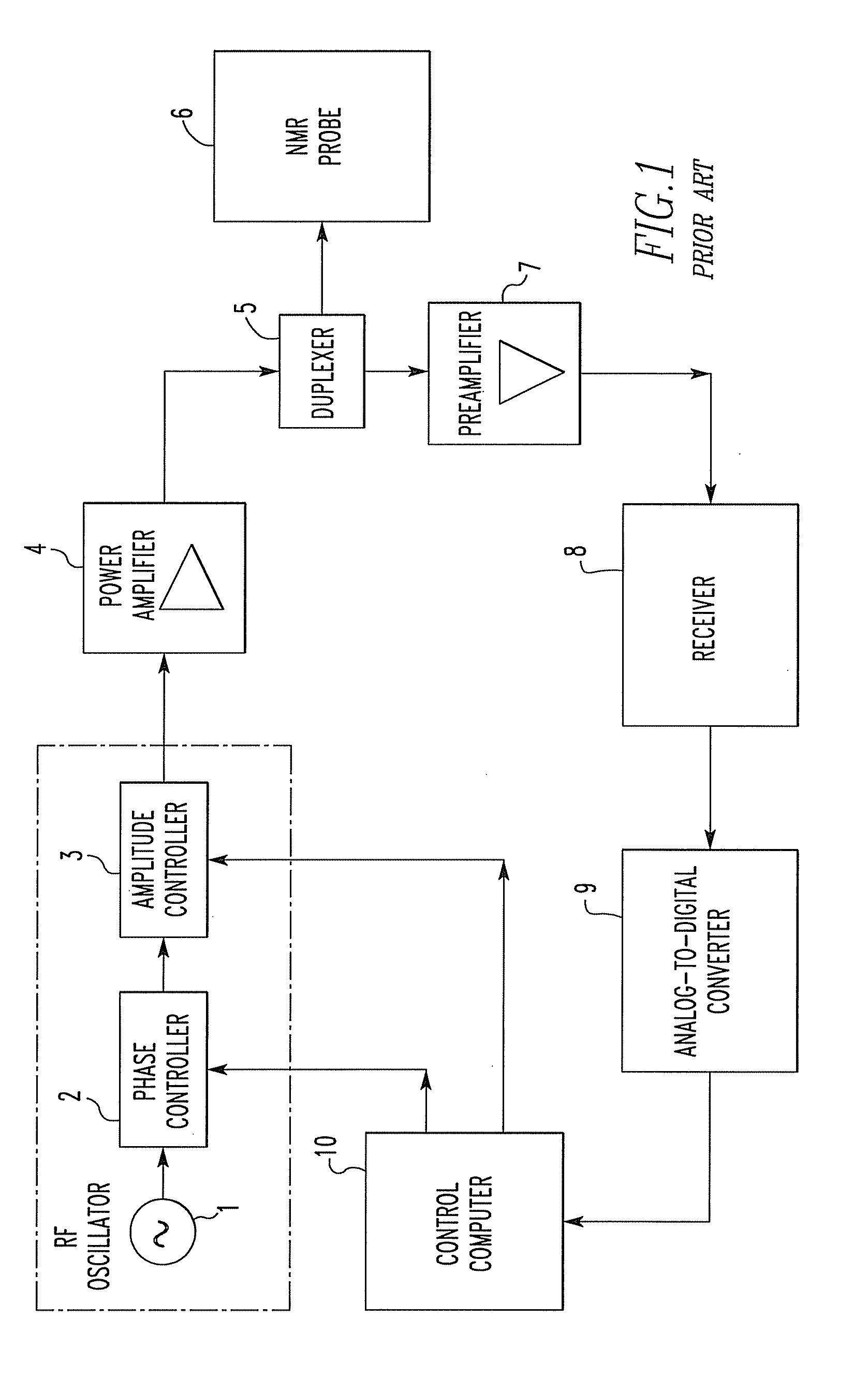
Patents
Literature
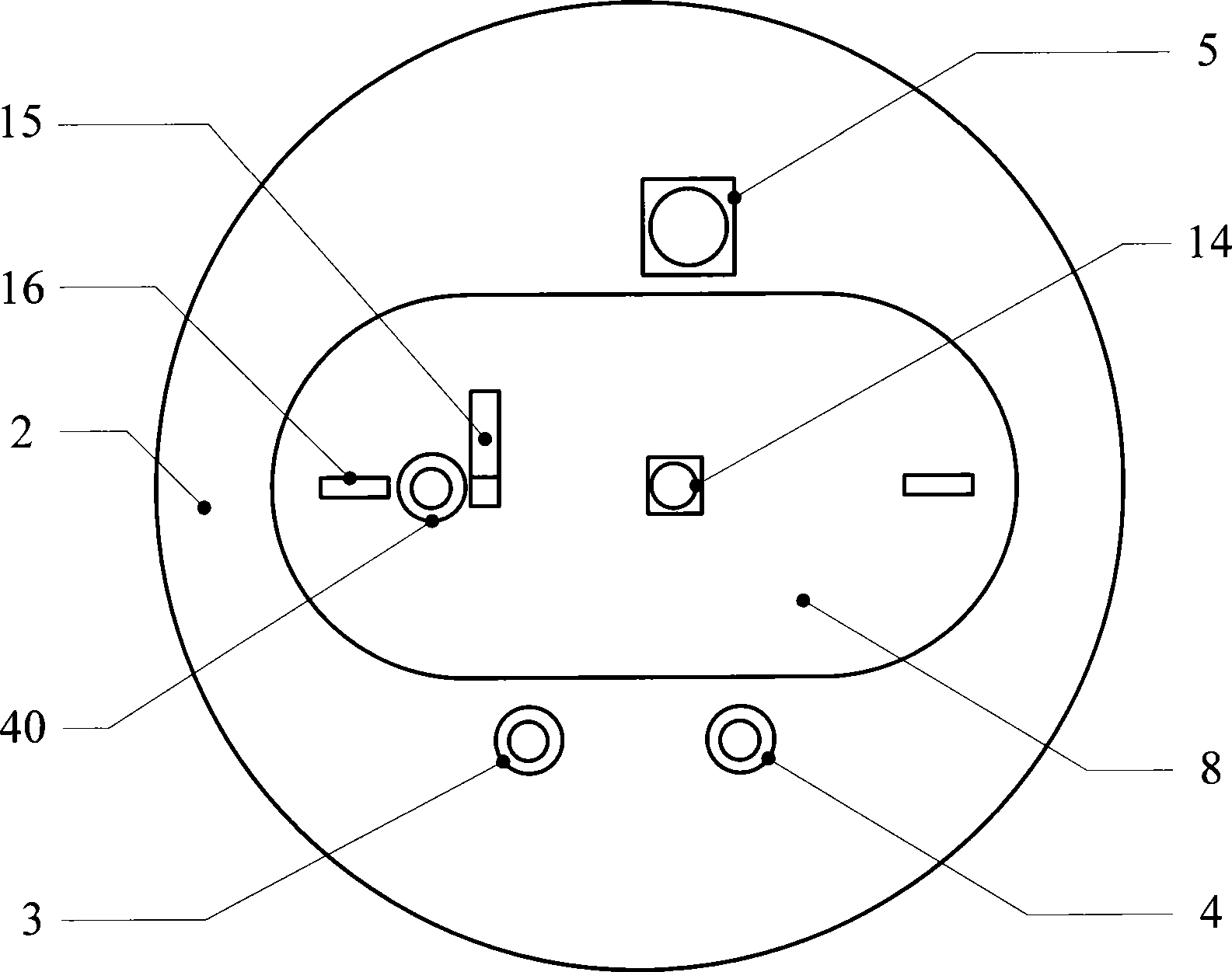
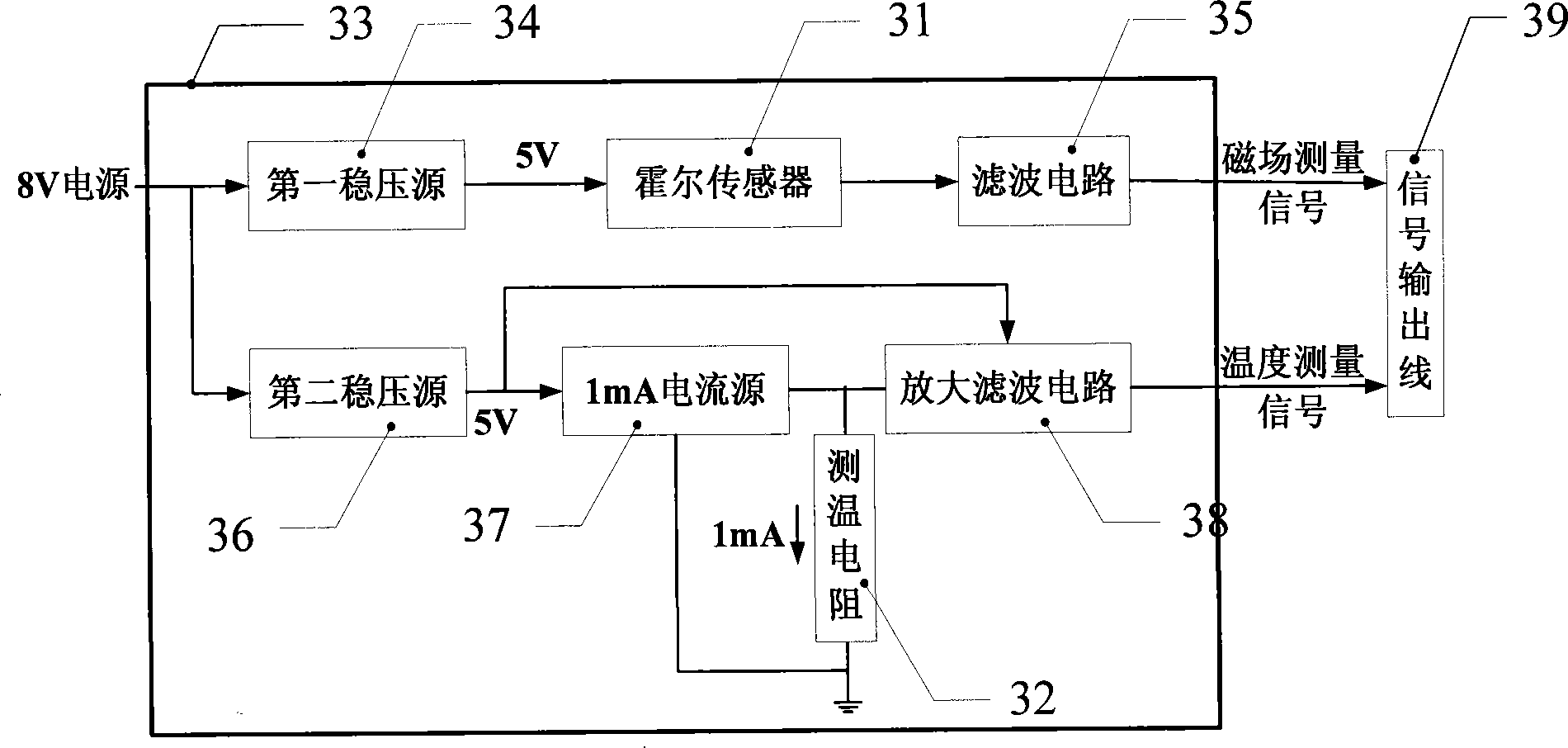
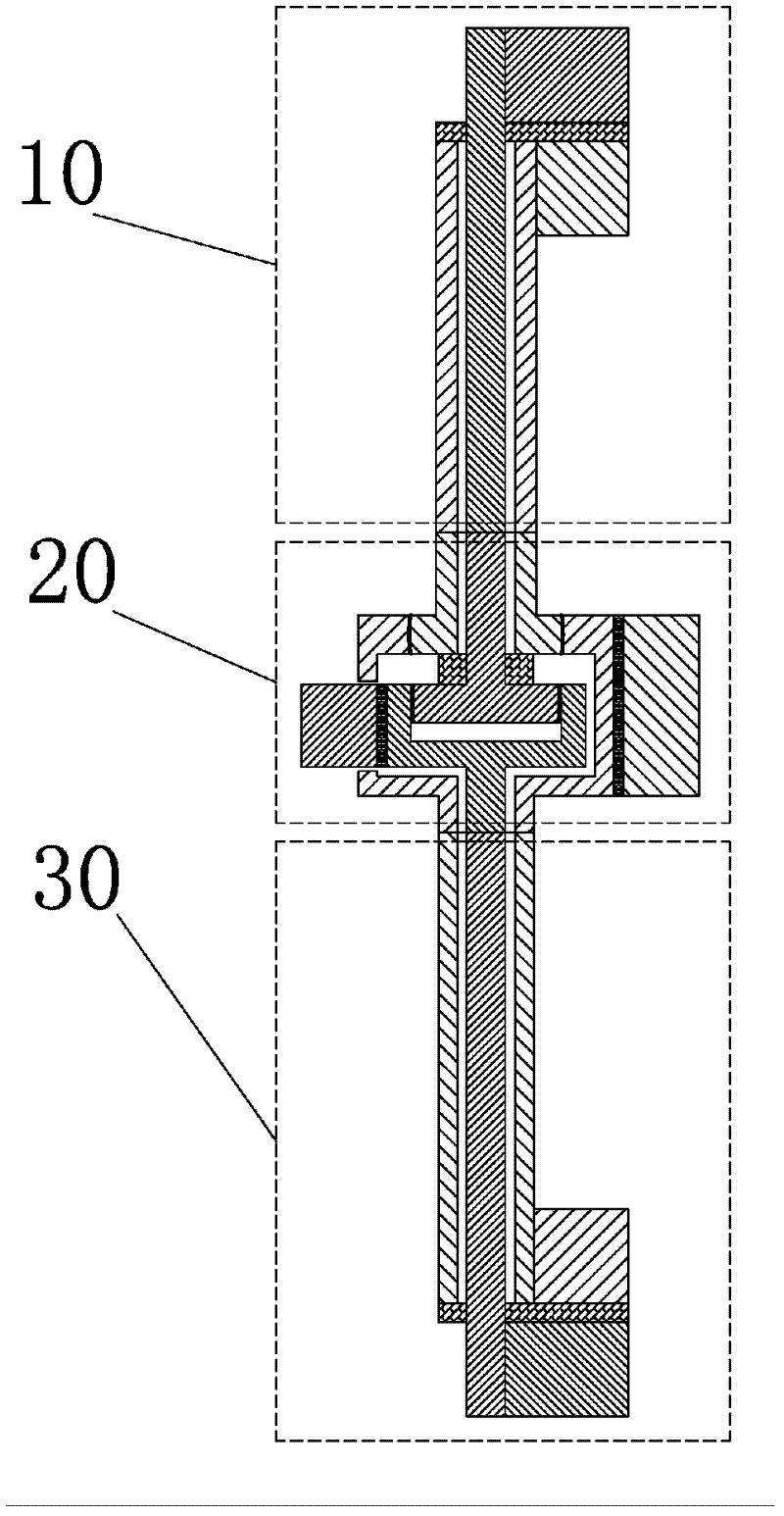
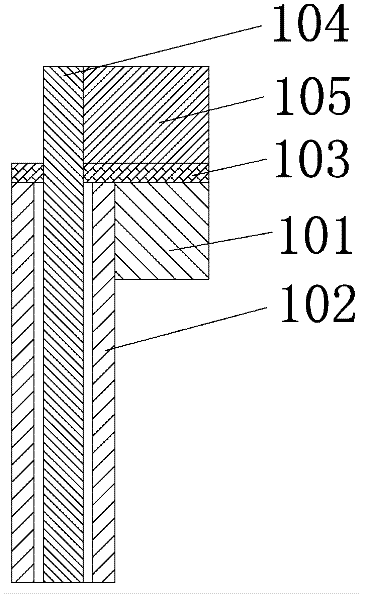
574 results about "Liquid helium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
At standard pressure, the chemical element helium exists in a liquid form only at the extremely low temperature of −269 °C (about 4 K or −452.2 °F). Its boiling point and critical point depend on which isotope of helium is present: the common isotope helium-4 or the rare isotope helium-3. These are the only two stable isotopes of helium. See the table below for the values of these physical quantities. The density of liquid helium-4 at its boiling point and a pressure of one atmosphere (101.3 kilopascals) is about 0.125 grams per cm³, or about 1/8th the density of liquid water.
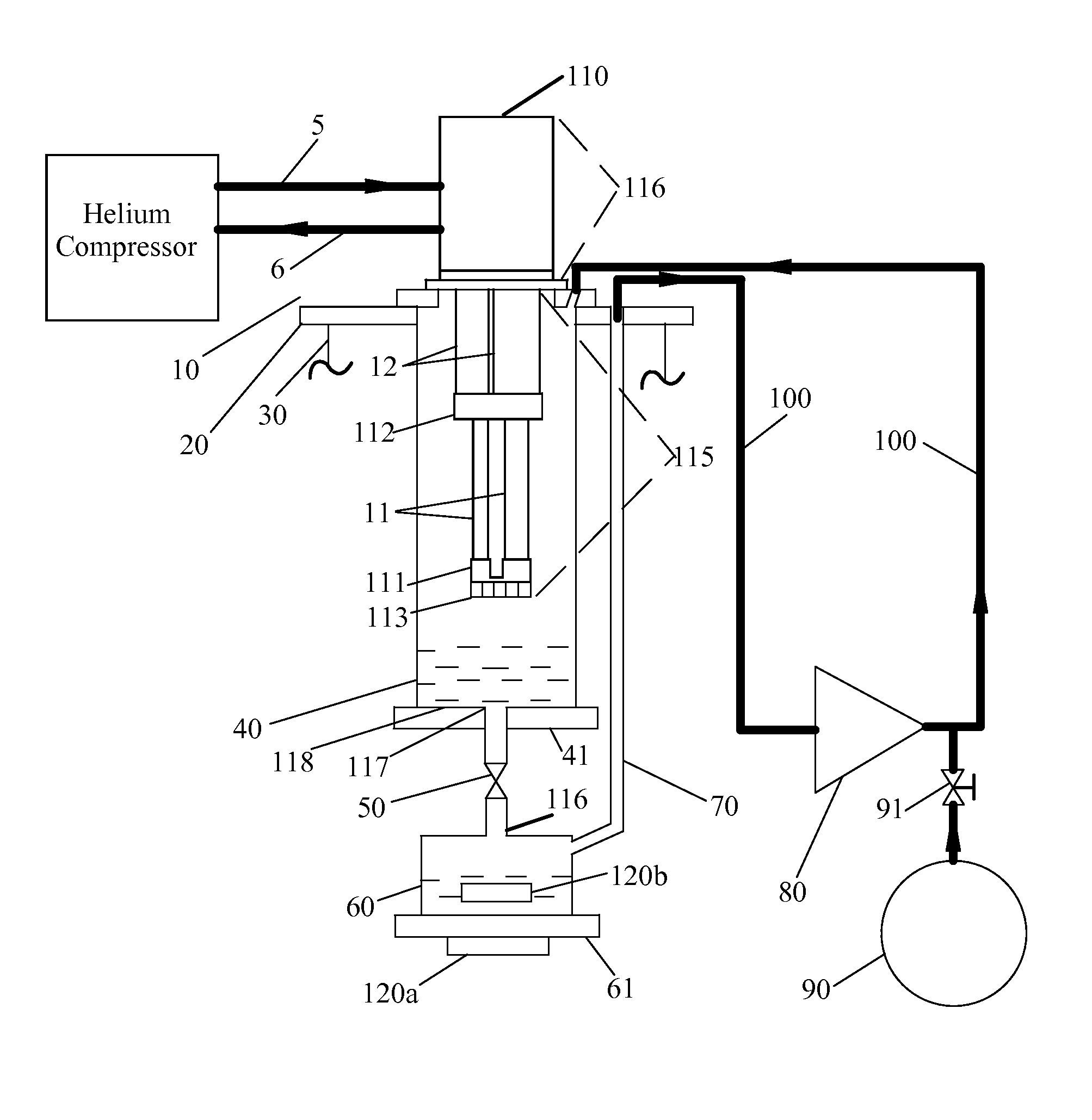
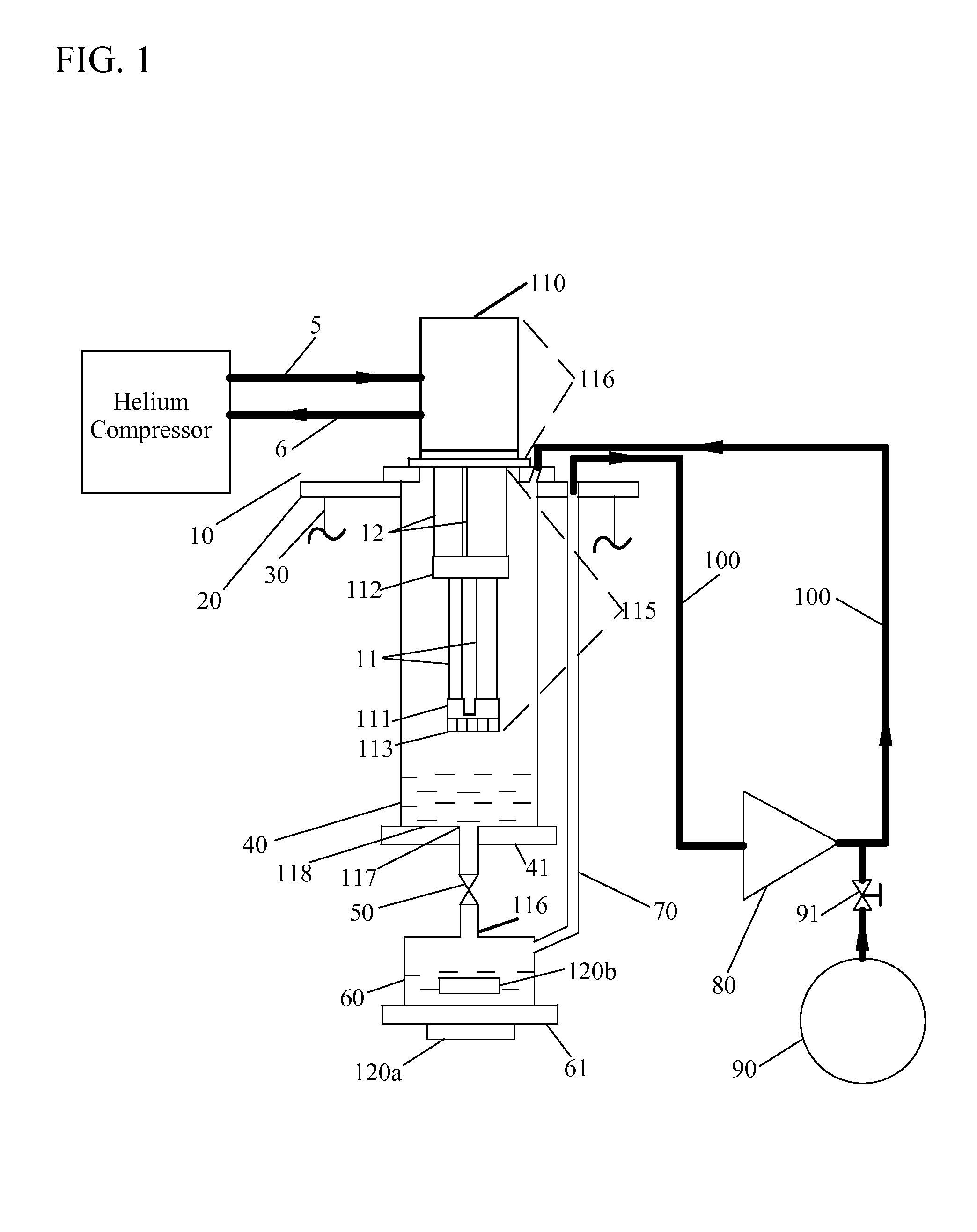
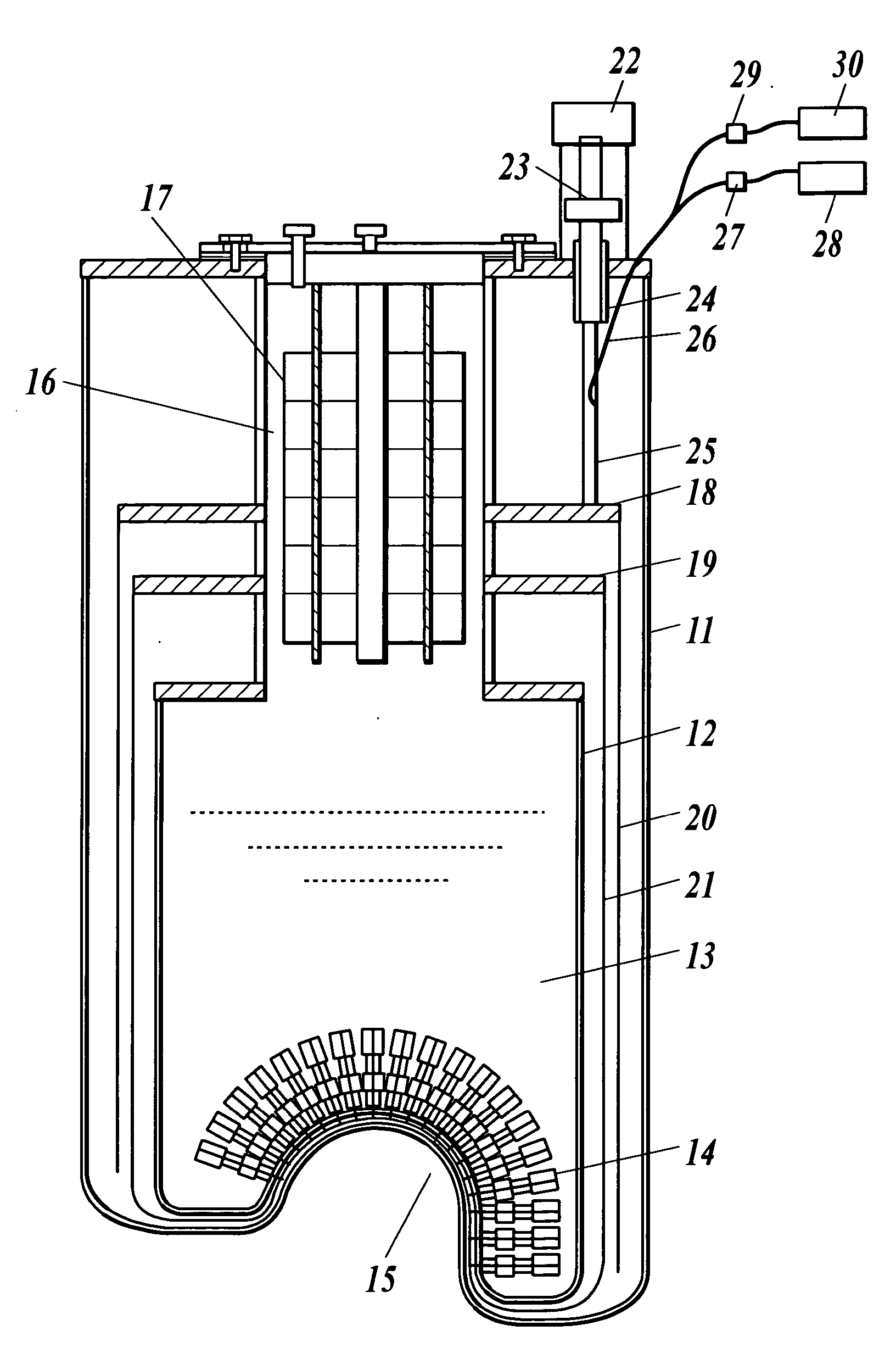
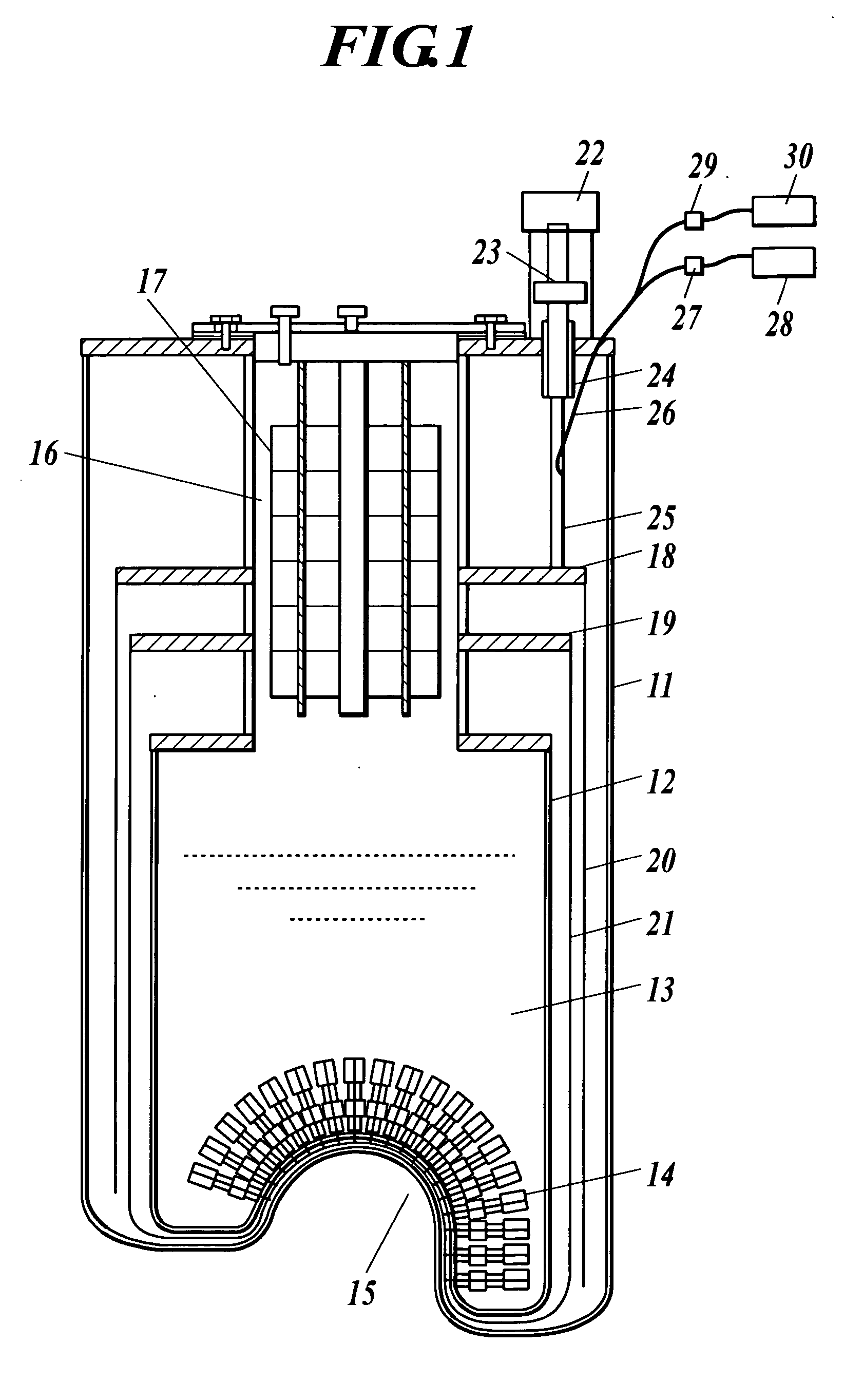
Closed Cycle 1 K Refrigeration System
InactiveUS20140202174A1Low vibration designReduce transferCompression machinesRefrigeration devicesCooling chamberEngineering
A closed-cycle refrigerator provides cooling to extremely low temperatures, particularly in the range of 0.5 K to 2.0 K. A 4 K pulse-tube cryocooler cold head or G-M cryocooler cold head liquefies helium in a first cooling chamber at a pressure at approximately 1 atmosphere. Liquid helium flows from the first cooling chamber, through a Joule-Thomson valve, and into a second cooling chamber under a pressure differential created by a pump. Helium vapor extracted from the second cooling chamber by the pump is routed back to the first cooling chamber to be re-condensed. This closed-cycle design provides continuous cooling below 2 K. Cryocooler cold head cold sections have no physical contact with subsequent cooling elements, such as the first and second cooling chambers to reduce vibration transfer. In some embodiments the cryocooler cold head is connected to a vacuum chamber via a vibration damping coupler to further reduce vibration transfer.
