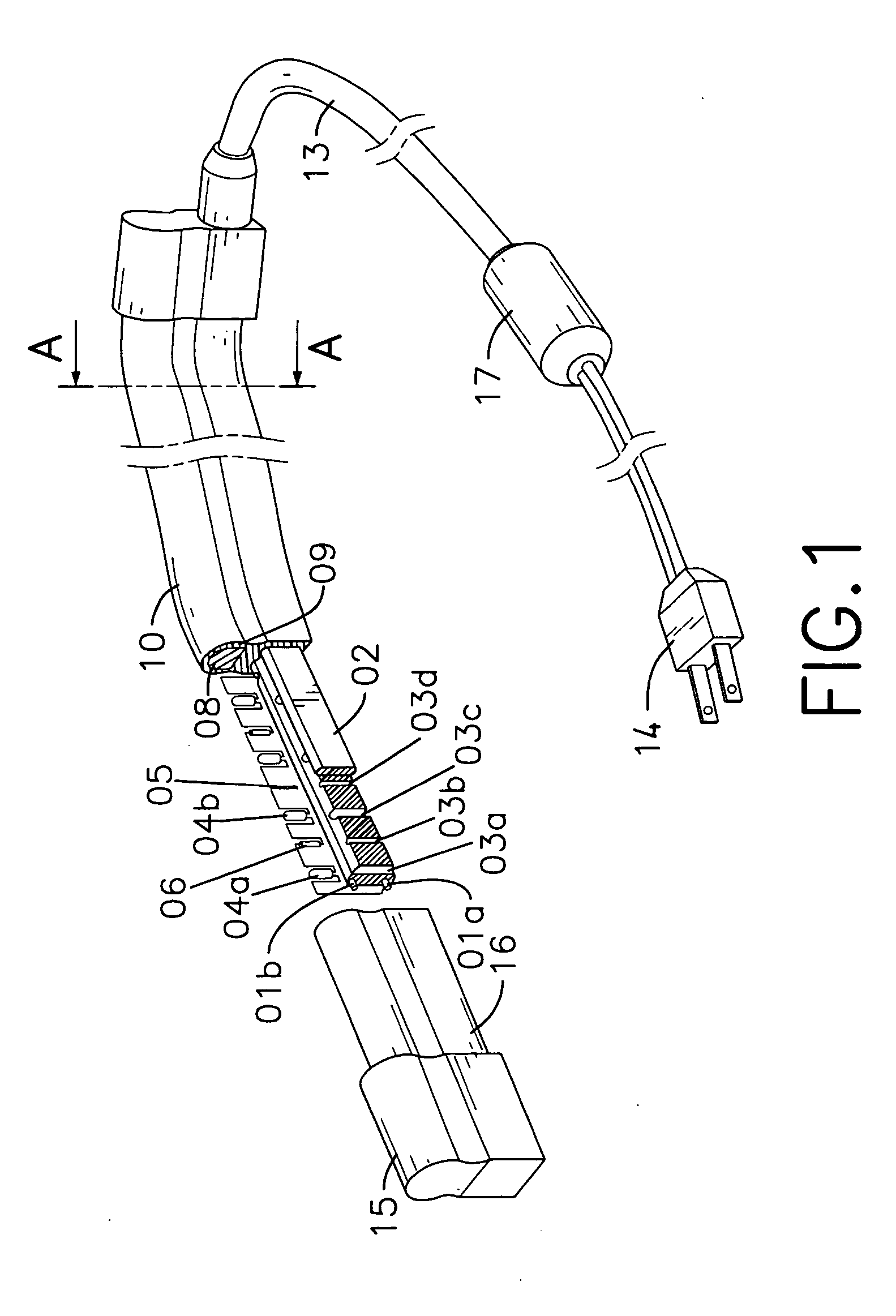
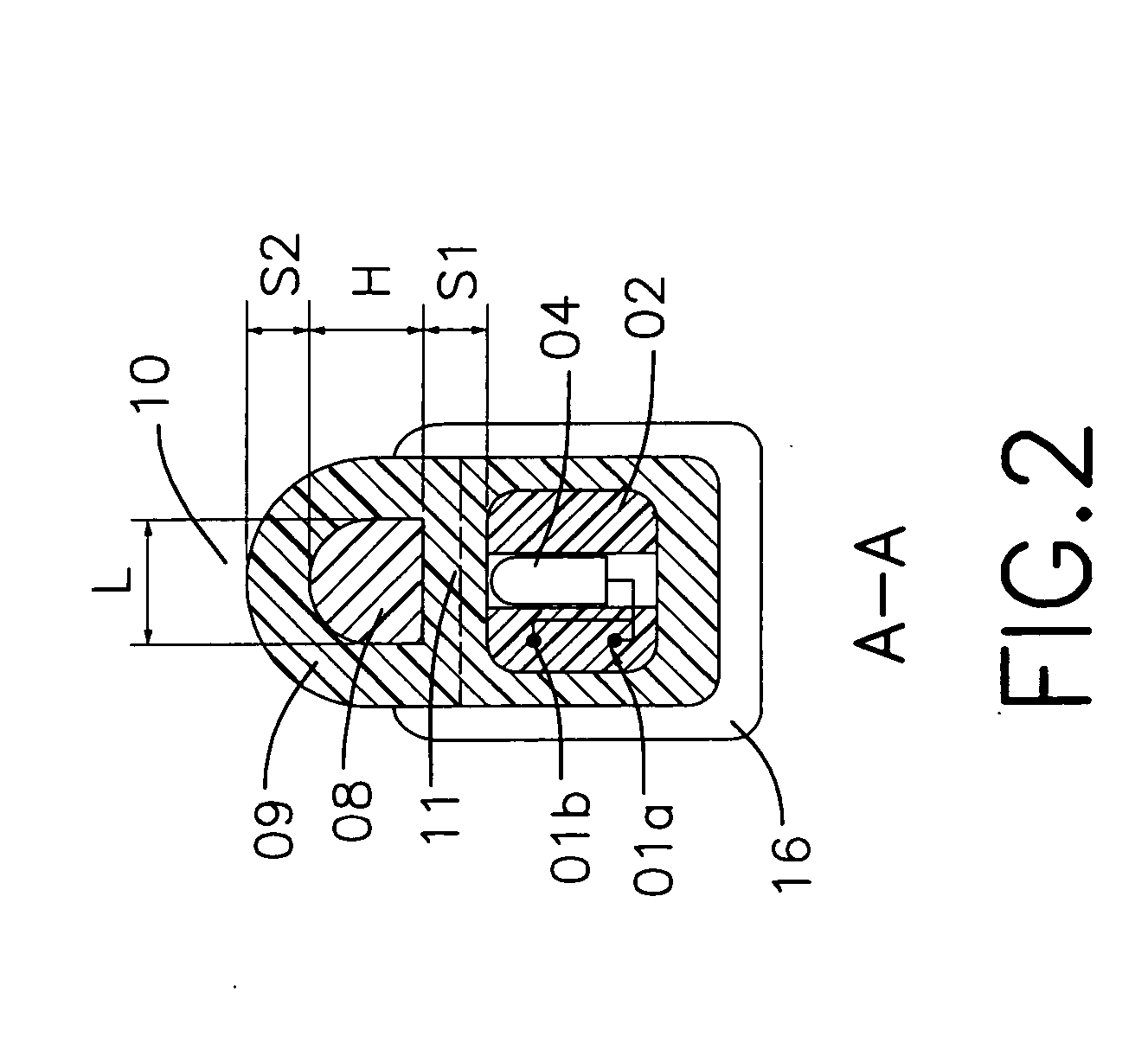
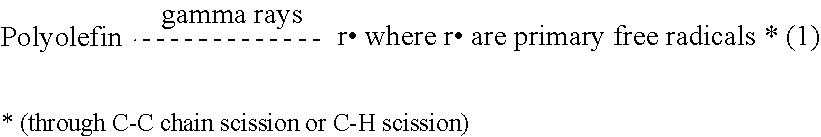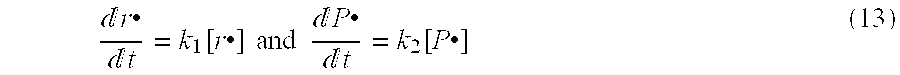Patents
Literature
739 results about "Neon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypton and xenon) in 1898 as one of the three residual rare inert elements remaining in dry air, after nitrogen, oxygen, argon and carbon dioxide were removed. Neon was the second of these three rare gases to be discovered and was immediately recognized as a new element from its bright red emission spectrum. The name neon is derived from the Greek word, νέον, neuter singular form of νέος (neos), meaning new. Neon is chemically inert, and no uncharged neon compounds are known. The compounds of neon currently known include ionic molecules, molecules held together by van der Waals forces and clathrates.
