Patents
Literature
696 results about "Joule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The joule (/dʒaʊl, dʒuːl/ jawl, jool; symbol: J) is a derived unit of energy in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy transferred to (or work done on) an object when a force of one newton acts on that object in the direction of the force's motion through a distance of one metre (1 newton metre or N⋅m). It is also the energy dissipated as heat when an electric current of one ampere passes through a resistance of one ohm for one second.
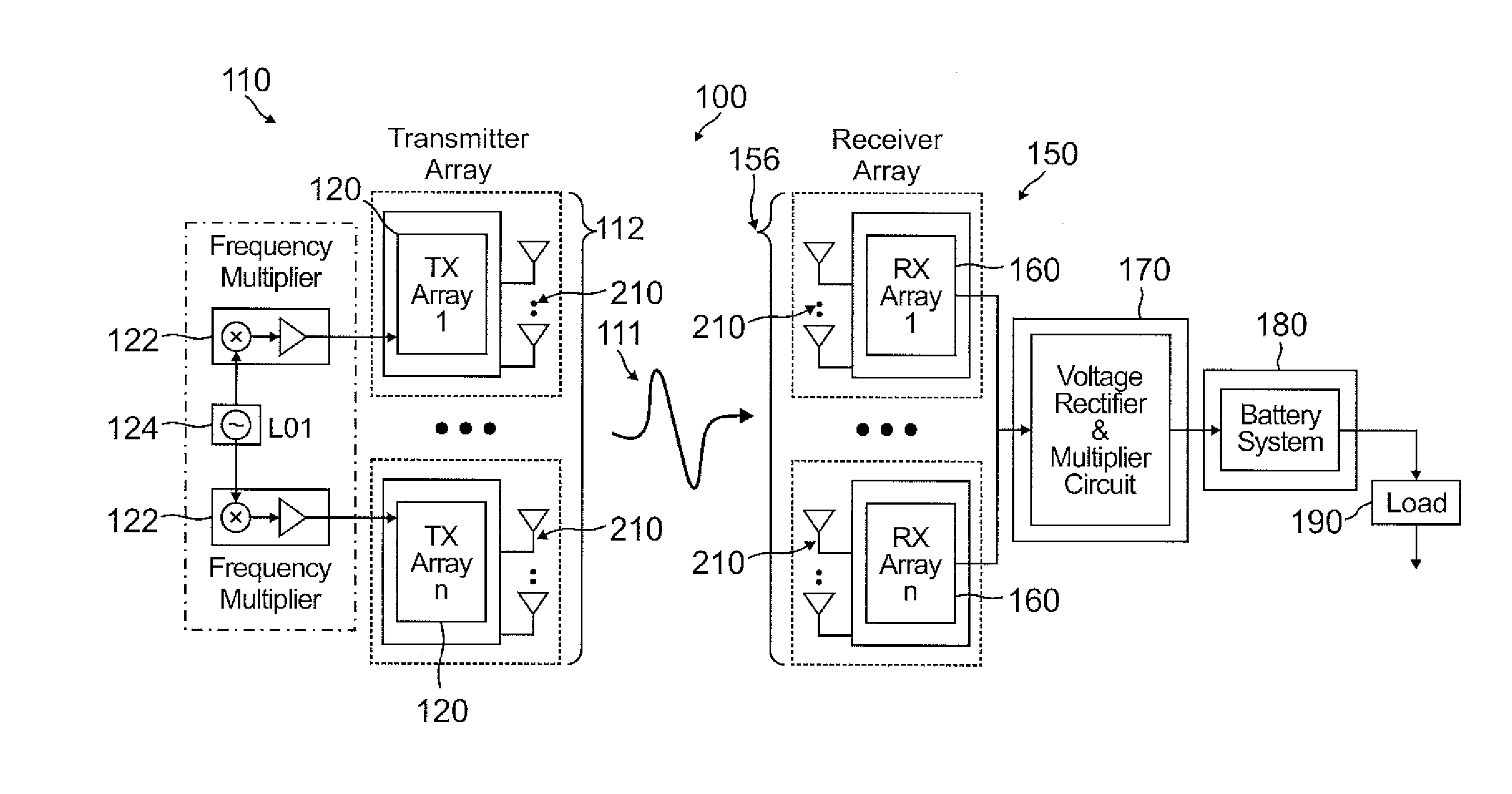
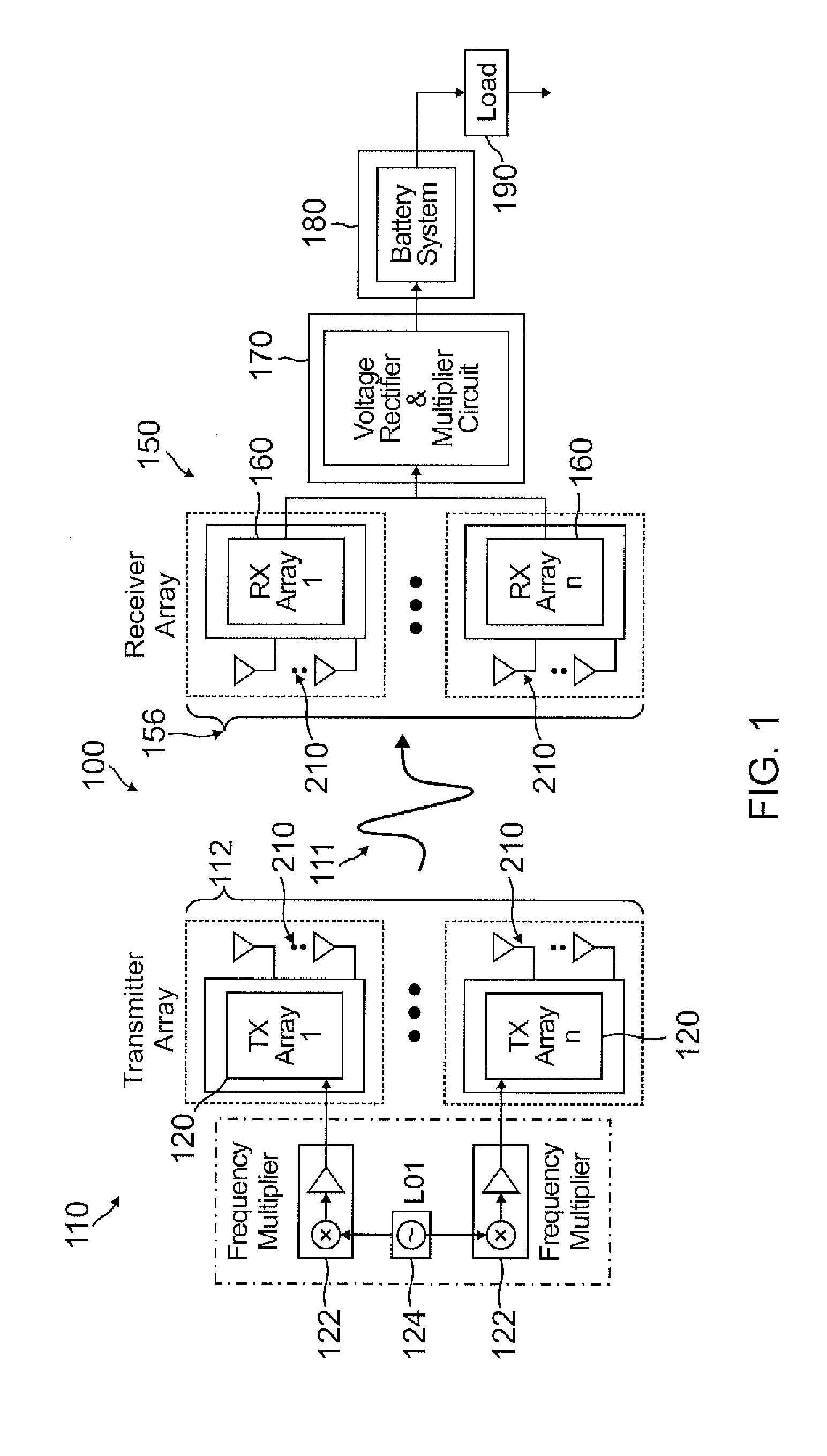
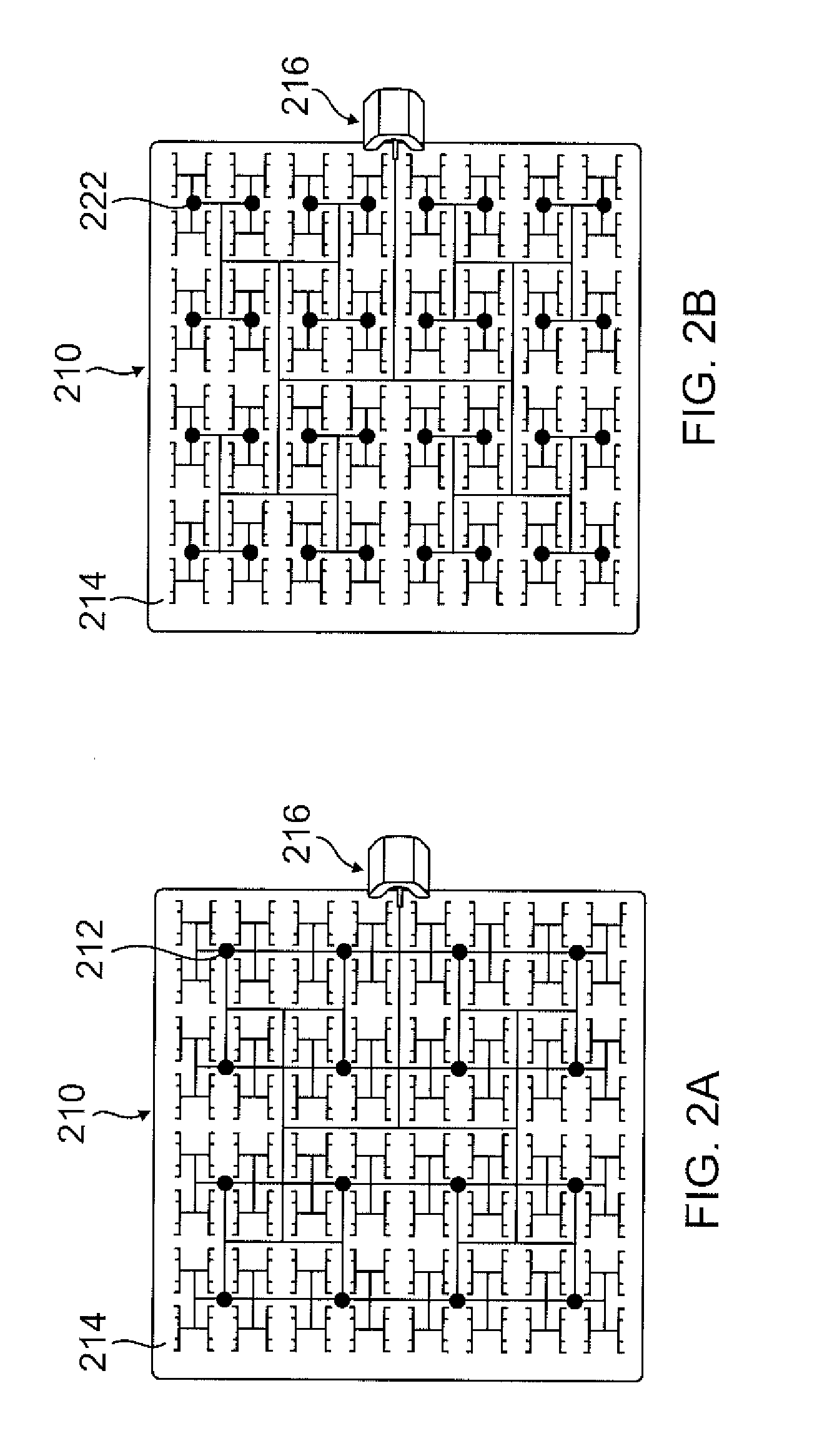
Flat panel, stationary or mobile, spatially beam-formed wireless energy delivery system
Methods and systems are provided for achieving delivery of power wirelessly using a highly beam-formed array of radio frequency (RF) transmitters as a source and a spatially beam-formed array of receivers that collect the impinged RF power and feed a multistage RF to direct current (RF-DC) conversion circuit that, for example, increases output voltage by doubling the voltage at each stage, while power delivery remains constant. One or more embodiments may provide energy wirelessly and—unlike conventional systems where the power flux density may be too low for applications where an energy density (specific energy) on the order of several mega-Joules per kilogram (MJ / Kg) is desired—may provide sufficient power flux density for many practical applications.
Owner:MOHAMADI FARROKH
Breathable composite sheet structure and absorbent articles utilizing same
A breathable composite sheet material, a method for making such a sheet material, and an absorbent article utilizing the sheet material are provided. The composite sheet material is comprised of a thermoplastic film adhered directly to a fibrous substrate. The thermoplastic film comprises at least 50% by weight of a polymer material from the group of block copolyether esters, block copolyether amides and polyurethanes. The substrate comprises a fibrous web of at least 50% by weight of polyolefin polymer synthetic fibers. The composite sheet exhibits a peel strength of at least 0.1 N / cm, a dynamic fluid transmission of less than about 0.75 g / m2 when subjected to an impact energy of about 2400 joules / m2, and a moisture vapor transmission rate, according to the desiccant method, of at least 1500 g / m2 / 24 hr. The absorbent article comprises (a) a topsheet; (b) a backsheet; and (c) an absorbent core located between the topsheet and the backsheet; wherein the backsheet comprises the non-porous, substantially fluid impermeable, moisture vapor permeable composite sheet material described above. The composite sheet material is oriented such that the film layer of the composite sheet material faces toward the absorbent core. The absorbent article may comprise a disposable diaper.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Low-EMI electronic apparatus, low-EMI circuit board, and method of manufacturing the low-EMI circuit board.
InactiveUS6353540B1Radiation suppressionHigh packageMagnetic/electric field screeningFinal product manufactureCapacitanceCountermeasure
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Power system for high temperature applications with rechargeable energy storage
ActiveUS20120268074A1Material nanotechnologyElectrolytic capacitorsCelsius DegreeElectric power system
A power system adapted for supplying power in a high temperature environment is disclosed. The power system includes a rechargeable energy storage that is operable in a temperature range of between about seventy degrees Celsius and about two hundred and fifty degrees Celsius coupled to a circuit for at least one of supplying power from the energy storage and charging the energy storage; wherein the energy storage is configured to store between about one one hundredth (0.01) of a joule and about one hundred megajoules of energy, and to provide peak power of between about one one hundredth (0.01) of a watt and about one hundred megawatts, for at least two charge-discharge cycles. Methods of use and fabrication are provided. Embodiments of additional features of the power supply are included.
Owner:FASTCAP SYST
Method for providing refrigeration
A method for providing refrigeration such as to an insulated enclosure wherein a defined multicomponent refrigerant fluid undergoes a phase change coupled with Joule-Thomson expansion to generate refrigeration over a wide temperature range which may comprise from ambient to low temperatures.
Owner:EDWARDS VACUUM LLC
Systems structures and materials for electronic device cooling
An electronic device having one or more components that generate heat during operation includes a structure for temperature management and heat dissipation. The structure for temperature management and heat dissipation comprises a heat transfer substrate having a surface that is in thermal communication with the ambient environment and a temperature management material in physical contact with at least a portion of the one or more components of the electronic device and at least a portion of the heat transfer substrate. The temperature management material comprises a polymeric phase change material having a latent heat of at least 5 Joules per gram and a transition temperature between 0° C. and 100° C., and a thermal conductive filler.
Owner:LATENT HEAT SOLUTIONS LLC
H-bridge circuit for generating a high-energy biphasic waveform in an external defibrillator using single SCR and IGBT switches in an integrated package
An external defibrillator with an output circuit having four legs arrayed in the form of an “H” (an “H-bridge”) is disclosed. The output circuit is designed to be able to conduct a range of defibrillation pulse energies, from below 50 joules to above 200 joules. Each leg of the output circuit contains a solid-state switch. By selectively switching on pairs of switches in the H-bridge, a biphasic defibrillation pulse may be applied to a patient. The switches in three of the legs of the H-bridge output circuit are preferably SCR switches, while the fourth leg includes an IGBT switch. In one embodiment, a single power switch is utilized in each of the legs of the H-bridge output circuit, and are included in a single integrated module or package. The use of single semiconductor switches in an integrated surface mountable module or package simplifies the assembly and manufacturing of the defibrillator device. The use of a single IGBT in a leg of the H-bridge (as opposed to two or more IGBTs in series) also greatly simplifies the drive circuitry required to turn on and off the IGBT.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
Therapeutic laser treatment
A method for treating selected tissue, including exposing the selected bone or tissue to laser light having a wavelength between approximately 600 and 1400 nm, and maintaining such exposure of the selected tissue or bone to the laser light for a period of time sufficient to deliver a laser light dosage of at least 7 Joules / cm2 per treatment and maintaining such exposure for a period of time sufficient to deliver a laser light dosage of at least 1500 Joules per treatment within a 24 hour period of time. The method also includes upcollimating the laser light such that the laser delivers to the selected tissue a substantially coherent beam of laser light having a cross-sectional area of at least 2 cm2, and, further, delivering the laser light to a depth of at least 5 mm in the selected tissue.
