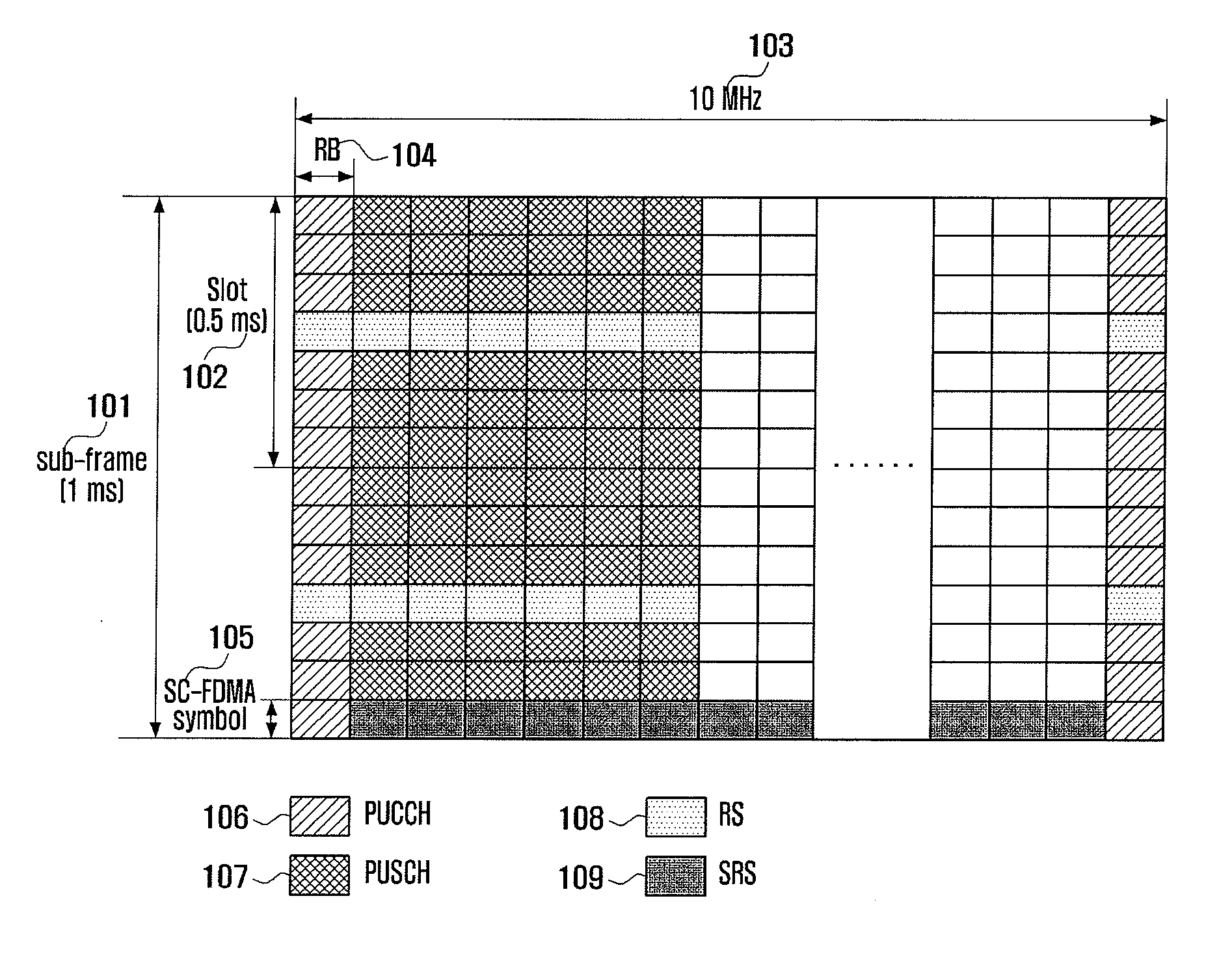
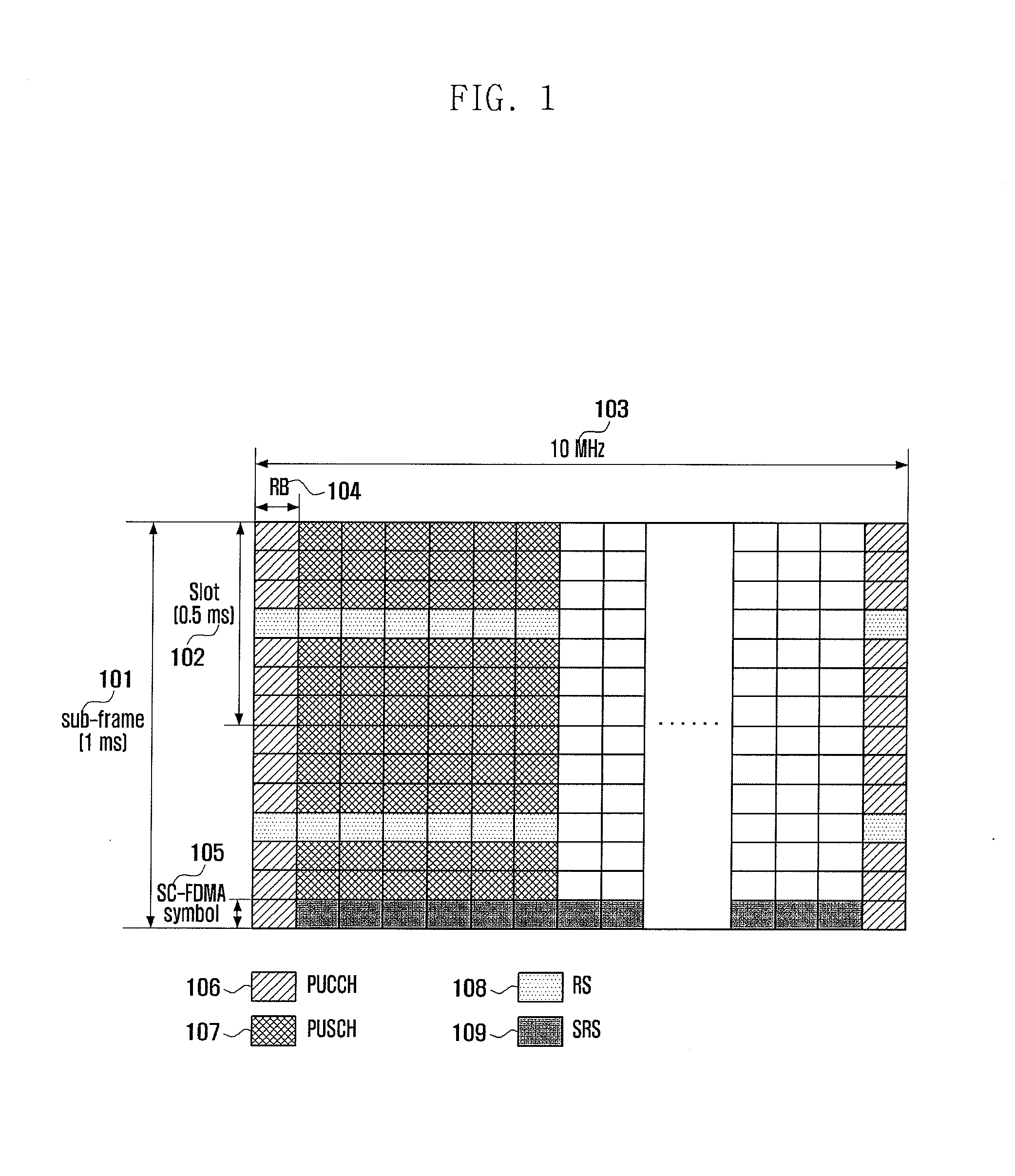
Patents
Literature
1630 results about "Phase correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
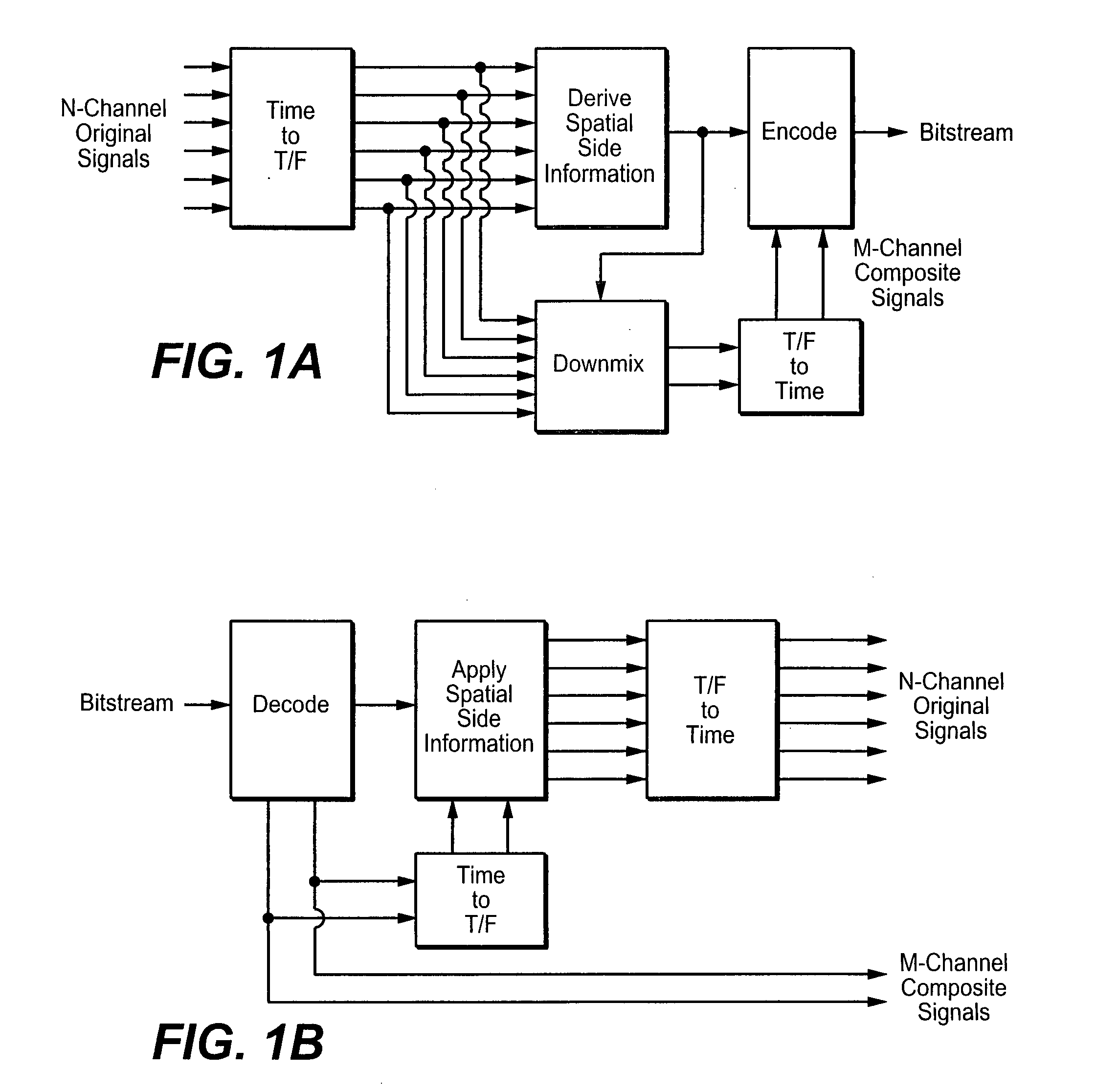
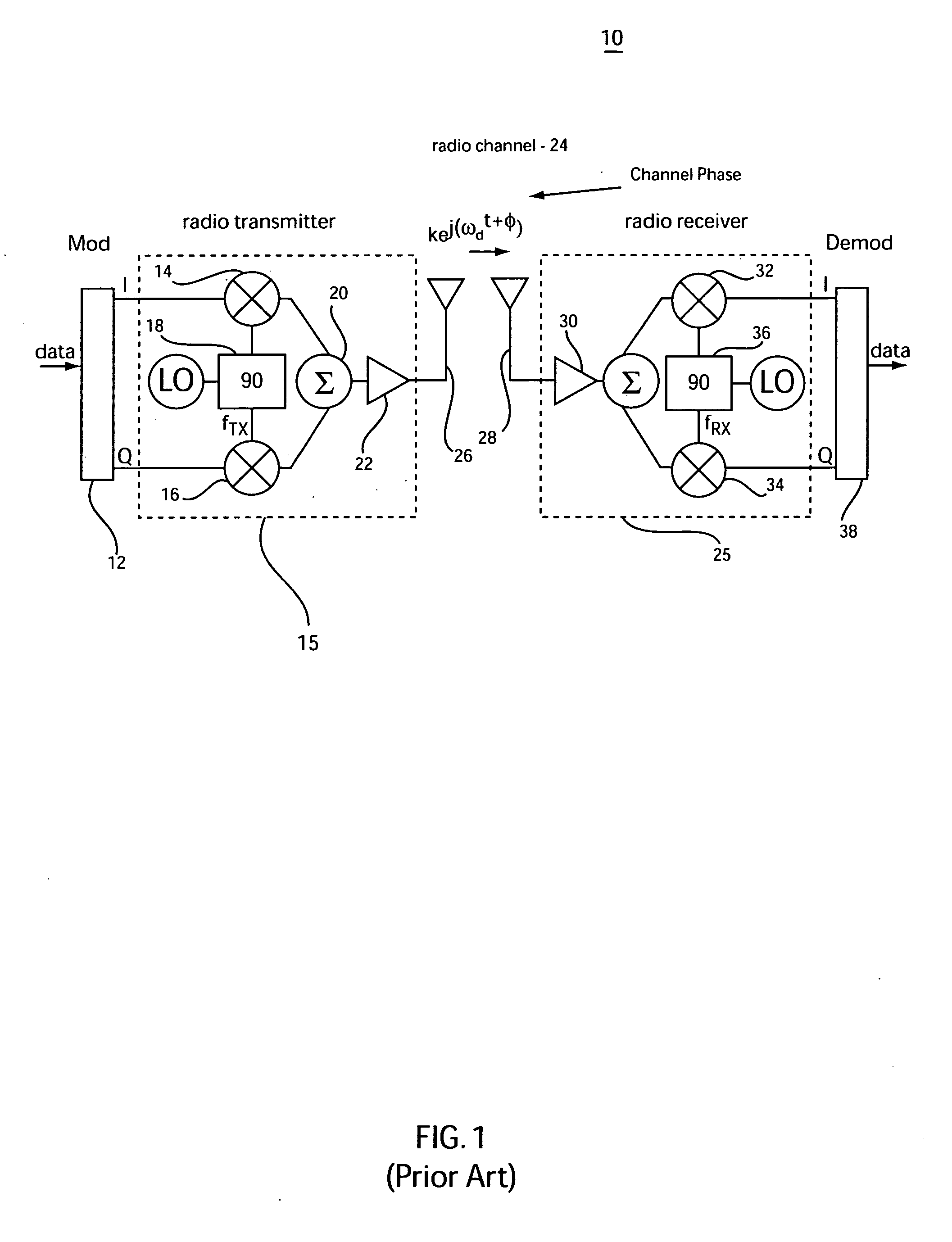
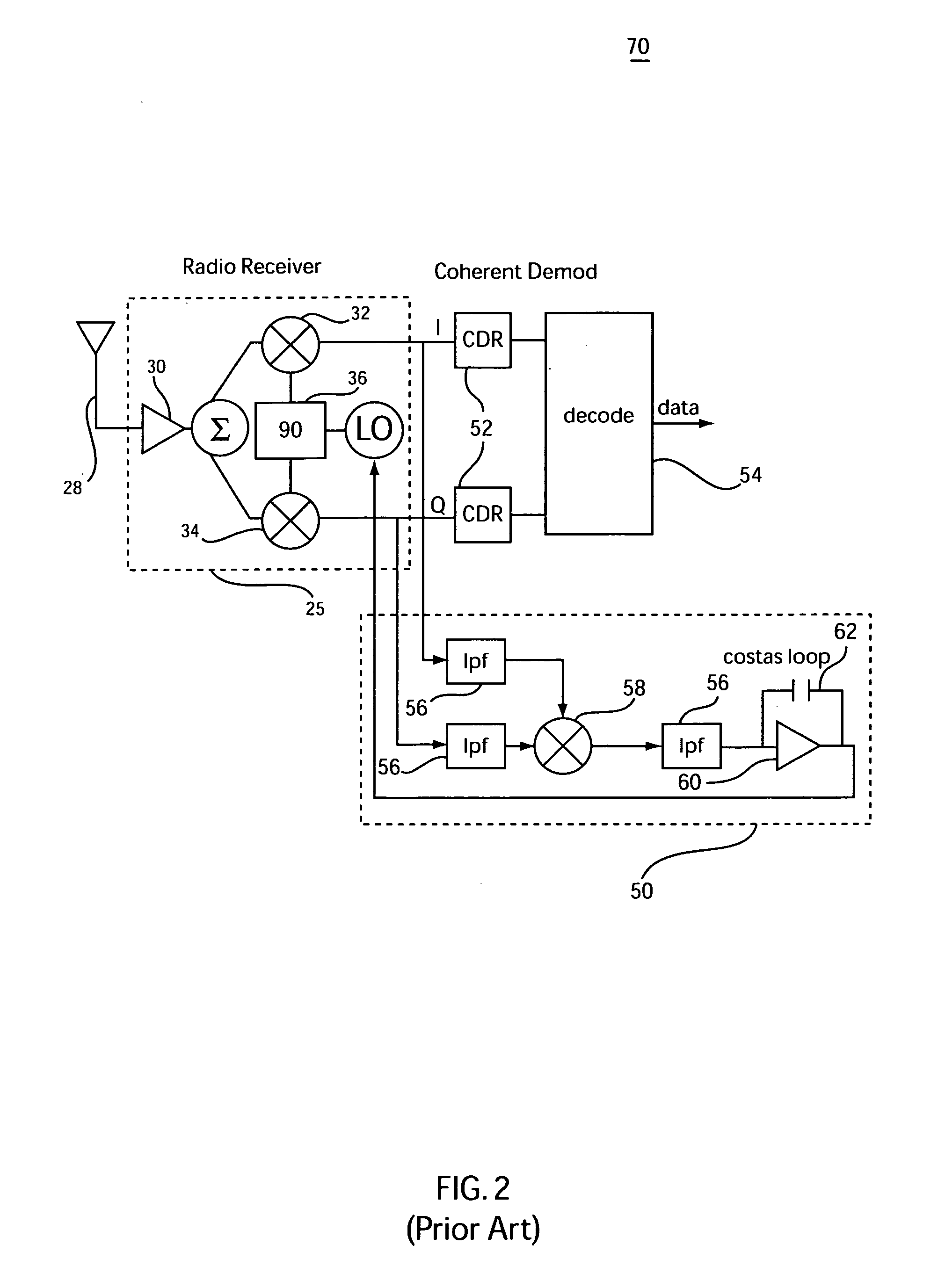
Communication method and system
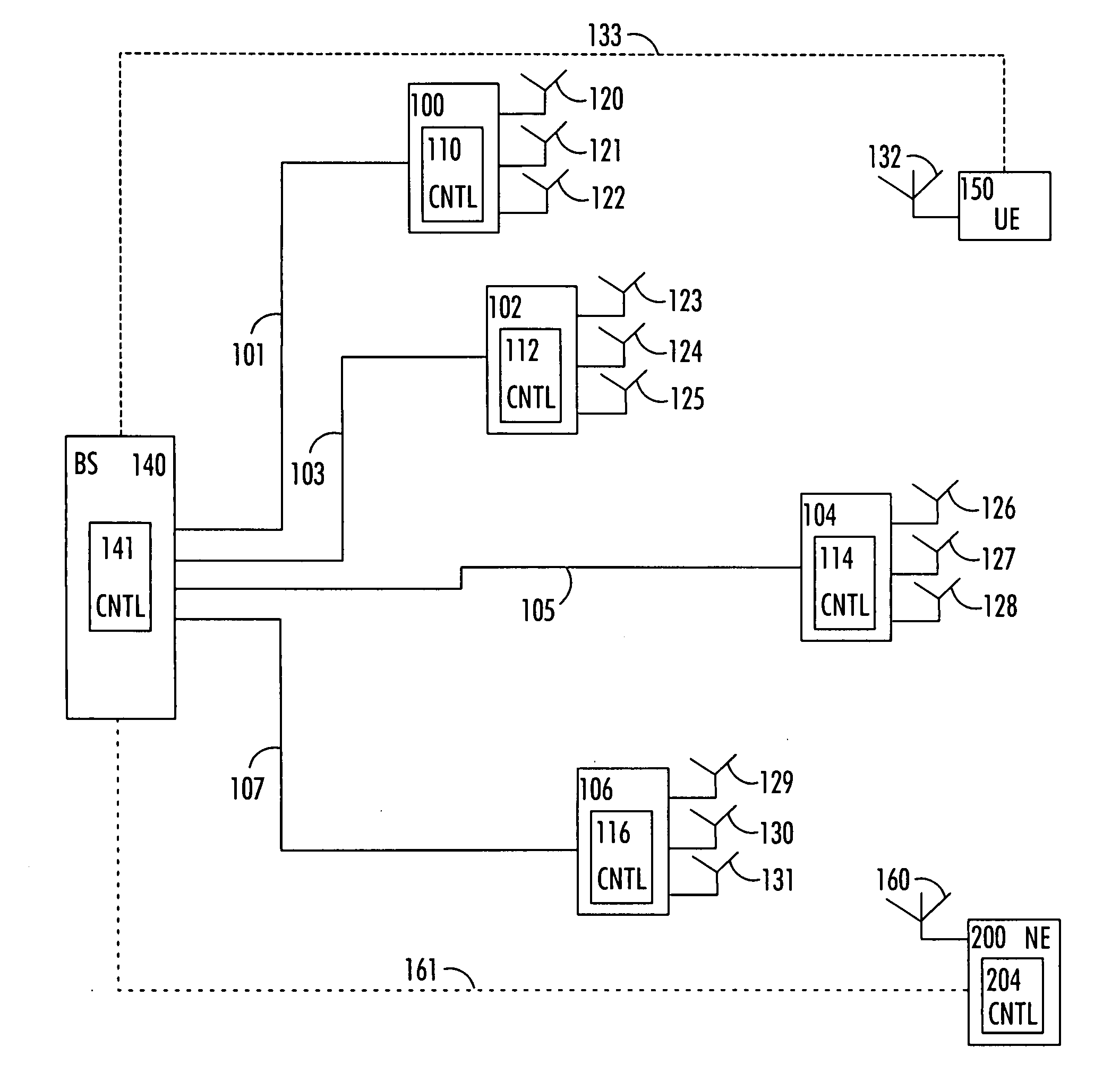
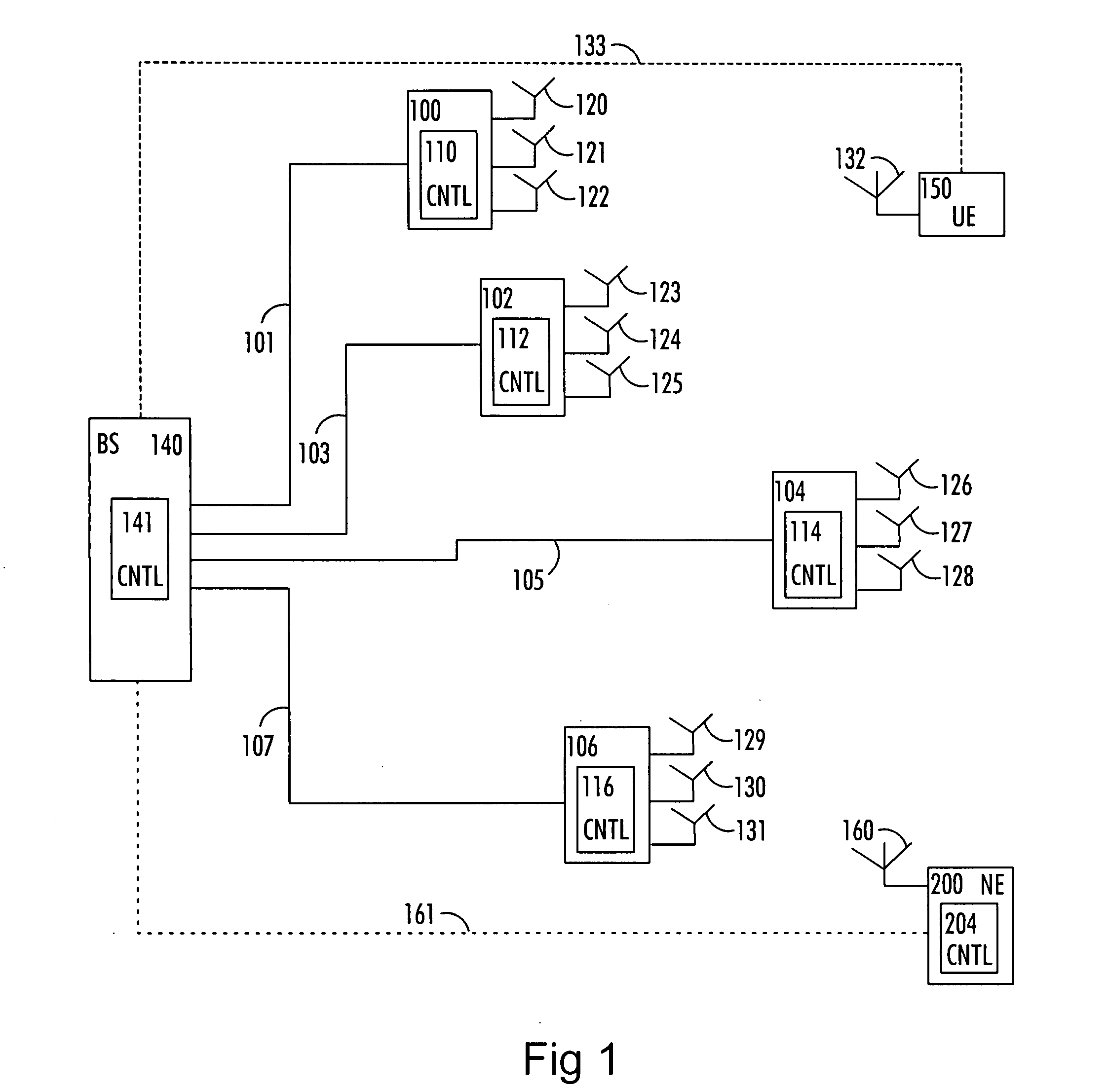
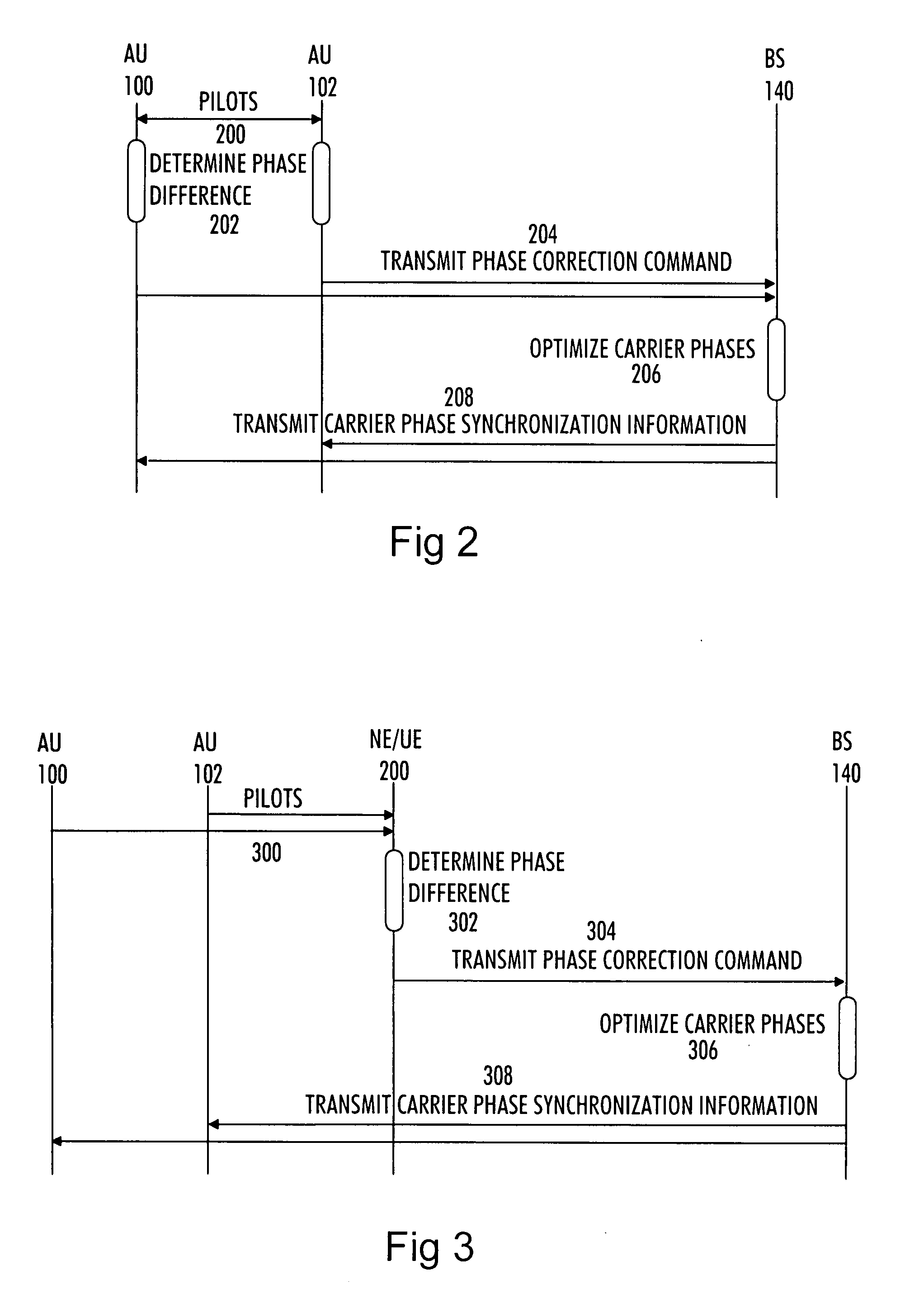
ActiveUS20080150514A1Increase network capacityCooperate fullySite diversityReceivers monitoringPhase correctionCommon base
There is provided a method comprising: determining a phase difference between at least two antenna units of a distributed antenna system on the basis of at least one pilot signal received from at least one of a plurality of antenna units; and transmitting phase correction commands to a common base station of the plurality of antenna units on the basis of the determined phase difference in order to synchronize carrier phases between at least two antenna units of the distributed antenna system.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and Apparatus for Radiance Processing by Demultiplexing in the Frequency Domain
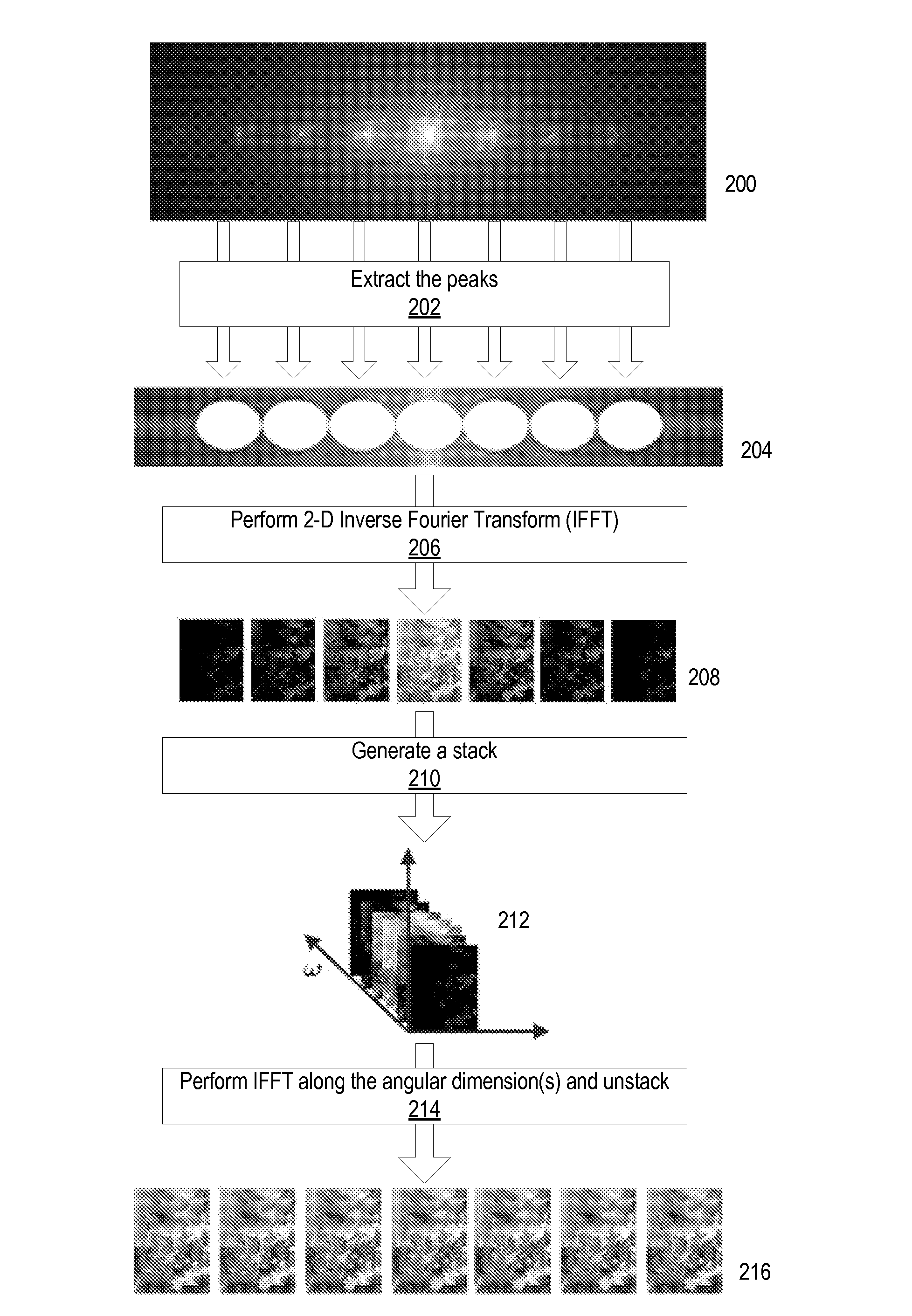
ActiveUS20090041381A1Guaranteed corrective effectPromote resultsTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionParallaxPhase correction
Method and apparatus for radiance processing by demultiplexing in the frequency domain. A frequency domain demultiplexing module obtains a radiance image captured with a lens-based radiance camera. The image includes optically mixed spatial and angular frequency components of light from a scene. The module performs frequency domain demultiplexing on the radiance image to generate multiple parallax views of the scene. The method may extract multiple slices at different angular frequencies from a Fourier transform of the radiance image, apply a Fourier transform to each of the multiple slices to generate intermediate images, stack the intermediate images to form a 3- or 4-dimensional image, apply an inverse Fourier transform along angular dimension(s) of the 3- or 4-dimensional image, and unstack the transformed 3- or 4-dimensional image to obtain the multiple parallax views. During the method, phase correction may be performed to determine the centers of the intermediate images.
