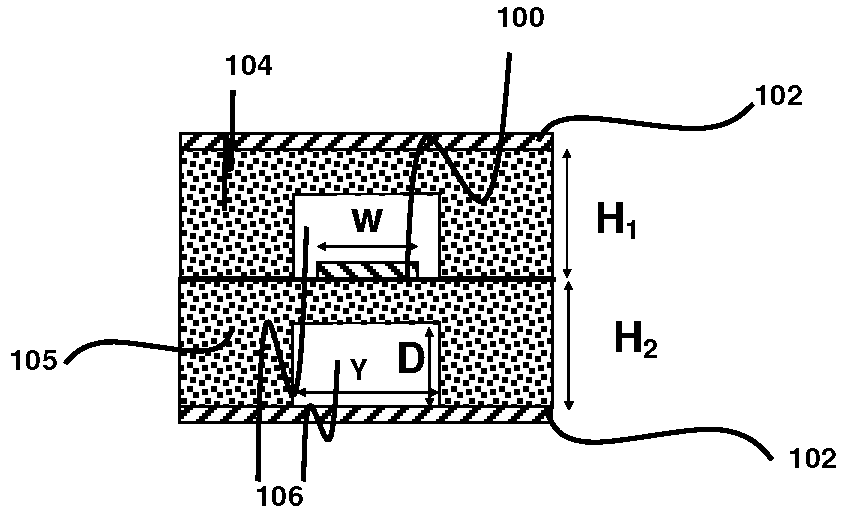
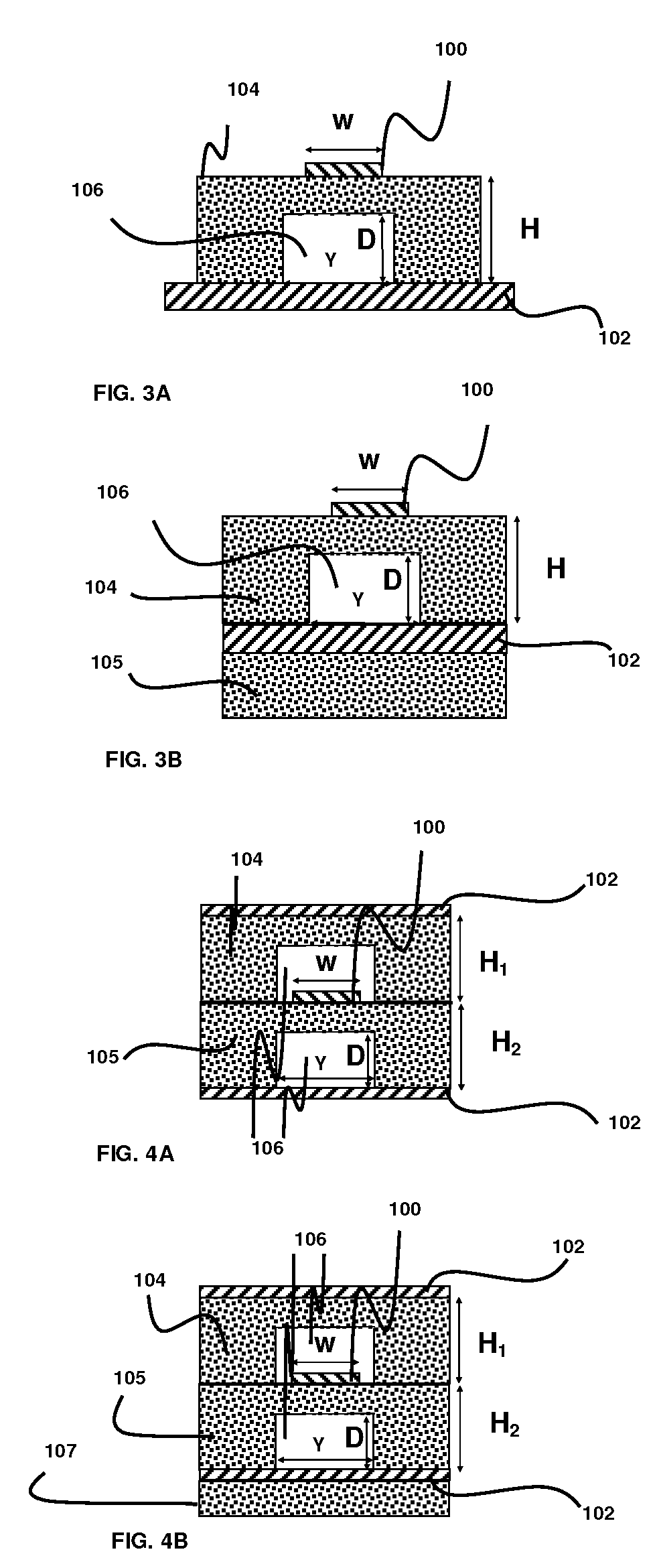
Patents
Literature
117 results about "Coplanar lines" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Coplanar Lines are lines which lie on the same plane. Two parallel lines or two intersecting lines always lie in a plane.
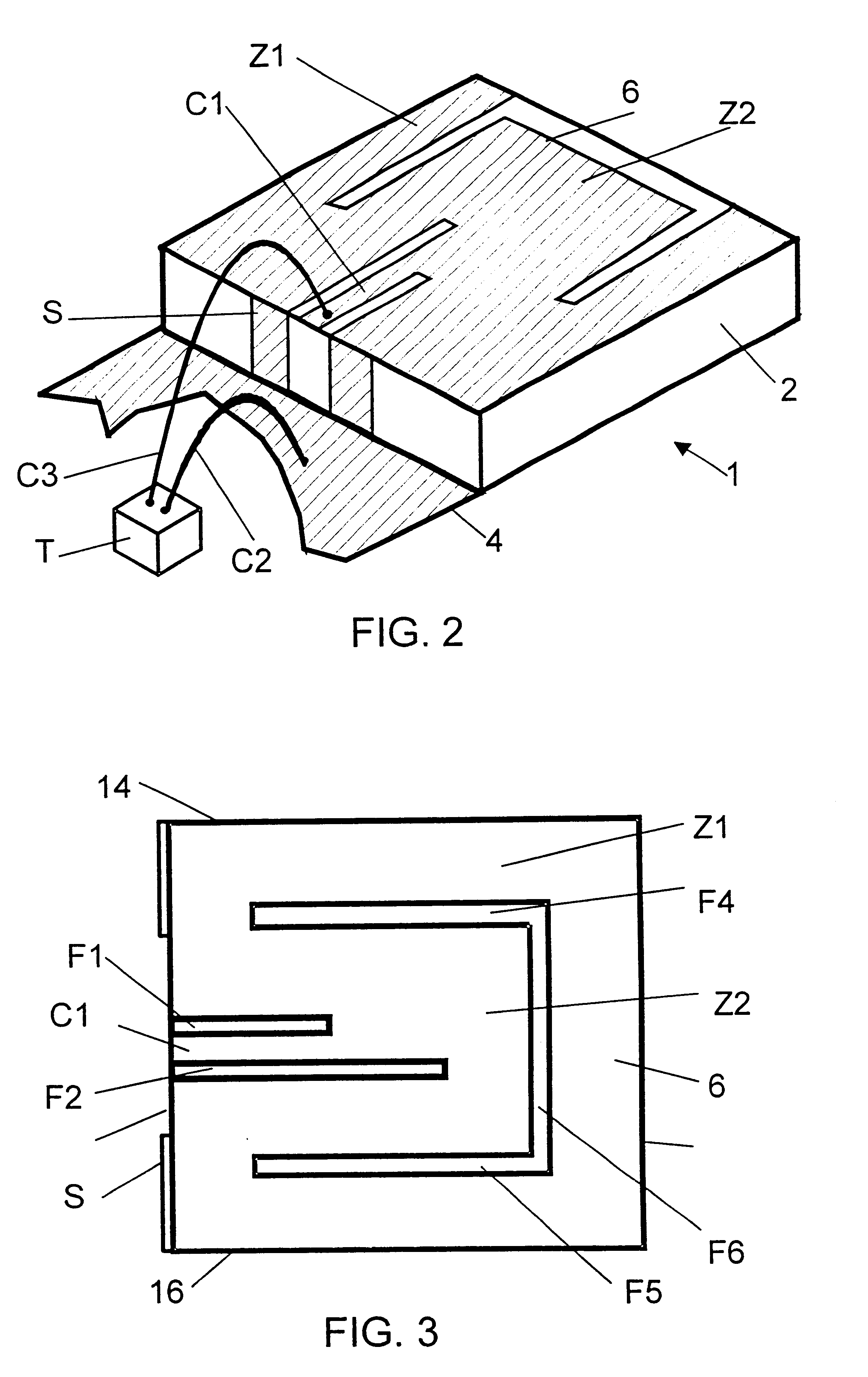
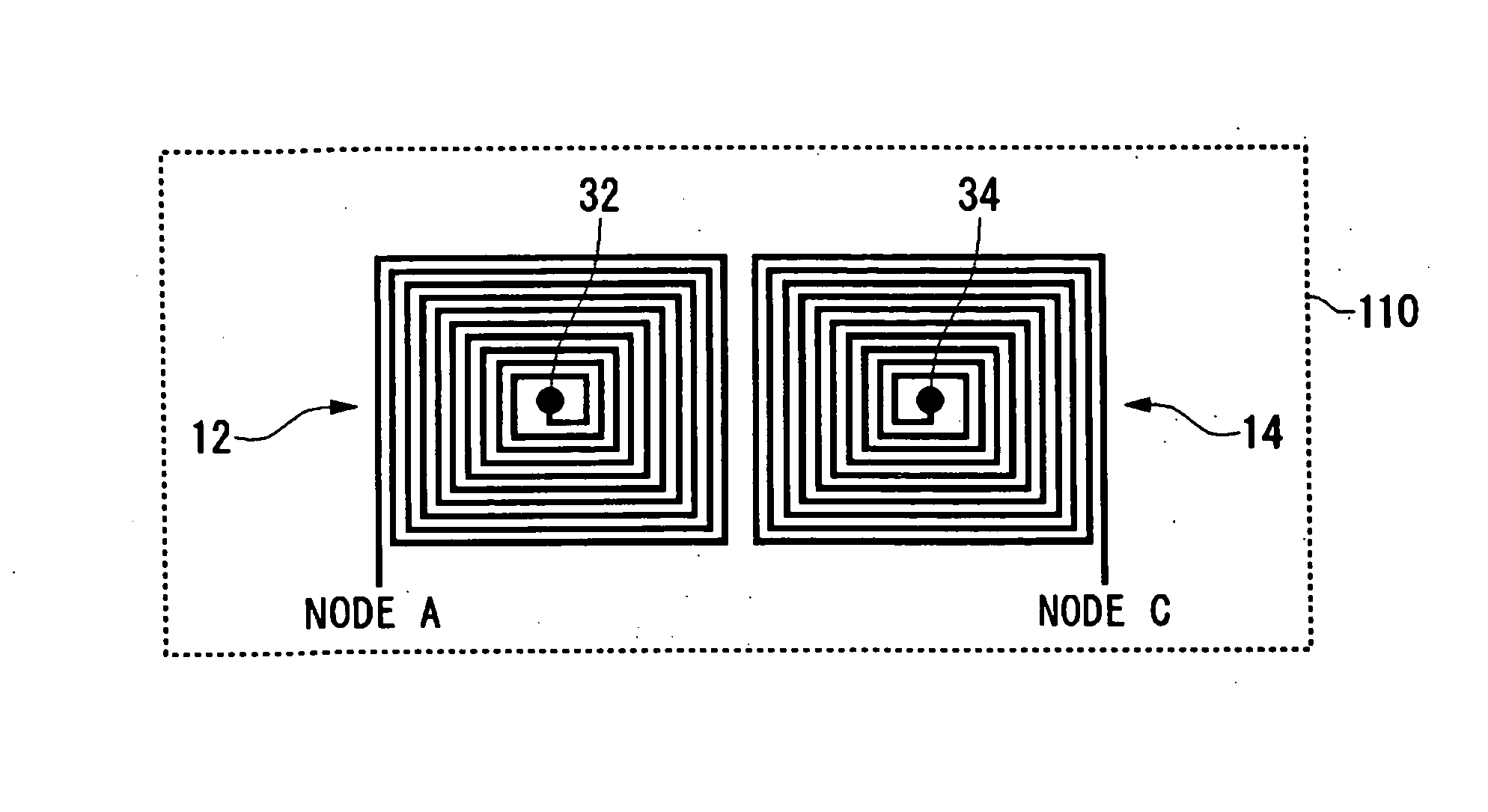
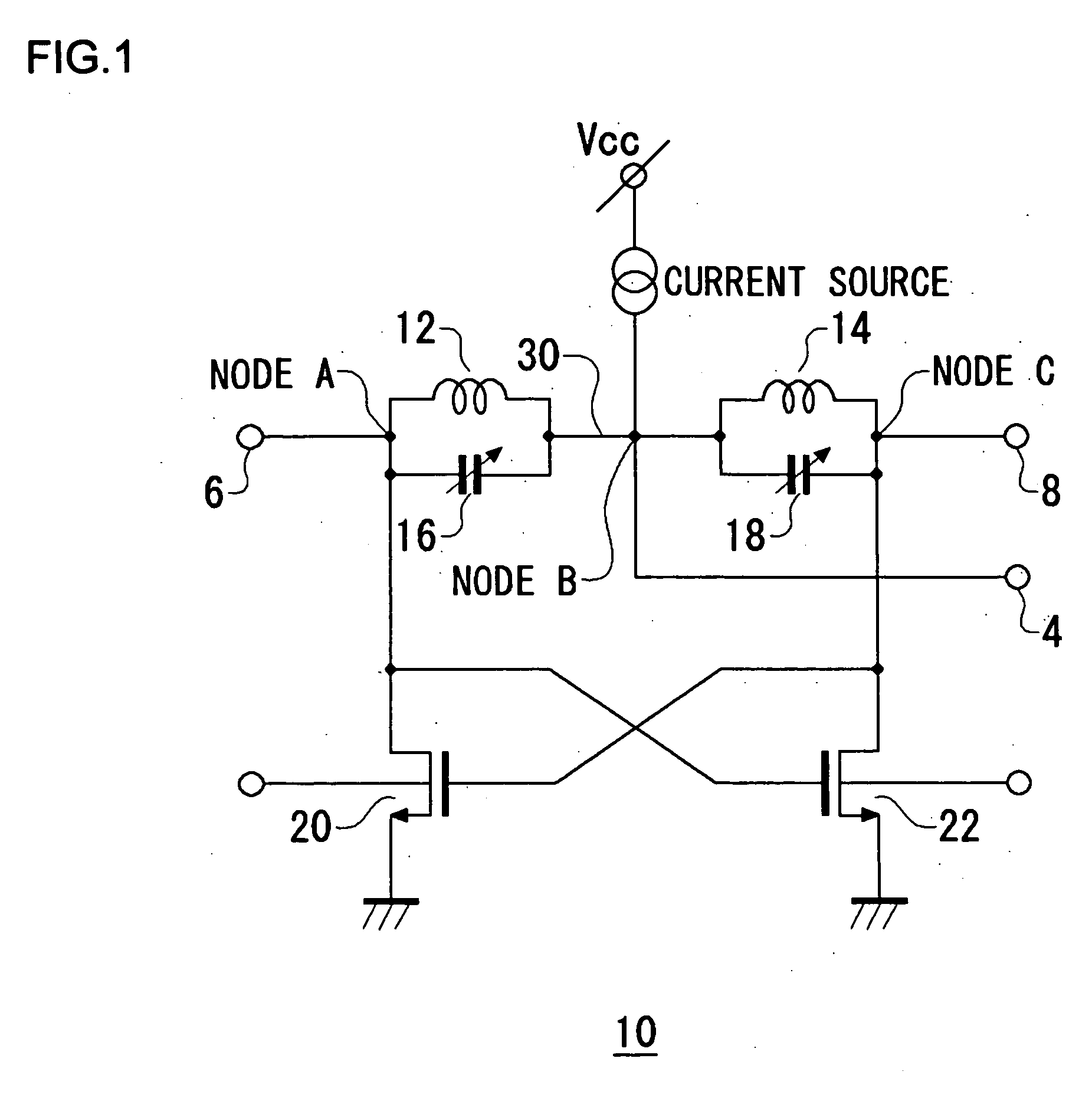
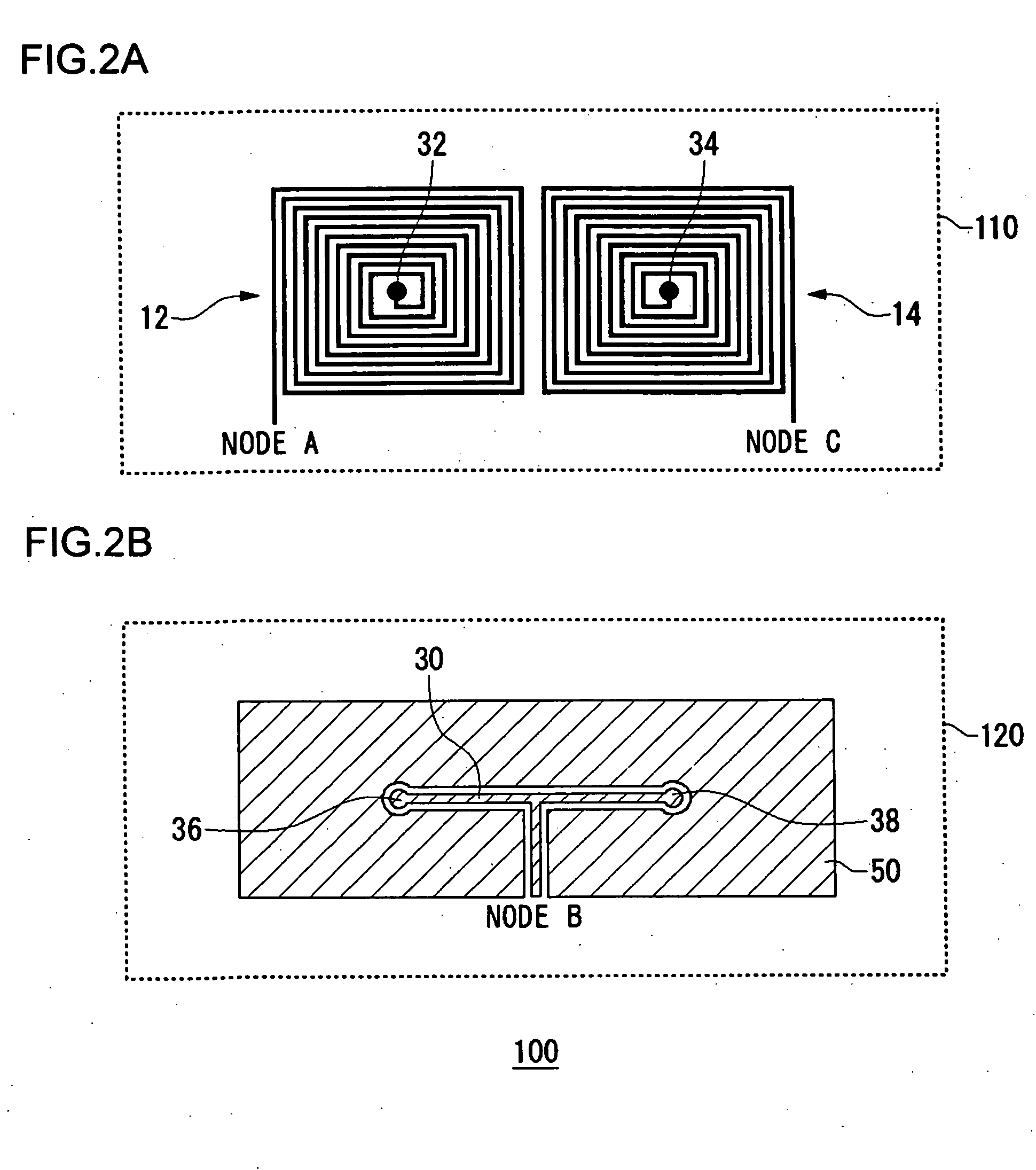
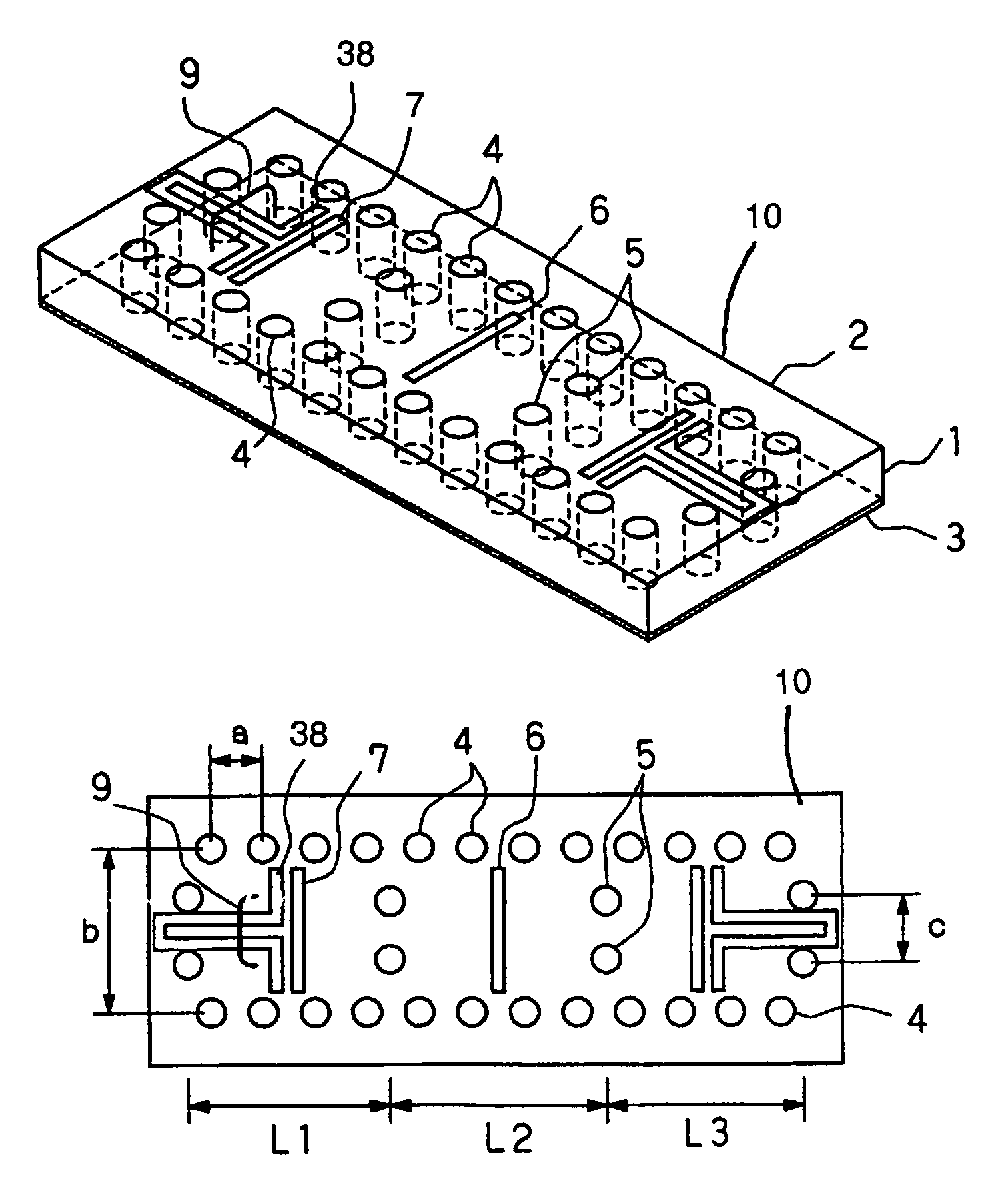
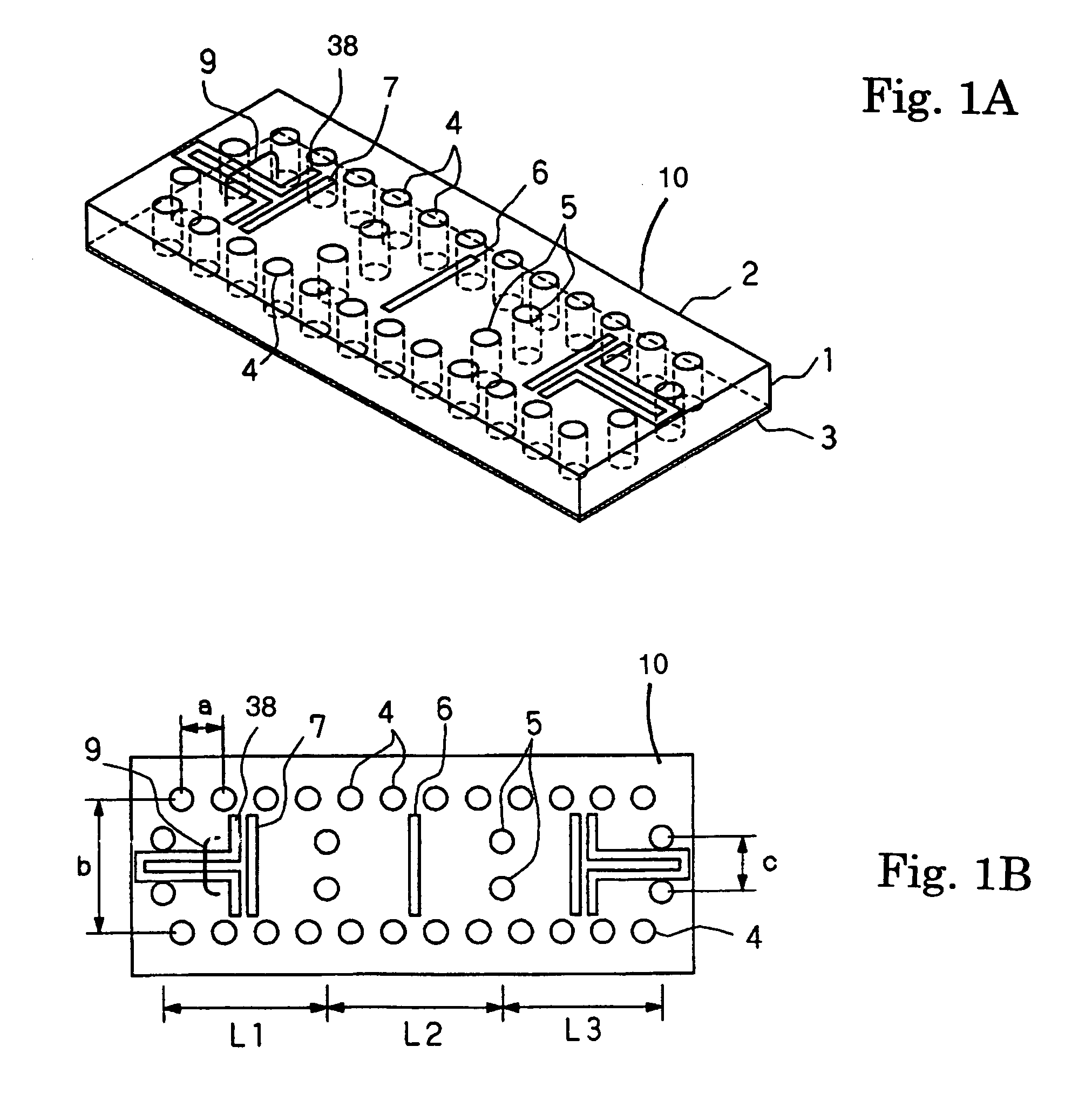
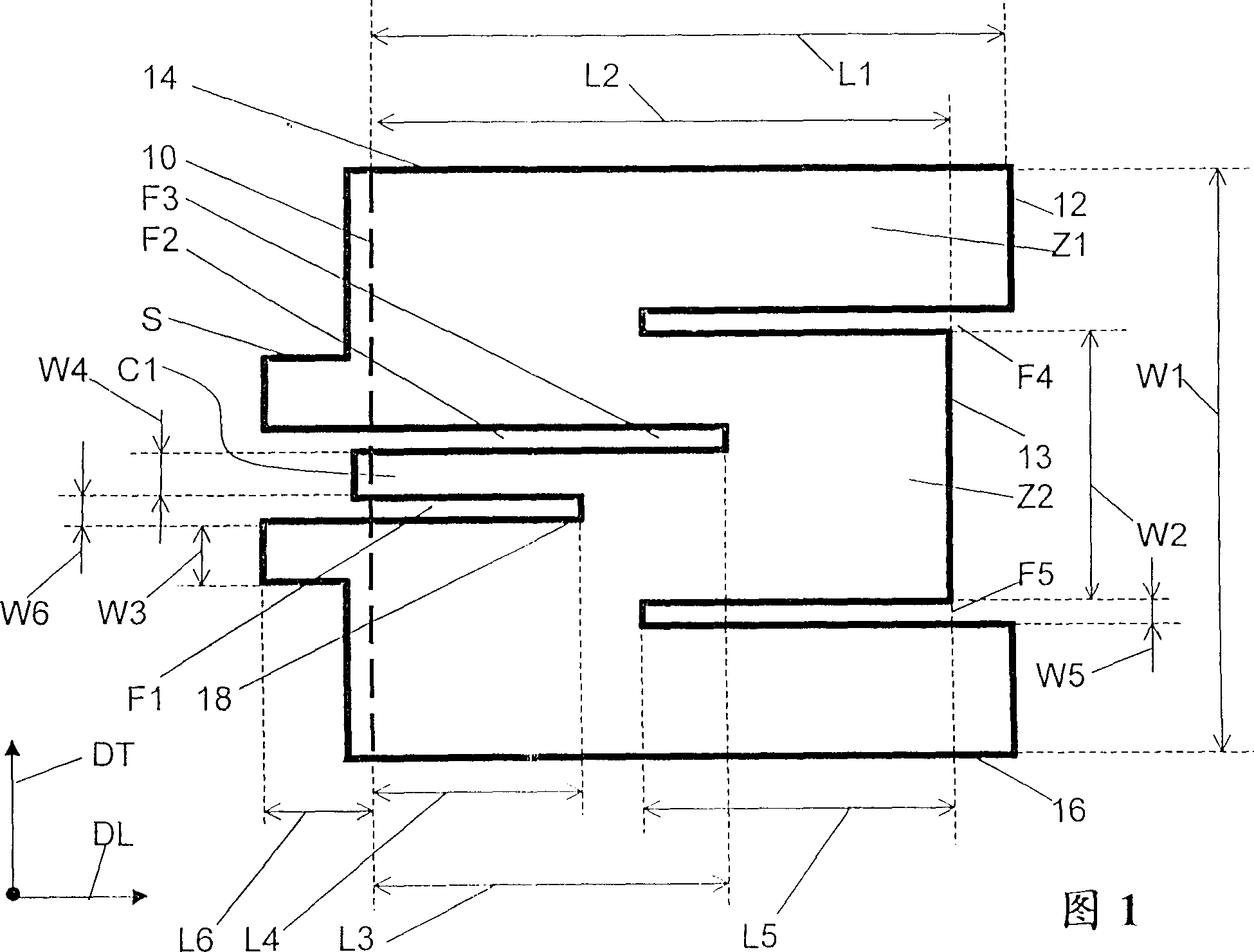
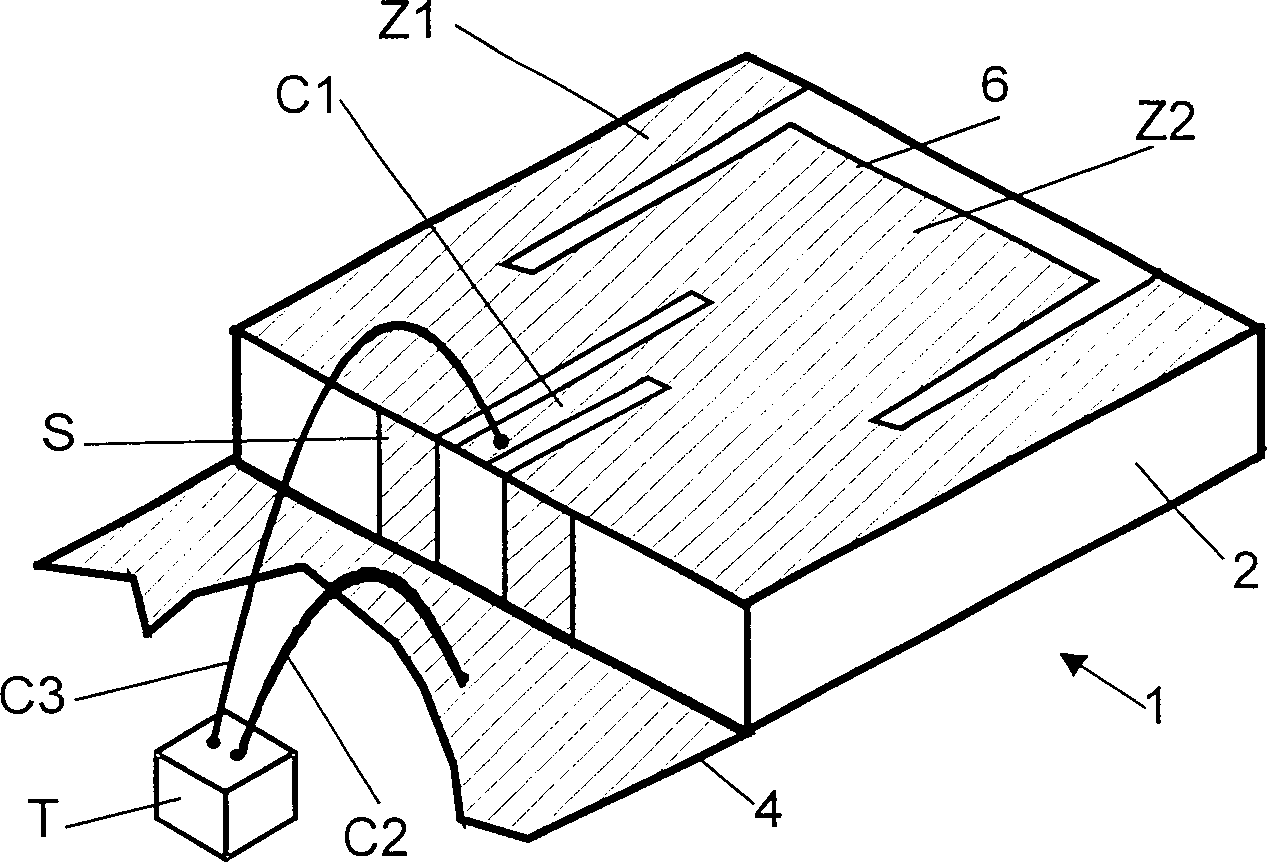
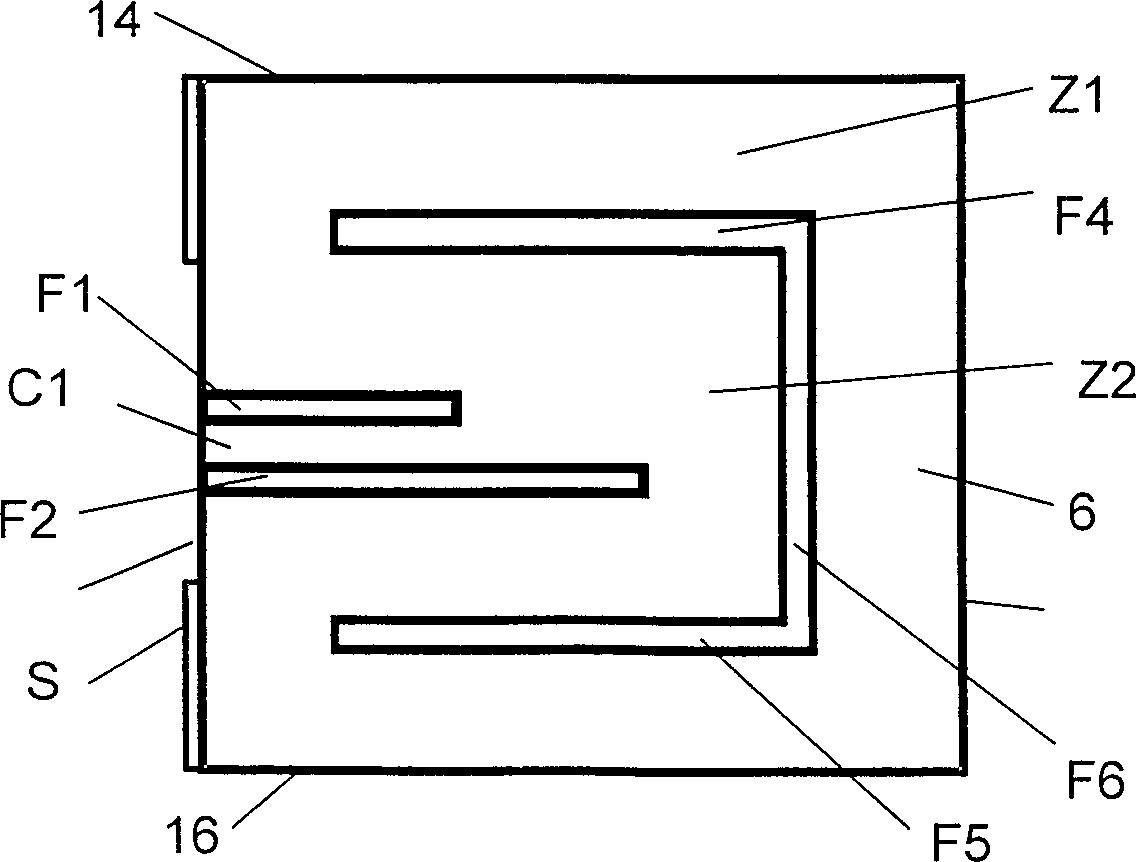
Antenna with a conductive layer and a two-band transmitter including the antenna
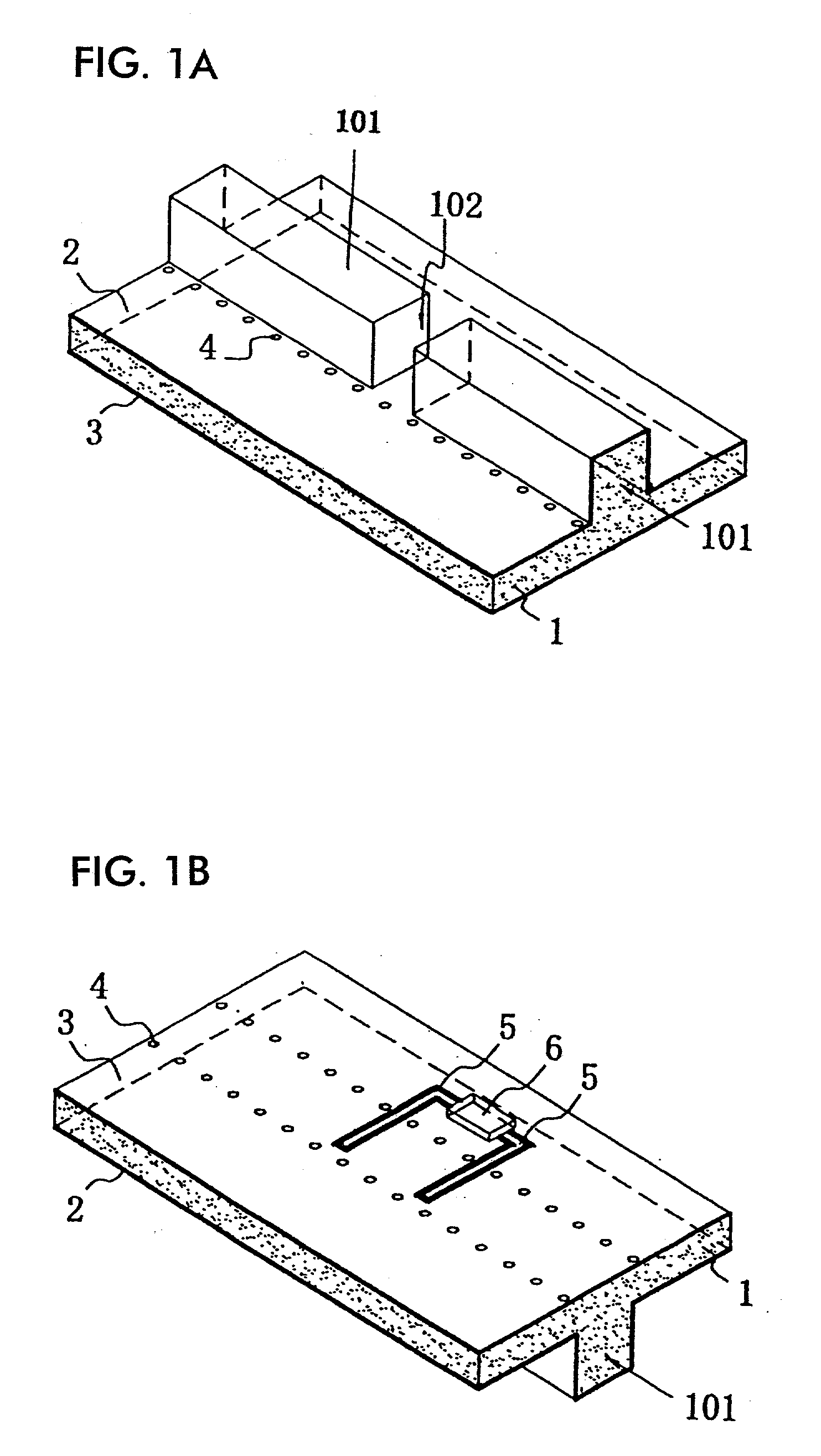
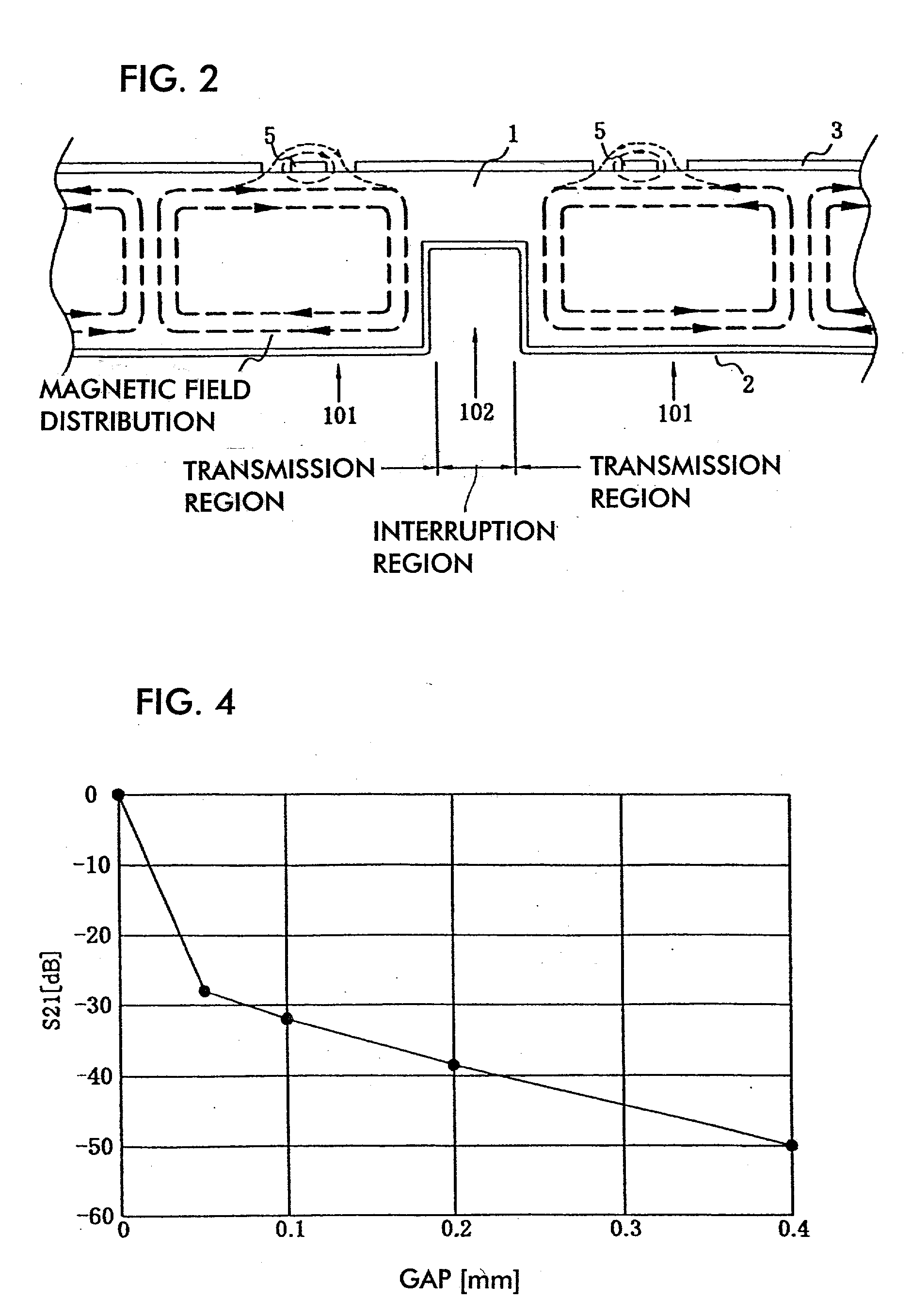
InactiveUS20020003499A1Improve matchSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual modeTwo band
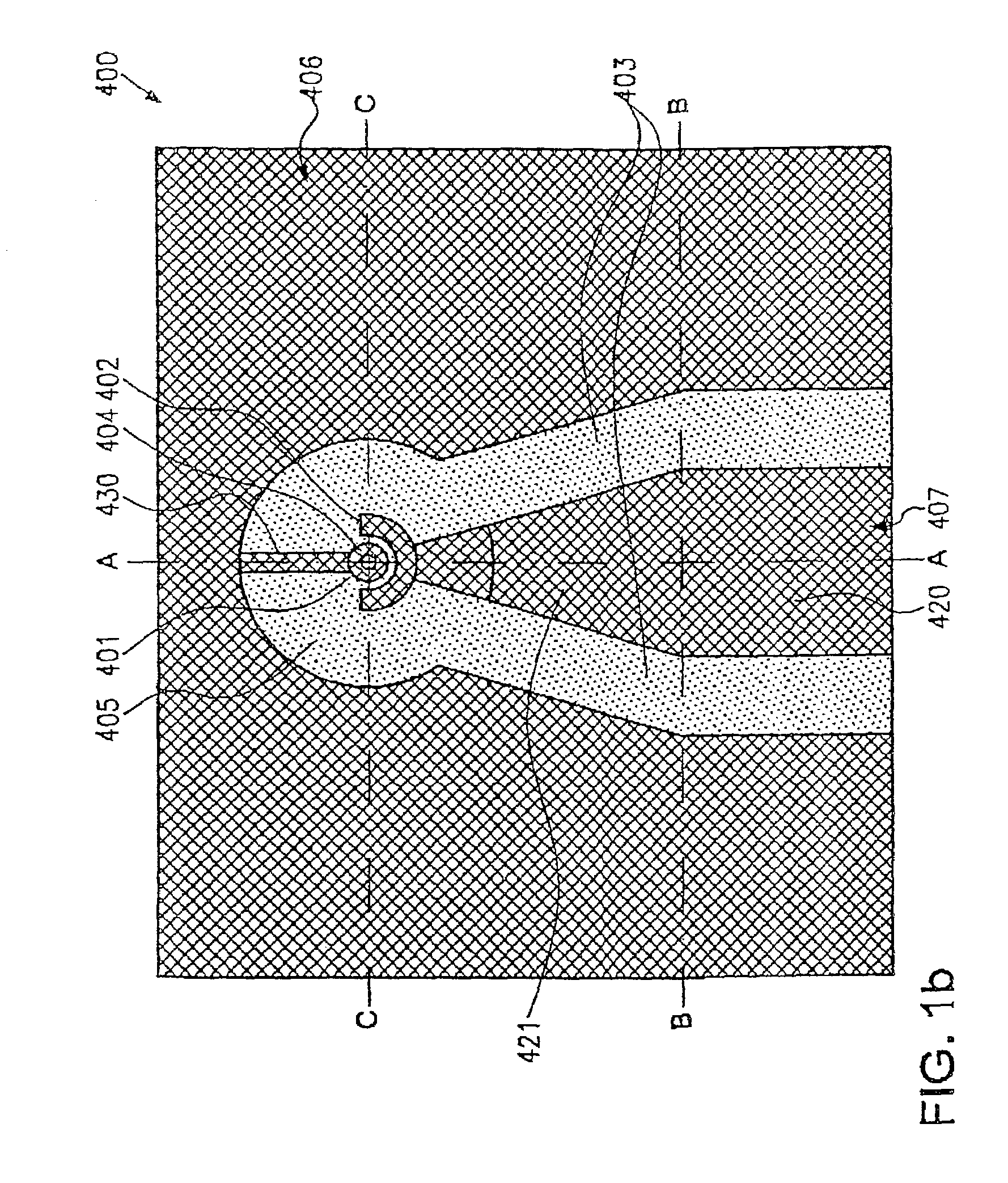
The antenna of said transmitter is a microstrip antenna. A rear edge of its patch is provided with a short circuit by means of which a quarter-wave primary resonance can be excited by a coplanar line formed by two coupling slots in an area. Separator slots separate said area from another area in which a secondary resonance can be established at twice the frequency of the primary resonance from a slotted line extending one slot of the coplanar line. The invention applies in particular to the production of a dual-mode mobile telephone to the GSM and DCS standards.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
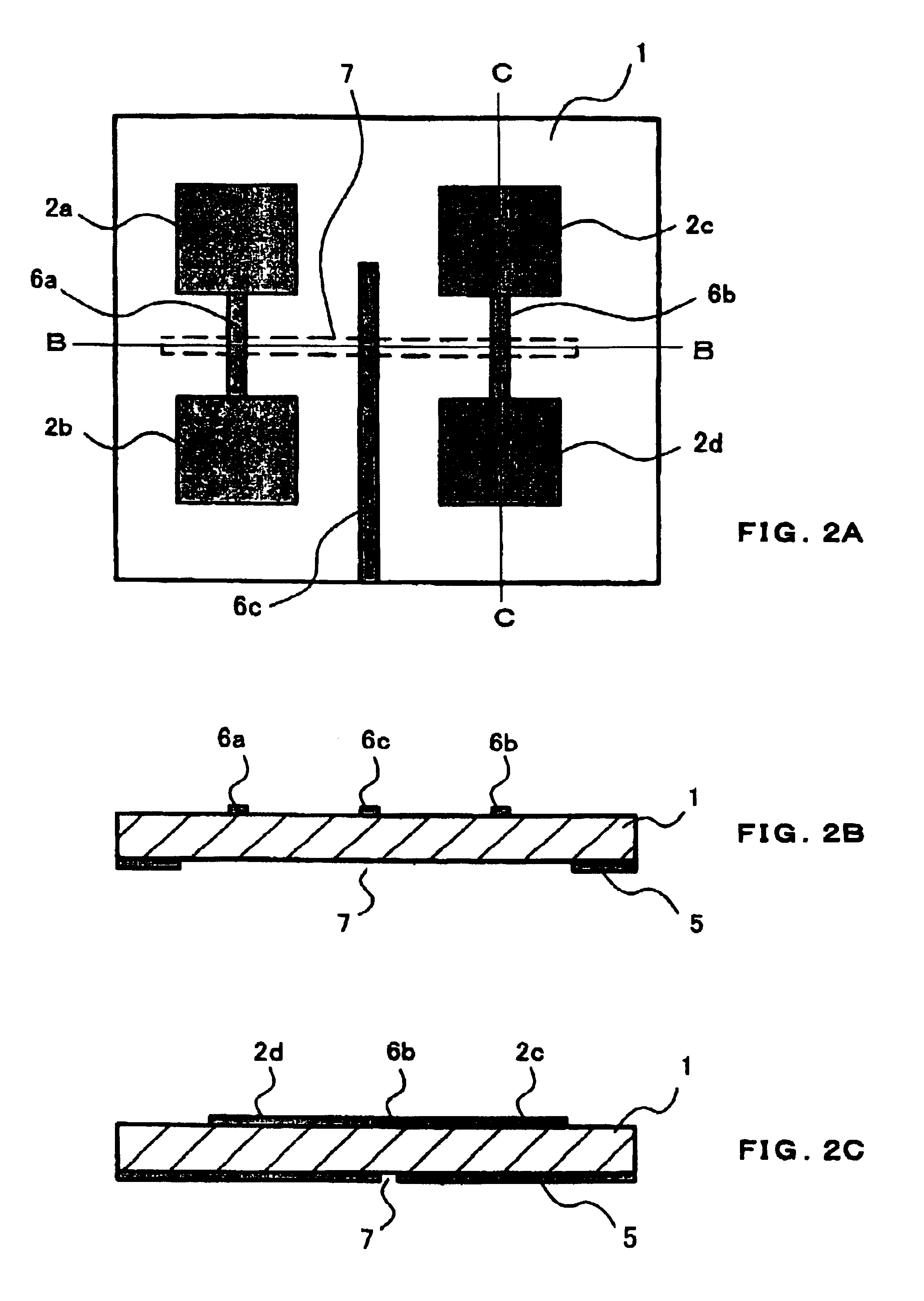
Dual-polarized antenna
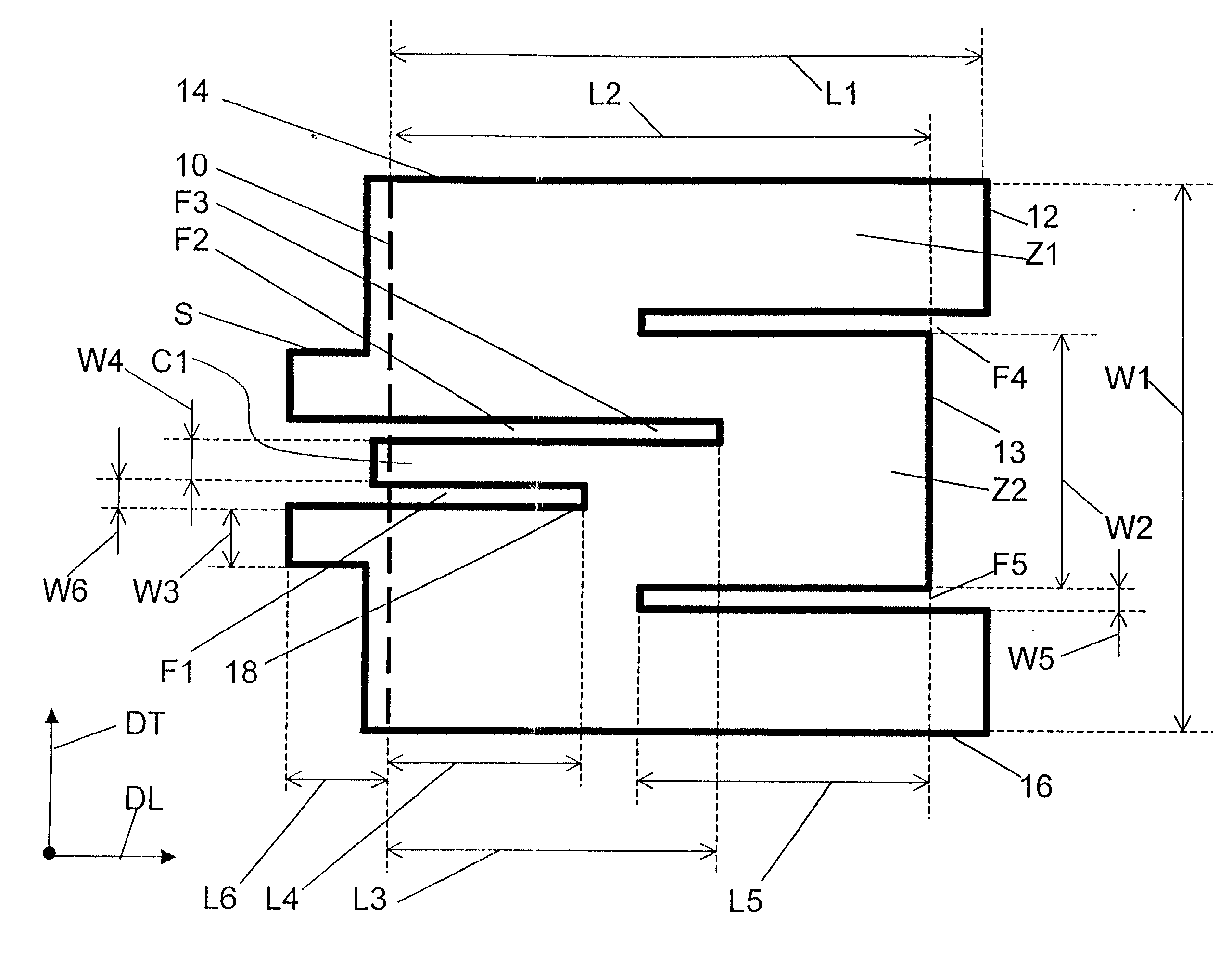
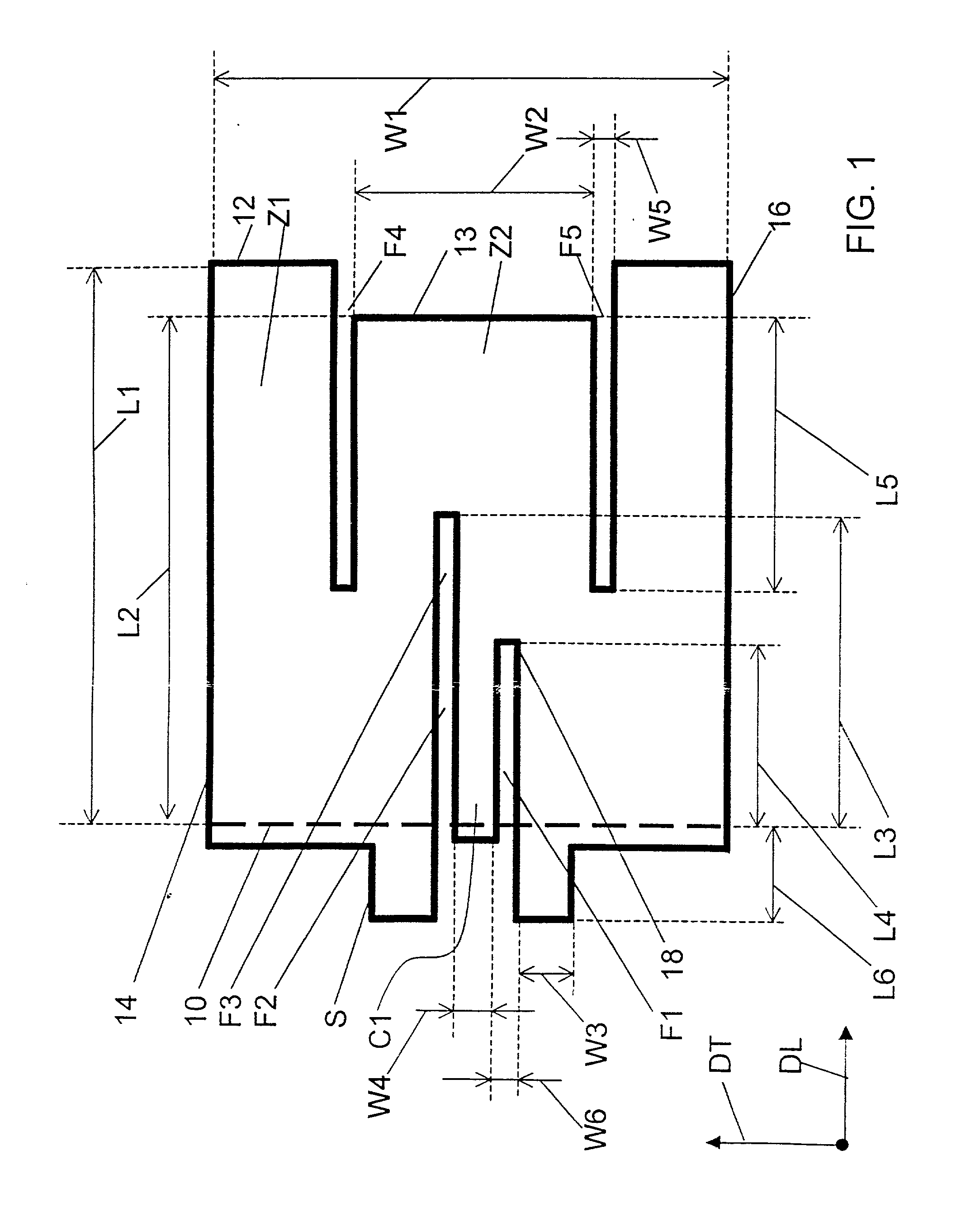
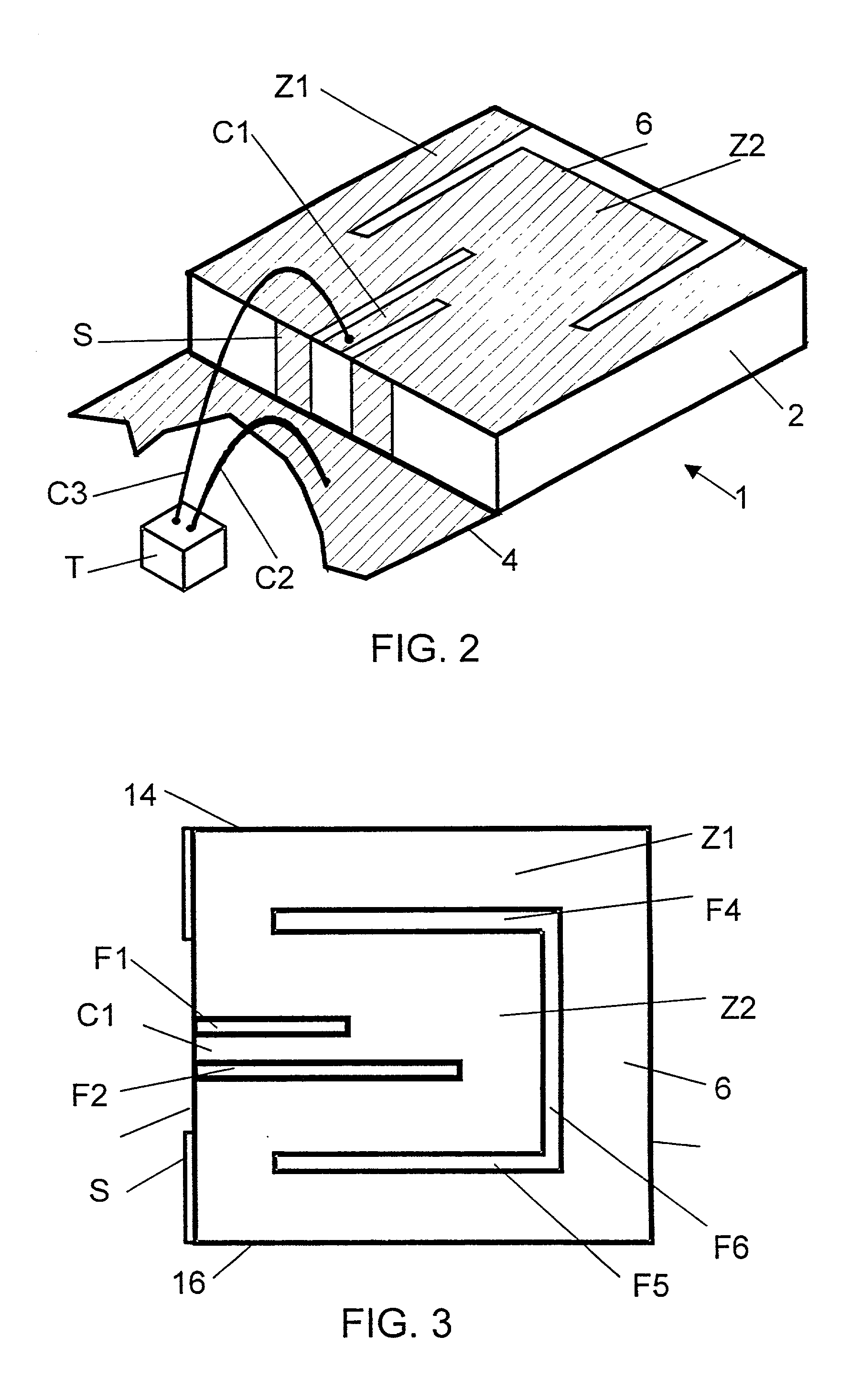
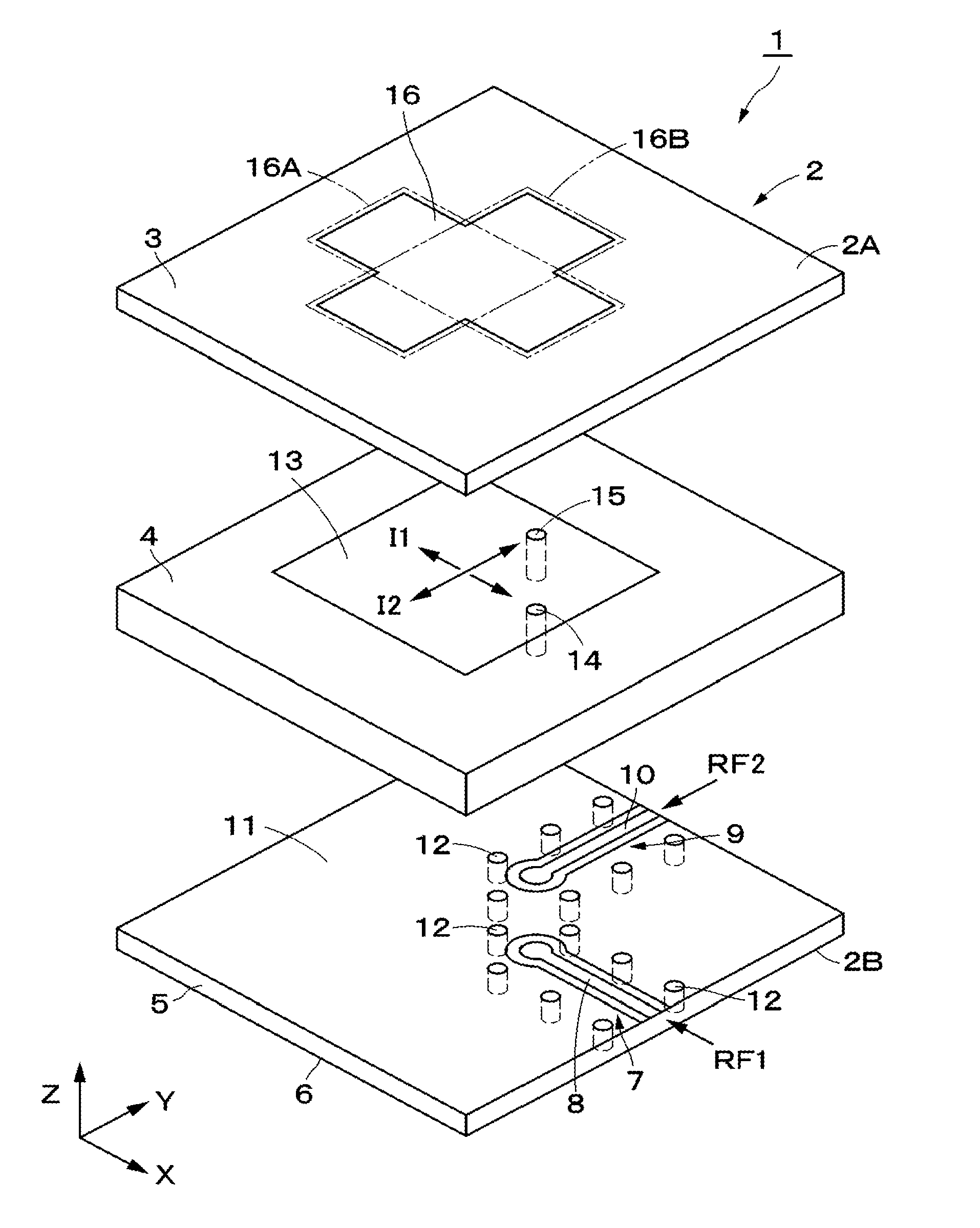
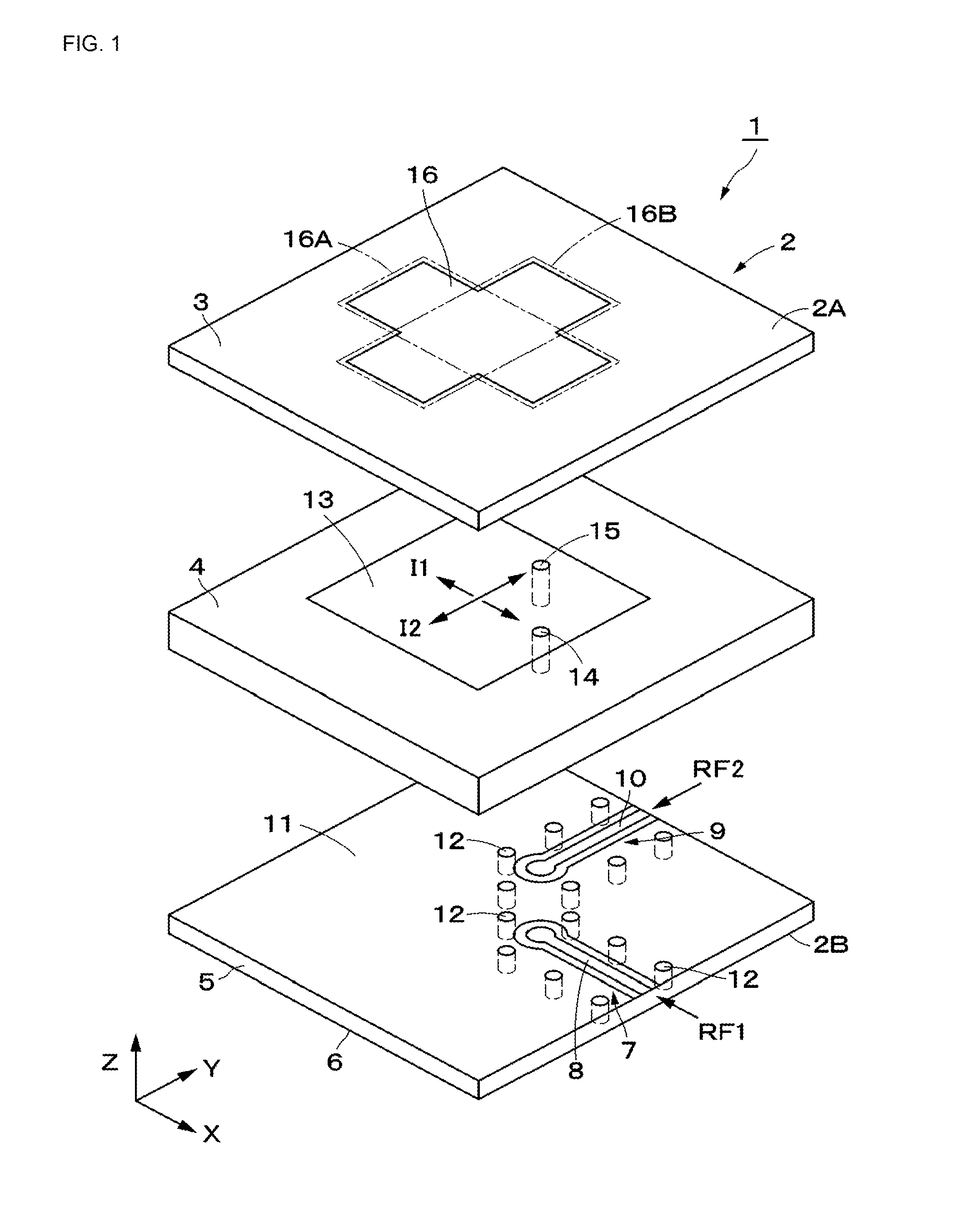
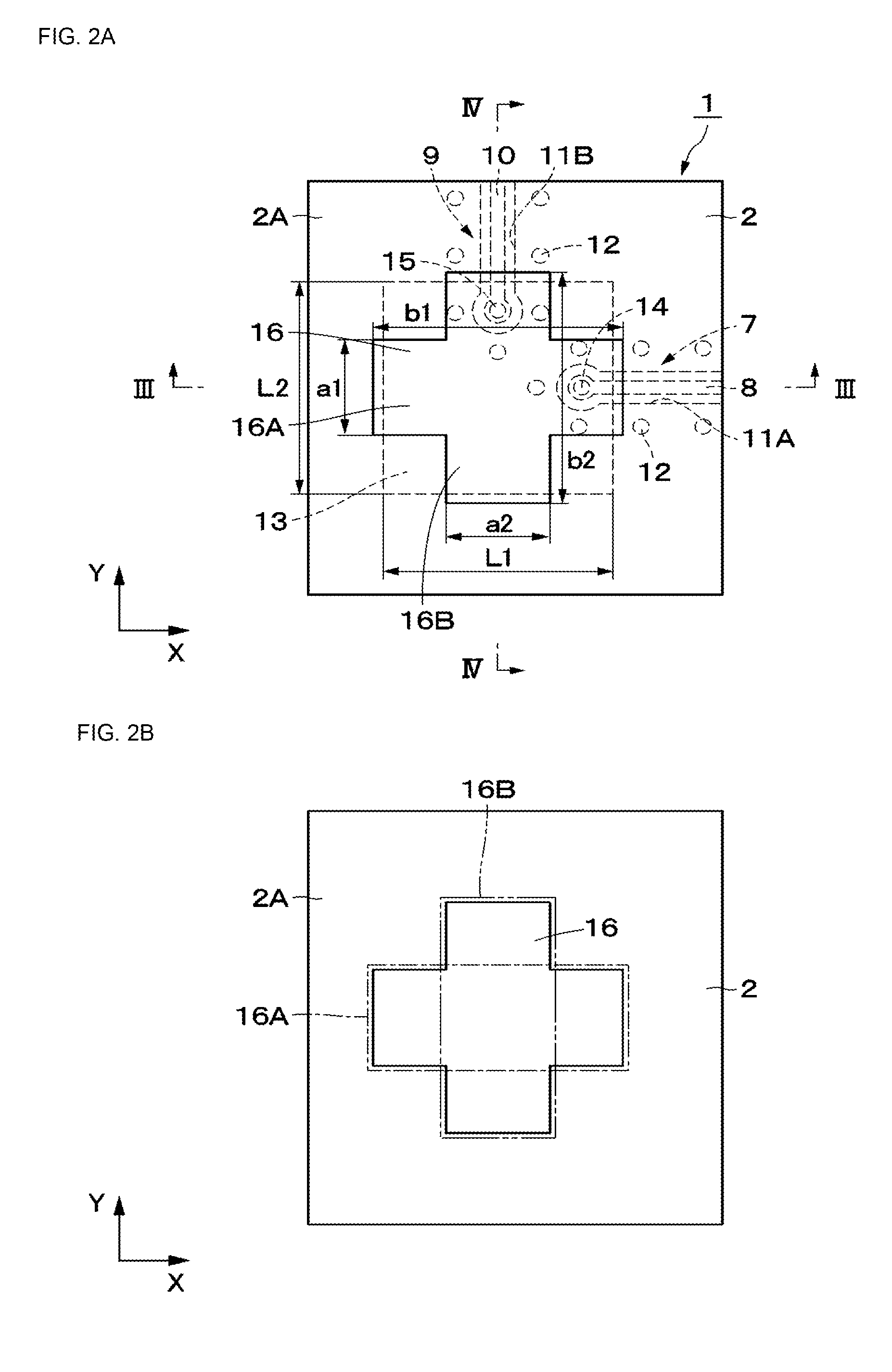
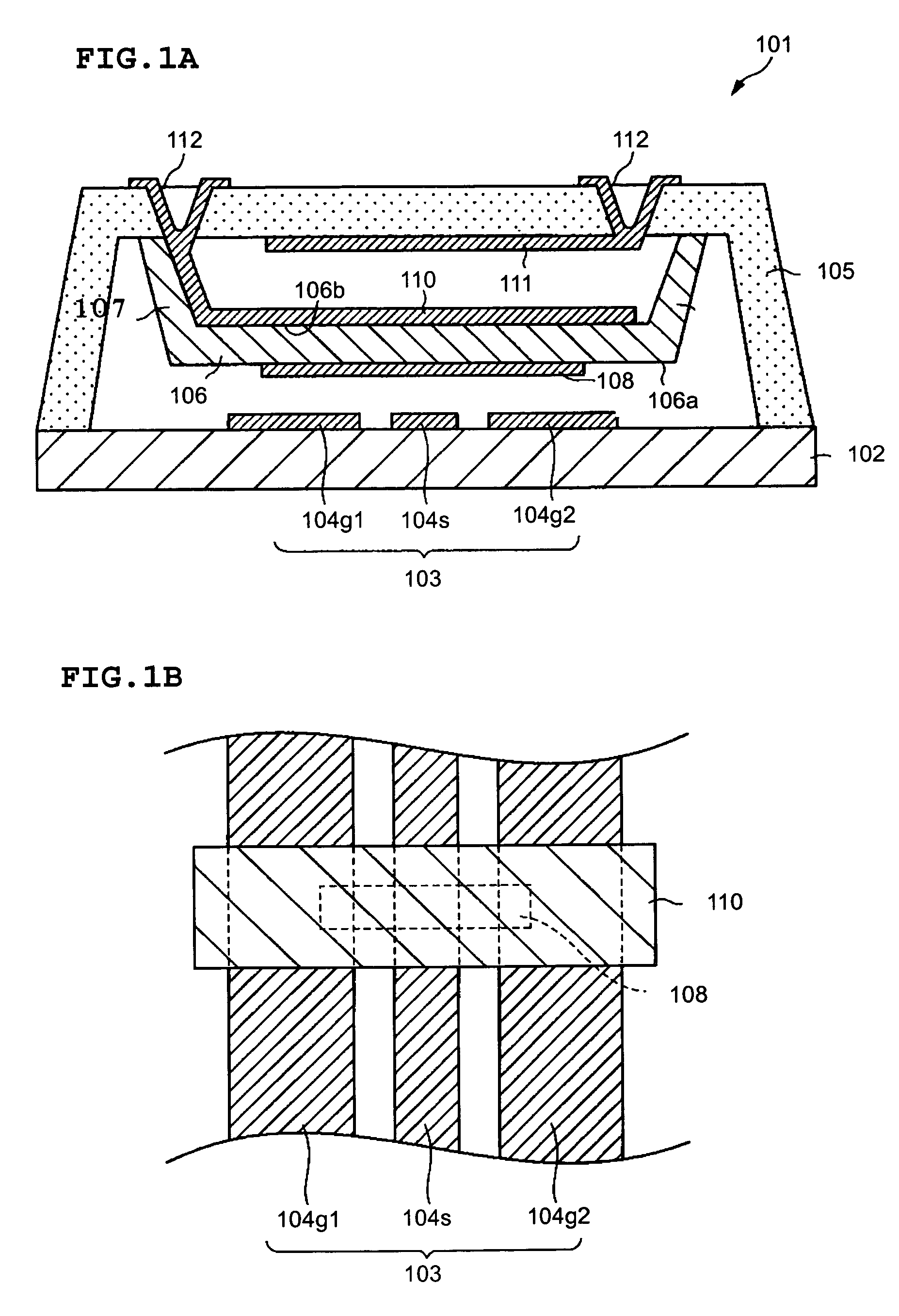
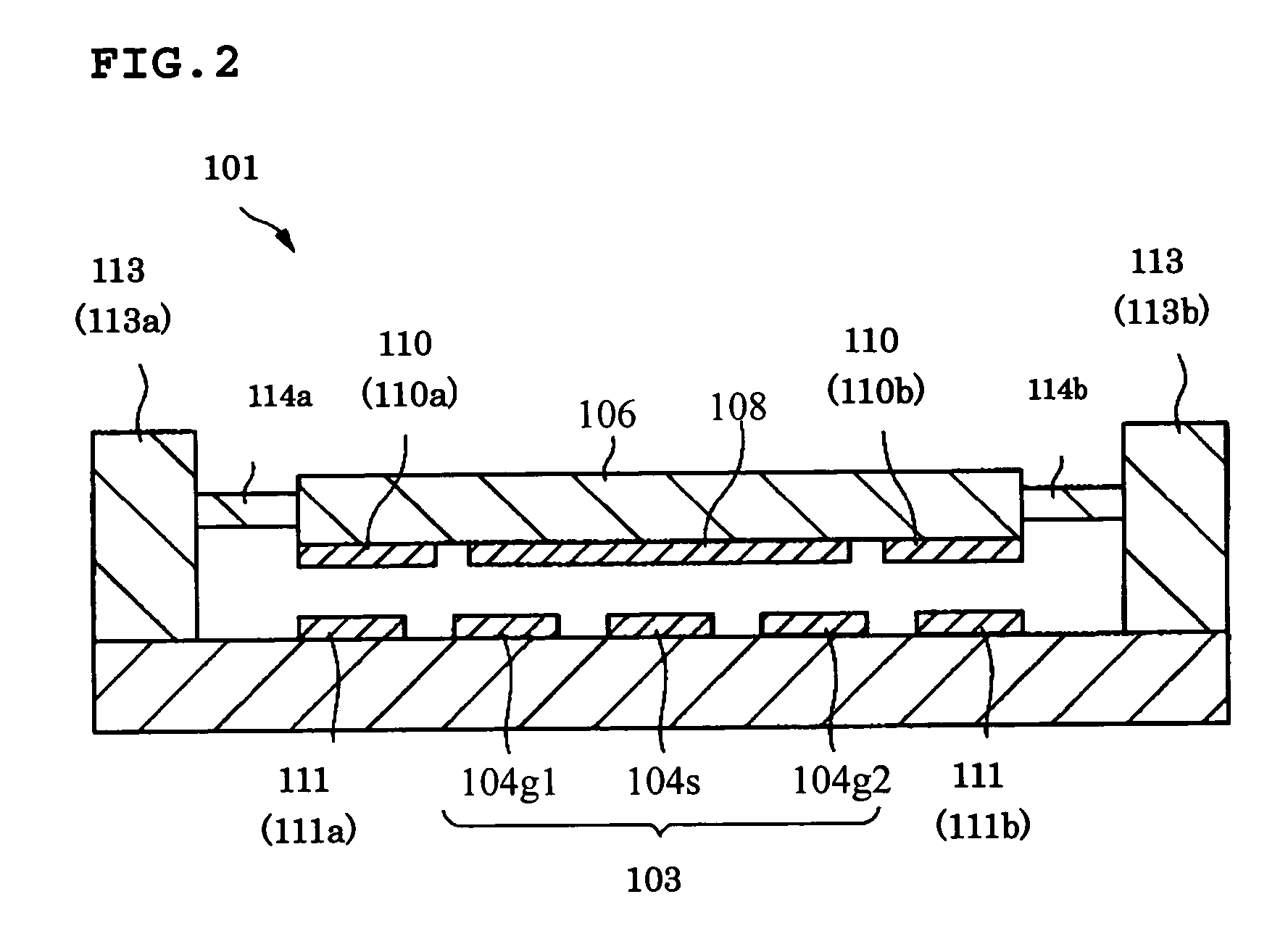
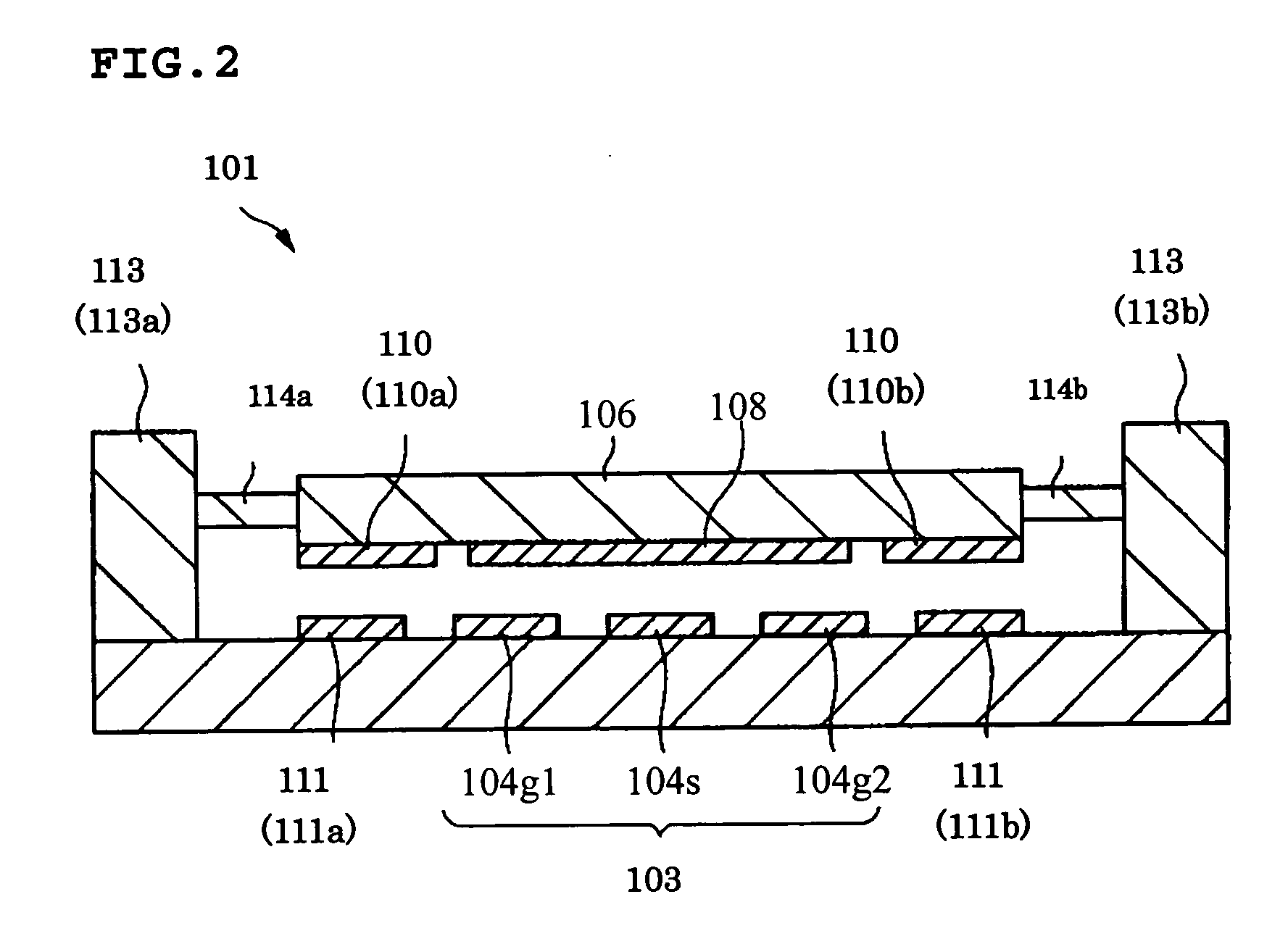
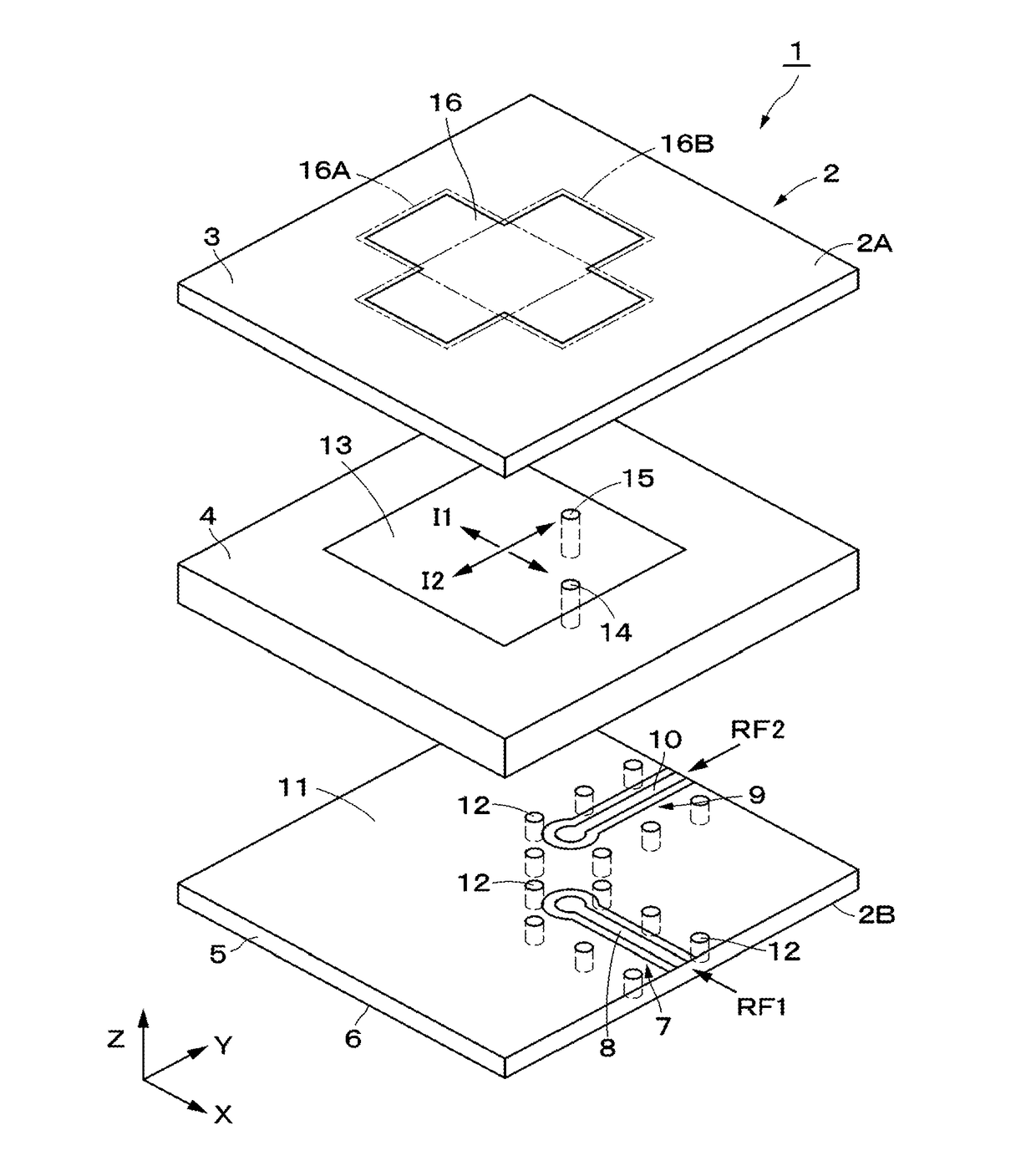
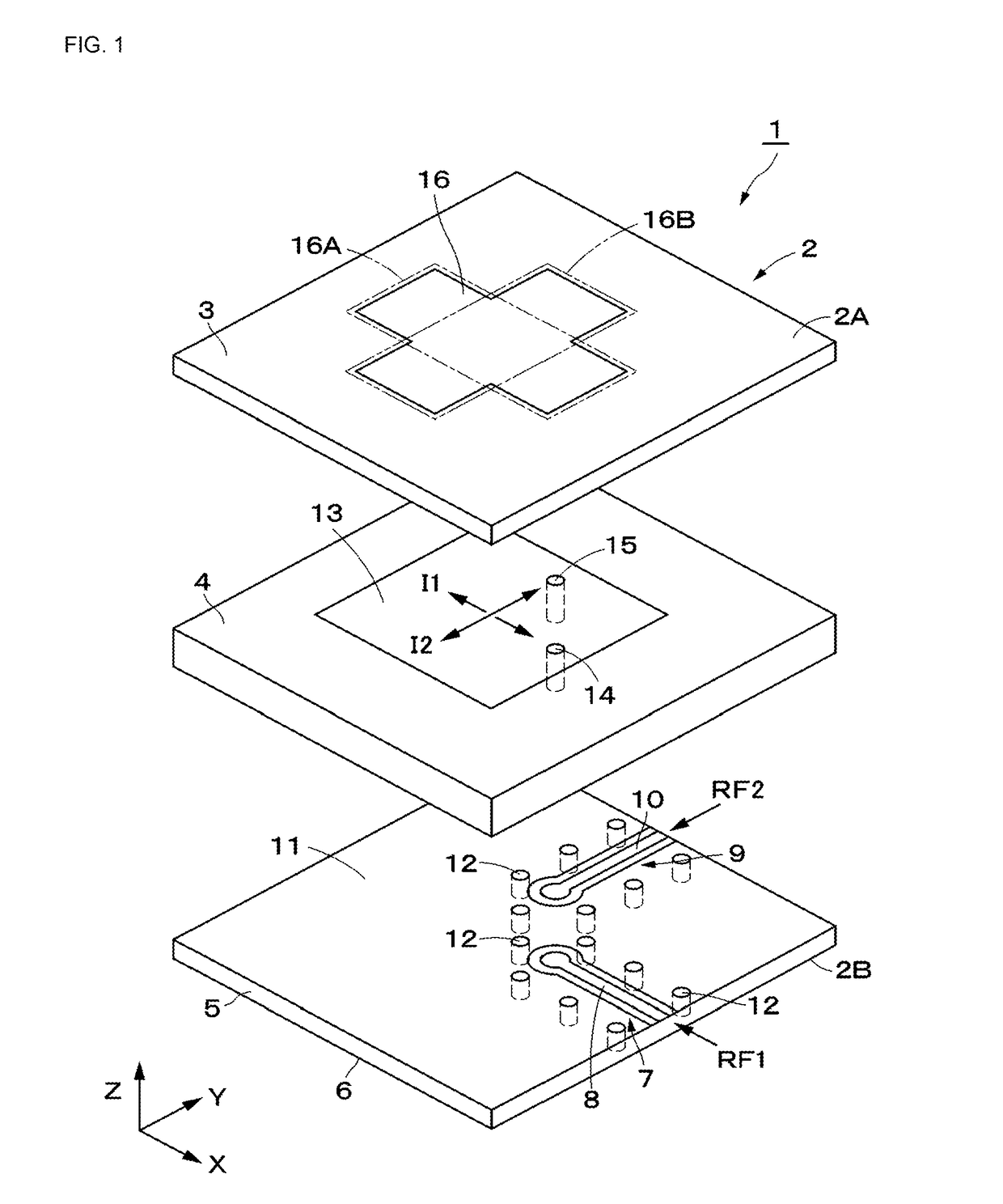
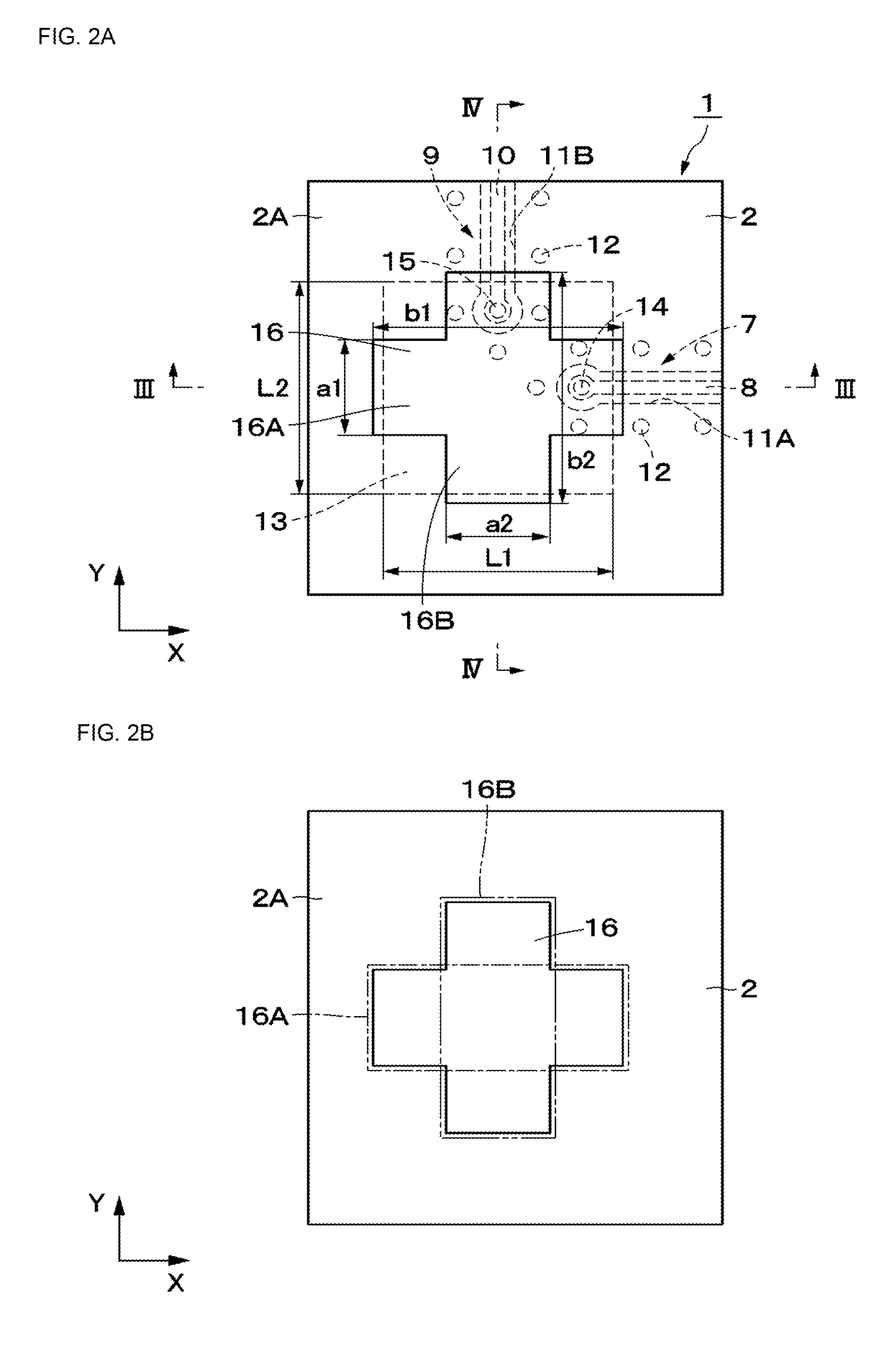
ActiveUS20150194730A1Bandwidth in which matching of the antenna can be ensured can be widenedHigh bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsRadiating elementCoplanar lines
In a multilayer substrate (2), an internal ground layer (11) is provided at a position between insulating layers (4) and (5) and a radiating element (13) is provided at a position between insulating layers (3) and (4). A first coplanar line (7) is connected to an intermediate position of the radiating element (13) in an X-axis direction, and a second coplanar line (9) is connected to an intermediate position of the radiating element (13) in a Y-axis direction. A passive element (16) is laminated on the upper surface of the radiating element (13) through the insulating layer (3). The passive element (16) is formed in a cross shape in which a first patch (16A) extending in the X-axis direction and a second patch (16B) extending in the Y-axis direction are orthogonal to each other.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device including microstrip line and coplanar line
