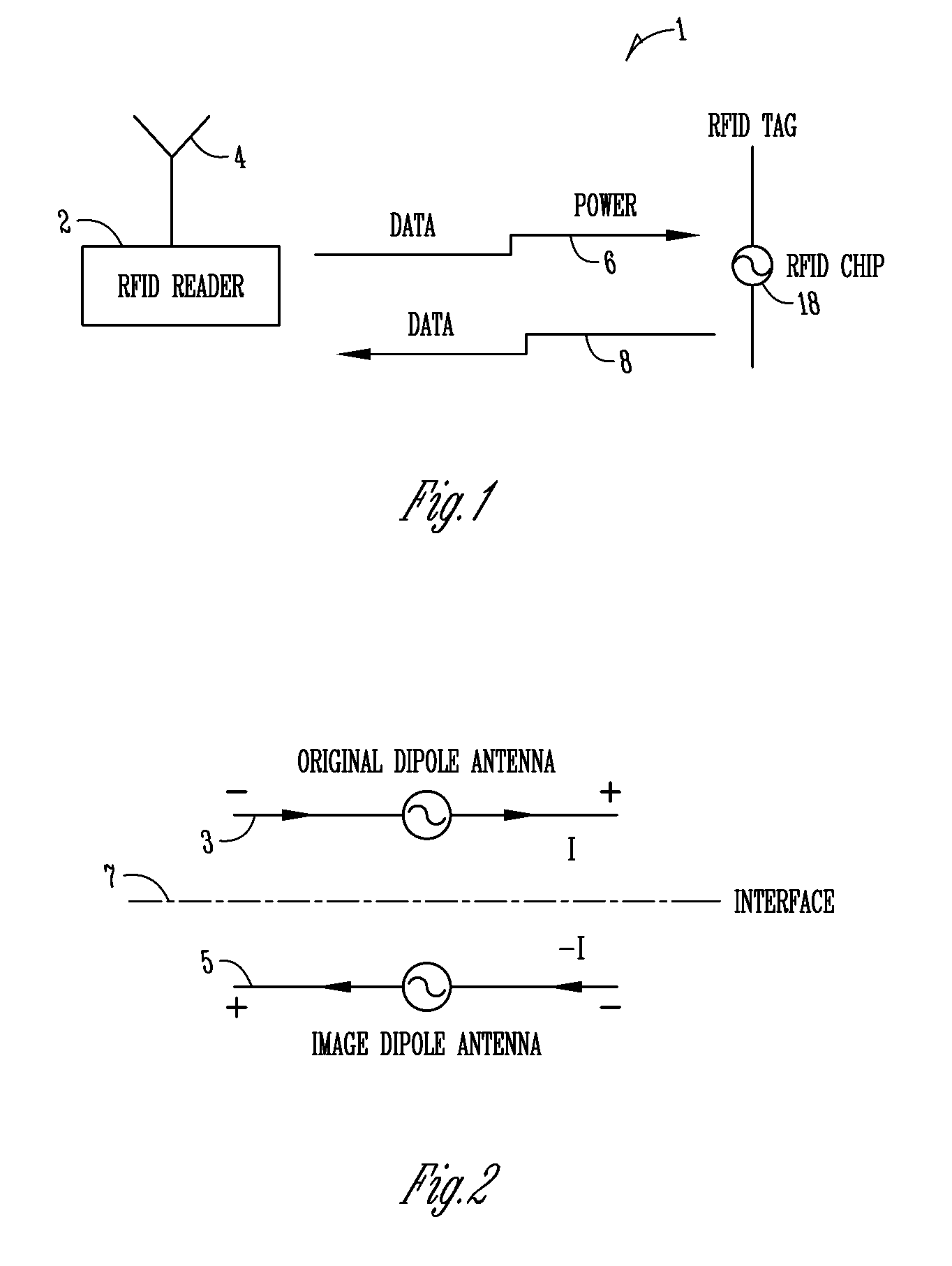
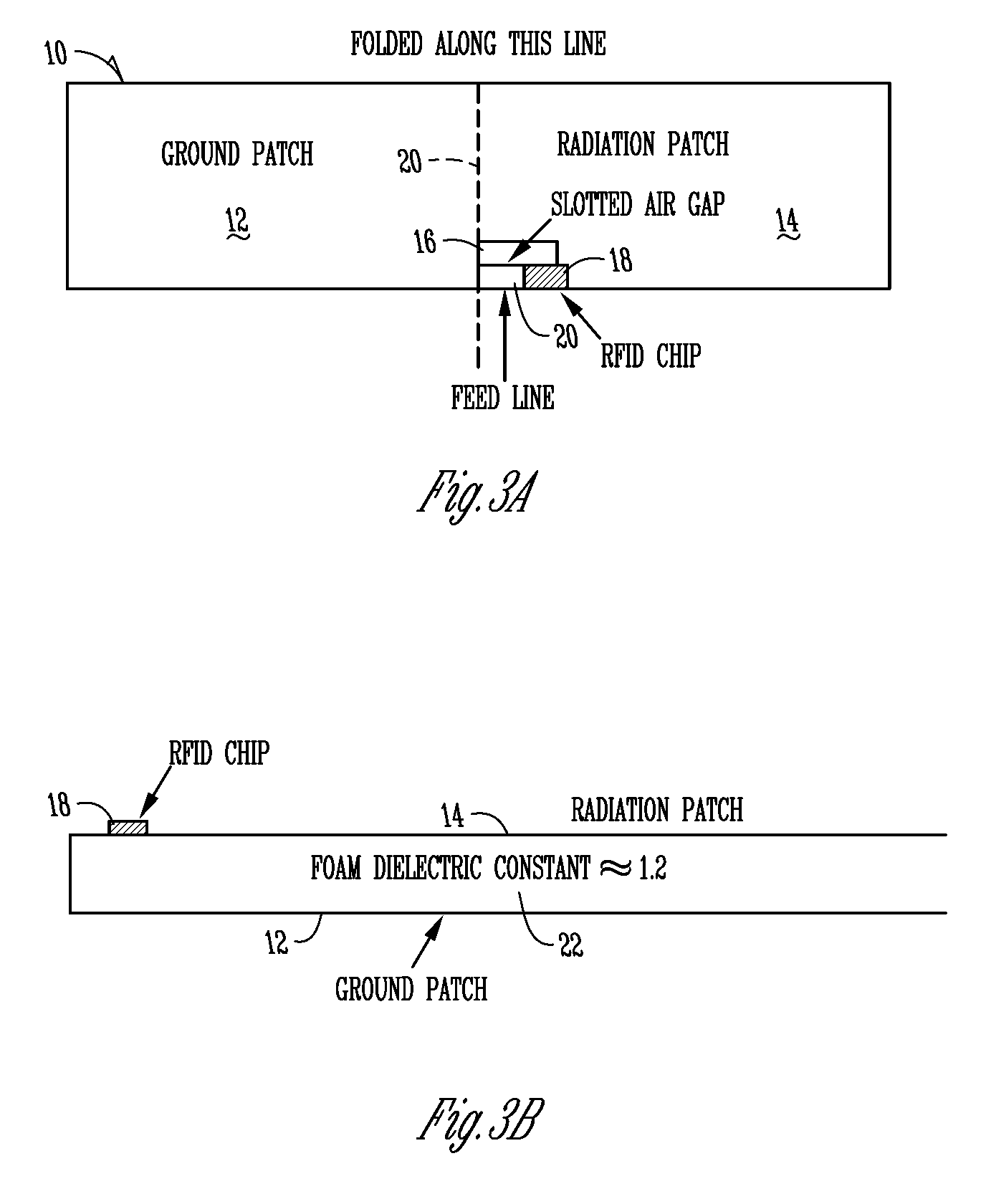
Patents
Literature
766 results about "Tag antenna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
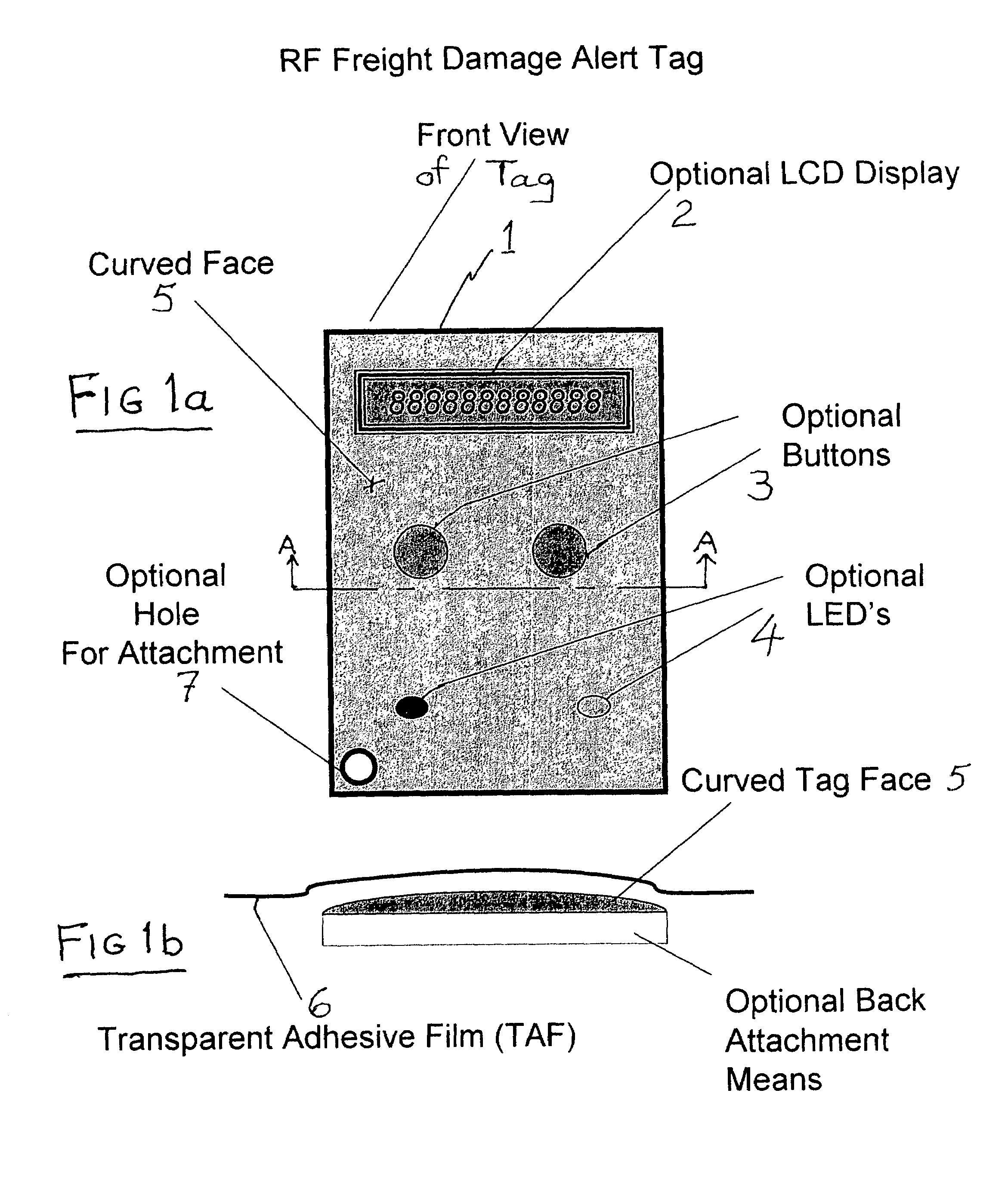
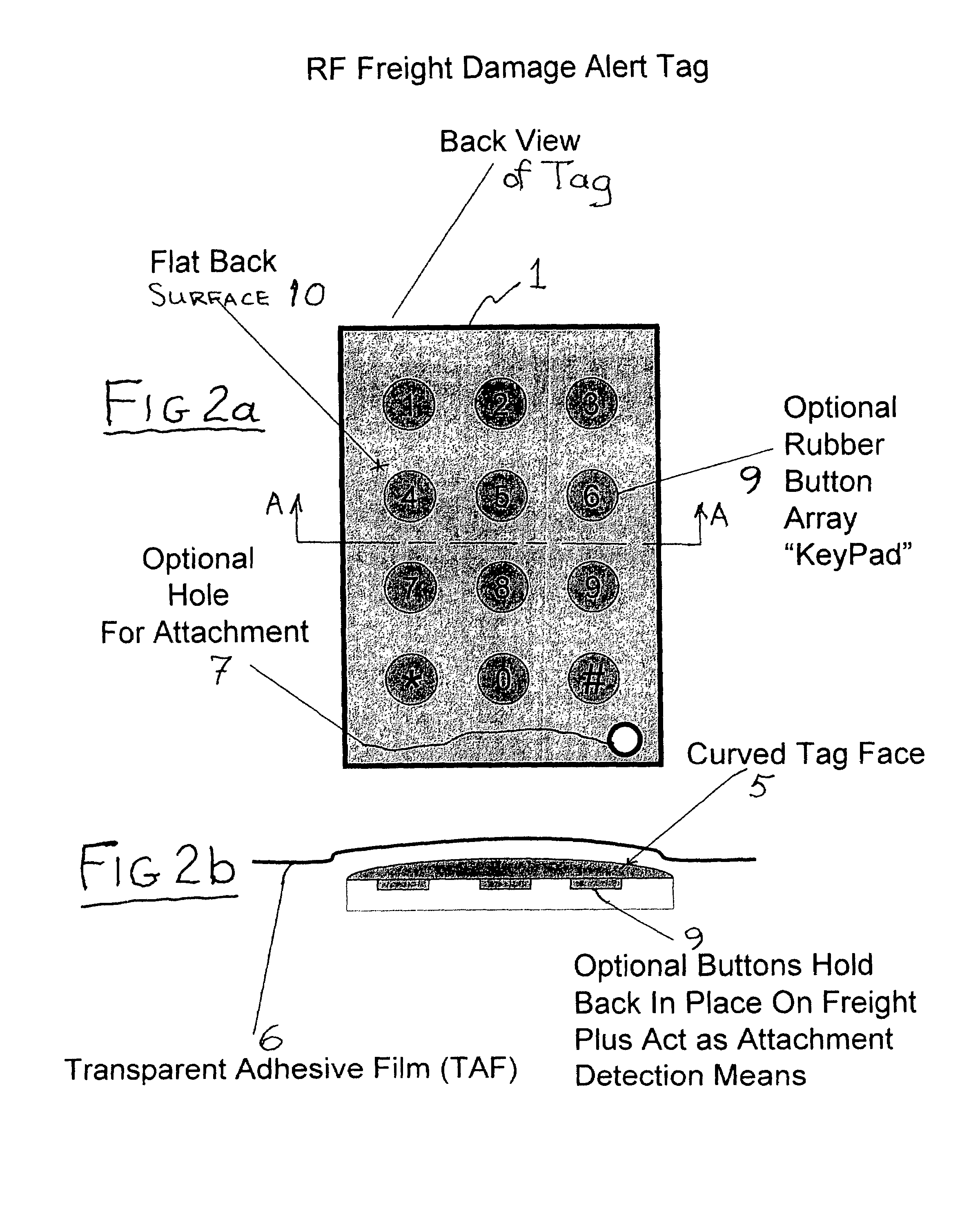
Safety charging system for surgical hand piece
InactiveUS20080030170A1Operational securitySatisfy safety performance requirementsElectric powerBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalTag antennaElectrical battery
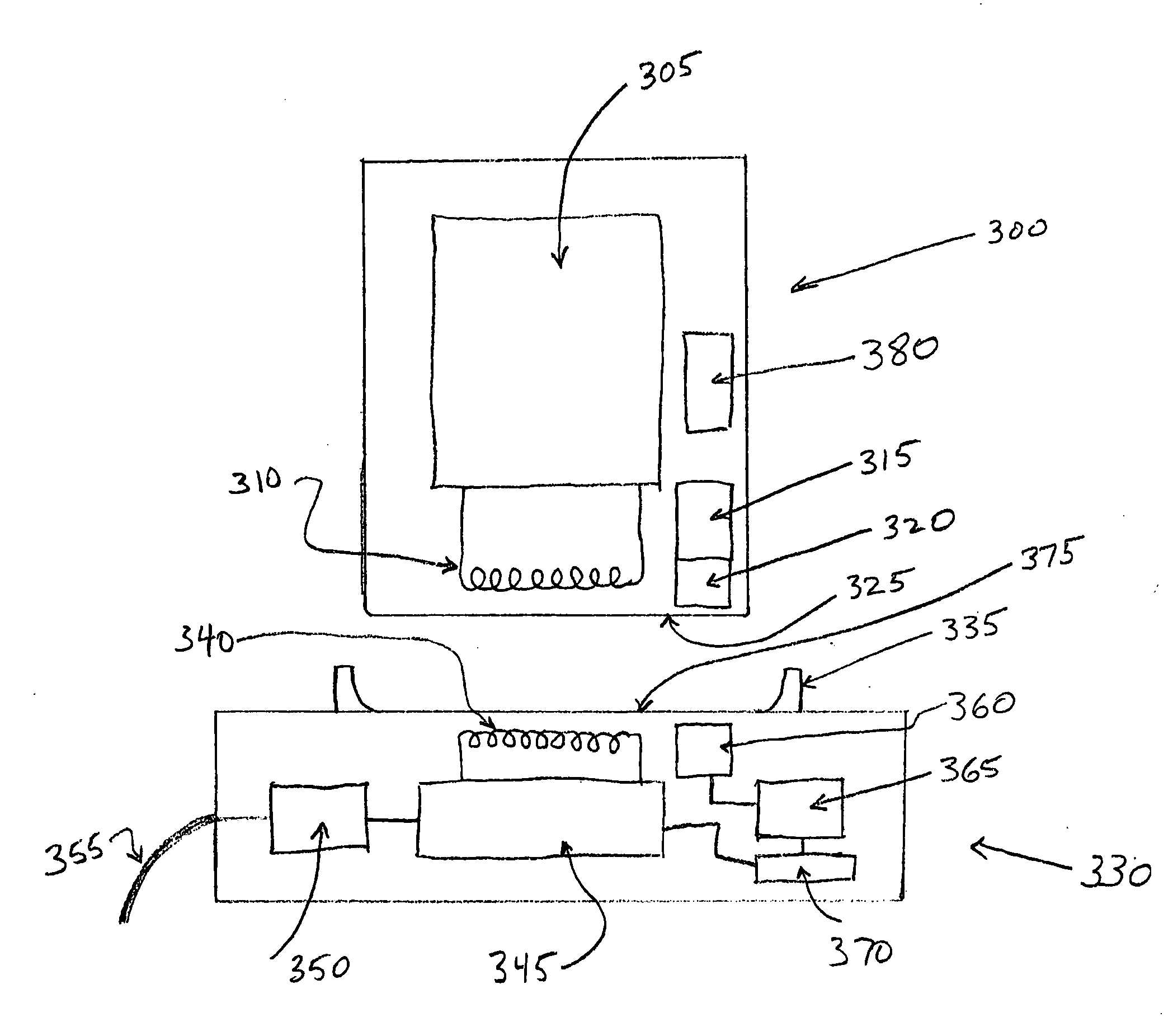
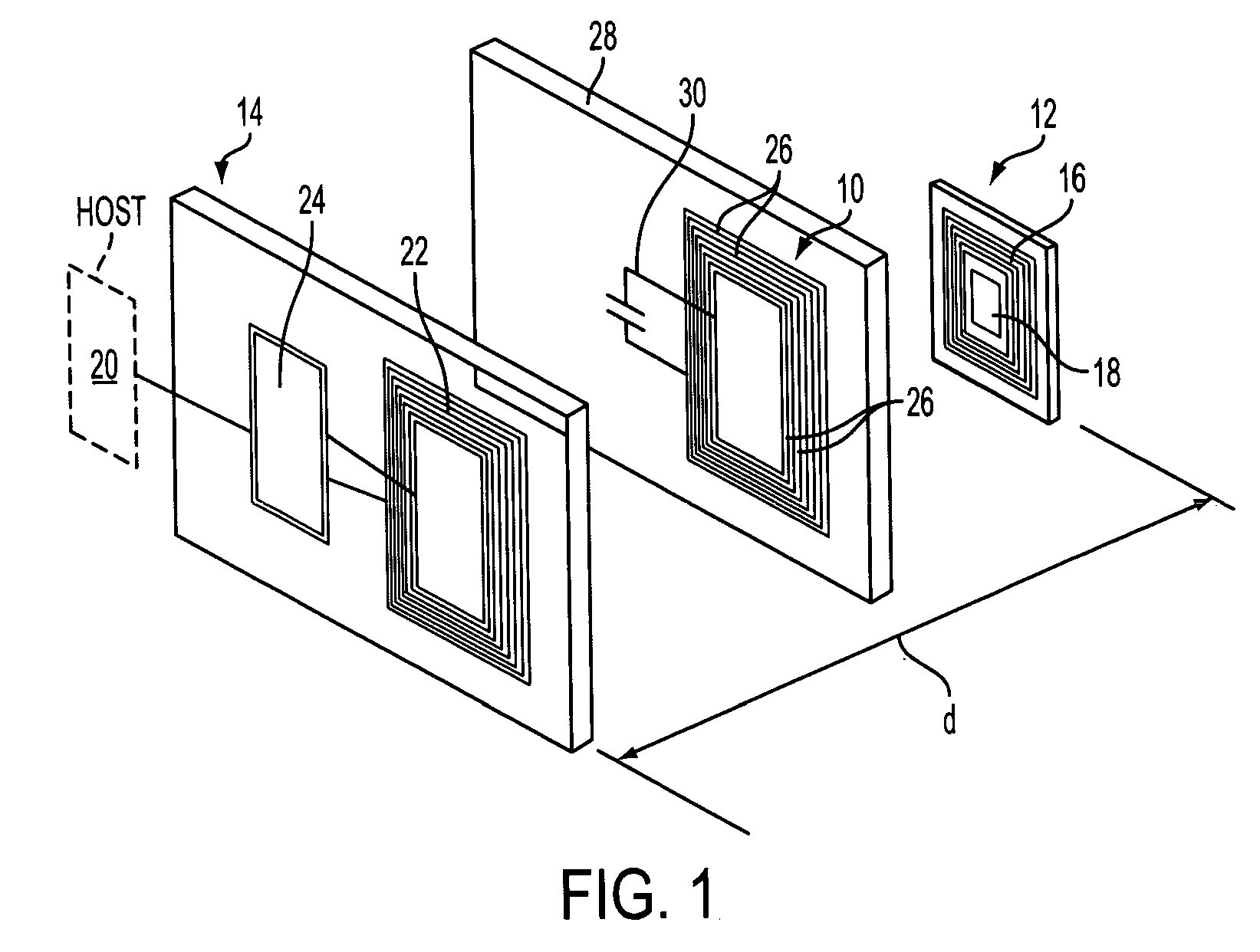
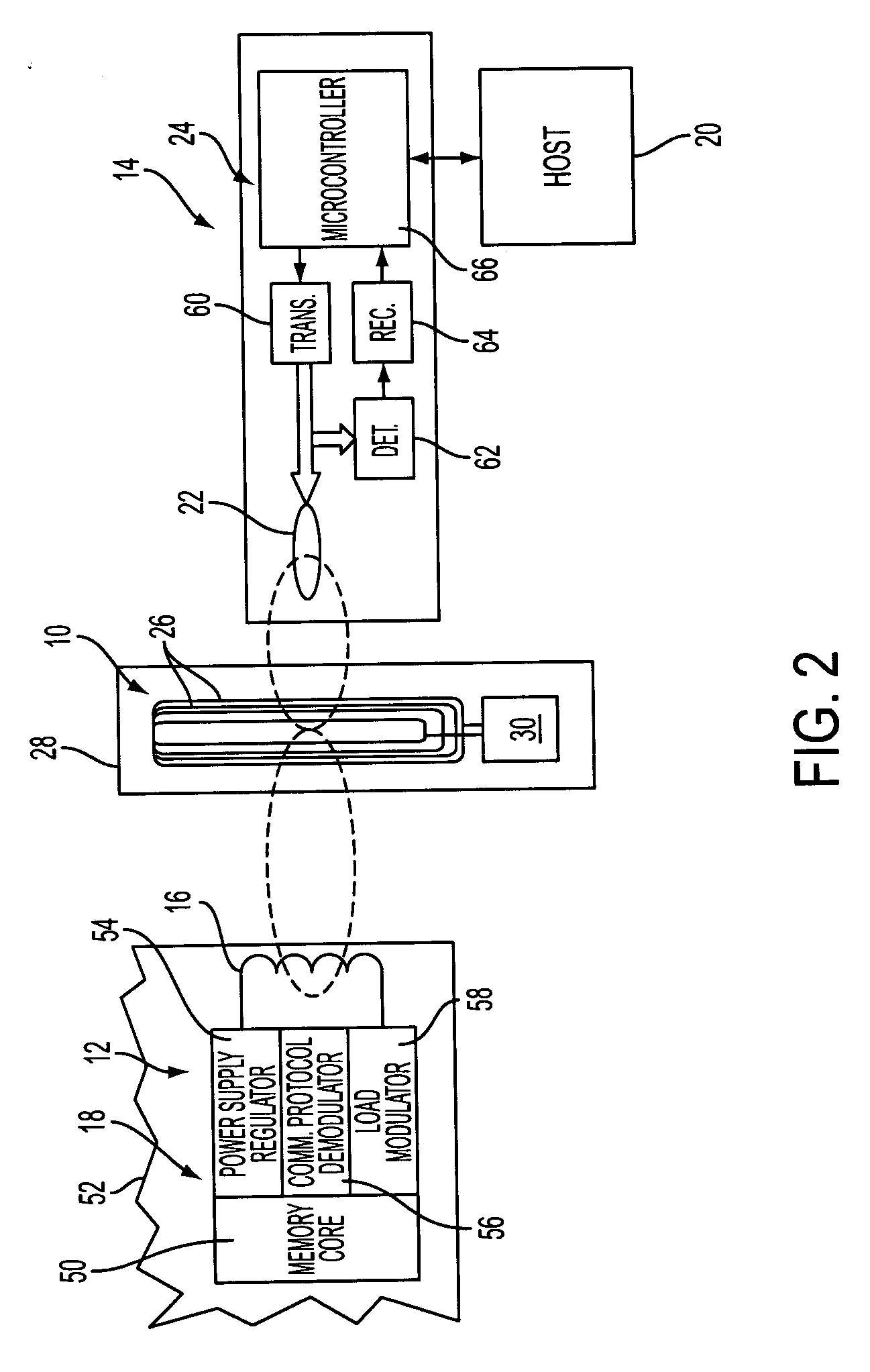
A safety charging system for a battery-operated surgical hand includes a charging base, a battery pack, and control logic. The charging base has an RFID reader antenna disposed near a top surface of the charging base and charge circuitry for charging the battery. The battery pack has the battery used with the hand piece and an RFID tag antenna disposed near a bottom surface of the battery pack. The control logic determines if the battery should be charged based on a data point read by the RFID reader antenna.
