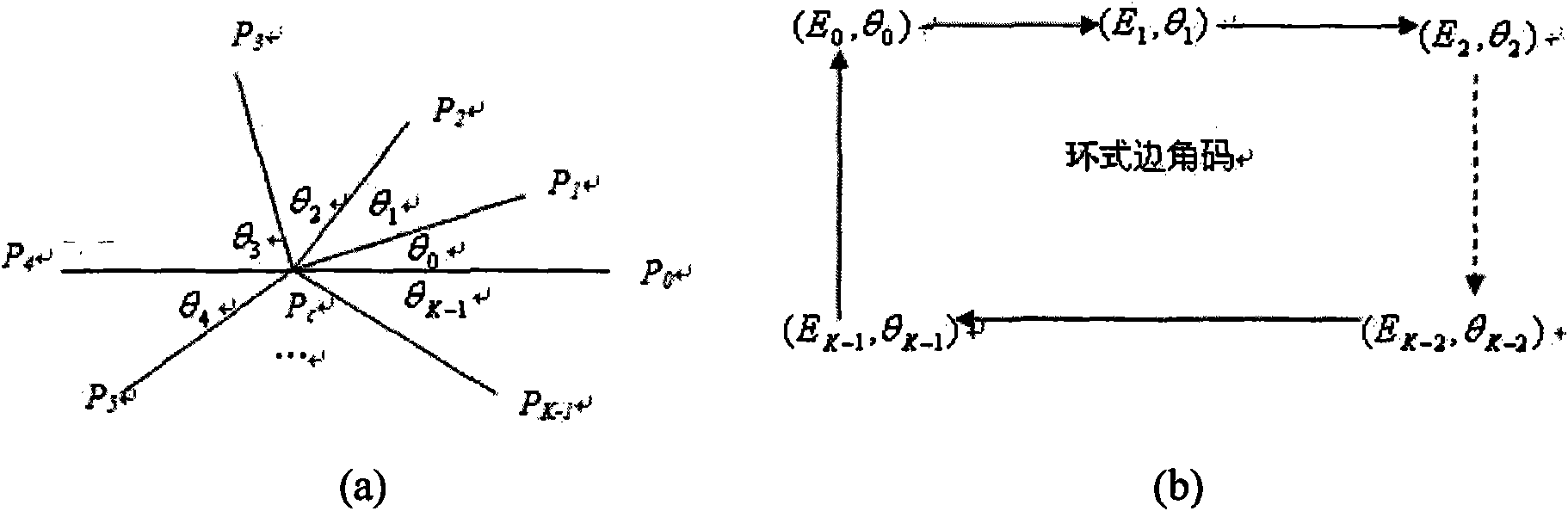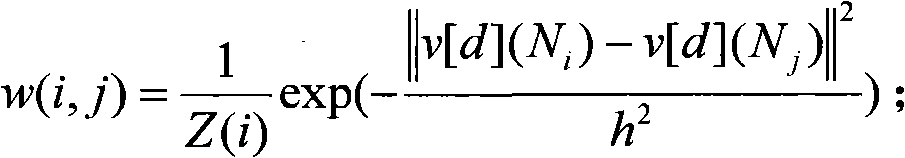Patents
Literature
670 results about "Local structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Software self-defense systems and methods
ActiveUS20050183072A1Error detection/correctionProgram/content distribution protectionTamper resistanceObfuscation
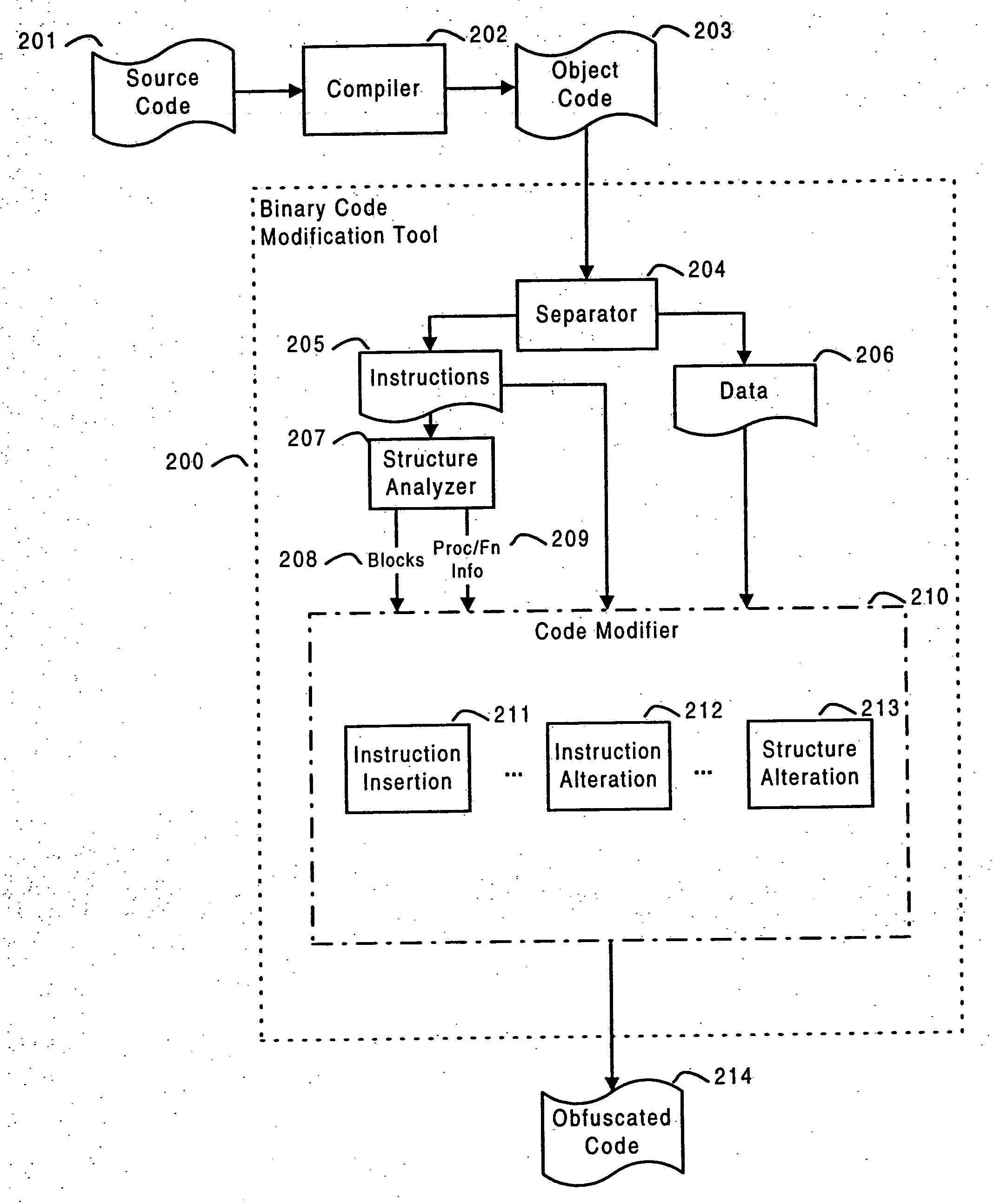
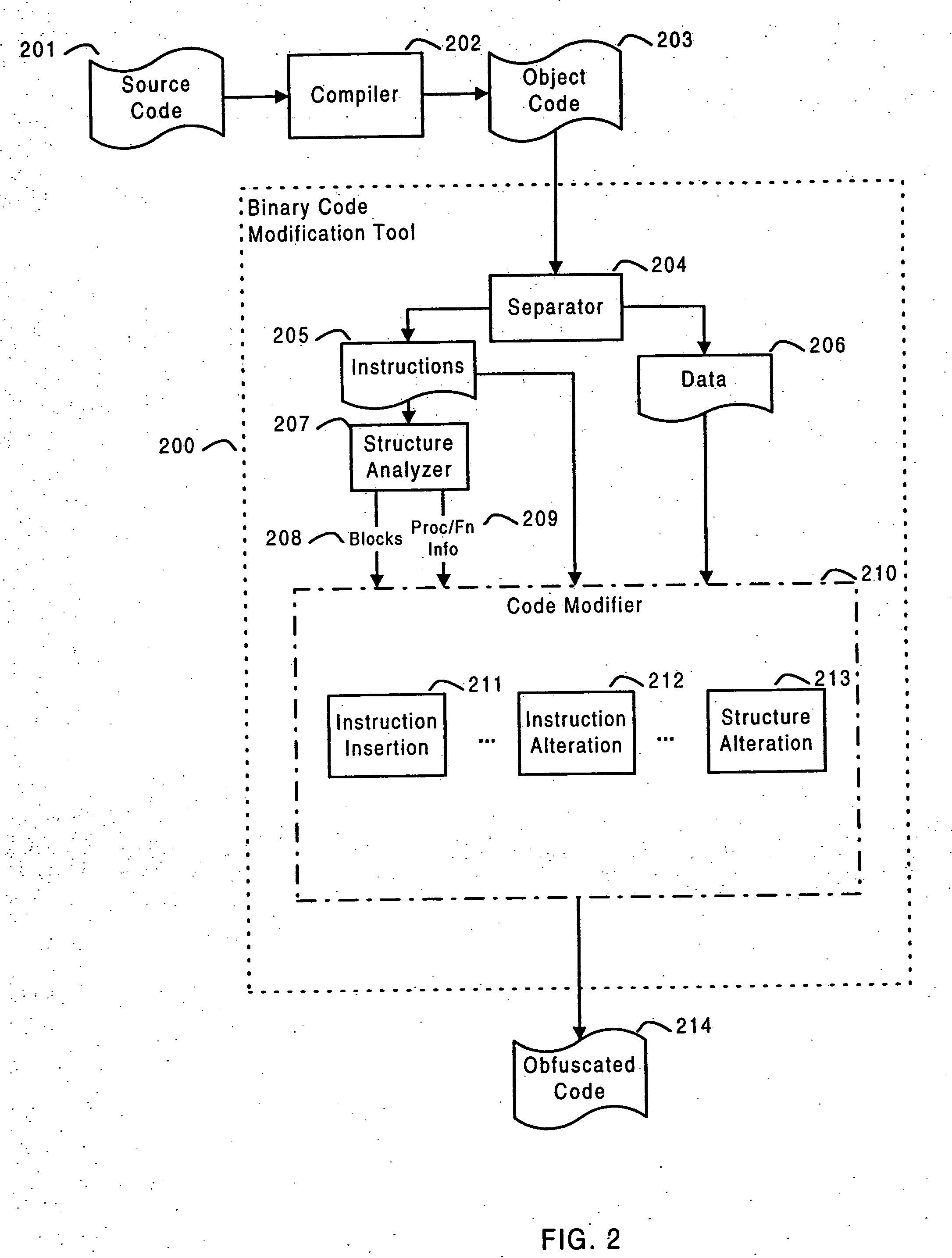
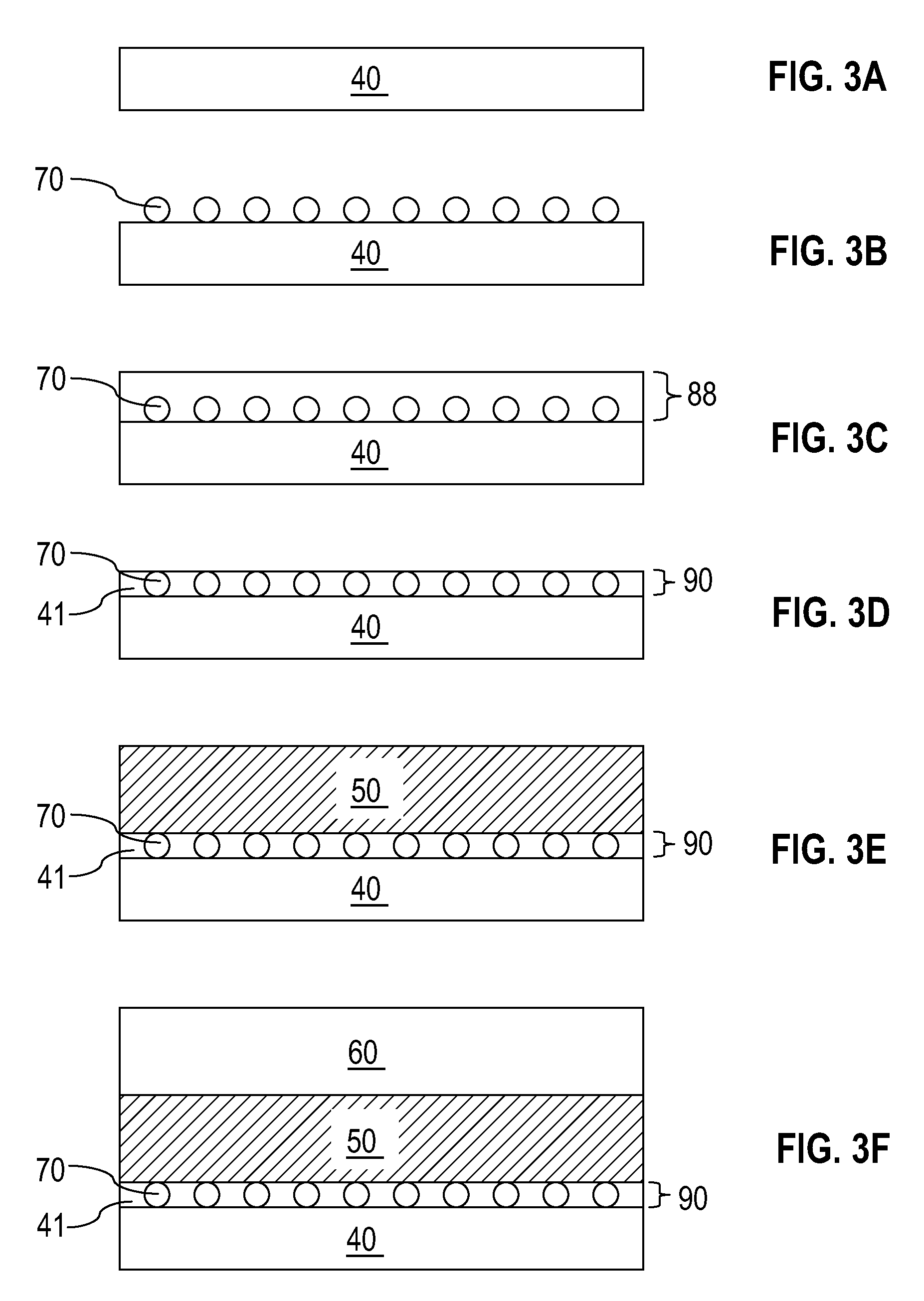
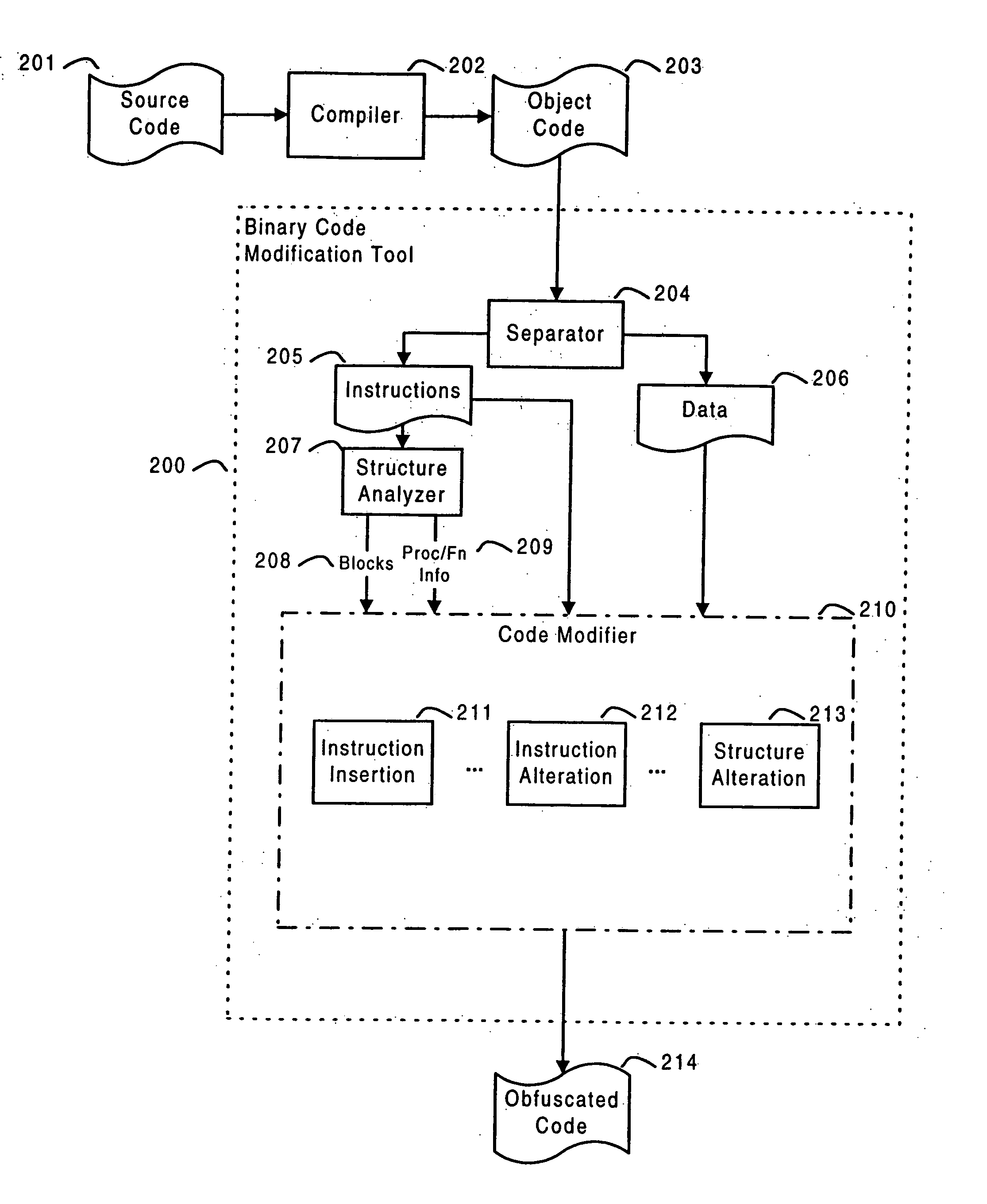
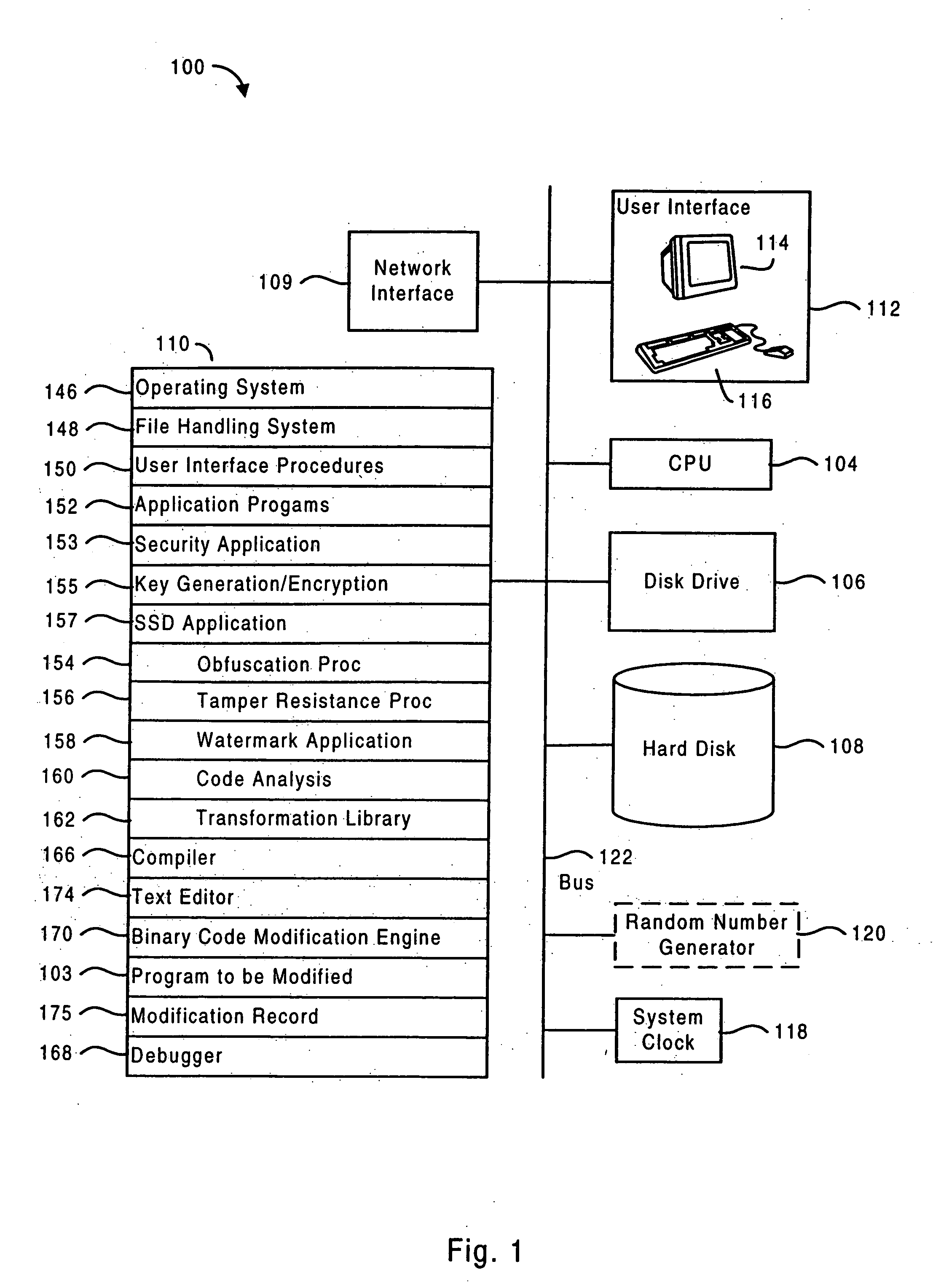
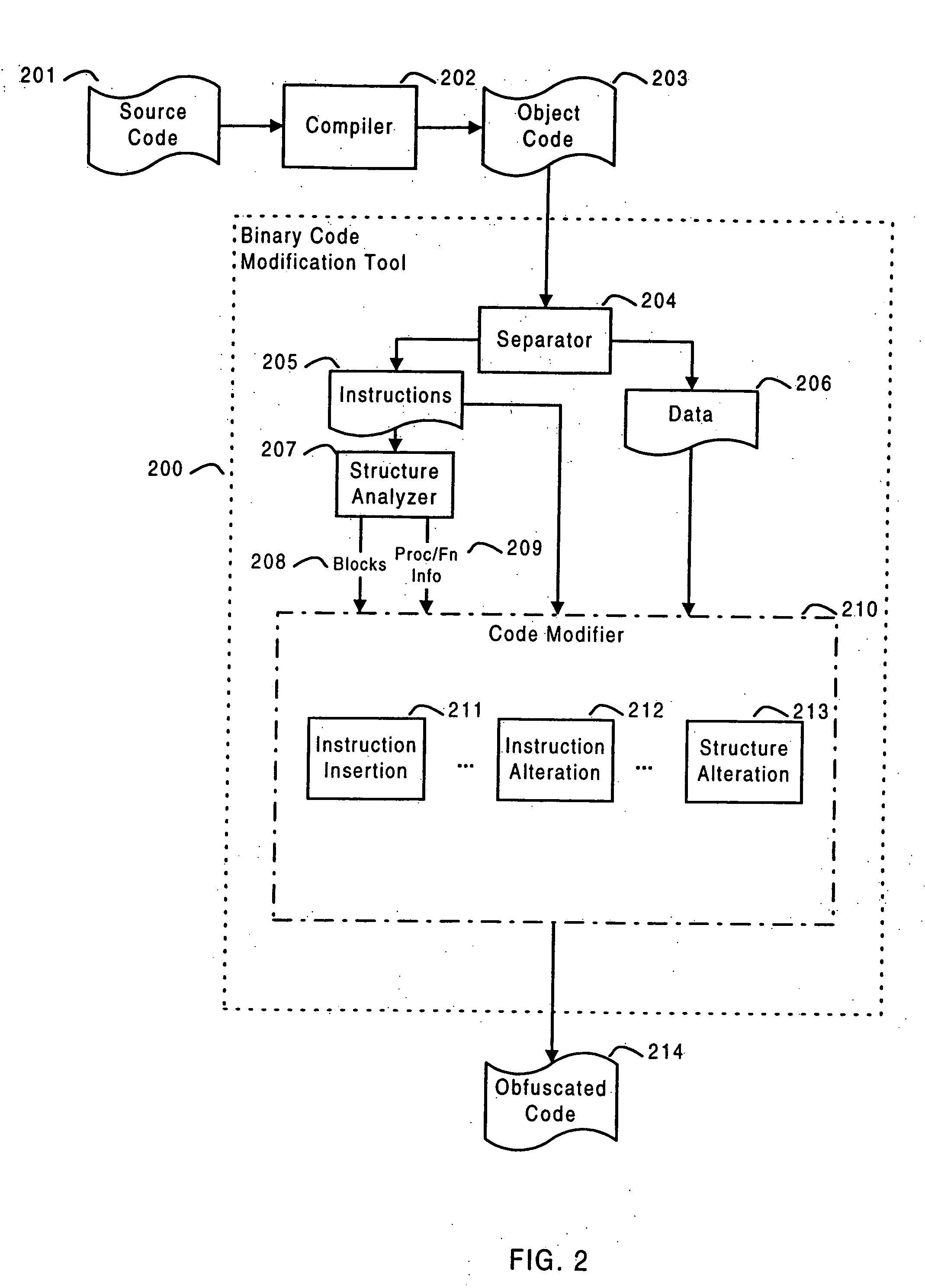
Systems and methods are disclosed for protecting a computer program from unauthorized analysis and modification. Obfuscation transformations can be applied to the computer program's local structure, control graph, and / or data structure to render the program more difficult to understand and / or modify. Tamper-resistance mechanisms can be incorporated into the computer program to detect attempts to tamper with the program's operation. Once an attempt to tamper with the computer program is detected, the computer program reports it to an external agent, ceases normal operation, and / or reverses any modifications made by the attempted tampering. The computer program can also be watermarked to facilitate identification of its owner. The obfuscation, tamper-resistance, and watermarking transformations can be applied to the computer program's source code, object code, or executable image.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
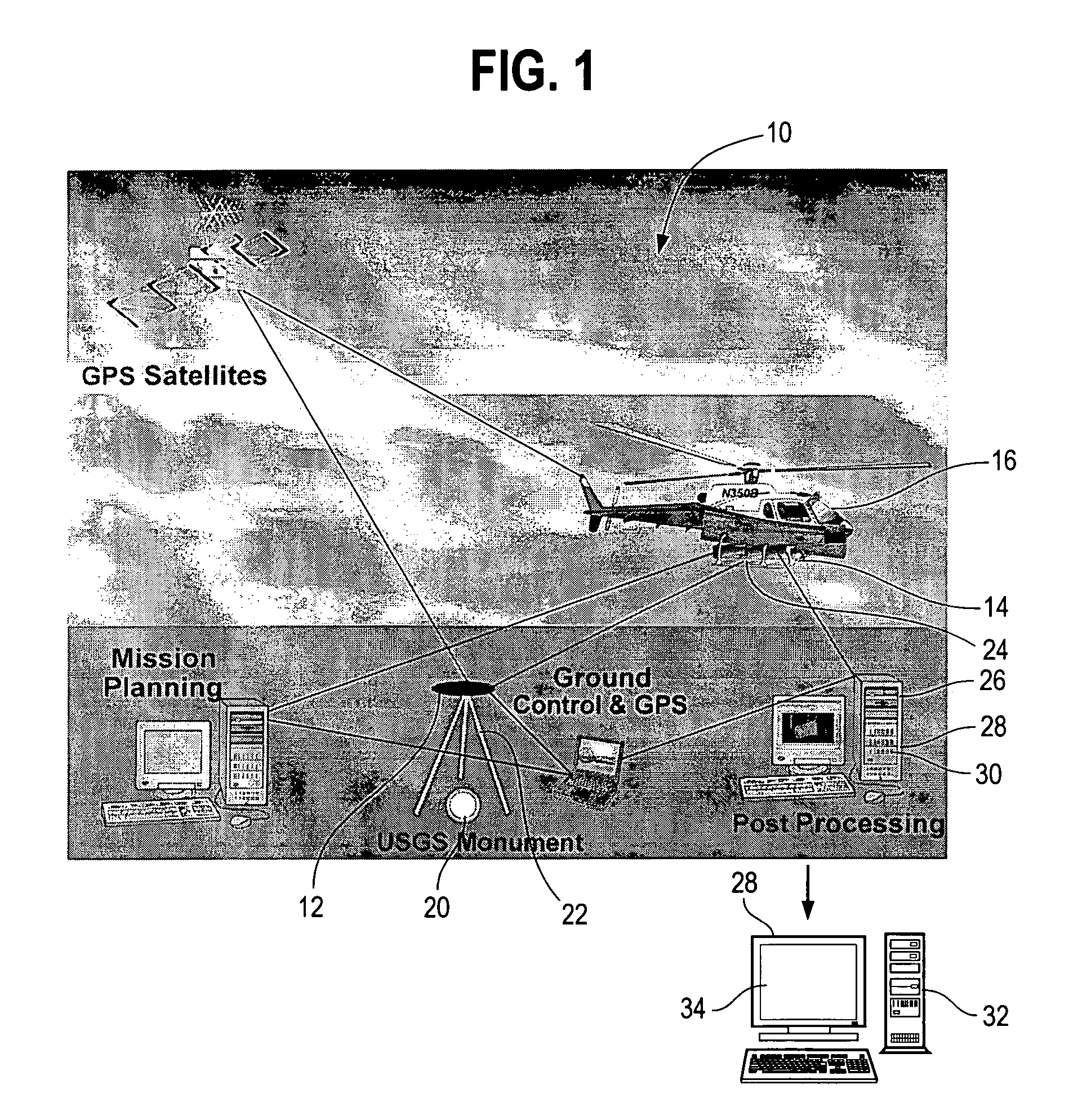
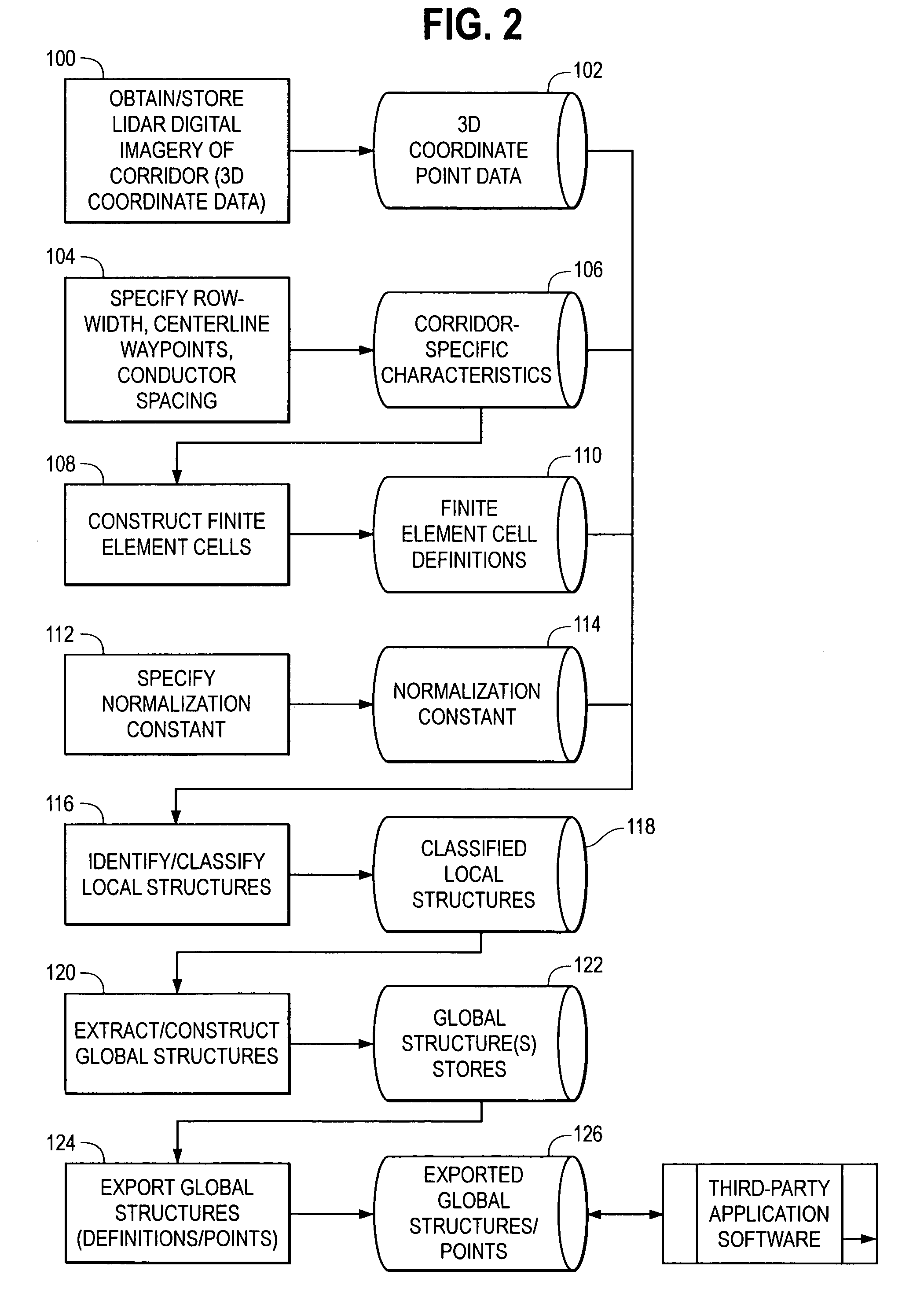
Method and system for direct classification from three dimensional digital imaging
An automated system and / or method is disclosed for rapidly, accurately, and efficiently processing bulk three-dimensional digital image data of both path / corridor and area scenes to discriminate different structures or classifications of objects from within the image. The method first decomposes the three-dimensional digital imagery coordinate points into simple local structures and then extracts the globally complex structures from the local structures. The system and / or method incorporates procedures for sub-dividing the three-dimensional image data into rectilinear and / or ellipsoidal finite element cells, mathematically analyzing the contents (point coordinates) of each individual cell to classify / define the local structure, and extracting the globally complex structure or object from the image. The system and / or method applies accepted mathematical formulas to filter or classify large volumes of apparently random three-dimensional point coordinate spatial data into simpler structures and then to extract more globally complex objects generally encountered within the real world imagery scene being investigated.
Owner:DOW JAMES W
Current constricting phase change memory element structure
InactiveUS20090014704A1Small sizeHigh local temperatureNanoinformaticsBulk negative resistance effect devicesPhase-change memoryCurrent limiting