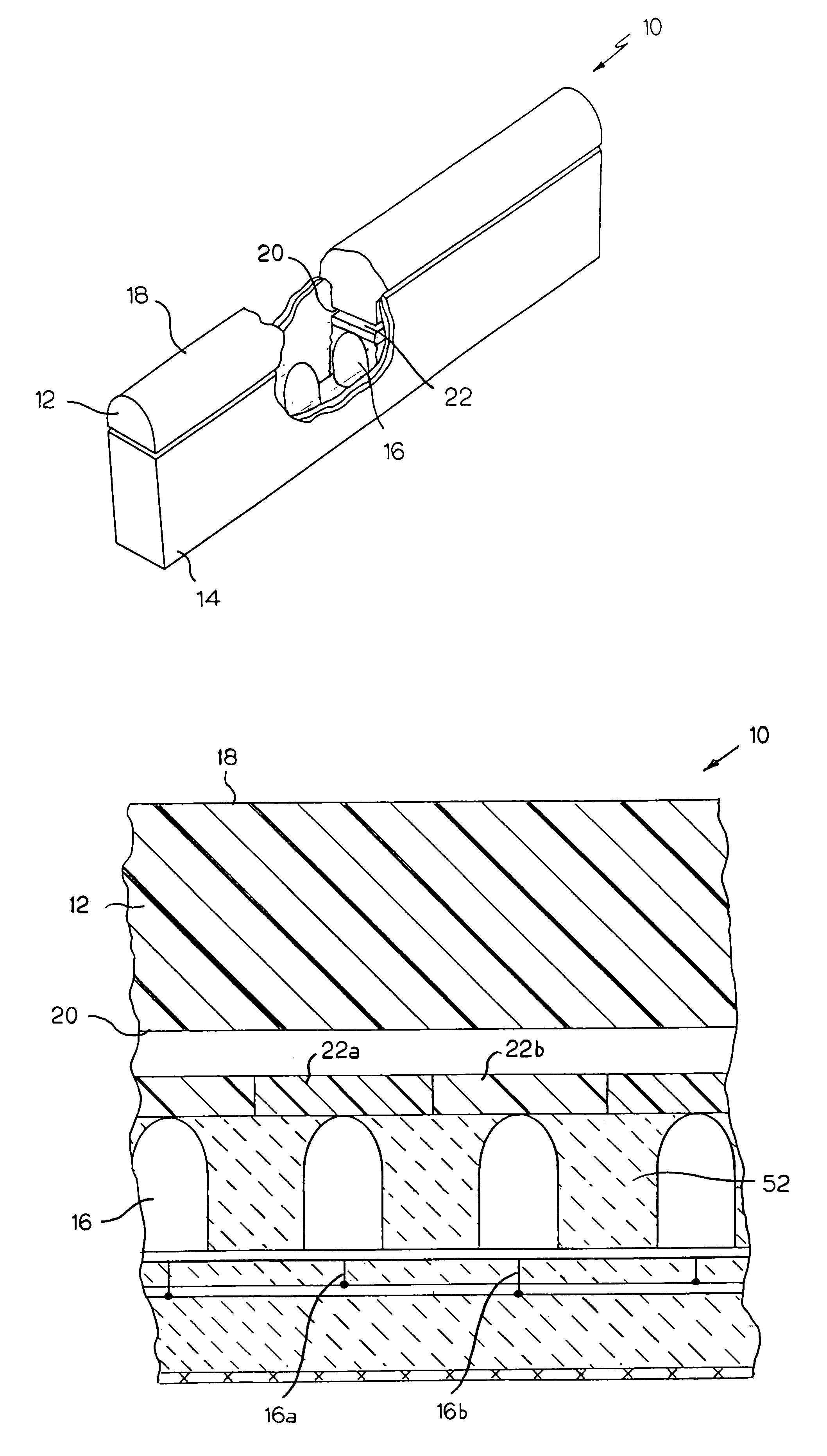
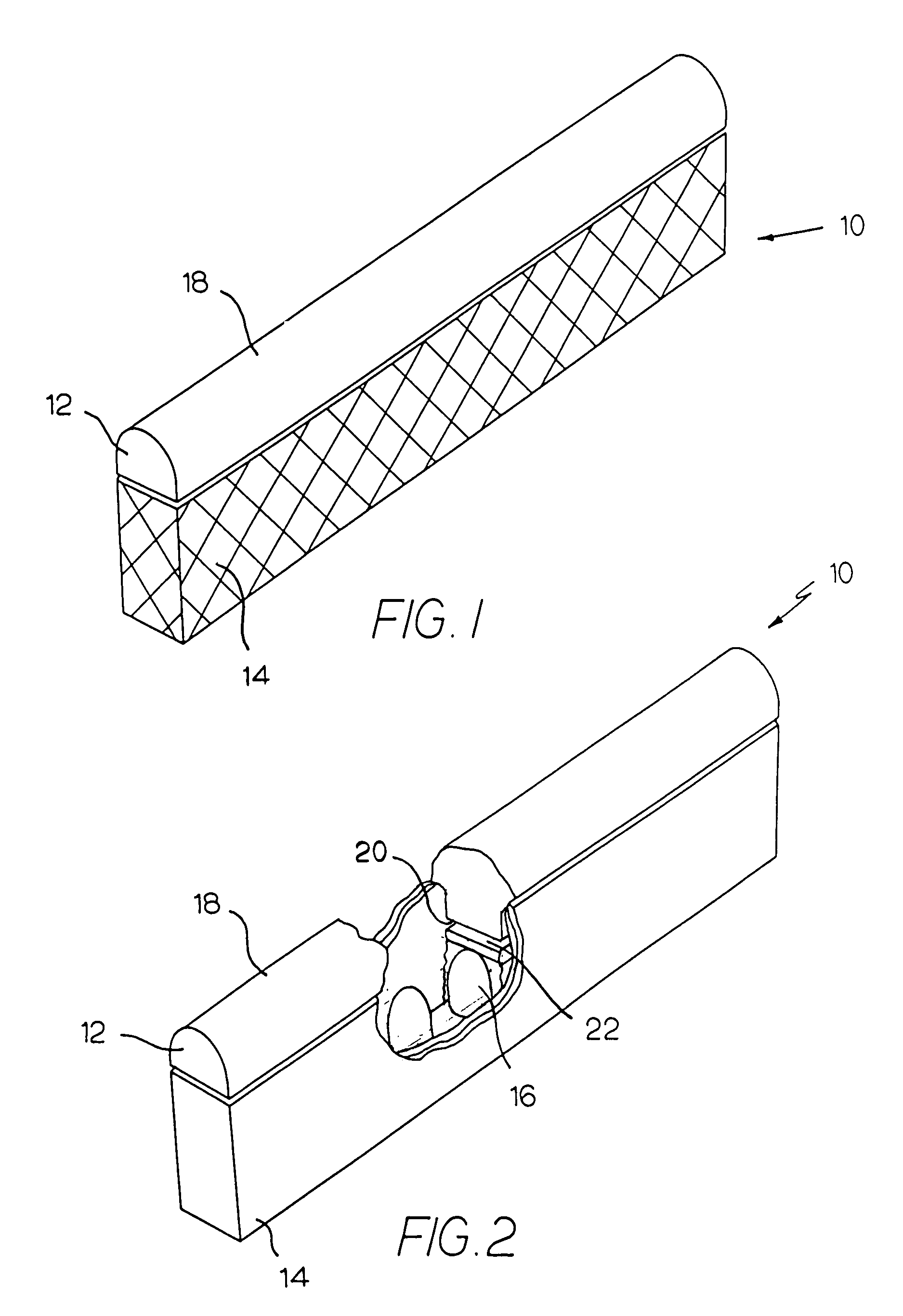
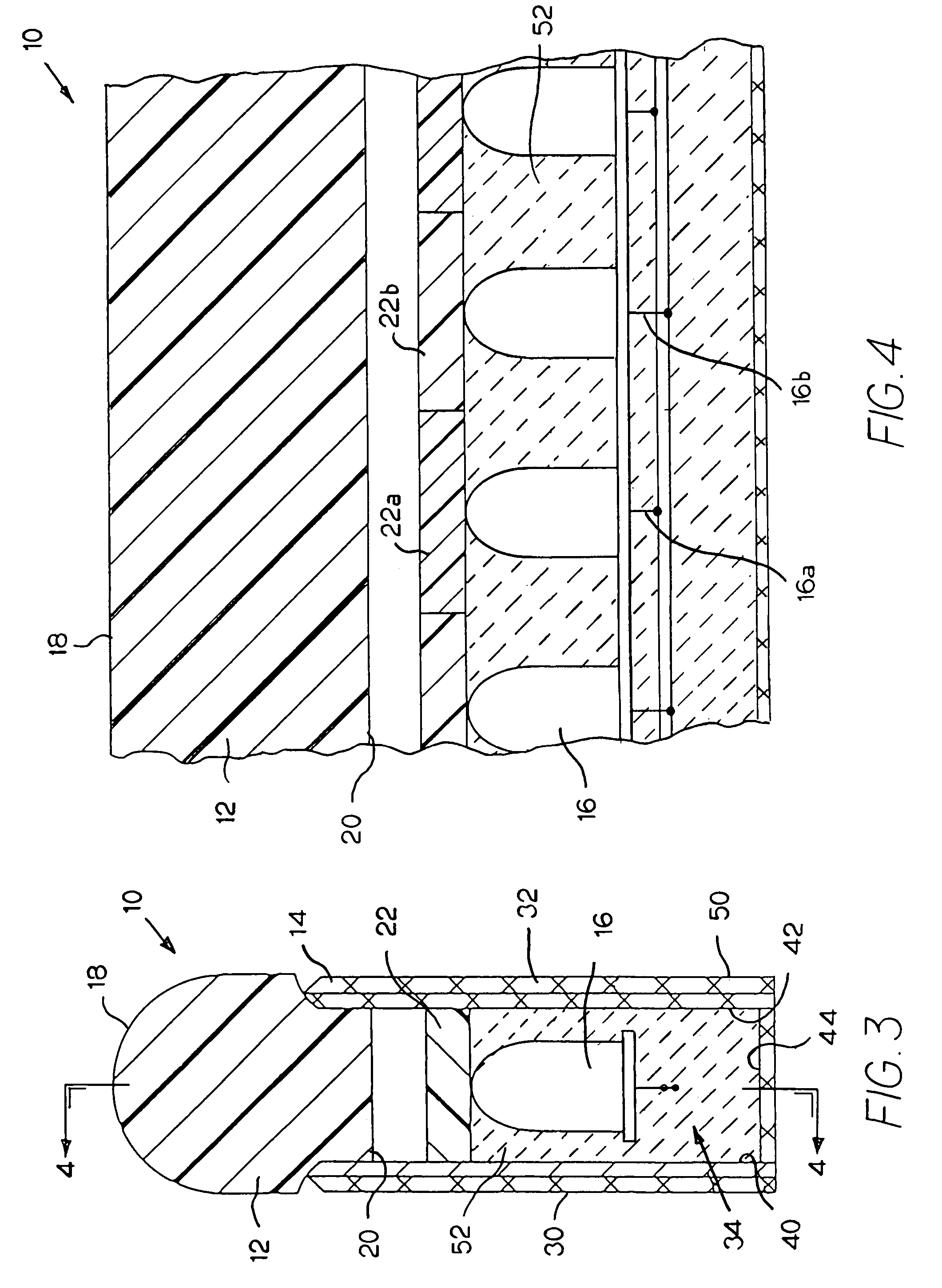
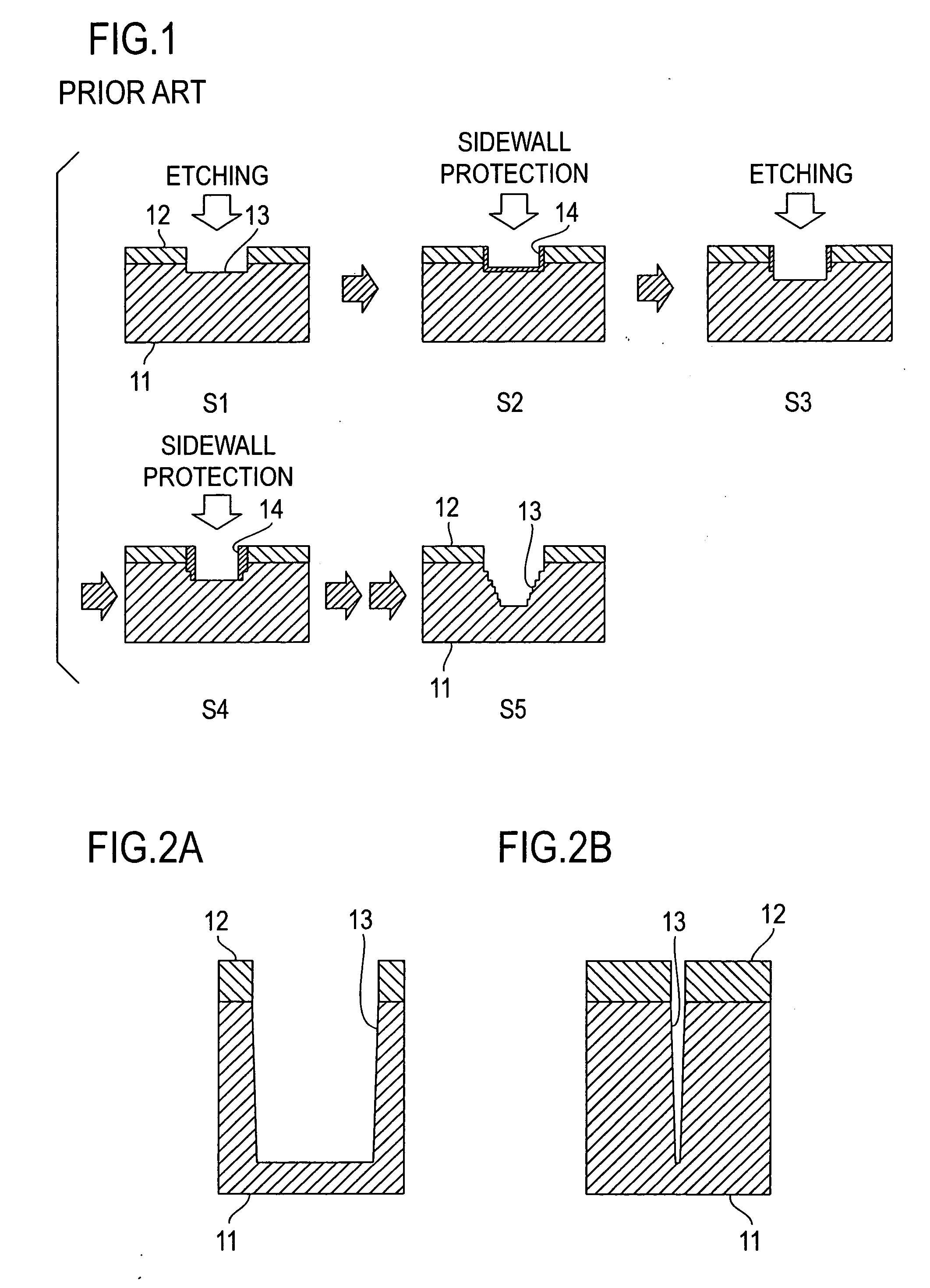
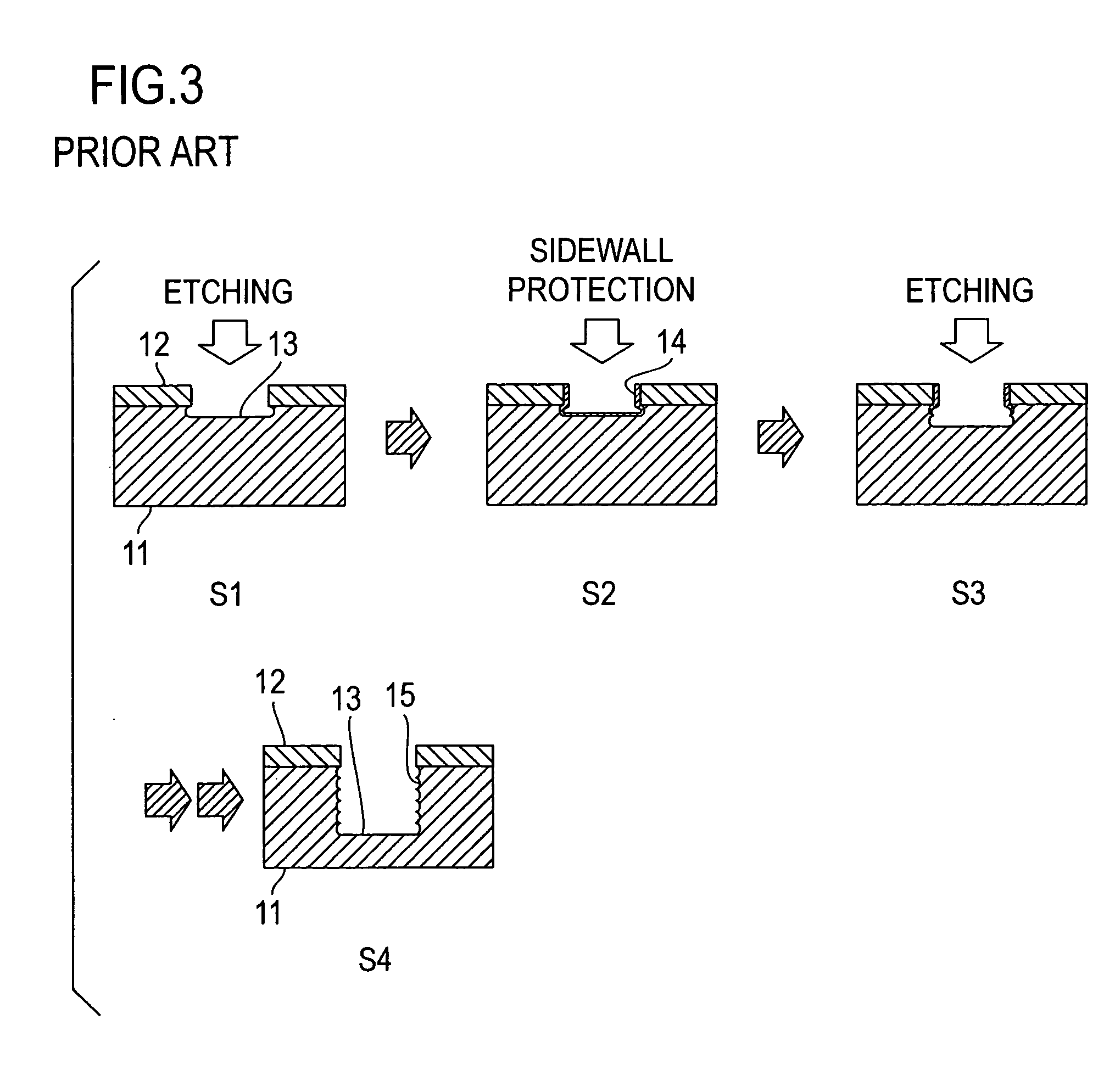
Methods of Forming Integrated Circuit Devices Having Ion-Cured Electrically Insulating Layers Therein
ActiveUS20090098706A1Quality improvementDegree of reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAtomic orderEngineering
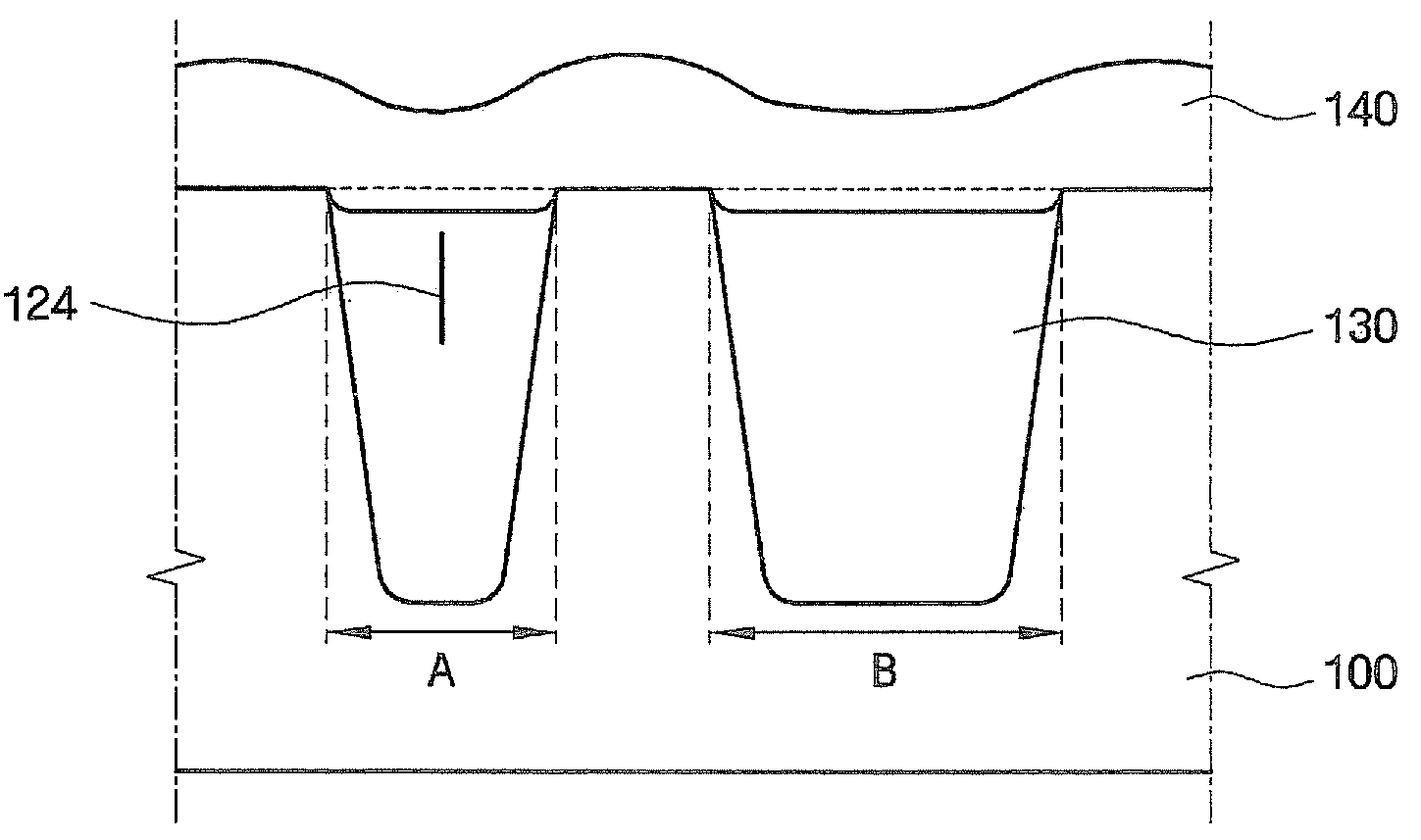
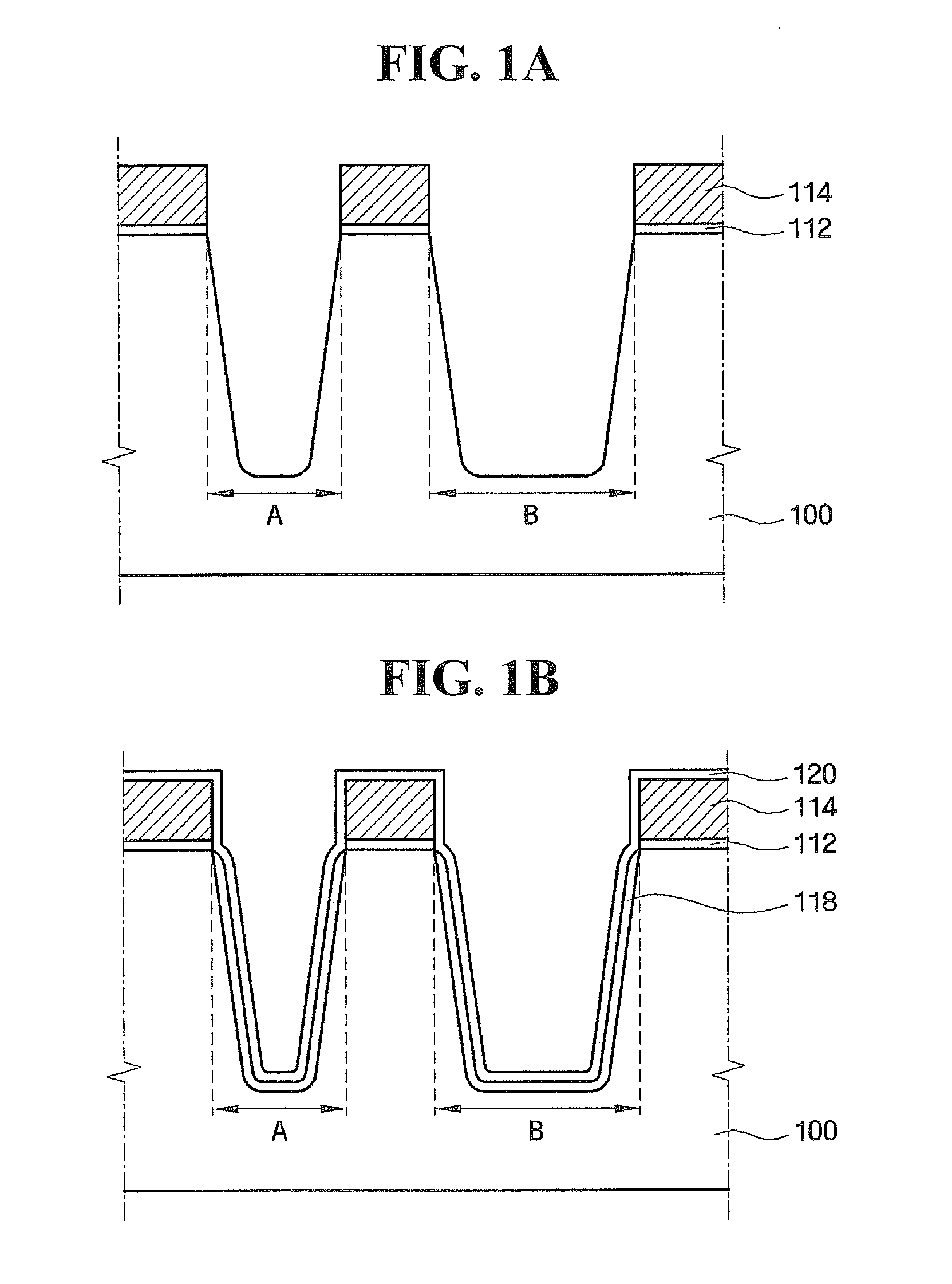
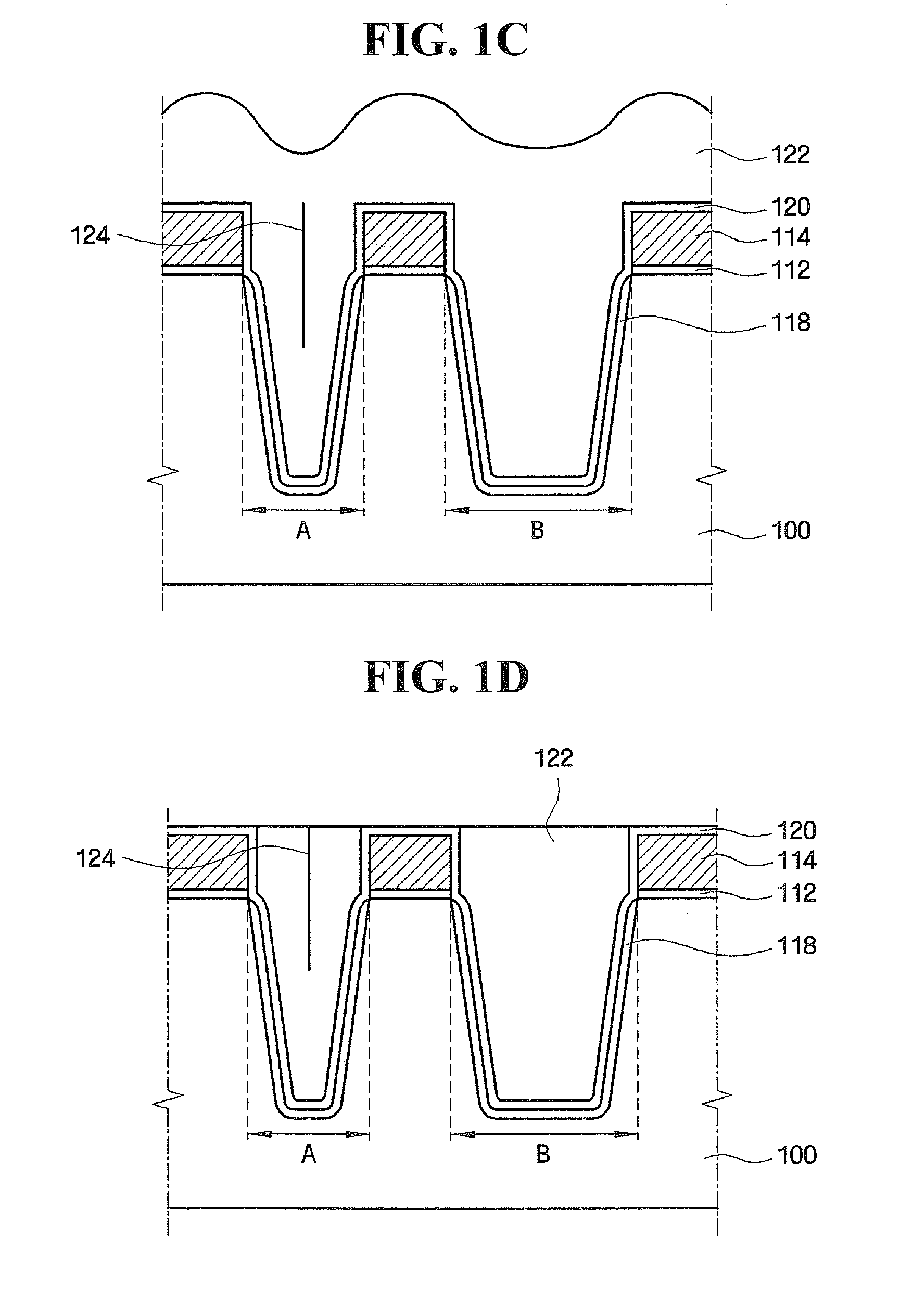
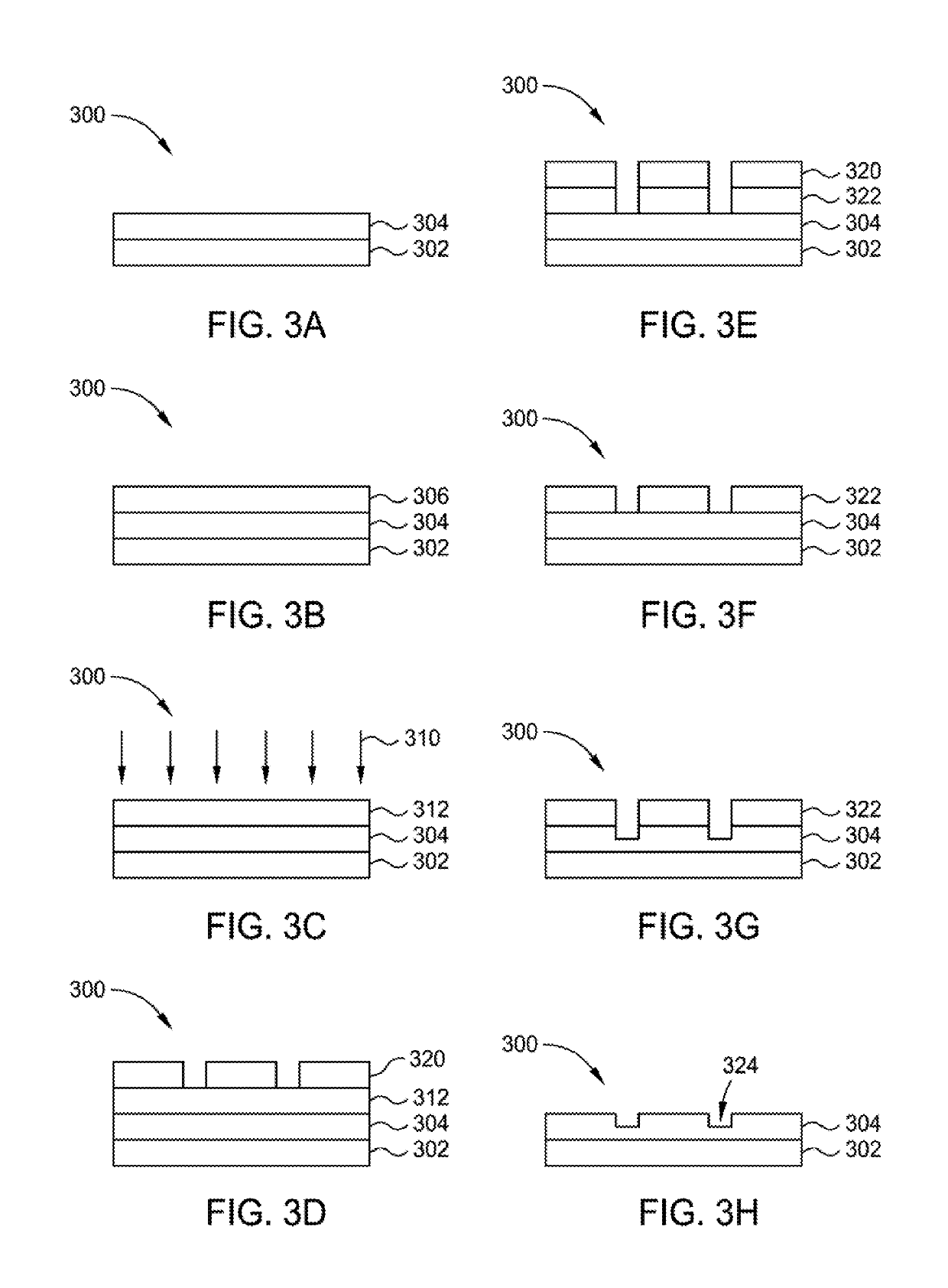
Methods of forming integrated circuit devices include forming a trench in a surface of semiconductor substrate and filling the trench with an electrically insulating region having a seam therein. The trench may be filled by depositing a sufficiently thick electrically insulating layer on sidewalls and a bottom of the trench. Curing ions are then implanted into the electrically insulating