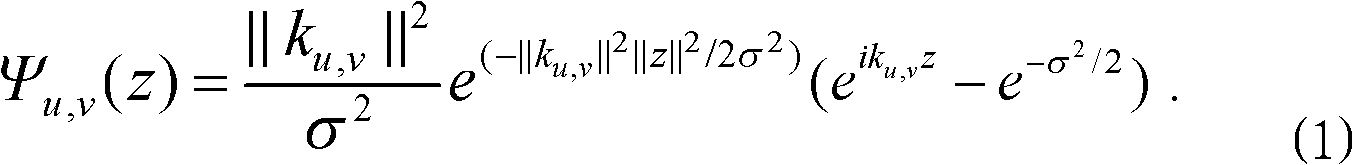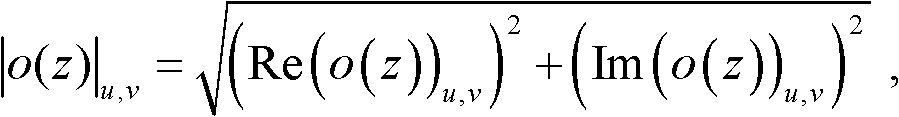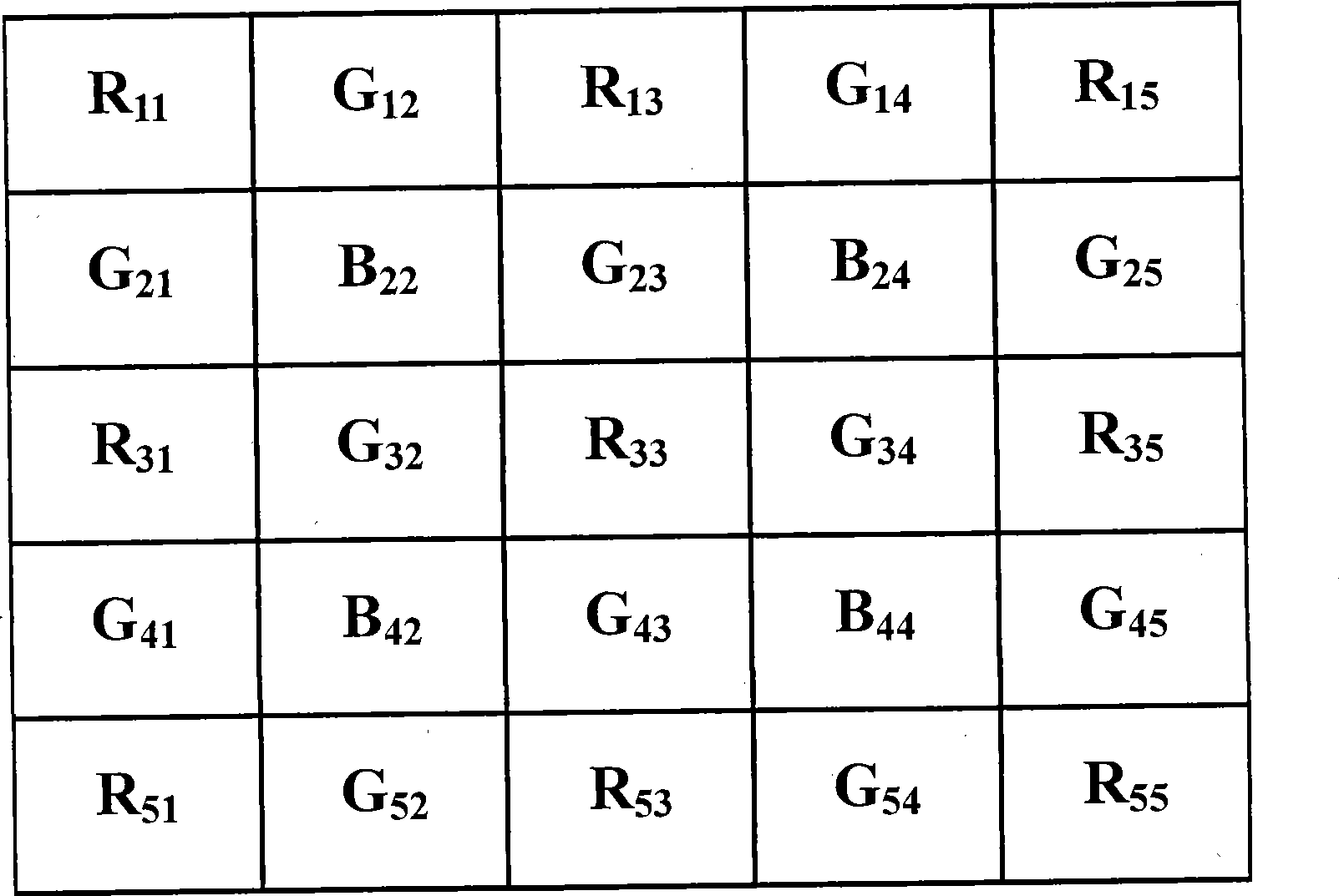Patents
Literature
78 results about "Edge orientation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
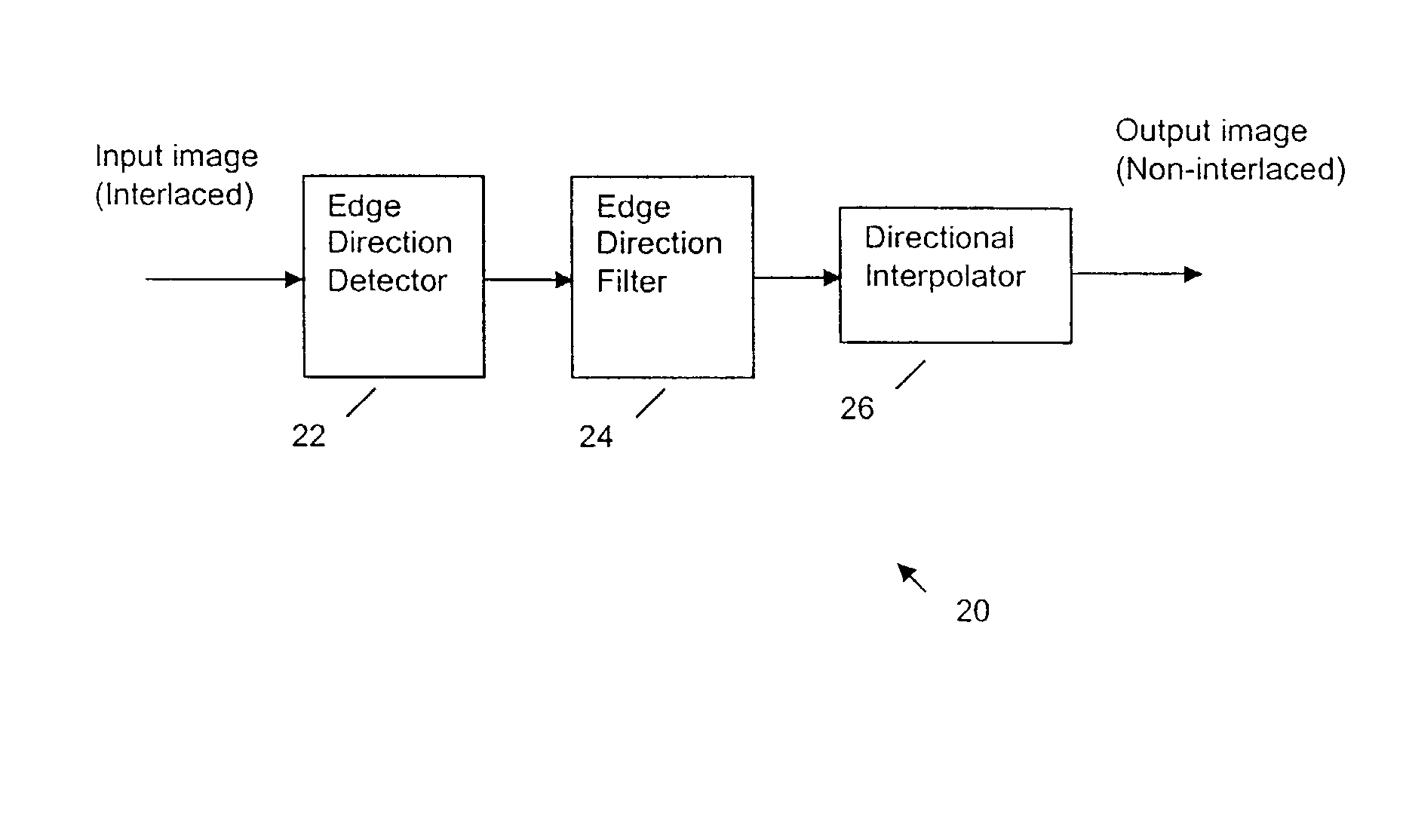
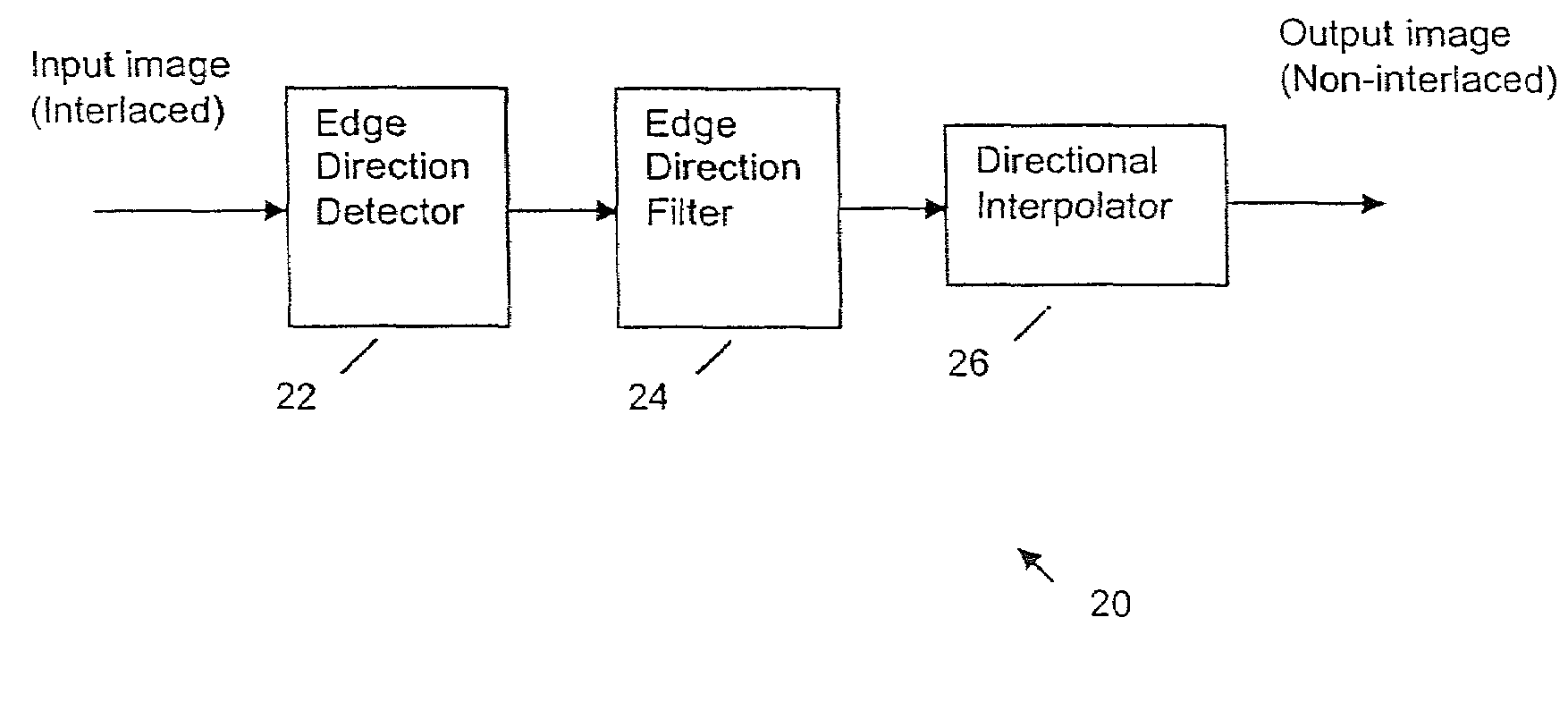
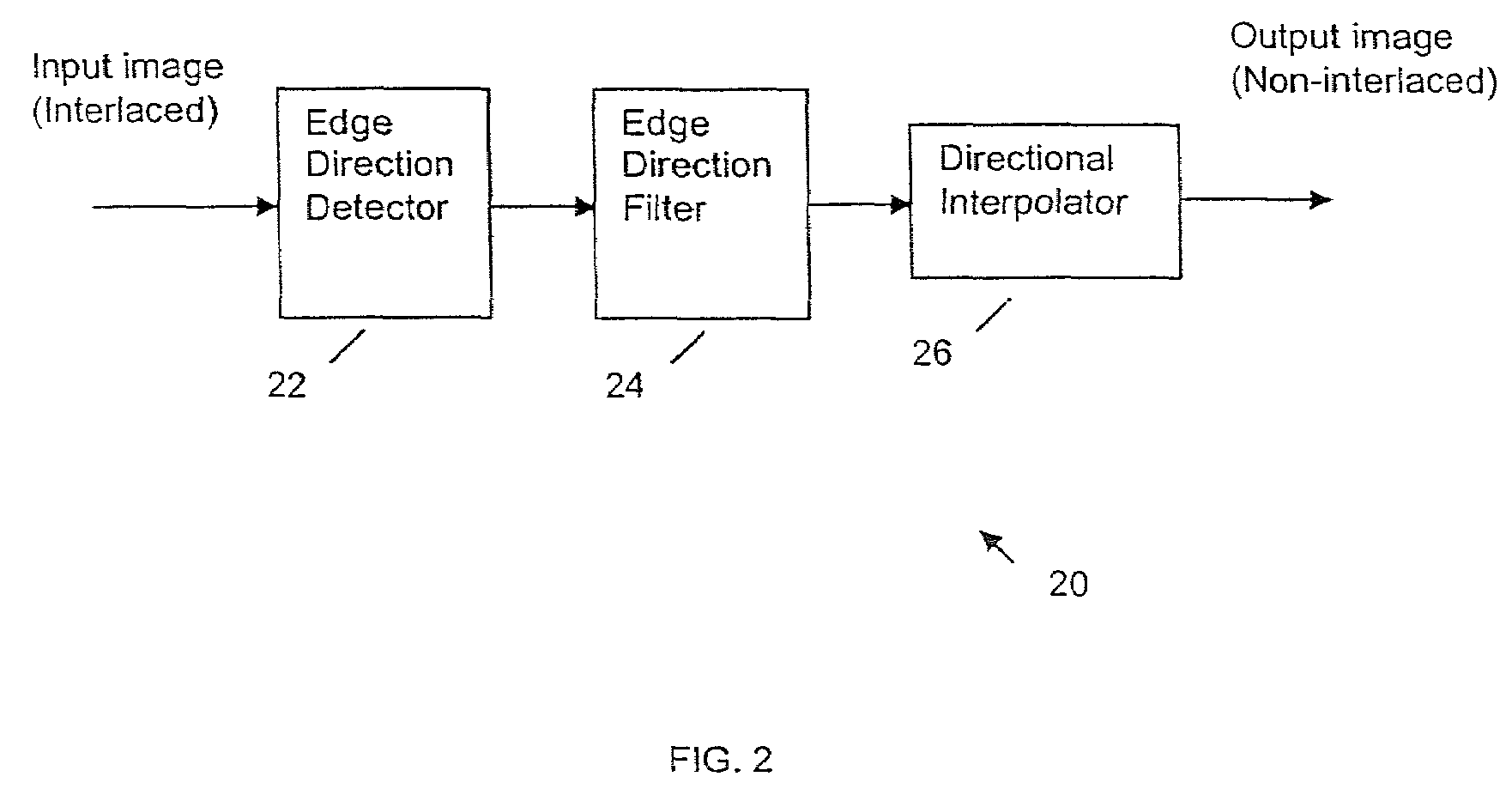
Deinterlacing of video sources via image feature edge detection
ActiveUS7023487B1Reduce artifactsPreserves maximum amount of vertical detailImage enhancementTelevision system detailsInterlaced videoProgressive scan
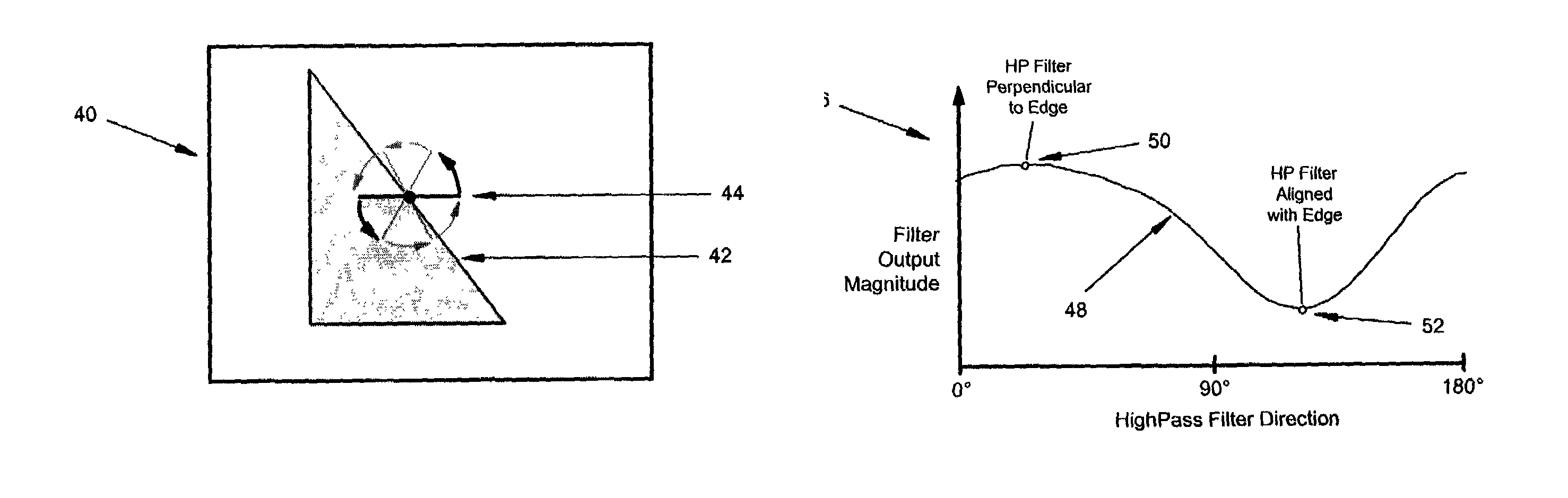
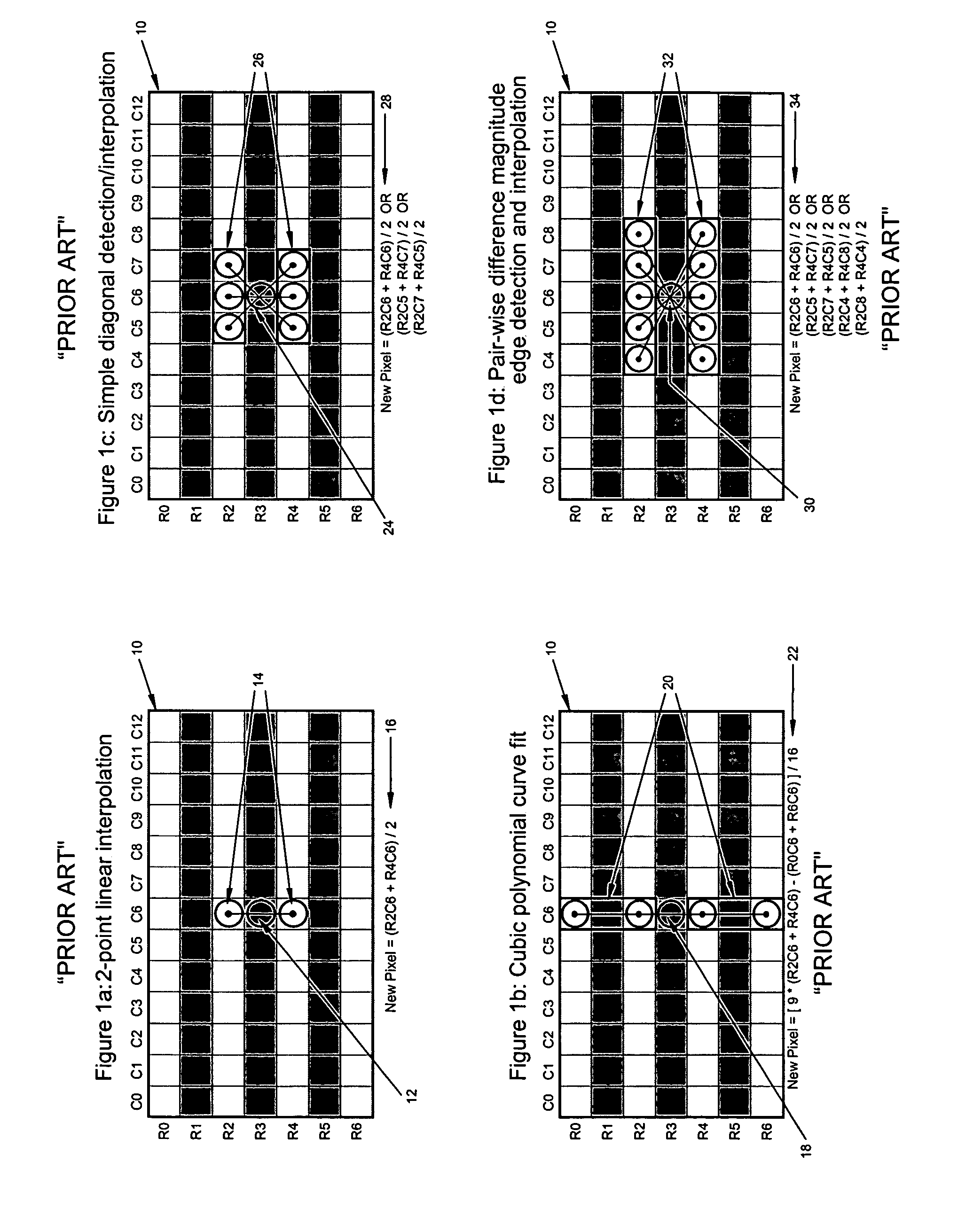
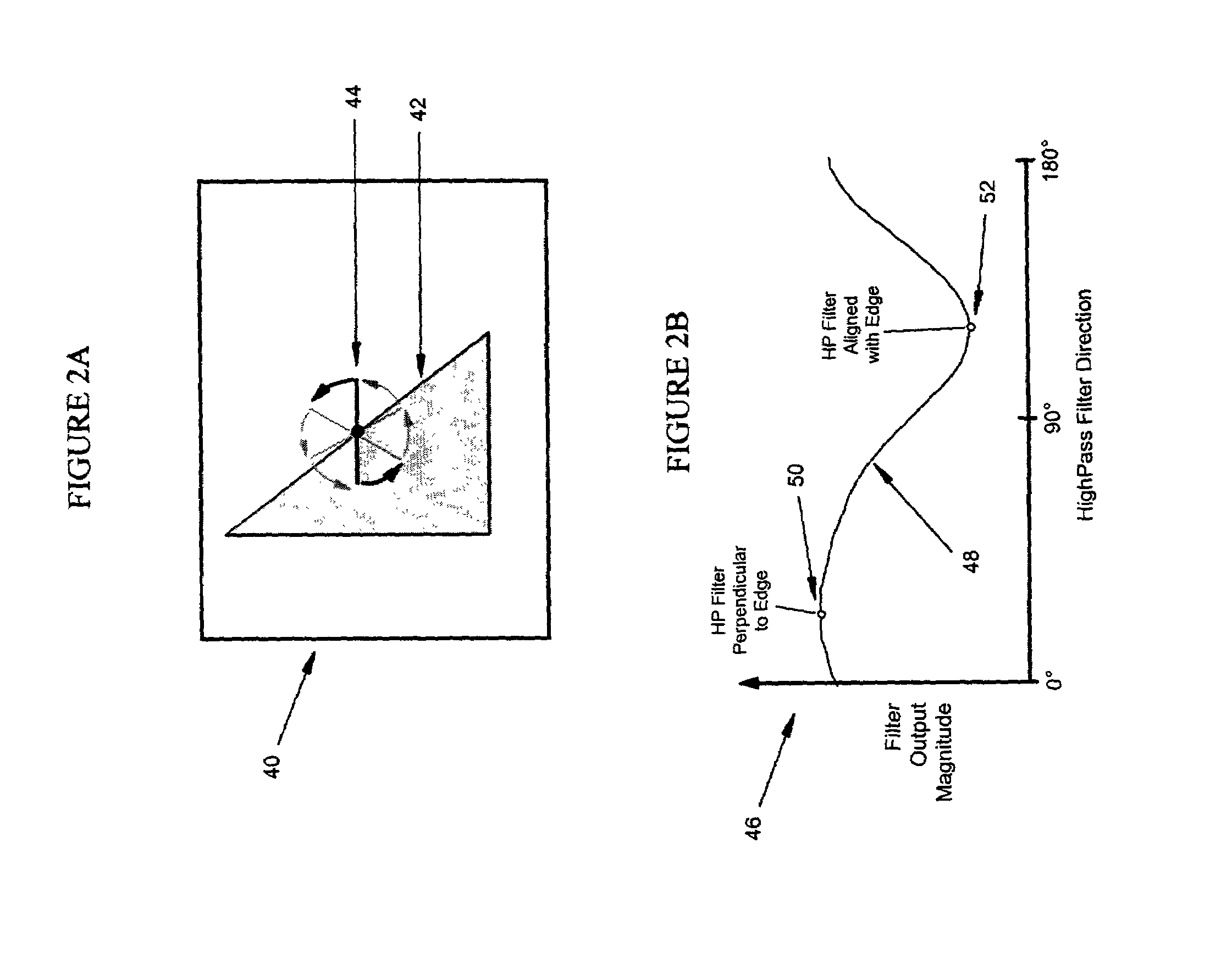
An interlaced to progressive scan video converter which identifies object edges and directions, and calculates new pixel values based on the edge information. Source image data from a single video field is analyzed to detect object edges and the orientation of those edges. A 2-dimensional array of image elements surrounding each pixel location in the field is high-pass filtered along a number of different rotational vectors, and a null or minimum in the set of filtered data indicates a candidate object edge as well as the direction of that edge. A 2-dimensional array of edge candidates surrounding each pixel location is characterized to invalidate false edges by determining the number of similar and dissimilar edge orientations in the array, and then disqualifying locations which have too many dissimilar or too few similar surrounding edge candidates. The surviving edge candidates are then passed through multiple low-pass and smoothing filters to remove edge detection irregularities and spurious detections, yielding a final edge detection value for each source image pixel location. For pixel locations with a valid edge detection, new pixel data for the progressive output image is calculated by interpolating from source image pixels which are located along the detected edge orientation.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
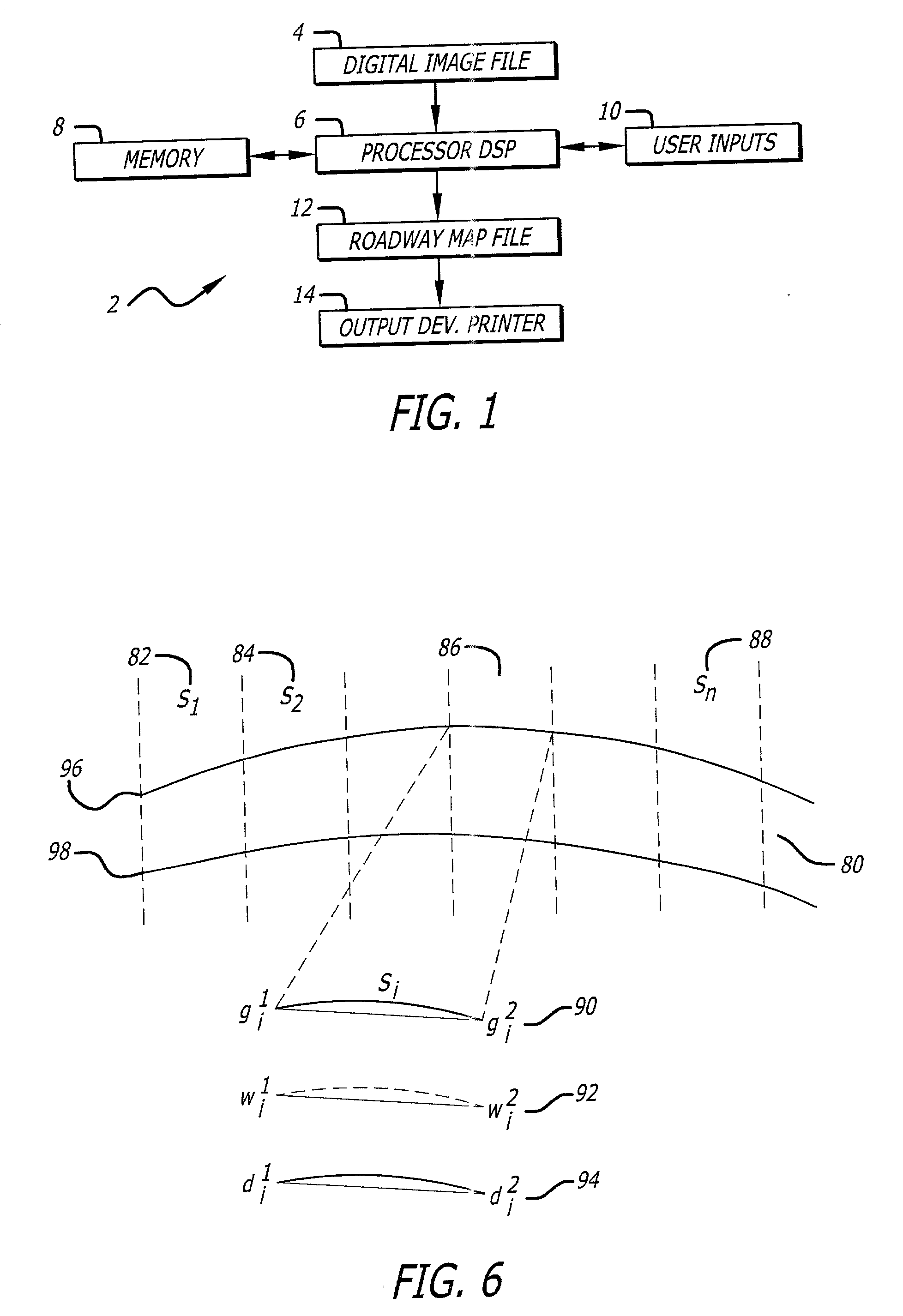
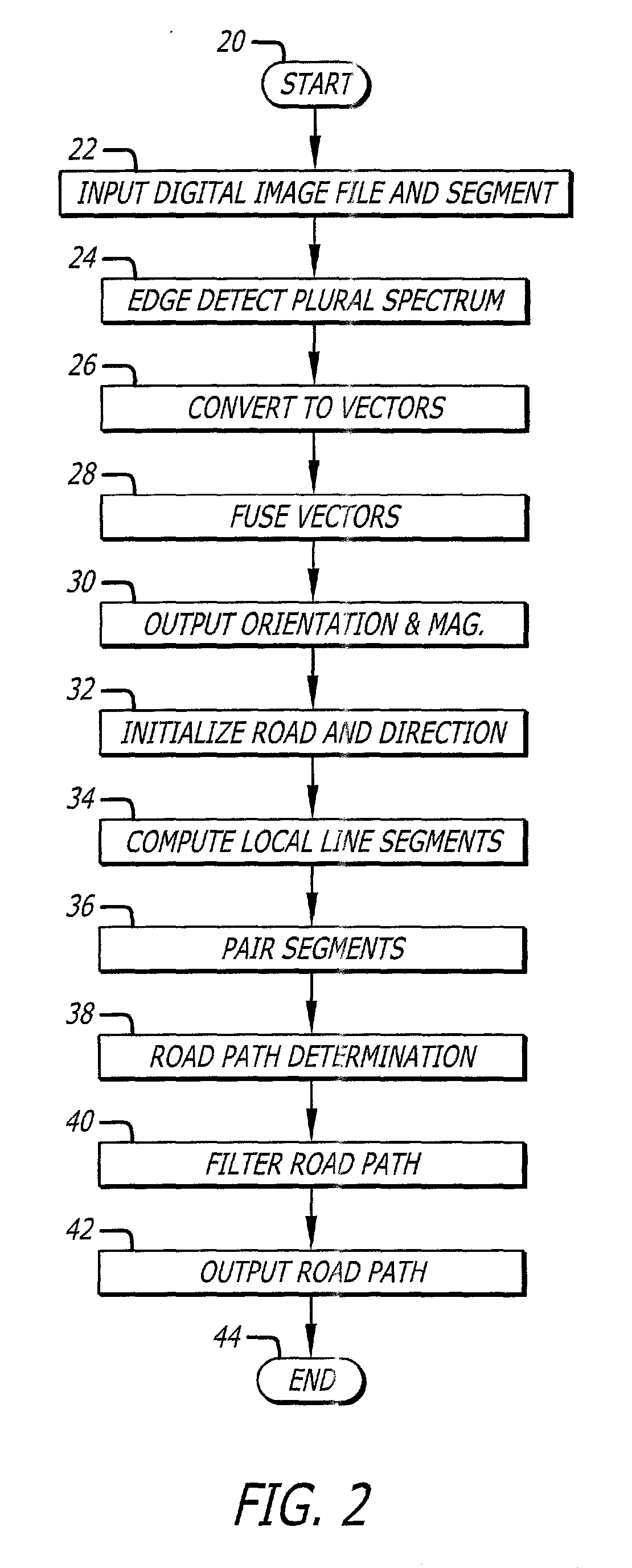
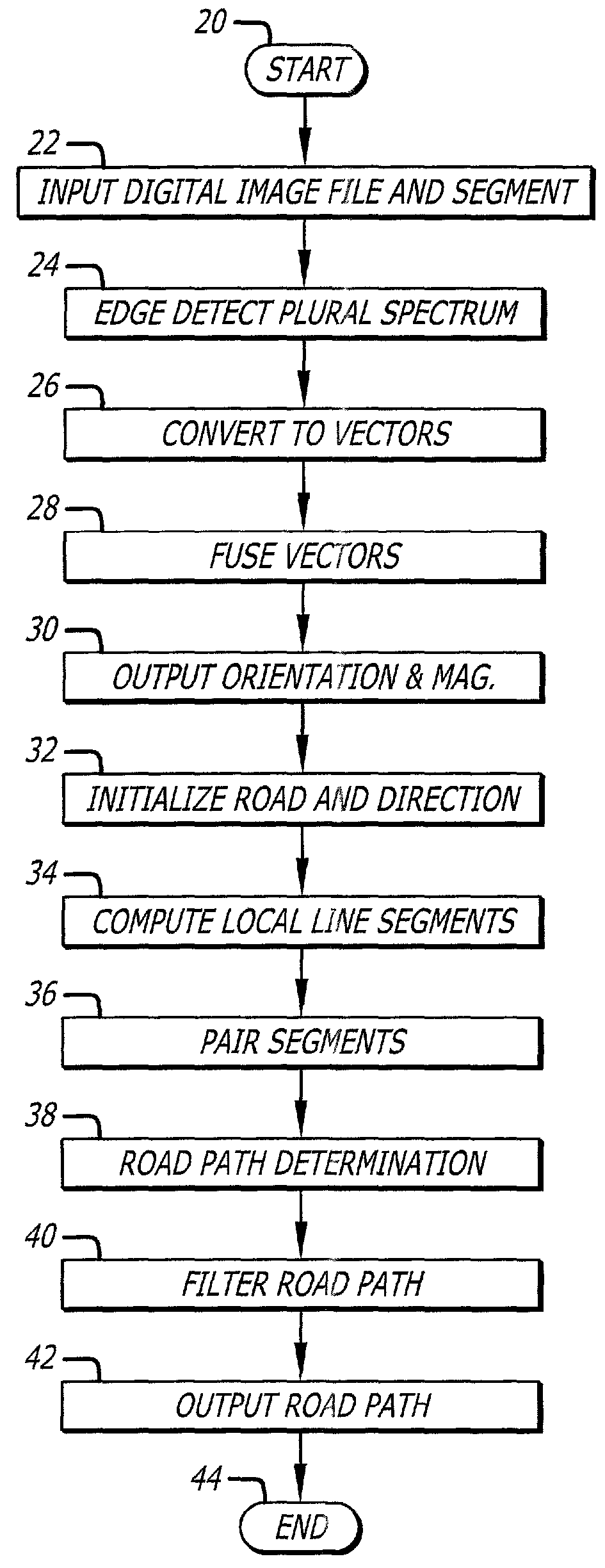
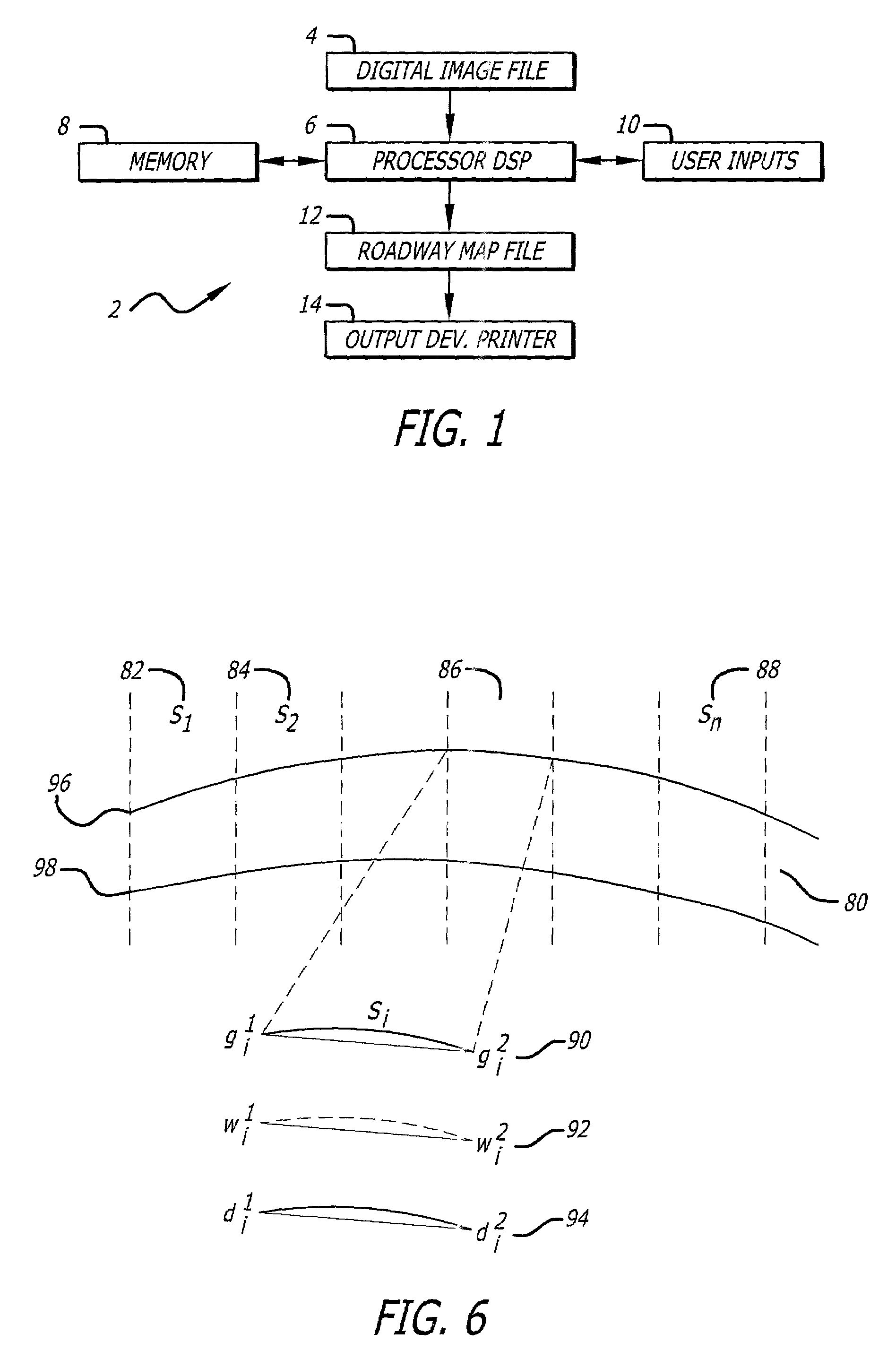
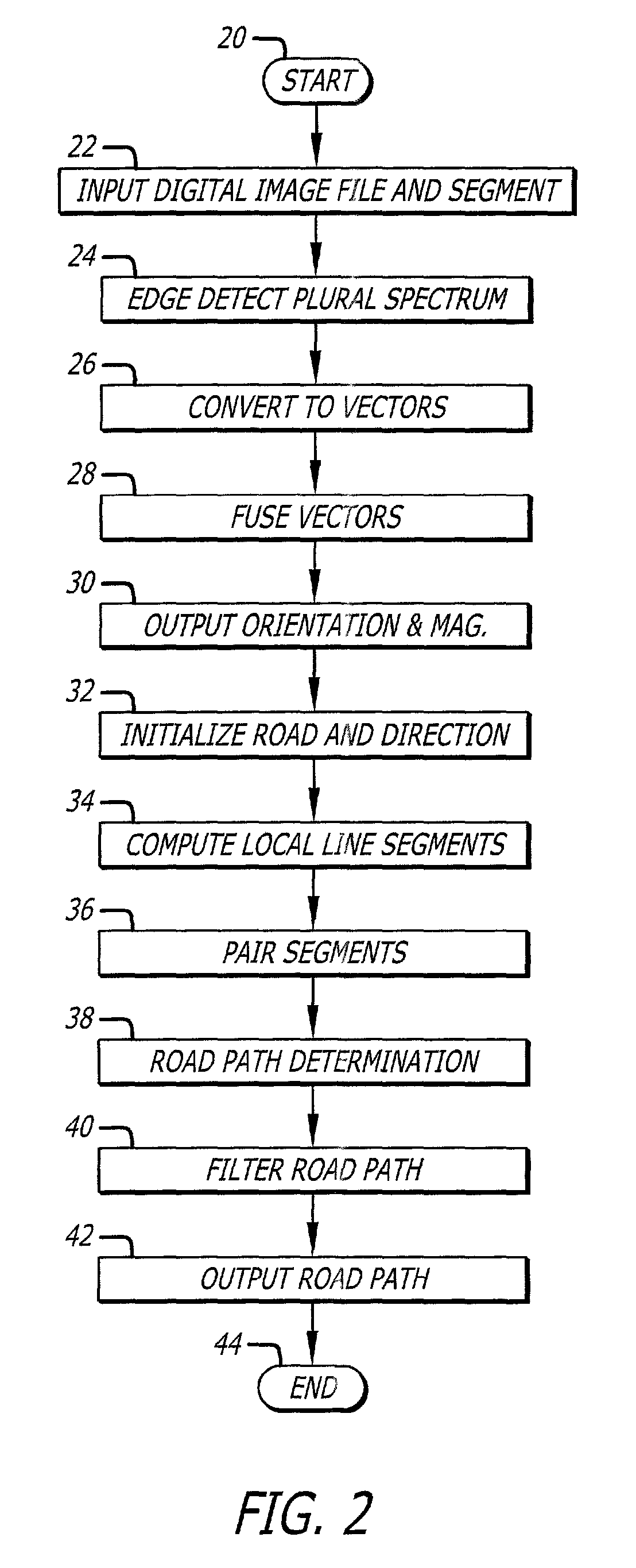
Digital image edge detection and road network tracking method and system