Owner:CURAELASE
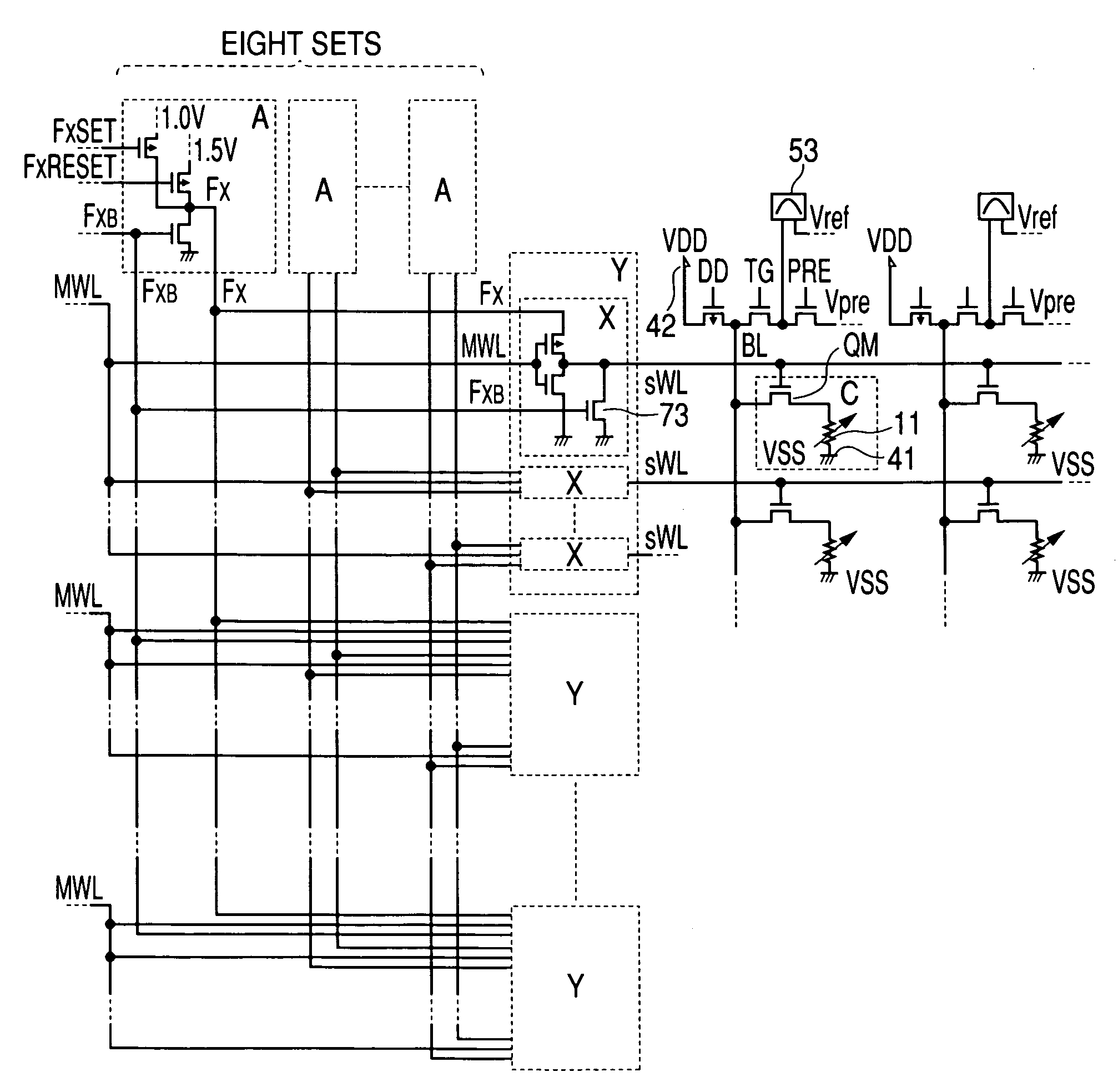
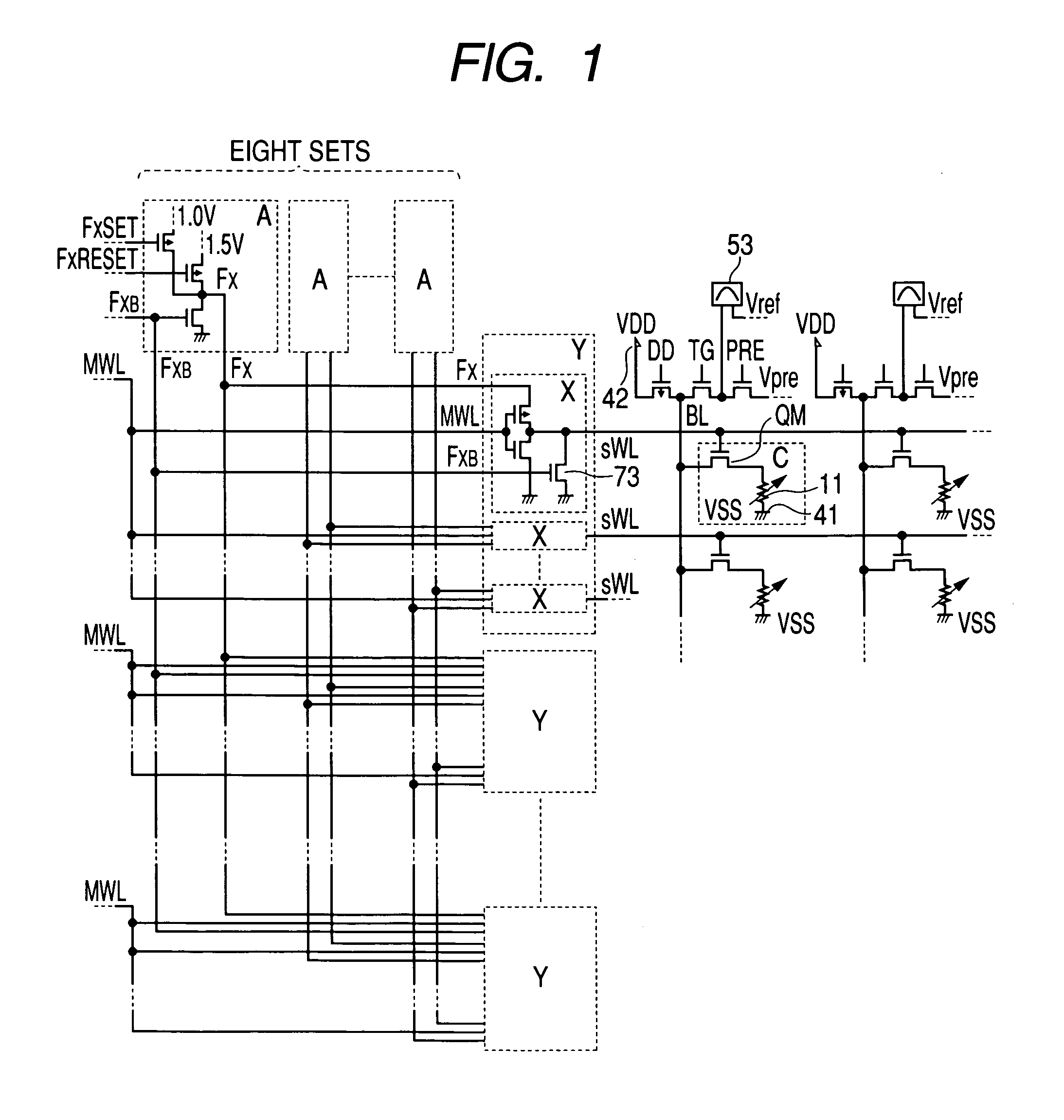
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20050128799A1Improve reliabilityIncrease heightSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
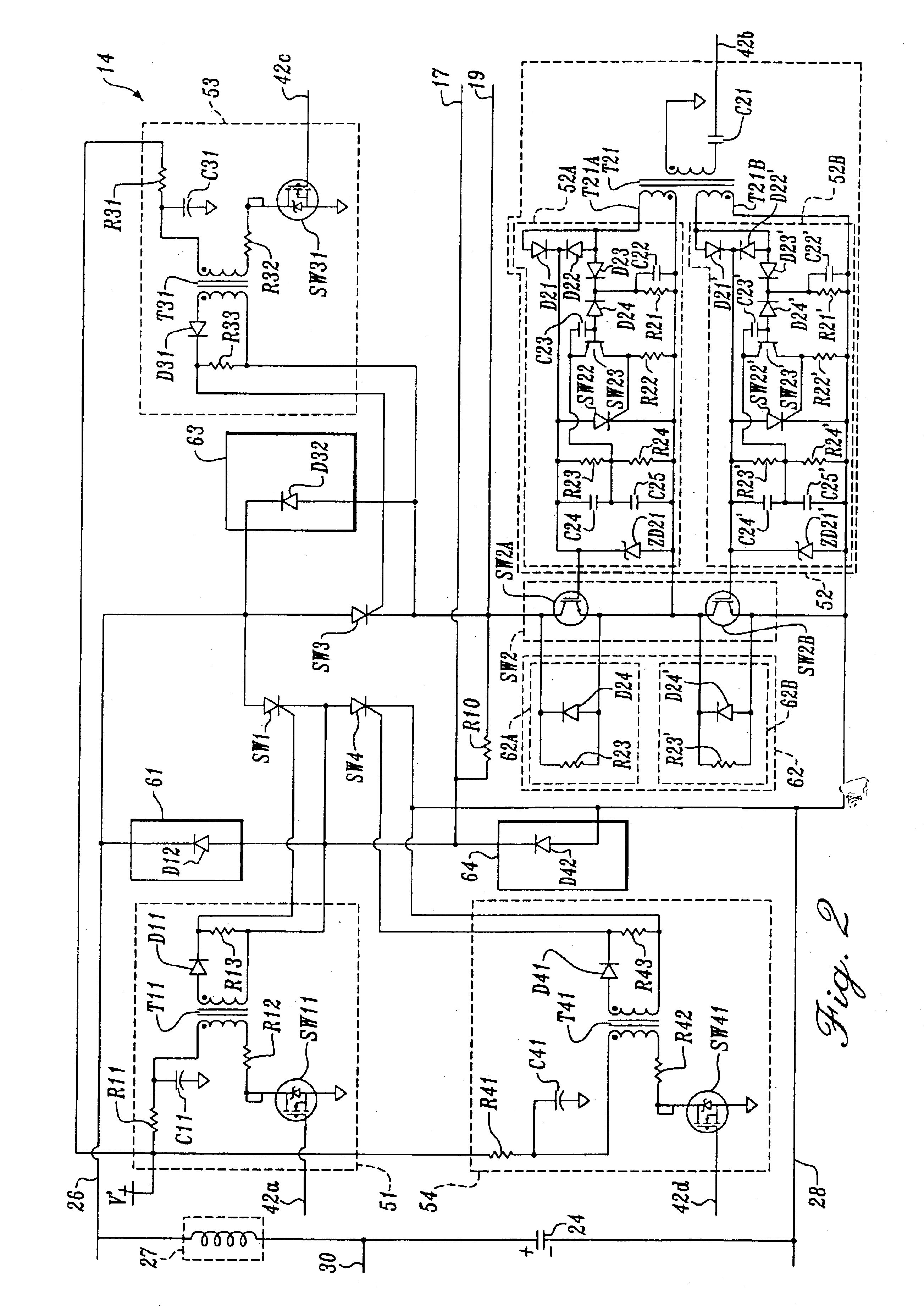
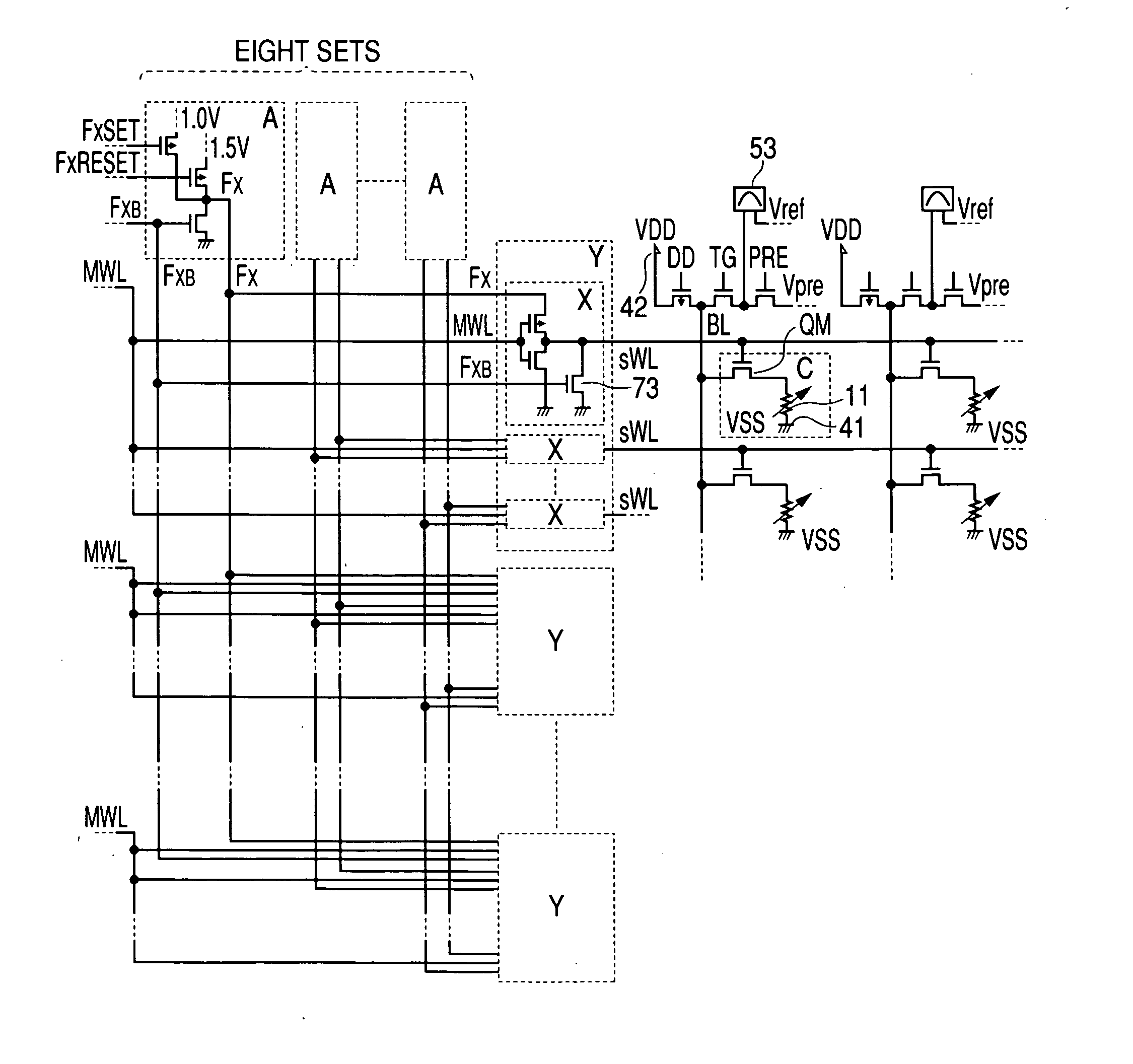
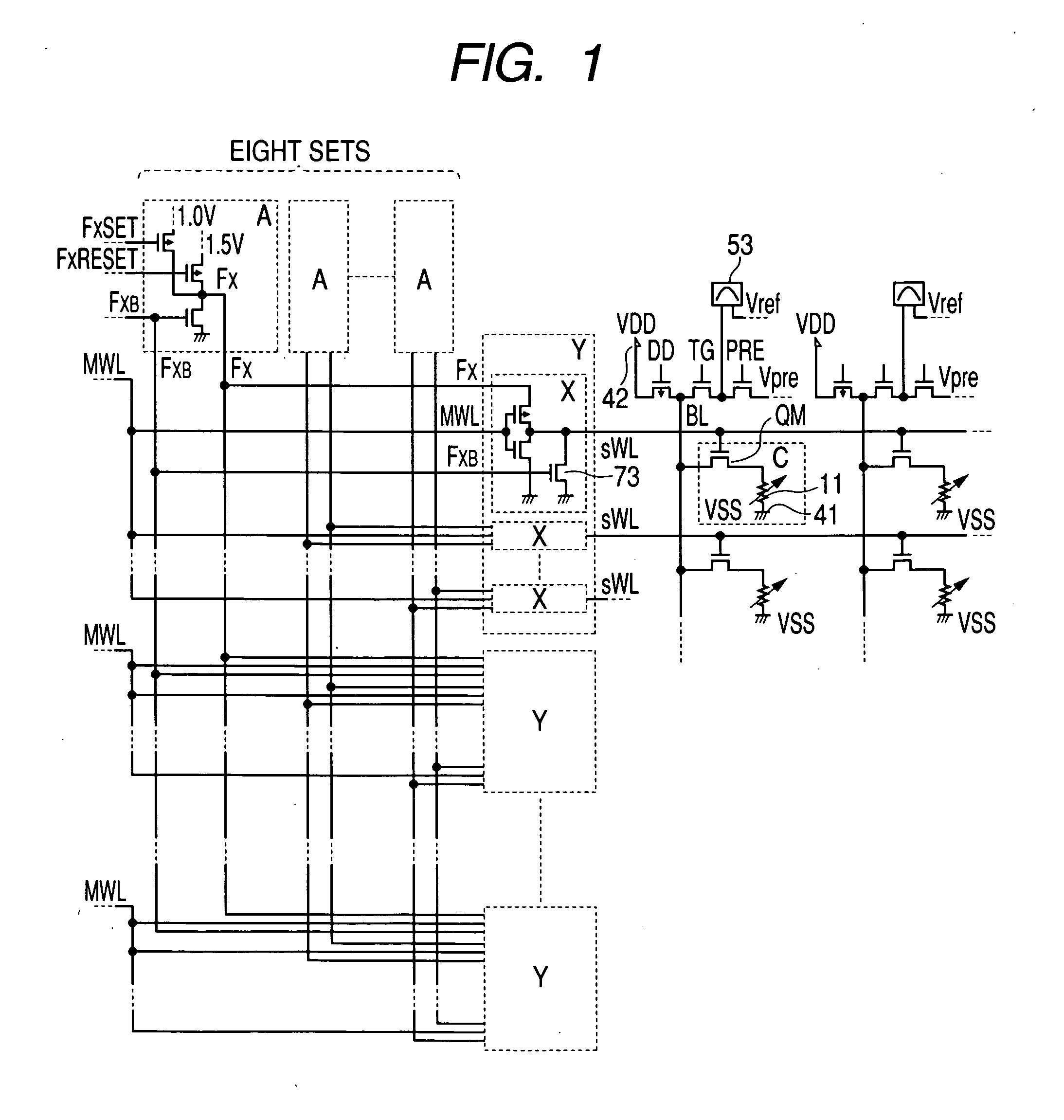
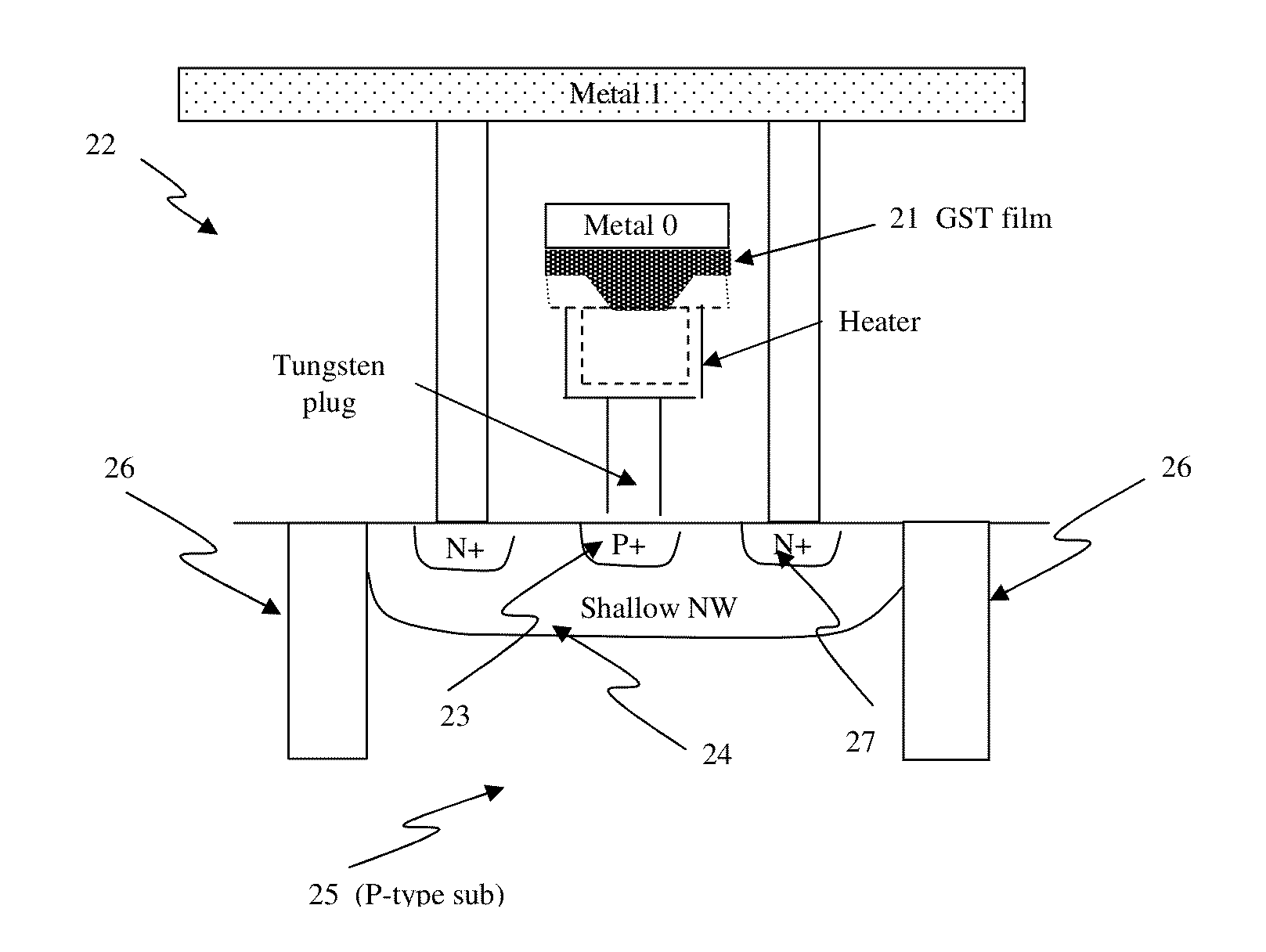
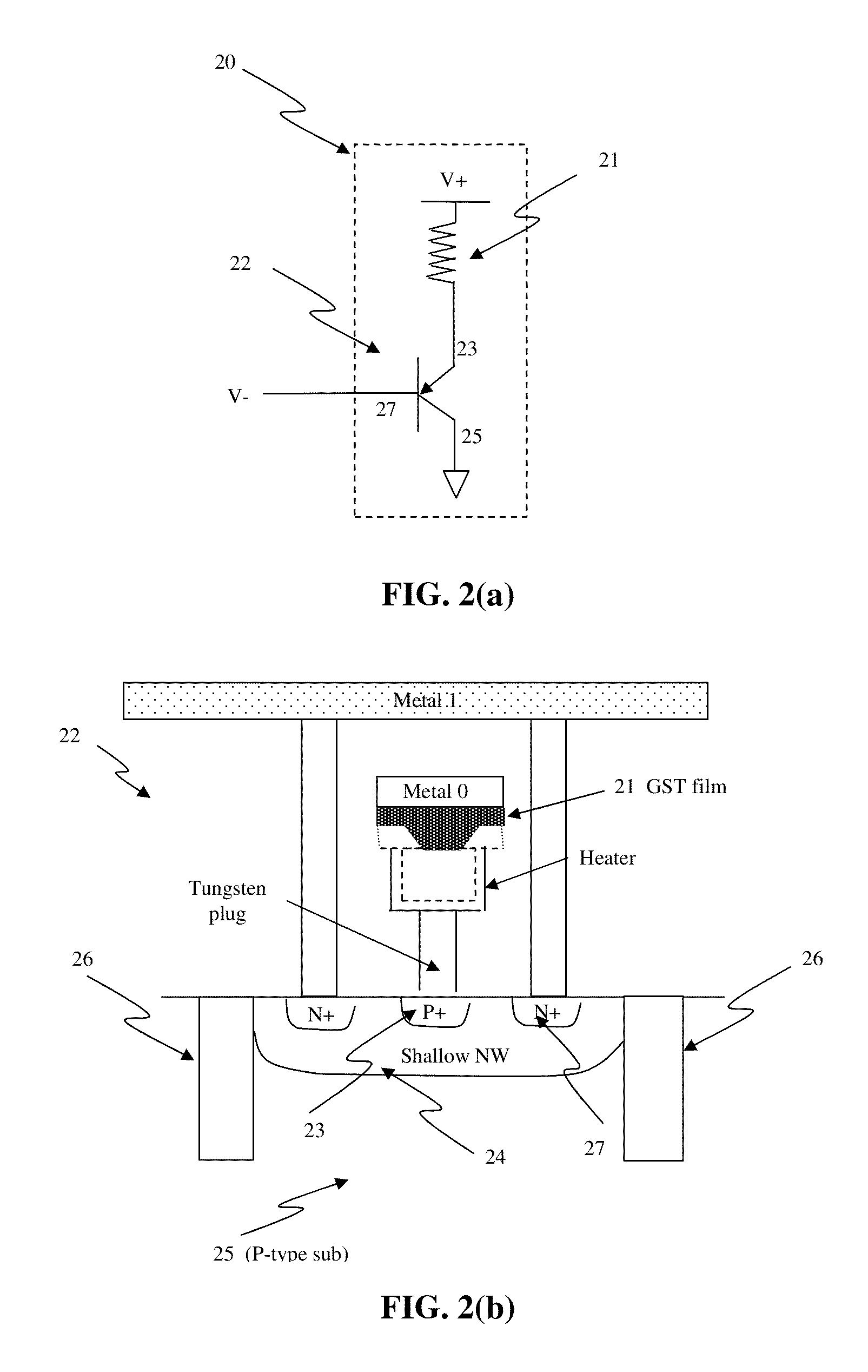
In a non-volatile phase change memory, information is recorded by utilizing a change in resistance of a phase change portion. When the phase change portion is allowed to generate Joule's heat and is held at a specific temperature, it goes into a state of a low resistance. At this time, if a constant voltage source is used, not only the phase change portion assumes a state of a low resistance, but also a large current flows, so that a sample concerned is overheated and goes into a state of a high resistance. Thus, it is difficult to make the phase change portion low in resistance stably. When the gate voltage of a memory cell selection transistor QM is controlled with MISFET to afford a low resistance state, the maximum amount of current applied to the sample is limited by the application of a medium-state voltage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
