Patents
Literature
54results about How to "Coupling efficiency is high" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
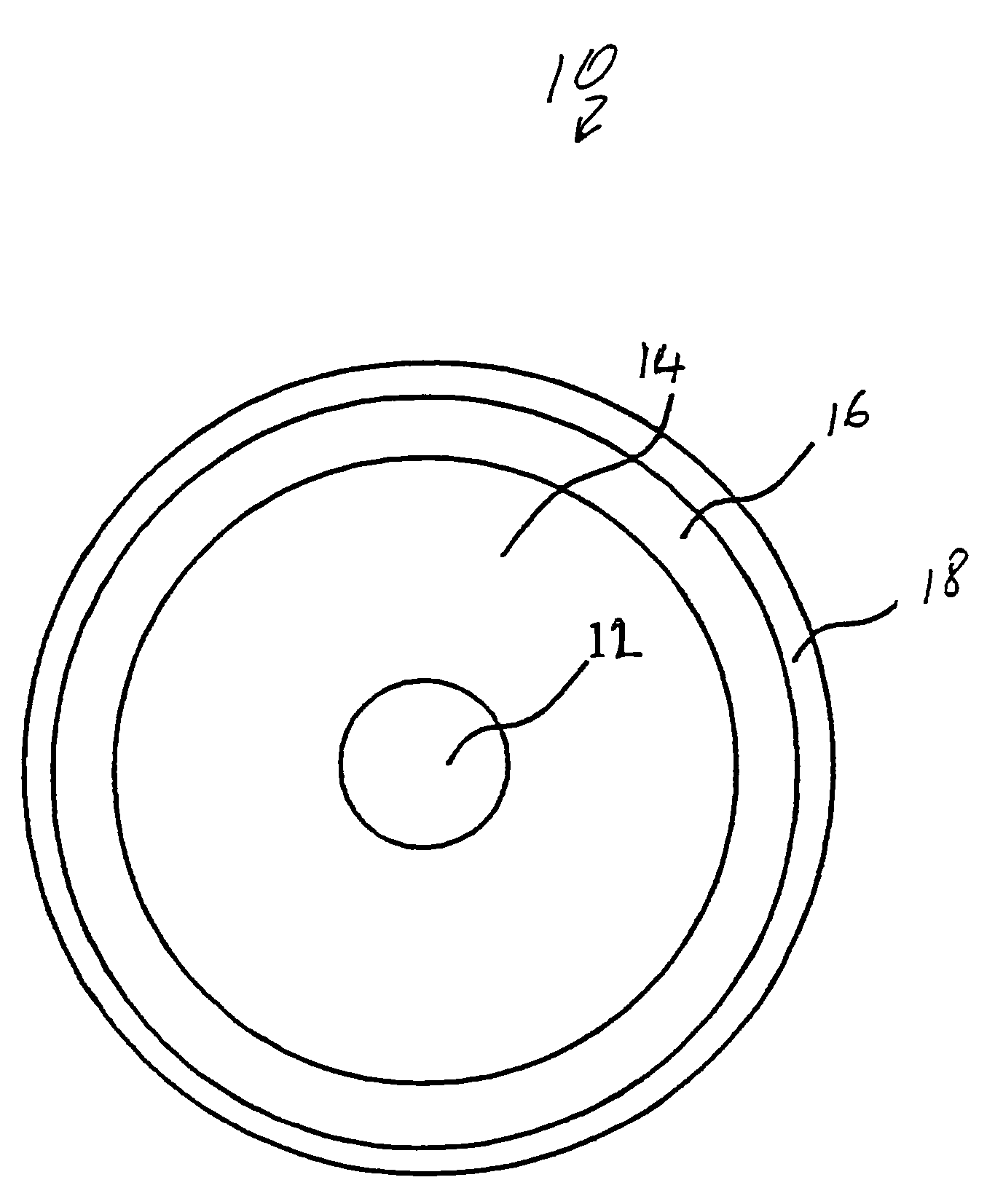
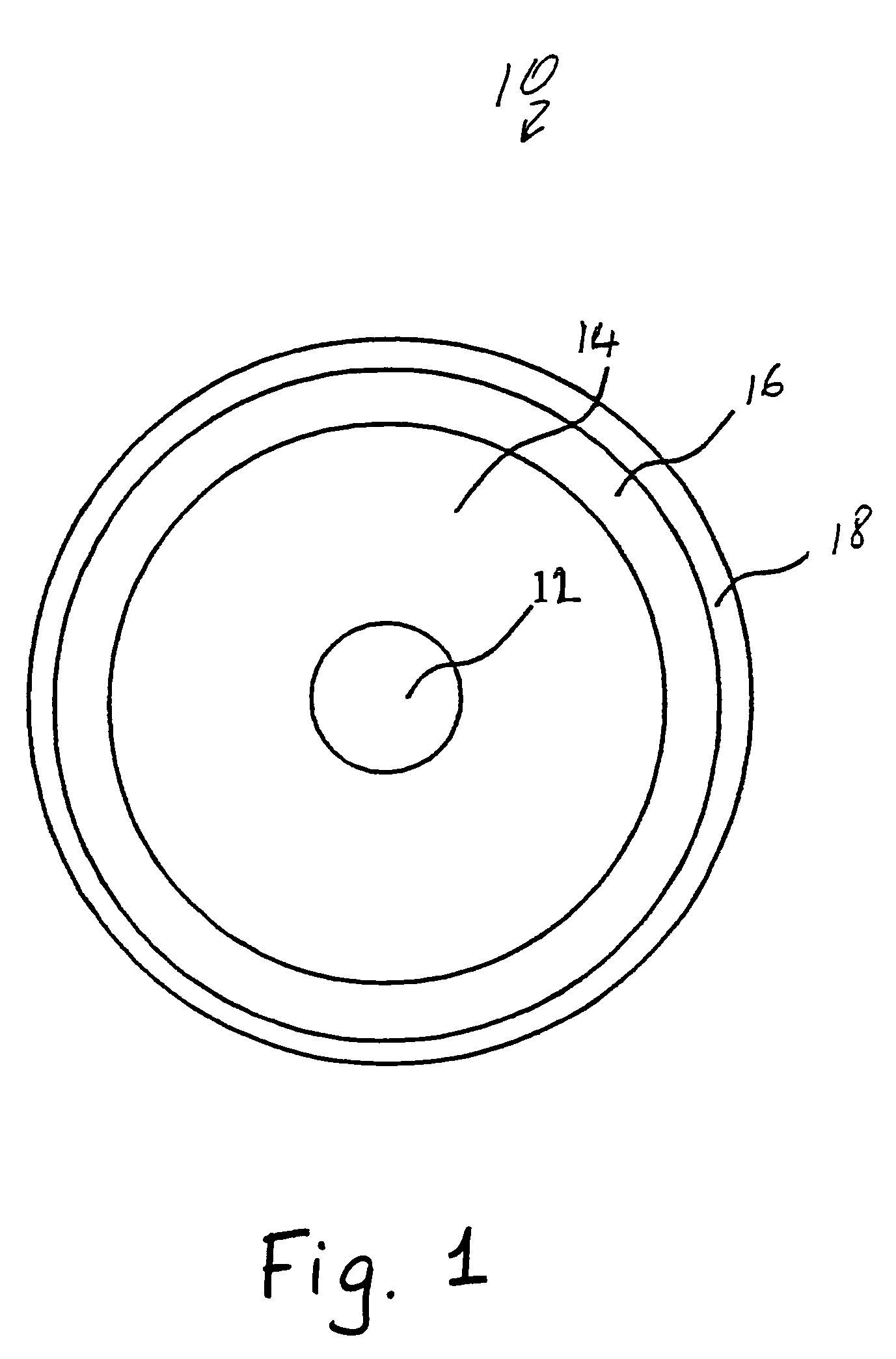
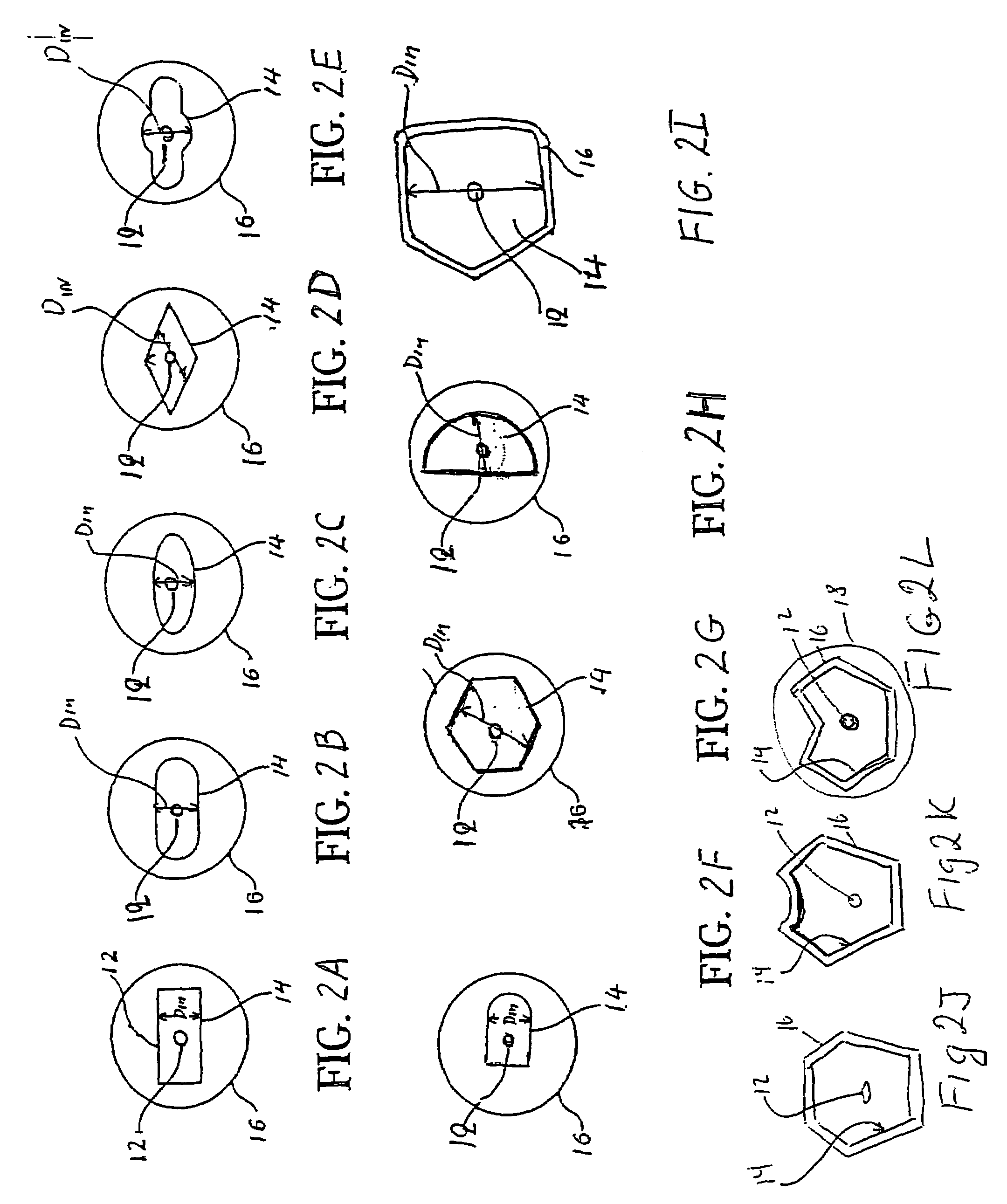
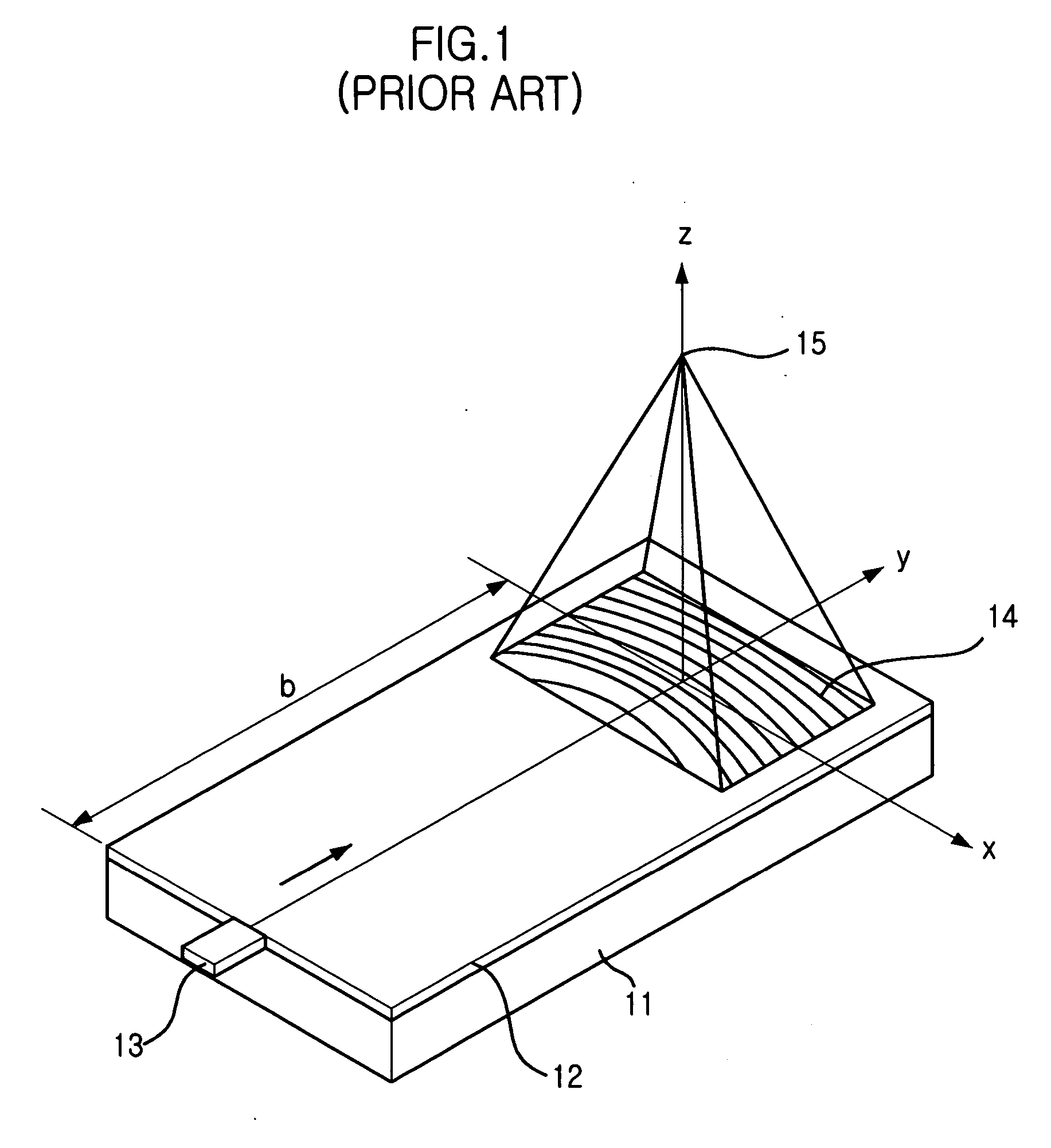
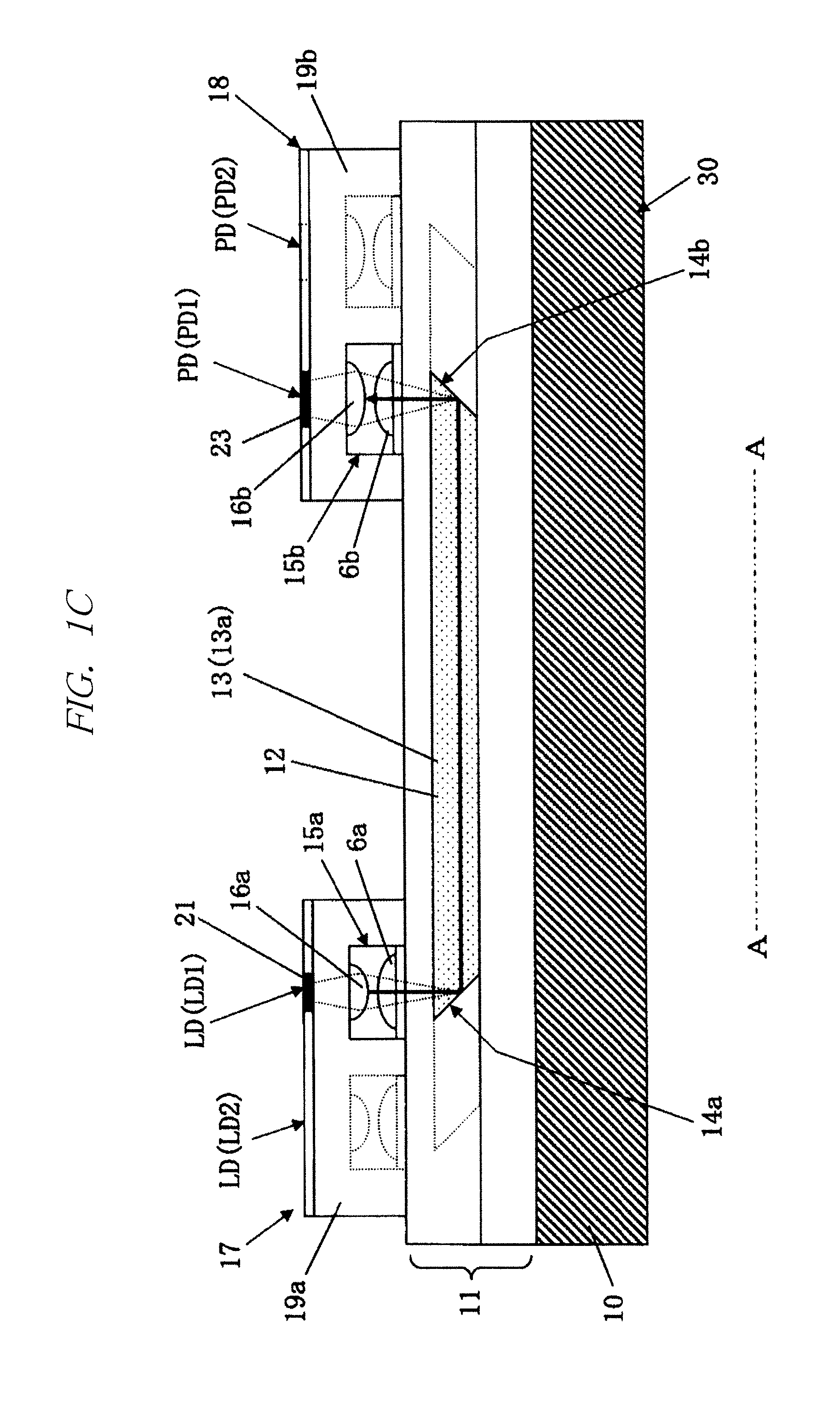
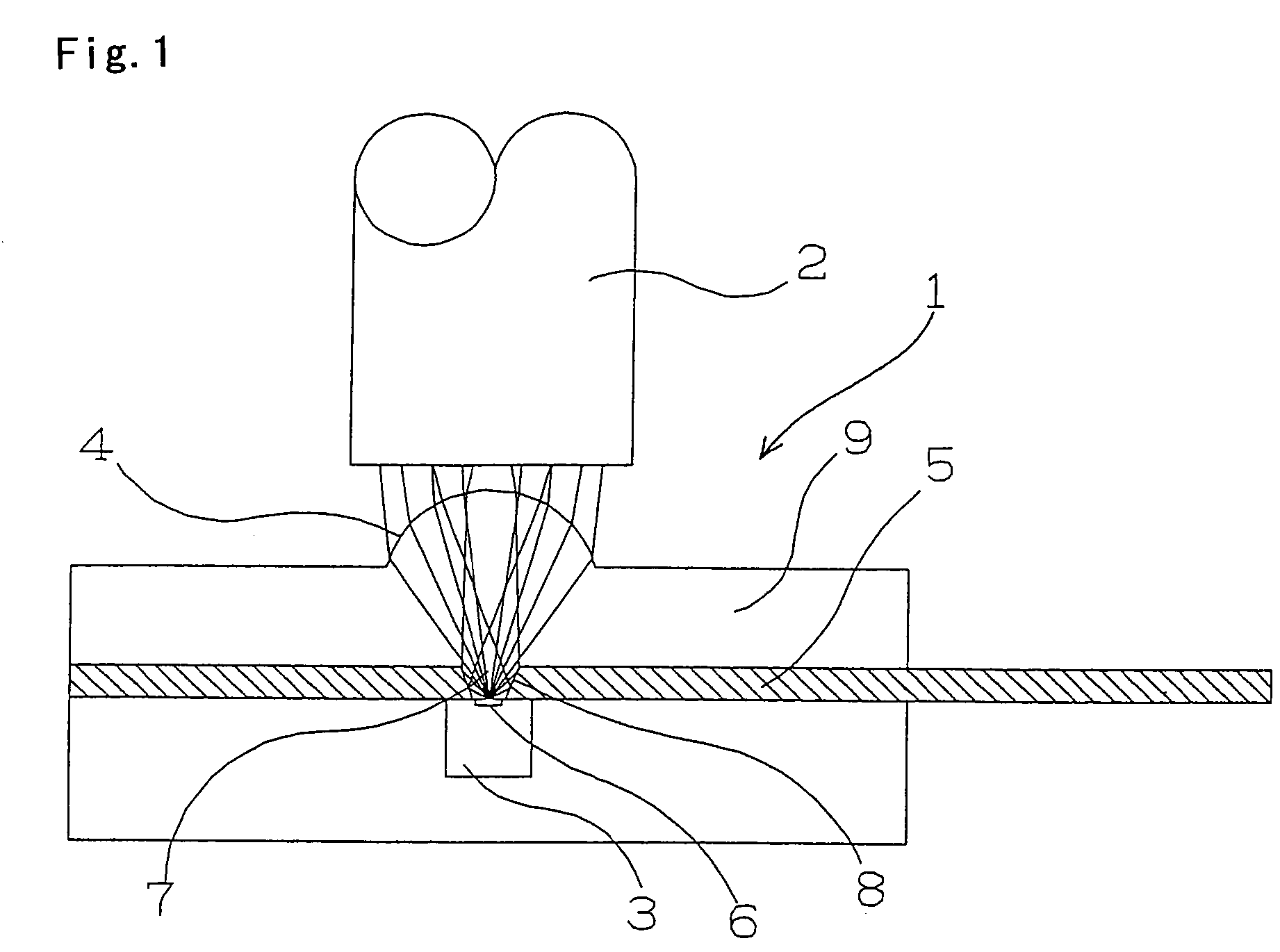
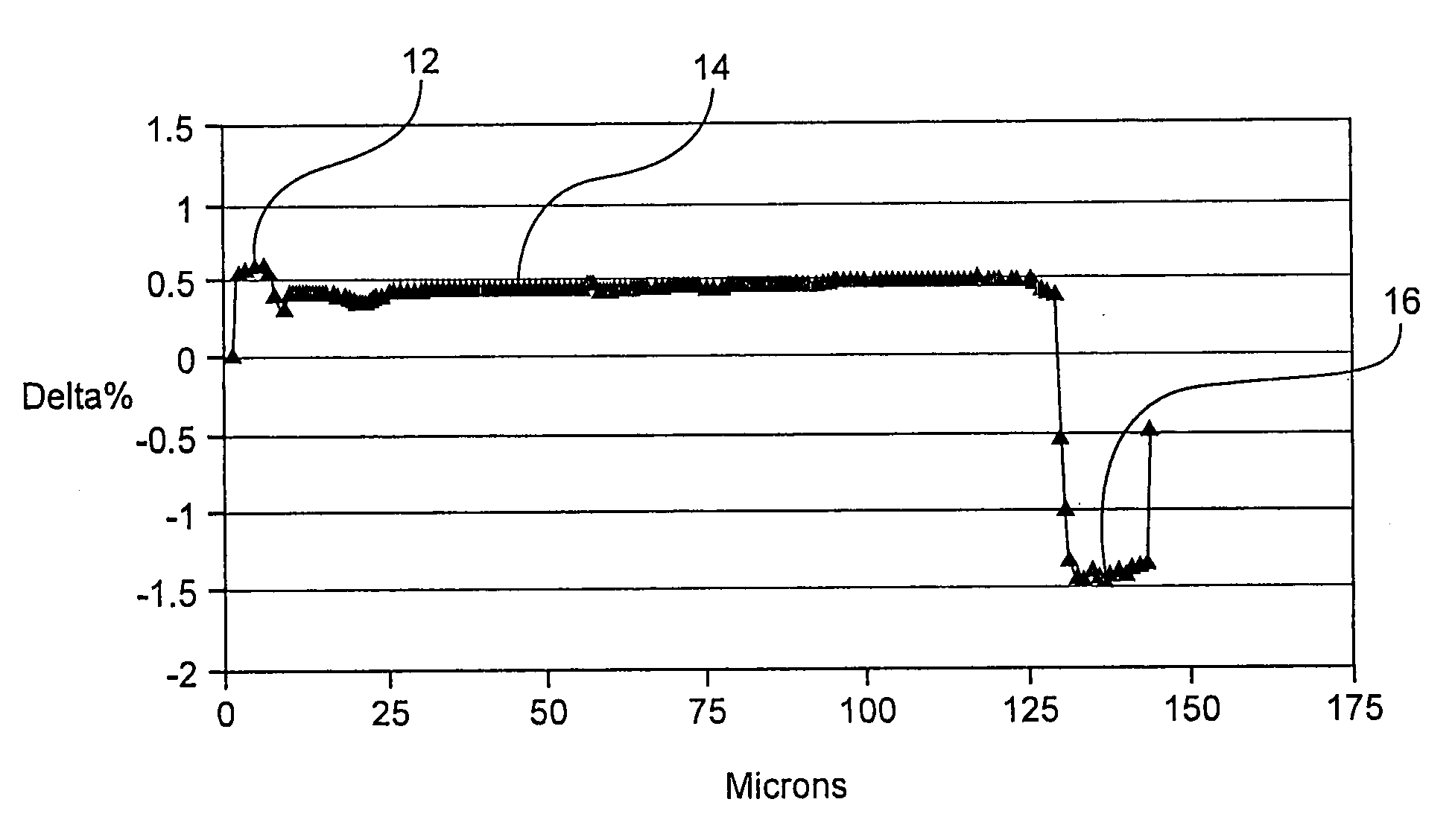
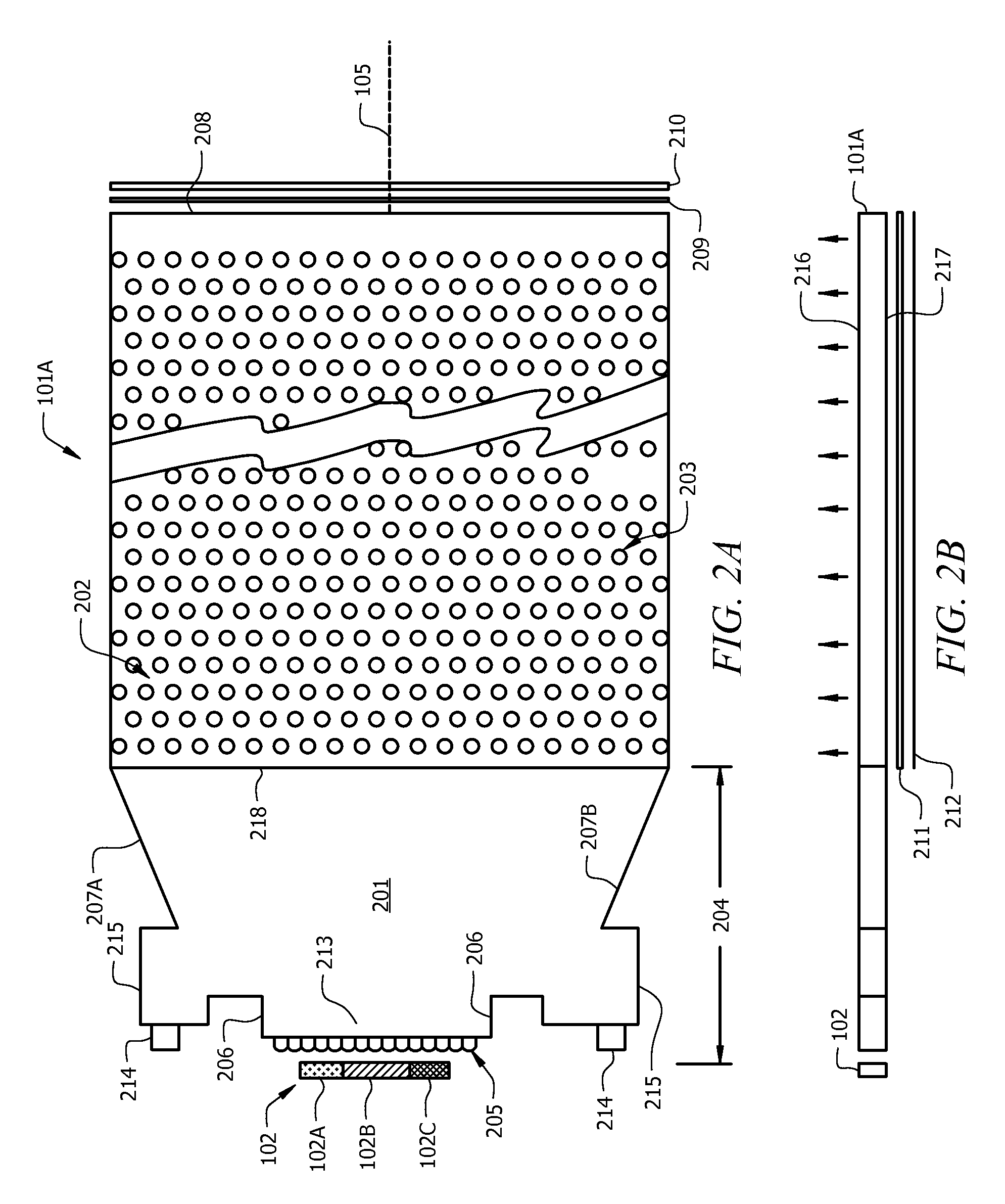
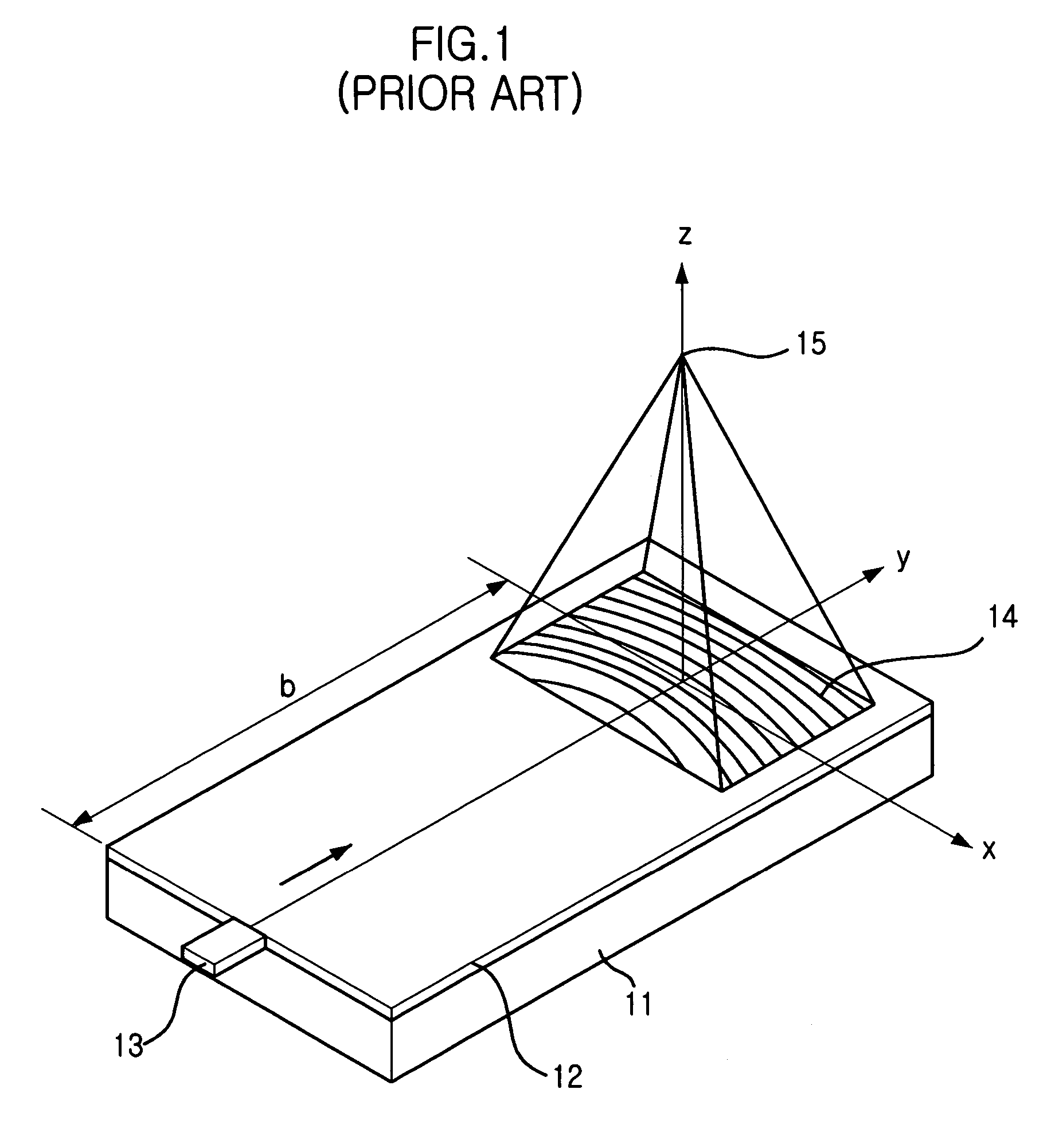
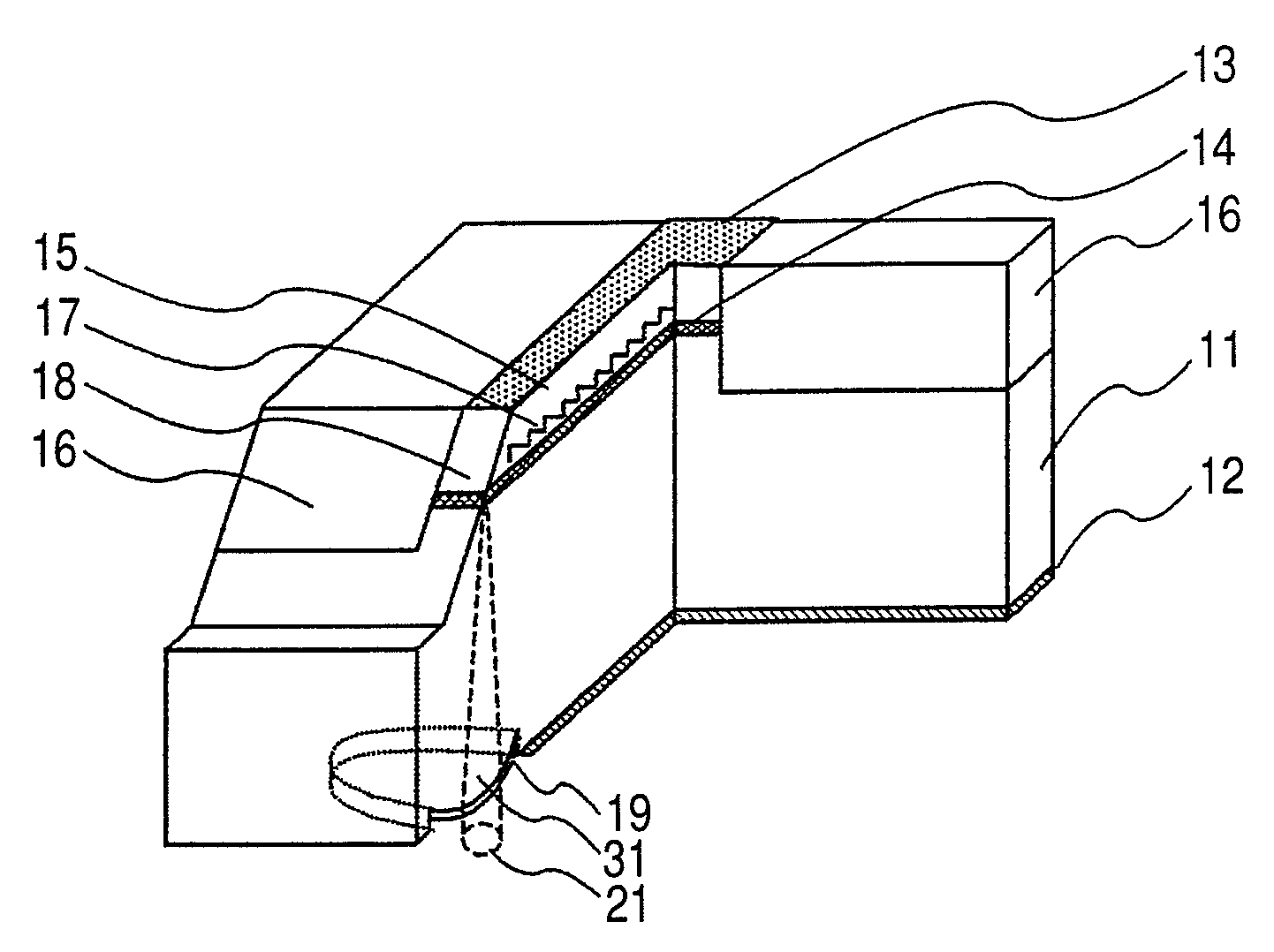
Optical fiber and method for making such fiber
ActiveUS7313312B2Coupling efficiency is highIncrease optical powerOptical fibre with polarisationOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRare earth
According to one example of the invention an optical fiber comprises: (i) silica based, rare earth doped core having a first index of refraction n1; (ii) at least one silica based cladding surrounding the core and having a second index of refraction n2, such that n1>n2; wherein at least one of the core or cladding is doped with Al2O3, such that the ratio of max wt % to min wt % of Al2O3 concentration is less than 2:1.