InactiveUS20080128916A1Reduce in quantityReduce layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringGround plane
Provided is a semiconductor device including an interconnect substrate, a transmission line which is formed on the interconnect substrate, and a circuit component which is mounted over the interconnect substrate and has a ground plane. The transmission line includes a first portion and a second portion that is connected to the first portion. The first portion and the ground plane constitute a microstrip line. The second portion and ground line constitute a coplanar line.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and system for a 60 ghz leaky wave high gain antenna
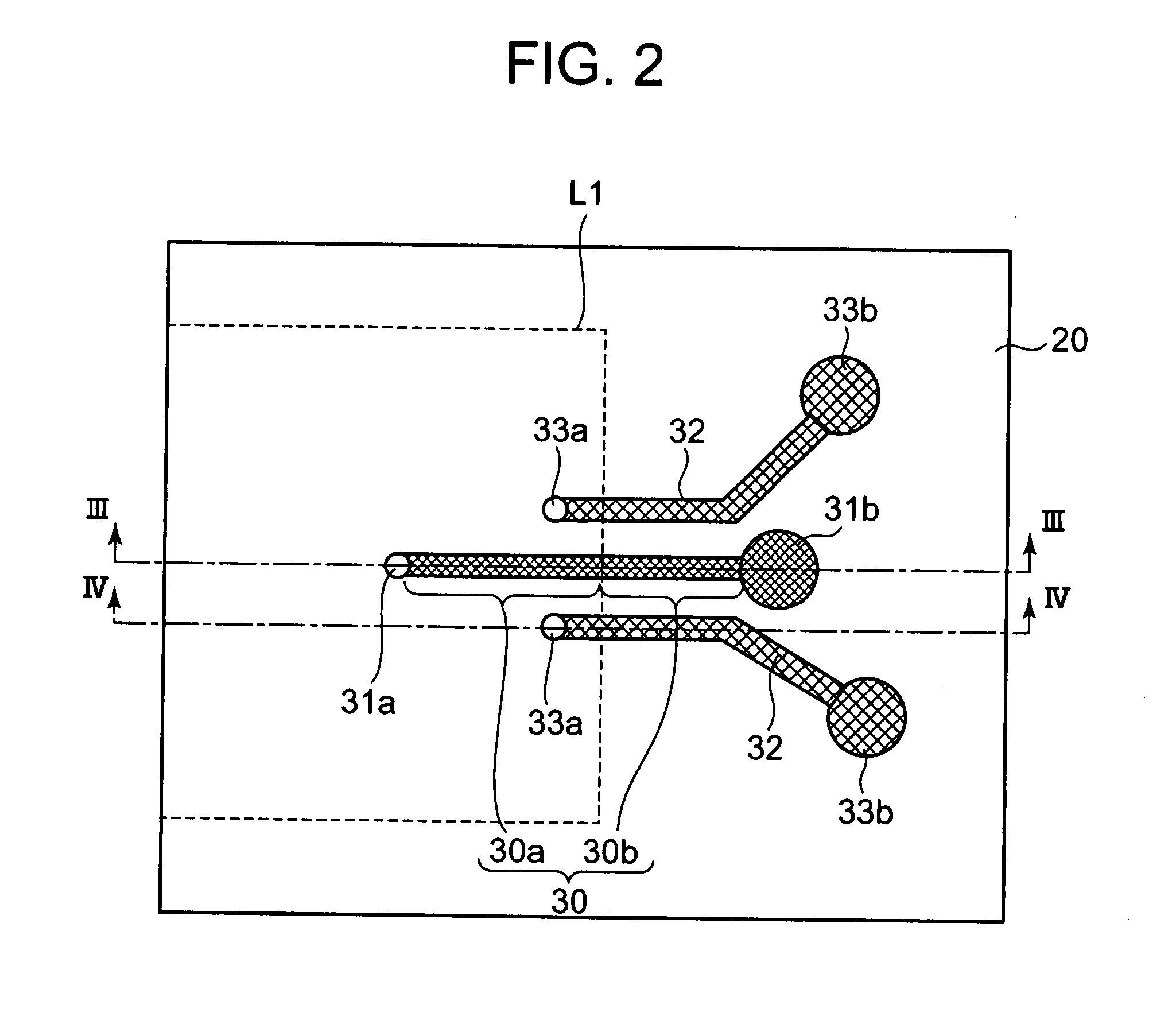
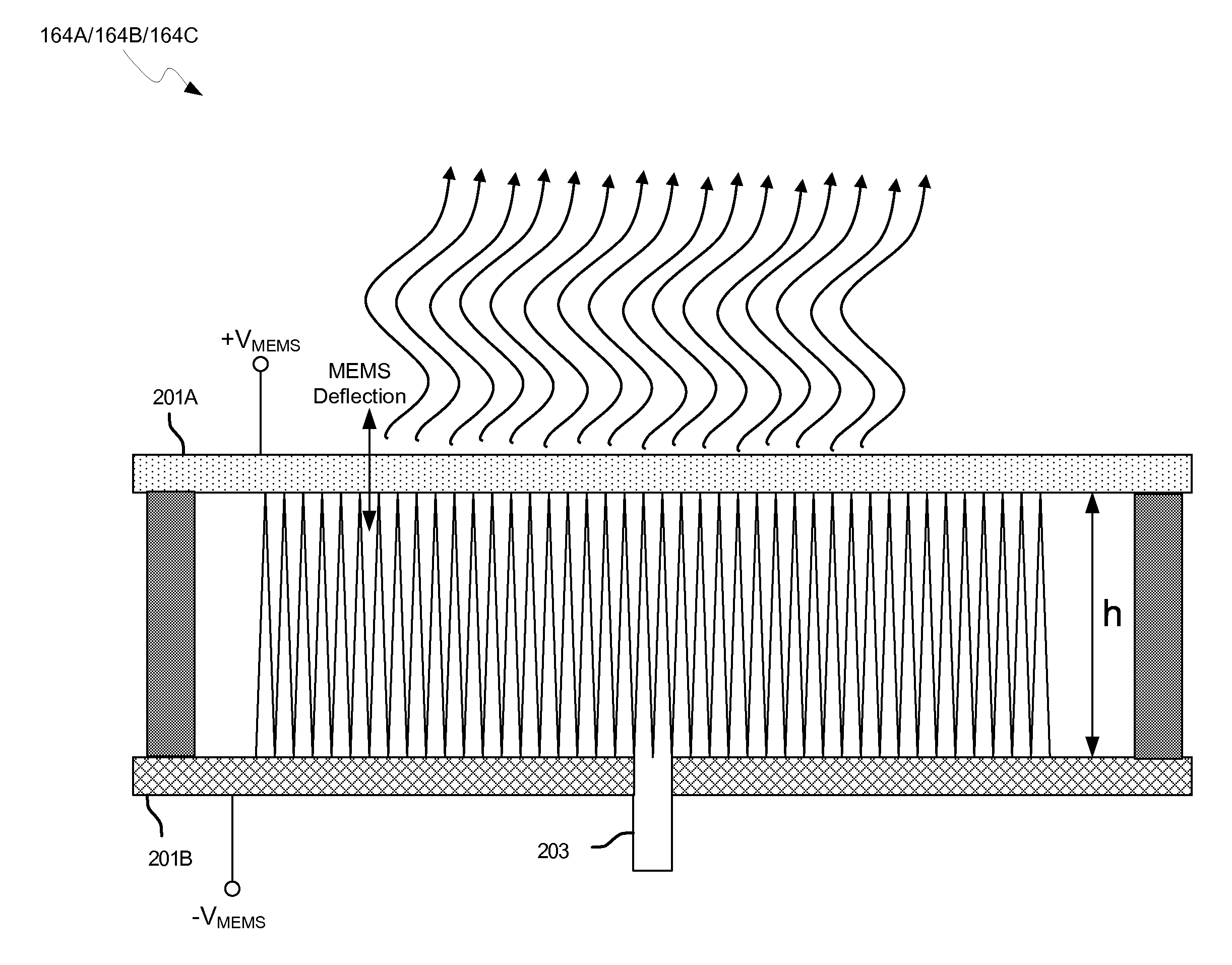
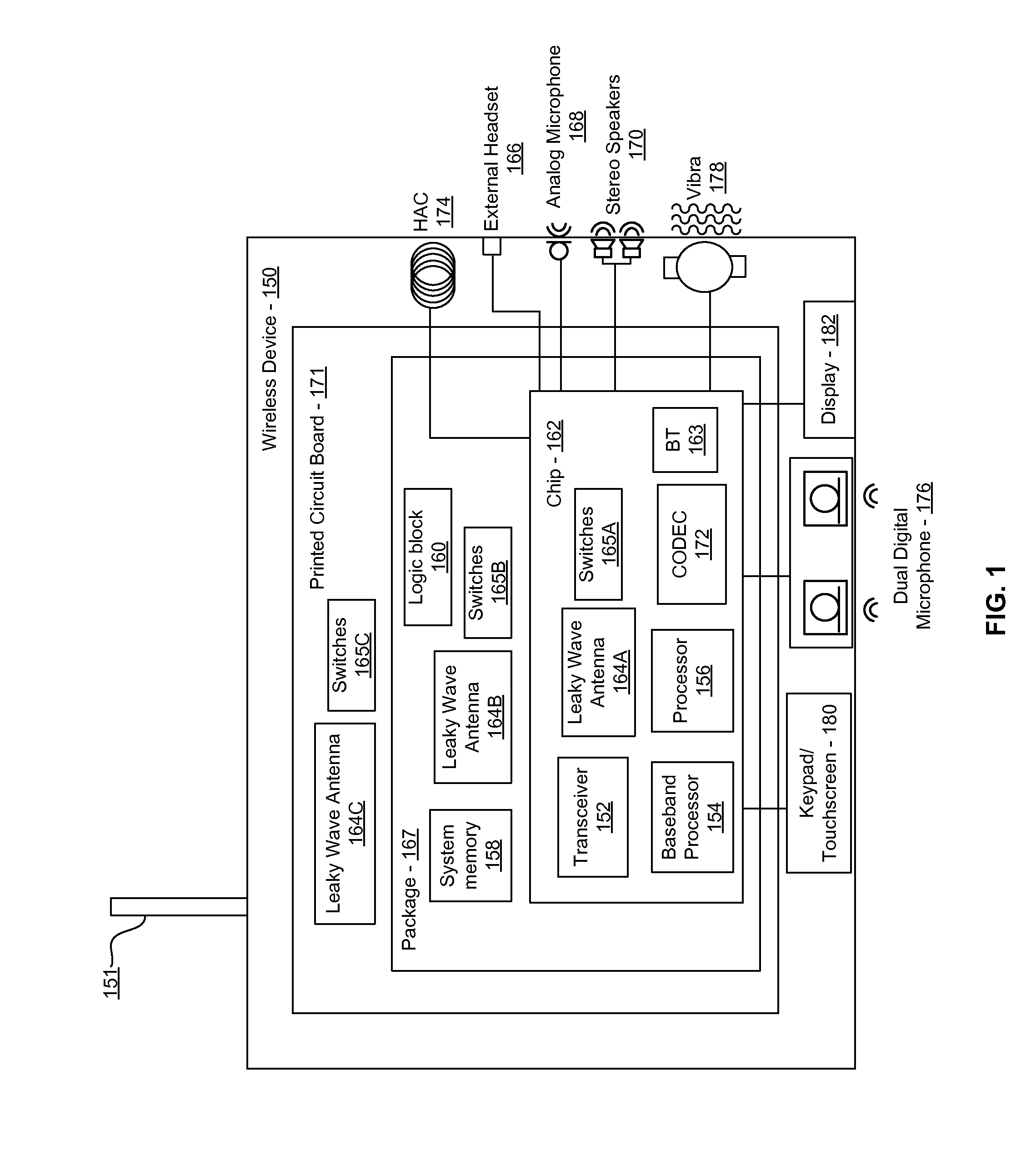
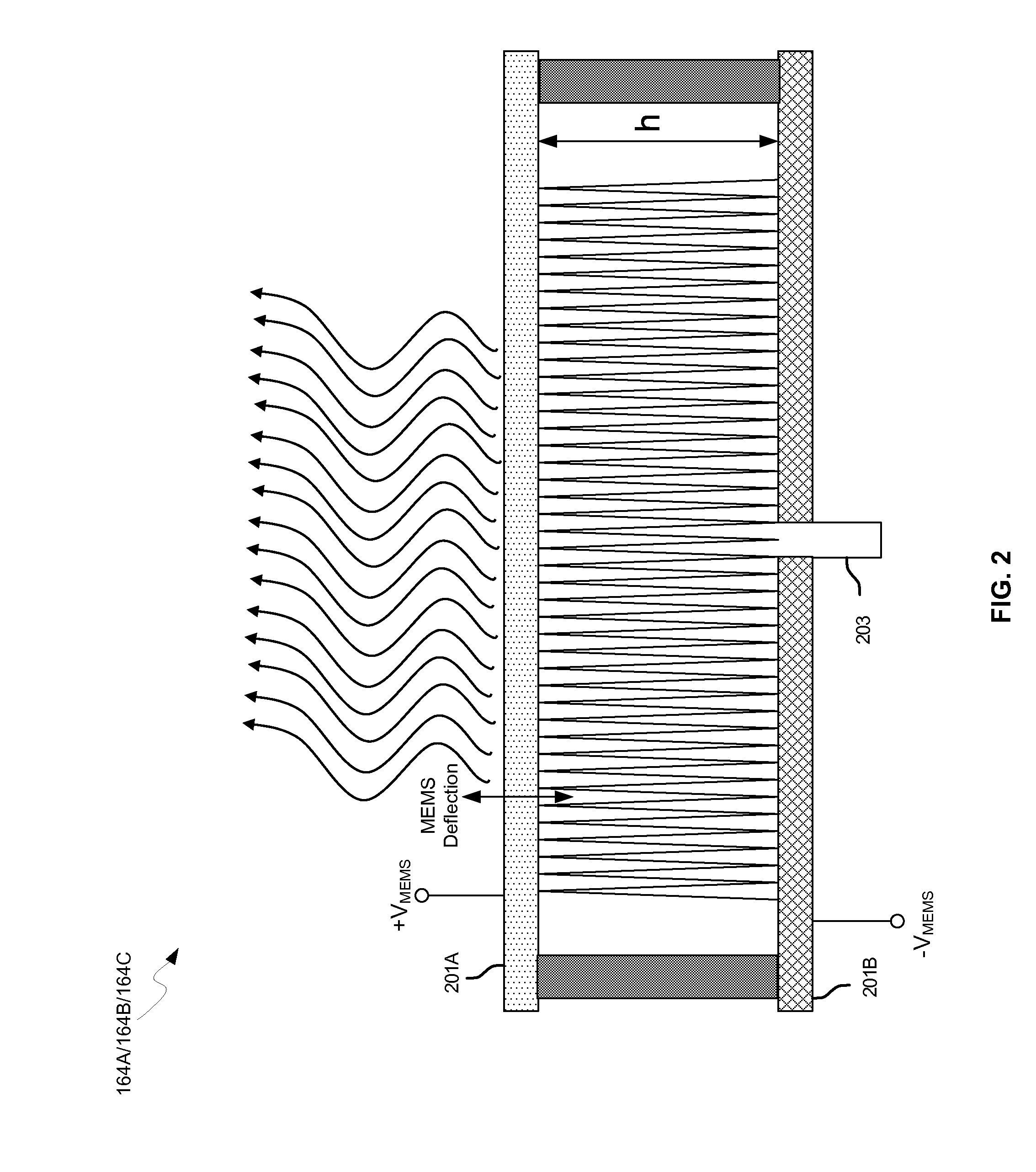
Methods and systems for a 60 GHz leaky wave high gain antenna are disclosed and may include communicating RF signals using one or more or more leaky wave antennas (LWAs) in a wireless device. The LWAs may be integrated in metal traces on a chip, a package, and / or a printed circuit board (PCB). The metal traces may supply voltage signals to one or more circuits on the chip, package, and / or PCB. The voltage signals may include DC bias voltages, and / or signals at a frequency that is lower than a resonant frequency of the LWAs. The LWAs may include microstrip or coplanar lines where a cavity height of the LWAs is dependent on a spacing between the lines. An angle of the wireless signals with a surface of the chip, package, and / or PCB may be dynamically configured. The LWAs may be configured via switches in the chip, package, and / or PCB.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Low loss electrical delay line
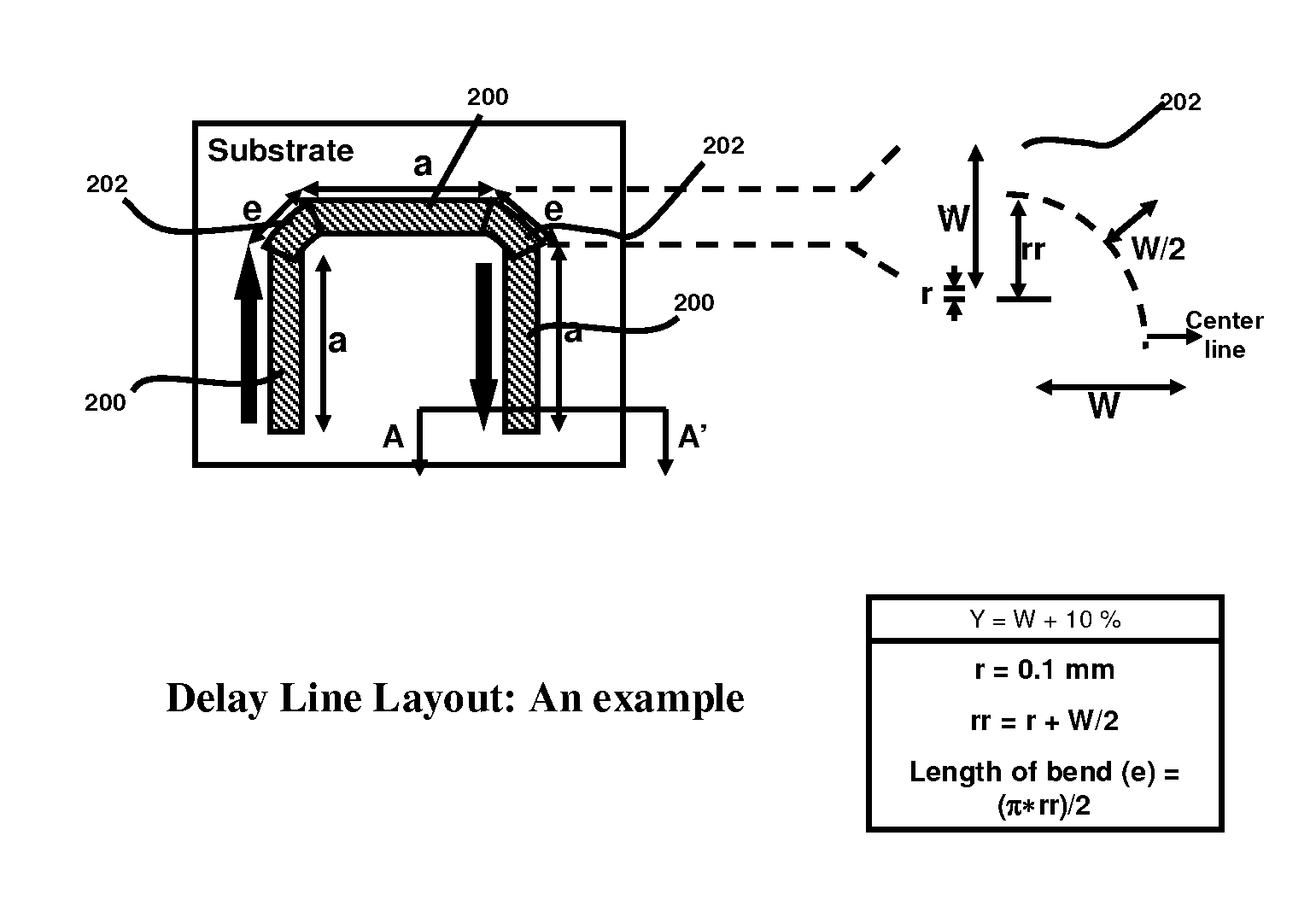
ActiveUS20080048800A1Decrease dielectric lossSimplified delay line solutionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityDielectric loss
A delay line system able to reduce the microwave loss by reducing the effective dielectric loss and dielectric constant of the system including a signal line, dielectric system with opened trench or slot filled up with the air or lower dielectric loss material, a ground plane, and a system of switches if the line is to be variable. The delay line proposed in this invention could be made of any type of signal line configuration, for example: micro-strip line, strip line, or coplanar line. The signal line can also be made as single ended or differential pairs of any configurations. The delay line systems based on the fundamental techniques provided in this invention can be used for on-chip devices where the delay line is laid on the oxide or dielectric material, or in a traditional PCB implementation such as FR4.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
