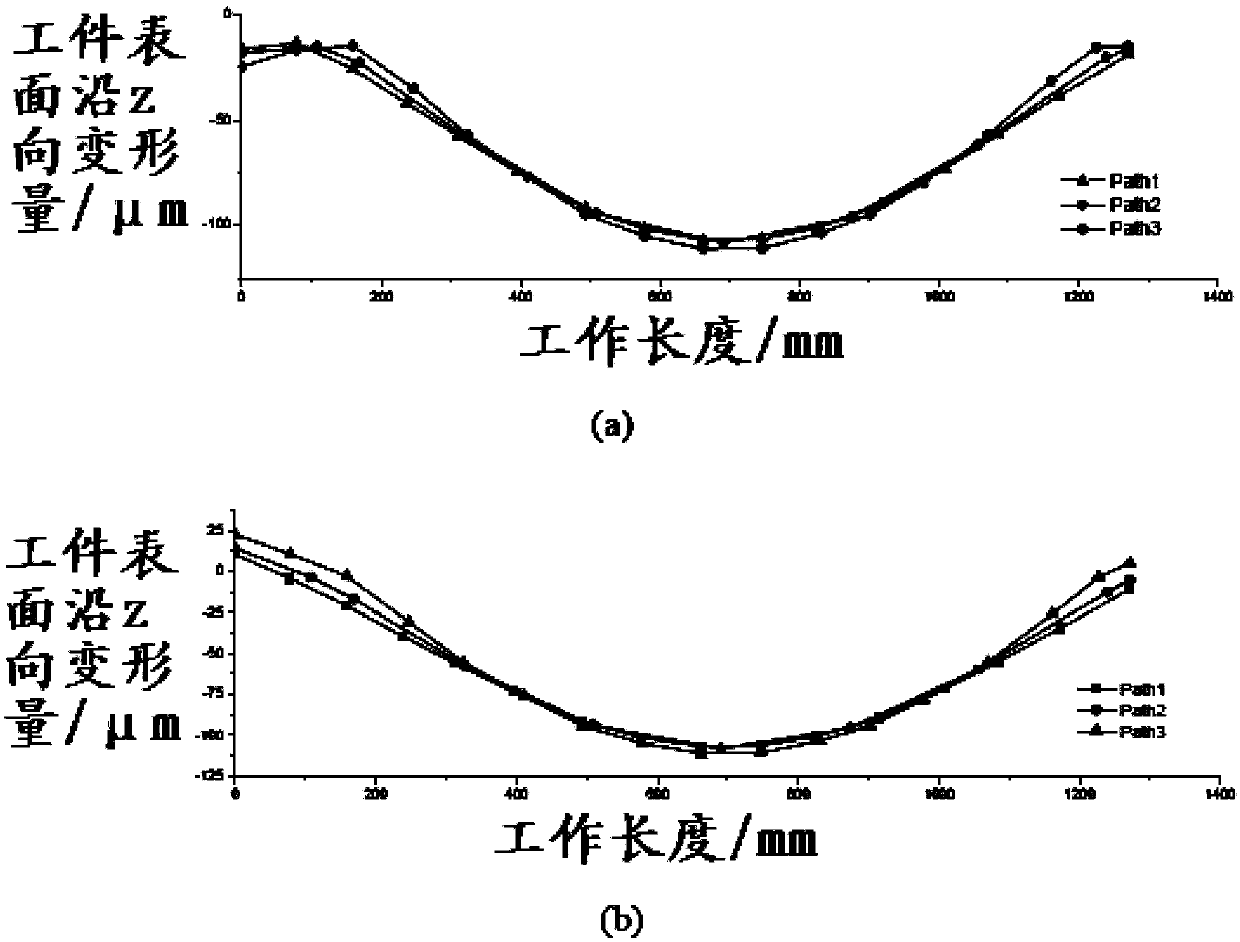
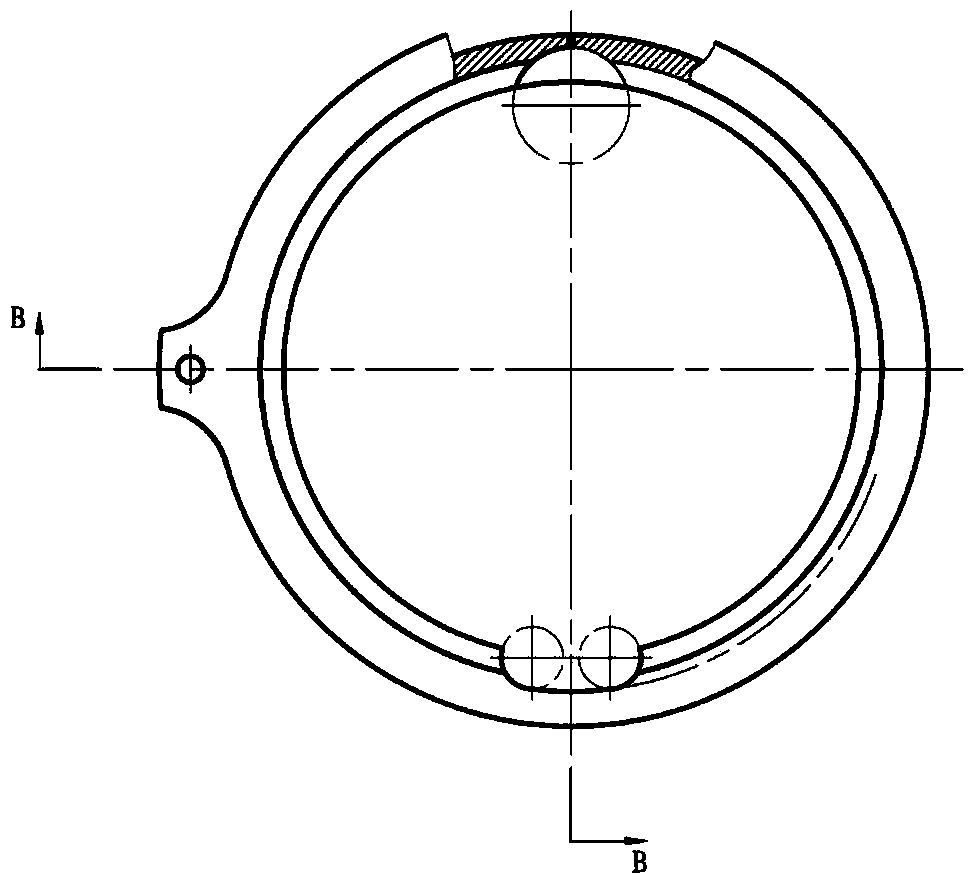
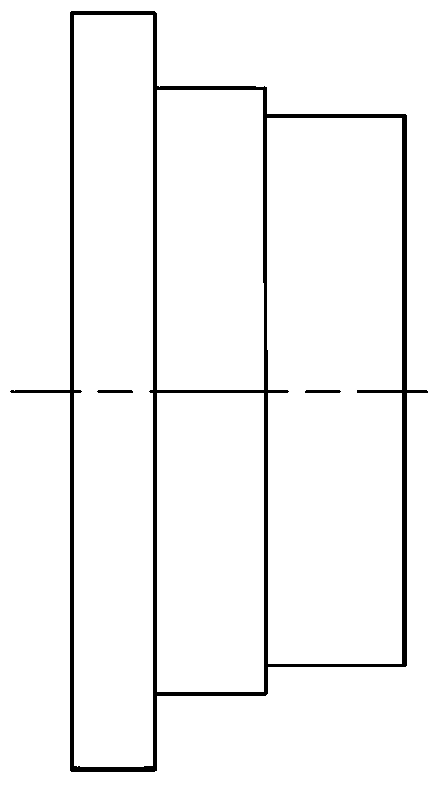
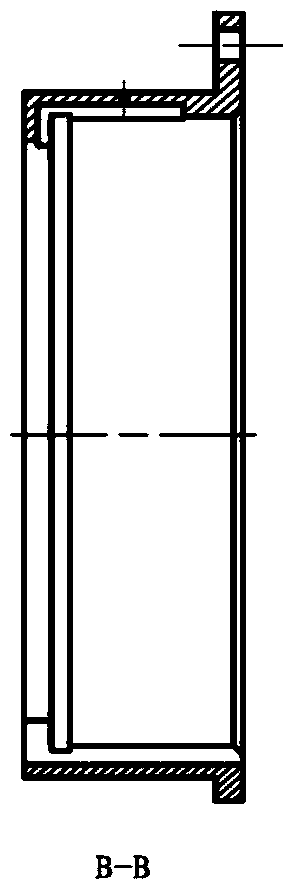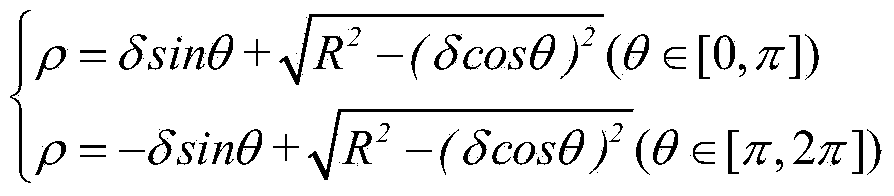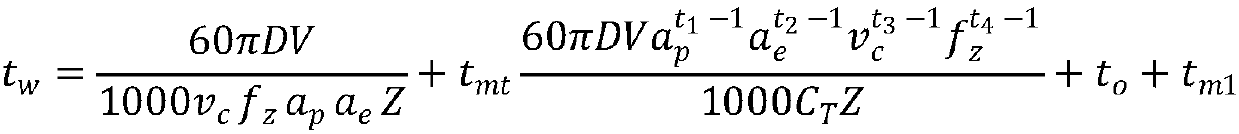Patents
Literature
597 results about "Machining deformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
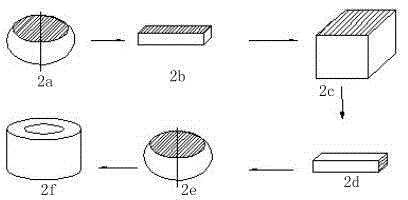
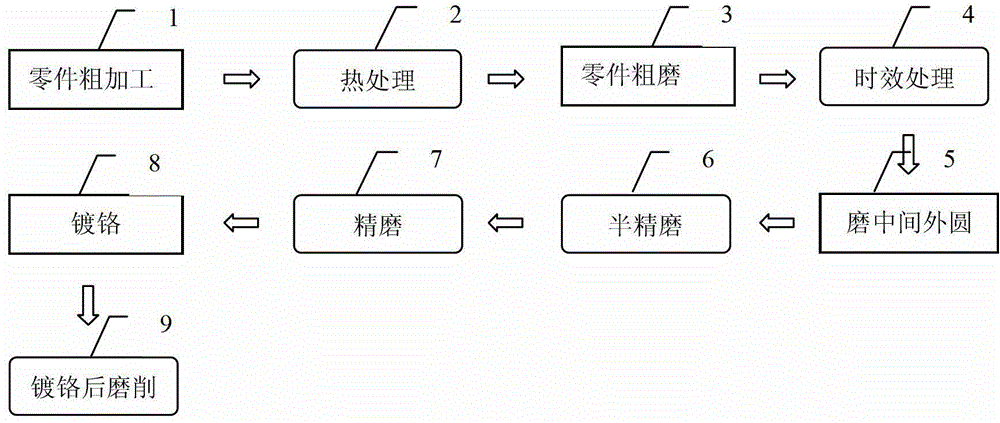
Machining method for large cast titanium alloy diamond-shaped cabin shell
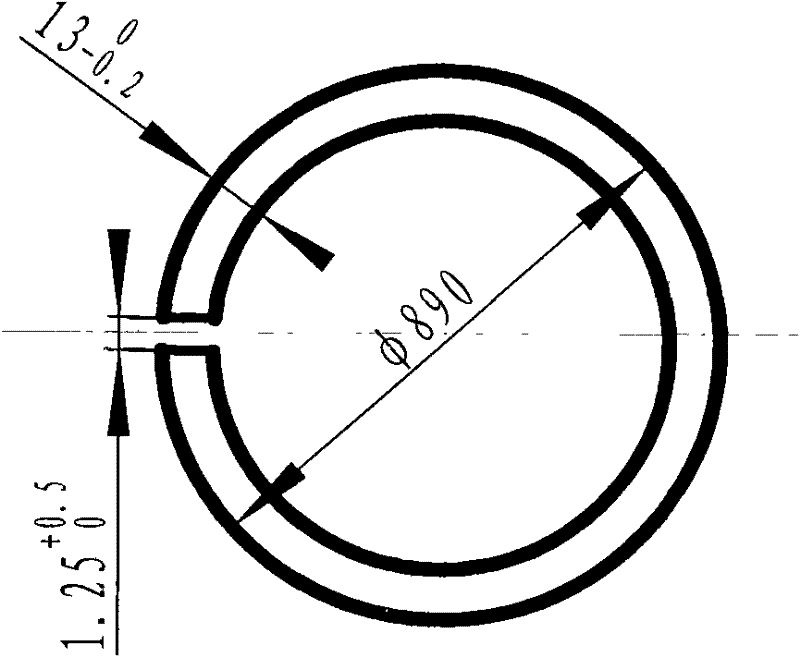
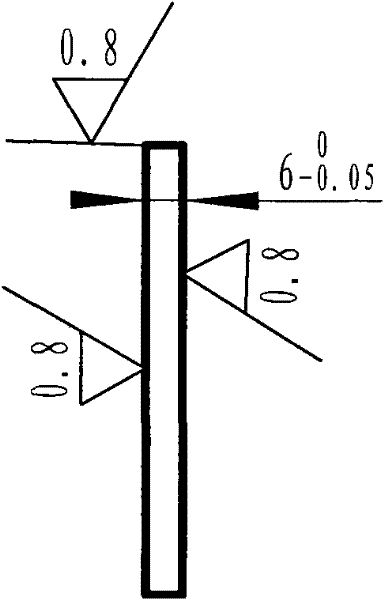
ActiveCN103753124AQuality assuranceControl Wall Thickness UniformityAircraft componentsMachining deformationTitanium alloy
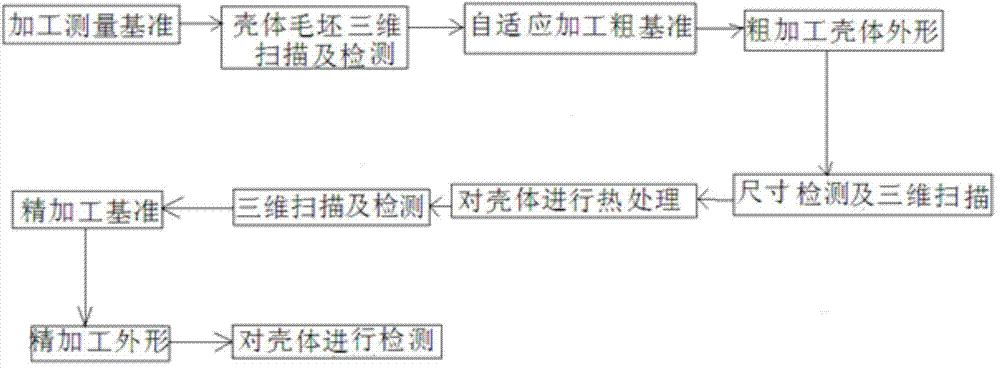
The invention discloses a machining method for a large cast titanium alloy diamond-shaped cabin shell and belongs to the machining method for a complex piece. The machining method for the large cast titanium alloy diamond-shaped cabin shell includes the following steps: step 1, machining a base and measuring; step 2, carrying out three-dimensional scanning on a blank and detecting; step 3, carrying out self-adaption machining on a rough base; step 4, roughly machining the shape; step 5, detecting the size and performing three-dimensional scanning; step 6, performing heat treatment; step 7, performing three-dimensional scanning and detecting; step 8, finishing the base; step 9, finishing the shape; step 10, detecting the shell. The machining method for the large cast titanium alloy diamond-shaped cabin shell is capable of comprehensively analyzing the cast size precision and allowance, quickly determining the machining base, controlling the wall thickness uniformity and guaranteeing the shell quality, has small machining deformation, and enables the manufacturing cycle to be shortened.