Owner:CORNING INC
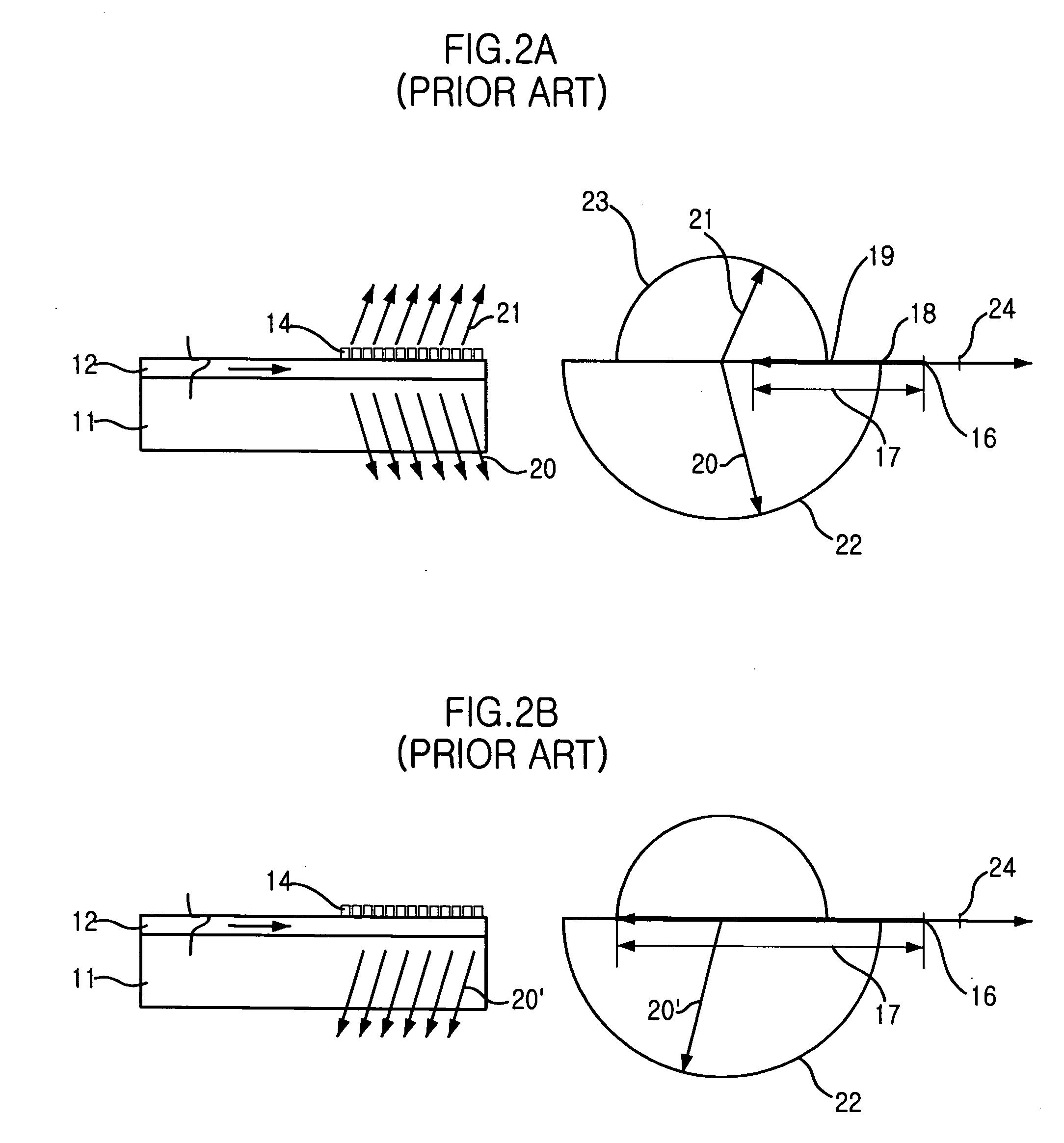
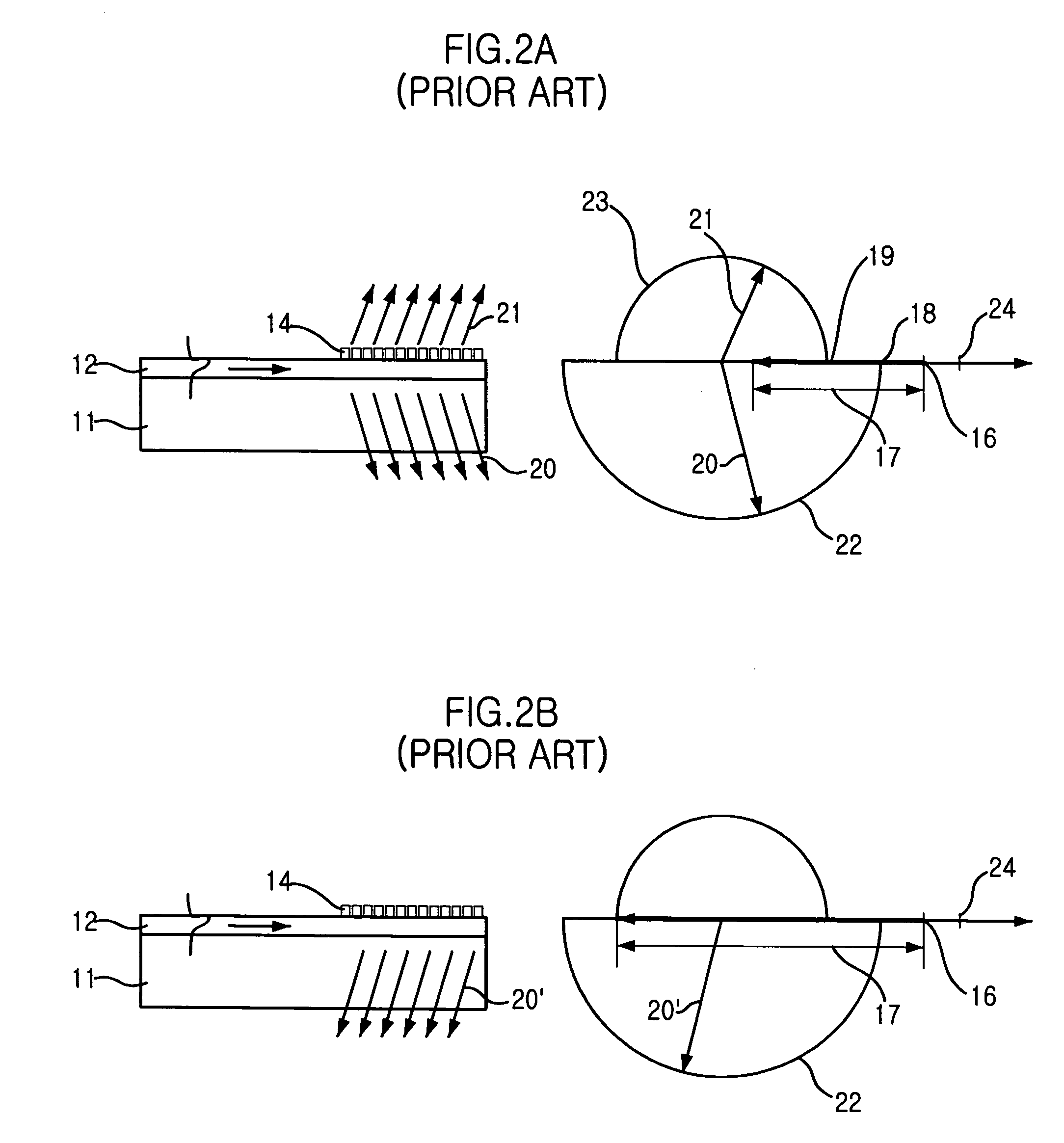
Reflective light coupler
InactiveUS20050117366A1Coupling efficiency is highEfficient couplingElectric discharge tubesDiffusing elementsLighting systemOptical coupling
An illumination system has individual light emitting diodes (LEDs) that are optically coupled via reflective couplers to respective optical fibers. The respective optical fibers may then be bundled. The shape of the reflective coupler may be selected to increase the coupling efficiency between the LED and its optical fiber. The reflective coupler may be formed as an aperture through a sheet, having a first shape at the input side and a second shape, different form the first shape, at the second side. The reflective coupler may be formed as an aperture through a body, where at least a first portion of the interior surface of the aperture conforms to a two-dimensional (2-D) surface and at least a second portion of the interior surface conforms to a three-dimensional (3-D) surface.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
High-brightness spatial-multiplexed multi-emitter pump with tilted collimated beam
ActiveUS20130148684A1Coupling efficiency is highReduce feedbackLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLight beamStep height
Multi-mode diode emitters are stacked in a staircase formation to provide a spatially-mulitplexed output. Improved coupling efficiency is achieved by providing tilted collimated output beams that determine an effective step height of the stepped structure. Since the effective step height is dependent on the tilt angle, a variable number of emitters can be used inside packages having a same physical step height, while still attaining high coupling efficiency.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
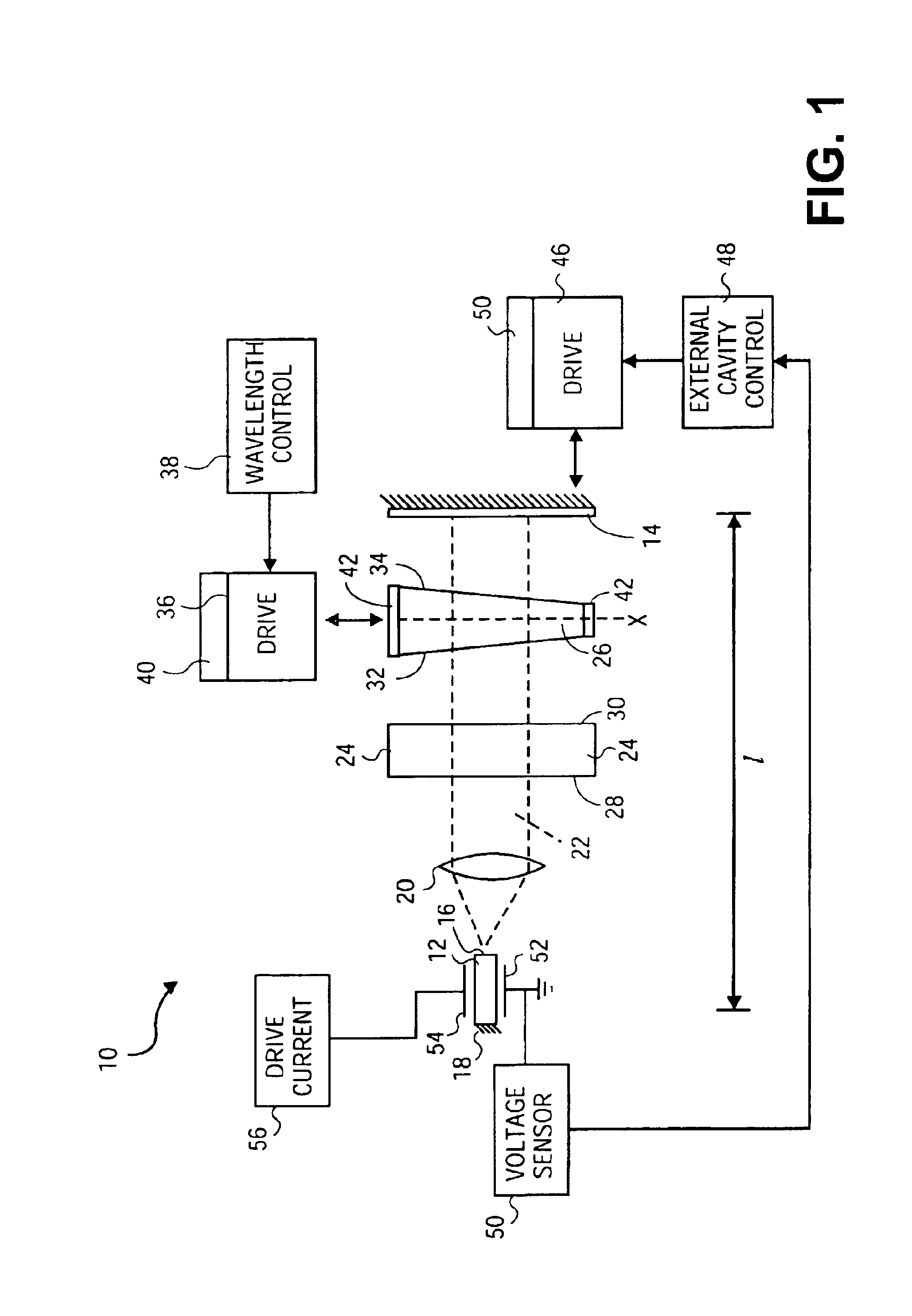
External cavity laser method and apparatus with orthogonal tuning of laser wavelength and cavity optical path length
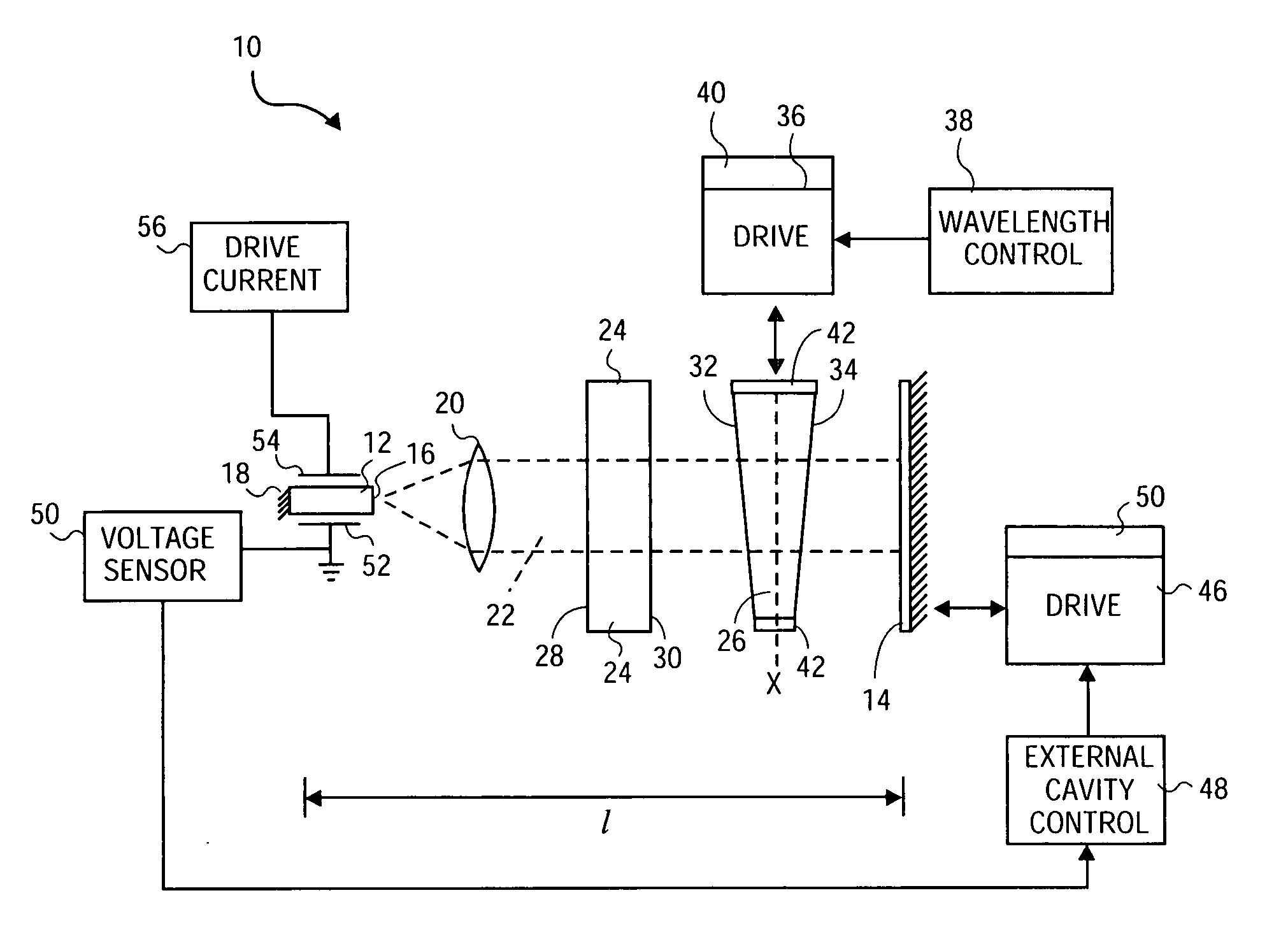
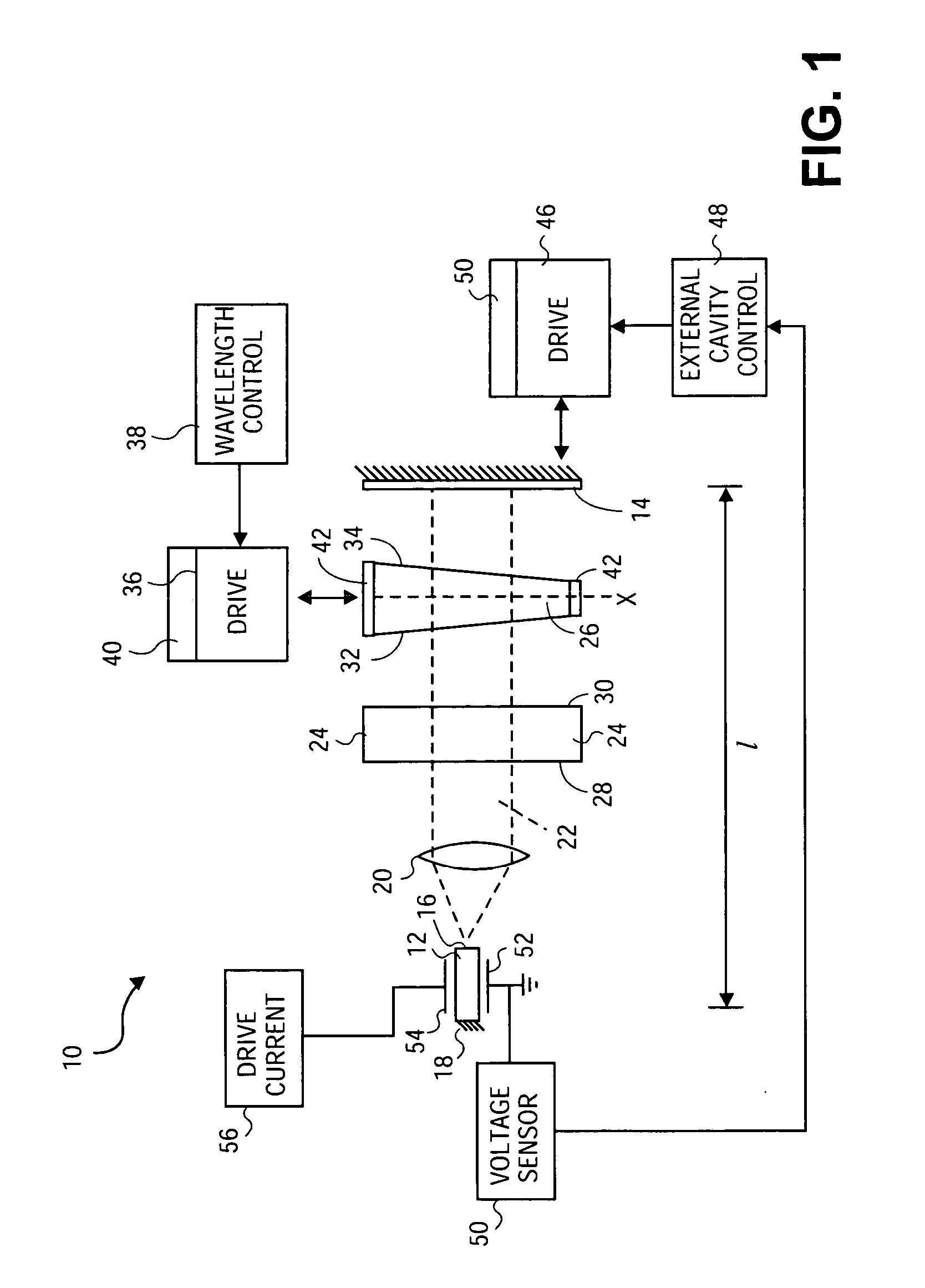
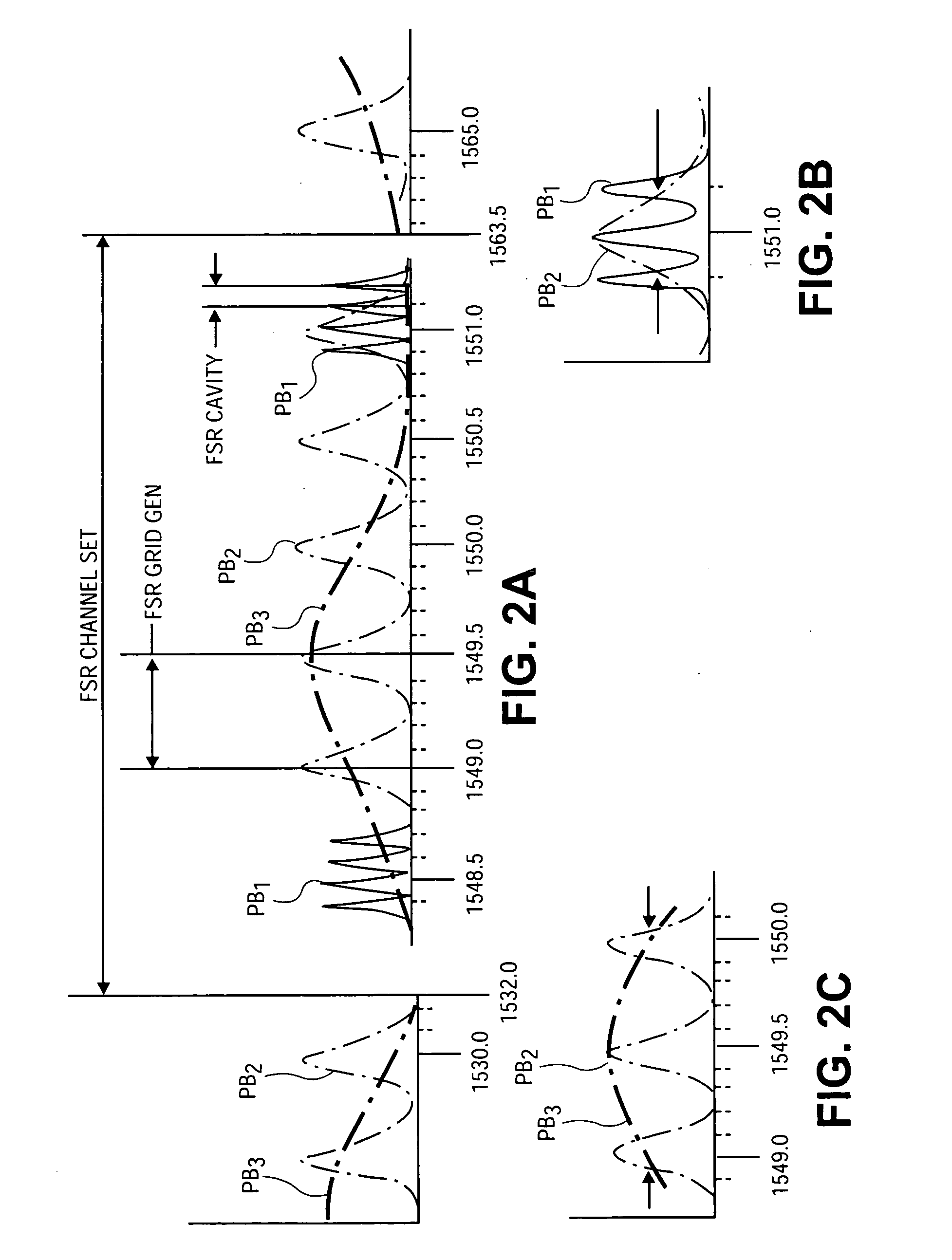
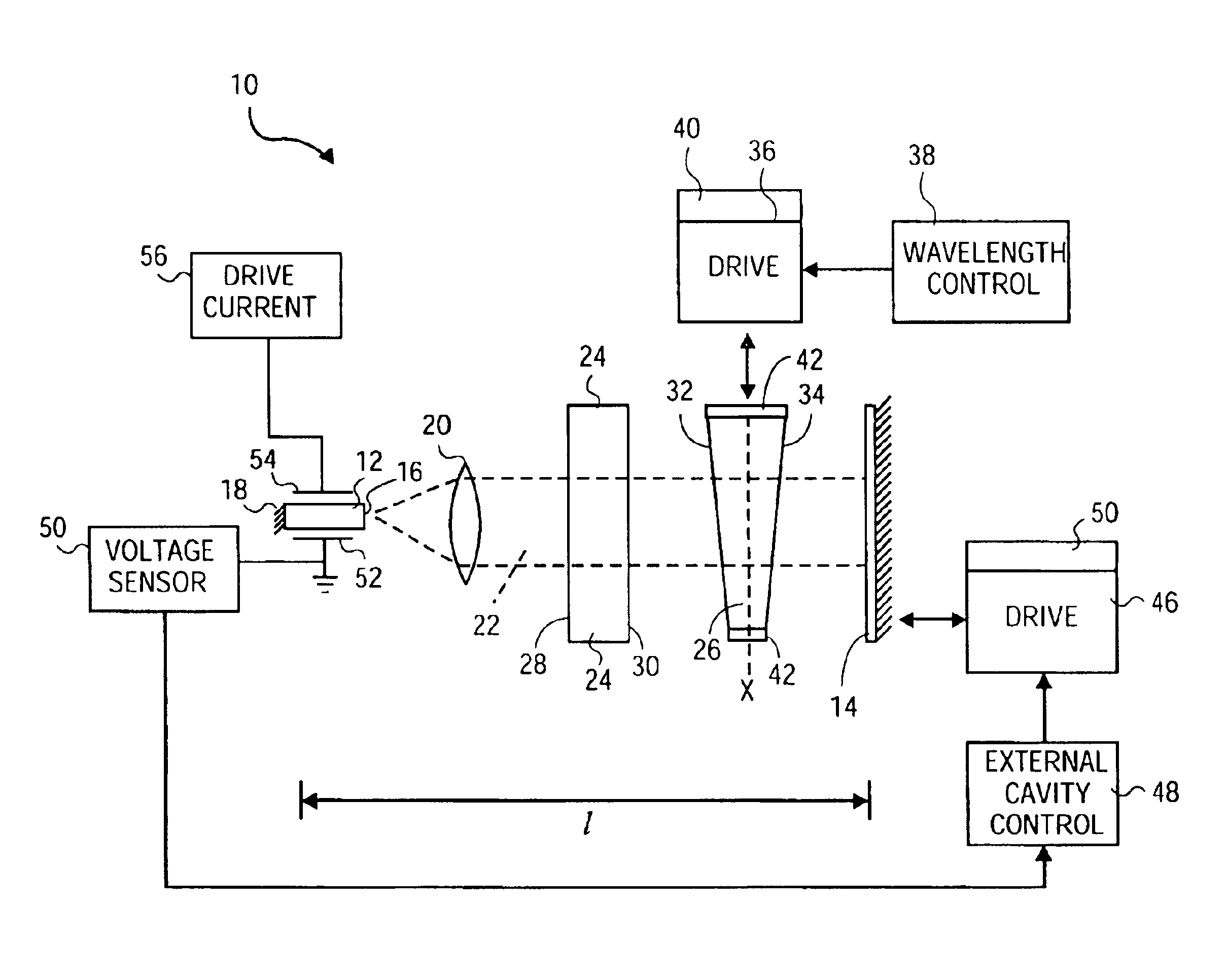
InactiveUS20050135439A1Large coupling efficiencyCoupling efficiency is highLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionExternal cavity laserLasing wavelength
An external cavity laser apparatus and method wherein wavelength or channel selection is carried independently from adjustment of external cavity optical path length. The apparatus comprises a wavelength or channel selector tuner and an external cavity tuner, wherein the wavelength tuner is uncoupled from the external cavity tuner. The tuning mechanisms for wavelength selection and cavity optical path length are configured to operate independently or orthogonally with respect to each other. The wavelength tuner may operate according to a first, channel selection signal, while the external cavity tuner operates according to a second, external cavity adjustment signal. The wavelength tuner and external cavity tuner may operate under the control of the same, or of separate controllers. The channel selection signal may be derived from a look-up table of adjustment parameter data accessed by a controller, and the external cavity adjustment signal may be derived from an error signal from a detector configured to measure external cavity loss.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Linear Optic Light Coupler
InactiveUS20080225549A1Coupling efficiency is highMechanical apparatusFibre light guidesLighting systemOptical communication
An illumination system includes a plurality of radiation generating sources, such as LED dies. A corresponding plurality of optical waveguides is also provided, with each waveguide having a first and a second end, with each first end being in optical communication with the corresponding LED die. An array of corresponding passive optical elements is interposed between the plurality of LED dies and the corresponding first ends of the plurality of optical waveguides. The illumination system provides for substantially high light coupling efficiency and an incoherent light output that can appear to the human observer as arising from a single point of light. In addition, the light can be output remotely at one or more locations and in one or more directions.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Reflective light coupler
InactiveUS7403680B2Coupling efficiency is highEfficient couplingCoupling light guidesCondensersLighting systemOptical coupler