region at a sufficient energy and dose to reduce a degree of atomic order therein. The curing ions may be ones selected from a group consisting of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), boron (B), arsenic (As), carbon (C), argon (Ar), germanium (Ge), helium (He), neon (Ne) and xenon (Xe). These curing ions may be implanted at an energy of at least about 80 KeV and a dose of at least about 5×1014 ions / cm2. The electrically insulating region is then annealed at a sufficient temperature and for a sufficient duration to increase a degree of atomic order within the electrically insulating region.
Owner:IBM CORP +2
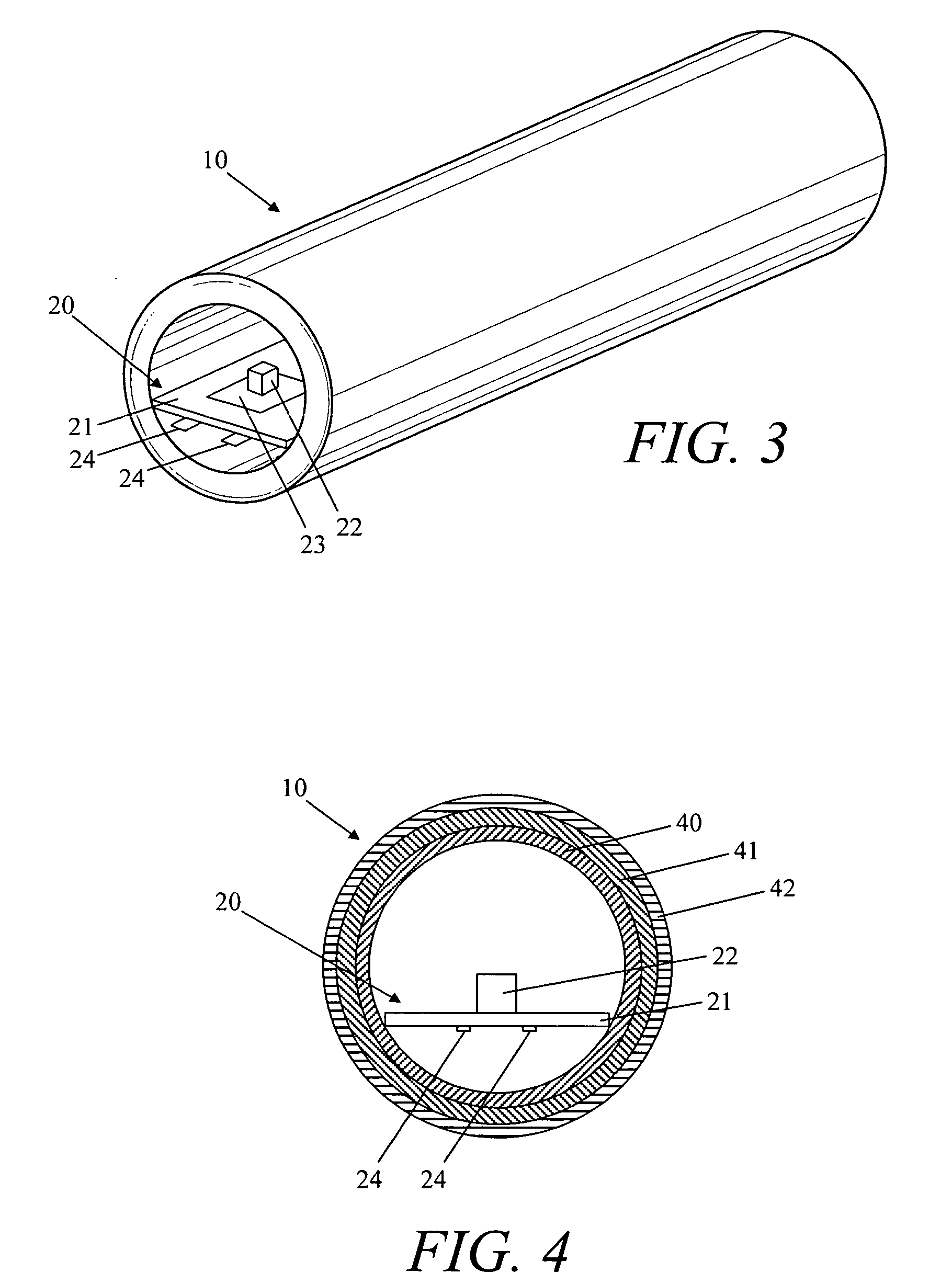
Curvilinear LED light source
ActiveUS20060028837A1Avoid easy installationEasily brokenLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceMulti materialLight guide
An LED system that simulates bare or exposed neon in appearance. The curvilinear LED light source comprises a rigid, formable light guide having a