Patents
Literature
2630 results about "Ground layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ground layer The lowest layer of a plant community, comprising especially mosses, lichens, and fungi, together with low-growing herb species which often have trailing stems or rosette forms. Cite this article.
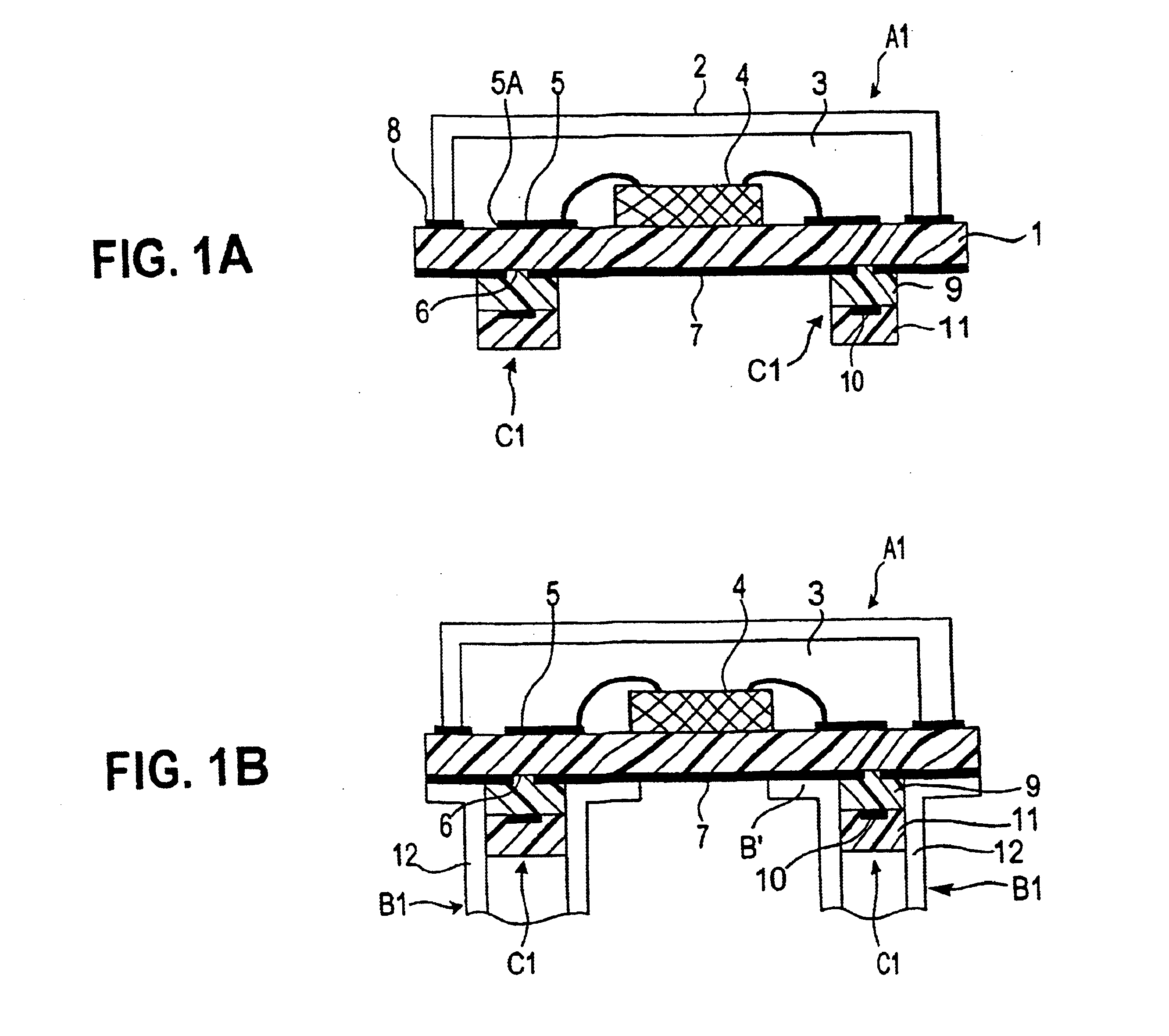
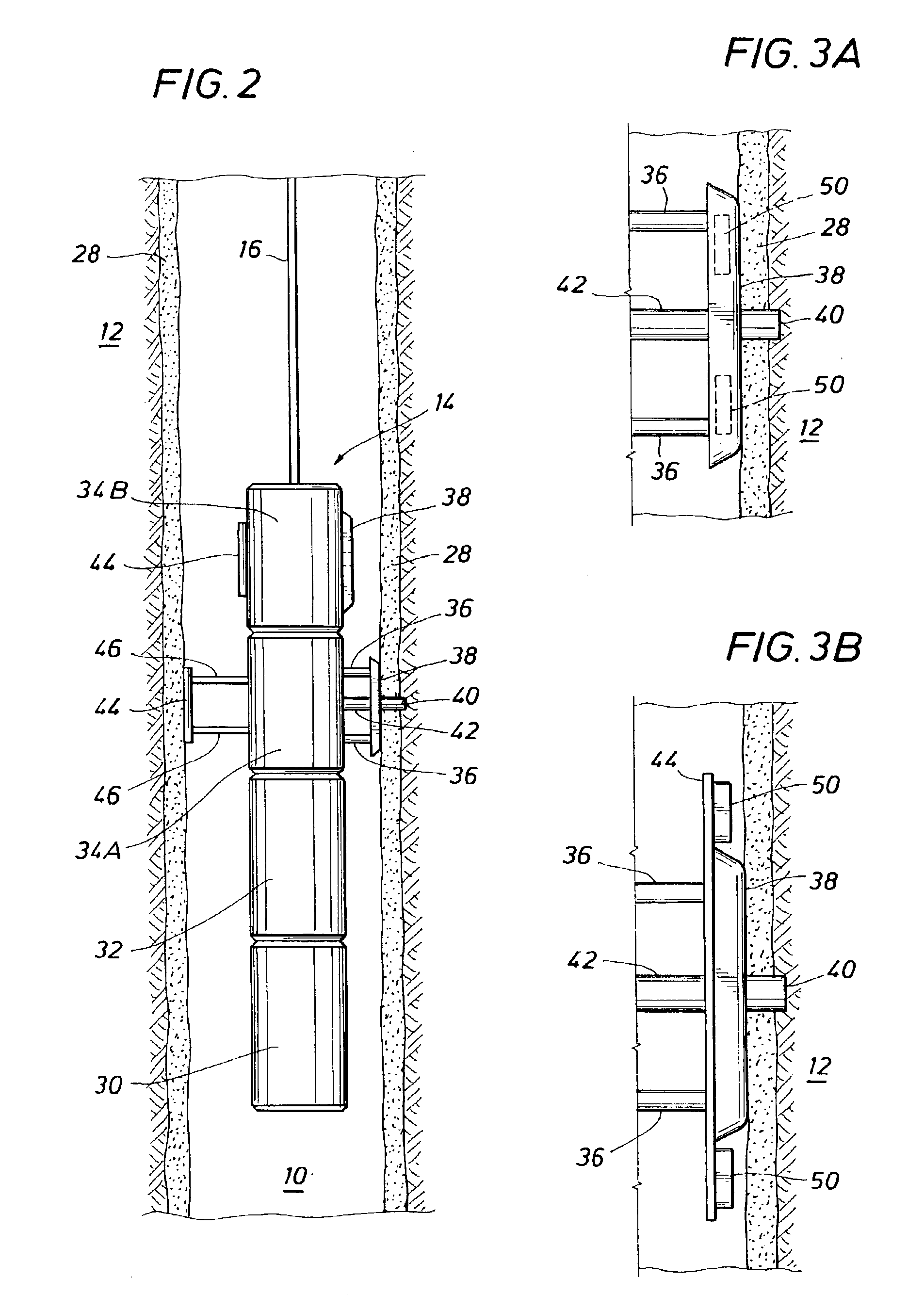
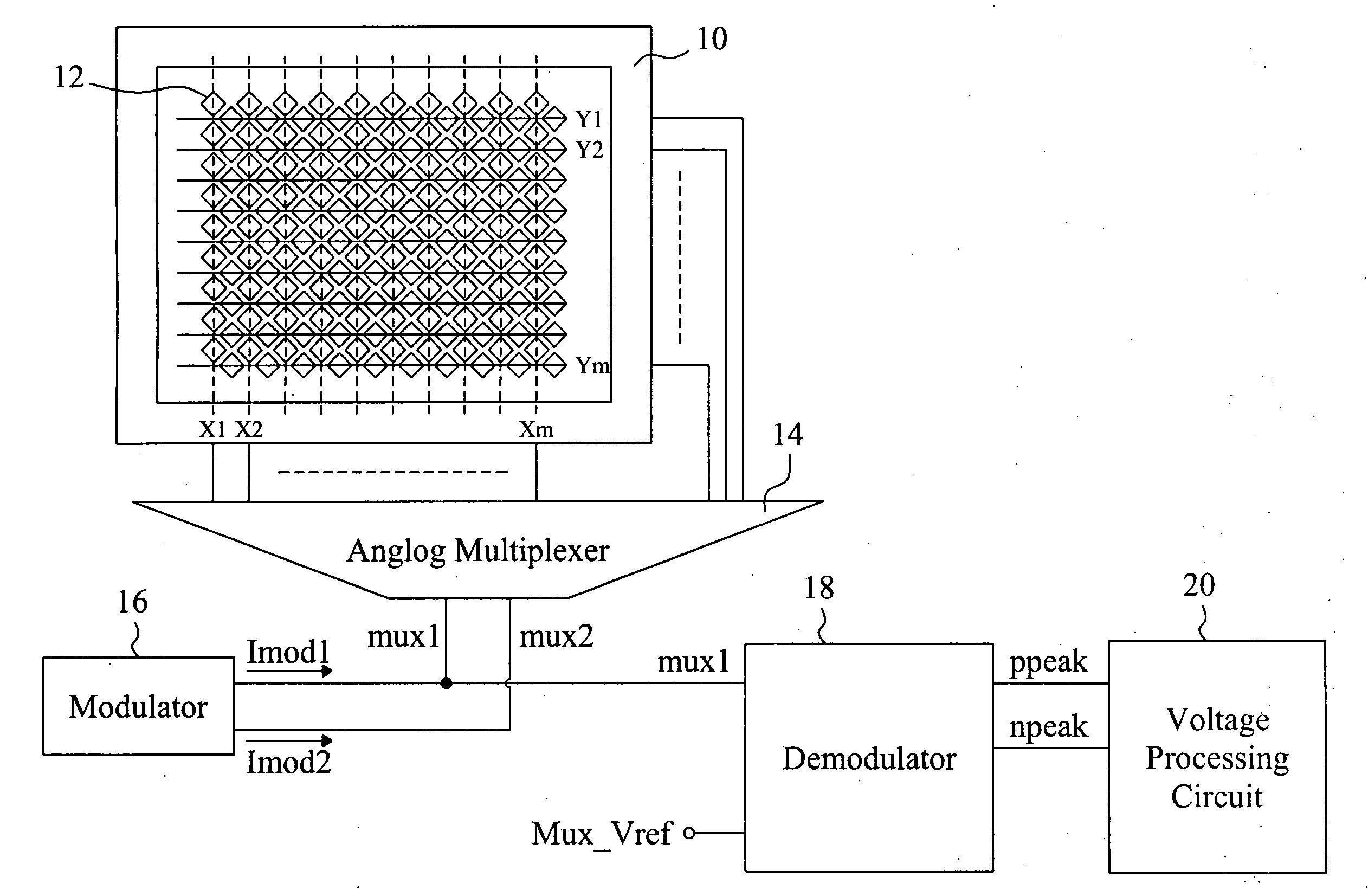
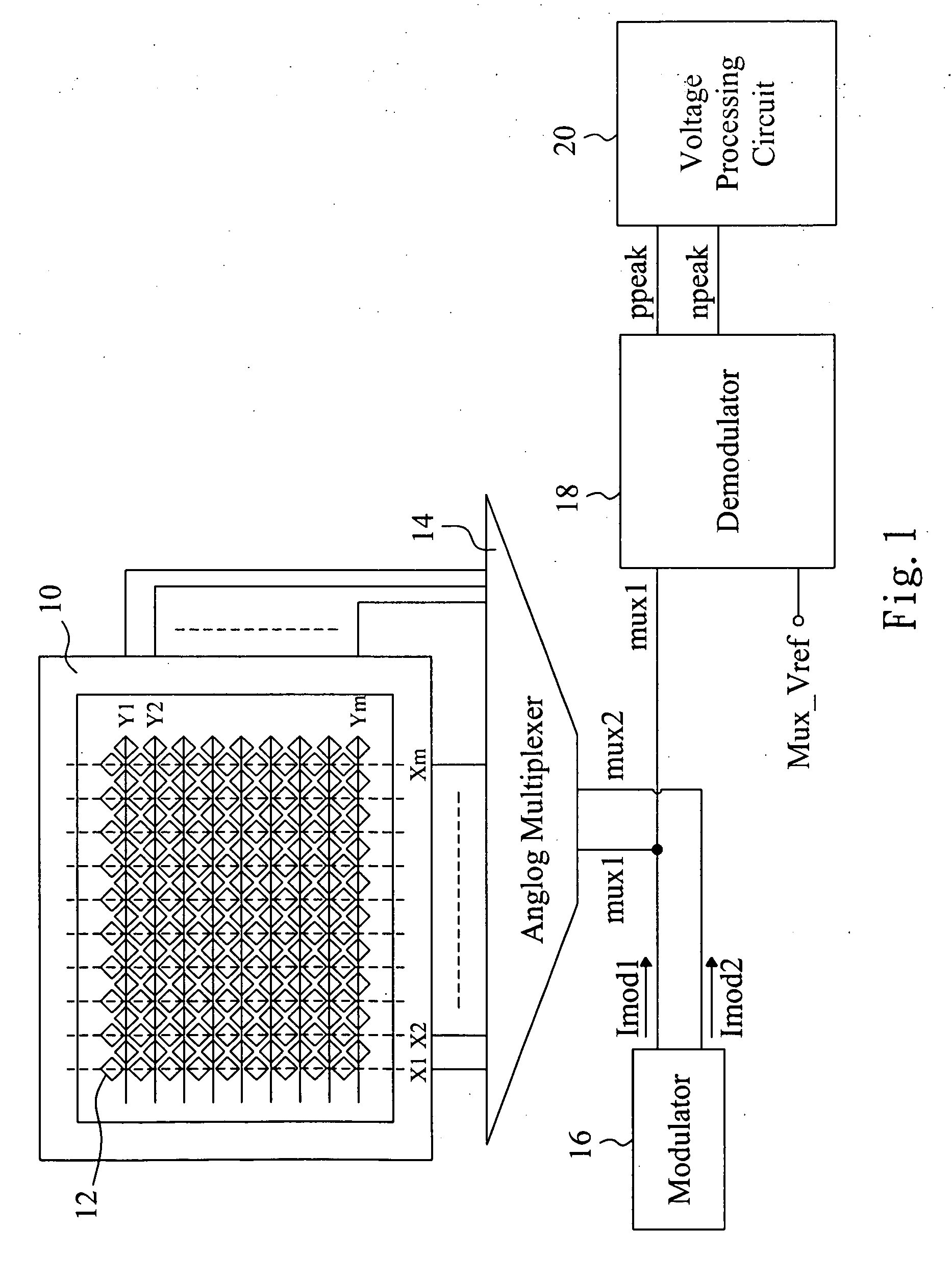
Simulation gridding method and apparatus including a structured areal gridder adapted for use by a reservoir simulator
InactiveUS6106561AHigh simulationSimulation results are accurateElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingComputation using non-denominational number representationHorizonTriangulation
A Flogrid Simulation Gridding Program includes a Flogrid structured gridder. The structured gridder includes a structured areal gridder and a block gridder. The structured areal gridder will build an areal grid on an uppermost horizon of an earth formation by performing the following steps: (1) building a boundary enclosing one or more fault intersection lines on the horizon, and building a triangulation that absorbs the boundary and the faults; (2) building a vector field on the triangulation; (3) building a web of control lines and additional lines inside the boundary which have a direction that corresponds to the direction of the vector field on the triangulation, thereby producing an areal grid; and (4) post-processing the areal grid so that the control lines and additional lines are equi-spaced or smoothly distributed. The block gridder of the structured gridder will drop coordinate lines down from the nodes of the areal grid to complete the construction of a three dimensional structured grid. A reservoir simulator will receive the structured grid and generate a set of simulation results which are displayed on a 3D Viewer for observation by a workstation operator.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Apparatus and method for heating subterranean formations using fuel cells
InactiveUS6684948B1Eliminate needAvoid inefficiencyFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingElectricityFuel cells
A fuel cell based subterranean heater for mineral extraction, in situ decontamination, or other applications. The fuel cells are preferably stacked within a casing which is then inserted into a hole bored, or otherwise formed, into the formation to be heated. Conduits within the casing, and preferably formed by adjacent, aligned holes formed through the plates of the individual fuel cells supply fuel and air and extract exhaust gases. An optional manifold is used to span the overburden without applying heat to it directly. The manifold may also function as a heat exchanger between incoming and exhaust gases. Preferably the fuel cell is fueled by gases produced by the formation and also generates electricity which is available for use or export.
Owner:IEP TECH INC
Dipole tag antenna structure mountable on metallic objects using artificial magnetic conductor for wireless identification and wireless identification system using the dipole tag antenna structure
InactiveUS20100007569A1Easy to manufactureEasy to installAntenna feed intermediatesRecord carriers used with machinesTag antennaElectrical conductor
Provided are a dipole tag antenna using an artificial magnetic conductor (AMC) for wireless identification and a wireless identification system using the dipole tag antenna. The dipole tag antenna includes: a substrate formed of a first dielectric material; a conductive ground layer formed underneath the substrate; an AMC layer formed on the substrate; the dipole tag antenna mounted on the AMC layer and comprising a wireless identification chip; and the AMC directly mounted on a conductor.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Microstrip antenna for an identification appliance
InactiveUS6888502B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringDegradation Problem
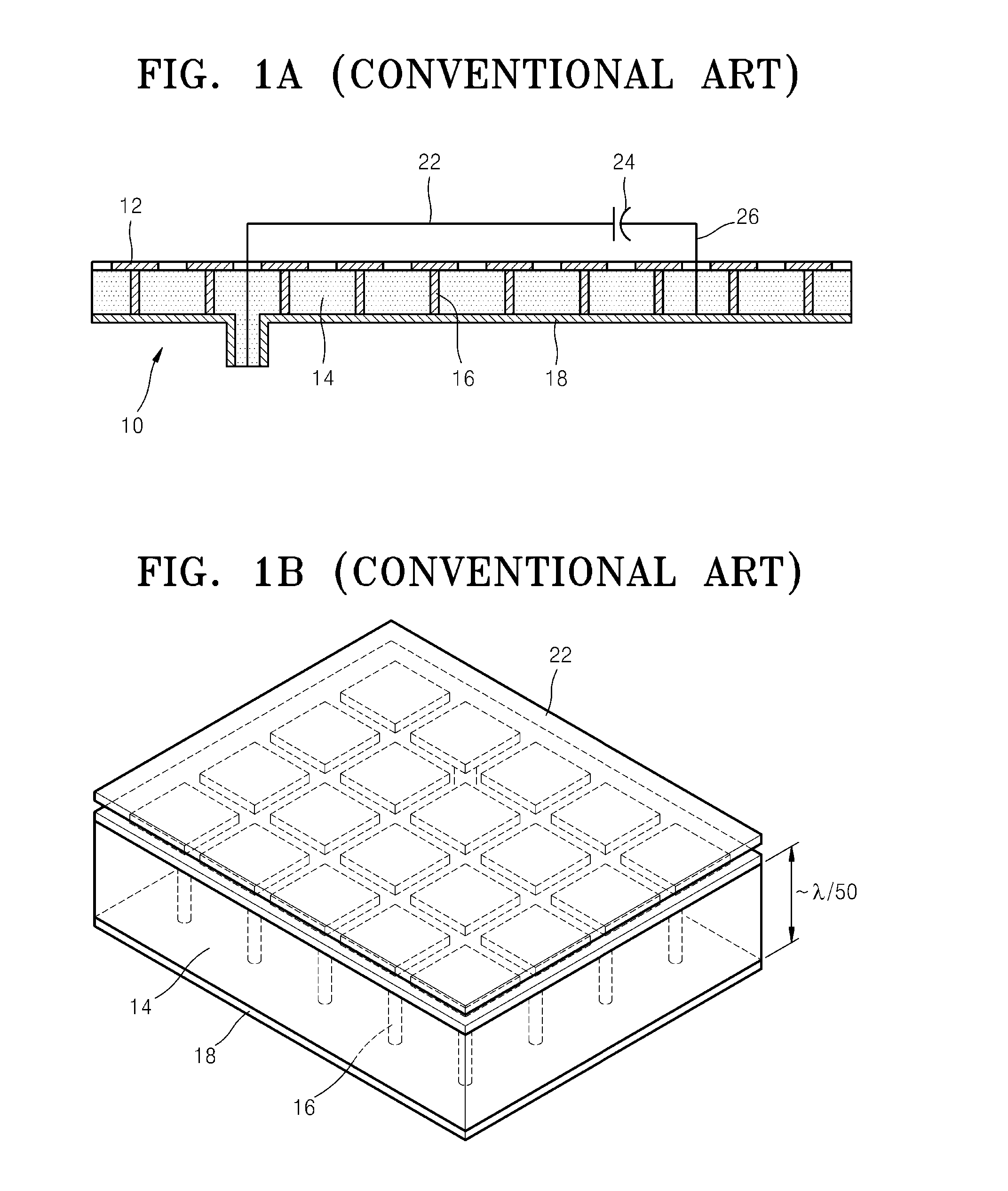
An identification appliance, such as a wristband, bracelet, patch, headband, necklace, card, sticker, or other wearable appliance, has an improved patch or microstrip antenna. The microstrip antenna comprises a conductive patch layer, a conductive ground layer and a dielectric layer in between the conductive layers. The microstrip antenna is mounted to or disposed in the identification appliance, where preferably the ground layer is closest to the user and the patch layer is furthest from the user. Electronic circuits may be located in the dielectric layer, on a surface of a conductive layer, or on another part of the identification appliance. Connecting holes through the dielectric layer may allow circuits to be connected to a conductive layer or layers. This improved antenna resolves detuning and communication degradation problems.
Owner:PRECISION DYNAMICS CORPORATION
Antennas
InactiveUS20150009089A1Radiating element housingsIndividually energised antenna arraysDielectric substrateConductive materials
One aspect of the invention provides an antenna including: a dielectric substrate and a plurality of antenna elements positioned on a surface of the dielectric substrate. Each antenna element includes: a sector-shaped sheet of conductive material and a conductive feed line coupled to the sector-shape sheet of conductive material. Another aspect of the invention provides an antenna including: a dielectric substrate, a plurality of antenna elements positioned on a surface of the dielectric substrate at substantially uniform angular intervals along an arc, and a ground layer mounted to an opposite side of the dielectric substrate from the plurality of antenna elements. Each antenna element includes: a sector-shaped sheet of conductive material having a central angle between about 90° and about 180° and a conductive feed line coupled to the sector-shape sheet of conductive material.
Owner:L COM
Low-EMI electronic apparatus, low-EMI circuit board, and method of manufacturing the low-EMI circuit board.
