Patents
Literature
350 results about "Coaxial waveguides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
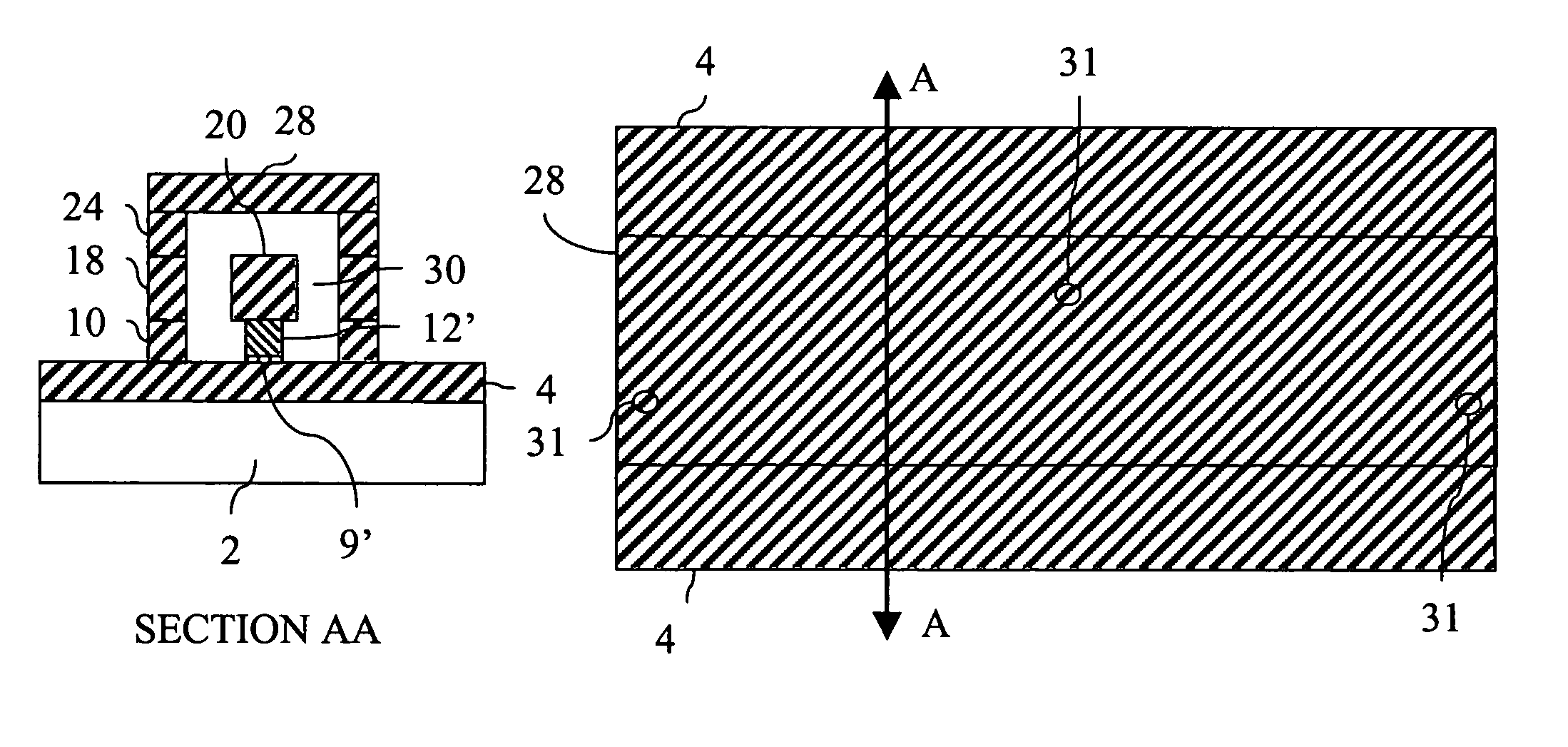
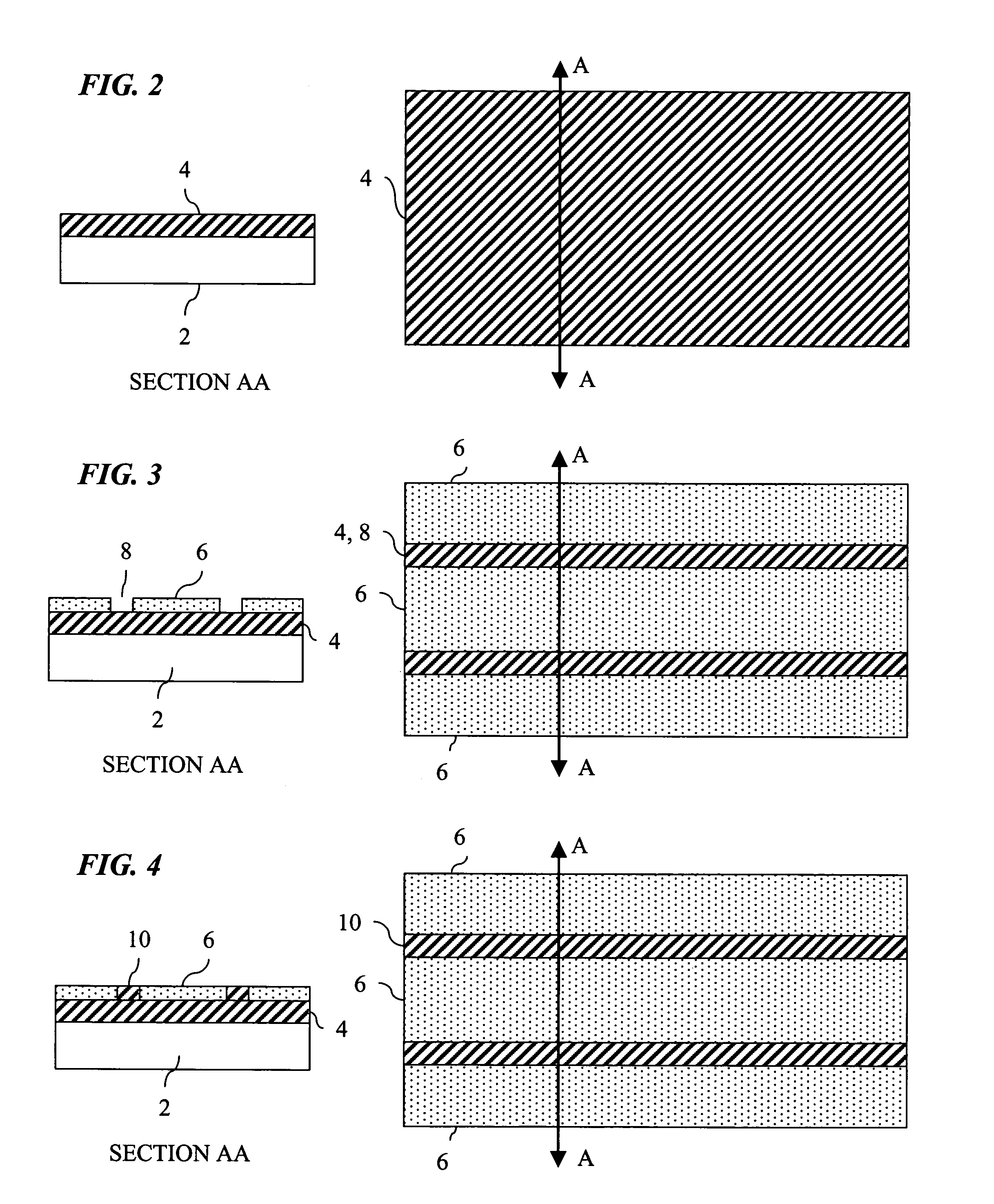
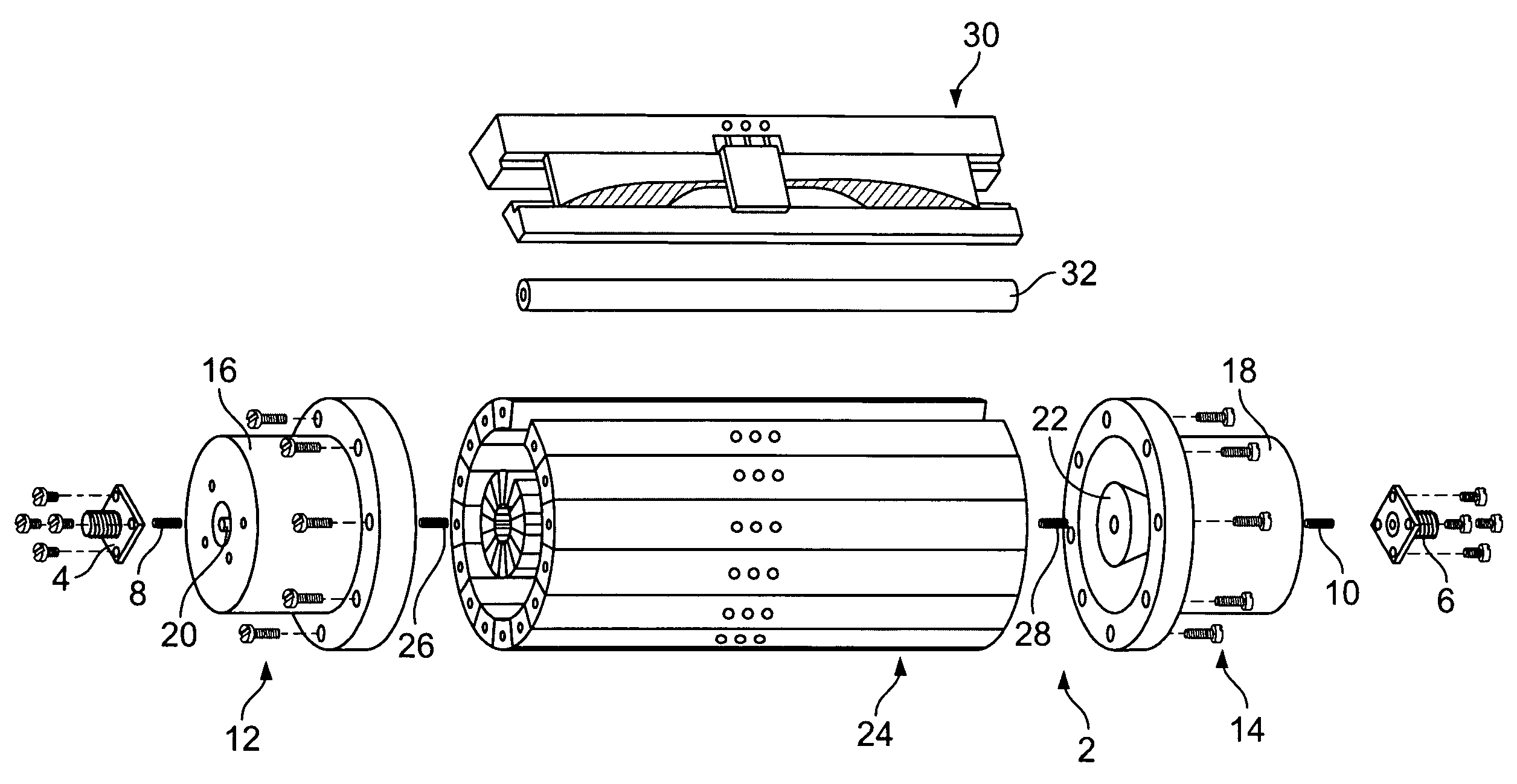
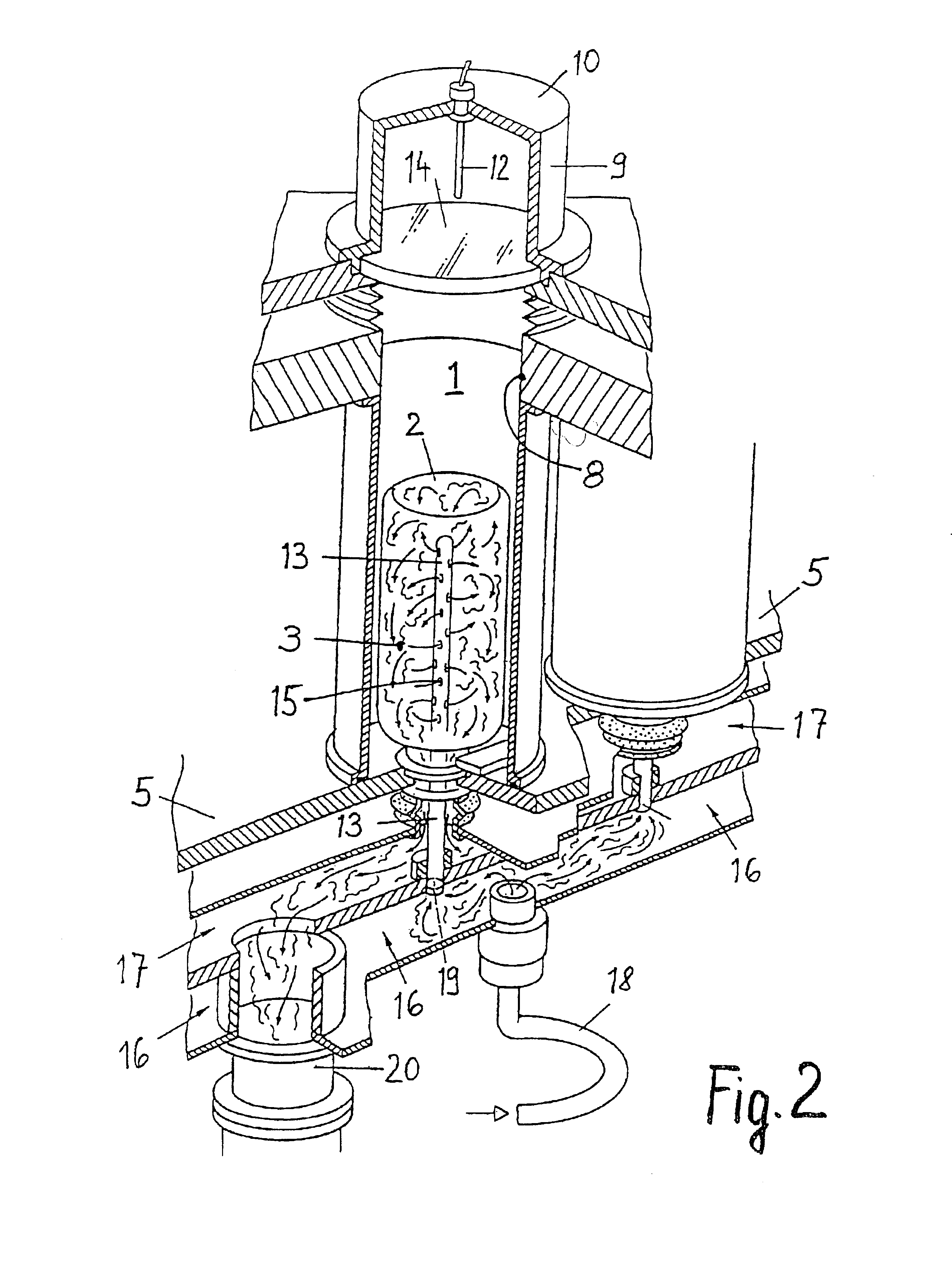
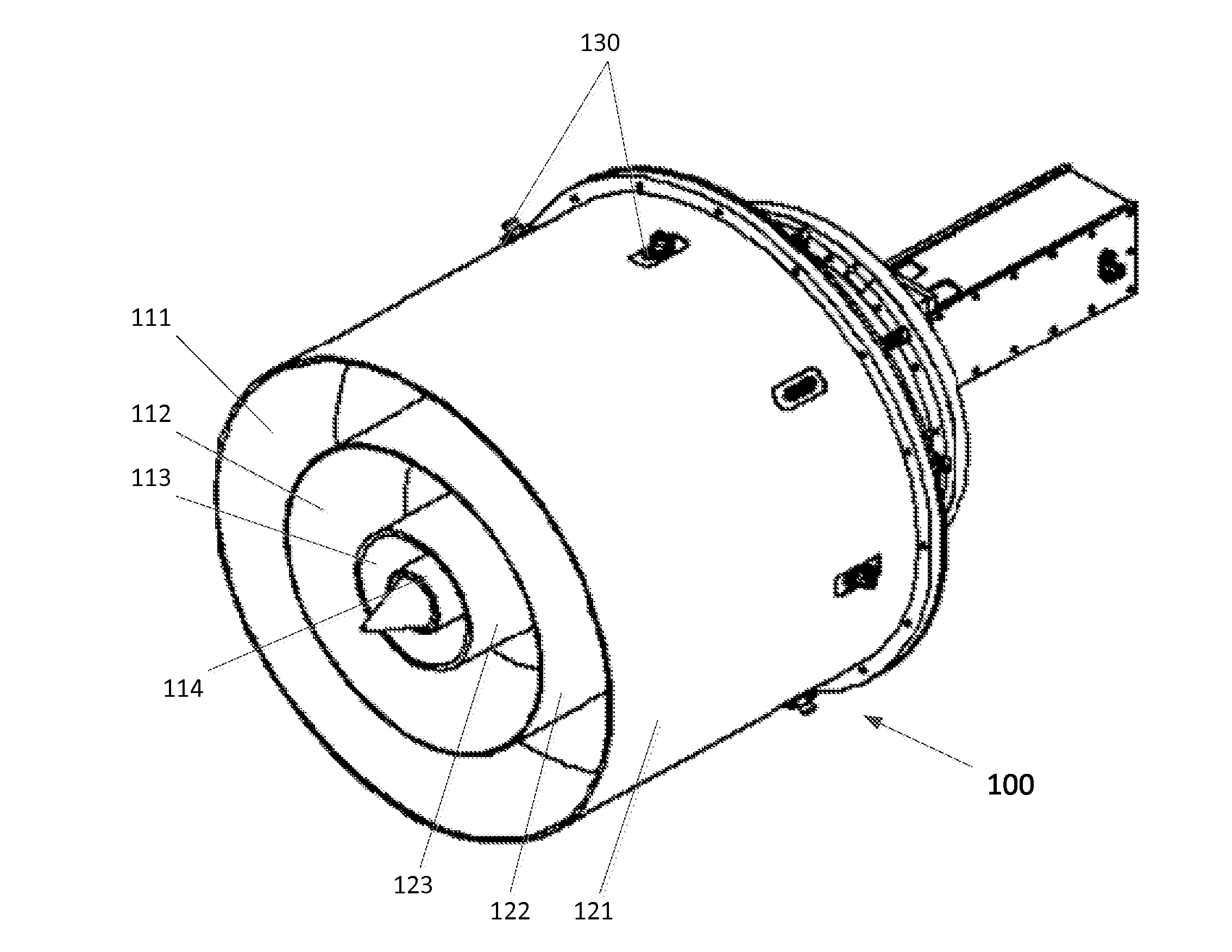
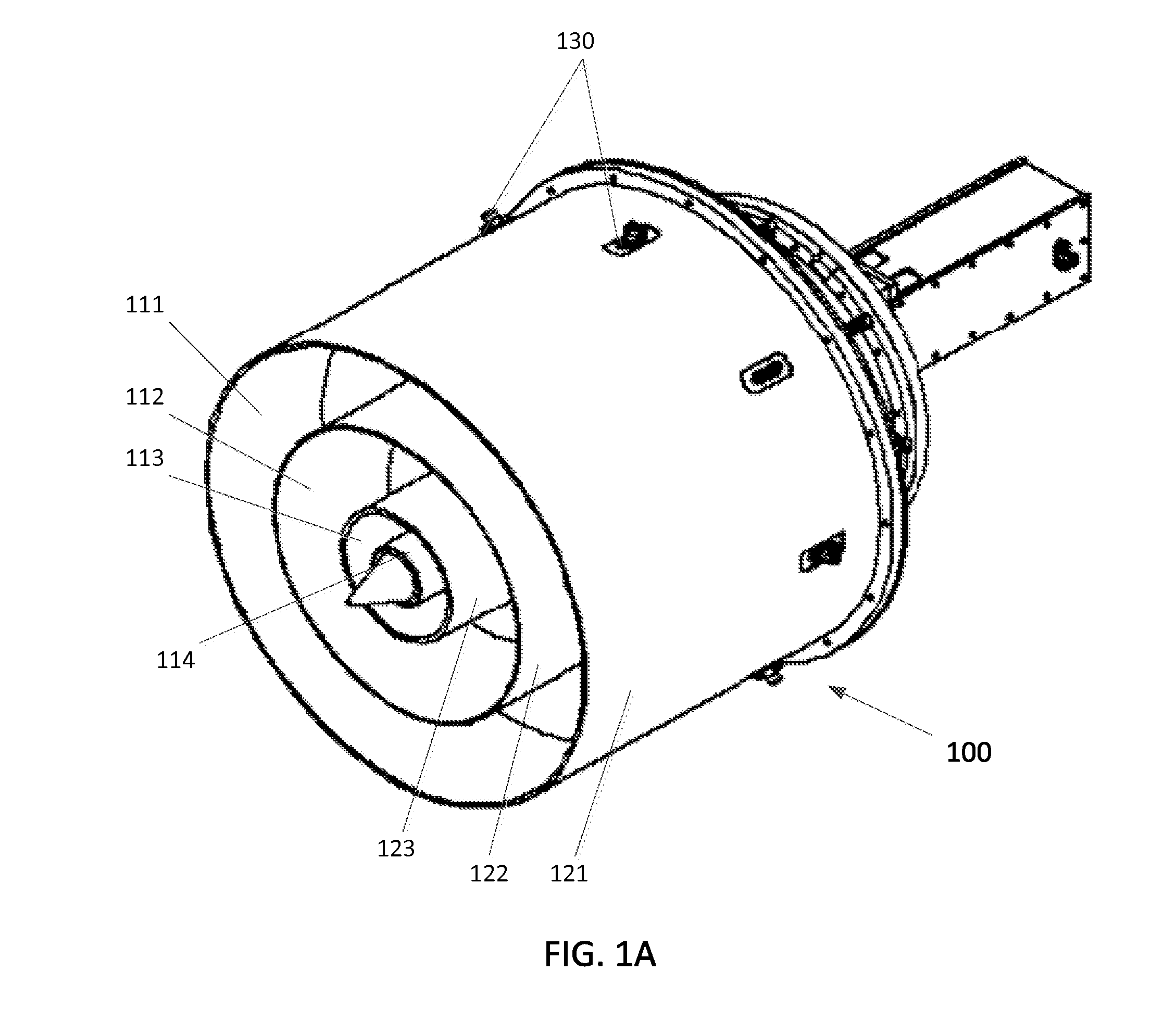
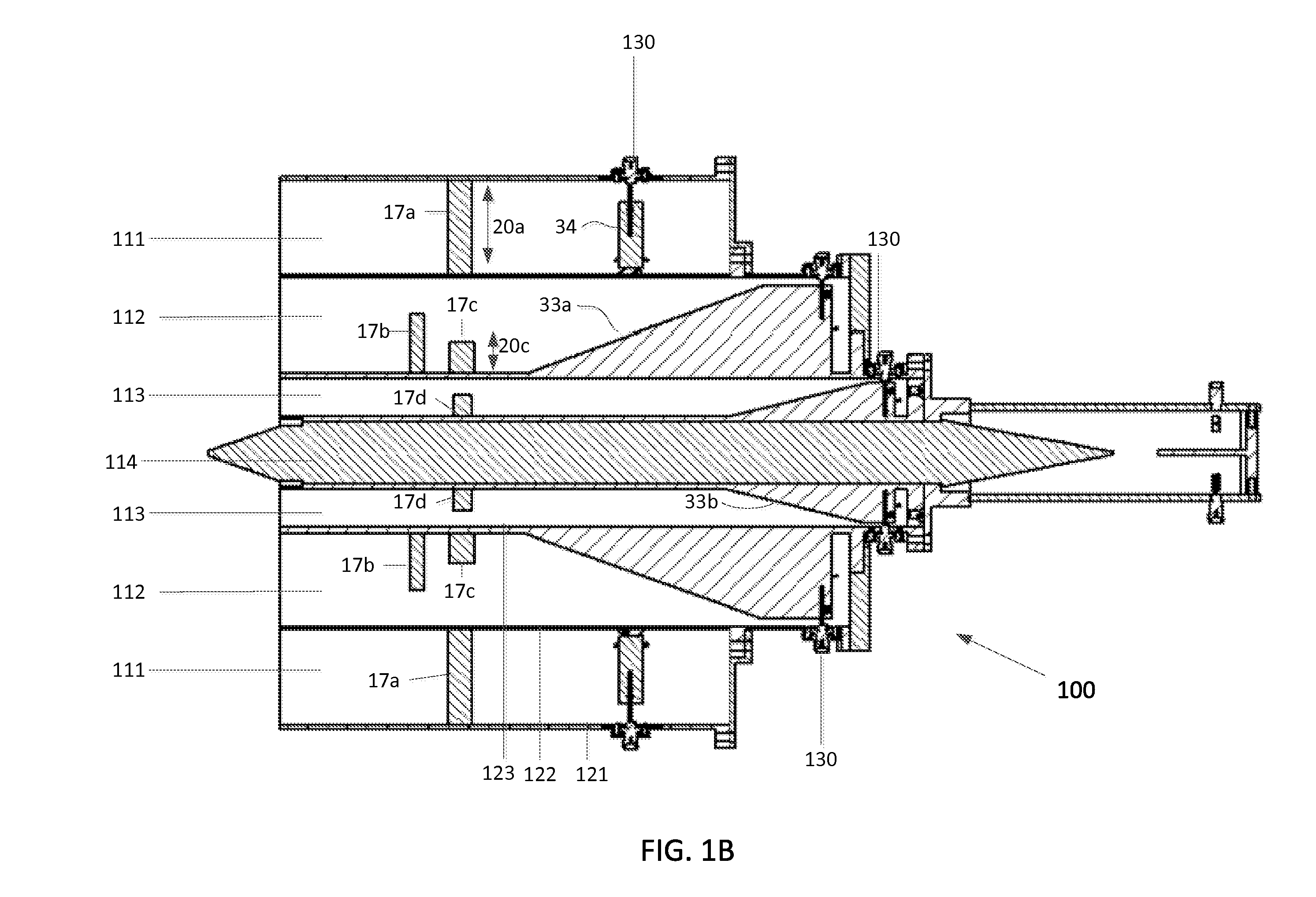
Coaxial waveguide microstructures and methods of formation thereof
ActiveUS7012489B2Printed circuit aspectsCircuit fluid transportElectrical conductorCoaxial waveguides
Provided are coaxial waveguide microstructures. The microstructures include a substrate and a coaxial waveguide disposed above the substrate. The coaxial waveguide includes: a center conductor; an outer conductor including one or more walls, spaced apart from and disposed around the center conductor; one or more dielectric support members for supporting the center conductor in contact with the center conductor and enclosed within the outer conductor; and a core volume between the center conductor and the outer conductor, wherein the core volume is under vacuum or in a gas state. Also provided are methods of forming coaxial waveguide microstructures by a sequential build process and hermetic packages which include a coaxial waveguide microstructure.
Owner:CUBIC CORPORATION
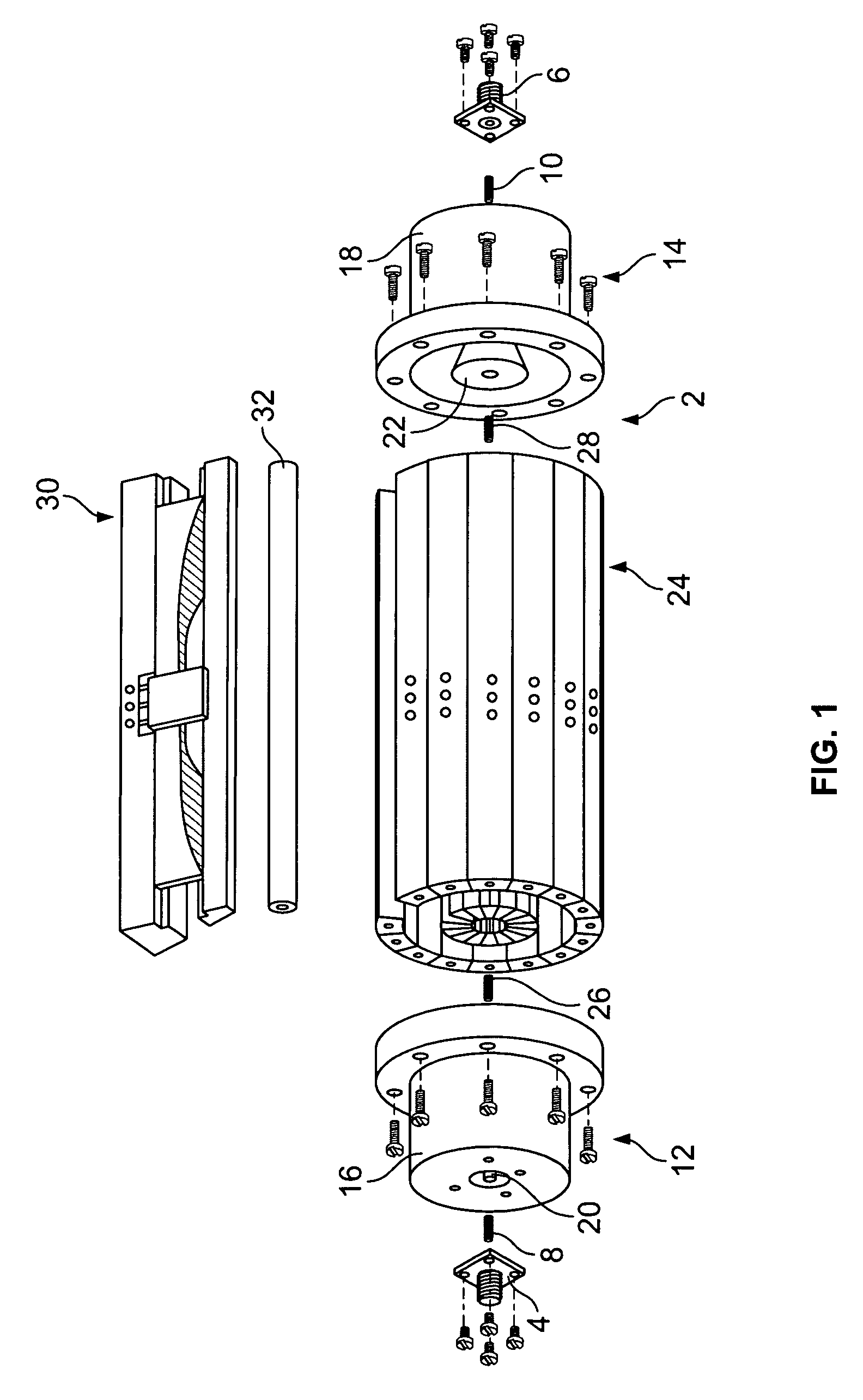
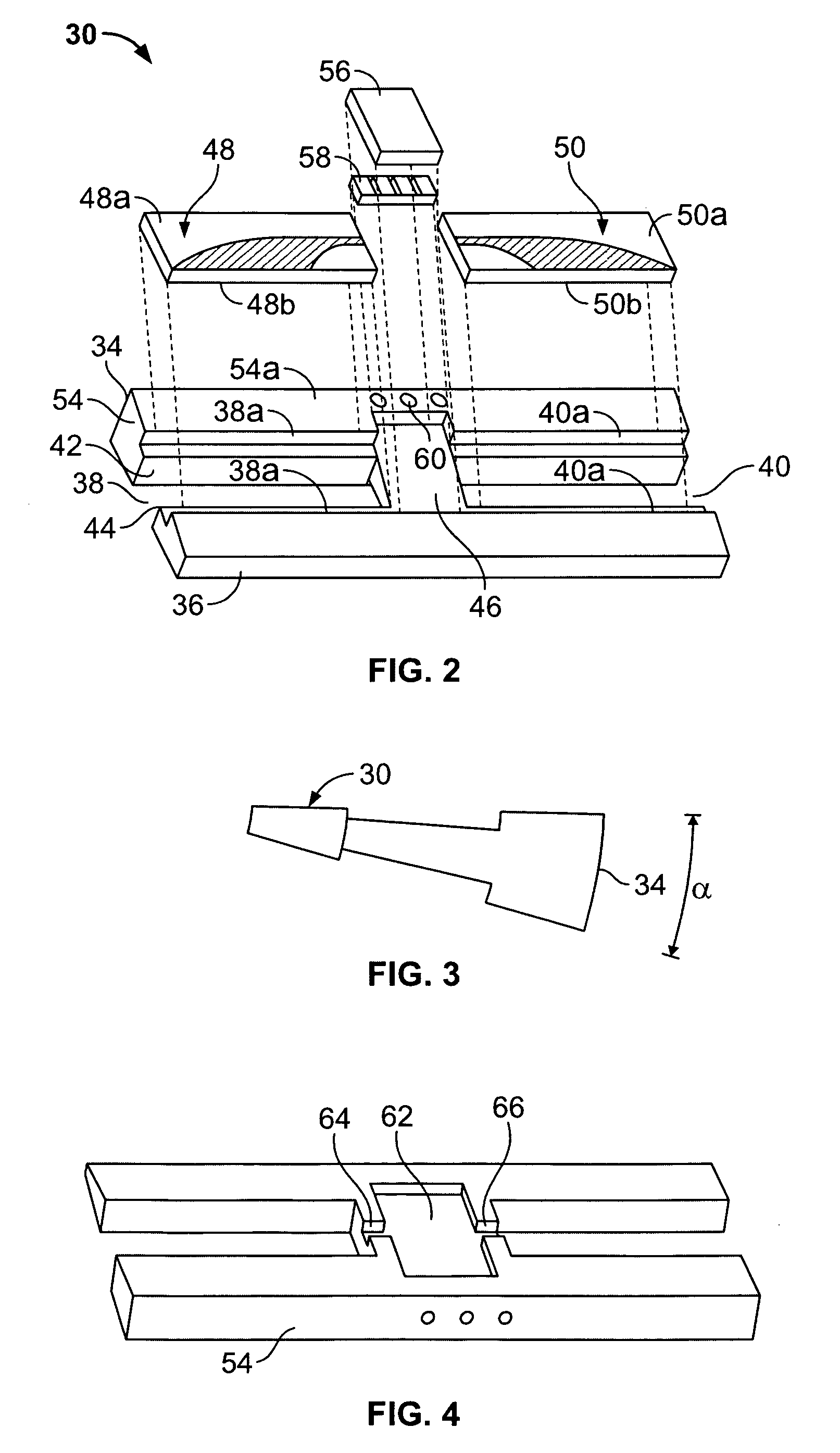
Broadband power combining device using antipodal finline structure
ActiveUS7215220B1Easy to manageThermal resistance minimizationWaveguidesCoupling devicesWedge angleHermetic seal
A broadband power combining device includes an input port, an input waveguide section, a center waveguide section formed by stacked wedge-shaped trays, an output waveguide section, and an output port. Each tray is formed of a wedge-shaped metal carrier, an input antipodal finline structure, one or more active elements, an output antipodal finline structure, and attendant biasing circuitry. The wedge-shaped metal carriers have a predetermined wedge angle and predetermined cavities. The inside and outside surfaces of the metal carriers and surfaces of the cavity all have cylindrical curvatures. When the trays are assembled together, a cylinder is formed defining a coaxial waveguide opening inside. The antipodal finline structures form input and output arrays. An incident EM wave is passed through the input port and the input waveguide section, distributed by the input antipodal finline array to the active elements, combined again by the output antipodal finlines array, then passed to the output waveguide section and output port. A hermetic sealing scheme, a scheme for improving the power combining efficiency and thermal management scheme are also disclosed. The broadband power combining device operates with multi-octave bandwidth and is easy to manufacture, well-managed thermally, and highly efficient in power combining.