An illumination system has individual light emitting diodes (LEDs) that are optically coupled via reflective couplers to respective optical fibers. The respective optical fibers may then be bundled. The shape of the reflective coupler may be selected to increase the coupling efficiency between the LED and its optical fiber. The reflective coupler may be formed as an aperture through a sheet, having a first shape at the input side and a second shape, different form the first shape, at the second side. The reflective coupler may be formed as an aperture through a body, where at least a first portion of the interior surface of the aperture conforms to a two-dimensional (2-D) surface and at least a second portion of the interior surface conforms to a three-dimensional (3-D) surface.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
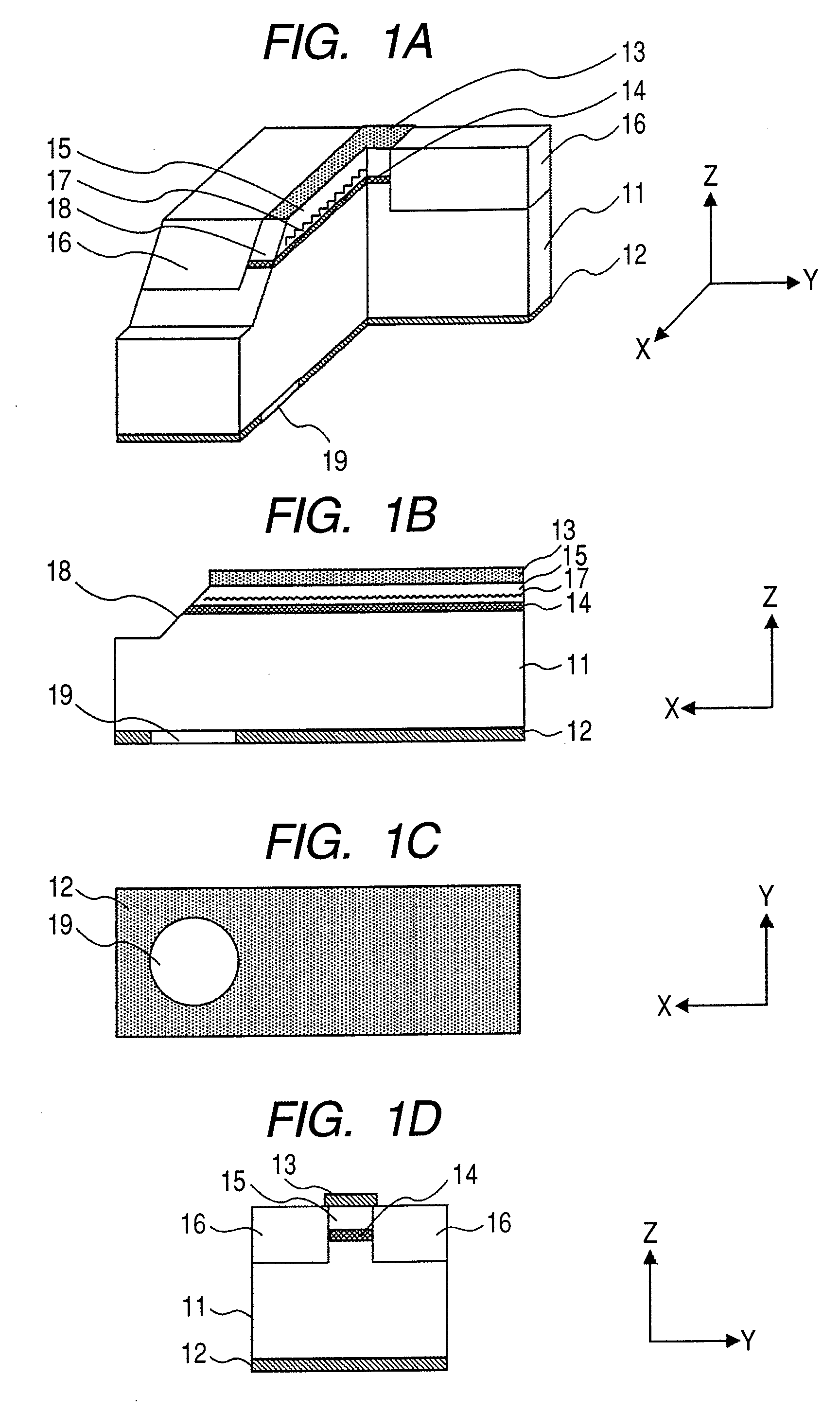
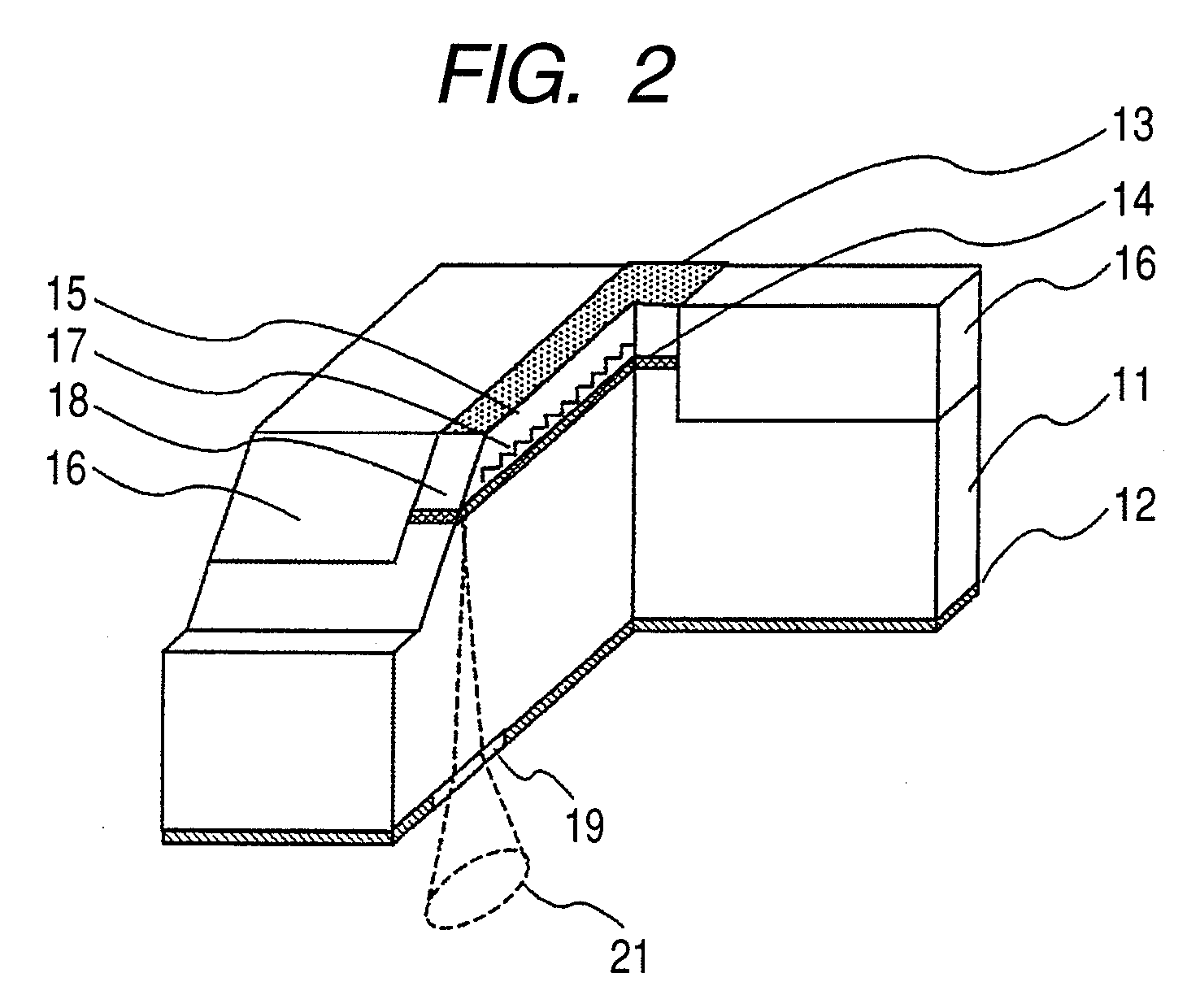
Optical transmitter
InactiveUS20060124946A1Increase efficiencyReduce depthSolid-state devicesCoupling light guidesCoupling efficiencyEngineering
The present invention provides an optical transmitter for transmitting an optical signal using an optical fiber as a transmission medium. The optical transmitter comprises: a substrate having a through hole; and a light-emitting element disposed on a rear surface of the substrate and having a light-emitting portion. The through hole has an inner wall. The through hole has an inside diameter increasing from a rear surface side of the substrate toward a front surface side thereof. The light-emitting element is disposed so that the light-emitting portion is exposed within the through hole. The light-emitting portion radiates light beams toward a front surface of the substrate. The through hole is such that part of the light beams goes out the through hole without being reflected, and that the other light beams go out the through hole after being reflected from the inner wall thereof. It is possible to increase the coupling efficiency of the optical transmitter by effectively utilizing a light beam light having a wide radiation angle, and improve heat dissipation thereof, while achieving miniaturization and cost reduction of the optical transmitter.
Owner:SHARP KK
Highly efficient focusing waveguide grating coupler using leaky mode
InactiveUS20050008294A1Coupling efficiency is highReduce dependenceCoupling light guidesFresnel lensManufacturing technology
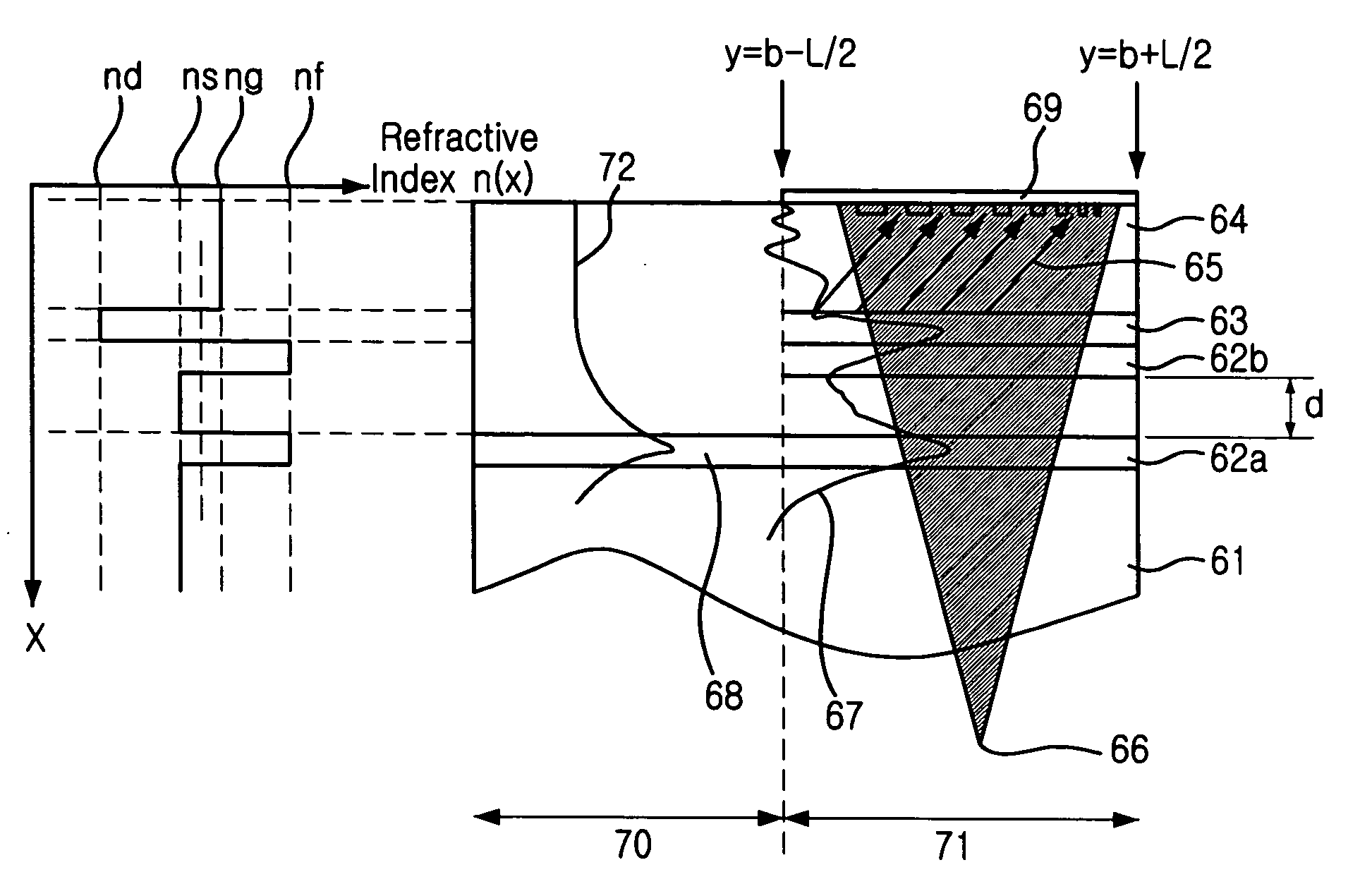
Provided is a focusing waveguide grating coupler using a leaky mode which can form single output beam while relieving the dependency on manufacturing processes. The focusing waveguide grating coupler of the present research includes: a substrate having a first refraction index n1; a first core layer having a second refraction index n2, the first core layer being formed on the substrate; a second core layer having a third refraction index n3, the second core layer being formed on the first core layer apart from the first core layer with a space d in between; a first cladding layer having a fourth refraction index n4, the first cladding layer being formed on the second core layer; a second cladding layer having a fifth refraction index n5, the second cladding layer being formed on the first cladding layer and inserted between the first core layer and the second core layer; and a Fresnel lens positioned on the second cladding layer, wherein the refractive indexes satisfy conditions of n5>(n2, n3)>n1 and n5>n4; and light inputted through the first and second core layers to the Fresnel lens as radiated leaky beam by a leaky mode formed according to the conditions, and the leaky beam forms an optical focus by performing single directional coupling.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Semiconductor laser and optical module
ActiveUS20080266638A1Coupling efficiency is highHigh in optical coupling efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsFiberOptical Module
In a horizontal cavity surface emitted laser, there is provided a device structure that is capable of obtaining a circular narrow-divergence emitted beam that is high in the optical coupling efficiency with a fiber. As a first means, there is provided a horizontal cavity surface emitting laser having a structure in which the plane mirror that is inclined by 45° and the bottom lens of the oval configuration are integrally structured. As a second means, there is provided a horizontal cavity surface emitting laser in which the mirror having the columnar front surface configuration inclined by 45° and the bottom lens of the columnar front surface configuration are integrally structured. Since the horizontal component and the vertical component of the laser beam can be shaped, independently, through the above means. As a result, it is possible to obtain the circular narrow-divergence emitted beam.