Voltage tunable laminated dielectric materials for a coplanor waveguide
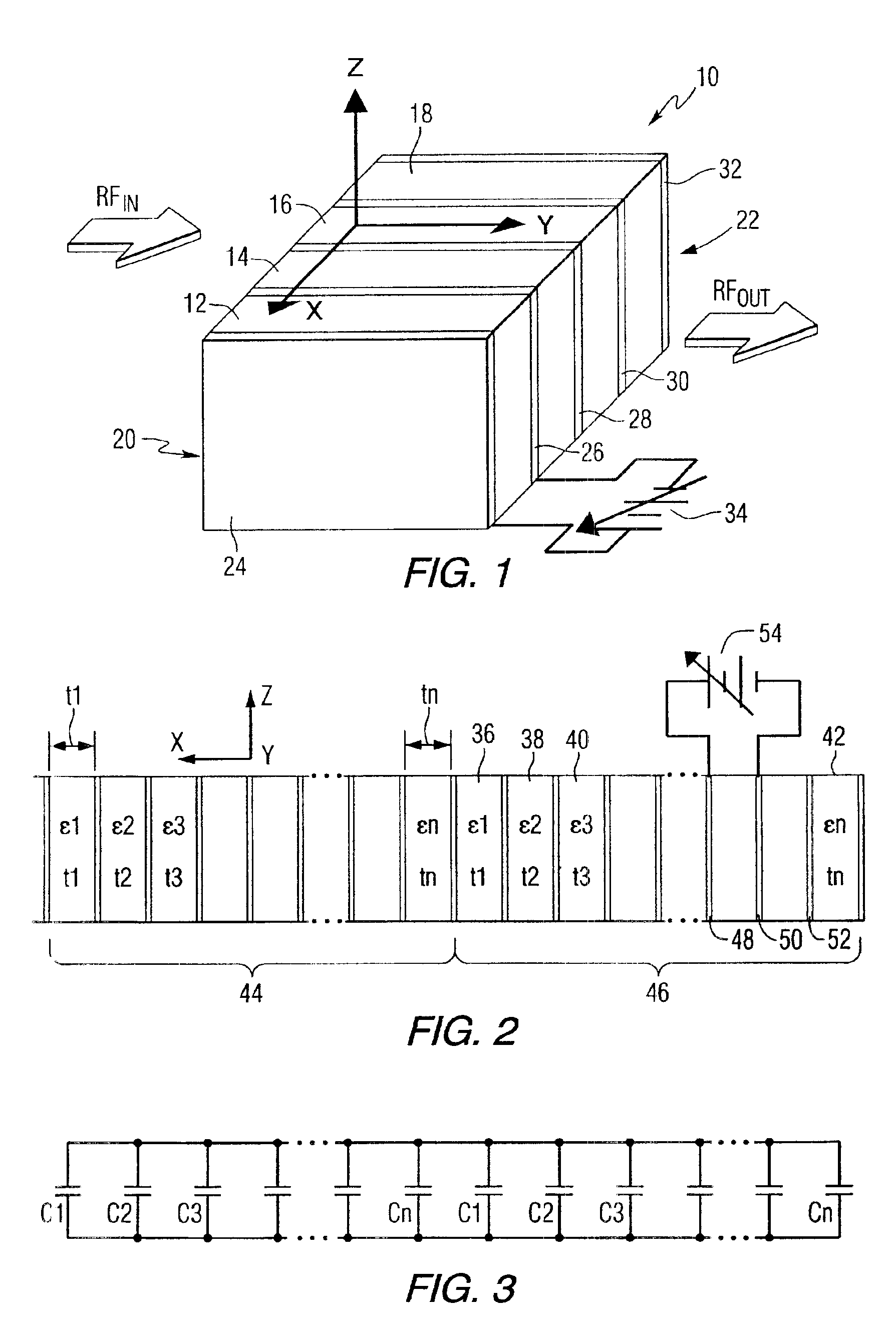
InactiveUS6876279B2Layered productsHigh frequency circuit adaptationsCoaxial cableCoplanar waveguide
A tunable dielectric structure includes a first layer of dielectric material, a second layer of dielectric material positioned adjacent to the first layer of dielectric material, with the second layer of dielectric material having a dielectric constant that is less than the dielectric constant of the first layer of dielectric material, and electrodes for applying a controllable voltage across the first dielectric material, thereby controlling a dielectric constant of the first dielectric material, wherein at least one of the electrodes is positioned between the first and second layers of dielectric material. The dielectric materials can be formed in various shapes and assembled in various orientations with respect to each other. The tunable dielectric structure is used in various devices including coaxial cables, cavity antennas, microstrip lines, coplanar lines, and waveguides.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Antenna with a conductive layer and a two-band transmitter including the antenna
InactiveUS6496148B2Improve matchSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual modeTwo band
The antenna of said transmitter is a microstrip antenna. A rear edge of its patch is provided with a short circuit by means of which a quarter-wave primary resonance can be excited by a coplanar line formed by two coupling slots in an area. Separator slots separate said area from another area in which a secondary resonance can be established at twice the frequency of the primary resonance from a slotted line extending one slot of the coplanar line. The invention applies in particular to the production of a dual-mode mobile telephone to the GSM and DCS standards.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
High frequency circuit element and high frequency circuit module
A high-frequency circuit device includes a dielectric member 1, a shielding conductor 2 surrounding the dielectric member 1, a support member 3 for fixing and supporting the dielectric member 1, and a pair of transmission lines 4 each of which is formed of a microstrip-line. Each of the transmission lines includes a substrate 6 formed of a dielectric material, a strip conductor 5, and an earth conductor layer 9. An end portion of the strip conductor 5 faces part of the dielectric member 1 and functions as a coupling probe for input / output coupling. Each of the transmission lines 4 is formed of a strip line, a mictostrip line, a coplanar line or the like, and has low-loss when connected to a circuit board.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Planar coupler and integrated antenna system
