Patents
Literature
299 results about "Ridge waveguides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
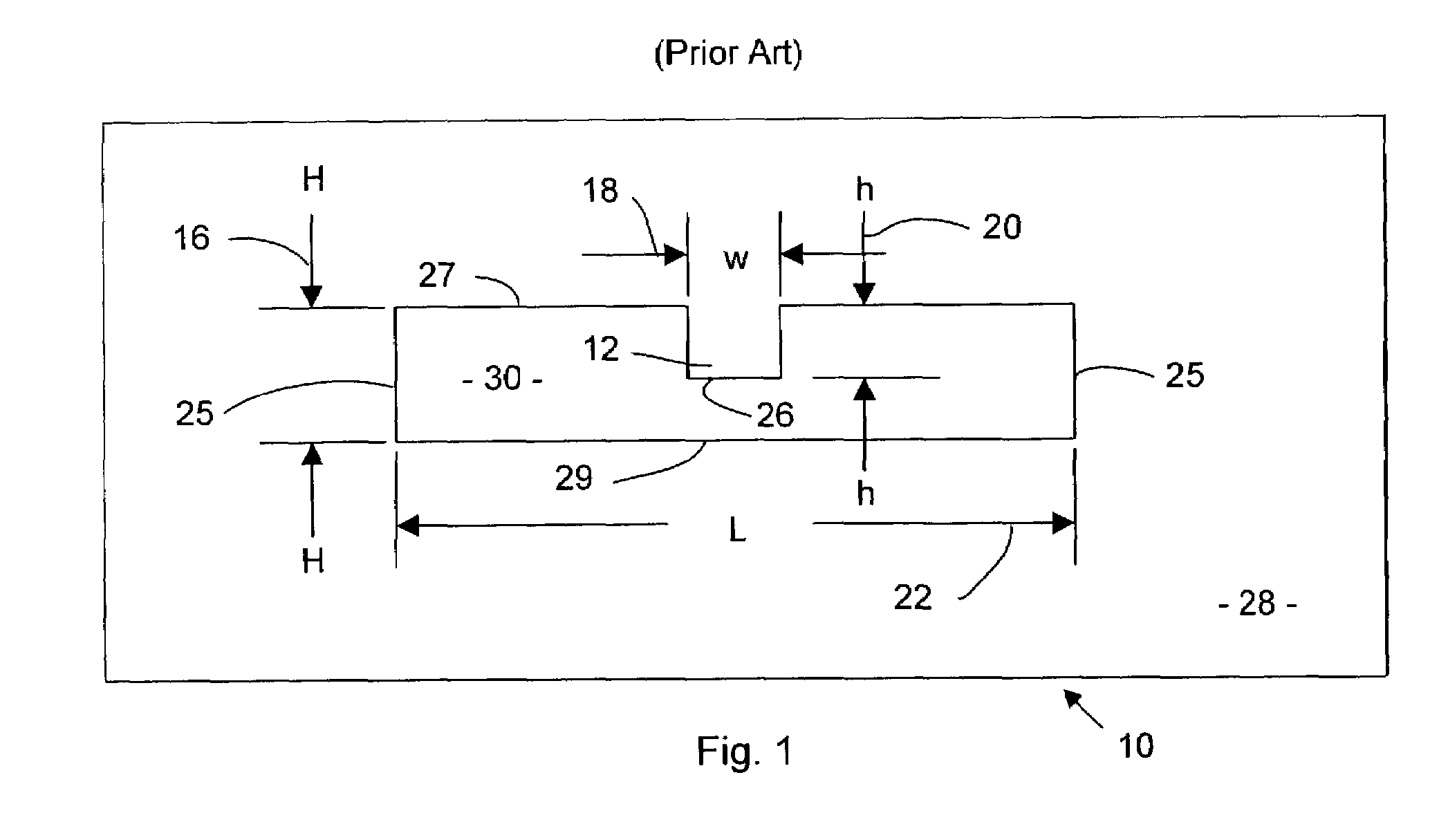
Ridge waveguide. [′rij ′wāv‚gīd] (electromagnetism) A circular or rectangular waveguide having one or more longitudinal internal ridges that serve primarily to increase transmission bandwidth by lowering the cutoff frequency.
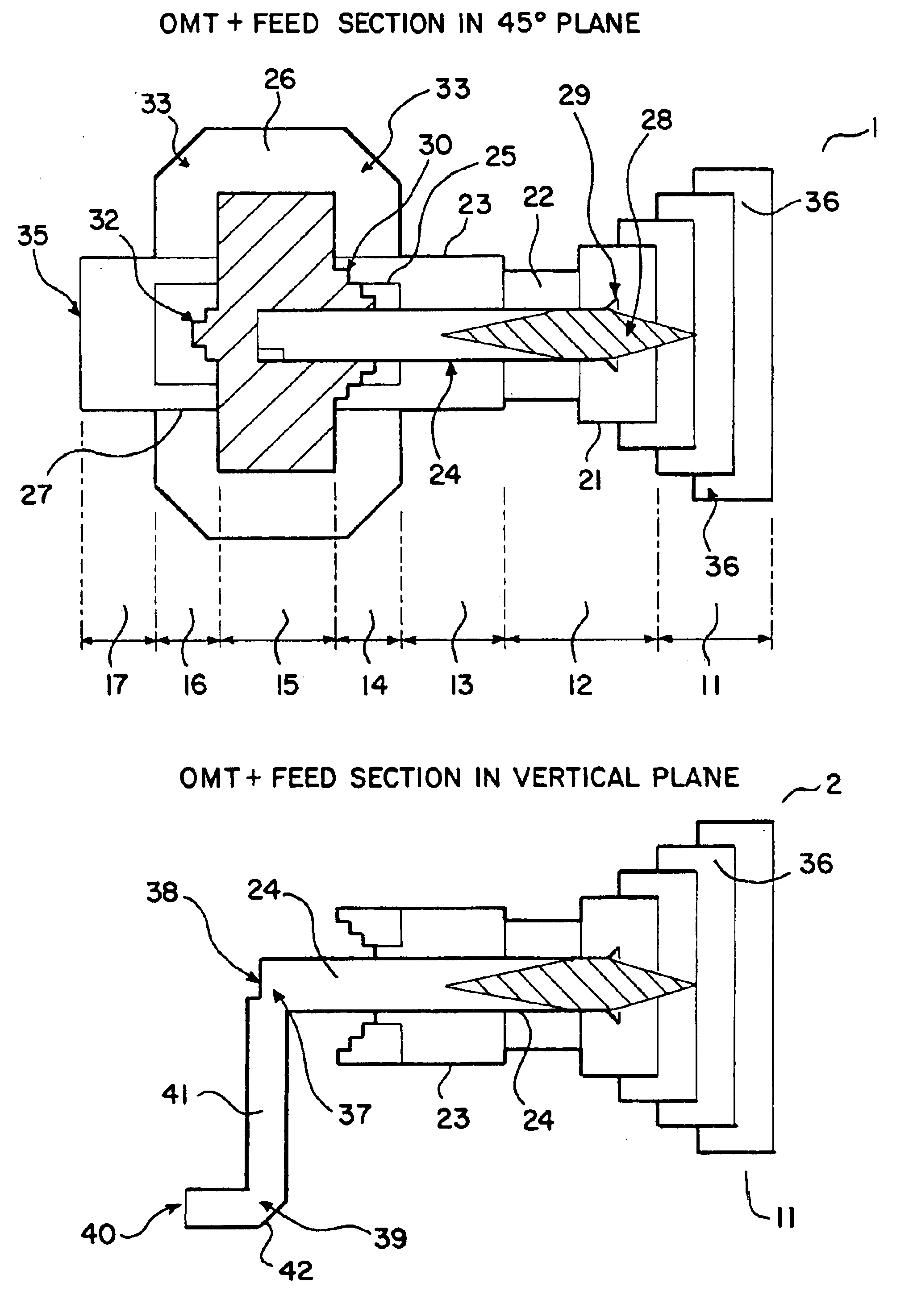
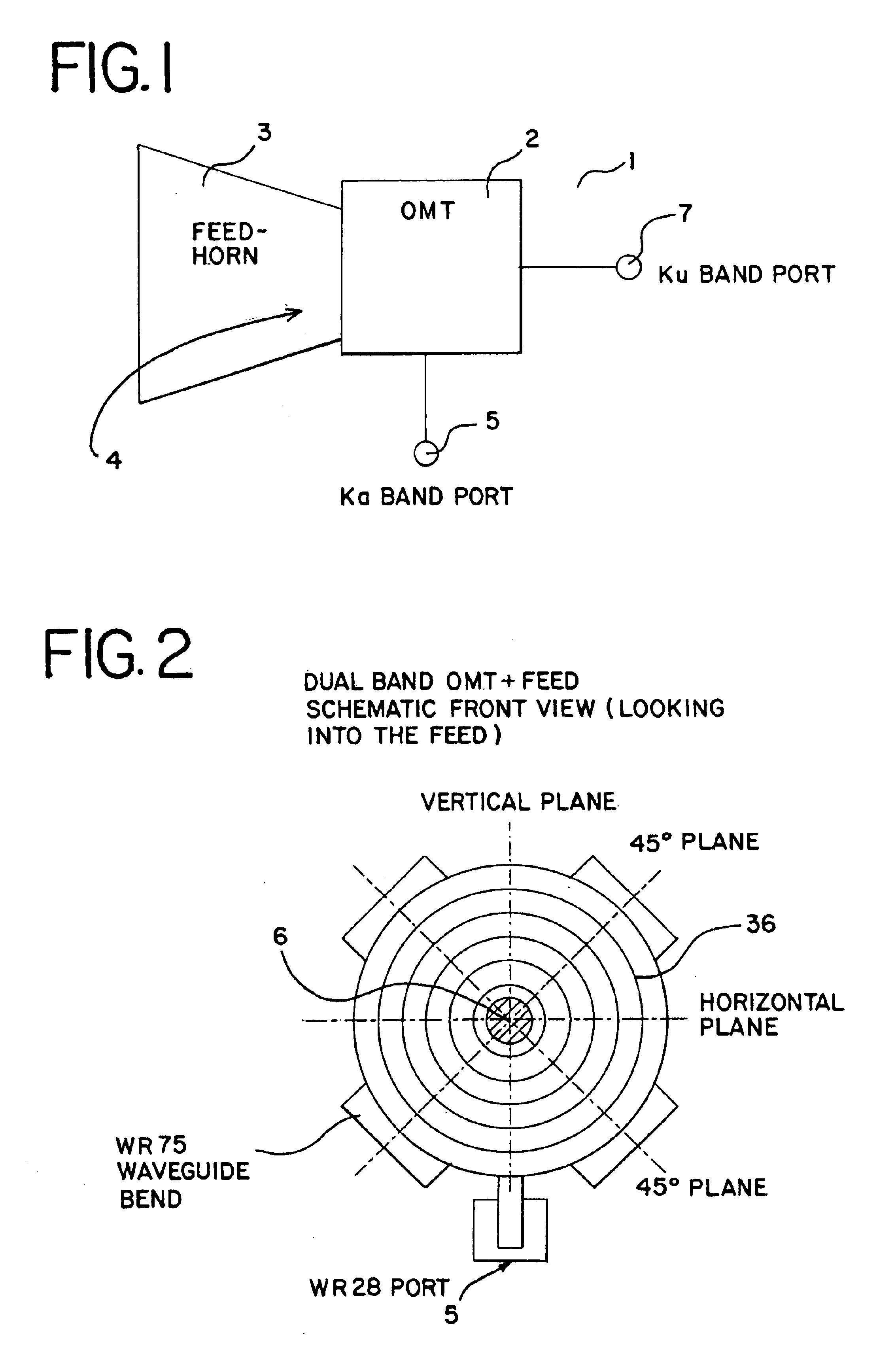
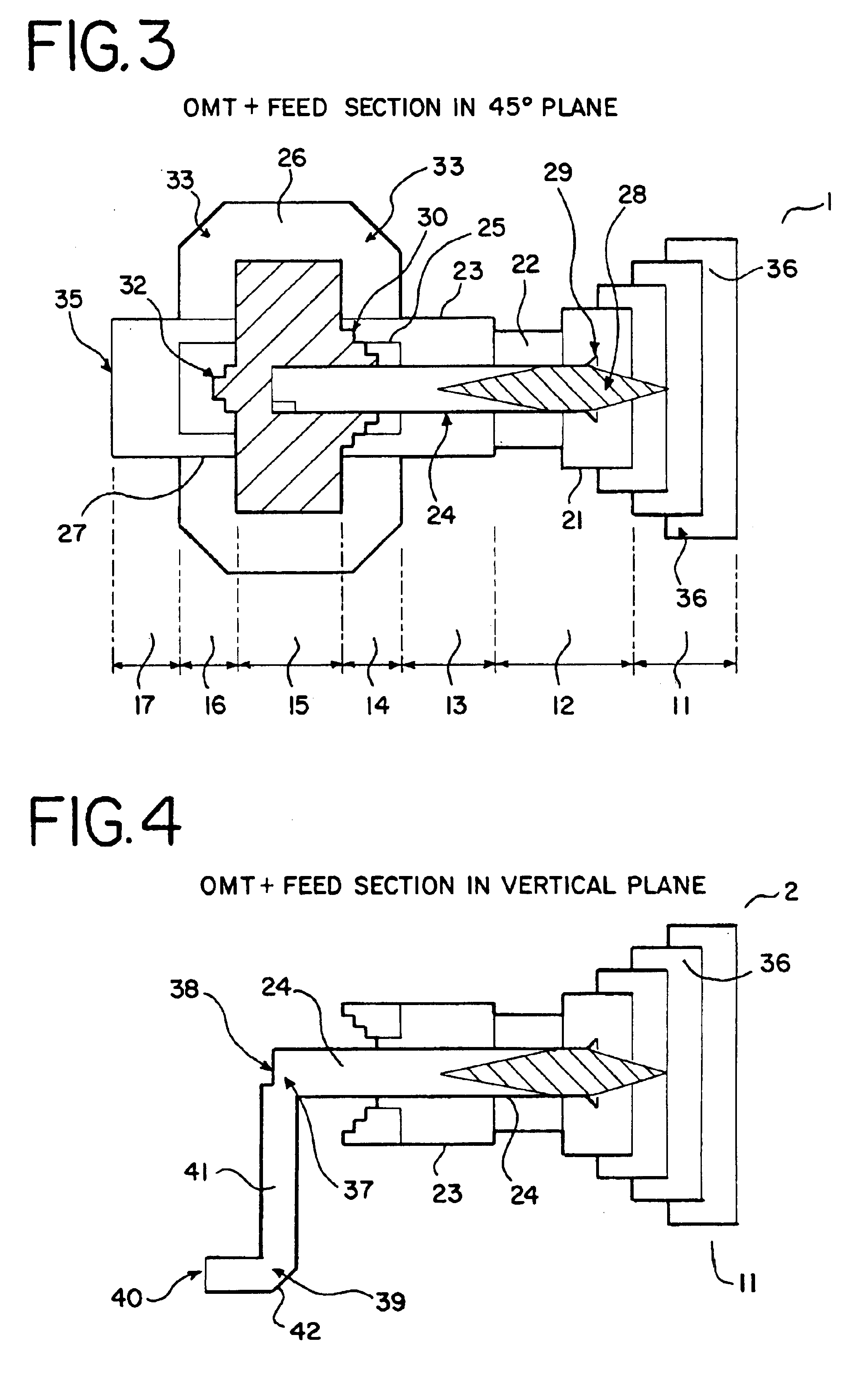
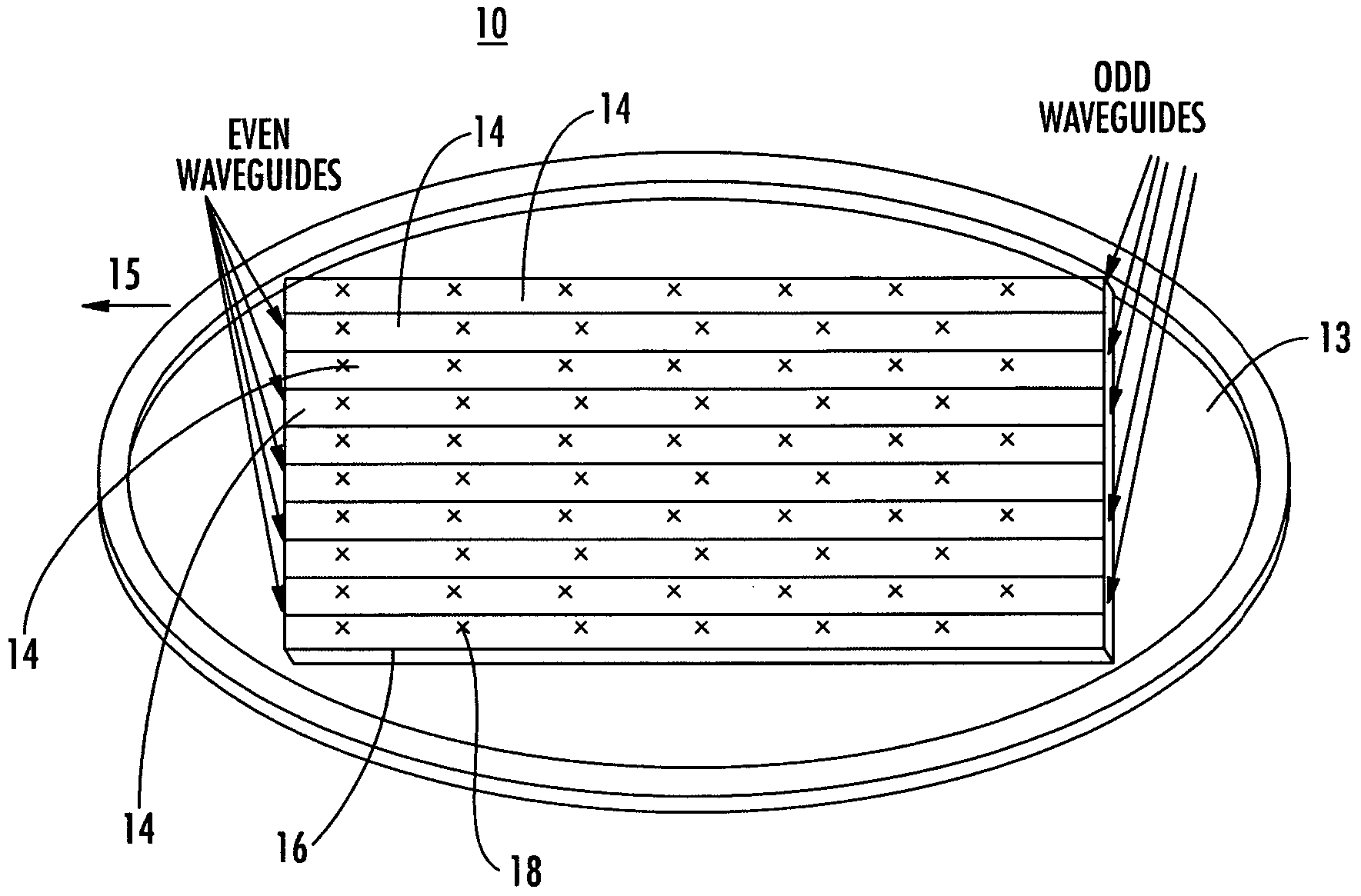
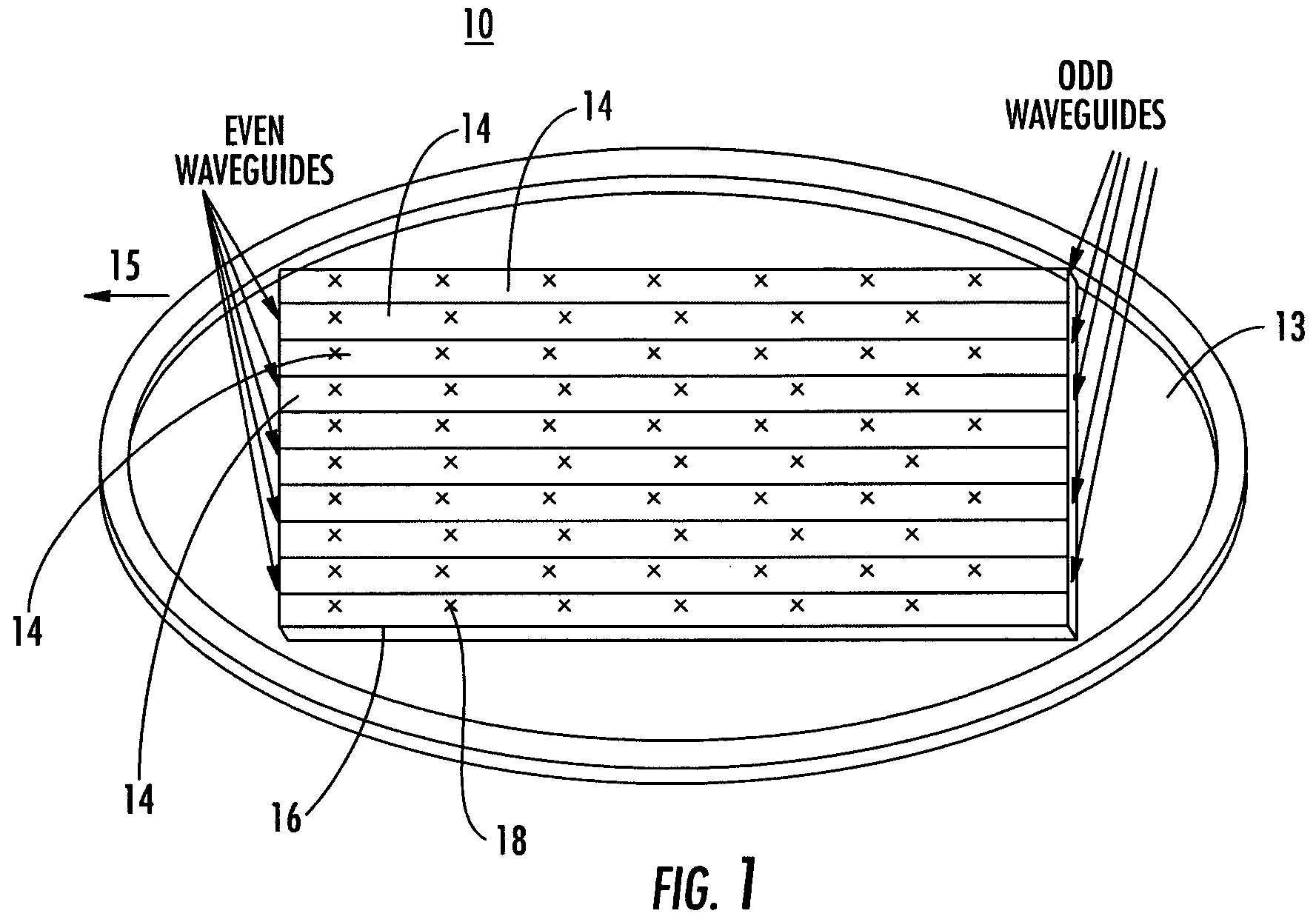
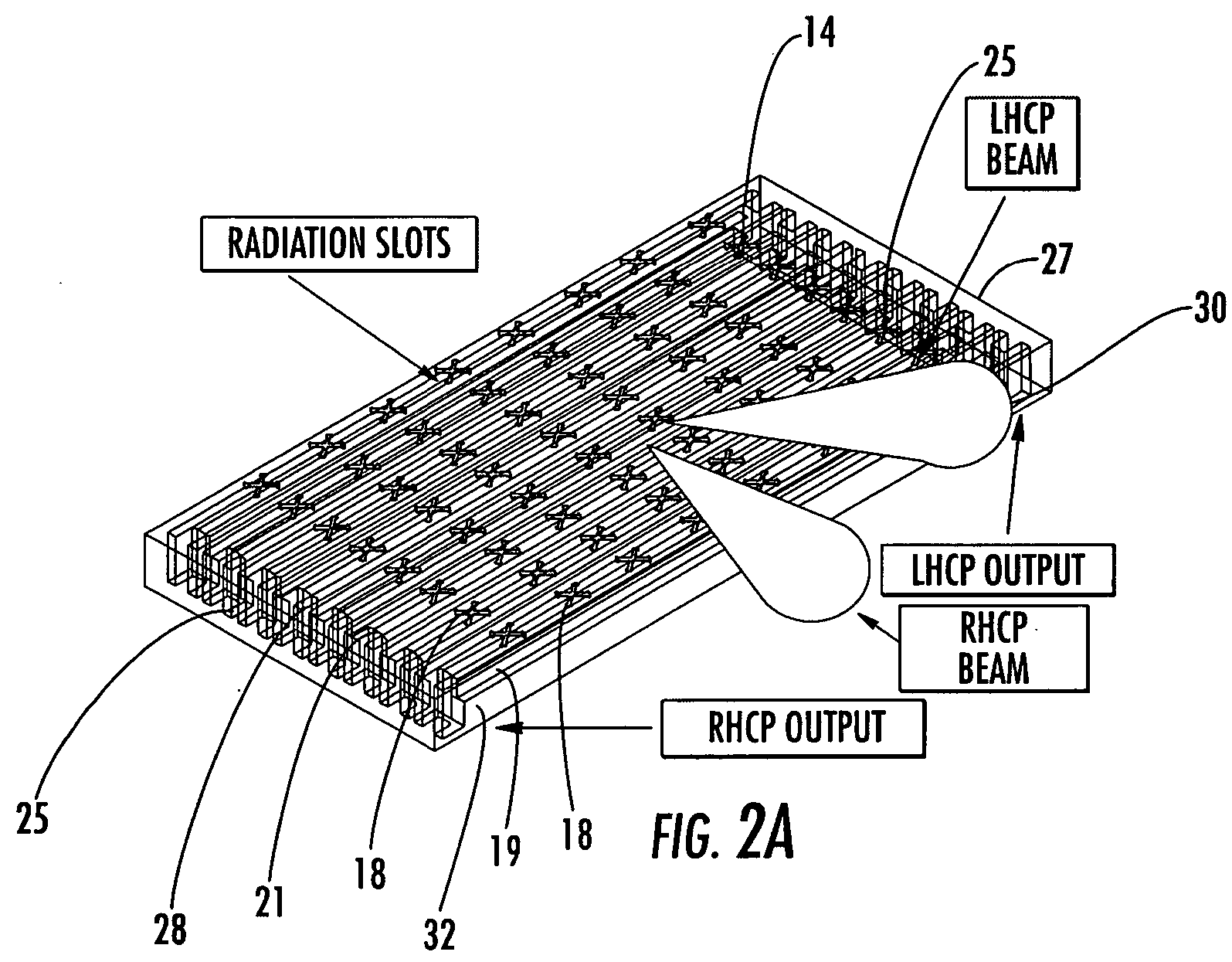
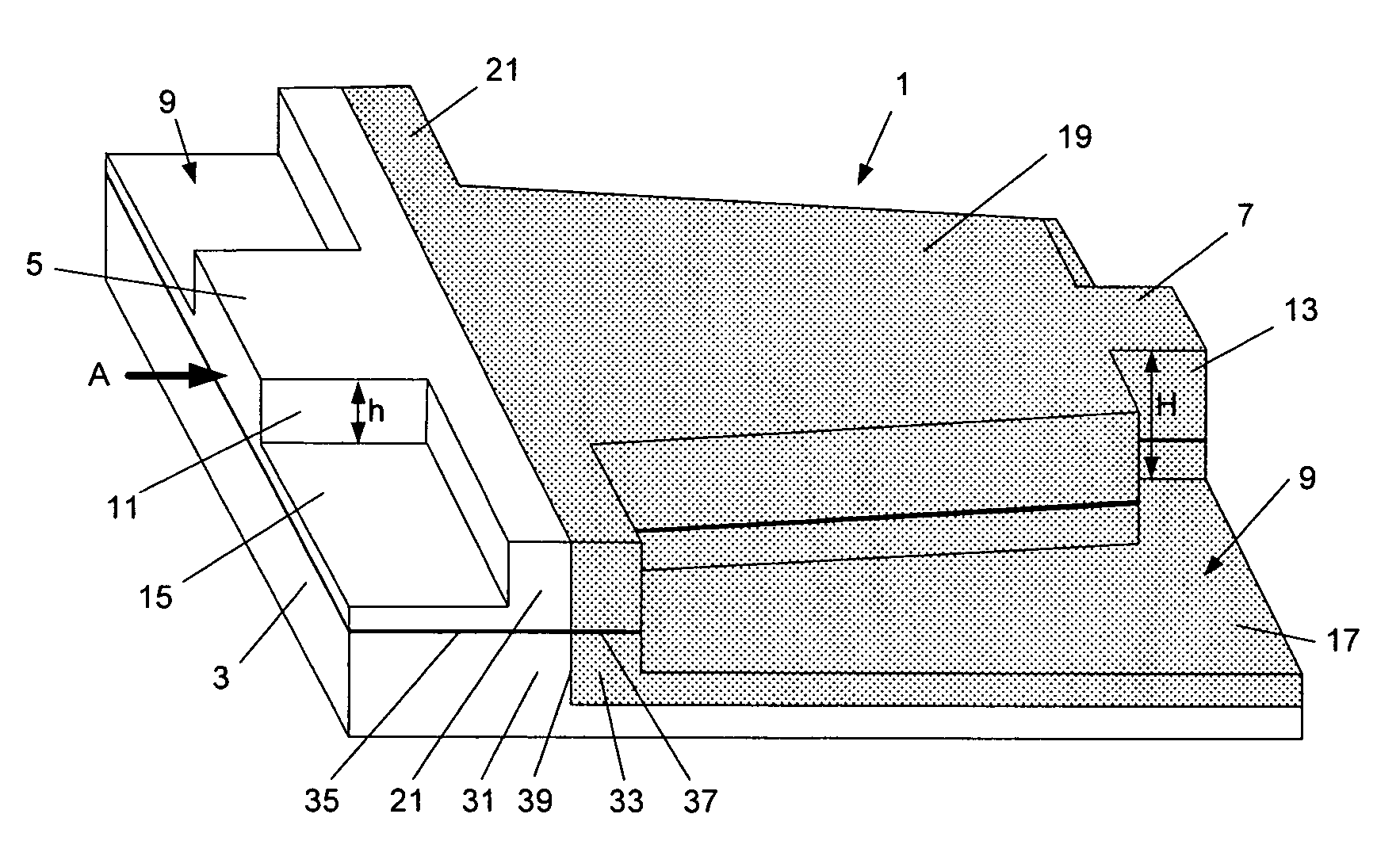
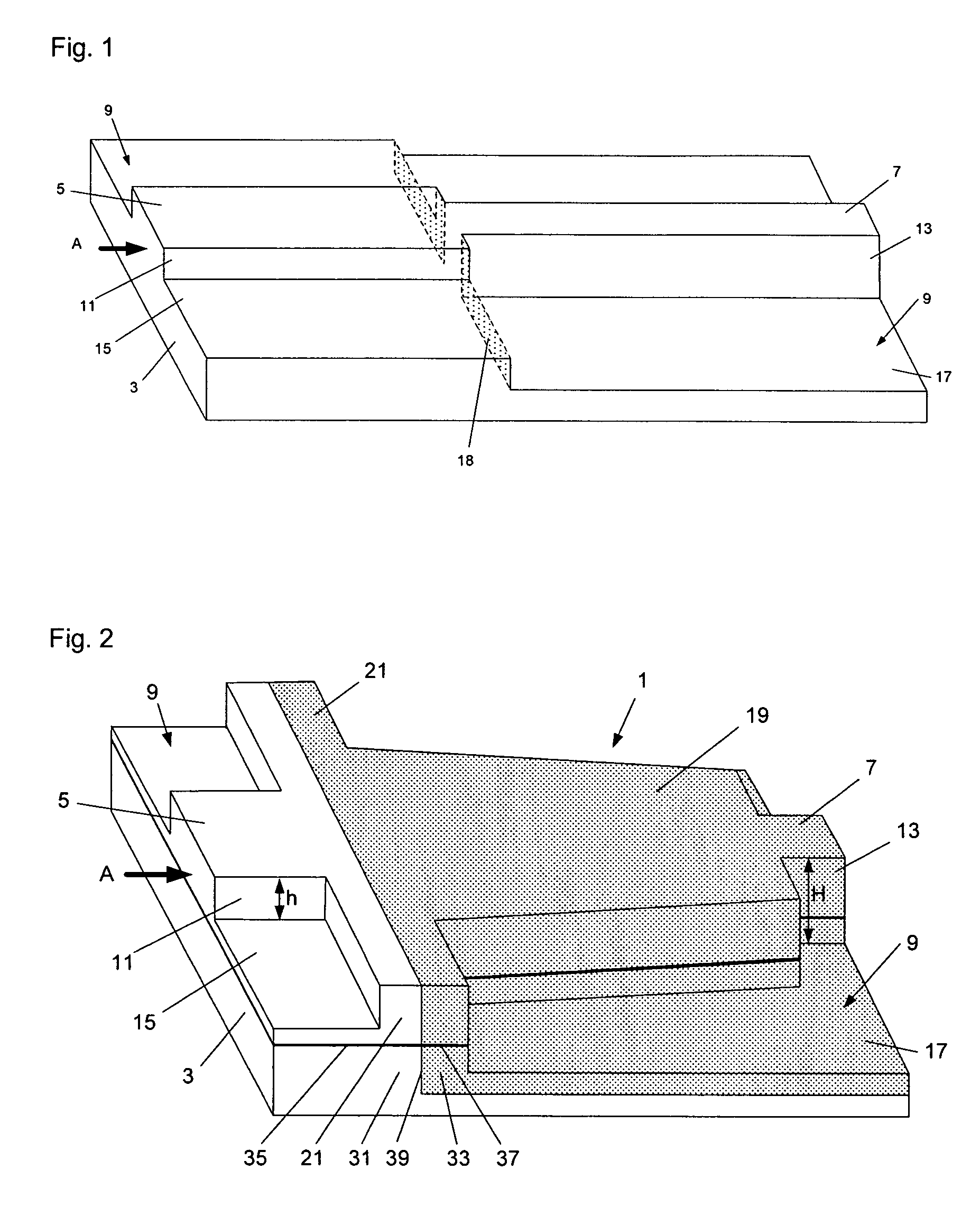
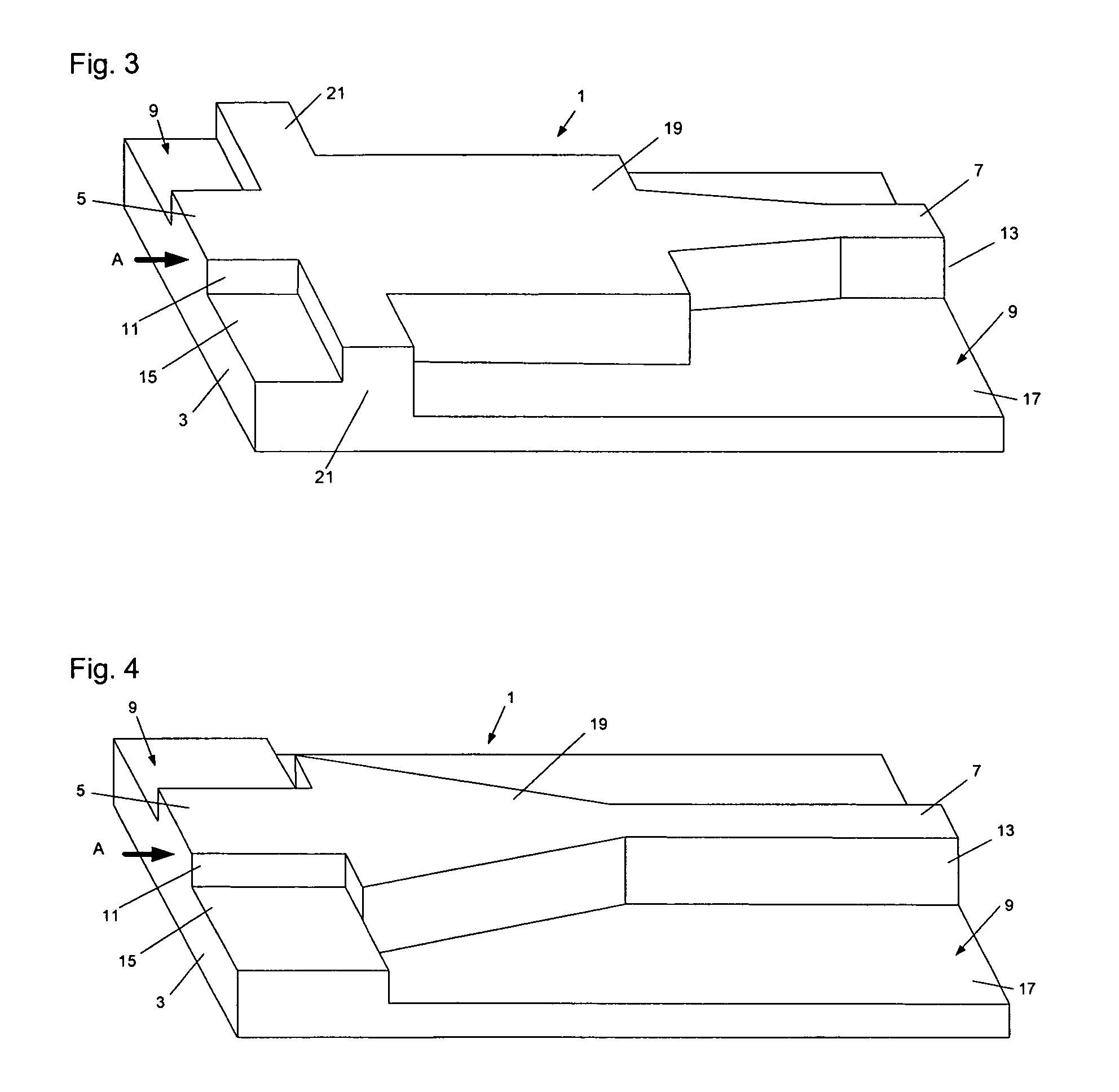
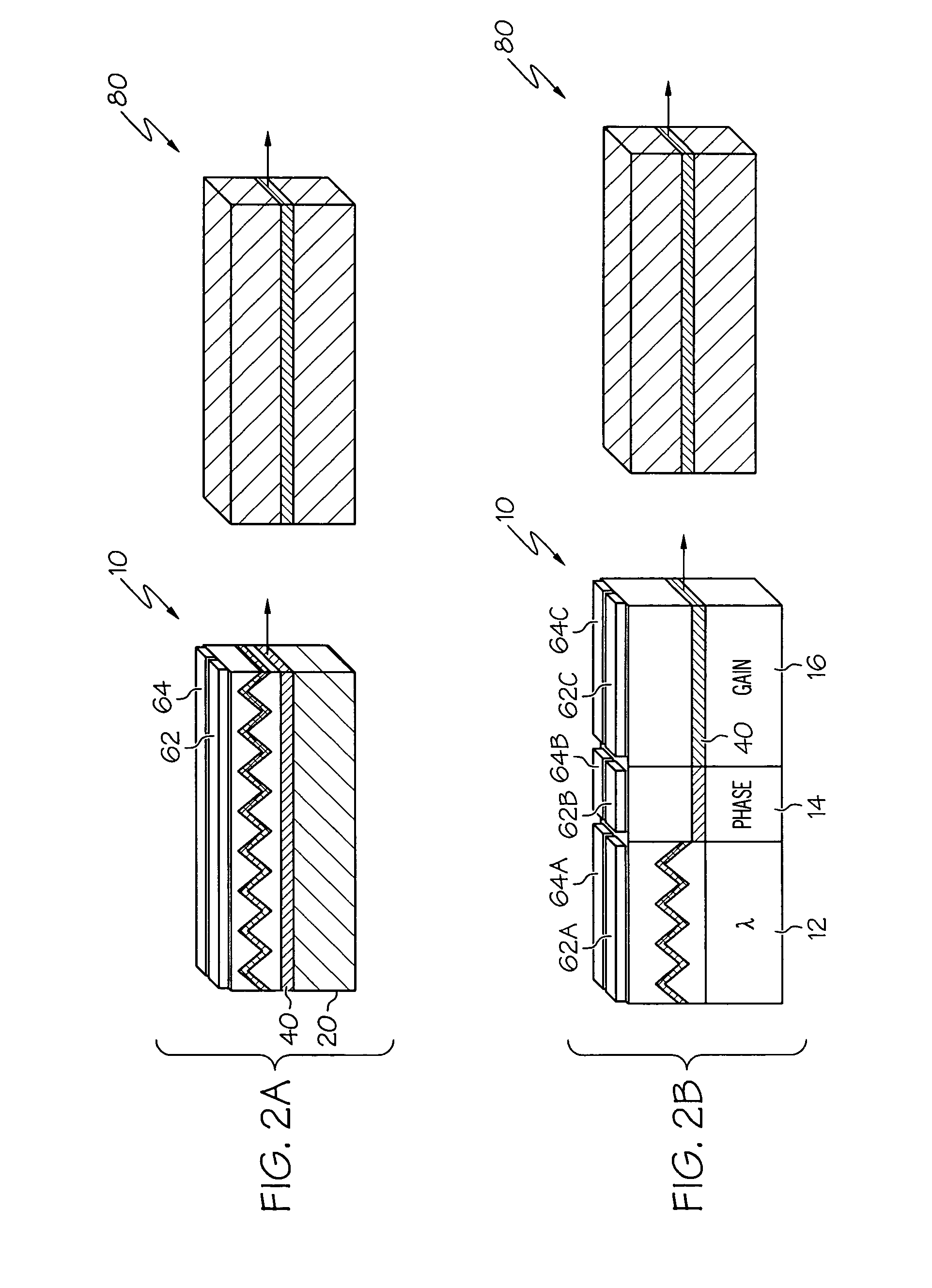
Ka/Ku dual band feedhorn and orthomode transduce (OMT)
InactiveUS6714165B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntennas earthing switches associationRidge waveguidesTransducer
A dual band, higher and lower frequency range transducer with a circular coaxial waveguide feed is described having a first junction for connection of a lower frequency range outer waveguide of the coaxial waveguide feed to at least two rectangular or ridge waveguides offset from the longitudinal axis of the transducer and a second junction for connection of the at least two rectangular or ridge waveguides to a further waveguide. A third junction is provided for connecting an inner waveguide of the coaxial waveguide feed to a higher frequency range waveguide. The transducer comprises at least first and second parts joined across a first plane substantially perpendicular to the longitudinal axis and including at least a portion of the higher frequency range waveguide extending within the first plane of the join. A seal such as an "O" ring seal may be placed easily in the plane of the join thus preventing moisture ingress. Similarly, a feed horn and input and output ports may be sealingly attached to the first and second parts of the transducer. The first and second junctions are preferably impedance matched turnstile junctions.
