Patents
Literature
499results about "Circuit fluid transport" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
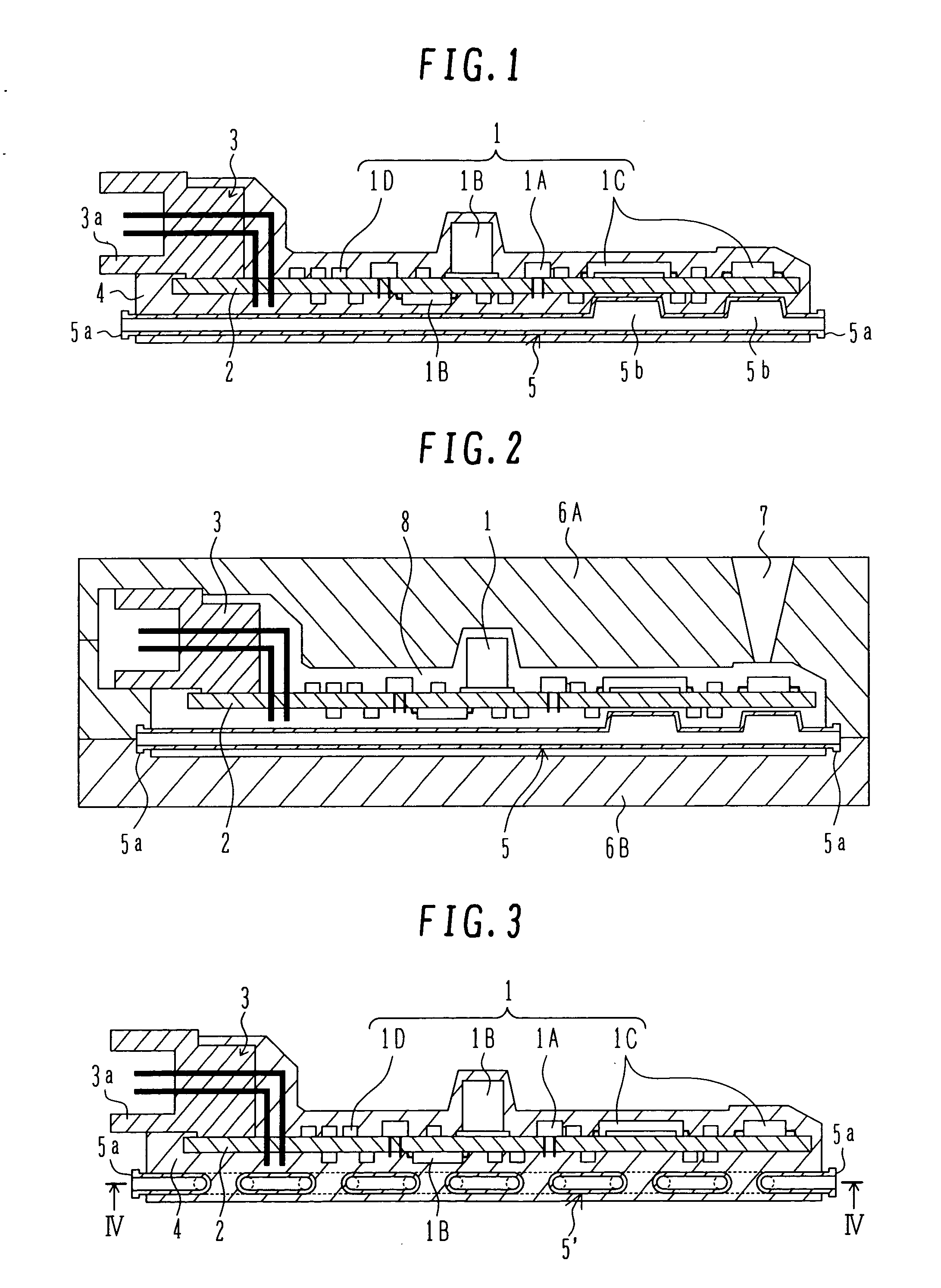
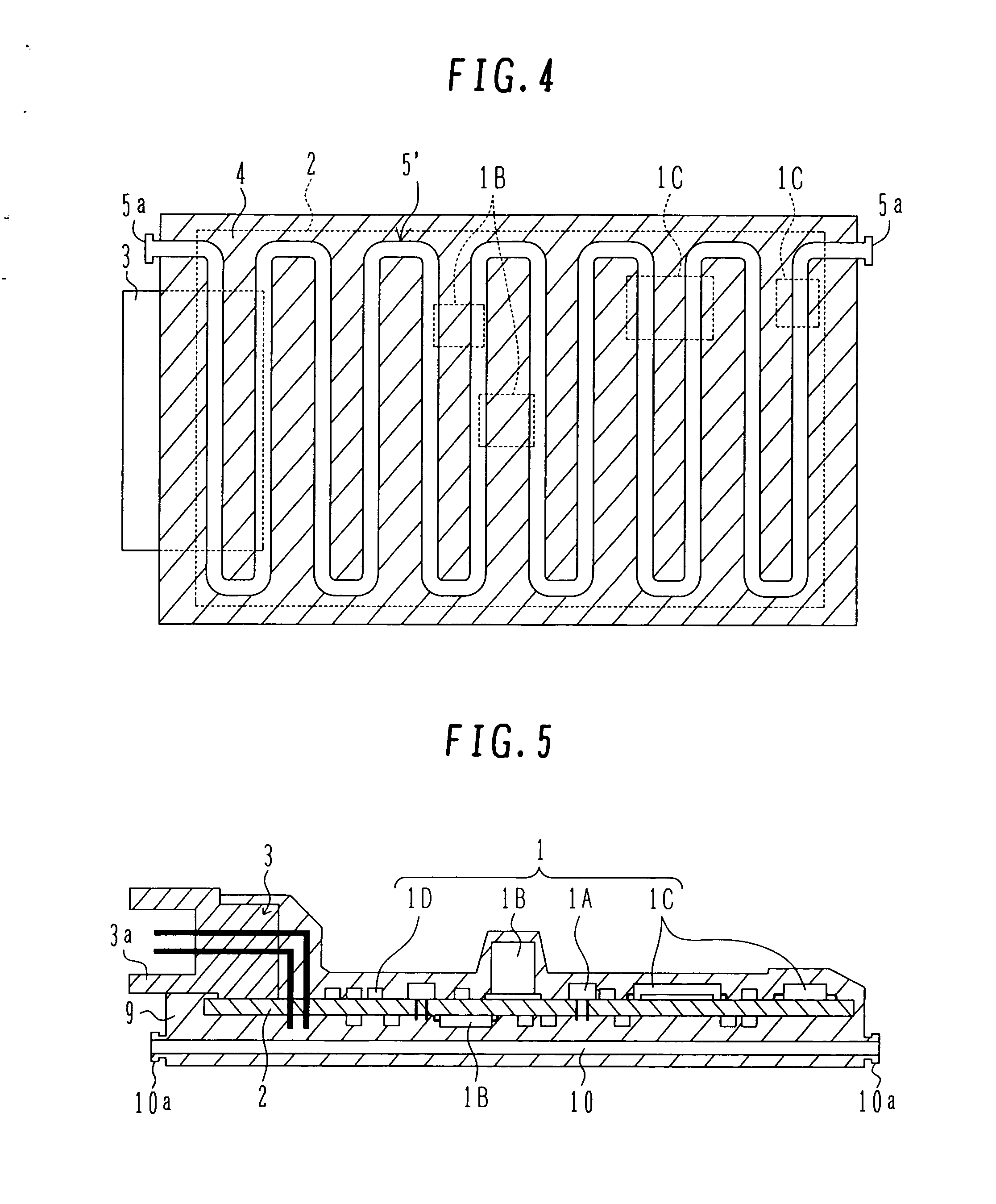
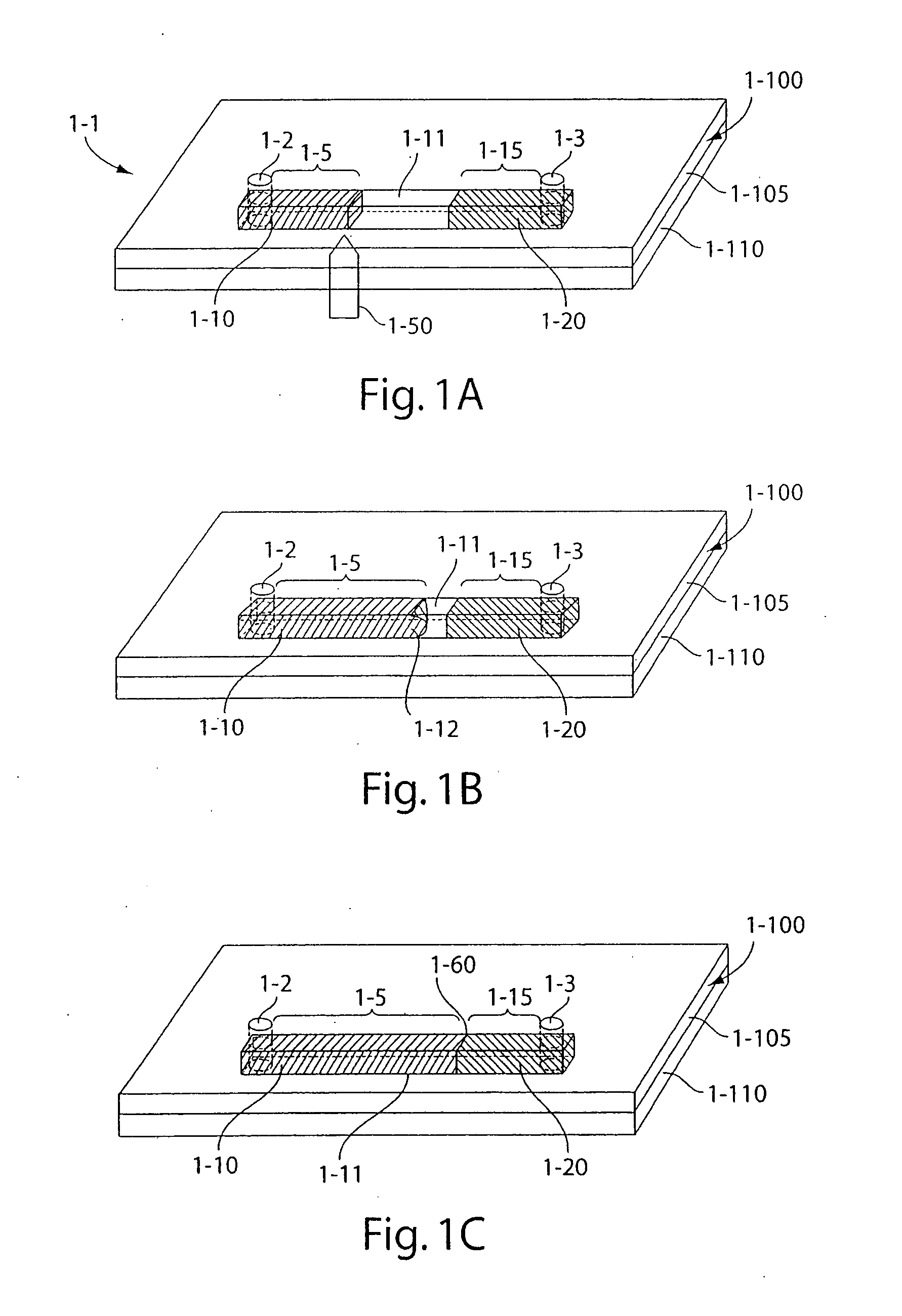
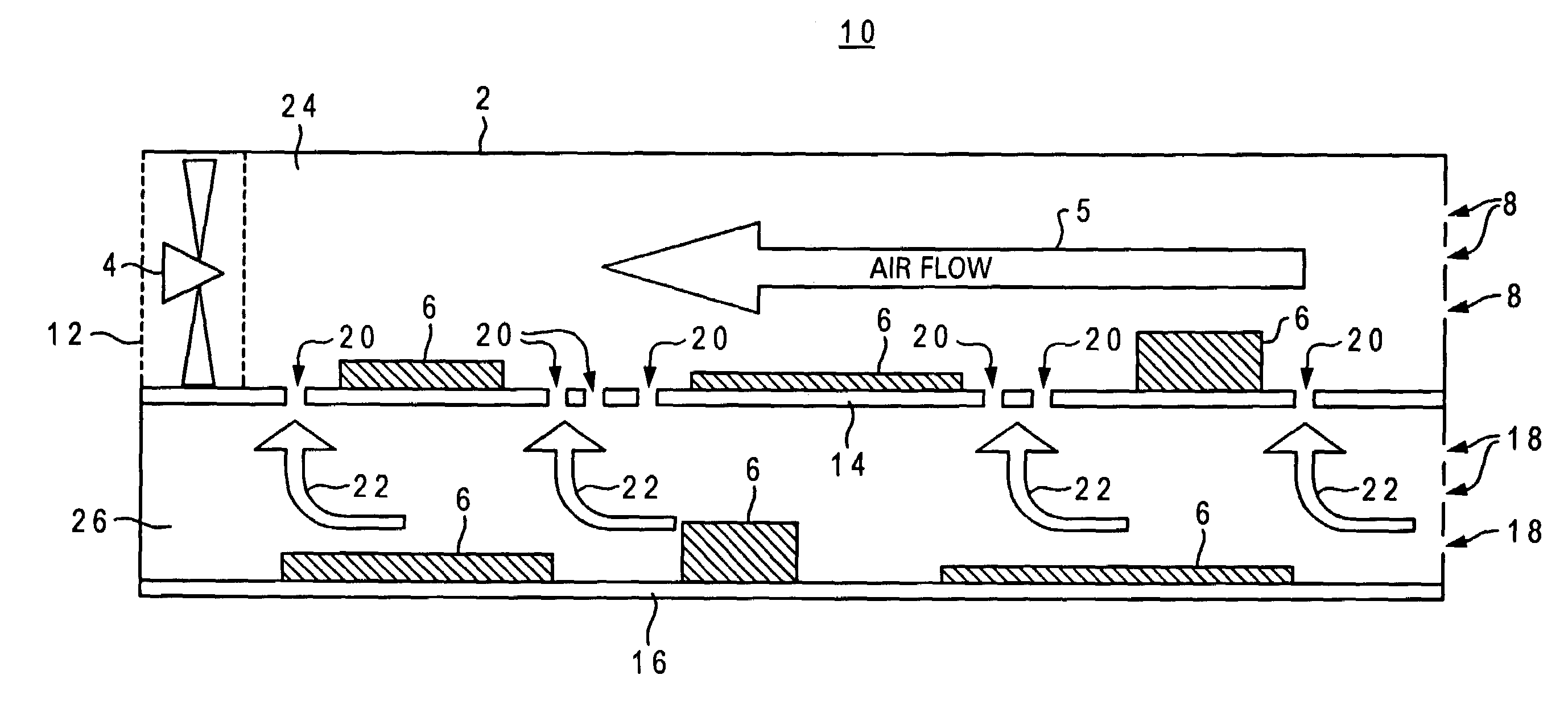
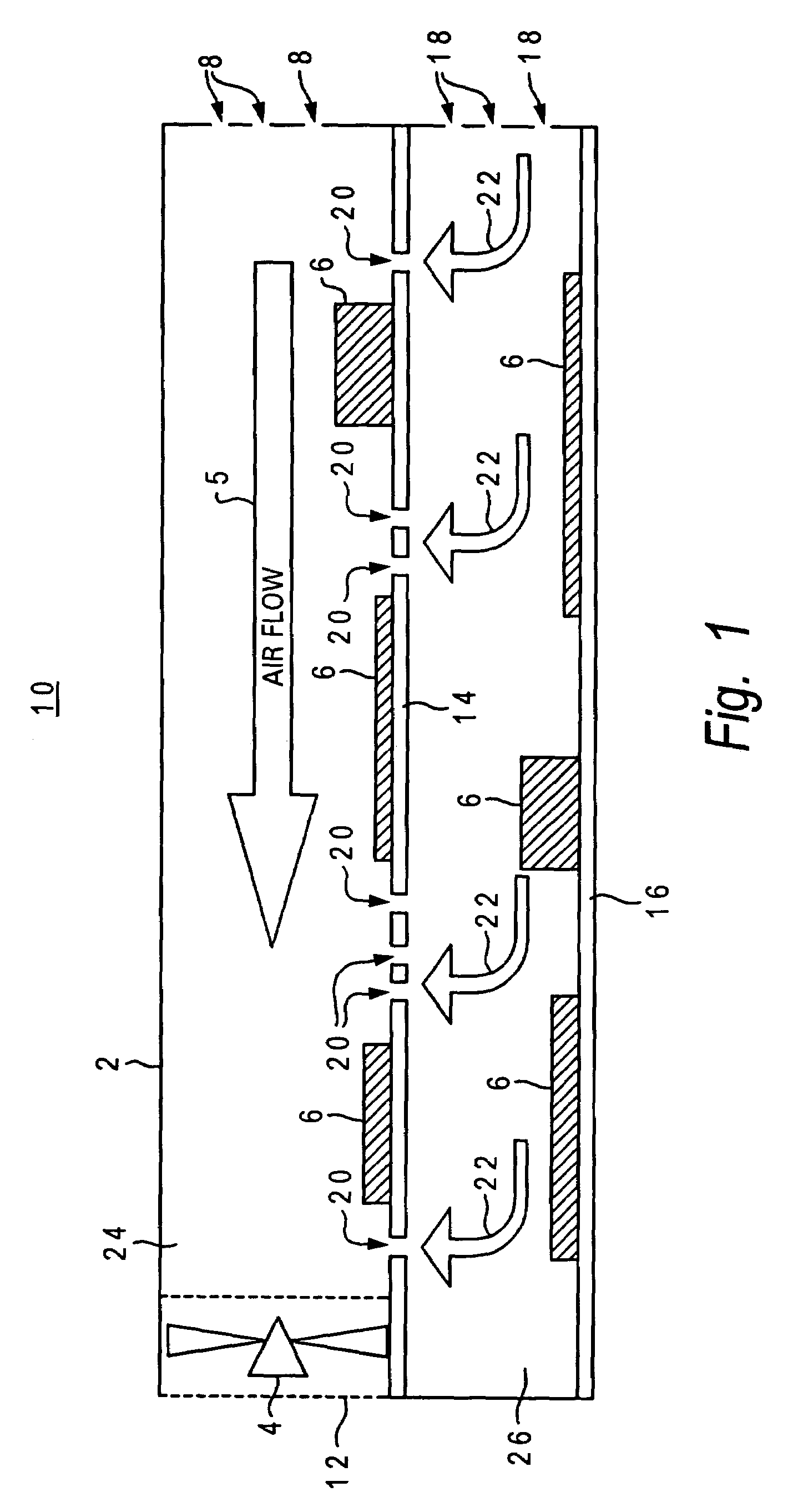
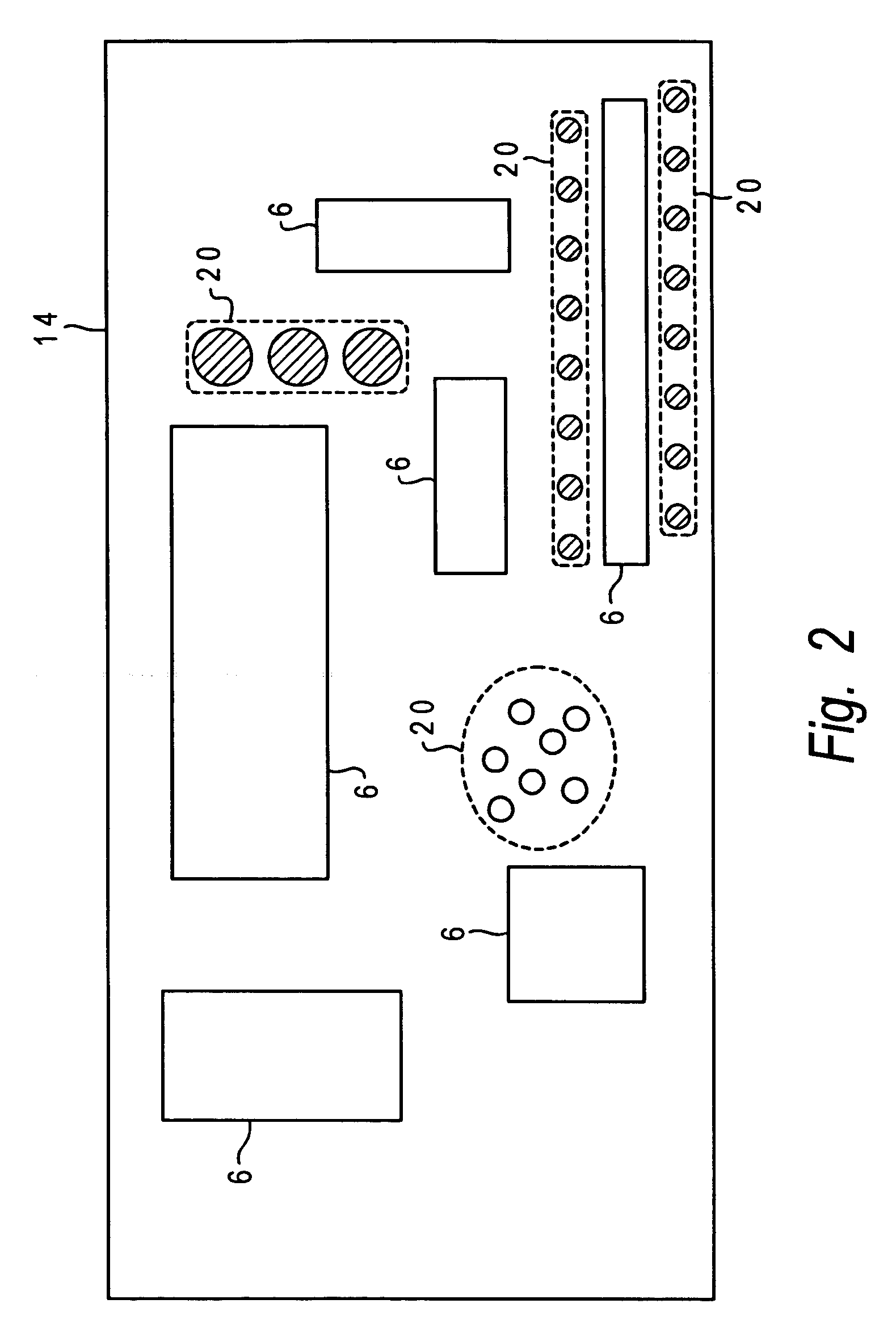
Coaxial waveguide microstructures and methods of formation thereof
ActiveUS7012489B2Printed circuit aspectsCircuit fluid transportElectrical conductorCoaxial waveguides
Provided are coaxial waveguide microstructures. The microstructures include a substrate and a coaxial waveguide disposed above the substrate. The coaxial waveguide includes: a center conductor; an outer conductor including one or more walls, spaced apart from and disposed around the center conductor; one or more dielectric support members for supporting the center conductor in contact with the center conductor and enclosed within the outer conductor; and a core volume between the center conductor and the outer conductor, wherein the core volume is under vacuum or in a gas state. Also provided are methods of forming coaxial waveguide microstructures by a sequential build process and hermetic packages which include a coaxial waveguide microstructure.
Owner:CUBIC CORPORATION
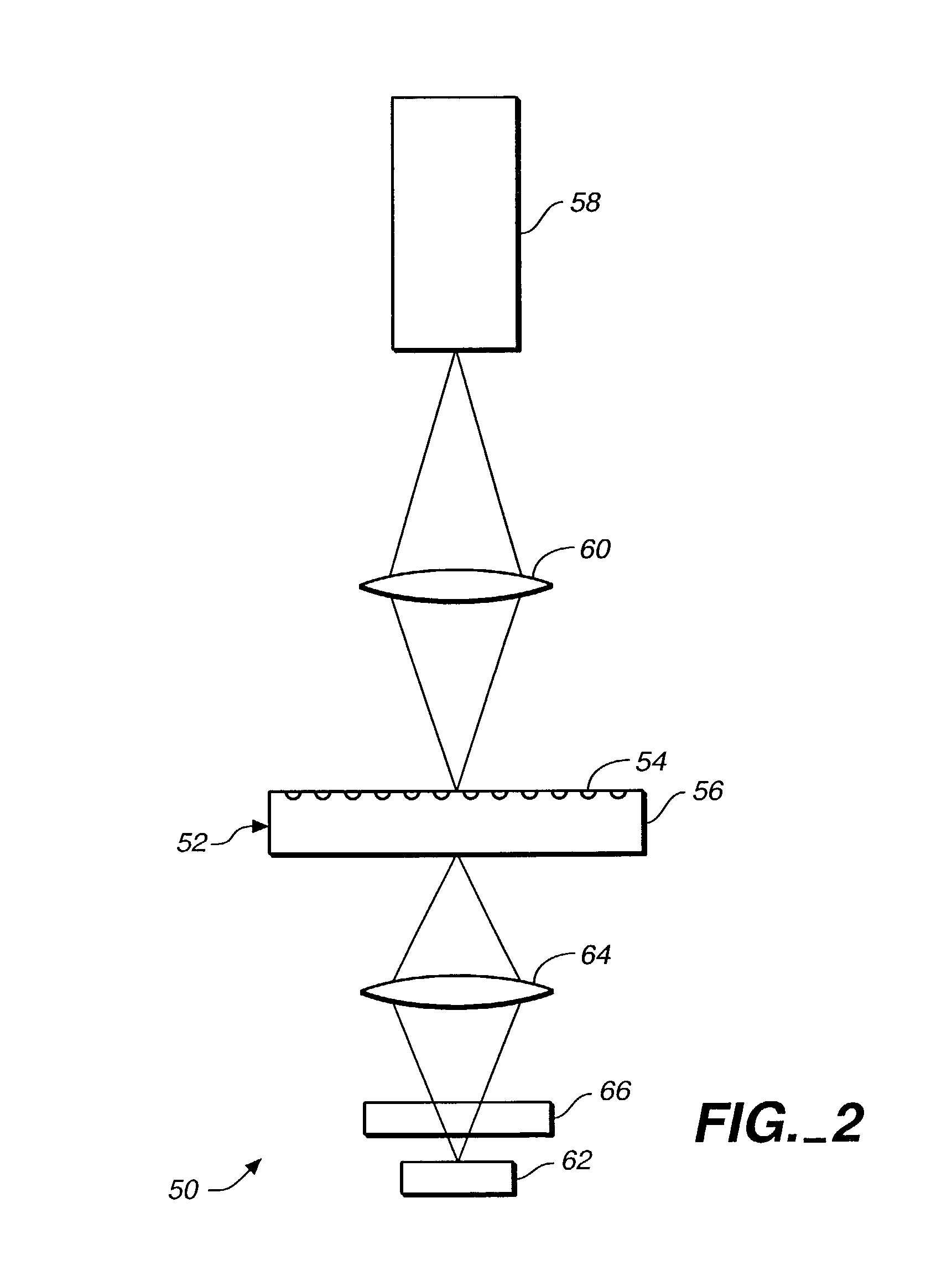
Multilayered microfluidic DNA analysis system and method
A multilayered microfluidic DNA analysis system includes a cell lysis chamber, a DNA separation chamber, a DNA amplification chamber, and a DNA detection system. The multilayered microfluidic DNA analysis system is provided as a substantially monolithic structure formed from a plurality of green-sheet layers sintered together. The substantially monolithic structure has defined therein a means for heating the DNA amplification chamber and a means for cooling the DNA amplification chamber. The means for heating and means for cooling operate to cycle the temperature of the DNA amplification chamber as required for performing a DNA amplification process, such as PCR.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
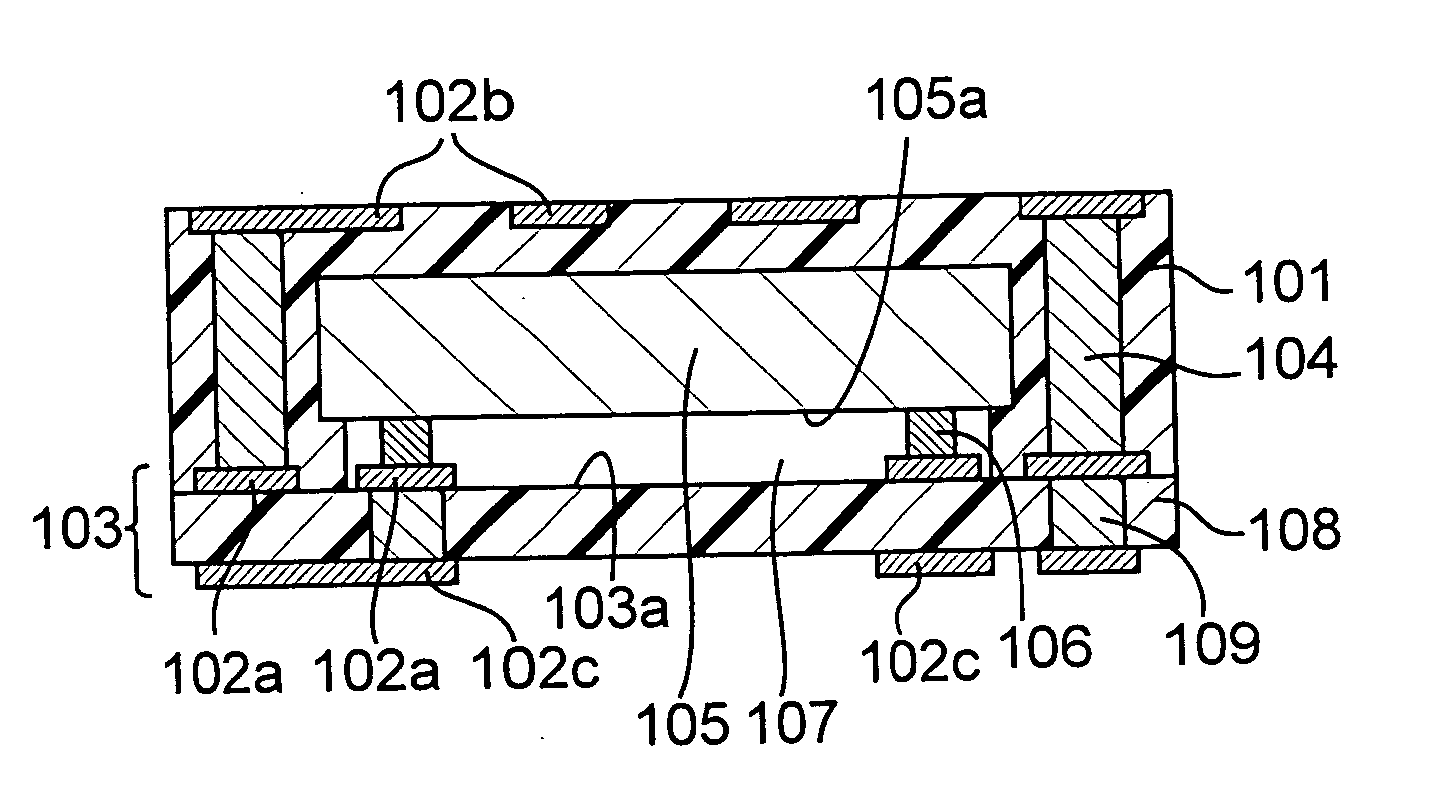
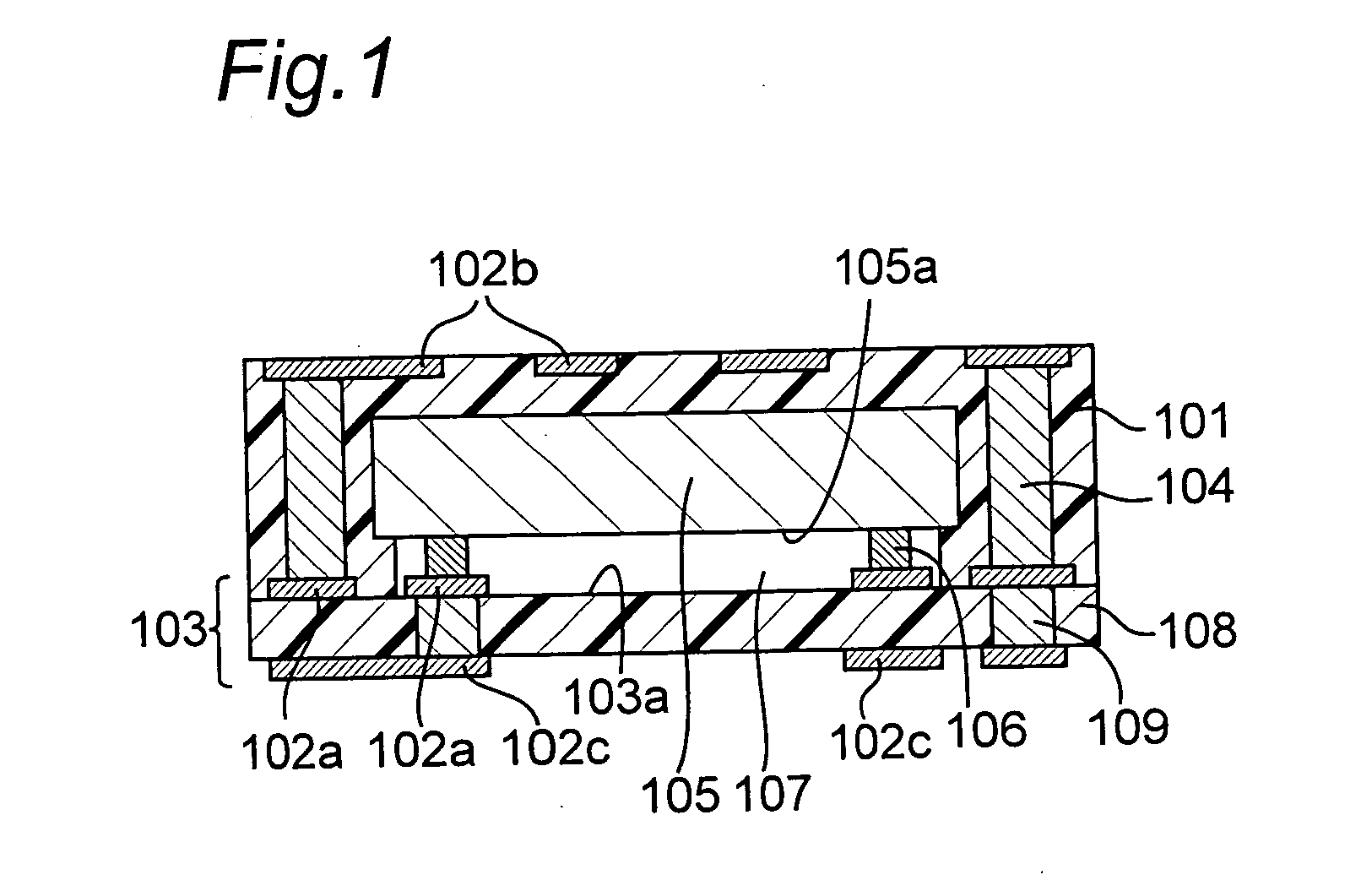
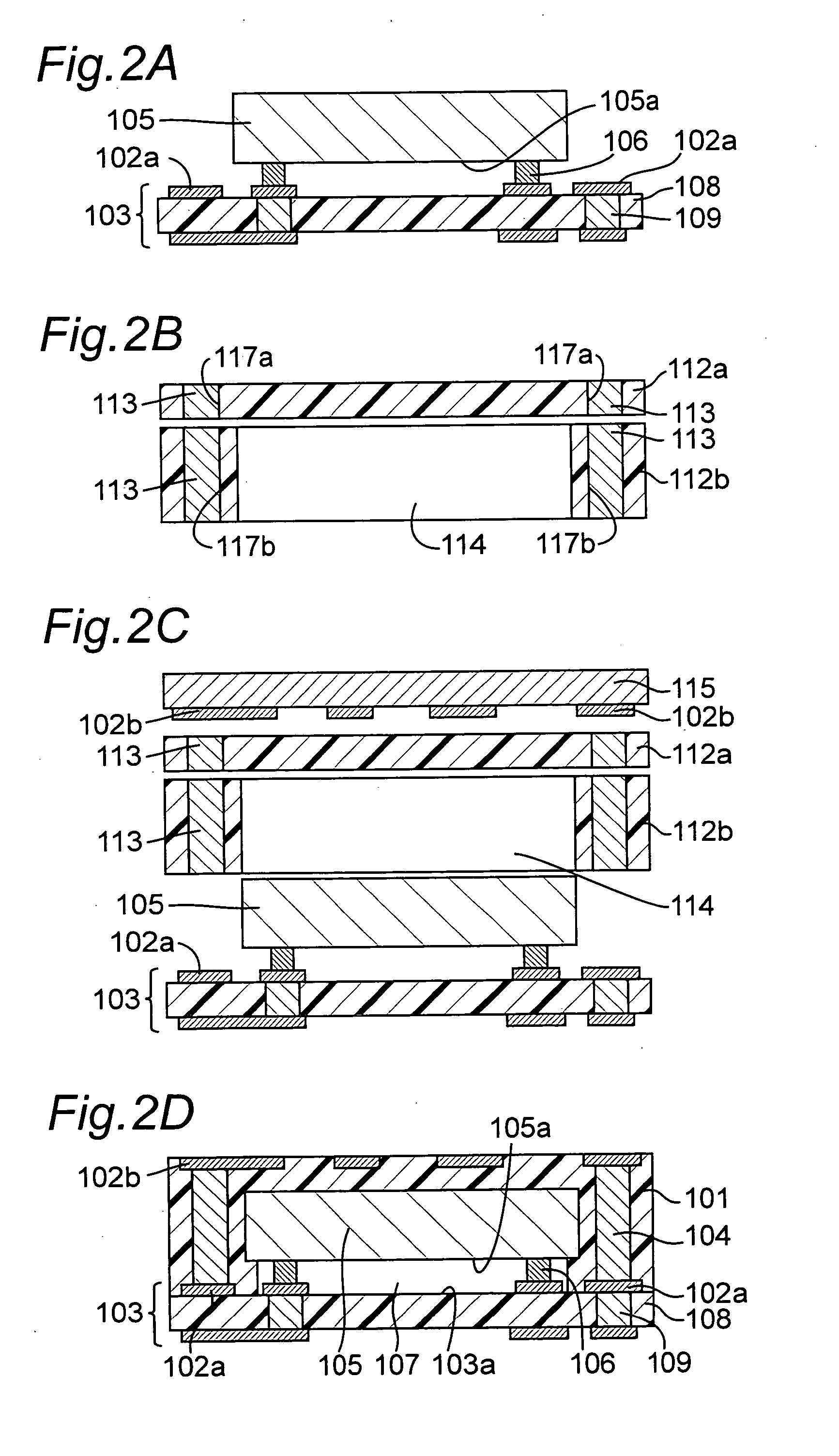
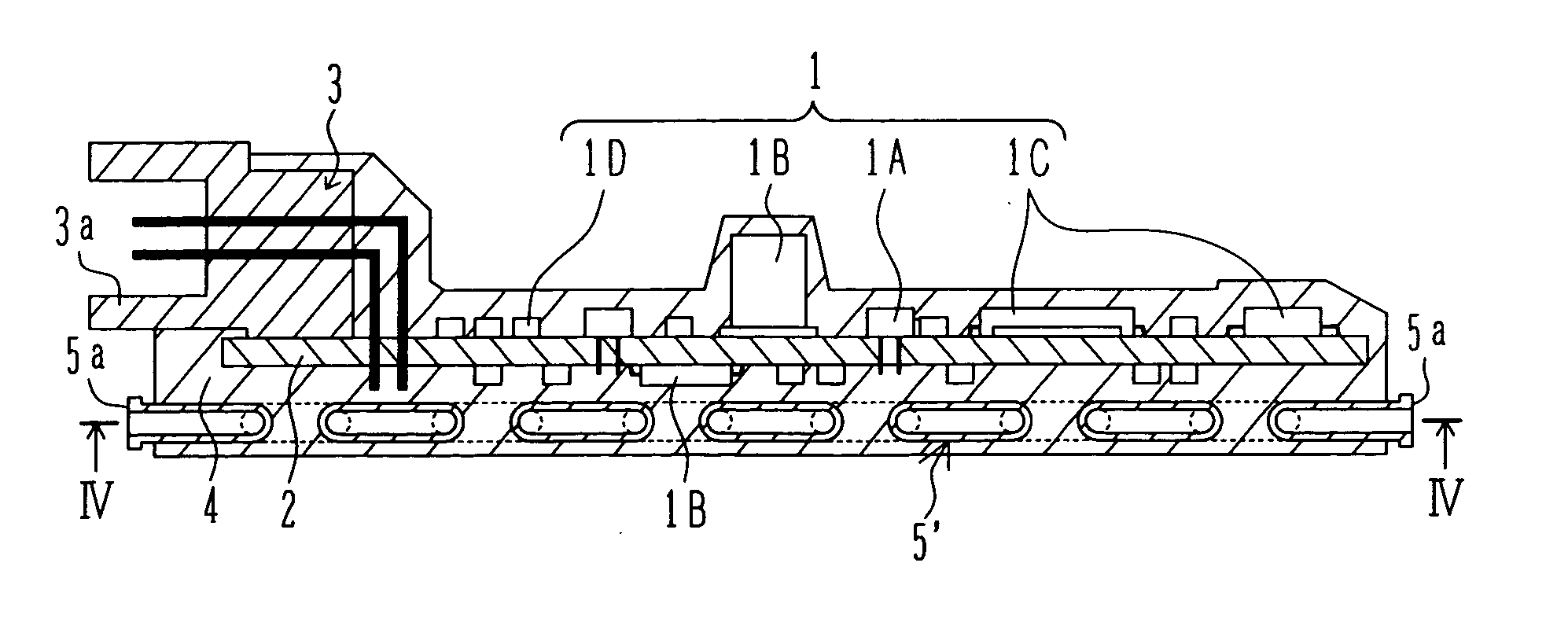
