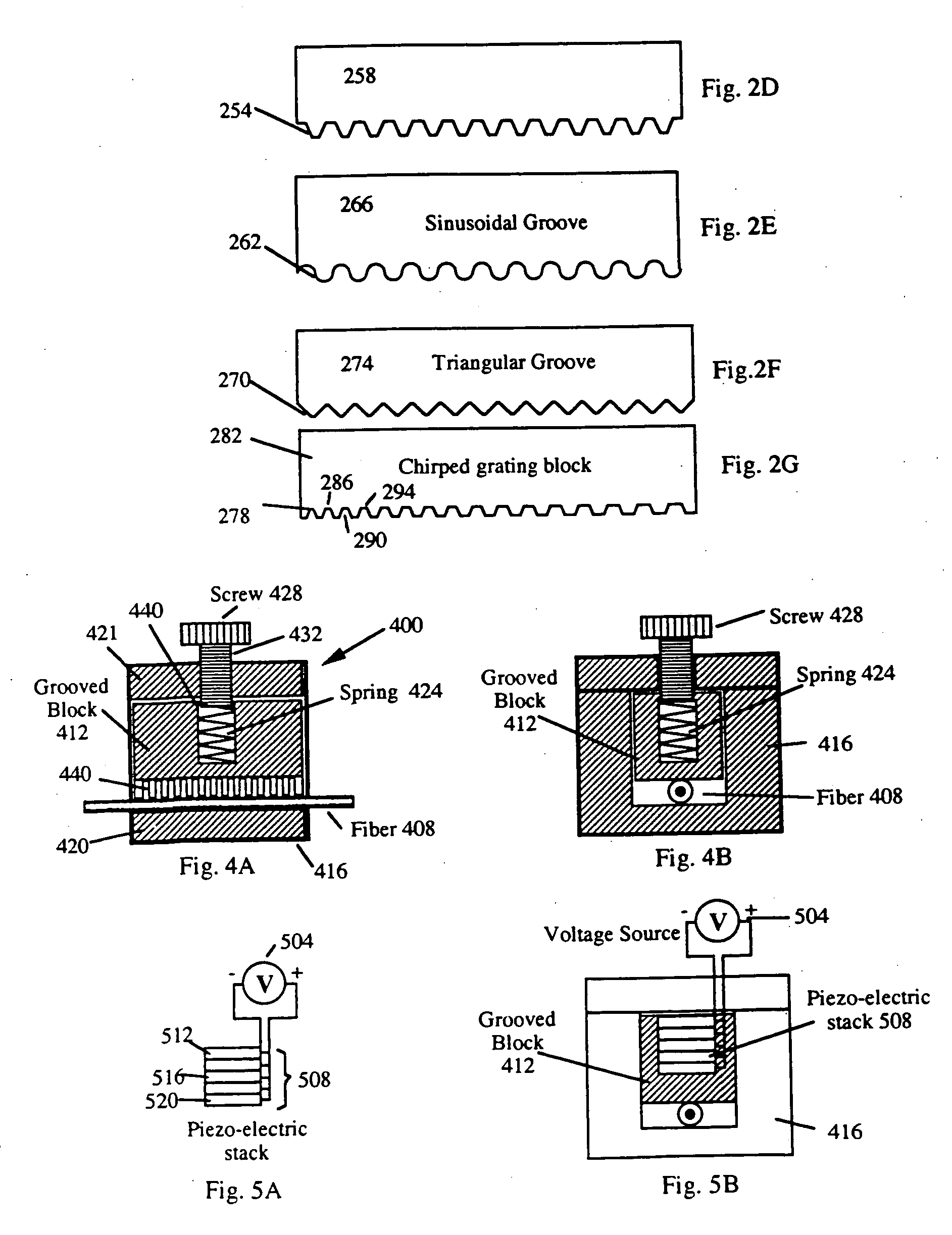
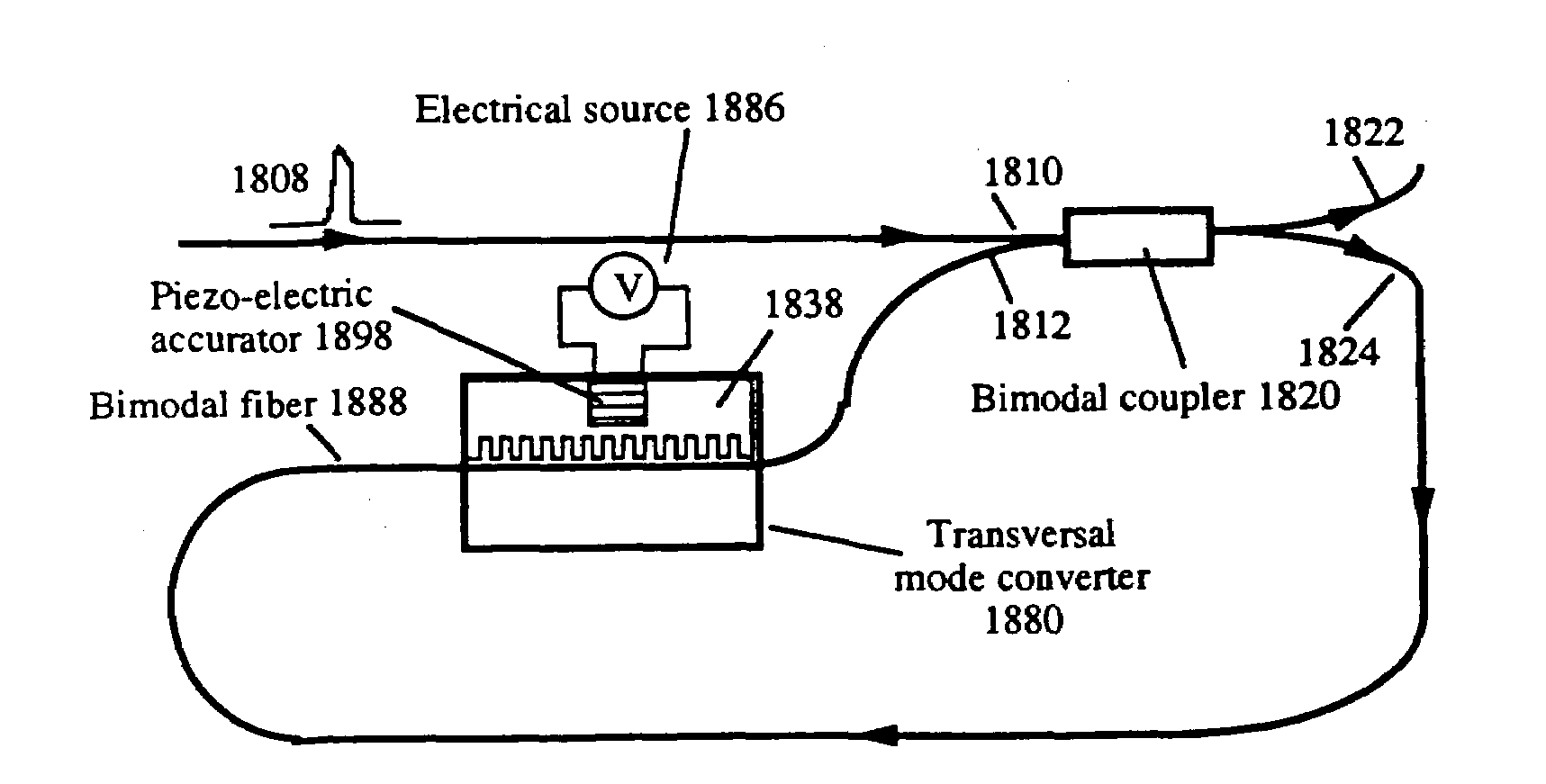
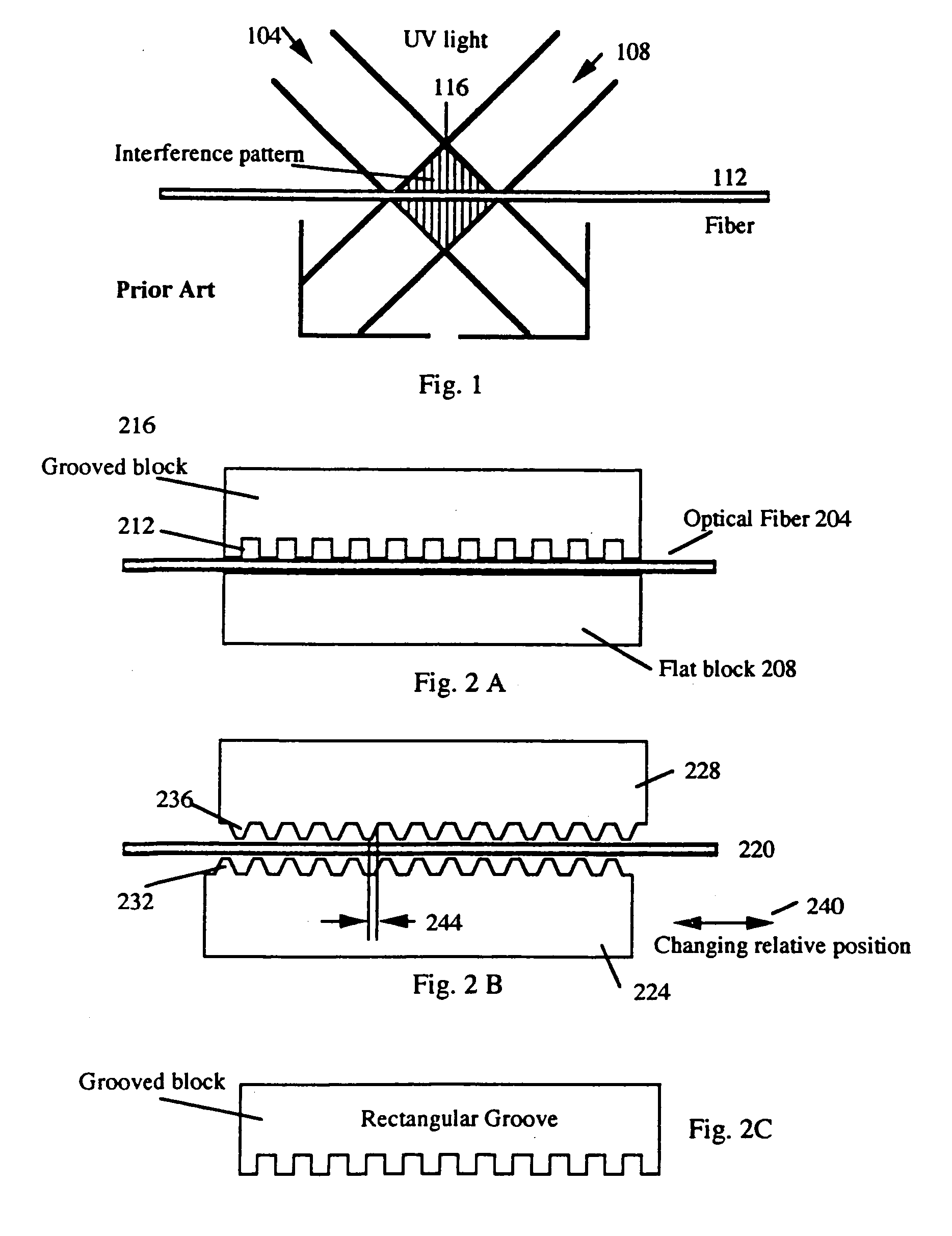
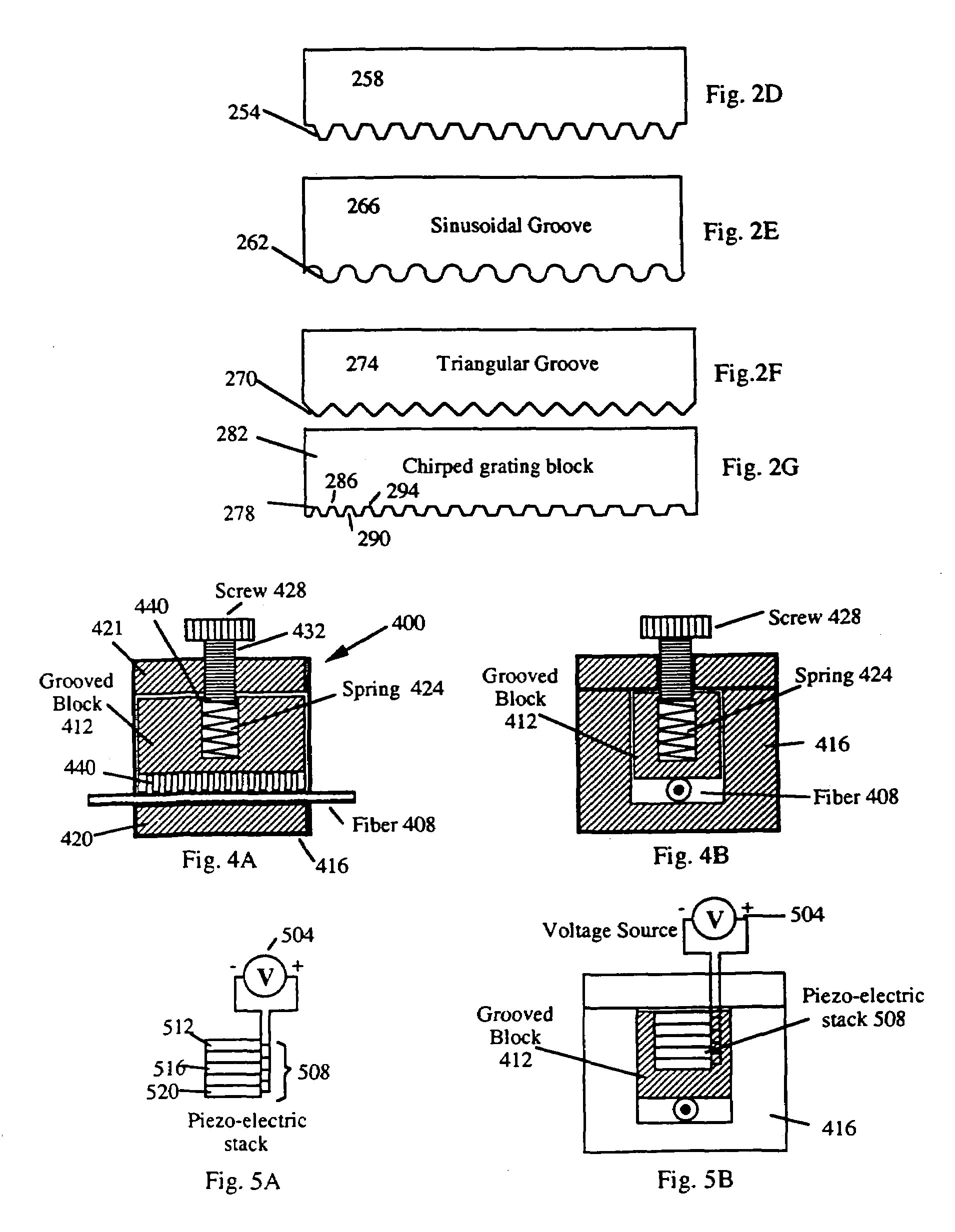
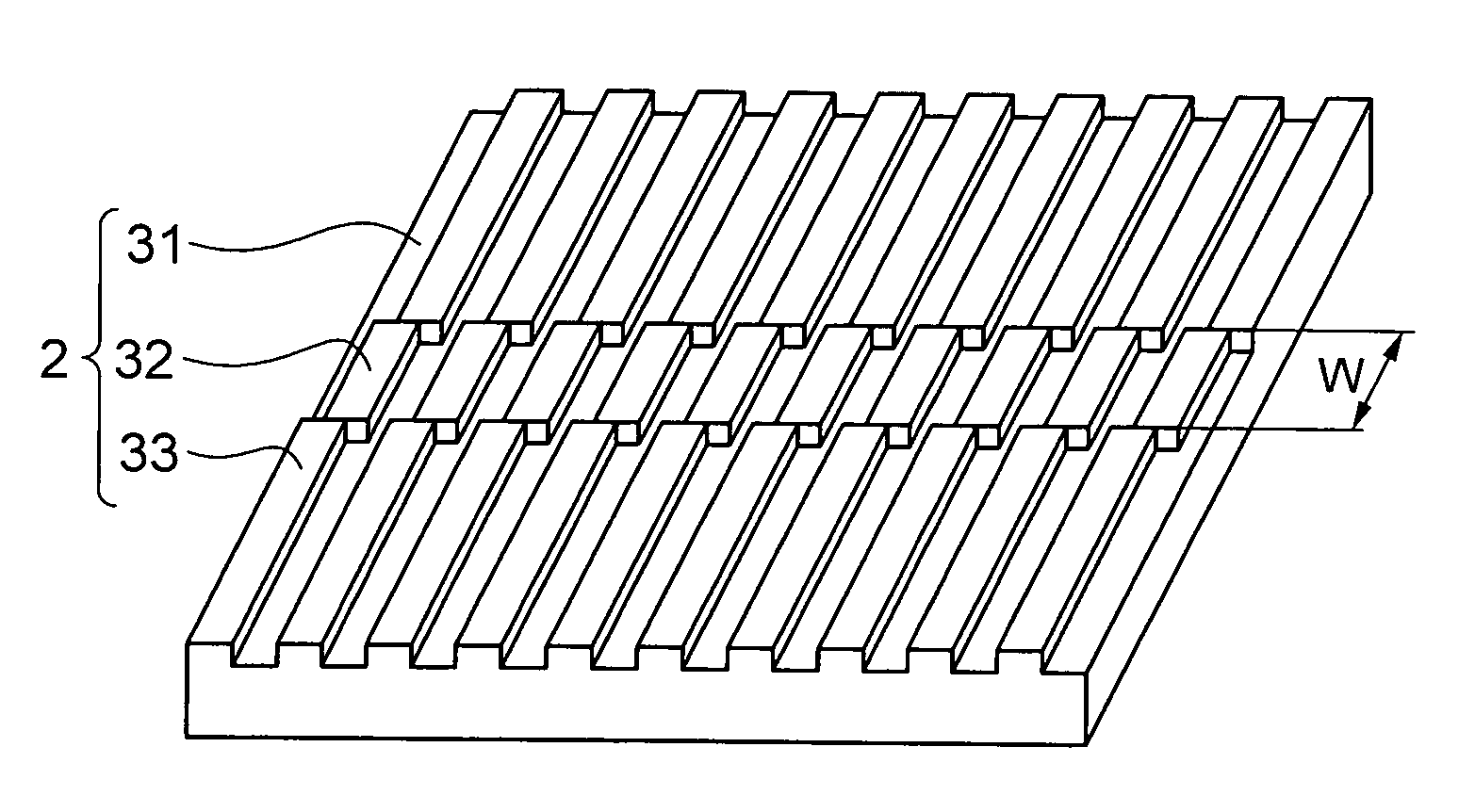
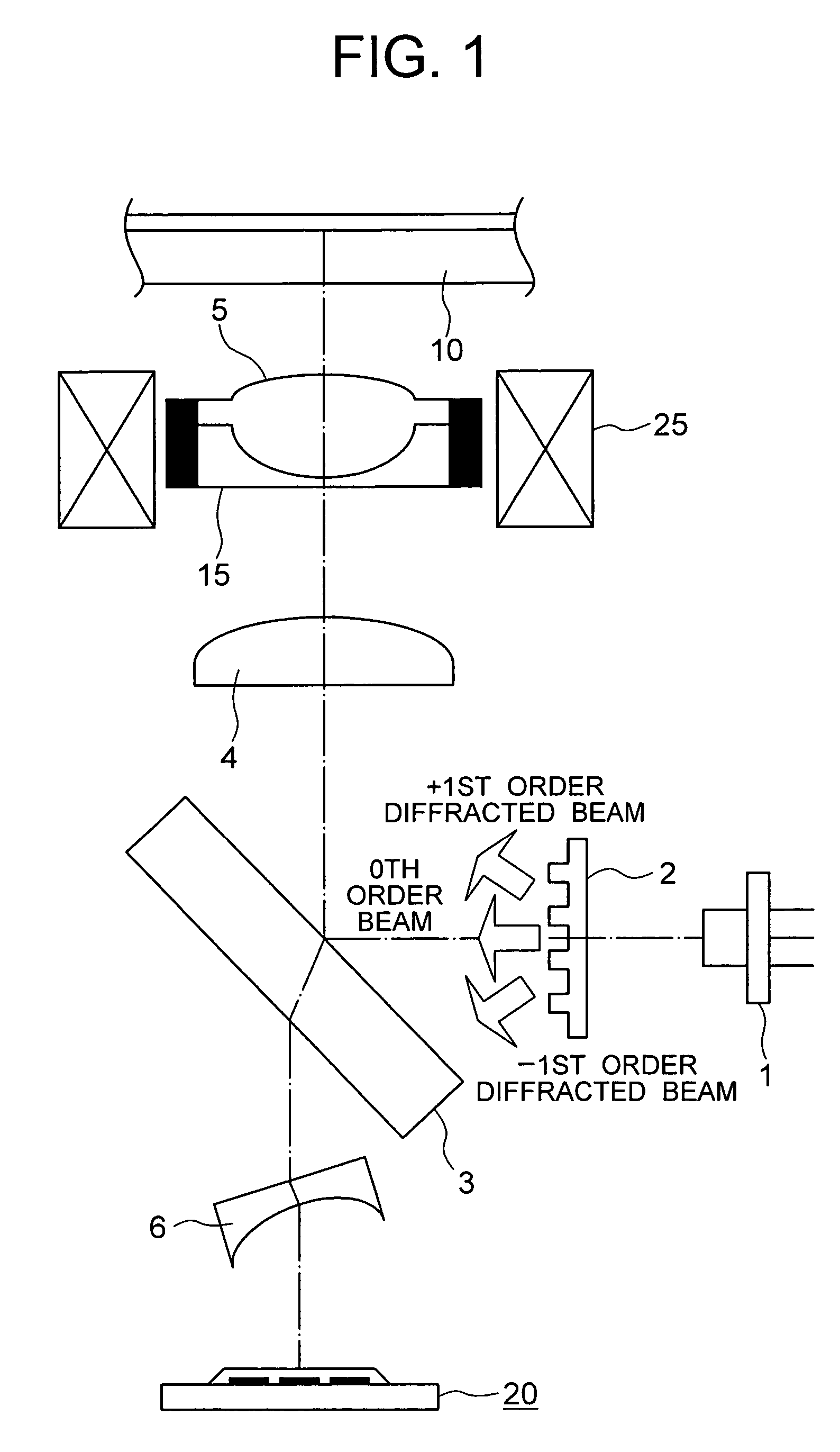
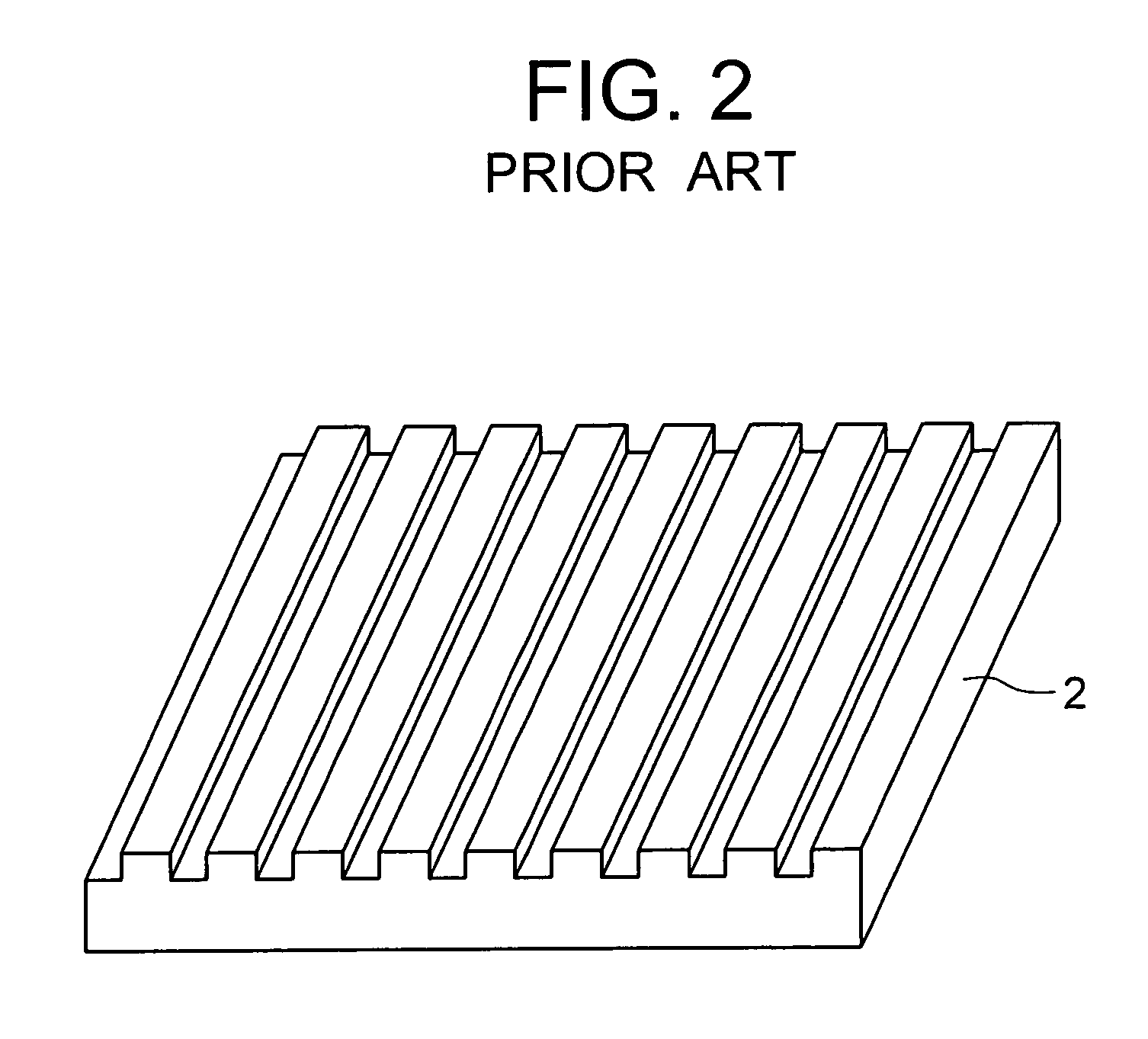
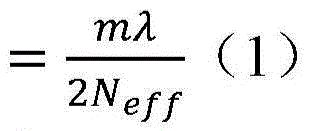Patents
Literature
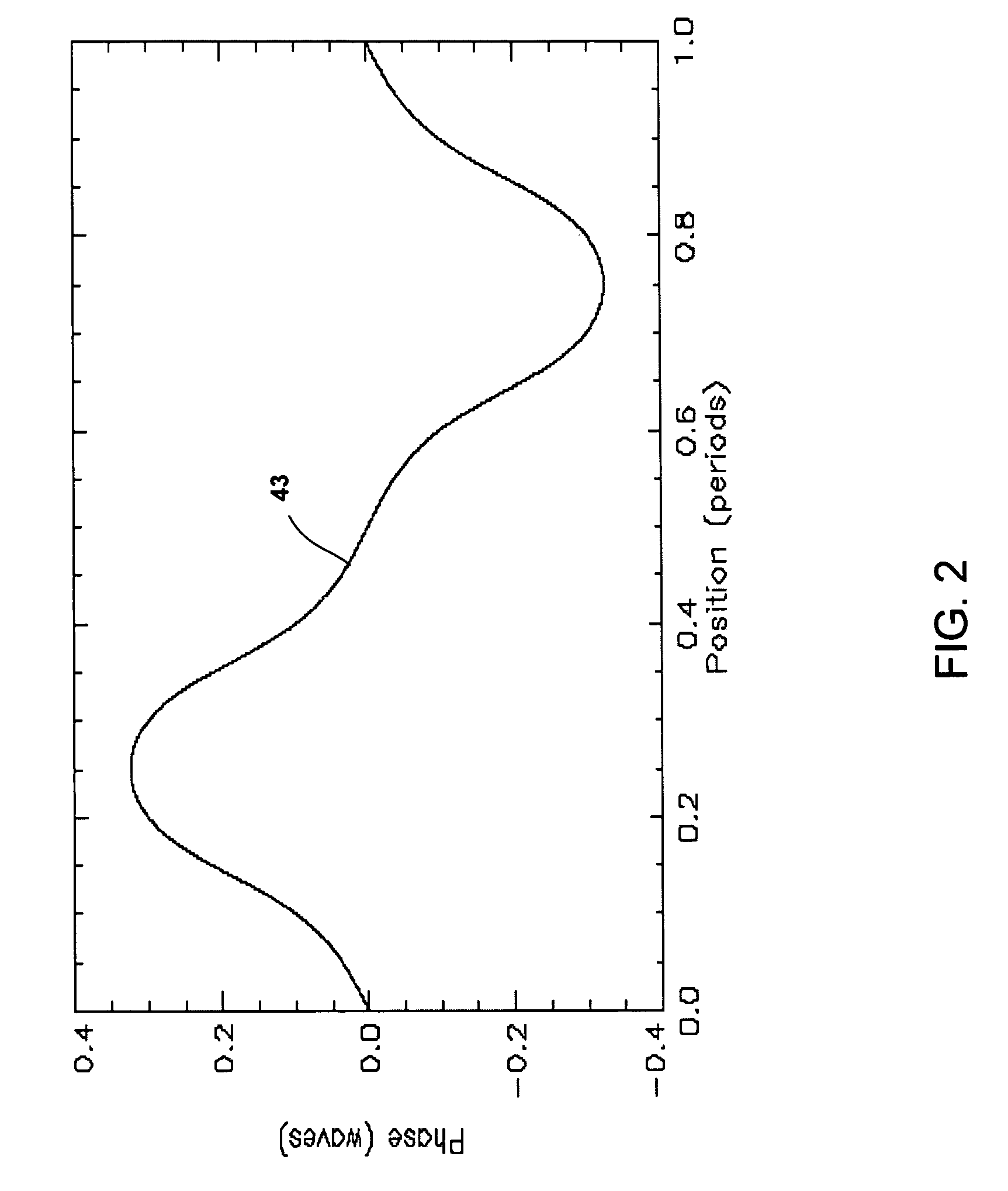
204 results about "Periodic grating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
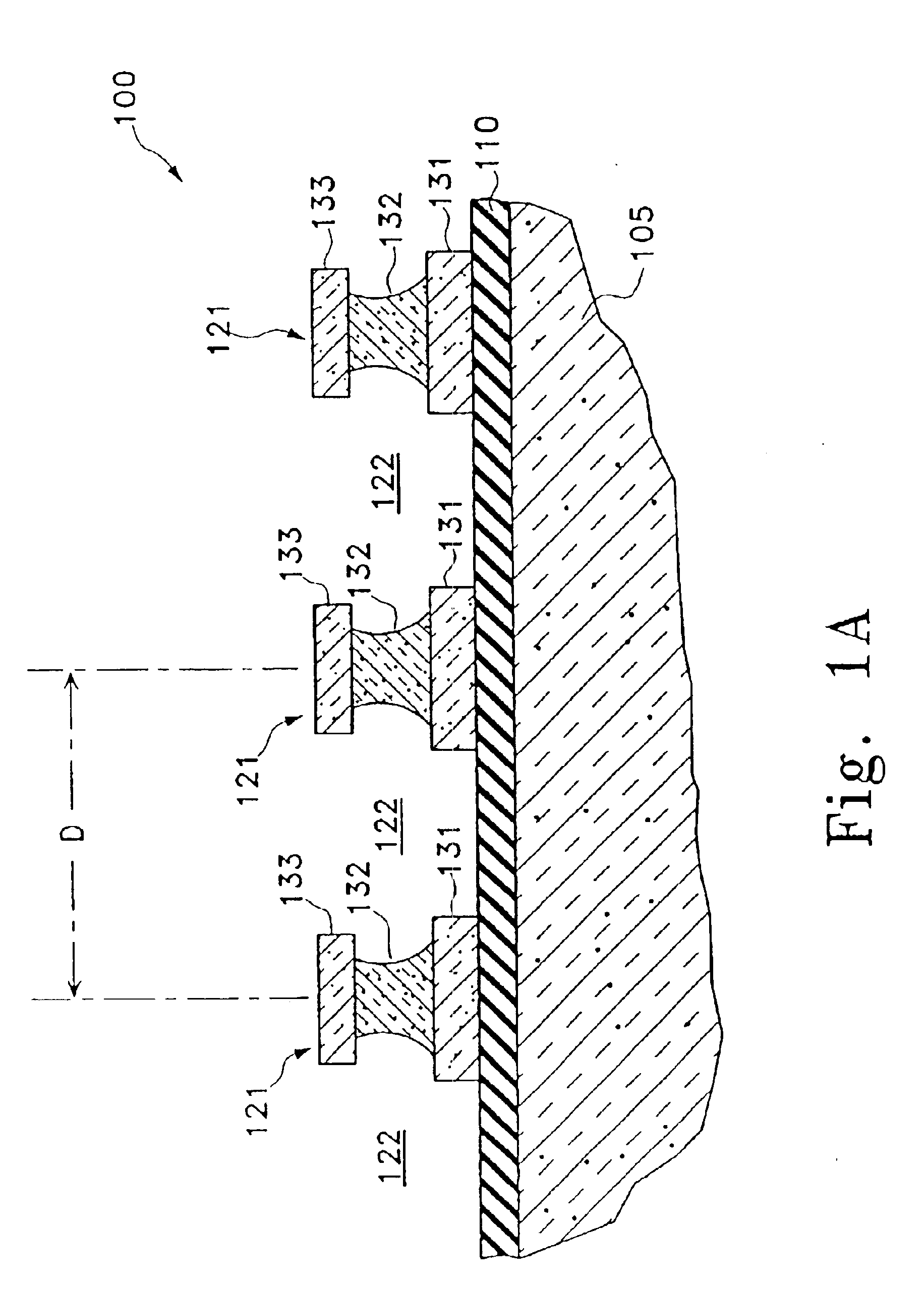
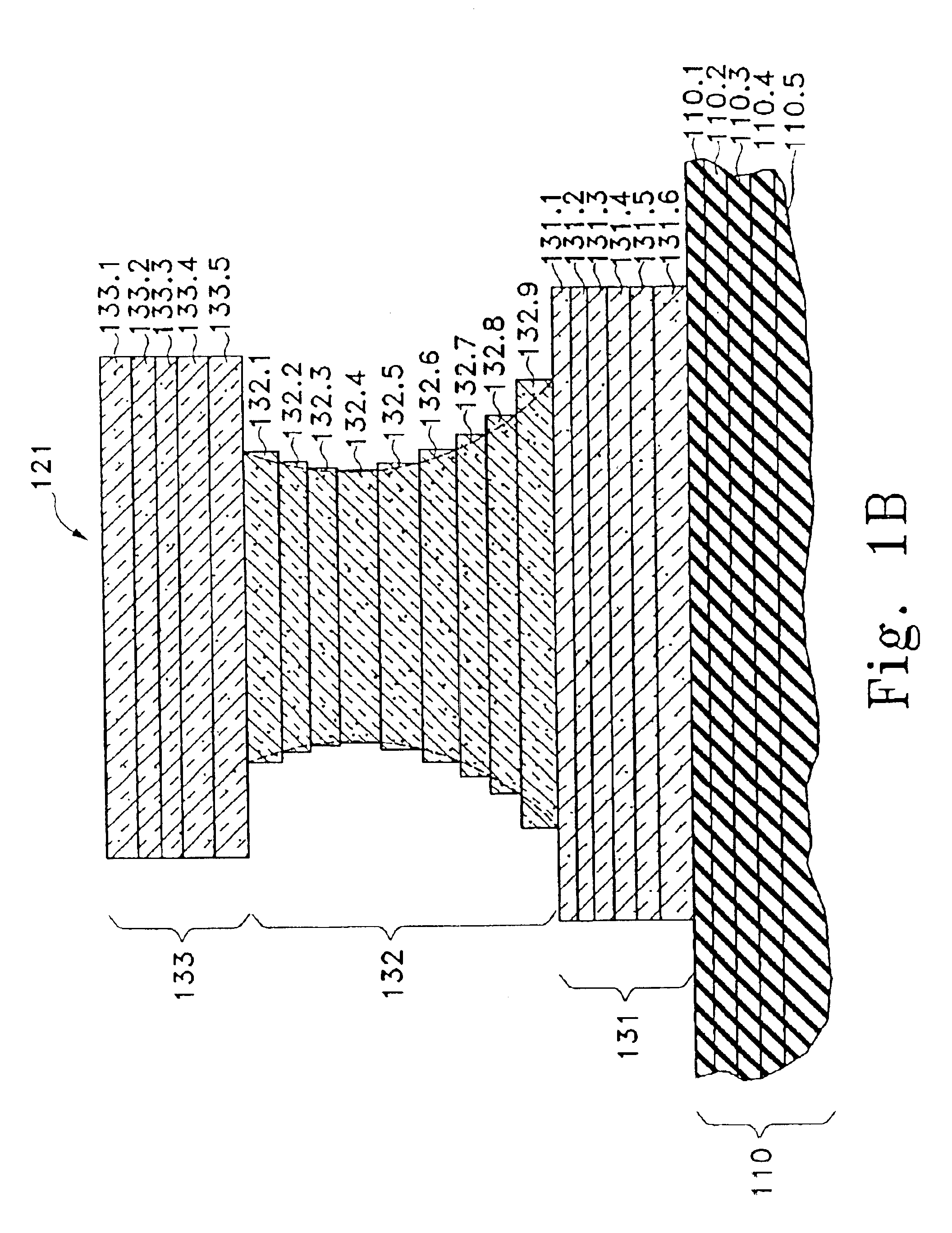
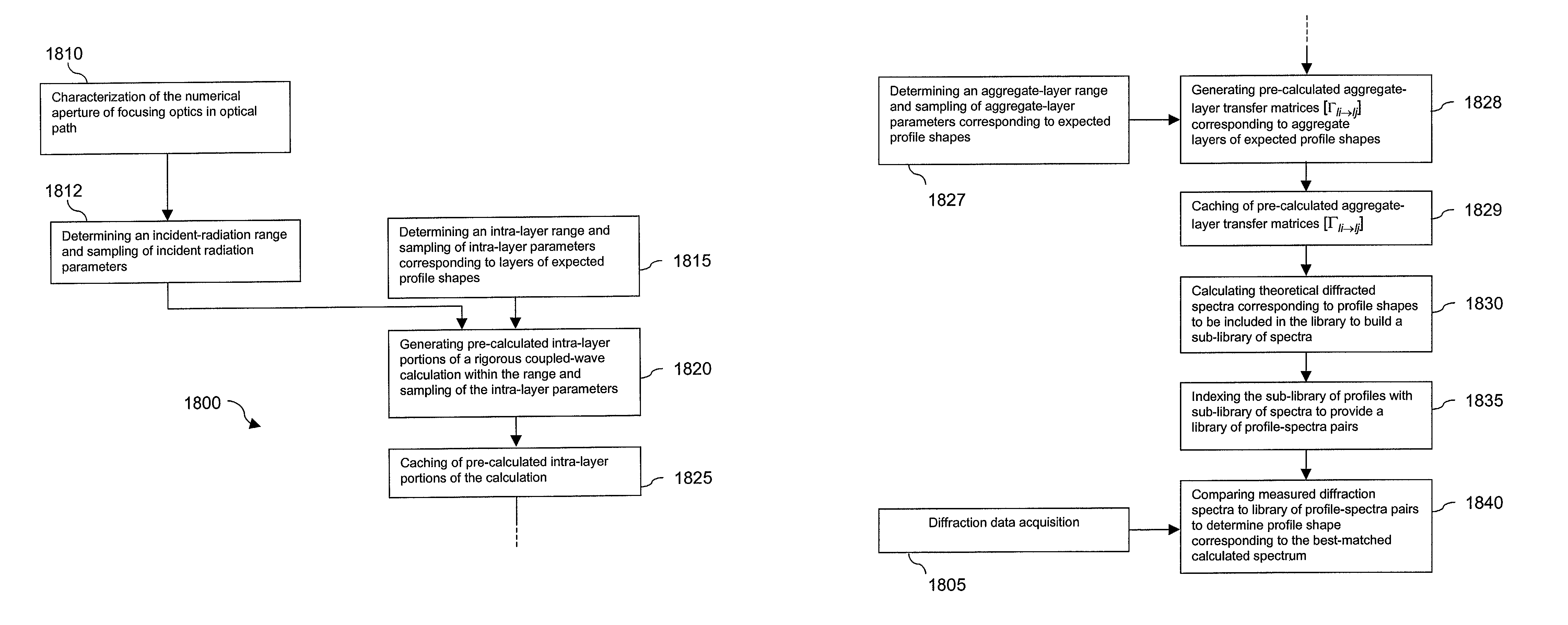
Caching of intra-layer calculations for rapid rigorous coupled-wave analyses
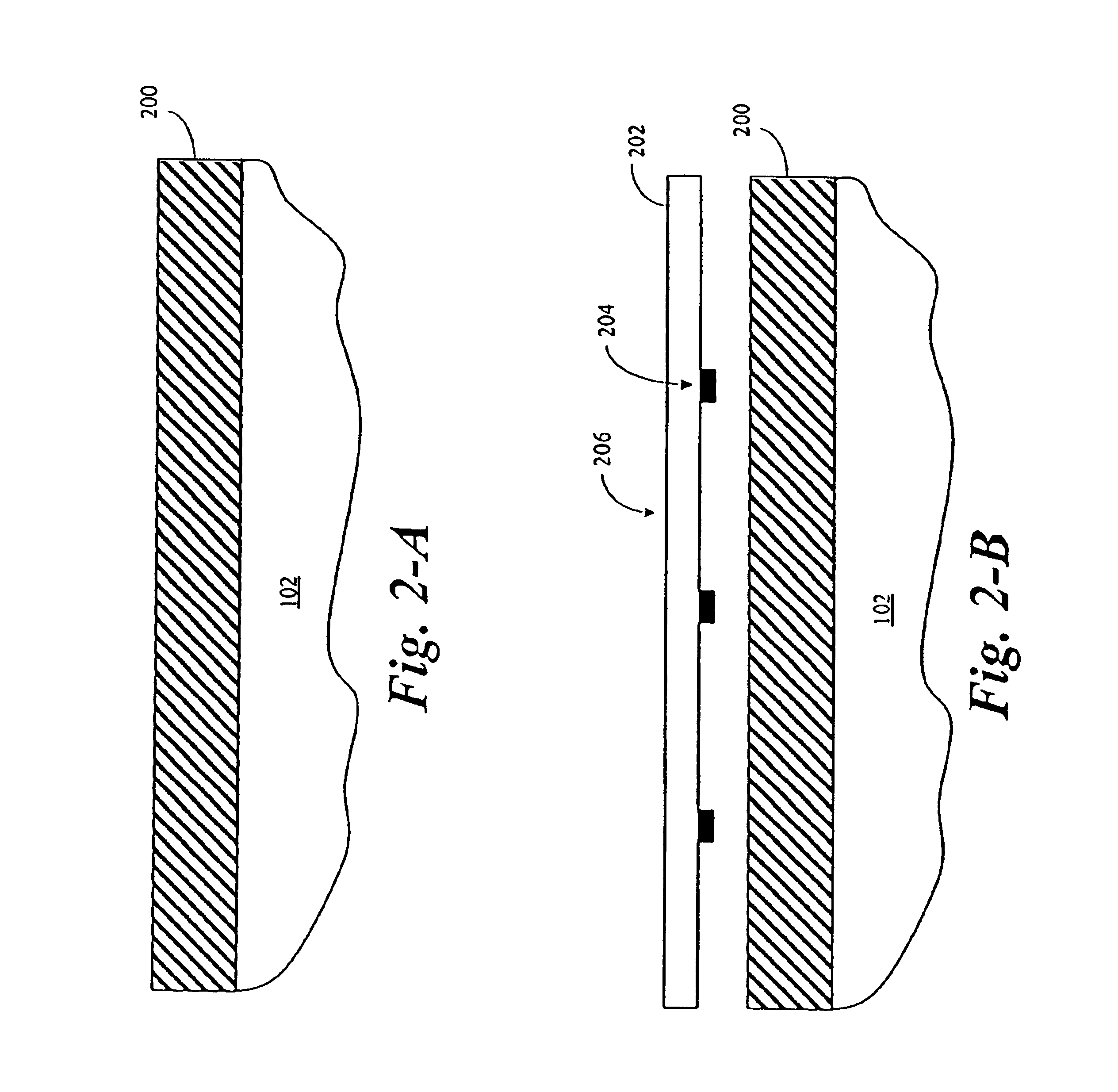
InactiveUS6891626B2Reduce computing timeCharacter and pattern recognitionDiffraction gratingsData setRigorous coupled-wave analysis
A library of simulated-diffraction signals for an integrated circuit periodic grating is generated by generating gets of intermediate layer data. Each set of intermediate layer data corresponding to a separate one of a plurality of hypothetical layers of a hypothetical profile of the periodic grating. Each separate hypothetical layer has one of a plurality of possible combinations of hypothetical values of properties for that hypothetical layer. The generated sets of intermediate layer data are stored. Simulated-diffraction signals for each of a plurality of hypothetical profiles are generated based on the stored generated sets of intermediate layer data.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON US HOLDINGS INC
Method and apparatus for the determination of mask rules using scatterometry
InactiveUS6433878B1Polarisation-affecting propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGrating patternPhotolithography
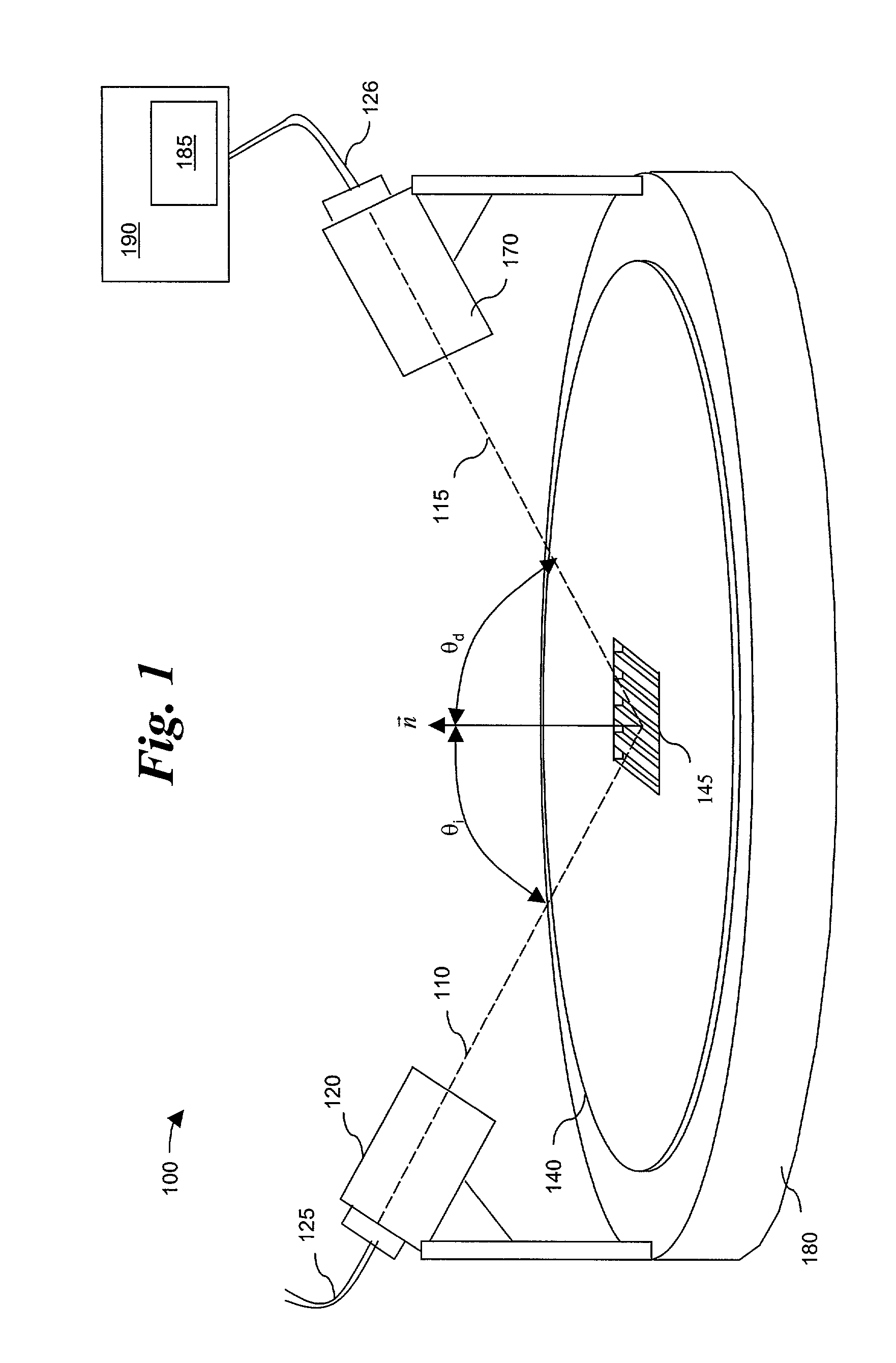
A method and apparatus for determining optical mask corrections for photolithography. A plurality of grating patterns is printed onto a wafer utilizing a photomask having at least one grating. Each grating pattern within the plurality of grating patterns is associated with known photolithographic settings. Each grating pattern is illuminated independently with a light source, so that light is diffracted off each grating pattern. The diffracted light is measured utilizing scatterometry techniques to determine measured diffracted values. The measured diffracted values are compared to values in a library to determine a profile match. A 2-dimensional profile description is assigned to each grating pattern based on the profile match. A database is compiled of the profile descriptions for the plurality of grating patterns. Photomask design rules are then generated by accessing the database containing the 2-dimensional profile descriptions. In preferred embodiments, the design rules are used to create and correct masks containing OPC corrections, phase-shifting mask corrections and binary masks. In a preferred embodiment the at least one grating is a bi-periodic grating. In a preferred embodiment, the scatterometry technique is optical digital profilometry utilizing a reflectometer or ellipsometer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON US HOLDINGS INC
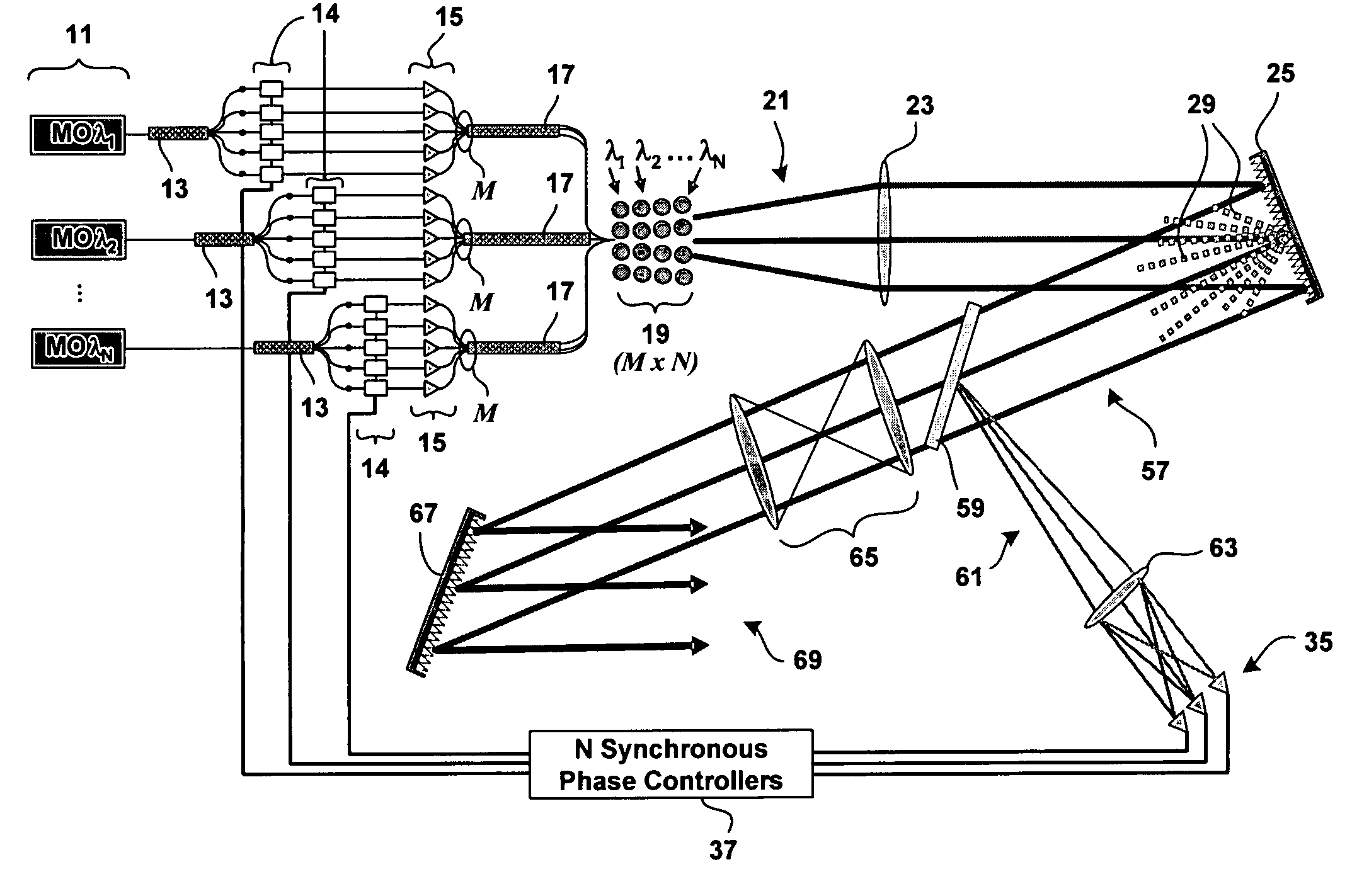
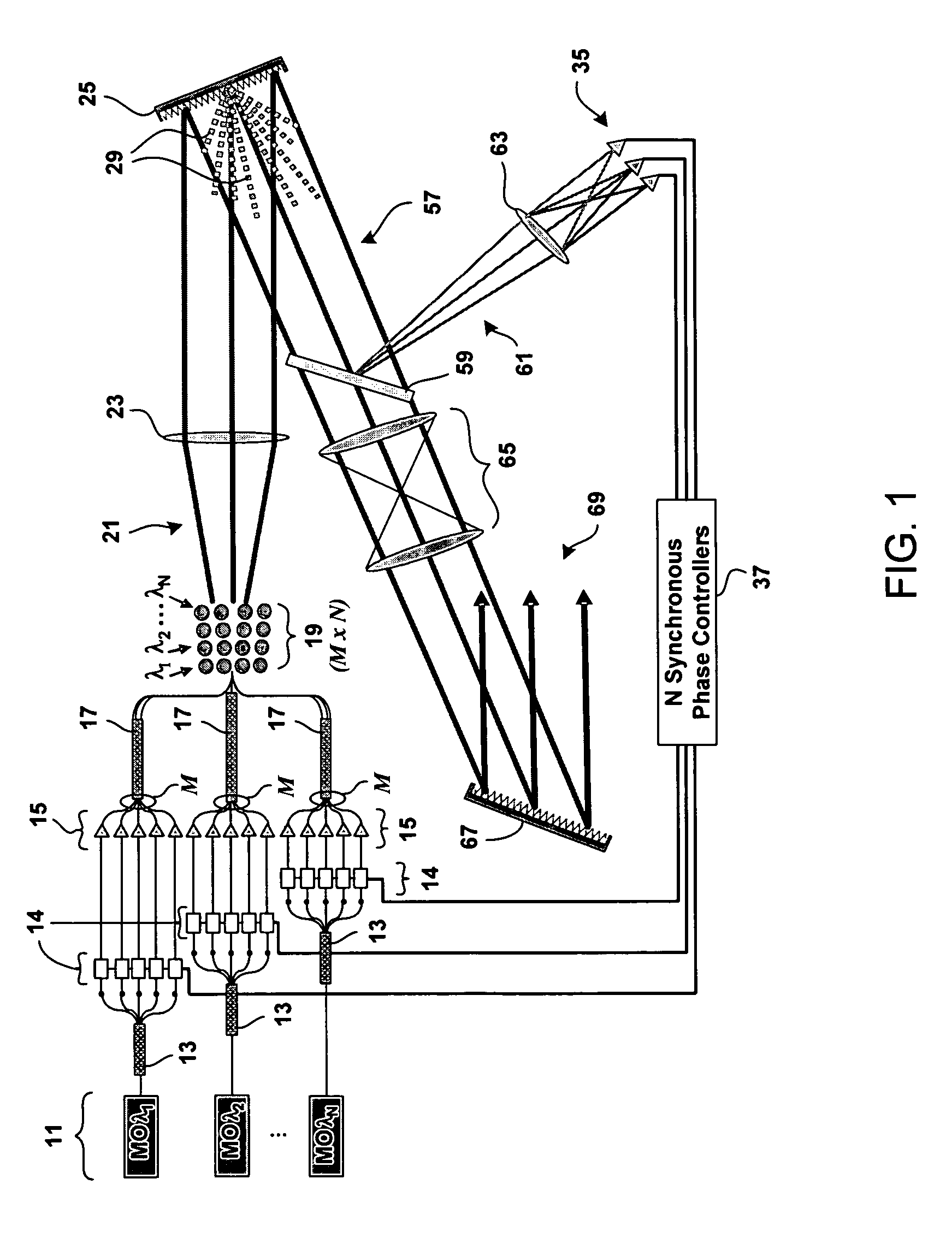
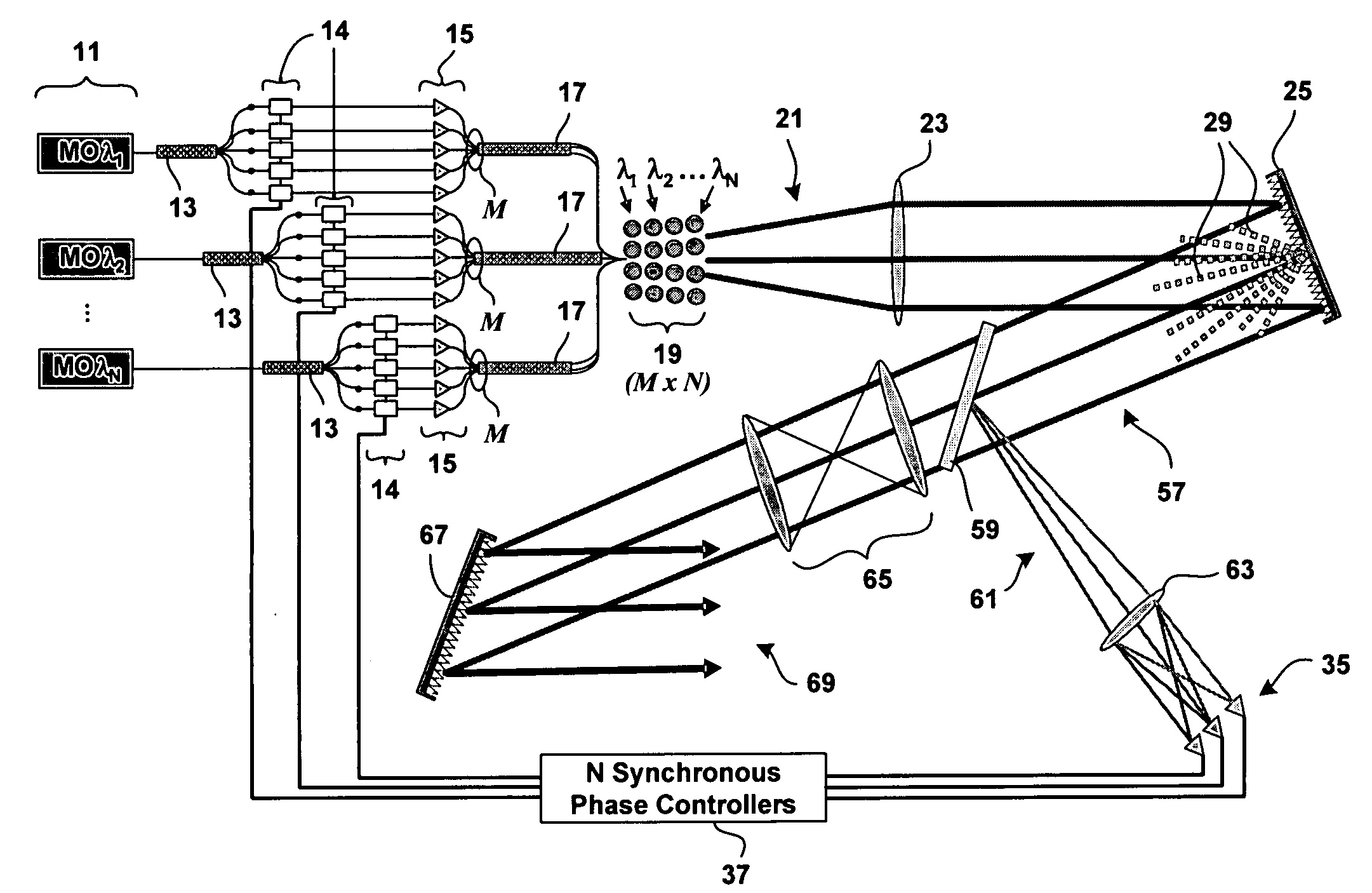
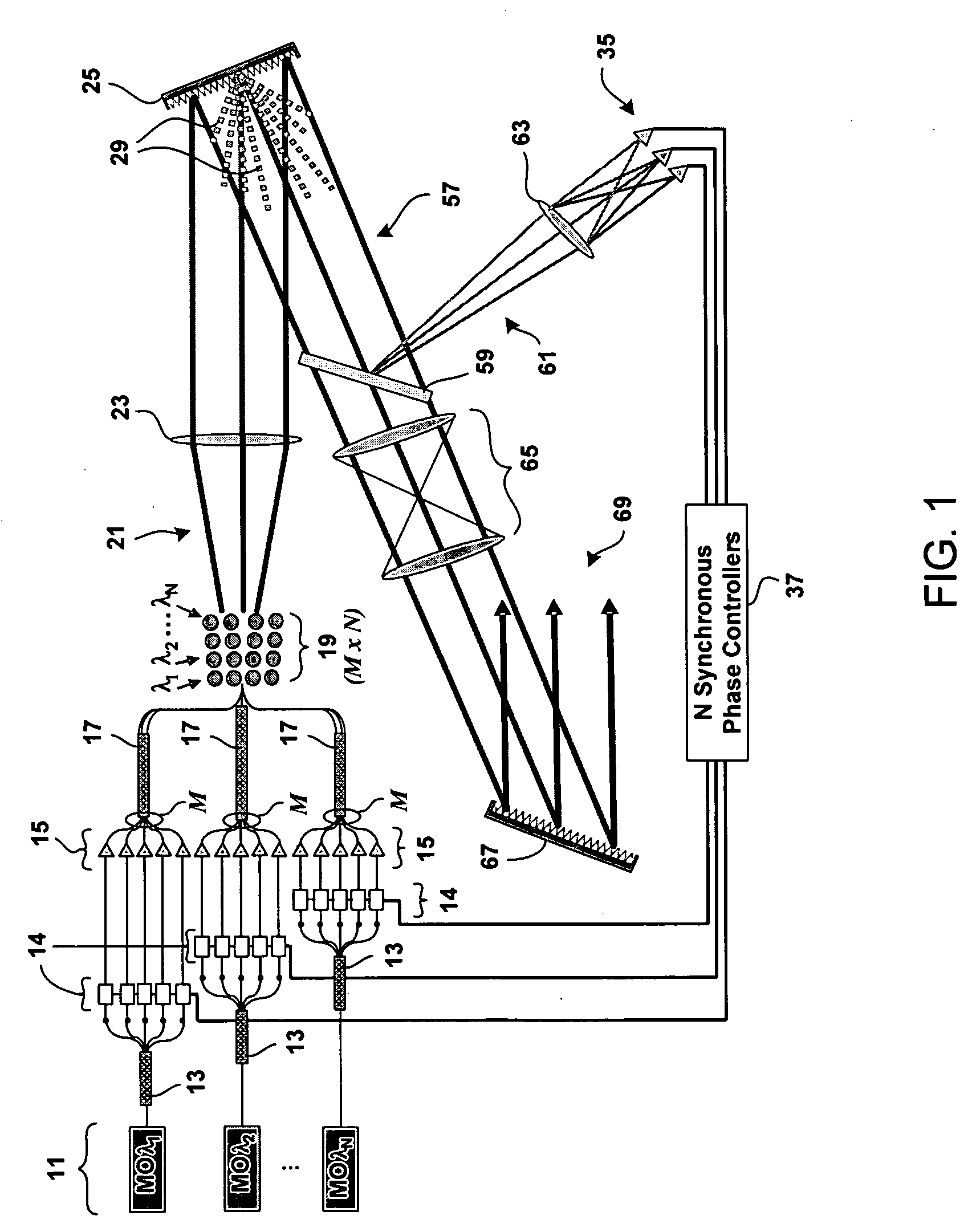
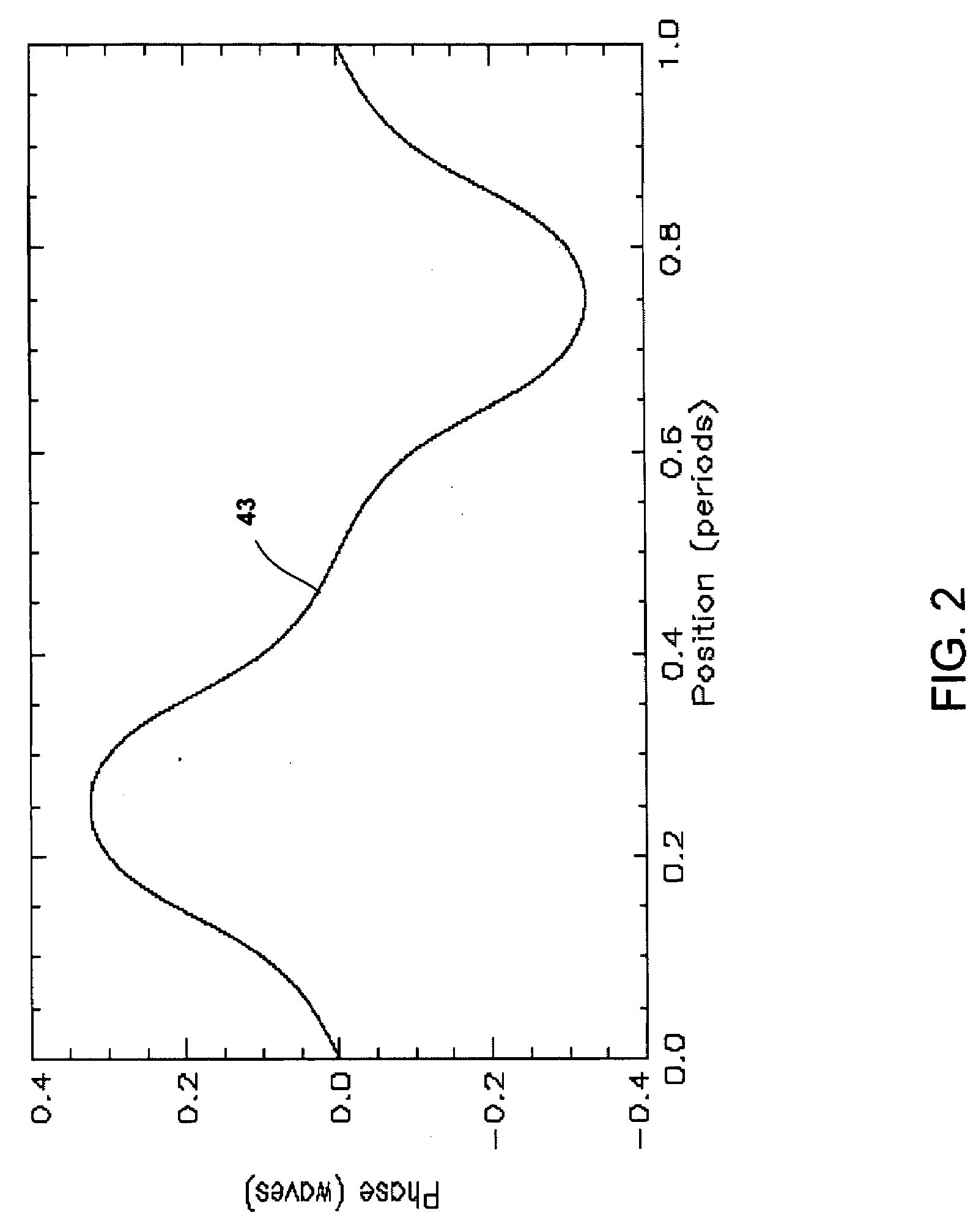
Method and system for hybrid coherent and incoherent diffractive beam combining
A hybrid beam combining system or method combines a plurality of coherent and incoherent light beams into a composite high power diffraction limited beam. N oscillators each transmit light at one of N different wavelengths and each wavelength is split into M constituent beams. M beams in each of N groups are phase locked by a phase modulator using phase correction signals. The phase locked beams are amplified and coupled into an M×N fiber array. Beams emerging from the array are collimated and incident on a diffractive optical element operating as a beam combiner combining the M outputs at each N wavelength into a single beam. The N single beams are incident and spectrally combined on a grating which outputs a composite beam at a nominal 100% fill factor. A low power sample beam, taken from the N beams emerging from the diffractive optical element, is measured for phase deviations from which the phase correction signals are derived and fed back to the phase modulators. The diffractive optical element may include a weak periodic grating for diffracting the low power sample. The diffractive optical element may also be combined with the spectral combining grating into a single optical element.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Organic polarized light emitting diode display with polarizer