A layer of nanopaiticles having a dimension on the order of 10 nm is employed to form a current constricting layer or as a hardmask for forming a current constricting layer from an underlying insulator layer. The nanoparticles are preferably self-aligning and / or self-planarizing on the underlying surface. The current constricting layer may be formed within a bottom conductive plate, within a phase change material layer, within a top conductive plate, or within a tapered liner between a tapered via sidewall and a via plug contains either a phase change material or a top conductive material. The current density of the local structure around the current constricting layer is higher than the surrounding area, thus allowing local temperature to rise higher than surrounding material. The total current required to program the phase change memory device, and consequently the size of a programming transistor, is reduced due to the current constricting layer.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD +2
Software self-defense systems and methods
ActiveUS20050204348A1Error detection/correctionProgram/content distribution protectionTamper resistanceObfuscation
Systems and methods are disclosed for protecting a computer program from unauthorized analysis and modification. Obfuscation transformations can be applied to the computer program's local structure, control graph, and / or data structure to render the program more difficult to understand and / or modify. Tamper-resistance mechanisms can be incorporated into the computer program to detect attempts to tamper with the program's operation. Once an attempt to tamper with the computer program is detected, the computer program reports it to an external agent, ceases normal operation, and / or reverses any modifications made by the attempted tampering. The computer program can also be watermarked to facilitate identification of its owner. The obfuscation, tamper-resistance, and watermarking transformations can be applied to the computer program's source code, object code, or executable image.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
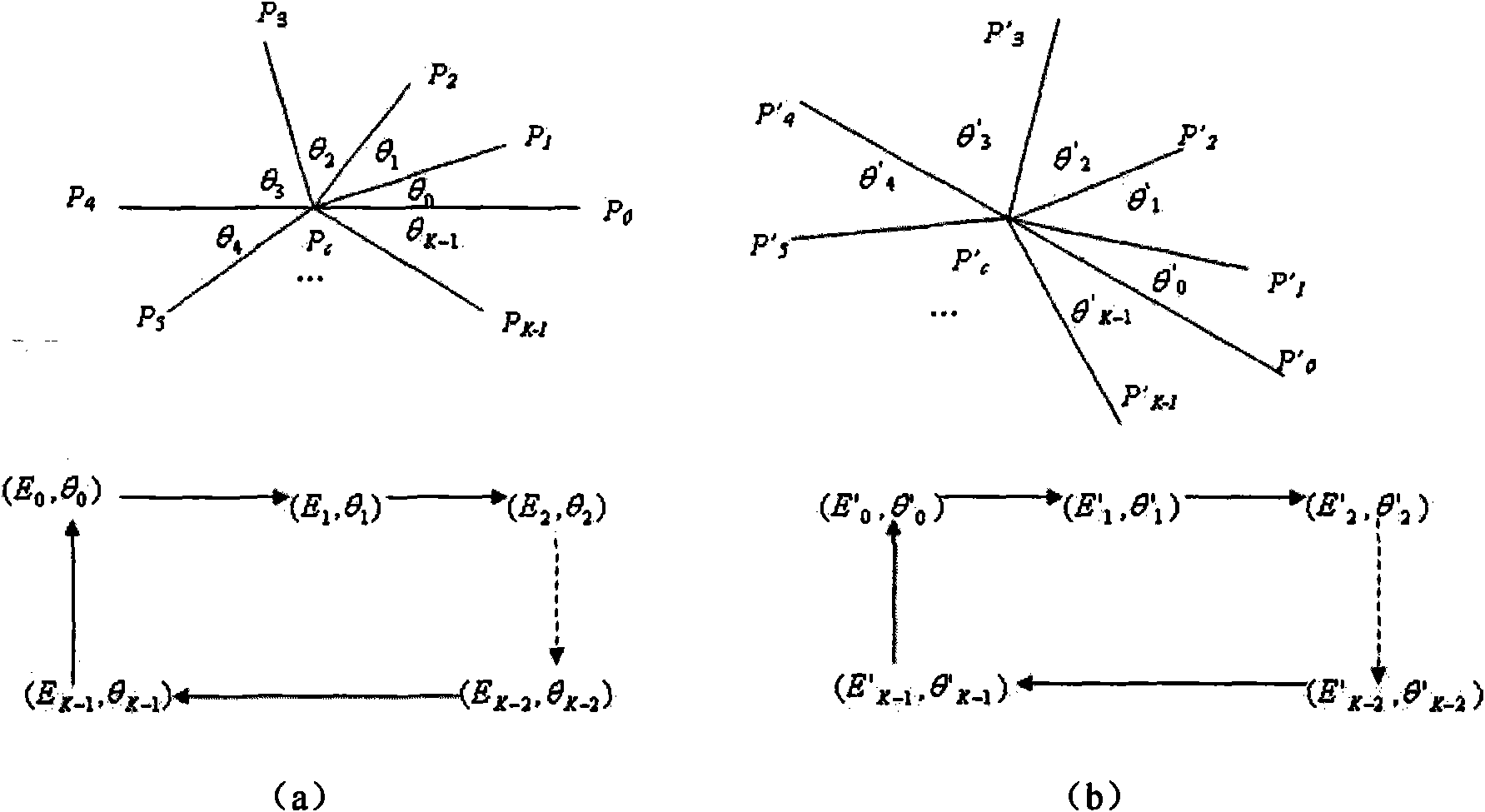
Fundamental entity-relationship models for the generic audio visual data signal description
InactiveUS6847980B1Enhanced content-sensitive general searchVideo data indexingData processing applicationsSemantic propertyData signal
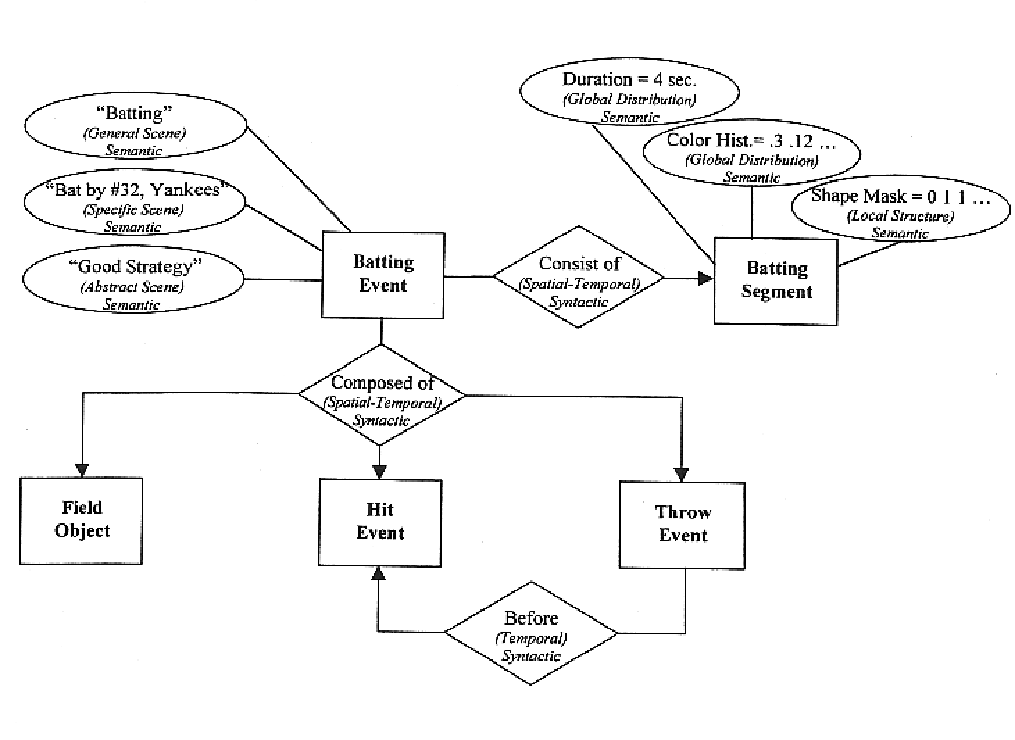
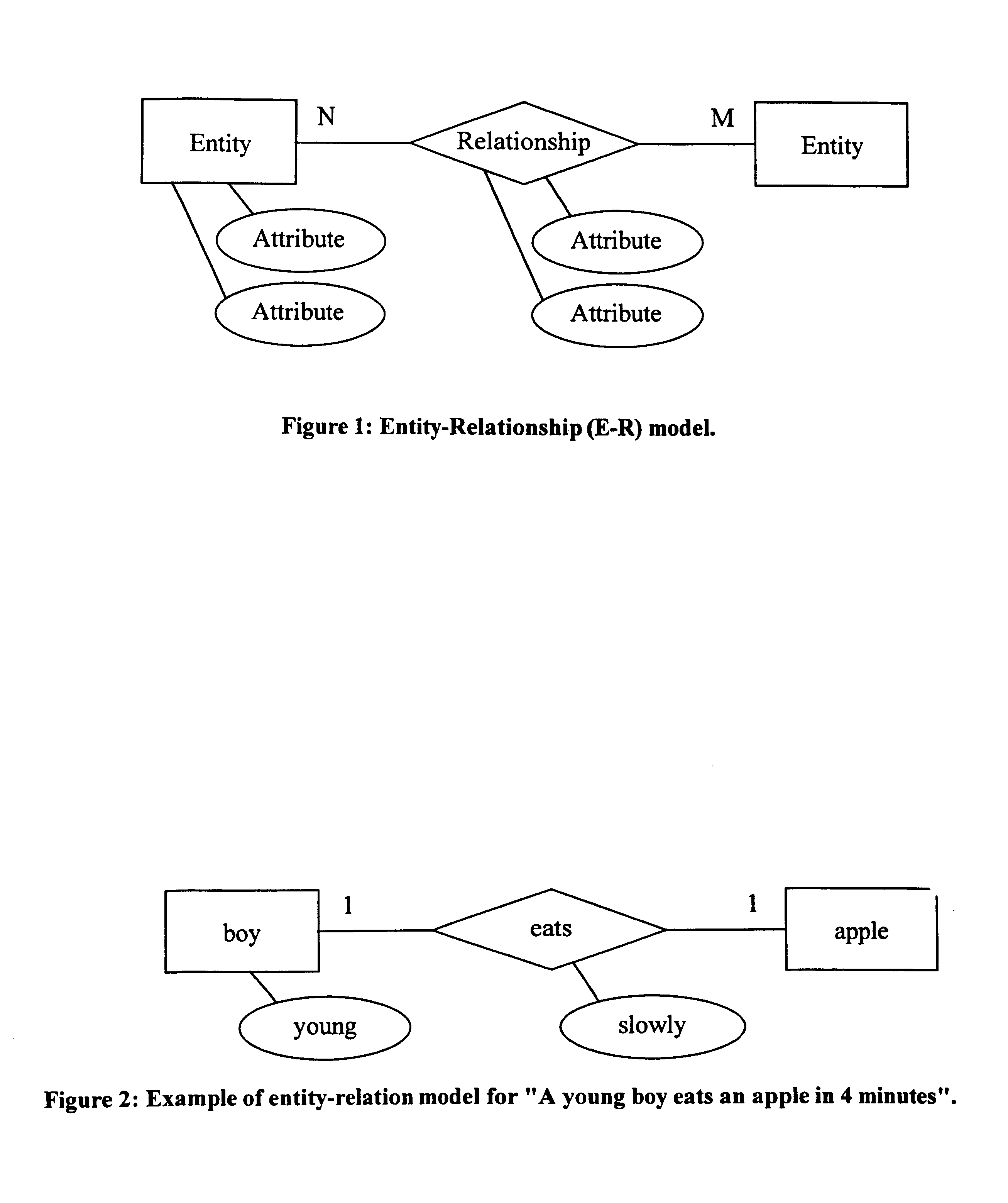
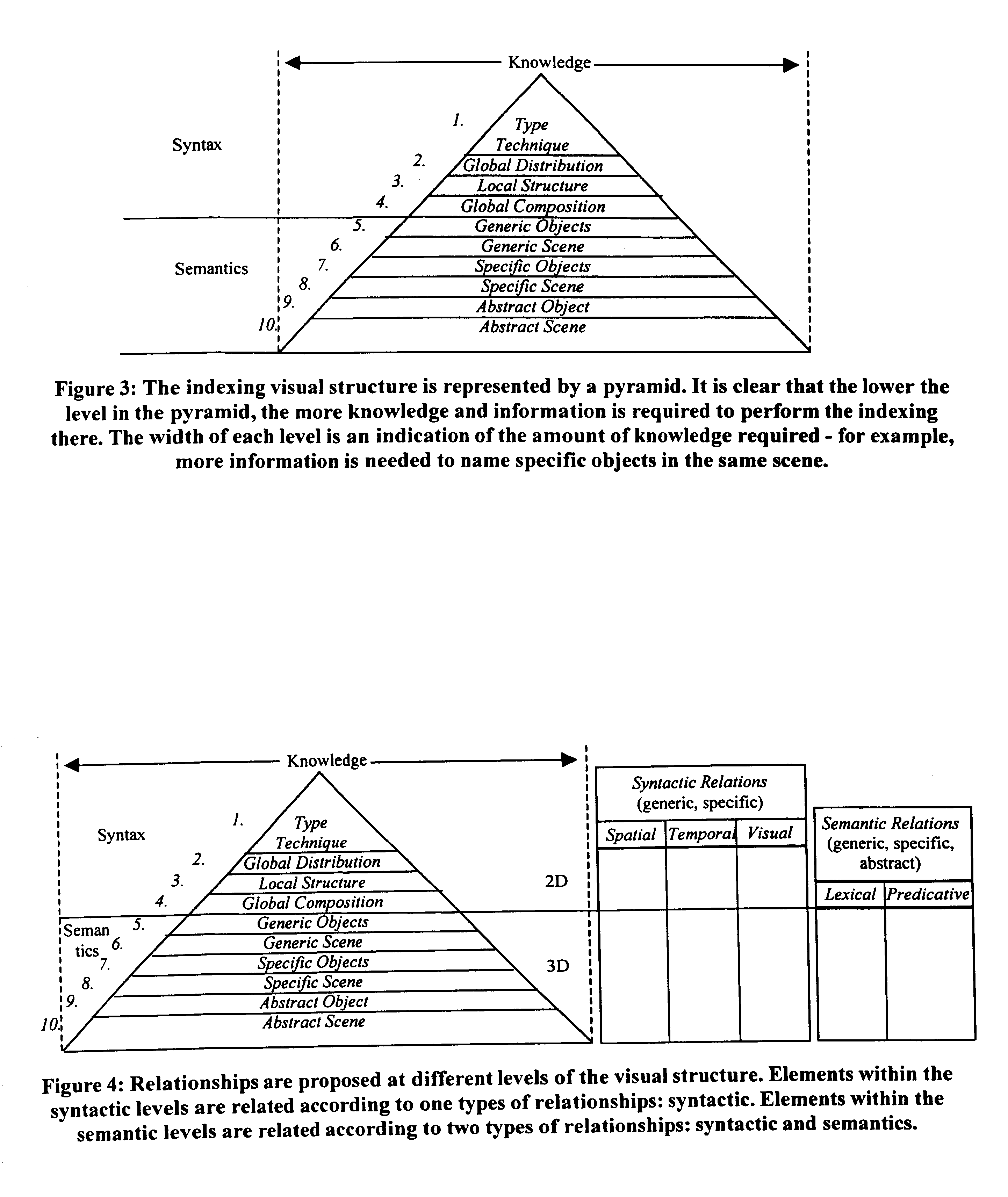
An invention for generating standard description records from multimedia information. The invention utilizes fundamental entity-relation models for the Generic AV DS that classify the entities, the entity attributes, and the relationships in relevant types to describe visual data. It also involves classification of entity attributes into syntactic and semantic attributes. Syntactic attributes can be categorized into different levels: type / technique, global distribution, local structure, and global composition. Semantic attributes can be likewise discretely categorized: generic object, generic scene, specific object, specific scene, abstract object, and abstract scene. The invention further classifies entity relationships into syntactic / semantic categories. Syntactic relationship categories include spatial, temporal, and visual categories. Semantic relationship categories include lexical and predicative categories. Spatial and temporal relationships can be topological or directional; visual relationships can be global, local, or composition; lexical relationships can be synonymy, antonymy, hyponymy / hypernymy, or meronymy / holonymy; and predicative relationships can be actions (events) or states.