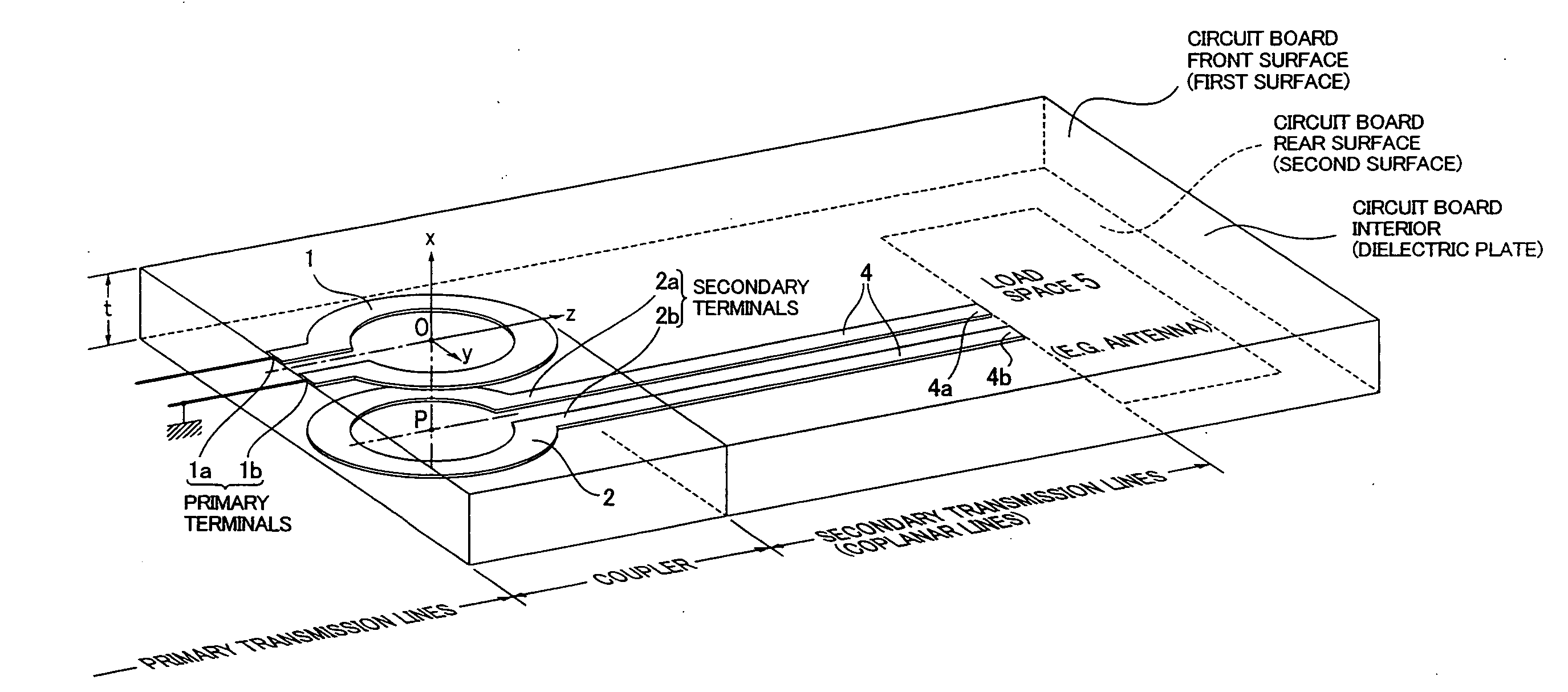
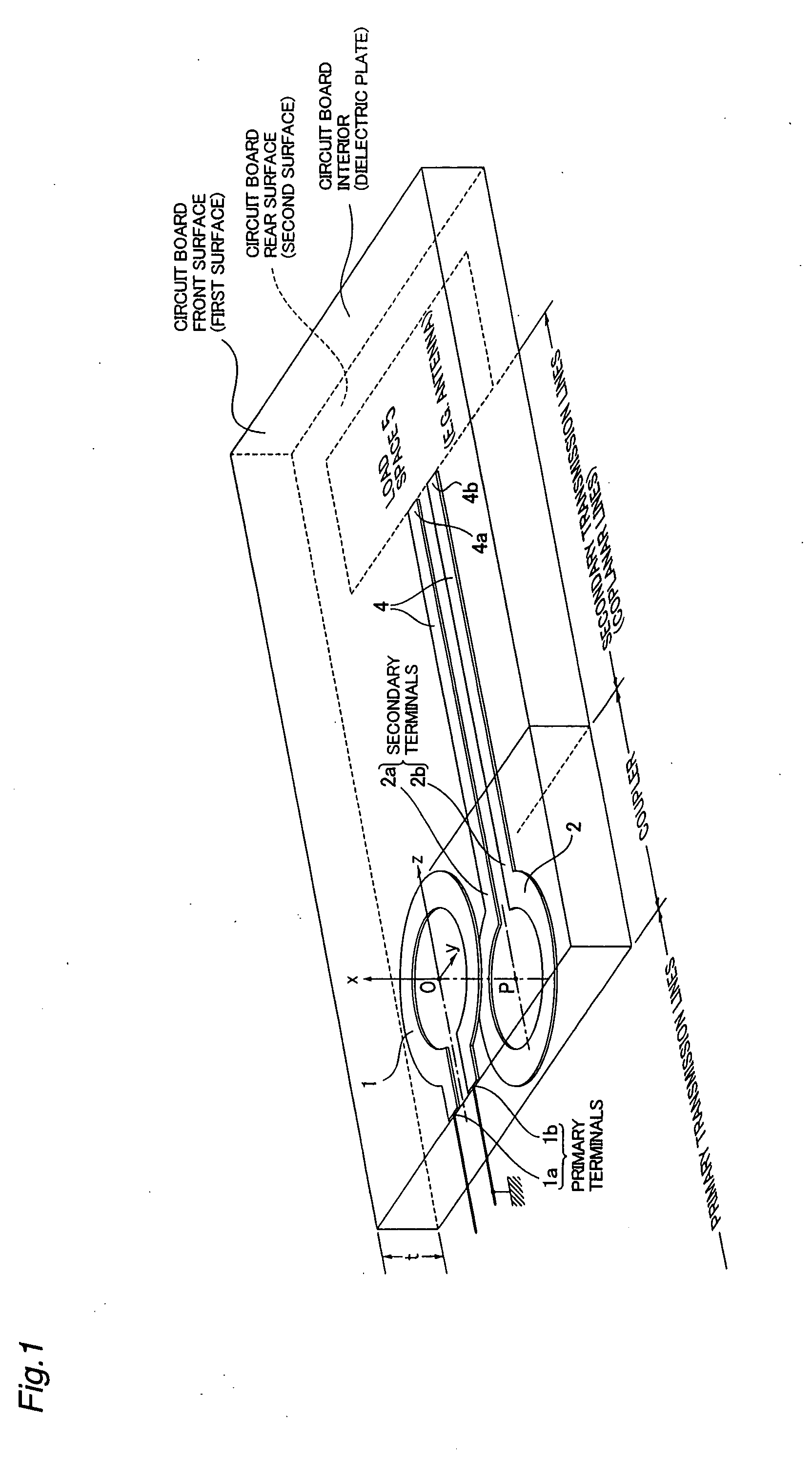
InactiveUS20070229368A1Reduce manufacturing costSmall sizeSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectromagnetic couplingDielectric plate
Owner:HATA HIROSHI +2
Variable capacitance element
InactiveUS7027284B2Guaranteed uptimeImprove reliabilityMechanically variable capacitor detailsElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysCapacitanceEngineering
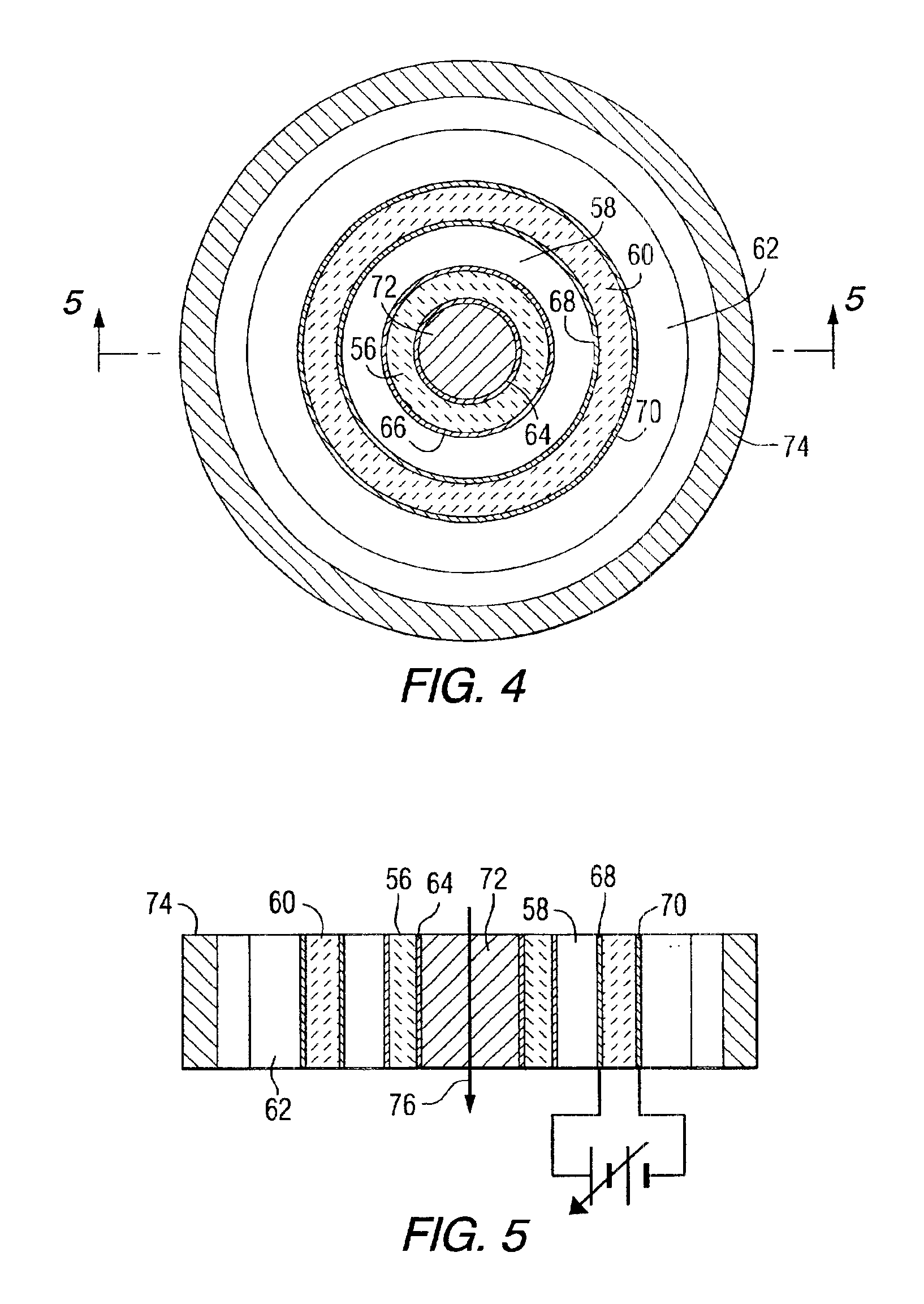
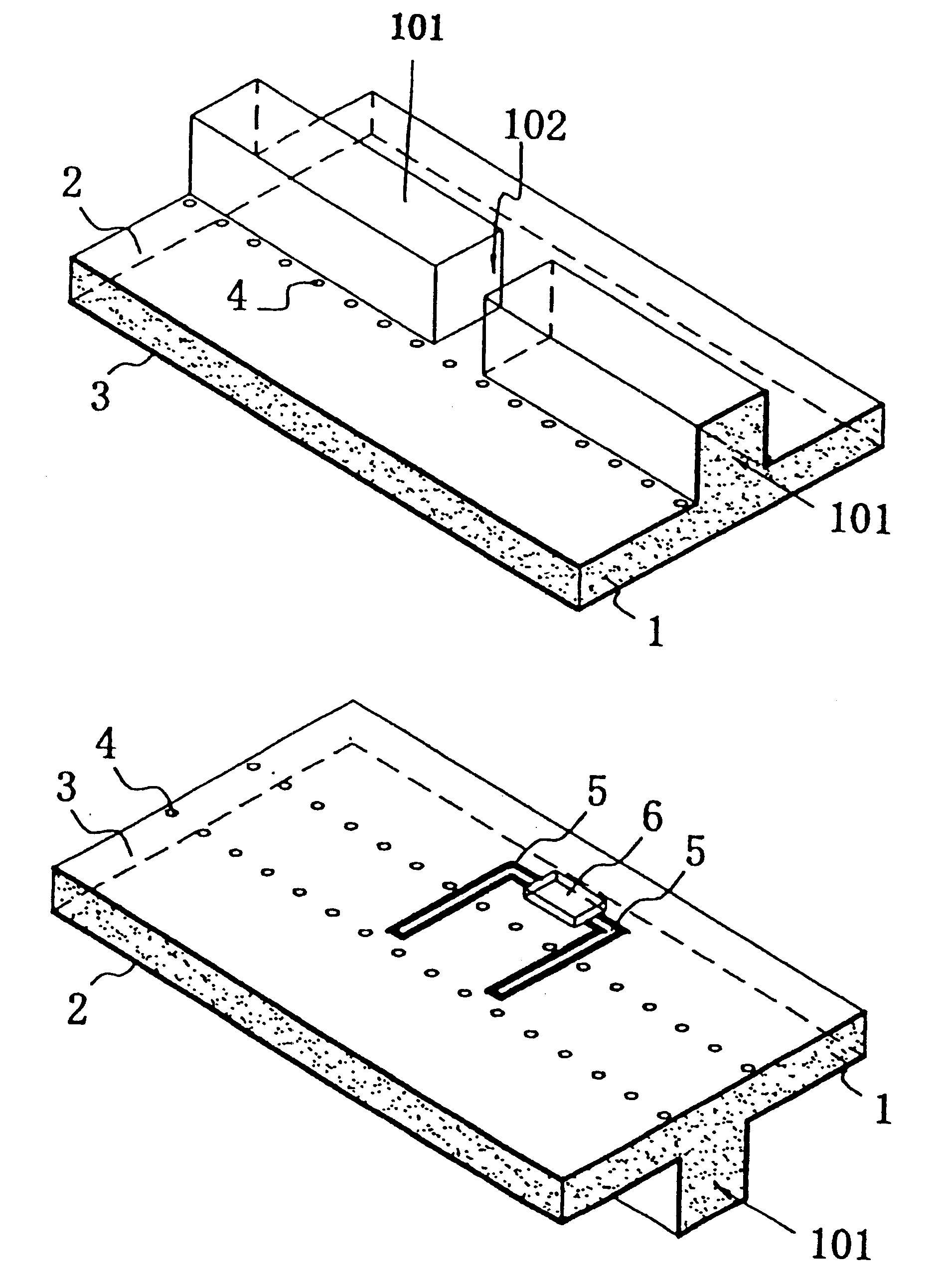
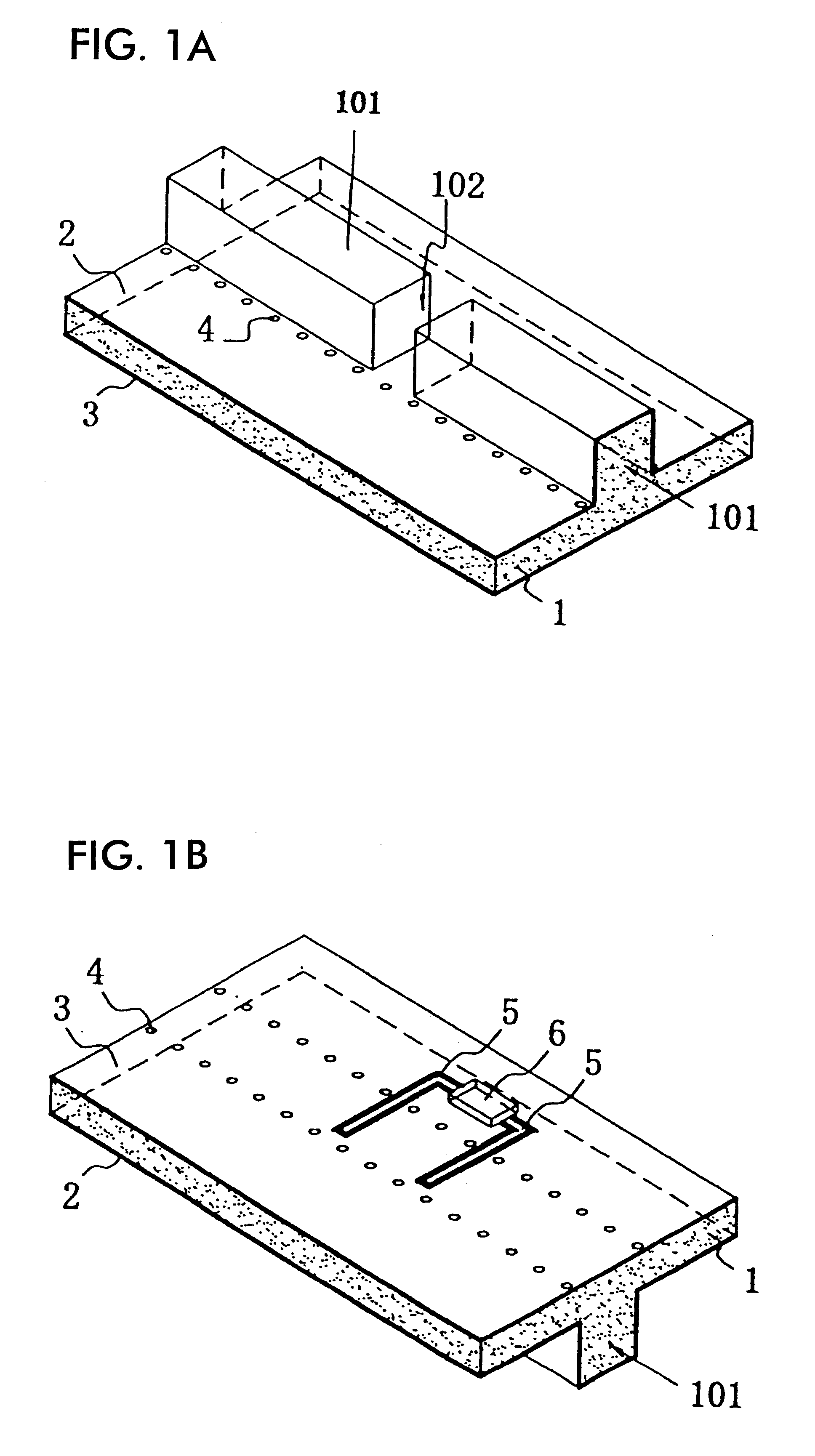
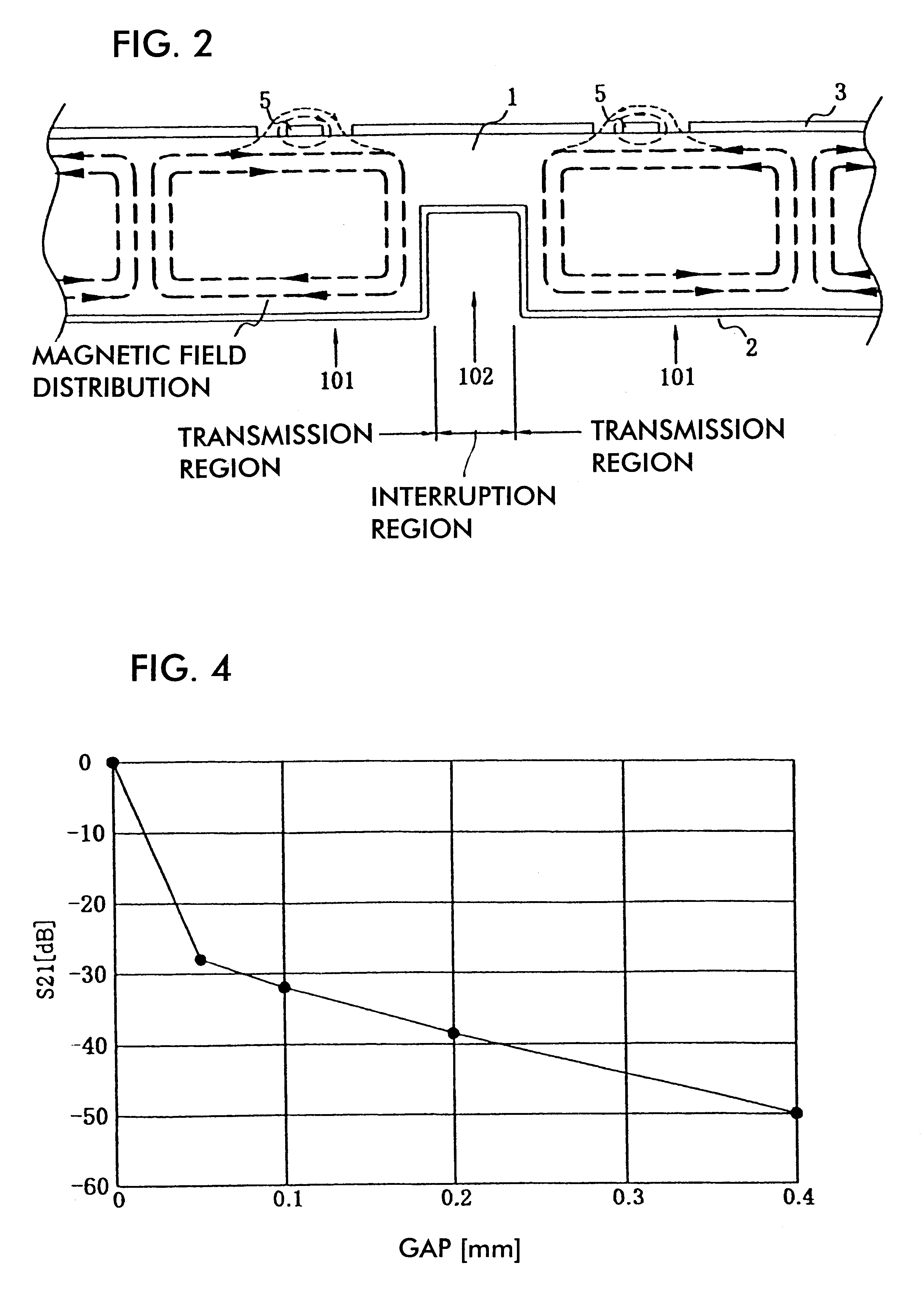
A variable capacitance element includes a coplanar line or signal conduction and a movable body, which are vertically displaced through a supporting bar and which are provided on a substrate. A movable electrode is provided between a first driving electrode and second and third driving electrodes which are movable electrodes. Voltage is applied between the movable electrodes, such that one of the movable electrodes is pressed against the coplanar line through a dielectric film. Thus, high frequency signals conducting through the coplanar line are shut off. When voltage is applied between the other electrodes, the movable electrode and the dielectric film are moved apart from the coplanar line. Thus, high frequency signals are conducted through the coplanar line.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Optical module
ActiveUS20100215324A1Deterioration of characteristicEasy to getCross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
An optical module having a flexible substrate having, even after actual manufacturing steps, excellent transmission characteristics of high-frequency signals and an advantage that electromagnetic field radiation is reduced even when it is connected with a package. The flexible substrate used in external connection of the package of the optical module uses a flexible substrate having a coplanar line to which a lead pin is fixedly attached, a grounded coplanar line which is in contact with the coplanar region, and a microstrip line which is in contact with the grounded coplanar line. The flexible substrate has an electrode layout in which an electromagnetic field component of a surface ground line and a signal line is more dominant than an electromagnetic field component of a back-surface ground line and the signal line in a region of the coplanar line adjacent to the grounded coplanar line.
Owner:LUMENTUM JAPAN INC
Low loss electrical delay line
ActiveUS7561006B2Reduce lossEffective dielectric constantSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityDielectric loss