Owner:CW ACQUISITION
Ku/Ka frequency band circularly polarization integrated receiving and transmitting feed source antenna
InactiveCN102136634ACompact and efficientExcellent transceiver isolationAntenna supports/mountingsPolarised antenna unit combinationsReflection lossAxial ratio
The invention provides a Ku / Ka frequency band circularly polarization integrated receiving and transmitting feed source antenna applied to antenna systems, such as a paraboloid antenna and the like, in satellite communication. The antenna adopts a coaxial nested compact structure, and is applied to Ku frequency band and Ka frequency band at the same time. The basic structure of a feed source comprises a circular waveguide, on which a pointed cone shaped dielectric rod is loaded, a flange, a coaxial waveguide, a symmetrical SMA connector pair, a circular polarizer and an orthogonal mode coupler, wherein the feed source in the Ka frequency band is applied to dual circular polarization, has rotary symmetrical radiation directional diagrams, the circularly polarization axial ratio in Ka double band is smaller than minus 2dB, and the transmitter-receiver isolation is smaller than minus 70dB; and the feed source in the Ku frequency band is applied to dual circular polarization, has rotary symmetrical radiation directional diagrams, a cross polarization level smaller than minus 40dB, and good transmitter-receiver isolation and reflection loss.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
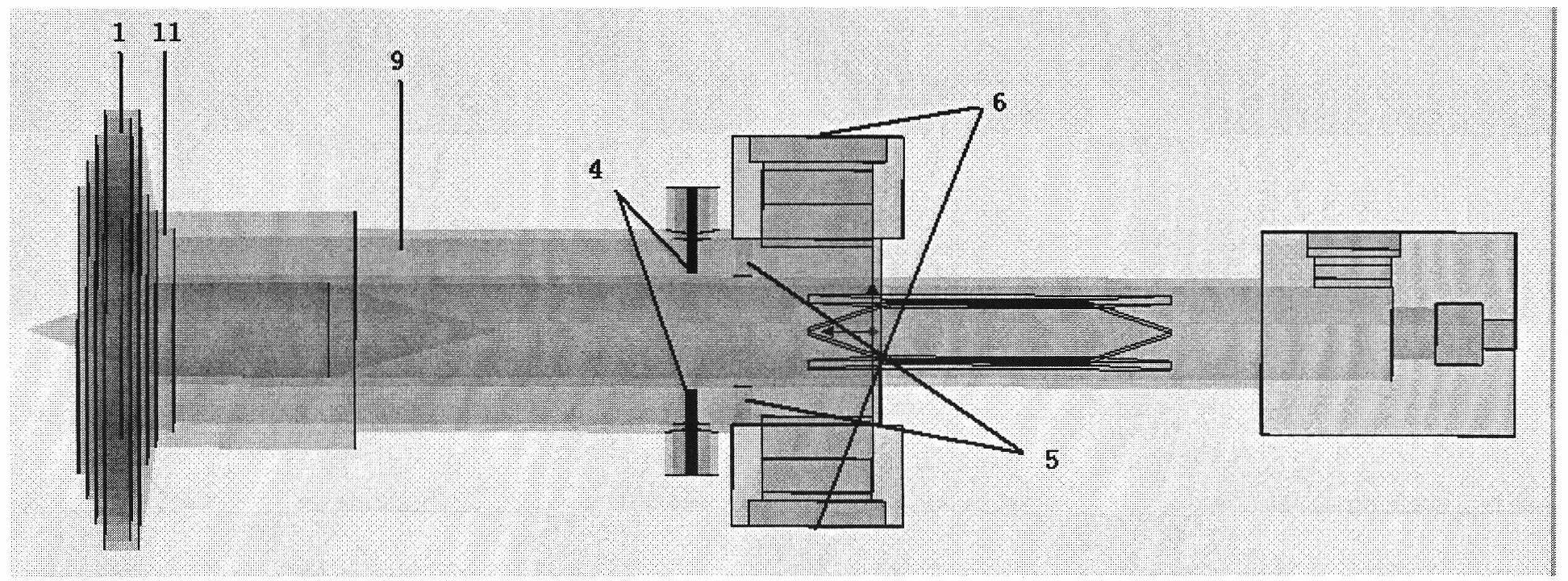
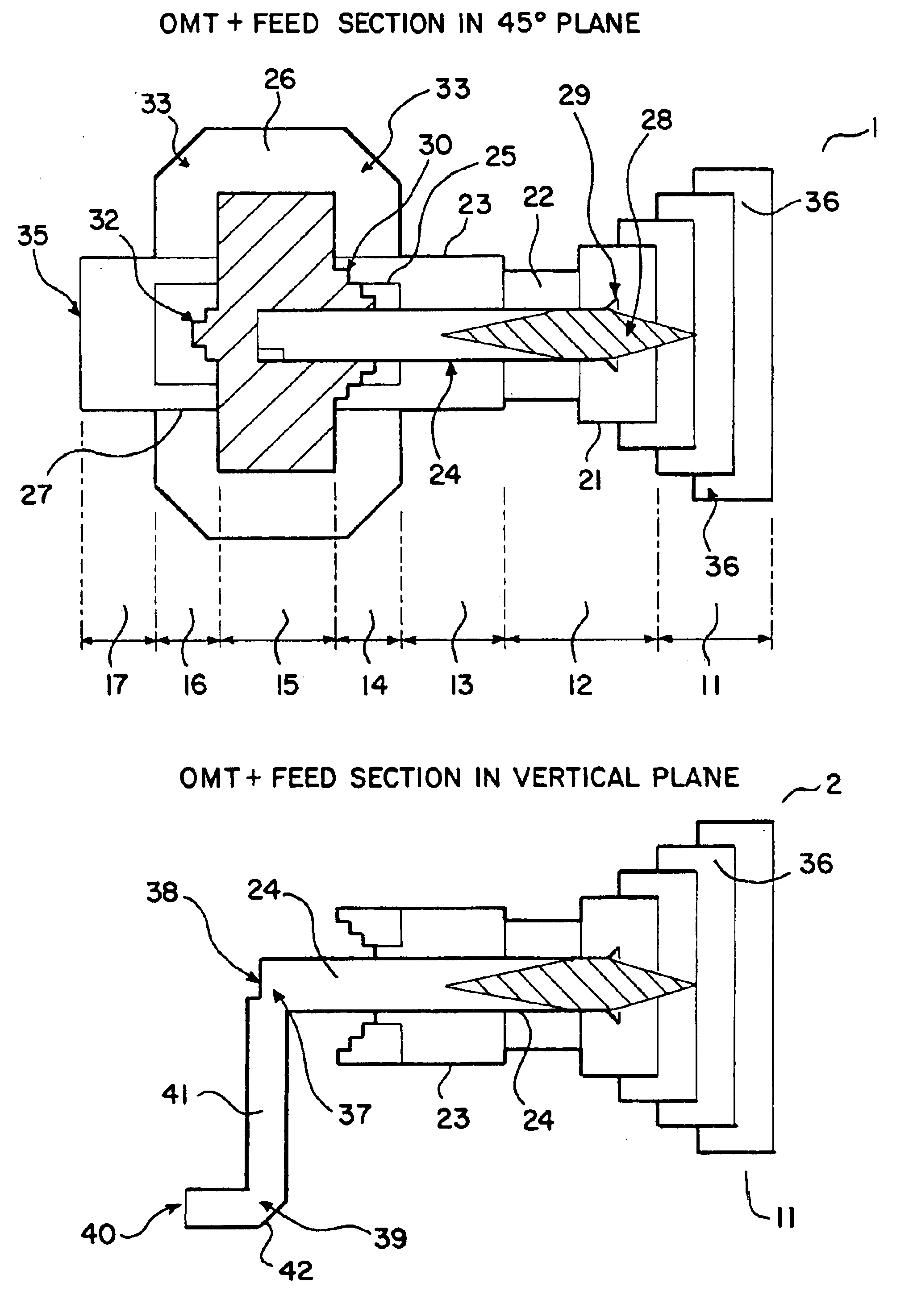
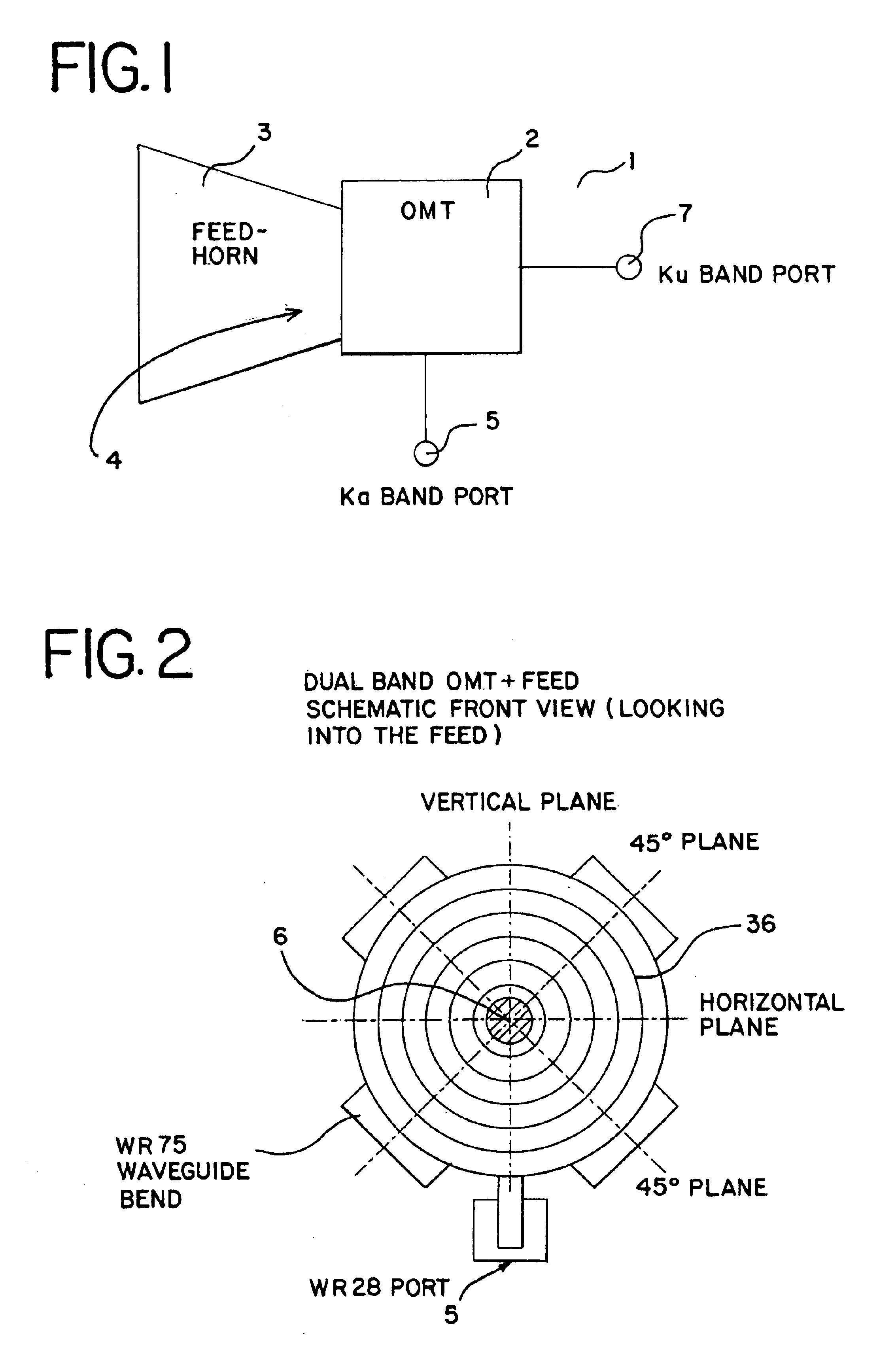
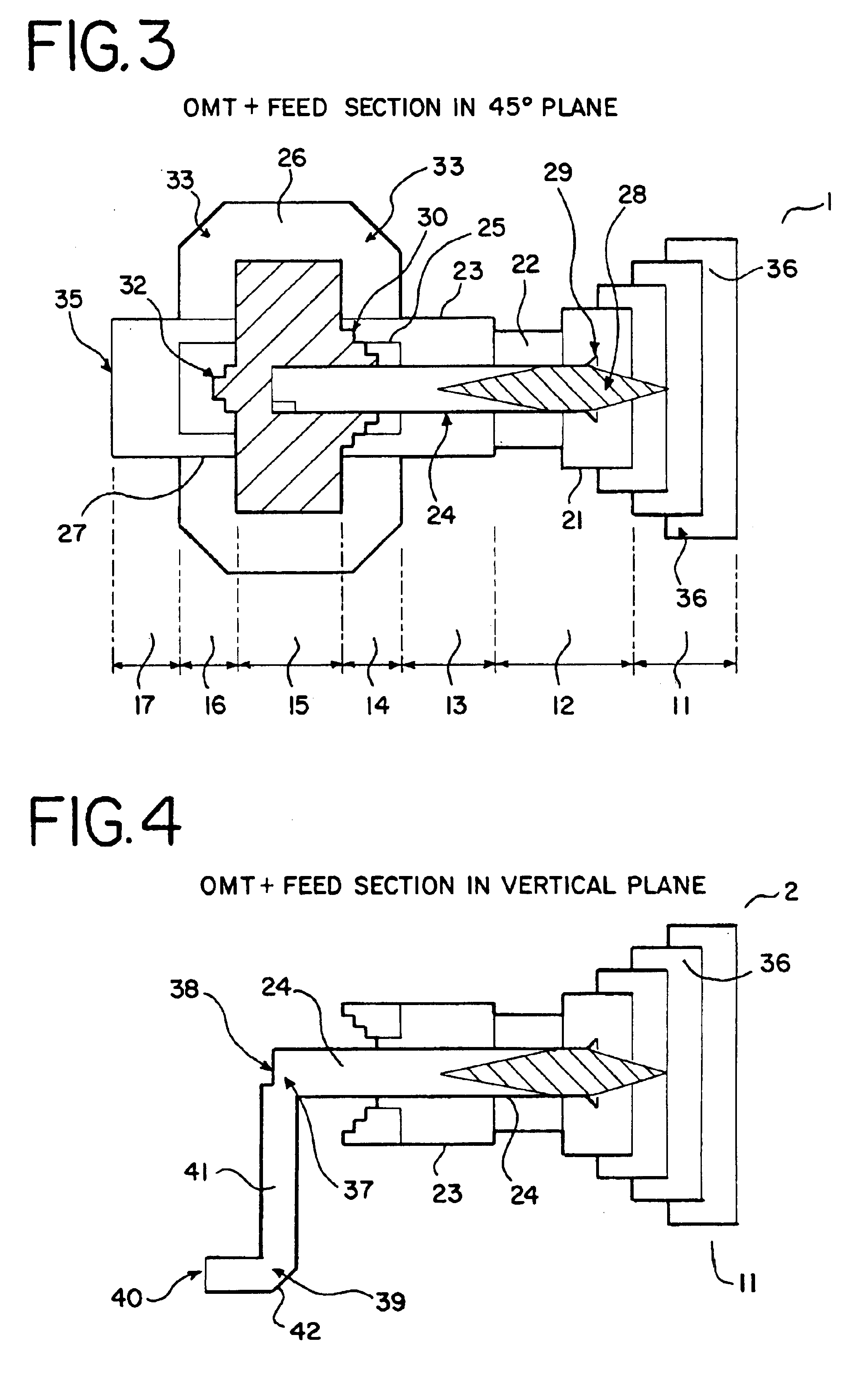
Ka/Ku dual band feedhorn and orthomode transduce (OMT)
InactiveUS6714165B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntennas earthing switches associationRidge waveguidesTransducer
A dual band, higher and lower frequency range transducer with a circular coaxial waveguide feed is described having a first junction for connection of a lower frequency range outer waveguide of the coaxial waveguide feed to at least two rectangular or ridge waveguides offset from the longitudinal axis of the transducer and a second junction for connection of the at least two rectangular or ridge waveguides to a further waveguide. A third junction is provided for connecting an inner waveguide of the coaxial waveguide feed to a higher frequency range waveguide. The transducer comprises at least first and second parts joined across a first plane substantially perpendicular to the longitudinal axis and including at least a portion of the higher frequency range waveguide extending within the first plane of the join. A seal such as an "O" ring seal may be placed easily in the plane of the join thus preventing moisture ingress. Similarly, a feed horn and input and output ports may be sealingly attached to the first and second parts of the transducer. The first and second junctions are preferably impedance matched turnstile junctions.
Owner:NEWTEC CY
Plasma processing system, antenna, and use of plasma processing system
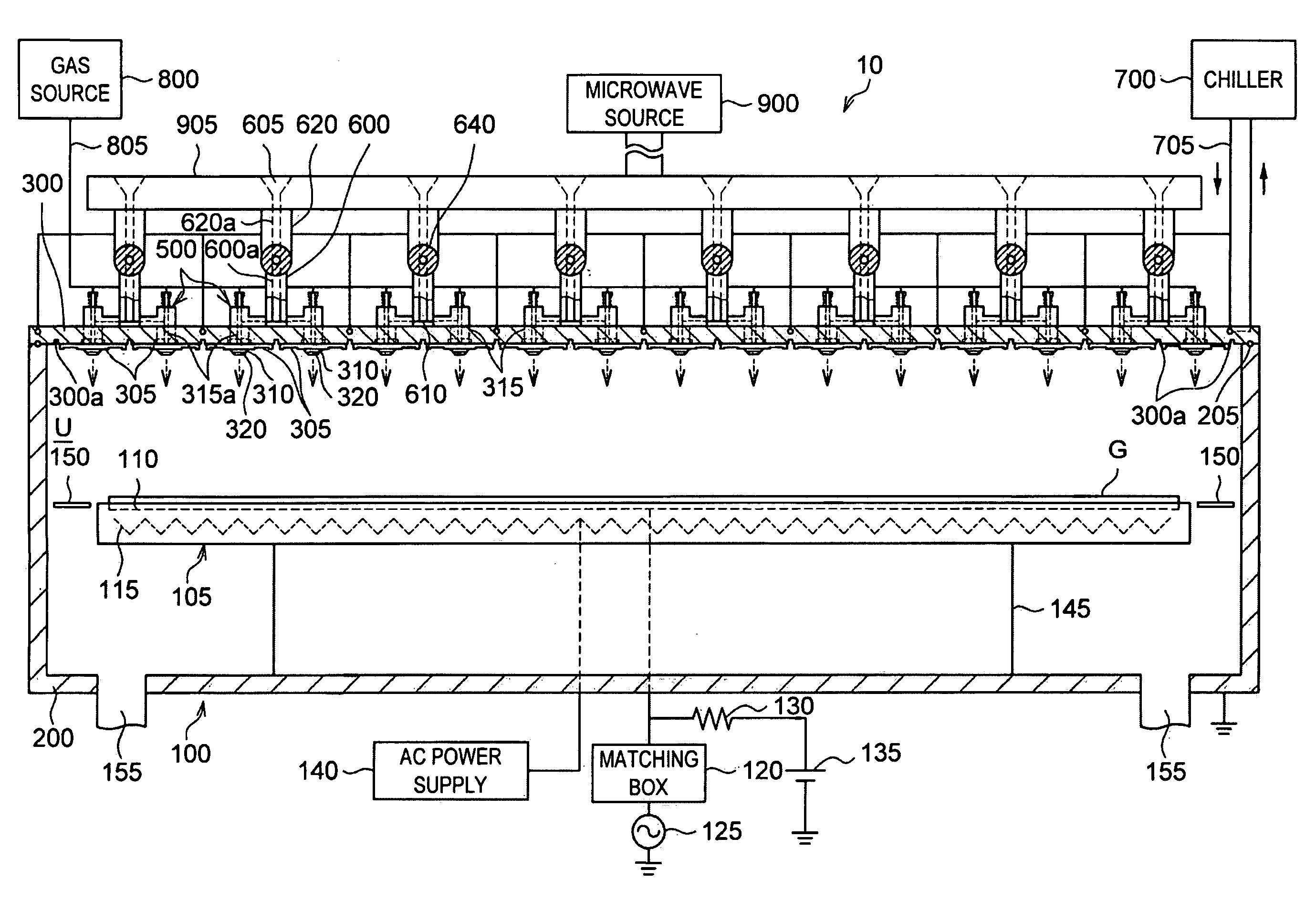
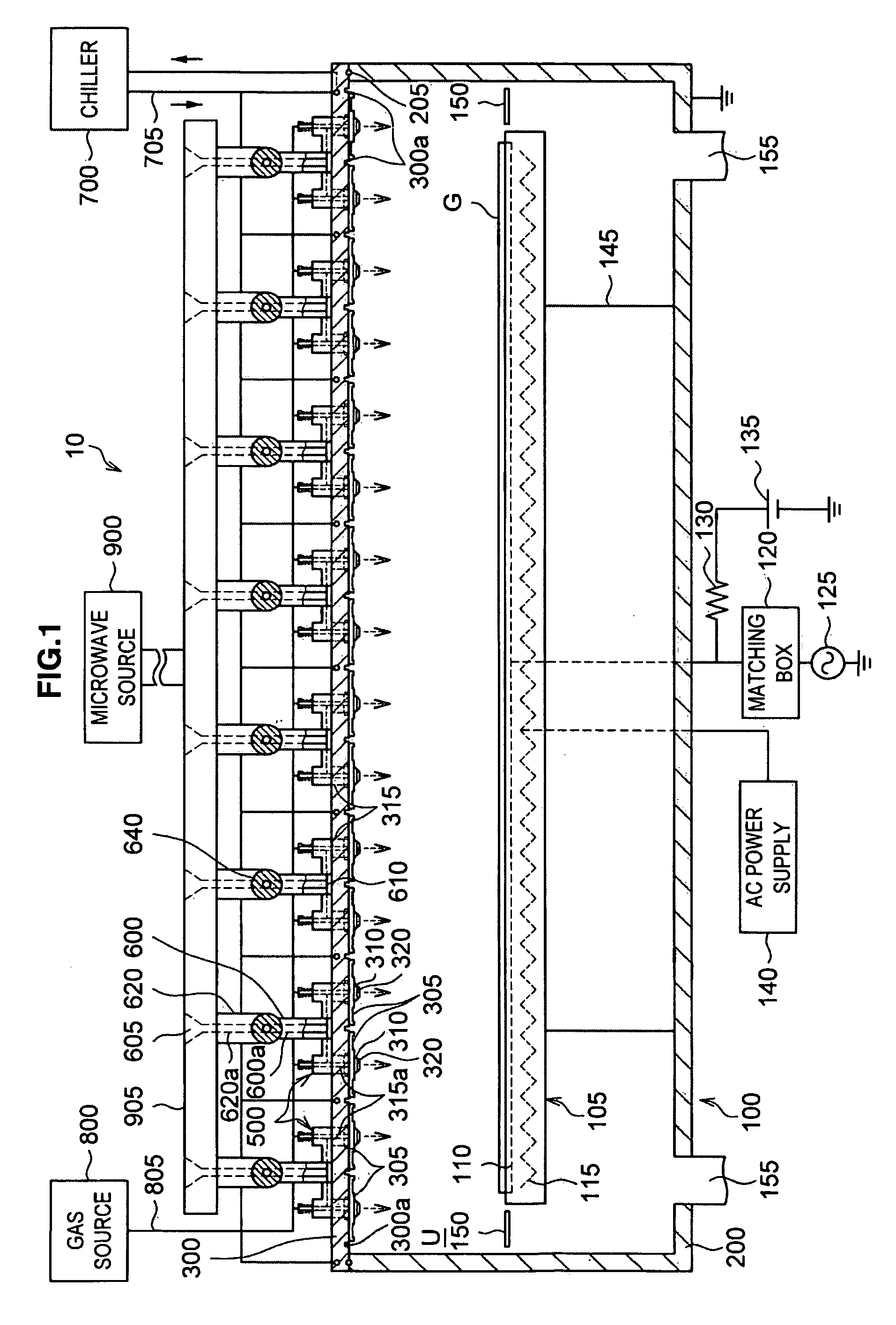
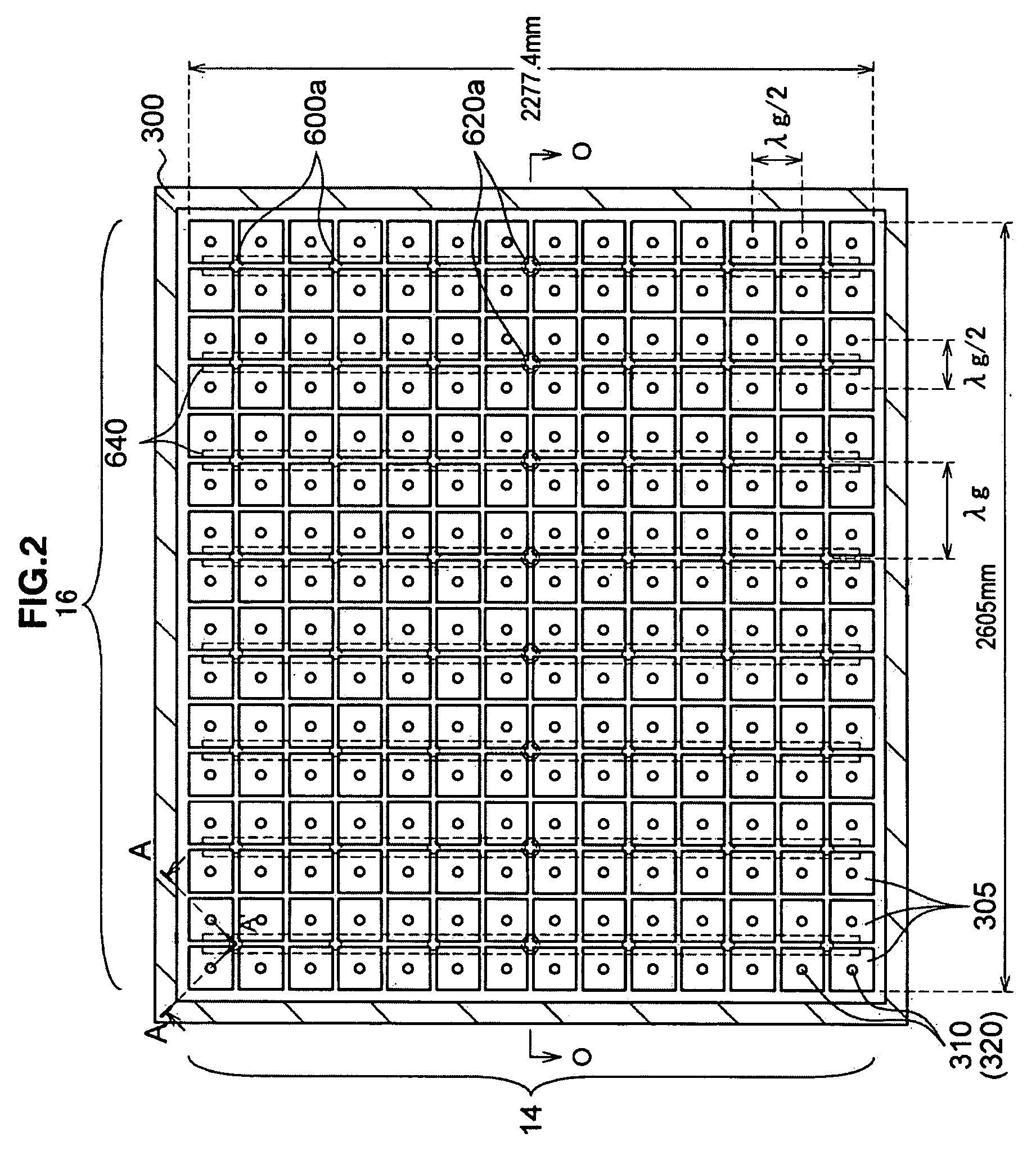
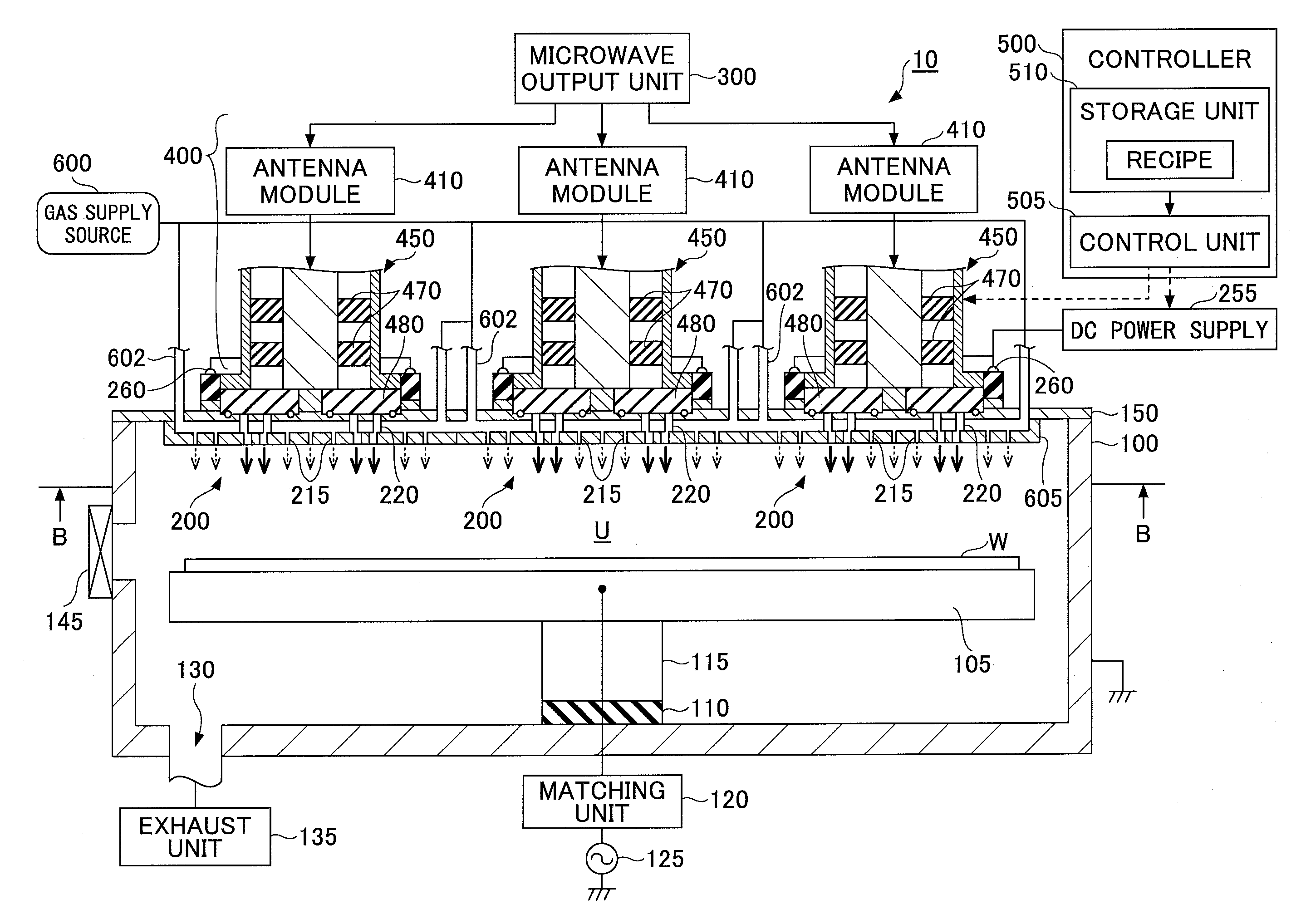
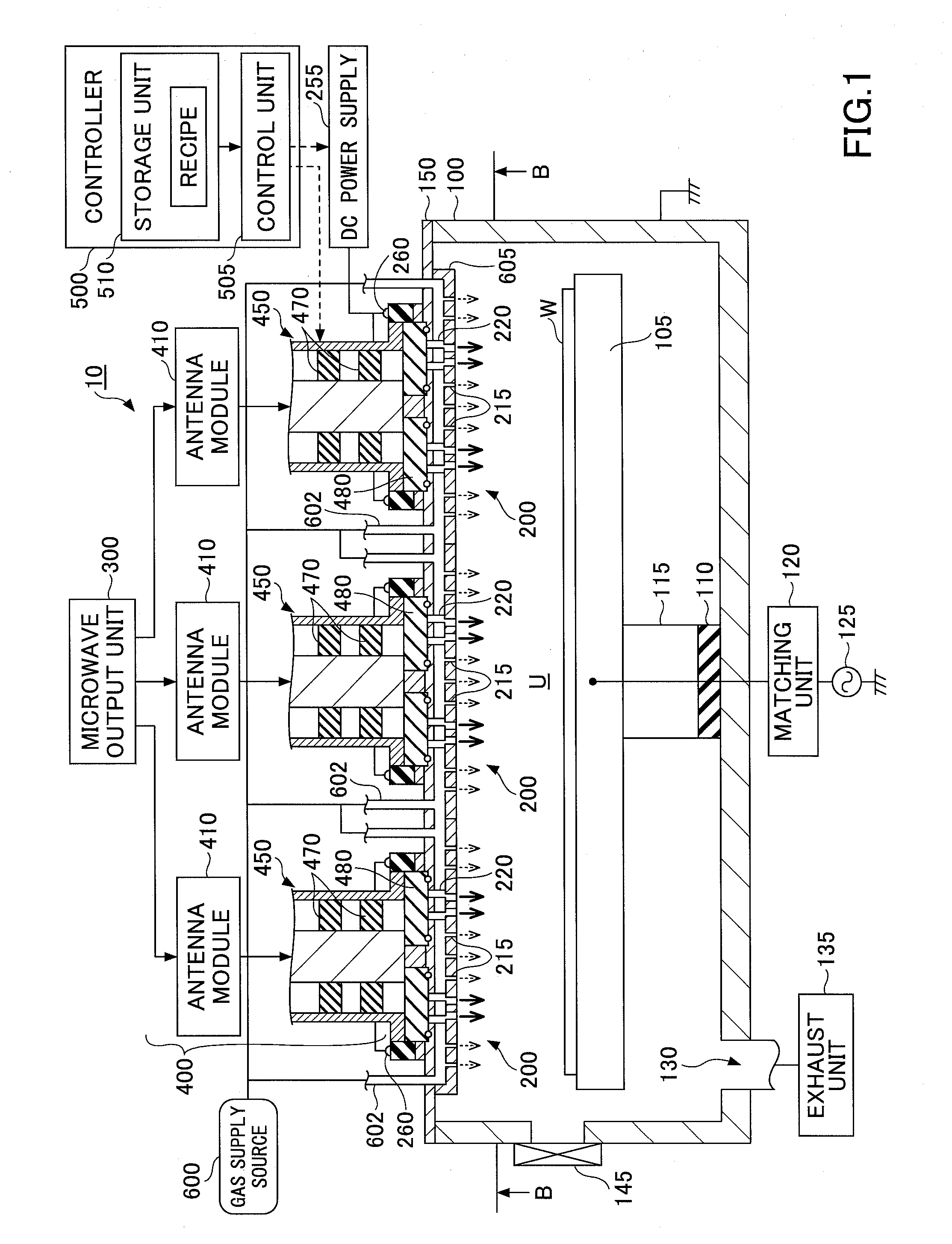
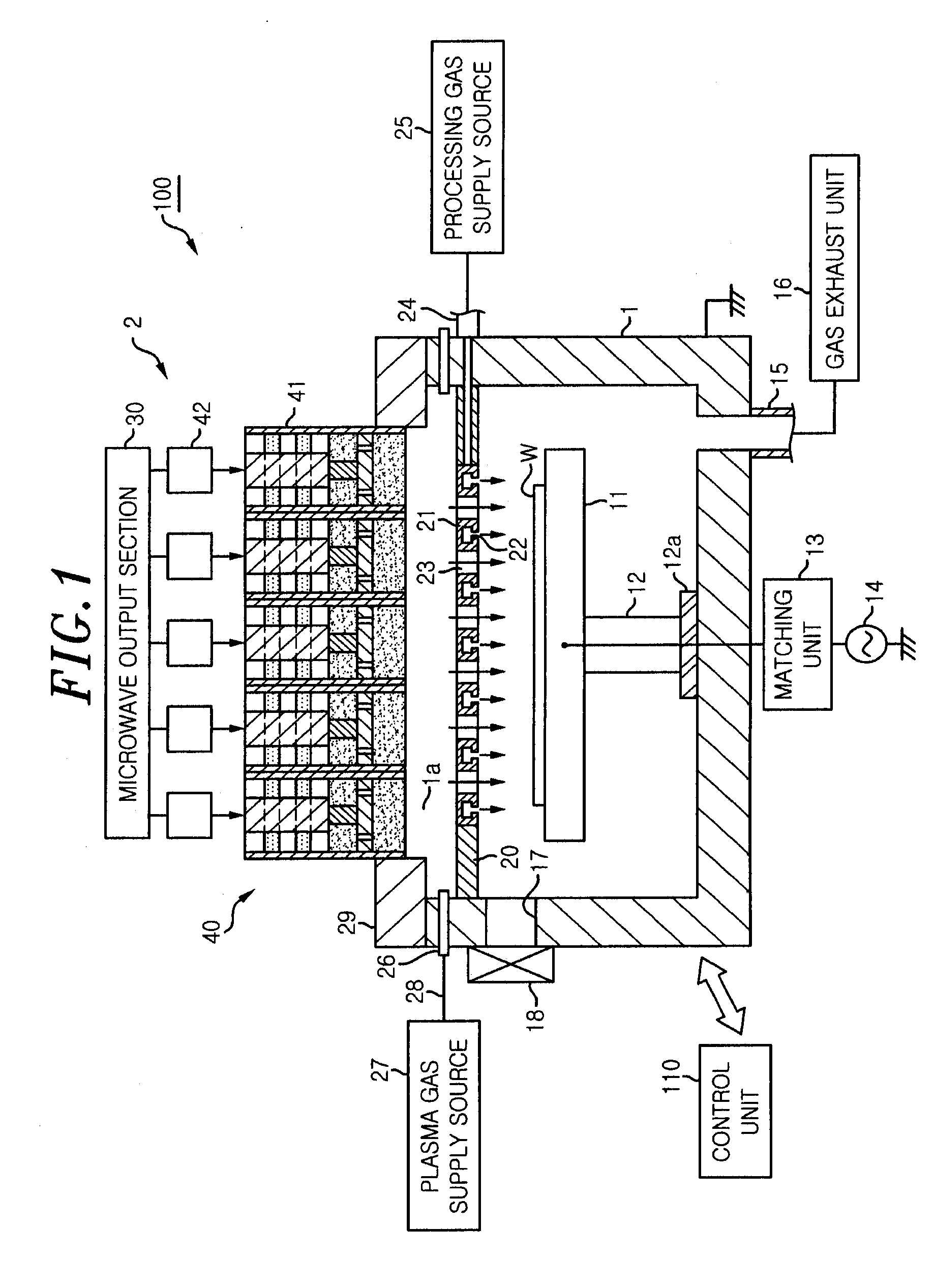
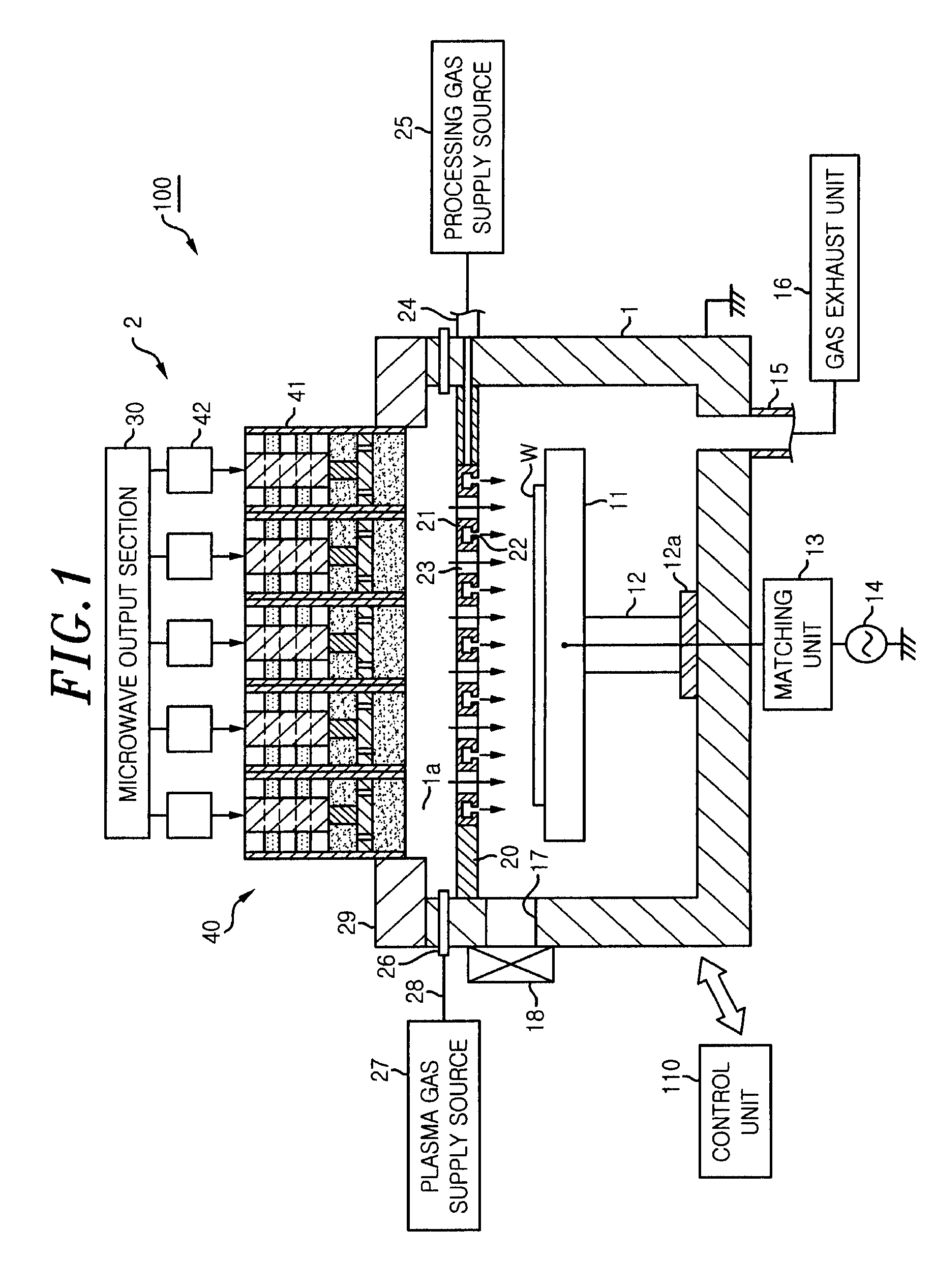
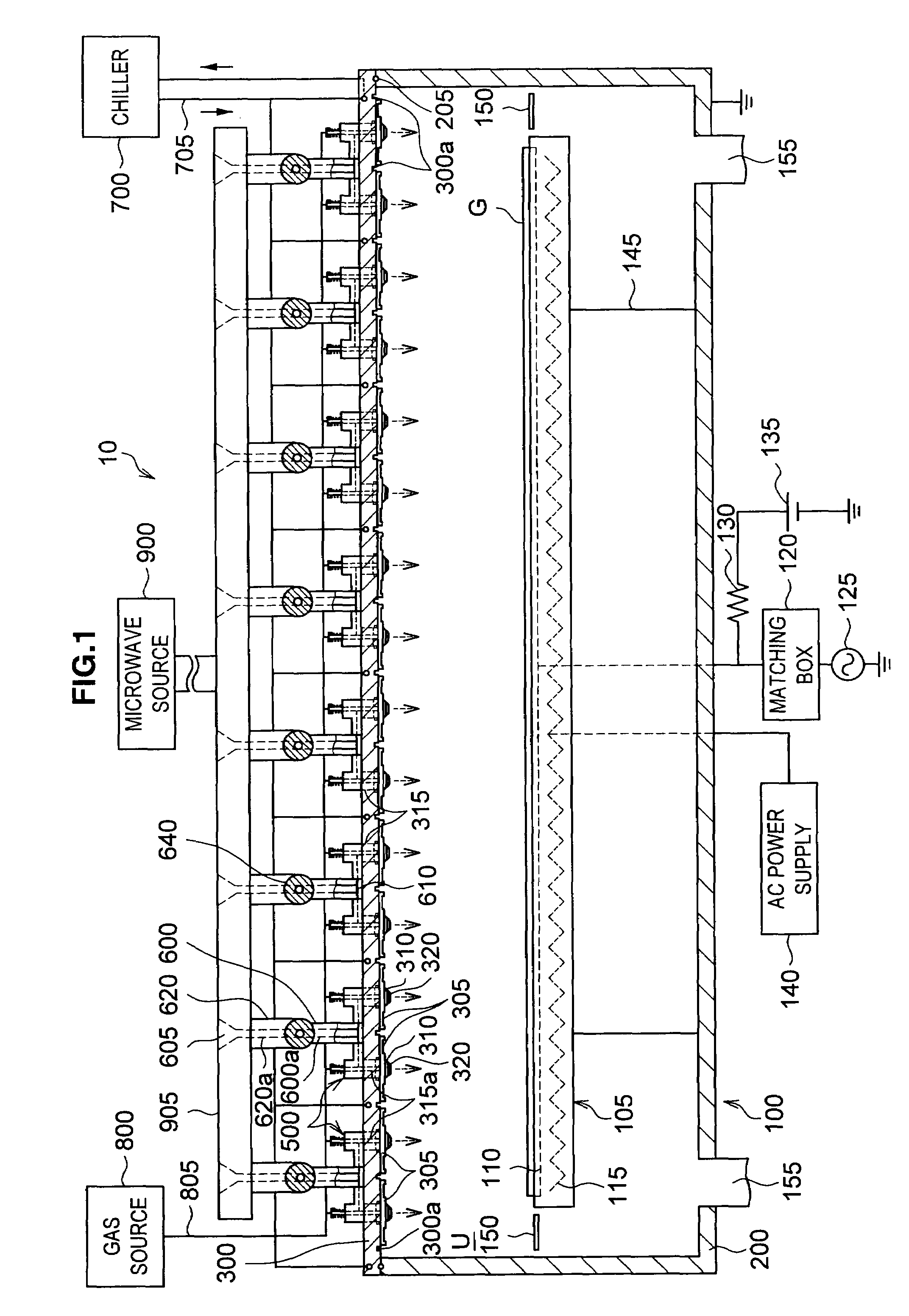
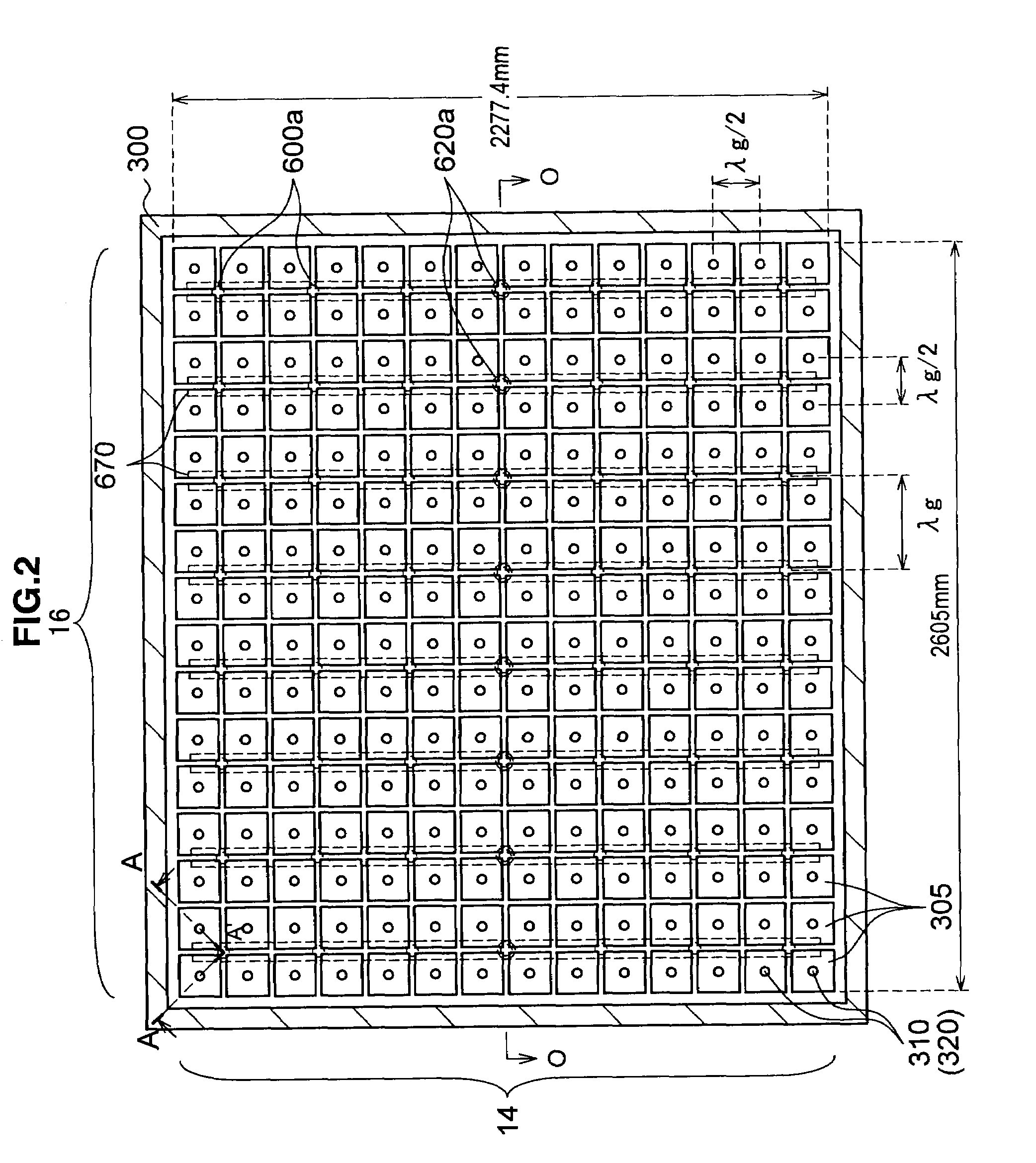
InactiveUS20080303744A1Reduce the electric fieldImprove uniformityElectric discharge tubesRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorDielectric plate
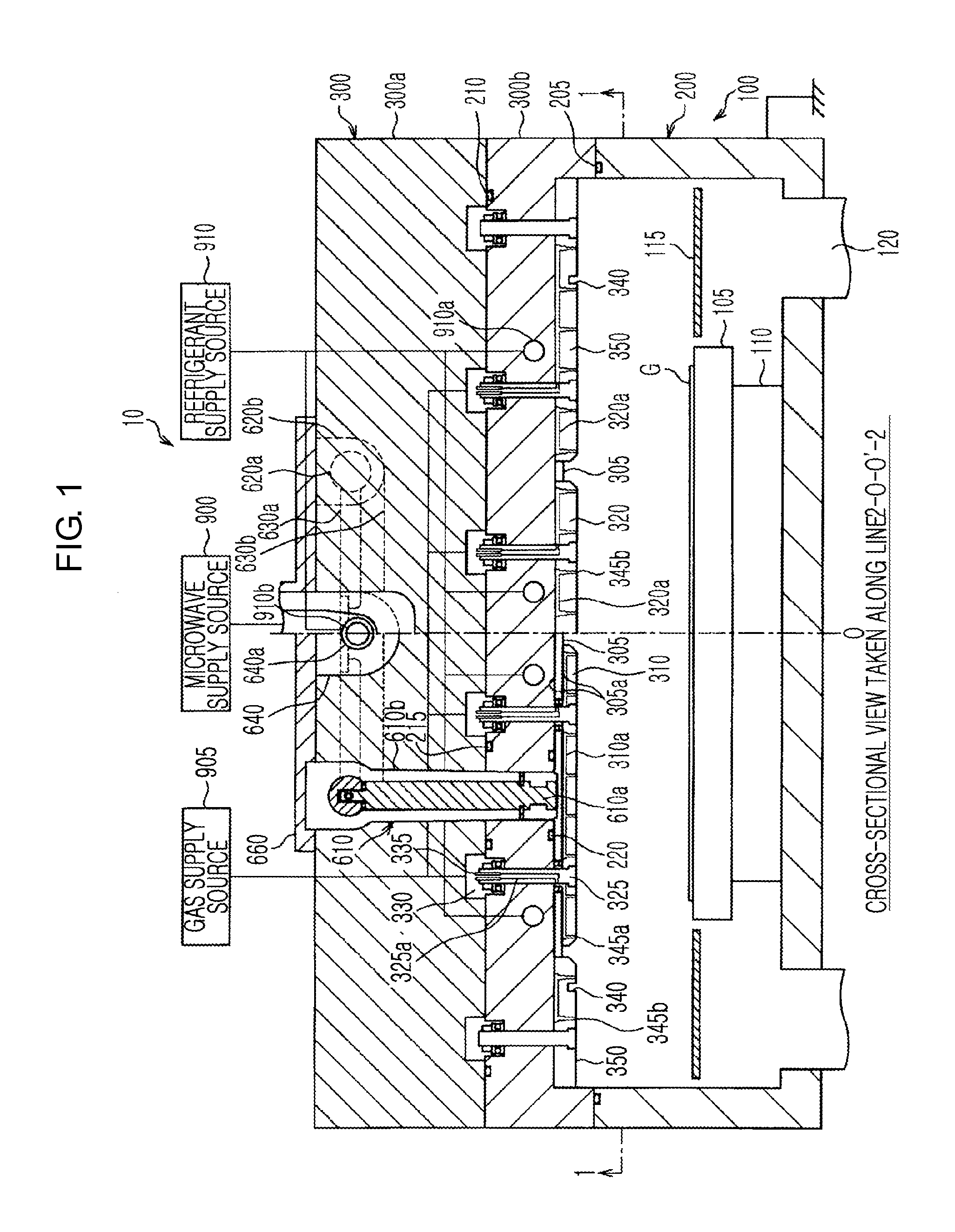
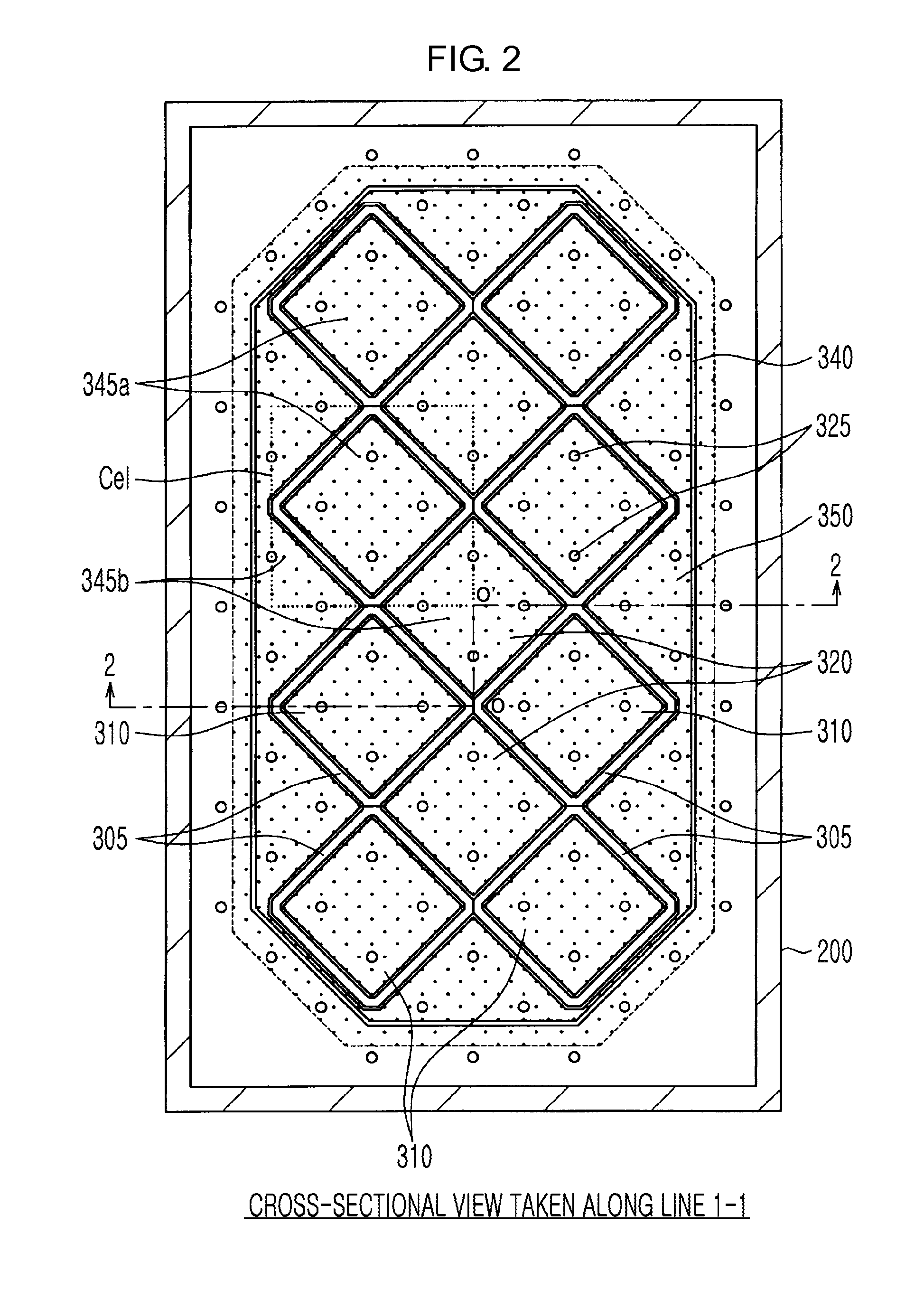
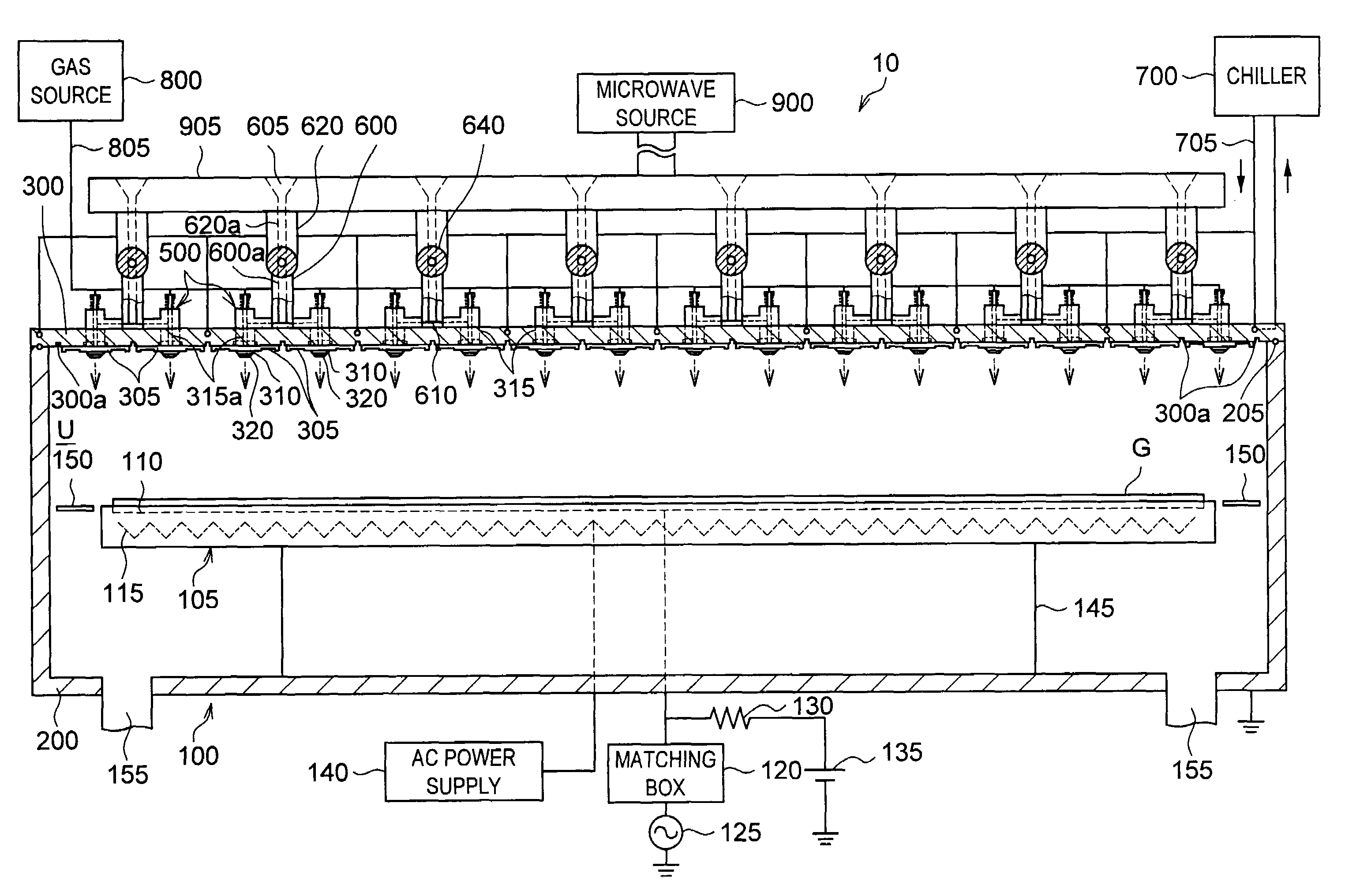