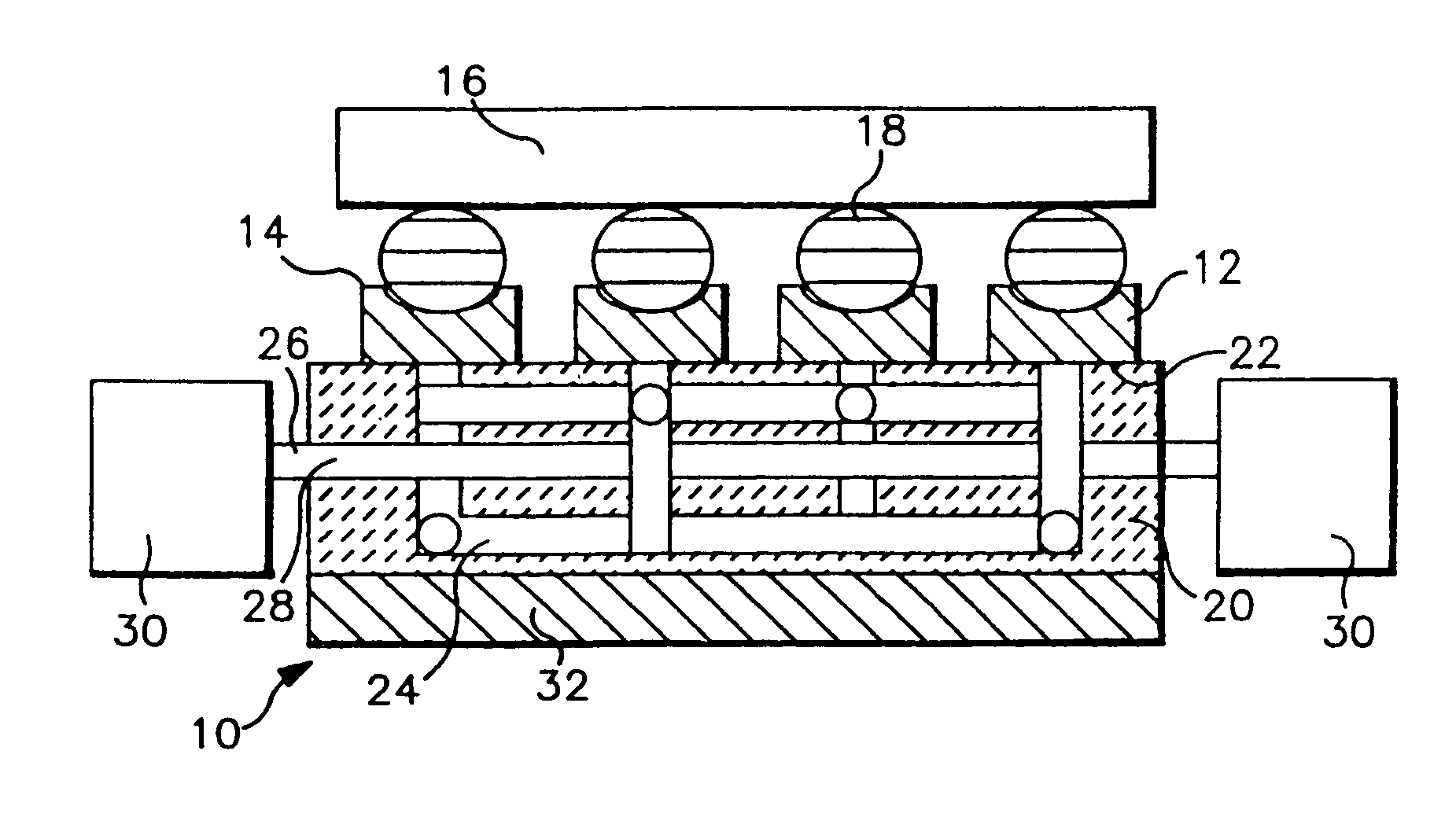
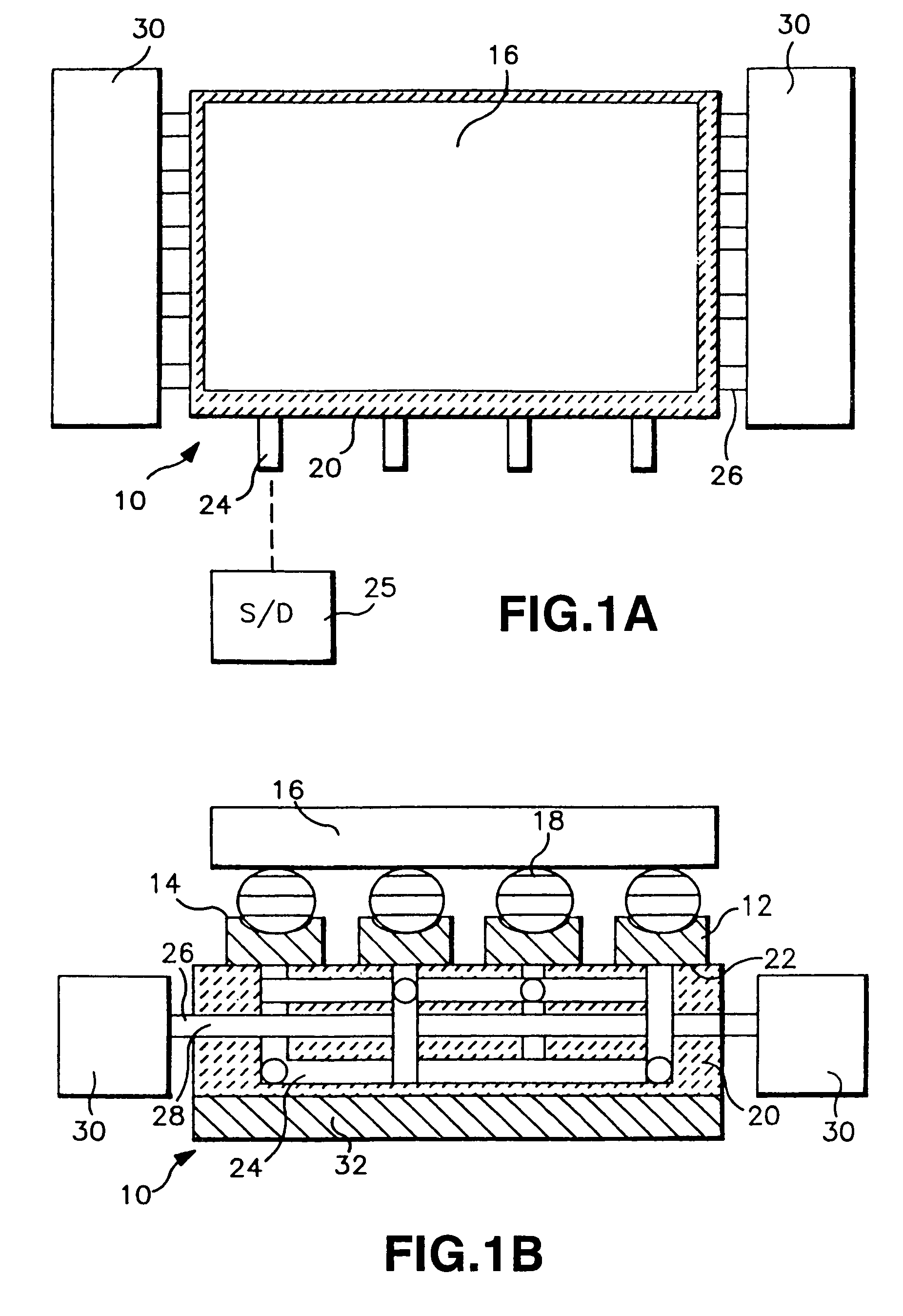
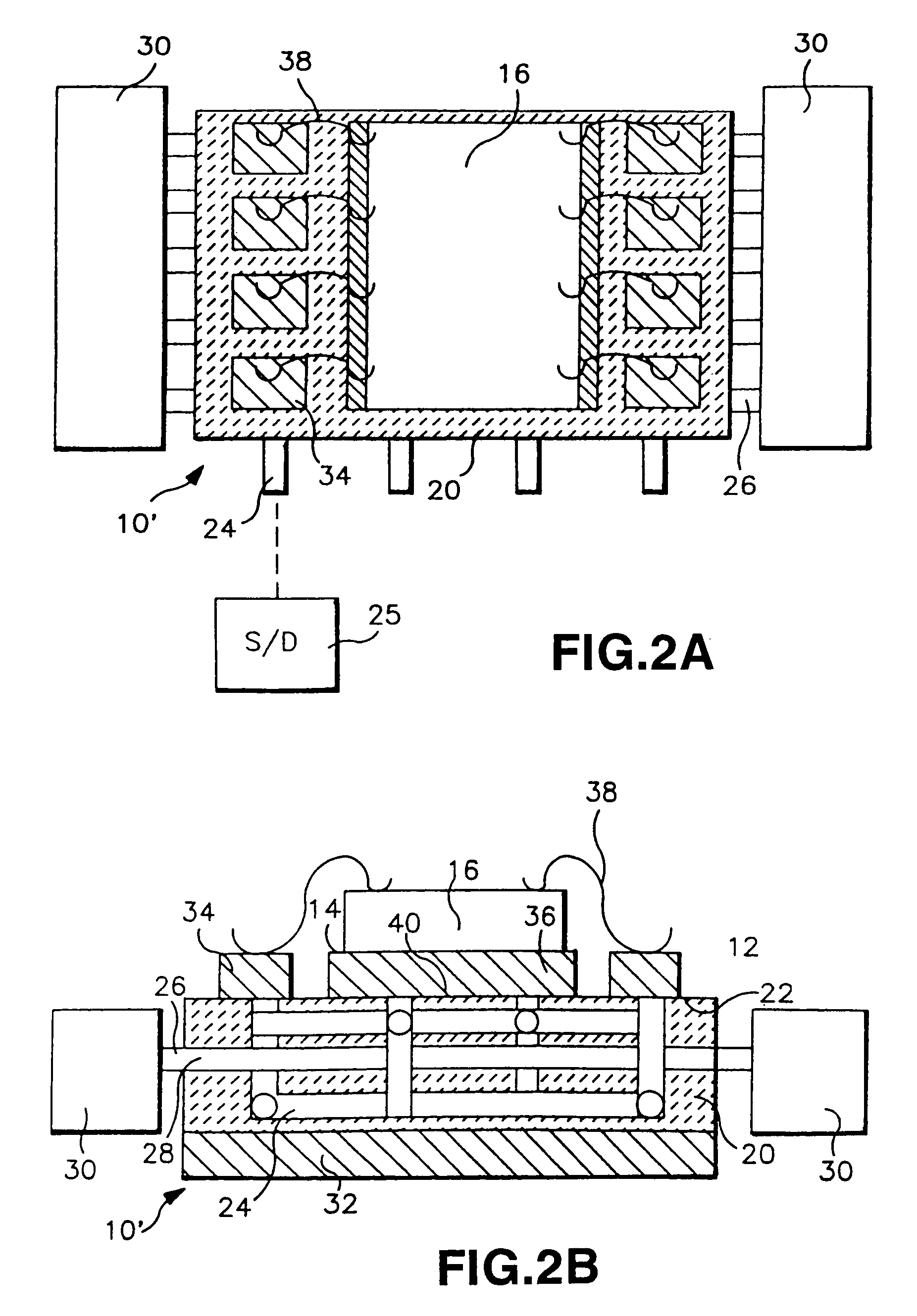
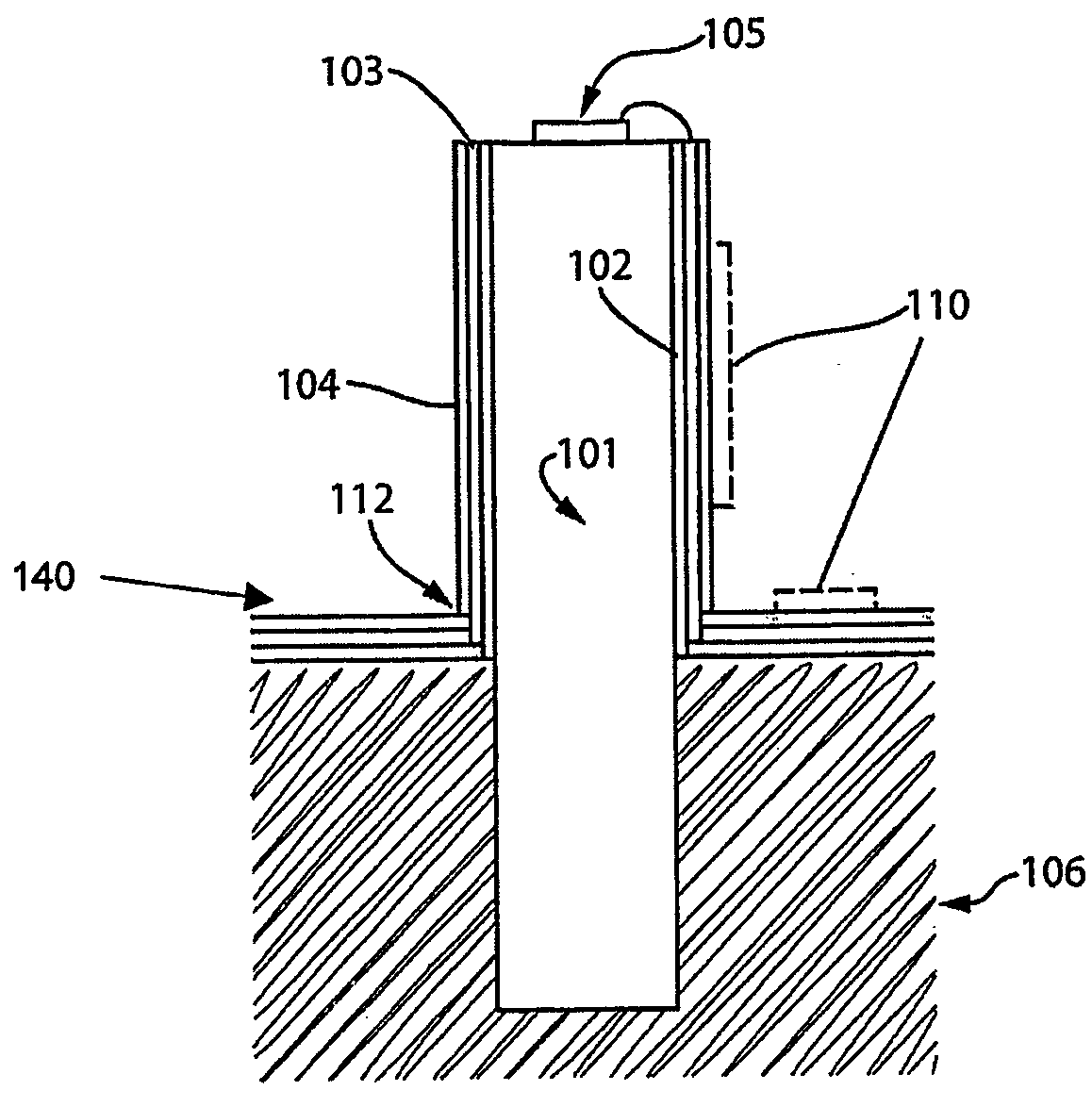
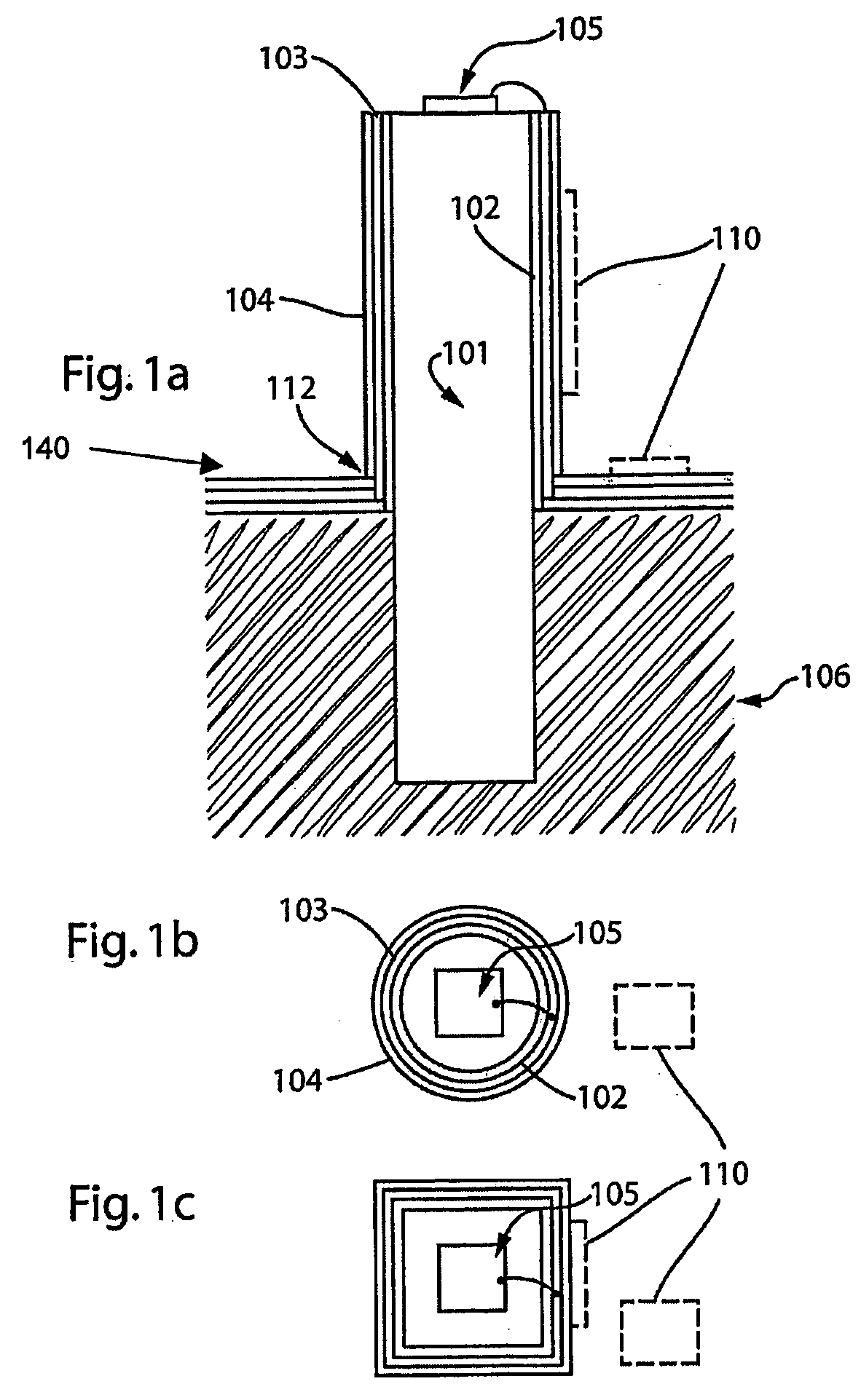
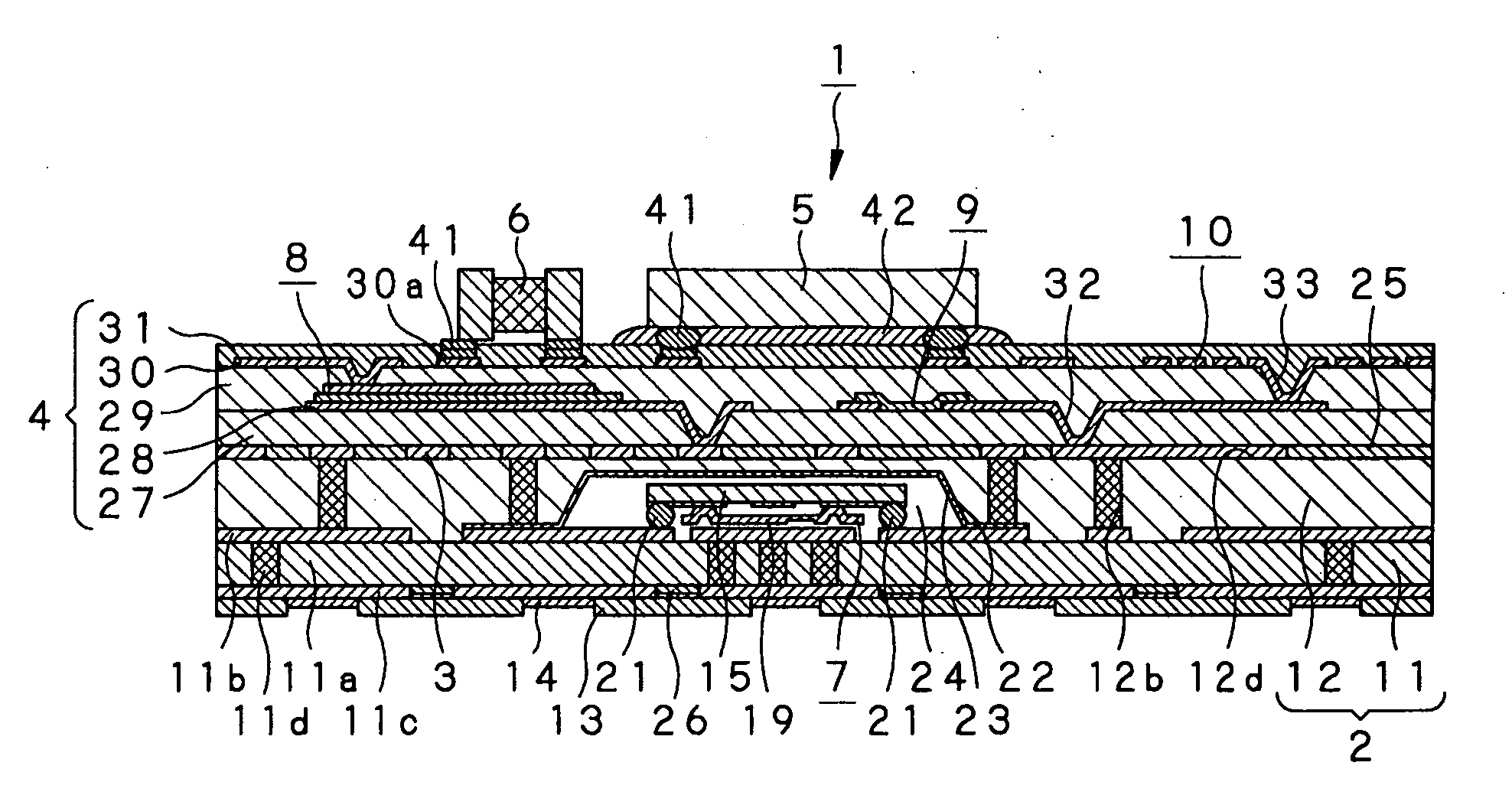
Module with a built-in semiconductor and method for producing the same
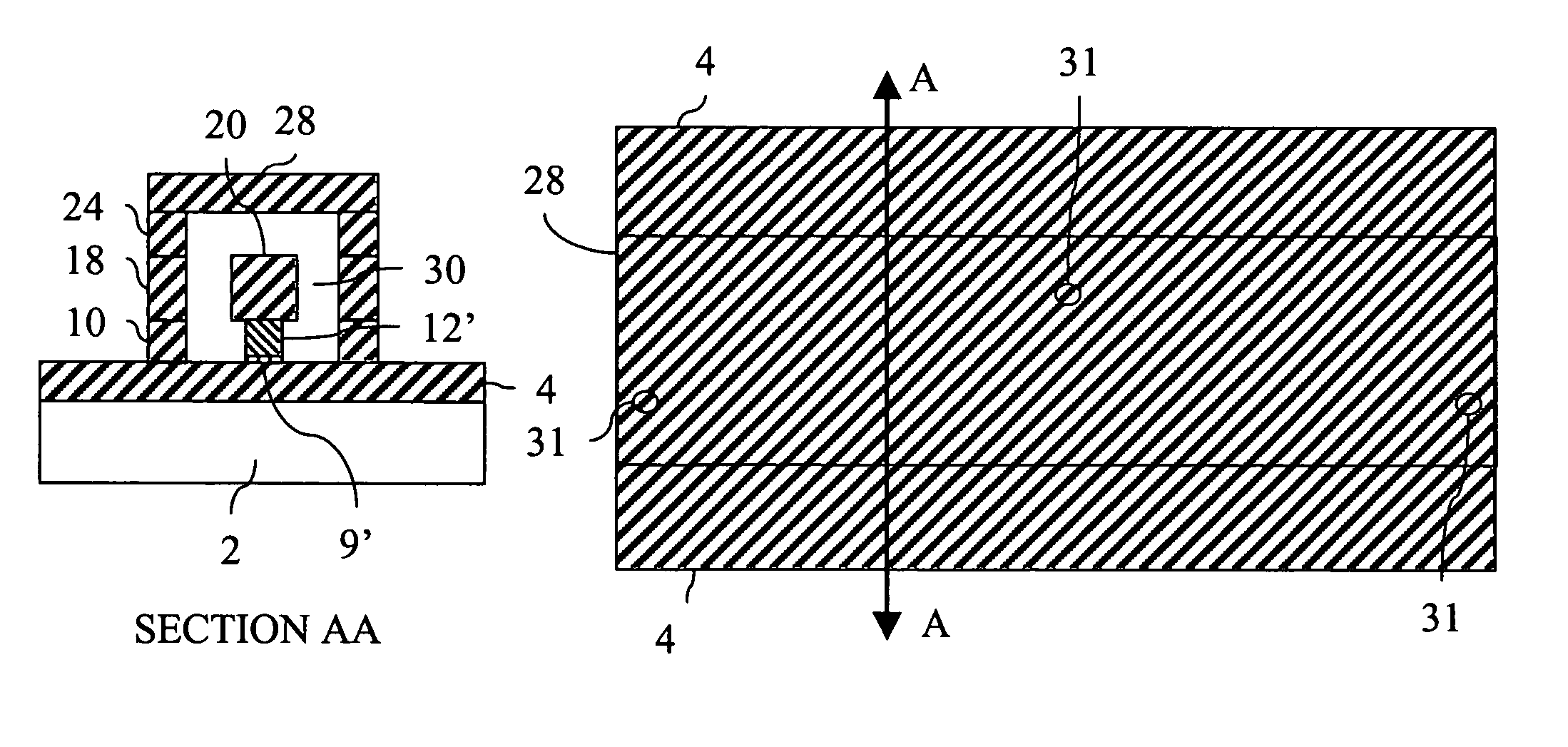
InactiveUS20050001331A1Easy to fillReduce areaTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive pasteDevice material
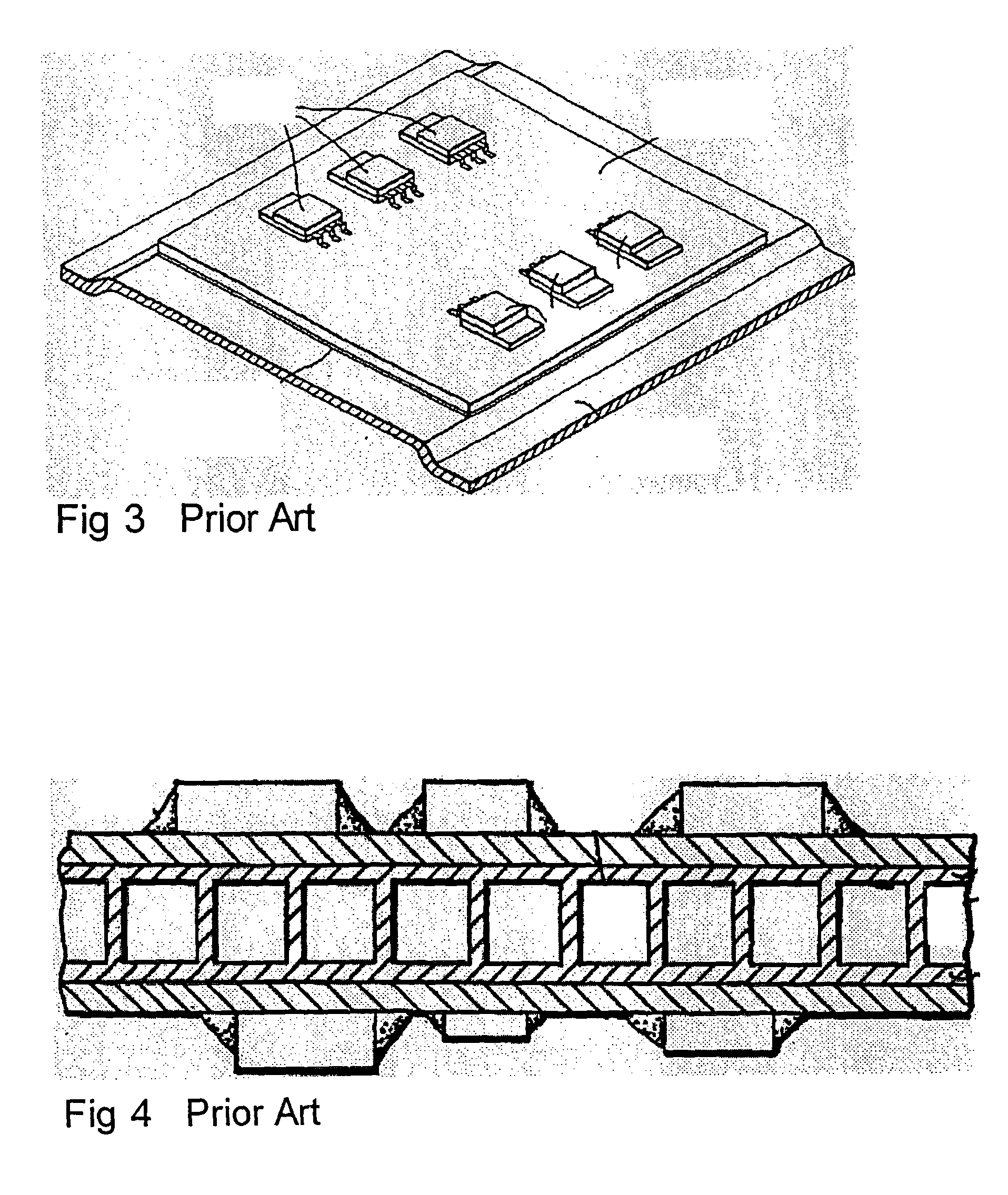
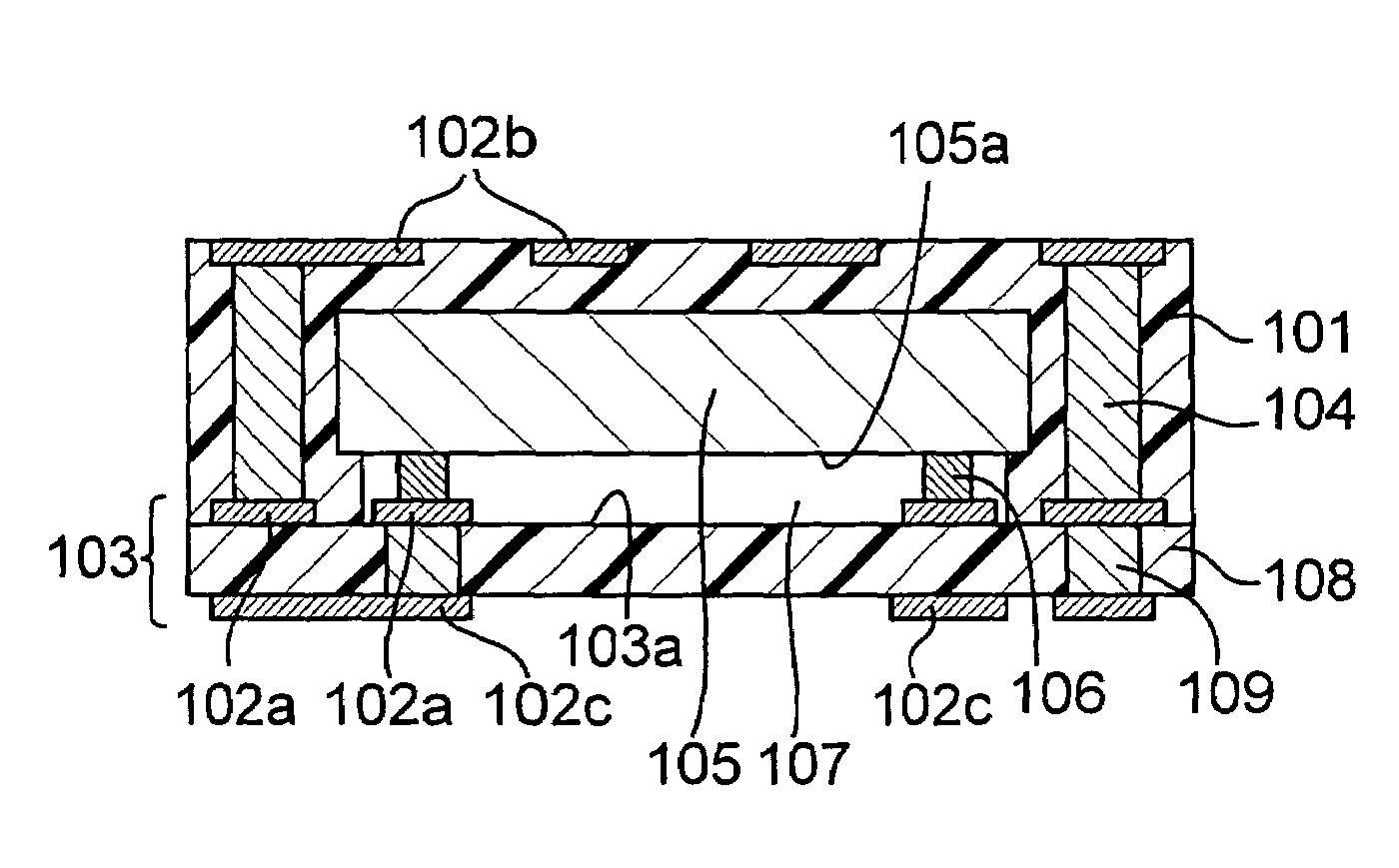
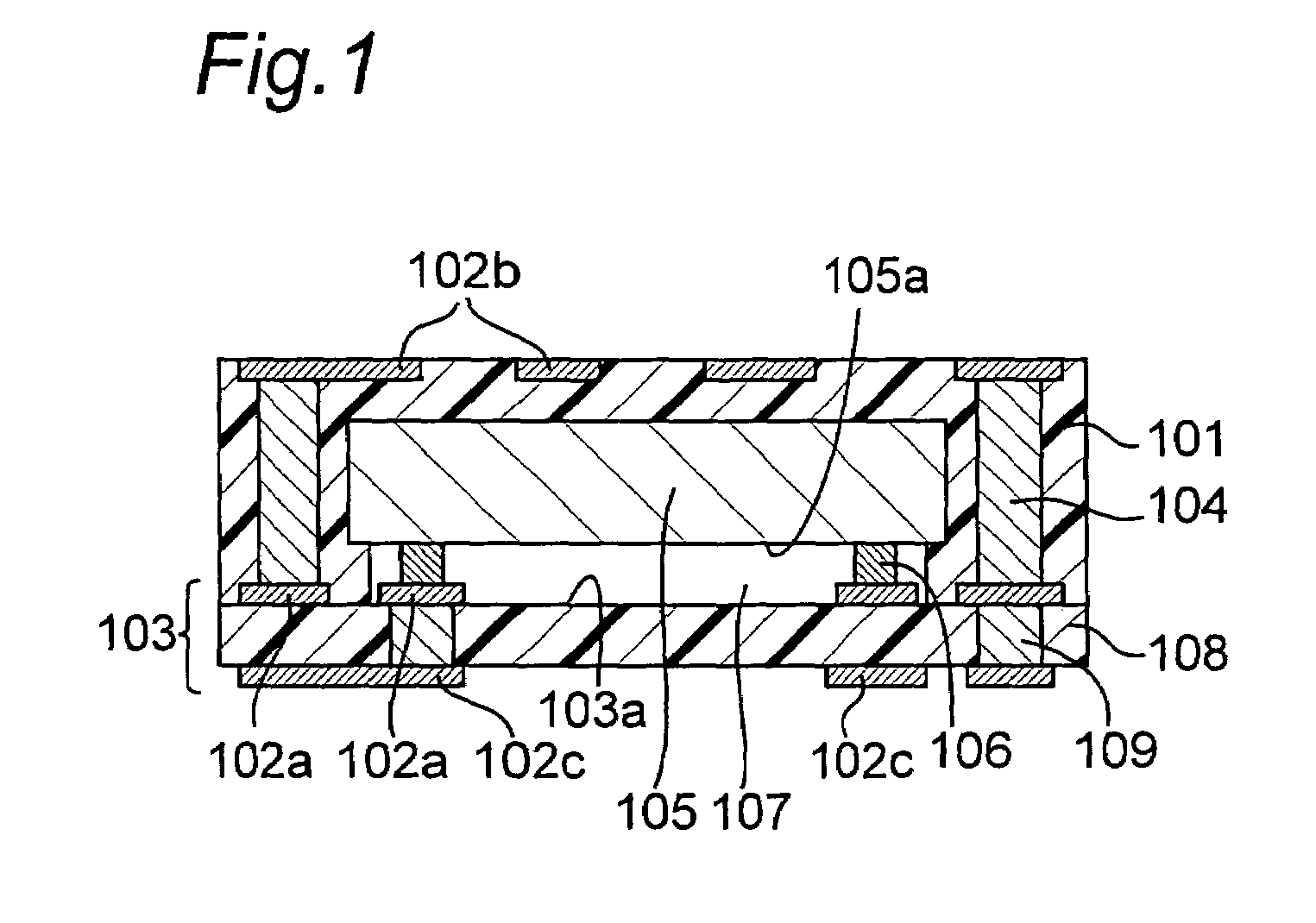
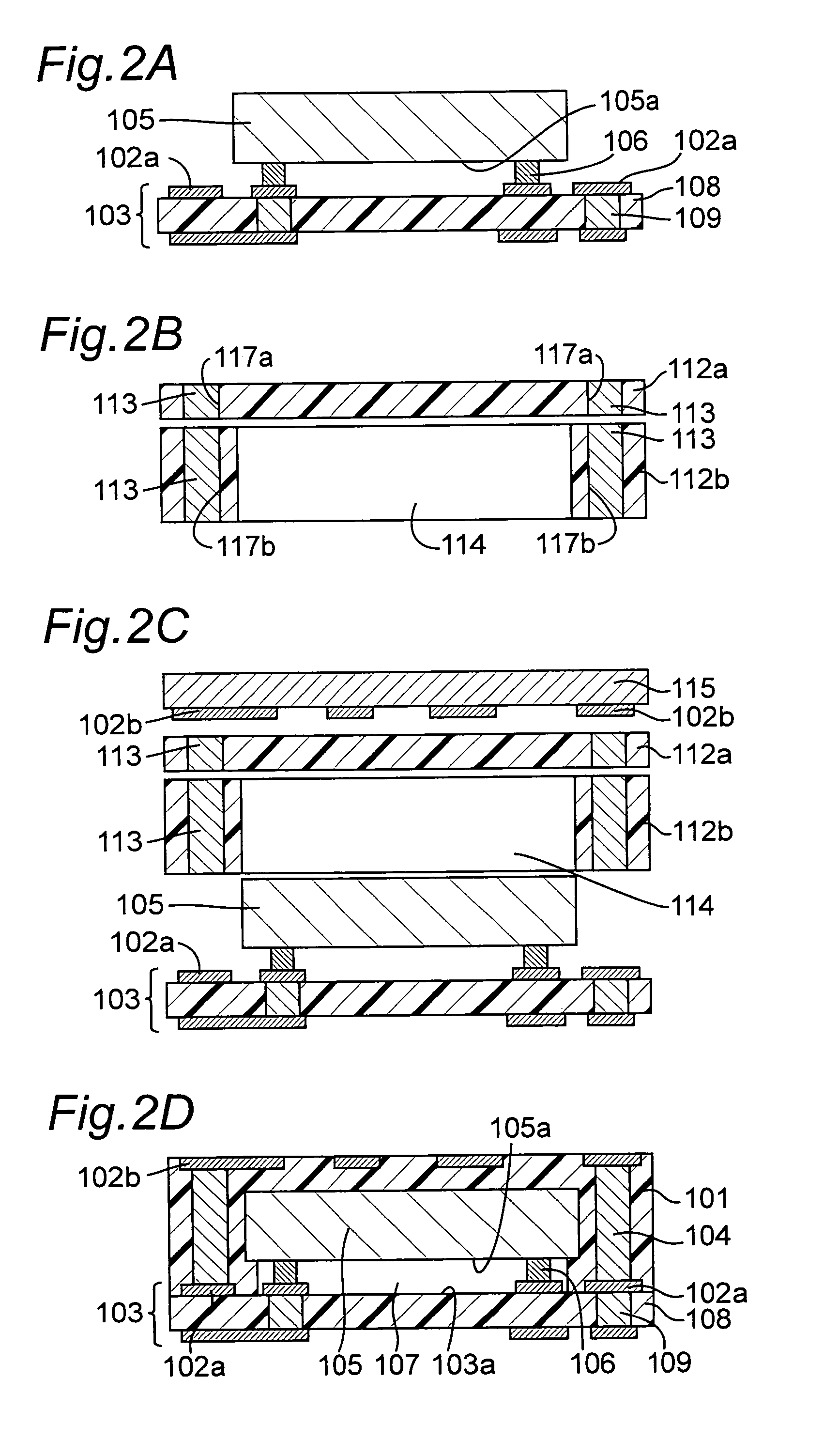
In a module with a built-in semiconductor, higher densification is achieved by disposing inner vias close to a semiconductor device. A module which has a space 107 between a first wiring layer 102a and a built-in semiconductor device 105 is obtained by: mounting the semiconductor device 105 on a first wiring layer 102a of a wiring board 103 without using a sealing resin; stacking on the circuit board an electrically insulating substrate having a through bore (inner via) 104 filled with a conductive paste and an opening for receiving the semiconductor device, and a mold release carrier having a second wiring layer 102b in the stated order; and heating and pressurizing so that the semiconductor device 105 is incorporated in a core layer 101 which is formed by curing the electrically insulating substrate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Stretchable electronic systems with fluid containment
ActiveUS20140220422A1Relieve pressureCircuit bendability/stretchabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsStretchable electronicsElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention provides electronic systems, including device arrays, comprising functional device(s) and / or device component(s) at least partially enclosed via one or more fluid containment chambers, such that the device(s) and / or device component(s) are at least partially, and optionally entirely, immersed in a containment fluid. Useful containment fluids for use in fluid containment chambers of electronic devices of the invention include lubricants, electrolytes and / or electronically resistive fluids. In some embodiments, for example, electronic systems of the invention comprise one or more electronic devices and / or device components provided in free-standing and / or tethered configurations that decouple forces originating upon deformation, stretching or compression of a supporting substrate from the free standing or tethered device or device component.