Owner:ALCON RES LTD
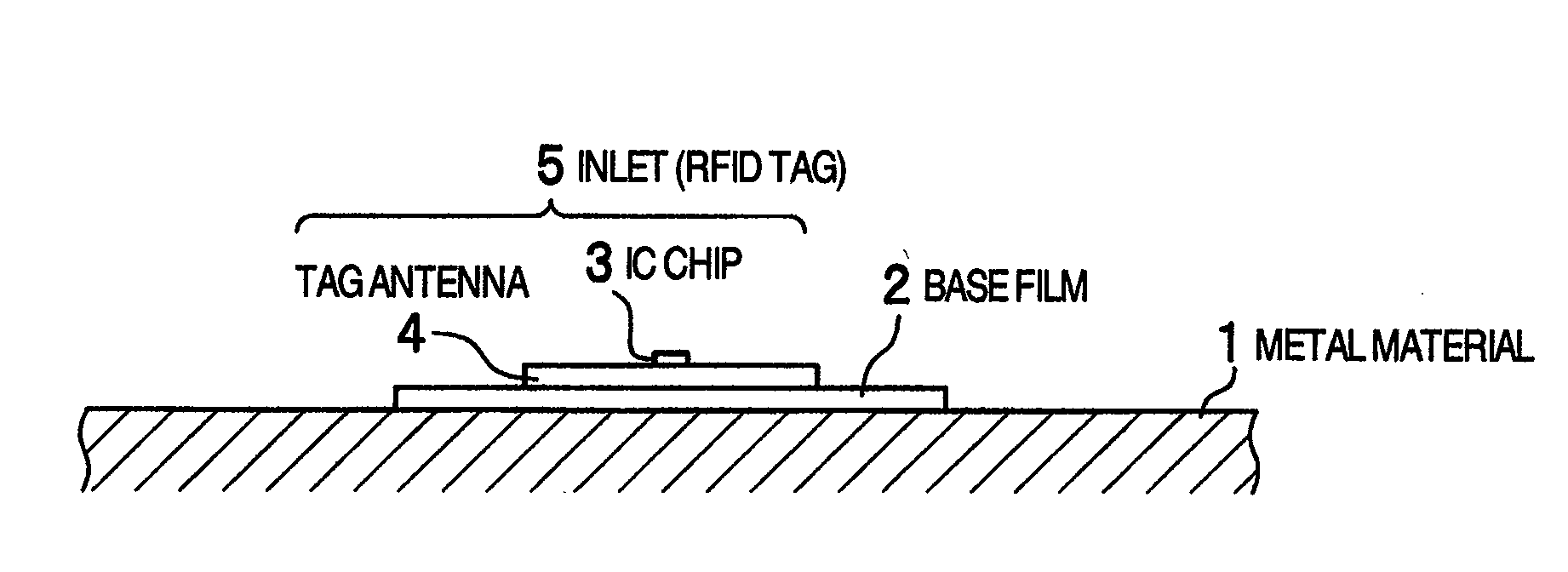
Dipole tag antenna structure mountable on metallic objects using artificial magnetic conductor for wireless identification and wireless identification system using the dipole tag antenna structure
InactiveUS20100007569A1Easy to manufactureEasy to installAntenna feed intermediatesRecord carriers used with machinesTag antennaElectrical conductor
Provided are a dipole tag antenna using an artificial magnetic conductor (AMC) for wireless identification and a wireless identification system using the dipole tag antenna. The dipole tag antenna includes: a substrate formed of a first dielectric material; a conductive ground layer formed underneath the substrate; an AMC layer formed on the substrate; the dipole tag antenna mounted on the AMC layer and comprising a wireless identification chip; and the AMC directly mounted on a conductor.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Passive transponder identification and credit-card type transponder
InactiveUS20030006901A1Simultaneous aerial operationsDetection of traffic movementCredit cardTag antenna
A passive transponder identification system and credit card type transponder are disclosed, particularly, the transponder identification system to utilize a transmitting manner of two different RF signals is provided. The present invention directly relates to a passive transponder without any kind of power source. Therefore, the present invention has advantages of having a constant gain value by developing a high-gain dual polarizing antenna for a small credit card type passive tranponder to identify at long distance, independently to any direction of the transponder; improving gain values than conventional transponder tag antenna by 6-9 dB to ensure a sub-permanent life time by providing the desired identification performance by means of a small credit card type passive transponder without power supply; and being applicable to any systems to identify and distinguish high-speed moving objects.
Owner:CREDIPASS
Radio frequency identification tag and radio frequency identification tag antenna
InactiveUS8098201B2Efficiently receiving electromagnetic wave transmittedMaximize readable rangeResonant long antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsTag antennaRadio frequency
An RFID tag includes an antenna and a chip, and the antenna includes a first polygonal dielectric material, first and second microstrip lines partially formed in the first dielectric material, a second polygonal dielectric material stacked on the first dielectric material, and a third microstrip line partially formed in the second dielectric material. According to the present invention, the RFID tag can efficiently receive electromagnetic waves to thereby maximize a readable range.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
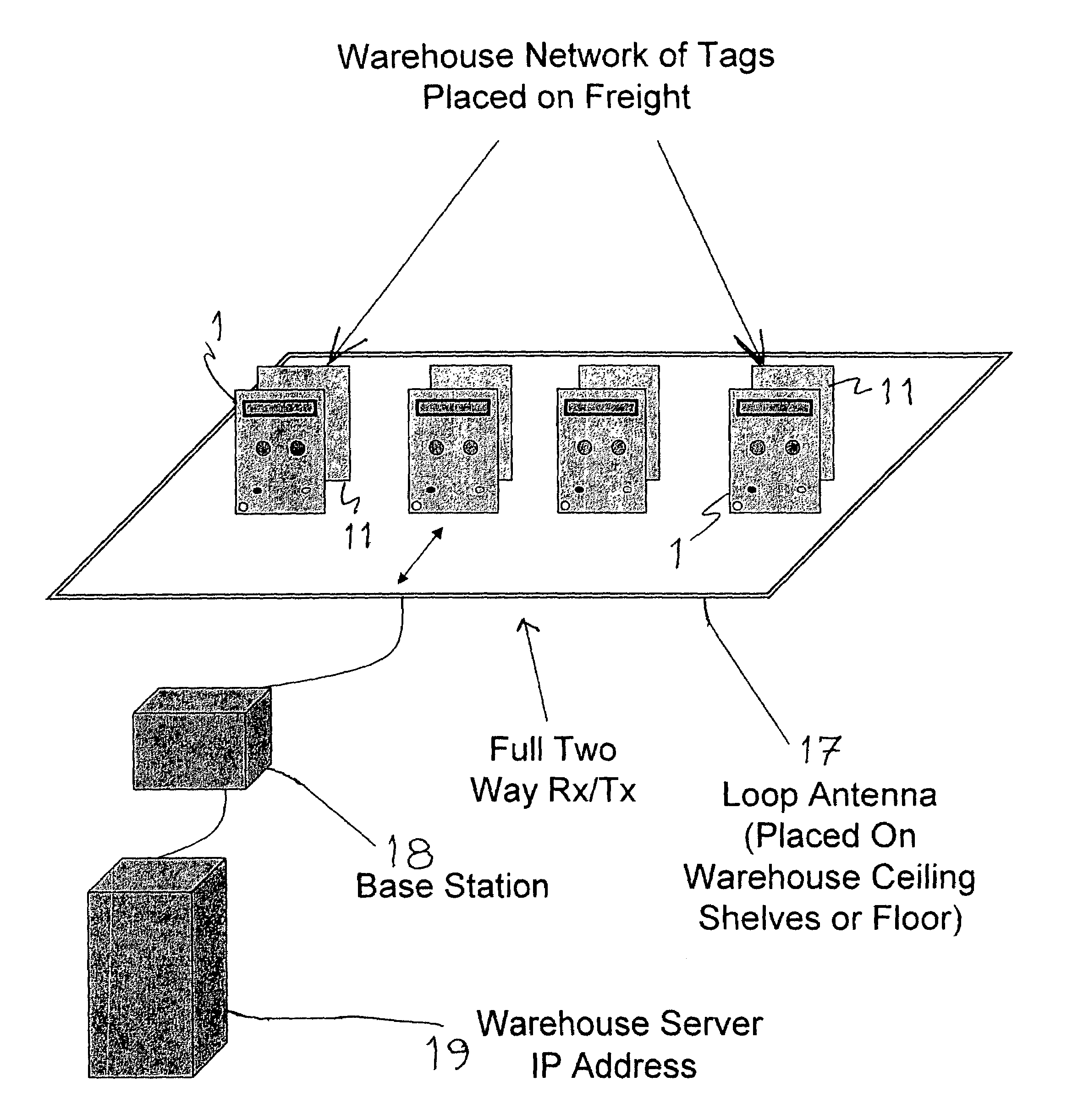
Networked RF tag for tracking freight
ActiveUS7049963B2Reduce slippagePrecise positioningHand manipulated computer devicesCo-operative working arrangementsTransceiverIp address
The invention disclosed provides a method, system, and associated tag for detection and tracking of inanimate and animate objects. The novel method broadly comprises the steps of: a) attaching a low radio frequency detection tag to each of the objects, each tag comprising a tag antenna operable at a low radio frequency not exceeding 1 megahertz (preferably not exceeding 300 kilohertz), a transceiver operatively connected to the tag's antenna, the transceiver being operable to transmit and receive data signals at the low radio frequency, a data storage device operable to store data comprising identification data for identifying said detection tag, a programmed data processor operable to process data received from the transceiver and the data storage device and to send data to cause the transceiver to emit an identification signal based upon the identification data stored in said data storage device, and an energy source for activating the tag's transceiver and data processor; b) storing, in the data storage device of each tag, shipping data selected from object description data, address-of-origin data, destination address data, object vulnerability data, and object status data; c) commingling the objects in a repository selected from a warehouse and a truck, the repository being provided with at least one large loop field antenna operable at said low radio frequency; the field antenna being disposed at a distance from each object that permits effective communication therewith at the low radio frequency, d) reading the identification data and shipping data from the transceiver of each tag by interrogating all tags commingled in said repository with data signals, such as specific IP addresses or other identification codes, via said field antenna; and e) transmitting the identification data and shipping data from each tag to a central data processor to provide a tally of the objects in said repository.
Owner:VISIBLE ASSET INC
High Sensitivity RFID TAG Integrated Circuits
InactiveUS20070046369A1Reduce the required powerMore sensitiveCharge amplifiersRecord carriers used with machinesElectricityTag antenna
A method and apparatus for an ultra-high sensitivity, low cost, passive (no battery) low-power energy harvesting data transmitting circuit energy, such as a RFID (Radio Frequency IDentification) tag integrated circuit “chip.” By using combinations of special purpose design enhancements, the low-power energy harvesting passive data transmitting circuit, such as the RFID tag chip, operates in the sub-microwatt power range. The chip power should be derived from a low-microwatt per square centimeter RF field radiated to the RFID tag antenna from the tag reader (interrogator) or derived from a suitable low signal source, such as a sonic transducer (e.g., a piezoelectric transducer or a low level DC source, such as a bimetallic or chemical source).
Owner:INNURVATION IP LLC
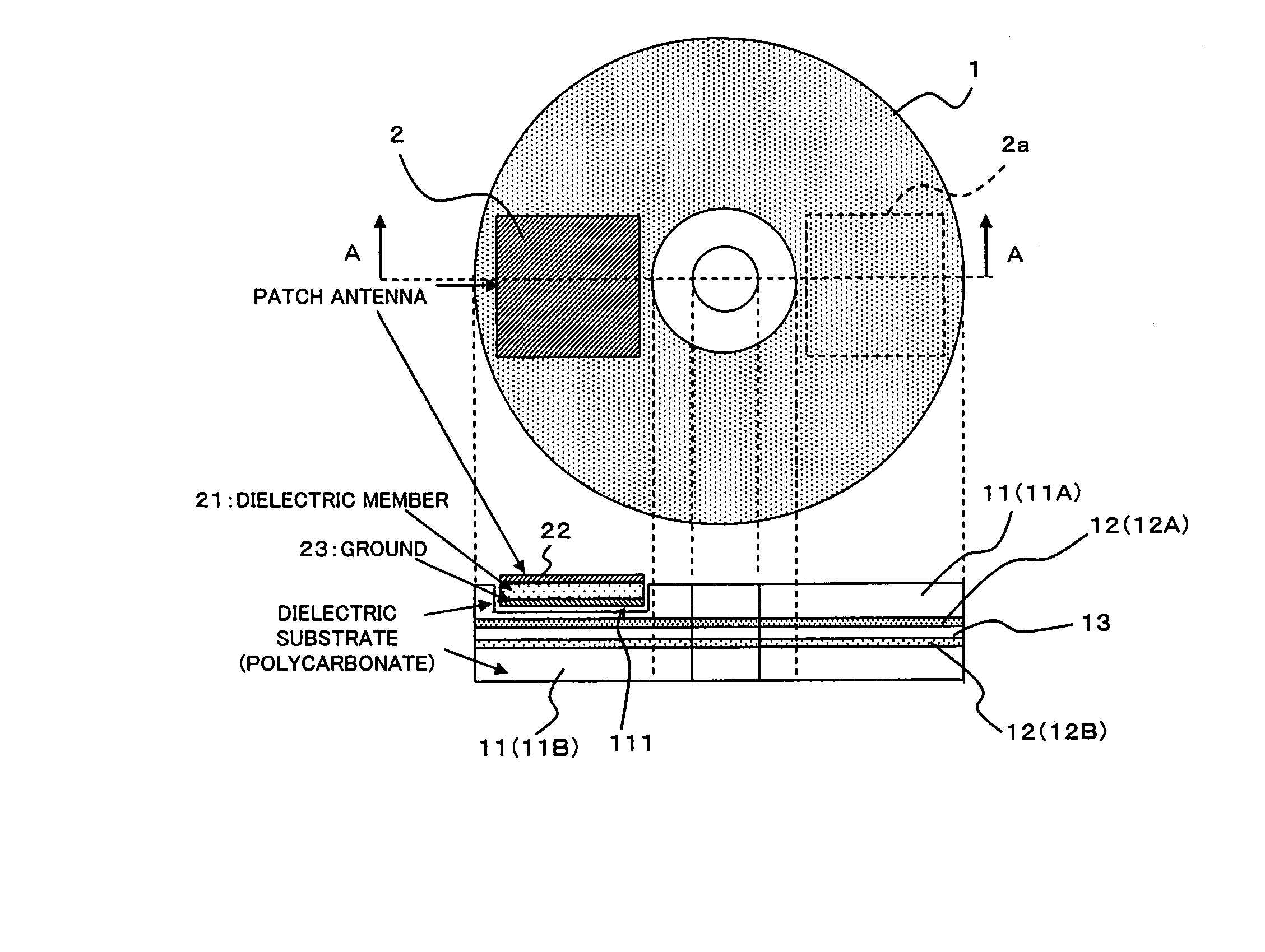
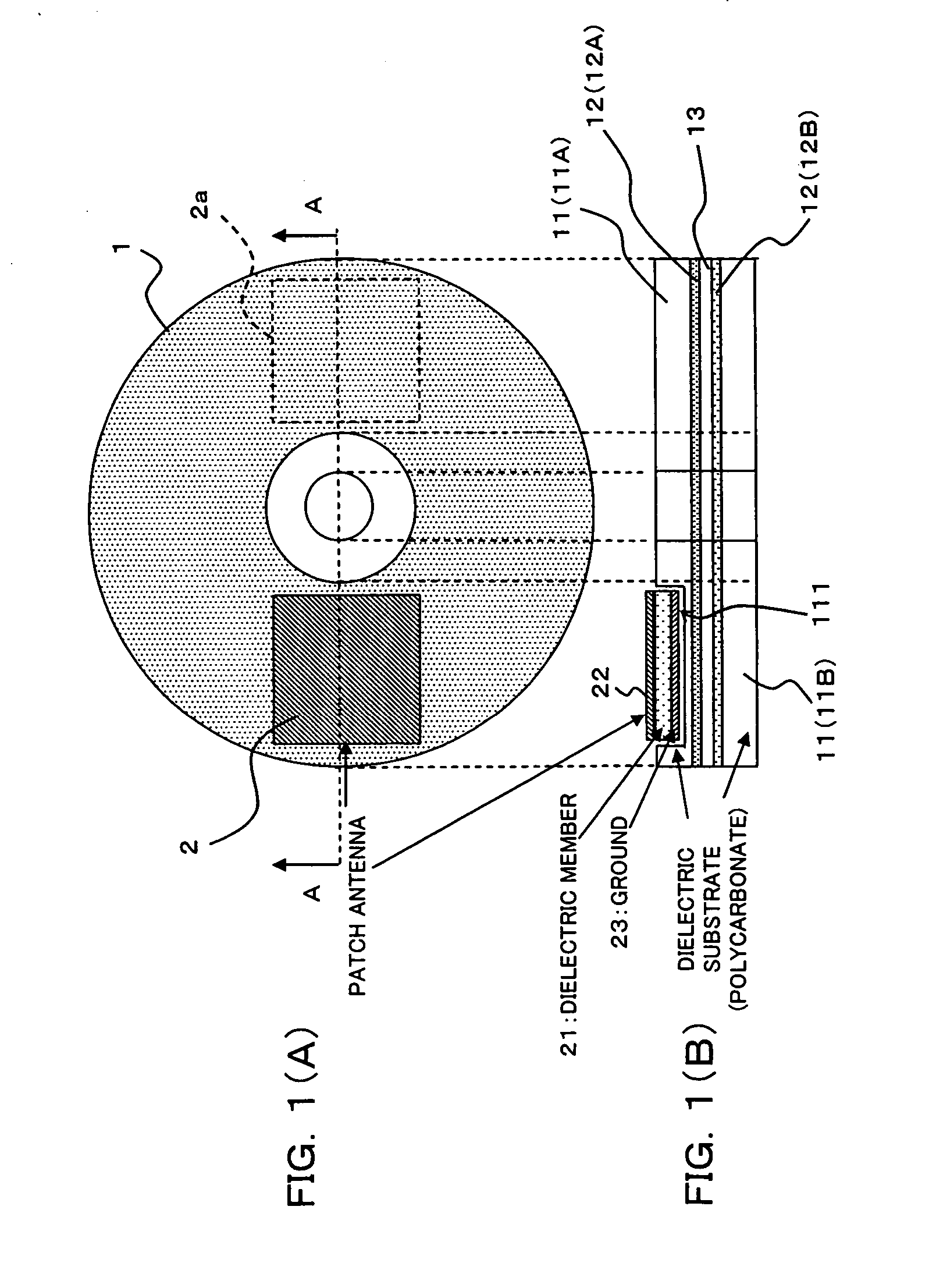
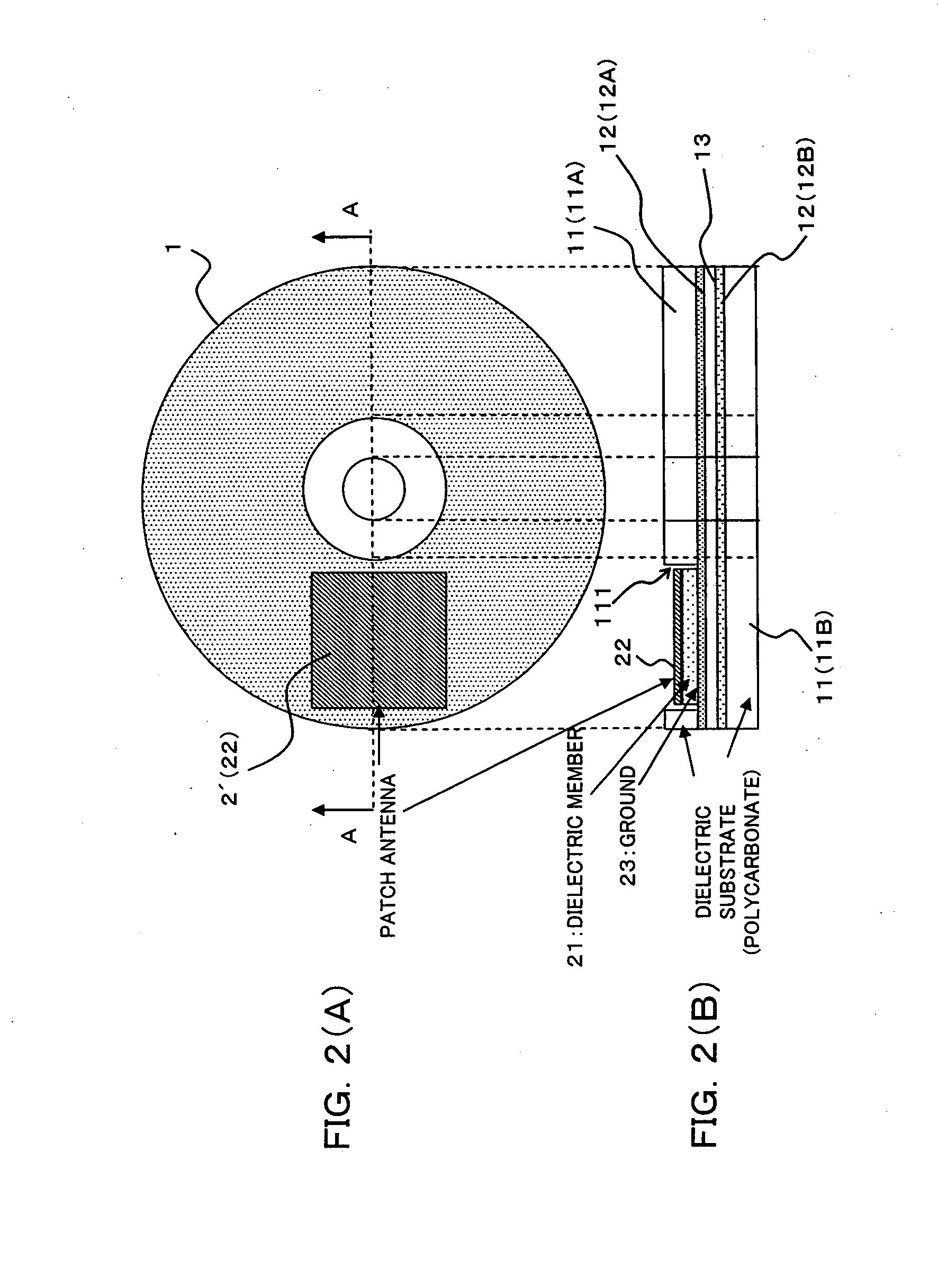
Radio tag antenna structure for an optical recording medium and a case for an optical recording medium with a radio tag antenna
InactiveUS20070018893A1Small-sizedSecure required reading performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsTag antennaOptical recording
An antenna comprises a dielectric member, an antenna pattern formed on one surface of the dielectric member, and a ground pattern formed on the other surface of the dielectric member. A part or the whole of the antenna is implanted in a dielectric layer on the side from which a laser beam does not come in of an optical recording medium symmetrically having a metal layer reflecting the laser beam and the dielectric layer, thereby to provide a radio tag antenna structure for an optical recording medium which is simple, is small-sized, and can secure necessary reading performance.