InactiveUS20050088084A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesMetallic electrodeLED display
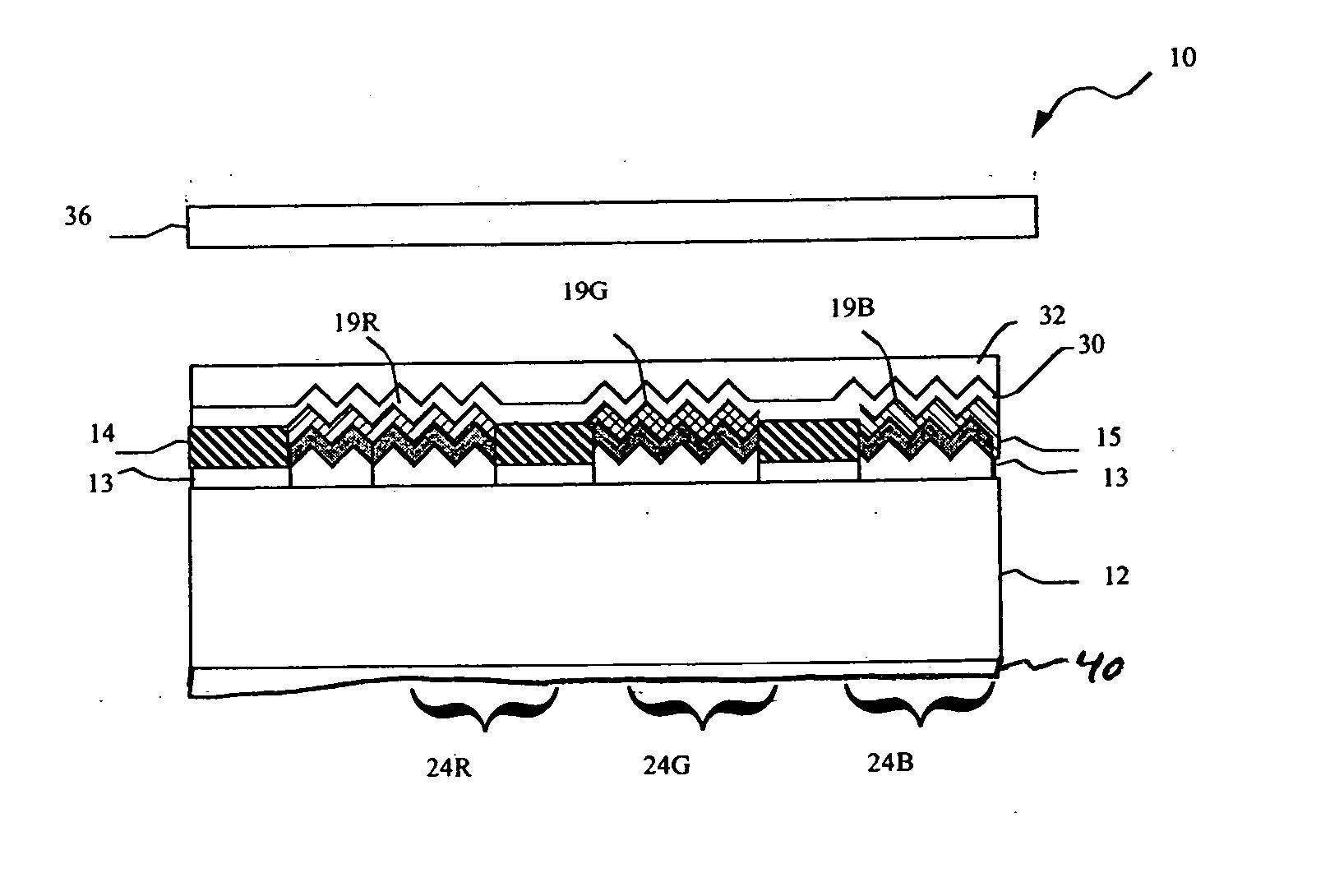
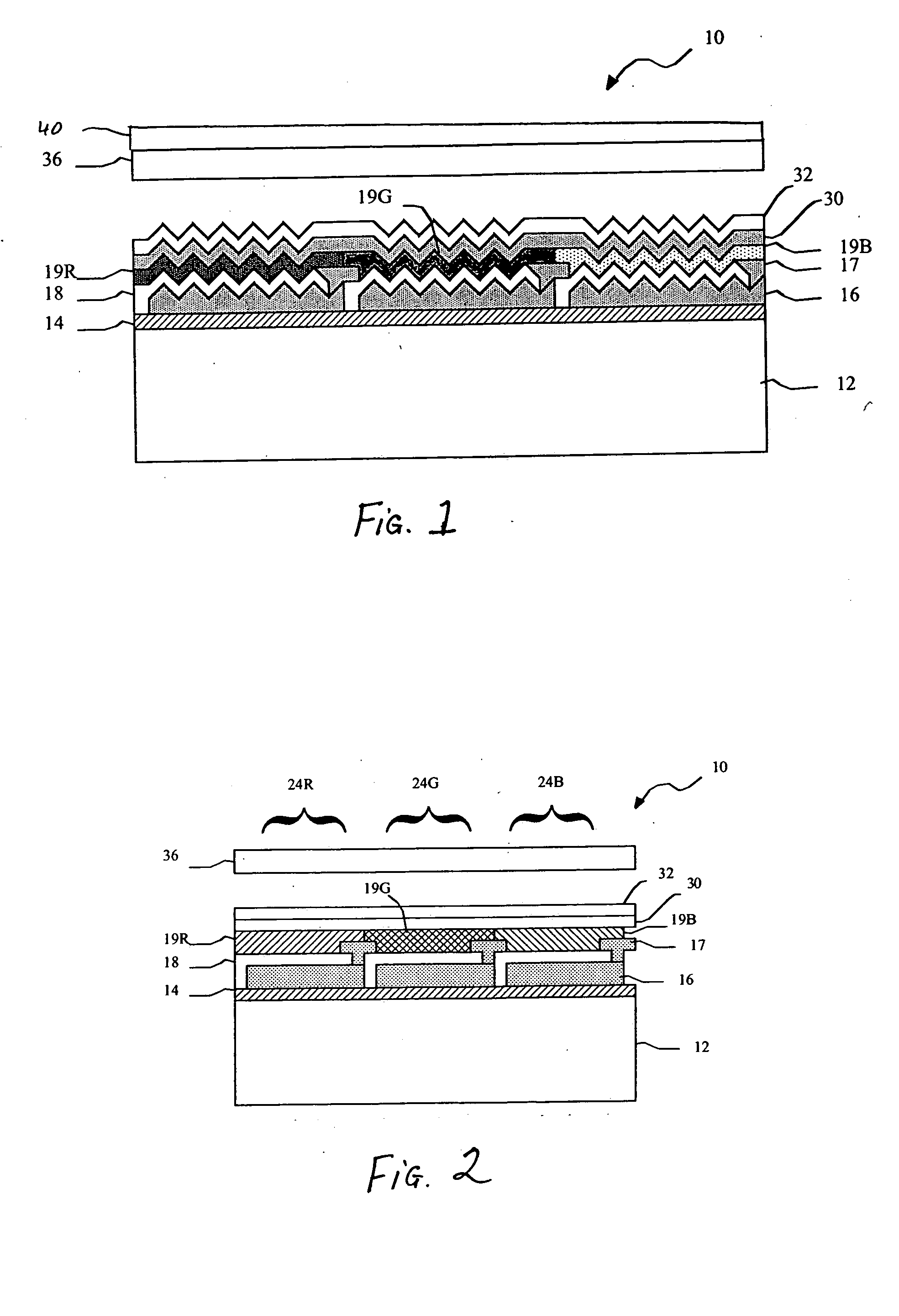
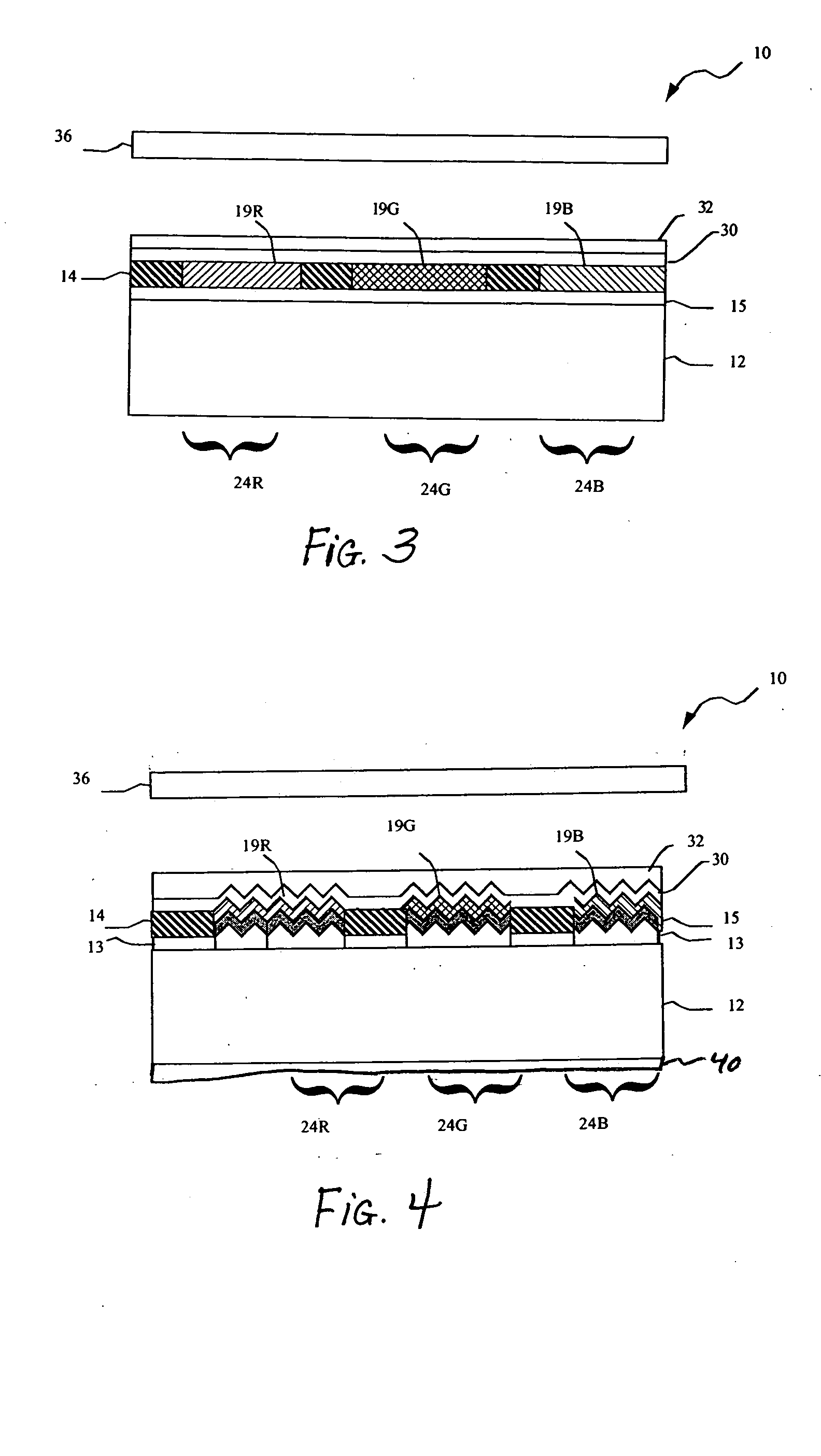
An organic light emitting diode display includes a substrate; a plurality of OLEDs formed on the substrate, the OLEDs emitting polarized light wherein the OLEDs comprise a layer defining a periodic grating structure; a first electrode layer conforming to the grating structure; an OLED material layer formed over the first electrode layer and conforming to the grating structure; and a second electrode layer formed over the OLED material layer and conforming to the grating structure, wherein the first and / or second electrode layers are metallic layers, whereby the periodic grating structure induces surface plasmon cross coupling in the metallic electrode layer(s) to emit polarized light; and a polarizer located over the substrate through which the polarized light is emitted.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Optical waveguide with non-uniform sidewall gratings
A diffraction grating of non-uniform strength is introduced into an optical waveguide by modulating its width. The waveguide may be fabricated using one of several planar processing techniques. Varying the size, position, and / or thickness of the grating teeth provides the desired variation of grating strength. Certain functional variations of grating strength suppress side-lobe levels in the grating reflection and transmission spectra. This process, termed apodization, is necessary for precise wavelength filtering and dispersion compensation. If desired, different periodicity gratings can be introduced in each side of the waveguide, multiple periodicities can be superimposed, the grating can be angled with respect to the waveguide, and the grating period and phase can be varied.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Metrology Method and Apparatus, and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20130100427A1Reduce the impactReduce impactScattering properties measurementsPhotomechanical apparatusMetrologyScatterometer
An approach is used to estimate and correct the overlay variation as function of offset for each measurement. A target formed on a substrate includes periodic gratings. The substrate is illuminated with a circular spot on the substrate with a size larger than each grating. Radiation scattered by each grating is detected in a dark-field scatterometer to obtain measurement signals. The measurement signals are used to calculate overlay. The dependence (slope) of the overlay as a function of position in the illumination spot is determined. An estimated value of the overlay at a nominal position such as the illumination spot's center can be calculated, correcting for variation in the overlay as a function of the target's position in the illumination spot. This compensates for the effect of the position error in the wafer stage movement, and the resulting non-centered position of the target in the illumination spot.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Overlay measurements using zero-order cross polarization measurements
InactiveUS6947141B2Measurement arrangements for variableDigital computer detailsPolarimetryCross polarization
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON US HOLDINGS INC
Method and apparatus for the determination of mask rules using scatterometry
InactiveUS20020131055A1Polarisation-affecting propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContour matchingGrating pattern