InactiveUS6353540B1Radiation suppressionHigh packageMagnetic/electric field screeningFinal product manufactureCapacitanceCountermeasure
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Multi-layered wiring board for slot coupling a transmission line to a waveguide
InactiveUS6870438B1Small signal lossSmall reflectionOne-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
A wiring board includes a dielectric substrate, a signal transmission line formed on one surface of the dielectric substrate, a grounded layer formed on the other surface of the dielectric substrate, and a connection portion for connecting portion for connecting the signal transmission line to a waveguide, the connection portion being formed on the grounded layer. The grounded layer has a slot at a position opposed to an end of the signal transmission line. The connection portion includes a first dielectric portion disposed to cover the slot of the ground layer, a second dielectric portion laminated on the first dielectric portion, and a patch conductor provided at a position opposed to said slot on an interface between the first dielectric portion and the second dielectric portion. The wiring board enables the signals to be efficiently transmitted from the signal transmission line to the waveguide with a small loss and a small reflection.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Marine electromagnetic measurement system
InactiveUS6842006B2Electric/magnetic detection for transportAcoustic wave reradiationOcean bottomMeasurement device
A sea-floor electromagnetic measurement device for obtaining underwater measurements of earth formations including a central structure and arms attached to the central structure so that they can pivot relative to the central structure. An electrode is attached to the end of each of the arms or to the central structure, and / or magnetometers are attached to the arms. A method for undertaking sea-floor electromagnetic measurements of earth formations including measuring electric fields at a selected distance from a central structure of an electromagnetic measurement system. Magnetic fields are then measured at the same location.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
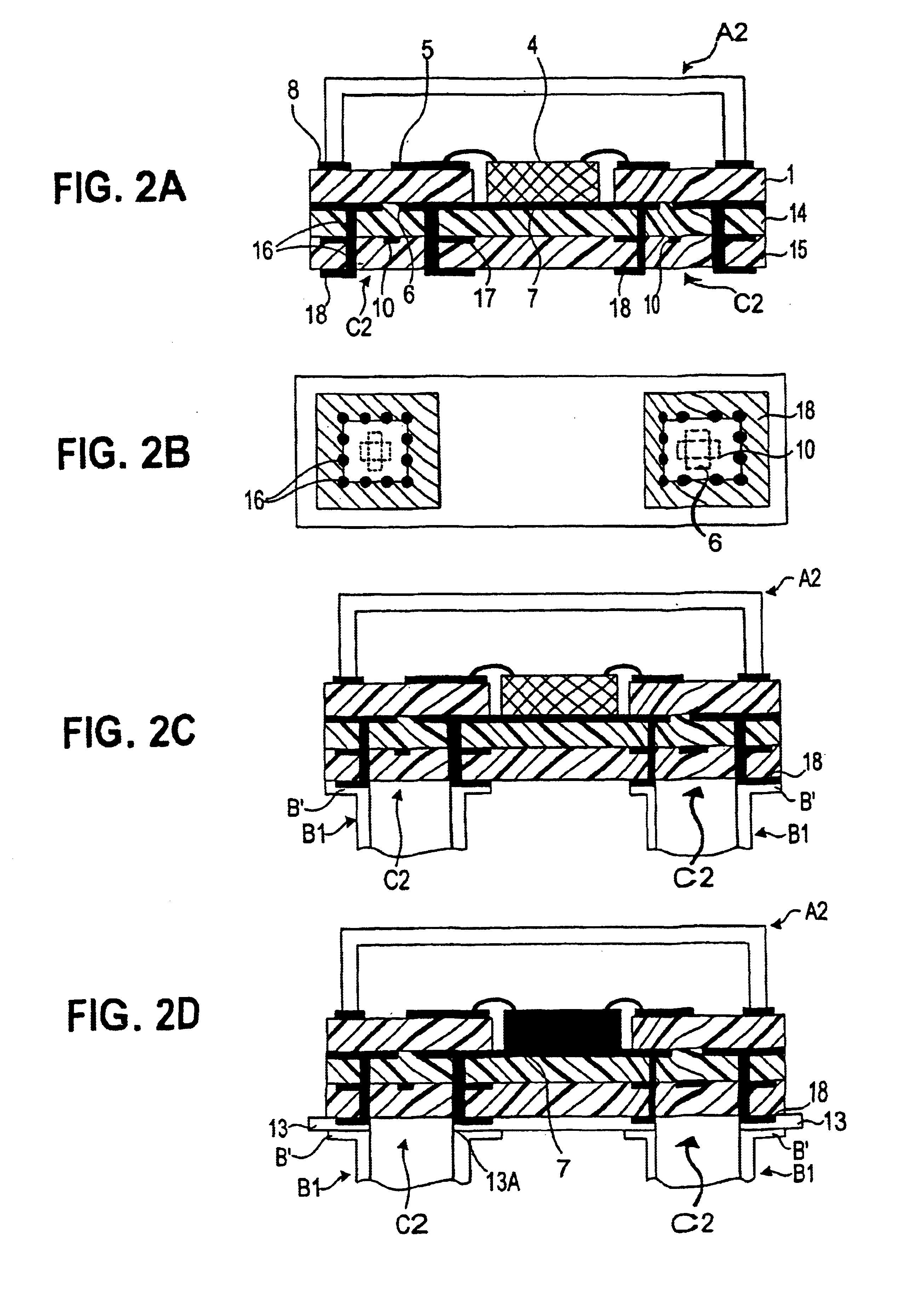
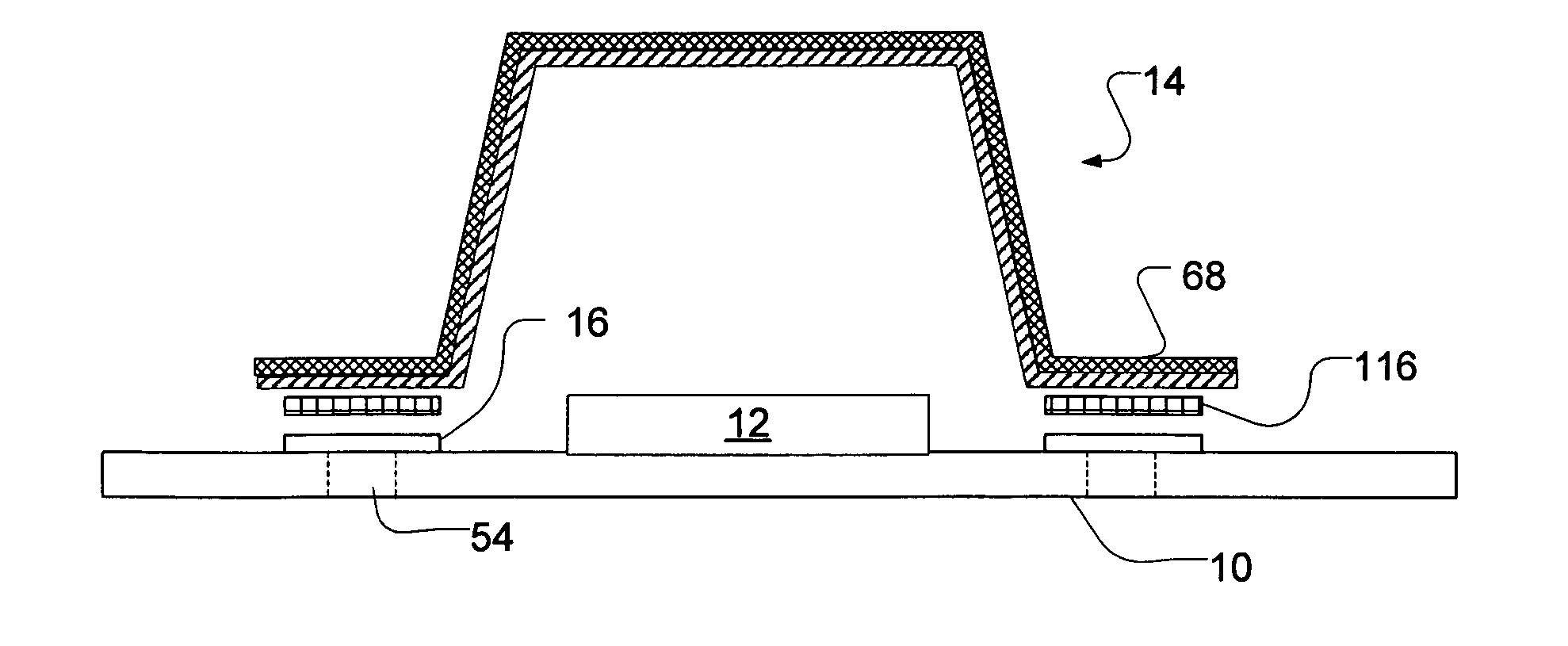
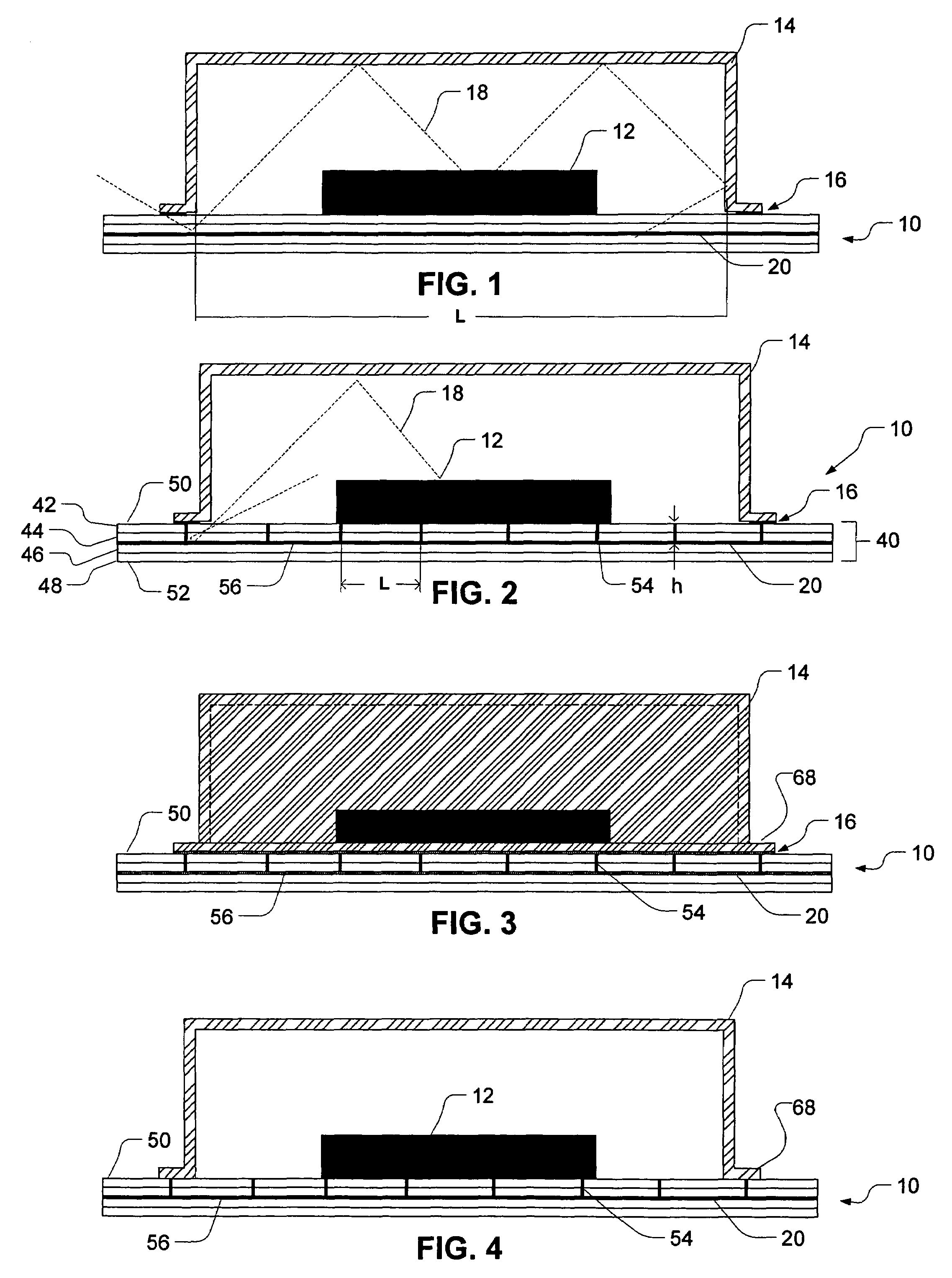
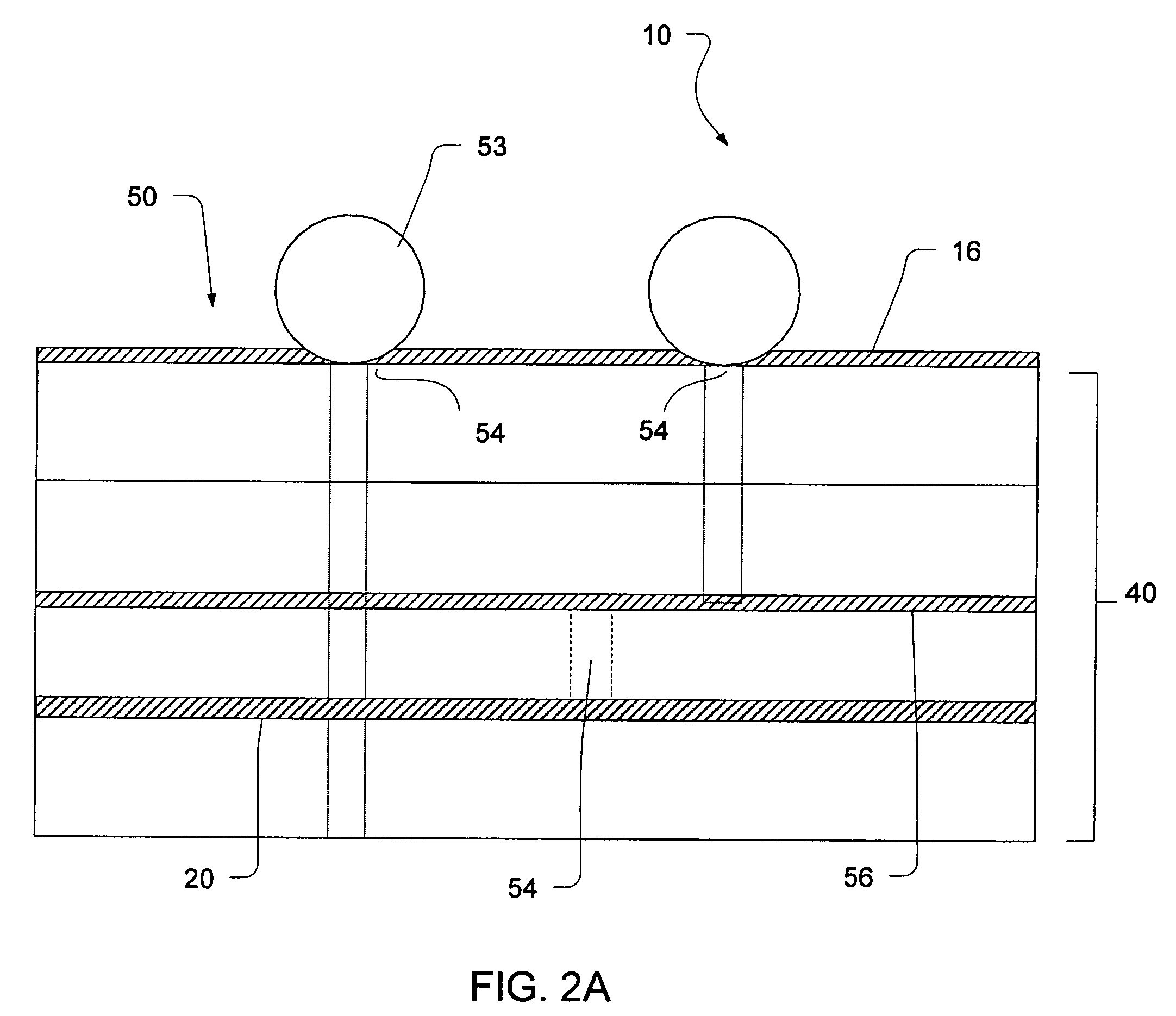
Printed circuit board with capacitors connected between ground layer and power layer patterns
InactiveUS6198362B1Magnetic/electric field screeningCurrent interference reductionEngineeringGround pattern
A printed circuit board is disclosed. A top layer power supply pattern and a top layer ground pattern are formed. The top layer power supply pattern and the top layer ground pattern are connected to a power supply layer and a ground layer through a plurality of viaholes, respectively. A plurality of capacitors or a plurality of capacitor resistor series circuits are disposed at predetermined intervals between the top layer power supply pattern and the top layer ground pattern.
Owner:NEC CORP
Semiconductor device incorporating a semiconductor constructing body and an interconnecting layer which is connected to a ground layer via a vertical conducting portion
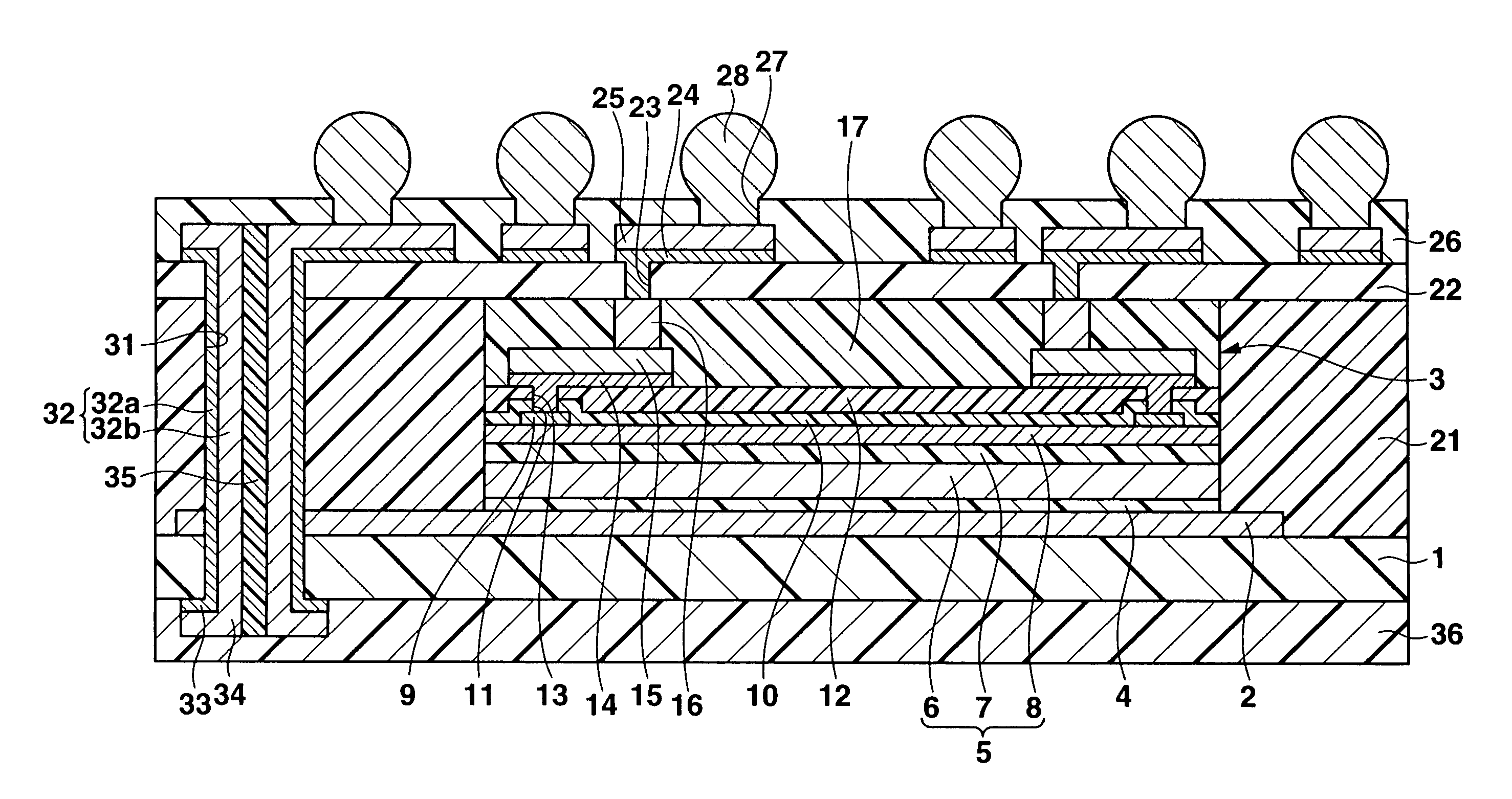
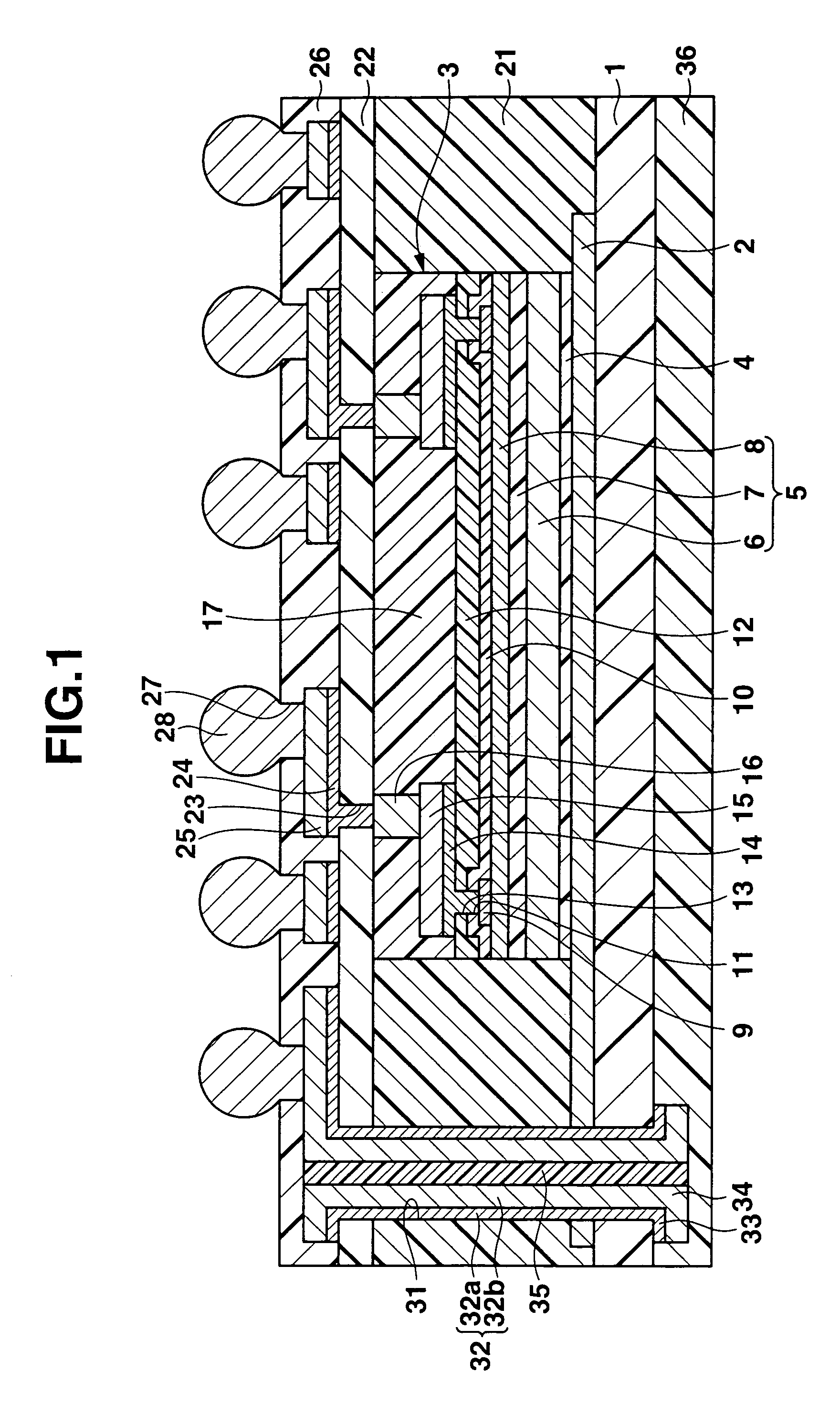
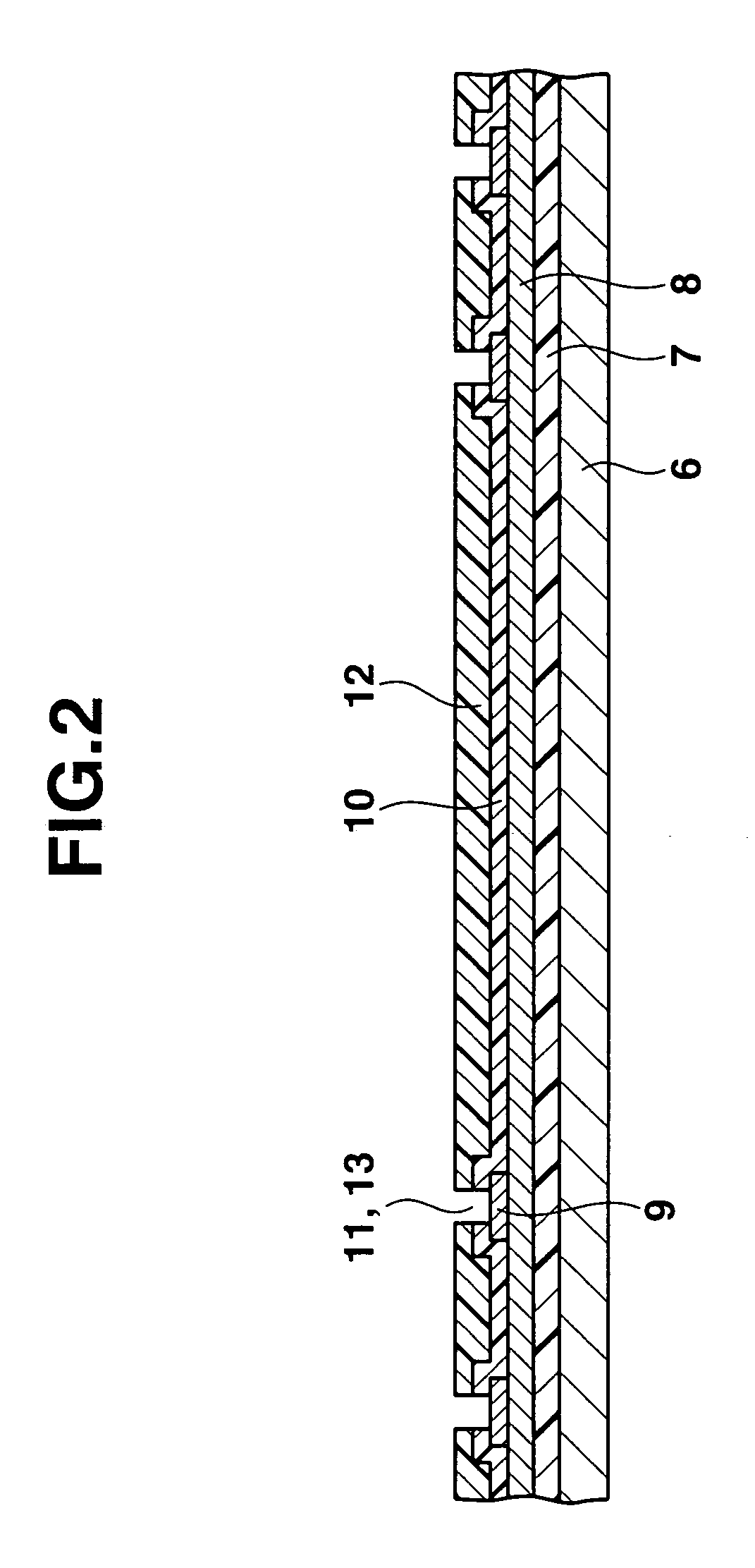
InactiveUS7279750B2Deterioration of characteristic can be suppressedDownsize the electronic apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNoise reduction constructionMetal foilSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes metal foil to which a ground potential is applied, at a semiconductor constructing body provided on the metal foil and having a semiconductor substrate and a plurality of external connection electrodes provided on the semiconductor substrate. An insulating layer is provided around the semiconductor constructing body and has a thickness substantially equal to the semiconductor constructing body. An one upper interconnecting layer is provided on the semiconductor constructing body and insulating layer, and electrically connected to the external connection electrodes. A vertical conducting portion extends through the insulating layer and electrically connects the metal foil and upper interconnecting layer.