Owner:KAI MANABU +4
RFID tag, RFID-tag antenna, RFID-tag antenna sheet, and method of manufacturing RFID tag
A radio-frequency-identification tag antenna includes a film base, a plurality of antenna patterns for transmission and reception, which is formed in parallel on the film base, and a cut line that is formed on the film base between adjacent antenna patterns along the antenna patterns from an inside to an outer edge of the film base. A part of the film base on which the antenna patterns are formed is folded or bent in a predetermined direction using the cut line.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Networked RF tag for tracking baggage
ActiveUS20070152826A1Reduce slippagePrecise positioningHand manipulated computer devicesCo-operative working arrangementsTransceiverIp address
The invention disclosed provides a method, system, and associated tag for detection and tracking of inanimate and animate objects. The novel method broadly comprises the steps of: a) attaching a low radio frequency detection tag to each of the objects, each tag comprising a tag antenna operable at a low radio frequency not exceeding 1 megahertz (preferably not exceeding 300 kilohertz), a transceiver operatively connected to the tag's antenna, the transceiver being operable to transmit and receive data signals at the low radio frequency, a data storage device operable to store data comprising identification data for identifying said detection tag, a programmed data processor operable to process data received from the transceiver and the data storage device and to send data to cause the transceiver to emit an identification signal based upon the identification data stored in said data storage device, and an energy source for activating the tag's transceiver and data processor; b) storing, in the data storage device of each tag, shipping data selected from object description data, address-of-origin data, destination address data, object vulnerability data, and object status data; c) commingling the objects in a repository selected from a warehouse and a truck, the repository being provided with at least one large loop field antenna operable at said low radio frequency; the field antenna being disposed at a distance from each object that permits effective communication therewith at the low radio frequency, d) reading the identification data and shipping data from the transceiver of each tag by interrogating all tags commingled in said repository with data signals, such as specific IP addresses or other identification codes, via said field antenna; and e) transmitting the identification data and shipping data from each tag to a central data processor to provide a tally of the objects in said repository.
Owner:VISIBLE ASSET INC
Multiple loop antenna for RFID reader, RFID reader having same and RFID system having the RFID reader
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND UNIV OF INCHEON
Networked RF tag for tracking freight
ActiveUS20060128023A1Precise positioningFacilitate attachment to surfaceHand manipulated computer devicesCo-operative working arrangementsTransceiverIp address
The invention disclosed provides a method, system, and associated tag for detection and tracking of inanimate and animate objects. The novel method broadly comprises the steps of: a) attaching a low radio frequency detection tag to each of the objects, each tag comprising a tag antenna operable at a low radio frequency not exceeding 1 megahertz (preferably not exceeding 300 kilohertz), a transceiver operatively connected to the tag's antenna, the transceiver being operable to transmit and receive data signals at the low radio frequency, a data storage device operable to store data comprising identification data for identifying said detection tag, a programmed data processor operable to process data received from the transceiver and the data storage device and to send data to cause the transceiver to emit an identification signal based upon the identification data stored in said data storage device, and an energy source for activating the tag's transceiver and data processor; b) storing, in the data storage device of each tag, shipping data selected from object description data, address-of- origin data, destination address data, object vulnerability data, and object status data; c) commingling the objects in a repository selected from a warehouse and a truck, the repository being provided with at least one large loop field antenna operable at said low radio frequency; the field antenna being disposed at a distance from each object that permits effective communication therewith at the low radio frequency, d) reading the identification data and shipping data from the transceiver of each tag by interrogating all tags commingled in said repository with data signals, such as specific IP addresses or other identification codes, via said field antenna; and e) transmitting the identification data and shipping data from each tag to a central data processor to provide a tally of the objects in said repository.
Owner:VISIBLE ASSET INC
Energy Harvesting for Low Frequency Inductive Tagging
InactiveUS20110163857A1Double communication speedIncrease rangeSubscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesTransceiverEngineering
A system for detection and tracking of objects which carry low radio frequency tags that comprise an inductive antenna and transceiver operable at a radio frequency below 1 megahertz, a transceiver operatively connected to that antenna, an ID data storage device, a microprocessor for handling data from the transceiver and data store, and an energy harvesting device to capture energy from an energy condition at said object. The system includes a field communication inductive antenna disposed, preferably at a distance of several feet from each object, and at an orientation that permits effective communication with the tag antennas at the aforesaid radio frequency, a data receiver, transmitter and reader data processor in operative communication with the field communication inductive antenna. The aforesaid tag communication inductive antenna may have a ferrite core to enhance data reception.
Owner:VISIBLE ASSET INC
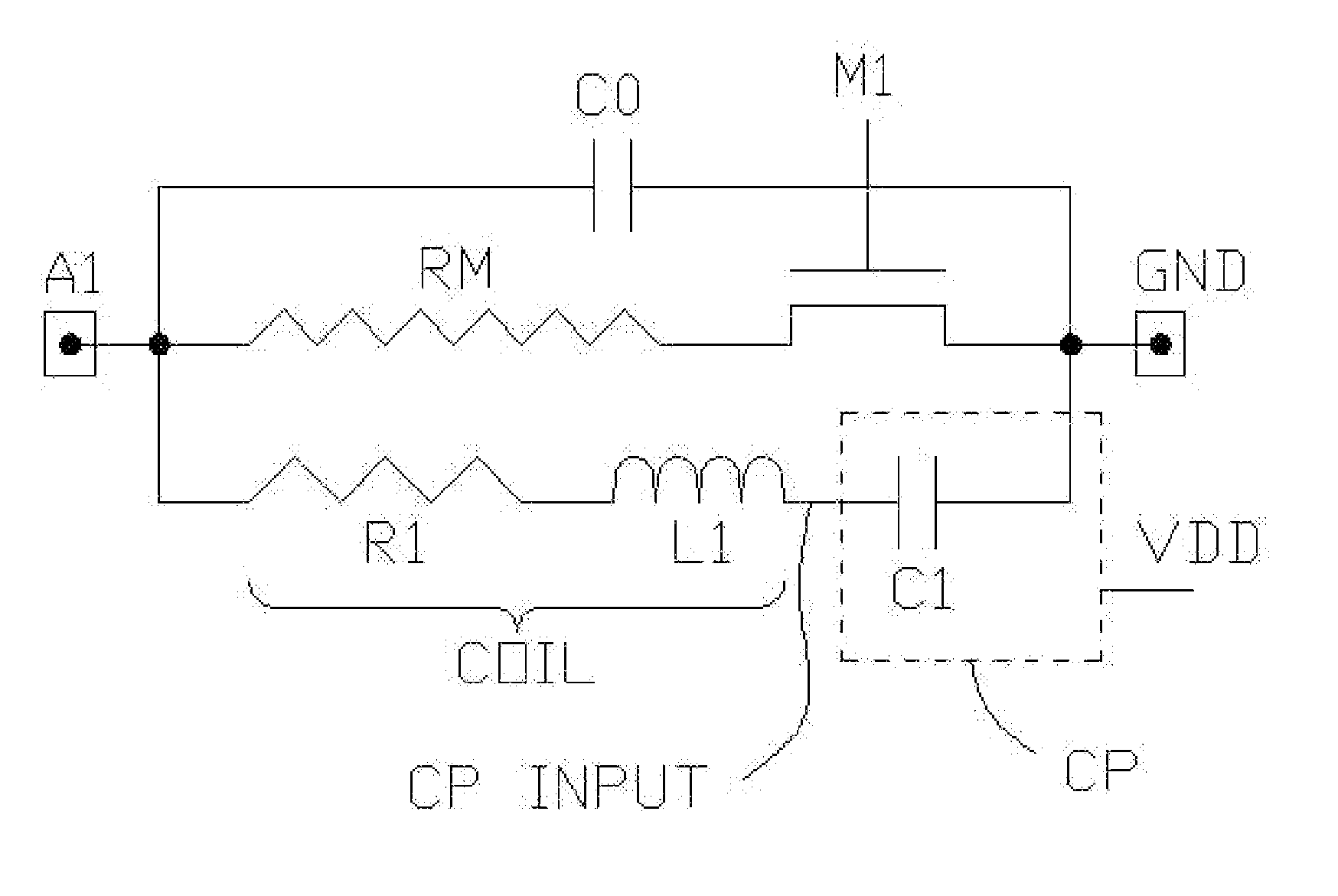
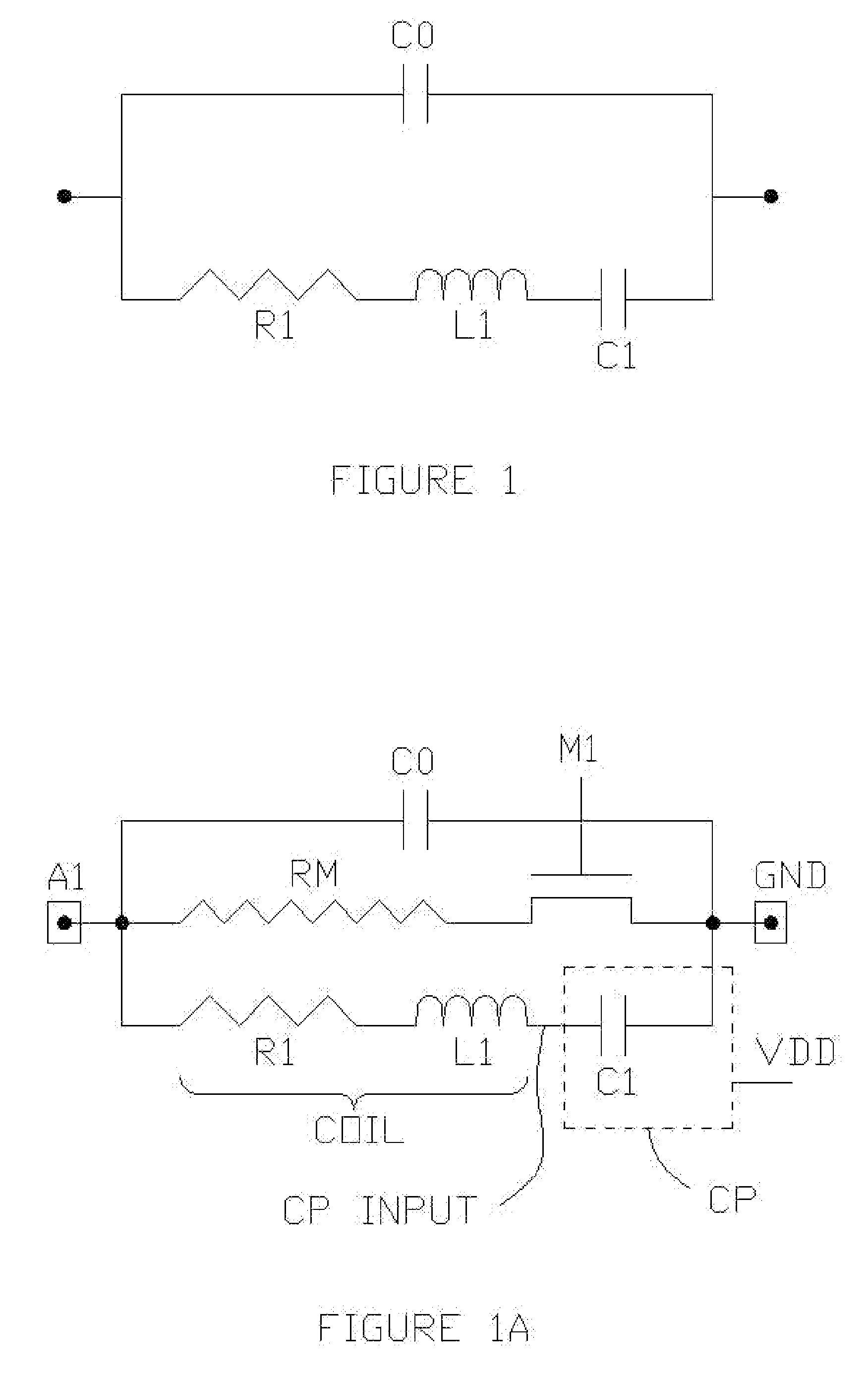
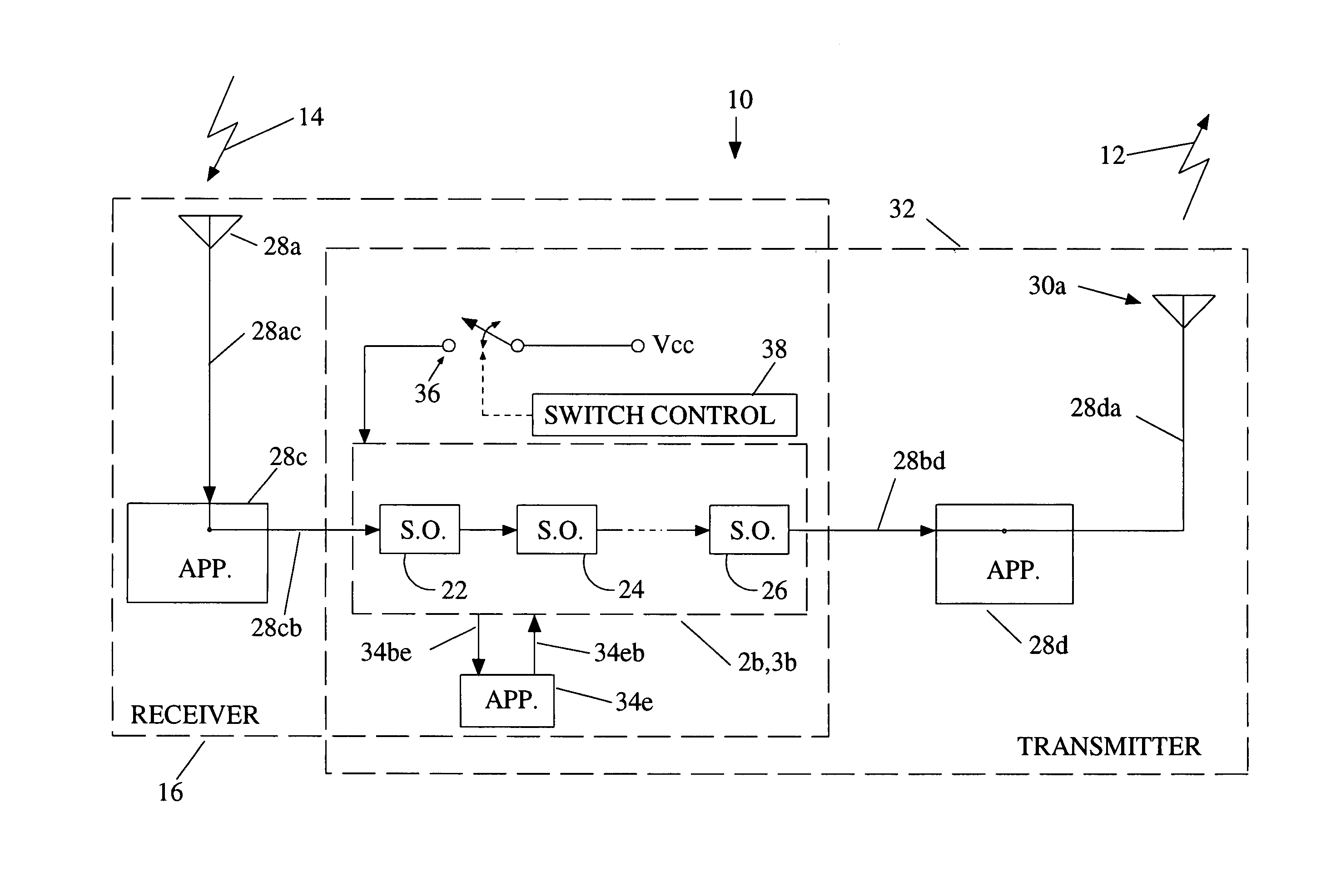
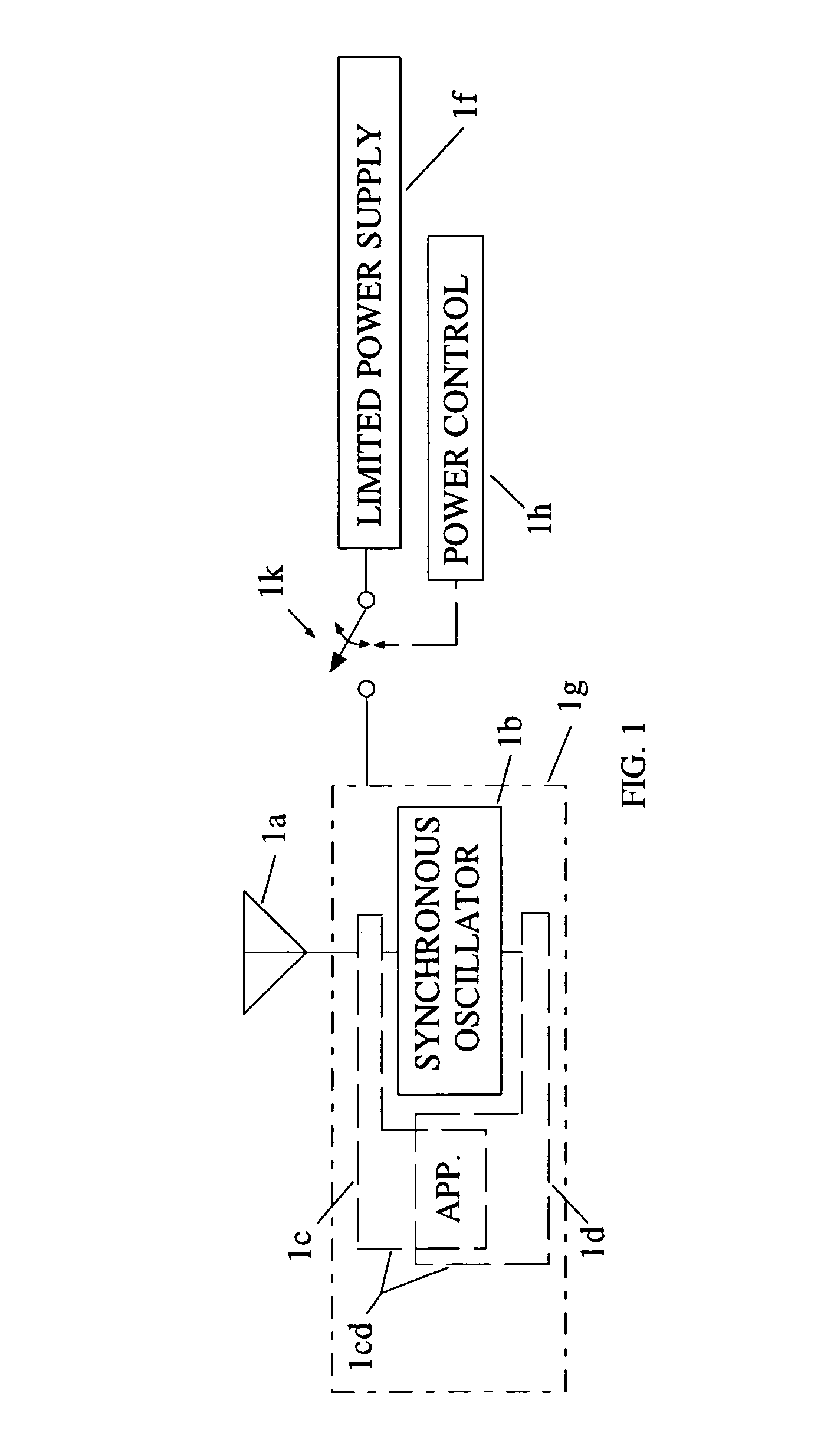
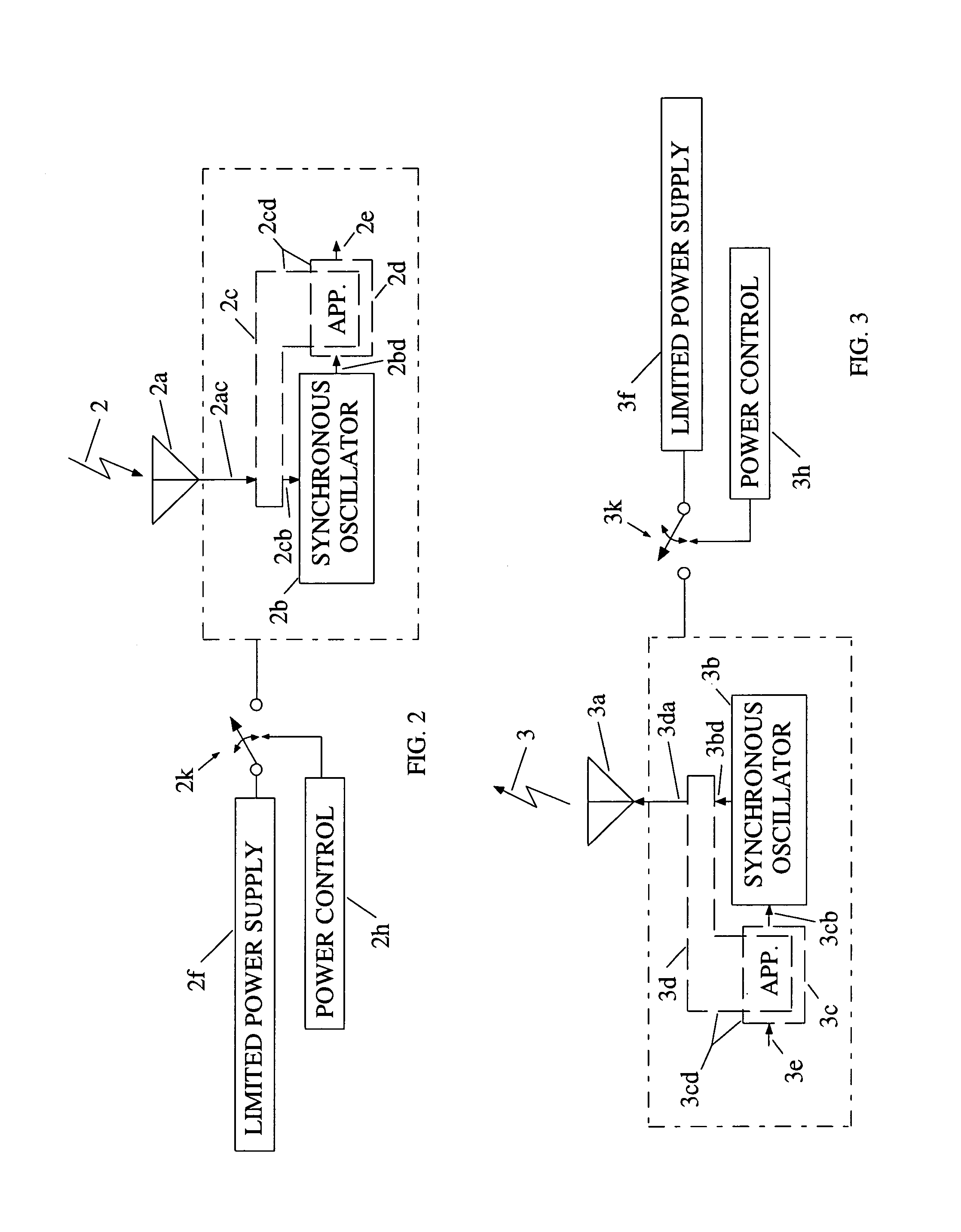
Oscillator coupled to an antenna and an application
ActiveUS7106246B1Improve power efficiencyLong period of timeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTag antennaRadio frequency
A radio frequency device has an antenna for capturing an incoming signal for processing by the device or for radiating an outgoing signal from the device and a signal processor having one or more synchronous oscillators responsive to an input signal for providing an amplified output signal without using much power. An application is a radio frequency (RF) transponder (tag) for receiving an RF signal from an interrogator includes a tag antenna for receiving the RF signal from the interrogator and a receiver section connected to the tag antenna wherein the receiver consumes a significantly lower amount of power than conventional receiver technologies by using one or more synchronous oscillators.
