Patents
Literature
16526 results about "Phase difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phase Difference. Definition: The phase difference between the two electrical quantities is defined as the angular phase difference between the maximum possible value of the two alternating quantities having the same frequency.
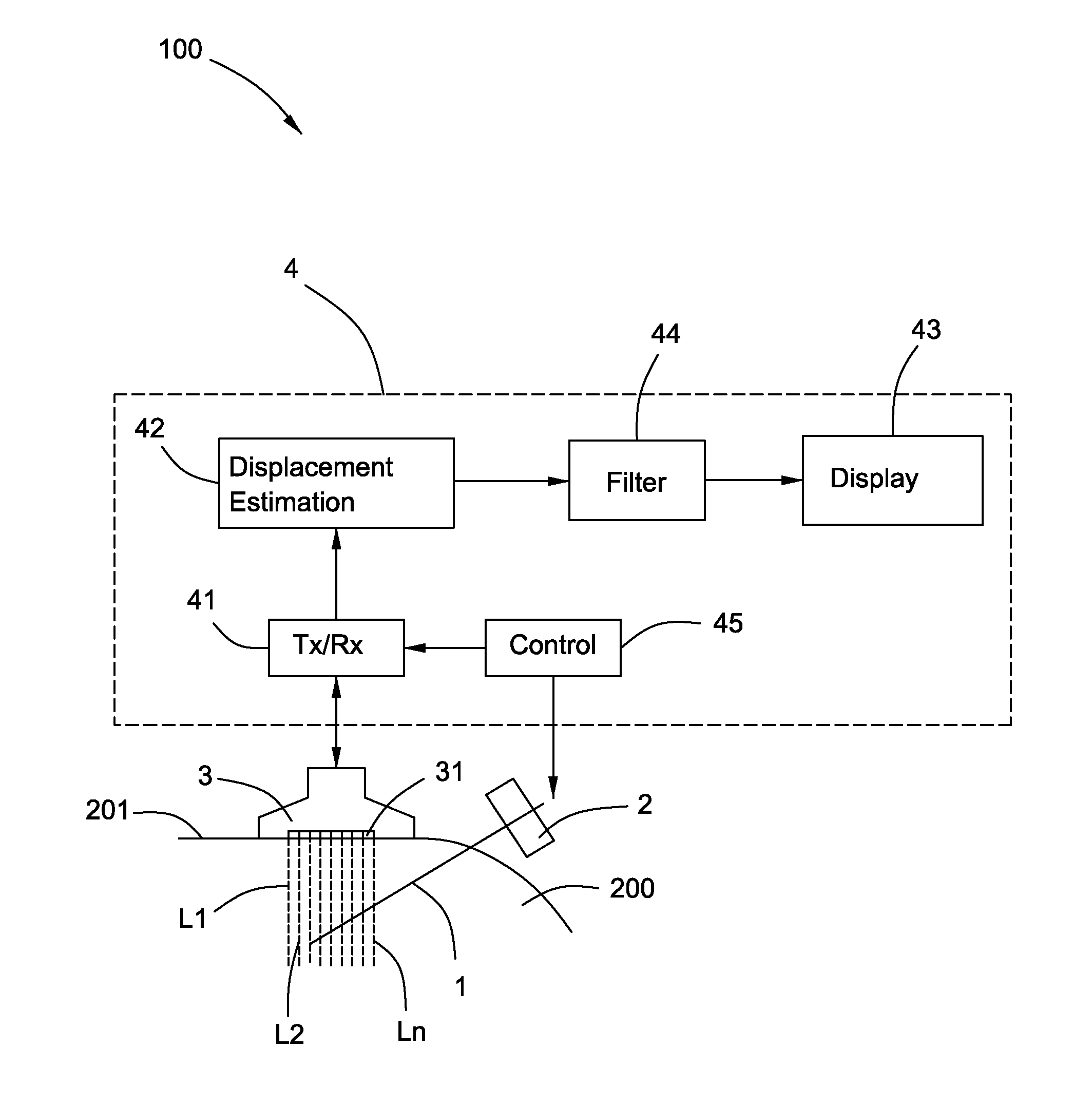
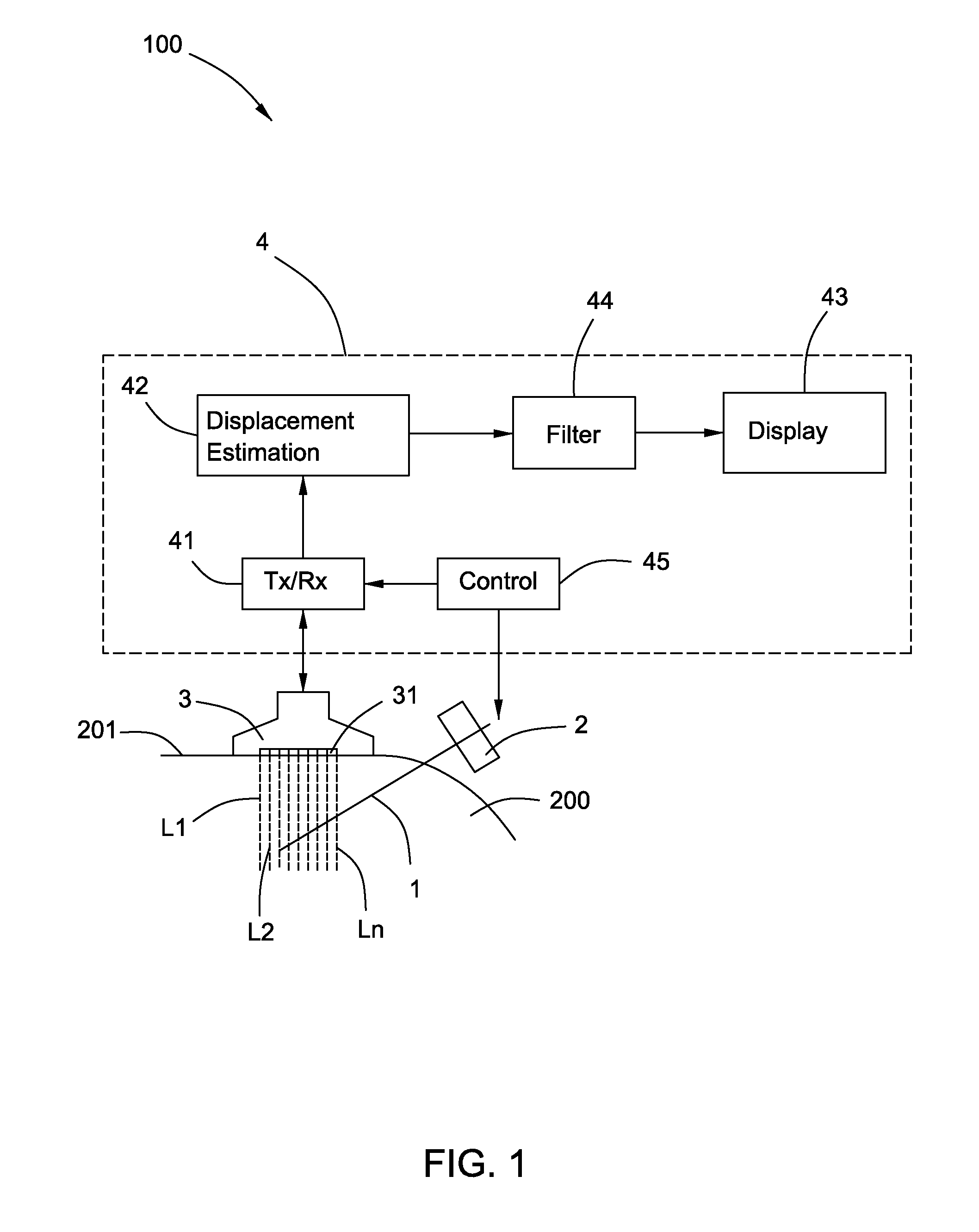
Ultrasonic needle guiding apparatus, method and system
InactiveUS20130158390A1Organ movement/changes detectionSurgical needlesPhase differenceDisplay device
An apparatus is provided. The apparatus comprises a vibrator configured to vibrate a needle, an ultrasonic scanhead configured to transmit ultrasonic pulses and to receive return signals, and an ultrasonic system coupled to the ultrasonic scanhead. The ultrasonic system comprises a transmitter and receiver module coupled to the ultrasonic scanhead, a displacement estimation module coupled to the transmitter and receiver module, and a display coupled to the displacement estimation module. The transmitter and receiver module is configured to supply energizing pulses to the ultrasonic scanhead to transmit the ultrasonic pulses and to receive electrical signals produced by the ultrasonic scanhead according to the return signals. The displacement estimation module is configured to calculate motion displacements based on phase differences of the electrical signals. The display is configured to display an image according to the motion displacements.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
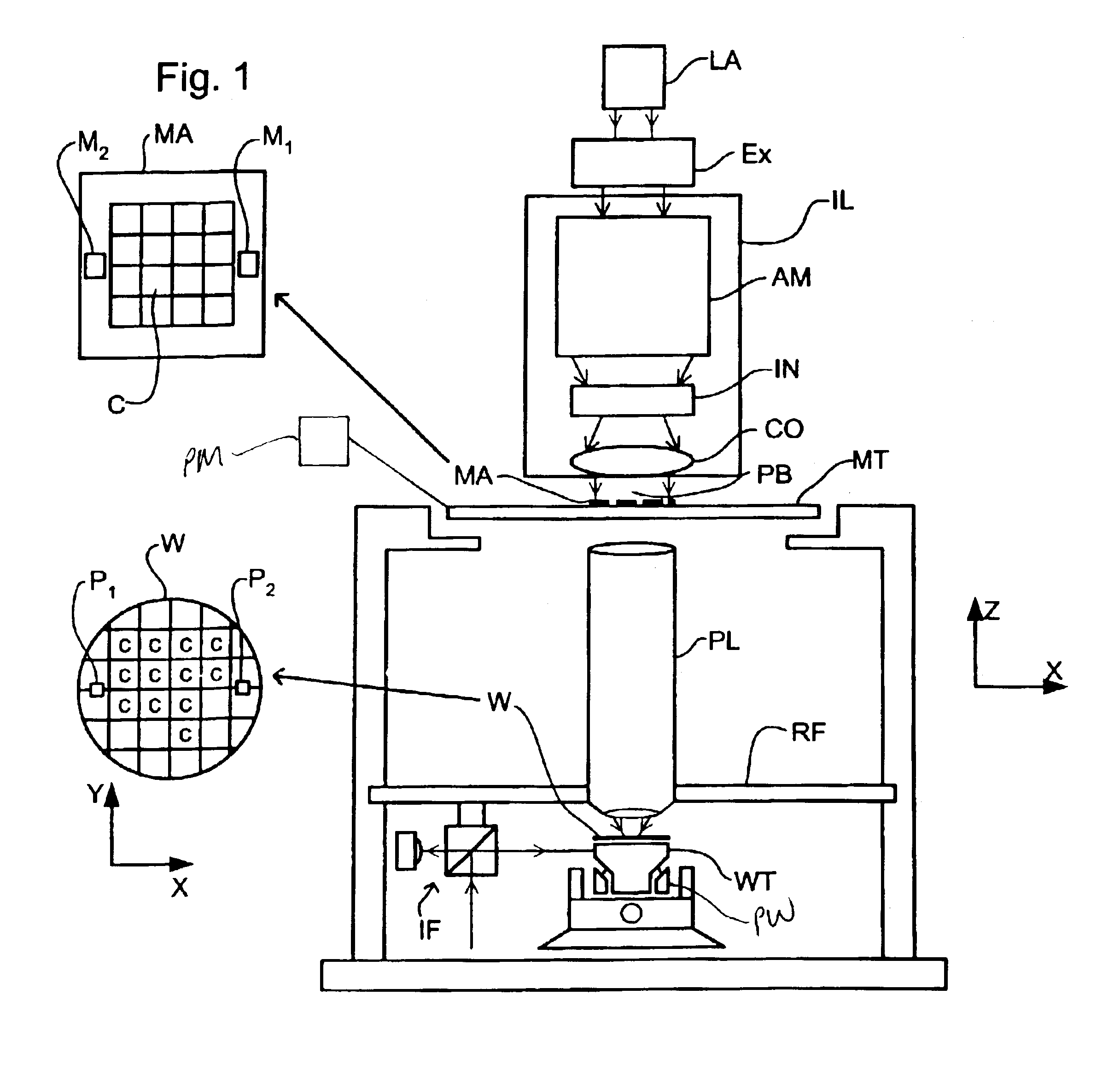
Lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
InactiveUS6961116B2Fine positioning informationLarge capture rangeDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsDiffraction orderPhase difference
An alignment system uses a self-referencing interferometer that produces two overlapping and relatively rotated images of an alignment markers. Detectors detect intensities in a pupil plane where Fourier transforms of the images are caused to interfere. The positional information is derived from the phase difference between diffraction orders of the two images which manifests as intensity variations in the interfered orders. Asymmetry can also be measured by measuring intensities at two positions either side of a diffraction order.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
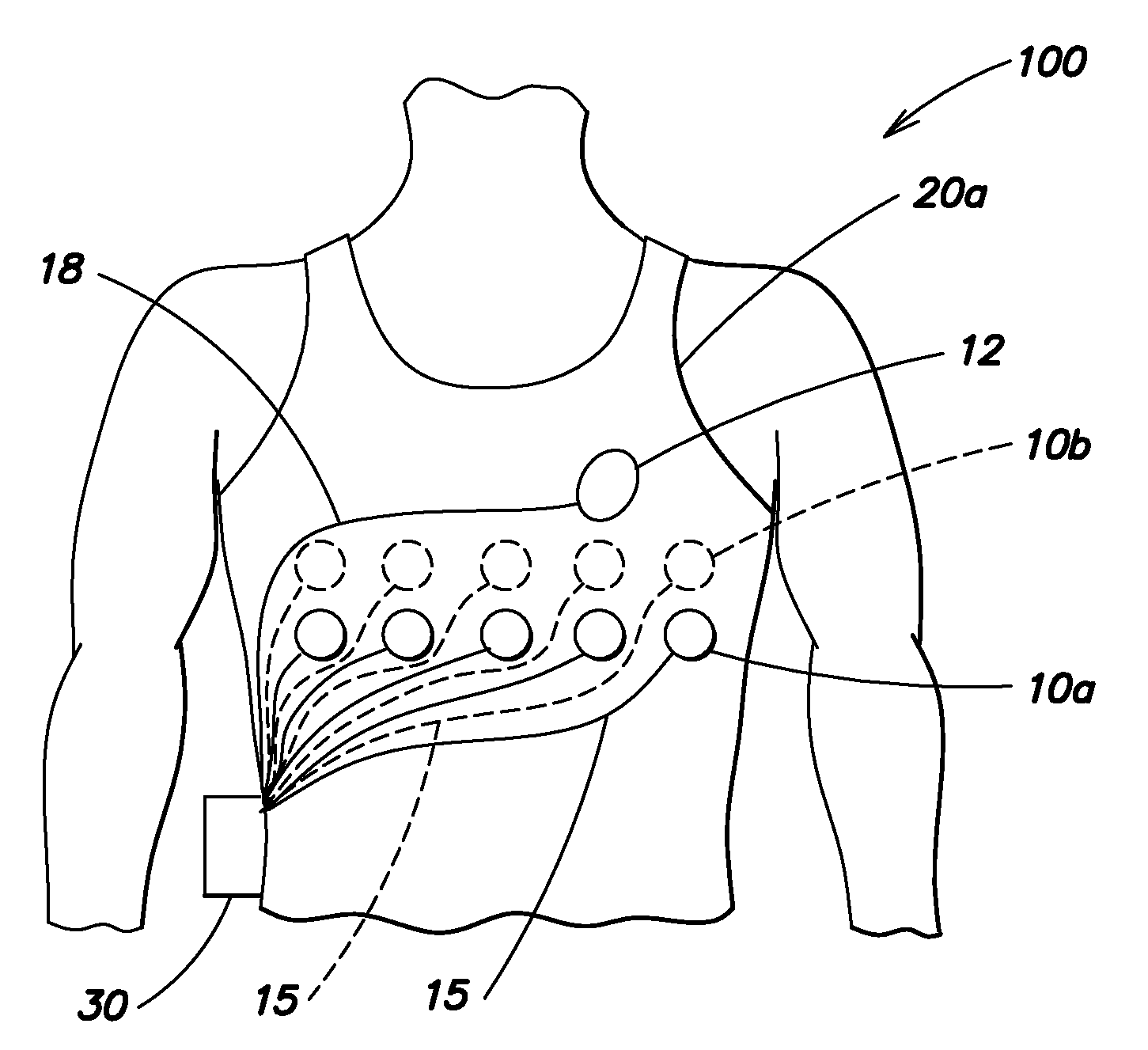
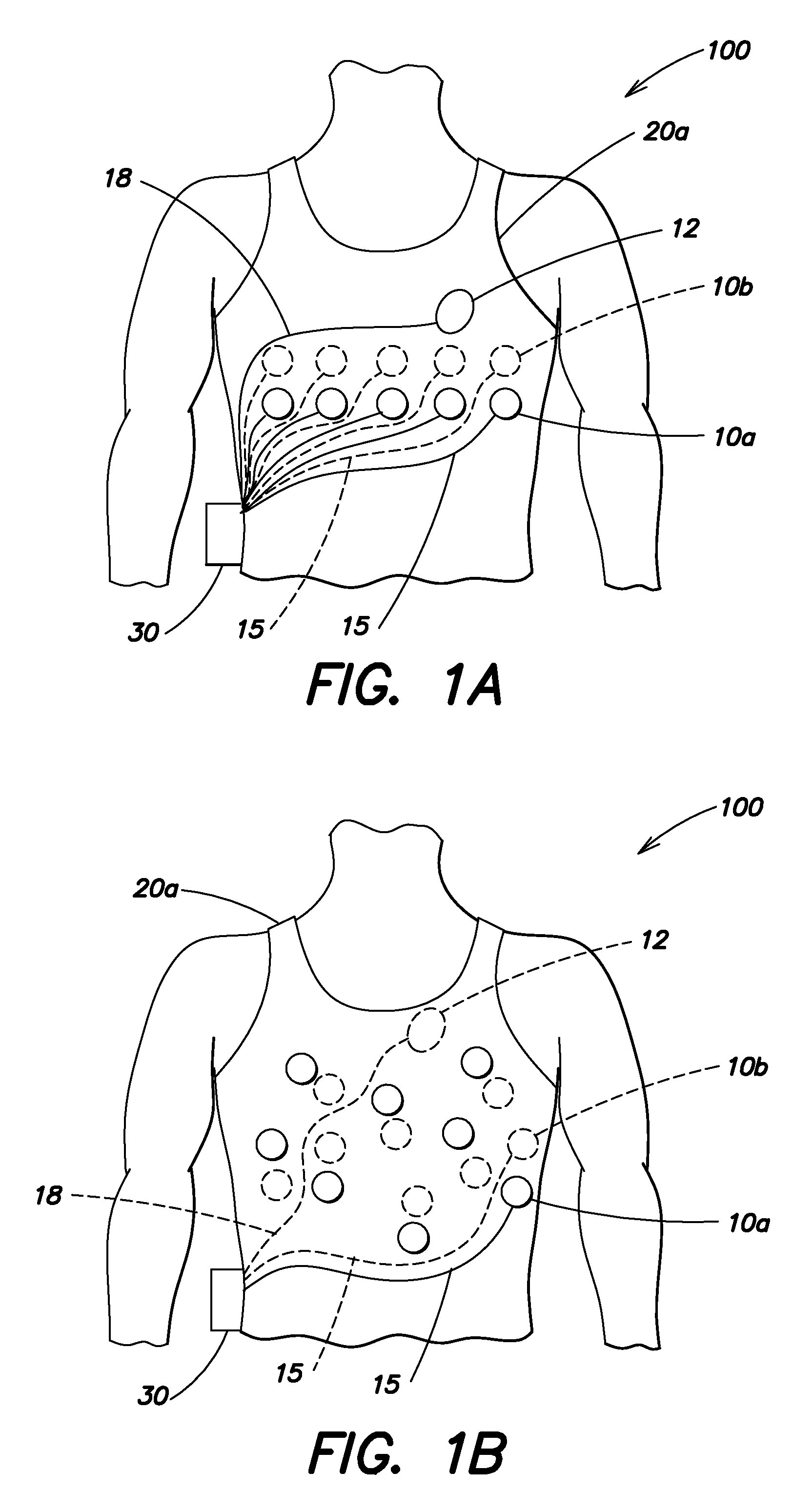
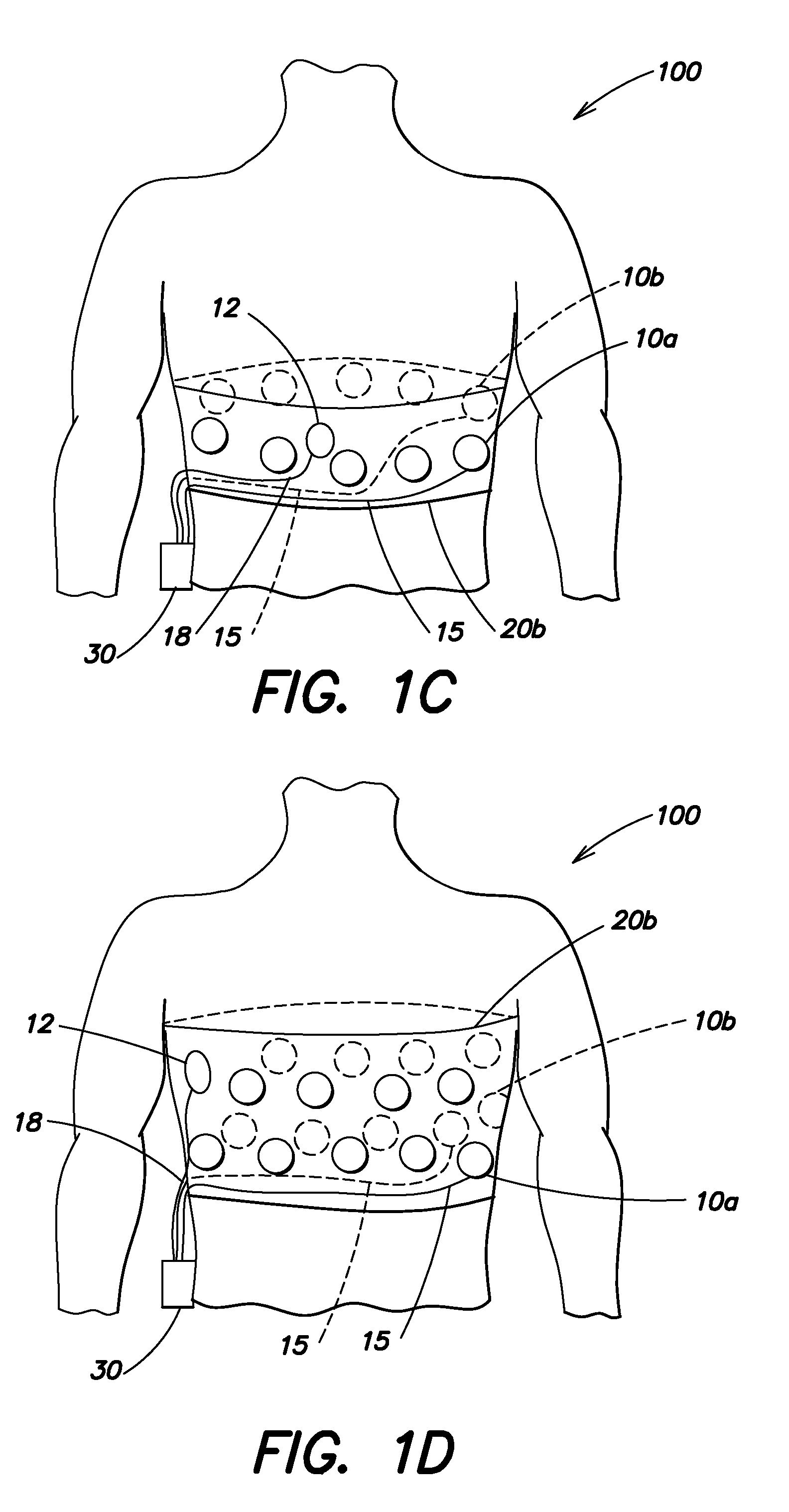
Wearable ambulatory medical device with multiple sensing electrodes
ActiveUS20110288605A1Quality improvementReduce noiseElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsElectricityPhase difference
An ambulatory medical device including a plurality of electrodes configured to be disposed at spaced apart positions about a patient's body, an electrode signal acquisition circuit, and a monitoring circuit. The acquisition circuit has a plurality of inputs each electrically coupled to a respective electrode of the plurality of electrodes and is configured to sense a respective signal provided by a plurality of different pairings of the plurality of electrodes. The monitoring circuit is electrically coupled to an output of the acquisition circuit and is configured to analyze the respective signal provided by each of the plurality of different pairings and to instruct the acquisition circuit to select at least one of the plurality of different to pairings to monitor based on at least one of the quality of the respective signal, a phase difference between the respective signal and that of other pairings, a position of electrodes relative to the patient's body, and other criteria.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Forward and reverse motor for improving forward and reverse efficiency, and control method thereof
PendingCN109889124ASolve the problem of not being able to achieve high efficiency in both forward and reverse directionsImprove efficiencyAC motor controlPhase differenceControl theory
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Electric processing system
InactiveUS20080082098A1Quality improvementSimple processSurgical instrument detailsSurgical forcepsElectricityHigh frequency power
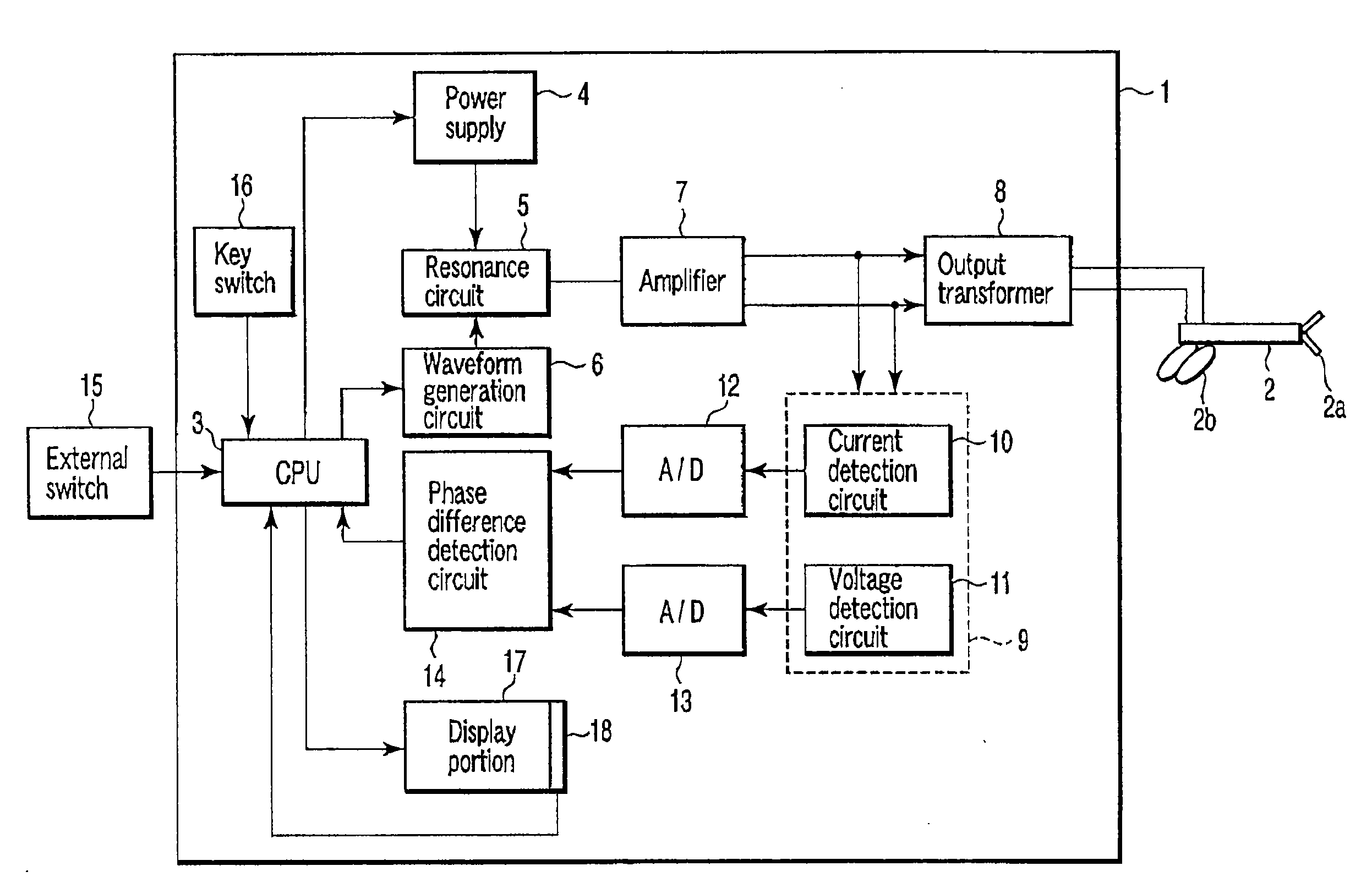