A plasma processing system 10 includes a processing chamber 100, a microwave source 900 that outputs a microwave, an inner conductor of a coaxial waveguide 315a that transfers the microwave, a through-hole 305a, a dielectric plate 305 that transmits the microwave transferred through the inner conductor 315a and discharges it into a processing chamber 100, and a metal electrode 310 that is coupled to the inner conductor 315a via the through-hole 305a, the metal electrode 310 being exposed on the surface of the dielectric plate 305 that faces the substrate with at least a portion of the metal electrode 310 being adjacent to the surface of the dielectric plate 305 that faces the substrate. A surface of the exposed surface of the metal electrode 310 is covered by the dielectric cover 320.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
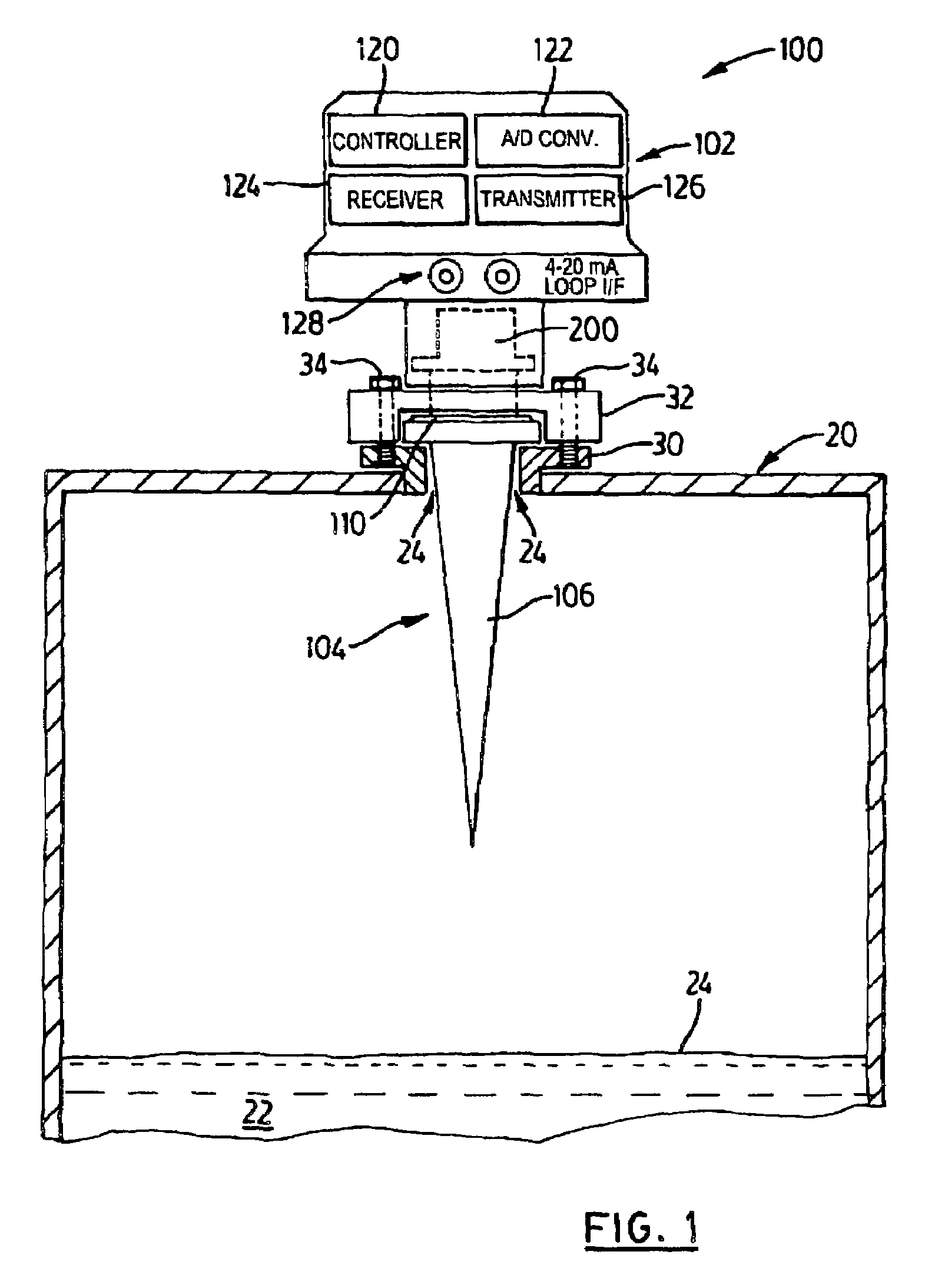
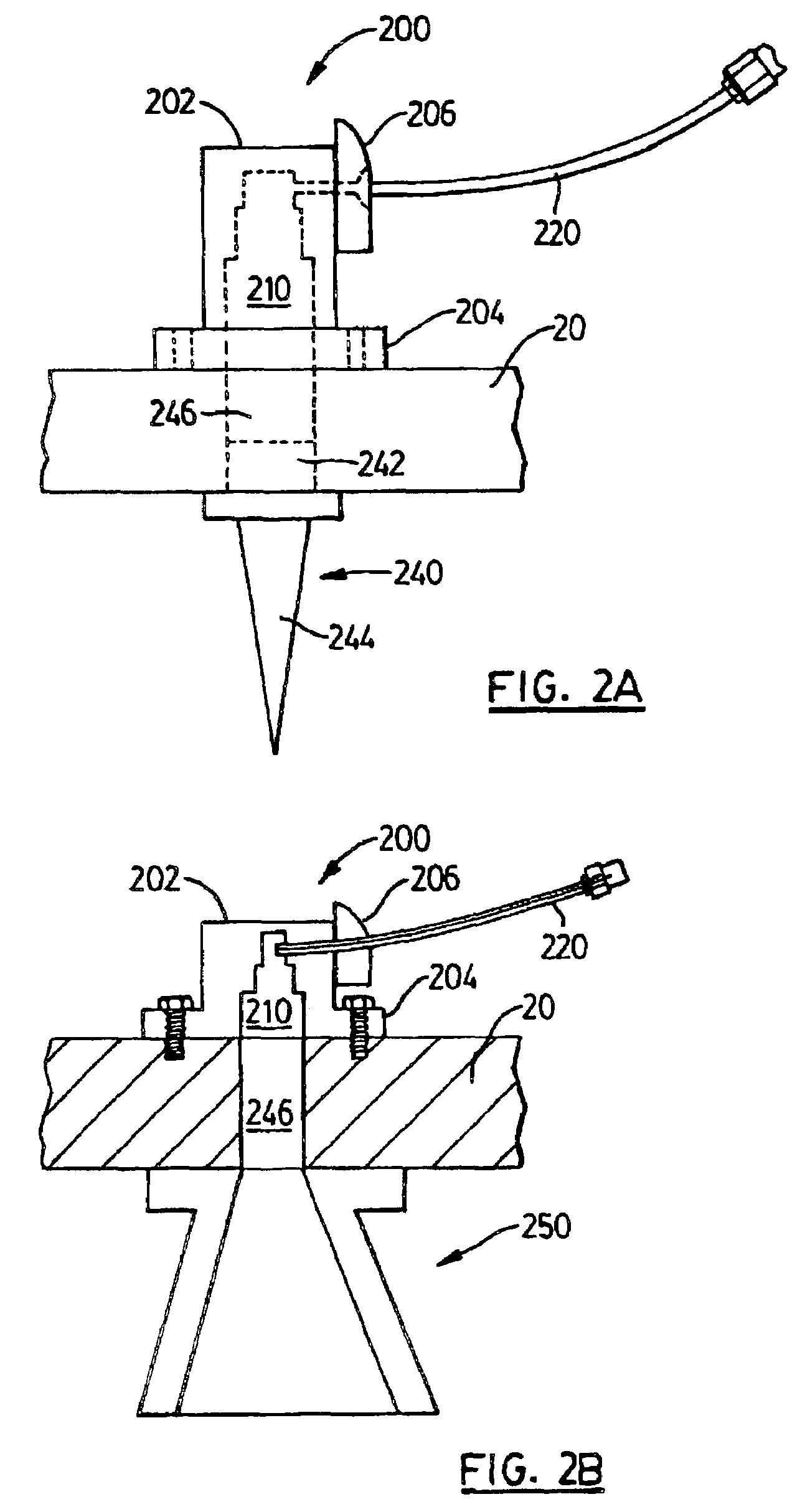
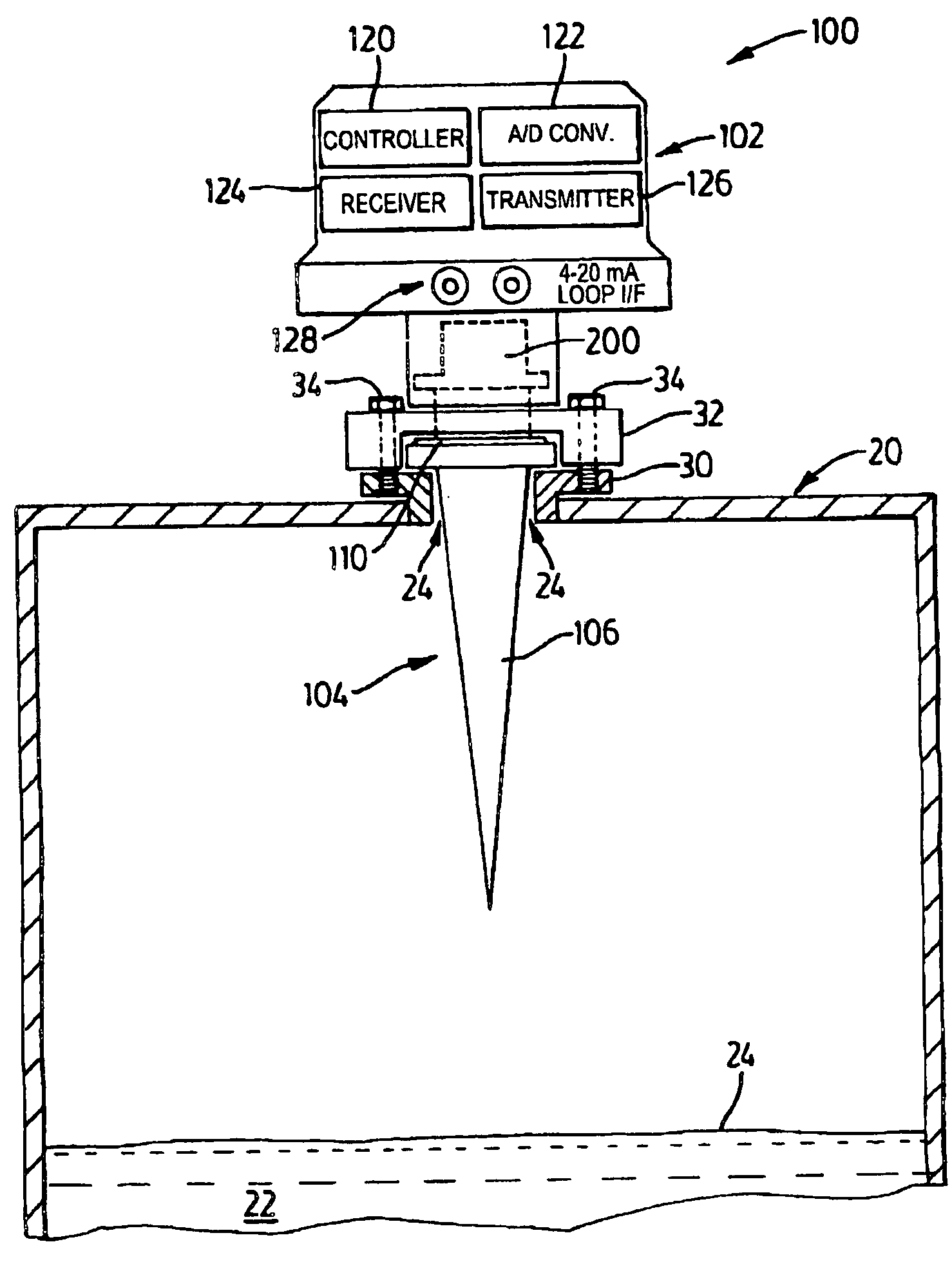
Coupler with waveguide transition for an antenna in a radar-based level measurement system
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Multiband waveguide reflector antenna feed
A multiband waveguide reflector antenna feed comprises waveguide feeds in a concentric architecture. A waveguide feed is located in the center and coaxial waveguide feeds are disposed around the center feed. The waveguide feeds may be all-metallic with the center feed operating in a TE11 mode and the coaxial feeds operating in a coaxial TE11 mode. The waveguide feeds may have electromagnetic band gap (EBG) surfaces on waveguide surfaces. The center waveguide feed may have an EBG outer conductor surface and operate in a circular waveguide TEM mode. The coaxial waveguide feeds may have EBG inner and outer conductors and operate in a circular waveguide TEM mode. The coaxial feeds may have EBG inner conductors and near perfect electrical conductor (PEC) outer conductors and operate in a circular waveguide-like TE11 mode or may comprise EBG outer conductors and PEC inner conductors and operate in a quasi-TEM waveguide mode.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
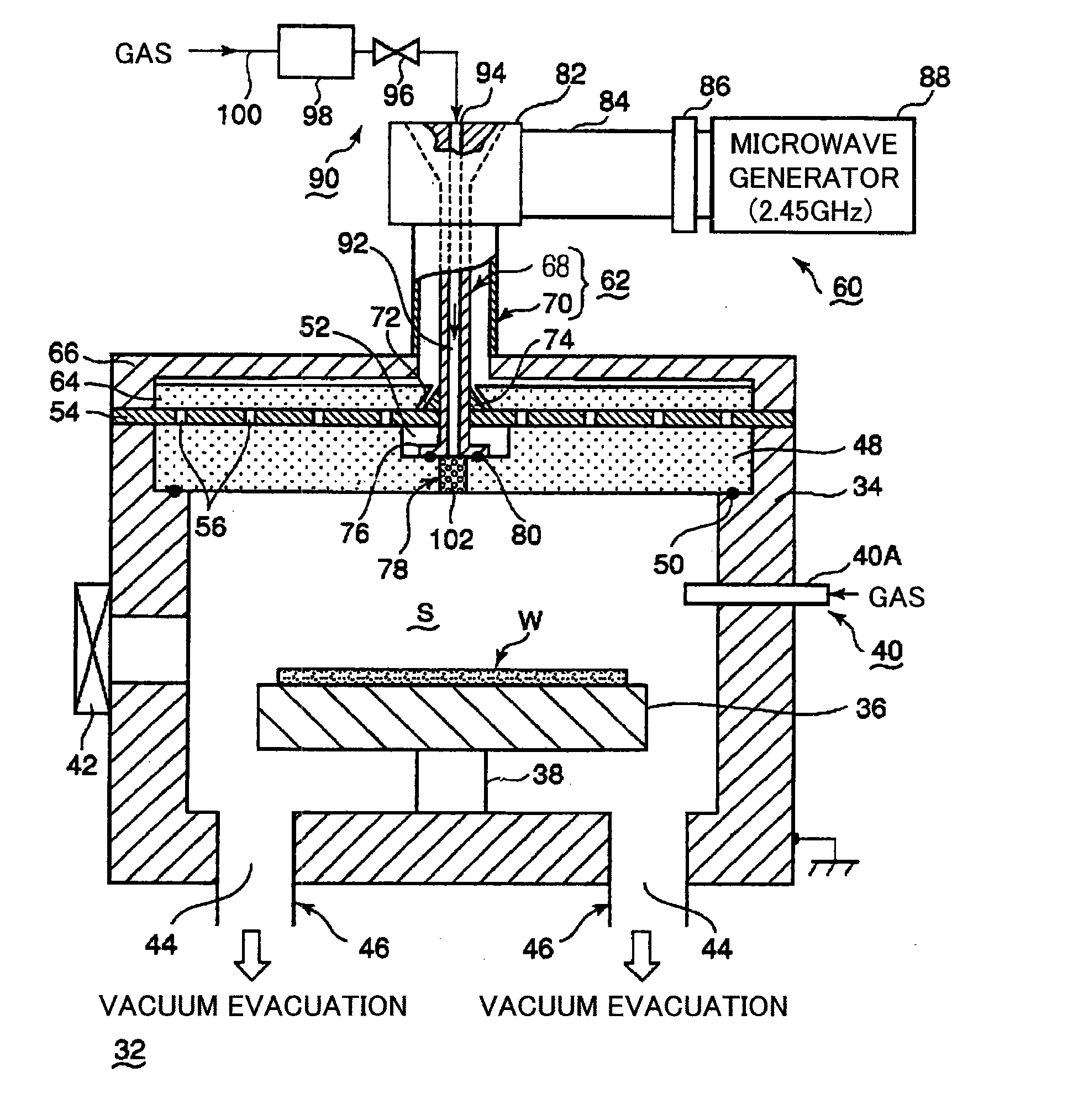
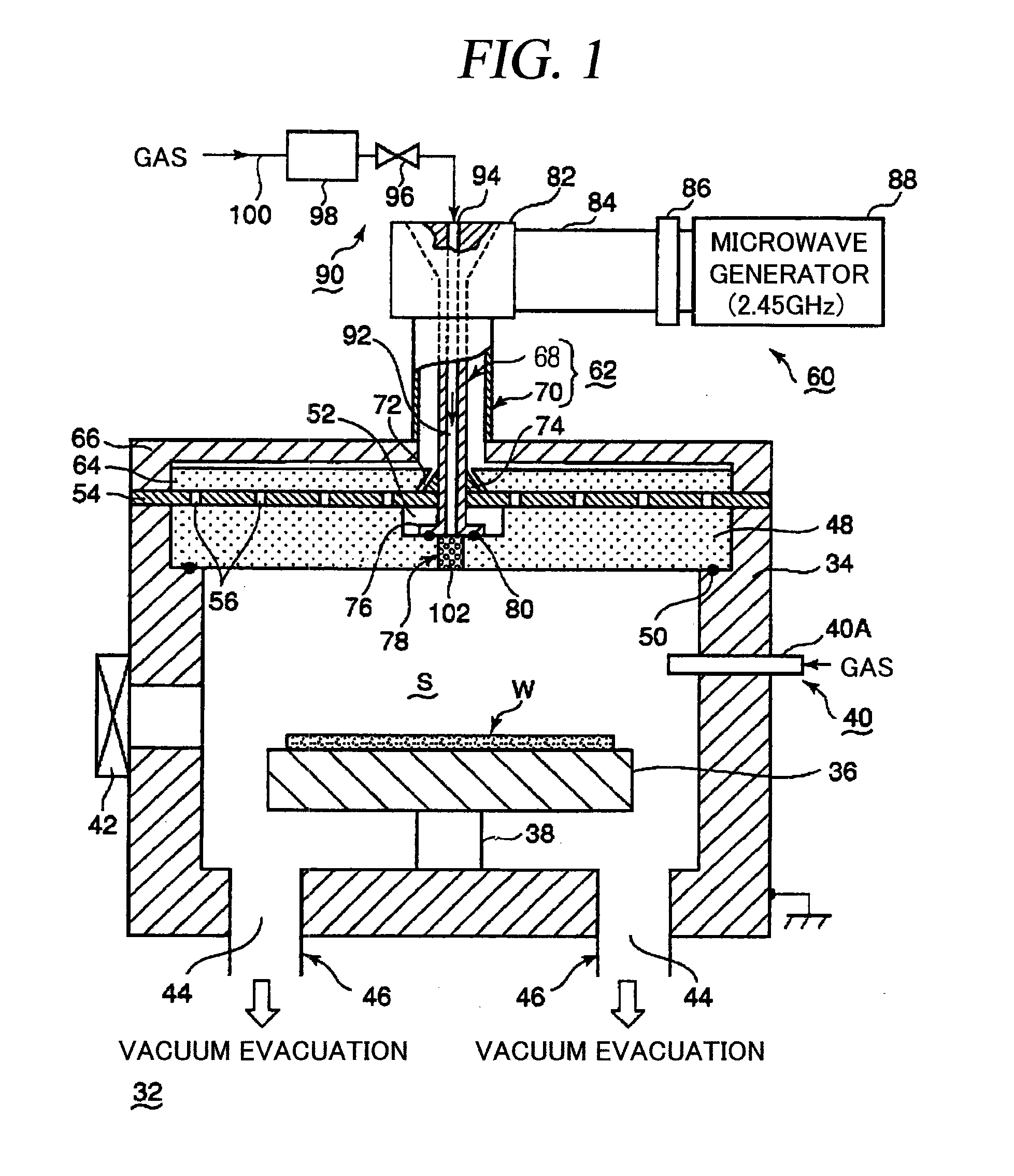
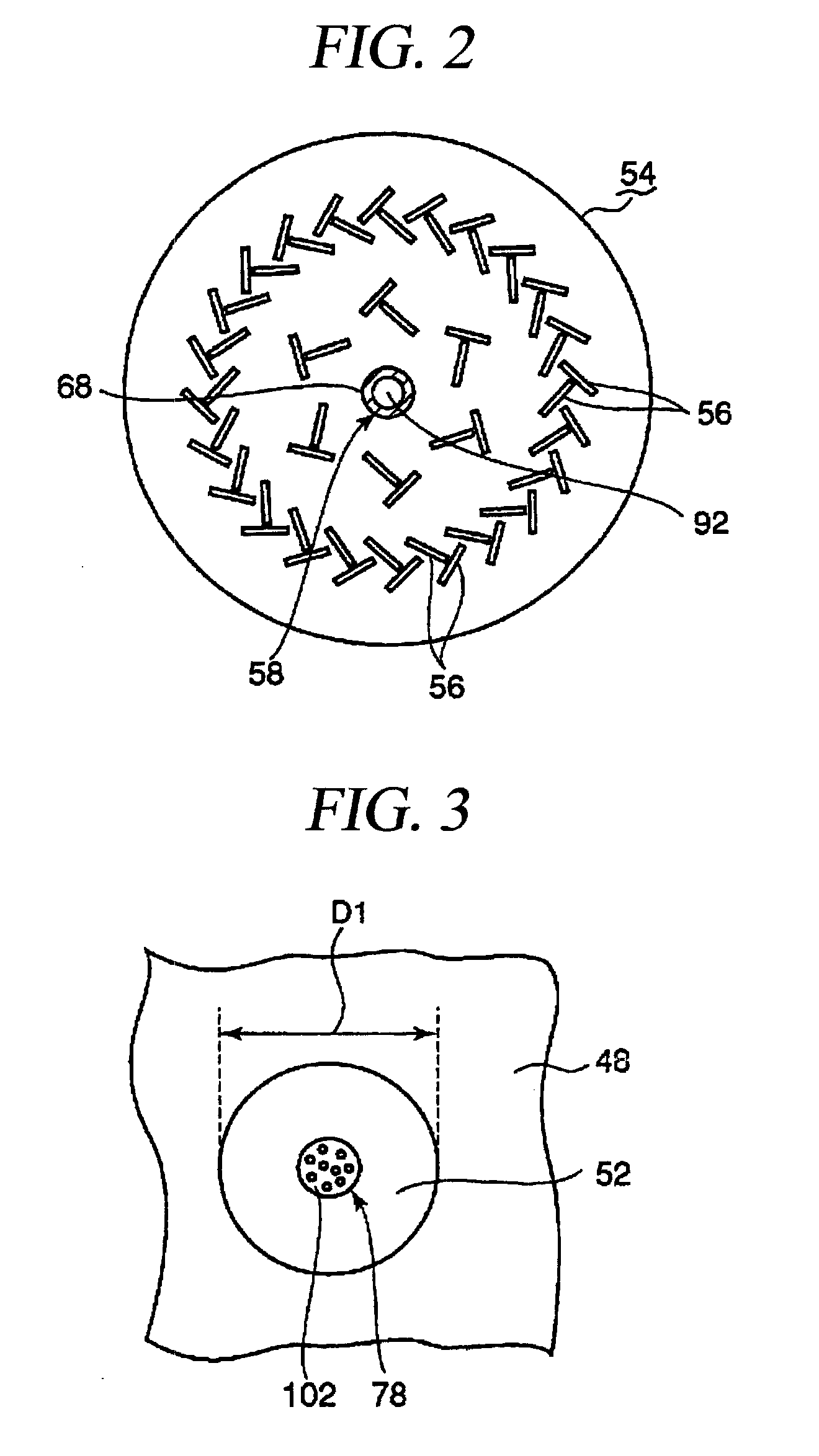
Plasma processing apparatus
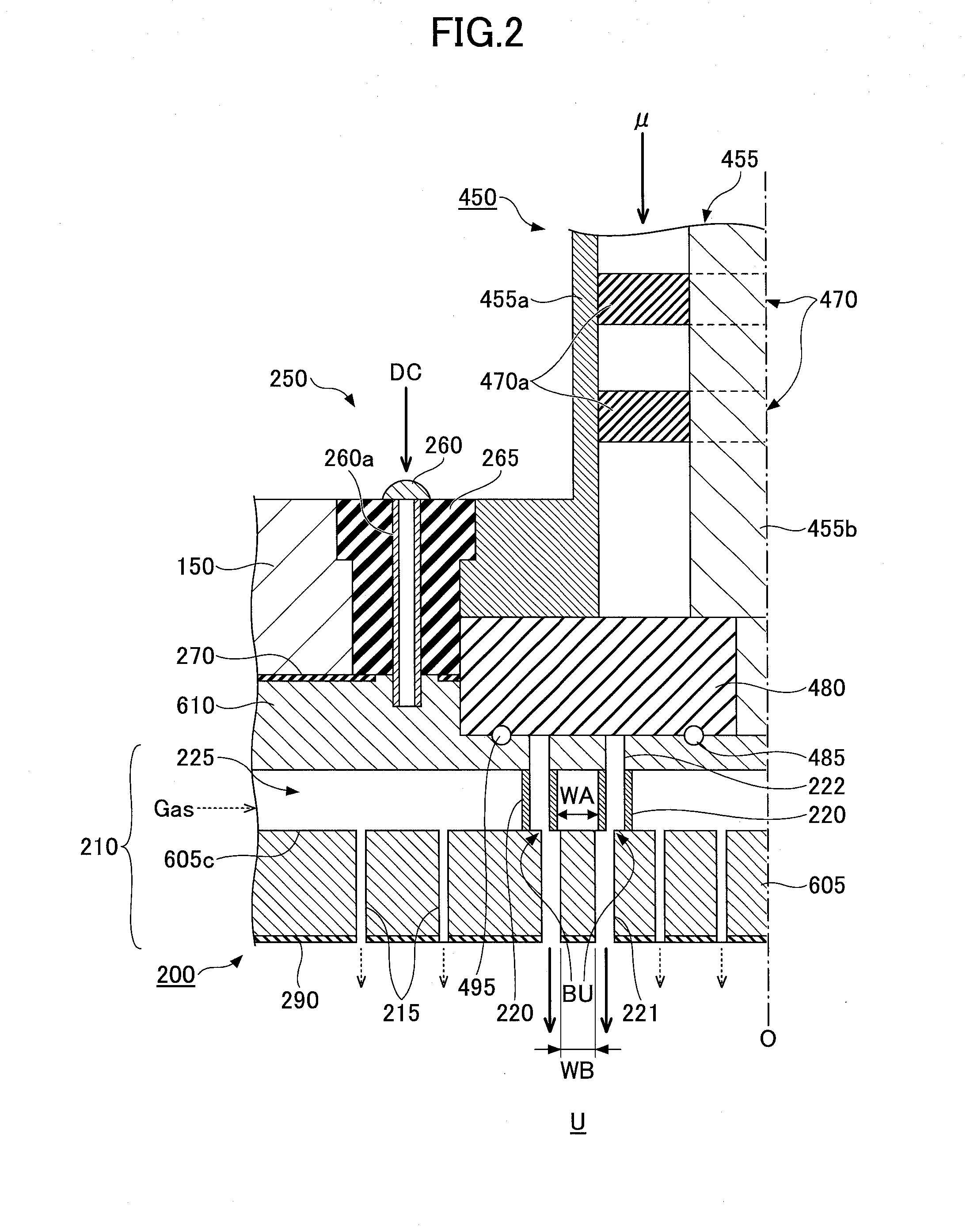
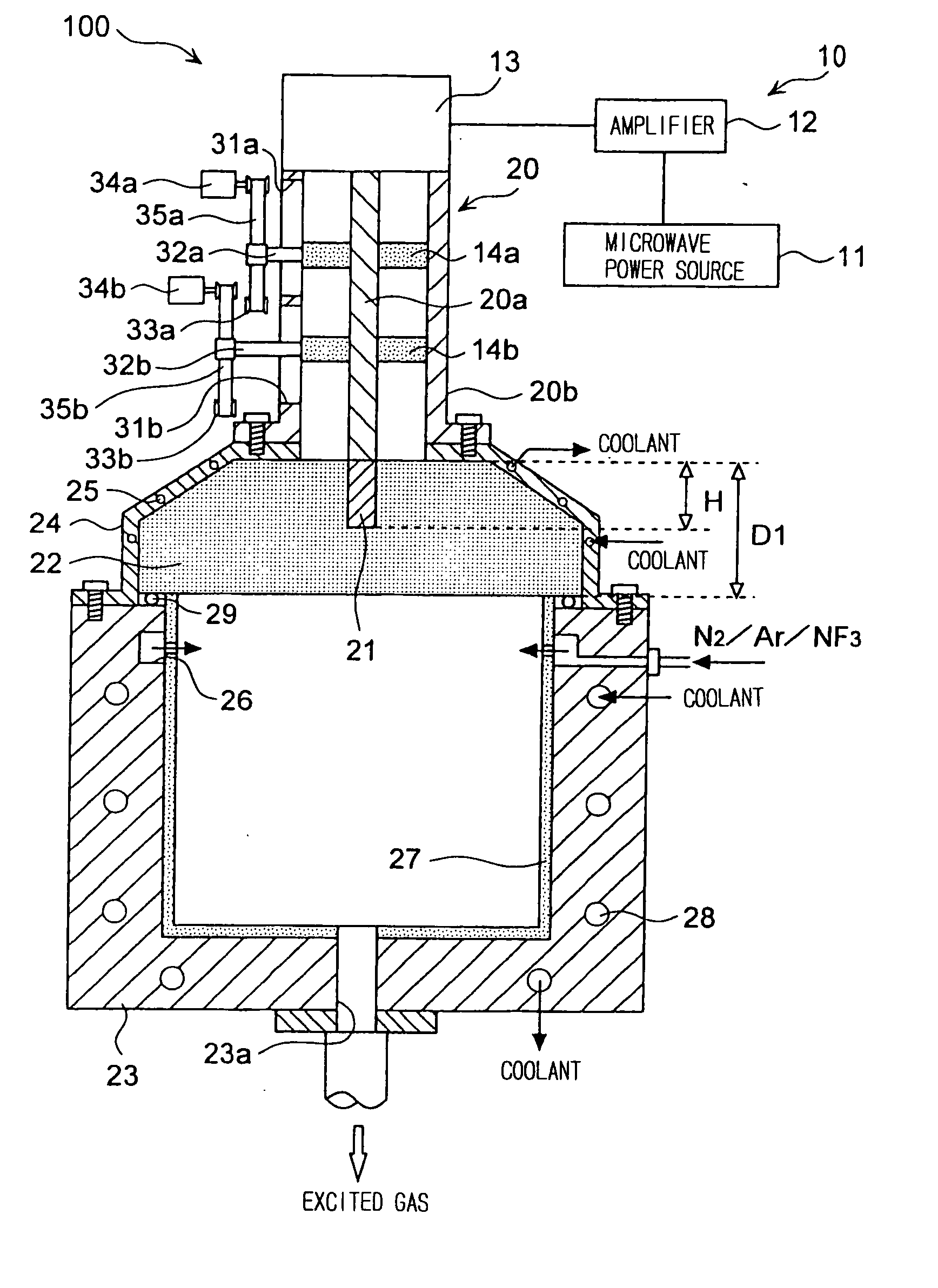
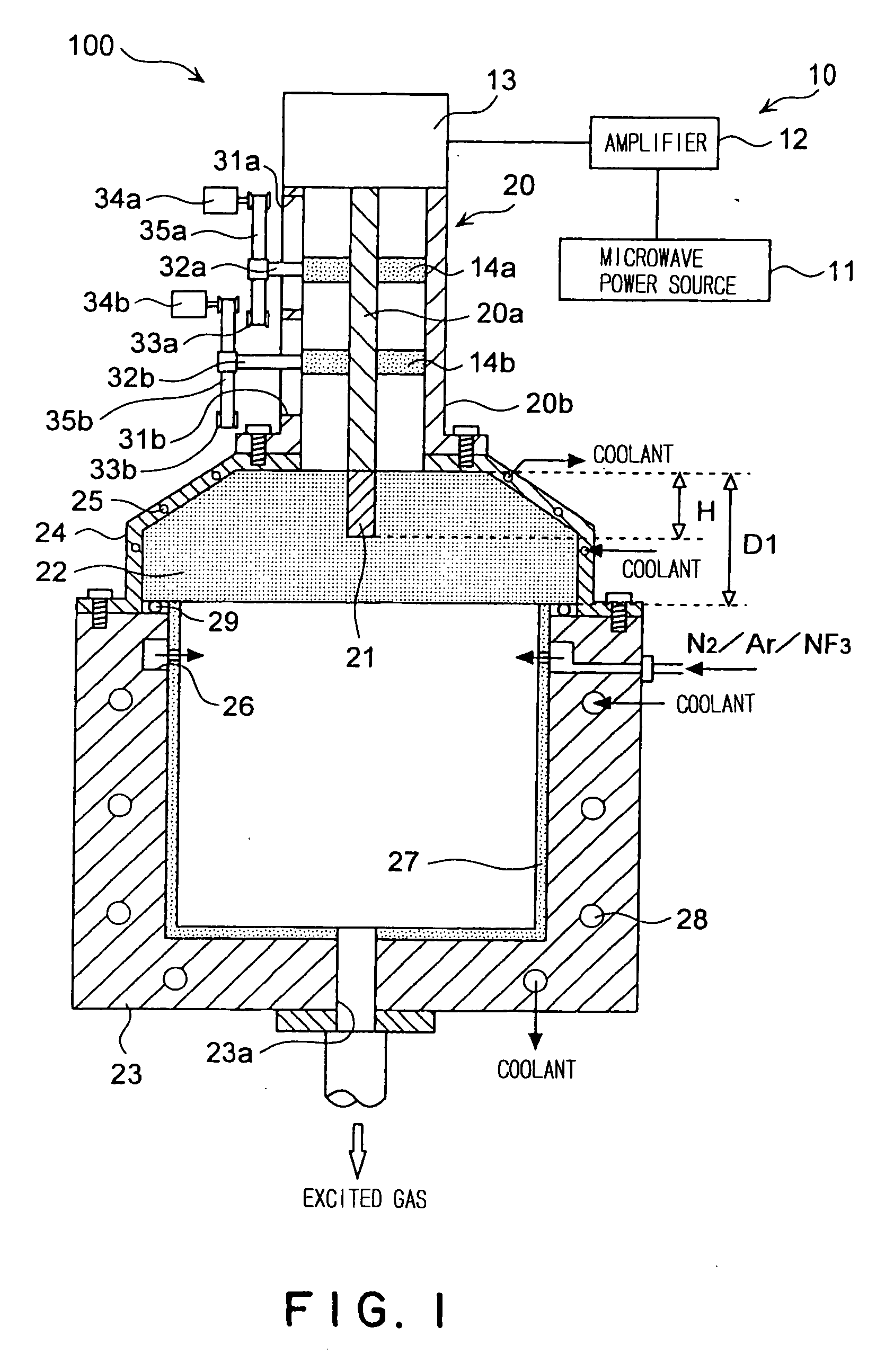
ActiveUS20090242130A1Efficient solutionSuppressing discharge of plasmaElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsElectrical conductorCoaxial waveguides
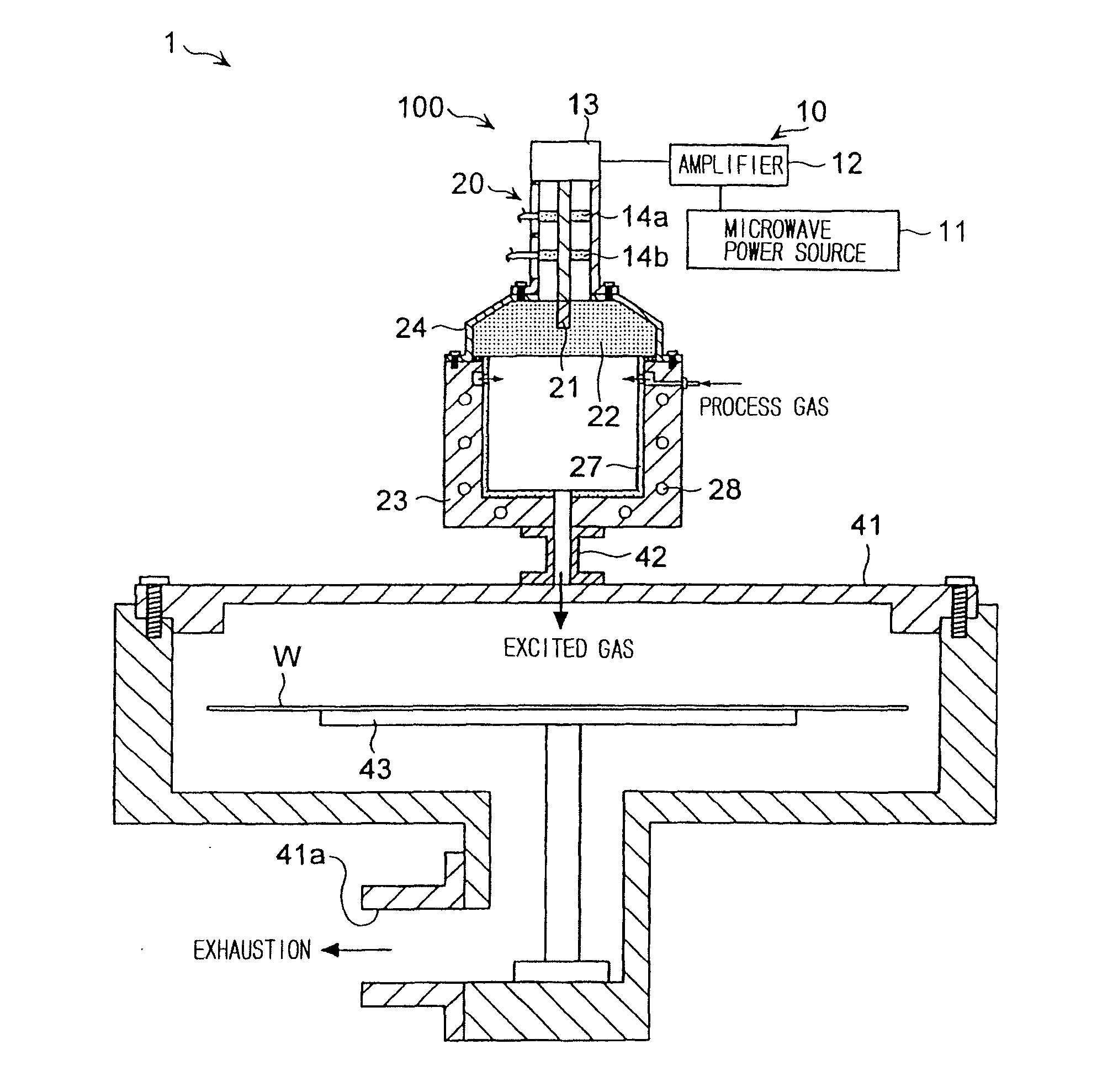
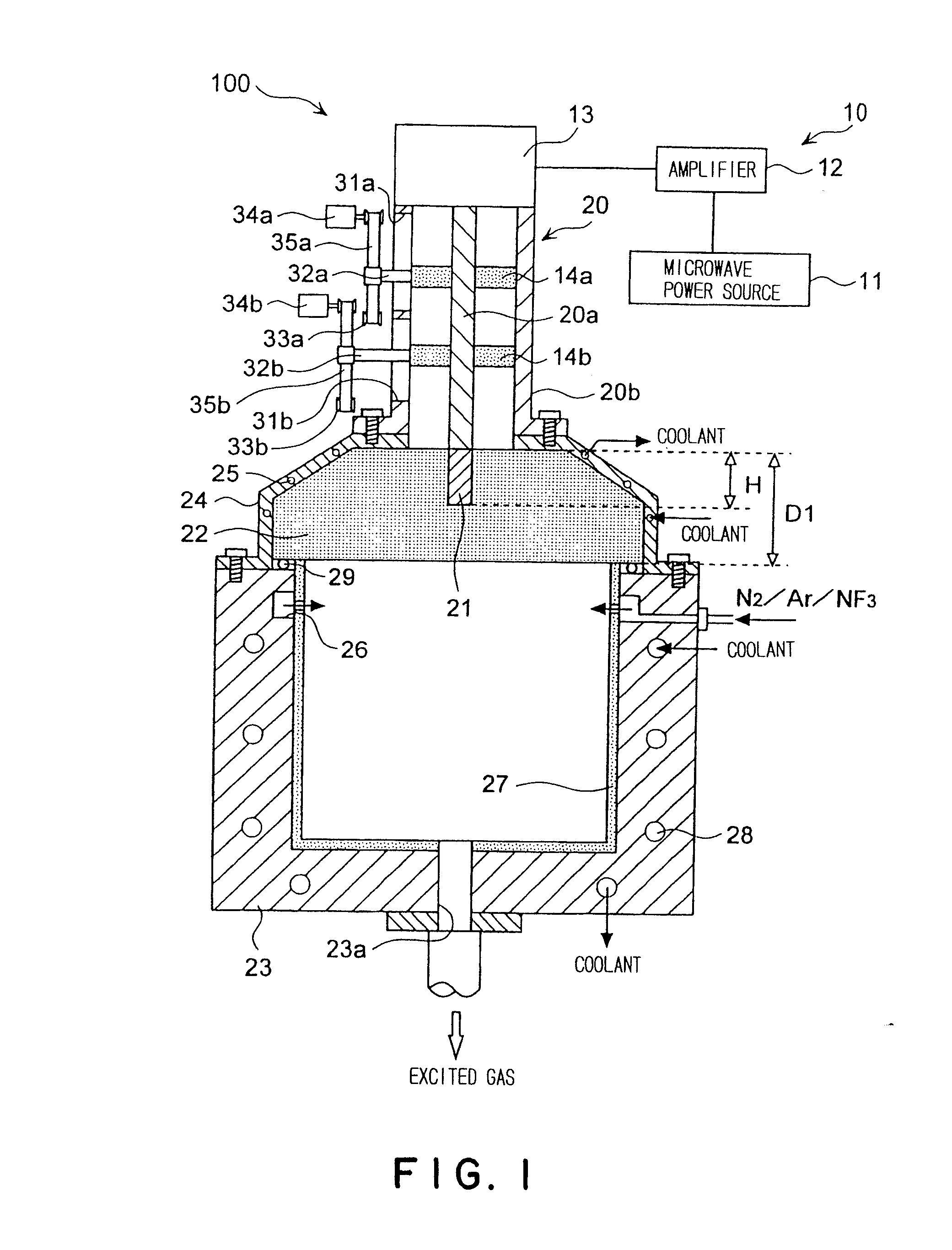
The present invention relates to a plasma processing apparatus including: a processing chamber whose ceiling portion is opened and the inside thereof can be evacuated to vacuum; a ceiling plate which is made of dielectric material and is airtightly mounted to an opening of the ceiling portion; a planar antenna member which is installed on a top surface of the ceiling plate, for introducing a microwave into the processing chamber; and a coaxial waveguide, which has a central conductor connected to the planar antenna member, for supplying the microwave, wherein a gas passage is formed to pass through the central conductor, the planar antenna member, and the ceiling plate, and an electric field attenuating recess for attenuating an electric field intensity of the center portion of the ceiling plate is installed on a top surface of a center area of the ceiling plate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Antenna for plasma generation, plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
ActiveUS20140339981A1Electric discharge tubesAntenna supports/mountingsMicrowave propagationCoaxial waveguides