Owner:LUMENTUM JAPAN INC
Optical Waveguide and Optical Waveguide Module
InactiveUS20110299808A1Easy to installHigh precision installationCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideWaveguideSemiconductor
An optical waveguide module which satisfies highly-accurate and stable optical connection between optical elements and optical waveguides and can be easily fabricated is provided. As means for it, in an optical waveguide module having: an optical waveguide surrounded by a cladding layer and provided with a mirror part formed of a tapered surface on a first end side; an optical element having a concave part in a first surface of a semiconductor substrate; and a convex member provided on the cladding layer so as to be planarly overlapped with the mirror part, the convex member is mated with the concave part of the optical element.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Optical fiber and method for making such fiber
ActiveUS20050271347A1Coupling efficiency is highIncrease optical powerOptical fibre with polarisationOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRare earth
According to one example of the invention an optical fiber comprises: (i) silica based, rare earth doped core having a first index of refraction n1; (ii) at least one silica based cladding surrounding the core and having a second index of refraction n2, such that n1>n2; wherein at least one of the core or cladding is doped with Al2O3, such that the ratio of max wt % to min wt % of Al2O3 concentration is less than 2:1
Owner:CORNING INC
Integrated optical circuit device and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20020154848A1Help positioningCoupling is not degradedLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionMultimode interferenceElectrical and Electronics engineering
An integrated optical circuit device includes: a first optical element section including first and second element regions deposited along a thickness direction; a second optical element section formed away from the first optical element section; and a multimode interference region provided between the first and second optical element sections, the multimode interference region including a buried portion formed along a light propagation direction. The first and second optical element sections are optically coupled to each other via the multimode interference region.
Owner:SHARP KK
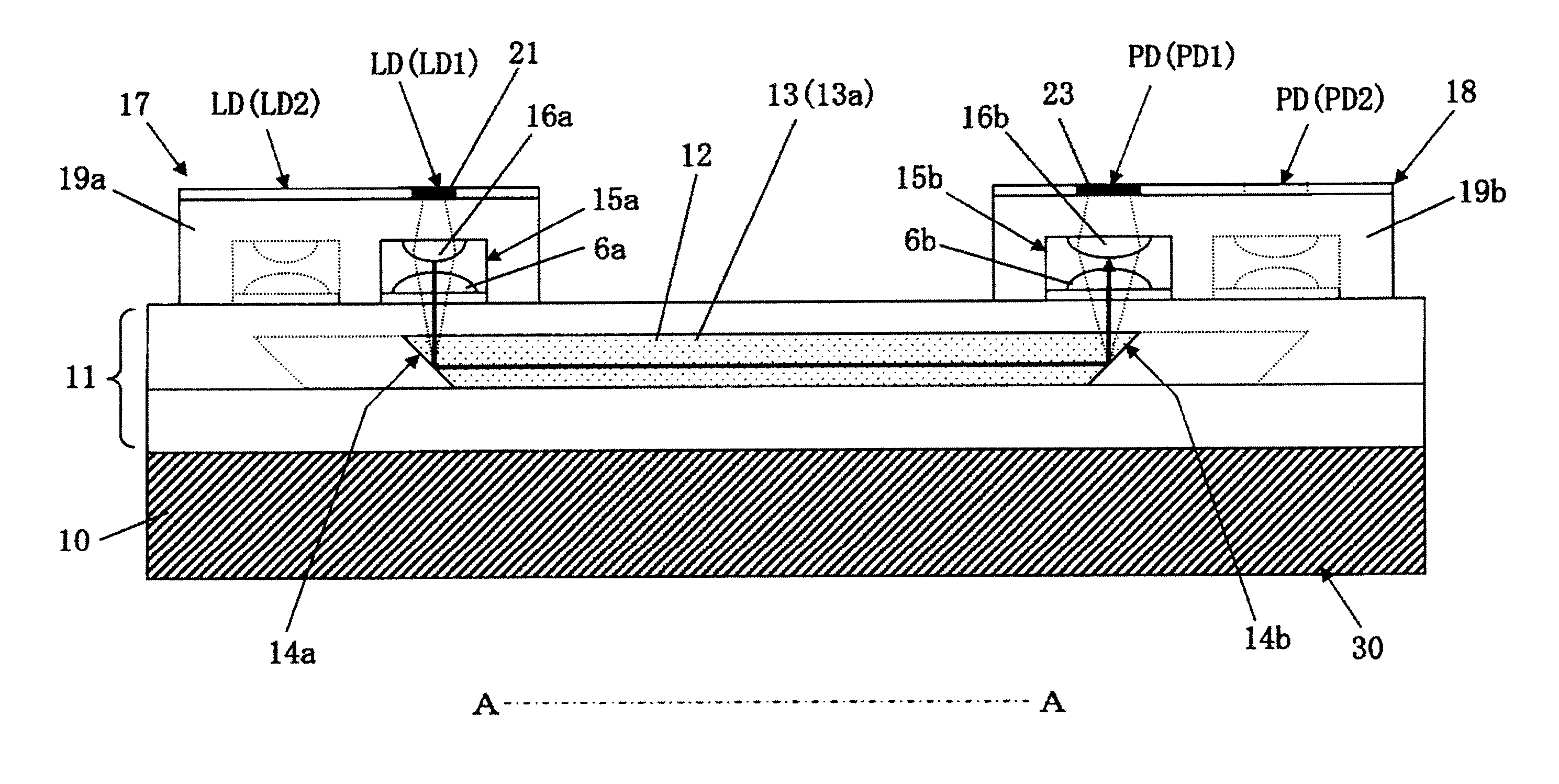
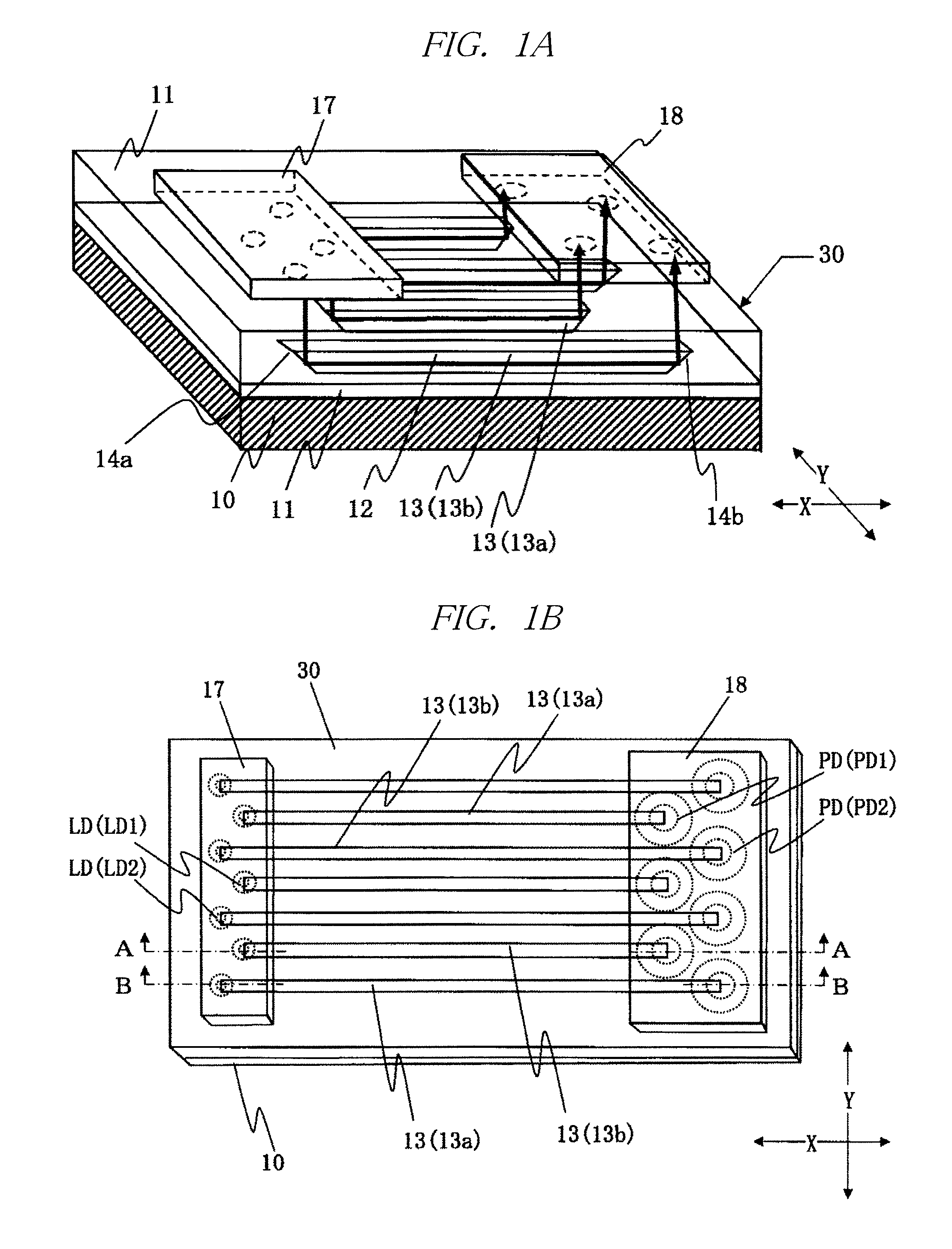
Optical transmitter
InactiveUS7281860B2Coupling efficiency is highLow costSolid-state devicesCoupling light guidesLight beamMiniaturization
Owner:SHARP KK
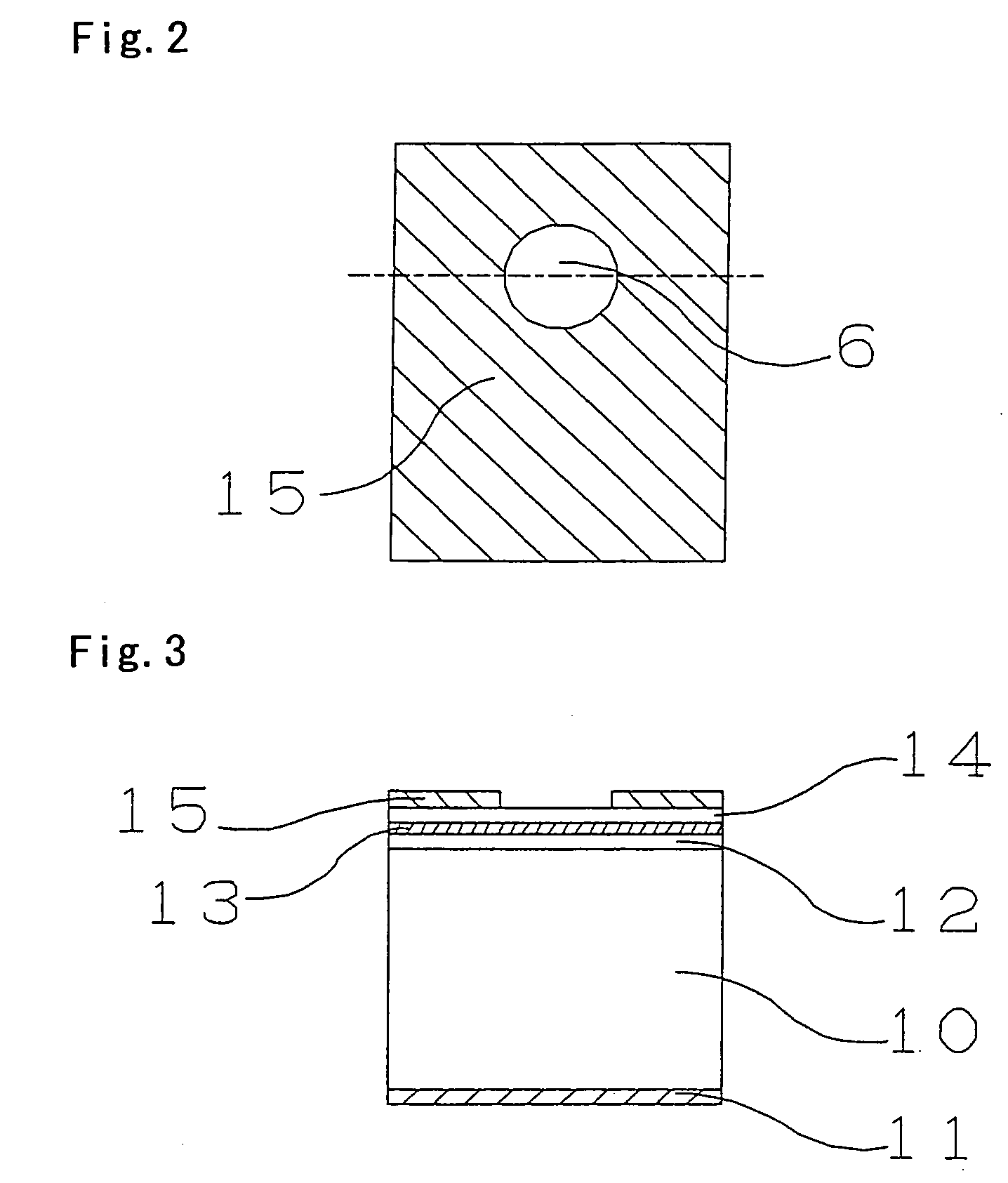
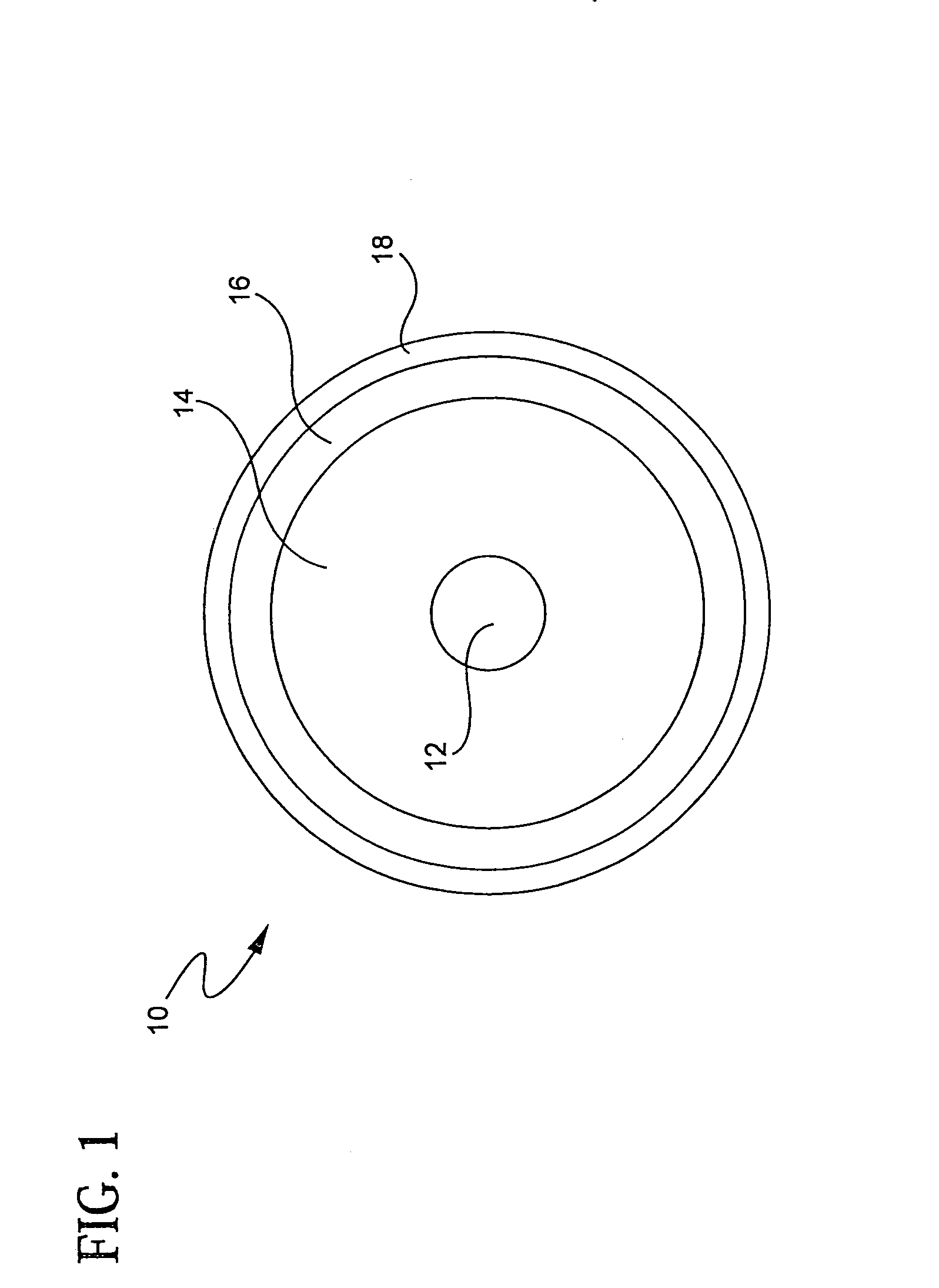
Double clad rare earth doped fiber
ActiveUS7139458B2Coupling efficiency is highProlong lifeOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingActive medium shape and constructionFiberRare earth
An optical fiber comprising: (i) a silica based, rare earth doped core having a first index of refraction n1; (ii) a silica based inner cladding surrounding the core having a second index of refraction n2, such that n1>n2; (iii) a silica based outer cladding surrounding the inner cladding having a third index of refraction n3 such that n2>n3, wherein inner cladding diameter is at least 125 μm.