generally circular cross-section and a flexible LED light engine. The light guide is made of a material or materials that can be heated and formed into a desired shape. The light guide retains the desired shape upon cooling. The flexible light engine is inserted into a groove in the light engine.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
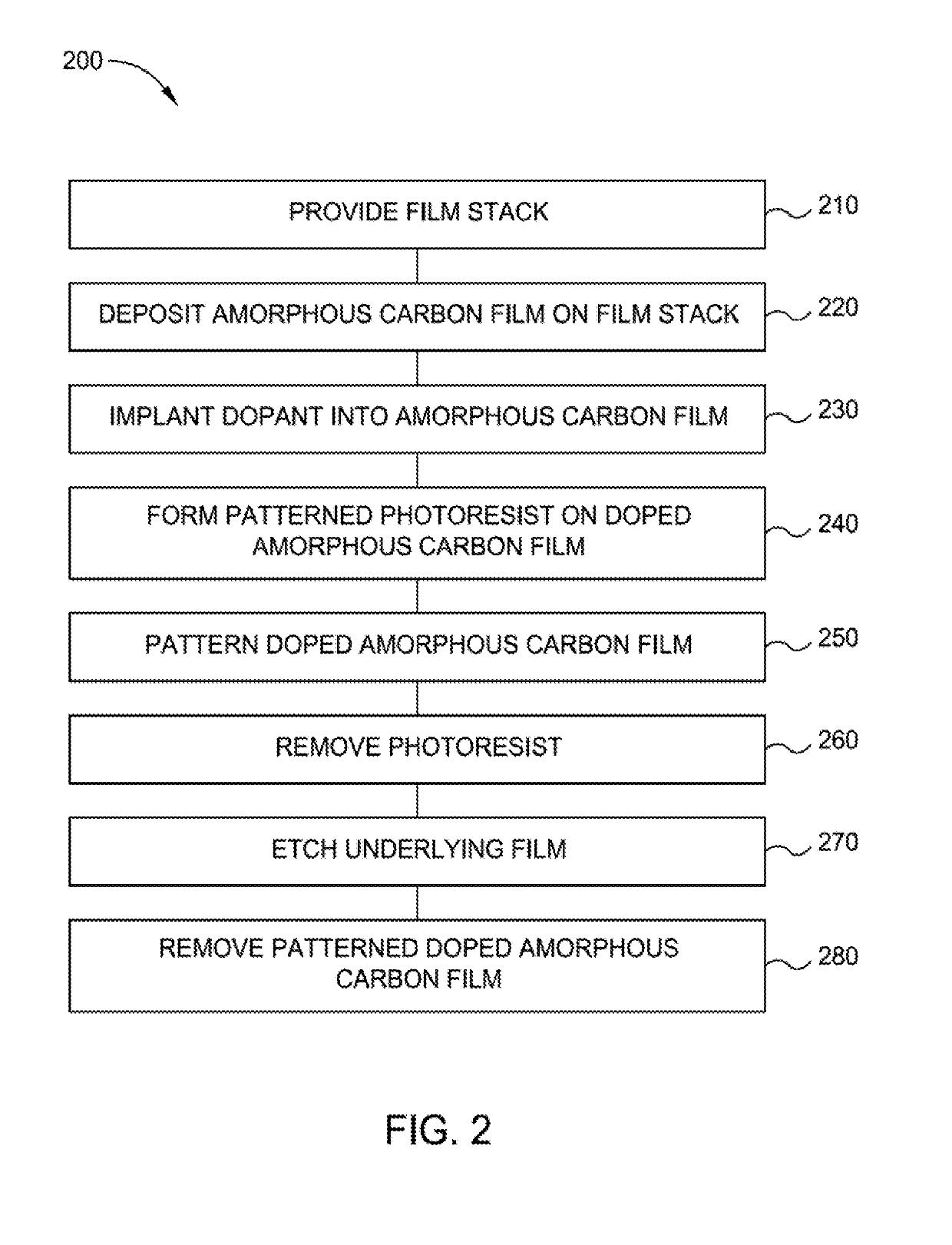
Highly etch selective amorphous carbon film
ActiveUS20190172714A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingKryptonDopant
Implementations described herein generally relate to the fabrication of integrated circuits. More particularly, the implementations described herein provide techniques for deposition of amorphous carbon films on a substrate. In one implementation, a method of forming an amorphous carbon film is provided. The method comprises depositing an amorphous carbon film on an underlayer positioned on a susceptor in a first processing region. The method further comprises implanting