Owner:LINDELL KEVIN W
System and method of optimizing the process of identifying items tagged with RFID tags in an enclosed shielded space
A system and method comprises a plurality of RF antennas having beams directed to a storage space in which medical items having RFID tags are stored. Each antenna is controlled to inject energy at a different frequency in a frequency-hopping set of frequencies to activate the tags. The return signal strength is monitored and for each tag that responds, the antenna location, frequency of the injected energy, identification response, and signal strength are stored as identification data. If a tag fails to respond in new scans, the antenna at which the tag last responded receives all the frequency-hopping frequencies in an attempt to locate the tag. If new tags are found, they are compared to a list of expected new medical items.
Owner:MEPS REAL TIME
Event driven context switching in passive radio frequency identification tags
InactiveUS20130033364A1Simple configurationLow costSensing detailsSubscribers indirect connectionEvent triggerDevice Monitor
The invention relates to an event driven content switching technology in a passive, batteryless radio frequency identification (RFID) tag. The RFID tag device monitors the occurence of an external event such as a change in the environment. The switching of the context of the tag is effected by sensors incorporated in the tag. An external event triggers the switch. An RFID reader may subsequently read out the occurrence of the event due to the switch change. Different alignments of the switch could bring about the closing or opening of specific electronic circuits within the RFID tag that effect the storing of information in a selected memory, or changing the ID transmitted by the tag. In a particular embodiment this latter is accomplished by shorting one or the other of two RFID tag antennas. When one antenna is shorted, the second tag's ID is sent, and vice versa.
Owner:R F KEEPER
Passive transponder identification and credit-card type transponder
InactiveUS6894624B2Reduce impactIncrease system bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsDetection of traffic movementCredit cardTag antenna
A passive transponder identification system and credit card type transponder are disclosed, particularly, the transponder identification system to utilize a transmitting manner of two different RF signals is provided. The present invention directly relates to a passive transponder without any kind of power source. Therefore, the present invention has advantages of having a constant gain value by developing a high-gain dual polarizing antenna for a small credit card type passive transponder to identify at long distance, independently to any direction of the transponder; improving gain values than conventional transponder tag antenna by 6-9 dB to ensure a sub-permanent life time by providing the desired identification performance by a small credit card type passive transponder without power supply; and being applicable to any systems to identify and distinguish high-speed moving objects.
Owner:CREDIPASS
Survival and location enhancement garment and headgear
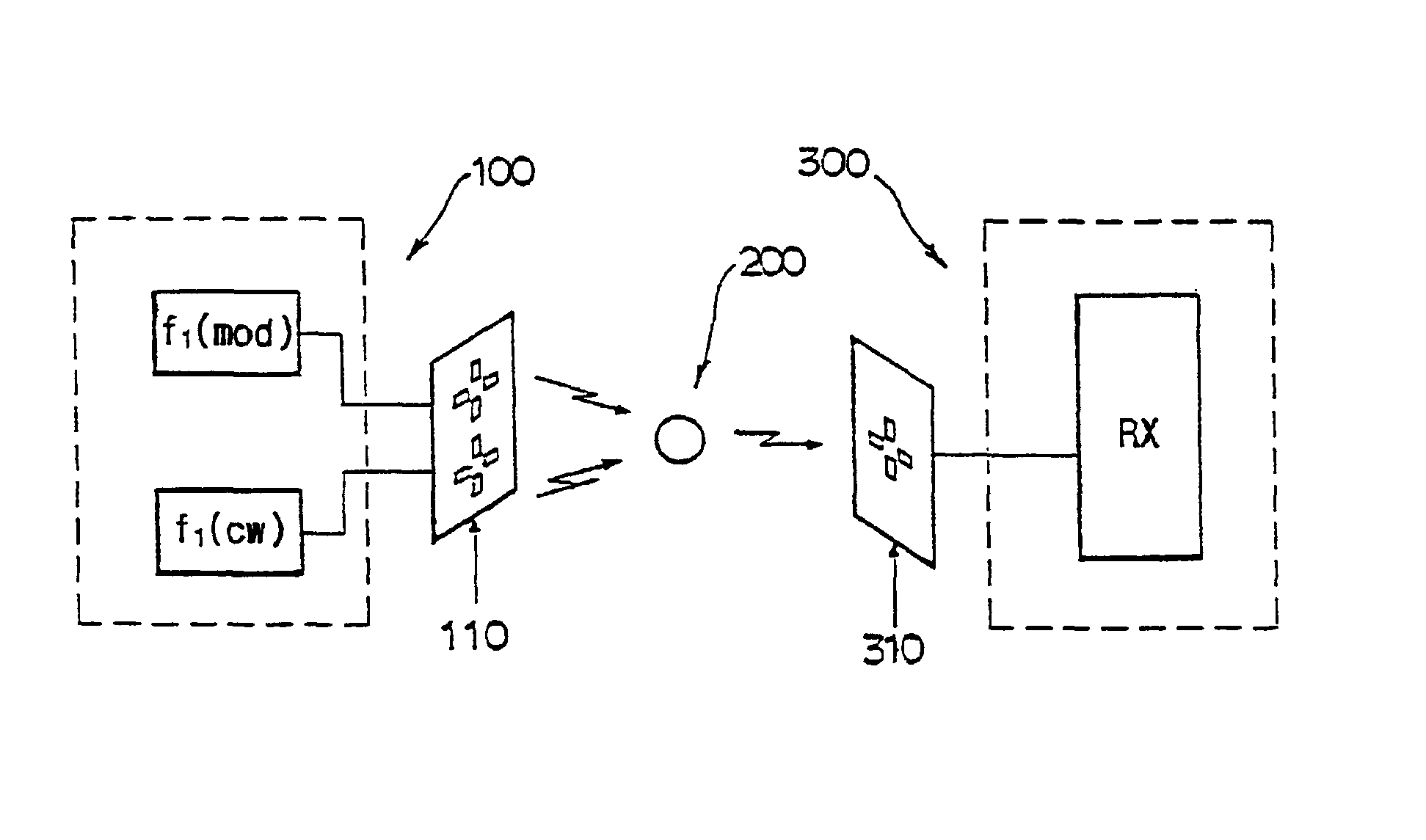
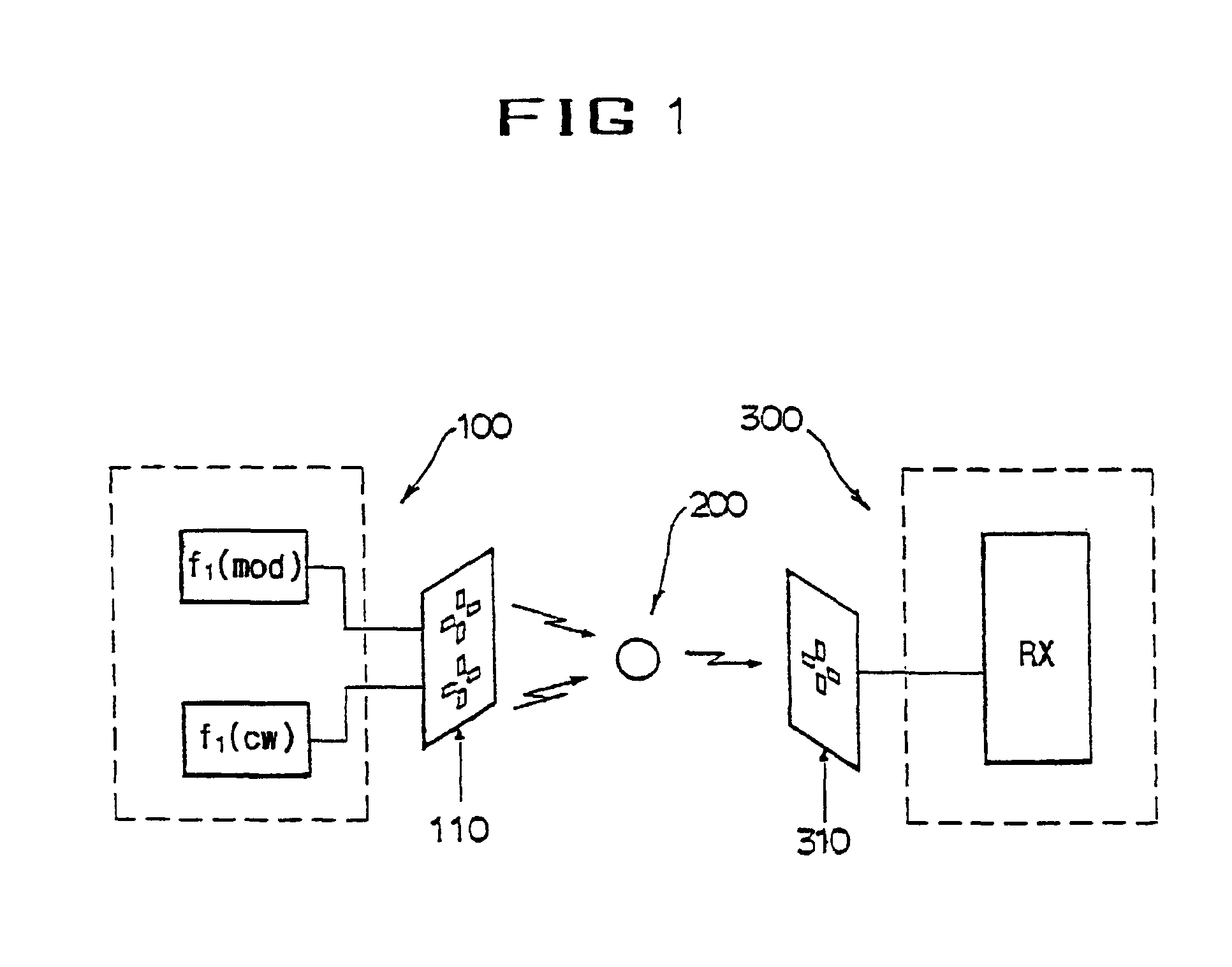
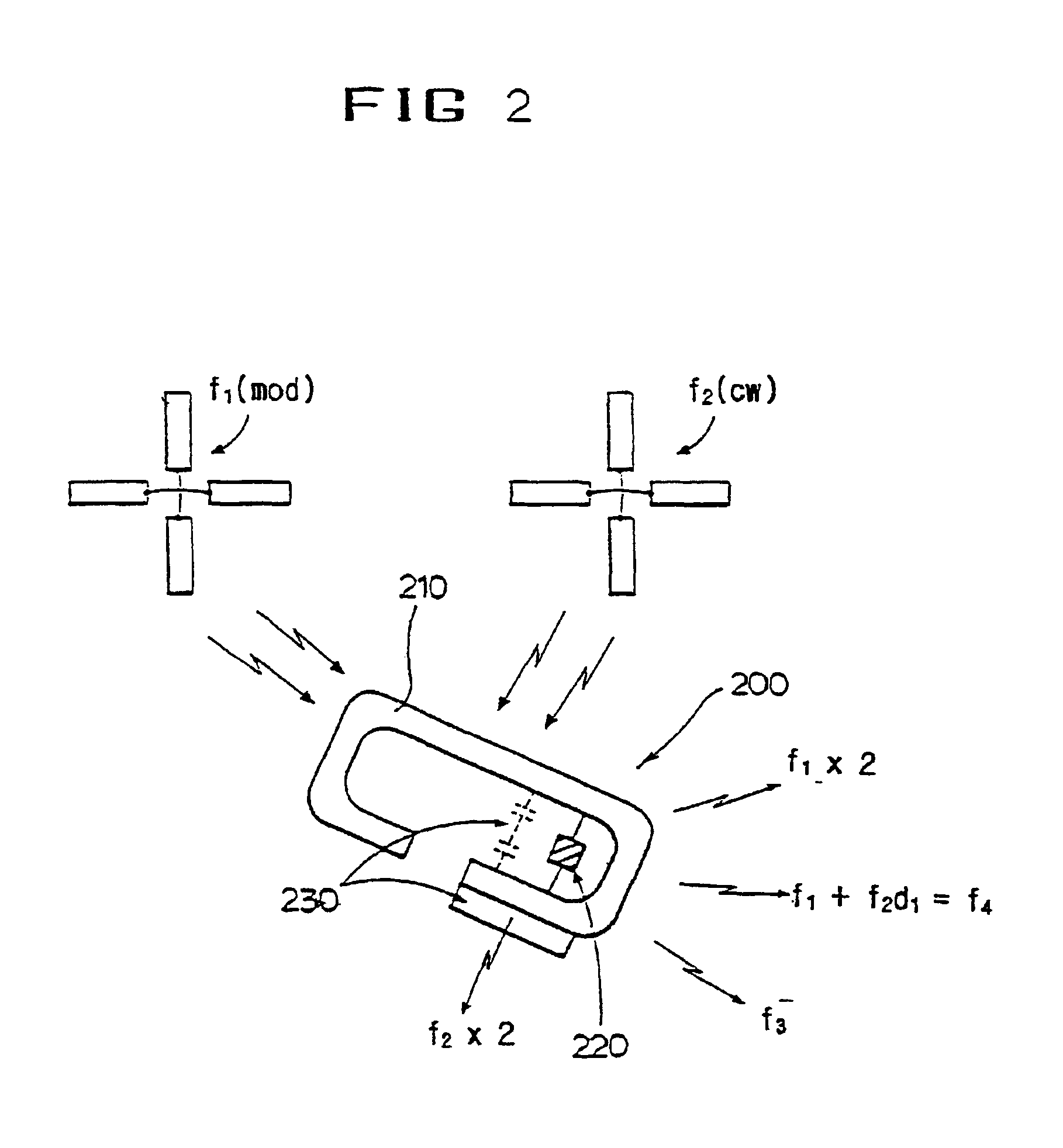
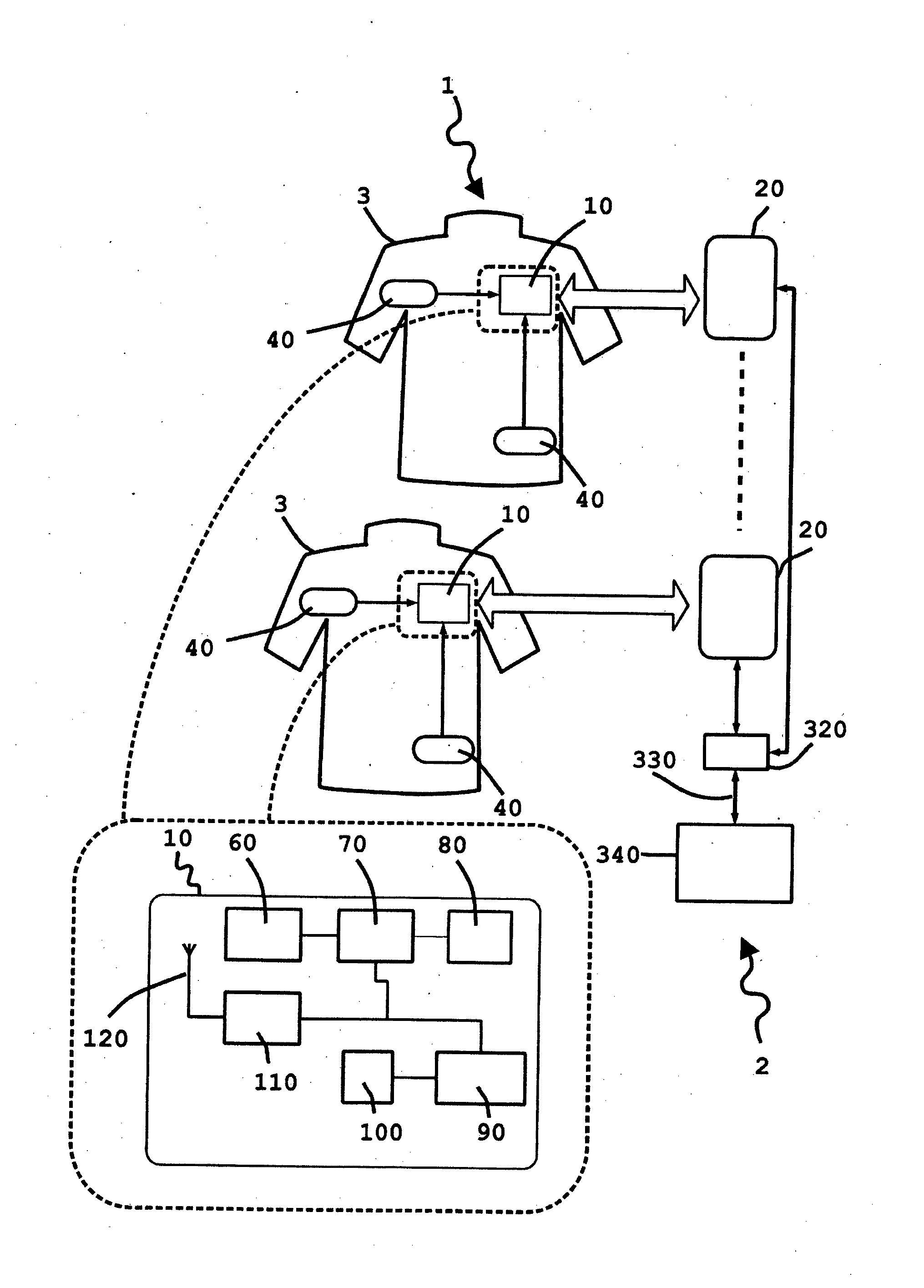
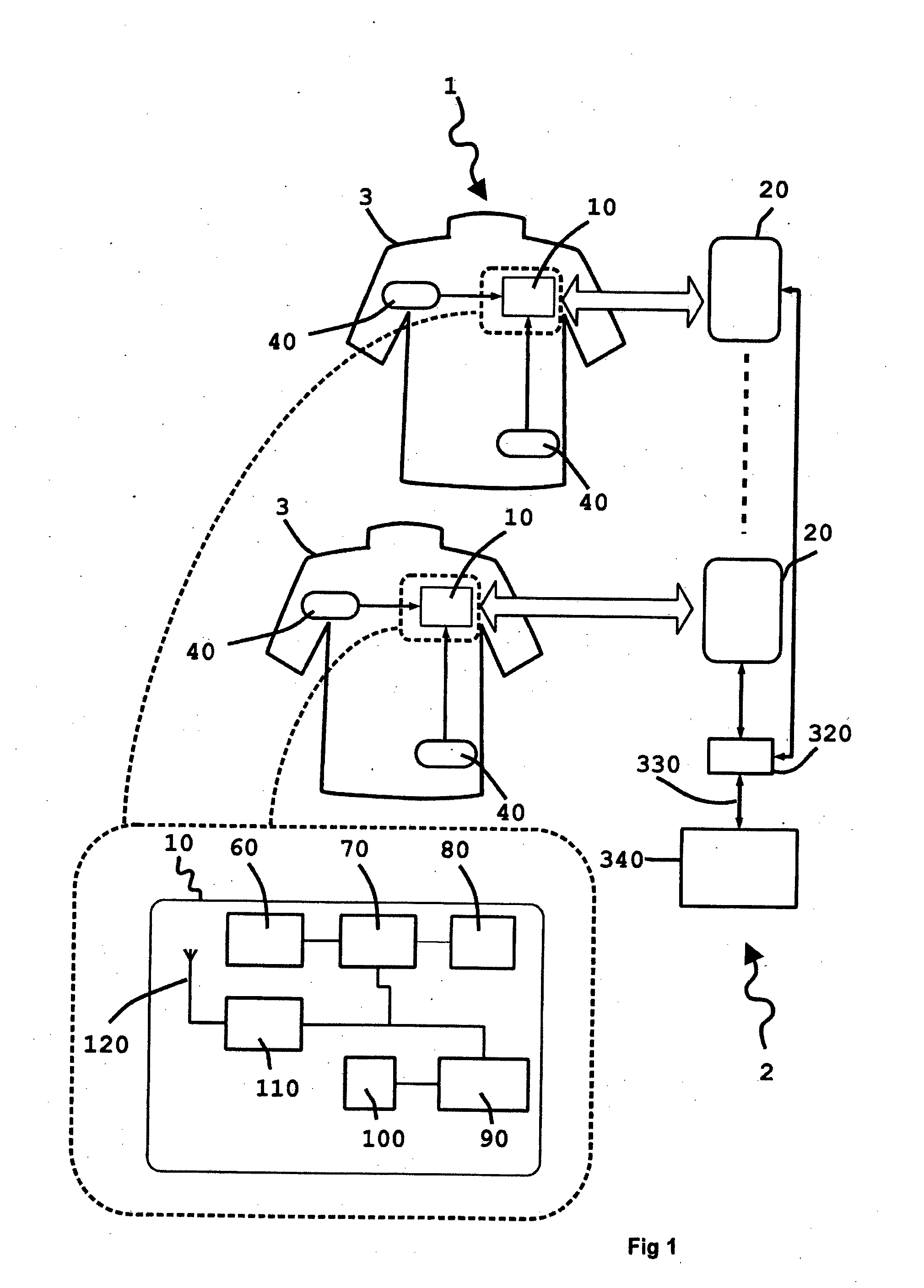
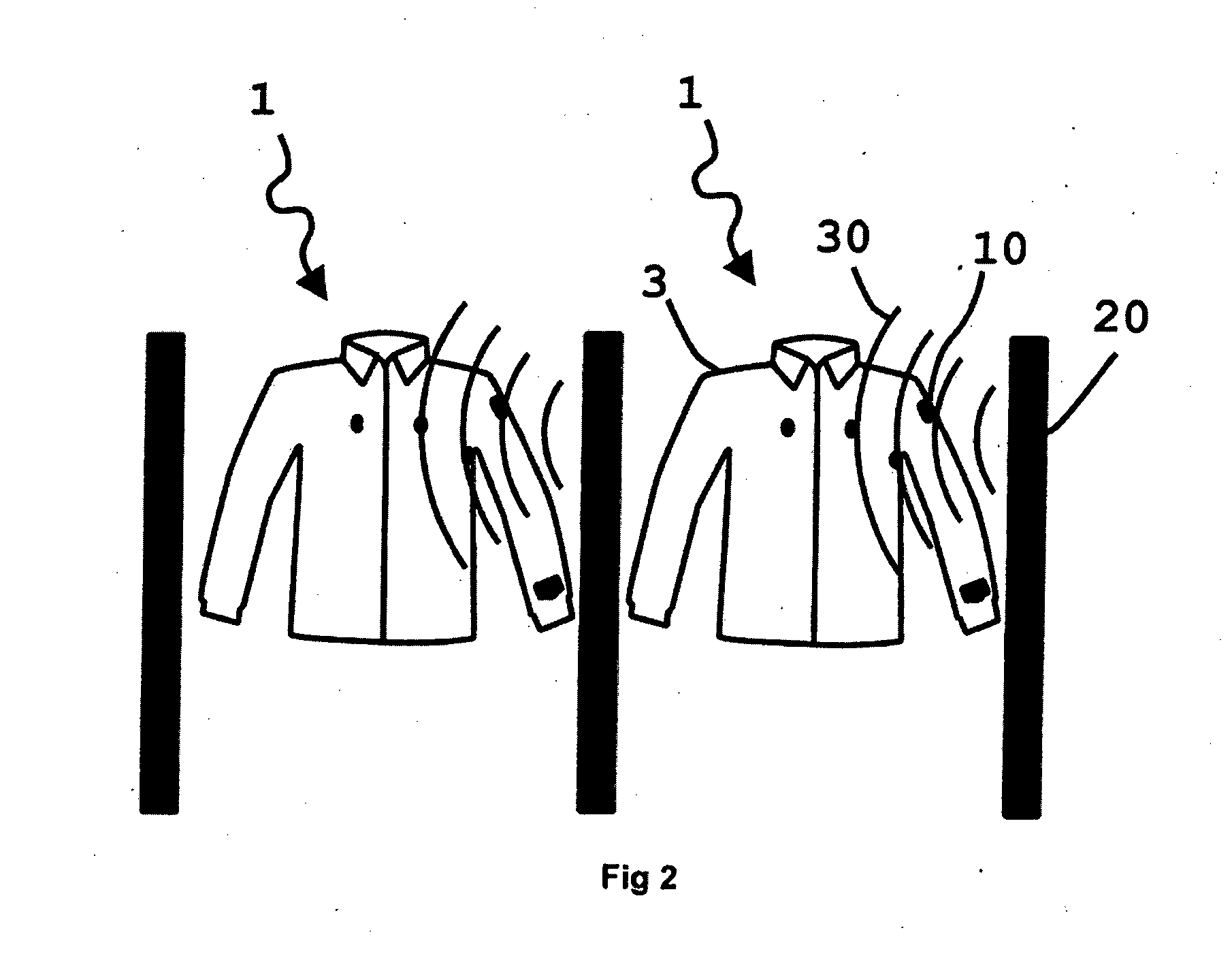
InactiveUS20130321168A1Improve survivabilityChemical protectionElectric signal transmission systemsMicrocontrollerSurvivability
The present invention provides system of active uniform and base station for sensing an aspect of the wearers environment or physiology. Active uniform (1) is comprised of uniform (3), electronic sensors (40) for sensing an aspect of the wearer's environment or of the wearer's physiology and an active tag (10). The system of active uniform (1) and base station (2) is used to collect data from wearers of the at least one item of active uniform which allows an assessment of the health of the wearer where said health assessment is subsequently used to enhance the survivability of the wearer. The active tag contains various components that allow it to communicate with the base station (2) including (i) sensor interface (80) for interfacing electronic sensors (40) to the active tag, (ii) a microcontroller (70), (iii) a data store (60) including flash memory, (iv) radio frequency interface (110), (v) at least one tag antenna (120) and (vi) a battery (100) and power management unit (90). The sensors (40) and active tag (10) are adapted to be retained on or in the item of uniform (3) such that the active uniform (1) is able to be washed without removing the electronic sensors (40) or the active tag (10). Base station (2) comprises base station antenna (20), base station transceiver (320) and data processing apparatus (340) connected to the base station transceiver, which is adapted to receive and store data transmitted by the active tag of the active uniform, including at least, sensor and identification data.