Owner:HUBEI SANJIANG AEROSPACE GRP HONGYANG ELECTROMECHANICAL
Copper-alloy pipe-material casting-milling technology parameter designing and optimizing method
InactiveCN1979496AOptimizing Graphical Result ExpressionAvoid breakingPhysical realisationSpecial data processing applicationsNerve networkMachining deformation
The invention discloses a method for designing and optimizing cast-rolling process parameters of copper alloy tubing, using database as design basic, using nerve network as design method of process parameters and indexes, and using genetic algorithm as process parameter optimizing means, integrating nerve network, genetic algorithm, finite element simulation, experiment design, CAD parameterized design and database technique into the process design and parameter optimization, designing and optimizing the cast-rolling process parameters of the copper alloy tubing. And the invention has high automation degree, and can be applied to machining deformation of copper alloy tubing, and make personnel short of special knowledge able to make accurate and standard machining process.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for controlling machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis
InactiveCN104077442AReduce machining accuracyShorten the processing cycleSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisMachining deformation
The invention discloses a method for controlling the machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, extracting local structural features of the large integrated thin-walled part; 2, performing finite element simulative analysis on local structural features to obtain an optimized cutting technology; 3, numerically modeling a large integrated workblank, and loading an initial internal stress; 4, protocoling a tool path, namely protocoling the machining sequence of the feature structures; 5, performing simulative analysis on the integrated structure to obtain a predicted deformation result under the condition of process technology; 6, regulating and optimizing a clamp scheme to control machining deformation. The method adopts finite element simulation, can analyze and predict in advance before the actual machining of the parts, and thereby corresponding machining strategy is adjusted, machining deformation is effectively controlled, production cycle of the parts is shortened, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING CHENGUANG GRP +1
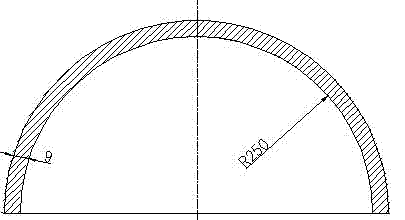
Method for machining large-radius thin-wall semi-annular part
InactiveCN103624497AControl processing deformationRealize machining errorTurning toolsMachining deformationEngineering
The invention discloses a method for machining a large-radius thin-wall semi-annular part, belongs to the technical field of aero-engines, and particularly relates to a method for machining the large-radius thin-wall semi-annular part. According to the method for machining the large-radius thin-wall semi-annular part, provided by the invention, the machining deformation of the large-radius thin-wall semi-annular part is effectively controlled, the machining error of the large-radius thin-wall semi-annular part is less than 0.05 millimeter, and the geometric accuracy of the large-radius thin-wall semi-annular part is increased, so that the yield of the part is increased. The method for machining the large-radius thin-wall semi-annular part comprises the following steps: I, roughly machining the profile of an entire ring; II, roughly machining pin holes, screw holes, a left shoulder and a right shoulder; III, cutting an entire ring part into a semi-annular part; IV, machining an integral molded surface in a semi-finishing way; V, finishing the integral profile.
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
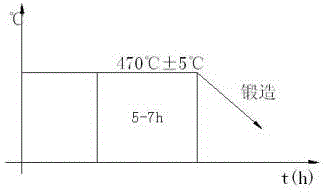
Forging forming process of high barrel-shaped aluminum alloy forged piece
ActiveCN104438419AReduce anisotropyIncrease radial elongationMetal rollingMachining deformationBarrel Shaped
The invention relates to a forging forming process of a high barrel-shaped aluminum alloy forged piece. A cross upsetting and rolling method is adopted in a forging process, so that on one hand, an aluminum alloy blank can be fully deformed, and a casting-state structure is enabled to be changed into a forged structure, on the other hand, by use of the cross upsetting and rolling method, the anisotropy of an aluminum alloy ring piece can be reduced and the radial elongation of the aluminum alloy ring piece can be improved. The feeding rate of a ring rolling machine during ring rolling is changed in a forging process, so that the aluminum alloy forged piece is prevented from being overheated on one hand, and the end surface of the aluminum alloy forged piece can be prevented from peeling and sinking; and besides, the aluminum alloy forged piece is subjected to heat treatment, so that the intensity of the forged piece can be improved, hardening constituents precipitated out from the aluminum alloy forged piece at the heat treatment temperature can be finely dispersed and distributed, the participating stress of the aluminum alloy forged piece can be reduced and the follow-up machining deformation can be prevented.
Owner:WUXI PAIKE HEAVY CASTING & FORGING
Laser cladding repair technique for engine crankshaft
InactiveCN101109083AMelting depth is smallSmall machining allowanceMetallic material coating processesNumerical controlOptoelectronics
The invention relates to an engine crankshaft laser cladding repairing technology based on the following steps. A: the crankshaft surface is treated with oil removing stain removal; B: a DL-HL-T10000 type CO2 laser is selected; a working table with numerically-controlled machine tool is applied; an auto-feeding powder apparatus for laser is used to delivered a Fe-based or Ni-base self-fusing alloy powder to a molten pool, and the Fe-based or Ni-base self-fusing alloy powder is repaired and strengthed on the surface of the crankshaft. The technological parameter features that the cladding power P ranges between 1,000w and 10,000w; the spot dismeter D is between 2mm and 20mm; the scanning speed is at 200 mm per min to 2000mm per min; the overlapping rate is from 20 per cent to 40 per cent. The laser cladding technology of the invention features no pollution, high productivity, low energy consumption, small machining allowance and lower comprehensive cost. In addition, the laser cladding is good to the repair of the wear parts, such as strong associativity, small residual stress, no machining deformation, high surface hardness as well as good abrasion resistance, and becomes a process technology with great developing potential in repairing the components.
Owner:SHENYANG DALU LASER COMPLETE EQUIP
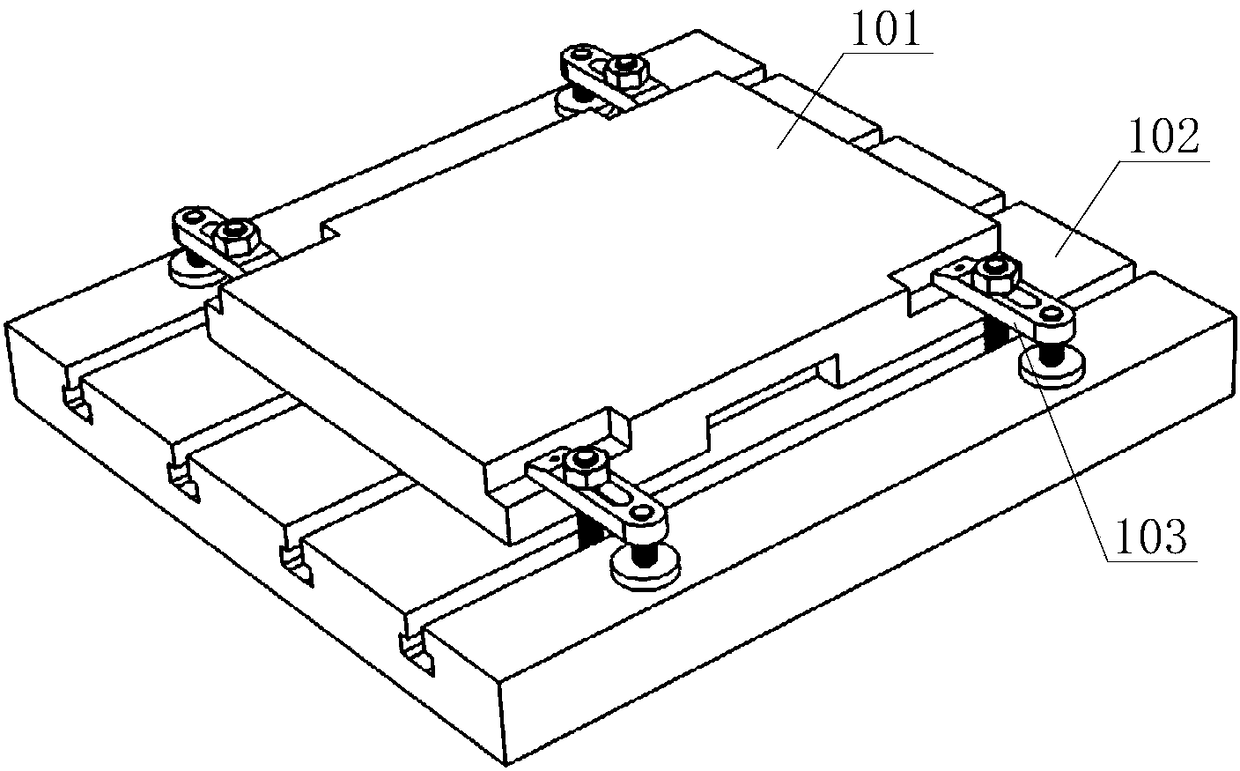
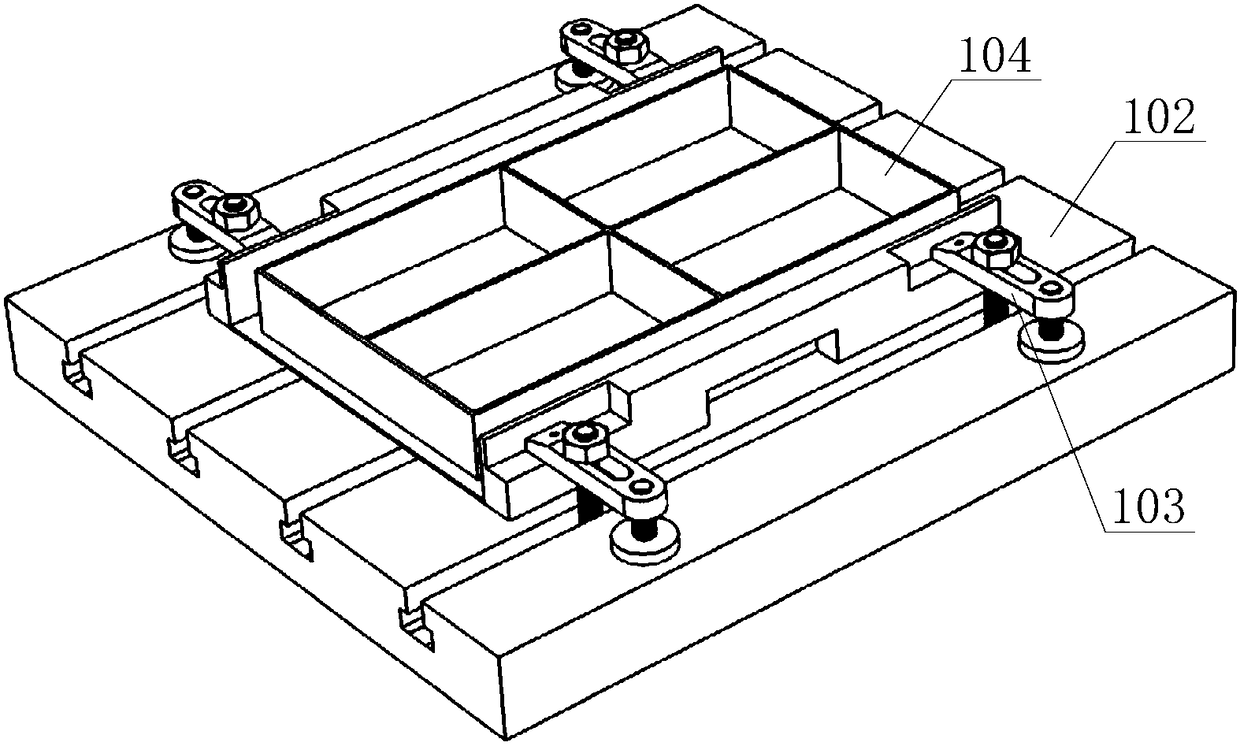
Flexible clamp for milling thin-walled workpiece with complex curved surface
ActiveCN106514369AEven by forceReduce processing deformationMilling equipment detailsPositioning apparatusMachining deformationMagnetorheological fluid
The invention discloses a flexible clamp for milling a thin-walled workpiece with a complex curved surface, and belongs to the field of machining. The flexible clamp comprises a vice clamp, a fluid carrying trough for accommodating a magnetorheological fluid, a magnetoresistive plate frame arranged at the upper part of the fluid carrying trough, and plate electrodes for providing a horizontal magnetic field, wherein the left side of the magnetoresistive plate frame is connected with a lead screw through threads; the right side of the magnetoresistive plate frame sleeves a supporting and positioning rod in a matching way; the upper end of the lead screw is connected with an operating crank; and the operating crank can drive the lead screw to rotate and drive the magnetoresistive plate frame to rise and fall. The flexible clamp provided by the invention can effectively reduce the machining deformation of the thin-walled workpiece with the curved surface, effectively restrains the vibration of the thin-walled workpiece with the curved surface during milling, lowers the machining noise, reduces the machining error, and guarantees high machining efficiency and high surface machining quality.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
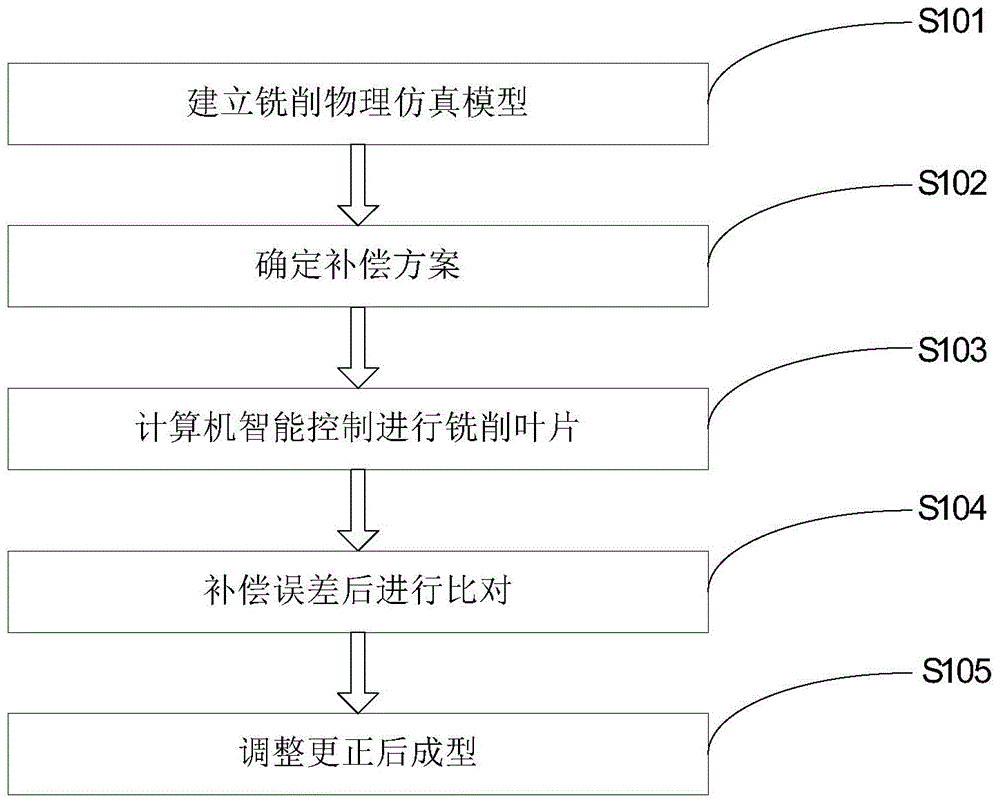
Aviation blade machining method based on error compensation
InactiveCN104096889AImprove machining accuracySmall processing deformationOther manufacturing equipments/toolsMilling equipment detailsAviationElement analysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of aviation blade machining, in particular relates to an aviation blade machining method based on error compensation. The aviation blade machining method is characterized by comprising the steps of building of a milling physical simulation model, determination of a compensation scheme, milling of a blade through computer intelligent control, comparison after the error compensation and formation after adjusting correction. The milling physical simulation model is built, and the deformation quantity in the blade machining engineering is accurately forecasted according to an error compensation principle, so that the milling error caused by the deformation of the blade and a milling cutter is largely reduced, the blade machining precision can be effectively improved, and the working efficiency is enhanced; and the blade deformation is controlled through the cutting surface finite element analysis and the cutter path finite element analysis, so that the blade machining deformation quantity is reduced, the cost is decreased, and the machining efficiency is improved.