Owner:ADOBE INC
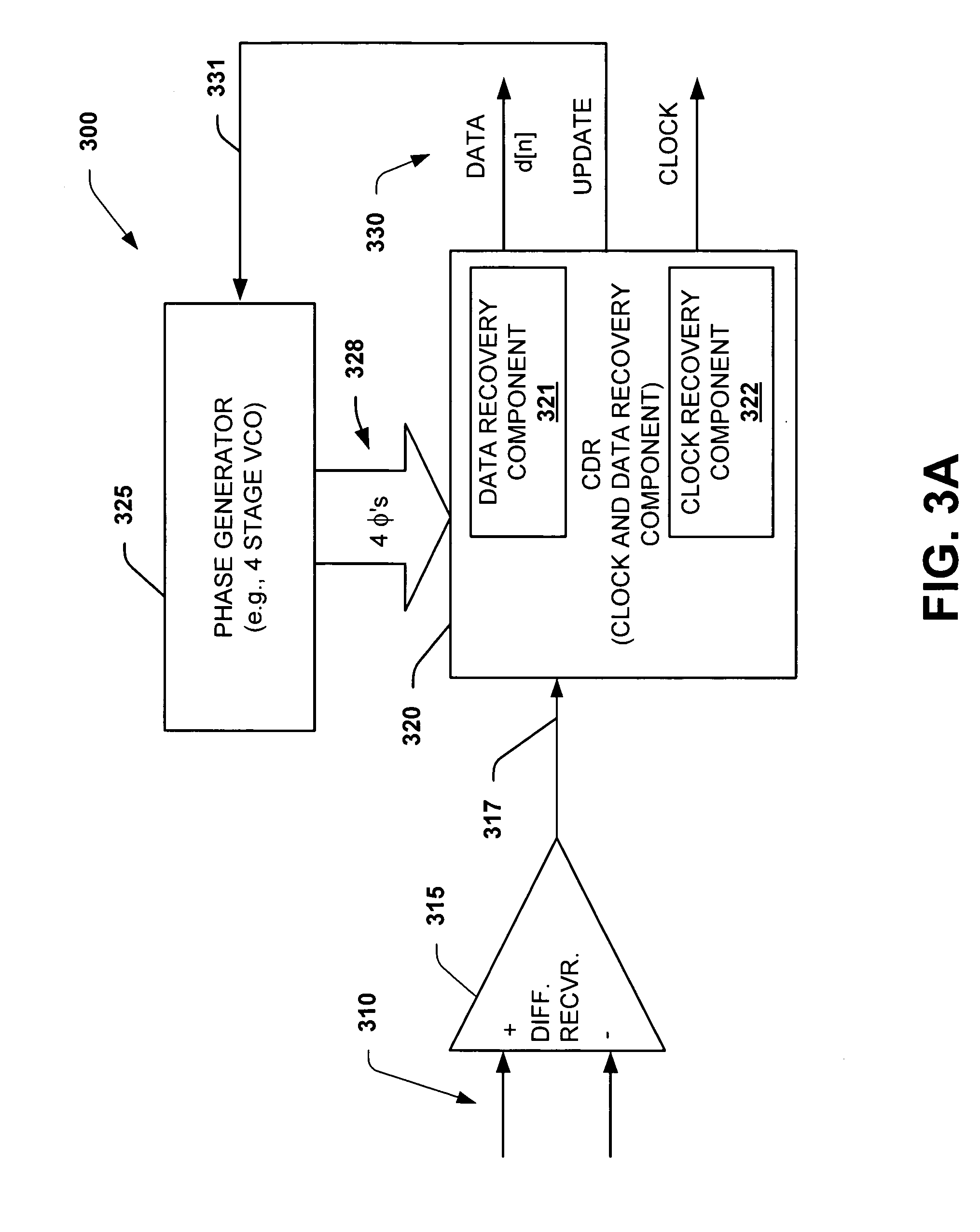
Interpolator based clock and data recovery (CDR) circuit with digitally programmable BW and tracking capability
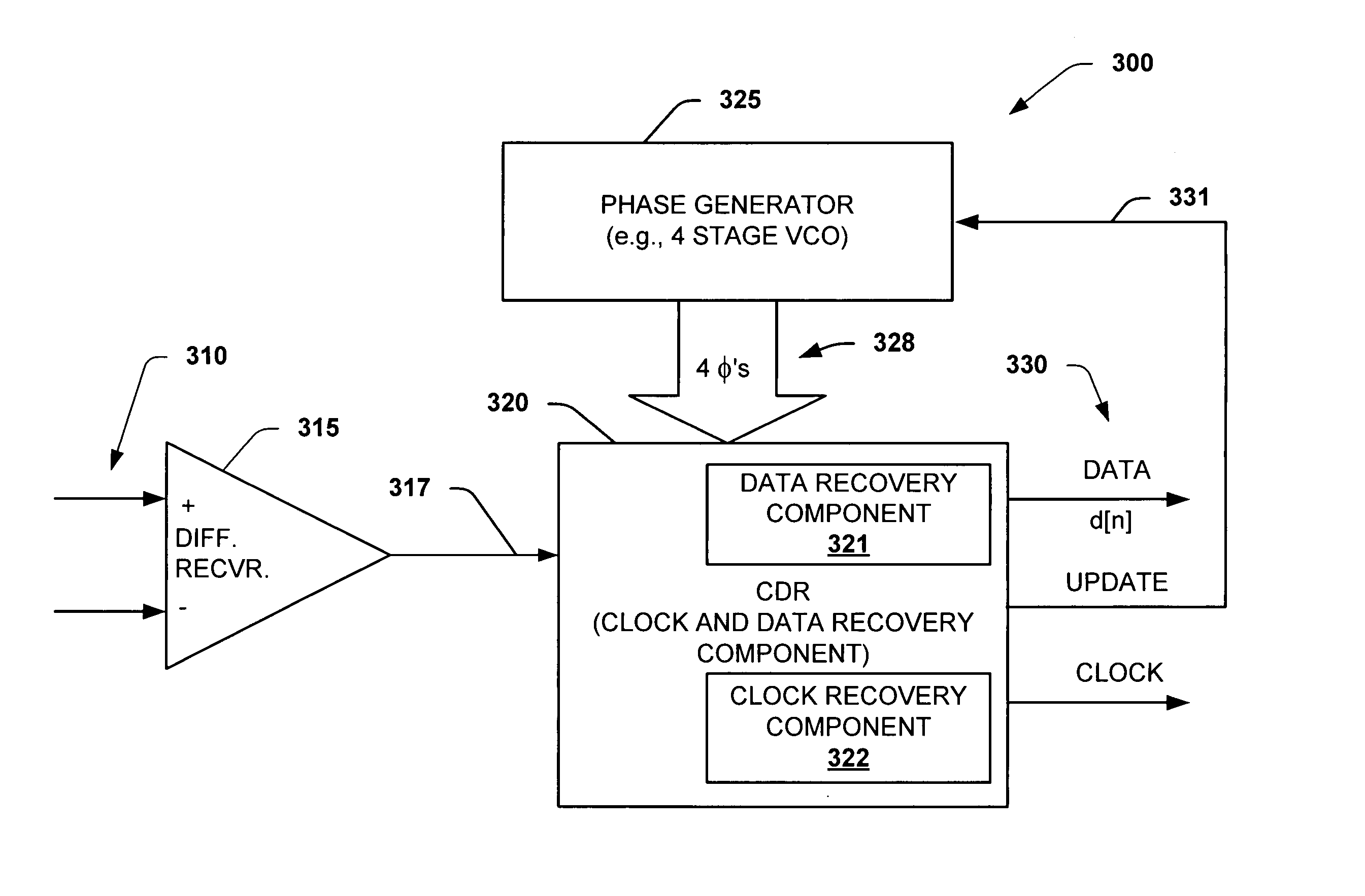
ActiveUS20050180536A1High bandwidthLower latencyPulse automatic controlSynchronising arrangementPhase correctionData stream
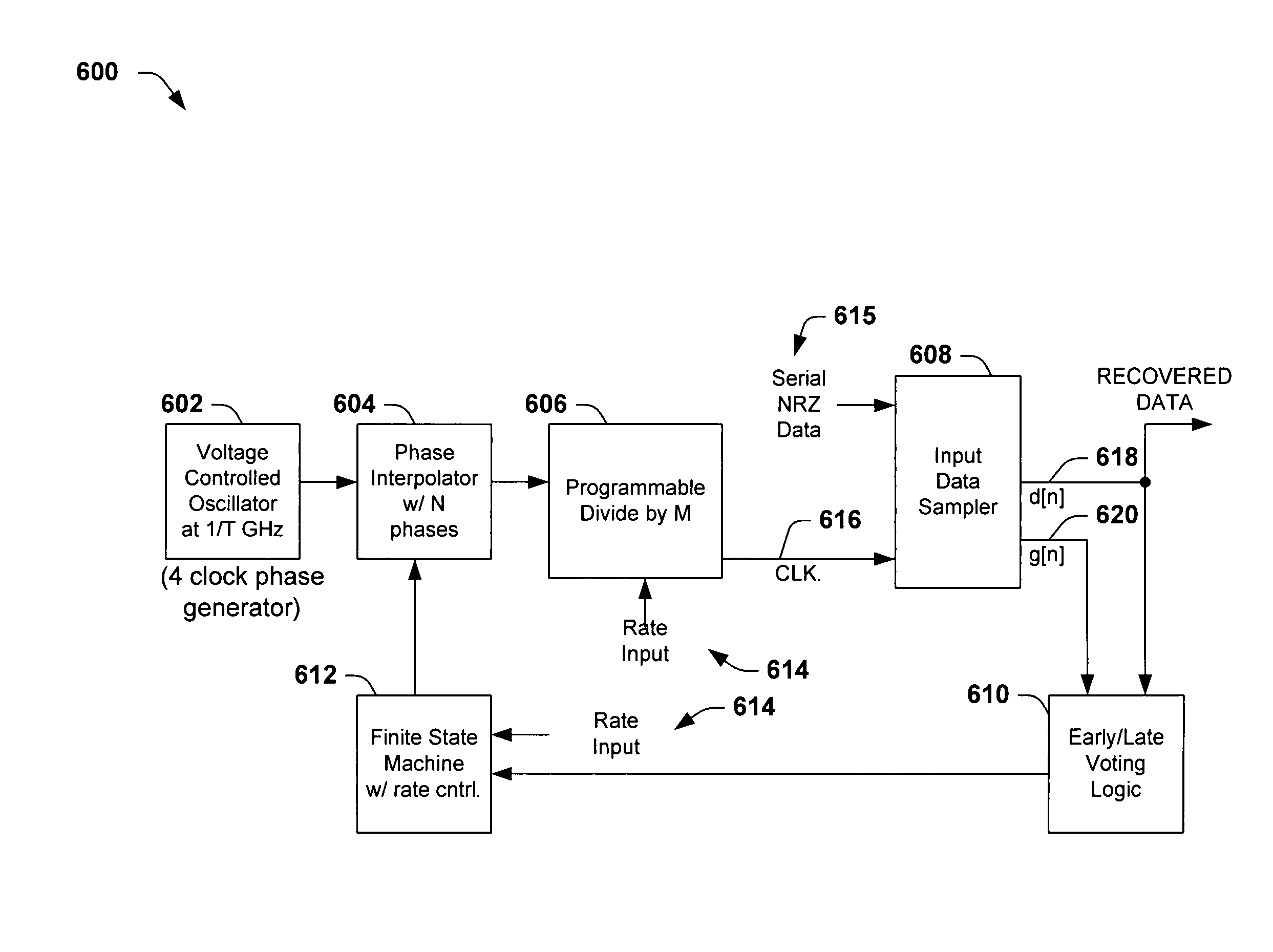
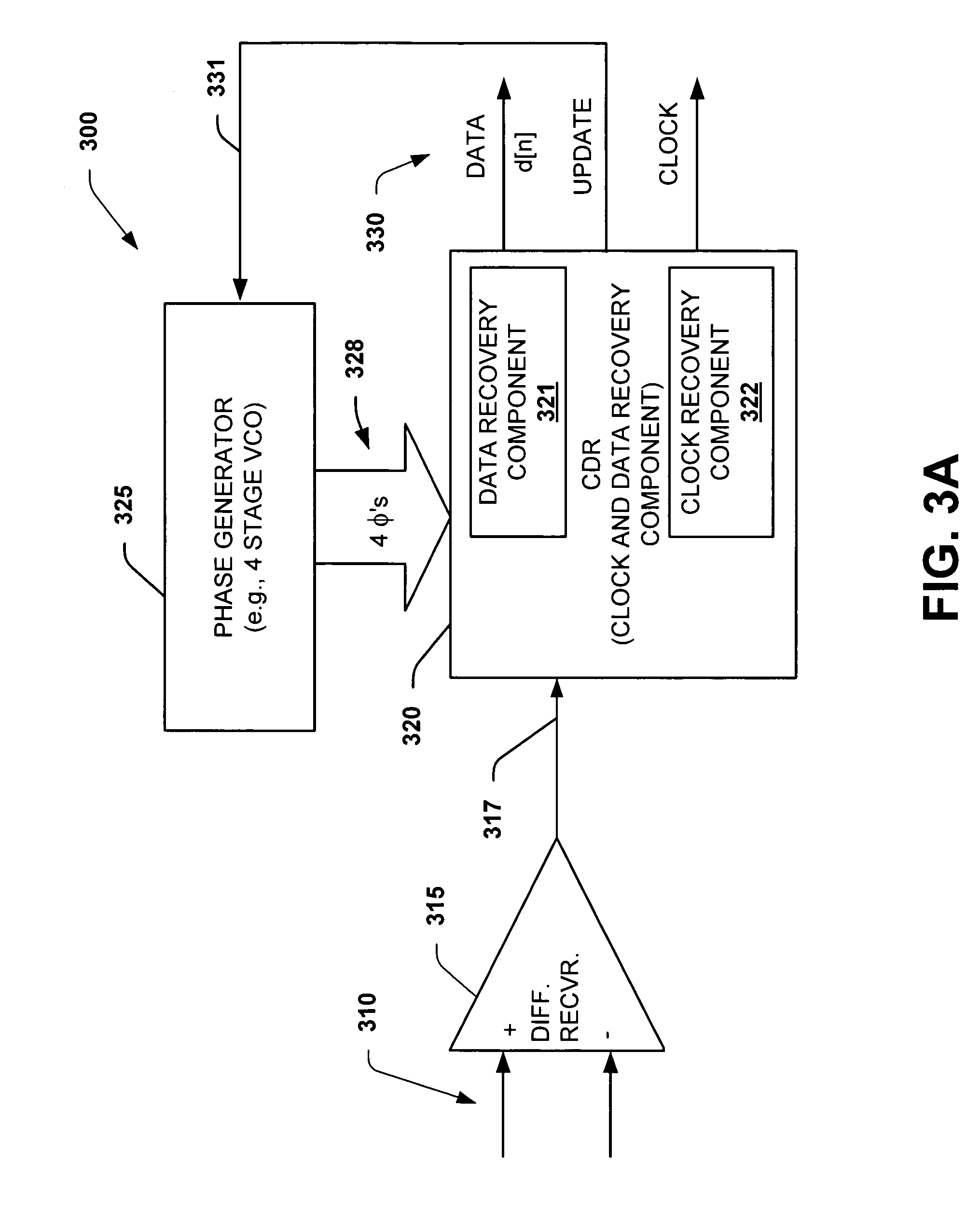
The present invention facilitates clock and data recovery (330,716 / 718) for serial data streams (317,715) by providing a mechanism that can be employed to maintain a fixed tracking capability of an interpolator based CDR circuit (300,700) at multiple data rates (e.g., 800). The present invention further provides a wide data rate range CDR circuit (300,700), yet uses an interpolator design optimized for a fixed frequency. The invention employs a rate programmable divider circuit (606,656,706) that operates over a wide range of clock and data rates (e.g., 800) to provide various phase correction step sizes (e.g., 800) at a fixed VCO clock frequency. The divider (606,656,706) and a finite state machine (FSM) (612,662,712) of the exemplary CDR circuit (600,650,700) are manually programmed based on the data rate (614,667). Alternately, the data rate may be detected from a recovered serial data stream (718) during CDR operations (on-the-fly) utilizing a frequency detection circuit (725) to automatically program the divider (706) and FSM (712) to provide CDR circuit operation at the nearest base clock rate (716).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Apparatus For And Method Of Controlling A Feedforward Filter Of An Equalizer
InactiveUS20070201544A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPhase correctionComplex representation
A method of controlling a feedforward filter of an equalizer includes the steps of generating a complex representation of an output of the feedforward filter and generating a representation of a decision from an output of the equalizer. The complex representation and the decision representation are correlated to obtain a phase error estimate. A phase correction value is generated based on the phase error estimate and used to adjust the phase of the output of the feedforward filter.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Method and apparatus for the modeling and synthesis of harmonic distortion
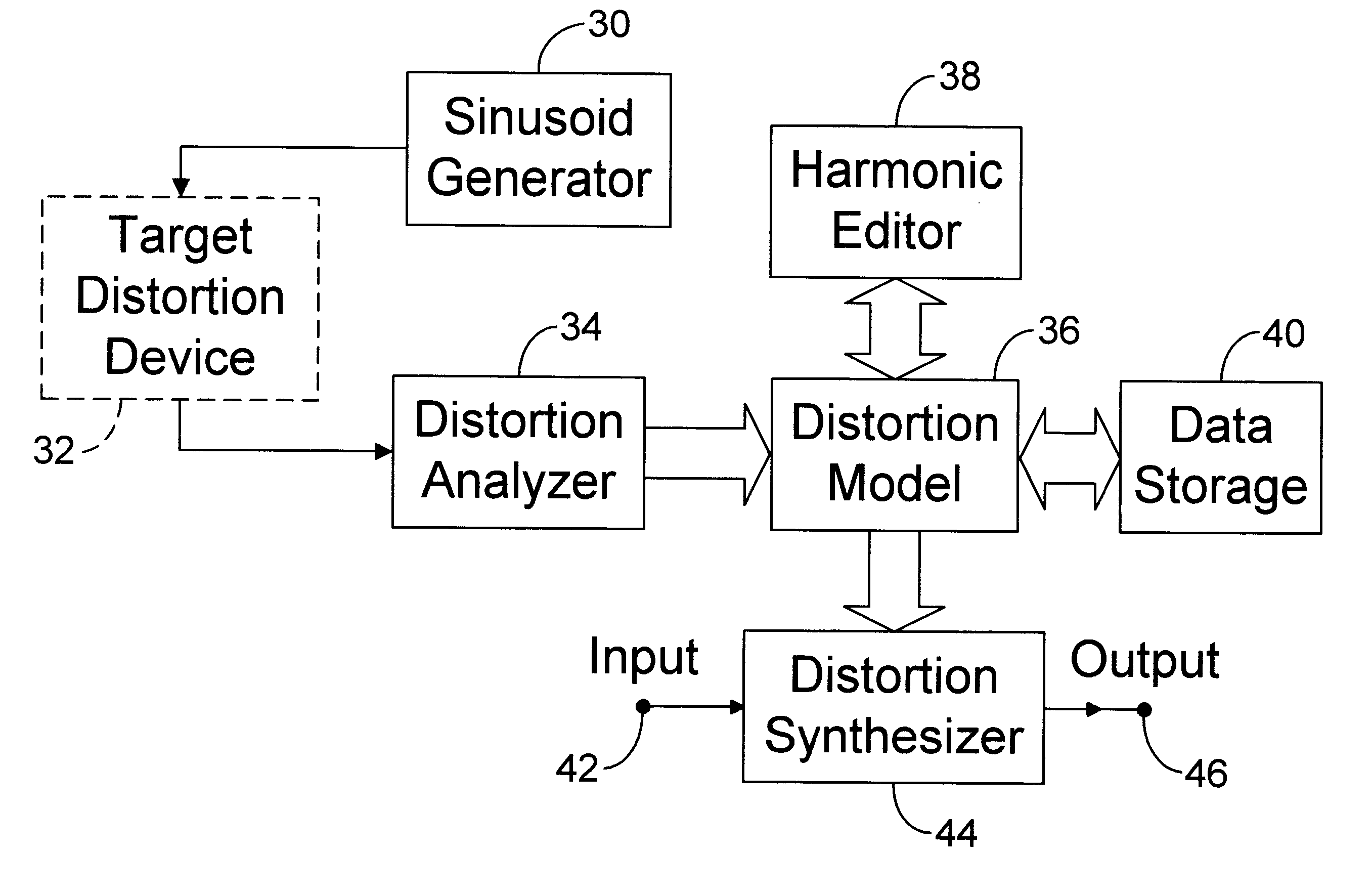
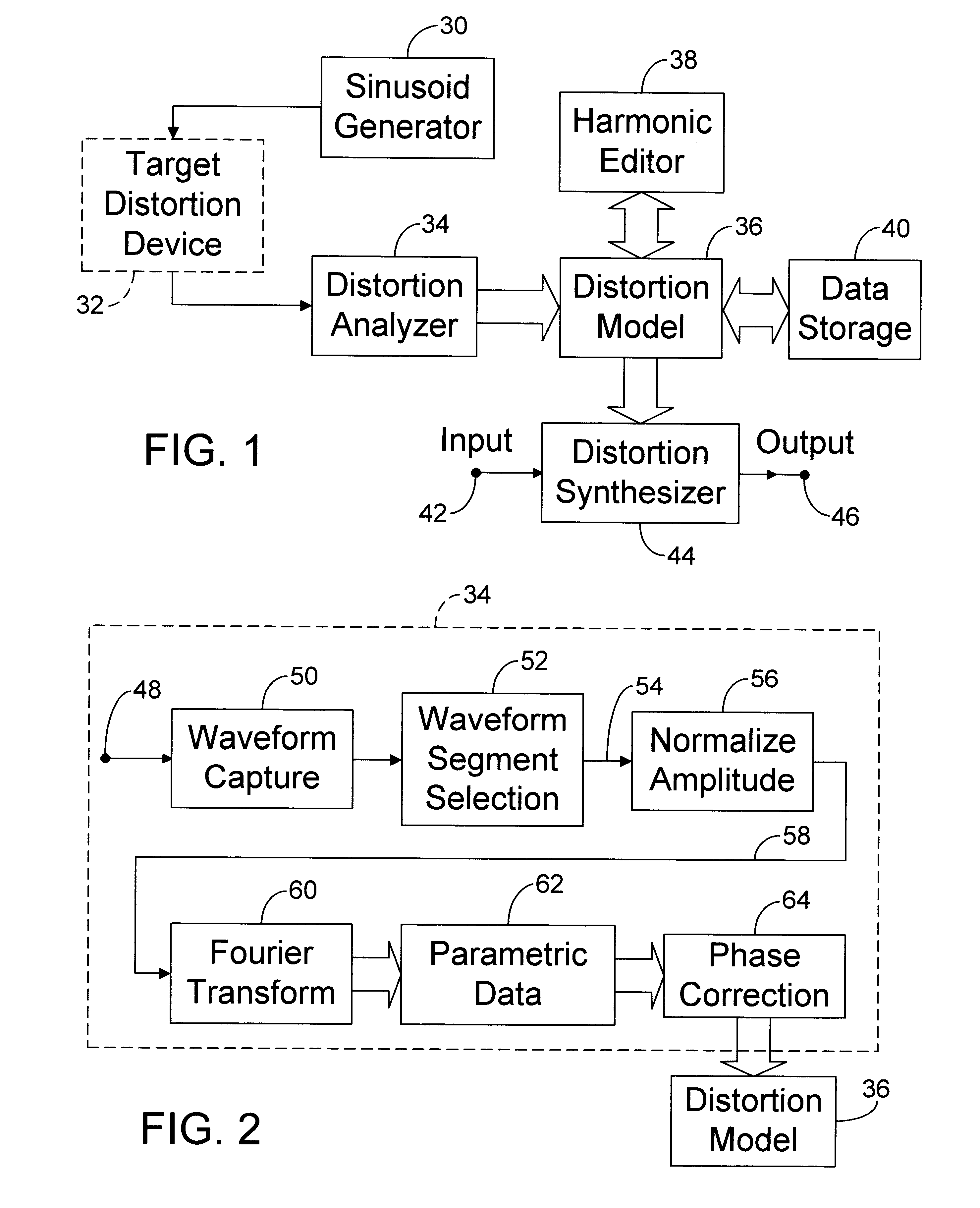
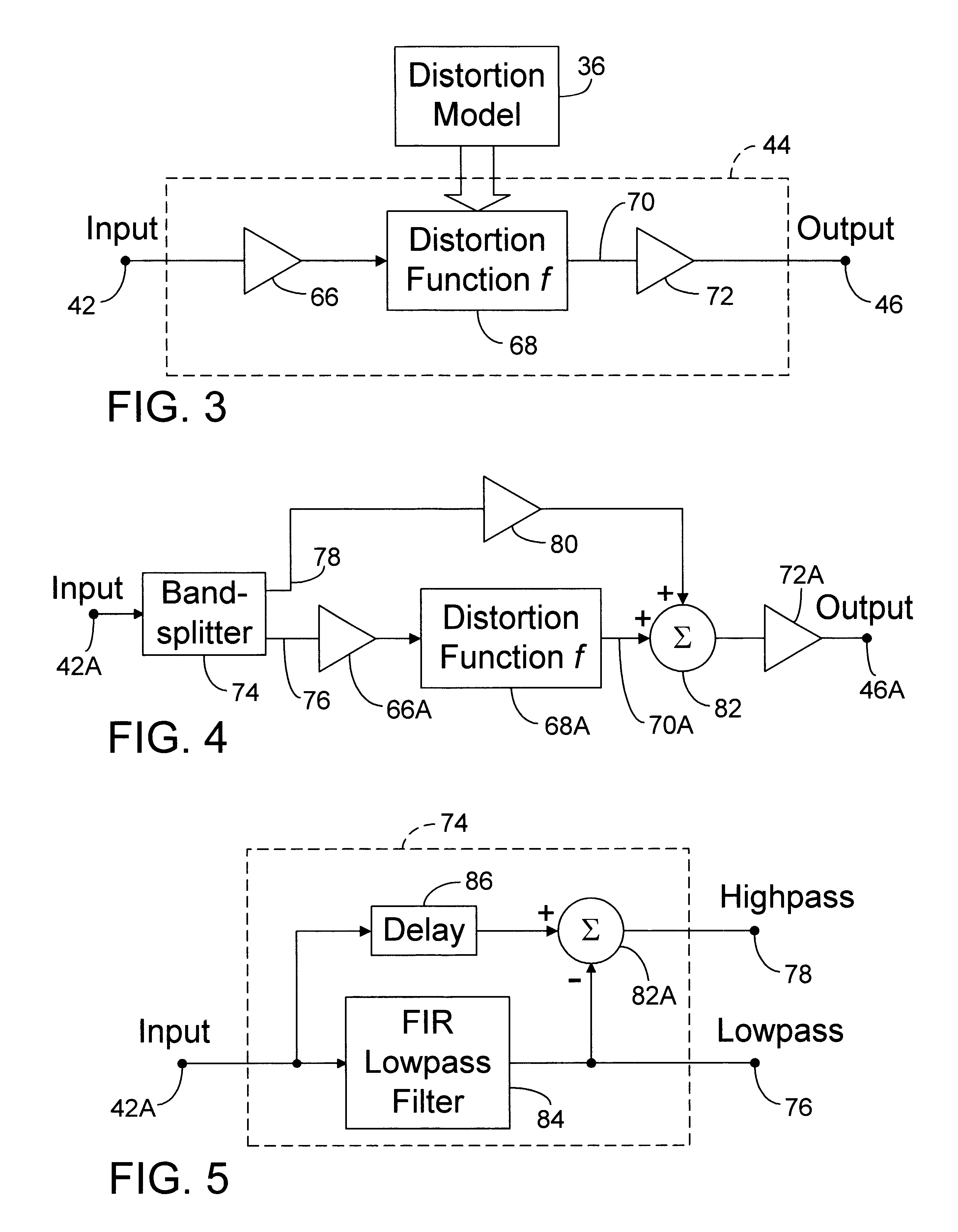
InactiveUS6504935B1Facilitates efficient storageImprove accuracyElectrophonic musical instrumentsGain controlFrequency spectrumTotal harmonic distortion
Distortion modeling produces distortion models for use by a distortion synthesizer to synthesize the harmonic distortion effects of audio distortion devices. A sinusoidal waveform is distorted by an audio distortion device and analyzed using a Fourier transform to produce a distortion model comprising harmonic amplitude and phase parameters. A phase correction process compensates for phase shifts induced by the audio distortion device. The distortion synthesizer uses a distortion function that distorts a digital audio signal according to the distortion model. The distortion model can be modified to alter the distortion effect and can be stored in a data-storage device for later retrieval. A frequency bandsplitter and signal mixer allow the distortion effect to be applied only to the low frequency content of the digital audio signal, thus providing spectral headroom to suppress the production of aliasing noise. Aliasing-noise suppression is provided for a full-bandwidth signal by up-converting the sampling rate of the signal before applying the distortion function and down-converting the sampling rate afterwards. A process is provided to remove the direct-current component that may be induced into the signal by the distortion function.