A method and apparatus for determining optical mask corrections for photolithography. A plurality of grating patterns is printed onto a wafer utilizing a photomask having at least one grating. Each grating pattern within the plurality of grating patterns is associated with known photolithographic settings. Each grating pattern is illuminated independently with a light source, so that light is diffracted off each grating pattern. The diffracted light is measured utilizing scatterometry techniques to determine measured diffracted values. The measured diffracted values are compared to values in a library to determine a profile match. A 2-dimensional profile description is assigned to each grating pattern based on the profile match. A database is compiled of the profile descriptions for the plurality of grating patterns. Photomask design rules are then generated by accessing the database containing the 2-dimensional profile descriptions. In preferred embodiments, the design rules are used to create and correct masks containing OPC corrections, phase-shifting mask corrections and binary masks. In a preferred embodiment the at least one grating is a bi-periodic grating. In a preferred embodiment, the scatterometry technique is optical digital profilometry utilizing a reflectometer or ellipsometer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON US HOLDINGS INC
Method and system for hybrid coherent and incoherent diffractive beam combining
A hybrid beam combining system or method combines a plurality of coherent and incoherent light beams into a composite high power diffraction limited beam. N oscillators each transmit light at one of N different wavelengths and each wavelength is split into M constituent beams. M beams in each of N groups are phase locked by a phase modulator using phase correction signals. The phase locked beams are amplified and coupled into an M×N fiber array. Beams emerging from the array are collimated and incident on a diffractive optical element operating as a beam combiner combining the M outputs at each N wavelength into a single beam. The N single beams are incident and spectrally combined on a grating which outputs a composite beam at a nominal 100% fill factor. A low power sample beam, taken from the N beams emerging from the diffractive optical element, is measured for phase deviations from which the phase correction signals are derived and fed back to the phase modulators. The diffractive optical element may include a weak periodic grating for diffracting the low power sample. The diffractive optical element may also be combined with the spectral combining grating into a single optical element.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
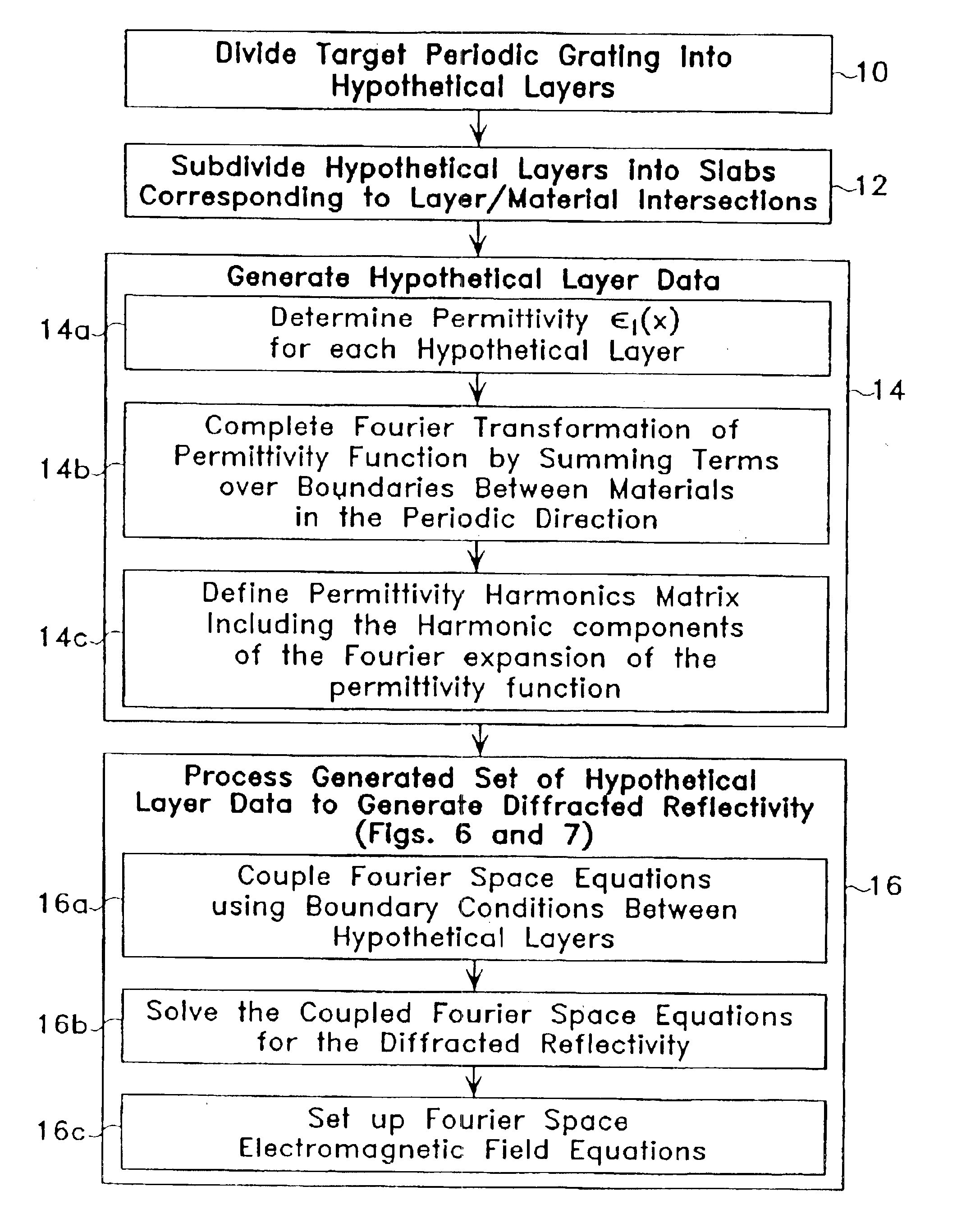
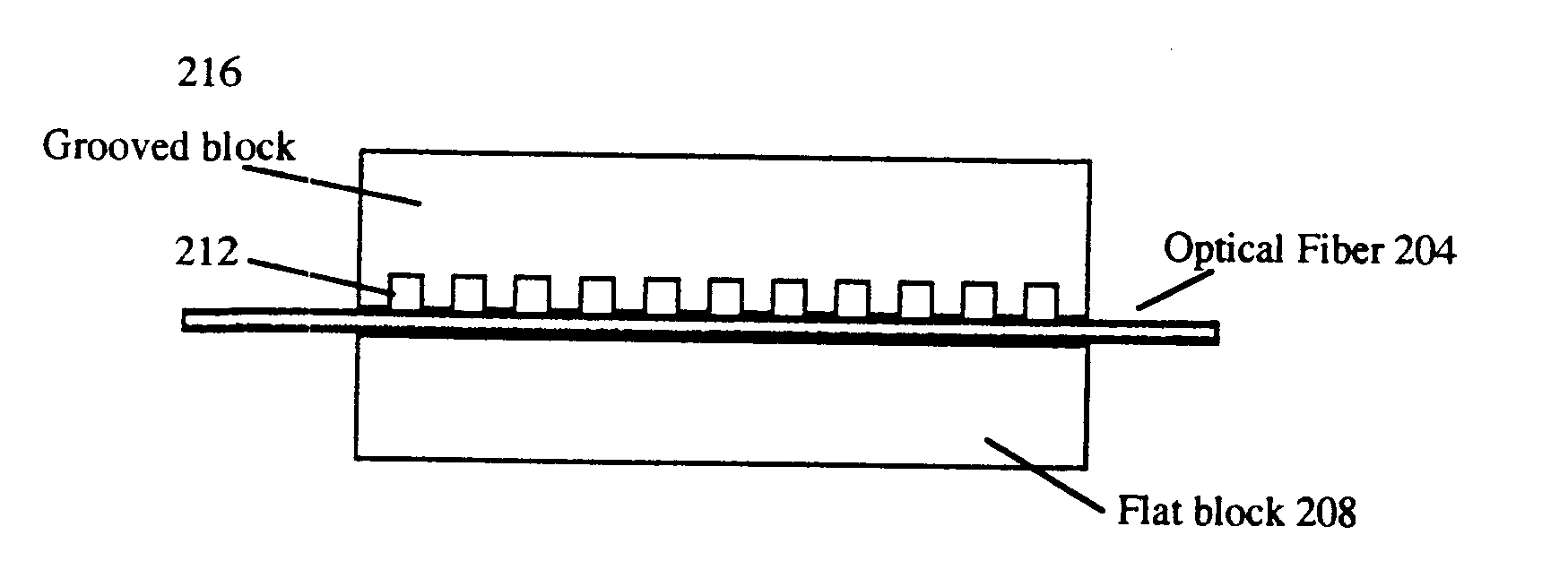
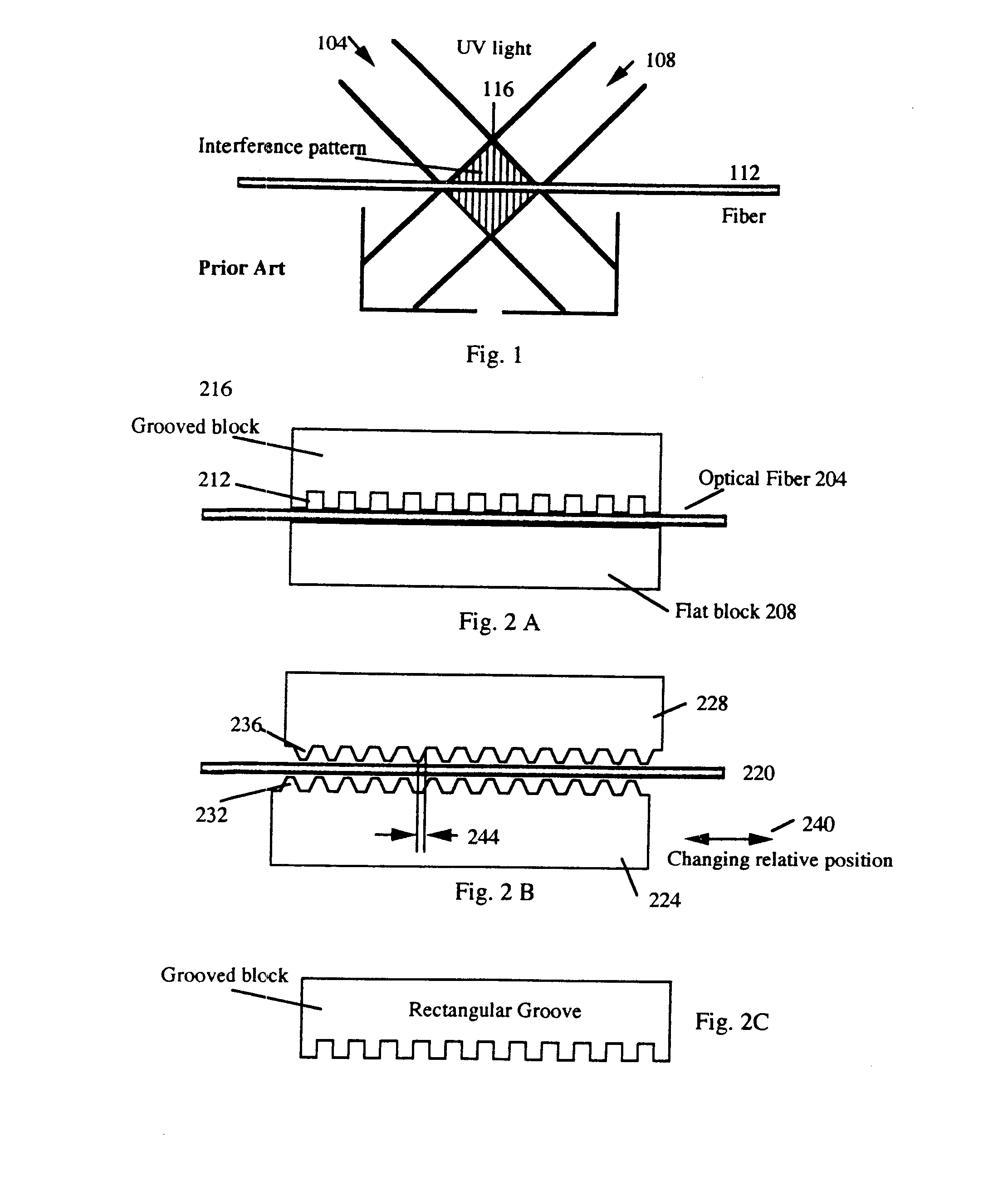
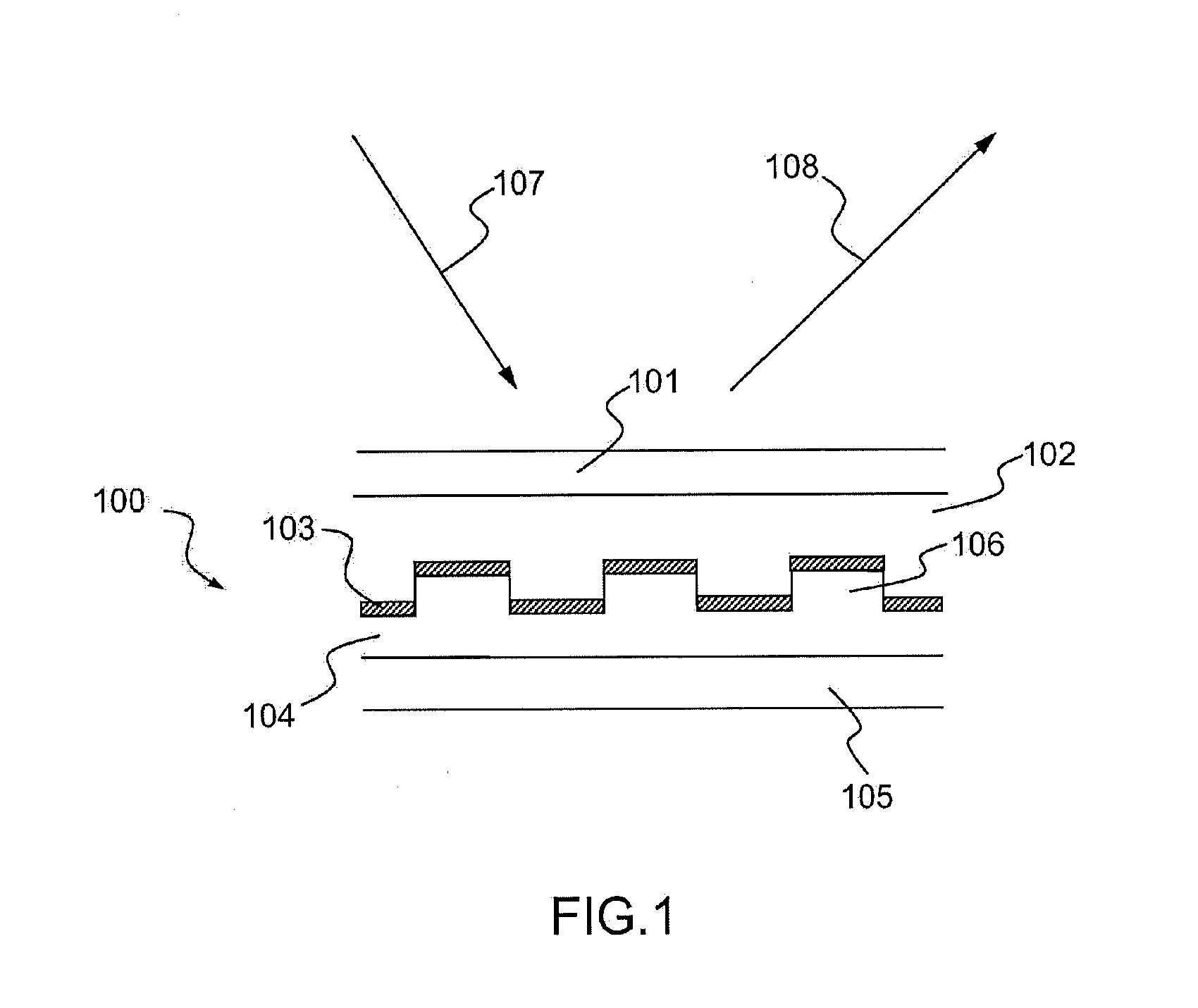
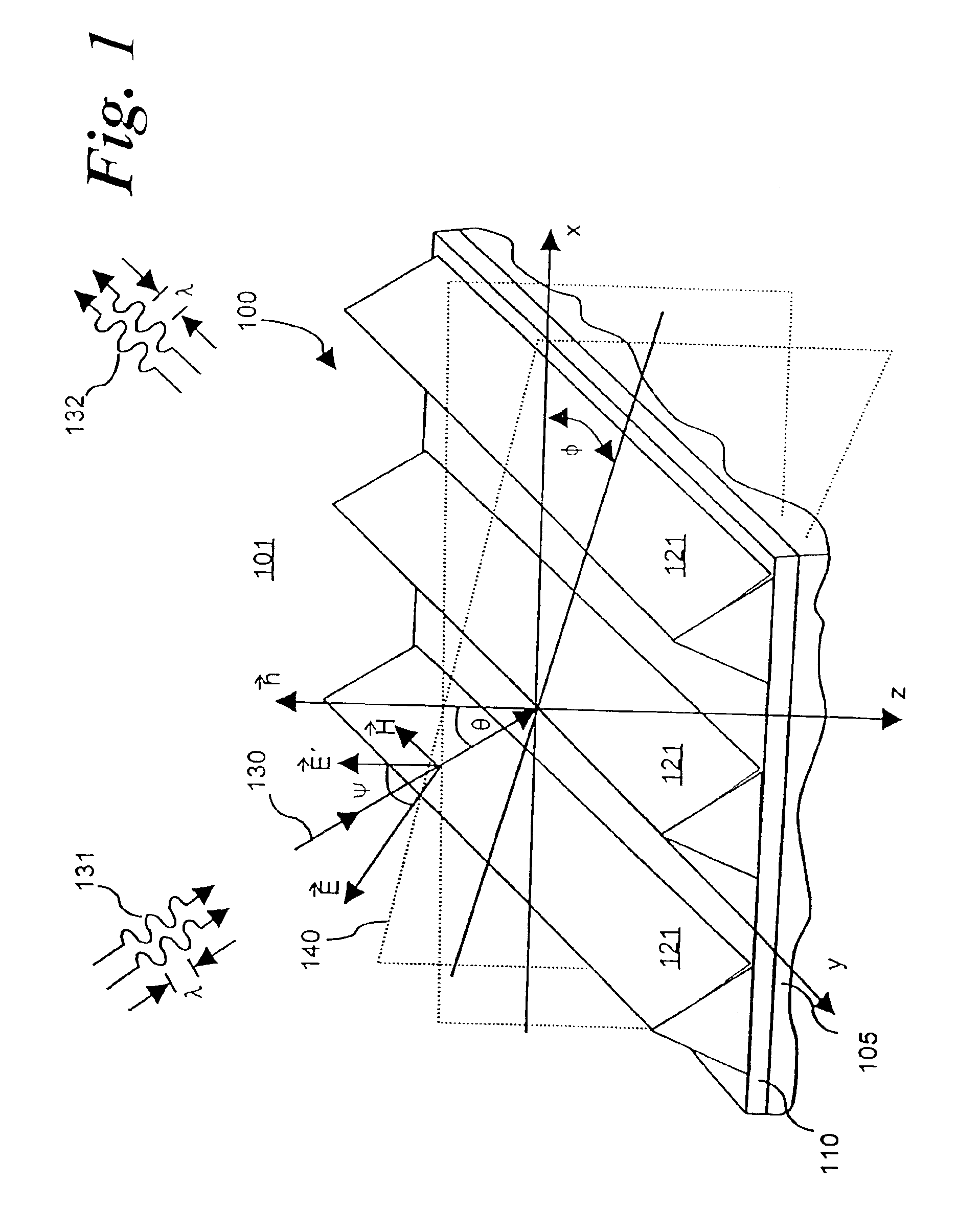
Optical profilometry of additional-material deviations in a periodic grating
Disclosed is a method and system for measurement of periodic gratings which have deviations which result in more than two materials occurring along at least one line in the periodic direction. A periodic grating is divided into a plurality of hypothetical layers, each hypothetical layer having a normal vector orthogonal to the direction of periodicity, each hypothetical layer having a single material within any line parallel to the normal vector, and at least one of the hypothetical layers having at least three materials along a line in the direction of periodicity. A harmonic expansion of the permittivity ε or inverse permittivity 1 / ε is performed along the direction of periodicity for each of the layers including the layer which includes the first, second and third materials. Fourier space electromagnetic equations are then set up in each of the layers using the harmonic expansion of the permittivity E or inverse permittivity 1 / ε, and Fourier components of electric and magnetic fields in each layer. The Fourier space electromagnetic equations are then coupled based on boundary conditions between the layers, and solved to provide the calculated diffraction spectrum.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON US HOLDINGS INC
Generating a library of simulated-diffraction signals and hypothetical profiles of periodic gratings
ActiveUS7031894B2Scattering properties measurementsComputation using non-denominational number representationLight beamComputational physics
A library of simulated-diffraction signals and hypothetical profiles of a periodic grating can be generated by generating diffraction calculations for a plurality of blocks of hypothetical layers. A diffraction calculation for a block of hypothetical layers characterizes, in part, the behavior of a diffraction beam in the block of hypothetical layers. Each block of hypothetical layers includes two or more hypothetical layers, and each hypothetical layer characterizes a layer within a hypothetical profile. The diffraction calculations for the blocks of hypothetical layers are stored prior to generating the library. The simulated-diffraction signals to be stored in the library are then generated based on the stored diffraction calculations for the blocks of hypothetical layers.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON US HOLDINGS INC