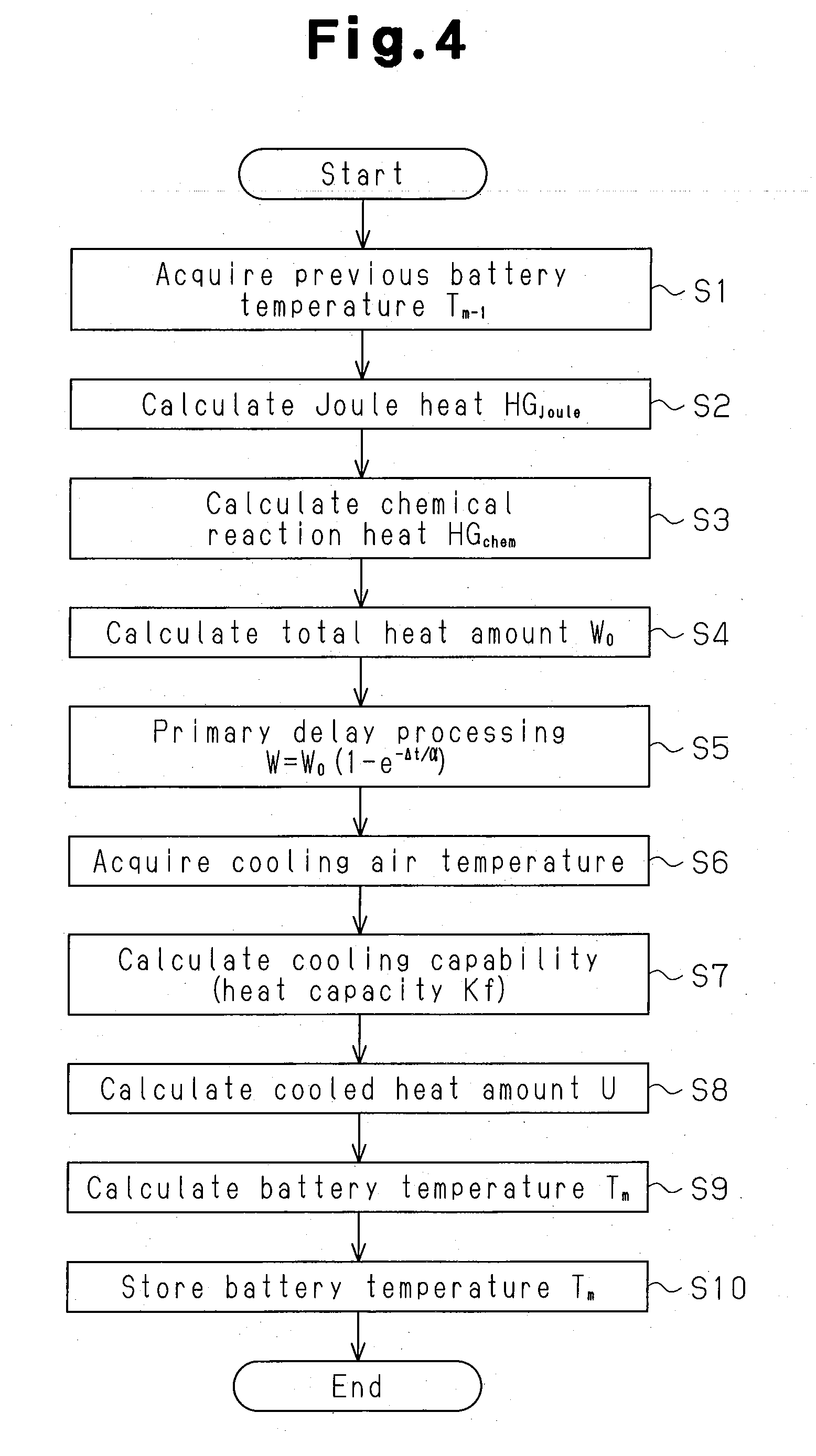
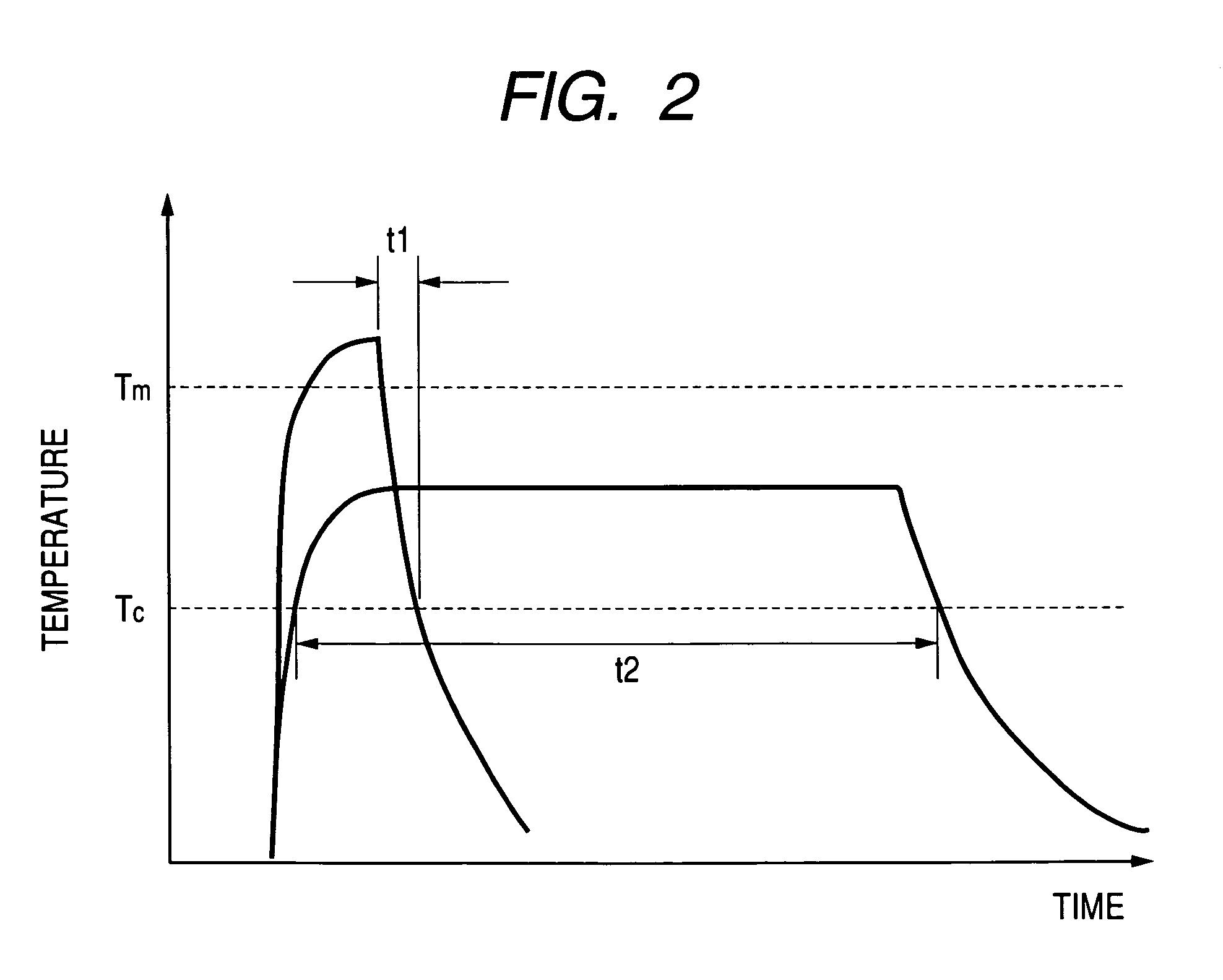
Controller for rechargeable battery and temperature estimation method and deterioration determination method for rechargeable battery
InactiveUS20070120537A1Accurate battery temperatureAccurate temperatureBatteries circuit arrangementsOperating modesChemical reactionEstimation methods
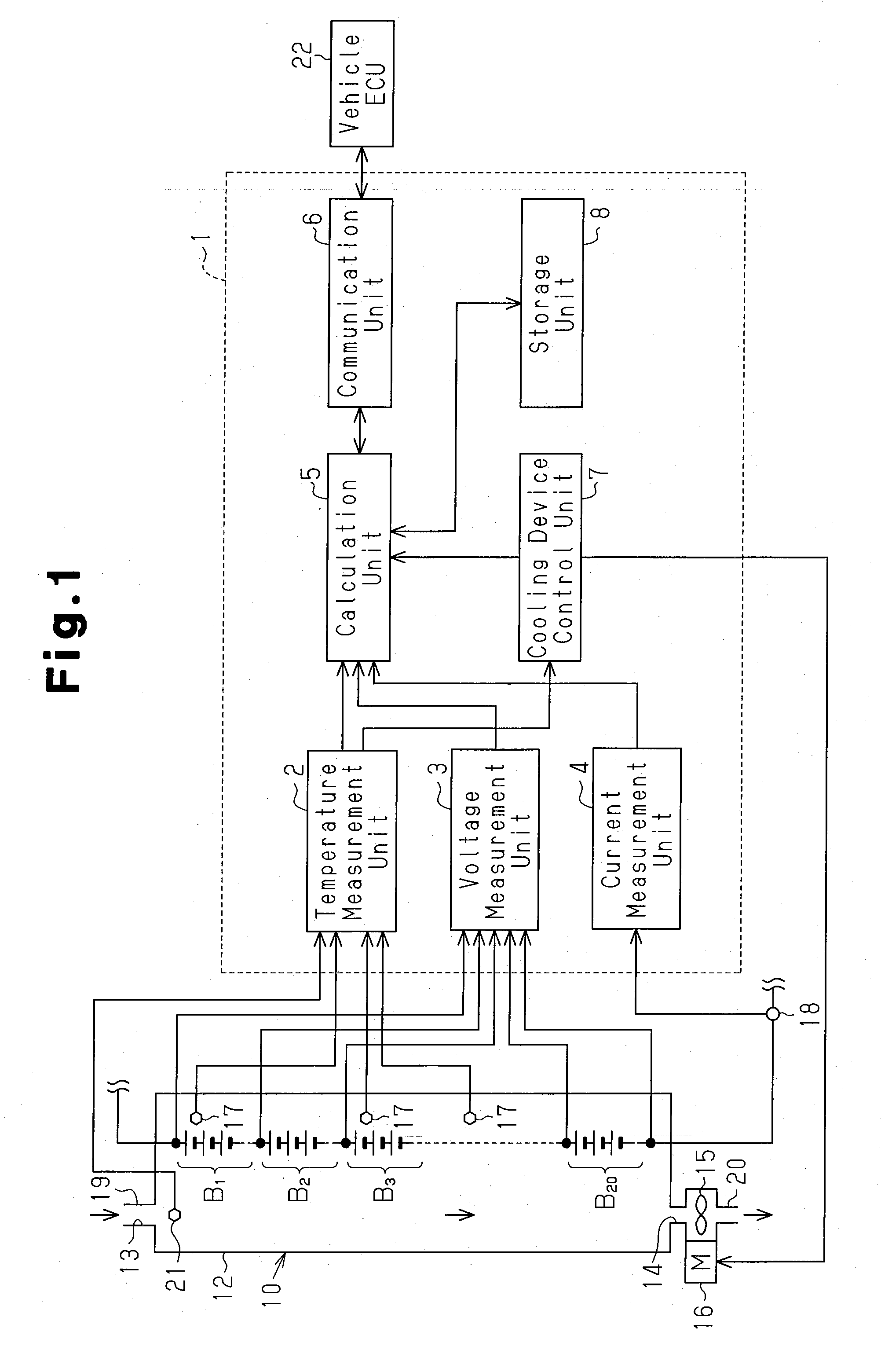
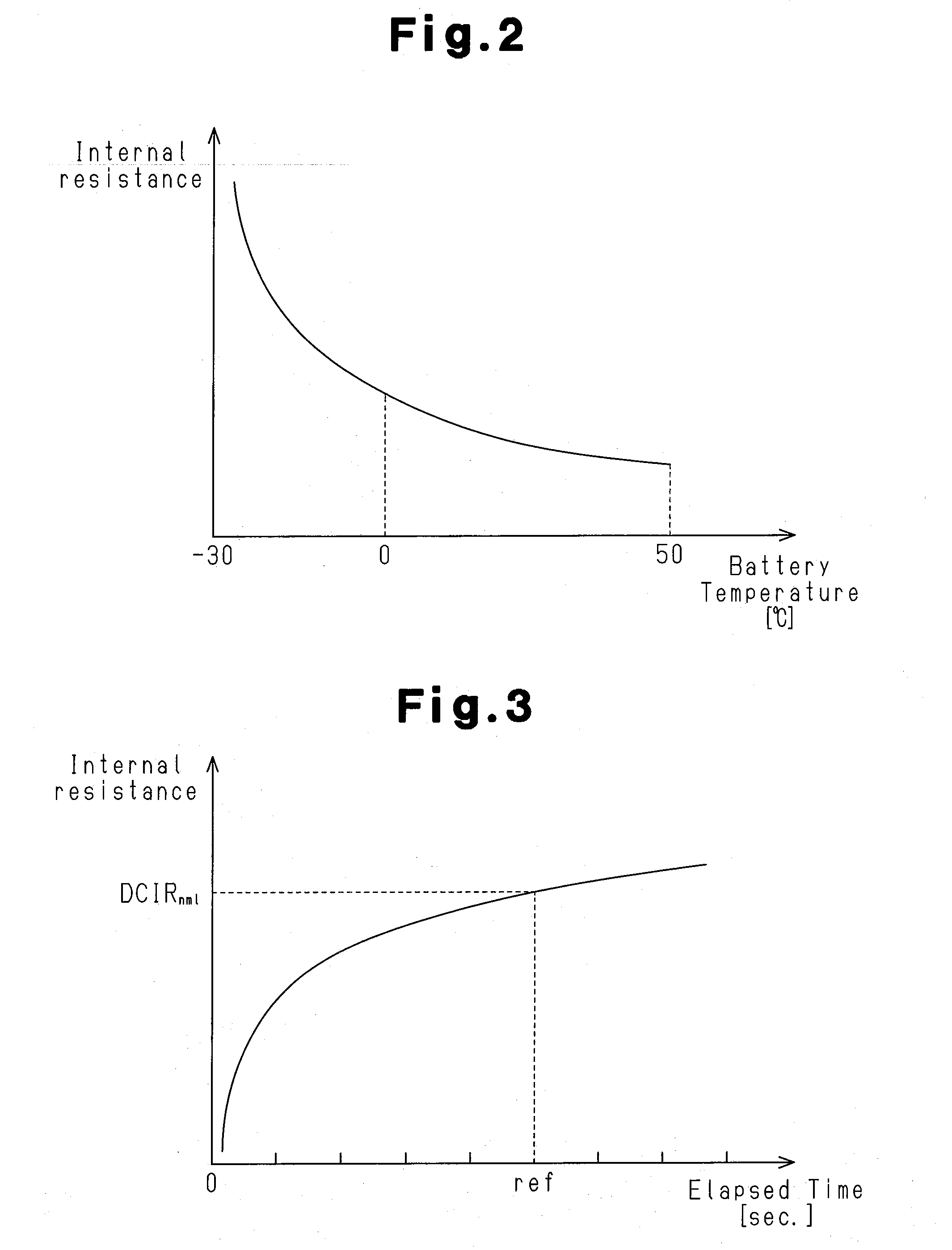
A controller for a rechargeable battery and a temperature estimation method and a deterioration determination method for a rechargeable battery enabling an accurate battery temperature to be obtained through calculation. The controller calculates a heat generation amount of Joule heat generated in the rechargeable battery and a heat generation amount of chemical reaction heat generated in the rechargeable battery to calculate the battery temperature of the rechargeable battery based on the calculated Joule heat generation amount and the calculated chemical reaction heat generation amount. When a cooling device is connected to the rechargeable battery, the controller preferably calculates the battery temperature of the rechargeable battery using the Joule heat generation amount, the chemical reaction heat generation amount, and a value indicating the cooling capability of the cooling device.