Owner:XIAN TECH UNIV
Numerical control machine heat error compensation temperature point position determination method
InactiveCN101290266AReduce the number of temperature measuring pointsImprove effectivenessStructural/machines measurementNumerical controlExperimental methods
The invention relates to a method for determining the position of a measuring point of a temperature sensor for thermal error compensation of a numerical control machine, comprising the following steps of: 1. analyzing a finite element of thermal property of the numerical control machine; 2. calculating mutual information quantity of numerical control machine deformation provided by a measuring point temperature value Ti (t) according to informationism; 3. calculating mutual information quantity of numerical control machine deformation Y(t) provided by a combination of m temperature measuring points. With the method, the problem of optimized calculation for determining the position of the temperature sensor during the process of thermal error modeling for the numerical control machine can be solved. The method uses the method of numerical calculation to replace the prior experimental method, and can realize prediction of thermal deformation of the numerical control machine with the least temperature sensors, thereby effectively reducing the number of temperature measuring points of the numerical control machine, saving time and cost, and improving the validity of the thermal error compensation model of the numerical control machine.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH +1
Double-S-shaped double-curve thin-walled part manufacturing process
ActiveCN104526270AImprove clamping stabilityImprove processing rigidityMachining deformationVibration Problem
The invention relates to the technical field of mechanical machining, in particular to a double-S-shaped double-curve thin-walled part manufacturing process. A five-coordinate high-speed mill is adopted to conduct rough machining on an inner curve and an outer curve with ribs and conduct semi-finish machining and finish machining on the inner curve and the outer curve with ribs, and a step cushion block positioning and gypsum filling method is adopted to perform clamping and positioning. The part clamping and positioning problems are solved, and part clamping stability and machining rigidity are improved. Regional segmented and layered machining is adopted for parts, machining deformation of ultra-complicated thin-walled curved surfaces is effectively controlled, the vibration problem in the machining process is avoided, and part size and accuracy are ensured.
Owner:JIANGXI HONGDU AVIATION IND GRP
Machining clamp for outer wall of blind-hole thin-wall sleeve part and using method thereof
ActiveCN103495755AImprove clamping effectAvoid clampingExpansion mandrelsMachining deformationEngineering
The invention discloses a machining clamp for the outer wall of a blind-hole thin-wall sleeve part and a using method of the machining clamp. The clamp comprises a core shaft and a fastening nut connected on the core shaft through threads. The core shaft is sleeved with an elastic clamping sleeve, the elastic clamping sleeve is overall cylindrical, cones with the large outsides and the small insides are arranged at the two ends of the elastic clamping sleeve, a conical surface is arranged at the tail end of the core shaft, the tail end of the core shaft is matched with the elastic clamping sleeve, the core shaft is further sleeved with a taper sleeve, the taper sleeve is arranged between the fastening nut and the elastic clamping sleeve, and the conical surface of the tapper sleeve is arranged in the elastic clamping sleeve. The design of the elastic clamping sleeve with two expansile ends is adopted in the clamp, the inner diameter of the part is centered when the elastic clamping sleeve expands, the opening end and the inner bottom end of the part are simultaneously clamped, the function of bidirectional clamping is achieved, then the locating and clamping effect of the clamp is enhanced, the clamping and machining deformation of the external circle of the thin-wall sleeve part can be effectively prevented when finish machining is carried out on a lathe and a grinding machine, machining quality is guaranteed and improved, and therefore production efficiency is improved, and machining cost is lowered.
Owner:贵州凯星液力传动机械有限公司
Method for predicting and analyzing cutting deformation of thin-walled structural parts
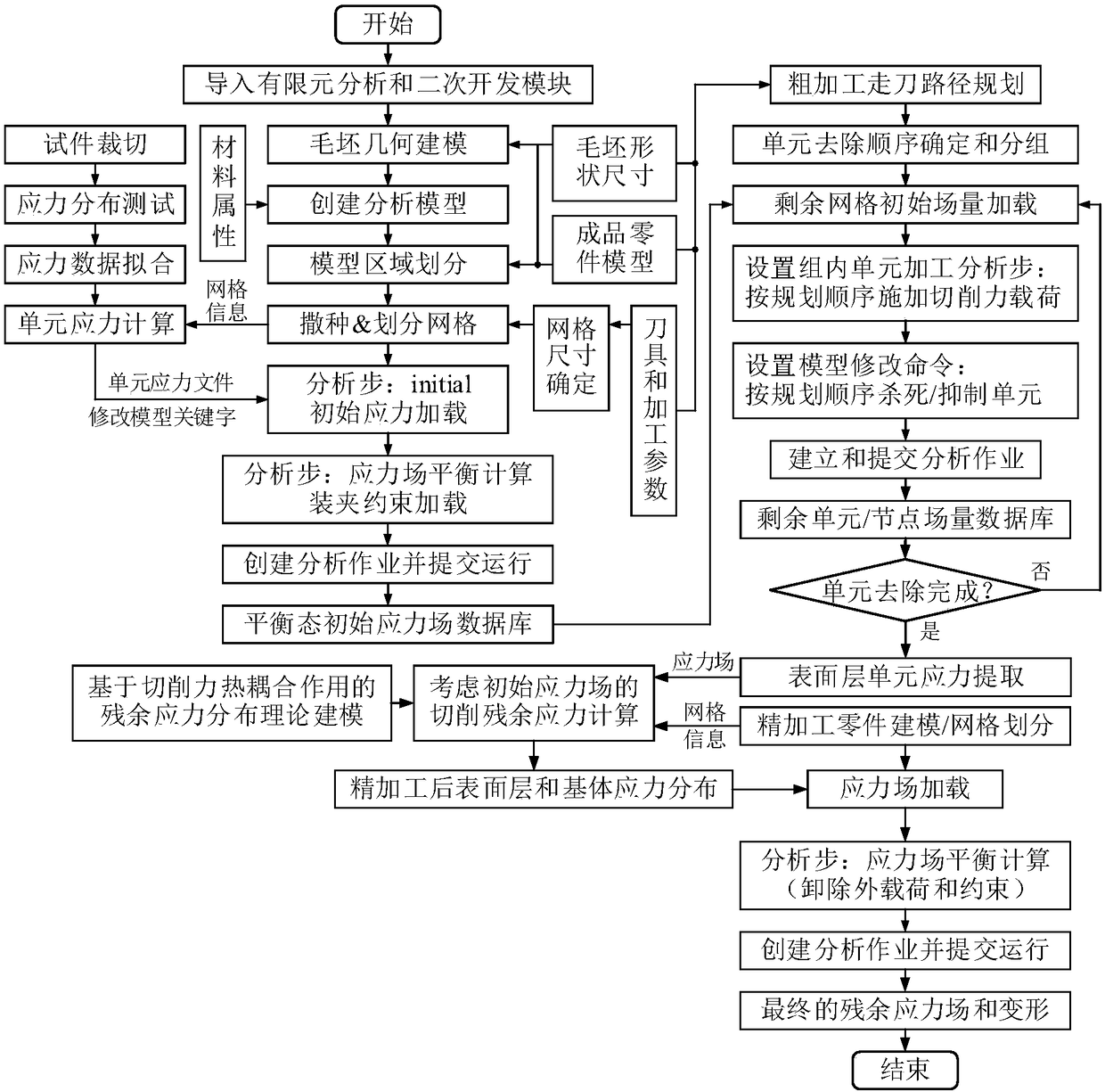
ActiveCN108182325ASimulation results are accurateImprove efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStress distributionSurface layer
The invention discloses a method for predicting and analyzing cutting deformation of thin-walled structural parts. Based on combination of finite element simulation analysis and cutting force thermalcoupling theoretical modeling, the evolution process of blank structural parts with initial residual stress in an internal stress field during the coarse and fine cutting process to better reflect theimpact of body residual stress distribution of the structural parts after coarse processing on cutting residual stress distribution of a finish machining surface layer, and the impact of stress release of the structural parts after completion of the whole cutting process on processing deformation, and finally the prediction of machining residual stress and machining deformation can be achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
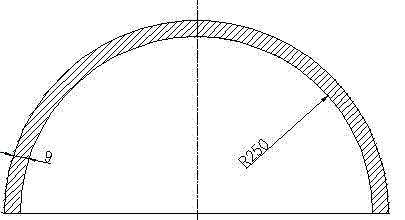
High-precision machining deformation control method for titanium alloy spherical shell
InactiveCN102335754ASolve the deformationSmall elastic deformationTurning machinesMetal working apparatusMachining deformationStress relief
The invention discloses a high-precision machining deformation control method for a titanium alloy spherical shell, which comprises the following steps of: performing rough machining, performing stress relief heat treatment for the first time, performing semi finish machining, performing stress relief heat treatment for the second time, and performing finish machining. During finish machining, a special anti-deformation tool is needed to be designed for the finish machining of a semispherical shell. By a processing technology of stage processing and repeated stress relief heat treatment, the problem that a titanium alloy is deformed in the machining forming process is well solved, yield is 100 percent, and quality meets a design requirement. The problem that a large-diameter thin-wall titanium alloy spherical shell is deformed in the machining process is solved, and production cost is saved; and a workpiece machined and formed by a forming method has ideal performance and size, the yield is 100 percent, and the method is suitable to be popularized to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
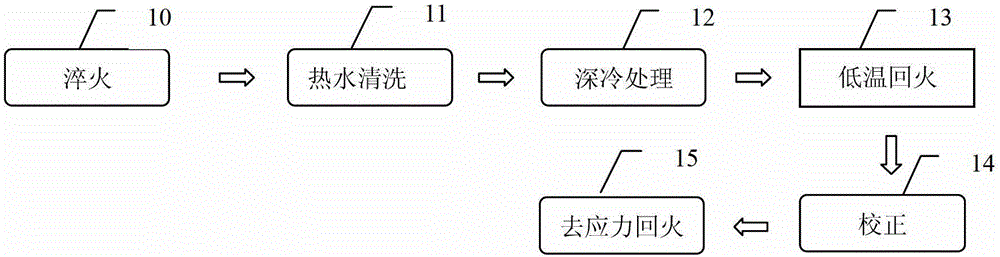
Technology treatment method of machining deformation of long and thin hole shaft type thin-wall part
InactiveCN103331651AImprove rigidityReduce unstable retained austeniteFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCold treatmentTempering
The invention provides a technology treatment method of machining deformation of a long and thin hole shaft type thin-wall part, and aims at providing a technology treatment method of the machining deformation, which is simple in flow, and high in machining precision and yield. The method adopts the following technical scheme that the method comprises the steps that the long and thin hole shaft type thin-wall part after mechanical rough machining and carburizing treatment is subjected to quenching heat treatment, subzero treatment and low temperature tempering treatment. During the quenching heat treatment, the quenching cooling time is 8-11S / mm; when a surface temperature of the part falls to 30-50 DEG C, the part is lifted up from oil; the surface temperature of the part rebounds in air after some time; and when the part is cooled to 30-50 DEG C again, residual oil is rinsed cleanly by hot water greater than or equal to 60 DEG C. During the subzero treatment, the part is transferred to a -70 DEG C to -80 DEG C refrigerator box to be refrigerated for 2-2.5h within 1h after quenching, and then subjected to air cooling for 60-90min till the part reaches a room temperature. During the low temperature tempering treatment, the part is subjected to heat preservation for 3-4h at 160-180 DEG C and the air cooling. The method solves the problem of the machining deformation of the long and thin hole shaft type thin-wall part due to heat treatment stress, grinding stress and the like, and the yield reaches 100%.