Devices Based on Optical Waveguides with Adjustable Bragg Gratings
A system for filtering light propagating in a waveguide is described. The system utilizes an adjustable periodic grating which induces mode coupling of predetermined frequencies of light propagating in the waveguide.
Owner:GENERAL PHOTONICS CORP
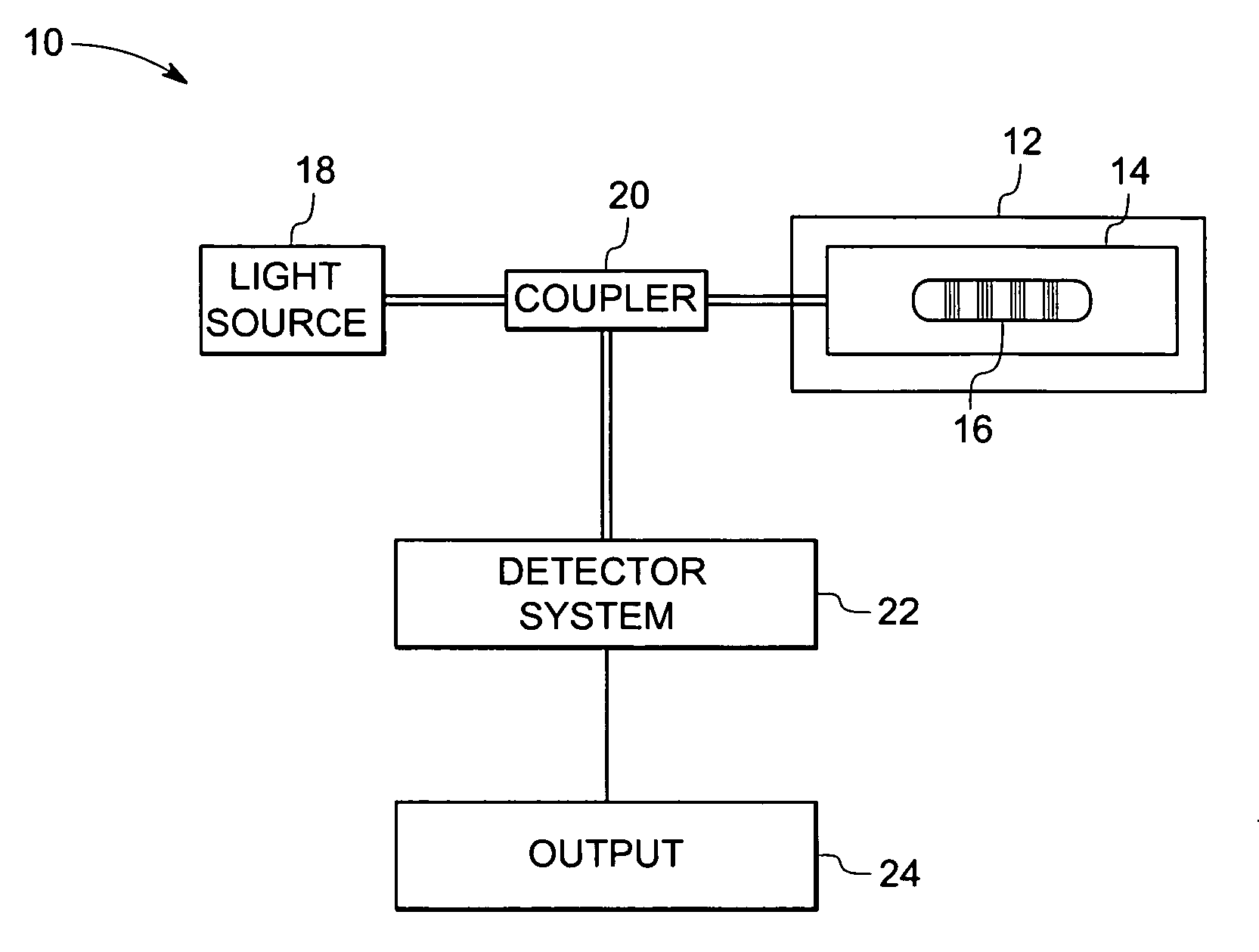
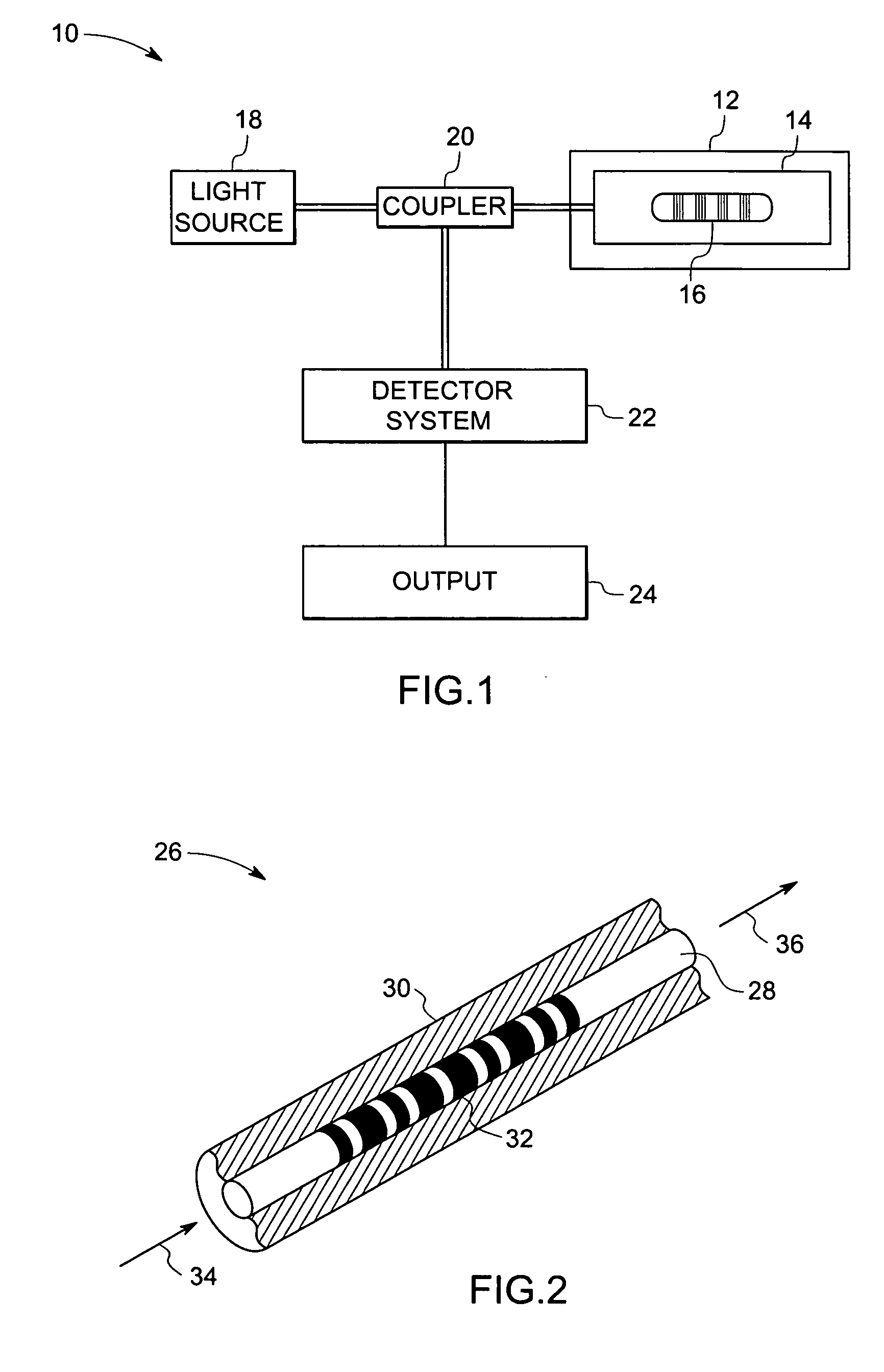
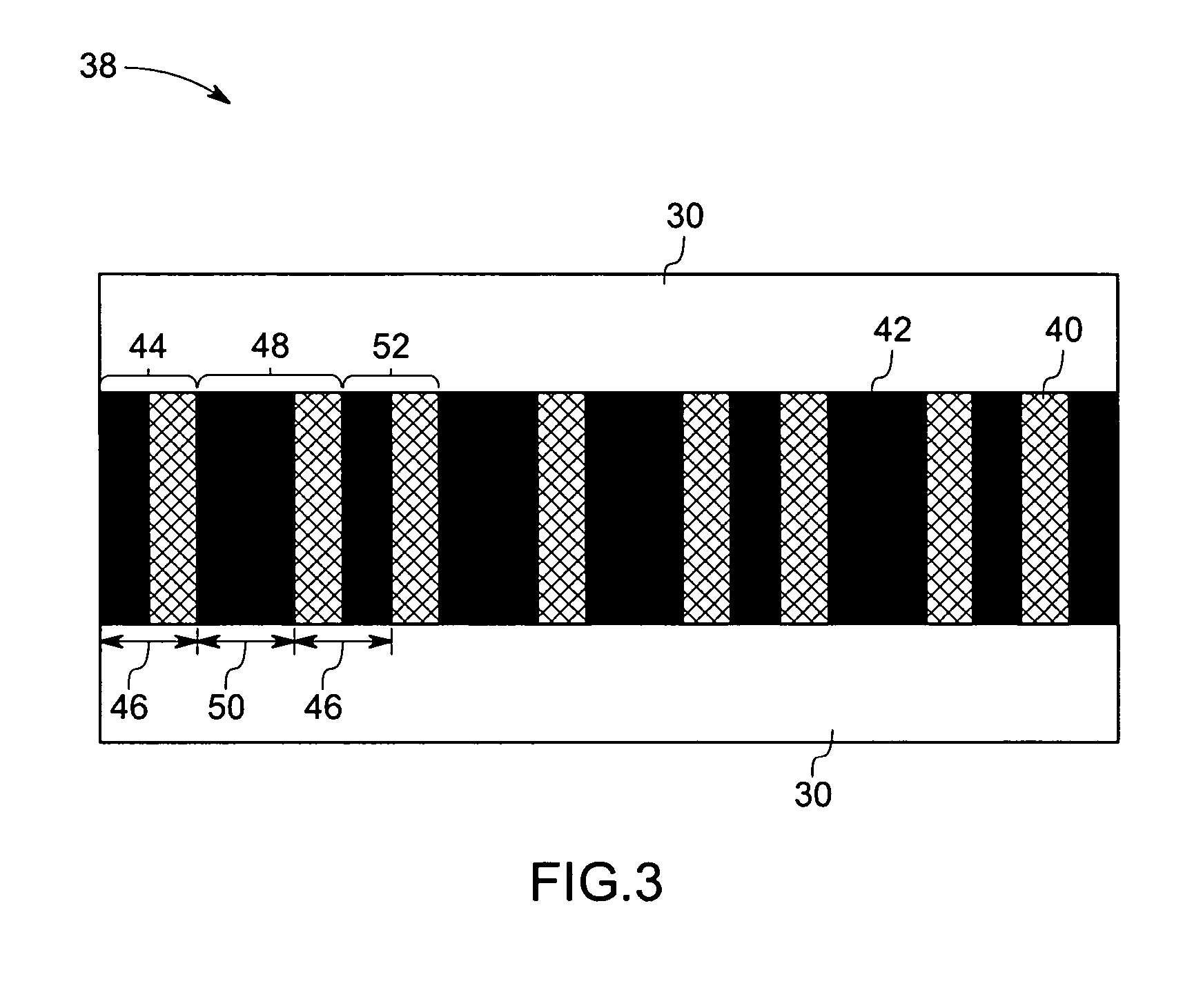
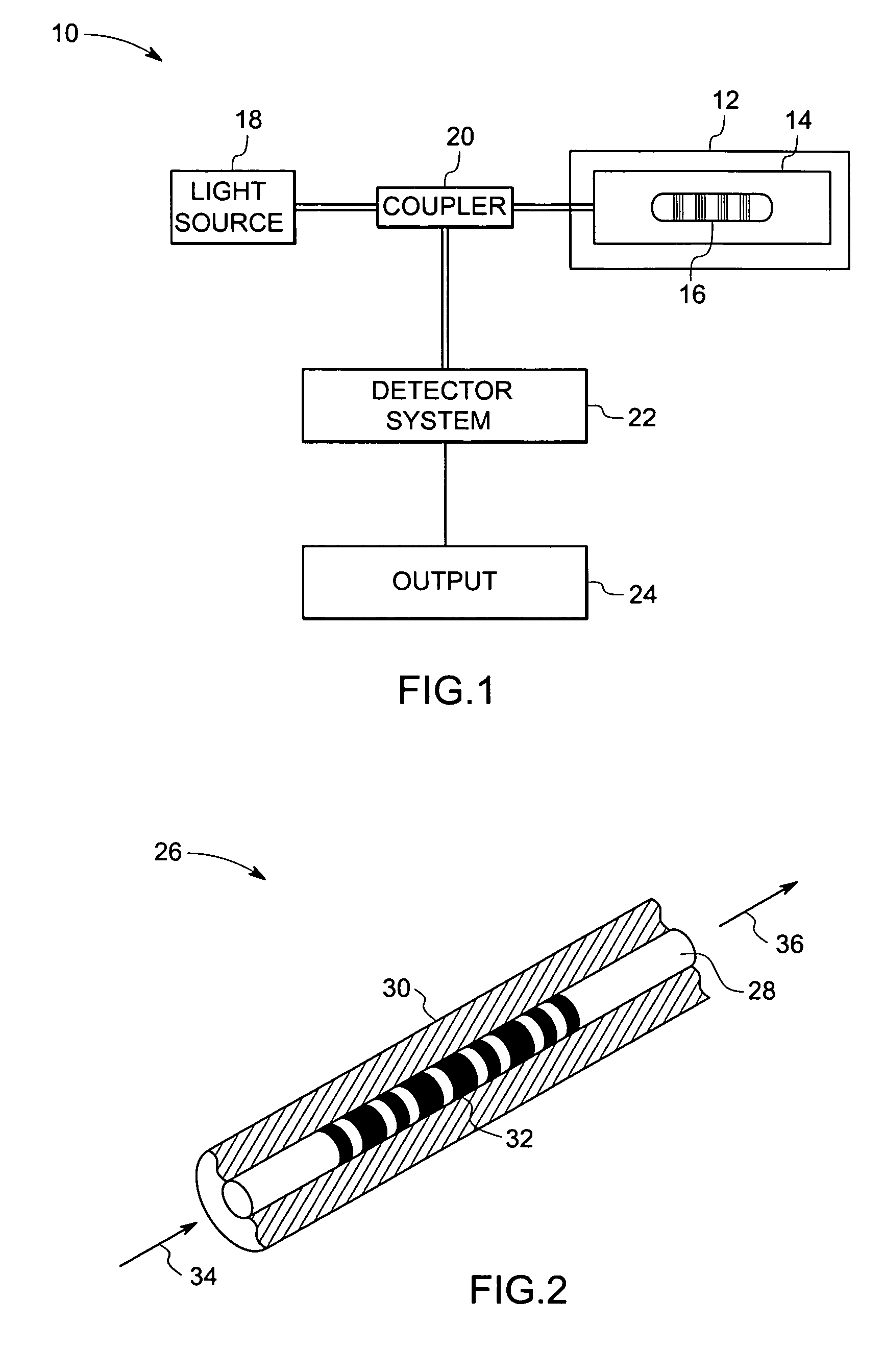
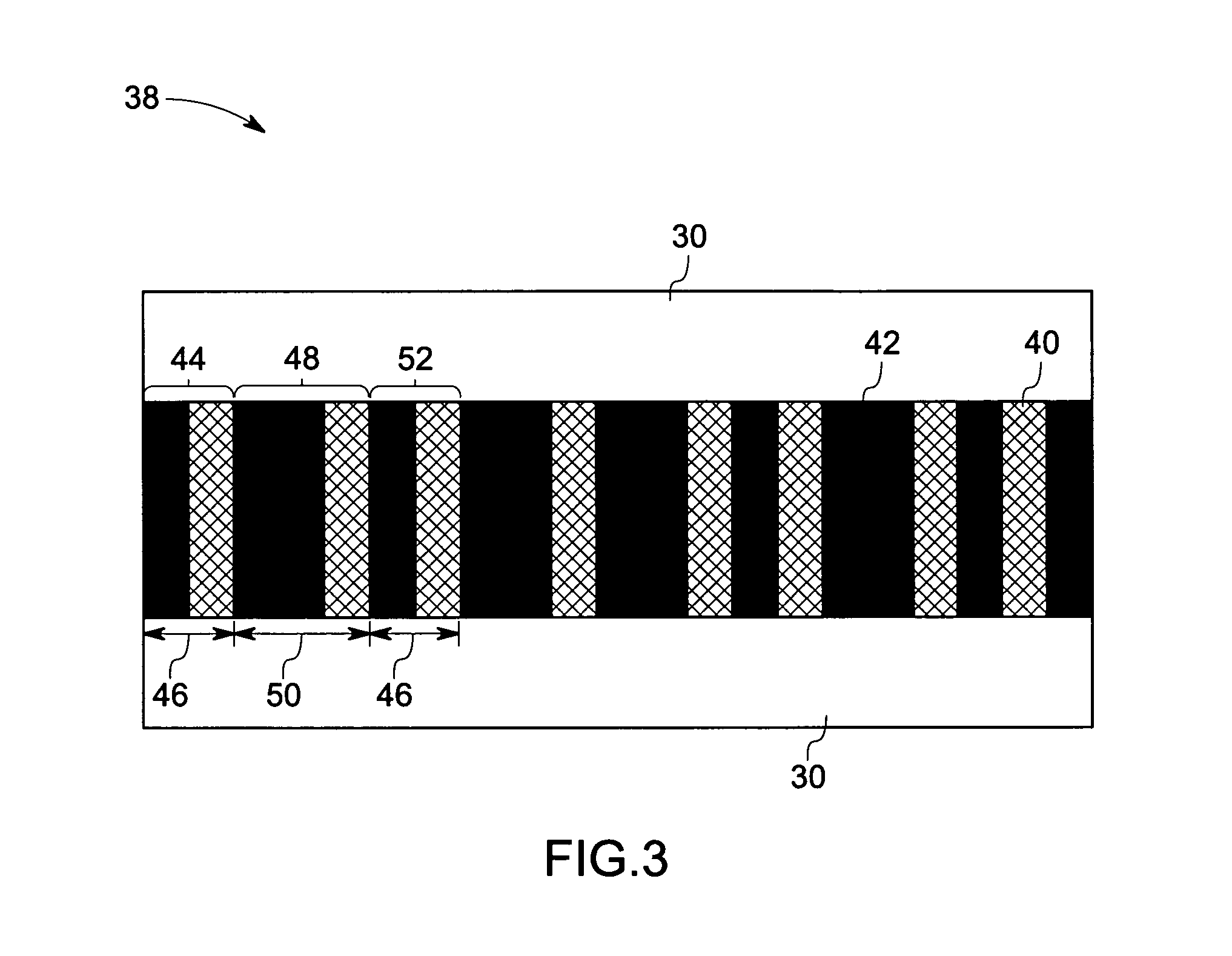
Fiber optic sensing device and method of making and operating the same
In accordance with one exemplary embodiment the invention provides a multi-parameter fiber optic sensing system with an aperiodic sapphire fiber grating as sensing element for simultaneous temperature, strain, NOx, CO, O2 and H2 gas detection. The exemplary sensing system includes an aperiodic fiber grating with an alternative refractive index modulation for such multi-function sensing and determination. Fabrication of such quasiperiodic grating structures can be made with point-by-point UV laser inscribing, diamond saw micromachining, and phase mask-based coating and chemical etching methods. In the exemplary embodiment, simultaneous detections on multi-parameter can be distributed, but not limited, in gas / steam turbine exhaust, in combustion and compressor, and in coal fired boilers etc. Advantageously, the mapping of multiple parameters such as temperature, strain, and gas using sapphire aperiodic gratings improves control and optimization of such systems directed to improve efficiency and output and reduce emissions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Optical authentication component and method of fabricating said component
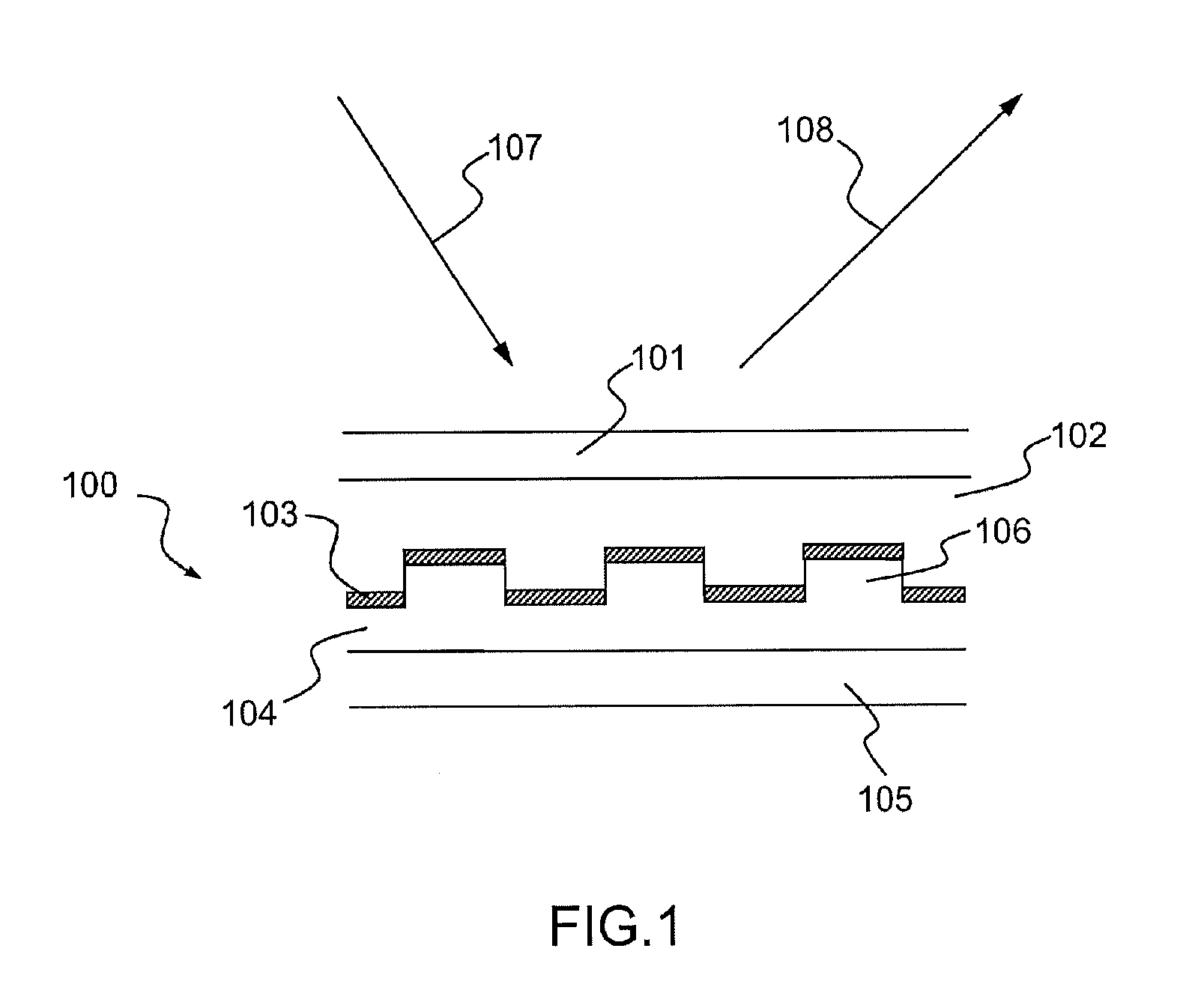
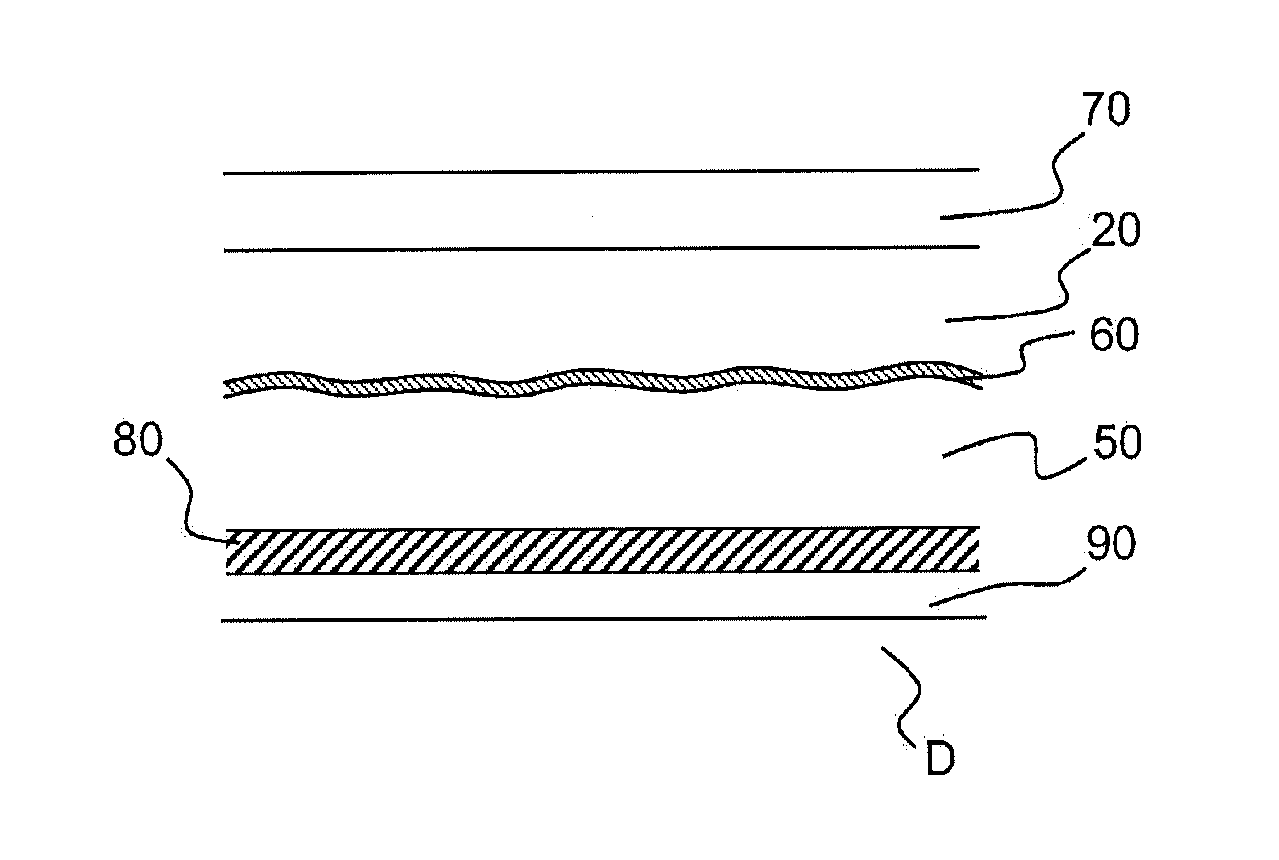
ActiveUS9134468B2Easy to recognizeEasily memorizeDiffraction gratingsInformation cardsRefractive indexThin layer
An optical authentication component visible in reflection having a structure imprinted on a substrate of index n0, a thin layer, made of a dielectric material having a refractive index n1, deposited on the structure, and a layer made of a material having an index n2 similar to n0, encapsulating the structure coated with the thin layer, is disclosed. The structure has a first pattern modulated by a second pattern, the first pattern is a bas-relief with an array of facets, having shapes which are defined to simulate an image in relief of an object in relief, and the second pattern is a periodic grating that modulates the first pattern which produces, after the thin layer has been deposited and the structure has been encapsulated, a first color at a first viewing angle and a different second color at a second viewing angle, obtained by azimuthal rotation of the component.
Owner:SURYS
Devices based on optical waveguides with adjustable bragg gratings
InactiveUS20050041922A1Time-division optical multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesWaveguideLight wave
A system for filtering light propagating in a waveguide is described. The system utilizes an adjustable periodic grating which induces mode coupling of predetermined frequencies of light propagating in the waveguide.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Devices based on optical waveguides with adjustable Bragg gratings
A system for filtering light propagating in a waveguide is described. The system utilizes an adjustable periodic grating which induces mode coupling of predetermined frequencies of light propagating in the waveguide.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Optical authentication component and method of fabricating said component
ActiveUS20130052373A1Easy to recognizeEasily memorizeOther printing matterLight effect designsRefractive indexMaterials science