Owner:CRYOMECH
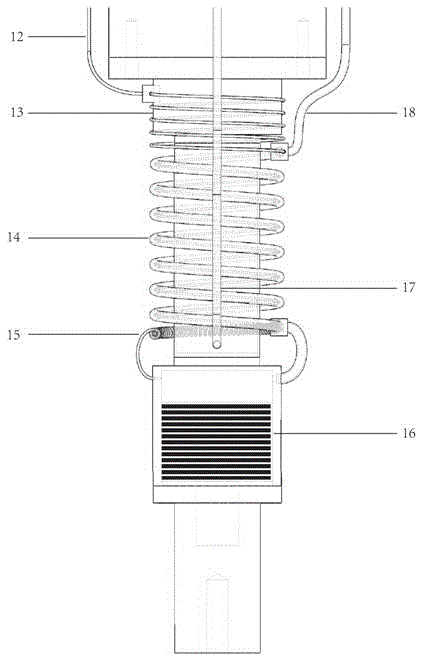
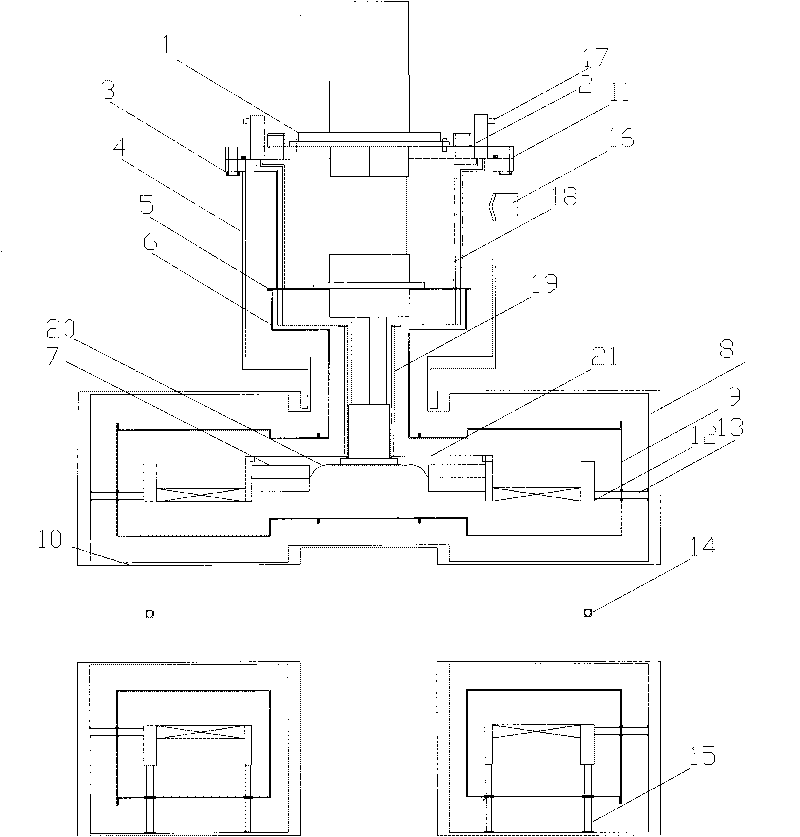
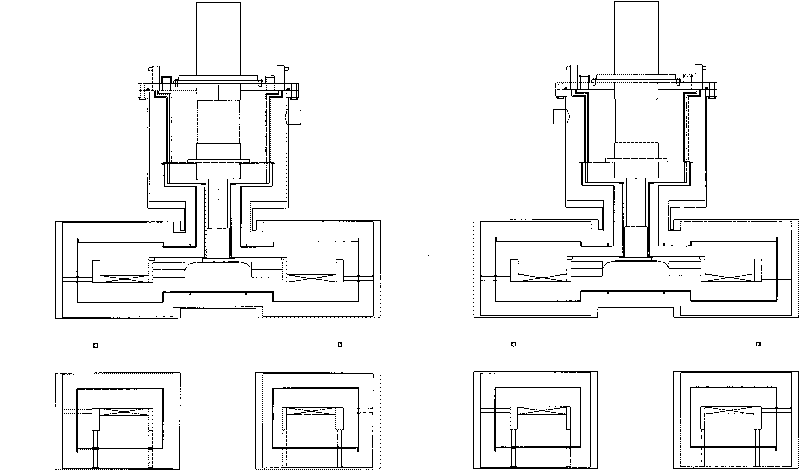
Conduction cooling superconducting magnet dewar convenient for loading and unloading
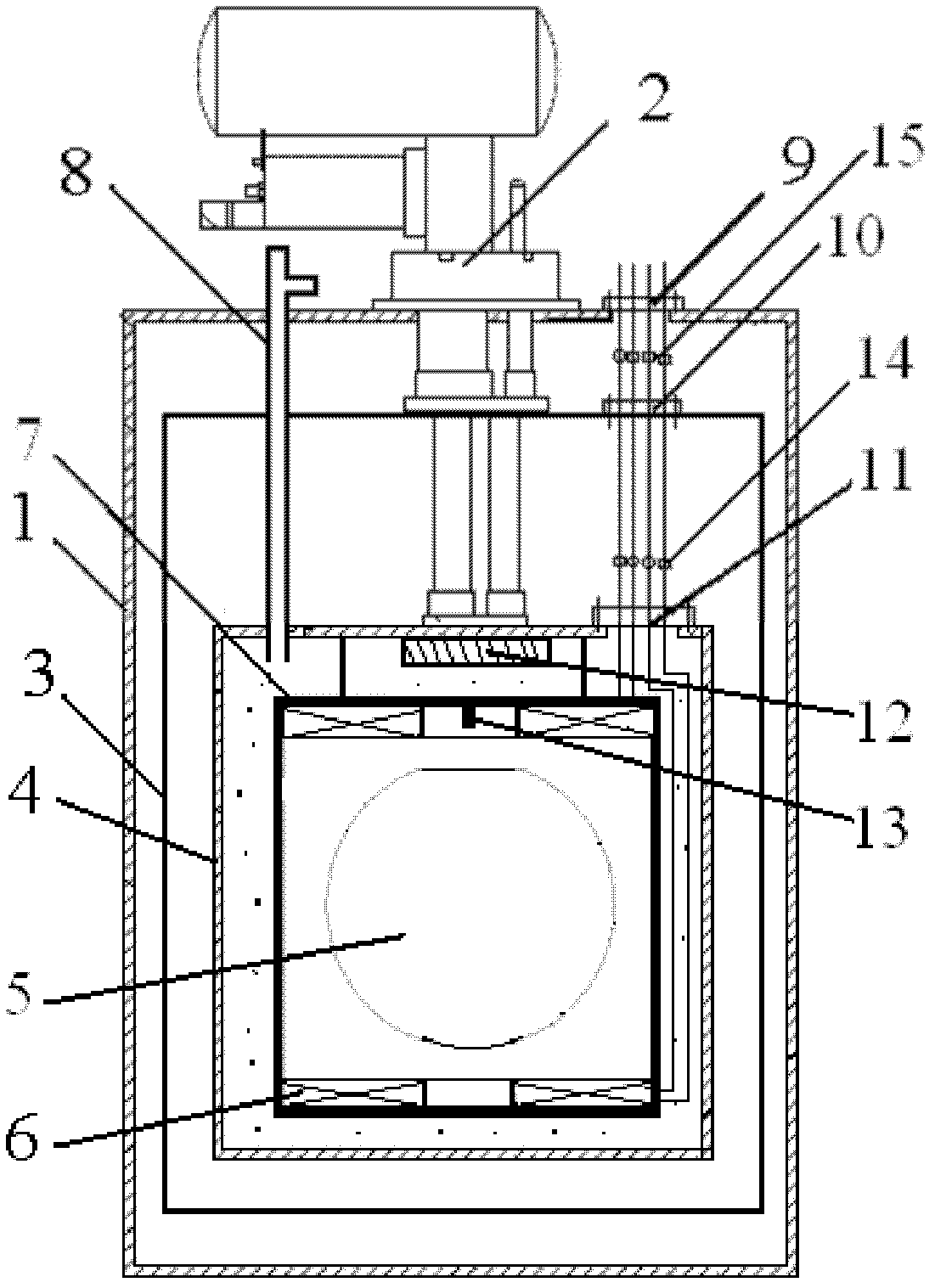
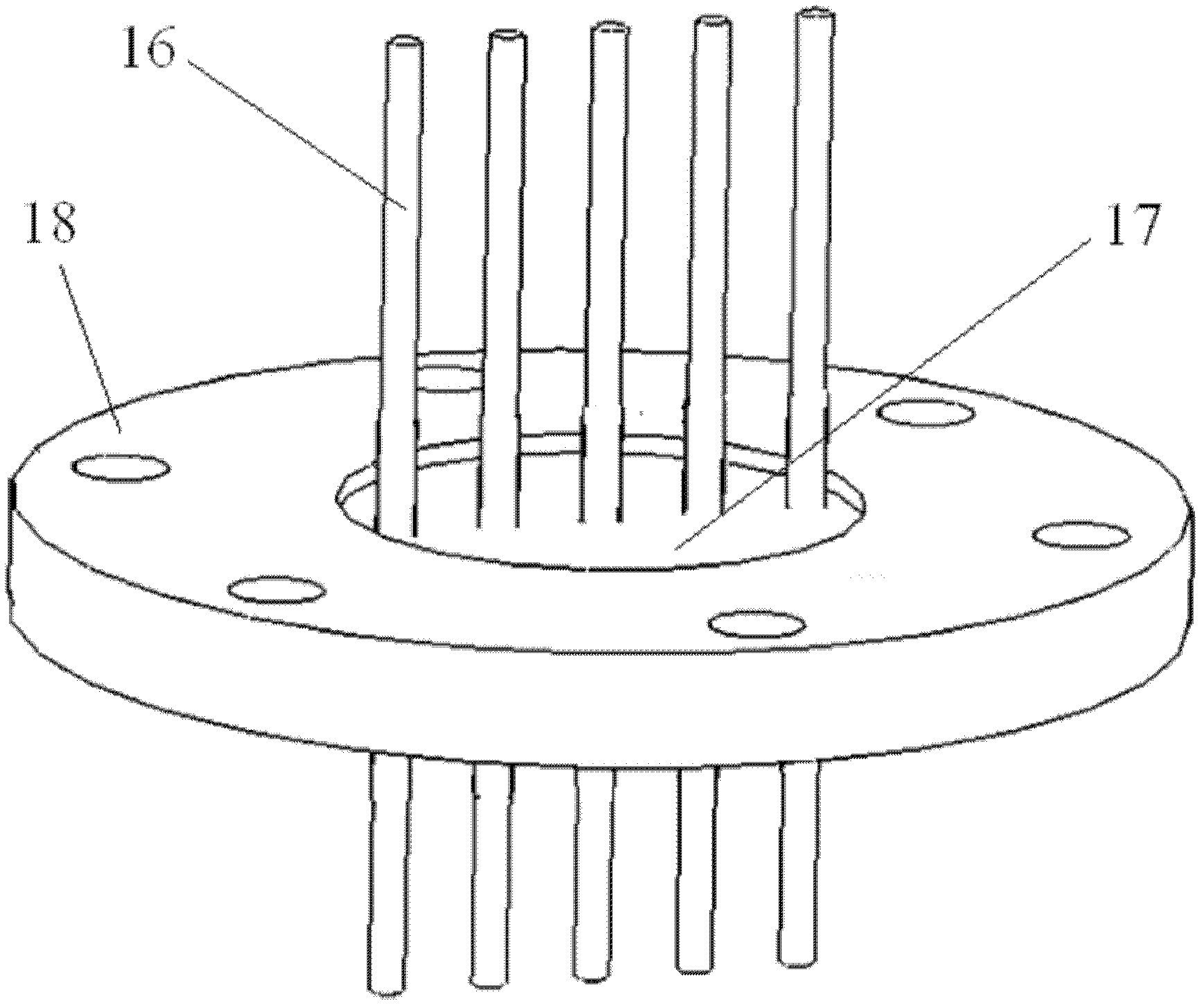
The invention relates to a conduction-cooled superconducting magnet Dewar with easy loading-unloading, comprising a Dewar cylinder. The conduction-cooled superconducting magnet Dewar is characterized in that the Dewar cylinder is a hollow annular cylinder, the middle of the annular cylinder is provided with a room temperature hole, an annular copper cold shield is arranged in the Dewar cylinder, a refrigerator and a superconducting magnet are arranged in the copper cold shield, a vacuum pumping port is arranged on the Dewar cylinder, a measuring device is arranged on an upper cover of the Dewar cylinder and the Dewar cylinder is in a vacuum state. Compared with the prior Dewar container, the conduction-cooled superconducting magnet Dewar is simpler, has small conduction heat leakage, and has the advantages of easy installation and disassembly; the refrigerator is used for conducting and cooling without a low temperature liquid (such as liquid helium and so on) cooling system; because of simple and safe system, a first-level cold junction of the refrigerator is operated under a temperature of 77K, thereby realizing heat sink of the copper cold shield, an electric lead and a support device; the first-level cold junction of the refrigerator adopts soft connection, thereby reducing temperature increment of the magnet due to vibration of the refrigerator; and the conduction-cooled superconducting magnet Dewar has the advantages of easy operation of manufacture, processing and installation, and is applicable to scale production.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