Owner:JACKSON DOUGLAS L
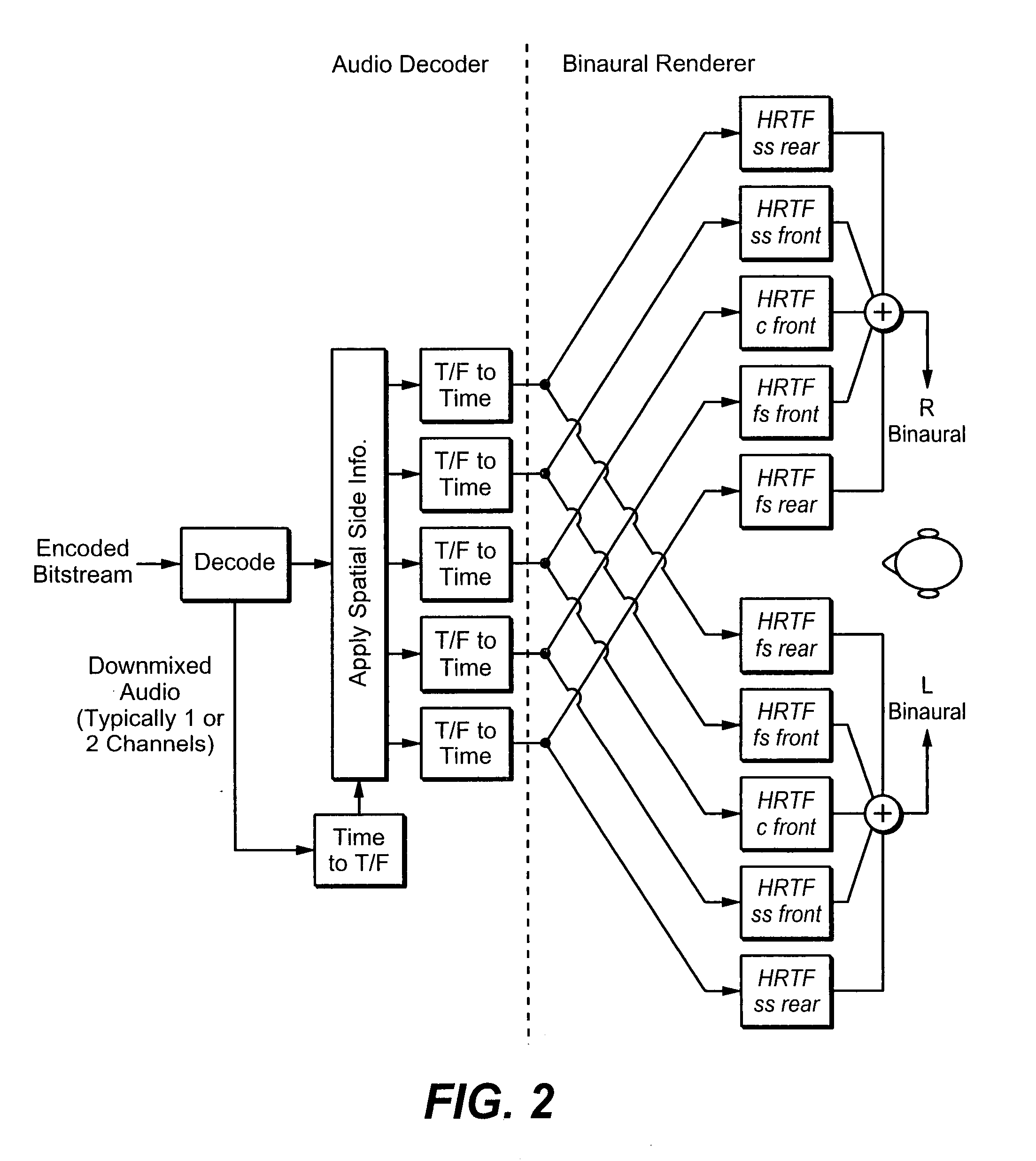
Binaural rendering using subband filters
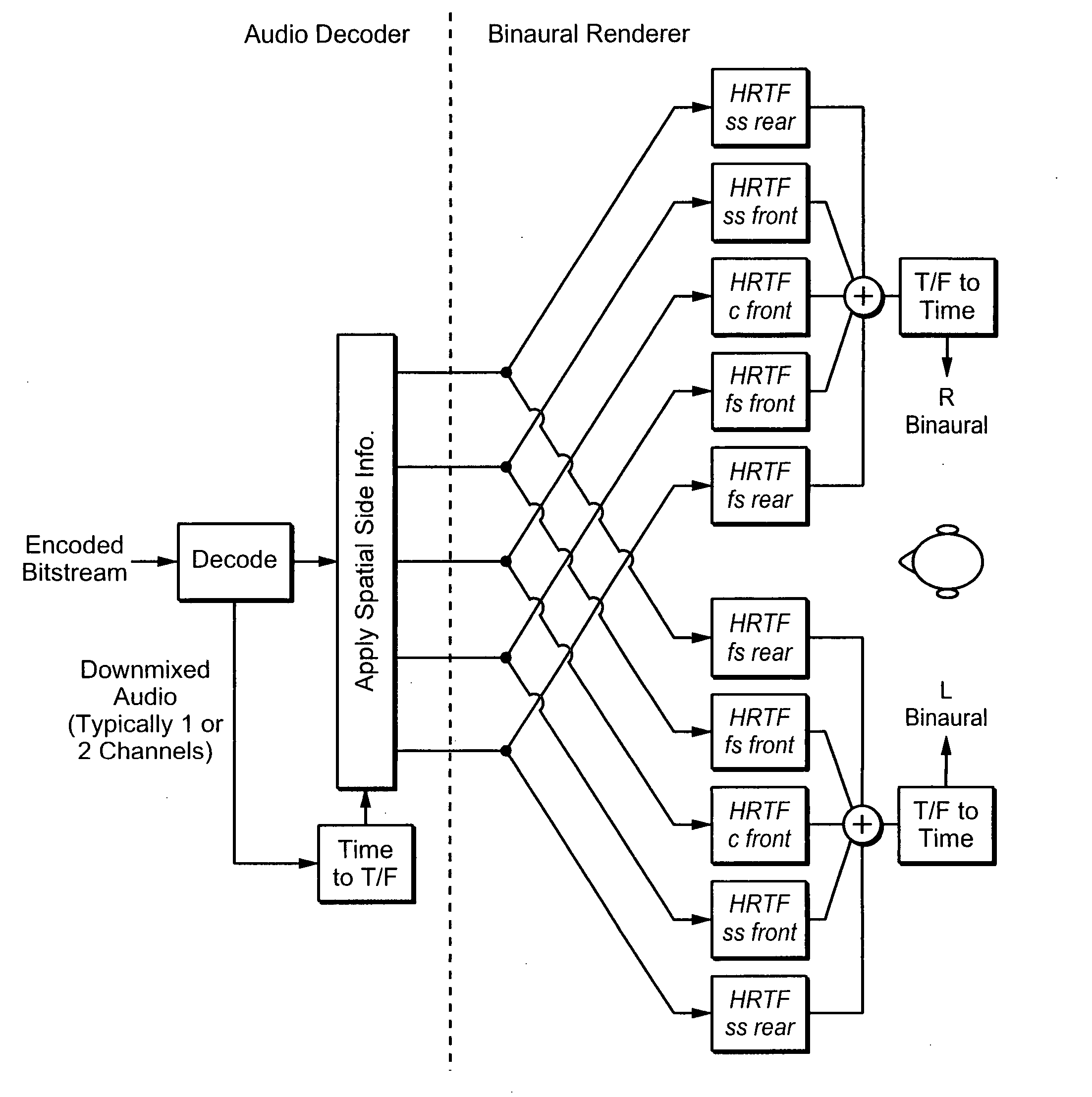
InactiveUS20080025519A1Efficient implementationComputational complexity is reducedSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsPhase correctionFrequency spectrum
Transfer functions like Head Related Transfer Functions (HRTF) needed for binaural rendering are implemented efficiently by a subband-domain filter structure. In one implementation, amplitude, fractional-sample delay and phase-correction filters are arranged in cascade with one another and applied to subband signals that represent spectral content of an audio signal in frequency subbands. Other filter structures are also disclosed. These filter structures may be used advantageously in a variety of signal processing applications. A few examples of audio applications include signal bandwidth compression, loudness equalization, room acoustics correction and assisted listening for individuals with hearing impairments.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
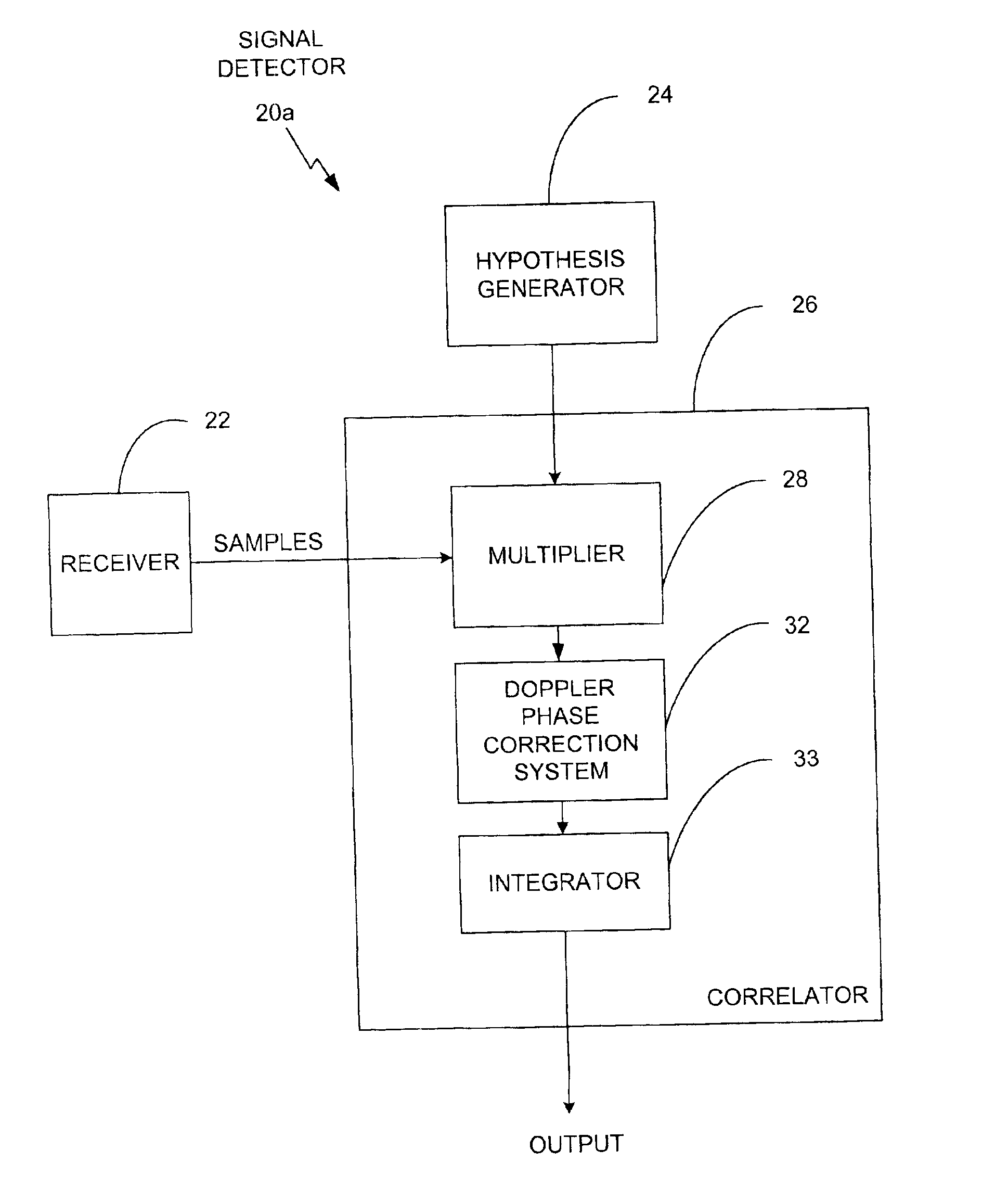
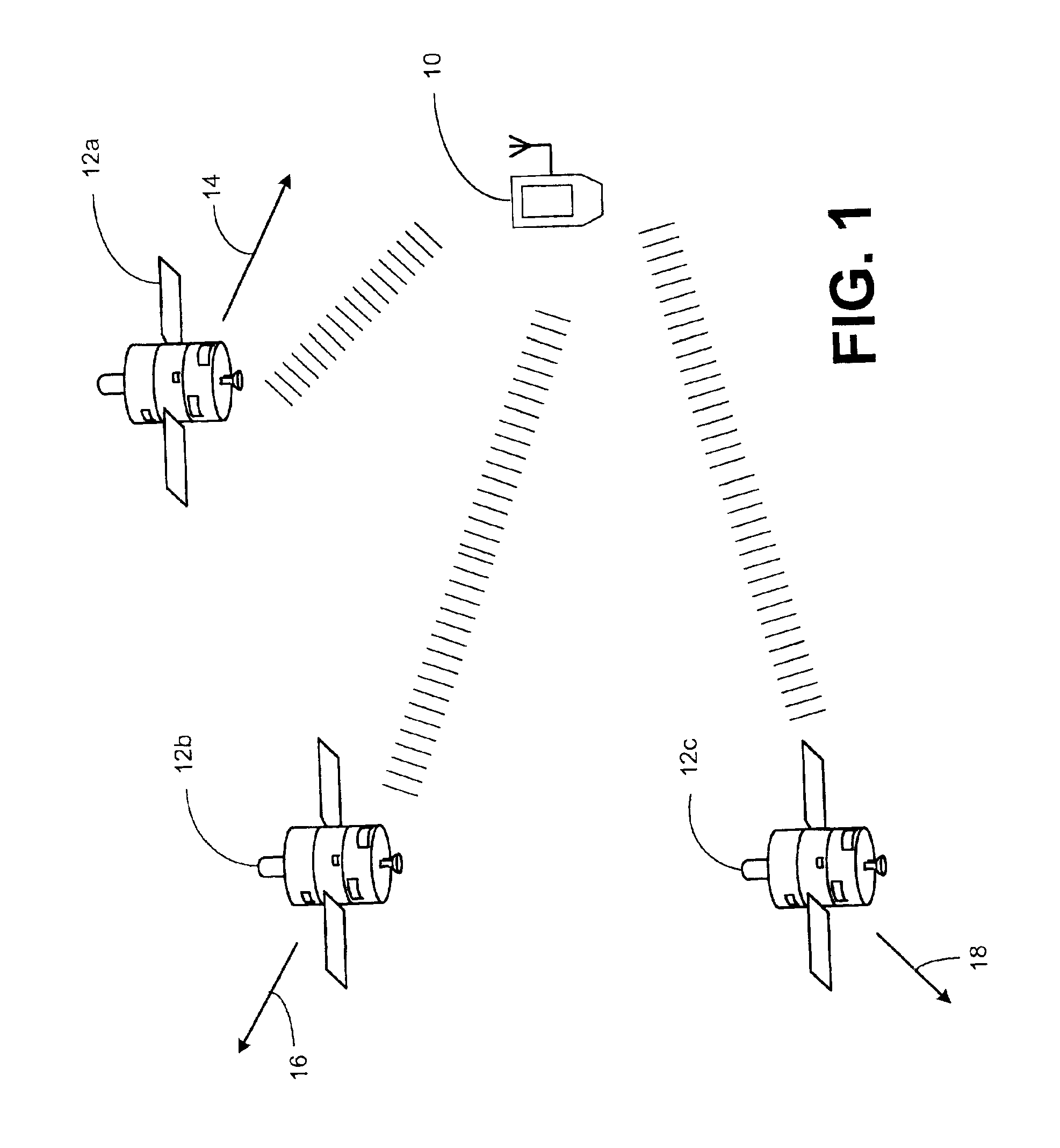
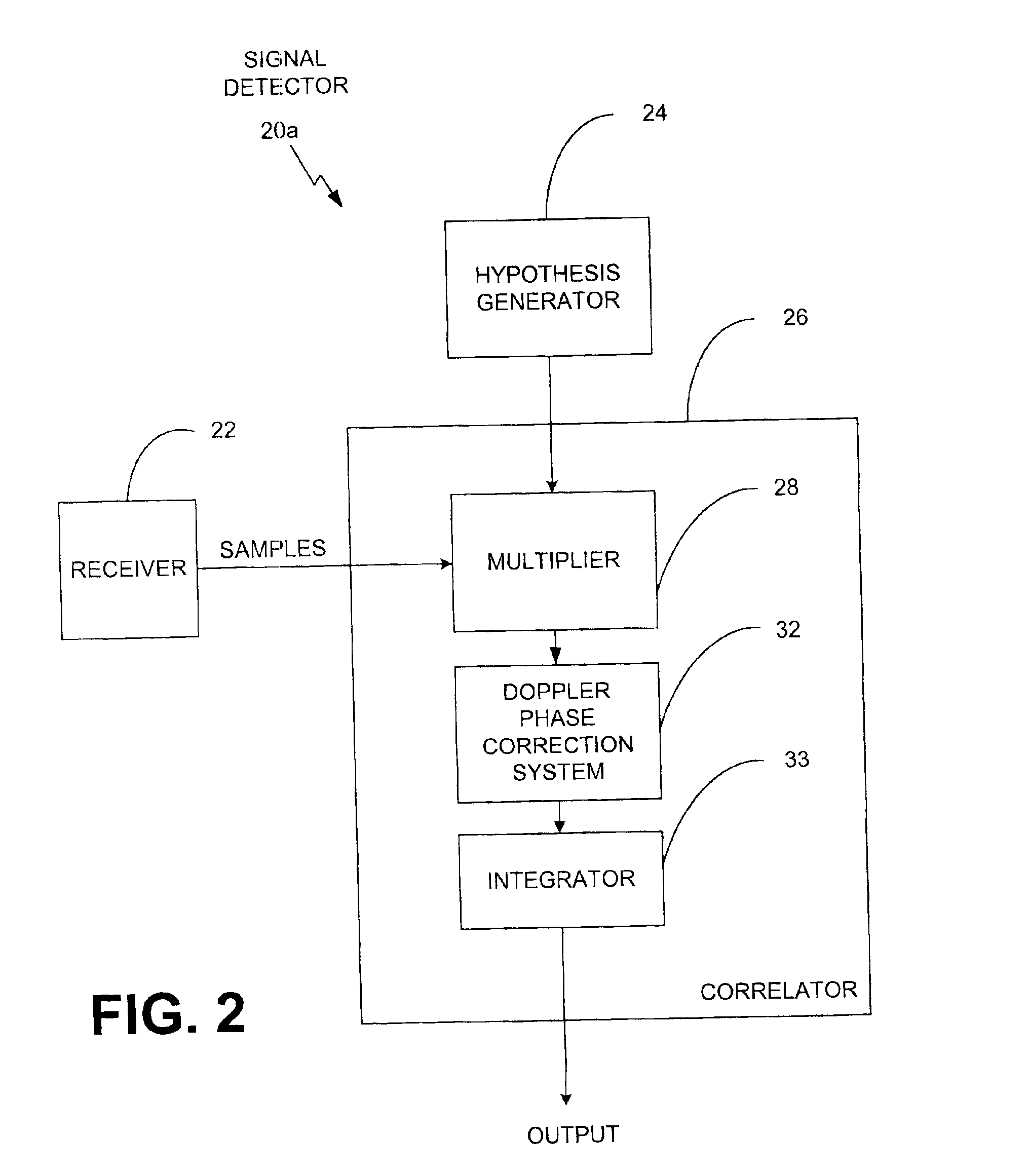
Signal detector employing a Doppler phase correction system
InactiveUS6952440B1Quick identificationEasy to optimizeError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionPhase correctionTime domain
A spread spectrum detector employs a Doppler phase correction system that improves correlation of pseudo-noise (PN) codes to a received spread spectrum signal by combining phase shifts, in the time domain, to correlation values that compensate for the Doppler shift error that is inherent in the signal and that is imposed upon the signal by movement between the signal source and receiver. In architecture, the Doppler phase correction system includes a receiver to receive a spread spectrum modulated signal having the Doppler shift error, a multiplier to produce a plurality of complex first correlation values based upon the signal and a code. A phase shifter generates a plurality of complex second correlation values respectively from the first correlation values. The second correlation values being phase shifted by respective different amounts from corresponding first correlation values, so that the second correlation values exhibit less of the Doppler shift error than the first correlation values. The phase shifter can be implemented with a look-up table that stores a plurality of phase shift values, a counter that produces indices for the look-up table, and a multiplier that multiplies the phase shift values that are output from the look-up table with the first correlation values to produce the second correlation values. Finally, a combiner, such as an integrator, combines, or integrates, the second correlation values to derive a third correlation that indicates a degree of correspondence of the code with the signal.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
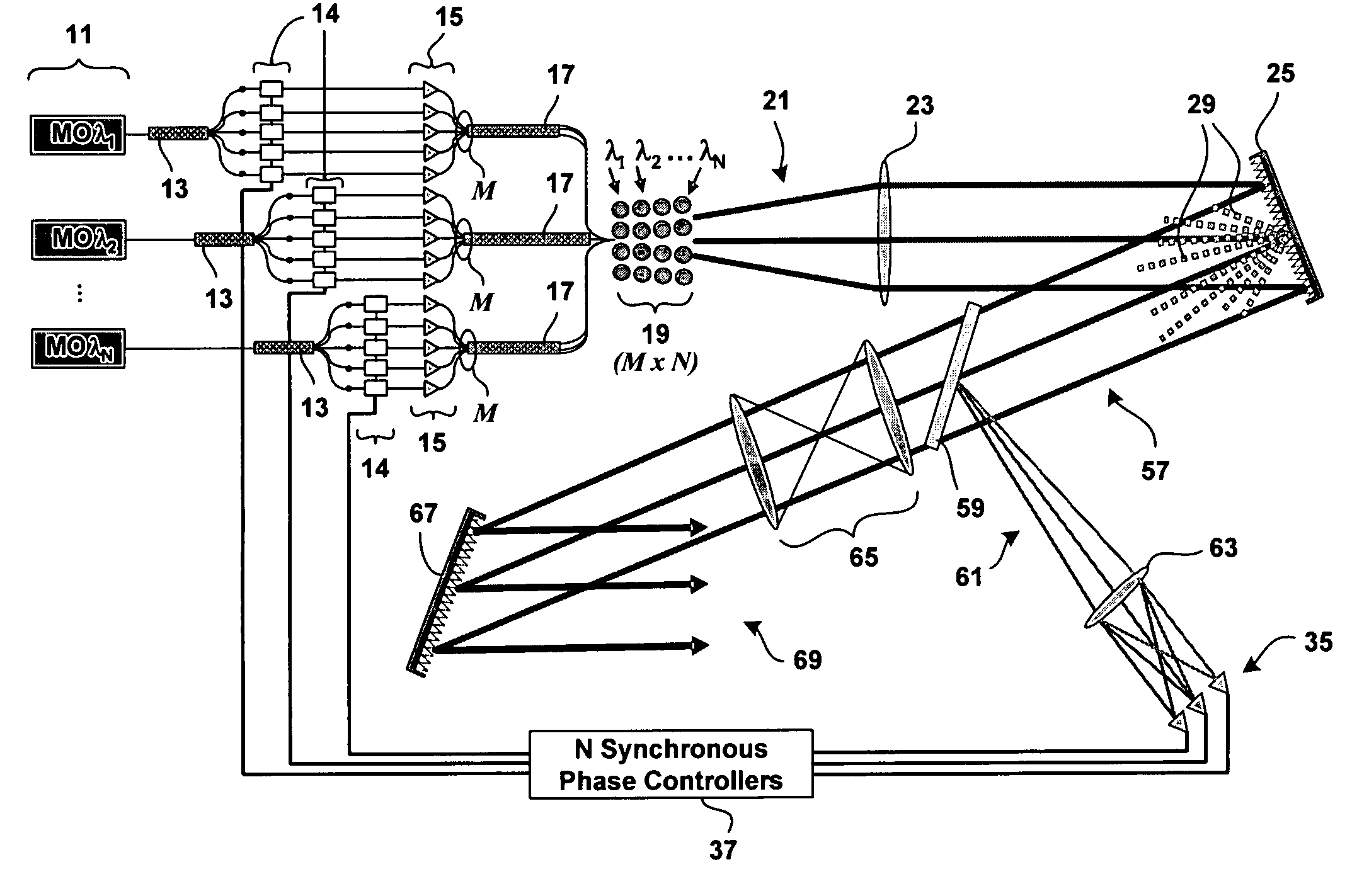
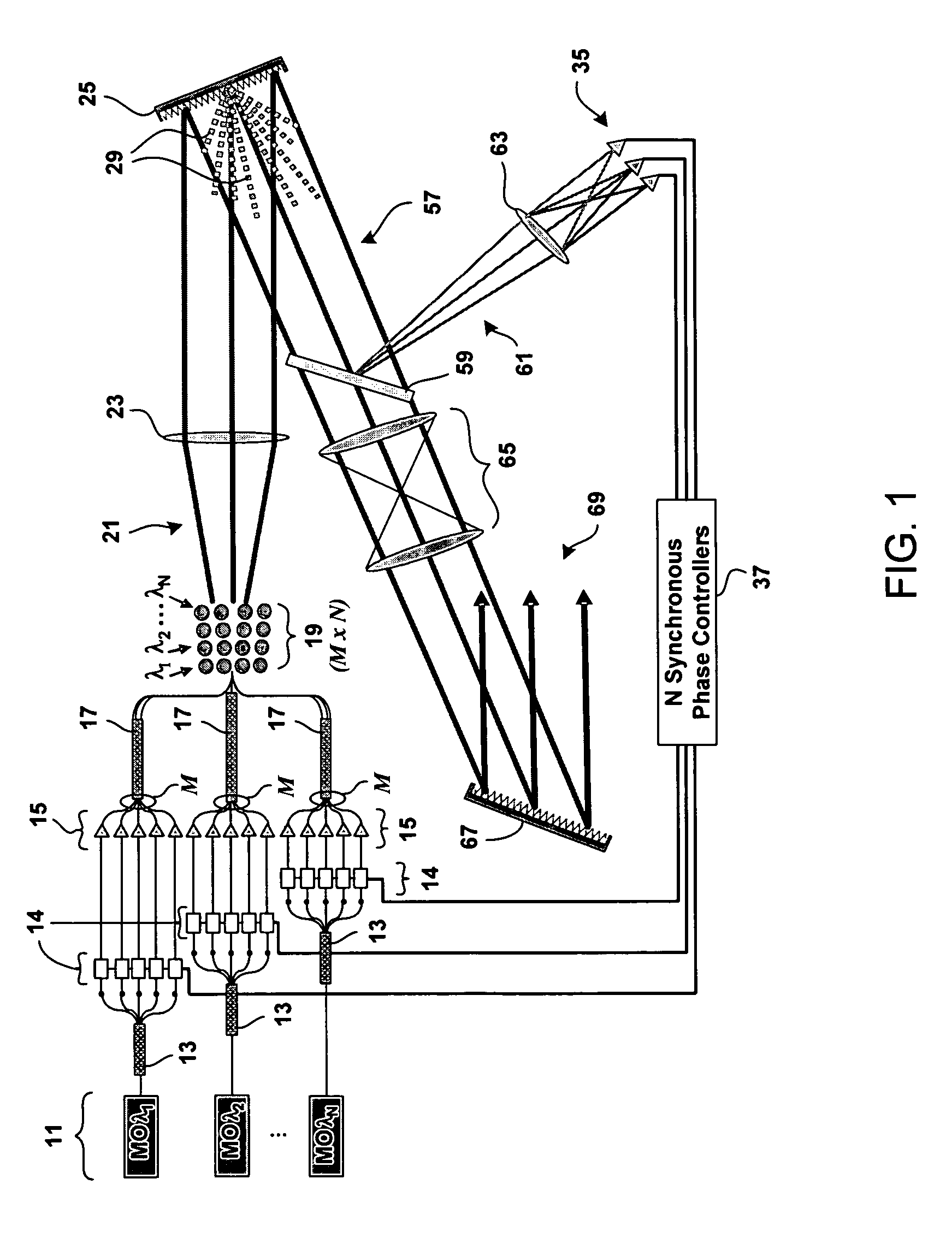
Method and system for hybrid coherent and incoherent diffractive beam combining
A hybrid beam combining system or method combines a plurality of coherent and incoherent light beams into a composite high power diffraction limited beam. N oscillators each transmit light at one of N different wavelengths and each wavelength is split into M constituent beams. M beams in each of N groups are phase locked by a phase modulator using phase correction signals. The phase locked beams are amplified and coupled into an M×N fiber array. Beams emerging from the array are collimated and incident on a diffractive optical element operating as a beam combiner combining the M outputs at each N wavelength into a single beam. The N single beams are incident and spectrally combined on a grating which outputs a composite beam at a nominal 100% fill factor. A low power sample beam, taken from the N beams emerging from the diffractive optical element, is measured for phase deviations from which the phase correction signals are derived and fed back to the phase modulators. The diffractive optical element may include a weak periodic grating for diffracting the low power sample. The diffractive optical element may also be combined with the spectral combining grating into a single optical element.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
External correction of errors between traffic and training in a wireless communications system
InactiveUS7221699B1Compensating for such errorTime-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase correctionTraffic capacity
A method and apparatus are provided that allows a training and traffic signal to be compensated for phase errors without modifying a receiver. In one embodiment, the invention encompasses an external error correction circuit having a signal input to receive training and traffic channel signals from a receive chain, a signal processing circuit to compute phase corrections to at least one of the training and traffic channel signals, and a signal generator to supply a compensation signal to effect the computed correction.