An optical authentication component visible in reflection having a structure imprinted on a substrate of index n0, a thin layer, made of a dielectric material having a refractive index n1, deposited on the structure, and a layer made of a material having an index n2 similar to n0, encapsulating the structure coated with the thin layer, is disclosed. The structure has a first pattern modulated by a second pattern, the first pattern is a bas-relief with an array of facets, having shapes which are defined to simulate an image in relief of an object in relief, and the second pattern is a periodic grating that modulates the first pattern which produces, after the thin layer has been deposited and the structure has been encapsulated, a first color at a first viewing angle and a different second color at a second viewing angle, obtained by azimuthal rotation of the component.
Owner:SURYS
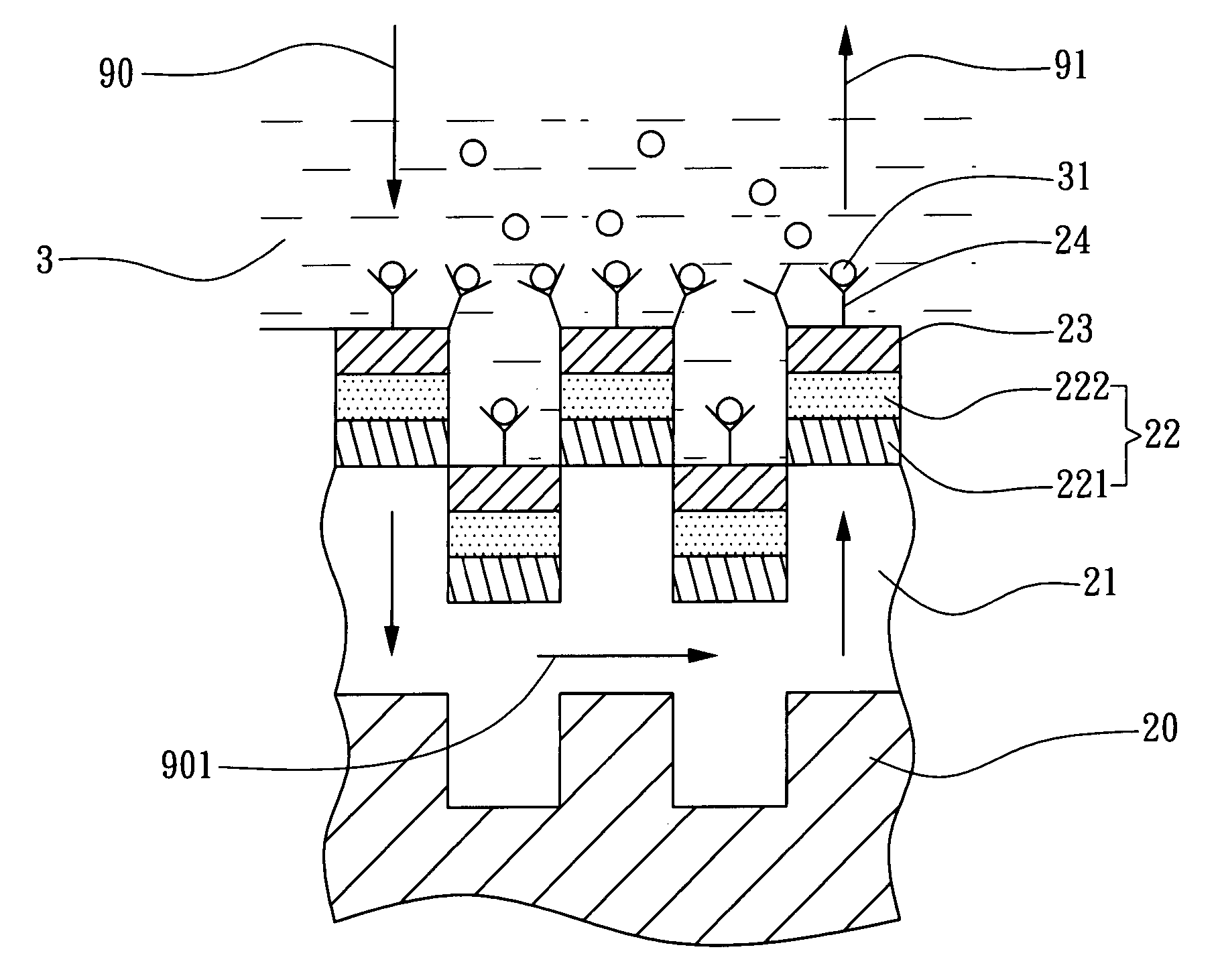
Coupled waveguide-surface plasmon resonance biosensor
ActiveUS20060238767A1High sensitivityHigh resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationResonanceRefractive index
The present invention discloses a coupled waveguide-surface plasmon resonance biosensor, comprising: a grating layer formed of a transparent material, the grating layer comprising a first periodic grating structure; a waveguide layer formed on the first periodic grating structure, the refractive index of the waveguide layer being larger than the refractive index of the grating layer; a plasmon resonance layer formed on the waveguide layer, capable of being optically excited to cause a plasmon resonance wave; and a ligand layer formed on the plasmon resonance layer; capable of being bound to react with receptors of a sample to be tested.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
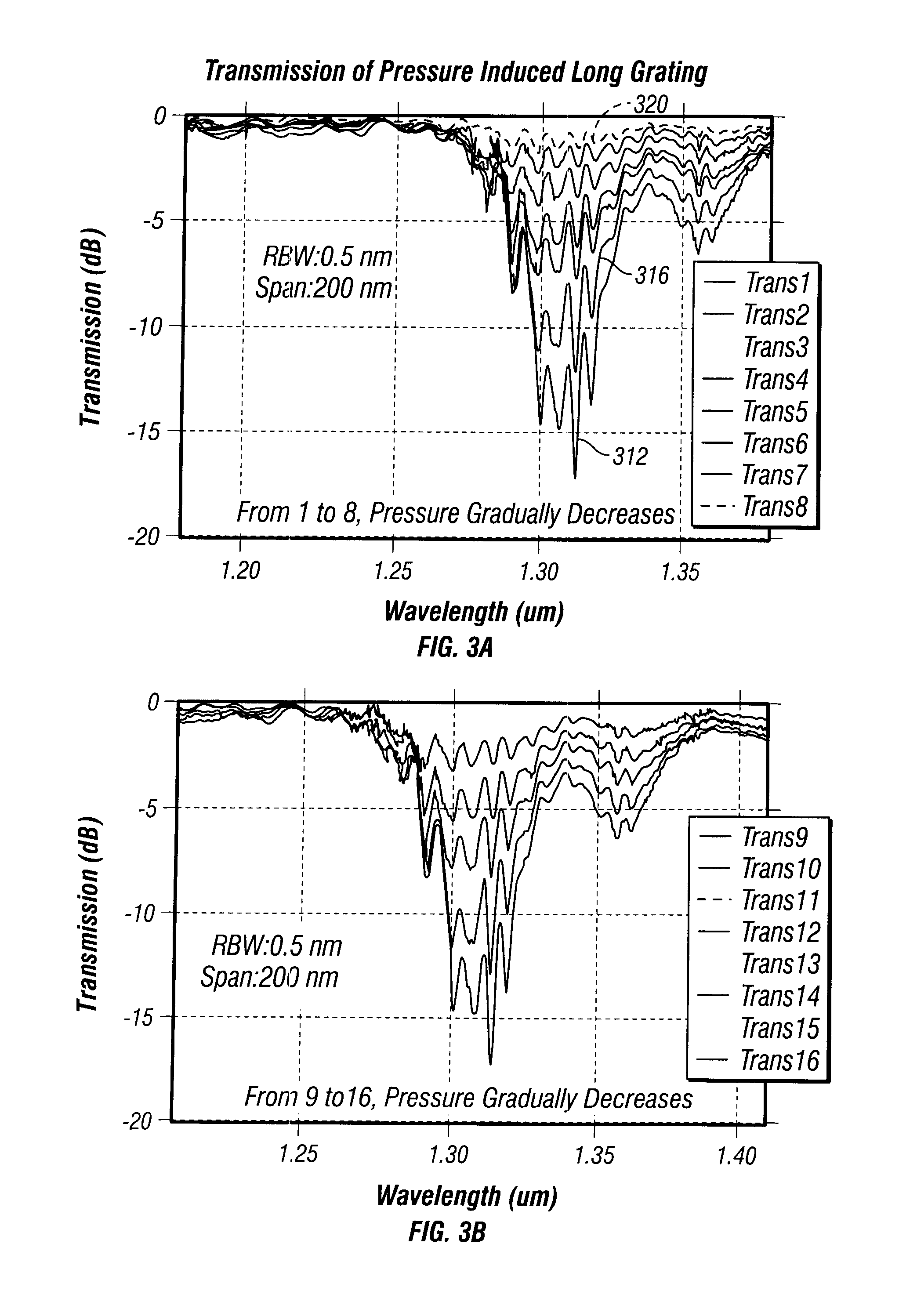
Damage assessment of a wafer using optical metrology
ActiveUS20070232045A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementNuclear monitoringEngineeringAssessment data
A method of assessing damage of a dual damascene structure includes obtaining a wafer after the wafer has been processed using a dual damascene process. A first damage-assessment procedure is performed on the wafer using an optical metrology process to gather damage-assessment data for a first set of measurements sites on the wafer. For each measurement site in the first set of measurement sites, the optical metrology process determines an amount of damage of a damaged area of a periodic grating in the measurement site. The damage-assessment data includes the amount of damage determined by the optical metrology process. A first damage-assessment map is created for the dual damascene process. The first damage-assessment includes the damage-assessment data and the locations of the first set of measurement sites on the wafer. One or more values in the damage-assessment map are compared to damage-assessment limits established for the dual damascene process to identify the wafer as a damaged or undamaged wafer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Graphene-based nanodevices for terahertz electronics
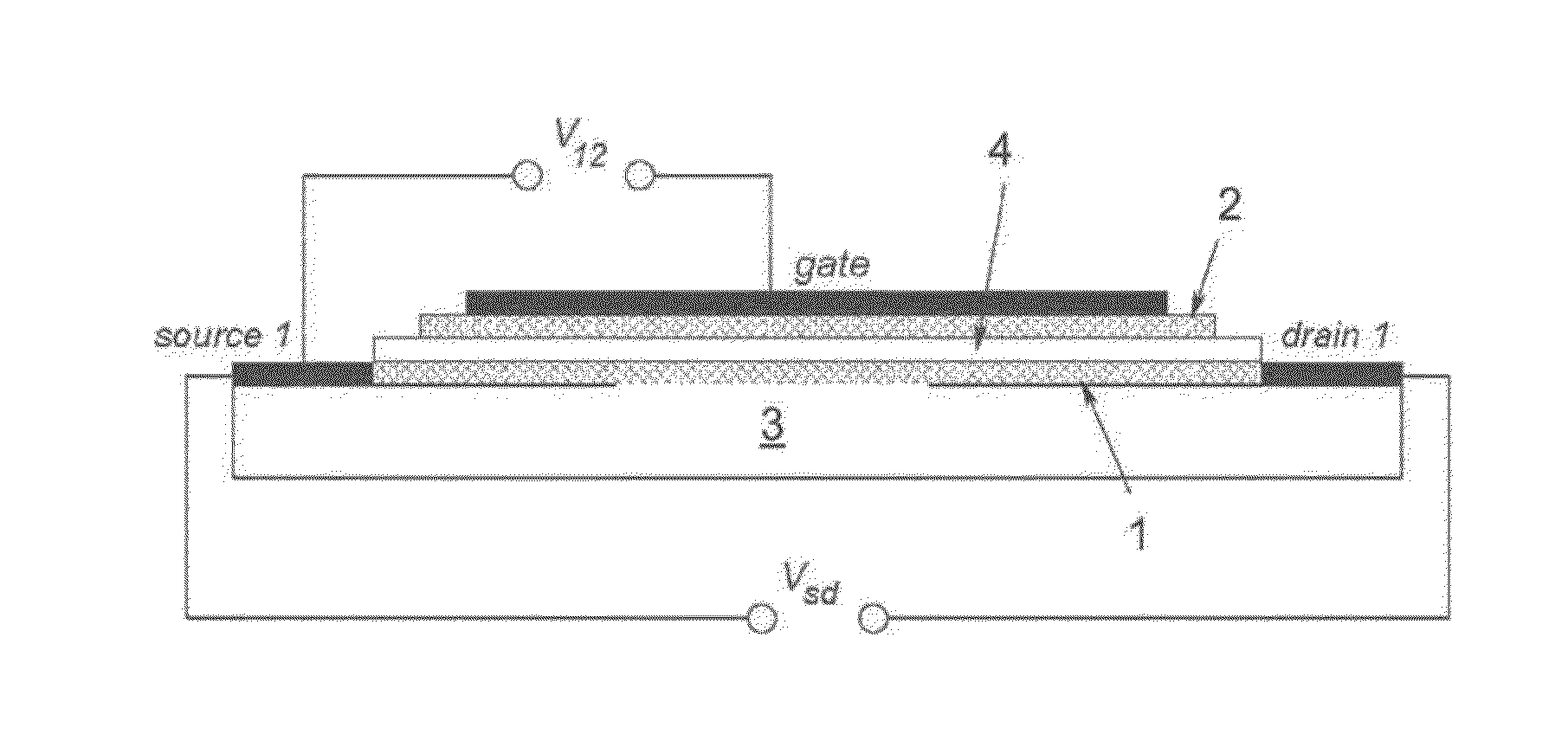
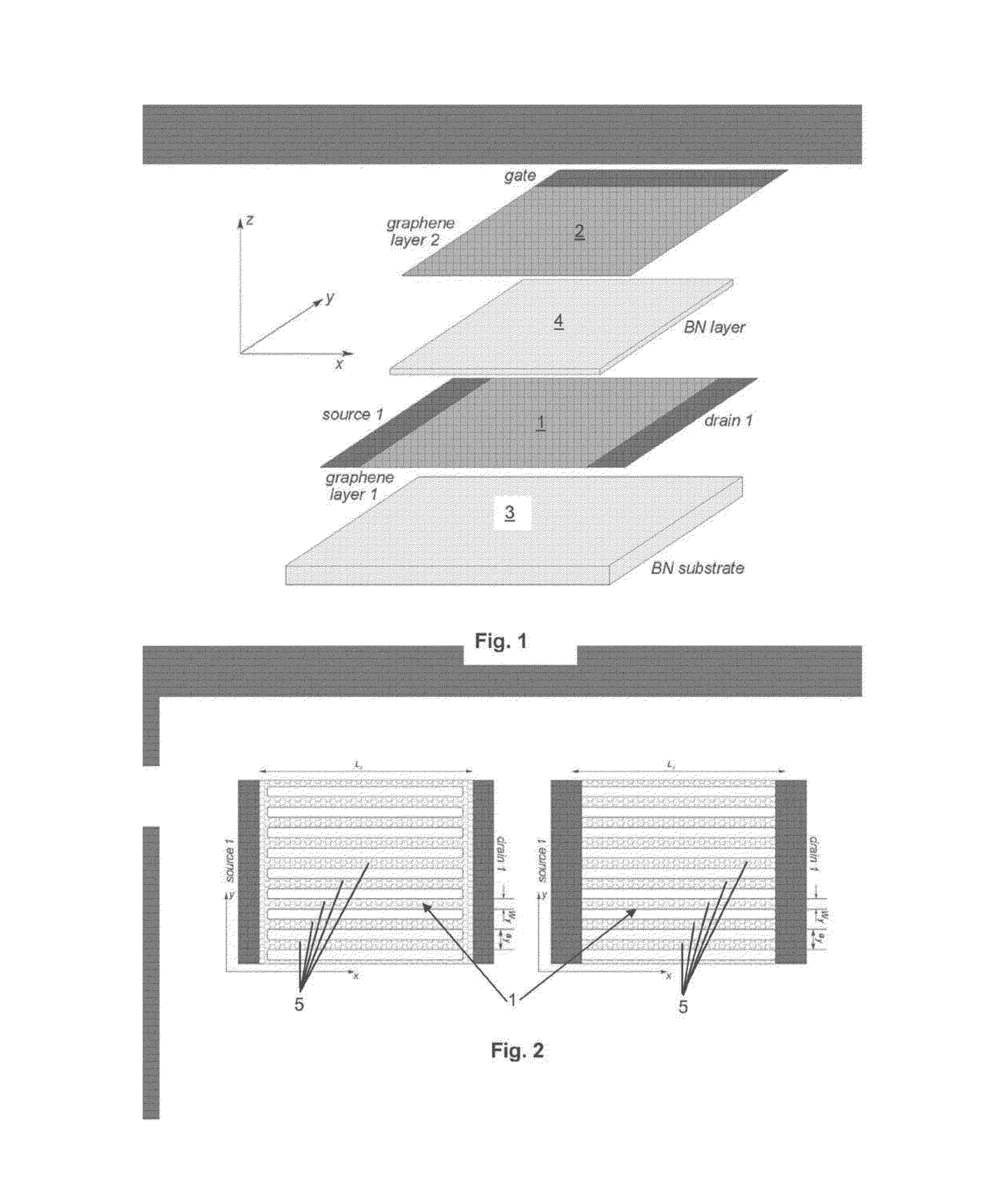
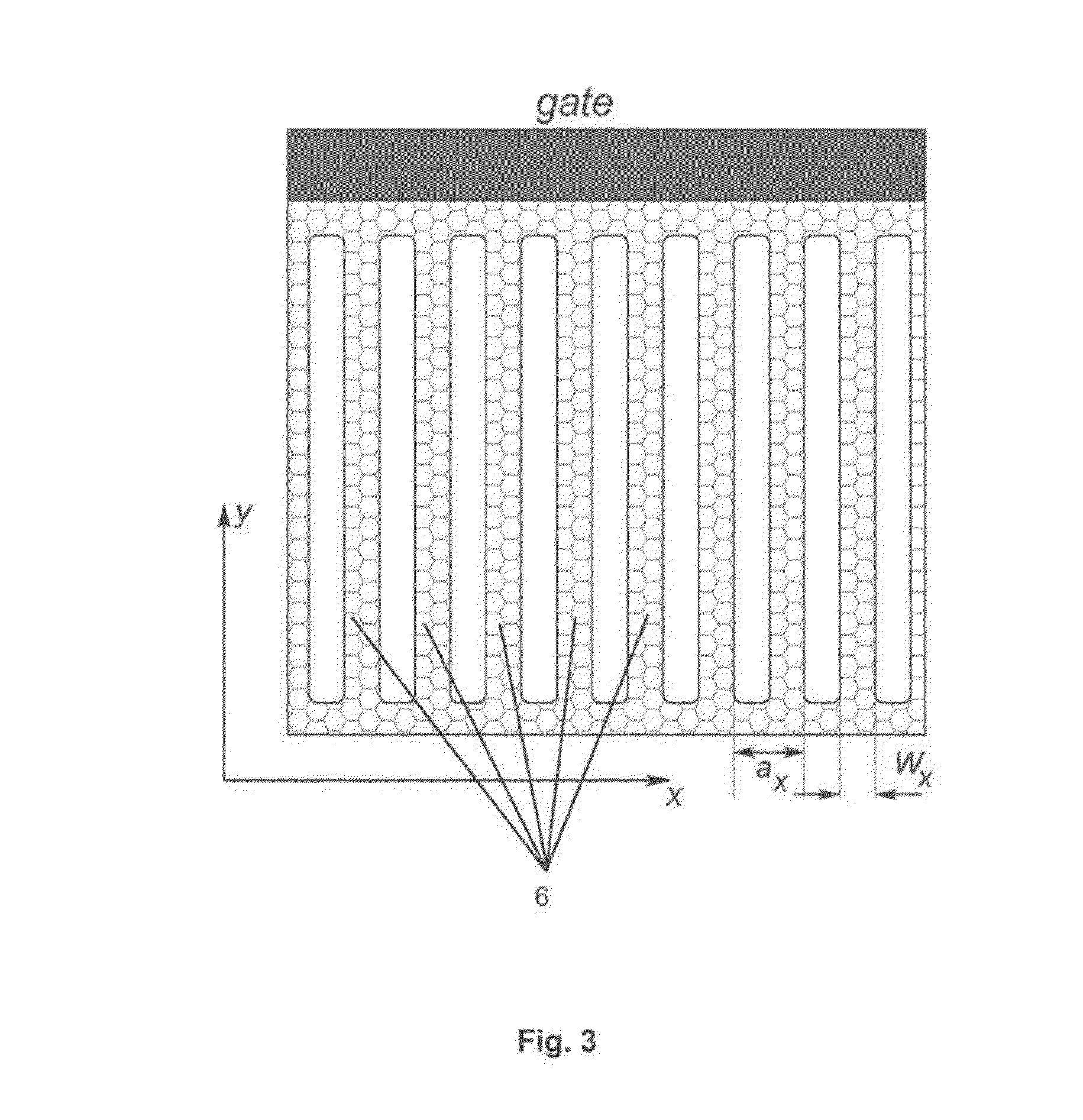
The invention refers to a nanodevice for generating electromagnetic radiation in the terahertz frequency range, the nanodevice comprising a substrate (3) made of a dielectric material, a first graphene layer (1) arranged on the substrate (3), having a first longitudinal end being electrically connected with a source contact (source 1) and having a second longitudinal end being connected with a drain contact (drain 1), an electrically conducting layer (2) having a periodic grating structure with grating stripes (6) extending substantially in transversal direction (y), and a dielectric layer (4) arranged between the first graphene layer (1) and the conducting layer (2).
Owner:UNIV AUGSBURG
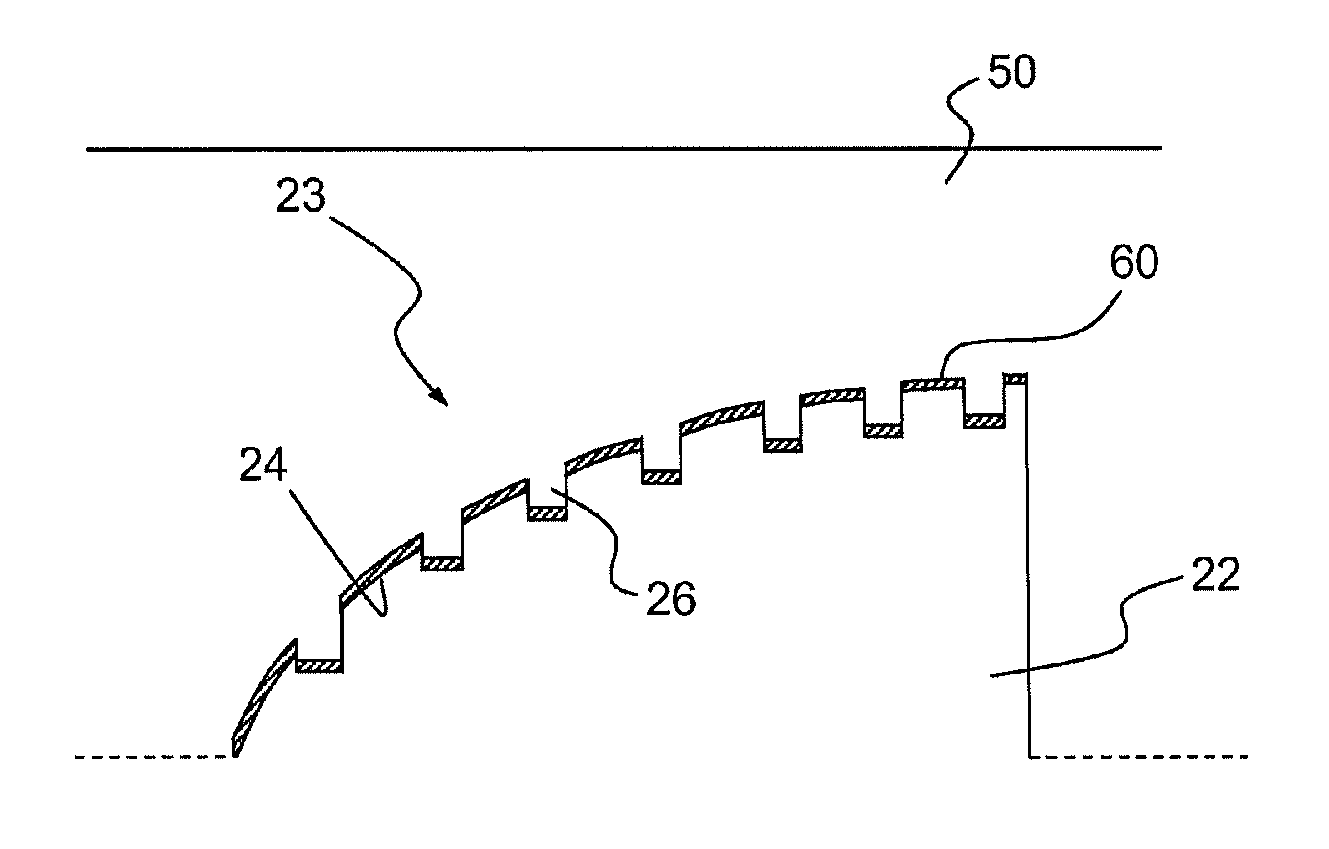
Optical position measuring device
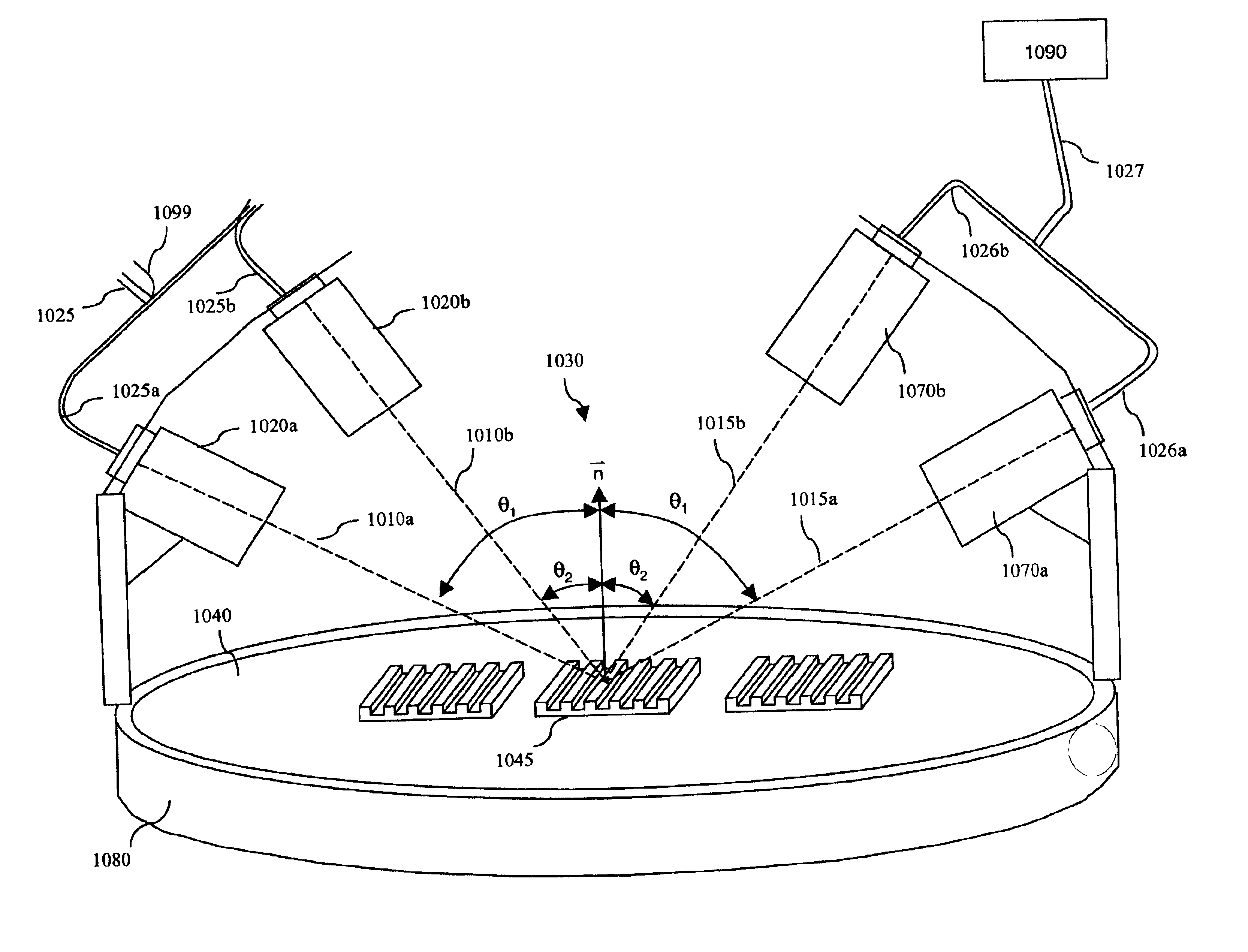
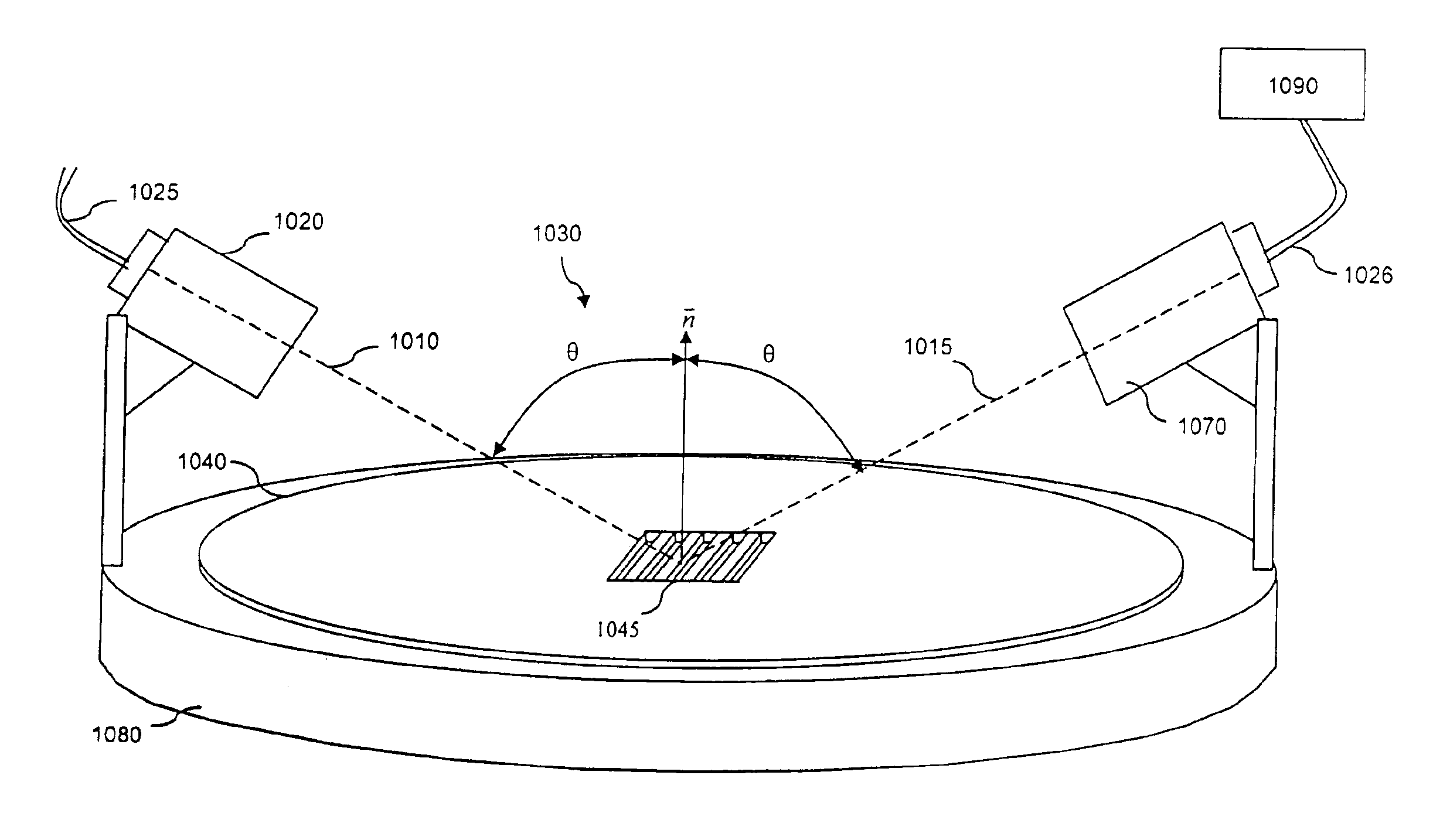
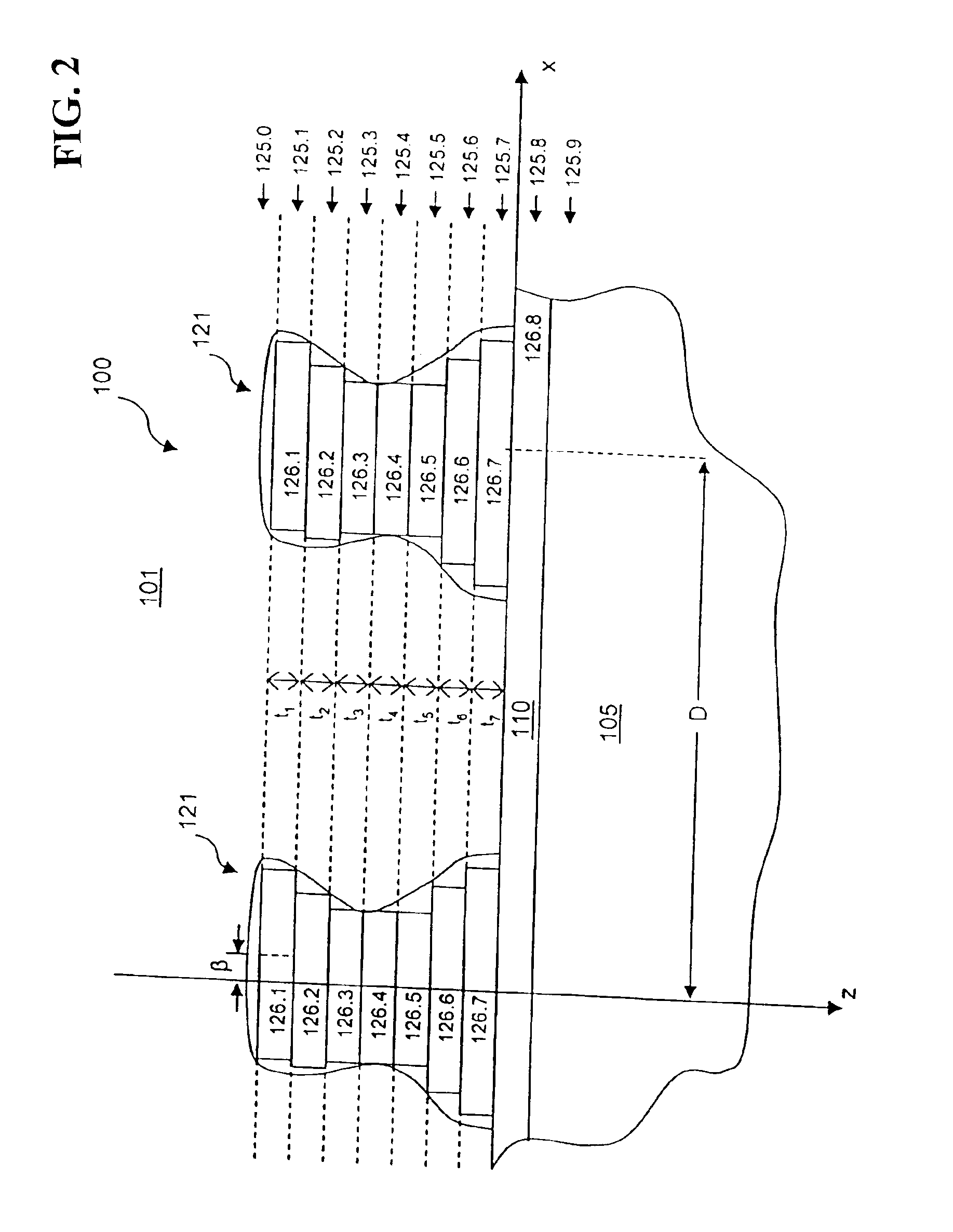
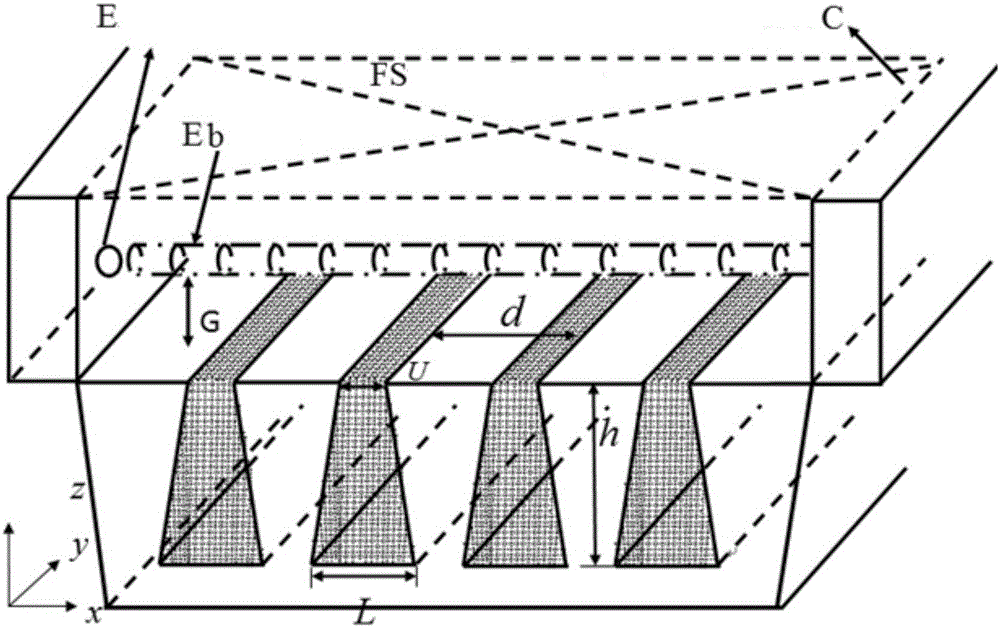
InactiveUS6963409B2Short focal lengthSmall structure sizeInvestigating moving sheetsUsing optical meansPhase shiftedMagnification
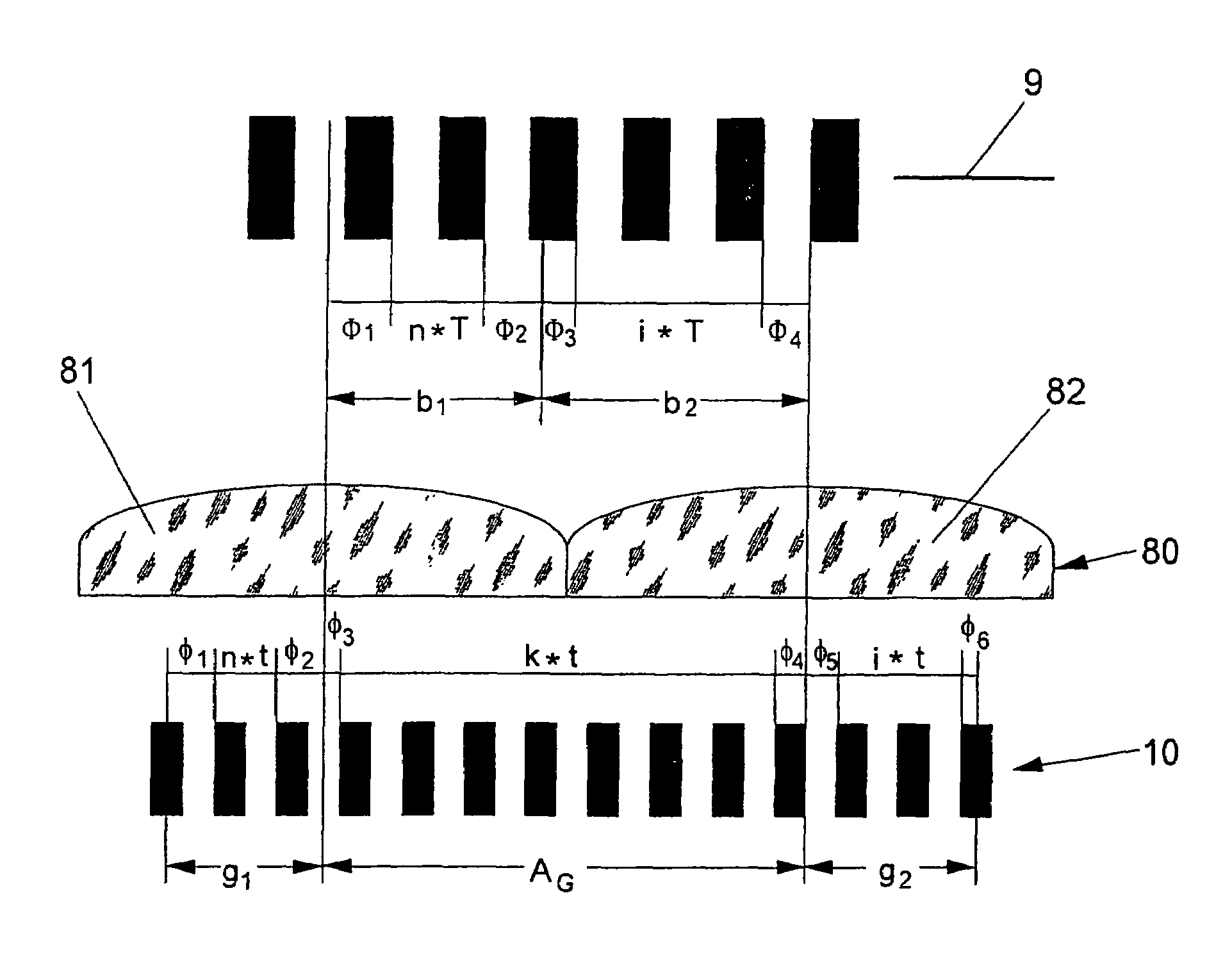
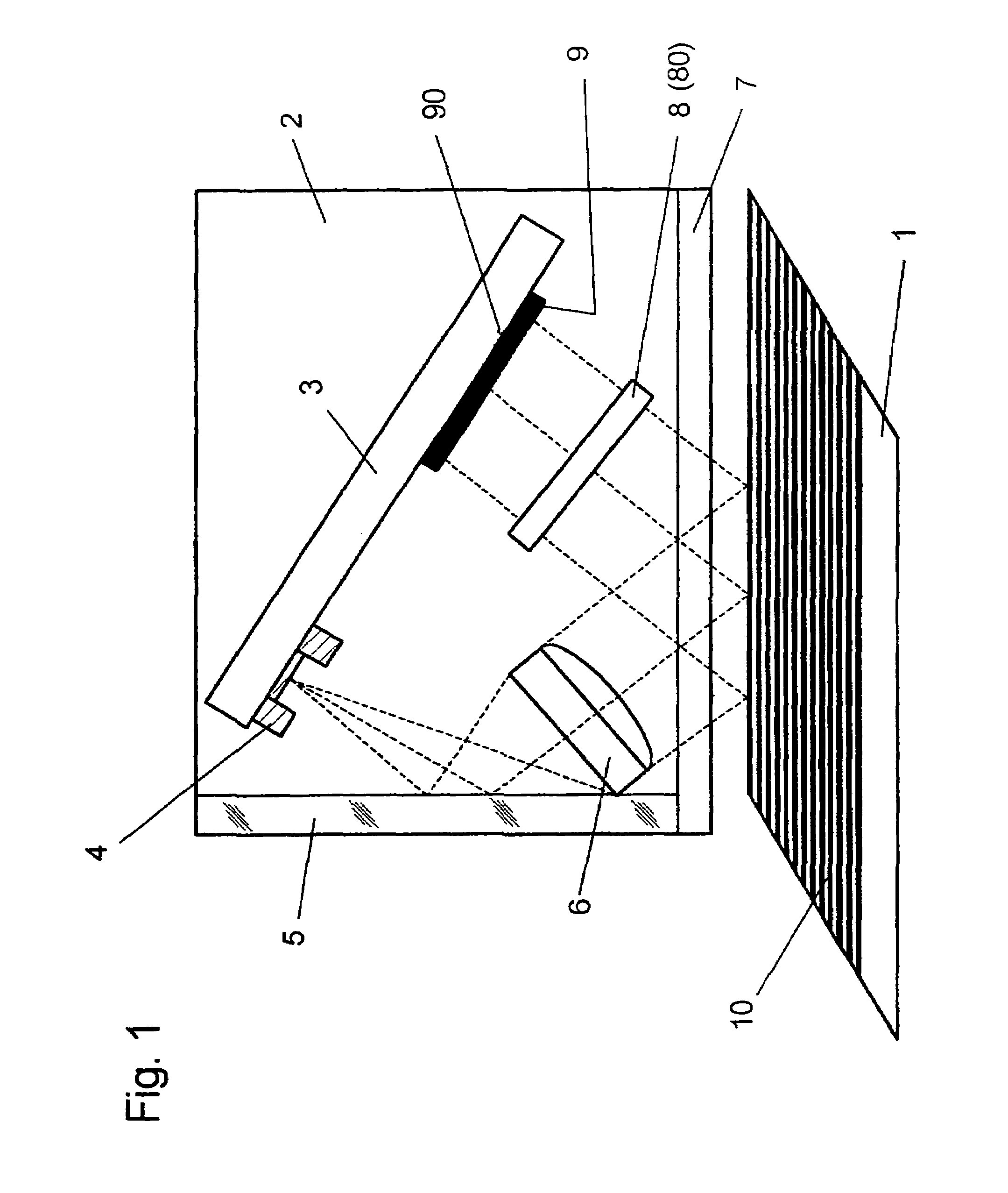
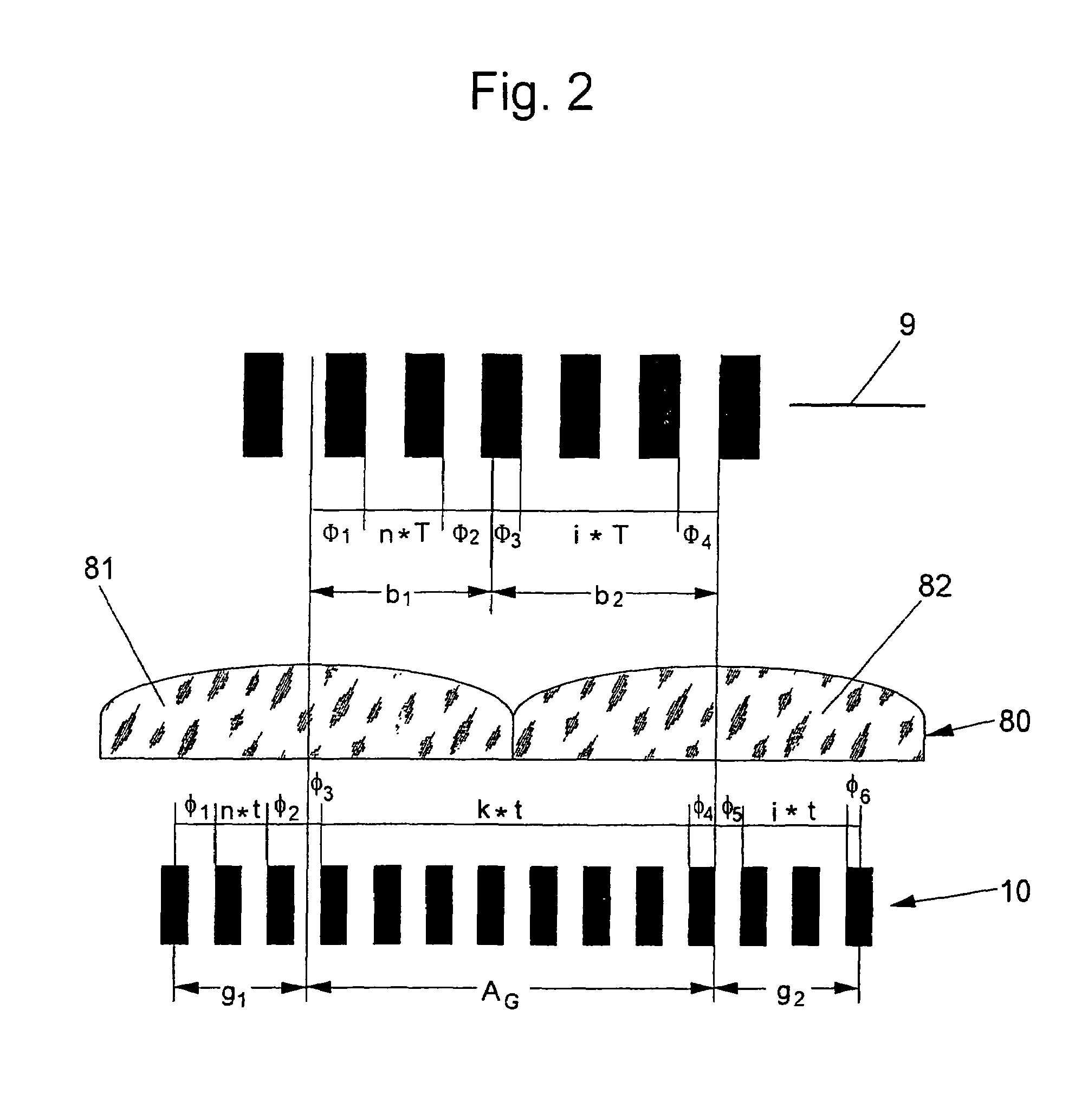