A system and method for finding edge orientation and magnitude, and extracting a road path from an image. An image is segmented into at least a first window and a second window. A first road segment having plural parameters within the first window is specified. Plural road segments are identified, each having plural parameters, in the second window. The orientation of plural line segments in the second window are determined, and paired, based on their orientation. The line segment orientations are determined by receiving a plurality of edge orientation estimates, transforming a portion of them, and aggregating the transformed portion into an edge orientation estimate. A stochastic process is performed on the plural parameters of the plural road segments to identify a second road segment having the maximum correlation with the plural parameters of the first road segment.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
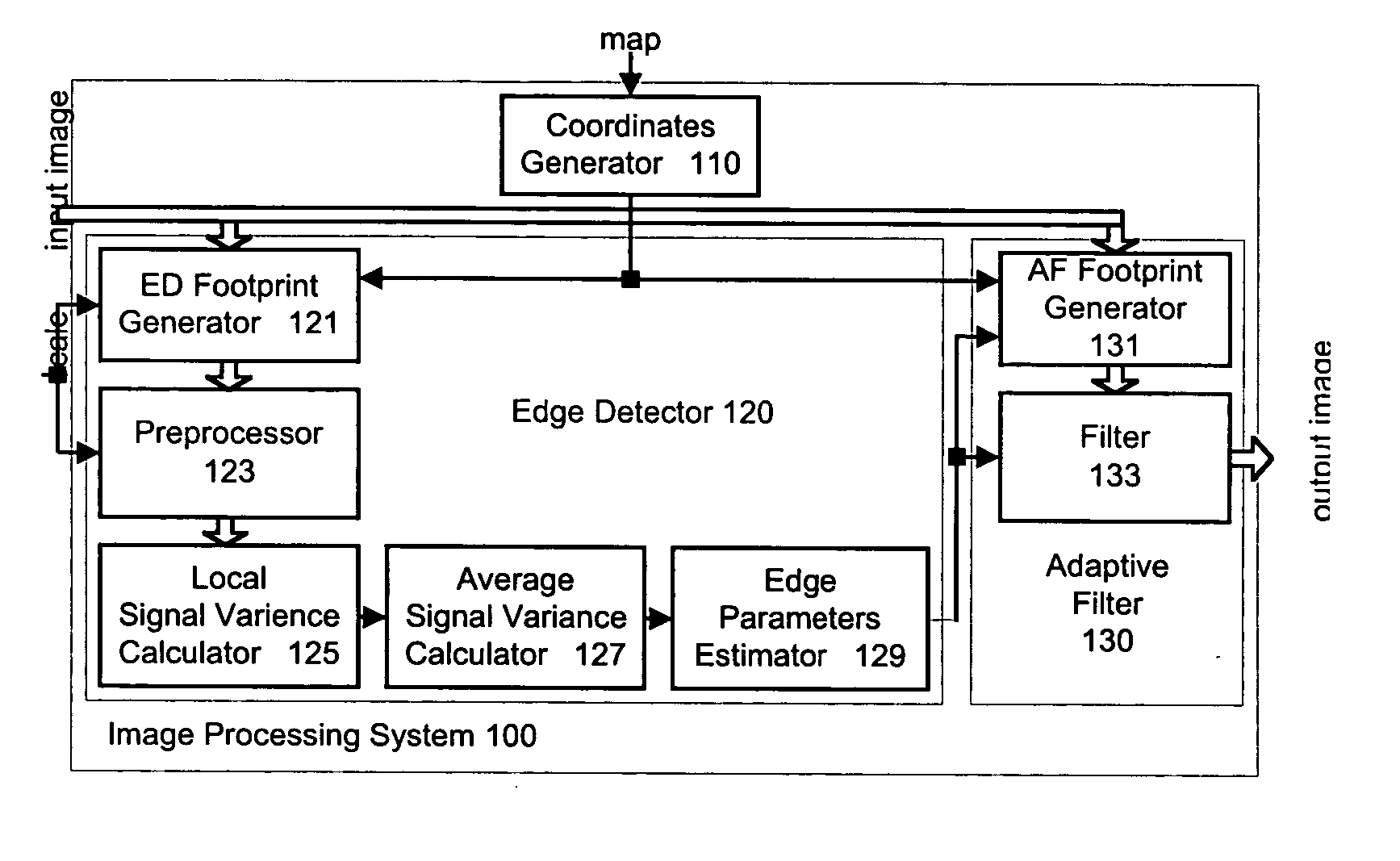
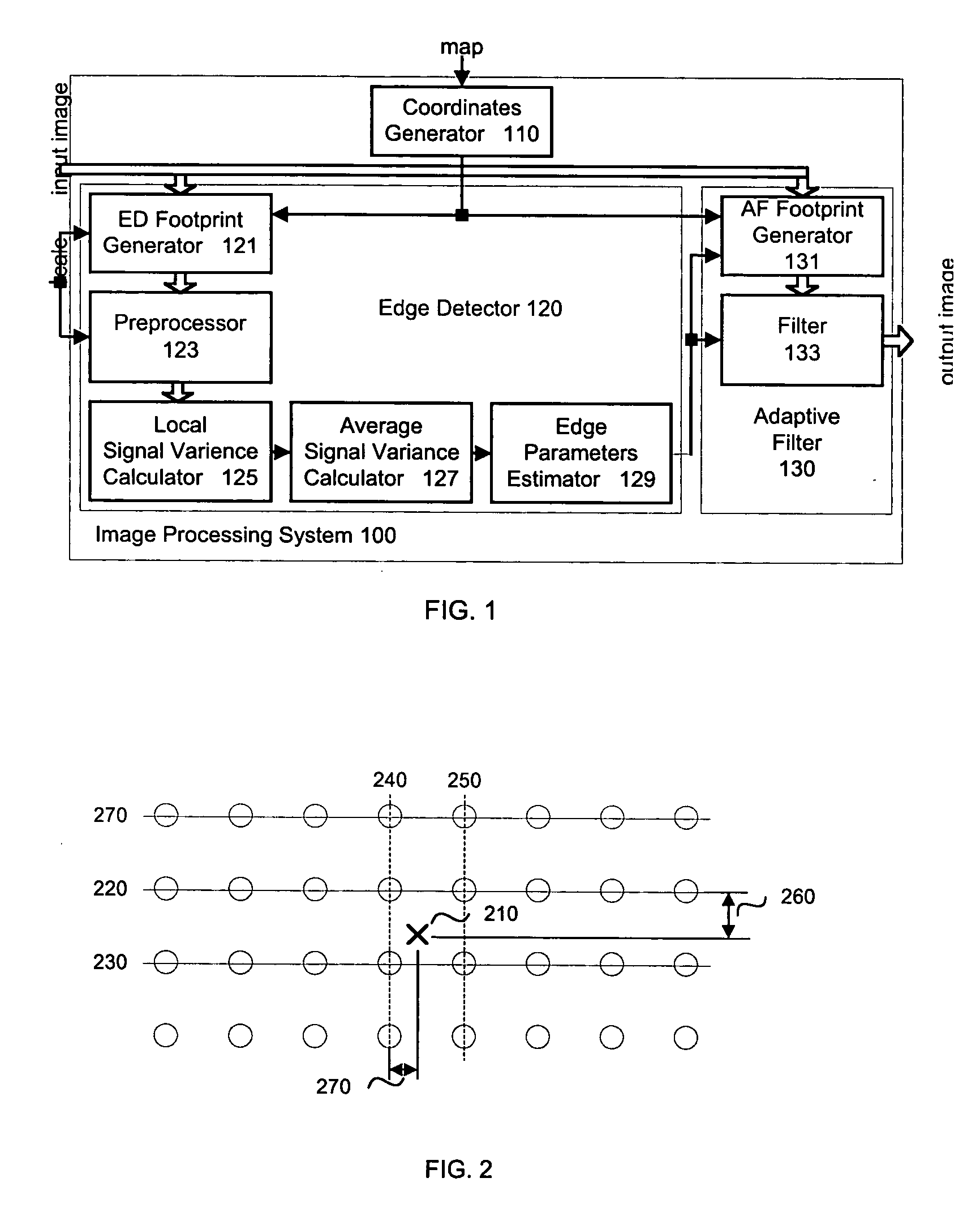
Edge adaptive image expansion and enhancement system and method
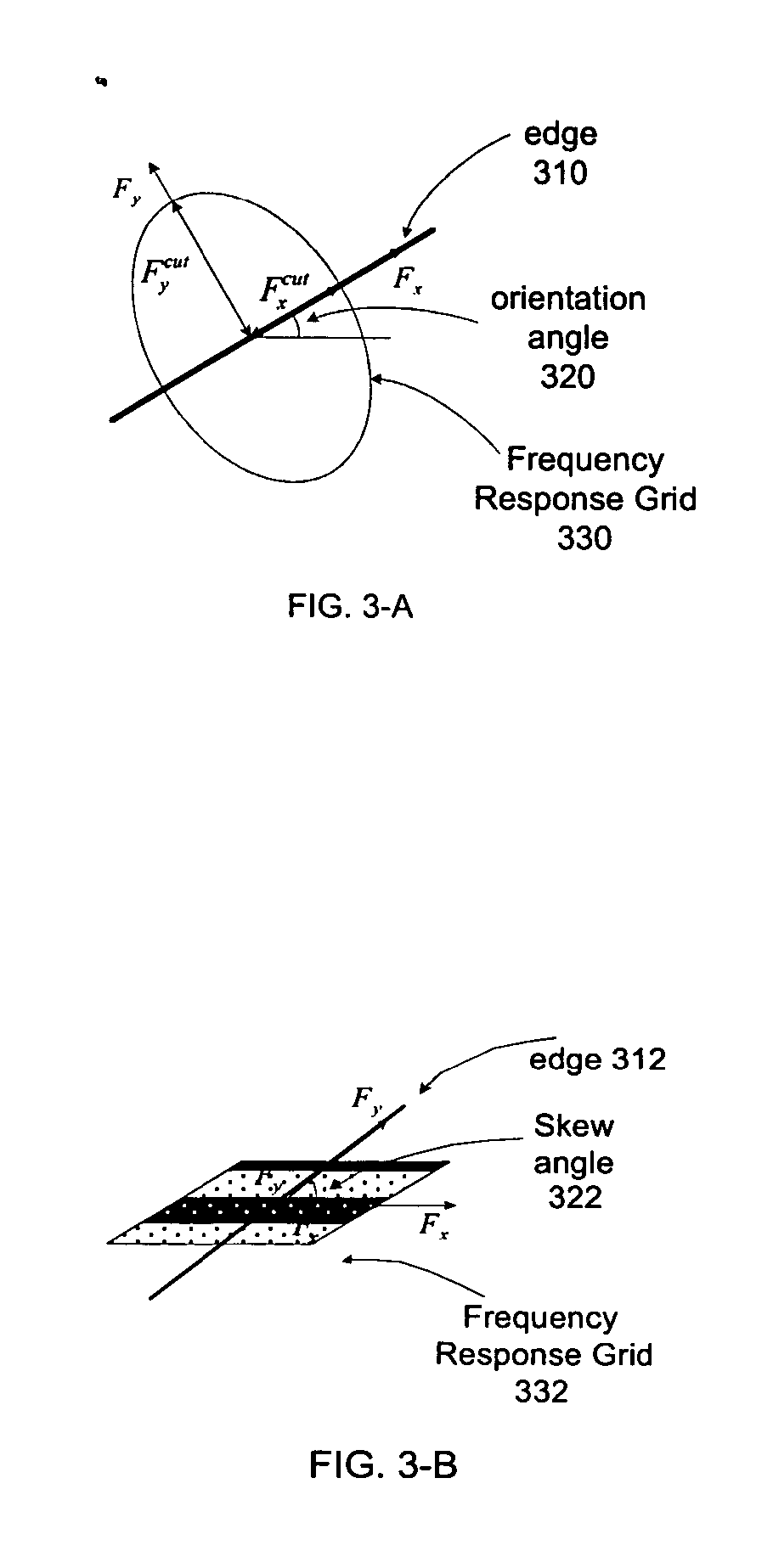
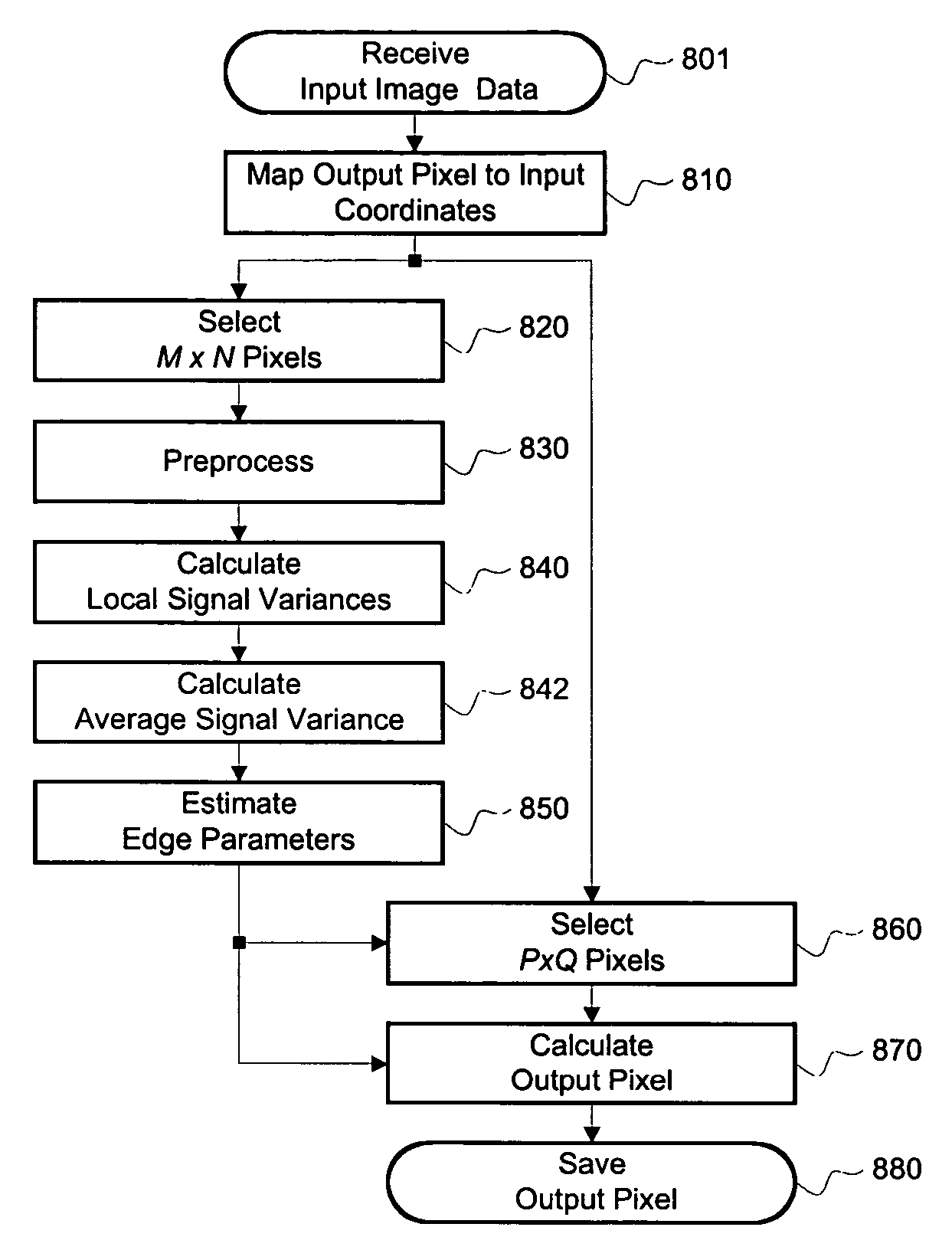
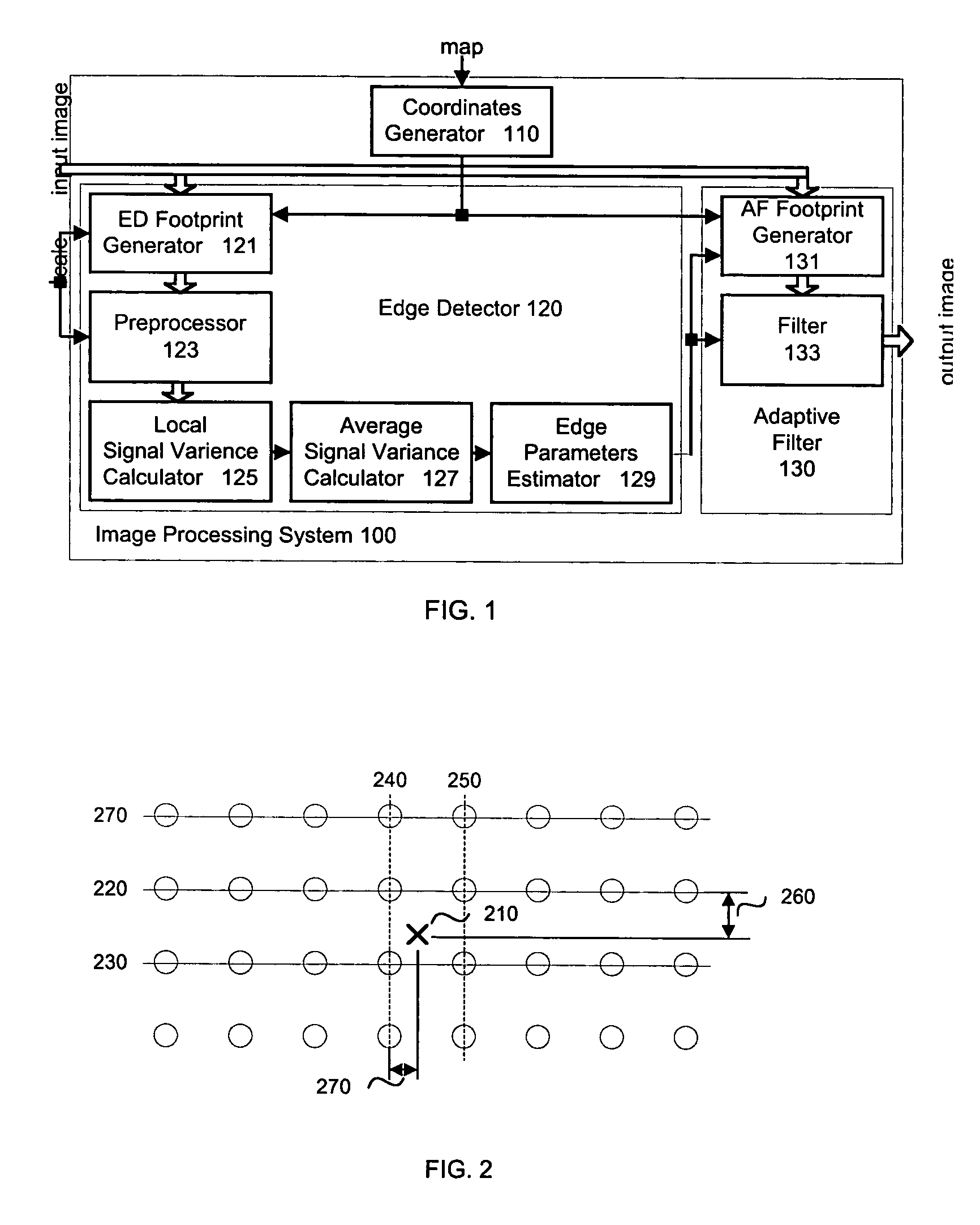
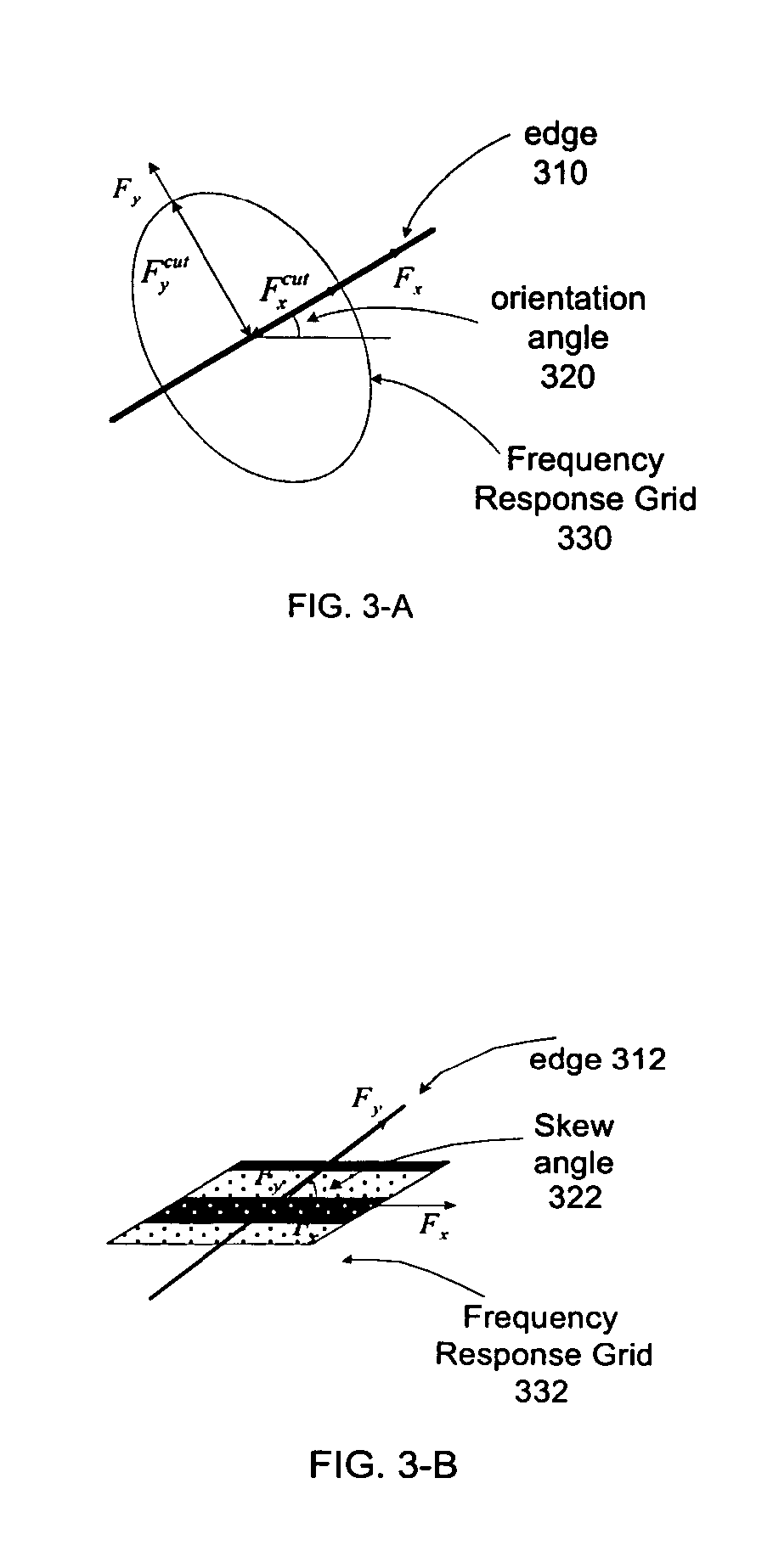
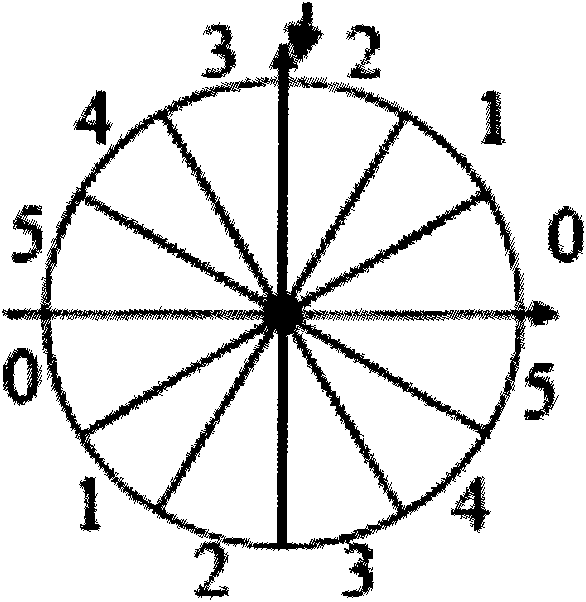
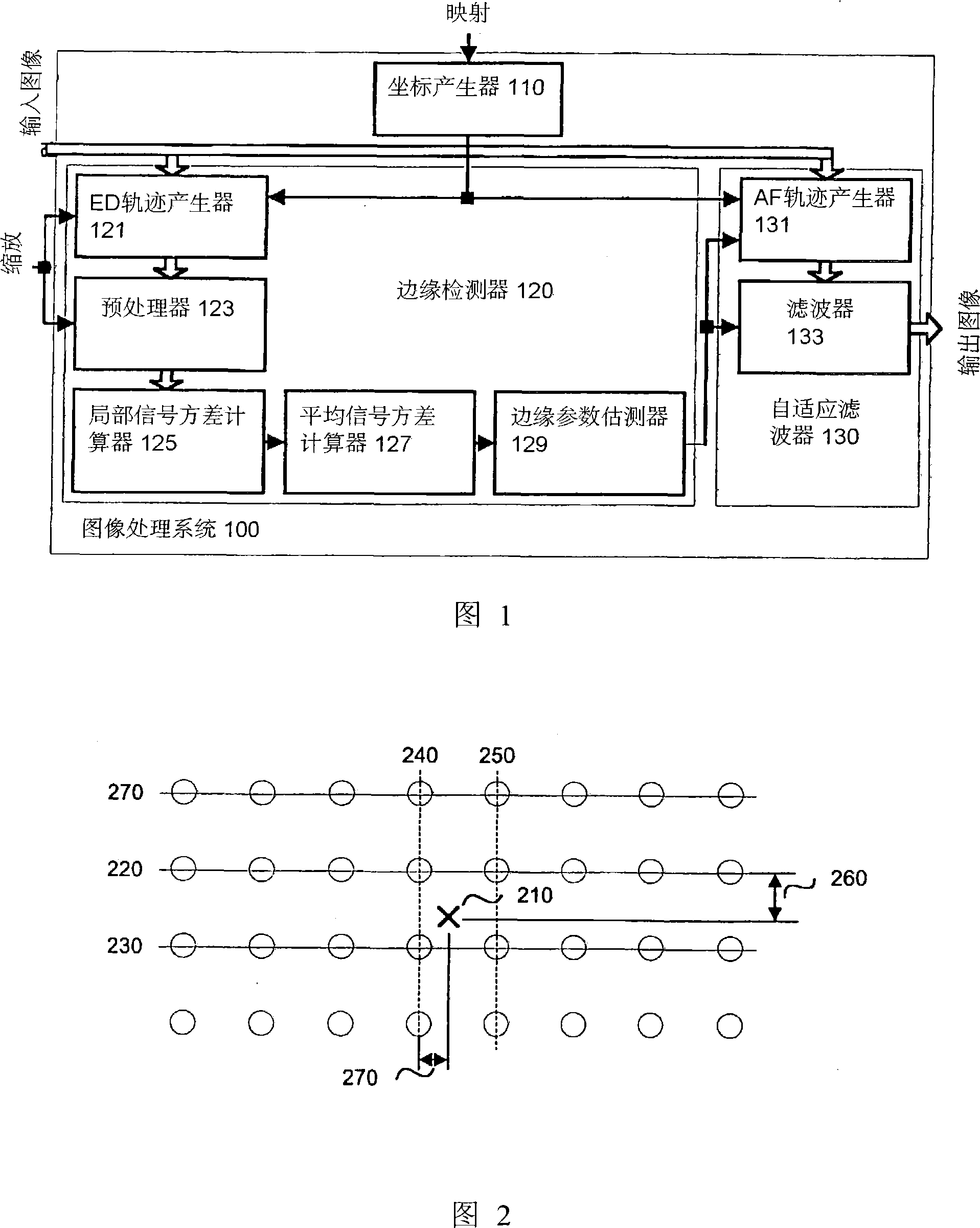
An edge adaptive system and method for image filtering. The method maps each output pixel onto input image coordinates and then prefilters and resamples the input image pixels around this point to reduce noise and adjust the scale corresponding to a particular operation. Then the edge in the input image is detected based on local and average signal variances in the input pixels. According to the edge detection parameters, including orientation, anisotropy and variance strength, the method determines a footprint and frequency response for the interpolation of the output pixel. In a more particular implementation, the method divides the input pixel space into a finite number of directions called skews, and estimates the edge orientation with the nearest skew direction. This further facilitates pixels inclusion in the interpolation of the output pixel.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Edge adaptive image expansion and enhancement system and method
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Condenser type touch screen