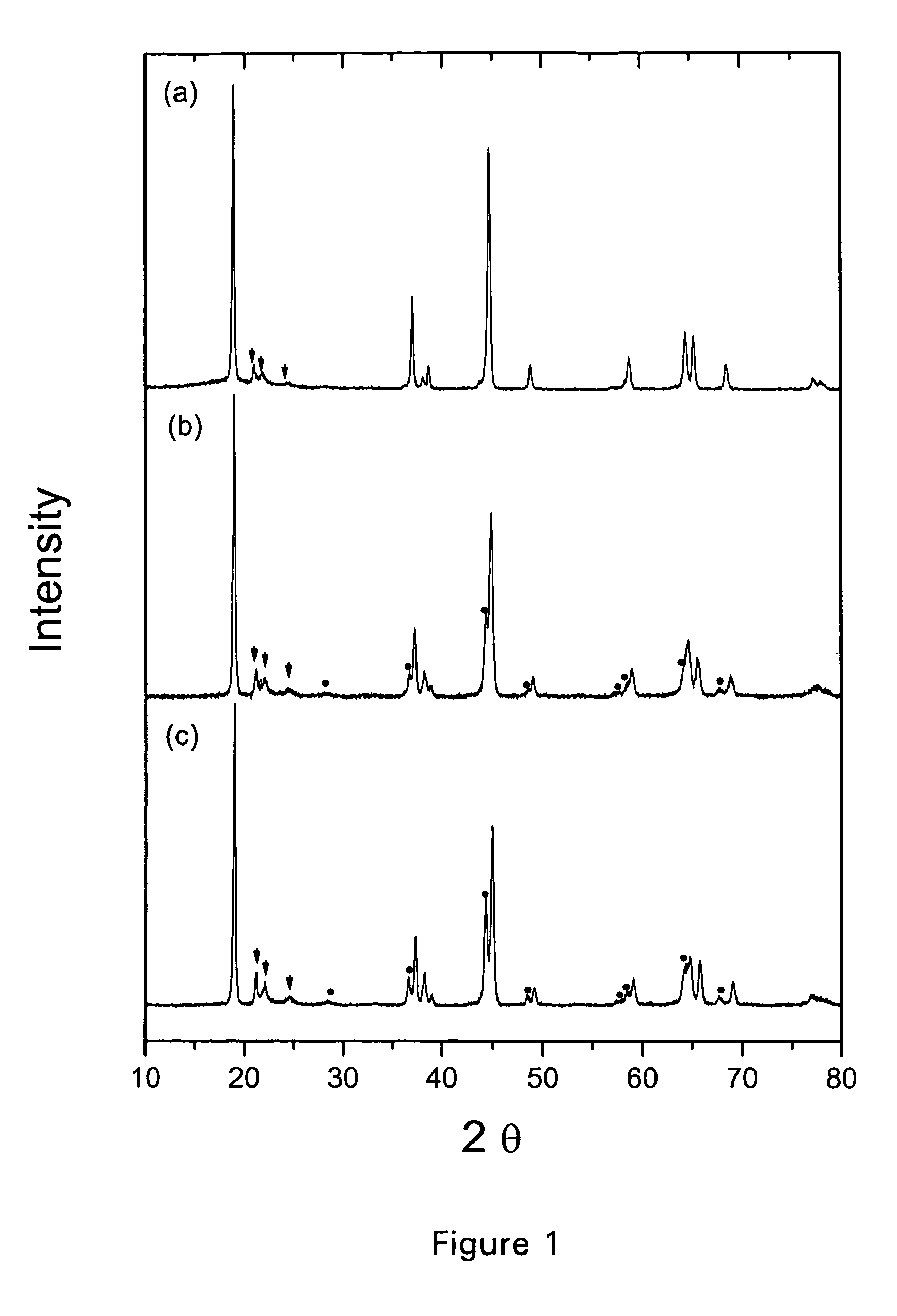
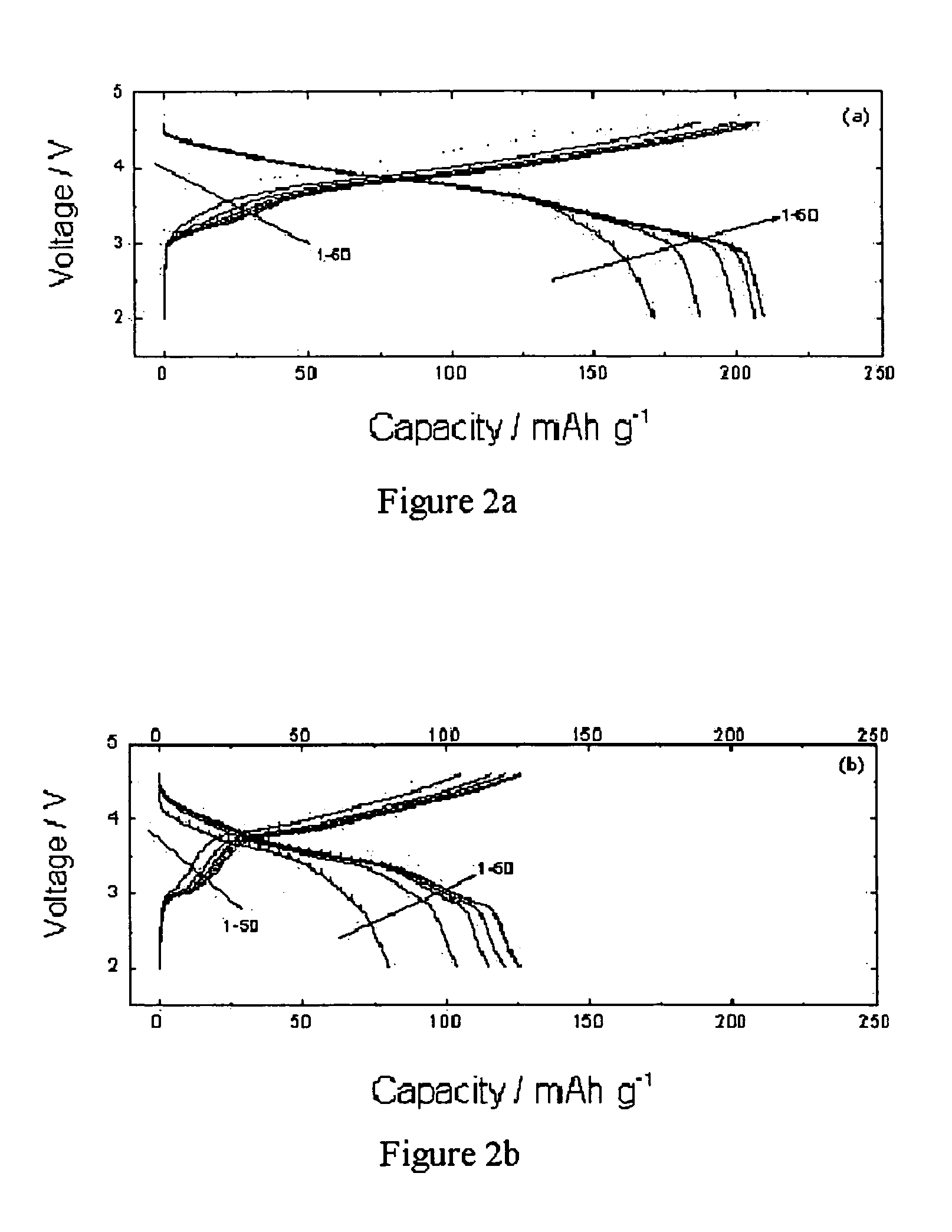
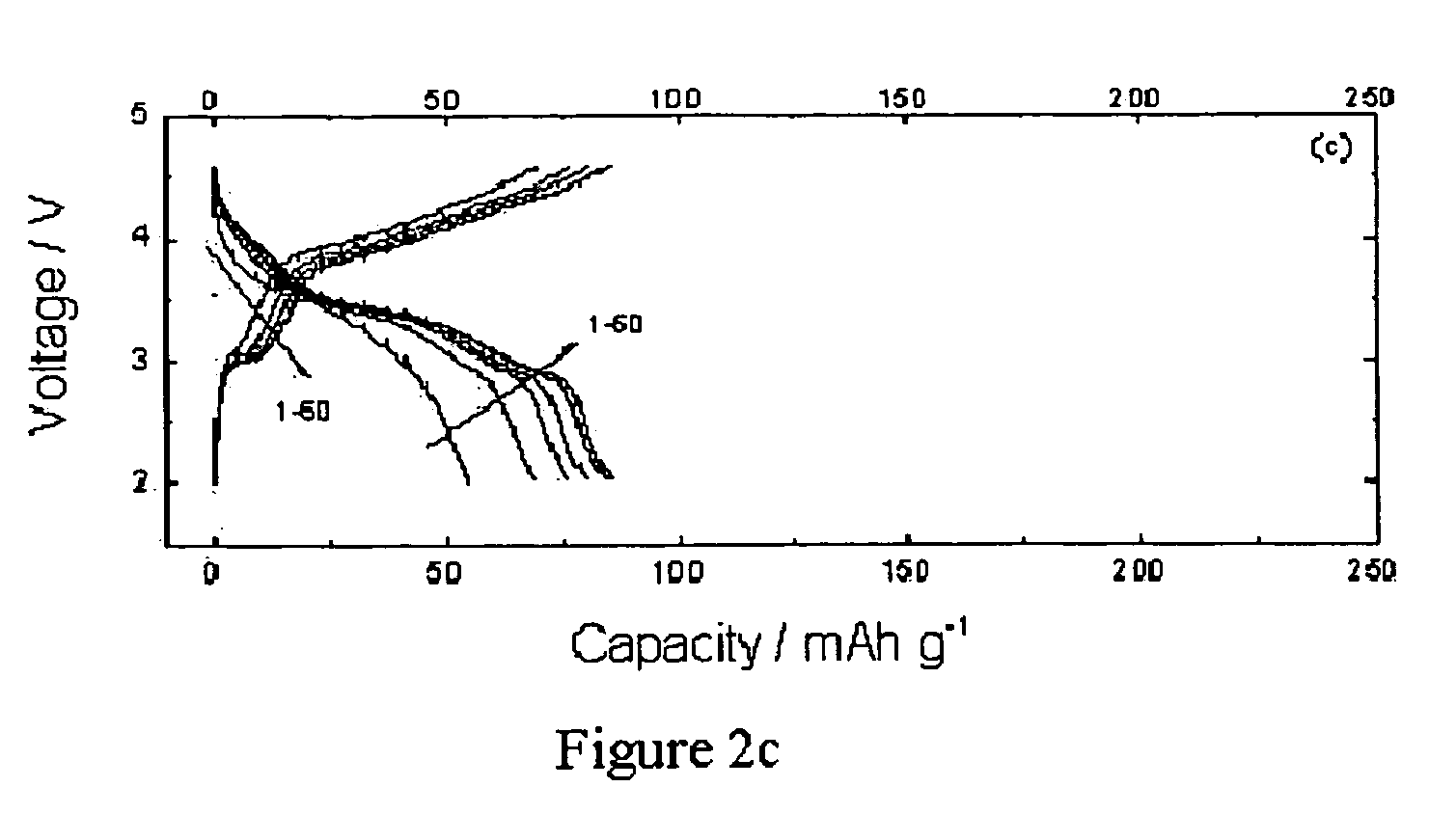
Layer cathode methods of manufacturing and materials for Li-ion rechargeable batteries
ActiveUS7314684B2Lower performance requirementsRapid coolingSecondary cellsAlkali metal oxidesLithiumSolid state reaction method
A positive electrode active material for lithium-ion rechargeable batteries of general formula Li1+xNiαMnβAγO2 and further wherein A is Mg, Zn, Al, Co, Ga, B, Zr, or Ti and 0<x<0.2, 0.1≦α≦0.5, 0.4≦β≦0.6, 0≦γ≦0.1 and a method of manufacturing the same. Such an active material is manufactured by employing either a solid state reaction method or an aqueous solution method or a sol-gel method which is followed by a rapid quenching from high temperatures into liquid nitrogen or liquid helium.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF THE +1
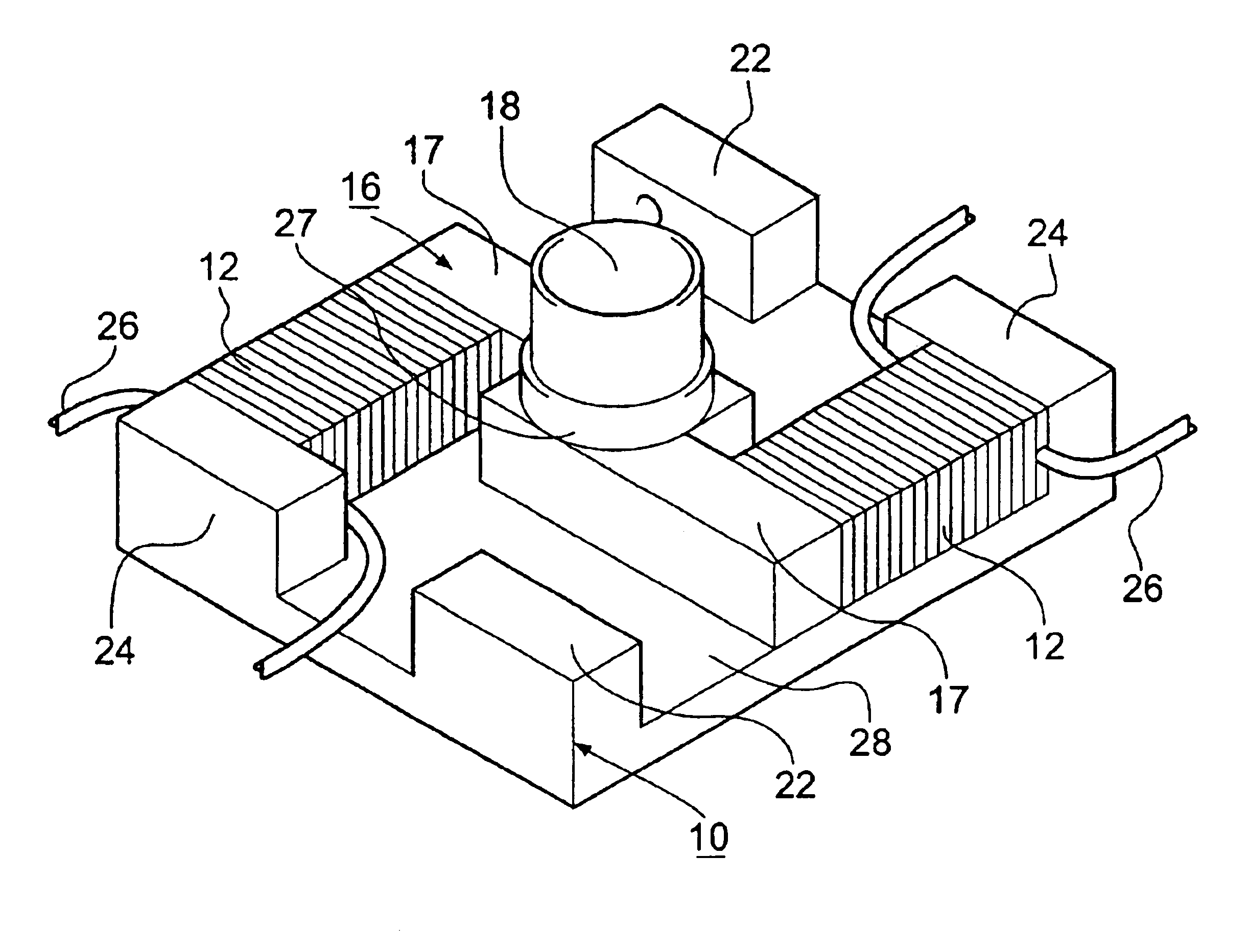
Inertial rotation device
InactiveUS6940210B2Reduce clamping forceEasy to operatePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesNanotechnologyElectricityPiezoelectric actuators
An inertial positioning device comprising: a base plate (10); a top plate (20) for mounting an element to be rotated; a rotation member (16) having a column (18) on which the top plate is mounted in frictional engagement for slip-stick rotational motion; and a pair of piezoelectric actuators (12) each secured to the base plate at one end and to lateral extensions (17) of the rotation member at their other ends. Simultaneous actuation of the piezoelectric actuators rotates the column of the rotation member about its axis. When a suitable asymmetric drive signal is supplied to the piezoelectric actuators, the top plate is rotated by slip-stick motion. The device is compact, has a good load capacity for an inertial motor and is operable in extreme environments such as liquid helium temperatures, high vacuum and high magnetic fields.