An optical position measuring system including a periodic grating structure and a scanning unit. The scanning unit includes a light source that directs light towards the periodic grating structure and an optical lens device that receives light from the periodic grating structure and creates an image of the periodic grating structure in an image plane, the optical lens device having a periodic lens array with a grating period, AG(r) or the mutual distance between adjoining lenses of said lens array defined by the equation: AG(r)=β(r)*[t(r)*[k+i+n]+ψ](β(r)+1)whereinAG(r) is the grating pert(r) the period of the periodic grating structure,|β(r)| the absolute amount of the image magnification factor β of the lens arrayΨ a presettable defined phase shiftr the radius of the grating arrangement, wherein inthe case of a linear grating r=∞ and AG,t and |β| are constants,i, k, n ε N, i.e. are natural numbers, including zero.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
Optical sensor based on surface electromagnetic wave resonance in photonic band gap materials
A sensing method and apparatus using photonic band gap multilayered material. Photonic band gap multi-layers are formed from alternating layers of higher refractive index and lower refractive index materials, and may be deposited or disposed on a optically transparent substrate or a reflecting face of a prism. Light is directed into the prism, directed to the photonic band gap multilayer, and reflected out of the prism, where it is captured and analyzed. Various sensor configurations keep light wavelength or coupling angle fixed, while monitoring the change in the other parameter. Also disclosed is a microarray configuration with an array of probe spots placed on one surface of the multilayer, which is mounted on an x-y translation stage. Also disclosed is a configuration where a cylindrical lens focuses an expanded and collimated light beam to a line that transects the rows of array elements sequentially, producing an image with shifted surface electromagnetic wave modes for each row, corresponding to individual elements of the array row. Further disclosed is a PBG multilayer with a periodic grating structure in or on the terminating layer.
Owner:ROBERTSON WILLIAM M
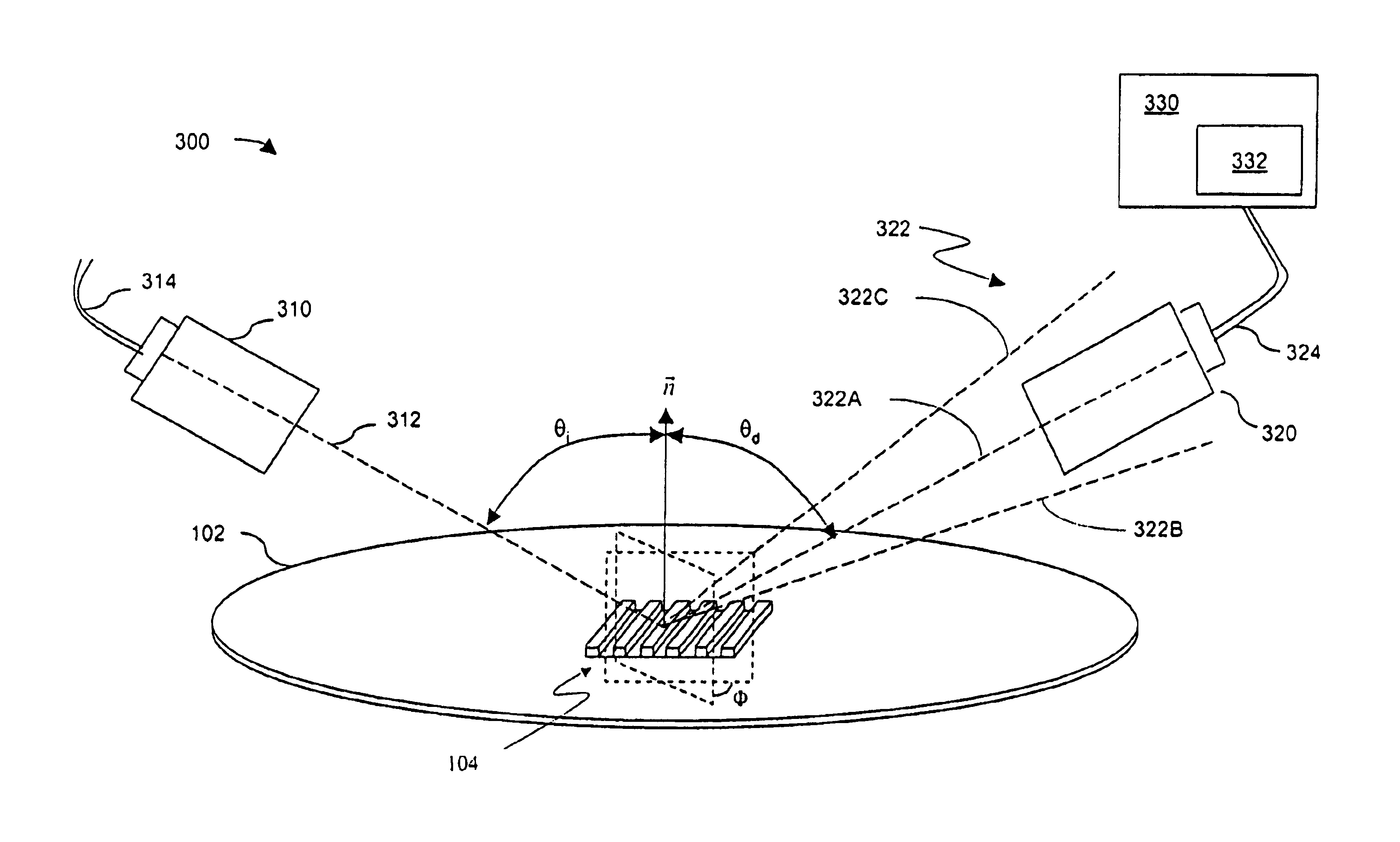
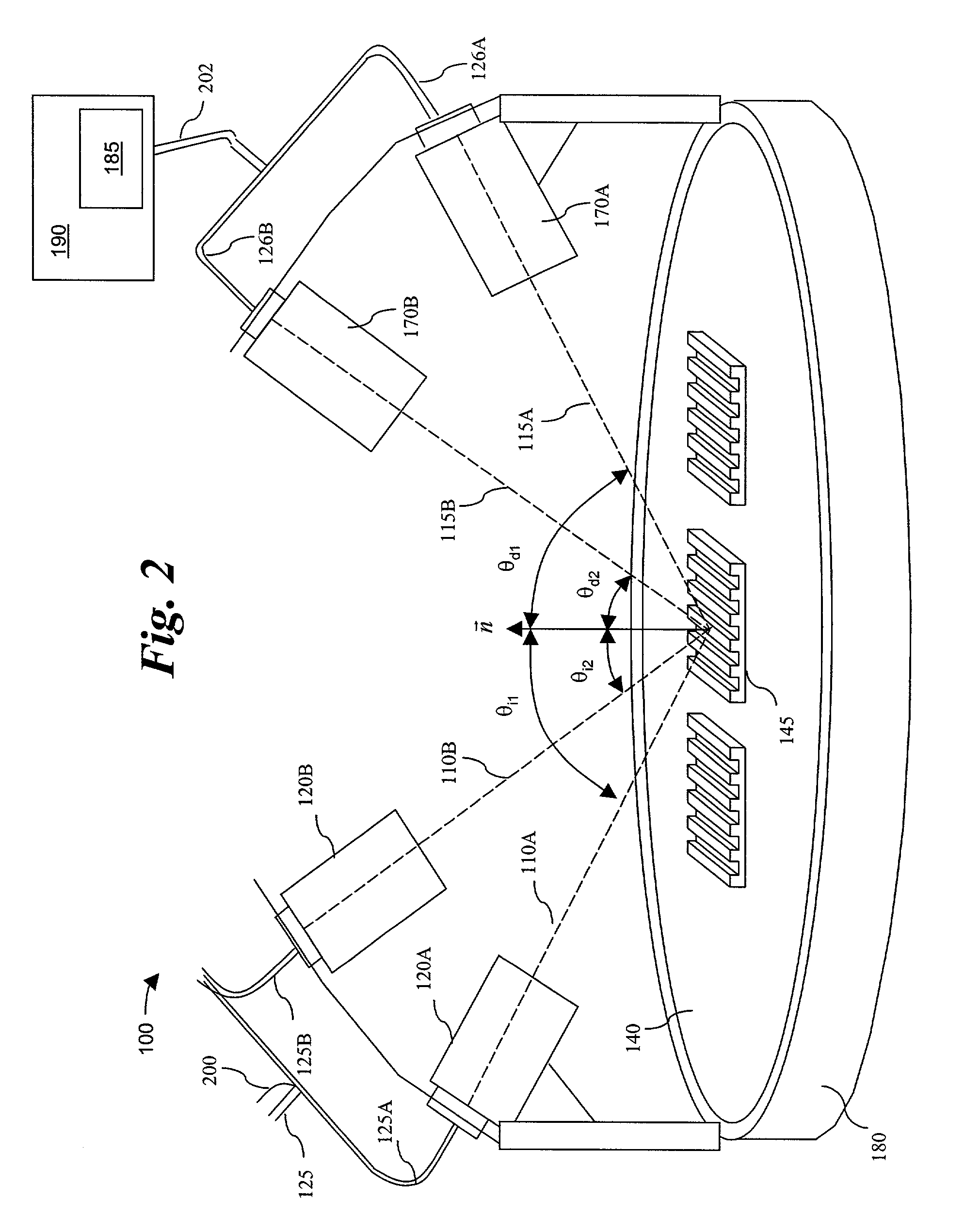
Alignment mark and its imaging optical system and imaging method
ActiveCN101149564ALarge capture rangeImprove alignment accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLight beamOptic system
This invention relates to a sort of alignment mark, and this alignment mark is the multiply periodic grating configuration. It consists of several group of the different periodic grating. This invention also offers a sort of imaging optical system of this alignment mark, and the alignment mark from the picture by this optical system, and it consists of this cohere imaging system at least. The first imaging system consists of frontal group lens, the first space wave filter, and the first back group lens. The second consists of the frontal group lens, the second space wave filter, and the second back group lens. This invention also offers a sort of the method which adopts this optical system to produce the picture to the alignment mark. This method consists of this approach: Offer and transfer the laser illuminating beam of light, and irradiate it to the alignment mark. Adopt the diffraction light and the reflex of the alignment mark. The diffraction light produces the picture by the first coheres imaging system and the second cohere imaging system of the optical system. This invention advances the detecting precision of the alignment mark availably.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Spectral synchronous phase-shift common-path interference microscopic-detection device and detection method
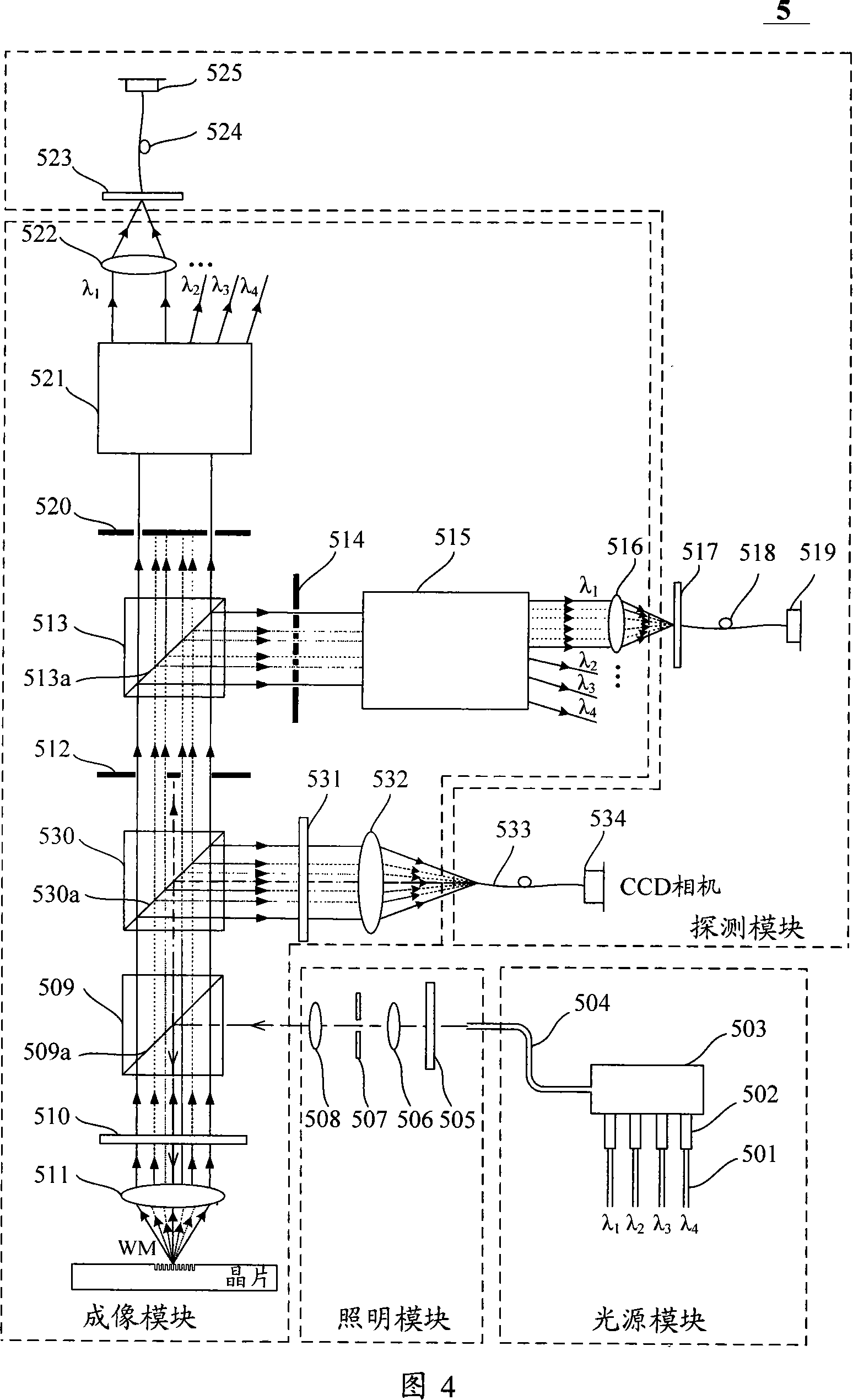
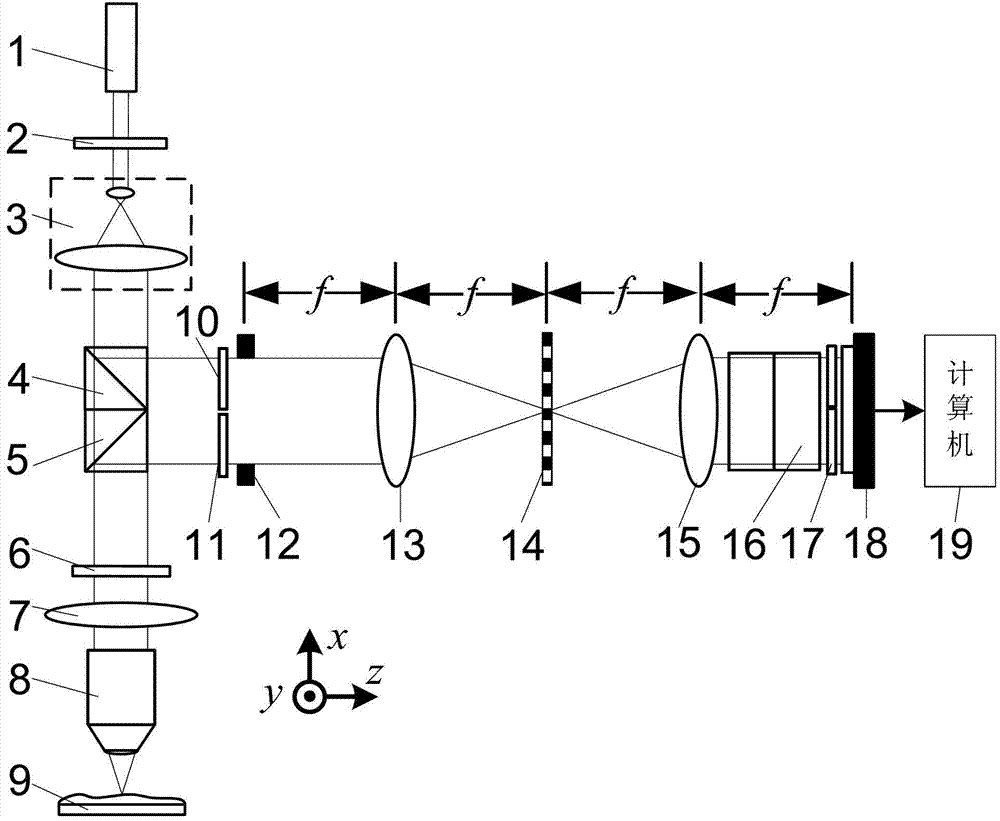
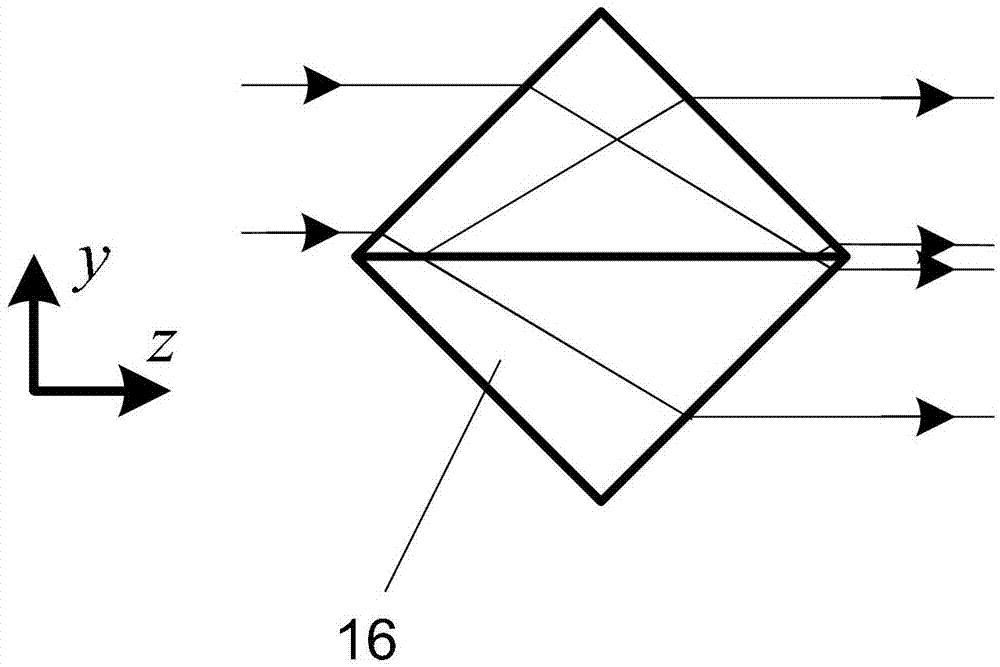
The invention discloses a spectral synchronous phase-shift common-path interference microscopic-detection device and a detection method, which belongs to the field of optical interference detection. The invention is designed for solving the problem that the existing optical phase-shift interference detection method is complicated and difficult in operation and low in measurement accuracy. The scheme of the invention is as follows: a beam emitted by a light source, after passing through a polaroid, enters into a light receiving surface of a beam collimating and expanding system, after the beam is subjected to beam collimating and expanding by the beam collimating and expanding system, an emergent beam enters into a first beam splitter prism, and then a reflected beam of the first beam splitter prism, as a reference beam, enters into a rectangular window after passing through a second lambda / 4 wave plate; the reference beam and object beams which are abreast converged into the rectangular window respectively pass through a first Fourier lens, a one-dimensional periodic grating, a second Fourier lens, a non-polarizing beam splitter prism and a four-quadrant polaroid set again, a polarized beam emitted from the four-quadrant polaroid set generates an interference pattern on a plane of an image sensor, and a computer carries out processing on the acquired interference pattern so as to obtain the phase distribution of an object to be detected.