Low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope using closed-cycle refrigerator to achieve refrigeration
A closed-cycle refrigerator and scanning tunnel technology, applied in the field of scanning probe microscopy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] In order to make the purpose, technical solution and advantages of the present invention more clear, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
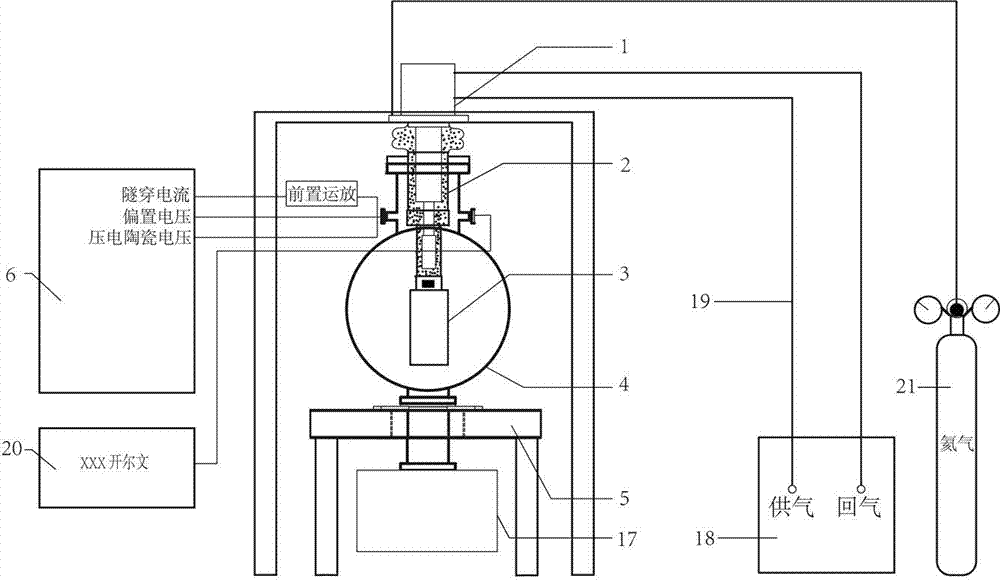
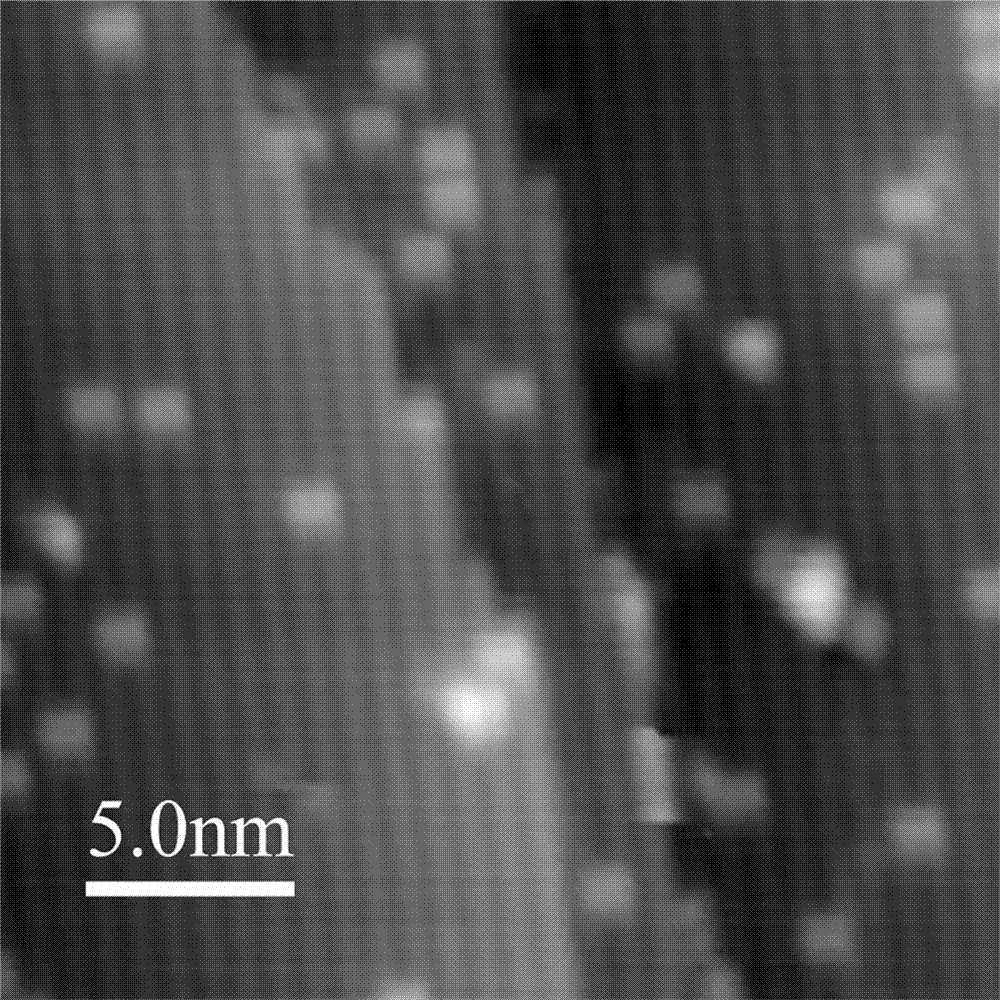
[0024] Almost all cryogenic scanning tunneling microscopes today are cooled using liquid helium based Dewar thermostats or continuous flow thermostats. This