Owner:CMK
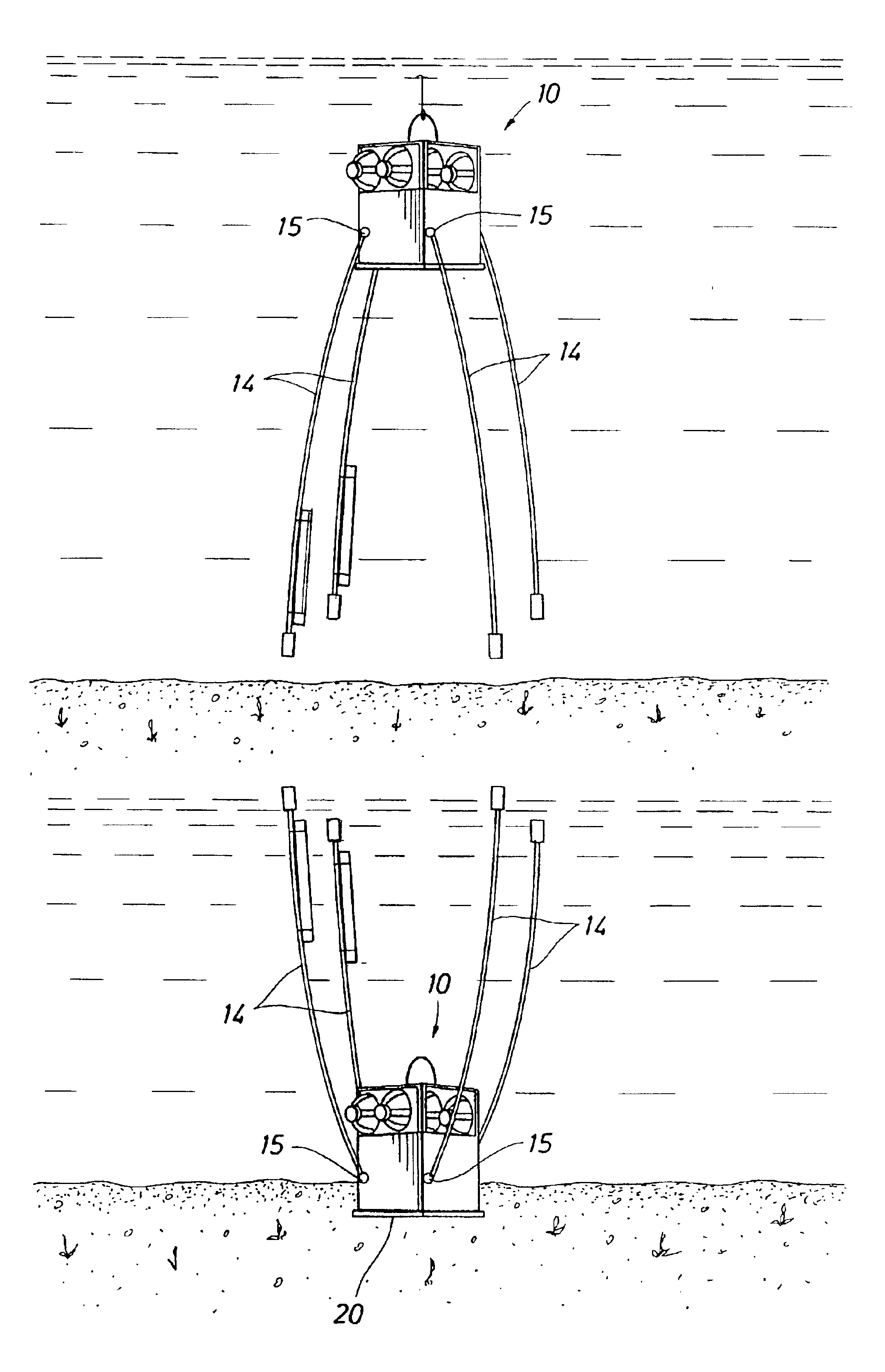
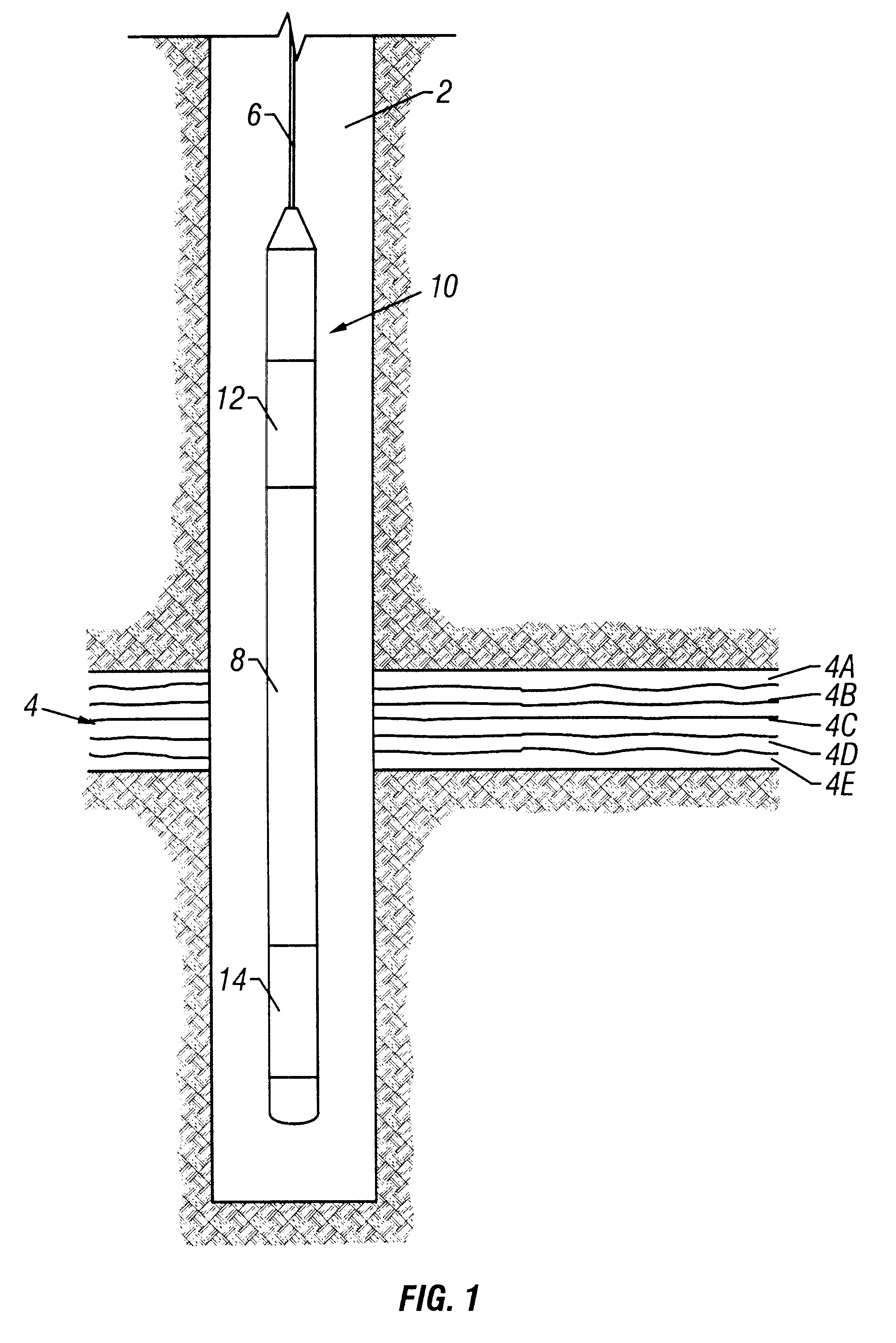
Acquisition method and device for seismic exploration of a geologic formation by permanent receivers set on the sea bottom
InactiveUS6932185B2Good flexibilityFine divisionSeismic energy generationSeismic signal receiversGeophoneHydrophone
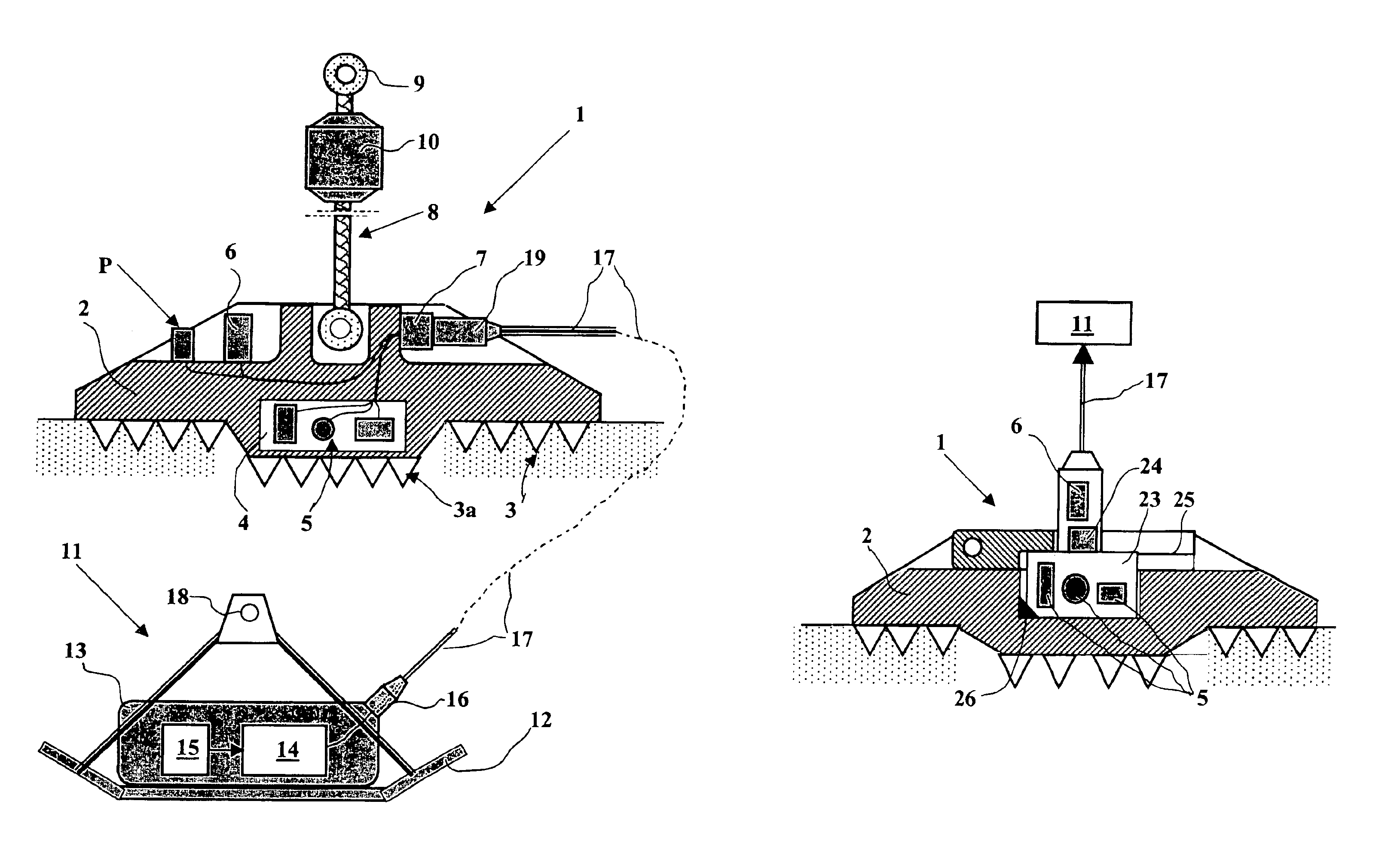
A method and device for seismic exploration of a subsea geologic formation by pickups set on the sea bottom and intermittently connectable to active data acquisition stations (11) brought nearby. Permanent passive reception stations (1) comprising a heavy pedestal provided with housings for seismic pickups (geophones (6), hydrophone (7) which receive acoustic or seismic signals from the underlying formation are arranged at the bottom of the water body. When collection sessions for the signals received by the pickups are scheduled, mobile active acquisition stations (11) connected to permanent passive reception stations (1) are positioned at the bottom of the water body. The signals picked up are then recorded, for the time required to carry out at least one session of acquisition and recording of the acoustic or seismic signals received by the passive stations in response to the emission of seismic waves by one or more seismic sources. The mobile active acquisition stations (11) are thereafter recovered at the surface and the records acquired by each one are transferred to a central collection laboratory.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method and apparatus for subterranean formation flow imaging
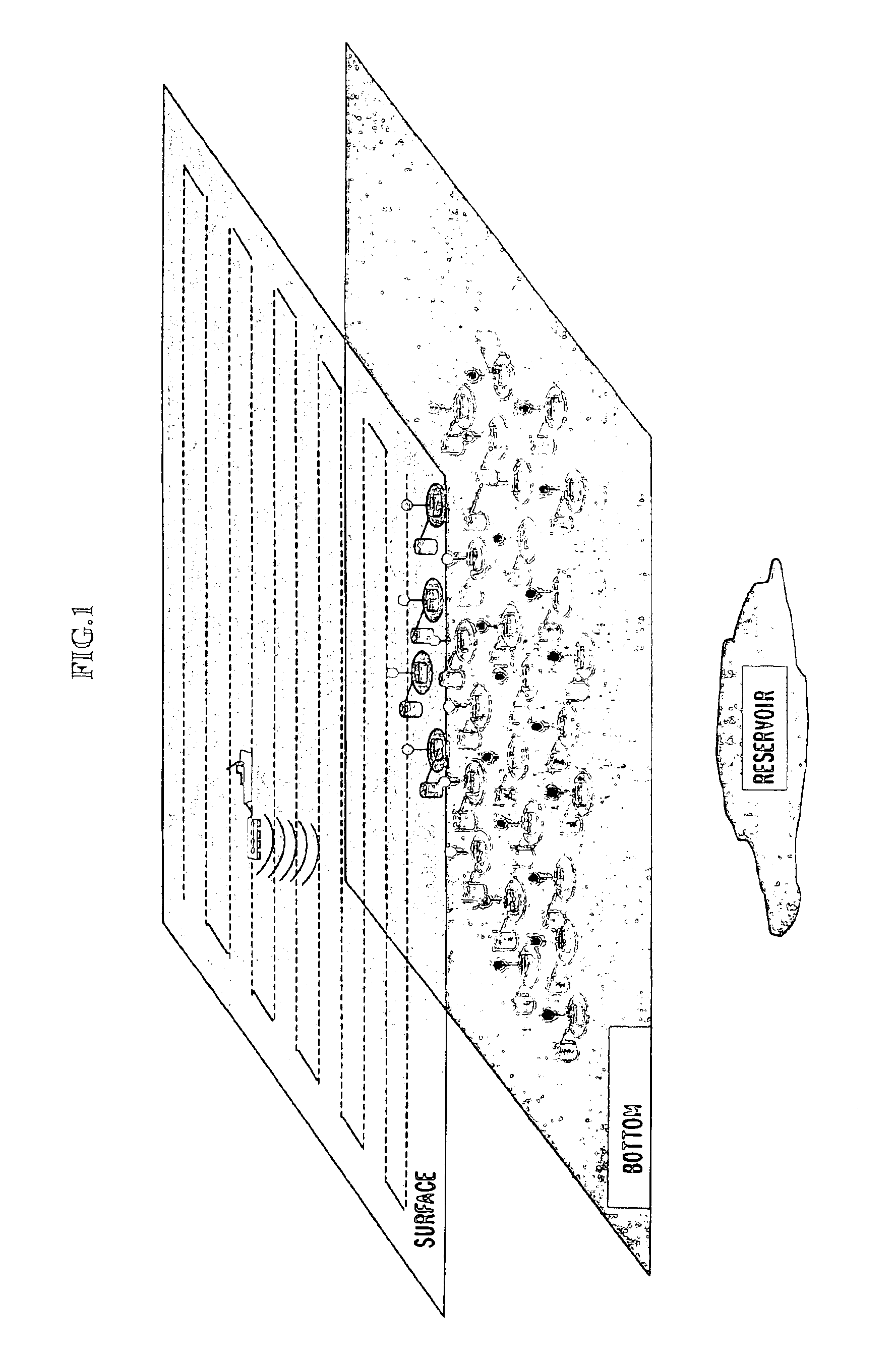
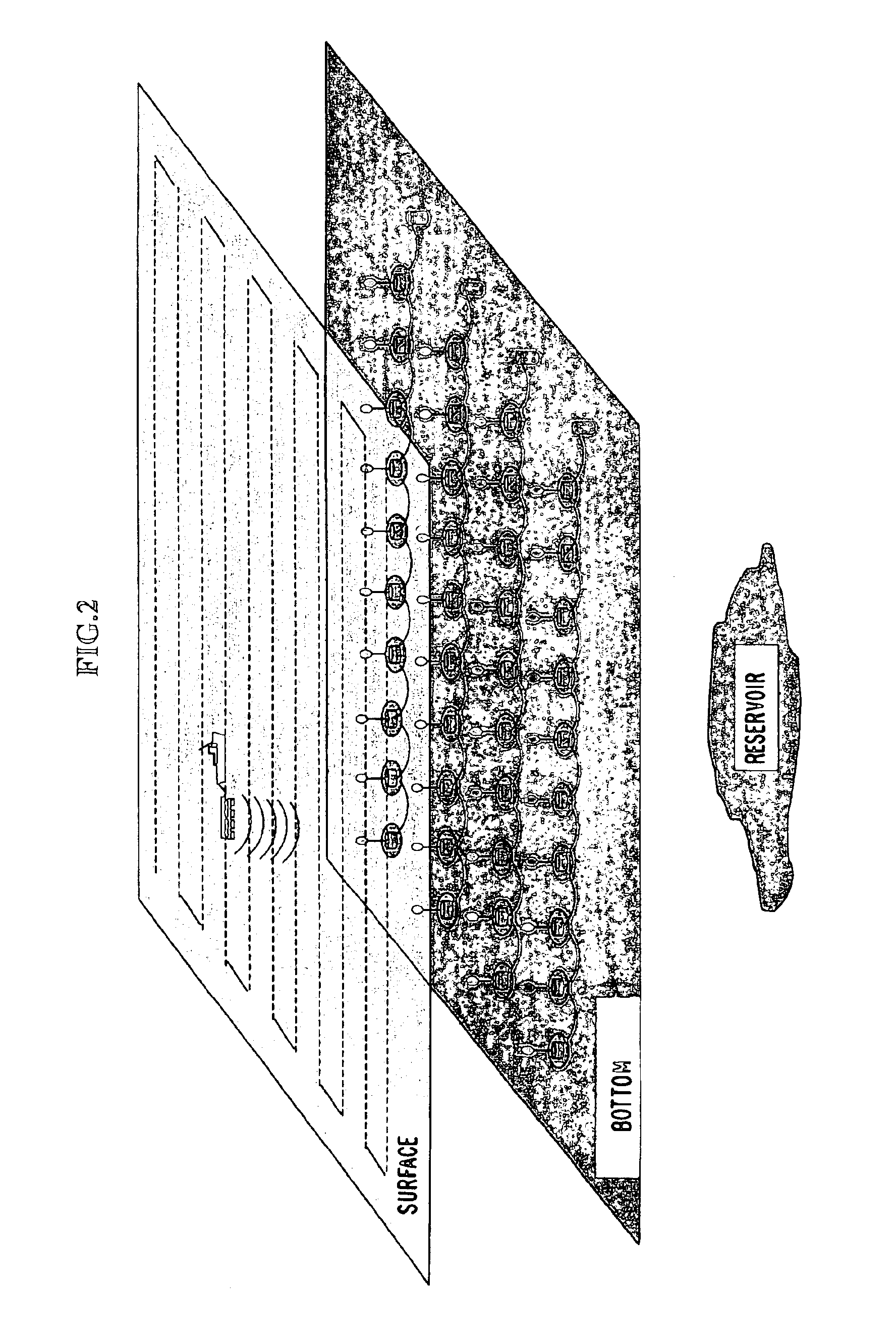
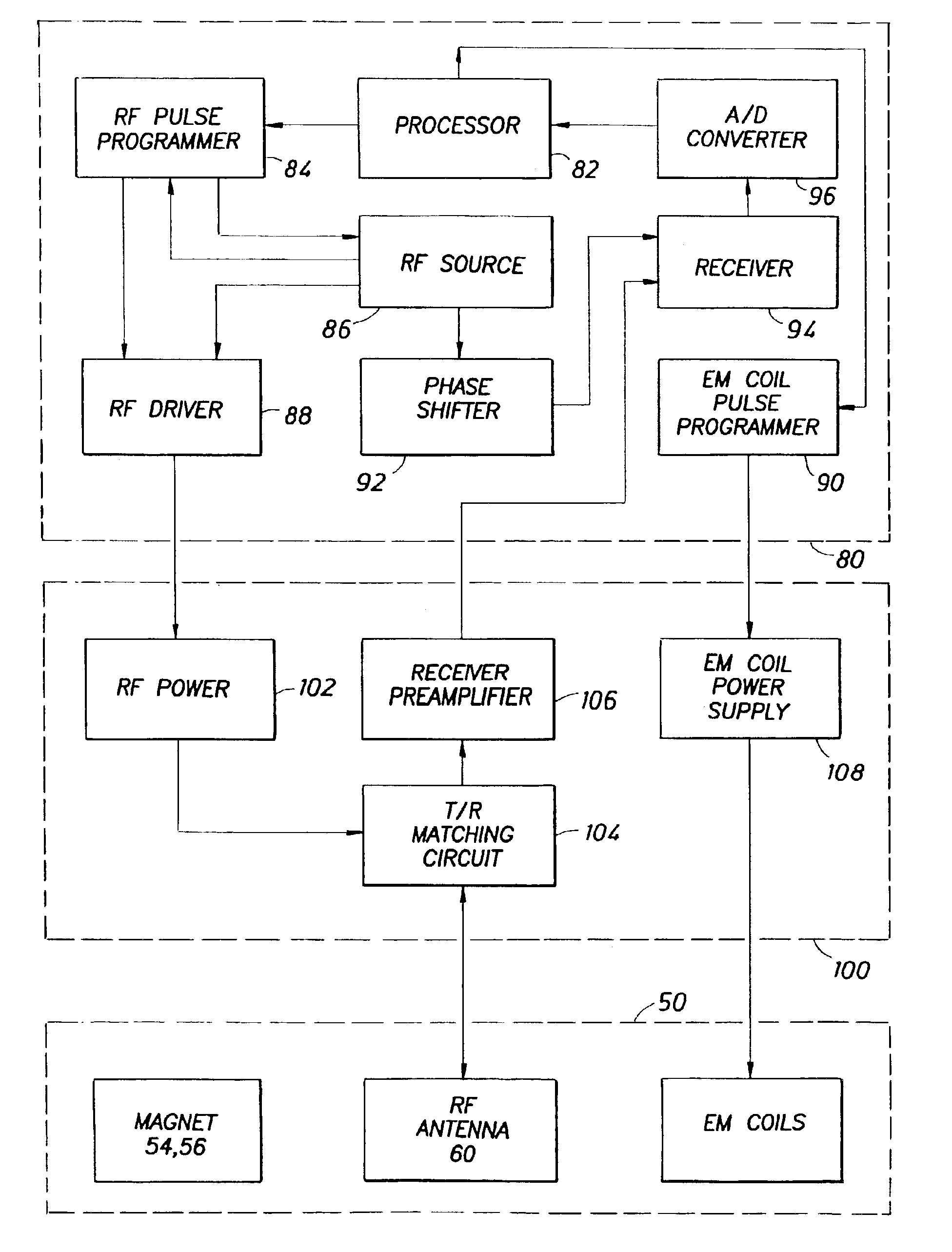
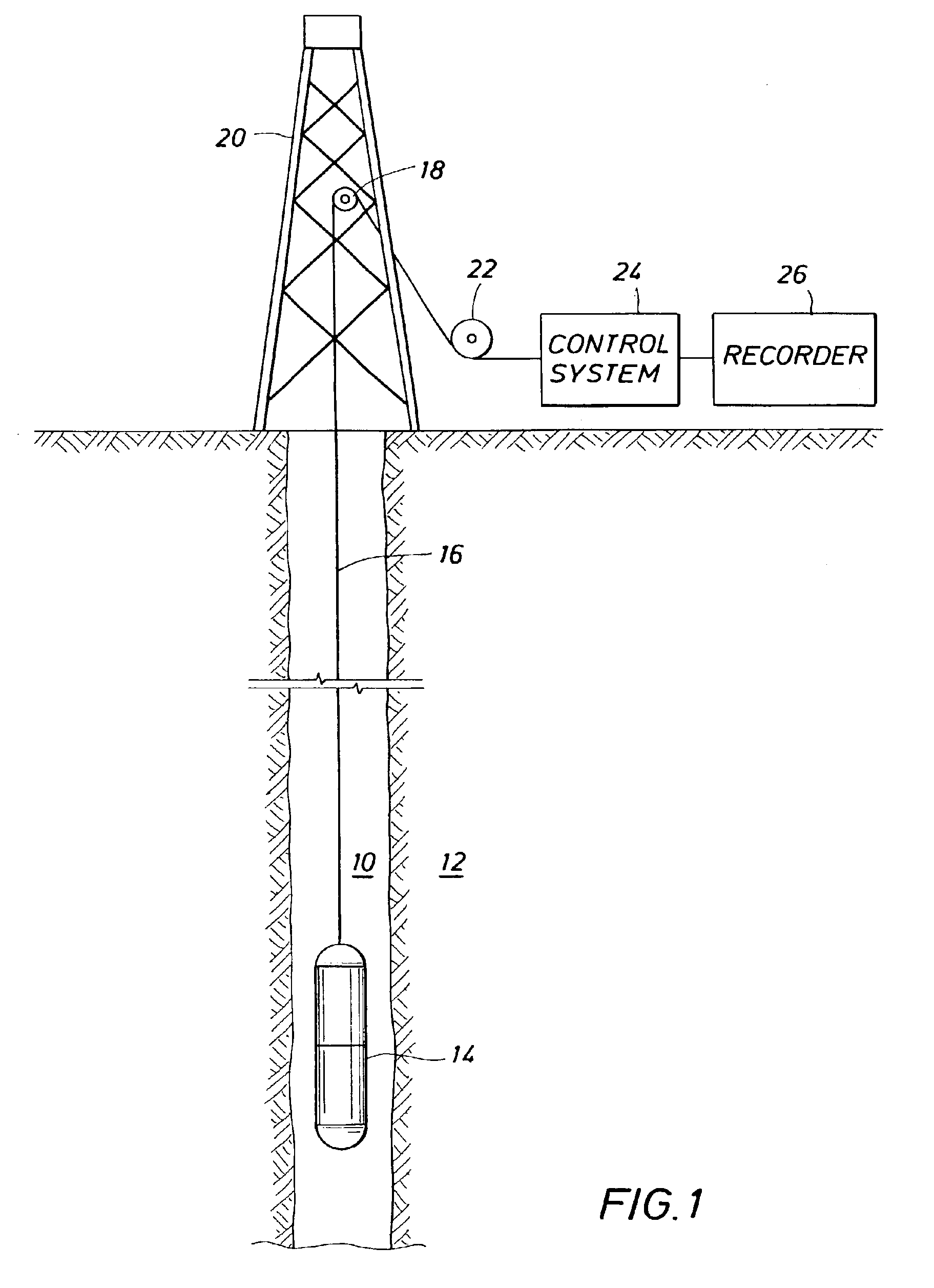
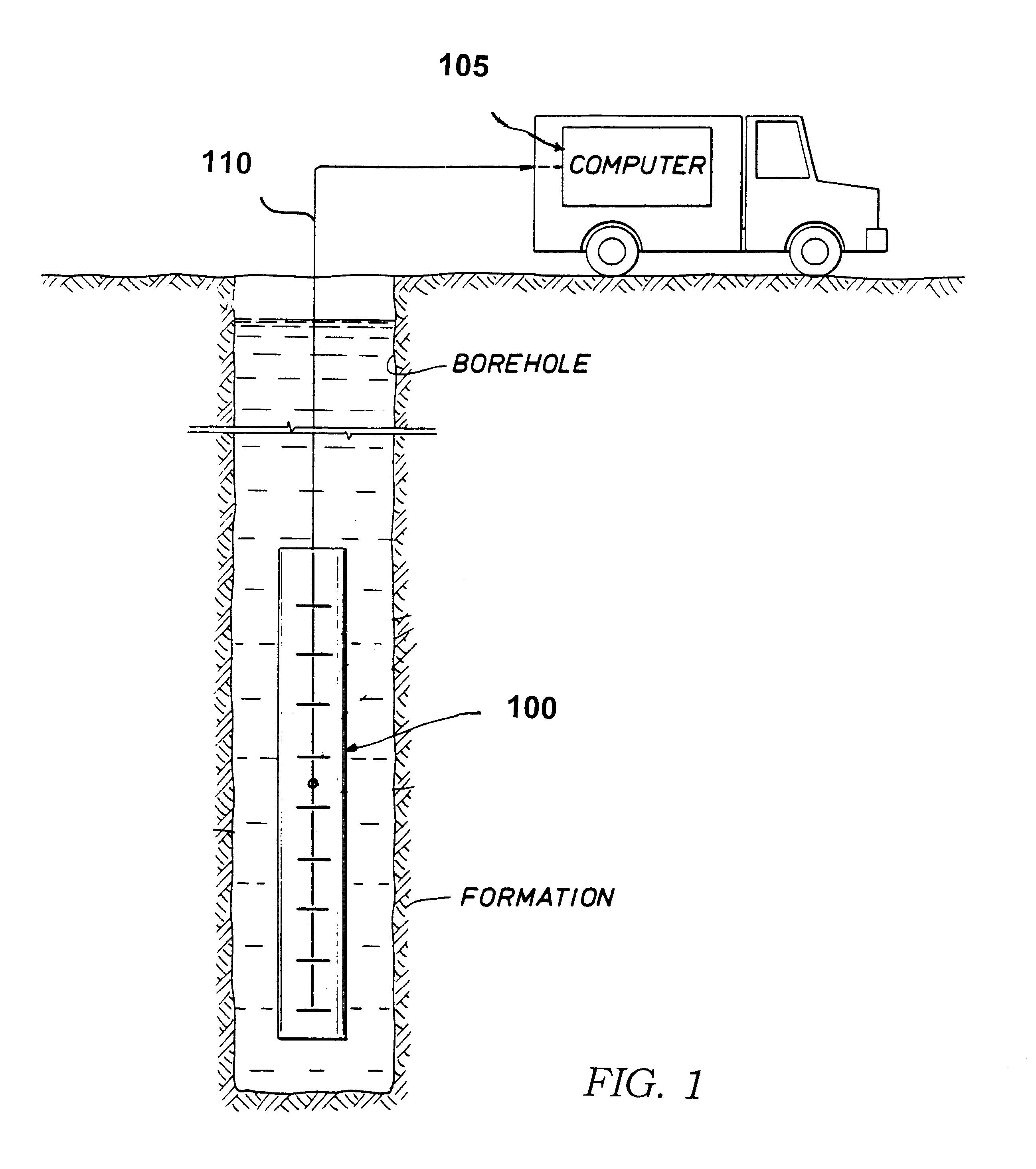
InactiveUS6856132B2Accurate measurementAccurately determineElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceMri imageGeophysics
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for measuring a property relating to fluid flow in an earth formation, more specifically to directly measuring formation permeability and other fluid characteristics. The present invention provides a method for determining the permeability of a hydrocarbon bearing earth formation, which method comprises the steps of: locating a tool at a selected position in a borehole penetrating the earth formation; inducing a flow of fluid within the earth formation to said tool; creating at least two MRI images of said fluid while flowing within the earth formation to said tool, said at least two images being created at different times; determining displacement of said fluid within the earth formation between said different times, using the at least two MRI images.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
