Patents
Literature
435 results about "Progressive scan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
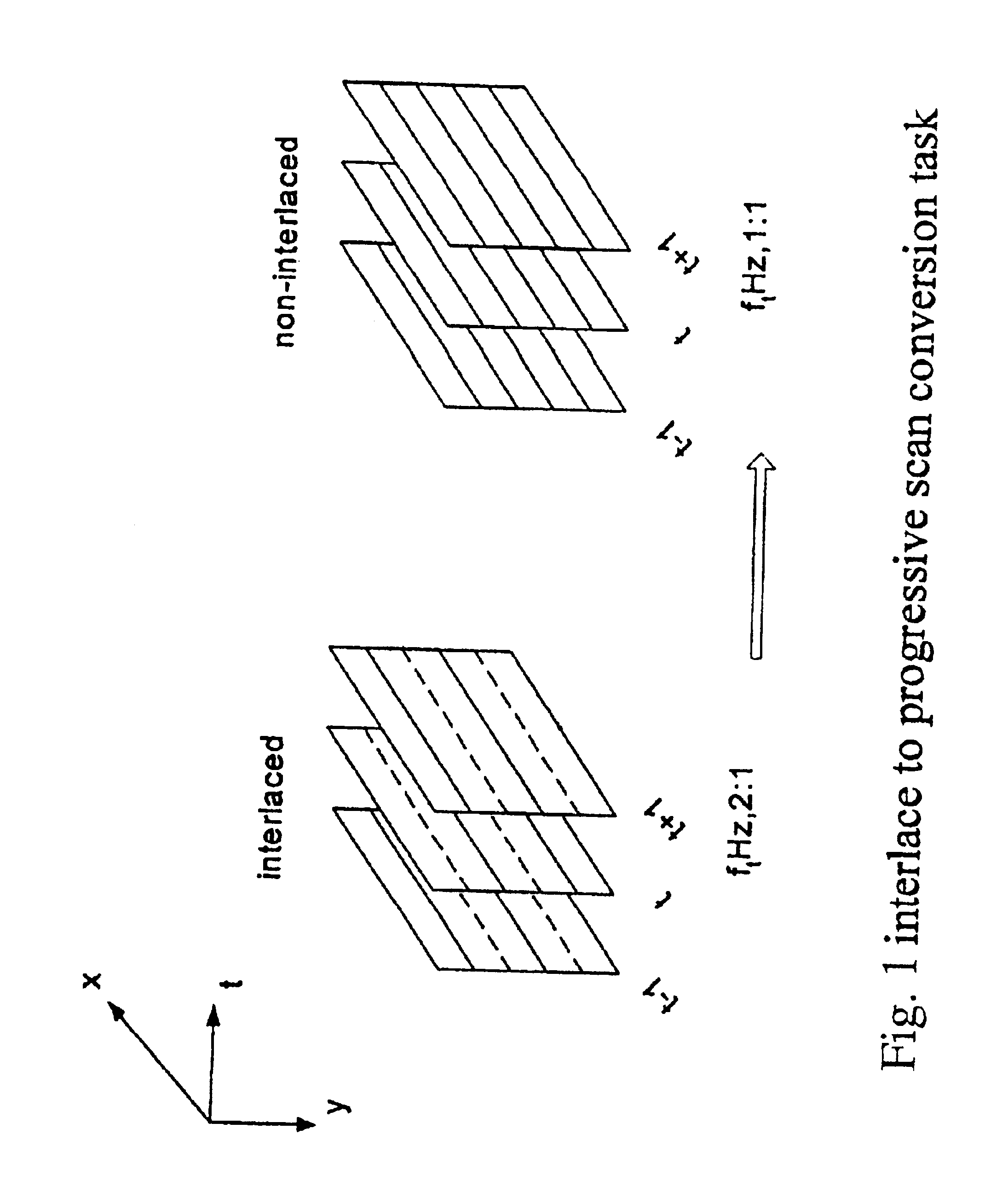
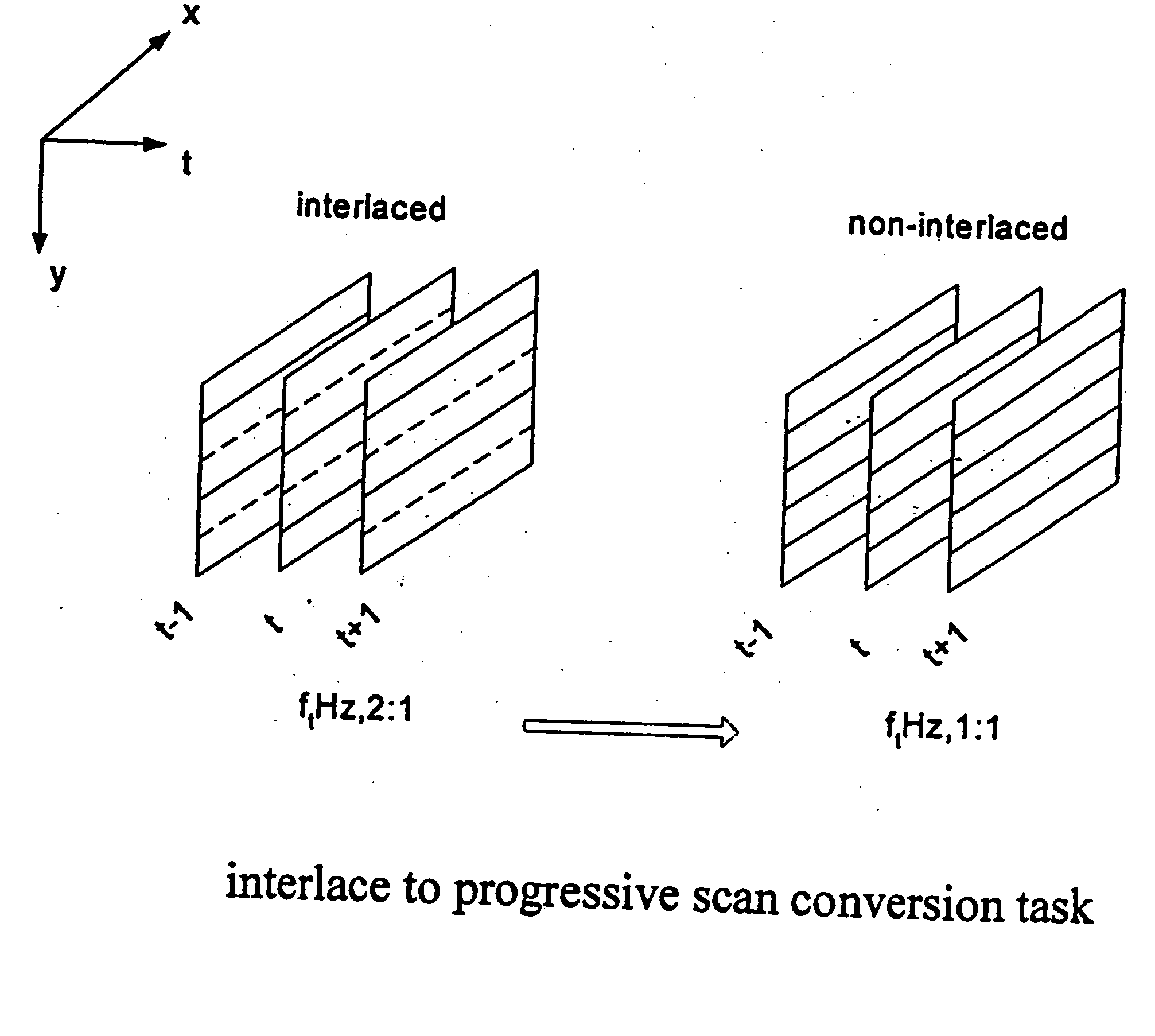
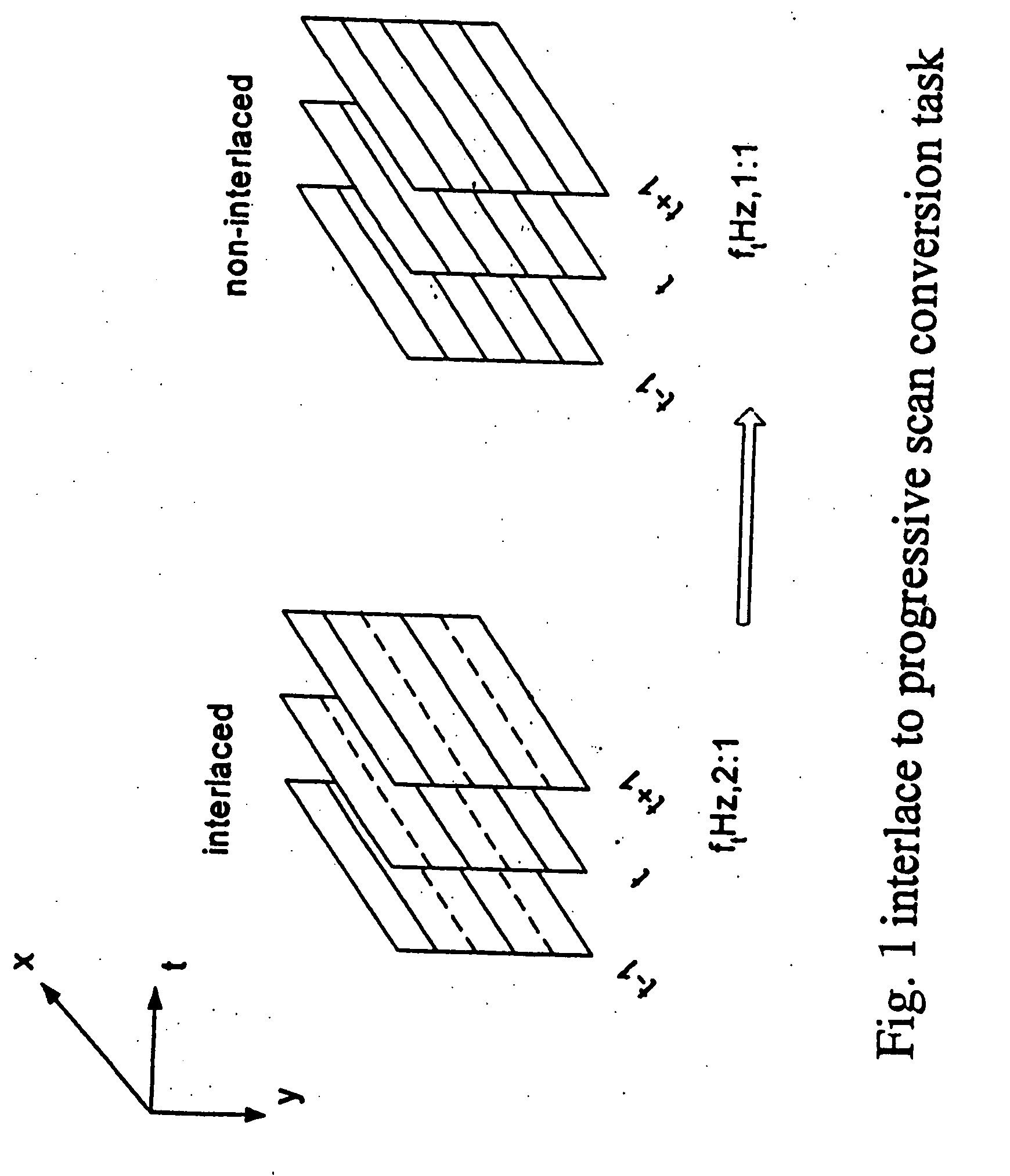
Progressive scanning (alternatively referred to as noninterlaced scanning) is a format of displaying, storing, or transmitting moving images in which all the lines of each frame are drawn in sequence. This is in contrast to interlaced video used in traditional analog television systems where only the odd lines, then the even lines of each frame (each image called a video field) are drawn alternately, so that only half the number of actual image frames are used to produce video. The system was originally known as "sequential scanning" when it was used in the Baird 240 line television transmissions from Alexandra Palace, United Kingdom in 1936. It was also used in Baird's experimental transmissions using 30 lines in the 1920s. Progressive scanning became universally used in computer screens beginning in the early 21st century.
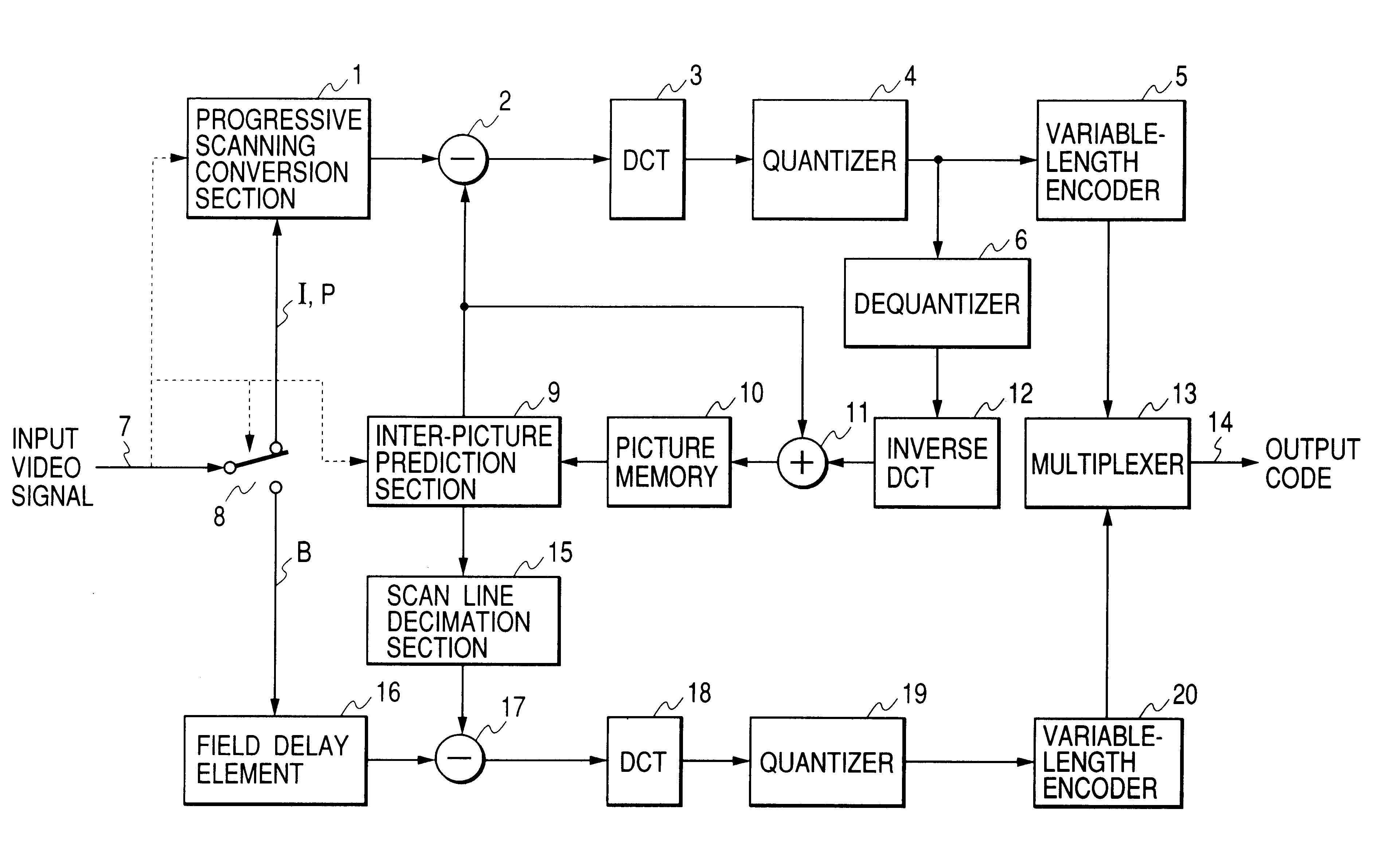
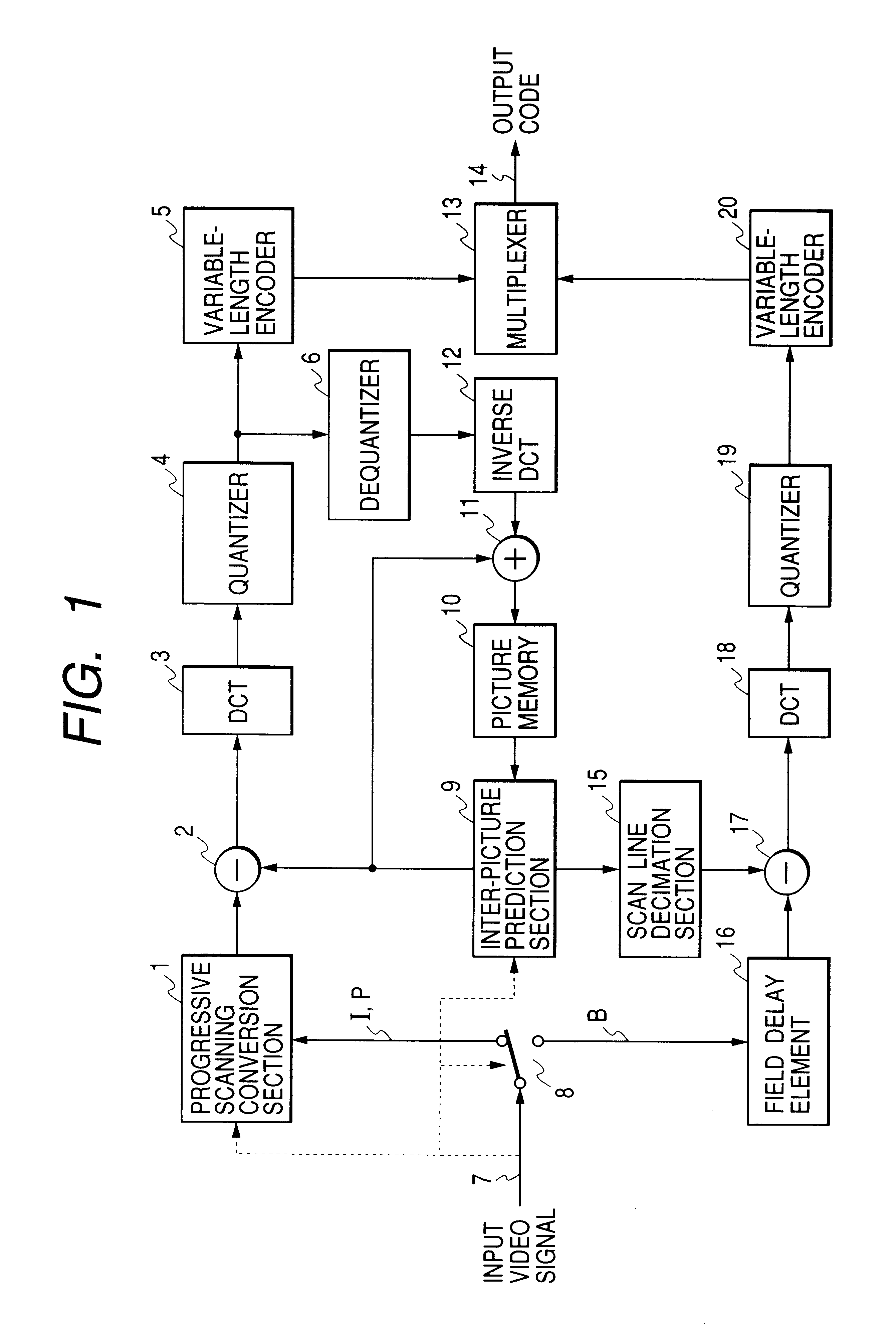
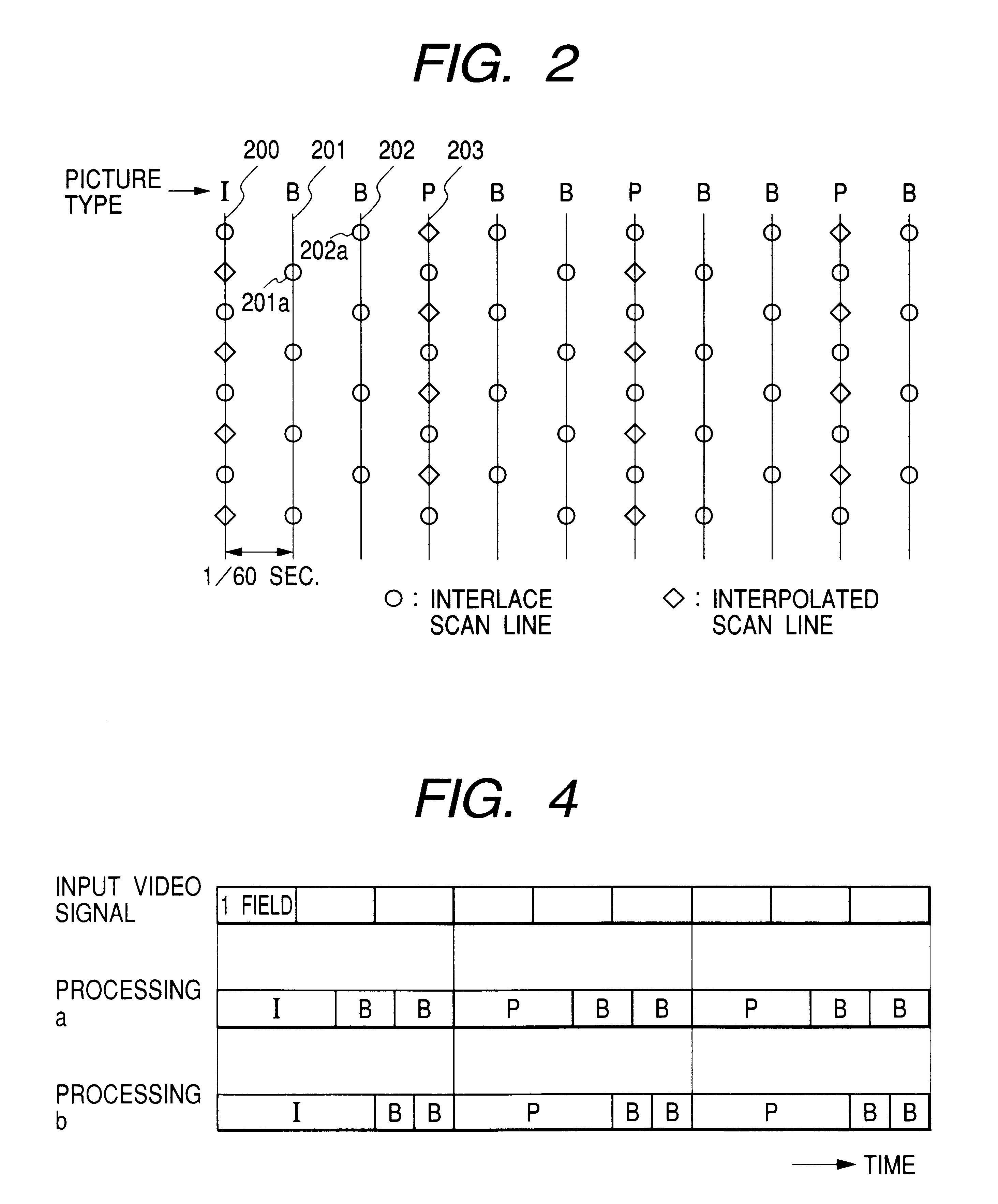
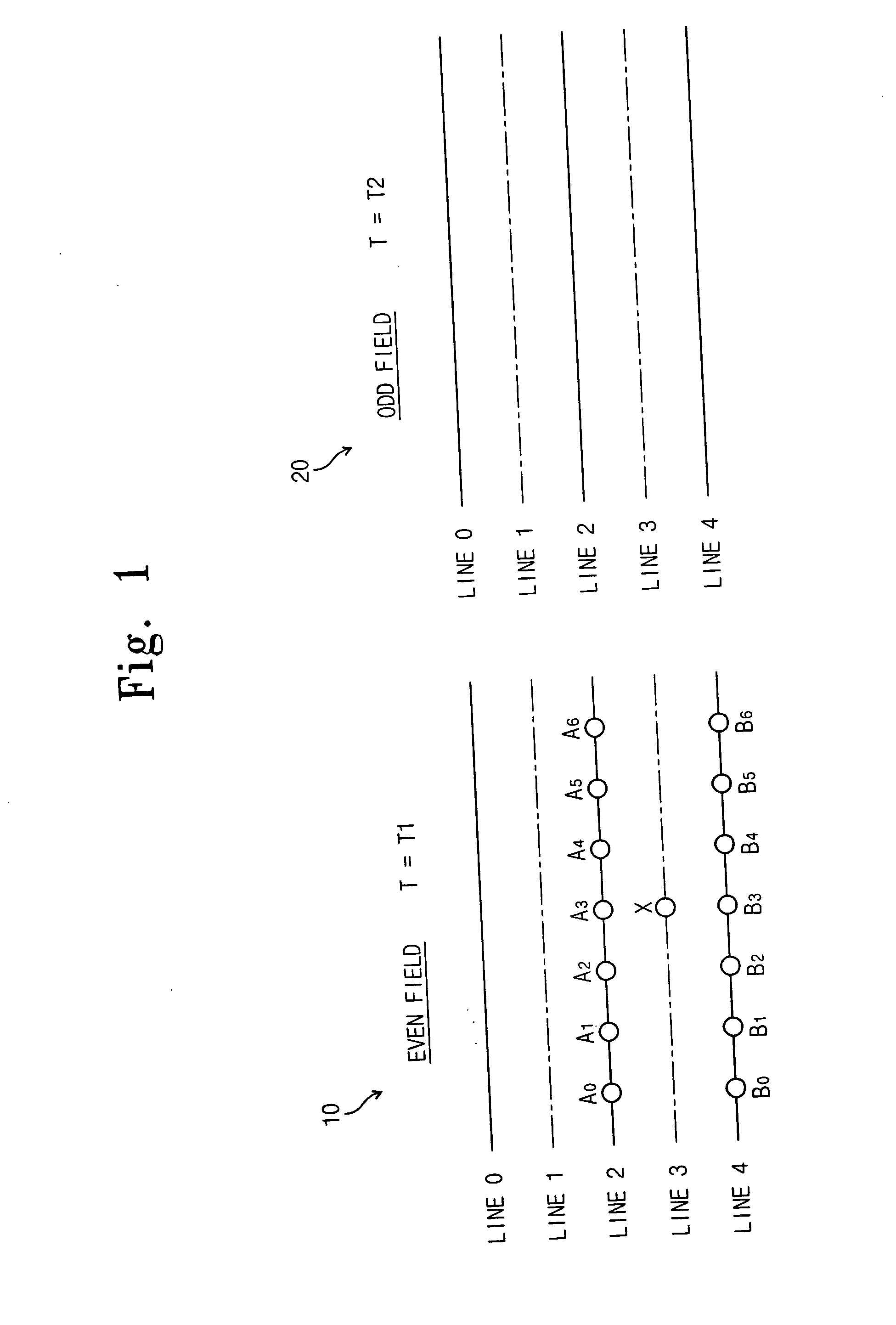
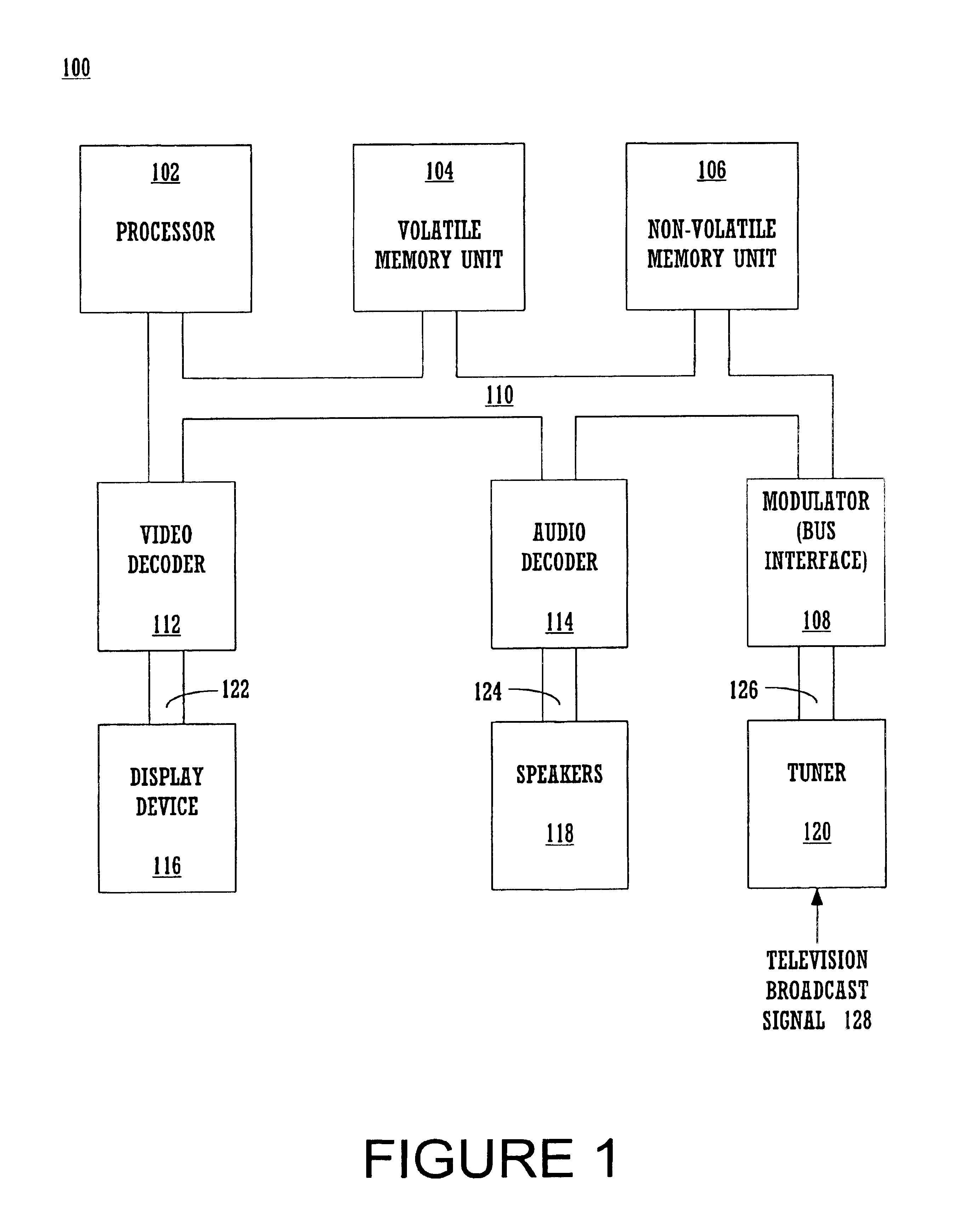
Interplaced video signal encoding and decoding method, and encoding apparatus and decoding apparatus utilizing the method, providing high efficiency of encoding by conversion of periodically selected fields to progressive scan frames which function as reference frames for predictive encoding
InactiveUS6188725B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesScan conversionInterlaced video
An encoding apparatus includes a selector for periodically selecting fields of an interlaced video signal to be converted to respective progressive scanning frames, by a scanning converter which doubles the number of scanning lines per field. The apparatus encodes these frames by intra-frame encoding or unidirectional predictive encoding using preceding ones of the frames, and encodes the remaining fields of the video signal by bidirectional prediction using preceding and succeeding ones of the progressive scanning frames for reference. The resultant code can be decoded by an inverse process to recover the interlaced video signal, or each decoded field can be converted to a progressive scanning frame to thereby enable output of a progressive scanning video signal. Enhanced accuracy of motion prediction for inter-frame encoding can thereby be achieved, and generation of encoded aliasing components suppressed, since all reference pictures are progressive scanning frames rather than pairs of fields constituting interlaced scanning frames.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
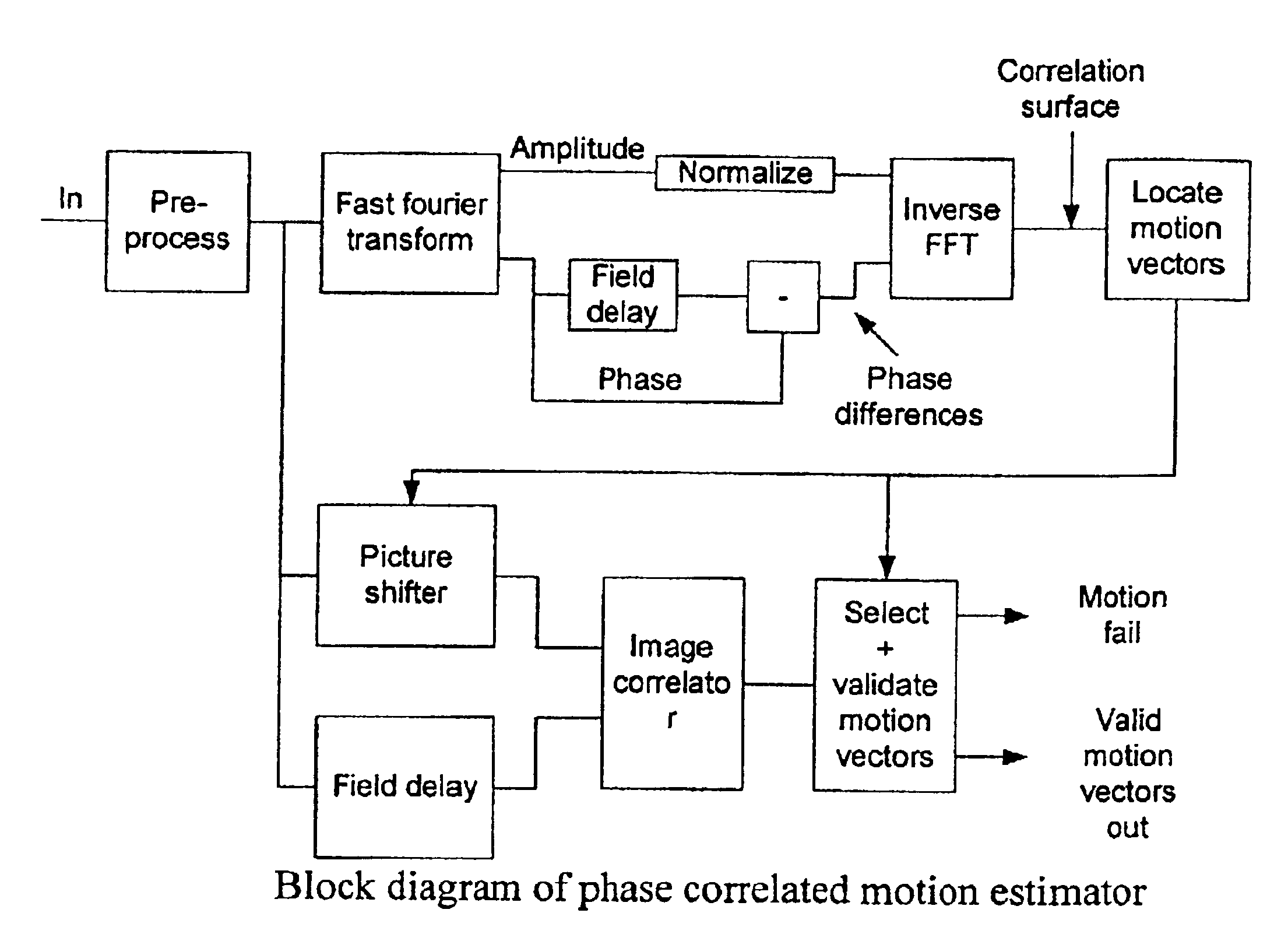
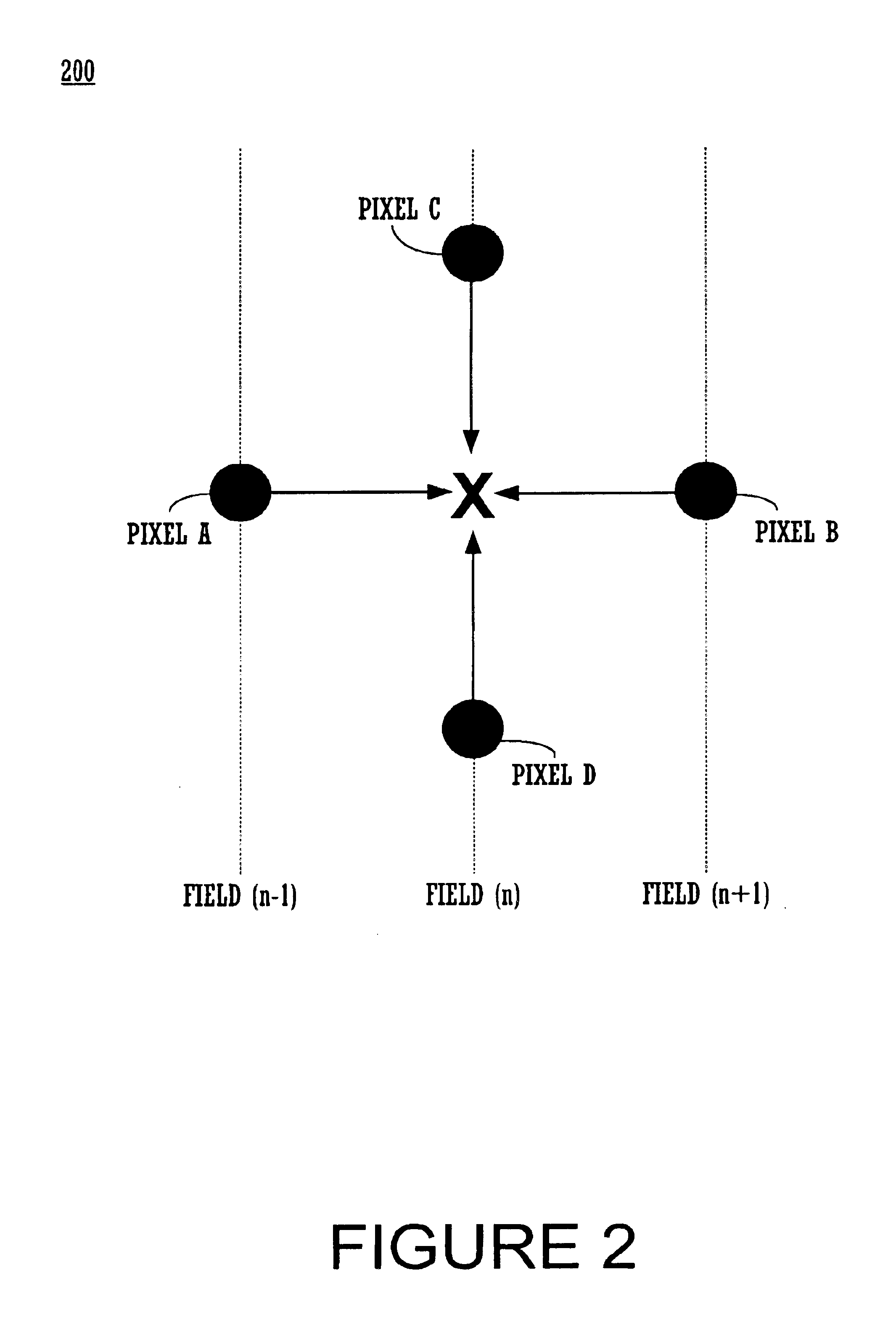
Adaptive interlace-to-progressive scan conversion algorithm
InactiveUS6940557B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsProgressive scanData set
An interlace-to-progressive scan conversion system comprises: a spatial line averaging prefilter; a motion estimator; a three-stage adaptive recursive filter. The motion estimator comprises: a 3-D recursive search sub-component having a bilinear interpolator; a motion correction sub-component having an error-function including penalties related to the difference between a given candidate vector and a plurality of neighboring vectors; a block erosion sub-component. The motion estimator assumes that motion is constant between fields. The three-stage adaptive recursive filter comprises: a first stage that selects between using static pixels data and moving pixels data from a next field; a second stage that selects a more valid set of data between motion compensated data from a previous field and the pixels selected by the first stage; a third stage that combines an intra-field interpolation with the more valid set of data selected by the second stage.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
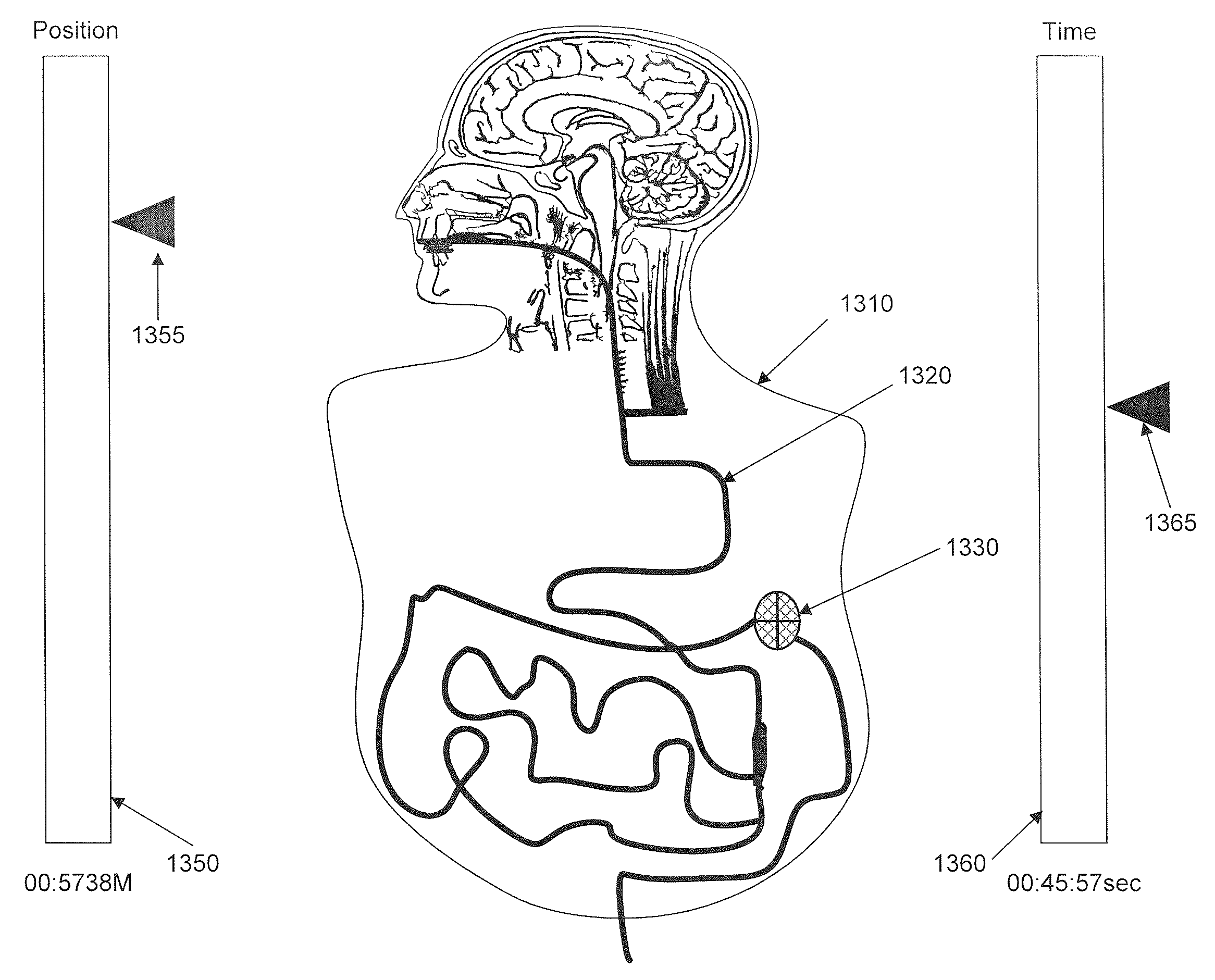
Displaying Image Data From A Scanner Capsule
An ingestible image scanning pill captures high resolution images of the GI tract as it passes through. Images communicated externally have exact location determination. Image processing software discards duplicate information and stitches images together, line scan by line scan, to replicate a complete GI tract as if it were stretched out in a straight line. A fully linear image is displayed to a medical professional as if the GI tract had been stretched in a straight line, cut open, laid flat out on a bench for viewing—all without making any incisions in a live patient.