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
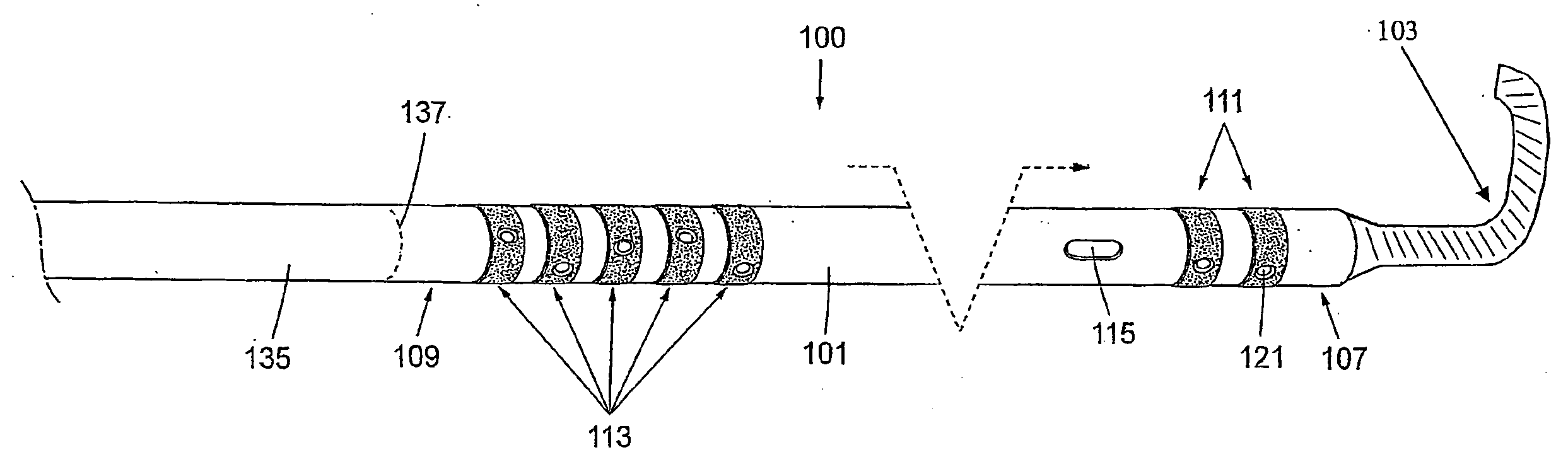
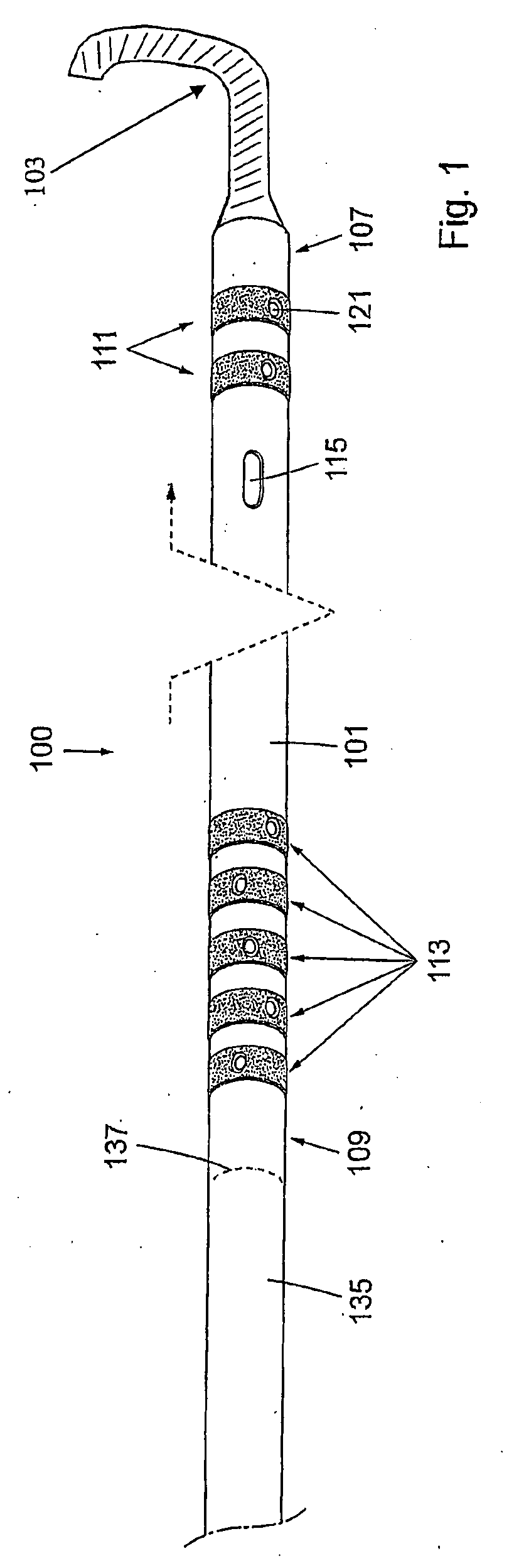
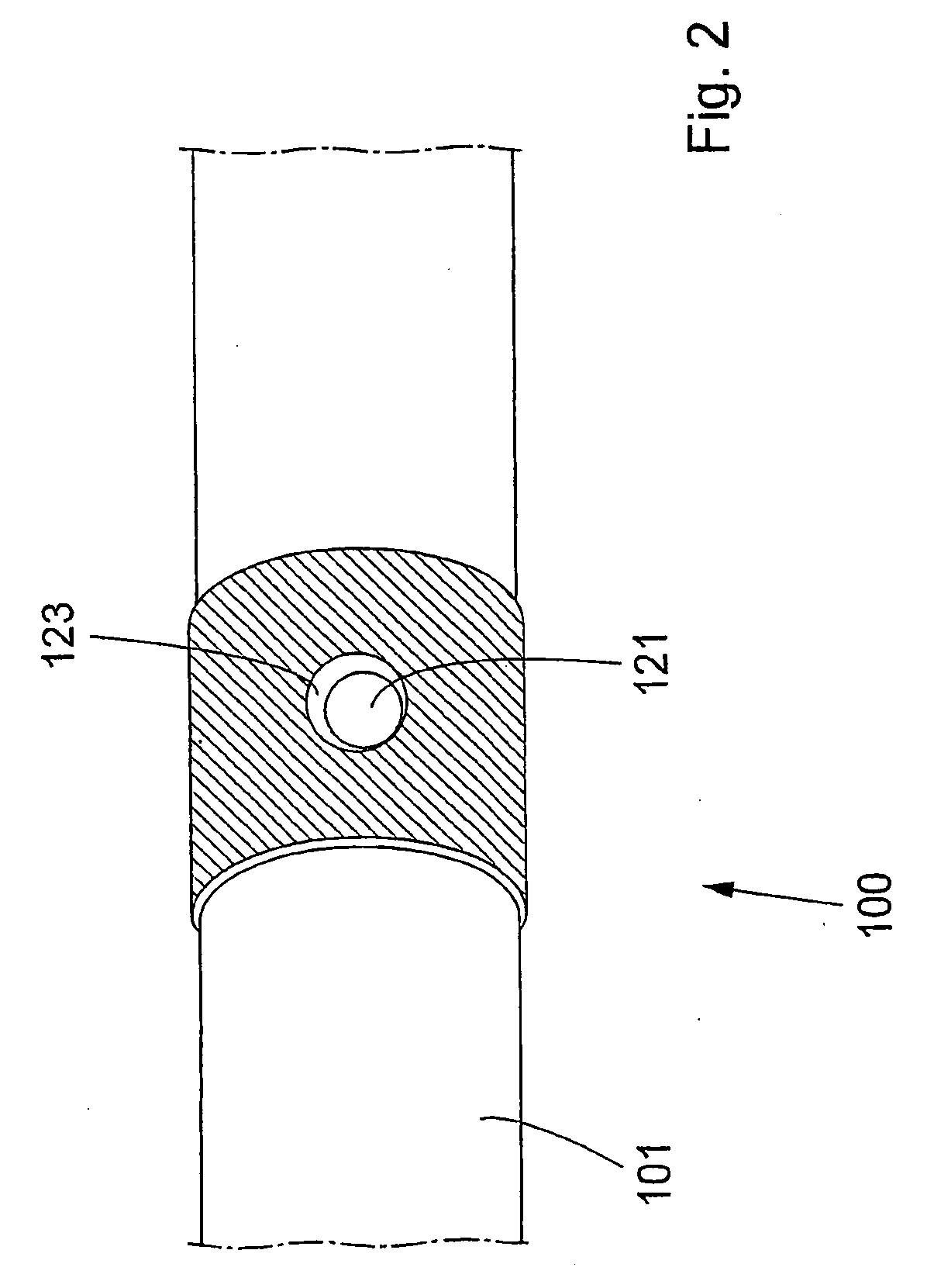
Device for Invasive Use
A device for invasive use, comprising a support member comprising a flexible material. The support member comprises a layer of a conductive line or pattern thereon. The support member is formed into an elongated tube shape, and the inside of the support member can be sealed from the outside of the support member. An electrically conductive line or pattern extends on the inside of the tube shaped support member, and the support member may comprise a sensing, stimulating and / or processing element. Furthermore, there is described a manufacturing method for the device, a system where the device is a part of the system and the use of the device for invasive use.
Owner:CATHPRINT
Engine control circuit device
InactiveUS20060012034A1Improve heat resistanceReduce expansionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsHeat resistanceControl circuit
An engine control circuit device which has higher heat resistance and can be installed in a place exposed to severe thermal environments. In an engine control circuit device comprising a circuit board on which a plurality of packaged electronic parts are mounted, and a connector mounted on the circuit board for connection to an external circuit, the device further comprises a resin portion formed of a thermo-setting resin and covering the connector except for a connecting portion thereof and the circuit board, and a cooling pipe integrally molded in the resin portion and allowing a coolant to flow through it, thereby cooling the resin portion.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
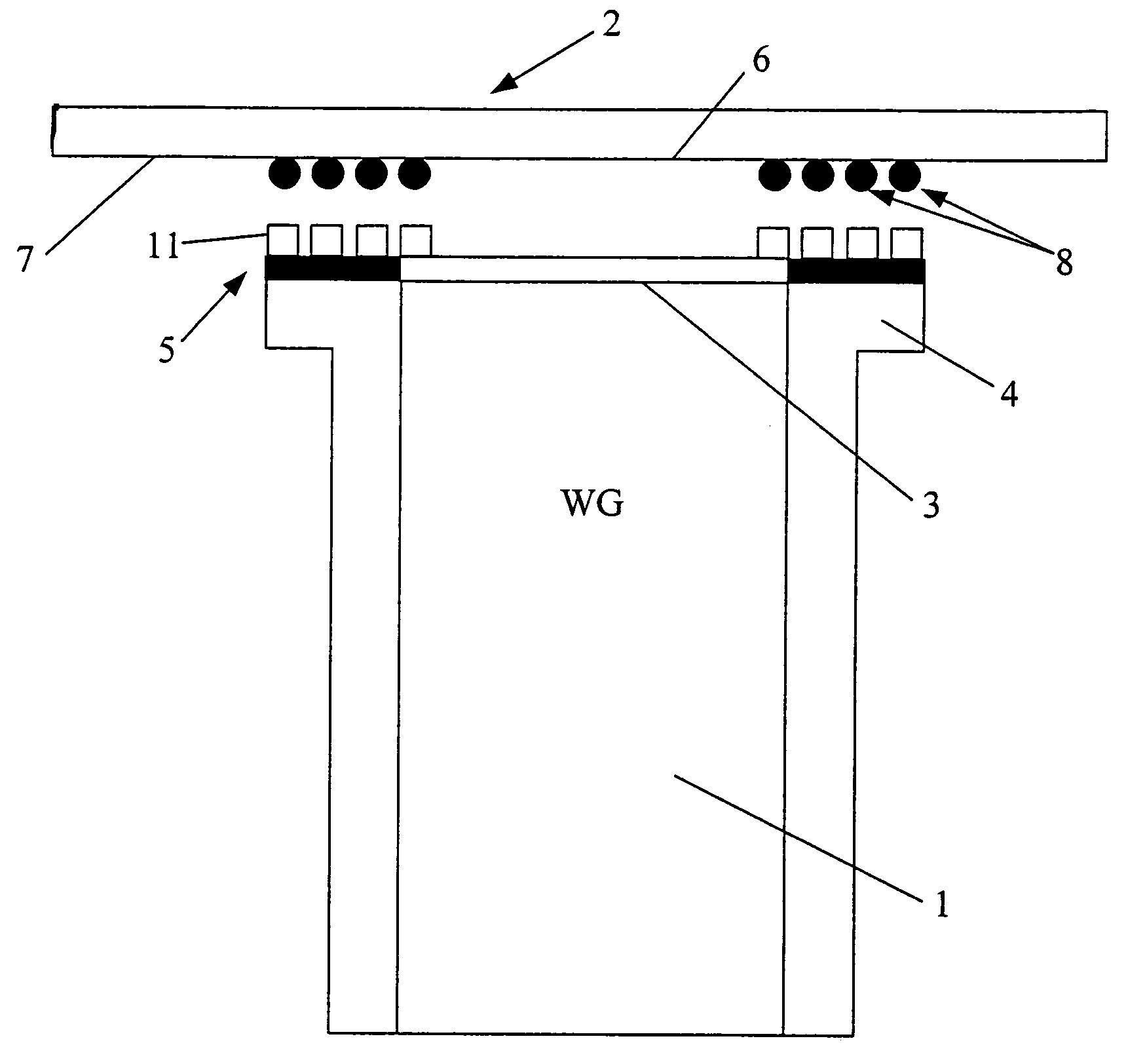
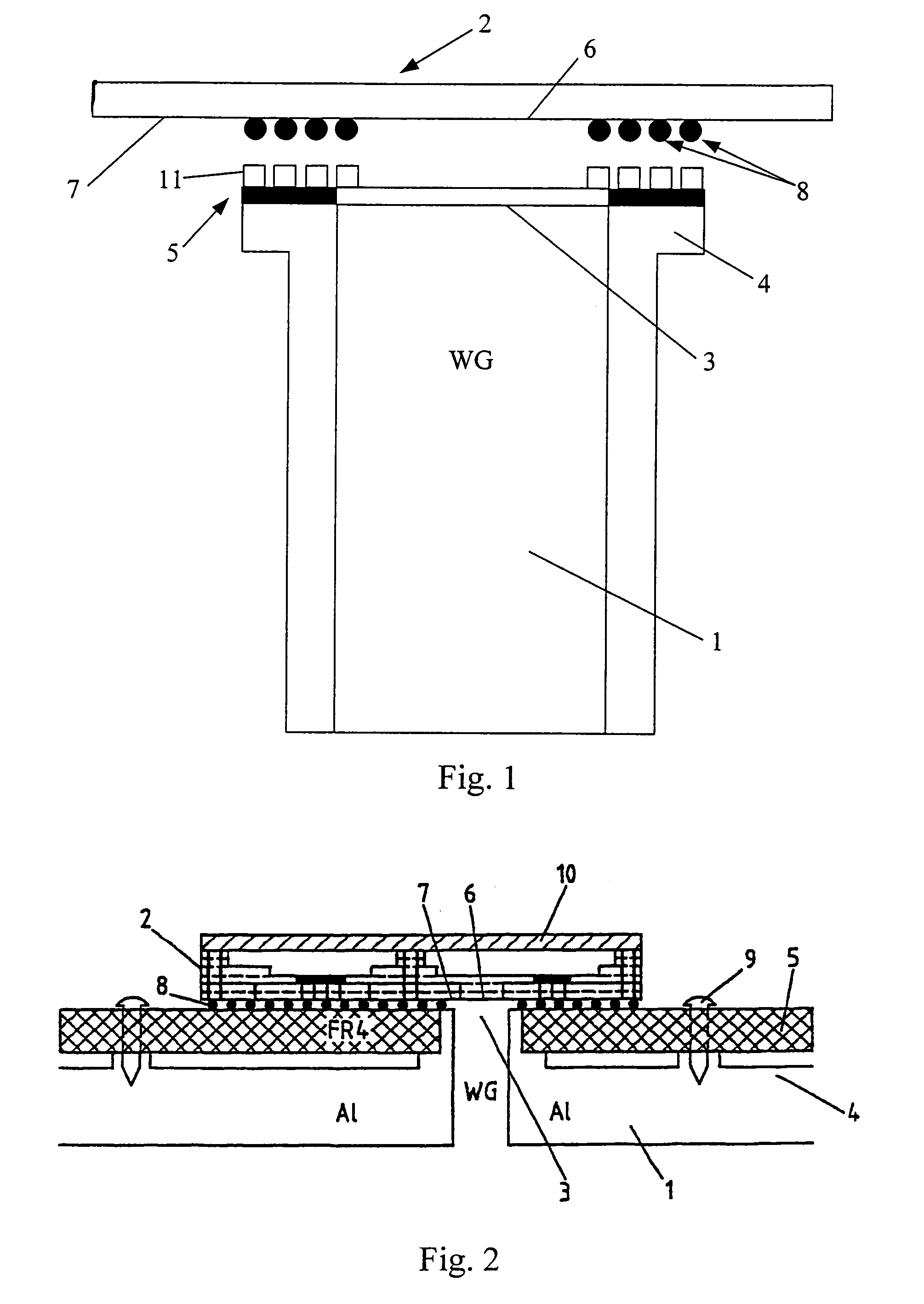
Self-aligned transition between a transmission line and a module
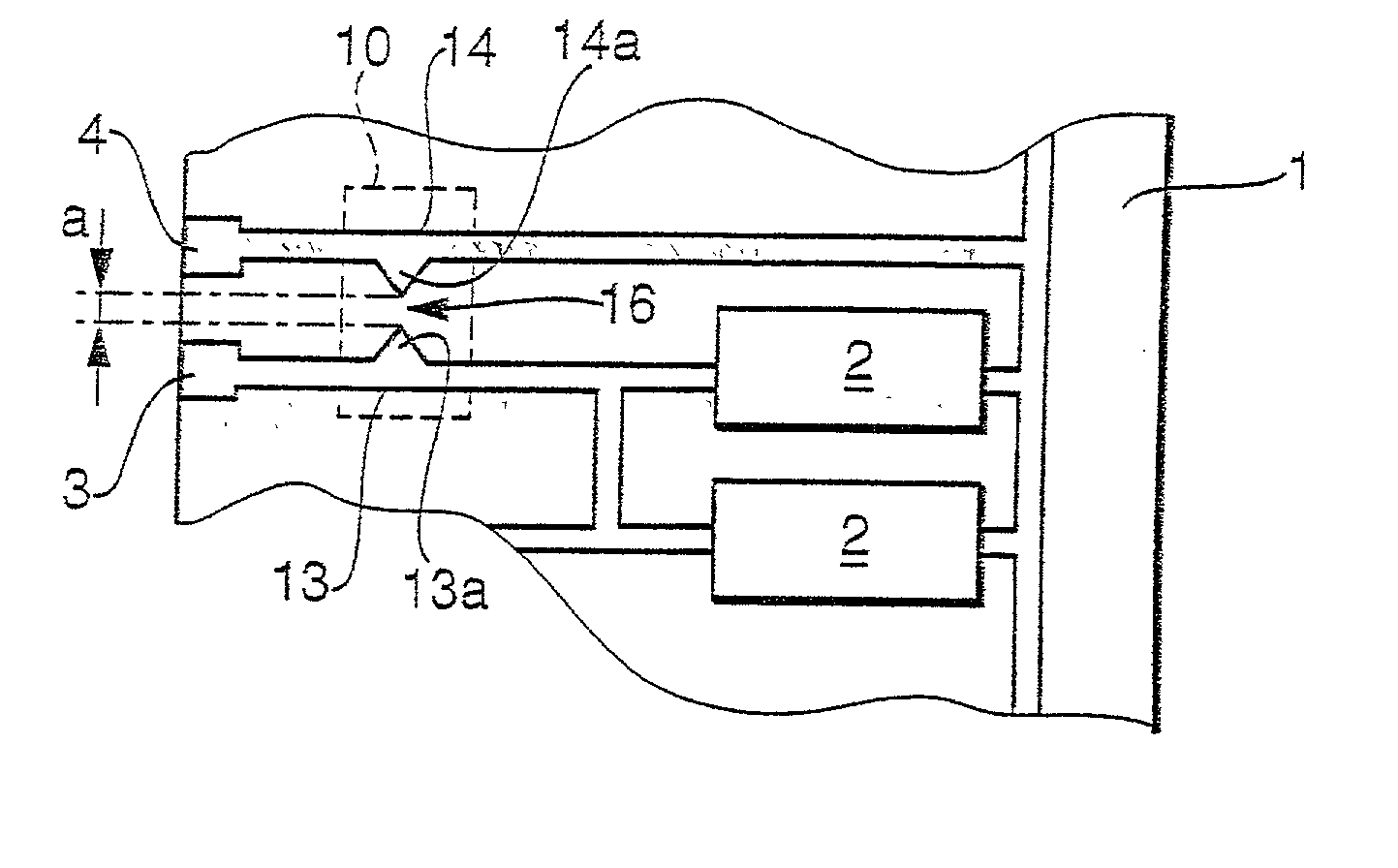