A delay line system able to reduce the microwave loss by reducing the effective dielectric loss and dielectric constant of the system including a signal line, dielectric system with opened trench or slot filled up with the air or lower dielectric loss material, a ground plane, and a system of switches if the line is to be variable. The delay line proposed in this invention could be made of any type of signal line configuration, for example: micro-strip line, strip line, or coplanar line. The signal line can also be made as single ended or differential pairs of any configurations. The delay line systems based on the fundamental techniques provided in this invention can be used for on-chip devices where the delay line is laid on the oxide or dielectric material, or in a traditional PCB implementation such as FR4.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
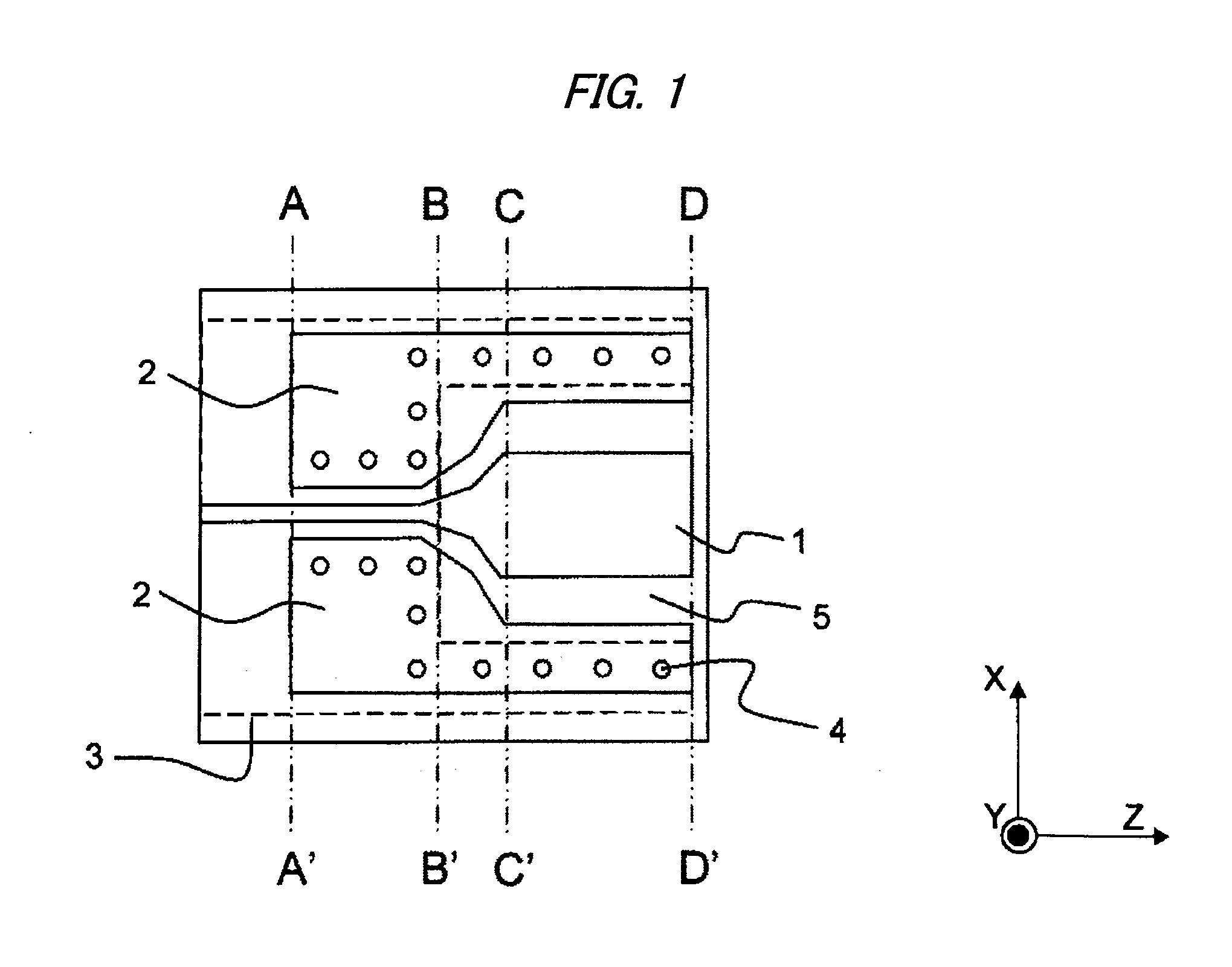
Circuit substrate structure and circuit apparatus
InactiveUS20060170071A1Improve performanceSuppresses electromagnetic leakageOne-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInductorEngineering
A first wiring layer in a circuit substrate structure is provided with a first inductor and a second inductor. A dielectric layer is provided with a first via and a second via electrically connected to the first inductor and the second inductor, respectively. A second wiring layer is provided with: abridge electrically connecting the first via and the second via; and a conductive pattern provided around the bridge, the outer edge of the conductive pattern being located outside the outer edge of the first wiring pattern and the second wiring pattern in the first wiring layer. The bridge functions as a coplanar line and suppresses generation of electromagnetic field.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
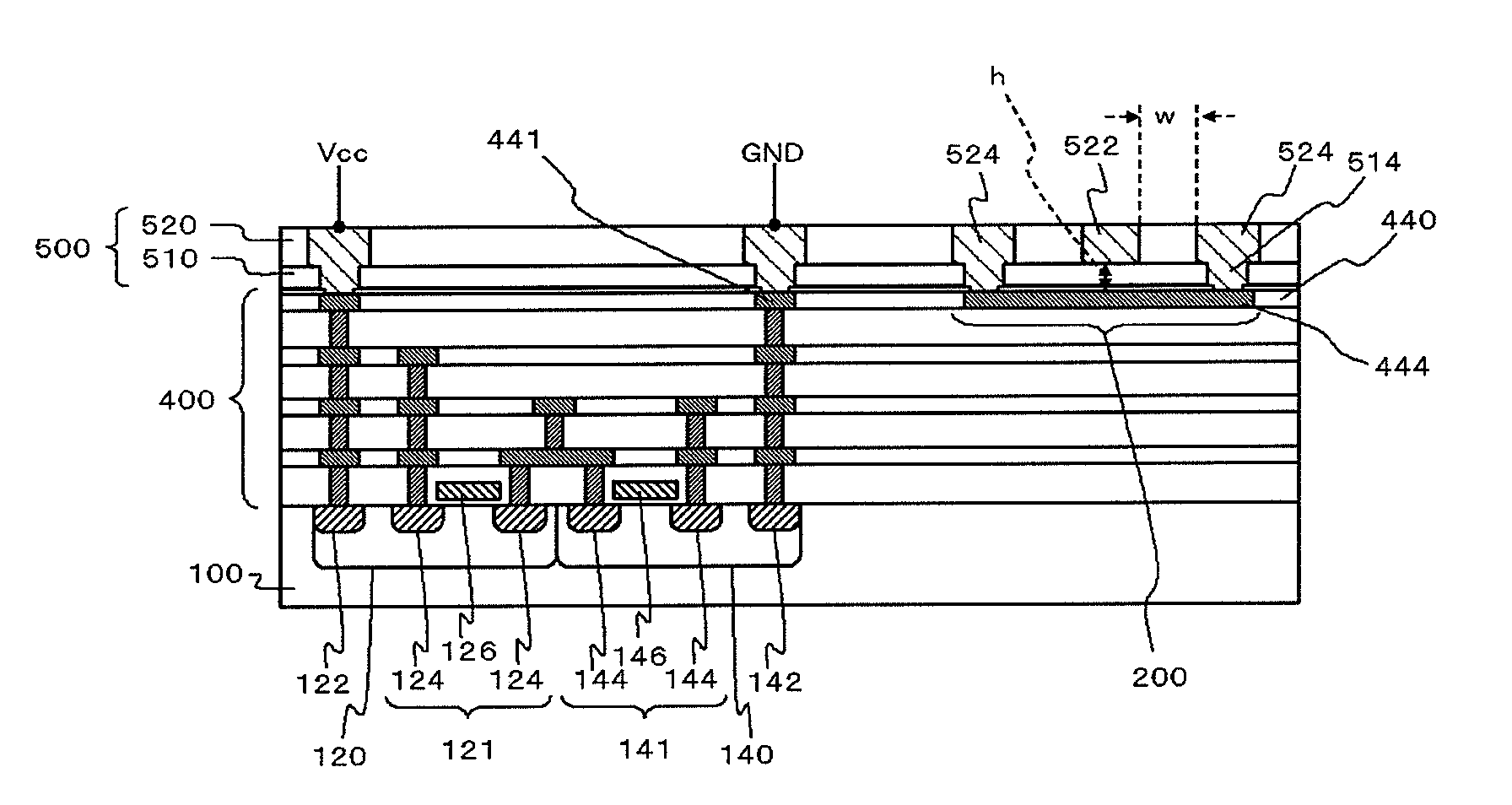
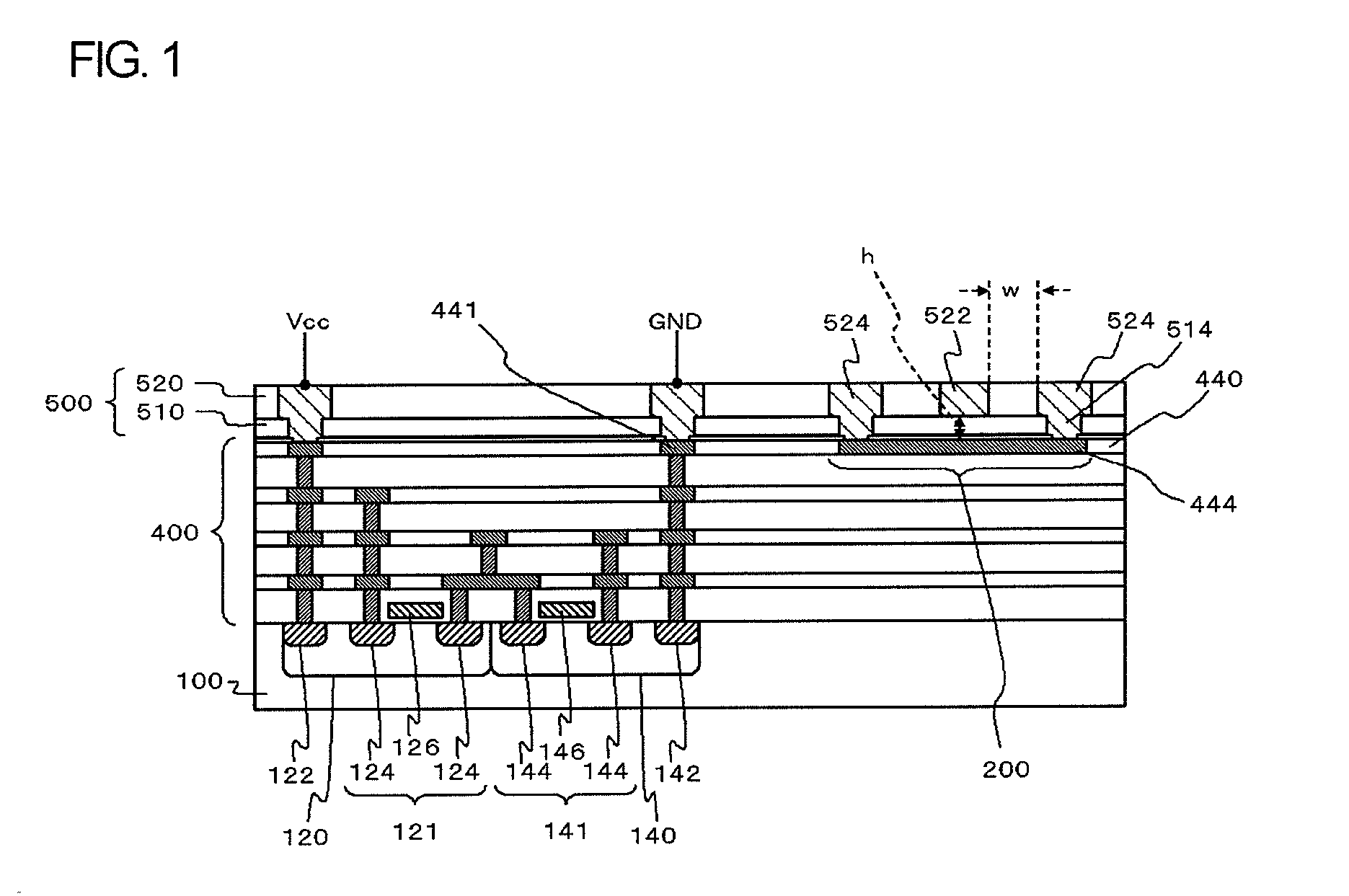
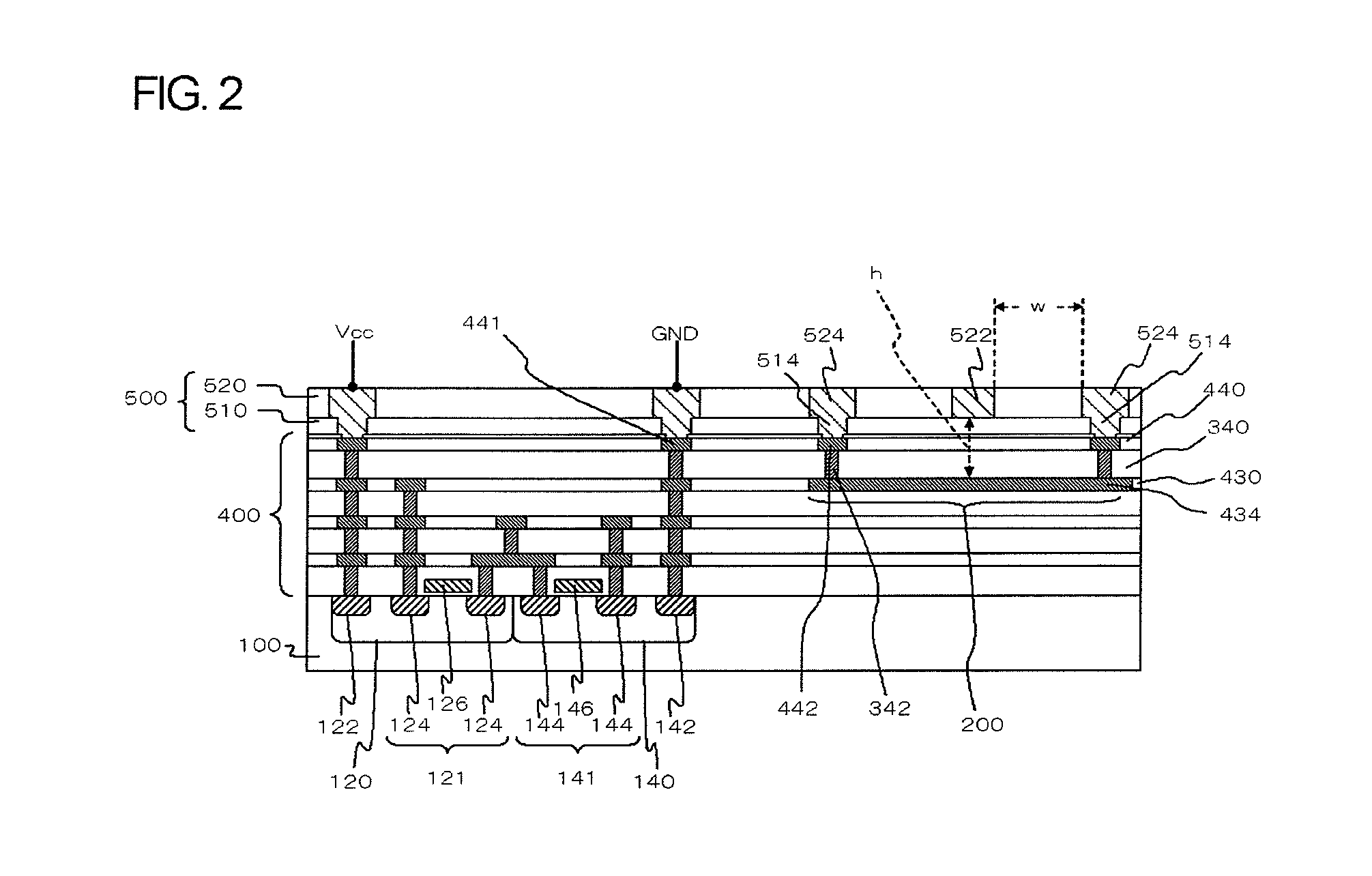
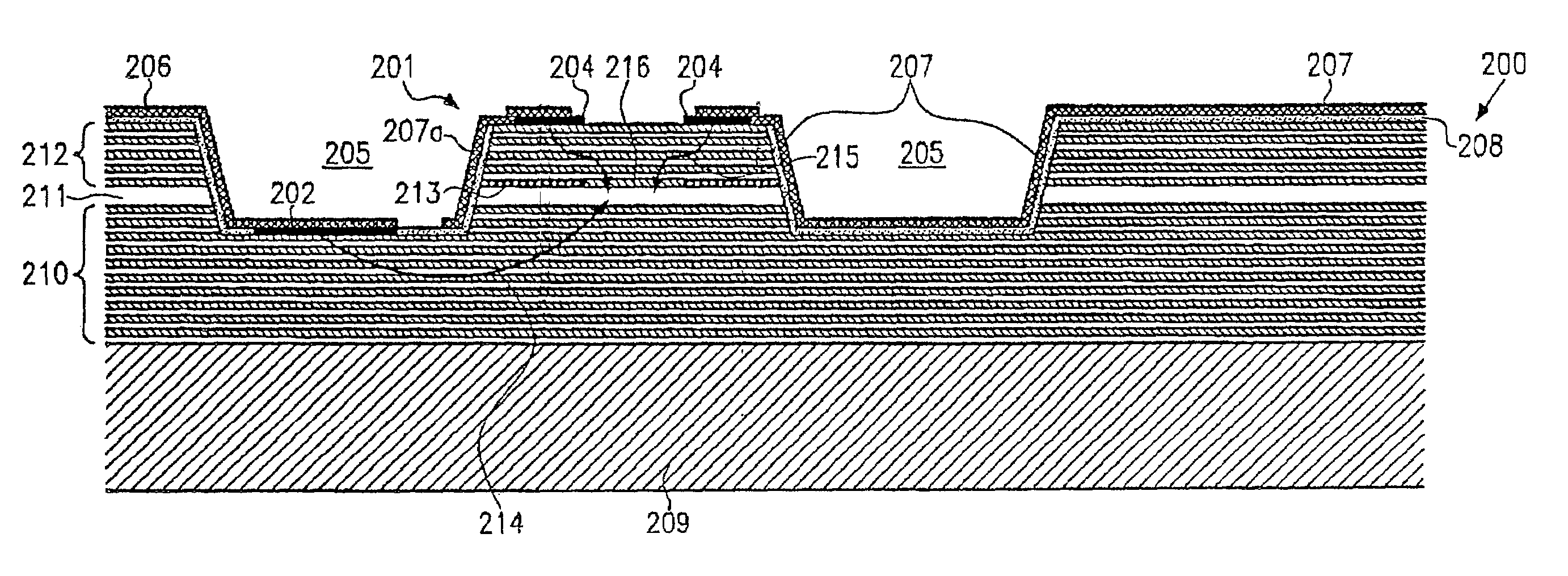
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120013019A1Suppress characteristicDeteriorating transmission characteristic of transmission lineSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRedistribution layerDevice material
A signal line is formed in the a-th layer (a≧2) of a multi-layered interconnect layer and a redistribution layer. A plain line is formed in the b-th layer (b<a) of the multi-layered interconnect layer and the redistribution layer and overlaps with the signal line when seen in a plan view. Two coplanar lines that are formed in the c-th layer (b≦c≦a) of the multi-layered interconnect layer and the redistribution layer, extend in parallel to the signal line when seen in a plan view, and interpose the signal line therebetween. A distance h from the signal line to the plain line is smaller than a distance w from the signal line to the coplanar lines. A power supply line, a ground line, and another signal line are not located within the range of the height equal to the distance w from the signal line above the signal line.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Variable capacitance element