An antenna for plasma generation radiates a microwave transmitted through a coaxial waveguide into a processing chamber and propagates the microwave on a metal surface of the processing chamber to convert gas into surface wave plasma. The antenna includes a gas flow path for passing the gas through the antenna, a plurality of gas holes that communicate with the gas flow path and introduce the gas into the processing chamber, and a plurality of slots that are separated from the gas flow path and penetrate through the gas flow path. The slots pass the microwave transmitted through the coaxial waveguide and a slow-wave plate to the processing chamber. A first space between portions of adjacent slots penetrating through the gas flow path is arranged to be wider than a second space between portions of the adjacent slots opening out to a plasma generation space of the processing chamber.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
ActiveUS20110121736A1Different characteristic impedancePrevent fallingElectric arc lampsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityElectrical conductor
Provided is a plasma processing apparatus having a coaxial waveguide structure in which characteristic impedance of an input side and characteristic impedance of an output side are different. A microwave plasma processing apparatus, which plasma-processes a substrate by exciting a gas by using a microwave, includes: a processing container; a microwave source, which outputs a microwave, a first coaxial waveguide, which transmits the microwave output from the microwave source; and a dielectric plate, which is adjacent to the first coaxial waveguide while facing an inner side of the processing container, and emits the microwave transmitted from the first coaxial waveguide into the processing container. A thickness ratio between an inner conductor and an outer conductor of the first coaxial waveguide is not uniform along a longitudinal direction.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
Microwave resonance plasma generating apparatus and plasma processing system having the same
ActiveUS20070045244A1Increase plasma producing efficiencySimple structureElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsHigh energyCoaxial waveguides
A microwave resonance plasma generating apparatus, a plasma processing system having the same and a method of generating a microwave resonance plasma are provided. The apparatus includes a microwave generating unit which generates a microwave, and a plasma producing unit which produces electrons and photons of high energy using the microwave generated from the microwave generating unit. The plasma producing unit includes a coaxial waveguide having an inner electrode disposed adjacent to the microwave generating unit, an outer electrode connected to the microwave generating unit and disposed to coaxially surround a portion of the inner electrode, the outer electrode being shorter than the inner electrode, and a dielectric tube disposed between the inner electrode and the outer electrode to insulate between the inner electrode and the outer electrode. The coaxial waveguide utilizes a principle of “cut or truncated electrode of coaxial waveguide” and a resonance phenomenon of Langmiur.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
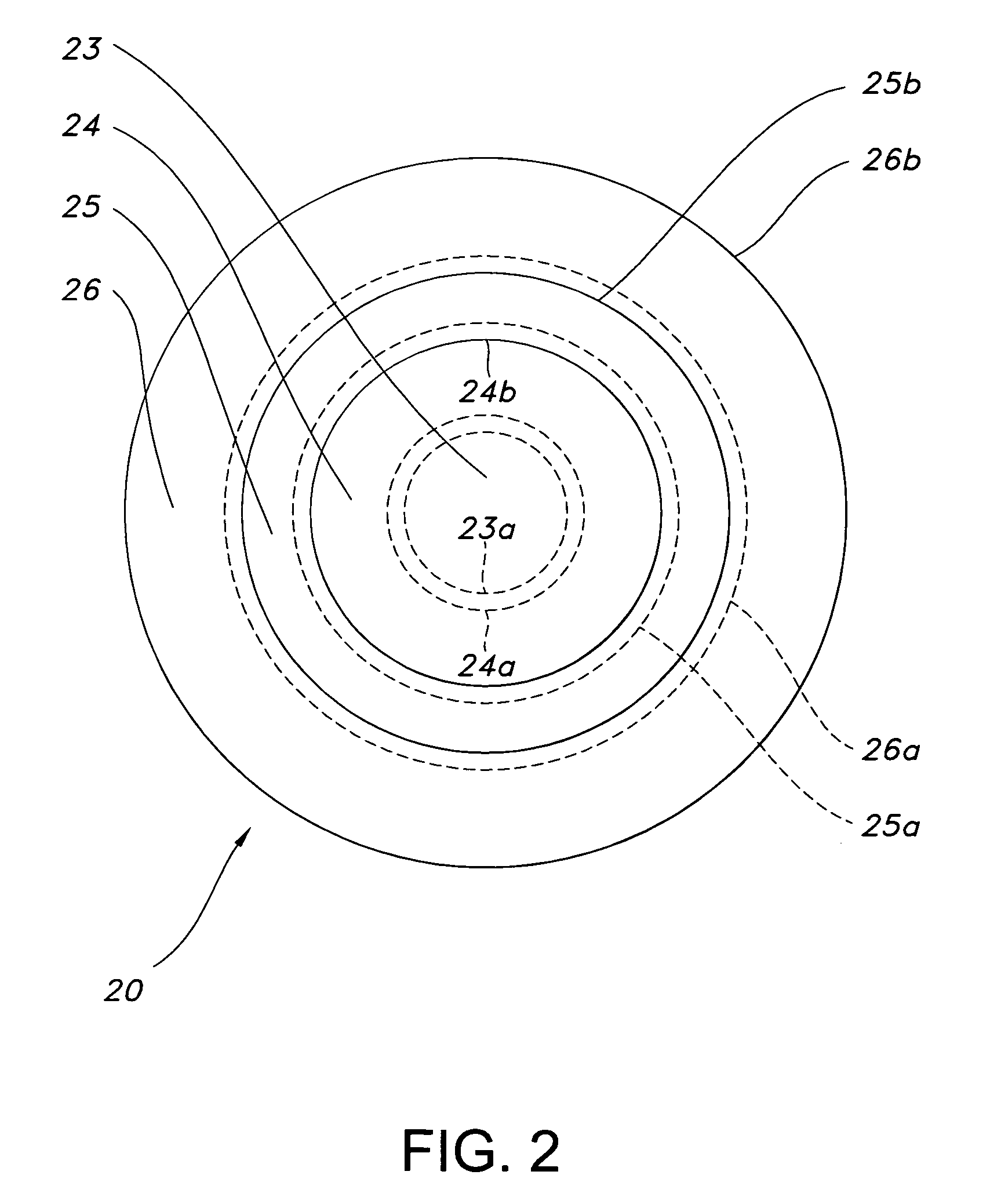
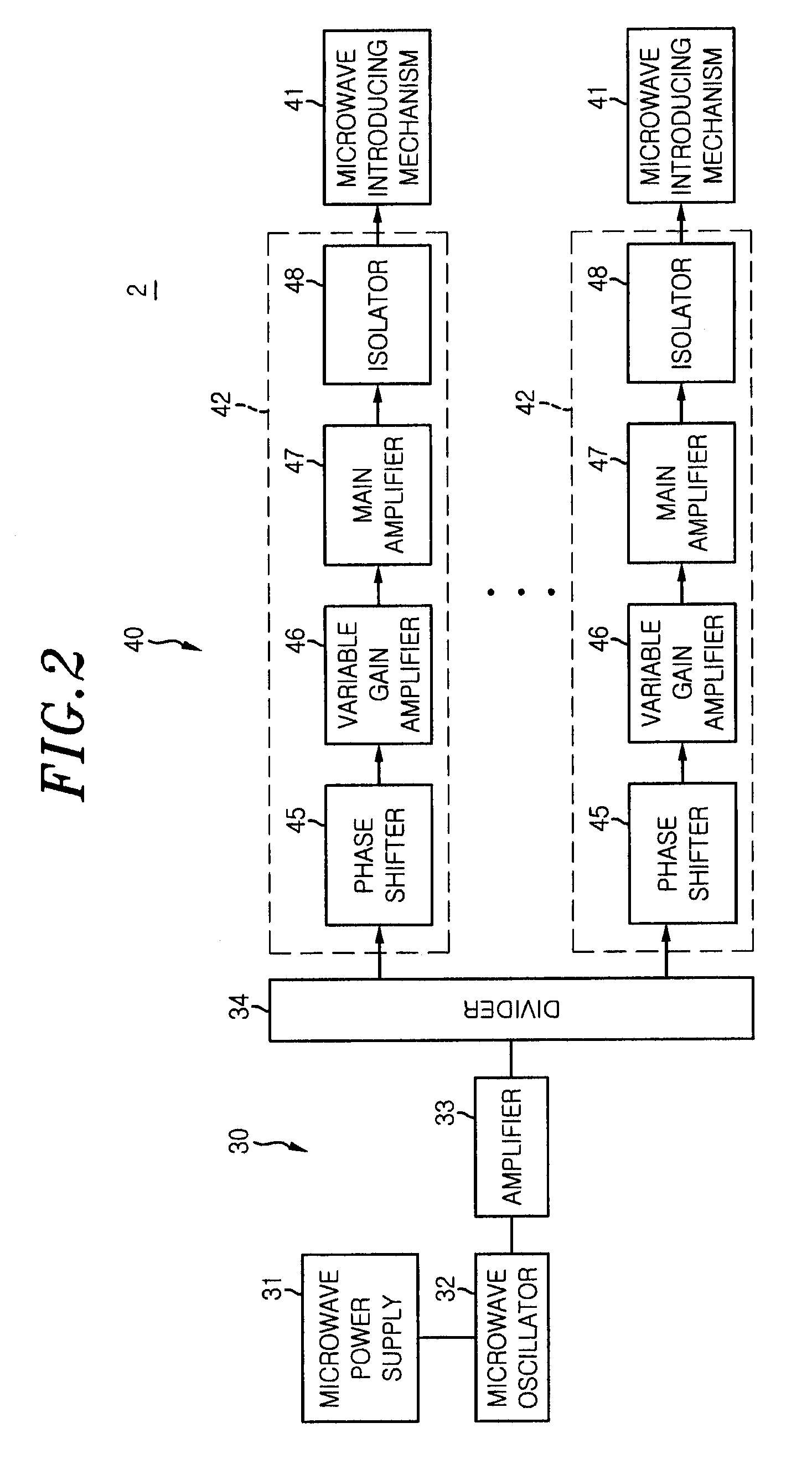
Electromagnetic-radiation power-supply mechanism and microwave introduction mechanism
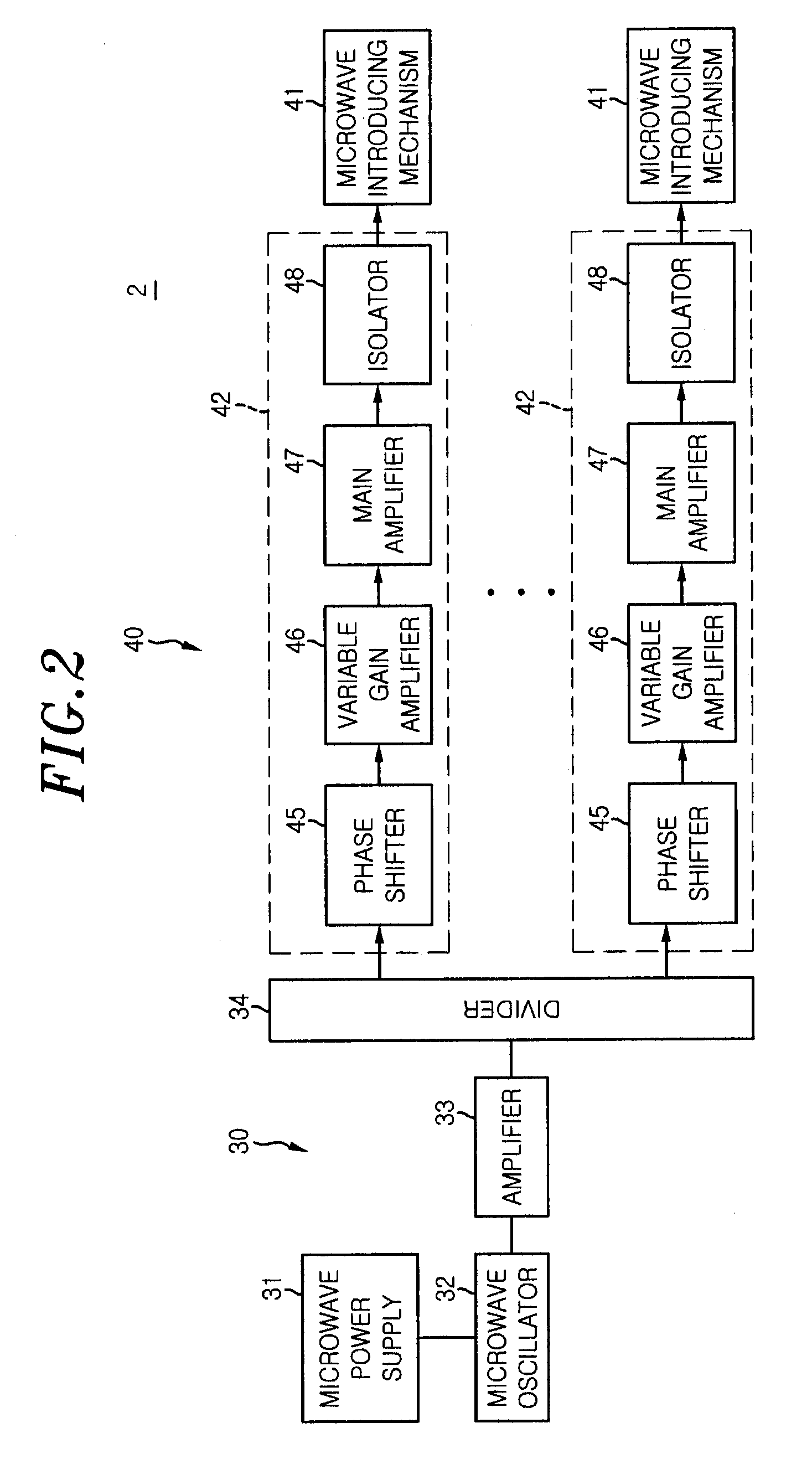
ActiveUS20120299671A1Efficient supplyShortening an effective wavelength of an electromagnetic waveElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorCoaxial waveguides
An electromagnetic-radiation power-supply mechanism includes a microwave power introduction port provided on the side of the coaxial waveguide, a power line being connected to the microwave power introduction port; and a power supply antenna for radiating the electromagnetic wave power into the waveguide, the power supply antenna being connected to the power line. The power supply antenna includes an antenna body having a first pole connected to the power line and a second pole connected to an inner conductor of the waveguide; and a ring-shaped reflection portion extending from opposite sides of the antenna body.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Multi-channel mode converter and rotary joint operating with a series of TE or TM mode electromagnetic wave