Owner:NEWTEC CY
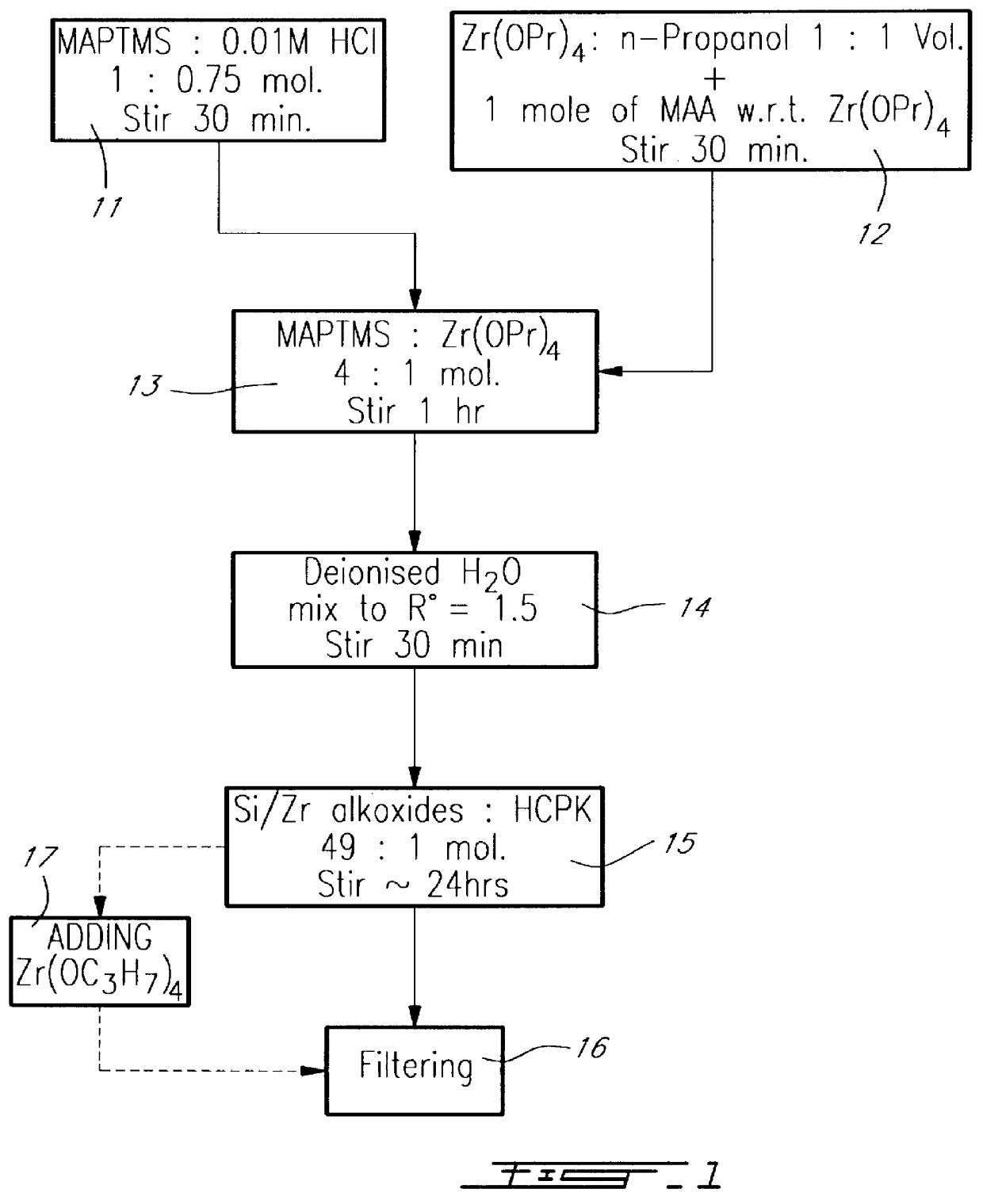
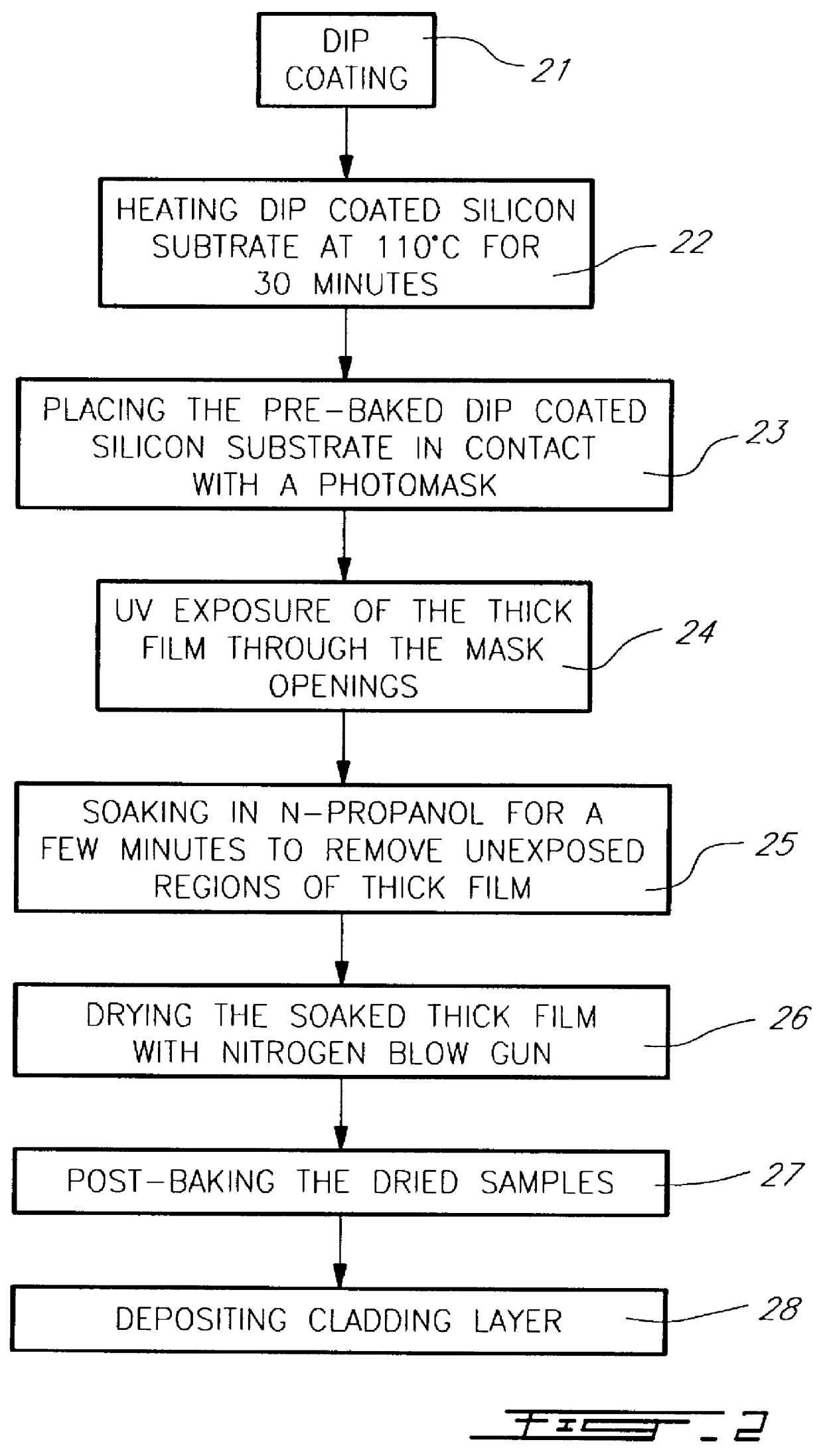
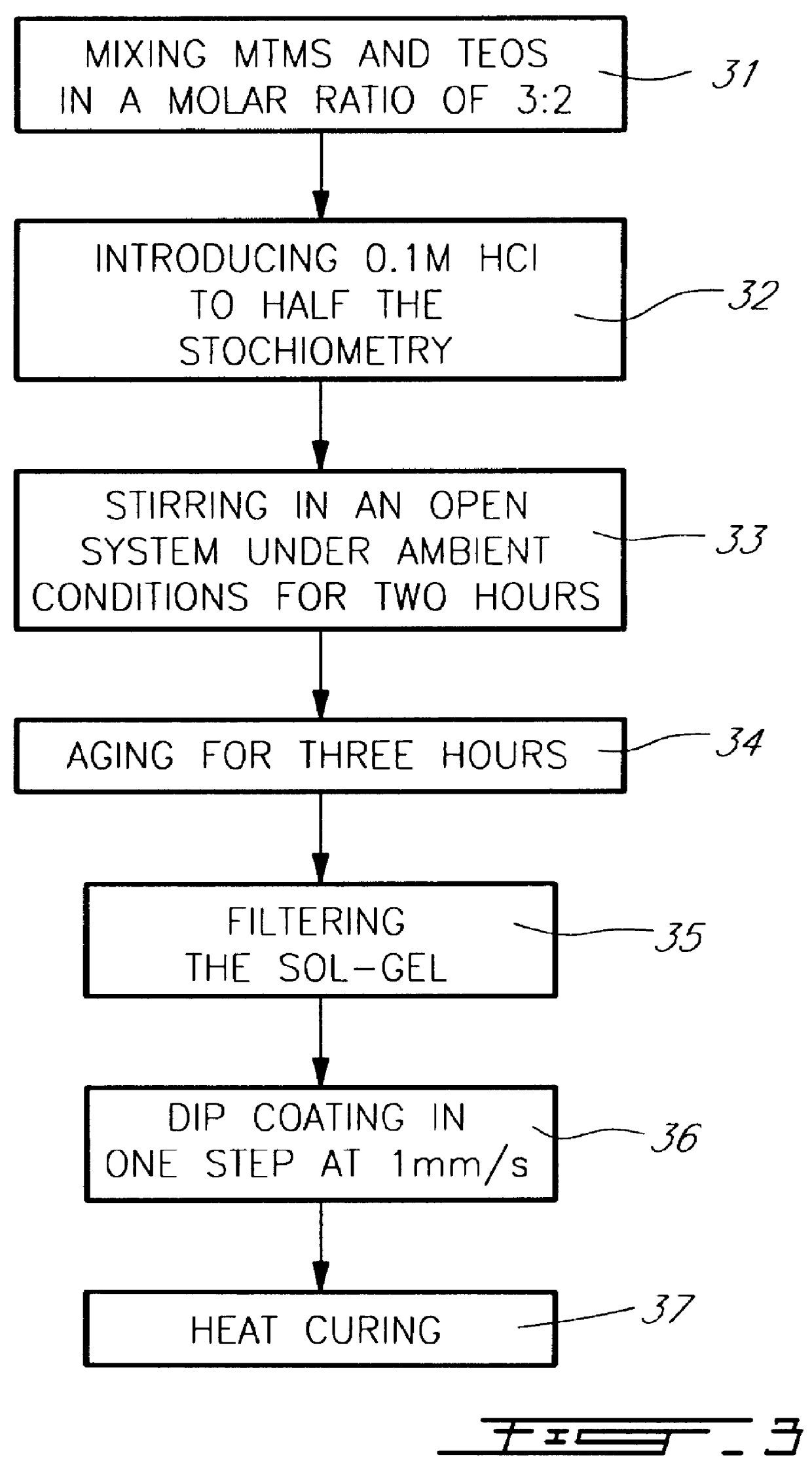
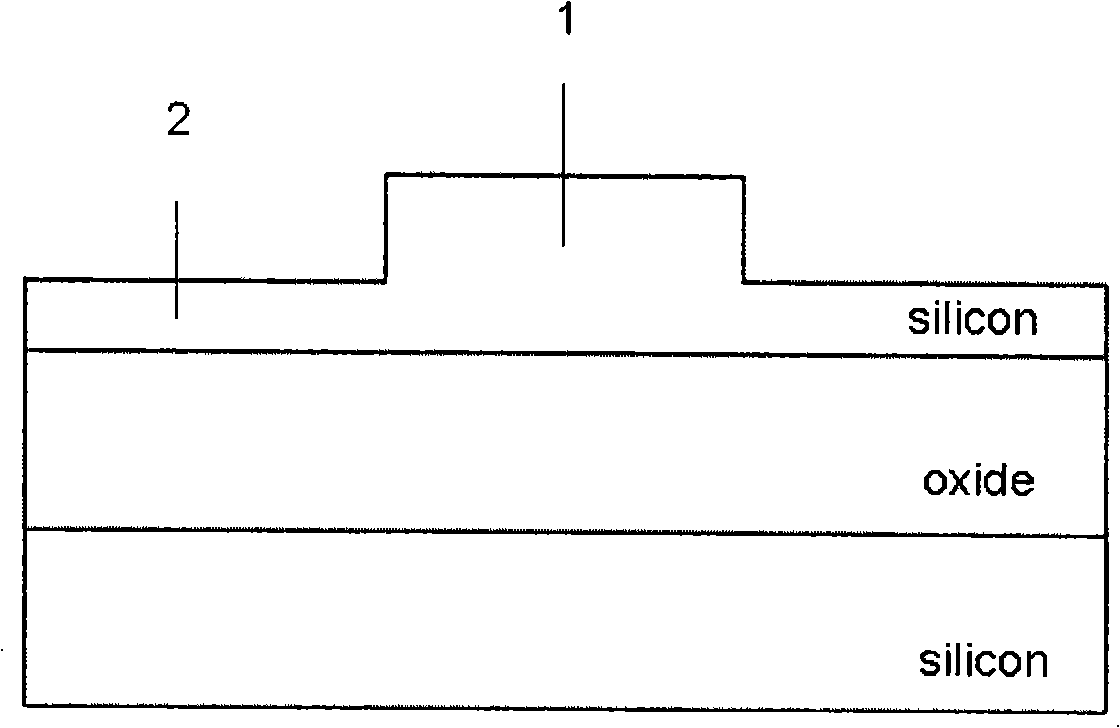
Solvent-assisted lithographic process using photosensitive sol-gel derived glass for depositing ridge waveguides on silicon
InactiveUS6054253ARapid thermal annealingSimple wayPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentRidge waveguidesSolvent
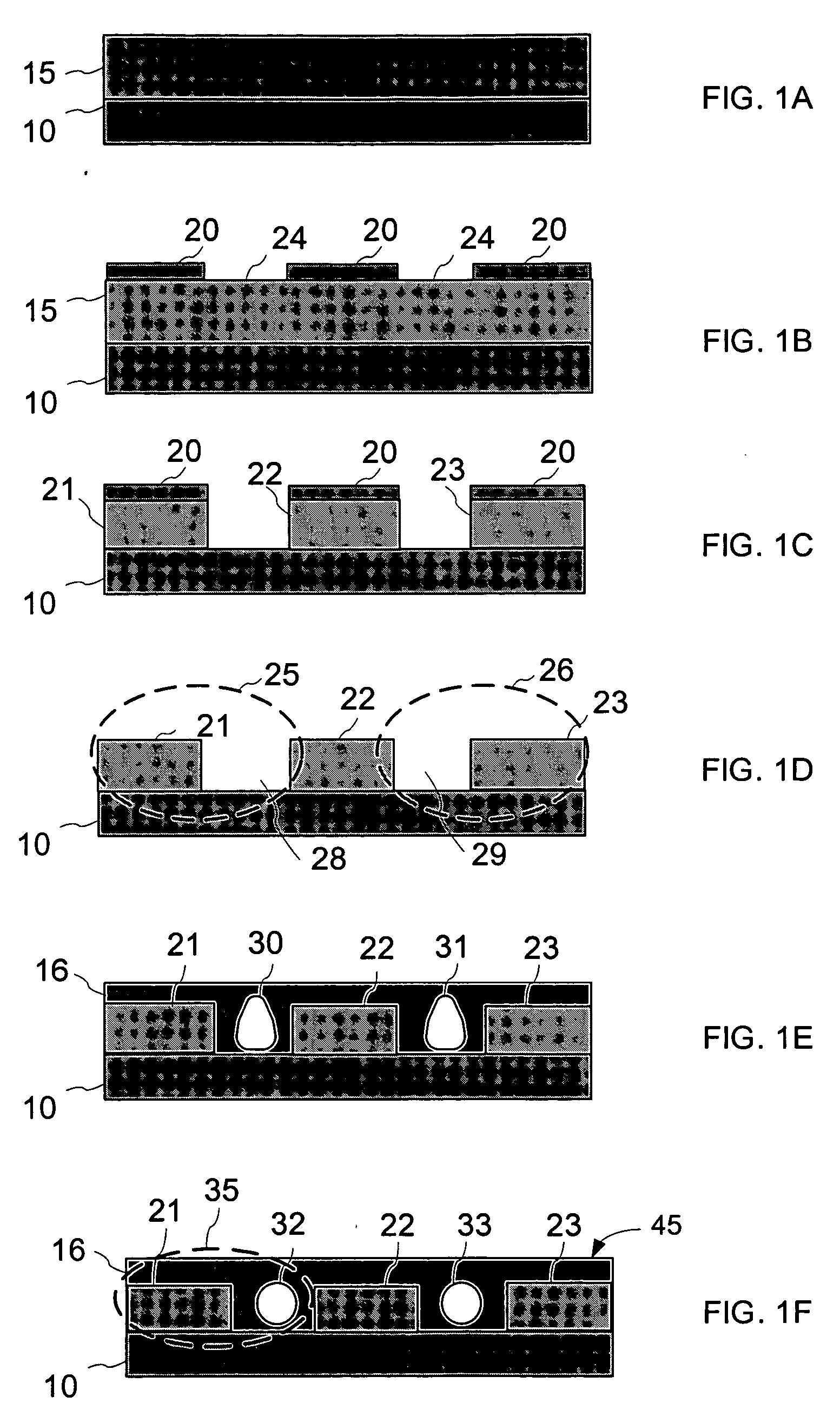
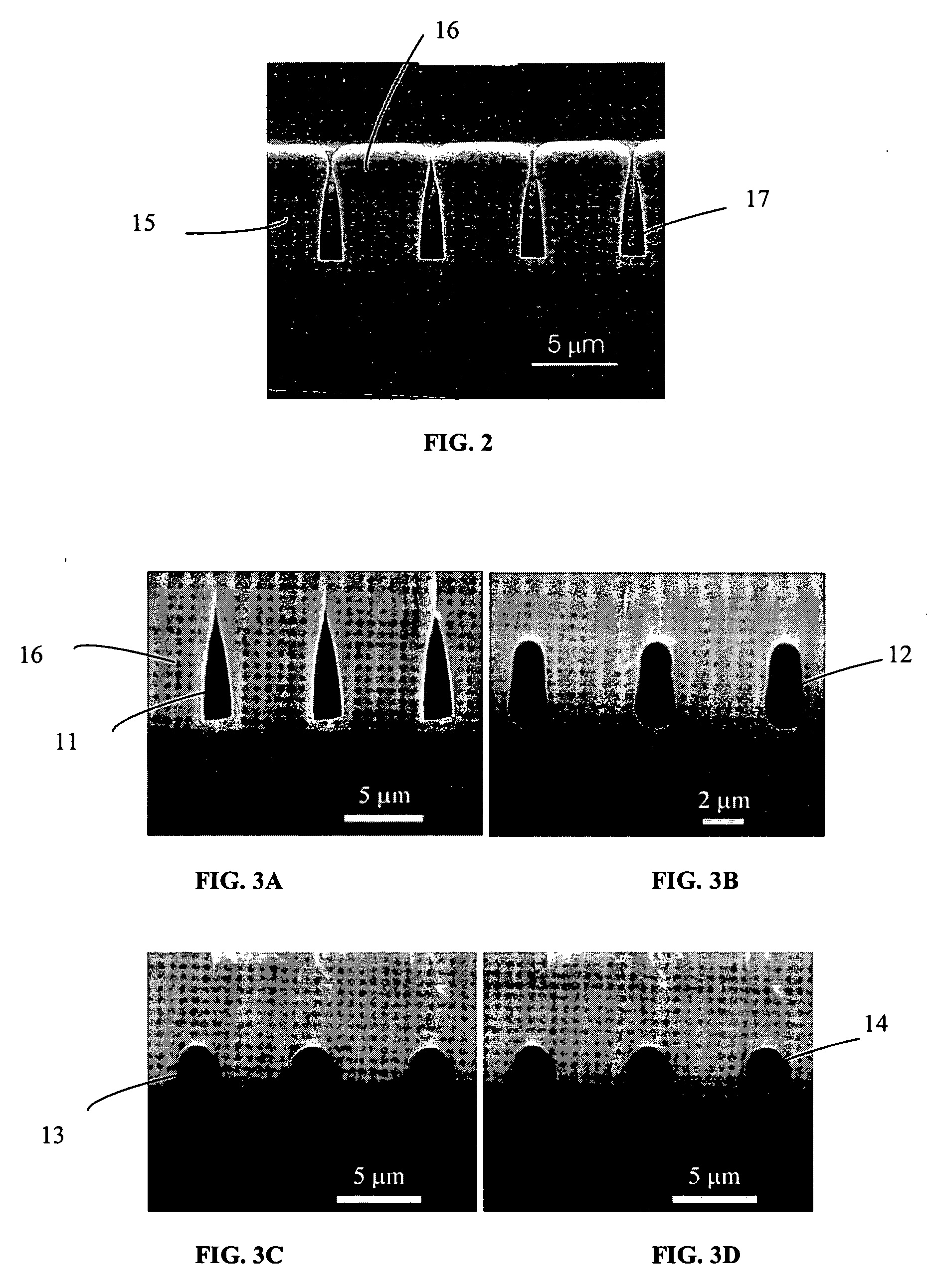
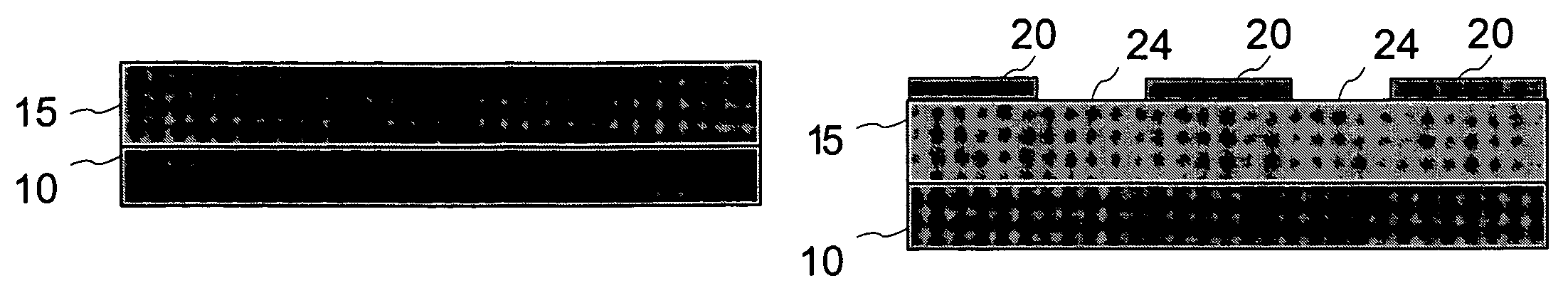
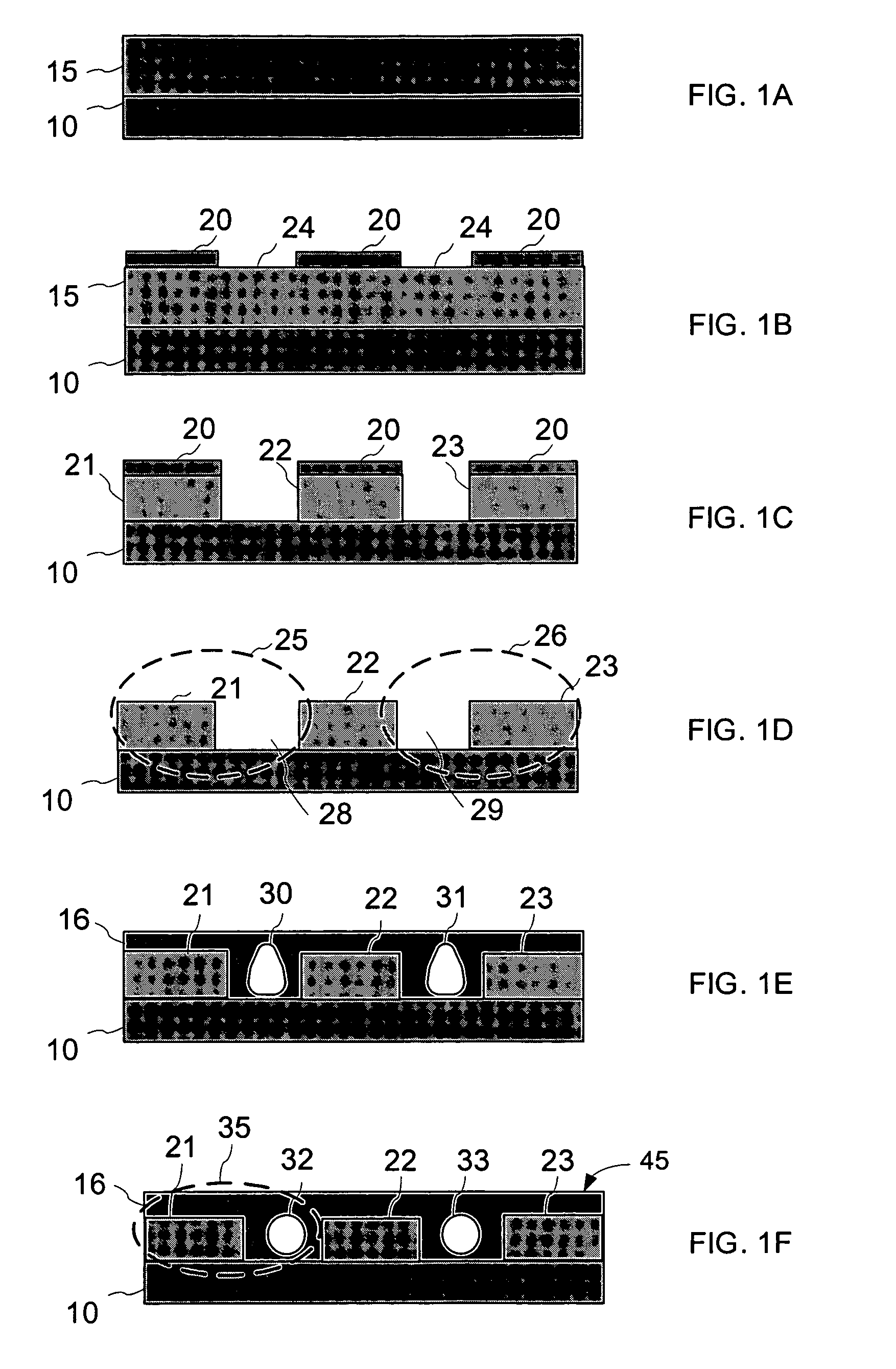
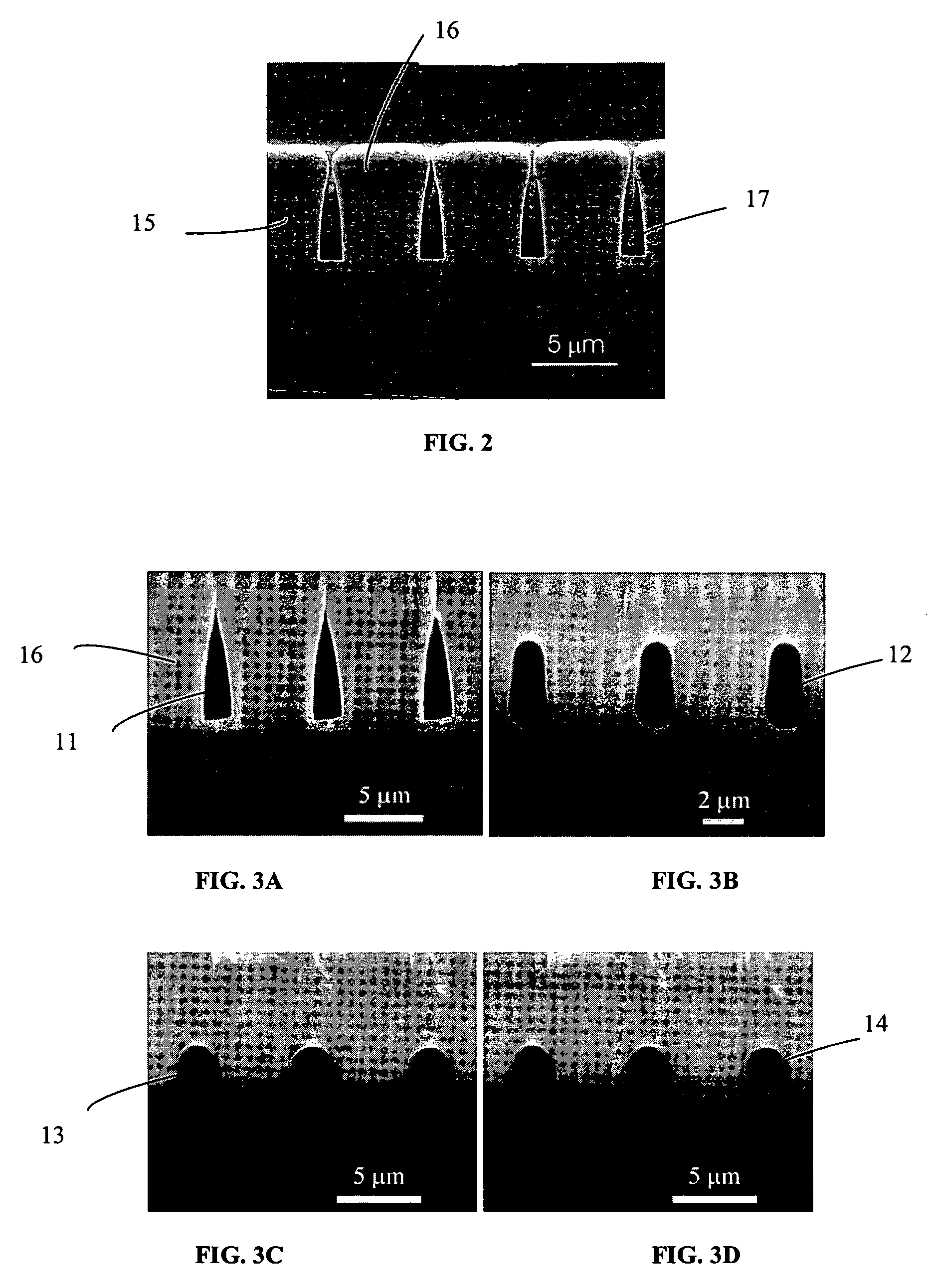
The process for fabricating a ridge waveguide on a substrate uses a photosensitive sol-gel glass material prepared, according to a first embodiment, by mixing methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (H2C=C(CH3)CO2(CH2)3Si(OCH3)3) and methacrylic acid (H2C=C(CH3)COOH) or, according to a second embodiment, by mixing methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (H2C=C(CH3)CO2(CH2)3Si(OCH3)3) with bis(s-butoxy)aluminoxytriethoxysilane. A thick film of photosensitive sol-gel glass material is first dip coated on at least a portion of the substrate. A photomask is applied to the film of photosensitive sol-gel glass material, and this sol-gel material is exposed to ultraviolet radiation through the opening(s) of the photomask to render a portion of the film insoluble to a given solvent and thereby imprint the ridge waveguide in that film. The thick film is then soaked in this solvent, for example n-propanol to dissolve the unexposed portion of the sol-gel film and leave on the substrate the exposed film portion and therefore the ridge waveguide. The ridge waveguide is heat cured and the heat cured ridge waveguide is covered with a cladding layer.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV - THE ROYAL INSTION FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF LEARNING
Integrated etched multilayer grating based wavelength demultiplexer
An integrated etched multilayer grating-based wavelength multiplexer / demultiplexer is disclosed wherein an etched multilayer grating structure is monolithically integrated within the optical waveguide stack of the multiplexer / demultiplexer to reflectively diffract an input optical beam. The multilayer grating structure is generally comprised of a series of etched diffractive elements and an etched multilayer reflector, the combined optical response of which providing the desired multiplexing / demultiplexing effect. The etched structures are generally comprised of shallow etch structures in a top surface of the multiplexer / demultiplexer waveguide stack. Monolithically integrated input and output ridge waveguides may also be provided, optionally fabricated in a same etching step as the etched multilayer grating.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Device with waveguide defined by dielectric in aperture of cross-track portion of electrical conductor for writing data to a recording medium
A device for writing data to a recording medium and a method for fabricating the device is presented. According to one embodiment, the device includes an electrical conductor having a cross-track portion, wherein the cross-track portion includes first and second opposing surfaces, and wherein the cross-track portion defines an aperture extending from the first surface to the second surface. The device also includes a dielectric portion disposed in the aperture such that the dielectric portion defines a ridge waveguide having a lowest-order mode cut-off frequency that is less than the frequency of incident optical energy used to heat the recording medium.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Waveguiding structures with embedded microchannels and method for fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20050287696A1NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotonic crystalRidge waveguides
The invention provides a method for fabricating planar waveguiding structures with embedded microchannels. The method includes the step of depositing, over a planar template having at least one indented feature comprising a ridge of a first optical material and a narrow trench adjacent thereto, a second optical material, and the step of subsequent annealing thereof, so that an embedded hollow microchannel forms within the trench. The method provides planar structures wherein the ridge and the embedded microchannel cooperate to form an optical waveguiding structure having a waveguiding direction collinear with the embedded microchannel. Embodiments of the method for forming microfluidic devices integrating ridge waveguides with hollow microchannels having surface access points for fluid delivery, and for forming photonic crystals, are disclosed together with corresponding device embodiments.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna system with ridged waveguide