ActiveCN101477430AGood display visual effectMinimize or avoid interference phenomenaInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceEdge orientation
A capacitive touch screen comprises at least one transparent insulated layer and at least one transparent electrode conducting layer, wherein, the transparent electrode conducting layer is arranged on the transparent insulated layer, and comprises a plurality of electrodes. The touch screen is characterized in that the edge of each electrode on the transparent electrode conducting layer is in the shape of a saw tooth in a visual area of the capacitive touch screen, so that the bending of the electrode edge can be utilized, to enable the edge orientation of the electrodes with smaller line width on the capacitive touch screen and the clearance between electrodes to incline with the arrange direction of pixel point arrays of a display device at a certain angle. Therefore, as far as the light interference is concerned, the slit direction is changed so that the generated interference fringes are not evident or disappear, the light interference in the visual area of the touch area is effectively weakened or avoided, and the better visual effect is possessed by the display device.
Owner:SHANTOU GOWORLD DISPLAY (PLANT II) CO LTD
Automatic micro-expression recognition method based on Gabor features and edge orientation histogram (EOH) features
ActiveCN103258204ARecognition speed is fastImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionEdge orientationVideo image
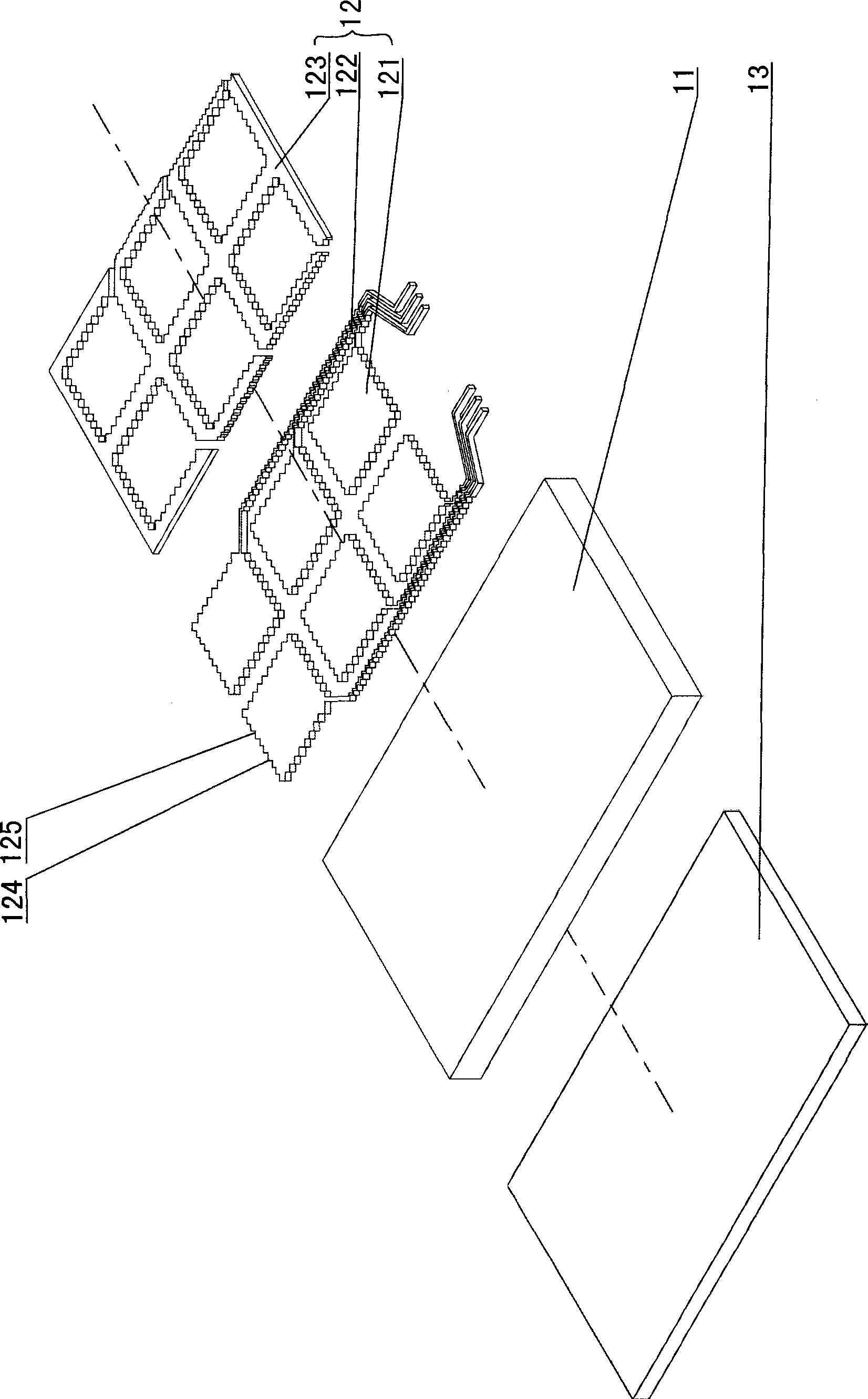
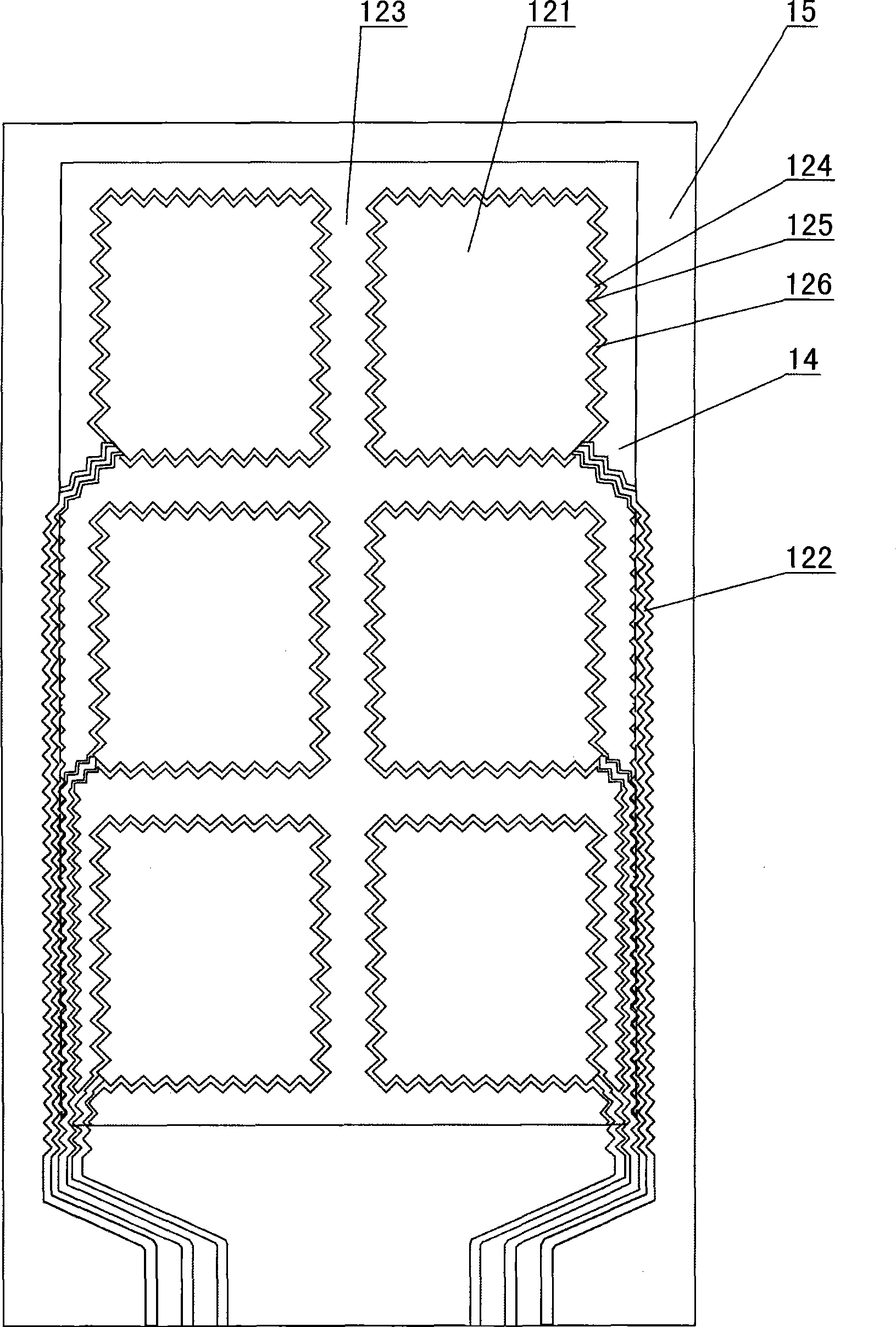
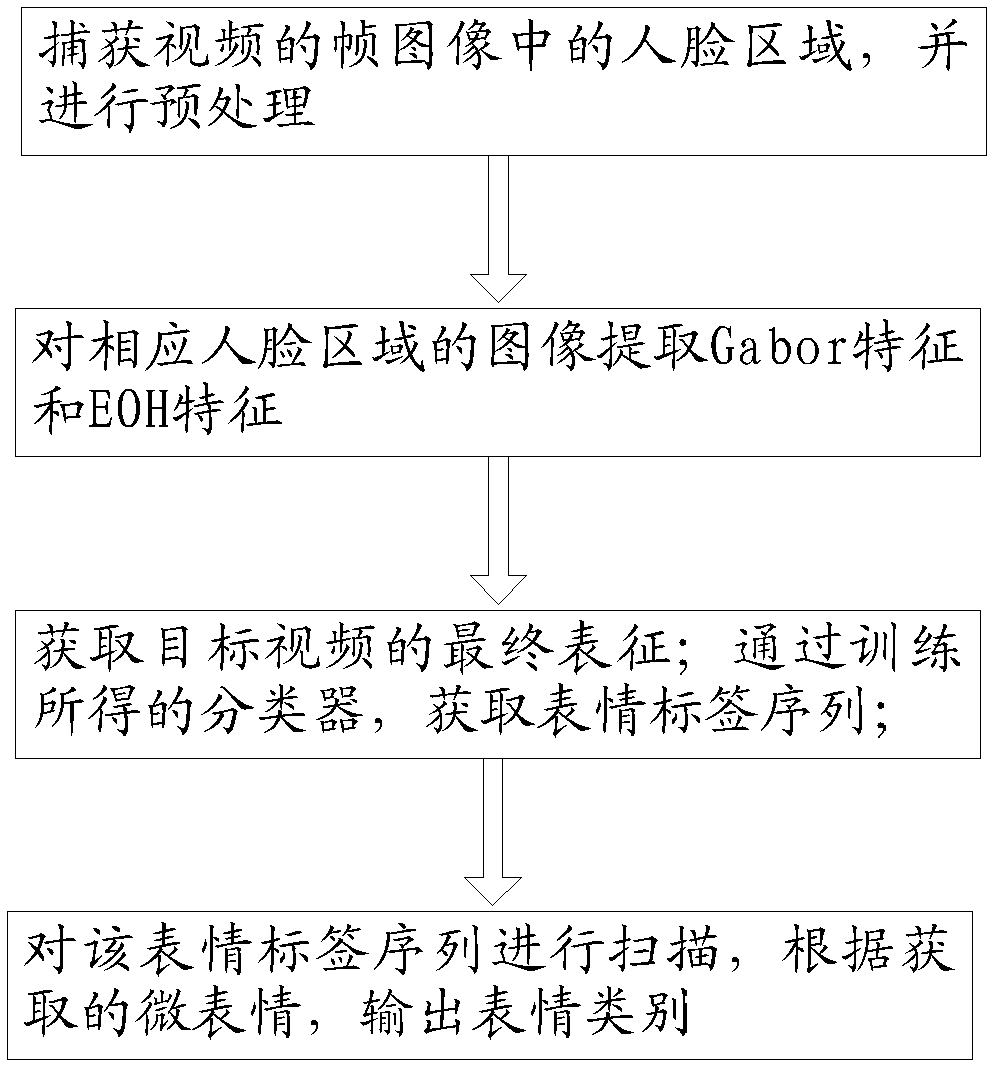
The invention provides an automatic expression recognition method. The method includes the following steps: step10, capturing face areas in frame images of a video and preprocessing the face areas, step20, extracting Gabor features and EOH features of images of the corresponding face areas, step30, integrating the corresponding features to acquire final superficial features of the target video and acquiring an expression tag sequence of each frame of video images through a classifier acquired by training, step 40, scanning the expression tag sequences, judging duration time of expressions and outputting expression classes according to the acquired micro- expressions.