InactiveUS20050052821A1Guaranteed uptimeImprove vibration resistanceMechanically variable capacitor detailsElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysCapacitanceCoplanar lines
A variable capacitance element includes a coplanar line or signal conduction and a movable body, which are vertically displaced through a supporting bar and which are provided on a substrate. A movable electrode is provided between a first driving electrode and second and third driving electrodes which are movable electrodes. Voltage is applied between the movable electrodes, such that one of the movable electrodes is pressed against the coplanar line through a dielectric film. Thus, high frequency signals conducting through the coplanar line are shut off. When voltage is applied between the other electrodes, the movable electrode and the dielectric film are moved apart from the coplanar line. Thus, high frequency signals are conducted through the coplanar line.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Optical module
ActiveUS8437583B2Decrease productivityDeterioration of characteristicCross-talk/noise/interference reductionHigh frequency circuit adaptationsEngineeringElectromagnetic field
Owner:LUMENTUM JAPAN INC
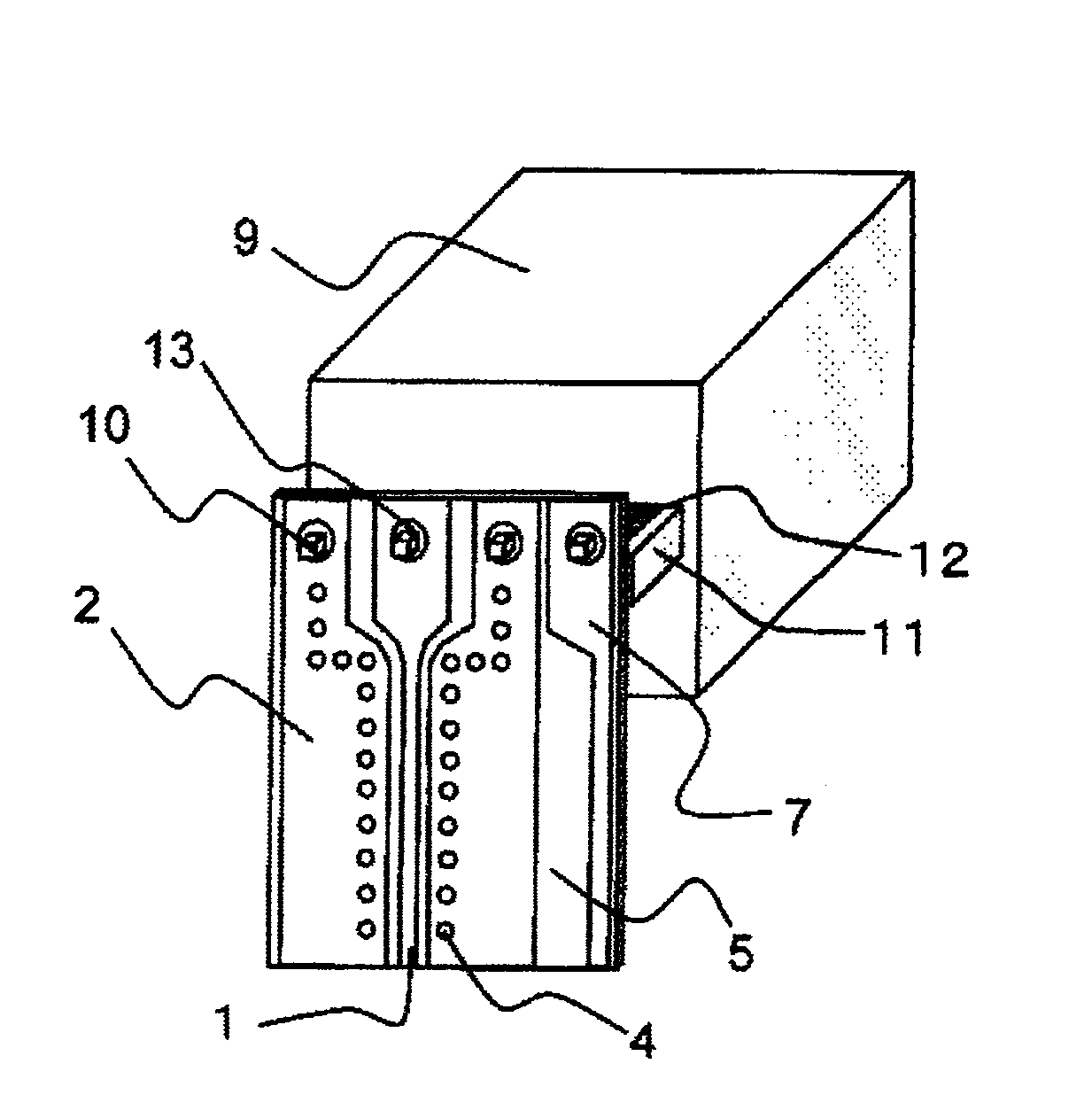
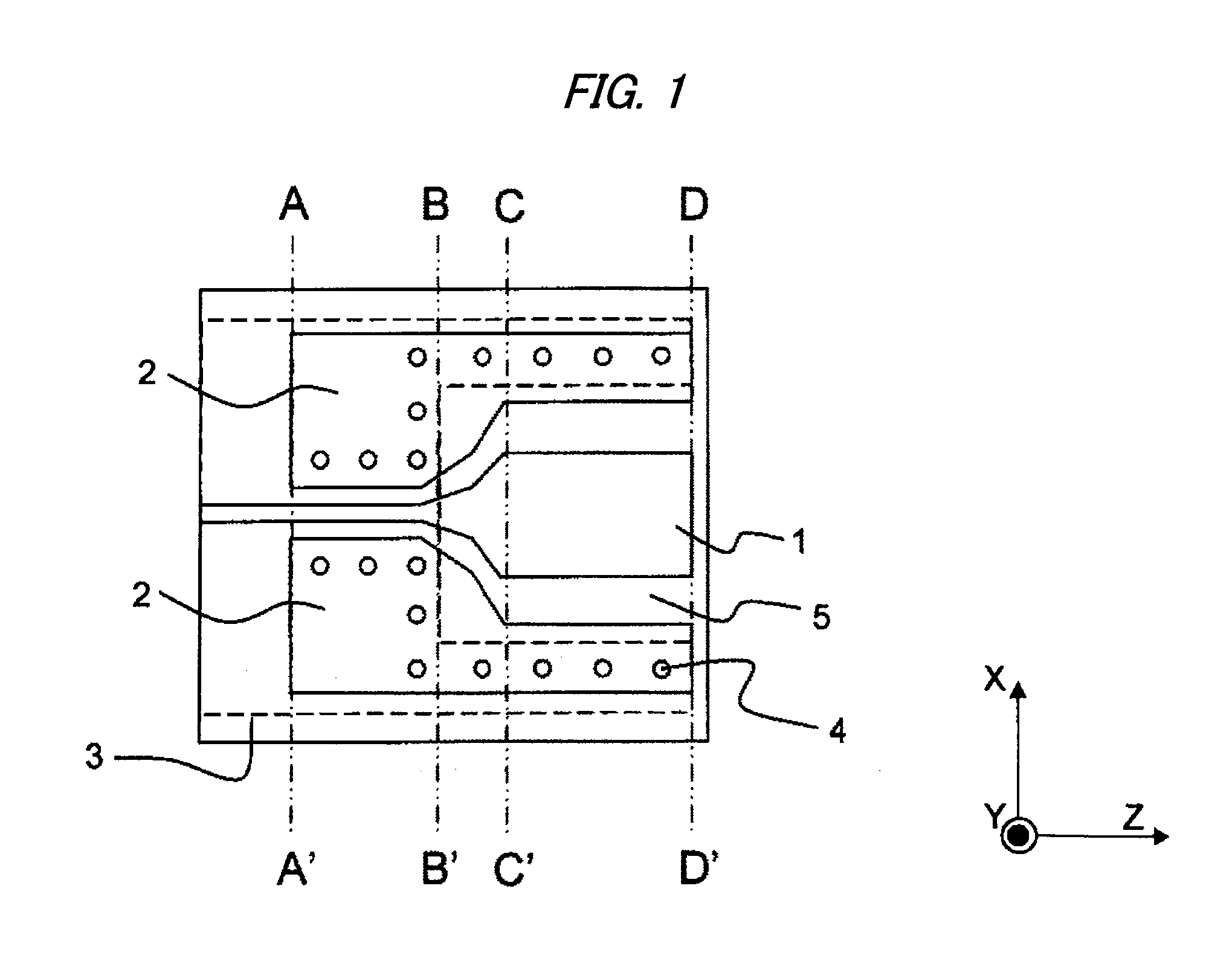
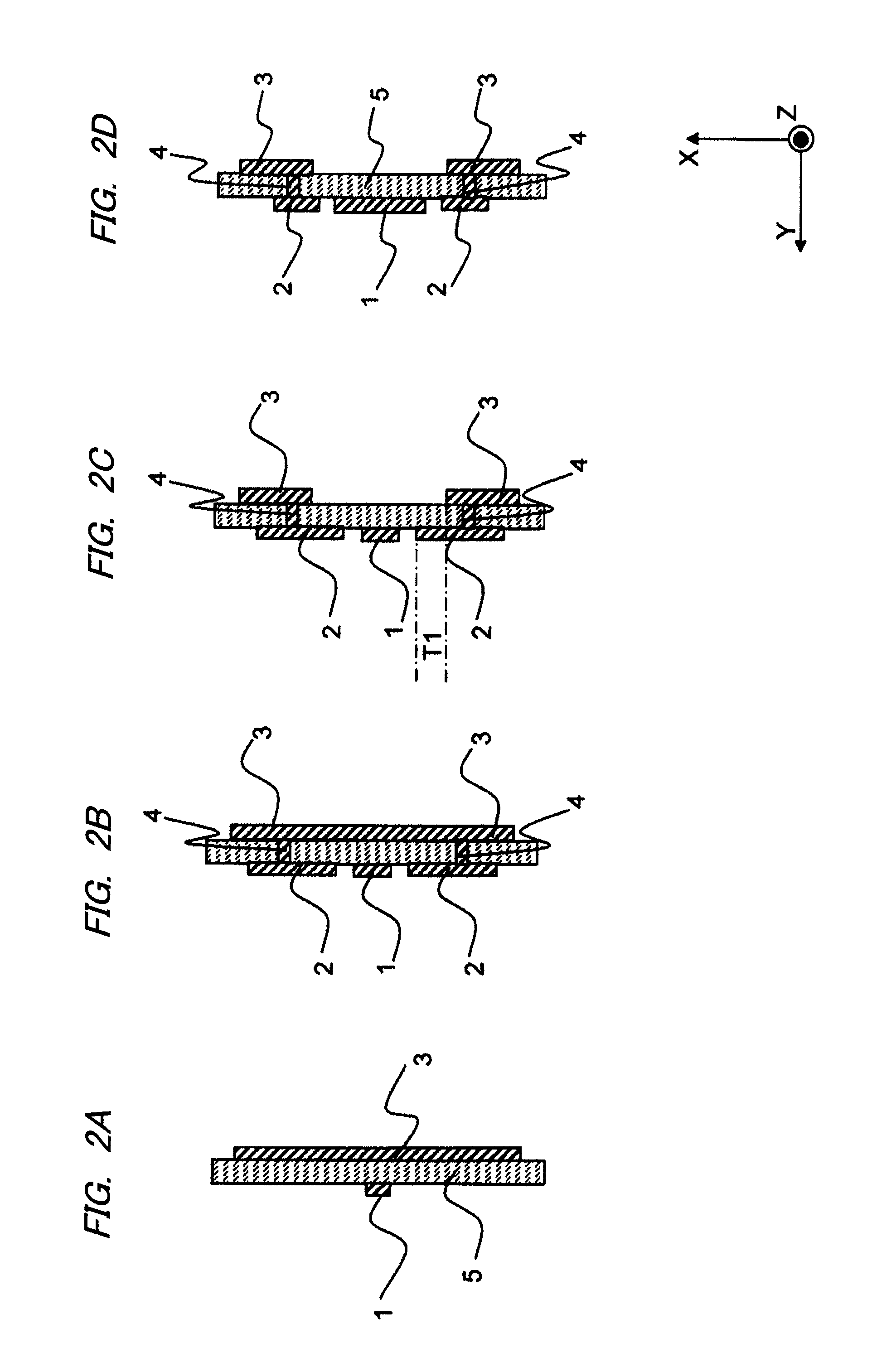
High-Frequency Wiring Board and High-Frequency Module That Uses the High-Frequency Wiring Board
InactiveUS20100254094A1Good reflective propertiesSolid-state devicesElectrical apparatus contructional detailsEngineeringGround pattern
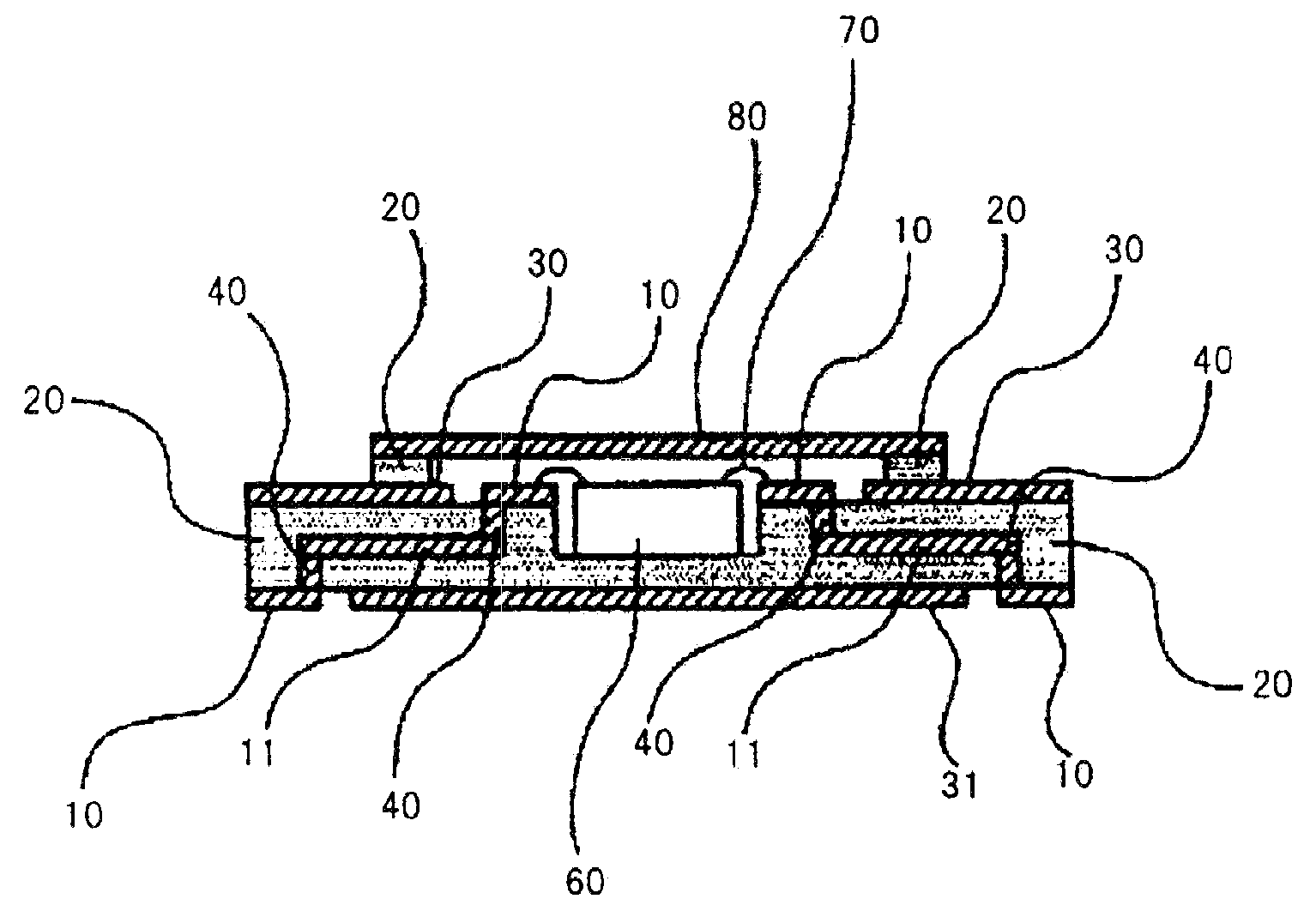
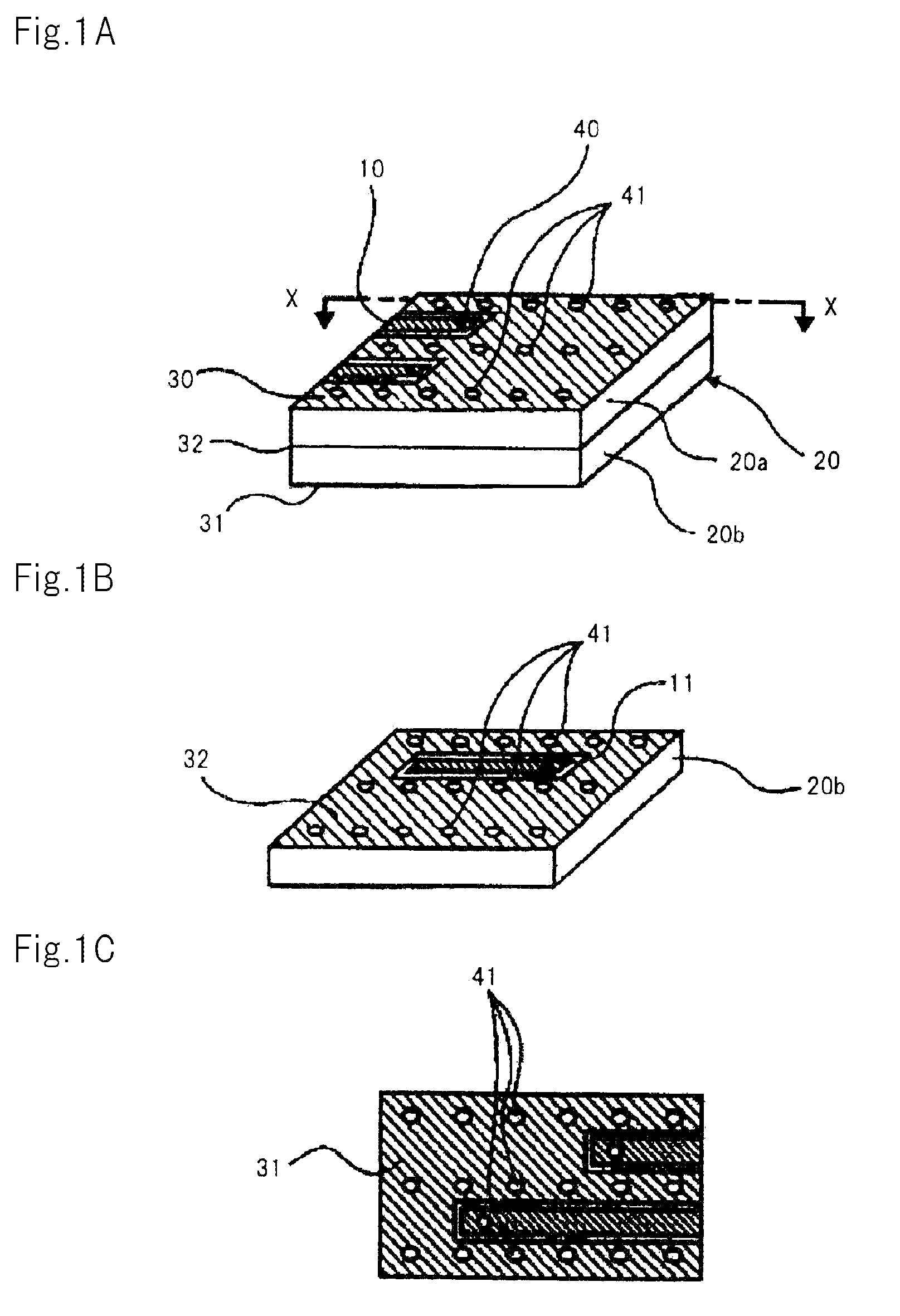
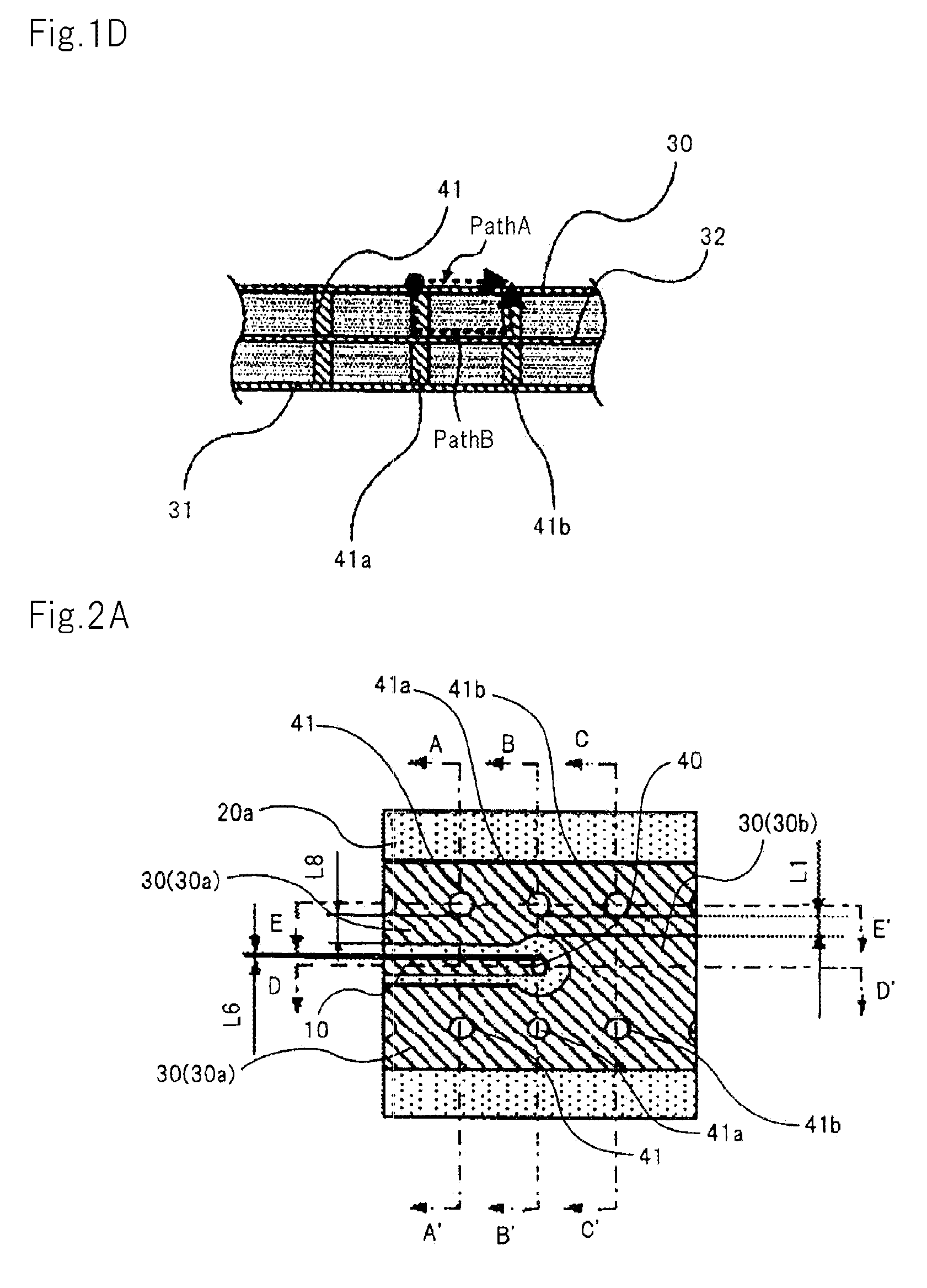
The high-frequency wiring board of the present invention is a wiring board that includes first coplanar lines and second coplanar lines formed on a different layer than the first coplanar lines; the first coplanar lines and second coplanar lines being connected at the line ends of each. The first coplanar lines are provided with a first signal line (10) and a first planar ground pattern (30a) formed on the same wiring layer as the first signal line (10). The second coplanar lines are provided with second signal line (11) formed on a wiring layer that differs from that of the first signal line (10), a second planar ground pattern 32 formed on the same wiring layer as the second signal line, and a first ground pattern (30b) formed on the same wiring layer as the first coplanar lines. The end of the first planar ground pattern (30a) and the end of the first ground pattern (30b) are connected and thus unified. In this high-frequency wiring board, the second planar ground pattern (32) is separated from the connection portion at the end of the first planar ground pattern (30a) in the direction in which the second coplanar lines extend from the vicinity of the connection portion of the first signal line and the second signal line.