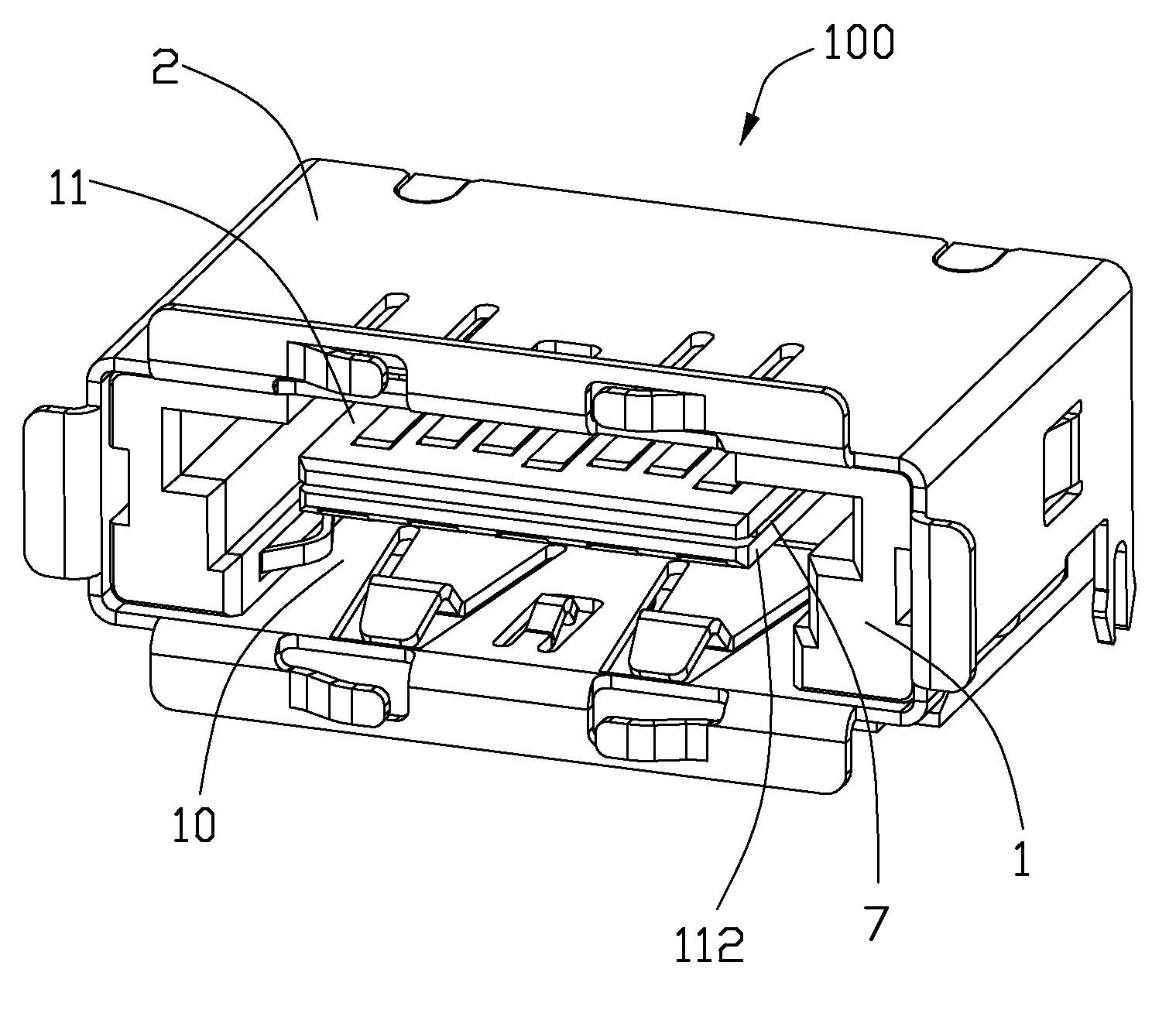
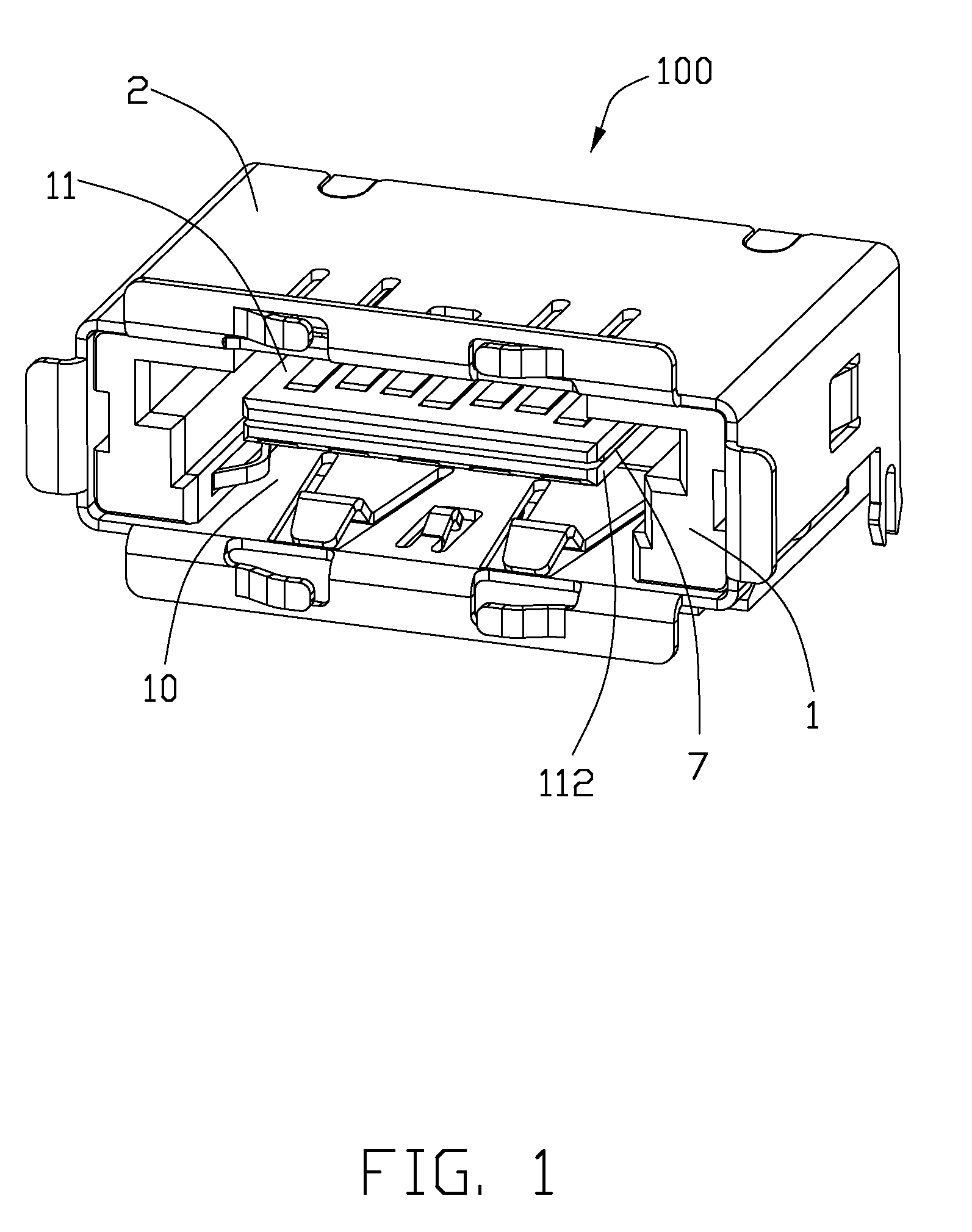
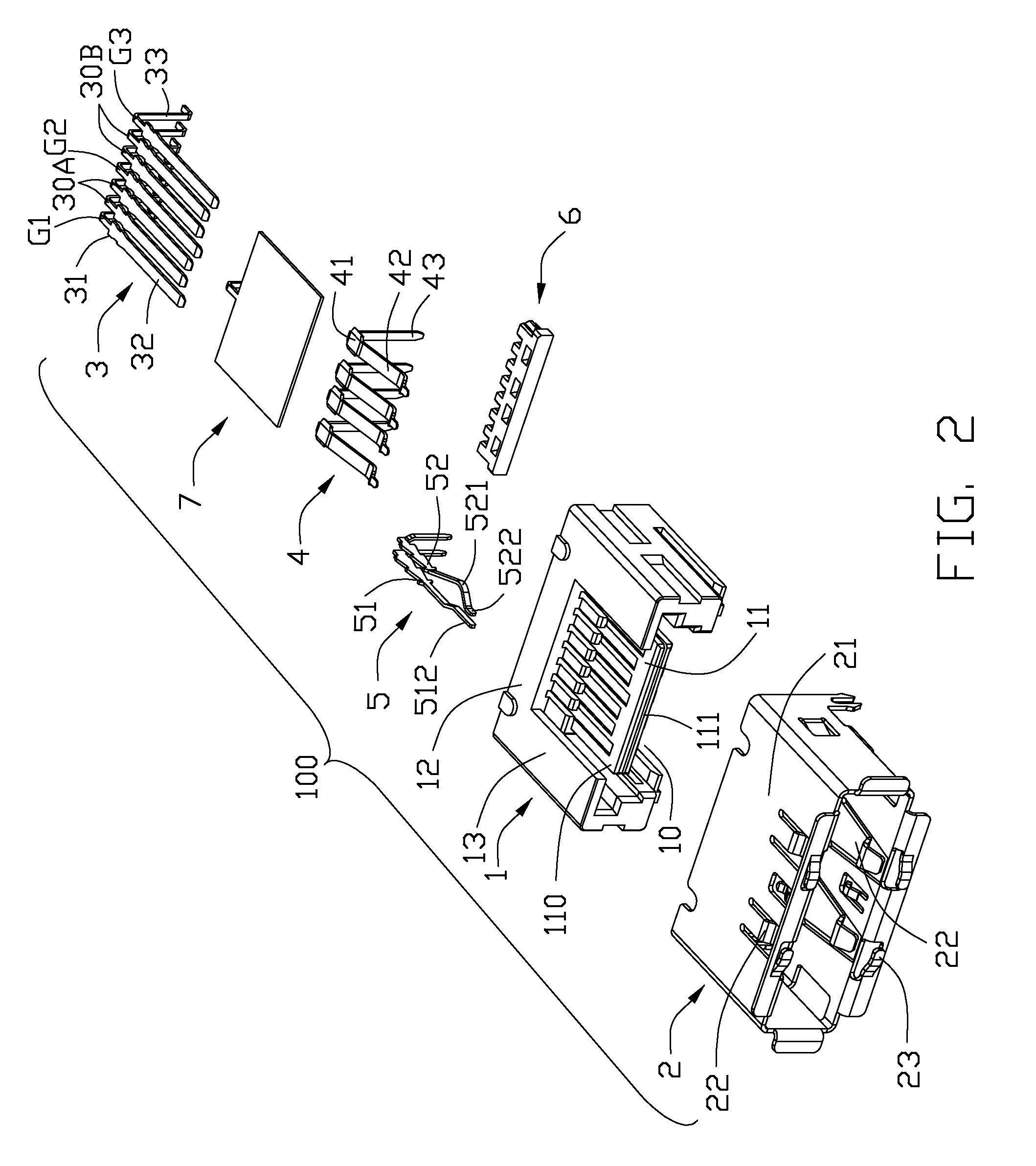
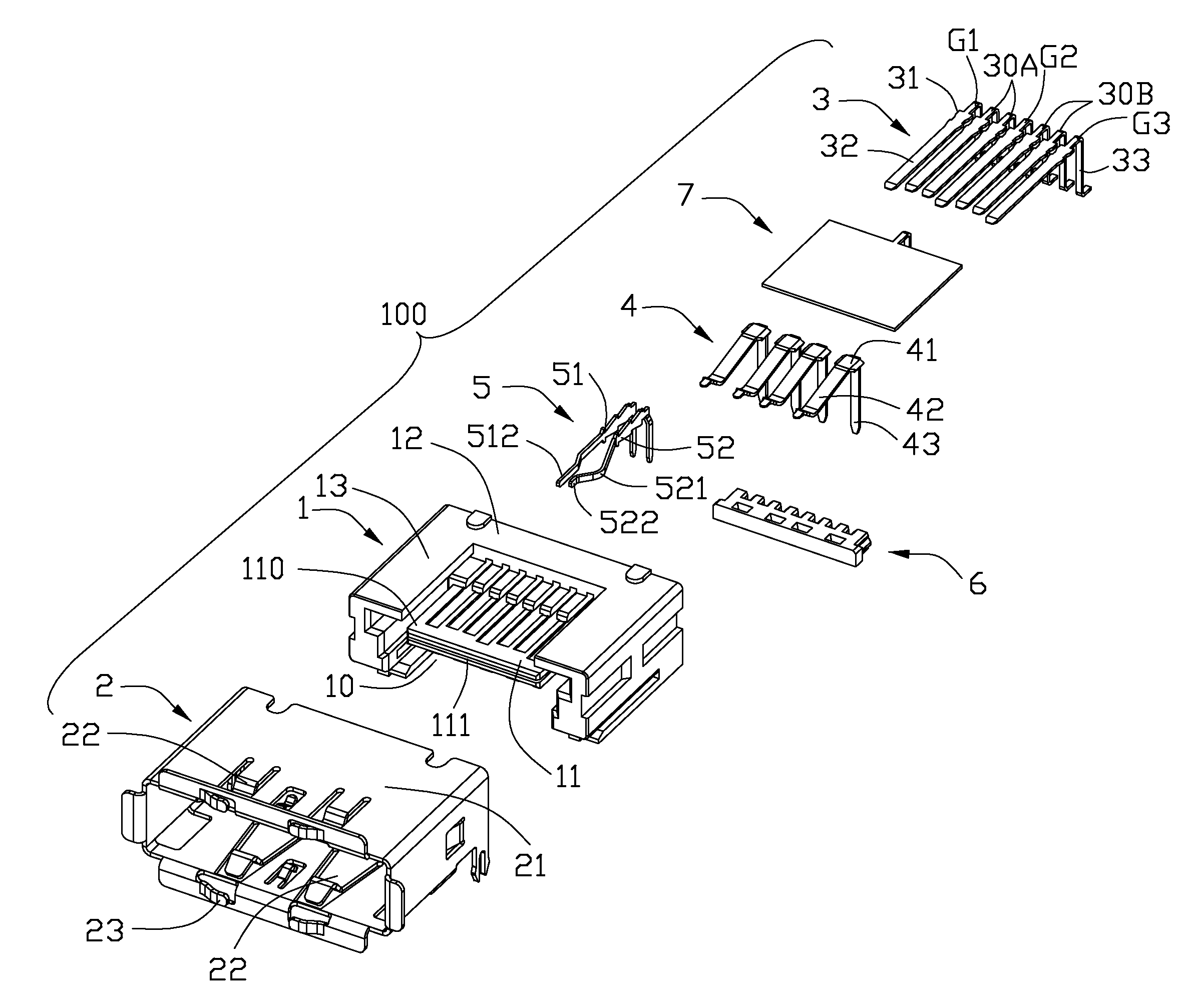
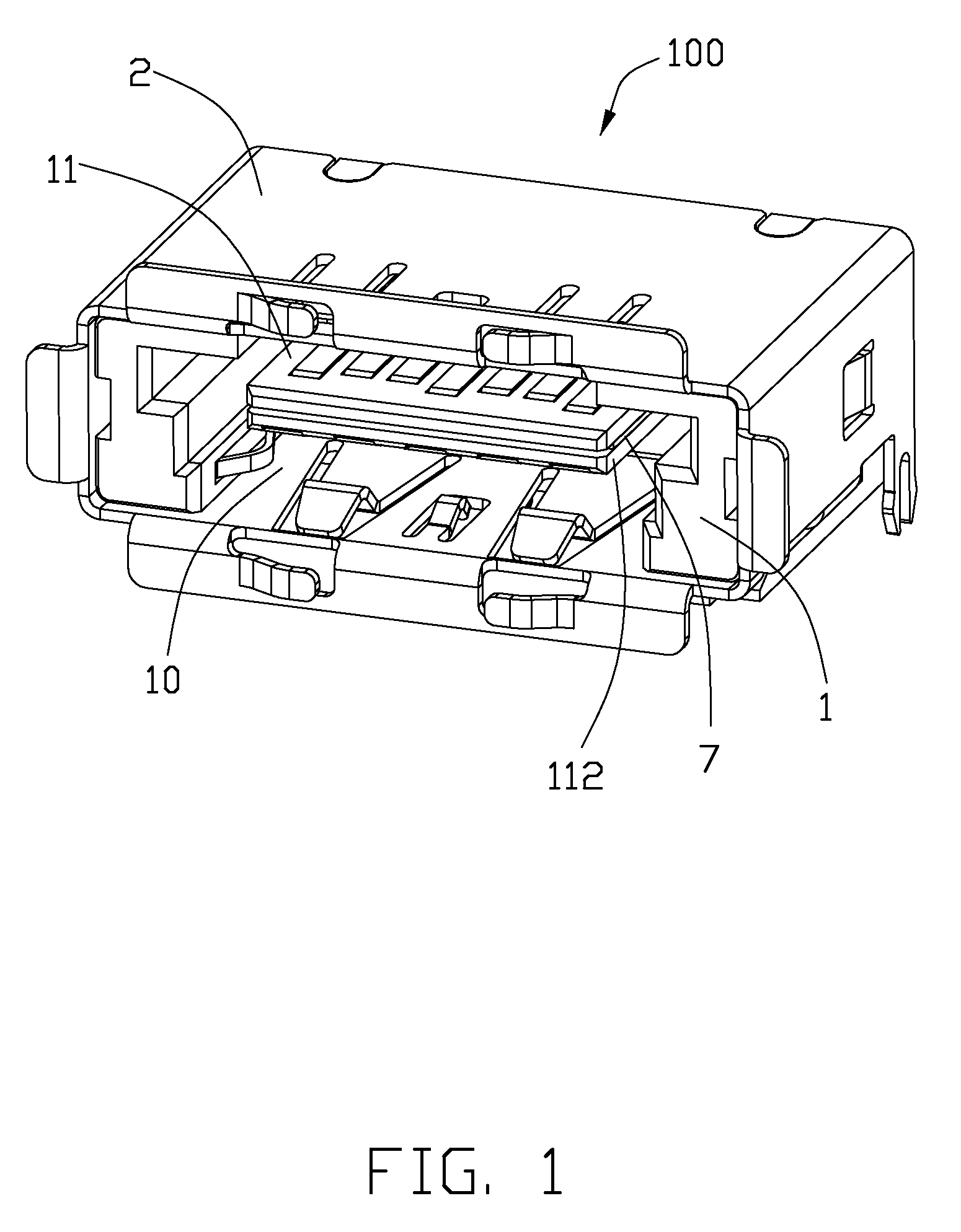
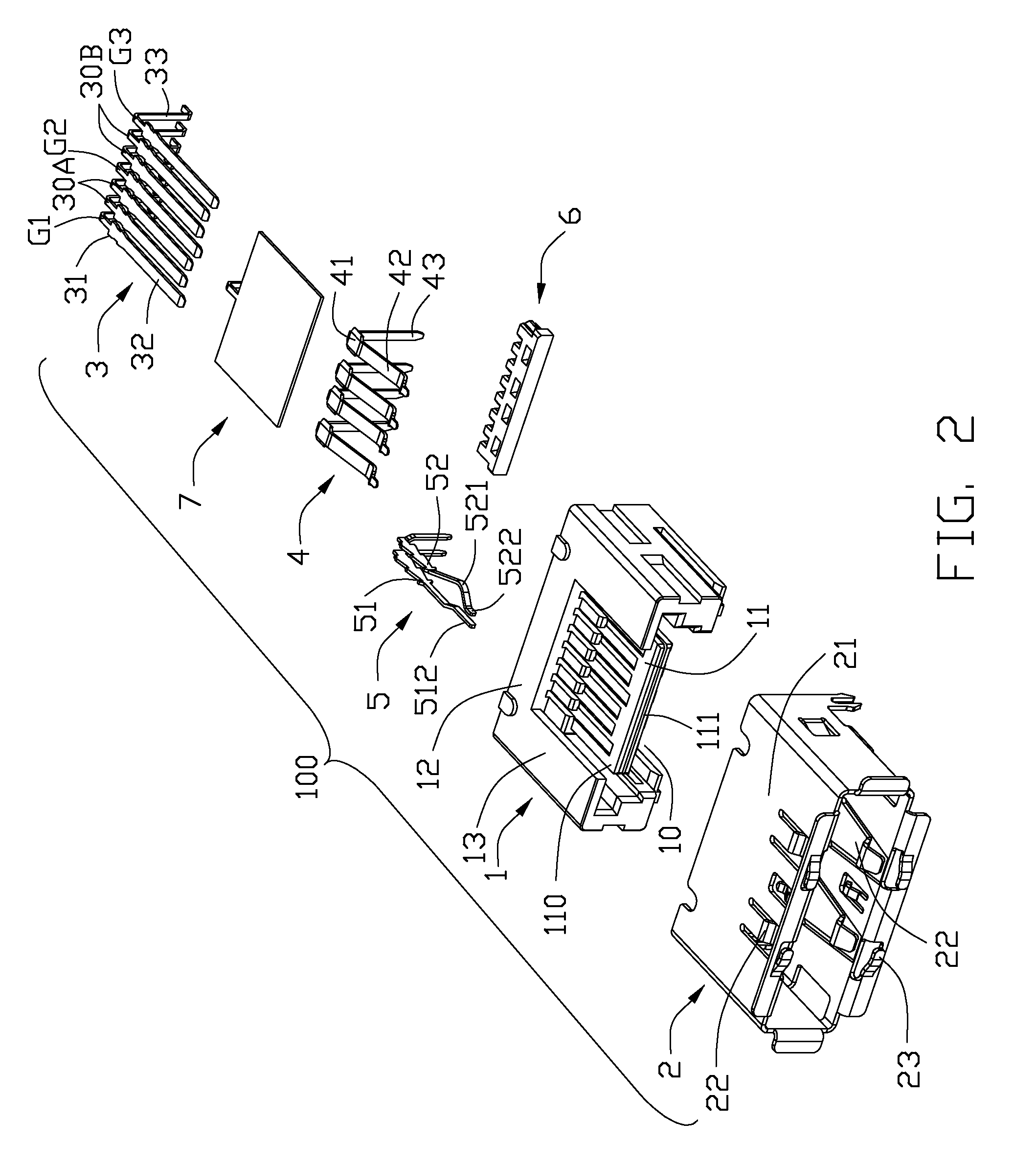
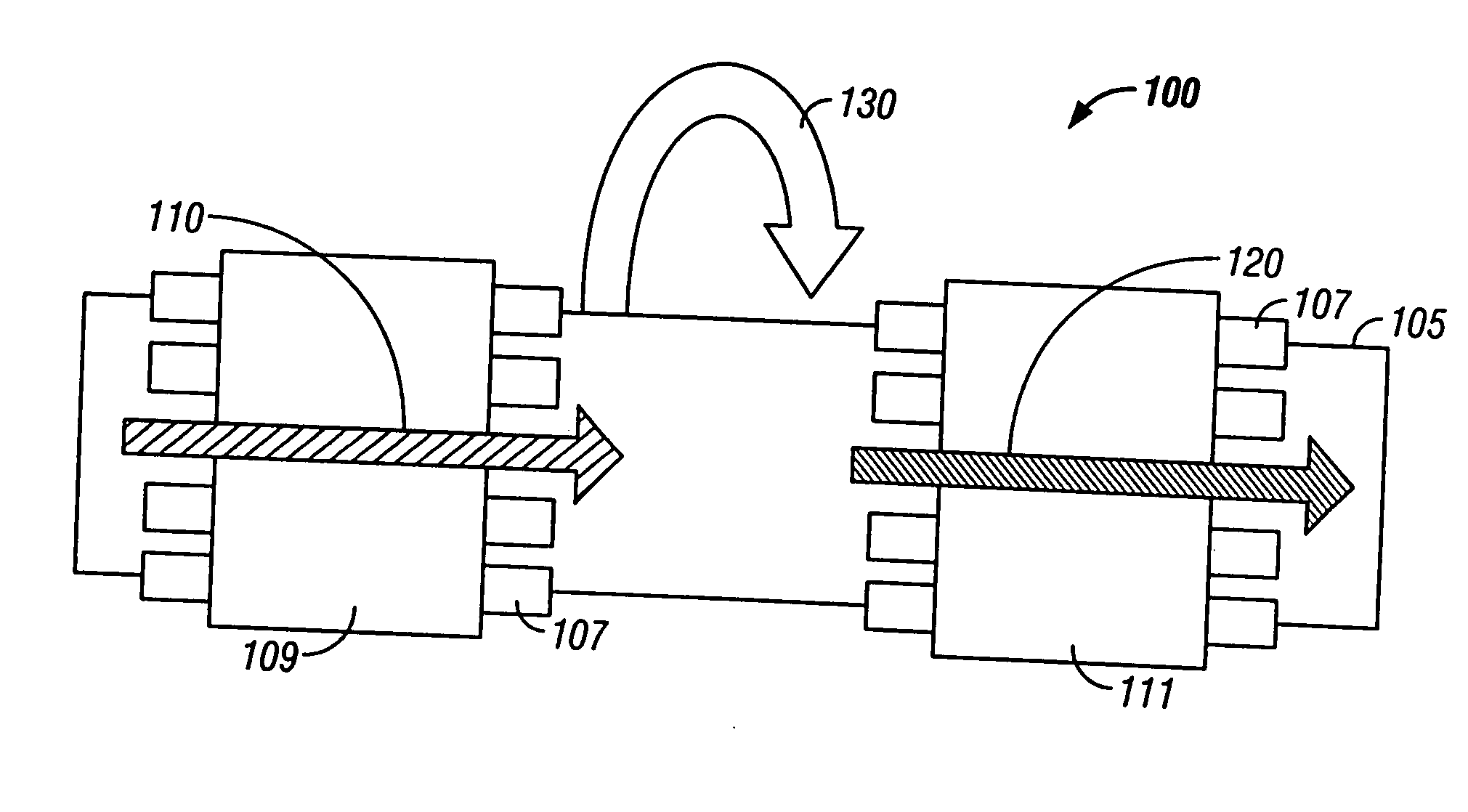
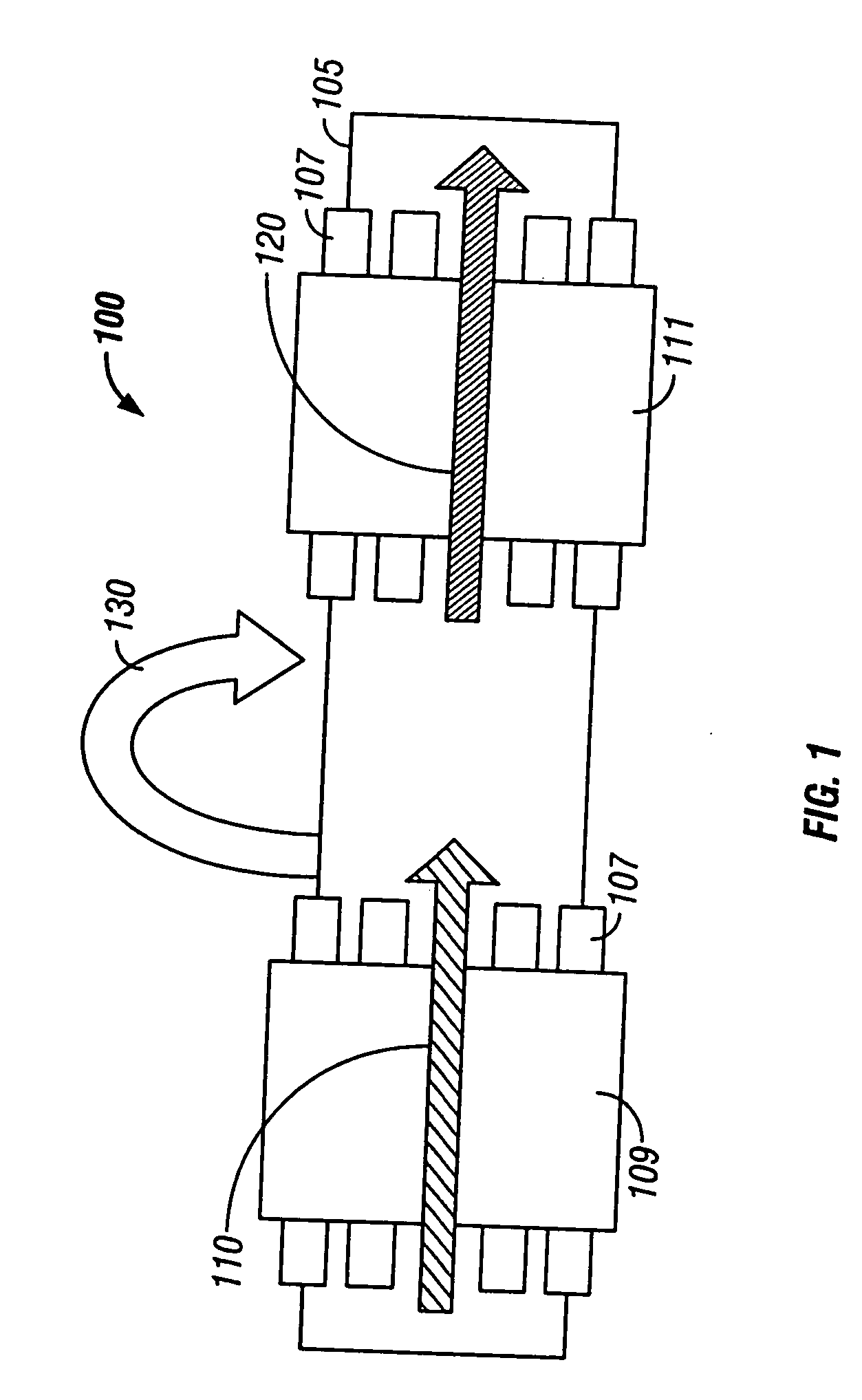
Usb/esata combo receptable featured with ground layer retarding interfaces therebetween
An electrical connector includes an insulative housing defining a mating cavity, two parallel and stacked mating portions respectively forwards extending into the mating cavity, sets of contact retained in the housing and a grounding member retained in the housing. The first mating portion defines thereon a first surface; the second mating portion spaces from the first mating portion and defines thereon a second surface opposite to the first surface. The sets of contact include a first set of contacts each defining a contacting section exposed upon the first surface and a second set of contacts each defining a deflectable cantilevered beam accessible from the second face. The grounding member is disposed between the first and second mating portions to reduce the cross-talk between the first and second sets of contacts.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
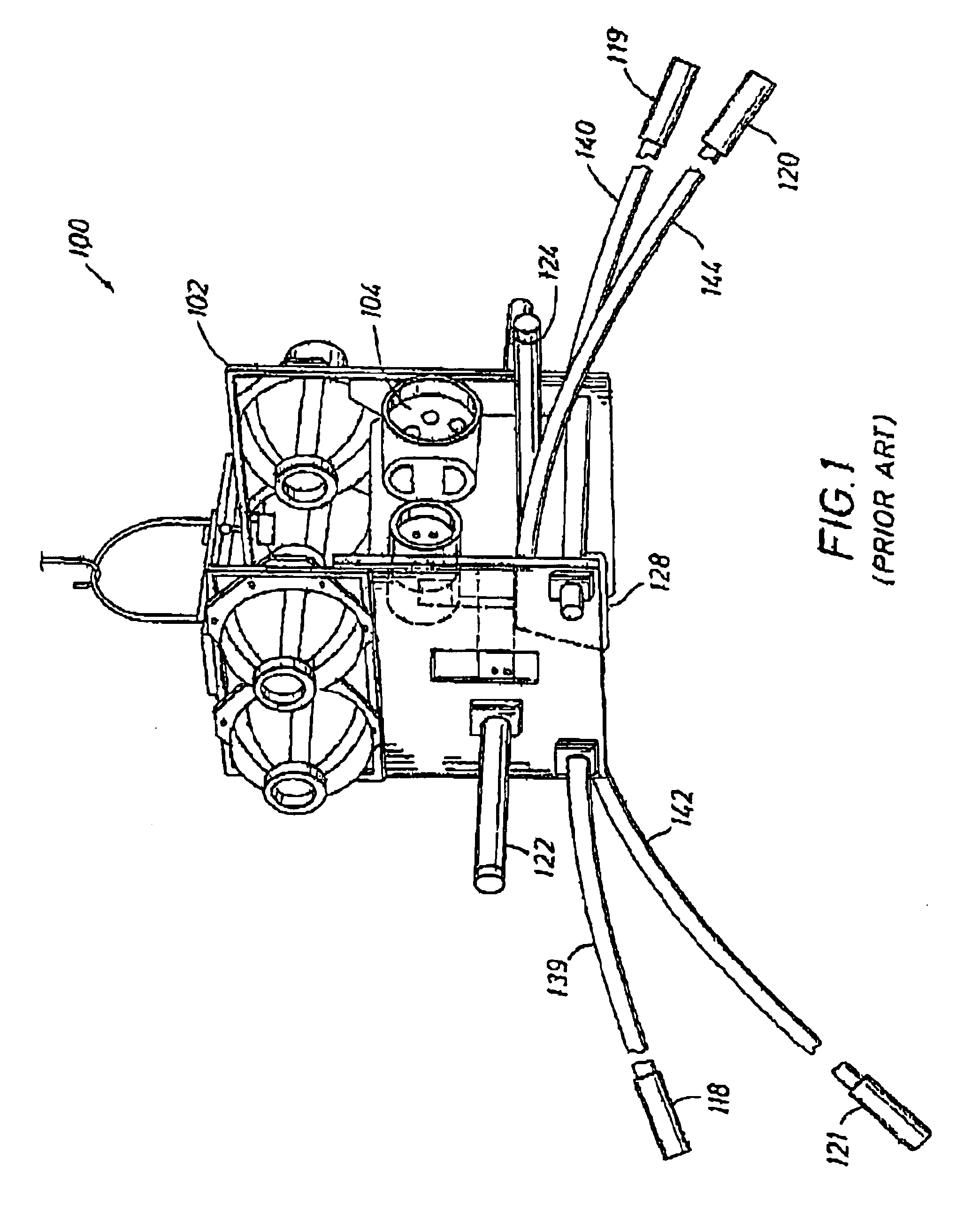
Seismic data acquisition system using acquisition stations set on the sea bottom
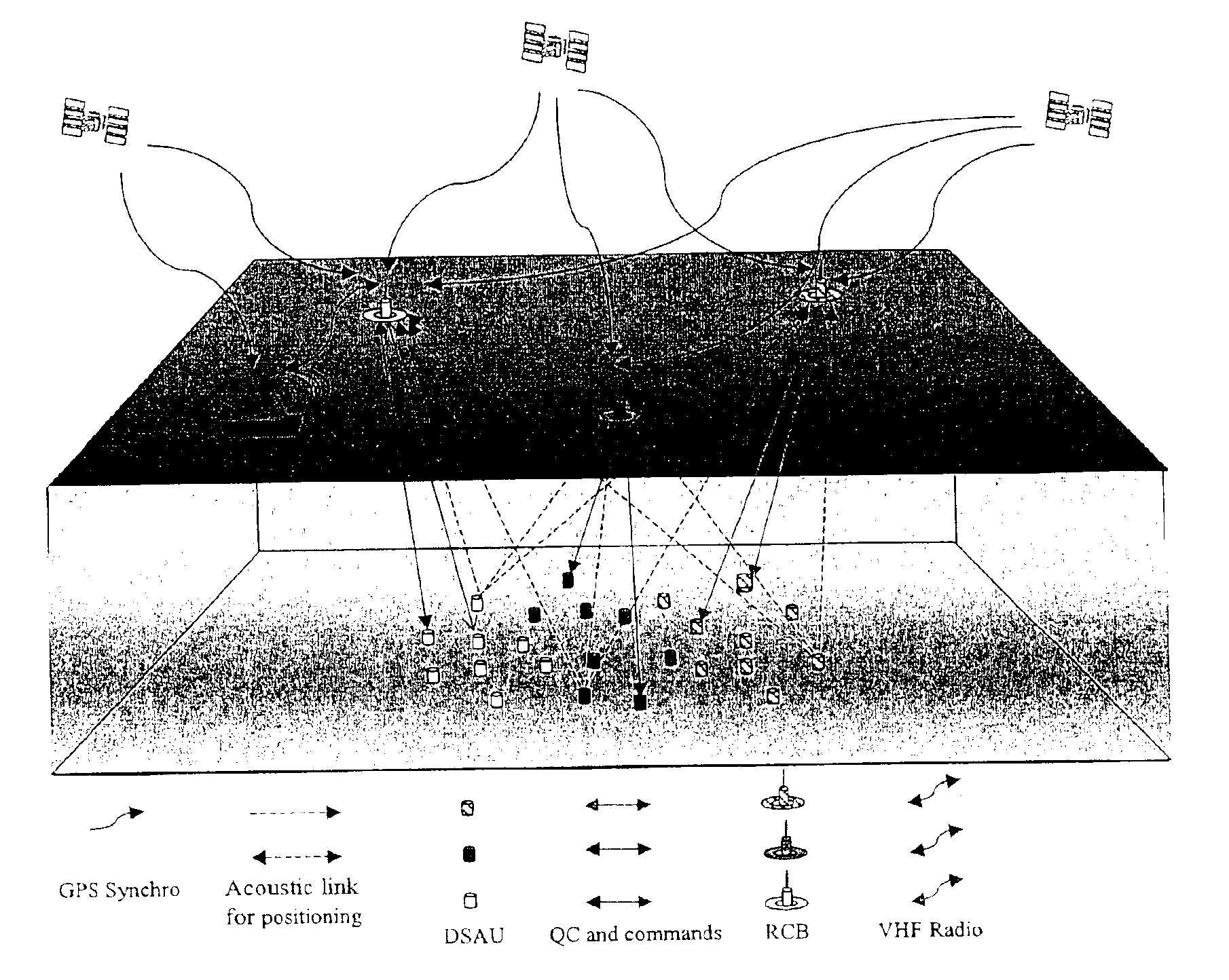
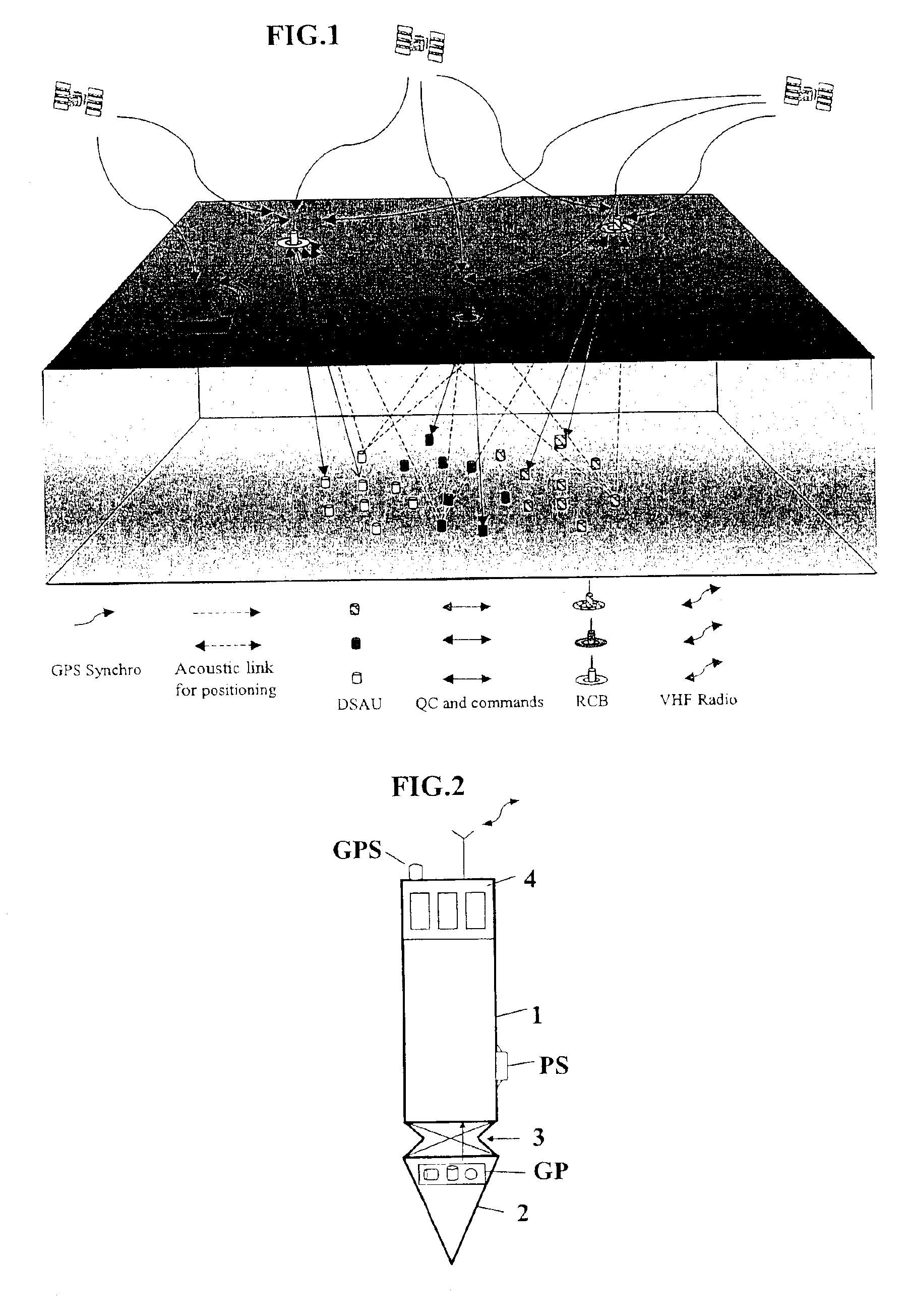
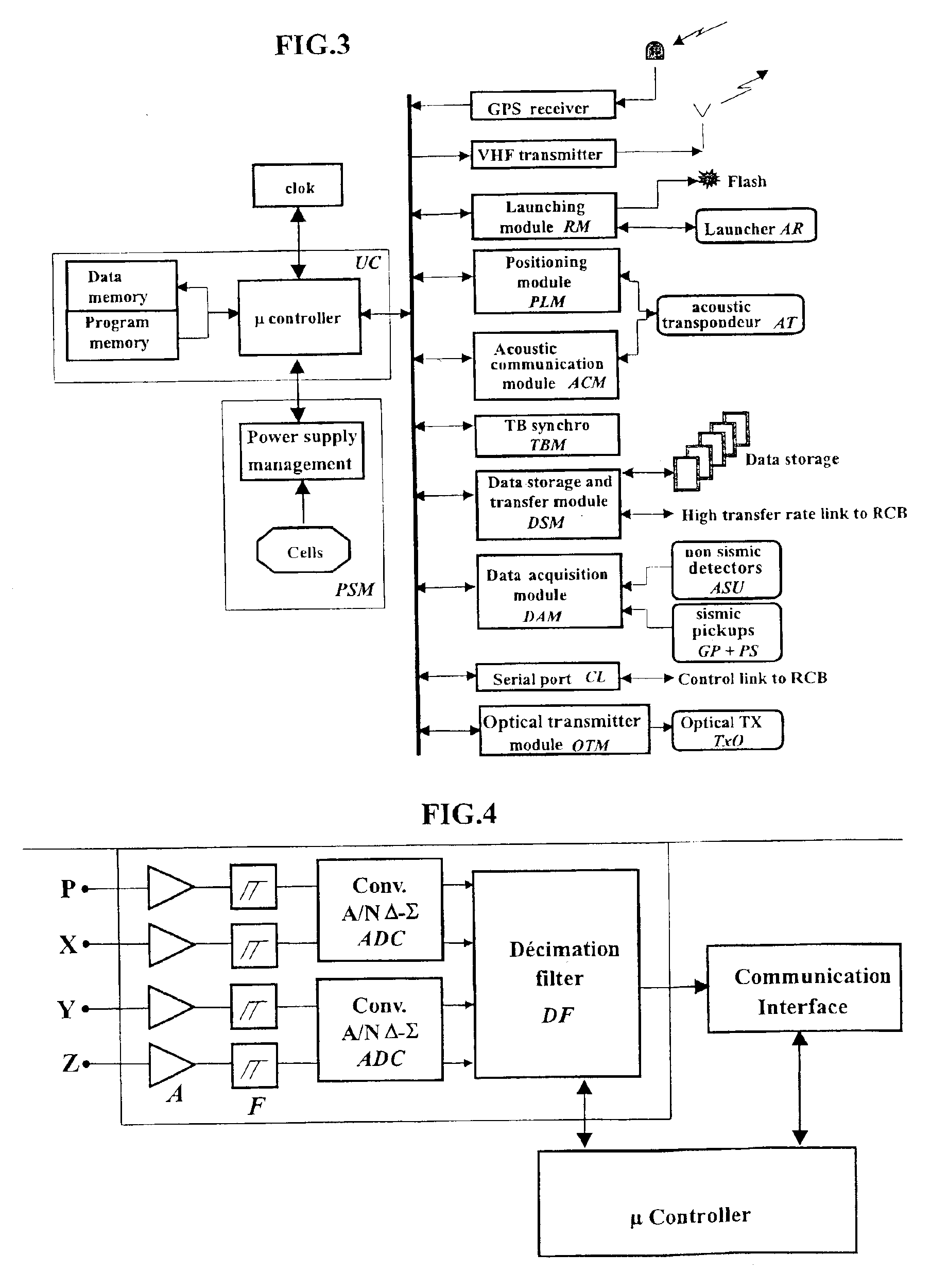
InactiveUS7016260B2Good synchronizationTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsTransmission systemsSystems designData acquisition
The invention is a system designed for acquisition of seismic data by means of acquisition stations set on water bottom of a water body. The system comprises acquisition stations (DSAU) combining a streamlined boom suited to penetrate the bottom and thus couple seismic receivers with the underlying formation, a sealed body for electronic data acquisition and communication modules. These acquisition stations (DSAU) are placed in the water and drop to the bottom under the effect of gravity. Relay buoys (RCB) are positioned at the surface, each with a GPS positioning module, a radio link with a central station (CCRU), on a ship for example, and modules providing acoustic communication with bottom acquisition stations (DSAU), which are used to determine the position of the stations in relation to the relay buoys and to exchange control data and seismic data (good running order data or possibly seismic traces acquired if the conditions lend themselves thereto) to provide seismic prospecting or monitoring of an underground formation.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Substrate for reducing electromagnetic interference and enclosure