A multi-channel mode converter operating with a series of TE or TM mode electromagnetic wave includes a plurality of coaxial waveguides arranged in overlay configuration. By controlling radius ratio and the number of coupling aperture of each coaxial waveguide, high power and high purity of operating mode of electromagnetic wave can be obtained and the major parasitic mode of electromagnetic wave can be suppressed, so as to avoid crosstalk between coaxial waveguides. A rotary joint including the above-mentioned mode converter with multi-channel is also disclosed.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Electromagnetic-radiation power-supply mechanism for exciting a coaxial waveguide by using first and second poles and a ring-shaped reflection portion
ActiveUS9072158B2Efficient supplyShortening an effective wavelength of an electromagnetic waveElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorCoaxial waveguides
An electromagnetic-radiation power-supply mechanism includes a microwave power introduction port provided on the side of the coaxial waveguide, a power line being connected to the microwave power introduction port; and a power supply antenna for radiating the electromagnetic wave power into the waveguide, the power supply antenna being connected to the power line. The power supply antenna includes an antenna body having a first pole connected to the power line and a second pole connected to an inner conductor of the waveguide; and a ring-shaped reflection portion extending from opposite sides of the antenna body.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
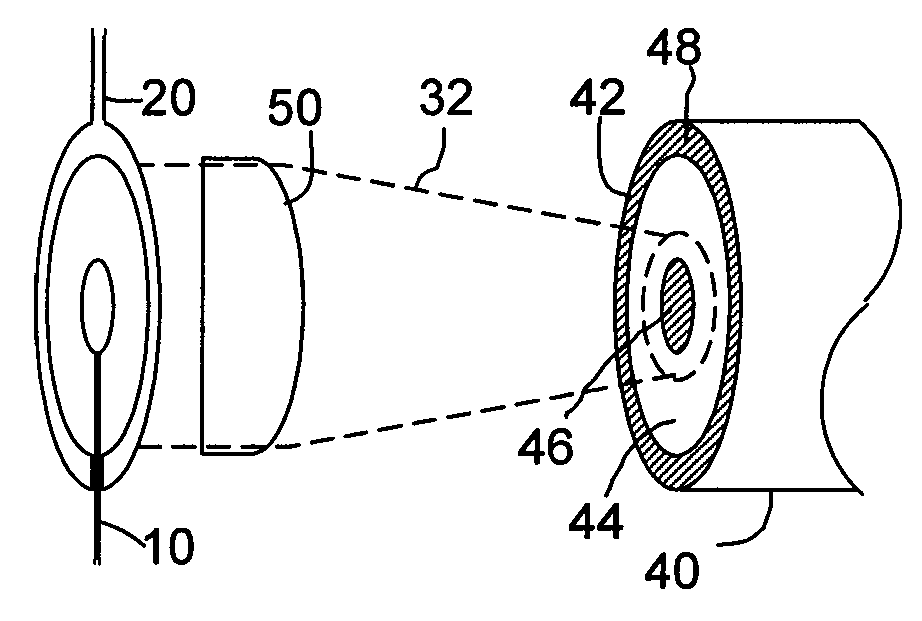
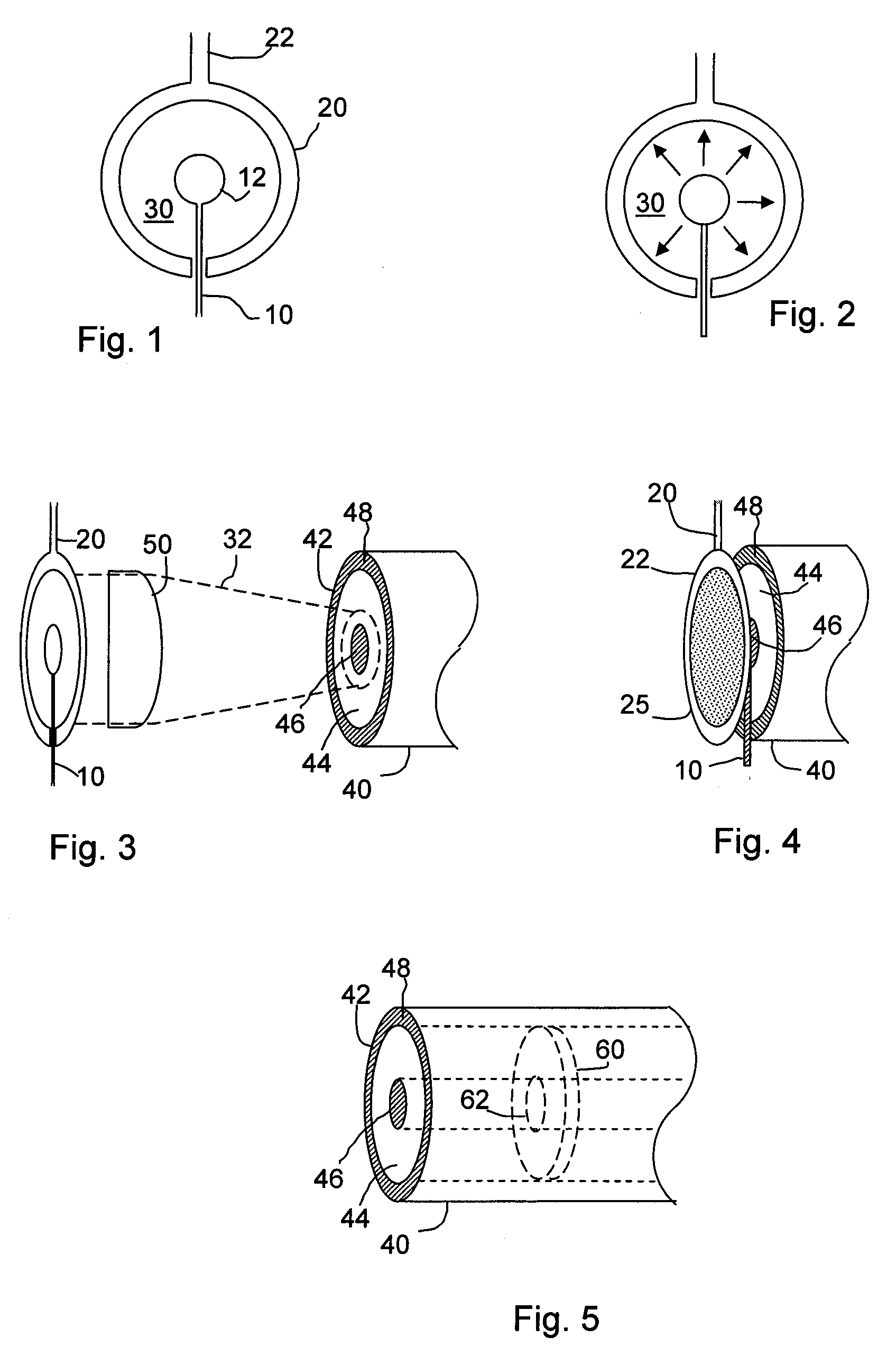
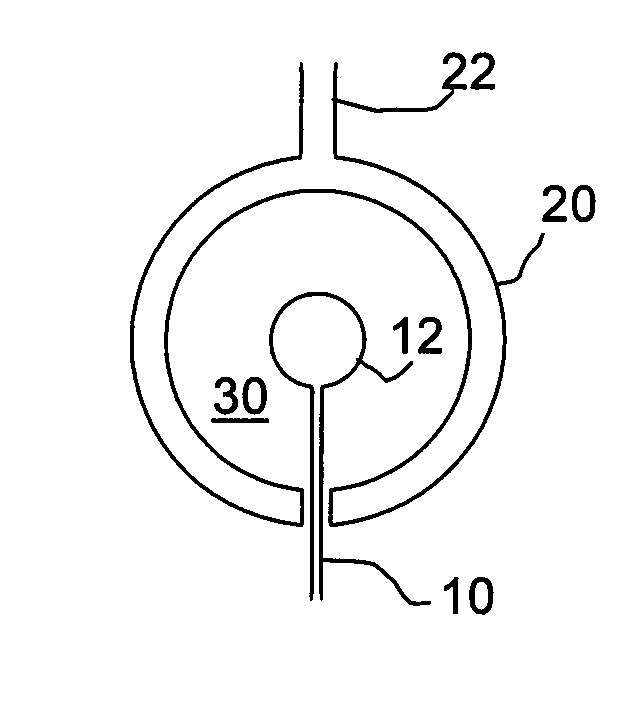
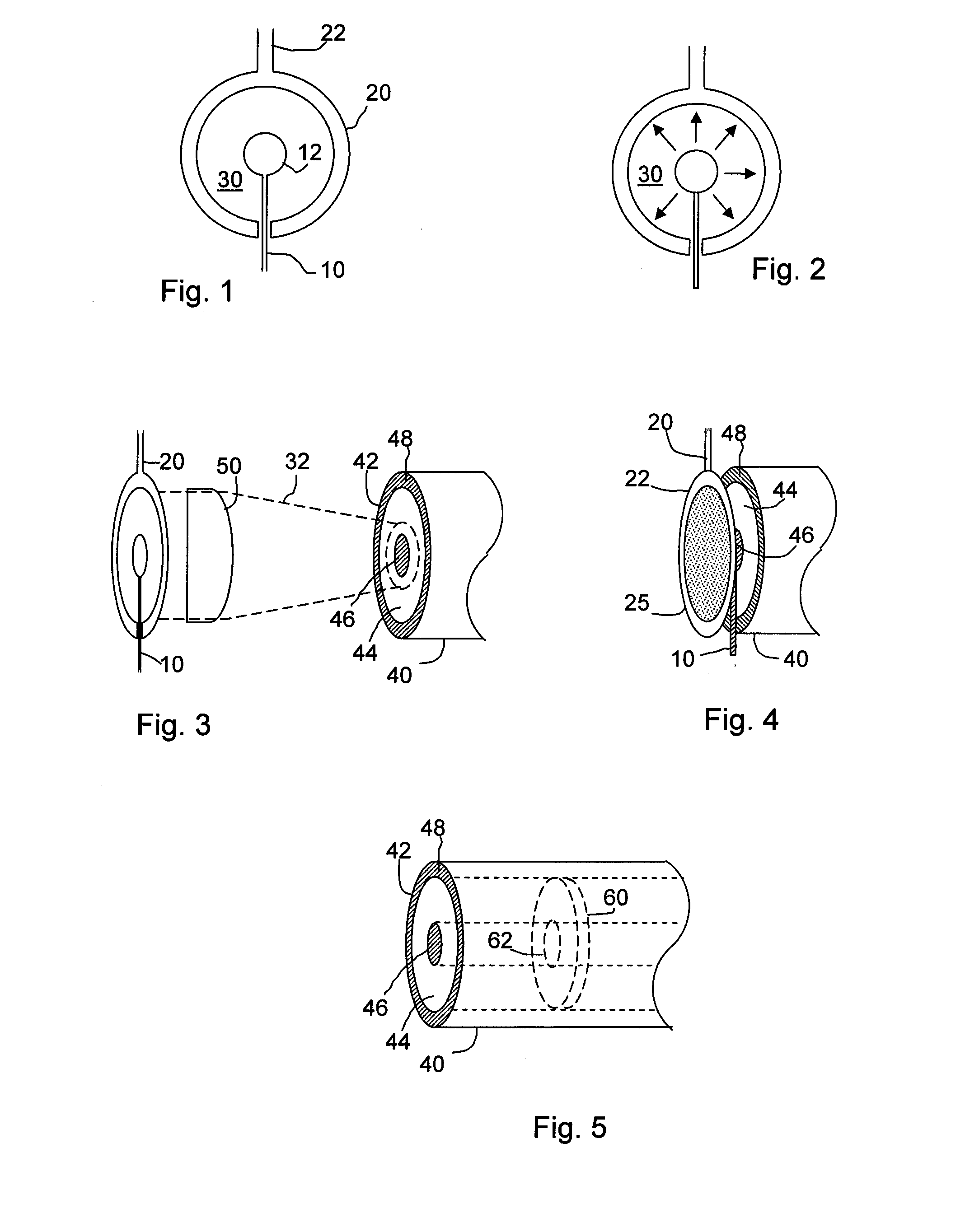
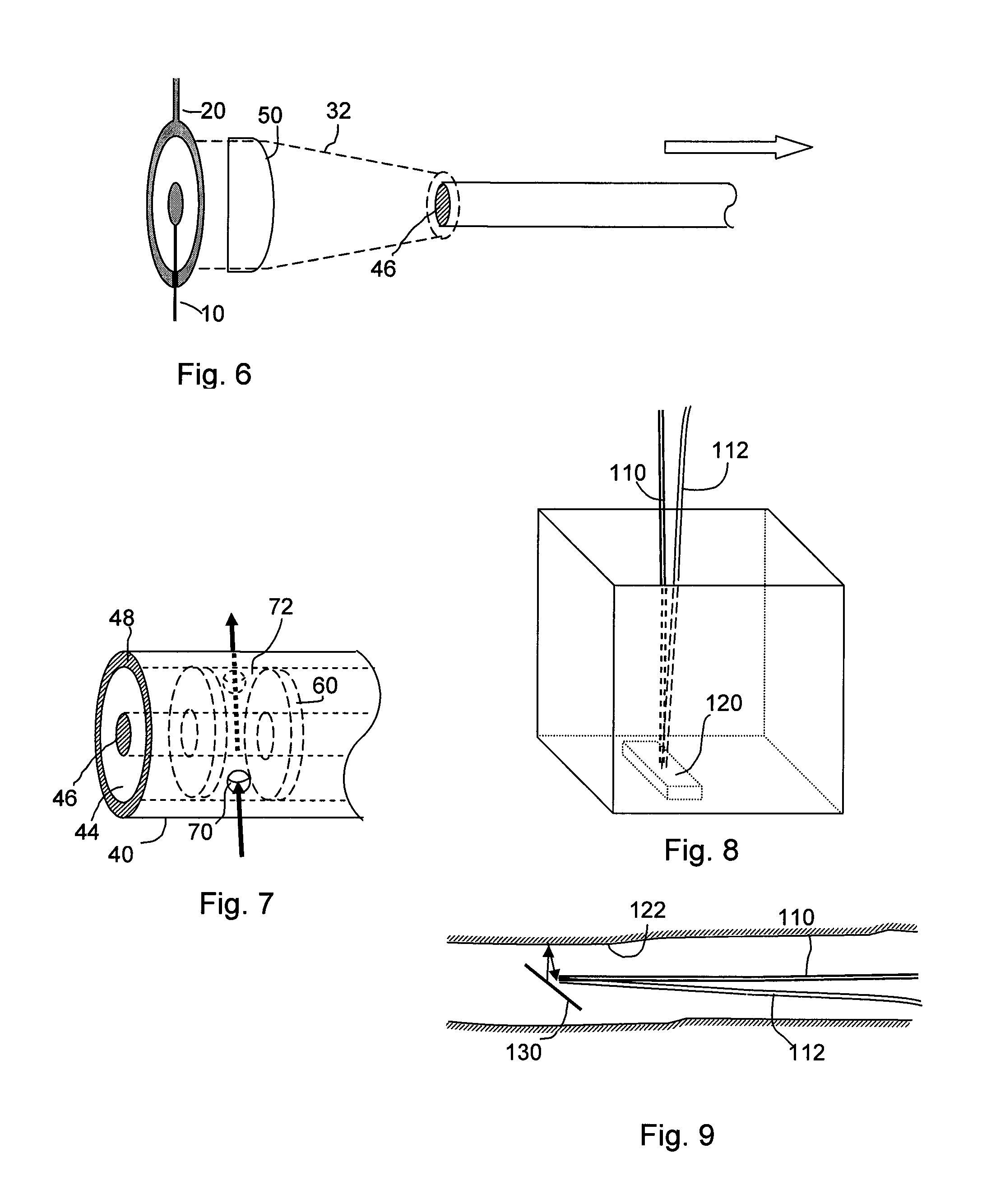
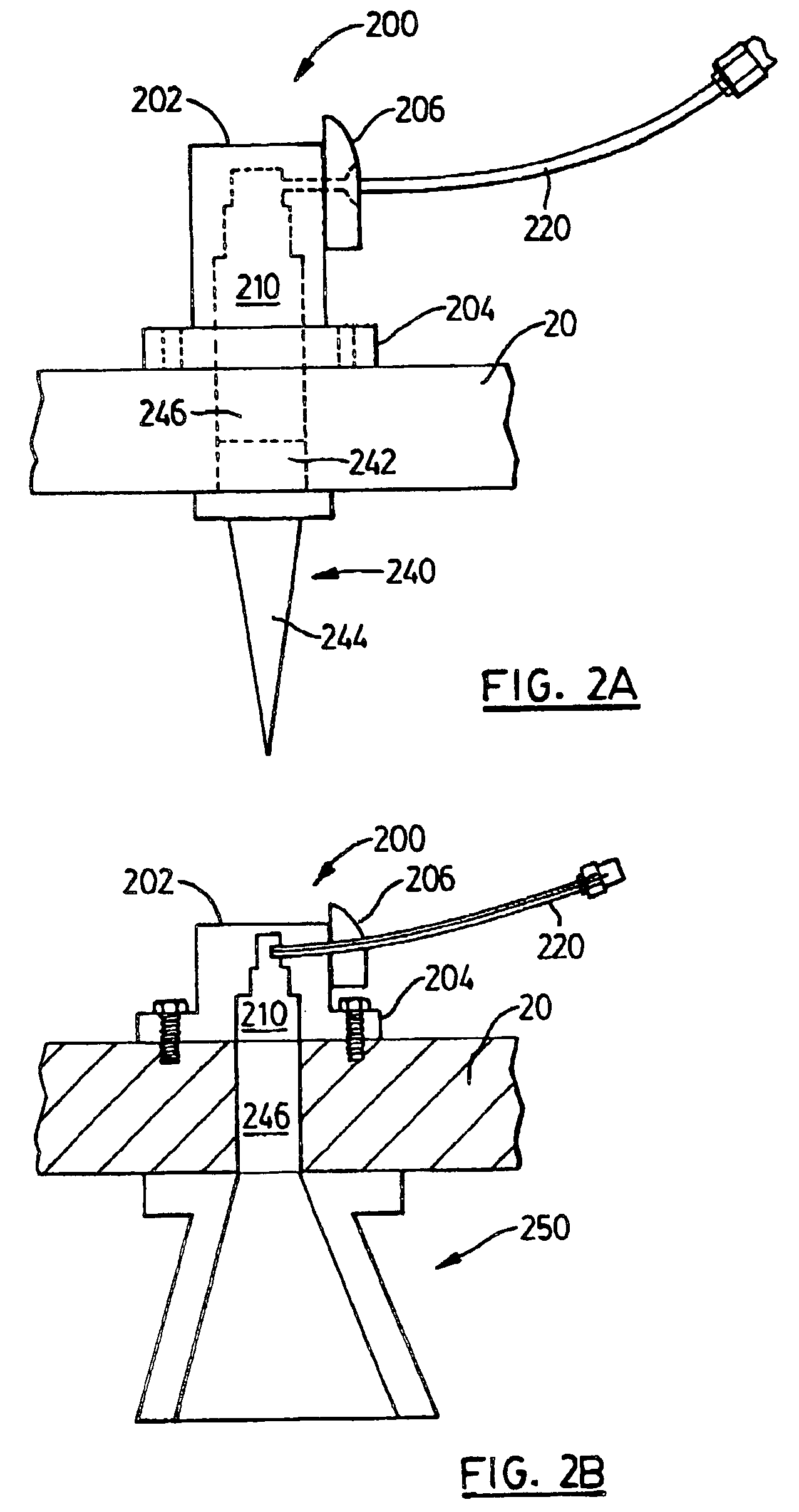
Method for coupling terahertz pulses into a coaxial waveguide
InactiveUS9178282B2Efficient couplingExclude influenceMaterial analysis by optical meansAntennas earthing switches associationCoaxial waveguidesWaveguide mode
A system for coupling teraherz (THz) radiation to a coaxial waveguide comprises an antenna that generates THz radiation having a mode that matches the mode of the waveguide. The antenna may comprise a pair of concentric electrodes, at least one of which may be affixed to or formed by one end of the waveguide. The radiation may have wavelengths between approximately 30 μm and 3 mm. The waveguide may comprise an inner core and an outer wall defining an annular region. A terahertz sensor system may comprise a terahertz antenna comprising first and second concentric electrodes, means for generating a field across the trodes and means for triggering the emission of terahertz radiation, a first waveguide having first and second ends, said first end being coupled to said antenna so as to receive at least a portion of said terahertz radiation, and a sensor for detecting said terahertz radiation.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Plasma generating apparatus, plasma generating method and remote plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20100224324A1Improve efficiencyImprove space efficiencyElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaCoaxial waveguides
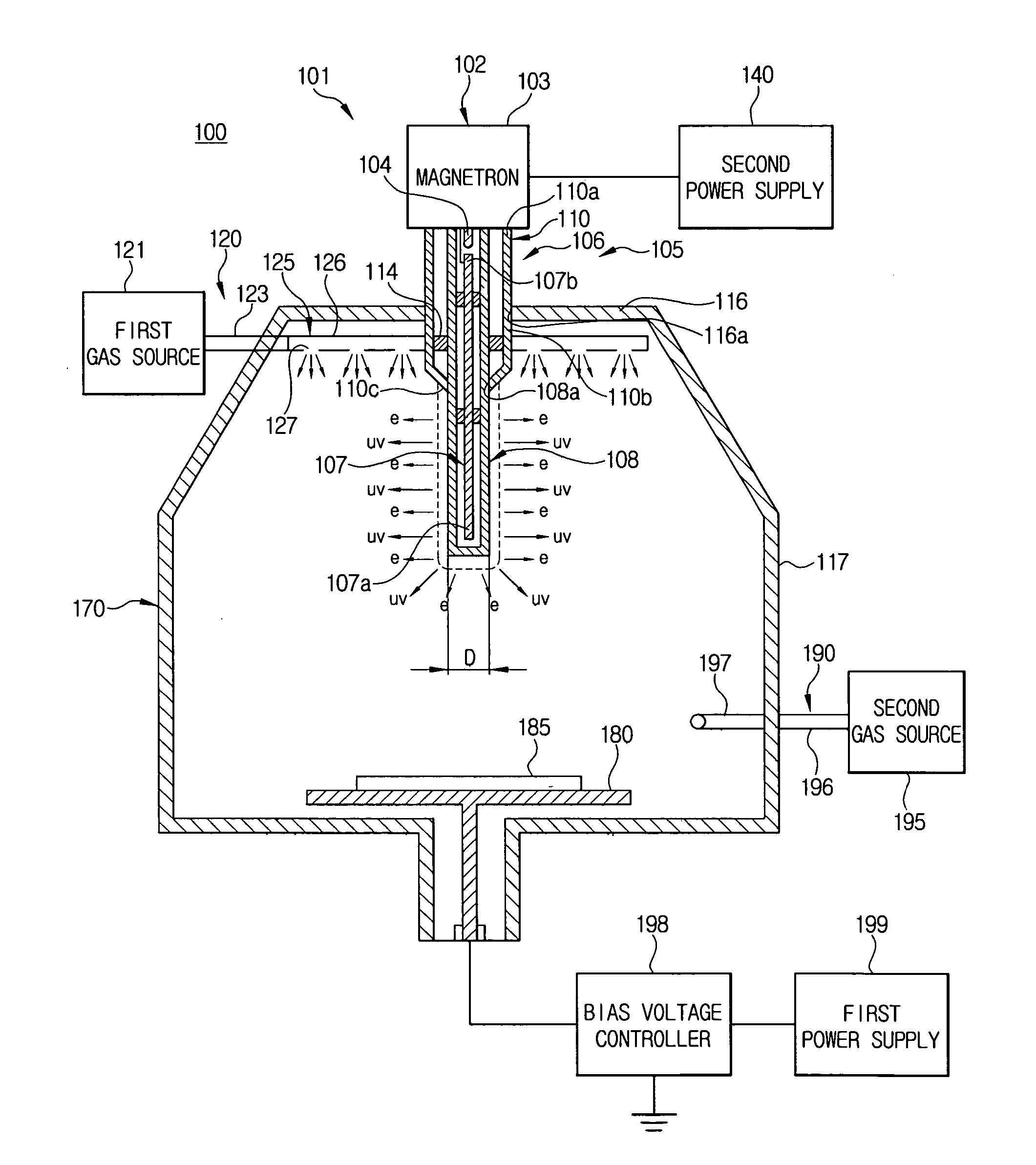
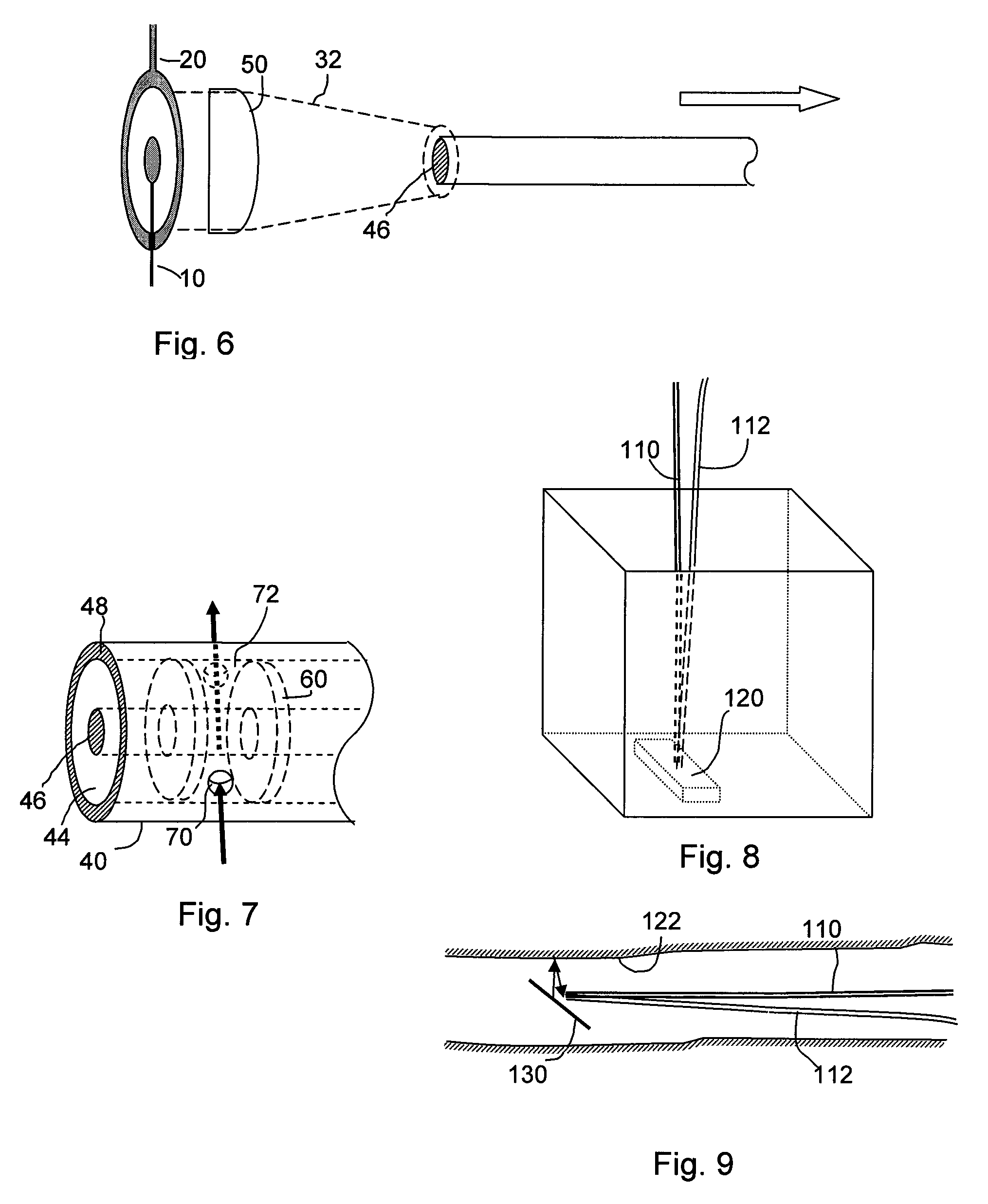