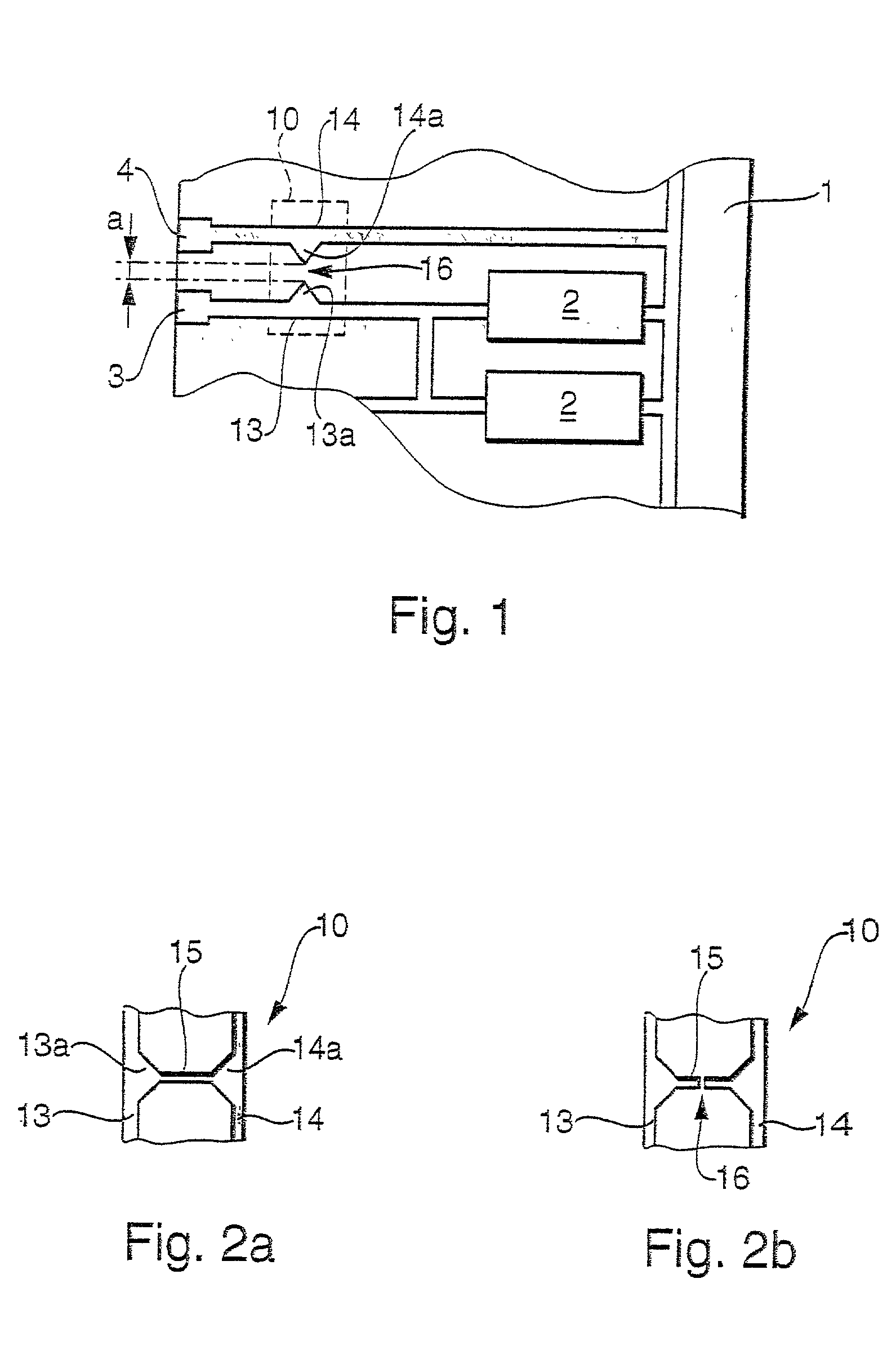
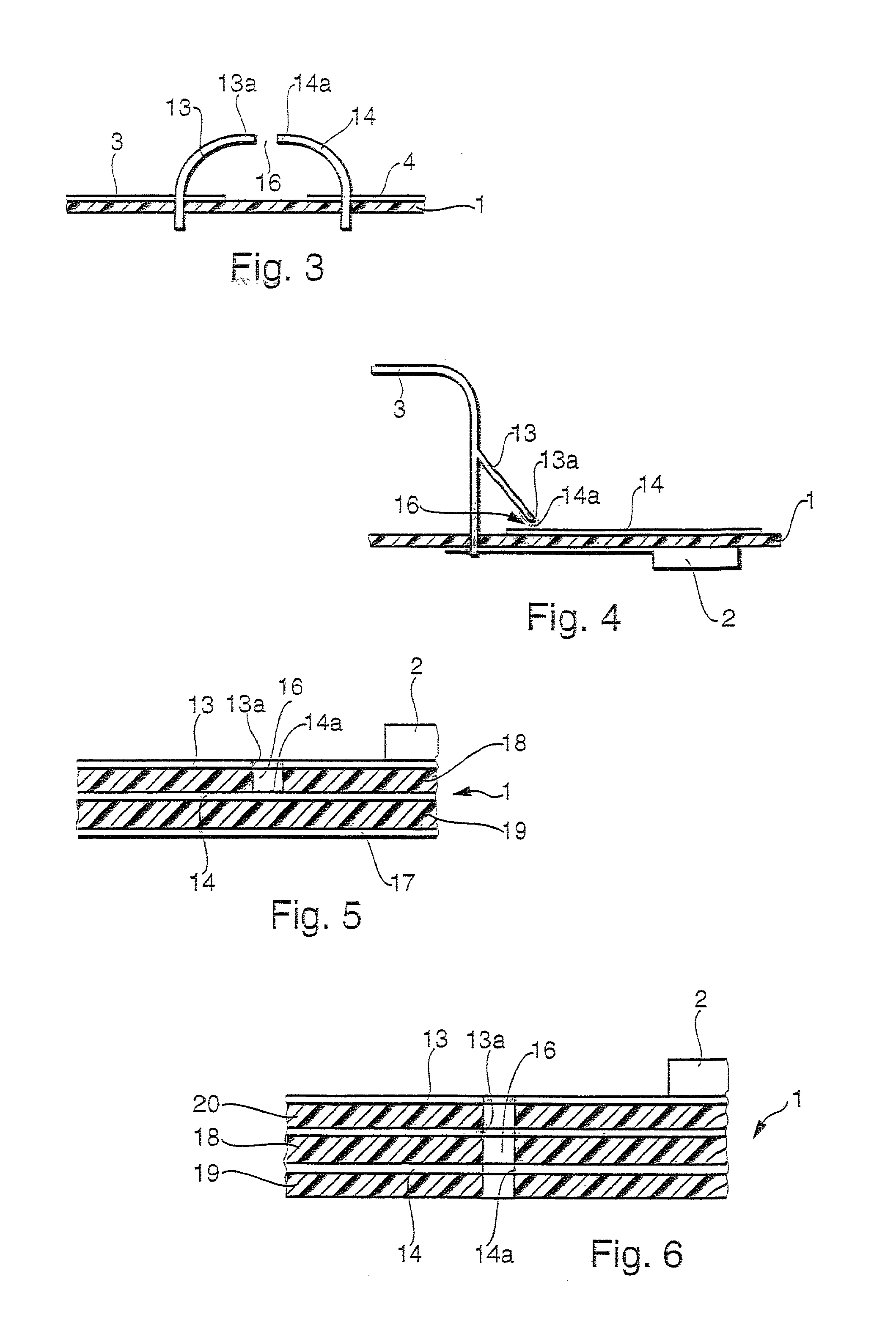
InactiveUS6940361B1Easy and accurate connectionSimple and precise connectionPrinted circuit assemblingOne-port networksEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a method for forming a self-aligned transition between a transmission line (1) and a module (2) to be connected to said transmission line (1). The invention equally relates to such a module (2), to such a transmission line (1), to an intermediate element (5) possibly to be positioned between such a module (2) and such a transmission line (1), and finally to a system comprising such a transition. In order to enable a simple and precise connection of a transmission line (1) with some other module (2), it is proposed to use matching solder particles (8) and soldering pads on module (2) and transmission line (1) or intermediate element (5) respectively, and to apply a reflow treatment to the joined elements (1) and (2) or (5) and (2), thereby forming a self-aligning connection. The invention is to be applied particularly to waveguide-to-microstrip transitions.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Integrated cooling system for electronic devices
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
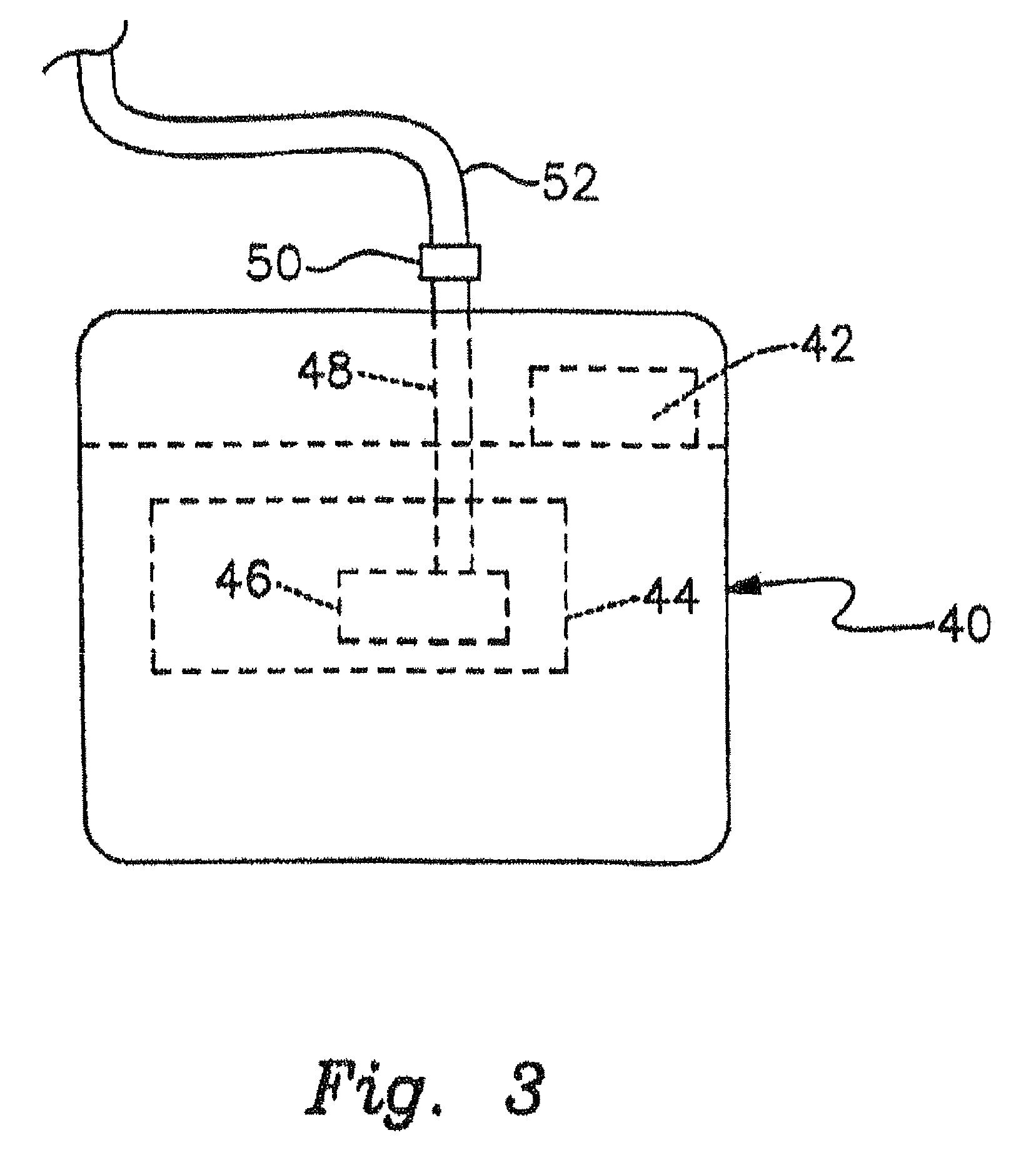
Battery module and battery module assembly using same
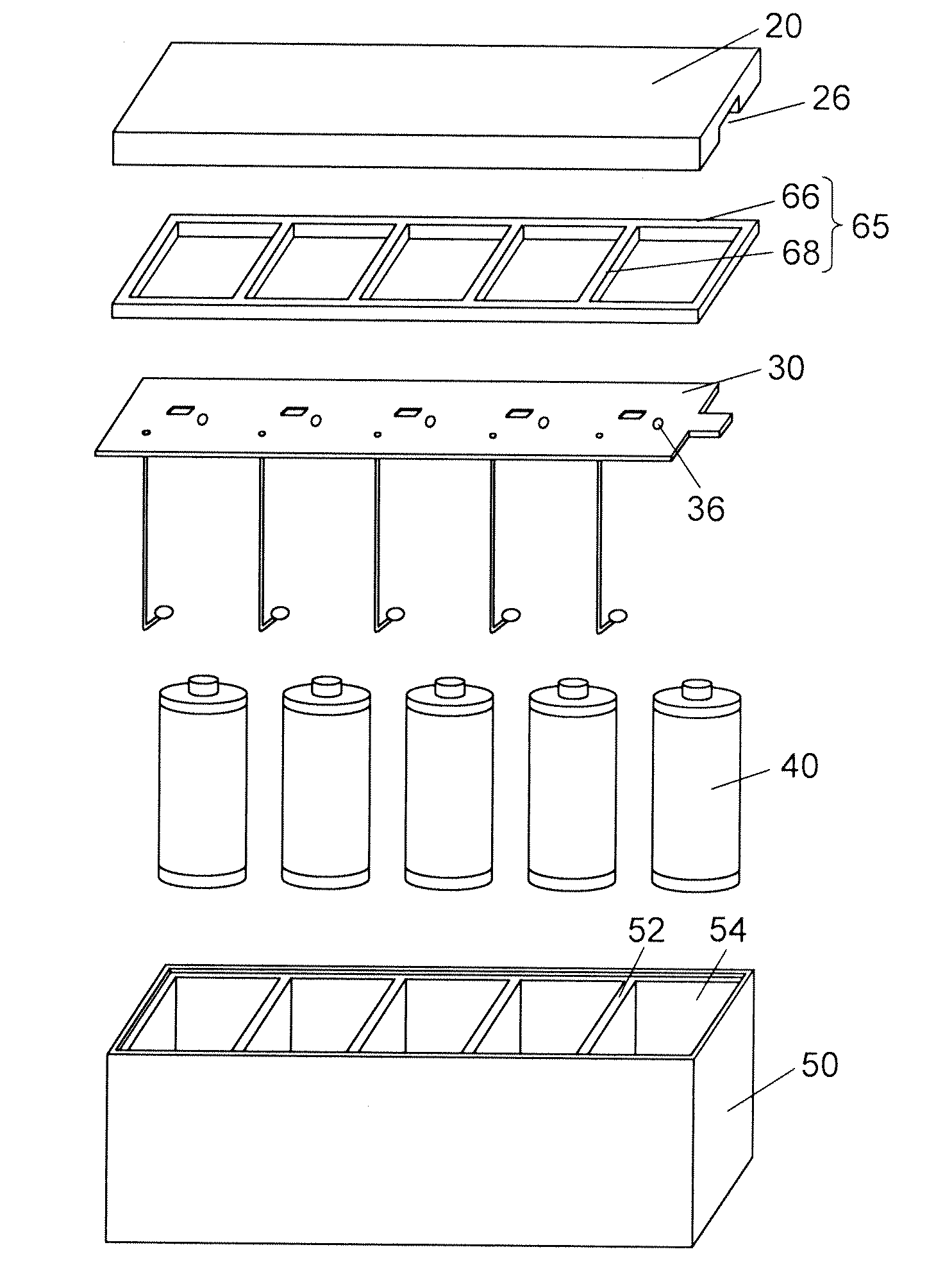
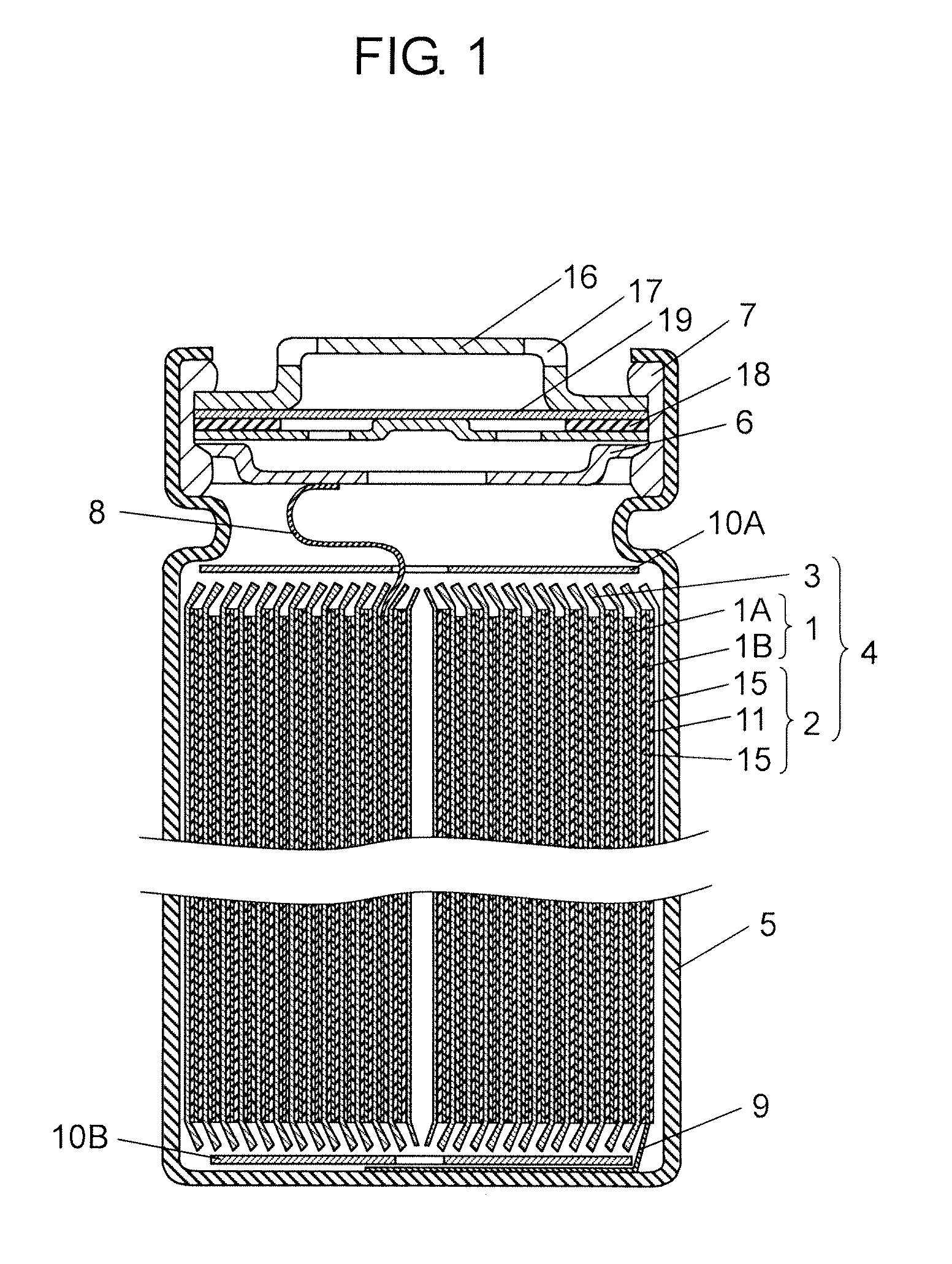
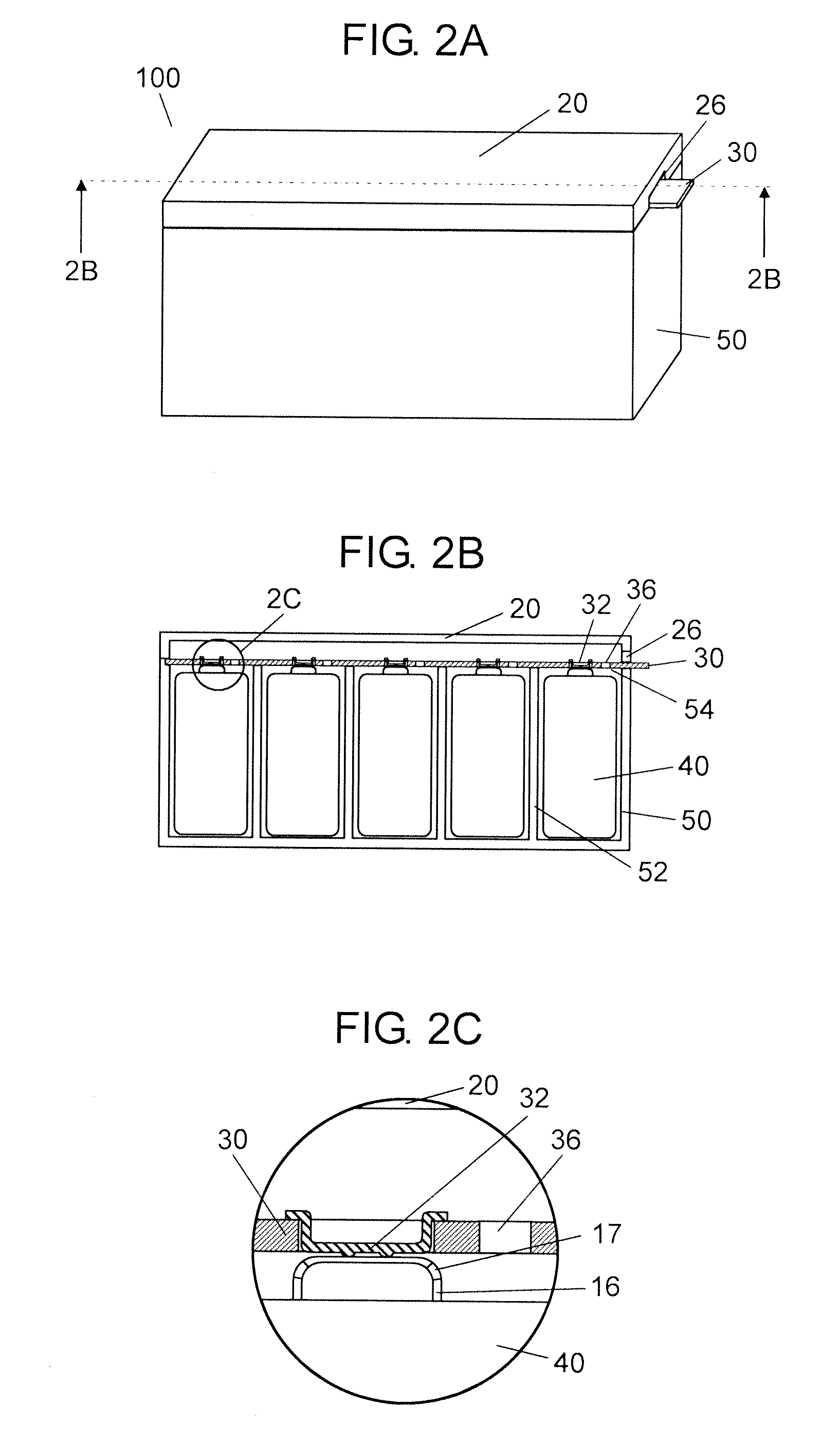
InactiveUS20110195284A1Reduce spacingMinimize impactVent arrangementsCircuit fluid transportBattery cellElectrical and Electronics engineering
The battery module includes a plurality of battery units, a housing, a wiring board, and a lid. The battery unit is composed of one or more battery cells each having a vent mechanism. At least one surface of the housing is an open end. The housing has a plurality of storage parts partitioned by one or more partition walls. Each battery unit is stored in each storage part. The wiring board covers the open end of the housing, is disposed at the vent mechanism side of the cell, and has connection terminals connected to the battery units. The lid covers the open end of the housing and the wiring board, and has an open part. Through holes are provided on the wiring board in positions facing the battery units and in a different region from that of the connection terminals.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electrical circuit board and method for making the same