Owner:NEC CORP
Device for connecting a coaxial line to a coplanar line
InactiveUS20060284699A1Increase distanceImprove featuresMultiple-port networksTwo pole connectionsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
The coaxial line comprises a coaxial inner conductor and a first dielectric layer encompassing the coaxial inner conductor and which is surrounded by a coaxial outer conductor. The coplanar line comprises a second dielectric layer with a coplanar inner conductor and a first and second coplanar outer conductor applied to the front side thereof and with a metallization layer followed by a substrate carrier layer on the rear side thereof. The first and second coplanar outer conductors are separated from the coplanar inner conductor by the second dielectric layer and the coaxial inner conductor is connected to the coplanar inner conductor and the coaxial outer conductor is connected to the first and second coplanar outer conductors. When high bit rate data signals are transmitted via the connecting point of the coaxial line and the coplanar line, the capacitative power is increased and undesirable reflections occur. In order to avoid this, a recess is provided in the metallization layer, beginning at the point of connection between the coaxial line and the coplanar line and extending in an approximately symmetrical manner with respect to the coplanar inner conductor, tapering in the direction of the coplanar inner conductor as the distance from the point of connection increases.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
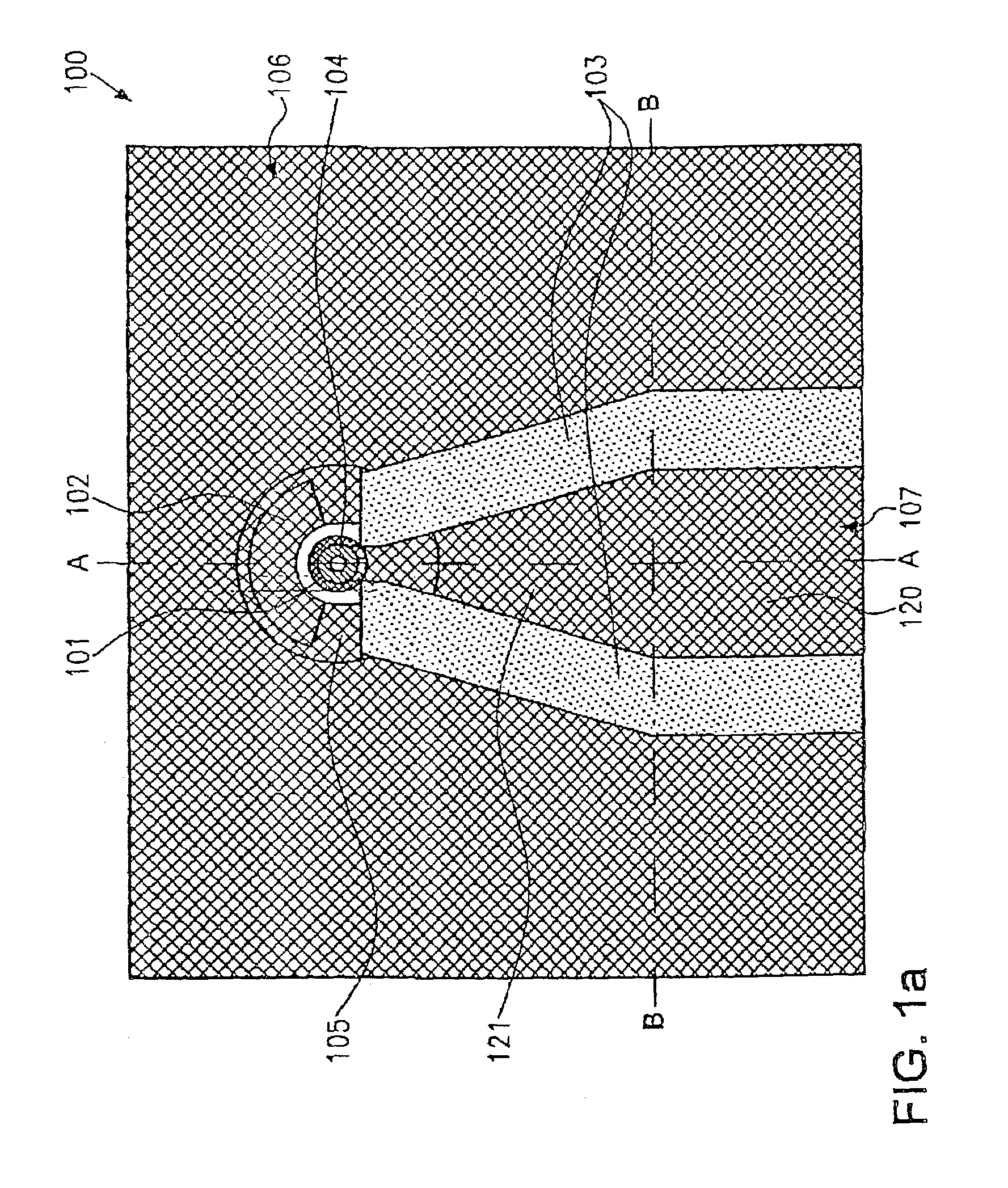
High-Frequency Coupler, Rf Guide, and Antenna
InactiveUS20080024241A1Improve transmission characteristicsOne-port networksTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsCapacitanceCoupling
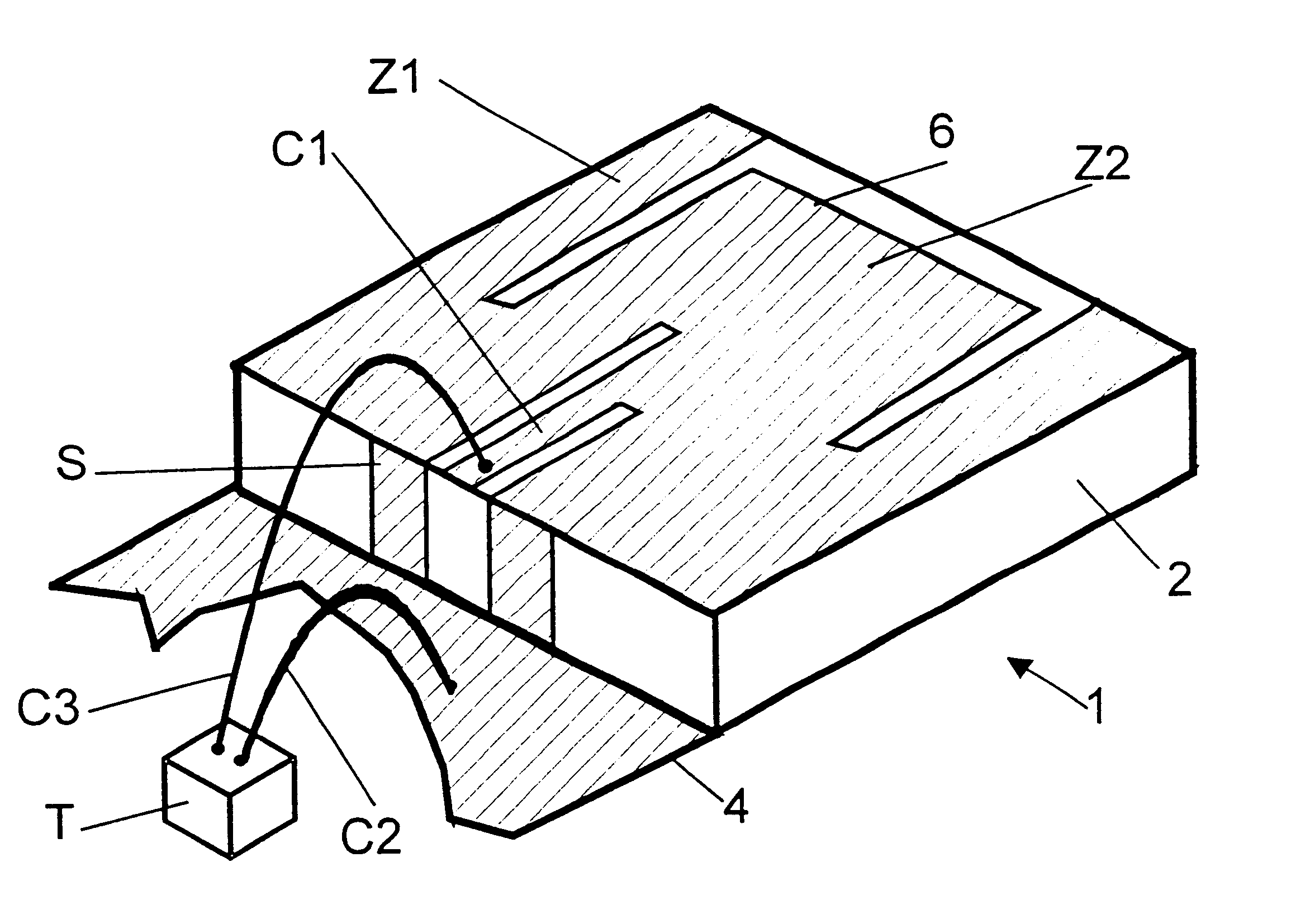
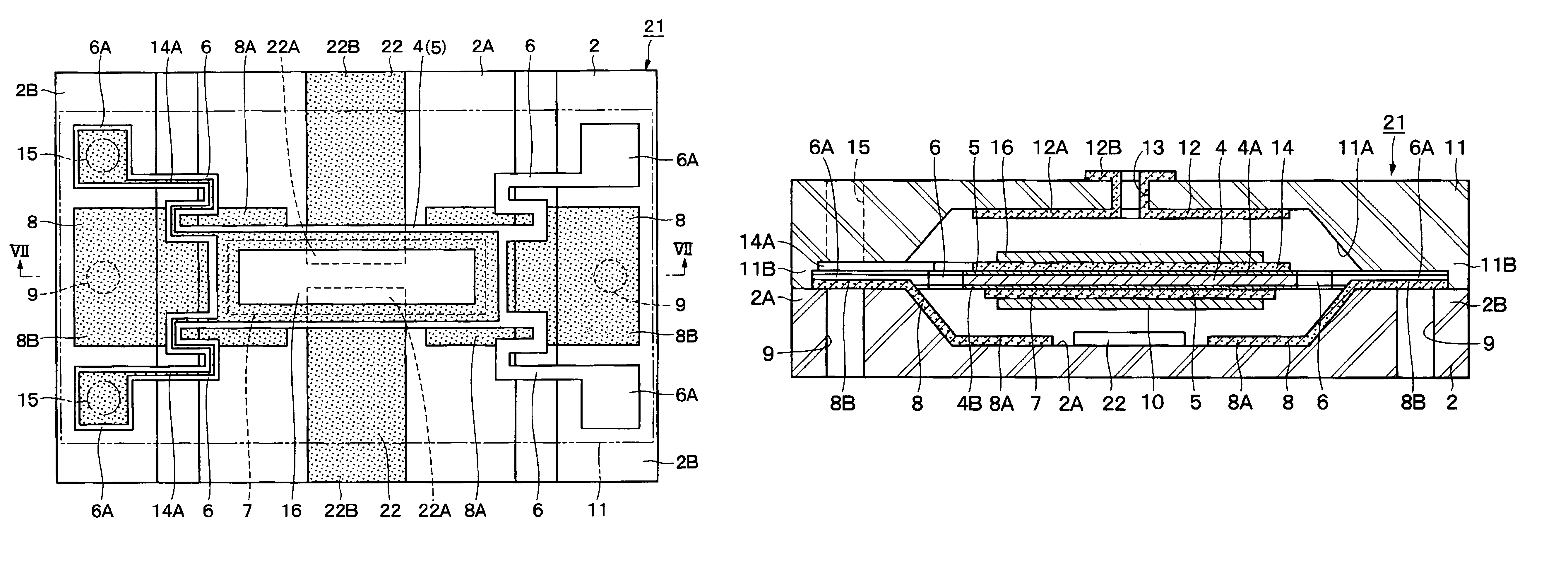
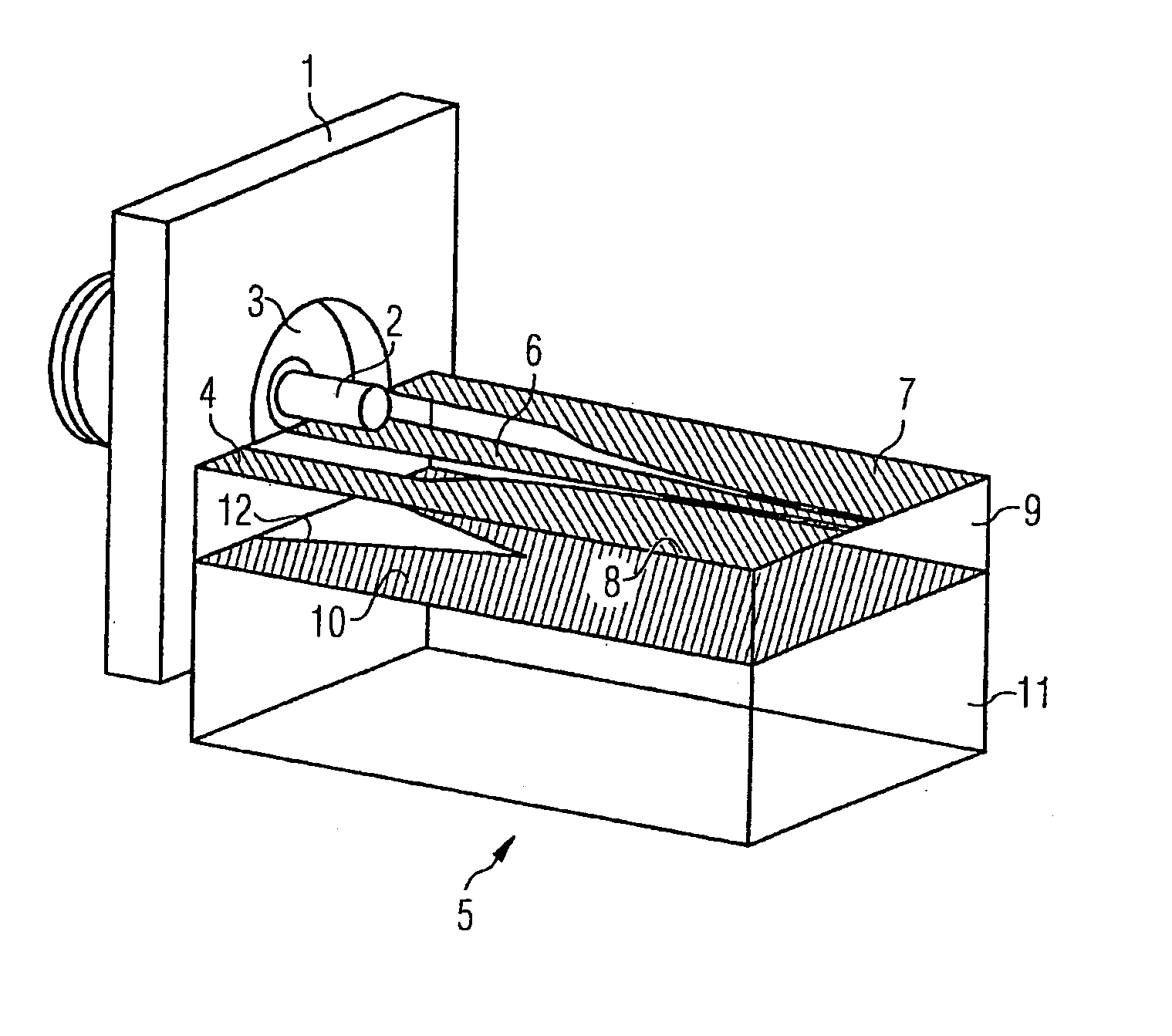
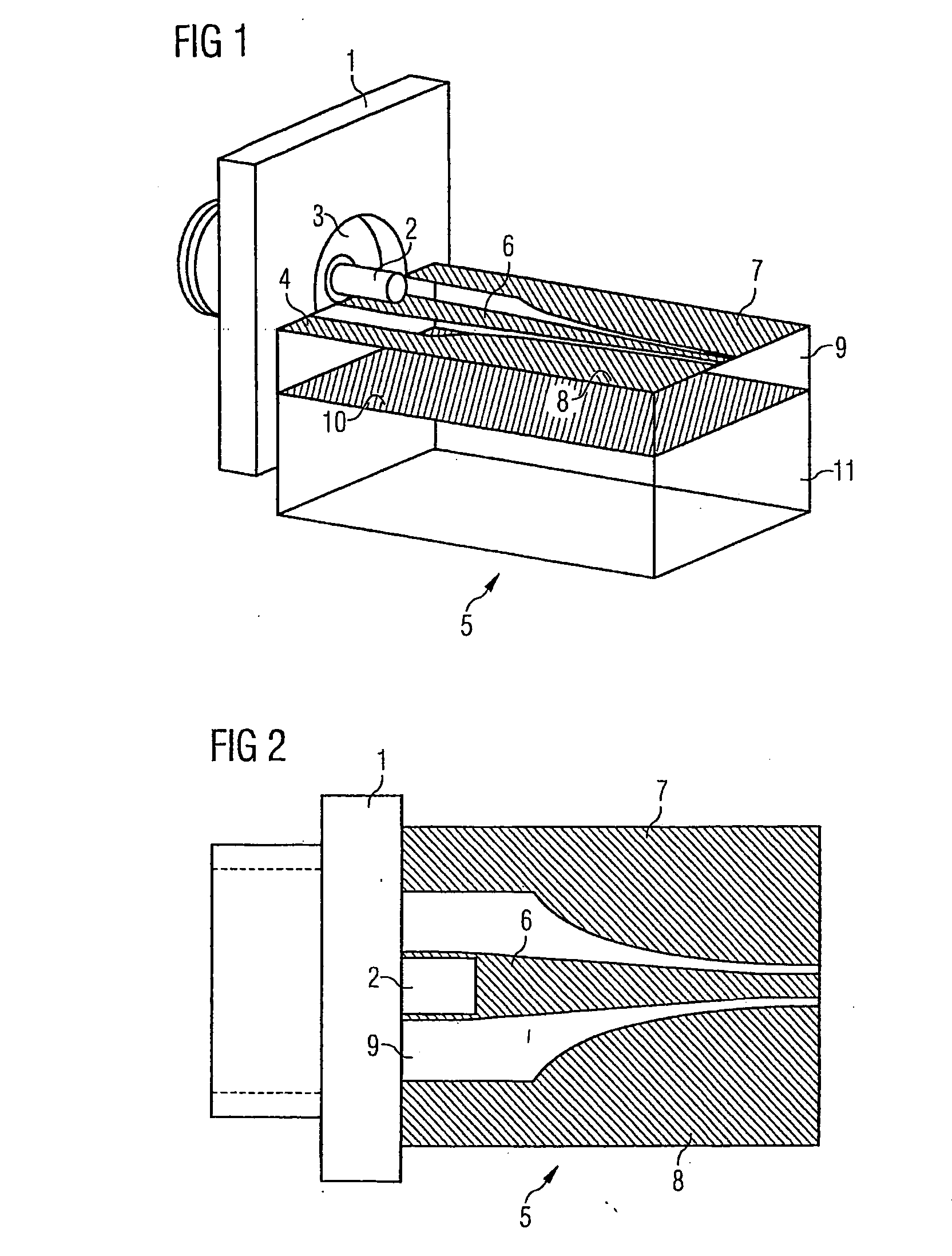
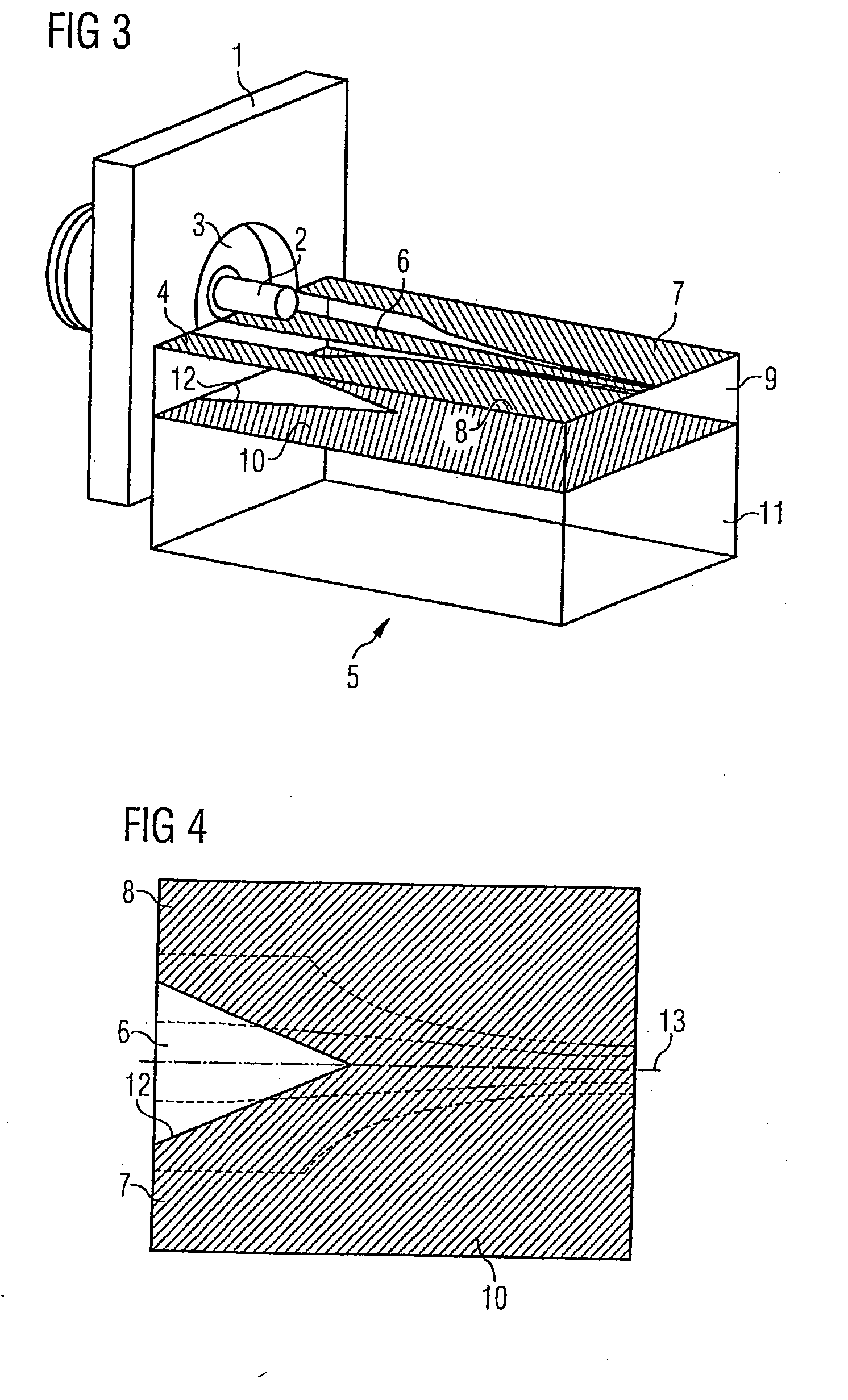
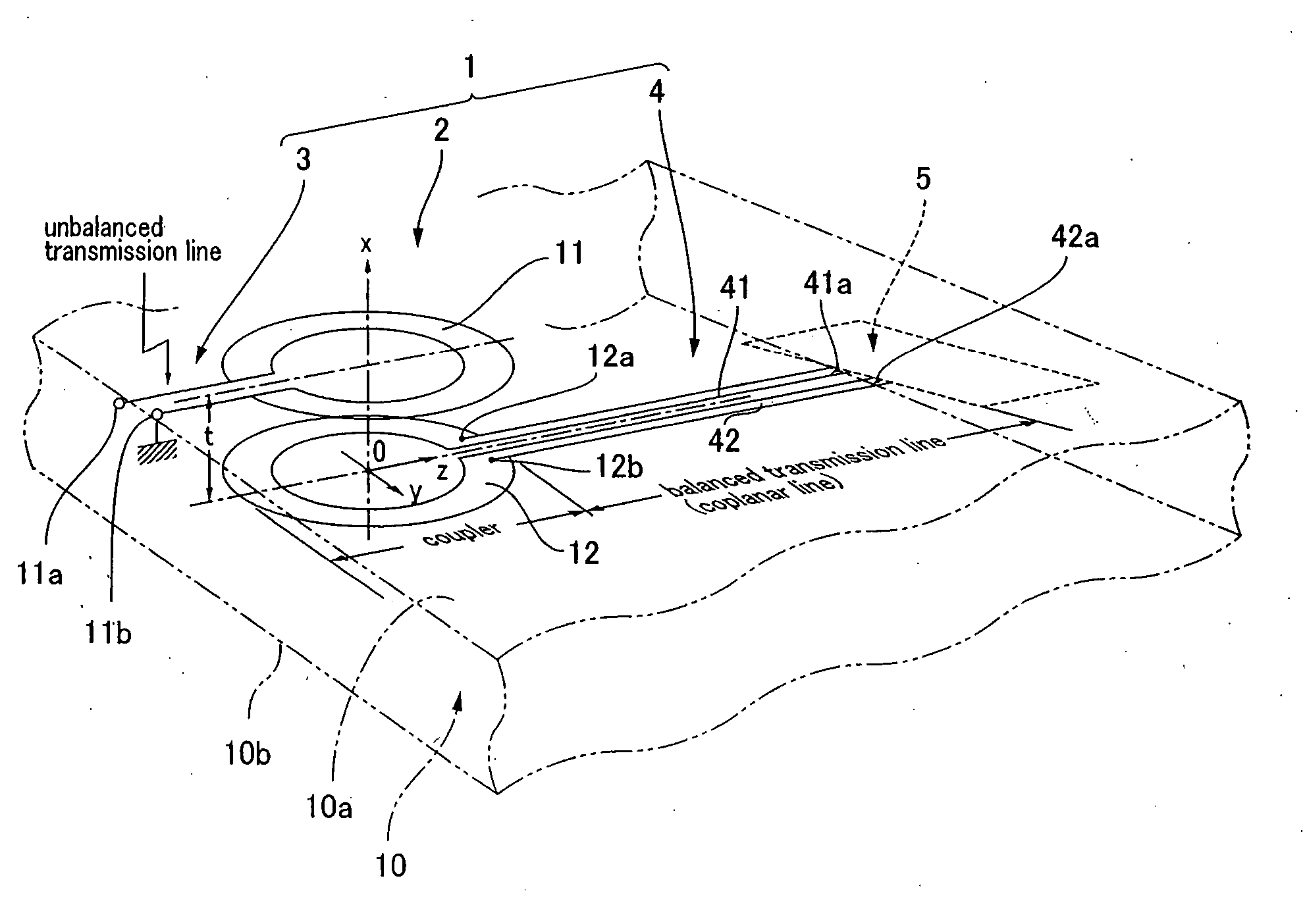
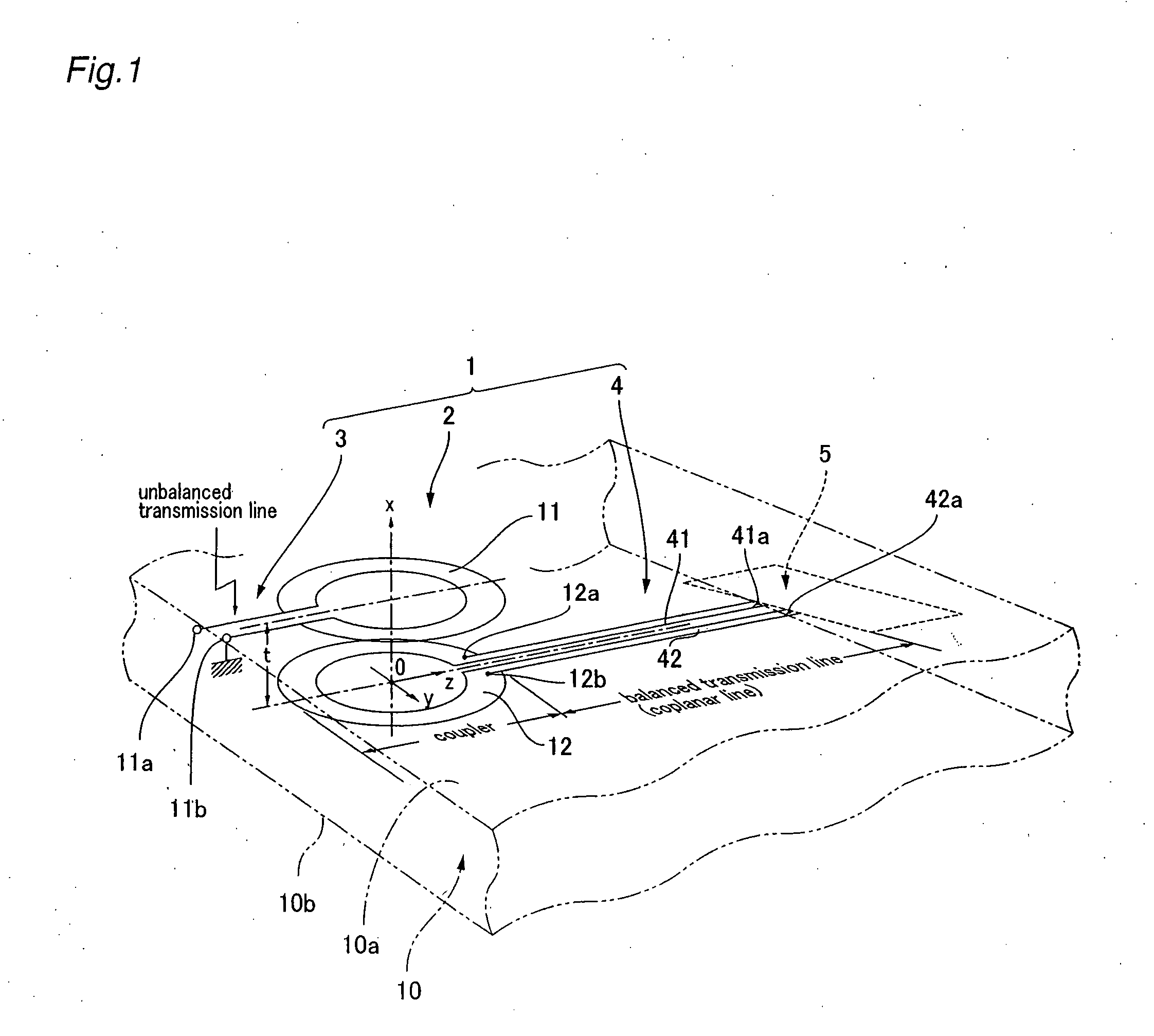
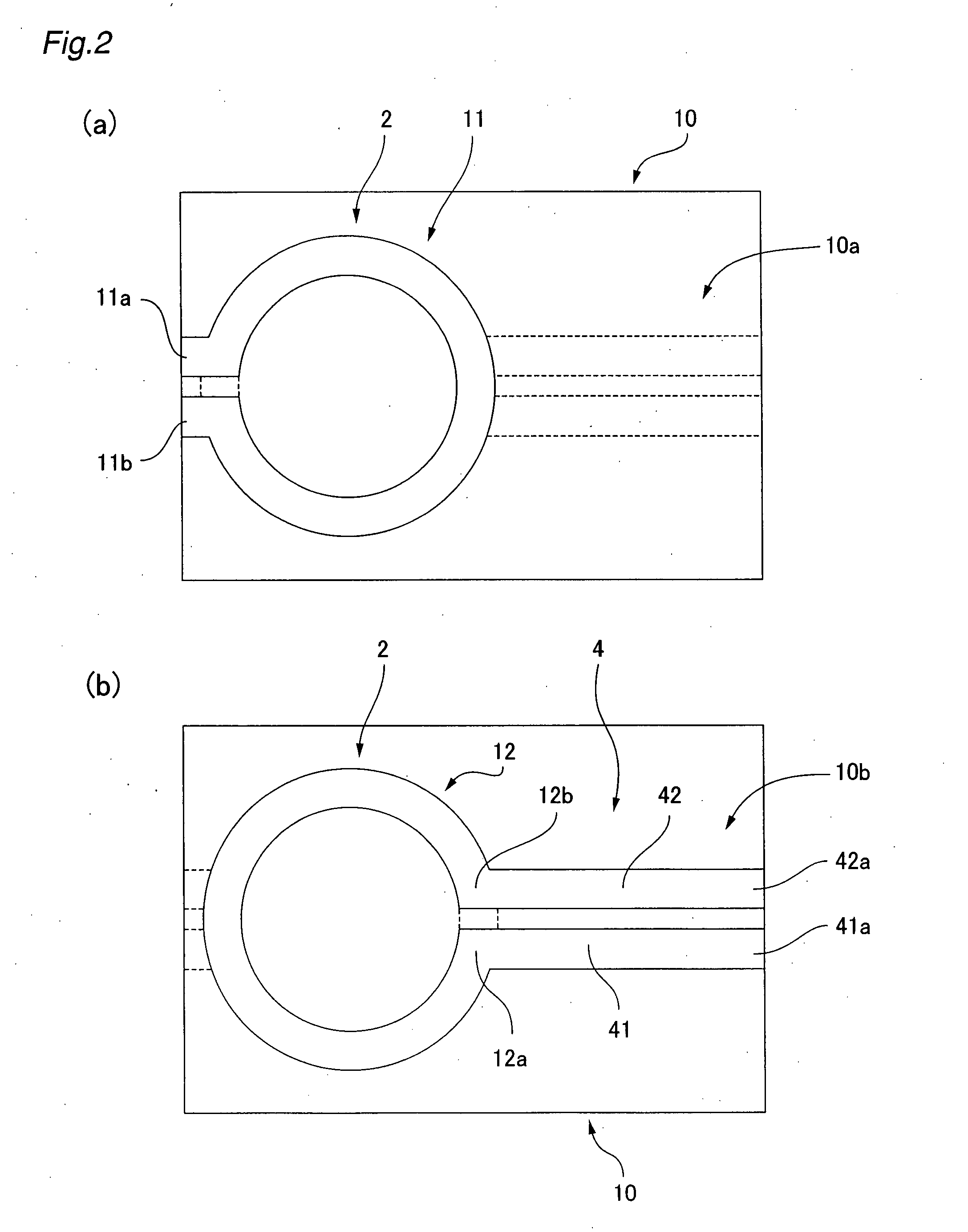
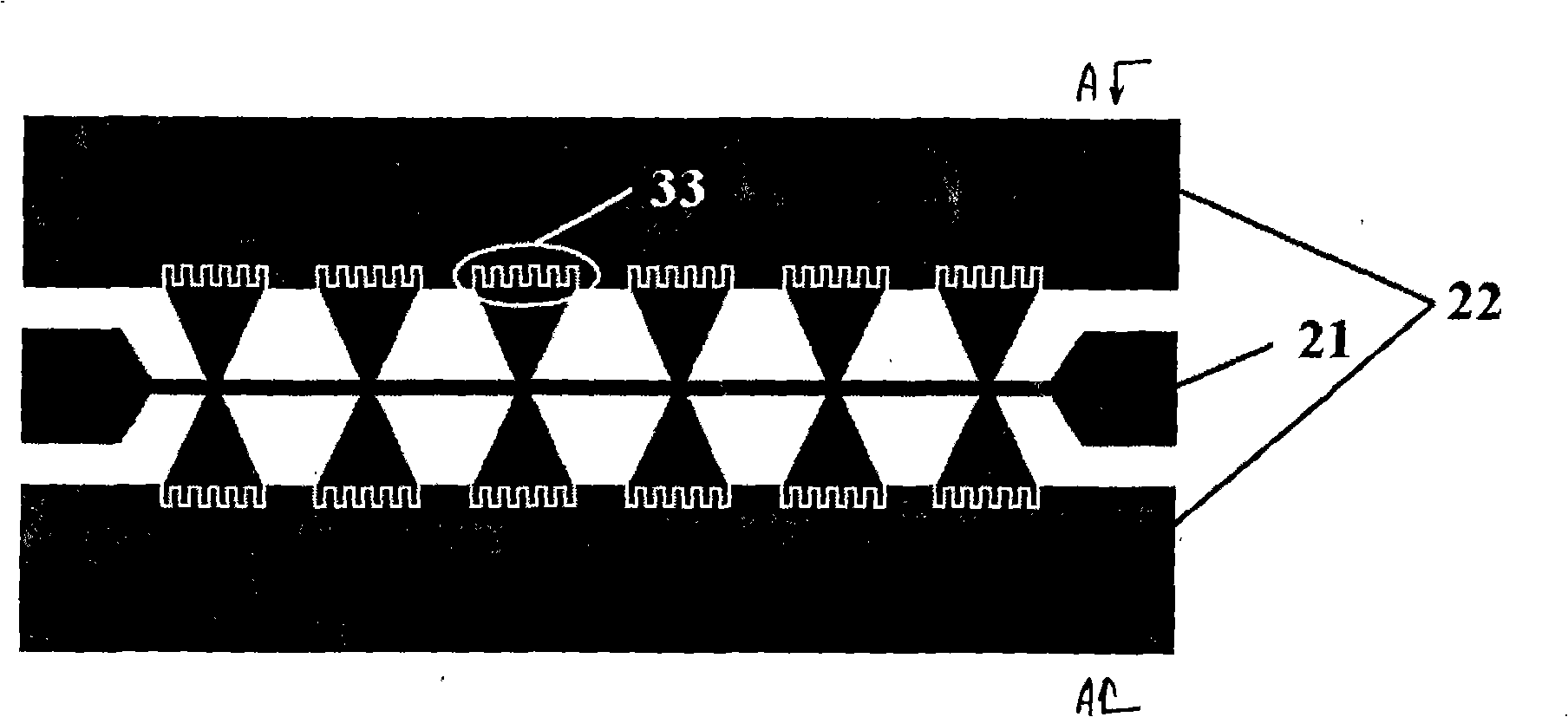
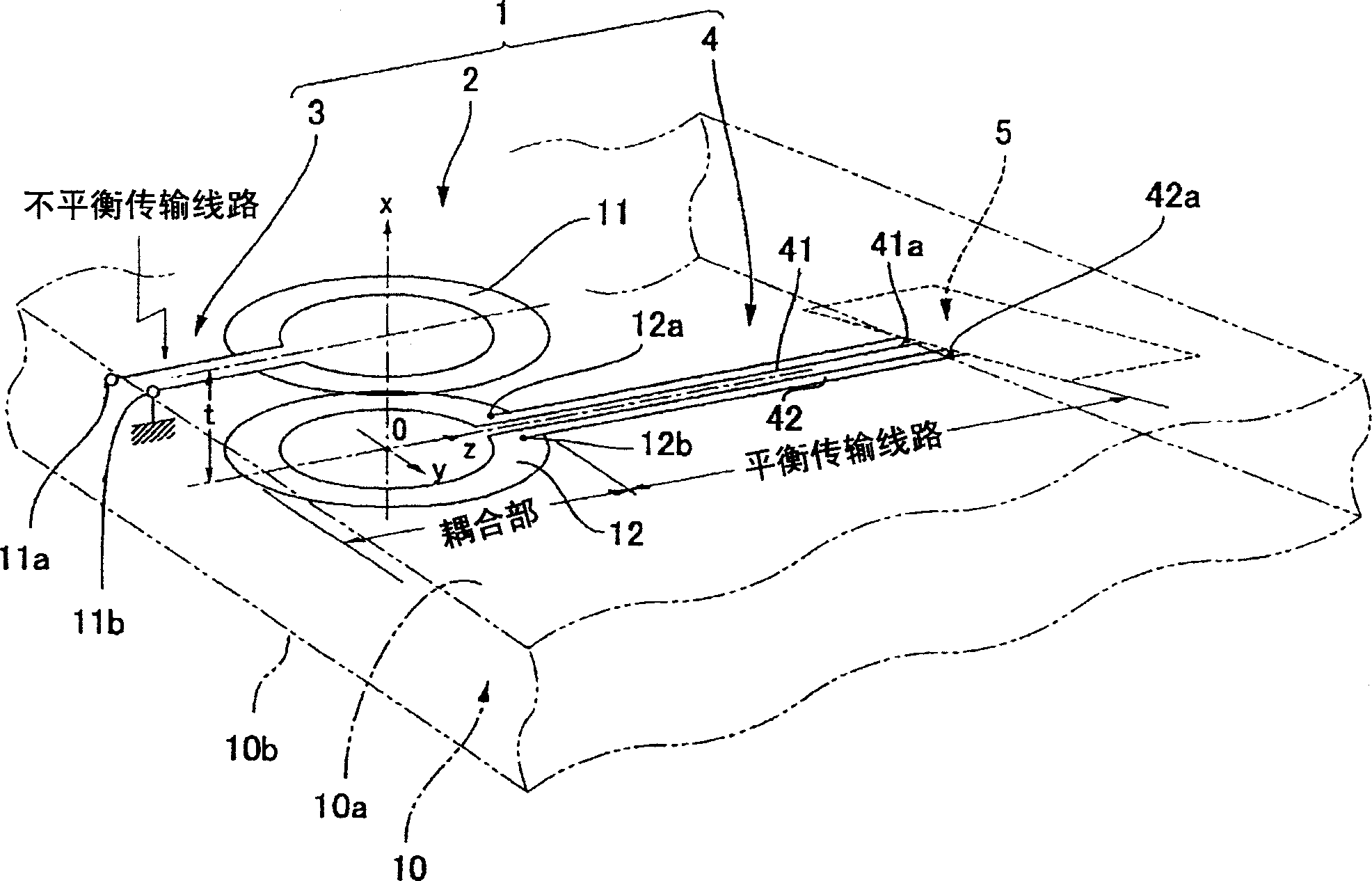
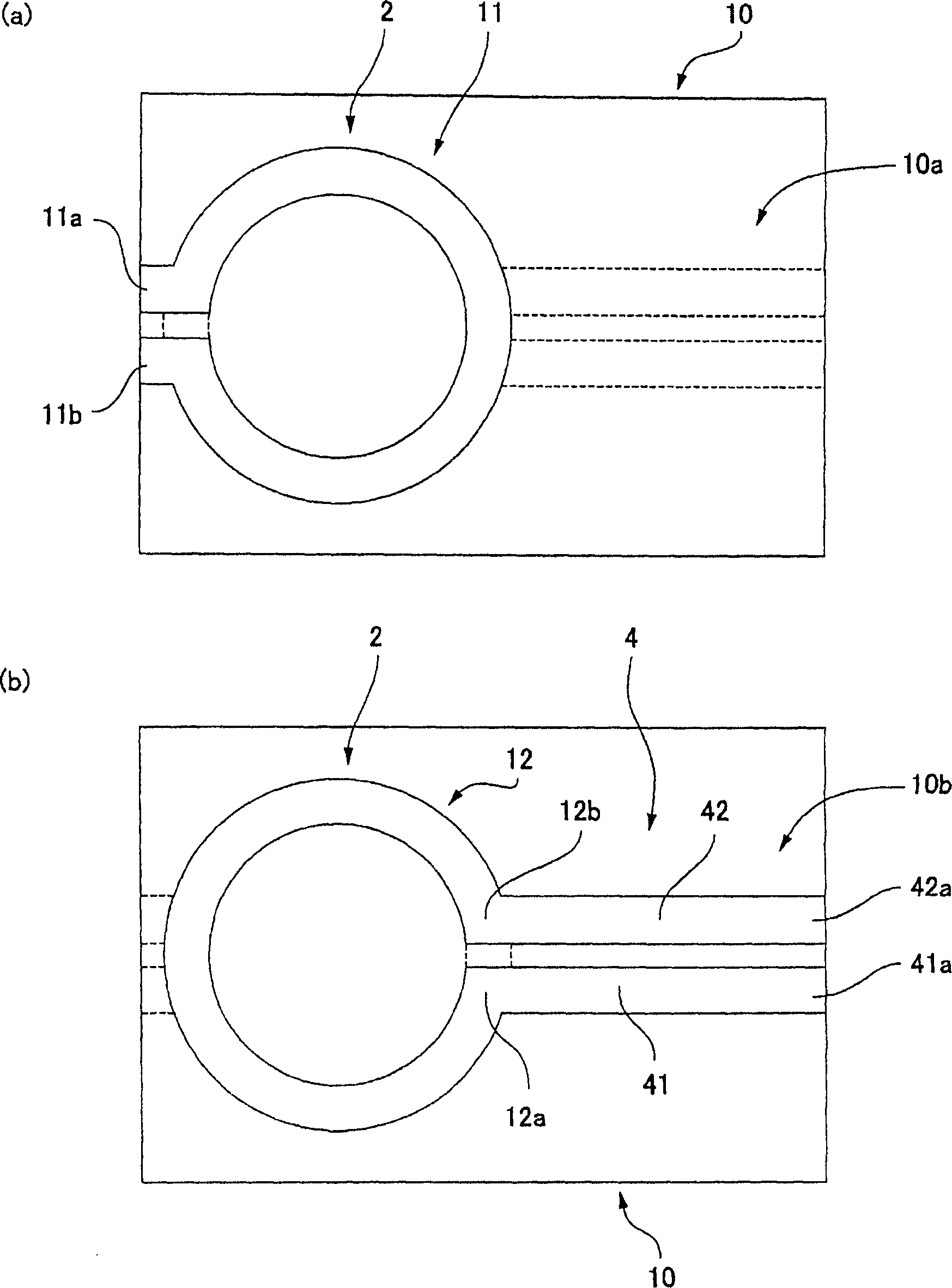
A high frequency coupler (2) comprising first and second coupler patterns (11, 12) each having an annular shape broken at one location and formed, facing each other, on the front and rear surfaces of a circuit board (10) consisting of a dielectric and being t thick. The terminals (11a, 11b) of the first coupler pattern (11) serve as unbalanced terminals, and the terminals (12a, 12b) of the second coupler pattern (12) serve as unbalanced terminals from which coplanar lines (41, 42) are led out along the rear surface and connected with a balanced antenna (5). Since the first and second coupler patterns (11, 12) are kept in an electrostatic capacity coupling state as well as in a magnetic induction coupling state, the coupler high in transmission efficiency in a broad band can be realized.