Owner:SICHUAN LINGFENG AVIATION HYDRAULIC MACHINERY
Process method for improving rigidity of large titanium alloy ring groove thin-wall part
InactiveCN103203592AIncrease stiffnessSolve problems such as easy deformationMolten stateMachining deformation
The invention discloses a process method for improving rigidity of a large titanium alloy ring groove thin-wall part. The process method includes the steps: (1) roughly machining the overall dimension of a ring groove of the part, precisely machining the internal dimension of the ring groove to meet design requirements, and heating low-melting-point alloy to a molten state; (2) uniformly filling the part to a preset depth; (3) waiting for sufficient cooling of the low-melting-point alloy; (4) inspecting whether the appearance of the part has pouring defects or not; and (5) subsequently machining the part when not detecting abnormal change of the overall dimension of the part. The process method has the advantages that by the aid of auxiliary reinforcement of the low-melting-point alloy, the system rigidity of a workpiece is improved, machining stability of the part is realized, the technical problems of machining deformation, ultra-poor dimension accuracy and the like in the machining process of the large ring groove thin-wall part are solved, the machining quality and the machining efficiency of the part are effectively improved, and the rejection rate of deep groove ring type and deep cavity shell type thin-wall parts in the machining process is reduced, and the process method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:GUIZHOU LIYANG INT MFG
Method for manufacturing large elastic obturating piston ring
The invention belongs to the field of machining process and discloses a method for manufacturing a large elastic obturating piston ring. The method comprises the following steps: (1), turning the outer diameter, inner diameter and thickness of the product through a lathe; (2), drilling a process compression hole through a drilling machine; (3), performing semi-finish turning to the thickness through the lathe; (4), conducting heat treatment; (5), grinding the thickness plane through a grinding machine; (6), cutting an inner circle, an outer circle and an opening through a linear cutting machine; (7), performing external grinding through the grinding machine; and (8), grinding an inner hole through the grinding machine. The invention has the benefits that the method for manufacturing the large elastic obturating piston ring with the pressure-equalizing radial sealing ring structure is devised; the deformation law of roughly machining the contour under the state without radial stress and the influence to the profile tolerance and the opening dimension of the piston ring during the process of finely machining the inner circle and the outer circle under the radial stress state are discovered; the difficult process problems that the structure rigidity of parts is poor, the machining deformation is easily caused, and the machining accuracy of the parts is affected are solved; and the method fills the gap in China.
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
Thin-wall aluminum alloy material tube-shell part cutting processing heat treatment process
InactiveCN104233125AImprove cutting performanceGuaranteed processing deformationSolution treatmentMachine parts
The invention relates to a thin-wall aluminum alloy material tube-shell part cutting processing heat treatment process which comprises the following steps: carrying out quenching and aging solution treatment by adopting a blank; improving the cutting property of a material; relieving stress by adopting aging heat treatment after rough machining; carrying out semi-finishing, and then carrying out the aging heat treatment to further relieve machining stress so as to ensure the stress inside a machined part is completely released; after turning is completed, carrying out low-temperature heat treatment for stabilizing machining size for the last time. Practices indicate that the heat treatment process method can be used for achieving the purposes of eliminating the machining deformation of the part and stabilizing the machining size and ensuring that the size accuracy and form and location tolerance of the part meet the technical requirements.
Owner:无锡市森信精密机械厂
Method for predicting and simulating errors of end-milled surface
ActiveCN104298818ASimple methodEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsRelational modelMachined surface
The invention discloses a method for predicting and simulating errors of an end-milled surface. The method includes the steps that various influence factors causing the machining deformation errors in the end-milling cutting process are analyzed, and a machined-surface single-factor and multi-factor error vector model and an error accumulation vector relation model are built in cooperation with end-milling characteristics; by virtue of a calculation and simulated analysis method, based on a solving method for the machined-surface flatness errors, according to a least regional method, the flatness errors are calculated with a self-adaptation genetic algorithm based on real number encoding, verification is carried out through living example calculation, and contrastive analysis is carried out on the errors and errors of a traditional genetic algorithm. The method is simple and convenient to operate, and the problems that heat stress is caused by cutting heat, residual stress is caused by unloading and loading loads, strict quantitative or logical relationships do not exist between the heat stress and the residual stress, and great difficulty is brought to analysis of the machined surface errors are well solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Machining deformation control method of bushing thin-wall part
ActiveCN104384825ASolve the processing stress problemReduce stressBearing componentsNumerical controlElement analysis
The invention provides a machining deformation control method of a bushing thin-wall part, and aims to provide a deformation control method for effectively controlling the machining deformation of an aluminum alloy thin-wall part, enabling the deformation in a controllable range and having stable and reliable quality. The method is realized through the following technical scheme: the stress finite element analysis and the stress strain state tendency analysis are performed by a finite element analysis model file and a simulation module; the meshing is performed by a partitioning second-order 20-node hexahedral unit to find out specific deformation areas and deflections; a smallest deformation scheme is selected to formulate a process machining scheme; and the heat treatment destressing is added after the semi-finishing for removing the machining stress deformation generated in the semi-finishing, and then, the finishing is performed for controlling the roundness of an outer circle and an inner hole within 0.02 mm. The inner hole and the outer circle are finished by the numerical control turning, so that the wall thickness difference is not bigger than 0.01; and a clamping part is cut off, and an end surface is machined, so that the total length is guaranteed. The method solves the machining difficulties of the bushing thin-wall part; and the pass percent can be improved above 90%.
Owner:PLA NO 5719 FACTORY
Three-dimensional elliptical ultrasonic vibration cutting device adopting longitudinal bending composite mode
InactiveCN108927572AIncreased power output capabilitySimple structureMechanical vibrations separationVibration amplitudePhase difference
The invention discloses a three-dimensional elliptical ultrasonic vibration cutting device adopting a longitudinal bending composite mode. The three-dimensional elliptical ultrasonic vibration cuttingdevice is composed of a pre-tightening bolt, a rear cover plate, a first excitation source, a second excitation source, a middle cover plate, a third excitation source and a flange front cover plate.The three-way excitation sources are driven by input signals with the same frequency, wherein the phase angles of the input signal are different in pairs. By adjusting the voltage and phase difference of driving signals of the three-way excitation sources, a tool nose point of a tool mounted at the output end of the three-dimensional elliptical ultrasonic vibration cutting device obtains spatialelliptic vibration trajectories with different vibration amplitudes and phase differences. According to the three-dimensional elliptical ultrasonic vibration cutting device, the assembly link is less,and mounting and dismounting of a blade are convenient; a flange structure is adopted, and the system stiffness is good; and the effect on the aspect of cutting machining of parts with hard machiningmaterials, weak stiffness and free curved surfaces is remarkable, cutting force and the cutting temperature can be significantly decreased, tool abrasion and machining deformation of the workpiece materials can be significantly reduced, the surface quality and form and position accuracy of the parts are improved, the subsequent machining process is reduced, and then the machining efficiency and economical efficiency are improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU AIRCRAFT EQUIP
Thin-walled bearing ring lathing process
InactiveCN104526284AReduce processing deformationRelieve cutting stressFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesNumerical controlMachining deformation
The invention discloses a thin-walled bearing ring lathing process. The thin-walled bearing ring lathing process includes the following steps of firstly, conducting rough lathing, wherein the outer circle, the inner hole, the ditch and the two end faces of a thin-walled bearing ring part are lathed in a numerical control mode, a balance of 0.3 mm to 0.5 mm is controlled to be reserved for the outer circle, a balance of 0.6 mm to 0.8 mm is reserved for the inner hole, a balance of 0.2 mm to 0.3 mm is reserved for the ditch, and a balance of 0.2 mm to 0.5 mm is reserved for the two end faces; secondly, conducting annealing, wherein the roughly-lathed thin-walled bearing ring part is annealed at a temperature of 650 DEG C to 680 DEG C for 3 hours to 4 hours and then cooled in a furnace till the temperature reaches 180 DEG C to 200 DEG C and cooled outside the furnace through air; thirdly, conducting fine lathing, wherein the outer circle, the inner hole, the ditch and the two end faces of the annealed thin-walled bearing ring part are latched in a numerical control module, and the sizes of the outer circle, the inner hole, the ditch and the two end faces are lathed into the sizes required by grinding. In this way, the machining deformation of a thin-walled bearing ring can be reduced, and the machining accuracy of a product can be ensured.
Owner:CHANGSHU CHANGZHOU BEARING
Method for positioning and homogenizing residual stress of thermal shock compounding
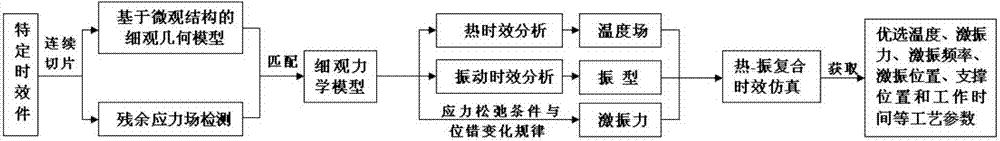
ActiveCN103488850AChange yield limitImprove molecular activitySpecial data processing applicationsMechanical modelsMachining deformation
The invention provides a method for positioning and homogenizing residual stress of thermal shock compounding. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a microscomic geometric model based on a microstructure of a workpiece material; (2) detecting a three-dimensional residual stress field of a workpiece; (3) matching the step (1) according to the step (2) to obtain a microscomic mechanical model; (4) carrying out a thermal aging analysis on the workpiece and establishing a temperature field and residual stress homogenizing relation; (5) carrying out a vibration aging analysis on the workpiece and selecting a suitable vibration mode; (6) determining a reasonable excitation force according to a residual stress relaxation condition and a dislocation changing principle; (7) carrying out simulation on thermal-vibration compounding aging and optimizing technological parameters including thermal aging temperatures, the excitation force, excitation frequencies, excitation positions, supporting positions, working time and the like; and (8) carrying out residual stress homogenization on the workpiece by using the step (7). According to the method provided by the invention, positioning relaxation and comprehensive homogenization of the residual stress of the workpiece are realized so as to obtain the workpiece with small machining deformation, stable service size and long fatigue life.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Experimental device for simulating aircraft wing stringer assembly
InactiveCN102721563AReasonable structurePrecise positioningStructural/machines measurementMachining deformationAirplane
The invention discloses an experimental device for simulating aircraft wing stringer assembly. The experimental device comprises a test table bottom platform, a stringer, skin, and an edge longitudinal positioning device, an edge vertical positioning device, a sliding transverse support force measuring device, a slider transverse positioning device and a sliding vertical clamping device which are arranged on the test table bottom platform and connected with the stringer and the skin. The experimental device has a rational structure, is stable in positioning and can realize the simulation of different machining deformation, clamping positions and clamping force; during the simulation of the aircraft wing stringer assembling process, different machining deformation, different positioning errors, different clamping force and different clamping areas can be simulated by various devices, and the assembling deformation of the stringer when the factors change can be measured, so that the relation between the assembling deformation of the stringer and the variables can be determined, and the law of the aircraft wing stringer assembly can be disclosed. The experimental device for simulating the aircraft wing stringer assembly has the advantages of multiple variable factors and high adaptability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Processing method for stop plate-free split casing
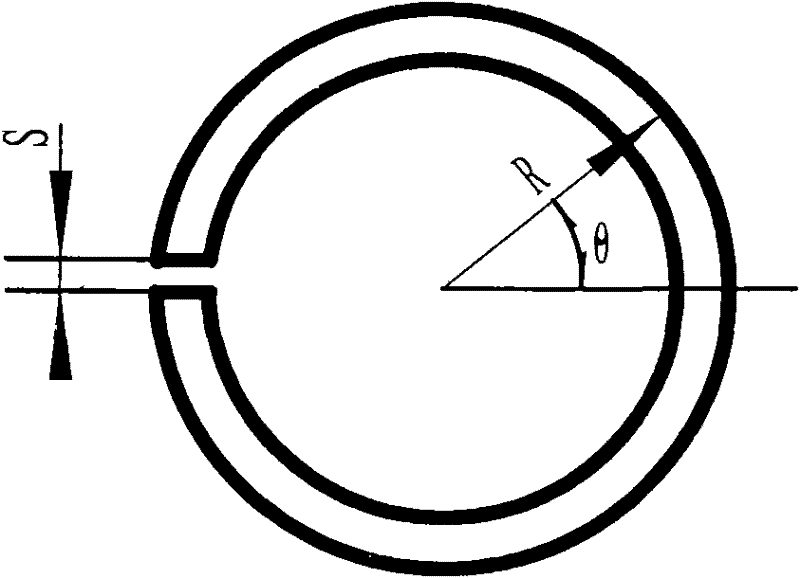
ActiveCN103769816AUniform finishing allowanceReduce processing difficultyOne passMachining deformation
The invention provides a processing method for a stop plate-free split casing. The processing method for the stop plate-free split casing comprises the following steps: milling the external profile section of a part into two semicircles with offset at a roughing stage; turning an internal profile section into a circle; performing finish milling on the back face of the junction surface of the casing to meet the set tolerance requirements; performing linear cutting along the junction surface of the casing to cut off the casing and performing the finish milling on the junction surface to meet the set tolerance requirements, and connecting the two half casings by using bolts at the junction surface of the casing to finish reassembly of the casing; performing finishing on the internal profile and the external profile of the casing. After roughing, the non-uniform wall thickness of the casing is formed; after the casing is cut off by the linear cutting, the finish milling is performed on the junction surface and the casing is reassembled, uniform finishing allowance can be obtained by the external profile of the casing, and the uniformization of the allowance of the external profile of the casing is realized, and therefore, the processing difficulty is lowered; the finishing of the external profile can be finished by one-pass, so that machining deformation is reduced, and the machining efficiency is improved.