InactiveUS6490159B1Quickly and efficiently dissipating heat from the circuit boardEfficient heatingCircuit fluid transportInsulated cablesEngineeringHeat pipe
A multi-layer circuit board with heat pipes and a method forming a multi-layer circuit board with heat pipes is disclosed. The circuit board includes a heat pump which communicates with the heat pipe to circulate an amount of cooling material within the heat pipe effective to efficiently dissipate heat from the circuit board.
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
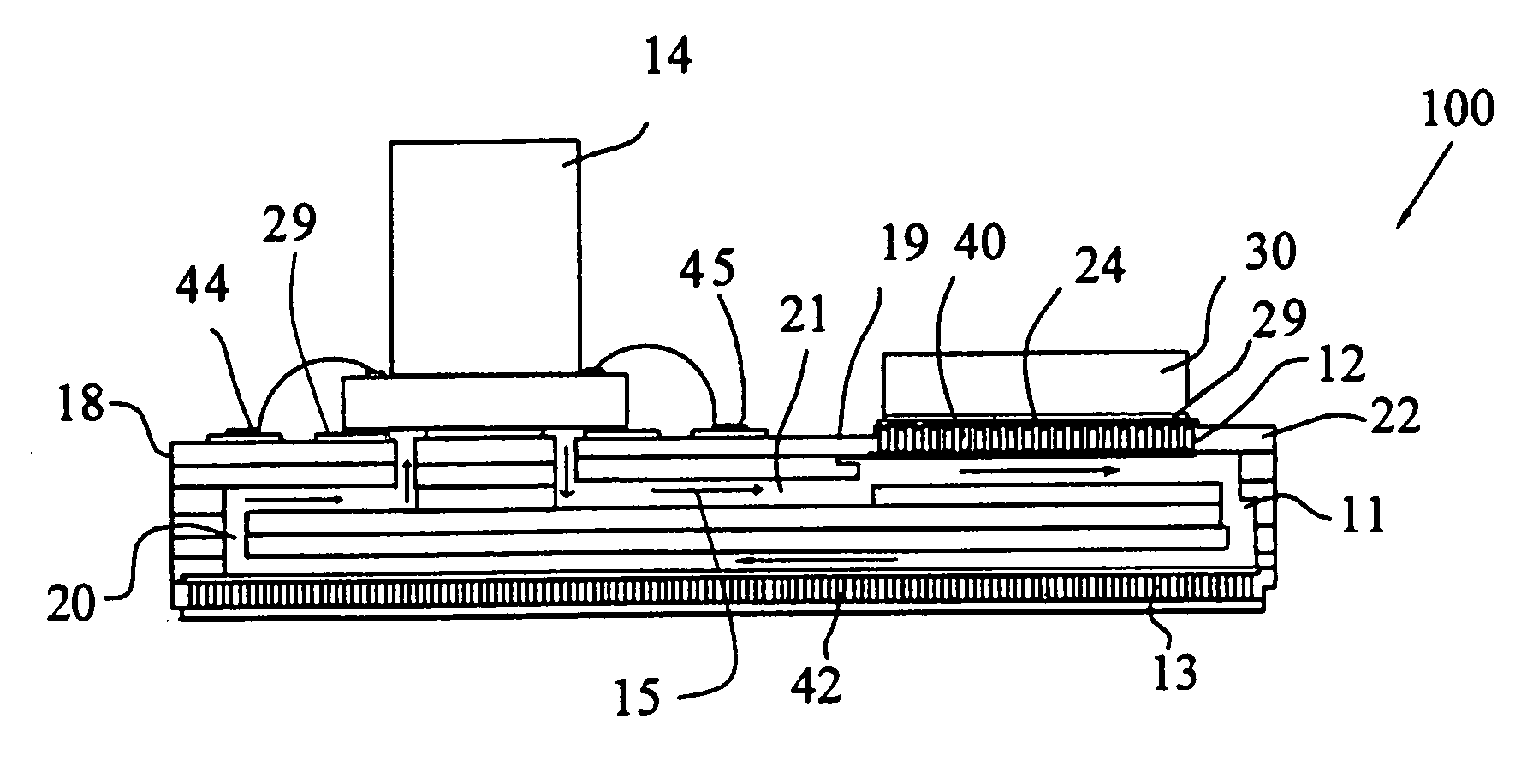
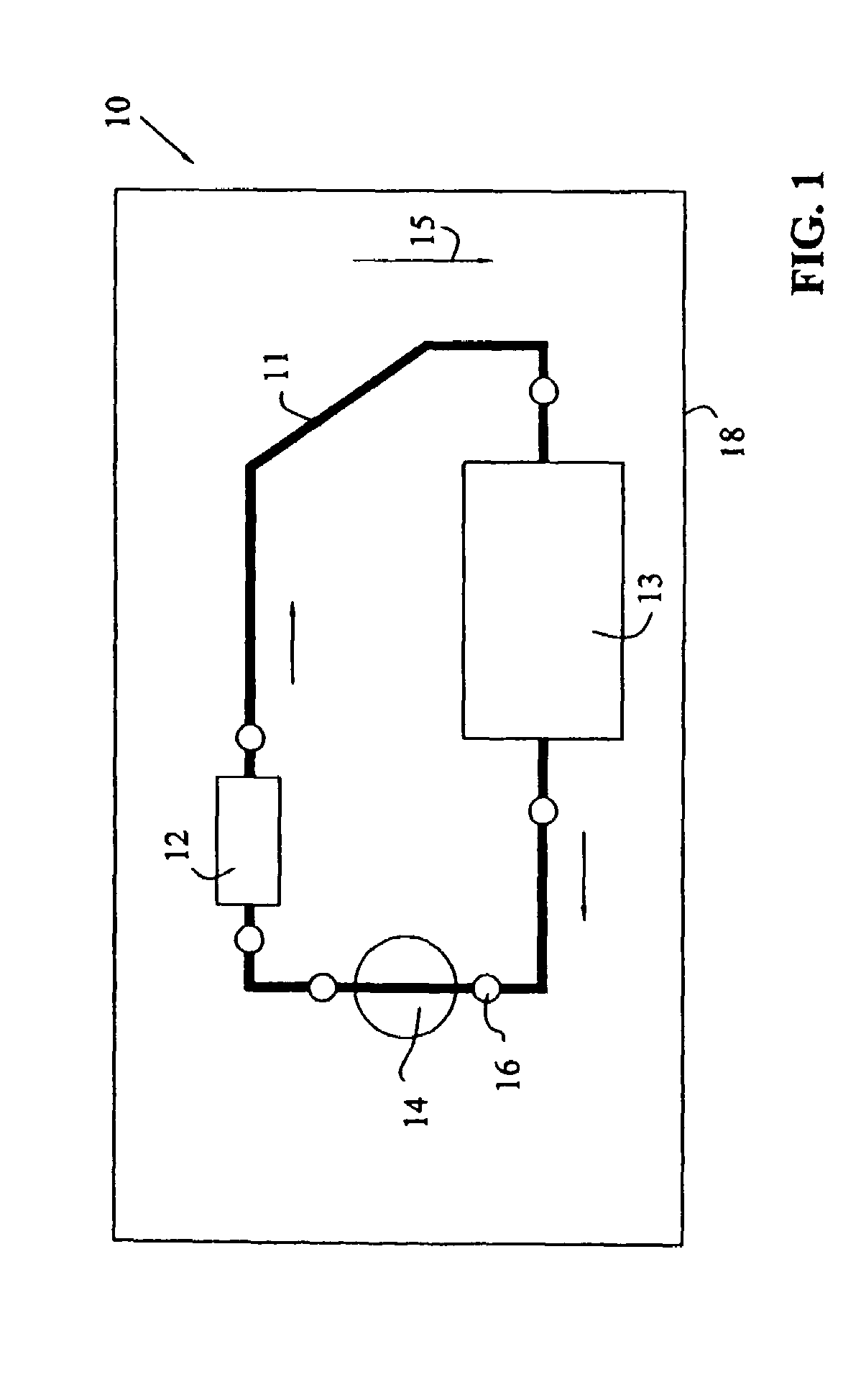
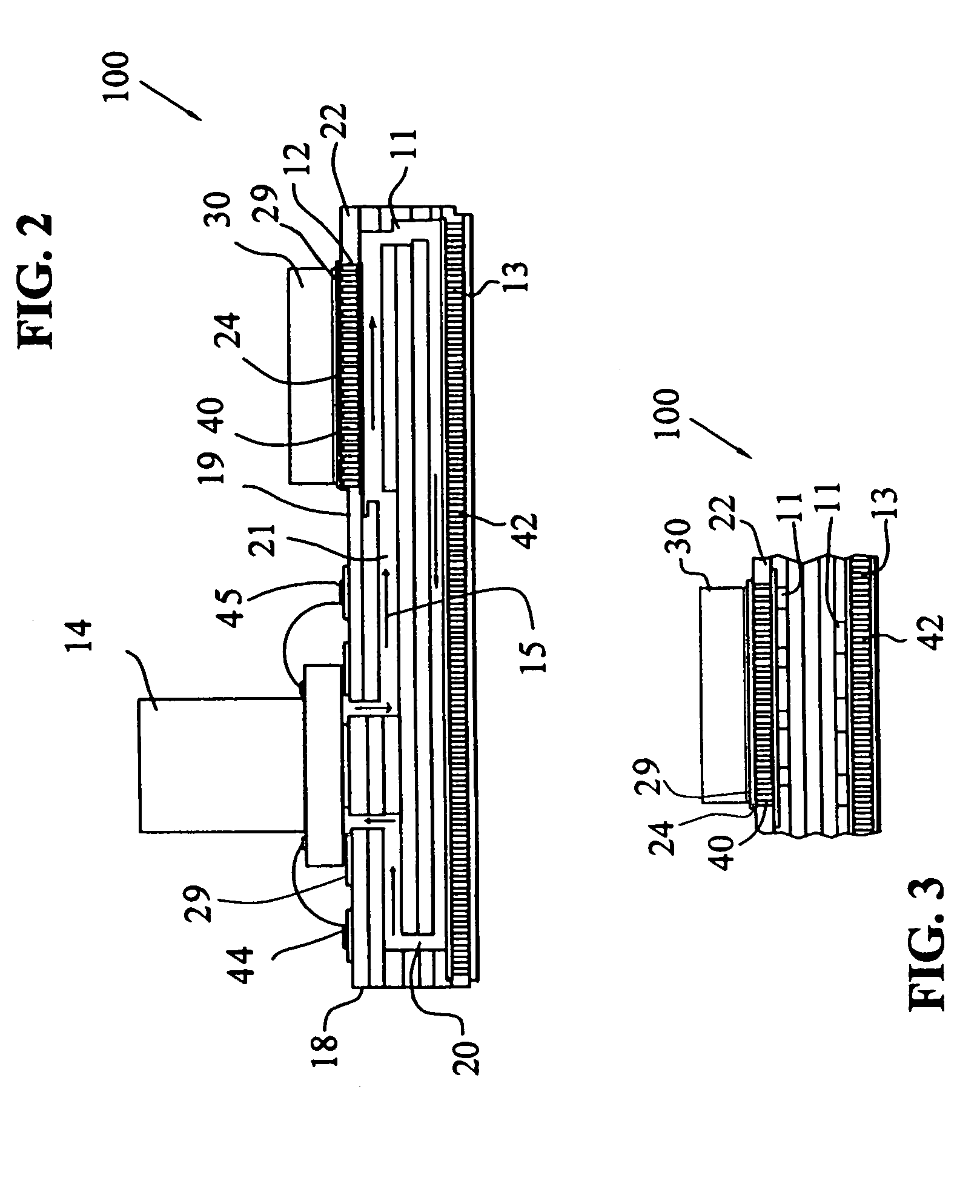
Cooling apparatus, system, and associated method
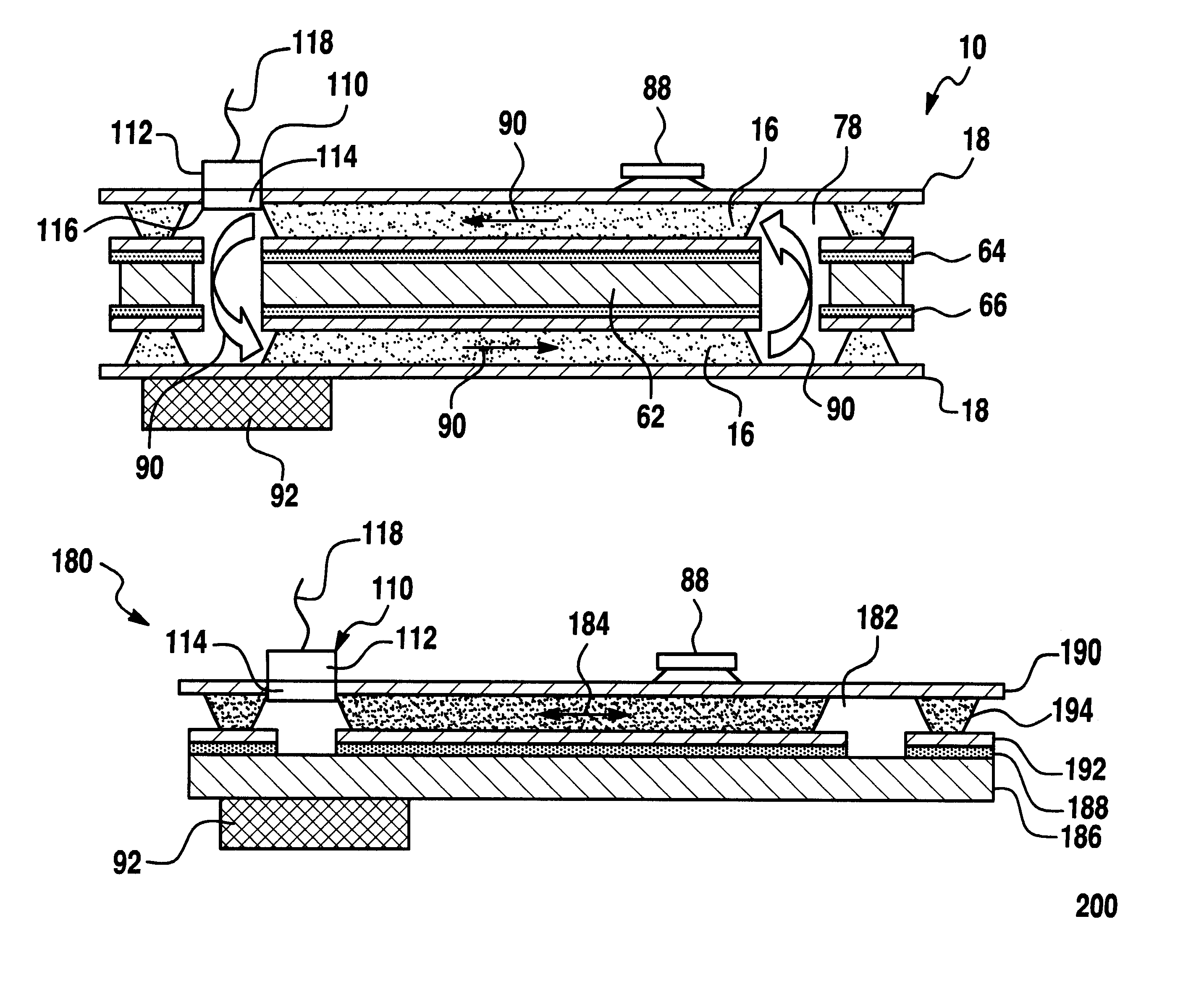
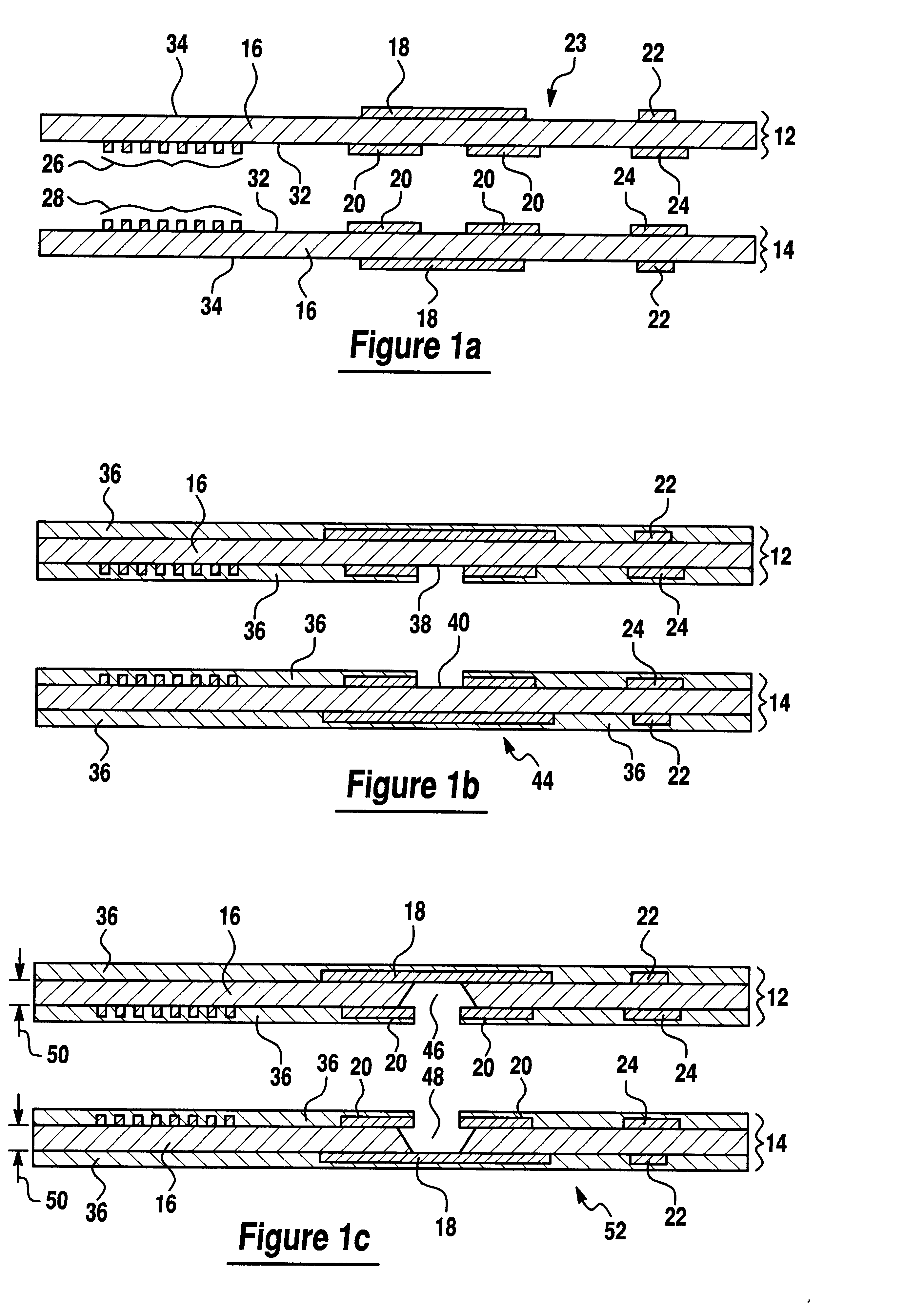
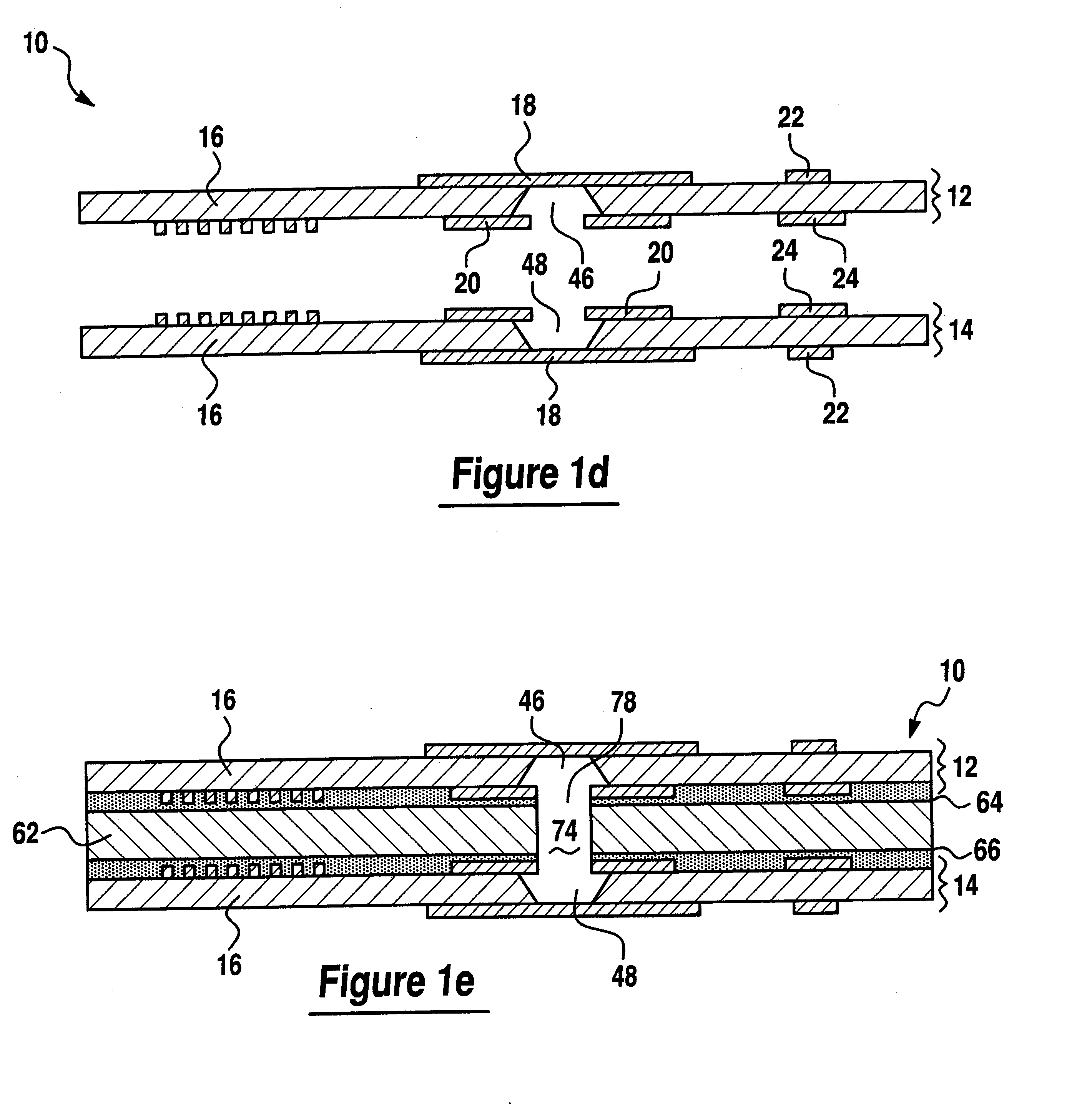
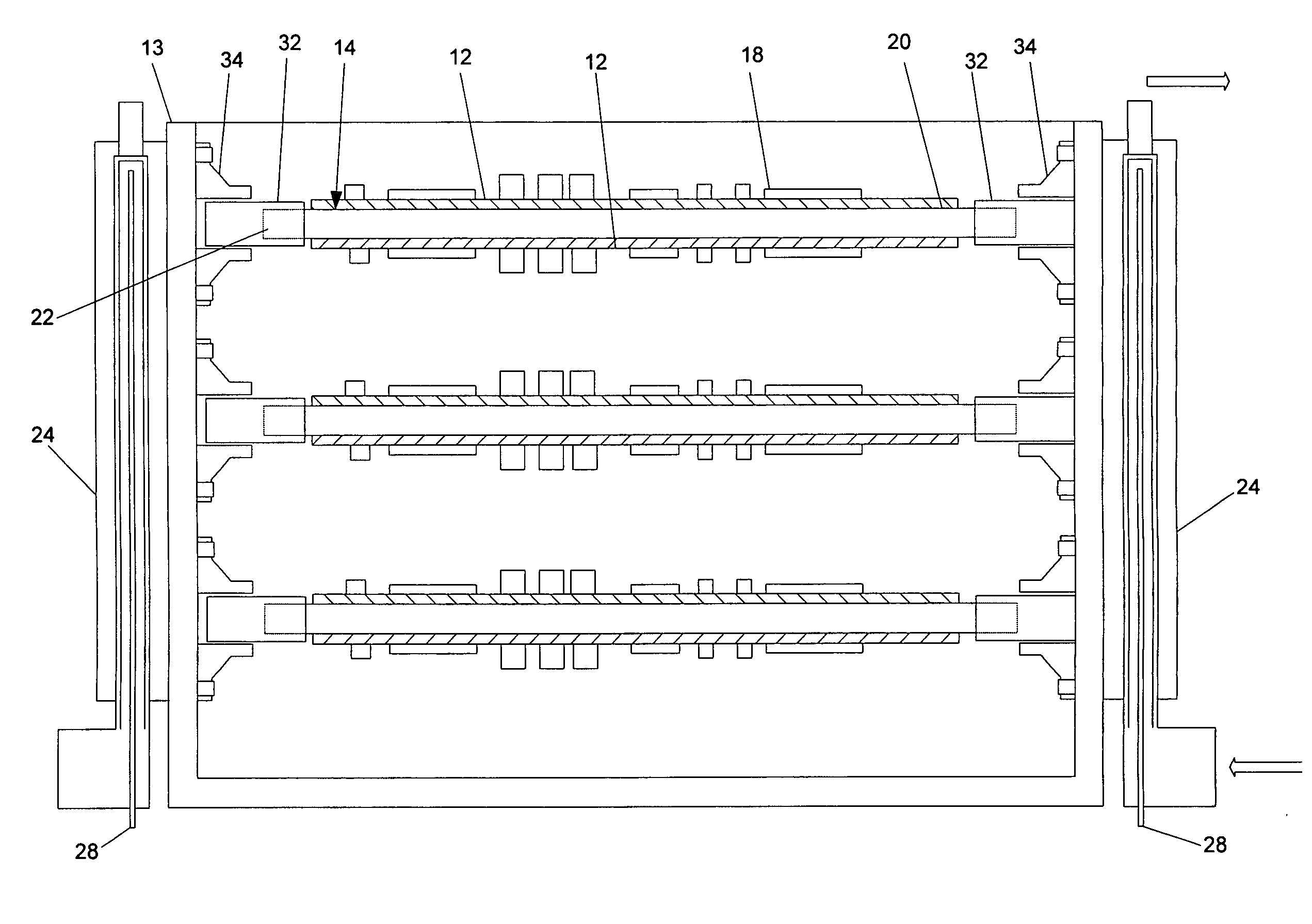
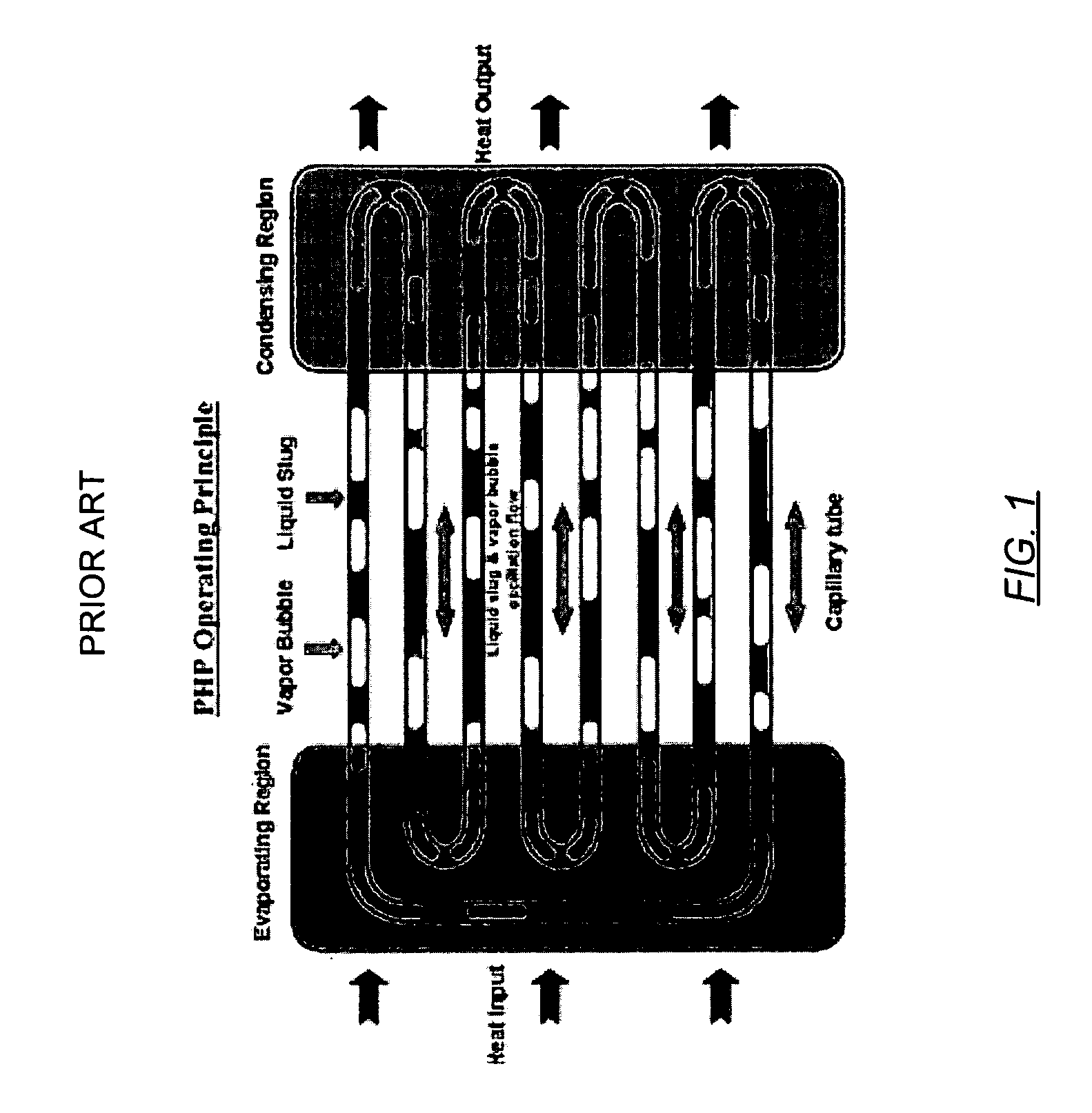
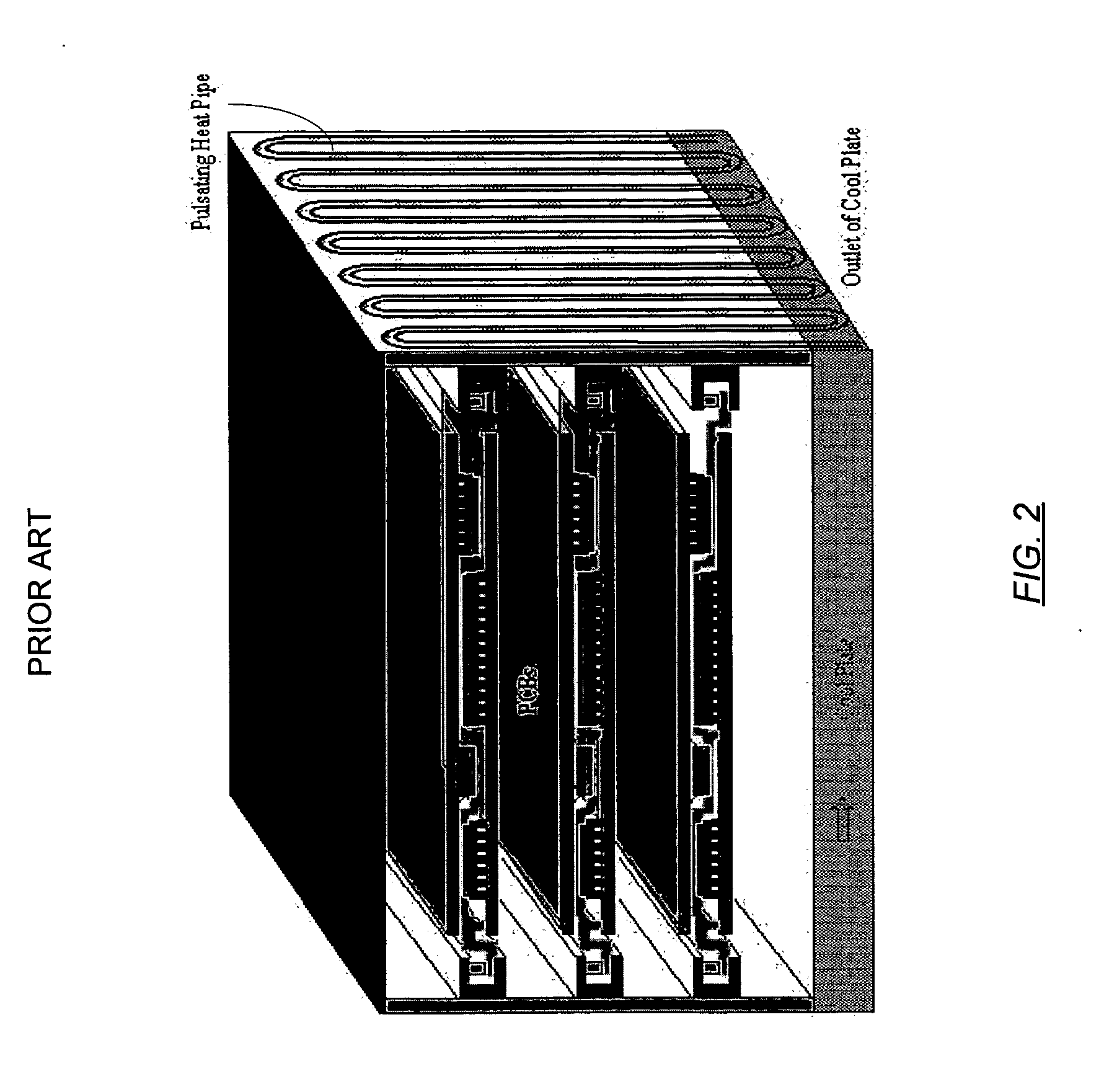
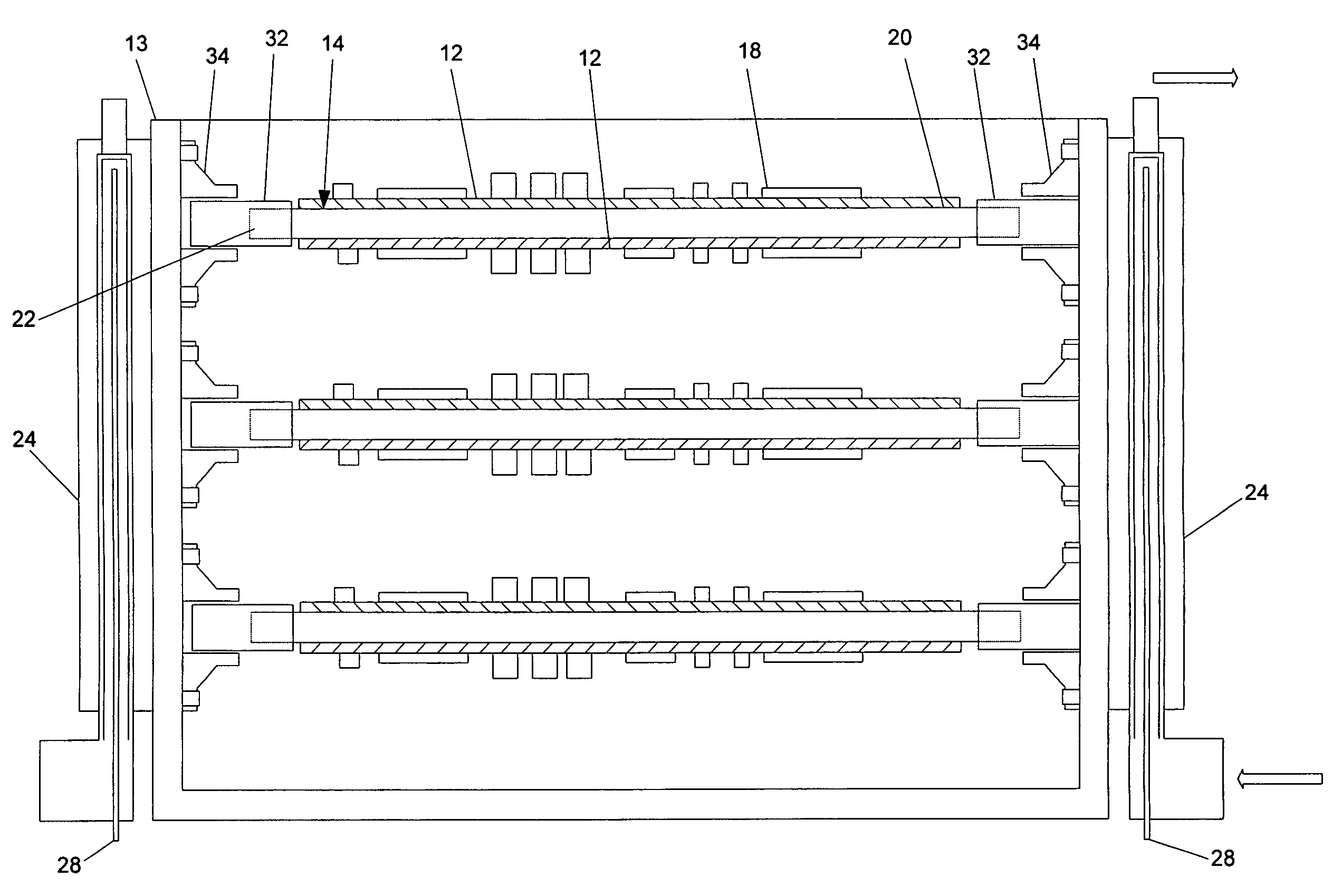
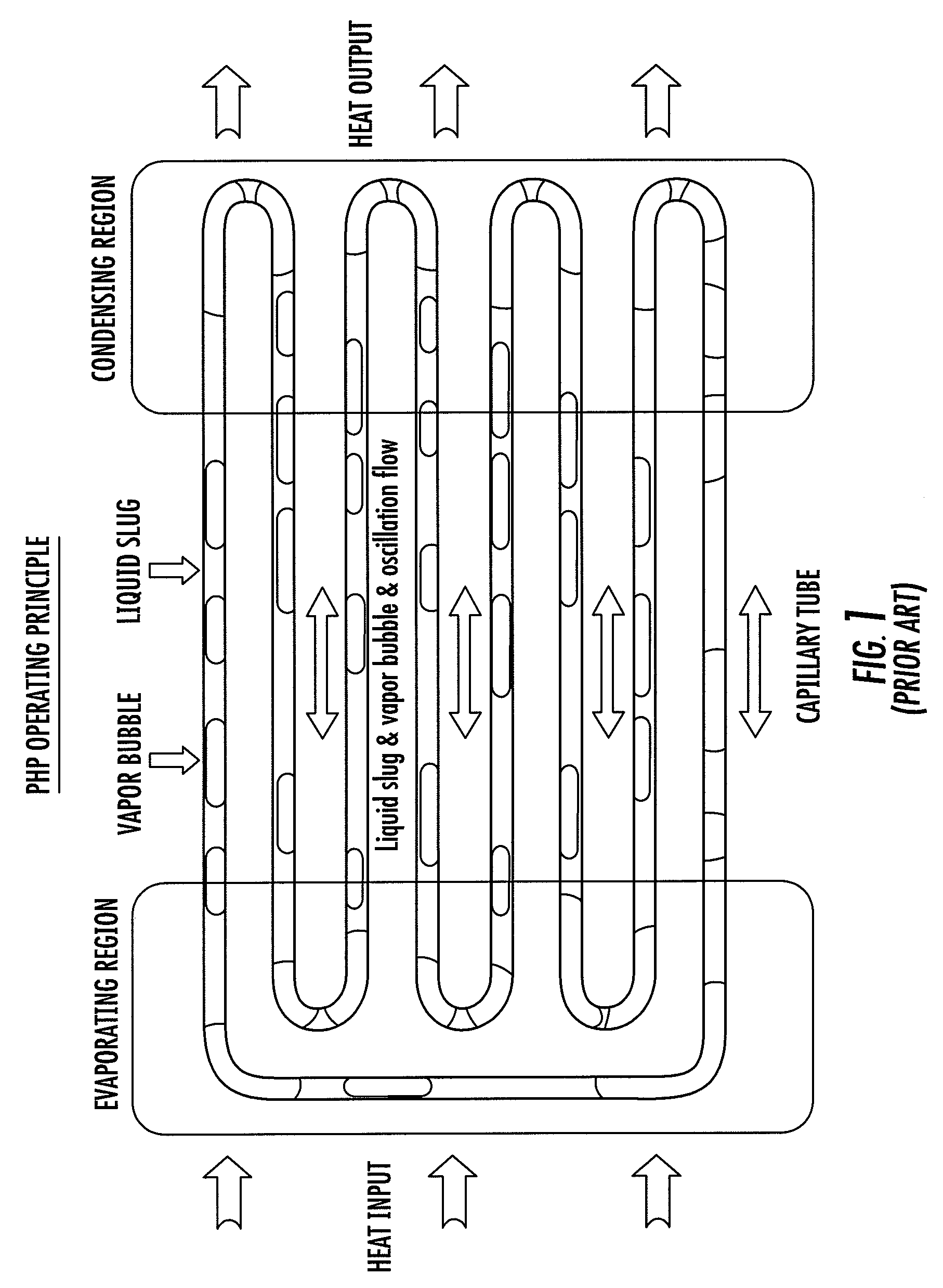
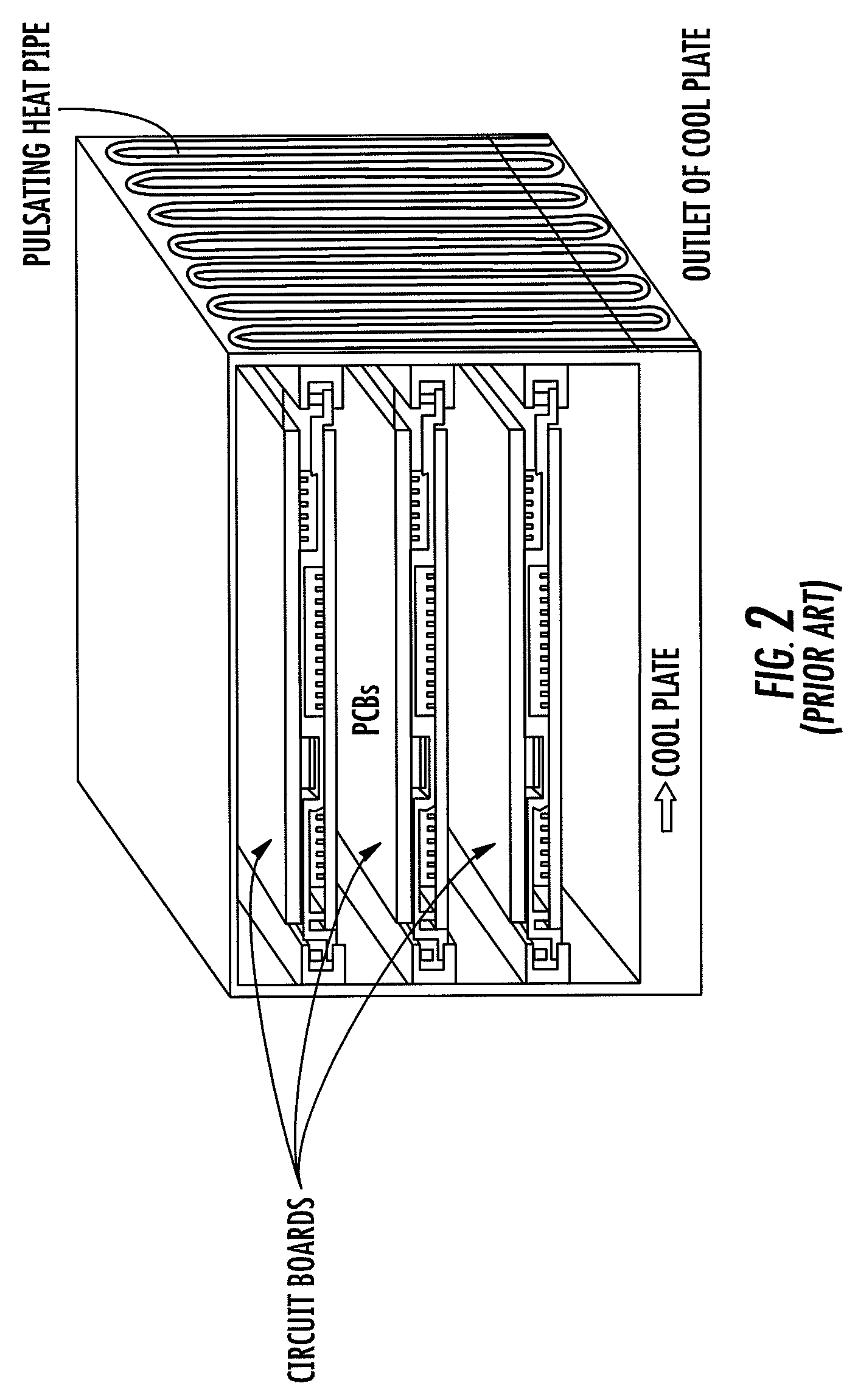
ActiveUS20060146496A1Readily and effectively transfer heat away from printed circuit boardMinimal amount of spaceCircuit fluid transportIndirect heat exchangersEngineeringPrinted circuit board
A cooling apparatus, system, and method are provided. The cooling apparatus includes at least one printed circuit board having opposed major surfaces, and at least one electrical component or other heat source positioned on one major surface of the printed circuit board. The cooling apparatus also includes a pulsating heat pipe having at least a portion that is positioned to either extend along and proximate to one of the major surfaces or be embedded within the printed circuit board. As such, the pulsating heat pipe is capable of transferring heat from the printed circuit board.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Light-emitting diode assembly and method of fabrication
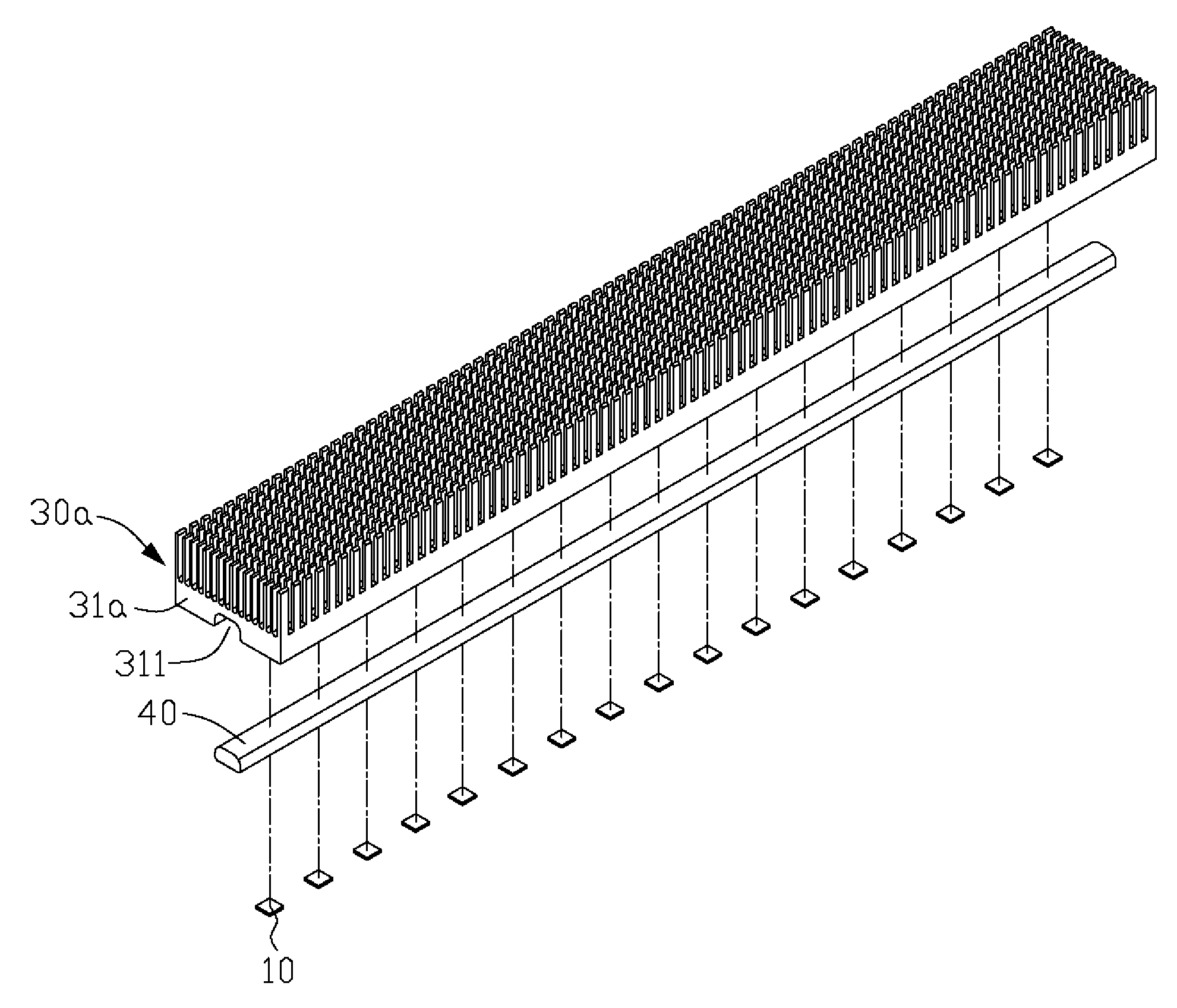
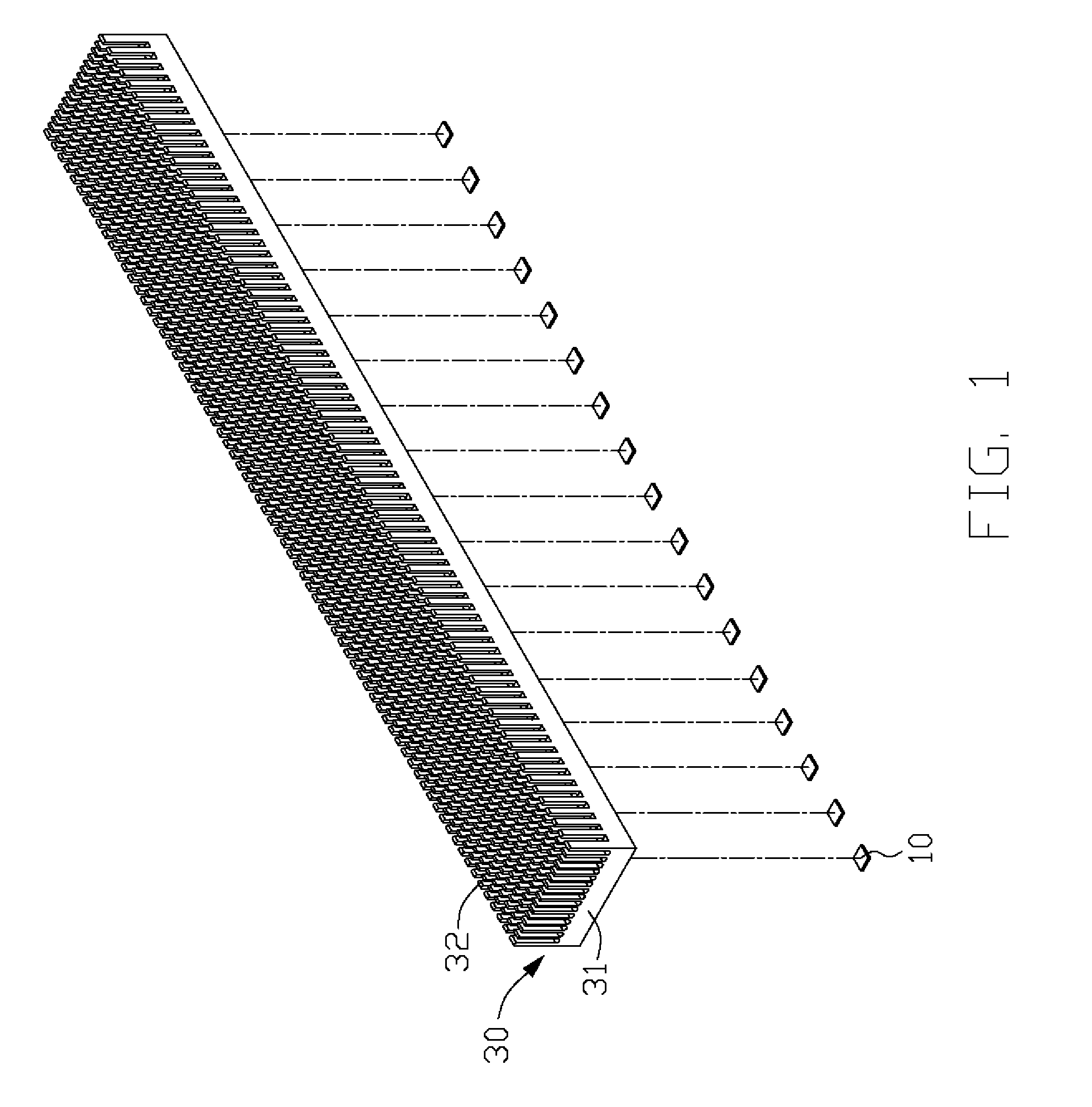
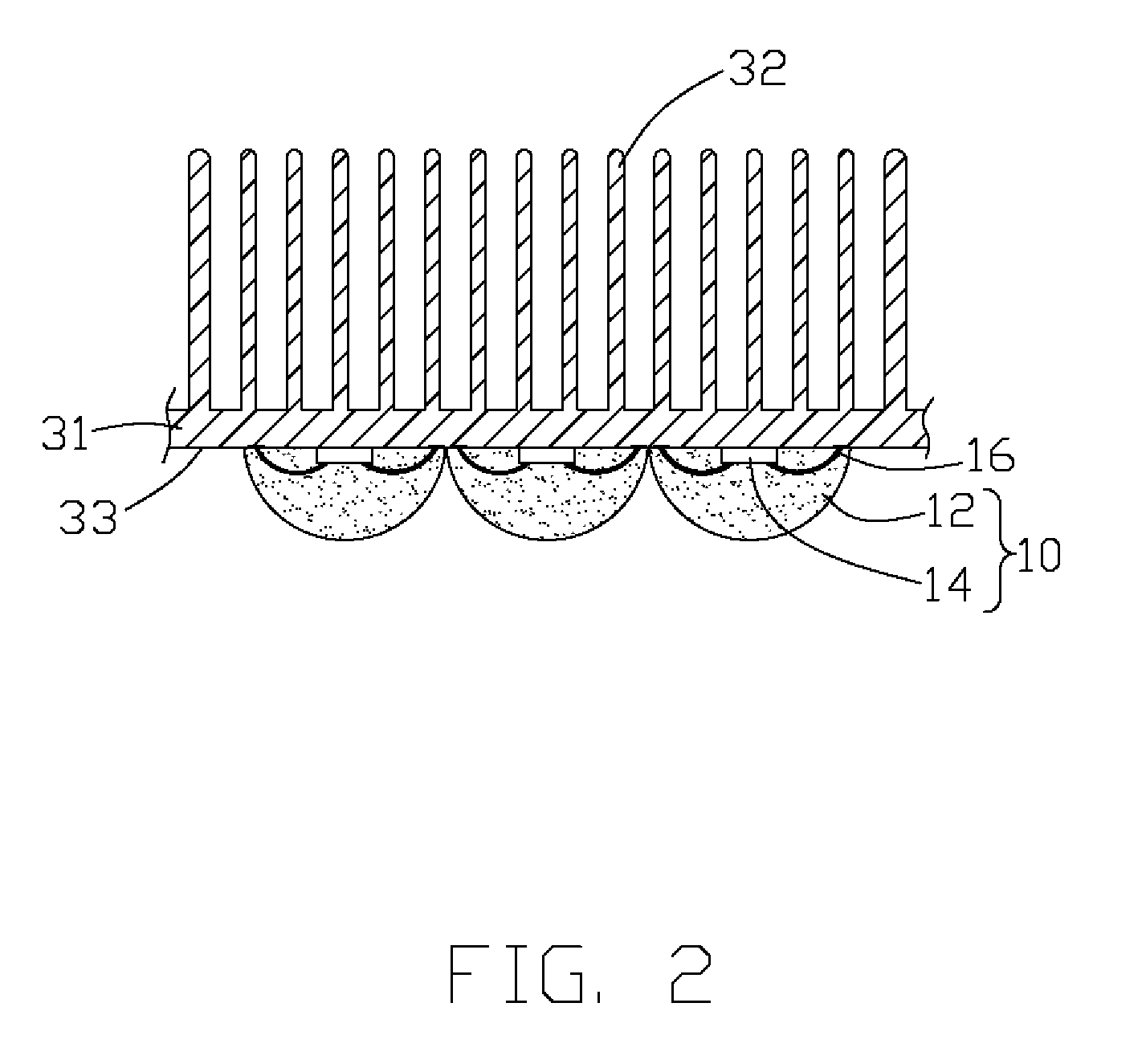