Owner:ATTOCUBE SYST AG
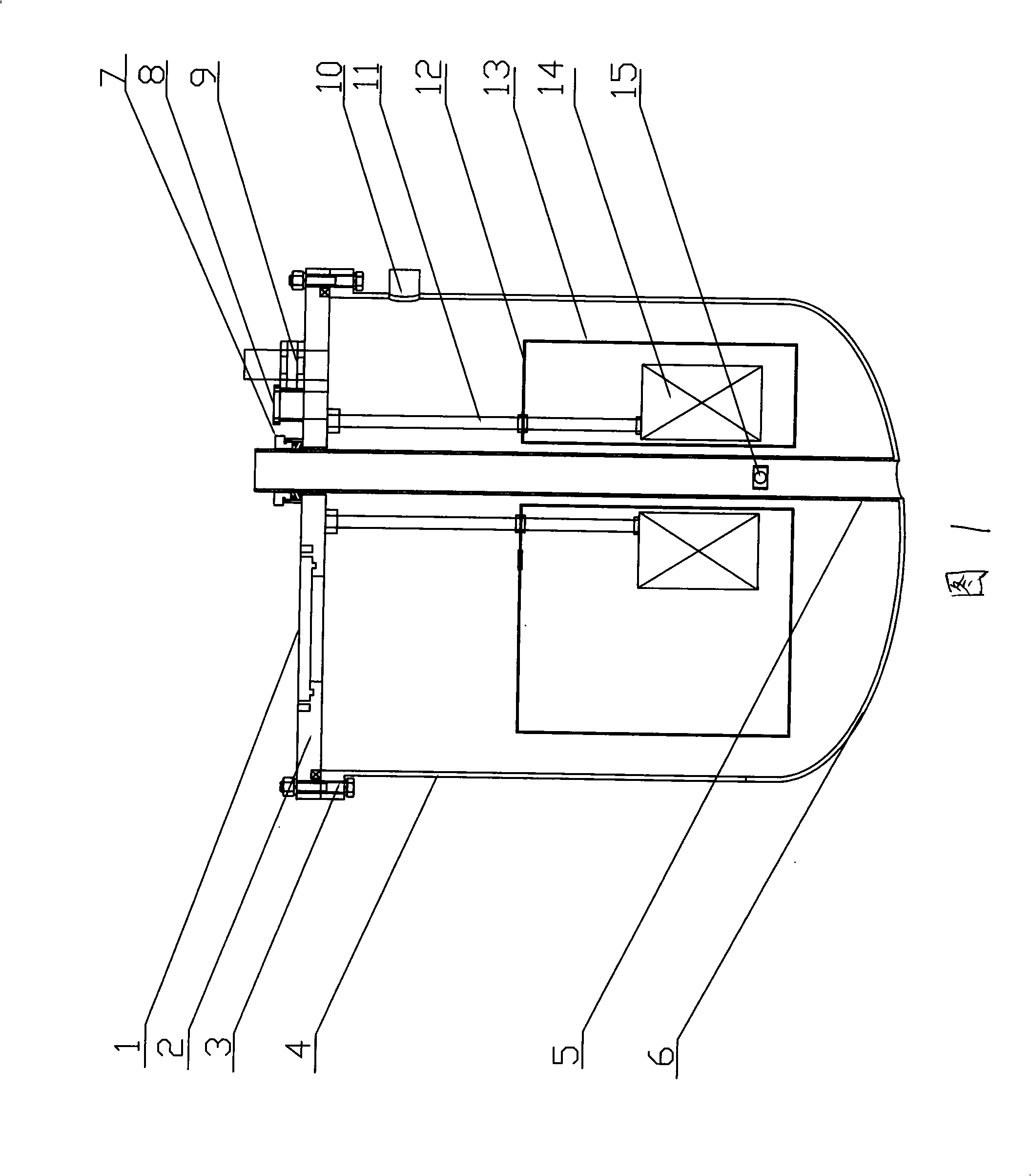
High-temperature superconducting magnetic levitation motor
InactiveCN103441648AReduce weightIncrease speedDynamo-electric machinesMagnetic holding devicesMagnetic bearingSuperconducting electric machine
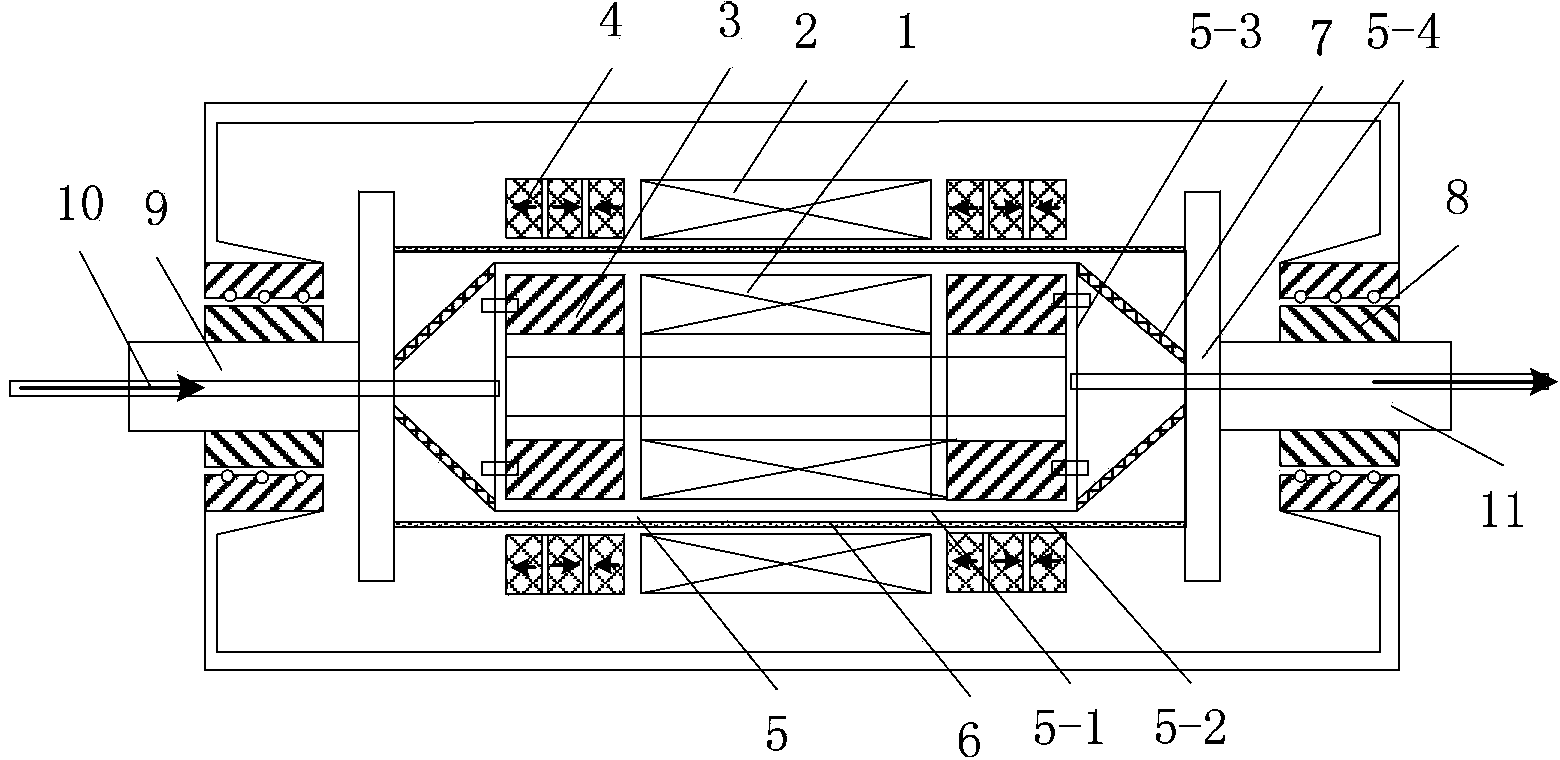
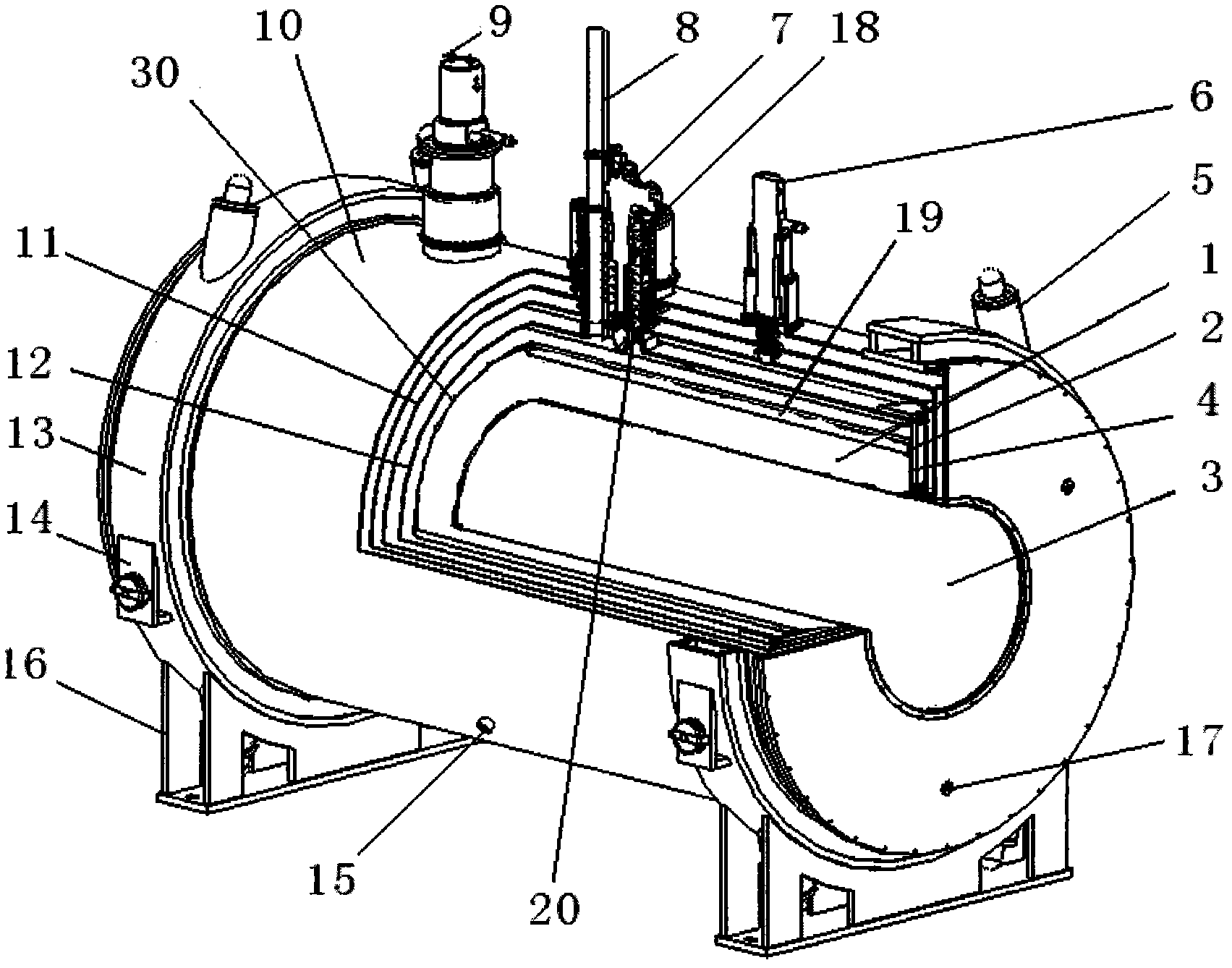
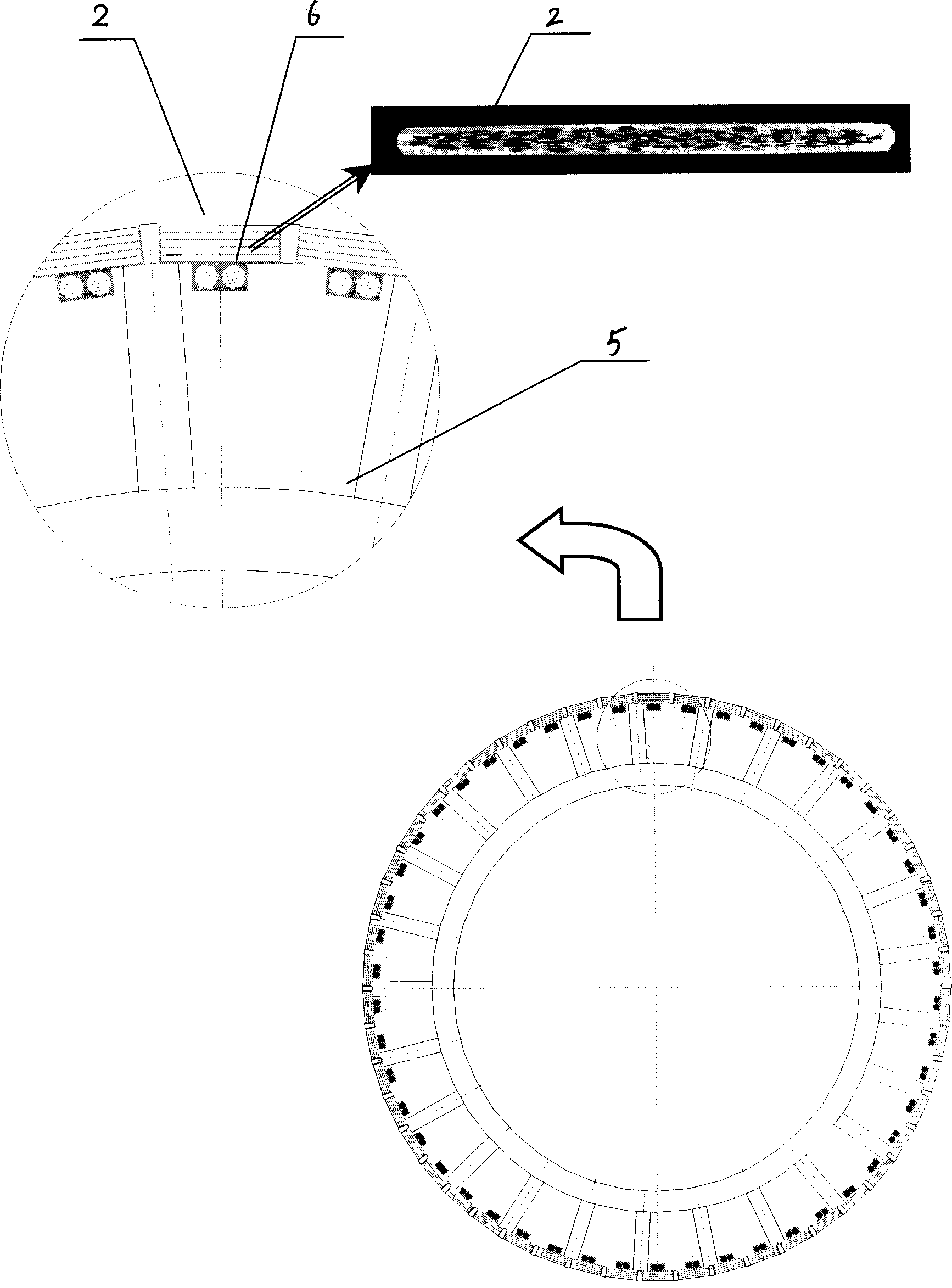
A high-temperature superconducting magnetic levitation motor is formed by a superconducting motor rotor (1), a motor stator (2), superconducting bearing rotors (3), permanent magnetic bearing stators (4), a rotary dewar (5), an electromagnetic screen (6), torque tubes (7), mechanical protection bearings (8), a main shaft (9), a low-temperature liquid (gas) inlet pipeline (10) and a low-temperature liquid (gas) outlet pipeline (11). The superconducting motor rotor (1) and the superconducting bearing rotors (3) are arranged in the rotary dewar (5) and are cooled by liquid nitrogen or liquid neon or liquid helium or cold helium, the motor stator (2) and the permanent magnetic bearing stators (4) are arranged outside the rotary dewar (5) and are coaxial with the rotary dewar (5), and the two mechanical protection bearings (8) are used in a left and right mode in the radial direction for protecting against the influence brought by the failure of superconducting bearings.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
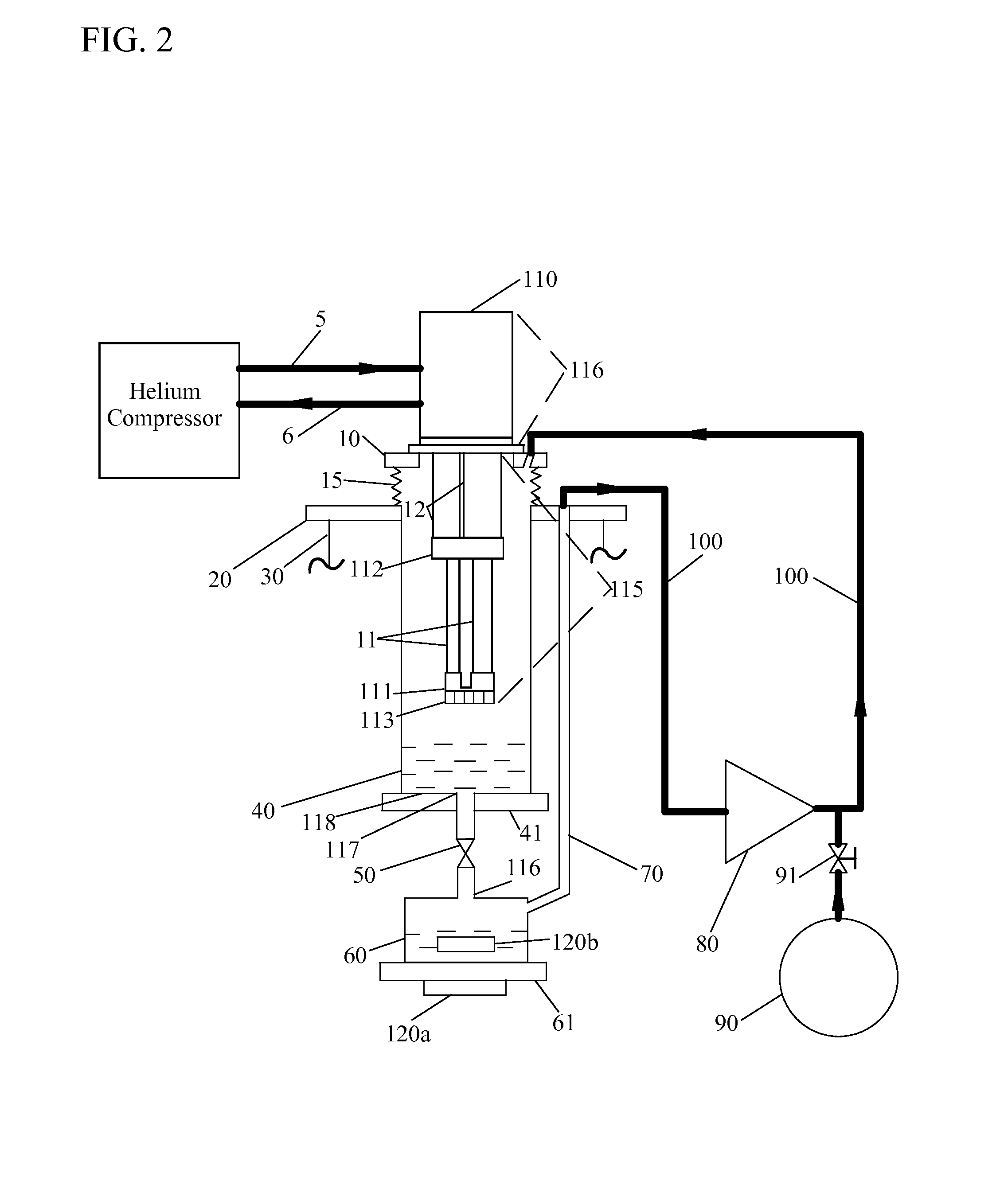
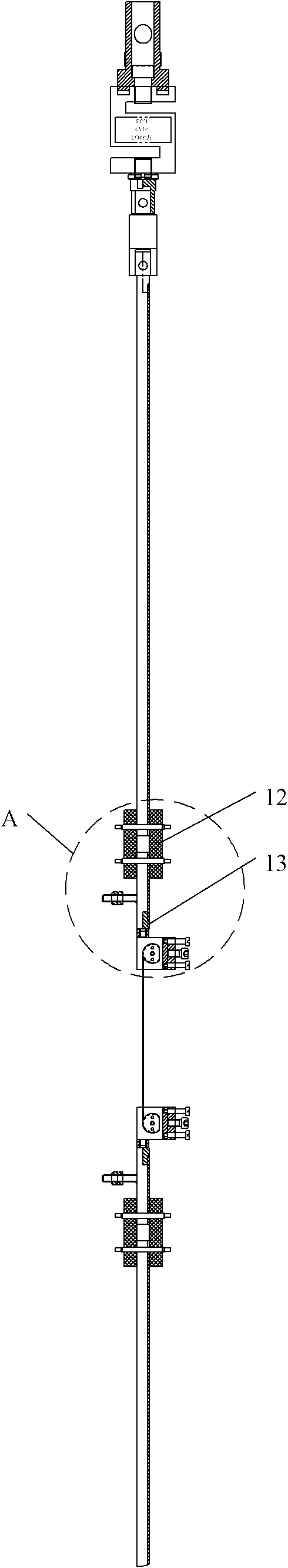
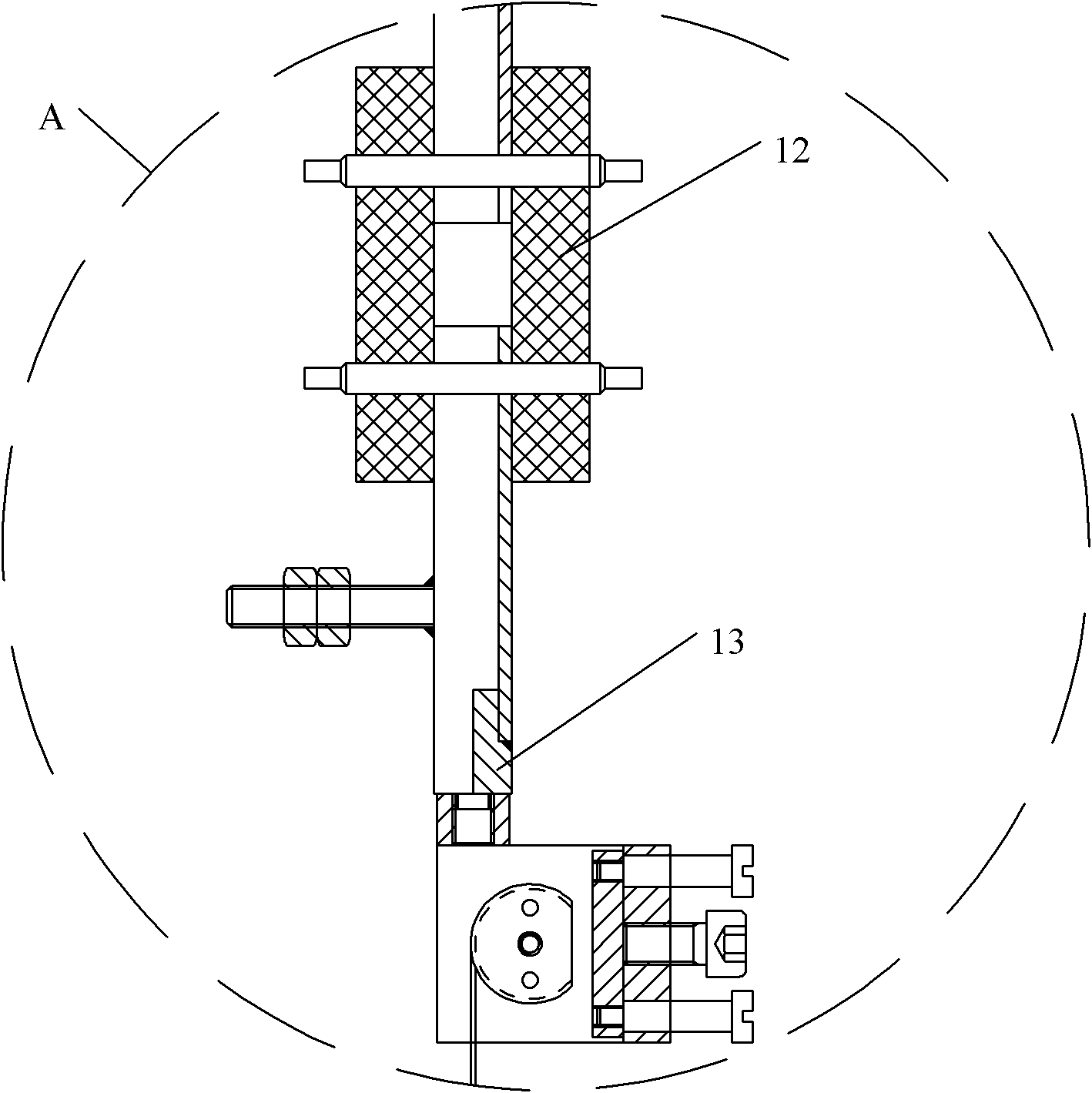
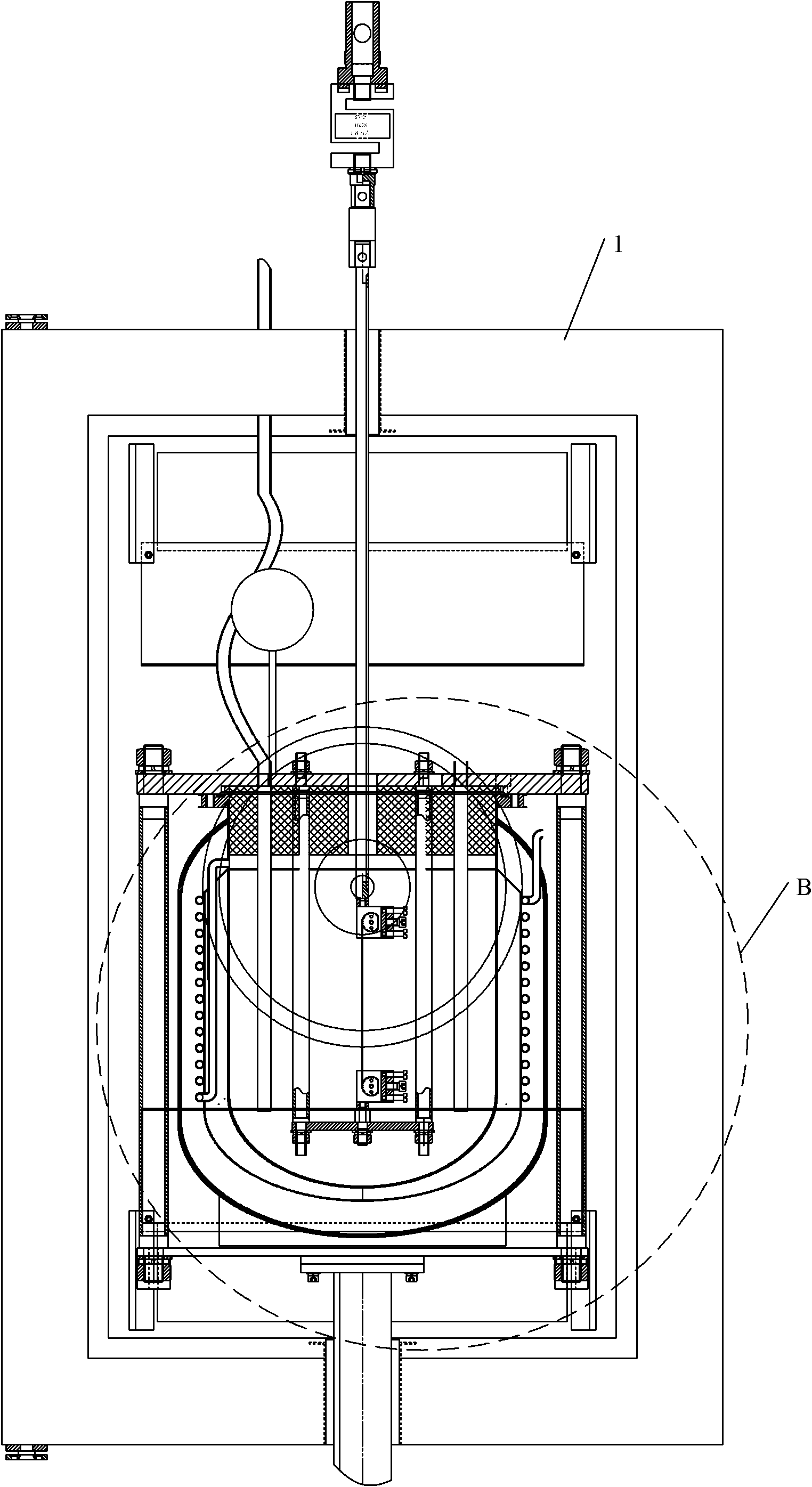
Low vibration liquid helium cryostat
An extra-low vibration cryostat, which incorporates a cryocooler and cryostat to cool and house a vibration-sensitive device, with the cryocooler and cryostat sealed gas-tight to each other, but mechanically isolated, so that vibration from the cryocooler does not affect the device.