Owner:JOELMAR
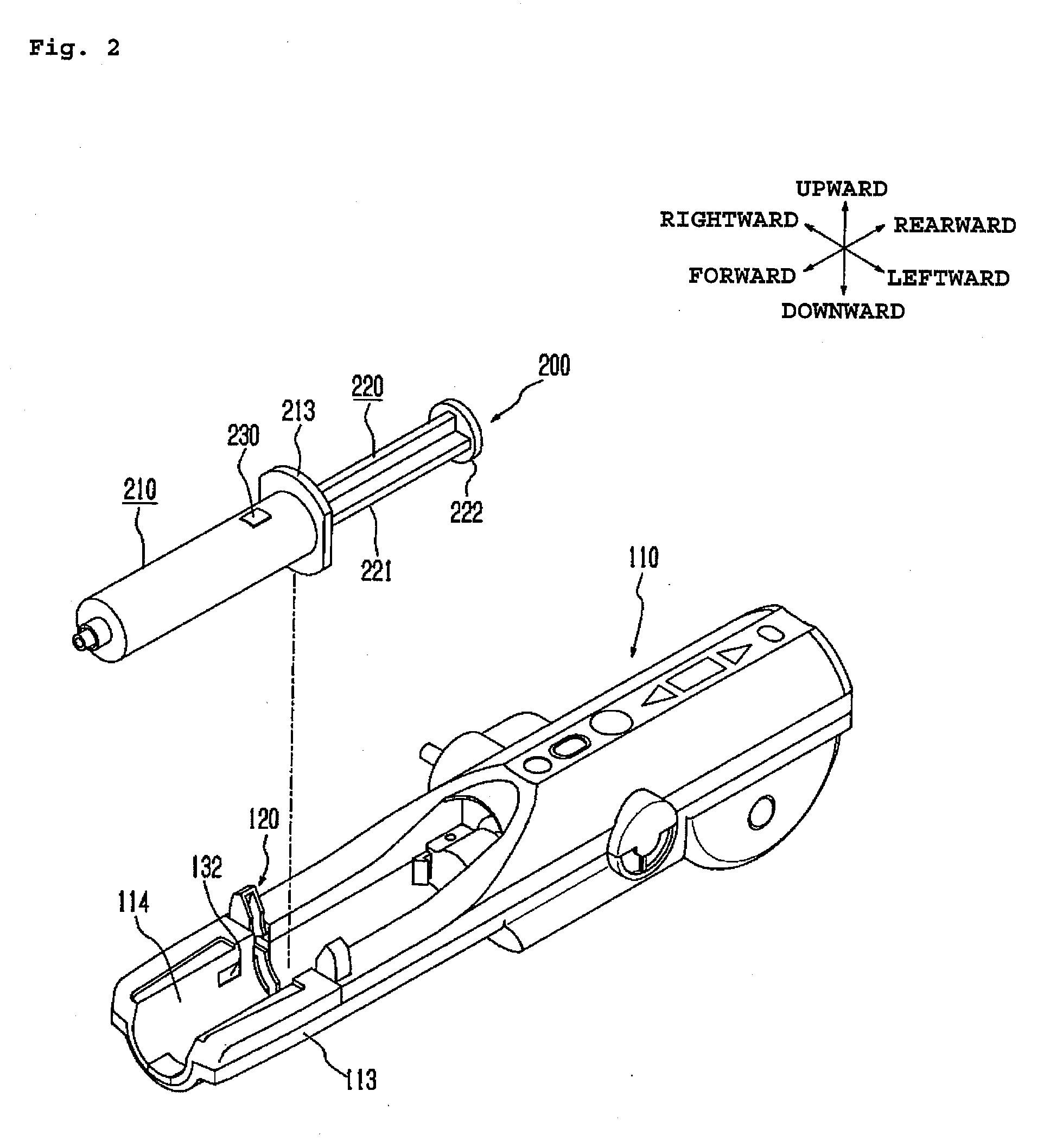
Chemical liquid injection system
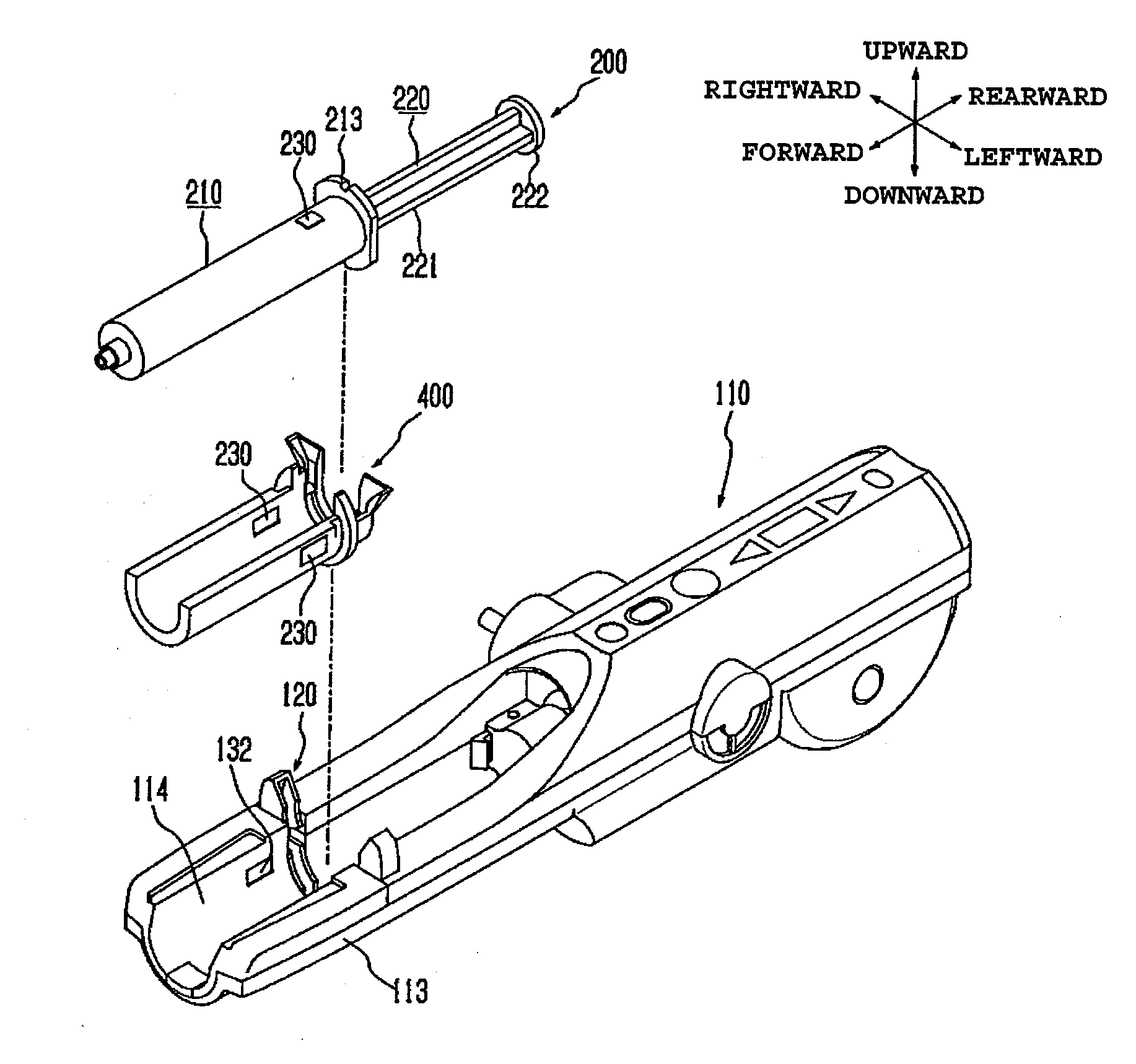
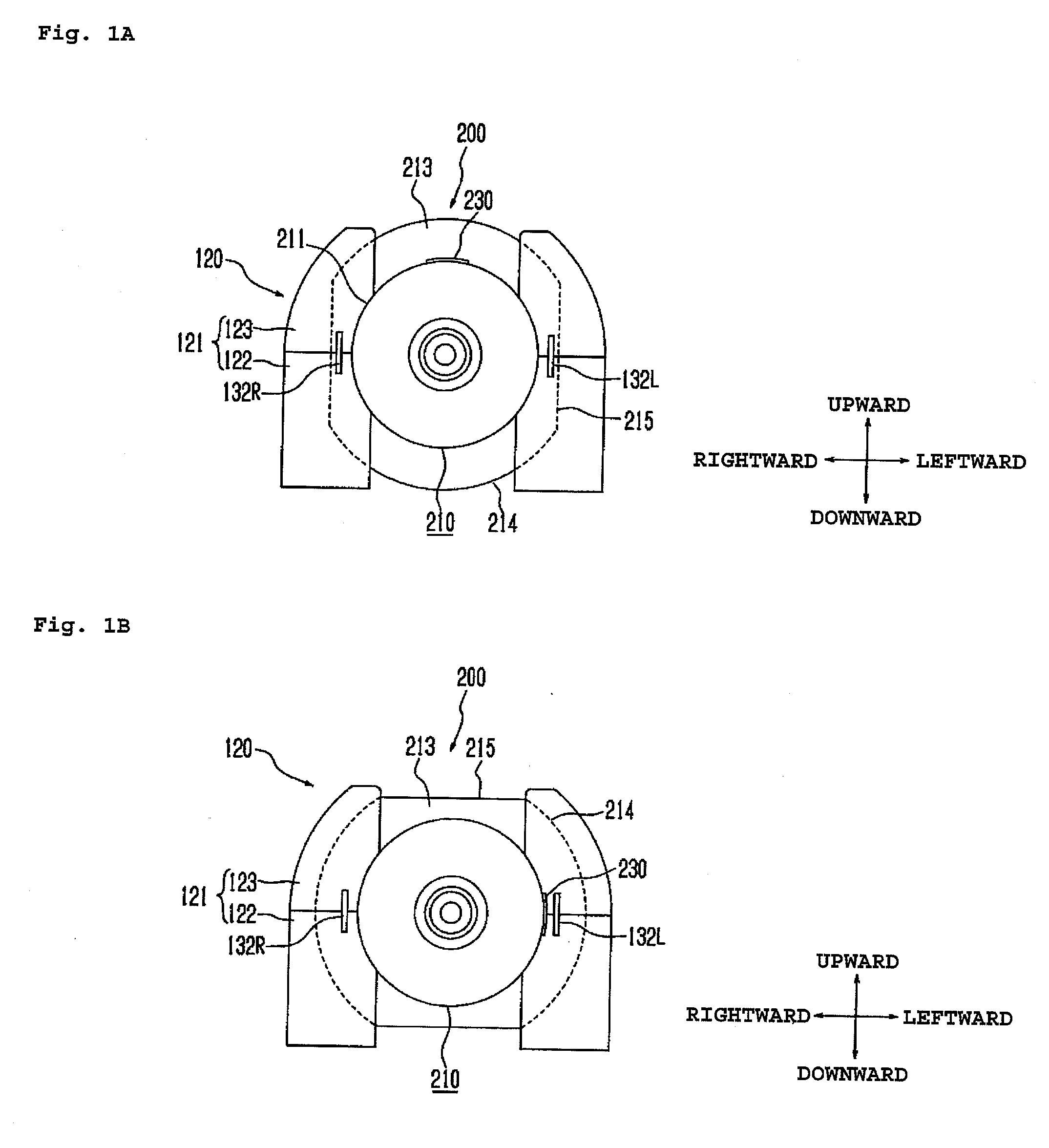
ActiveUS20090156931A1Avoid pressingAvoid drivingMedical devicesIntravenous devicesTag antennaEngineering
A chemical liquid injector comprises liquid syringe 200 and a chemical liquid injector. Liquid syringe 200 has cylinder member 210, a piston member and RFID tag 230 put on an outer circumference of cylinder member 210. The chemical liquid injector has cylinder holding mechanism 120 for holding cylinder member 210, a piston driving mechanism for driving the piston member and an RFID reader. The RFID reader has reader antennas 132L, 132R placed opposite to a tag antenna so as to be able to receive data from RFID tag 230 with cylinder member 210 is appropriately held by the cylinder holding mechanism. The piston driving mechanism is permitted to operate only when the RFID reader receives data from RFID tag 230.
Owner:NEMOTO KYORINDO KK
Networked RF tag for tracking baggage
ActiveUS7489244B2Precise positioningFacilitate attachment to surfaceHand manipulated computer devicesElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingTransceiverIp address
The invention disclosed provides a method, system, and associated tag for detection and tracking of inanimate and animate objects. The novel method broadly comprises the steps of: a) attaching a low radio frequency detection tag to each of the objects, each tag comprising a tag antenna operable at a low radio frequency not exceeding 1 megahertz (preferably not exceeding 300 kilohertz), a transceiver operatively connected to the tag's antenna, the transceiver being operable to transmit and receive data signals at the low radio frequency, a data storage device operable to store data comprising identification data for identifying said detection tag, a programmed data processor operable to process data received from the transceiver and the data storage device and to send data to cause the transceiver to emit an identification signal based upon the identification data stored in said data storage device, and an energy source for activating the tag's transceiver and data processor; b) storing, in the data storage device of each tag, shipping data selected from object description data, address-of-origin data, destination address data, object vulnerability data, and object status data; c) commingling the objects in a repository selected from a warehouse and a truck, the repository being provided with at least one large loop field antenna operable at said low radio frequency; the field antenna being disposed at a distance from each object that permits effective communication therewith at the low radio frequency, d) reading the identification data and shipping data from the transceiver of each tag by interrogating all tags commingled in said repository with data signals, such as specific IP addresses or other identification codes, via said field antenna; and e) transmitting the identification data and shipping data from each tag to a central data processor to provide a tally of the objects in said repository.
Owner:VISIBLE ASSET INC
Techniques for folded tag antennas
ActiveUS20070046475A1Improved multi-axis performanceLessAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna feed intermediatesTag antennaEngineering
Techniques for an RFID device with improved multi-axis performance are provided. The device includes a flexible substrate with an antenna pattern formed thereon. A fold in the flexible substrate results in the antenna pattern crossing over itself and disposes a distal region of the antenna pattern away from a proximal region at about a predetermined angle. An integrated circuit is electrically coupled to the antenna pattern. In a specific embodiment, the antenna pattern is slit along a major axis to allow folding a segment of an antenna pattern.
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
RFID tag incorporating at least two integrated circuits
ActiveUS20070085689A1Minimizes inter-chip interferenceImprove abilitiesSubscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesTag antennaSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Multiple RFID integrated circuit microradio chips are located at the feed point of an RFID tag antenna for greater reliability, elimination of testing and to take advantage of coherent microradio operation for increased gain and power, better signal-to-noise ratios, improved range and low bit error rates.
Owner:RADIOFIDO
Self-checkout system
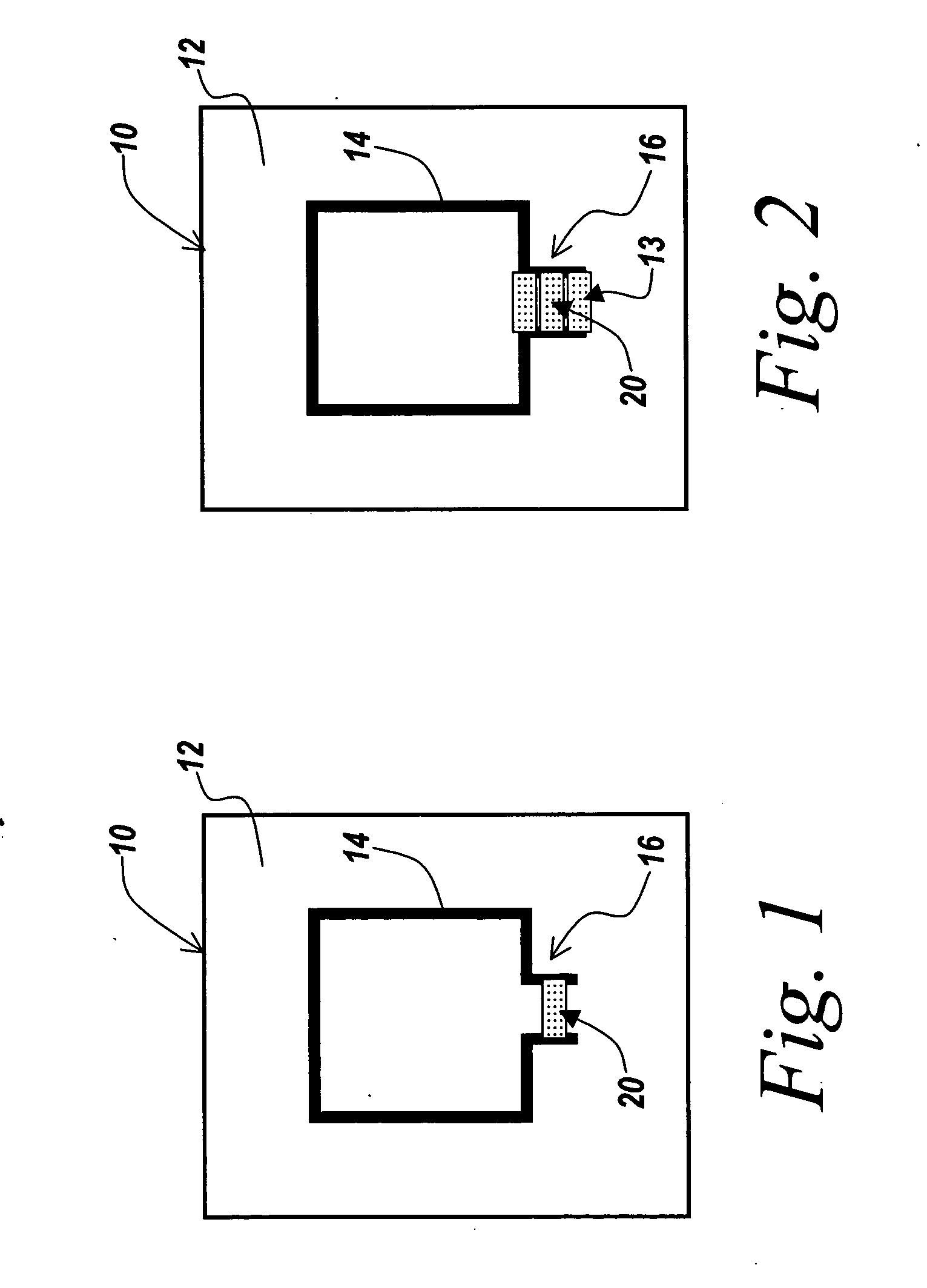
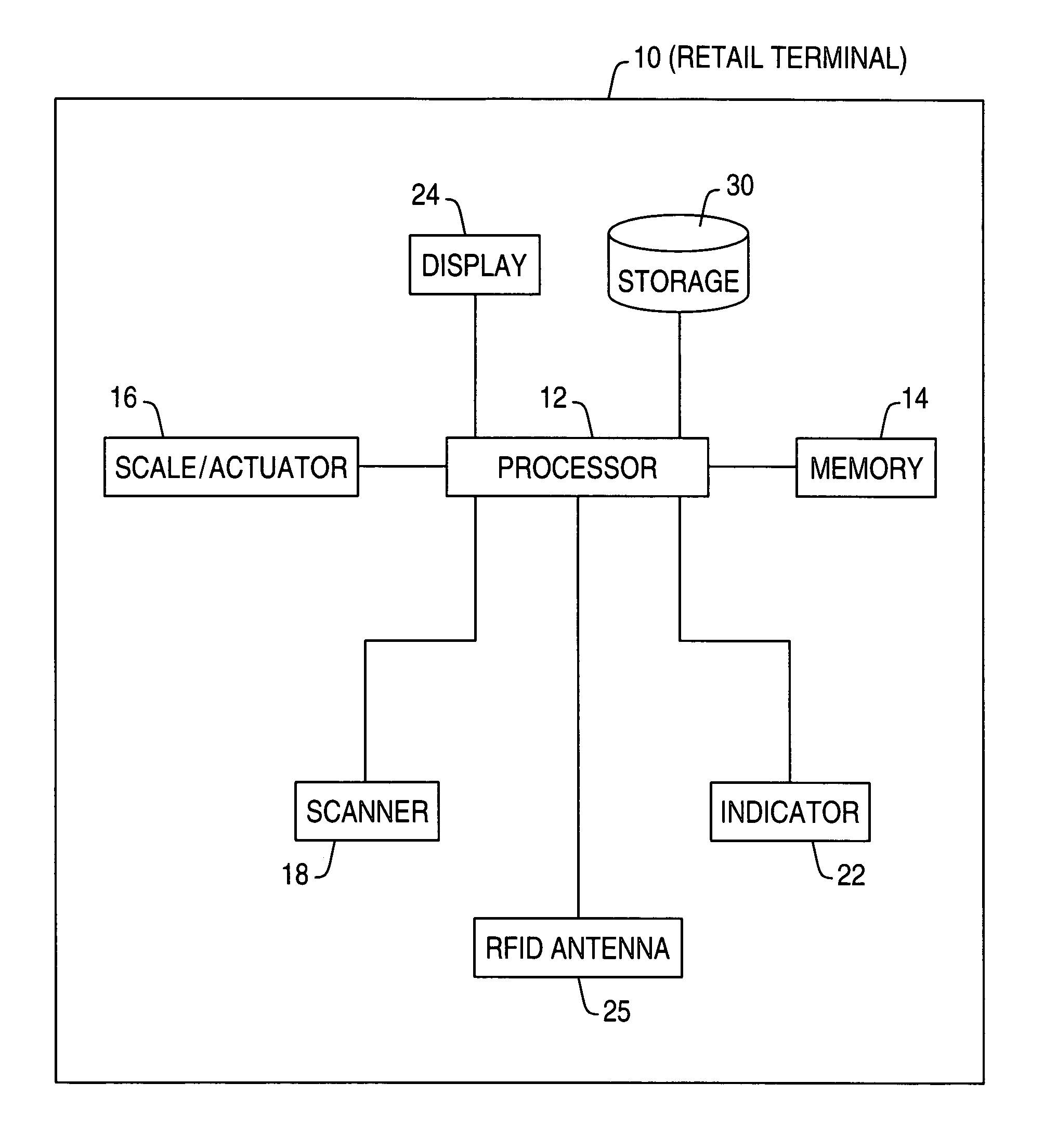
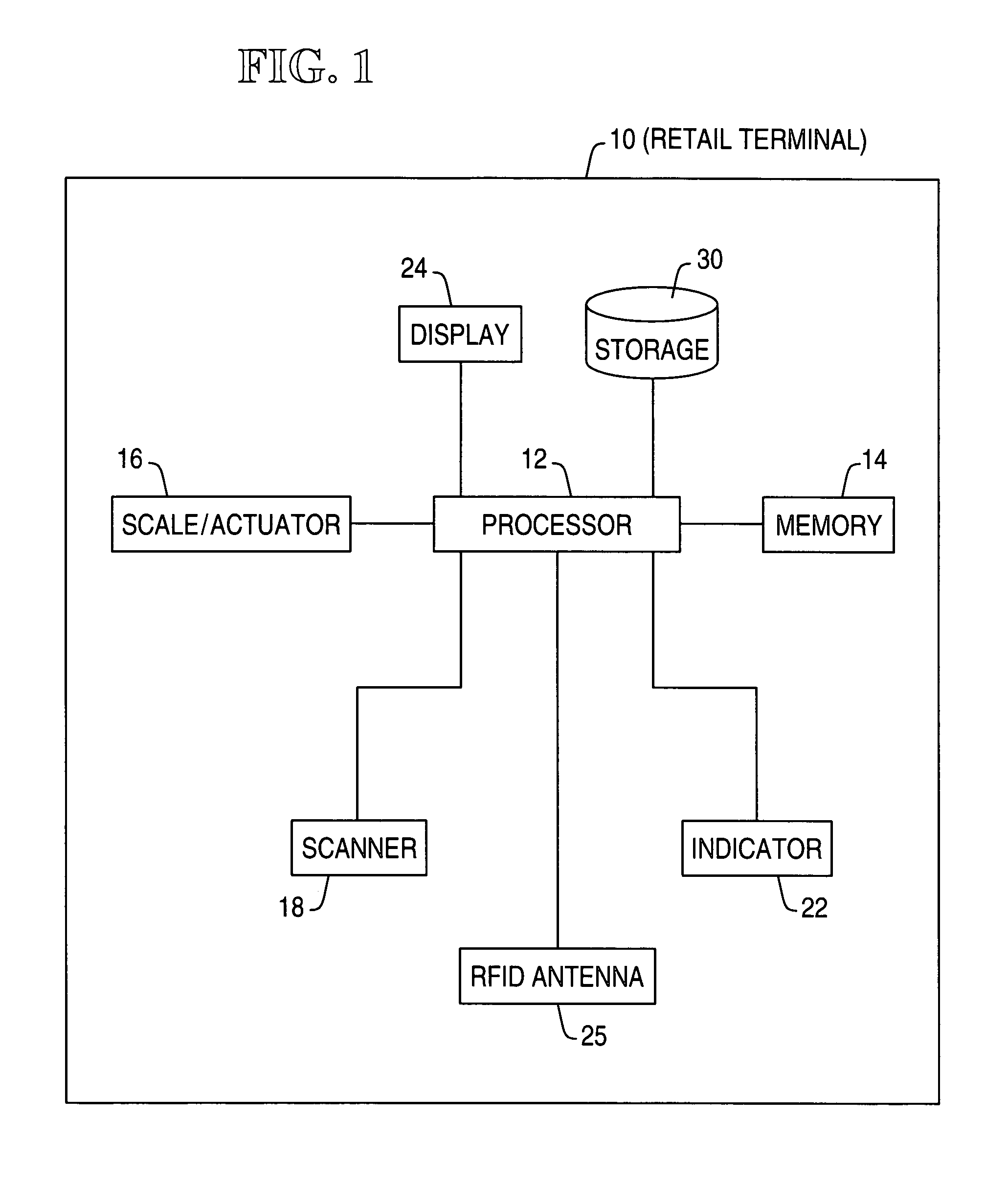
A retail terminal and method of operation thereof. The retail terminal has a weight scale, a bar code scanner, RFID tag antenna, a scan error indicator, means for communicating with a processor and a memory containing a weight learning database (WLDB). The method comprises the steps of: allowing placement of an item, having an RFID tag, to be weighed on the weight scale; allowing scanning of the item via the bar code scanner; allowing RFID tag to be read by antenna located in the scanner; obtaining a weight measurement of the item on the scale upon successful scanning of the item; and comparing the measured weight of the scanned item with a predetermined weight for that item stored in the WLDB. Wherein the comparison detects a discrepancy between the measured and pre-determined weights for the item actuating the RFID antenna in order to detect the RFID tag on the scanned item; and wherein the item identified by the RFID tag matches the scanned item de-actuating the scan error indicator, which would otherwise have been actuated by the discrepancy between the stored and measured weights for the scanned item.