a dopant or inert species into the amorphous carbon film in a second processing region. The dopant or inert species is selected from carbon, boron, nitrogen, silicon, phosphorous, argon, helium, neon, krypton, xenon or combinations thereof. The method further comprises patterning the doped amorphous carbon film. The method further comprises etching the underlayer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Curvilinear LED light source
An LED system that simulates bare or exposed neon in appearance. The curvilinear LED light source comprises a rigid, formable light guide having a generally circular cross-section and a flexible LED light engine. The light guide is made of a material or materials that can be heated and formed into a desired shape. The light guide retains the desired shape upon cooling. The flexible light engine is inserted into a groove in the light engine.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Fluorescent illumination device
InactiveUS7192161B1Increased complexityIncrease costPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesFluorescenceEffect light
An illumination device for simulating neon or similar lighting uses fluorescent dyes, thus allowing for emission of light in colors that cannot ordinarily be achieved by use of LEDs alone. Such an illumination device is generally comprised of an elongated diffusing member enclosing a string of continuously mounted LEDs. An intermediate light-transmitting medium including a predetermined combination of one or more fluorescent dyes is interposed between the light source and the diffusing member, such that light from the LEDs is partially absorbed by each of the fluorescent dyes, and a lower-energy light is then emitted from each of the fluorescent dyes and into the light-receiving surface of the diffusing member, producing a substantially uniform light along the light-emitting surface of the diffusing member with perceived a color different than that of the LEDs.