A compact plasma generating apparatus providing high efficiency of plasma excitation is presented. A plasma generating apparatus (100) comprises a microwave generating apparatus (10) for generating microwaves, a coaxial waveguide (20) having a coaxial structure comprising an inner tube (20a) and an outer tube (20b), a monopole antenna (21) being attached to one end of said inner tube (20a), for directing the microwaves generated by said microwave generating apparatus (10) to the monopole antenna (21), a resonator (22) composed of dielectric material for holding the monopole antenna (21), and a chamber (23) in which a specific process gas is fed for plasma excitation. The chamber (23) has an open surface and the resonator (22) is placed on this open surface, and the process gas is excited by the microwaves radiated from the monopole antenna (21) through the resonator (22) into the interior of the chamber (23) to generate plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Plasma generating apparatus, plasma generating method and remote plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20060137613A1Improve plasma excitation efficiencySmall sizeElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingRemote plasmaCoaxial waveguides
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Plasma Generator
InactiveUS20080029030A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingElectrical conductorPlasma generator
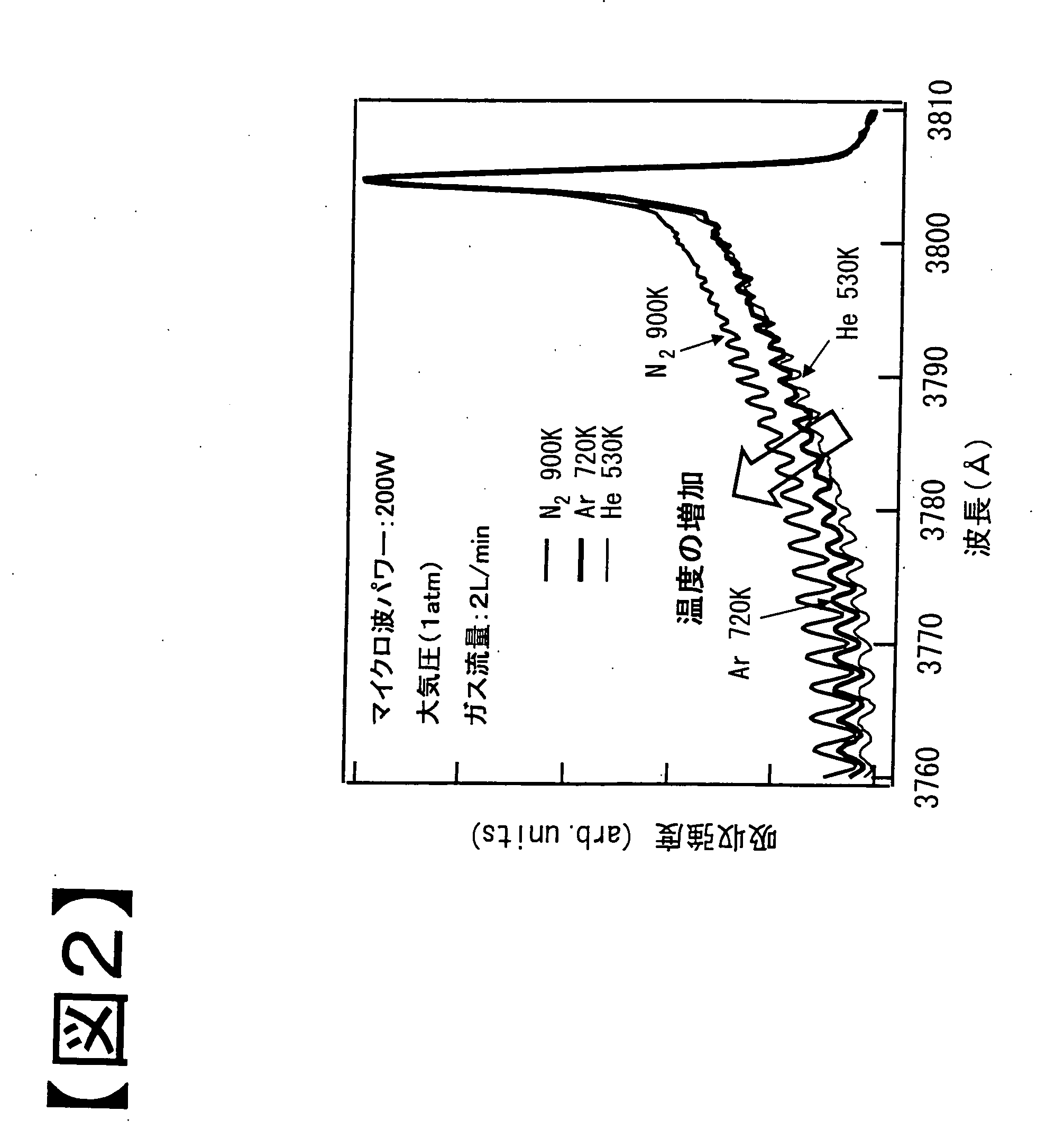
[Object] To stably generate plasma at atmospheric pressure.[Solving Means] There are provided a tubular casing 10 into which a gas and a microwave are introduced, a hole 30 provided in a bottom surface of this casing, and a columnar conductor 40 which is provided in an axis direction of the casing, a bottom surface of the conductor 40 having a contour placed inside the contour of the hole. A minute gap A formed between the contour of a bottom surface 41 of the conductor 40 and the contour of the hole, a coaxial waveguide formed of the conductor and the casing, and an insulating film 22 formed at least on a contour portion forming the hole at the minute gap are provided. In the structure described above, the microwave is guided to the minute gap by the coaxial waveguide, and the gas is made to pass through the minute gap, so that the gas is placed in a plasma state at the minute gap. The microwave is a pulse wave and is duty-controlled, and the contour portion forming the hole 30 is cooled with a cooling medium from the inside of an electrode 20. Accordingly, the increase in plasma temperature can be prevented, and as a result, stable plasma can be generated.
Owner:GOTO TOSHIO +3
Arrangement for coupling microwave energy into a treatment chamber
InactiveUS6952949B2Moderate reflection factor drop in powerReduce reflected powerElectric discharge tubesUsing liquid separation agentElectrical conductorCoaxial waveguides
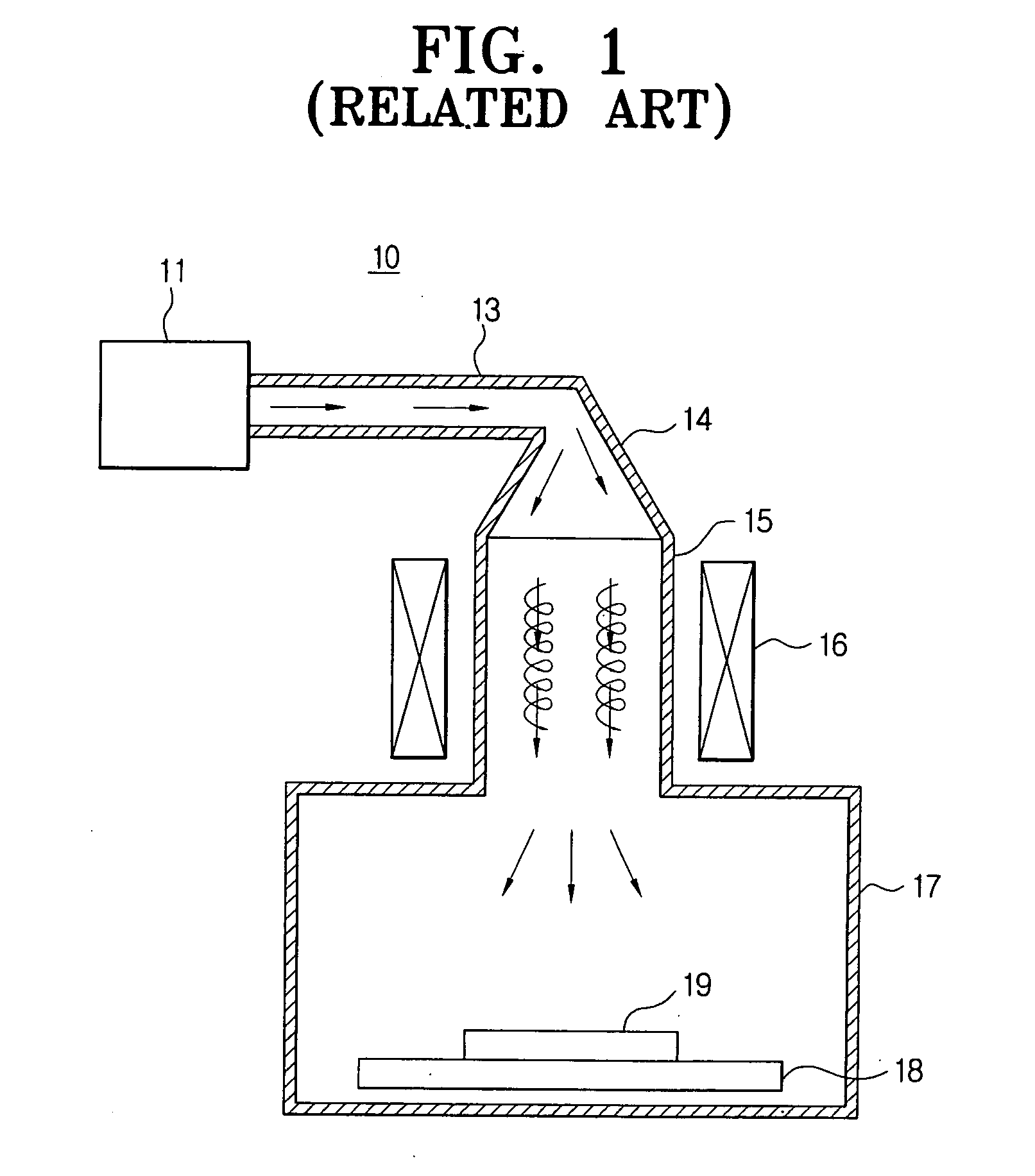
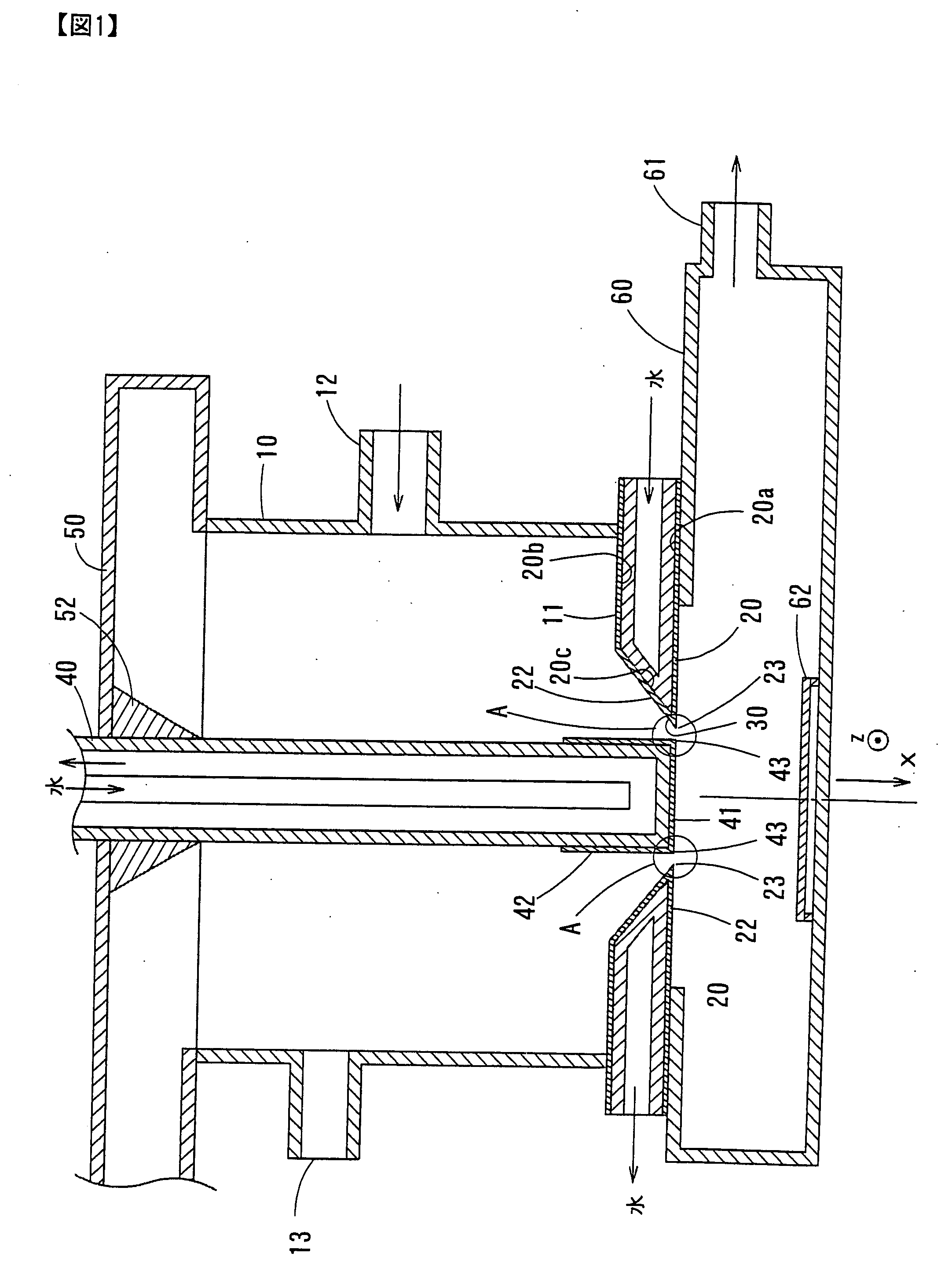
An arrangement for coupling microwave energy into a plasma CVD coating chamber (3) disposed in a cavity resonator (1) has a microwave feed (11) and a microwave waveguide (9, 1). So that a plastic container of a size and configuration which differ to a certain degree can be effectively coated in its interior, it is provided that the arrangement is of a substantially cylindrical structure, such that provided at the rear end is a first coaxial waveguide (in the region a) with an internal conductor in the form of an antenna (12), an approximately cylindrical waveguide (in the region b) follows in the centre of the arrangement and provided at the front end (in the region c) is a second coaxial waveguide (1) with internal conductor (13), wherein gas can be introduced through a gas feed tube (13) into the second coaxial waveguide (in the region c), which gas can be activated into the plasma state by the coupled-in microwave energy, and wherein a TM-mode is produced by the antenna (12) in the plasma region (1, c).