Owner:CRYOMECH
Highfield high uniformity nuclear magnetic resonance superconducting magnet system
ActiveCN102136337ALarge apertureImprove uniformityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRoom temperature
The invention provides a highfield high uniformity nuclear magnetic resonance superconducting magnet system. The highfield high uniformity nuclear magnetic resonance superconducting magnet system comprises a main winding (1) and a magnetic field uniformity compensation winding (19) having a positive and negative current combination; the main winding (1) and the magnetic field uniformity compensation winding (19) consist of 24 superconducting windings coiled by NbTi / Cu low temperature superconducting lines; a 9.4T magnetic field is generated in a room temperature space which is 800 millimeters high, so that the non-uniformity of the magnetic field within the range of 300 millimeters is less than 0.1ppm. A low temperature container (2) of a superconducting magnet and liquid helium (4) is arranged inside the superconducting magnet system, so a 4K low temperature environment required by the normal running of the superconducting magnet can be provided for the superconducting magnet. By a ferromagnetic shielding system, the superconducting magnet has high electromagnetic compatibility. The superconducting magnet system has the advantages of compact structure and low running cost.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cold end of heavy current lead out wire made from high-temperature superconductor, and low resistance connector of superconducting transmission line
InactiveCN1873847ASave cooling capacityLess investmentSuperconducting magnets/coilsEngineeringSuperconducting transmission lines
The disclosed adaptor between cold junction of leading wire in heavy current of high-temperature superconductor and low resistance of superconducting transmission line includes structure: welding piles of high-temperature superconductor arranged in spaces to outer wall of support tube made from stainless steel in low thermal conductance; welding warm end in piles of high-temperature superconductor to transition piece of copper; through braze welding, cold end in piles is joined to NbTi / Cu superconducting line; cross winding NbTi / Cu line on inner copper tube sheathed inside outer copper tube; cooling superconducting line and copper connector by using liquid helium between inner and outer copper tubes. Features are: simple structure, suitable to connection under 20kA. In the invention, resistance of adaptor is lowered as 1.4-4.6n ohm. In supercritical quantity of helium flow 4g / s, all loss of 6 pieces of adaptor and 12 pieces of butt end of transmission line is less than 0.1Mpa.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus of fabricating semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070166892A1Increase amount of introductionFacilitated DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPlasma nitridationEngineering
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Preparation method of black phosphorus alkene-graphene composite material hollow microsphere
ActiveCN105129789ARealize large-scale preparationMeet different application requirementsPhosphorus preparationMicrosphereFiltration
The invention discloses a preparation method of a black phosphorus alkene-graphene composite material hollow microsphere. The preparation method comprises the steps of adding a black phosphorus alkene nanosheet or black phosphorus alkene quantum dot dispersion liquid into oxidized graphene nanosheet dispersion liquid firstly, and mixing the black phosphorus alkene and the oxidized graphene by adopting a mechanical agitation method; spraying the mixed dispersion liquid of the black phosphorus and the oxidized graphene into liquid helium by a spraying method and rapidly freezing the mixed dispersion liquid into microballoons; then putting the obtained black phosphorus alkene and oxidized graphene composite material microballoons into a freezer dryer for freeze-drying, so as to obtain the black phosphorus alkene and oxidized graphene composite material hollow microballoons; reducing the oxidized graphene into graphene at high temperature under the protection of nitrogen or argon, so as to obtain the balck phosphorus alkene and graphene composite material hollow miroballoons at last. The prepared black phosphorus alkene and graphene composite material hollow miroballoons have a potential application prospect in the fields such as lithium ion batteries, supercapacitors, sensors and filtration purification.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
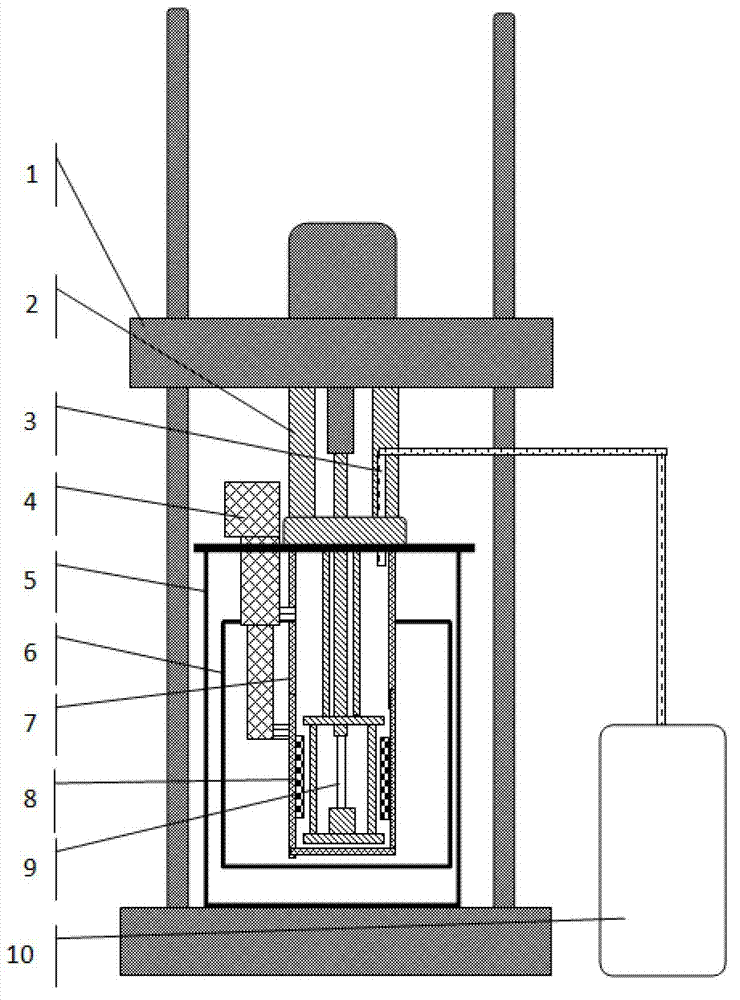
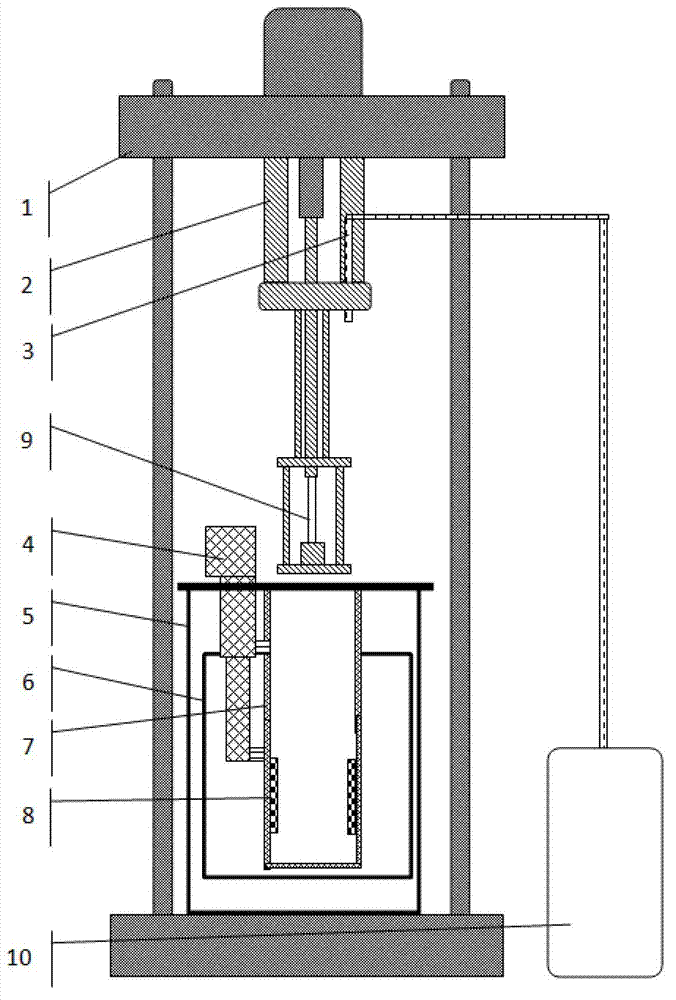
Multi-field coupling test system for superconducting material at temperature of between 373 and 4.2K
InactiveCN102323160AEasy to replaceImprove performanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMulti fieldTest sample
The invention discloses a multi-field coupling test system for a superconducting material at the temperature of between 373 and 4.2K. The system comprises a large-sized temperature alternating experiment box, a liquid helium ultralow temperature vacuum Dewar flask, a Dewar flask bracket, a mechanical test experiment device, a liquid helium injection pipe, a plurality of heating bodies, an air circulating device and an air circulating fan, wherein the liquid helium ultralow temperature vacuum Dewar flask is sleeved inside the large-sized temperature alternating experiment box; the Dewar flask bracket is arranged at the bottom of a box body at the bottom of the liquid helium ultralow temperature vacuum Dewar flask; the mechanical test experiment device and the liquid helium injection pipe are arranged in coordination with the liquid helium ultralow temperature vacuum Dewar flask and the large-sized temperature alternating experiment box; the plurality of heating bodies are arranged inside the large-sized temperature alternating experiment box; the air circulating device is arranged behind the box body of the large-sized temperature alternating experiment box; and the air circulating fan is connected with the air circulating device through a bearing. By the multi-field coupling test system for the superconducting material at the temperature of between 373 and 4.2K, the defects of poor functions, small application ranges, long test time, high cost and the like in the prior art can be overcome, so that the system has the advantages of making a test sample conveniently replaced and saving test time, along with a powerful function, a wide application range and low cost.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
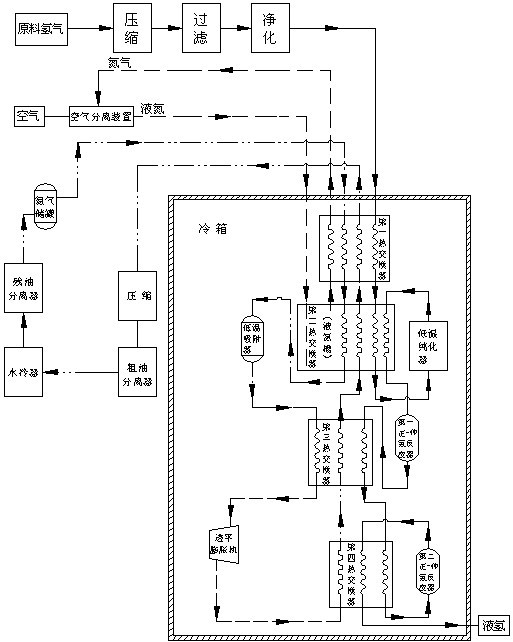
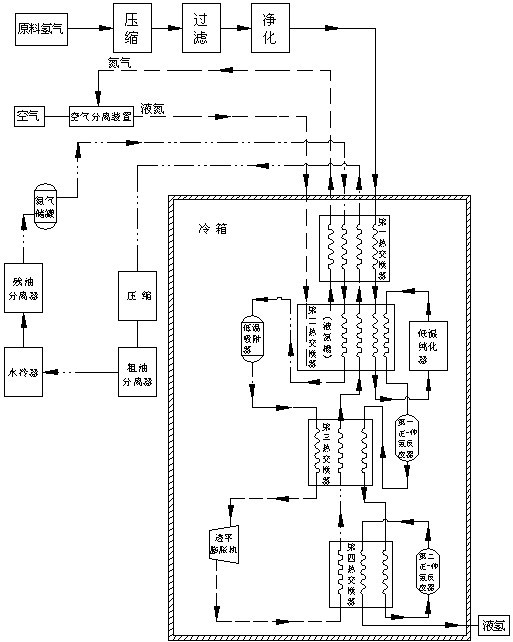
Hydrogen liquefaction process
The invention discloses a hydrogen liquefaction process comprising a nitrogen refrigeration cycle, a helium refrigeration cycle and a hydrogen refrigeration cycle. In the technical scheme, liquid helium generated by a liquid helium and air separating device is used as a refrigeration working medium, refrigerating capacity required by hydrogen condensation and liquefaction is provided by the liquid helium, rewarmed helium gas and nitrogen gas are respectively recycled and can be turned into the liquid helium and liquid nitrogen after being processed correspondingly when the refrigerating capacity is provided for the hydrogen liquefaction by the liquid helium and the liquid nitrogen, thus the continuous refrigerating capacity is provided for the hydrogen refrigeration cycle by the helium refrigeration cycle and the nitrogen refrigeration cycle, waste caused by directly discharging the helium gas or the nitrogen gas is avoided, and energy sources are saved. In the intention, operation that any one of the three refrigeration cycles is independent of the other two refrigeration cycles is realized, and heat quantity exchange is carried out among the three refrigeration cycles, thus liquid hydrogen generation is finally completed, and the liquefaction of hydrogen gas is realized by sequentially utilizing the refrigerating capacity of the liquid helium and the liquid nitrogen in the hydrogen refrigeration cycle.
Owner:ALLY HI TECH CO LTD
Super-conduction magnetic levitation device without liquid helium volatilization
ActiveCN102545725AReduce volatilityNon-pressured vesselsRefrigeration devicesLevitationHigh-temperature superconductivity