Owner:CORNING INC
Mobile Communication Device
InactiveUS20080207282A1Avoid disadvantagesImprove communication performanceNear-field systems using receiversTelephone set constructionsEngineeringElectromagnetic shielding
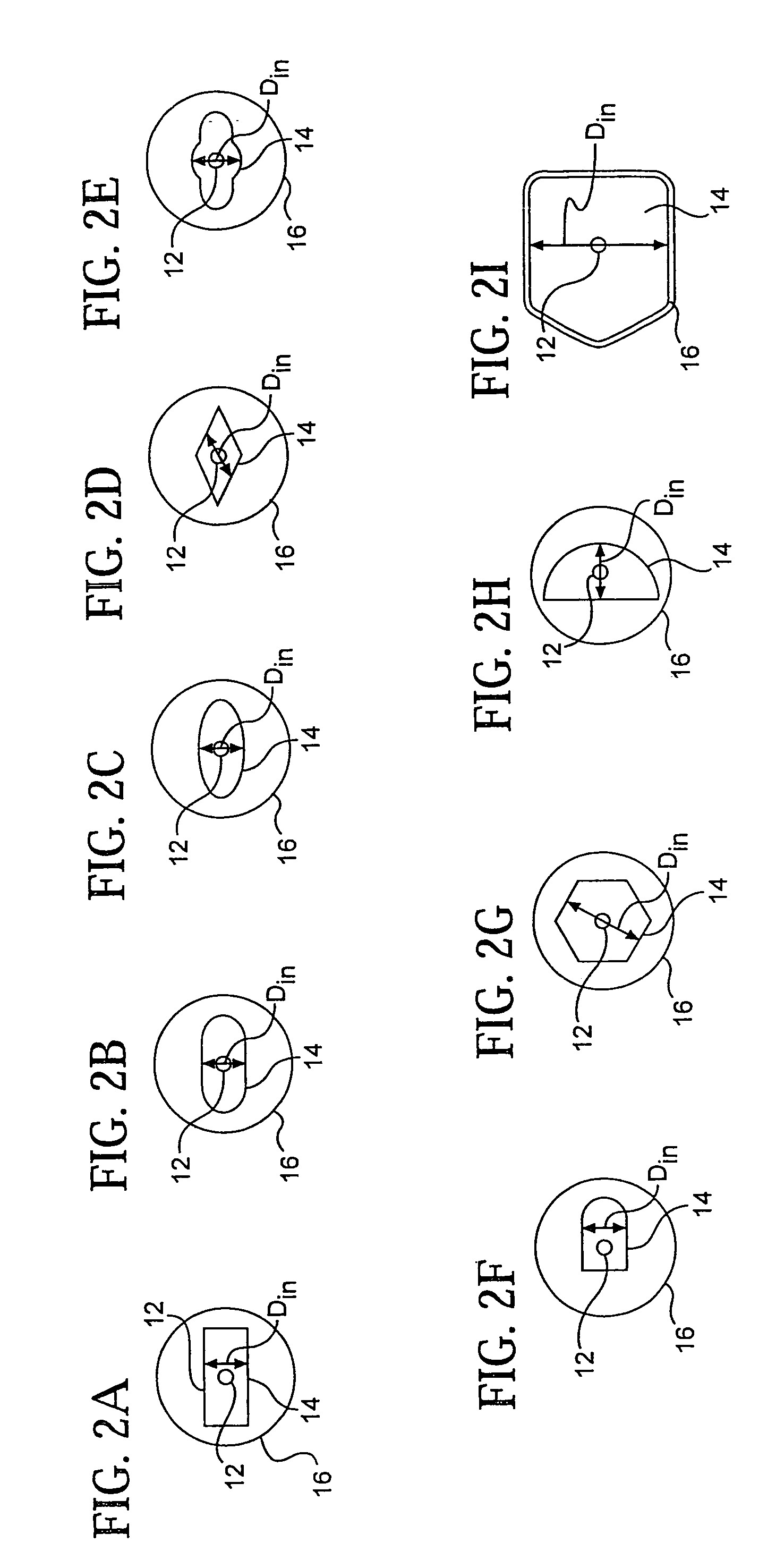
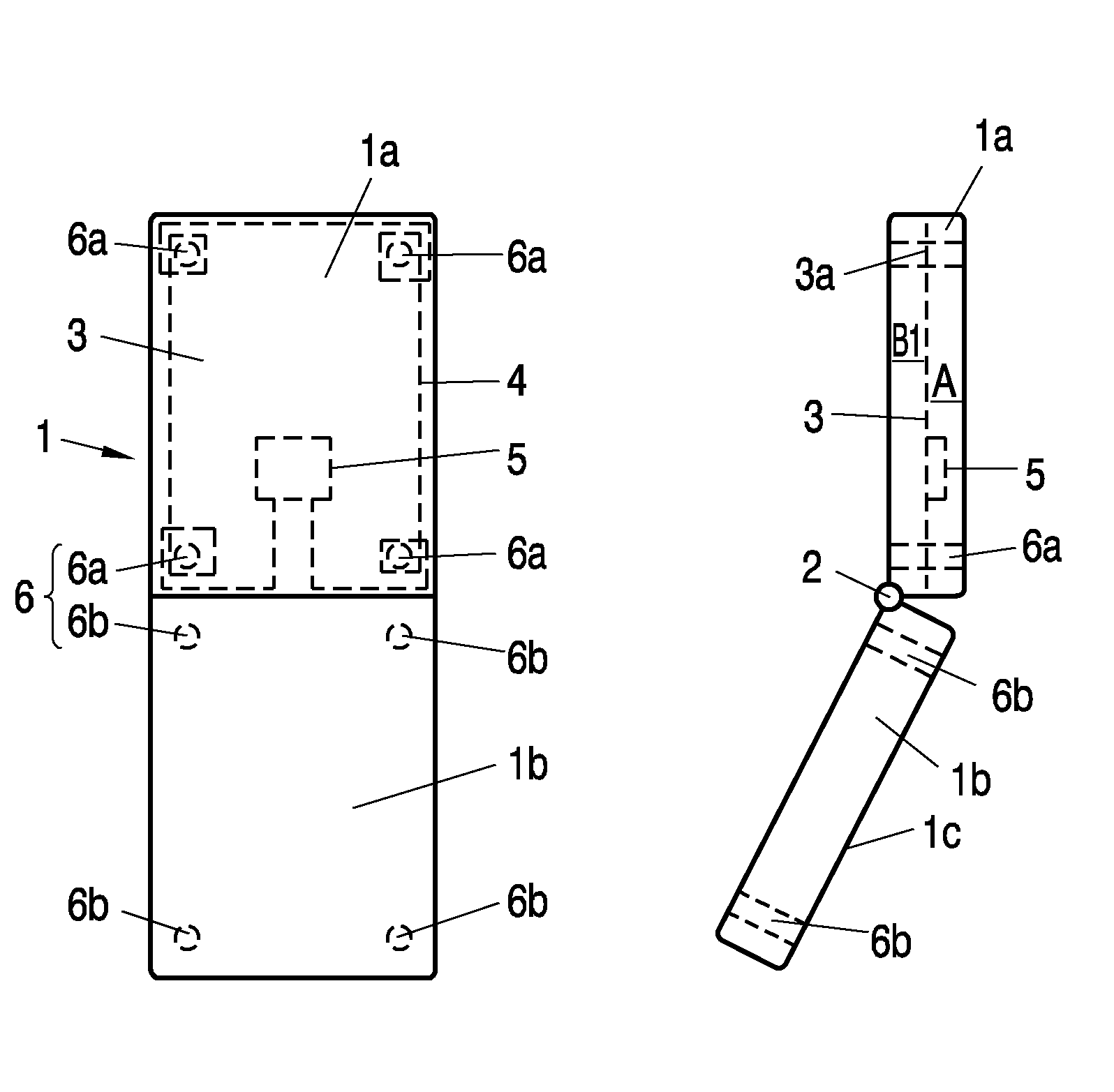
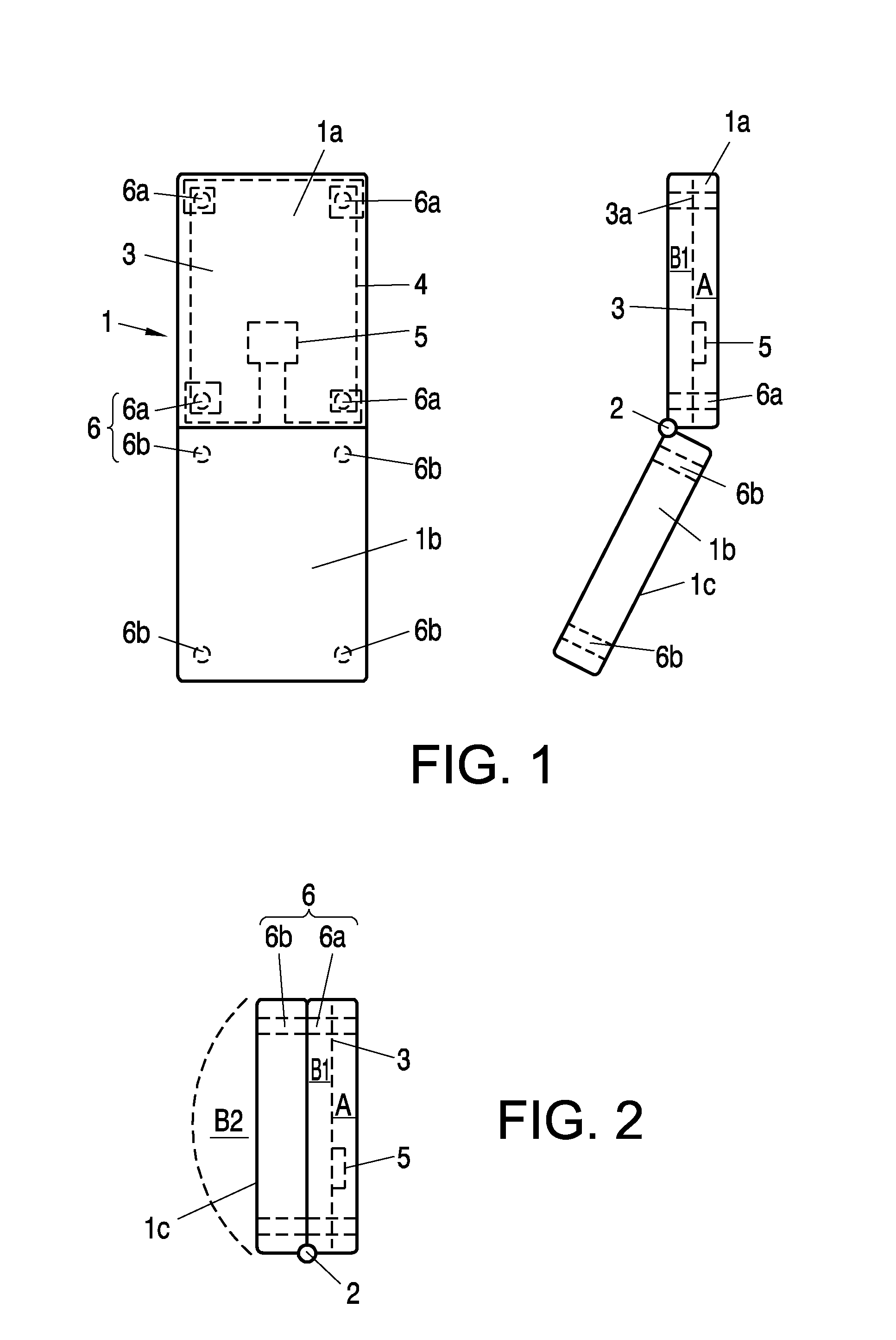
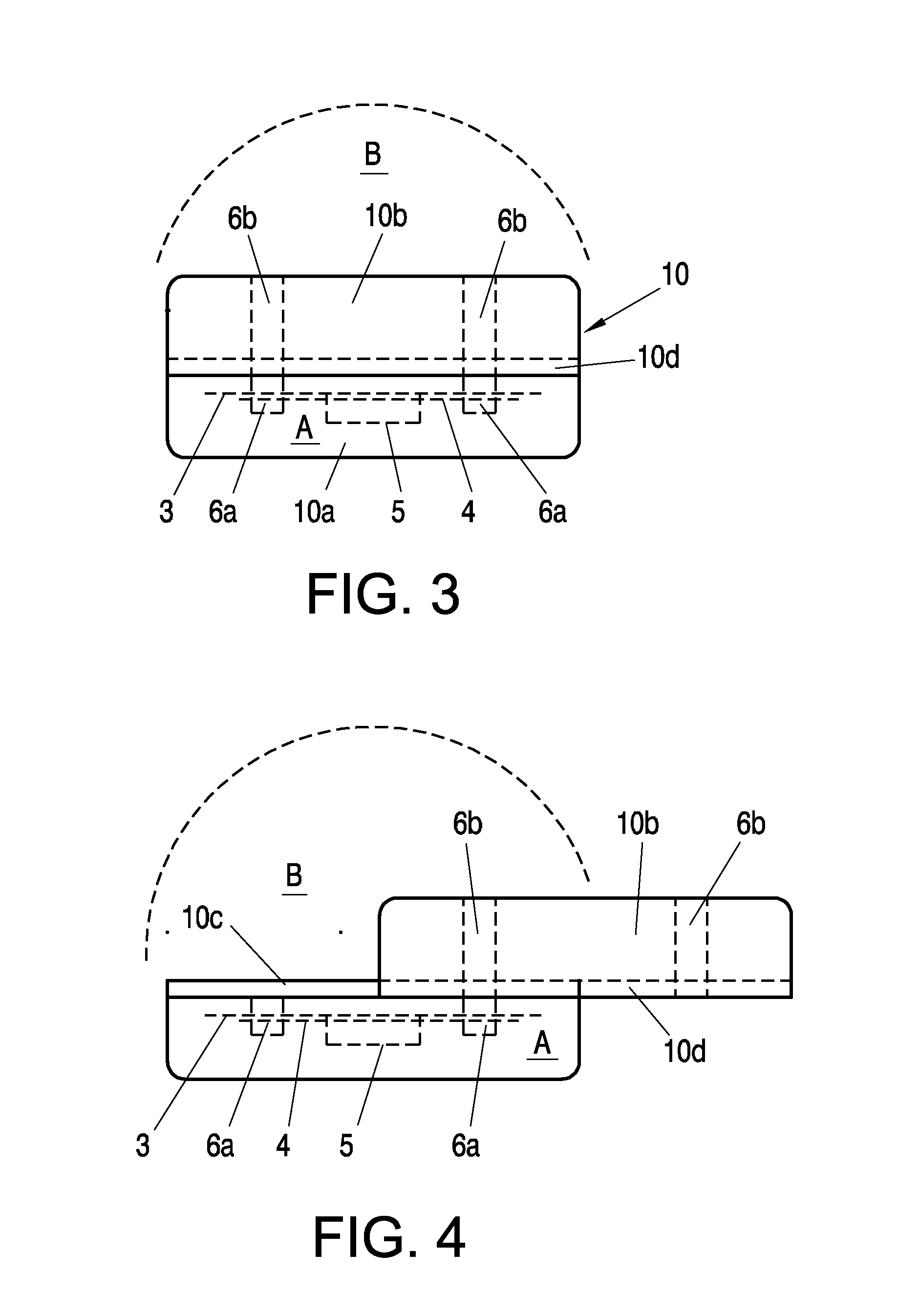
A mobile communication device (1, 10) comprises shielding components that provide electromagnetic shielding or attenuation between a first area (A) and a second area (B, B1, B2) within and / or external of the communication device (1, 10). In said first area (A) an antenna (4) and at least one ferrite (6) are arranged, which ferrite (6) is provided to interact with said antenna (4) and to guide a magnetic flux between said first area (A) and said second area (B, B1, B2).
Owner:NXP BV
Light emitting apparatus, backlight apparatus, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS7490959B2Coupling efficiency is highReduce radiationLighting heating/cooling arrangementsSolid-state devicesElectrode placementLight emitting device
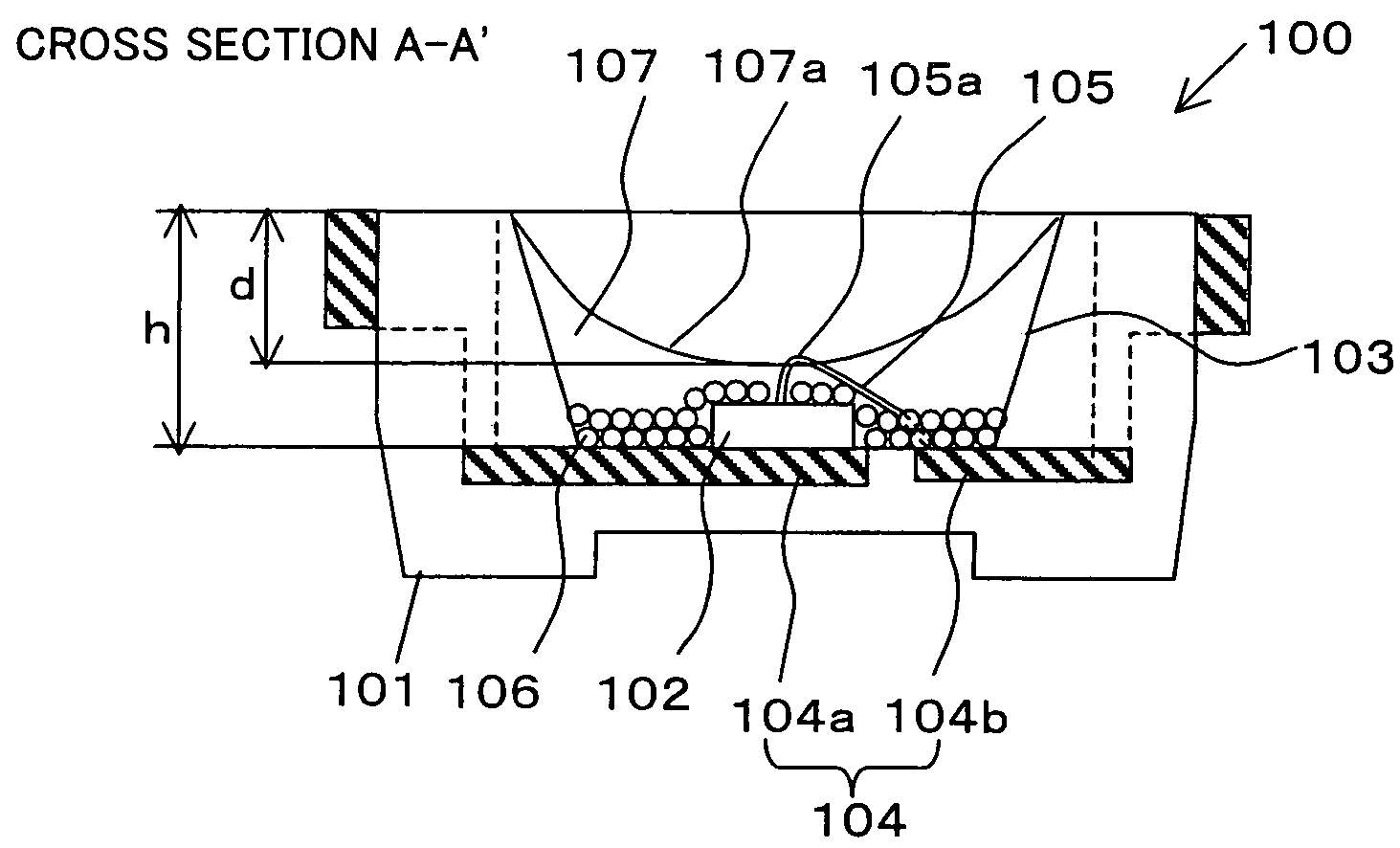
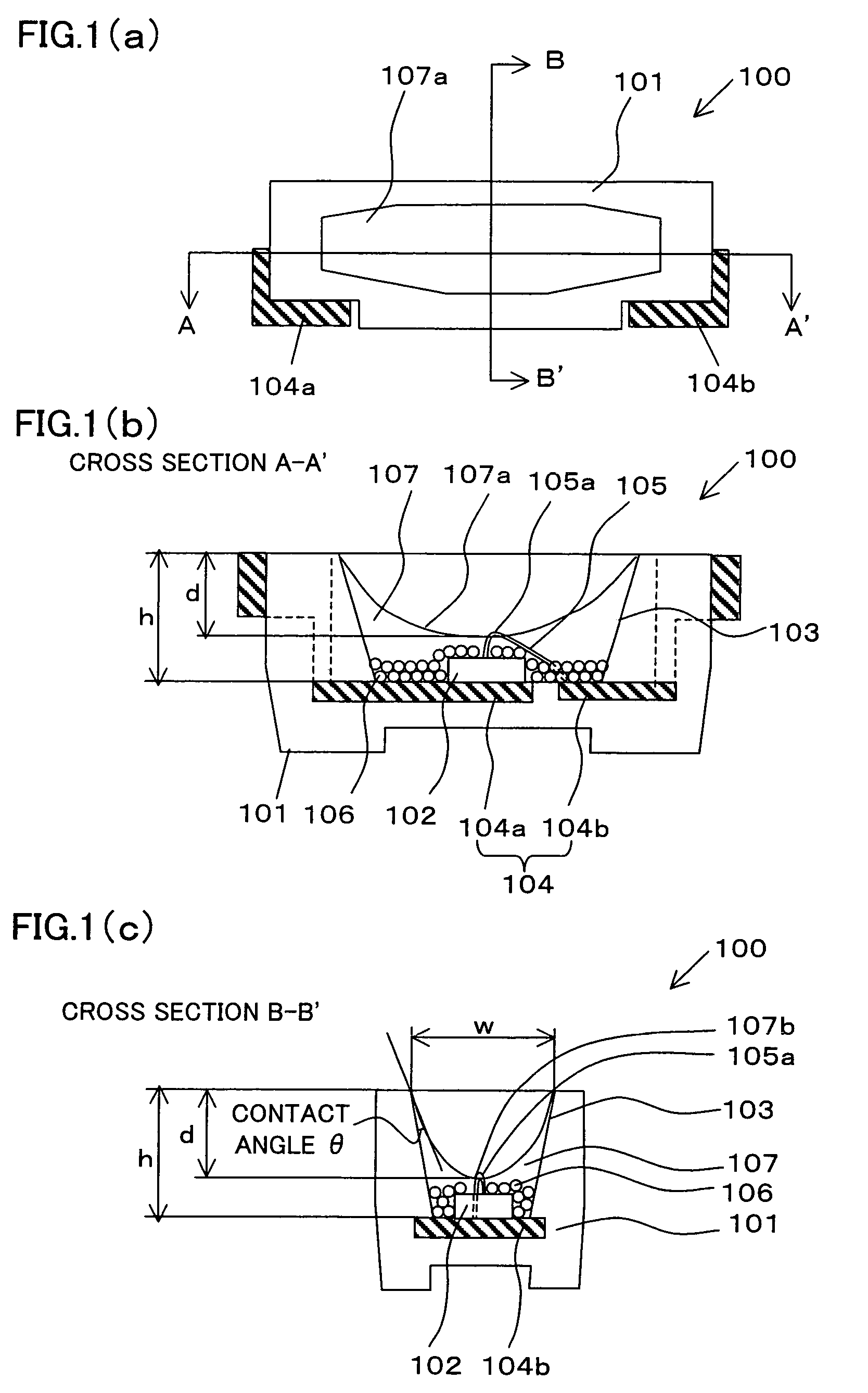
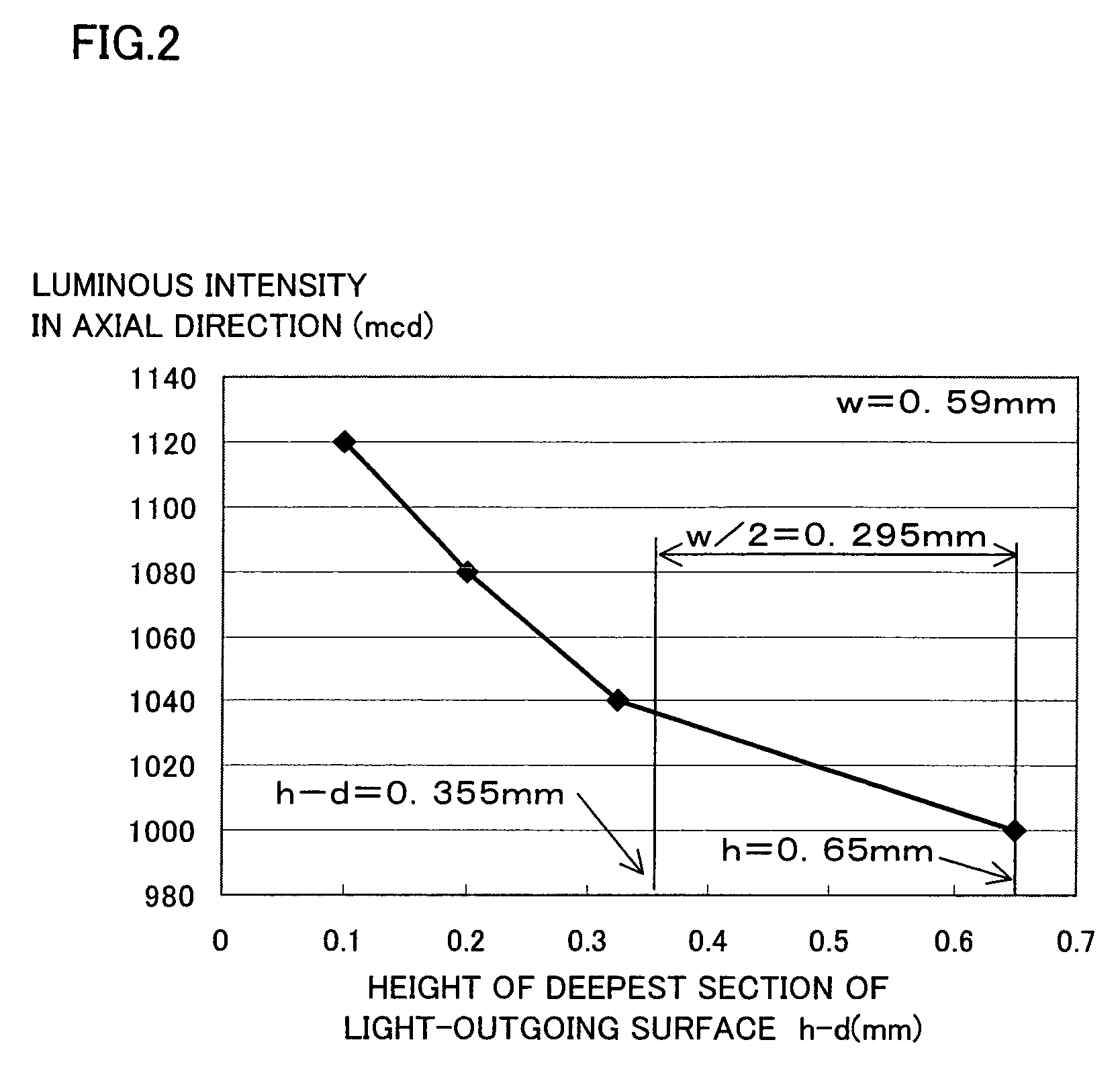
A light emitting apparatus according to the present invention includes: a placement surface that includes an electrode; a light emitter that is placed on the placement surface; and a transparent sealing resin that seals the light emitter, and forms a concave surface that is a light-outgoing surface via which light outgoes. The concave surface faces a surface of the light emitter, from which surface light is emitted. The light emitter and the electrode are connected via a wire that is curved in such a way that a top section of the curved wire substantially coincides with a deepest section of the concave surface.