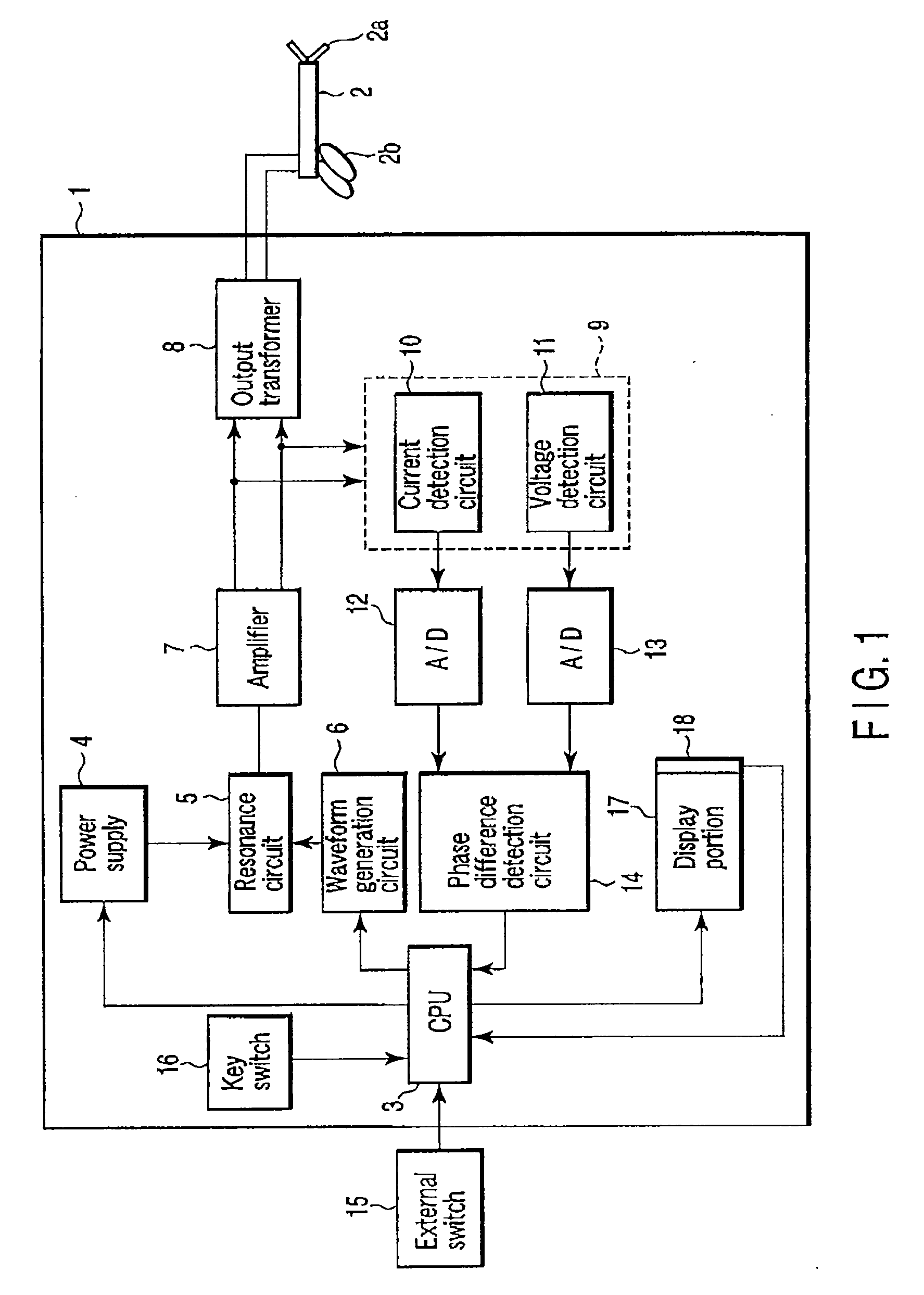
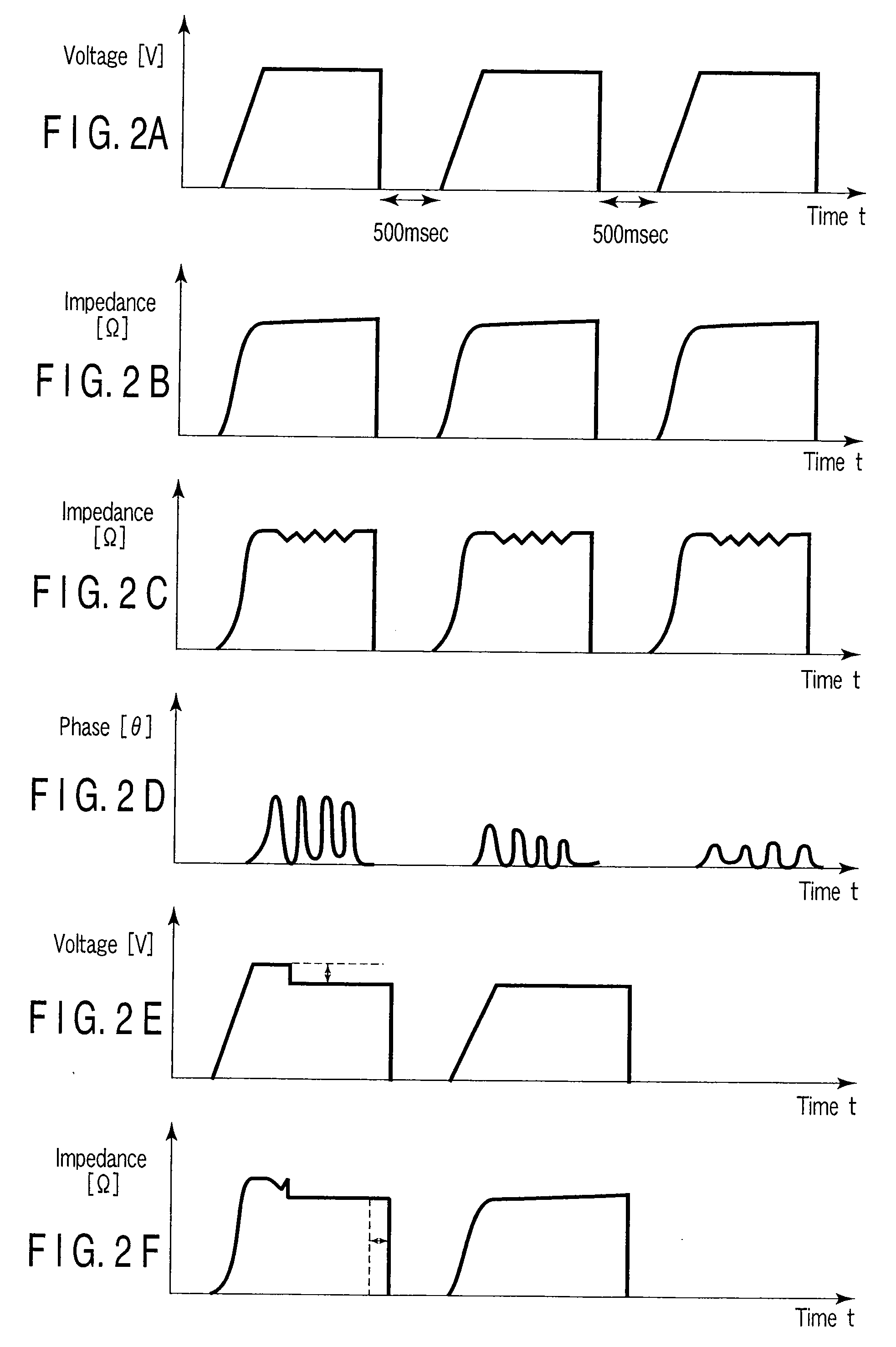
There is provided an electric processing system which sequentially monitors a phase difference of intermittently output high-frequency powers in the case of performing feedback control with respect to a high-frequency power applied to bipolar type sealing forceps, reduces the high-frequency power and prolongs an application time at the time of occurrence of abnormal discharge (a spark) at distal ends, thereby terminating the abnormal discharge (extinguishing the spark) to carry out sealing processing.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
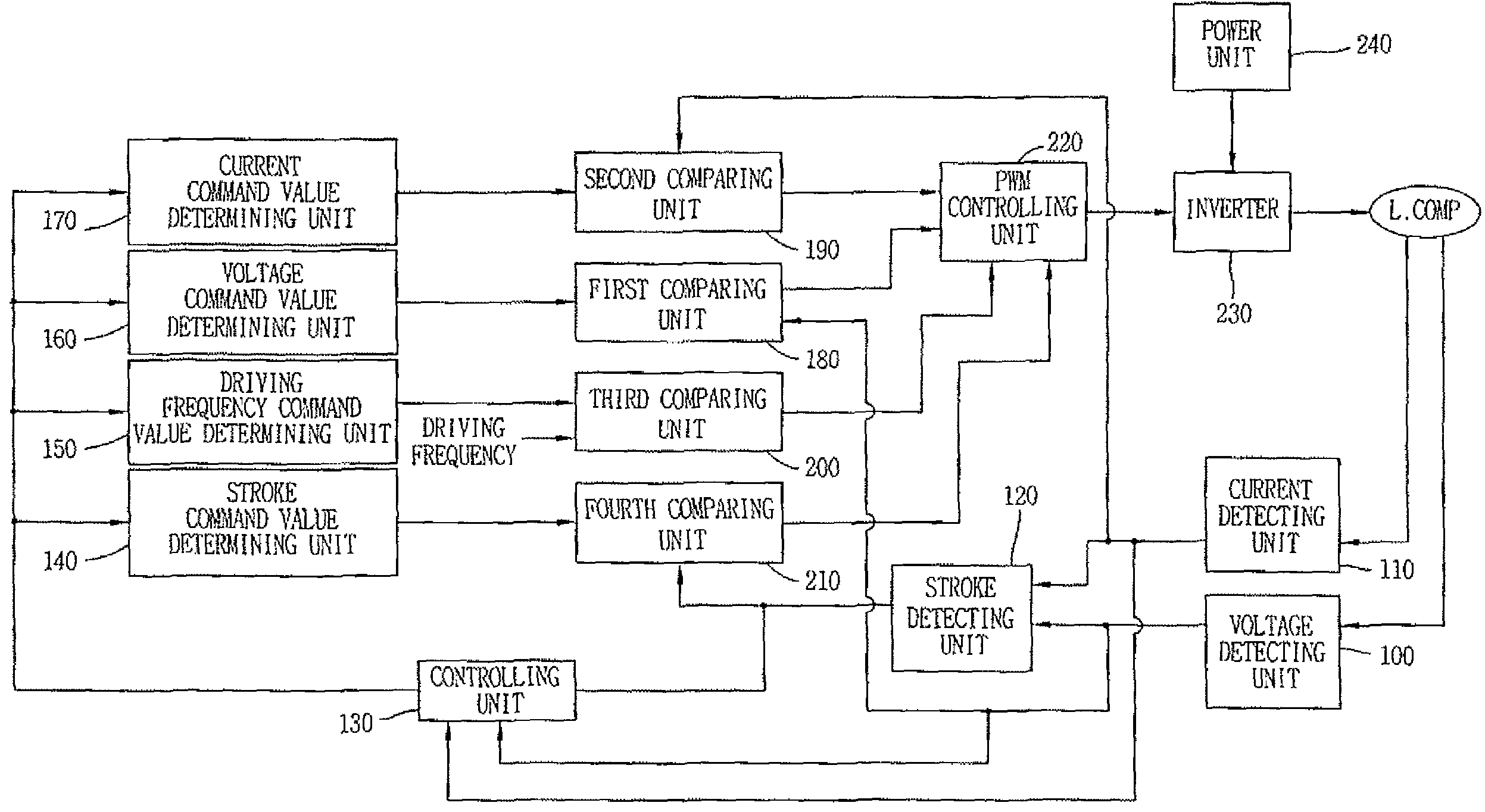
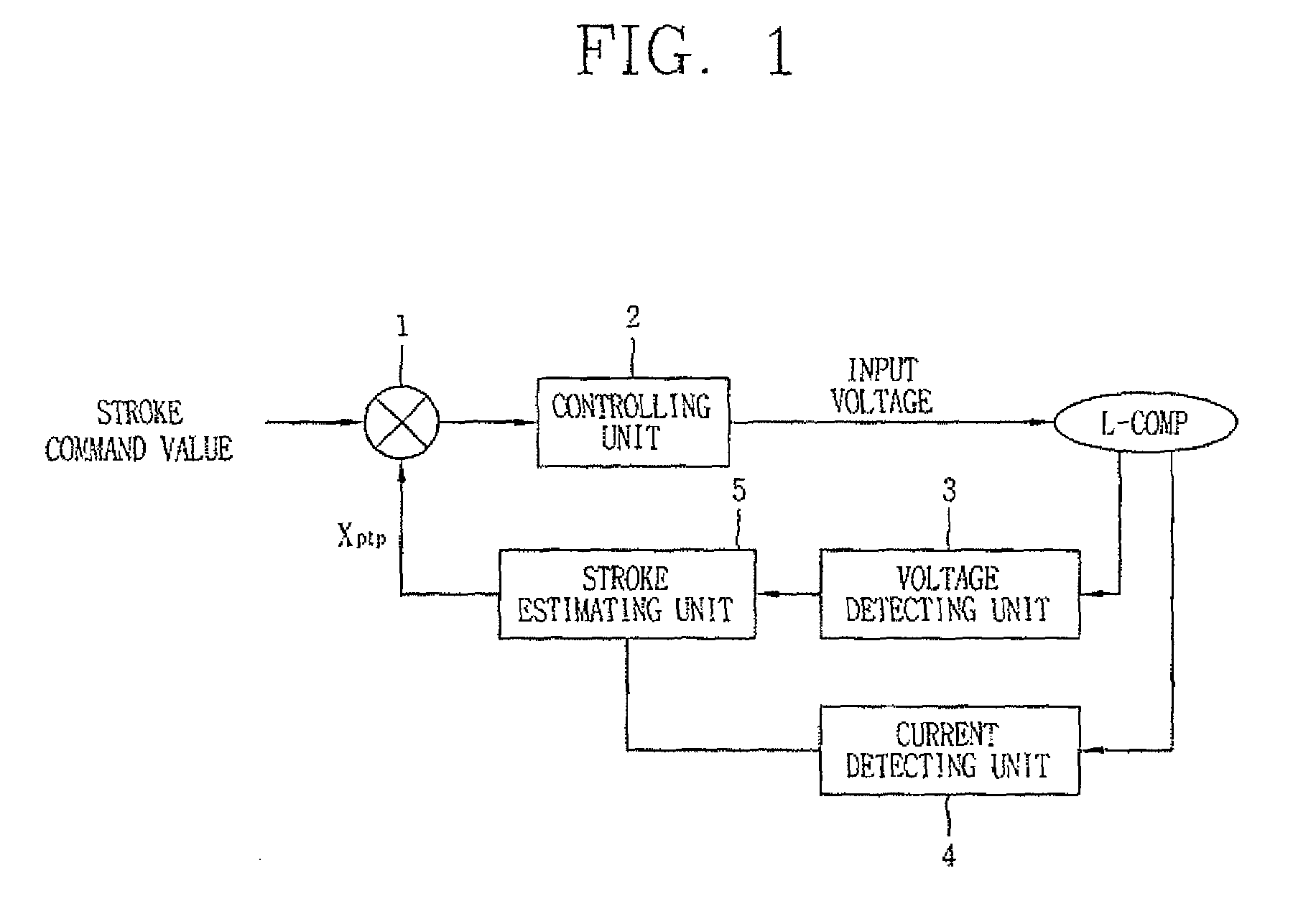
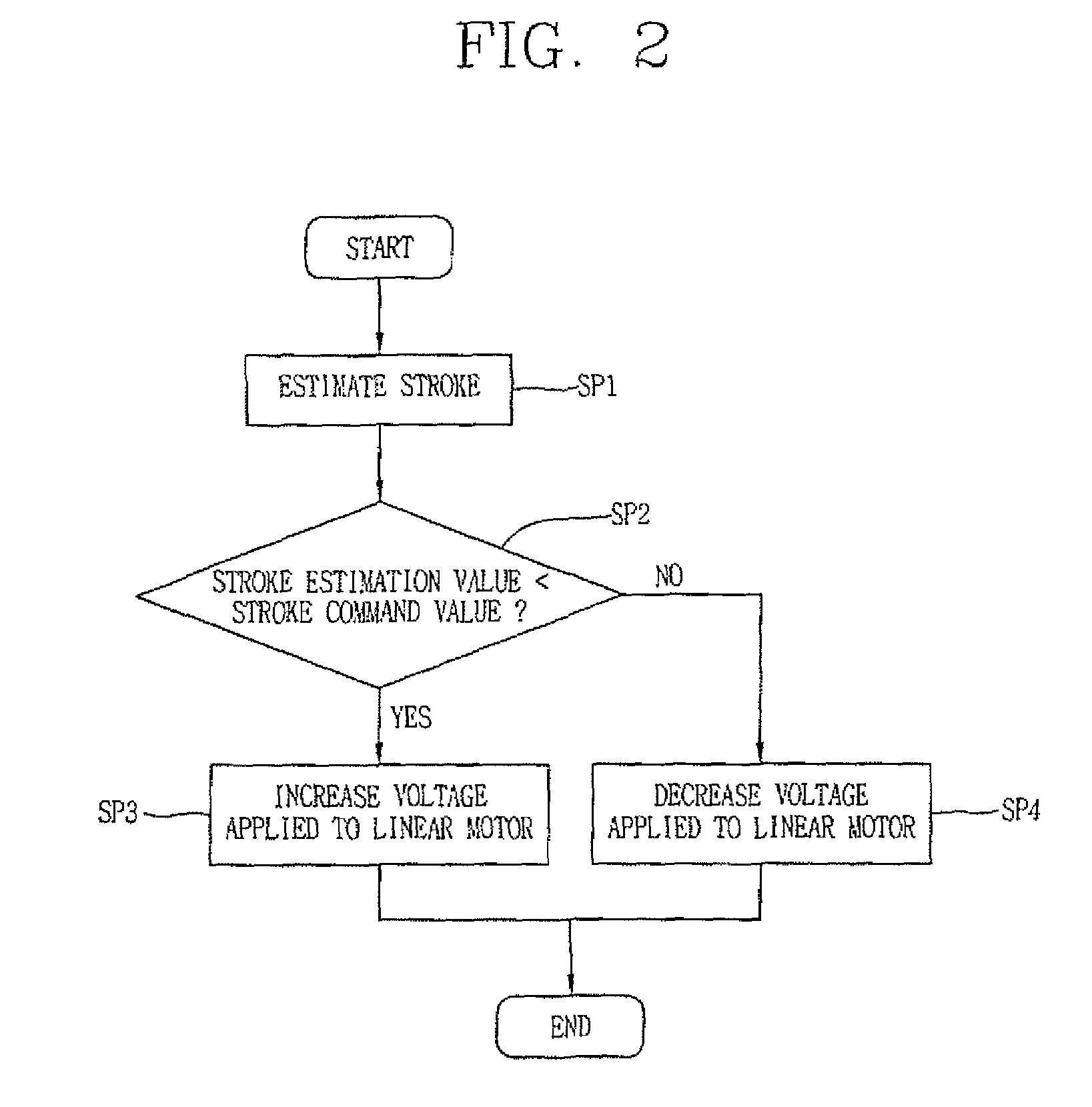
Driving controlling apparatus for linear compressor and method thereof
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Transmitting/receiving antenna, isolator, high-frequency oscillator, and high-frequency transmitter-receiver using the same
InactiveUS20050190101A1Satisfactory characteristicOscillation stabilityWaveguide type devicesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDielectricPhase difference
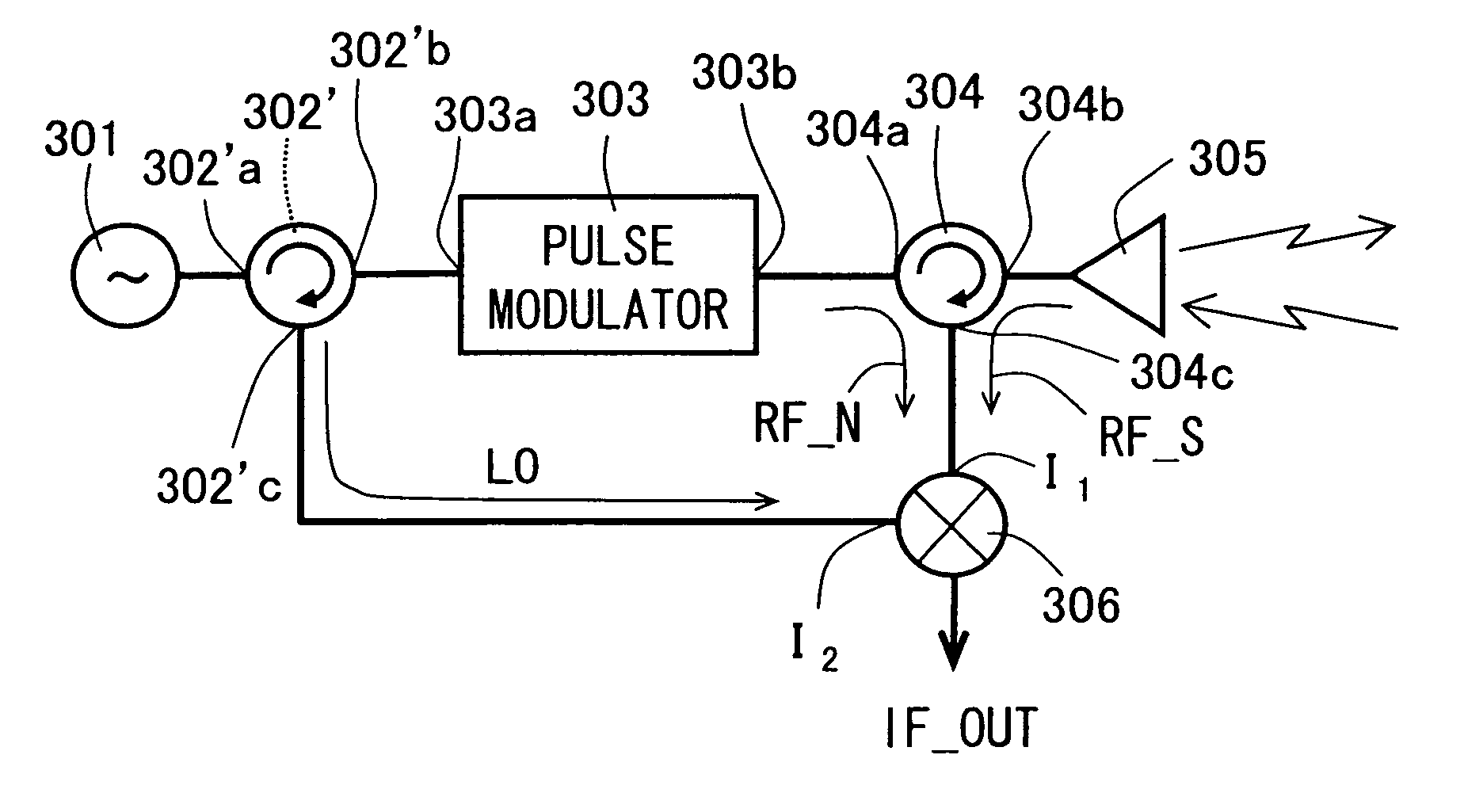
A millimeter-wave transmitter-receiver uses an NRD guide as a fundamental configuration and includes a millimeter-wave signal oscillator, a pulse modulator, a circulator, an antenna and a mixer. In the millimeter-wave transmitter-receiver, a line length of a third dielectric guide is set so that δ=±π in which δ is a phase difference at a center frequency between a portion of a transmission millimeter-wave signal, which is reflected via a third dielectric guide on the leading end portion of the third dielectric guide and returned to leak to a third connecting portion of the circulator, and another portion of the millimeter-wave signal, which leaks from a first connecting portion to the third connecting portion of the circulator. It is possible to reduce the change in the mixer output and enhance the millimeter-wave transmission / reception performance.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Calibration apparatus for smart antenna and method thereof
This invention is related to the calibration apparatus and method for compensating the phase characteristics in the receiving and transmitting signal paths of array antenna system, especially adaptive array antenna system operating as the base station system. The objective of this invention is to provide the calibration apparatus and method for the array antenna system to be able to compensate its phase differences or irregularities without any restrictions on the array structure or position of additional antenna or antenna toplogies while the array antenna system is in its operational mode such that the signals used by the subscribers are received or transmitted together with the signals used for the calibration. In this invention the phase delay between the additional antenna element and each of the antenna elements of the array antenna system is measured in advance of the calibration procedure to be used when the phase differences or irregularities are measured during the calibration procedure. The test signals used for the calibration is distinguishable from the signals used by the subscribers. Furthermore, each of the transmitting calibration signals itself is distinguishable from one another when the plural transmitting signal paths are to be calibrated simultaneously.
Owner:SASTECH +1
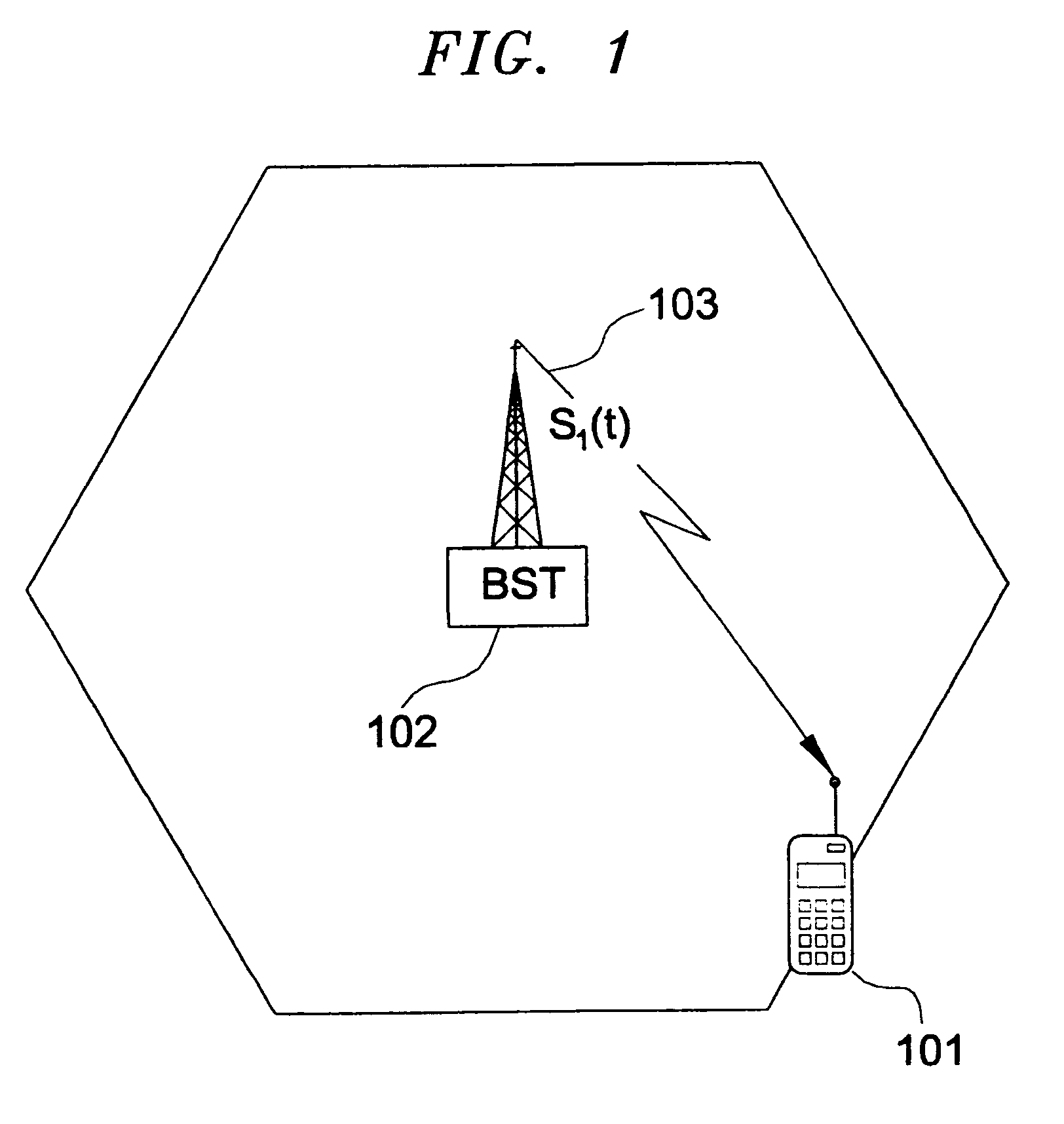
Methods and apparatus to position a mobile receiver using downlink signals part IV
The invention consists of methods and apparatus to estimate the position and velocity of a Mobile Receiver (MR) using either the Time Of Arrival (TOA) of signals received by the MR, their Phase Of Arrival (POA), their Strength Of Arrival (SOA), their Frequency Of Arrival (FOA), or a combination thereof, with respect to a reference produced by a Reference Receiver (RR) of known location. In order to solve for the coordinates of the MR, the invention uses either hyperbolic multilateration based on Time Difference Of Arrival (TDOA), or linear multiangulation based on Phase Difference Of Arrival (PDOA), or both. In order to solve for the velocity of the MR, the patent uses FOA based on Frequency Difference Of Arrival (FDOA).