Owner:INST OF PSYCHOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Digital image edge detection and road network tracking method and system
ActiveUS7636455B2Maximize joint probabilityReduce errorsImage enhancementImage analysisEdge orientationRoad networks
A system and method for finding edge orientation and magnitude, and extracting a road path from an image. An image is segmented into at least a first window and a second window. A first road segment having plural parameters within the first window is specified. Plural road segments are identified, each having plural parameters, in the second window. The orientation of plural line segments in the second window are determined, and paired, based on their orientation. The line segment orientations are determined by receiving a plurality of edge orientation estimates, transforming a portion of them, and aggregating the transformed portion into an edge orientation estimate. A stochastic process is performed on the plural parameters of the plural road segments to identify a second road segment having the maximum correlation with the plural parameters of the first road segment.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
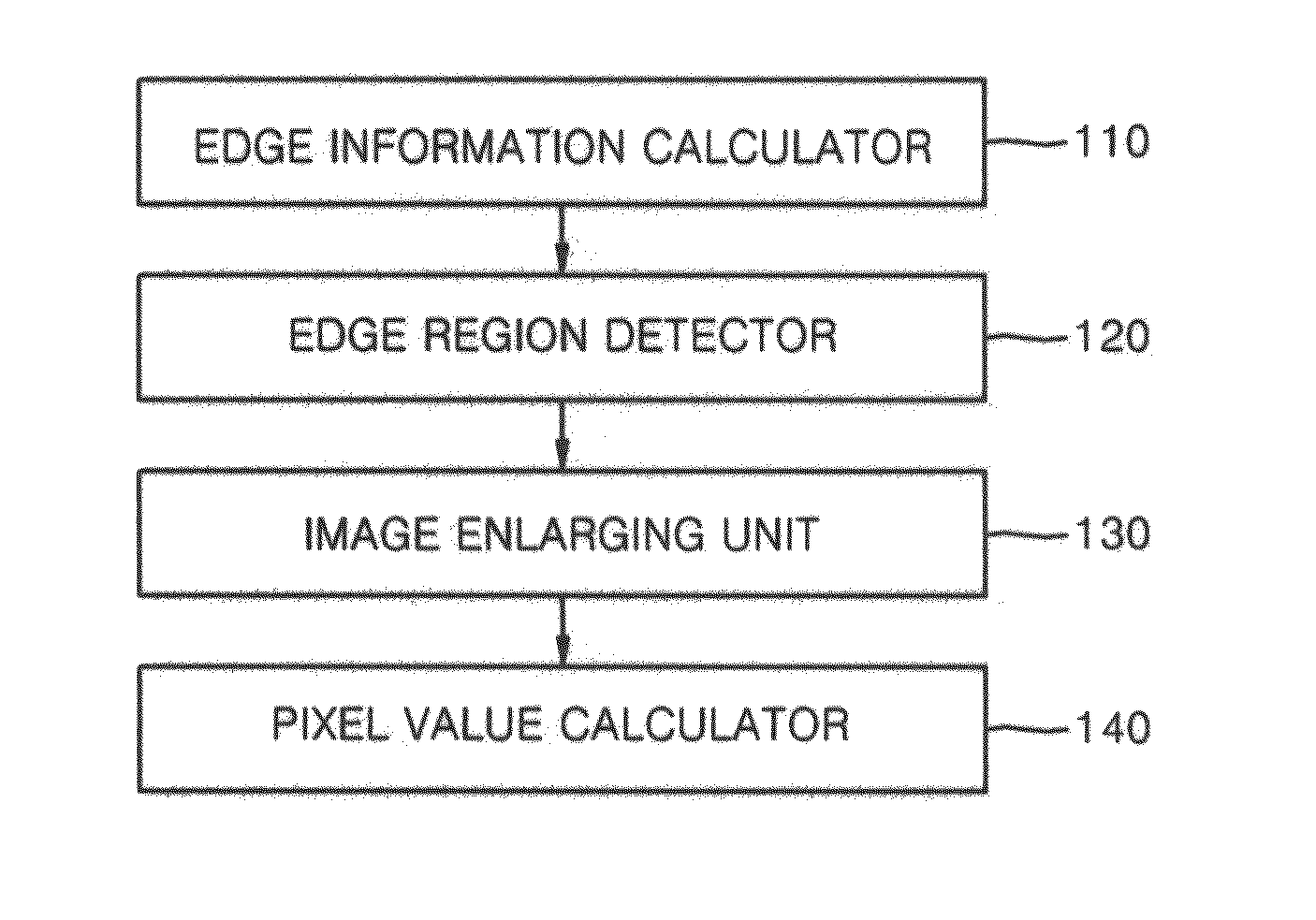
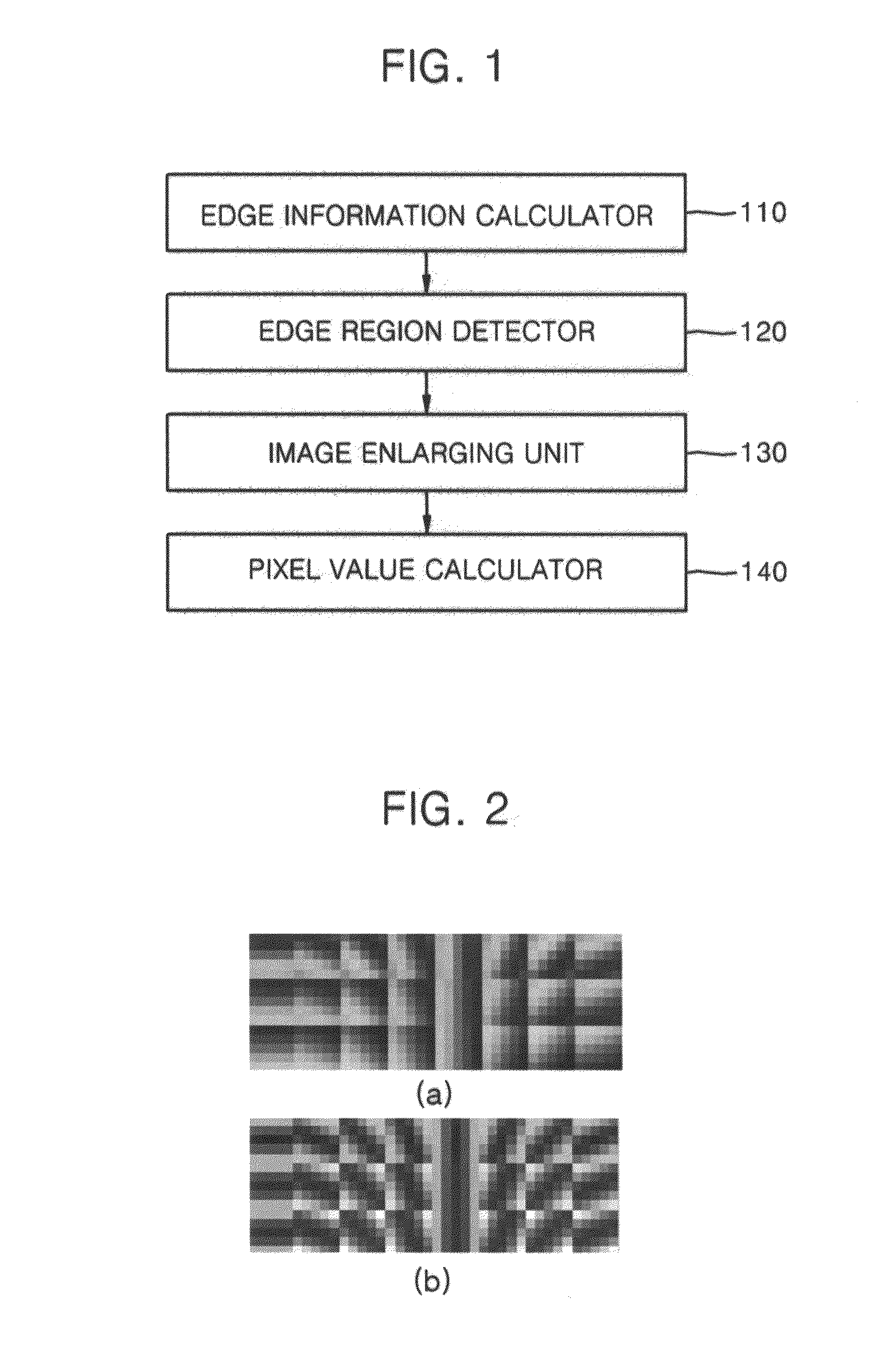
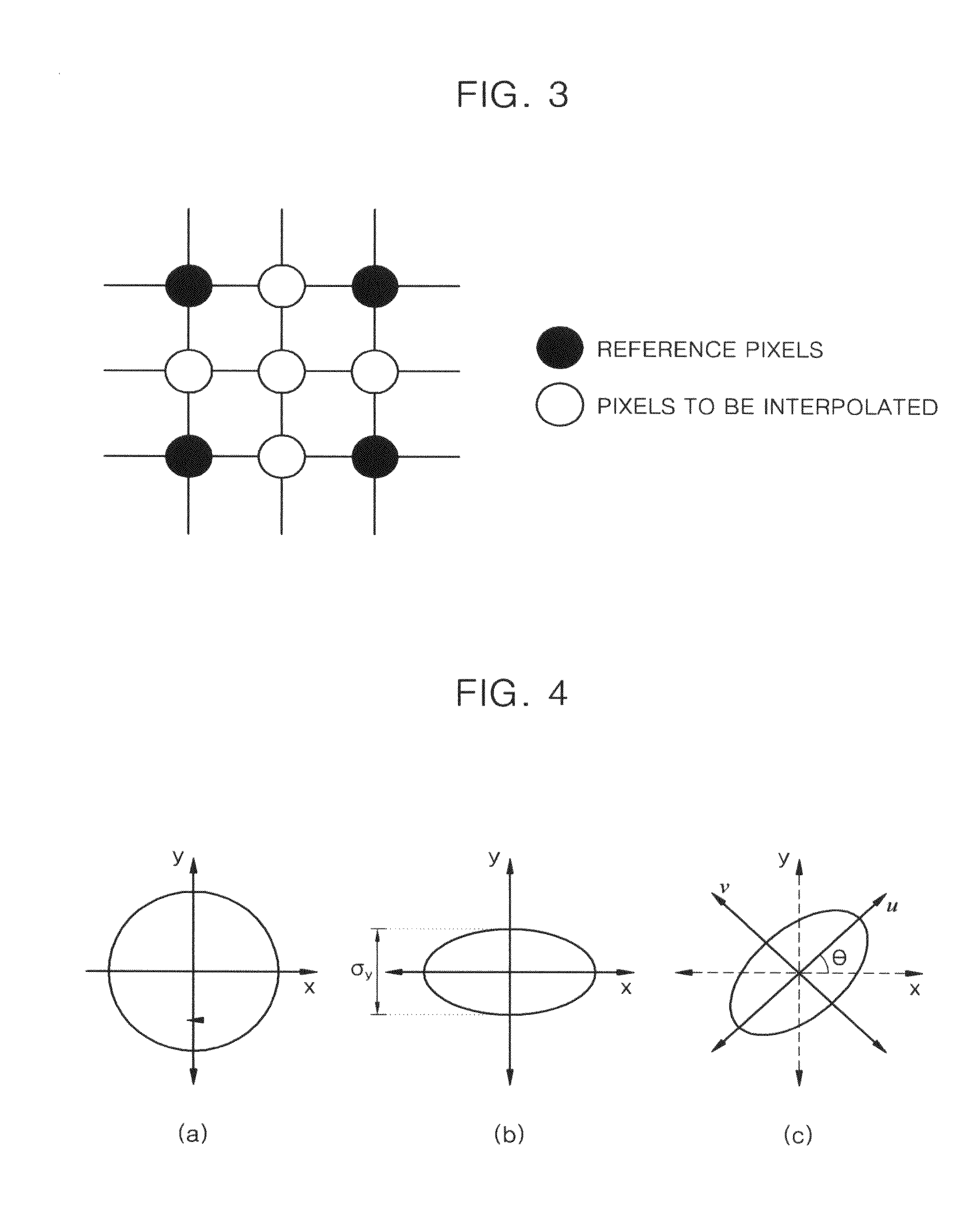
Apparatus and method for image interpolation using anisotropic gaussian filter
InactiveUS20110176744A1High resolutionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityImage resolution
An apparatus and method for image interpolation using an anisotropic Gaussian filter, the image interpolation apparatus including: an edge information calculator calculating a first edge orientation that is an orientation of an edge of each of a plurality of pixels that constitute an input low resolution image, and first edge orientation energy that is a maximal strength of the edge corresponding to the first edge orientation; an image enlarging unit calculating a second edge orientation and second edge orientation energy of each of pixels to be interpolated, which are obtained by subtracting reference pixels corresponding to each of the pixels of the low resolution image among a plurality of pixels that constitute the high resolution image that is obtained by enlarging the low resolution image, based on the first edge orientation and the first edge orientation energy of the adjacent reference pixels; and a pixel value calculator calculating a value of each of the pixels to be interpolated, by using an interpolation filter having a direction and a width determined according to the second edge orientation and the second edge orientation energy of each of the pixels to be interpolated. The Gaussian filter having a direction and a width that are adaptively adjusted according to an orientation and strength of an edge is used to interpolate values of pixels of a high resolution image that is obtained by image enlargement so that deterioration of image quality can be minimized with a small amount of calculation and an image with high quality and high resolution can be generated.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
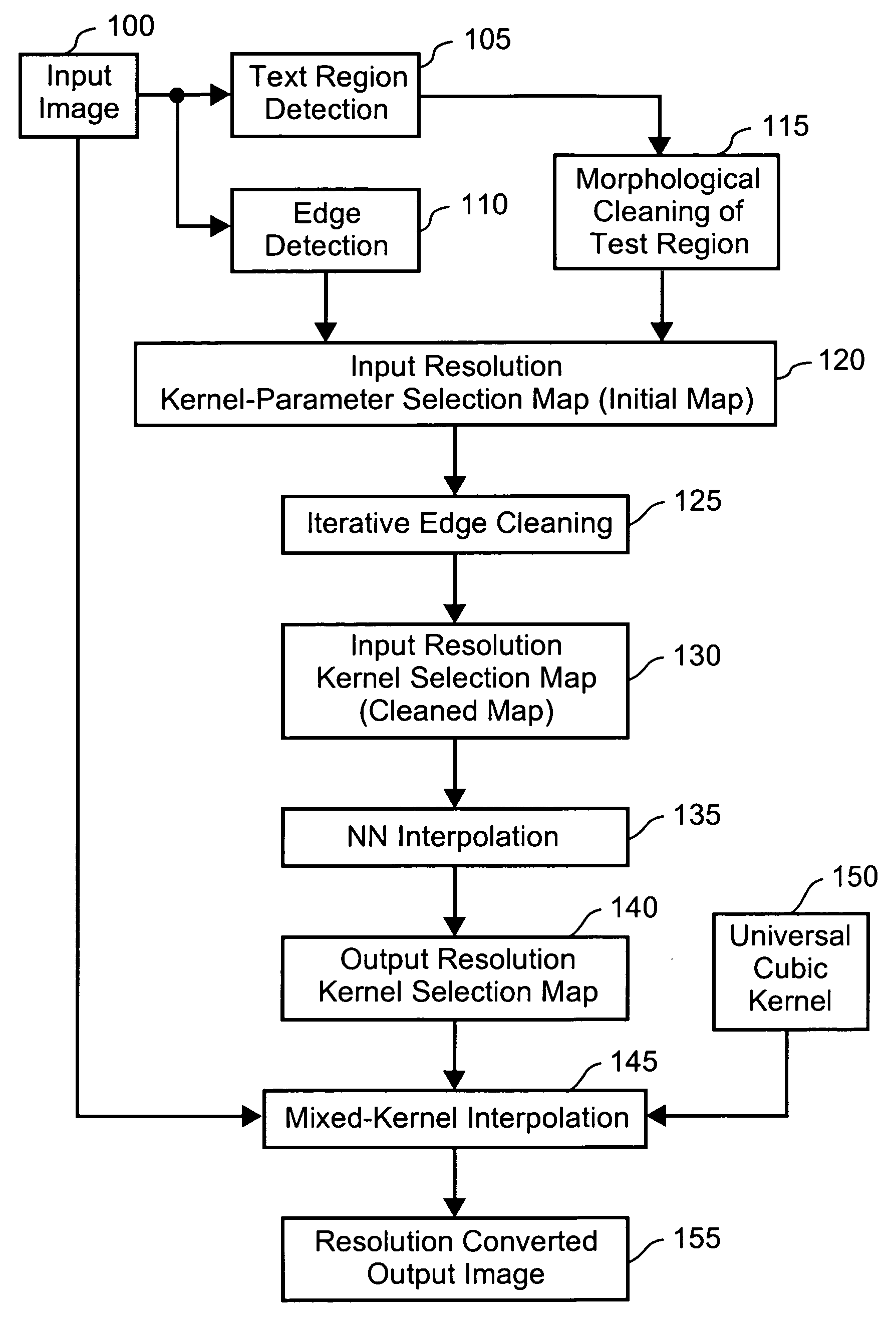
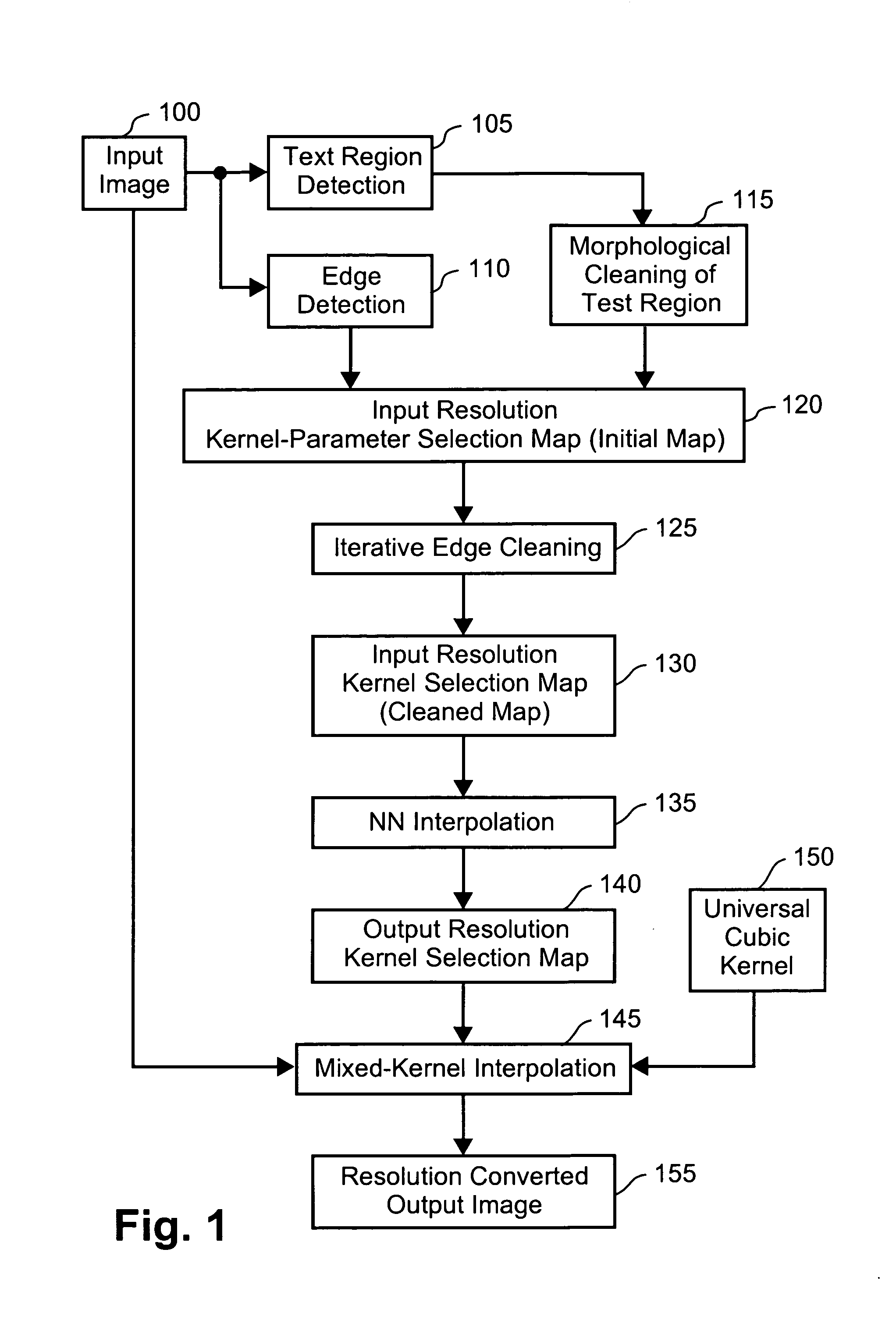
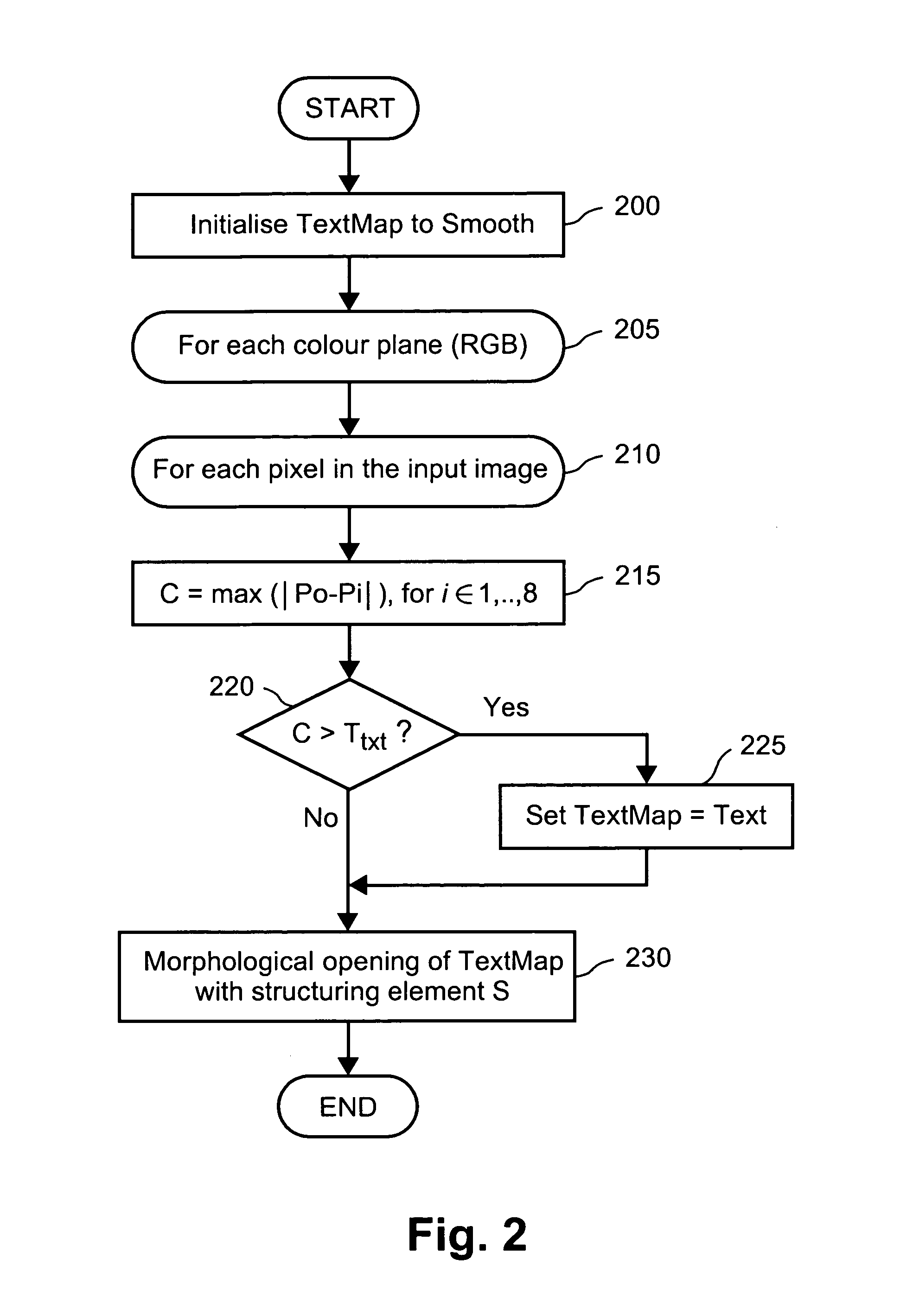
Method of kernel selection for image interpolation
InactiveUS7054507B1Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionEdge orientationEdge strength
A method of interpolating image data is disclosed. The method accesses a first set of discrete sample values of the image data and calculates kernel values for each of the discrete sample values using one of a plurality of kernels. The kernel is selected depending upon an edge orientation indicator, an edge strength indicator, and an edge context indicator for each of the discrete sample values. The calculated kernel values are convolved with the discrete sample values to provide a second set of discrete sample values.
Owner:CANON KK
System and method for robust multi-frame demosaicing and color super-resolution
ActiveUS7412107B2Quality improvementBlur artifactImage enhancementImage analysisMulti inputImage fusion algorithm
An integrated method for both super-resolution and multi-frame demosaicing includes an image fusion followed by simultaneous deblurring and interpolation. For the case of color super-resolution, the first step involves application of recursive image fusion separately on the three different color layers. The second step is based on minimizing a maximum a posteriori (MAP) cost function. In one embodiment, the MAP cost function is composed of several terms: a data fidelity penalty term that penalizes dissimilarity between the raw data and the super-resolved estimate, a luminance penalty term that favors sharp edges in the luminance component of the image, a chrominance penalty term that favors low spatial frequency changes in the chrominance component of the image, and an orientation penalty term that favors similar edge orientations across the color channels. The method is also applicable to color super-resolution (without demosaicing), where the low-quality input images are already demosaiced. In addition, for translational motion, the method may be used in a very fast image fusion algorithm to facilitate the implementation of dynamic, multi-input / multi-output color super-resolution / demosaicing.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