Owner:INNURVATION
System and method for playback of digital video pictures in compressed streams
ActiveUS20060013568A1Television system detailsColor television signals processingDigital videoProgressive scan
A video decompression system and method are disclosed. In one preferred embodiment, the video decompression system comprises a memory with logic, and a processor configured with the logic to receive a compressed video stream that includes frame pictures and detect a scan mode indicator in the compressed video stream, wherein the scan mode indicator indicates whether a progressive scan format was used during the creation of the frame pictures.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
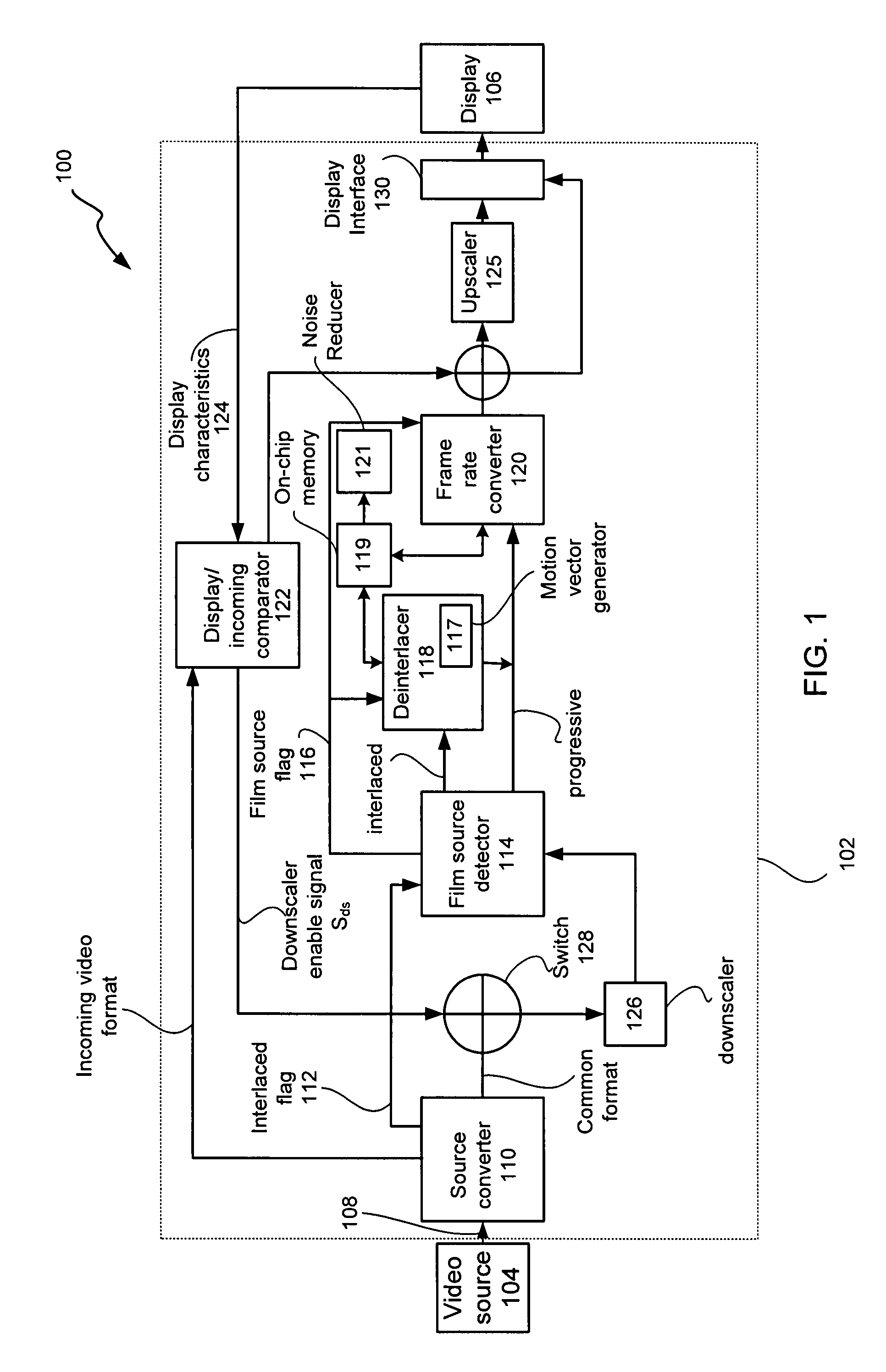
Adaptive display controller
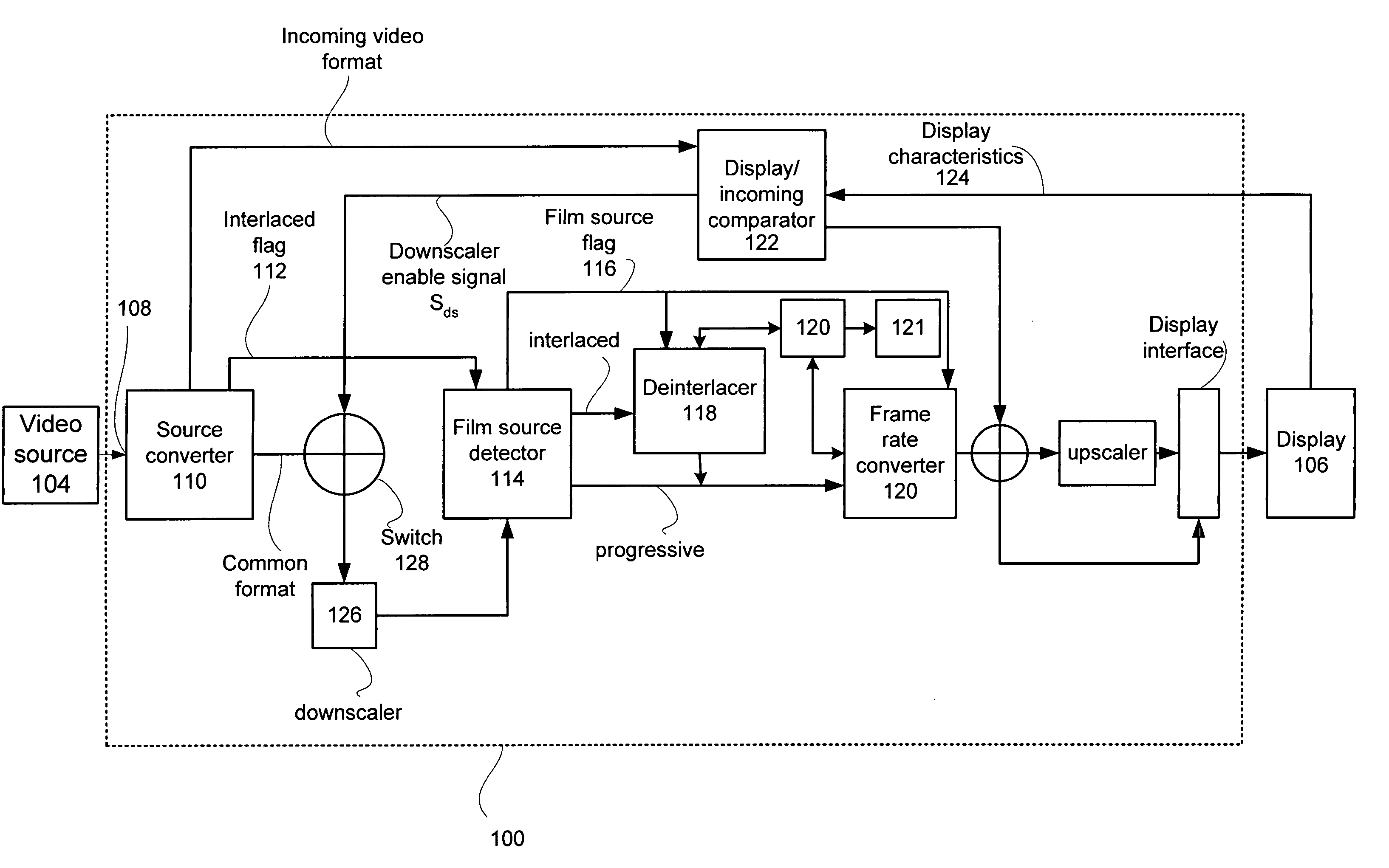
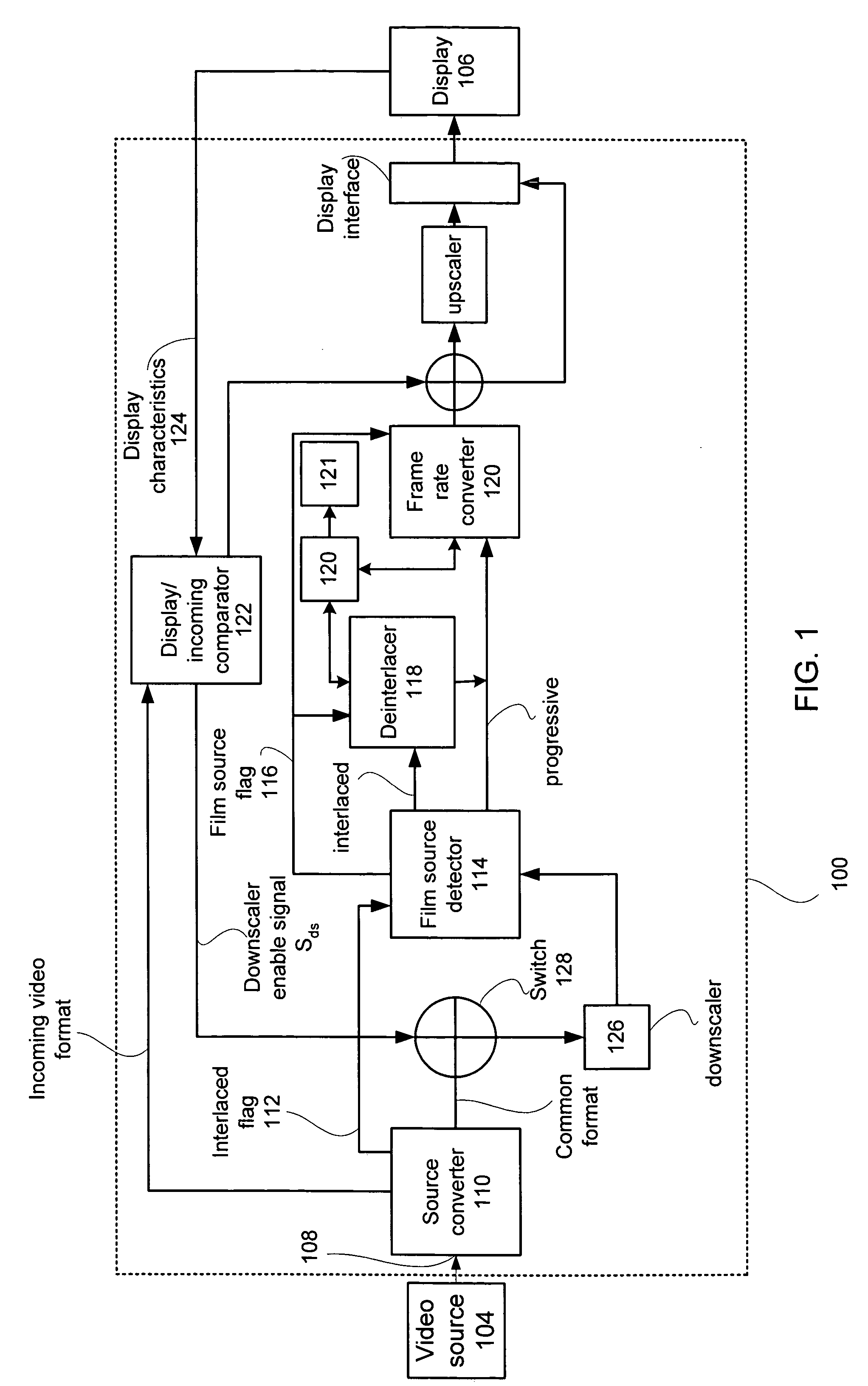
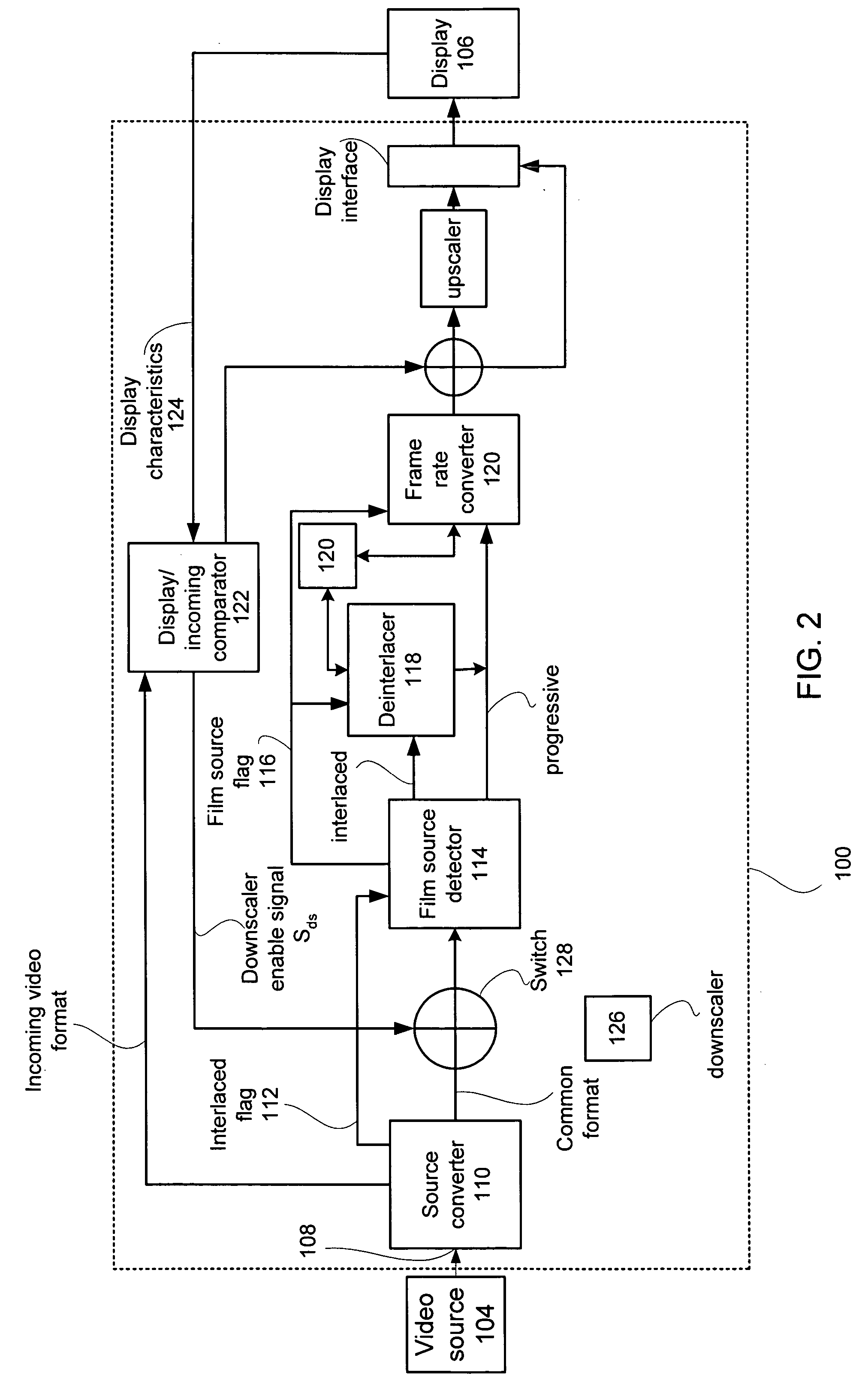
ActiveUS20050134735A1Cancel noiseBandwidthTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMulti-function displayProgressive scan
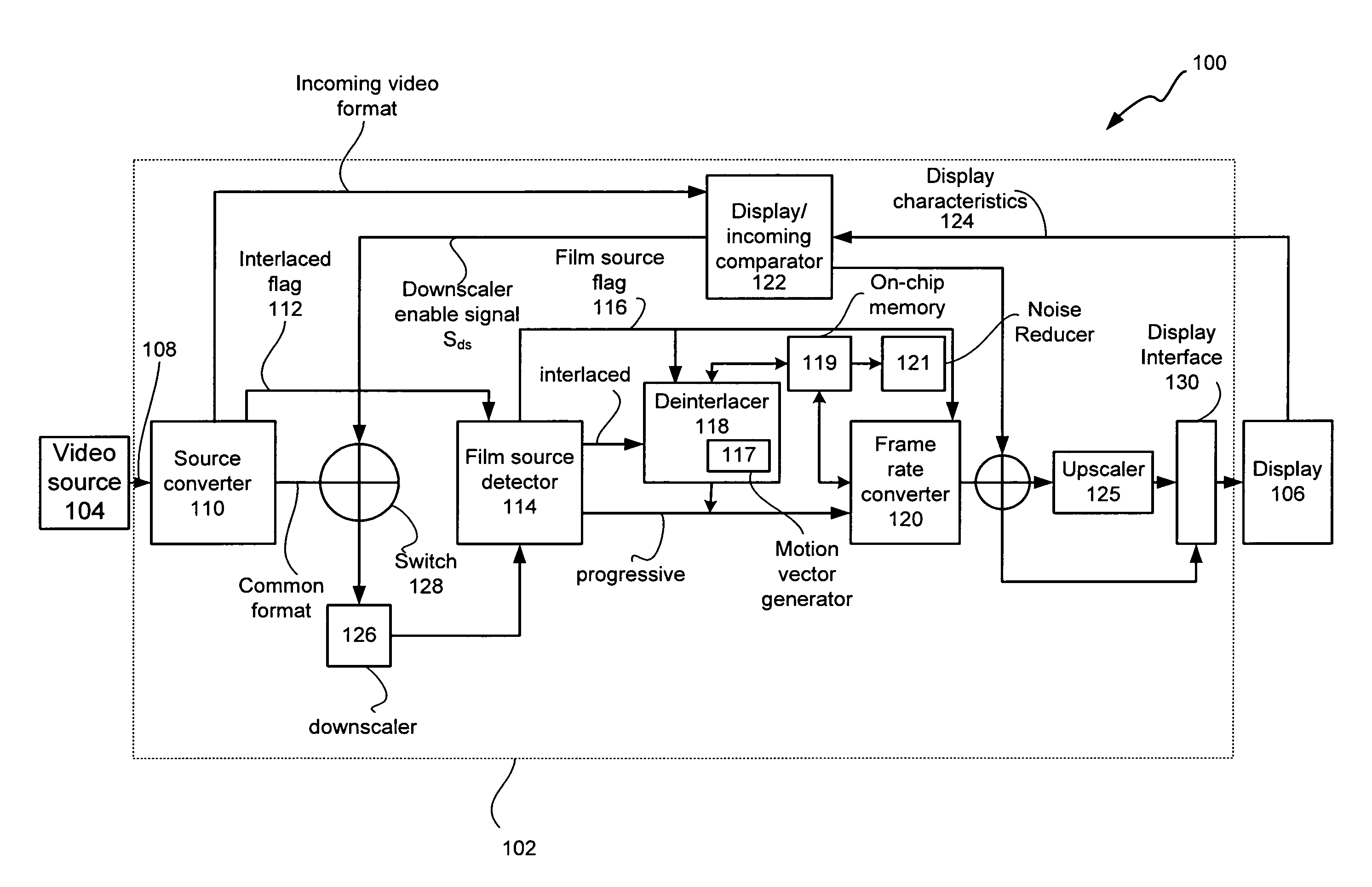
A multi-function display controller that includes a source detector unit for determining if the source of an input stream is either film originated source originated or video source originated. A source converter unit for converting the input image stream to a common signal processing format is coupled to the source detector unit. Once converted to the common signal processing format, a determination is made if the input image stream is interlaced or non-interlaced (progressive scan). If the input image stream is interlaced, a de-interlace unit converts the interlaced signal to progressive scan using either motion adaptive or motion compensated de-interlacing techniques. It should be noted that in the described embodiment, motion vectors generated for use by the motion compensated de-interlace can be optionally stored in a memory unit for use in subsequent operations, such as motion compensated frame rate conversion or noise reduction (if any).