Owner:CELL LOC LOCATION TECH
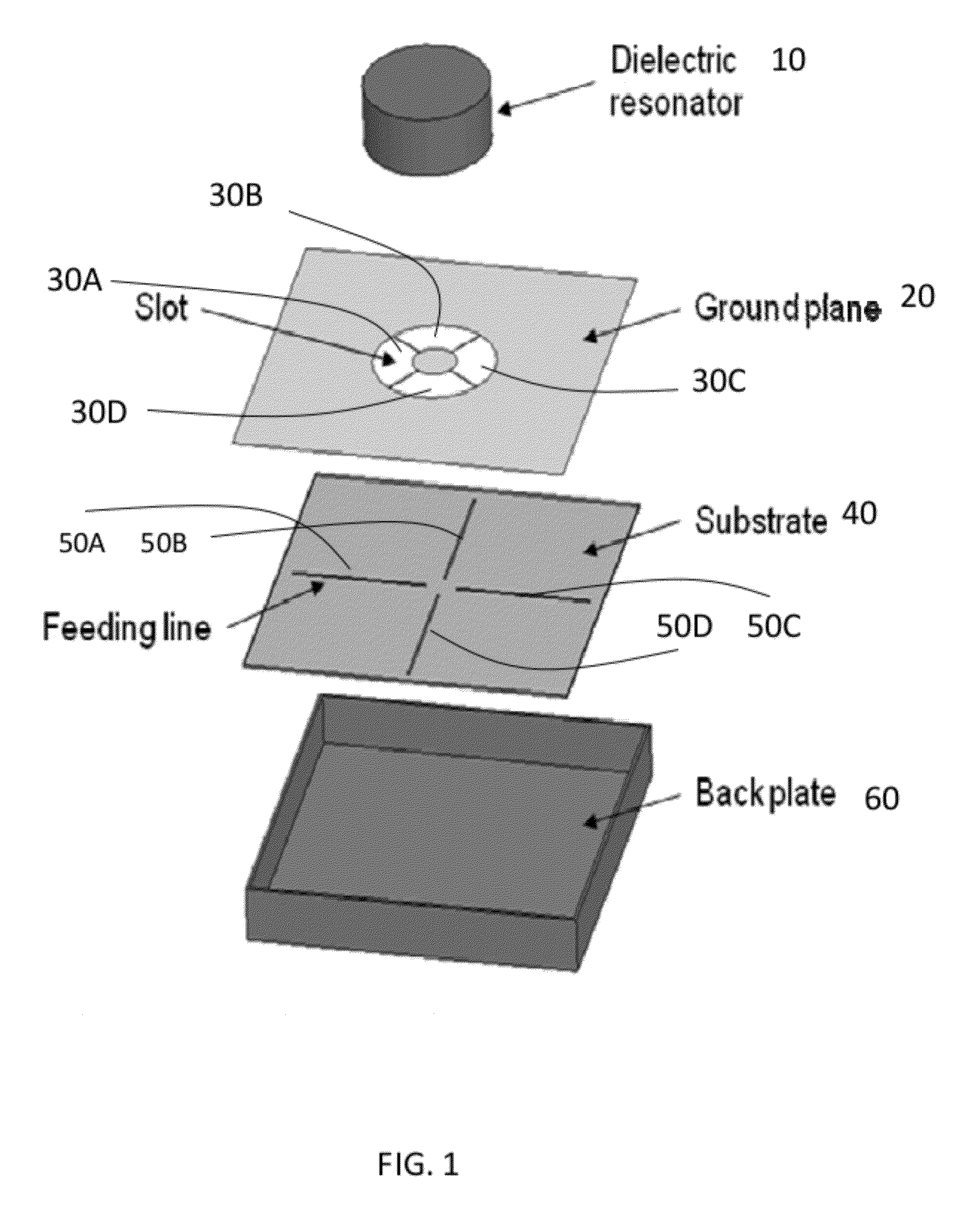
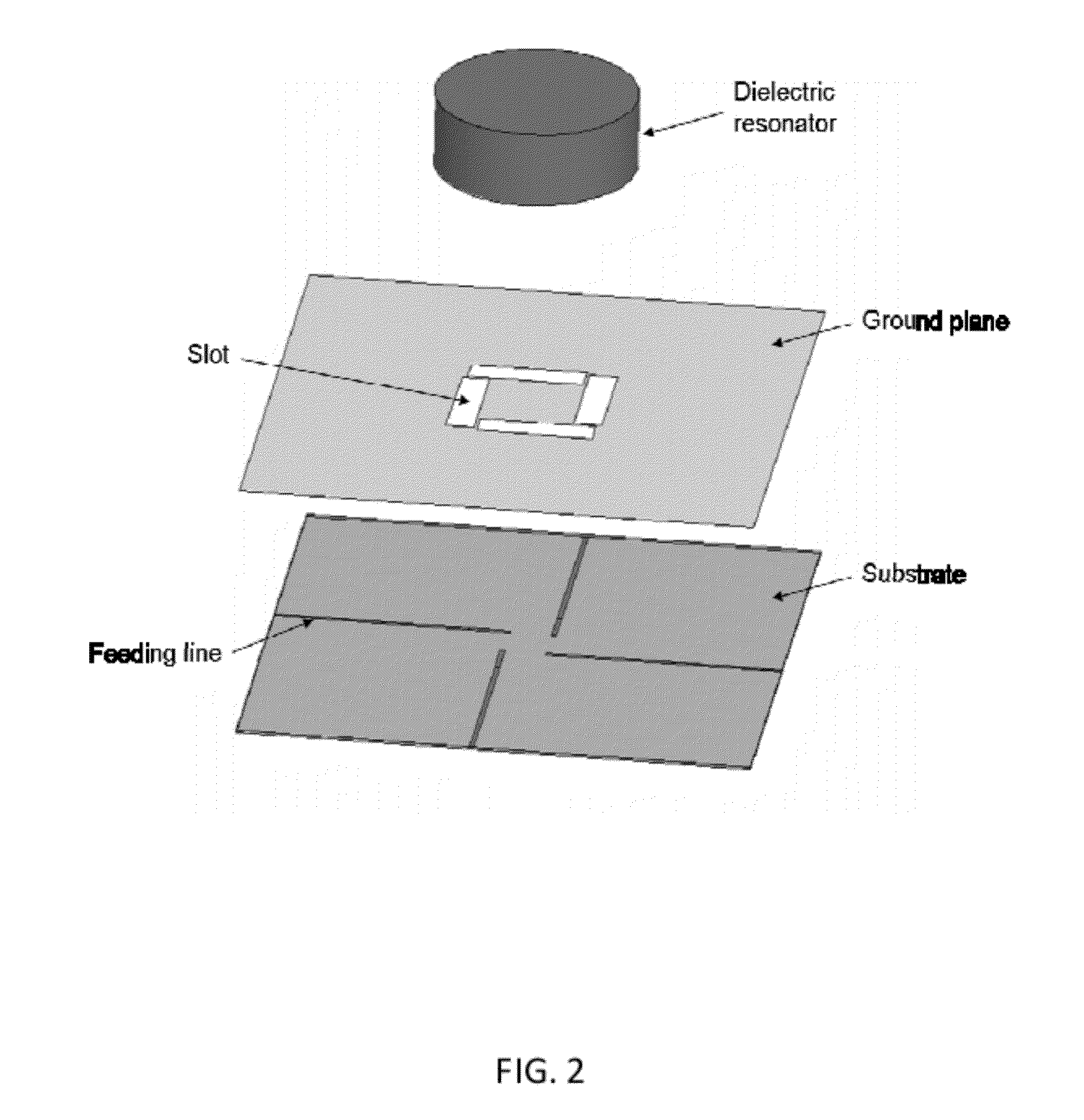
Wideband circularly polarized hybrid dielectric resonator antenna
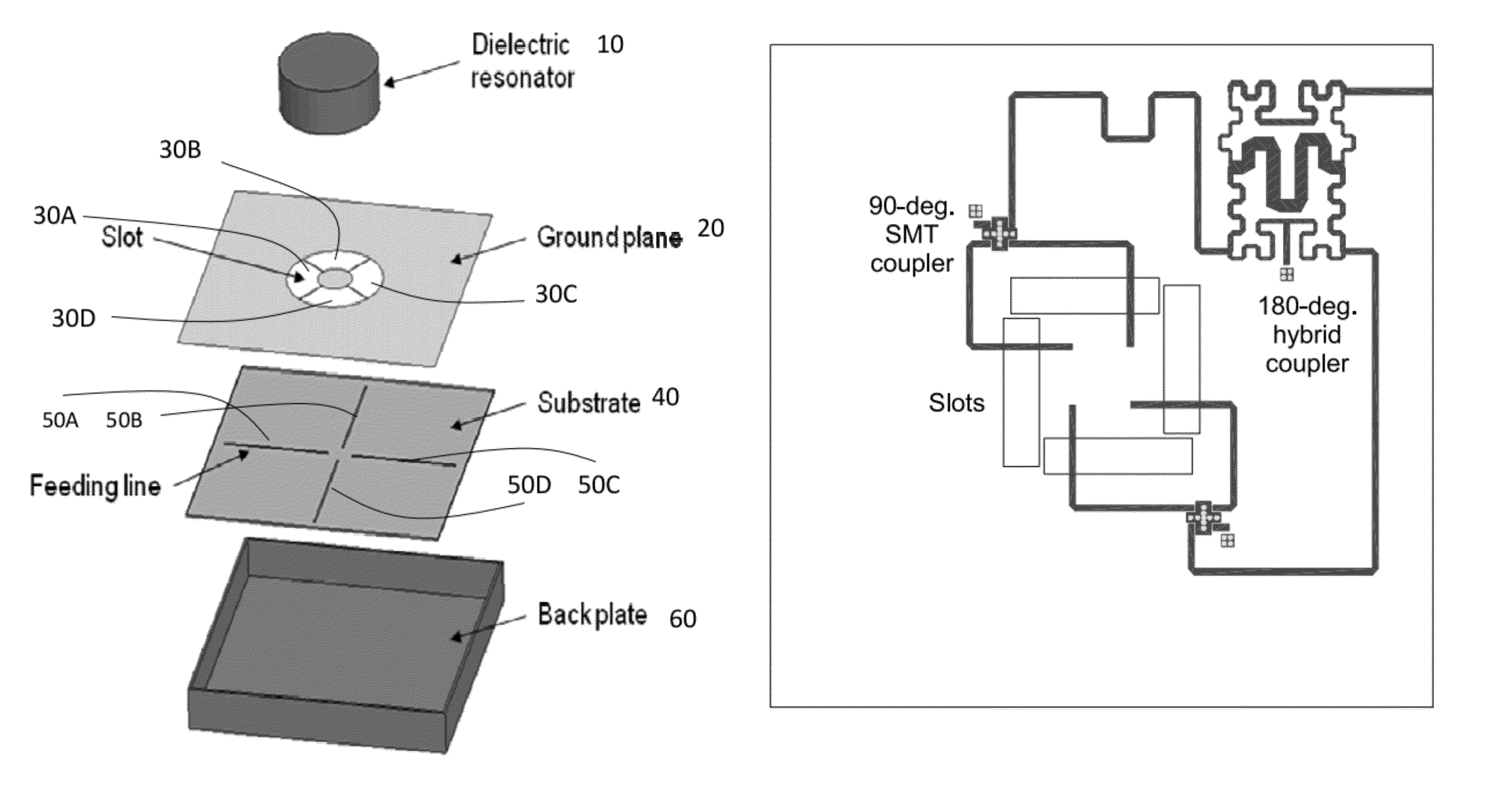
ActiveUS8928544B2High bandwidthCompact geometryAntenna supports/mountingsAntennas earthing switches associationDielectric resonator antennaPhase difference
The present invention provides a dielectric resonator antenna comprising: a dielectric resonator; a ground plane, operatively coupled with the dielectric resonator, the ground plane having four slots; and a substrate, operatively coupled to the ground plane, having a feeding network consisting of four microstrip lines; wherein the four slots are constructed and geometrically arranged to ensure proper circular polarization and coupling to the dielectric resonator; and wherein the antenna feeding network combines the four microstrip lines with a 90 degree phase difference to generate circular polarization over a wide frequency band.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
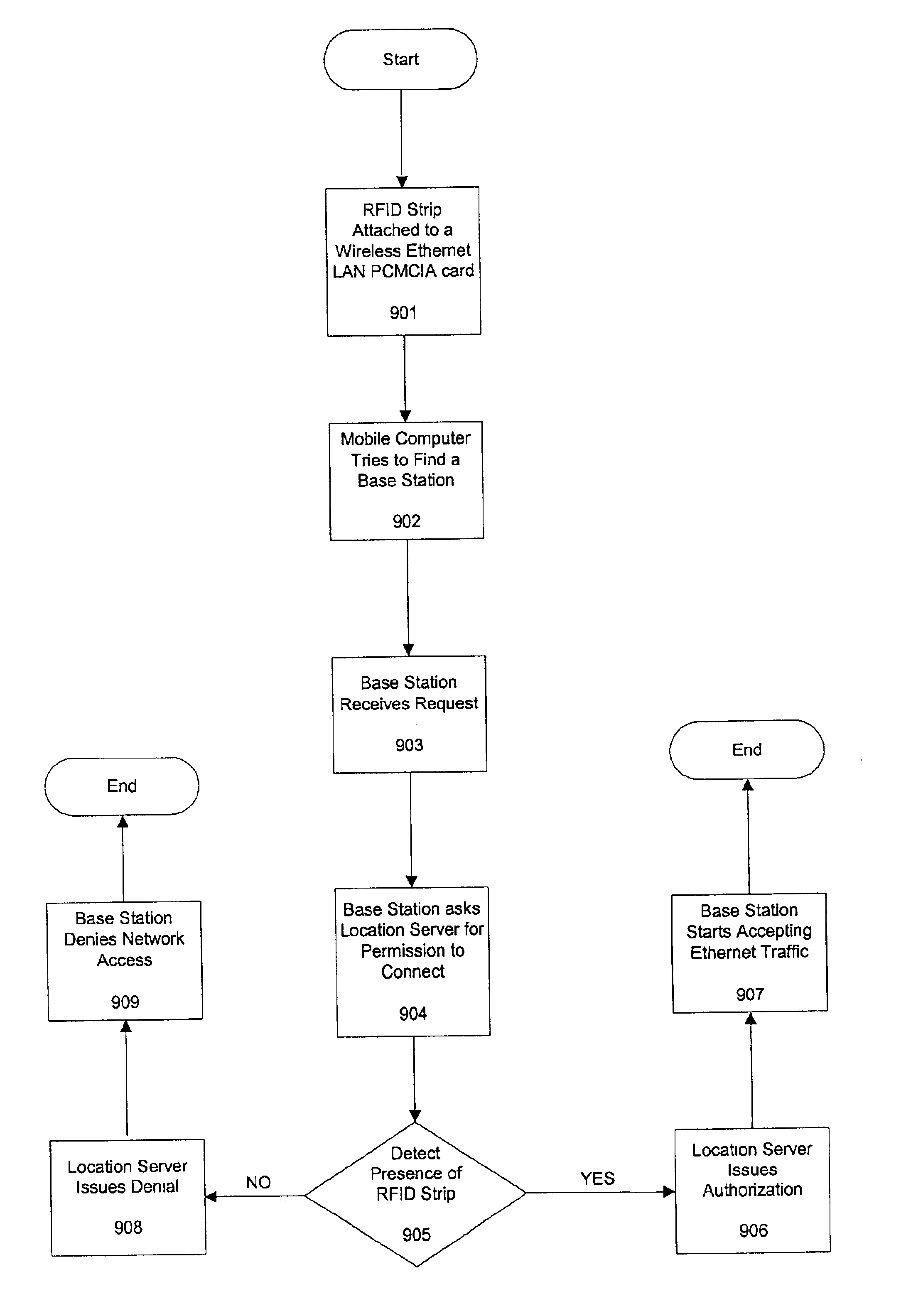
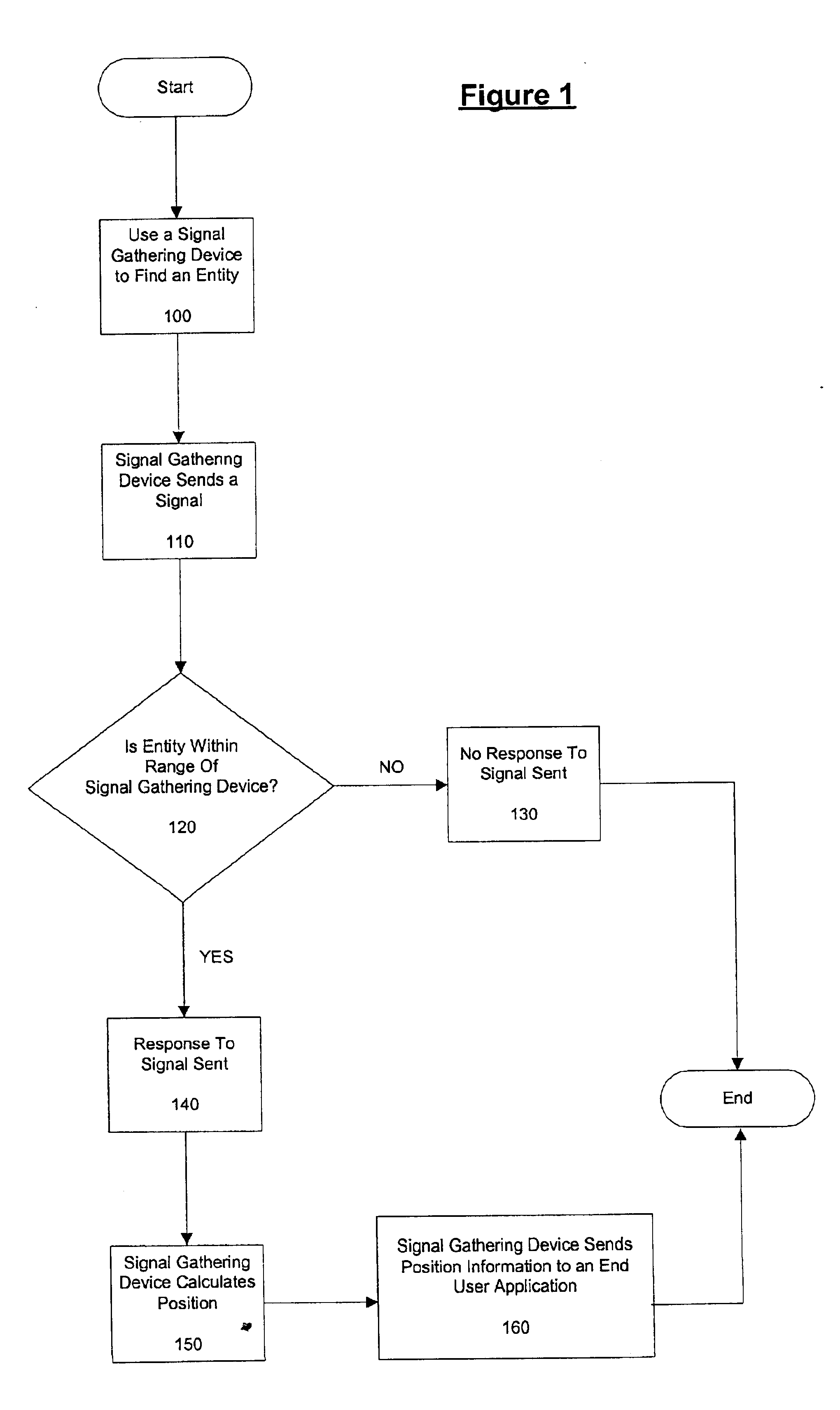
Apparatus and method for the use of position information in wireless applications
InactiveUS6920330B2Direction finders using radio wavesAssess restrictionWireless Application ProtocolPhase difference
Embodiments of the present invention are directed at gathering position information of mobile and stationary entities and using the position information in a wide variety of applications. Various embodiments use a plurality of signal transmitting devices and / or a plurality of signal gathering devices to gather position information. In one embodiment, the signal transmitting device is an existing mobile electronic device. In another embodiment, the signal transmitting device is a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag attached to an entity. In another embodiment, the signal gathering device is a collection of wall mounted antennas. The entity location is calculated by gathering the phase difference or other timing information of signal generated by the signal transmitting device on the entity. This location information is then given to end user applications. One embodiment is a network security application using gathered location information of wireless ethernet cards. Another embodiment is a network resource locator application.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
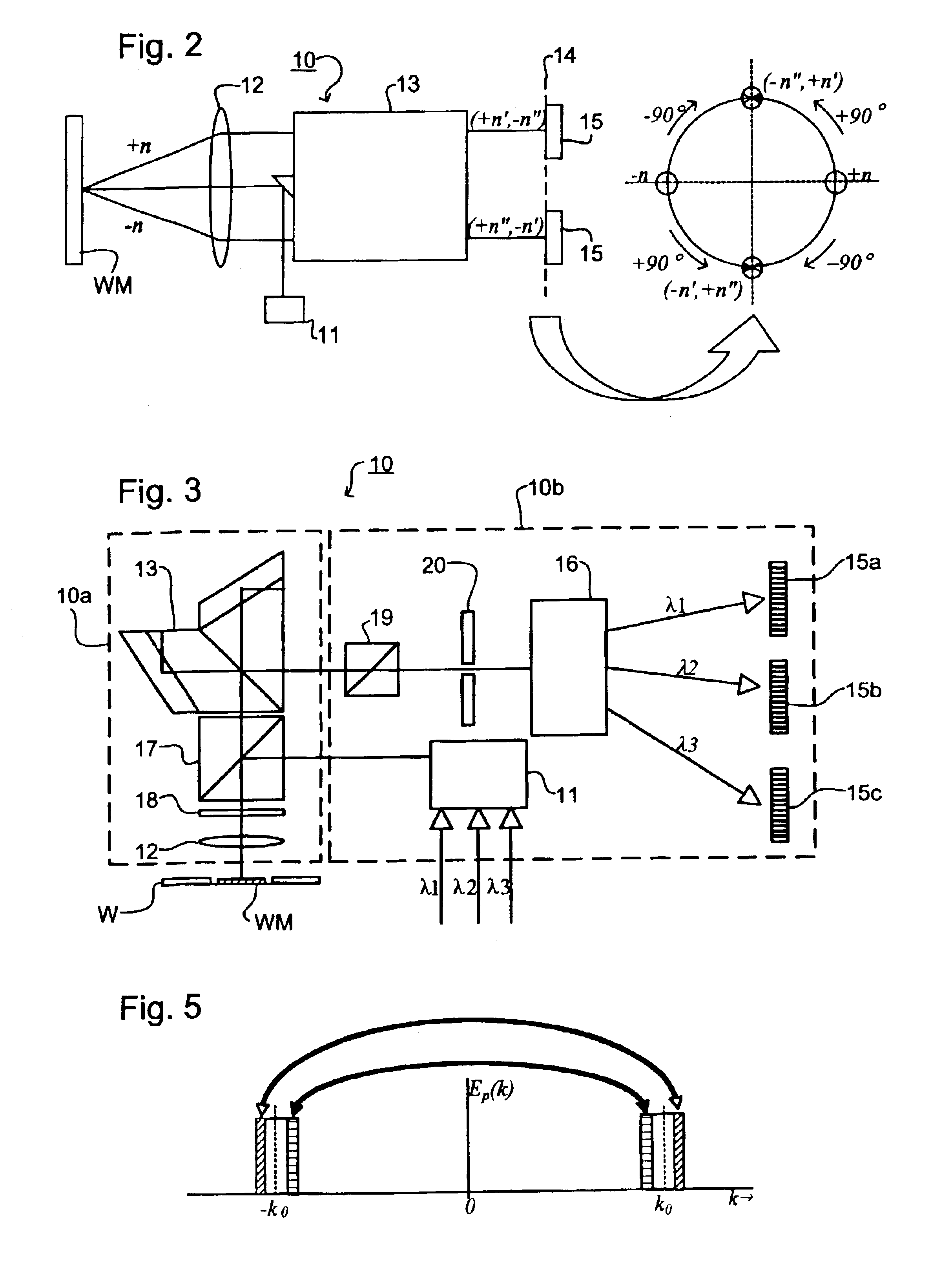
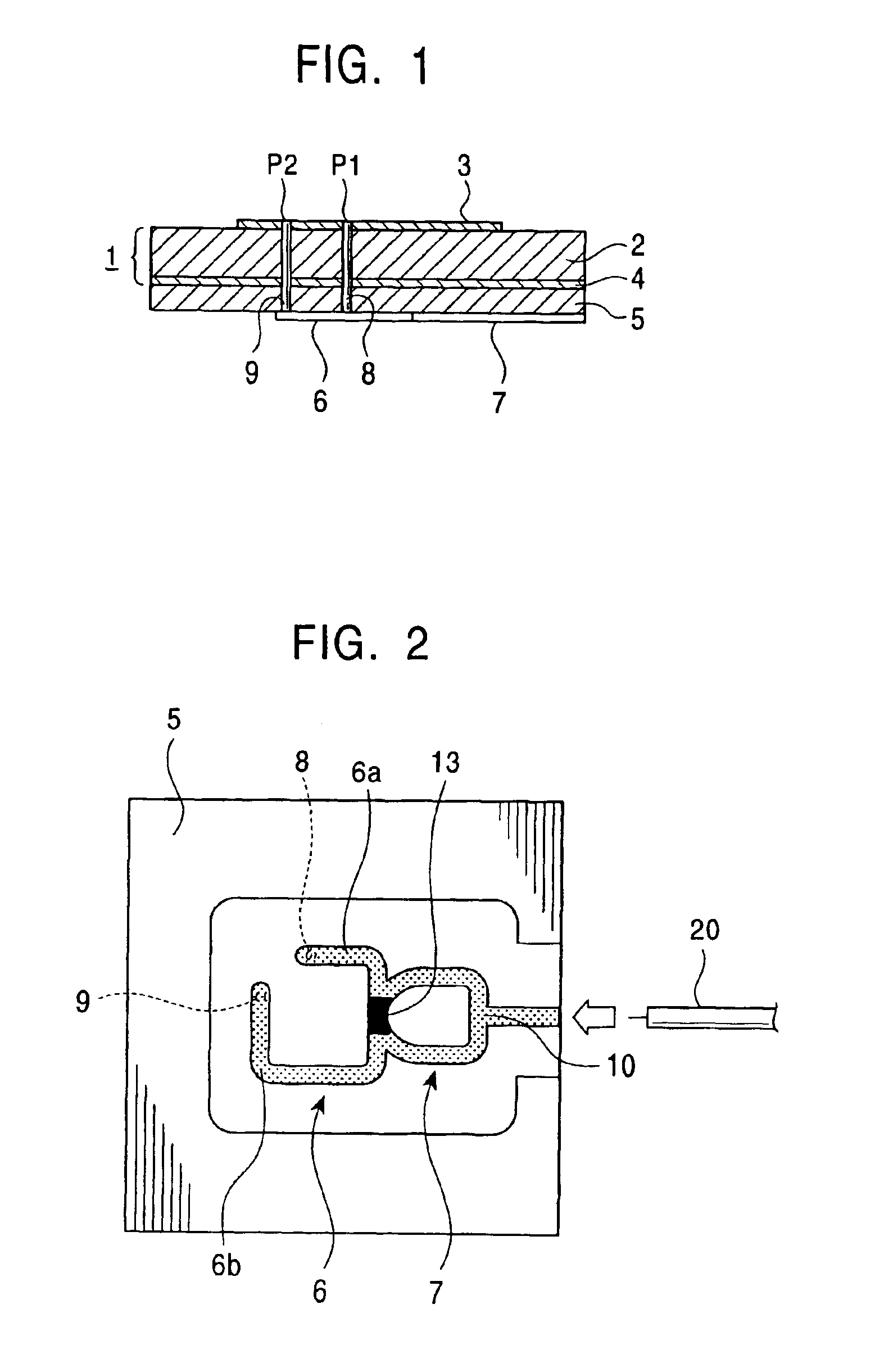
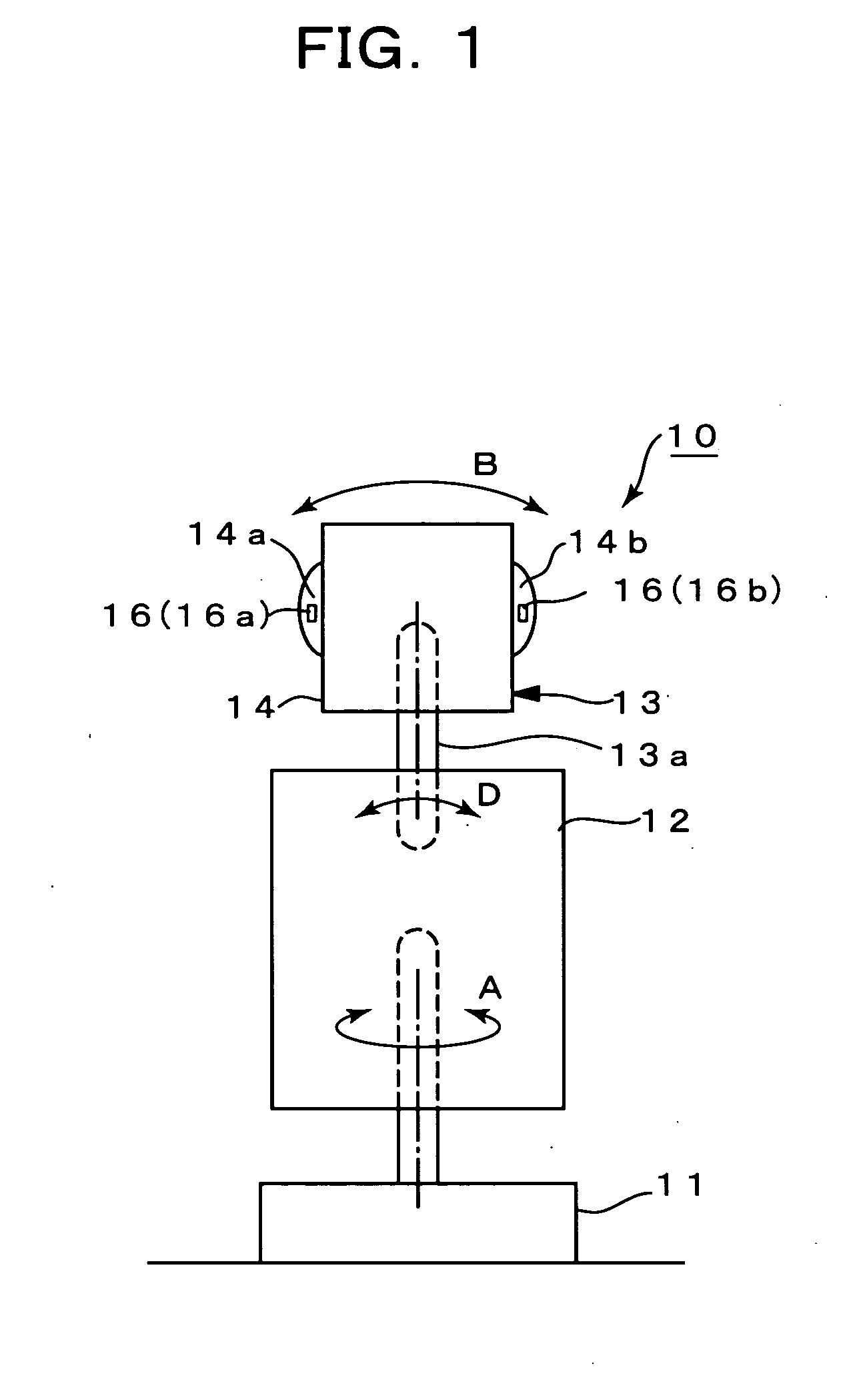
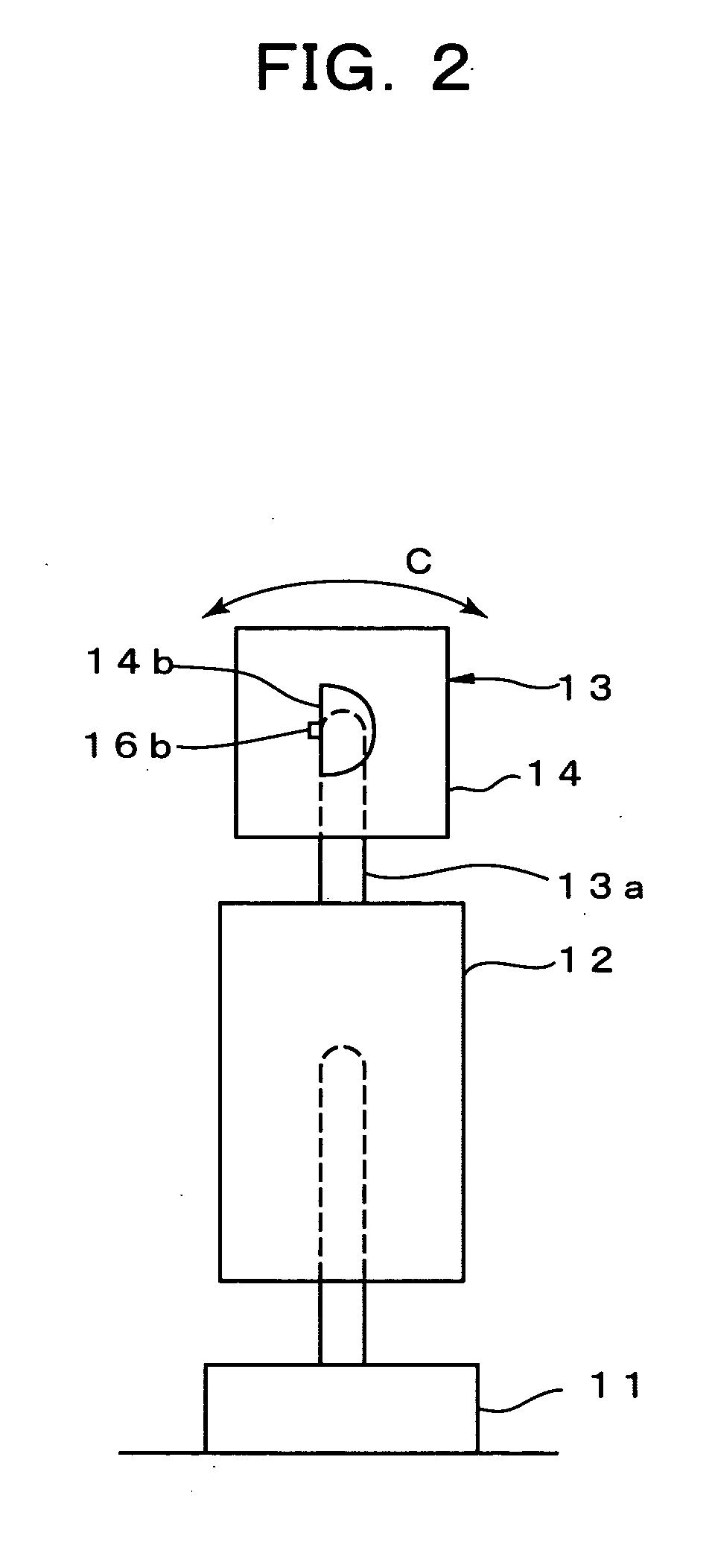
Phase difference film and production method therefor
InactiveUS20060192913A1Low costElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLiquid crystallinePhase difference
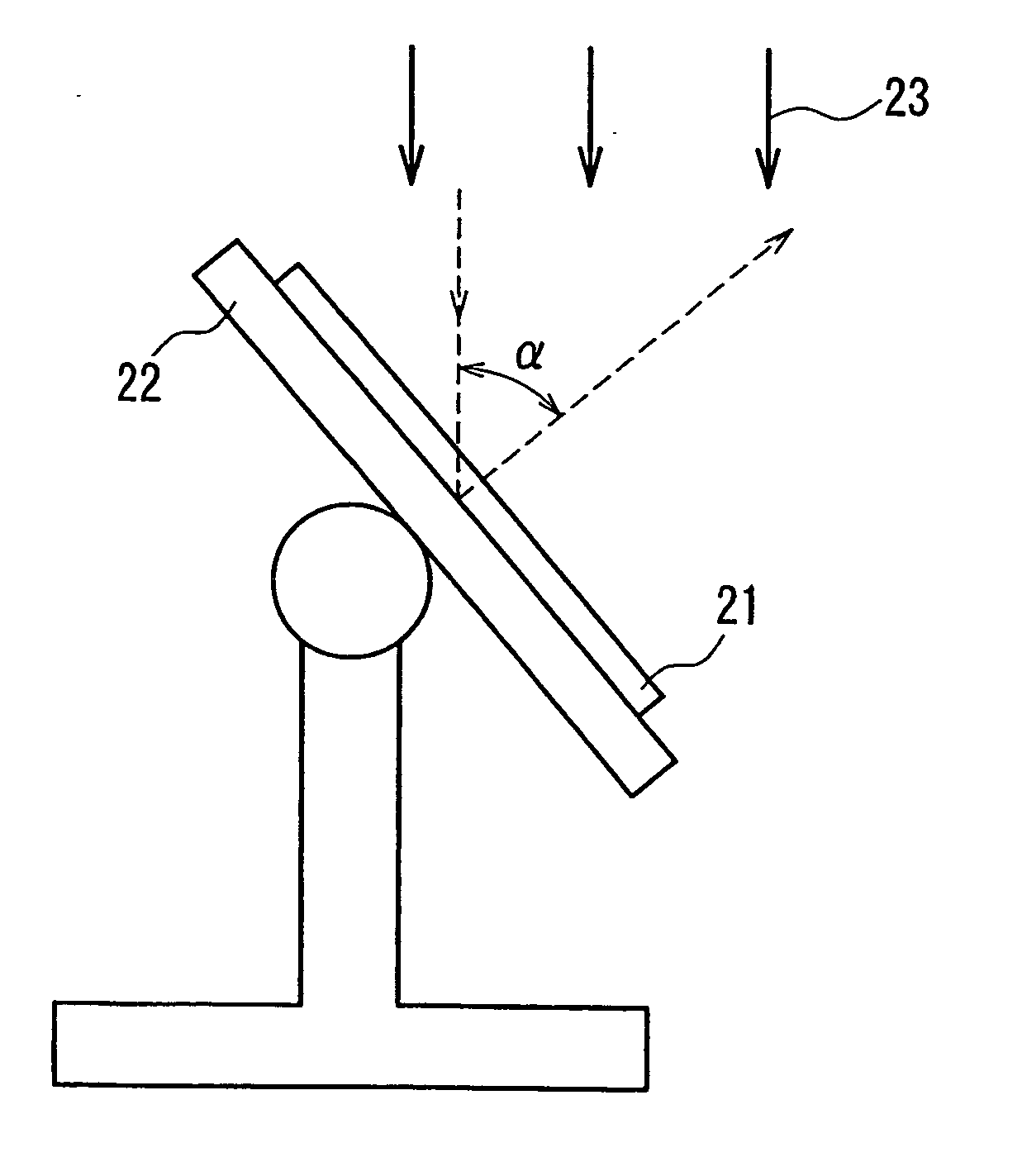
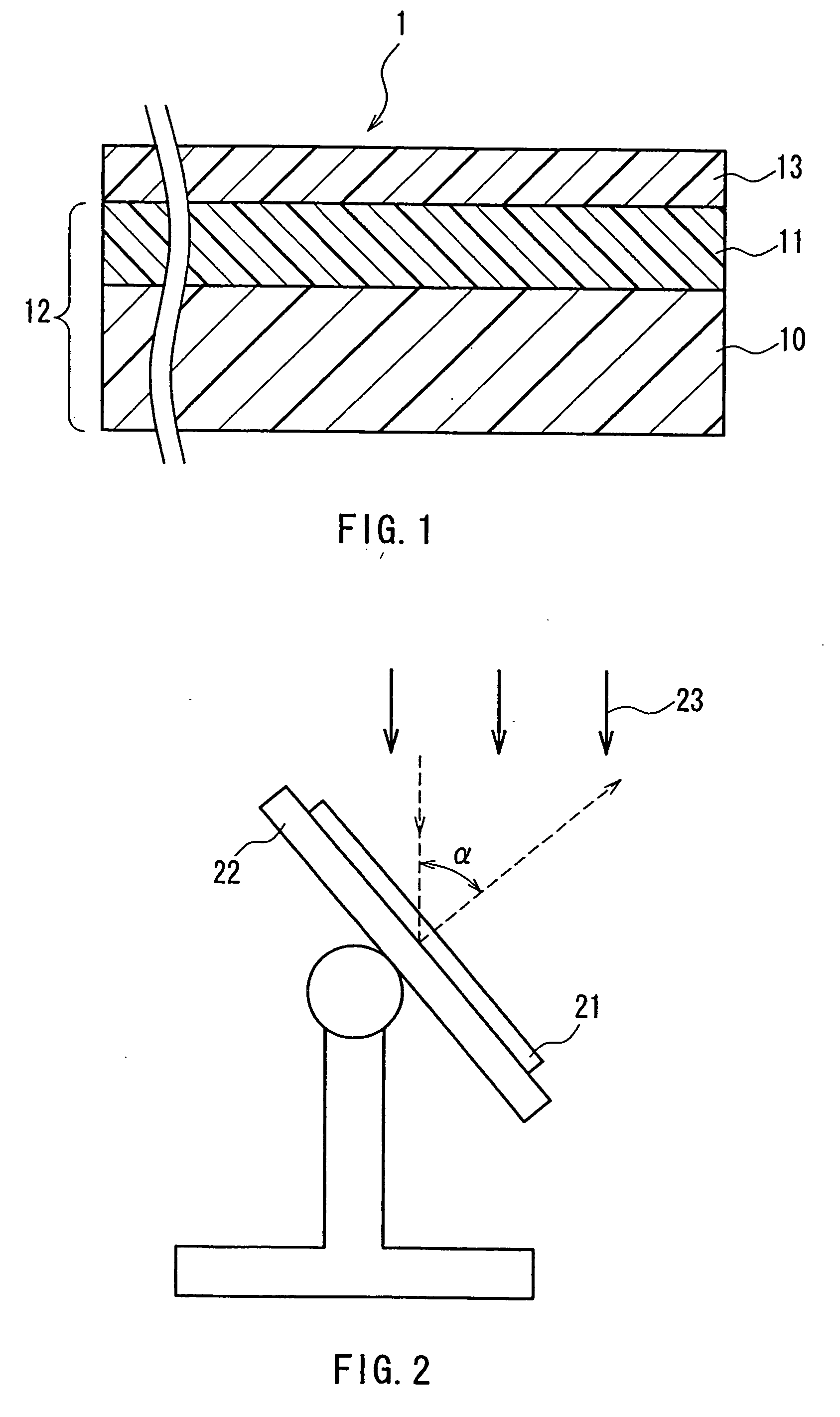
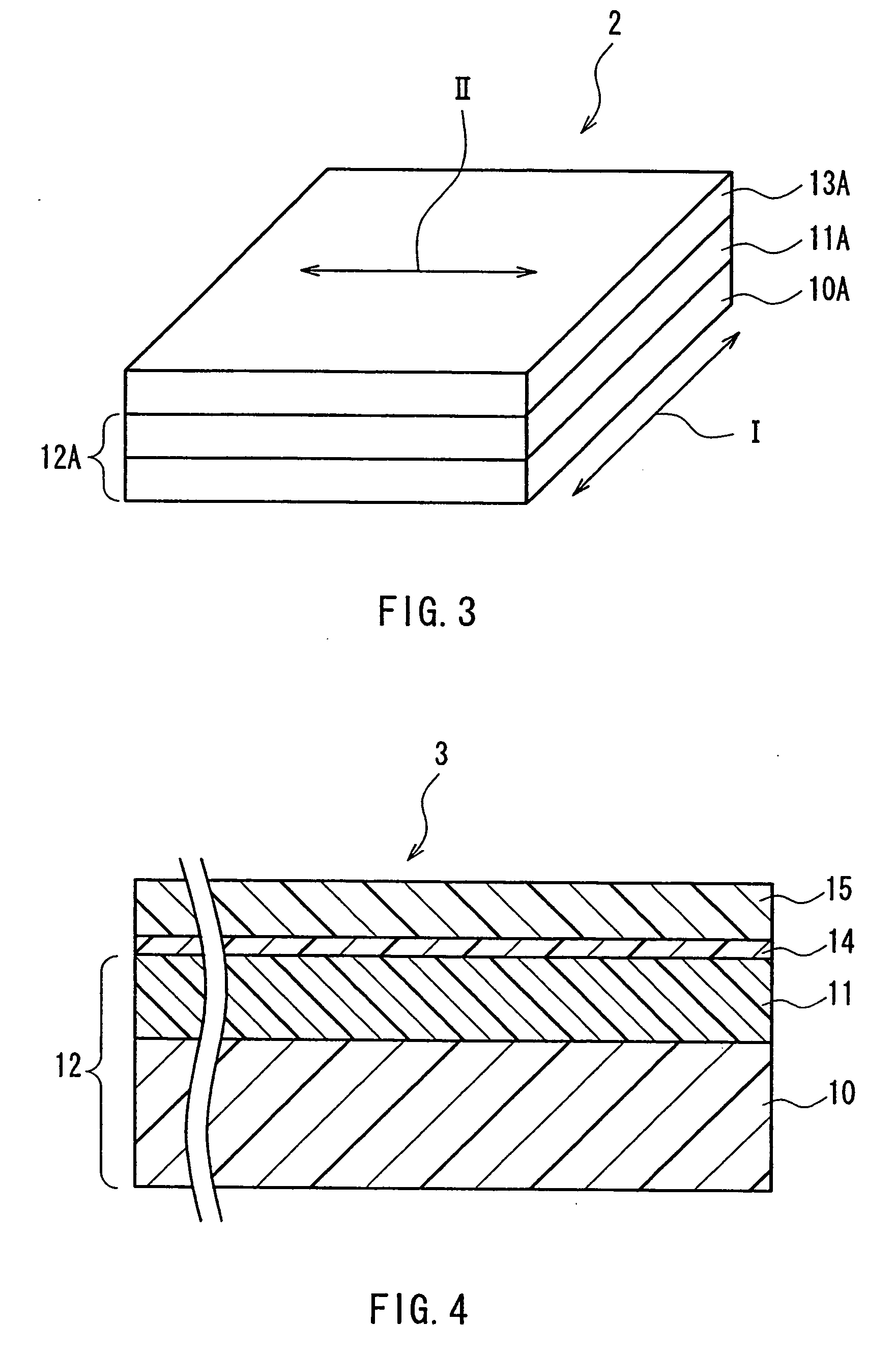
A retardation film that has an optical retardation layer whose alignment direction is controlled precisely and that is produced at a low cost, and also a method for producing the same, are provided. The explanation below relates to FIG. 1. First, a base-attached anisotropic layer 12 is prepared by laminating an optically anisotropic layer 11 on a transparent base 10. Next, on the optically anisotropic layer 11, a solution containing a polymer reacting with polarized ultraviolet light and a liquid crystalline compound is coated and dried. Then, it is irradiated with polarized ultraviolet light so as to align the liquid crystalline compound, and irradiated further with unpolarized ultraviolet light as required to crosslink the liquid crystalline compound, thereby forming a retardation film 1 having an optical retardation layer 13 that is directly formed on the optically anisotropic layer 11.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