Owner:PANASONIC EV ENERGY CO LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
InactiveUS7123535B2Increase resistanceResistance of the phase change portion becomes lowerSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPhase-change memoryGate voltage
In a non-volatile phase change memory, information is recorded by utilizing a change in resistance of a phase change portion. When the phase change portion is allowed to generate Joule's heat and is held at a specific temperature, it goes into a state of a low resistance. When the gate voltage of a memory cell selection transistor QM is controlled to afford a low resistance state, the maximum amount of current applied to the phase change portion is limited by the application of a medium-state voltage to the control gate, thereby avoiding overheating of the phase change portion.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Low-EMI electronic apparatus, low-EMI circuit board, and method of manufacturing the low-EMI circuit board
InactiveUS20020015293A1Suppress spurious radiationIncrease costMagnetic/electric field screeningFinal product manufactureCapacitanceCountermeasure
A low-EMI circuit which realizes a high mounting density by converting the potential fluctuation of a power supply layer with respect to a ground layer which occurs on switching an IC device etc., into Joule's heat in the substrate without using any parts as a countermeasure against the EMI. Its structure, a circuit board using it, and a method of manufacturing the circuit board are also disclosed. Parallel plate lines in which the Q-value of the stray capacitance between solid layers viewed from the power supply layer and ground layer is equivalently reduced and which are matchedly terminated by forming a structure in which a resistor (resistor layer) and another ground layer are provided in addition to the power supply layer and the ground layer on a multilayered circuit board. A closed shield structure is also disclosed. This invention can remarkably suppress unwanted radiation by absorbing the potential fluctuation (resonance) which occurs in a power supply loop by equivalently reducing the Q-value of the stray capacitance, absorbing the standing wave by the parallel plate lines matchedly terminated and, closing and shielding the parallel plate lines.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
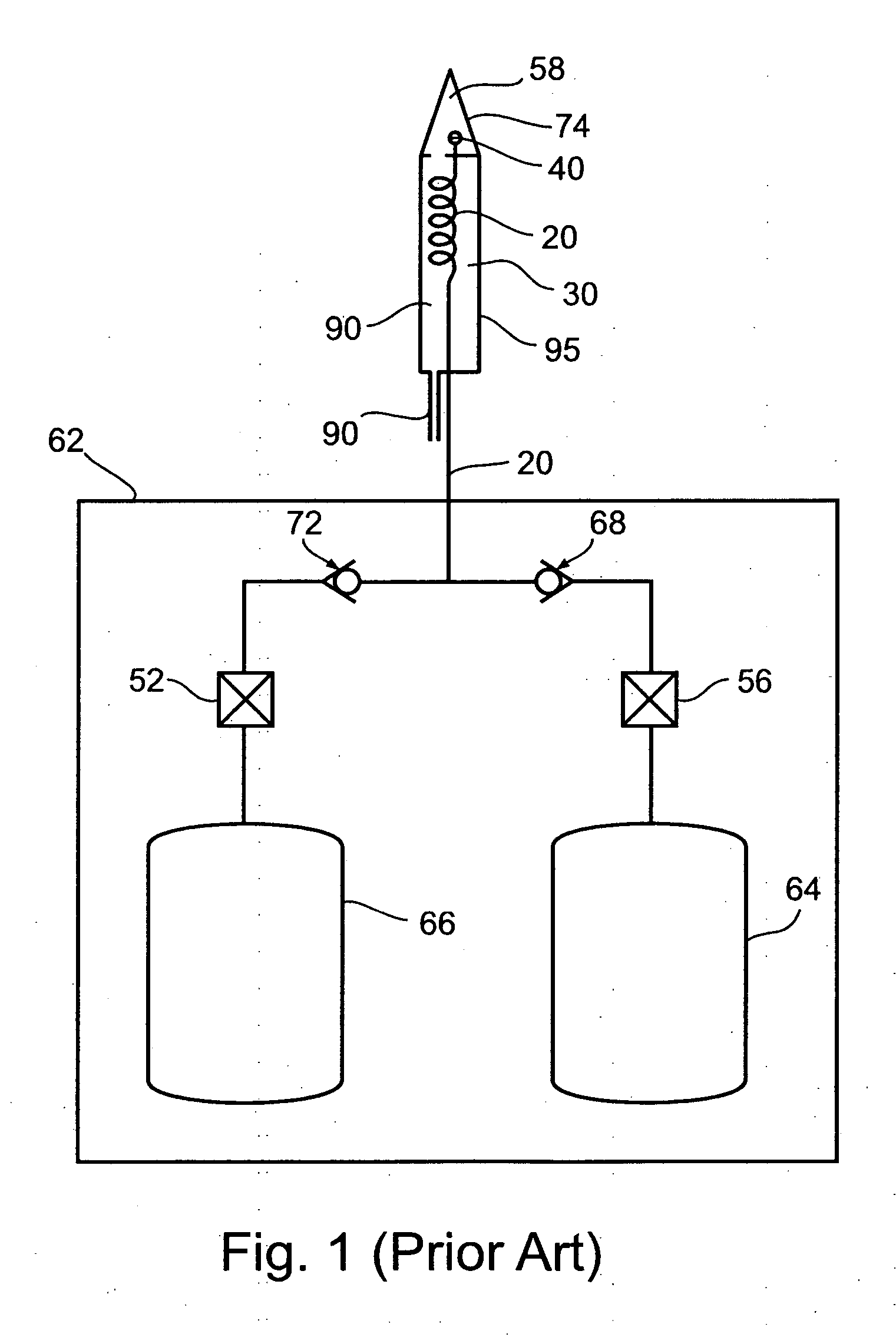
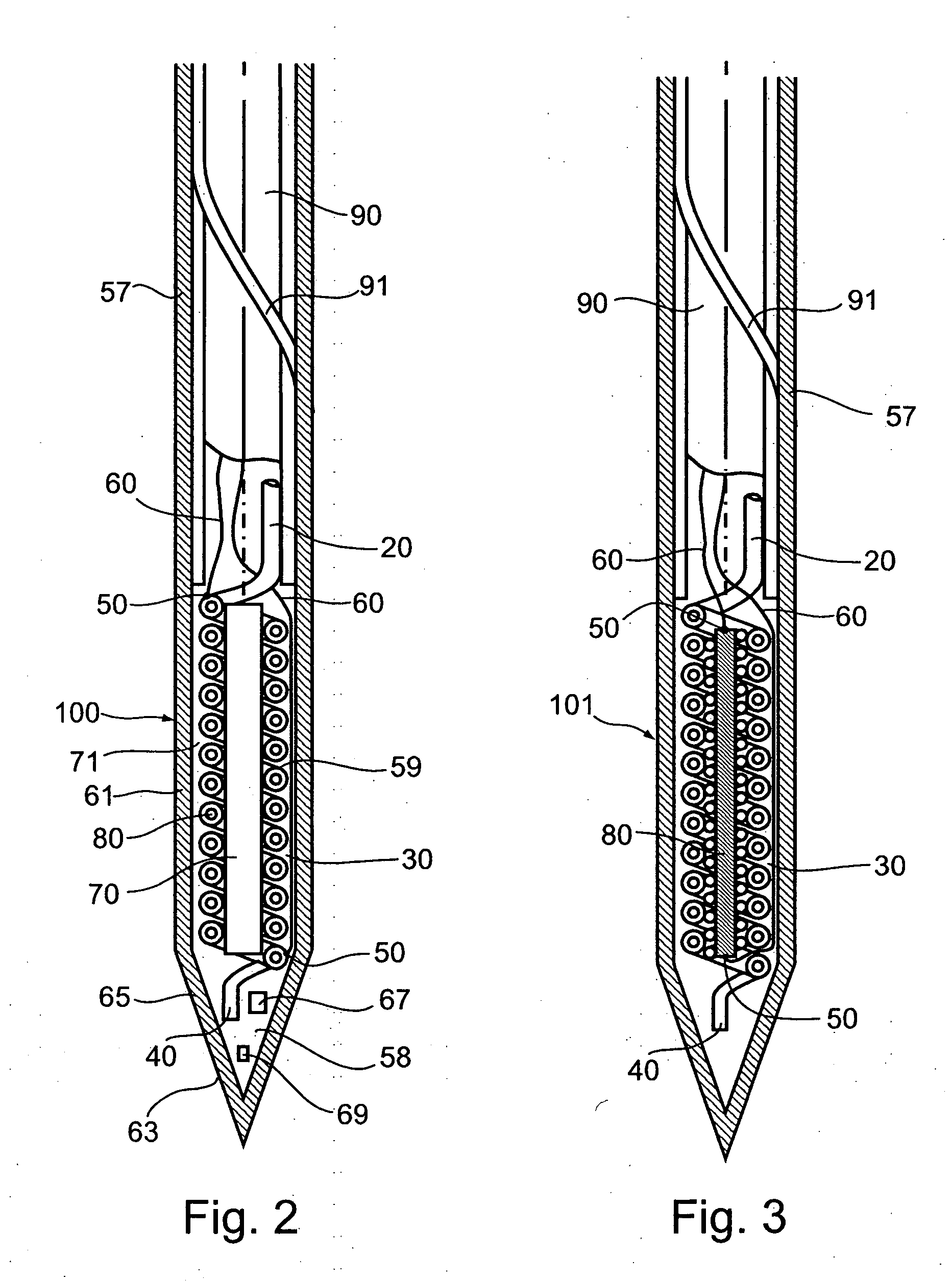
Gas-heated gas-cooled cryoprobe utilizing electrical heating and a single gas source
ActiveUS20060122590A1Quick switchHeating fastSurgical instruments for coolingElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The present invention is of device, system, and method for cooling and heating an operating tip of a cryoprobe using a single source of compressed gas. Cooling of the operating tip is effected by Joule-Thomson expansion of a high-pressure cooling gas through a Joule-Thomson orifice into an expansion chamber. Heating of the operating tip is effected by electrical resistance heating. In preferred embodiments, heating of the operating tip is effected by electrical resistance heating of low-pressure gas flowing towards the operating tip. Preferably, gas from a single gas source is supplied to the probe during both cooling and heating phases, a cooling gas being supplied at high pressure when used for cooling and at low pressure when used for heating. Low-pressure gas supplied during the heating phase is heated as it flows towards the operating tip, preferably by electrical resistance heating within the body of the probe. A single gas input lumen is used during both cooling and heating phases to transport gas into the probe, and a single gas exhaust lumen is used during both cooling and heating phases to conduct gas out of the probe.
Owner:GALIL MEDICAL
Glass-plate cutting machine
InactiveUS7642483B2Improve cut qualityQuality improvementFine working devicesGlass reforming apparatusLight beamEngineering
A glass plate cutting machine using a laser beam is provided to solve problems, such as uneven glass section and slanting cutting. By using the glass plate cutting machine of the current invention, the glass plate is irradiated with a first carbon dioxide laser beam of 0.05-2 joule / mm2 on a long oval shaped area of 20-200 mm2 according to an expected cutting line thereof, and immediately cooled with water, to generate a scribe line, which is then further irradiated with a second carbon dioxide laser beam of 0.1-0.5 joule / mm′ on the area of 20-200 mm2 thus obtaining a superior glass section.
Owner:RORZE SYST
Fibers and articles having combined fire resistance and enhanced reversible thermal properties
A fabric, fiber or article comprising a plurality of fiber bodies, the plurality of fiber bodies including a first fiber material and a second fiber material, wherein the first fiber material comprises a cellulosic material and a phase change material dispersed in the cellulosic material, the phase change material forming a plurality of domains dispersed in the cellulosic material, the phase change material having a latent heat of at least 5 Joules per gram and a transition temperature in the range of 0° C. to 100° C., the phase change material providing thermal regulation based on at least one of absorption and release of the latent heat at the transition temperature. Wherein the second fiber material comprises a fire resistant material.
Owner:OUTLAST TECH LLC
Systems, structures and materials for electronic device cooling
Owner:LATENT HEAT SOLUTIONS LLC
Current collector, pole piece using same and battery
InactiveCN106910897AImprove securityIncrease resistanceElectrode carriers/collectorsSecondary cellsElectrical resistance and conductanceForeign matter
The invention relates to the field of batteries, in particular to a current collector, a pole piece using the same and a battery. The current collector comprises a PPTC (polymeric positive temperature coefficient) material layer and a metal layer, wherein the PPTC material layer is used for bearing the metal layer; the metal layer is used for bearing an electrode active material layer and is located on at least one surface of the PPTC material layer. The PPTC material layer not only is used for bearing the metal layer, but also can have a rapid resistance increasing function at the stage of temperature rising caused by overcharge and short circuiting because of characteristics of the PPTC material, and generation of joule's heat is inhibited by reducing current value. By means of the current collector, the short-circuiting safety performance because of foreign matter can be improved, and the overcharge safety performance can also be improved.