Owner:AECC AVIATION POWER CO LTD
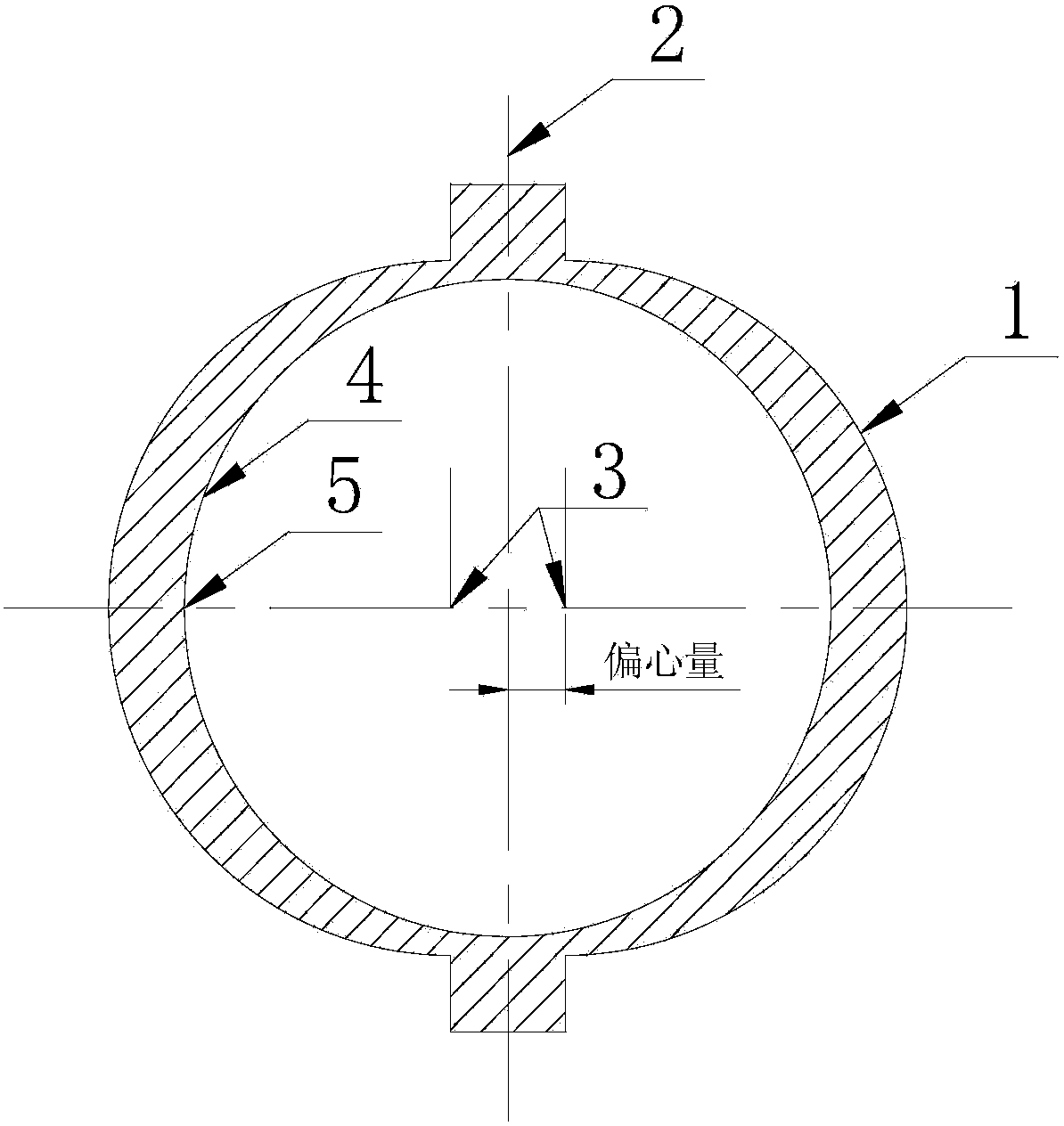
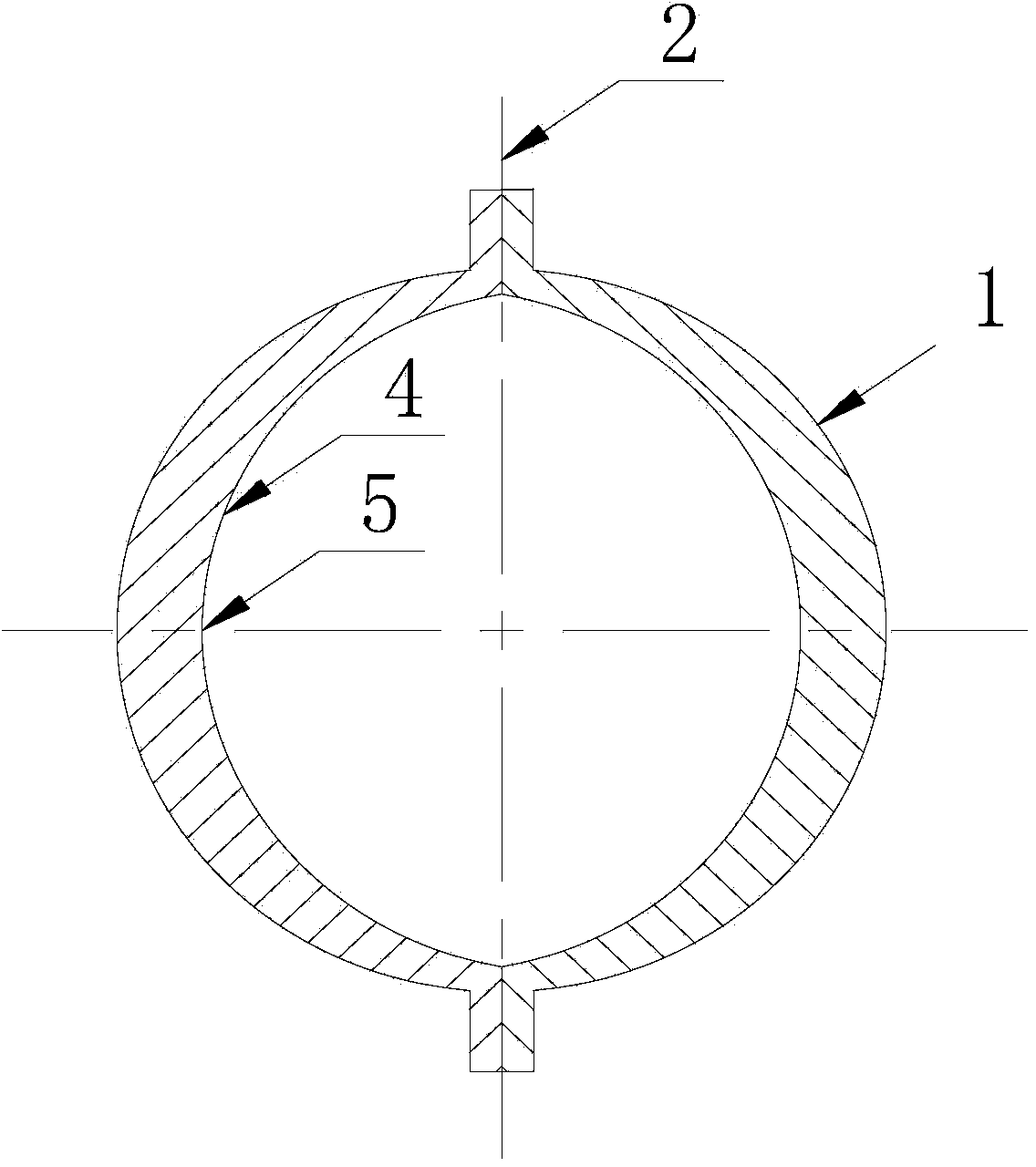
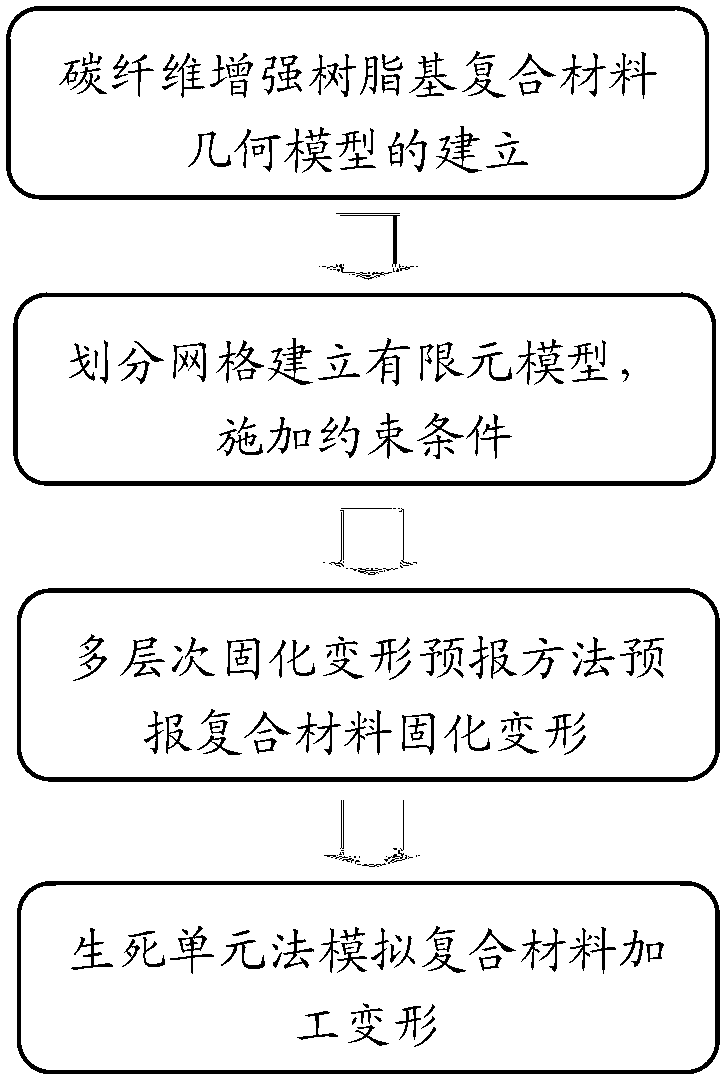
Simulation method for machining deformation of carbon-fiber-reinforced resin matrix composite
InactiveCN103294862ASolve the real problemEasy to masterSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelCarbon fibers
The invention provides a simulation method for machining deformation of carbon-fiber-reinforced resin matrix composite. The method includes: a, inputting modeling parameters in ANSYS software to build a geometric model; b, meshing the geometric model built in step a by a solid 185 unit, building a finite element model, and limiting the finite element model; c, simulating an autoclave process, calculating a solidification deformation value of the composite, and extracting a stress and strain distribution cloud graph; d, simulating a composite machining process by a method of killing or activating element to obtain machining deformation of the machined composite; and e, calculating the machining deformation value of the machined composite. The method has the advantages that simulation of accurate deformation prediction for the machining deformation of the carbon-fiber-reinforced resin matrix composite is realized, and the practical problems in composites engineering application are solved. The method is simple to operate and convenient to use. The software platform ANSYS is used, so that the method is well compatible and is convenient for technicians to master and use.
Owner:SHANGHAI AIRCRAFT MFG +1
Method for manufacturing multi-core MgB2 superconductive wires through extrusion technology
ActiveCN104091651AImprove compactnessHigh yield strengthCable/conductor manufactureComposite strengthMachining deformation
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing multi-core MgB2 superconductive wires through the extrusion technology. The method includes the steps that first, precursor powder is prepared; second, the precursor powder is installed in a pipe to prepare a primary complex, and single-core wires are obtained through drawing machining; third, the precursor powder is installed in a pipe to prepare a secondary complex; fourth, the secondary complex processed through pre-heating seal welding is extruded, and multi-core rods are obtained; fifth, the multi-core rods are stripped and drawn to obtain multi-core wires, the multi-core wires are subjected to heat treatment, and then the multi-core MgB2 superconductive wires are obtained. According to the method, on the basis of a traditional power pipe-installing technology, a large single-pass machining deformation amount is adopted for manufacturing the multi-core MgB2 superconductive wires, in other words, the extrusion technology is adopted for manufacturing the multi-core MgB2 superconductive wires, because the secondary complex is in a very favorable three-dimensional stress state in extrusion, good metallurgical bonding will be achieved between different metal interfaces in the secondary complex along with the large extrusion deformation amount, the manufactured multi-core rods are high in composite strength, and the compactness and the yield strength of the multi-core MgB2 superconductive wires can be significantly improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
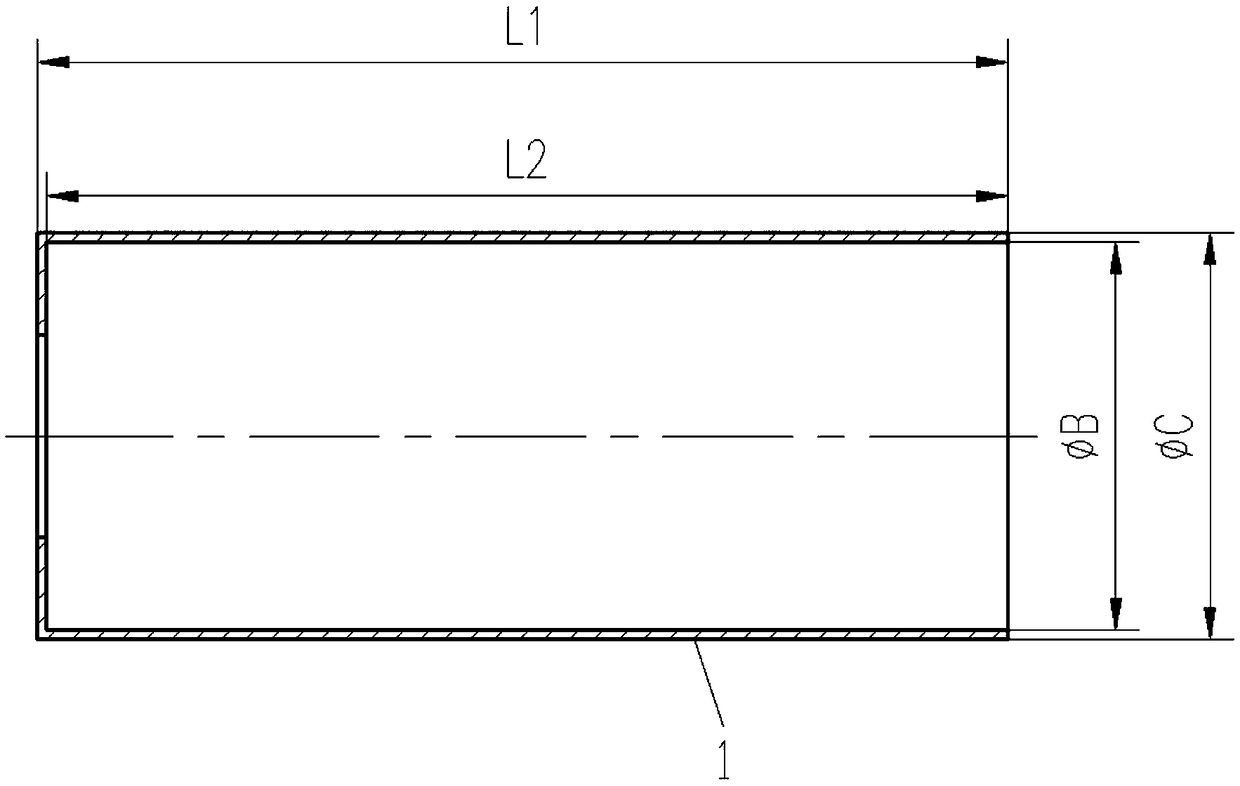
Machining method of high-precision deep and long hole thin-walled sleeve part
The invention provides a machining method of a high-precision deep and long hole thin-walled sleeve part. The machining method comprises the following steps that a rod is clamped and subjected to rough-machining forming, the machining allowance is reserved, and a process chuck is reserved; a roughly-machined workpiece is subjected to thermal treatment aging; and the process chuck of the workpieceis clamped by a lathe, finish machining of the workpiece is completed during primary clamping machining according to a workpiece drawing, and finish machining is divided into the following working steps that a core shaft, a lining and a screw are manufactured; the process chuck is clamped on the lathe, the core shaft is crammed into roughly-machined inner holes of the workpiece, and an outer circle of the part is machined to the required dimension; the screw is screwed into a core shaft threaded hole, and the core shaft is taken out of the workpiece; the lining sleeves the machined outer circle of the workpiece, the outer end face of the workpiece is machined, and the large and small inner holes and the bottom face are bored; tool setting is conducted from the bottom face, the outer end face of the workpiece is machined, and the length dimension L2 of the workpiece is ensured; and the workpiece is cut off, and the total length L1 of the workpiece is ensured. According to the machiningmethod of the high-precision deep and long hole thin-walled sleeve part, the rigidity of the part is improved, machining deformation of the part is reduced, vibration during thin-walled part machiningis reduced, and the machining quality and surface roughness are improved.