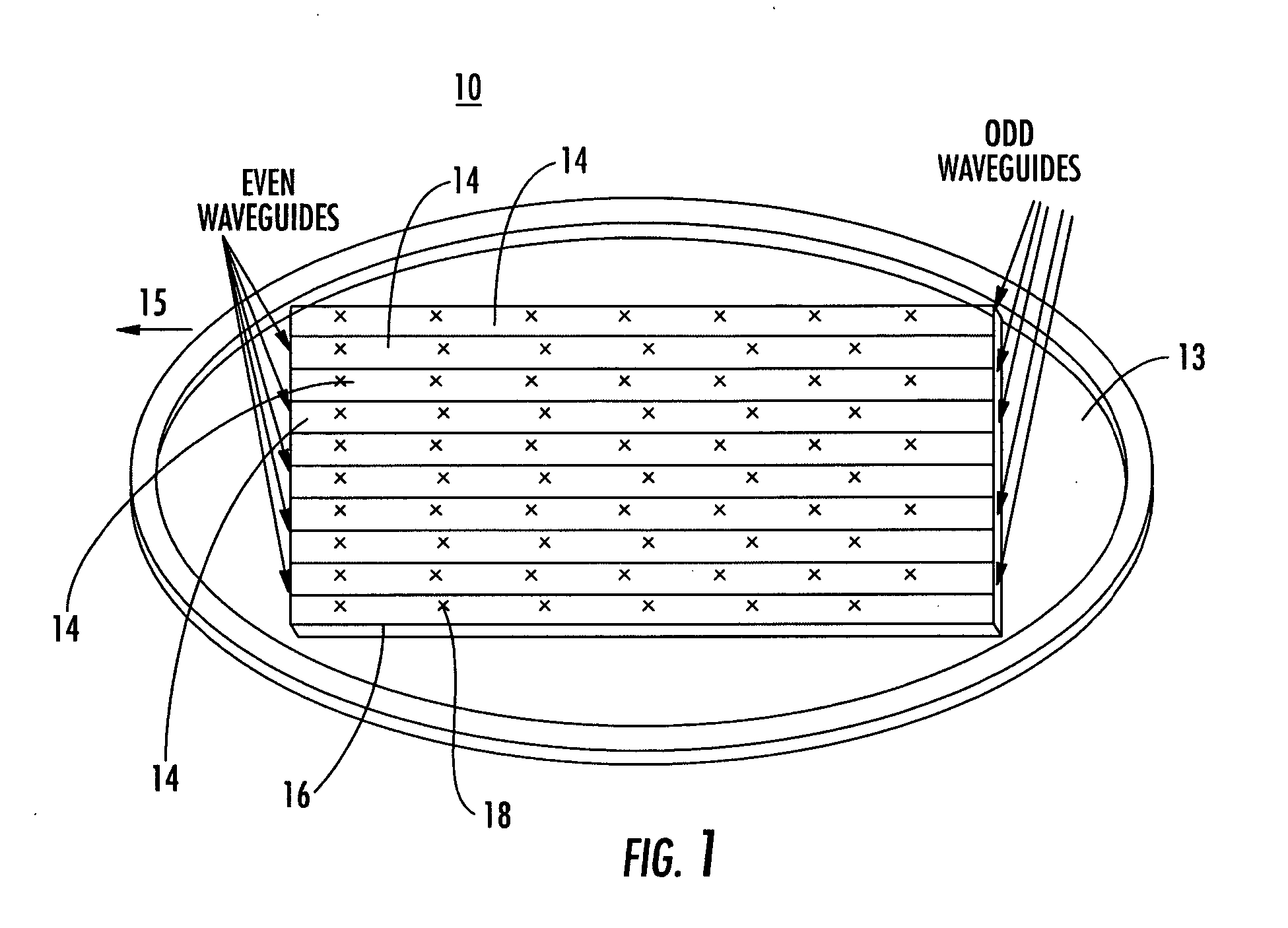
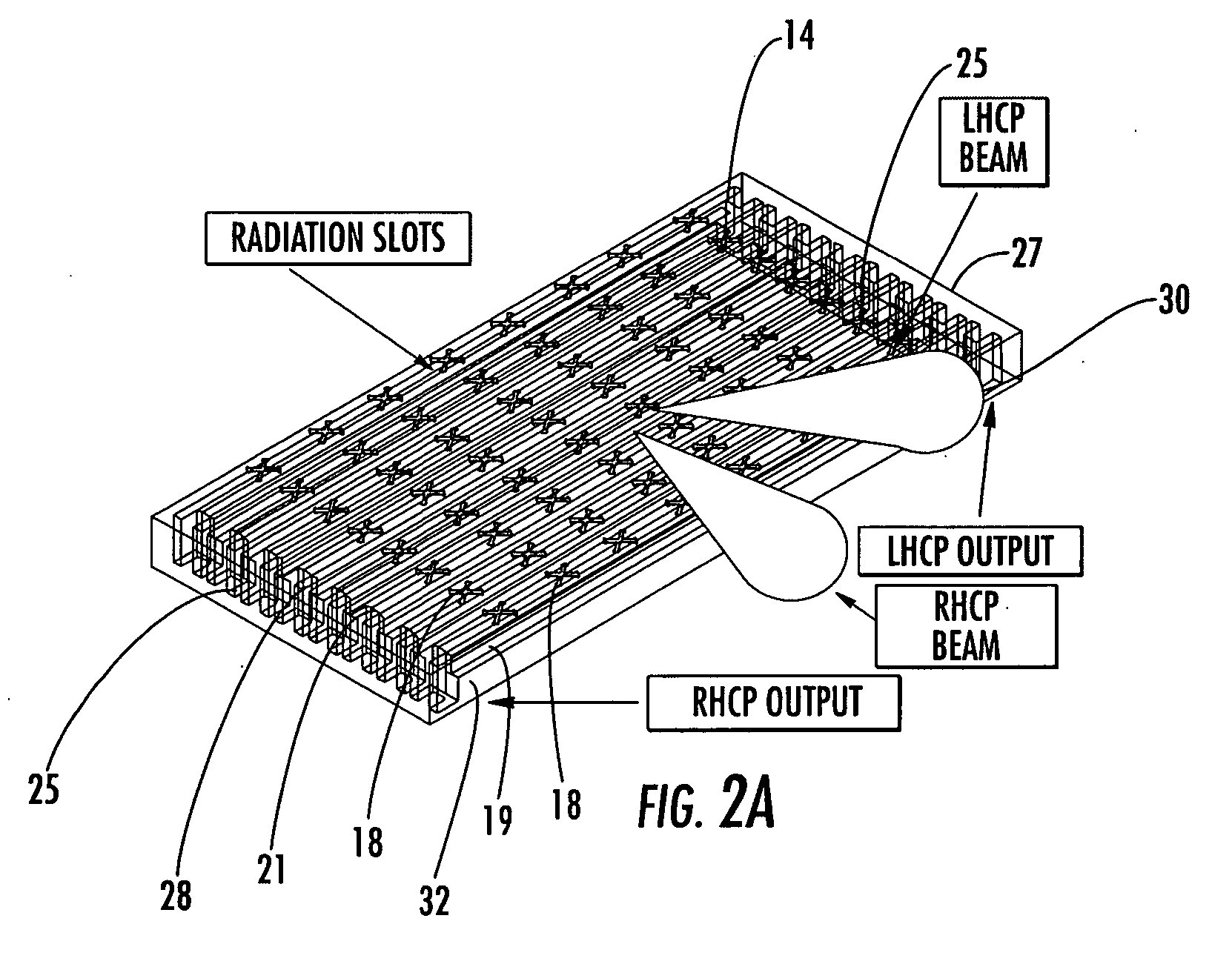
ActiveUS20060132374A1Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesLinear waveguide fed arraysAxial ratioRidge waveguides
The present invention relates to a vehicle mountable satellite antenna as defined in the claims which is operable while the vehicle is in motion. The satellite antenna of the present invention can be installed on top of (or embedded into) the roof of a vehicle. The antenna is capable of providing high gain and a narrow antenna beam for aiming at a satellite direction and enabling broadband communication to vehicle. The present invention provides a vehicle mounted satellite antenna which has low axial ratio, high efficiency and has low grating lobes gain. The vehicle mounted satellite antenna of the present invention provides two simultaneous polarization states. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a ridged waveguide instead of a conventional rectangular waveguide to alleviate the effects of grating lobes. The ridge waveguide provides a ridged section longitudinally between walls forming the waveguide. A plurality of radiating elements are formed in a radiating surface of the ridged waveguide.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
Microwave antenna transmission device having a stripline to waveguide transition via a slot coupling
InactiveUS6081241AImprove efficiencySmall demand on spaceOne-port networksCoupling devicesLeveling effectElectrical conductor
A device for the power transmission of microwaves between a strip-line and a number of parallel cavity waveguides arranged in a group antenna. The strip-line includes H-shaped slots. These slots are centered with respect to a central conductor. Opposite each of the slots, a corresponding slot is arranged through the wall of the cavity waveguide. Electrically conducting seals are arranged to follow immediately outside the contours of the slots. The strip-line is fixedly fastened to the seals and the ridge waveguide, whereby good electrical coupling is achieved. Simultaneously, small cavities are formed between the slots. These cavities have a leveling effect such that the demands on mechanical precision is appreciably lowered, such that the tolerance to placement of the slots opposite to each other is increased substantially as compared to the case of the waveguides directly abutting the strip-line.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Lateral heat spreading layers for epi-side up ridge waveguide semiconductor lasers
InactiveUS7061022B1Reduce thermal resistanceMaximum device performanceOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsRidge waveguidesWaveguide
Disclosed are a semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same comprising a substrate, a mesa region adjacent to the substrate, an electroplated metal layer, for reducing the thermal resistance of the device, surrounding the mesa region, an insulator layer separating a side portion of the mesa region from the electroplated metal layer, a heat sink, a bonding layer adjacent to the heat sink, and a second metal layer in between the substrate and the heat sink, wherein the substrate is adjacent to the bonding layer, and wherein the electroplated metal layer dimensioned and configured to have a thickness of at least half a thickness of the mesa region; and to laterally spread heat away from the mesa region. The mesa region comprises a first cladding layer adjacent to the substrate, an active region adjacent the first cladding layer, and a second cladding layer adjacent to the active region.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Vehicle mounted satellite antenna system with ridged waveguide
ActiveUS7202832B2Low axle ratioImprove efficiencyAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesLinear waveguide fed arraysAxial ratioRidge waveguides
Owner:RENDA TRUST
Frontlight unit for enhancing illumination of a reflective display
InactiveUS8596846B2Improve efficiencyImprove image qualityCosmonautic condition simulationsLaser using scattering effectsPhase shiftedRidge waveguides
The frontlight illumination system is intended for enhancing illumination of a reflective display having pixels arranged in a matrix pattern and using monochromatic laser lights as light sources. The unit contains a network of light-distributing planar ridge waveguides with holograms arranged in a matrix pattern that corresponds to the matrix pattern of the reflective display. The light-distributing holograms of the system are formed on opposite sides of each core of respective light-distributing planar ridge waveguides. Neighboring holograms located on opposite sides of the core are combined into pairs and are arranged on each core in positions at which they interact with a predetermined phase shift that doubles the intensity of light directed to the reflective display and extinguishes light directed to the external surface.