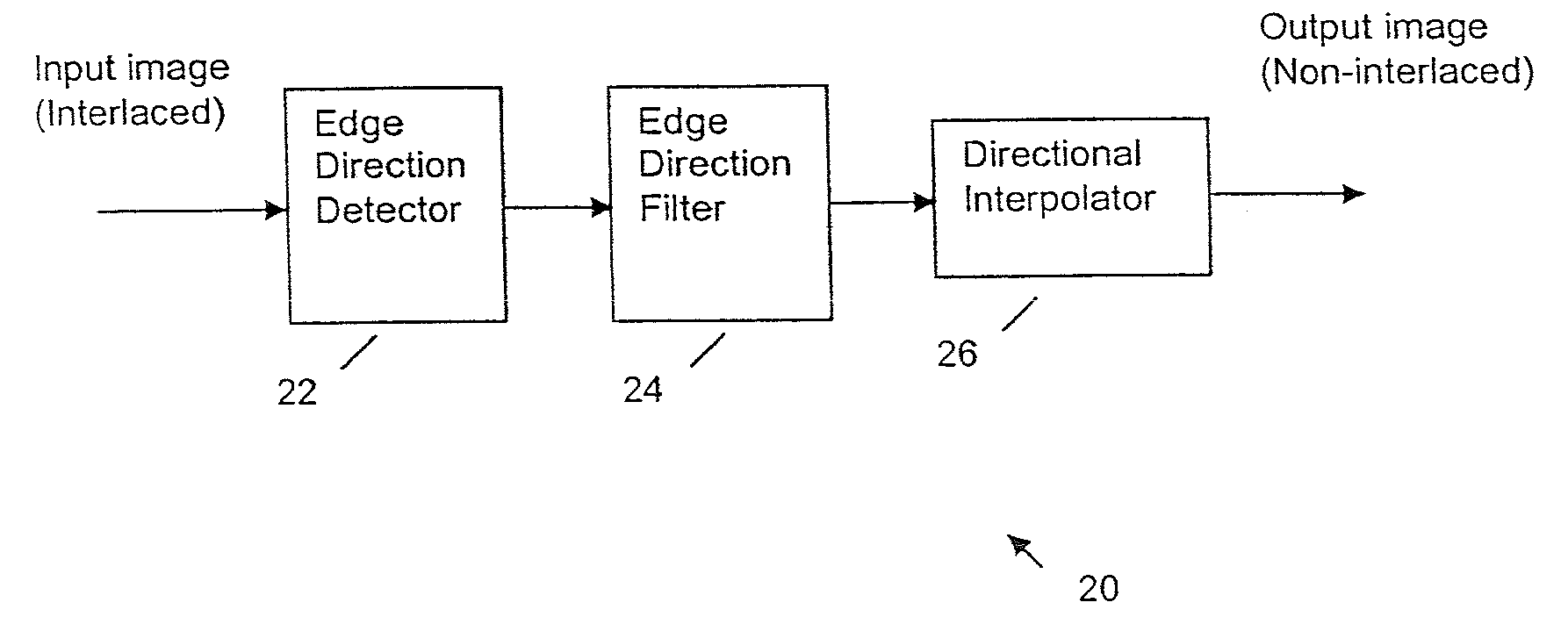
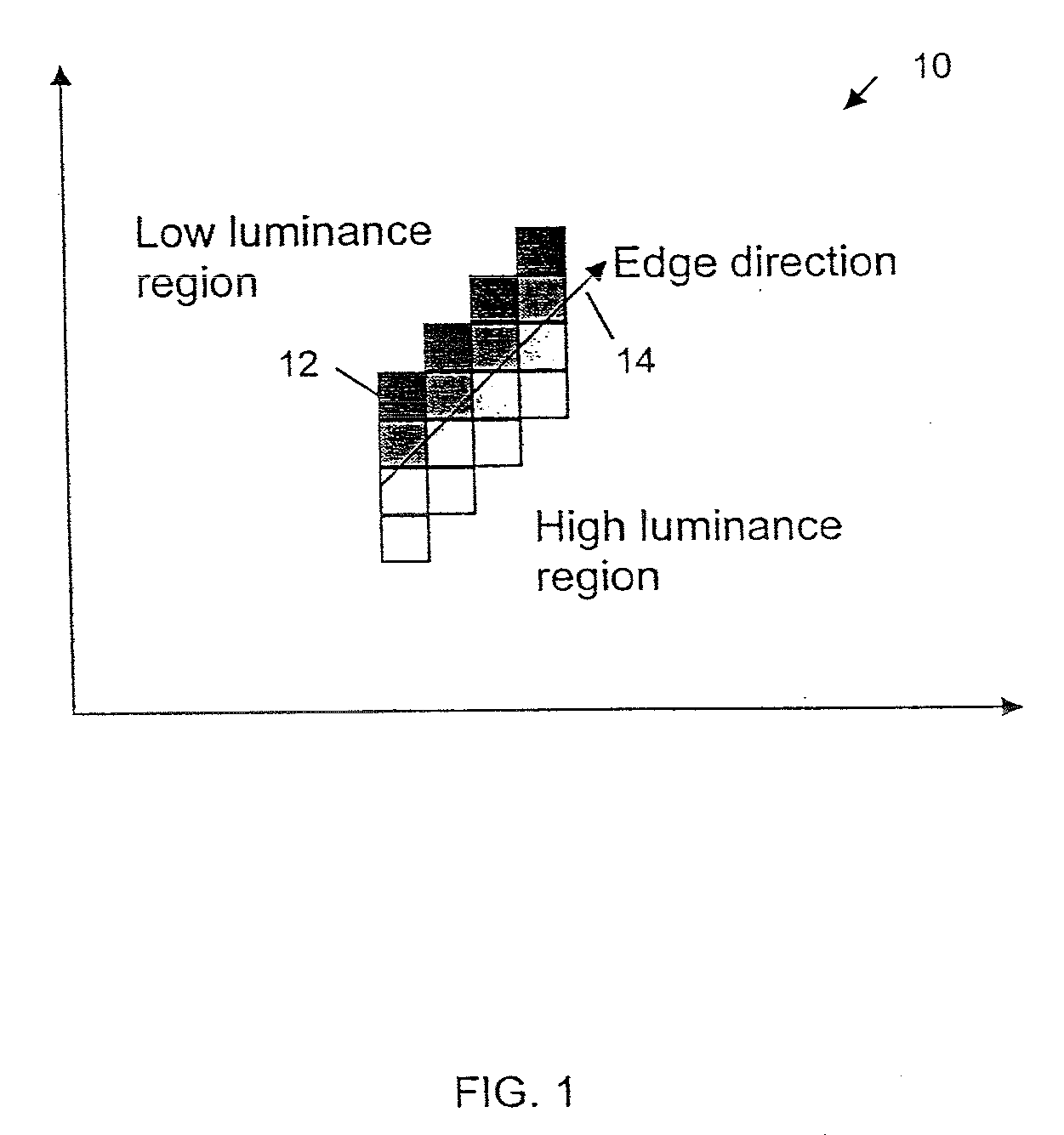
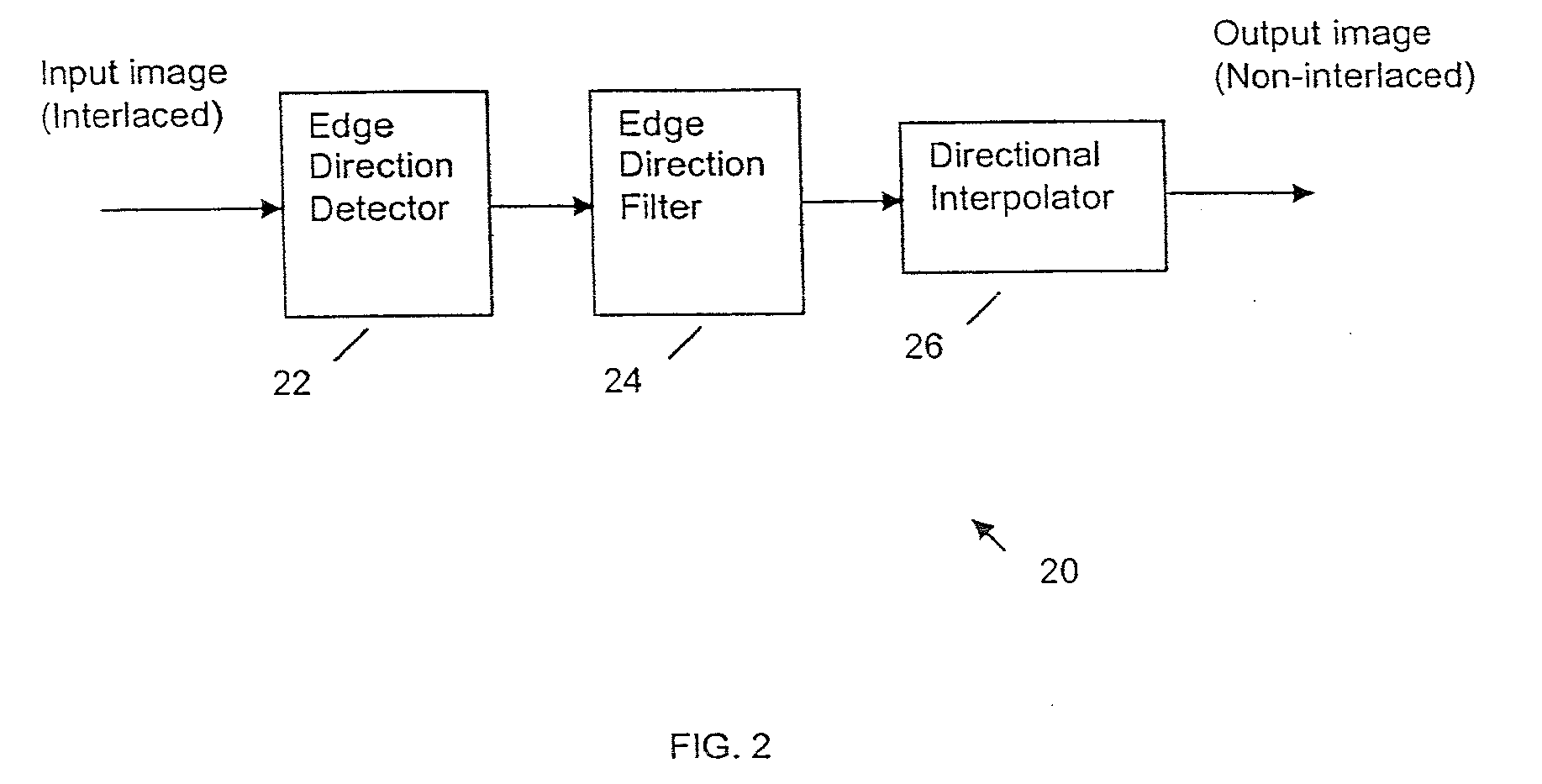
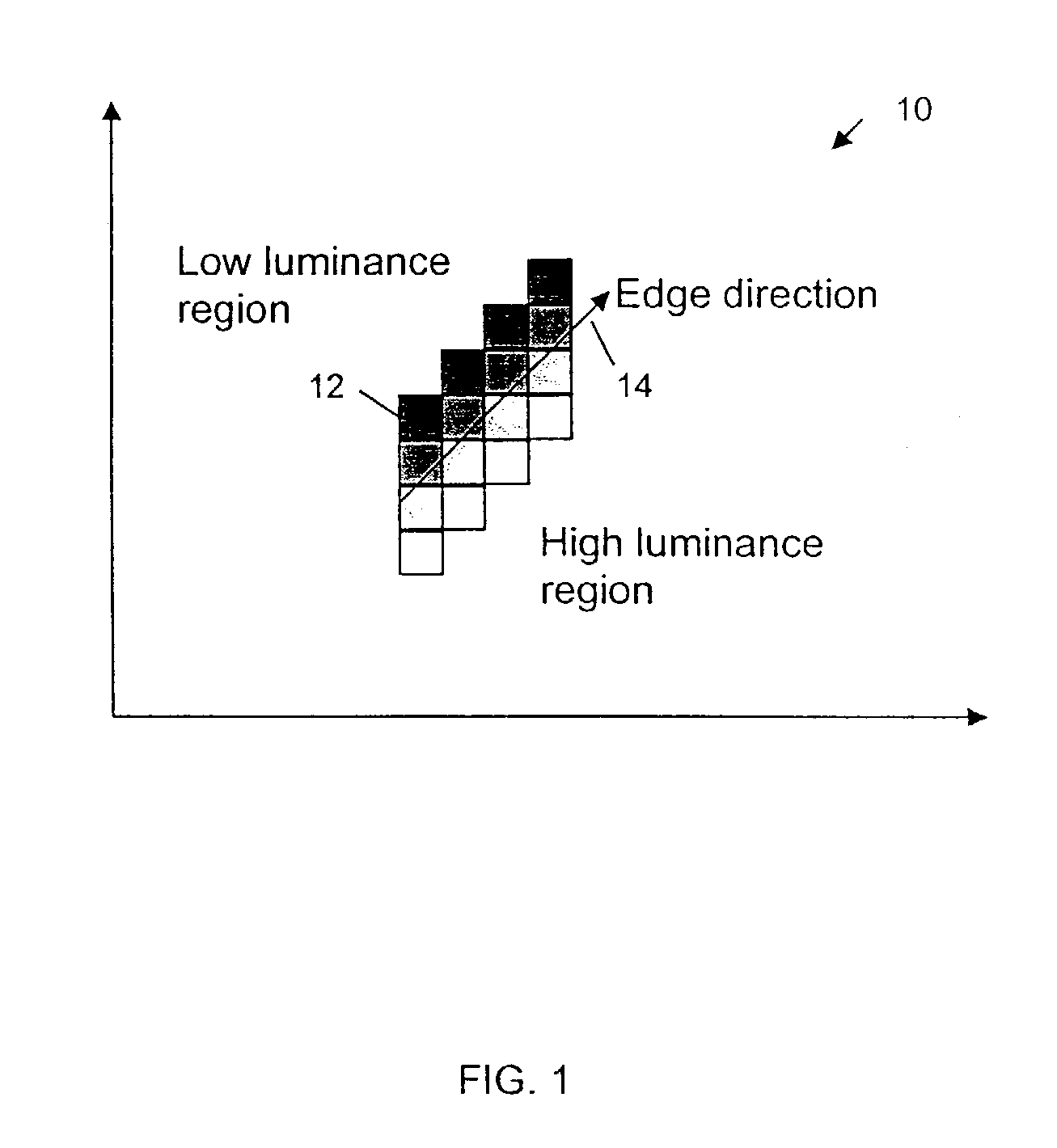
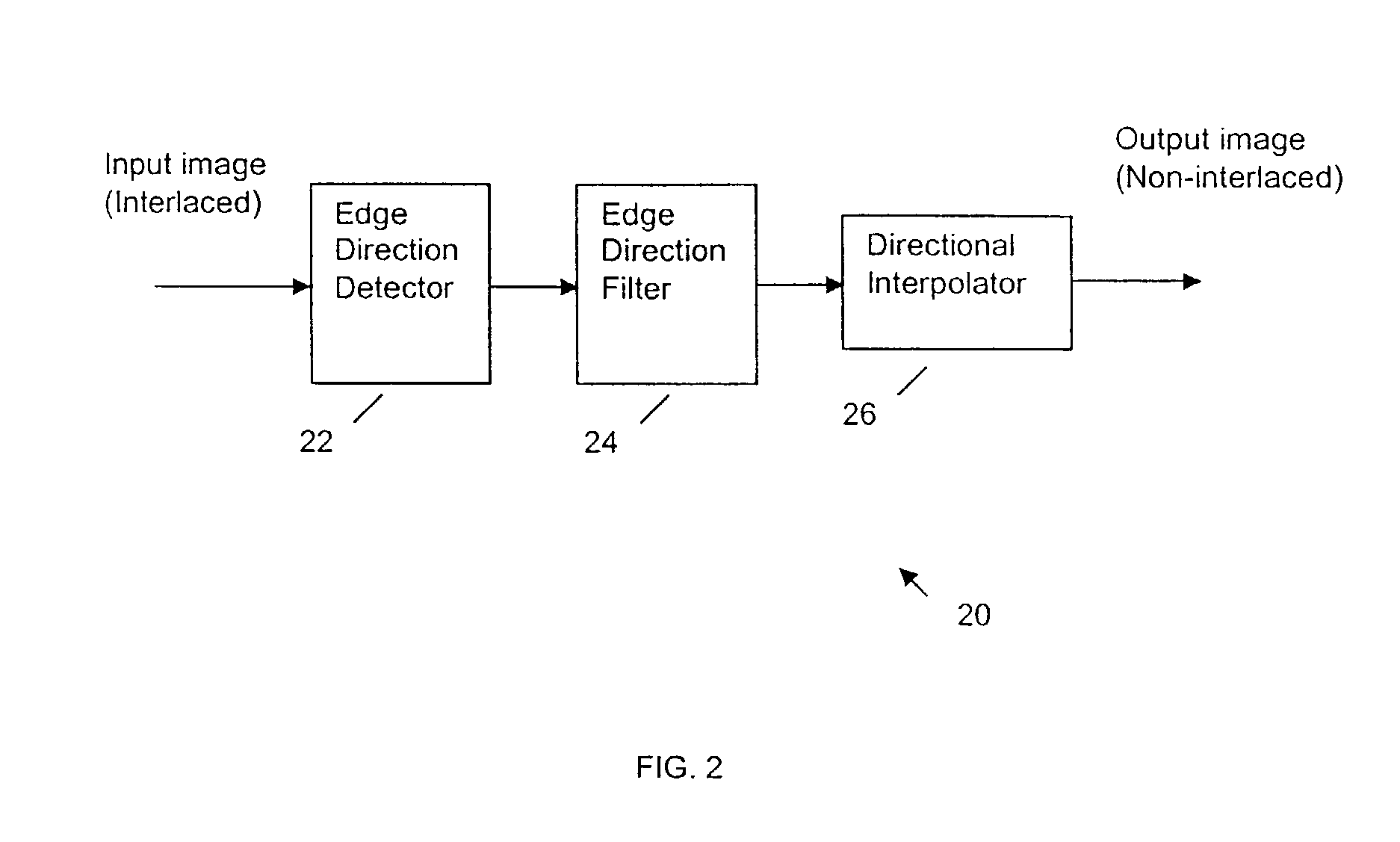
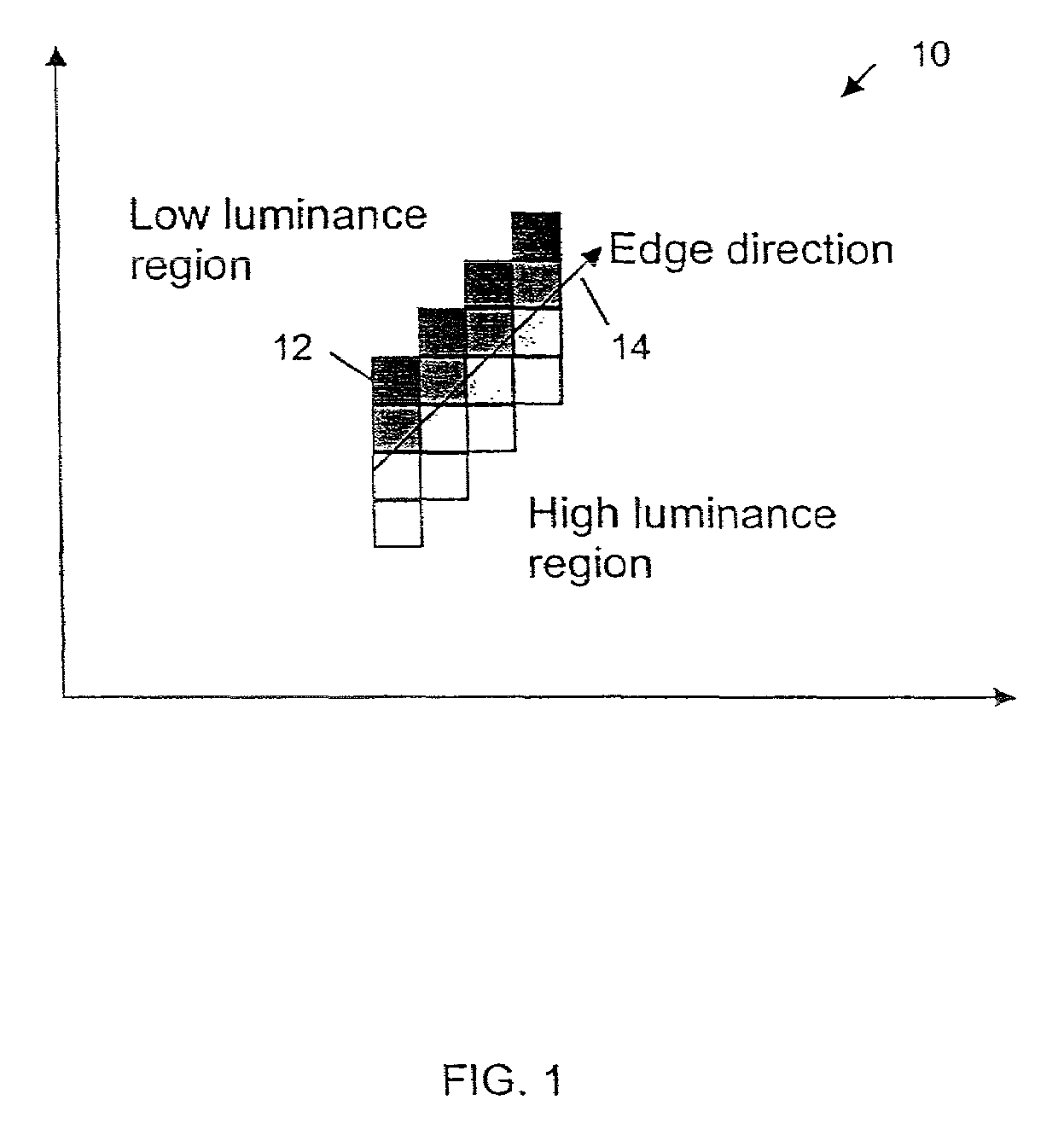
Edge direction based image interpolation method
InactiveUS20080024658A1Efficient detectionEfficient comprehensive utilizationImage enhancementImage analysisLocation detectionInterlaced video
A method for interpolating pixel data of an omitted line by use of pixel data from an interlaced scan, for de-interlacing an interlaced video image. Image edge direction is detected at the center position of every two neighboring scan lines in an interlaced scan. All the directions detected in a given field constitute an edge orientation map. Edge directions are filtered to remove false and unreliable edge directions from the edge orientation map. If an edge direction is removed, the vertical edge direction is used to replace that direction in the edge orientation map. For interpolating a new pixel at the center of two neighboring scan lines, the corresponding direction for that position is used as the interpolation direction to calculate the value of the new pixel. If the direction is vertical, a filter is used along the vertical direction to calculate the interpolation value. If the direction is non-vertical, and has an integer value, then interpolation is performed by taking the average of the two neighboring sample values along the direction. If the direction is non-vertical and has a non-integer value, then an interpolation value is calculated using a directional bilinear method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
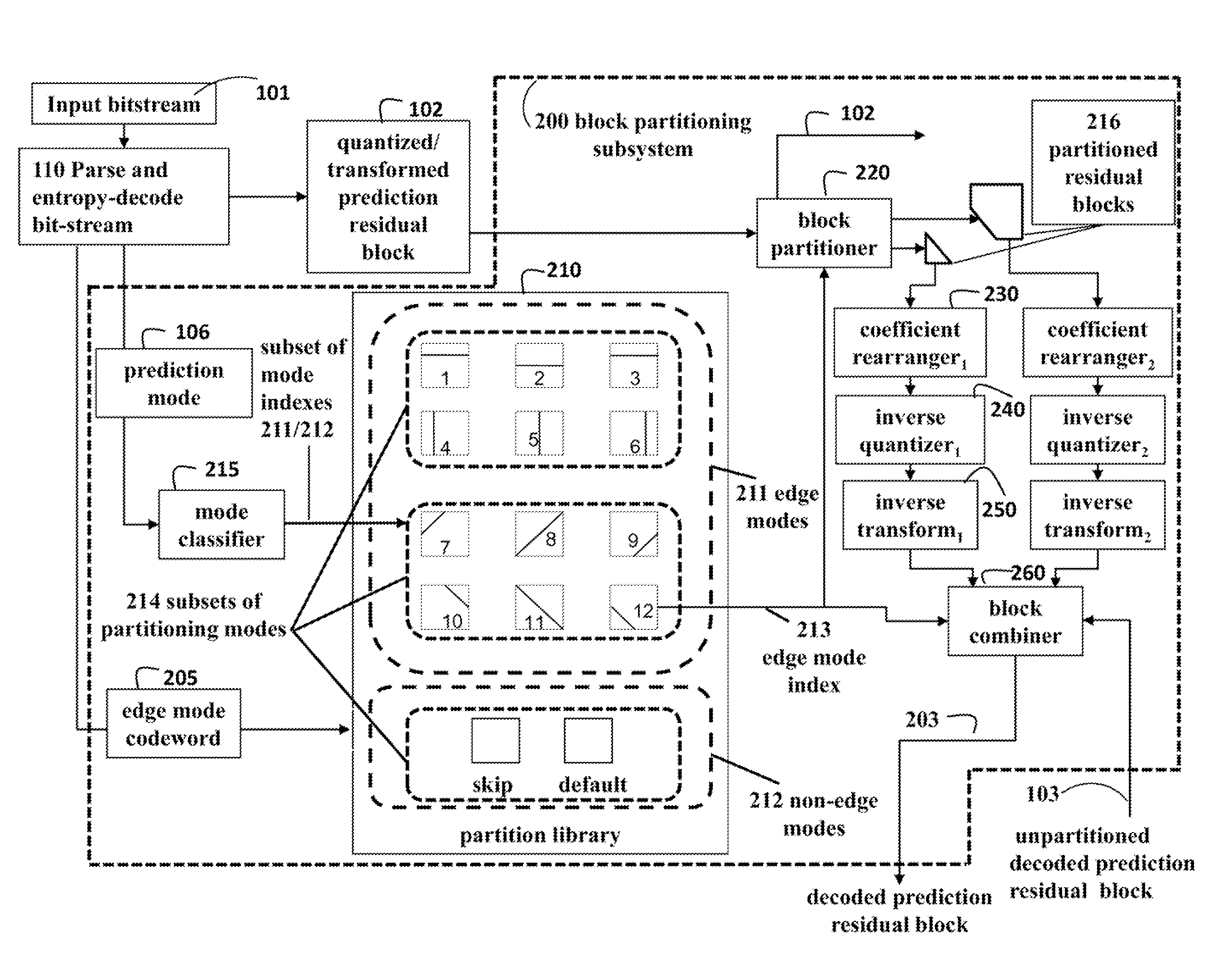
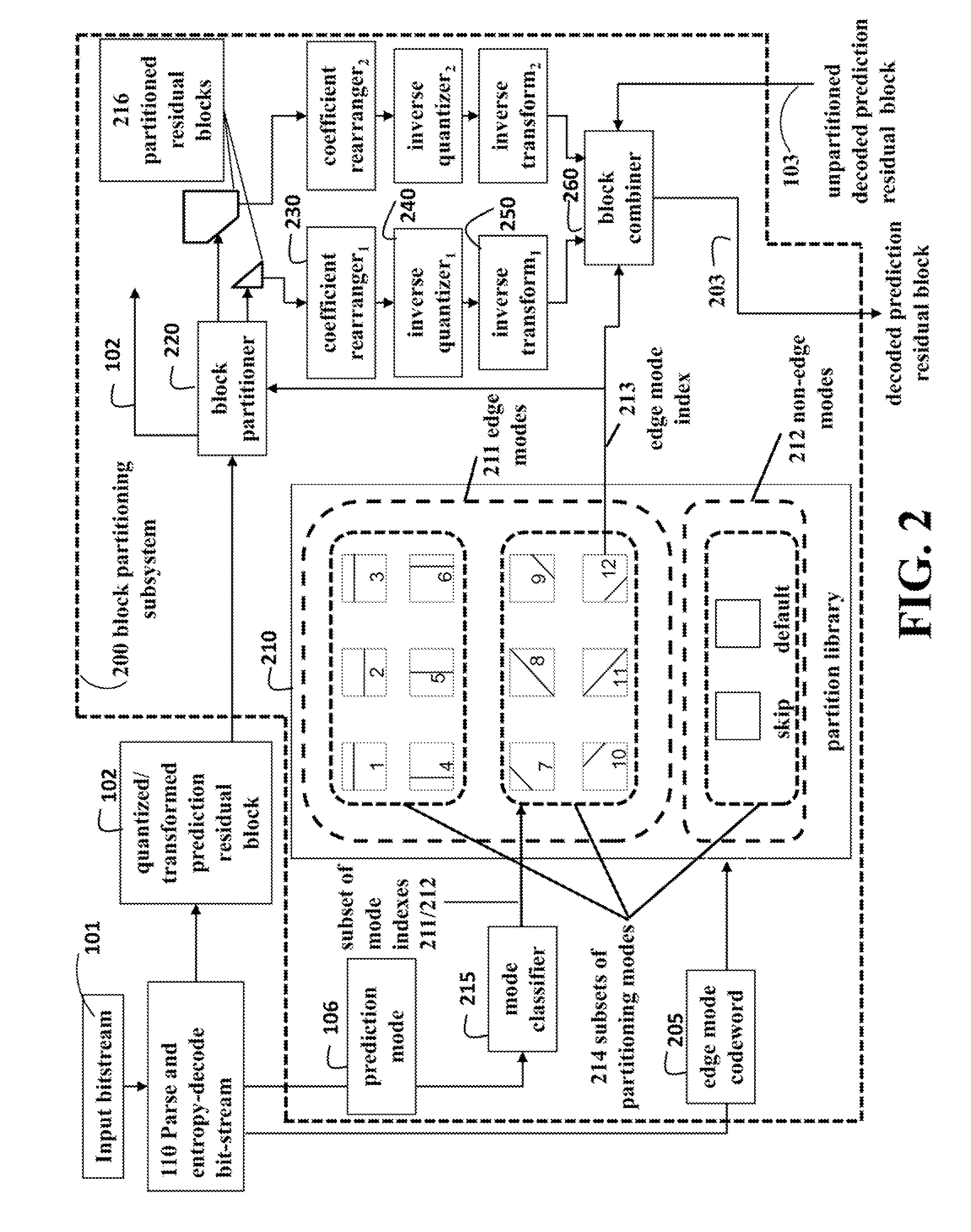
Method for Video Coding Using Blocks Partitioned According to Edge Orientations
InactiveUS20140307780A1Reduce in quantityReduce complexityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionEdge orientationInverse quantization
A bitstream corresponding to an encoded video is decoded. The encoded video includes a sequence of frames, and each frame is partitioned into encoded blocks. For each encoded block, an edge mode index is decoded based on an edge mode codeword and a prediction mode. The edge mode index indicates a subset of predetermined partitions selected from a partition library according to the prediction mode. The encoded block is partitioned based on the edge mode index to produce two or more block partitions. To each block partition, a coefficient rearrangement, an inverse transform and an inverse quantization is applied to produce a processed block partition. The processed block partitions are then combined into a decoded block for a video.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
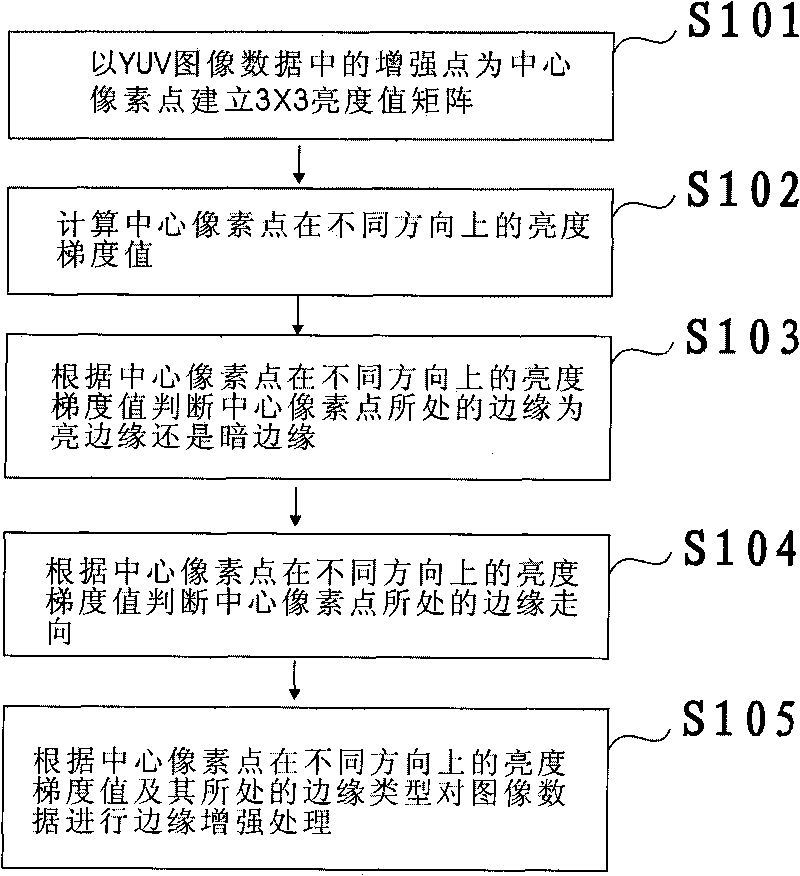
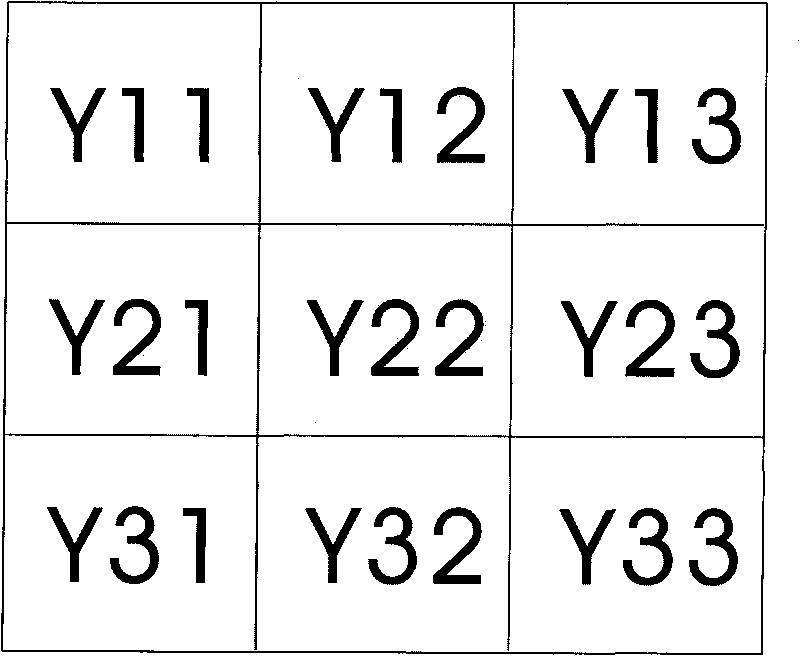
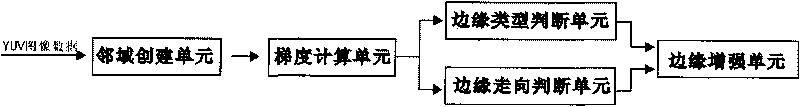
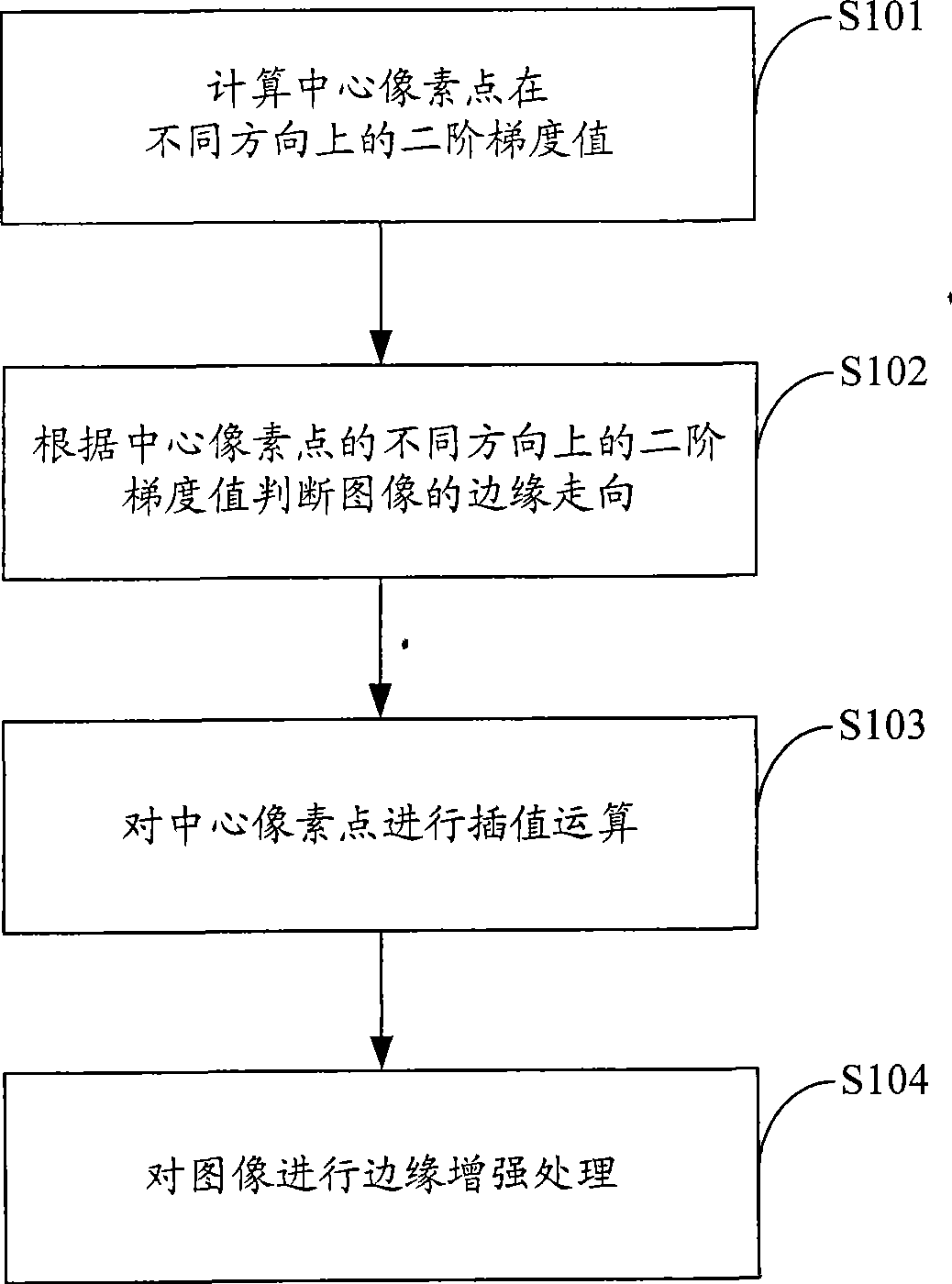
Method and system for enhancing image edge
ActiveCN101727659AImprove contrast between light and darkAvoid transition distortion effectsImage enhancementEdge typeEdge orientation
The invention discloses a method for enhancing an image edge. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a matrix with a 3x3 brightness value by taking an enhanced point in a YUV image data as a central pixel; calculating gradient brightness values of the central pixel in different directions and judging whether the edge of the central pixel is a bright edge or a dark edge according to the gradient brightness values of the central pixel in the different directions; judging the edge orientation of the central pixel according to the gradient brightness values in different directions; and enhancing the edge of the image data according to the edge orientation of the central pixel and the edge types thereof. In the invention, the image edge is divided into the dark edge and the bright edge and the dark edge and the bright edge are processed separately, so different enhancement values can be superposed to make control and adjustment very convenient and flexible, and the brightness contrast of the edge is enhanced to make the edge look sharper; and meanwhile, the phenomenon that the transient distortion of the edge caused by enhancing the edge can be avoided.