Owner:临沂产业研究院有限公司
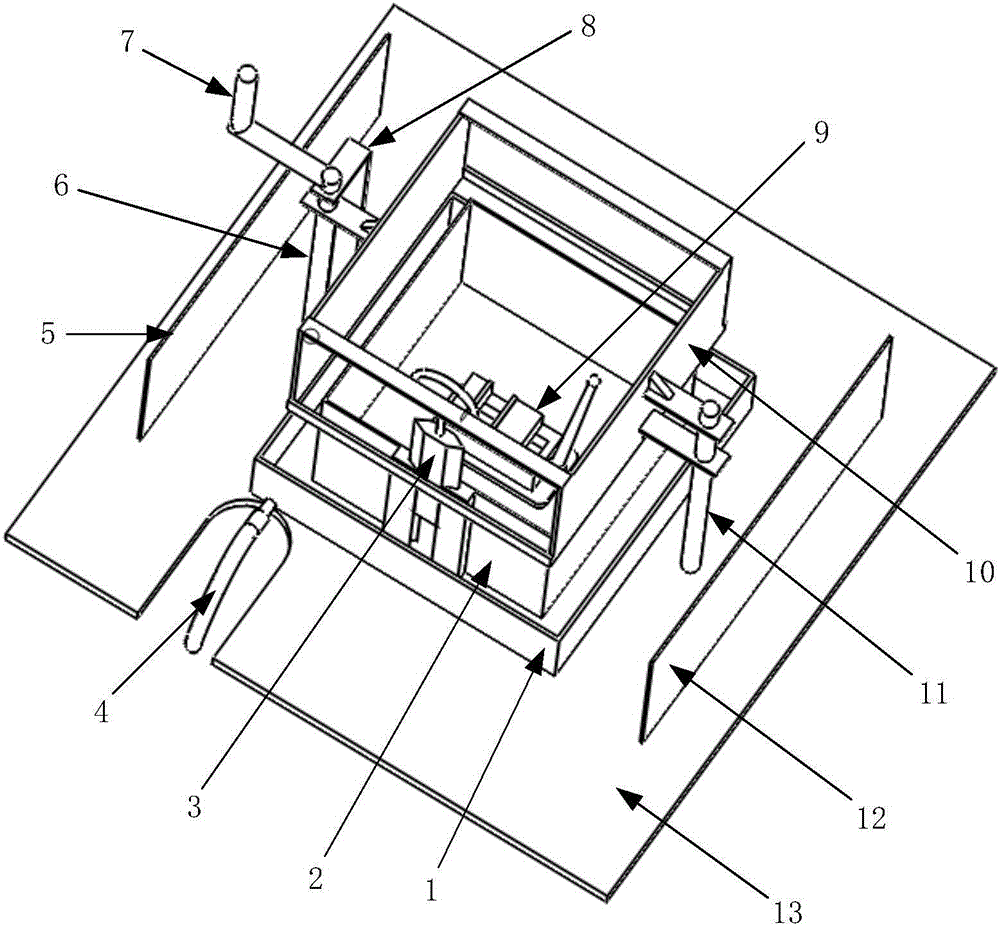
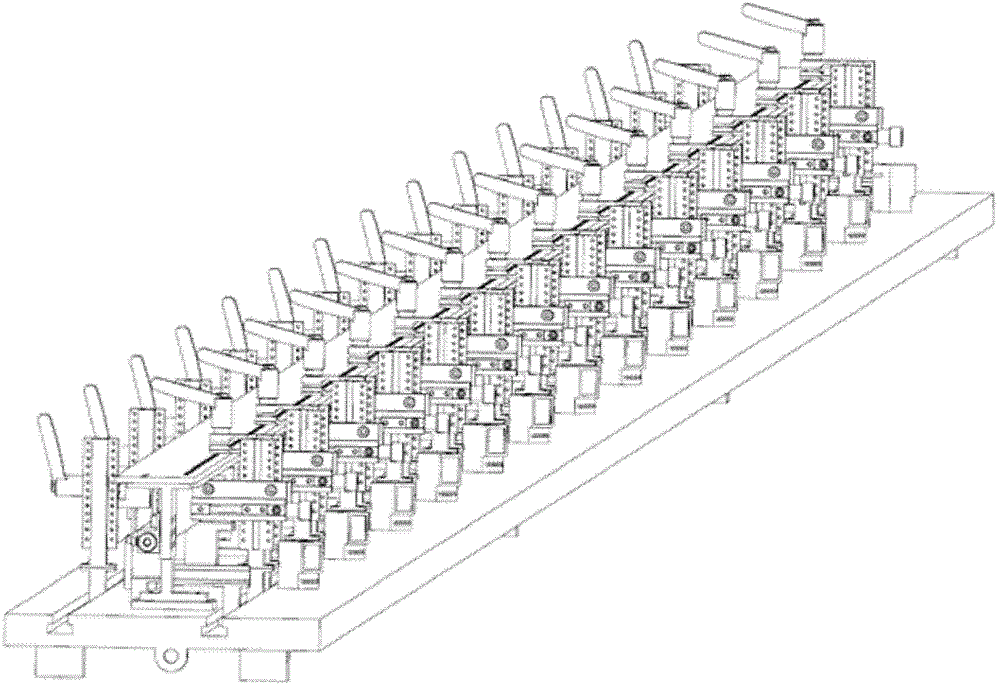
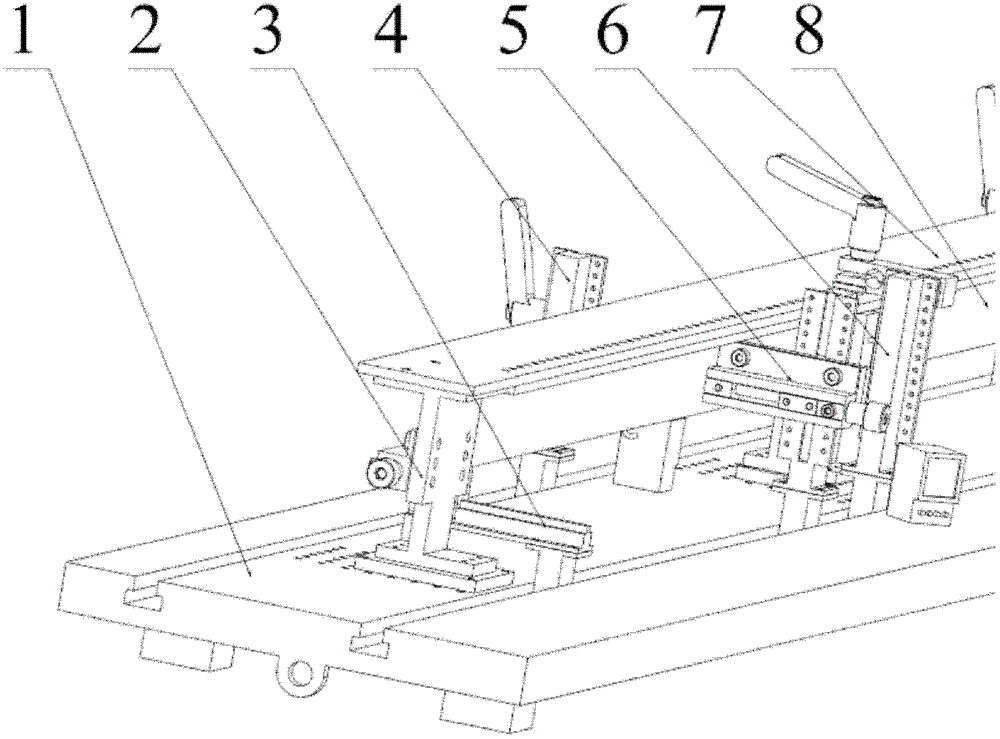
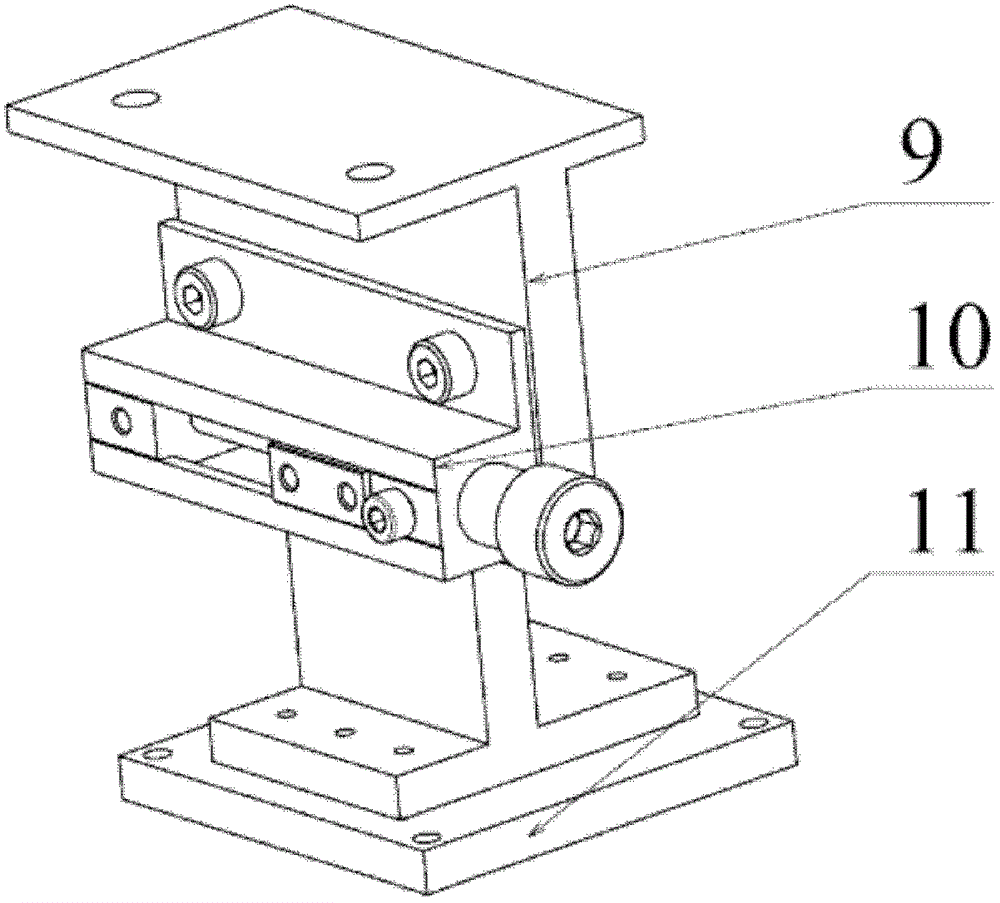
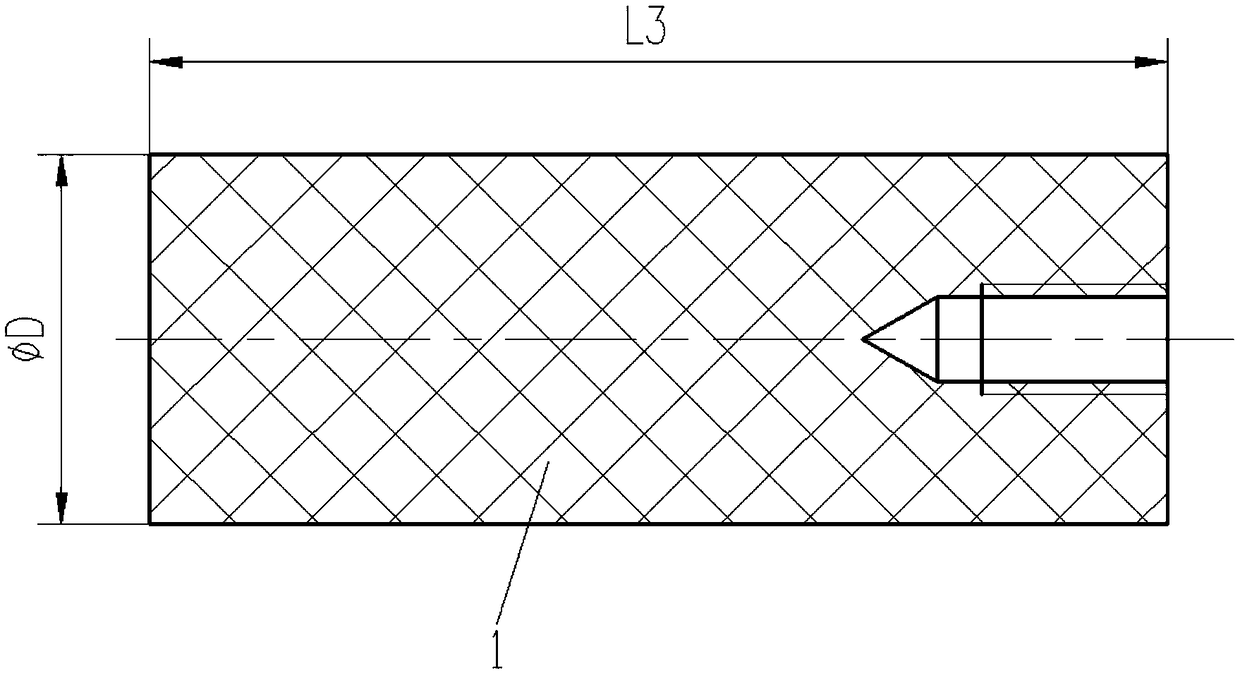
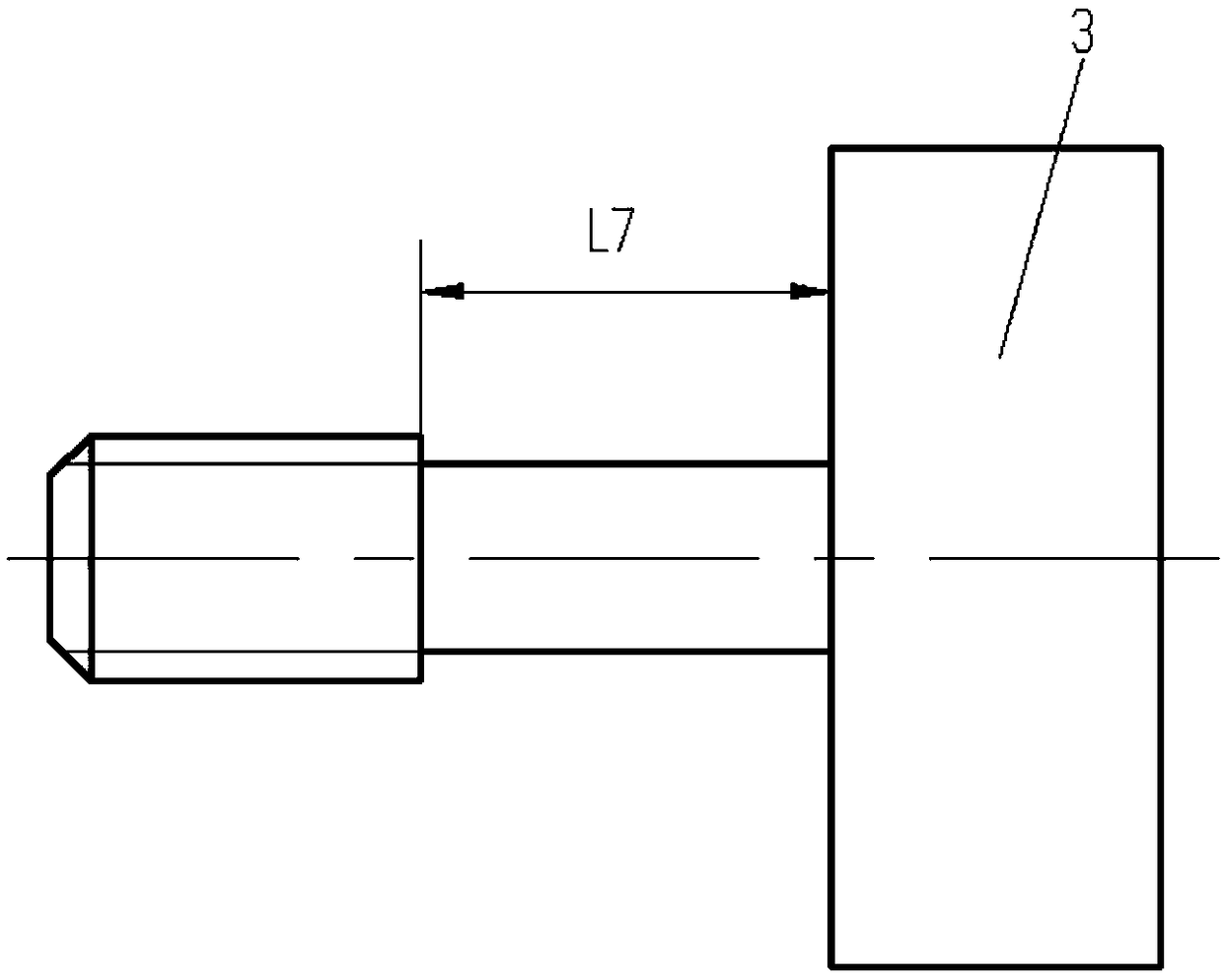
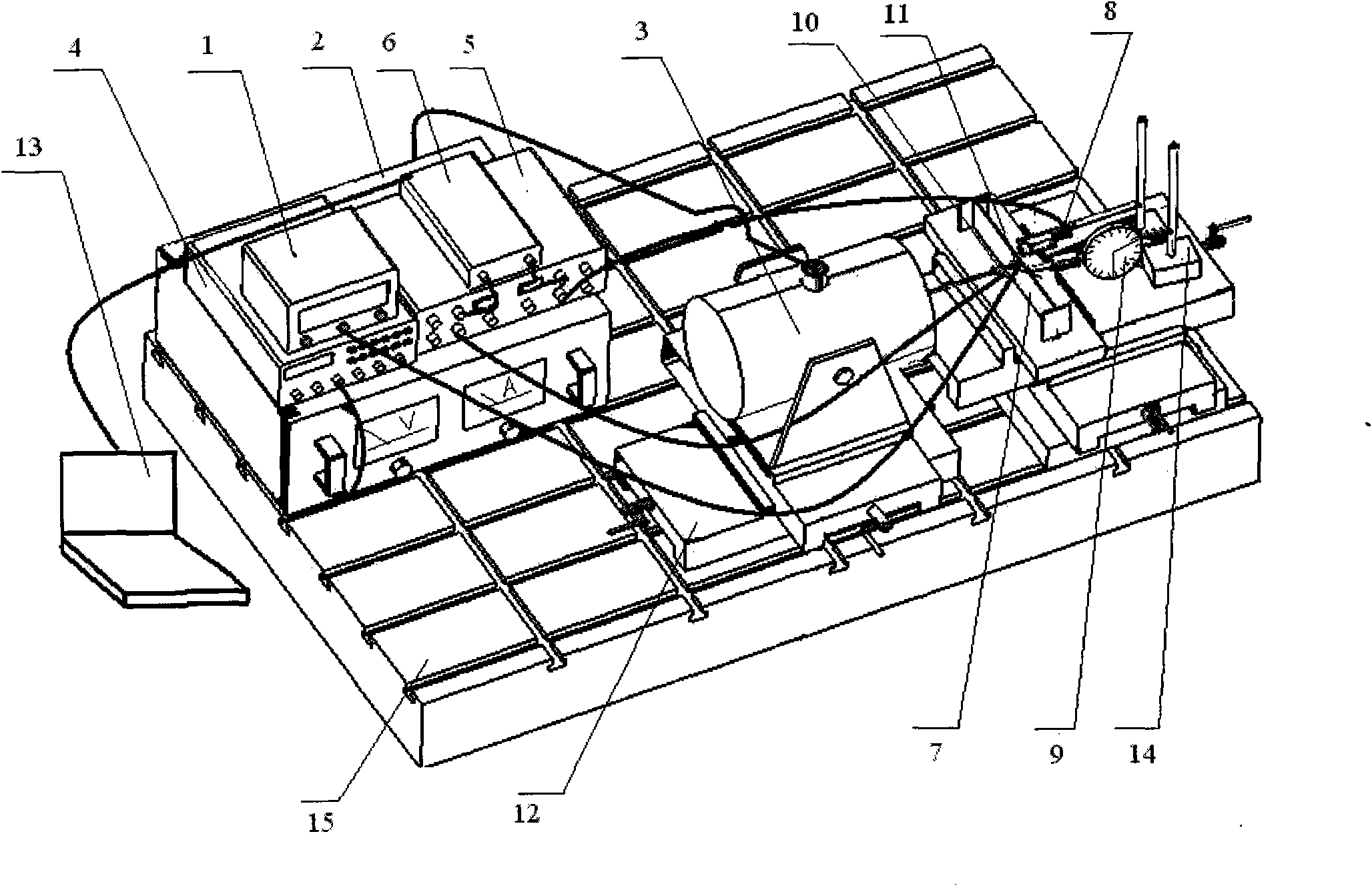
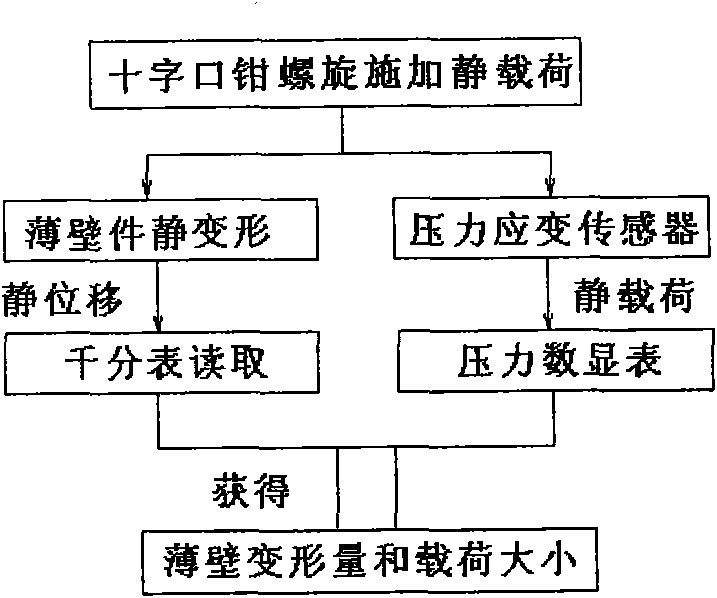
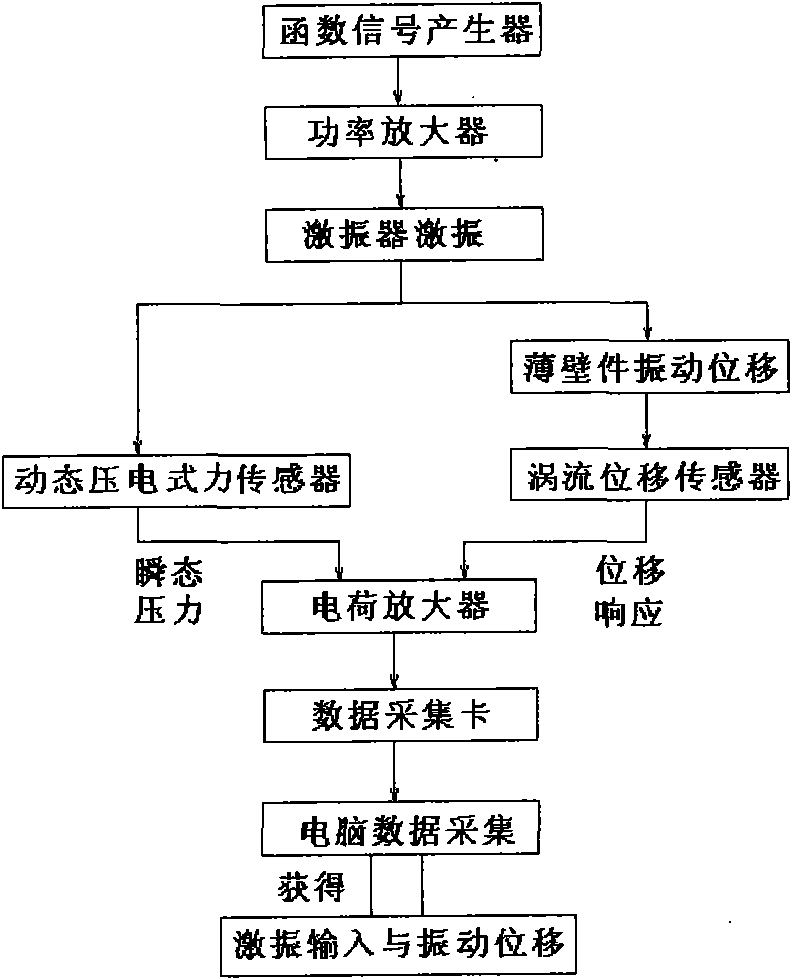
Measure apparatus of machining deformation and dynamic response for thin-wall part of aircraft
A measure apparatus of machining deformation and dynamic response for thin-wall parts of aircraft comprises a pressure signal digital display meter, a power amplifier, a vibration exciter, a function generator, a charge amplifier, a signal collection card, a thin-wall part to be measured, a non-contact eddy current displacement sensor, a dial indicator, a dynamic piezoelectric force sensor, a static pressure sensor, a cross flat-nose pliers assembly, a data acquisition software, a computer system, a magnetic base and an experiment platform. In the measure apparatus, the cross flat-nose pliersand the vibration exciter generate static and dynamic load force; the dial indicator and the dynamic piezoelectric force sensor measure the deformation and dynamic response of the part; the exciting force with required frequency is obtained through the function generator and the power amplifier to simulate the cutting force. The measure apparatus provides a simulation environment and an experiment platform for the parameters selection and optimization during machining process of thin-wall parts. The invention has a good practical value and broad application prospects in fields of high precisemilling study and detection technology.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Milling parameter optimization method for thin-walled workpiece
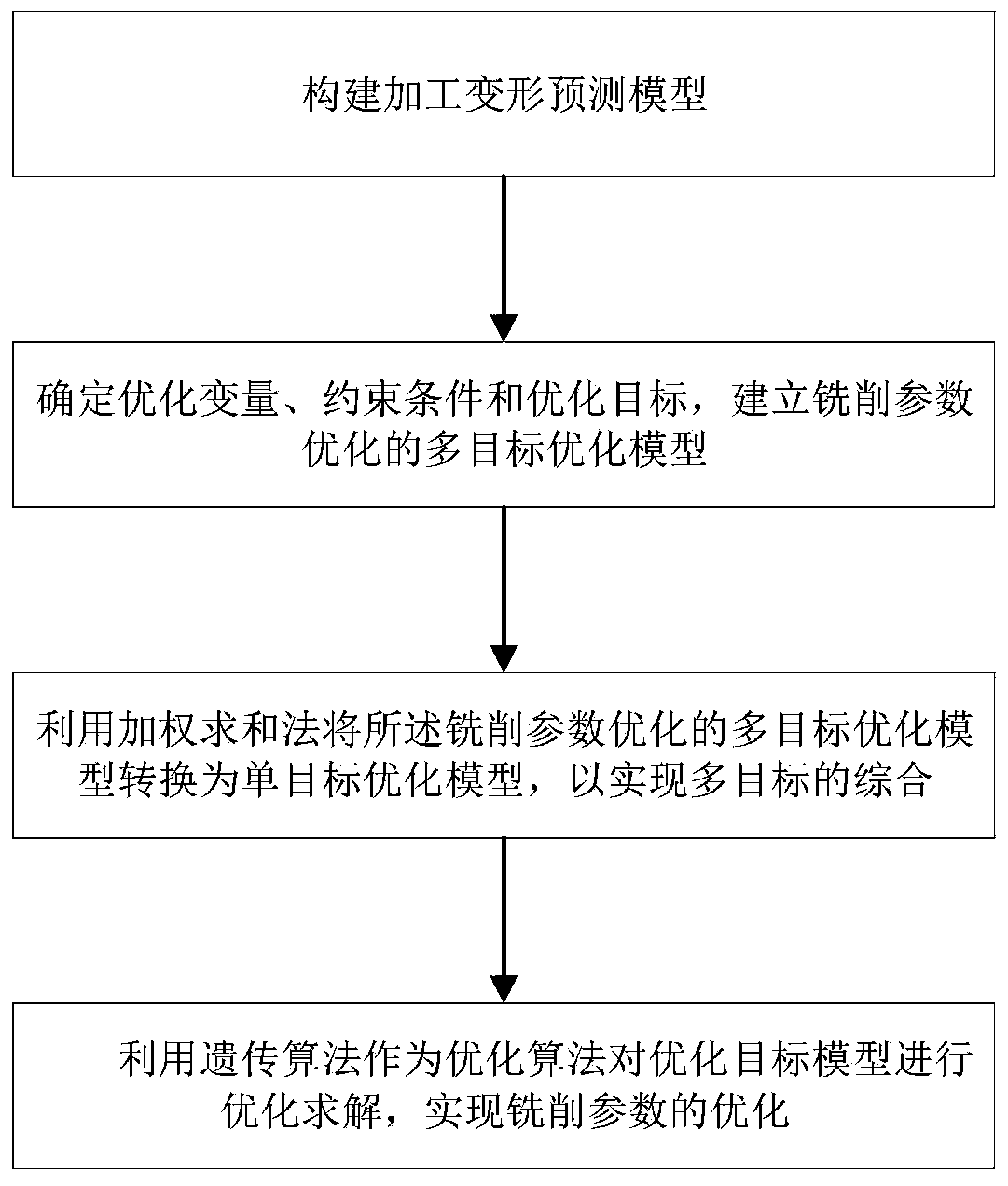