Owner:GENESIS MICROCHIP
Deinterlacing of video sources via image feature edge detection
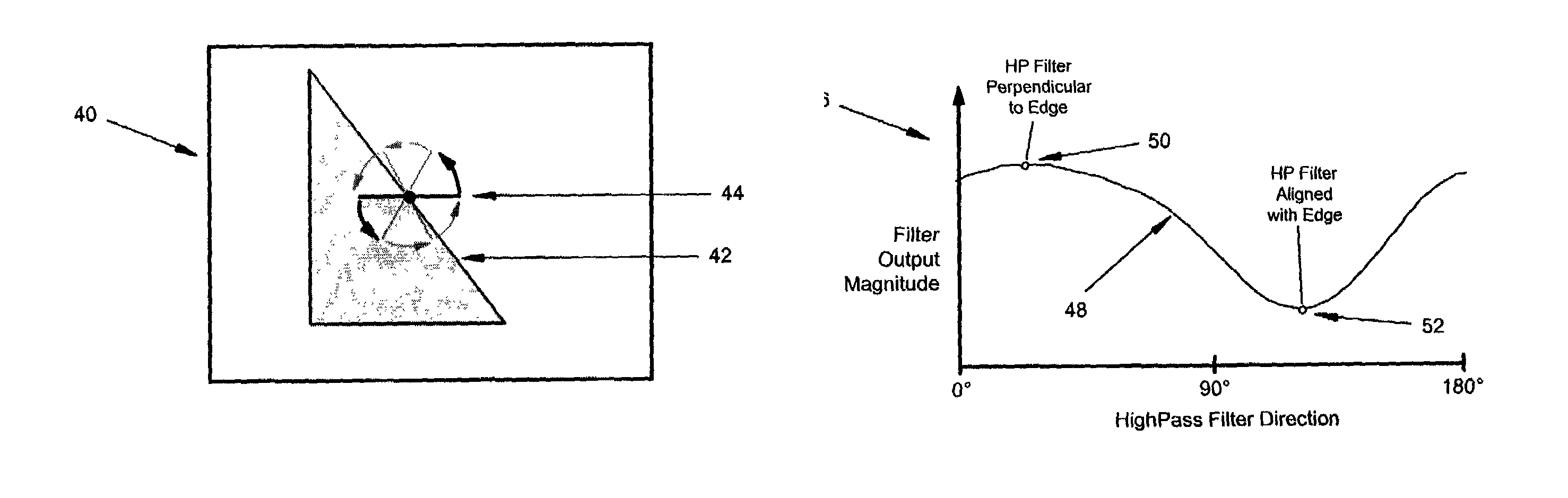
ActiveUS7023487B1Reduce artifactsPreserves maximum amount of vertical detailImage enhancementTelevision system detailsInterlaced videoProgressive scan
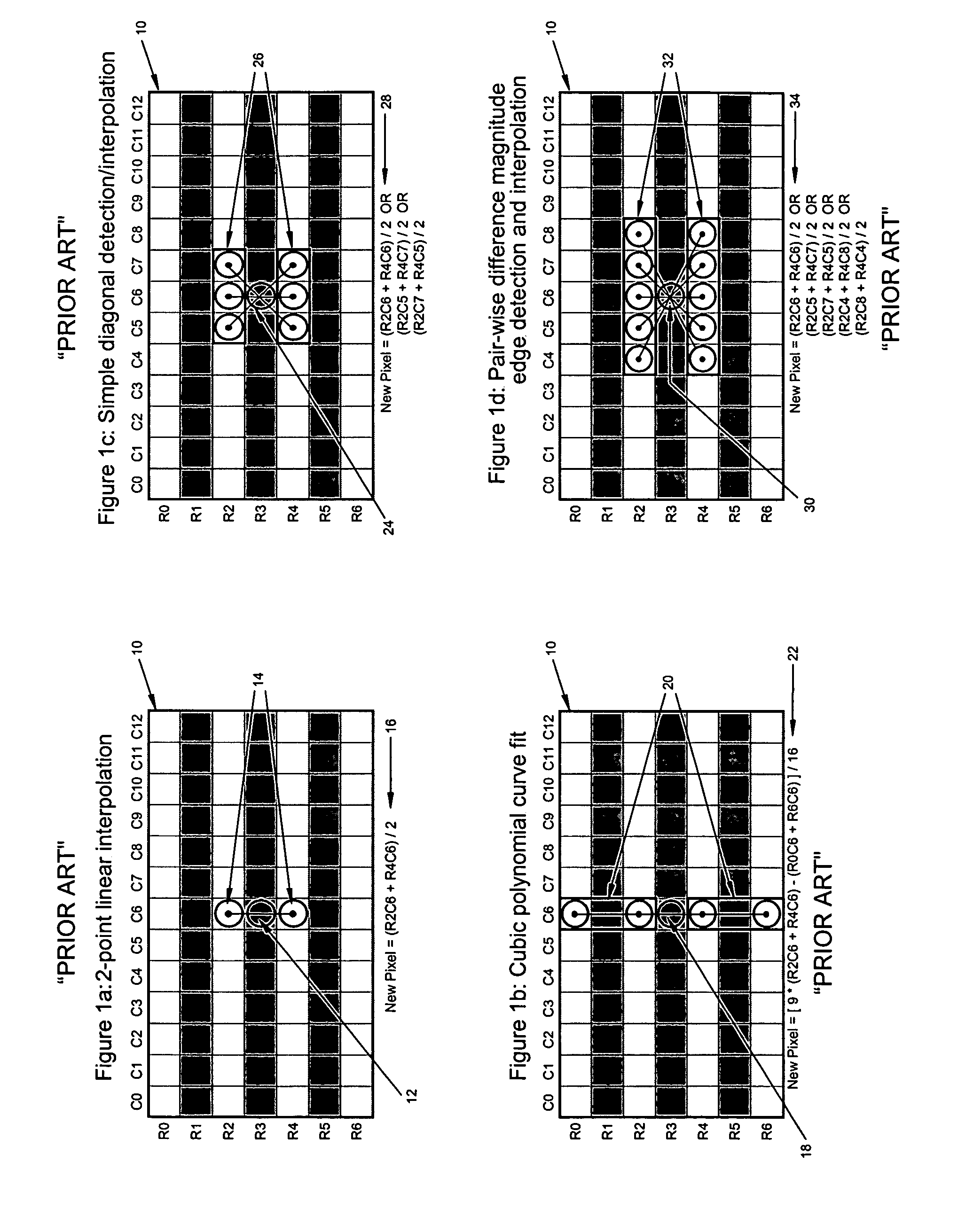
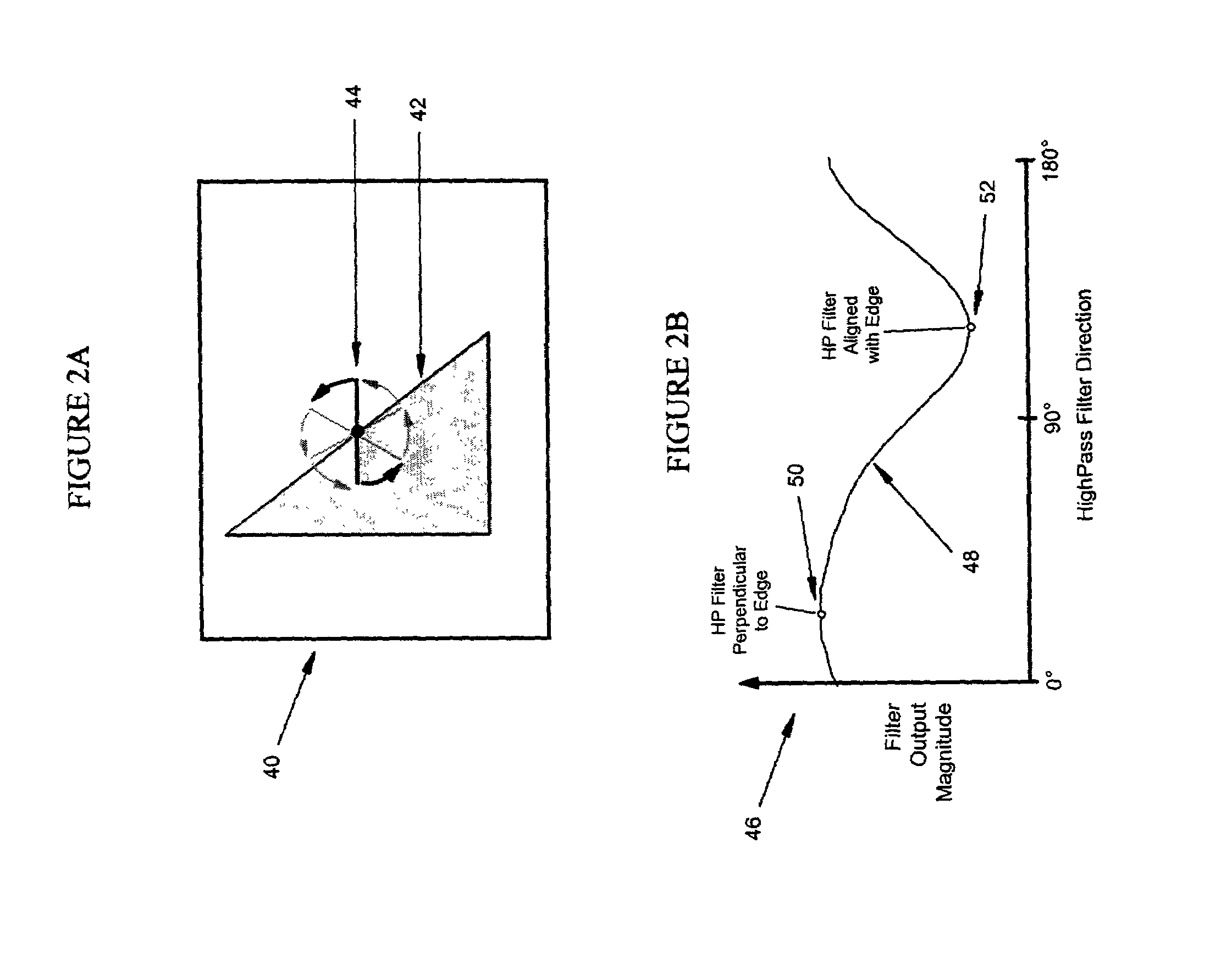
An interlaced to progressive scan video converter which identifies object edges and directions, and calculates new pixel values based on the edge information. Source image data from a single video field is analyzed to detect object edges and the orientation of those edges. A 2-dimensional array of image elements surrounding each pixel location in the field is high-pass filtered along a number of different rotational vectors, and a null or minimum in the set of filtered data indicates a candidate object edge as well as the direction of that edge. A 2-dimensional array of edge candidates surrounding each pixel location is characterized to invalidate false edges by determining the number of similar and dissimilar edge orientations in the array, and then disqualifying locations which have too many dissimilar or too few similar surrounding edge candidates. The surviving edge candidates are then passed through multiple low-pass and smoothing filters to remove edge detection irregularities and spurious detections, yielding a final edge detection value for each source image pixel location. For pixel locations with a valid edge detection, new pixel data for the progressive output image is calculated by interpolating from source image pixels which are located along the detected edge orientation.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Device and method for decoding HDTV video
InactiveUS6104753AImprove picture qualityQuality improvementPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesProgressive scanComputer graphics (images)
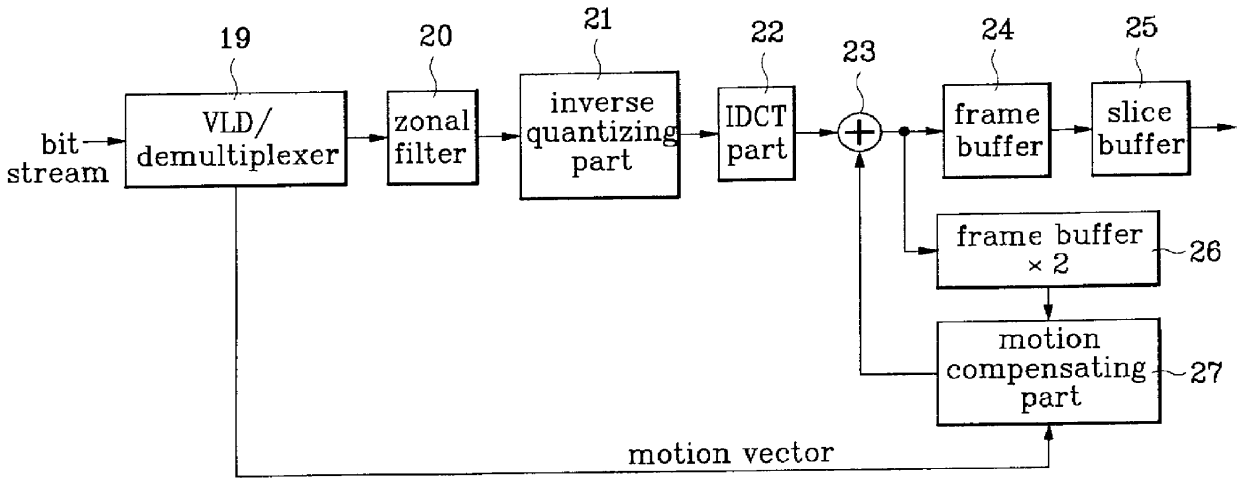
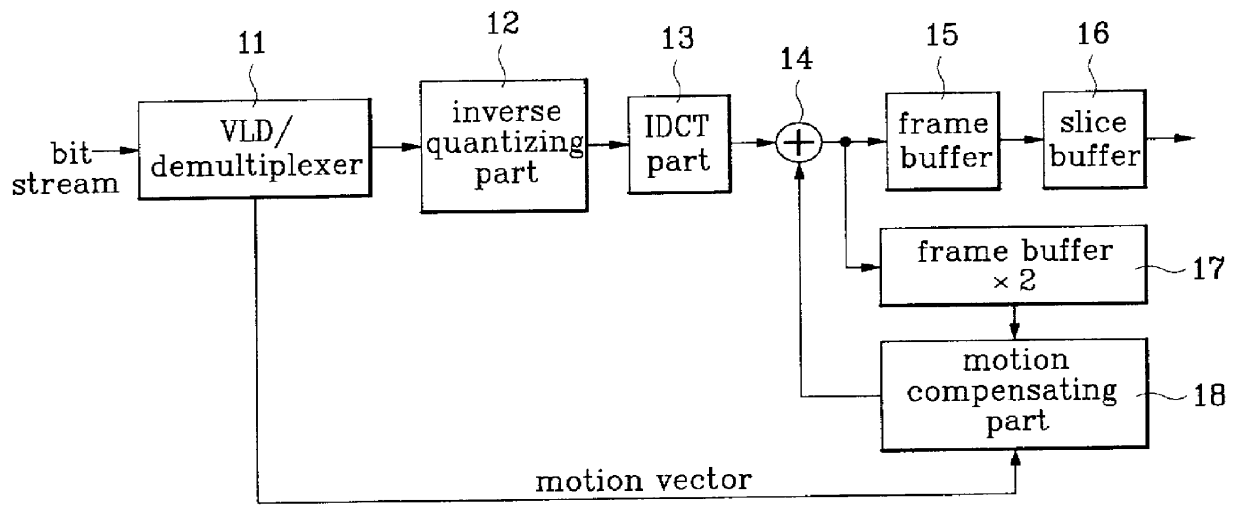
HDTV video decoder circuit is disclosed, which has an +E,fra 1 / 4+EE size frame memory for a progressive scanned or interlace scanned video and yet can conduct IDCT and motion compensation to fit to the reduced frame memory size, which, in comparison to a conventional MPEG-2 video decoder which uses a 4x4 IDCT that requires +E,fra 1 / 4+EE frame memory in encoding an interlace scanned image into frame picture only to lose field information of the image resulting in a significant damage to the picture quality, facilitates to maintain the field information as it was resulting in an improvement in the picture quality.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
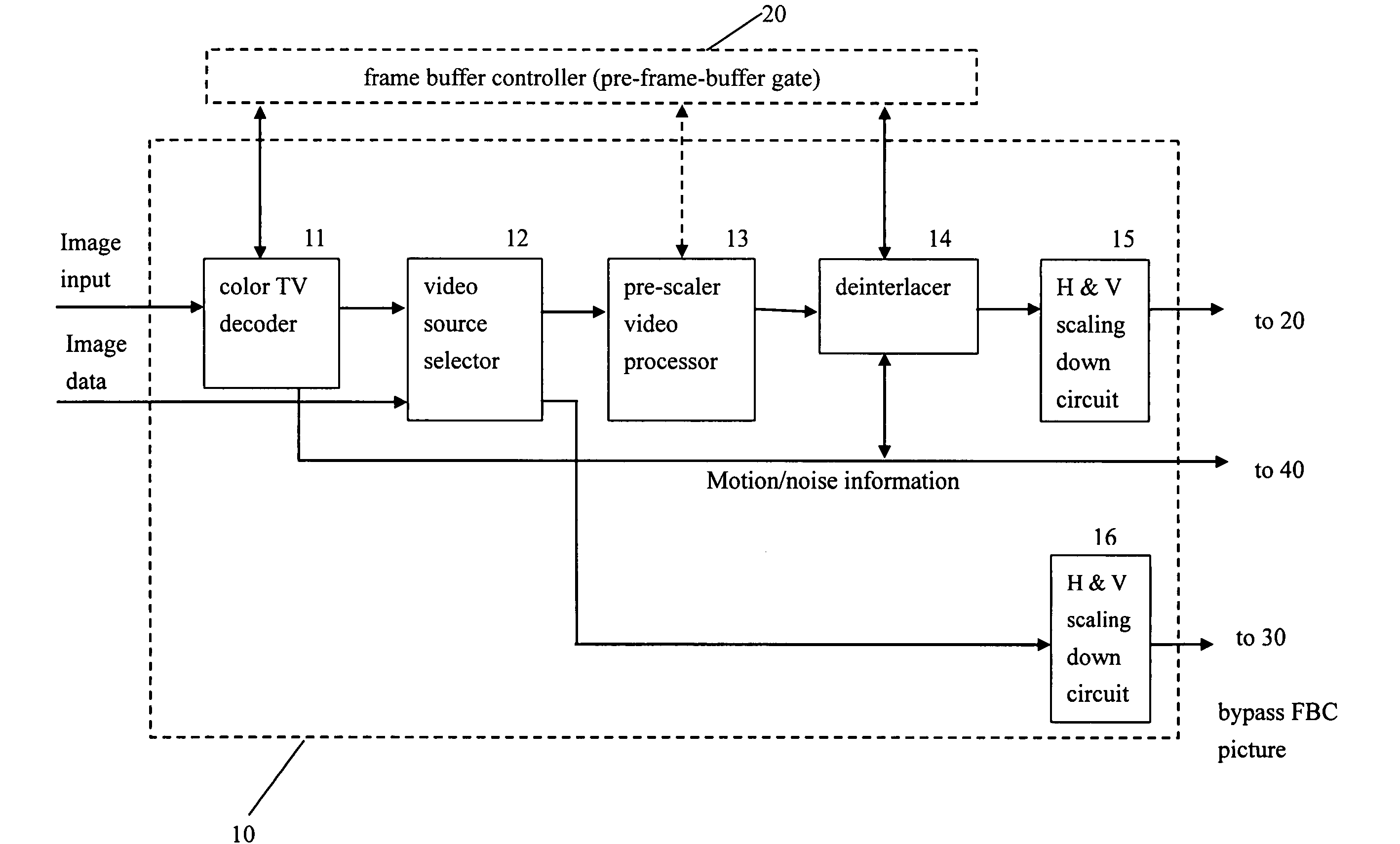
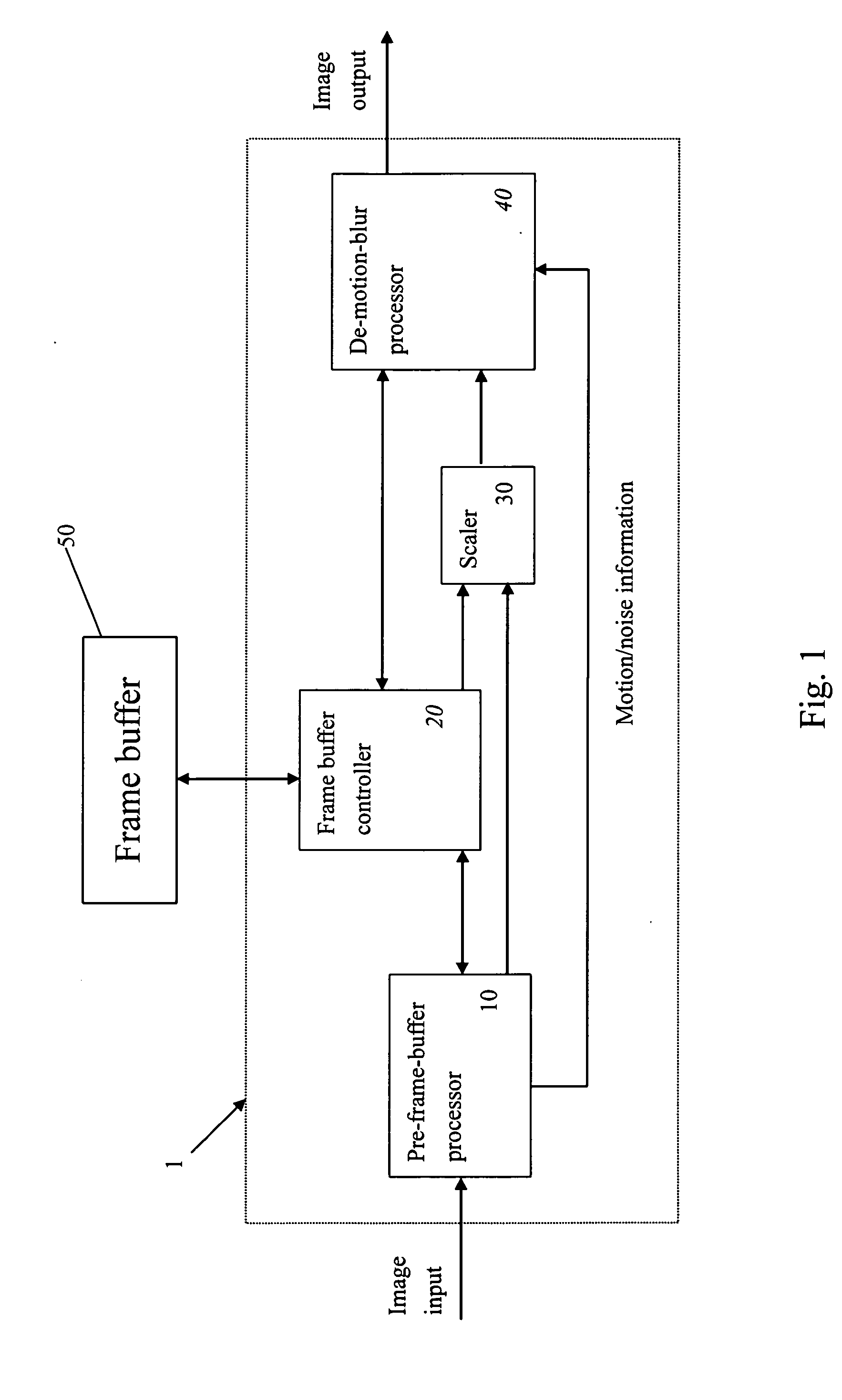
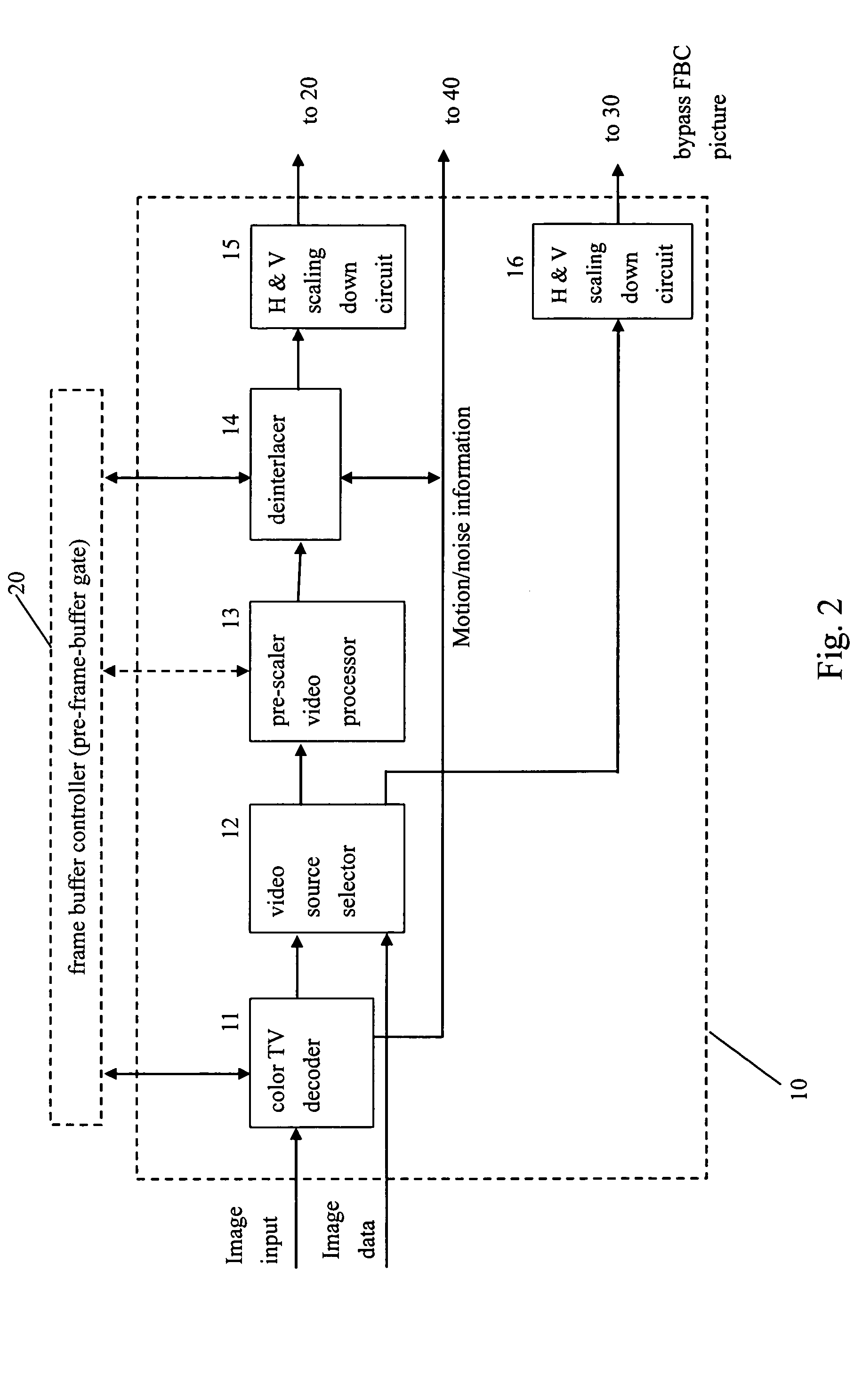
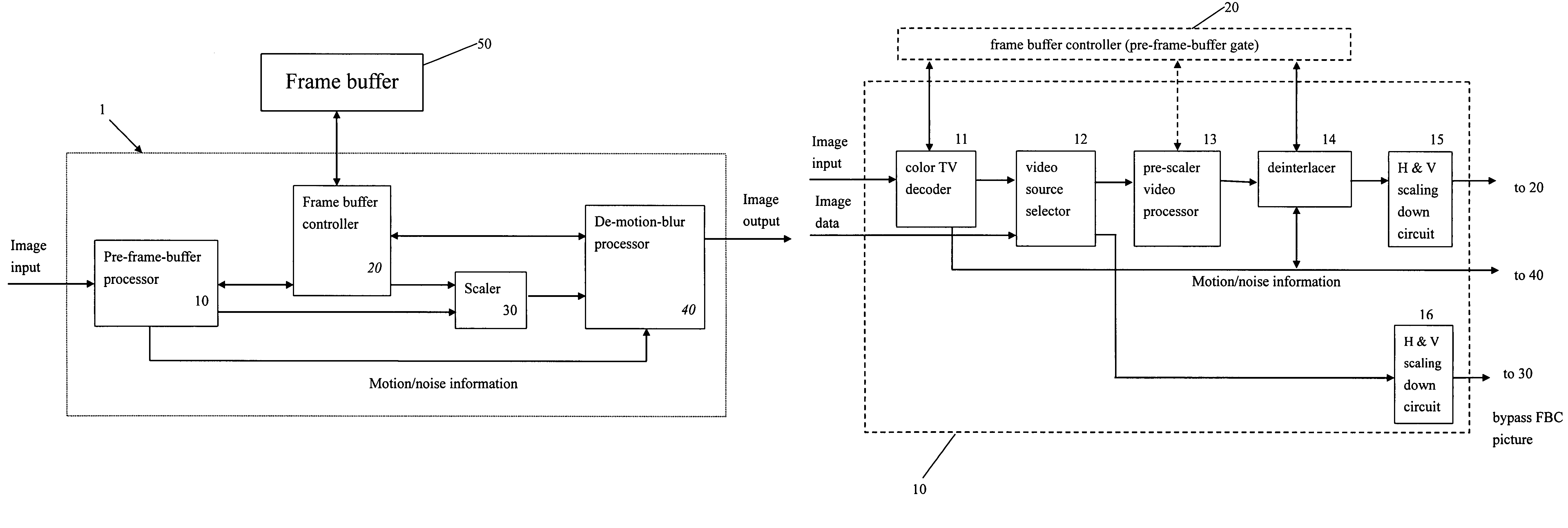
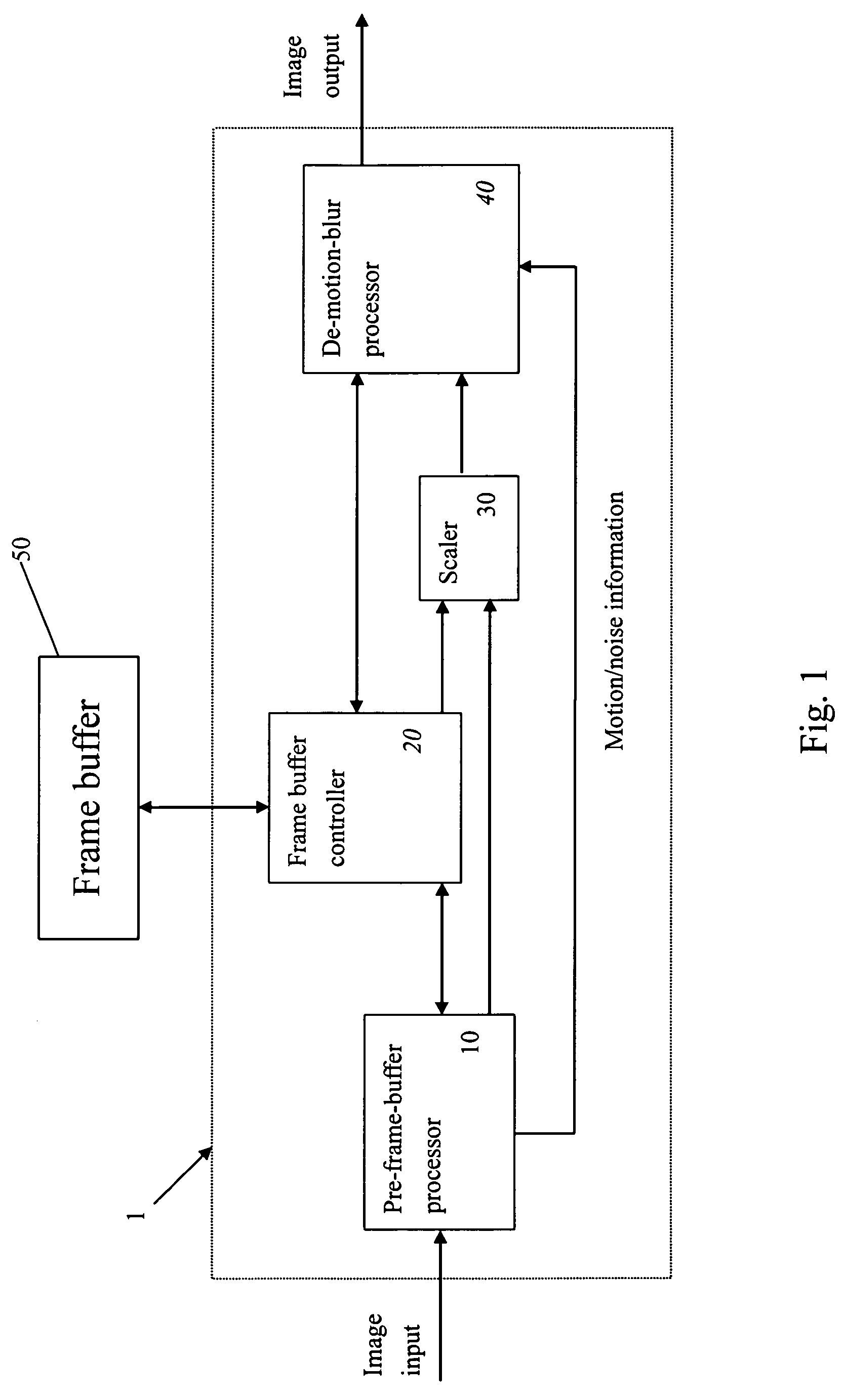
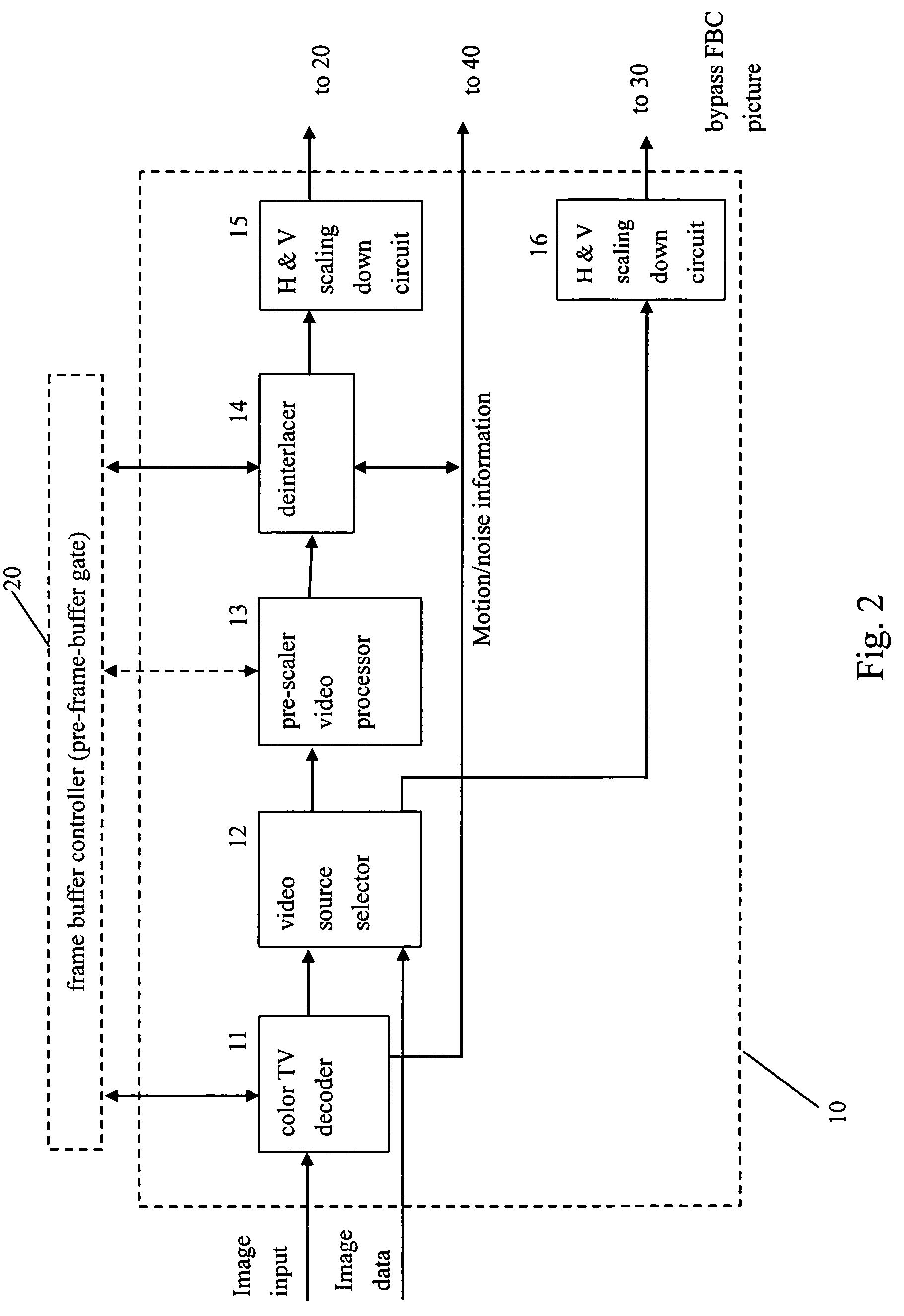
Video system with de-motion-blur processing
ActiveUS20050162566A1Short response timeQuality improvementImage enhancementTelevision system detailsProgressive scanImage resolution
A video system that performs TV signal decoding, deinterlacing, and de-motion-blurring for progressive scan flat panel display is introduced. The system embeds a frame buffer and a scaler for conducting format and resolution conversions for display panels of different sizes. The output of the scaler is sent to a de-motion-blur processor for reducing the blurriness due to the motion of image objects and the slow response time of flat panel display devices. The de-motion-blur processor gets the motion and noise indication signal from scaler or the pre-frame-buffer video processor. Based on the motion and noise information and the information of temporal difference, the de-motion-blur processor performs over driving for the display panel interface and improves the rising and falling response time of the flat panel display. The decoding, deinterlacing, and de-motion-blur processing share the same frame buffer controller so the entire system can be optimized in cost and performance.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
System for digitally capturing and recording panoramic movies
InactiveUS20020046218A1Flexible and convenient controlEffective apertureTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingCamera lensData compression
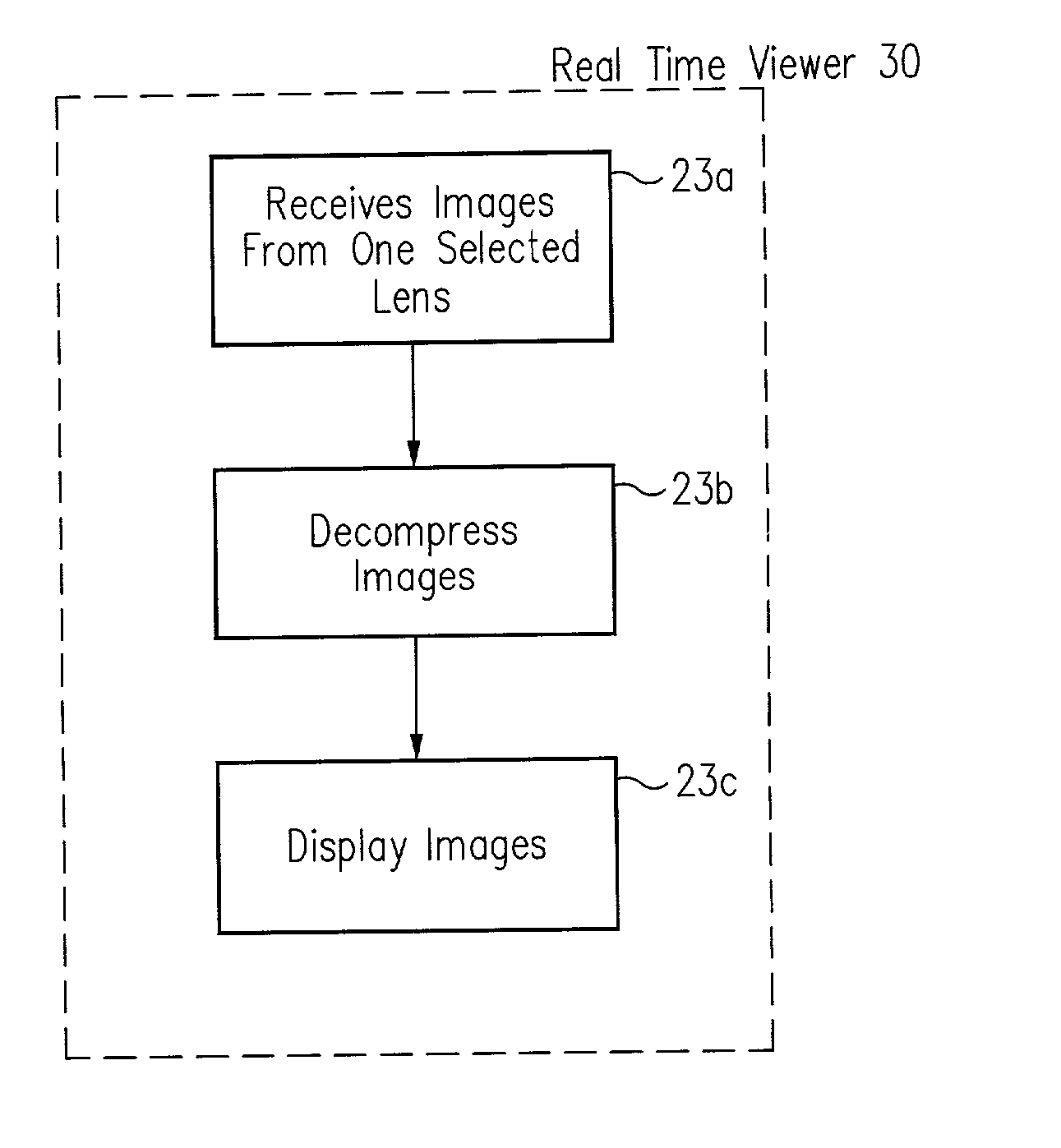
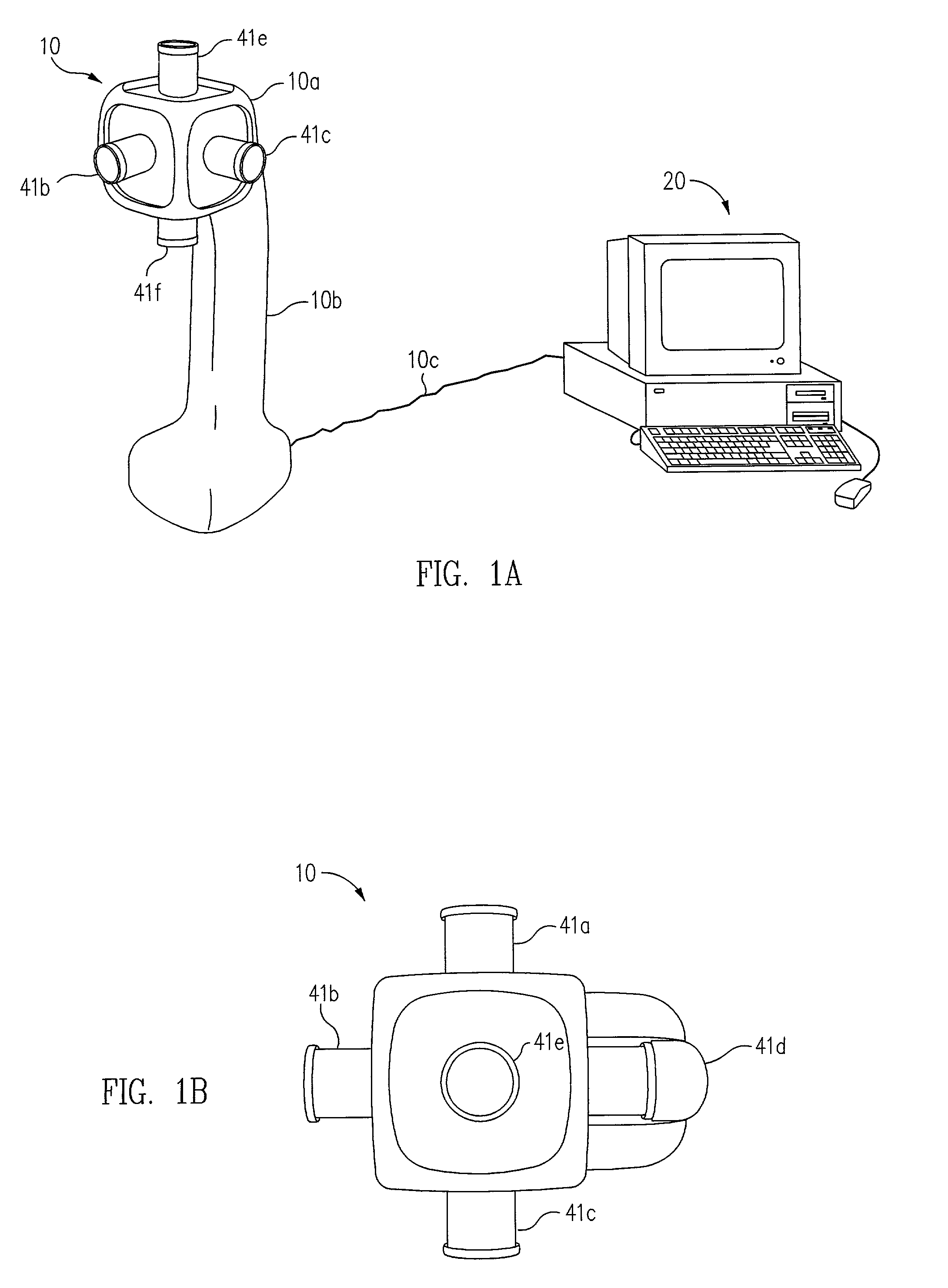
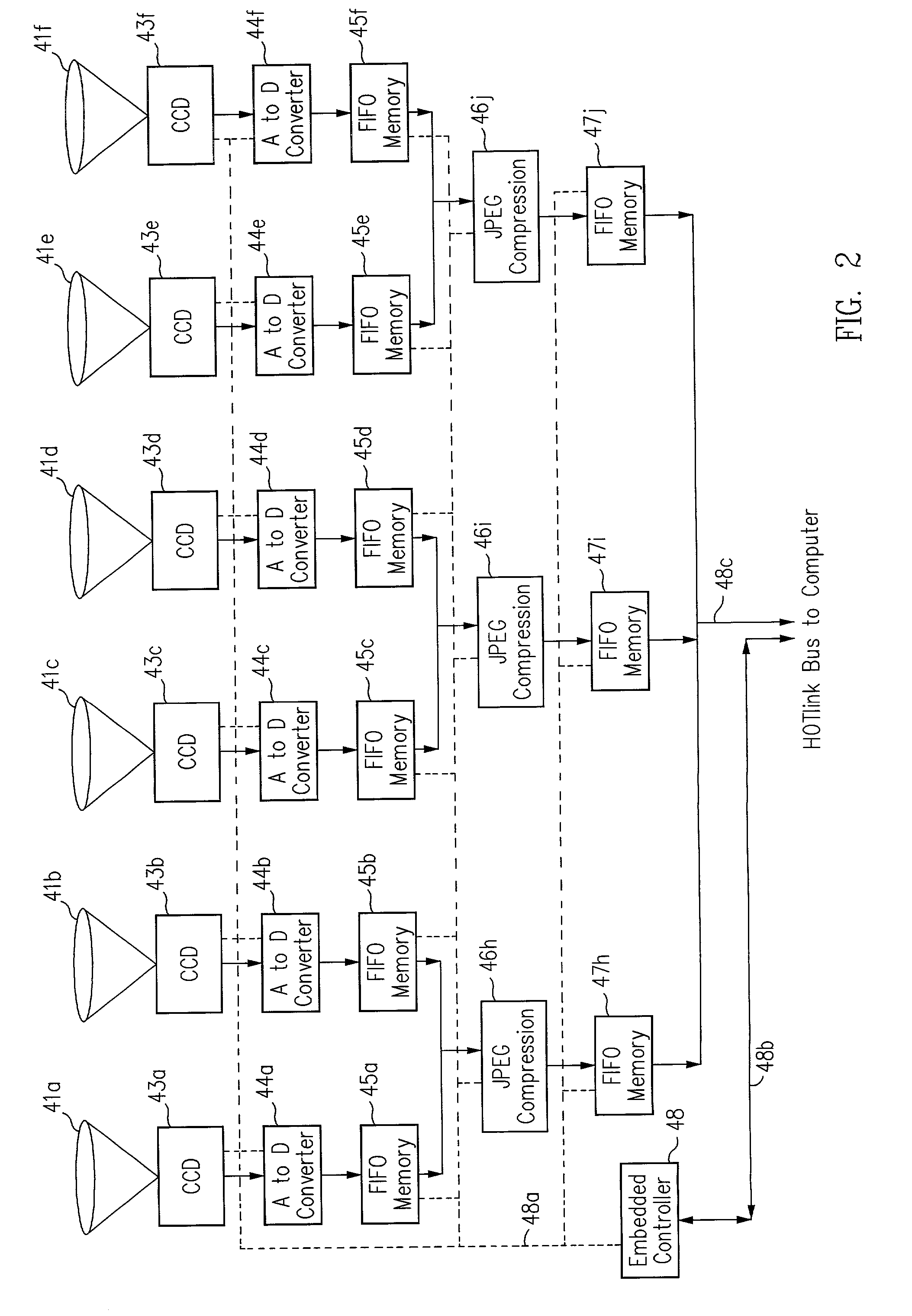