InactiveUS6191475B1Magnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectromagnetic interferenceEngineering
A substrate for reducing electromagnetic emissions is provided. The substrate may include a plurality of ground layers, signal layers and power layers. All of the layers other than the ground layer are provided with a ground ring that may extend around the perimeter of the layer. The ground rings are electrically coupled together by ground stitching or vias that are randomly spaced. The random spacing of the ground stitching is based on the operating frequencies of the integrated circuit devices mounted on the substrate. Additional shielding may be provided by providing a cover assembly made of any conductive material that is coupled to the exposed ground rings on the uppermost and lowermost surfaces of the substrate. The cover assembly is coupled to the exposed ground rings in a randomized pattern. The device provides a virtual electrical ground cage in which the internal signal layers are totally enclosed, thereby reducing electromagnetic emissions.
Owner:INTEL CORP
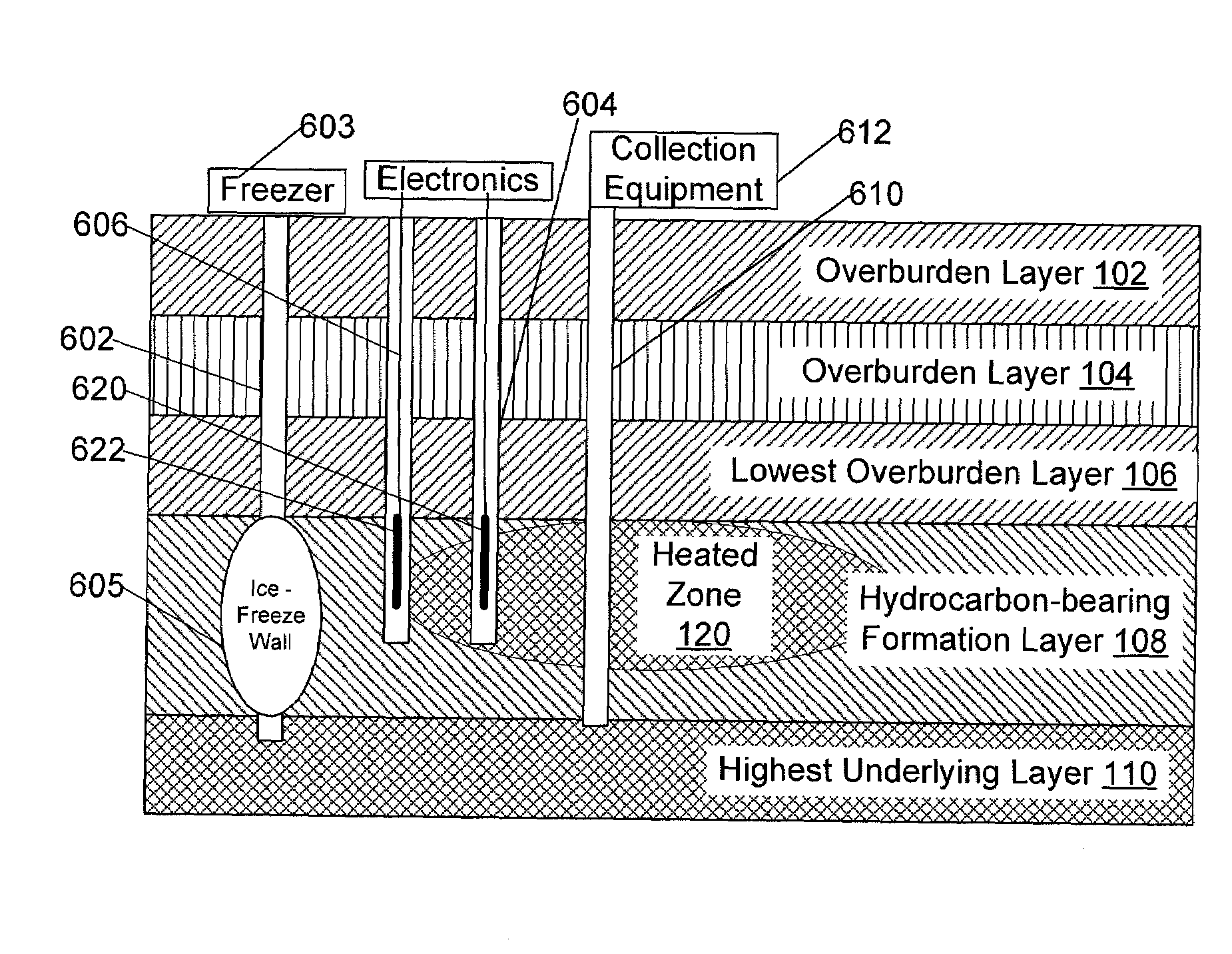
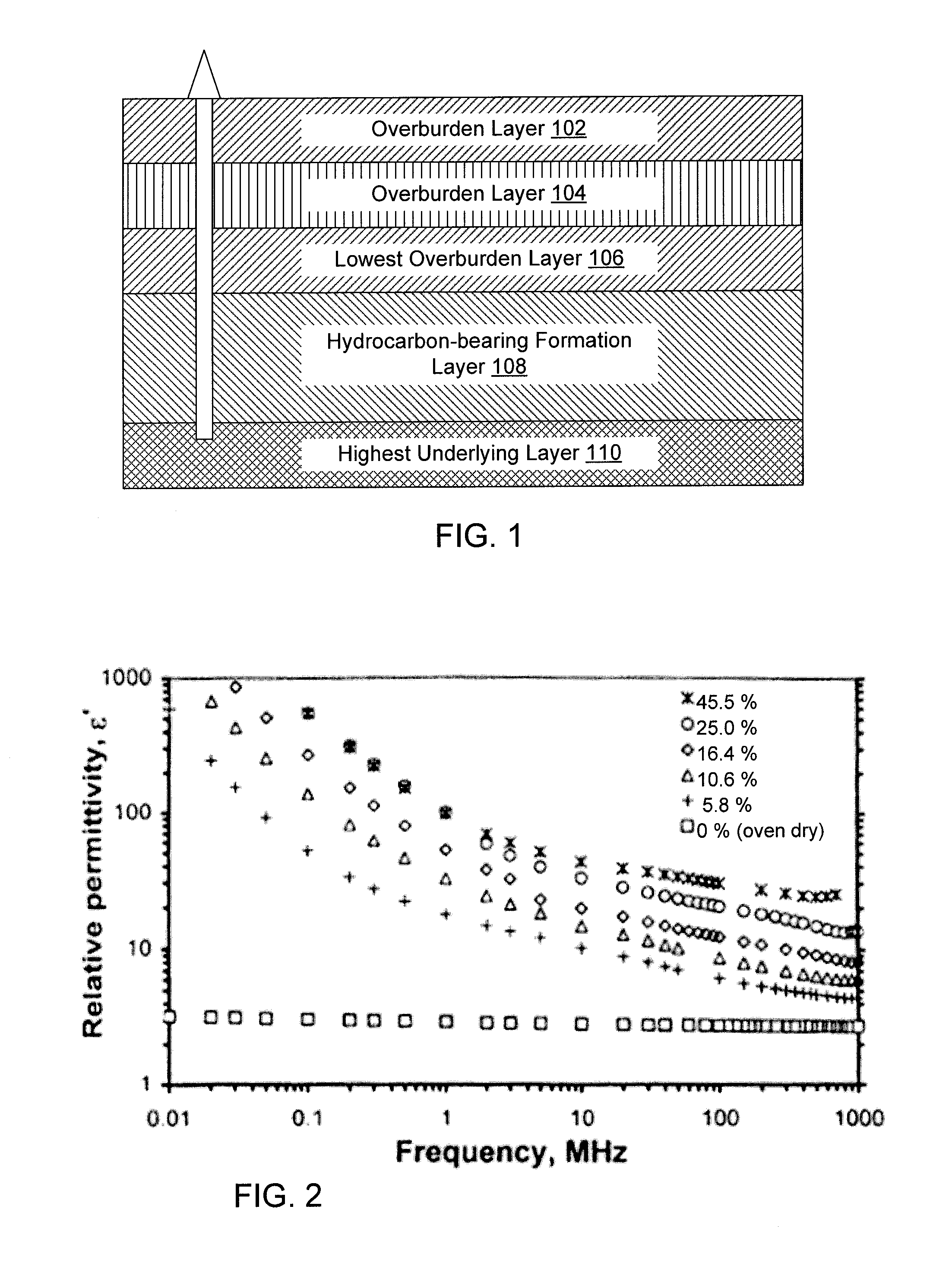
System and method for extraction of hydrocarbons by in-situ radio frequency heating of carbon bearing geological formations
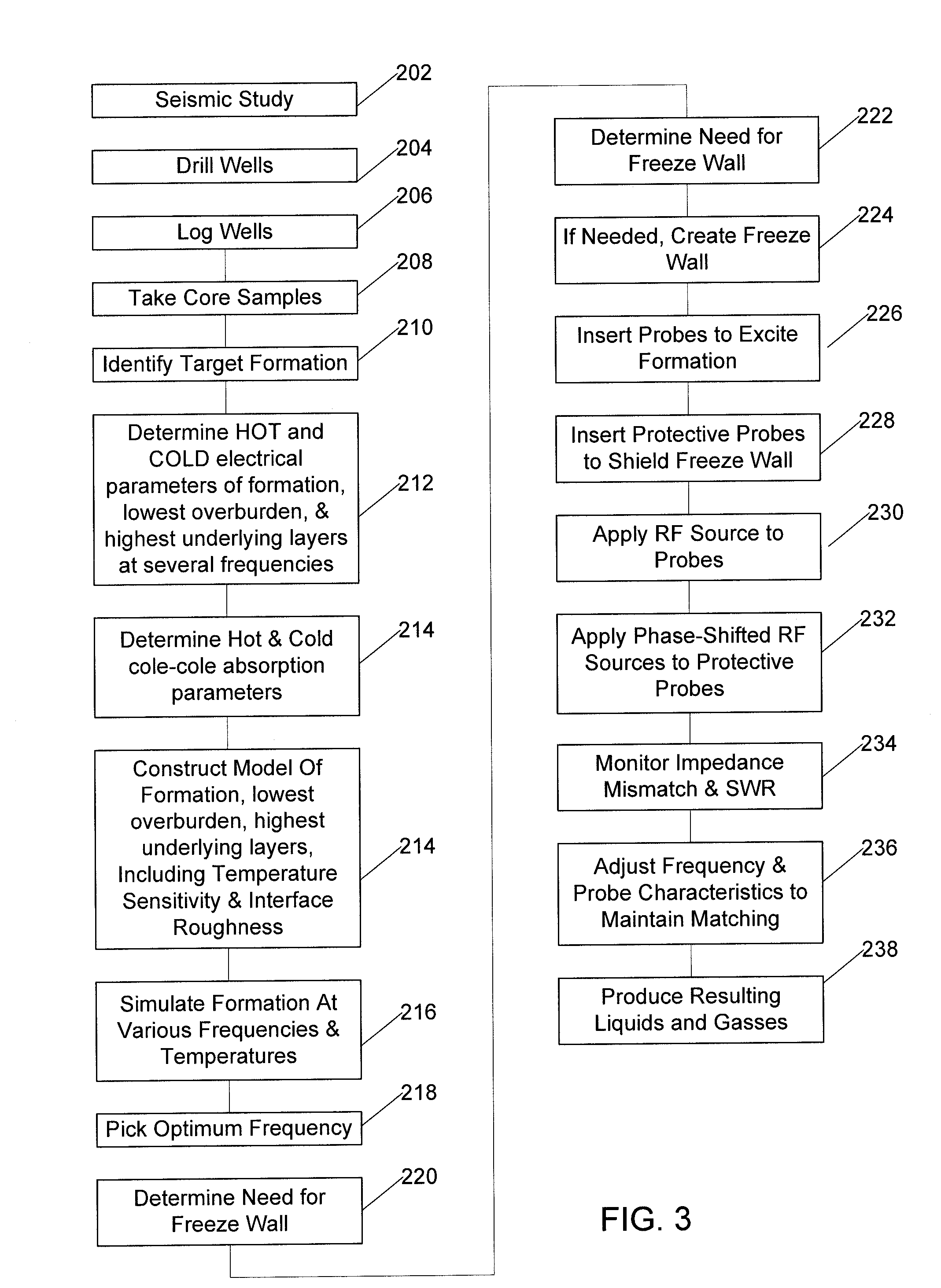
A method of producing liquid hydrocarbons from a hydrocarbon-bearing rock in situ in a geological formation begins with exploring the formation by drilling a plurality of boreholes into the formation and taking core samples of the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and at least one overburden layer. Electrical parameters of the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and the overburden layer are determined, as well as a roughness of a boundary between the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and the at least one overburden layer. These electrical parameters are used to construct a computer model of a portion of the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and at least one overburden layer, the computer model based upon modeling the formation as a rough-walled waveguide. This computer model is used to simulate propagation of radio frequency energy within the hydrocarbon-bearing rock, including simulation of radio frequency wave confinement within the hydrocarbon-bearing rock, at several frequencies and temperatures. A frequency for retorting is selected based upon simulation results. Radio frequency couplers are installed into at least one borehole in the hydrocarbon-bearing rock and driven with radio frequency energy to heat the hydrocarbon-bearing rock. As the rock heats, it releases carbon compounds and these are collected.