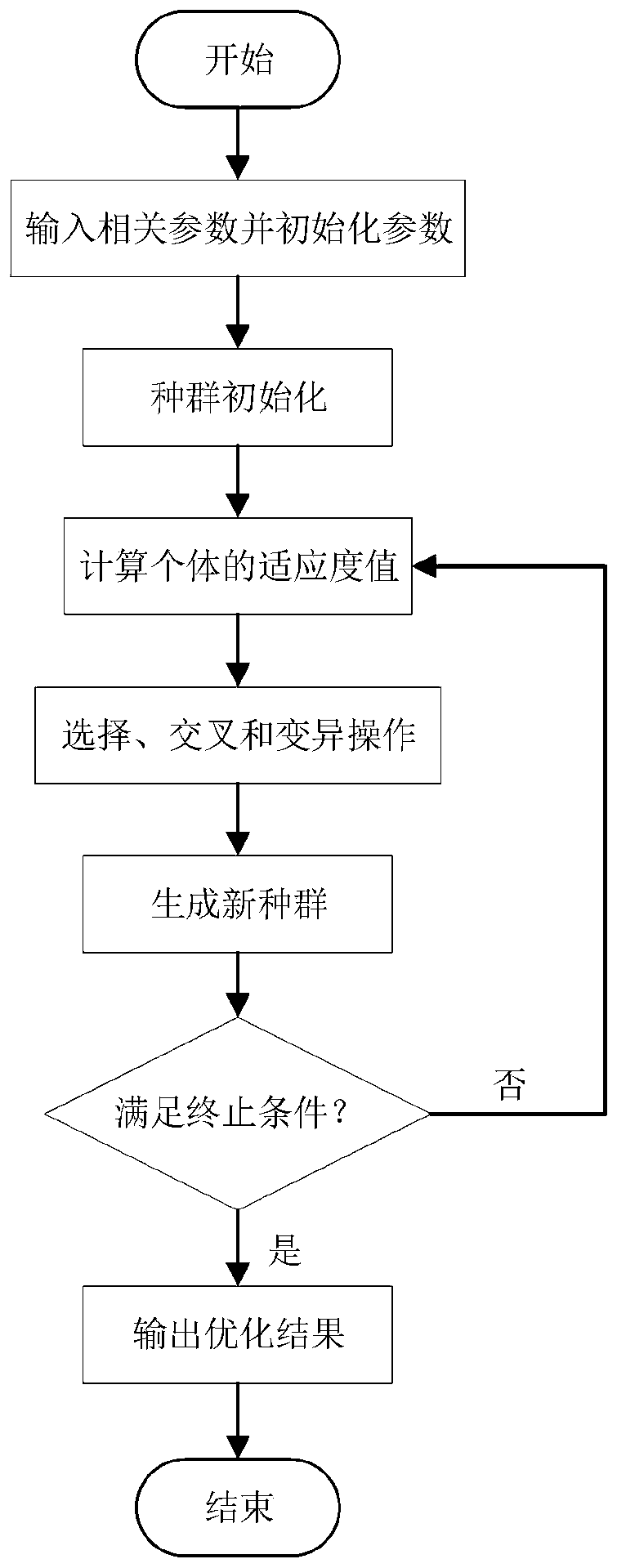
PendingCN111563301AImprove search capabilitiesGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMachining deformationGenetics algorithms
The invention discloses a milling parameter optimization method for a thin-walled workpiece. The method comprises the steps that firstly, creating a BP neural network to complete establishment of a workpiece maximum machining deformation prediction model; establishing a multi-objective optimization model of milling parameter optimization by taking a machine tool, a cutter and machining deformationas constraints, taking machining time and cutting energy consumption as optimization objectives and taking a cutting speed, a feed rate of each tooth, an axial cutting depth and a radial cutting width as optimization variables; converting the milling parameter optimized multi-objective optimization model into a single-objective optimization model by using a weighted summation method so as to realize multi-objective integration; and using a genetic algorithm as an optimization algorithm to carry out optimization solution on the optimization target model to optimize milling parameters. The influence of machining deformation of the thin-walled workpiece on an optimization result is considered while the machining time and the cutting energy consumption are taken as optimization objectives tooptimize the cutting parameters, so that the optimization result is more accurate, the problem of conservative milling machining parameters of the thin-walled workpiece at present is solved, and machining efficiency of the workpiece is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
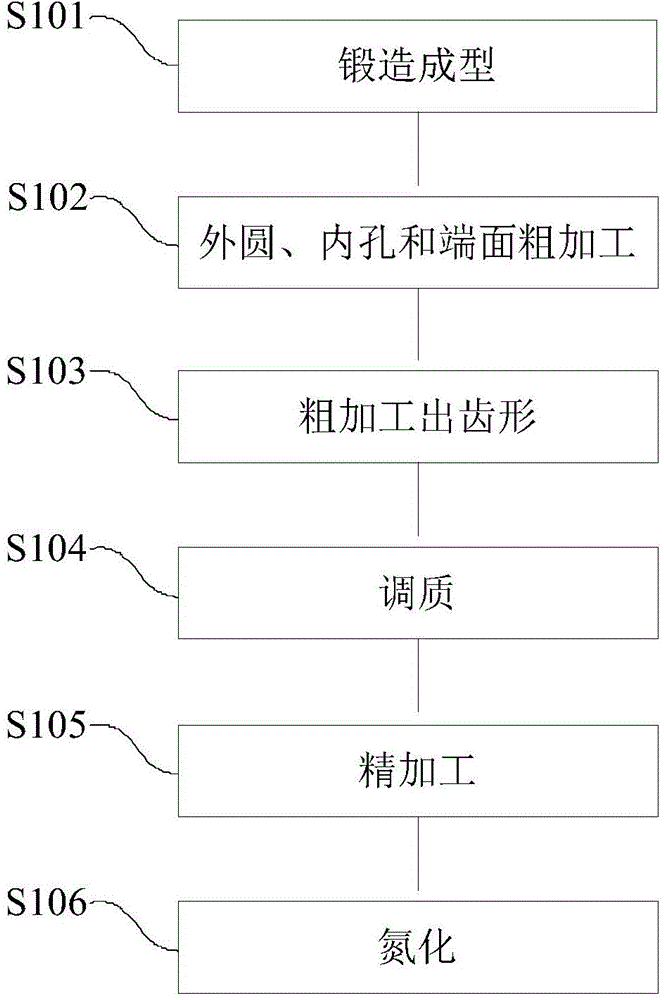
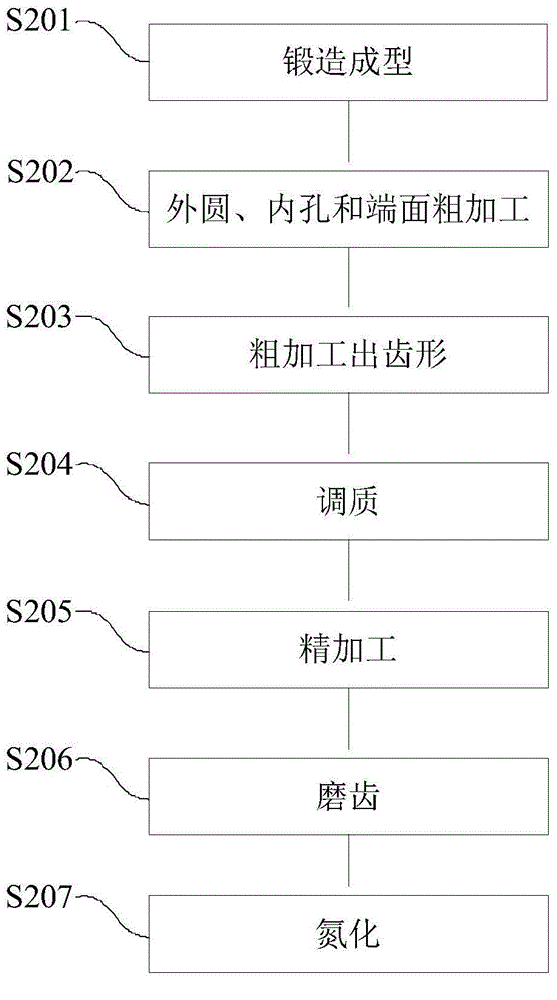
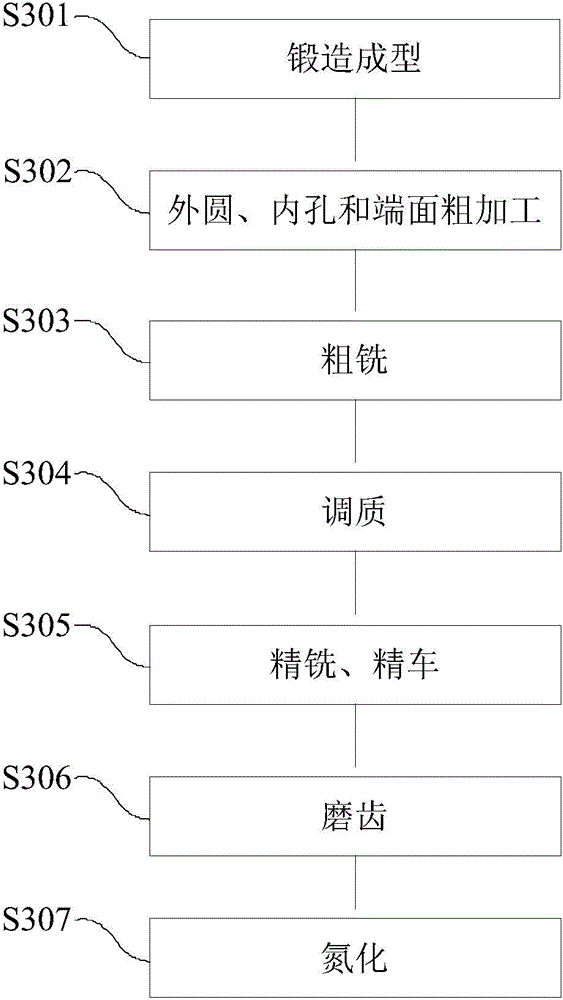
Method for machining large inner gear ring of wind turbine gear box