The present invention provides a very flexible, digital system for capturing and storing panoramic images using progressive scan (that is, non interlaced) technology. The system includes a digital image input device and an associated control computer. Since the image capture device is digital it can be easily and flexibly controlled by software in the control computer. The image input device has six lenses positioned on the six faces of a cube. While the image input system can have other lens configurations, the use of six lenses in a cubic configuration is optimal for a system that is used to capture a spherical panorama. The six lenses simultaneously focuses different images on six CCDs (Charge Coupled Devices). The image input device also includes an embedded controller, and data compression circuitry. The embedded controller controls the exposure time of the CCDs (i.e. the effective aperture and effective shutter speed) and reads image data from the CCDs. The image data read from the CCDs is compressed, multiplexed, and sent to the control computer. The control computer stores the images in frames, each of which have one image from each of the six lenses. Each frame includes six images that were simultaneously recorded and any associated information, such as audio tracks, textual information, or environmental information such as GPS (Global Position System) data or artificial horizon data. The control computer includes a user interface which allows a user to specify control information such as frame rate, compression ratio, gain, etc. The control computer sends control information to the embedded controller which in turn controls the CCDs and the compression circuitry. The images can be sent from the control computer to a real time viewer so that a user can determine if the correct images are being captured. The images stored at the control computer are later seamed into panoramas and made into panoramic movies.
Owner:GILBERT SCOTT +3
Remote control of image sensing apparatus
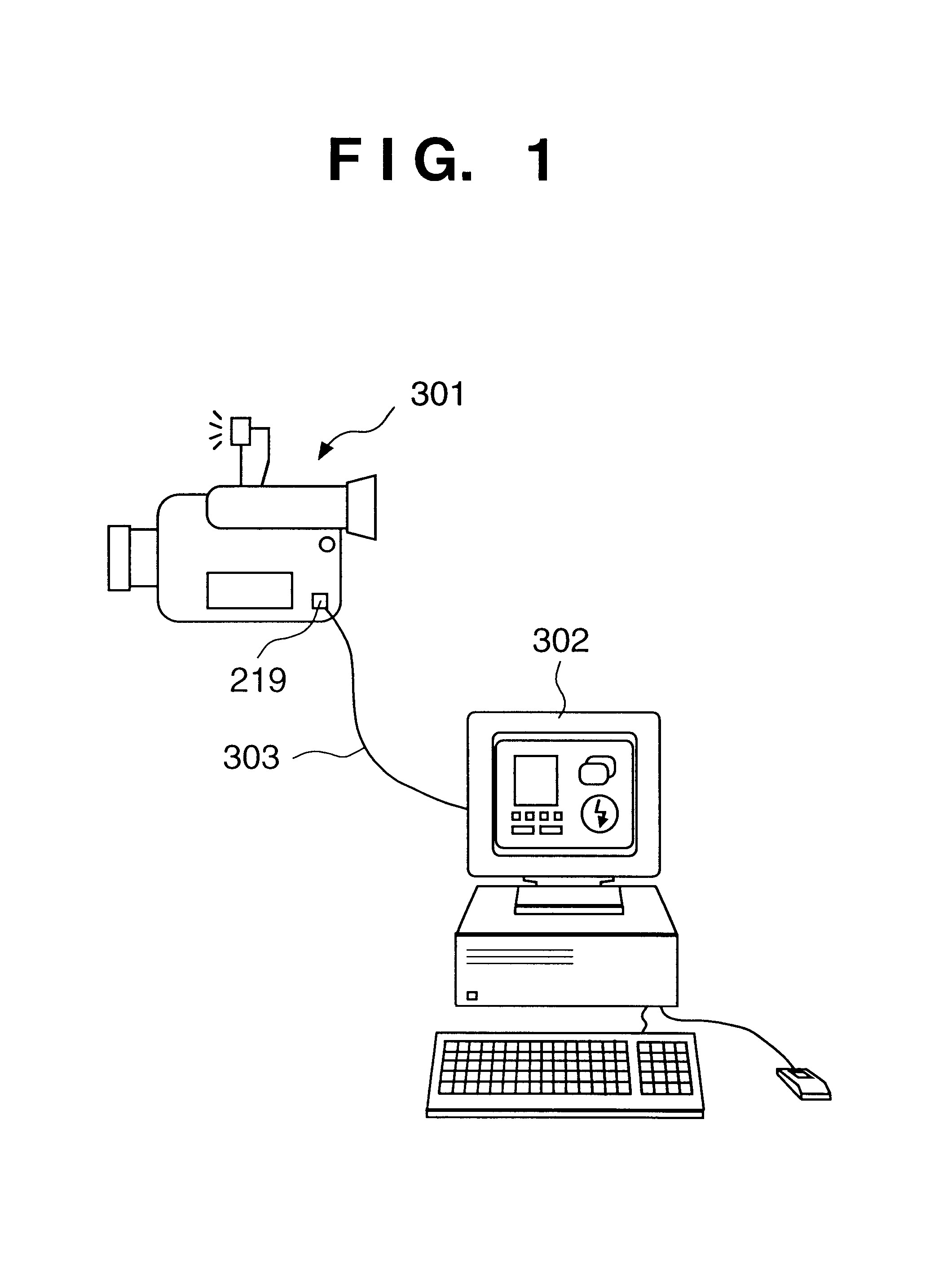
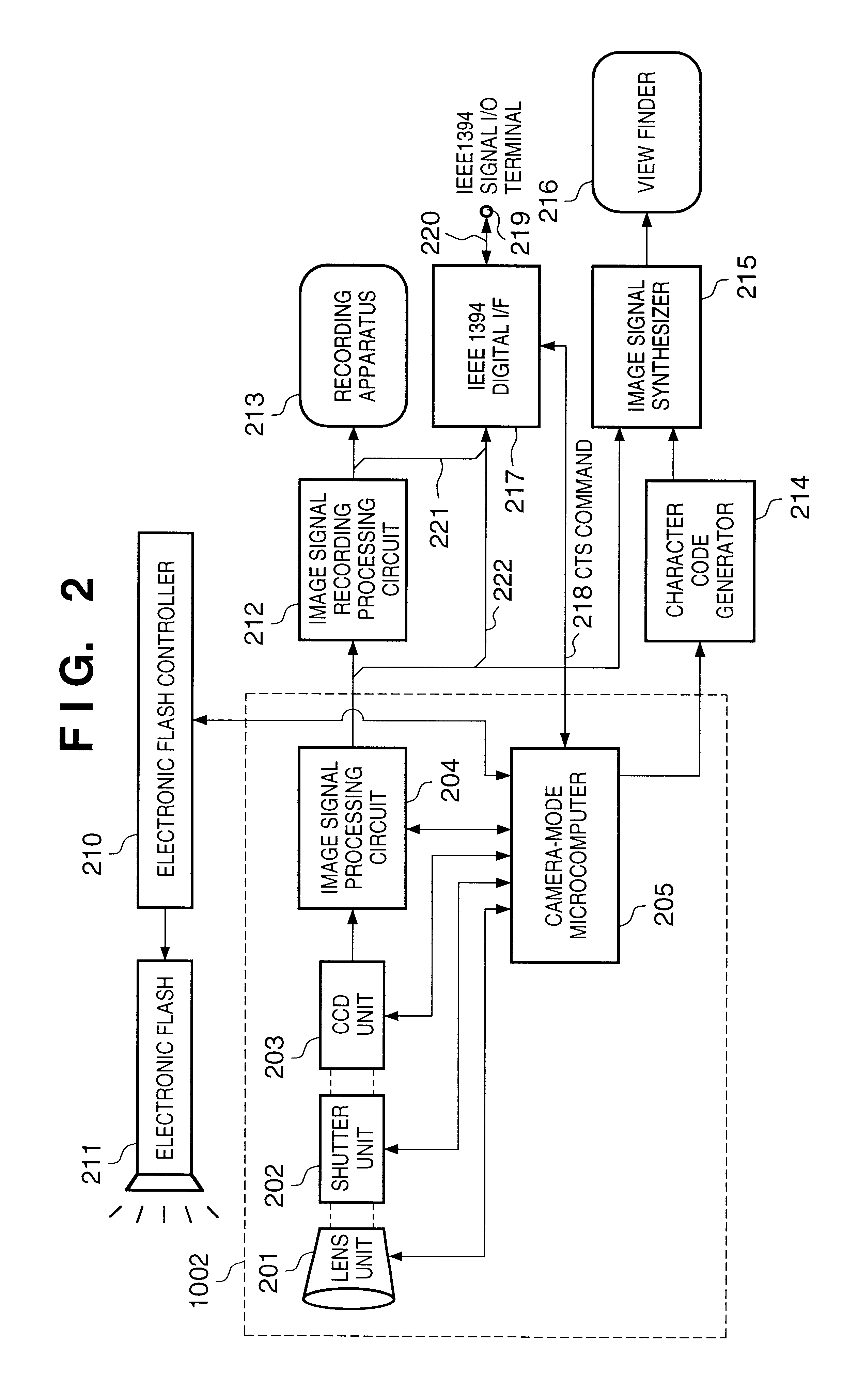
InactiveUS6850282B1Good effectConfirm amount of movementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsProgressive scanRemote control
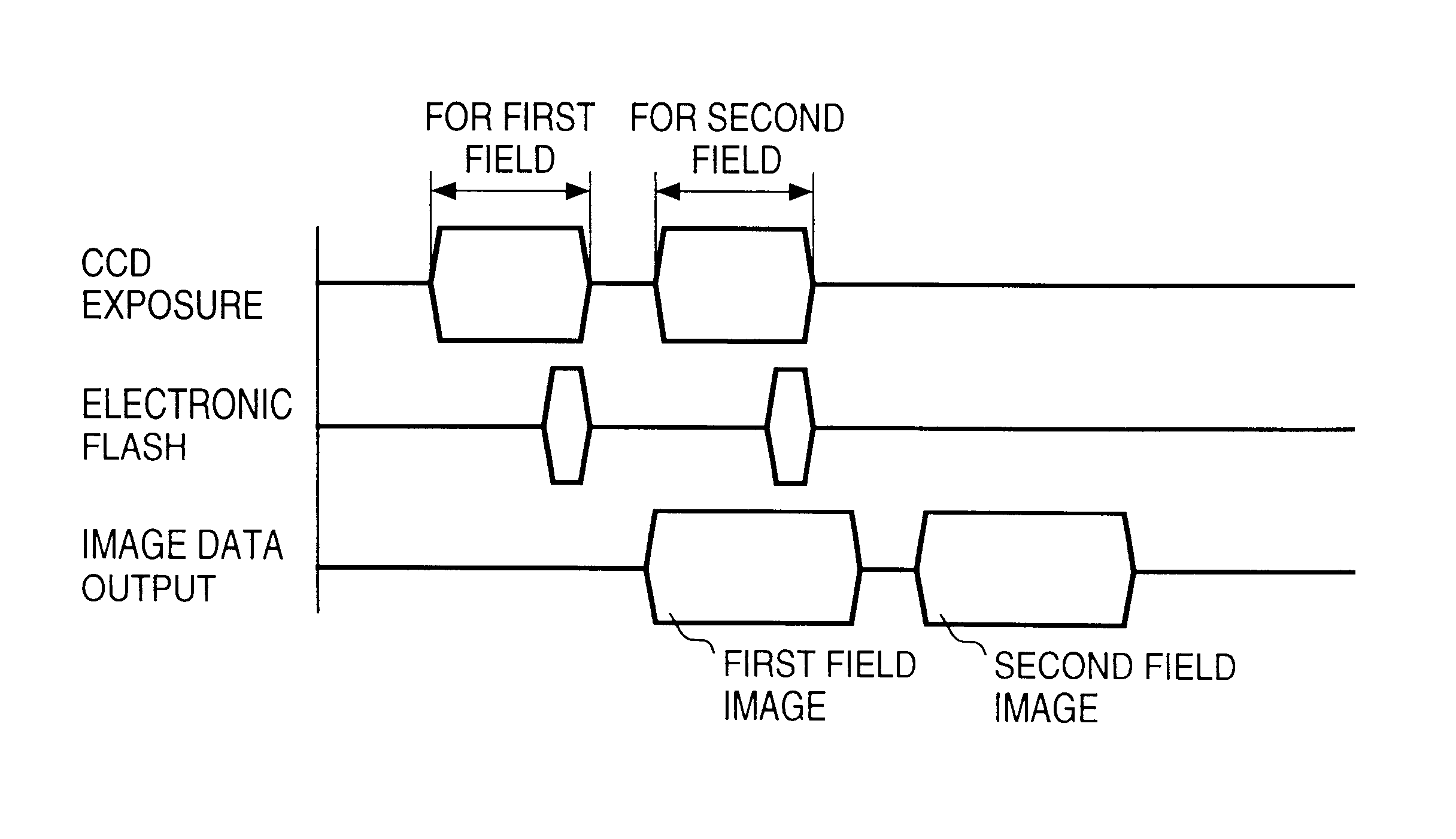
In a method having an image sensor capable of selectively sensing an image in progressive scanning method and in interlace scanning method, when performing an image sensing operation using an electronic flash, if the image sensing operation is performed in the progressive scanning method, the electronic flash is controlled to flash once for each frame, and if the image sensing operation is performed in the interlace scanning method, the electronic flash is controlled to flash twice for each frame, once for each field.
Owner:CANON KK
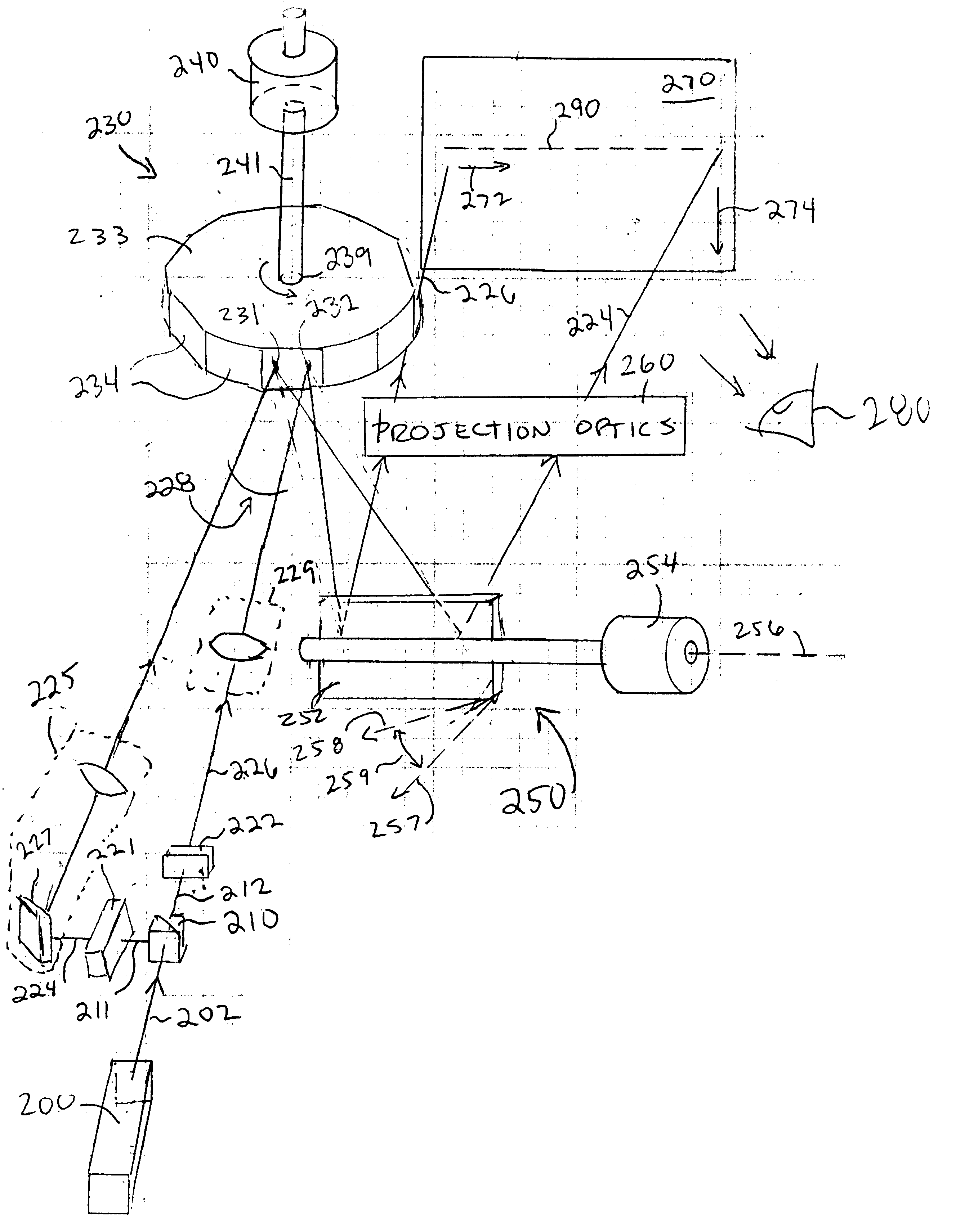
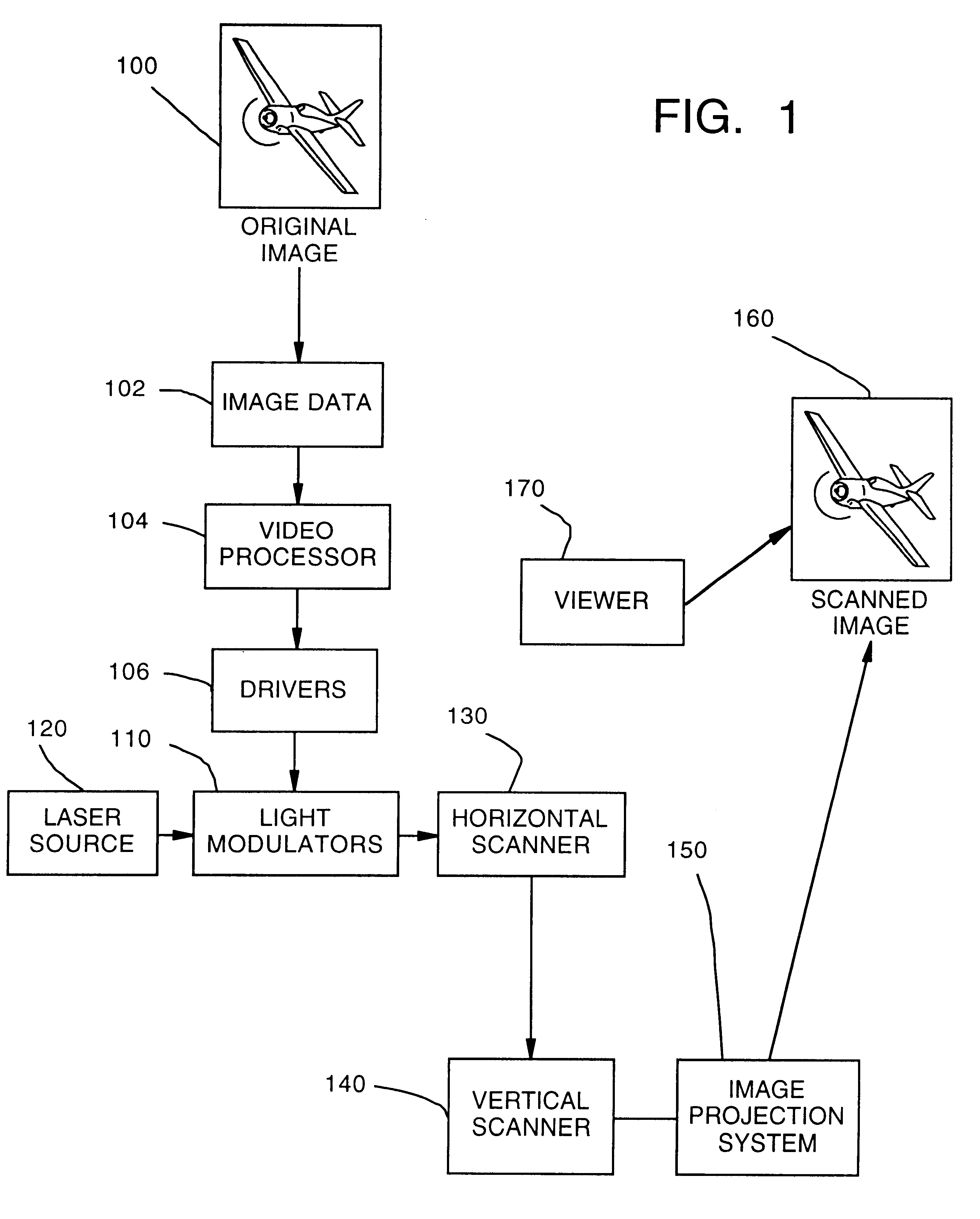
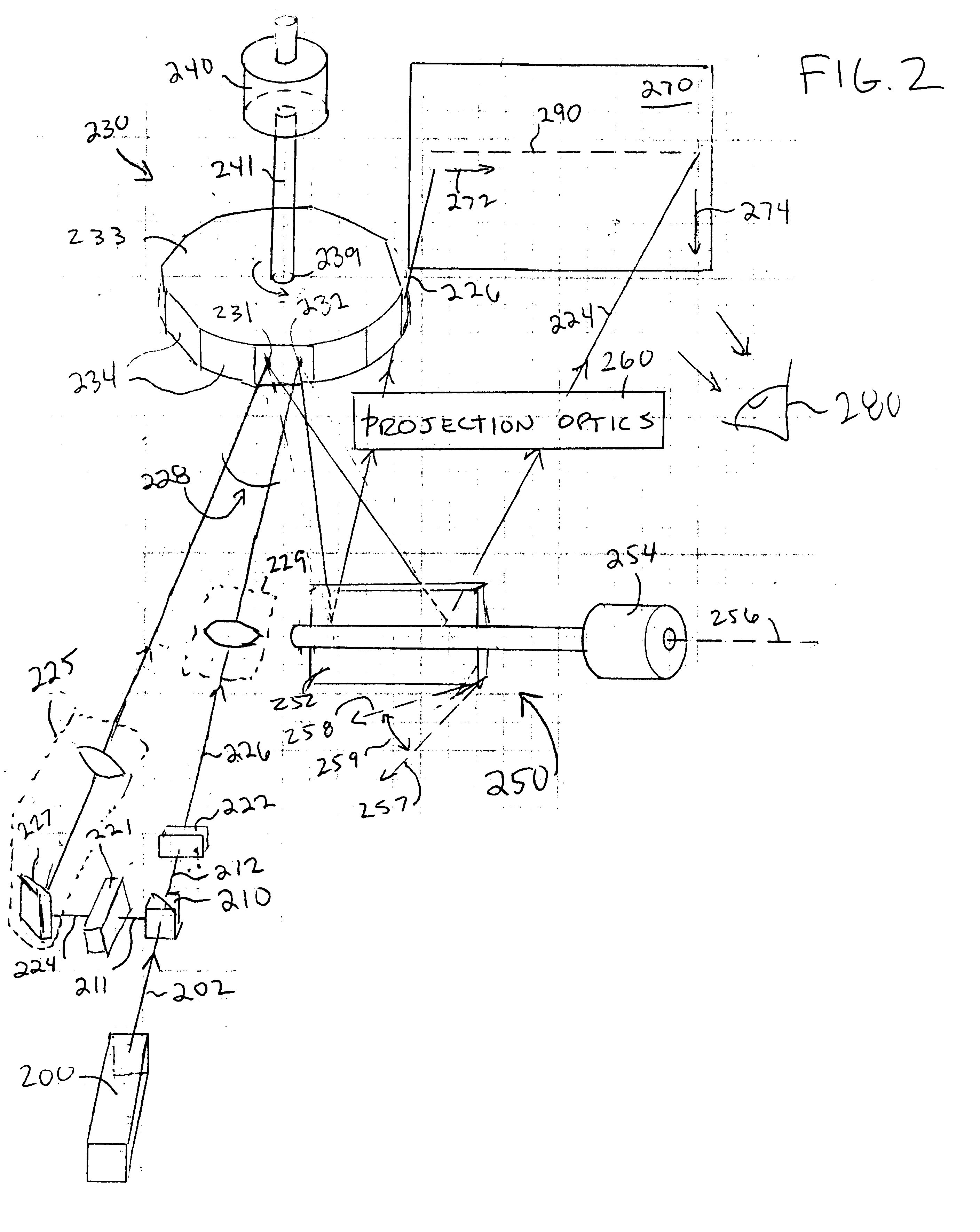
Laser imaging system with progressive multi-beam scan architecture
InactiveUS6351324B1Big cost advantageImprove system efficiencyPicture reproducers using projection devicesPicture signal generatorsColor imageBeam scanning
A progressive scan architecture for displaying a two-dimensional image by alternately scanning two or more laser beams, one after the other with a time delay between adjacent beams. The beams are arranged to become incident upon a polygon scanner in a row with an approximately uniform spatial separation and an approximately equal angle between adjacent beams. The polygon scanner scans horizontally and a galvanometer-driven mirror scans vertically. Adjacent lines are progressively scanned in sequence from top to bottom, which advantageously reduces or eliminates psycho-visual effects and is tolerant of non-linearities in the vertical scanner, allowing use of a low-cost galvo mirror. Typically, the beams in the row are arranged in pairs, and only one beam from each pair will be scanning at any one time. Embodiments are described in which the duty cycle is slightly less than 50% and the laser illumination is switched between two interleaved beam scans thereby allowing a single modulator to be used for both beams which provides significant cost advantages and improves system efficiency. For full-color images, each of the beams described can incorporate separate red, green and blue (RGB) components which are individually modulated by separate red, green, and blue modulators. The system can be scaled up with one or more additional pairs of beams to improve resolution and / or increase pixel count without requiring a high-speed polygon scanner or a highly-linear galvo scanner. Furthermore, the height of each facet in the polygon mirror need be only one beam diameter and its length need only be two beam diameters, which allows the system to approach the minimum pixel size attainable, which is useful to provide high efficiency and high brightness in the image.