Owner:VELIKOV LEONID MR +1
High-nonlinearity micro-ring waveguide optical device
InactiveCN103576413AEnhance nonlinear effectsLower the thresholdNon-linear opticsRidge waveguidesLogic gate
The invention relates to a micro-ring waveguide optical device capable of realizing all-optical signal processing by utilizing a high-nonlinearity effect, and aims to overcome the defect that nonlinear coefficients are insufficient when a conventional micro ring performs all-optical signal processing. The provided micro-ring waveguide optical device comprises a straight waveguide and a parallel growth micro ring on a substrate, wherein the micro ring is an annular resonant cavity; the ridge waveguide part of the micro ring adopts a parallel slot structure instead of a single ridge waveguide structure; and the straight waveguide is coupled with the micro ring. According to the micro-ring waveguide optical device, one parallel slot micro-ring waveguide structure is innovated; and when light is coupled into the parallel slot micro-ring waveguide structure, the slot waveguide structure can well limit a light field, the light intensity of resonance light is enhanced greatly due to the resonance effect of the micro ring, accordingly, various nonlinear effects of the micro ring are enhanced, the threshold value is reduced, the efficiency is improved, and the device can be applied to the all-optical signal processing fields such as optical frequency comb, wavelength conversion, logic gate, format conversion and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
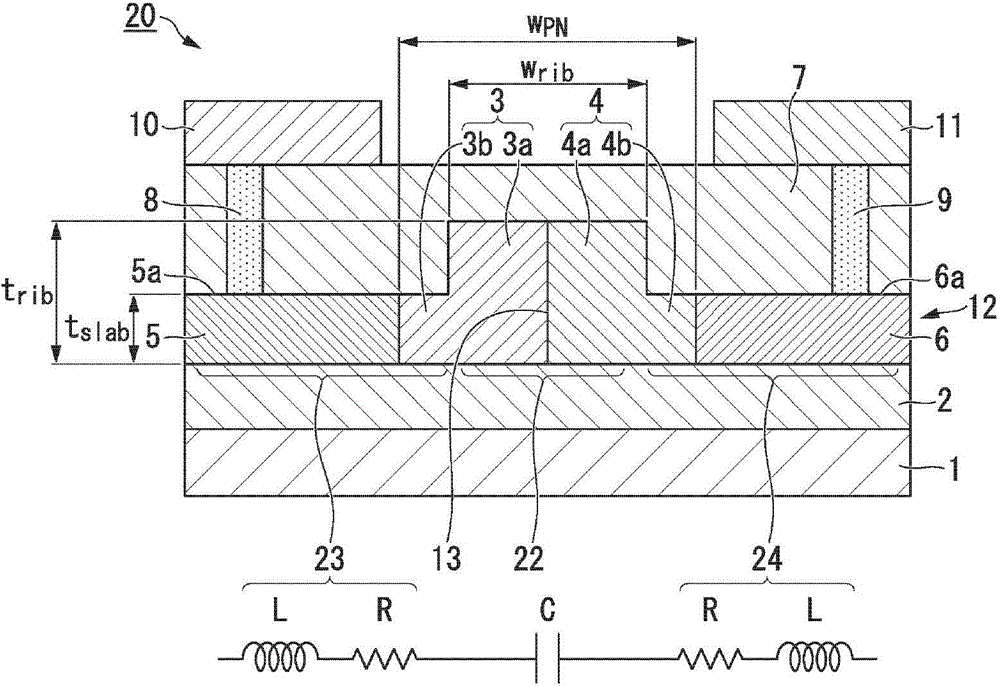
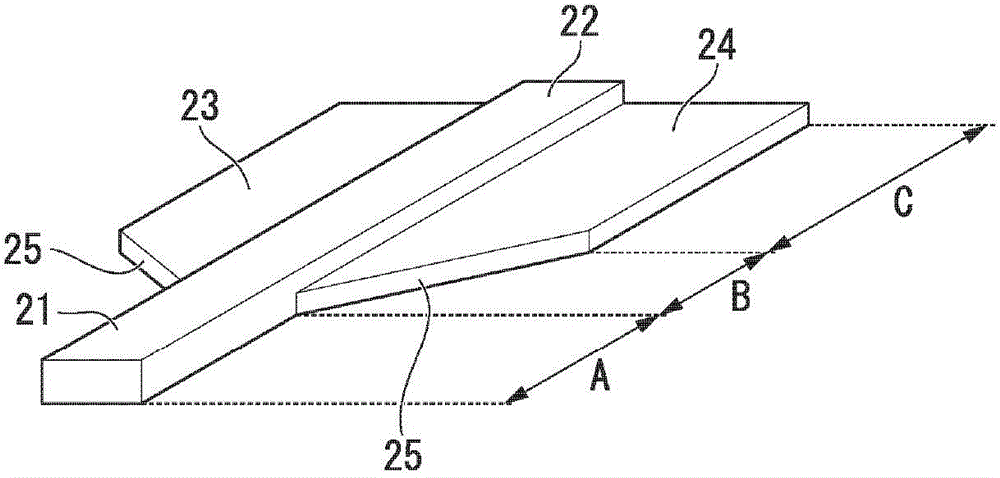
Electro-optice device comprising a ridge waveguide and a PN junction and method of manufacturing said device
ActiveUS20130058606A1Decrease device performance variationIncrease productionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideRidge waveguidesWaveguide
An electro-optic device, comprising an insulating layer and a layer of light-carrying material adjacent the insulating layer. The layer of light-carrying material, such as silicon, comprises a first doped region of a first type and a second doped region of a second, different type abutting the first doped region to form a pn junction. The first doped region has a first thickness at the junction, and the second doped region has a second thickness at the junction, the first thickness being greater than the second thickness, defining a waveguide rib in the first doped region for propagating optical signals. Since the position of the junction coincides with the sidewall of the waveguide rib a self-aligned process can be used in order to simplify the fabrication process and increase yield.
Owner:POINTCLOUD INC
Semiconductor optical device
ActiveUS7184207B1Avoid bad consequencesEfficiently modulate substantially the entire optical modeLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersSemiconductor structureMultimode interference
An optical device comprises a semiconductor structure including first and second ridge waveguides, each waveguide comprising a ridge extending across a surface of the semiconductor structure. The ridge of the first waveguide has a first height above a first region of the surface, and the ridge of the second waveguide has a second, greater, height above a second region of the surface. The semiconductor structure includes a multimode interference (MMI) region situated between the first and second ridge waveguides, which provides a transition between them. At least a part of the MMI region is tapered in width and / or at least a part of the first and / or second ridge waveguide is tapered in width in a direction extending away from the MMI region.
Owner:LUMENTUM TECH UK LTD
Ridge gap waveguide and multilayer antenna array including the same
ActiveUS20200185802A1Prevent leakageParticular array feeding systemsRadiating elements structural formsRidge waveguidesEngineering physics
Disclosed is a ridge guide waveguide including a conductive base, a conductive ridge protruding upward from the conductive base and extending along a predetermined wave transmission direction, an upper conductive wall located over the conductive base and the conductive ridge and spaced apart from the conductive ridge by a gap, and an electromagnetic bandgap structure arranged adjacent to the conductive ridge between the conductive base and the upper conductive wall.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
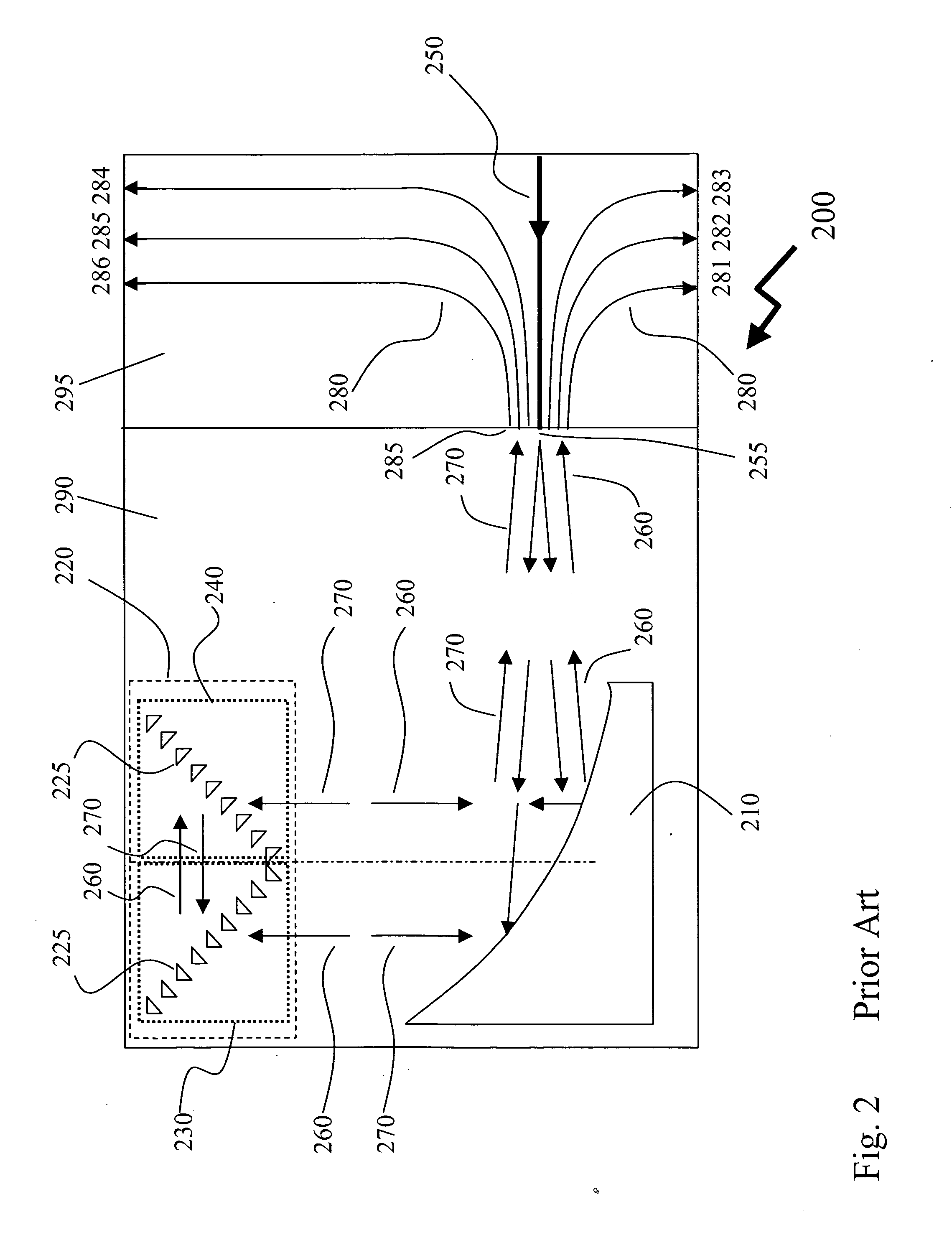
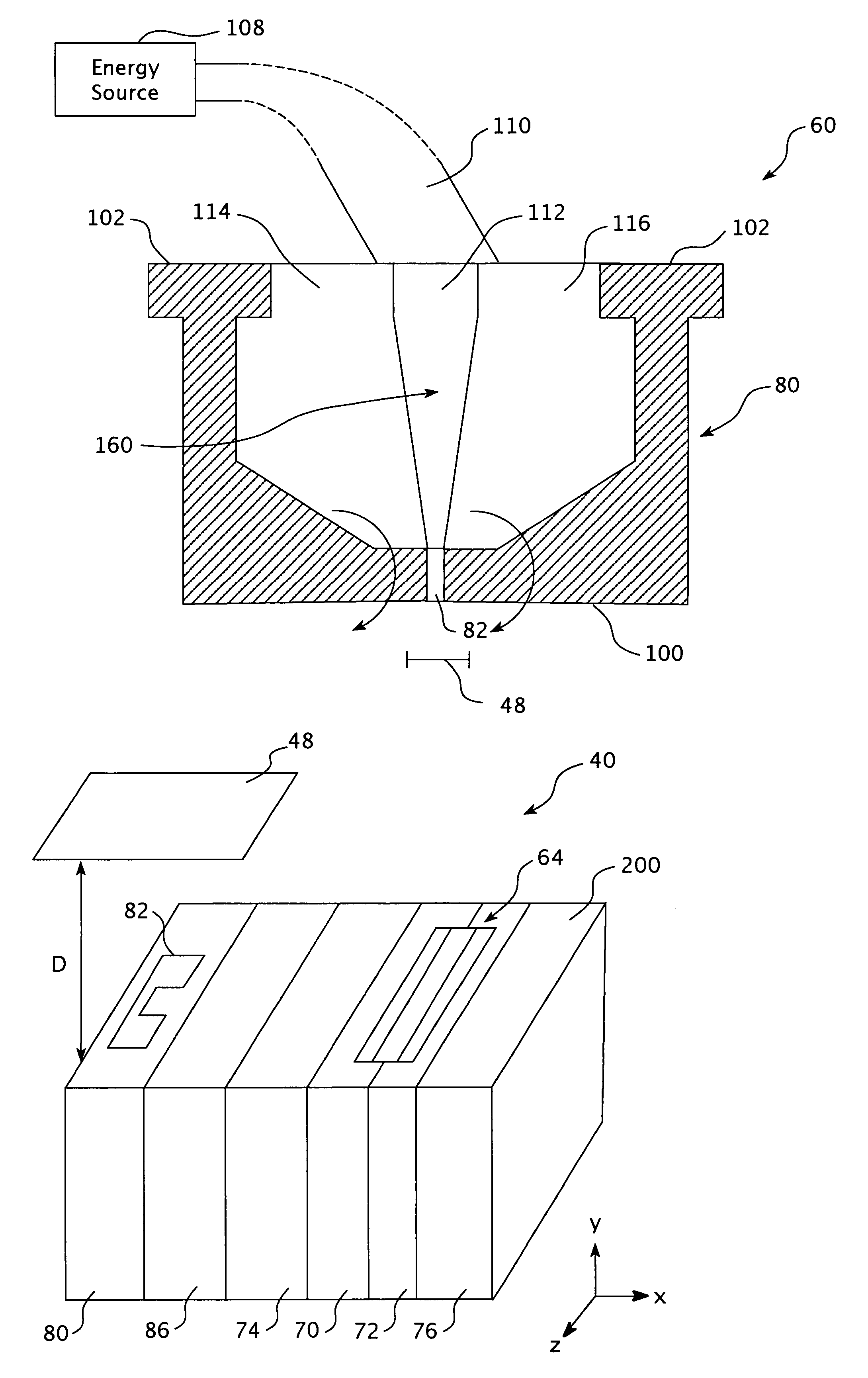
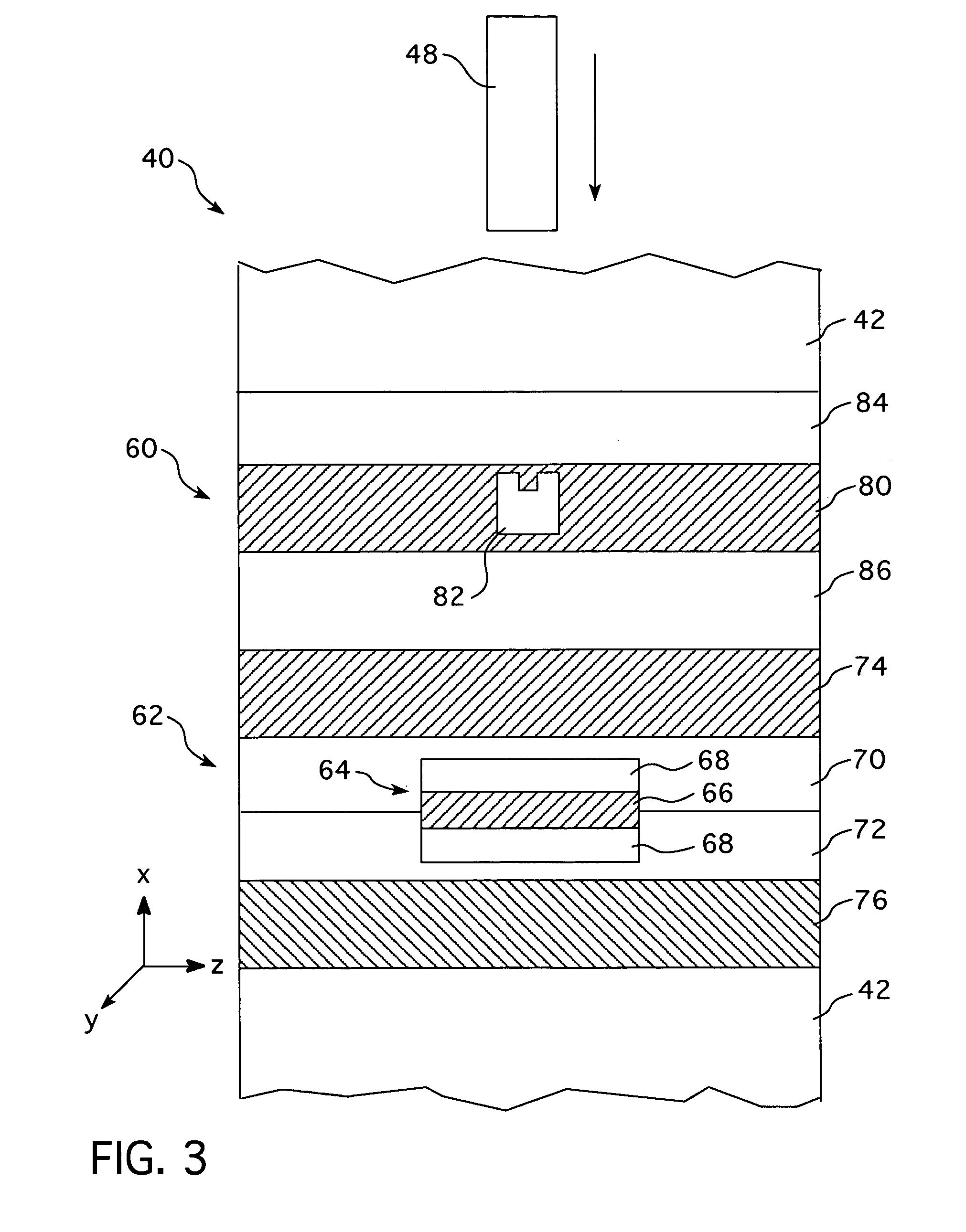
Ridge waveguide with recess
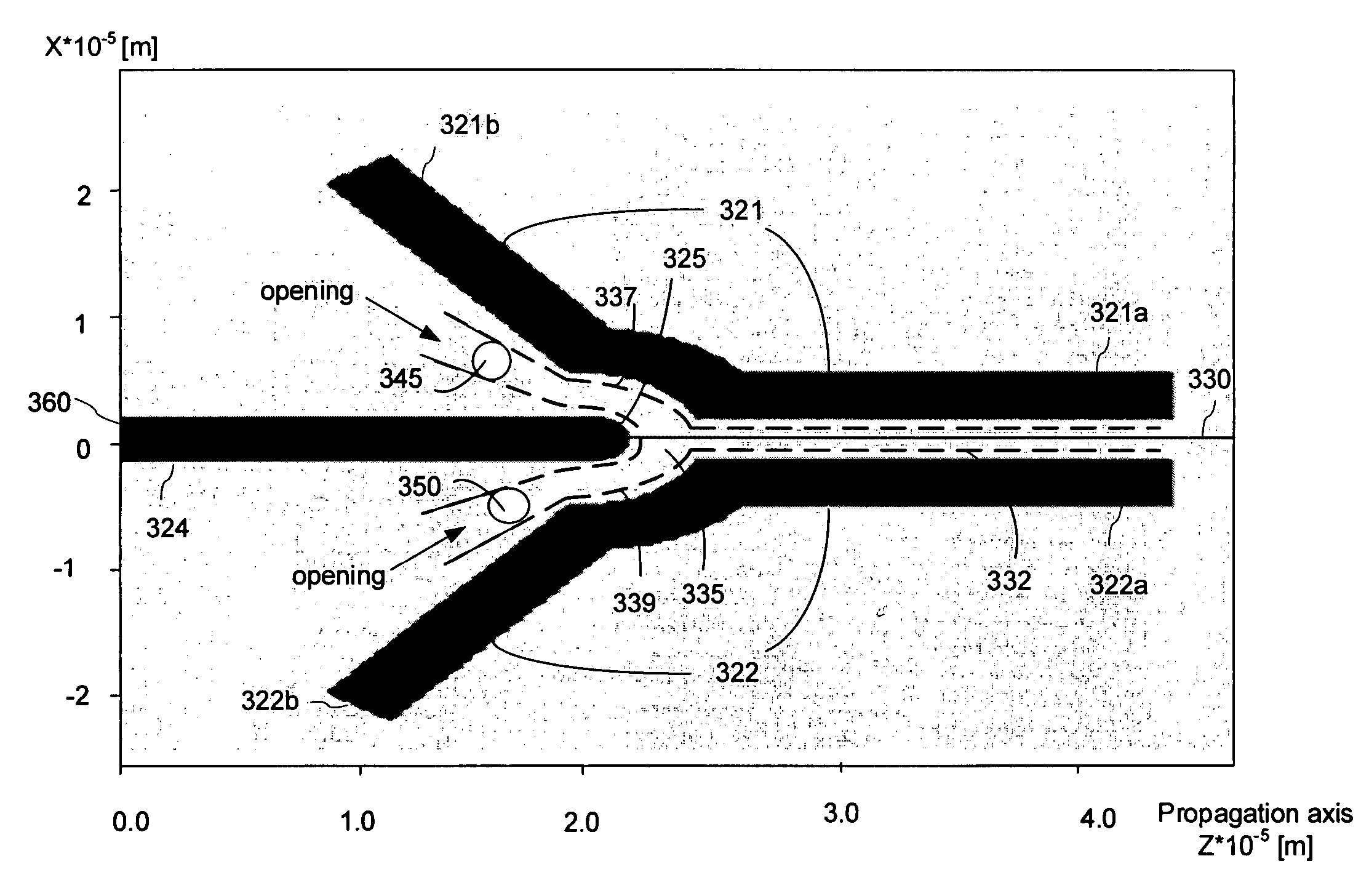
A ridge waveguide having a recessed ridge forming an isolated tip at a terminal end of the waveguide's aperture efficiently couples light into a spot adjacent to the tip in a medium below the terminal end of the waveguide which is significantly smaller than the light's wavelength. The waveguide is used to heat a recording medium via the small spot for heat assisted recording or to pattern substrates by photolithography with line width exposures that are significantly smaller than the wavelength of light. The body of the waveguide may also be recessed away from the medium in an area surrounding the waveguide's aperture to further confine the energy emerging from the waveguide to the small spot adjacent the tip in the medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
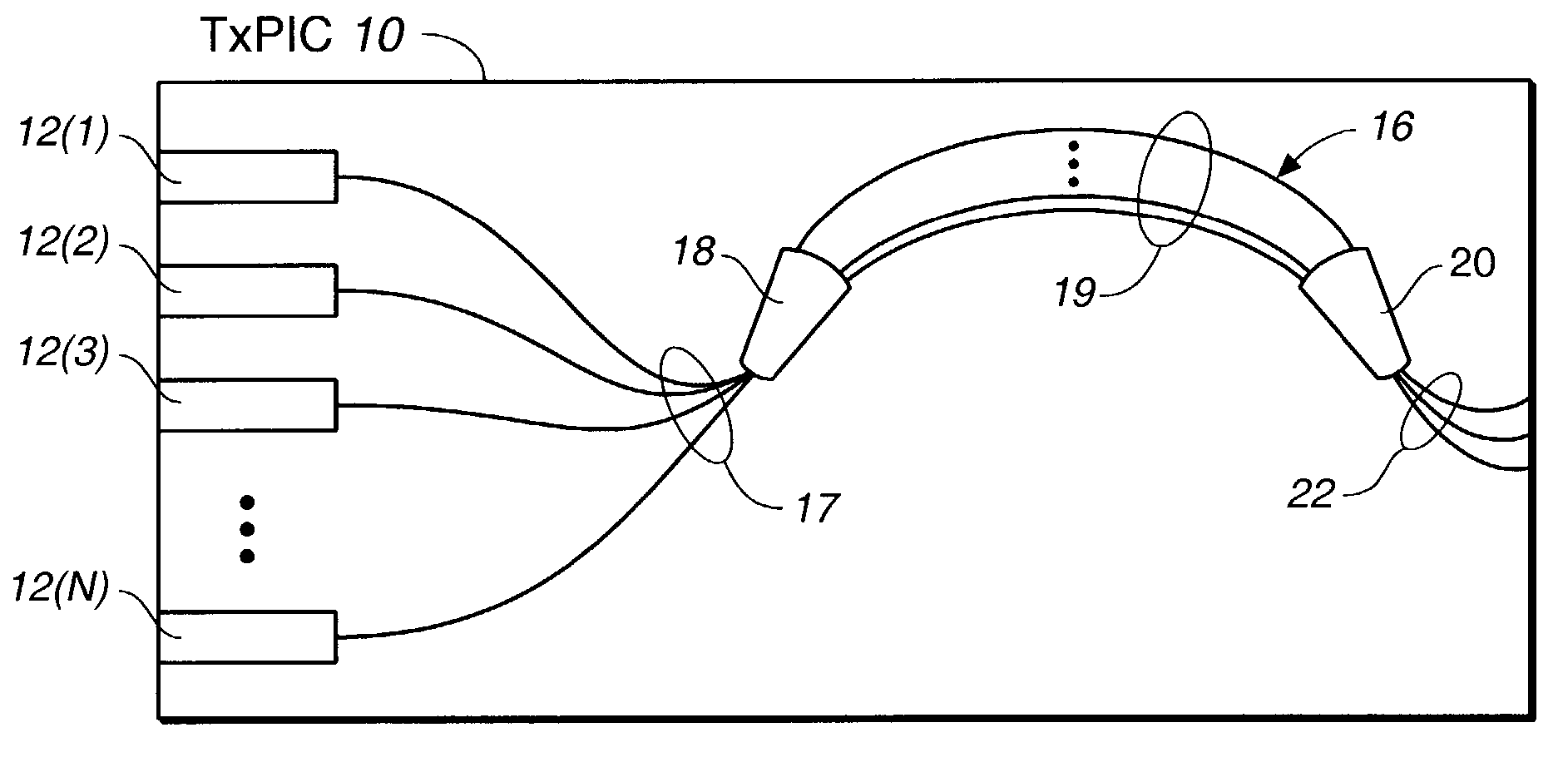
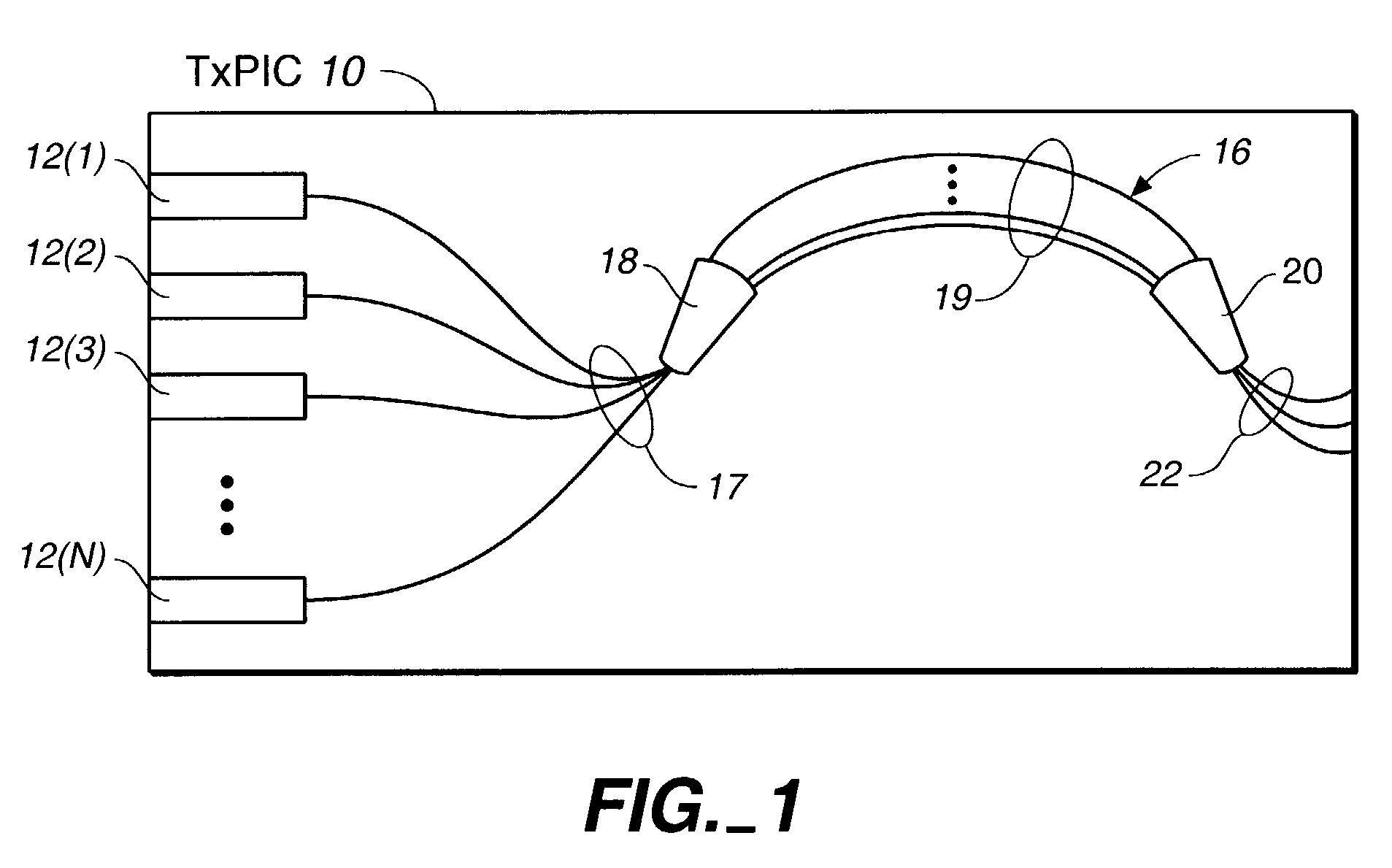
Transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC) chip with enhanced power and yield without on-chip amplification
ActiveUS7058246B2Improve output performanceQuality improvementOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionRidge waveguidesLength wave
A monolithic photonic integrated circuit (PIC) chip comprises an array of modulated sources providing a plurality of channel signals of different wavelengths and an optical combiner coupled to receive the channel signals and produce a combined output of the channel signals. The arrays of modulated sources are formed as ridge waveguides to enhance the output power from the respective modulated sources so that the average output power from the sources is approximately 2 to 4 times higher than in the case of comparable arrays of modulated sources formed as buried waveguides.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Waveguiding structures with embedded microchannels and method for fabrication thereof