Owner:INTEL CORP
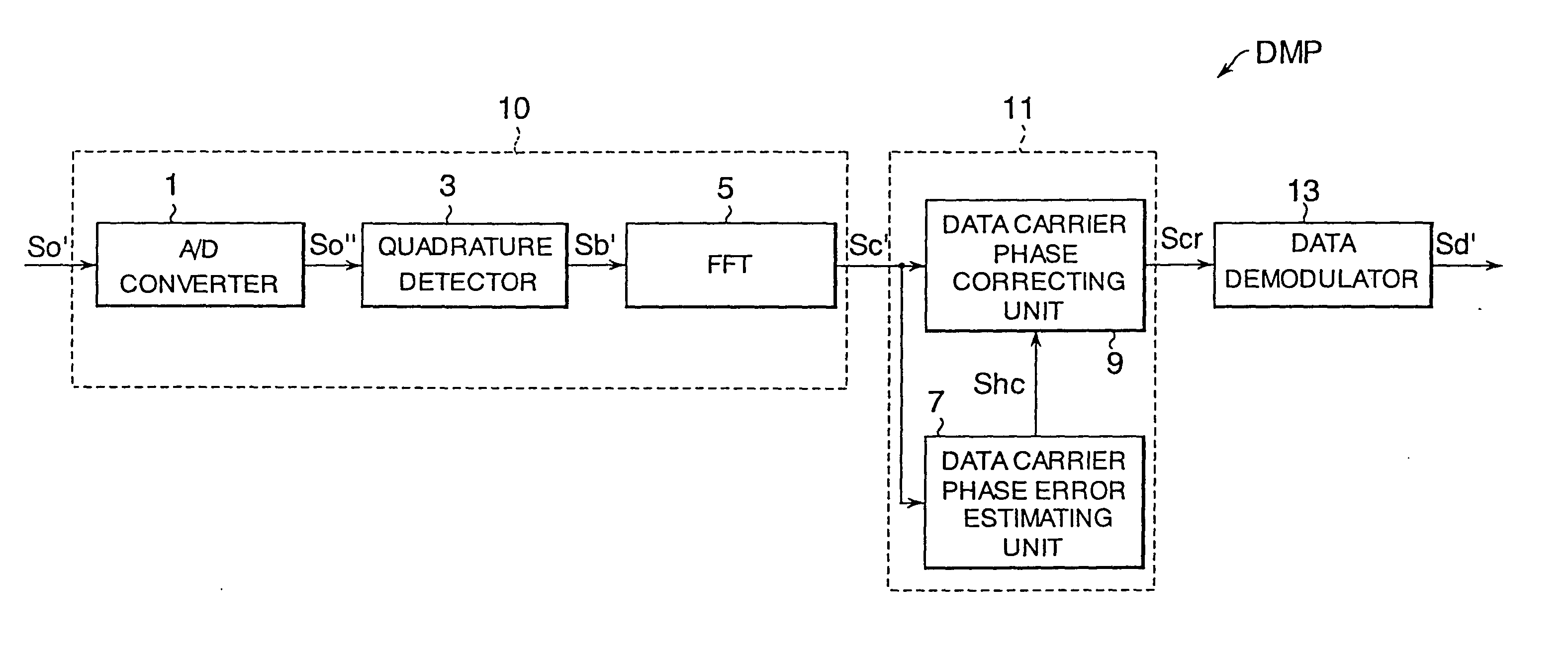
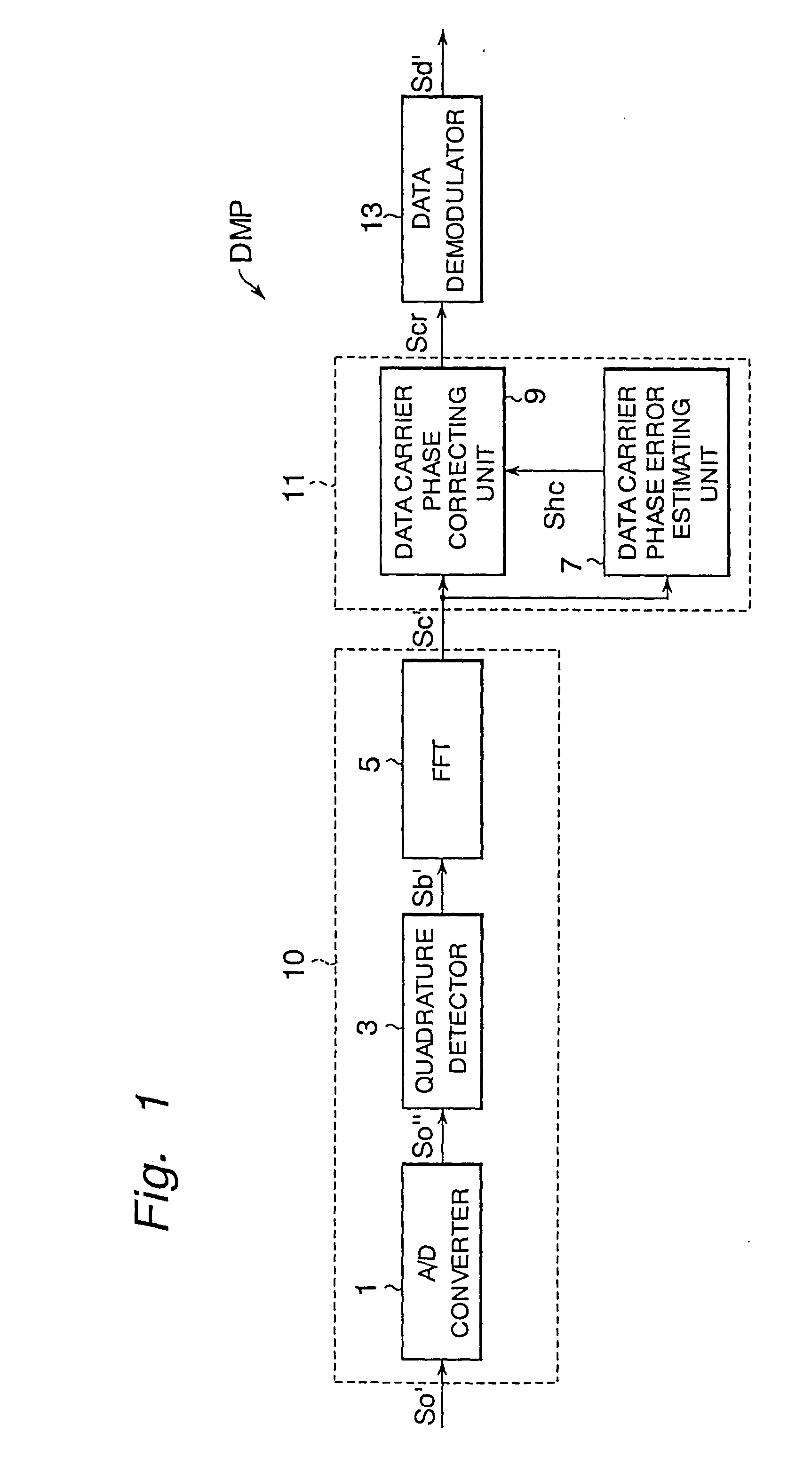
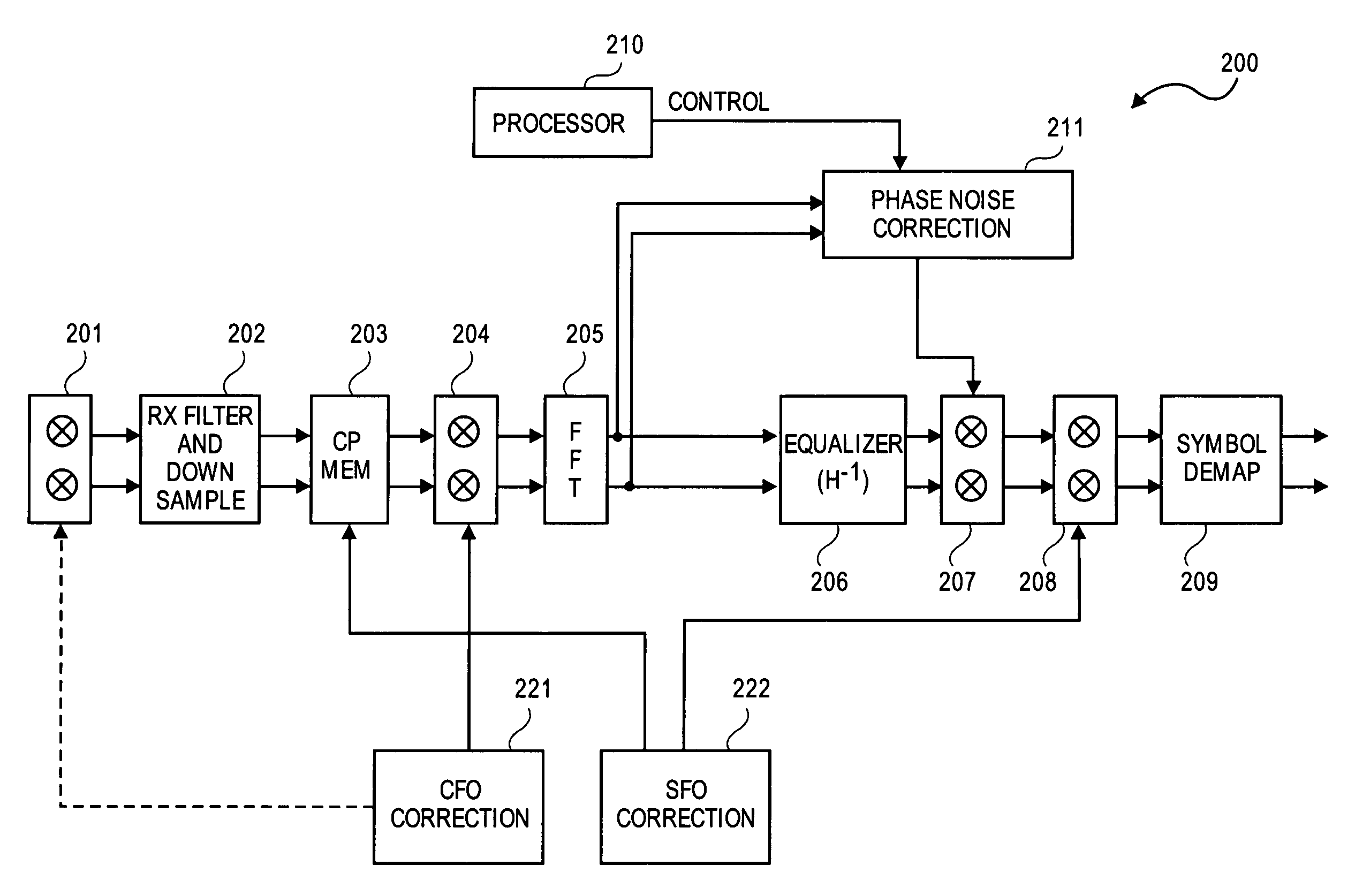
Modulator, demodulator, and transmission system for use in OFDM transmission
An input of an OFDM signal containing known pilot carriers among given subcarriers is separated into subcarriers through Fourier transform in a fast Fourier transform unit. A data carrier phase error estimating unit obtains an amount of phase correction of each subcarrier on the basis of the pilot carriers in the separated subcarriers. A data carrier phase correcting unit corrects the phase of the separated subcarrier signal on the basis of the amount of phase correction. Thus, the phase errors of the subcarriers can be corrected and the OFDM symbols can be demodulated even if a frequency error and a timing error are occurring between the transmitter and receiver.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Method and apparatus for locating the source of an unknown signal
InactiveUS6618009B2Direction finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesPhase correctionUnknown Source
A method of determining the location of an unknown source 10 transmitting a signal to satellite relays 14 and 16 comprises receiving replicas of the signal from the relays at receivers 18. The receivers 18 also transmit and receive reference signals via respective relays 14 and 16. All signals are downconverted, digitized and correlated with one another in pairs using a correlation function including a term which compensates for time varying differential frequency offset (DFO). Compensation for time varying differential time offset or time dilation is achieved by replicating or adding to signal samples and applying phase corrections. This procedure enables a correlation maximum and associated measurement results to be obtained despite the effects of relay satellite motion which mitigate against this. Results are used in a prior art geometrical technique to locate the unknown transmitter.
Owner:KRATOS INTEGRAL HLDG LLC
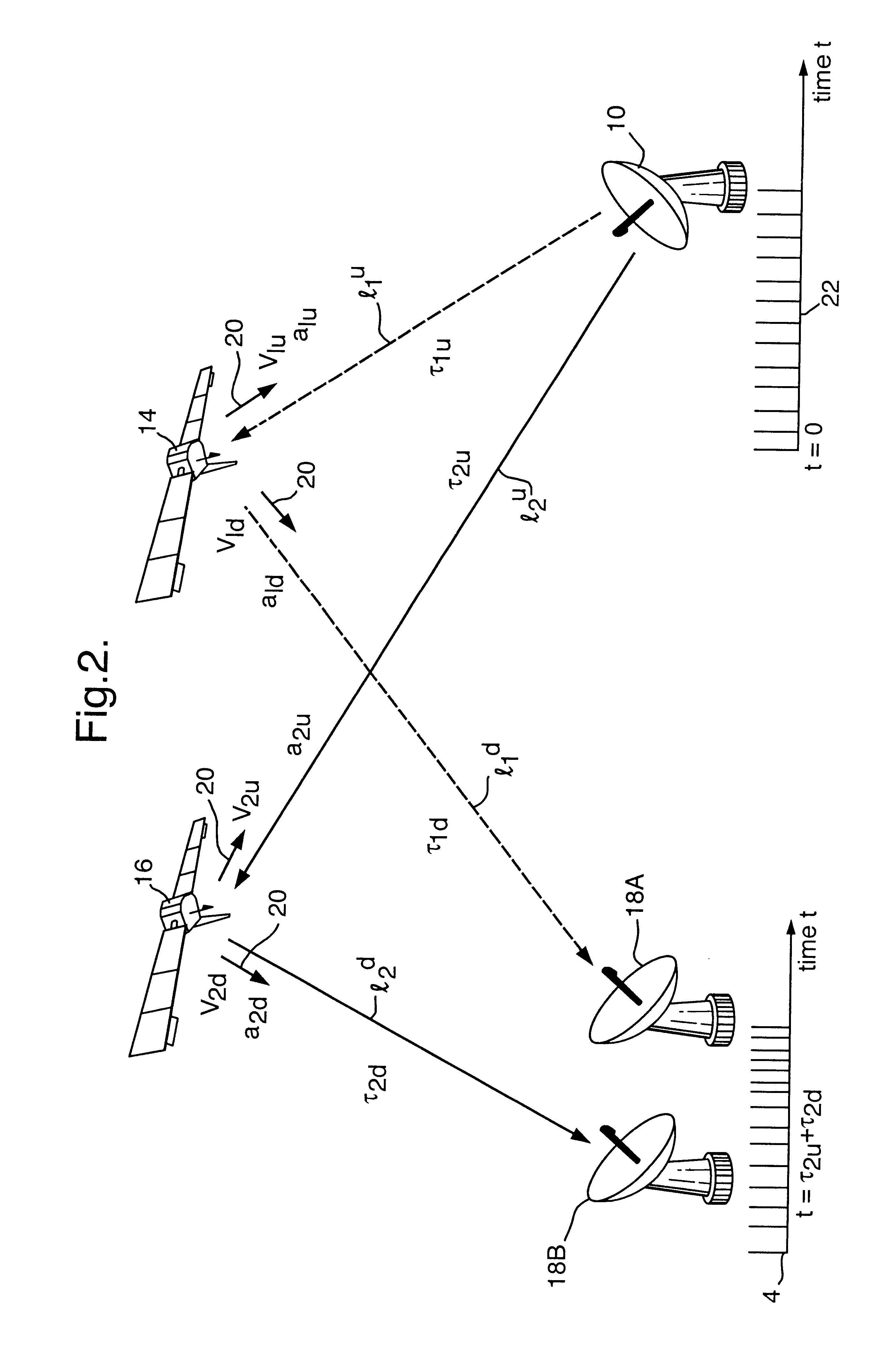
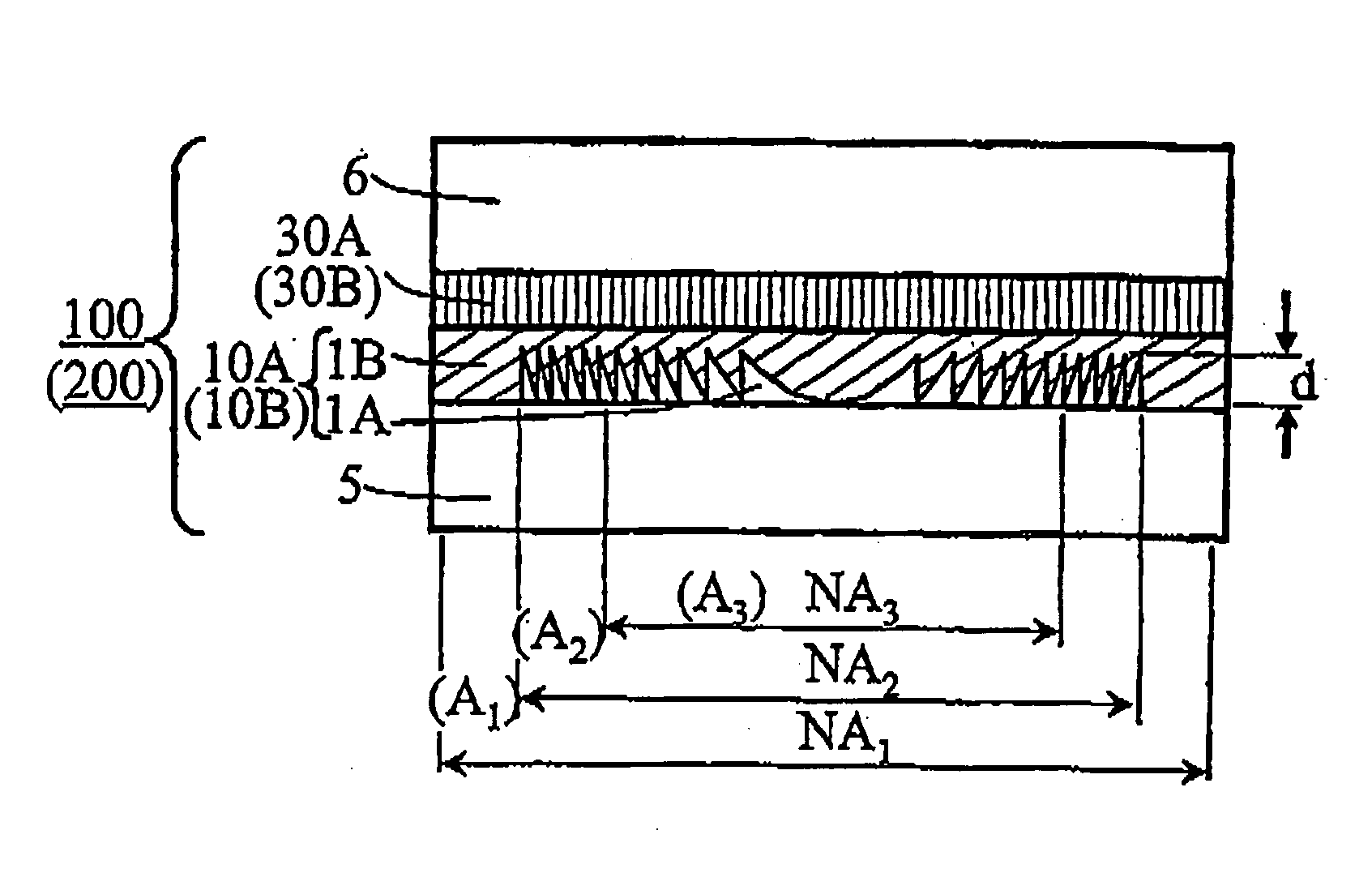
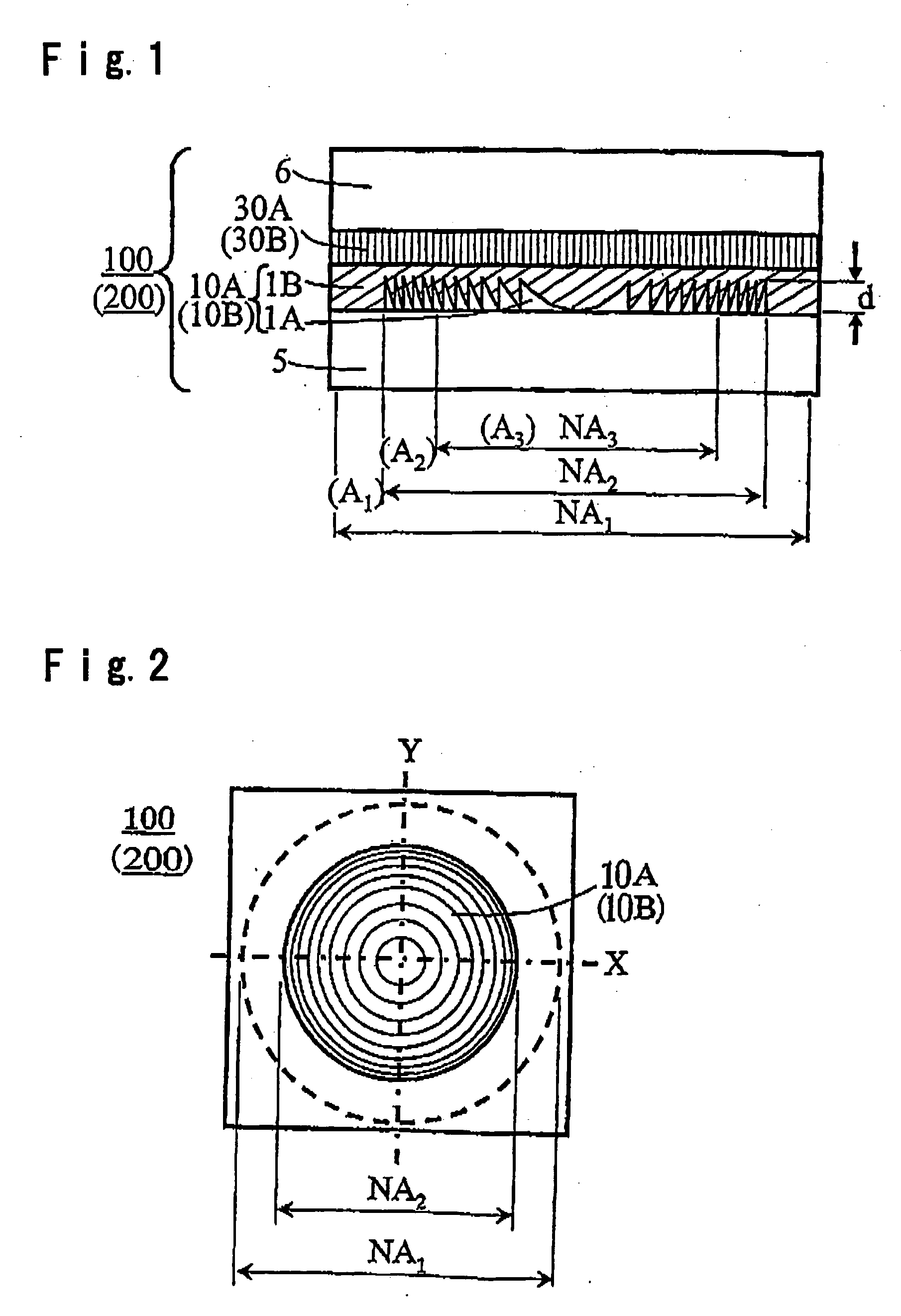
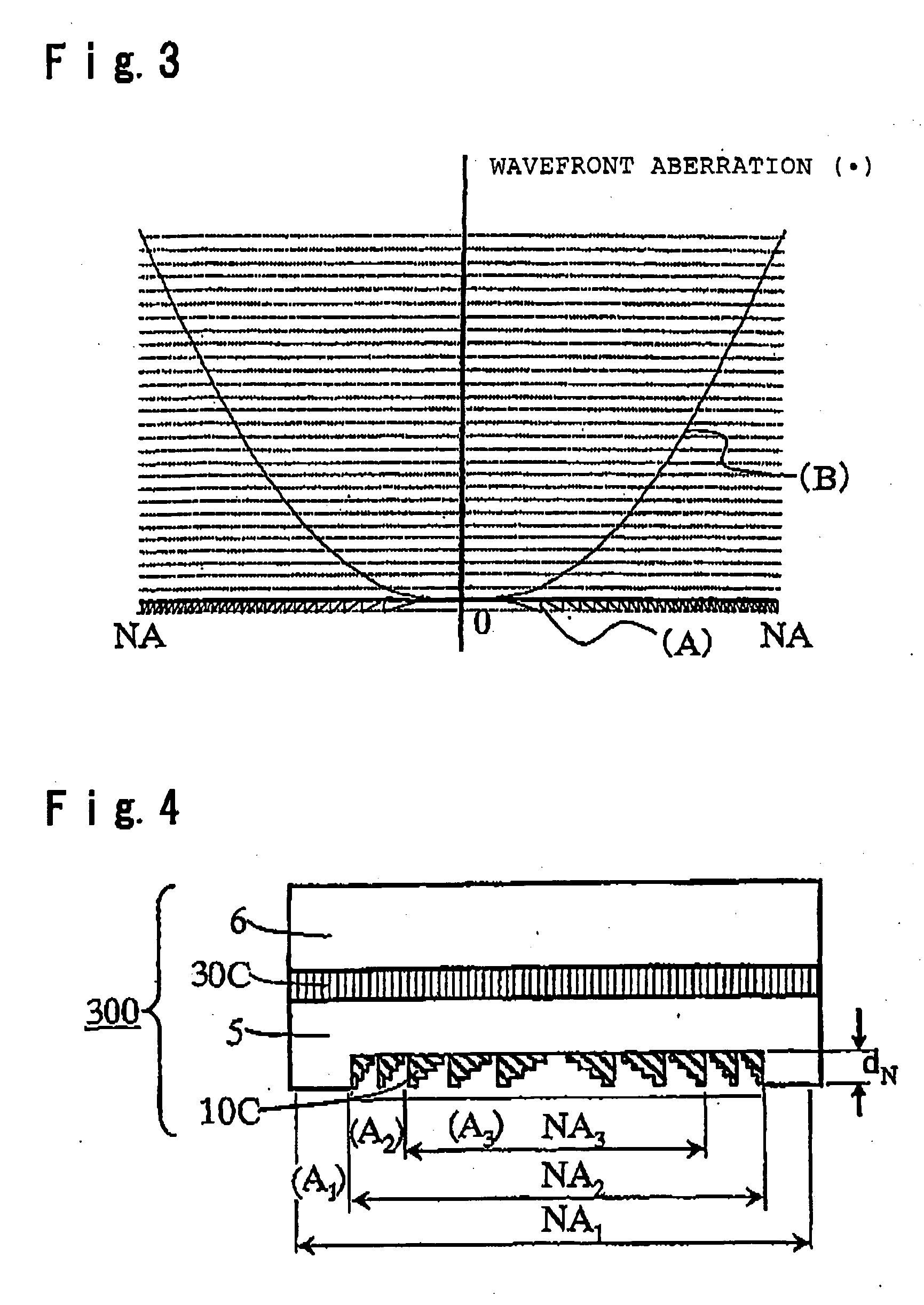
Phase correction element and optical head device
InactiveUS20050226122A1Polarising elementsRecord information storagePhase differenceNumerical aperture
The present invention provides a phase correction element which can be used for recording and / or reproducing an information of three types of optical disks for HD, DVD and CD by employing a single objective lens for HD, and an optical head device. The phase correction element 100 of present invention comprises a first phase correction layer 10A formed in a region of numerical aperture NA2, and a first phase plate 30A integrally formed; the first phase correction layer 10A comprising a concavo-convex portion having a rotational symmetry with respect to the optical axis of incident light and having a cross-sectional shape of a saw-tooth-form or a saw-tooth-form whose convex portions are each approximated by a step form; the first phase plate 30A generating a birefringent phase difference of about an odd number times of π / 2 for linearly polarized light having a wavelength of λ1; and the phase correction element 100 having a function of not changing a transmitted wavefront of the wavelength of λ1 and changing a transmitted wavefront of the wavelength of λ2 or transmitted wavefront of both wavelengths of λ2 and λ3 when three types of incident light in a λ1=410 nm wavelength band, a λ2=650 nm wavelength band and a λ3=780 nm wavelength band respectively, are incident.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
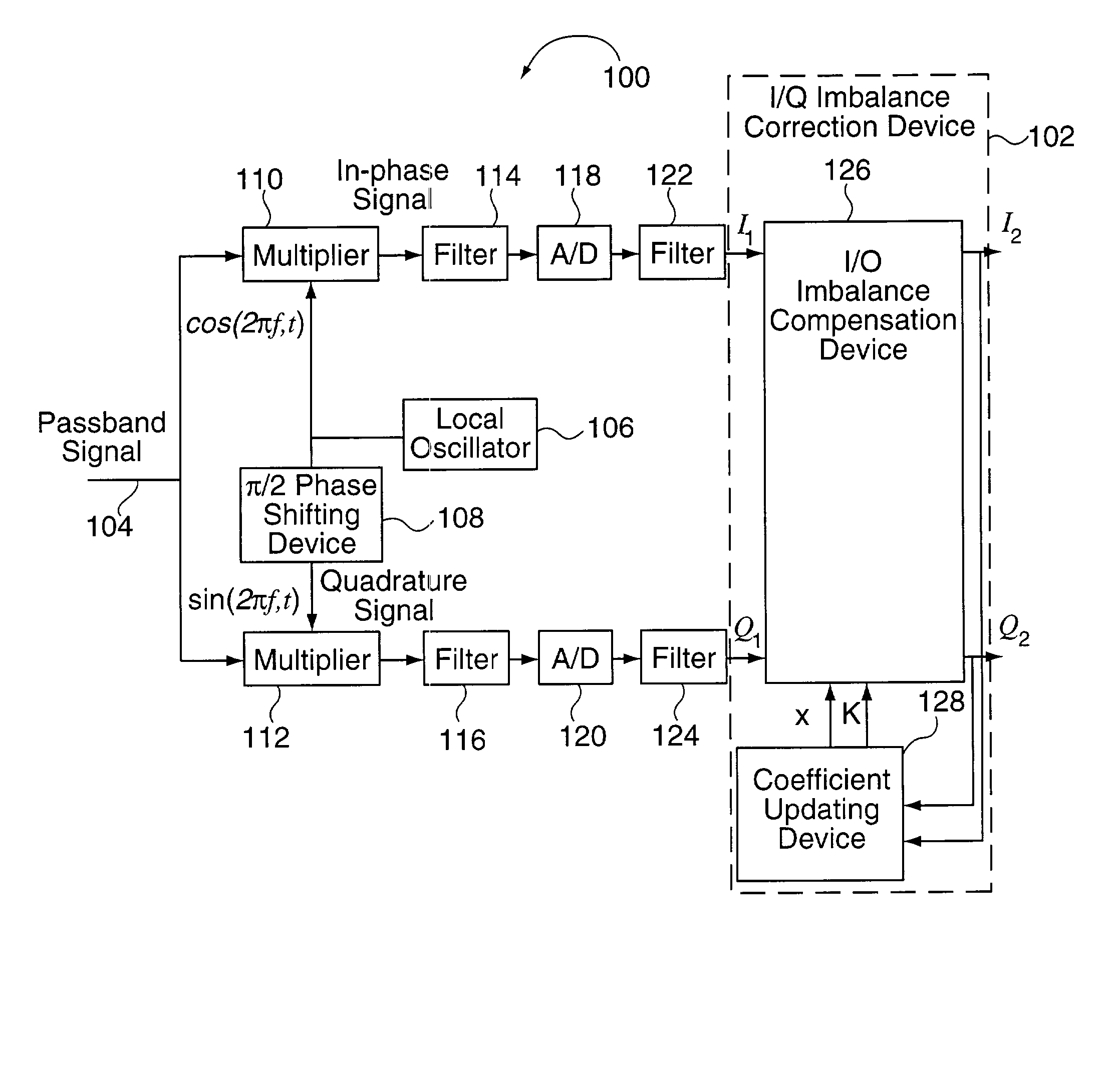
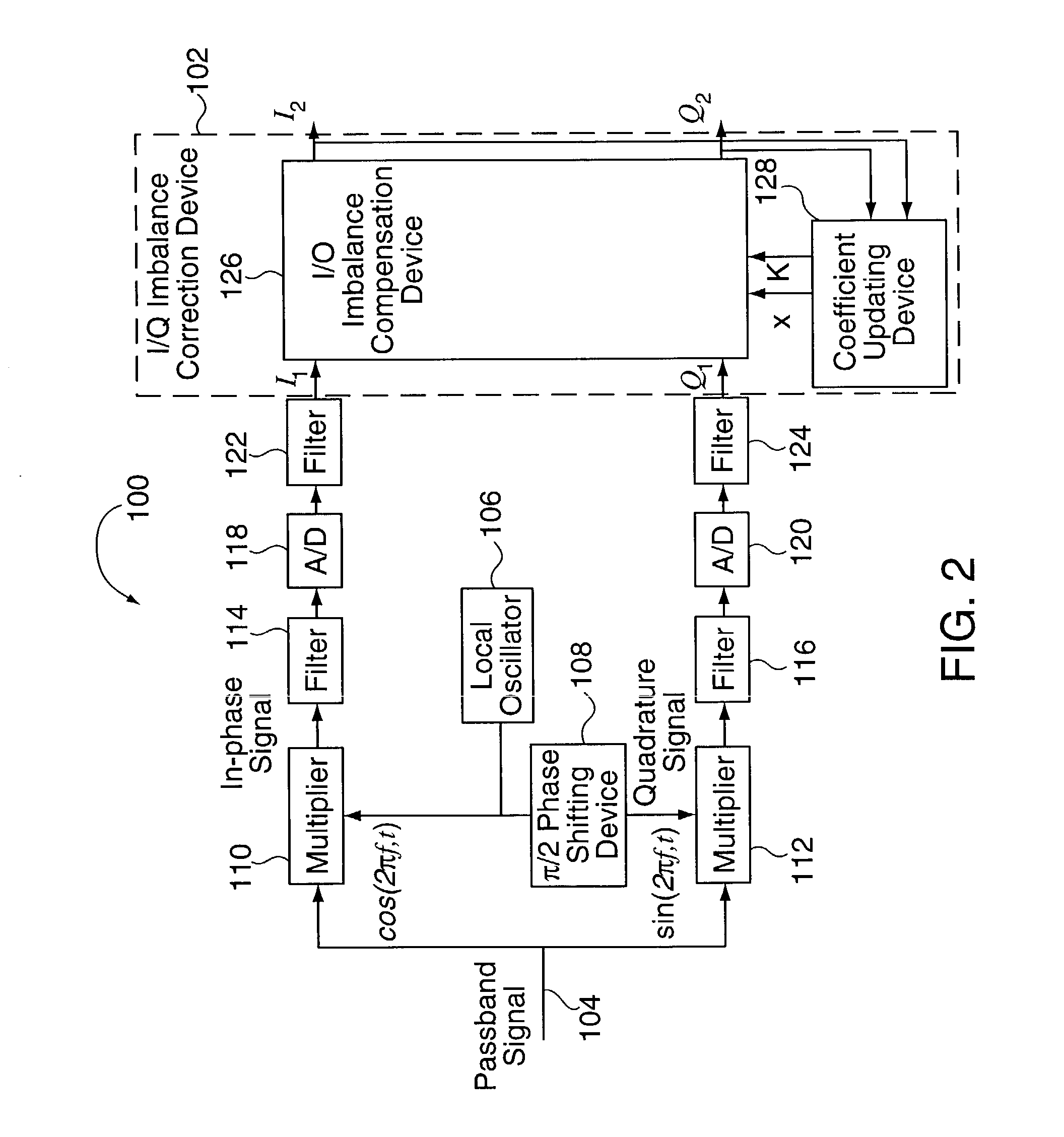
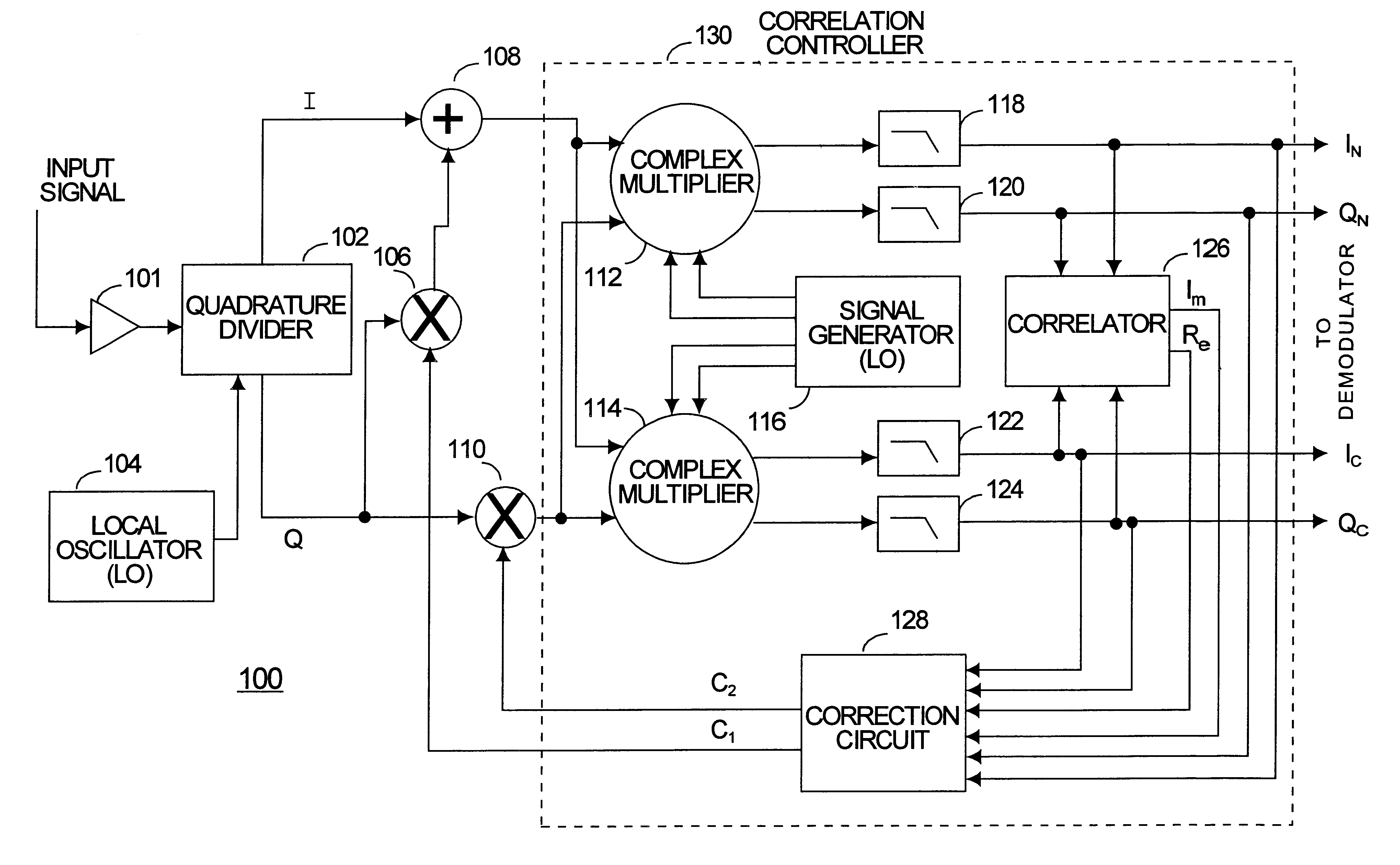
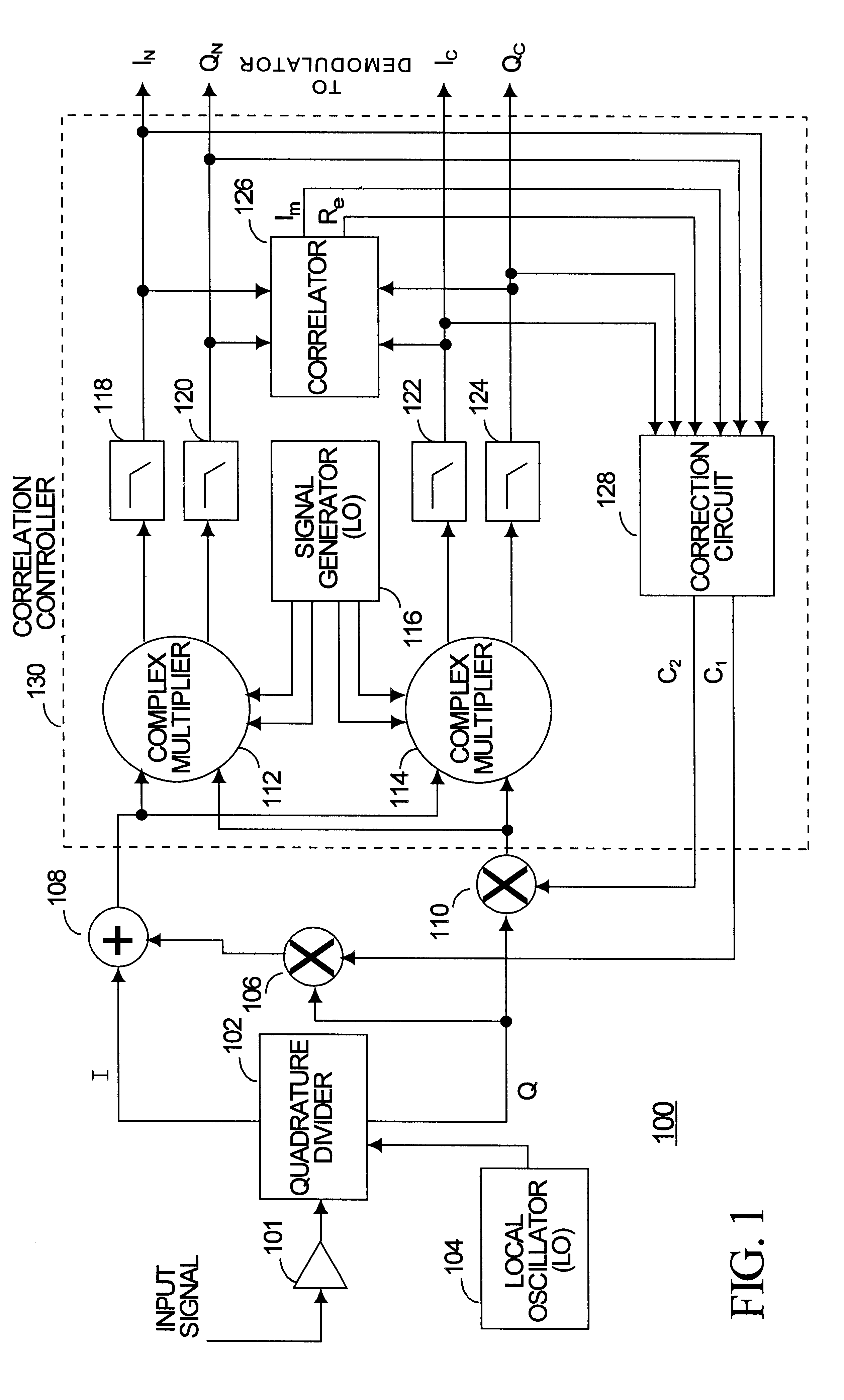
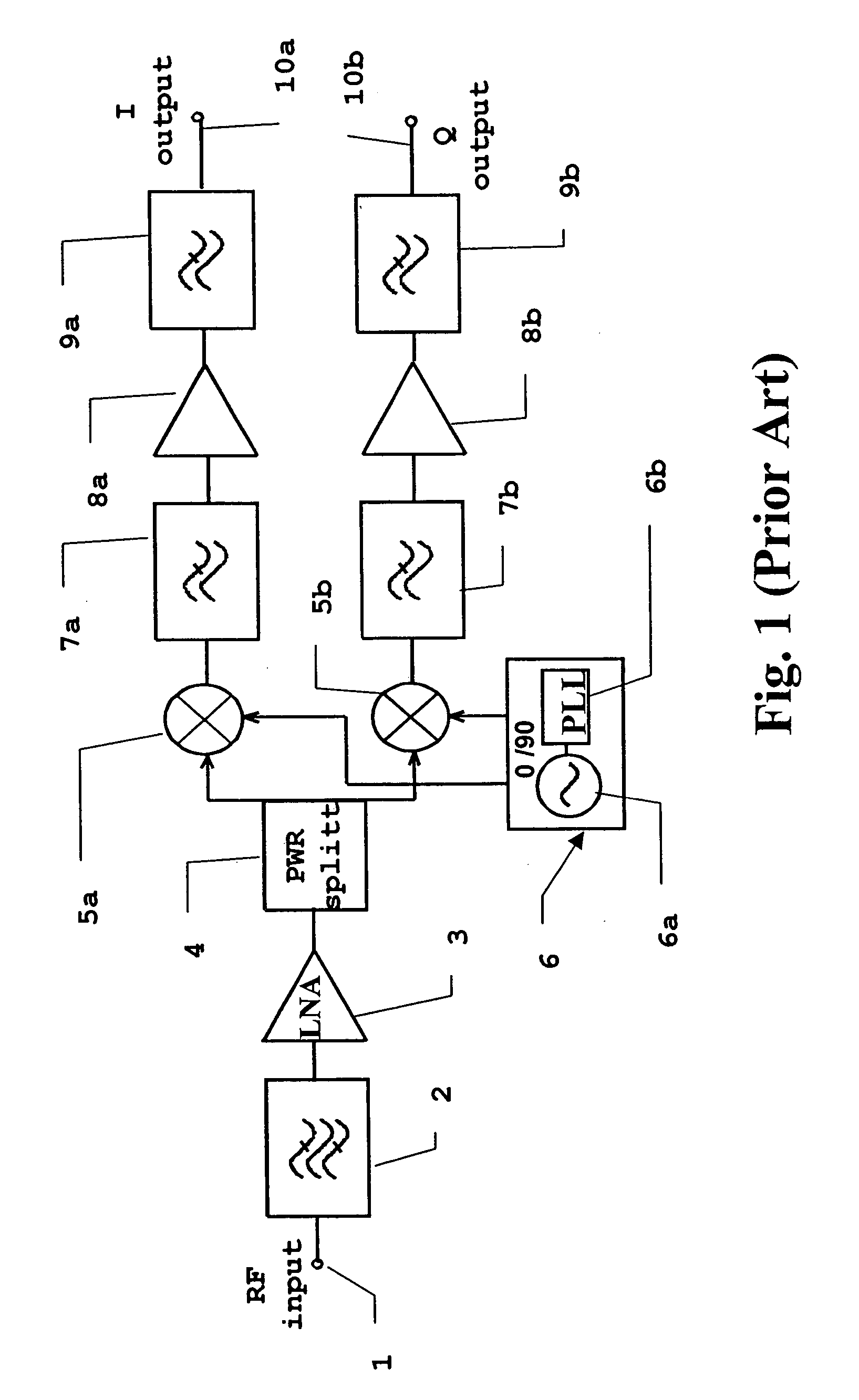
Methods and apparatus for I/Q imbalance compensation
InactiveUS20030007574A1Carrier regulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase correctionPhase imbalance
Methods and apparatus for performing amplitude and phase imbalance correction operations on in-phase and quadrature phase signal components corresponding to a received signal are described. The imbalance correction operations relay on the use of relatively simple to implement feedback loops. The phase imbalance feedback loop relies on the tendency of transmitted symbols to be distributed uniformly around the origin of the I / Q plane if proper phase balance is present in the processed signal. Phase correction coefficients are generated over time as a function of the negated product of the processed in-phase and quadrature phase signal components. Amplitude correction coefficients are generated over time as a function of the difference in the squared values of the I and Q processed signal components.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