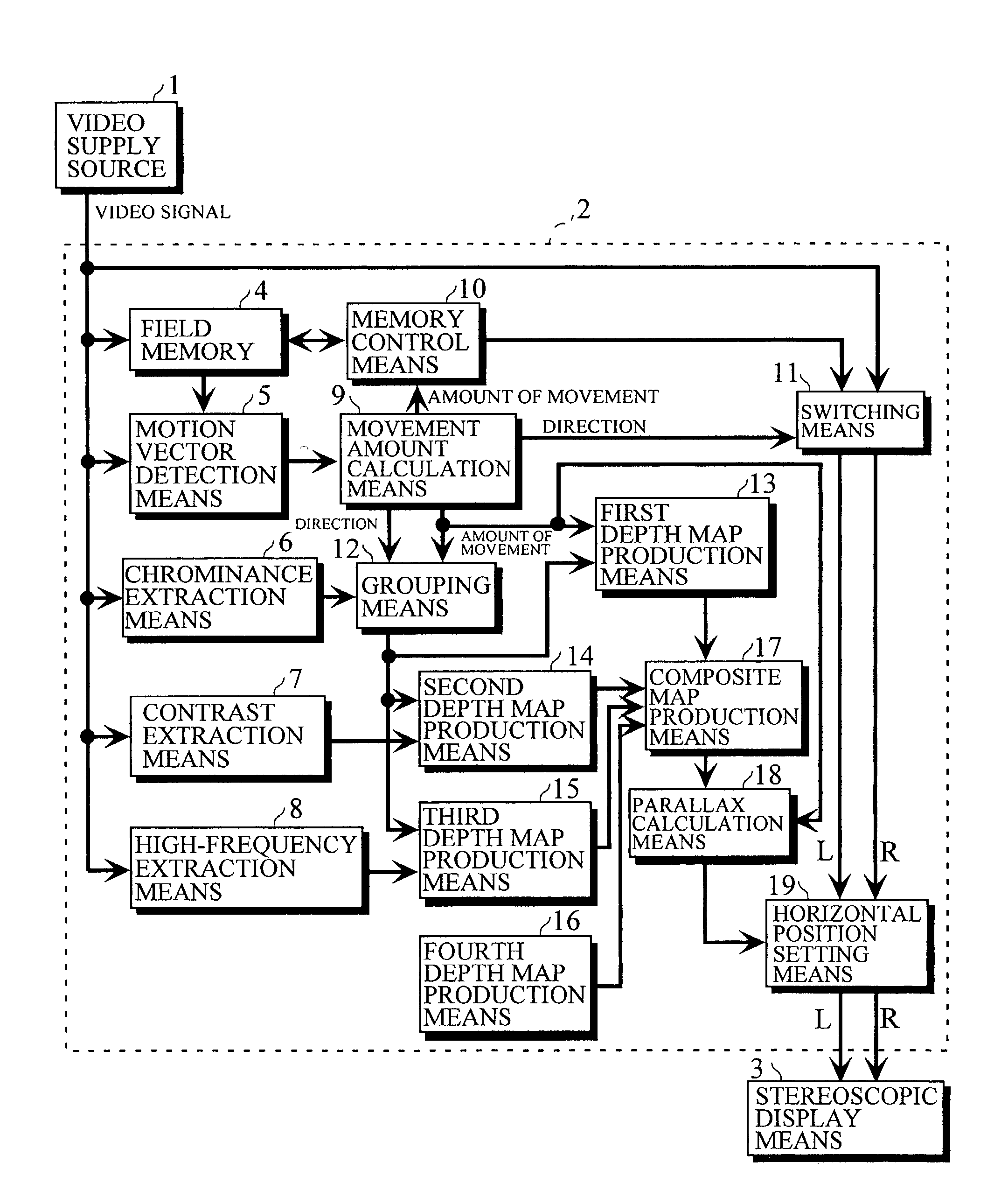
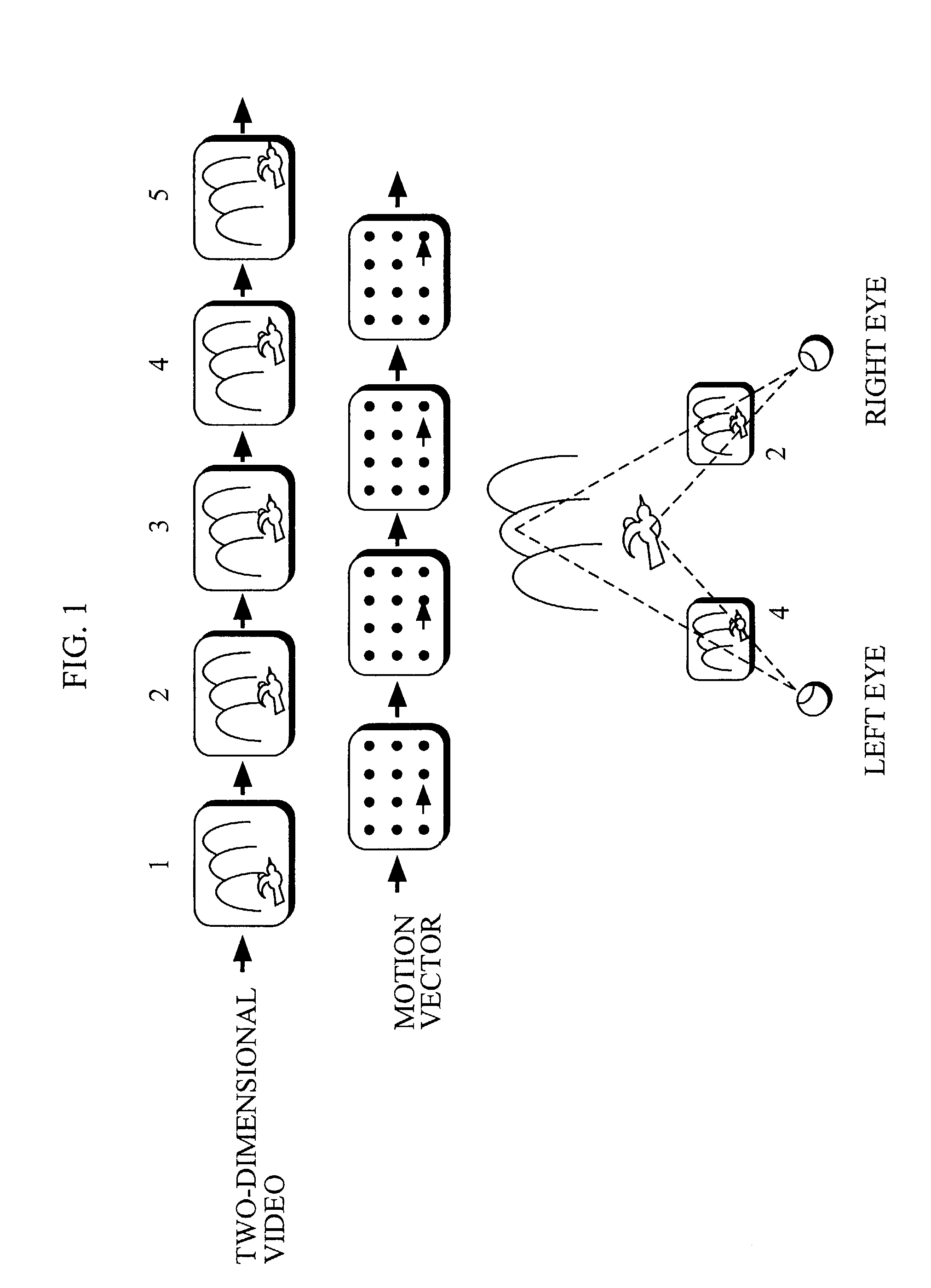
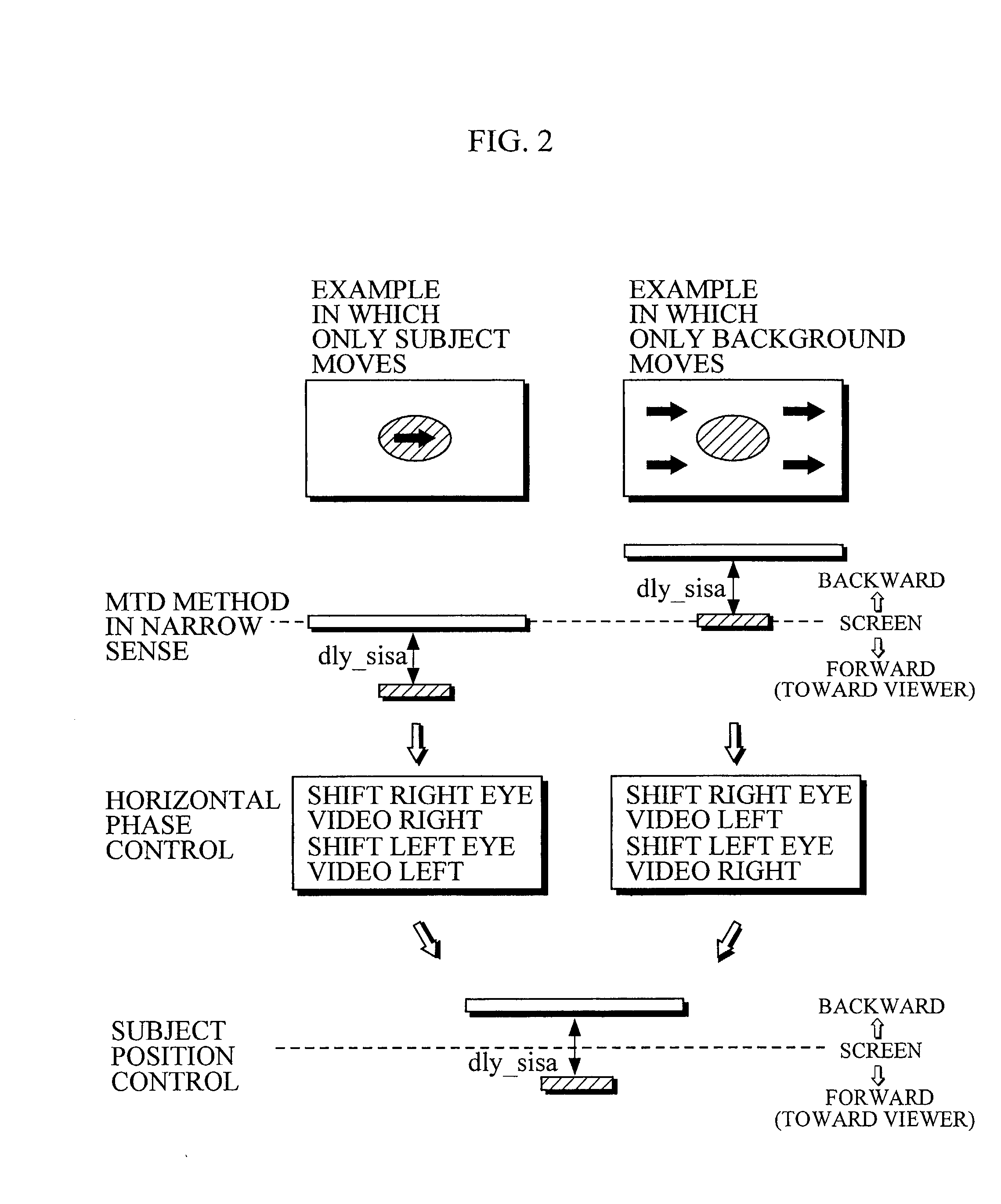
Device and method for converting two-dimensional video to three-dimensional video
There is provided parallax correction means for correcting a parallax for each area calculated by parallax calculation means in accordance with the magnitude of a motion vector for the area detected by motion vector detection means in order to prevent the three-dimensional effect of a conversion video from greatly differing depending on an input video when the MTD method and the CID method are simultaneously used.When a depth estimate is converted into a parallax, the depth estimate is subjected to distance scale conversion in order to suppress the distortion of the conversion image, to find a tentative target phase for each parallax calculation area, and a dynamic range in which a phase difference between the parallax calculation areas is within a distortion allowable range is searched for and is subjected to distance scale conversion, to find a tentative target phase, which operations are repeated.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
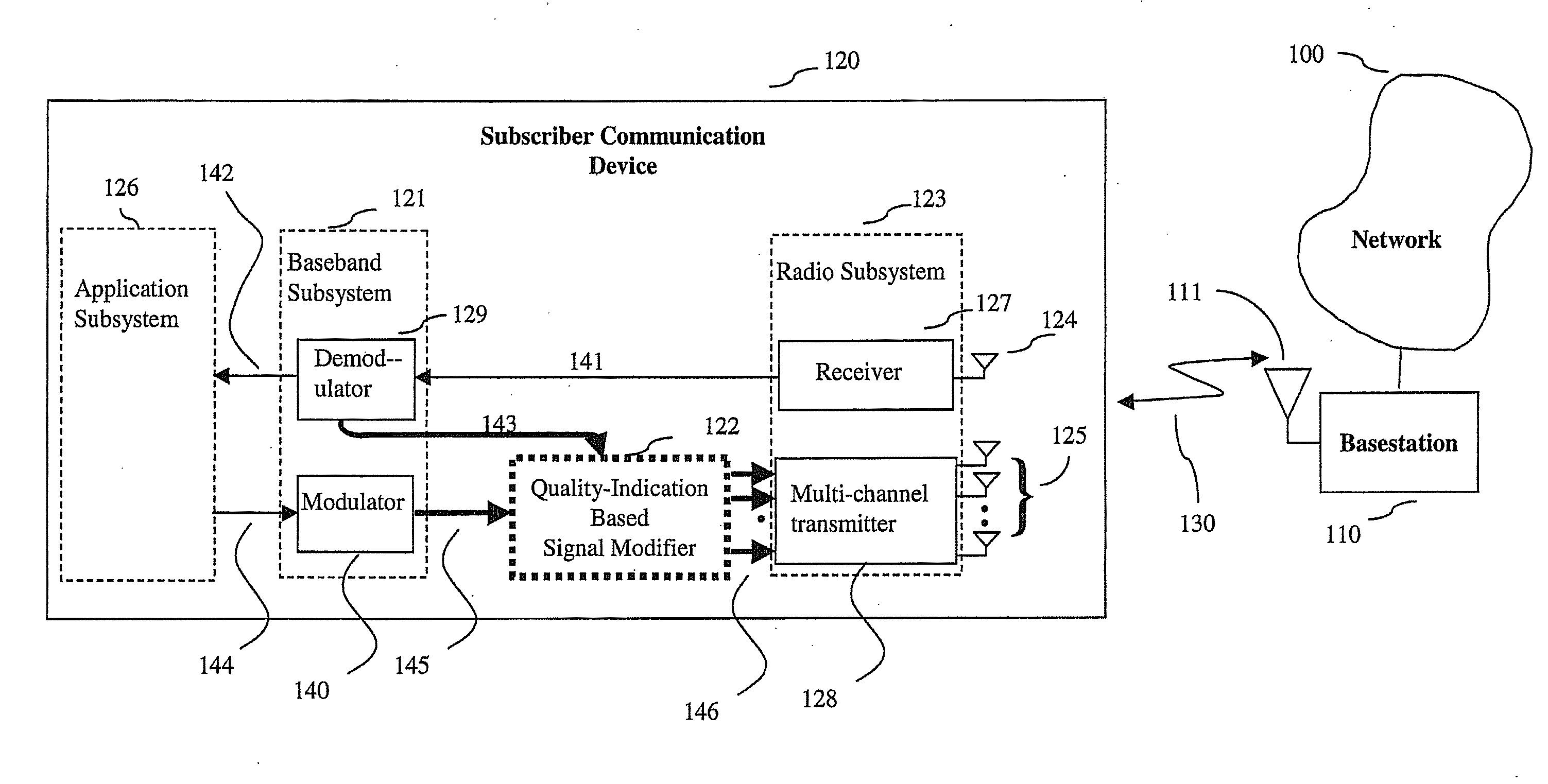
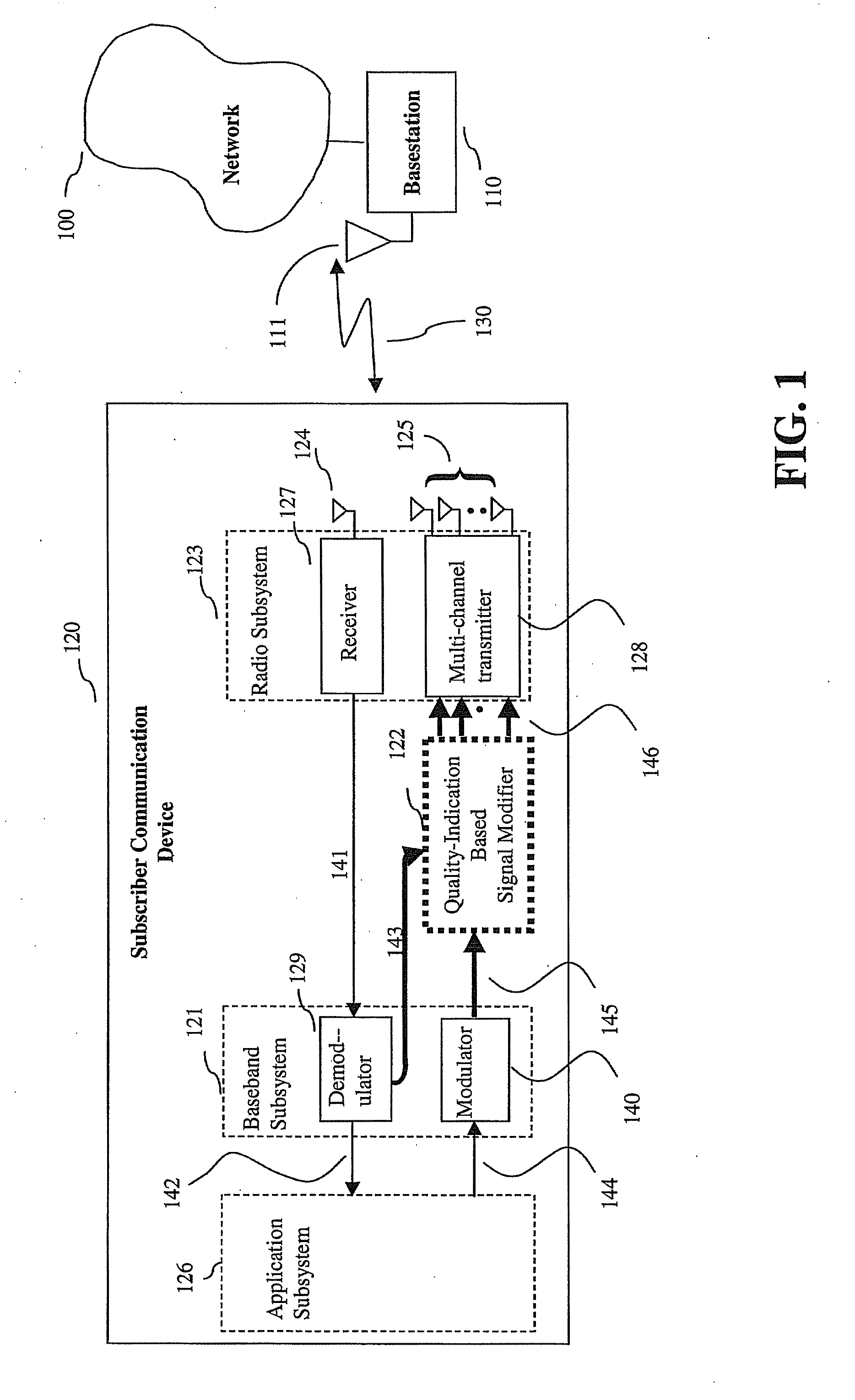
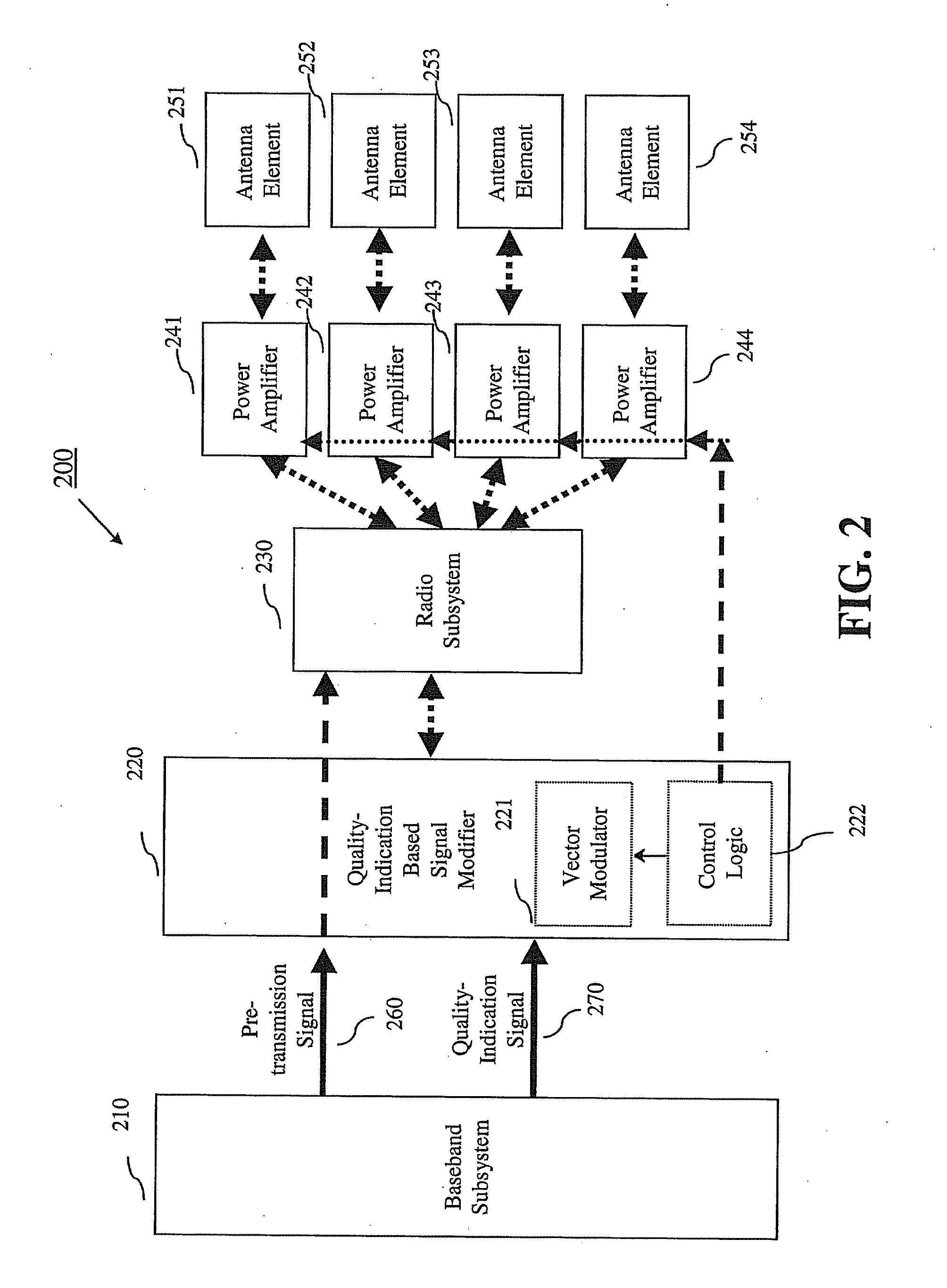
System, method and apparatus for mobile transmit diversity using symmetric phase difference
InactiveUS20100266063A1Easy to receiveQuality improvementPower managementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase differenceDiversity scheme
Communication is performed for a first communication device having a set of antenna elements. A quality-indication signal is received from a second communication device (e.g., a basestation). A complex weighting is calculated based on the quality-indication signal. A pre-transmission signal is modified based on the complex transmit diversity weighting to produce a set of modified-pre-transmission signals, wherein the modifications are symmetric by making approximately half the magnitude of the transmit diversity modification to one signal in a first direction, and approximately half the magnitude of the transmit diversity modification to the other signal in a second direction, opposite the first direction. Each modified pre-transmission signal from the set of modified-pre-transmission signals is uniquely associated with an antenna element from the set of antenna elements. The set of modified-pre-transmission signals is sent from the set of antenna elements to produce a transmitted signal.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Power converter and power unit
InactiveUS6963147B2Solve large capacityMinimal energyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectDc-dc conversionPhase differenceWave shape
Control means is provided, in which the whole of the phase difference of a power waveform of each phase is matched to a value dividing a cycle of the power waveform into n-equal portions, and at the same time, the whole of the power value of each phase is controlled to be identical, so that the power conversion unit having a n-alternating current output (n is an integer numeral serving as n≧2) connected to the direct current power source and smoothing means provided between the direct current power source and the power conversion unit are made small in capacity.