The invention discloses a method for machining a large inner gear ring of a wind turbine gear box. The method includes the steps that 1, an inner gear ring blank is formed in a forging forming mode according to the specification and forging standard of the inner gear ring; 2, outer circle rough machining, inner hole rough machining and end face rough machining are conducted on the inner gear ring blank, the outer circle, an inner hole and an end face are primarily formed, and allowance is reserved; 3, rough machining is conducted on the inner gear ring obtained after outer circle rough machining, inner hole rough machining and end face rough machining are conducted to enable the inner gear ring to be in a tooth shape; 4, quenching and tempering are conducted on the tooth-shaped inner gear ring obtained after rough machining is conducted; 5, the profile and the inner hole of the inner gear ring obtained after quenching and tempering are machined through finish machining; 6, nitrogen treatment is conducted on the inner gear ring obtained after finishing machining is conducted. By means of the method for machining the large inner gear ring of the wind turbine gear box, quenching and tempering are conducted on the inner gear ring which is machined to be in the tooth shape through rough machining, the quenching and tempering effects on the tooth top, the tooth root and the tooth surface are the same, the uneven quenching and tempering effect caused by the limited quenching and tempering hardenability is avoided, and the comprehensive mechanical performance of the interior of the inner gear ring is improved; meanwhile, working allowance of follow-up finishing machining is lowered, and machining deformation is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING GEARBOX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com