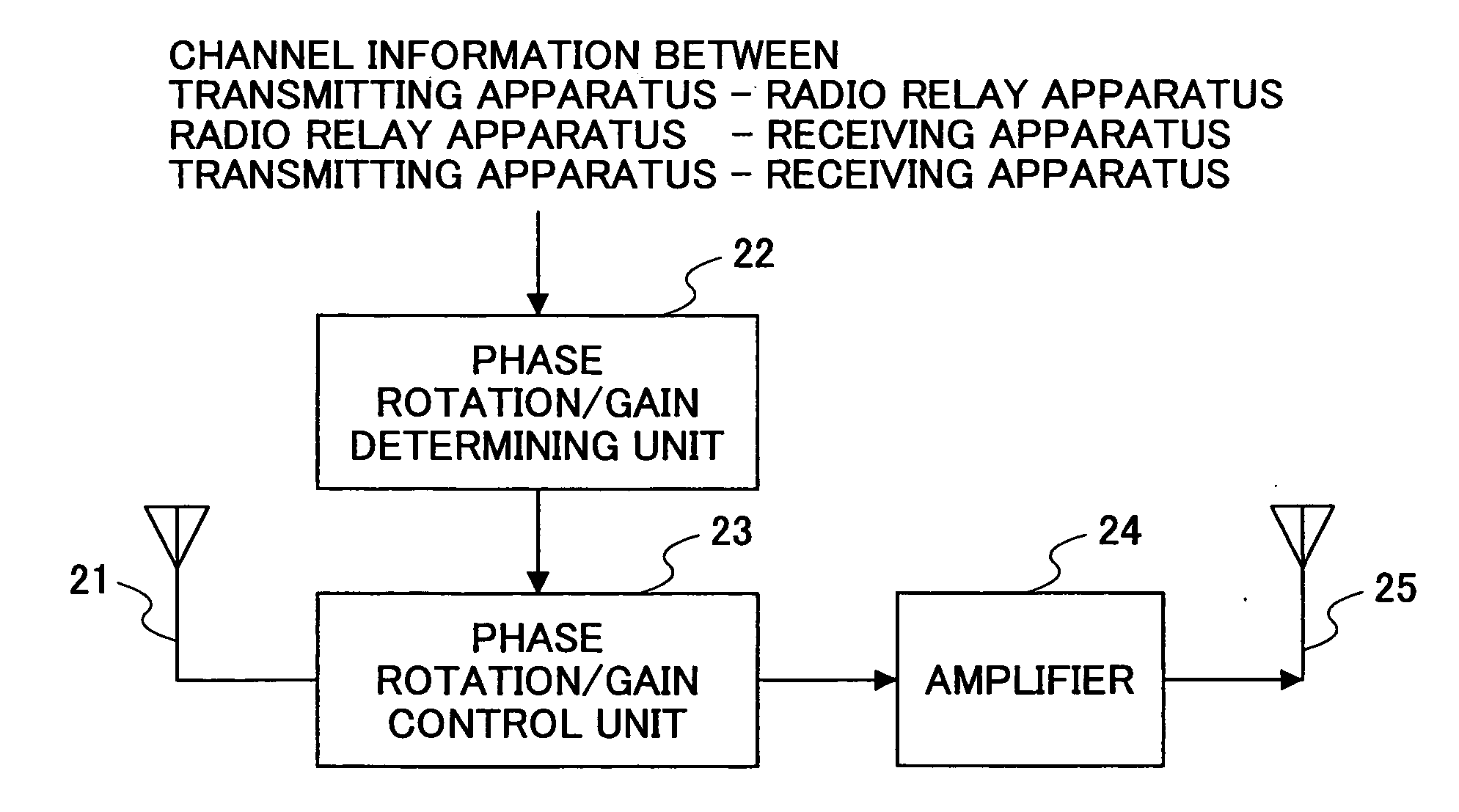
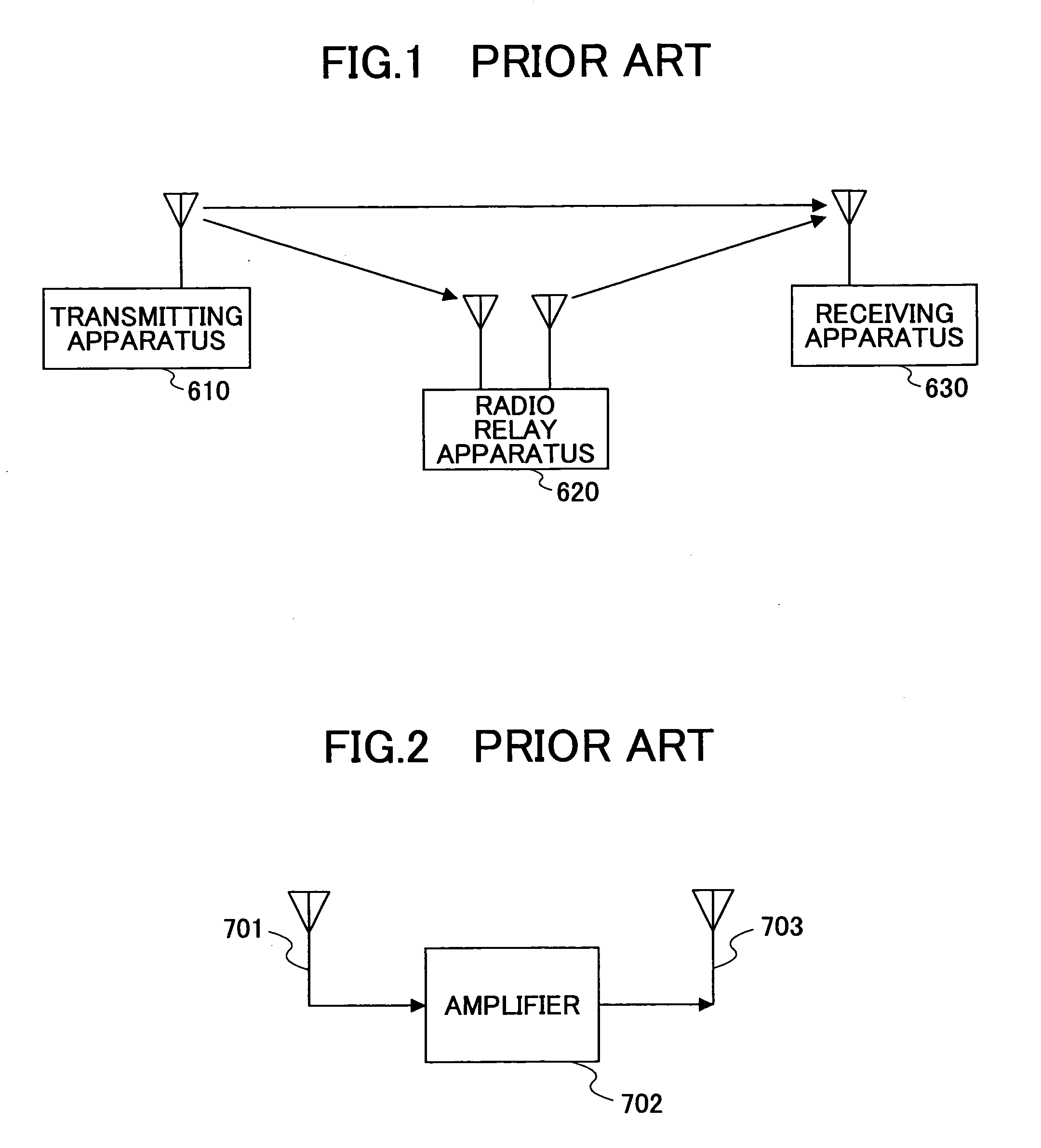
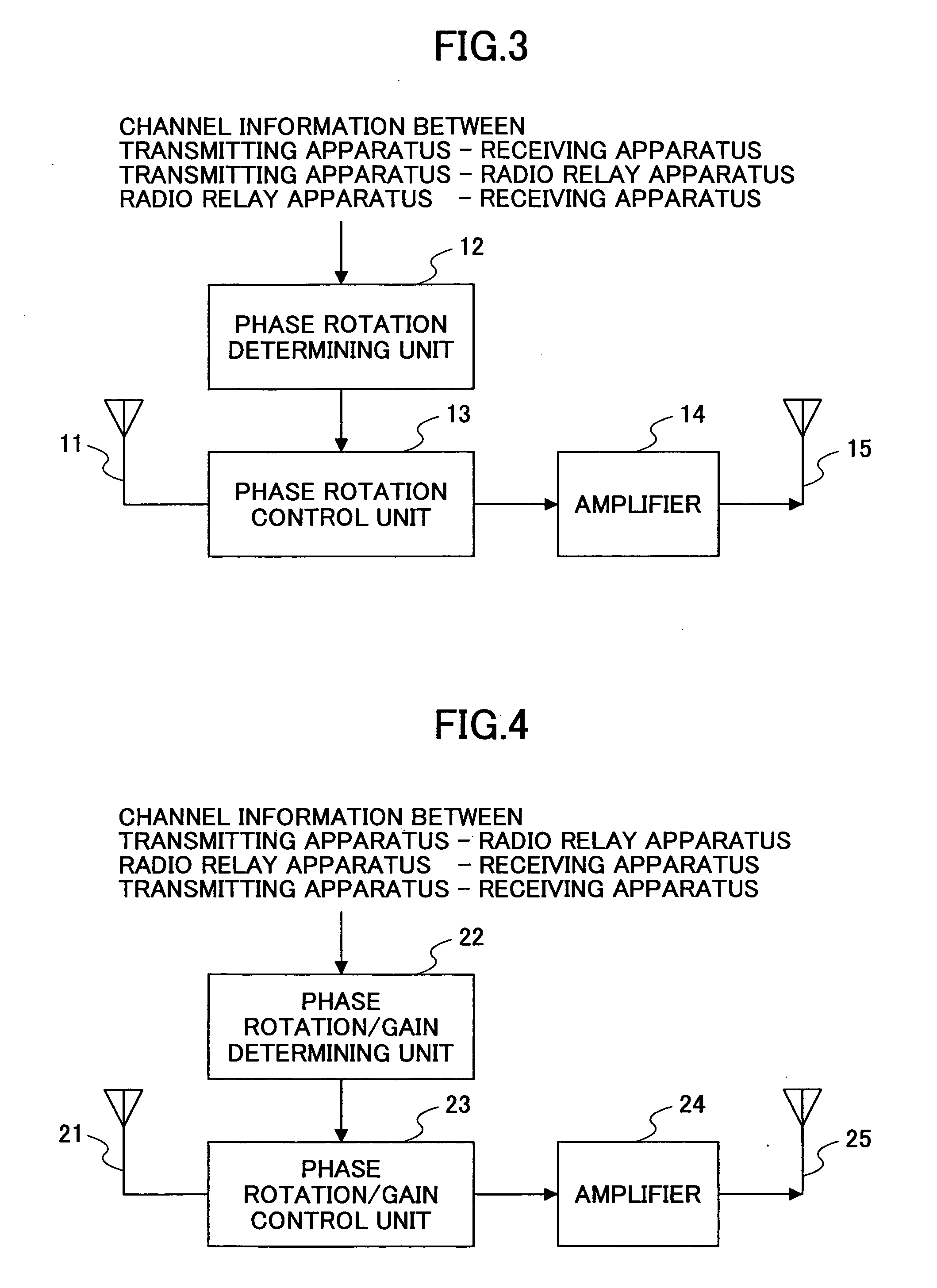
Radio relay system, radio relay apparatus, and radio relay method
InactiveUS20050190821A1Reduce communication qualityQuality improvementSpatial transmit diversityRepeater/relay circuitsFrequency bandPhase correction
A radio relay system is disclosed that is capable of preventing communication degradation in a case where radio signals are relayed using the same frequency band in a mobile communication environment. The radio relay system includes a first radio station, a second radio station, and a radio relay apparatus for relaying a radio signal that is exchanged between the first radio station and the second radio station. The radio relay apparatus includes a phase correction determining unit that determines a phase correction amount of the relayed signal based on channel information pertaining to channels established between the first radio station, the second radio station, and the radio relay apparatus, and a phase correction unit that corrects the relayed signal based on the phase correction amount determined by the phase correction determining unit.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
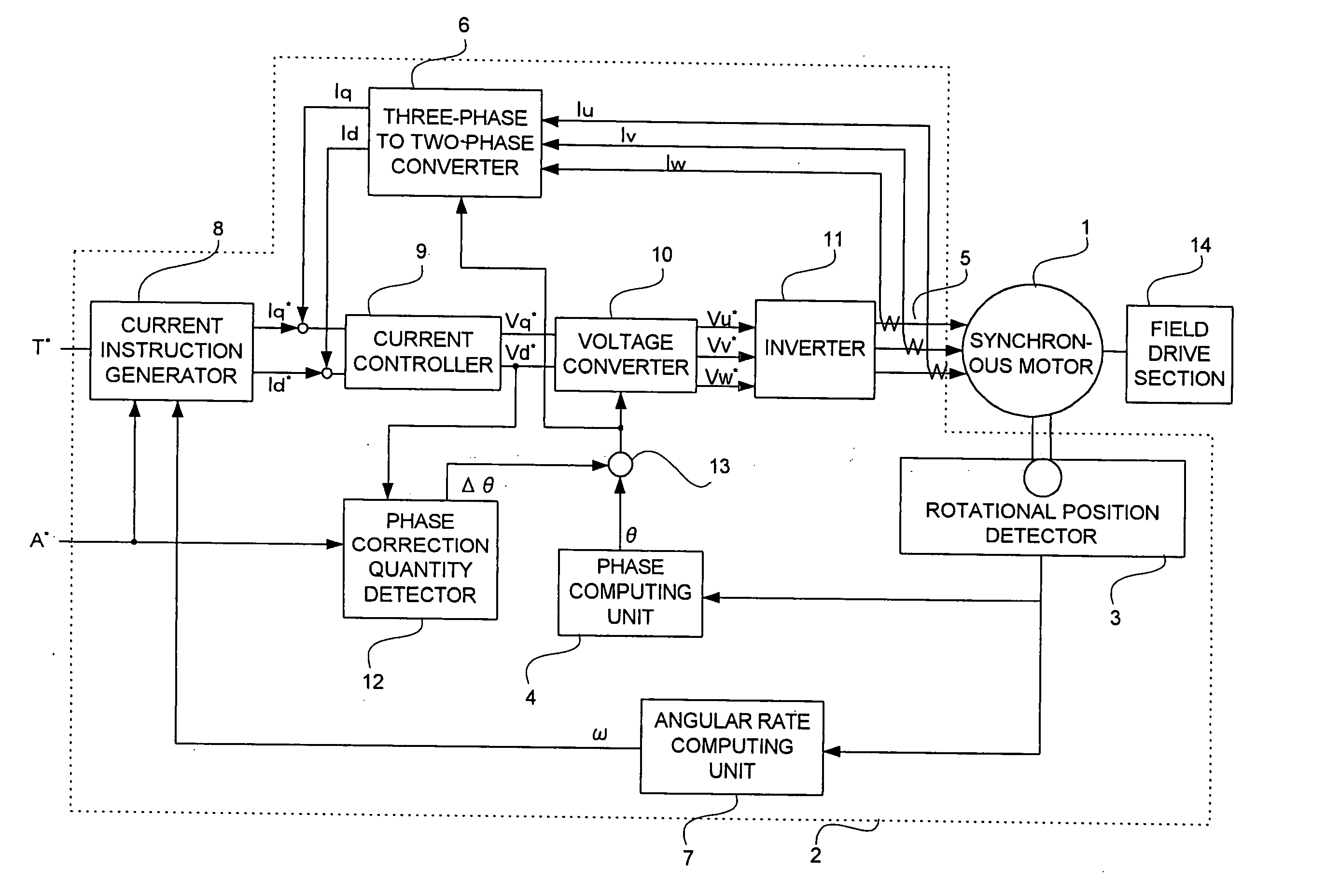
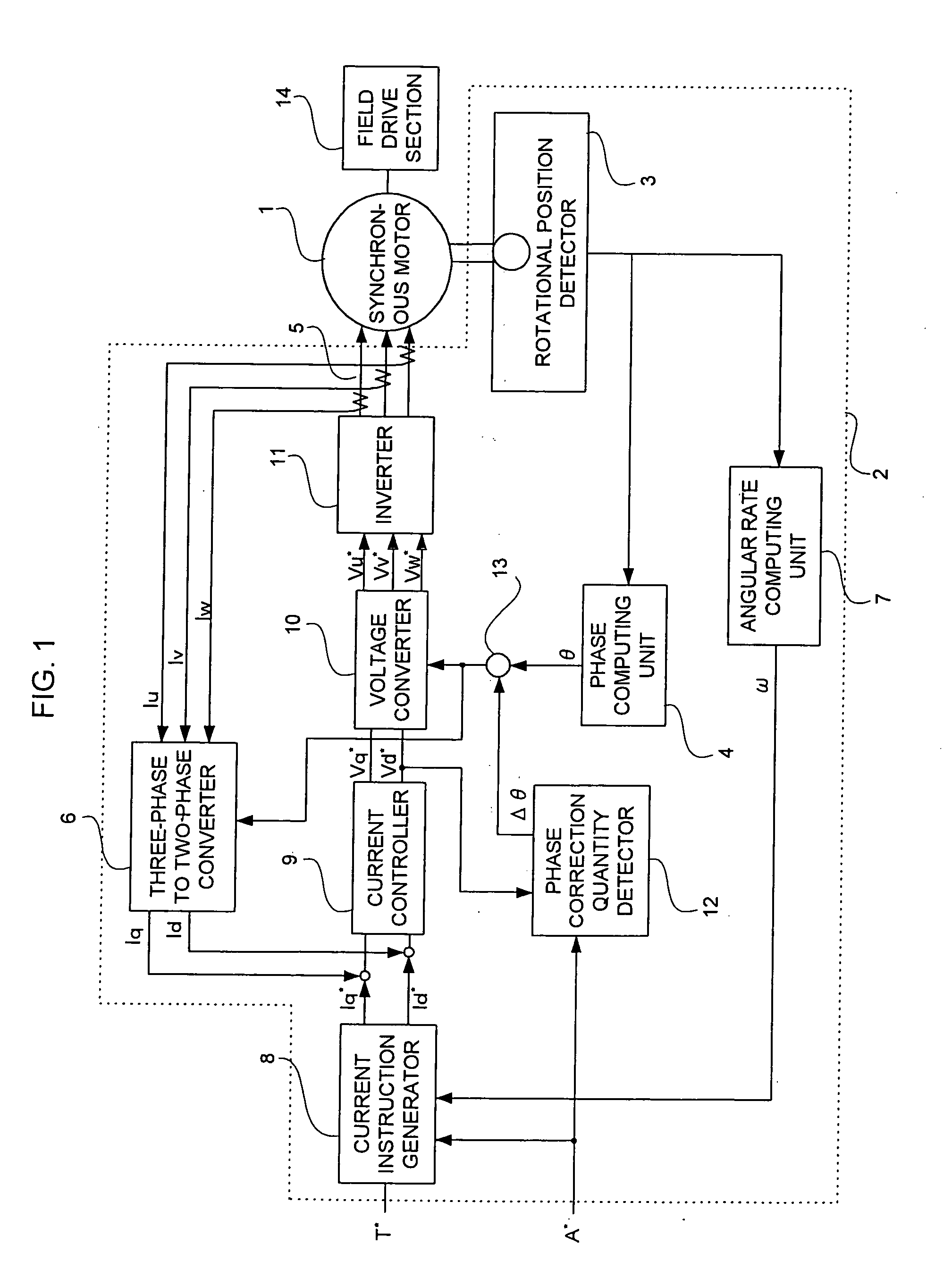
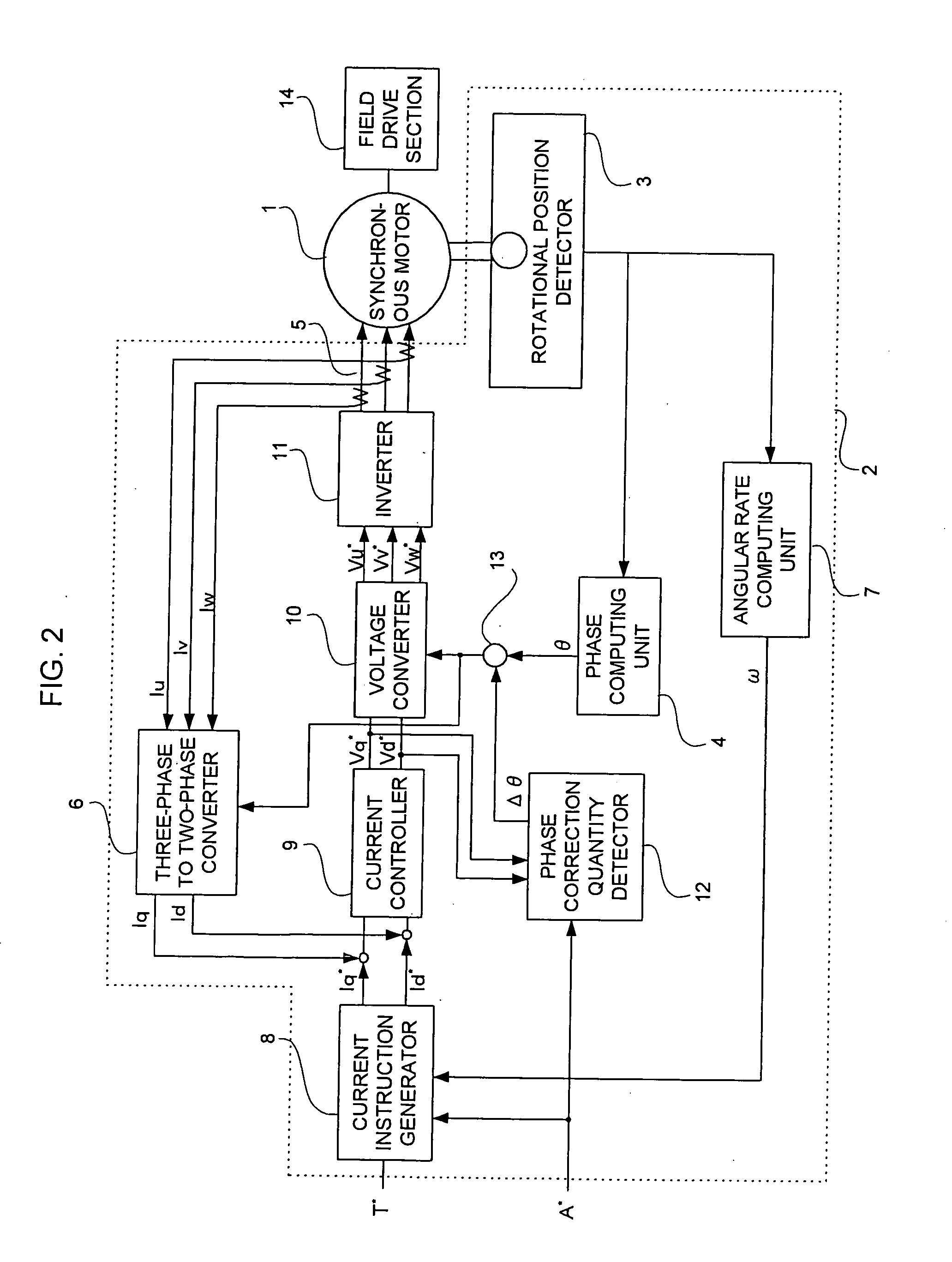
Synchronous motor control device and method of correcting deviation in rotational position of synchronous motor
ActiveUS20050104551A1Correct deviationAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlPhase correctionVoltage converter
In a synchronous motor control device that corrects a deviation in rotational position which is related to a rotational position detector for a synchronous motor on which vector-control is performed, the synchronous motor control device includes: a current instruction generator that disables a torque instruction to set d-axis and q-axis current instructions as zero when a phase correction instruction is inputted; a current controller that outputs d-axis and q-axis voltage instructions based on the d-axis and q-axis current instructions; a phase correction quantity detector for determining the amount of offset in which the d-axis voltage instruction becomes zero when the phase correction instruction is inputted and the d-axis voltage instruction is not zero; an adder for adding a rotor positional angle and the amount of offset; and a voltage converter for determining three-phase voltage instructions based on the additional value, the d-axis and q-axis voltage instructions.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
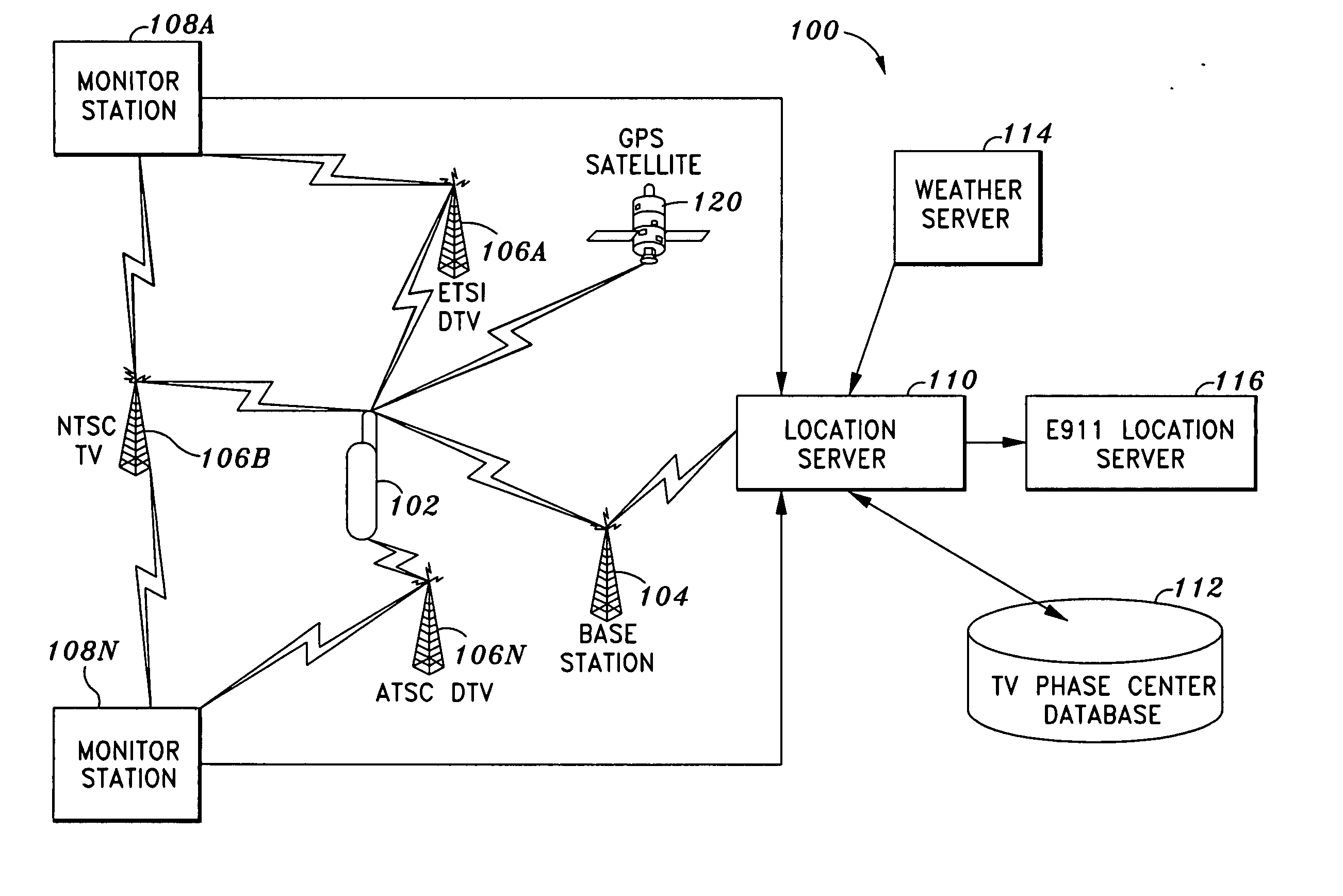
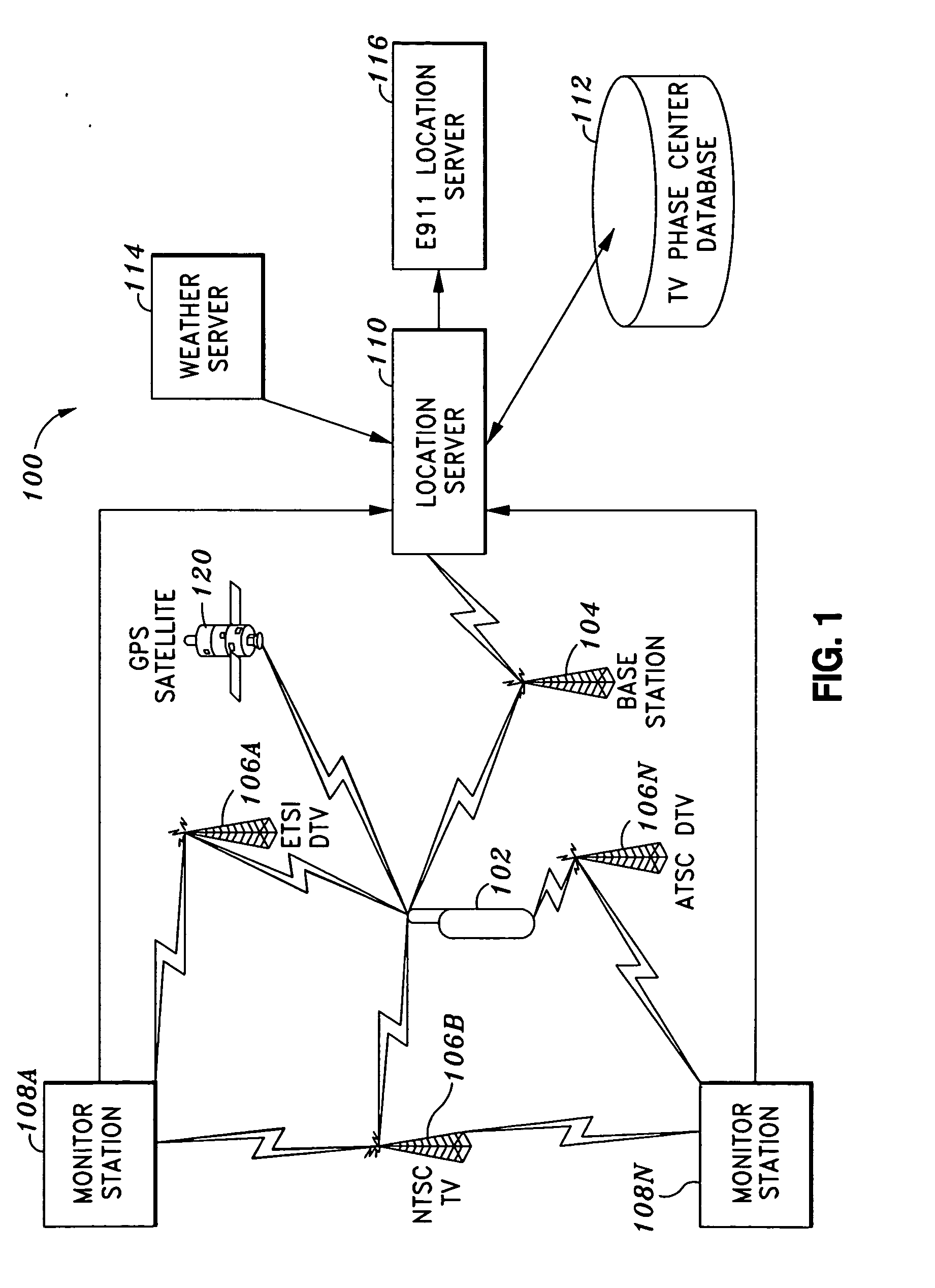
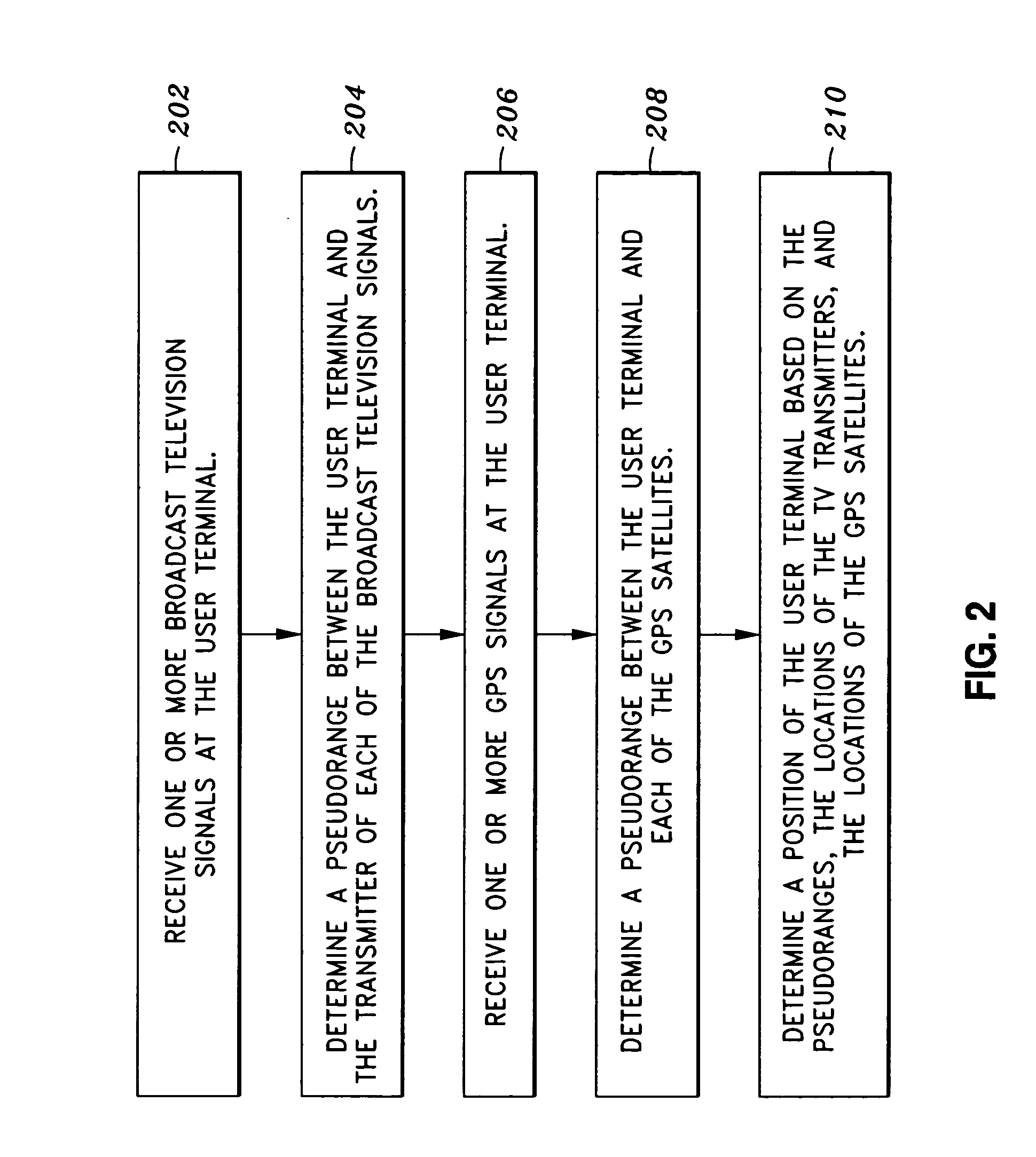
Pilot acquisition and local clock calibration with reduced MIPS
The present invention provides a method, system, and apparatus for estimating a pilot frequency of a television broadcast signal at a receiver. In one aspect, the receiver constitutes a mobile device that uses the estimated pilot frequency to facilitate the determination of position location of the mobile device. The receiver includes a processor which estimates the pilot frequency by computing a baseband version of the pilot signal relative to a reference frequency, defining time-shifted segments for the pilot signal and its baseband version, computing phase correction terms using the pilot signal and its baseband version, phase correcting each received signal segment, and estimating the pilot frequency. In another aspect of the invention, a phase-locked-loop is used to track the phase of the incoming pilot signal. The loop filter and / or the phase of the numerically controlled oscillator is scaled to account for the non-integer nature of samples within the received segments.
Owner:ROSUM CORP
Interpolator based clock and data recovery (CDR) circuit with digitally programmable BW and tracking capability
ActiveUS7315596B2Easy to operateWide data rate rangePulse automatic controlSynchronising arrangementPhase correctionData stream
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Apparatus and method for signal phase control in an integrated radio circuit
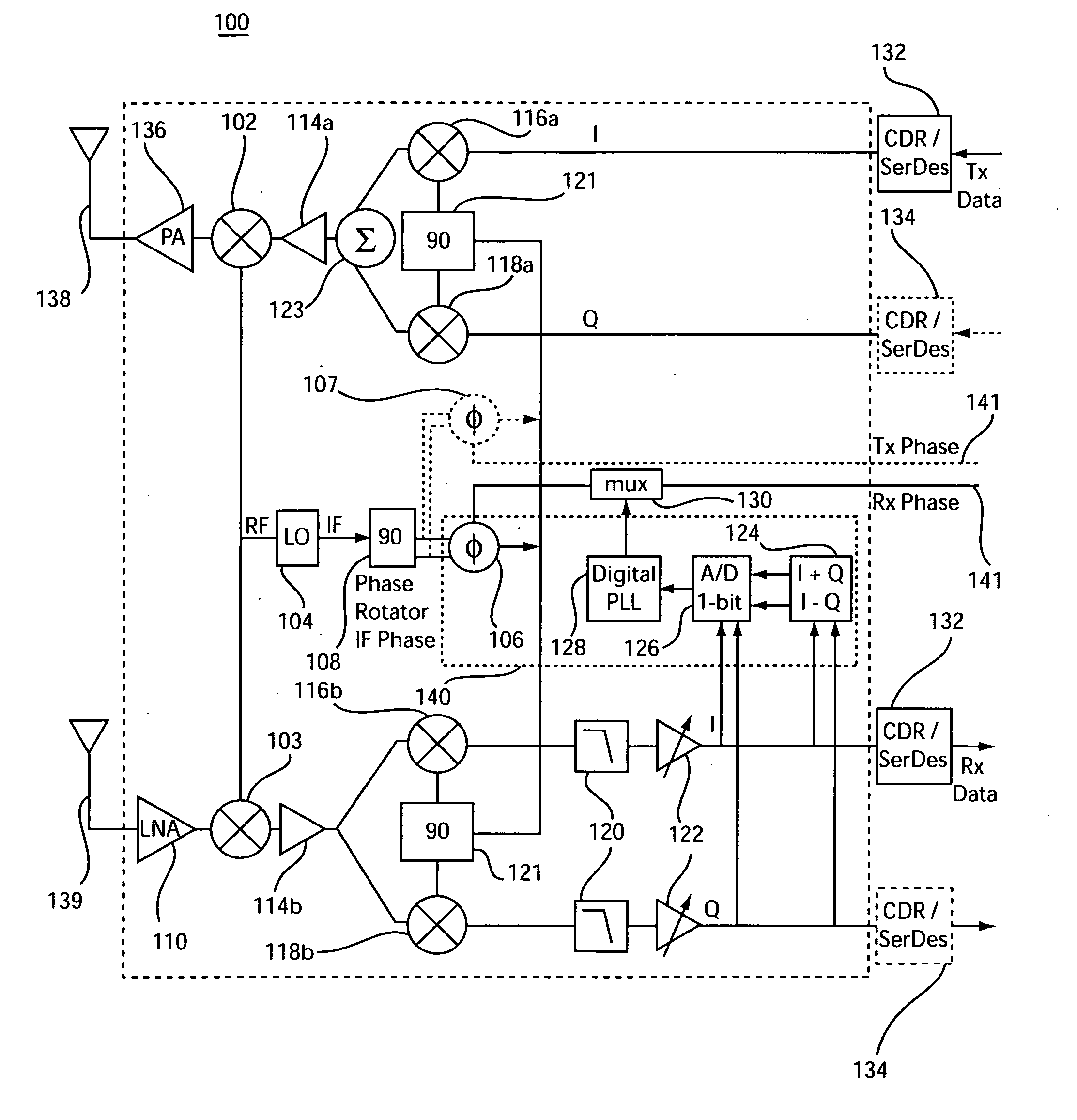
An apparatus and method to control signal phase in a radio device includes a phase rotator configured to control a phase of a local oscillator. A phase error determination module is configured to determine phase error information based on received in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) (IQ) signal values. A phase correction module is configured to derive from the received IQ signal values a correction signal and apply the correction signal to the phase rotator in a path of the local oscillator.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for improving dynamic range in a receiver