InactiveUS7753568B2Lighting heating/cooling arrangementsCircuit fluid transportElectricityEngineering
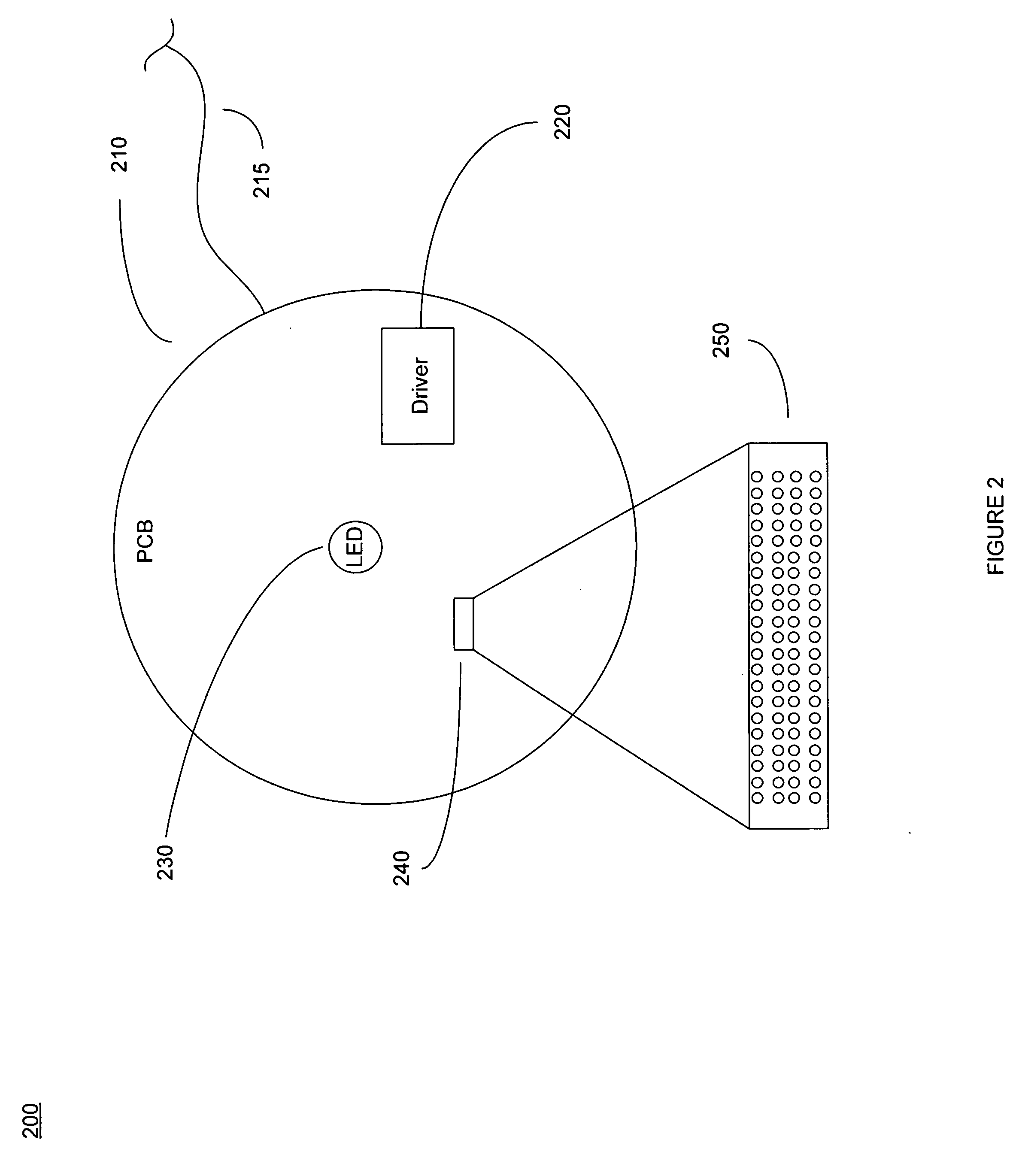
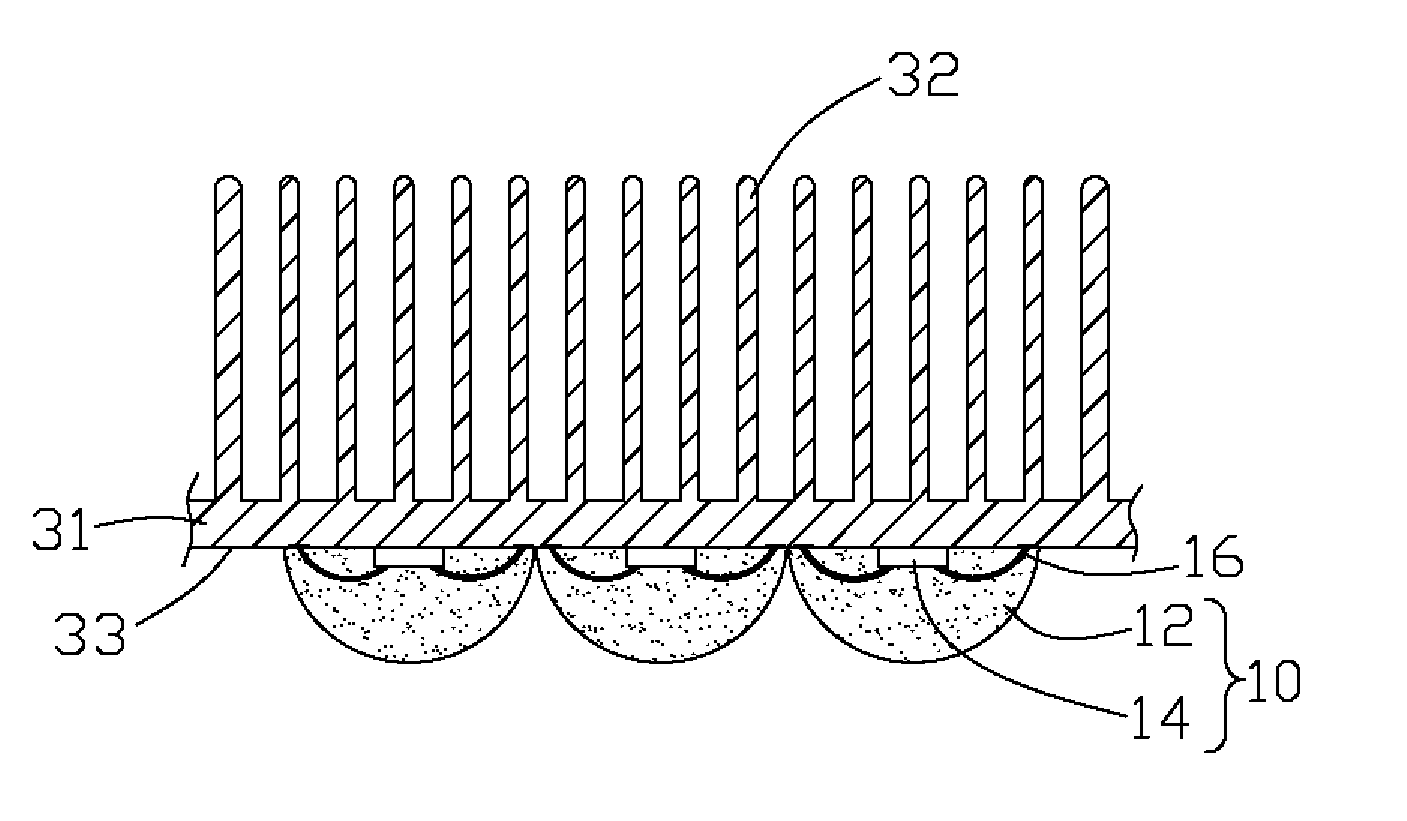
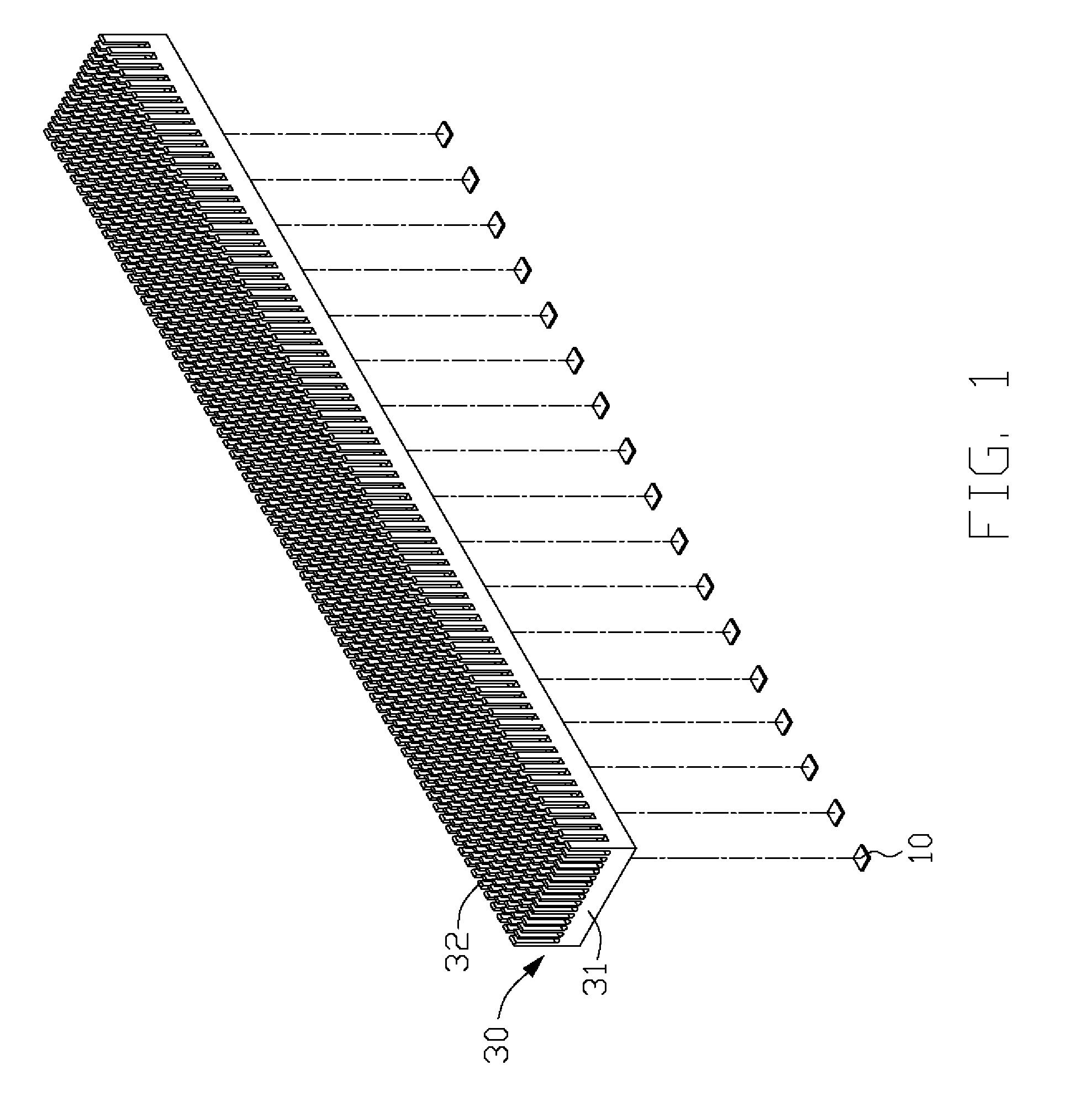
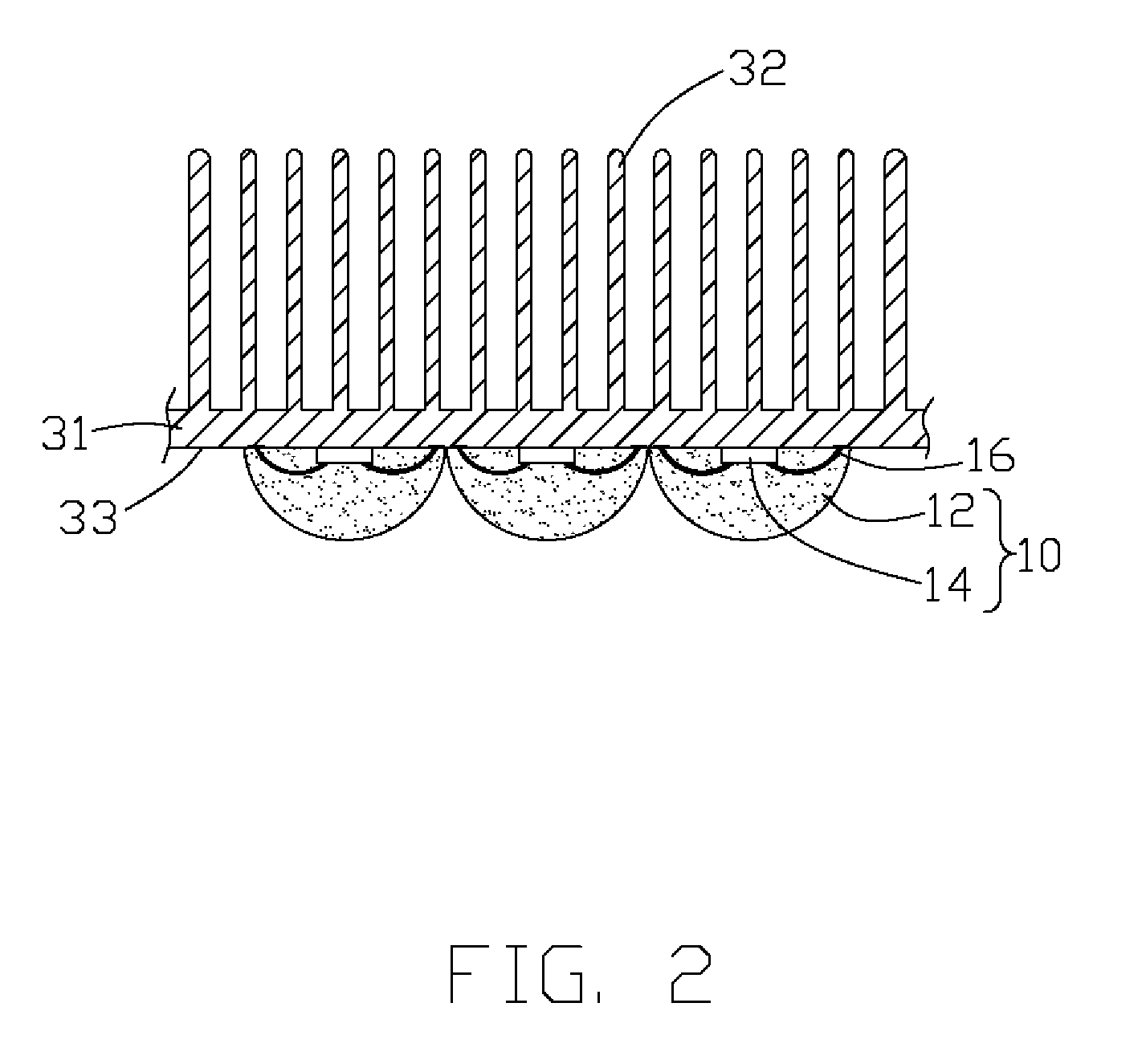
A light-emitting diode (LED) assembly includes a heat dissipation device (30) and at least one LED (10). The heat dissipation device has a connecting surface (33) with circuitry (20) being directly formed thereon. The at least one LED is electrically connected with the circuitry, and is maintained in thermal and mechanical contact with the connecting surface to dissipate heat generated thereby through the heat dissipation device. A method for making the LED assembly includes steps of: (A) providing a heat dissipation device having a surface for the LED to be mounted thereon; (B) insulating the surface; (C) forming circuitry on the insulated surface directly to obtain a connecting surface; (D) attaching the LED to the connecting surface of the heat dissipation device thermally and mechanically, and connecting the LED with the circuitry electrically to form the LED assembly.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Method of manufacture of ceramic composite wiring structures for semiconductor devices
InactiveUS7047637B2Increase volume fractionEasy to removeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricCeramic composite
Method of manufacture of a composite wiring structure for use with at least one semiconductor device, the structure having a first conductive member upon which the semiconductor device can be mounted for electrical connection thereto. A dielectric member, made of ceramic or organo-ceramic composite material, is bonded to the first conductive member and contains embedded therein a conductive network and a thermal distribution network. A second conductive member may be incorporated with the composite wiring structure, with a capacitor electrically connected between the conductive network and the second conductive member. Bonding between the dielectric member and the conductive members may be in the form of a direct covalent bond formed at a temperature insufficient to adversely effect the structural integrity of the conductive network and the thermal distribution network.