Owner:CONTEMPORARY AMPEREX TECH CO
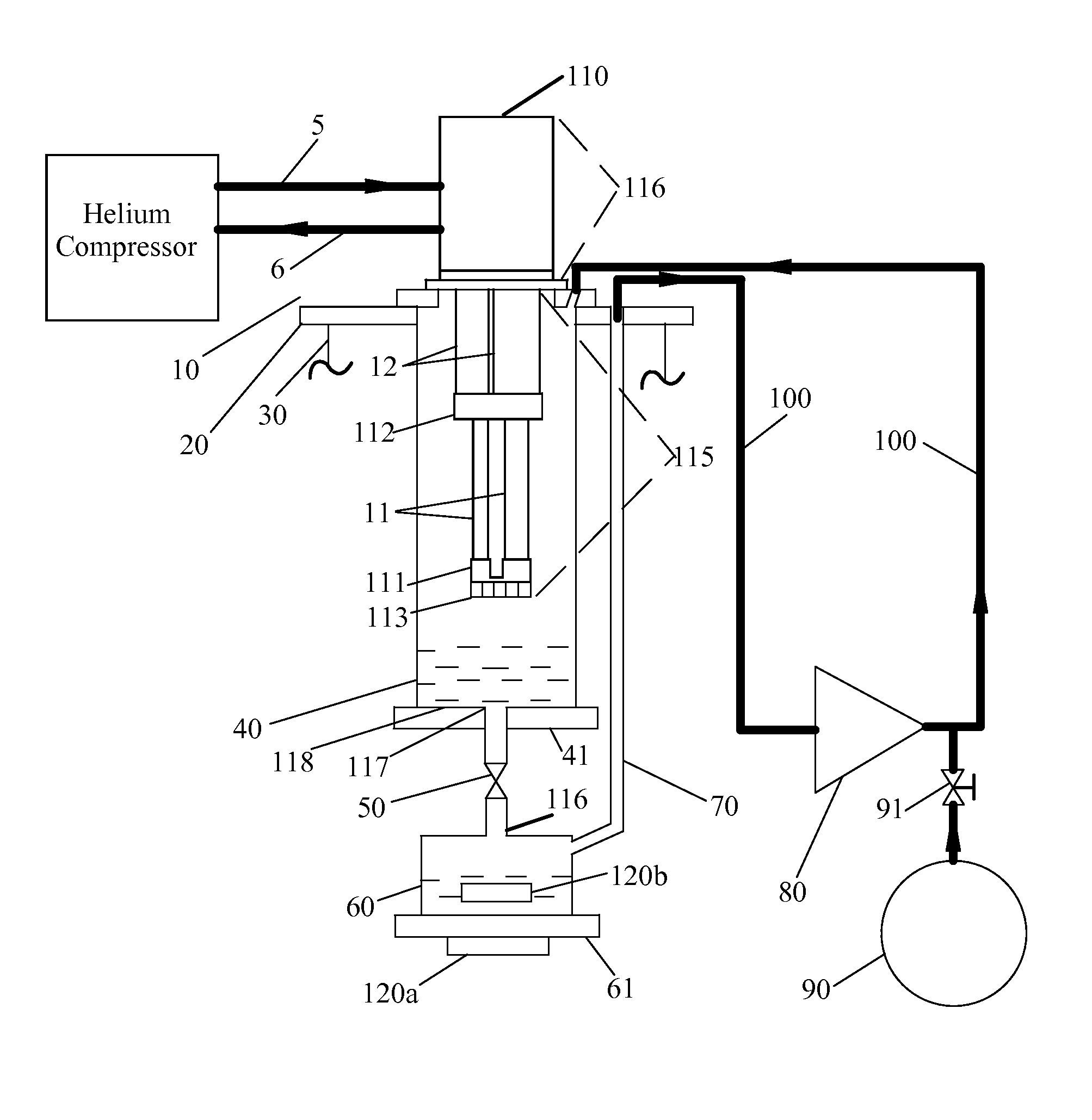
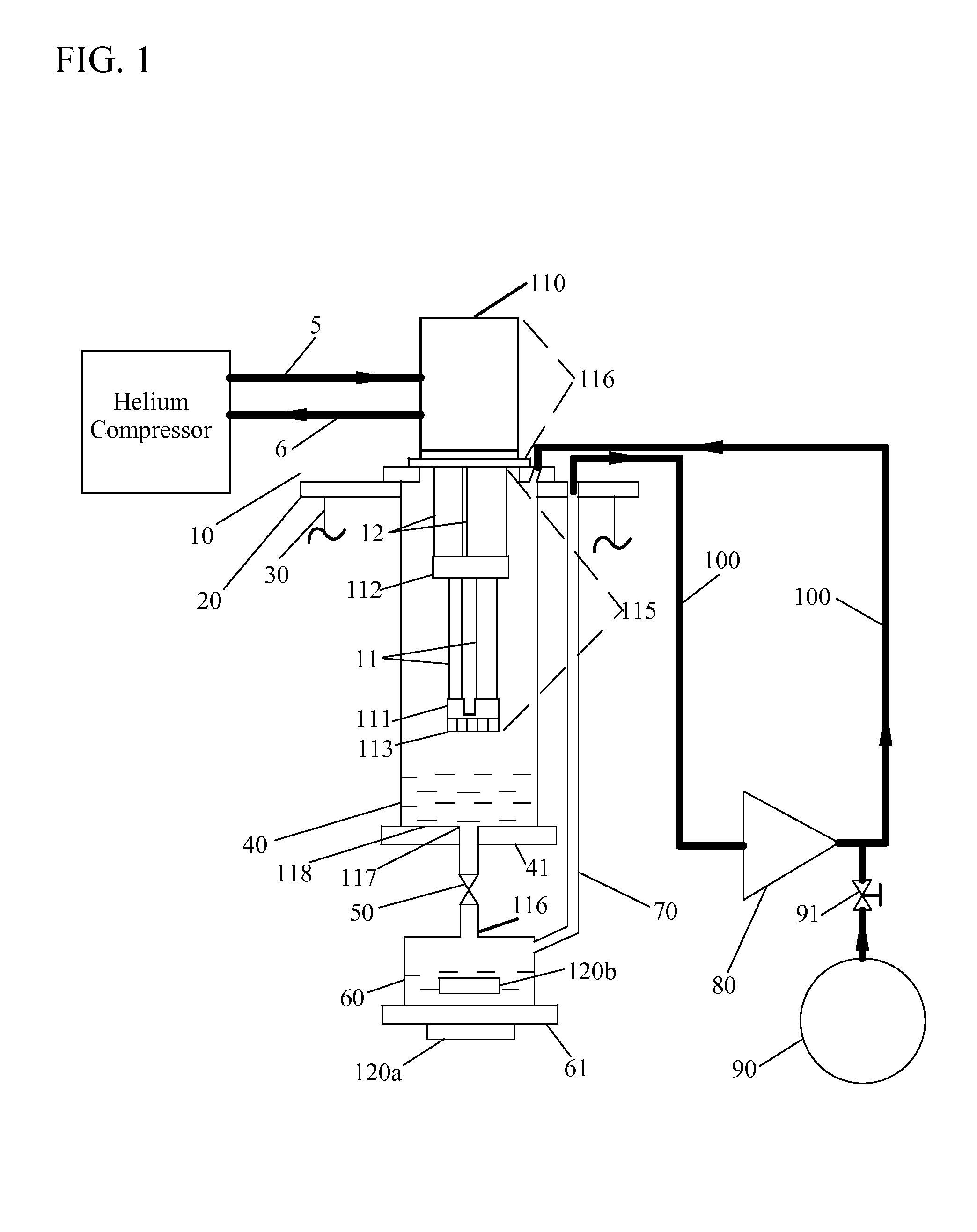
Closed Cycle 1 K Refrigeration System
InactiveUS20140202174A1Low vibration designReduce transferCompression machinesRefrigeration devicesCooling chamberEngineering
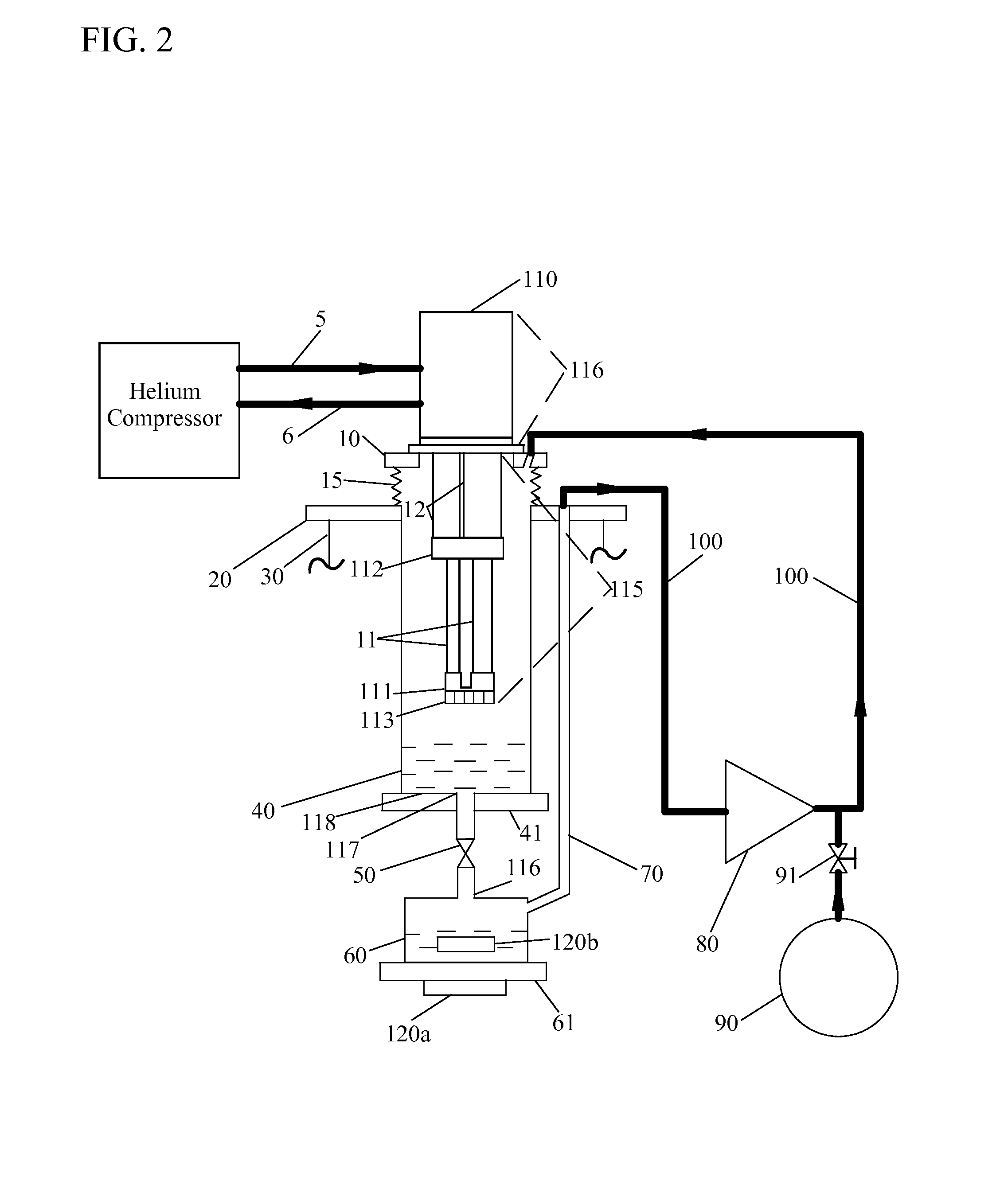
A closed-cycle refrigerator provides cooling to extremely low temperatures, particularly in the range of 0.5 K to 2.0 K. A 4 K pulse-tube cryocooler cold head or G-M cryocooler cold head liquefies helium in a first cooling chamber at a pressure at approximately 1 atmosphere. Liquid helium flows from the first cooling chamber, through a Joule-Thomson valve, and into a second cooling chamber under a pressure differential created by a pump. Helium vapor extracted from the second cooling chamber by the pump is routed back to the first cooling chamber to be re-condensed. This closed-cycle design provides continuous cooling below 2 K. Cryocooler cold head cold sections have no physical contact with subsequent cooling elements, such as the first and second cooling chambers to reduce vibration transfer. In some embodiments the cryocooler cold head is connected to a vacuum chamber via a vibration damping coupler to further reduce vibration transfer.
Owner:CRYOMECH
System and method for improved film cooling
ActiveUS20100282721A1Prolongs effectiveness of coolerSimple technologyEngine fuctionsEfficient propulsion technologiesLight beamSystem configuration
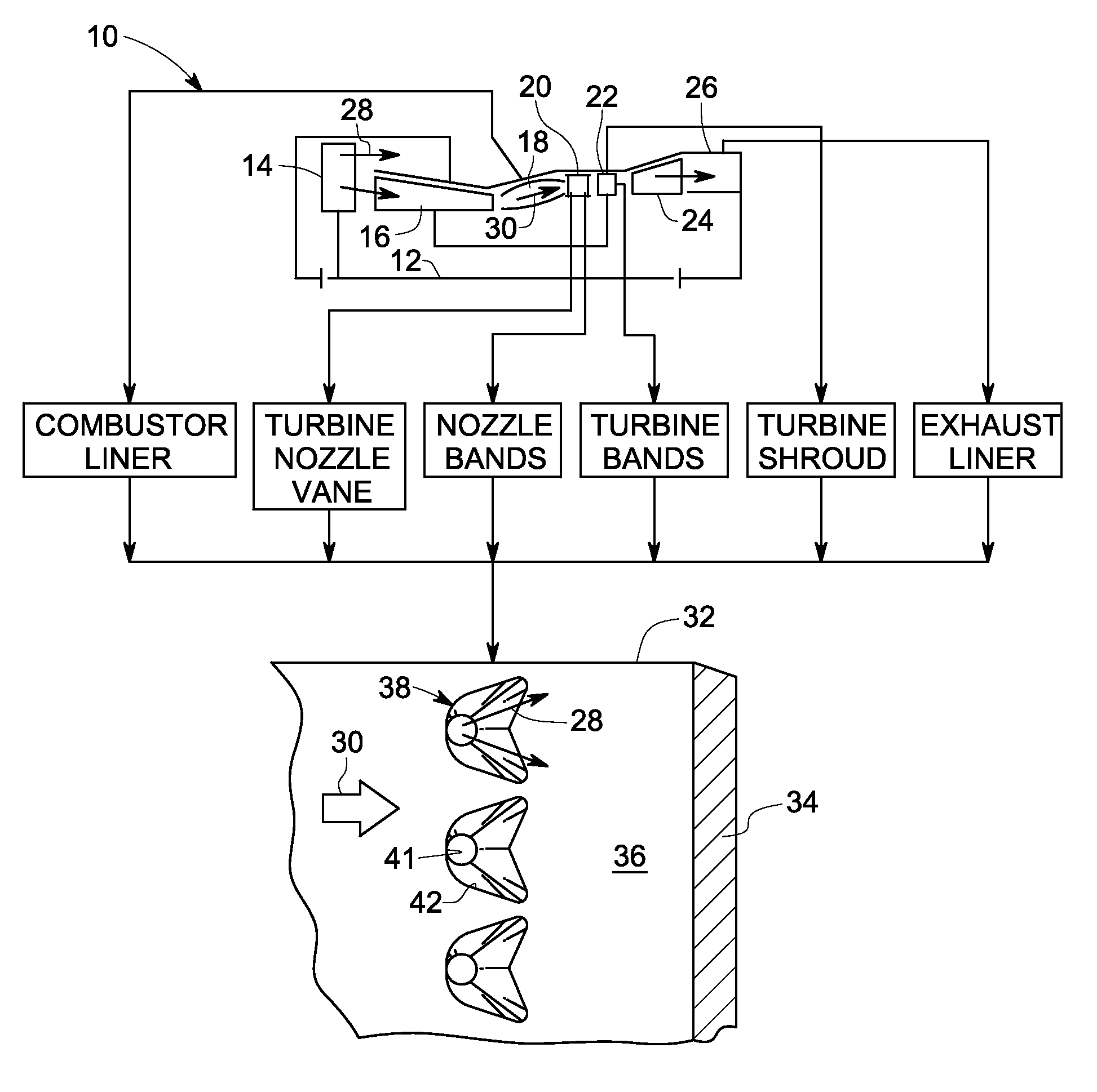
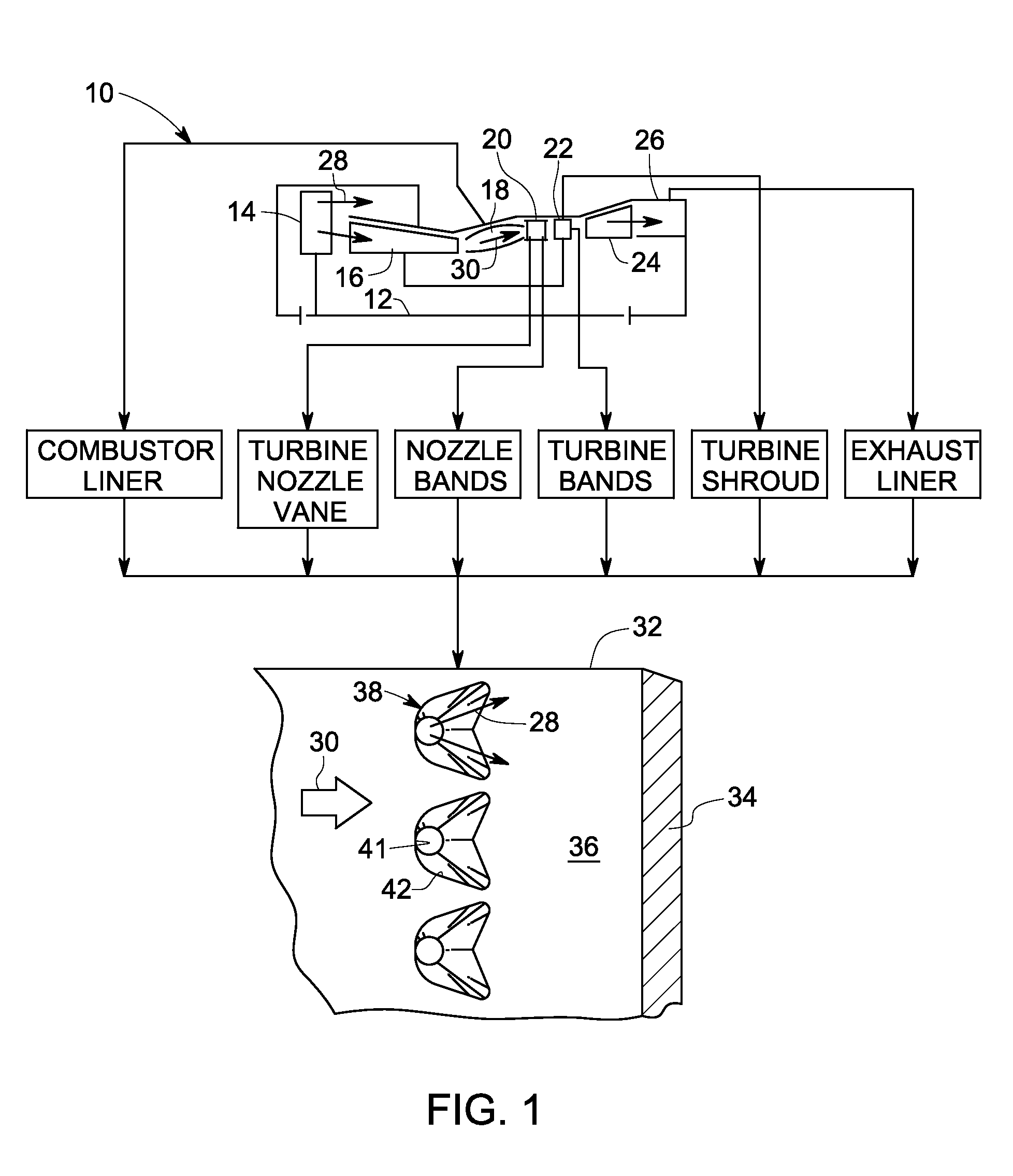
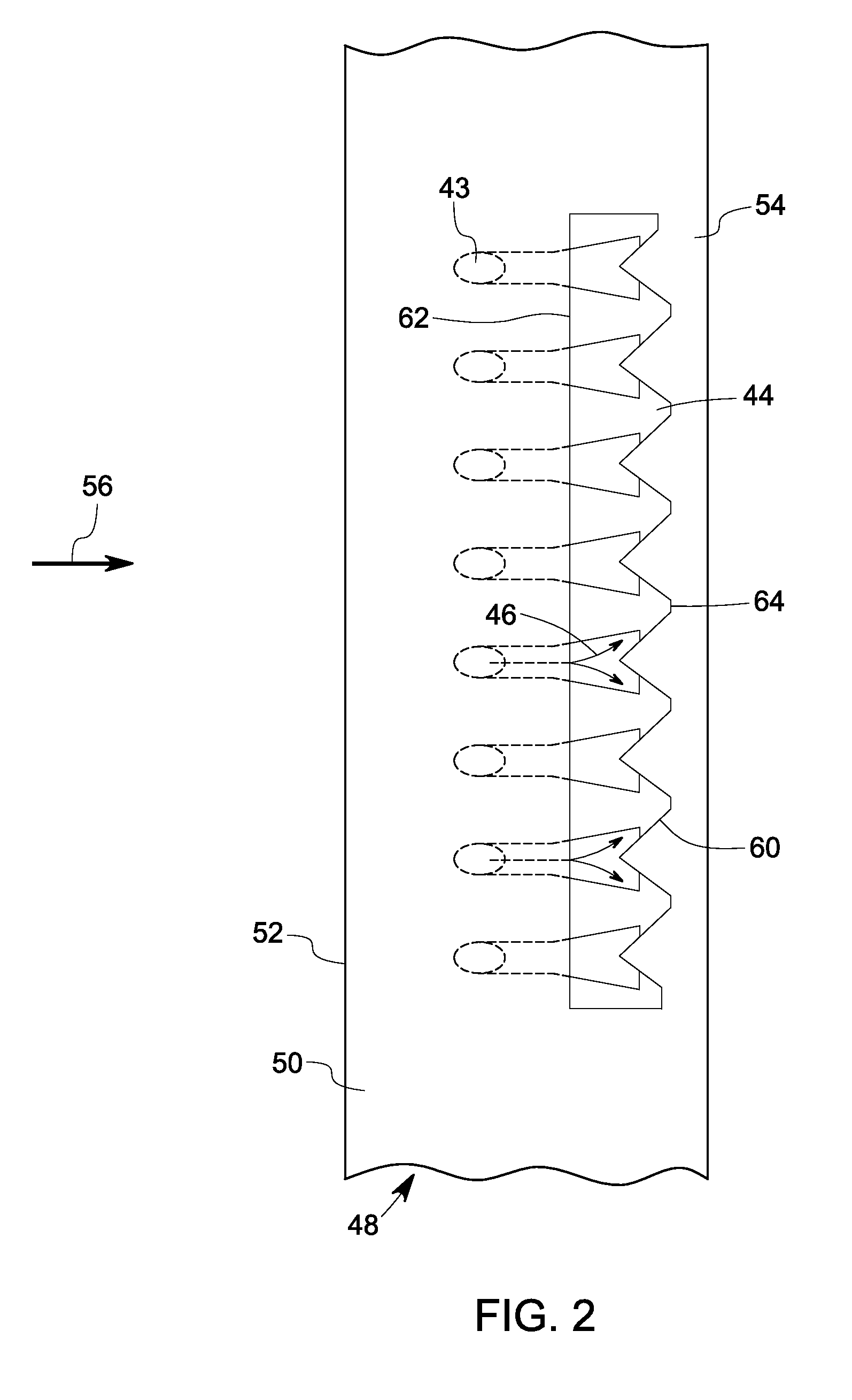
A system for producing at least one trench to improve film cooling in a sample is provided. The system includes at least one laser source outputting at least one pulsed laser beam. The pulsed laser beam includes a pulse duration including a range less than about 50 μs, an energy per pulse having a range less than about 0.1 Joule, and a repetition rate with a range greater than about 1000 Hz. The system also includes a control subsystem coupled to the laser source, the control subsystem configured to synchronize a position of the sample with the pulse duration and energy level in order to selectively remove at least one of a thermal barrier coating, a bondcoat and a substrate metal in the sample to form the at least one trench.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ccircuit and system of using junction diode as program selector for metal fuses for one-time programmable devices