InactiveUS6289048B1Multiple-port networksWave based measurement systemsPhase correctionIntermediate frequency
Phase errors and gain errors are reduced in a receiver to increase the dynamic range of the receiver. An input signal is shifted to an intermediate frequency (IF) and divided into a first channel and a second channel. The first and second channels are multiplied by a complex intermediate frequency signal having a frequency equal to the negative of the IF and by the complex conjugate of the intermediate frequency signal to produce a complex normal signal and a complex conjugate signal. A gain correction factor and a phase correction factor are adjusted based on a correlation signal produced by multiplying the complex normal signal by the complex correlation signal.
Owner:CUBIC COMM
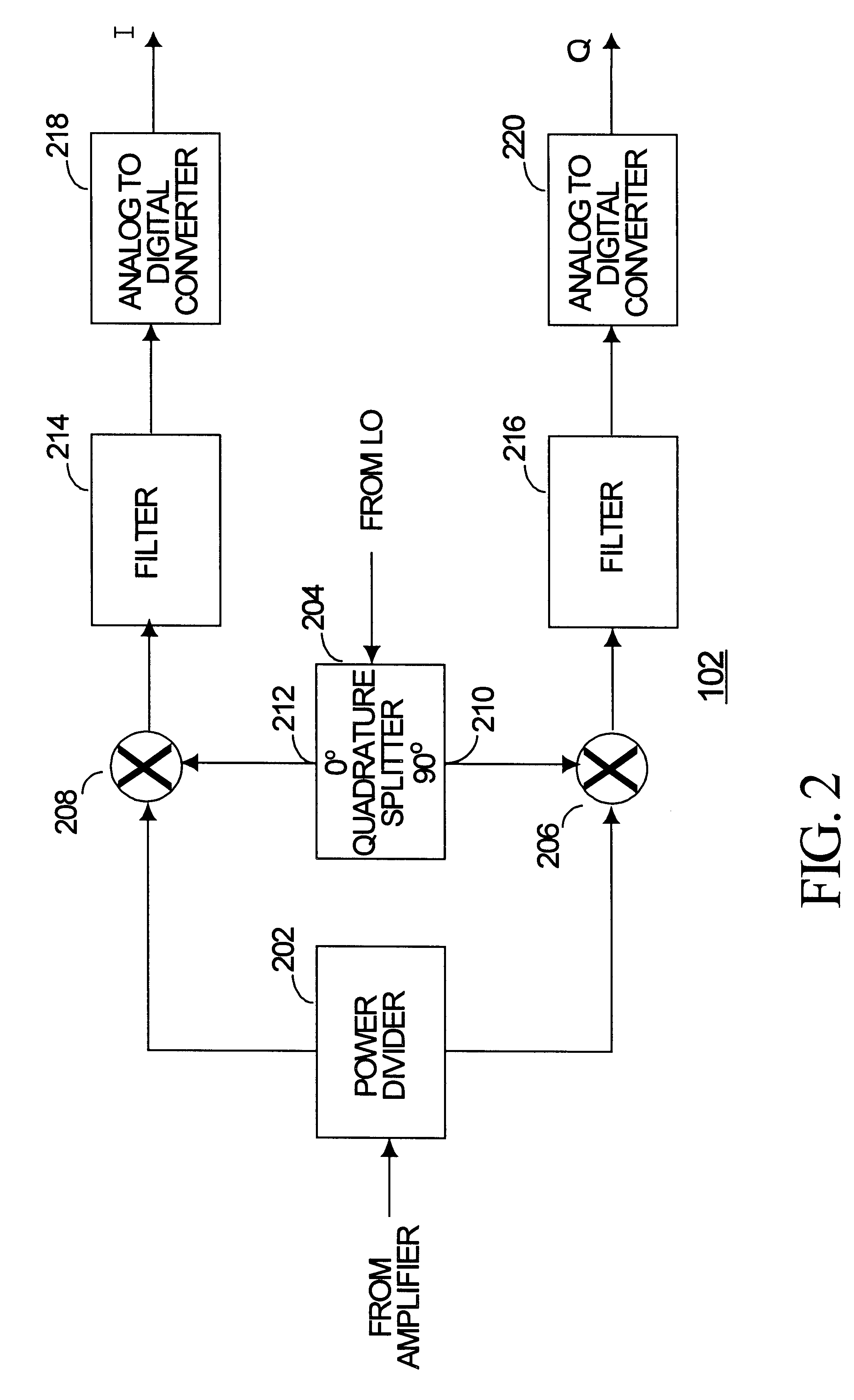
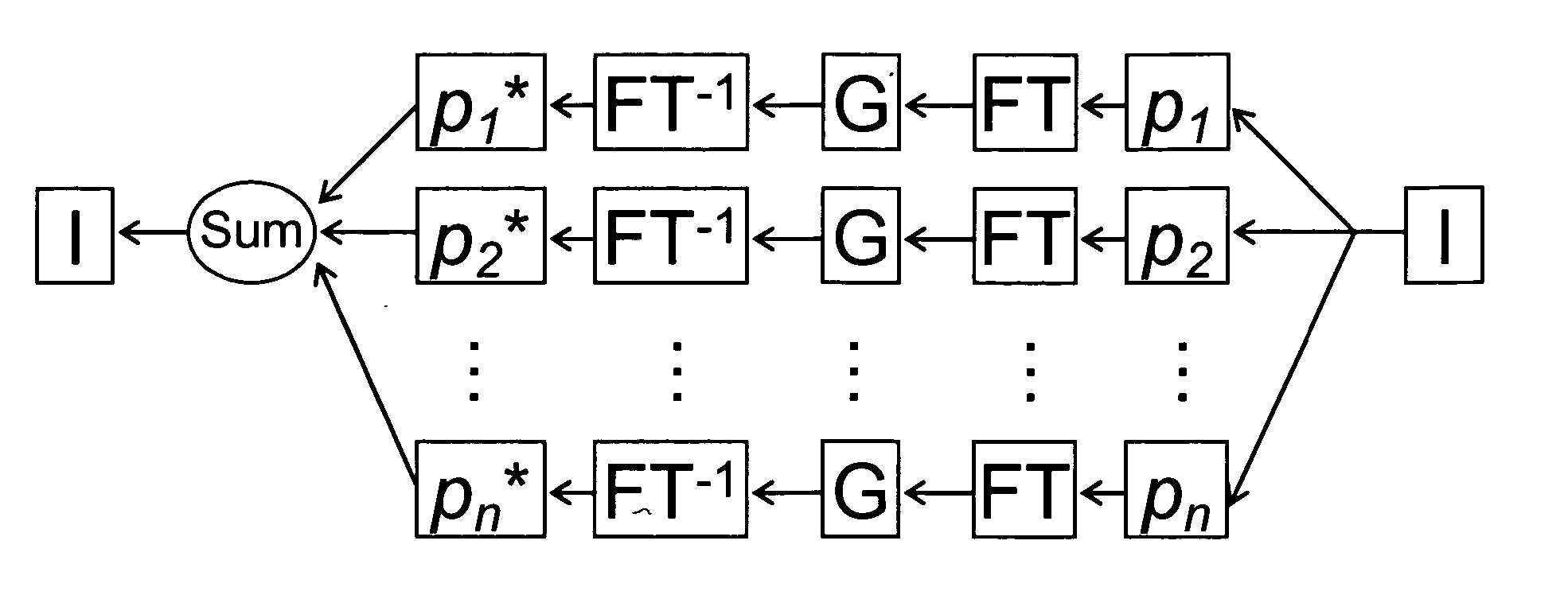
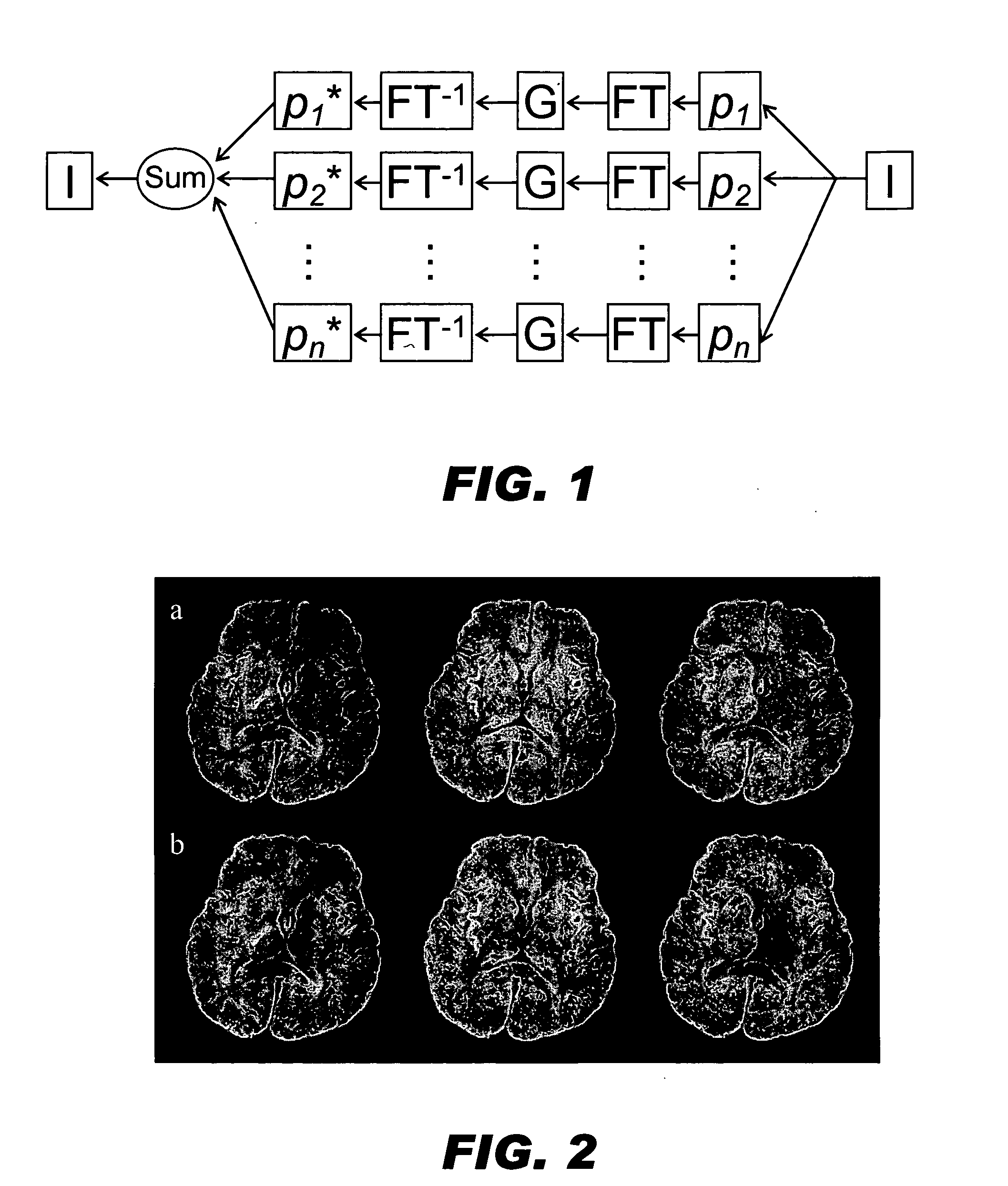
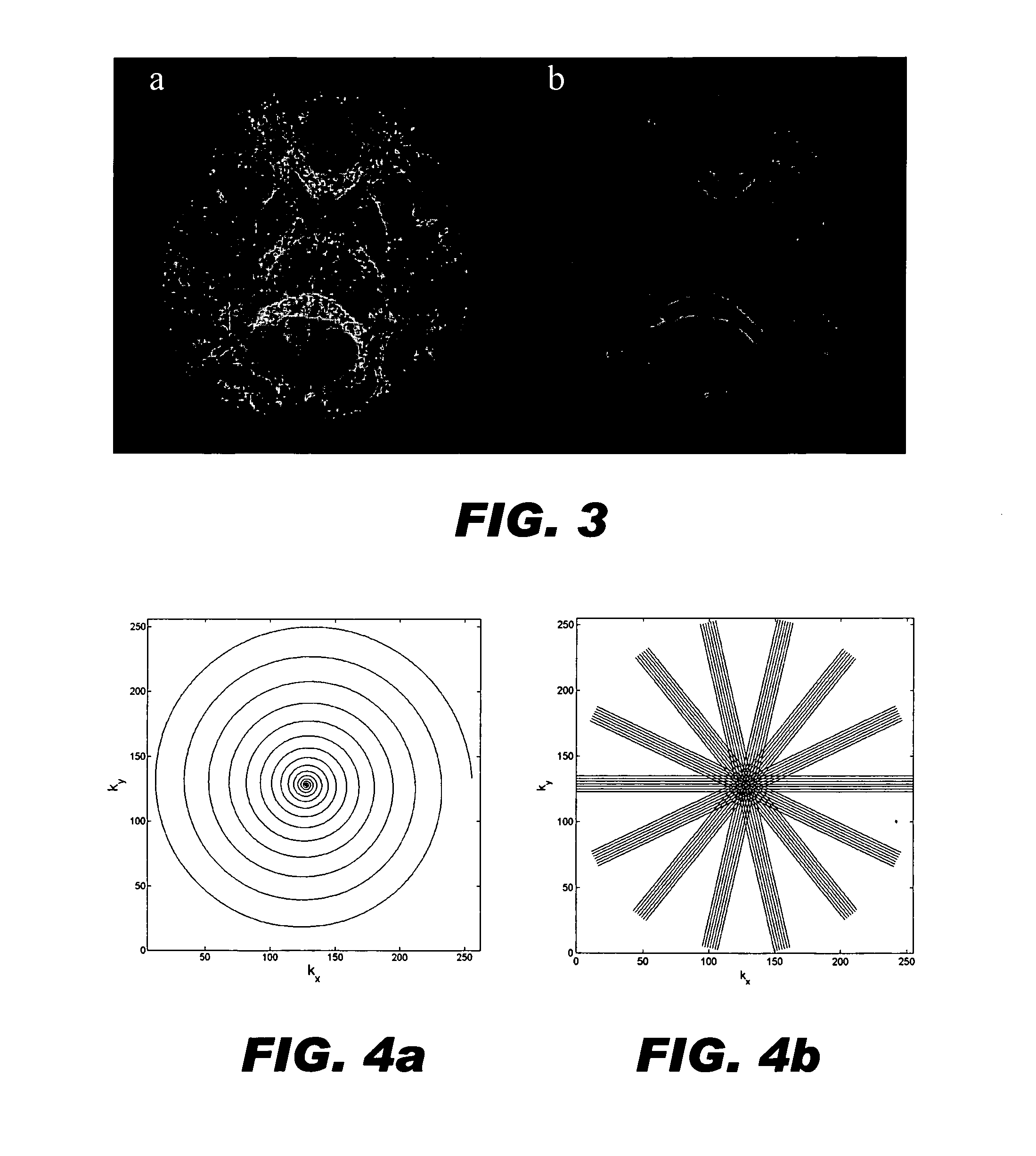
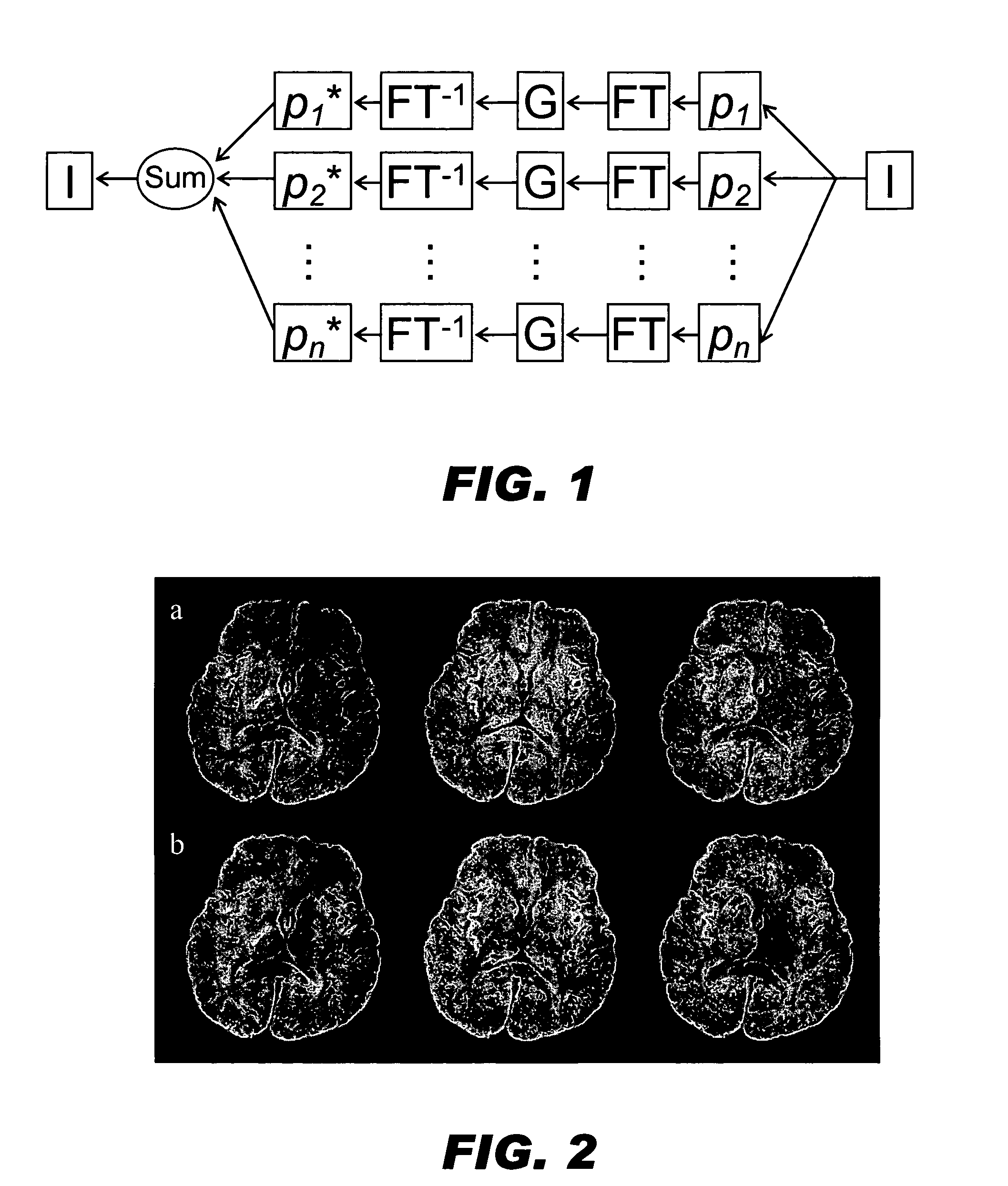
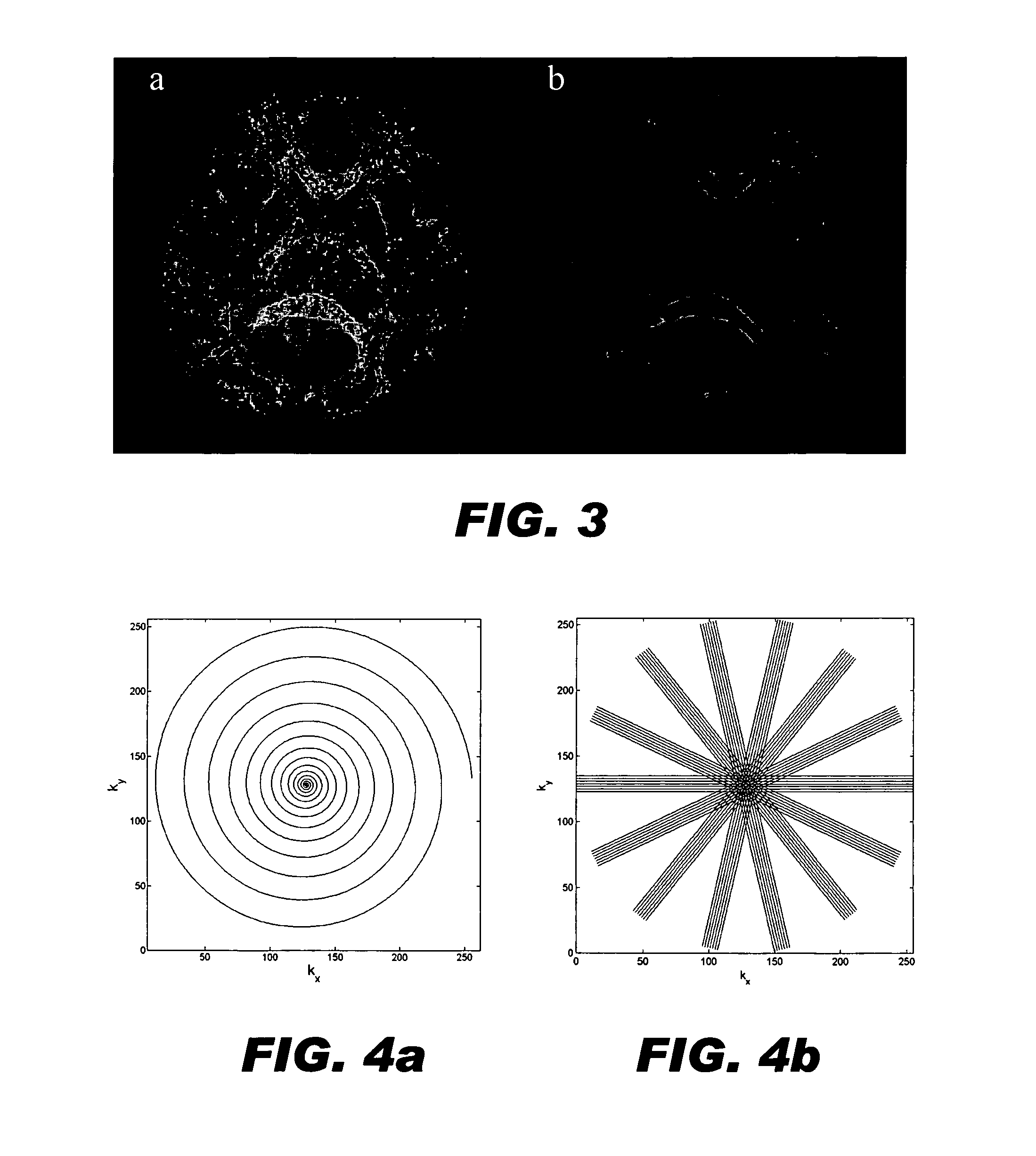
Generalized MRI reconstruction with correction for multiple image distortion
Disclosed is an effective algorithm to correct motion-induced phase error using an iterative reconstruction. Using a conjugate-gradient (CG) algorithm, the phase error is treated as an image encoding function. Given the complex perturbation terms, diffusion-weighted images can be reconstructed using an augmented sensitivity map. The mathematical formulation and image reconstruction procedures are similar to the SENSE reconstruction. By defining a dynamic composition sensitivity, the CG phase correction method can be conveniently incorporated with SENSE reconstruction for the application of multi-shot SENSE DWI. Effective phase correction and multi-shot SENSE DWI (R=1 to 3) are demonstrated on both simulated and in vivo data acquired with PROPELLER and SNAILS.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
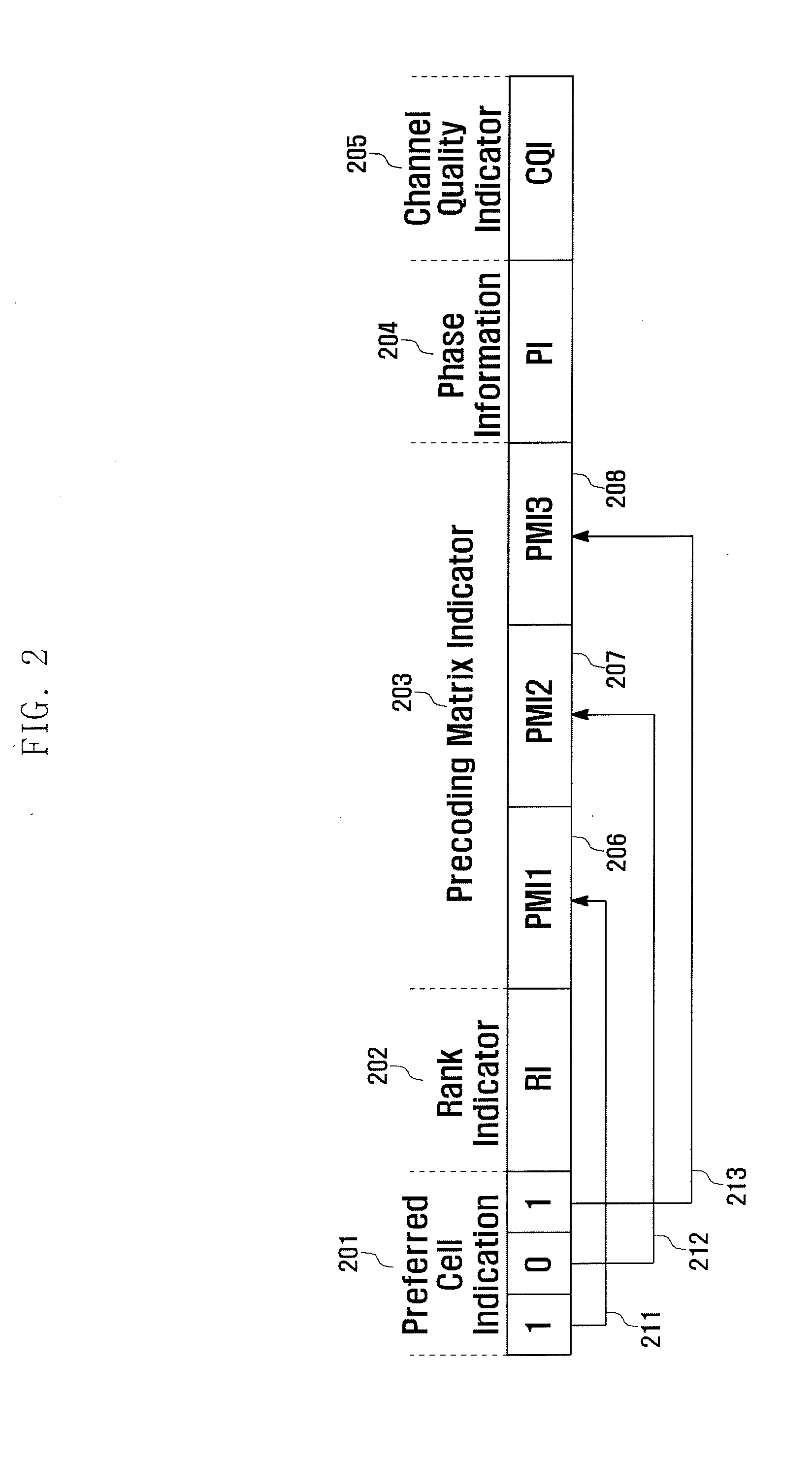
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving feedback information for inter-cell cooperative transmission in wireless communication cellular system
InactiveUS20120088514A1High gainEfficient managementSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityPhase correctionCode book
A method for transmitting feedback information for cooperative transmission in a wireless communication cellular system comprises: receiving information on cells that can be cooperatively transmitted from a base station; determining cells that prefer the cooperative transmission among the cells that can be cooperatively transmitted; generating feedback information, which includes a preference cell indicator representing preferred cells and non-preferred cells for the cooperative transmission among the cells that can be cooperatively transmitted, precoding matrix information for the respective cell that can be cooperatively transmitted, phase information representing a phase correction value of each of the preferred cells for the cooperative transmission, and a channel quality indicator; and transmitting the feedback information through a control channel or a data channel. Accordingly, the present invention provides a method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving a report of implicative feedback information on code books that can be designed for the gain improvement of a high-level inter-cell cooperative transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
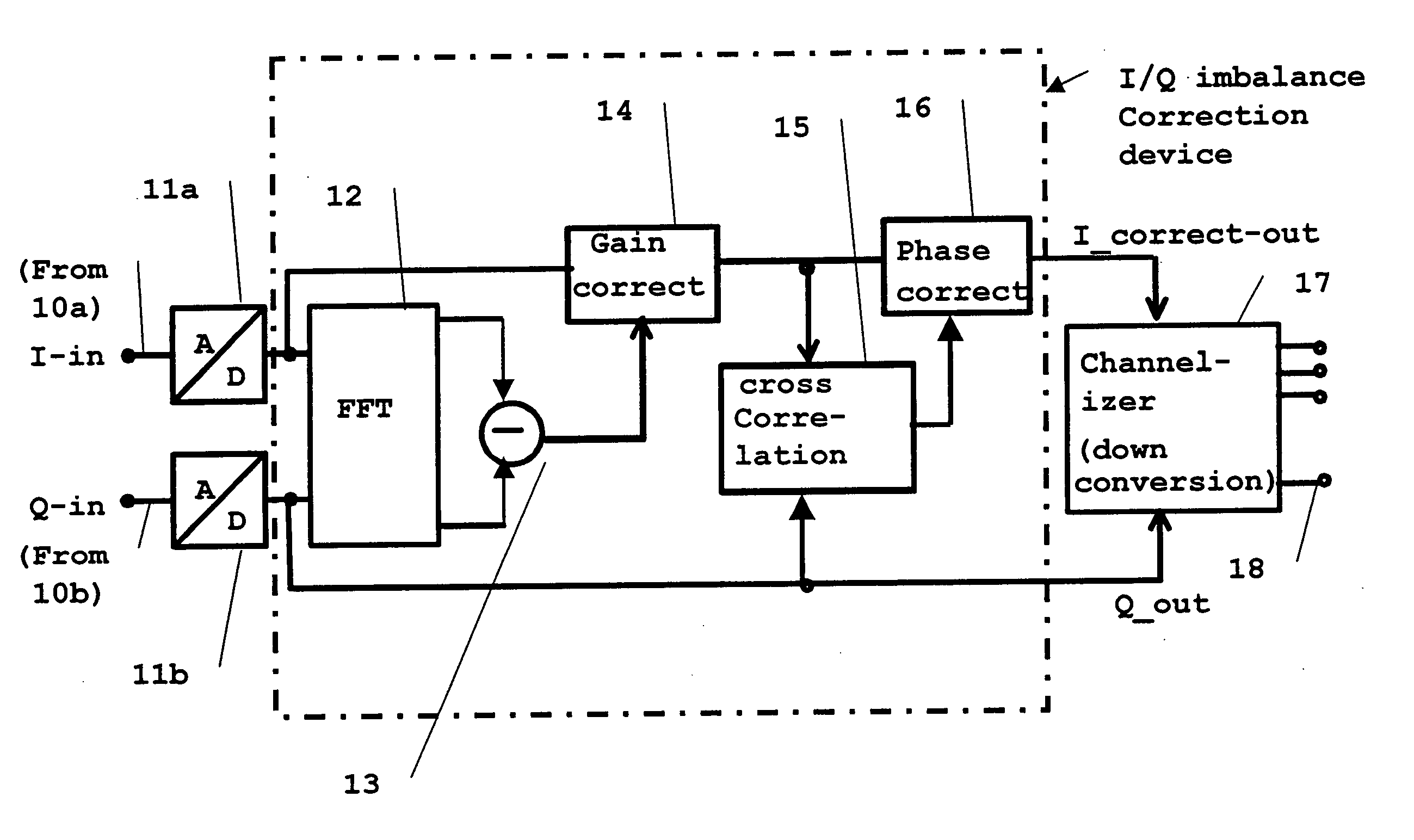
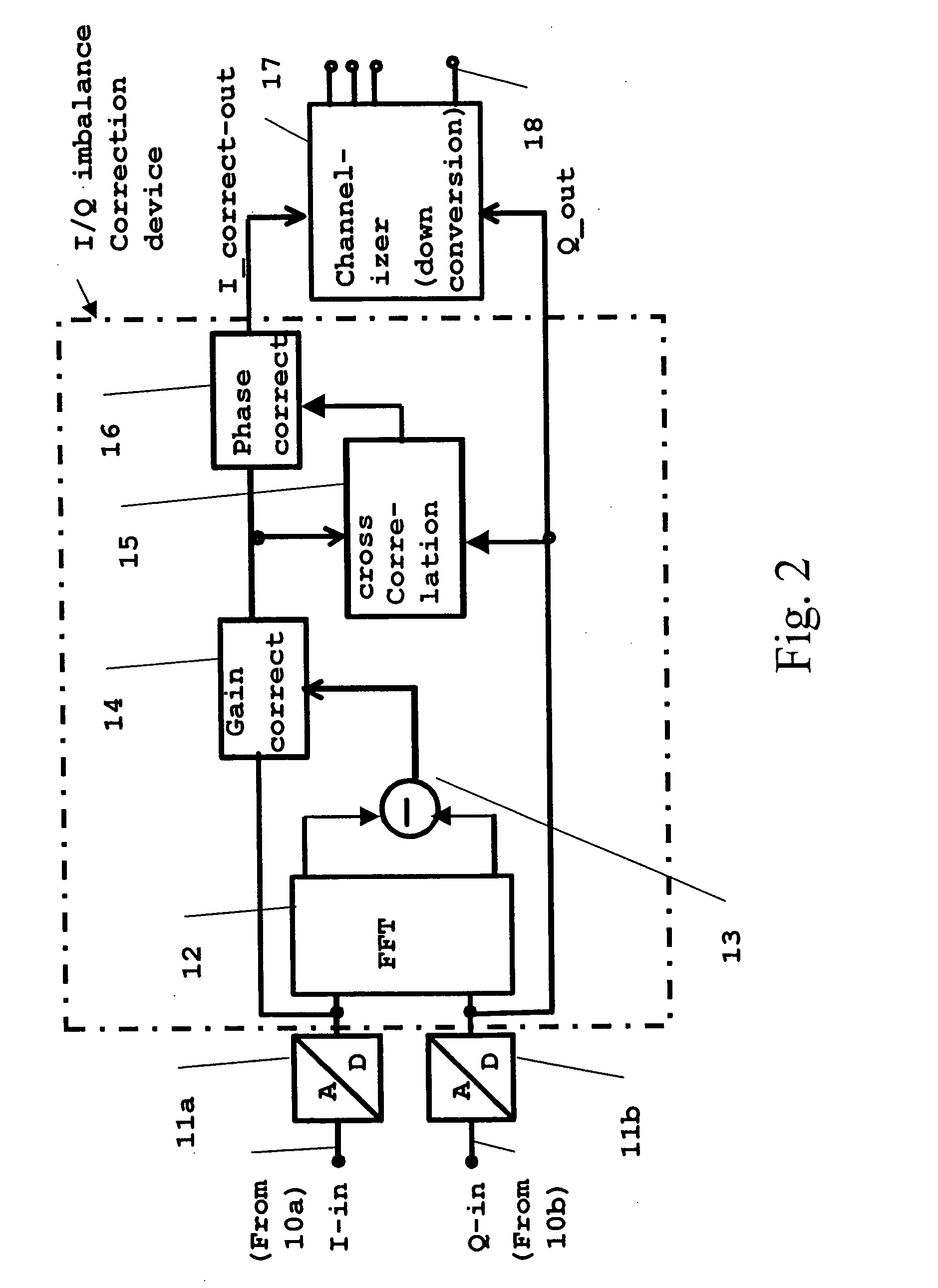
Digital imbalance correction method and device
InactiveUS20040082300A1Cost of complexityAvoids very tedious frequency planning processResonant long antennasInterconnection arrangementsPower differencePhase correction
The present invention concerns a digital imbalance correction device, comprising input means adapted to receive first input signals I-in, Q-in containing a plurality of channels from an I / Q converter stage at respective input terminals, each input terminal being associated to a respective signal branch, a time-to-frequency-domain-transforming means FFT adapted to perform a transformation of said first input signals from time-domain into frequency-domain, the transformation result being represented as a power spectrum of said respective first input signals, a subtracting means arranged to receive at its inputs second input signals which are represented by the power spectra of said respective transformed first input signals and to output the gain difference as a function of frequency at its output, a cross-correlation means arranged to receive at its inputs third input signals based on said input signals, and to output a cross-correlation of said third input signals, said cross-correlation output being proportional to a phase error between