Owner:L PIERRE DEROCHEMONT C2 TECH
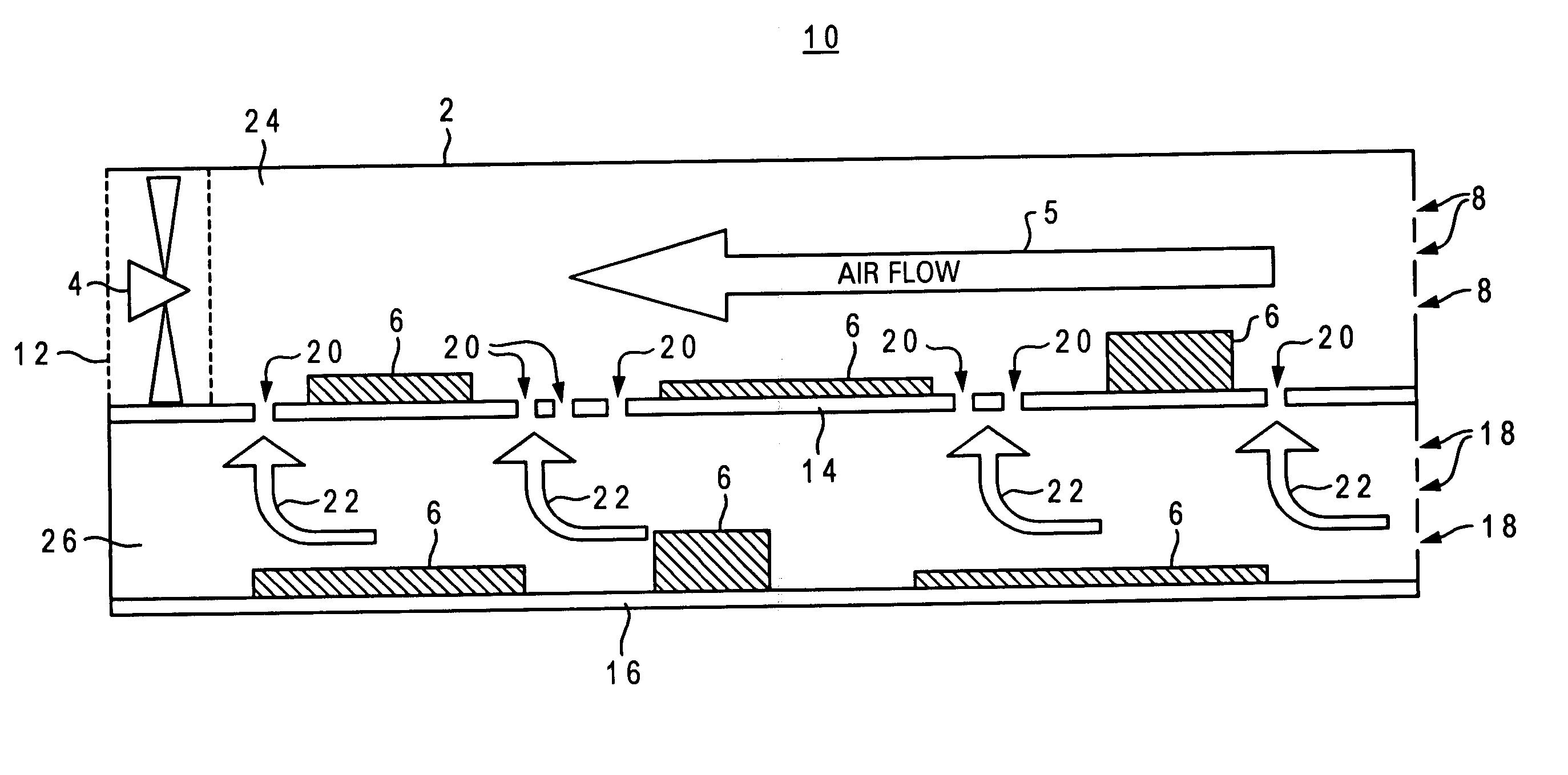
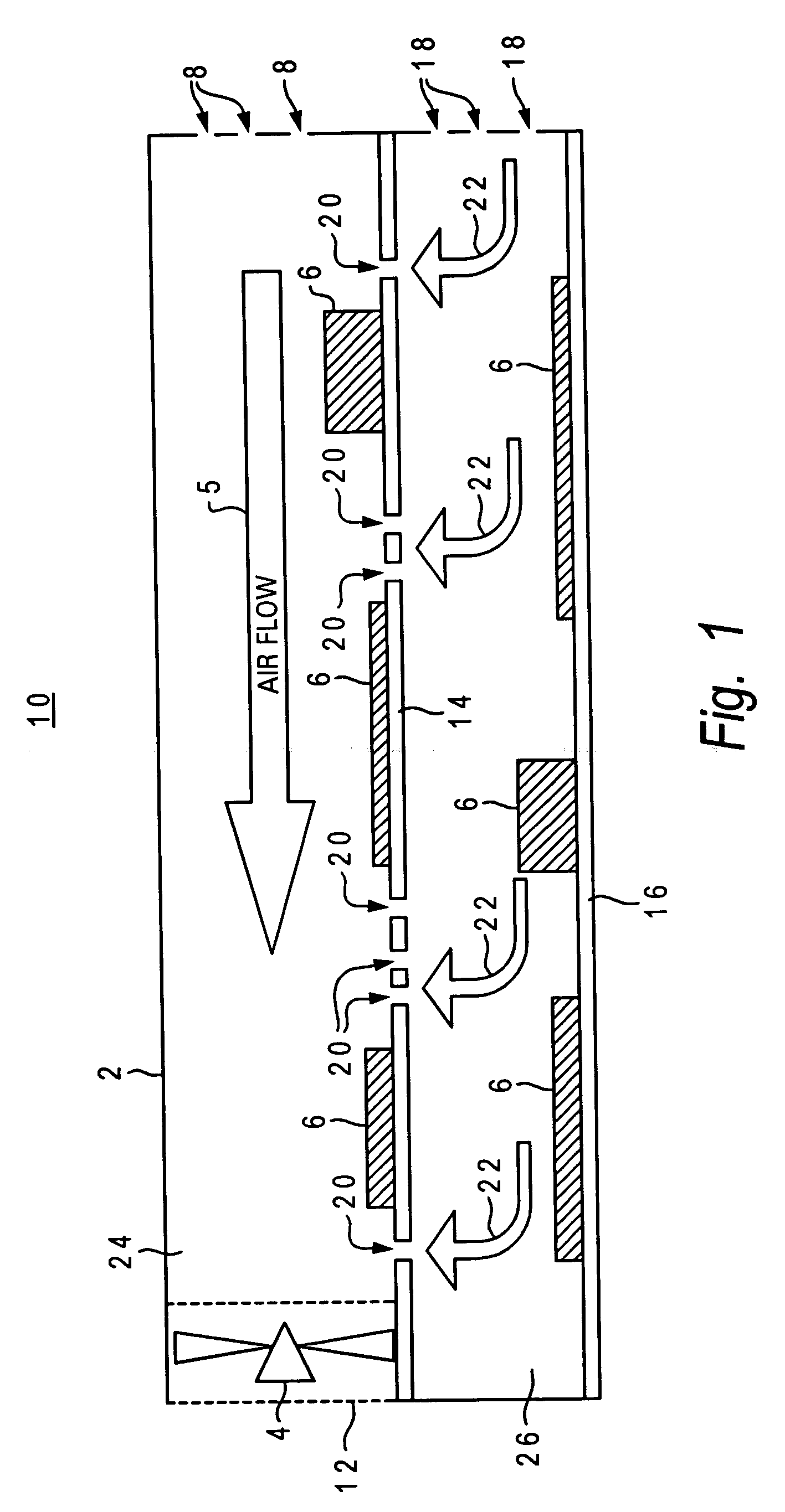
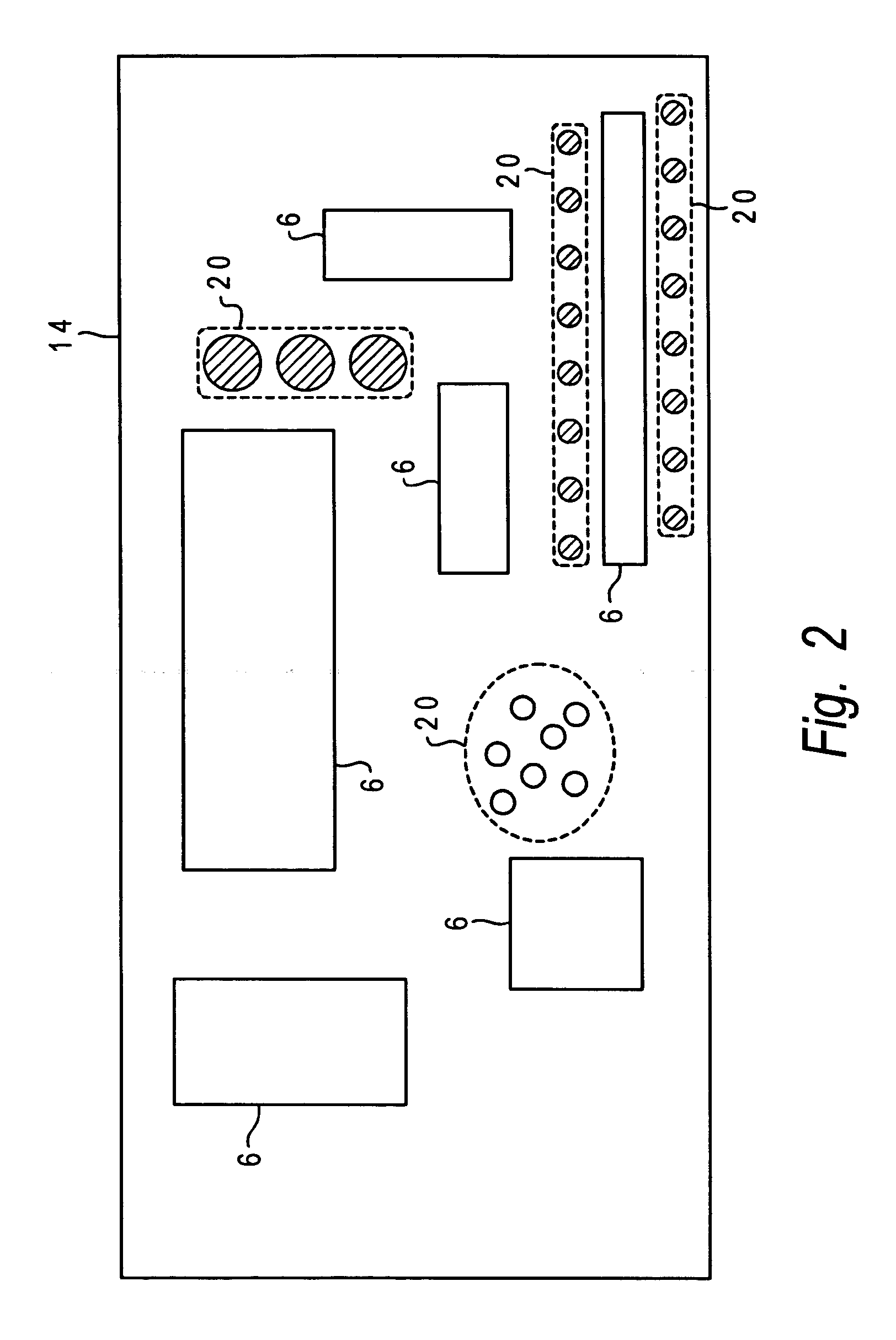
Cooling apparatus for vertically stacked printed circuit boards
An apparatus, system and method for cooling vertically stacked printed circuit boards (PCBs). In one embodiment, a first PCB is disposed within a substantially enclosed lower chamber inside a PCB containment housing. A second PCB is disposed above the first PCB within the housing to define a substantially enclosed upper chamber above the lower chamber. The second PCB includes one or more airflow apertures defined therethrough and providing vertical air flow coupling between the upper and lower chambers. An airflow actuating device is utilized to generate a primary forced airflow within the upper chamber which is substantially parallel to the surface plane of the second PCB. The primary forced airflow further induces a negative air pressure in the upper chamber such that a mixed convection airflow is established between the upper and lower chambers via the second PCB apertures.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Thermally and Electrically Conductive Apparatus
ActiveUS20080239675A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsLighting heating/cooling arrangementsElectric forceCoating system
The present invention provides a thermally and electrically conductive apparatus that can provide both thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity for one or more electronic devices connected thereto. The apparatus comprises a thermally conductive element that is in thermal contact with one or more electronic devices and optionally in contact with a heat dissipation system. A portion of the thermally conductive element is surrounded by a multilayer coating system comprising two or more layers. The multilayer coating system includes alternating electrically insulating and electrically conductive layers in order to provide paths for the supply of electric current to the one or more electronic devices. A conductive layer of the multilayer coating system may be selectively patterned to connect to one or more electronic devices. In this manner, the combination of an electronic circuit carrier and a thermally conductive element can unify thermal conductivity with the provision of power and / or communication into a single integrated unit for use with electronic devices.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Dual sided board thermal management system
ActiveUS7477513B1Efficiently thermally managingDomestic cooling apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermal management systemElectronic component
A dual sided board thermal management system for efficiently thermally managing a printed circuit board having electronic components on opposing sides thereof. The dual sided board thermal management system generally includes a housing surrounding a portion of a printed circuit board, and a plurality of coolant dispensing units within the housing directed towards opposite sides of the printed circuit board to thermally manage electronic components on opposite sides of the printed circuit board.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
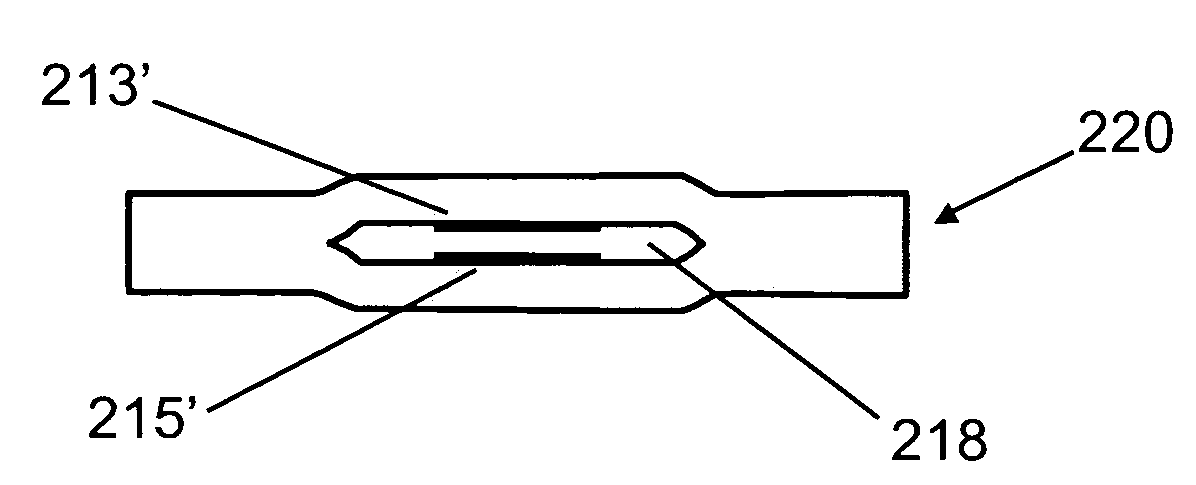
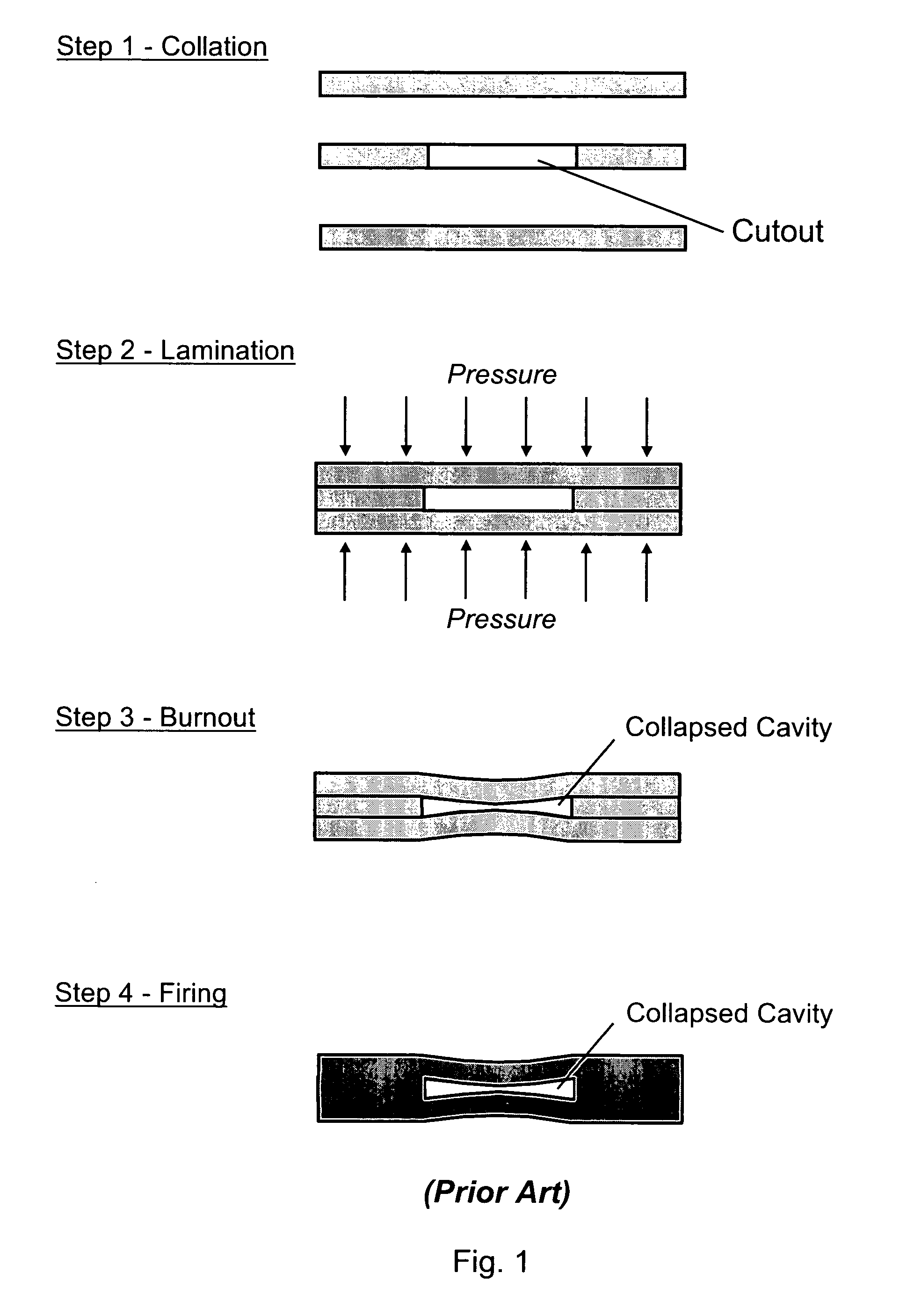
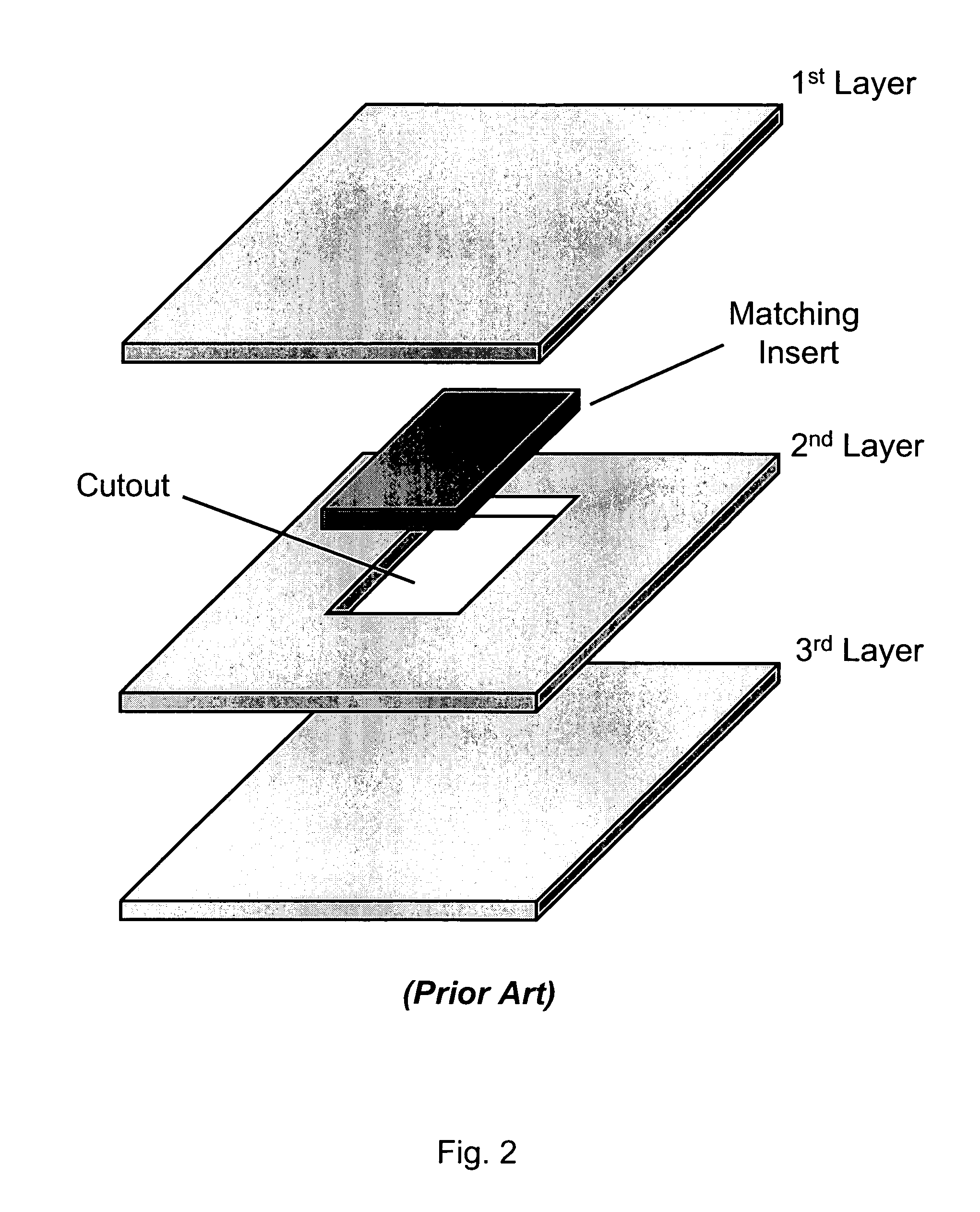
Method of using sacrificial materials for fabricating internal cavities in laminated dielectric structures
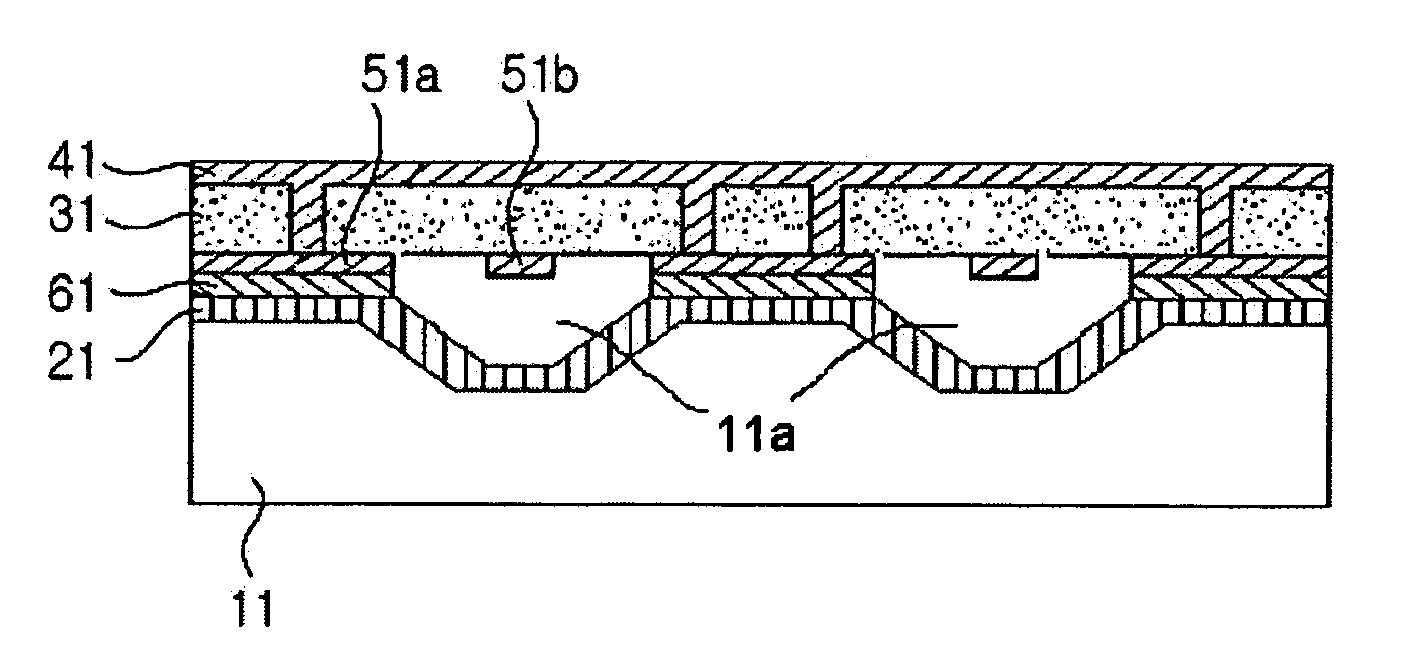
A method of using sacrificial materials for fabricating internal cavities and channels in laminated dielectric structures, which can be used as dielectric substrates and package mounts for microelectronic and microfluidic devices. A sacrificial mandrel is placed in-between two or more sheets of a deformable dielectric material (e.g., unfired LTCC glass / ceramic dielectric), wherein the sacrificial mandrel is not inserted into a cutout made in any of the sheets. The stack of sheets is laminated together, which deforms the sheet or sheets around the sacrificial mandrel. After lamination, the mandrel is removed, (e.g., during LTCC burnout), thereby creating a hollow internal cavity in the monolithic ceramic structure.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
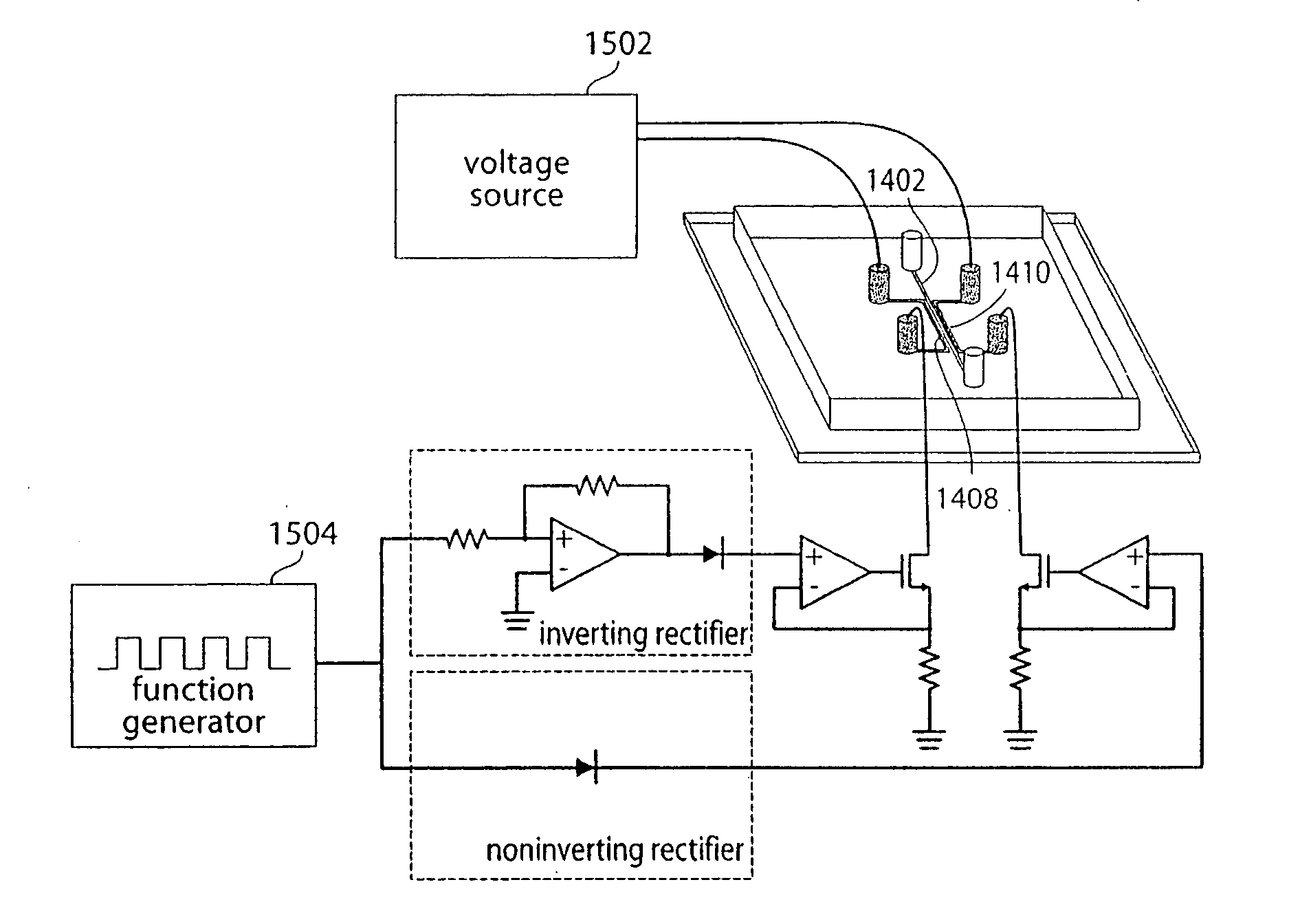
Fabrication of conductive pathways, microcircuits and microstructures in microfluidic networks
ActiveUS20110045577A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsThermal energyElectricity
Disclosed herein are a variety of microfluidic devices and solid, typically electrically conductive devices that can be formed using such devices as molds. In certain embodiments, the devices that are formed comprise conductive pathways formed by solidifying a liquid metal present in one or more microfluidic channels (such devices hereinafter referred to as “microsolidic” devices). In certain such devices, in which electrical connections can be formed and / or reformed between regions in a microfluidic structure; in some cases, the devices / circuits formed may be flexible and / or involve flexible electrical components. In certain embodiments, the solid metal wires / conductive pathways formed in microfluidic channel(s) may remain contained within the microfluidic structure. In certain such embodiments, the conductive pathways formed may be located in proximity to other microfluidic channel(s) of the structure that carry flowing fluid, such that the conductive pathway can create energy (e.g. electromagnetic and / or thermal energy) that interacts withy and / or affects the flowing fluid and / or a component contained therein or carried thereby. In other embodiments, a microsolidic structure may be removed from a microfluidic mold to form a stand-alone structure. In certain embodiments, the solid metal structures formed may interact with light energy incident upon a structure or may be used to fabricate a light-weight electrode. Another aspect of the invention relates to the formation of self-assembled structures that may comprise these electrically conductive pathways / connections.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
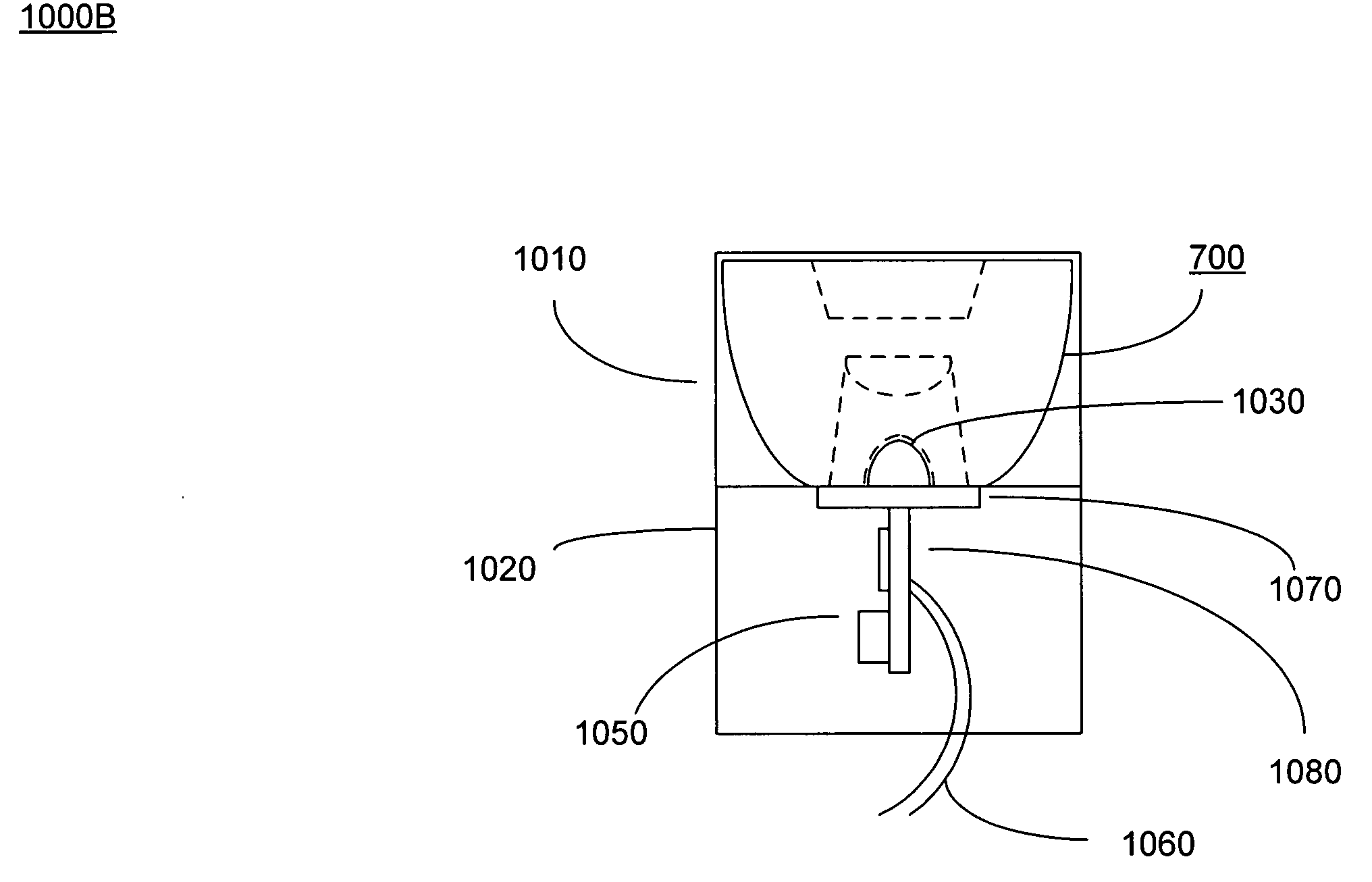
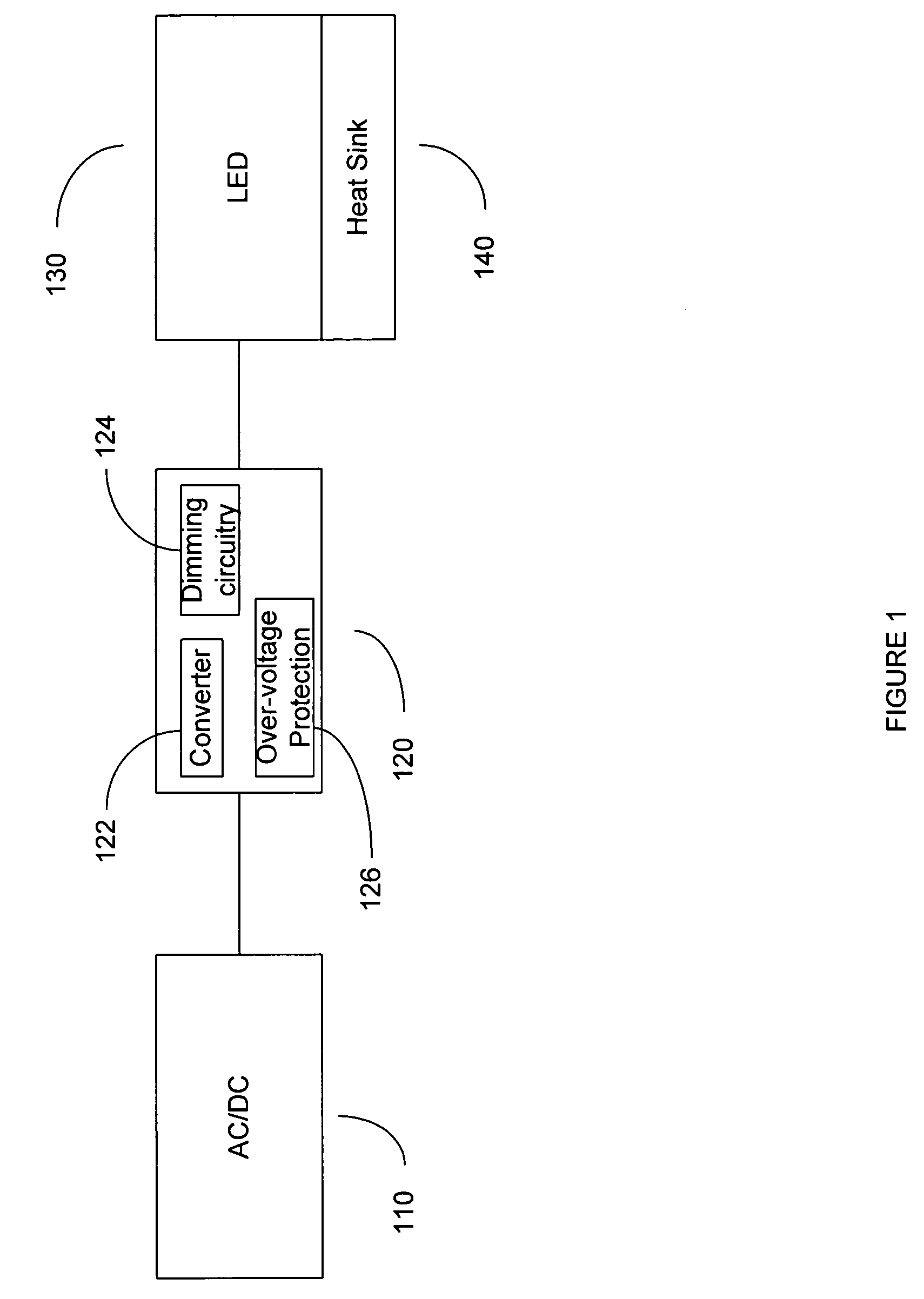
Light device having LED illumination and electronic circuit board in an enclosure
InactiveUS20080123340A1Avoid potential damageIncrease flexibilityPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesDriver circuitEngineering
A light device having a light source, lenses adjacent to the light source, a housing for securing the light source and the lenses, and a light fixture for securing the housing. The light source includes high efficiency light emitting diodes (LEDs), driver circuitry, and a heat sink mounted and integrated on a common board. The driver circuitry receives multiple input voltages, supplies an appropriate power signal, provides over-voltage protection and controls dimming for the LEDs. Lenses magnify and focus light emitting from the LEDs at a diffusion angle between 10° and 100°. The housing comprises a first and a second portion fittable together (e.g., threads, screws and openings). LEDs are operable between 250 mA to 1 A at 3.2 volts and produce at least 55 lumens per LED. The light fixture may be rotateable to adjust the direction of the light from the LED. The light fixture may be puck-shape.