Owner:CANON KK
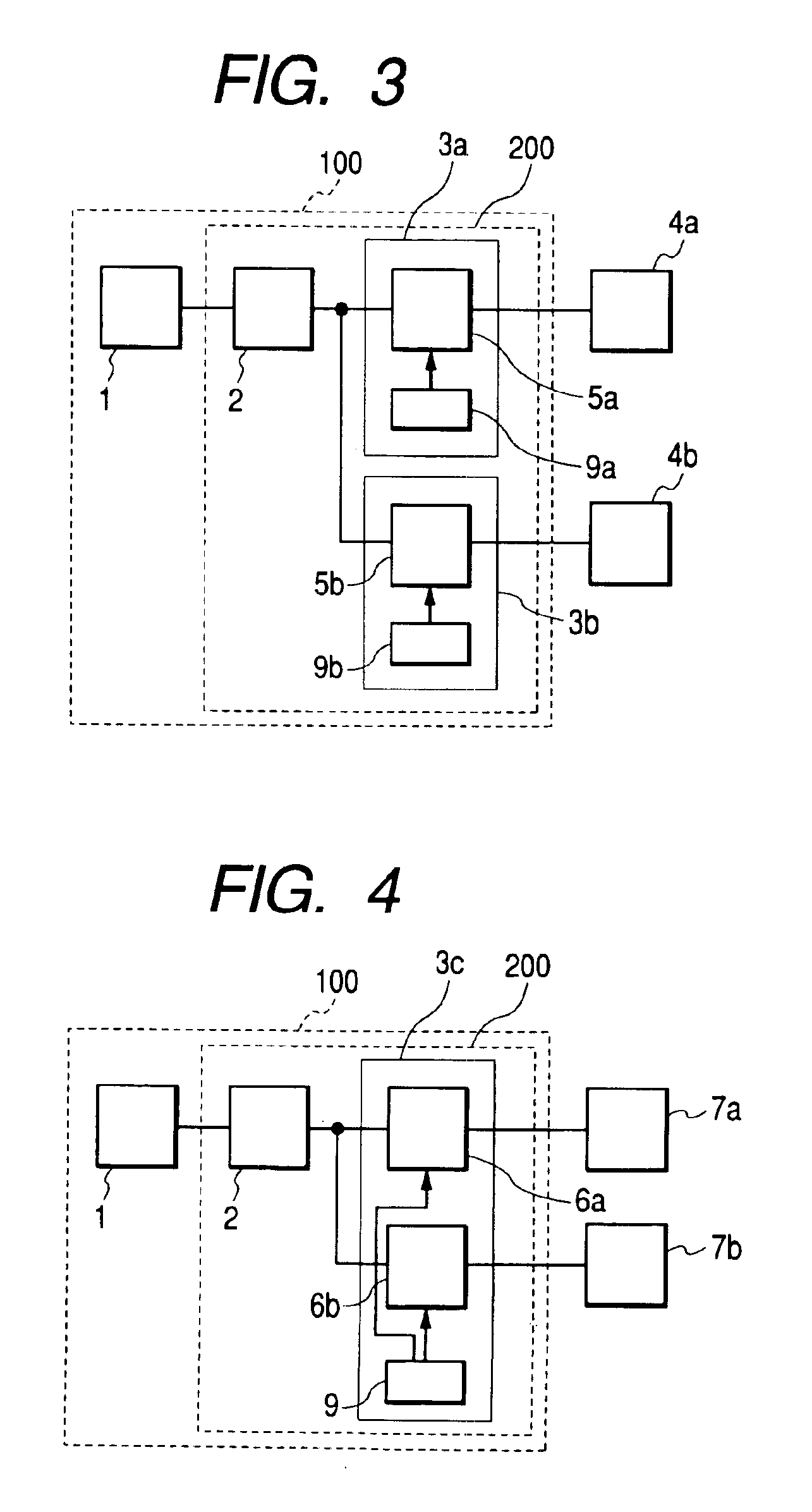
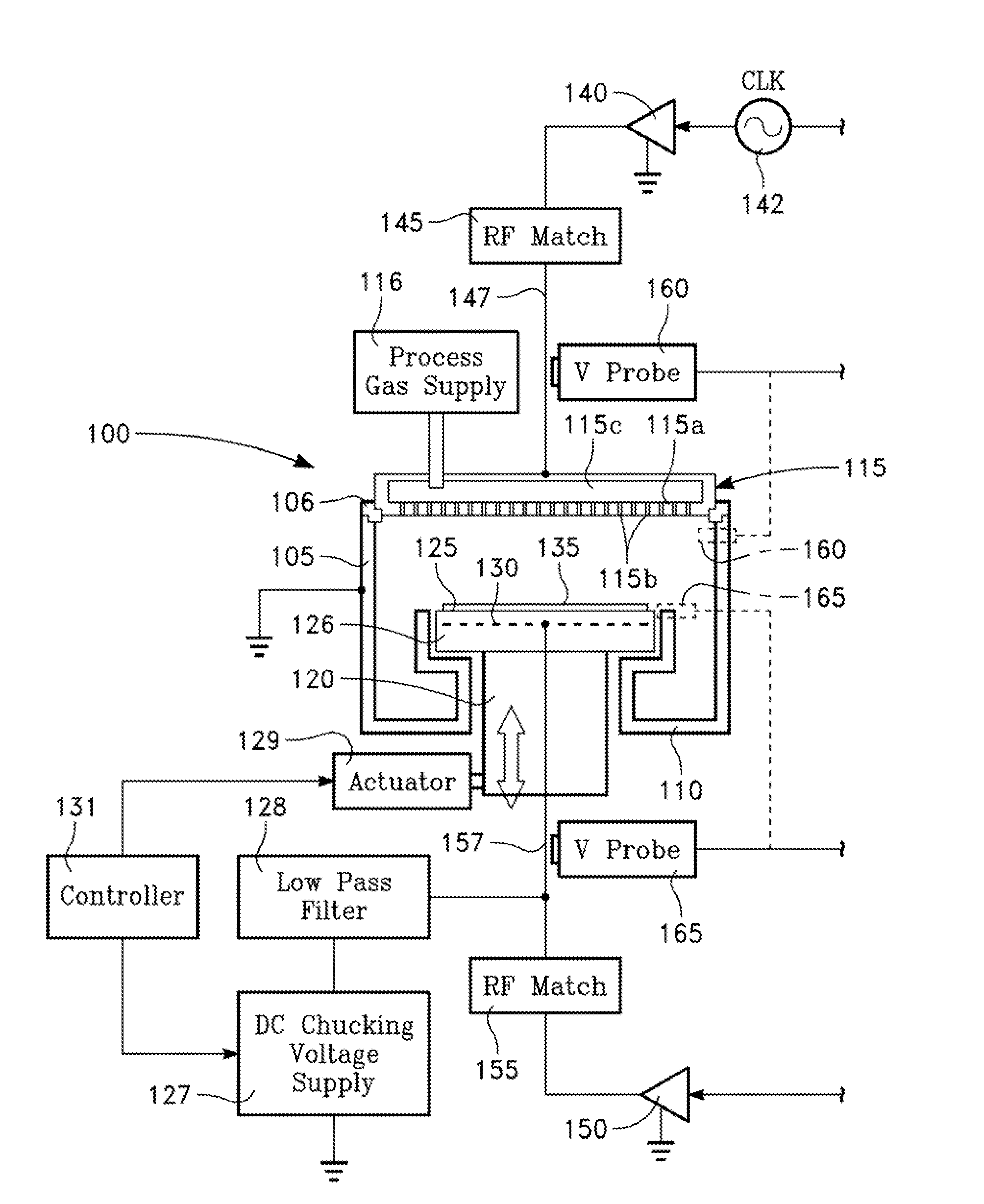
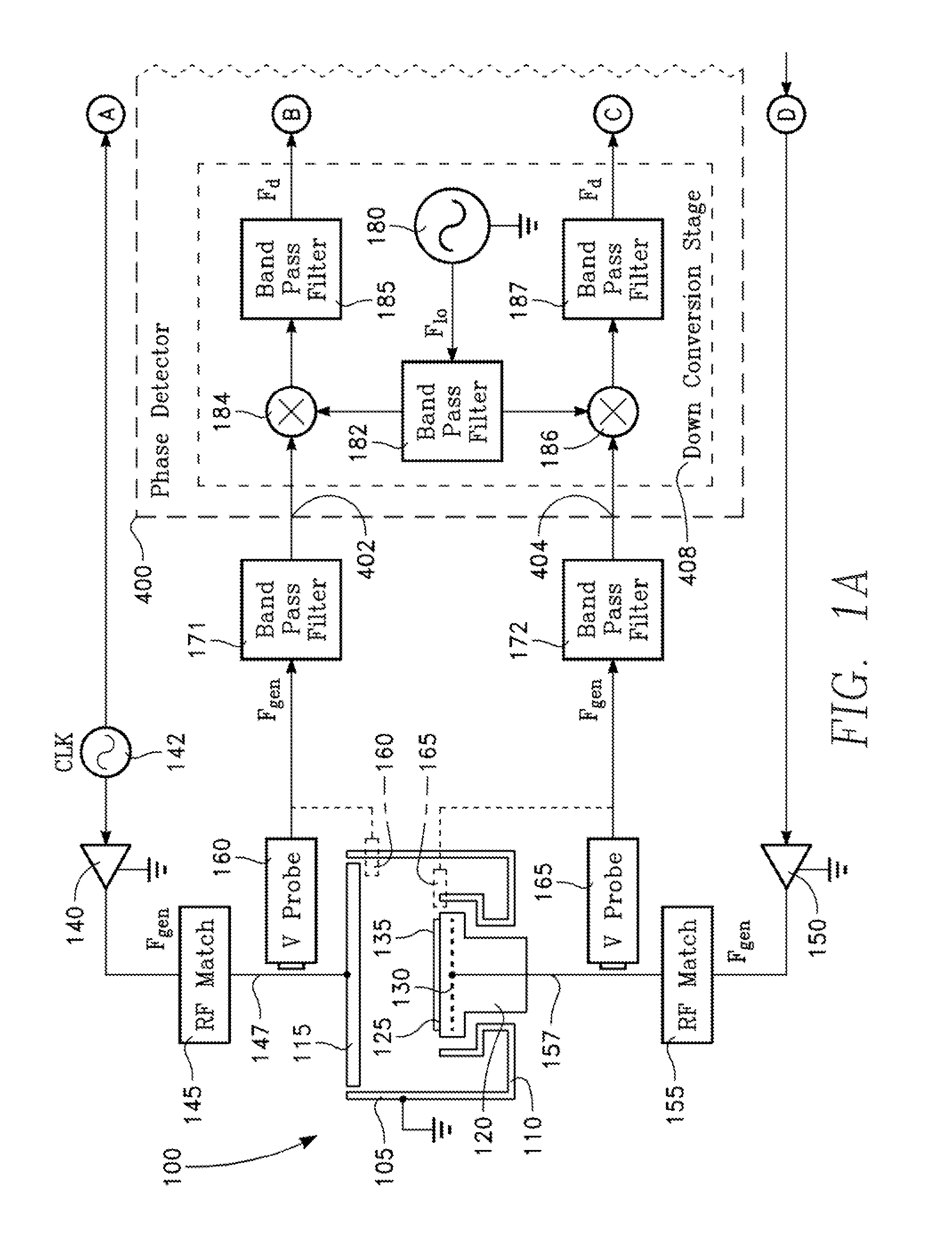
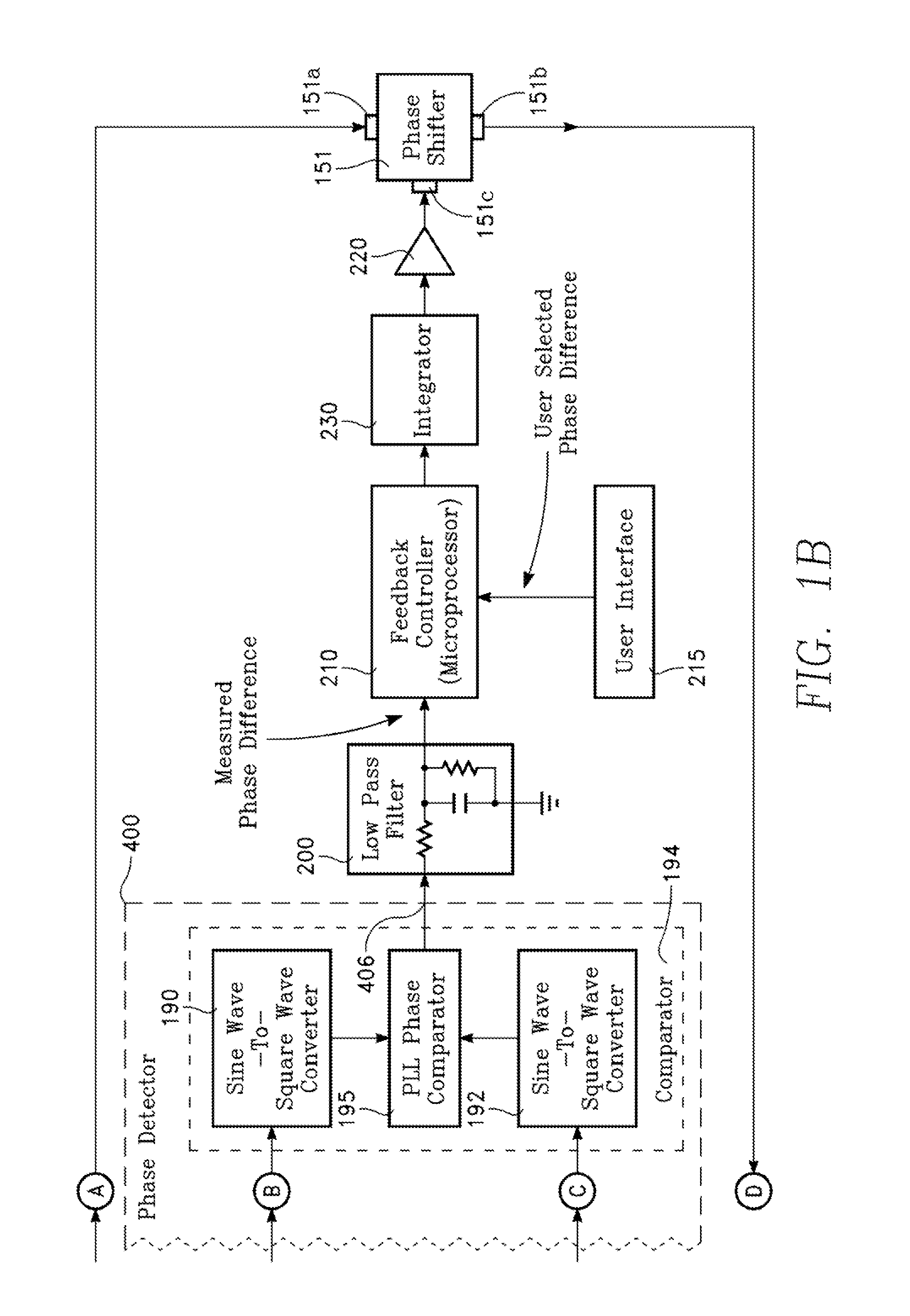
Two-phase operation of plasma chamber by phase locked loop
InactiveUS20130284369A1Liquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesPhase differenceEngineering
Plasma distribution is controlled in a plasma reactor by controlling the phase difference between opposing RF electrodes, in accordance with a desired or user-selected phase difference, by a phase-lock feedback control loop.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
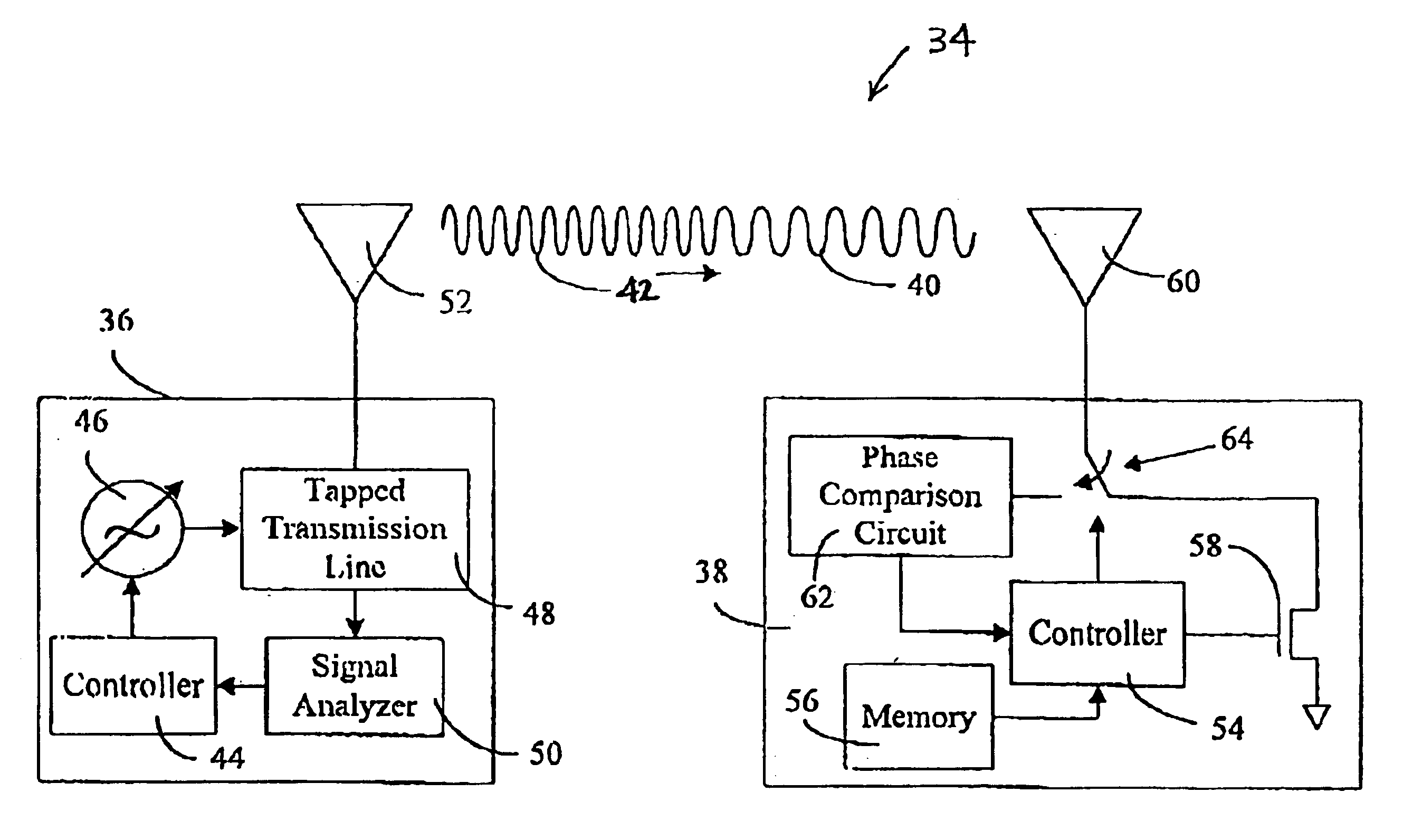
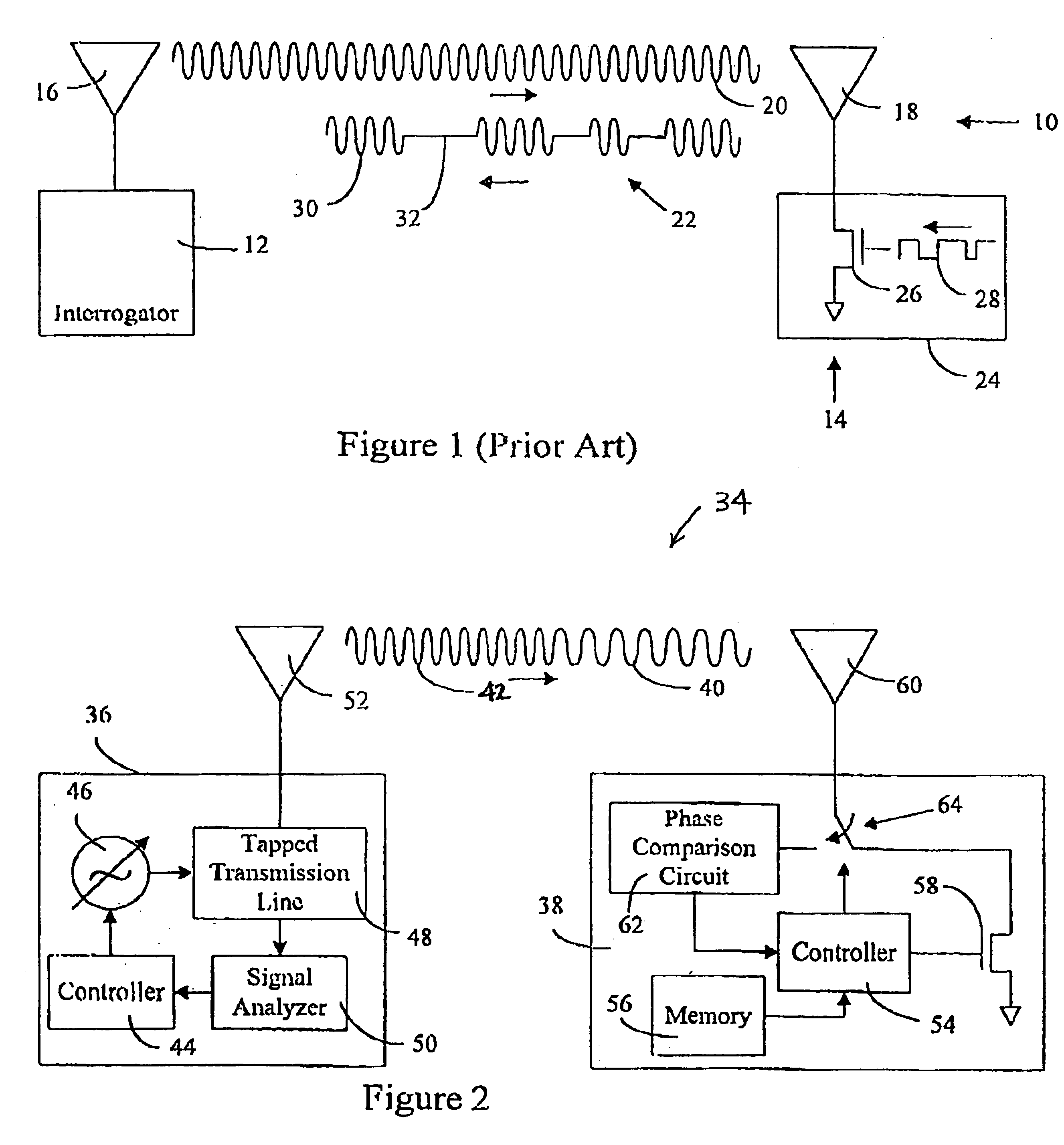
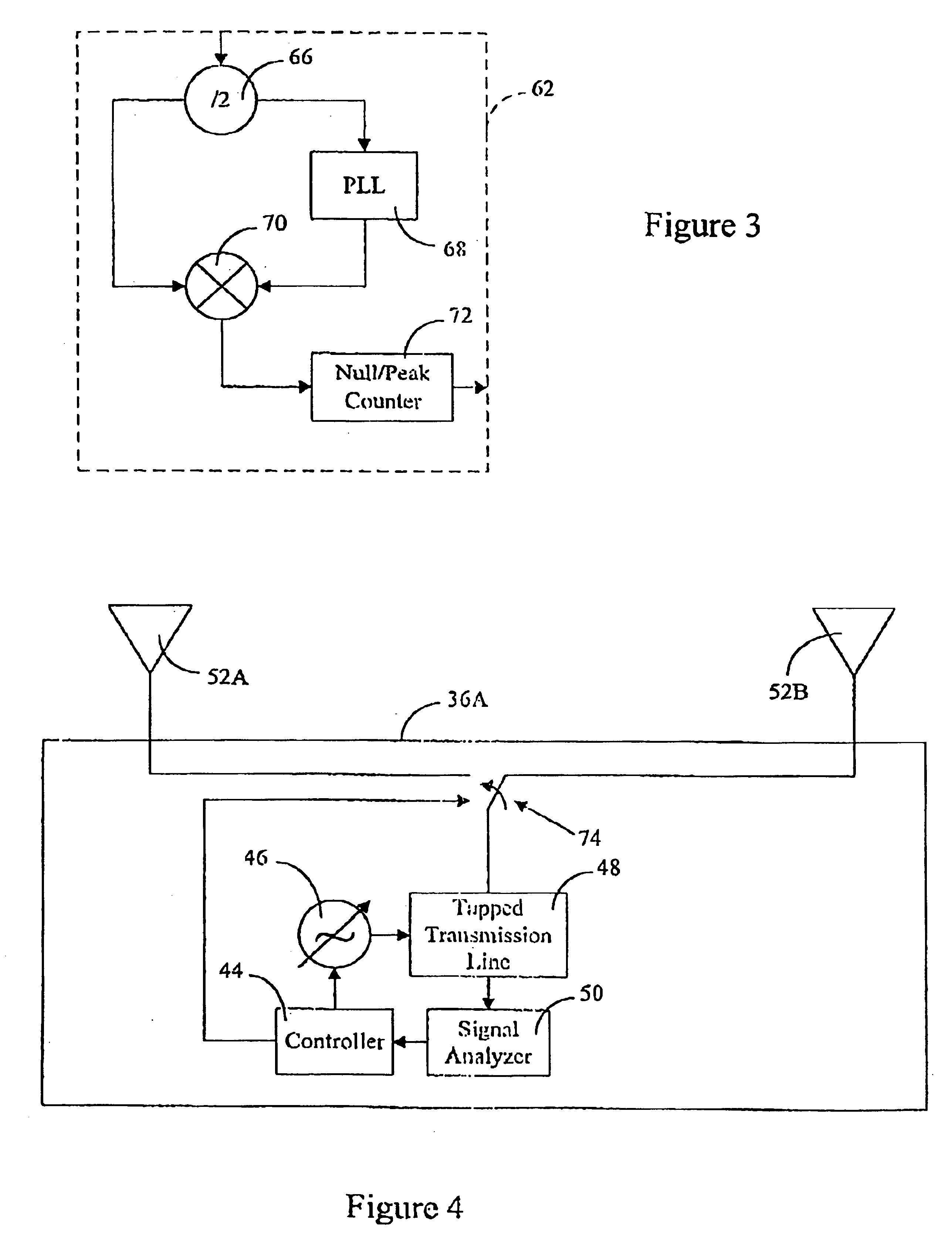
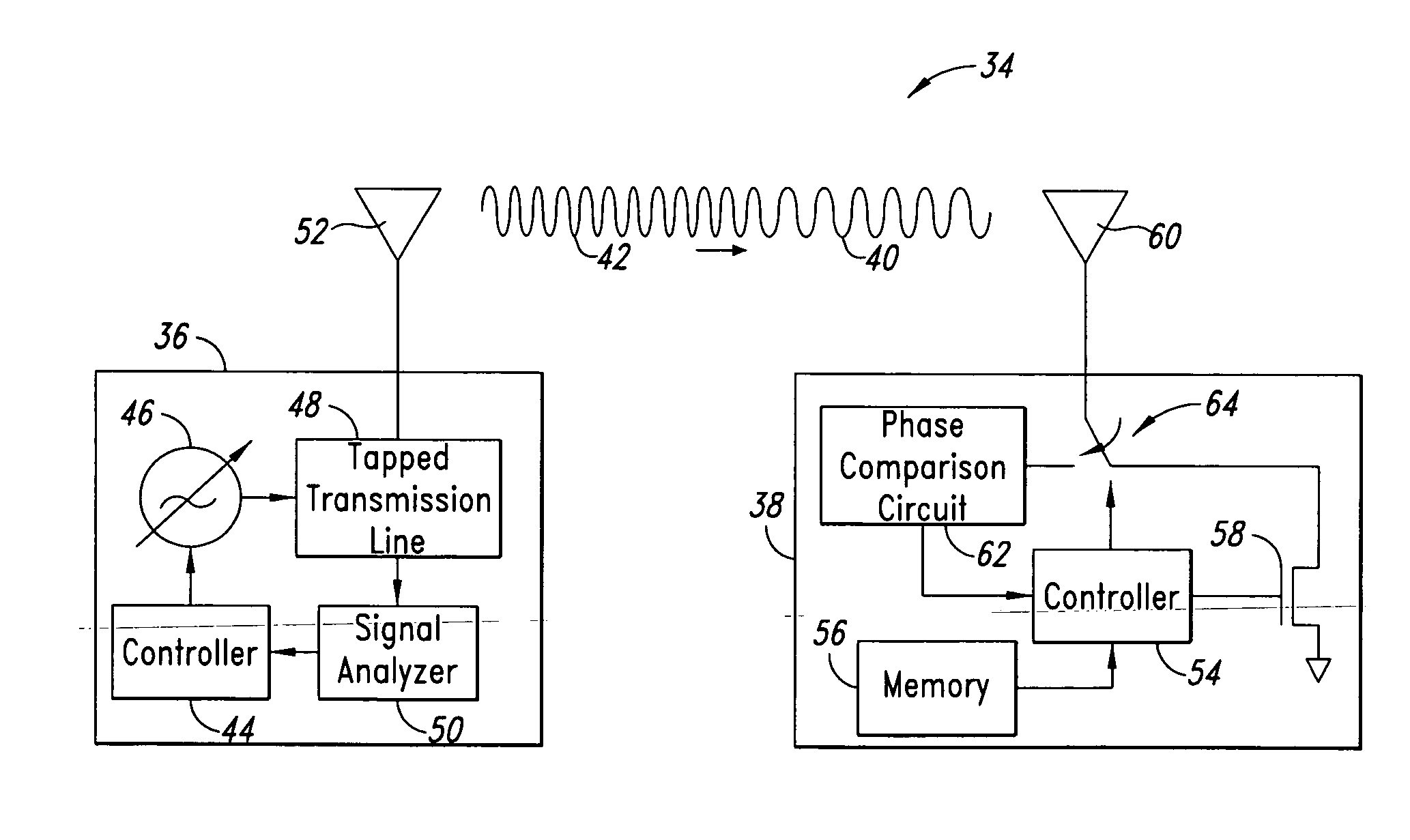
Distance/ranging by determination of RF phase delta
A method and system can locate an RF transponder based on phase differences between signals transmitted to the RF transponder. The method transmits from a first transponder to a second transponder first and second signals at first and second frequencies, respectively. The second signal is compared with the first signal and a distance between the first and second transponders is determined based on the phase difference between the first and second signals. In one embodiment, the first transponder is an interrogator, the second transponder is an RF tag, and the RF tag determines the phase difference between the two signals. In another embodiment, the first and second transponders are the interrogator and RF tag, respectively, but the interrogator determines the phase difference between the two signals after the two signal are reflected back to the interrogator. The method can also determine a position (distance and direction) of the RF tag by measuring the distances from two different locations of the interrogator to the RF tag. In one embodiment, the two distances are measured from two spaced-apart antennas of the interrogator. In another embodiment, the interrogator is moved from one known location to another known location. With distance measurements from both known locations, the location of the RF tag can be determined by simple geometry.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Circularly-polarized-wave patch antenna which can be used in a wide frequency band
InactiveUS6952183B2Wide bandImprove axle ratioSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsAxial ratioCoaxial cable
A circularly-polarized-wave patch antenna includes a main body having a patch electrode provided with two feeding points and a circuit for generating a phase difference of 90° between signals supplied to the feeding points. A Wilkinson distribution circuit is provided between the 90°-phase-difference generating circuit and a coaxial cable (feeder line) so as to improve a reflection characteristic. The patch antenna includes two feeding points, and thus a favorable axial ratio characteristic can be obtained in a wide band. Also, a favorable reflection characteristic can be obtained in a wide band because of the Wilkinson distribution circuit. Accordingly, the patch antenna can be used in a wider frequency band.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
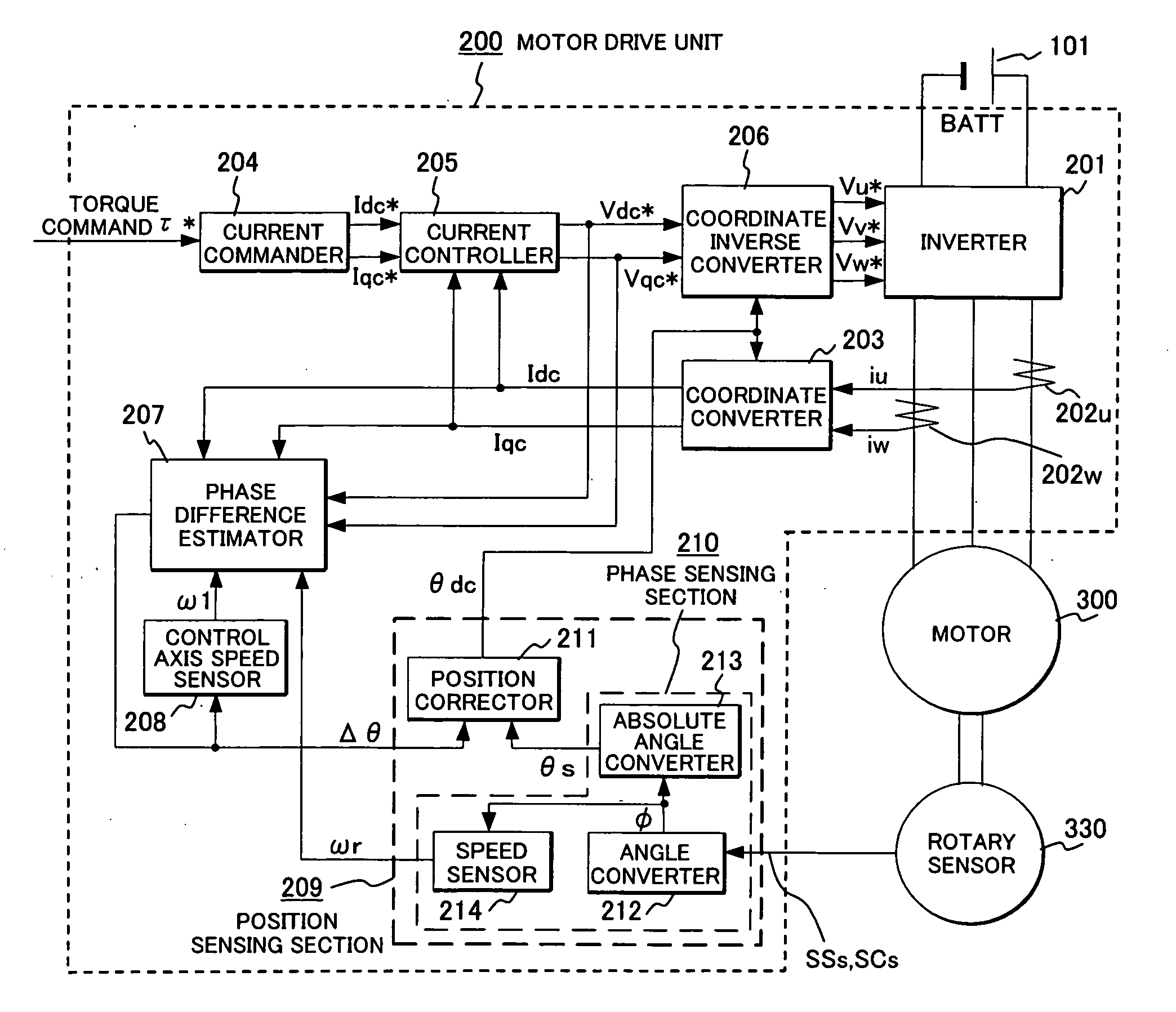
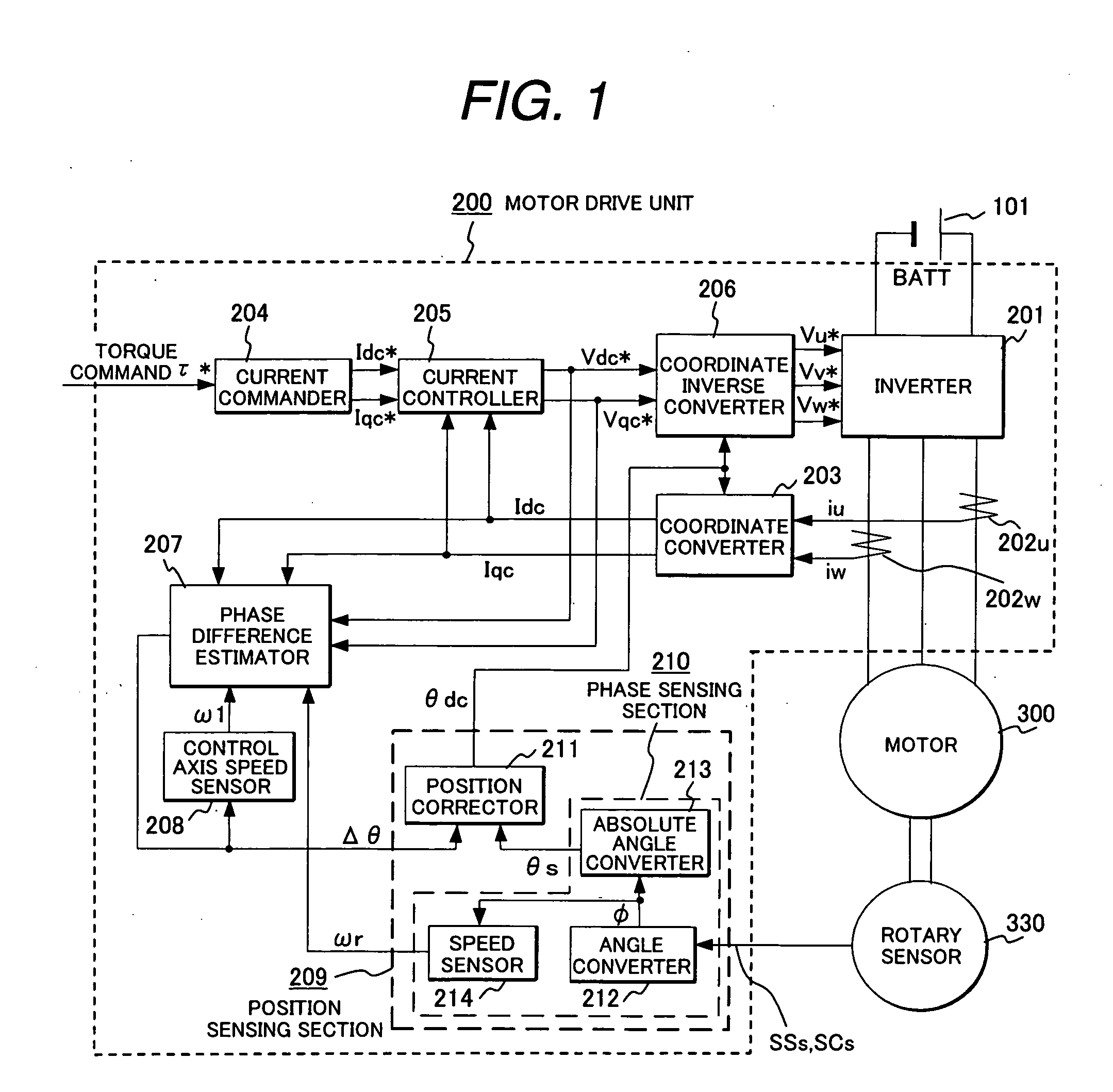
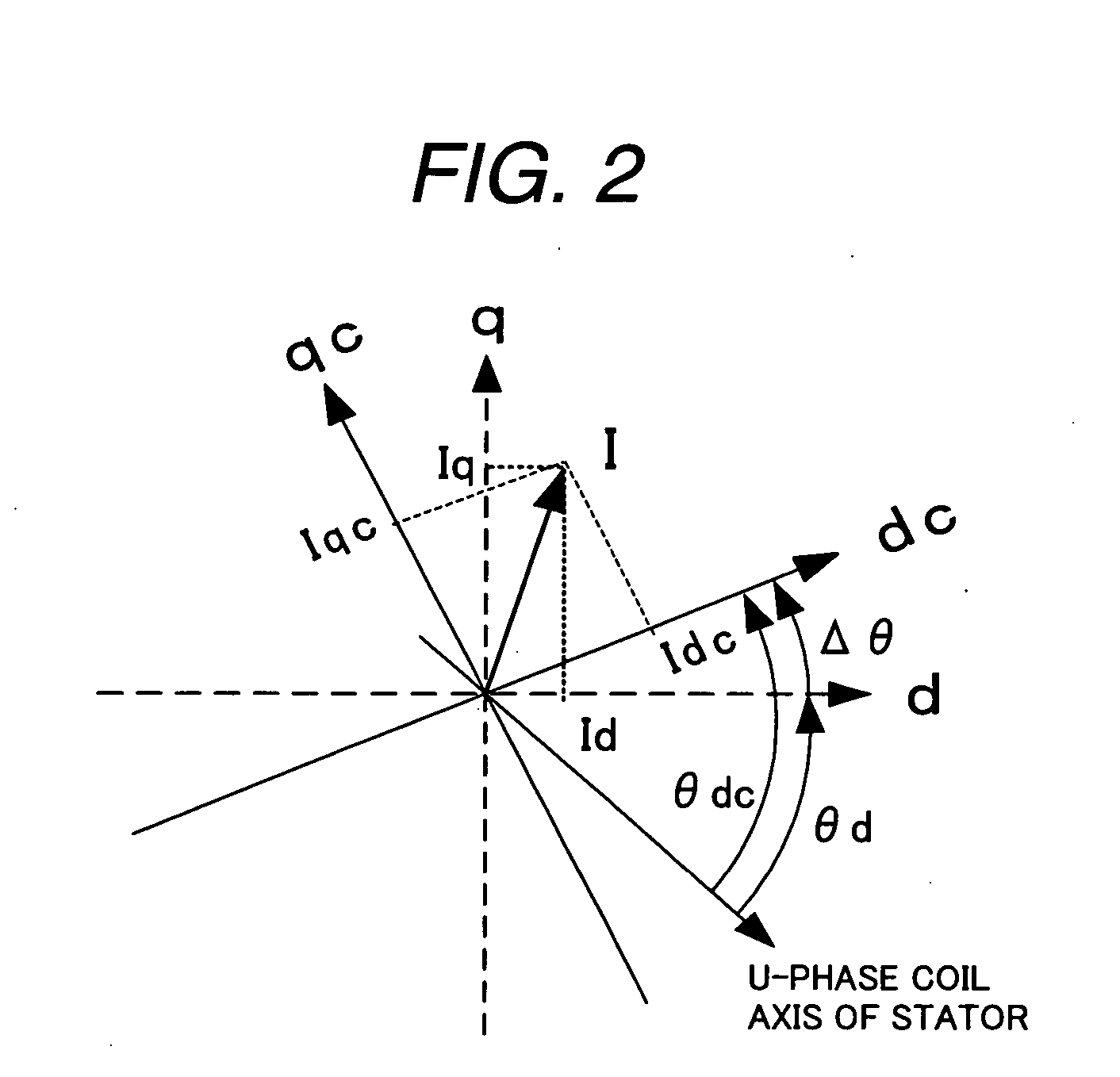
Synchronous motor drive unit and a driving method thereof
InactiveUS20060125439A1Efficient driveImprove maintainabilityAsynchronous induction motorsElectric energy vehiclesSynchronous motorPhase difference
A rotary sensor that outputs two analog signals, such as one sine wave and one cosine wave and has multiple periods within one period of the electrical angle of a motor is employed. The motor is energized at each position for a specified length of time upon its startup by using multiple electrical angles corresponding to the multiple candidate absolute angles obtained from the rotary sensor signal as the initial position of the motor, and the electrical angle at which the motor acceleration becomes maximum is determined as the absolute angle. While the motor drive is in operation, on the other hand, the phase difference Δθ between the phase of the motor at the counter electromotive voltage and the control phase is directly computed from the parameters of the motor, sensed current, voltage command and angle speed so as to correct the shifted position. A high-efficiency motor drive unit with improved maintainability of rotary sensor and improved accuracy of sensing the magnet pole position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor that accelerates and decelerates very quickly in a wide range of speed is realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Circular-polarization dipole helical antenna