Junction diodes fabricated in standard CMOS logic processes can be used as program selectors for One-Time Programmable (OTP) devices. An OTP device can have at least one OTP element coupled to at least one diode in a memory cell. With a metal fuse is used by the OTP element, at least one contact and / or a plurality of vias can be built (possibly with use of one or more jumpers) in the program path to generate more Joule heat to assist with programming. The jumpers are conductive and can be formed of metal, metal gate, local interconnect, polymetal, etc. The metal fuse can also have an extended area that is longer than required by design rules for enhanced programmability. The OTP element can be polysilicon, silicided polysilicon, silicide, polymetal, metal, metal alloy, local interconnect, thermally isolated active region, CMOS gate, or combination thereof.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
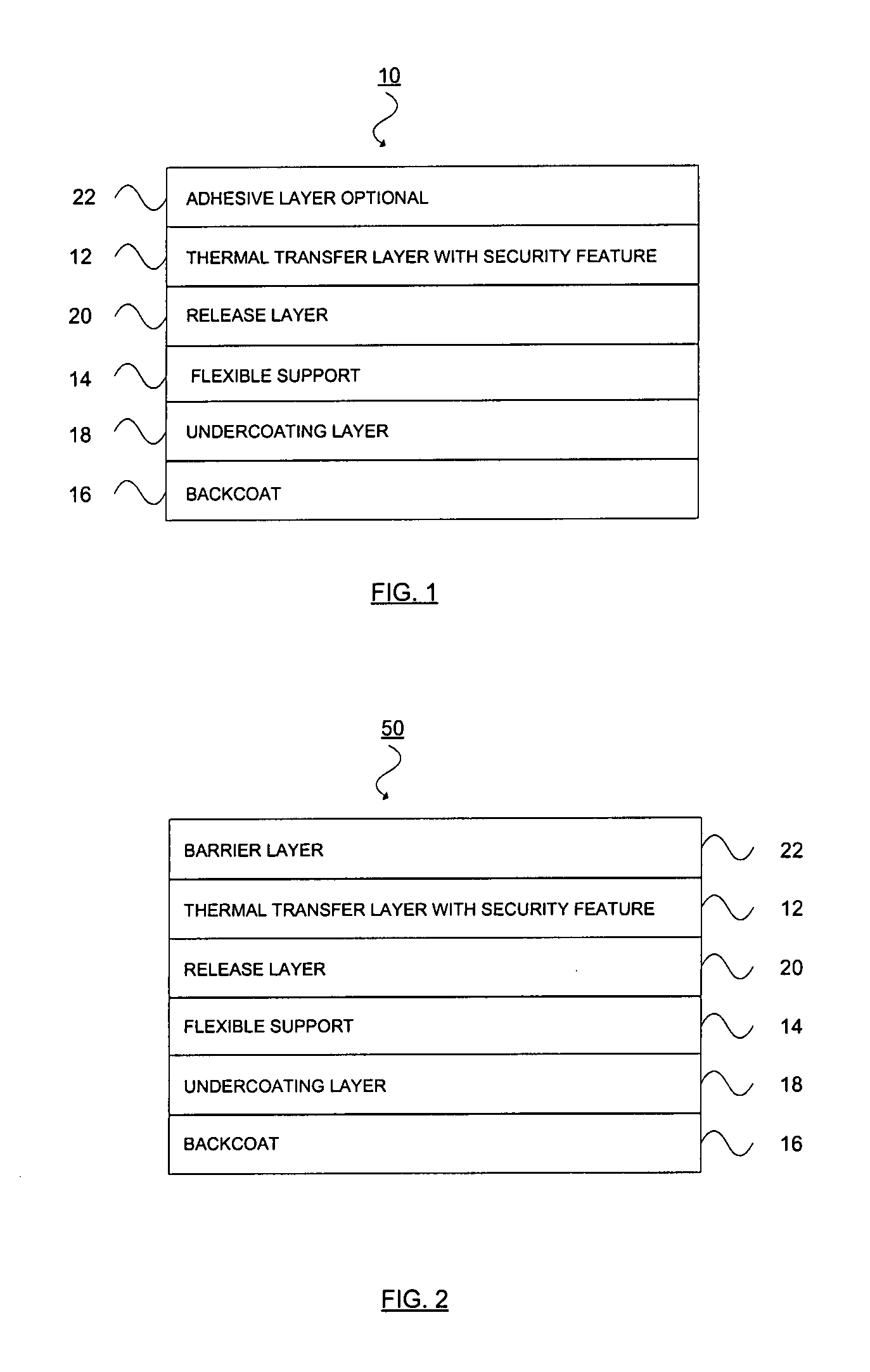
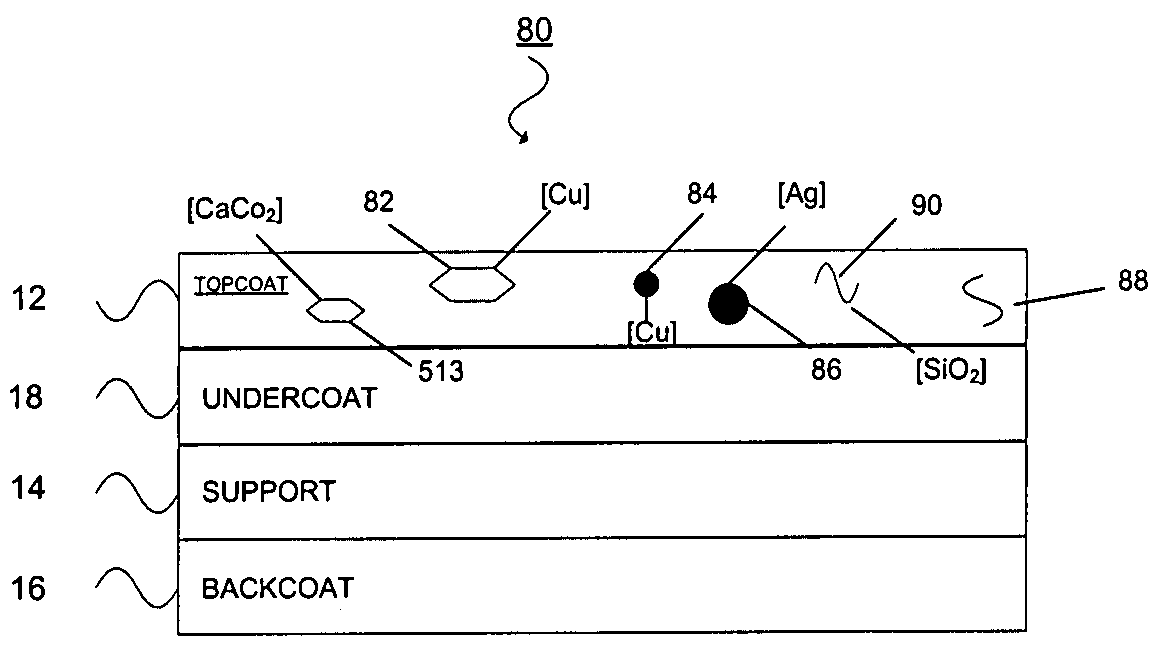
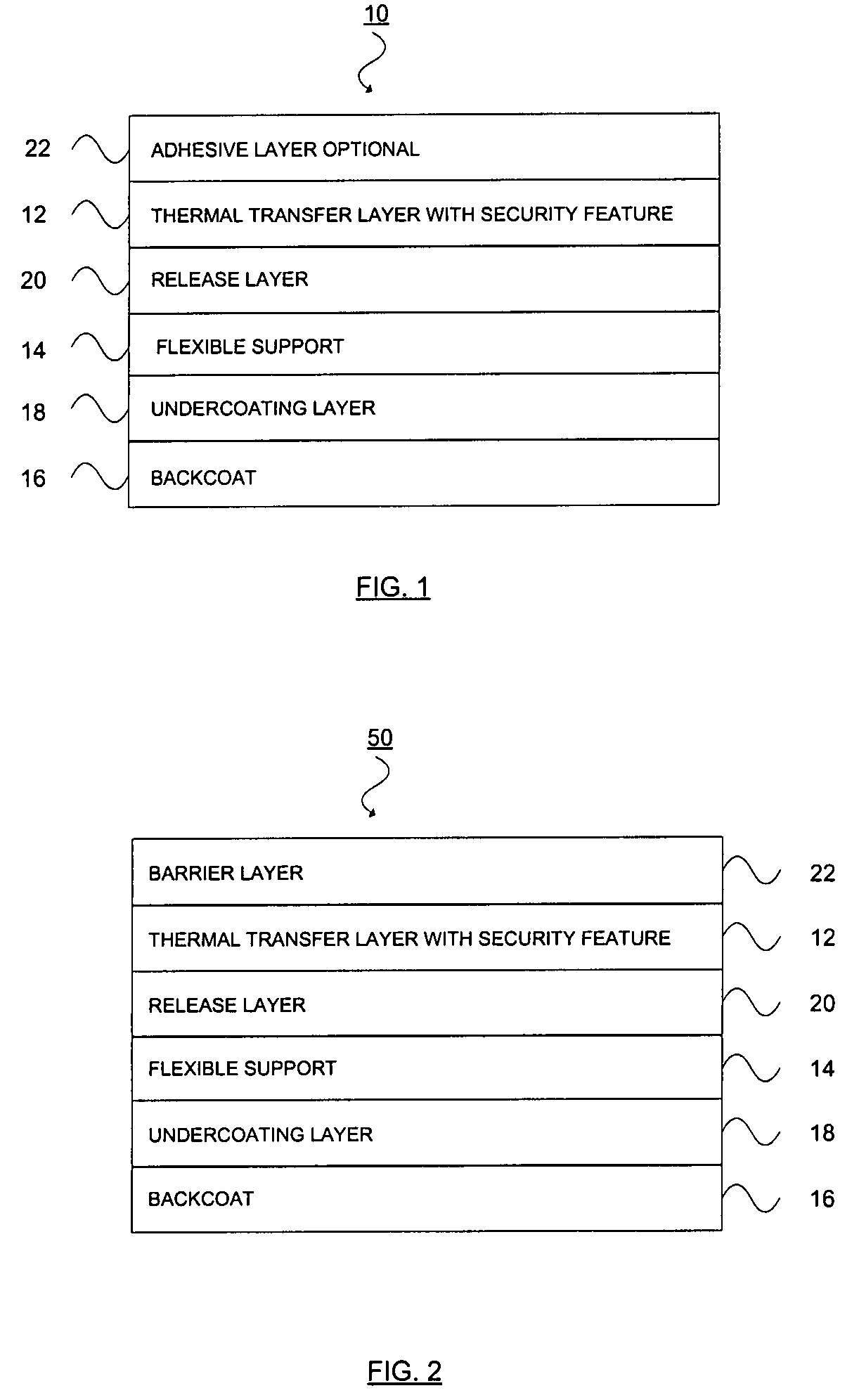
Thermal transfer ribbon
A thermal transfer printing medium that contains a thermal transfer layer which contains a first taggant and colorant, wherein: the first taggant comprises a fluorescent compound with an excitation wavelength selected from the group consisting of wavelengths of less than 400 nanometers, wavelengths of greater than 700 nanometers. When the thermal transfer layer is printed onto a white polyester substrate with a gloss of at least about 84, a surface smoothness Rz value of 1.2, and a reflective color represented by a chromaticity (a) of 1.91 and (b) of −6.79 and a lightness (L) of 95.63, when expressed by the CIE Lab color coordinate system, and when such printing utilizes a printing speed of 2.5 centimeters per second and a printing energy of 3.2 joules per square centimeter, a printed substrate with certain properties is produced. The printed substrate has a reflective color represented by a chromaticity (a) of from −15 to 15 and (b) from −18 to 18, and the printed substrate has a lightness (L) of less than about 35, when expressed by the CIE Lab color coordinate system. When the printed substrate is illuminated with light source that excites the first taggant with an excitation wavelength selected from the group consisting of wavelengths of less than 400 nanometers, wavelengths greater than 700 nanometers, the printed substrate produces a light fluorescence with a wavelength of from about 300 to about 700 nanometers.