Owner:PHOTERA TECH
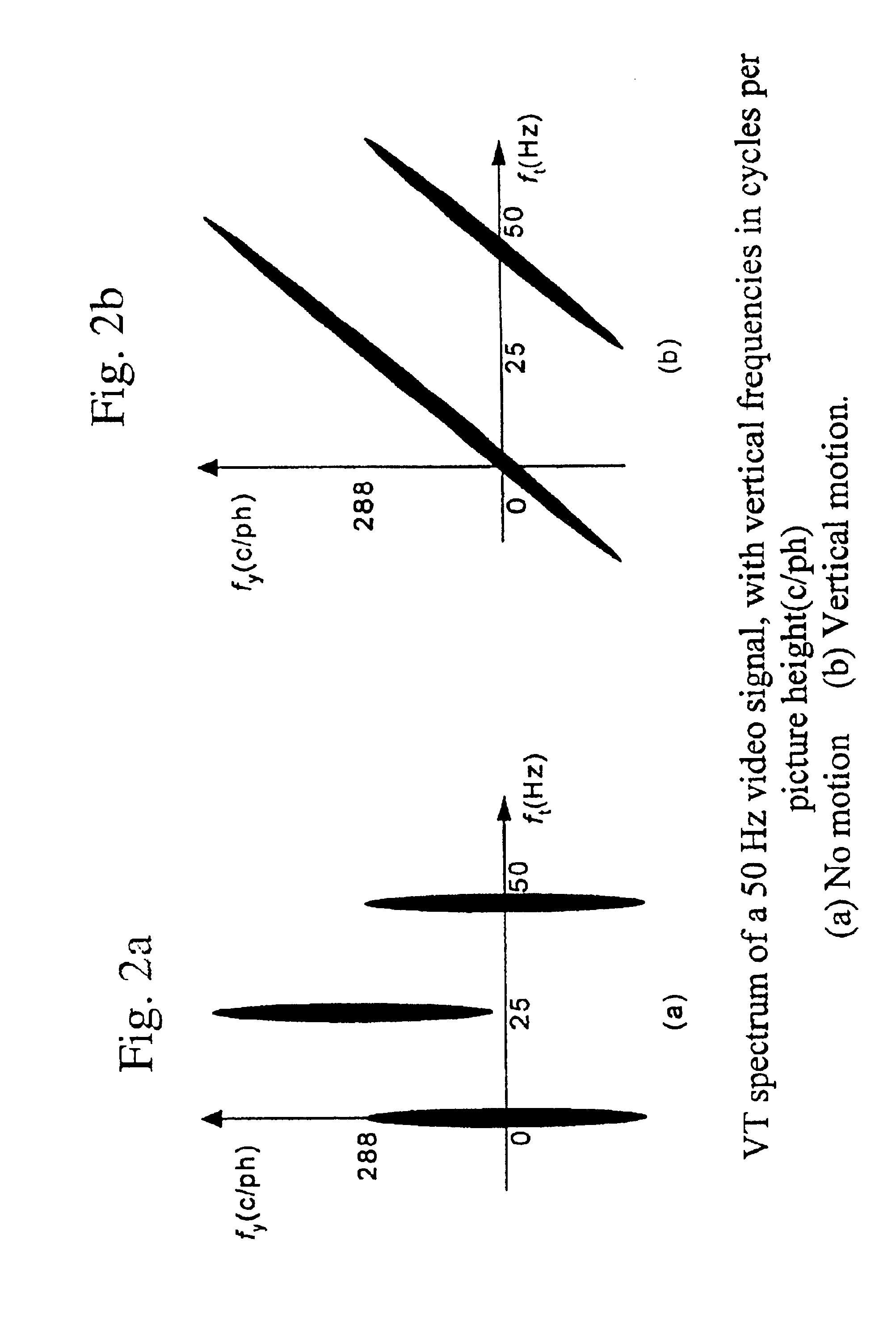
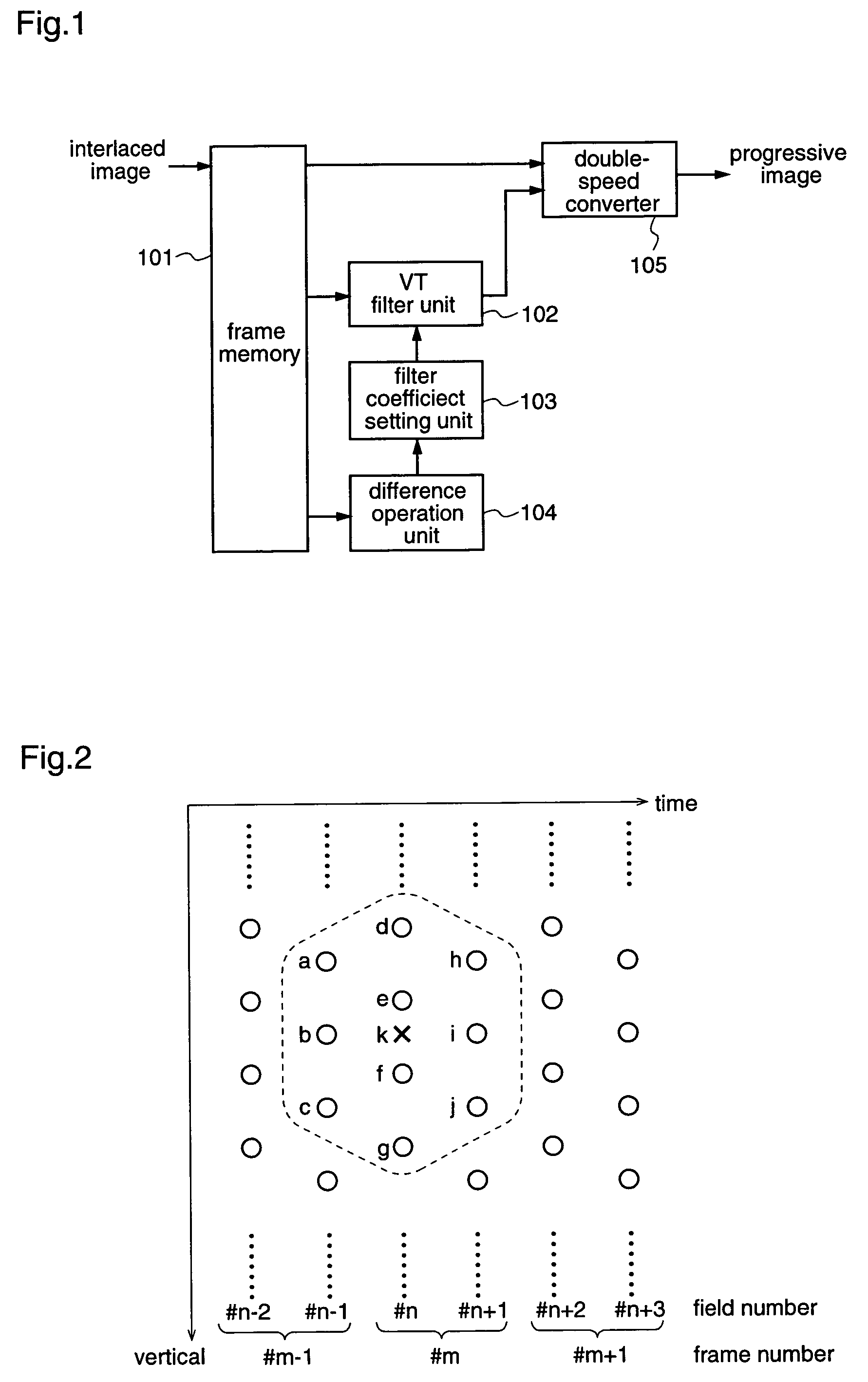
Method and apparatus for deinterlacing
InactiveUS7116372B2Improve accuracyReduce gainTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesProgressive scanInterlaced video
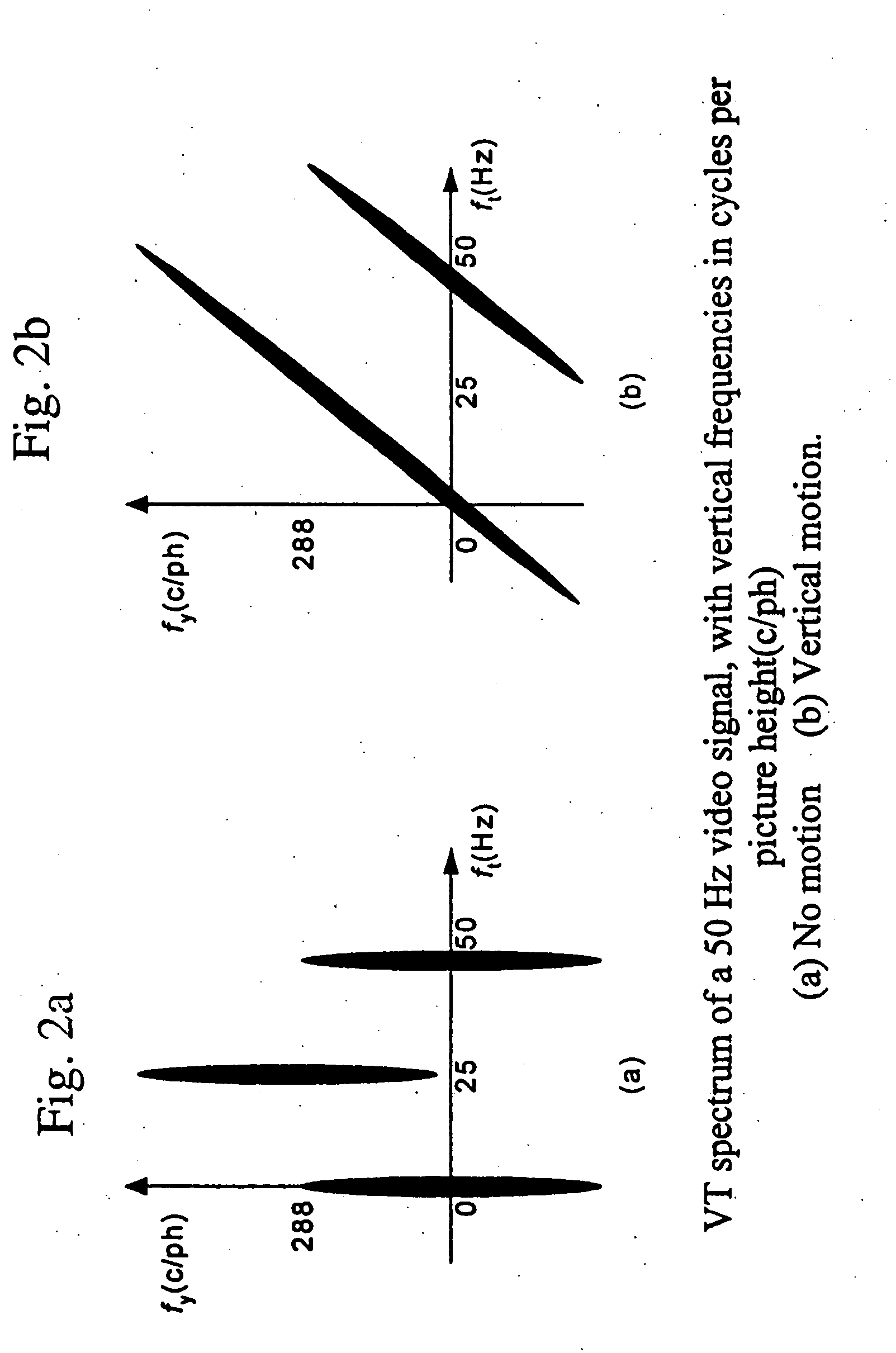
An apparatus and method for improving the VT filter performance for moving pictures by deinterlacing. A VT filter unit receives data of a deinterlacing target field (field #n) and data of forward and backward fields of the target field (fields #n−1 and #n+1). A difference operation unit receives data of two frames including the field #n, and calculates the sum of the absolute values of differences between these frames. A filter coefficient setting unit decides a filter coefficient based on the sum of the absolute values of the differences. The VT filter unit subjects the inputted pixels to the filtering by using the filter coefficient to generate an interpolation pixel, and outputs the generated interpolation pixel. A double-speed converter composes the interlaced image and the interpolation pixel to convert the frame rate to be doubled, and outputs the converted image as a progressive image.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
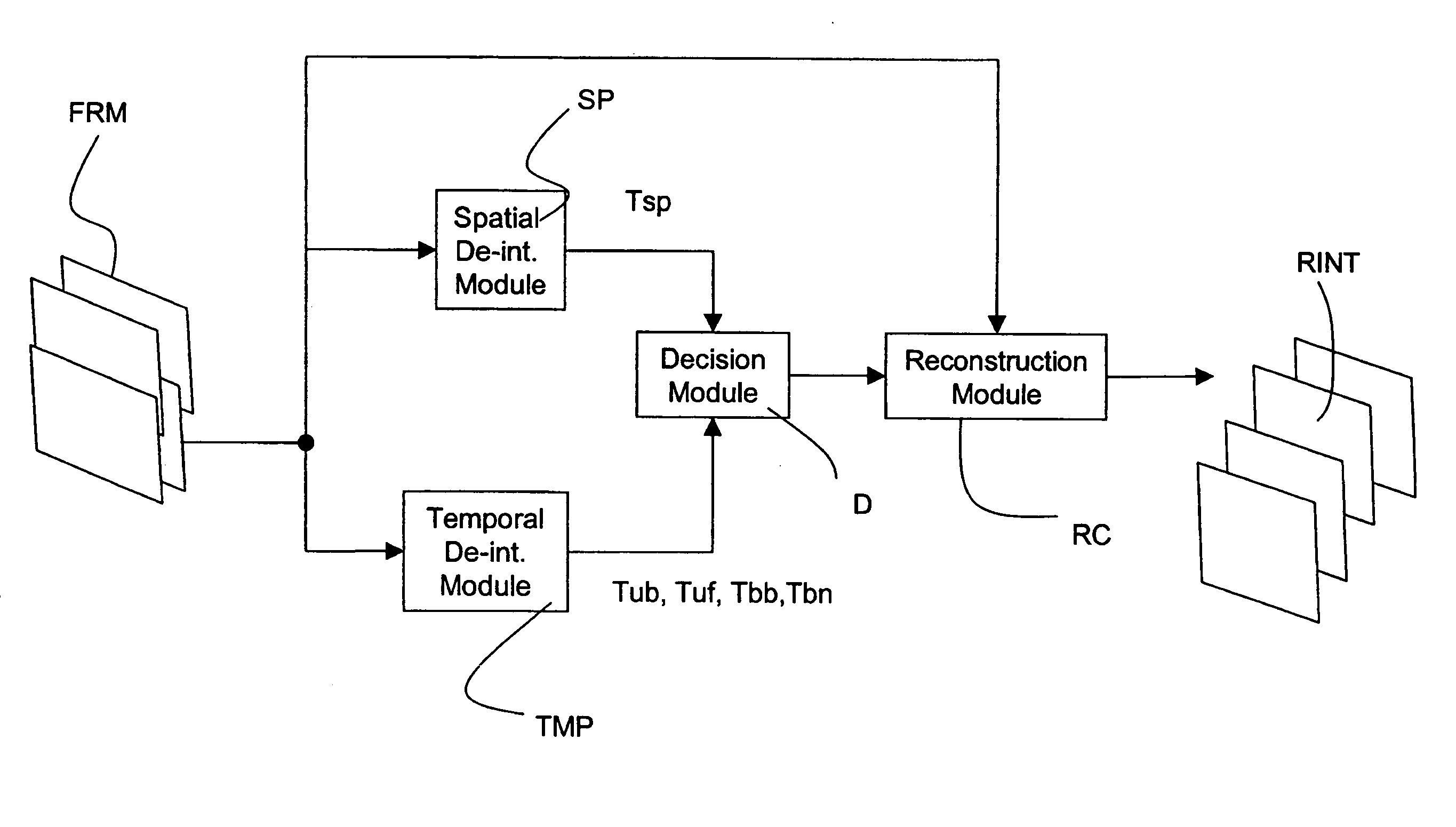
Method and system for de-interlacing digital images, and computer program product therefor
InactiveUS20050179814A1Easy to operateGood Performance GuaranteedTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesProgressive scanDigital image
A spatial-type de-interlacing process to be applied to a digital image for obtaining a spatial reconstruction. Furthermore, to the digital image there are also applied one or more temporal-type motion compensation de-interlacing processes for obtaining one or more temporal reconstructions, and the spatial reconstruction and the one or more temporal reconstructions are sent to a decision module. The decision module applies a cost function to the spatial reconstruction and the temporal reconstructions and chooses from among the spatial reconstruction and the temporal reconstructions the one that minimizes the cost function. Preferential application is to display systems, in particular displays of a cathode-ray type, liquid-crystal type, and plasma type which use a mechanism of progressive scan.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
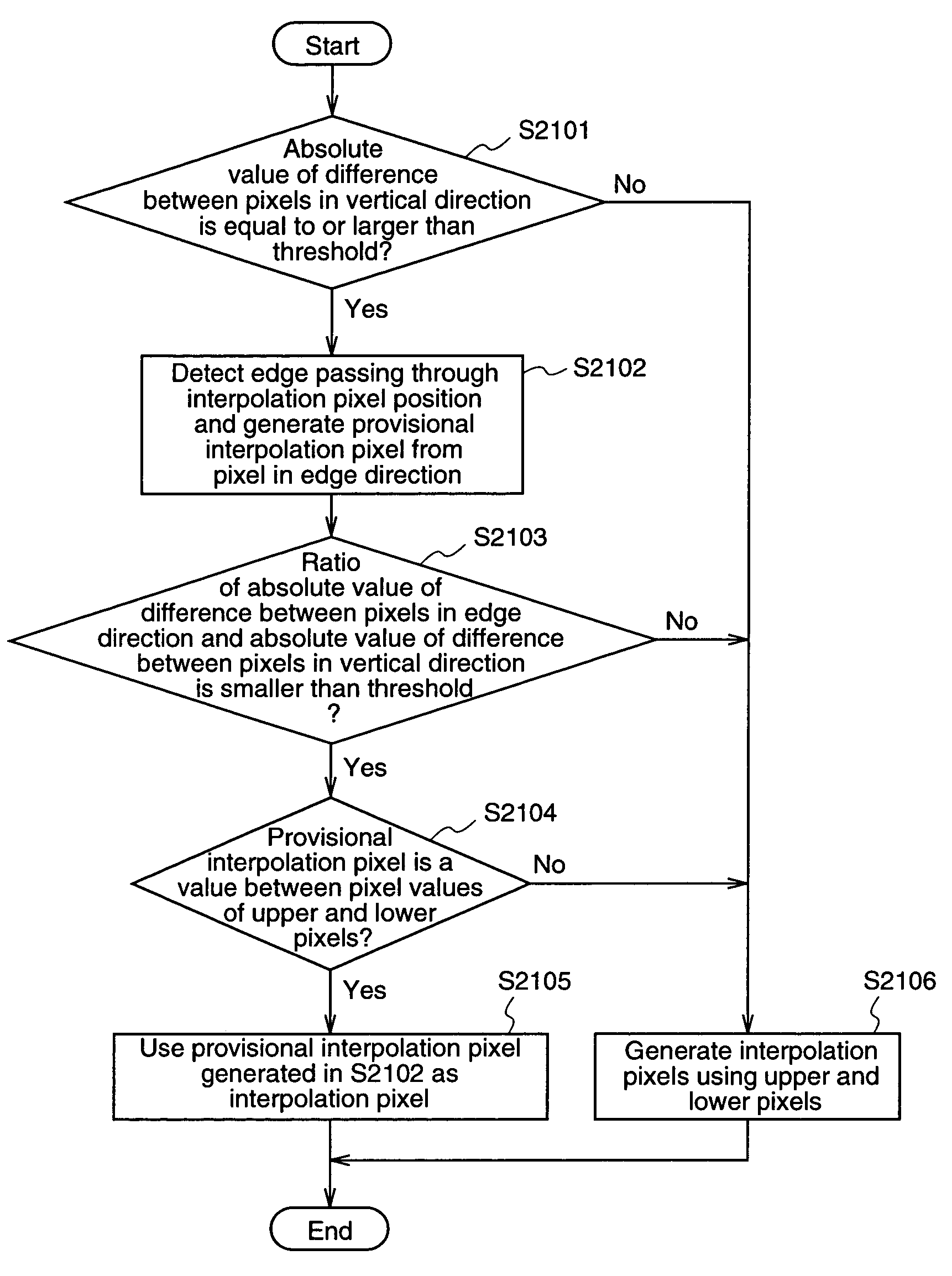
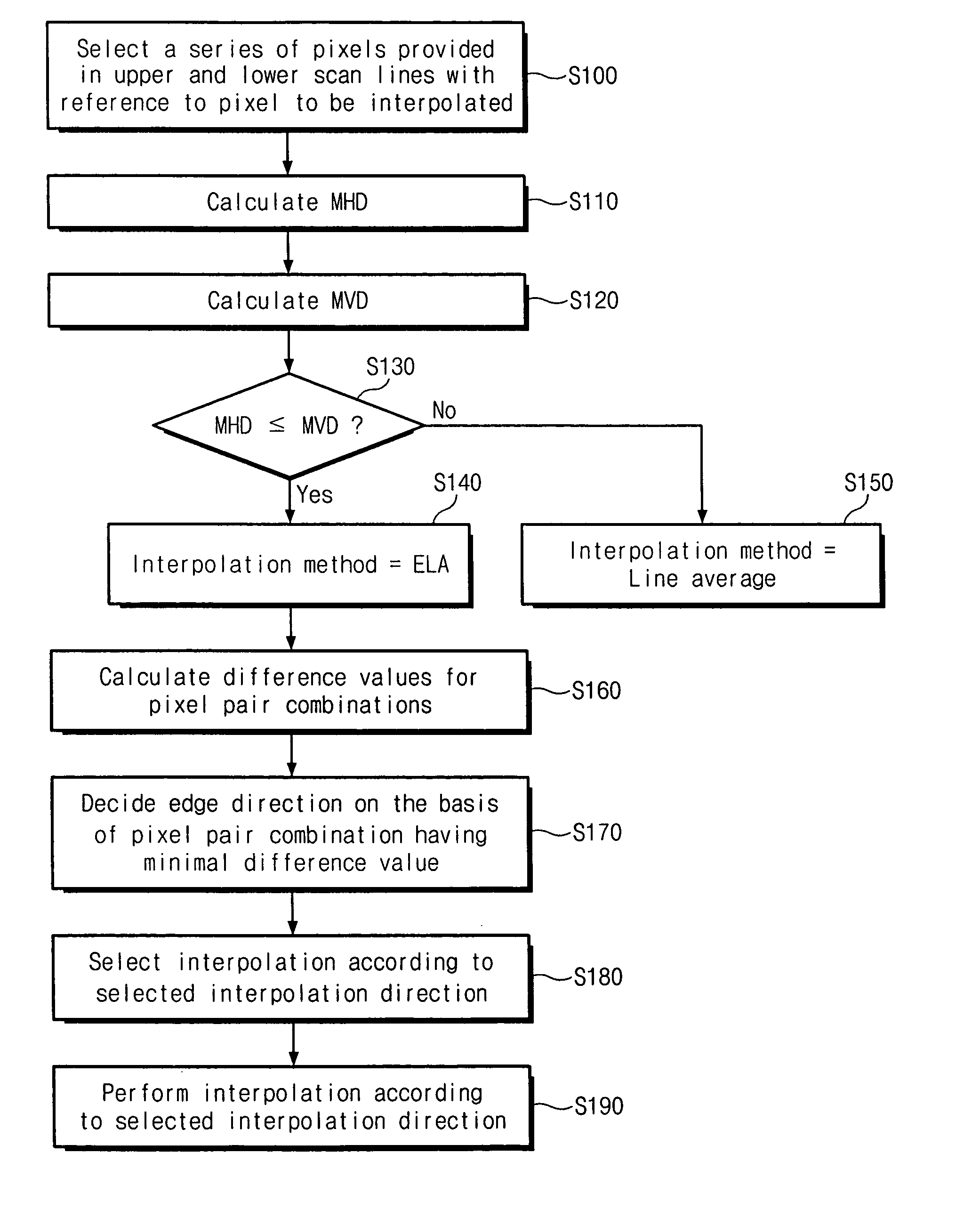
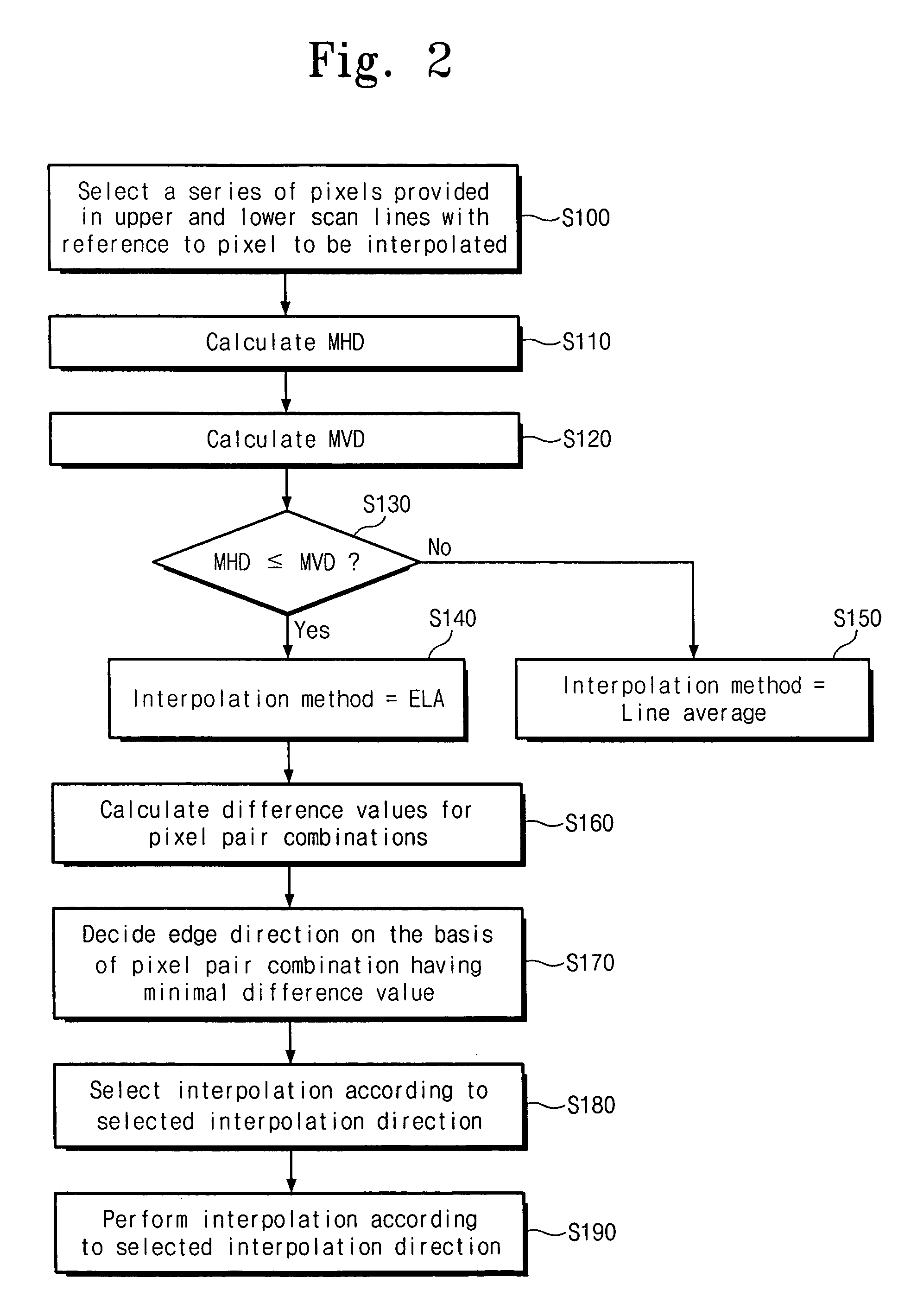
Image adaptive deinterlacing method and device based on edge
ActiveUS20050073607A1Improve picture qualityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionProgressive scan
The present invention relates to a deinterlacing device and method for converting a video signal of an interlaced scan format into a video signal of a progressive scan format. The deinterlacing method including the steps of: measuring an edge gradient from a series of pixels provided in an upper scan line and a series of pixels provided in a lower scan line with reference to a pixel to be interpolated; determining an interpolation method on the basis of the measured edge gradient; calculating a difference value for each of pixel pair combinations, each of the pixel pair combinations having at least one pixel pair, the pixel pair having two pixels each one from each of the upper and lower scan lines with reference to the pixel to be interpolated, each of the pixel pair combinations having the pixel pairs that are adjacent to one another, the pixel pair combinations having different directions from one another; determining an edge direction on the basis of a direction of the pixel pair combination having the smallest difference value; and performing an interpolation for the pixel depending on the determined interpolation method and the determined edge direction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
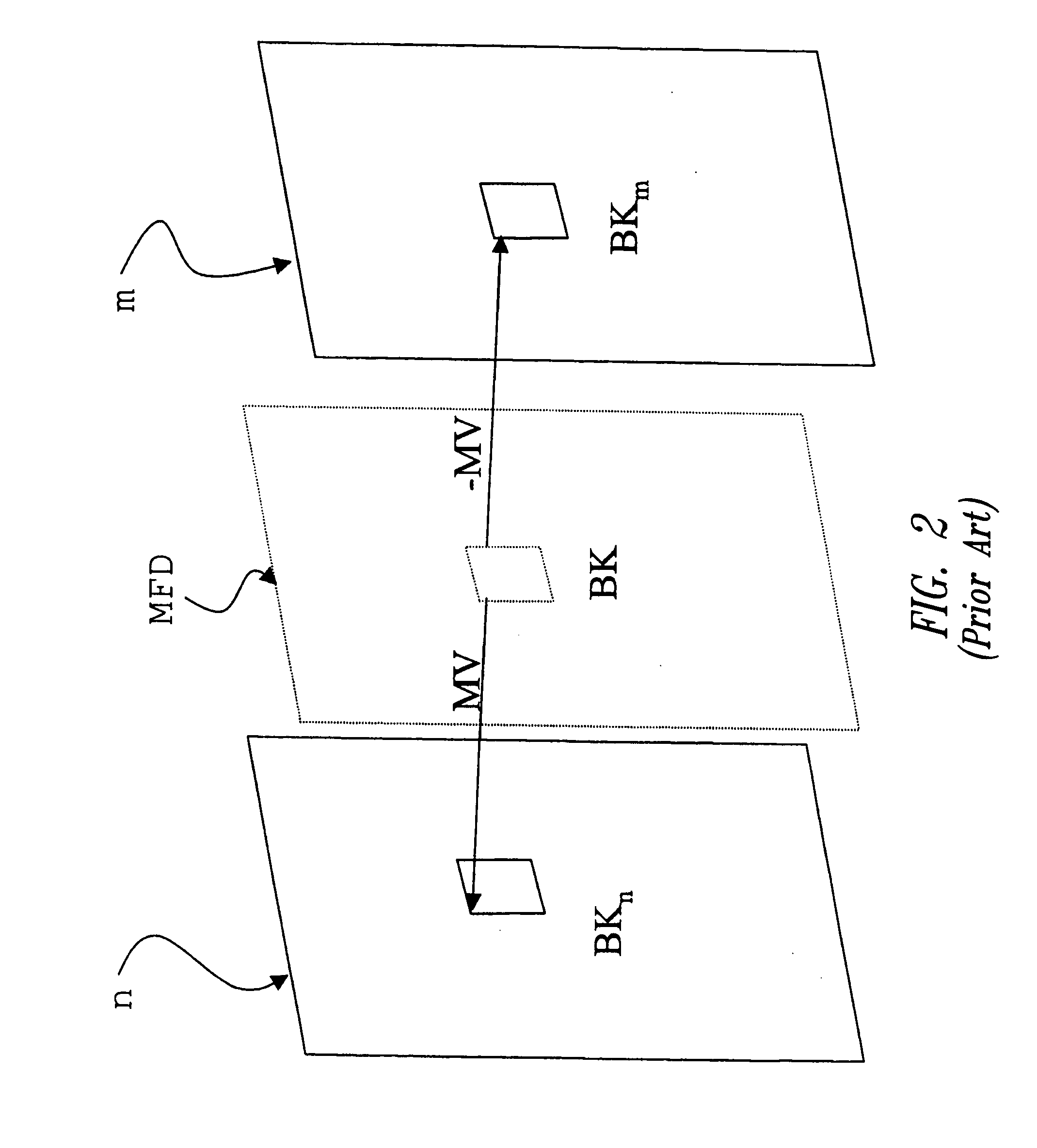
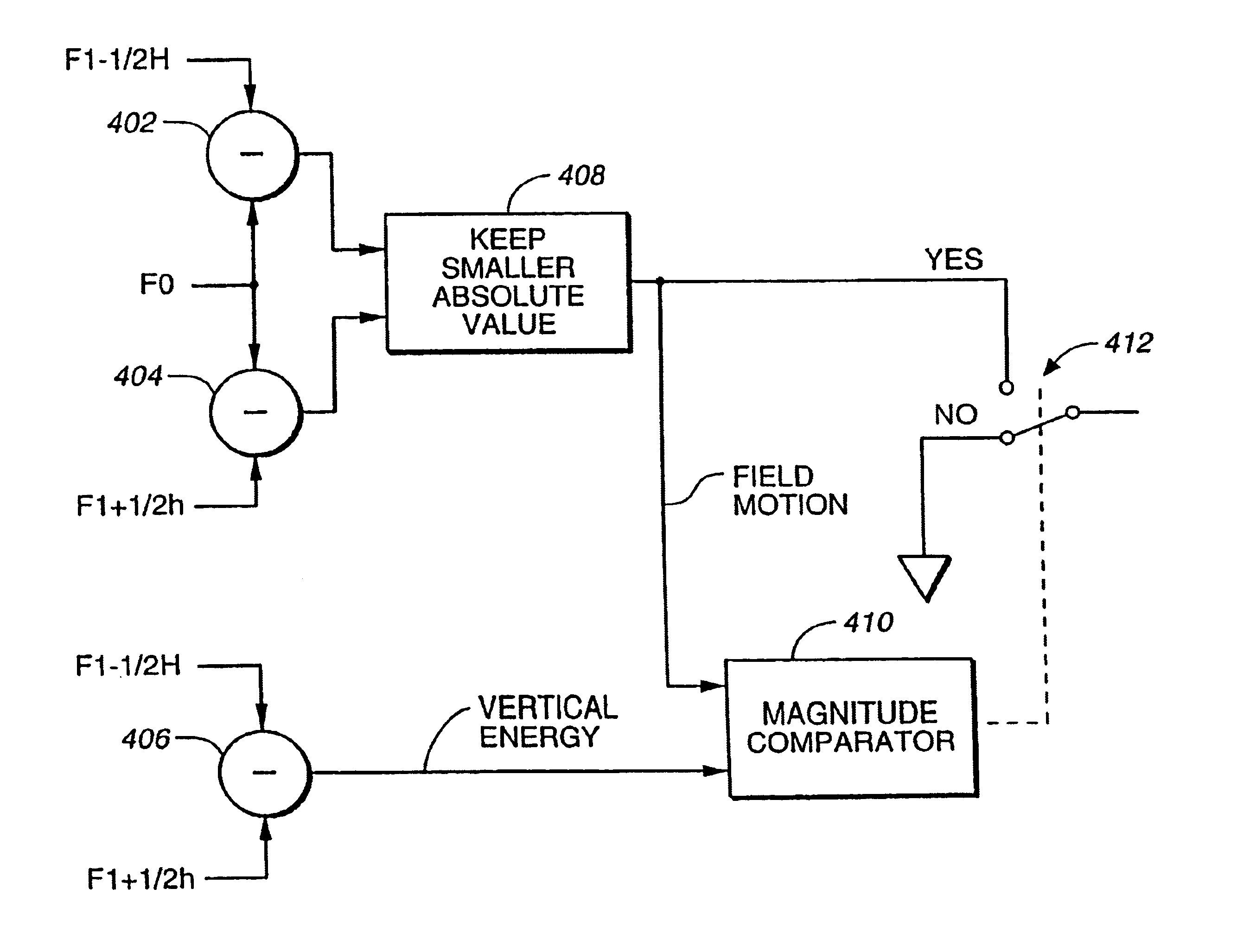
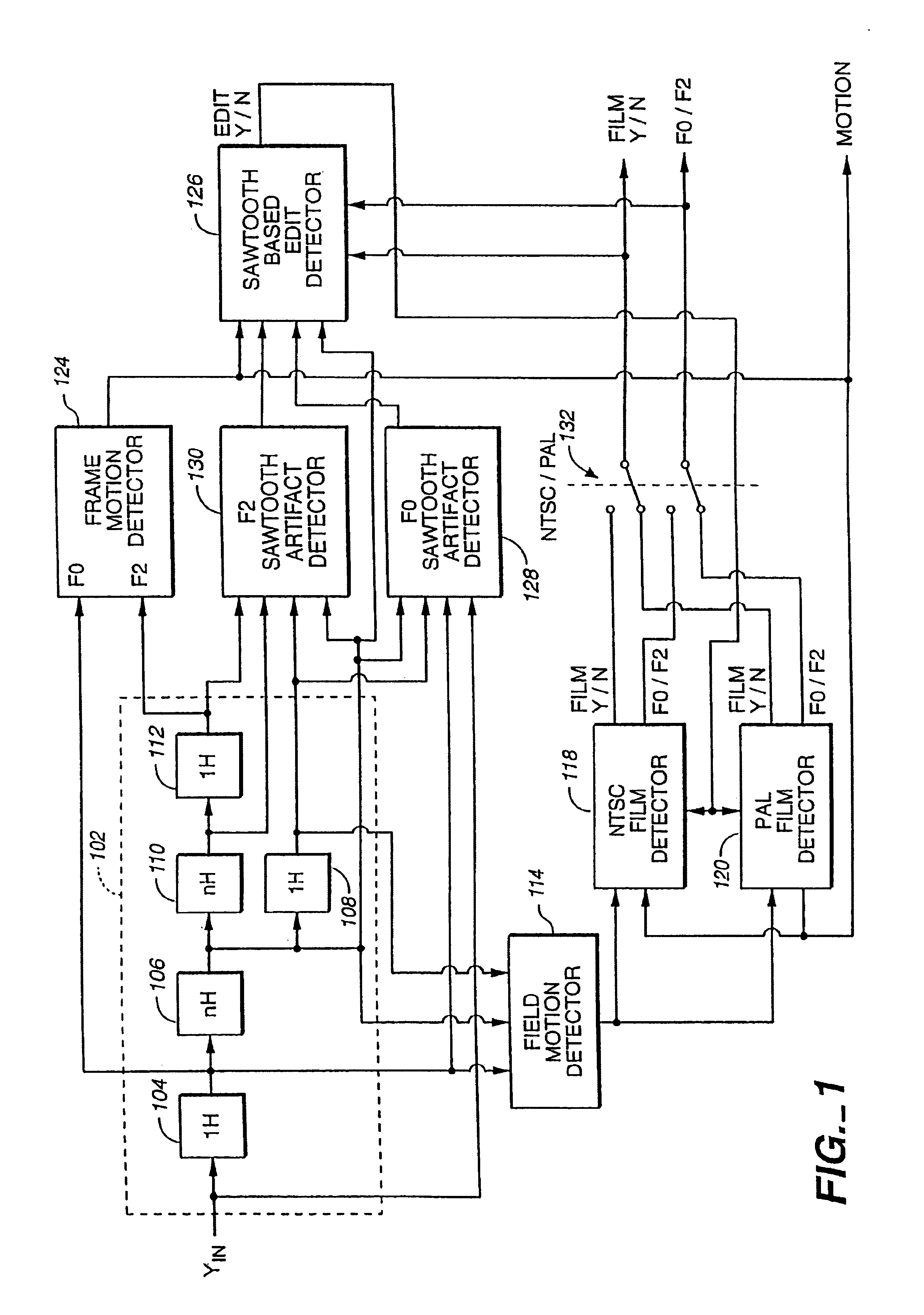
Film source video detection
InactiveUS6859237B2Improve abilitiesIncrease differentiationTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsMotion detectorPattern sequence
A television line doubler (interlaced to progressive scan converter) incorporating the following aspects—an improved field motion detector which does not treat low frequency vertical transitions as motion; a frame motion detector having an improved ability to differentiate motion from subcarrier signal components; a sawtooth artifact detector; a sawtooth artifact detector in combination with a film pattern detector, such that the artifact detector can take the film pattern detector out of film mode earlier than it would if it only were responsive to a break in the film pattern; tandem field motion detectors; an improved field based film detector; film pattern detectors and motion detectors used therewith which operate by performing end-of-field calculations; the combination of a field motion detector and a frame motion detector such that the frame motion detector provides a motion signal used as a verification by the field motion detector; an improved NTSC film detector requiring a minimum number of NTSC film pattern sequences; and an improved PAL film detector employing a minimum motion threshold detector.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