A super-conduction magnetic levitation device without liquid helium volatilization comprises a low temperature container (1), a refrigerating machine (2), a refrigerated screen (3), a liquid helium container (4), a super-conduction rotor (5), a levitation coil (6), a rotor cavity (7), an infusion tube (8), a condenser (12) and a polar axis displacement sensor (13). Heat generated by a current lead wire of the levitation coil (6) after the levitation coil (6) is powered on cannot be transmitted into the liquid helium container (4) through a room temperature current lead wire connector (9), a high temperature super-conduction current lead wire connector (10) and a low temperature super-conduction current lead wire connector (11), so that volatilization of liquid helium in the liquid helium container (4) is reduced. Helium in the condenser (12) is refrigerated through the refrigerating machine (2) to be liquefied so that zero volatilization of liquid helium in the liquid helium container (4) is achieved. The super-conduction magnetic levitation device without liquid helium volatilization does not need to be infused with liquid helium for many times and can independently run for a long period.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope using closed-cycle refrigerator to achieve refrigeration
ActiveCN103901232ASolve the scarcity of consumption reservesSettle the priceScanning probe microscopyControl systemEngineering
The invention discloses a low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope using a closed-cycle refrigerator to achieve refrigeration. The low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope comprises a closed-cycle refrigerator system, a helium heat exchange gas refrigeration vibration isolation interface system, a low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope scanning head system, a vacuum system, a vibration reduction platform and a scanning tunnel microscope control system. According to the low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope, under the condition that no liquid helium is consumed, atomic-scale resolution low-temperature ultrahigh-vacuum scanning tunnel microscopy space imaging and high-energy resolution scanning tunnel spectrum accurate measurement can be achieved like a liquid helium refrigeration system. The technical scheme of closed-cycle refrigeration can also be used for other applications needing lower temperature and low-vibration environments like other members of scanning probe microscope families. Large-range temperature changes can also be achieved through feedback combination of heating elements and temperature measuring elements.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
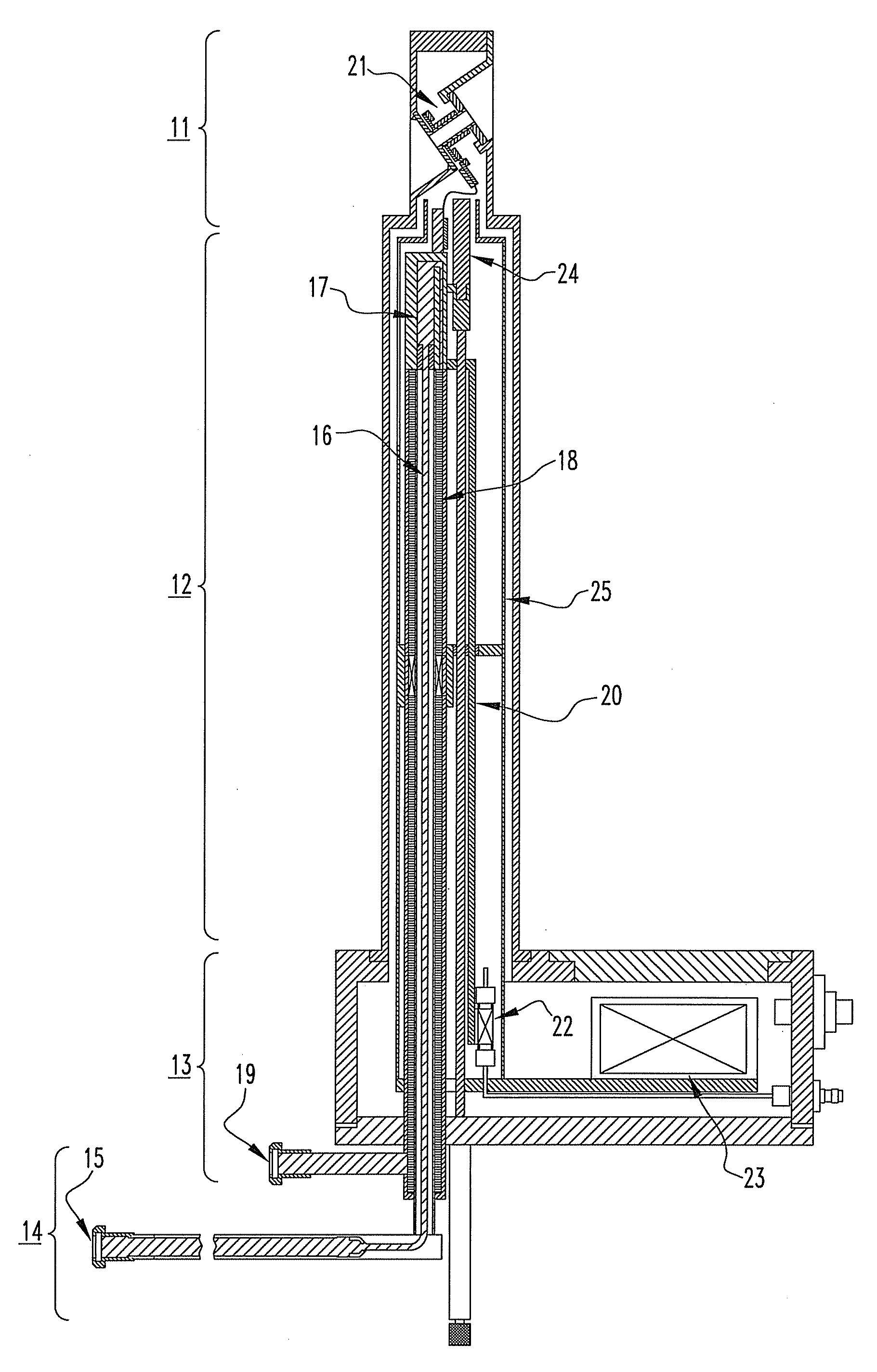
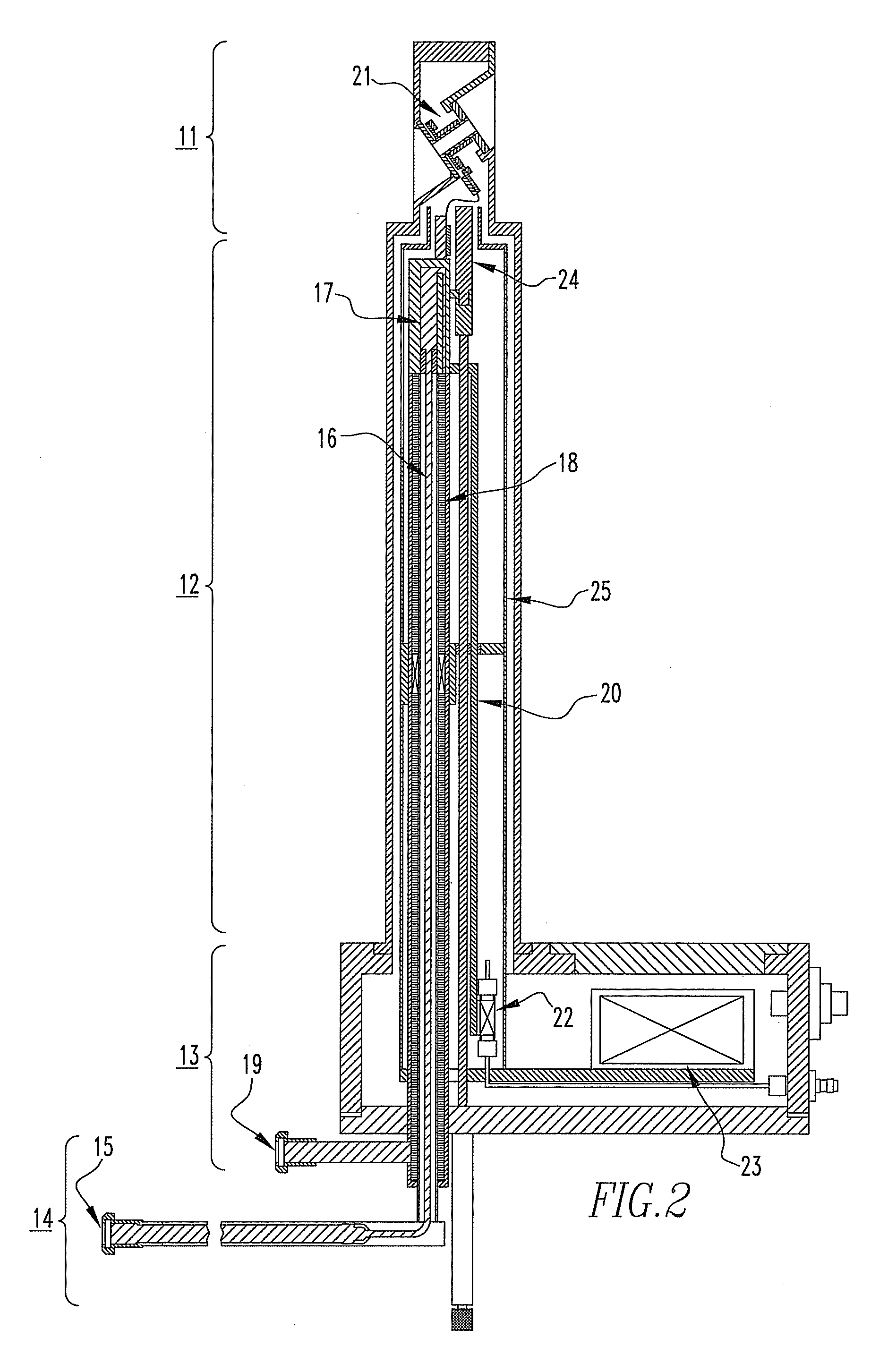
High-Resolution NMR Probe
ActiveUS20100321018A1Simple structureInexpensive to fabricateElectrical testingMeasurement leads/probesEngineeringRadiation shield
Owner:JEOL RESONANCE
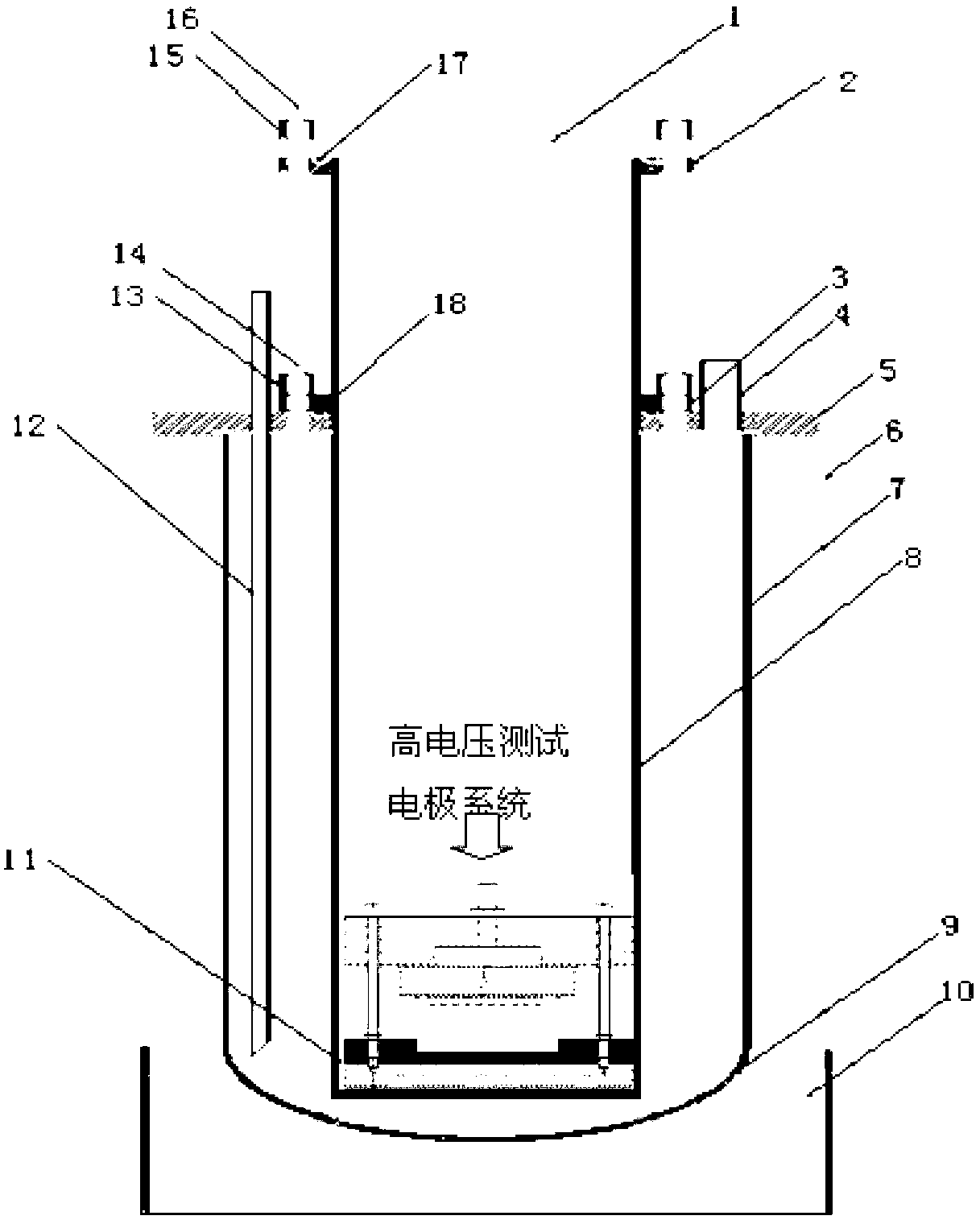
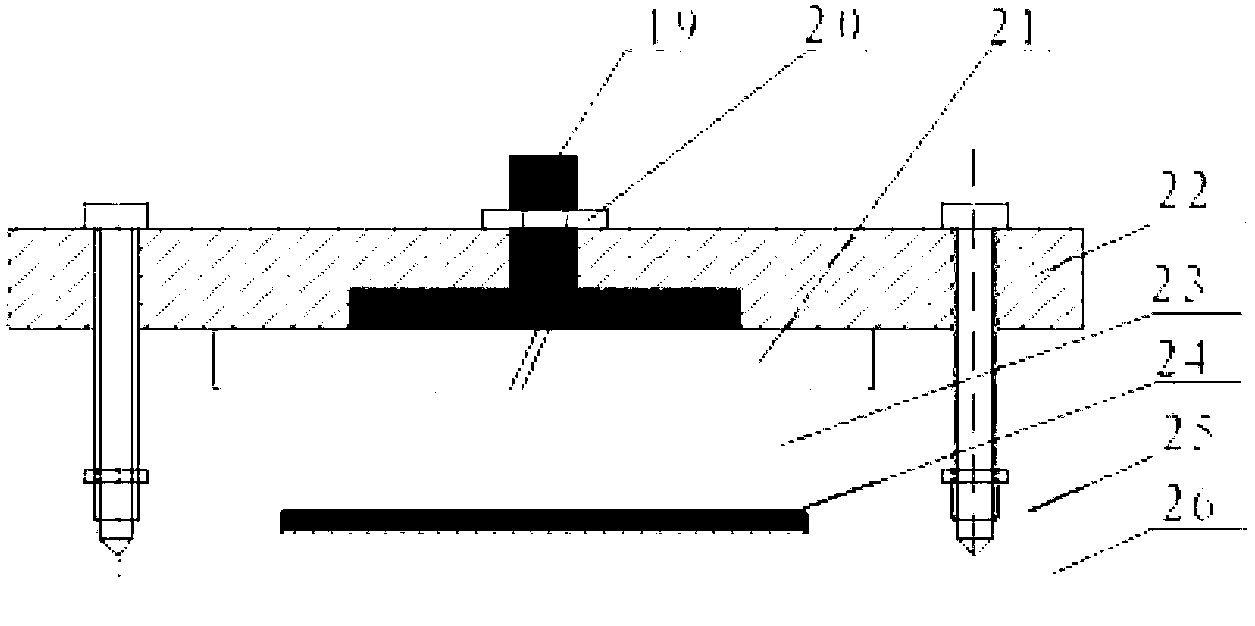
Testing experimental platform for performing disruptive discharge on insulation sample under low-temperature vacuum environment
InactiveCN102707204AGuaranteed strict isolationAffect the vacuumTesting dielectric strengthElectrical measurement instrument detailsHeat conductingEngineering
The invention discloses a testing experimental platform for performing disruptive discharge on an insulation sample under a low-temperature vacuum environment. The testing experimental platform mainly comprises a three-layered experimental Dewar type container and a high-voltage testing electrode system; the three-layered experimental Dewar type container comprises a vacuum testing container, a liquid helium (or liquid nitrogen), a cooling cylinder, and an outer vacuum insulation cylinder; the high-voltage testing electrode system is mainly composed of negative and positive electrodes, an insulating sample, upper and lower insulation supporting epoxy boards, polyimide insulating layer, a heat conducting copper supporting plate, and on the like. A cathode copper plate is used for connecting a low-potential lead and a leakage current testing lead; the leakage current testing lead is externally connected with the test system to strictly detect the disruptive discharge rule of the insulating sample. An anode copper plate is used for connecting a high-potential lead. The invention can realize the disruptive discharge performance test on various tested insulating samples under different low temperatures and vacuum degrees. According to the invention, the test temperature is ranged from 4.5 K to 300 K; and the air pressure test is ranged from 10-2 to 105 Pa.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
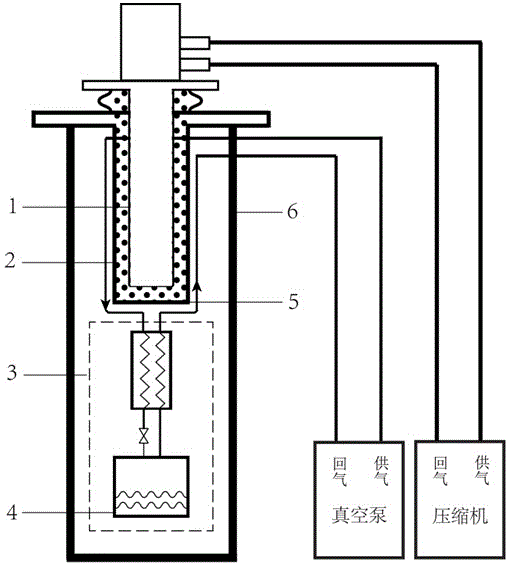
Mechanical vibration isolation liquid-helium-consumption-free extremely-low-temperature refrigerating system
ActiveCN105571190ASolve the problem of not being able to obtain extremely low temperatureIsolation of low frequency mechanical vibrationCompression machinesRefrigeration safety arrangementTemperature controlUltra-high vacuum
The invention belongs to the technical field of extremely-low-temperature refrigerating equipment, and particularly relates to a mechanical vibration isolation liquid-helium-consumption-free extremely-low-temperature refrigerating system. The system comprises a closed-cycle refrigerator system, a helium heat exchange air cooling vibration isolation system, an extremely-low-temperature throttle valve refrigerating system and a temperature feedback control system. According to the refrigerating manner provided by the system, the extremely-low temperature lowering to 1.4 K (based on helium-4 media) or 0.2 K (based on helium-3 media) can be achieved under the condition without consuming liquid helium, and meanwhile, the inherent mechanical vibration of the closed-cycle refrigerator system can be quite effectively isolated; and through the temperature feedback control system, variable temperature control can be achieved. The system is further suitable for an ultrahigh-vacuum environment needing to be subject to high-temperature baking.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Material low-temperature mechanics performance testing device using refrigerator as cold source
InactiveCN102854056AAccurate temperature controlSimple structureStrength propertiesMaterials testingTest sample
The invention discloses a material low-temperature mechanics performance testing device using a refrigerator as a cold source. The device comprises a vacuum heat preservation barrel, a test sample cavity, a heat radiation preventing barrel, an outer gas storage bag and the refrigerator, wherein the vacuum heat preservation barrel is placed on a base in a universal material testing machine; the test sample cavity is arranged in an internally-built temperature controller which is arranged in the heat preservation barrel; the test sample cavity covers the heat radiation preventing barrel which is positioned in the heat preservation barrel; helium is arranged in the outer gas storage bag which is communicated with the test sample cavity; a sample to be tested is rigidly connected with a mechanics support frame by a measuring clamp and moves up and down; the testing machine is provided with a mechanics and displacement sensor and supplies the mechanics power source for the test sample to be tested; the mechanics support frame transmits a mechanics signal and a displacement signal of the test sample to be tested to a mechanics sensor and a displacement sensor; the refrigerator is arranged in the heat preservation barrel; a cooling head is in contact with the test sample cavity by virtue of bridge connection; and cold energy is supplied to the test sample cavity. By utilizing the device, the refrigerator is used as the cold source, liquid helium or liquid nitrogen are not needed to be consumed, so that the material mechanics test of any of the temperature points in the temperature area of 4.2-300K can be realized; and moreover, the temperature is accurately controlled, and the device has a simple structure, and is easy to operate and high in efficiency.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
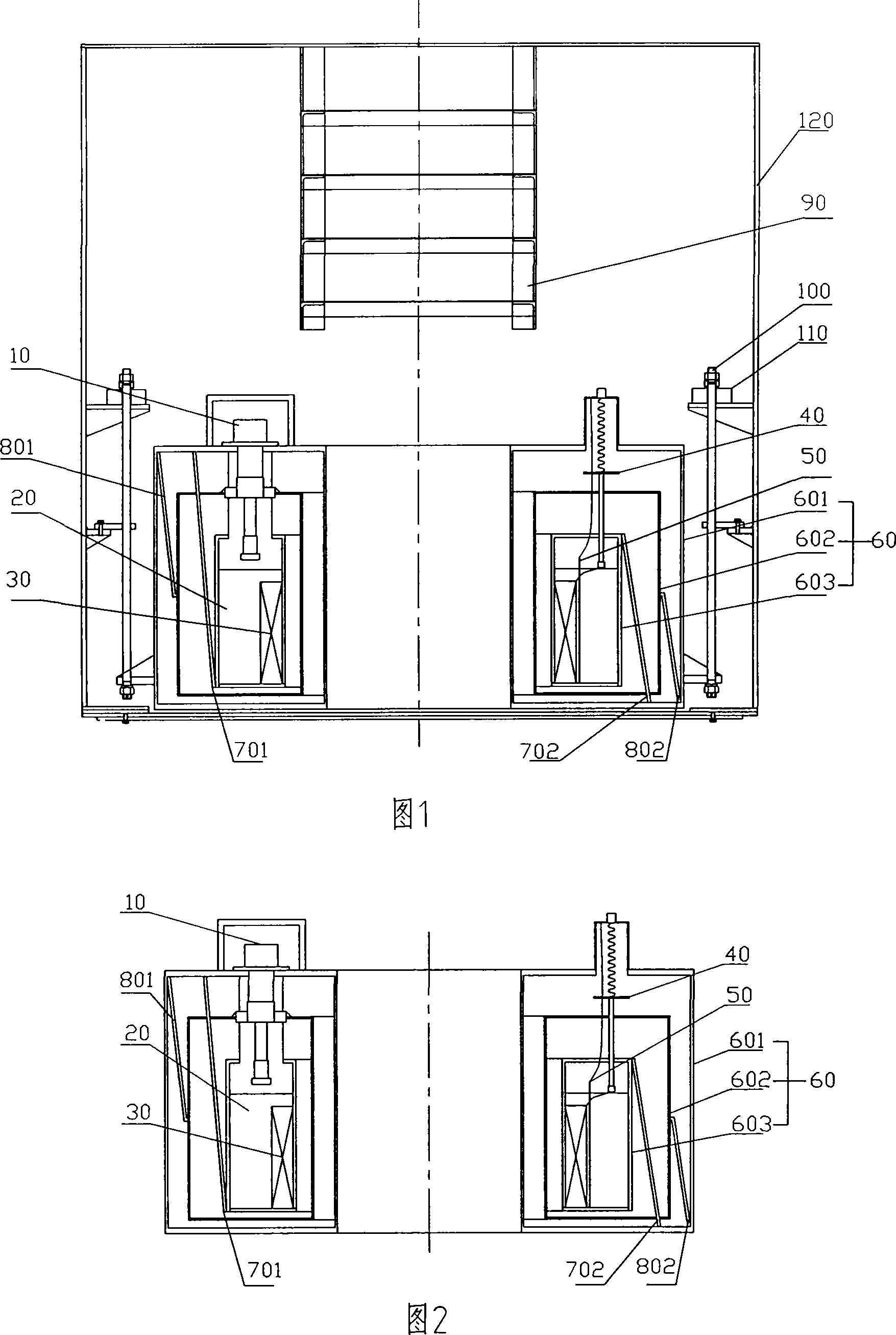
Low temperature superconductivity ferromagnetic deironing device
ActiveCN101195108AReduce heat leakageImprove stabilityOpen gradient mangetic separatorsSuperconducting magnets/coilsSuperconducting CoilsSuperconductivity