Owner:PAO HSUEH YUAN
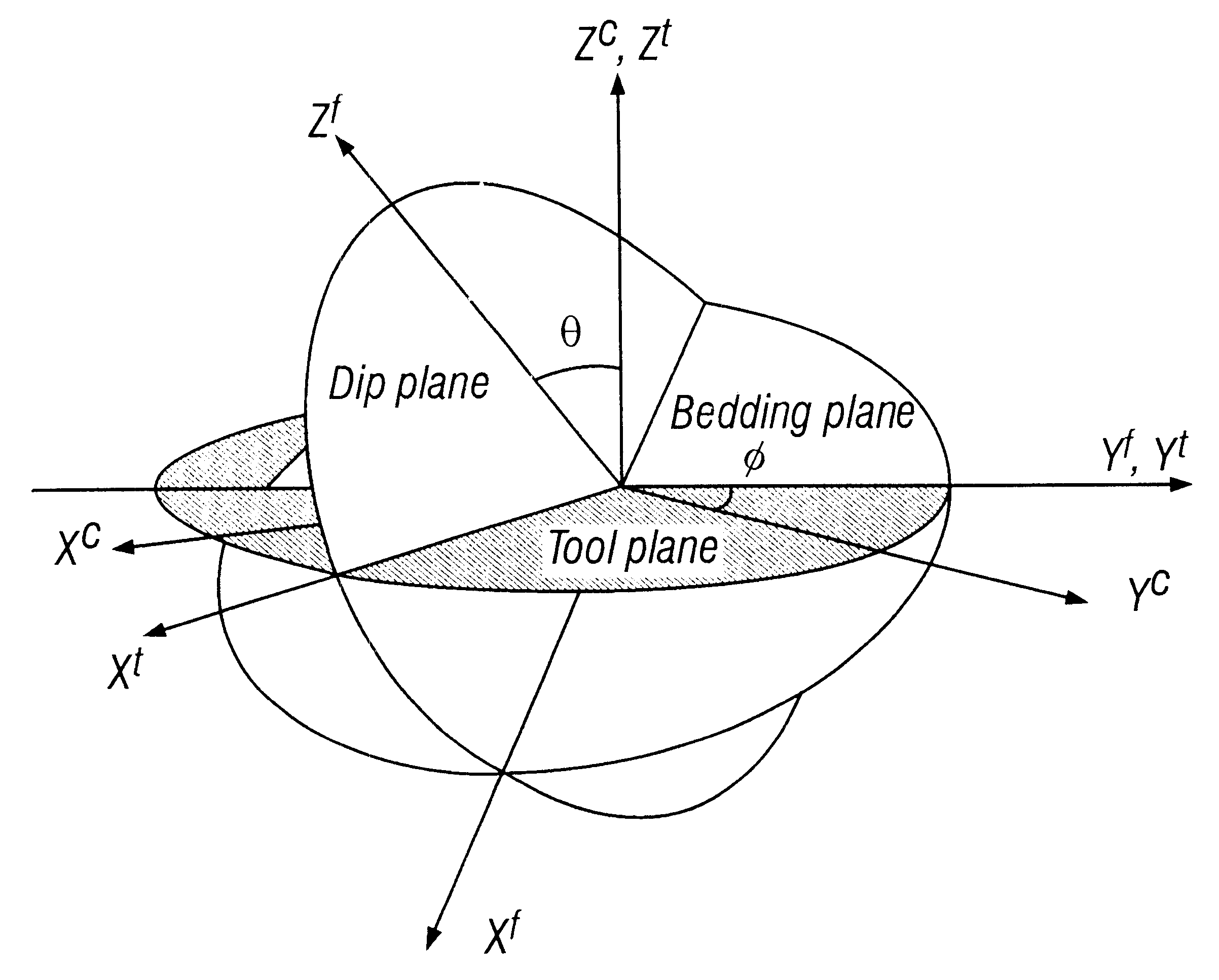
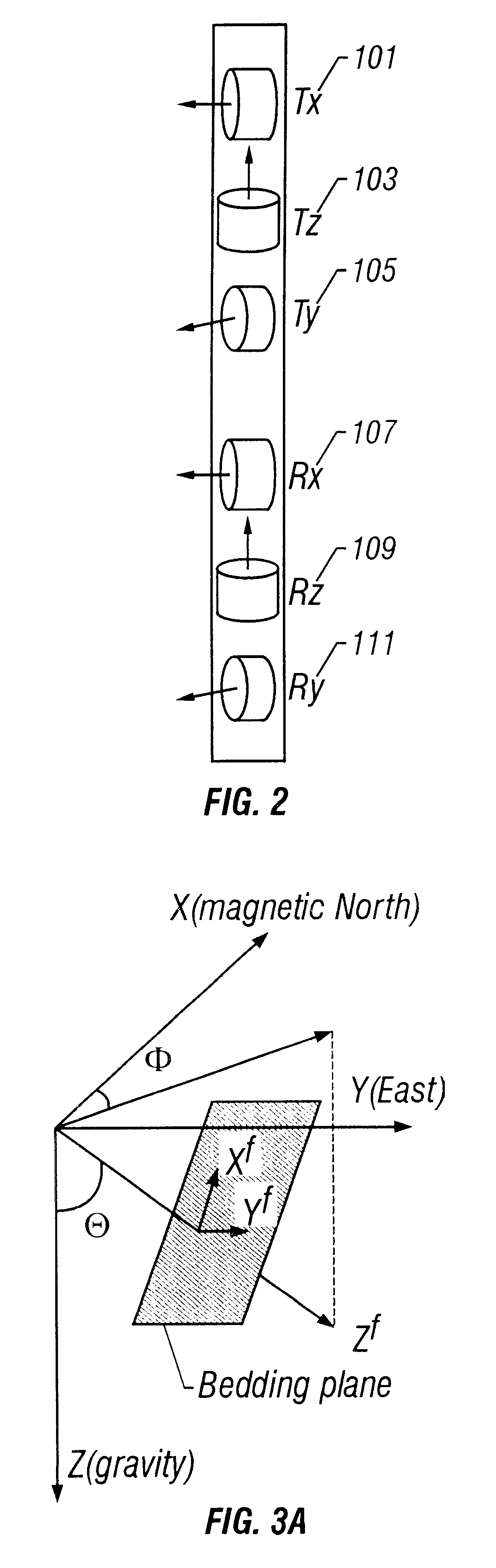
Simultaneous determination of formation angles and anisotropic resistivity using multi-component induction logging data
InactiveUS6643589B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingHorizontal and verticalObject function
Measurements made by a multicomponent logging tool in a borehole are inverted to obtain horizontal and vertical resistivities and formation dip and azimuth angles of a formation traversed by the borehole. The inversion is performed using a generalized Marquardt-Levenberg method. In this generalized Marquardt-Levenberg method, a data objective function is defined that is related to a difference between the model output and the measured data. The iterative procedure involves reducing a global objective function that is the sum of the data objective function and a model objective function related to changes in the model in successive iterations. In an alternate embodiment of the invention, the formation azimuth angle is excluded from the iterative process by using derived relations between the multicomponent measurements.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Integrated Filter Feedthrough Assemblies Made From Low Temperature Co-Fired (LTCC) Tape
InactiveUS20070217121A1Prevent leakageAvoid spreadingAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyScreen printingState of art
A filter capacitor comprising a substrate of at least one layer of a low temperature co-fires ceramic (LTCC) tape supporting alternating active and ground electrode layers segregated by a dielectric layer is described. The substrate is preferably a laminate of three LTCC tapes pieces that are heated under pressure and at a relatively low temperature to become a laminate that maintains its shape and structure dimensions even after undergoing numerous sintering steps. Consequently, relatively thin active and ground electrode layers along with the intermediate dielectric layer can be laid down or deposited on the LTCC substrate by a screen-printing technique. A second laminate of LTCC tapes is positioned on top of the active / dielectric / ground layers to finish the capacitor. Consequently, a significant amount of space is saved in comparison to a comparably rated capacitor or, a capacitor of a higher rating can be provided in the same size as a conventional prior art capacitor.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
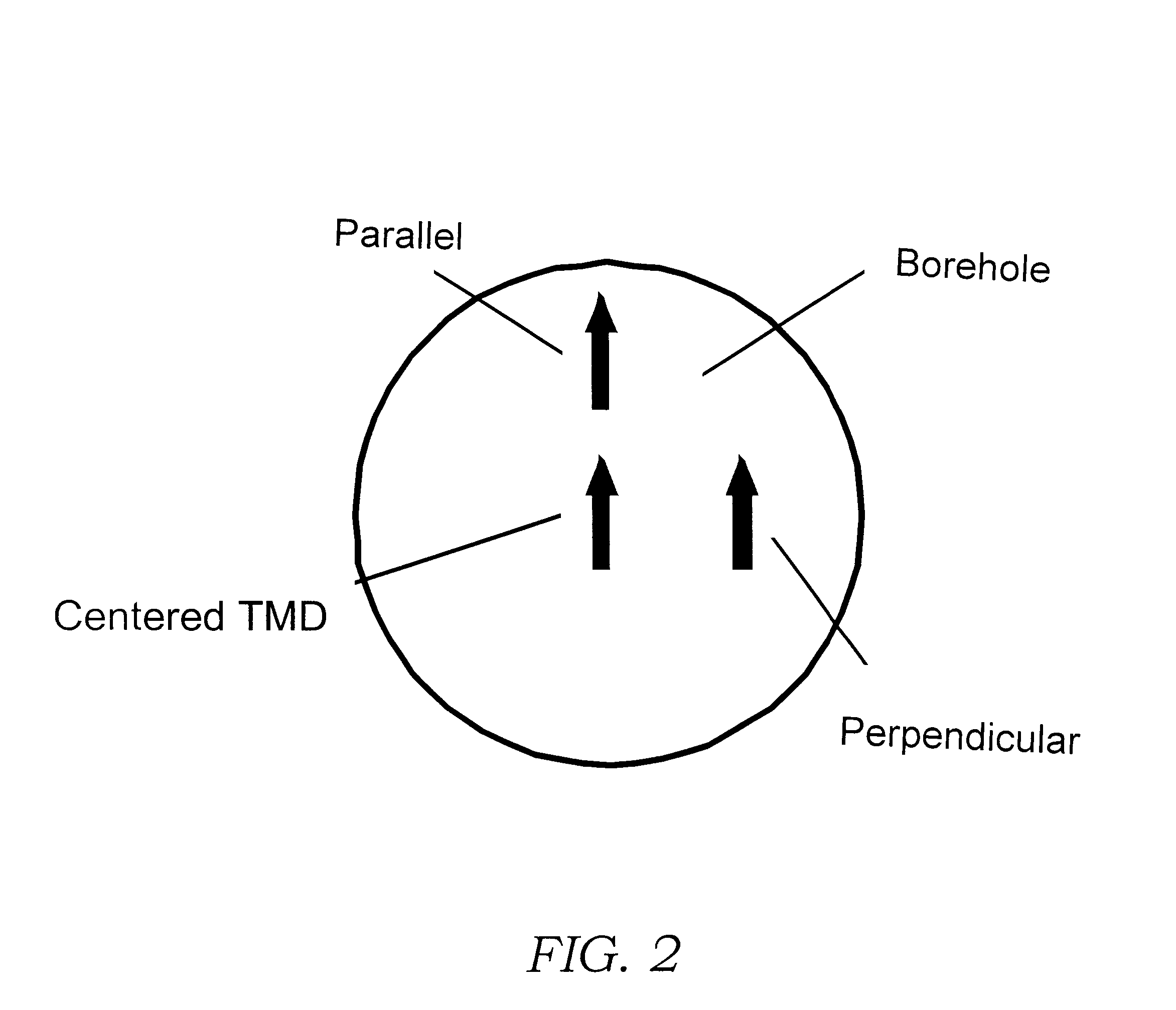
Multi-coil electromagnetic focusing methods and apparatus to reduce borehole eccentricity effects
InactiveUS6541979B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationElectrical resistance and conductanceCurrent sensor
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for canceling or eliminating borehole eccentricity effects on a formation resistivity measurement obtained with transmitter and / or receiver antennas which are substantially time varying magnetic dipoles with their dipole moments aligned at an angle to the axis of the borehole. Various apparatus are configured with a plurality of antennas having tilted or transverse magnetic dipole moments, at least one current sensor, means for conducting alternating current through one or more of the antennas, and means for calculating a scaling factor from signal measurements and for scaling the alternating current with the factor. One method includes scaling an alternating current and passing said current through one or more antennas to obtain the resistivity measurement. Another method includes calculating scaling factors based on spacings between antennas and / or current sensors disposed on an instrument and passing alternating currents scaled by said factors through one or more antennas to obtain the resistivity measurement. Another embodiment includes inputting a borehole fluid resistivity value to derive the formation resistivity.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
USB/ESATA combo receptable featured with ground layer retarding interfaces therebetween
An electrical connector includes an insulative housing defining a mating cavity, two parallel and stacked mating portions respectively forwards extending into the mating cavity, sets of contact retained in the housing and a grounding member retained in the housing. The first mating portion defines thereon a first surface; the second mating portion spaces from the first mating portion and defines thereon a second surface opposite to the first surface. The sets of contact include a first set of contacts each defining a contacting section exposed upon the first surface and a second set of contacts each defining a deflectable cantilevered beam accessible from the second face. The grounding member is disposed between the first and second mating portions to reduce the cross-talk between the first and second sets of contacts.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Electromagnetic interference shielding for a printed circuit board
ActiveUS7443693B2Reduce the amount requiredEmission reductionPrinted circuit assemblingLocalised screeningElectromagnetic interferenceEngineering
The present invention provides shielded printed circuit boards and electronic devices. The printed circuit board may comprise an internal network of grounded conductive elements that are coupleable to an EMI shield that is mounted on the printed circuit board. The network of grounded conductive elements are coupleable to a grounded layer and to the EMI shield and provides improved EMI shielding through the volume of the printed circuit board below an electronic component mounted on the printed circuit board.
Owner:DEEP COAT +1
Method and apparatus for subterranean formation flow imaging
InactiveUS20040090230A1Accurately determine formation parameterAccurate measurementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceMri imageGeophysics
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for measuring a property relating to fluid flow in an earth formation, more specifically to directly measuring formation permeability and other fluid characteristics. The present invention provides a method for determining the permeability of a hydrocarbon bearing earth formation, which method comprises the steps of: locating a tool at a selected position in a borehole penetrating the earth formation; inducing a flow of fluid within the earth formation to said tool; creating at least two MRI images of said fluid while flowing within the earth formation to said tool, said at least two images being created at different times; determining displacement of said fluid within the earth formation between said different times, using the at least two MRI images.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
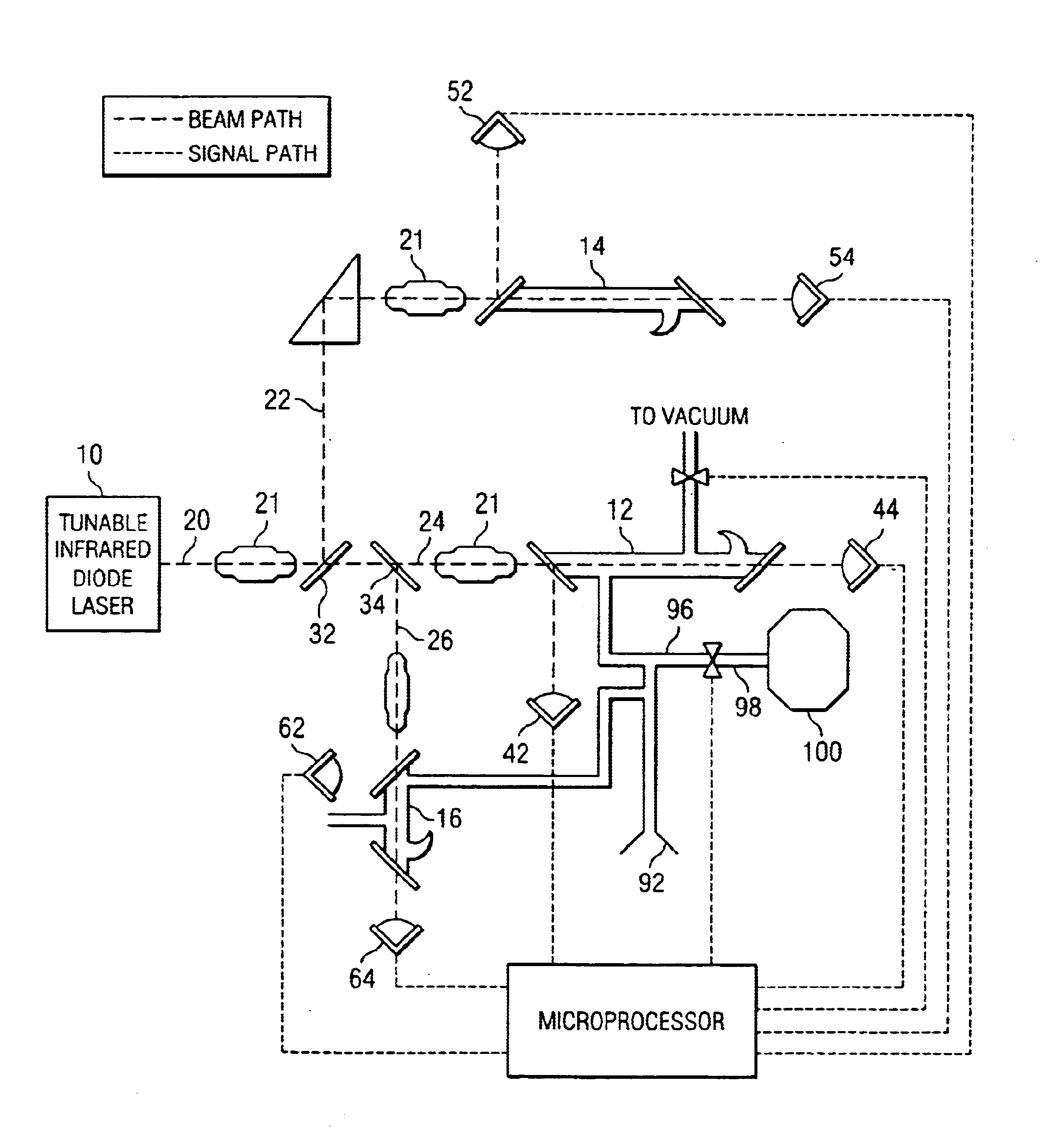
Method and apparatus for performing rapid isotopic analysis via laser spectroscopy
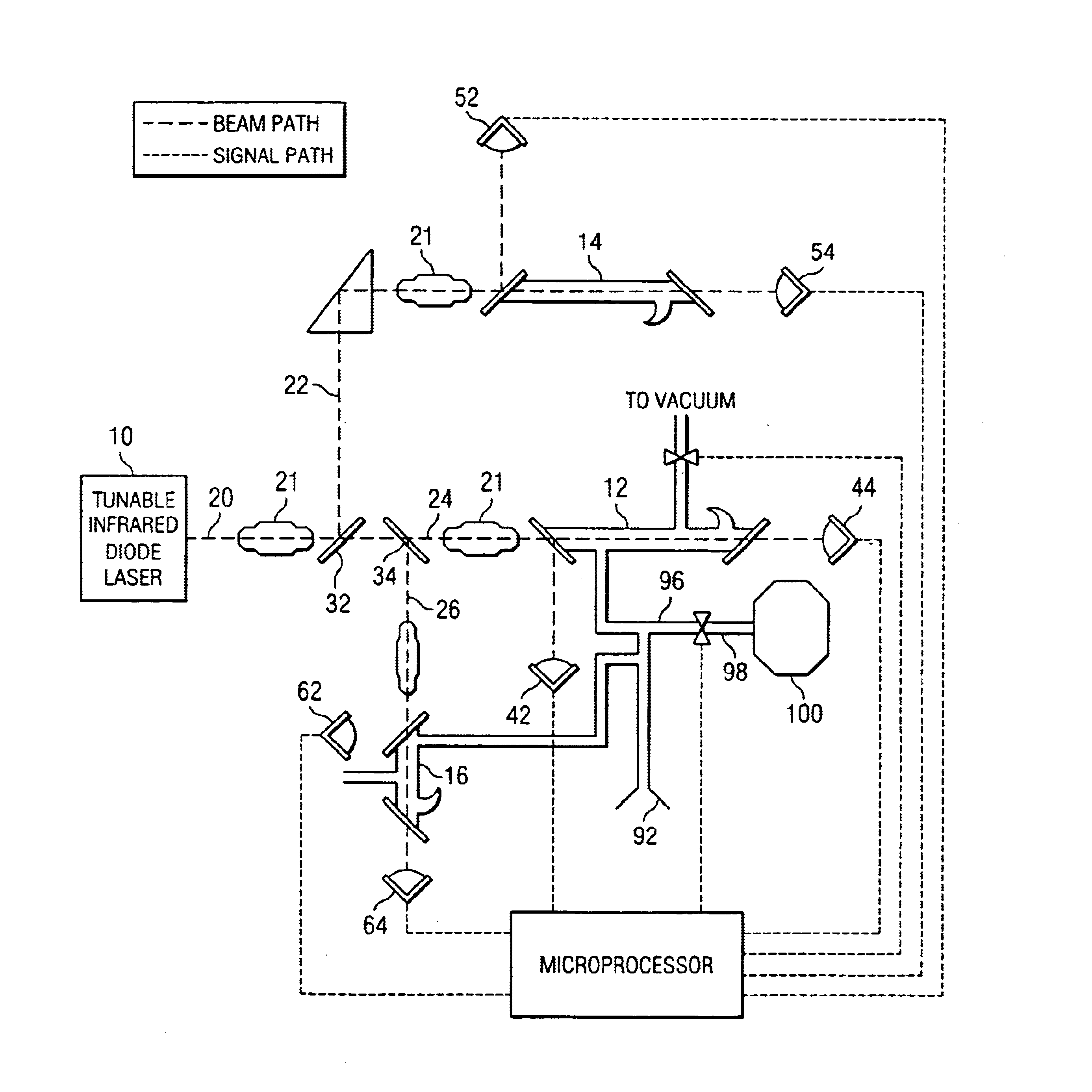
InactiveUS6888127B2Accurate and preciseAccurate and Precise MeasurementsRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsIsotopeLaser beams
Method and apparatus for providing real-time data indicative of the isotopic composition of formation fluids during drilling. The method includes the steps of: (a) providing a reference fluid having a known isotopic composition in a reference cell; (b) capturing a sample of formation; (c) providing at least one laser beam; (e) passing a beam through the reference fluid, measuring the reference-measurement beam before and after it passes through the reference fluid; (f) and passing a beam through the sample, measuring the beam before and after it passes through the sample, and calculating a first isotope concentration from those measurements. The measurements can provide information relating to the carbon isotopic composition of individual compounds in hydrocarbon gas mixtures, with the individual compounds including methane, ethane, propane, iso- or normal butane, or iso- or normal pentane.