said respective correlation input signals, a gain correction means arranged in one of said respective signal branches and receiving at its input a fourth input signal based said associated first input signal, wherein a gain of said fourth input signal is corrected based on said power difference spectrum such that said gain of said fourth input signal equals the gain of the other one of said first input signals, and a phase correction means arranged in one of said respective signal branches and receiving at its input a fifth input signal based said associated first input signal, wherein a phase of said fifth input signal is corrected based on said cross-correlation output, such that said phase of said fifth input signal is in quadrature relation to the other one of said first input signals. The present invention also concerns a corresponding method.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
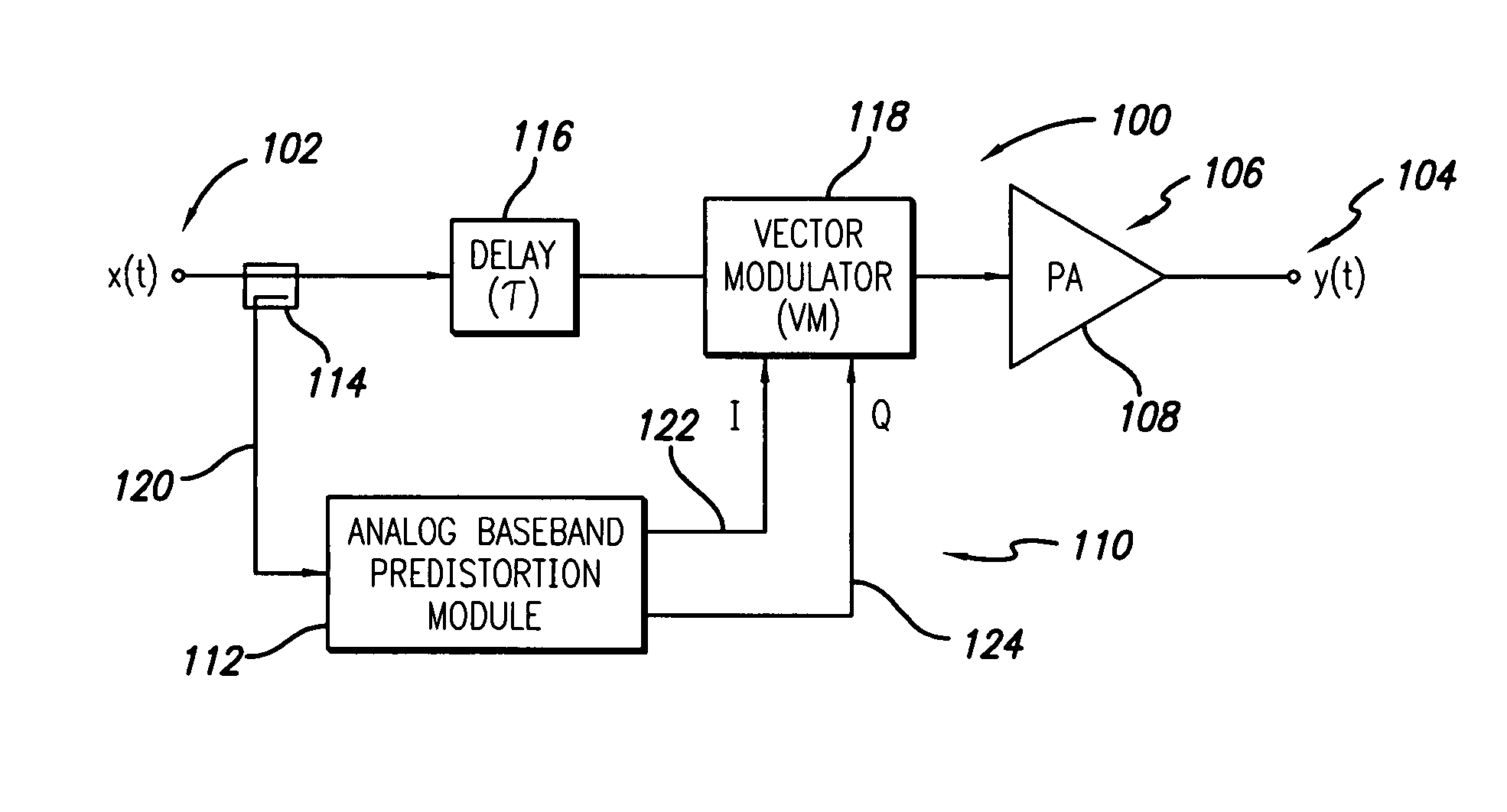
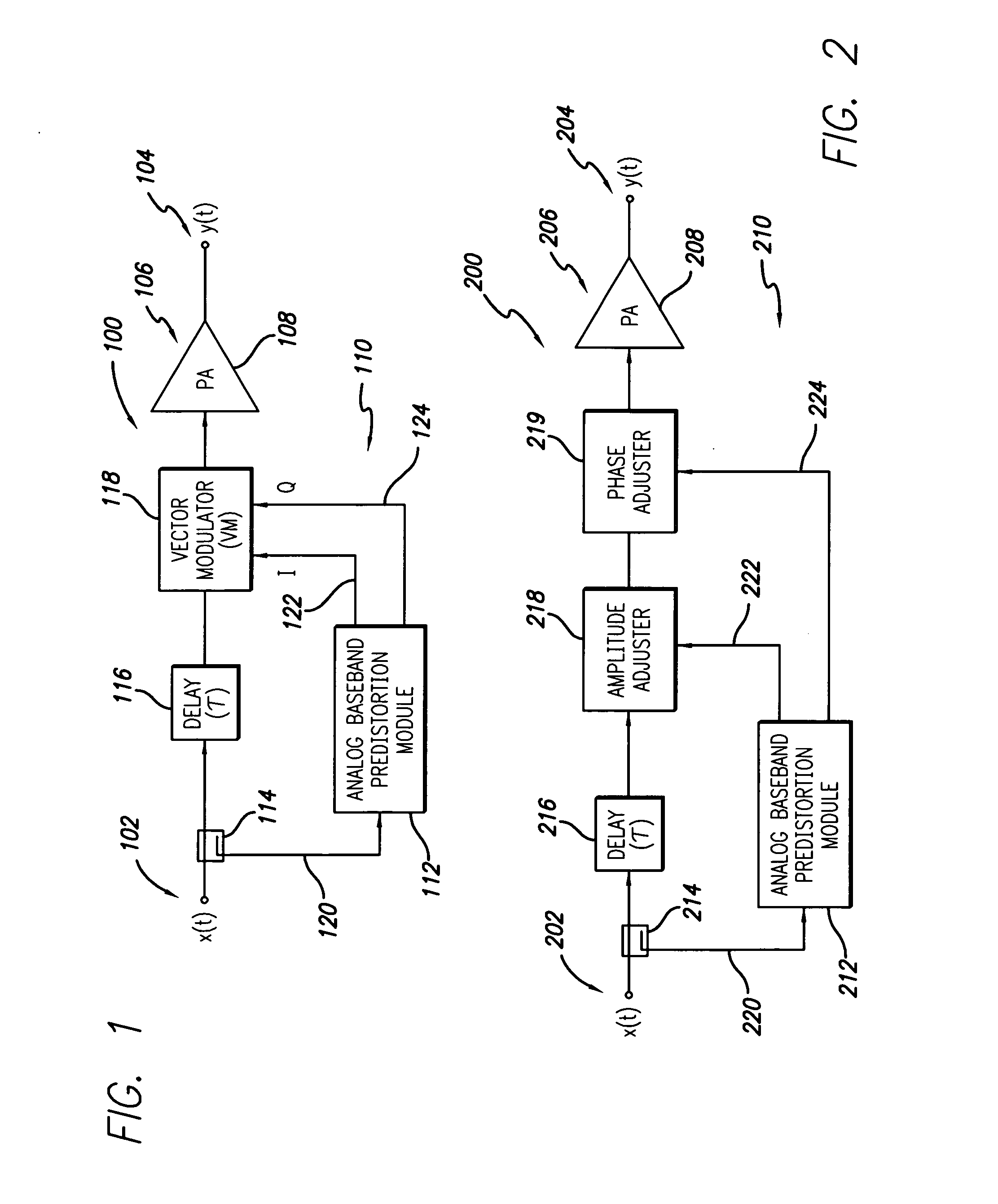
RF power amplifier system employing an analog predistortion module using zero crossings
ActiveUS20060217083A1Correct nonlinearityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationPhase correctionAudio power amplifier
An RF amplifier system employing an analog predistortion module is disclosed. The disclosed analog predistortion module is based on zero crossings of the gain error curves (AM-AM and AM-PM curves minus DC). The hardware structure uses the product of first-order functions avoiding the need for large differential swings in the coefficients to shape the lower part of the gain curves. The higher-order nonlinear functions are preferably derived from a single envelope detector. An equal number of multipliers are preferably used in each path when the order of the magnitude and phase corrections are equal or differ by one, thus reducing delay mismatches between the magnitude and phase correction signals.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for phase-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging
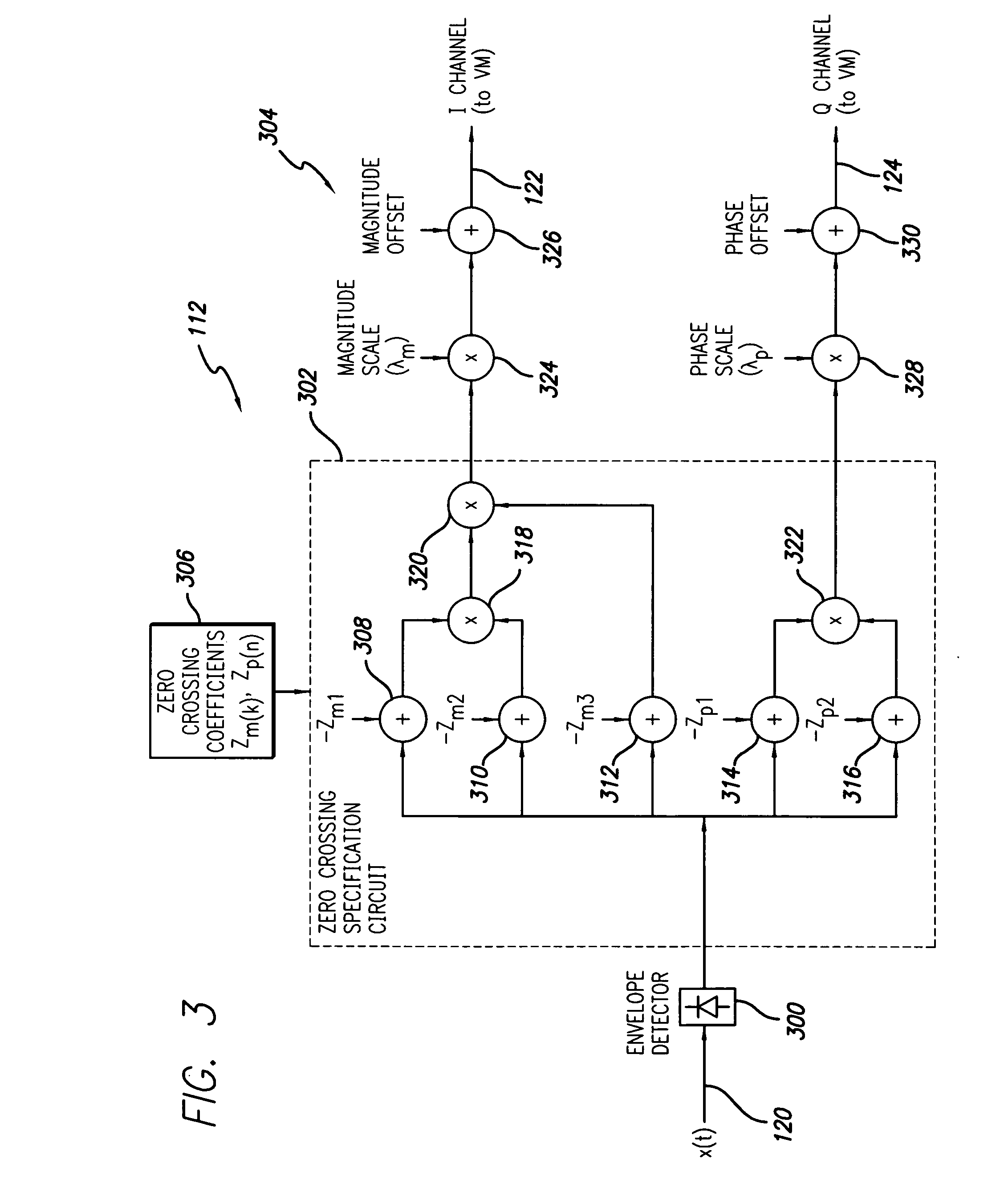
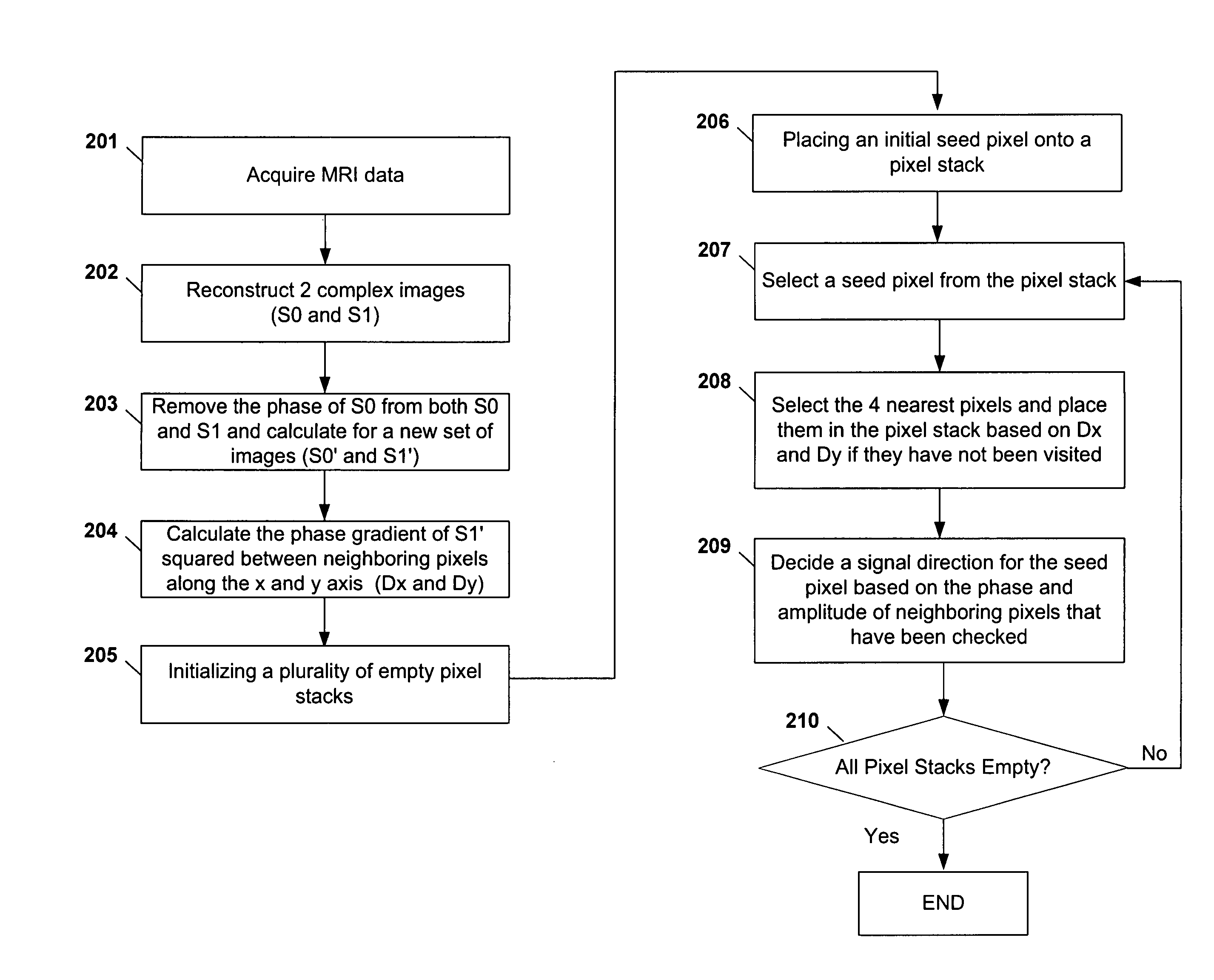
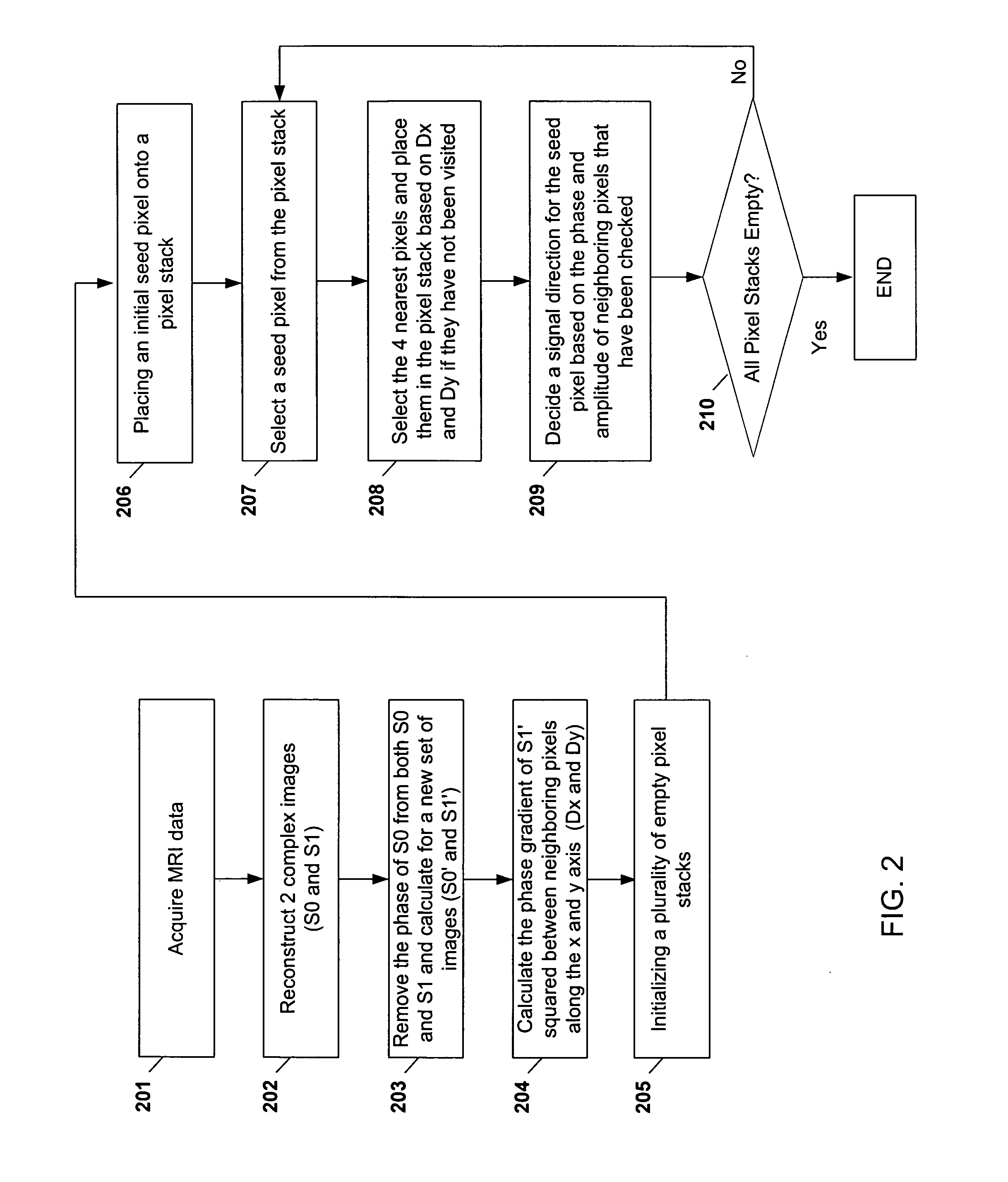
ActiveUS20050165296A1Maintain consistencyAccurate identificationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase correctionInversion recovery
Systems and methods are described for phase-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging using an efficient and robust phase correction algorithm. A method includes obtaining a plurality of MRI data signals, such as two-point Dixon data, one-point Dixon data, or inversion recovery prepared data. The method further includes implementing a phase-correction algorithm, that may use phase gradients between the neighboring pixels of an image. At each step of the region growing, the method uses both the amplitude and phase of pixels surrounding a seed pixel to determine the correct orientation of the signal for the seed pixel. The method also includes using correlative information between images from different coils to ensure coil-to-coil consistency, and using correlative information between two neighboring slices to ensure slice-to-slice consistency. A system includes a MRI scanner to obtain the data signals, a controller to reconstruct the images from the data signals and implement the phase-correction algorithm, and an output device to display phase sensitive MR images such as fat-only images and / or water-only images.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
MIMO phase noise estimation and correction
InactiveUS20080101497A1Modulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsPhase correctionPhase noise
A technique to estimate phase noise across a multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) communication channel, in which phase noise estimation is obtained by solving a matrix equation that has more unknowns than available equations. Once the phase noise estimate is determined, appropriate phase correction is applied to correct for phase noise induced errors in the received signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
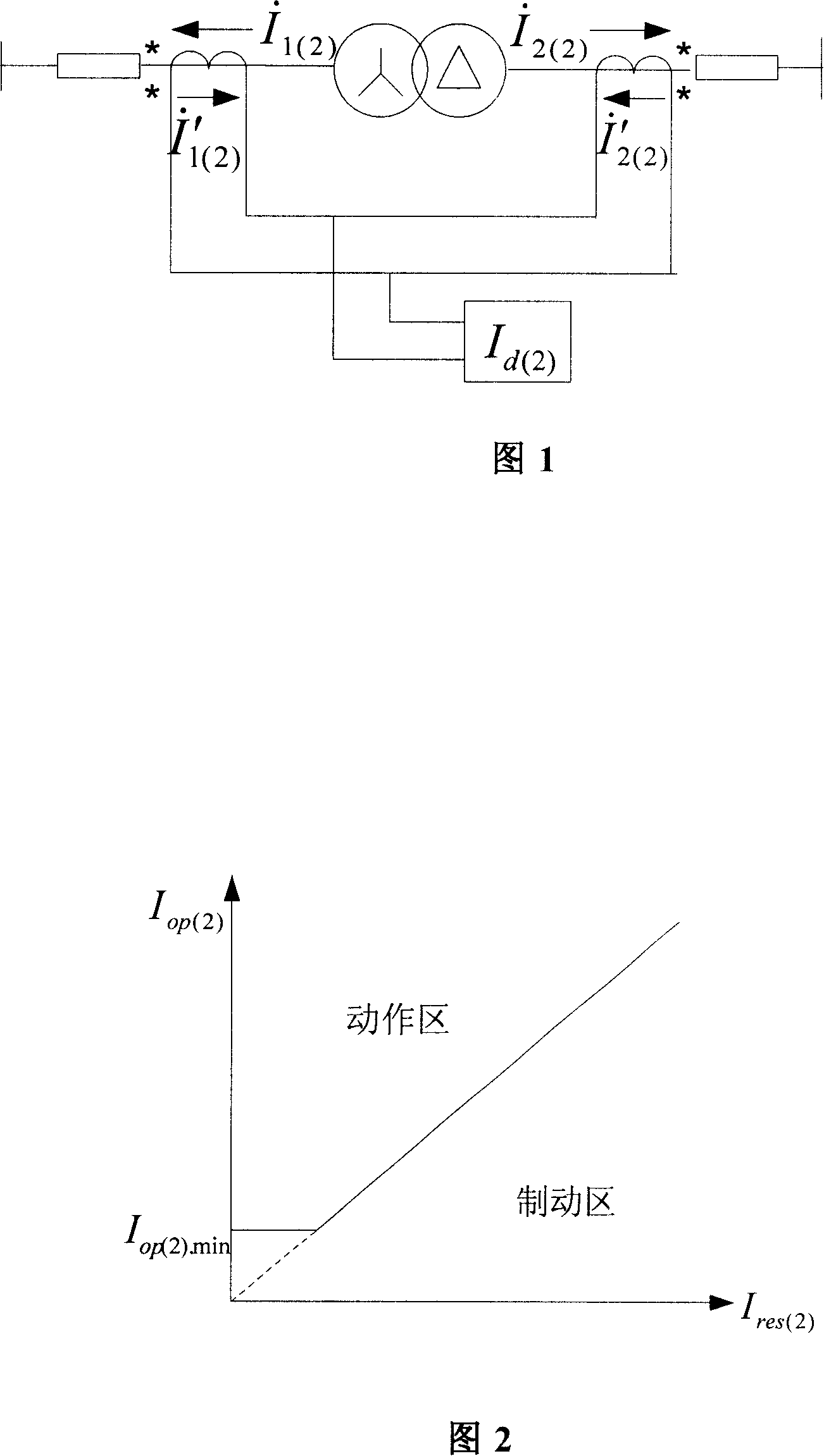
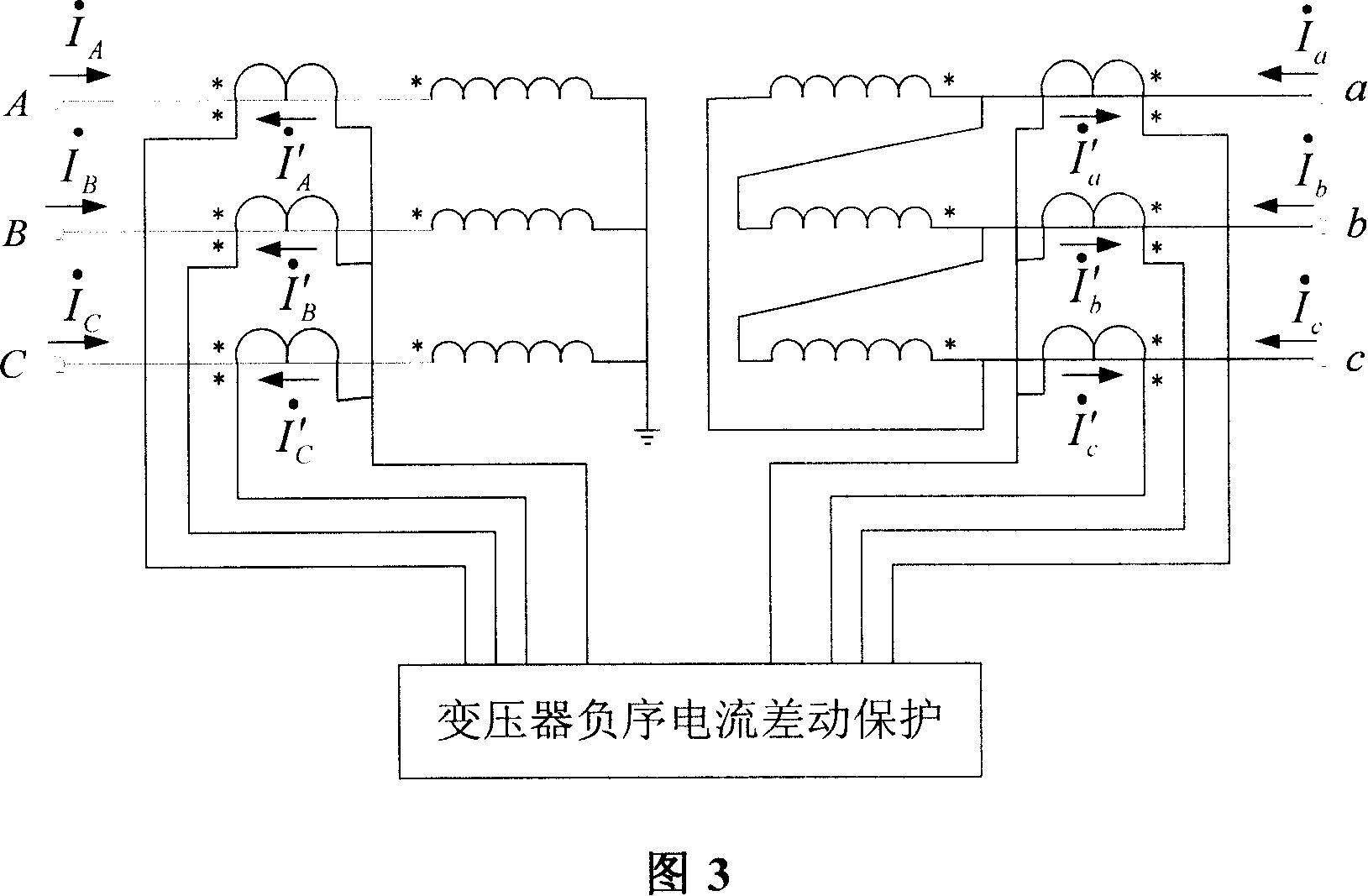
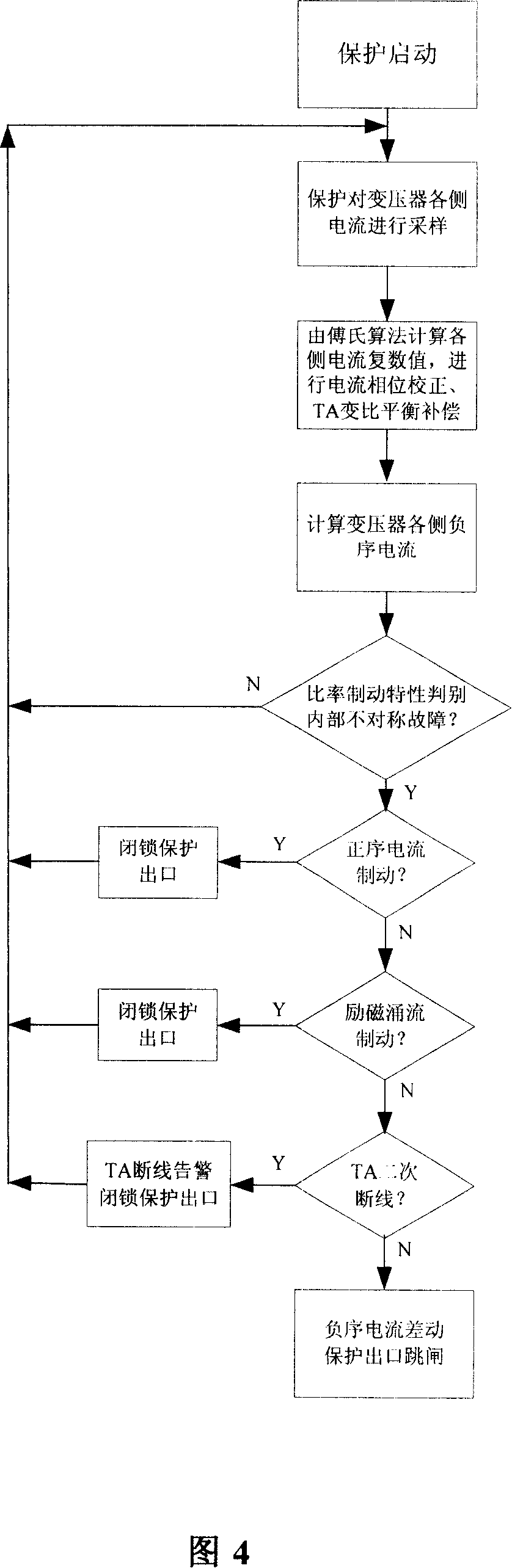
A differential protection method for negative sequence current of large power transformer
ActiveCN1964149AHigh protection sensitivityClearly distinguish internal and external asymmetrical faultsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPhase correctionSecondary loop