Owner:NCR CORP
RFID tag
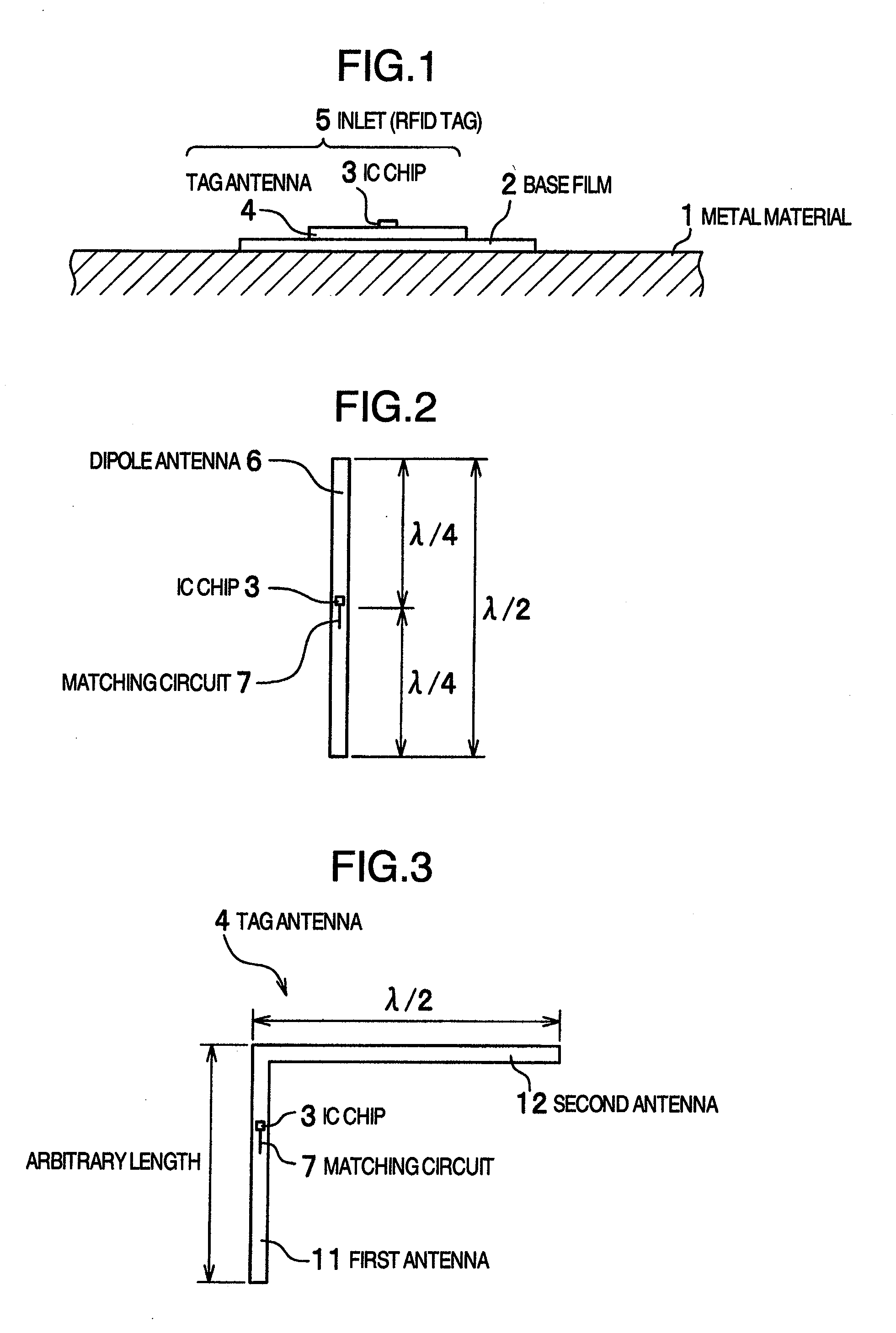
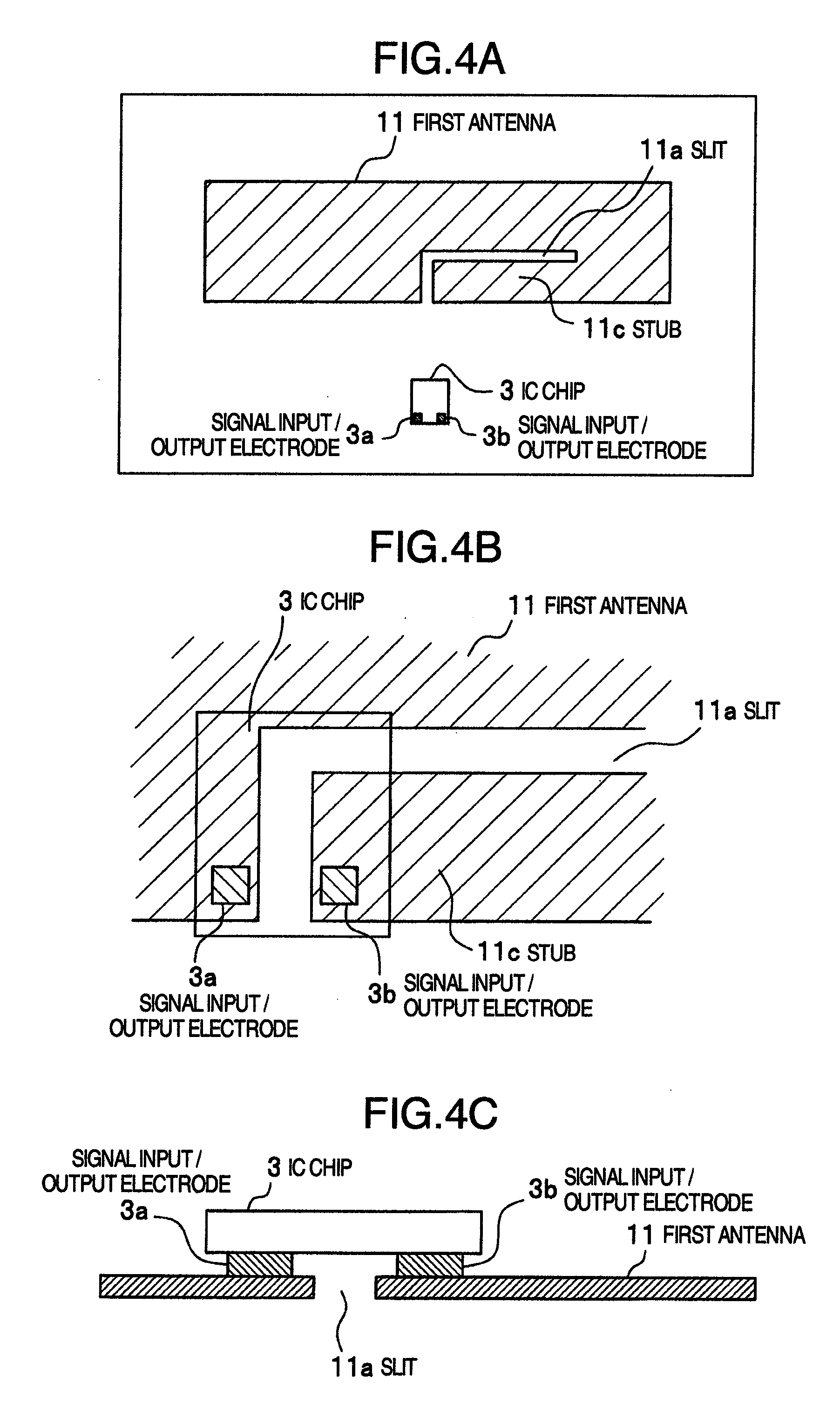
InactiveUS20080252462A1Slow changeReduce variationSubscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesTag antennaElectrical length
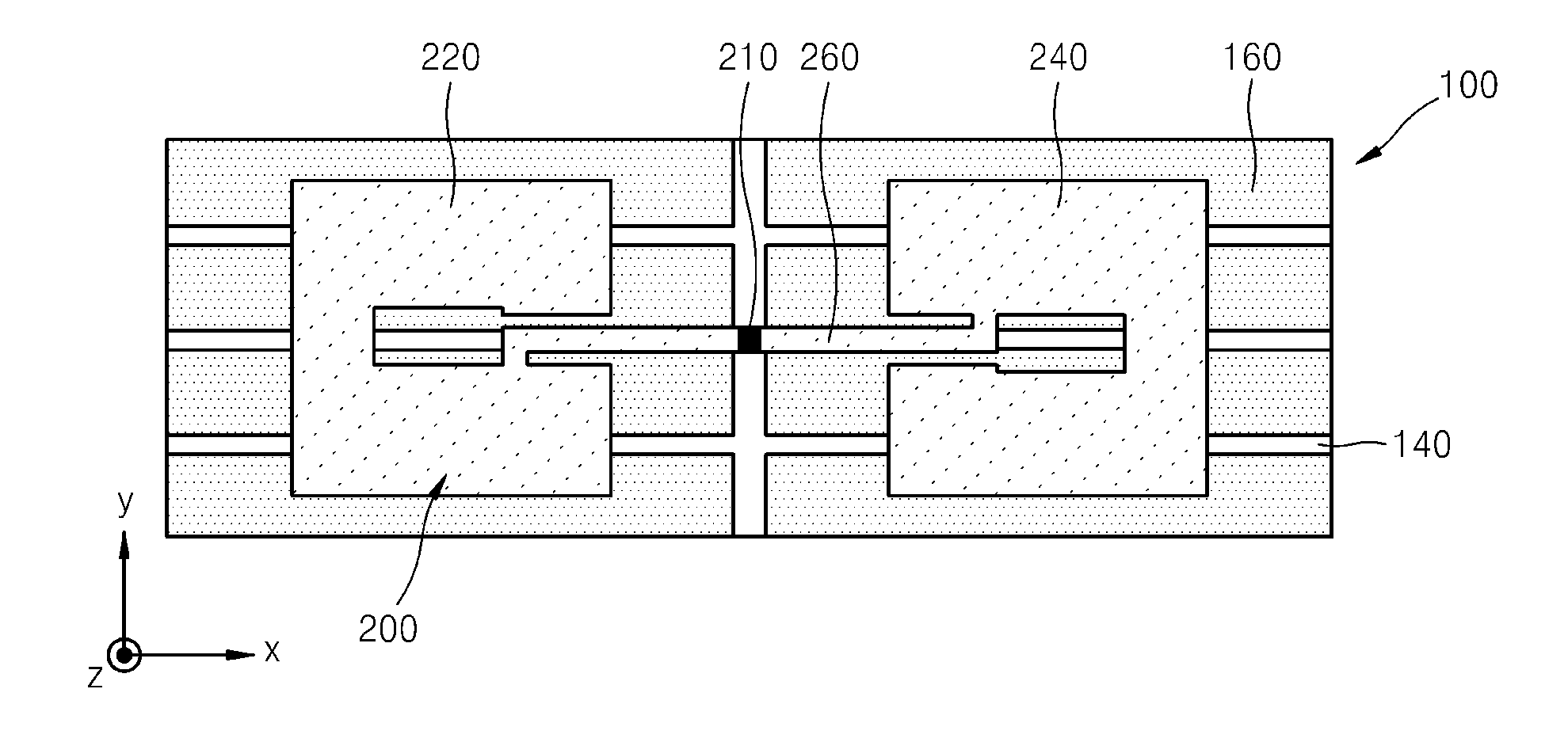
An RFID tag according to the present invention includes a first antenna on which an IC chip is mounted and a second antenna extending from an end of the first antenna in a direction at right angles to the first antenna. The first antenna has an arbitrarily electrical length and the second antenna has an electrical length of λ / 2 or an integral multiple of λ / 2. A resin base film having a thickness of approximately 50 μm is disposed on the back side of the first antenna and the second antenna. With this configuration of a tag antenna, the second antenna resonates with the first antenna to exhibit a radio wave amplifying effect. Therefore, a long communication distance can be achieved even if the electrical length of the first antenna is chosen to be short or the thickness of the base film is chosen to be thin.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Radio frequency identification tagging
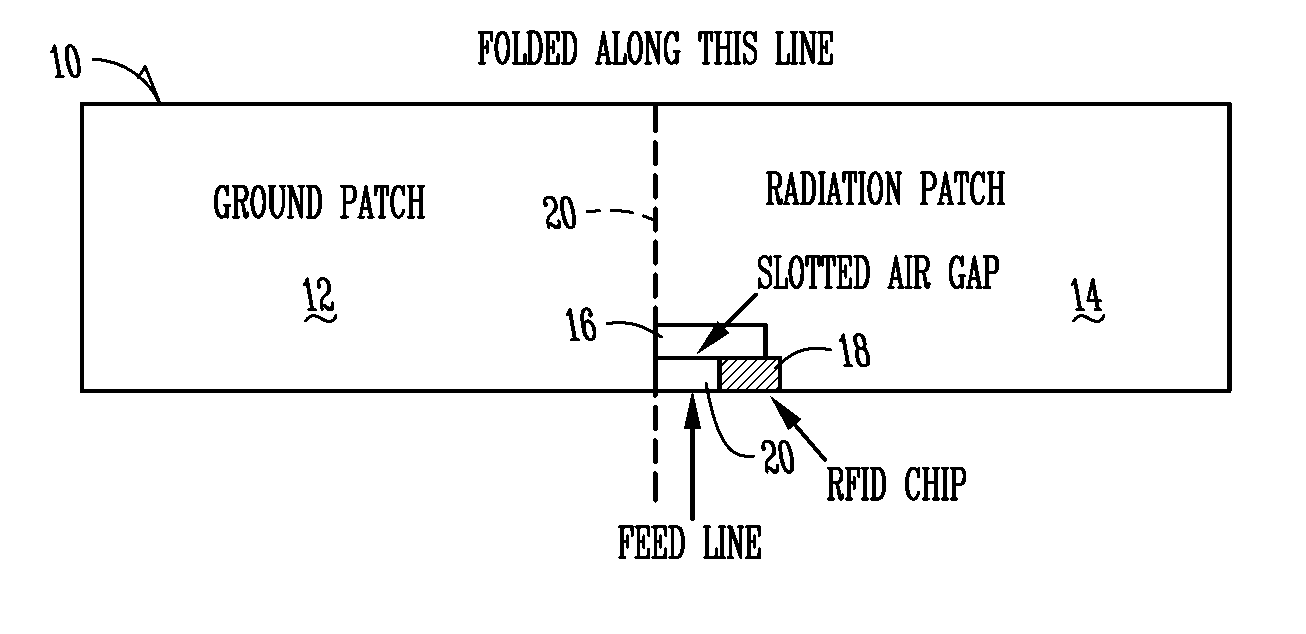
ActiveUS20090015377A1Easily used to tag objectSmall sizeContainer decorationsLevel indicationsElectronic identificationTag antenna
A RFID tag or label comprises a RFID tag module (comprising an electronic identification circuit and a coupling means) and an antenna structure coupled to the coupling means. The RFID tag module is separate from, separable or arranged to be severable from, the antenna structure. The tag module can be placed in or on an object and the antenna structure in or on packaging material for use with the object. A patch antenna type RFID tag antenna structure has a ground plane spaced from the patch antenna so as to increase the range of the tag. The ground plane is not substantially larger than, and electrically insulated from, the patch antenna. The ground plane is flexible, so the RFID tag structure can be worn by a human, and can be incorporated into a piece of clothing. A RFID antenna structure for use with a tag reader is made flat and robust so that it can be mounted on the ground to be walked upon or driven over. A bi-directional YAGI type RFID tag antenna structure has director elements on two opposite sides so that the YAGI antenna radiates in two opposite directions. An object includes a gain increasing metallic structure for increasing the gain of a RFID tag when placed near the object so as to form a RFID tag antenna structure.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
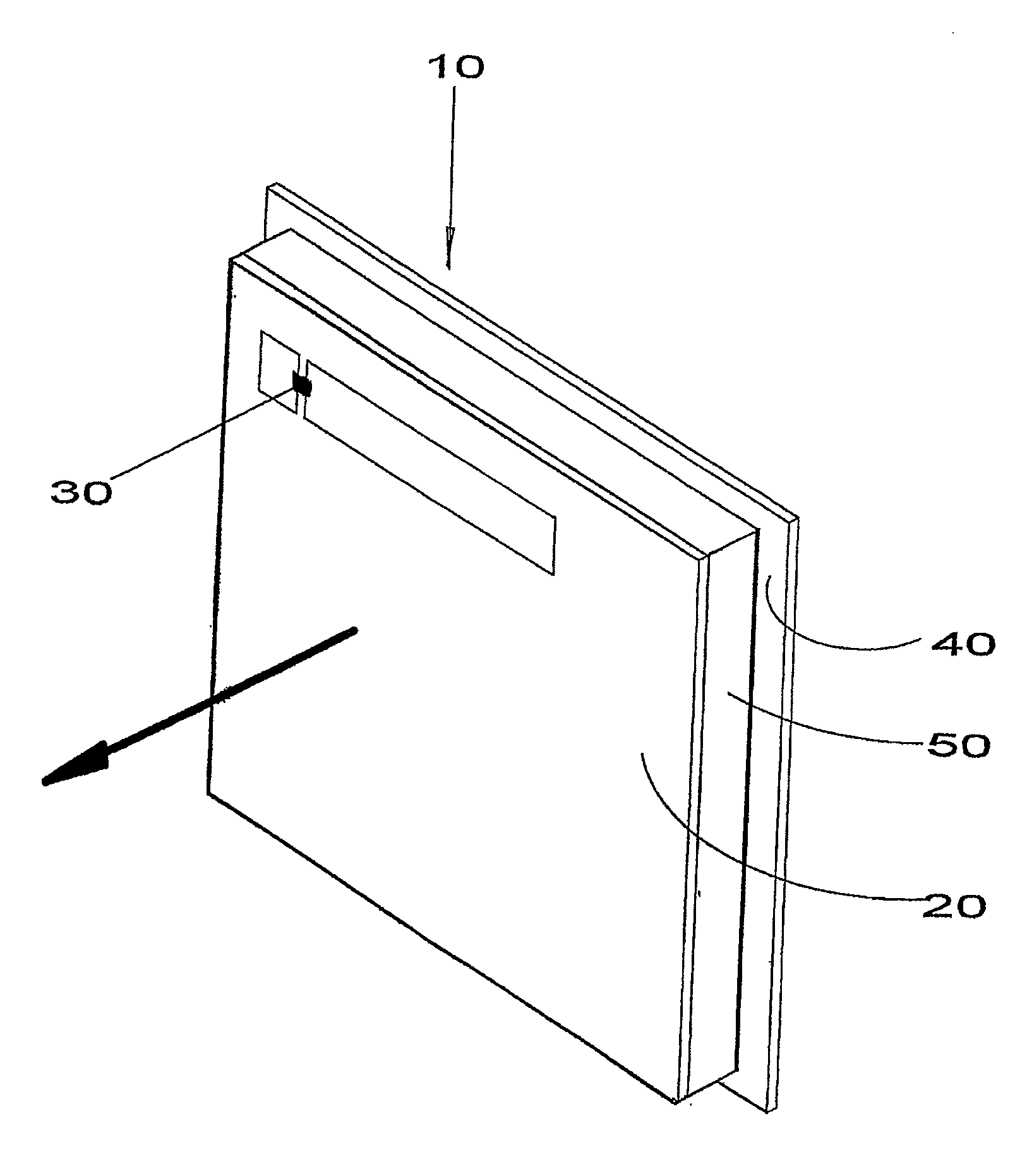
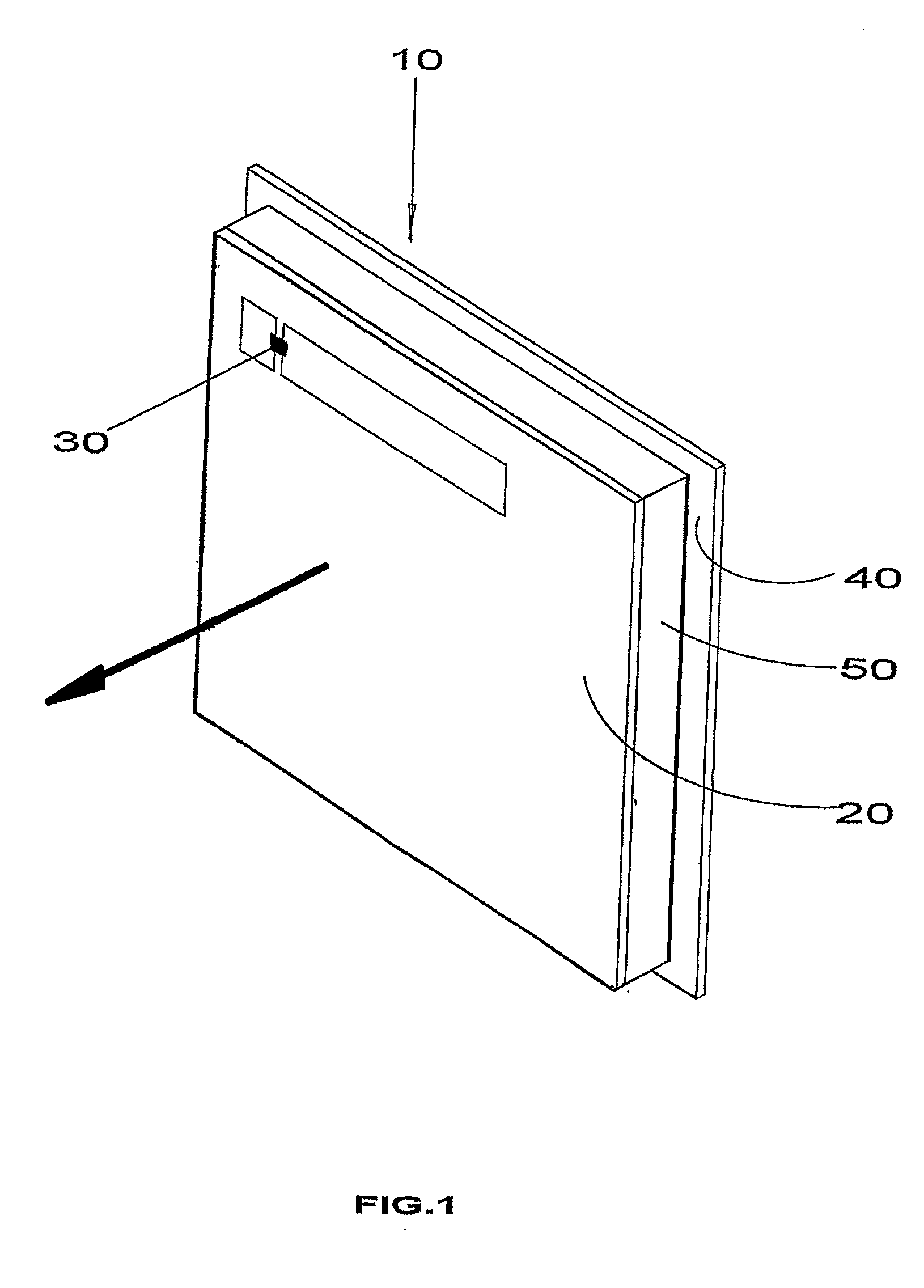
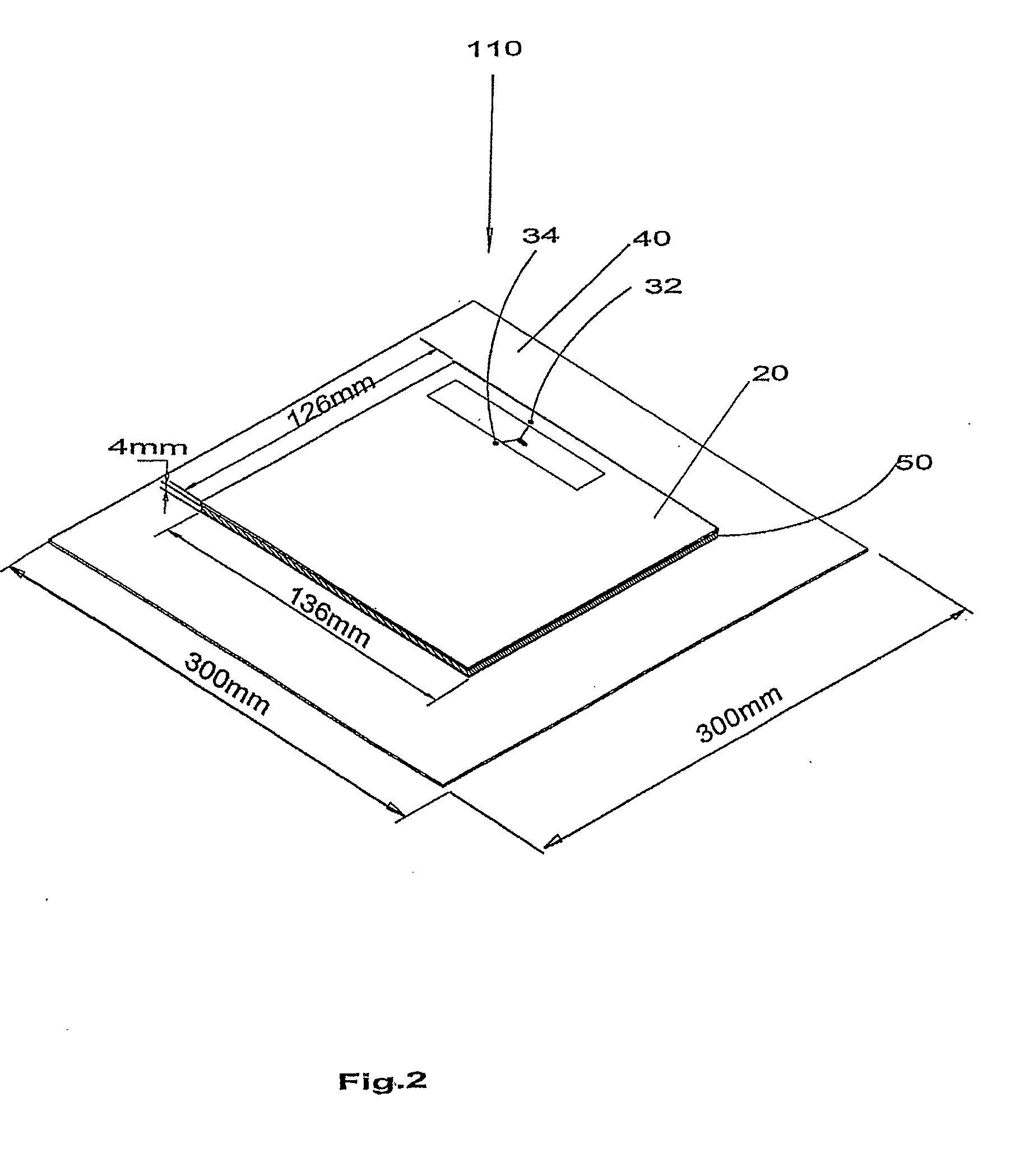
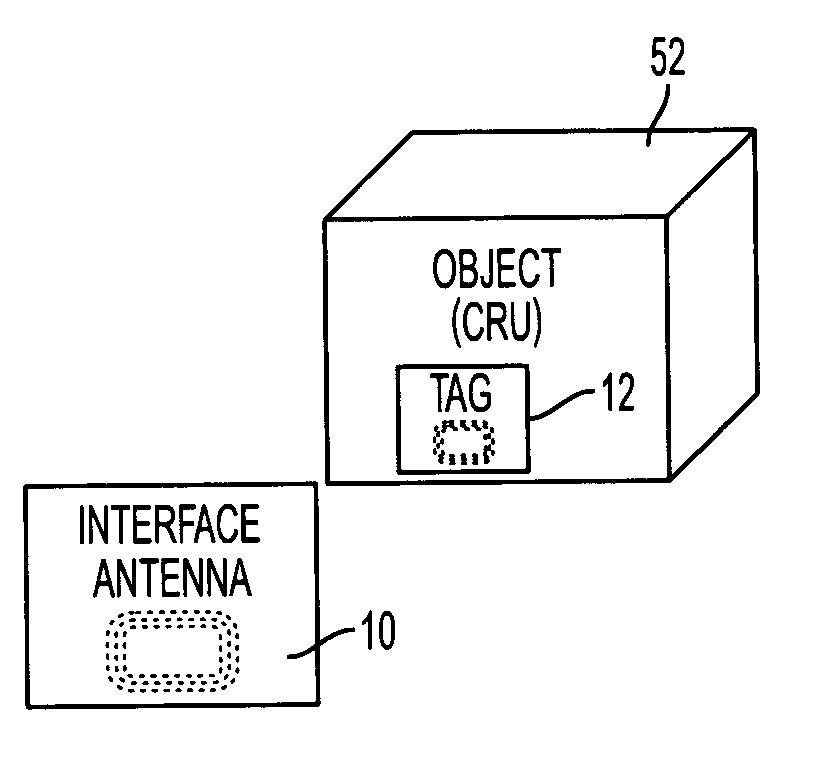
Interface antenna
ActiveUS20070146138A1Increase distanceResonant long antennasMemory record carrier reading problemsTag antennaCarrier signal
An interface antenna is positioned between a tag antenna associated with a tag and a reader antenna associated with a reader. The interface antenna receives an electromagnetic carrier signal transmitted by the reader antenna and causes an increase in intensity of the electromagnetic carrier signal at the location of the tag antenna, thereby increasing the distance over which the tag can communicate with the reader. Where the tag is attached to a packaged object, the interface antenna may be included in the package to allow wireless data communication between the tag and a reader external to the package. For example, the interface antenna may be attached to a label on the package. At least a portion of the interface antenna may be formed from a conductive ink applied to the label and / or the container. The object may be a module, also known as a customer replaceable unit (CRU), and the tag may be configured as a customer replaceable unit monitor (CRUM).