Owner:BYD SEMICON CO LTD
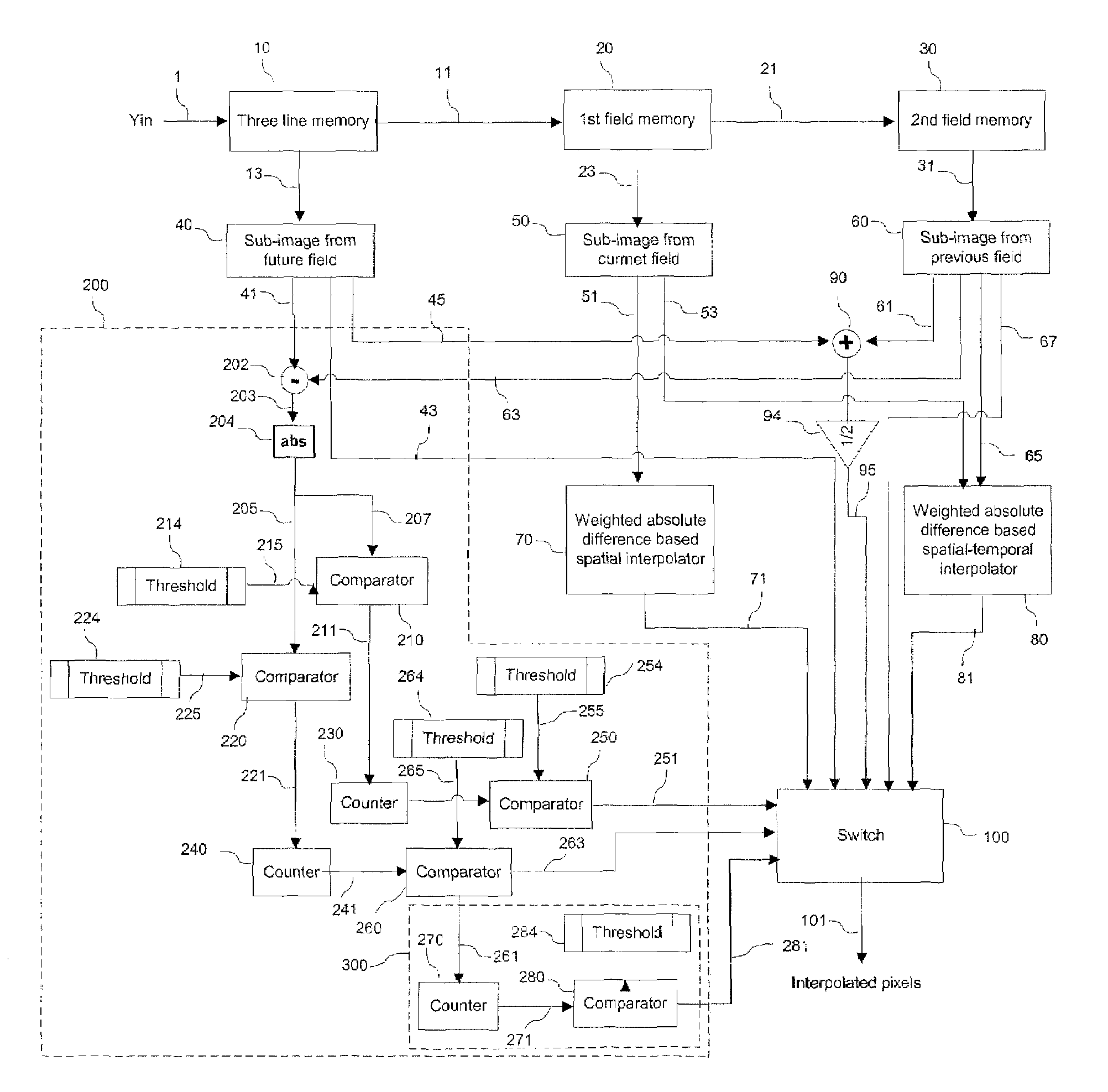
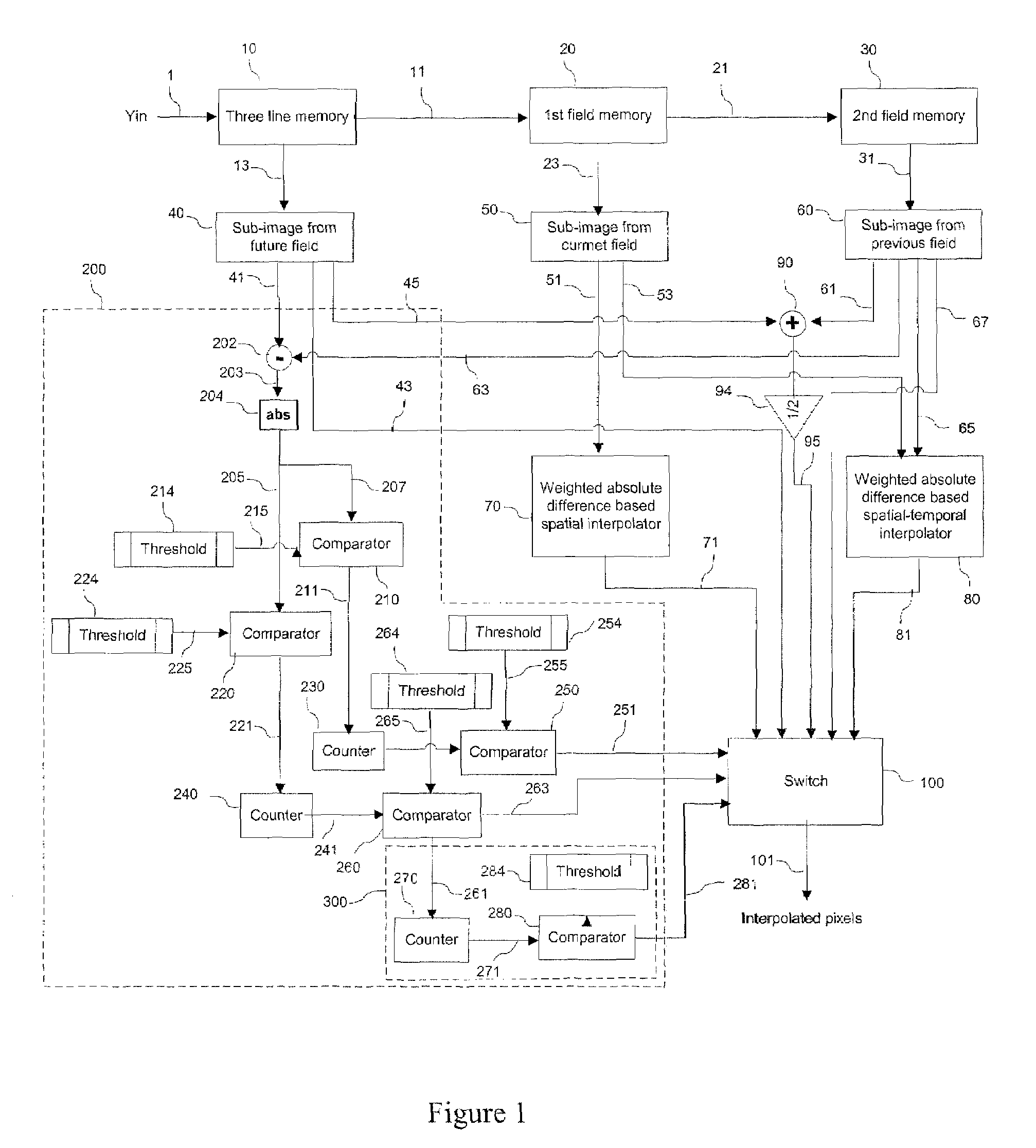
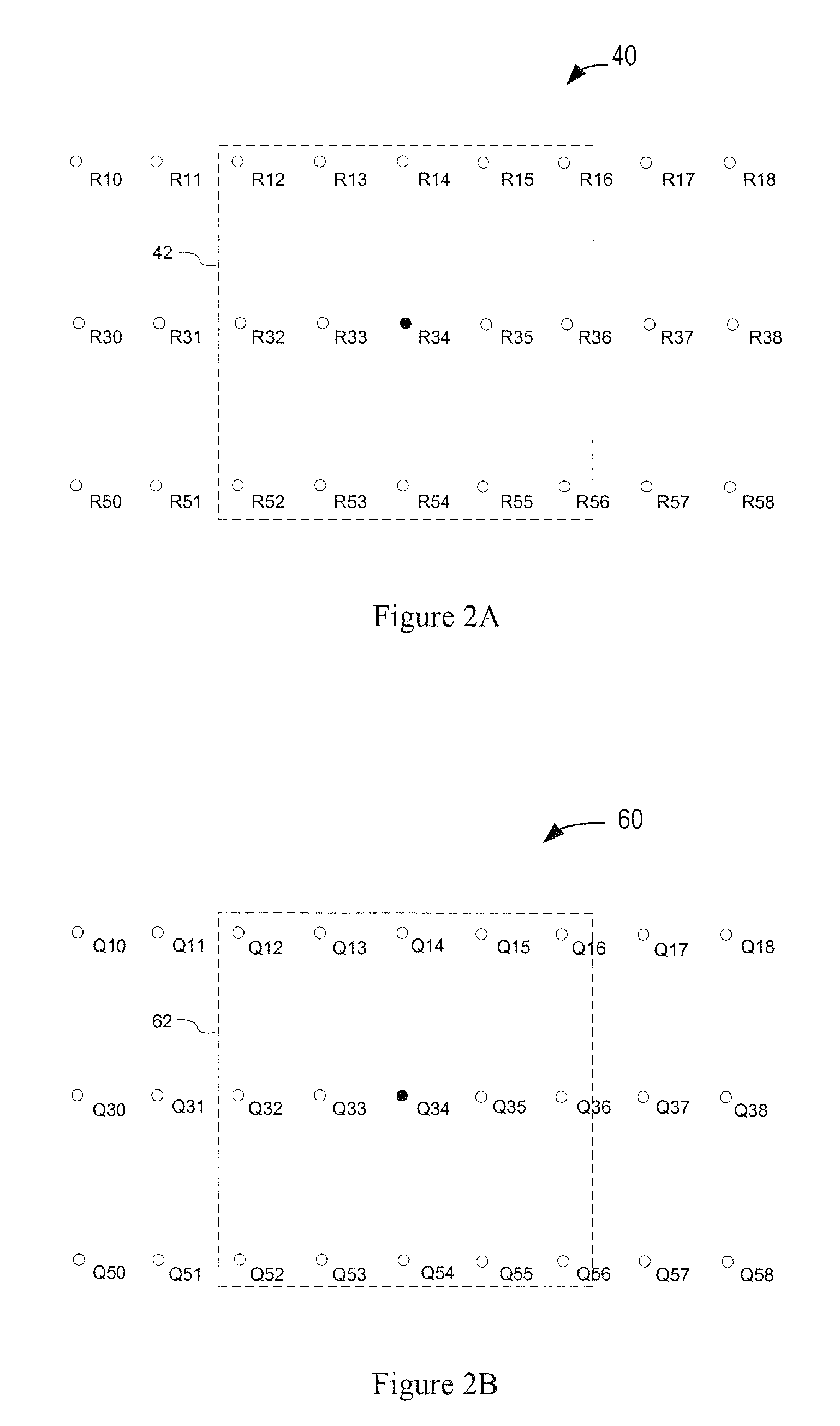
Weighted absolute difference based deinterlace method and apparatus
InactiveUS7515205B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMotion detectorAbsolute difference
We describe a weighted absolute difference based deinterlace method and apparatus. The deinterlace method and apparatus uses weighted absolute differences along different directions as means for interpolating pixel data using edge orientation detection. The apparatus includes a memory adapted to store a current and previous fields and predetermined portions of a future field of an input signal. A motion detector is adapted to detect motion between the future and previous fields. An interpolating circuit is adapted to generate a plurality of output pixels using a corresponding plurality of methodologies. And a switch is adapted to select between the plurality of output pixels responsive to the motion detector.
Owner:PIXELWORKS SEMICON TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Image edge enhancing method
The invention is applicable to the field of digital image processing and provides an image edge enhancing method. The method comprises: according to the two-step gradients of central pixel point in different directions, judging the edge orientation of an image; carrying out the interpolation of the central pixel point and calculating the lost color component of pixel points; and on the basis of Bayer data, enhancing the edge of the image in an interpolation template according to the color of the original component of the central pixel point and the edge orientation of the image. The embodiment of the invention takes the influences of green component values of different pixel points around the central pixel point into full consideration while carrying out edge enhancement of the image, adopts an adaptive edge enhancement algorithm, eliminates the possible influences of noises on the edge, achieves uniform image edge and helps the processed images to achieve good effect. Meanwhile, due to the edge enhancement processing in the interpolation template on the basis of Bayer data, the method saves SRAM required by single edge enhancement processing, as well as saves large areas of elements and costs.
Owner:BYD SEMICON CO LTD
Structural camouflage system
InactiveUS20070006909A1Prevent glareEliminate needAnimal huntingTents/canopiesEdge orientationEngineering
A structural camouflage system includes as the primary structural component a planar panel with a reflective outer face, formed in a trapezoidal configuration with upper and lower edges of the panel in parallel relation, the panels connected in edge to edge orientation to form an enclosed structure with the reflective faces of the panels facing outward of the structure and inclined toward the surface upon which the structure rests, so that the panels reflect an image of the immediate foreground to more distant observer looking toward the structure, camouflaging the structure. In an alternative embodiment, a plurality of reflective strips are connected to vertical supports with each strip disposed at an angle so as to reflect a composite image of the immediate foreground to a more distant observer.
Owner:LEWIS ROGER D
Thermal Interface Structure and the Manufacturing Method Thereof
InactiveUS20080074847A1High thermal conduction efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEdge surfaceCarbon nanotube
A thermal interface structure includes a carbon nanotube layer, in which the carbon nanotubes are oriented parallel to the direction of thermal transmission and metal layers provided on two edge surfaces of the carbon nanotube layer, the edge surfaces being perpendicular to the direction of the thermal transmission and located substantially parallel to the orientation direction at which edges of the carbon nanotubes are oriented.
Owner:IBM CORP
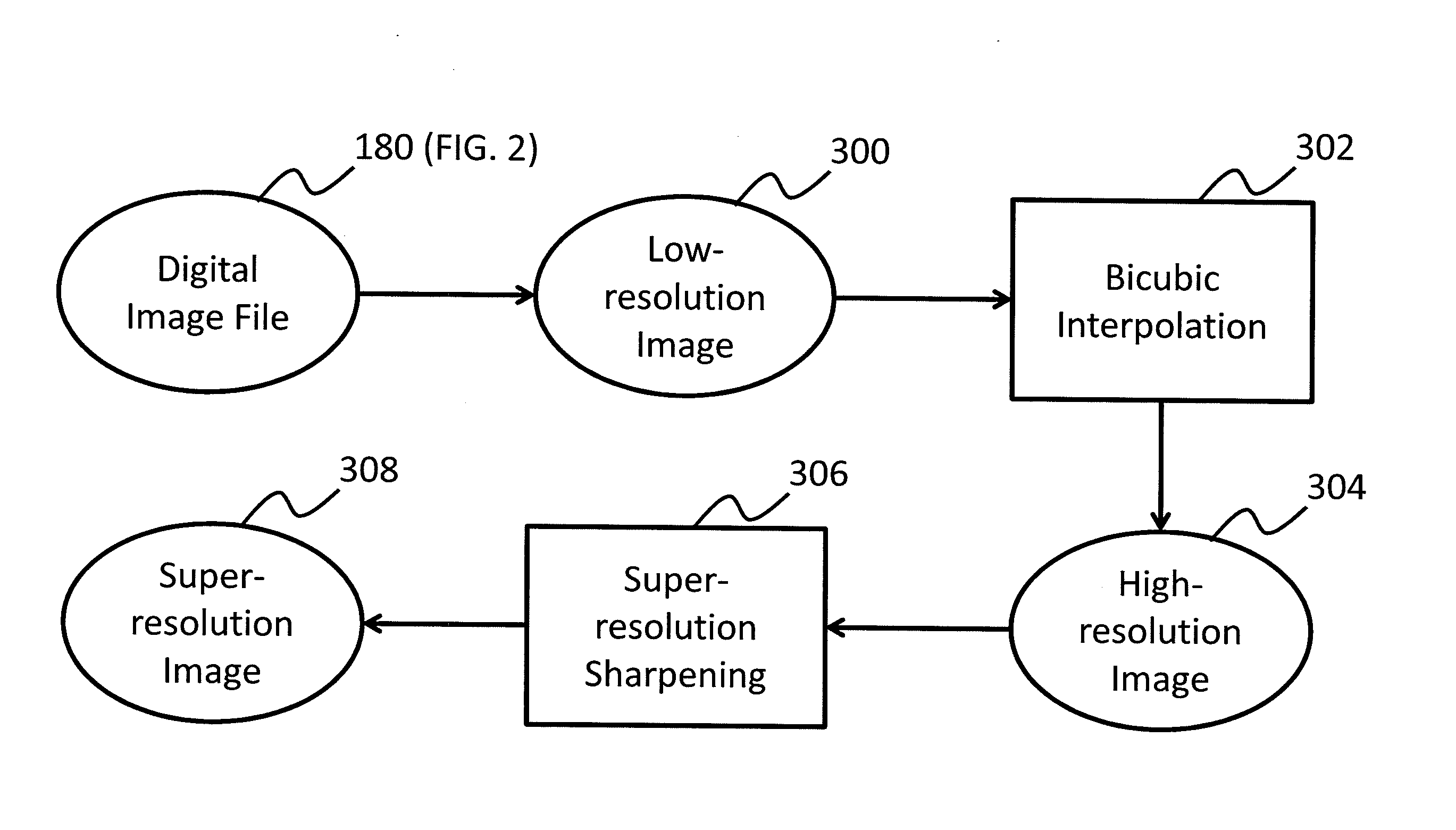
Super-resolution image using selected edge pixels
InactiveUS20130177242A1Reduce processing timeLower requirementGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionEdge orientation
Owner:APPLE INC
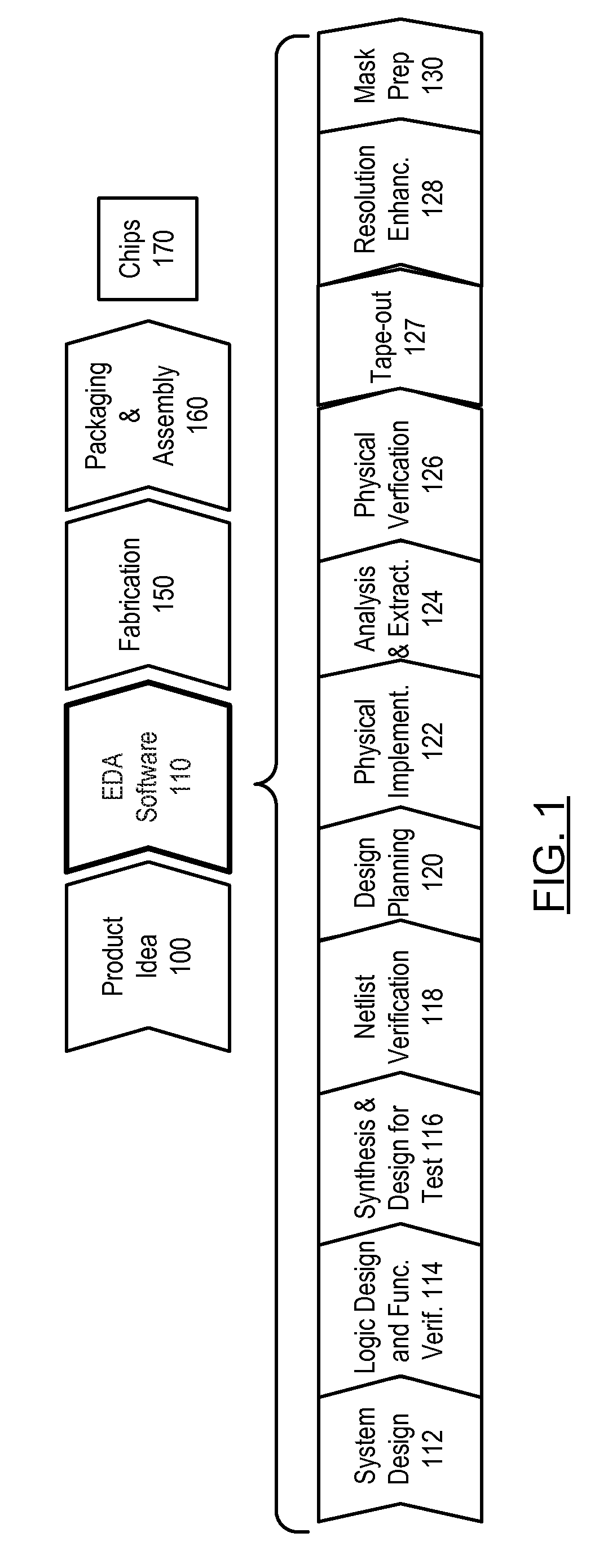
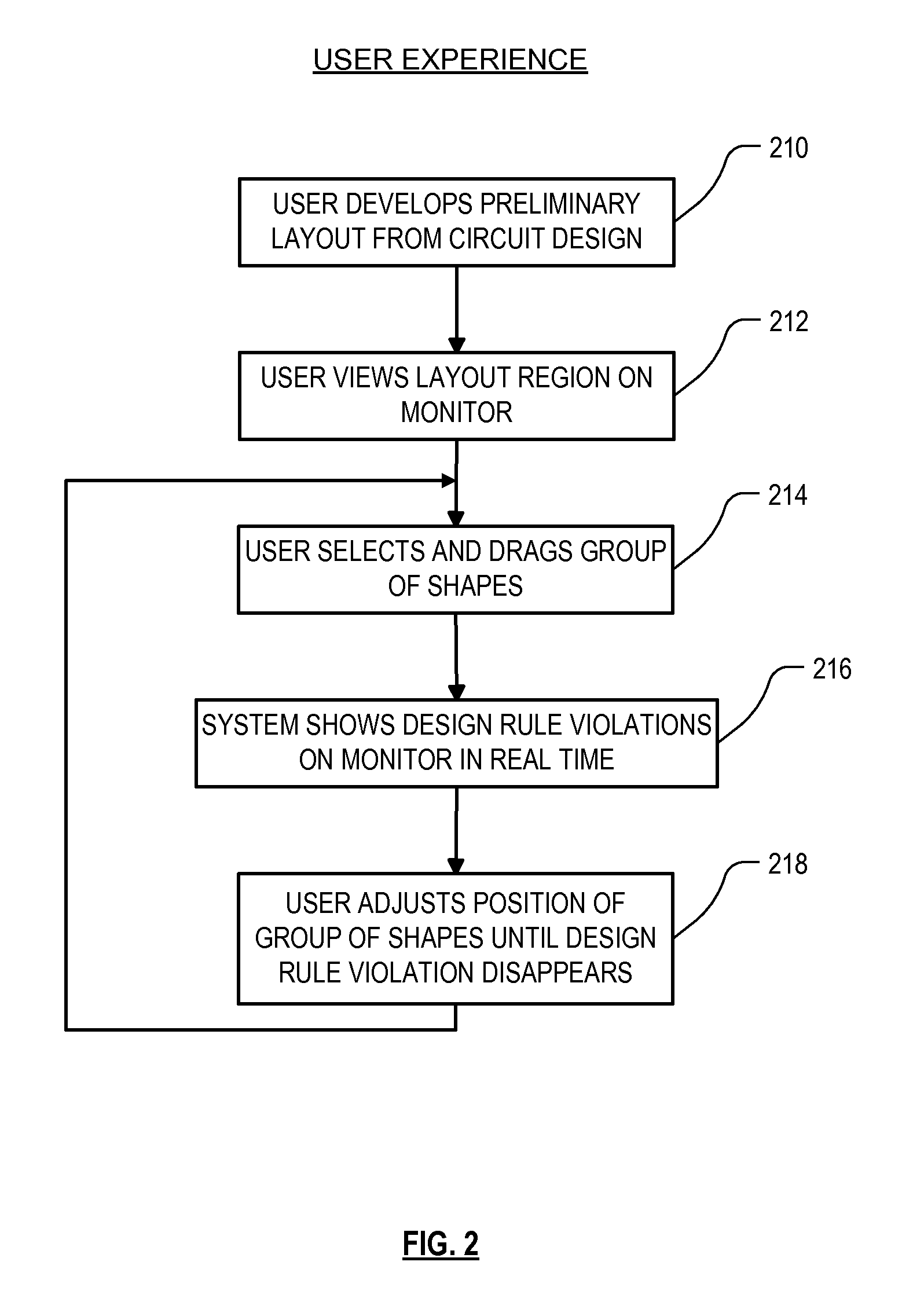
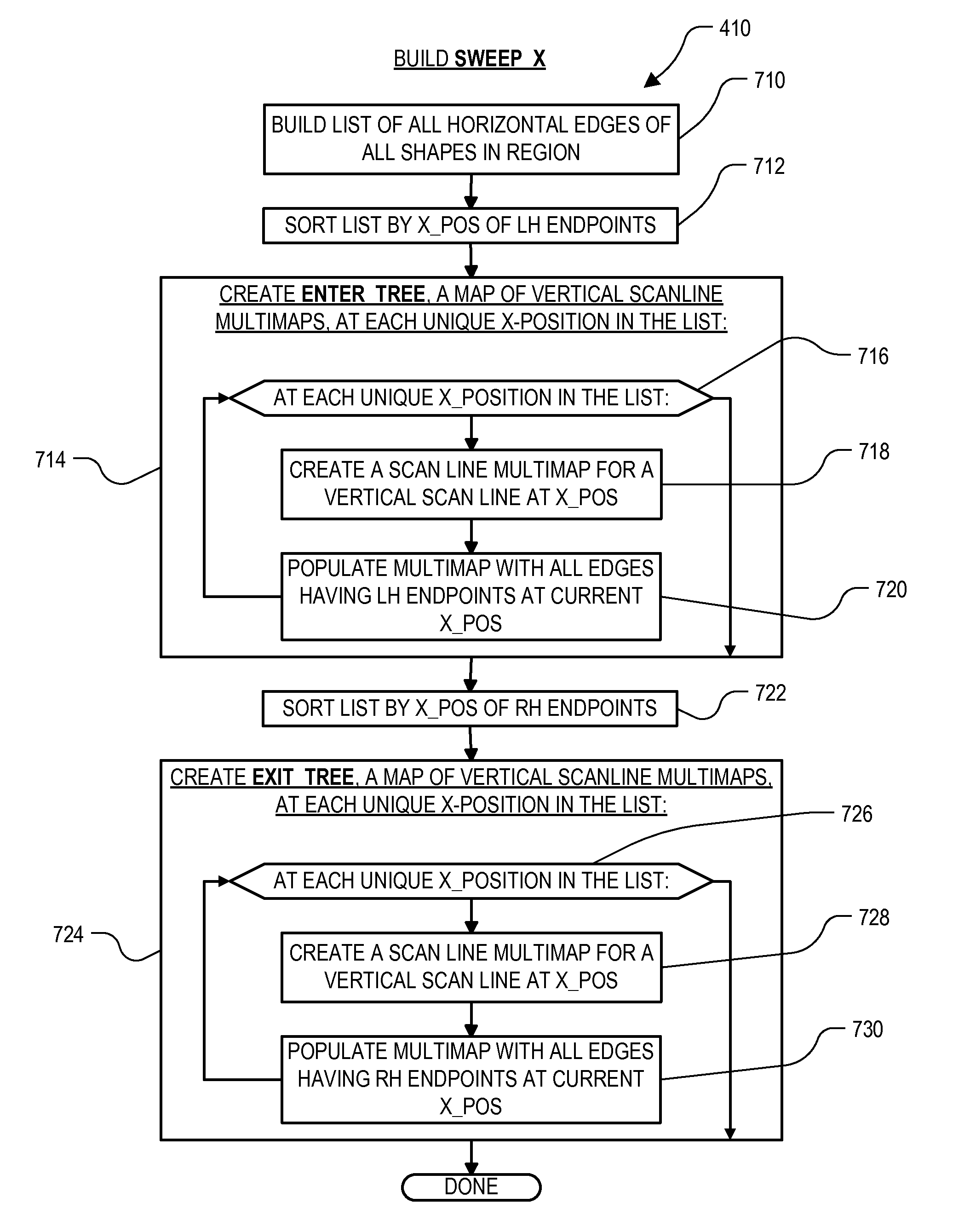
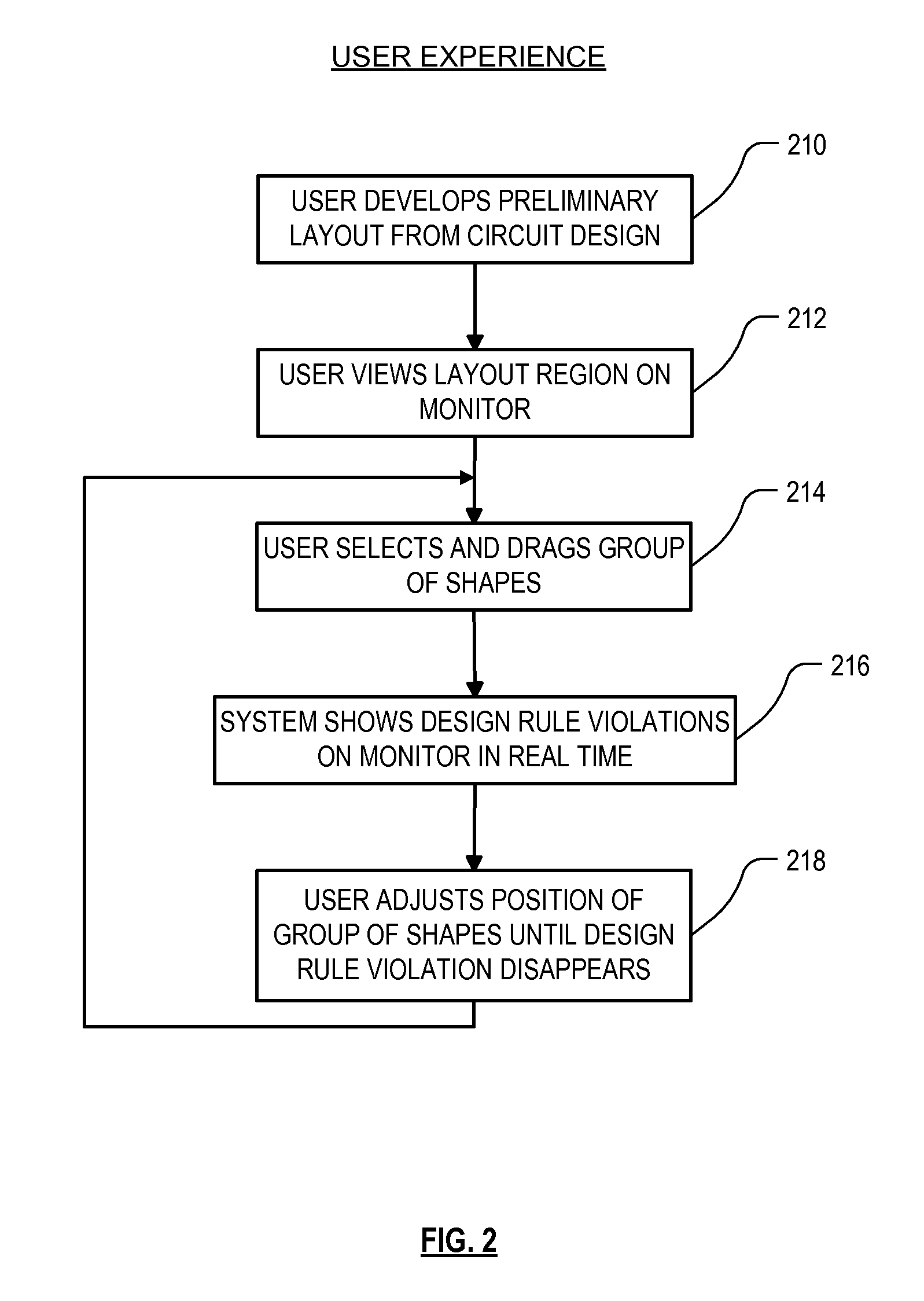
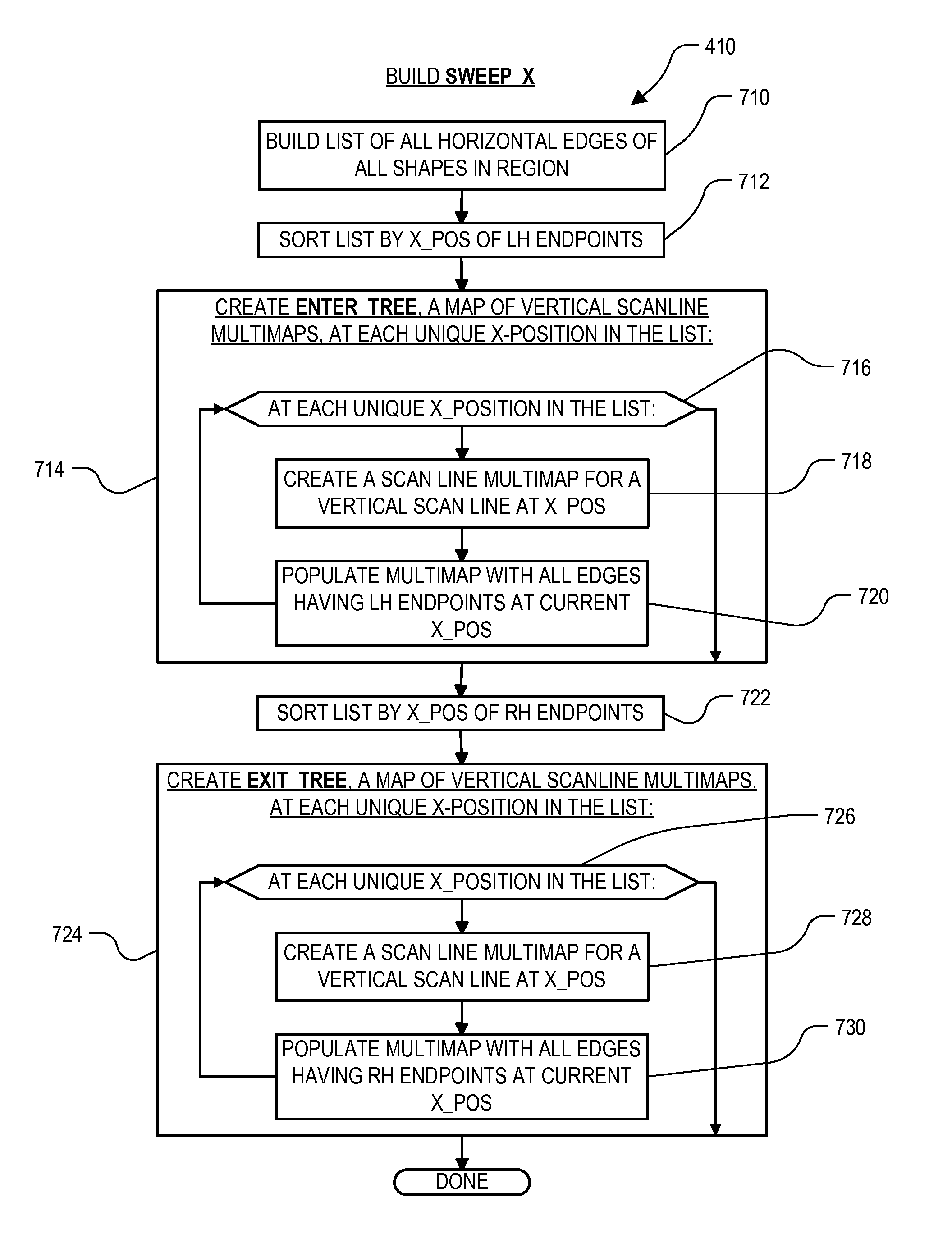
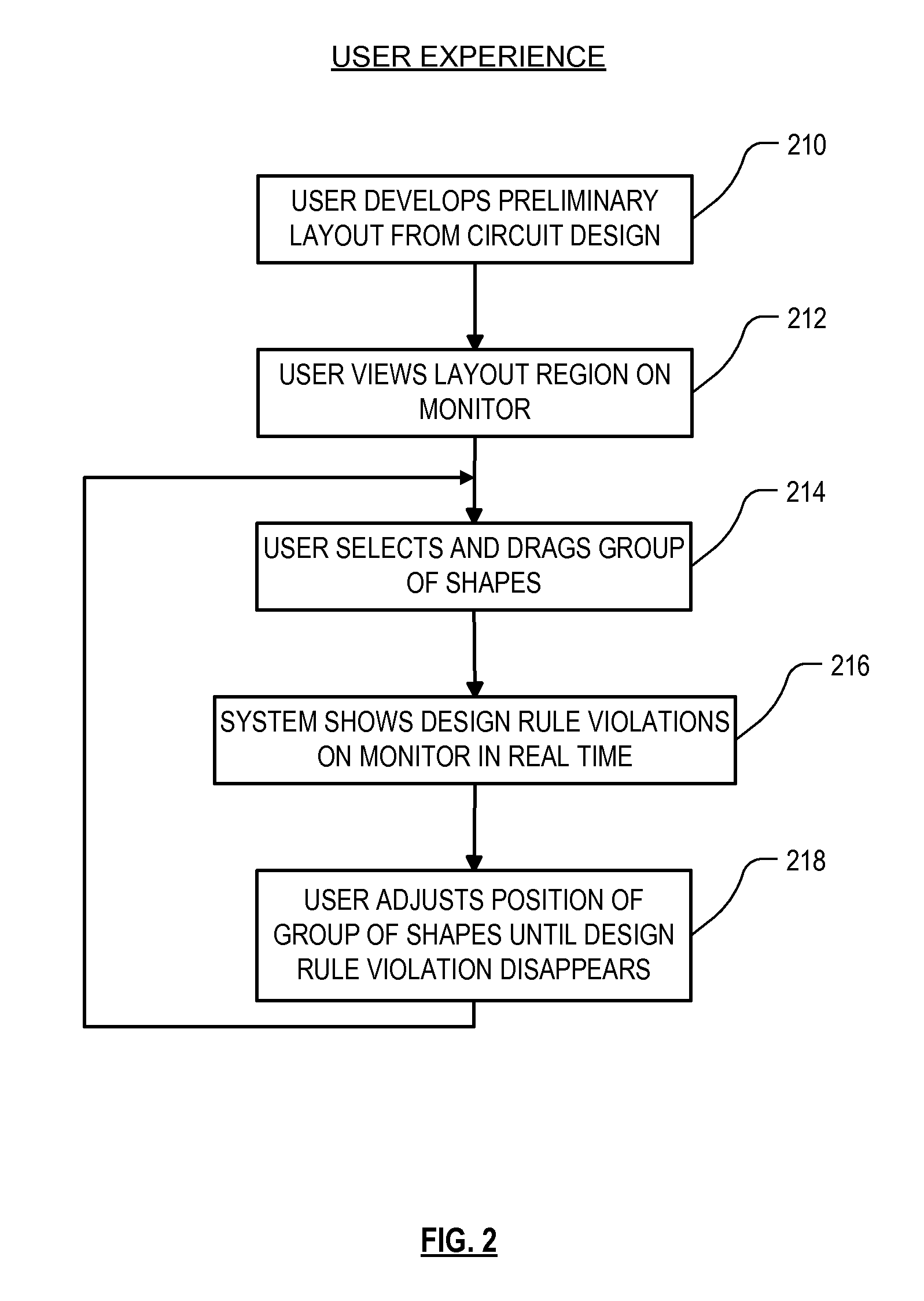
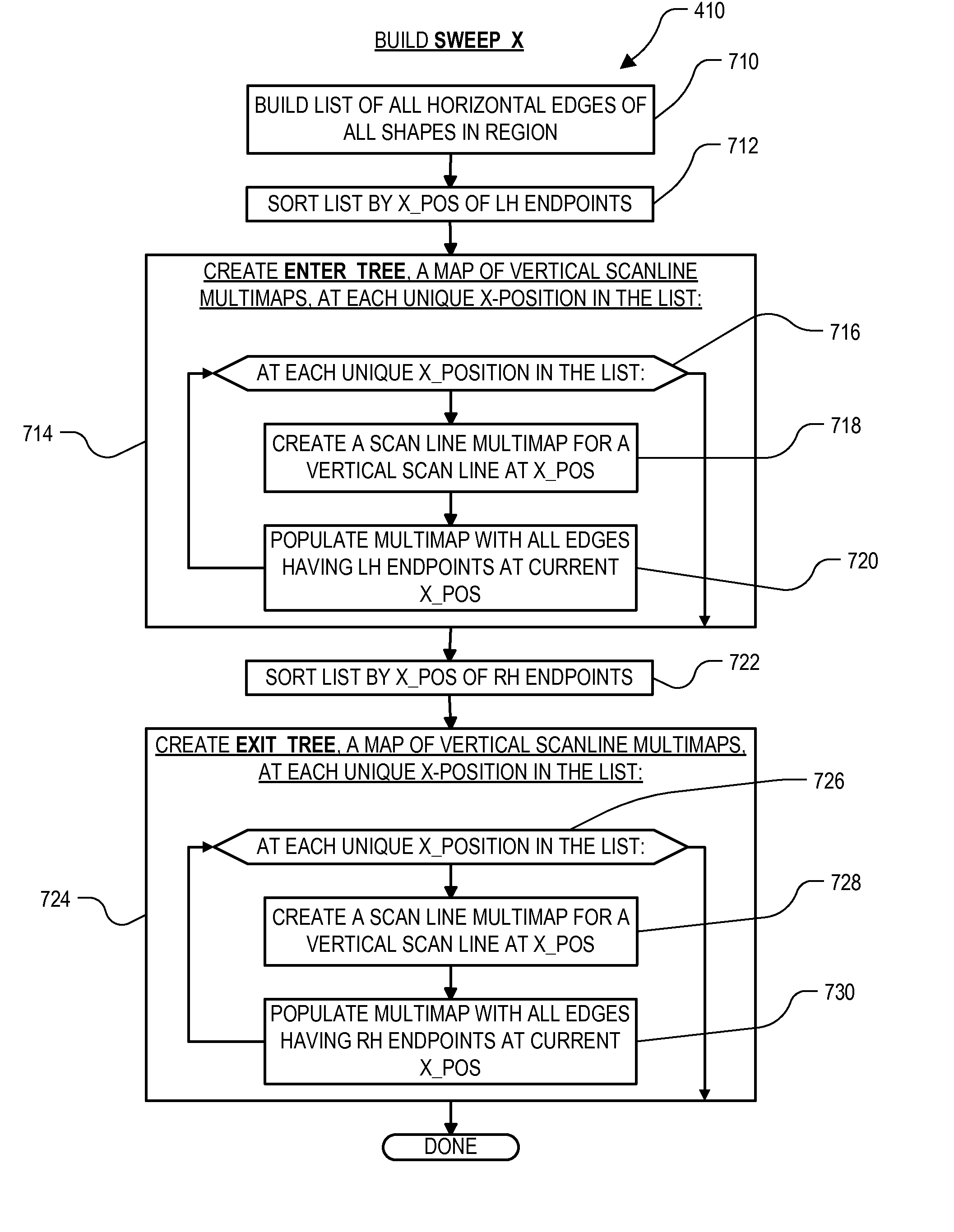
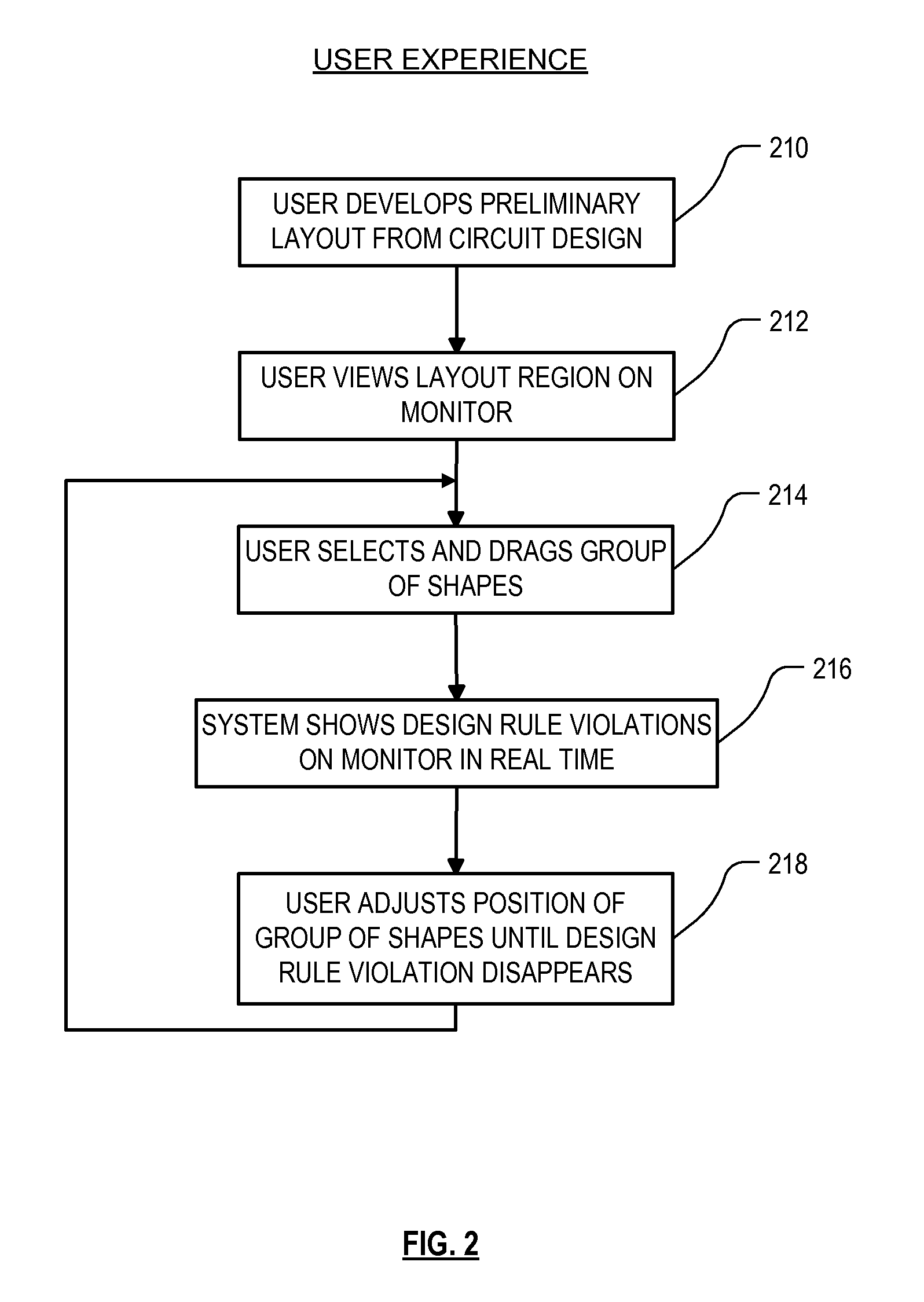
High performance design rule checking technique
ActiveUS20120144355A1Robust solutionConstraint-based CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationData setComputer architecture