InactiveUS20060232493A1Quick fine-tuningReduce lossRadiating elements structural formsHelical antennasElectrical conductorPhase difference
A circular-polarization dipole helical antenna is used for electronic device and satellite terminal and includes a base, and an antenna conductor arranged on surface of the base. The antenna conductor includes a plurality of metal conductors with high Q value and anti-oxidation property and continuously and helically coated on surface of the base. The base is made of low loss and high dielectric constant material. An unbalance-to-balance circuit module connects two signal-feeding ends to the base with phase difference of 180 degree. The problems of narrow bandwidth, low efficiency, complicated structure and precise manufacture can be solved.
Owner:CIREX TECH CORP
Distance/ranging determination using relative phase data
InactiveUS20050237953A1Transmission control/equalisingPosition fixationRelative phasePhase difference
A method and system for locating an RF transponder based on phase differences between signals received from the RF transponder. The method includes receiving a signal from the transponder and calculating distance, relative movement, and position by comparing I-Q phase angle vectors of the signals. Global scroll commands can be used following receipt of signals at first and second frequencies to quickly determine distance.
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
Robotics visual and auditory system
InactiveUS20090030552A1Accurate collectionAccurately localizeProgramme controlComputer controlSound source separationPhase difference
It is a robotics visual and auditory system provided with an auditory module (20), a face module (30), a stereo module (37), a motor control module (40), and an association module (50) to control these respective modules. The auditory module (20) collects sub-bands having interaural phase difference (IPD) or interaural intensity difference (IID) within a predetermined range by an active direction pass filter (23a) having a pass range which, according to auditory characteristics, becomes minimum in the frontal direction, and larger as the angle becomes wider to the left and right, based on an accurate sound source directional information from the association module (50), and conducts sound source separation by restructuring a wave shape of a sound source, conducts speech recognition of separated sound signals from respective sound sources using a plurality of acoustic models (27d), integrates speech recognition results from each acoustic model by a selector, and judges the most reliable speech recognition result among the speech recognition results.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Methods and apparatus to position a mobile receiver using downlink signals, part I
InactiveUS6208297B1Reduce the impactReduce impactDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationPhase differenceImage resolution
The invention comprises of methods and apparatus to estimate the position and velocity of a Mobile Receiver (MR) using either the Time Of Arrival (TOA) of signals received by the MR, their Phase Of Arrival (POA), their Strength Of Arrival (SOA), their Frequency Of Arrival (FOA), or a combination thereof, with respect to a reference produced by a Reference Receiver (RR) of known location. In order to solve for the coordinates of the MR, the invention uses either hyperbolic multilateration based on Time Difference Of Arrival (TDOA), or linear multiangulation based on Phase Difference Of Arrival (PDOA), or both. In order to solve for the velocity of the MR, the patent uses FOA based on Frequency Difference Of Arrival (FDOA). An important contribution of this invention is the way the MR receives, processes and combines available signals for location purposes. Another important contribution of this invention is the way the RR receives, processes and combines available signals for reference purposes. Yet another important contribution of the invention is the application of Super-Resolution (SR) techniques at both the MR and the RR to increase the resolution of the estimated TOAs, POAs, SOAs, or FOAs.