The disclosed protection method for internal fault of large power transformer comprises: the protector samples the secondary current of current transformers on power transformer sides to obtain current instantaneous value and calculate complex number form of electric values by Fourier algorithm, corrects phase of connection form, and balances amplitude of transformation ratio; then, it calculates the complex number form of negative sequence current according to three-phase ac complex form, and computes negative sequence differential current and break current as the negative sequence differential protection principle to decide asymmetric inside and outside fault and drop out all breakers. This invention also contains exactly the negative sequence differential rate breaking feature and protection criterion, the adjusting means for protection values, the positive sequence current breaking criterion, and the block function for error action protection.
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG JIBAO AUTOMATION +1
Cycle slip location and correction
Methods and techniques are disclosed for correcting the effect of cycle slips in a coherent communications system. A signal comprising SYNC bursts having a predetermined periodicity and a plurality of known symbols at predetermined locations between successive SYNC bursts is received. The received signal is partitioned into data blocks. Each data block encompasses at least data symbols and a set of check symbols corresponding to the plurality of known symbols at predetermined locations between a respective pair of successive SYNC bursts in the signal. Each data block is processed to detect a cycle slip. When a cycle slip is detected, the set of check symbols of the data block are examined to identify a first slipped check symbol, and a phase correction applied to data symbols of the data block lying between the first slipped check symbol and an end of the data block.
Owner:CIENA
Communication terminal apparatus and radio communication method
InactiveUS6980612B1Improve reception performanceLower performance requirementsSpatial transmit diversityError preventionPhase correctionSignal on
In closed-loop transmission diversity, a communication terminal apparatus calculates a phase correcting value for compensating for an effect of phase rotation due to the transmission diversity, using known feedback information, and corrects a received signal on a communication channel based on the phase correcting value, or corrects a channel estimation value based on the phase correcting value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for forming distributed aerial array beam based on channel correction
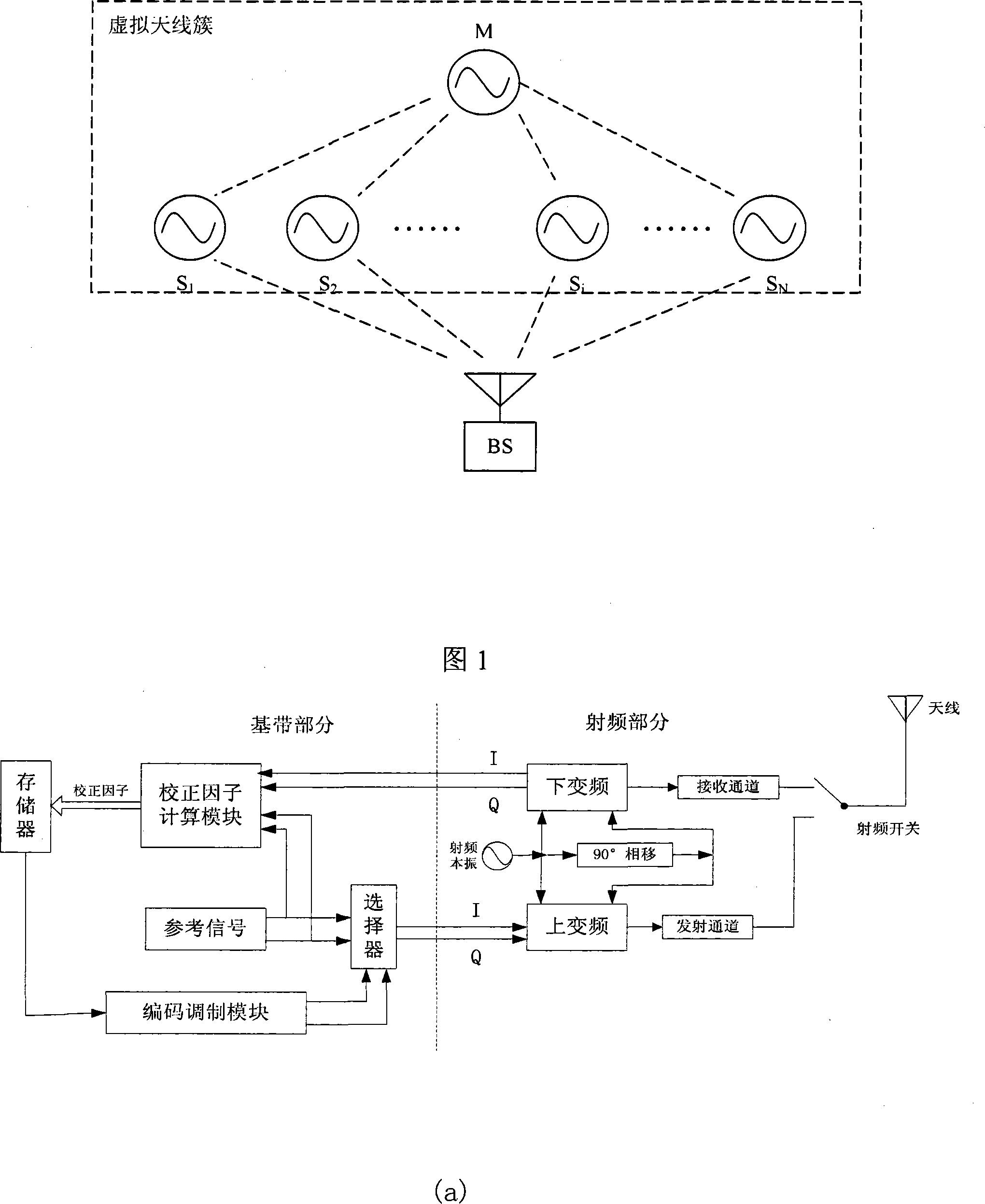
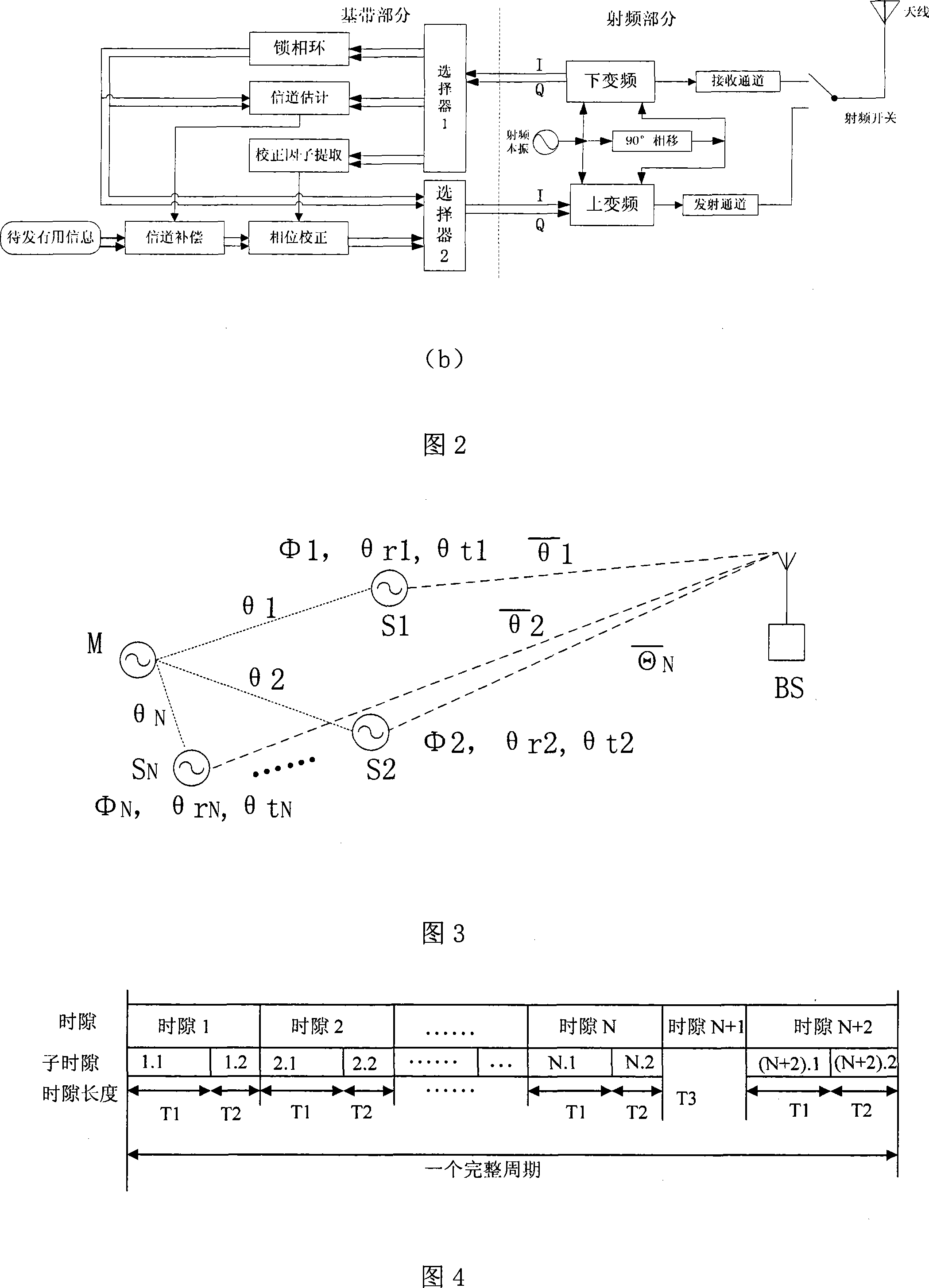
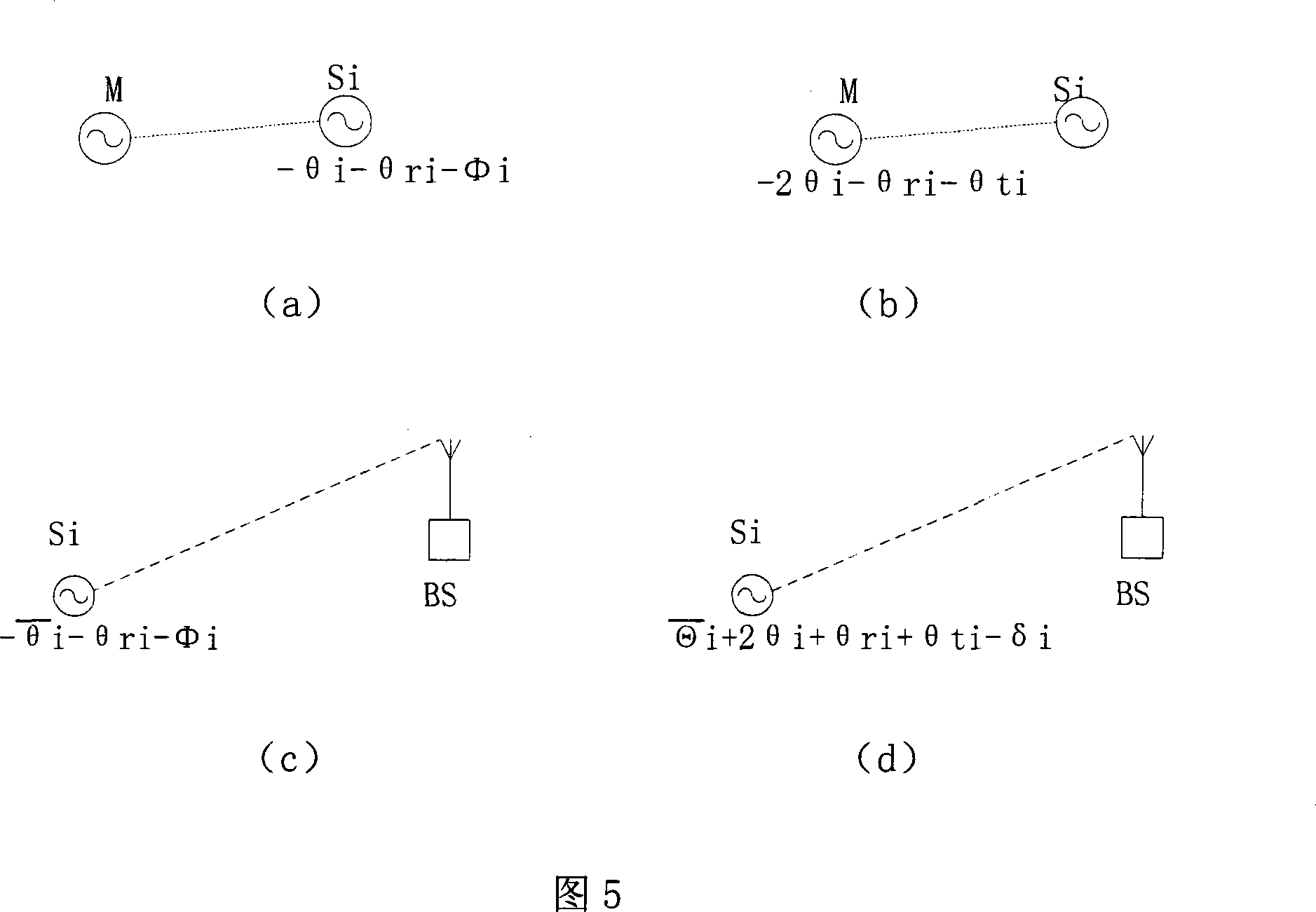
InactiveCN101227242ATo achieve the purpose of long-distance transmissionImprove signal-to-noise ratioTransmitters monitoringPhase correctionComputer science
The invention discloses a method for shaping distributed array aerial beams on the basis of channel calibration, which comprises building a 'virtual' aerial cluster and adopting master-salve structures between each node in the cluster, emitting reference signals to all slave nodes by a master node simultaneously according to preset transceiving time slots, utilizing phase-locked loops to phase-lock received reference signals after each slave node receives the reference signals, then, sending baseband reference signals which are outputted by each phase-locked loop back to the master node in turn through a feedback mode, calculating out corresponding correction factors according to signals which are returned back from each slave node by the master node and storing, broadcasting in a data mode after obtaining the correction factors of each slave node and abstracting each correction factor from data broadcast by each slave node, finally, utilizing obtained correction factor to phase-correct signals which will be sent after estimating and complementing each slave node according to the reference signals which are sent by a receiving key station by each slave node, superimposing in-phase after all signals which are sent by the slave nodes reach the key station, and forming beams on the key station direction.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Generalized MRI reconstruction with correction for multiple image distortion
Disclosed is an effective algorithm to correct motion-induced phase error using an iterative reconstruction. Using a conjugate-gradient (CG) algorithm, the phase error is treated as an image encoding function. Given the complex perturbation terms, diffusion-weighted images can be reconstructed using an augmented sensitivity map. The mathematical formulation and image reconstruction procedures are similar to the SENSE reconstruction. By defining a dynamic composition sensitivity, the CG phase correction method can be conveniently incorporated with SENSE reconstruction for the application of multi-shot SENSE DWI. Effective phase correction and multi-shot SENSE DWI (R=1 to 3) are demonstrated on both simulated and in vivo data acquired with PROPELLER and SNAILS.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com