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
Method for Coupling Terahertz Pulses Into a Coaxial Waveguide
InactiveUS20080309577A1Efficient couplingExclude influenceMaterial analysis by optical meansAntennas earthing switches associationCoaxial waveguidesWaveguide mode
A system for coupling teraherz (THz) radiation to a coaxial waveguide comprises an antenna that generates THz radiation having a mode that matches the mode of the waveguide. The antenna may comprise a pair of concentric electrodes, at least one of which may be affixed to or formed by one end of the waveguide. The radiation may have wavelengths between approximately 30 μm and 3 mm. The waveguide may comprise an inner core and an outer wall defining an annular region. A terahertz sensor system may comprise a terahertz antenna comprising first and second concentric electrodes, means for generating a field across the trodes and means for triggering the emission of terahertz radiation, a first waveguide having first and second ends, said first end being coupled to said antenna so as to receive at least a portion of said terahertz radiation, and a sensor for detecting said terahertz radiation.
Owner:RICE UNIV
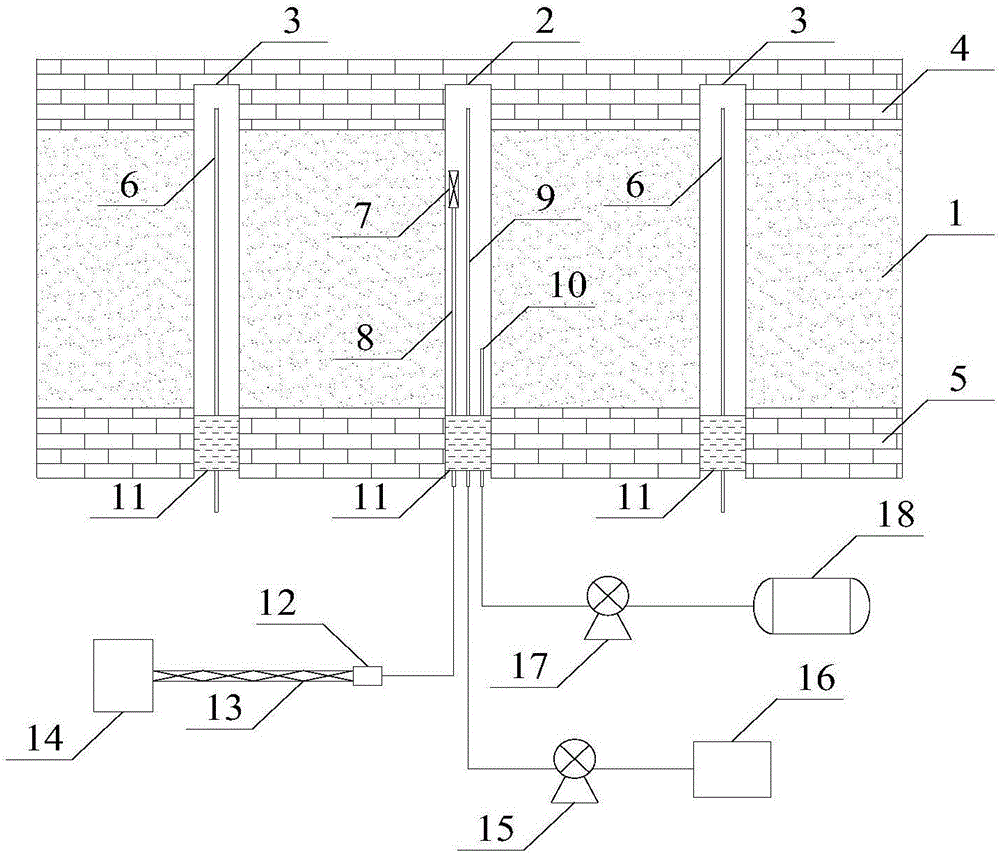
Microwave liquid nitrogen synergic freeze thawing coal seam anti-reflection method
ActiveCN106285605AHigh porosityImprove permeabilityFluid removalMicrowave heatingPorosityFreezing thawing
The invention relates to a microwave liquid nitrogen synergic freeze thawing coal seam anti-reflection method. According to the method, a freeze thawing drill hole is drilled in a coal seam, and two gas extraction drill holes are constructed at two sides of the freeze thawing drill hole. A microwave antenna, a coaxial waveguide, a water injection tube and a liquid nitrogen tube are sent into the freeze thawing drill hole together; firstly, a water injection pump is started, and water is injected into the freeze thawing drill hole; then a liquid nitrogen pump is started, and liquid nitrogen is injected into the freeze thawing drill hole to freeze water in the hole into ice so as to fracture the coal seam; and finally, a microwave generator is started, and produced microwave reaches the microwave antenna via a rectangular waveguide, a waveguide converter and the coaxial waveguide and is radiated to the freeze thawing drill hole by the microwave antenna, so that ice in the hole is quickly melted and gasified, high-temperature high-pressure water steam continues to fracture the coal seam, and gas is continuously desorbed at high temperature and rushes to the gas extraction drill holes along fractures in coal. According to the invention, microwave radiation is combined with liquid nitrogen freeze thawing, thus greatly improving the porosity and the permeability of the coal seam, promoting gas desorption, and further greatly improving the gas extraction efficiency and having wide practicability.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
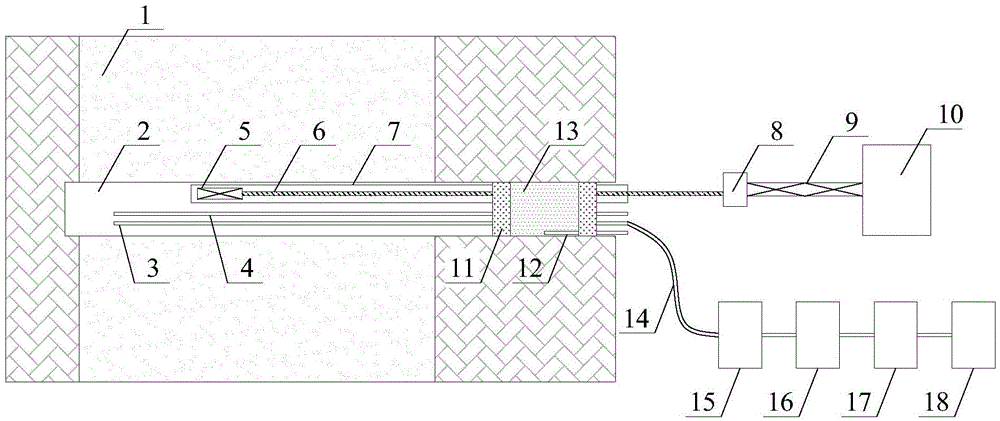
Microwave-assisted extraction and hydrofracture cooperative coal seam anti-reflection method
ActiveCN105484720ADredging holes and fissuresIncrease contact areaFluid removalGas removalPorosityDesorption
The invention provides a microwave-assisted extraction and hydrofracture cooperative coal seam anti-reflection method and belongs to the technical field related to coal mine down-hole hydraulic fracturing. The method includes the steps that a microwave antenna is connected to the innermost end of a coaxial waveguide tube and sent into a fracturing drill hole, the outer most end of the coaxial waveguide tube is connected with a waveguide tube converter, the waveguide tube converter is connected with a rectangular waveguide tube, and the rectangular waveguide tube is connected with a microwave generator; organic solvent and high pressure water are mixed, hydrofracture is conducted on the drill hole through a fracturing tube, meanwhile, the microwave generator is turned on, radiation drilling is conducted through the microwave antenna, fracturing is conducted, a seepage is provided for the solvent, the organic solvent dissolves small organic molecules in coal so that a chambering effect is generated, and methane desorption is promoted through the heat effect of microwaves. According to the method, hydrofracture, solvent extraction and microwave radiation are combined, the porosity and permeability of the coal seam are greatly improved, methane desorption is promoted, and thus the methane extraction effect is greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
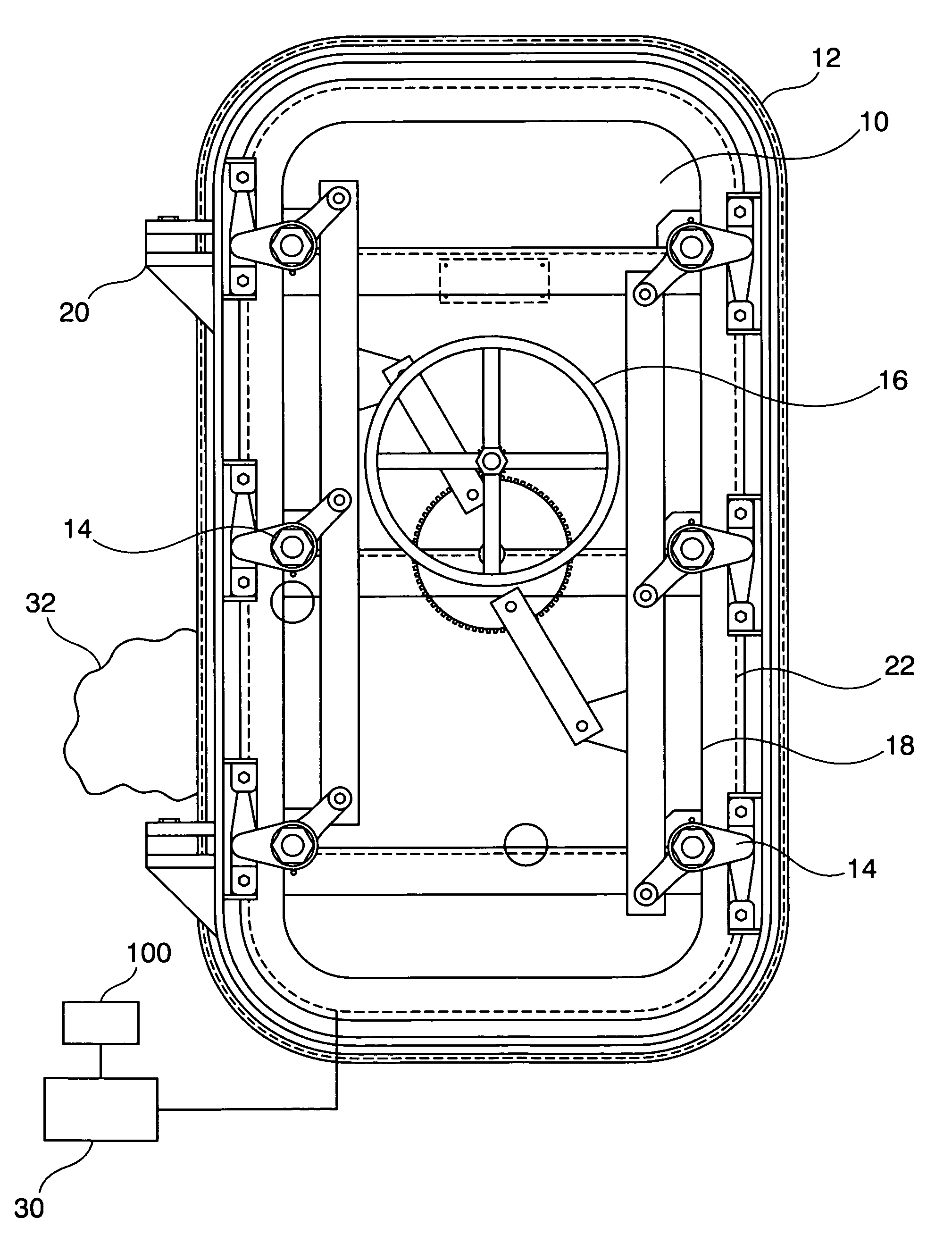
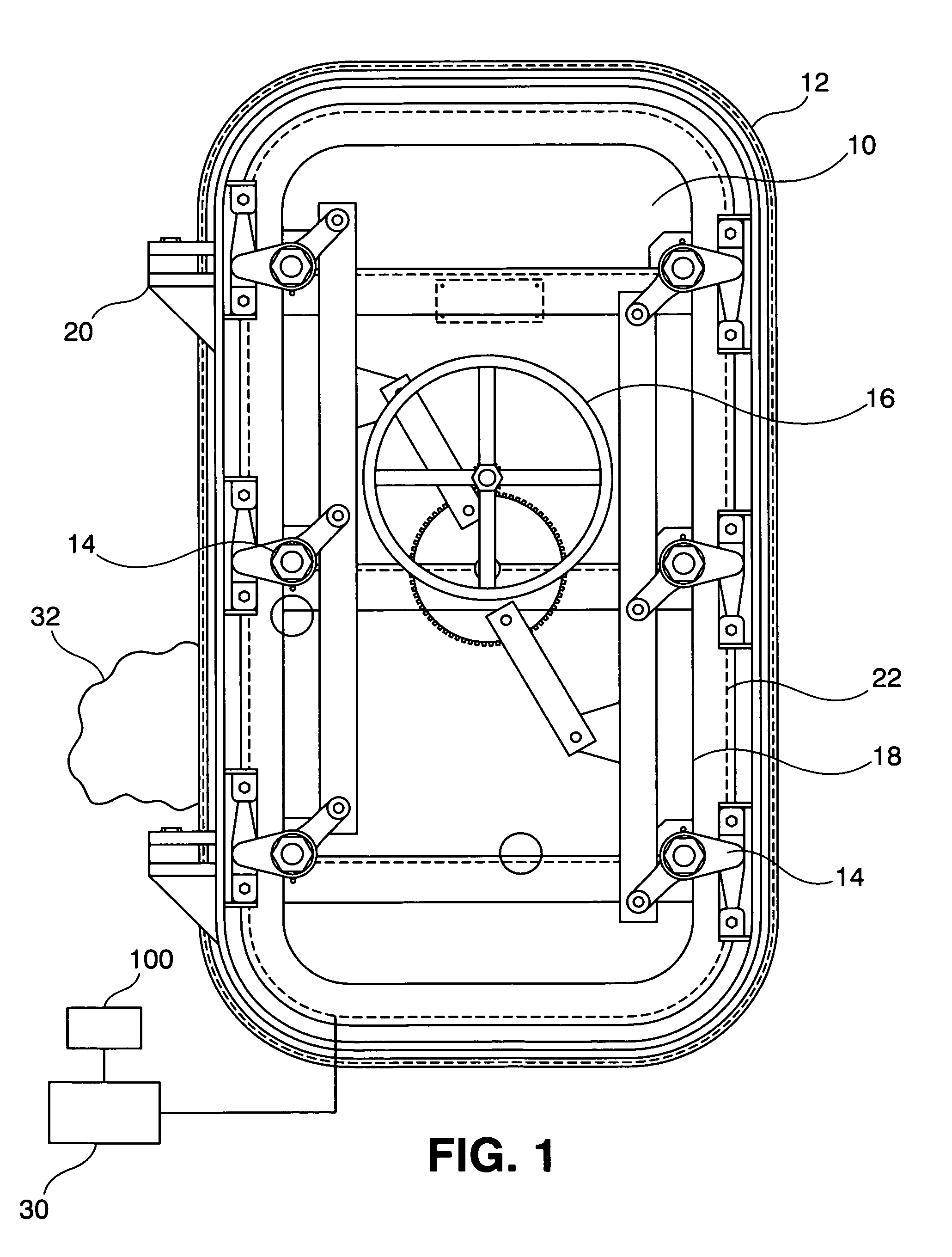
Seal integrity detection system
A seal integrity verification system scans for changes in impedance in a seal with integral coaxial waveguide, twisted pair wires, parallel ribbon wires or parallel wires. The wires are monitored by a TDR to note changes in impedance. The changes indicate the location where the seal is not under proper compression to ensure a tight fit. This is especially useful in verifying that watertight doors on ships or submarines are sealing properly when shut.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
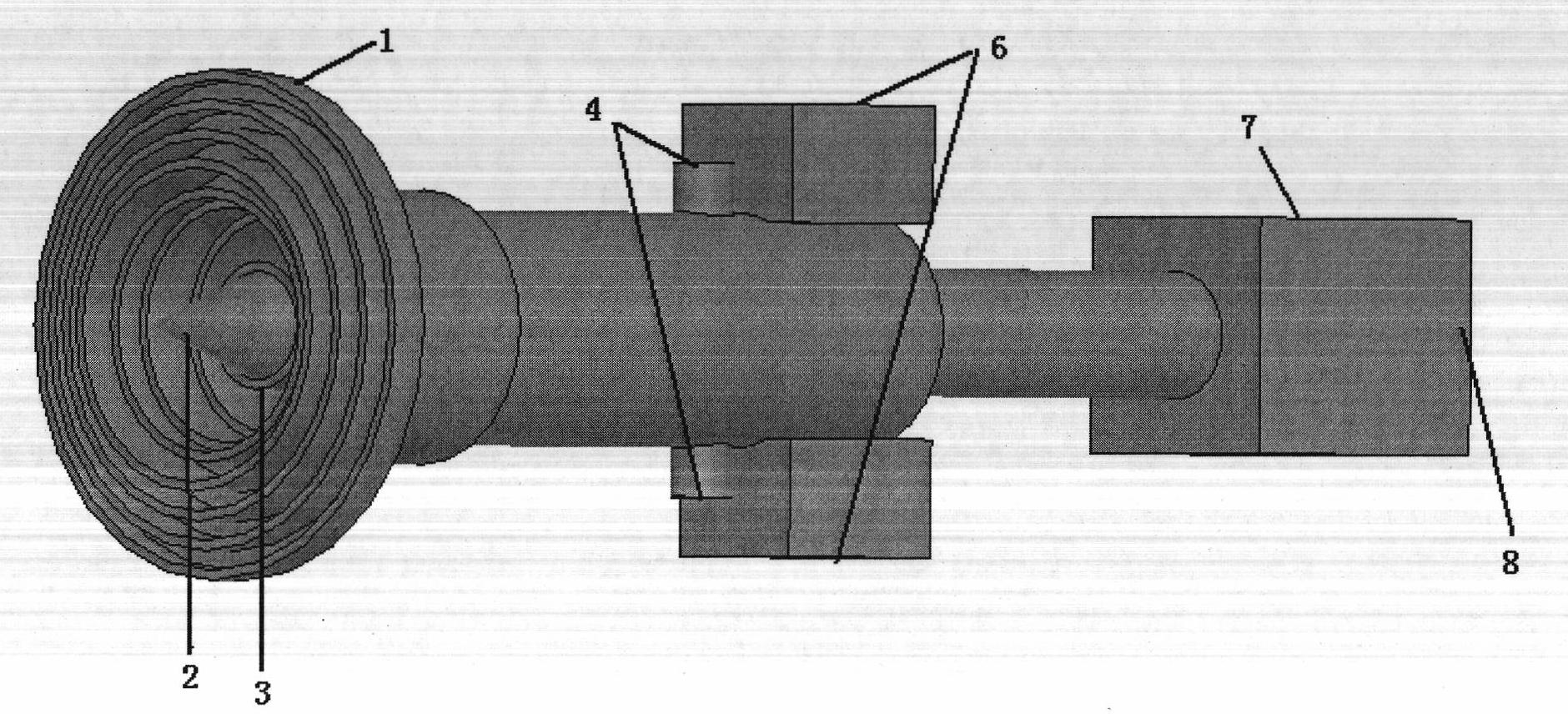
Coaxial-ridge waveguide-microstrip conversion structure power divider
InactiveCN102280681AAxisymmetricEqual signal amplitudeCoupling devicesUltra-widebandAxis of symmetry
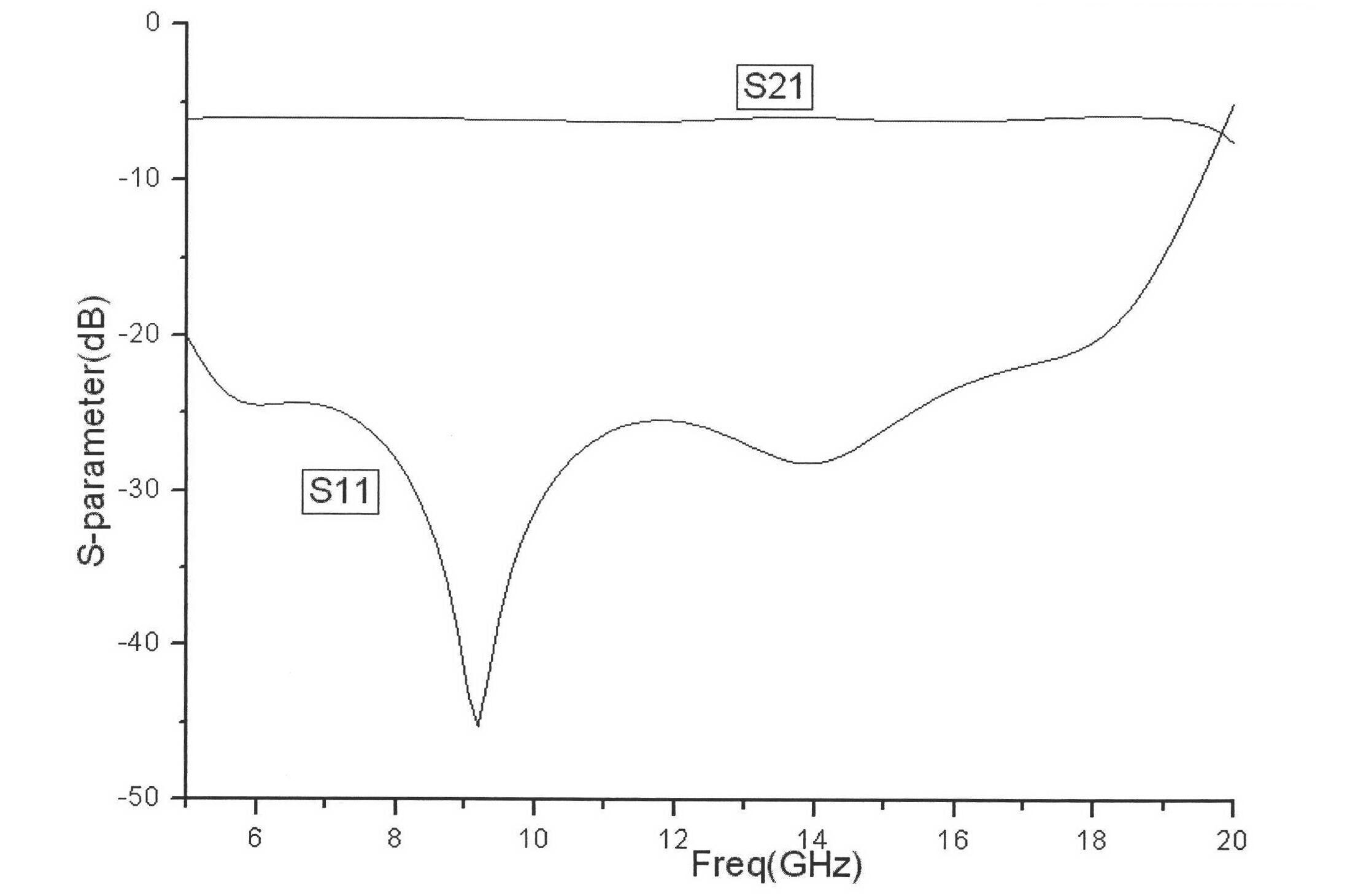
The invention relates to a coaxial-ridge waveguide-microstrip conversion structure ultra-broadband multi-channel power splitter. The input coaxial joint and the extended coaxial waveguide adopt a tapered coaxial gradual transition, and the tapered coaxial gradual transition And the ridge waveguide-microstrip conversion structure can realize ultra-wideband impedance matching; N ridge waveguide-microstrip conversion structures are uniformly distributed along the circumference in the extended coaxial waveguide to realize N-way parallel power division, and the entire power division circuit has axisymmetric To ensure that the signal amplitudes and phases of the N-channel power division signals are equal, the N-channel signal power division can be realized in one step, which can minimize the signal transmission loss. The present invention has ultra-wideband, low transmission loss, can realize any multi-channel power division output, each power division output signal has good amplitude and phase consistency, flat group delay characteristics in the band, and is easy to integrate with other peripheral planar circuits, etc. advantage. The invention is mainly used in microwave and millimeter wave power synthesis amplification systems, array antennas, etc., and has broad application prospects in microwave and millimeter wave systems such as communication and radar.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