Owner:CAPITOL ENERGY RESOURCES INC +1
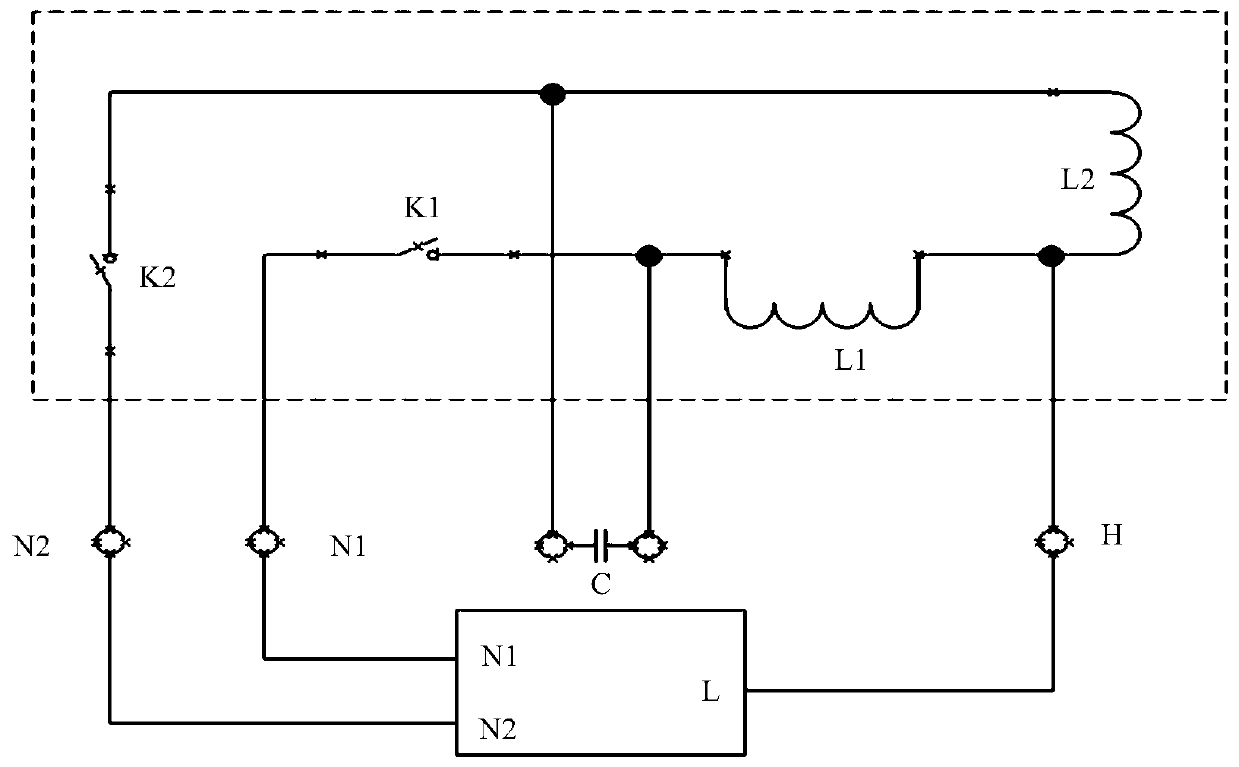
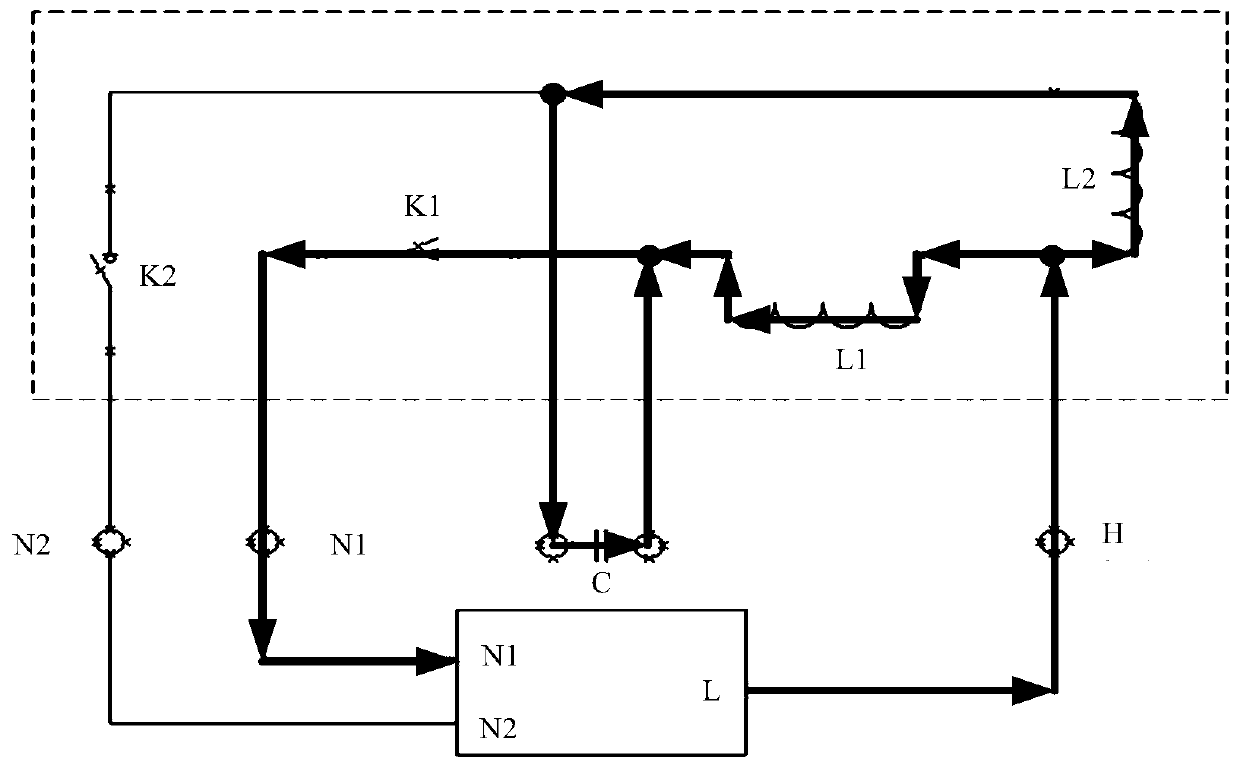
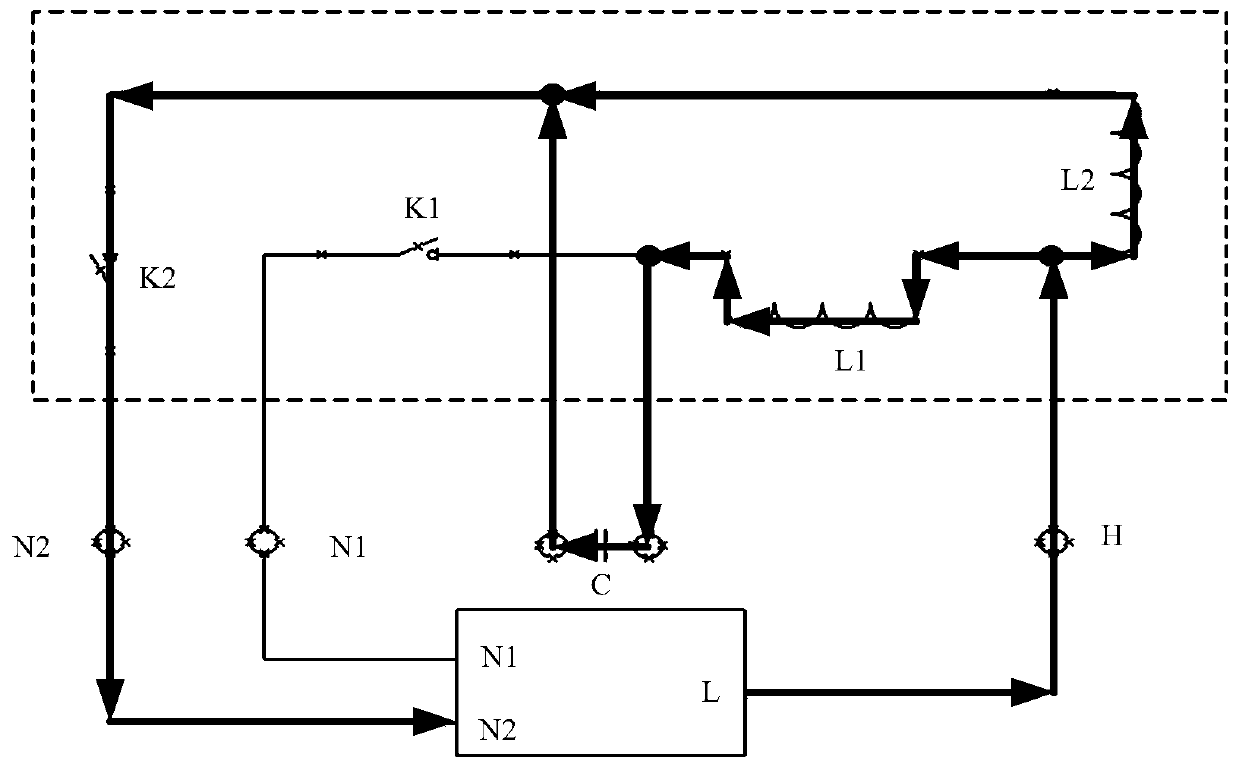
Wireless power feeder and wireless power transmission system
InactiveUS20110049997A1Improve efficiencySuppressing influence on the resonance characteristics of the feeding coilElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersPhase differenceResonance
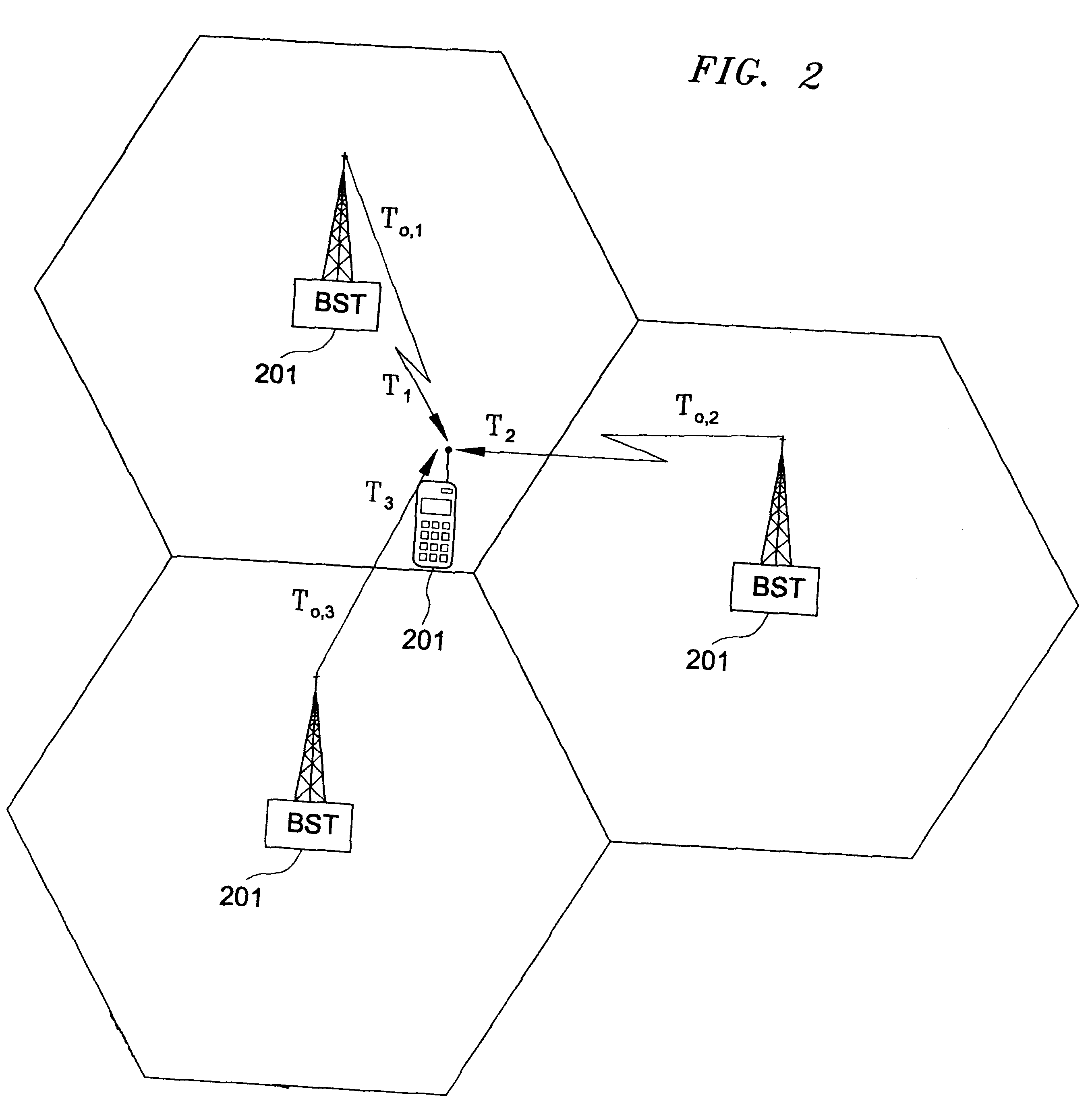
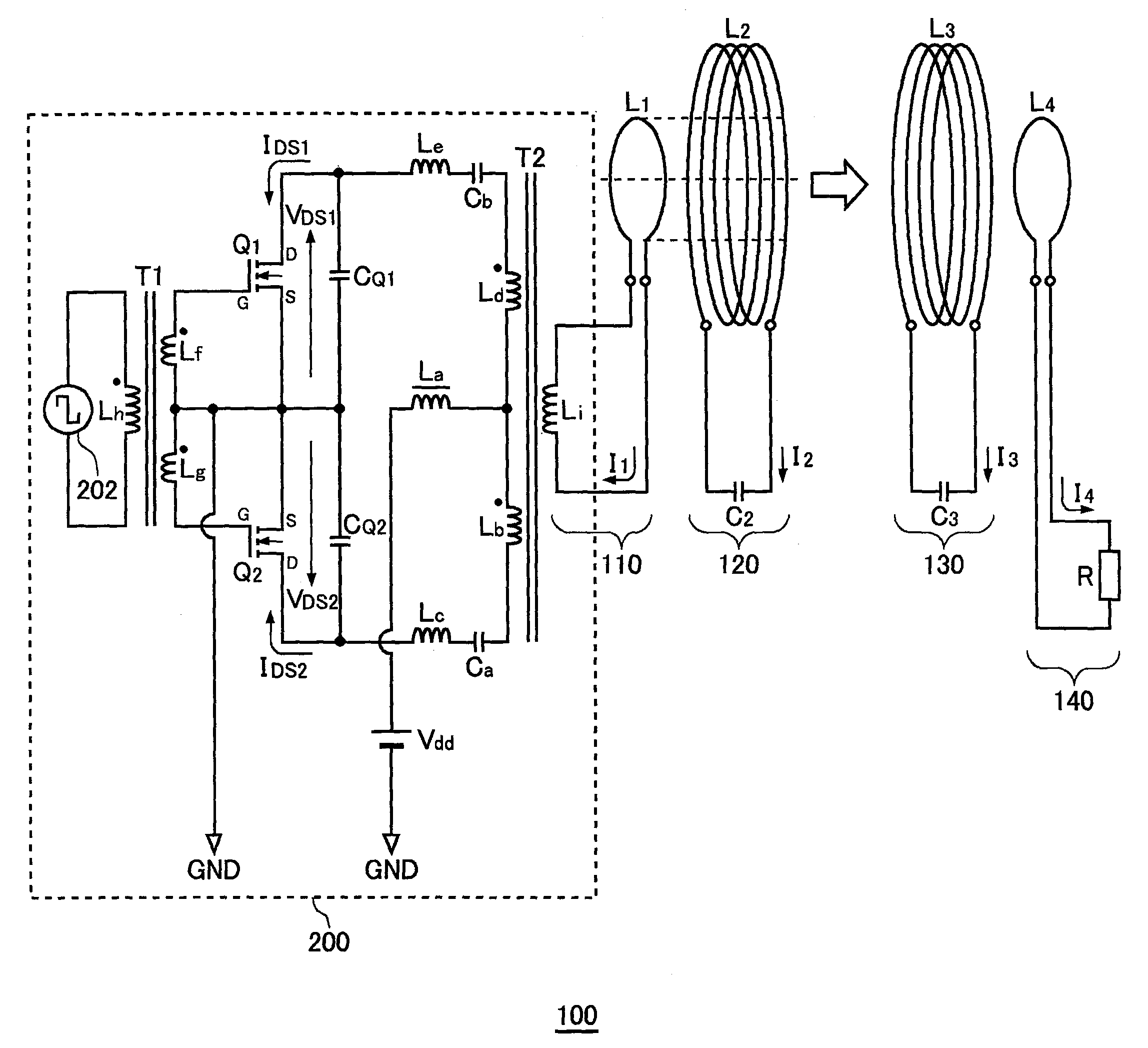
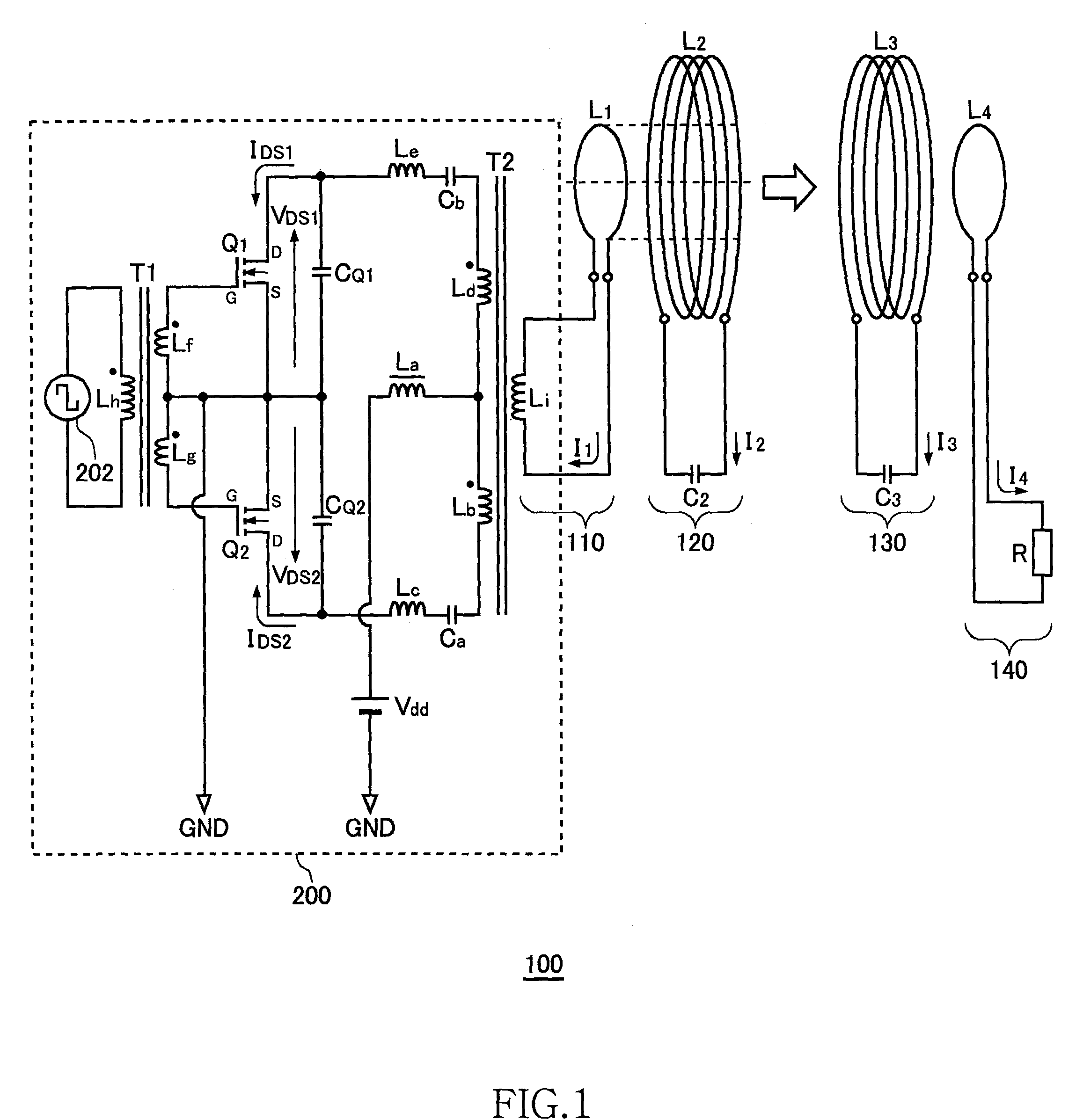
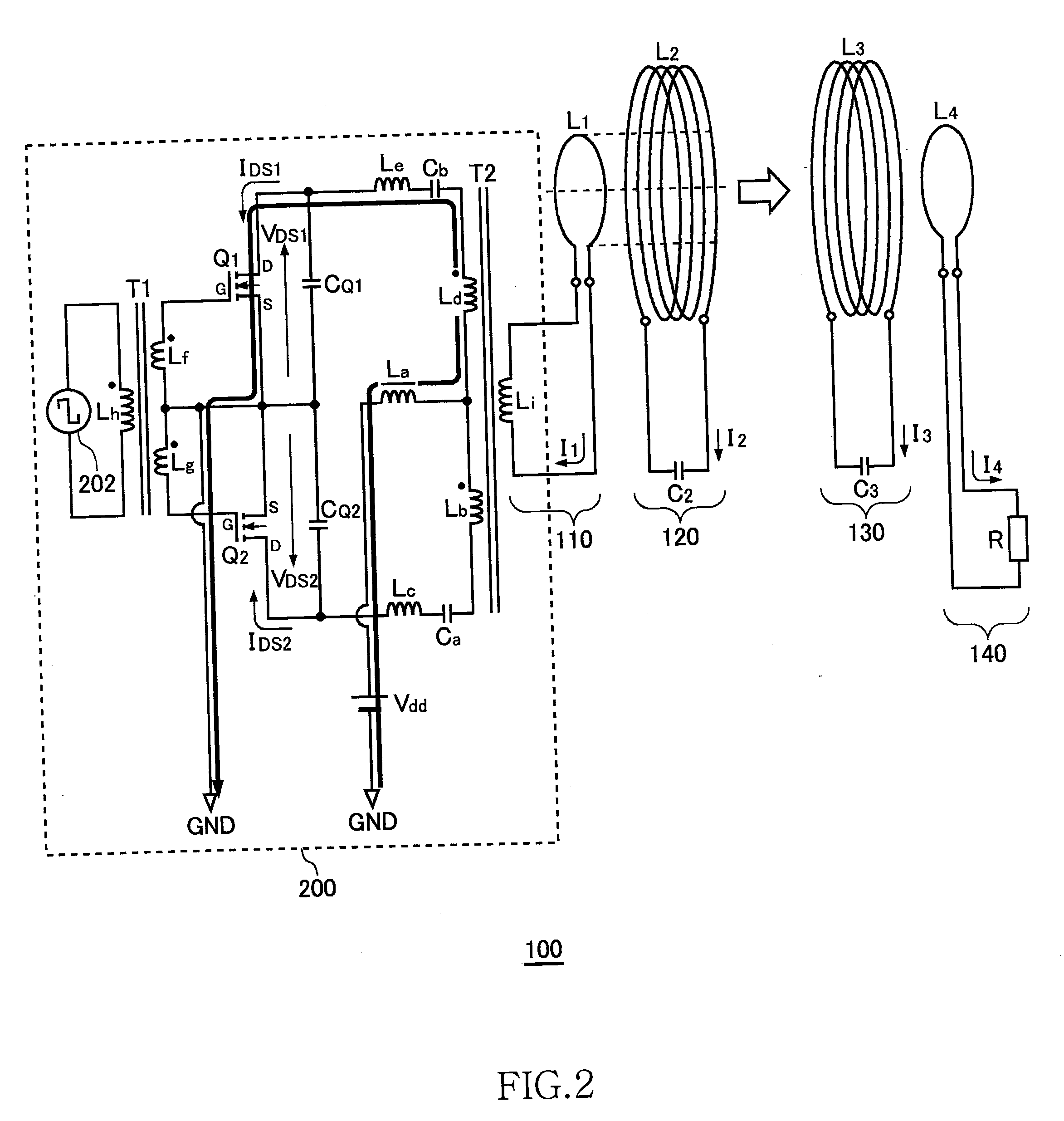
Power is transmitted from a feeding coil L2 to a receiving coil L2 by magnetic resonance. A power circuit 200 turns ON / OFF switching transistors Q1 and Q2 to feed AC current to an exciting circuit 110, whereby the AC power is fed from an exciting coil L1 to a feeding coil L2. A phase detection circuit 150 sets the switching transistor Q2 of the power circuit 200 as a measurement target and detects the phase difference between source-drain current IDS2 and source-drain voltage VDS2 from the current phase and voltage phase thereof.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical proximity correction method
InactiveUS20050009344A1Reduce the differenceEasy to operateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentGraphicsPhase difference
An integrated circuit layout includes dense figures and at least one isolated figure. A plurality of dummy patterns are formed to surround the isolated figure, so as to reduce the difference in pattern density of the integrated circuit layout. A transmitted light of the dummy patterns provides a phase difference of 0 or 180 degrees relative to a transmitted light of the integrated circuit layout. The integrated circuit layout and the plurality of dummy patterns are formed on a photo-mask.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Communication method and system
ActiveUS20080150514A1Increase network capacityCooperate fullySite diversityReceivers monitoringPhase correctionCommon base
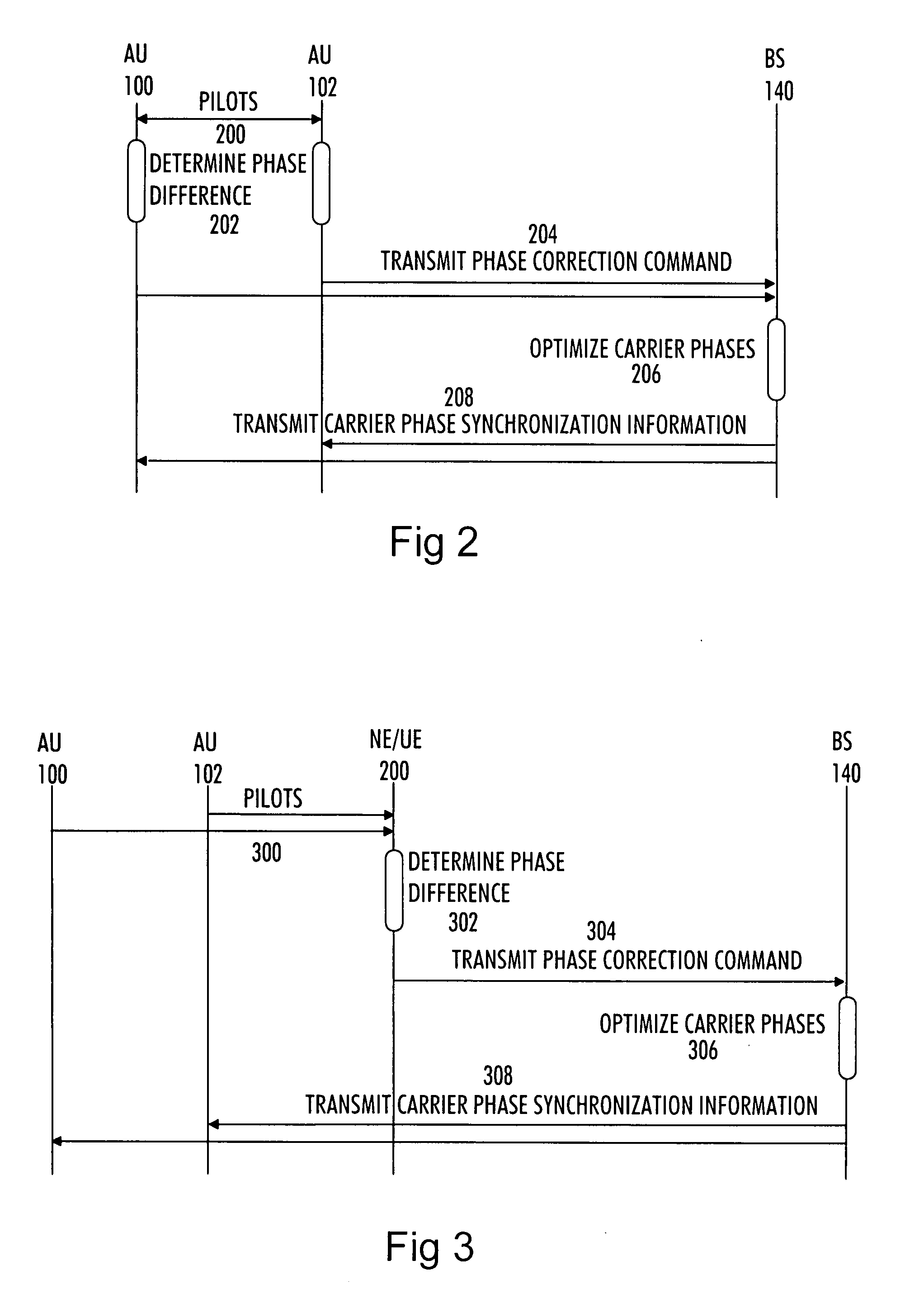
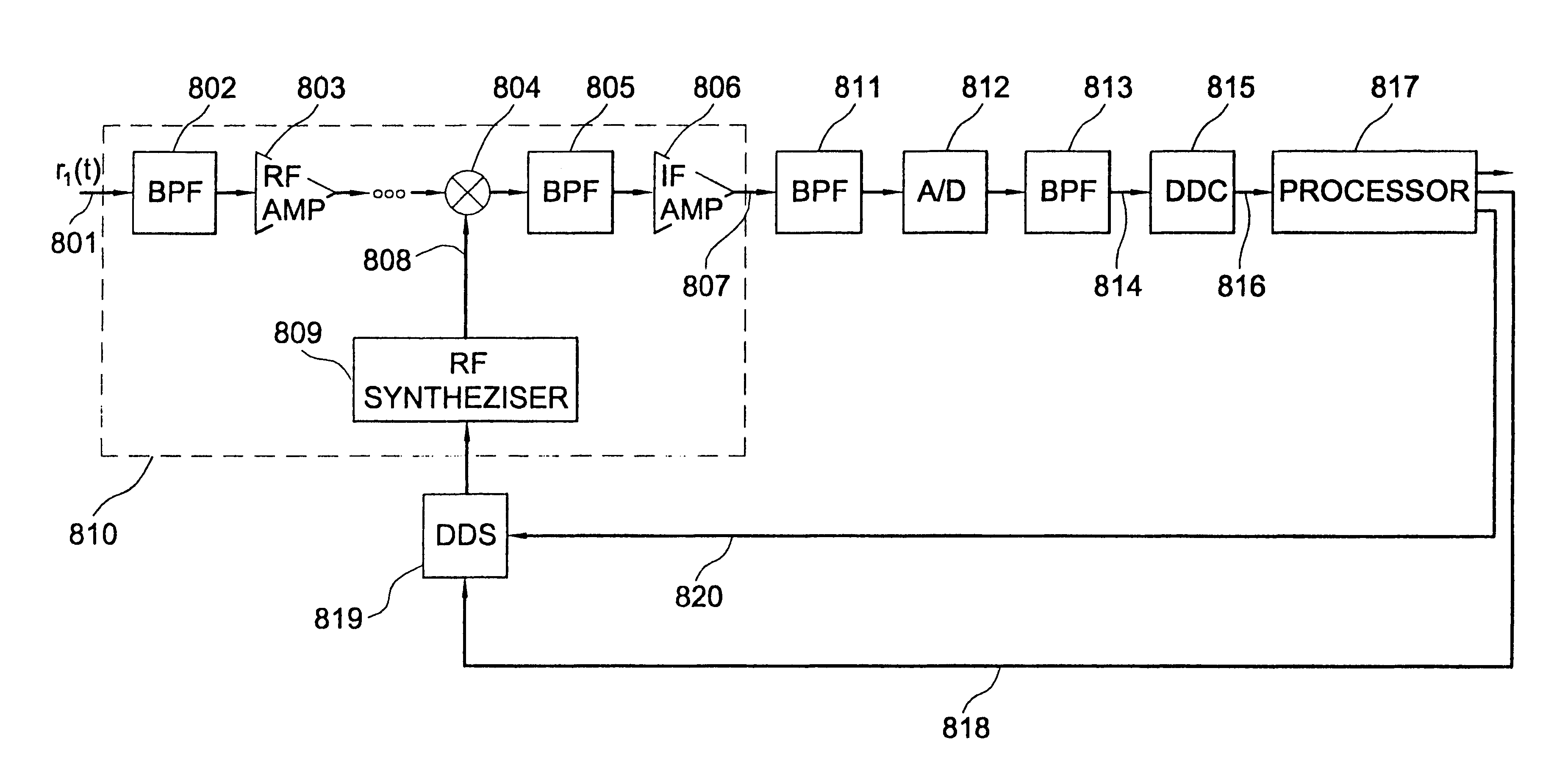
There is provided a method comprising: determining a phase difference between at least two antenna units of a distributed antenna system on the basis of at least one pilot signal received from at least one of a plurality of antenna units; and transmitting phase correction commands to a common base station of the plurality of antenna units on the basis of the determined phase difference in order to synchronize carrier phases between at least two antenna units of the distributed antenna system.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Methods and apparatus to position a mobile receiver using downlink signals, part II
InactiveUS6204812B1Use minimizedLow costDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationPhase differenceMultilateration
The invention consists of methods and apparatus to estimate the position and velocity of a Mobile Receiver (MR) using either the Time Of Arrival (TOA) of signals received by the MR, their Phase Of Arrival (POA), their Strength Of Arrival (SOA), their Frequency Of Arrival (FOA), or a combination thereof, with respect to a reference produced by a Reference Receiver (RR) of known location. In order to solve for the coordinates of the MR, the invention uses either hyperbolic multilateration based on Time Difference Of Arrival (TDOA), or linear multiangulation based on Phase Difference Of Arrival (PDOA), or both. In order to solve for the velocity of the MR, the patent uses FOA based on Frequency Difference Of Arrival (FDOA). An important contribution of this invention is the way the MR receives, processes and combines available signals for location purposes. Another important contribution of this invention is the way the RR receives, processes and combines available signals for reference purposes.