Owner:LEDCOMM LLC
External cavity laser apparatus with orthogonal tuning of laser wavelength and cavity optical pathlength
InactiveUS6901088B2Minimize couplingMinimal effectLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionExternal cavity laserLasing wavelength
An external cavity laser apparatus and method wherein wavelength or channel selection is carried independently from adjustment of external cavity optical path length. The apparatus comprises a wavelength or channel selector tuner and an external cavity tuner, wherein the wavelength tuner is uncoupled from the external cavity tuner. The tuning mechanisms for wavelength selection and cavity optical path length are configured to operate independently or orthogonally with respect to each other. The wavelength tuner may operate according to a first, channel selection signal, while the external cavity tuner operates according to a second, external cavity adjustment signal. The wavelength tuner and external cavity tuner may operate under the control of the same, or of separate controllers. The channel selection signal may be derived from a look-up table of adjustment parameter data accessed by a controller, and the external cavity adjustment signal may be derived from an error signal from a detector configured to measure external cavity loss.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Light guide blade with color balancing structures and blue absorption compensation for large screen LED backlight unit
ActiveUS20090316077A1Improve efficiencyPrevent leakagePlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsColor shiftProgressive scan
One or more embodiments of the present invention provide apparatuses, methods and systems to form a thin LED backlight unit for a large-screen flat-panel display. The backlight unit is able to achieve improved color mixing within a shorter mixing distance than the conventional art, while maintaining desired brightness uniformity, thereby allowing for a shorter bezel of a display device. One or more embodiments of the present invention include one or more light guides, which, by operating together, provide thin backlight units. High system efficiency is provided by introducing a recycling enhancement component, and uniform color distribution is achieved by incorporating color shift compensation. Multiple light guides are arranged adjacent to one another can offer a progressive scan illumination feature.
Owner:JABIL CIRCUIT INC
Microbubble optical resonator
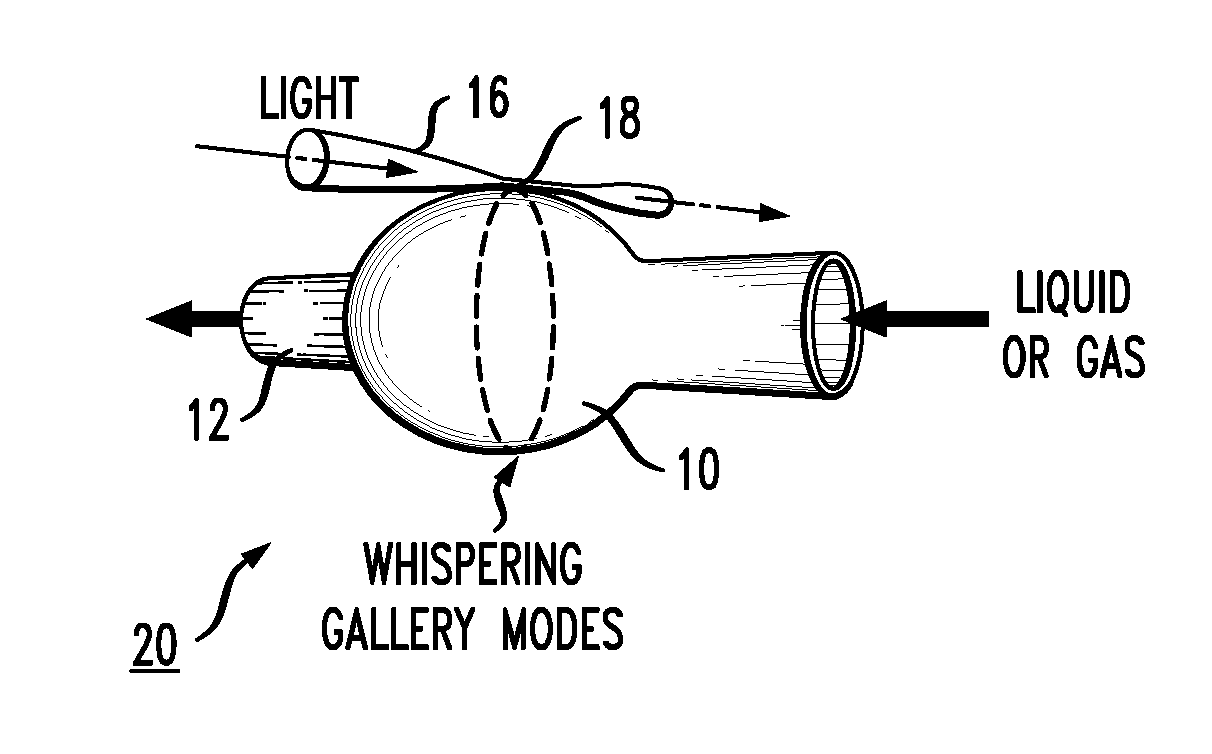
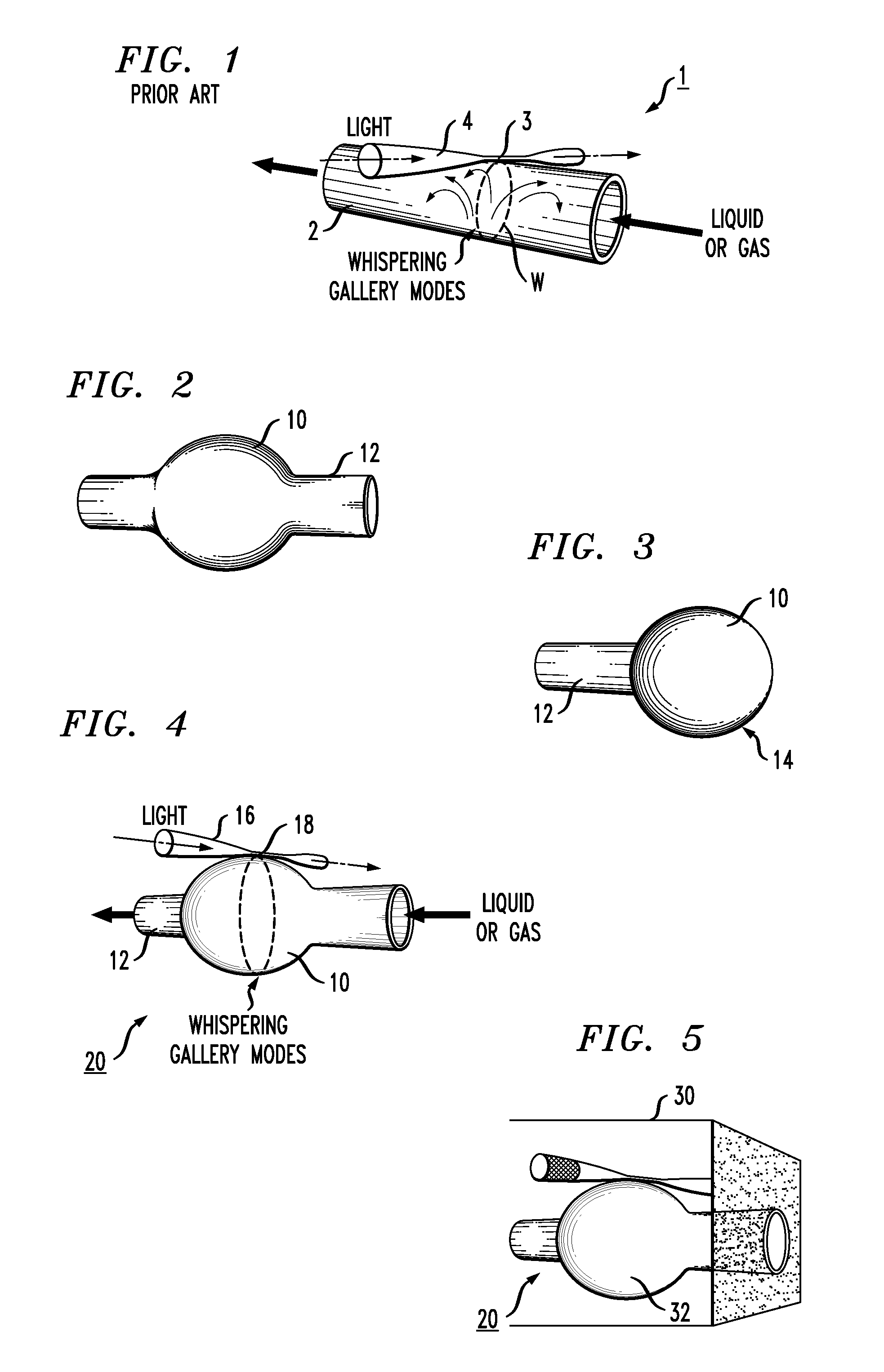
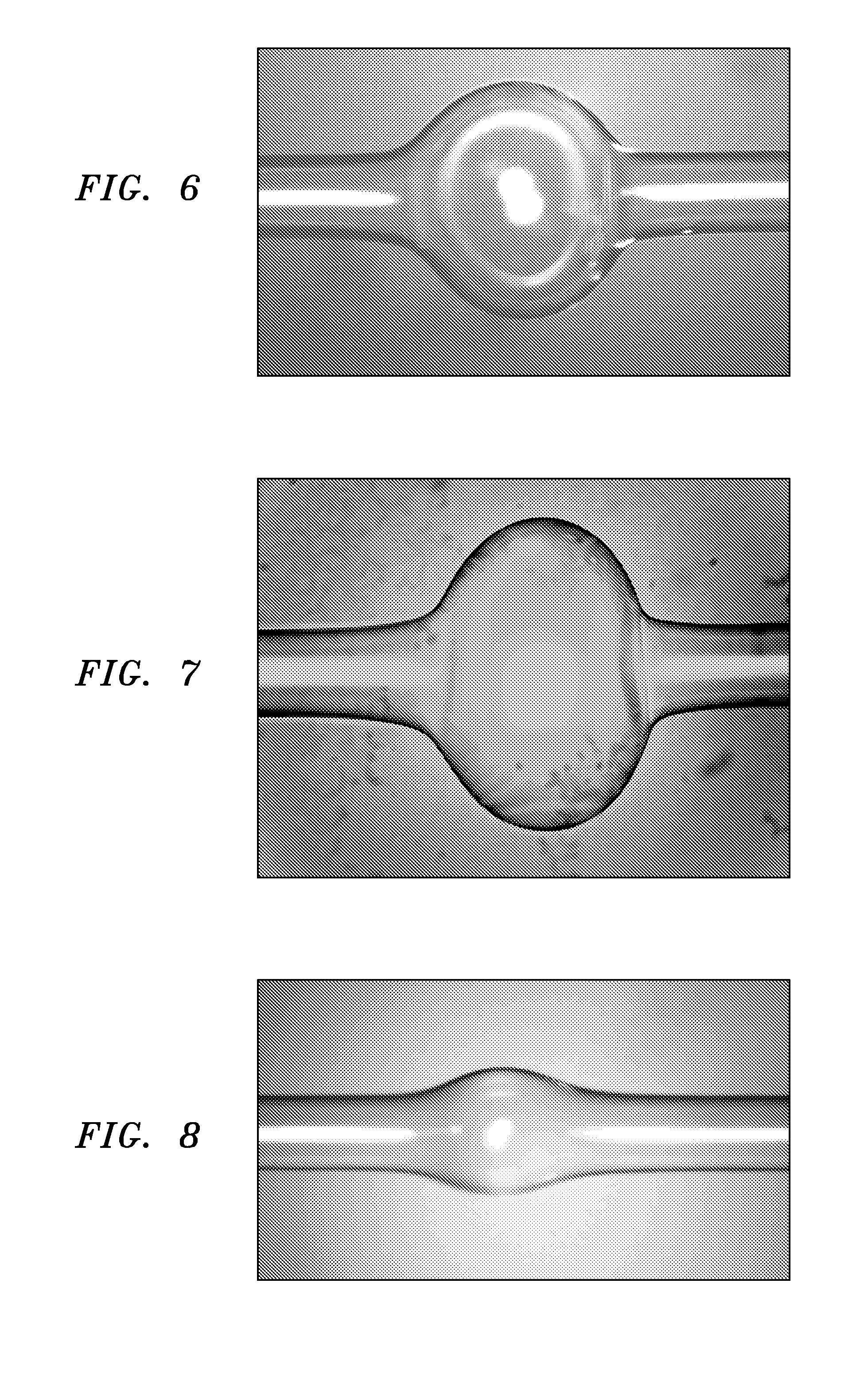
ActiveUS20100231903A1Coupling efficiency is highPreferable qualityLaser optical resonator constructionWithdrawing sample devicesPhysical propertyResonator
An optical microresonator is configured as an optical microbubble formed along a section of an optical microcapillary. The curvature of the outer surface of the microbubble creates an optical resonator with a geometry that encourages the circulating WGMs to remain confined in the central region of the bubble, creating a high Q optical resonator. The resonator may be tuned by modifying the physical properties of the microbubble, allowing the resonator to be used as an optical filter. The resonator may also be used as a sensor or laser by introducing the material to be sensed (or the active laser material) into the microcapillary along which the microbubble is formed.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Optical collimator-use lens component, optical collimator, and method of assembling these
InactiveUS20050123240A1Coupling efficiency is highHigh-quality communication performanceCoupling light guidesOptical axisAdhesive
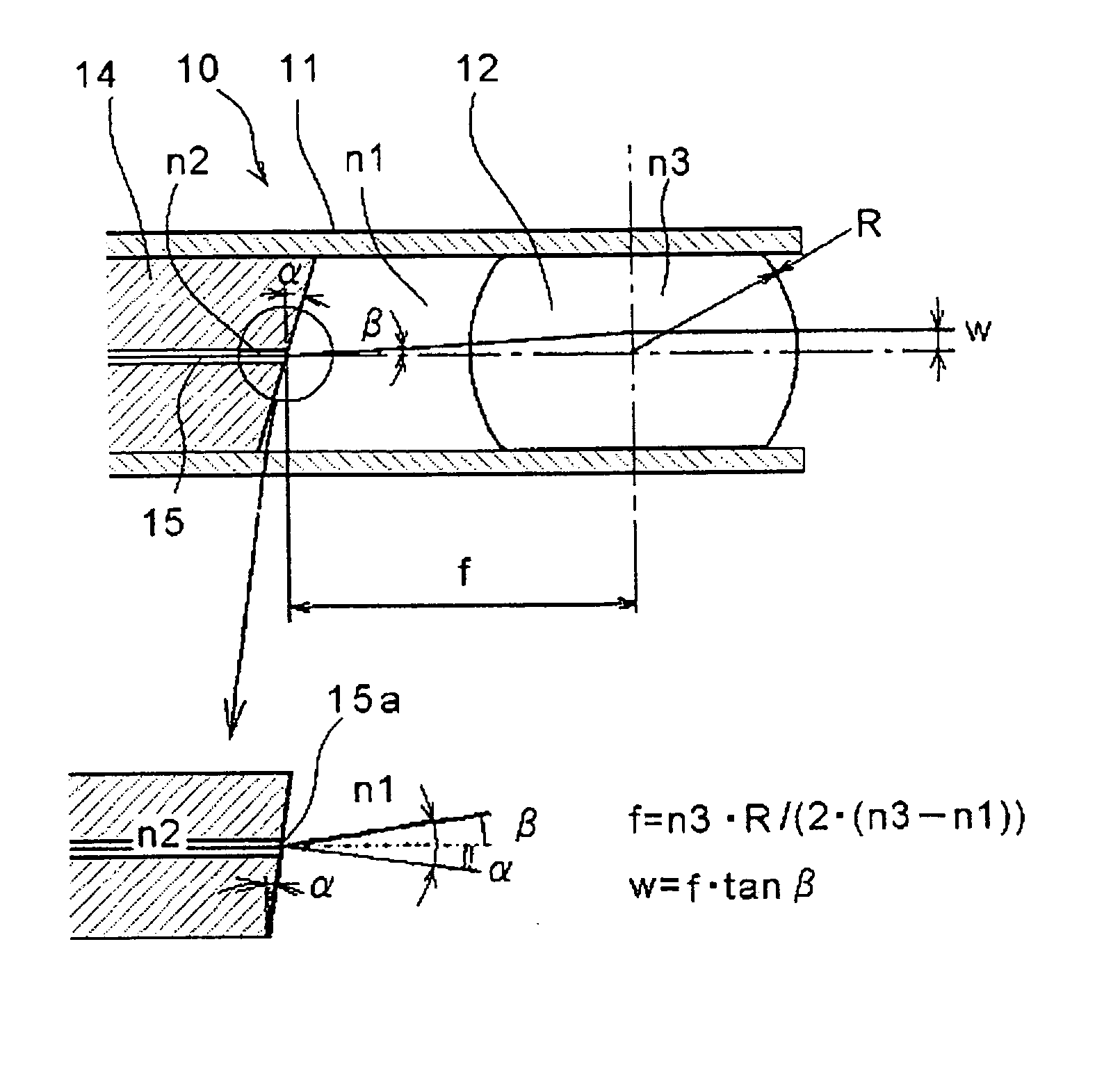
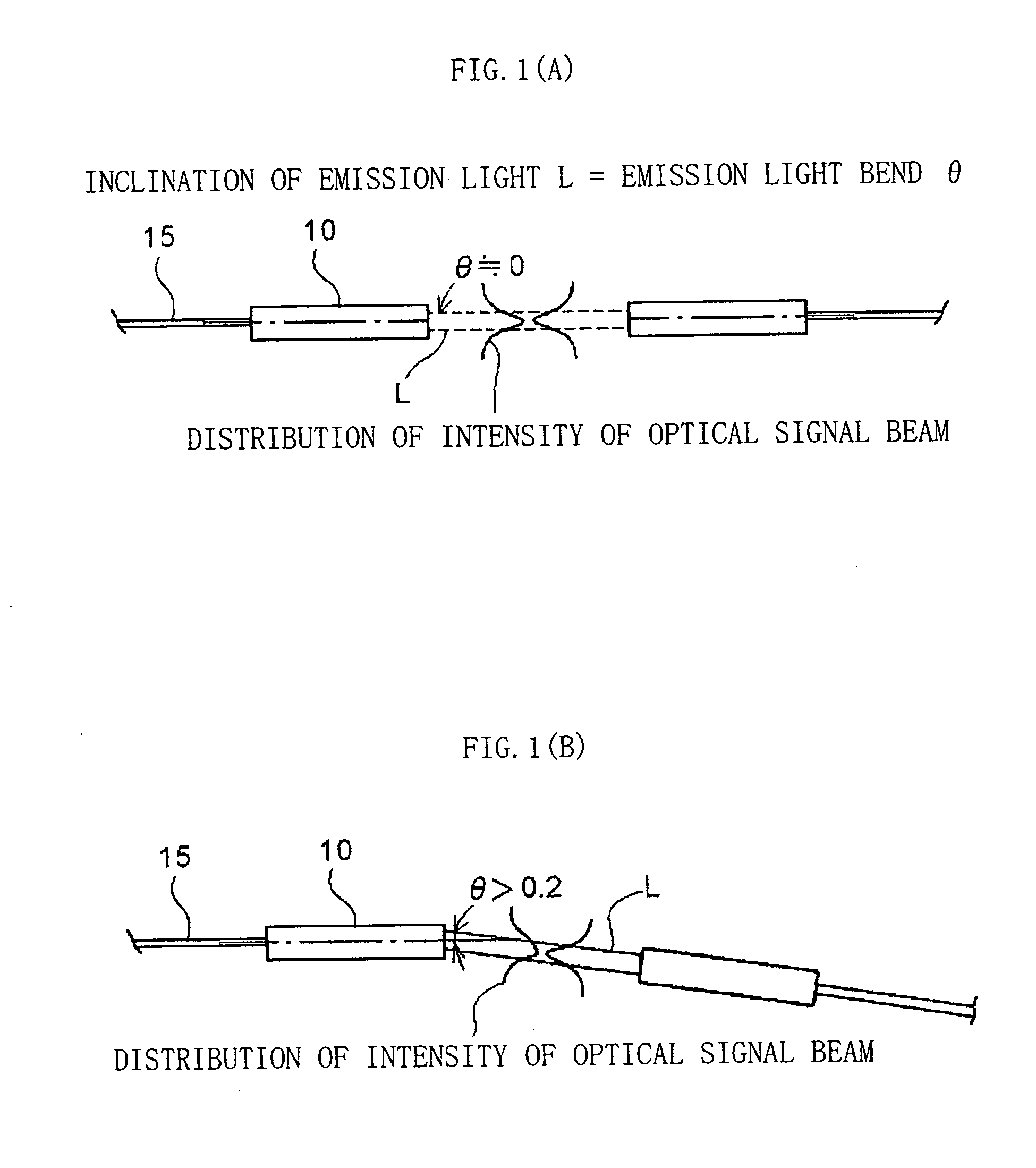
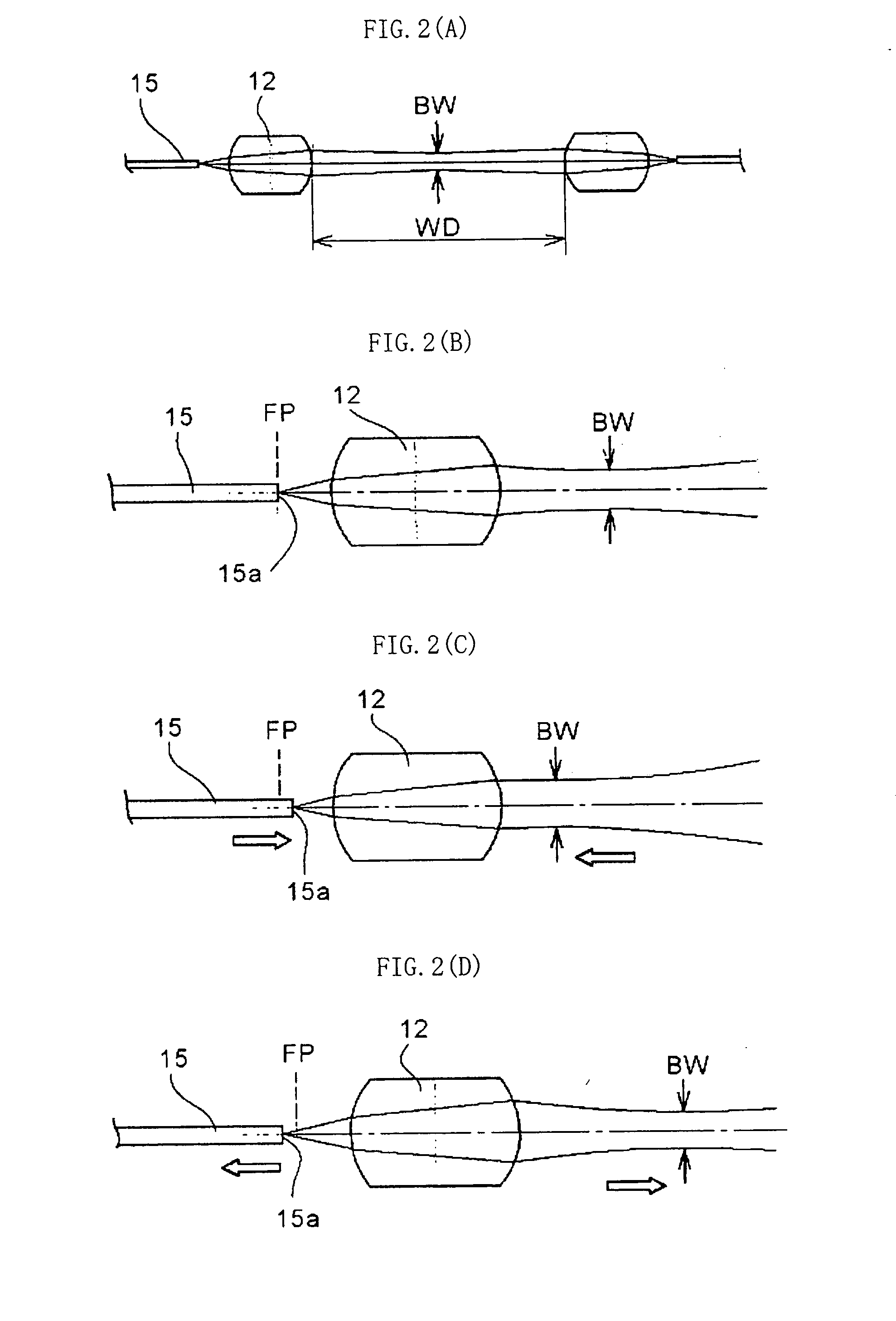
Disclosed is an optical collimator-use lens component including: a thin tube; a partially spherical lens that has been fixed in an inner hole of the thin tube so that an insertion portion having a predetermined length is left, is made of glass whose refractive index is approximately uniform, and has translucent spherical surfaces, whose centers of curvature are approximately the same, at both ends of a cylindrical portion of the partially spherical lens; and an adhesive that bonds the partially spherical lens to the thin tube. An axial deviation amount between a center axis of the thin tube and an optical axis of the partially spherical lens is 5 μm or less. When a capillary tube, in whose inner hole an optical fiber has been fixed and whose axial deviation amount between an outer peripheral surface of the capillary tube and a core center of an end surface of the optical fiber is 1.5 μm or less, is inserted into the insertion portion of the thin tube and the end surface of the optical fiber is fixed at a position at which a distance of the end surface to a focal point position of the partially spherical lens becomes ±40 μm or less, emission light has an emission light bend of 0.2° or less with respect to the center axis of the thin tube.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
Styrenic block copolymers and compositions containing the same
InactiveUS20090062457A1High viscosityCoupling efficiency is highSpecial tyresCoatingsThermoplasticFiber
A block copolymer of the formula [S-I-(I / B)]nX or [S-I-(I / B)- / B]nX or mixtures thereof wherein each S is independently a polymer block of an alkenyl arene; each I is a polymer block of isoprene; each B is a polymer block of butadiene and each (I / B) is a mixed random polymer block of isoprene and butadiene in a weight ratio I:B of from about 10:90 to about 90:10, n is an integer equal to or greater than 2, X is the residue of a coupling agent, and wherein the alkenyl arene content of the block copolymer represents a weight ratio of the alkenyl arene block to conjugated diene block of the total block copolymer and is in the range of from about 15 to about 35 wt %. Compositions for the manufacture of transparent, gel-free films, adhesives, fibers, injection molded articles, dipped goods, oil gels, and bitumen are also disclosed and comprise from about 3 to about 90 wt % of the claimed block copolymer and one or more components selected from thermoplastic resins, polyolefins, tackifying resins, end block resins, polystyrene, oils, engineering thermoplastics, fillers, and antioxidants.
Owner:KRATON POLYMERS US LLC
Optoelectronic transmission and/or reception arrangement
ActiveUS7270488B2Coupling efficiency is highProduced cost-effectivelyCoupling light guidesEngineeringOpto electronic
The invention relates to an optoelectronic transmission and / or reception arrangement. The arrangement includes a transmission and / or reception module containing an optoelectronic transmission and / or reception component, and a plug interface for the coupling of an optical fiber thereto. An optical waveguide section is arranged in the plug interface, and at one of its ends is optically coupled to the transmission and / or reception component. At its other end, the optical waveguide section is configured to be coupled to an optical fiber. The arrangement may further include a lens for optical coupling of the light between the optical waveguide section and the transmission and / or reception component. The lens and the optical waveguide section, in one example, are formed as a prefabricated subassembly, in which the lens is fixedly arranged at a defined distance from one end face of the optical waveguide section.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Light projector and sensor