InactiveUS7471866B2NanoinformaticsMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotonic crystalRidge waveguides
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Low power consumption electro-optical modulator with silicon-based cascade resonator structure
InactiveCN101639576ARaise the F valueImprove FSRCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideGratingRidge waveguides
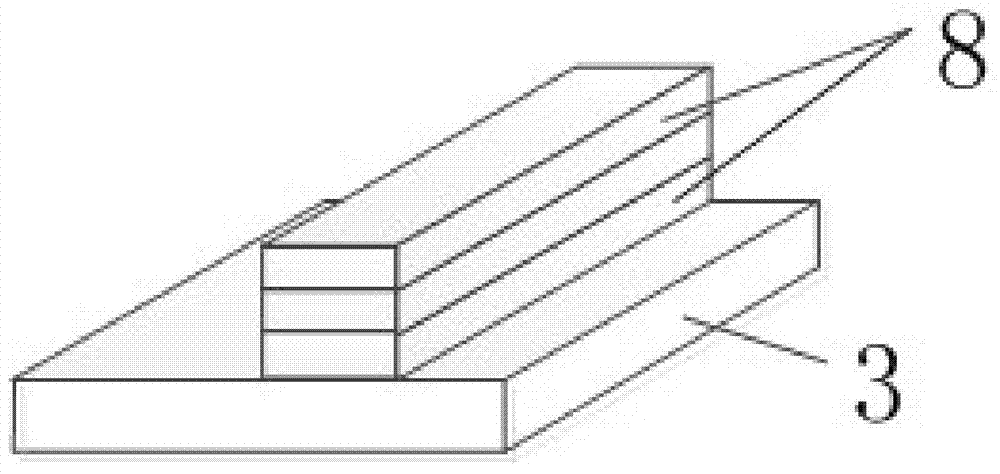
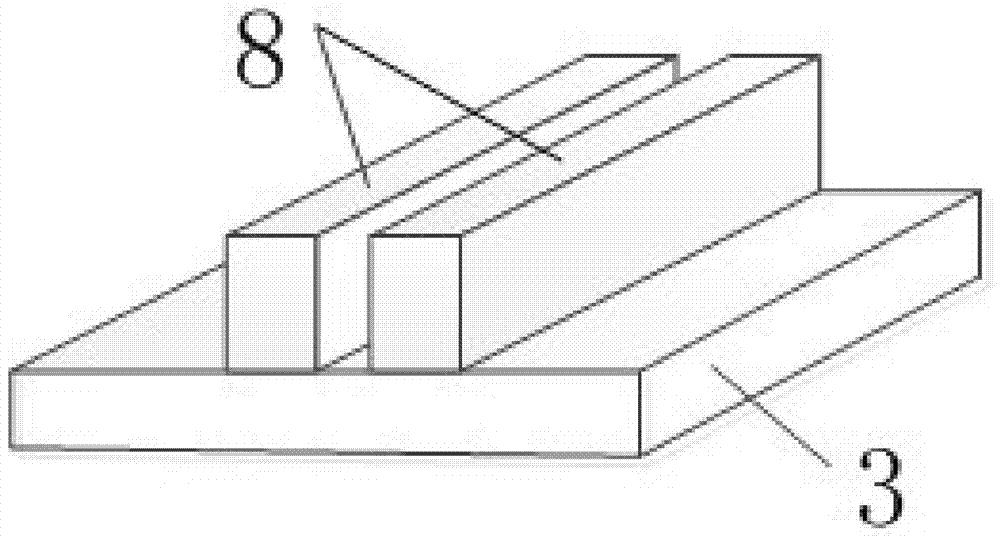
The invention discloses a low power consumption electro-optical modulator with a silicon-based cascade resonator structure, which is formed by serially connecting two Fabry-Perot resonant cavities (4)manufactured on an silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate on an insulator, wherein the two Fabry-Perot resonant cavities (4) are serially connected by adopting a form of cursor cascade to form a low power consumption electro-optical modulator with a cascade resonator structure. Each Fabry-Perot resonant cavity (4) consists of two Bragg gratings (3) and a ridge waveguide (1) positioned between the two Bragg gratings, and the Bragg gratings (3) are taken as reflecting mirrors of the Fabry-Perot resonant cavities (4). The low power consumption electro-optical modulator greatly improves parametersof the resonant cavities such as F values, FSR, Q values and the like, ensures that the extinction ratio of the electro-optical modulator is greatly increased, needs lower power consumption for the modulation, and has quicker speed; a device has a compact structure; and the production technology is compatible with a mature microelectronic CMOS process.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical waveguide element and optical modulator
InactiveCN104885003AHigh extinction ratioOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsSection planeRidge waveguides
An optical waveguide element is provided with a rib-type waveguide having a core that has a rib portion, and a pair of slab portions including a first slab portion and a second slab portion that are connected respectively to both ends of the rib portion so as to sandwich the rib portion. The rib portion has a cross-sectional dimension that allows the propagation of light of a basic mode and a high-order mode in a preset single polarization state, and has a first P-type semiconductor and a first N-type semiconductor that form a PN junction. The first slab portion has a second P-type semiconductor and a P-type conductor that are connected to each other, the second P-type semiconductor being connected to the first P-type semiconductor of the rib portion. The second slab portion has a second N-type semiconductor and an N-type conductor that are connected to each other, the second N-type semiconductor being connected to the first N-type semiconductor of the rib portion.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD
Waveguide Bragg grating based on SiO2 strip-loaded waveguide and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105607186AHigh transparencyGood optical consistencyOptical waveguide light guideGratingRidge waveguides
The invention discloses a waveguide Bragg grating based on a SiO2 strip-loaded waveguide and a manufacturing method thereof. The waveguide Bragg grating comprises a substrate layer, a flat core layer, a guide core layer and an upper coating, wherein the flat core layer covers the front side of the substrate layer, the guide core layer is positioned on the front side of the flat core layer, and the upper coating covers the front side of the flat core layer and wraps the guide core layer. The waveguide Bragg grating has the advantages of simplicity in process, low cost, good consistency, large-scale production and the like; and compared with a manufacturing process of an outer ridge modulation type waveguide Bragg grating based on a ridge waveguide, the manufacturing method has the advantages that the process is simple, the cost is low, the size is small and the like.
Owner:HENAN SHIJIA PHOTONS TECH
Ridge waveguide serial interferometers
ActiveUS20120134623A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePhase differenceRidge waveguides
In a ridge waveguide serial interferometer mode conversion is induced by a first mode conversion section, a phase difference between modes is introduced by propagation over a length of waveguide and optical interference is produced following further mode conversion induced in a second mode conversion section. The first mode conversion section has a first radius of curvature, which is equal to a second radius of curvature of the second mode conversion section. The ridge waveguide interferometer advantageously provides an equal phase dependency as a function of temperature.
Owner:LUMENTUM TECH UK LTD
Laser diode with ridge waveguide structure and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110164642A1Heat dissipation function can be improvedLow thermal conductivityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsRidge waveguidesWaveguide
An LD with an improved heat dissipating function in the edge regions is disclosed. The LD provides the core region including the active layer and extending whole of the substrate, and the ridge waveguide structure on the core region that extends in a direction along which the light generated in the active layer is guided. The ridge waveguide structure is buried by a thick resin layer in both sides thereof, but the resin layer is removed in the edge regions close to respective facets of the LD.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Semiconductor laser micro-heating element structure
InactiveUS7486709B2Optical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionRidge waveguidesSemiconductor package
A semiconductor laser is provided comprising a semiconductor substrate, an active region, a ridge waveguide, a driving electrode structure, and a micro-heating element structure. The micro-heating element structure comprises a pair of heating element strips extending along the longitudinal dimension of the semiconductor laser. The heating element strips are on opposite sides of the ridge waveguide such that one of the heating element strips extends along one side of the ridge waveguide while a remaining heating element strip extends along another side of the ridge waveguide.