Owner:NAT SCI FOUND NSF
Gas Purification Process Utilizing Engineered Small Particle Adsorbents
ActiveUS20120222555A1Great diffusion rateLower Level RequirementsCarbon compoundsSulfur compoundsParticulatesSorbent
A gas separation process uses a structured particulate bed of adsorbent coated shapes / particles laid down in the bed in an ordered manner to simulate a monolith by providing longitudinally extensive gas passages by which the gas mixture to be separated can access the adsorbent material along the length of the particles. The particles can be laid down either directly in the bed or in locally structured packages / bundles which themselves are similarly oriented such that the bed particles behave similarly to a monolith but without at least some disadvantages. The adsorbent particles can be formed with a solid, non-porous core with the adsorbent formed as a thin, adherent coating on the exposed exterior surface. Particles may be formed as cylinders / hollow shapes to provide ready access to the adsorbent. The separation may be operated as a kinetic or equilibrium controlled process.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
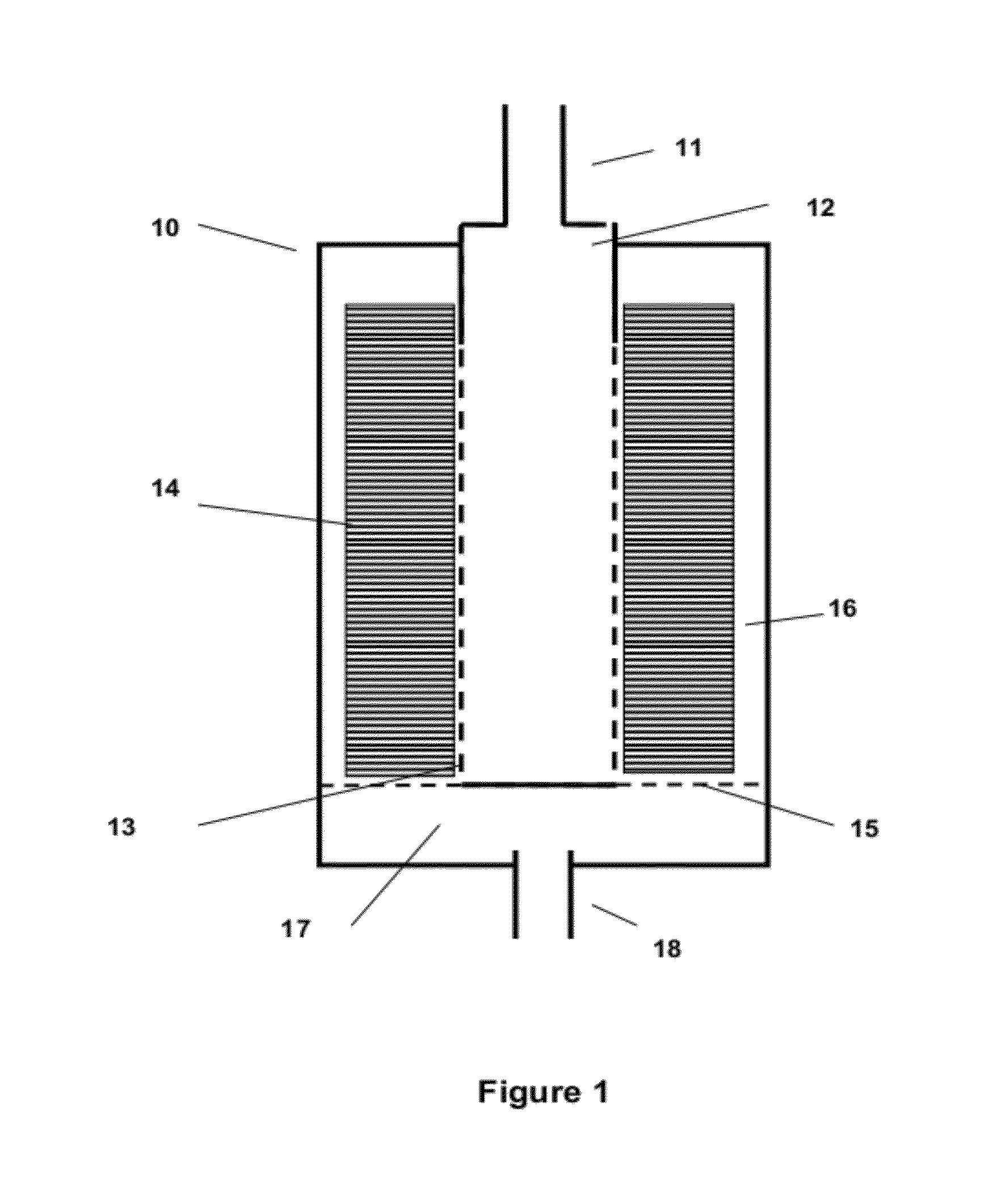
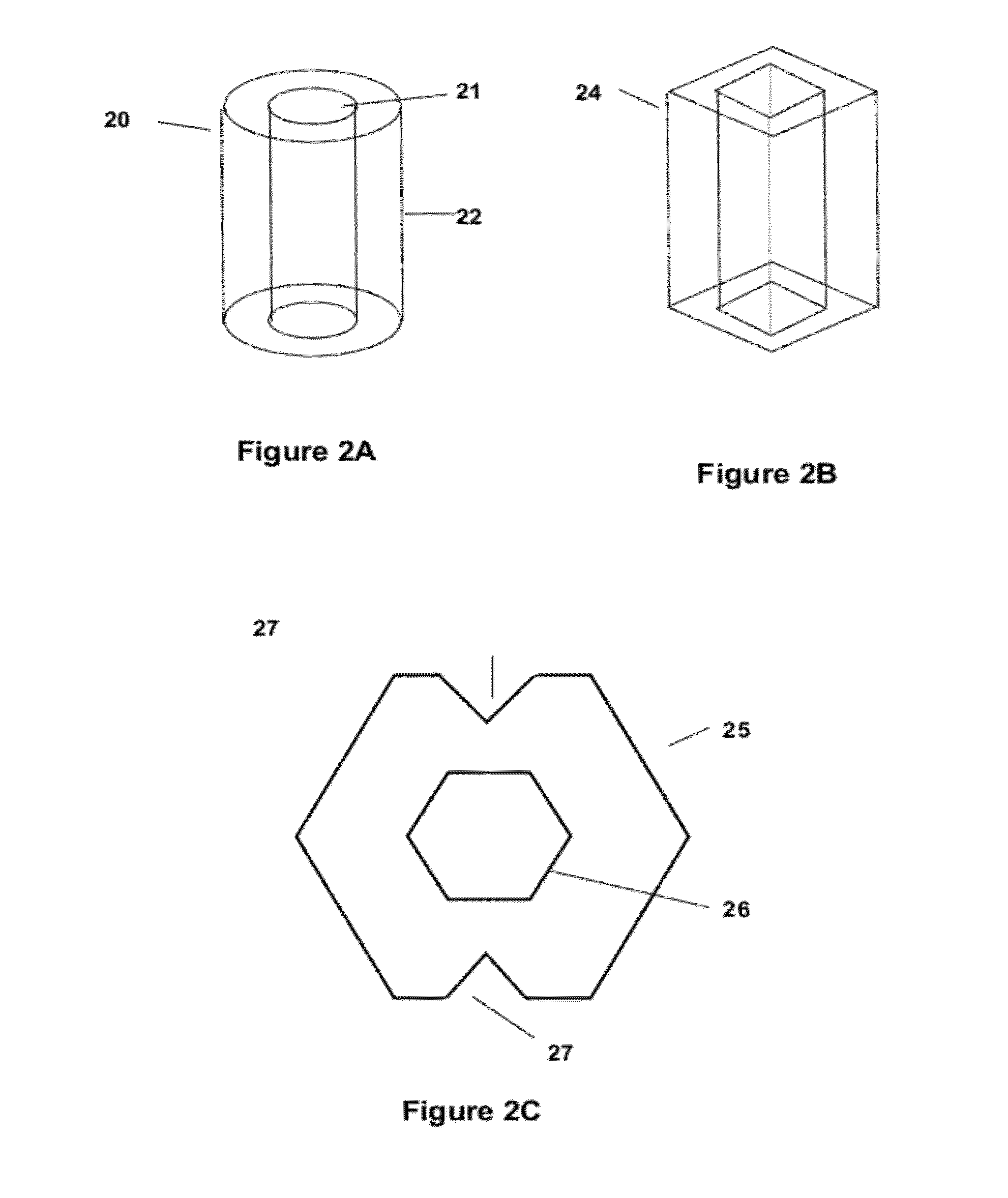
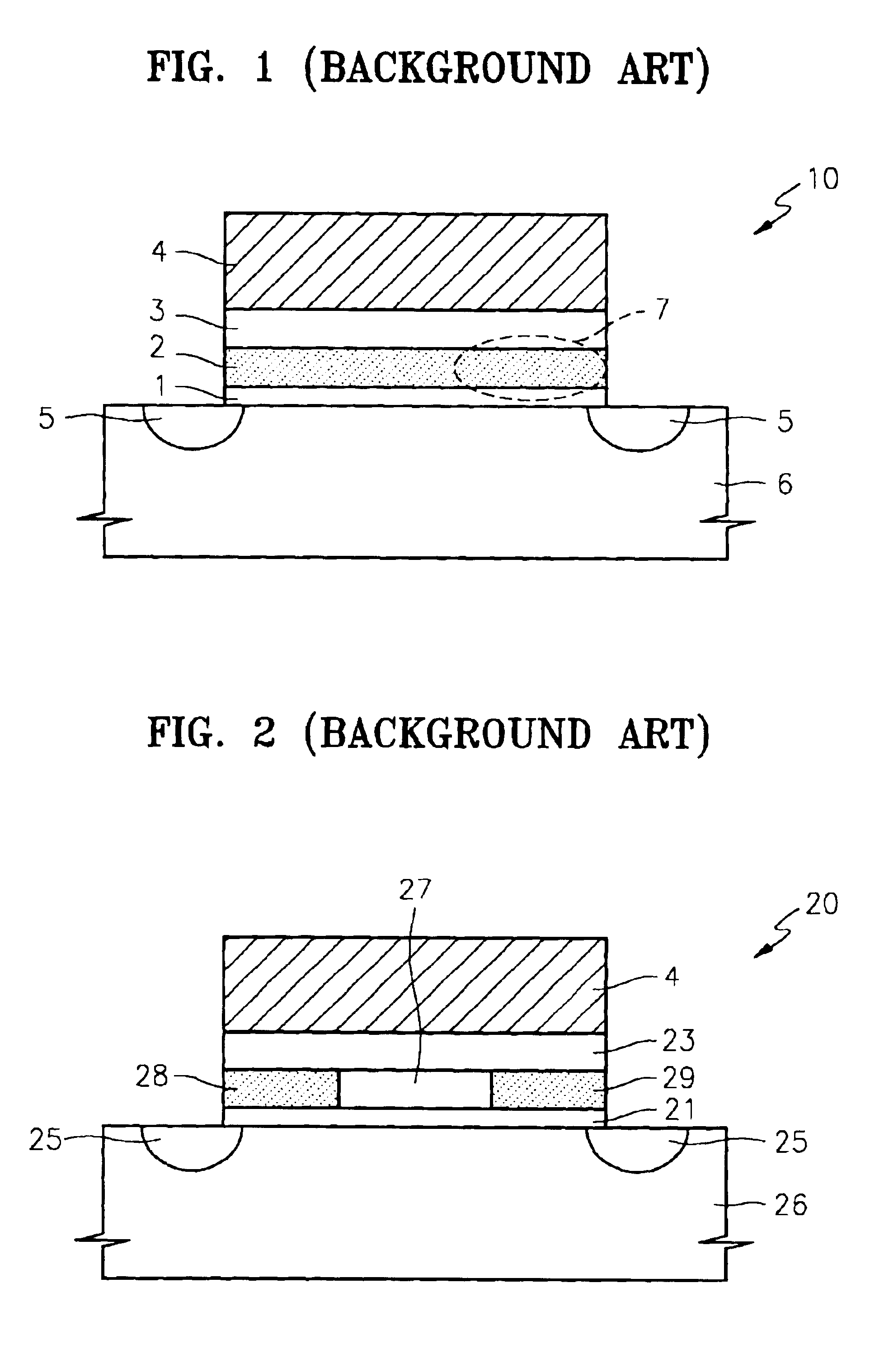
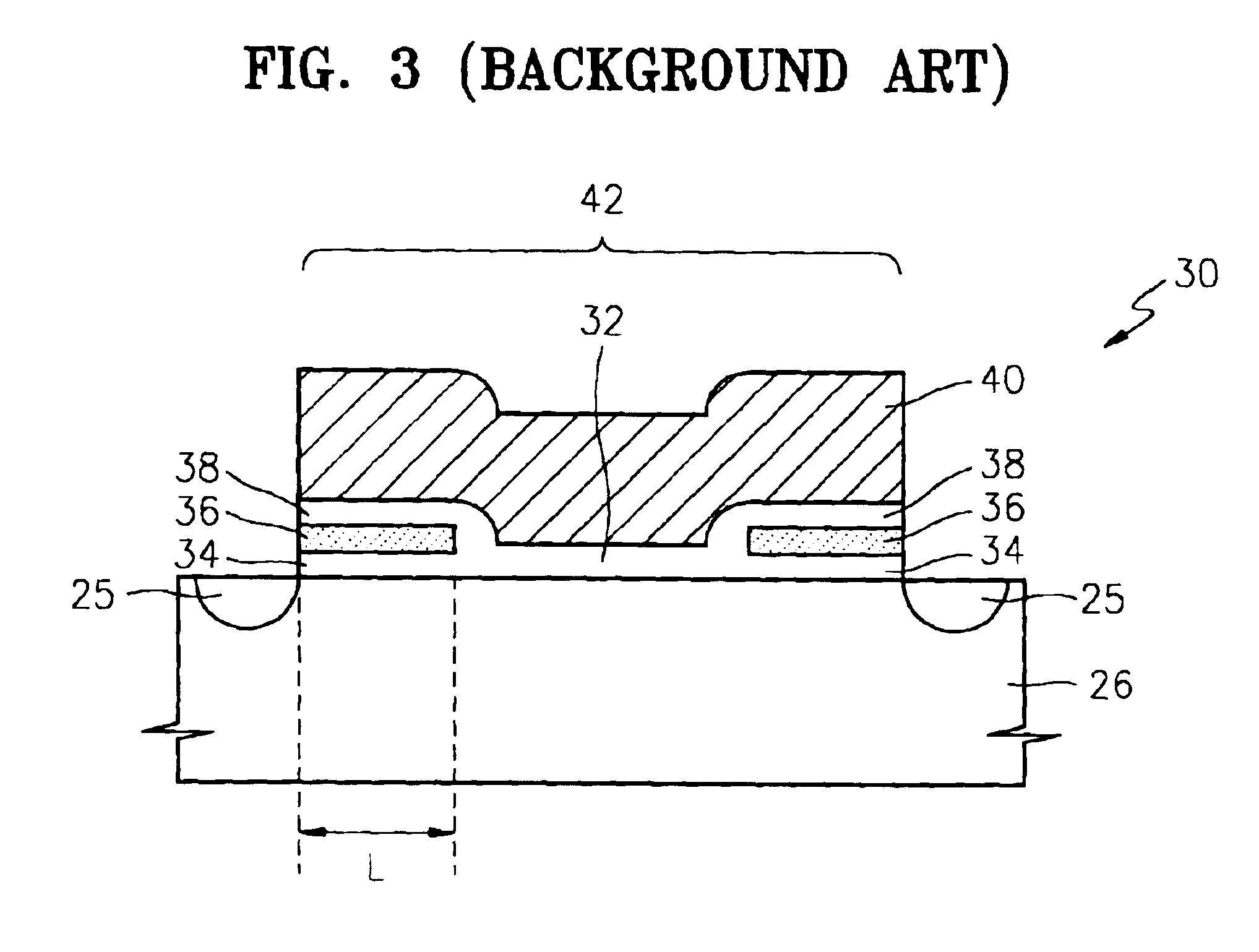
Local sonos-type structure having two-piece gate and self-aligned ono and method for manufacturing the same
A local SONOS structure having a two-piece gate and a self-aligned ONO structure includes: a substrate; an ONO structure on the substrate; a first gate layer on and aligned with the ONO structure; a gate insulator on the substrate aside the ONO structure; and a second gate layer on the first gate layer and on the gate insulator. The first and second gate layers are electrically connected together. Together, the ONO structure and first and second gate layers define at least a 1-bit local SONOS structure. A corresponding method of manufacture includes: providing a substrate; forming an ONO structure on the substrate; forming a first gate layer on and aligned with the ONO structure; forming a gate insulator on the substrate aside the ONO structure; forming a second gate layer on the first gate layer and on the gate insulator; and electrically connecting the first and second gate layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
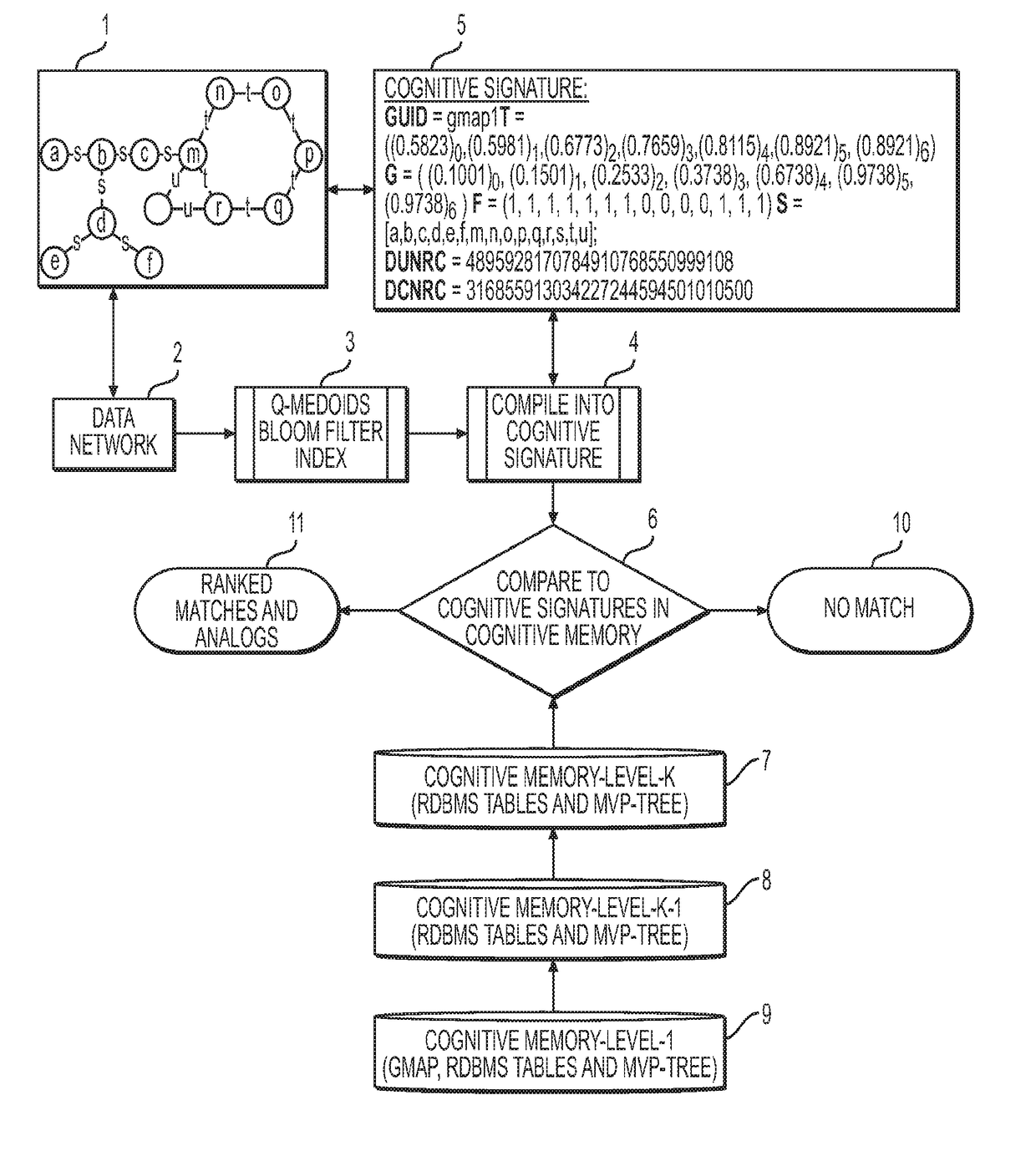
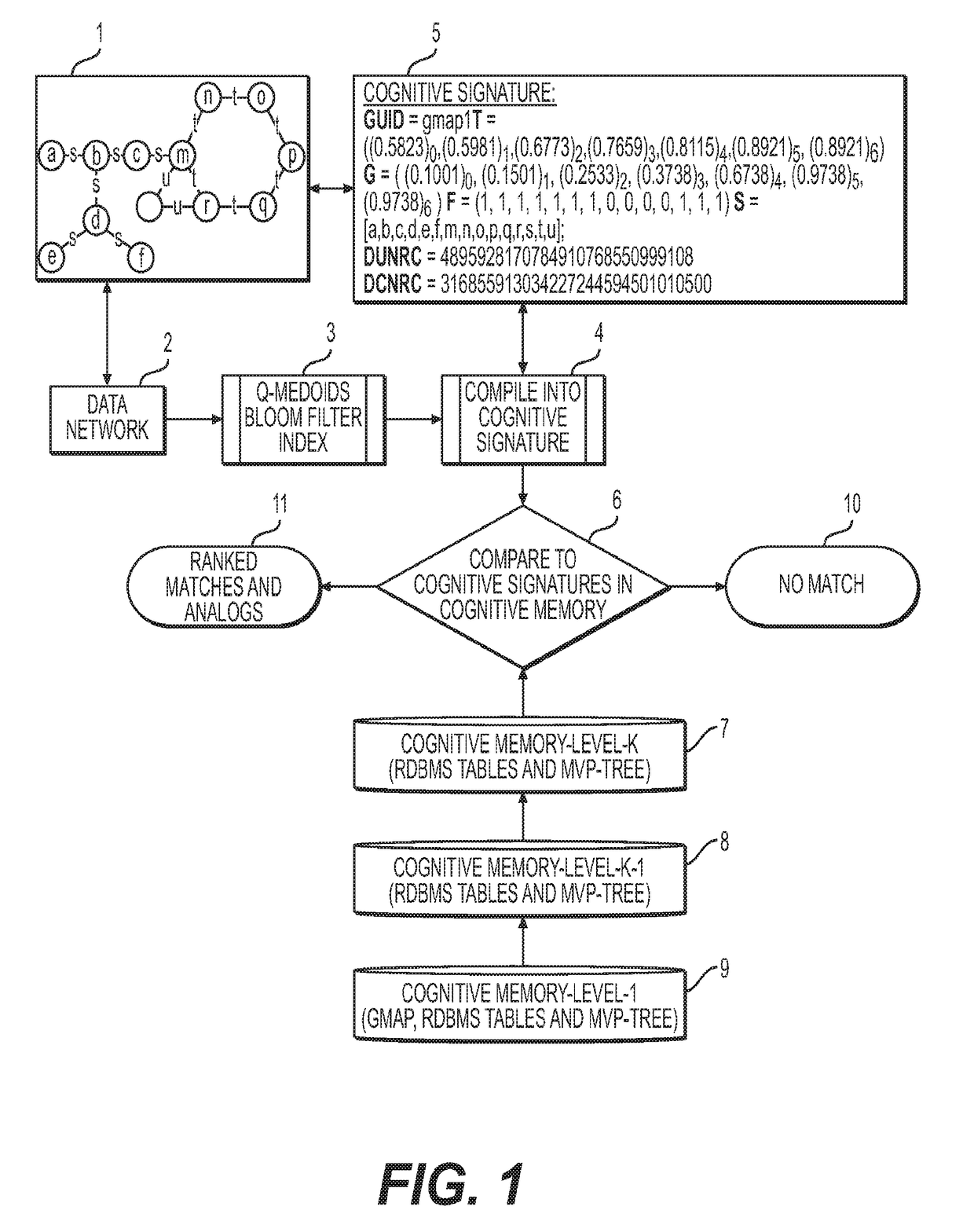
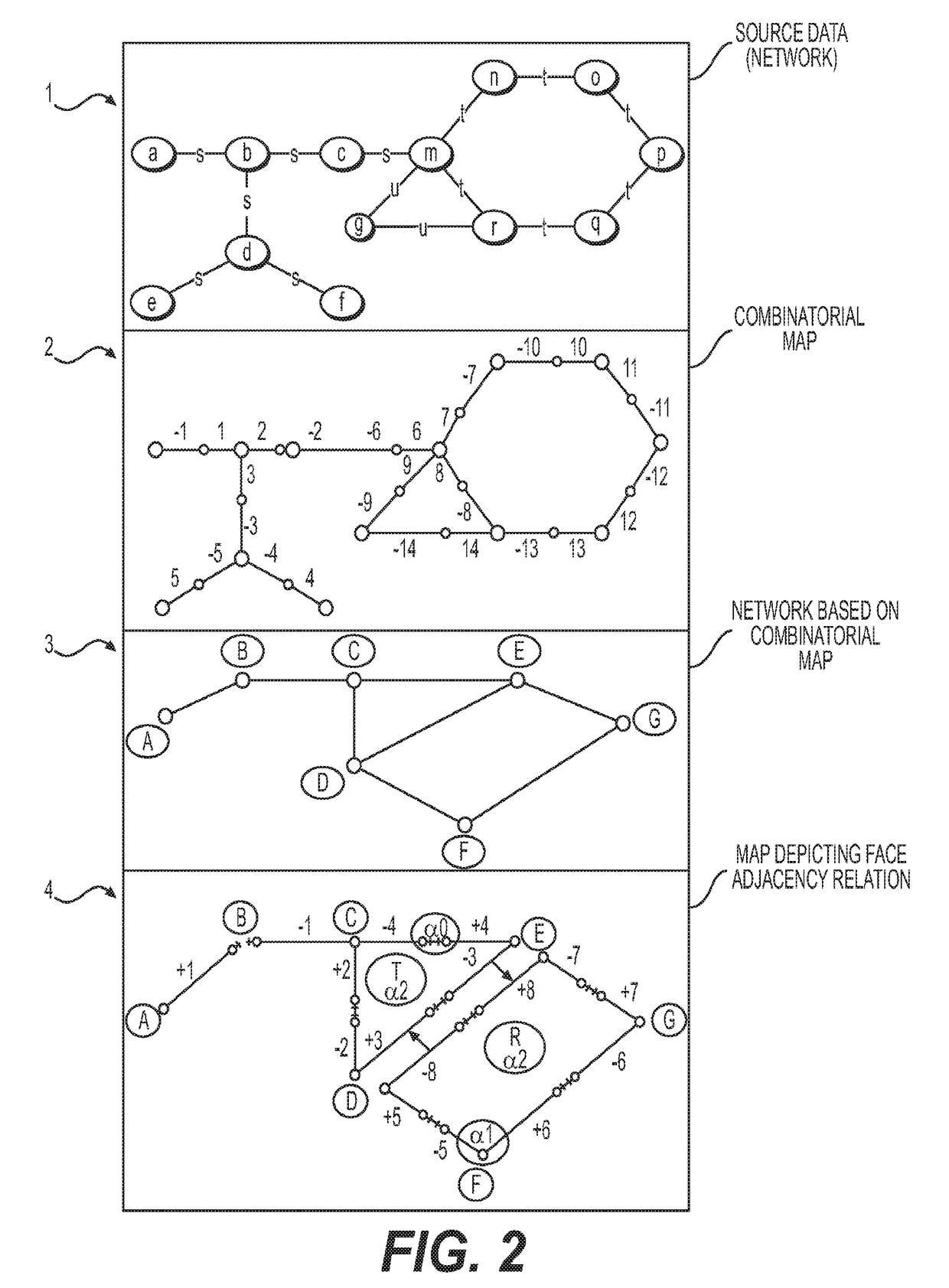
Cognitive memory graph indexing, storage and retrieval
The present disclosure provides a fast approximate as well as exact hierarchical network storage and retrieval system and method for encoding and indexing graphs or networks as well as for identifying substructure matches or analogs within graph data. Cognitive Memory encodes graphs via generalized combinatorial maps and a new quantum-inspired Q-Hashing algorithm to summarize local structures of the graph along with a contraction and graph property calculation to build an index data structure called the Cognitive Signature for property based, analog based or structure or sub-structure based search. The system and method of the present invention is ideally suited to store and index all or parts or substructures or analogs of graphs as well as dynamically changing graphs such as traffic graphs or flows and motion picture sequences of graphs. The system and method has the advantage that properties of the Cognitive Signature of the graph can be used in correlations to the properties of the underlying data making the system ideal for semantic indexing of massive scale graph data sets.