ActiveUS20110199781A1Coupling efficiency is highElectric discharge tubesDiffusing elementsOptical axisRefractive index
A light projector has a light emitting device having a light emitting surface, an optical fiber having an incident end-face to which light emitted from the light emitting surface enters, and a lens arranged between the light emitting surface of the light emitting device and the incident end-face of the optical fiber. The light emitting device, the optical fiber and the lens are arranged on one optical axis. The optical fiber includes a core region as a region including a single core of uniform refractive index or a region collectively encompassing a plurality of cores having uniform refractive index. The lens converts diffused light emitted from the light emitting surface to diffused light that widens more moderately.
Owner:ORMON CORP
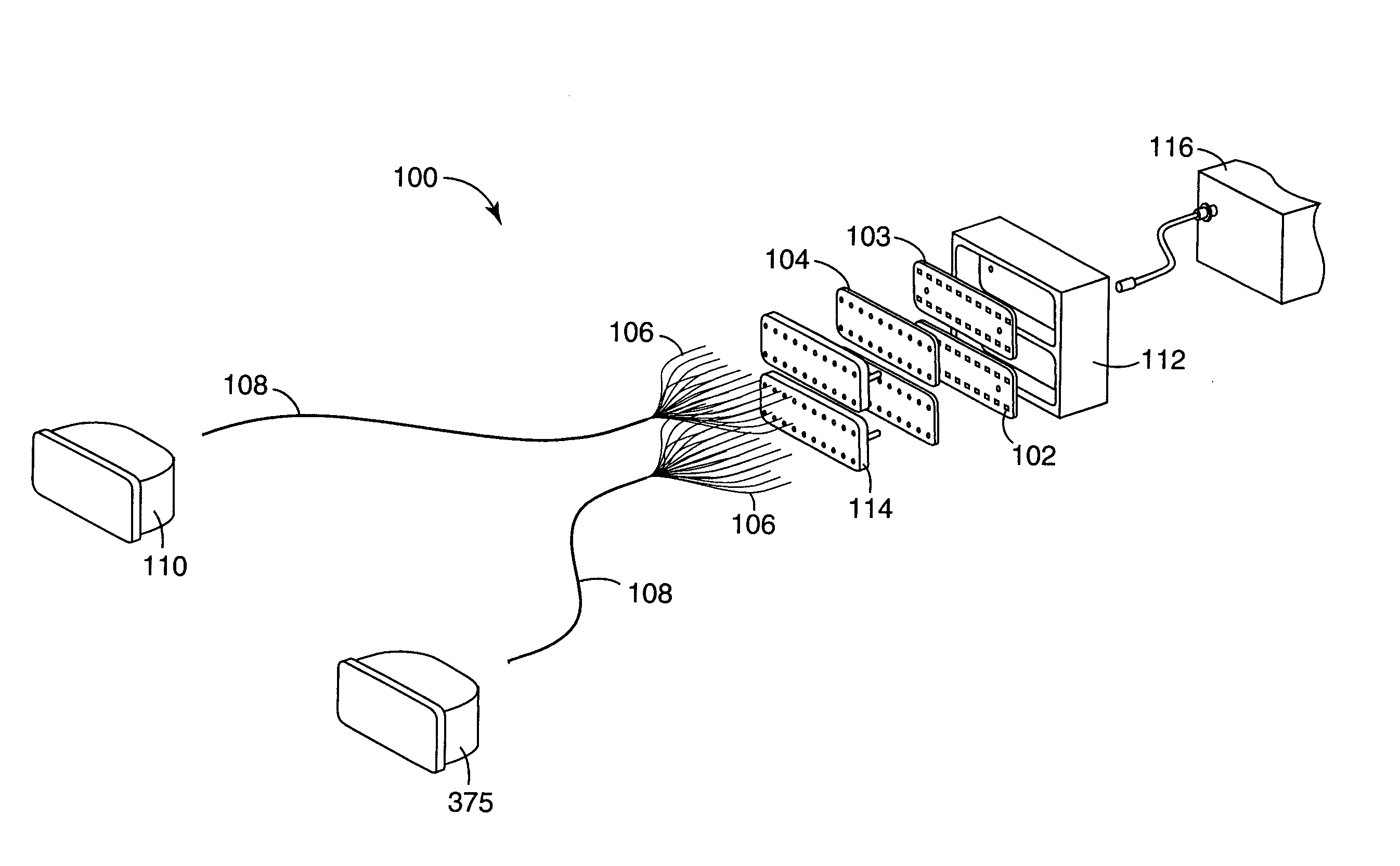
Bi-Directional Fiber Optic Transceivers, Housings Therefor, and Methods for Making and Using the Same
ActiveUS20130004132A1Coupling efficiency is highSmall outlineLaminationLamination apparatusFiberTransceiver
A bi-directional fiber optic transceiver includes a laser diode, a photodiode, first and second lenses, all of which share a common linear optical axis, and a housing. The first lens may have transmission increasing film thereon. The second lens may have a reflection increasing film thereon. An optical splitter may be between the first and second lenses. The first and / or second lenses may be spherical, hemispherical or aspheric. The transceiver size is reduced so that a circuit board can accommodate more components or be smaller in size. Utilizing hemispherical lenses can greatly increase the coupling ratio of the optical links between the photodiode, fiber and laser diode. Utilizing aspheric lenses with high coupling can serve high power output requirements. Use of spherical lenses (which extend the focal length) with aspheric lenses enables LD TO assemblies in individual housings to serve in various products.
Owner:SOURCE PHOTONICS
Fiber optic rotary joints and methods of using and manufacturing same
ActiveUS20180348439A1Compact structureCoupling efficiency is highDianostics using fluorescence emissionCatheterFluorescenceOptical instrument
One or more fiber optic rotary joints (FORJ), free space beam combiners, OCT, SEE and / or fluorescence devices and systems for use therewith, methods of manufacturing same and storage mediums are provided. One or more embodiments of FORJs may be used with numerous applications in the optical field, including, but not limited to, OCT and fluorescence applications. Examples of such applications include imaging, evaluating and diagnosing biological objects, such as, but not limited to, for Gastro-intestinal, cardio and / or ophthalmic applications, and being obtained via one or more optical instruments.
Owner:CANON USA
Highly efficient focusing waveguide grating coupler using leaky mode
InactiveUS6999660B2Coupling efficiency is highReduce dependenceCoupling light guidesFresnel lensManufacturing technology
Provided is a focusing waveguide grating coupler using a leaky mode which can form single output beam while relieving the dependency on manufacturing processes. The focusing waveguide grating coupler of the present research includes: a substrate having a first refraction index n1; a first core layer having a second refraction index n2, the first core layer being formed on the substrate; a second core layer having a third refraction index n3, the second core layer being formed on the first core layer apart from the first core layer with a space d in between; a first cladding layer having a fourth refraction index n4, the first cladding layer being formed on the second core layer; a second cladding layer having a fifth refraction index n5, the second cladding layer being formed on the first cladding layer and inserted between the first core layer and the second core layer; and a Fresnel lens positioned on the second cladding layer, wherein the refractive indexes satisfy conditions of n5>(n2, n3)>n1 and n5>n4; and light inputted through the first and second core layers to the Fresnel lens as radiated leaky beam by a leaky mode formed according to the conditions, and the leaky beam forms an optical focus by performing single directional coupling.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Particle characterisation
ActiveUS20190078990A1Fast measurement timeReduced measurement timeParticle size analysisScattering properties measurementsLight beamLight detector
An apparatus for particle characterisation, comprising: a sample cell for holding a sample; a light source configured to illuminate the sample with an illuminating beam and a plurality of light detectors, each light detector configured to receive scattered light resulting from the interaction between the illuminating beam and the sample along a respective detector path, wherein each respective detector path is at substantially the same angle to the illuminating beam.
Owner:MALVERN INSTRUMENTS
Optical module including an optoelectronic device
An optical module includes a support substrate, and an optoelectronic device on the support substrate. A coupling device provides optical coupling of the optoelectronic device with an optical fiber. The coupling device is integrated in the substrate, and is a reflection device inserted into an optical path between the optoelectronic device and the optical fiber.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Semiconductor laser and optical module
ActiveUS7502403B2Coupling efficiency is highHigh in optical coupling efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser optical deviceFiberOptical Module
In a horizontal cavity surface emitted laser, there is provided a device structure that is capable of obtaining a circular narrow-divergence emitted beam that is high in the optical coupling efficiency with a fiber. As a first means, there is provided a horizontal cavity surface emitting laser having a structure in which the plane mirror that is inclined by 45° and the bottom lens of the oval configuration are integrally structured. As a second means, there is provided a horizontal cavity surface emitting laser in which the mirror having the columnar front surface configuration inclined by 45° and the bottom lens of the columnar front surface configuration are integrally structured. Since the horizontal component and the vertical component of the laser beam can be shaped, independently, through the above means. As a result, it is possible to obtain the circular narrow-divergence emitted beam.
Owner:LUMENTUM JAPAN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com