Owner:INT IMAGING MATERIALS
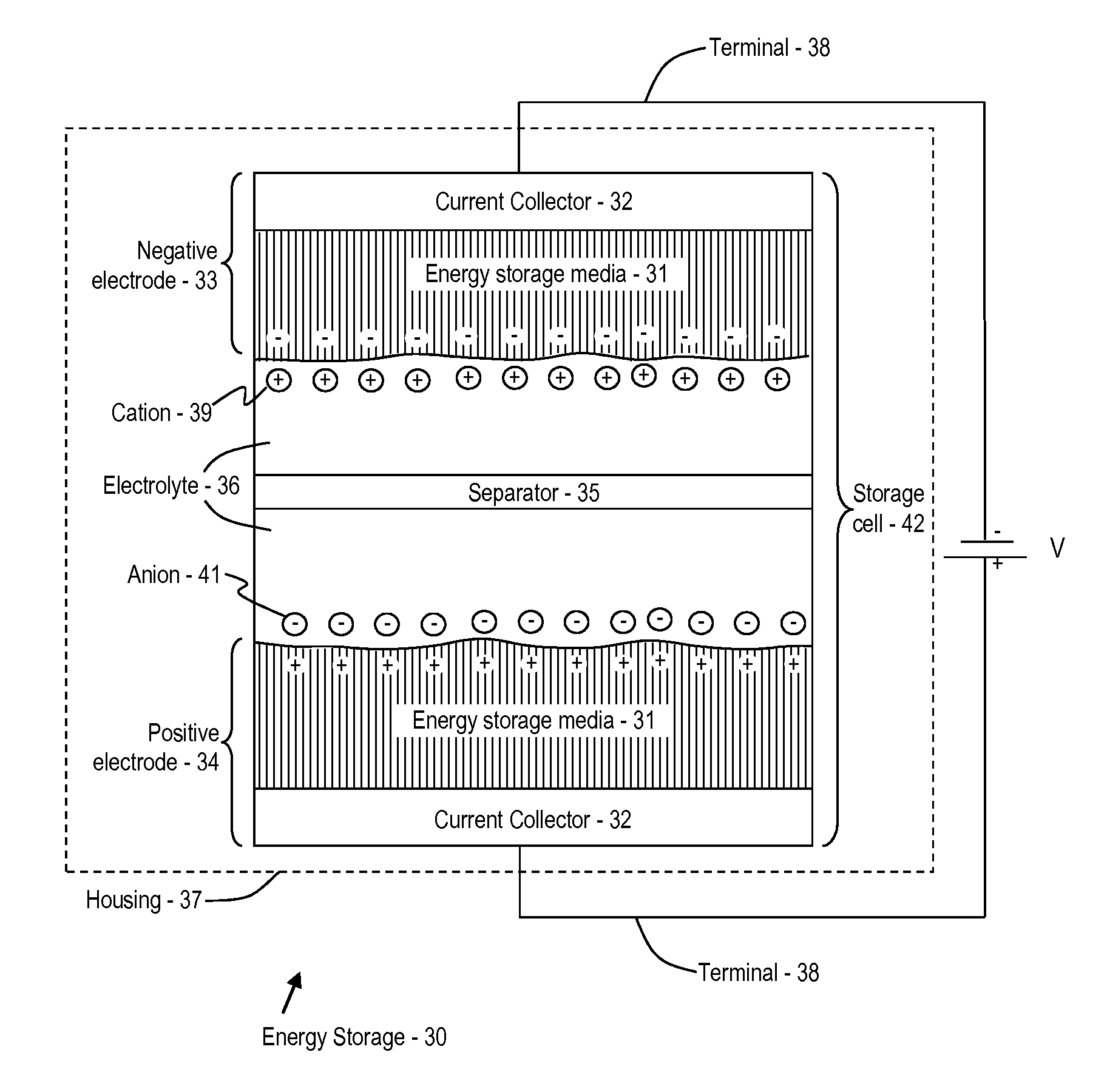
Systems, structures and materials for electrochemical device thermal management
ActiveUS20160226042A1Protecting/adjusting hybrid/EDL capacitorSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsElastomerGram
This disclosure provides a casing for the thermal management and protection of an electrochemical cell. The casing may comprise an inner surface configured to be in physical contact with at least a portion of an outer surface of an electrochemical cell. The inner surface may be substantially solid at room temperature. The casing may also comprise a polymer matrix which itself comprises two or more temperature management materials. At least one of the two or more temperature management materials may comprise a microencapsulated phase change material having a latent heat of at least 5 Joules per gram and a transition temperature between 0° C. and 100° C., and at least one other of the two or more temperature management materials may comprise an elastomeric material. The polymer matrix may be substantially homogeneous.
Owner:LATENT HEAT SOLUTIONS LLC
Hybrid high power laser to achieve high repetition rate and high pulse energy
ActiveUS20060029111A1Reduce outputEnhanced spontaneous emissionLaser using scattering effectsOptical light guidesHigh power lasersWaveguide
A fiber laser cavity that provides a new pulse shaping and spectral shaping technique is disclosed in this invention to achieve the purpose of resolving the difficulties arising from the issues related to Q-switched solid state lasers. The laser system achieves high repetition rate (1 kHz-100 kHz) and high pulse-to-pulse energy stability with small timing jitter of the laser pulses and scalable to the Joule pulse energy level. The laser system of this invention employs new approach with a hybrid fiber / waveguide master Oscillator-High Power Amplifier (MOPA) laser system in combination with the pulse shaping technology that allows not only to scale the fiber laser pulse energy to the multi-Joule level with high pulse-to-pulse energy stability but also achieve precise control of laser pulse timing jitter in a scale of <100 ps that is at least 5 to 10 time more accurate than for Q-switched systems where the same parameter reaches 500-1000 ps range.
Owner:LIU JIAN
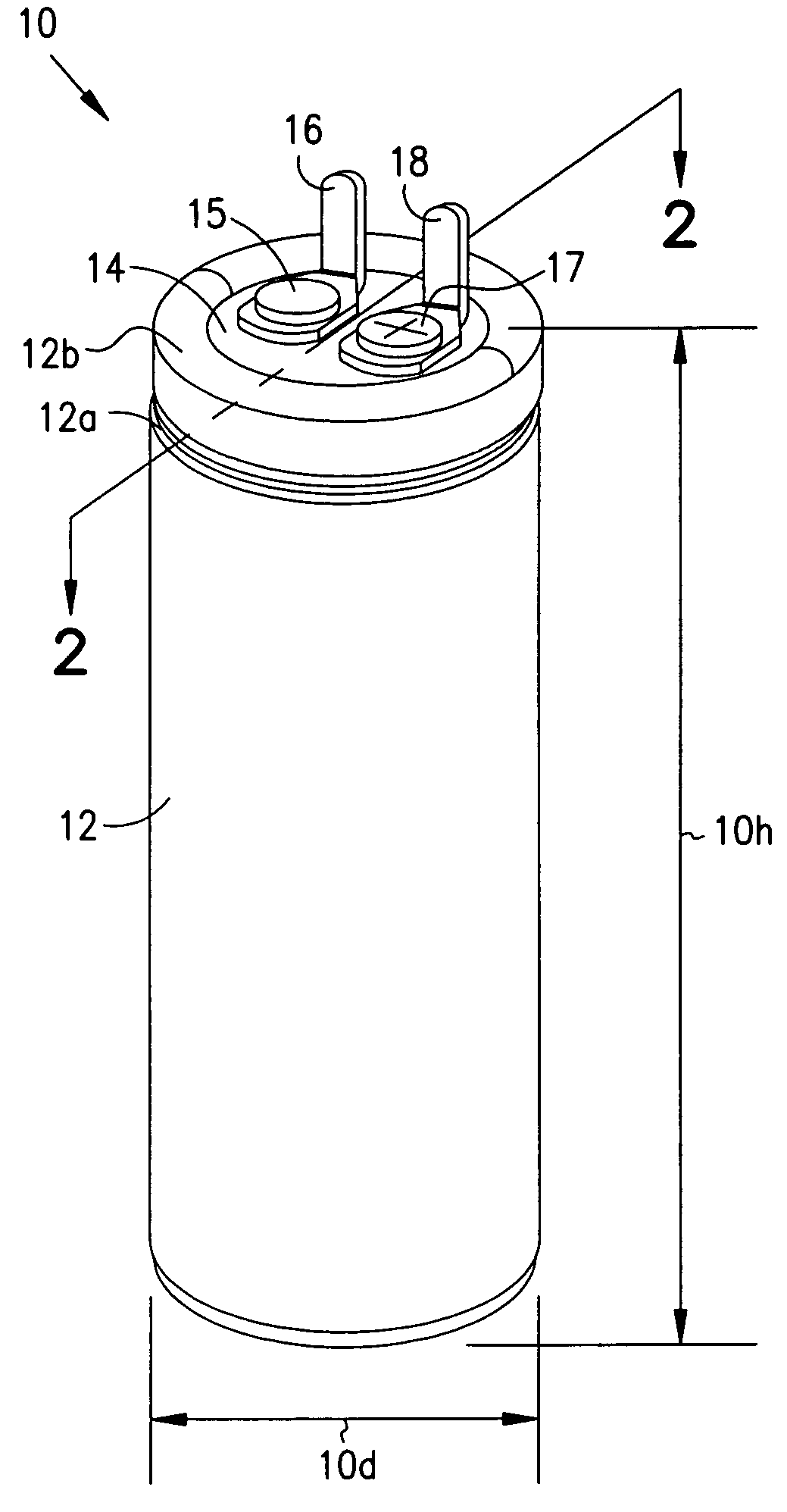
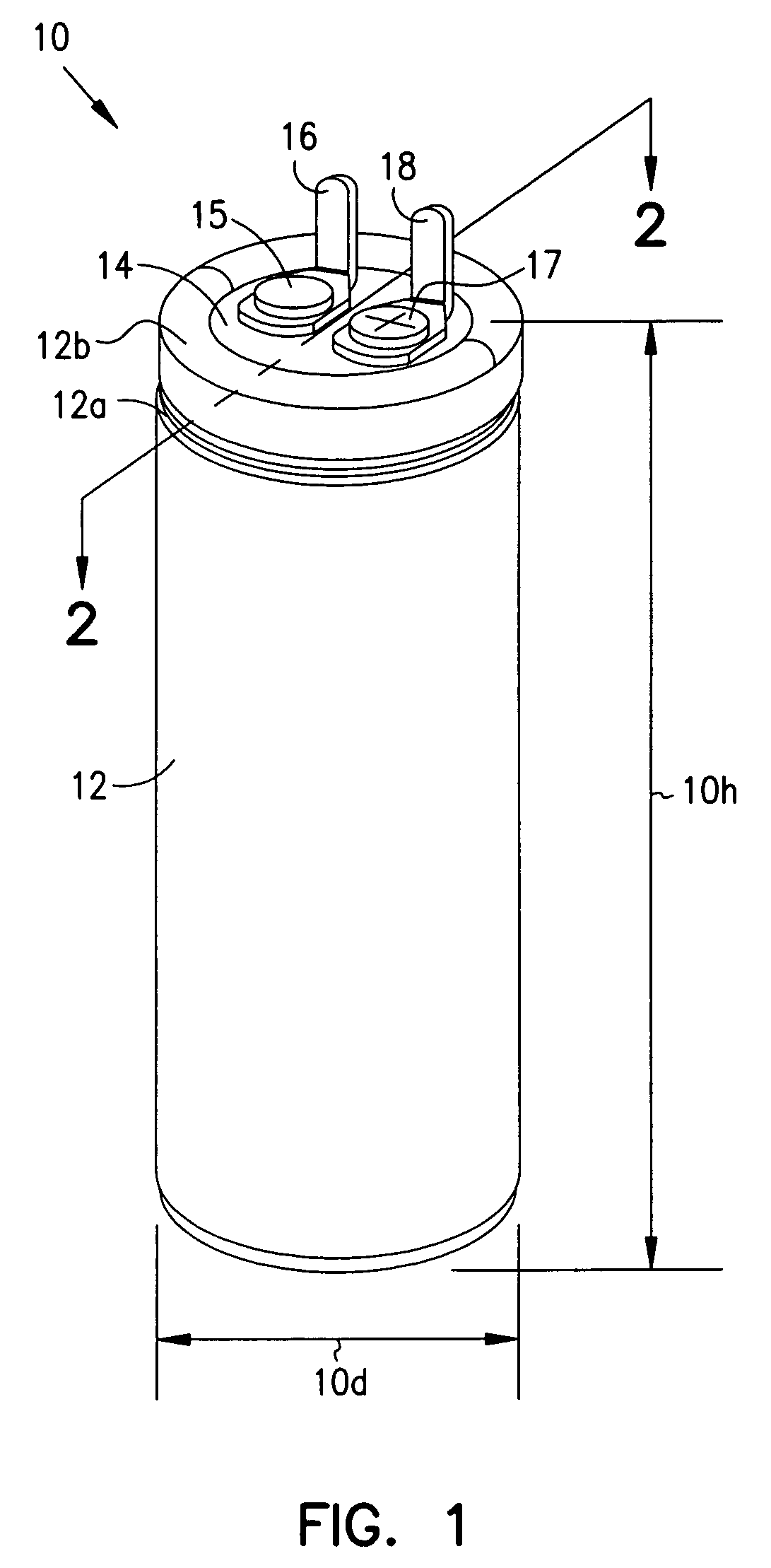
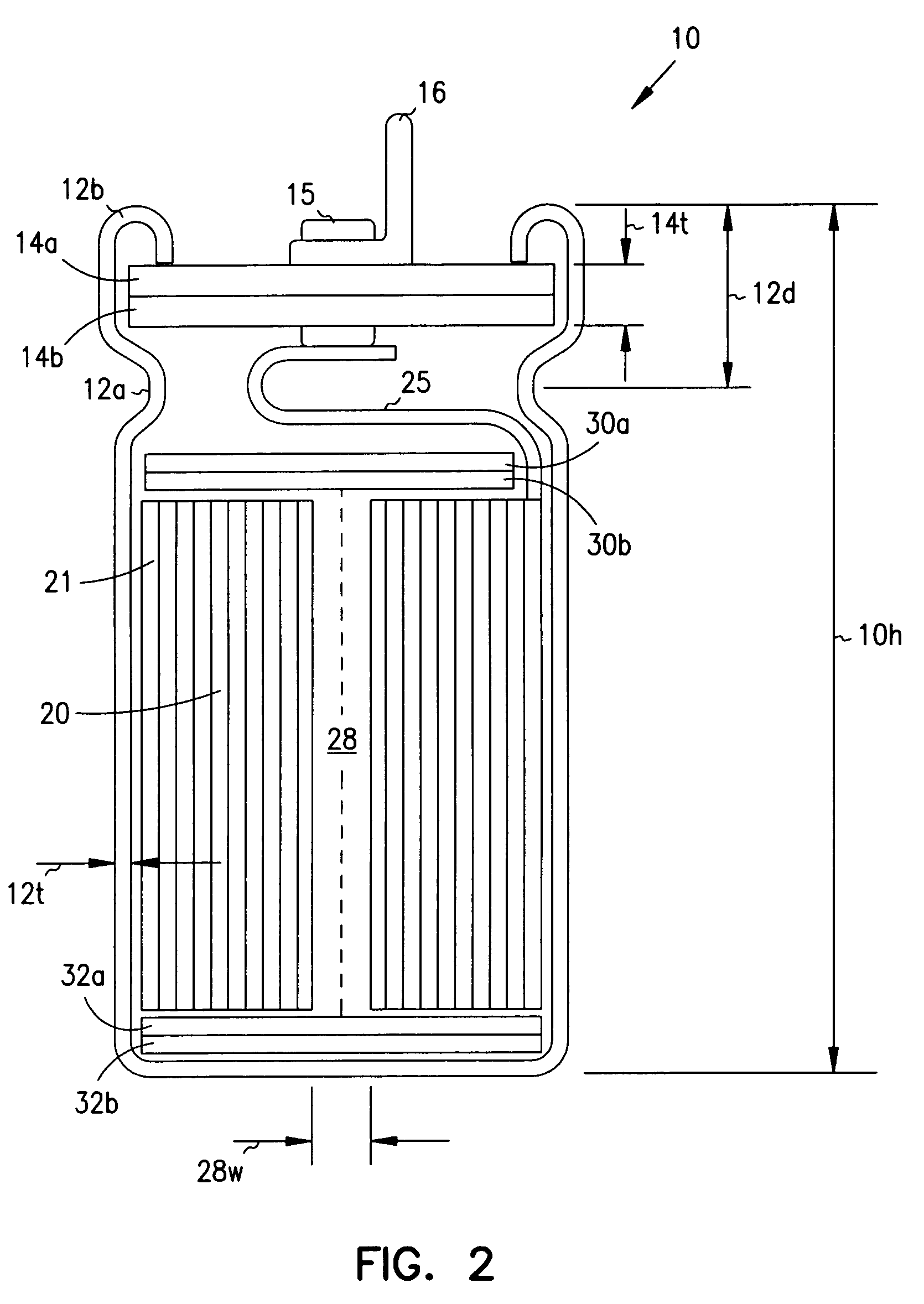
Smaller electrolytic capacitors for implantable defibrillators
InactiveUS7251123B2Reduce the overall diameterReduce volumeLiquid electrolytic capacitorsHeart defibrillatorsFiberElectrolysis
Implantable defibrillators are implanted into the chests of patients prone to suffering ventricular fibrillation, a potentially fatal heart condition. A critical component in these devices is an aluminum electrolytic capacitors, which stores and delivers one or more life-saving bursts of electric charge to a fibrillating heart. These capacitors make up about one third the total size of the defibrillators. Unfortunately, conventional manufacturers of these capacitors have paid little or no attention to reducing the size of these capacitors through improved capacitor packaging. Accordingly, the inventors contravened several conventional manufacturing principles and practices to devise unique space-saving packaging that allows dramatic size reduction. One embodiment of the invention uses thinner and narrower separators and top and bottom insulative inserts to achieve a 330-volt operating, 390-volt surge, 190-microfarad, 30-Joule aluminum electrolytic capacitor which is 33 percent smaller than conventional capacitors having similar electrical traits.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Power system for high temperature applications with rechargeable energy storage
ActiveUS9013144B2Material nanotechnologyCells structural combinationCelsius DegreeElectric power system
A power system adapted for supplying power in a high temperature environment is disclosed. The power system includes a rechargeable energy storage that is operable in a temperature range of between about seventy degrees Celsius and about two hundred and fifty degrees Celsius coupled to a circuit for at least one of supplying power from the energy storage and charging the energy storage; wherein the energy storage is configured to store between about one one hundredth (0.01) of a joule and about one hundred megajoules of energy, and to provide peak power of between about one one hundredth (0.01) of a watt and about one hundred megawatts, for at least two charge-discharge cycles. Methods of use and fabrication are provided. Embodiments of additional features of the power supply are included.