Owner:HATA HIROSHI +1
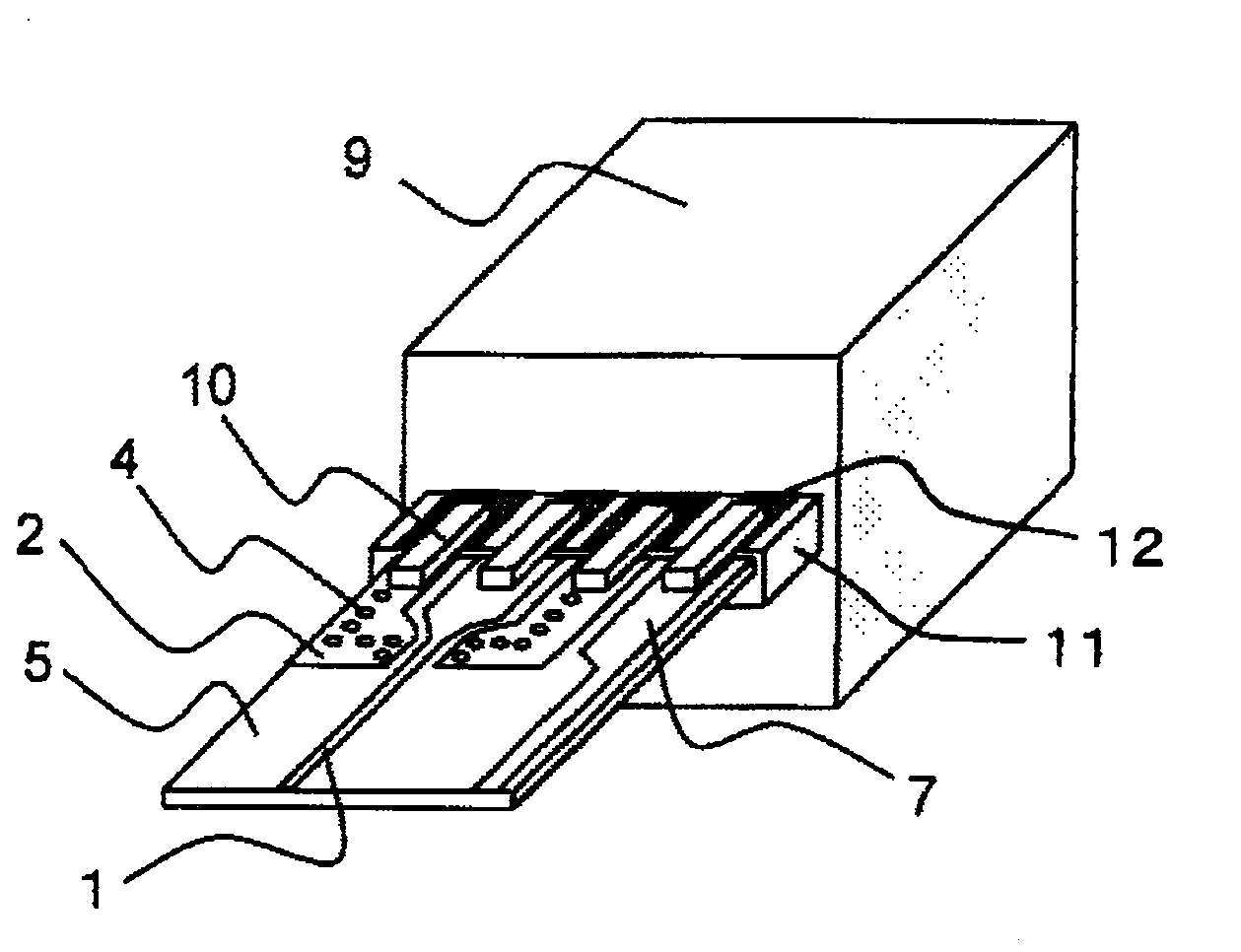
High-frequency transmission line and an optical module incorporating the same line
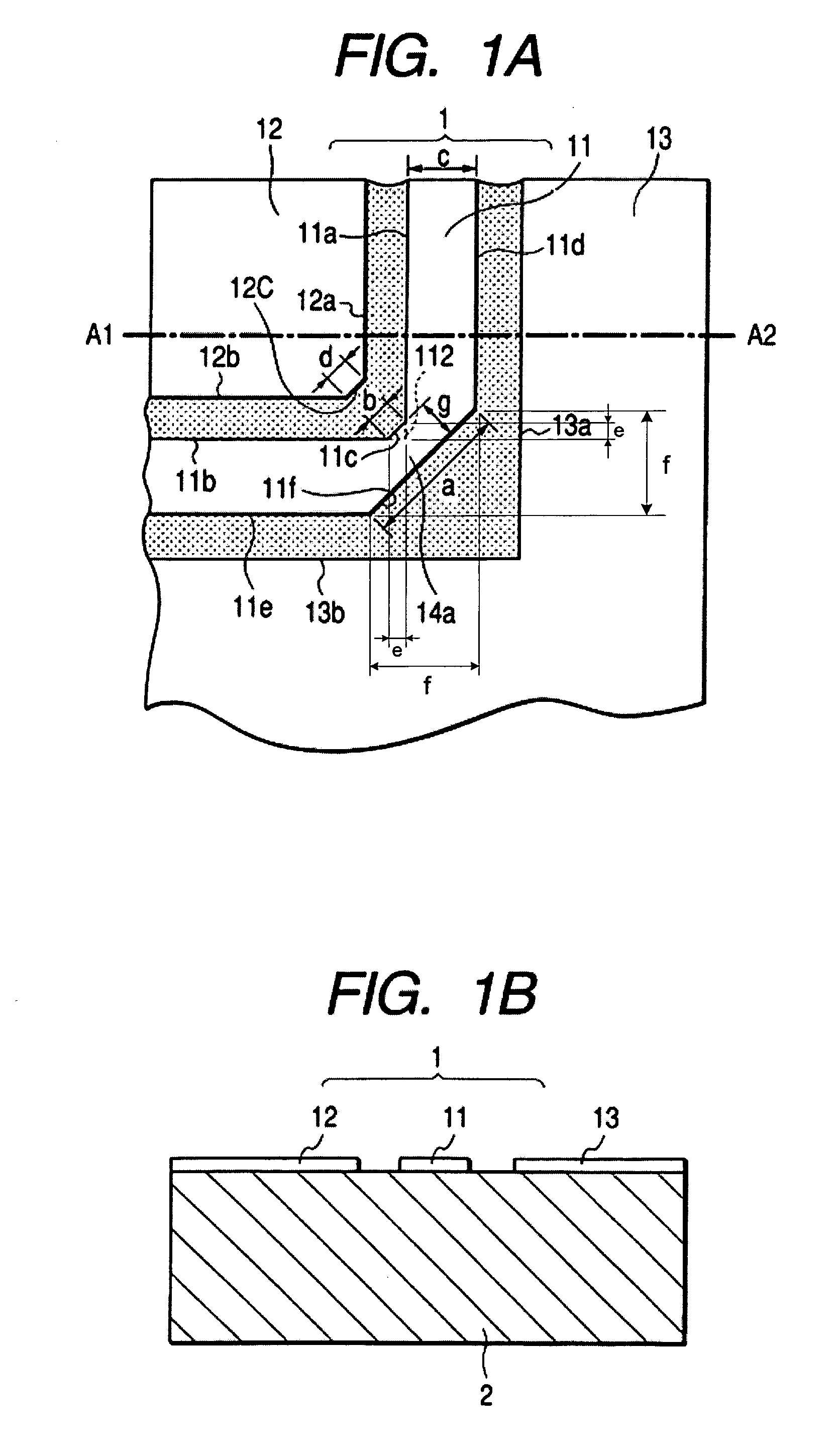
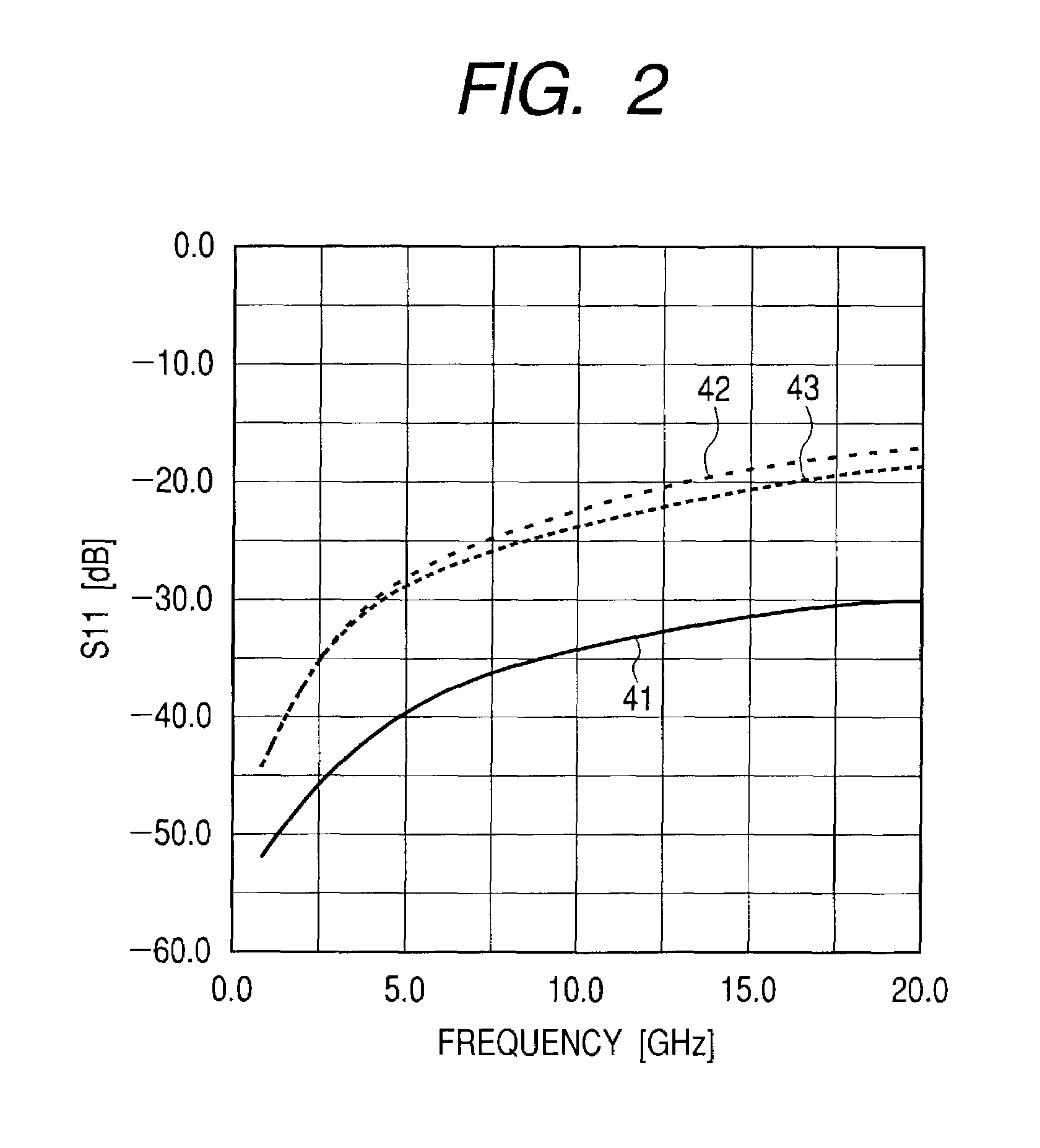
ActiveUS7177549B2Increase reflection lossLarge componentLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmittersReflection lossElectrical conductor
A transmission line with a bending portion is provided, which line comprises any one of a coplanar line, another coplanar waveguide line formed on the dielectric substrate under which a ground layer is provided and a coplanar strip line. A chamfered portion is provided on the outer angular portion of the bending portion of the signal wiring conductor and a triangular conductor is disposed to an inner angular portion thereof. Given that length of the chamfered portion is defined as a, and length of the wiring edge side of the triangular conductor is defined as b and width of the signal wiring conductor is defined as c, it is arranged such that a is greater than b+c×square root of 2. Thereby, a transmission line or an optical module of smaller reflection loss at the bending portion thereof and of improved high-frequency characteristics is provided.
Owner:LUMENTUM JAPAN INC
Multielement planar antenna
InactiveUS6917332B2Simple designLength minimizationParticular array feeding systemsSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrical conductorEngineering
A multielement planar antenna has a substrate, a plurality of antenna element pairs disposed on a first main surface of said substrate, each of the antenna element pairs including first and second antenna elements each made of a circuit conductor, a metal conductor disposed on a second main surface of the substrate, and a slot line defined in the metal conductor. Each of the antenna element pairs has a microstrip line interconnecting the first and second antenna elements. The slot line crosses the microstrip lines and is electromagnetically coupled to the microstrip lines for feeding the first and second antenna elements. The slot line is fed at its central area by a microstrip line or a coplanar line.
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD +1
Transmission line, integrated circuit, and transmitter receiver
InactiveUS20020175784A1Prevent leakageTransmitted signalWaveguidesCoupling devicesDielectric substrateEngineering
In a transmission line, protrusions extend in line one after another in a direction perpendicular to the cross section in a part of a dielectric substrate, with a discontinuous portion therebetween. A lower-surface electrode is formed on a main surface of the dielectric substrate provided with the protrusions and on the outer surfaces of the protrusions. An upper-surface electrode is formed on substantially the whole area of the surface opposite to the lower-surface electrode. Further, a plurality of through-holes for connecting the lower-surface electrode and the upper-surface electrode, which are formed on both surfaces of the dielectric substrate, are aligned on both sides of the protrusions along the direction in which the protrusions extend. Also, coplanar lines and a circuit element are mounted on the upper-surface electrode. The coplanar lines are coupled at a predetermined position to a transmission path formed by the protrusions.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
High speed vertical cavity surface emitting laser device (VCSEL) with low parasitic capacitance
ActiveUS7061956B2Reduced electrical parasiticsReliable fabricationLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserParasitic capacitance
A design of a vertical cavity surface emitting laser chip suitable for high speed data communication. An intracavity contact to the doped layers of the bottom mirror is formed so that both contacts are on the top epitaxial side of the wafer. These main structural features can be used to reduce the bond pad capacitance by a suitable spatial separation of metallizations of the p and n contact. The bond pads are processed as a short symmetric coplanar line in a ground signal ground configuration which allows flexible device testing and packaging. A significant capacitance between the pads of the center strip and the outer ground strips is avoided by etching the doped semiconductor layers between these strips down to the semi-insulating substrate. This design avoids pad metallizations and the corresponding critical photolithographic steps over large height differences from the vertical cavity surface emitting laser mesa top to the substrate. This insures good lithographic fidelity and makes the process reproducible.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Transmission line, integrated circuit, and transmitter receiver
InactiveUS6614332B2Prevent leakageTransmitted signalWaveguidesCoupling devicesDielectric substrateEngineering
In a transmission line, protrusions extend in line one after another in a direction perpendicular to the cross section in a part of a dielectric substrate, with a discontinuous portion therebetween. A lower-surface electrode is formed on a main surface of the dielectric substrate provided with the protrusions and on the outer surfaces of the protrusions. An upper-surface electrode is formed on substantially the whole area of the surface opposite to the lower-surface electrode. Further, a plurality of through-holes for connecting the lower-surface electrode and the upper-surface electrode, which are formed on both surfaces of the dielectric substrate, are aligned on both sides of the protrusions along the direction in which the protrusions extend. Also, coplanar lines and a circuit element are mounted on the upper-surface electrode. The coplanar lines are coupled at a predetermined position to a transmission path formed by the protrusions.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Ferroelectric thin-membrane phase shifter and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101335371ASimple preparation processImprove Modulation CapabilitiesWaveguide type devicesCapacitanceManufacturing technology
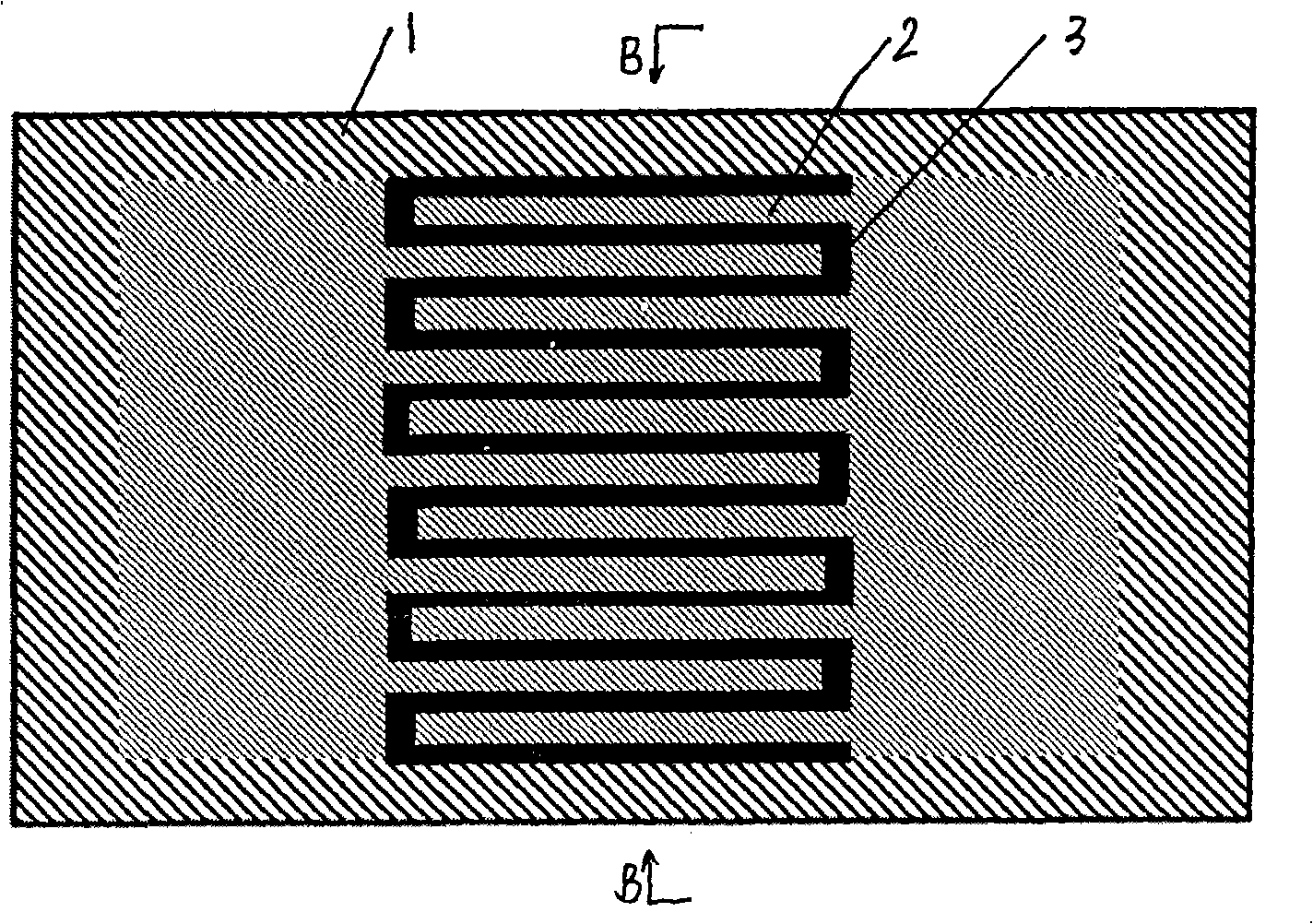
The invention relates to a ferro-electricity film phase shifter, pertaining to the field of microwave engineering technology, which comprises a coplanar line structure that comprises a transmission line constituted by a general conductive film and ground planes on both sides thereof. Aequilate slots are arranged between the ground planes and the transmission line, interdigited capacitor structures are arranged mutually and periodically on the transmission line and the ground planes on both sides thereof, the conductive film is directly fixed on to the substrate of an underlay, and ferro-electricity films are provided in the slots between the mutually interdigited transmission line and the ground planes. The intedigited capacitor structure of the invention places equal attention to advantages of simple manufacturing technology of a general intedigited capacitor and to that a parallel plate capacitor structure can highly concentrate impressed electric field into the ferro-electricity film, thus realizing the advantage of large phase shifting capacity under low voltage and having potential and broad practical prospect.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High frequency coupler, high frequency tansmitter and antenna
InactiveCN1914763AImprove transmission characteristicsImprove magnetic induction coupling stateCoupling devicesCouplingBroadband
The present invention provides a high frequency coupler(2) comprising first and second coupler patterns(11, 12) each having an annular shape broken at one location and formed, facing each other, on the front and rear surfaces of a circuit board(10) consisting of a dielectric and being t thick. The terminals(11a, 11b) of the first coupler pattern(11) serve as unbalanced terminals, and the terminals(12a, 12b) of the second coupler pattern(12) serve as unbalanced terminals from which coplanar lines(41, 42) are led out along the rear surface and connected with a balanced antenna(5). Since the first and second coupler patterns(11, 12) are kept in an electrostatic capacity coupling state as well as in a magnetic induction coupling state, the coupler high in transmission efficiency in a broad band can be realized.
Owner:樋口 俊昭 +2
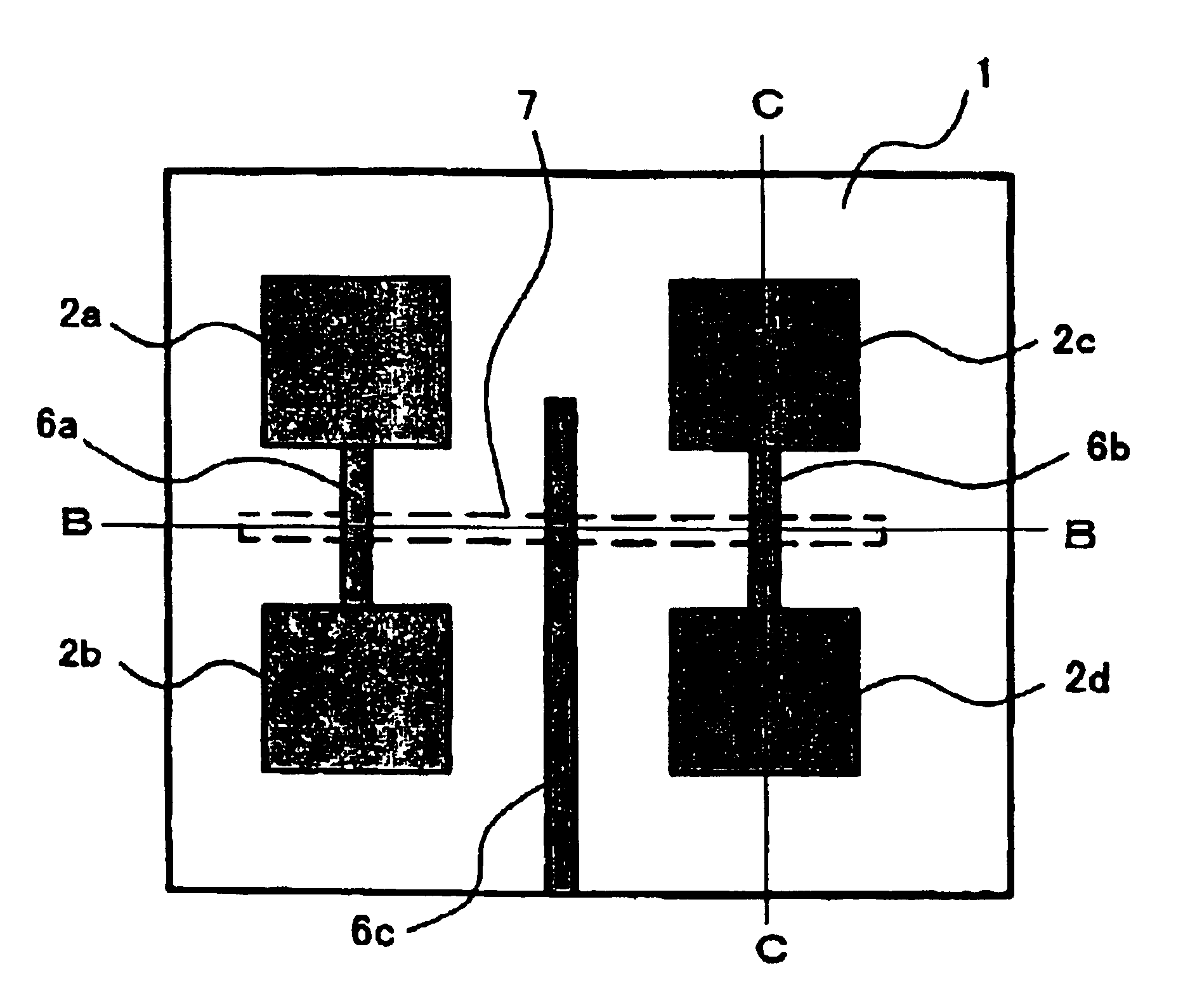
Dual-polarized antenna
ActiveUS9865928B2Bandwidth in which matching of the antenna can be ensured can be widenedHigh bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringRadiating element
In a multilayer substrate (2), an internal ground layer (11) is provided at a position between insulating layers (4) and (5) and a radiating element (13) is provided at a position between insulating layers (3) and (4). A first coplanar line (7) is connected to an intermediate position of the radiating element (13) in an X-axis direction, and a second coplanar line (9) is connected to an intermediate position of the radiating element (13) in a Y-axis direction. A passive element (16) is laminated on the upper surface of the radiating element (13) through the insulating layer (3). The passive element (16) is formed in a cross shape in which a first patch (16A) extending in the X-axis direction and a second patch (16B) extending in the Y-axis direction are orthogonal to each other.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Dielectric waveguide filter with inductive windows and coplanar line coupling
InactiveUS7196598B2Improve filter characteristicsFibre mechanical structuresResonatorsElectrical conductorCoupling
The present invention provides a filter exhibiting excellent filter characteristics and having less number of stages. A dielectric substrate (1) has one surface connected to a top conductor (2) and an opposite surface connected to a bottom conductor (3). A pair of rows of via-holes connecting together the top conductor (2) and the bottom conductor (3) are formed along the signal transfer direction. A slit (6) is formed in a portion of the top conductor (2) overlying the central resonator among a plurality of resonators. The slit (6) extends in a direction perpendicular to the signal transfer direction. Slits (7, 8) are formed in each of portions of the top conductor (2) overlying resonators disposed at both ends. A coplanar waveguide (9) mounted on the top conductor (2) is connected to the slit (7).
Owner:NEC CORP
Antenna with an electric conductive layer and dual band emitter therewith
The antenna of said transmitter is a microstrip antenna. A rear edge of its patch is provided with a short circuit by means of which a quarter-wave primary resonance can be excited by a coplanar line formed by two coupling slots in an area. Separator slots separate said area from another area in which a secondary resonance can be established at twice the frequency of the primary resonance from a slotted line extending one slot of the coplanar line. The invention applies in particular to the production of a dual-mode mobile telephone to the GSM and DCS standards.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
High speed electronics interconnect and method of manufacture
ActiveUS20090058567A1Effective dielectric constantIncrease bandwidth of interconnectionMultiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityDielectric loss
Fundamental interconnect systems for connecting high-speed electronics elements are provided. The interconnect systems consists of signal line, dielectric system with open trench or slot filled up with air or lower dielectric loss material, and the ground plane. The signal line could be for example, microstripline, strip line, coplanar line, single line or differential pairs. The interconnect system can be used for on-chip interconnects or can also be used for off-chip interconnects. The fundamental techniques provided in this invention can also be used for high-speed connectors and high-speed cables.
Owner:BANPIL PHOTONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com