Owner:KYNDI
Kernel regression for image processing and reconstruction
ActiveUS20070047838A1Improve local image structure informationImproves gradient and pixel valueImage enhancementImage analysisSingular value decompositionKernel regression
A method of image processing using kernel regression is provided. An image gradient is estimated from original data that is analyzed for local structures by computing a scaling parameter, a rotation parameter and an elongation parameter using singular value decomposition on local gradients of the estimated gradients locally to provide steering matrices. A steering kernel regression having steering matrices is applied to the original data to provide a reconstructed image and new image gradients. The new gradients are analyzed using singular value decomposition to provide new steering matrices. The steering kernel regression with the new steering matrices is applied to the noisy data to provide a new reconstructed image and further new gradients. The last two steps are repeated up to ten iterations to denoise the original noisy data and improve the local image structure.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
Local SONOS-type structure having two-piece gate and self-aligned ONO and method for manufacturing the same
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
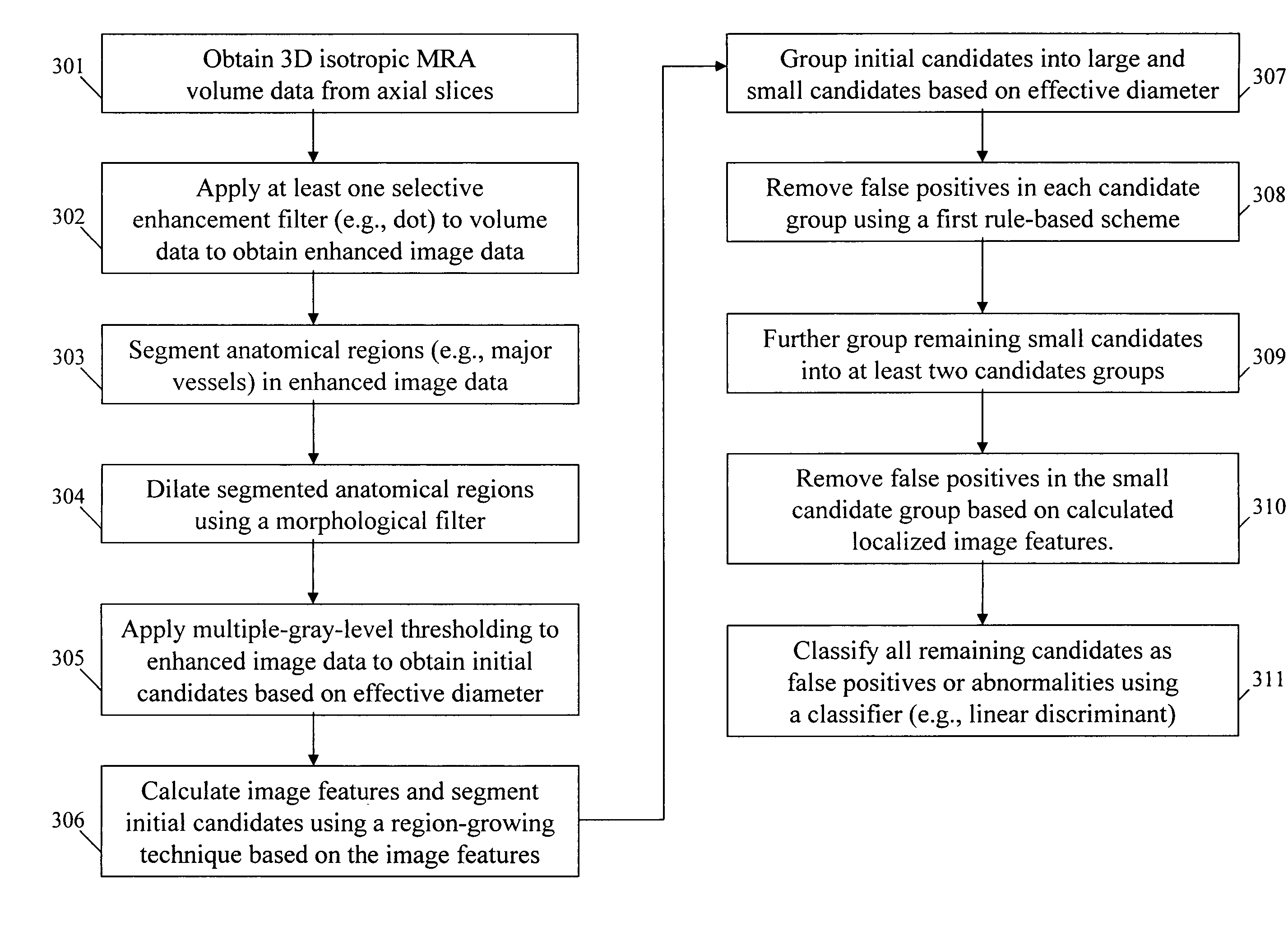
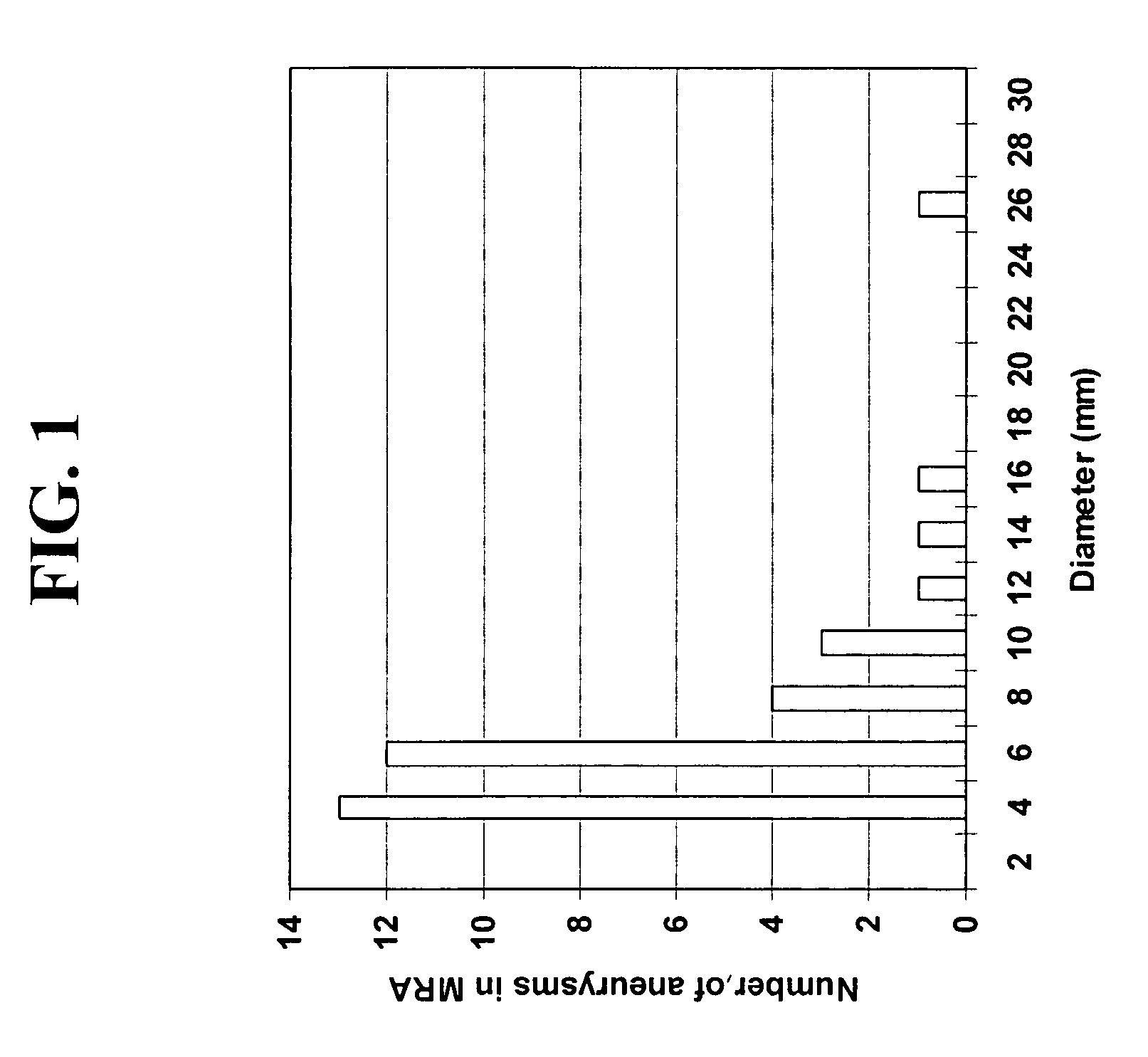
Method for detection of abnormalities in three-dimensional imaging data
A method, system, and computer program product for determining existence of an abnormality in a medical image, including (1) obtaining volume image data corresponding to the medical image; (2) filtering the volume image data using an enhancement filter to produce a filtered image in which a predetermined pattern is enhanced; (3) detecting, in the filtered image, a first plurality of abnormality candidates using multiple gray-level thresholding; (4) grouping, based on size and local structures, the first plurality of abnormality candidates into a plurality of abnormality classes; (5) removing false positive candidates from each abnormality class based on class-specific image features to produce a second plurality of abnormality candidates; and (6) applying the at least one abnormality to a classifier and classifying each candidate in the second plurality of abnormality candidates as a false positive candidate or an abnormality.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
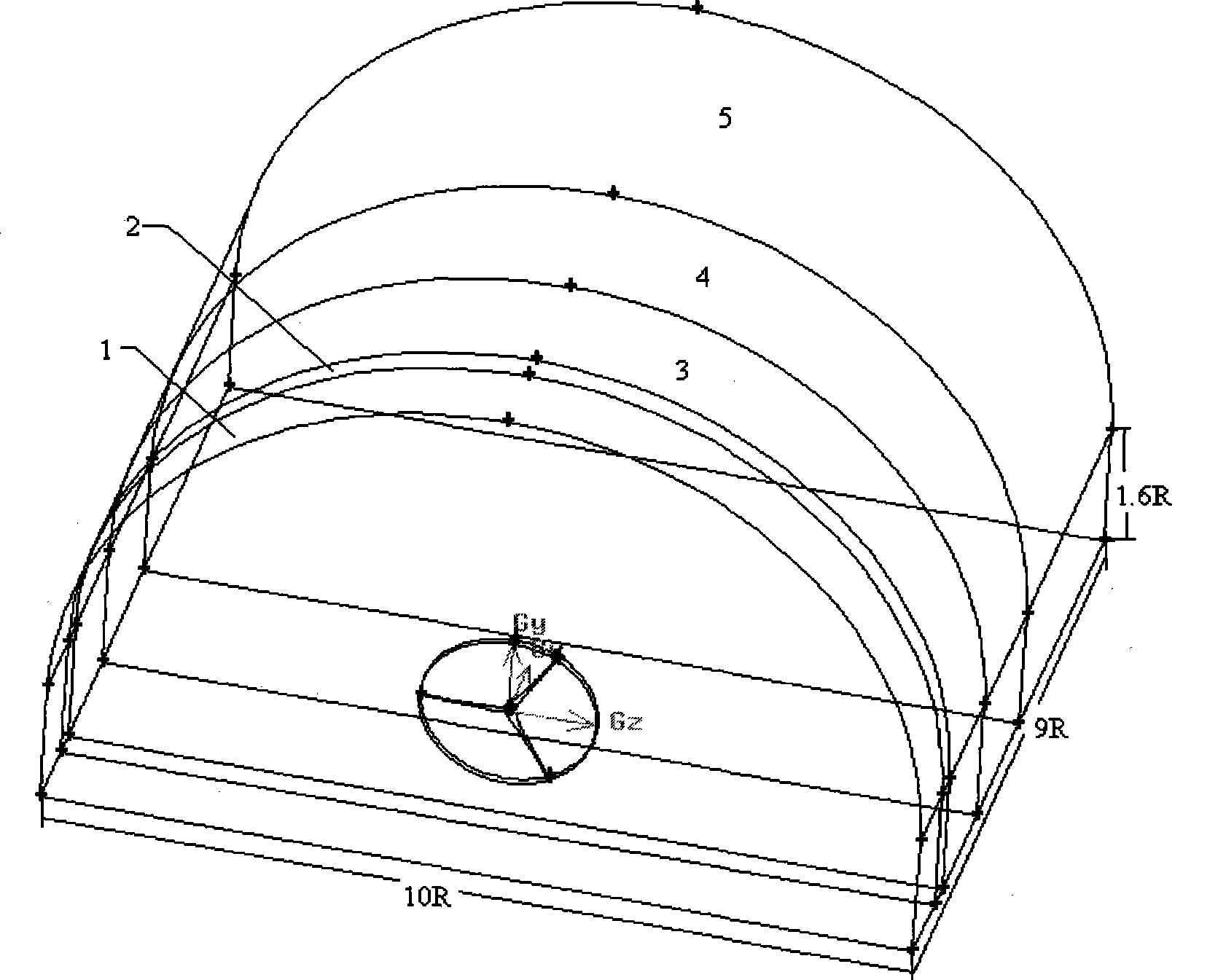
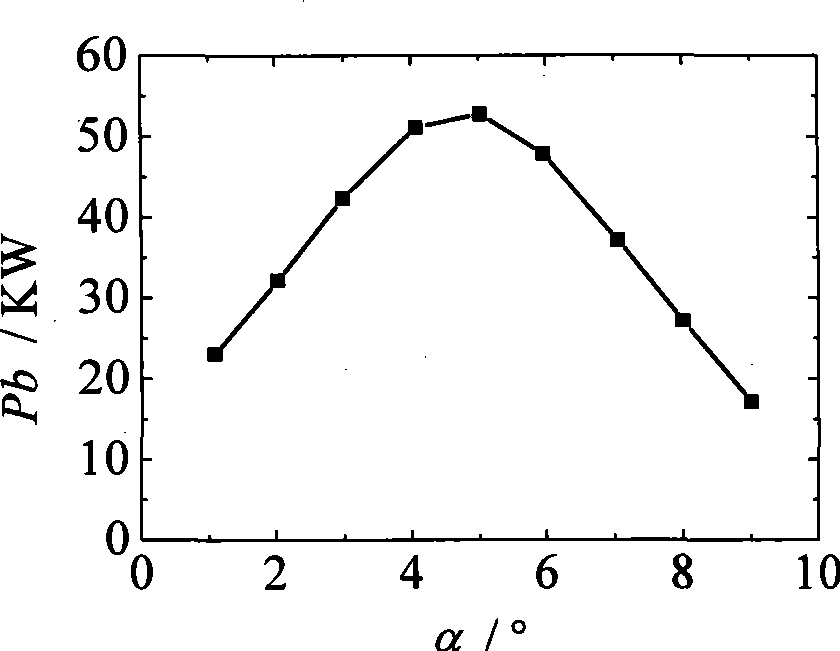
Method for analyzing fluid dynamics and structural mechanics of wind generator blades
InactiveCN101532906AReduce windward angleReduce the required powerMachine part testingAerodynamic testingEngineeringEntity model
The invention discloses a method for analyzing fluid dynamics and structural mechanics of wind generator blades, which comprises the following steps: combining CFD and CAE methods, determining each parameter of an impeller model by adopting the momentum blade element theory, designing an entity model of the blade, establishing a three-dimensional model of a windmill blade, a hub and a peripheral wind site based on a Gambit software platform, meshing the model by adopting a partial structuring method, setting a proper boundary condition, calculating the performance of a finite element based on a Fluent software platform, extracting the blade torsion and calculating the blade power and the blade efficiency, establishing a blade structural model based on an ansys software platform and meshing the blade structural model, applying load and restraint condition to the blade structural model, analyzing the mode of the blade structure, performing equal torque treatment for pressure distribution acquired by the Fluent software platform, applying pressure surface load to the ansys software platform, calculating the structural mechanics characteristics of the wind generator blades, and extracting blade deformation and stress distribution characteristics.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
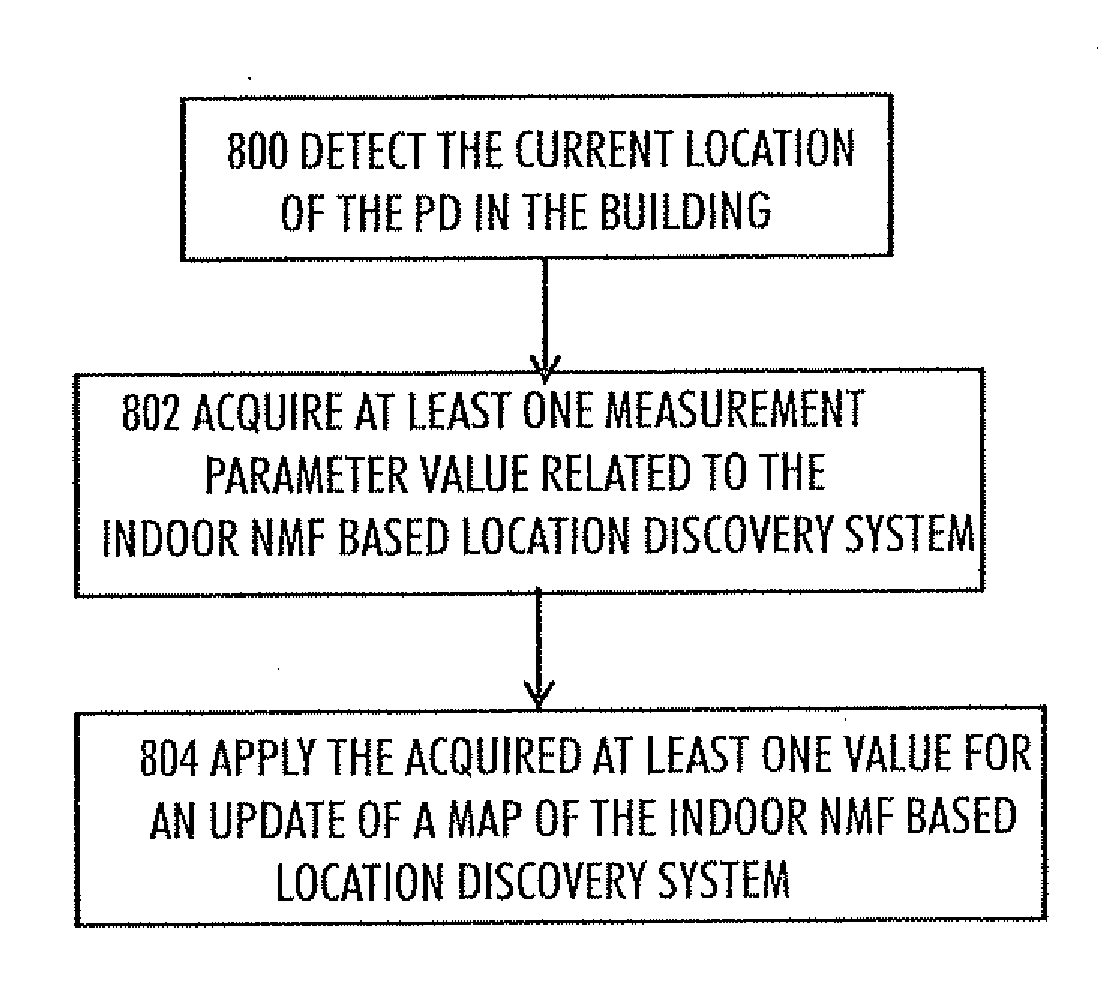
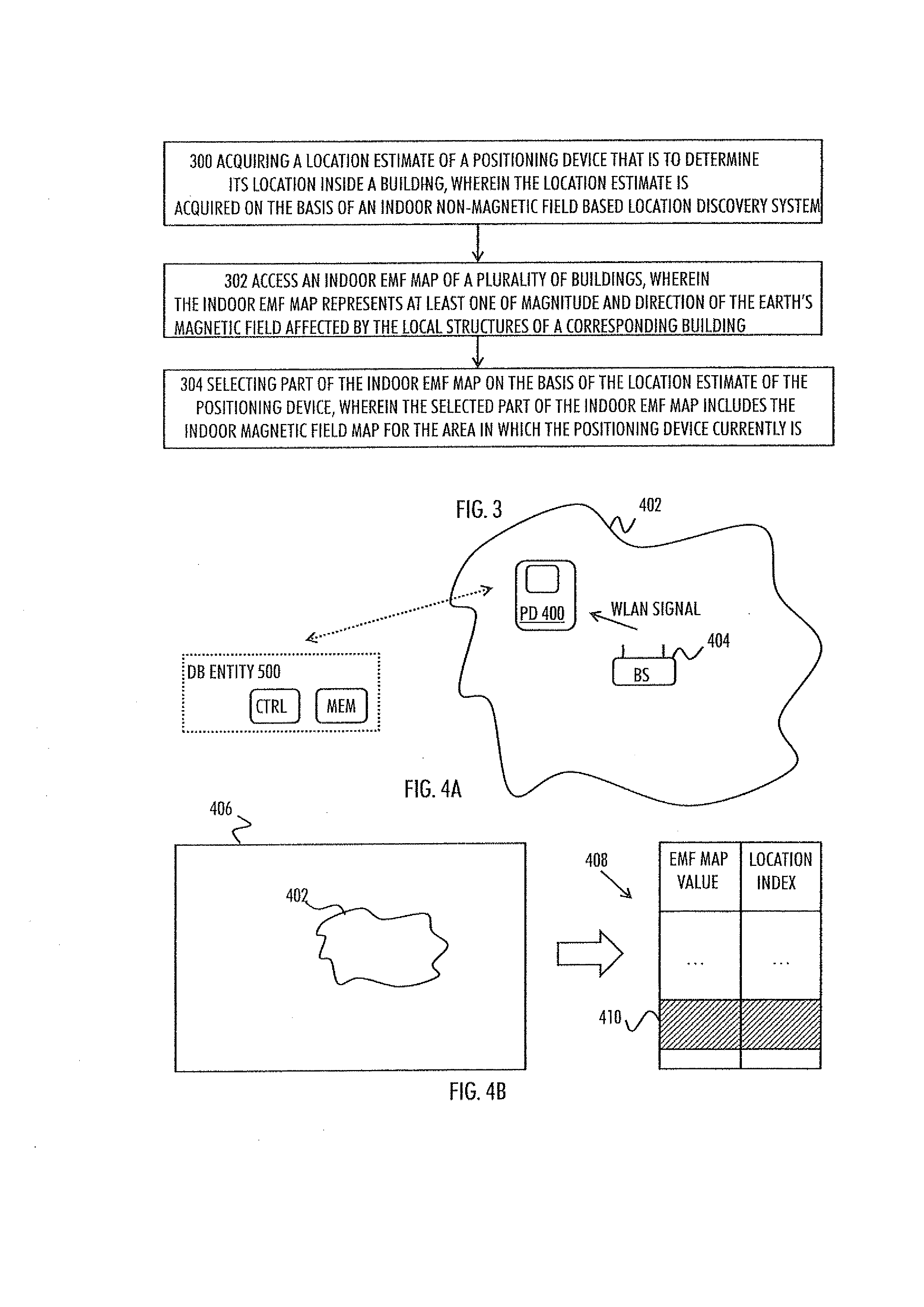
Indoor magnetic field based location discovery
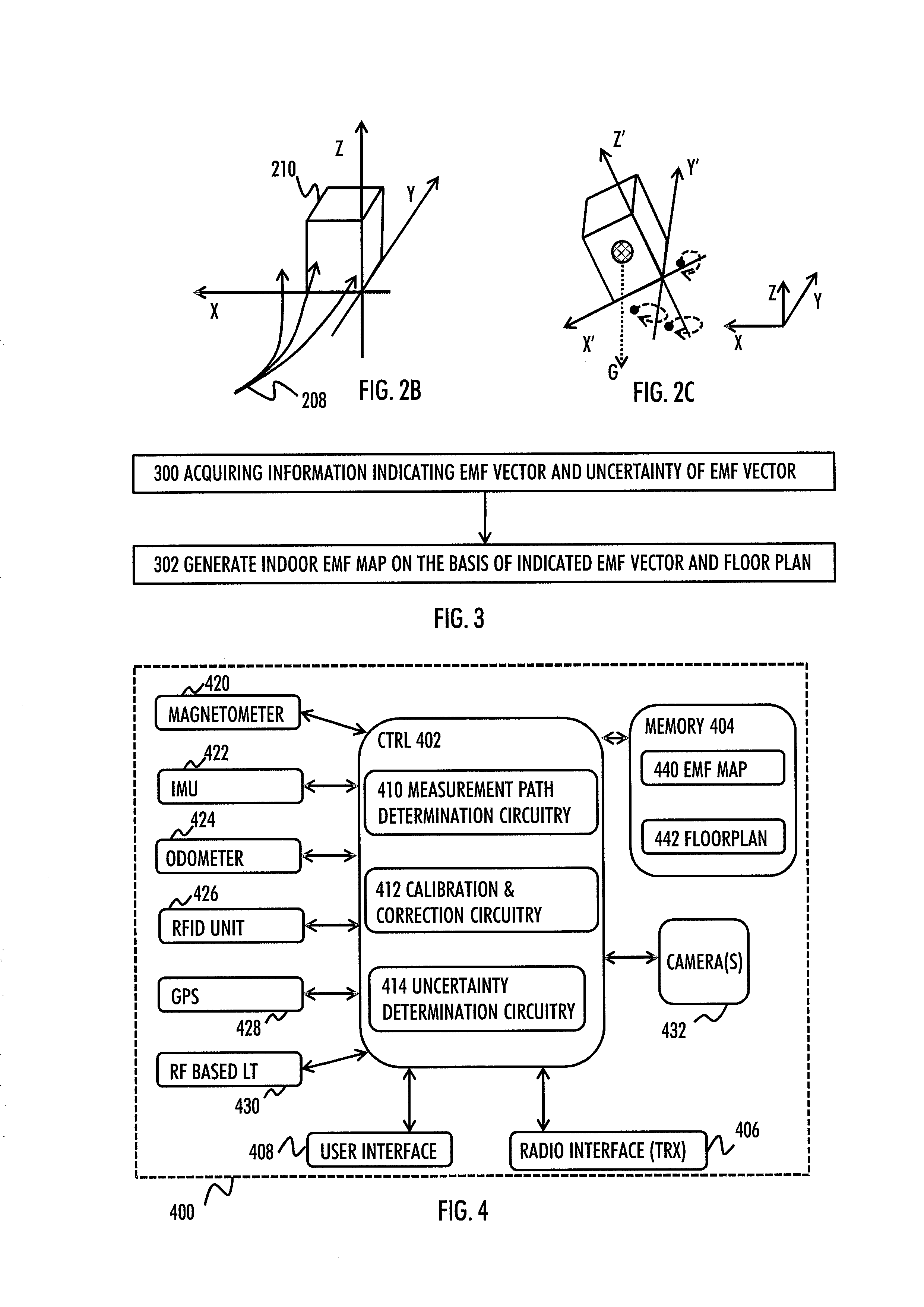
There is provided an apparatus, wherein the apparatus is caused to acquire a location estimate of a positioning device that is to determine its location inside a building, wherein the location estimate is acquired on the basis of an indoor non-magnetic field based location discovery system; access an indoor Earth's magnetic field, EMF, map of plurality of buildings, wherein the indoor EMF map represents at least one of magnitude and direction of the Earth's magnetic field affected by the local structures of a corresponding building; and select a part of the indoor EMF map on the basis of the location estimate of the positioning device, wherein the selected part of the indoor magnetic field map includes the indoor EMF map for the area in which the positioning device currently is.