Owner:CALEB BRETT USA
Method and apparatus for a multi-component induction instrument measuring system for geosteering and formation resistivity data interpretation in horizontal, vertical and deviated wells
InactiveUS20040196047A1Reduce the overall transmitter momentMinimize eddy currentElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyGeosteeringElectromagnetic launch
An improved induction tool for formation resistivity evaluations. The tool provides electromagnetic transmitters and sensors suitable for transmitting and receiving magnetic fields in radial directions that are orthogonal to the tool's longitudinal axis with minimal susceptibility to errors associated with parasitic eddy currents induced in the metal components surrounding the transmitter and receiver coils. Various transmitter receiver combinations are provided to select sensitivity to a desired reservoir formation properties, for example, different orientations xy, xz, yz, 20-40, 20-90, and combinations, such as, Symmetric-symmetric; Asymmetric-symmetric; and Asymmetric-asymmetric. Measurements made with a multi-component logging instrument when used in a substantially horizontal, vertical or deviated borehole in earth formations are diagnostic of the direction of resistive beds relative to the position of the borehole.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
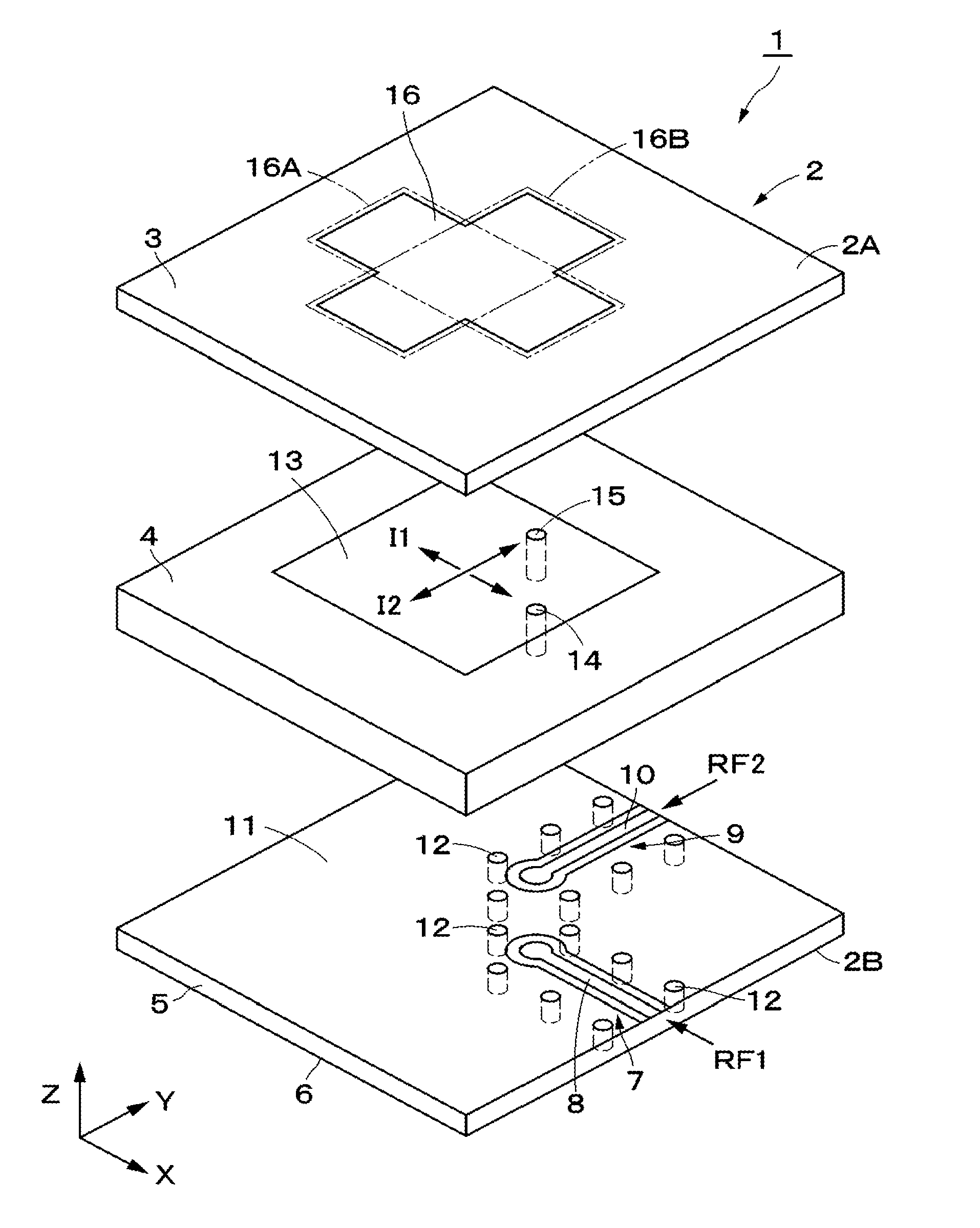
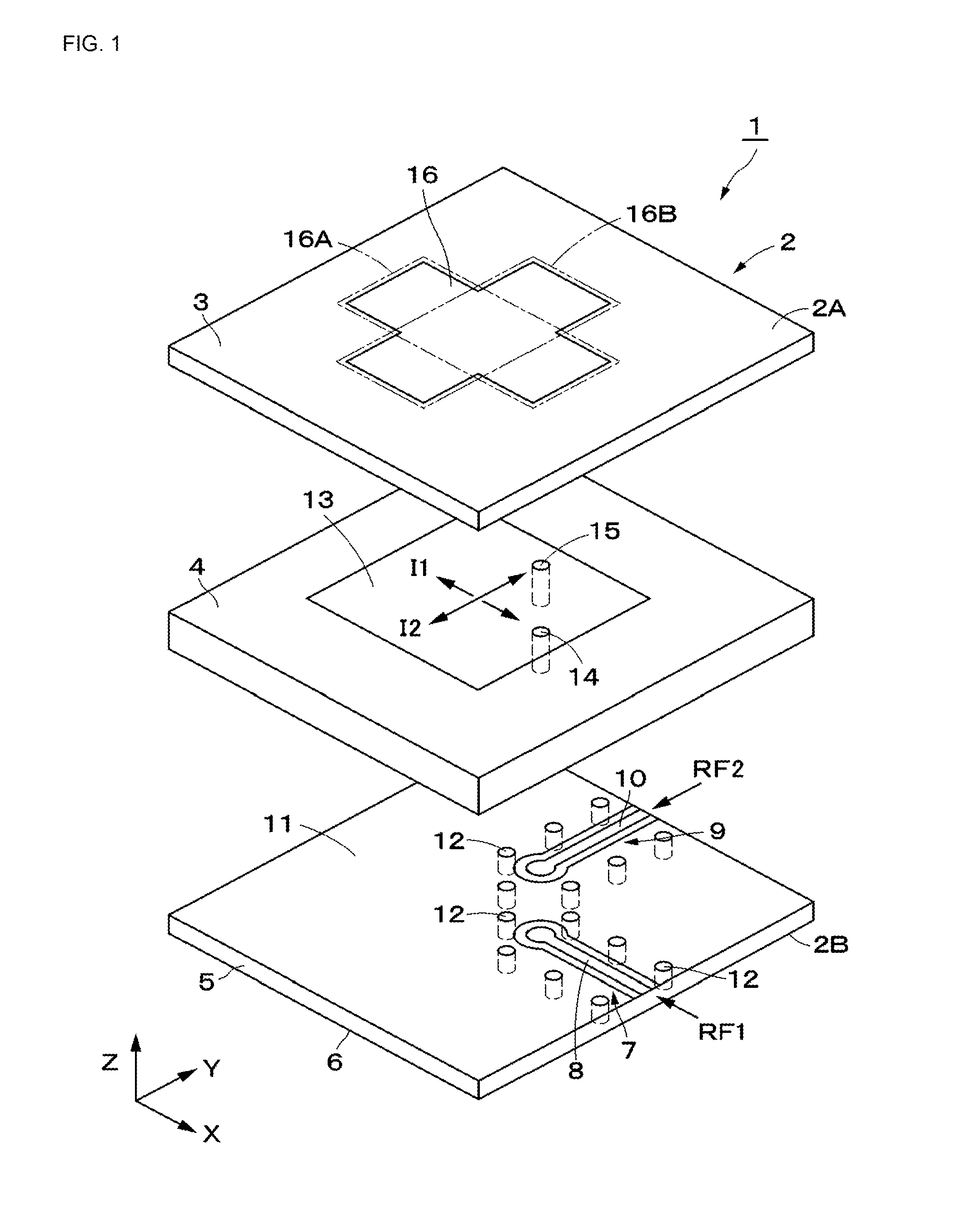
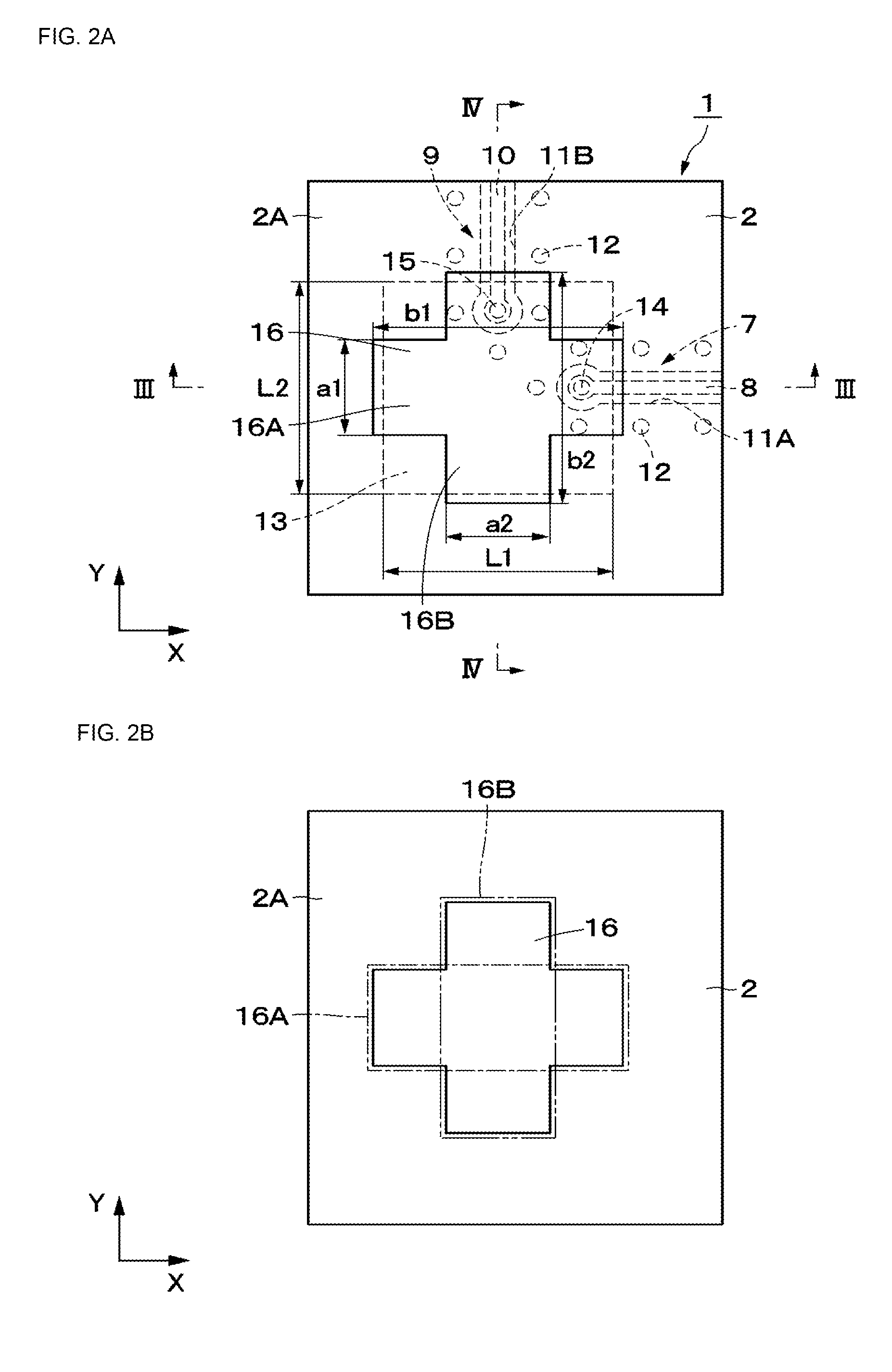
Dual-polarized antenna
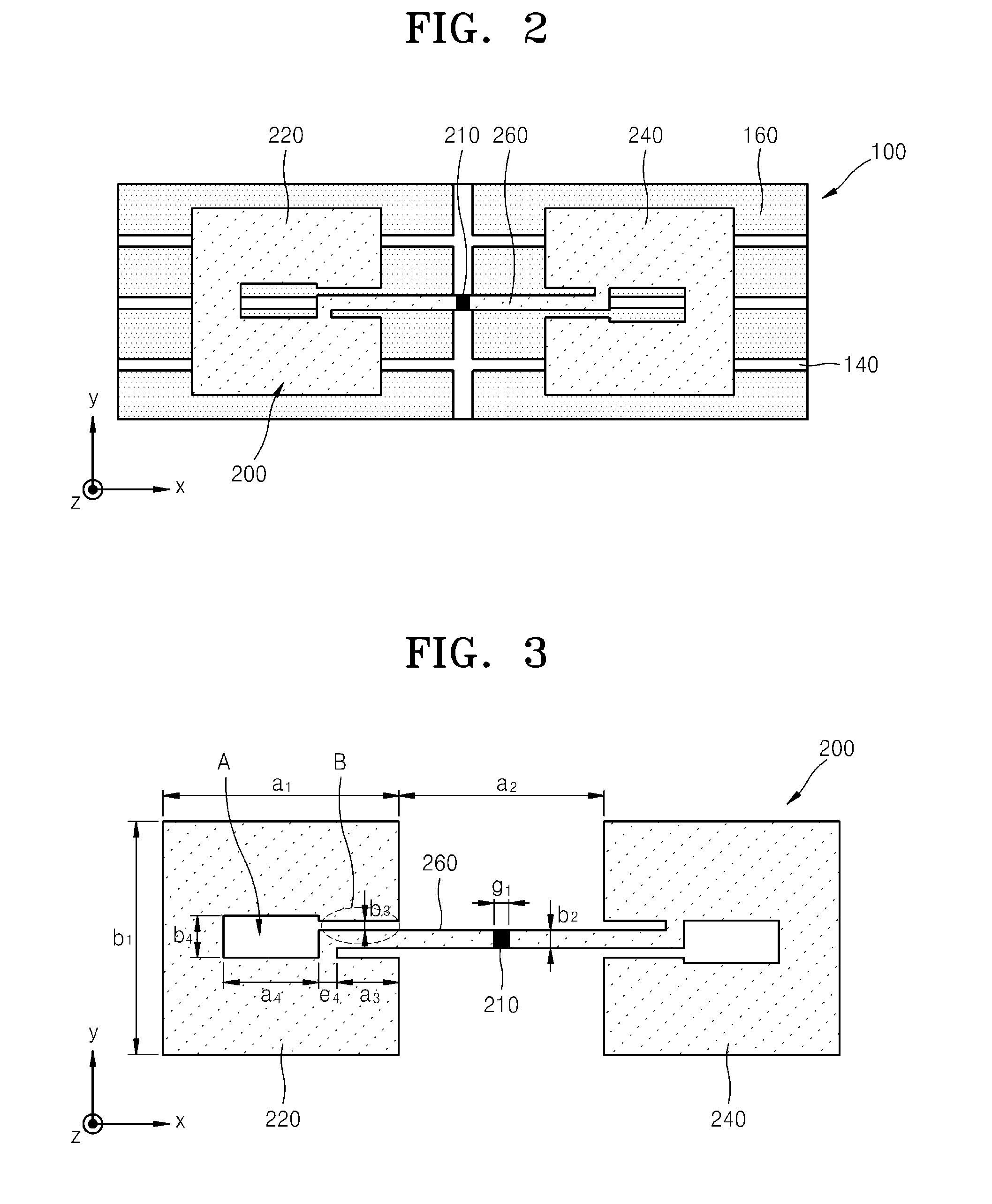
ActiveUS20150194730A1Bandwidth in which matching of the antenna can be ensured can be widenedHigh bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsRadiating elementCoplanar lines
In a multilayer substrate (2), an internal ground layer (11) is provided at a position between insulating layers (4) and (5) and a radiating element (13) is provided at a position between insulating layers (3) and (4). A first coplanar line (7) is connected to an intermediate position of the radiating element (13) in an X-axis direction, and a second coplanar line (9) is connected to an intermediate position of the radiating element (13) in a Y-axis direction. A passive element (16) is laminated on the upper surface of the radiating element (13) through the insulating layer (3). The passive element (16) is formed in a cross shape in which a first patch (16A) extending in the X-axis direction and a second patch (16B) extending in the Y-axis direction are orthogonal to each other.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
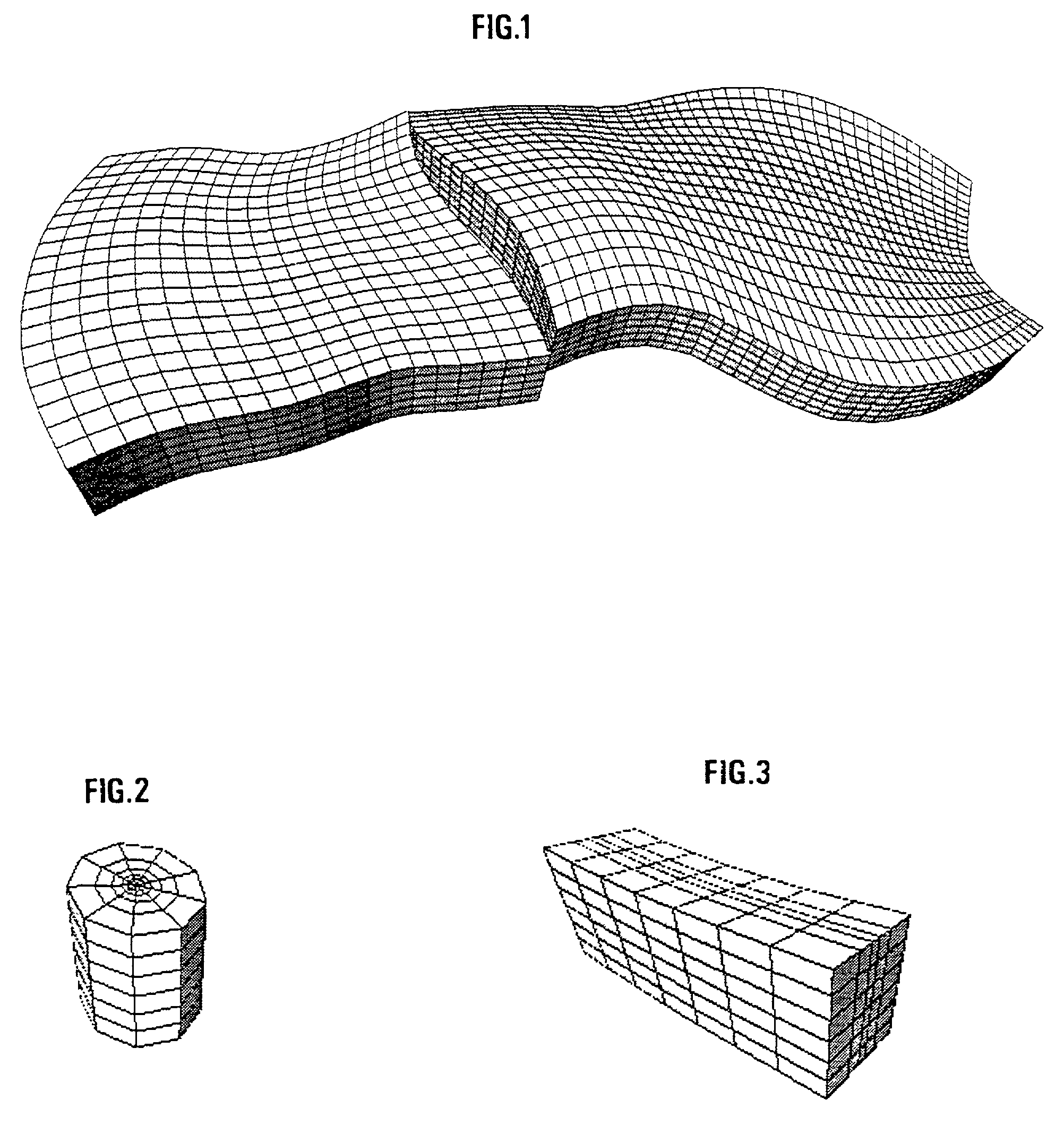
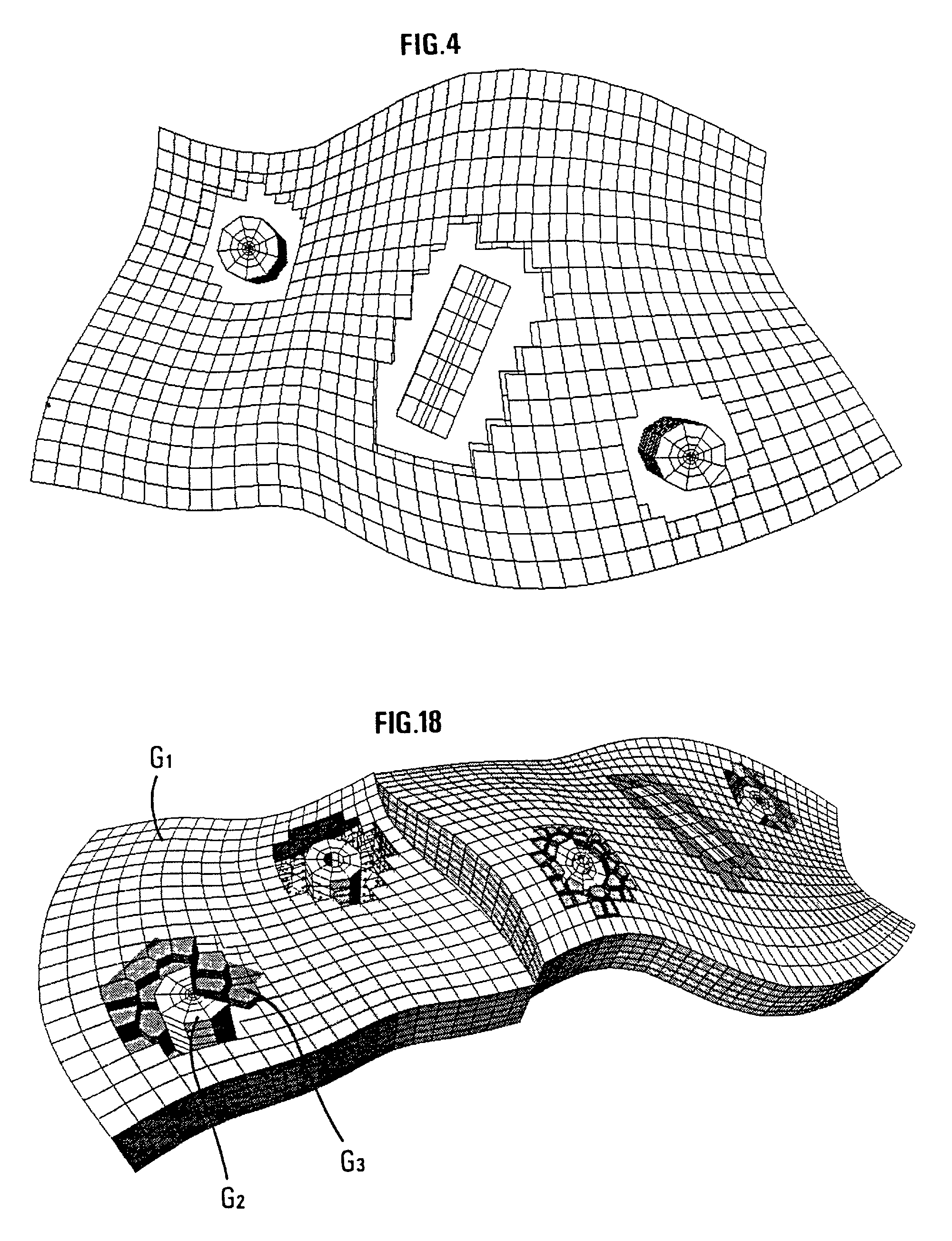
Method of generating a grid on a heterogenous formation crossed by one or more geometric discontinuities in order to carry out simulations
InactiveUS7047165B2GeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationPower diagramEngineering
A method of generating a hybrid grid of a heterogeneous formation crossed by one or more geometric discontinuities such as, for example, an underground formation where one or more wells have been drilled, or a fractured formation, by combining structured grids and non-structured grids in order to carry out simulations in accordance with a defined numerical pattern is disclosed. Hybrid gridding is performed by associating a first structured grid (G1) for gridding of the heterogeneous medium considering discontinuities thereof with second structured, radial type grids (G2) for gridding of a zone around each pipe or well, which allows better consideration of constraints linked with flows in the zone. In order to connect the first grid of the medium and the second well grids, non-structured transition grids (G3) are interposed there between. A power diagram technique is used, which is particularly advantageous in that it allows appropriate connection of non-regular structured grids. An application is hydrocarbon reservoir simulation.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Control circuit and control method for capacitive touch panel
InactiveUS20100110037A1Enhance sensing resultImprove performanceInput/output processes for data processingTouchpadParasitic capacitance
A control circuit and a control method for a capacitive touch panel are provided. Therein, while a scanning signal charges and discharges each trace on the capacitive touch panel, a signal in phase with the scanning signal is provided to traces adjacent to the scanned trace or a ground layer under the scanned trace so as to lower parasitic capacitances between the scanned trace and the ground layer or other traces, thereby decreasing a base capacitance of the capacitive touch panel and enhancing a sensing result of the control circuit as well as providing a shielding effect and reducing noise interference so that the capacitive touch panel has improved performance.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Solution method and apparatus for large-scale simulation of layered formations
ActiveUS7596480B2Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSupercomputerTypes of mesh
A targeted heterogeneous medium in the form of an underground layered formation is gridded into a layered structured grid or a layered semi-unstructured grid. The structured grid can be of the irregular corner-point-geometry grid type or the simple Cartesian grid type. The semi-unstructured grid is really unstructured, formed by arbitrarily connected control-volumes derived from the dual grid of a suitable triangulation; but the connectivity pattern does not change from layer to layer. Problems with determining fluid movement and other state changes in the formation are solved by exploiting the layered structure of the medium. The techniques are particularly suited for large-scale simulation by parallel processing on a supercomputer with multiple central processing units (CPU's).