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Caching of intra-layer calculations for rapid rigorous coupled-wave analyses
InactiveUS6952271B2Reduce computing timeRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationData setRigorous coupled-wave analysis
A library of simulated-diffraction signals for an integrated circuit periodic grating is generated by generating sets of intermediate layer data. Each set of intermediate layer data corresponding to a separate one of a plurality of hypothetical layers of a hypothetical profile of the periodic grating. Each separate hypothetical layer has one of a plurality of possible combinations of hypothetical values of properties for that hypothetical layer. The generated sets of intermediate layer data are stored. Simulated-diffraction signals for each of a plurality of hypothetical profiles are generated based on the stored generated sets of intermediate layer data.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON US HOLDINGS INC
Fiber optic sensing device and method of making and operating the same
In accordance with one exemplary embodiment the invention provides a multi-parameter fiber optic sensing system with an aperiodic sapphire fiber grating as sensing element for simultaneous temperature, strain, NOx, CO, O2 and H2 gas detection. The exemplary sensing system includes an aperiodic fiber grating with an alternative refractive index modulation for such multi-function sensing and determination. Fabrication of such quasiperiodic grating structures can be made with point-by-point UV laser inscribing, diamond saw micromachining, and phase mask-based coating and chemical etching methods. In the exemplary embodiment, simultaneous detections on multi-parameter can be distributed, but not limited, in gas / steam turbine exhaust, in combustion and compressor, and in coal fired boilers etc. Advantageously, the mapping of multiple parameters such as temperature, strain, and gas using sapphire aperiodic gratings improves control and optimization of such systems directed to improve efficiency and output and reduce emissions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
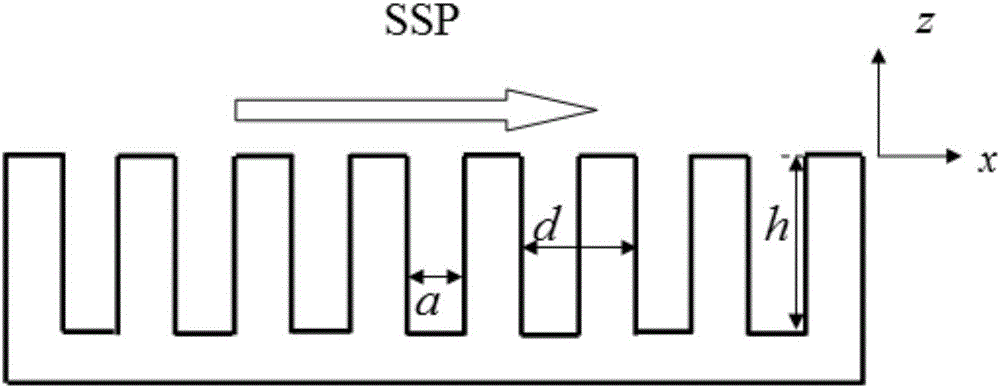
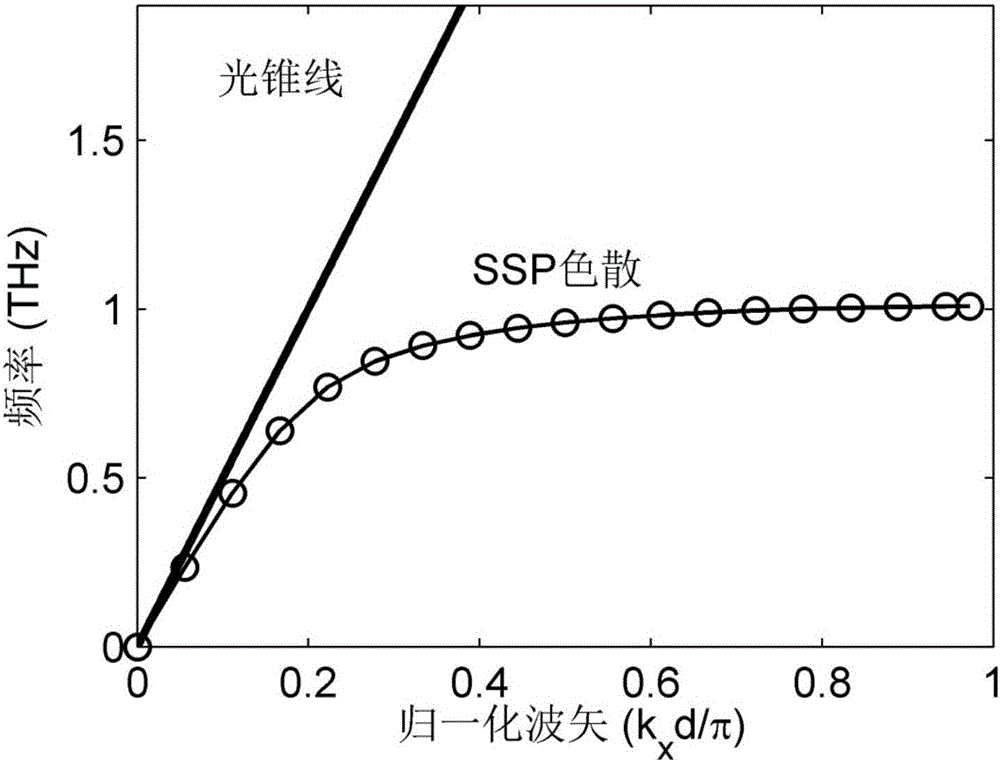
Mixed metal-dielectric SSP (Spoof Surface Plasmon) periodic grating system as well as application and method thereof
InactiveCN106054291AGood horizontal restraint abilityIncrease powerOptical light guidesHybrid typeDielectric surface
The invention discloses a mixed metal-dielectric SSP (Spoof Surface Plasmon) periodic grating system as well as application and a method thereof. By adopting a mixed metal-dielectric SSP periodic grating, the technical advantages of the existing SSP periodic metal waveguide can be adopted, and near-field propagation of terahertz wave can be limited more effectively by dielectric filling, so that the system has the characteristic of low loss; external electron beams excite surface plasmon polaritons on the mixed metal-dielectric SSP periodic grating, so that efficient spoof surface plasmon polaritons can be obtained under the condition that the SSP dispersion is matched with the dispersion of the external electron beams; moreover, a periodic metal-dielectric surface is formed by dielectric filling, so that the spoof surface plasmon polaritons can be limited more effectively relative to a pure metal periodic grating; meanwhile, an implementation diagram of the system principle of electron beam excited SSP is given, so that the defect of low-power excitation in the existing optical excitation mode can be overcome, and the system has the characteristics of high power and high efficiency.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Optical position measuring arrangement
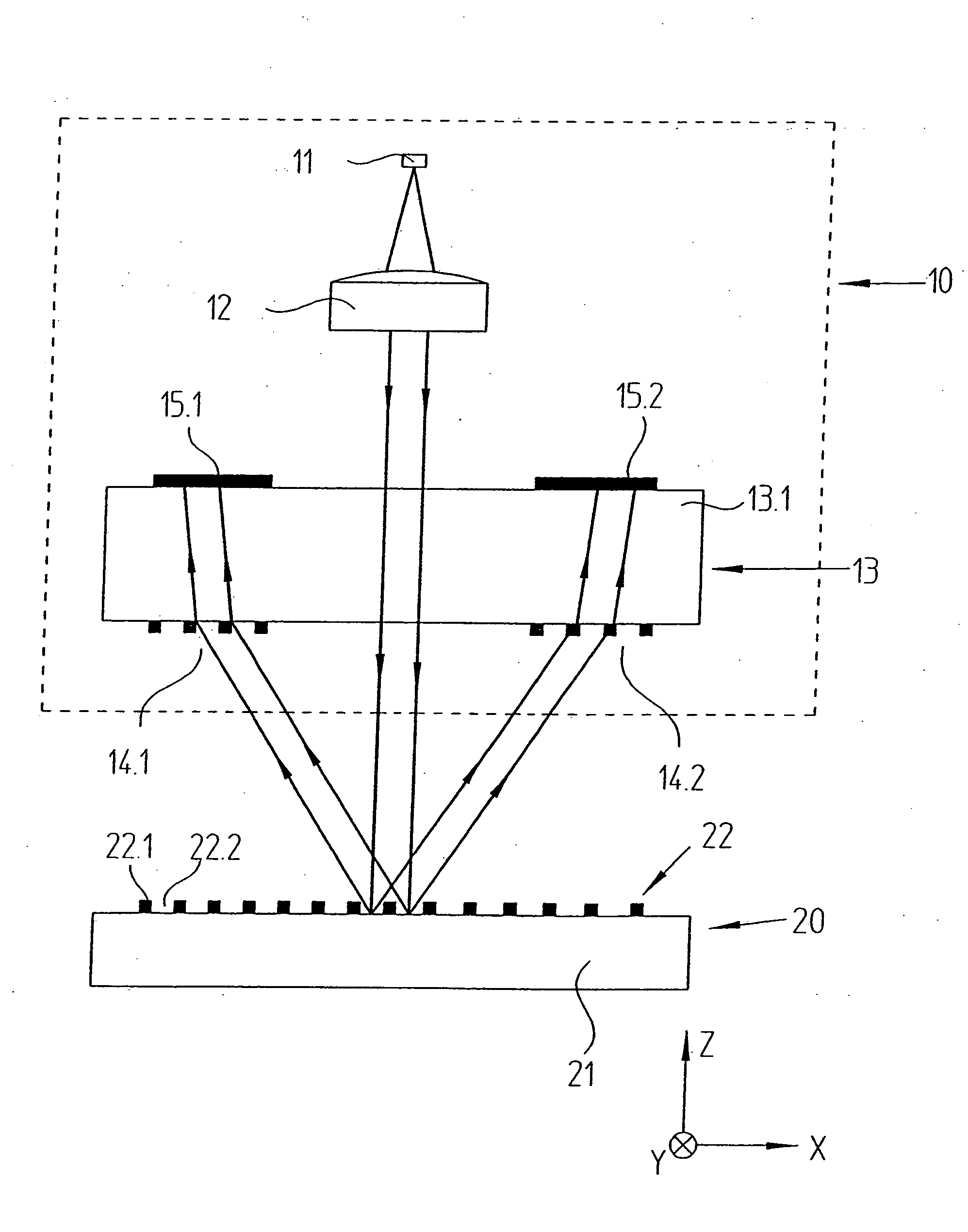
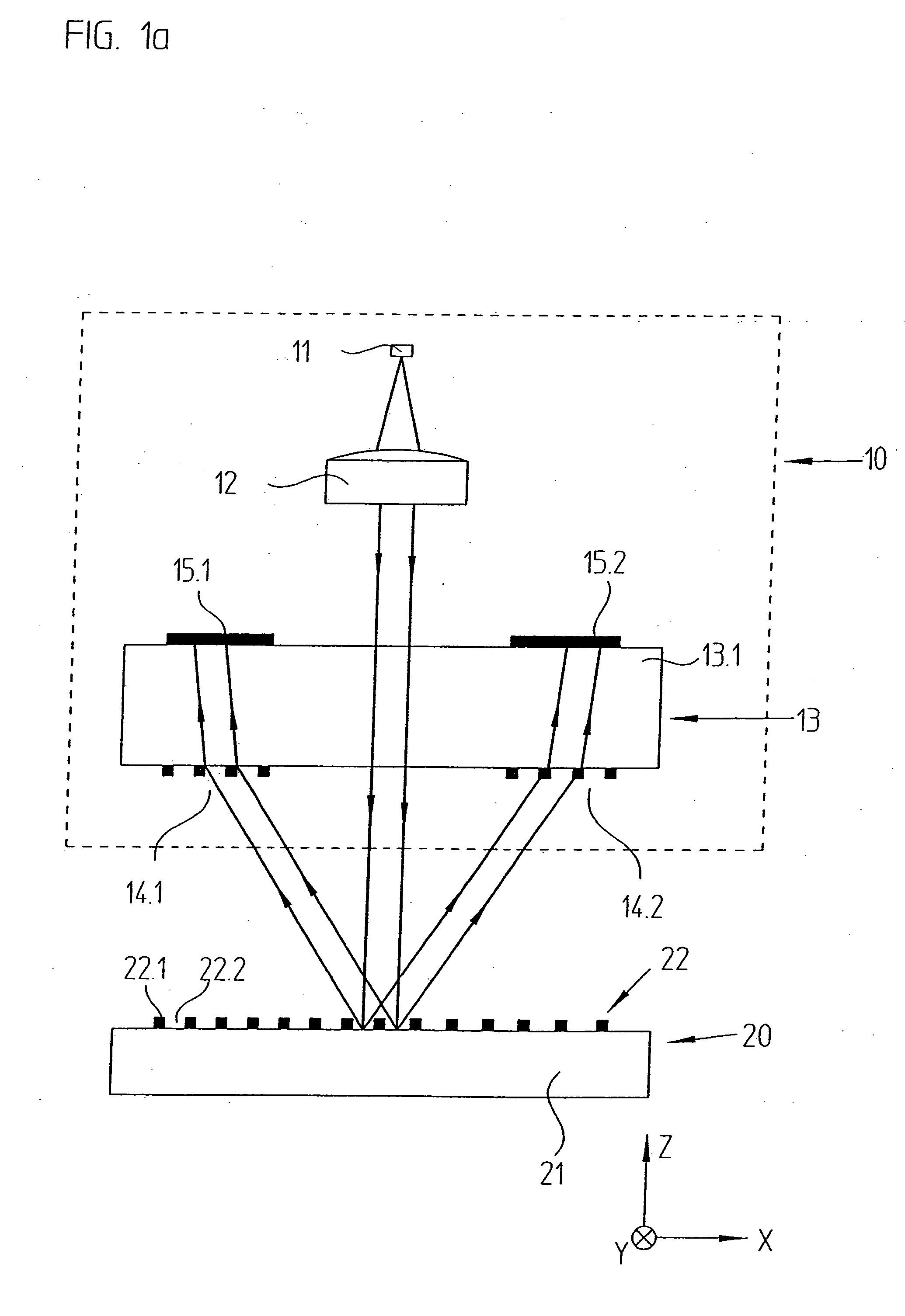
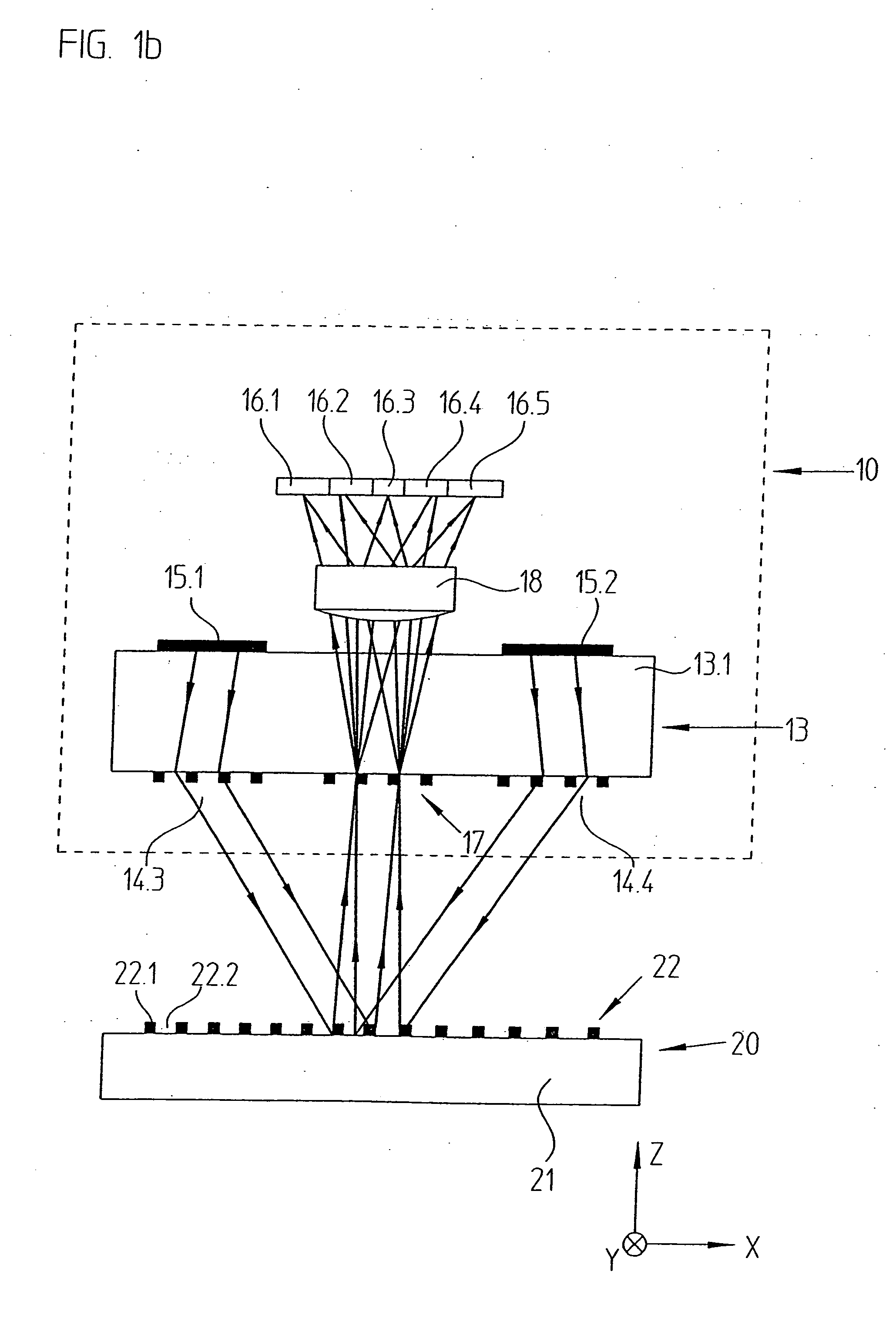