Owner:INDOORATLAS
Body structure for vehicle
The pillar structure to which the passenger cabin end of the hood ridge panel is connected, is arranged have different localized structural deformation resistances which buckle / deform in a manner which causes the hood ridge panel to reorient in response to a vehicle structure deforming force being applied to the front of the vehicle during a collision, and results in the force, which passes through the hood ridge panel, being redirected by a load-converting and transmitting member included in the pillar, up and along an upper rearwardly angled upper portion of the pillar. This force redirection produces sufficient resistance to induce compressive bucking in the structure forward of the passenger cabin and thus attenuate damage to the cabin structure.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
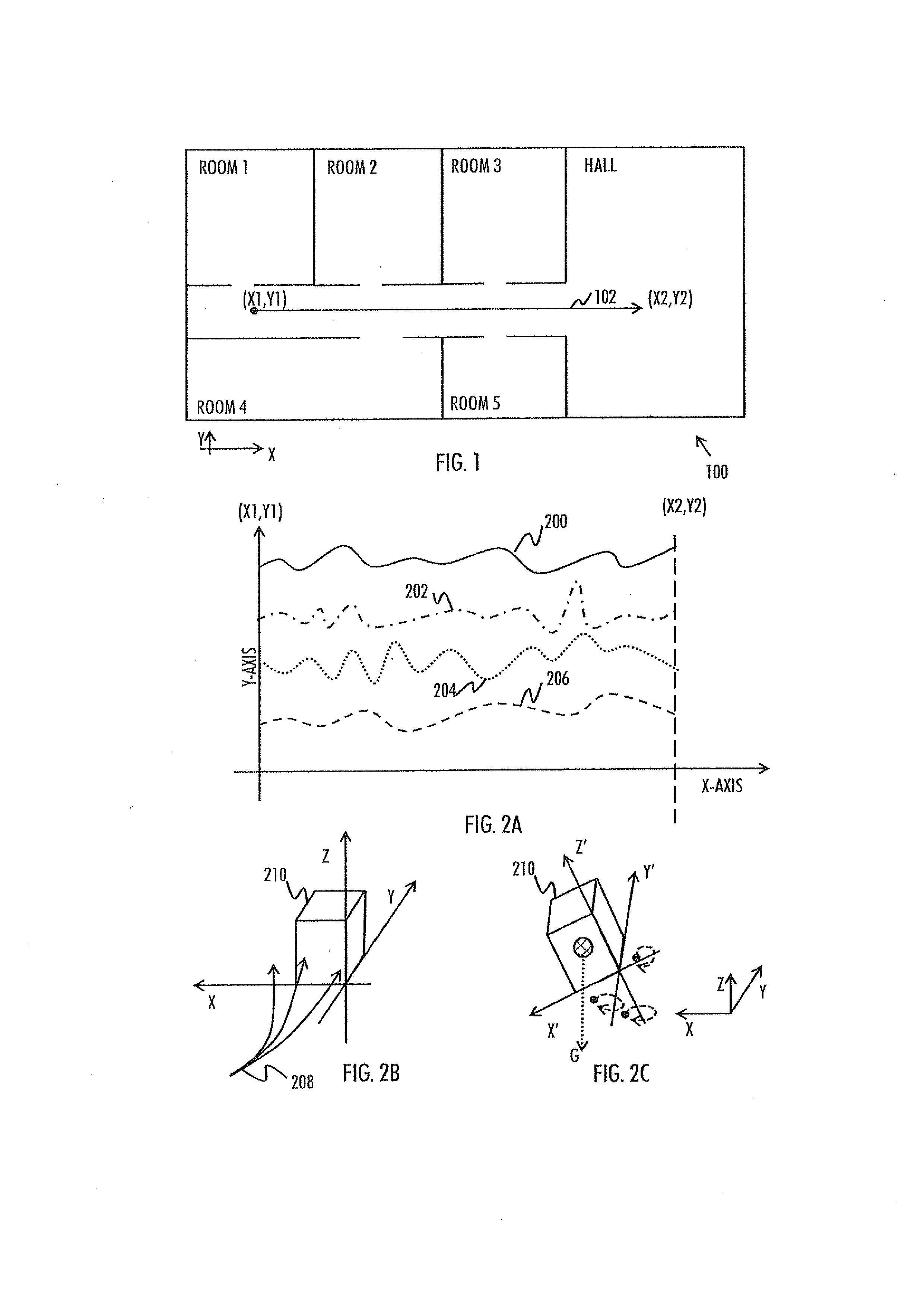
Generating magnetic field map for indoor positioning
There is provided an apparatus caused to acquire information indicating a measured magnetic field vector and information relating to an uncertainty measure of the measured magnetic field vector in at least one known location inside the building, wherein the indicated magnetic field vector represents magnitude and direction of the earth's magnetic field affected by the local structures of the building, and to generate the indoor magnetic field map for at least part of the building on the basis of at least the acquired information and the floor plan.
Owner:INDOORATLAS
Negative obstacle detection method based on local structure feature of laser radar point cloud
ActiveCN106650640ADetection results are not affected by light conditionsMeasure distance directlyScene recognitionPattern recognitionPoint cloud
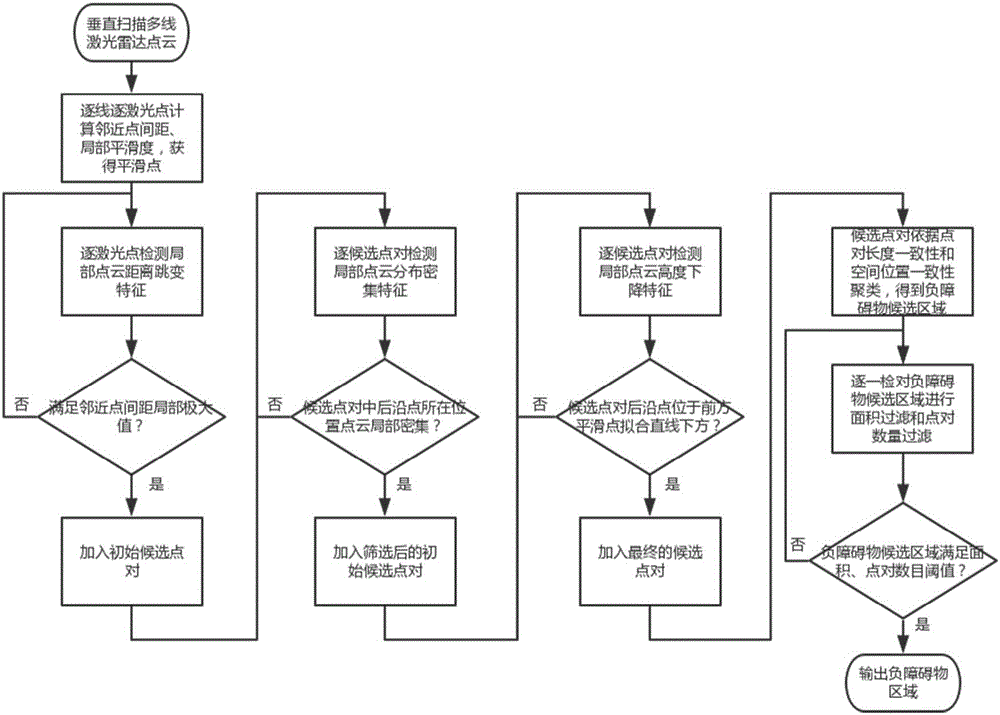
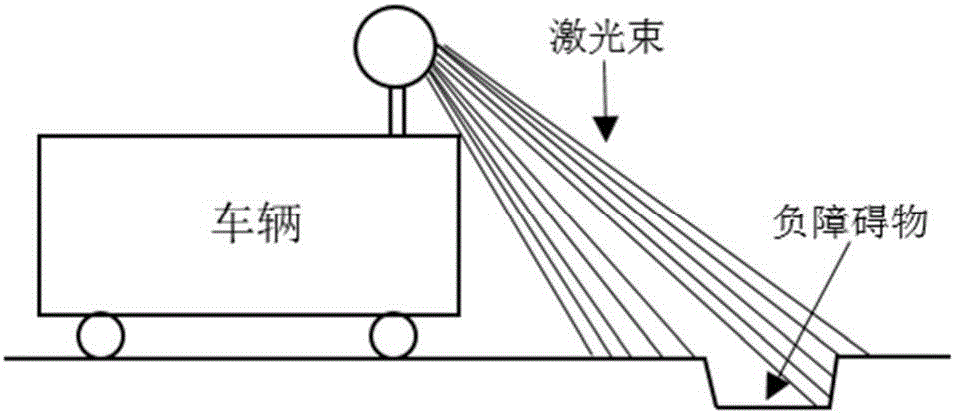
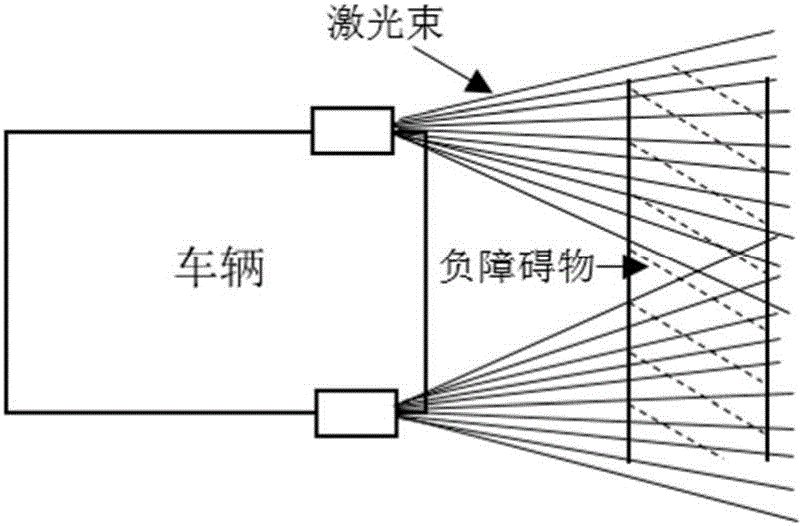
The invention discloses a negative obstacle detection method based on the local structure feature of a laser radar point cloud. In collected laser radar point cloud data, three structure features including local point cloud distance hopping, local point cloud dense distribution and local point cloud height decreasing are detected line by line; on the basis of the three structure features, candidate point pairs which may belong to a negative obstacle are obtained through extraction and screening in single line laser point cloud; all candidate point pairs obtained by the laser point cloud of each line laser are clustered on the basis of point pair length consistency and spatial position consistency to obtain a negative obstacle candidate area; and through area filtering and point pair amount filtering, obtaining a negative obstacle area. By use of the method, the negative obstacle in environment can be effectively detected, and the method has the advantages of good detection success rate, small calculation cost and high instantaneity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Flash memory having local SONOS structure using notched gate and manufacturing method thereof
A notched gate SONOS transistor includes: a substrate having source / drain regions; a gate insulator layer on the substrate between the source / drain regions; a notched gate structure, on the gate insulator leyer, having at least one notch; and at least one ONO wedge structure in the at least one notch, respectively, of the gate structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
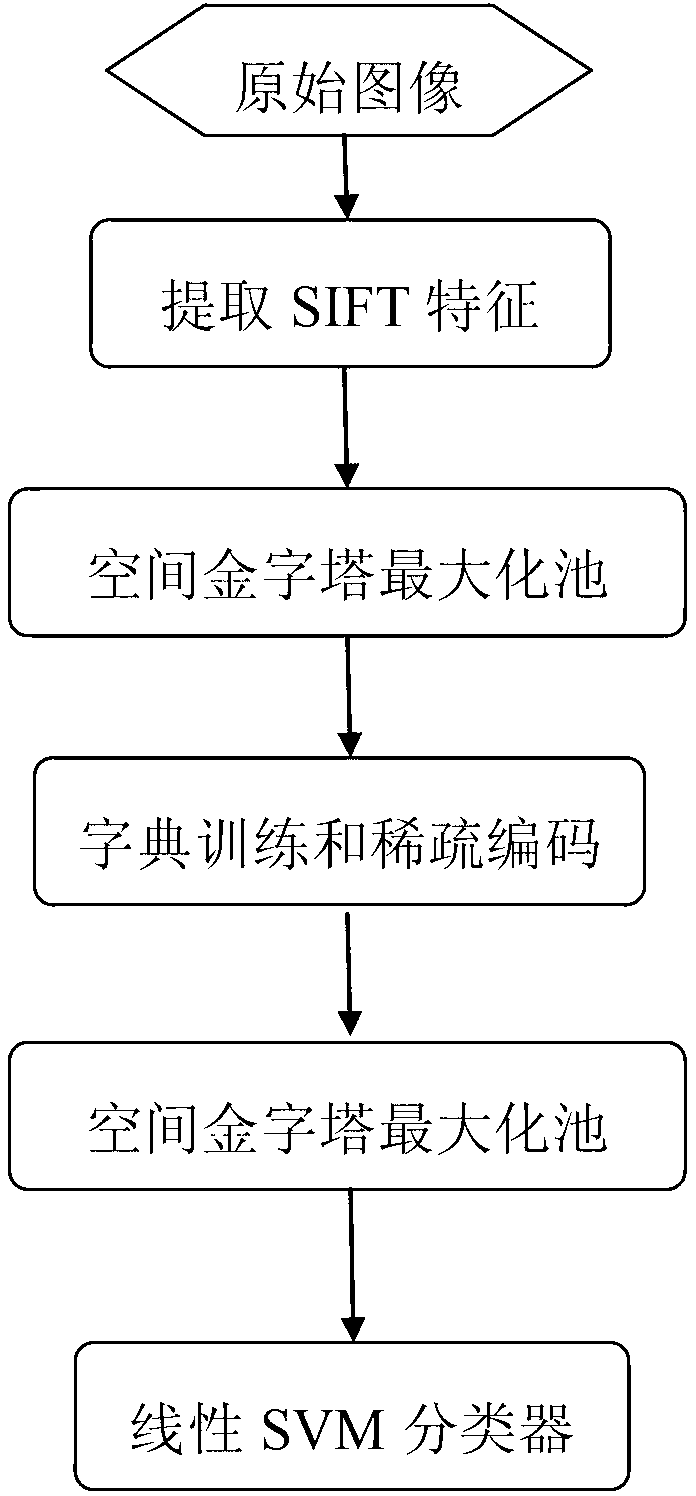
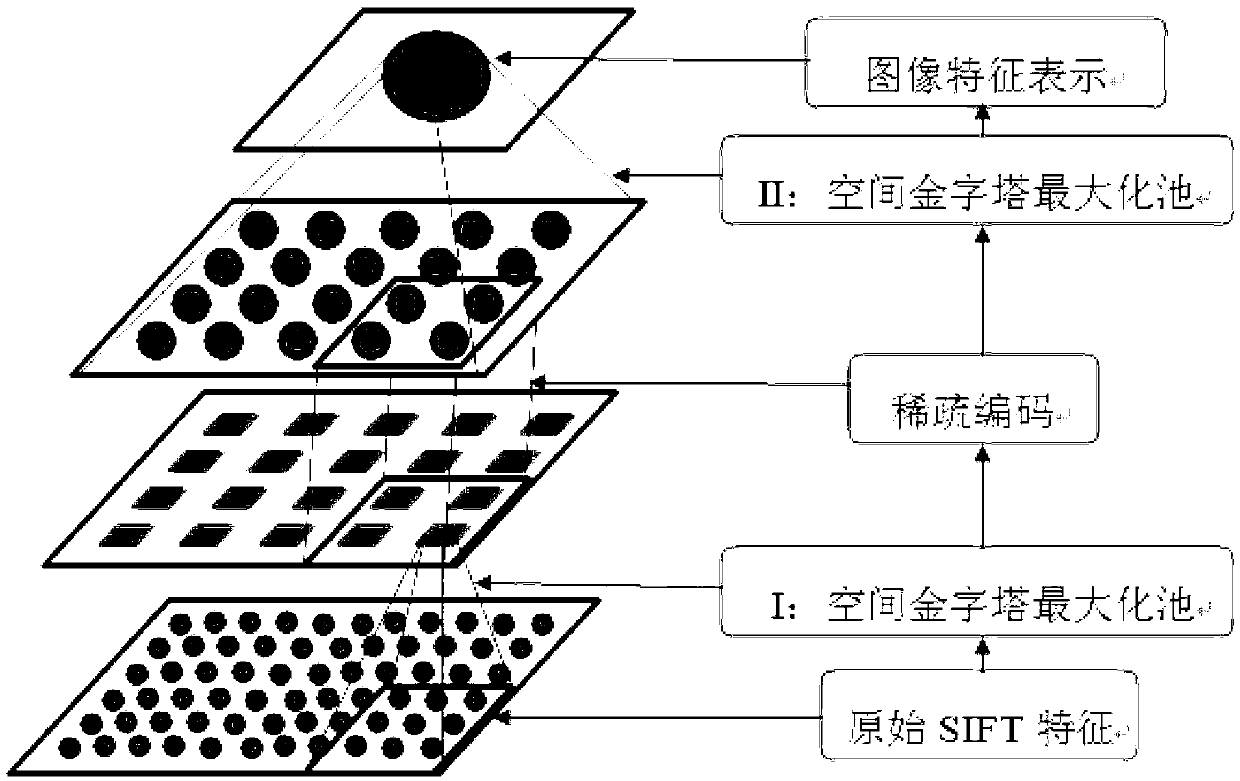
Image classification method based on hierarchical SIFT (scale-invariant feature transform) features and sparse coding
InactiveCN103020647AReduce the dimensionality of SIFT featuresHigh simulationCharacter and pattern recognitionSingular value decompositionData set
The invention discloses an image classification method based on hierarchical SIFT (scale-invariant feature transform) features and sparse coding. The method includes the implementation steps: (1) extracting 512-dimension scale unchanged SIFT features from each image in a data set according to 8-pixel step length and 32X32 pixel blocks; (2) applying a space maximization pool method to the SIFT features of each image block so that a 168-dimension vector y is obtained; (3) selecting several blocks from all 32X32 image blocks in the data set randomly and training a dictionary D by the aid of a K-singular value decomposition method; (4) as for the vectors y of all blocks in each image, performing sparse representation for the dictionary D; (5) applying the method in the step (2) for all sparse representations of each image so that feature representations of the whole image are obtained; and (6) inputting the feature representations of the images into a linear SVM (support vector machine) classifier so that classification results of the images are obtained. The image classification method has the advantages of capabilities of capturing local image structured information and removing image low-level feature redundancy and can be used for target identification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
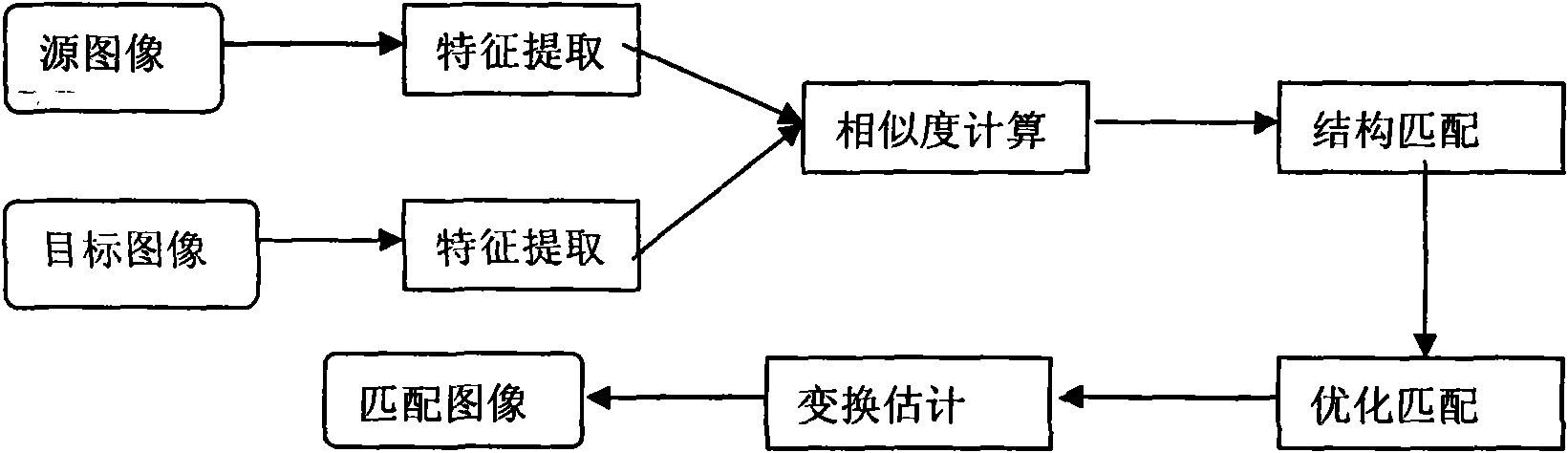
Image matching method based on characteristic points