Owner:CELL LOC LOCATION TECH
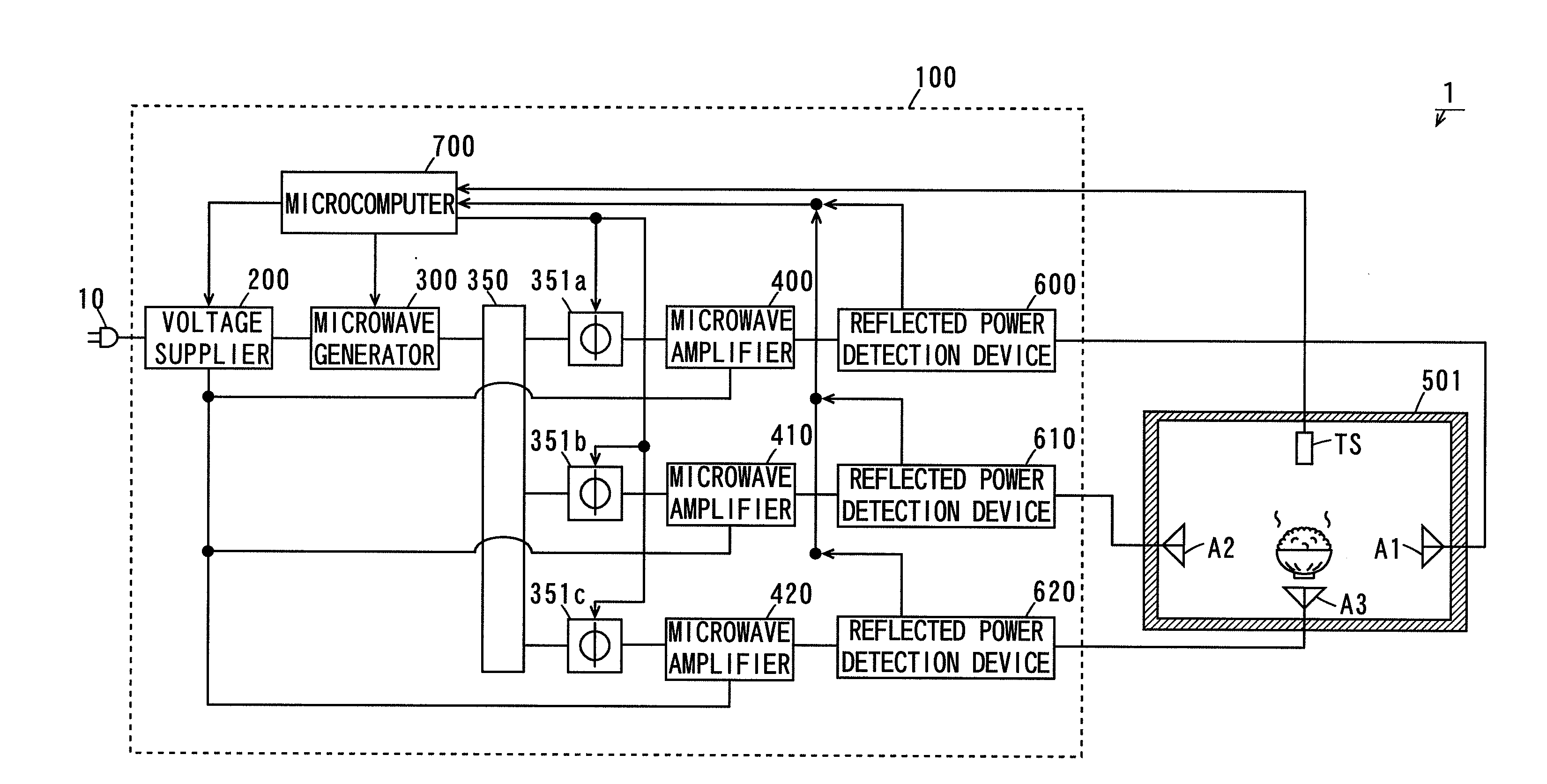
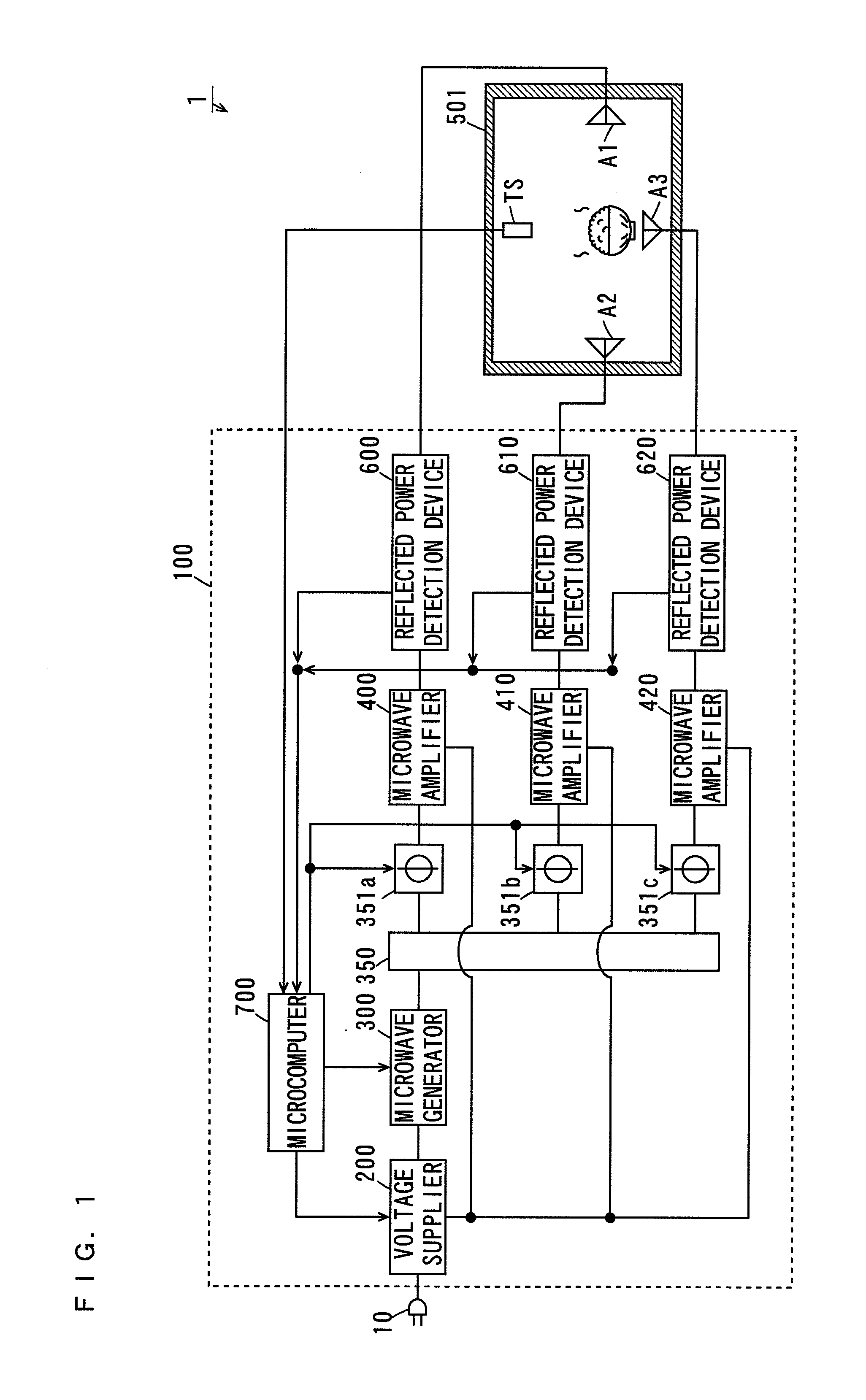
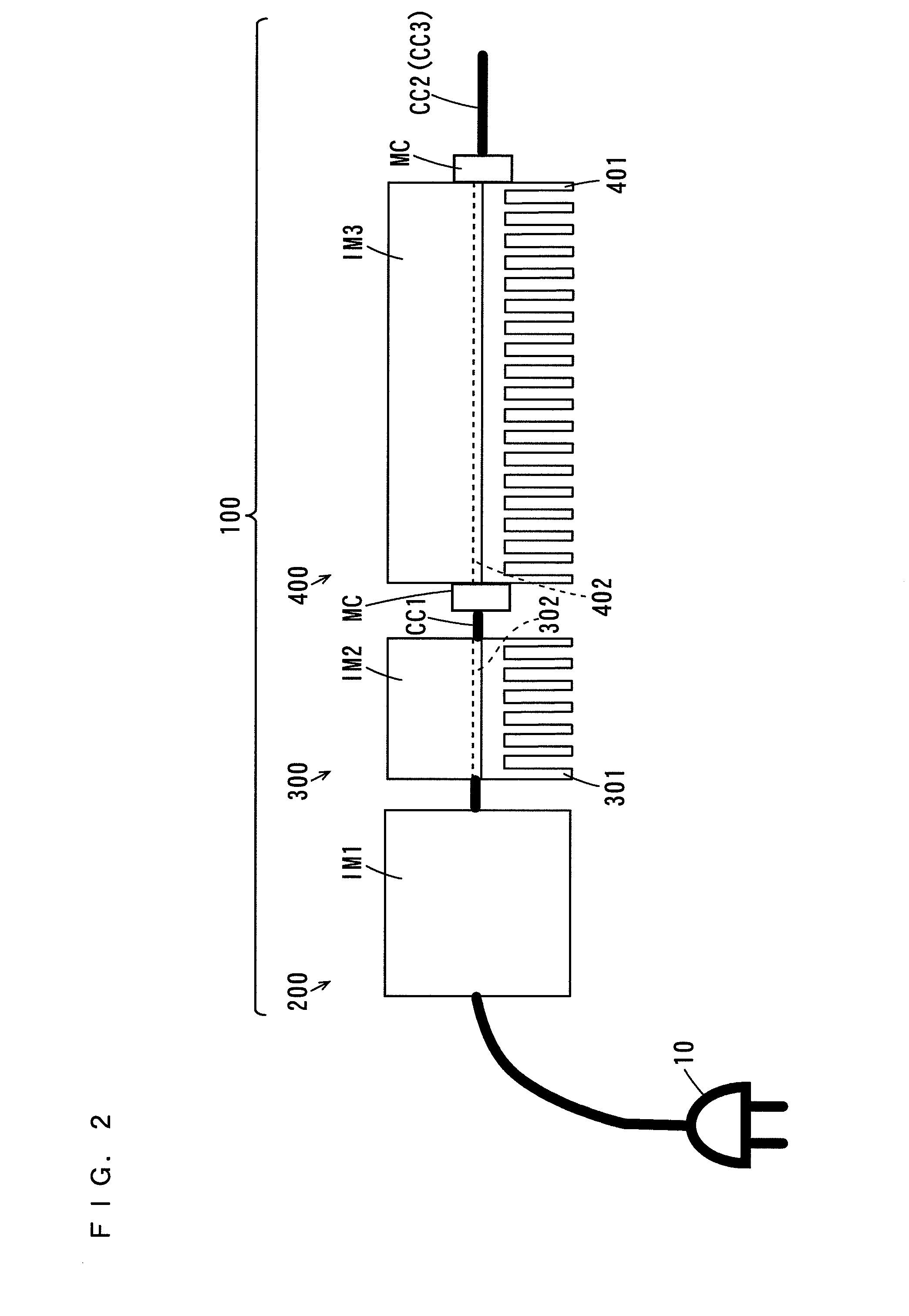
Microwave processing apparatus
InactiveUS20100176121A1Uniform processingLow costOhmic-resistance heatingMicrowave heatingMicrowave ovenPhase difference
A microwave oven includes a microwave generation device and a case. Three antennas are provided in the case. The two antennas are opposite each other along a horizontal direction. In the microwave generation device, a power distributor almost equally distributes a microwave generated by a microwave generator among phase variators. Each of the phase variators adjusts the phase of the fed microwave. This causes a phase difference between microwaves respectively radiated from the opposite two antennas to change. The microwaves are respectively radiated from the antennas.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Microscope generating a three-dimensional representation of an object and images generated by such a microscope
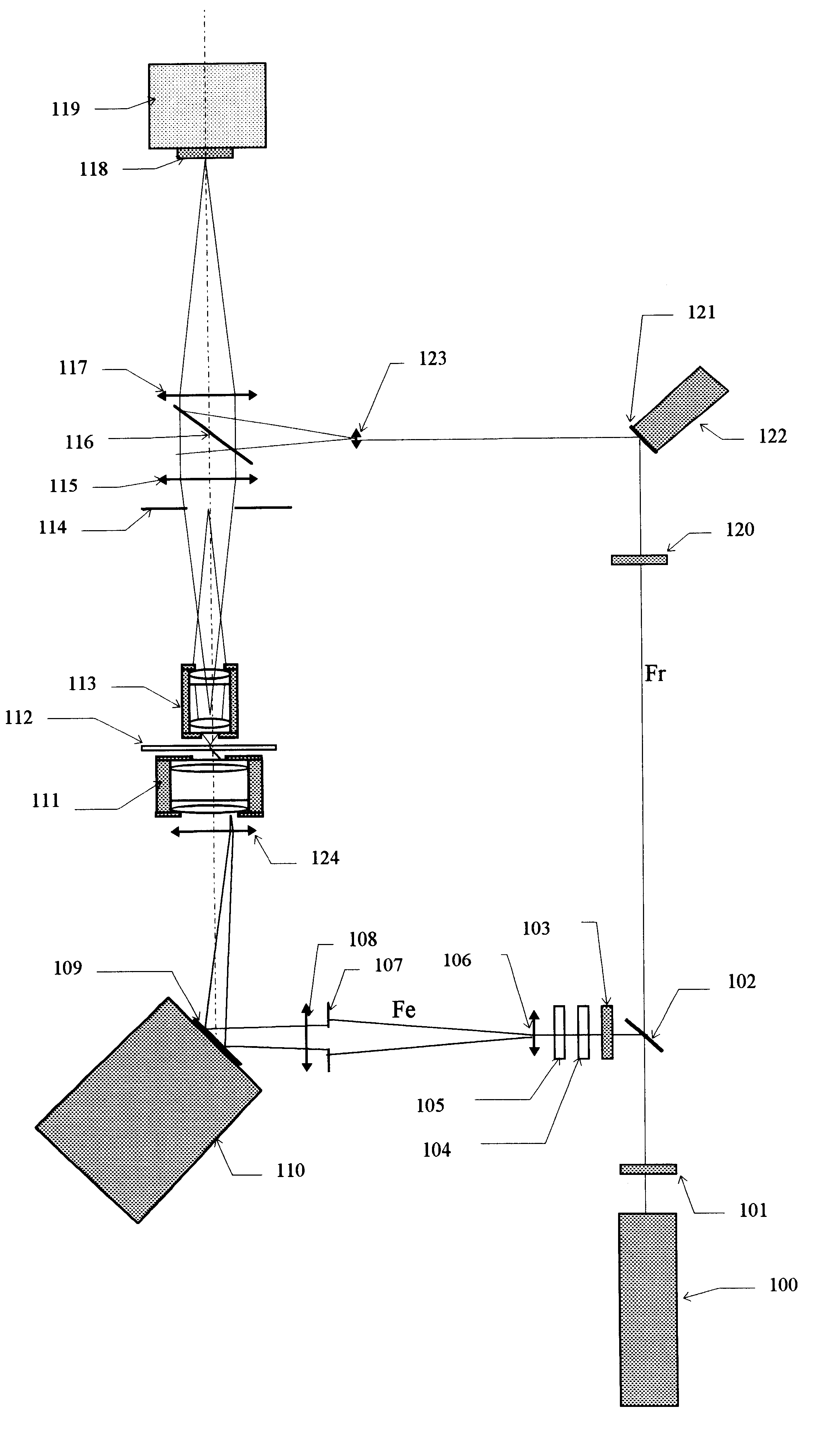
InactiveUS6525875B1Not possibleHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesMicroscopesObject basedPhase difference
A microscope is disclosed which determines a complex three-dimensional representation of an object based on a series of recordings of the light wave diffracted by the object, wherein the direction of the wave lighting of the object varies between two succesive recordings. The diffracted wave interferes with a reference wave on a receiving surface and a frequency representation of the diffracted wave is computed from interference patterns received on the receiving surface. A plurality of frequency representations of diffracted waves are then superimposed yielding a frequency representation of the object. The phase of each frequency representation of a diffracted wave is shifted in order to compensate for variations of the phase difference between the reference wave and the wave lighting of the object.
Owner:LAUER VINCENT
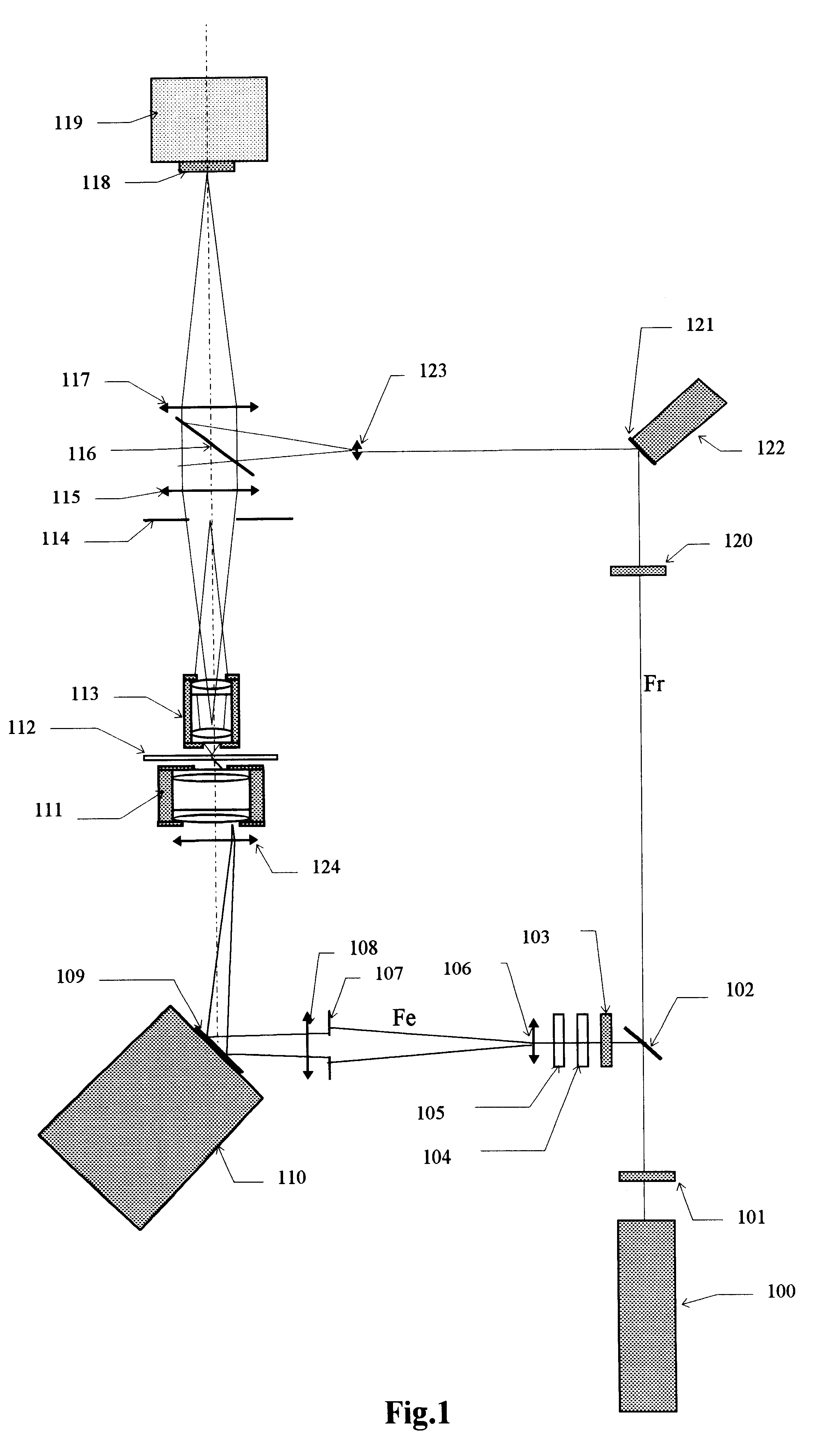
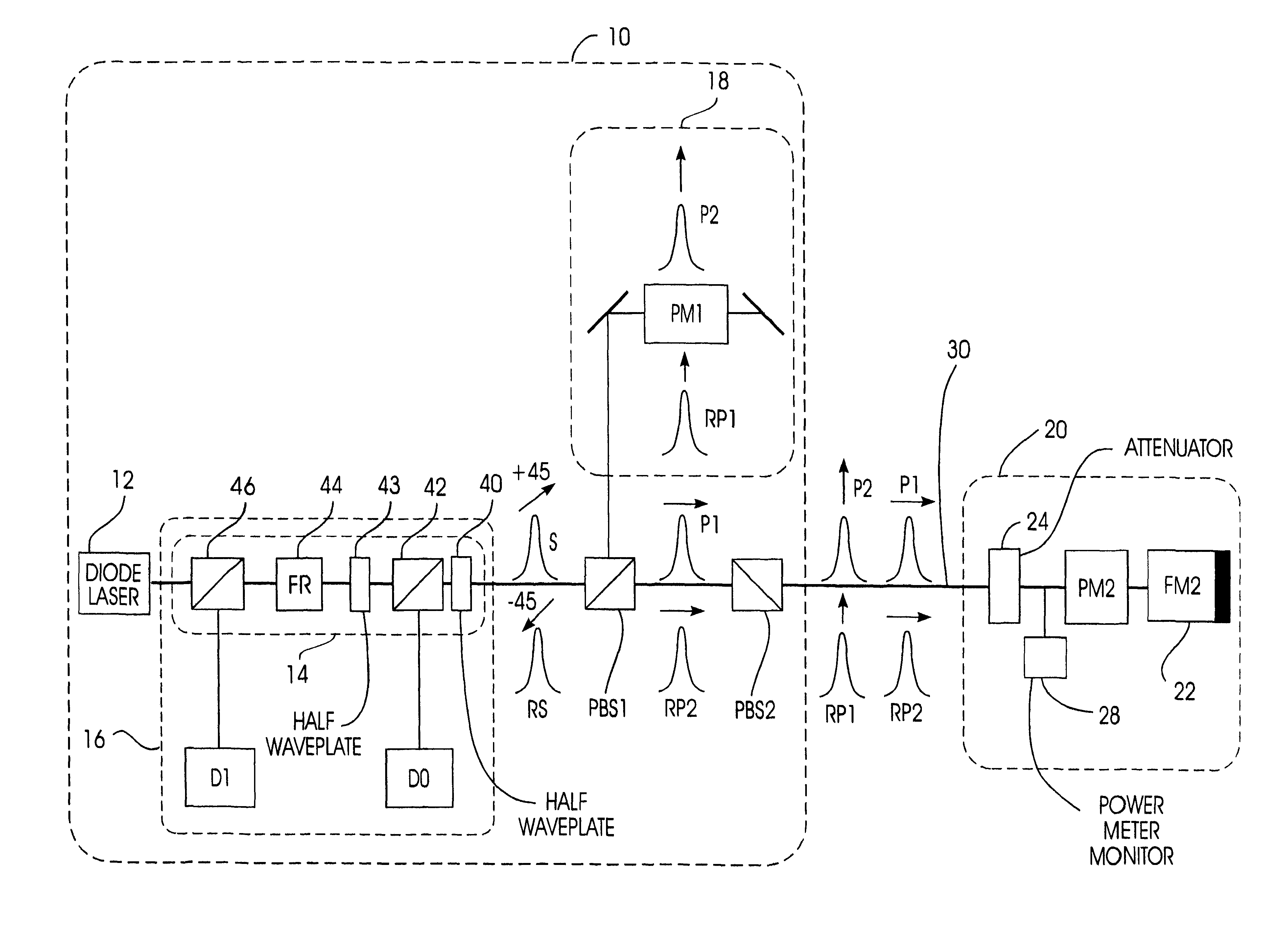
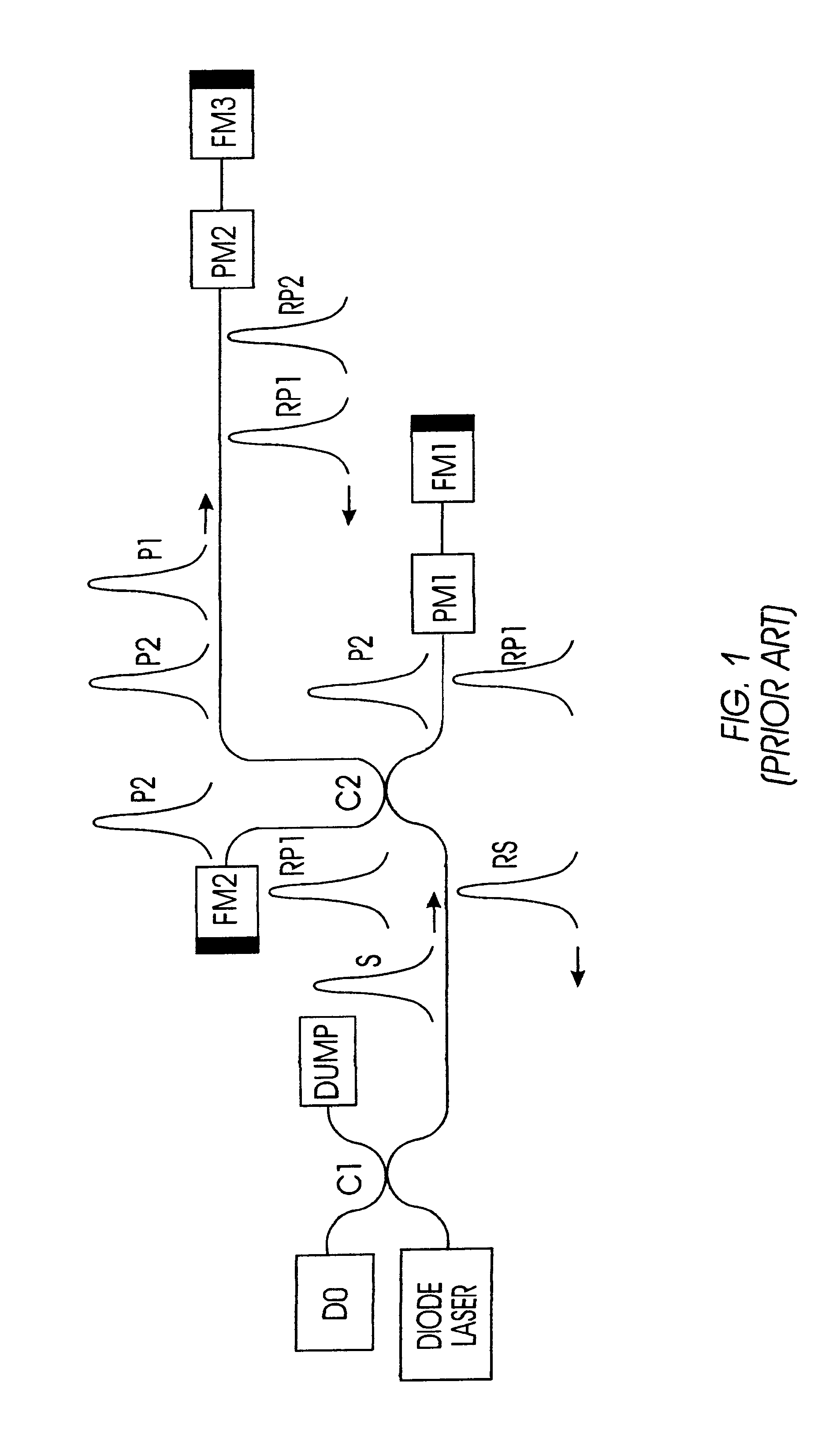
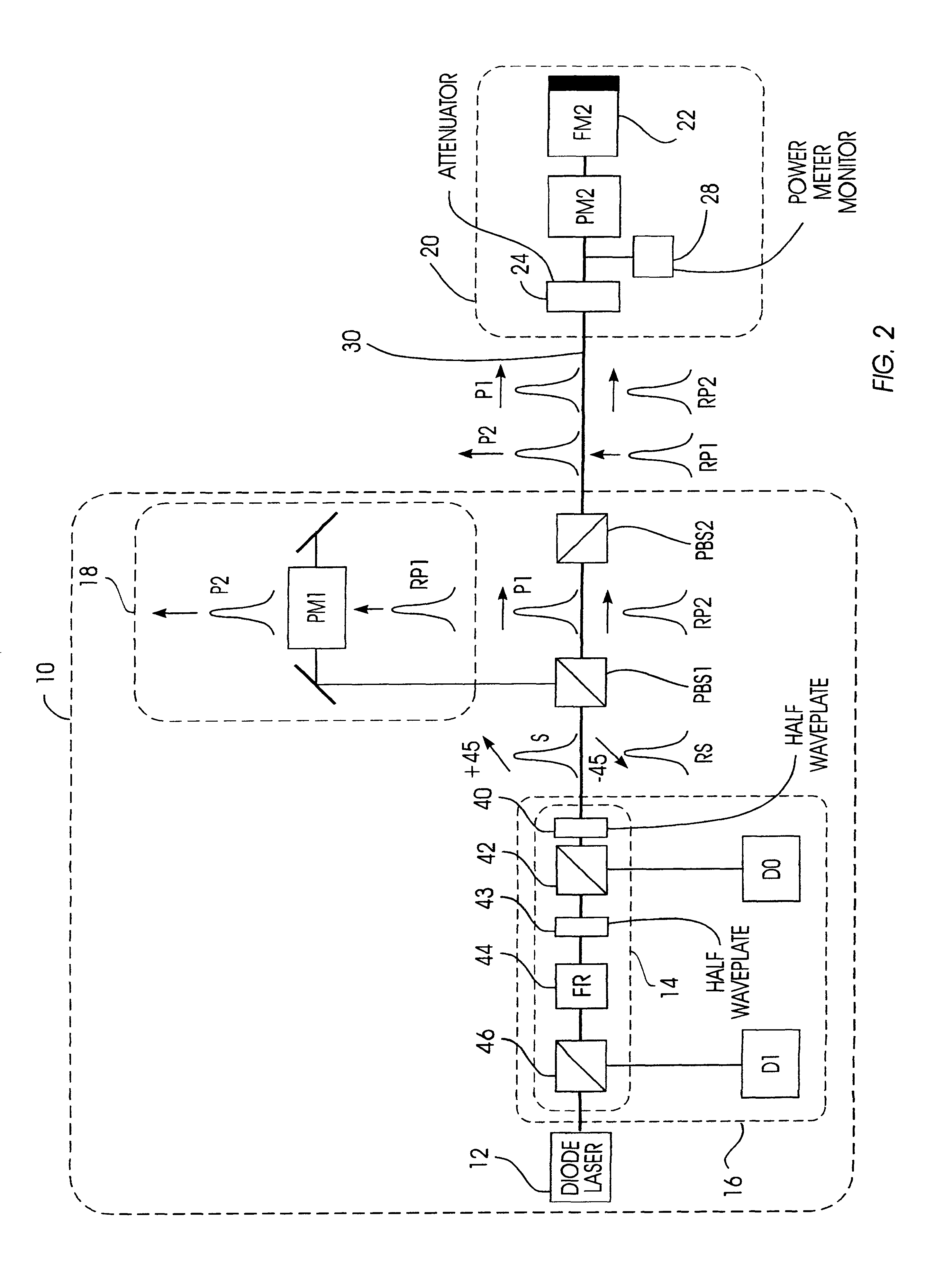
Autocompensating quantum cryptographic key distribution system based on polarization splitting of light
A quantum cryptographic key distribution (QKD) system splits discrete light signals from a laser source into a pair of light pulses that are orthogonally polarized with respect to each other, imparts a phase shift to one or both of these separate pulses during their round trip from the sender to the receiver and back, assures that the return pulses from the receiver are attenuated to single-photon pulses, recombines the phase-shifted pulses at the sender, and then detects from the recombined signal its polarization state, which is representative of the net phase shift imparted by the sender and receiver. The phase modulator at the receiver transmits only one polarization (e.g., vertical), but is used in a manner that permits it to equally modulate both polarization components of an arriving pulse. In this arrangement, when both components of a pulse reach the phase modulator at the receiver, they are both entirely vertically polarized and a phase shift is imparted at that time. This has the advantage that the effect of any time variation or phase errors in the phase modulator will be the same on both components. The key information is decoded at a detection stage at the sender that uses two detectors, one of which detects a first polarization state corresponding to the phase difference between the two phase shifts being 0 and the other of which detects a second polarization state corresponding to the phase difference between the two phase shifts being pi.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com