ActiveUS20090195792A1Improve efficiencyIncrease insensitivityUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyPhase shiftedLight beam
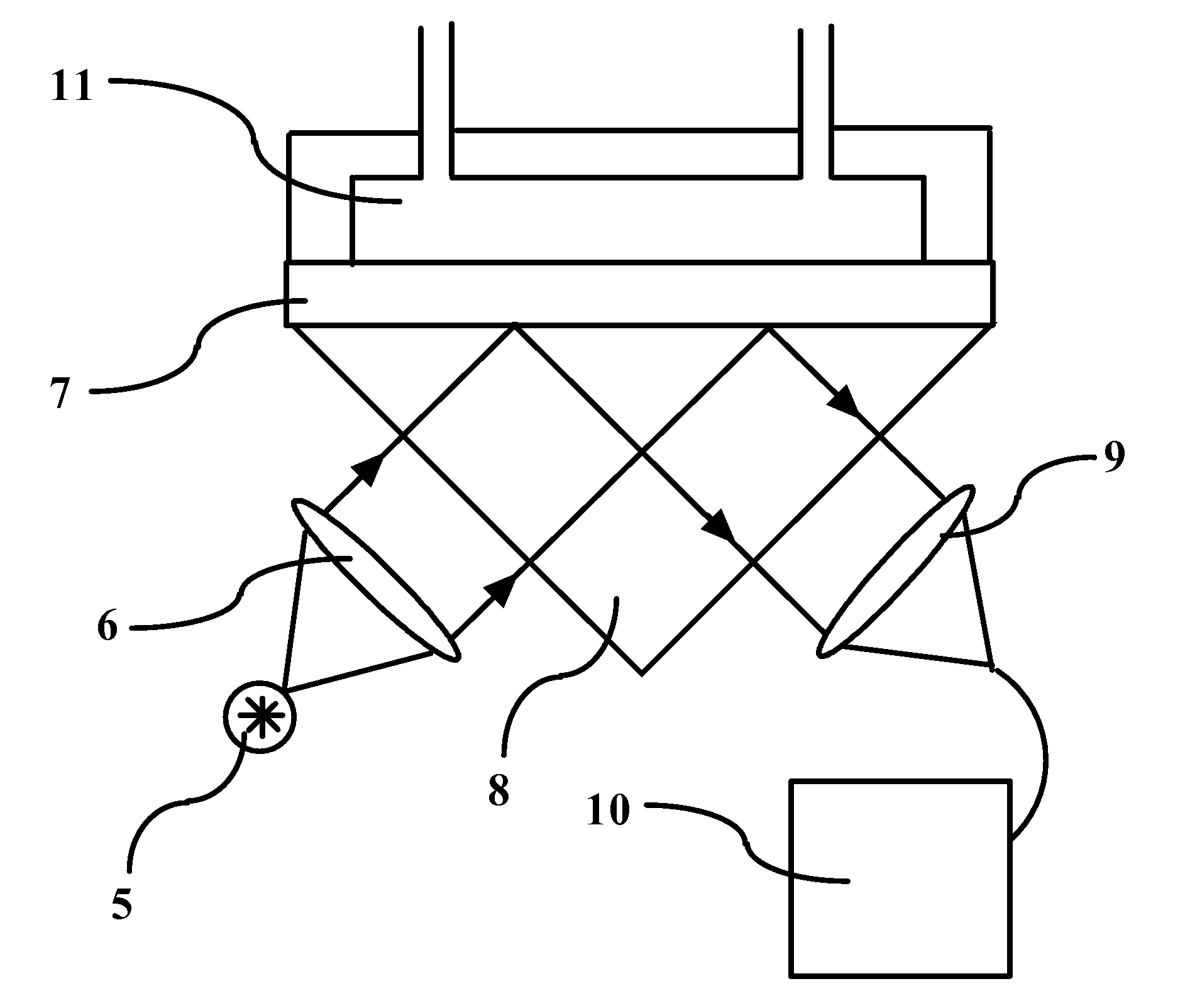
An optical position measuring arrangement for the generation of n>1 phase-shifted incremental signals characterizing relative positions of two objects which are movable with respect to each other along a measuring direction. The optical position measuring arrangement includes a light source that emits bundles of beams, a measurement grating, a plurality of optional gratings and a scanning unit. The scanning unit includes a scanning grating arranged in a scanning plane, wherein the scanning grating includes a plurality of blocks arranged periodically along the measuring direction with a scanning grating periodicity TPAG equaling a fringe pattern periodicity TPS, and each block includes n grating sections (n=1, 2, 3, . . . ) of a width bx=TPAG / n, exclusively arranged along the measuring direction, and each of the n grating sections has a periodic grating structure, which causes a deflection of the bundles of beams propagated through each of the n grating sections in several spatial directions, in which resulting spatial directions of the n grating sections in a block differ. The scanning unit further includes a plurality of detector elements arranged downstream of the scanning grating, wherein the detector elements are arranged in the spatial directions in the detector plane, and wherein the detector plane is located in an area in which the bundles of beams coming from the scanning grating are completely spatially separated. The fringe pattern having a periodicity TPS is formed in the scanning plane by an interaction of the bundles of beams emitted by the light source with the measurement grating and the further optional gratings.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
Optical pickup and optical information recording apparatus using the same
ActiveUS7327661B2Improved versatility and reliabilityRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupPush pull
An optical pickup includes a diffraction grating partitioned into three areas, in which the phase of periodic grating groove structure in an area is successively shifted from that in the adjacent area by 90°. In the generation of a differential push-pull signal, an amplification factor K for sub push-pull signals is varied depending on the type of the optical disk. By such composition of the optical pickup, amplitude deterioration of the tracking error signal accompanying displacement of the object lens is reduced.
Owner:HITACHI MEDIA ELECTORONICS CO LTD +1
Fabrication method for integrated semiconductor laser
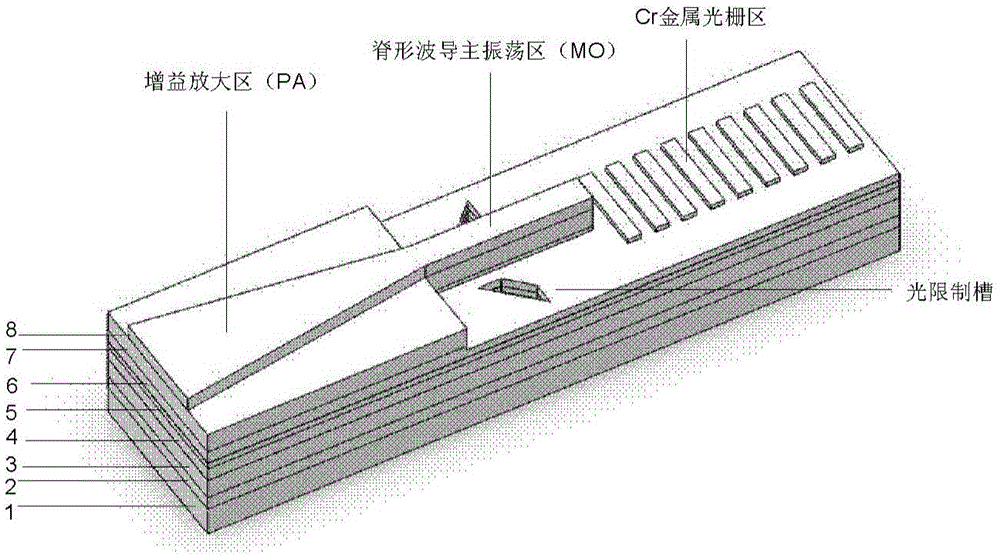
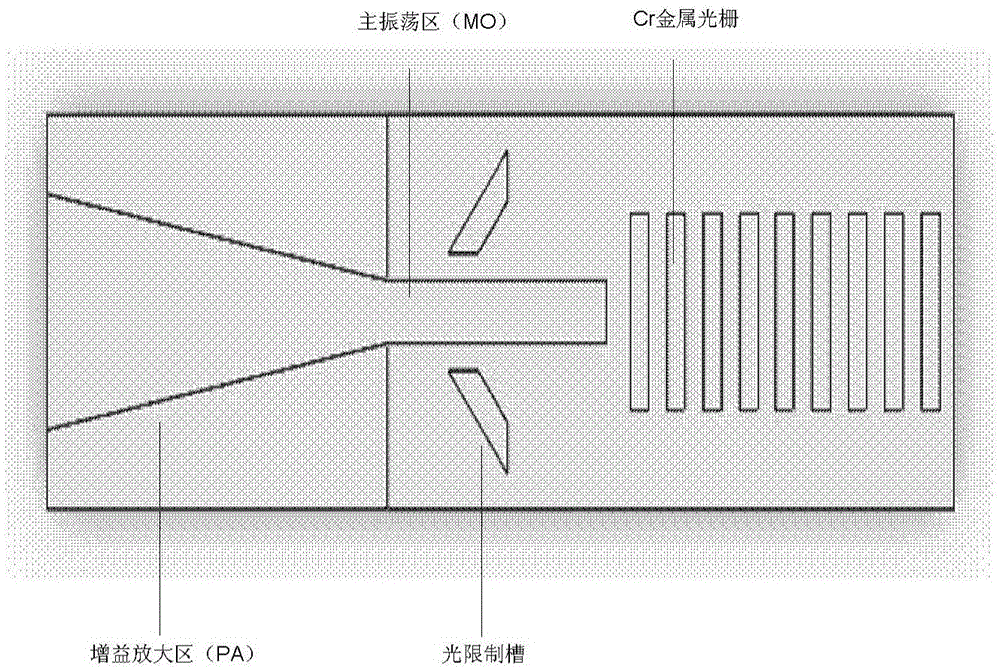
InactiveCN105098595AStable working modeAvoid oscillatory feedbackOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsIsosceles trapezoidRidge waveguides
The invention discloses an integrated semiconductor laser of a 2-micrometer single-mode high-power GaSb-based metal grating master oscillator power amplifier and a fabrication method of the integrated semiconductor laser. The semiconductor laser comprises a substrate, an epitaxial structure, a gain amplification region, a master oscillator region, a metal grating region and light limitation grooves, wherein the epitaxial structure is grown on the substrate and comprises an N-type lower contact layer, an N-type lower limitation layer, a lower waveguide layer, an active region, an upper waveguide layer, a P-type upper limitation layer and a P-type upper contact layer from bottom to top, the gain amplification region is arranged at the front part, namely an emergent light part of the semiconductor laser and is of an isosceles trapezoid structure formed by downwards etching the P-type upper contact layer, the master oscillator region is arranged at the rear part of the gain amplification region and is of a ridged waveguide structure formed by downwards etching the P-type upper contact layer and the P-type upper limitation layer, the metal grating region is arranged at the rear part of the master oscillator region and is of a periodic grating structure formed on the surface of the upper waveguide layer, the light limitation grooves are symmetrically arranged at the two sides of ridged waveguide structure, and the light limitation grooves and the ridged waveguide structure are arranged in an inclining manner.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com