The invention belongs to the technical fields of mode indentifying and image processing, and relates to an image matching method based on characteristic points. The image matching method based on characteristic points defines an annular corner code model according to the K neighboring structure of the characteristic points and applies the model to point mode matching. Similar annular corner codes not only describe the similarity of the space structures of two characteristic points, but also can be used for local mapping estimation. The similarity of the two characteristic points is confirmed by the similar length of the largest similar annular corner codes associated with the two characteristic points. The image matching method based on characteristic points carries out structure matching according to the similarity of the local space structures of the characteristic points, and uses the local mapping and clustering to carry out optimization matching. The optimization matching result is used for optimizing the mapping estimation. The method can be used for the image matching based on the characteristic points, image jointing and embedding, motion tracing, information fusion of medical single-mode and multi-mode images, as well as image searching based on contents.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
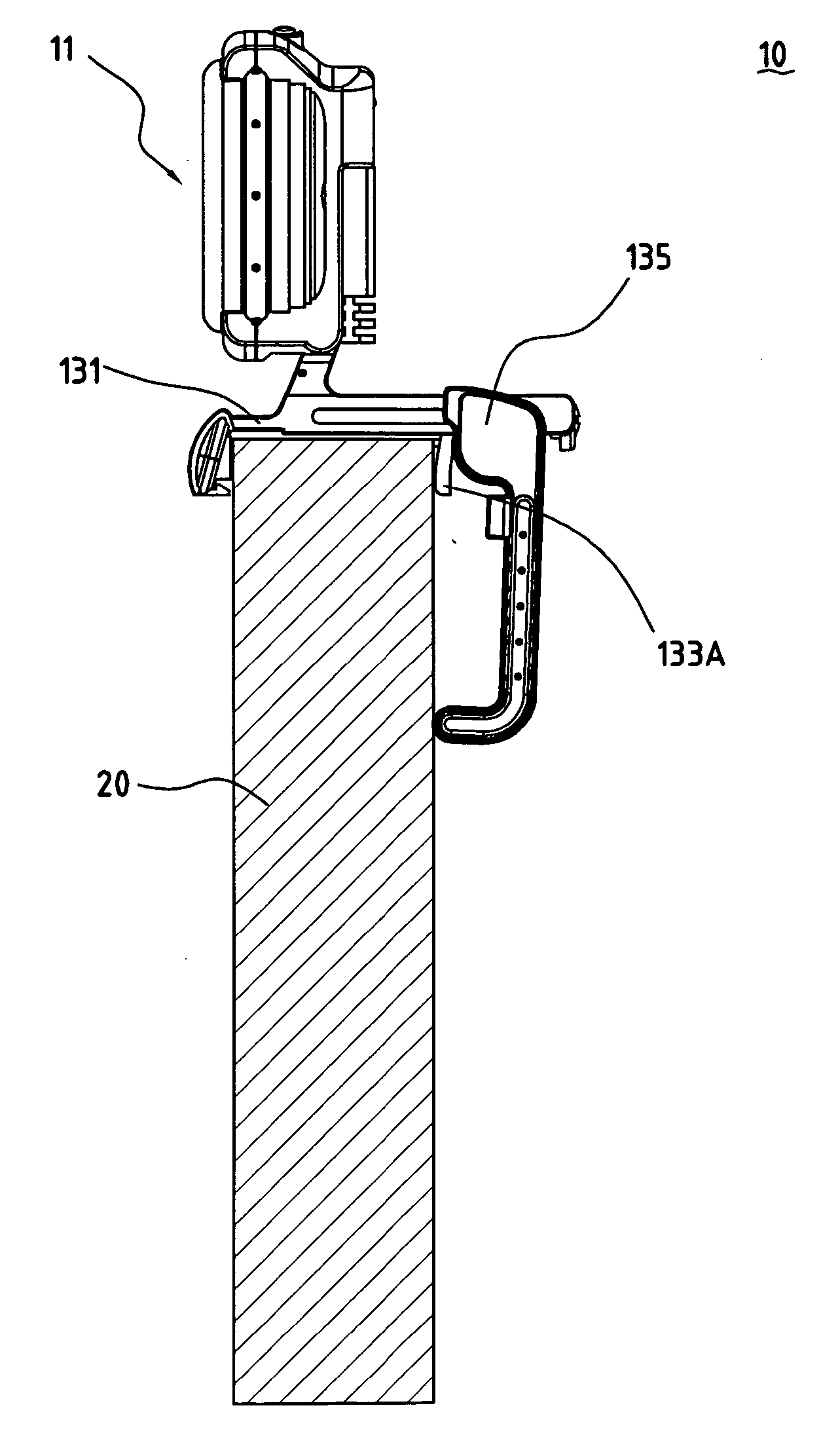
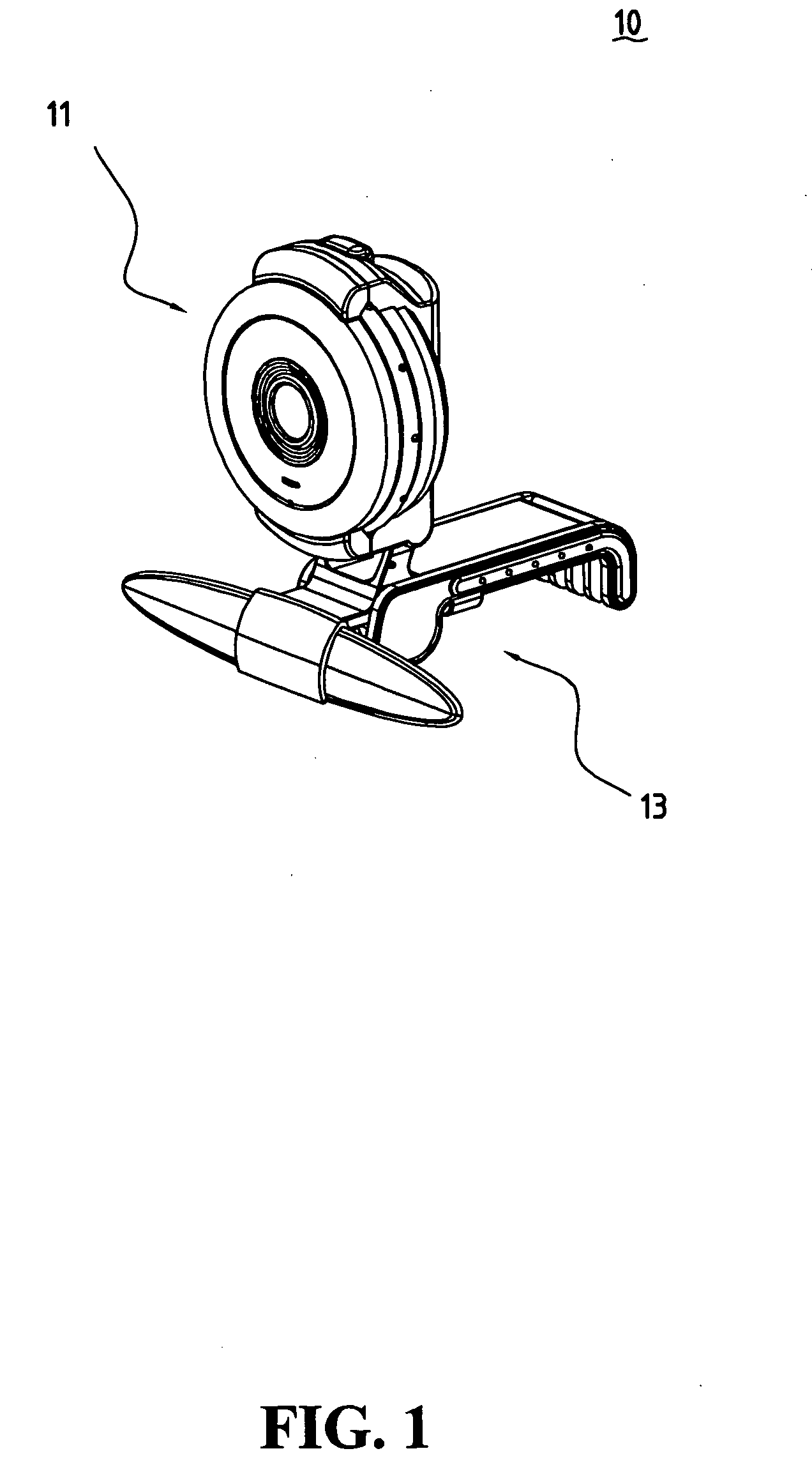
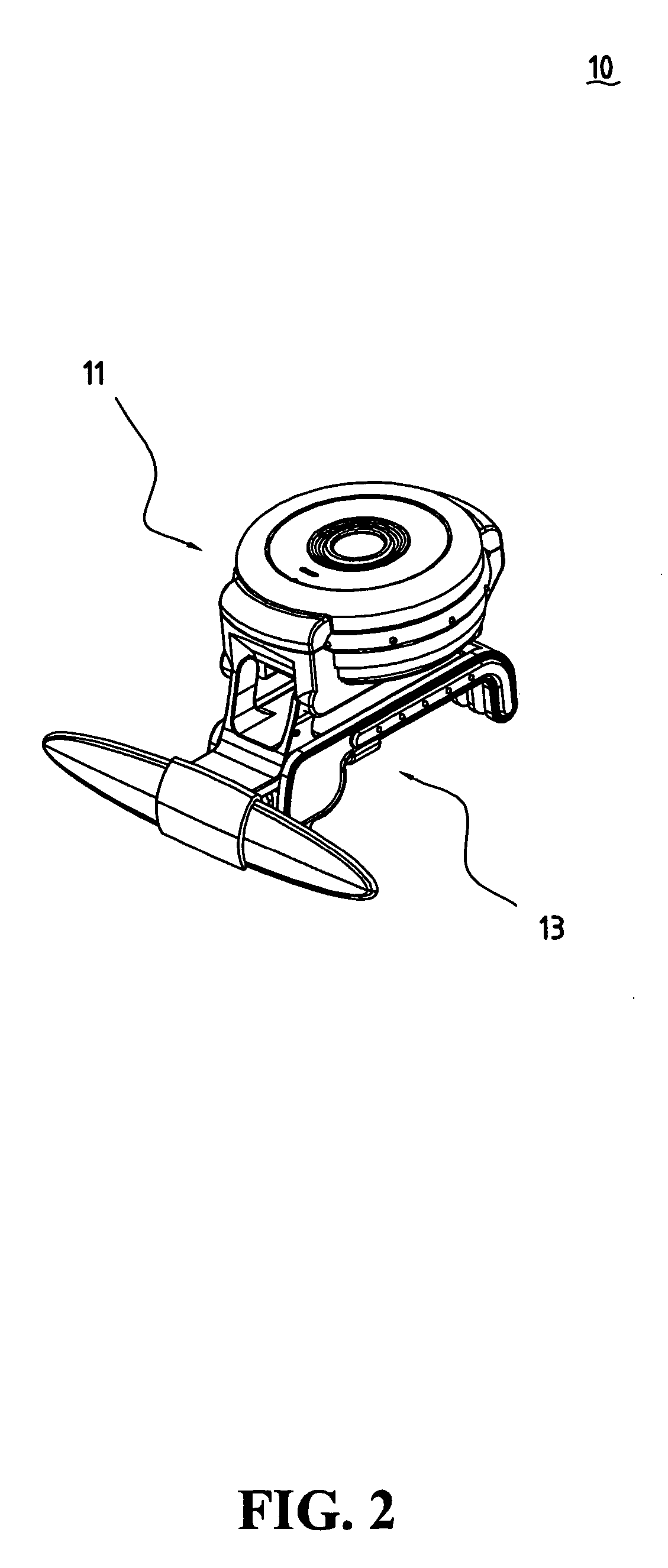
Camera assembly structure
InactiveUS20060170817A1Small sizeEasy to carryTelevision system detailsColor television detailsElastic componentLocal structure
The present invention is a camera assembly structure having a body and a base. The body, having a front cover, a back cover and a focus ring clamped between the front and back covers, is connected at the base and can rotate in relation to the base. The base has a front base, an elastic component, and a back base. The front base has two side troughs for inserting the elastic component, and the elastic component can move along the side troughs. The back base engaging with partial structure of the front cover is connected at the elastic component and can use the elastic component as an axis so as to rotate downward.
Owner:BEHAVIOR TECH COMPUTER
Method for controlling machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis
InactiveCN104077442AReduce machining accuracyShorten the processing cycleSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisMachining deformation
The invention discloses a method for controlling the machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, extracting local structural features of the large integrated thin-walled part; 2, performing finite element simulative analysis on local structural features to obtain an optimized cutting technology; 3, numerically modeling a large integrated workblank, and loading an initial internal stress; 4, protocoling a tool path, namely protocoling the machining sequence of the feature structures; 5, performing simulative analysis on the integrated structure to obtain a predicted deformation result under the condition of process technology; 6, regulating and optimizing a clamp scheme to control machining deformation. The method adopts finite element simulation, can analyze and predict in advance before the actual machining of the parts, and thereby corresponding machining strategy is adjusted, machining deformation is effectively controlled, production cycle of the parts is shortened, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING CHENGUANG GRP +1
Human face detection method based on picture geometry
InactiveCN101236608ASuitable for transplantQuick exclusionCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionFeature vector
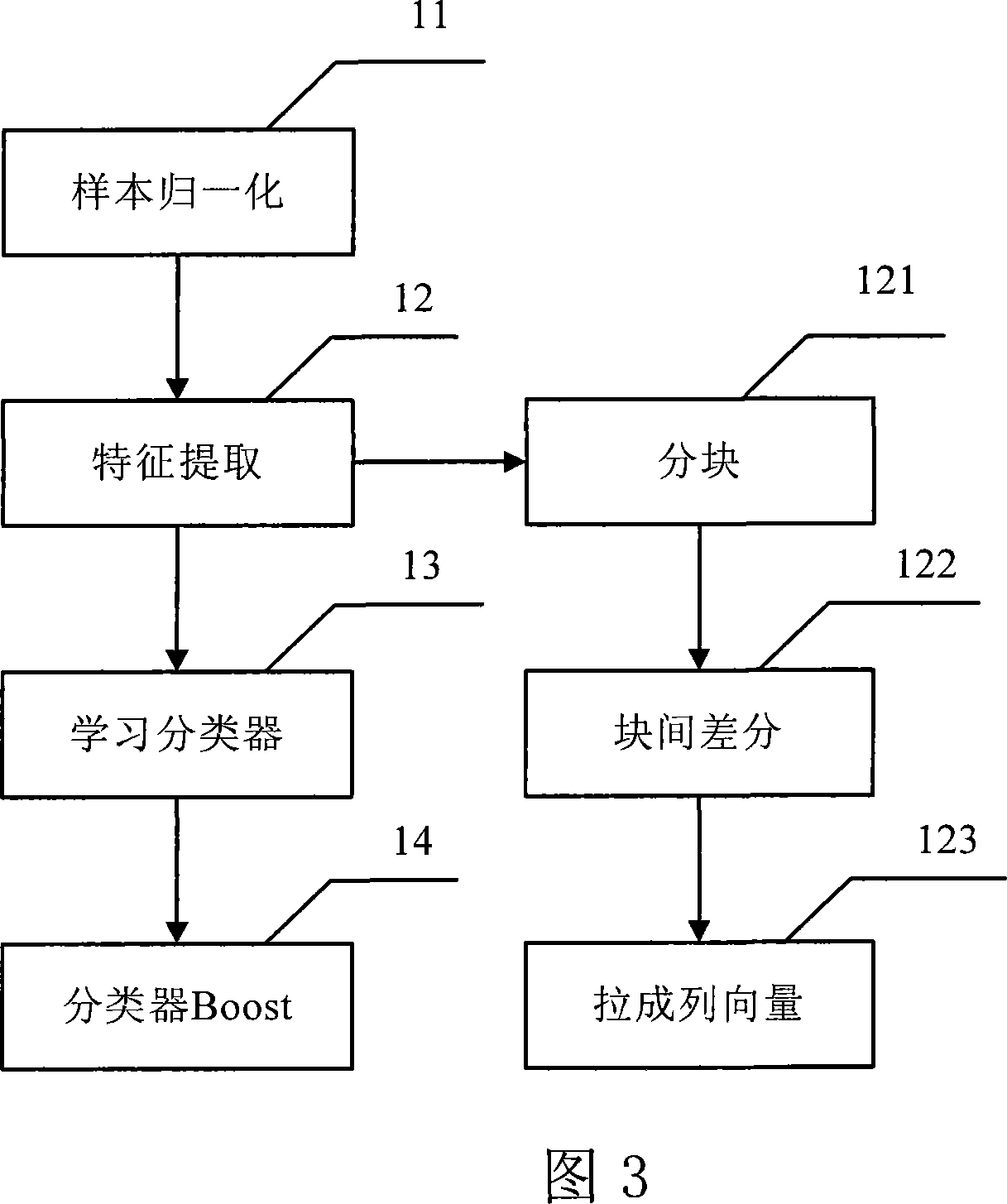
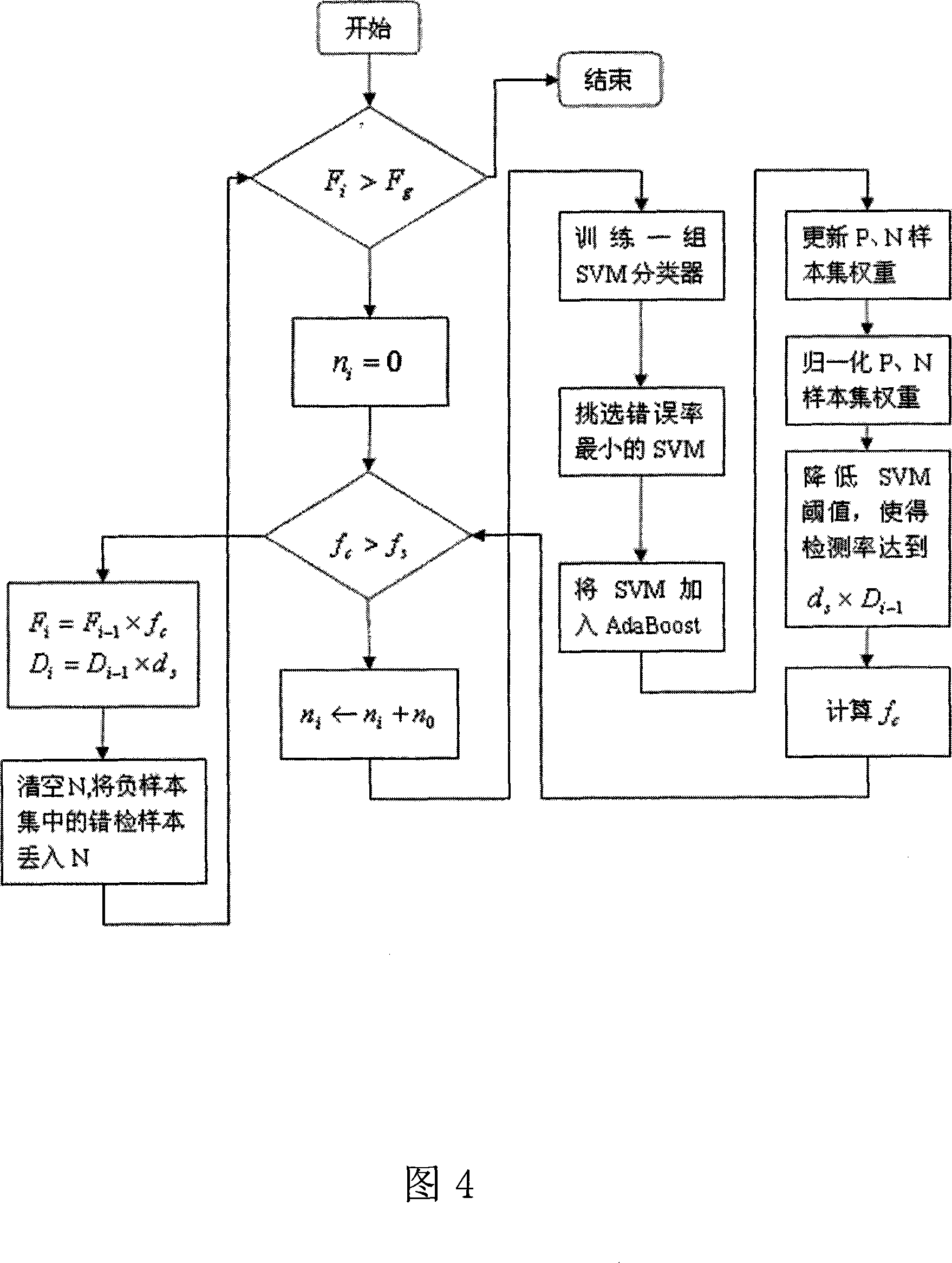
The invention discloses a face detection method based on a picture geometric structure, comprising a training process of face models and a detecting process of face images. The method comprises the following: the step of the training process of face models is divided into a step of training sample normalization, a step of feature extraction, a partitioning step of dividing a sample by adopting a block with a proper size, a step of drawing all differential values acquired by operations into a feature column vector to submit to a classifier for learning, a learning process of a fall type support vector machine and a classification against a sample picture in each window by using a cascade classifier; and the step of the detection of face images is to mark a detected face. The face detection method solves the problem generally existed in the field that the prior art aims at the local structure of a picture but can not completely and accurately express global information of the picture, and can detect a face quickly and accurately.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Regularized parameter adaptive sparse representation image reconstruction method
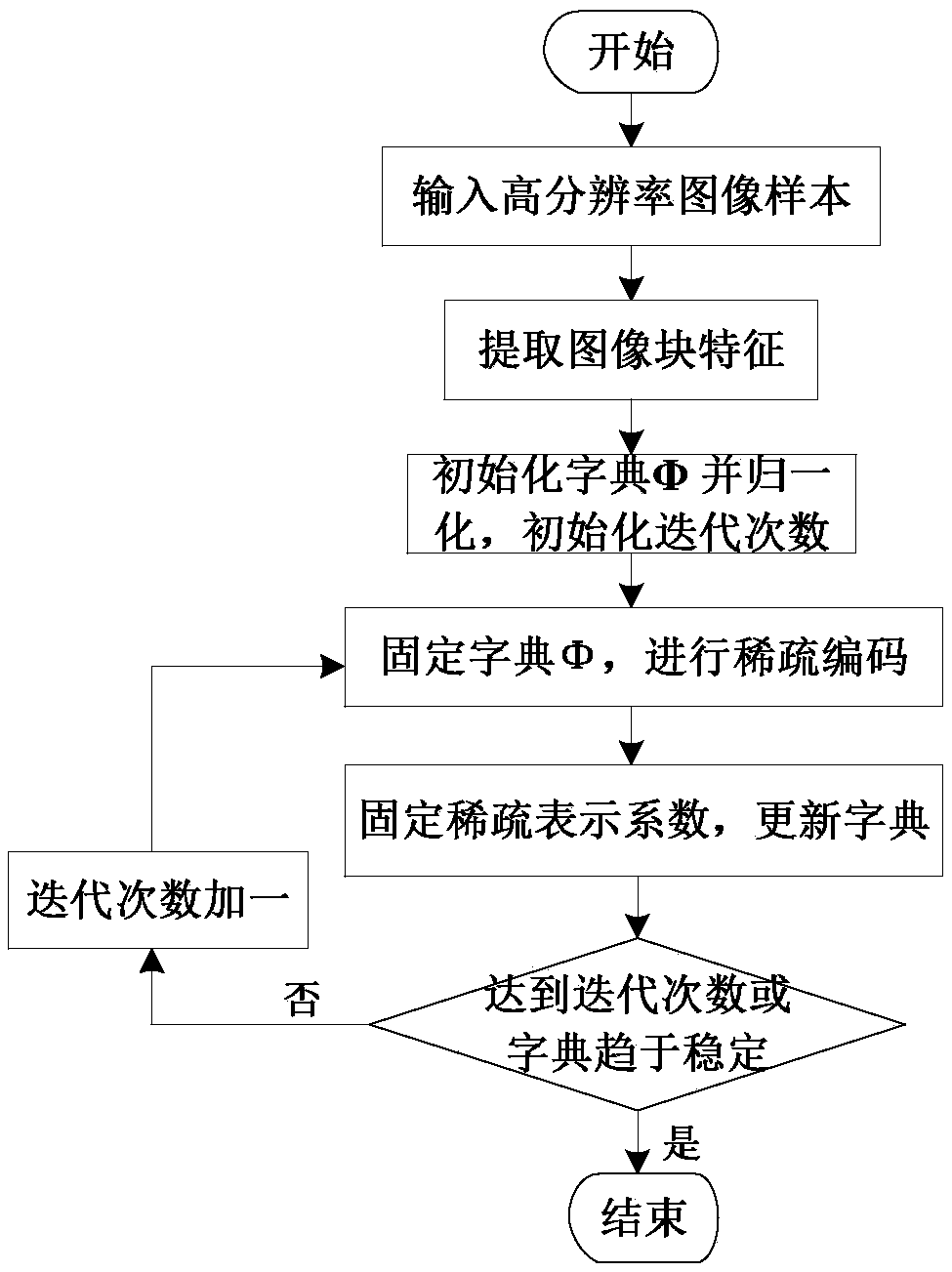
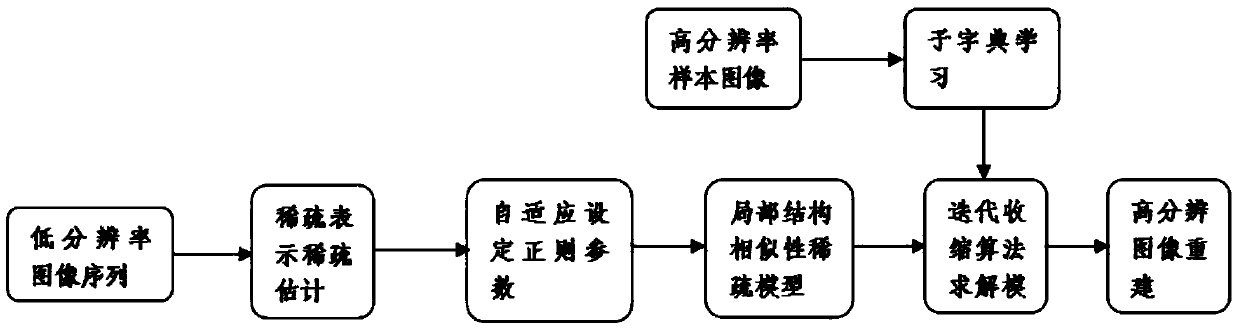