Owner:LUMINII PURCHASER LLC
Non-oxidizing polymeric medical implant
InactiveUS20050059750A1Improve antioxidant capacityPrevent further oxidationSurgeryPharmaceutical containersCross-linkNitrogen gas
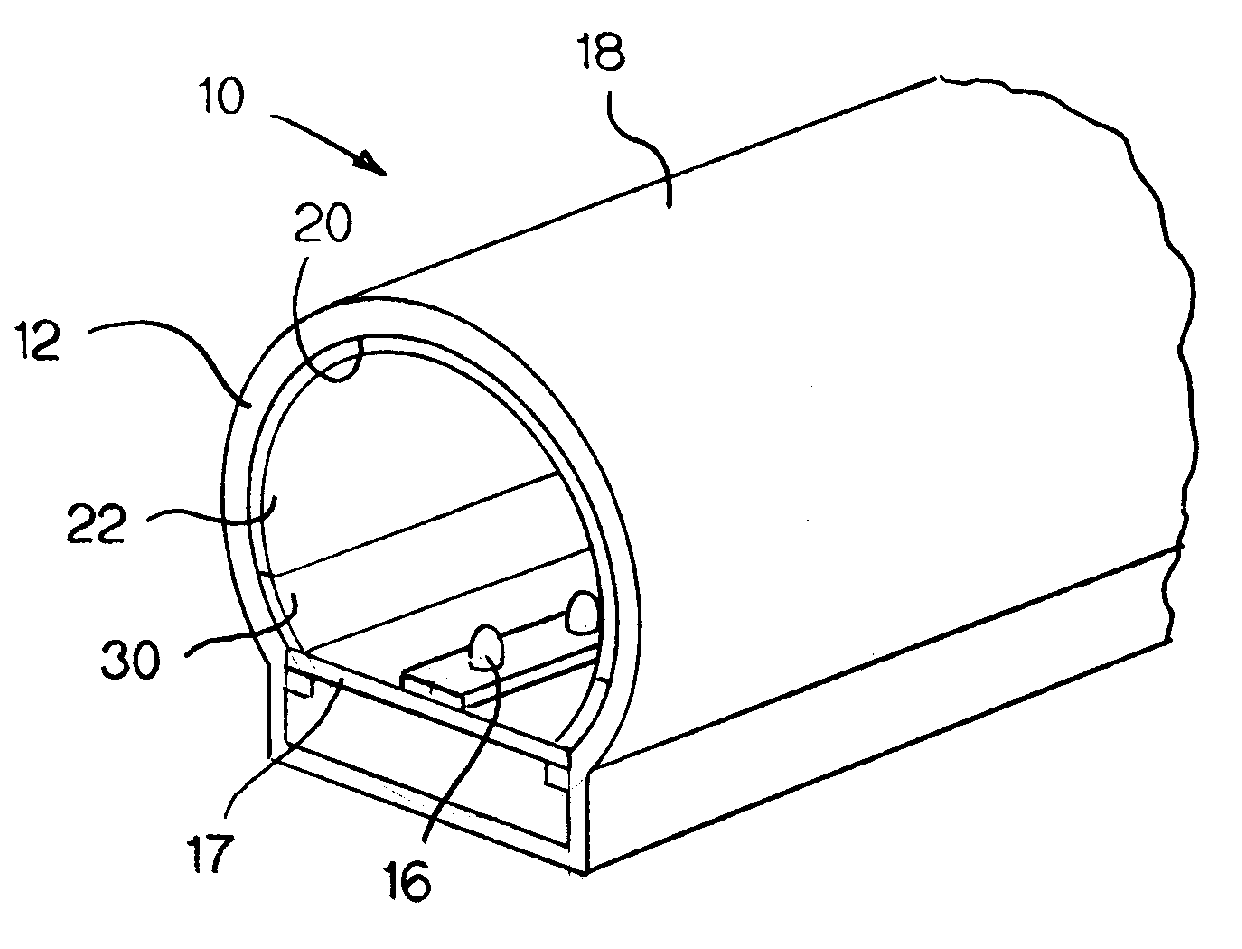
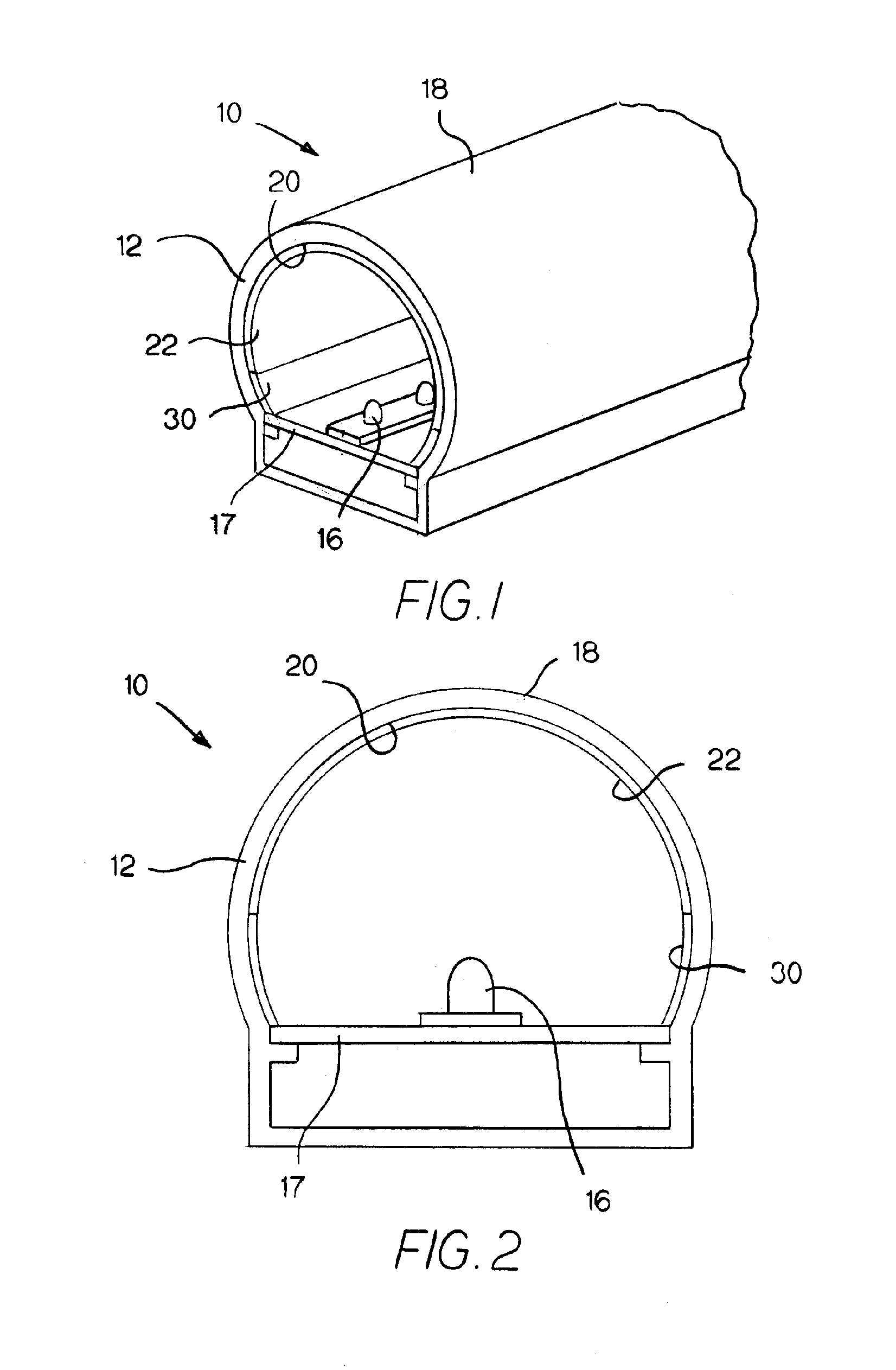
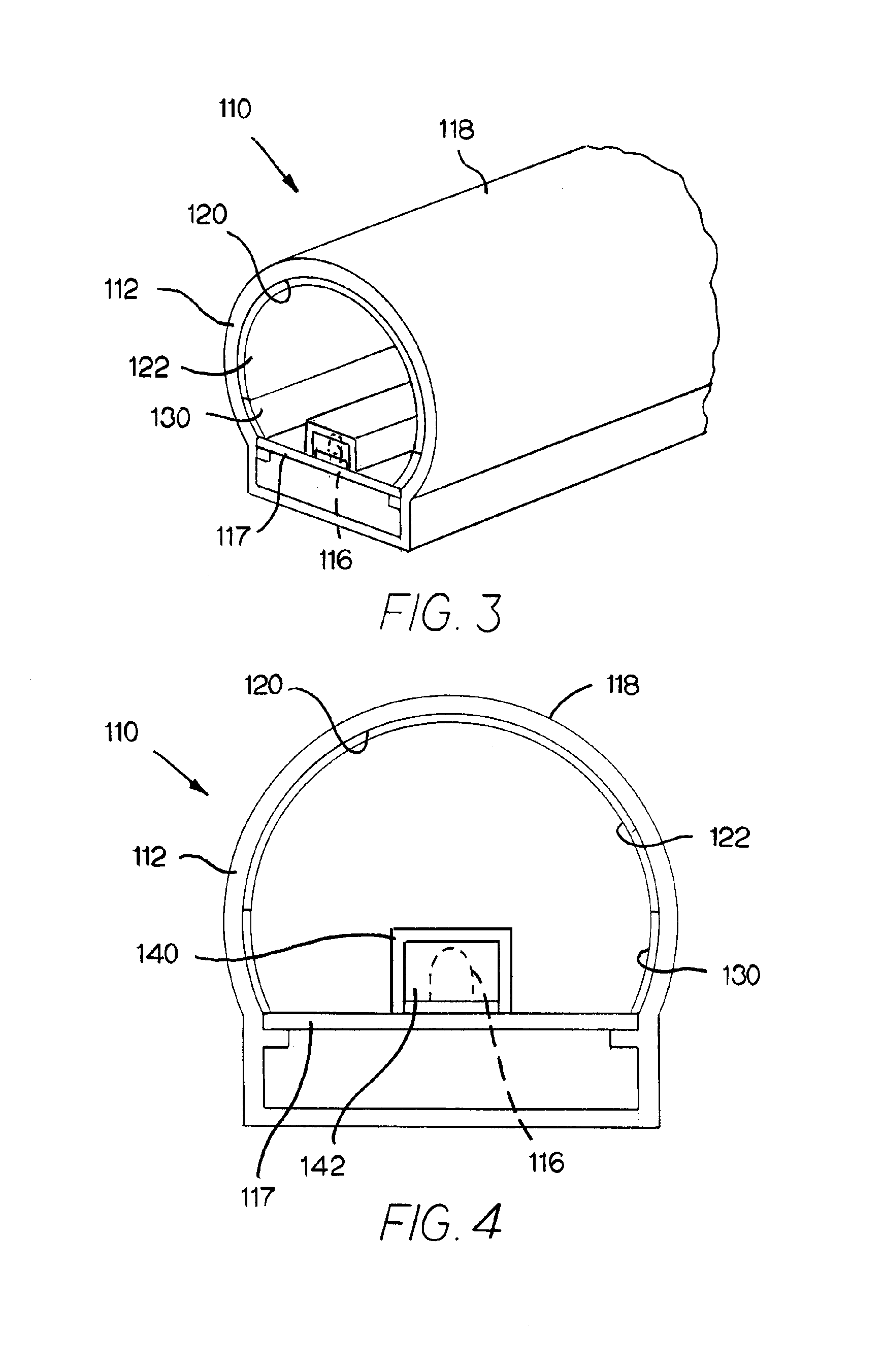
A medical implant made of polymeric material having an increased oxidation resistance is formed by a method including the steps of placing a resin powder in a sealed container. A substantial portion of the oxygen is removed from the sealed contained by either a vacuum, an oxygen absorbent or by flushing with inert gas. The container is then repressurized with a gas such as nitrogen, argon, helium or neon so that long term storage may be possible. On use, the resin in transferred to a forming device which both melts and forms the resin in an oxygen reduced atmosphere to produce a polymeric raw material such as a rod or bar stock. The medical implant is then formed from this raw material annealed and sealed in an airtight package in an oxygen reduced atmosphere. The implant is then radiation sterilized and thereafter annealed in the package for a predetermined time and temperature sufficient to form cross-links between any free radicals in neighboring polymeric chains.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Color-changing illumination device
An illumination device for simulating neon or similar lighting is generally comprised of a rod-like member, a housing, a light source, and an intermediate light-transmitting medium extending along and positioned adjacent the light source with a light-receiving surface for receiving light emitted from said light source and a light-emitting surface for emitting light into the rod-like member. This intermediate light-transmitting medium is preferably composed of a matrix of a substantially translucent acrylic, polyurethane, or similar material tinted with a predetermined combination of one or more fluorescent and / or phosphorescent dyes. The intermediate light-transmitting medium is subdivided into independent sections, each of which is provided with differing combinations of fluorescent dye, phosphorescent dye, and / or no dye at all.