makes the amount of liquid helium consumed by the system operation very considerable, and the operation cost is high. To obtain a low temperature comparable to that of a liquid helium refrigeration system without using liquid helium, an effective way is to use a closed-cycle refrigerator to cool down. However, the closed-cycle refrigerator has strong mechanical vibration and noise, which limits the application of the closed-cycle refrigerator in the field of low-temperature scanning tunneling microscope with atomic resolution.
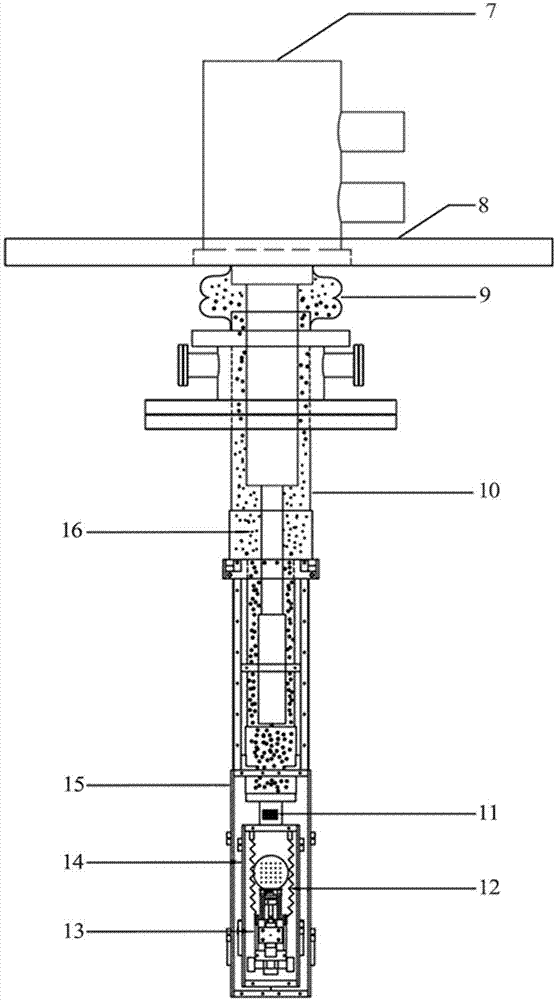
[0025] figure 1 Shown is a schema...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com