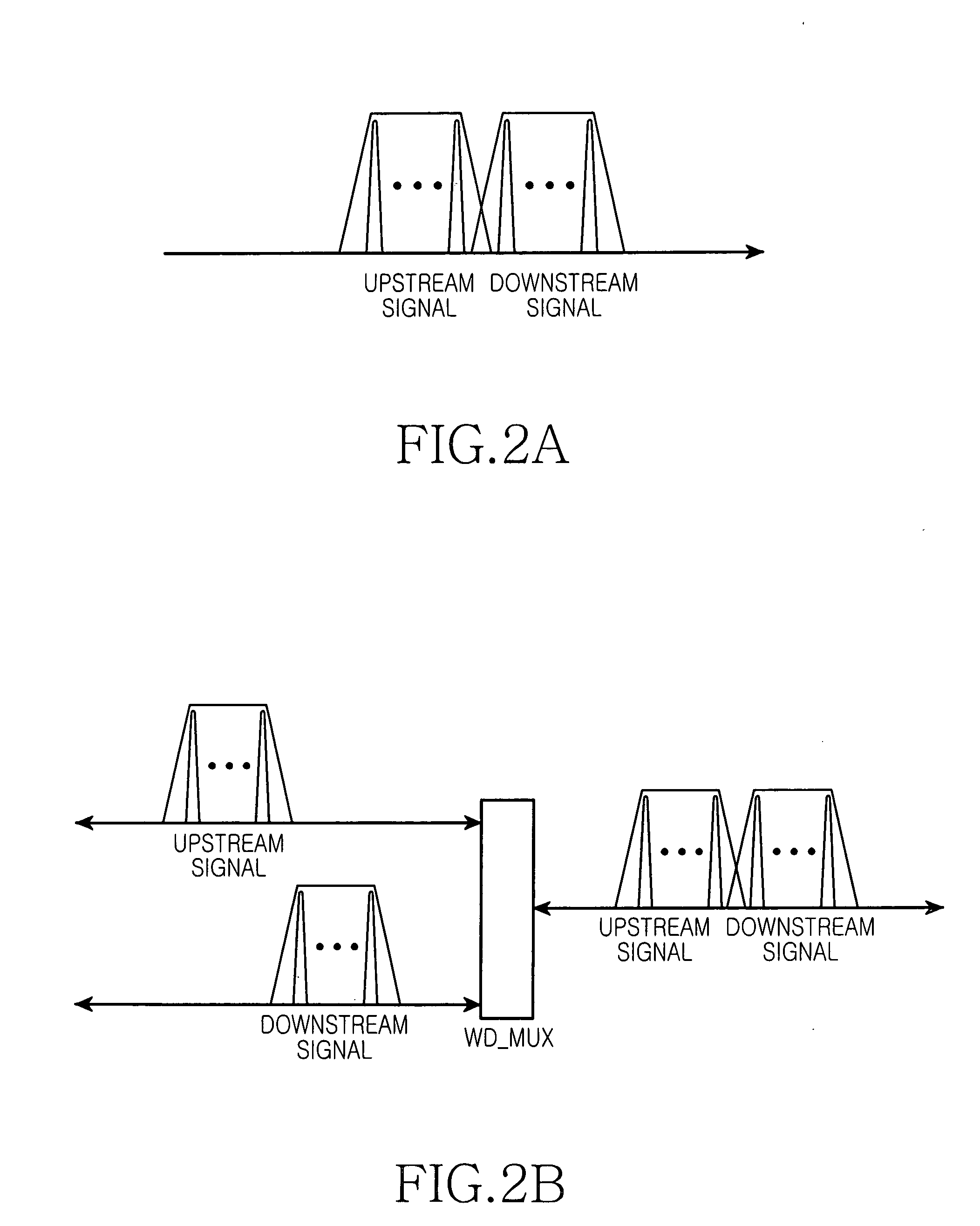
Wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network system using wavelength-seeded light source
InactiveUS20050074240A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionWdm optical networksSingle strand
An economical wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network (WDM-PON) system is realized by directly modulating a wavelength-seeded light source to