Owner:FASTCAP SYST
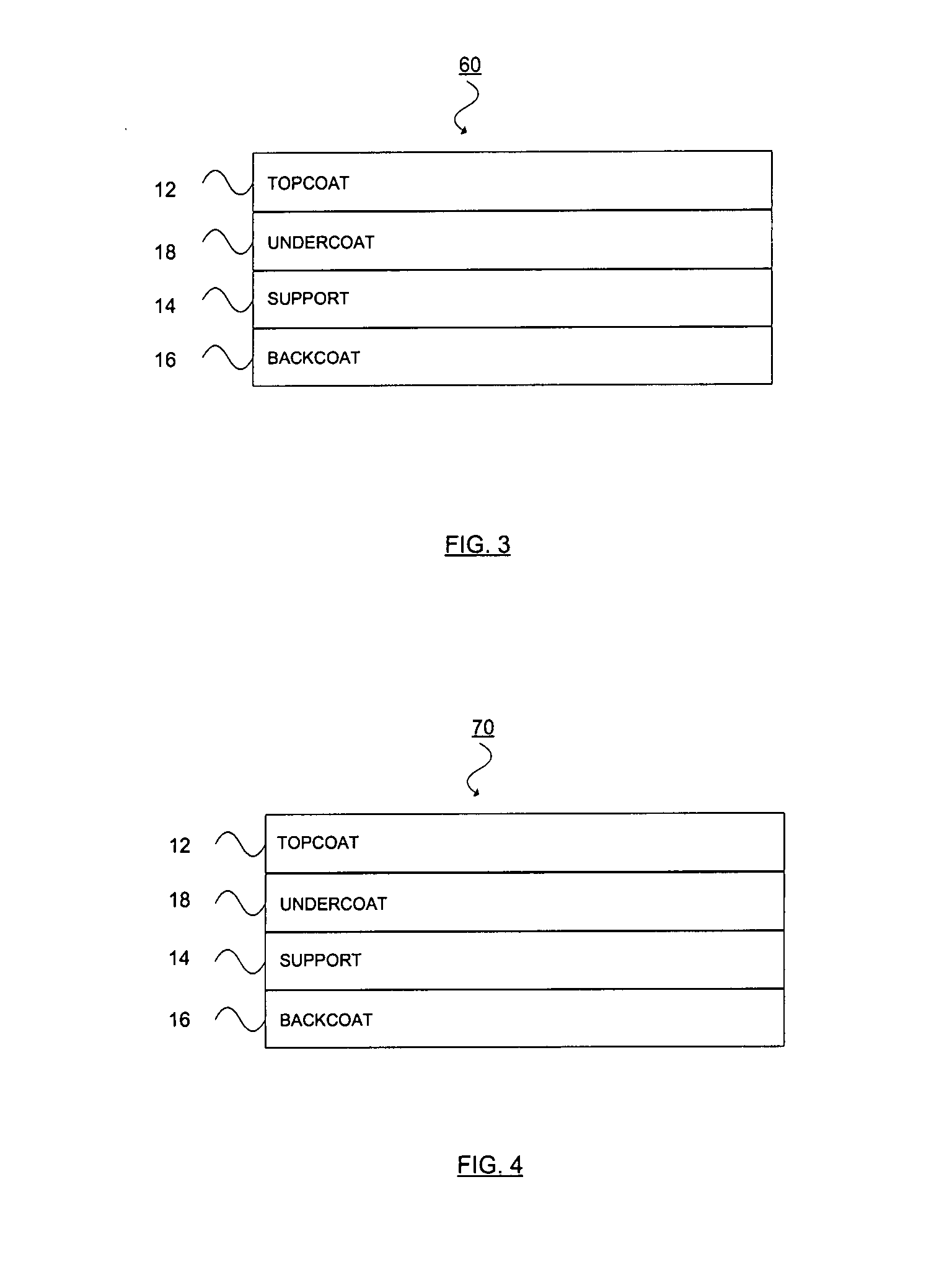
Thermal transfer ribbon
A thermal transfer printing medium that contains a thermal transfer layer which contains a first taggant and colorant, wherein: the first taggant comprises a fluorescent compound with an excitation wavelength selected from the group consisting of wavelengths of less than 400 nanometers, wavelengths of greater than 700 nanometers. When the thermal transfer layer is printed onto a white polyester substrate with a gloss of at least about 84, a surface smoothness Rz value of 1.2, and a reflective color represented by a chromaticity (a) of 1.91 and (b) of −6.79 and a lightness (L) of 95.63, when expressed by the CIE Lab color coordinate system, and when such printing utilizes a printing speed of 2.5 centimeters per second and a printing energy of 3.2 joules per square centimeter, a printed substrate with certain properties is produced. The printed substrate has a reflective color represented by a chromaticity (a) of from −15 to 15 and (b) from −18 to 18, and the printed substrate has a lightness (L) of less than about 35, when expressed by the CIE Lab color coordinate system. When the printed substrate is illuminated with light source that excites the first taggant with an excitation wavelength selected from the group consisting of wavelengths of less than 400 nanometers, wavelengths greater than 700 nanometers, the printed substrate produces a light fluorescence with a wavelength of from about 300 to about 700 nanometers.
Owner:INT IMAGING MATERIALS
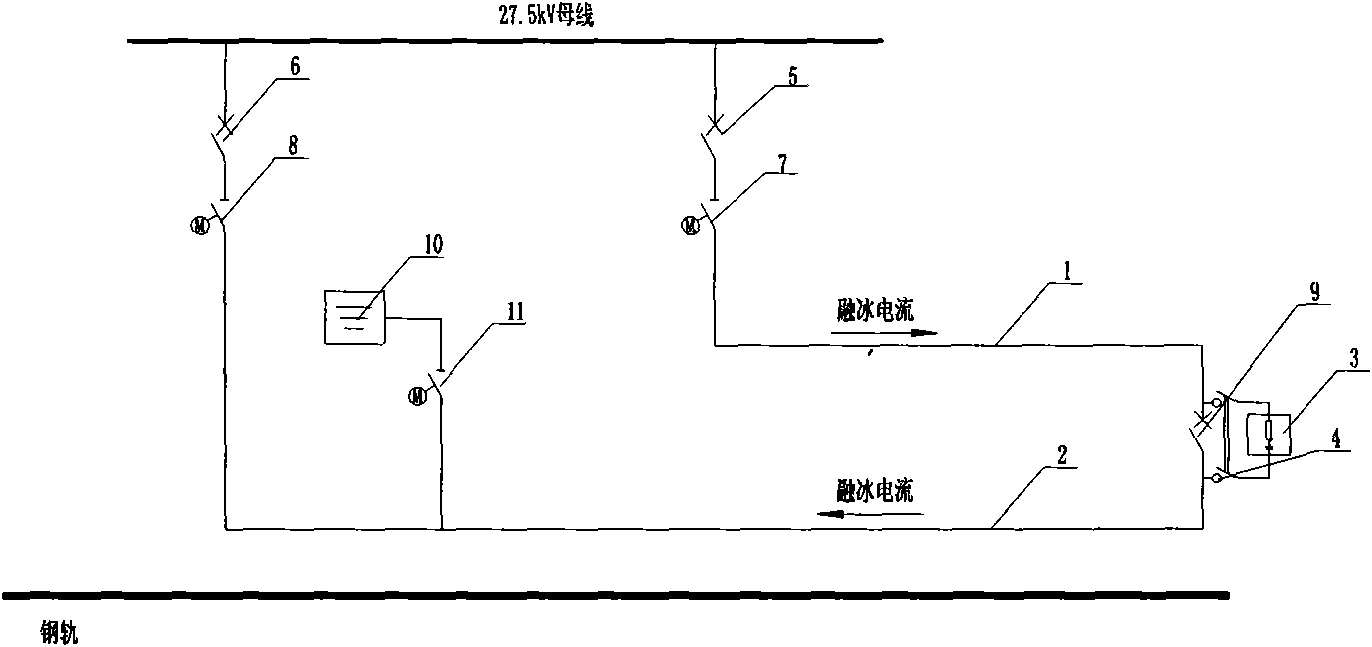
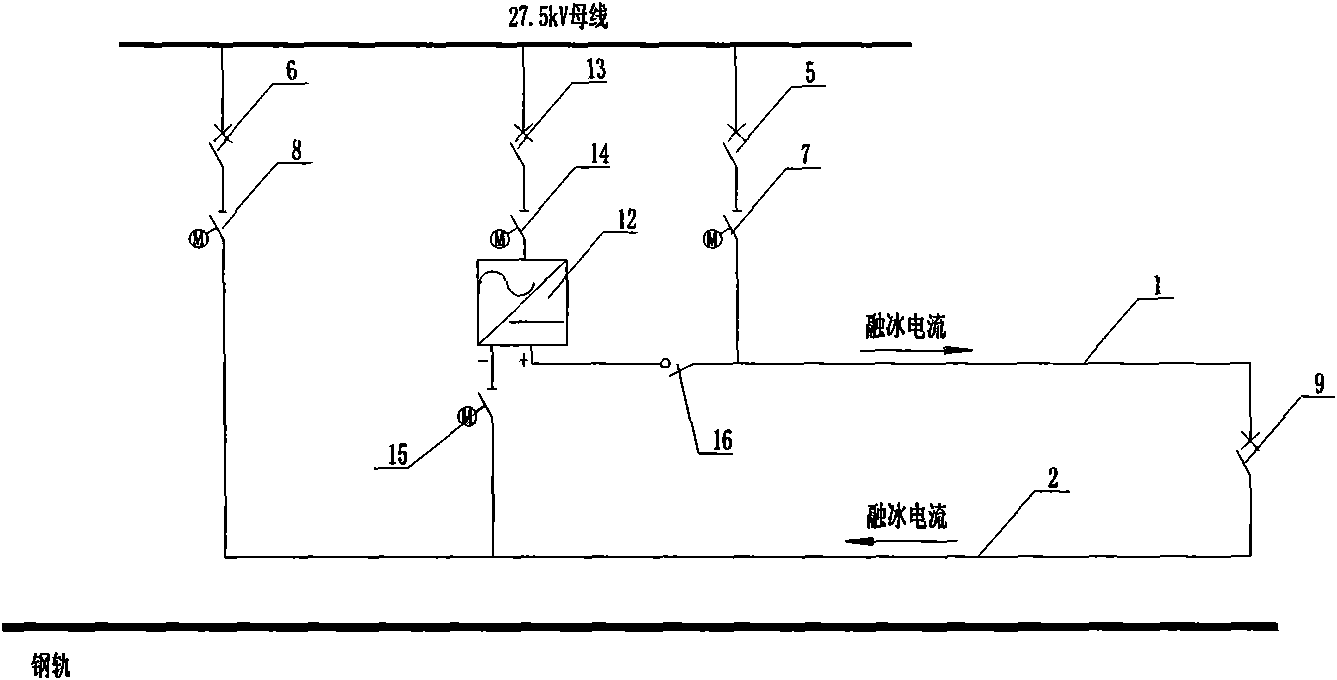
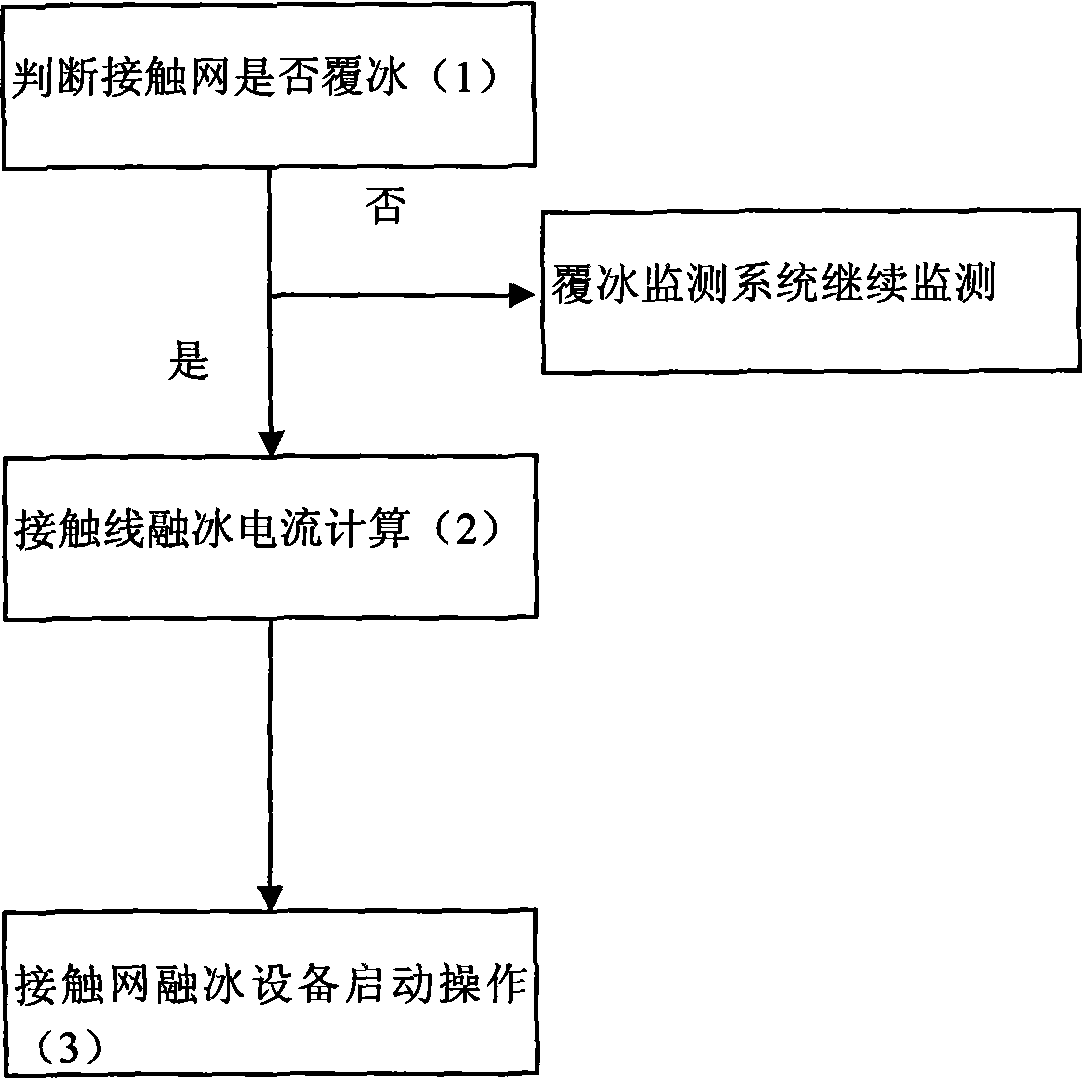
Ice melting method for overhead contact system of electrified railway and ice melting system thereof
InactiveCN101640400AEliminate damageReduce the impactOverhead installationTrolley linesEngineeringContact line
The invention relates to an ice melting method for overhead contact system of an electrified railway and an ice melting system thereof. Major hazards of ice coating of the overhead contact system include accidents that pantograph of electric locomotives can not contact with a contact line to obtain current, contact system brandishes, even falls of piles and collapses, and the like. In the ice melting method and the ice melting system thereof, an upper overhead contact system and a lower overhead contact system are connected in series to form a circuit by a section post, AC or DC ice melting current is input at the head end of the circuit, ice coating thickness and safe ice melting current value are obtained by analyzing meteorological and overhead contact system parameters with an ice coating data processing and control module, and then the ice melting system is controlled to output the ice melting current at the end of the circuit, thus ice is molten by Joule heat generated by the current. In the ice melting method and the ice melting system thereof, ice attached to the contact line is molten by joule heat, and compared with the deicing modes of artificial knock and the like of operation departments, the ice melting method and the ice melting system thereof greatly improve deicing efficiency, thus reducing the effect on railway transport, and eliminating damages of external force on the contact line.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY FIRST SURVEY & DESIGN INST GRP
Electrical heating numerical control incremental forming processing method and device for plate
The invention relates to a device and a method of the electrical heating numerical control incremental forming processing of a sheet metal and belongs to the technical field of the sheet metal incremental forming processing. The key points of the device and the method lie in that a large current-carrying wire is used for forming an auxiliary power supply, a forming pressure head, a forming clamp and the sheet metal into a current loop; the power supply provides a low-voltage large current to cause the materials in a processing area to generate joule heat and to be softened in the sheet metal processing and forming so as to ensure the smooth implementation of the incremental forming processing. The heating method is fast in temperature rising, convenient in control and low in price, thus solving the problem that other heating methods are complex to control, improving the processing precision and being favorable for forming complex parts. At the same time, the method is suitable for the incremental processing of sheet metals such as the titanium magnesium sheet metal, and the like, which are hard to be plastically formed at normal temperature.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
Laser-induced plasma micromachining
A method and system for laser ablating a target material in an ambient atmosphere are disclosed. The method includes generating one or more laser pulses, each of the laser pulses having a pulse width of 1 picosecond (ps) or less and a pulse energy of 50 micro joules (μJ) or more. The laser pulses are directed towards the target material such that the laser pulses interact with a gas to form a plasma. The plasma removes a portion of the target material by interaction of the plasma with the target material.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Low-temperature impact-resistant polyamide-based stretch-oriented mutilayer film
InactiveUS20030157350A1High low temperature impact resistanceIncrease elasticityFlexible coversWrappersSurface layerPolyamide
A stretch-oriented multilayer film suited for use as a freeze packaging material, a deep drawing packaging material, a vertical pillow packaging material, etc., is provided as a stretch-oriented multilayer film, comprising at least three layers including a surface layer (a) comprising a thermoplastic resin, an intermediate layer (b) comprising a polyamide resin and a surface layer (c) comprising a sealable resin, said multilayer film exhibiting an impact energy of at least 1.5 Joule at a conversion thickness of 50 mum at -10° C. The multilayer film is produced through an inflation process using water having a large capacity as a cooling and a heating medium and including a combination of a high degree of stretching and a high degree of relaxation heat treatment not exercised heretofore.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com