Owner:CORNING INC
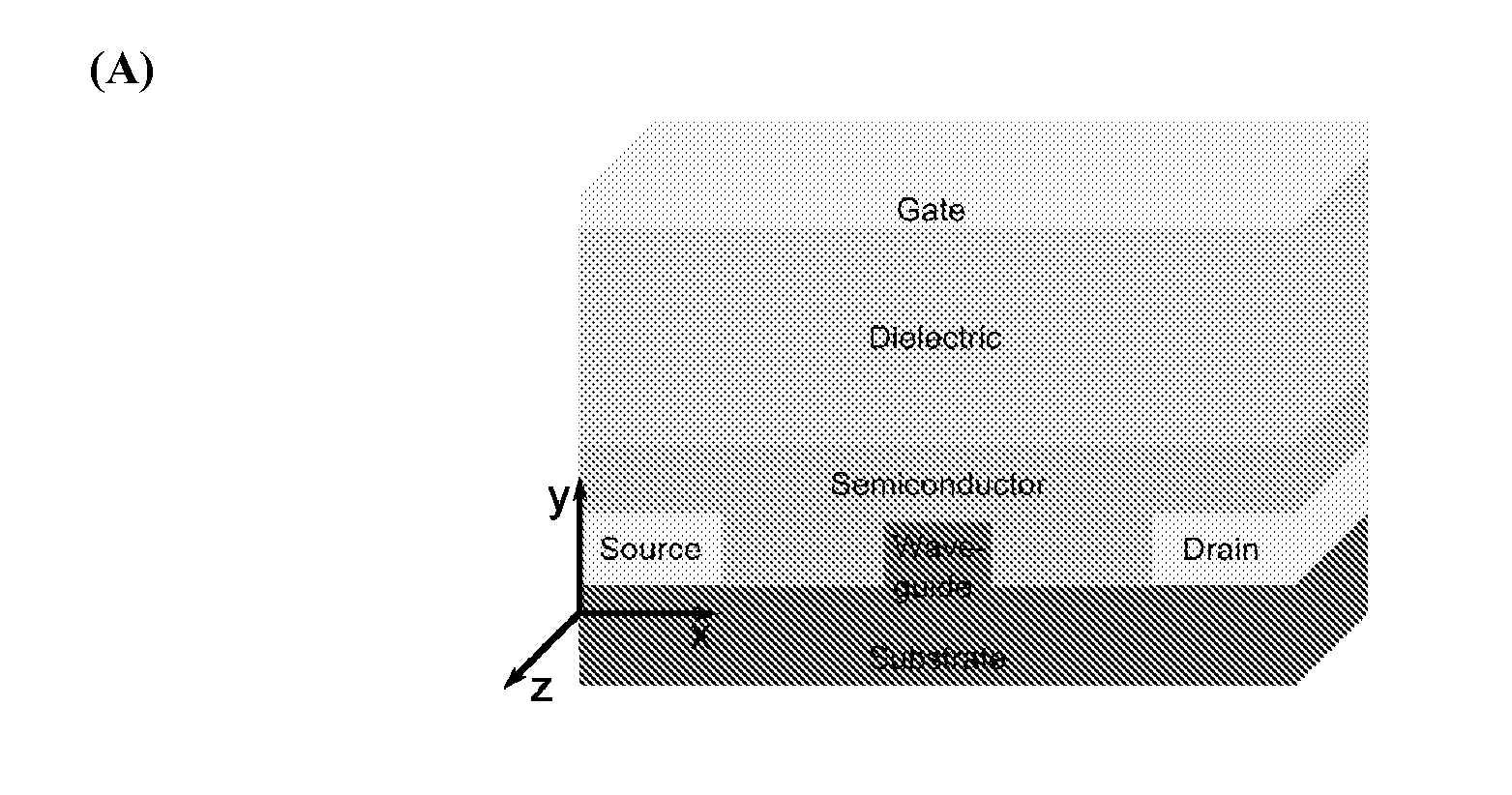
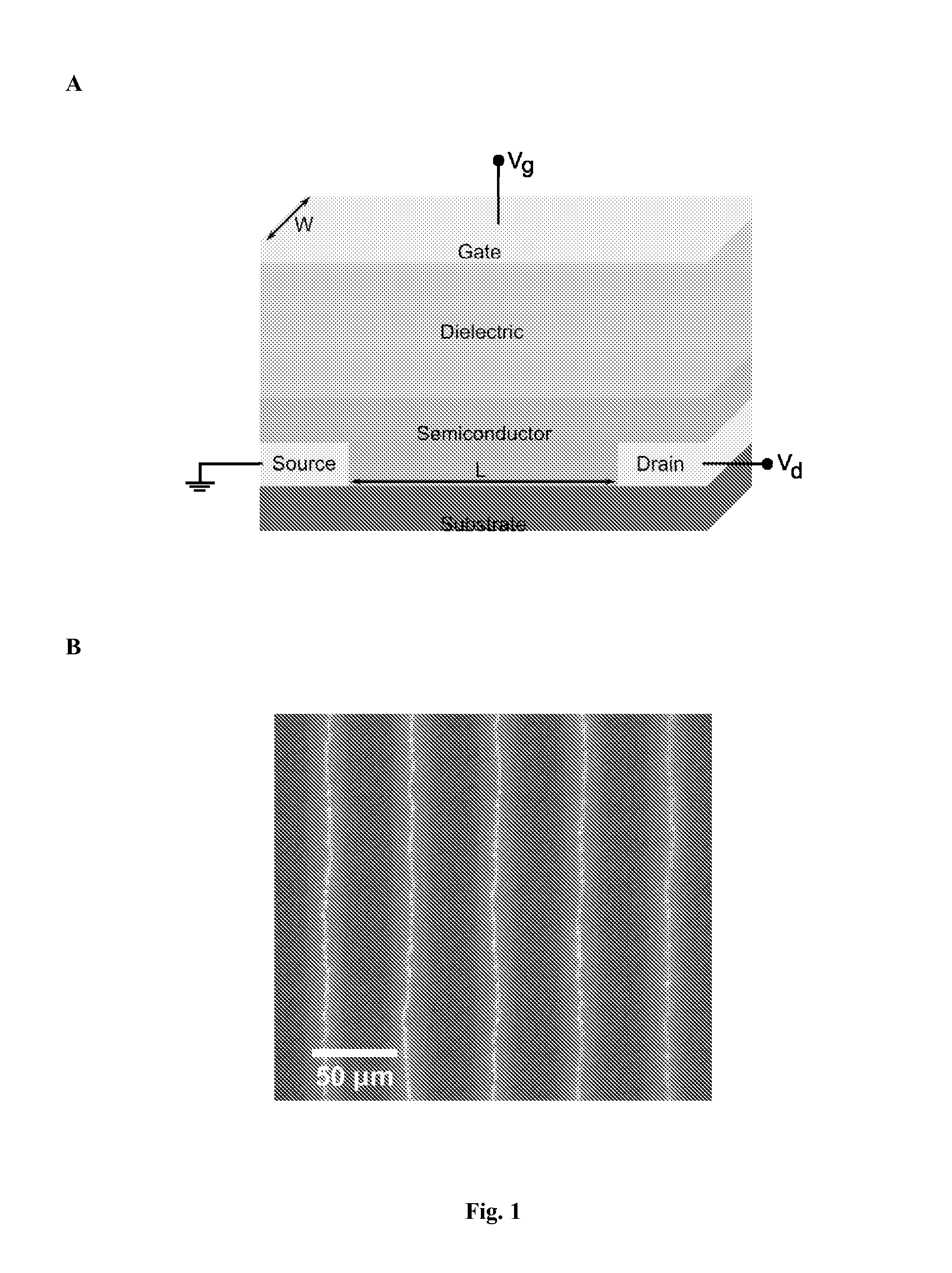
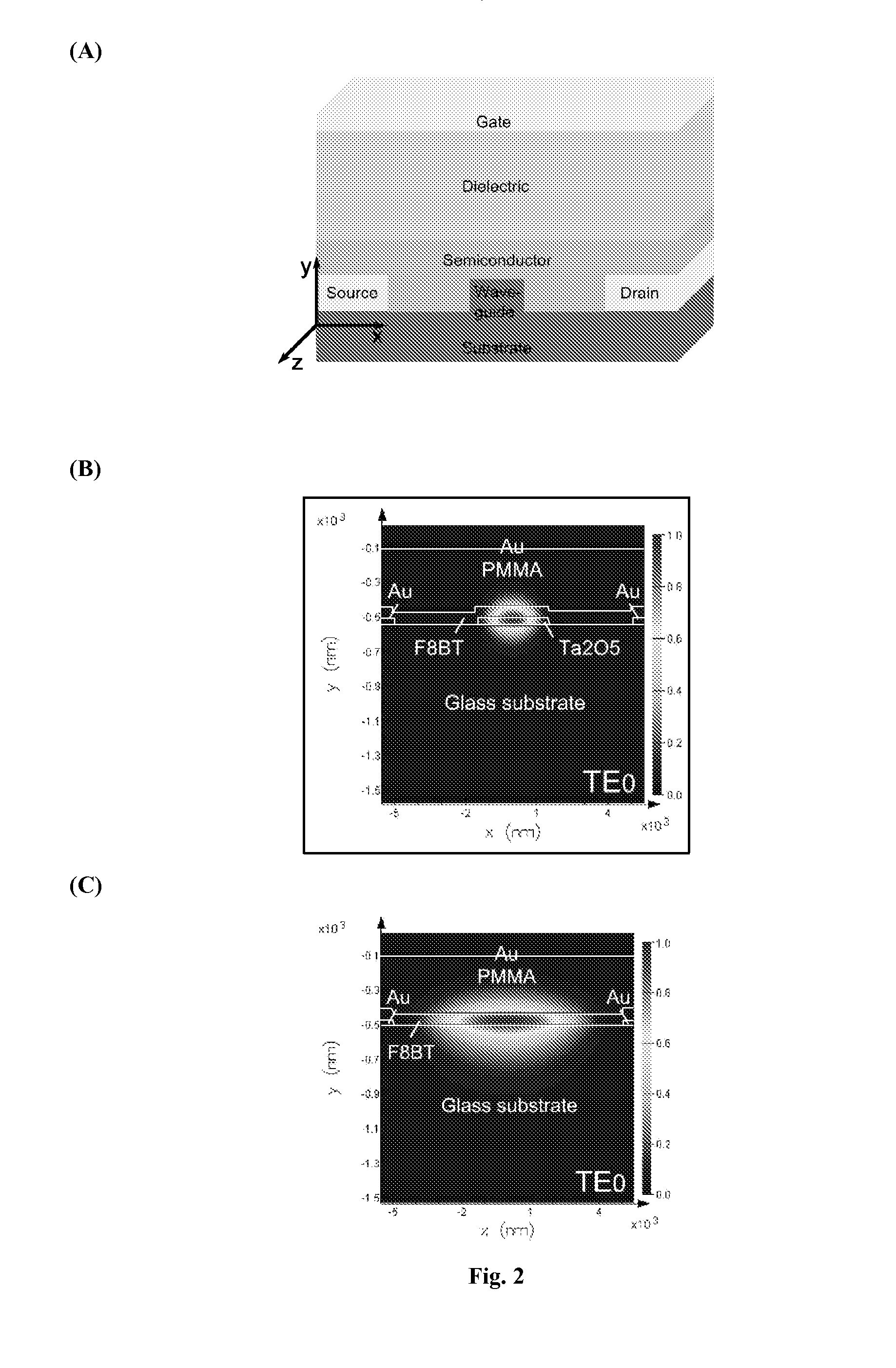
Optoelectronic Devices
ActiveUS20110229073A1Reduce light lossHigh LFET currentOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOrganic field-effect transistorRidge waveguides
The present invention relates integrated optoelectronic devices comprising light emitting field-effect transistors. We describe an optoelectronic device comprising a light-emitting field effect transistor (LFET) with an organic semiconductor active layer and a waveguide integrated within the channel of the light-emitting field effect transistor, wherein said waveguide comprises a material which has a higher refractive index than said organic semiconductor. We also describe a light-emitting organic field transistor integrated with a ridge or rib waveguide incorporated within the channel of the LFET; and a similar light-emitting organic field effect transistor in which the waveguide incorporates an optical feedback mechanism.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
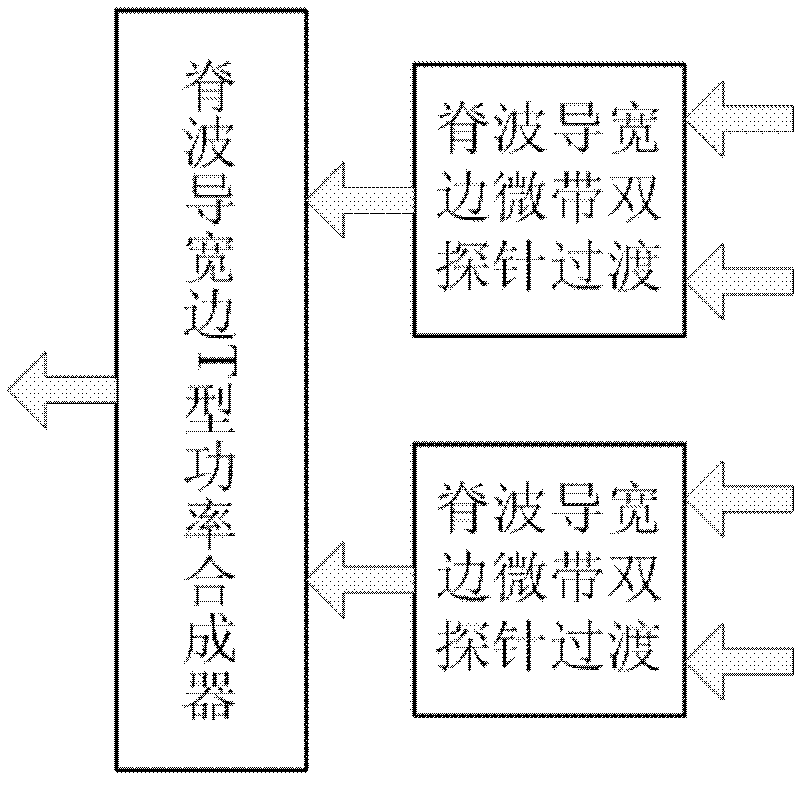
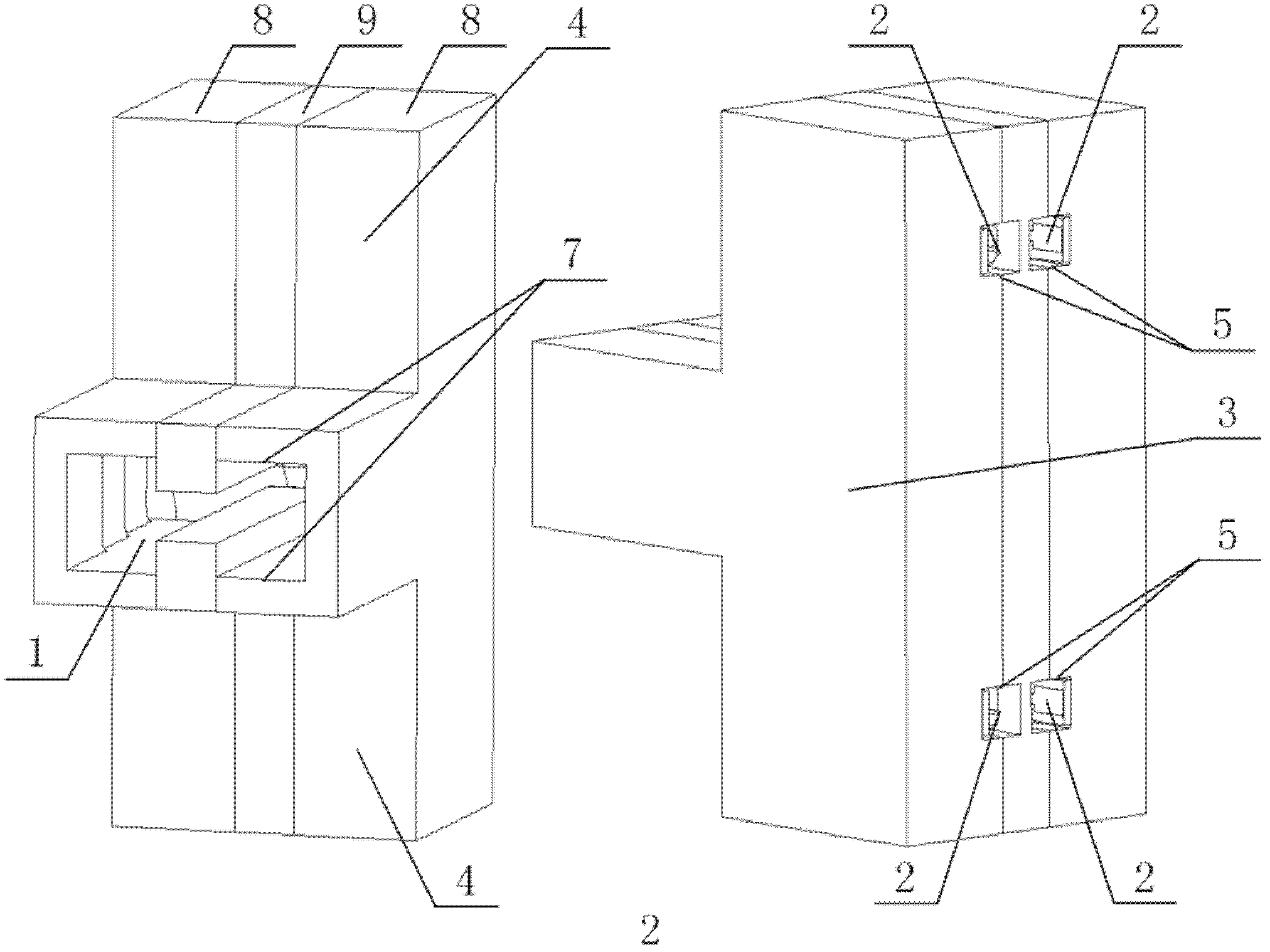
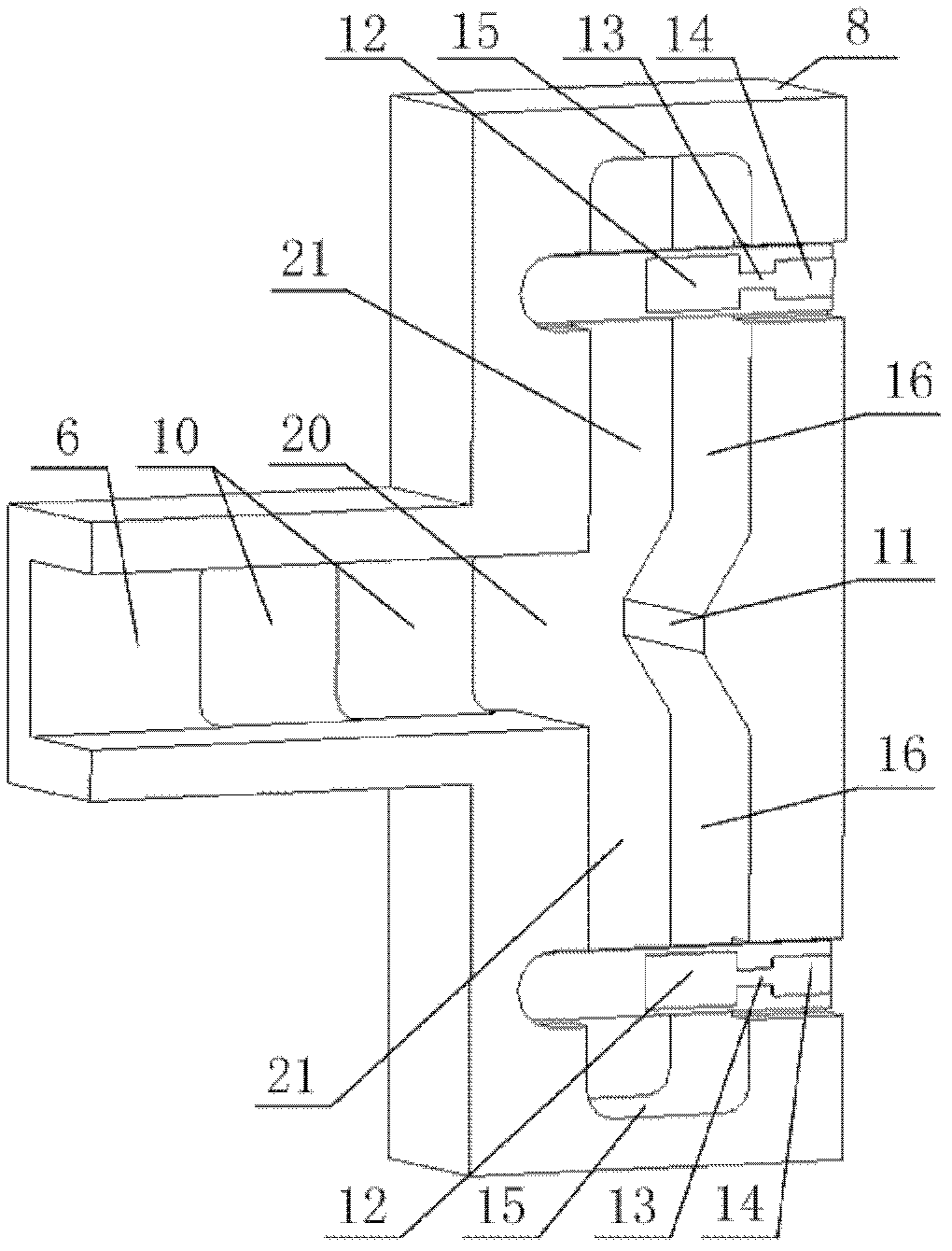
Millimeter wave ultra-wideband spatial power combining network
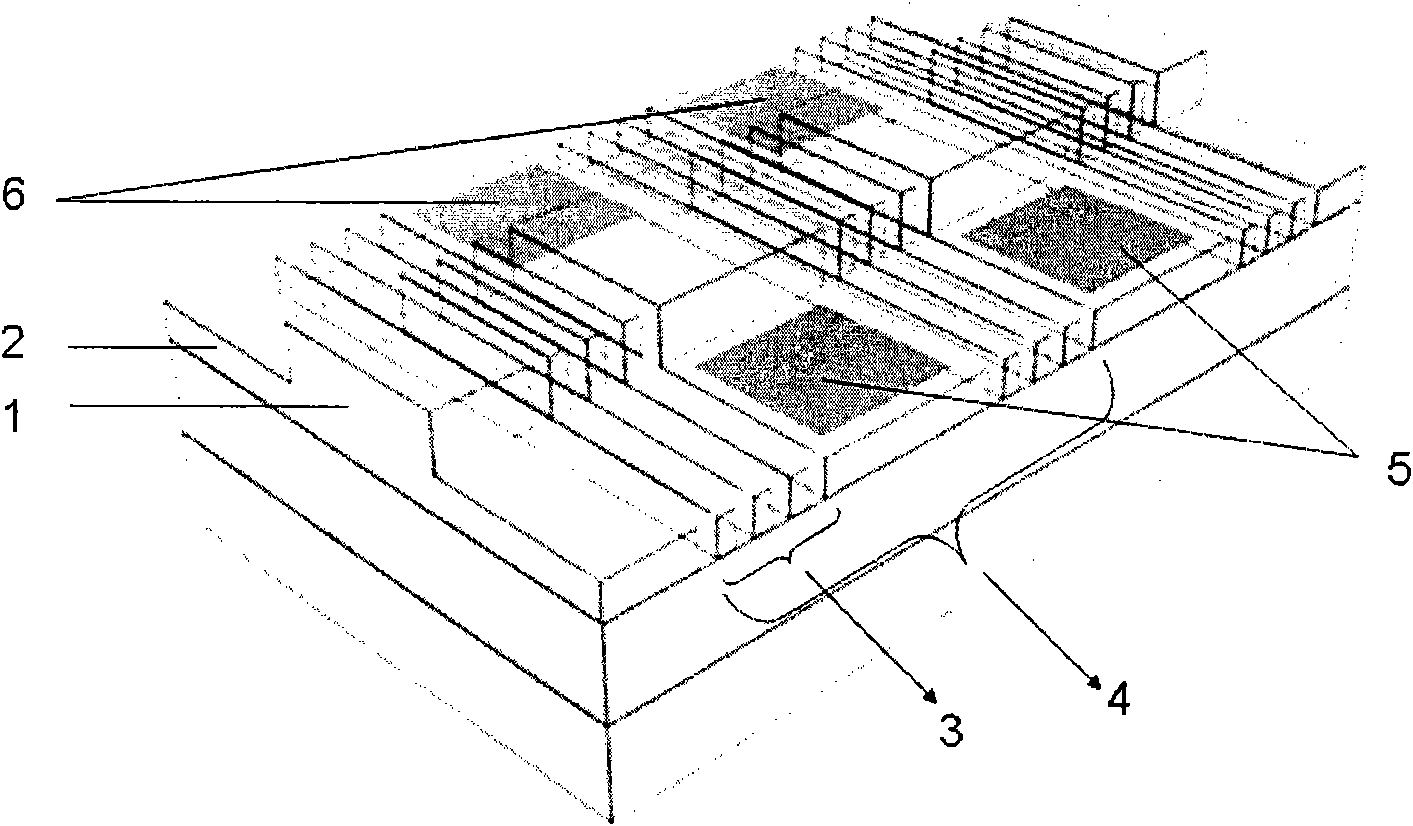
The invention provides a millimeter wave ultra-wideband spatial power combining network. Radio-frequency signals are combined to a standard double-ridge-waveguide output port (1) from four micro-strip transmission line input ports (2). Micro-strip double probes (12) are vertically inserted in from a single-ridge-waveguide broadside (16) and are distributed on two sides of waveguide single ridges (19) in a face-to-face mode. Radio-frequency signals on micro-strip transmission lines (14) are transferred into non-standard single ridge waveguides (21), and the radio-frequency signals which are transferred into an upper non-standard single ridge waveguide and a lower non-standard single ridge waveguide are combined to a non-standard double-ridge-waveguide (20) through a T-joint (3). A two-stage impedance conversion step (10) is manufactured on the inner wall of a U-shaped slot bottom of a T-shaped outer layer (8). The non-standard double-ridge-waveguide is converted into a standard double-ridge-waveguide (6), and at the same time, the radio-frequency signals are transferred to the standard double-ridge-waveguide output port (1). The waveguide single ridges (19) of the upper non-standard single ridge waveguide and the lower non-standard single ridge waveguide are respectively turned, extend to pass through the non-standard double-ridge-waveguide and ultimately enter into the standard double-ridge-waveguide to form a double-ridge (17).