Owner:XEROX CORP
Wireless functional testing of RFID tag
Wirelessly testing an RFID tag before it is packaged or otherwise entered into a process reserved for “working” RFID tags is described. Various processes that employ such wireless testing as well as various “on-die” RFID tag antenna designs for facilitating the wireless testing are also described.
Owner:IMPINJ
Module with RFID tag and associated bridge antenna
ActiveUS20070222606A1Increase distanceBridging the gapVoting apparatusAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorTag antenna
An RFID bridge antenna is positioned between a tag antenna associated with a tag and a reader antenna associated with a reader. The bridge includes at least two RF antenna elements spaced apart from one another and coupled together by an electrical conductor. The first RF antenna element is located proximate to the tag antenna and the second RF antenna element is located proximate to the reader antenna. An electromagnetic carrier signal transmitted by the reader antenna is received by one of the RF antenna element and retransmitted to the tag antenna by the other RF antenna element, increasing the distance over which the tag can communicate with the reader. Where the tag is attached to a packaged object, the RFID bridge antenna may be included in the package to allow wireless data communication between the tag and a reader. The reader may also be located external to the package. For example, one of the RF antenna elements may be attached to a label on the package, allowing data stored in the tag to be extracted by the external reader. The object may be a module, also known as a customer replaceable unit (CRU), and the tag may be configured as a customer replaceable unit monitor (CRUM). The module may take the form of a container having a closure cap equipped with a tag and the container may be stored in a cabinet along with an RFID bridge antenna mounted on the cabinet door to establish data communication between the tag and a reader.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Multiband RFID tag
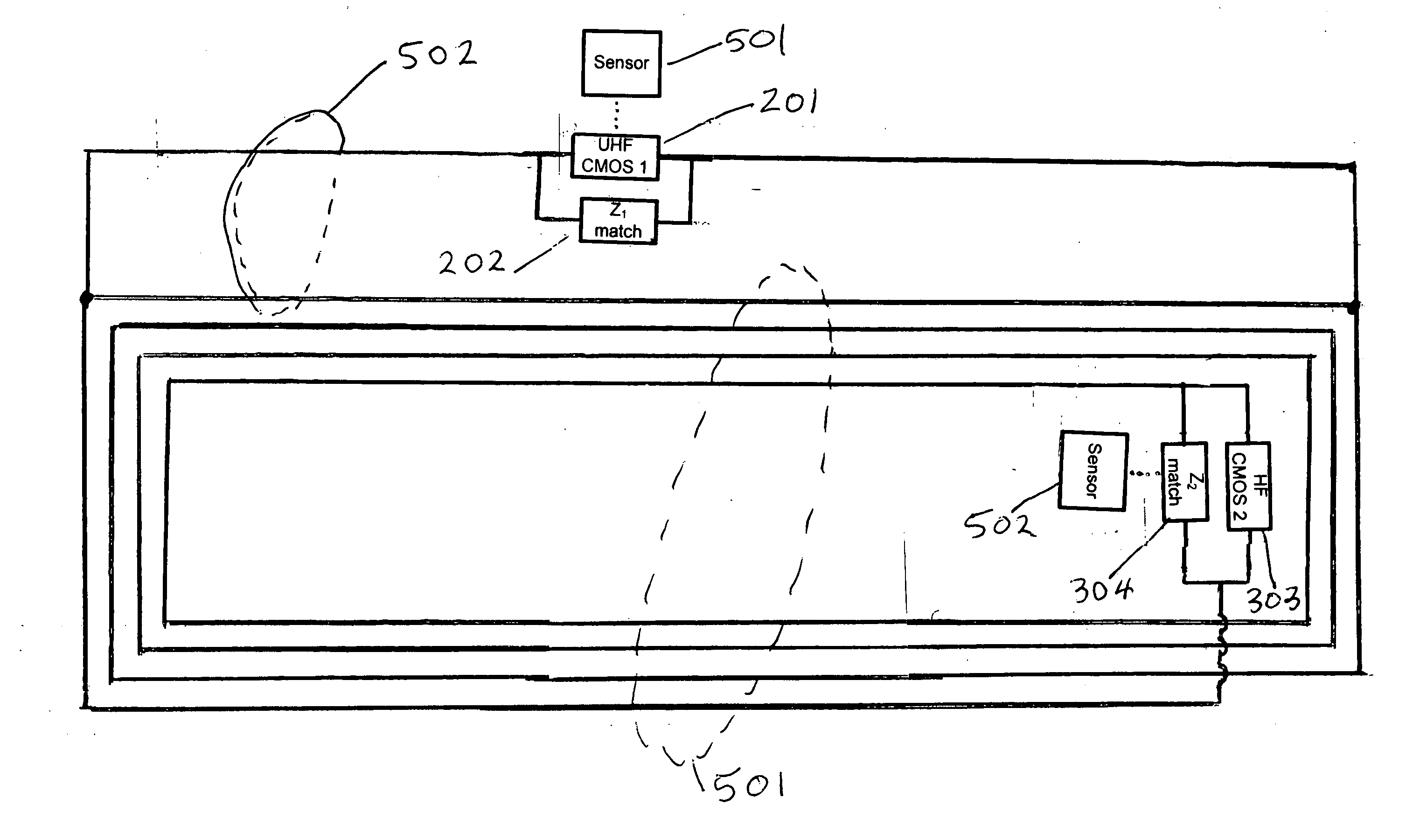
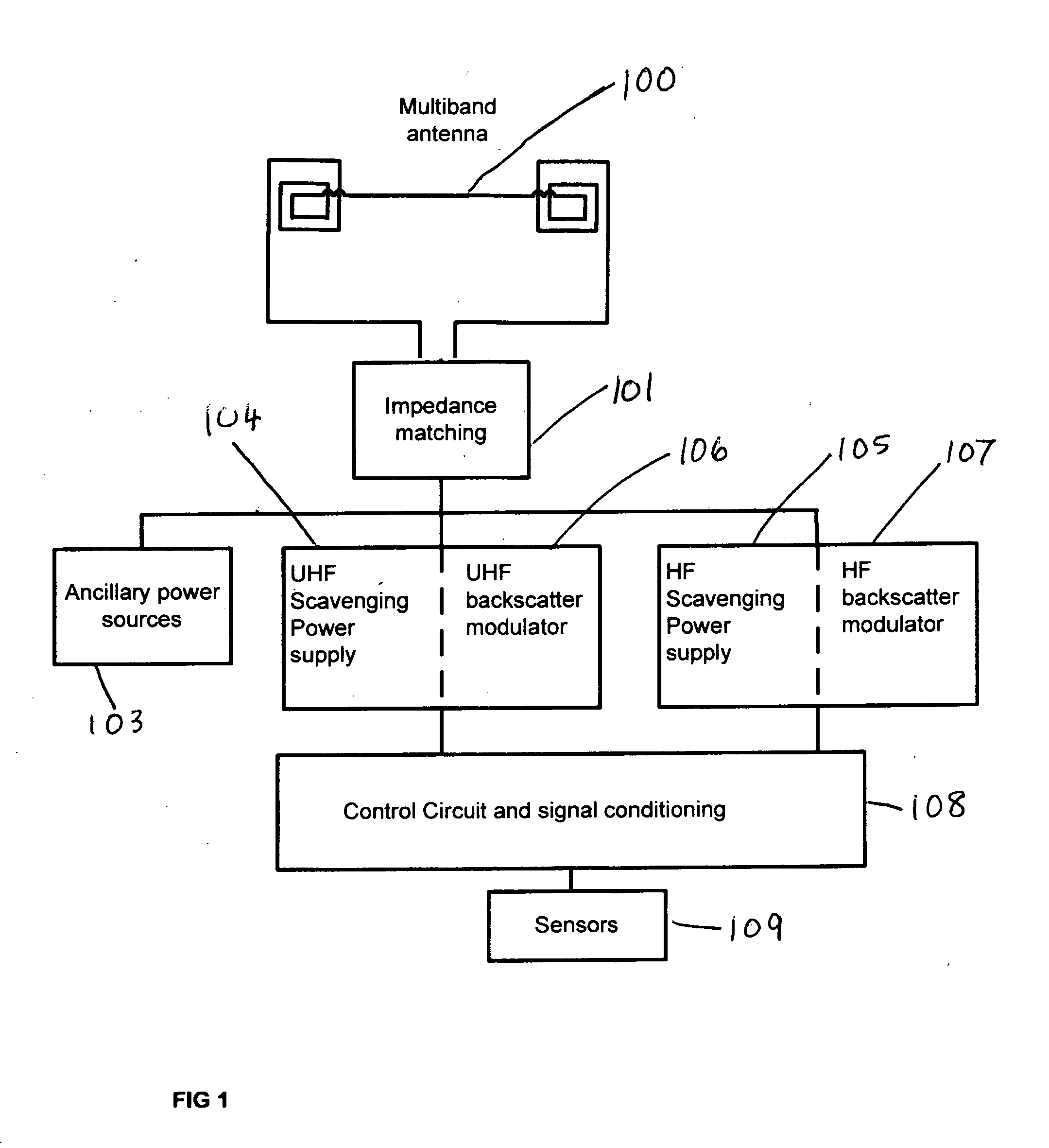
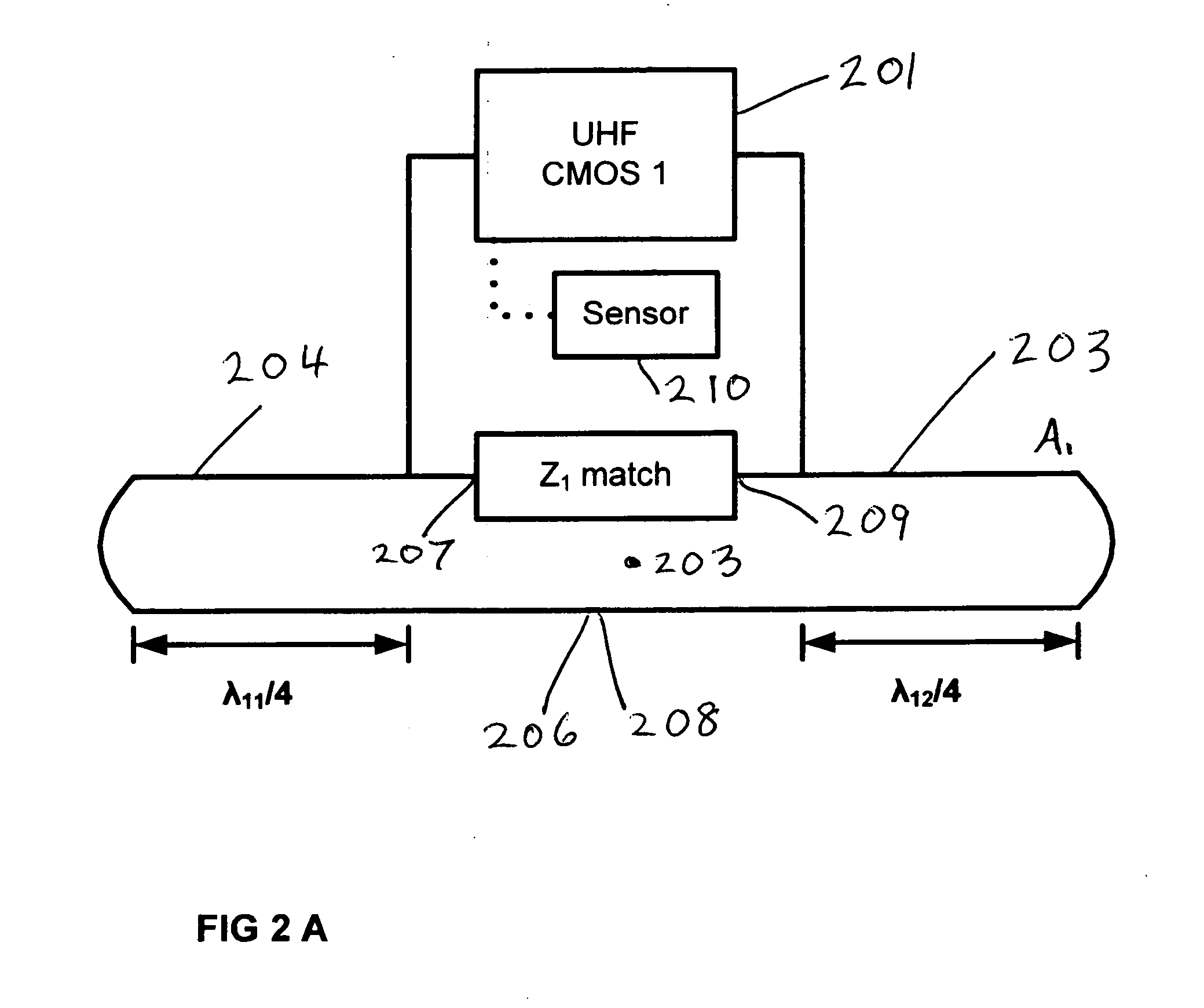
An RFID tag communicating with a wireless reader interrogator on more than one frequency band. In one embodiment the tag contains independent sensor circuits for a ultra high frequency UHF band and a lower frequency band. The UHF antenna element used in the tag is a double-resonant antenna typically operating in the 860-960 MHz frequency range providing both near and far field sensitivity. Separate resonant antenna structures a the lower frequency band is connected in series with the UHF antenna substructure. The high frequency HF antenna element contains a coil for magnetic induction pickup of signals typically in the 7-14 MHz frequency band but can also be used for the entire spectral range 100 KHz to 100 MHz. The tag antenna is an integrated structure providing for operation in both the UHF and a lower frequency band. In a separate embodiment the tag is configured with the UHF double-dipole antenna structure only and operates in a single UHF band.