Owner:LED GREEN POWER
Light-emitting diode assembly and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20080175008A1Wave amplification devicesLighting heating/cooling arrangementsEngineeringLight-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) assembly includes a heat dissipation device (30) and at least one LED (10). The heat dissipation device has a connecting surface (33) with circuitry (20) being directly formed thereon. The at least one LED is electrically connected with the circuitry, and is maintained in thermal and mechanical contact with the connecting surface to dissipate heat generated thereby through the heat dissipation device. A method for making the LED assembly includes steps of: (A) providing a heat dissipation device having a surface for the LED to be mounted thereon; (B) insulating the surface; (C) forming circuitry on the insulated surface directly to obtain a connecting surface; (D) attaching the LED to the connecting surface of the heat dissipation device thermally and mechanically, and connecting the LED with the circuitry electrically to form the LED assembly.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Cooling apparatus, system, and associated method
ActiveUS7345877B2Readily and effectively transfer heat away from printed circuit boardMinimal amount of spaceCircuit fluid transportIndirect heat exchangersEngineeringPrinted circuit board
A cooling apparatus, system, and method are provided. The cooling apparatus includes at least one printed circuit board having opposed major surfaces, and at least one electrical component or other heat source positioned on one major surface of the printed circuit board. The cooling apparatus also includes a pulsating heat pipe having at least a portion that is positioned to either extend along and proximate to one of the major surfaces or be embedded within the printed circuit board. As such, the pulsating heat pipe is capable of transferring heat from the printed circuit board.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
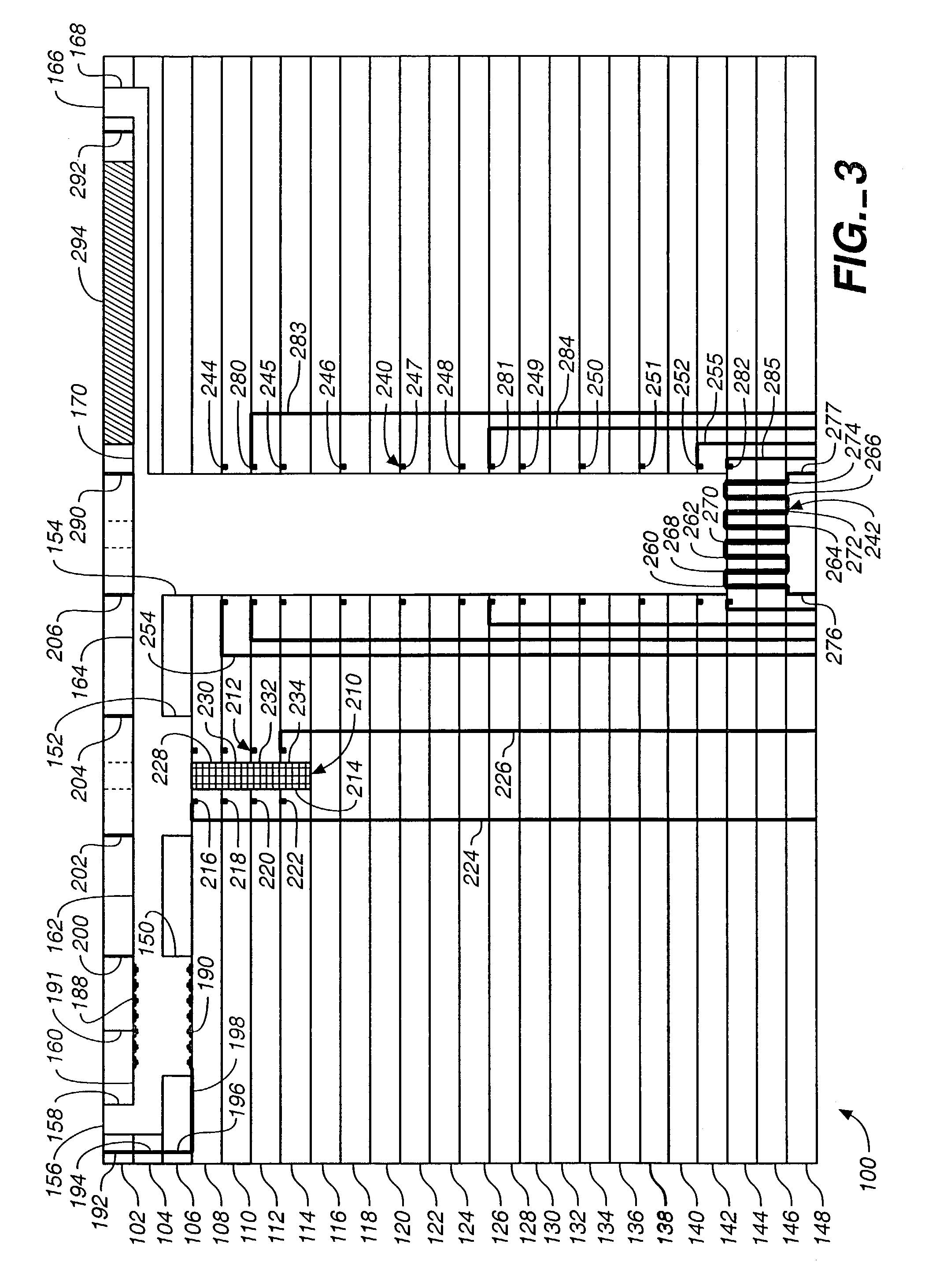
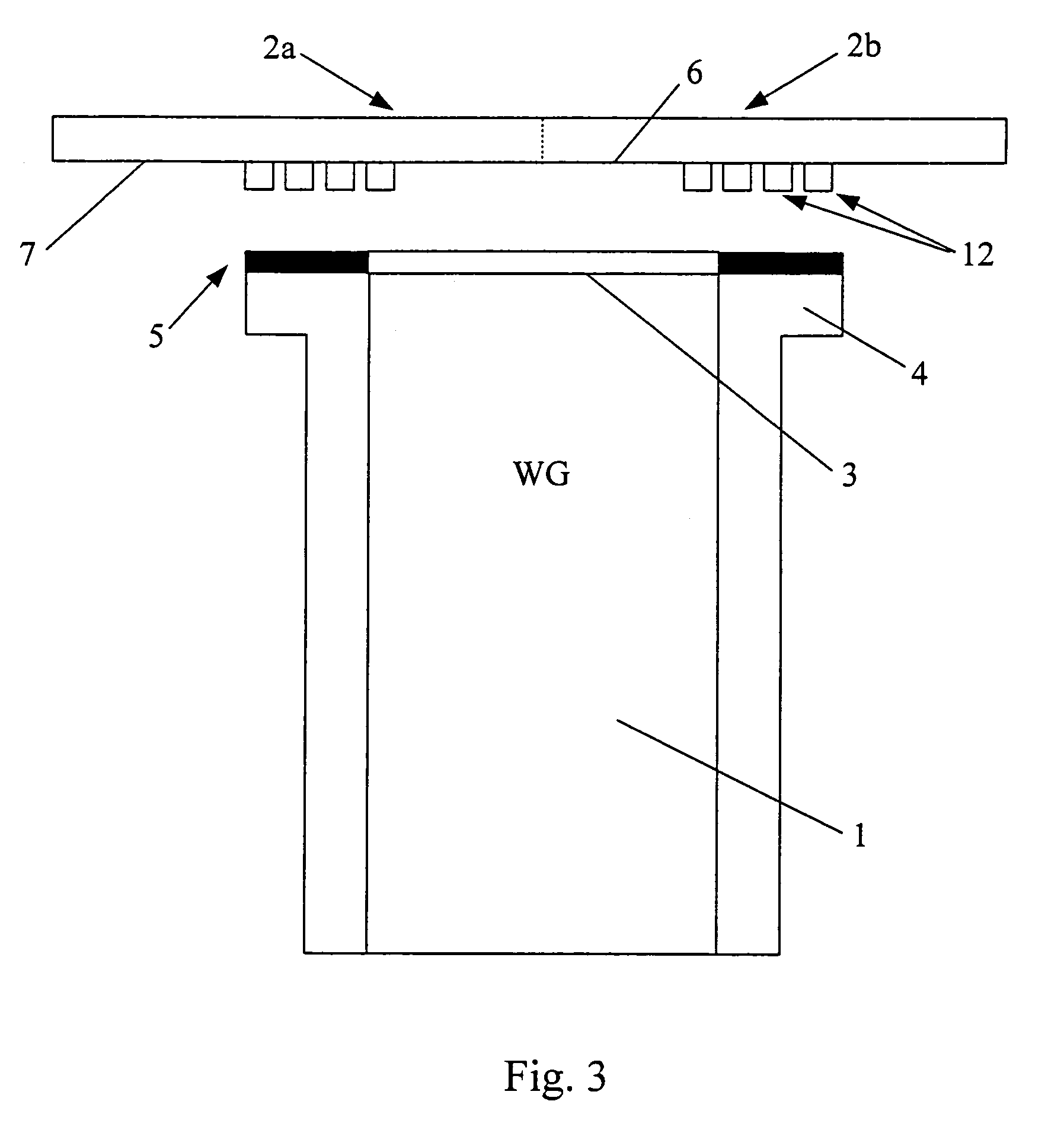
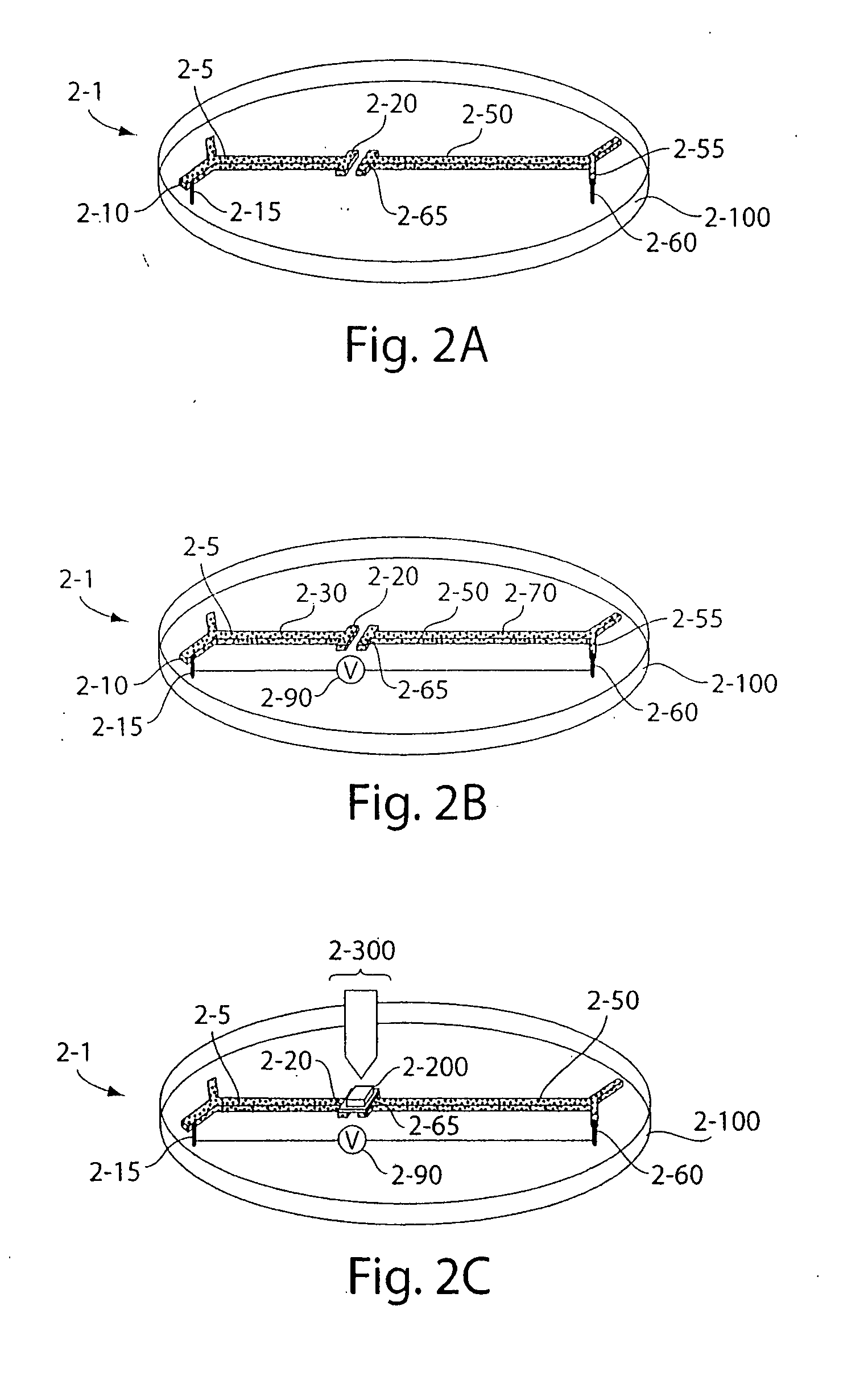
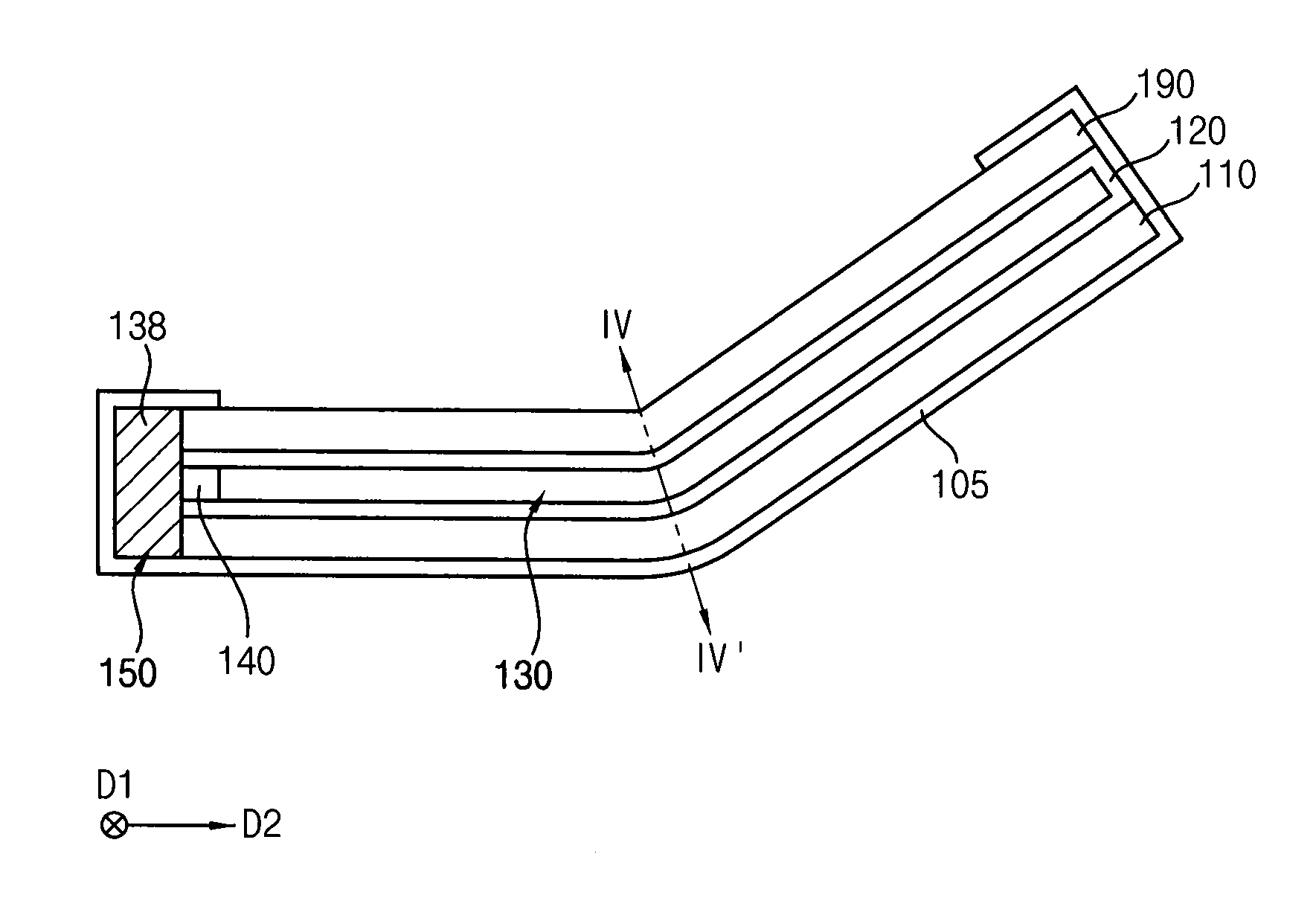
Grooved coaxial-type transmission line, manufacturing method and packaging method thereof
InactiveUS7400222B2Avoid signal lossReduced dimensionPrinted circuit aspectsSolid-state devicesEpoxyTransfer procedure
Disclosed herein are a transmission line of coaxial type and a manufacturing method thereof, capable of preventing a radiative signal loss of signal lines during transmission of an RF signal and removing signal interference between adjacent signal lines, thus allowing signal lines to be compactly arrayed during a manufacture of IC, and reducing a dimension of the IC. The transmission line of coaxial type includes grooves provided on a semiconductor substrate, a first ground layer, an electrically conductive epoxy coated on a flat part of the first ground layer except the grooves, second ground layers provided on the electrically conductive epoxy, a dielectric film provided at a position above the grooves and the second ground layers, a third ground layer provided on an upper surface of the dielectric film, and signal lines placed in spaces defined by the grooves and a lower surface of the dielectric film. In this case, the electrically conductive epoxy is coated on only contact surfaces of the first and second ground layers, and the signal lines are attached to the lower surface of the dielectric film.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
LED cooling system
InactiveUS20100046231A1High strengthEasy to operatePoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsElectricityEngineering
The invention relates to a LED cooling system that effects cooling of the LED's during use, and helps the LED's have a longer operating function, and uses less electricity for the LED's to operate. The use of cooling also provides a steadier light and has greater efficiency.
Owner:HAWKEYE DISTRIBUTING
Modular board device, high frequency module, and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080178463A1Solve the real problemLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMoisture resistanceEngineering
The present invention is directed to a high frequency module used for wireless communication module, and comprises a first organic substrate (11) in which conductive pattern or patterns are formed on the principal surface thereof and one element body (7) or more are mounted, and a second organic substrate (12) in which a recessed portion (22) is formed in correspondence with the area where the element body or bodies (7) are mounted at the connecting surface to the first organic substrate (11). In the state where the second organic substrate (12) is connected to the first organic substrate (11), an element body accommodating portion (24) which seals the element body or bodies (7) is constituted by the recessed portion (22), wherein the element body accommodating portion (24) is adapted so that moisture resistance characteristic and oxidation resistance characteristic are maintained.
Owner:SONY CORP
Cooling apparatus for vertically stacked printed circuit boards
An apparatus, system and method for cooling vertically stacked printed circuit boards (PCBs). In one embodiment, a first PCB is disposed within a substantially enclosed lower chamber inside a PCB containment housing. A second PCB is disposed above the first PCB within the housing to define a substantially enclosed upper chamber above the lower chamber. The second PCB includes one or more airflow apertures defined therethrough and providing vertical air flow coupling between the upper and lower chambers. An airflow actuating device is utilized to generate a primary forced airflow within the upper chamber which is substantially parallel to the surface plane of the second PCB. The primary forced airflow further induces a negative air pressure in the upper chamber such that a mixed convection airflow is established between the upper and lower chambers via the second PCB apertures.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
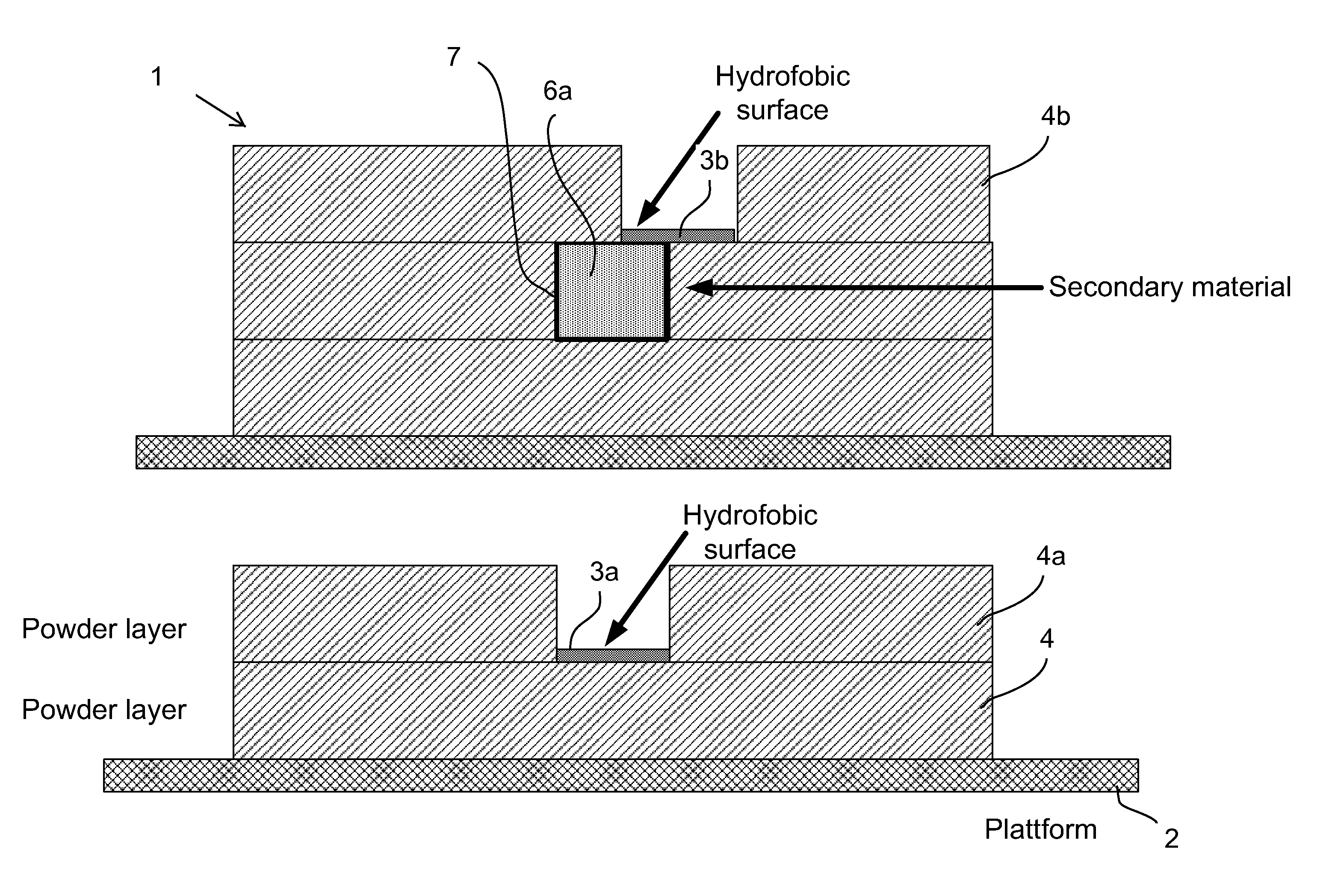
Layered manufacturing of free-form multi-material micro-components
ActiveUS20150306664A1Efficient productionAdditive manufacturing apparatusCircuit optical detailsMulti materialElectricity
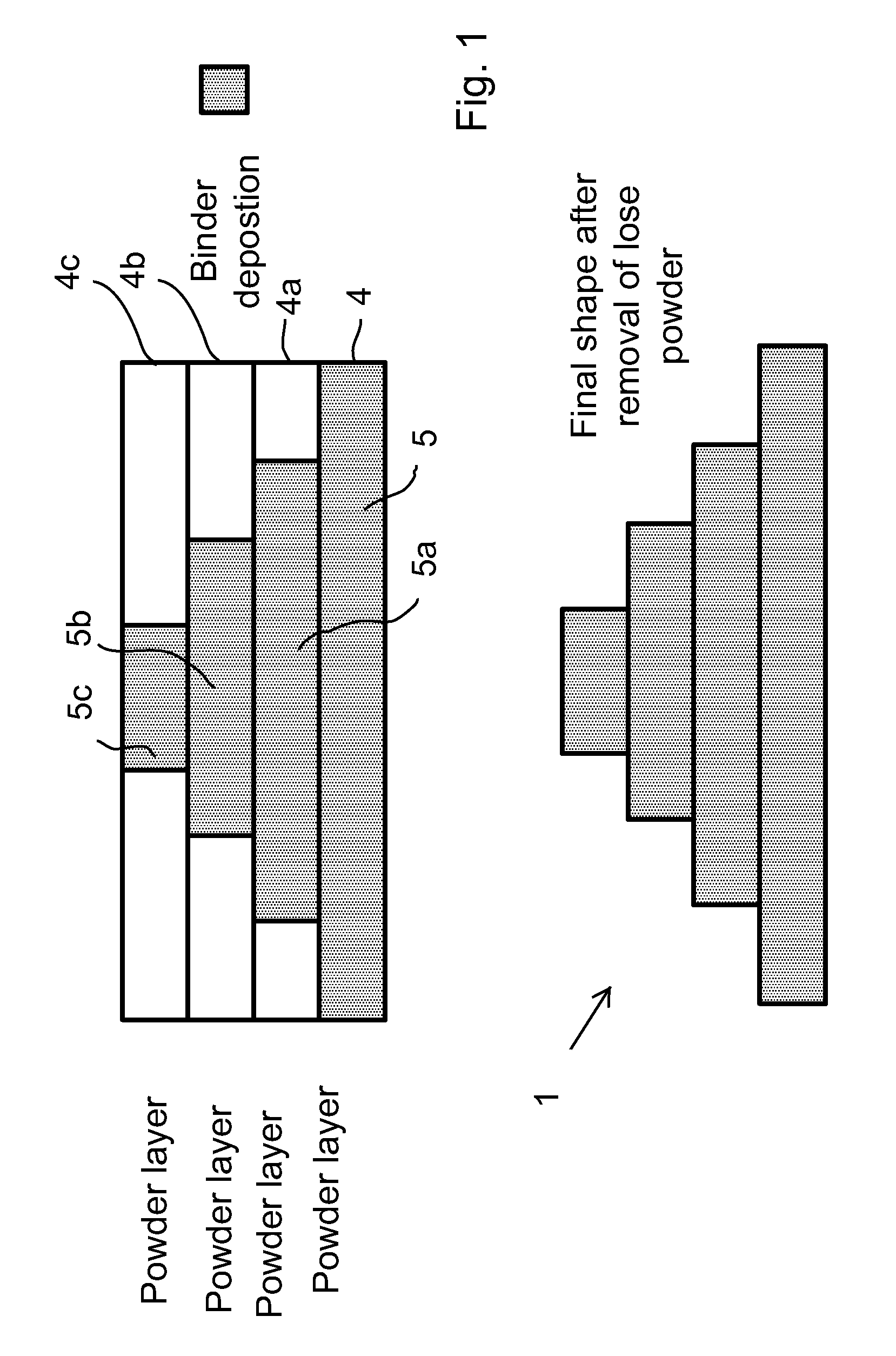
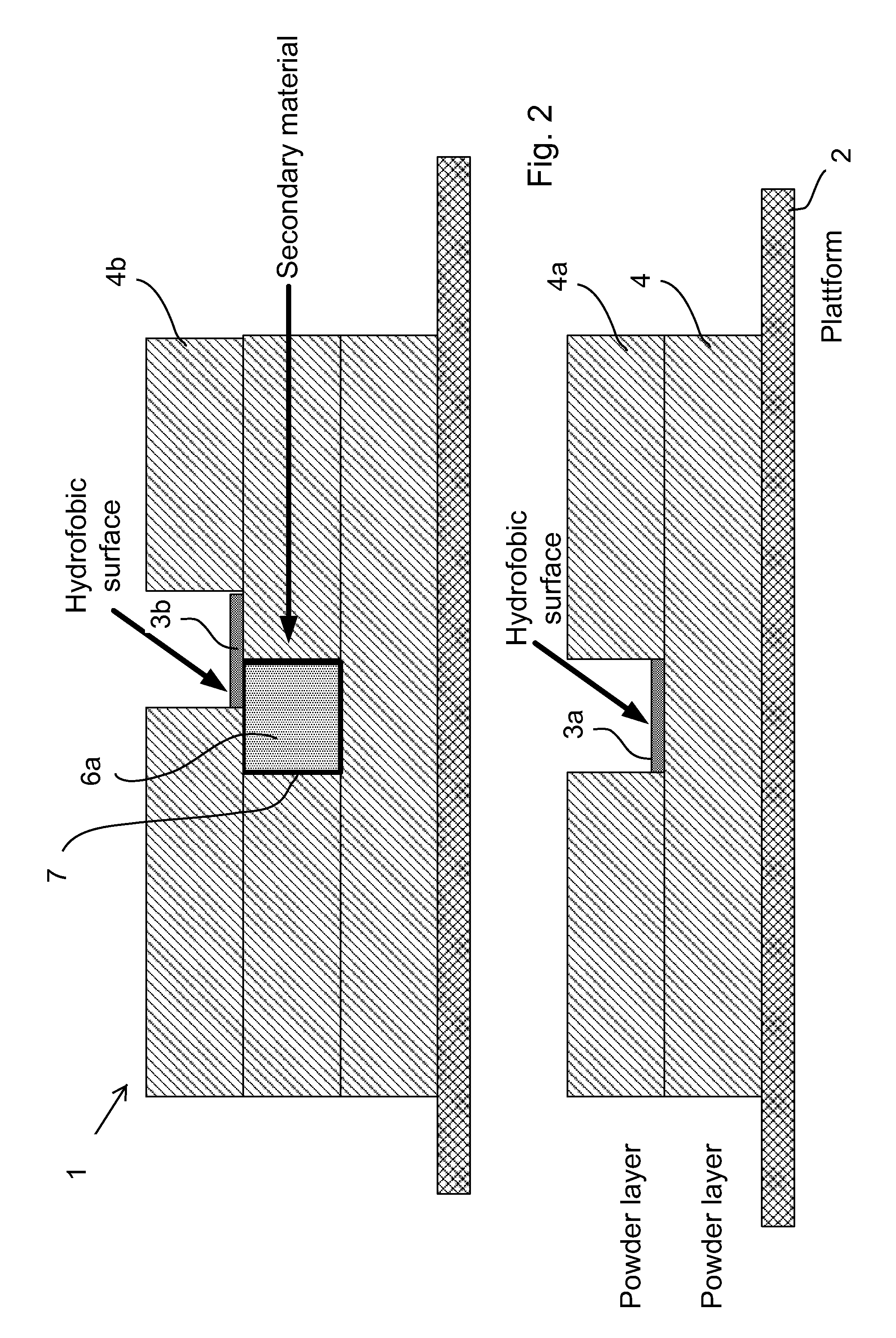
The present invention relates to layer manufacturing, more particularly to a method for additive layer manufacturing of objects comprised of more than one material with free-form capability for all included materials. The invention can for example be used for producing packaging for Microsystems where the ceramic acts as an insulator and the secondary material is used to produce electrical or optical 3D conductor lines or electrical or optical 3D vias. The fine powder used in this method enables it to be used for building components with small feature size and demand for high precision. Other intended uses for this method is to build small mechanical precision parts or grinding tools, dental objects or medical implants.
Owner:DIGITAL METAL
Circuit board unit and method for production thereof
InactiveUS7948758B2Printed circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHigh heat
The invention relates to a circuit board unit and a method for production thereof. The circuit board unit comprises a circuit board topmost laminate with conductive tracks on the upper side for mounting surface-mountable devices. The circuit board topmost laminate features a thickness dimensioned such that the anticipated heat dissipated by the surface-mountable devices is transported from the upper side to the underside of the circuit board laminate to good effect. The circuit board unit further comprises an electrically insulating laminate arranged under the circuit board topmost laminate, inserts made of a material with good heat conductivity and electrical insulation embedded in the electrically insulating laminate at sites below surface-mountable devices with high heat dissipation, and a cooling plate arranged below the electrically insulating laminate and the inserts.
Owner:CHARMILLES TECH SA +1
Module with a built-in semiconductor and method for producing the same
InactiveUS7141884B2Easy to fillReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesConductive pasteEngineering
In a module with a built-in semiconductor, higher densification is achieved by disposing inner vias close to a semiconductor device. A module which has a space (107) between a first wiring layer (102a) and a built-in semiconductor device (105). The module is obtained by: mounting the semiconductor device (105) on a first wiring layer (102a) of a wiring board (103) without using a sealing resin; stacking on the circuit board an electrically insulating substrate having a through bore (inner via) (104) filled with a conductive paste and an opening for receiving the semiconductor device, and a mold release carrier having a second wiring layer (102b) in the stated order; and heating and pressurizing so that the semiconductor device (105) is incorporated in a core layer (101) which is formed by curing the electrically insulating substrate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Device for protecting an electric and/or electronic component arranged on a carrier substrate against electrostatic discharges
InactiveUS20020151200A1Low production costReduce discharge voltagePrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureOvervoltageContact element
The proposal relates to a device for protecting an electrical and / or electronic component, arranged on a carrier substrate, from electrostatic discharges, an overvoltage occurring in the case of discharge at a carrier-substrate contact element connected to the component being diverted to a ground connection, bypassing the component. It is proposed that the protective device include a first electroconductive structure conductively connected to the jeopardized contact element, and a second electroconductive structure arranged adjacent to the first structure on the carrier substrate and conductively connected to the ground connection. Mutually facing sections of the electroconductive structures are set apart spatially from one another by a defined gap in such a way that an overvoltage transmitted to the contact element is transferred by a spark discharge in the gap from the section of the first electroconductive structure to the section of the second electroconductive structure, and is diverted to the ground connection.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
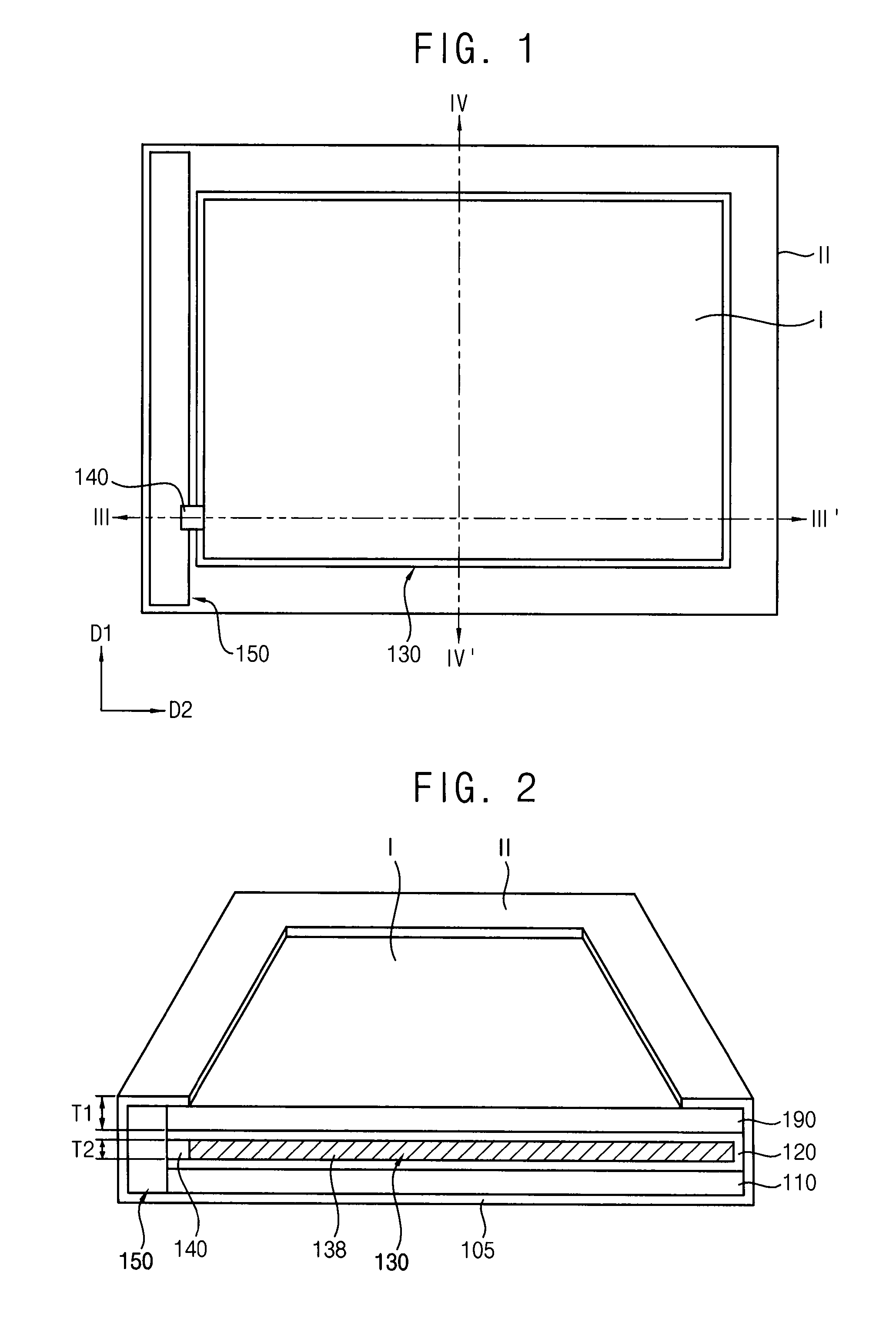
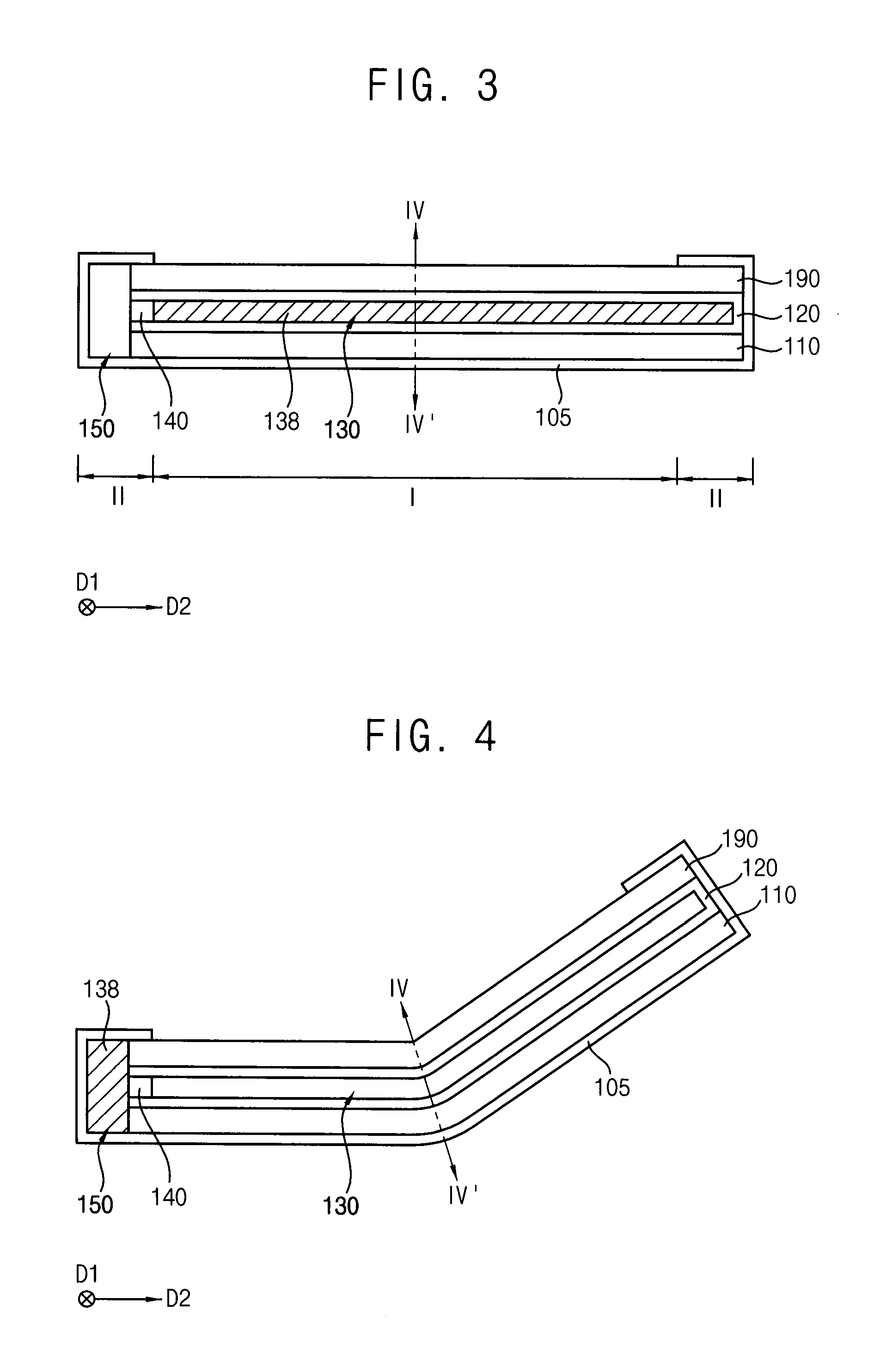
Flexible display apparatus
ActiveUS20150220117A1Relieve pressureIncrease flexibilityCasings with display/control unitsCircuit fluid transportEngineeringFace sheet
A flexible display apparatus is disclosed. The flexible display apparatus includes a display panel, a cover substrate, a first receiving portion and a first fluid. The display panel includes a first region and a second region surrounding at least one sides of the first region. The cover substrate is disposed over the display panel. The first receiving portion is disposed between the display panel and the cover substrate. The first receiving portion overlaps the first region of the display panel and has an empty space. The first fluid is disposed in the first receiving portion.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com