PendingCN109064406AImprove effectivenessMaintain structureGeometric image transformationDictionary learningMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention provides a regularized parameter adaptive sparse representation image reconstruction method, comprising the following steps: adopting a sparse dictionary learning algorithm, extracting image edge features to train a compact sparse dictionary, and adaptively allocating sub-dictionaries to each image block for sparse coding; Learning the Sparse Estimation of Sparse Coding from an Overcomplete Dictionary; Making full use of the local structure similarity of images, the regularization parameters are adaptively solved by using the method based on the maximum a posteriori probability.Adaptive sparse representation model of regularized parameters is established. The invention improves the effectiveness of sparse representation by utilizing the local structure similarity, and the edge and the structure of the image are well maintained. Adaptively adjusting the regularization parameters based on the maximum a posteriori probability, updating the regularization parameters in eachiteration process, better adapting to the current situation, greatly reducing the workload of manual selection of the regularization parameters; It has good image reconstruction effect and strong robustness to noise and motion blur.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
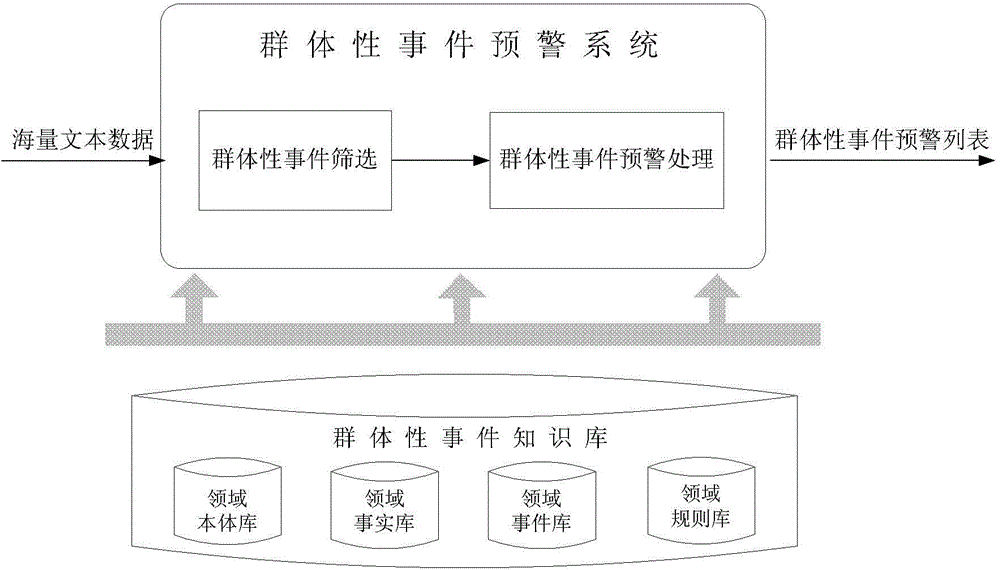
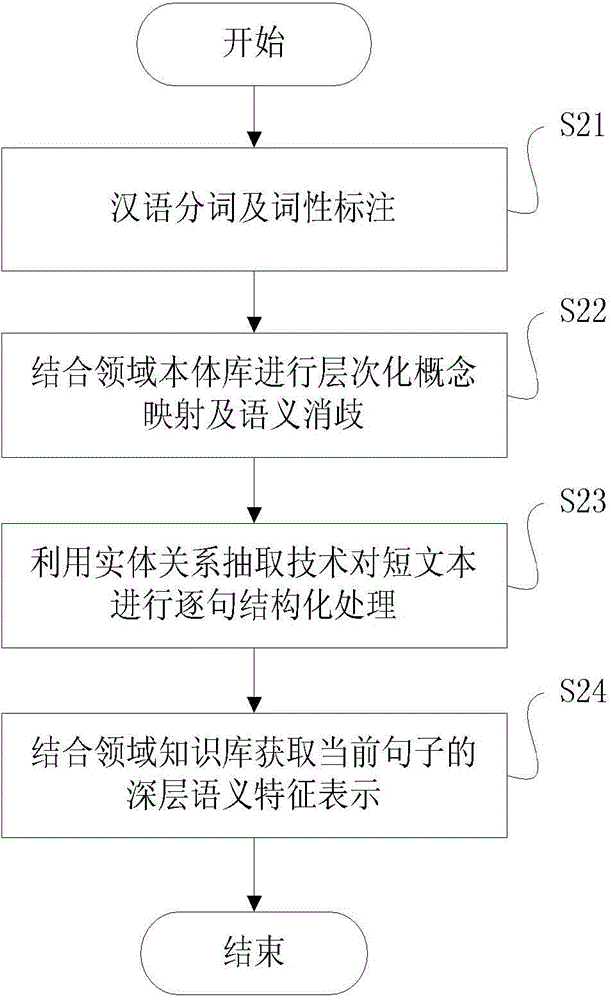
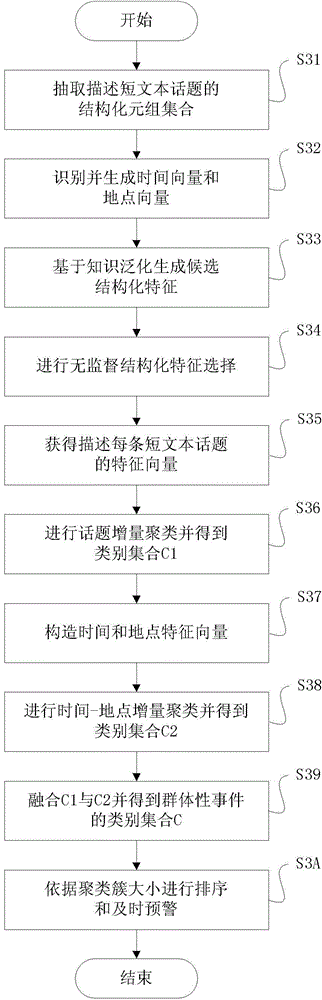
Mass disturbance warning method and system applied to short texts
ActiveCN104091054AGuaranteed timelinessImprove responseSpecial data processing applicationsA domainData mining
The invention discloses a mass disturbance warning method and system applied to short texts. The method comprises the following steps of automatically structuring a domain knowledge database applied to mass disturbances; combined with the domain knowledge database, performing local structured extraction and online classification on the short texts to screen out mass disturbance texts with potential risks from mass short texts; combined with the domain knowledge database, performing overall structured extraction and online clustering on identified short texts, and according to whether the number of short texts contained in every cluster exceeds a preset threshold value, determining whether to perform timely alarming. The mass disturbance warning method applied to the short texts has the advantages of fully integrating domain background knowledge, context, shallow semantic expression and deep semantic computation, achieving collaborative analysis and predication of mass disturbances and improving the timeliness, accuracy and recall rate of screening, tracking and alarming of the mass disturbances.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Privacy protecting method for social network based on undirected graph modification
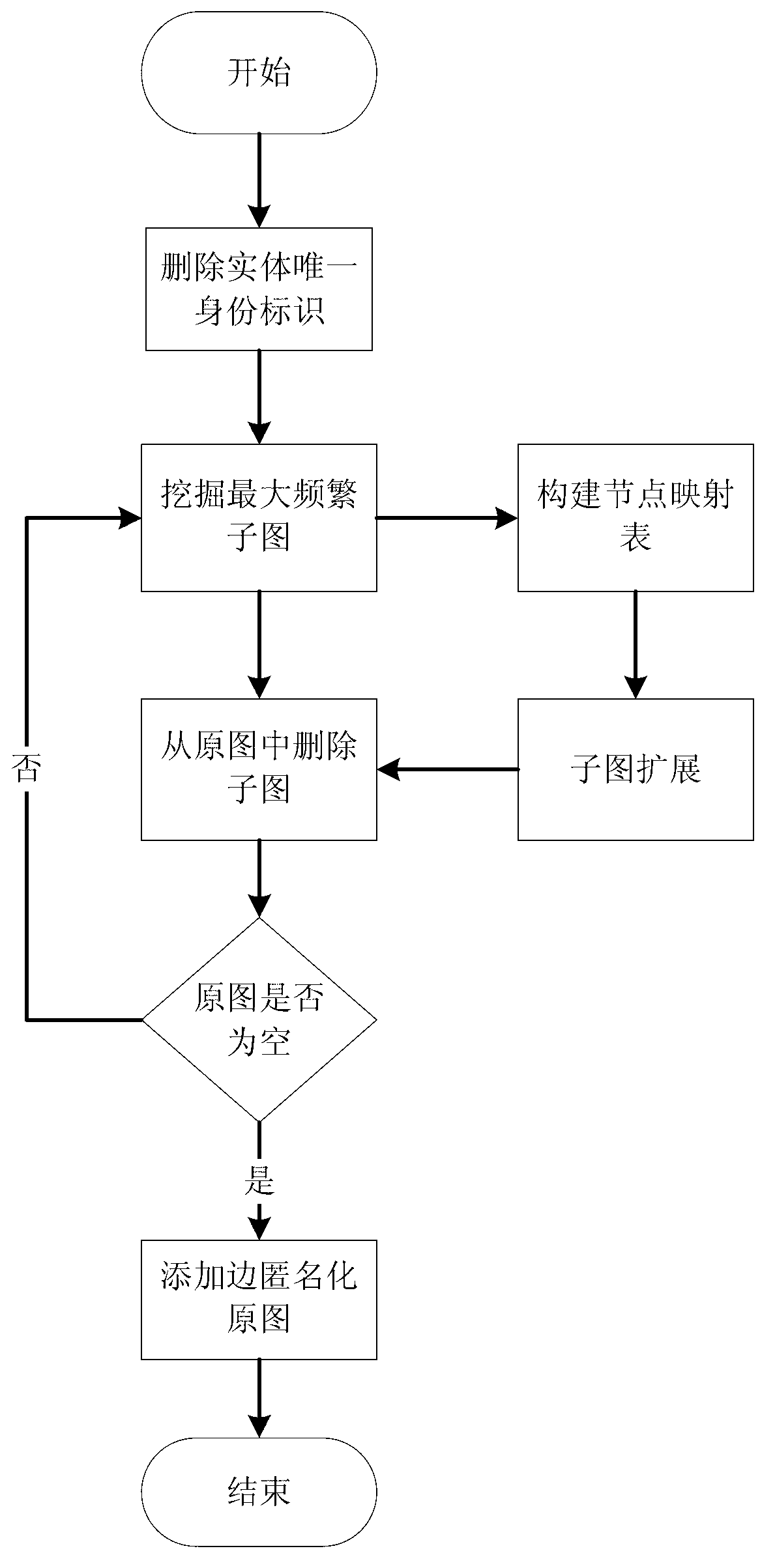
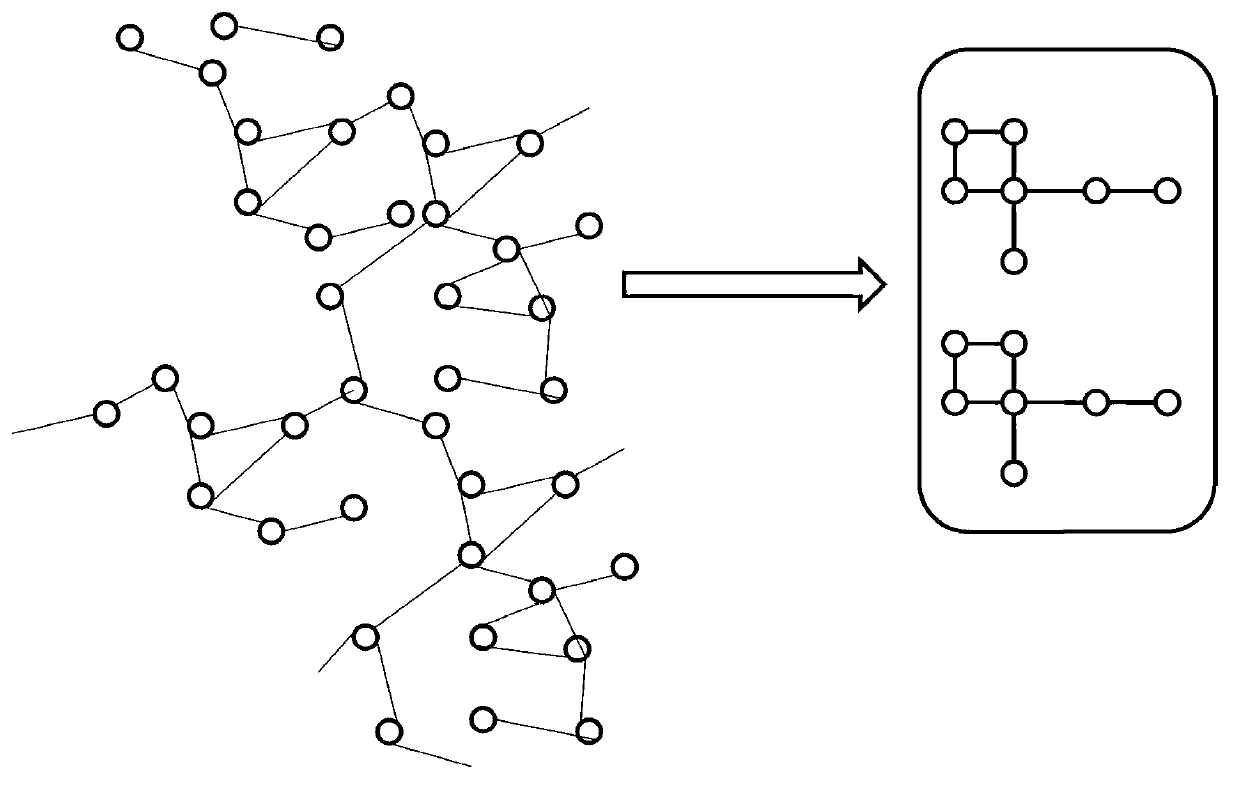
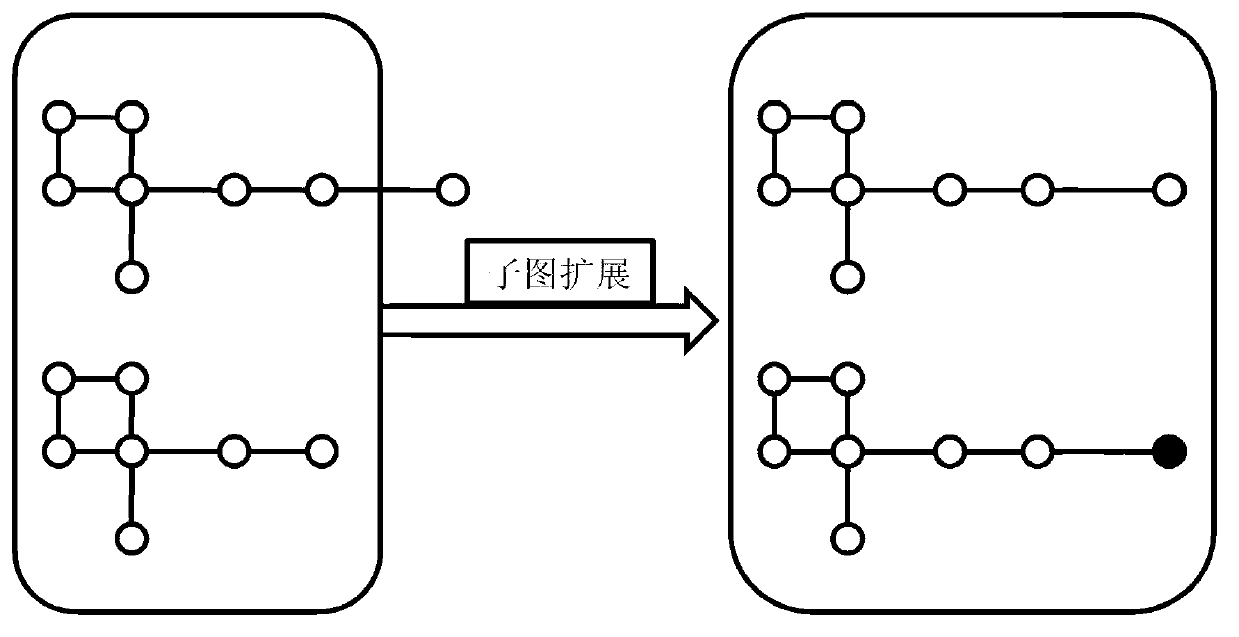
ActiveCN103218397AAvoid repositioningProtect personal privacyDigital data protectionSpecial data processing applicationsNODALUndirected graph
The invention discloses a privacy protecting method for a social network based on undirected graph modification. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing an undirected graph of the social network; (2) digging the maximum frequent subgraph; (3) establishing a node mapping relation; (4) iteratively expanding the subgraph and improving the mapping table; and (6) forming an anonymity isomorphic graph by adding mapping lines and virtual nodes to the undirected graph. According to the method, the virtual nodes are added, so that each node has other nodes symmetrical thereto, so that re-positioning of user identity is avoided, and personal privacy safety of the user is effectively protected. In addition, the local structure of the social network is finely modified, social network graph data can be externally and safely issued, so that the method is suitable for researching characteristic analysis and statistics of the local structure of the social network, and promotes data digging technology in research and application in the field of social network.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
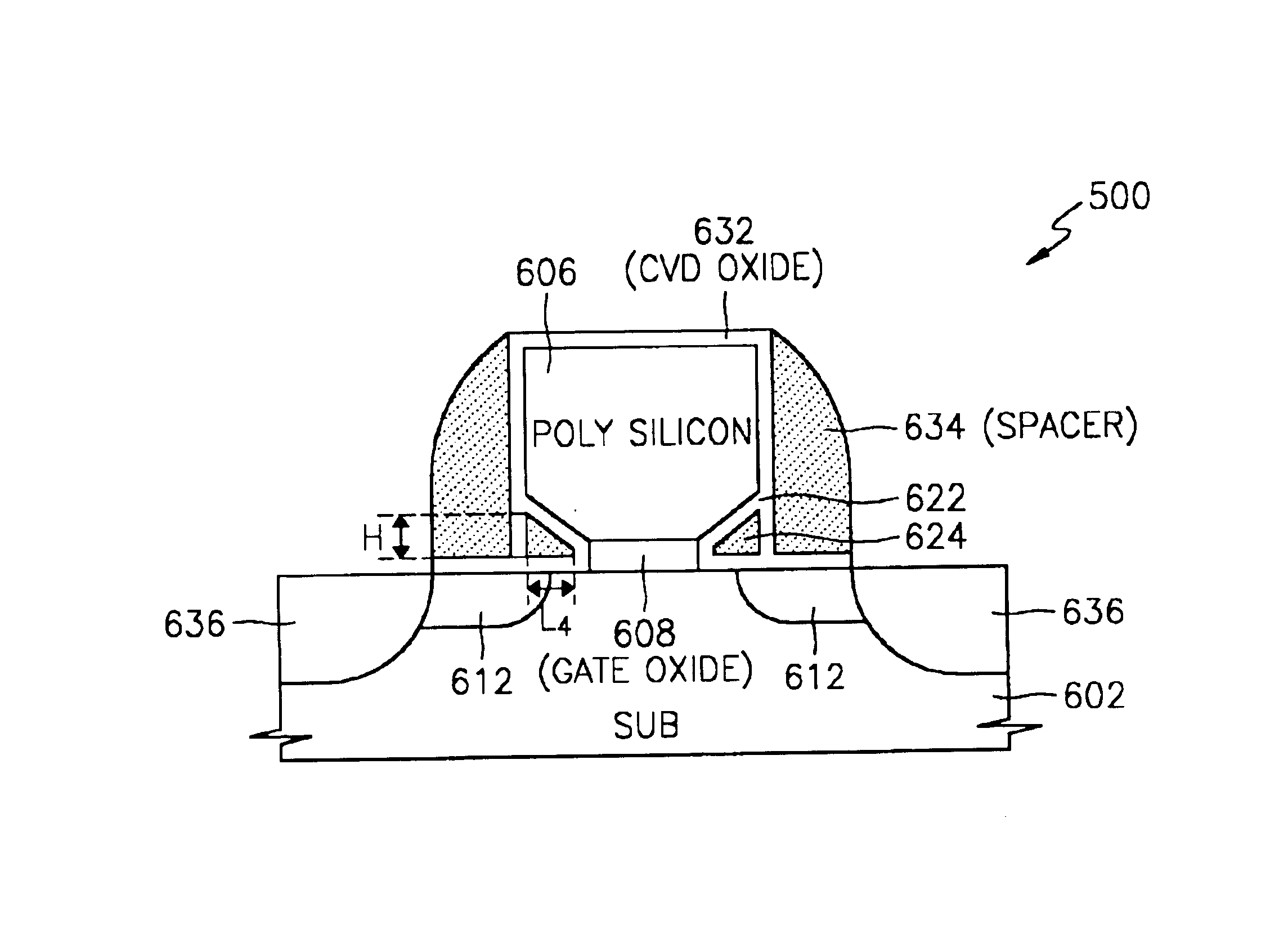
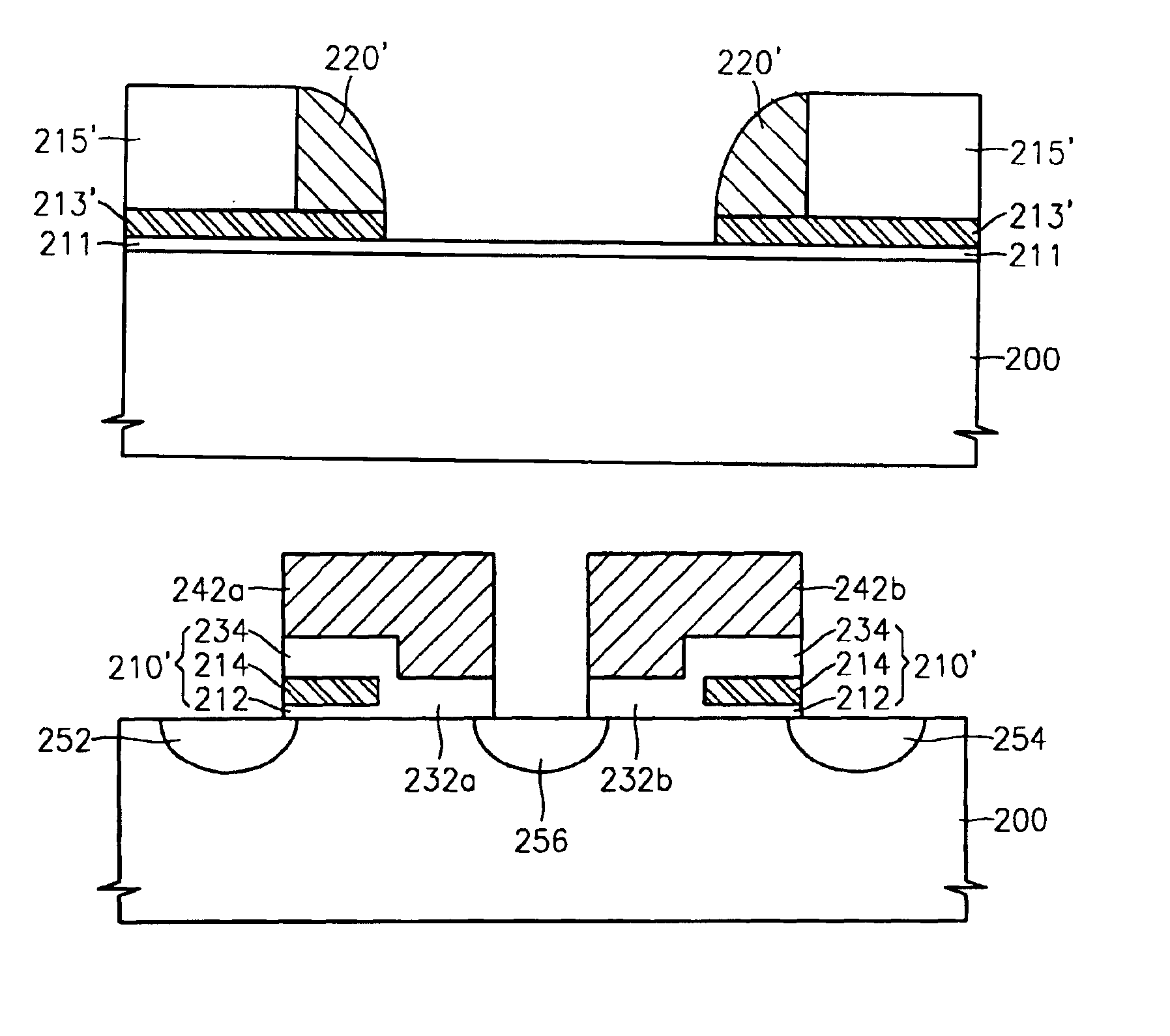
Methods of forming a nonvolatile memory device having a local SONOS structure that use spacers to adjust the overlap between a gate electrode and a charge trapping layer
A nonvolatile memory device is formed by forming a first oxide layer on a substrate. A nitride layer is formed on the first oxide layer. A second oxide layer is formed on the nitride layer. The second oxide layer is patterned so as to expose the nitride layer. A first polysilicon layer is formed on the second oxide layer and the exposed portion of the nitride layer. The first polysilicon layer and the nitride layer are etched so as to expose the second oxide layer and the first oxide layer and to form polysilicon spacers on the nitride layer. The polysilicon spacers are etched so as to expose portions of the nitride layer. The exposed portions of the nitride layer may function as charge trapping layers. The exposed portion of the first oxide layer is etched to expose a portion of the substrate. A third oxide layer is formed on the exposed portion of the substrate, the exposed portions of the nitride layer, and the second oxide layer. A second polysilicon layer is formed on the third oxide layer. The second polysilicon layer is planarized so as to expose the second oxide layer. The second polysilicon layer may function as a gate electrode that overlaps portions of the charge trapping layers. The third oxide layer may function as a gate-insulating layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
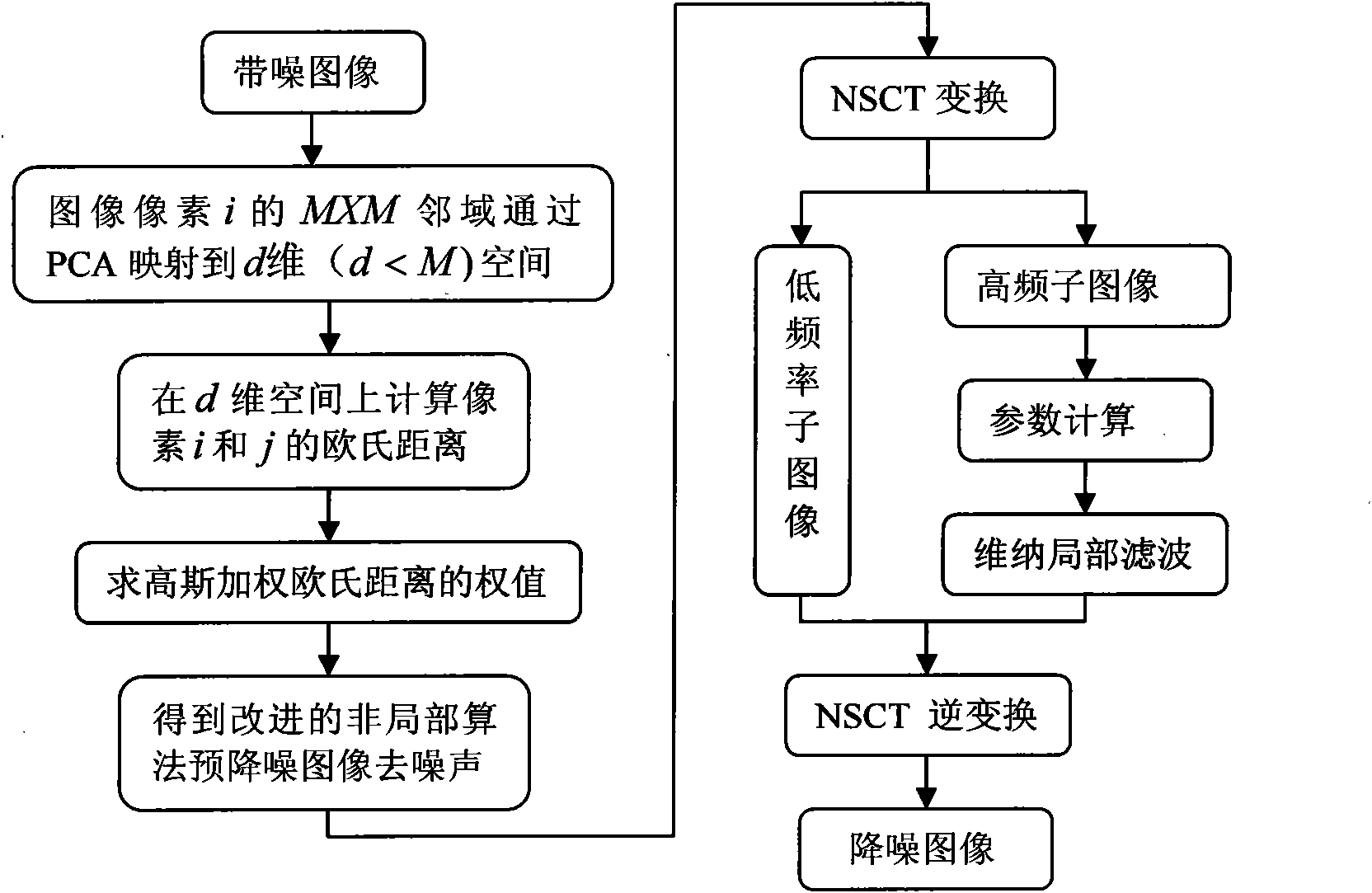
Image denoising method based on non-local means and multi-level directional images