Roughly described, a design rule data set is developed offline from the design rules of a target fabrication process. A design rule checking method involves traversing the corners of shapes in a layout region, and for each corner, populating a layout topology database with values that depend on respective corner locations. After the layout topology database is populated, the values are compared to values in the design rule data set to detect any design rule violations. Violations can be reported in real time, while the user is manually editing the layout. Preferably corner traversal is performed using scan lines oriented perpendicularly to edge orientations, and scanning in the direction of the edge orientations. Scans stop only at corner positions and populate the layout topology database with what information can be gleaned based on the current scan line. The different scans need not reach each corner simultaneously.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Edge direction based image interpolation method
InactiveUS7379625B2Effectively detect and utilizeImage enhancementImage analysisInterlaced videoVertical edge
A method for interpolating pixel data of an omitted line by use of pixel data from an interlaced scan, for de-interlacing an interlaced video image. Image edge direction is detected at the center position of every two neighboring scan lines in an interlaced scan. All the directions detected in a given field constitute an edge orientation map. Edge directions are filtered to remove false and unreliable edge directions from the edge orientation map. If an edge direction is removed, the vertical edge direction is used to replace that direction in the edge orientation map. For interpolating a new pixel at the center of two neighboring scan lines, the corresponding direction for that position is used as the interpolation direction to calculate the value of the new pixel. If the direction is vertical, a filter is used along the vertical direction to calculate the interpolation value. If the direction is non-vertical, and has an integer value, then interpolation is performed by taking the average of the two neighboring sample values along the direction. If the direction is non-vertical and has a non-integer value, then an interpolation value is calculated using a directional bilinear method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
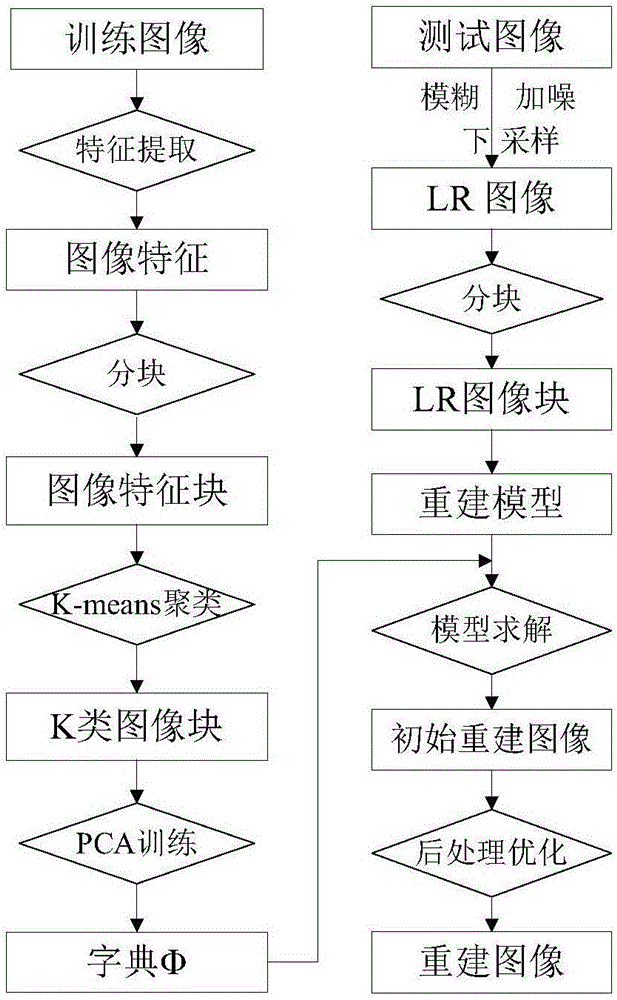
Single-image super-resolution reconstruction method based on edge difference constraint
ActiveCN106558022ARich edgeRich textureGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPrincipal component analysisHistogram of oriented gradients
Provided is a single-image super-resolution reconstruction method based on edge difference constraint. The method includes following three steps: step 1, extracting a texture principal direction characteristic of a training image through a Gabor filter, and performing a principal component analysis dictionary training to obtain a training dictionary; step 2, constructing a reconstruction model by employing the dictionary, and obtaining an initial reconstruction high-resolution image with a good edge structure through iterative threshold shrinkage; and step 3, describing an operator, a spatial distance, a pixel intensity, and edge orientation information by employing a histogram of oriented gradients between image blocks, establishing a non-local structure tensor optimization model, further optimizing and processing the initial reconstruction high-resolution image, and obtaining a final reconstruction high-resolution image with a substantial edge structure and abundant detail information. According to the method, by considering the difference between the initial reconstruction high-resolution image and an original clear image, the post-processing optimization method is further proposed, and the detail information of image edges and textures is abundant.
Owner:上海厉鲨科技有限公司
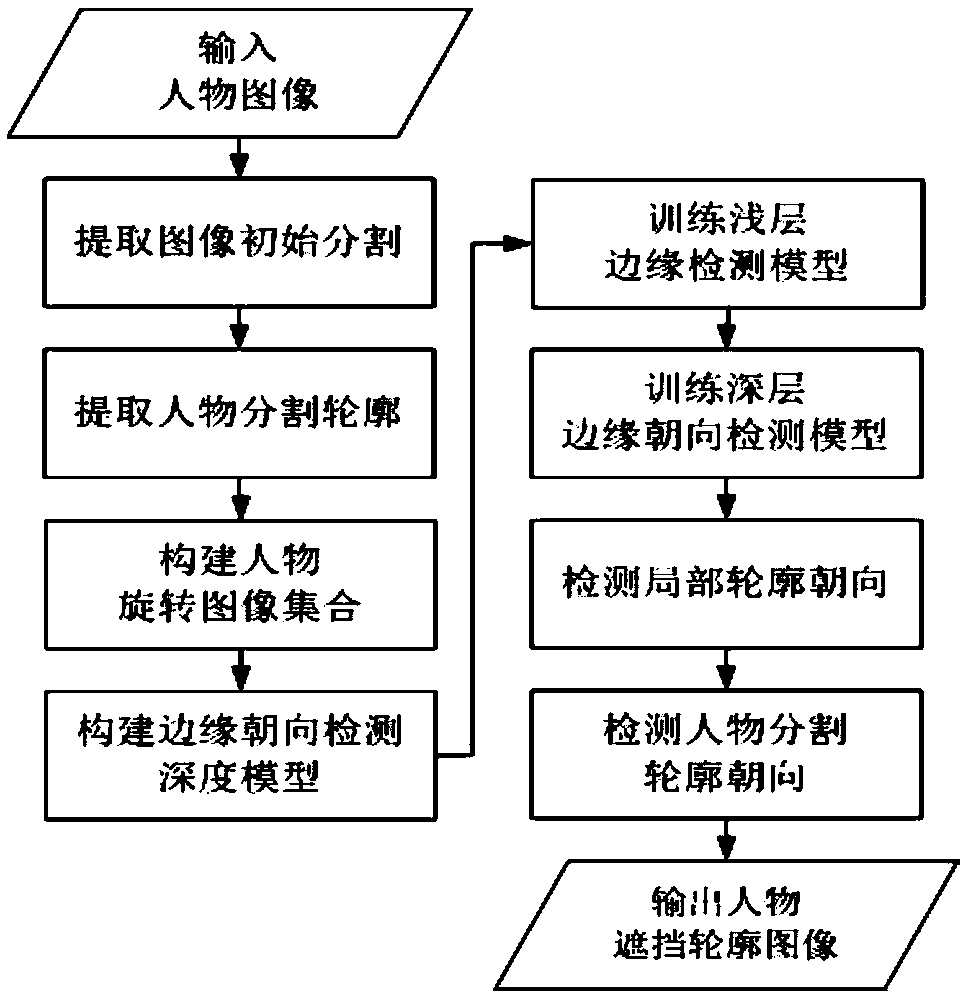
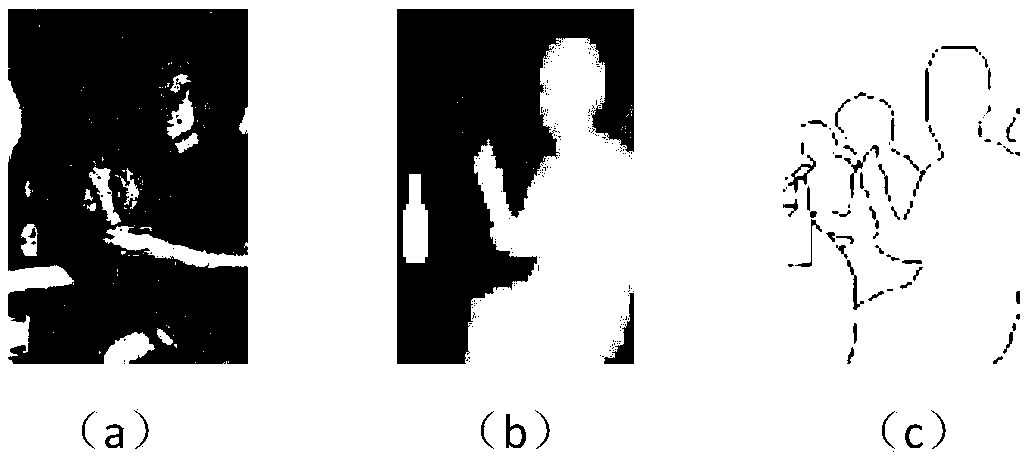
Method for human shielded contour detection based on rotational depth learning
ActiveCN108764186ASolve the accuracy problemImprove accuracyBiometric pattern recognitionNeural architecturesEdge orientationConvolutional neural network
The invention discloses a method for human shielded contour detection based on rotational depth learning. Firstly, the initial segmentation of an image is obtained by dividing and merging an input person image, and a segmentation contour of a target is extracted by regional merging of the color and the content; secondly, according to a rotation angle set, the image is rotated, sampled and labeledto obtain an edge image block set, based on a convolutional neural network, a depth model of the edge orientation detection is constructed, and a rotation image block acquisition set is used to traina shallow layer model and a deep layer model; and finally, the trained depth model of the edge orientation detection is used to detect the local contour orientation, the local contour orientation is evaluated for consistency, and the character segmentation contour orientation is extracted.