Method of low latency interlace to progressive video format conversion
InactiveUS7423691B2Efficiently determinedTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesInterlaced videoProgressive scan
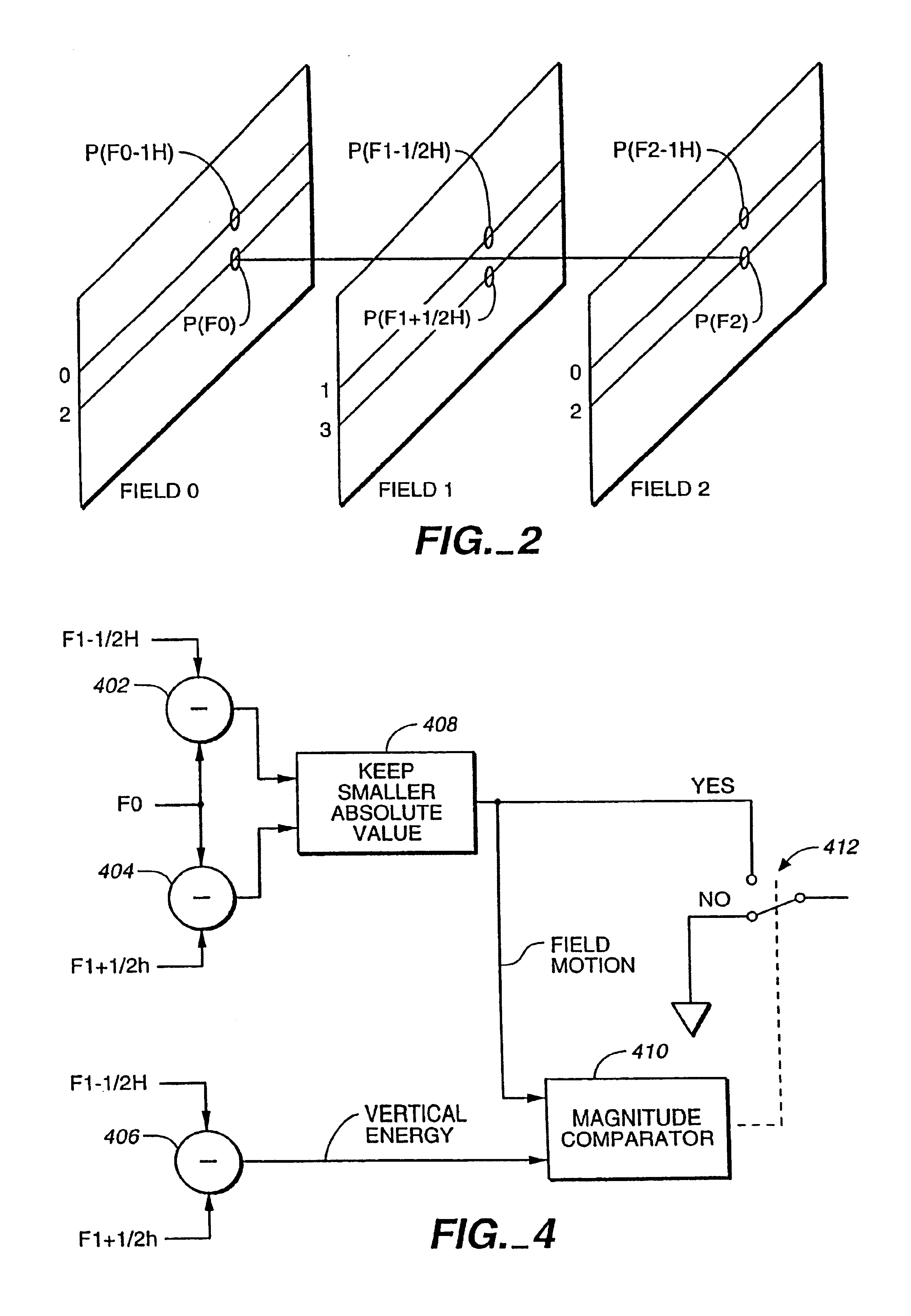
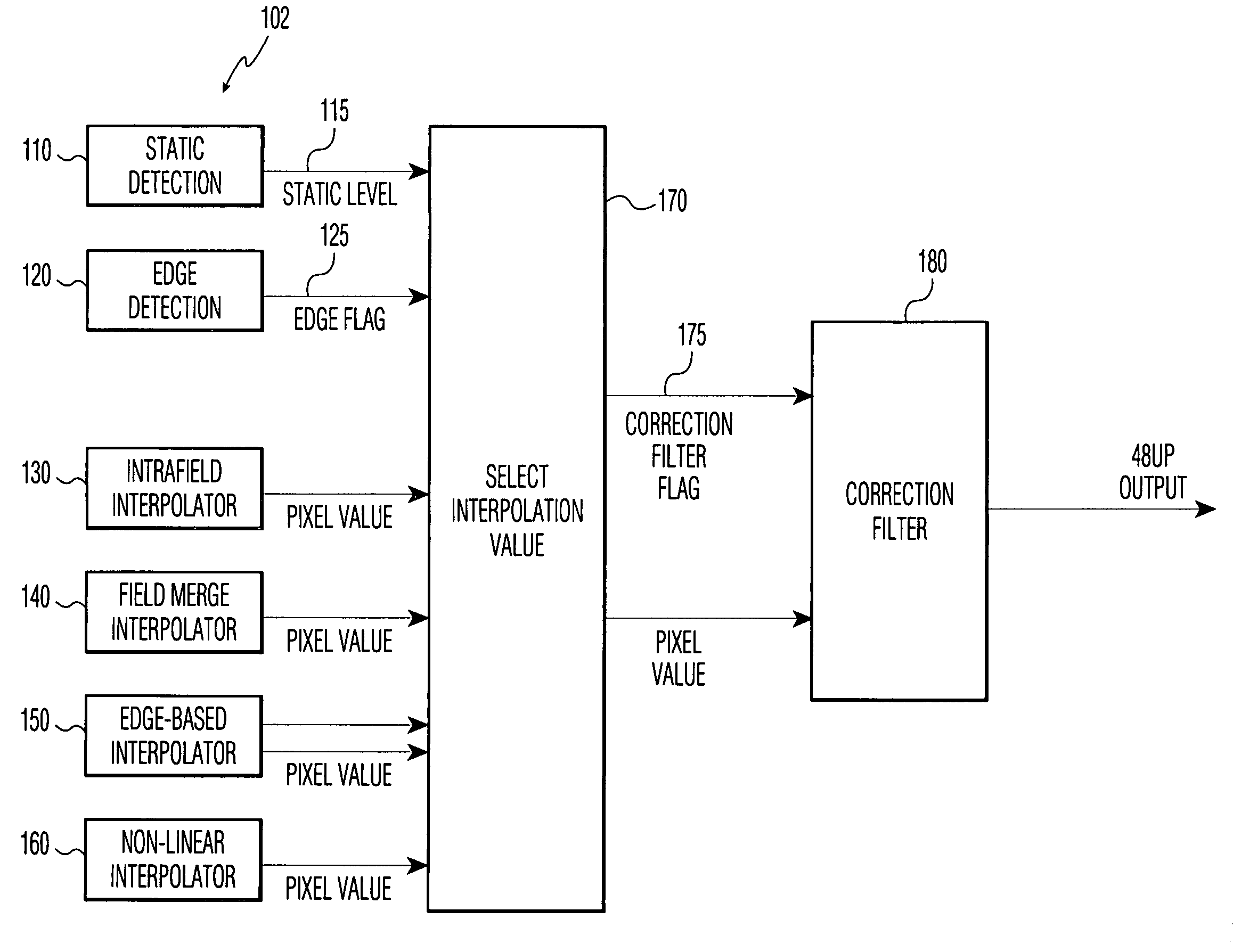
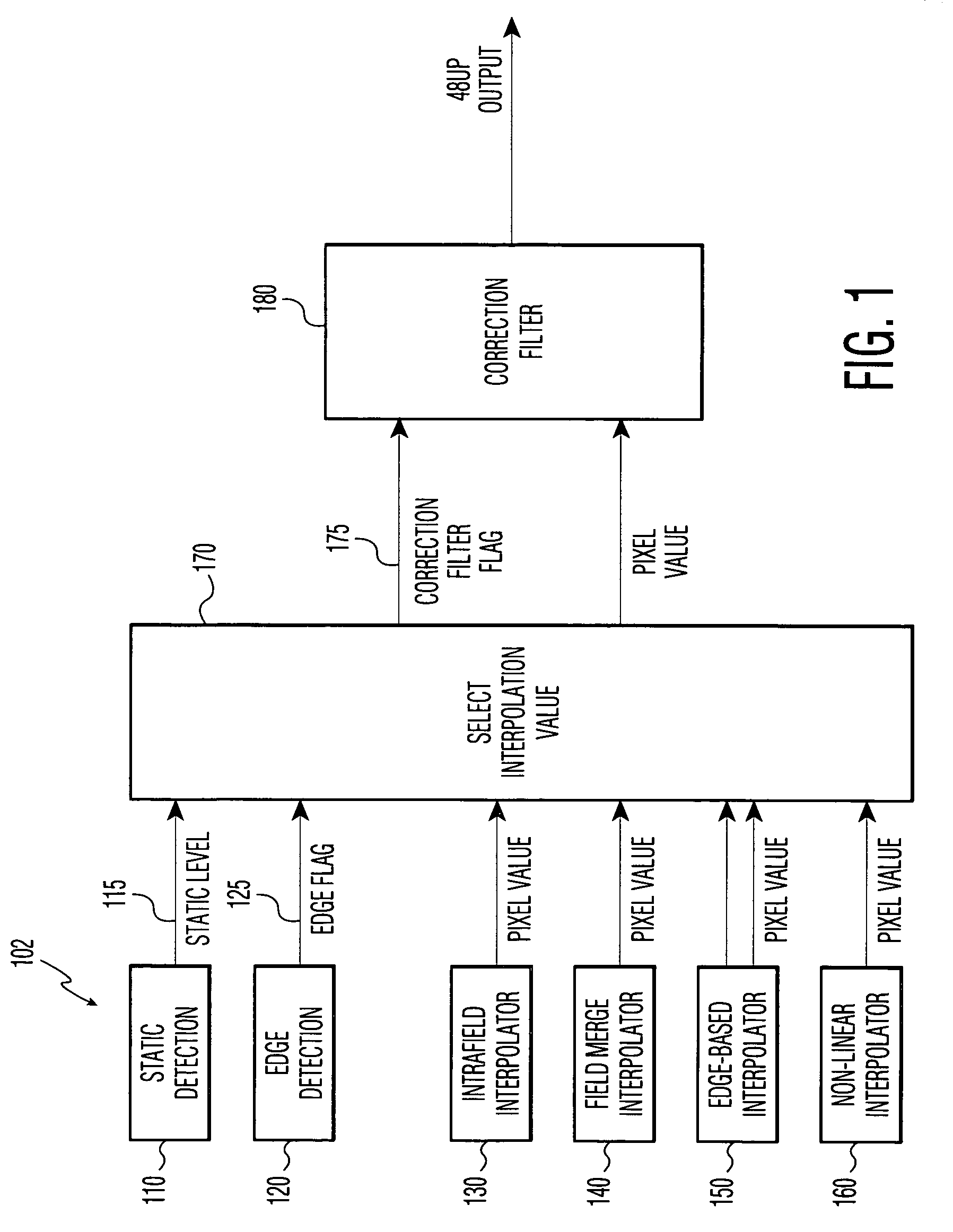
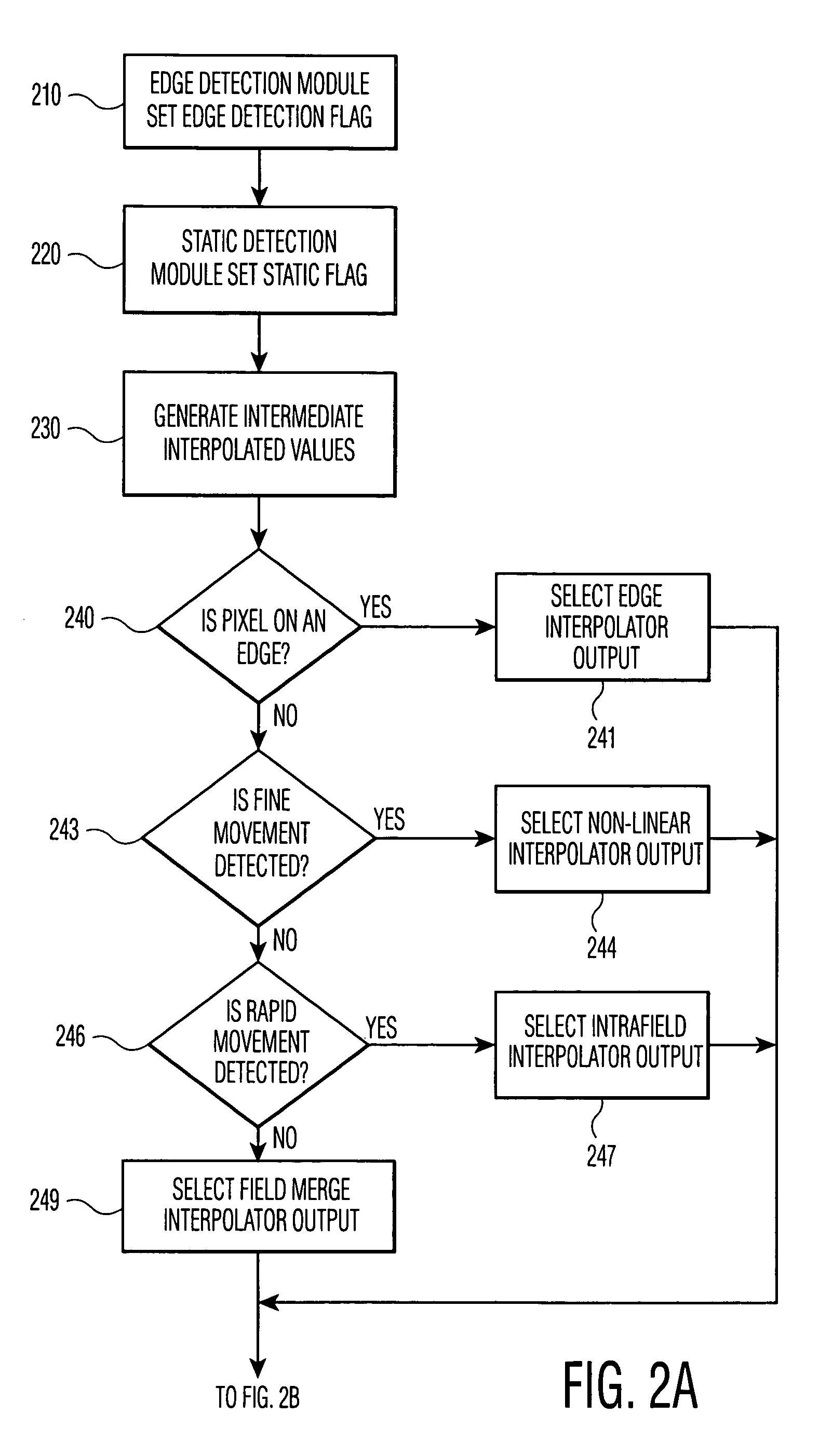
The invention includes a method for converting from an interlace scan image to a progressive scan image. Interpolated rows of pixels, lying between successive rows of the interlace scan image, are generated based upon the received interlace scan rows. The method determines a degree of movement, if any, in the region of a target pixel, and whether a target pixel lies on an edge between visually distinct regions. Multiple potential interpolated values for the target pixel are generated by several interpolation methods, including edge interpolation, inter-field interpolation, non-linear interpolation, and intra-field interpolation. The system uses the degree of movement and edge detection to select or combine one or more of the potential values for the target pixel. At least one correction filter is applied to the result, to correct errors caused by electrical noise in the interlace scan image.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for detecting interlaced material and field order
ActiveUS20060139491A1Solve problemsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSpatial correlationProgressive scan
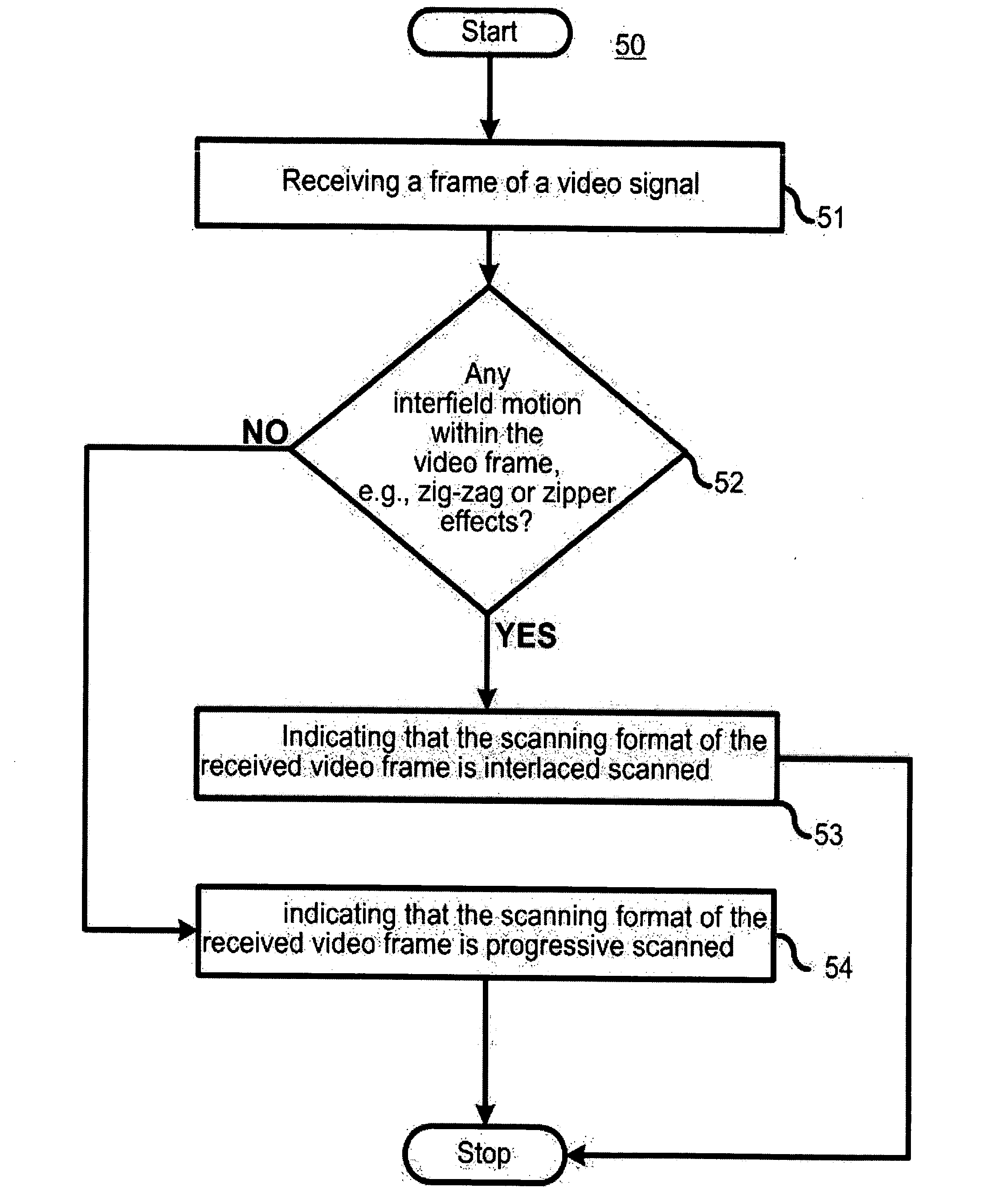
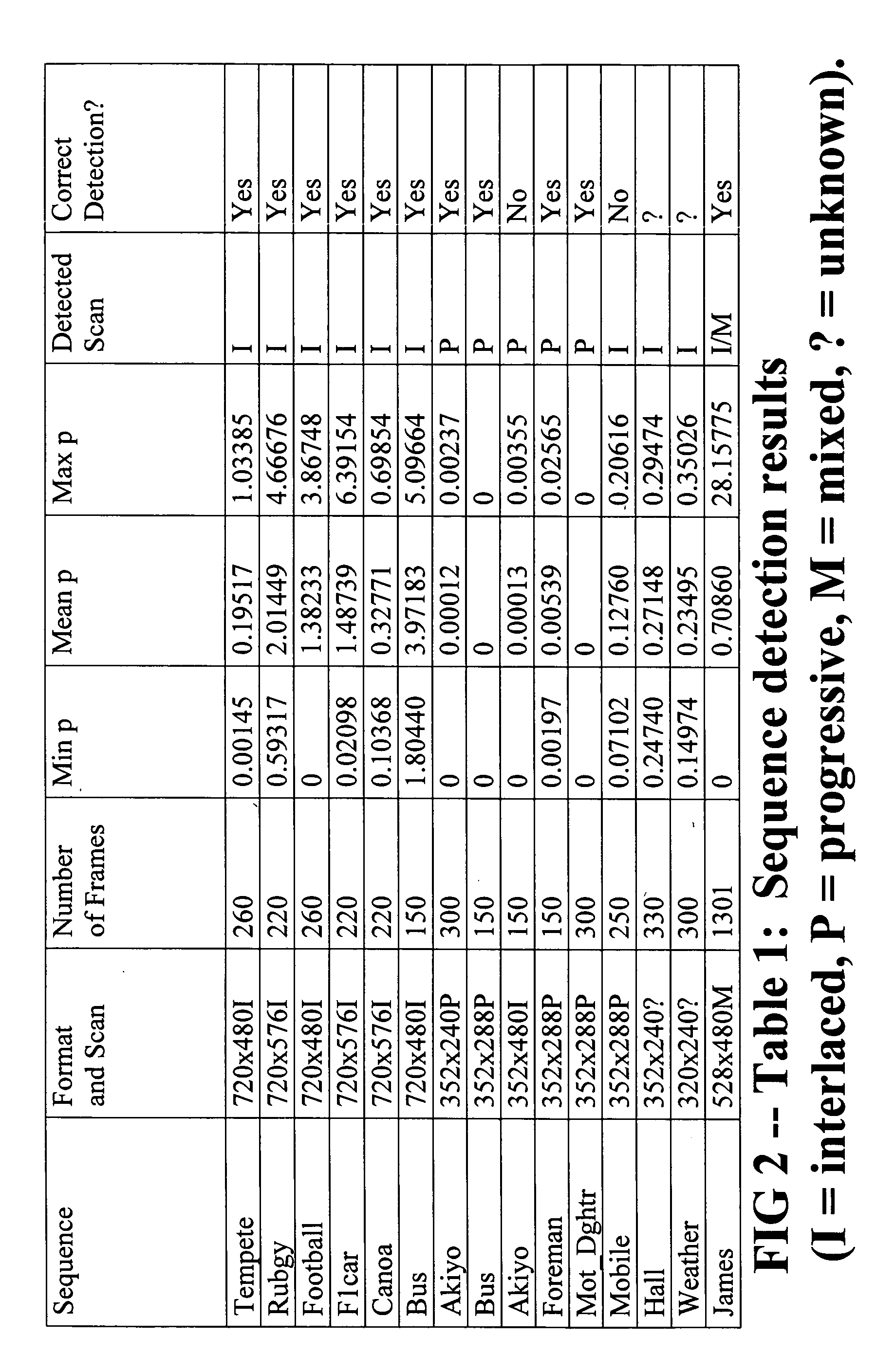
A (50) method and apparatus (110) for determining a scanning format of a frame of a video signal determines (52) if any interfield motion exists within the frame; and indicates (53) that the frame is interlaced scanned if interfield motion is detected and indicates (54) that the frame is progressive scanned if interfield motion is not detected. The determination is based on spatial correlation within and around one or more edges of one or more objects in the frame. This can be accomplished by identifying zig-zag or zipper effects near one or more edges of one or more objects in the frame, identifying motion between fields or identifying motion near one or more edges of one or more objects. A method (100) for determining a field order of two interlaced frames of a video sequence of frames assigns (101) one of the two interlaced frames to be a first frame and the other of the two interlaced frames to be a second frame and assembles (102) two new frames from the two interlaced frames by combining a bottom field of the first frame with the top field of the second frame and by combining a top field of the first frame with a bottom field of the second frame. The number of zipper points in each of the two new frames is then determined and compared. If the number of zipper points in the first frame is smaller than the number of zipper points in the second frame, that the field order of the two frames is top field first, otherwise the field order is bottom field first.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
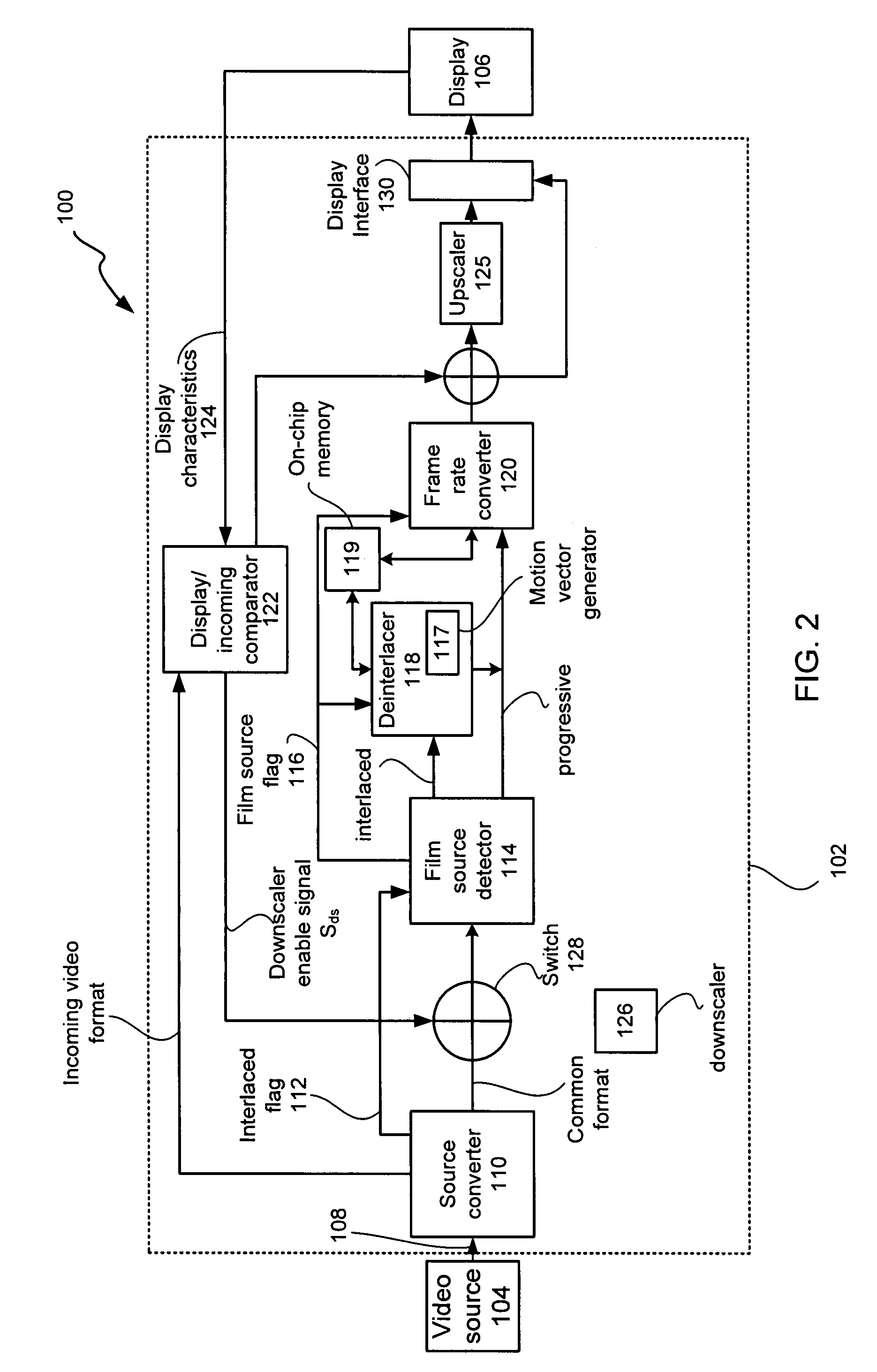
Single chip multi-function display controller and method of use thereof
ActiveUS7420618B2Cancel noiseBandwidthTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMulti-function displayInterlaced video
A multi-function display controller that includes a source detector unit for determining if the source of an input stream is either film originated source originated or video source originated. A source converter unit for converting the input image stream to a common signal processing format is coupled to the source detector unit. Once converted to the common signal processing format, a determination is made if the input image stream is interlaced or non-interlaced (progressive scan). If the input image stream is interlaced, a de-interlace unit converts the interlaced signal to progressive scan using either motion adaptive or motion compensated de-interlacing techniques. It should be noted that in the described embodiment, motion vectors generated for use by the motion compensated de-interlace can be optionally stored in a memory unit for use in subsequent operations, such as motion compensated frame rate conversion or noise reduction (if any).