ActiveCN101847257AQuality improvementAccurate targetImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionPrincipal component analysisDecomposition
The invention relates to an image denoising method based on non-local means and multi-level directional images, comprising the steps of: firstly, carrying out preprocessing on an image with noise in an empty space by utilizing a non-local mean arithmetic of a small window and the similarity of the local structure of the image, and mapping the local window to a low-dimensional space to improve the speed of the arithmetic by utilizing principal component analysis (PCA); then carrying out multi-scale multi-direction sparse decomposition on the preprocessed image through NSCT (Non-subsampled Contourlet); eliminating low-frequency noise by adopting Wiener filtering in an NSCT transform domain by utilizing the neighborhood statistical property of the coefficient; and obtaining the denoised image through NSCT inverse transformation. The method improves the quality of the denoised image, provides more comprehensive and accurate targets and background information, and achieves relatively ideal denoising effect. The invention has wide application prospect in systems in the military field and the non-military field such as optical imaging, target detection, safety monitoring, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER +1
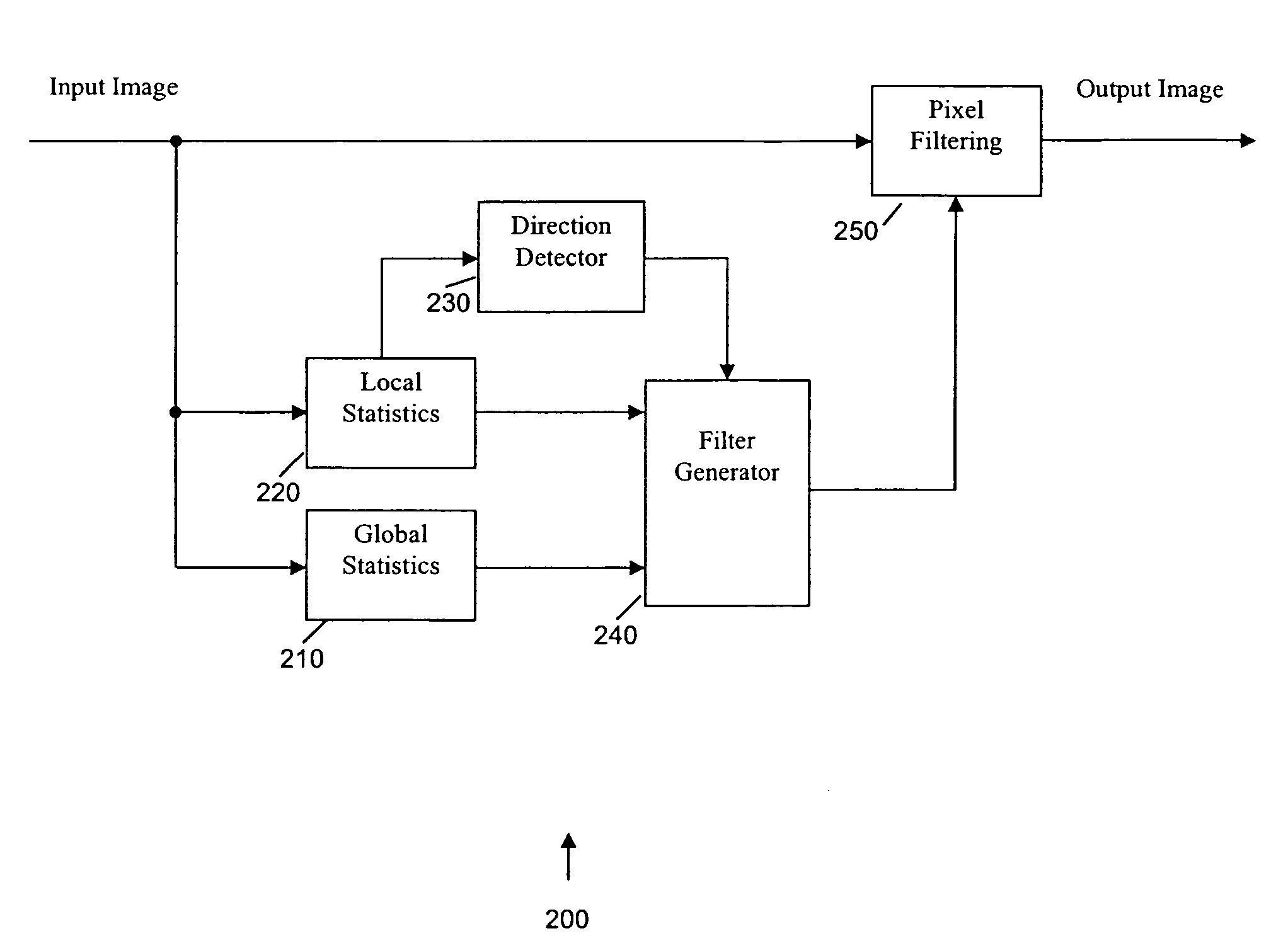
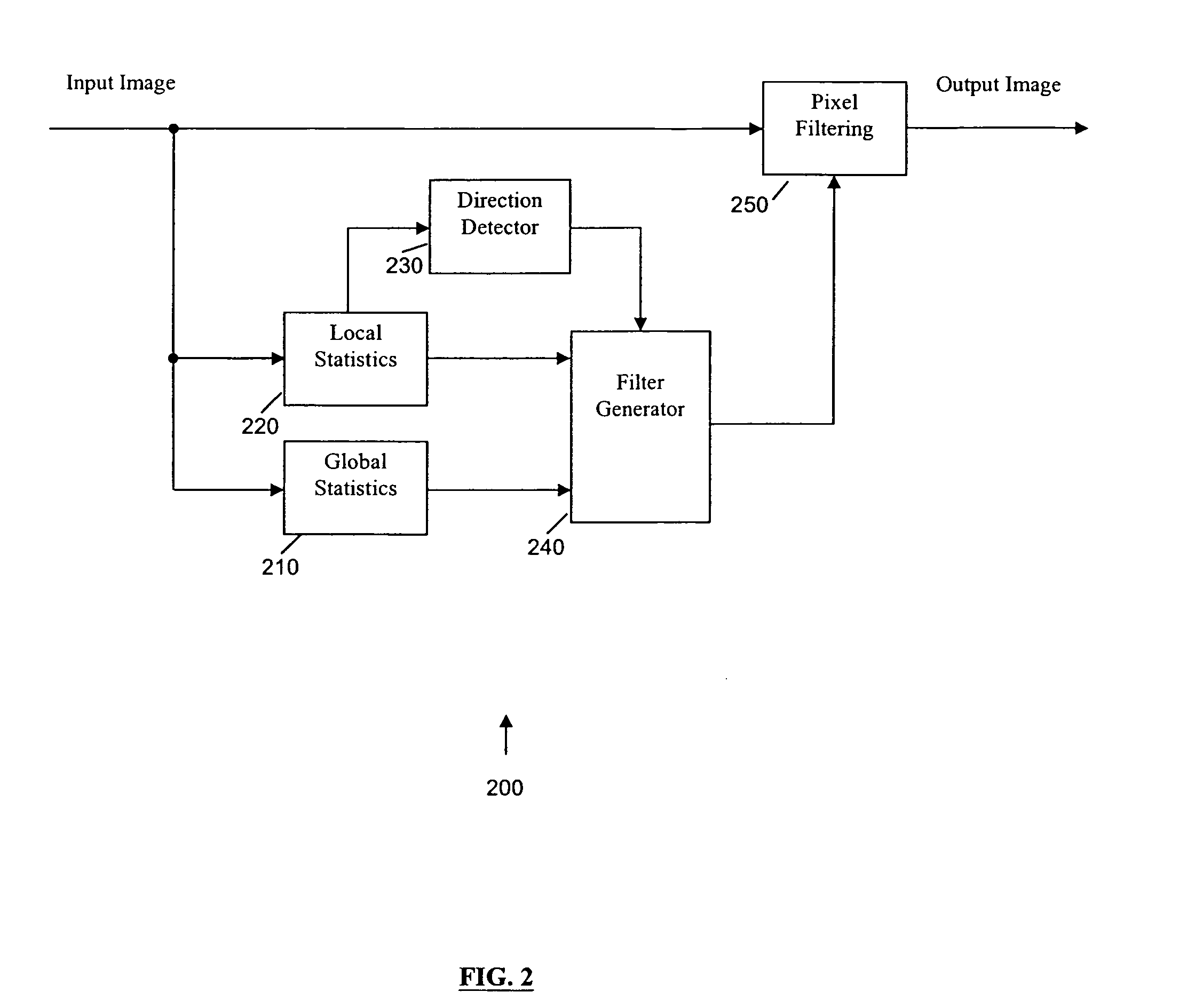
Global and local statistics controlled noise reduction system
InactiveUS20050094889A1Reliable global noise statisticAdapt effectivelyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage denoisingNoise level
A global and local statistics controlled noise reduction system in which the video image noise reduction processing is effectively adaptive to both image local structure and global noise level. A noise estimation method provides reliable global noise statistics to the noise reduction system. The noise reduction system dynamically / adaptively configures a local filter for processing each image pixel, and processes the pixel with that local filter. The filtering process of the noise reduction system is controlled by both global and local image statistics that are also computed by the system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for manufacturing casting blank of die for inner containers of household appliances on basis of metal cavity with cold iron structure
InactiveCN102773409AQuality improvementImprove pass rateFoundry mouldsFoundry coresSurface finishFree cooling
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a casting blank of a die for inner containers of household appliances on the basis of a metal cavity with a cold iron structure, and relates to the technical field of aluminum alloy casting. The method includes particular steps of constructing an outer cavity by cold iron blocks on the periphery of a manufactured wood mold in a form following manner; filling gaps among the cold iron blocks by clay sand, tightly filling the corresponding cold iron blocks by clay sand after each local structure is completed, and compacting a sand mould to prevent the cold iron blocks from moving; constructing a sand core of an inner cavity by the same method after the outer cavity is constructed; opening a case to take out the wood mould after the sand core of the inner cavity is manufactured so that a cavity of a casting is formed; drying the cavity of the casting and the sand core consisting of clay sand; preheating the cavity of the casting at the preheating temperature of 200 DEG C before pouring of the cavity of the casting; casting melted aluminum alloy into the cavity of the casting; and opening the case to take out the casting after the cavity of the casting is cooled naturally. The method is mainly used for casting the die for the inner containers of the household appliances, the surface of a casting product produced by the process is high in smoothness and does not have sand holes or pin holes after the surface of the casting product is treated in a follow-up machining process, and accordingly yield of molded inner container products is greatly increased.
Owner:CHUZHOU JINNUO INDAL
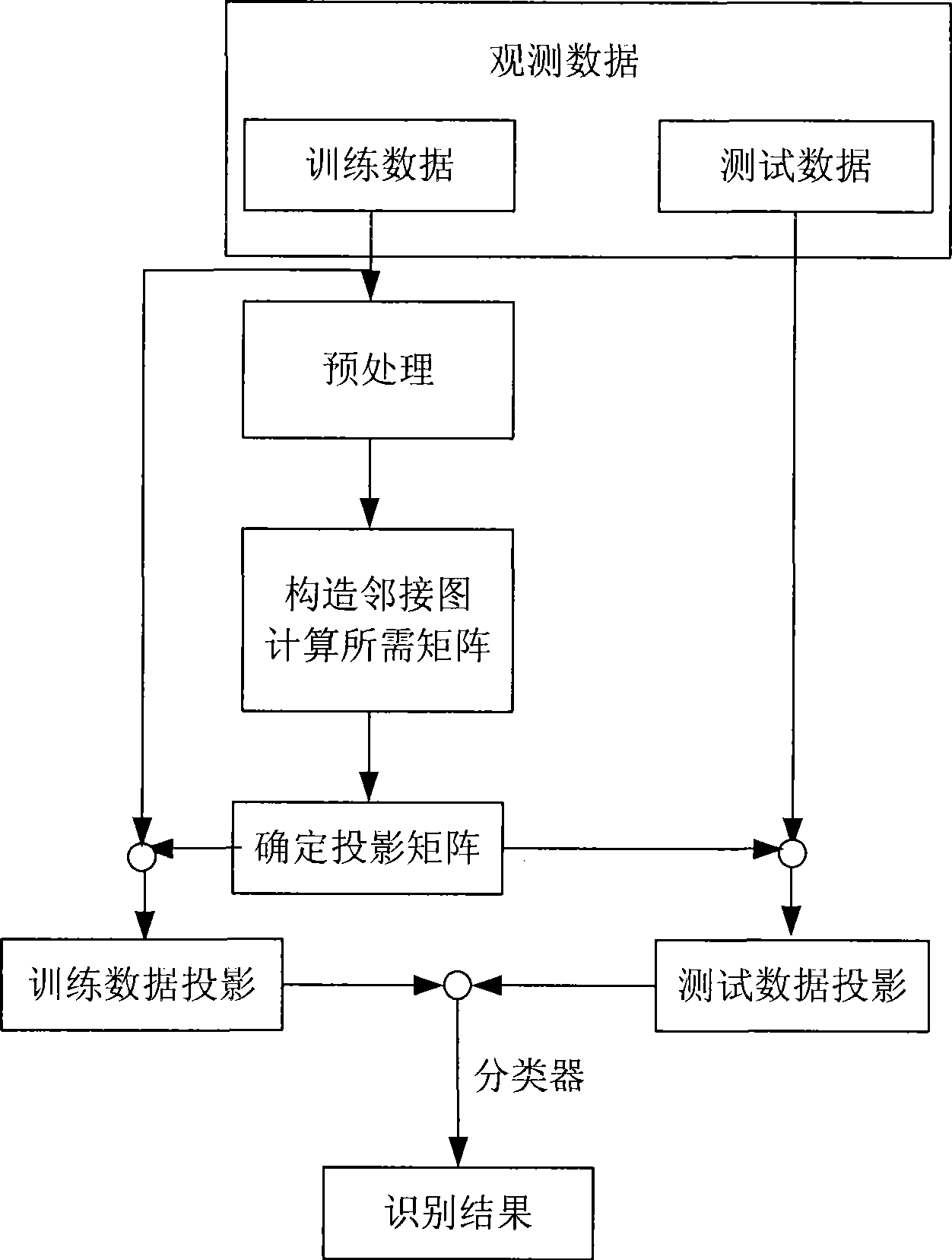
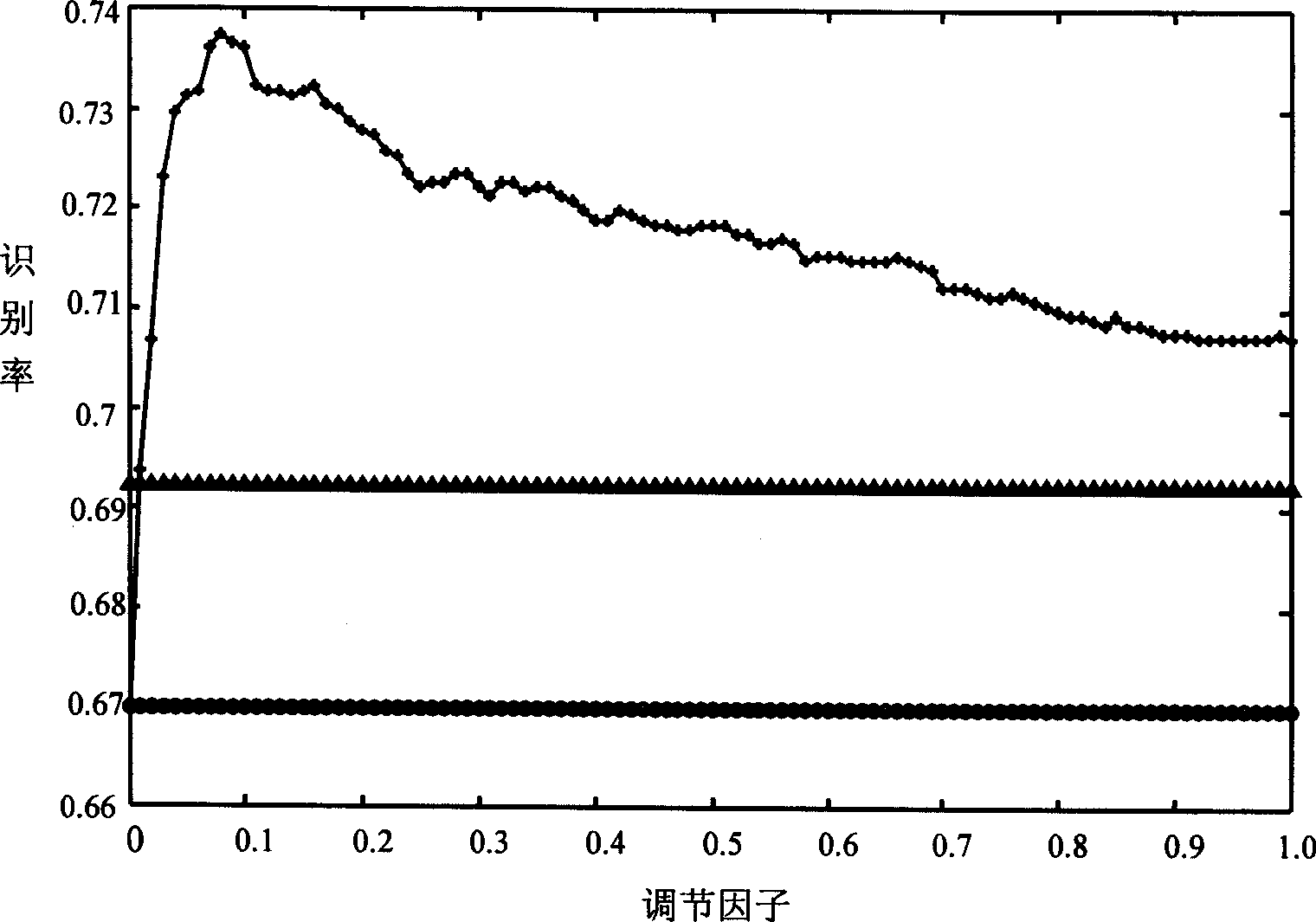
Image characteristics extraction method based on global and local structure amalgamation
Provided is an image feature extraction method based on global and local structure fusion, characterized by comprising: 1) constructing a weight adjacent map; 2) determining laplacian matrix of similar matrix, degree matrix and images, 3) determining scatter matrix inside the kind and between the kind; 4) determining projection matrix, 5) identifying. The invention provides a feature extraction method of fusing the global structure information and the local structure information, wherein complex features fused of the global feature and the local feature are extracted, thereby the method has strong resolving power. The method not only has the characteristics of holding the reflection method locally, namely holding the characteristics of manifold structure of data; moreover has the characteristics of linear discrimination analysis method, namely assembling the date of the kind more compact to enlarge the distance between the kinds. The invention is applied in image recognition, thereby increasing identifying performance.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com