The invention discloses a strong magnetic iron remover with low temperature superconductivity, a cryostat is arranged on an outer cover of the invention, and the cryostat is hoisted on an inner wall of the outer cover through a pull-rod. The cryostat is provided with an indoor temperature Dewar, a 4.2K Dewar is arranged in the indoor temperature Dewar, a heat radiation screen is arranged between the indoor temperature Dewar and the 4.2K Dewar, gaps are arranged in perimeters between the indoor temperature Dewar and the heat radiation screen and between the heat radiation screen and the 4.2K Dewar, a superconducting coil can be coiled in insulation on an inner cylinder of the 4.2K Dewar, and power can be provided for the superconducting coil by a pair of two-dimensional electric currents lead-in wires. A vacuum state is between the indoor temperature Dewar and the 4.2K Dewar, and the 4.2K Dewar is filled with liquid helium20. The invention has great magnetic induction intensity, and can suck out tiny iron magnetic substances from materials, and has high working stability.
Owner:SHANDONG HUATE MAGNET TECH +1
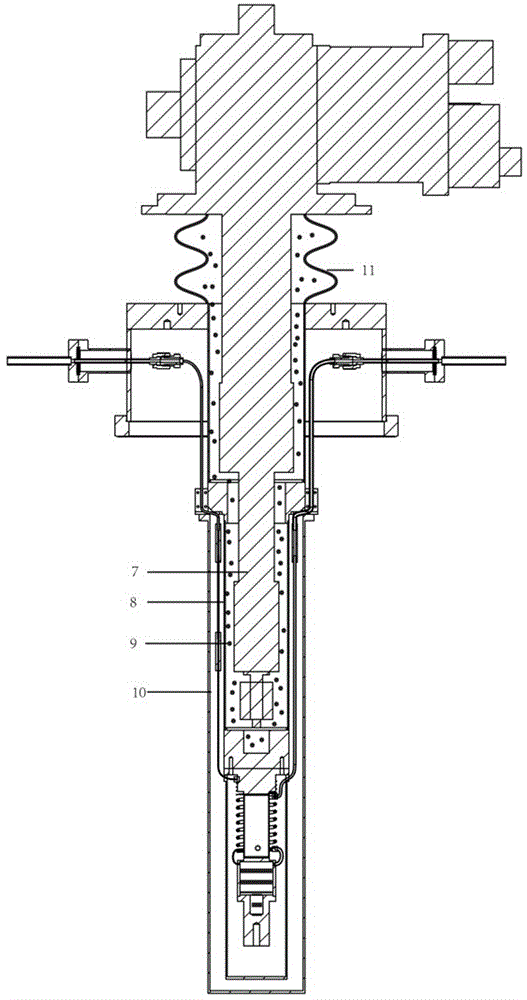
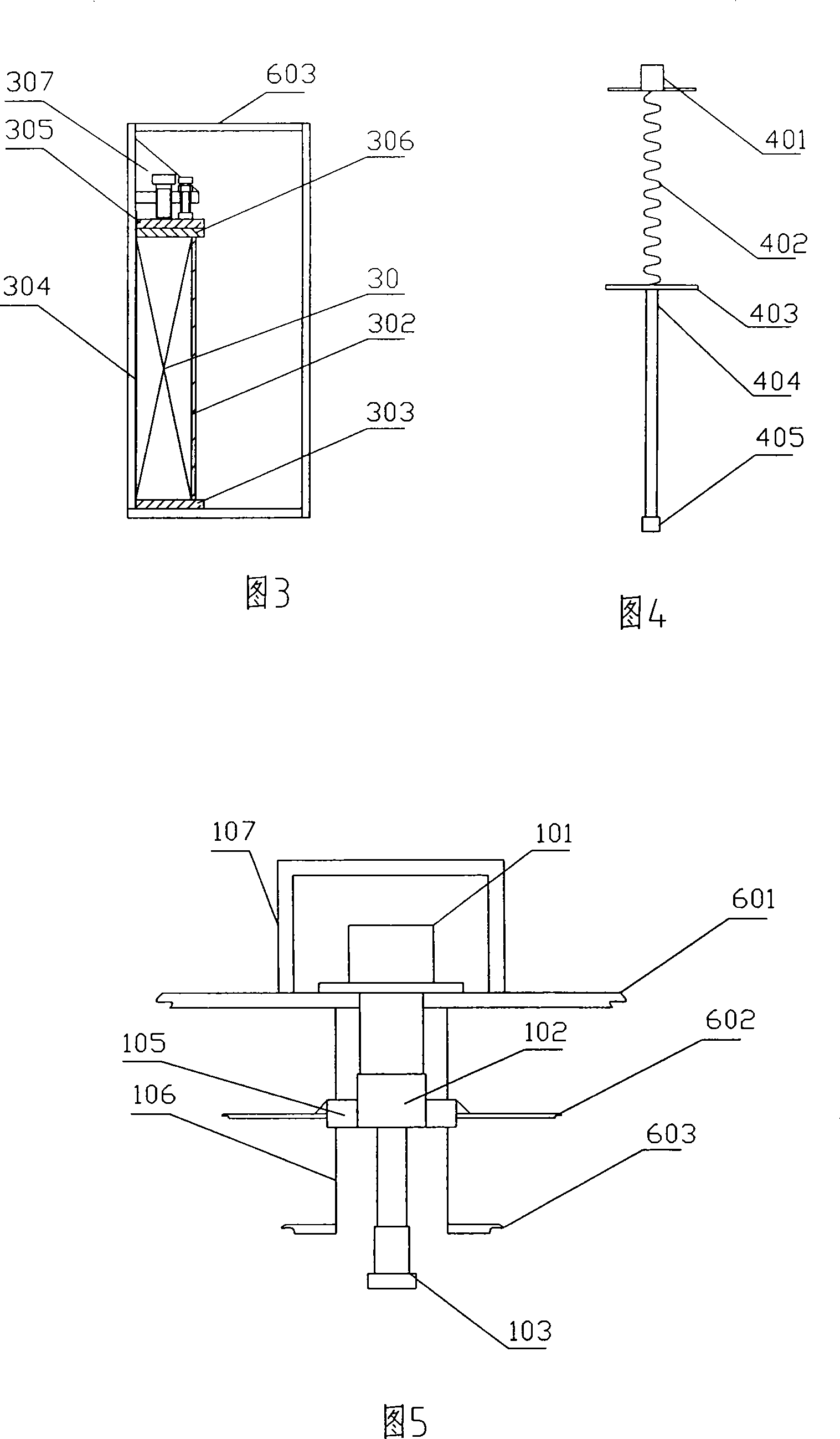
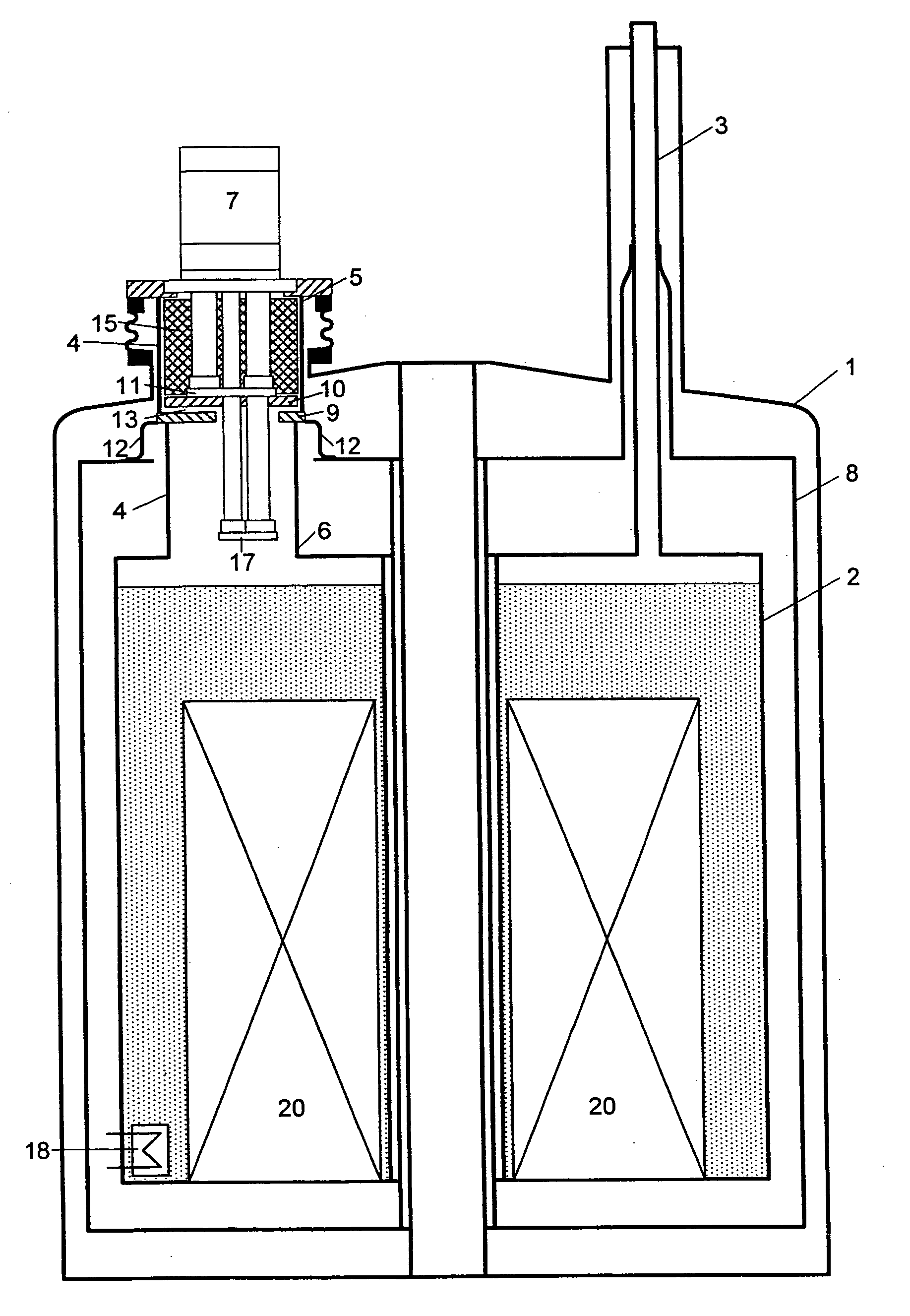
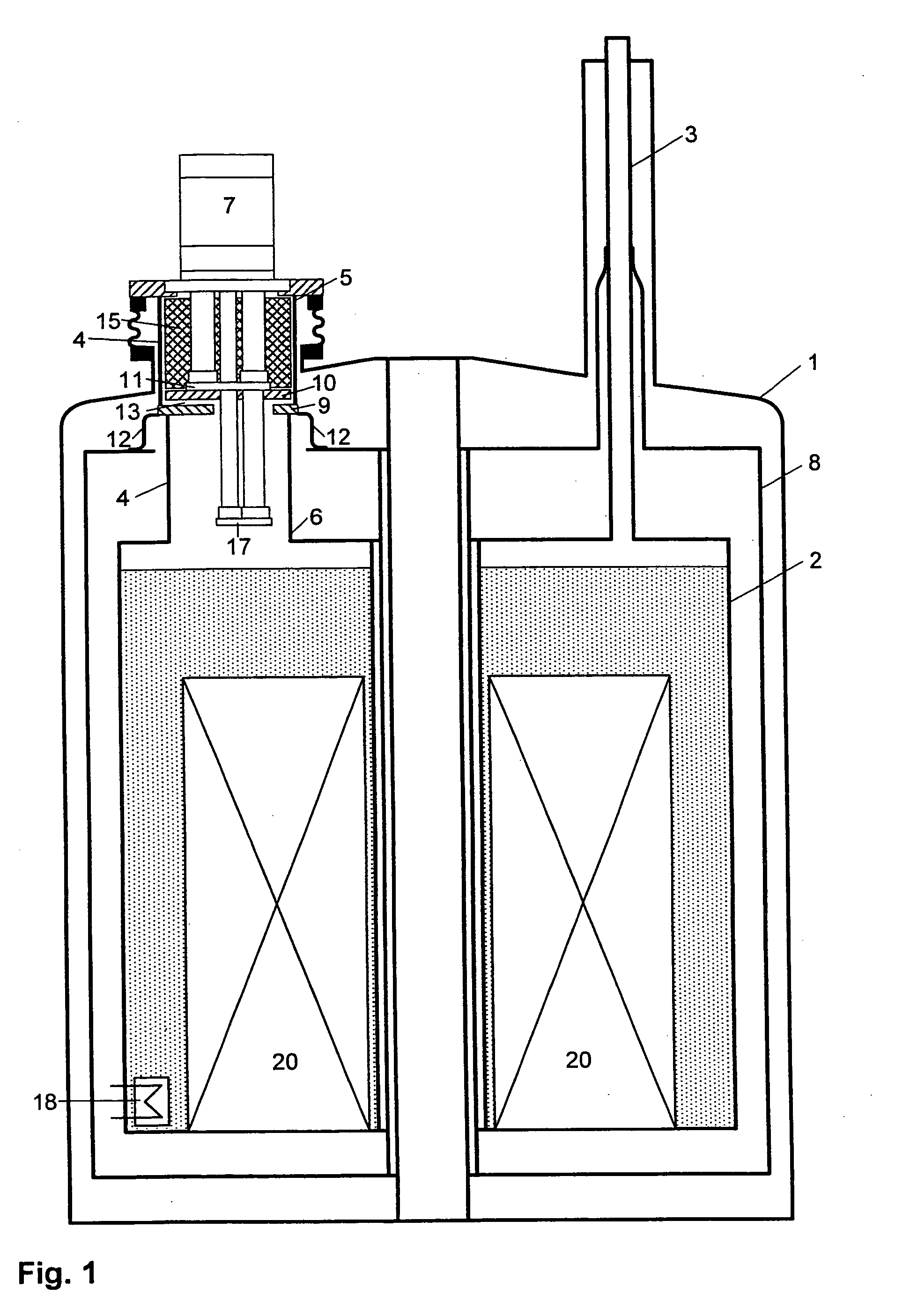
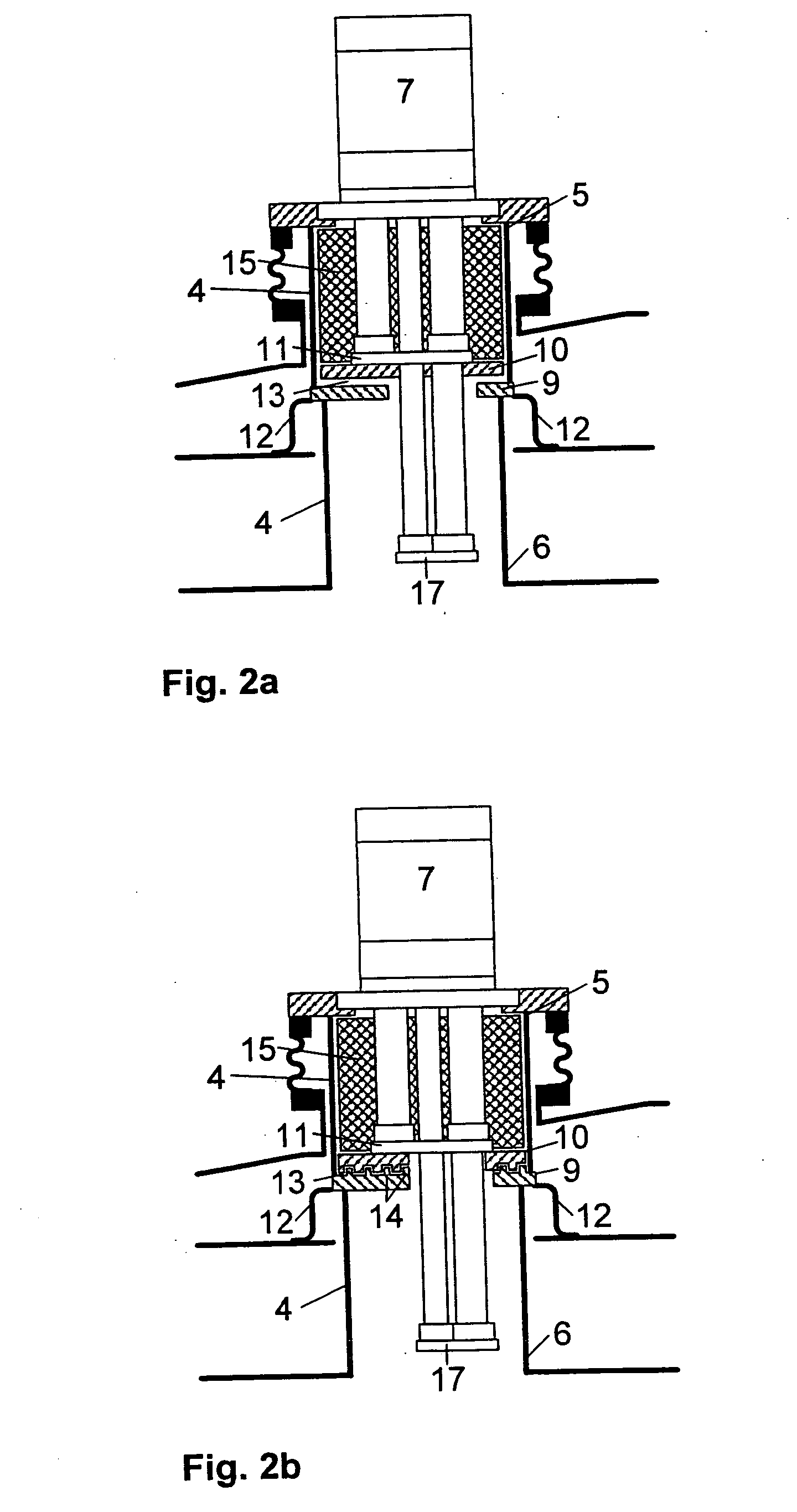
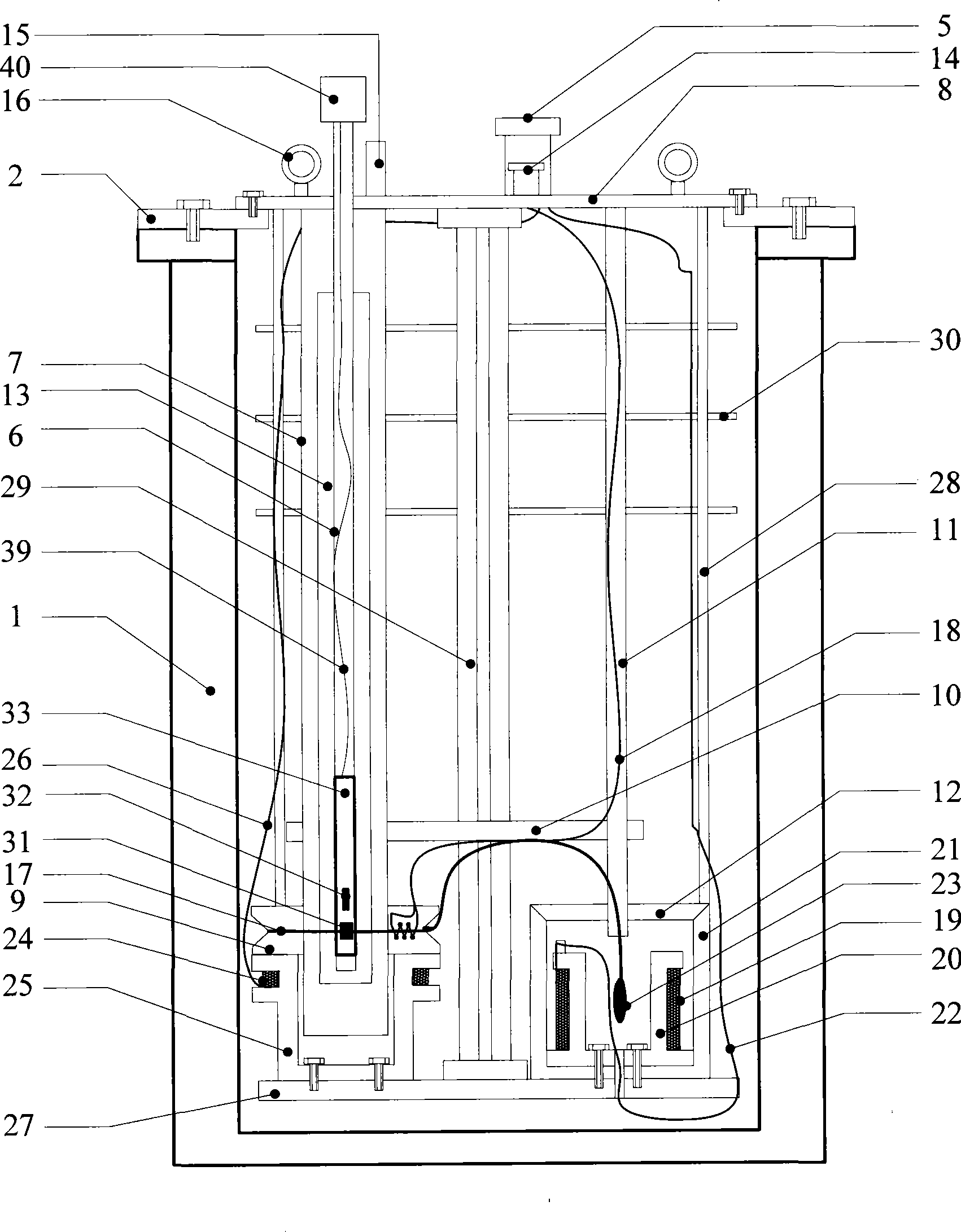
Cryostat configuration with cryocooler and gas gap heat transfer device
InactiveUS20070051115A1Reduce vibrationEffect spectrum qualityCompression machinesRefrigeration devicesHeat conductingThermal bridge
A cryostat configuration for keeping liquid helium comprises an outer jacket (1) surrounding a helium container (2) connected at at least two suspension tubes (3) to the outer jacket (1), and with a neck tube (4) whose upper warm end (5) is connected to the outer jacket (1) and whose lower cold end (6) is connected to the helium container (2) and into which a multi-stage cold head of a cryocooler (7) is installed, wherein the outer jacket (1), the helium container (2), the suspension tubes (3) and the neck tube (4) delimit an evacuated space, and the helium container (2) is surrounded by at least one radiation shield (8) which is connected in a heat-conducting fashion to the suspension tubes (3) and also to a contact surface (9) on the neck tube (4) of the helium container (2). The cryostat configuration is characterized by a gas gap (13) between one or more cold stages of the cold head (7) and one or more contact surfaces (9) in the neck tube (4) which are each connected in a heat-conducting manner to a radiation shield (8) via a fixed, rigid or flexible thermal bridge (12), heat being transferred through the gas gap (13) from the respective radiation shield (8) to the corresponding cold stage of the cold head (7). A cryostat configuration of this type ensures that no vibrations of the cold head (7) stages pass detectably into the cryostat configuration, wherein the quality of the thermal connection between the cold head (7) and the radiation shield(s) (8) is nevertheless sufficient.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
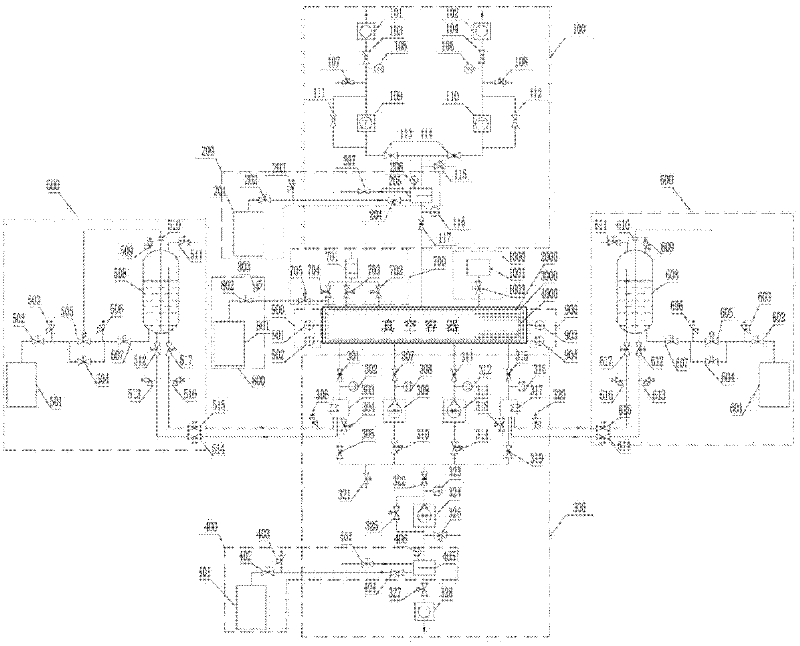
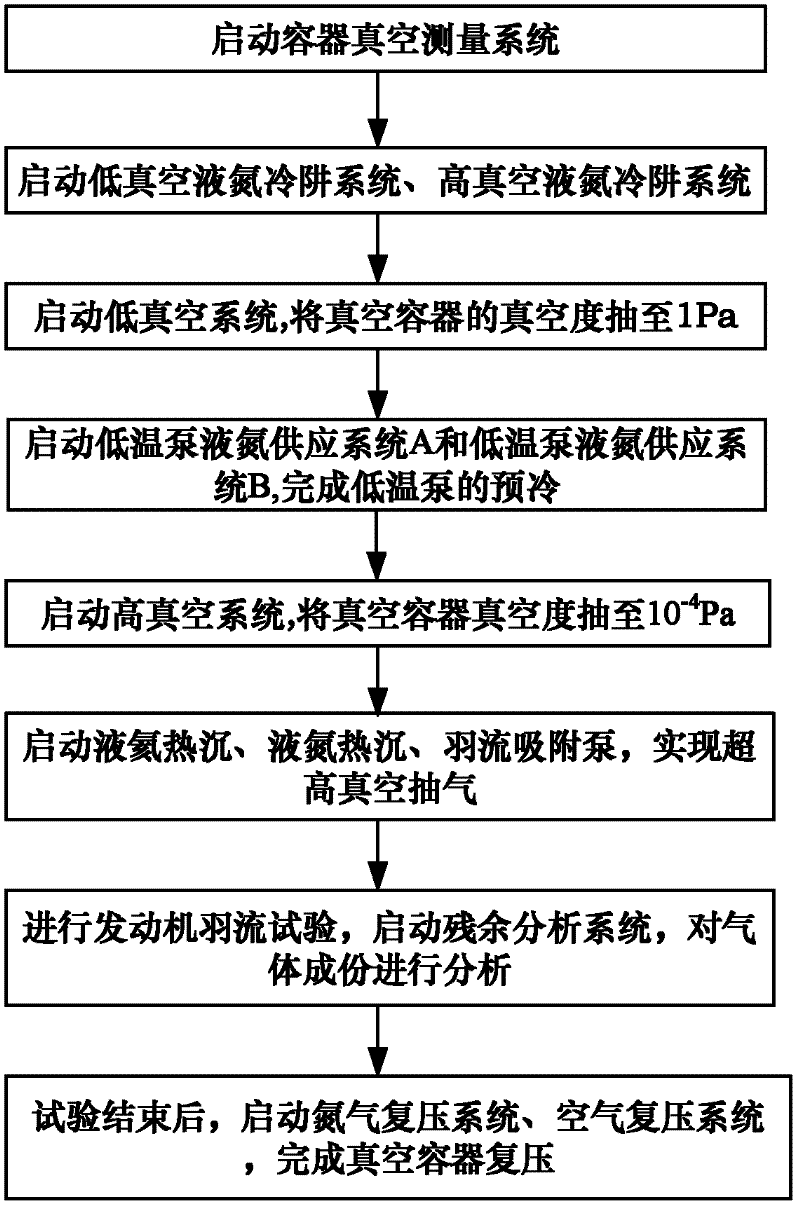
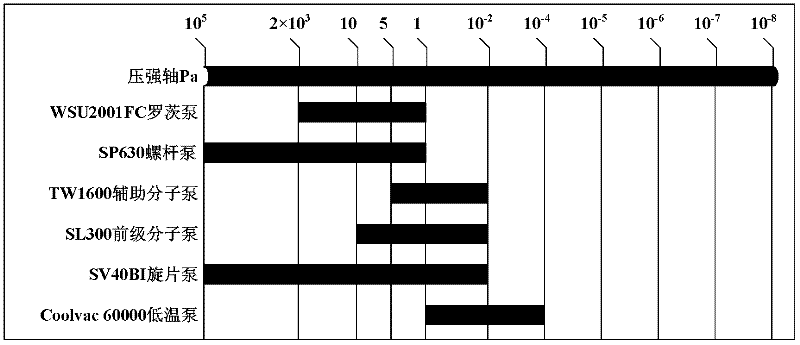
Clean vacuum system used for engine plume test research and vacuumizing and repressing method thereof
InactiveCN102359859AVarious working modesThe pumping speed is adjustableAerodynamic testingEngine testingGas analysisNitrogen
The invention provides a clean vacuum system used for engine plume test research and a vacuuminzing and repressing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of engine vacuum science. The clean vacuum system comprises a low vacuum system, a low vacuum liquid nitrogen cold trap system, a high vacuum system, a high vacuum liquid nitrogen cold trap system, a low temperature pump liquid nitrogen supply system A, a low temperature pump liquid nitrogen supply system B, an air repressing system, a nitrogen repressing system, a container vacuum measuring system, a residual gas analysis system, a liquid nitrogen heat sink, and a liquid nitrogen heat sink and plume adsorption pump. In the clean vacuum system, the vacuum is obtained mainly relying on the clean low vacuum system, the high vacuum system and the liquid nitrogen heat sink, the liquid nitrogen heat sink and plume adsorption pump; various clean vacuum degrees required by the plume test can be obtained, and the highest ultrahigh dynamic vacuum degree of 10<-6> Pa can be obtained. Both the low vacuum system and the high vacuum system are configured with the liquid nitrogen cold trap system which is used for absorbing the oil steam produced by working of a mechanical pump, so that the cleanness of the vacuum container can be ensured.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
High-temperature superconductive magnet system for magnetically confined plasma propeller
InactiveCN101692368AEliminate dangerIncrease the critical currentMagnetic induction acceleratorsSuperconducting magnets/coilsEvaporationConduction cooling
The invention discloses a high-temperature superconductive magnet system for a magnetically confined plasma propeller, which comprises two magnetic mirror units in the same structure, wherein each magnetic mirror unit comprises a Dewar barrel and two high-temperature superconductive magnets; and a refrigerator is used for cooling the two high-temperature superconductive magnets in each magnetic mirror unit. mode by a conductive cooling mode and uses the refrigerator to cool the two superconductive magnets in a conductive manner, so that the high-temperature superconductive magnet system for the magnetically confined plasma propeller greatly simplifies the structure, realizes high vacuum, reduces dependence on liquid nitrogen and high-cost operations, avoids a large-size low-temperature system and equipment used in the low-temperature liquid cooling mode, eliminates risks caused by the evaporation of a low-temperature liquid, cools the magnet to a temperature below 77 K and realizes a high field by increasing the critical current of the magnets, thus a superconductive low-temperature system is compact, efficient, safe and convenient, and is beneficial for integrating a superconductive apparatus with a low-temperature device.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High voltage insulation current lead for superconductive electric device
InactiveCN102568696ASolve the technical problems of high voltage insulationMeet the needs of high temperature gradientsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectric connection structural associationsCopper conductorRoom temperature
The invention relates to a high voltage insulation current lead for a superconductive electric device. A low temperature end B of a red copper conductor (1) is inserted into a low temperature container, and the tail end of the low temperature end B is provided with a connection terminal (2). The red copper conductor (1) is inserted into an insulation sleeve (3) from a room temperature end C of the insulation sleeve (3), a room temperature end A of the red copper conductor (1) is exposed out of the room temperature end C of the insulation sleeve (3); and screw threads (4) are arranged in the middle of the insulation sleeve (3). A connection nose (6) is pressed and connected with the end of the part of the room temperature end A of the red copper conductor (1), which is exposed out of the insulation sleeve (3), so as to form an insulation lead main body (7). A low temperature end F of the insulation lead main body (7) is arranged below the liquid level of liquid nitrogen or liquid helium in the low temperature container. A seal O ring and an insulator (11) are axially fixed on a low temperature container flange (14) by nuts and coaxial with the insulation lead main body (7). The room temperature end of the red copper conductor adopts a variable cross-section truncated cone structure from the flange position of the low temperature container to the low temperature end.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Chromatograph on-line analysis method for source rock by closed ball milling, heating analysis and cold trap trapping