Owner:GENESIS MICROCHIP
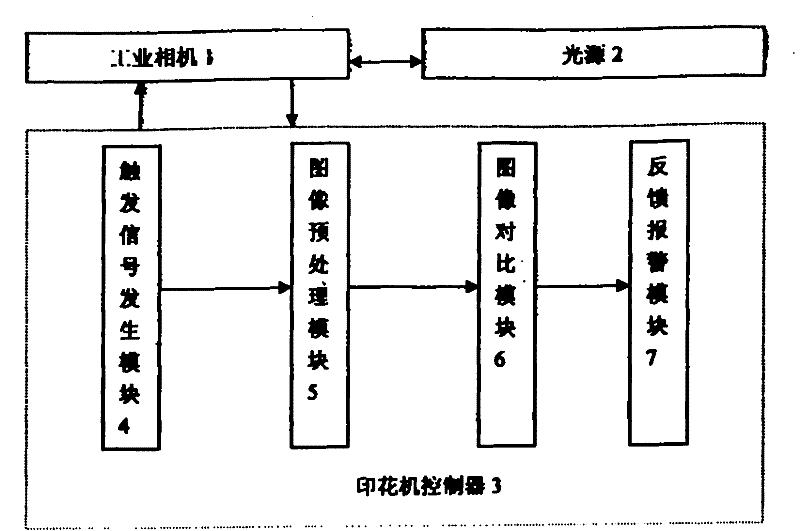
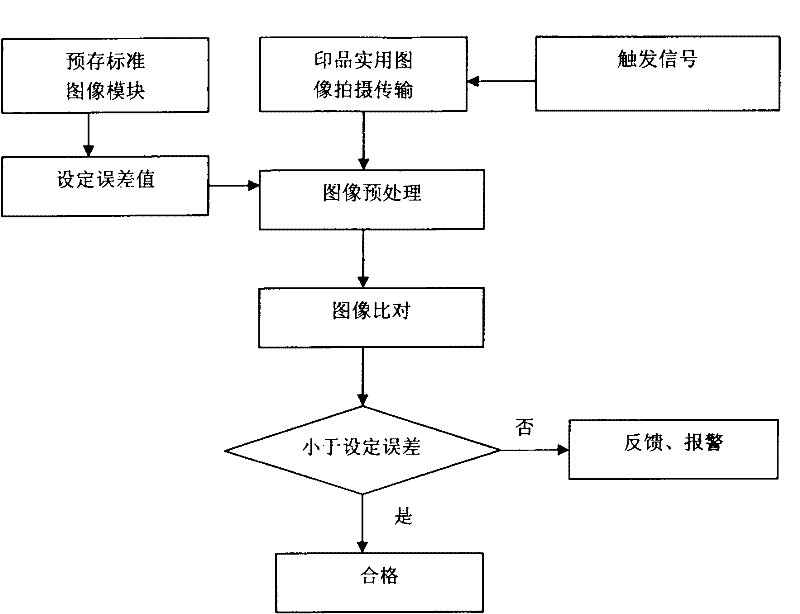
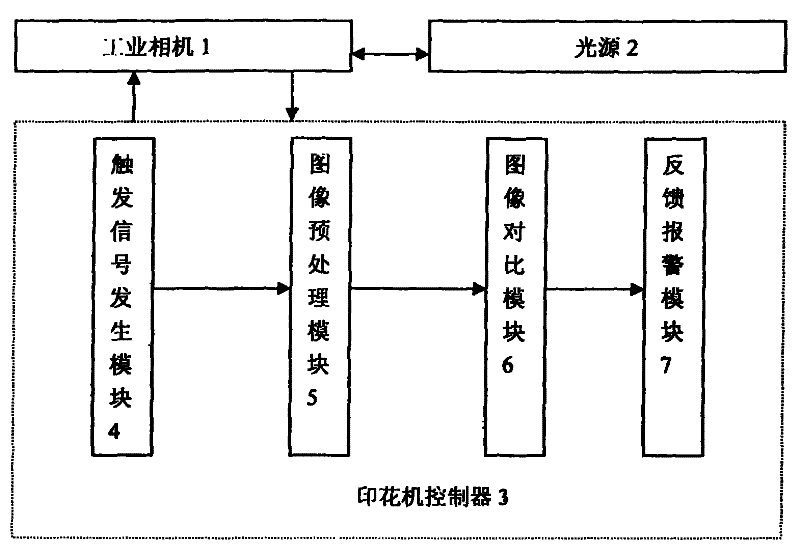
Online detection method of printing machine based on machine vision
InactiveCN102262093AQuick responseCan not eliminate the phenomenon of defectsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationTime responseData segment
The invention relates to the field of machine vision, in particular to a printing machine vision online detection method. It solves the problems of poor real-time response, heavy labor, high labor intensity and low detection level of manual detection of printed defective products. The present invention uses the image scanning device to scan the image of the printed product line by line and transmit it to the controller of the printing machine. After image processing, it is compared with the data segment corresponding to the printed image file prestored in the vision controller. If there is inaccurate registration, For defects such as missing printing, ghosting, and color difference, the interface circuit of the machine vision controller outputs a fault signal to prompt the operator to dispose of it or feedback the fault code to the upper controller, and the upper controller performs the next step of control. The invention has fast detection response speed, high precision, real-time detection during the printing process, and avoids printing defective products to the greatest extent.
Owner:张爱明
Video system with de-motion-blur processing
ActiveUS7262818B2Short response timeQuality improvementTelevision system detailsImage enhancementProgressive scanDisplay device
A video system that performs TV signal decoding, deinterlacing, and de-motion-blurring for progressive scan flat panel display is introduced. The system embeds a frame buffer and a scaler for conducting format and resolution conversions for display panels of different sizes. The output of the scaler is sent to a de-motion-blur processor for reducing the blurriness due to the motion of image objects and the slow response time of flat panel display devices. The de-motion-blur processor gets the motion and noise indication signal from scaler or the pre-frame-buffer video processor. Based on the motion and noise information and the information of temporal difference, the de-motion-blur processor performs over driving for the display panel interface and improves the rising and falling response time of the flat panel display. The decoding, deinterlacing, and de-motion-blur processing share the same frame buffer controller so the entire system can be optimized in cost and performance.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Online detecting device and method based on computer vision for soft capsule quality
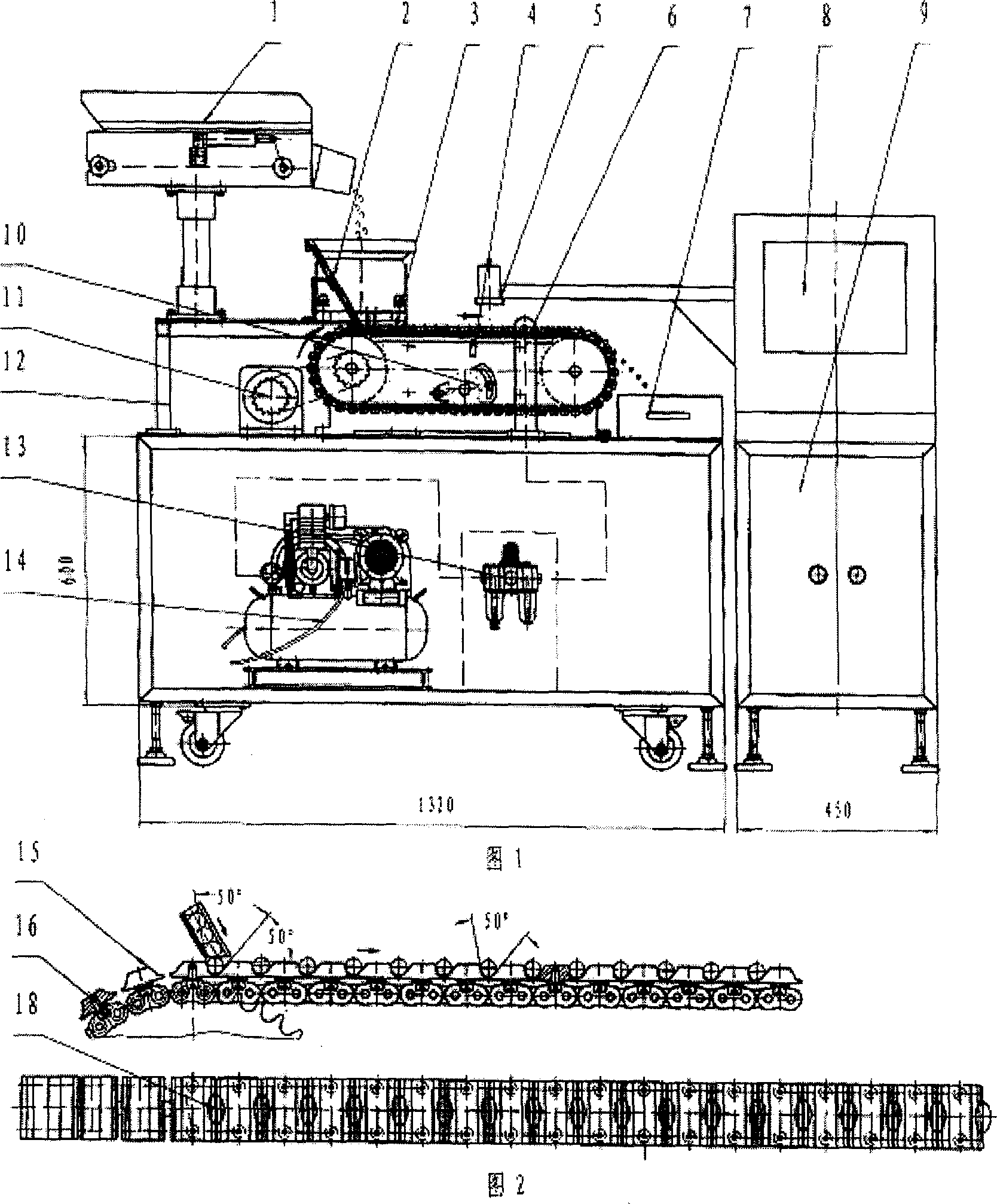
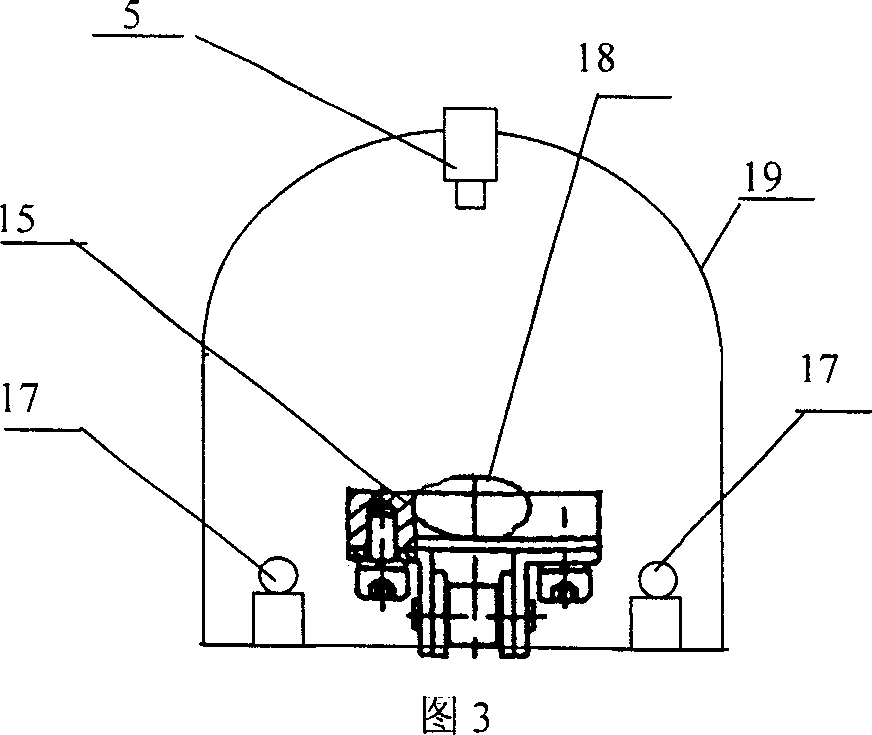
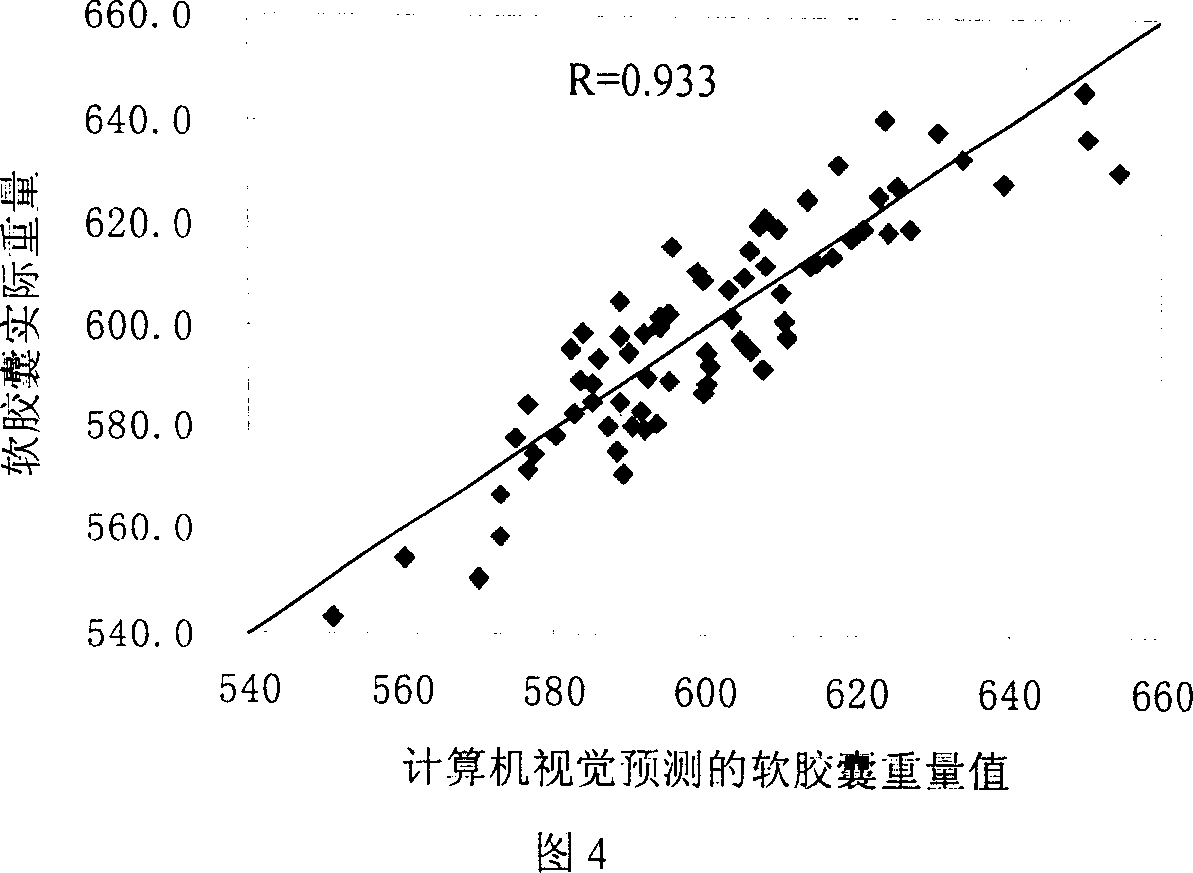
InactiveCN1943886AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed detection speedInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareMachine vision
The present invention is computer vision detecting device and method for real-time on-line detection based on the characteristics of article. The device consists of one capsule arranging and conveying unit, one computer vision recognizing unit and one capsule eliminating unit; and features the computer vision recognizing unit with CCD camera mounted over the capsule arranging and conveying unit and the capsule eliminating unit mounted beside the conveying chain of the capsule arranging and conveying unit. The capsule arranging and conveying unit includes one vibrating feeder and one conveying chain mainly; the capsule eliminating unit eliminating soft capsules in unqualified weight and shape consists of air source, solenoid valve and nozzle connected successively; and the computer vision recognizing unit consists of video camera system, lighting box, photoelectronic sensor, control module and corresponding software.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Motion-adaptive de-interlacing method and system for digital televisions
InactiveUS6847405B2Improve imaging resolutionCost-effectiveTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsVideo bitstreamProgressive scan
One embodiment of the present invention provides a method and system for transforming a video bitstream in an interlaced format into a progressive format which can be displayed by a digital television. For example, the present embodiment utilizes the pixel information of a current field, previous field, and future field of the interlaced video bitstream to try to determine what the original content is of the missing lines of the current field. Specifically, the present embodiment utilizes different sets of pixel information in order to estimate the amount of motion that exist within a video bitstream. In this manner, the present embodiment is able to more closely determine the original value of the missing pixels of each field of the interlaced video bitstream. Therefore, the present embodiment provides a de-interlacing function enabling digital televisions to receive interlaced video bitstreams and display them in the progressive format.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Adaptive interlace-to-progressive scan conversion algorithm
InactiveUS20060146187A1Improve performanceImprove forecast accuracyTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesProgressive scanData set
Owner:MICRONAS SEMICON
Liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS20040046705A1Inexpensive driving circuitCathode-ray tube indicatorsProgressive scanLiquid-crystal display
A liquid crystal display apparatus which has a first display panel and a second display panel which use liquid crystal as display media, a driving circuit which scans matrix-arranged pixels of each of the panels line by line, and a controller which controls the driving circuit. The controller changes the rate of the length of a delay step Td which is inserted between scanning lines to be sequentially scanned to the length of a scanning time Tss in accordance with circumstantial temperature. Also, the way of changing the rate of Td to Tss in a single writing mode and the way of changing the rate Td to Tss in a double writing mode are different.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
Method for processing TOPS (Terrain Observation by Progressive Scan)-SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar)-Raw Data
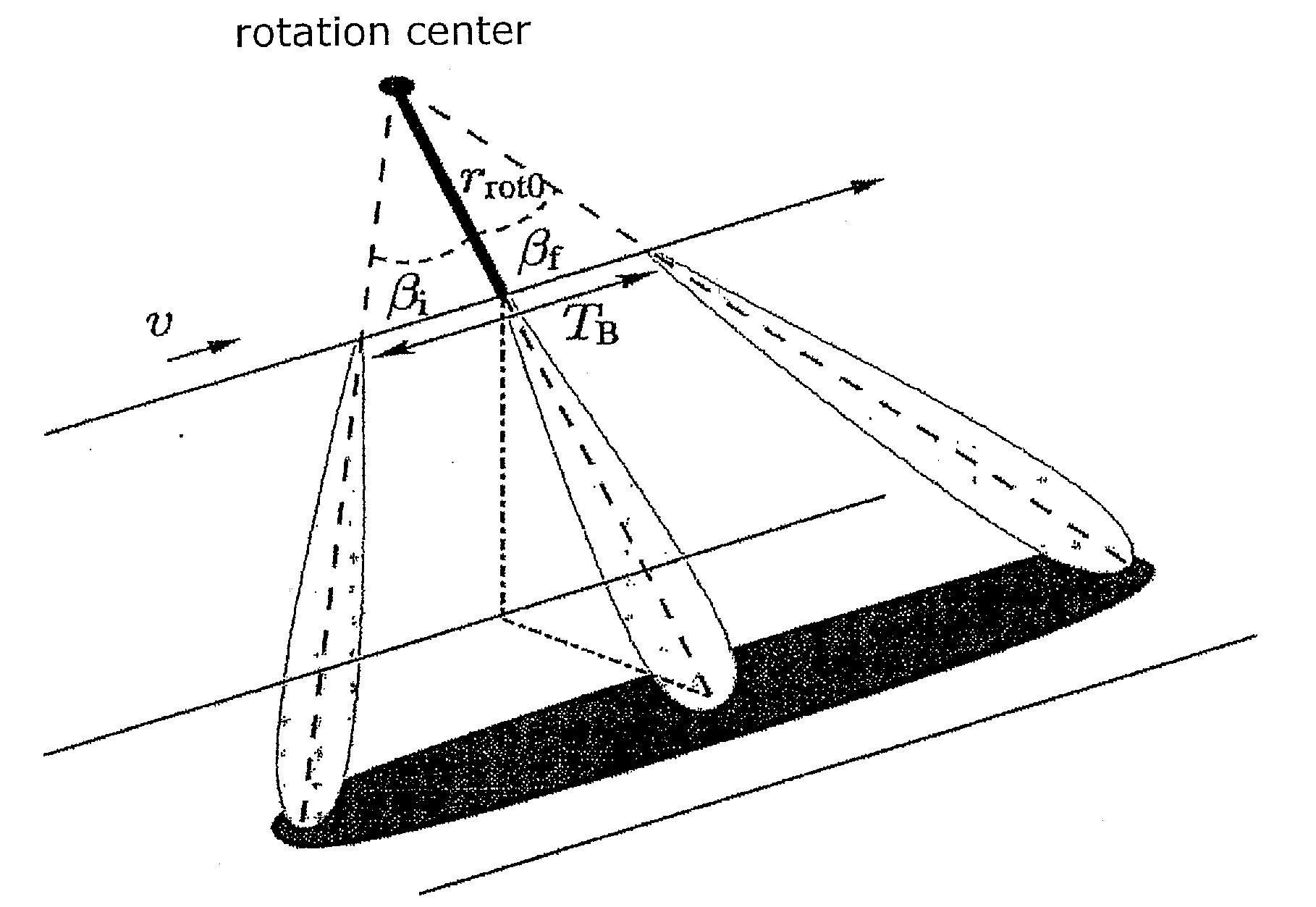
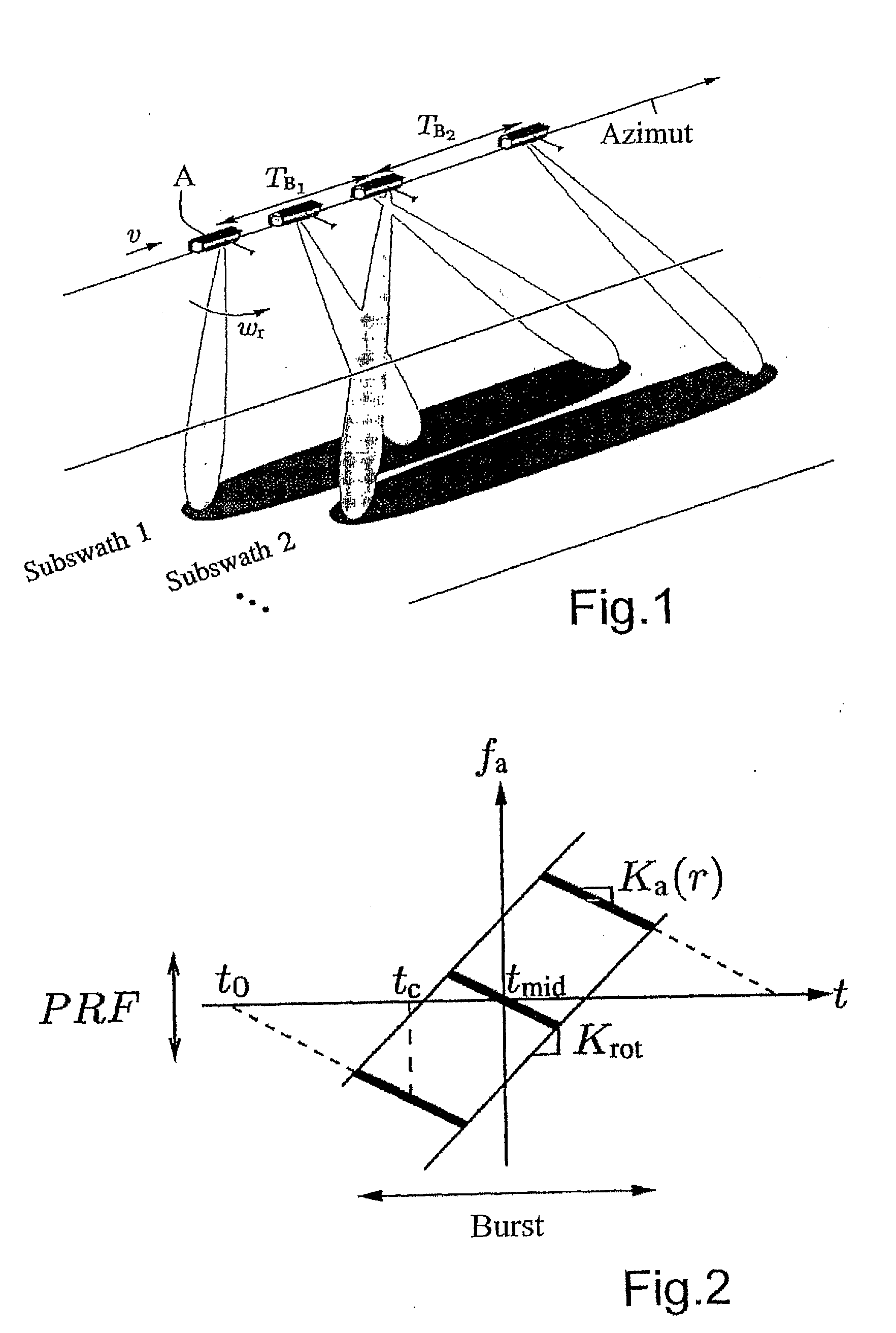
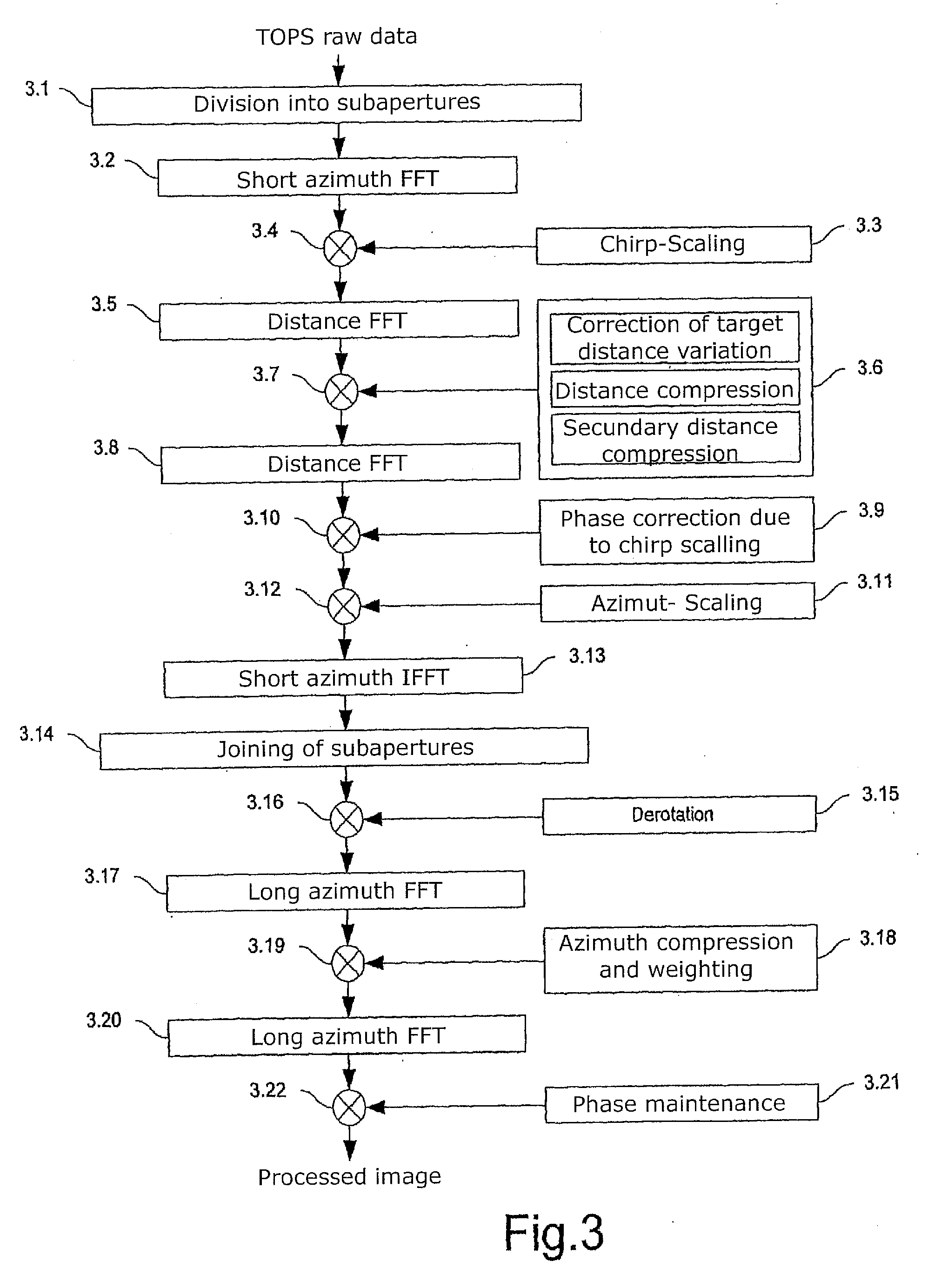
ActiveUS20100207808A1Improve accuracyAvoiding azimuth aliasing (backfoldingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEuclidean vectorLandform
Sub-aperture processing is carried out. Within each sub-aperture, range compression and a correction for the target range variation are carried out. Baseband azimuth scaling is used for processing the azimuth signal, wherein a long azimuth reference function and thus a wide azimuth dimension are prevented. The scaling range is not constant and depends on the range, which is not equal to the original range vector. It is calculated such that, in combination with a subsequent derotation step, constant azimuth scanning is achieved for all ranges. The selected derotation function, which is applied in the azimuth time domain, makes it possible for all the targets to be in base band, in this way varying the effective chirp rate. Since the phase is purely quadratic because of the azimuth scaling step, it is thus possible to use an optimal filter which takes account of the effective chirp rate. IFFT results in a focused image, and a final phase function in the time domain allows phase maintenance. Application for SAR, SONAR and seismic raw data processing in the TOPS mode, as well as other modes which make use of the antenna polar diagram being scanned in the azimuth and / or elevation direction.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
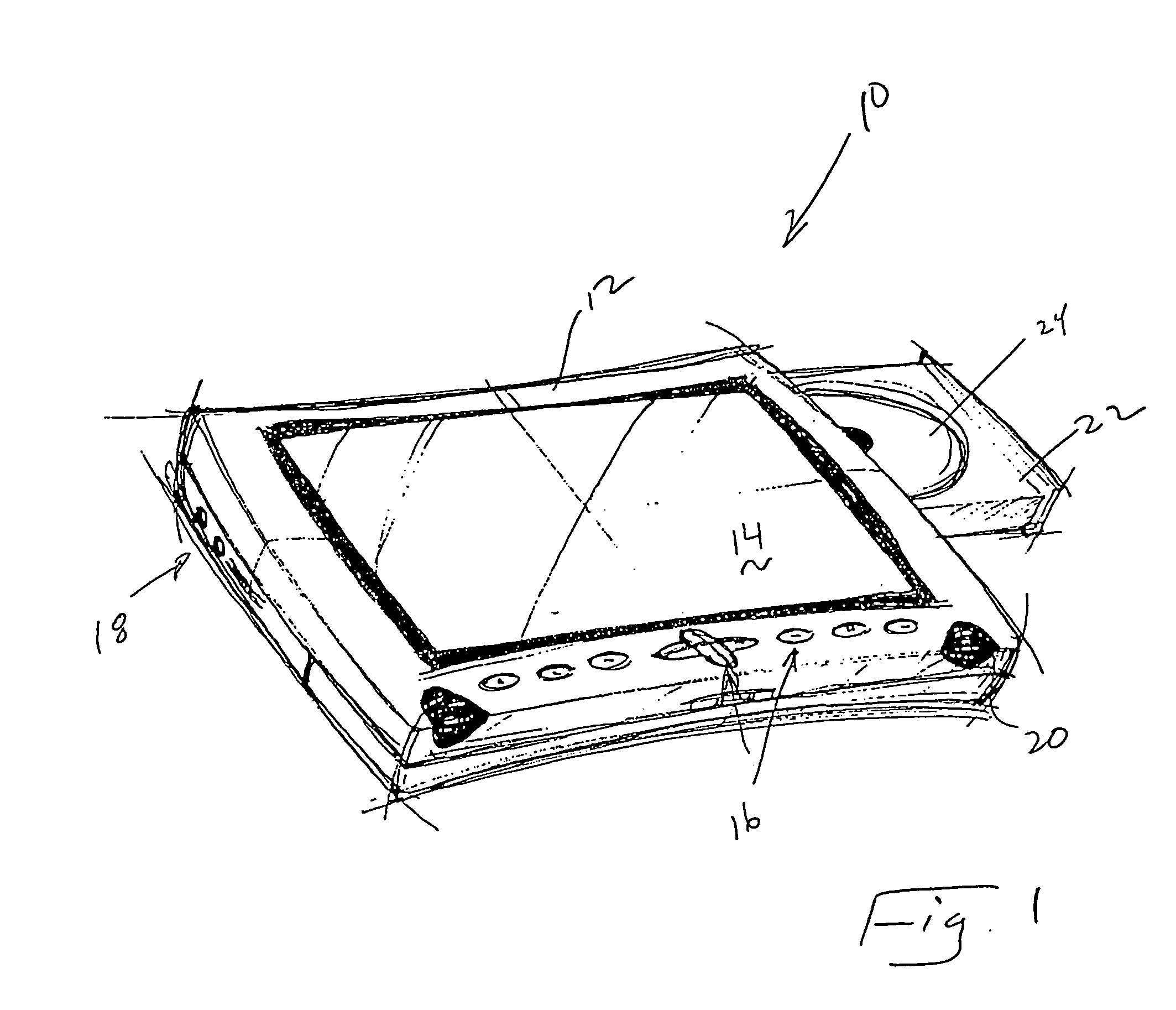
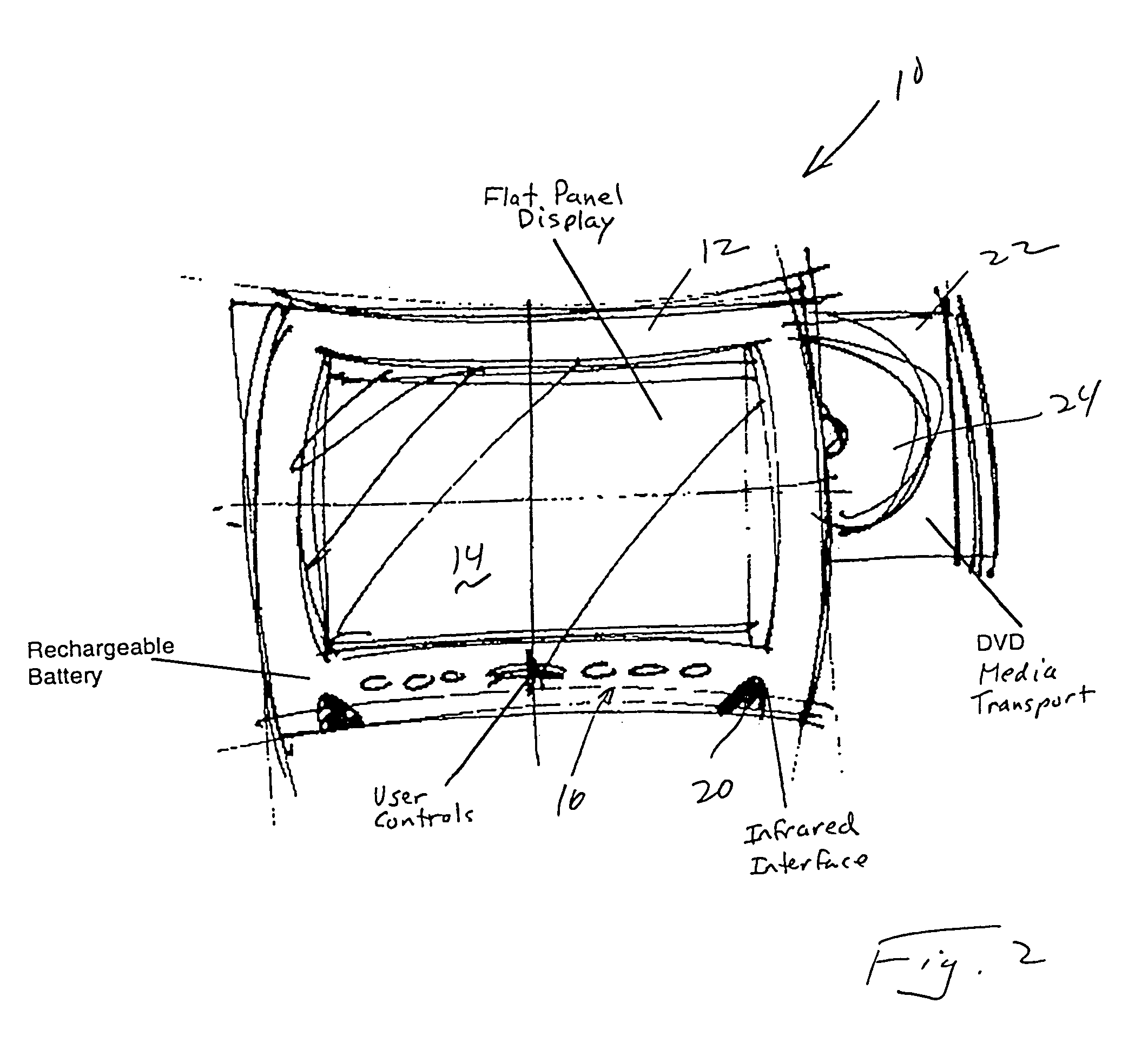
Portable DVD player
InactiveUS7359624B2Easy to useEasy to transportCarrier indicating/warning arrangementsTelevision system detailsProgressive scanInterlaced video
A portable DVD player includes a generally thin prismatic enclosure having a first major surface, a second major surface separated from the first major surface, and side surfaces connecting the first major surface to the second major surface. At least a portion of the first major surface includes a video display. The enclosure further includes a DVD entry port such that a DVD can be inserted into the enclosure. A digital processing system within the enclosure includes a decoder, a deinterlacer, and a display controller. The decoder receives signals from a DVD inserted into the enclosure to provide a decoded, interlaced video signal, the deinterlacer converts the interlaced video signal to a deinterlaced video signal, and the display controller uses the deinterlaced video signal to provide progressively scanned video on the video display. Preferably, the portable DVD player is both mechanically and electronically isolated for physical shocks to the player.