transmit upstream or downstream data, without using an expensive external modulator. A multiplexed signal having the same wavelength as the waveguide grating is generated and used to control the temperature of the waveguide grating and adjust the wavelength of a wavelength-division-multiplexed signal routed to a transfer link. The wavelength selectivity and stabilization of each light source are not required. Since upstream and downstream signals can be multiplexed and demultiplexed concurrently by each waveguide grating located in the central office and the remote node, it is possible to reduce the number of waveguide gratings used in a WDM optical network. In addition, upstream and downstream signals can be transmitted concurrently using a single-strand transfer optical fiber, thereby realizing an economical and efficient WDM-PON.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
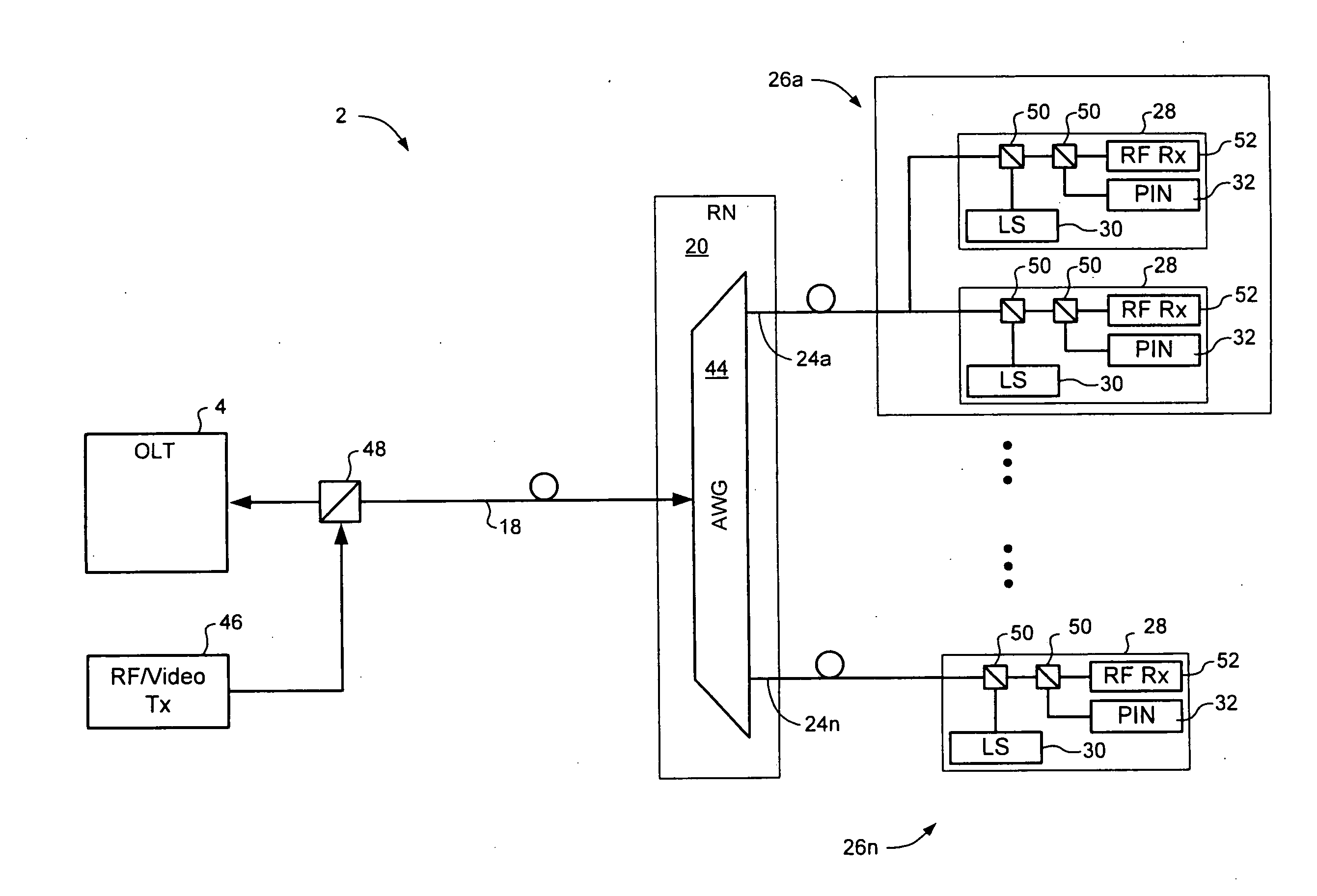
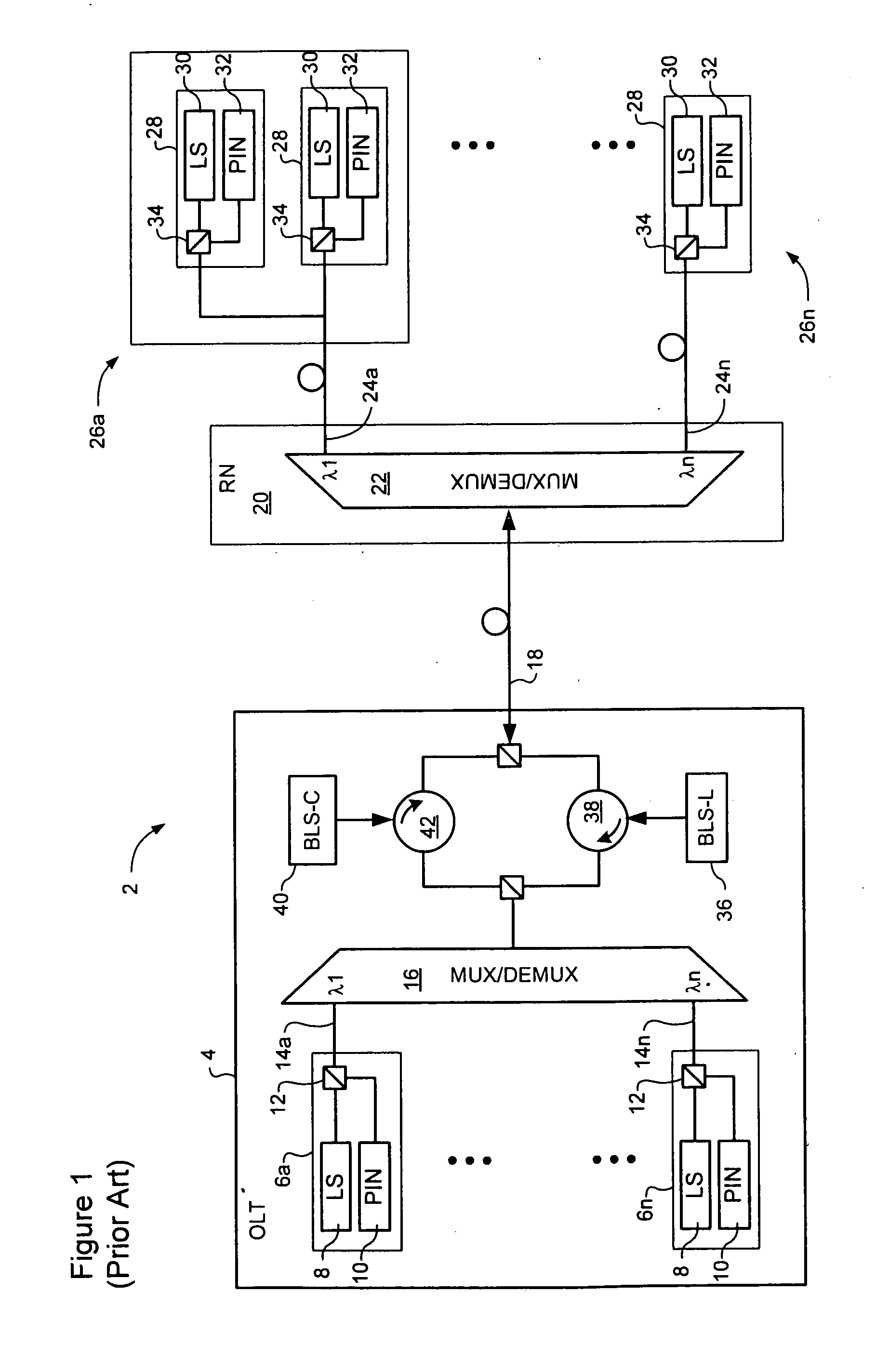
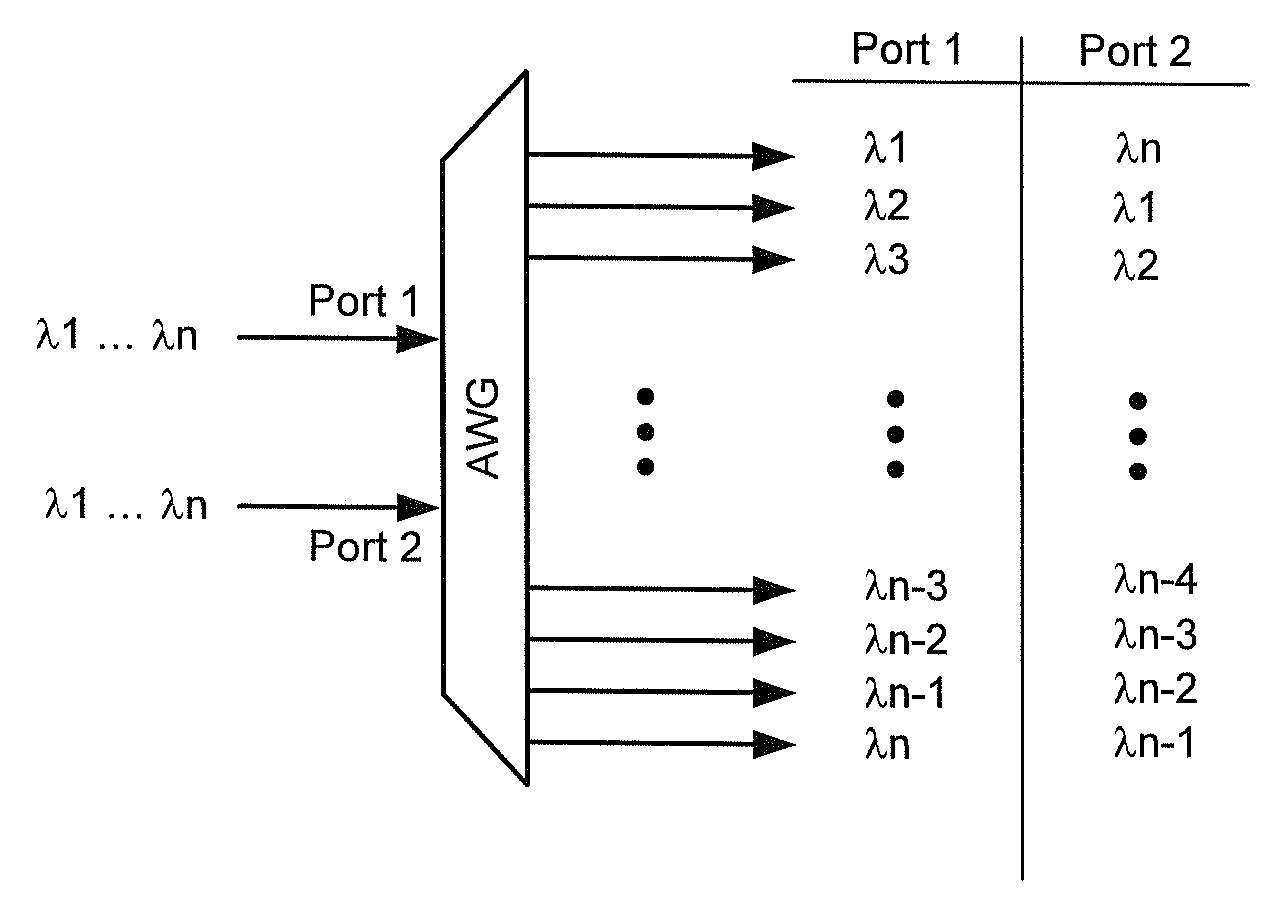
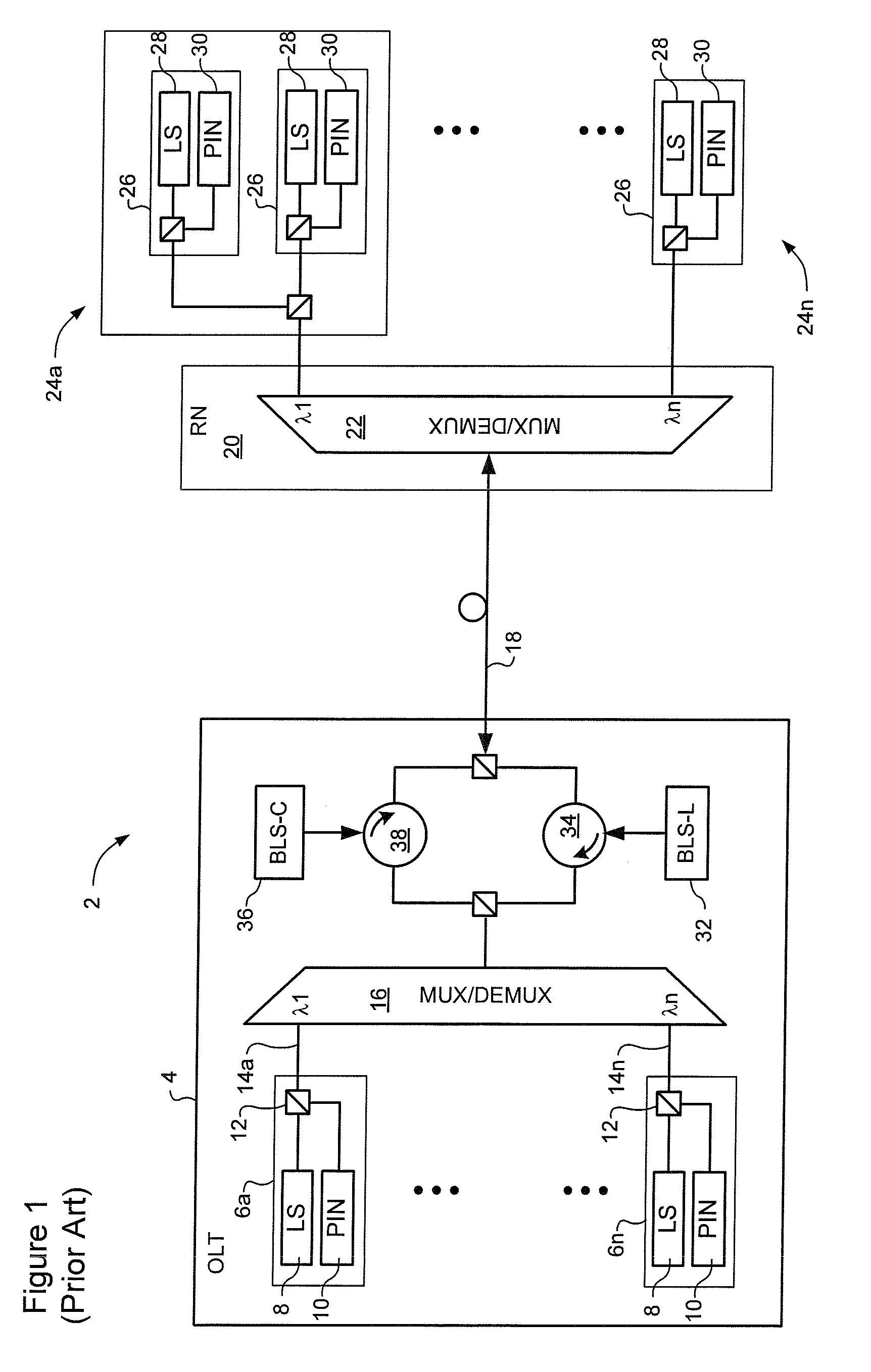
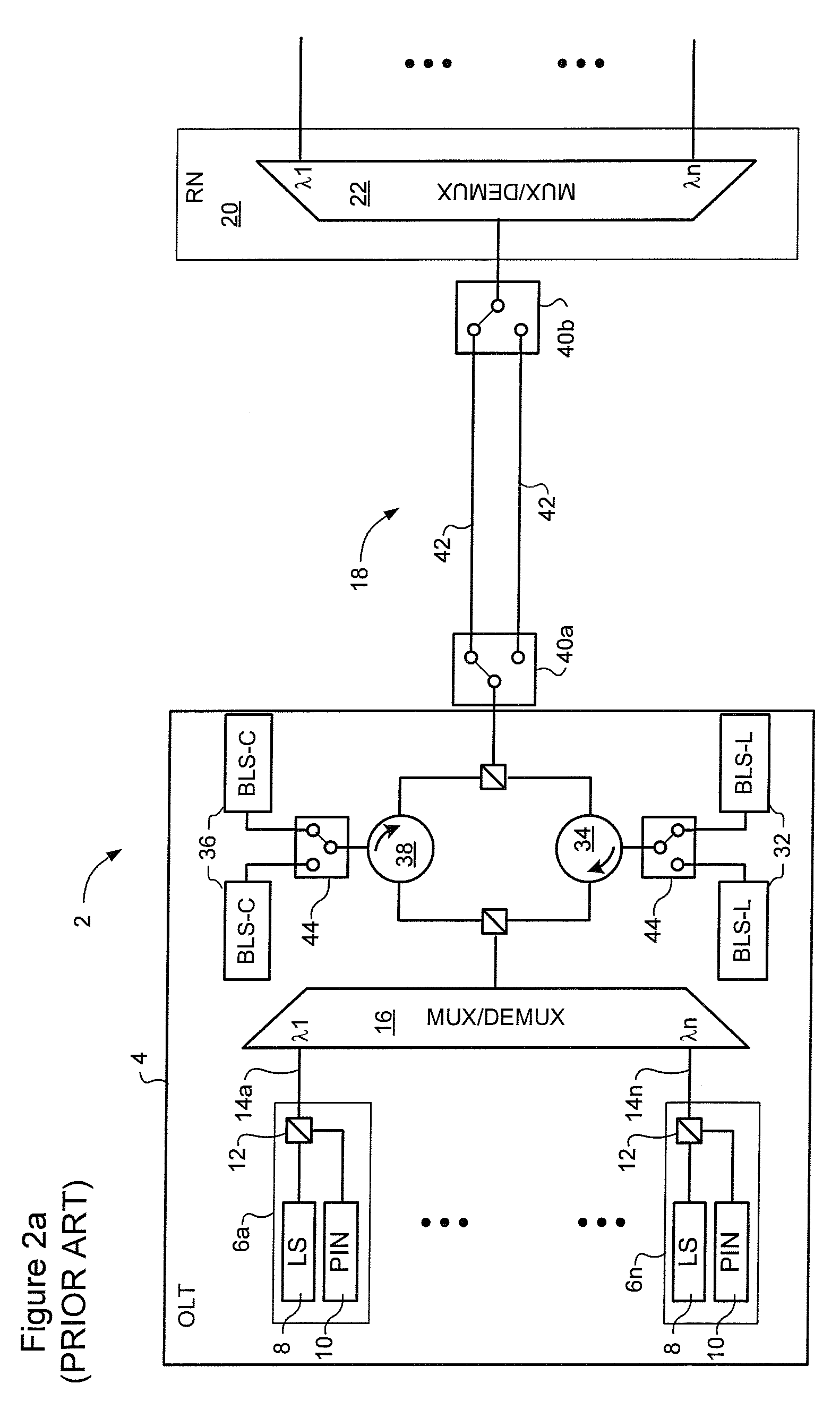
WDM PON protection scheme using a dual port arrayed waveguide grating (AWG)
A Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network (WDM-PON) includes an Optical Line Terminal (OLT) including a first Arrayed Waveguide Grating (AWG) MUX / DEMUX, and a remote node including a second AWG MUX / DEMUX. Each AWG MUX / DEMUX has at least two input ports for receiving a respective wavelength division multiplexed optical signal, and a plurality of output ports. Each output port of the Optical Line Terminal AWG MUX / DEMUX is coupled to a respective transceiver of the OLT. Each output port of the remote node AWG MUX / DEMUX is coupled to a respective PON having at least one optical network terminal (ONT). Respective first and second optical paths are coupled between corresponding input ports of the first and second AWG MUX / DEMUXs. Means are provided for sourcing seed light of the WDM-PON into a selected one the first and second optical paths.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com