Owner:NEW JERSEY MICROSYST
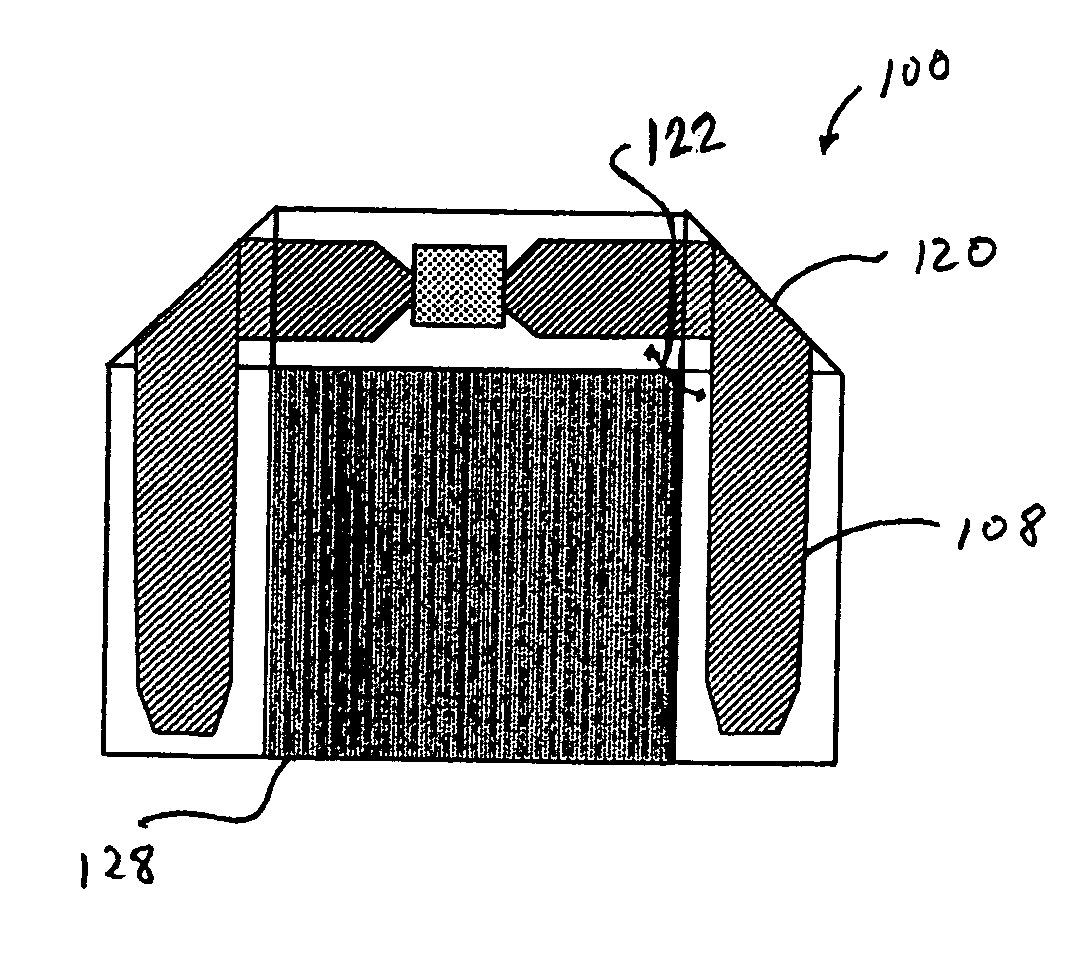
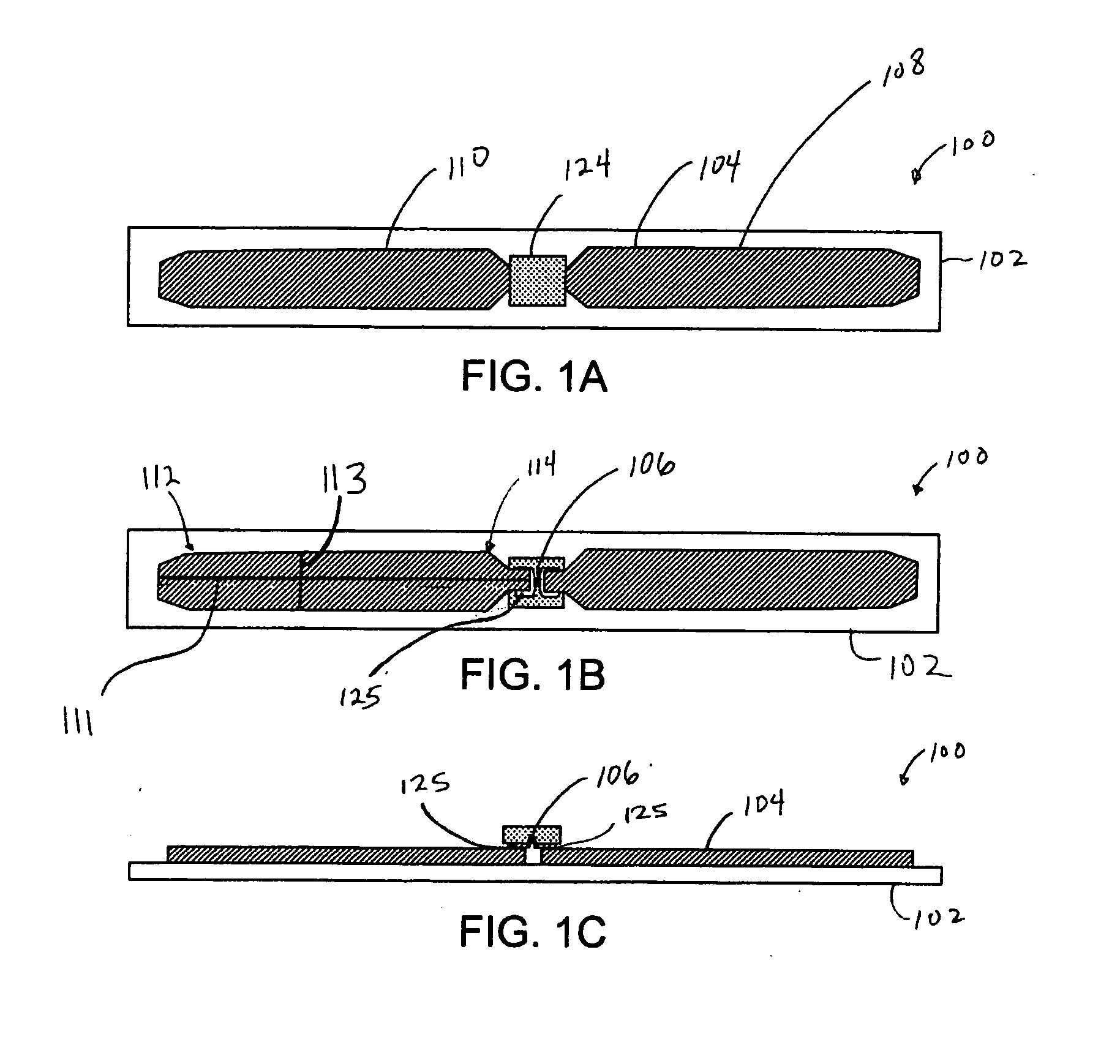
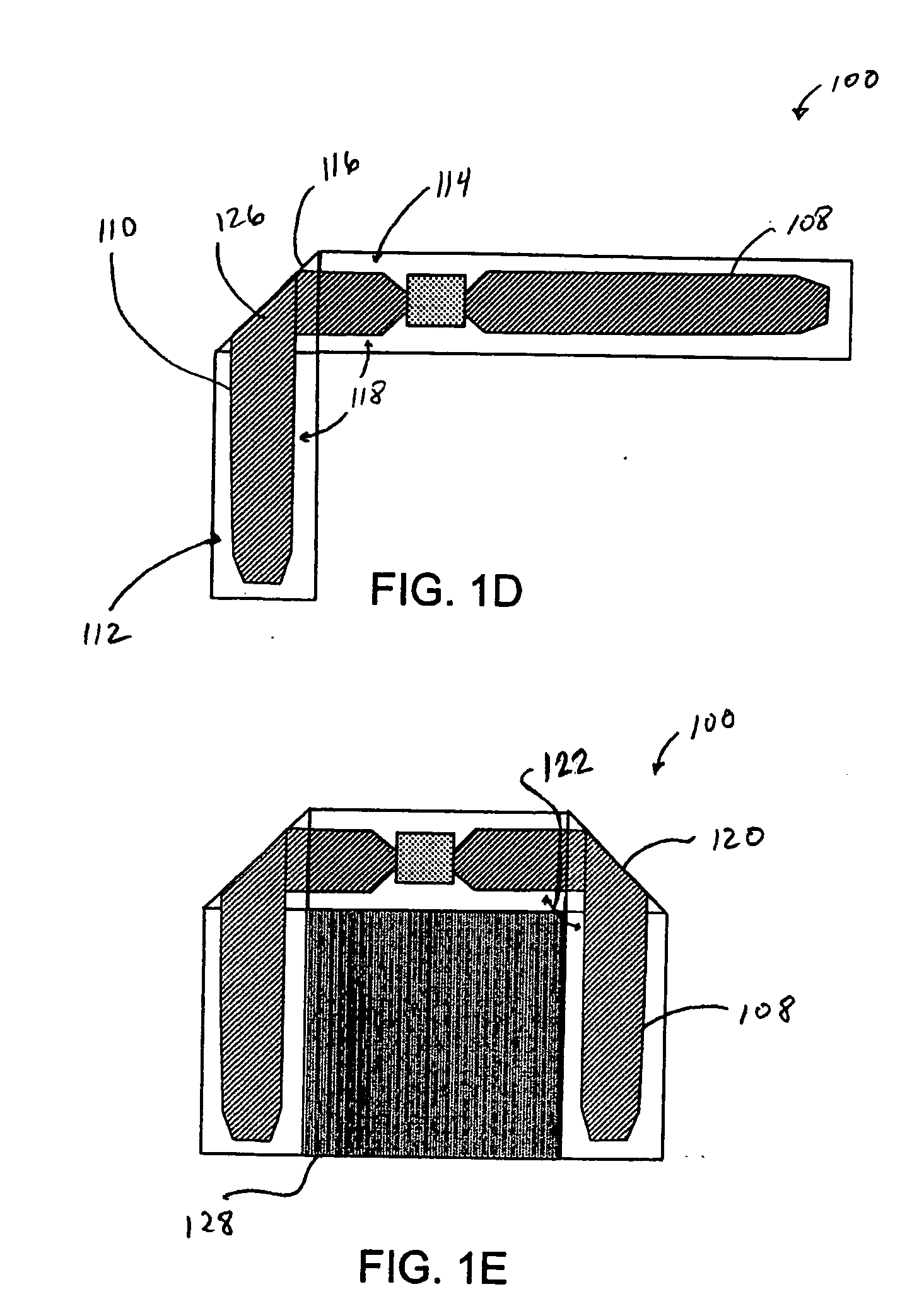
Low profile metal-surface mounted RFID tag antenna
ActiveUS8169322B1Cheap manufacturingEconomical to useSubscribers indirect connectionElectric signalling detailsTag antennaSurface mounting
A passive RFID tag suitable for attachment to an electrically conductive surface is provided. The passive RFID tag includes a dielectric substrate, an RFID chip for storing data, and an RFID antenna structure operatively connected to the RFID chip wherein the RFID antenna structure comprises a slotted inverted L-shape. A method of manufacturing a passive RFID tag includes forming an antenna structure on a conductive layer, the antenna structure comprising a slotted inverted L-shape. The method further includes operatively connecting an RFID chip with the antenna structure. A method associated with a passive RFID tag includes providing a passive RFID tag. The passive RFID tag includes a dielectric substrate, an RFID chip for storing data, and an RFID antenna structure operatively connected to the RFID chip wherein the RFID antenna structure comprises a slotted inverted L-shape. The method further includes operatively connecting the passive RFID tag to a conductive surface.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
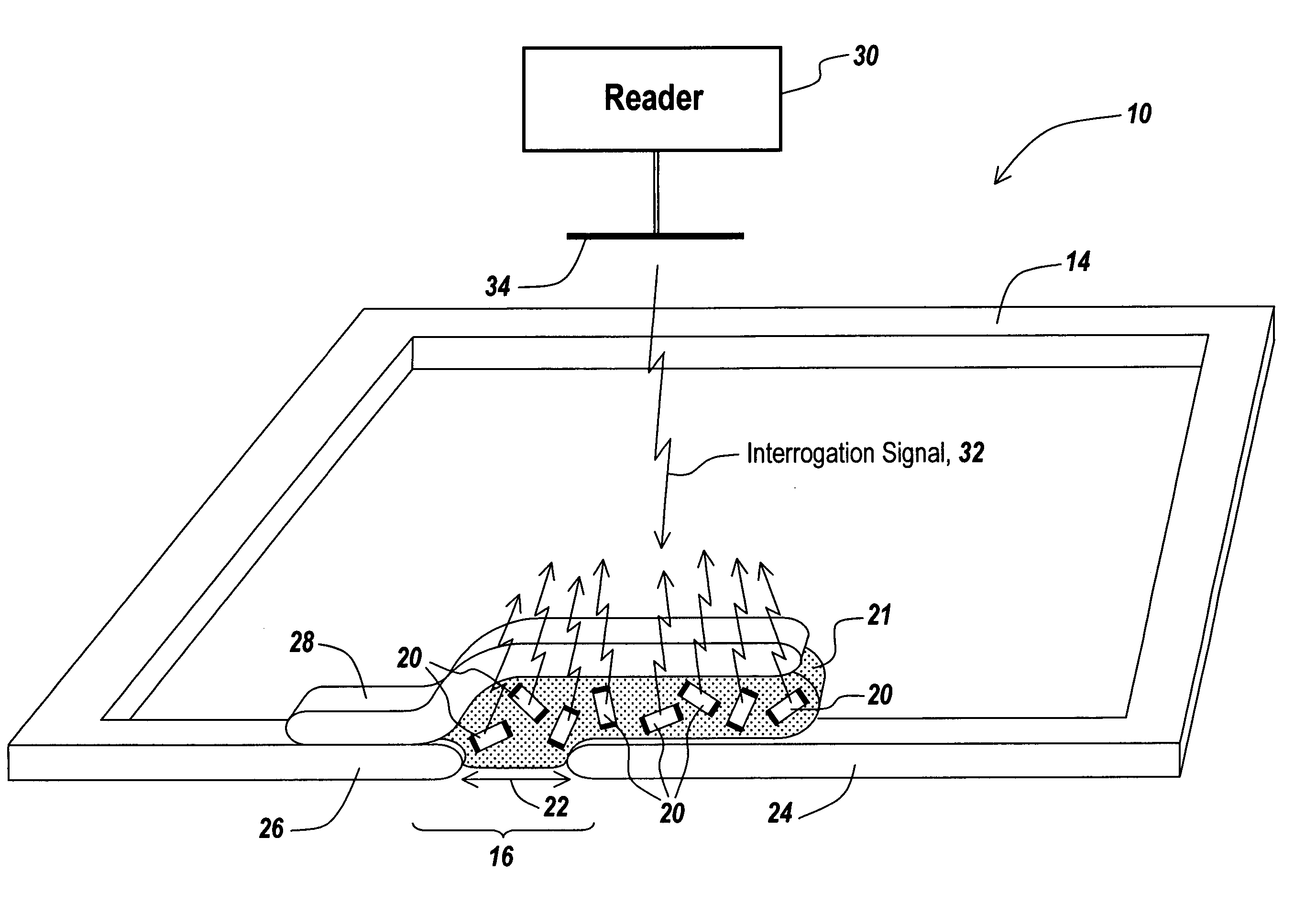
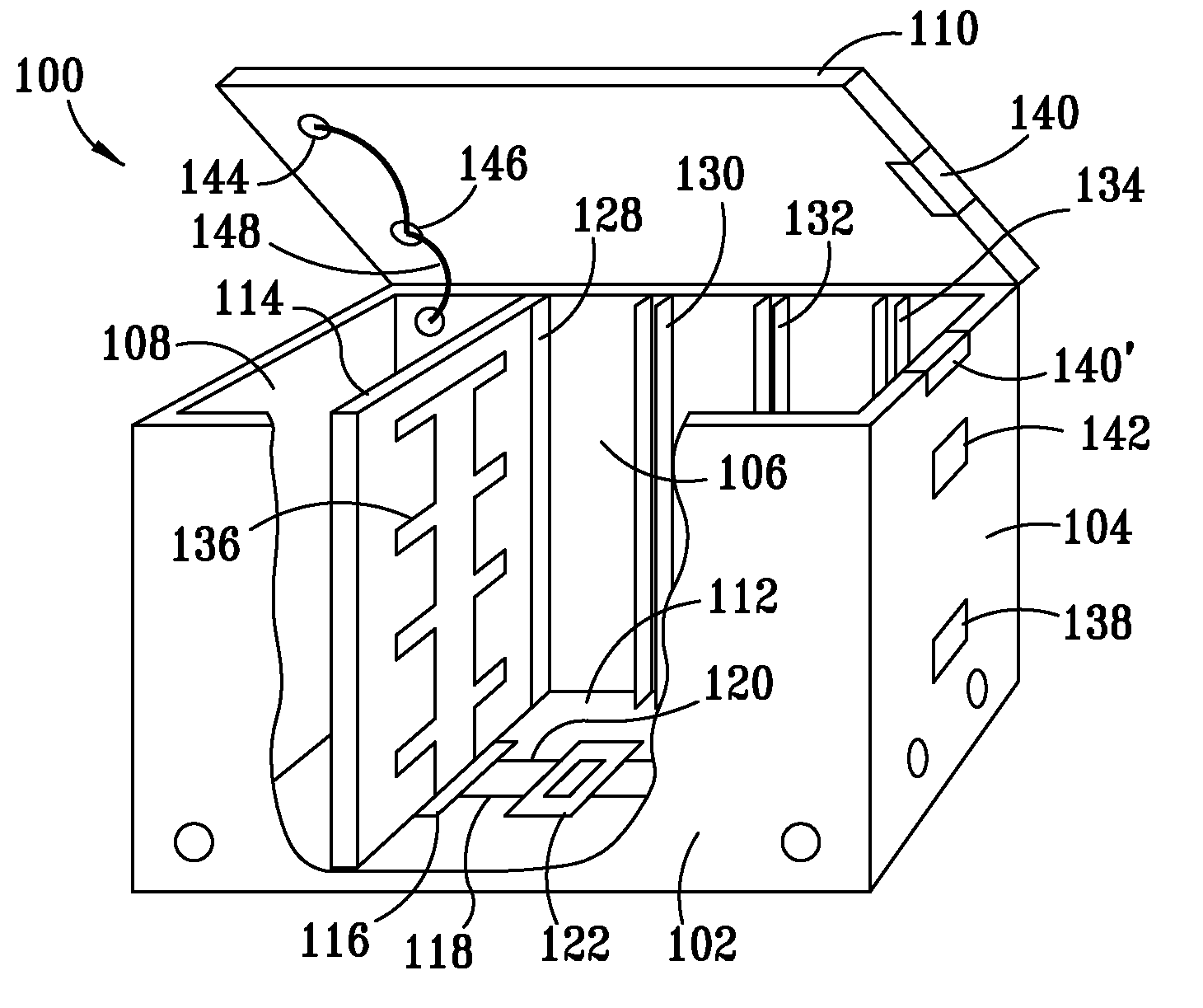
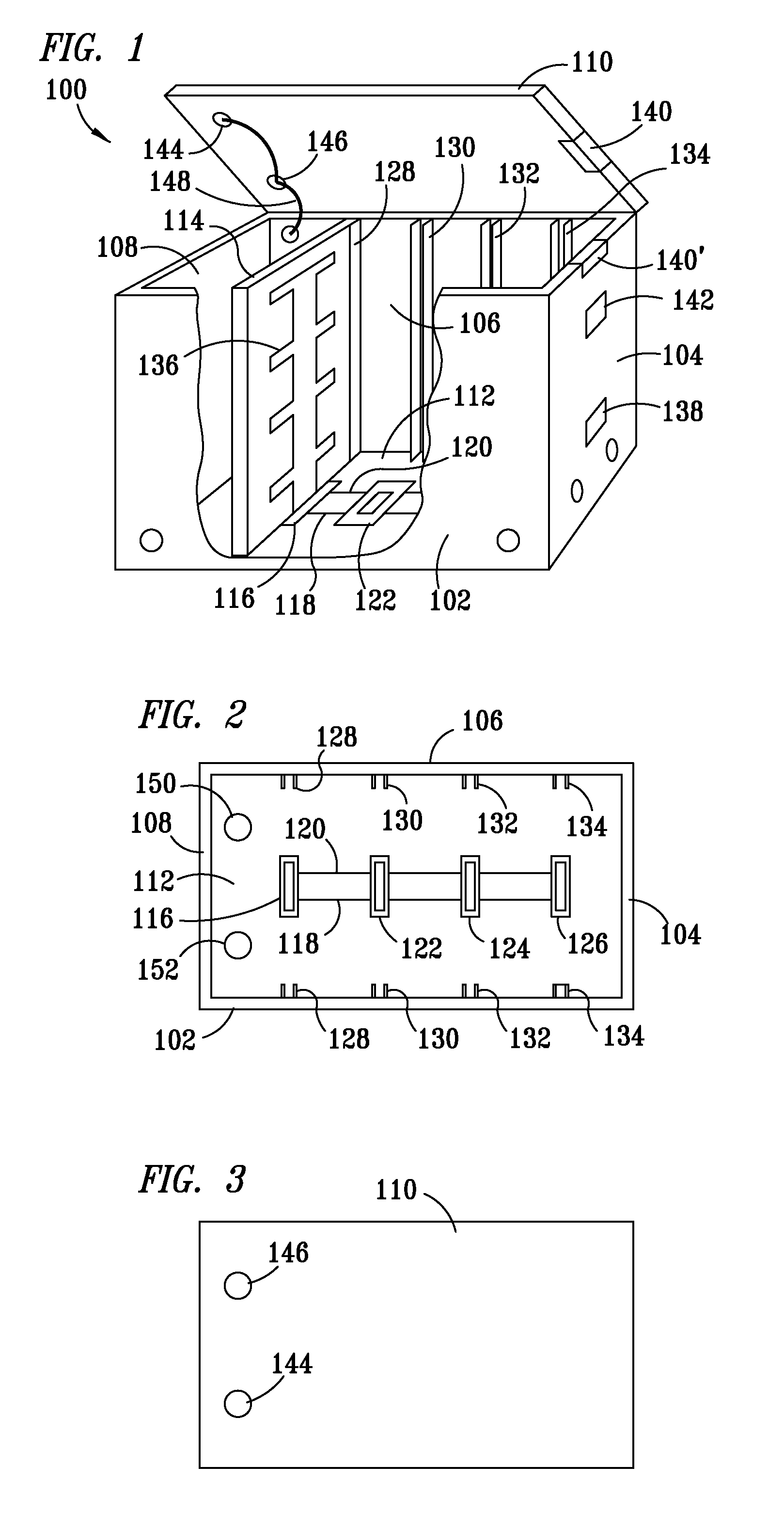
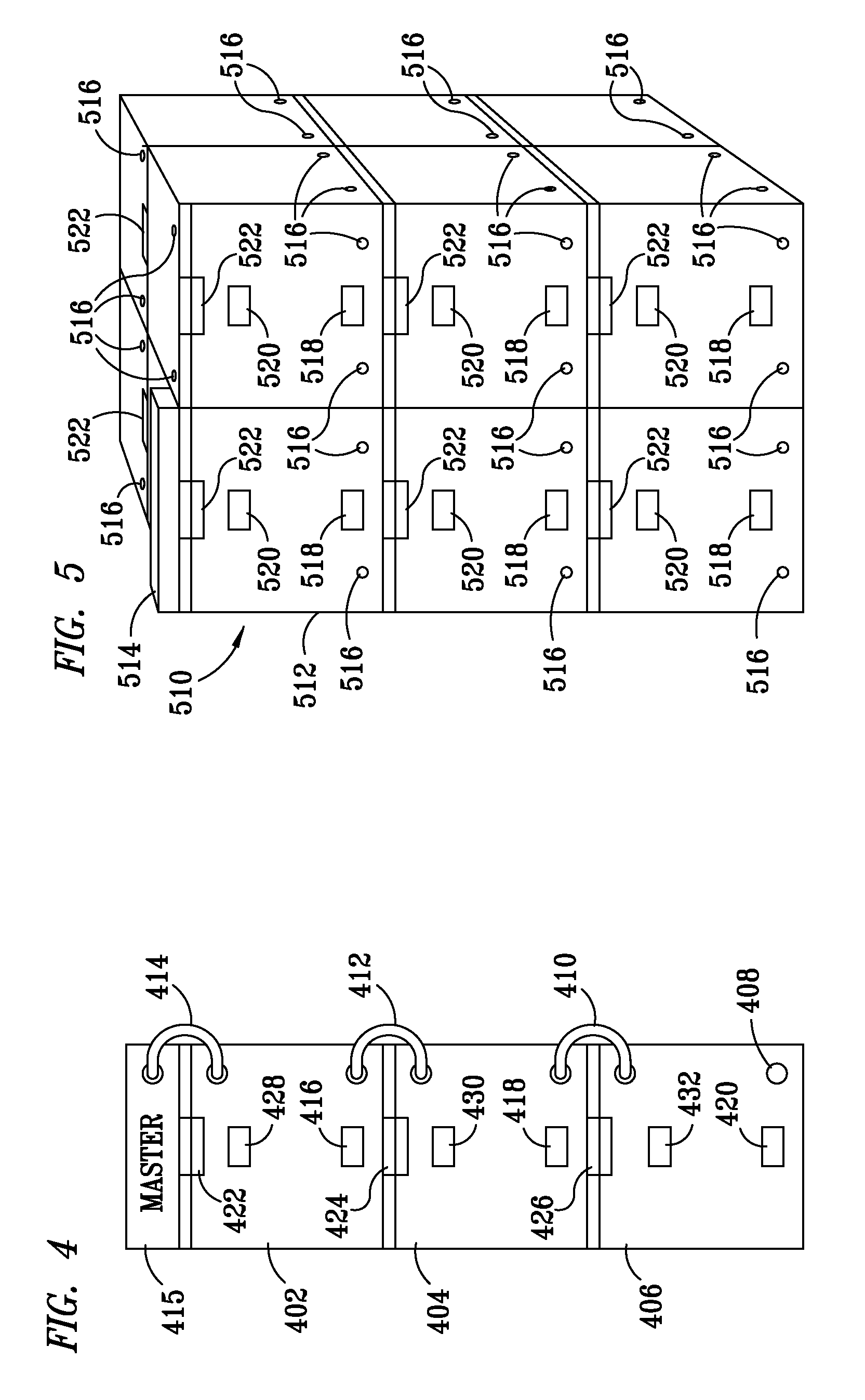
Method and apparatus for monitoring containerized ID tagged assets
A method and apparatus is provided for strategically arranging ID tag antennas in a container to accommodate various sizes of tagged assets and to assure a reading of all assets in the container when the tagged assets have different packing densities. An antenna bus in each container, that is connected to a container ID tag reader, allows bus connector insertable antennas to be strategically placed for accommodating various asset packing densities. The containers are designed to readily interconnect the data outputs of all the tag readers when the containers are stacked in any of three dimensions whereby a single master unit collects data from all the readers and transmits the data to a central data collection point.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com