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Determining formation parameters using electromagnetic coupling components
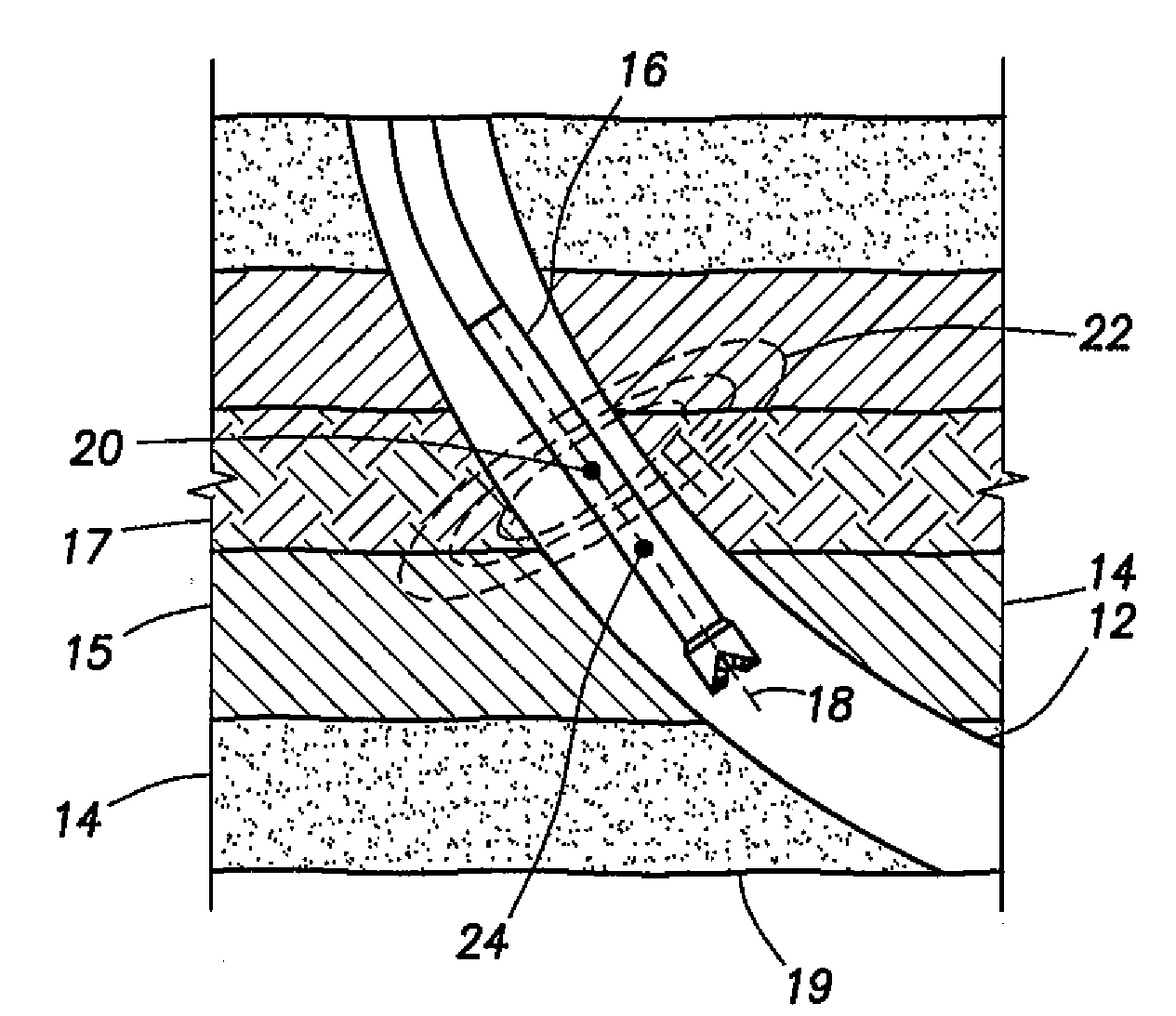
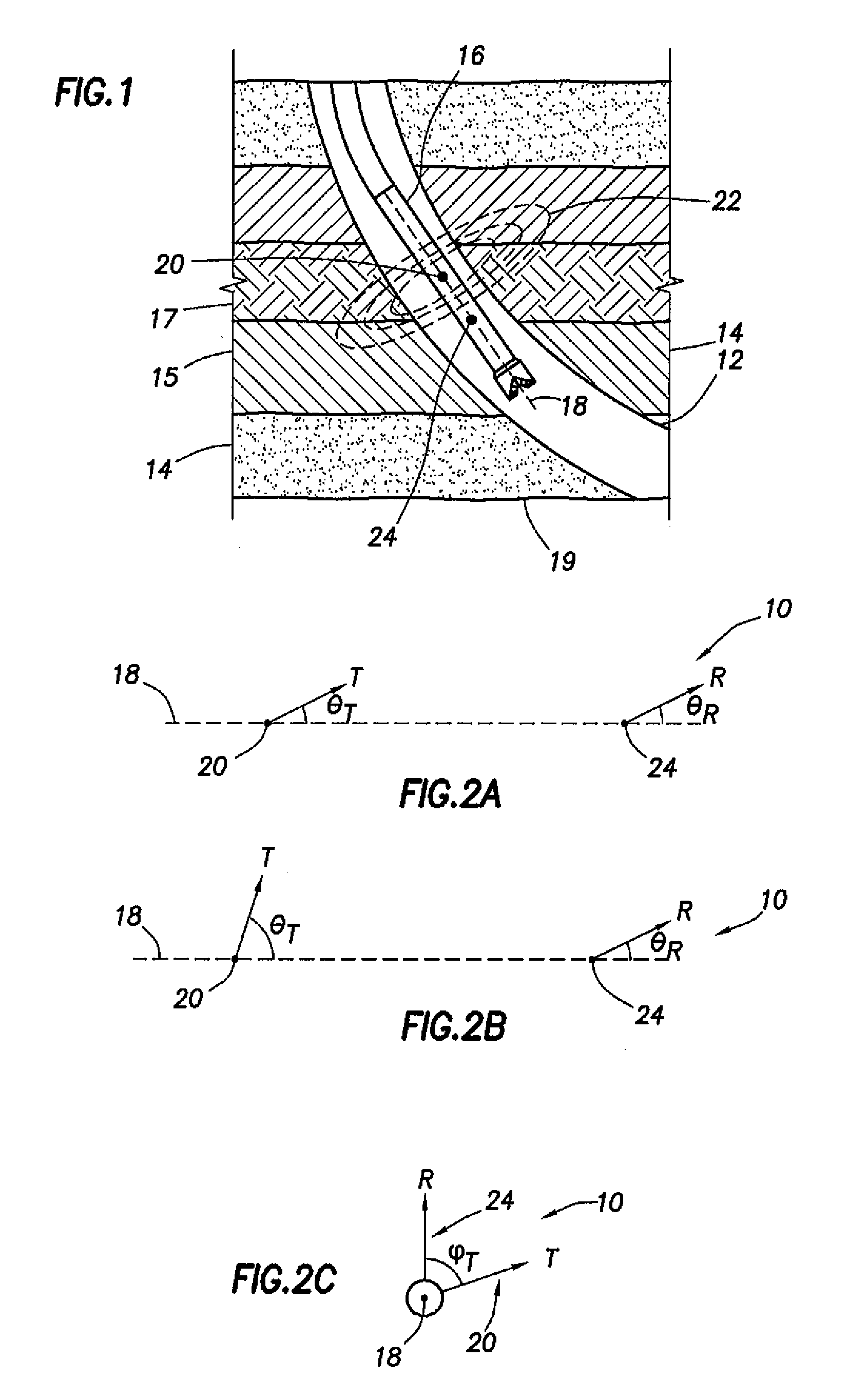
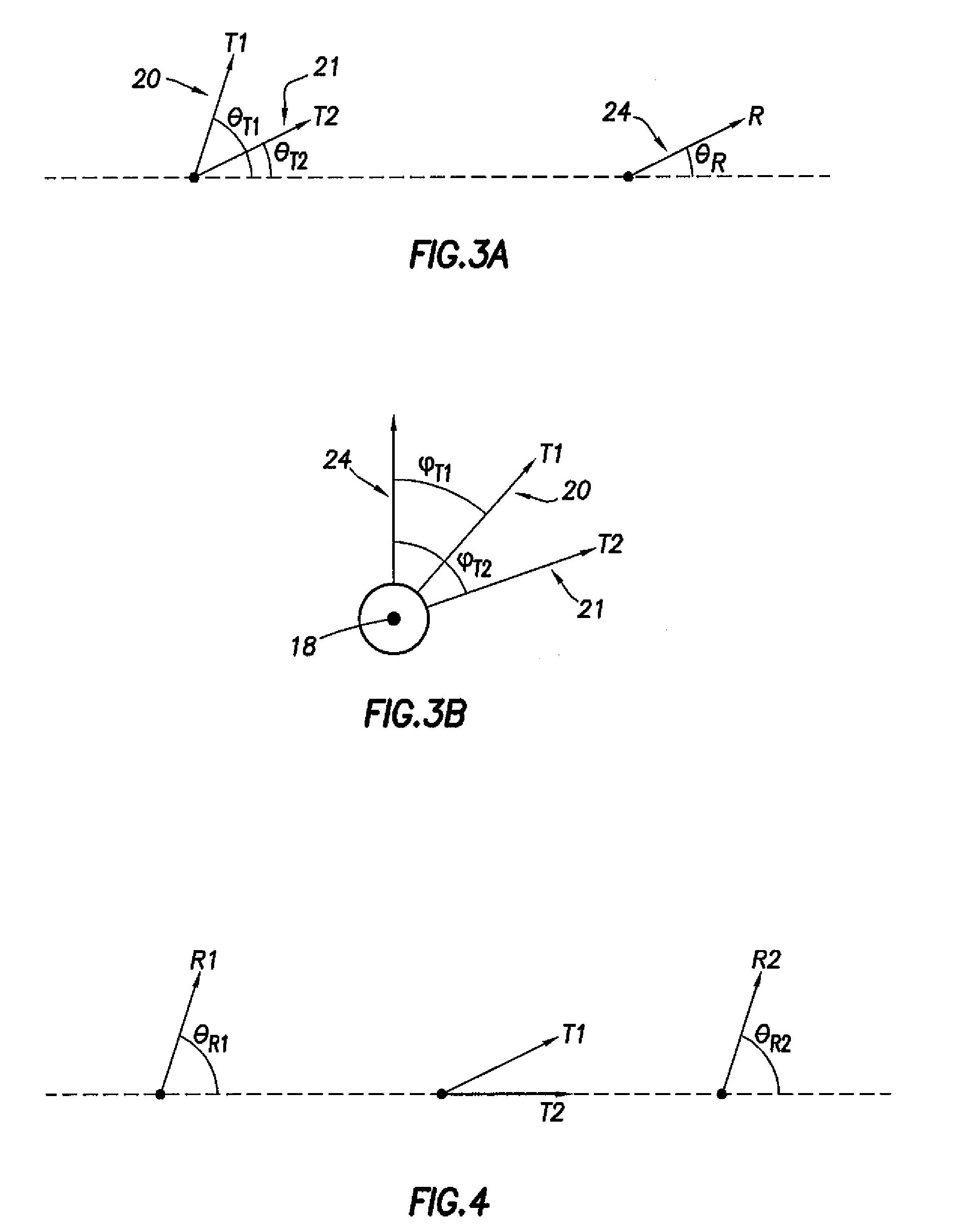
InactiveUS20090015261A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyGround layerEnvironmental geology
A method to determine one or more parameters of a formation traversed by a borehole, at least a portion of the formation having substantially parallel boundaries, the method comprising disposing a tool in the borehole, wherein the tool includes a transmitter having a dipole moment at an angle θT with respect to a longitudinal axis of the tool and a receiver having a dipole moment at an angle θR with respect to the longitudinal axis of the tool, the transmitter and receiver comprising a transmitter-receiver pair; transmitting an electromagnetic signal while rotating the tool; receiving the electromagnetic signal to produce a measured signal from the transmitter-receiver pair; and determining the one or more formation parameters for the portion of the formation having substantially parallel boundaries based on the measured signal from the transmitter-receiver pair. A tool disposed in a borehole penetrating a formation, at least a portion of the formation having substantially parallel boundaries, the tool comprising a single transmitter having a transmitter dipole moment at an angle θT with respect to a longitudinal axis of the tool; a single receiver having a receiver dipole moment at an angle θR with respect to the longitudinal axis of the tool; and a rotational position indicator.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Low-EMI electronic apparatus, low-EMI circuit board, and method of manufacturing the low-EMI circuit board
InactiveUS20020015293A1Suppress spurious radiationIncrease costMagnetic/electric field screeningFinal product manufactureCapacitanceCountermeasure
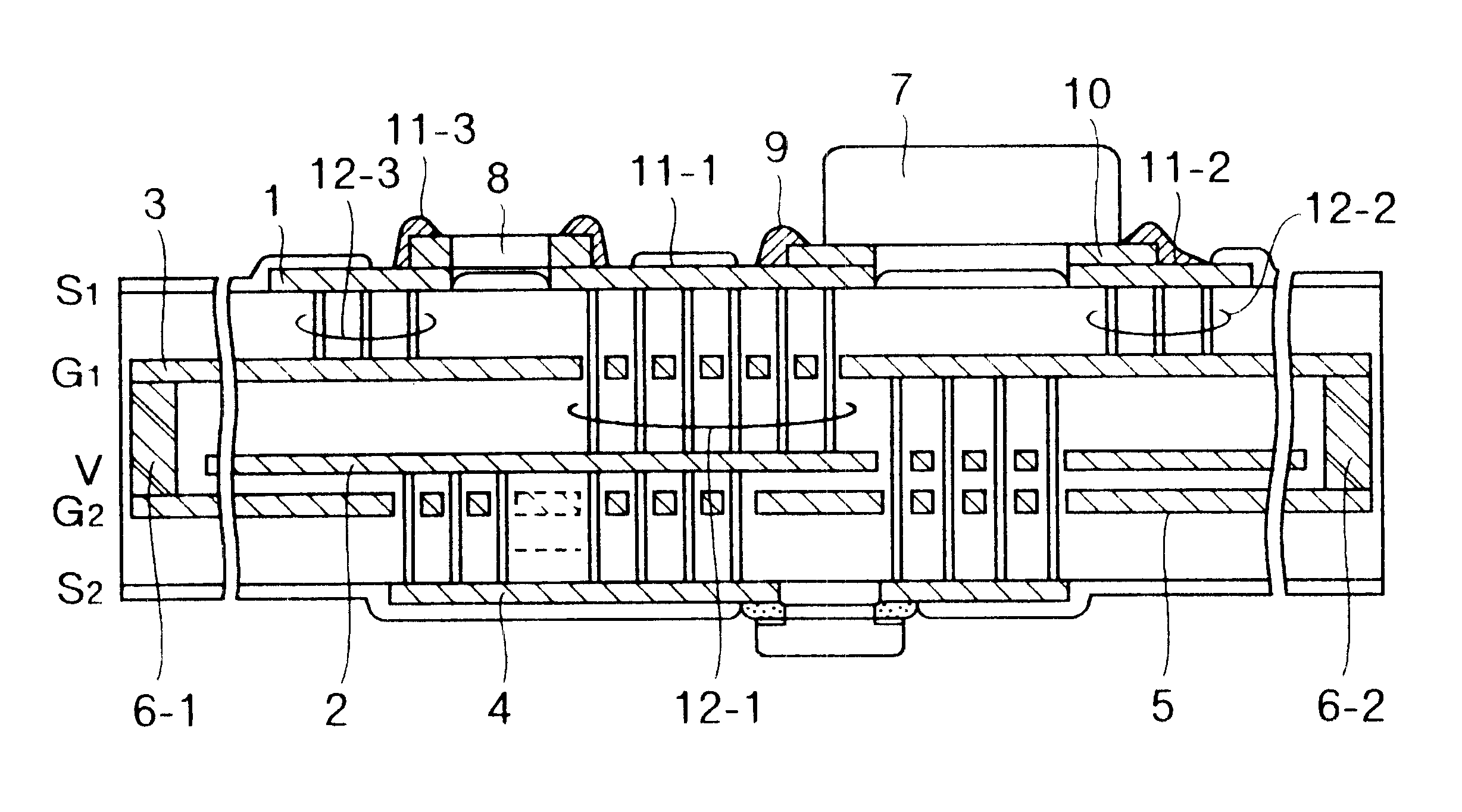
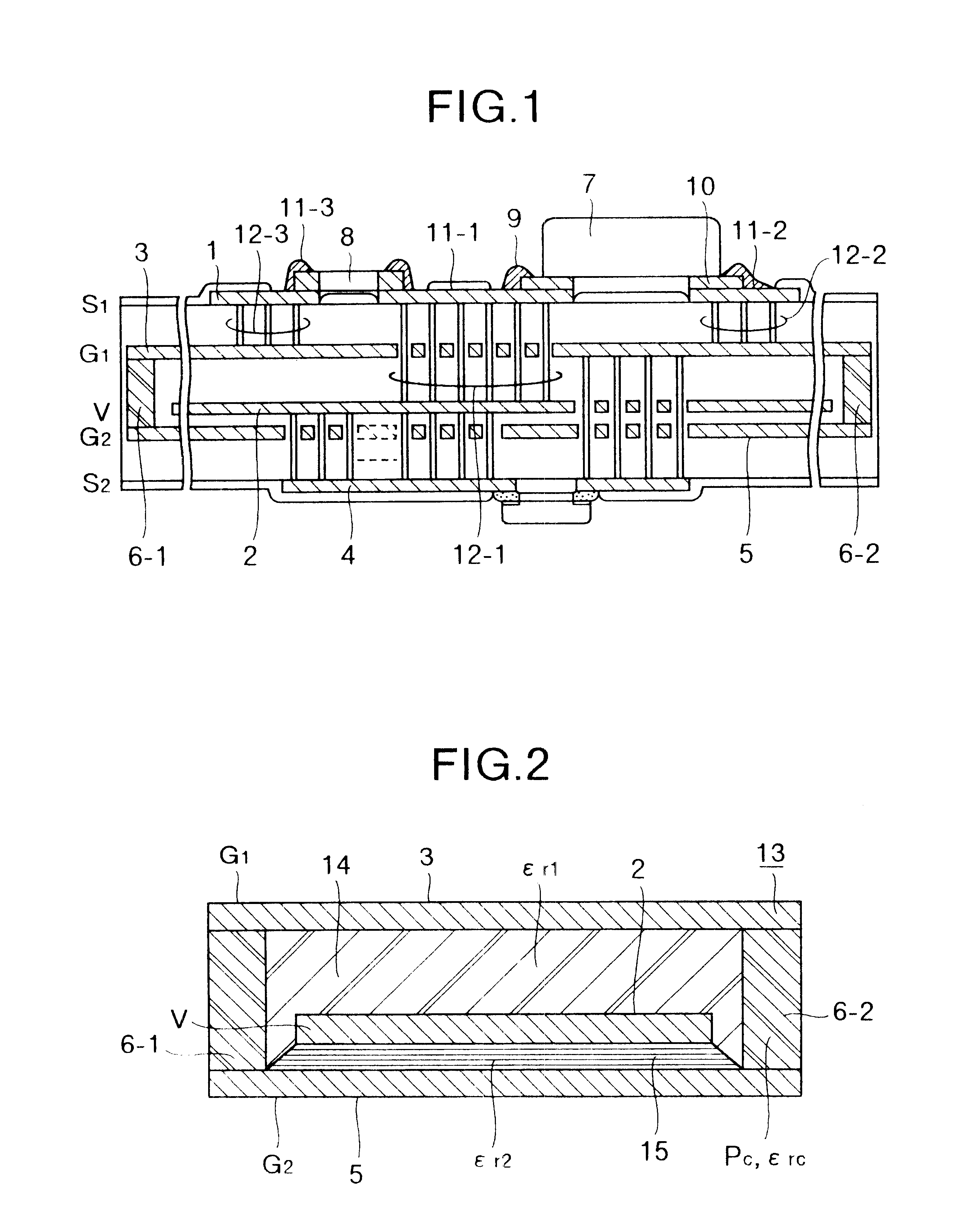
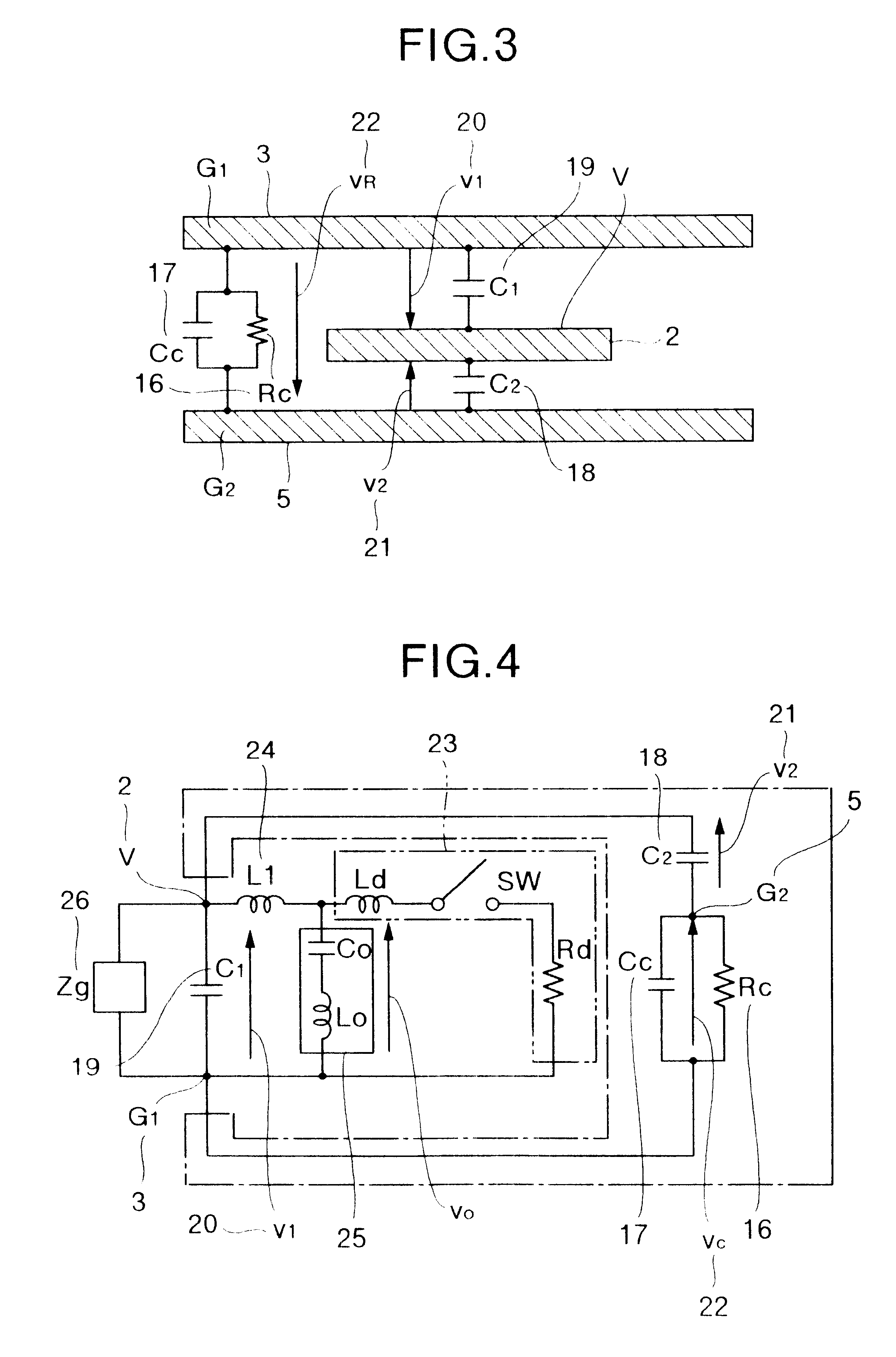
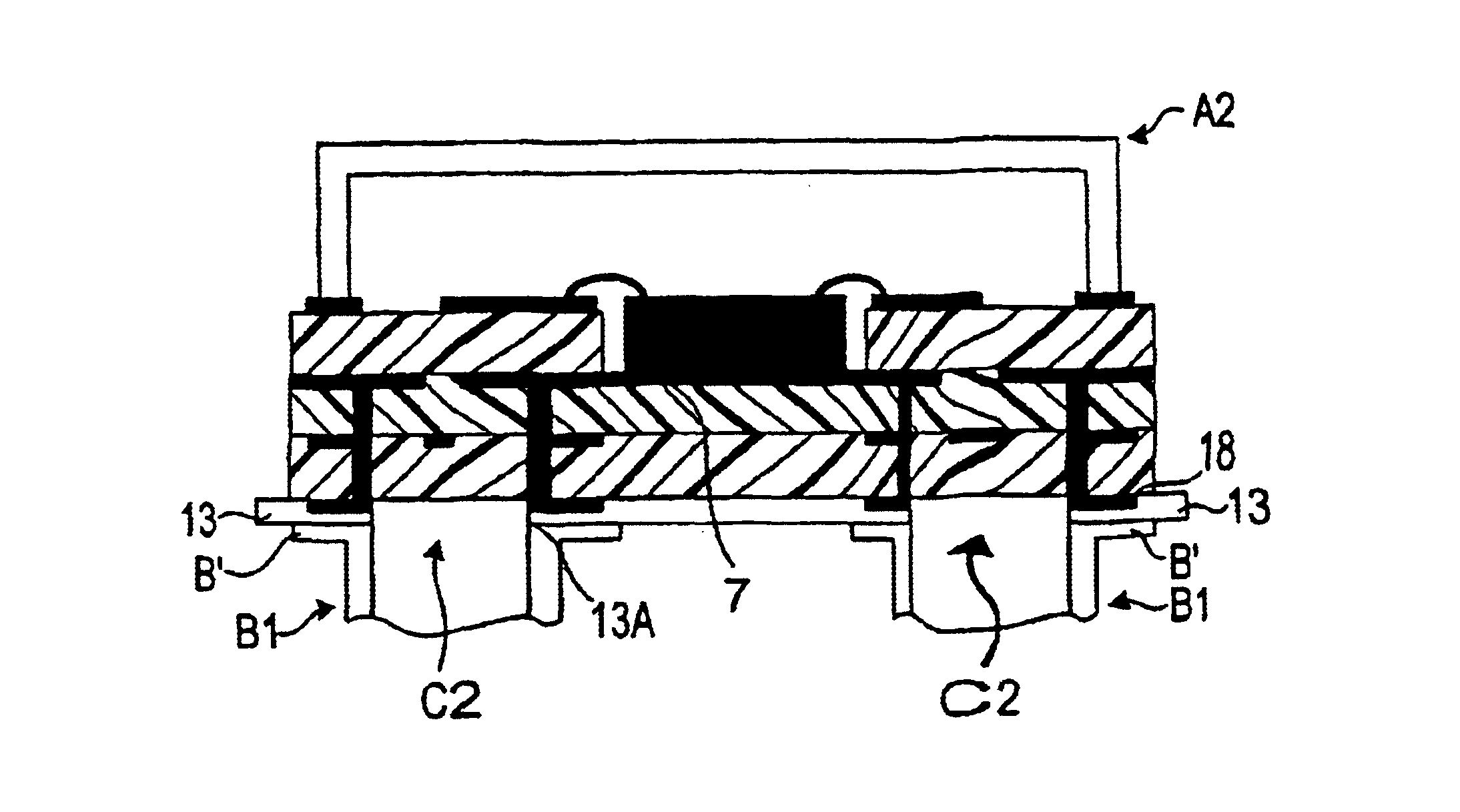
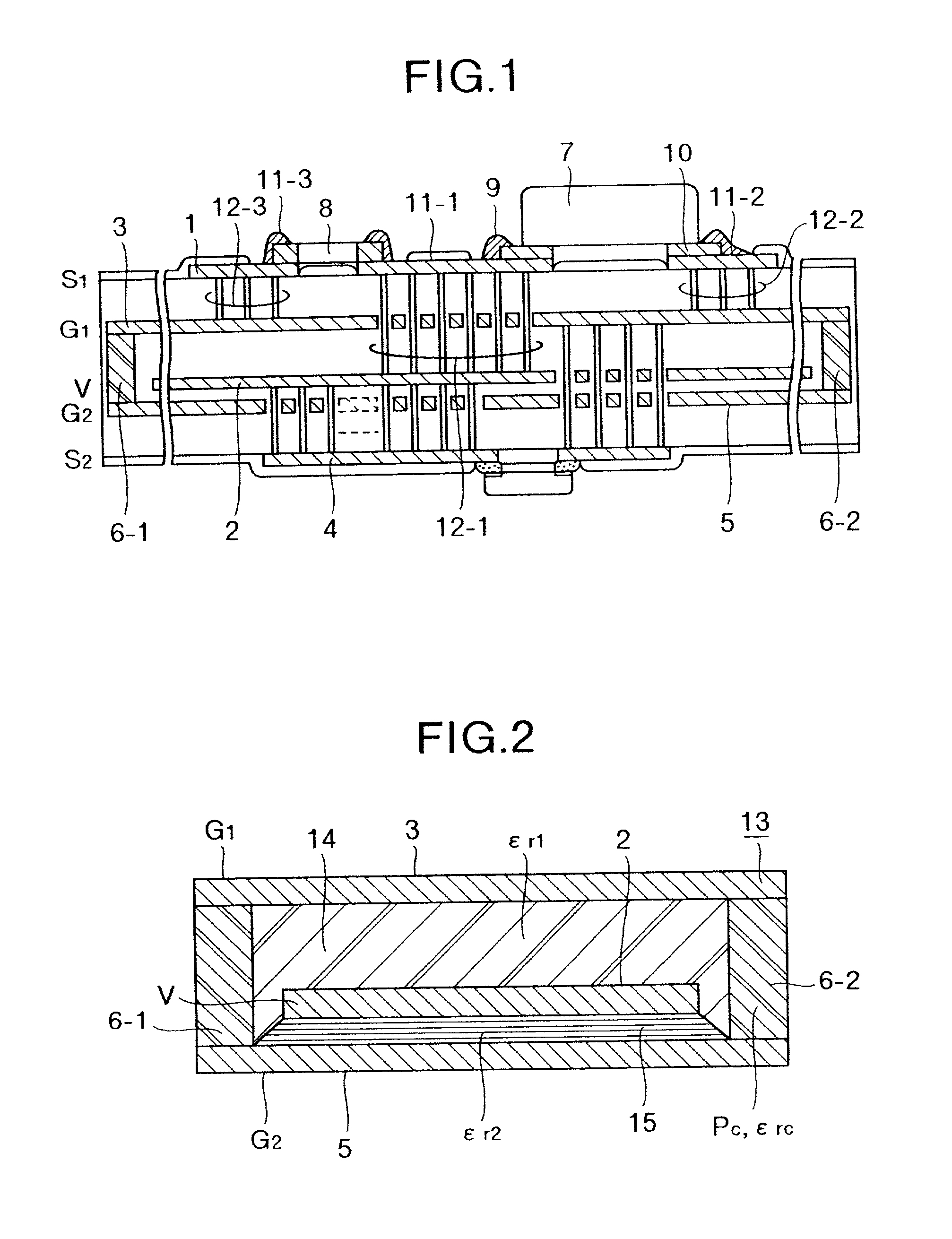
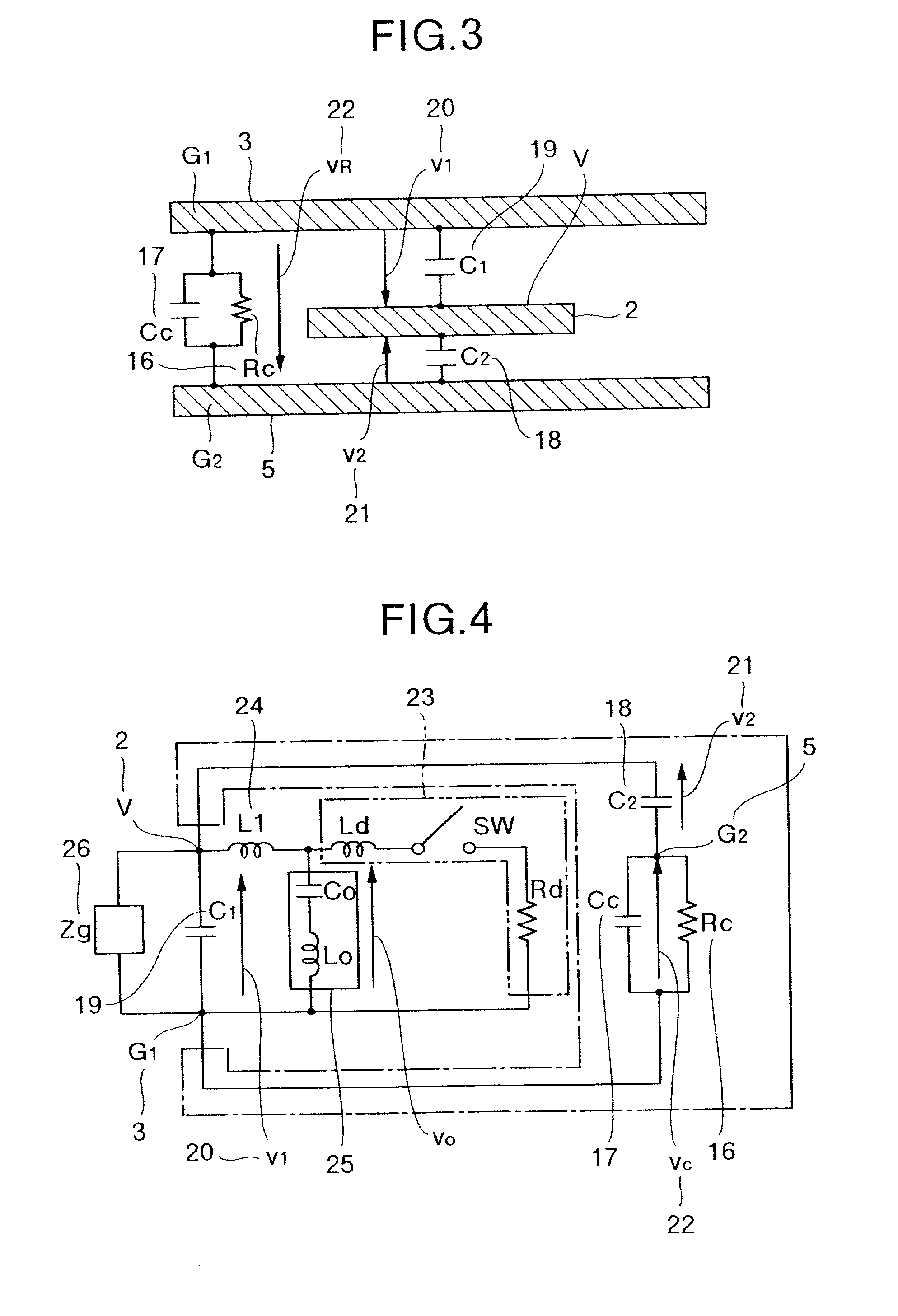
A low-EMI circuit which realizes a high mounting density by converting the potential fluctuation of a power supply layer with respect to a ground layer which occurs on switching an IC device etc., into Joule's heat in the substrate without using any parts as a countermeasure against the EMI. Its structure, a circuit board using it, and a method of manufacturing the circuit board are also disclosed. Parallel plate lines in which the Q-value of the stray capacitance between solid layers viewed from the power supply layer and ground layer is equivalently reduced and which are matchedly terminated by forming a structure in which a resistor (resistor layer) and another ground layer are provided in addition to the power supply layer and the ground layer on a multilayered circuit board. A closed shield structure is also disclosed. This invention can remarkably suppress unwanted radiation by absorbing the potential fluctuation (resonance) which occurs in a power supply loop by equivalently reducing the Q-value of the stray capacitance, absorbing the standing wave by the parallel plate lines matchedly terminated and, closing and shielding the parallel plate lines.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com