Owner:DVDO
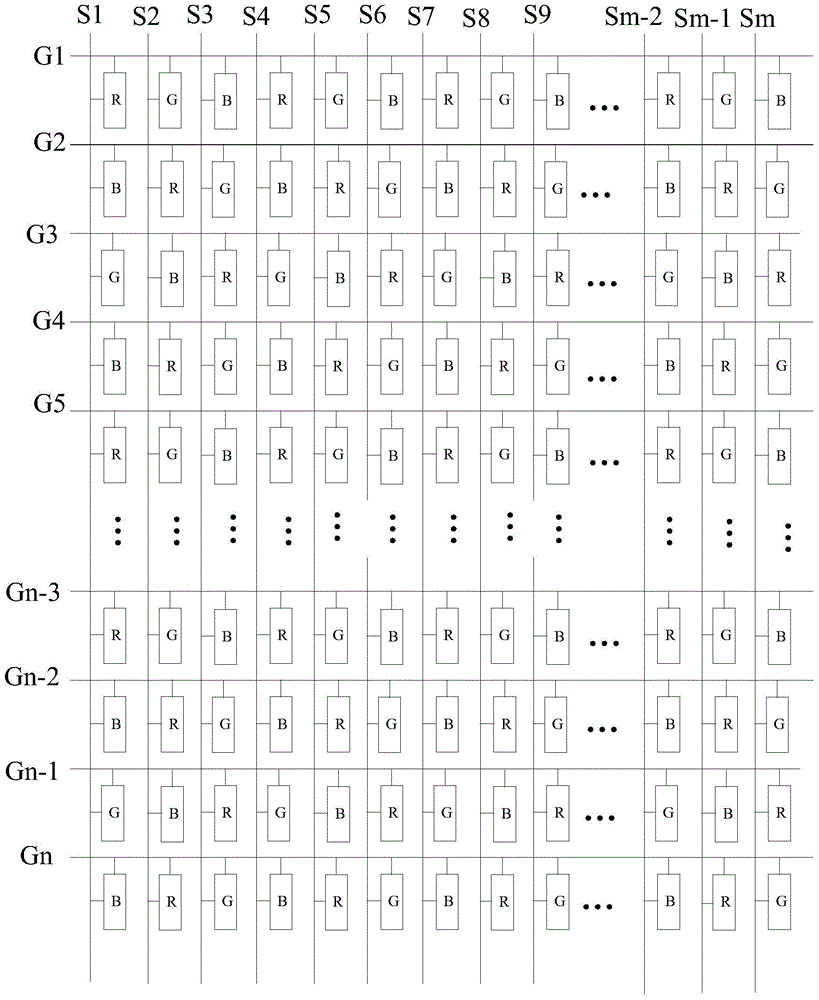
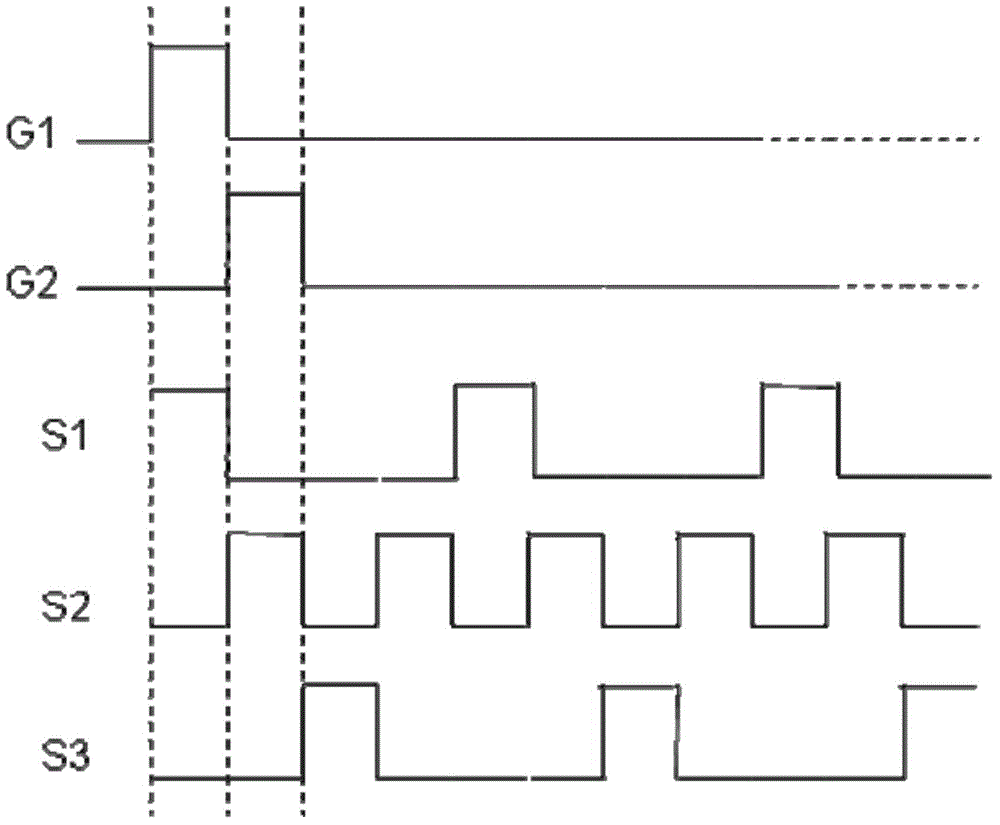
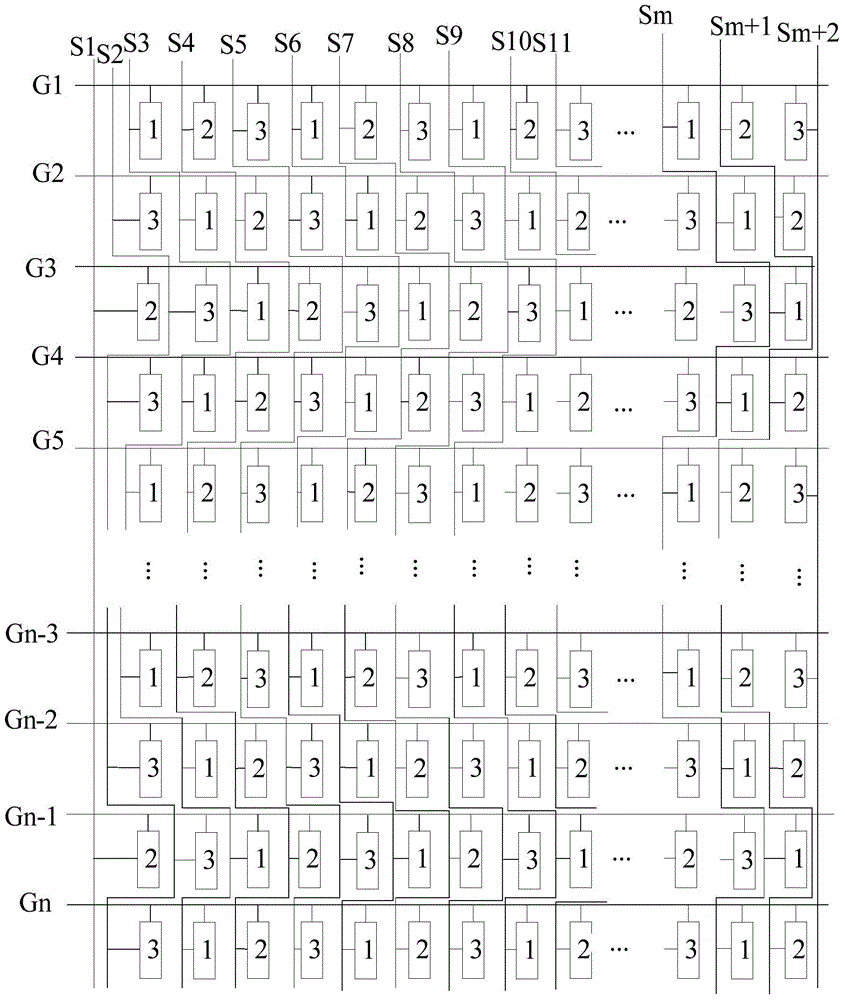
Array substrate, display panel, driving method of display panel and display device
ActiveCN104483794AReduce the number of voltage flipsReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectricityProgressive scan
The invention discloses a display panel, a driving method of the display panel and a display device. An array substrate comprises a plurality of sub-pixel units and a plurality of data lines. The sub-pixel units are arrayed in the row direction and the list direction, and in the row direction, the sub-pixel units with N sorts of colors are arrayed in an alternately cyclic mode; in the list direction, the sub-pixel units of different colors are arrayed in an alternately cyclic mode. Each data line is electrically connected with the sub-pixel units of the same color, and at most one sub-pixel unit is electrically connected into each row of sub pixels. According to the array substrate, each data line is electrically connected with the sub-pixel units of the same color, the sub-pixel units of different colors are electrically connected to different data lines, hence, when the display panel including the array substrate displays full-color images, in the row-by-row scanning process of each frame of display picture, each data line only needs to provide the voltage corresponding to the sub pixels of the same color, the potential does not need to be changed all the time, and therefore the power consumption of the display panel is lowered.
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
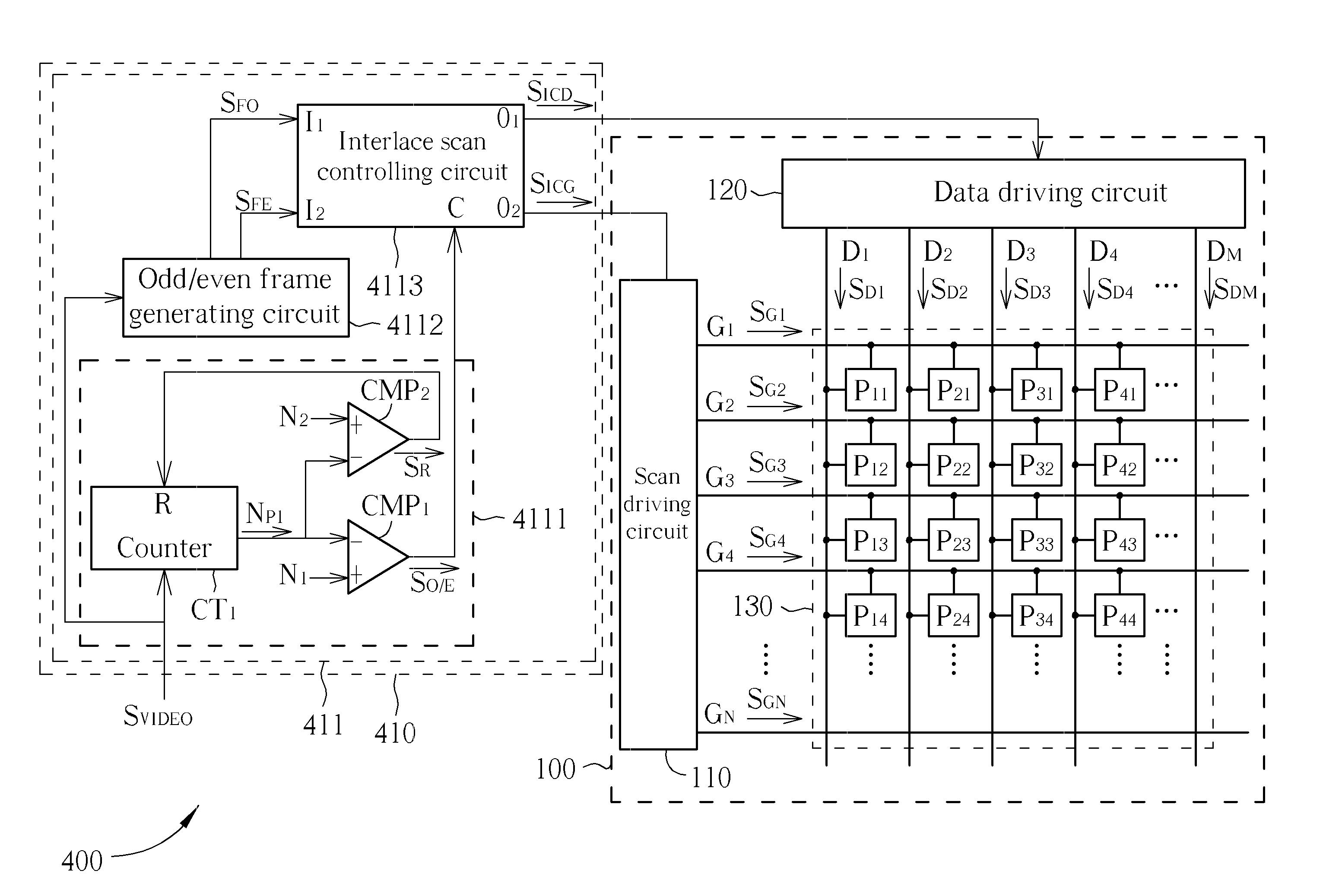
Timing controller with power-saving function
InactiveUS20100277463A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningInterlaced videoProgressive scan
A time controller with power-saving function is utilized for selecting to drive a display with progressive or interlace scan method based on if two continuous frames are dynamic. The time controller comprises an interlace scan control module, a progressive scan control module, a motion detecting circuit, a scan selecting circuit, and a data selecting circuit. The interlace scan and the progressive scan control modules are utilized for generating control signals of interlace scan and progressive scan according to a video signal, respectively. The motion detecting circuit select the control signals of interlace scan or progressive scan based on if the two continuous frames are dynamic, so as to drive the display. In this way, consumed power of the display is saved and a saw-tooth effect on the video frame is avoided.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
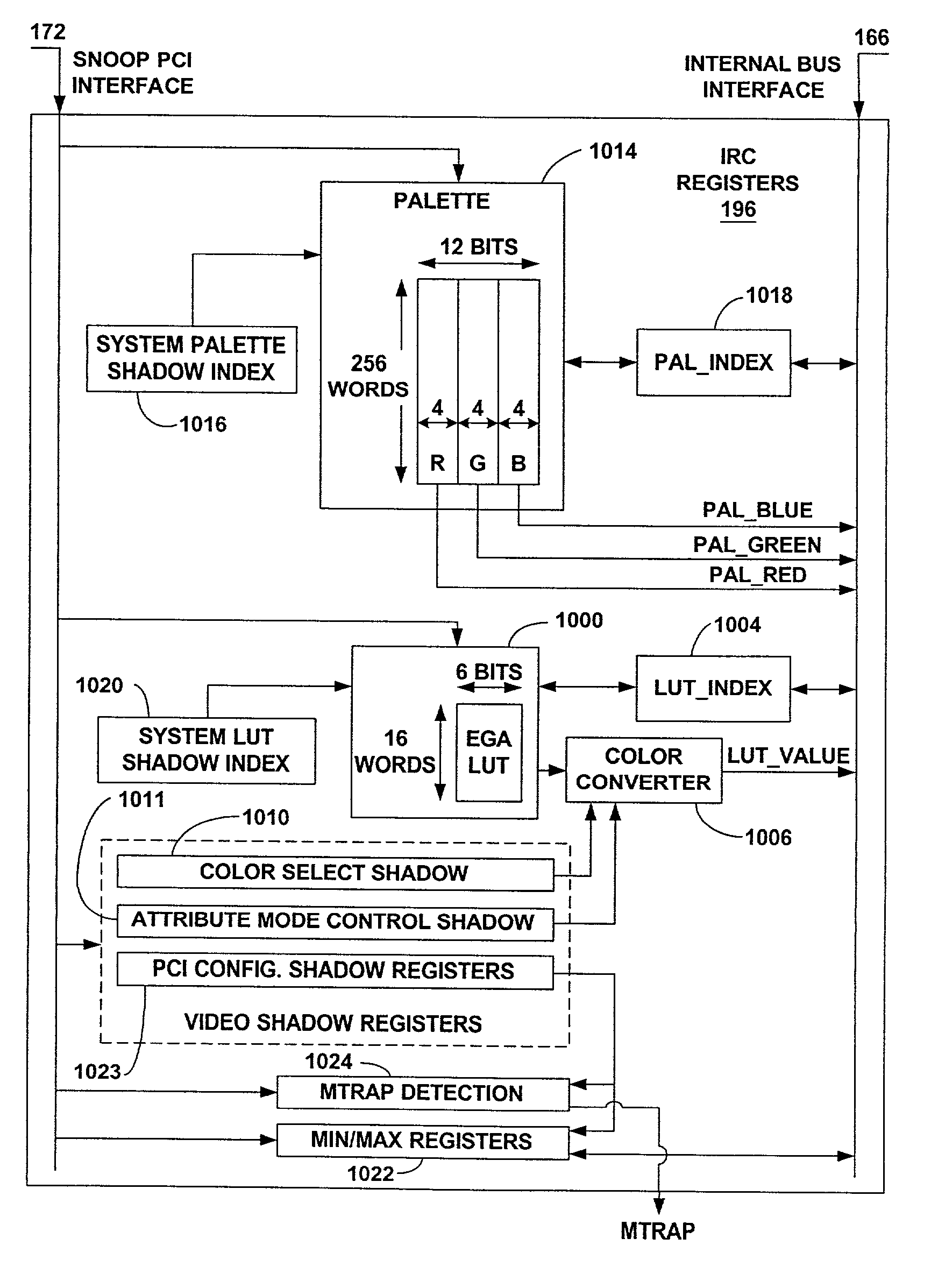
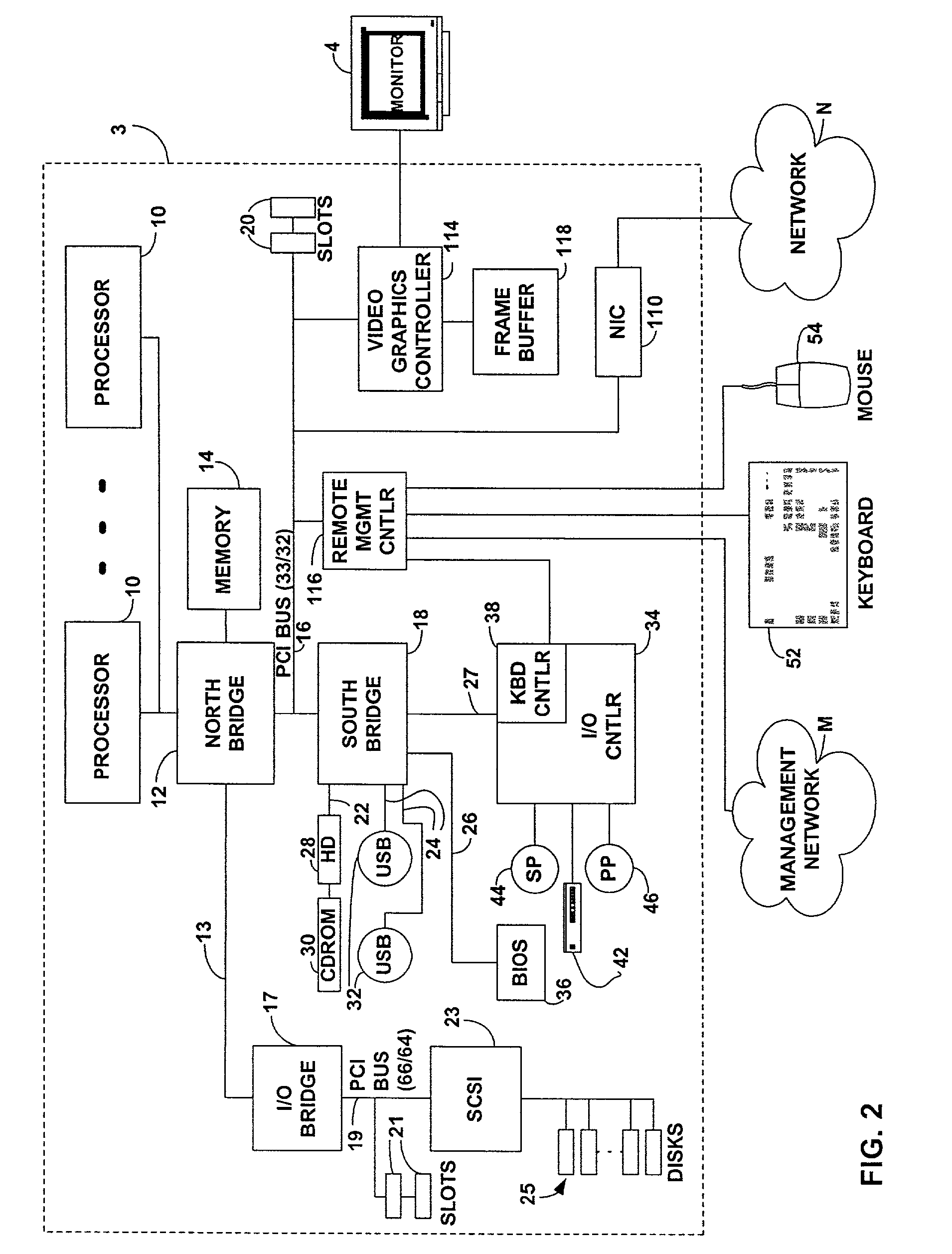
Operating system independent method and apparatus for graphical remote access having improved latency
InactiveUS20030169264A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital output to display deviceRemote computerGraphics
A method and apparatus updates video graphics changes of a managed computer to a remote computer. These updates may be performed independent of the operating system. In one embodiment, the screen (e.g., frame buffer) of the managed computer is divided into a number of blocks. A remote management controller snoops a bus coupling a processor to a video graphics controller to determine whether the processor has changed the contents of some blocks. If so, the location of the first changed block and the last changed block is stored in a pair of registers. The registers are periodically checked during the normal row-by-row scanning of the blocks. If the registers contain information indicating that a portion of the frame buffer has been changed, the remote management controller may temporarily terminate normal scanning in favor of scanning the changed portion. In one embodiment, a rectangle may be inferred using the minimum and maximum block locations, so that only blocks within the rectangle will be scanned prior to resumption of normal row-by-row scanning.
Owner:MEIZU TECH CO LTD
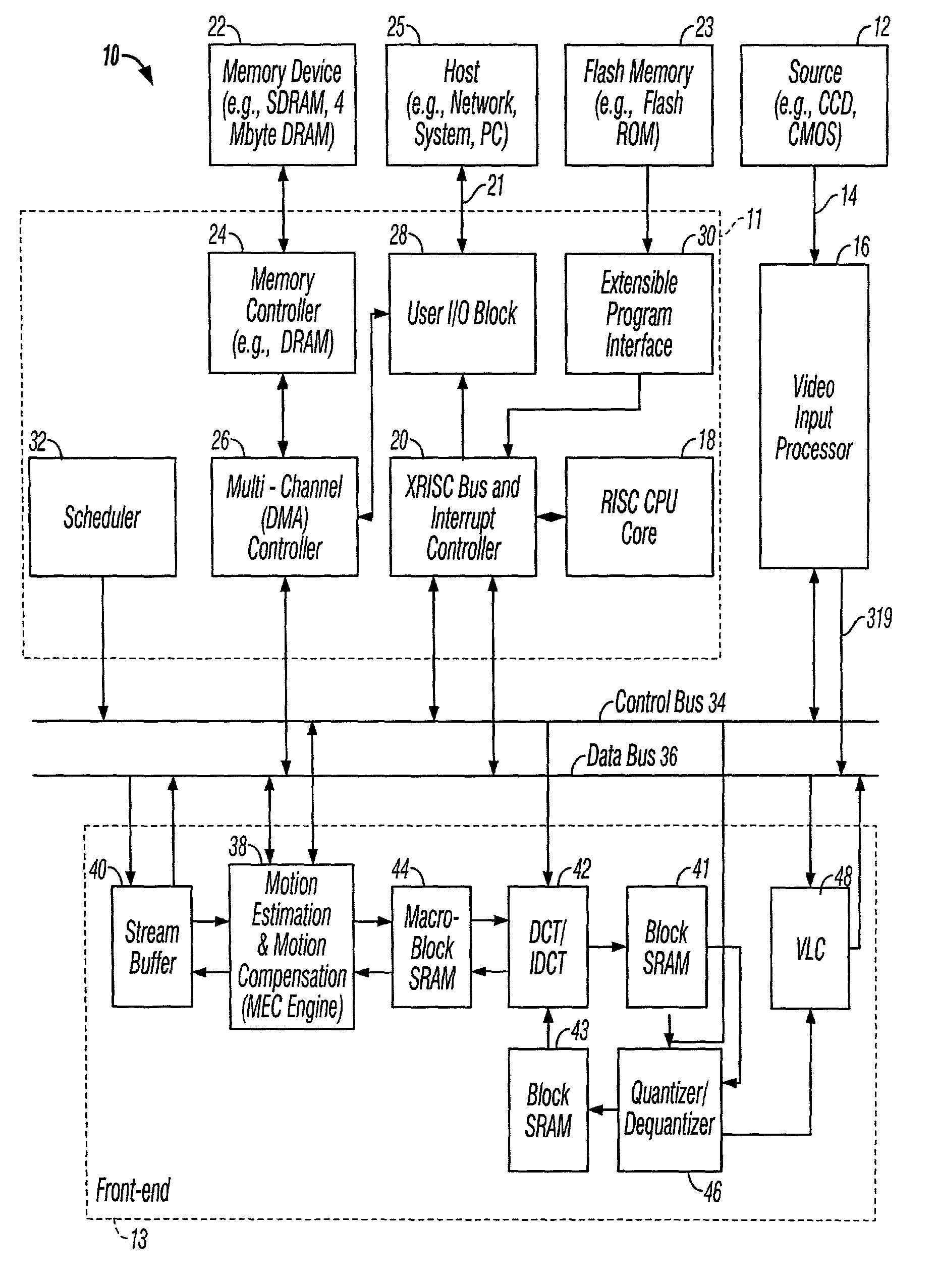
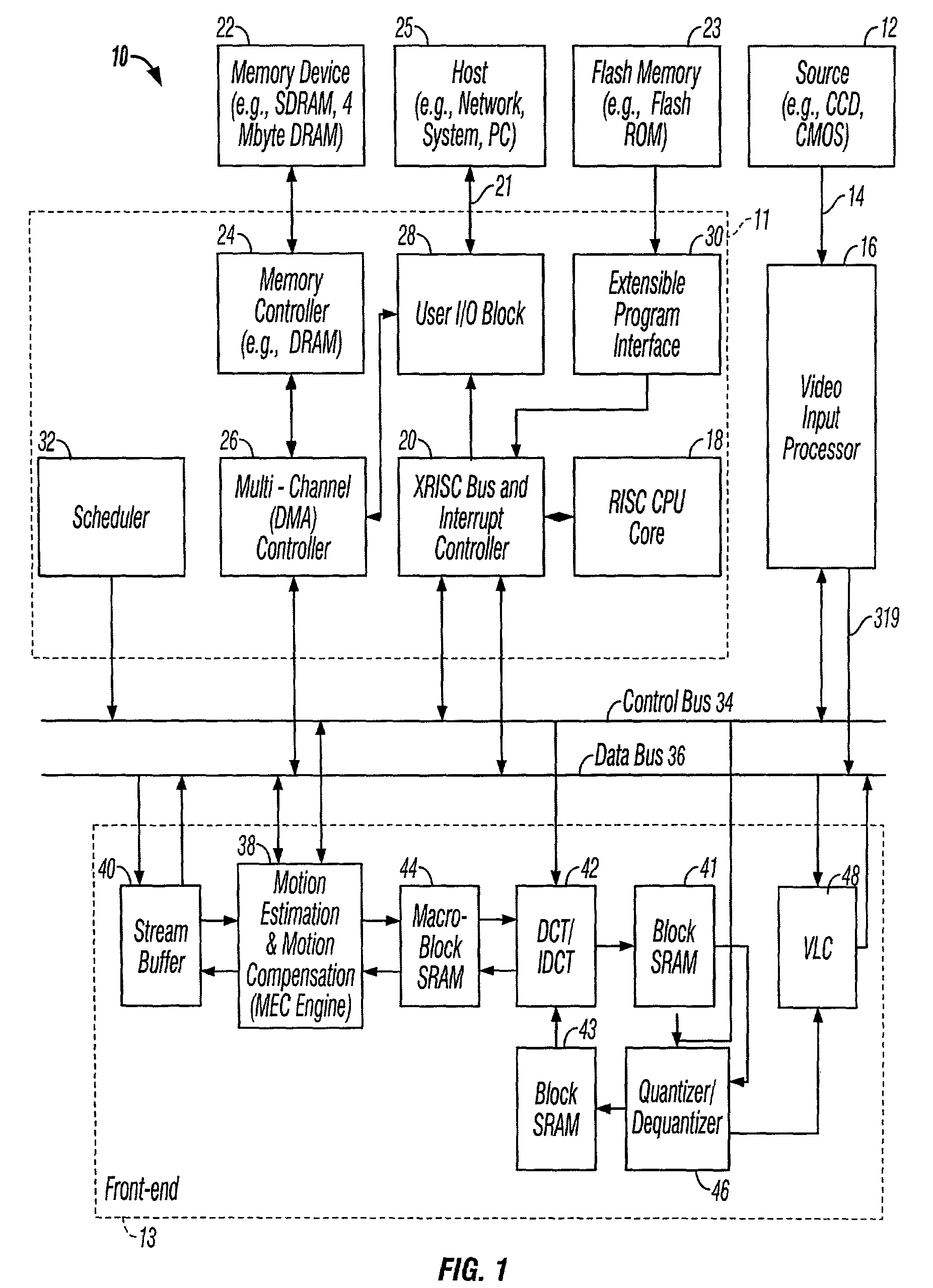
Video input processor in multi-format video compression system
InactiveUS7142251B2Increase investmentHigh frequencyTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsProgressive scanComputer graphics (images)
A video input processor is provided to process different input video format, including RGB, RGB Bayer, YUV 4:2:2 interlaced and progressive video data. The video input processor also uses an advanced algorithm to efficiently convert video data in RGB color space to YUV color space. The video input processor further enables multi-functions such as video image scaling, video image filtering before the video data are output for further video compression.
Owner:MICRONAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com