Owner:合肥捷玛智能科技有限公司
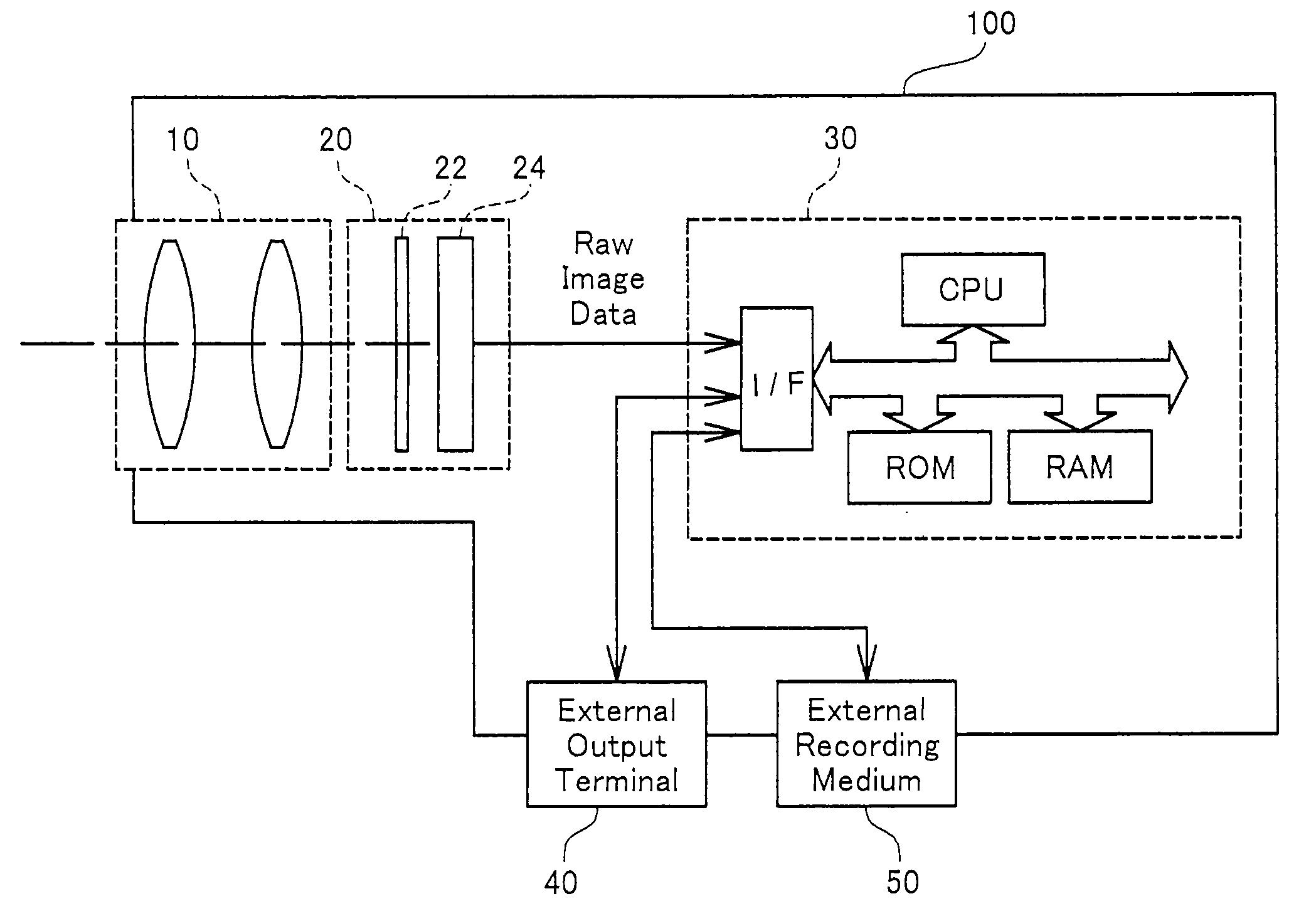
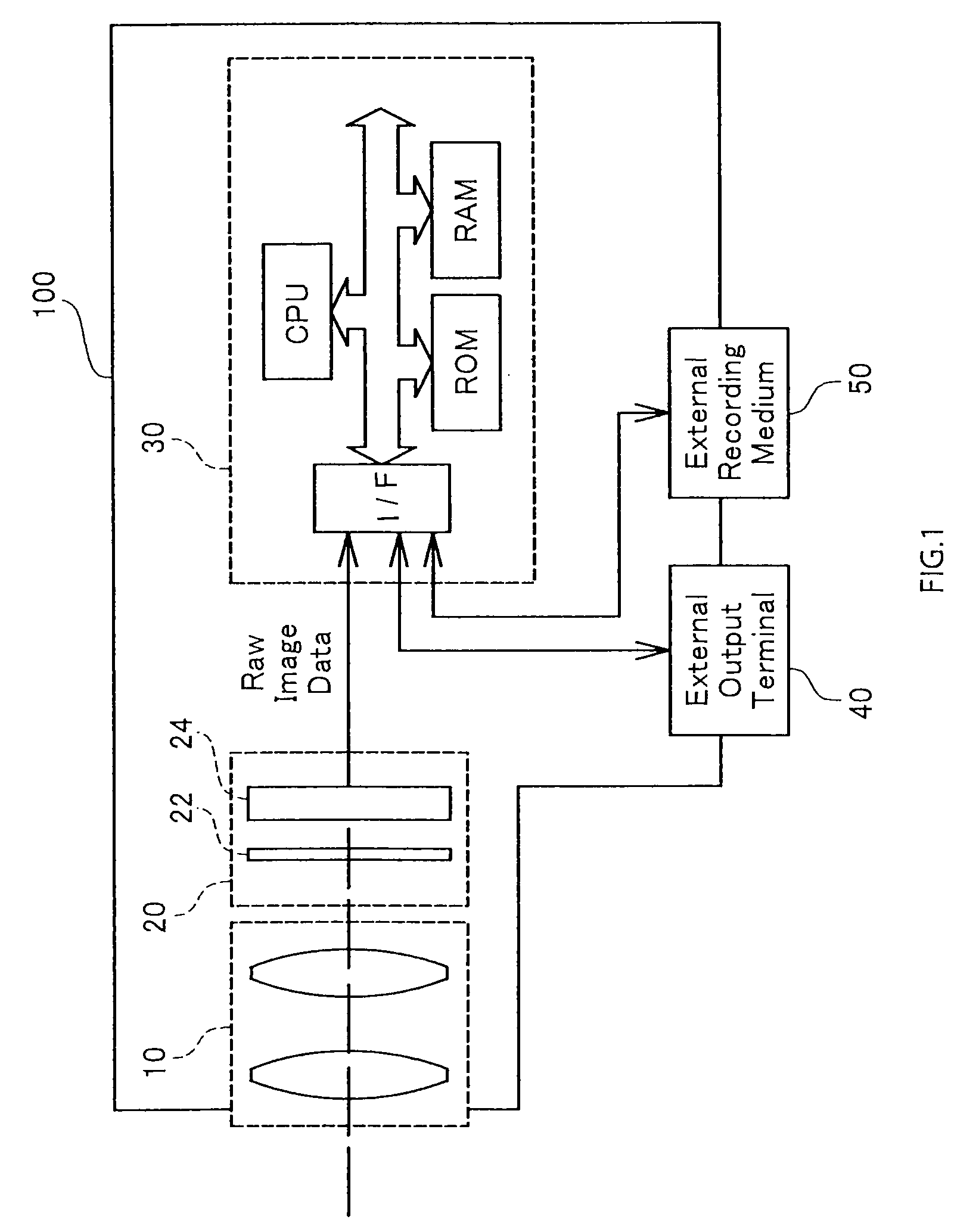
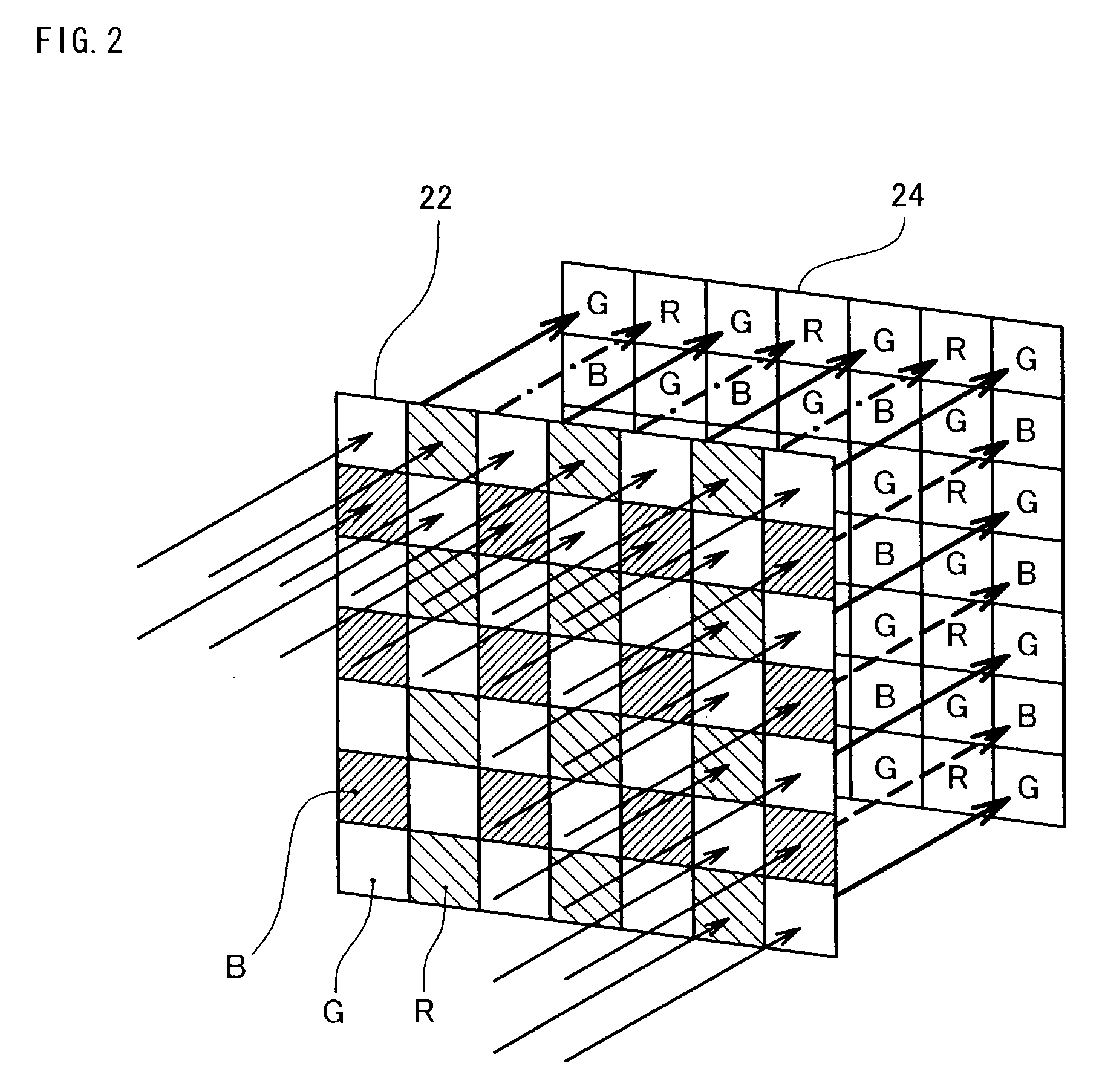
Image Processing Apparatus, Image Processing Method, And Program For Attaining Image Processing
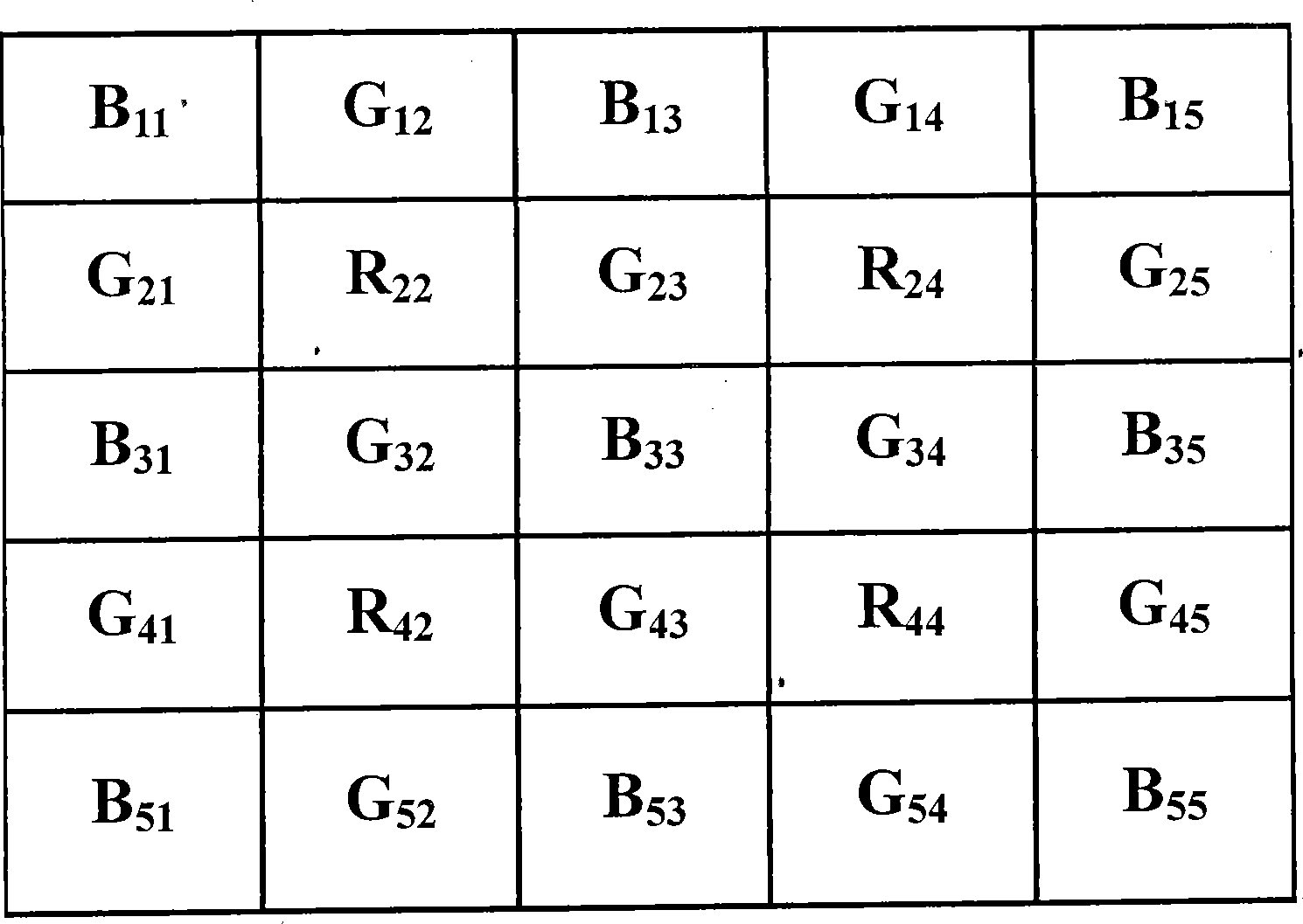
ActiveUS20090244333A1High-speed generationEffectively preventing occurrenceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingEdge orientation
The image processing procedure of the invention receives mosaic image data and calculates a vertical-direction color difference component with regard to each of pixel columns in the mosaic image data in a vertical direction and a horizontal-direction color difference component with regard to each of pixel rows in the mosaic image data in a horizontal direction. The mosaic image data is expressed by a combination of pixel columns with alternate arrangement of pixels of a G component and pixels of an R component in the vertical direction, pixel columns with alternate arrangement of pixels of the G component and pixels of a B component in the vertical direction, pixel rows with alternate arrangement of pixels of the G component and pixels of the R component in the horizontal direction, and pixel rows with alternate arrangement of pixels of the G component and pixels of the B component in the horizontal direction. The image processing procedure subsequently selects pixels of the R component and pixels of the B component from the mosaic image data, and compares a variation of the vertical-direction color difference component with a variation of the horizontal-direction color difference component with regard to each of at least the selected pixels to detect edge orientations of the at least selected pixels. The image processing procedure refers to the detected edge orientations, and interpolates a missing color component in each pixel of the mosaic image data with the settings of one color component in each pixel in the mosaic image data.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
Edge direction based image interpolation method
InactiveUS7590307B2Effectively detect and utilizeImage enhancementImage analysisInterlaced videoComputer graphics (images)
A method for interpolating pixel data of an omitted line by use of pixel data from an interlaced scan, for de-interlacing an interlaced video image. Image edge direction is detected at the center position of every two neighboring scan lines in an interlaced scan. All the directions detected in a given field constitute an edge orientation map. Edge directions are filtered to remove false and unreliable edge directions from the edge orientation map. If an edge direction is removed, the vertical edge direction is used to replace that direction in the edge orientation map. For interpolating a new pixel at the center of two neighboring scan lines, the corresponding direction for that position is used as the interpolation direction to calculate the value of the new pixel. If the direction is vertical, a filter is used along the vertical direction to calculate the interpolation value. If the direction is non-vertical, and has an integer value, then interpolation is performed by taking the average of the two neighboring sample values along the direction. If the direction is non-vertical and has a non-integer value, then an interpolation value is calculated using a directional bilinear method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High performance DRC checking algorithm for derived layer based rules
Roughly described, a design rule data set includes rules on derived layers. The rules are checked by traversing the corners of physical shapes, and for each corner, populating a layout topology database with values gleaned from that corner location, including values involving derived layers. After the layout topology database is populated, the values are compared to values in the design rule data set to detect any design rule violations, including violations of design rules defined on derived layers. Violations are reported in real time during manual editing of the layout. Preferably corner traversal is performed using scan lines oriented perpendicularly to edge orientations, scanning in the direction of the edge orientations. Scans stop only at corner positions on physical layers, and populate the layout topology database with what information can be gleaned based on the current scan line, including information about derived layers. The scans need not reach corners simultaneously.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
High performance drc checking algorithm for derived layer based rules
ActiveUS20120144349A1Robust solutionComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationData setAlgorithm
Roughly described, a design rule data set includes rules on derived layers. The rules are checked by traversing the corners of physical shapes, and for each corner, populating a layout topology database with values gleaned from that corner location, including values involving derived layers. After the layout topology database is populated, the values are compared to values in the design rule data set to detect any design rule violations, including violations of design rules defined on derived layers. Violations are reported in real time during manual editing of the layout. Preferably corner traversal is performed using scan lines oriented perpendicularly to edge orientations, scanning in the direction of the edge orientations. Scans stop only at corner positions on physical layers, and populate the layout topology database with what information can be gleaned based on the current scan line, including information about derived layers. The scans need not reach corners simultaneously.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
High performance design rule checking technique
ActiveUS8352887B2Constraint-based CADSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationData setComputer architecture
Roughly described, a design rule data set is developed offline from the design rules of a target fabrication process. A design rule checking method involves traversing the corners of shapes in a layout region, and for each corner, populating a layout topology database with values that depend on respective corner locations. After the layout topology database is populated, the values are compared to values in the design rule data set to detect any design rule violations. Violations can be reported in real time, while the user is manually editing the layout. Preferably corner traversal is performed using scan lines oriented perpendicularly to edge orientations, and scanning in the direction of the edge orientations. Scans stop only at corner positions and populate the layout topology database with what information can be gleaned based on the current scan line. The different scans need not reach each corner simultaneously.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method and system for human detection
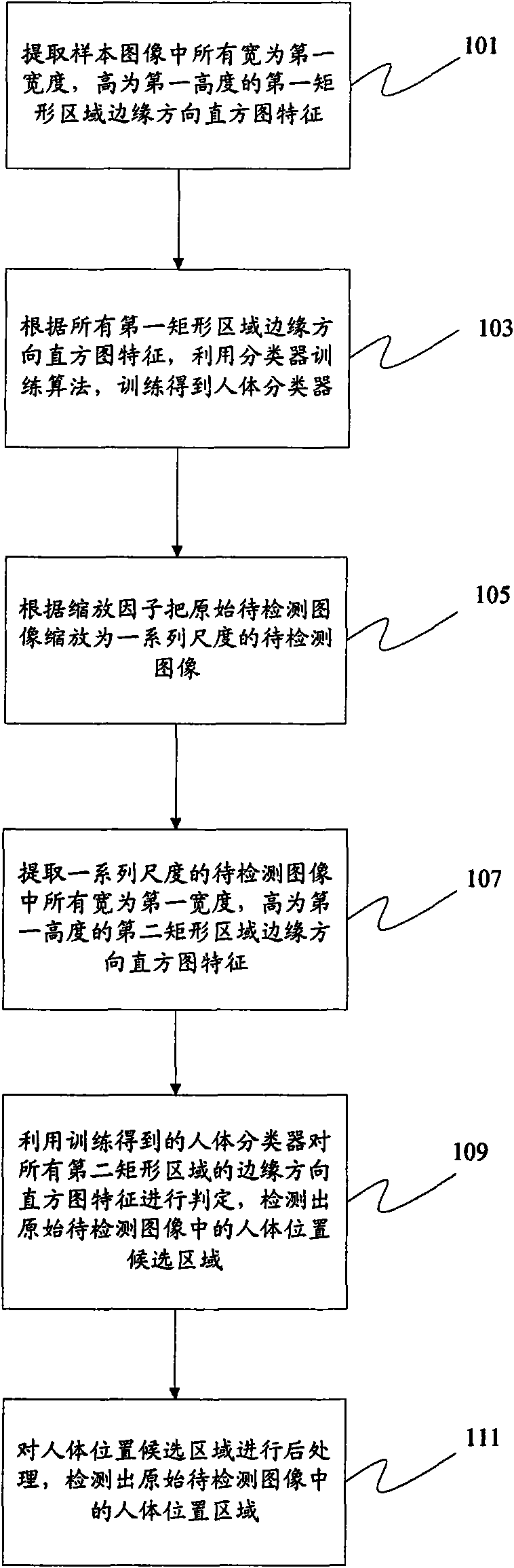
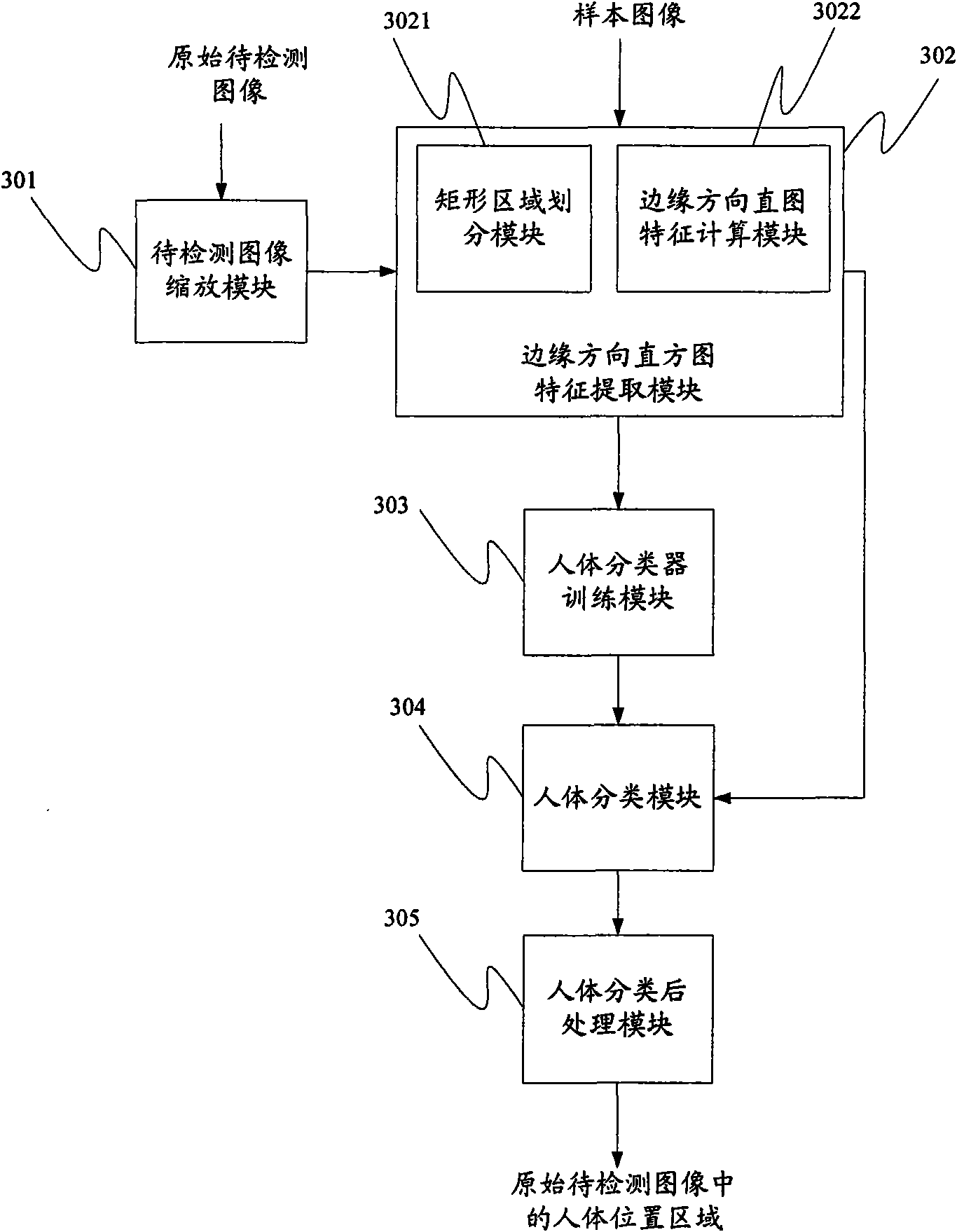
InactiveCN101645135AReduce computationHigh speedCharacter and pattern recognitionEdge orientationSample image
The invention provides a method and a system for human detection. The method comprises the following steps: extracting all the edge orientation histogram (EOH) features of a first rectangular region with the width thereof being a first width and the height thereof being the first height from a sample image; training according to all the EOH features of the first rectangular region by using a classifier training algorithm, to obtain a human classifier; scaling the original image to be detected to images to be detected on a series of scales according to scaling factors; extracting all the EOH features of a second rectangular region with the width thereof being the first width and the height thereof being the first height from the images to be detected on a series of scales; judging all the EOH features of the second rectangular region by the human classifier obtained from training, so as to detect the candidate region of human positions in the original image to be detected; and carryingout the post-treatment on the candidate region of the human positions in the original image to be detected, so as to detect the region of the human position in the original image to be detected.
Owner:VIMICRO CORP
Edge adaptive image expansion and enhancement system and method
An edge adaptive system and method for image filtering. The method maps each output pixel onto input image coordinates (110) and then prefilters and resamples the input image pixels around this point to reduce noise and adjust the scale corresponding to a particular operation. Then the edge in the input image is detected based on local (125) and average (127) signal variances in the input pixels. According to the edge detection parameters (129), including orientation, anisotropy and variance strength, the method determines a footprint and frequency response for the interpolation of the output pixel. In a more particular implementation, the method divides the input pixel space into a finite number of directions called skews, and estimates the edge orientation with the nearest skew direction. This further facilitates pixel inclusion in the interpolation of the output pixel.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
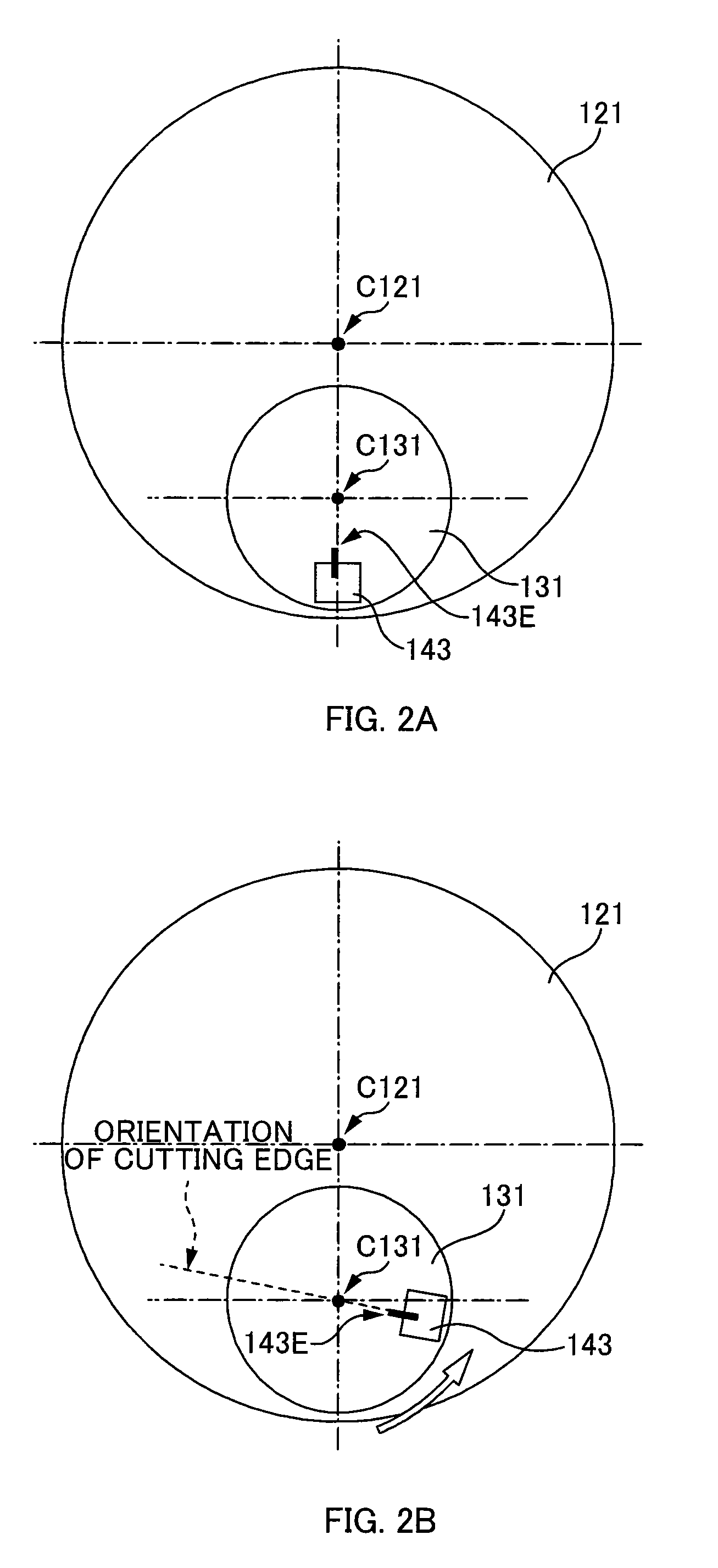
Machining unit and machine tool
ActiveUS20090214313A1Improve cutting effectSleeve/socket jointsMilling machinesEdge orientationEngineering
A machining unit that is supported on a machine tool and machines a workpiece by a revolving tool with a main spindle section being driven and rotated includes an eccentric rotational section, a tool holder, a tool revolution-radius changing mechanism, and a cutting-edge-orientation correcting mechanism. The eccentric rotational section is disposed on the main spindle section, and is rotatable about an eccentric axis that is located eccentrically at any distance in a radial direction of the main spindle section from a rotation center of the main spindle section. The tool holder is disposed on the eccentric rotational section, and supports the tool. The tool revolution-radius changing mechanism moves the tool in the radial direction, and changes the radius of the revolution of the tool by rotating the eccentric rotational section about the eccentric axis. The cutting-edge-orientation correcting mechanism corrects the orientation of a cutting edge of the tool by making the tool holder spin about an axis of the tool holder, the axis being parallel to the rotation center of the main spindle section.
Owner:SANKYO SEISAKUSHO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com