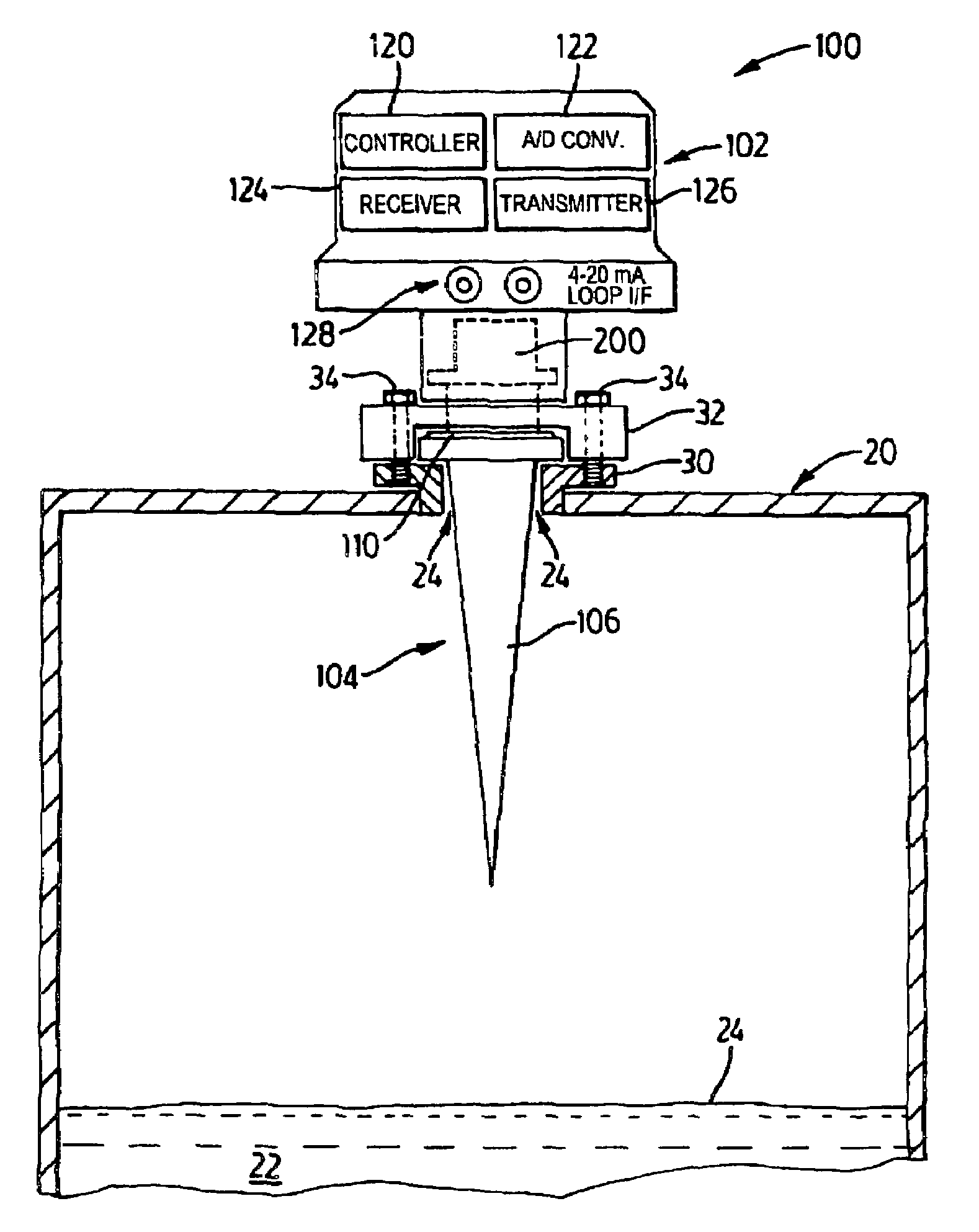
Coupler with waveguide transition for an antenna in a radar-based level measurement system
A mechanism for coupling a coaxial waveguide to another waveguide. The mechanism includes a lower or matching waveguide and an impedance transformer. A coaxial port couples the coaxial waveguide to the matching waveguide. The matching waveguide has a waveguide impedance which is close to the impedance of the coaxial waveguide. This arrangement allows matching between the coaxial waveguide and the matching waveguide over a wider frequency band. The impedance transformer couples the matching waveguide to the other waveguide. The impedance transformer comprises a single-stage, double-stage, or multi-stage transformer. The mechanism is suitable for coupling an antenna to a coaxial cable interface in a radar or microwave based level measurement or time of flight ranging systems.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
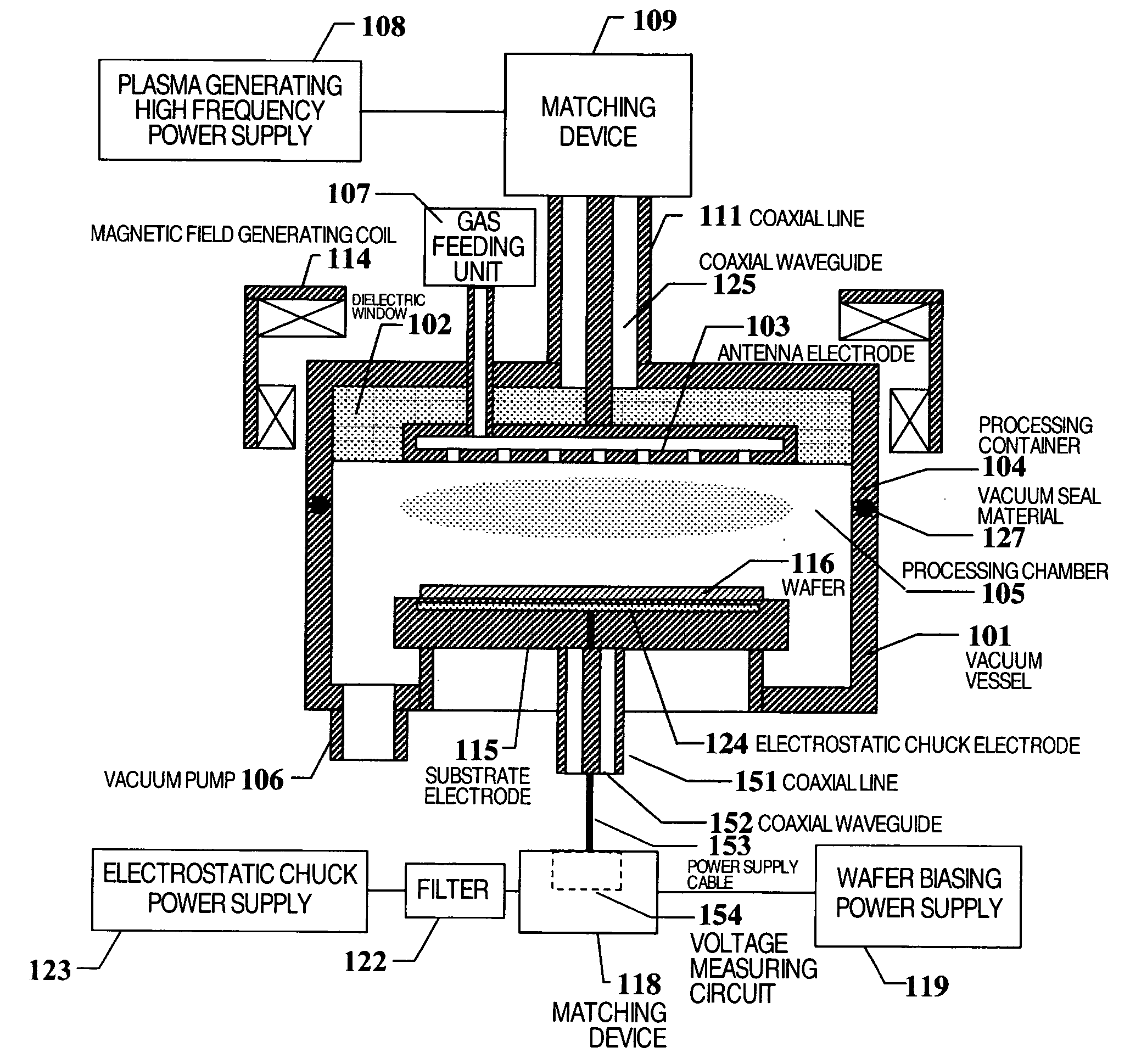
Plasma processing apparatus with resonance countermeasure function
InactiveUS20070181254A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh capacitanceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInternal pressureHigh frequency power
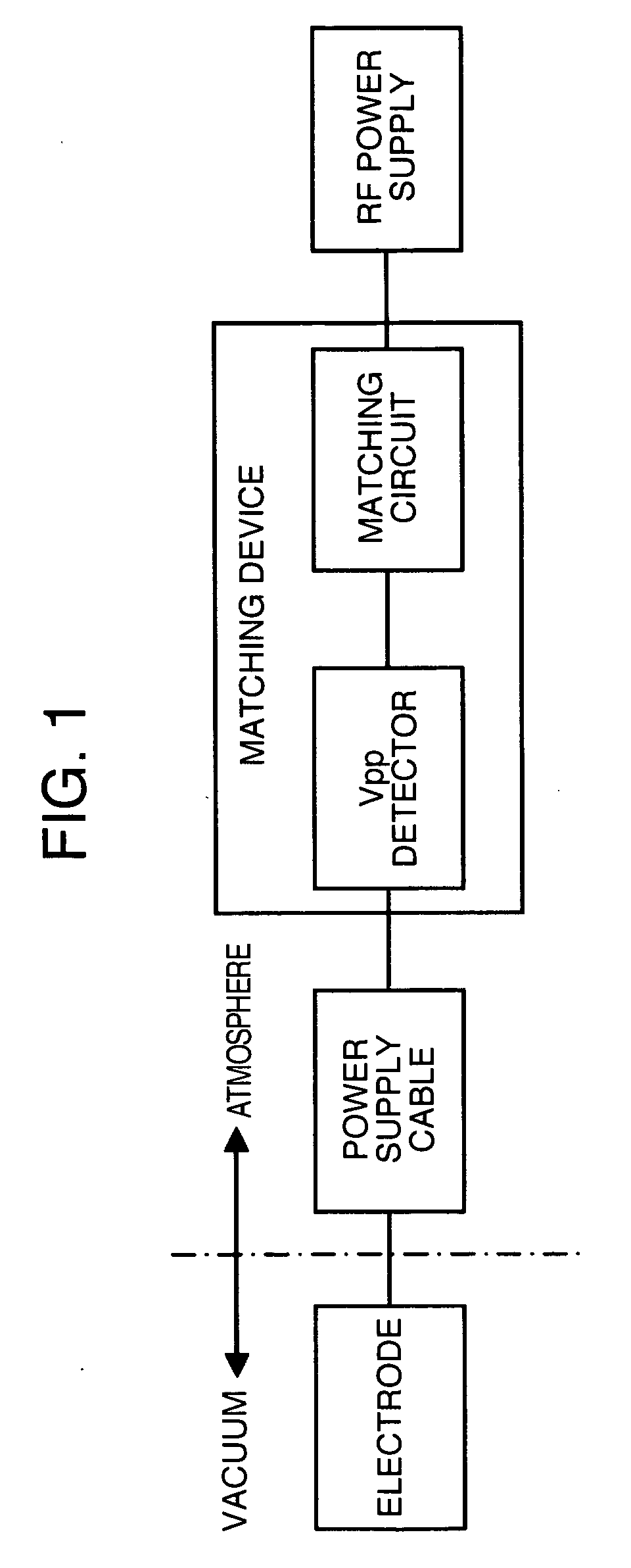
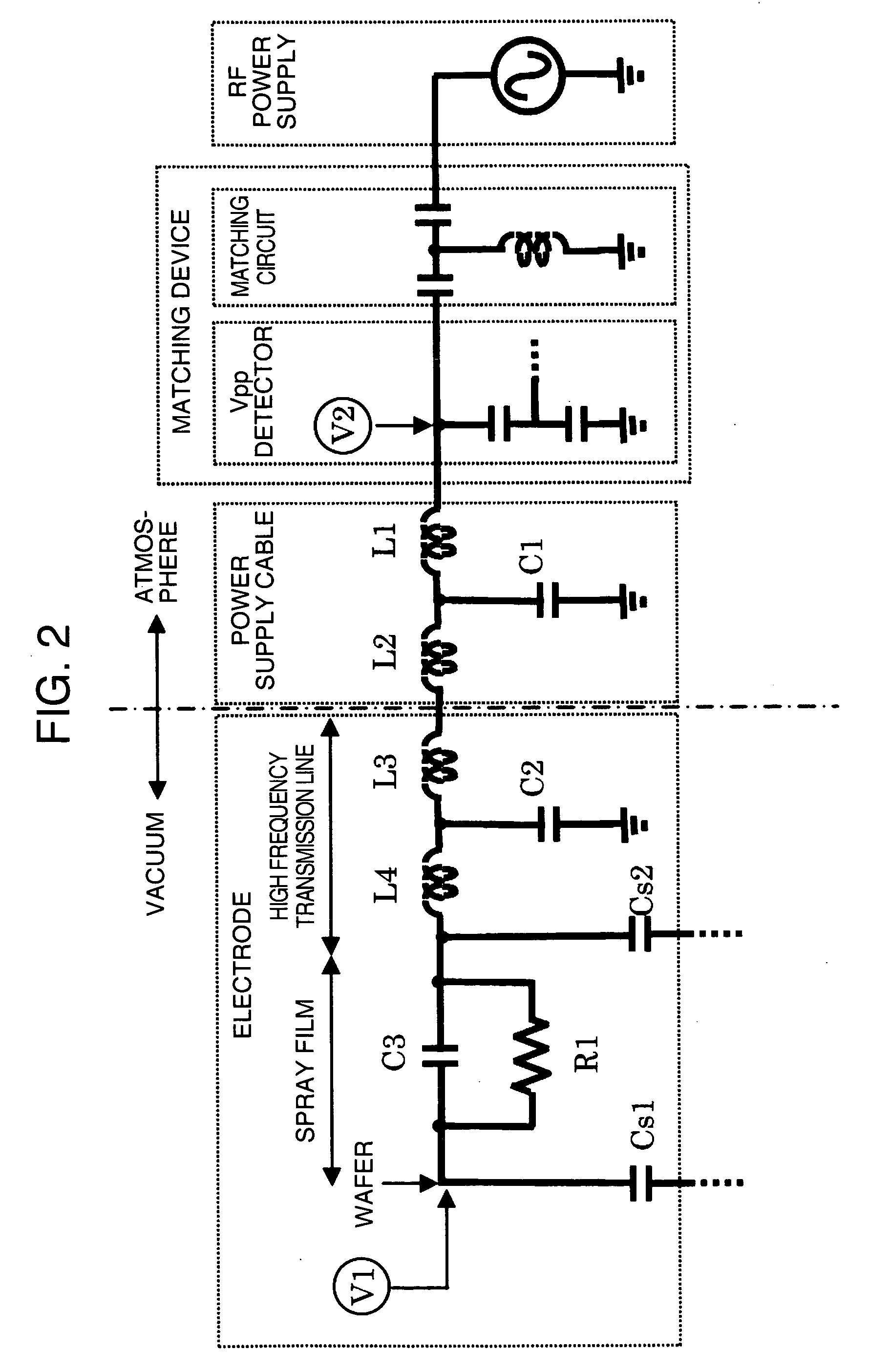
A plasma processing apparatus has a processing chamber connected to an exhaust system so that the inside pressure can be reduced, a gas feeding unit for supplying gas to the processing chamber, a wafer, and a substrate electrode on which the wafer can be placed. The plasma processing apparatus also has an antenna electrode provided in opposition to the substrate electrode to generate plasma, a plasma generating high-frequency power supply connected to the antenna electrode, and a wafer biasing power supply connected to the substrate electrode. In addition, a coaxial line and a coaxial waveguide are optimized by using a coaxial model, and a voltage measuring circuit is mounted right under the coaxial line.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Plate inserted coaxial micro-wave mode converter
InactiveCN1681154ADoes not cause concentrationSimple structureCoupling devicesElectrical conductorPhase difference
AT the place between inner and outer conductors of coaxial waveguide, along axial direction, the first, second, third and fourth metal plates are inserted. The angle between any neighboring plate is 90 degree. The first metal plate is shortest. The second and fourth metal plates are longest and have same length. The difference of metal plate length between third metal plate and first metal plate must meet following condition: the microwave electric field mode, in 180 degree scallop section waveguide composed of second and fourth metal plate, has a 180 degree phase difference with the microwave electric field mode, in 90 degree scallop section waveguide composed of second and third metal plate or third and fourth metal plate.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Microwave Plasma Sterilizing Method and Device
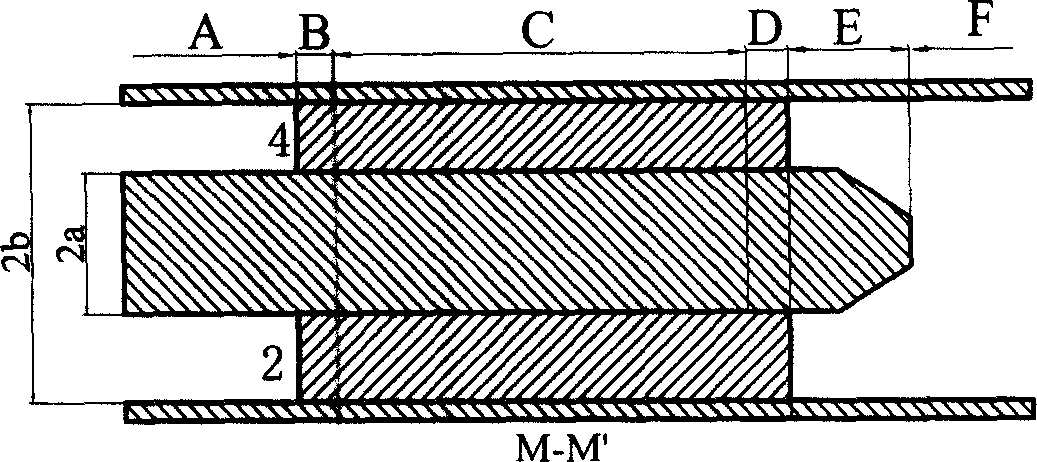
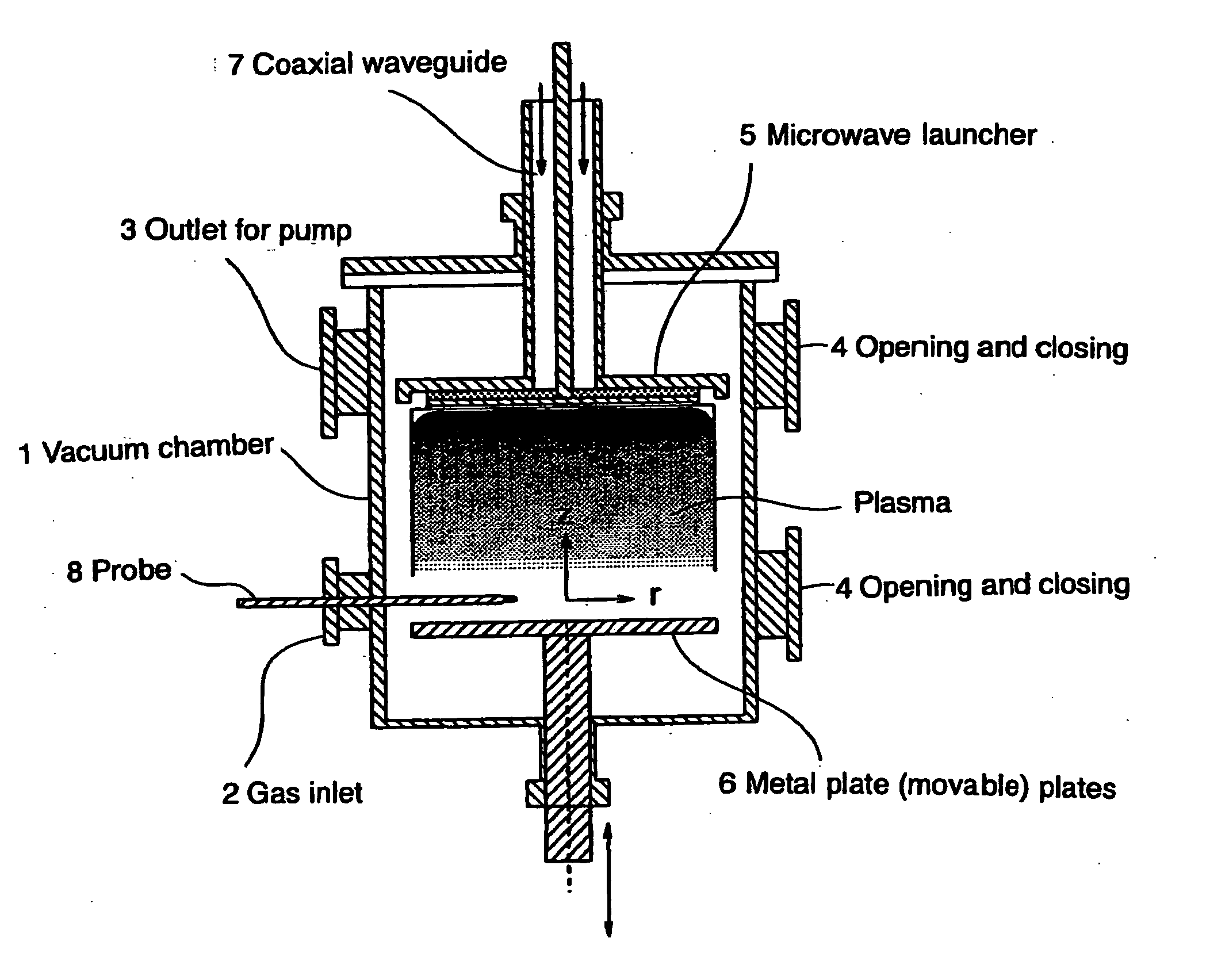
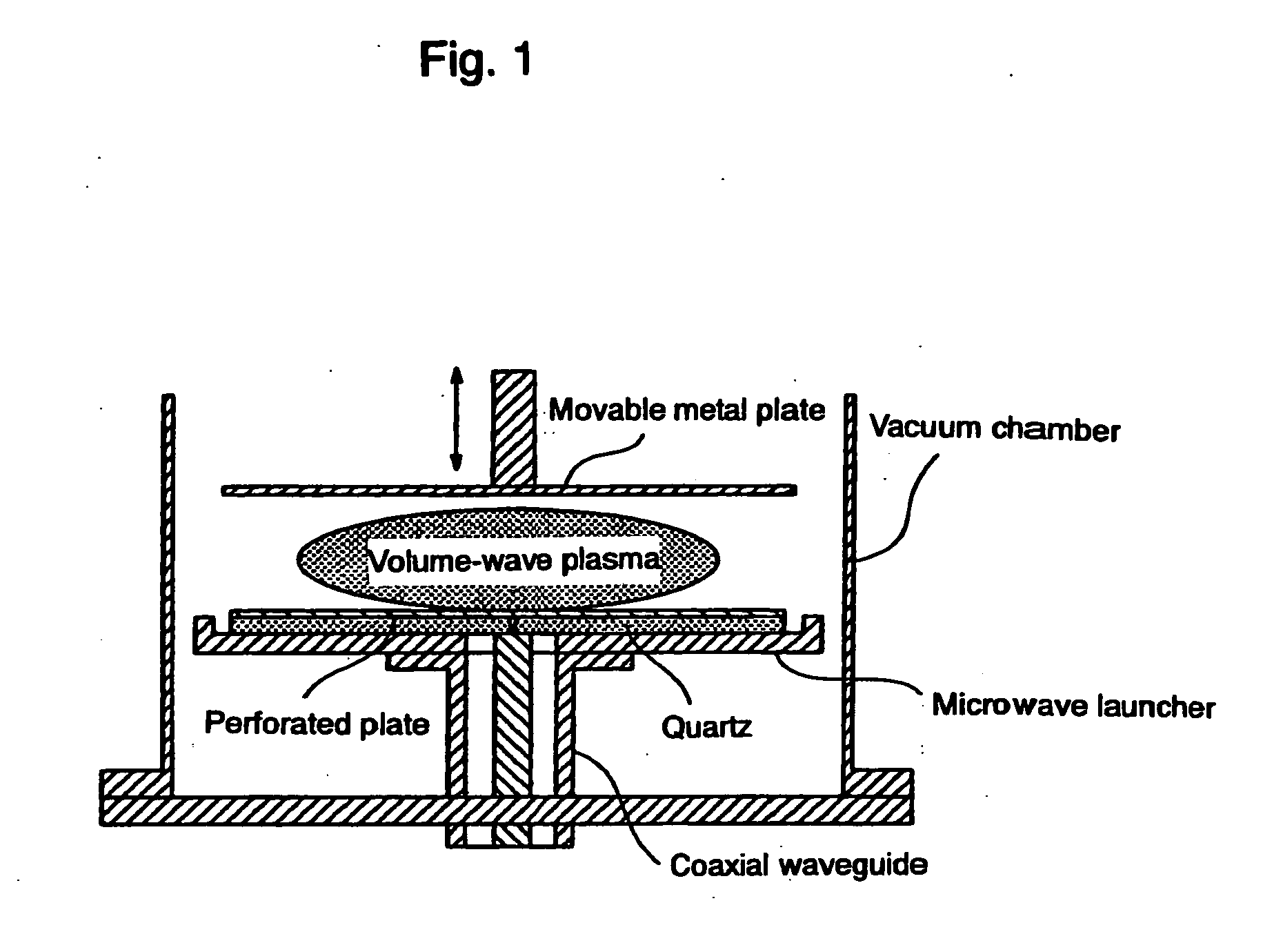
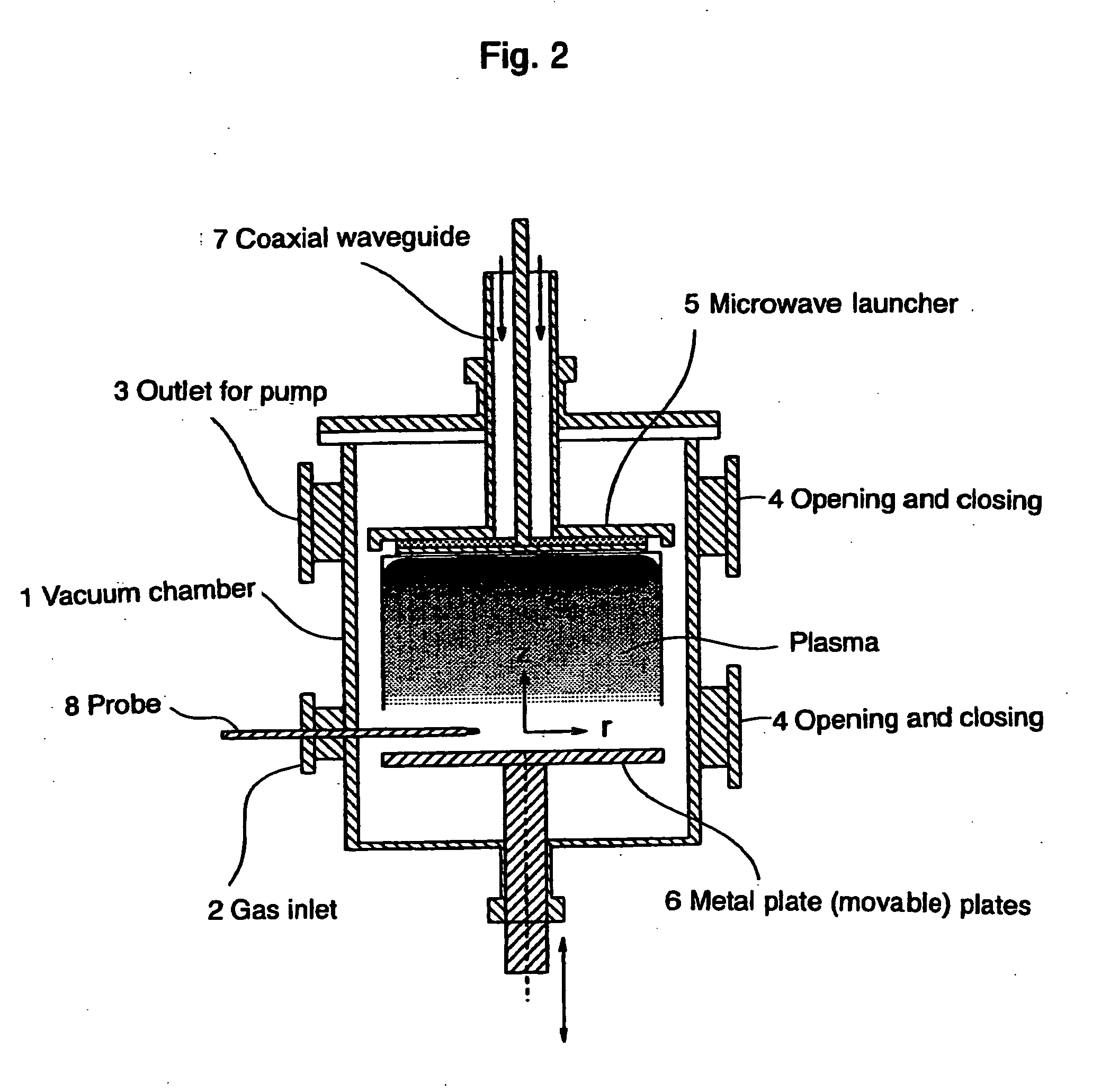
InactiveUS20070212254A1High-speed processing timeEffective sterilizationBacterial antigen ingredientsElectric discharge tubesVolume waveEngineering
A microwave inlet for introducing microwaves (coaxial waveguide) and a microwave launcher for generating volume-wave plasma are arranged on one side in a vacuum chamber, and a movable metal plate is arranged opposite to the microwave launcher on the other side in the vacuum chamber. The microwave launcher has a sandwiched structure where a quartz plate is sandwiched by a perforated plate having many holes of a specified diameter. Microwaves are introduced from an external microwave generator to the microwave launcher in, for example, oxygen gas, a mixture of helium gas and oxygen gas, a mixture of argon gas and oxygen gas, or a mixture of oxygen gas and nitrogen gas to change the spatial distribution of the electric field intensity, whereby the volume-wave plasma discharge is diffused to the entire inner space of the vacuum chamber by microwaves leaking through the holes in the perforated plate. The sterilizing method and the device of this invention use microwave discharge plasma that enables sterilization inside a perforated resinous package, such as a package of medical instruments in a vacuum chamber.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
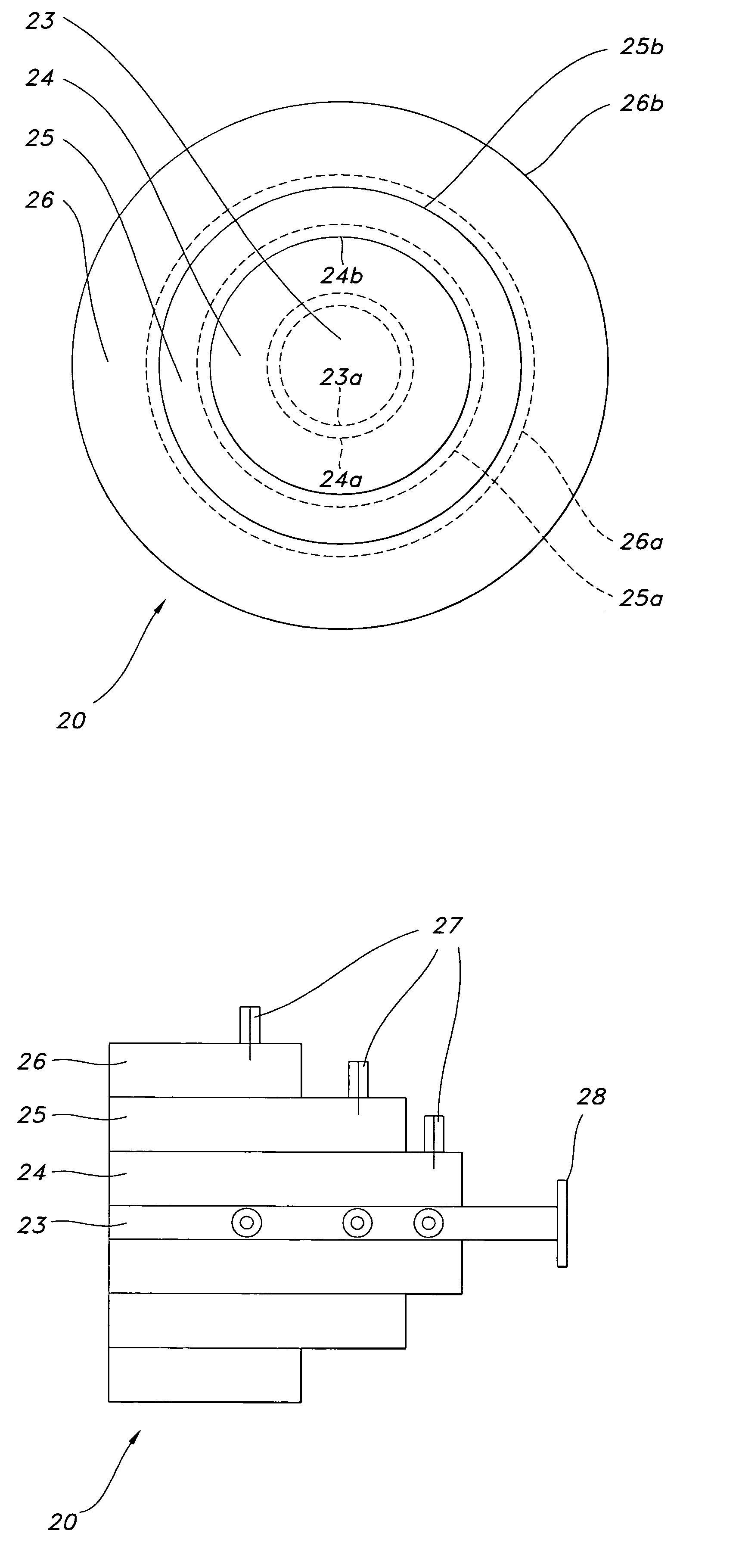
Multi band telemetry antenna feed
A multi band antenna feed, for supporting multiple frequency bands, is coupled to a reflector and includes a cylindrical core waveguide and at least three coaxial cylinders, encircling said cylindrical core waveguide and forming at least three coaxial waveguides, bounded between pairs of consecutive coaxial cylinders. The cylindrical core waveguide and the at least three coaxial waveguides provide a pair of sum and difference radiation patterns, for each frequency band: a C-band, an S-band and an L-band.
Owner:ORBIT COMM SYST
Plasma processing system and use thereof
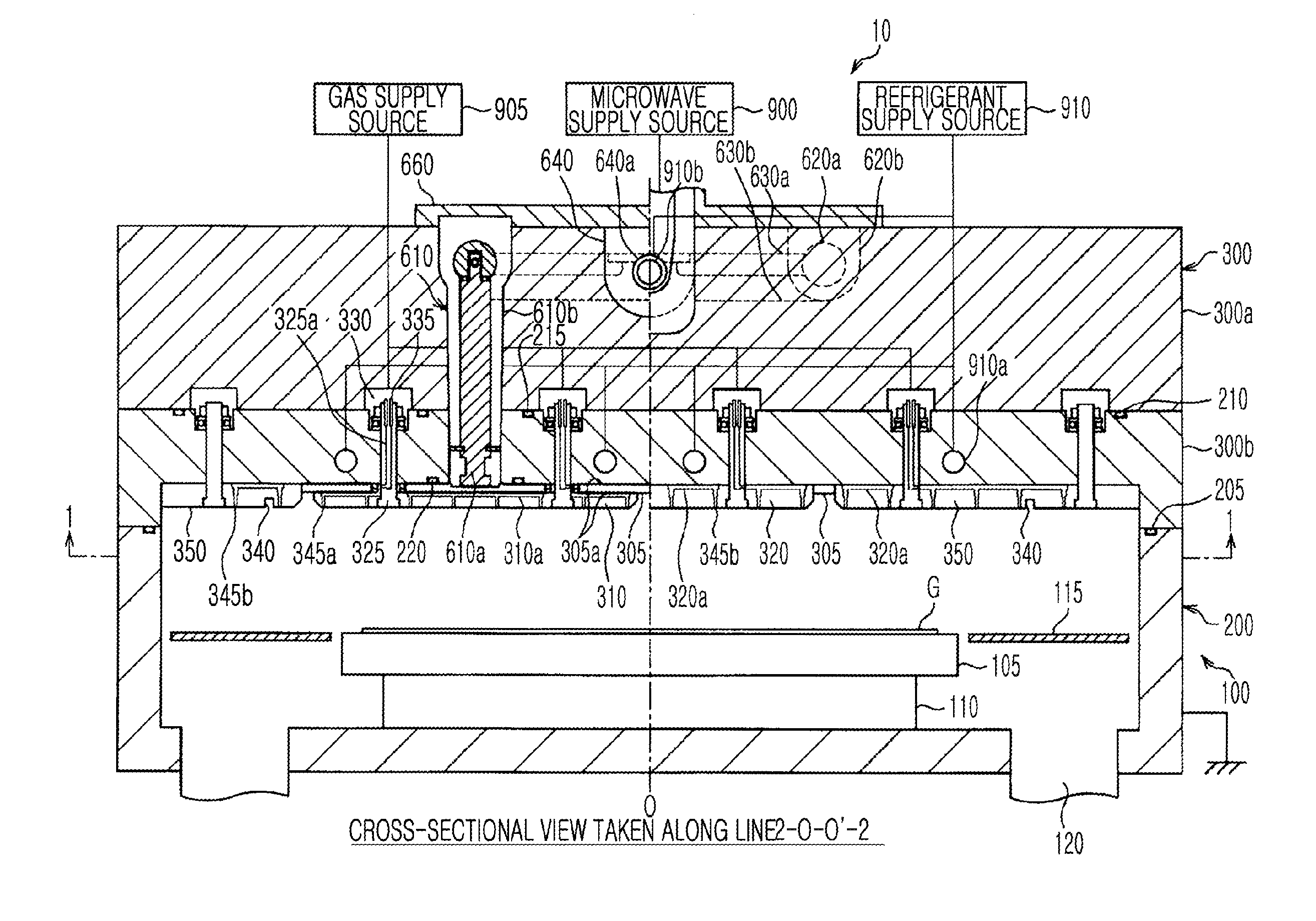
InactiveUS20080302761A1Clean interiorIncrease pressureElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsElectricityDielectric plate
A plasma processing system 10 includes a processing chamber 100, a microwave source 700 that outputs a microwave, a coaxial waveguide 315 that transfers the microwave from the microwave source, a plurality of dielectric plates 305 that transmit the microwave transferred through the coaxial waveguide 315 and discharge the microwave into the processing chamber 100, and a metal electrode 310 having a first end and a second end, the first end coupled to the coaxial waveguide 315, the second end disposed on the surface of the dielectric plate 305 facing the substrate. The coaxial waveguide 315 holds the dielectric plate 305 and metal electrode 310 and is securely fastened by a fastening mechanism 500. The coaxial waveguide 315 is given a force by the spring member 515, the force being directed away from the processing chamber 100.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com