The invention discloses a chromatograph on-line analysis method for source rock by closed ball milling, heating analysis and cold trap trapping, which is used for analyzing light fraction compound and percentage composition thereof in the dispersed organic matter of the source rock, and is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out vacuum sealing and ball milling on a source rock sample, carrying out ball milling, crushing, then heating to 300DEG C, and carrying out thermal desorption; blowing the pyrolysed hydrocarbon to a liquid helium cold trap by utilizing helium; placing the cold trap into a chromatograph furnace; and trapping, then carrying out chromatograph or Chromatographic-MS on-line analysis to obtain the qualitative data of chromatograph fine separation and / or Chromatographic-MS analysis of the light fraction in the source rock. The separation degree of the sample can approximate to the separation effect of the light dydrocarbon chromatograph separation of crude oil; the invention has good repeatability, reduces the volatilization loss of the light fraction in the crushing process because of the large volume of the sample before being put in a ball milling tank; and the qualitative analysis result can be used for researching the maturity and the environment of sedimentation of the source rock and carrying out oil source comparison.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
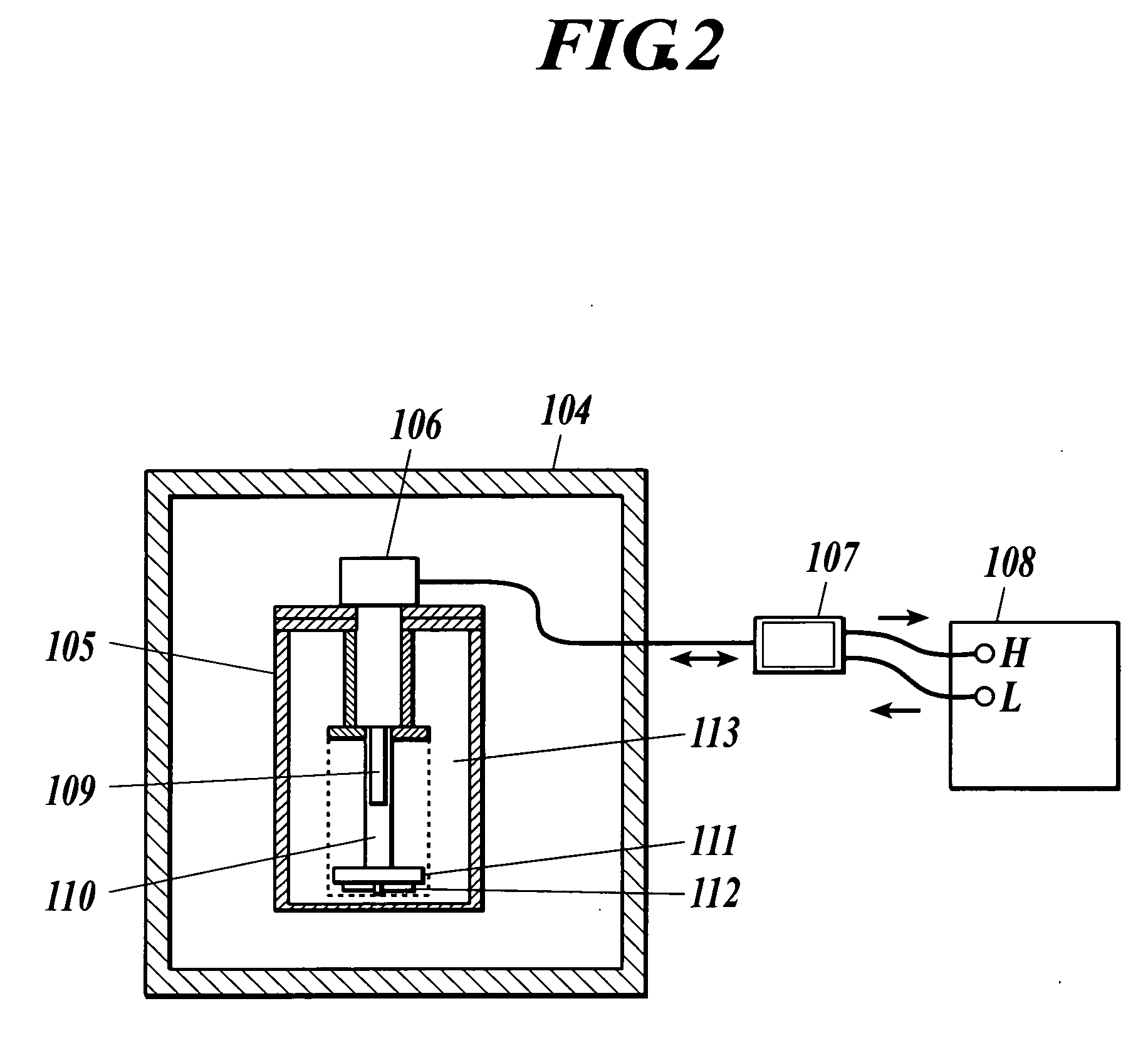
Ultracryostat and frigidity supplying apparatus
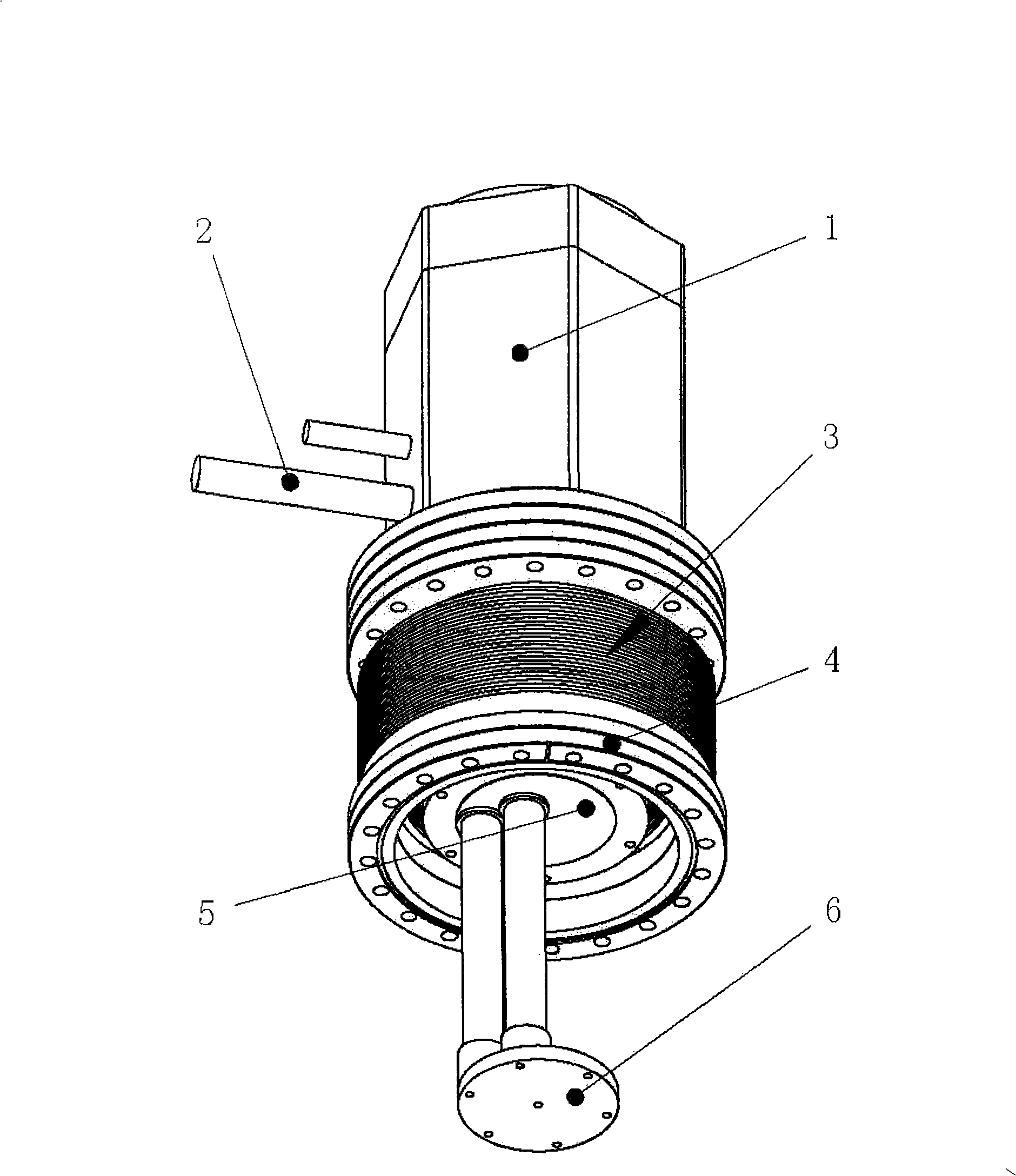
A ultracryostat is provided with a frigidity supplying member to supply frigidity to the ultracryostat which uses cryogen such as liquid helium, wherein the frigidity supplying member comprises a heat pipe and one end of the heat pipe is connected to a frigidity generating member of a cryocooler and the other end of the heat pipe is connected to a thermal anchor of a cryostat.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Special purpose device for measuring superconducting line joint resistance
InactiveCN101251558AEasy to replaceReduce volatilityMagnetic measurementsResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical resistance and conductanceHall element
The present invention discloses a specialized device for measuring the resistance of a superconducting line joint, comprising a low temperature Dewar unit, a room temperature tube unit, a background magnet unit, an excitation magnet unit, a linkage frame unit, a weakening magnetic field measuring unit, etc. The specialized device has the advantages that only the room temperature tube is required to be moved out from the low temperature Dewar via a guide rail when a sample loop of the measured superconducting line joint is replaced, so that the volatilization amount of the liquid helium in an experimental process is reduced. The background magnet is positioned on the lateral side of a Hall element which measures the weakening magnetic field of the sample loop of the superconducting line joint. Compared with being positioned at the lower side of the Hall element, the background magnet positioned at the lateral side of the Hall element reduces the influence of the background magnet to the fact that the Hall element measures the weakening magnetic field generated by the sample loop of the superconducting joint. With the room temperature tube technical, the Hall element is arranged inside the room temperature tube, namely a normal temperature Hall sensor measures the weakening magnetic field of the sample loop of the superconducting joint. The cost of the device is reduced and the reliability of the measurement is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
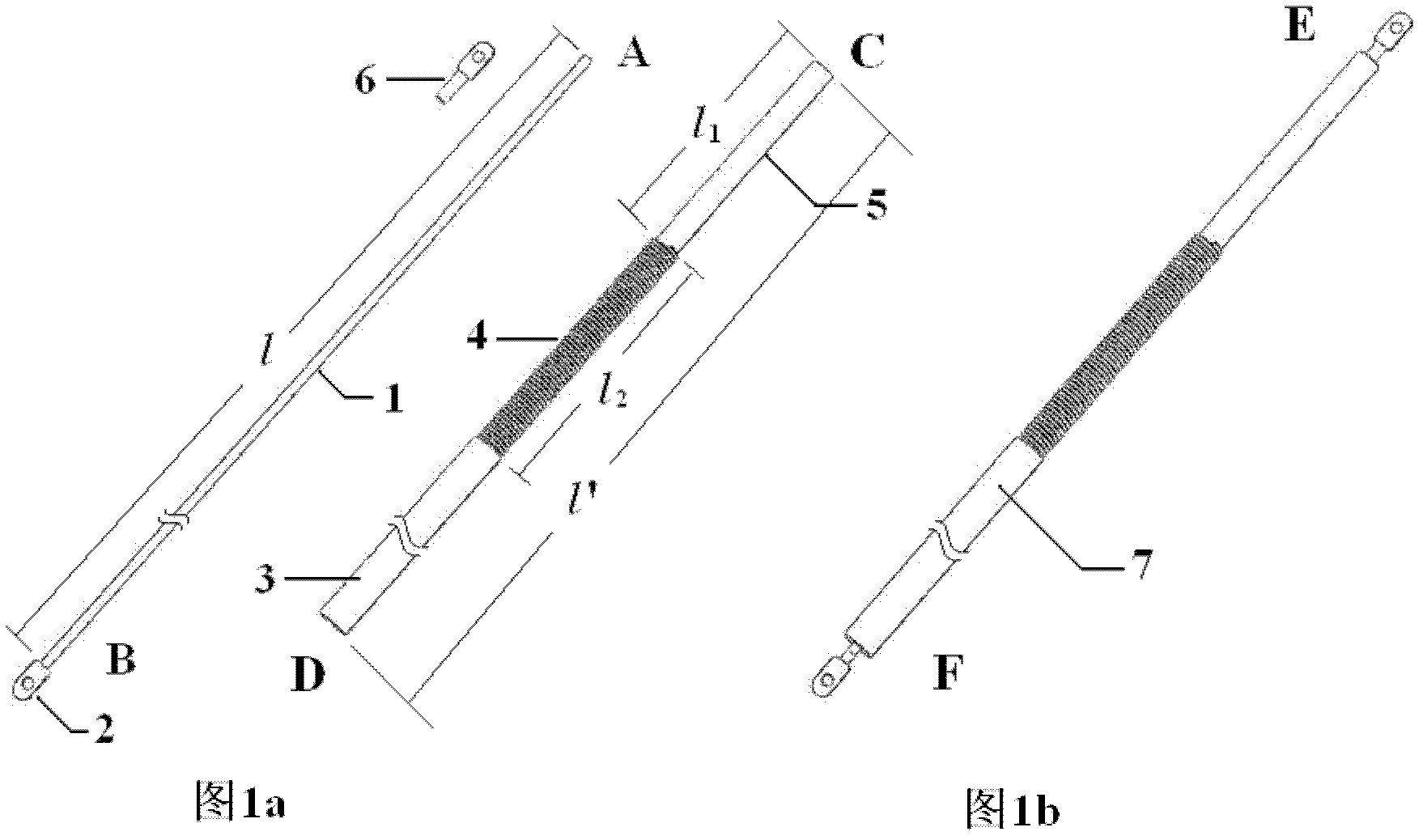
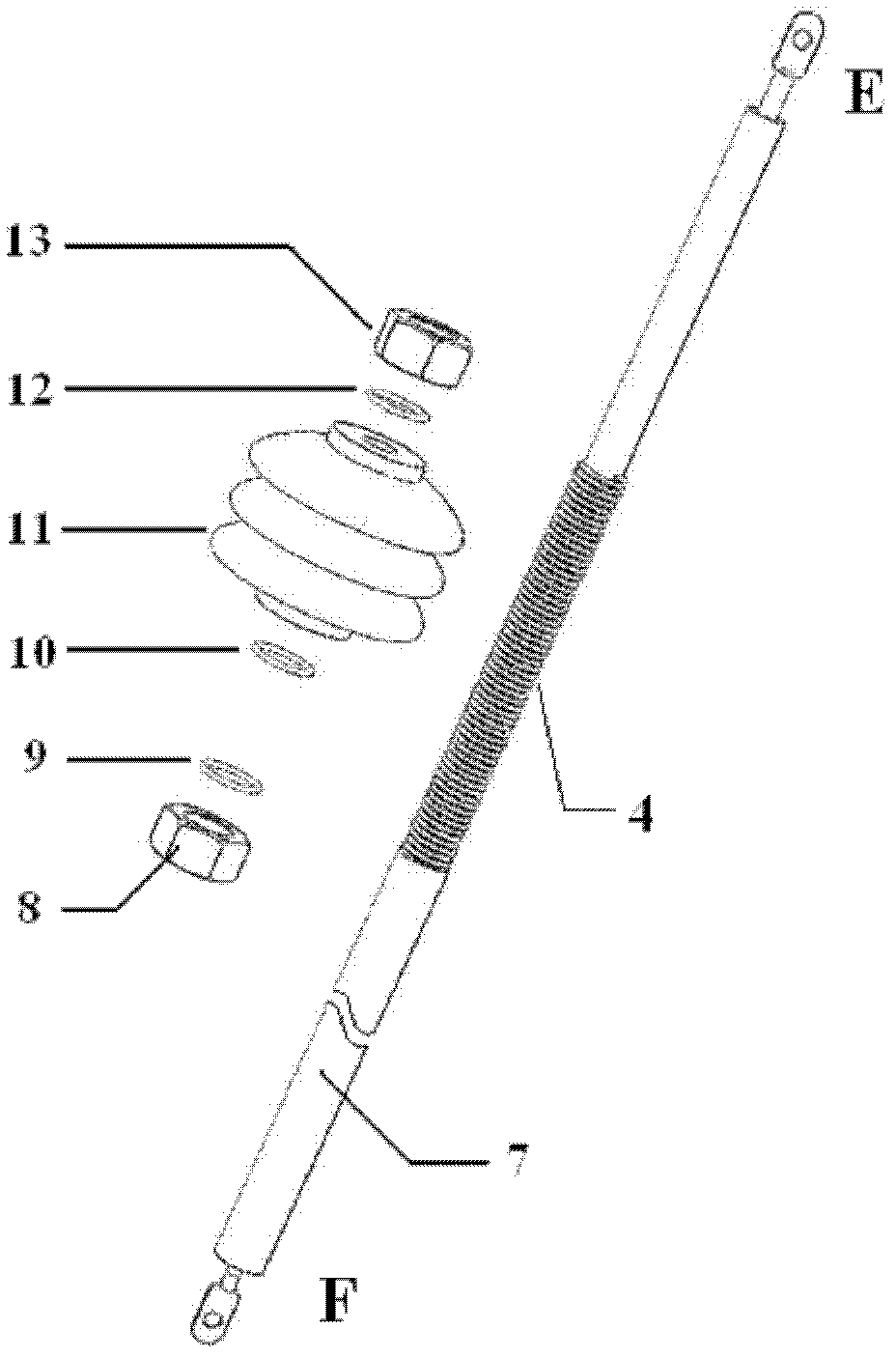
First-stage pullable binary coaxial current lead structure
InactiveCN102360694AReduce quench problemsAvoid the problem of excessive Joule heatingCoupling contact membersSuperconducting magnets/coilsHigh magnetic field strengthPower flow
The invention discloses a first-stage pullable binary coaxial current lead structure, and relates to a binary current lead technology. The structure comprises a first-stage current lead connected with a high-temperature part, a second-stage current lead connected with a low-temperature part and a pullable heat exchanger which is connected with the first-stage current lead and the second-stage current lead respectively and is positioned between the first-stage current lead and the second-stage current lead. The first-stage pullable binary coaxial current lead structure has the advantages of compact structure, stable performance, reliable operation, low heat leakage and convenience in disassembly and assembly, has the capacity of reducing heat leakage in an entire excitation process and subsequent normal operation, and is particularly suitable for a superconducting magnet with conduction cooling, less liquid helium and high magnetic field strength and operating in a closed loop.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Superconducting magnet system of inserted YBCO-Bitter type high-temperature superconducting coil
ActiveCN101577165AQuench preventionSimple structureInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureSuperconducting magnets/coilsEpoxyHigh-temperature superconductivity
The invention relates to a superconducting magnet system of an inserted YBCO-Bitter type high-temperature coil. The inserted YBCO-Bitter type high-temperature superconducting coil (8) is inserted into an inner hole of a peripheral superconducting coil (10) formed by NbTi and Nb3Sn. The inserted YBCO-Bitter type high-temperature superconducting coil (8) is positioned in a low-temperature container (9); the peripheral superconducting coil (10) is arranged in a low-temperature container (11); and the low-temperature containers (9 and 11) are filled with liquid helium (12). The inserted YBCO-Bitter type high-temperature superconducting coil (8) is formed by superposing of multiple YBCO ring pieces (1) which are embedded in a stainless steel ring (6). High-purity copper ring pieces (2) plated with an aluminum nitride film are arranged between the YBCO ring pieces (1). The multiple YBCO ring pieces (1) and the multiple high-purity copper ring pieces (2) are superposed along the same shaft, are assembled together by a stainless steel central hole tube (3) and an end flange (4), and are cured into a whole body after being soaked by epoxy resin. The superconducting magnet system has simplified structure, little heat leakage of system and stable generated magnetic field.
Owner:NINGBO JANSEN NMR TECH CO LTD
Connector between high-temperature superconductive magnet double-cake coils and its welding method
InactiveCN101075496AImprove stabilityLow running costSuperconducting magnets/coilsSuperconducting CoilsHigh temperature superconducting
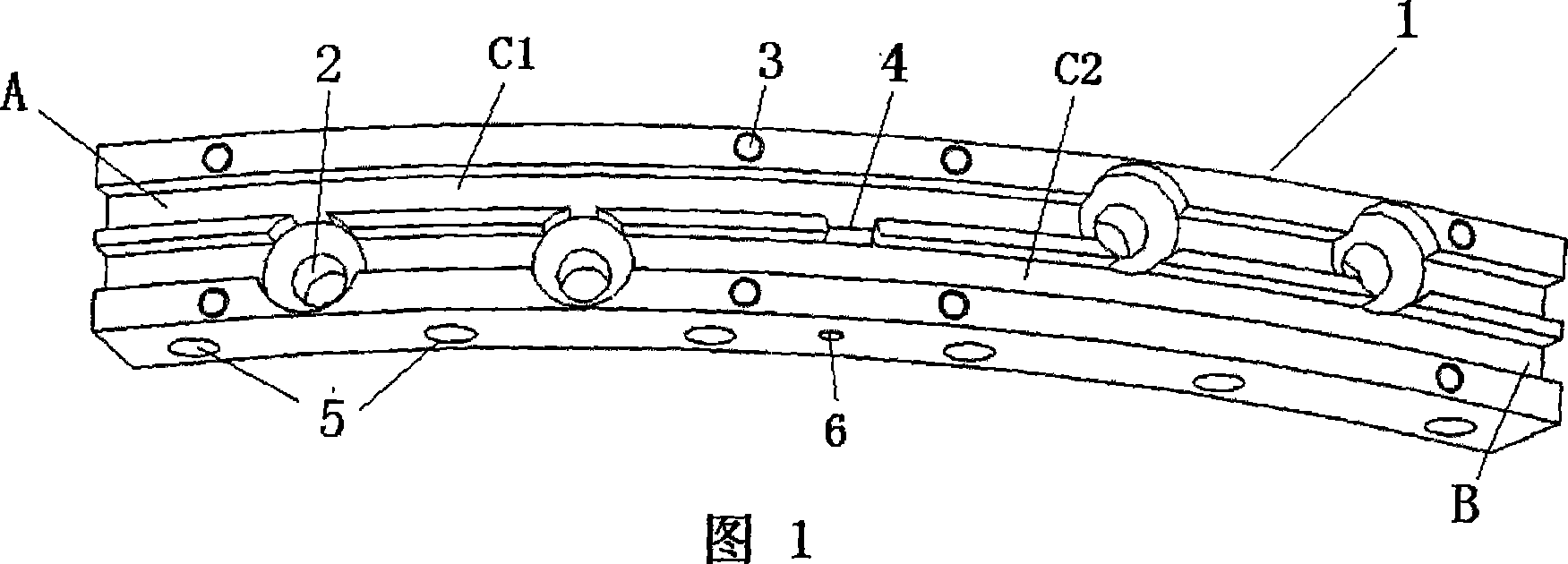
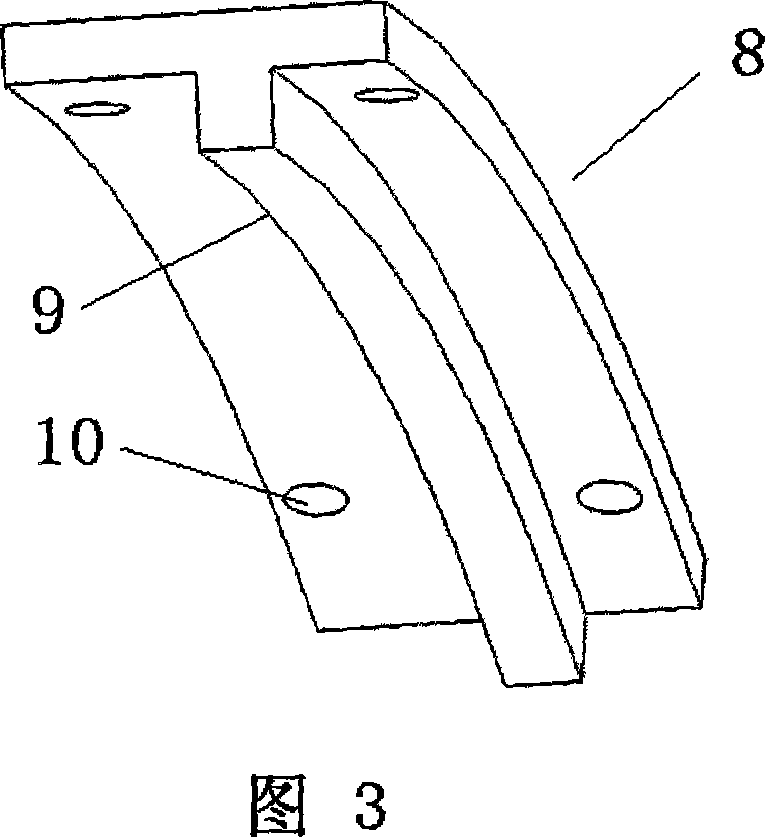
This is a tie-in of double pie loop for high temperature super conducting magnet and its jointing method. The tie-in composes a concave base, NbTi bridge and a convex cover. The concave base is the matrix of the tie-in and made by metal like copper of low resistivity, of a shape in arc and radial section in rectangle and is fixed to a magnet. The NbTi bridge is embedded in the groves[C1, C2] on the base, and the convex beam on the convex cover is also embedded in the groves to fix the NbTi bridge.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low temperature scanning probe microscope system based on pulsatron refrigeration technology
ActiveCN101294889ALow running costEliminate vibrationSurface/boundary effectInstrumental componentsRetention timeDigital signal processor
The invention relates to a low temperature scanning probe microscope system based on pulse tube refrigeration technology. Aimed at vibration source and characteristics, a multistage active / passive damping device, including a sylphon bellowss, a piezoelectric ceramic tube and a spring are adopted. The sylphon bellowss is used for connecting a main system cavity and a refrigeration head of the pulse tube to realize vibration isolation of the whole system. As for low frequency vibration unique to a pulse tube refrigerator, an active damping device with a piezoelectric ceramic tube and a digital signal processor as the core is adopted. A beryllium copper spring and a damping magnet form a first stage passive damping device to isolate vibration. The system eliminates the vibration from the pulse tube refrigerator and the refrigeration head to the scanning probe, applies to other vibration sensitive occasions that require low temperature, saves a large amount of liquid helium refrigerant, simplifies equipment operation and maintenance, and significantly prolongs the retention time at low temperature.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com