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Flat plane antenna applicable to mobile satellite communication terminal
ActiveCN101710651AReduce complexityReduce volumeAntenna supports/mountingsSlot antennasRidge waveguidesCoupling
The invention relates to an antenna applicable to mobile satellite communication terminal. The antenna comprises two vertically-polarized arrays, two horizontally-polarized arrays and two feeding waveguides, the vertically-polarized arrays are ridge waveguides with broad side radiate longitudinal seam, the horizontally-polarized arrays are rectangular radiate waveguides with narrow side radiate inclined seam. The invention is characterized in that the two ridge waveguides and the two radiate waveguides are arranged parallel in a stagger way to form a double-polarized array; the height of the radiate waveguides is higher than that of the ridge waveguides; one v is arranged on the bottom of one end of the double-polarized array in an orthogonal way; the inclined coupling seam and the coupling longitudinal seam which are communicated are respectively arranged between the two ridge waveguides and the feeding waveguides and between the two radiate waveguides and the feeding waveguides. Theinvention integrates the antenna with the feeder by coupling and feeding, thus greatly reducing height and weight of the antenna, and simplifying the structure of the antenna and the design of the feeding network. The invention has low profile but high gain, and is very suitable for satellite communication terminal of mobile carrier.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
An arrangement for electrical magnetic medium electromagnetic quantity temperature variation testing using ridge waveguide
InactiveCN1448726AResistance/reactance/impedenceMagnetic property measurementsTemperature controlRidge waveguides
The measurement equipment consists of vector network analyzer, temperature control system, TRL correcting part and ridged waveguide transmission system. The ridged waveguide transmission system consists of two coaxial converting joints connected to the ridged waveguide, two heat-dissipating ridged waveguides, two heat-isolating ridged waveguides, ridged waveguide heating seat, measured ridged waveguide and ridged waveguide temperature measuring seat. By using ridged waveguide as transmission line, the present invention has the features of relatively wide measurement frequency range, easy-to-make correcting part, measured specimen and transmission line. The present invention is especially suitable for measuring electromagnetic parameters of electromagnetic medium in different temperature and wide frequency band.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
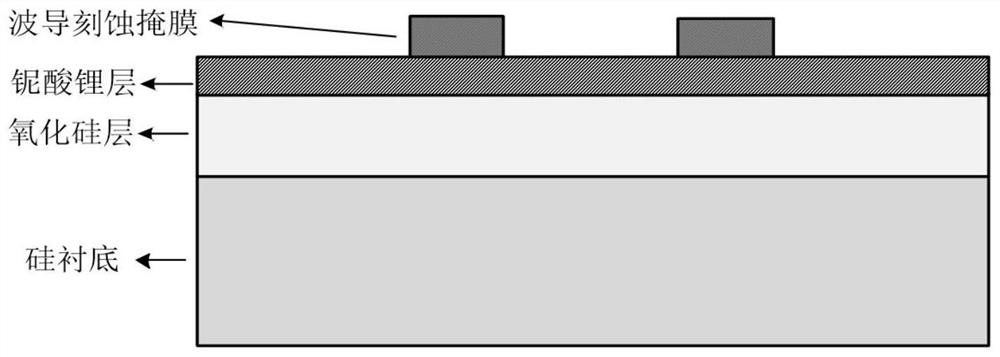
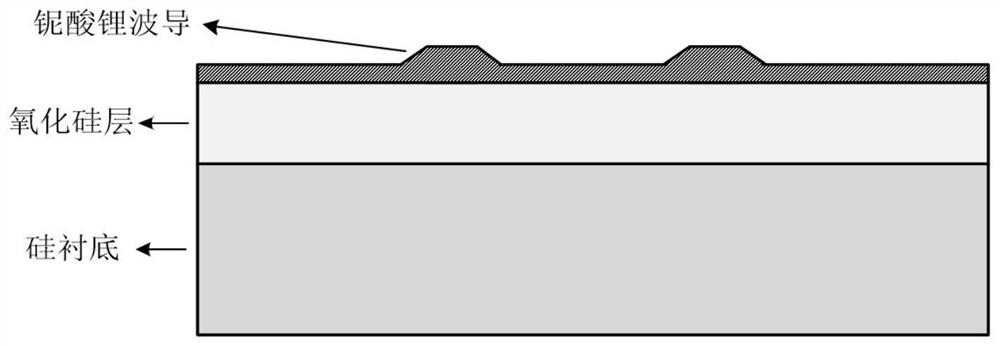
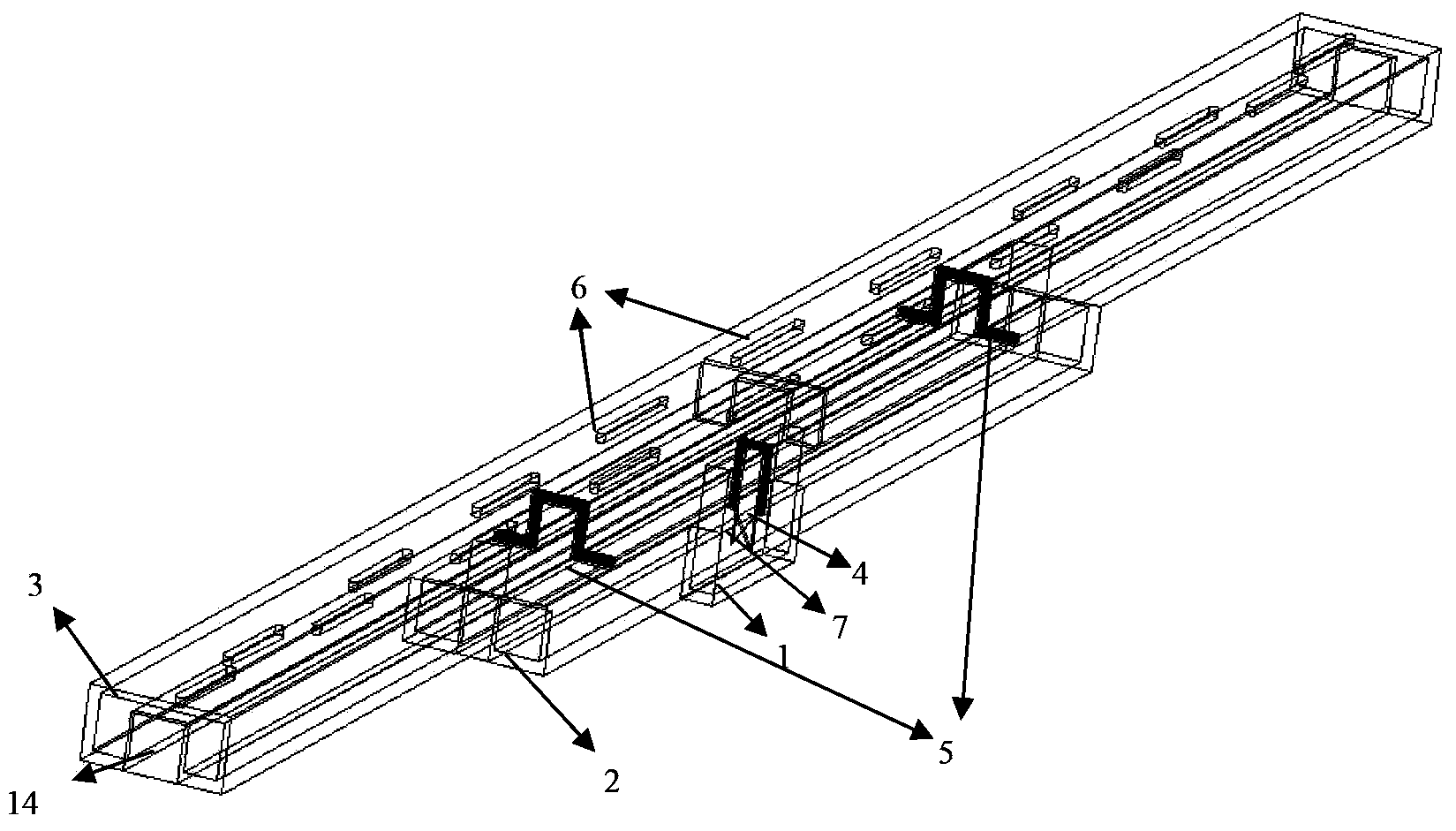
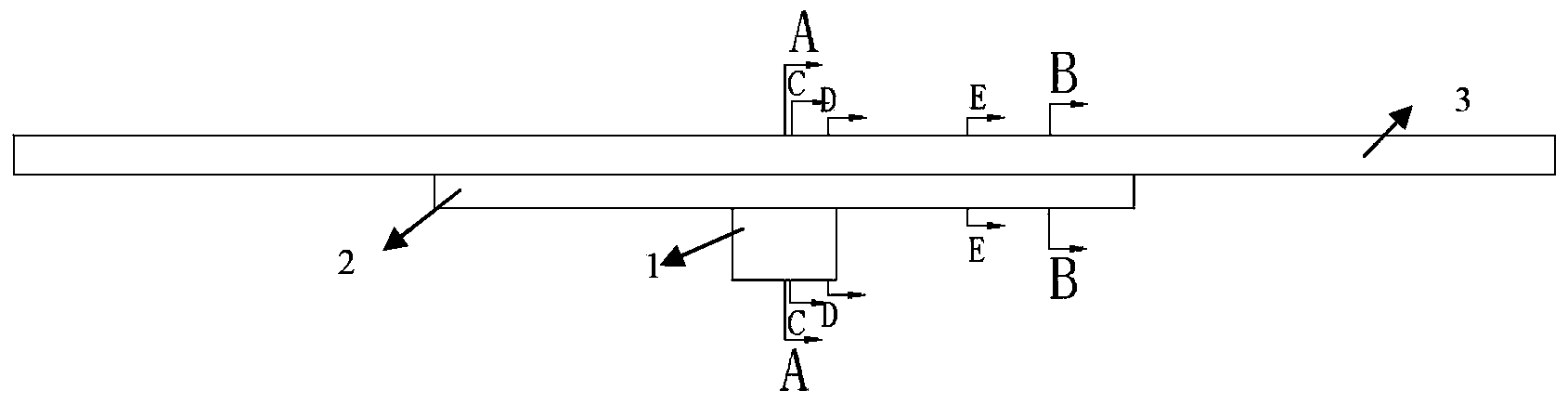
Thin-film lithium niobate-based integrated chip and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111736370ARealize the filtering functionRealize the delay functionNon-linear opticsRidge waveguidesCarrier signal
The invention discloses a thin-film lithium niobate-based integrated chip and a preparation method thereof. A substrate material is silicon-based thin film lithium niobate; the waveguide is a lithiumniobate ridge waveguide; the structure comprises an input / output port, a Mach-Zehnder electro-optic intensity modulator and a coupled double-ring resonator, a Mach-Zehnder modulator comprises two 1*2multimode interference couplers, two modulation arms and a GSG electrode, two coupling regions of the coupled double-ring resonator adopt coupling coefficient tuning units based on a Mach-Zehnder interference structure, and regulation and control electrodes are arranged in the coupling regions and the cavity; a radio frequency signal is loaded to an optical carrier through the modulator and thenis processed by the resonator, and the output signal is output to a detector or other unit chips through the output end, so that the functions of filtering, time delay and the like are realized. The electro-optical modulator and the micro-ring resonator are integrated, the filtering and time-delay functions are achieved, the all-silicon-based thin film lithium niobate material is adopted, and theadvantages of being large in bandwidth and rapid in tuning are achieved.
Owner:南京中电芯谷高频器件产业技术研究院有限公司
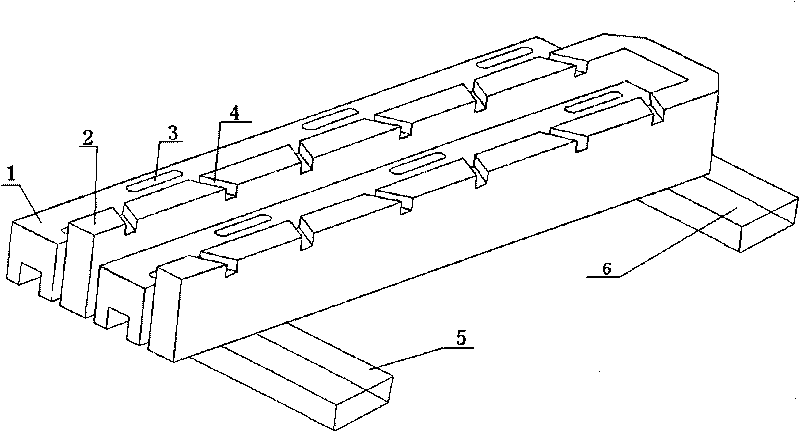
Broadband low minor lobe ridge waveguide gap array antenna
InactiveCN103384032AReduce the impactGuaranteed performanceAntenna arraysSlot antennasRidge waveguidesCoupling
The invention provides a broadband low minor lobe ridge waveguide gap array antenna. A radiation single-ridge waveguide (3) is an antenna array surface coalition formed by connecting two identical ridge waveguides in a butt joint mode, wherein the metal outer wall at the joint divides two waveguide cavities into two subarrays. A feed gap (4) is formed in the end portion of the center of a feed rectangular waveguide (1), wherein the feed rectangular waveguide (1) is nested in a concave ridge of a concave-convex double-ridge waveguide (2), a coupling gap (5) is formed in a convex ridge of the concave-convex double-ridge waveguide, and the convex ridge is embedded in a concave ridge of the radiation single-ridge waveguide. Feed is conducted in two stages, wherein the rectangular waveguide at the bottom conducts feed on the concave-convex double-ridge waveguide in the middle in the first stage, the concave-convex double-ridge waveguide conducts feed on the radiation single-ridge waveguide on the top in the second stage, the rectangular waveguide utilizes the feed gap formed in the rectangular waveguide to complete the feed on the concave-convex double-ridge waveguide, the concave-convex double-ridge waveguide utilizes the coupling gap formed in the concave-convex double-ridge waveguide to complete the feed on the radiation single-ridge waveguide, a radiation gap (6) completes aerial radiation, and the complete ridge waveguide gap array antenna is formed. The broadband low minor lobe ridge waveguide gap array antenna is wide in frequency band, low in minor lobe, and simple and compact in structure.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
DFB laser based on surface gating
ActiveCN106848835AImprove coupling coefficientReduce manufacturing difficultyOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionManufacturing technologyGrating
The invention discloses a DFB laser based on surface gating. The laser is of a ridge waveguide structure, and comprises a substrate, a lower waveguide cover layer, an active layer and an upper waveguide cover layer from the bottom up, wherein Bragg grating is etched in the surface of the ridge waveguide; the ridge area adopts high refractive material, so that the gating has a large coupling coefficient; no electrode is formed on the ridge waveguide, and the electrodes are positioned on two sides of the ridge waveguide; a groove is etched between the ridge waveguide and each of the electrodes on two sides; in the laser, the lower waveguide cover layer comprises one or more current limitation areas, or a buried tunnel junction is manufactured in the upper waveguide cover layer to limit current. According to the laser provided by the invention, secondary epitaxial growth of the material is not needed, the manufacturing technology is simple and convenient, and thus the manufacturing cost of the device is reduced, and the reliability of the device is improved. In addition, the laser provided by the invention can acquire the maximum coupling coefficient, so that the laser performance of low threshold and high-speed direct adjustment can be acquired in the case that the cavity length of the laser is extremely short.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com