Owner:ILIGHT TECH INC
All solid-state omni directional luminary and flashlight
InactiveUS6371625B2Guaranteed normal transmissionLight source combinationsLighting elementsCamera lensAll solid state
A laser lens glow baton is a hand held, dual purpose, visual signaling baton. This device can be used as a flashlight that projects a well-defined beam of light via its laser lens and assembly or as a highly visible luminary that radiates an intense flux of light similar to neon tube. The laser lens glow baton is useful as a visual-signaling device because the colors of the main body and the colors of the projected beam emitted from the laser lens assembly are easily changed. The laser lens glow baton may be easily fabricated in different lengths because of its compartmentalization of the components.
Owner:GRACE INDS
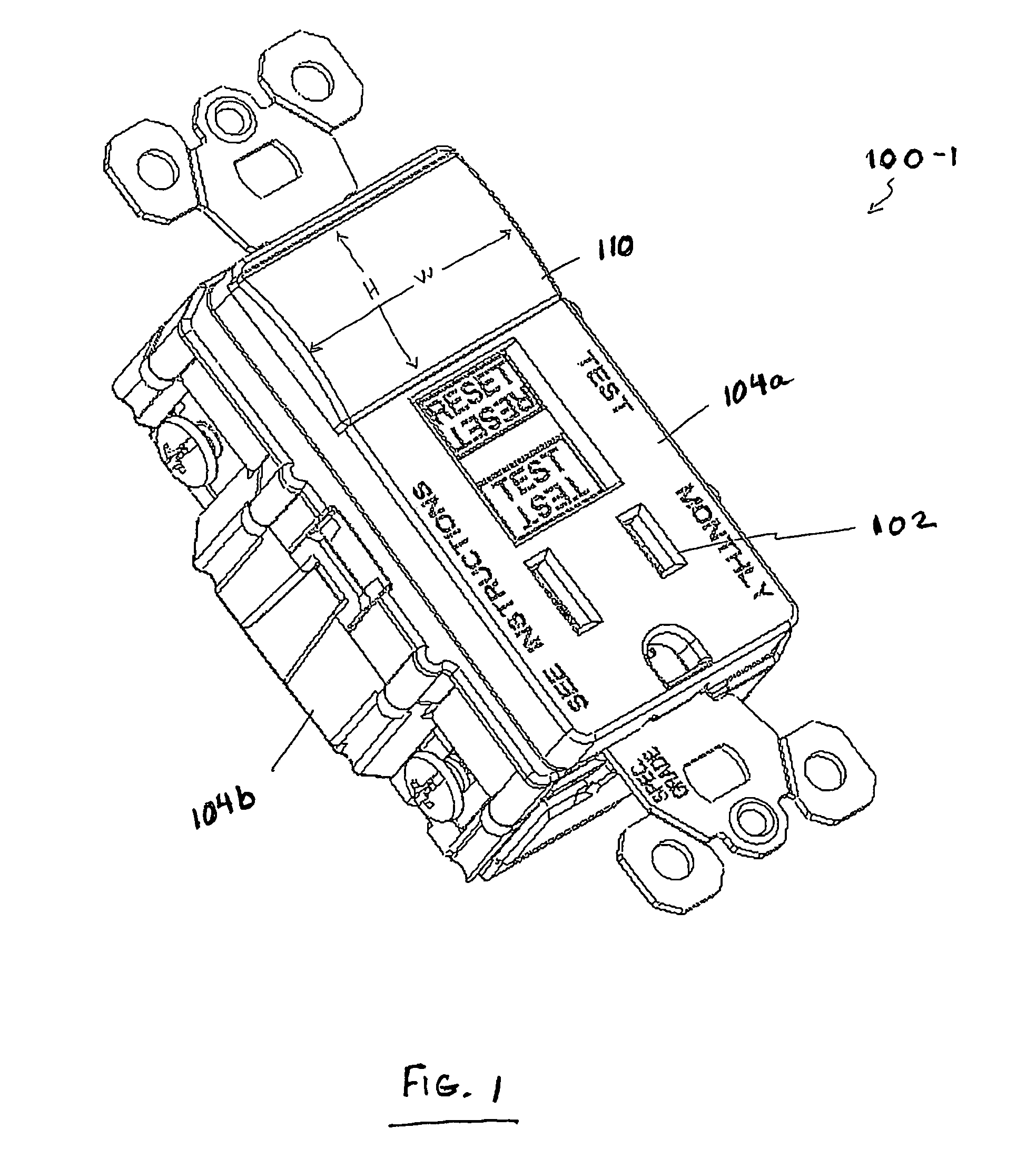
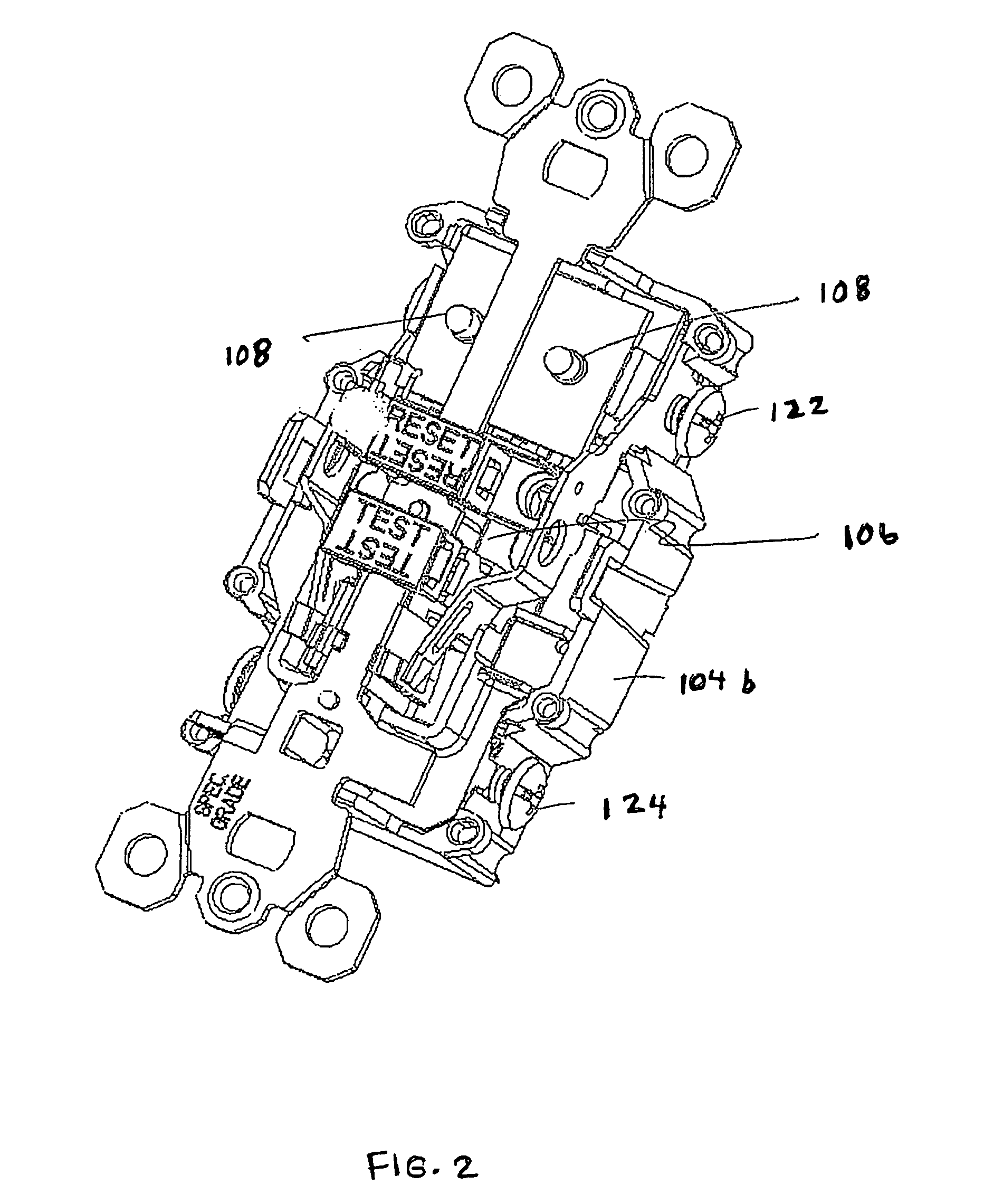
Electrical device with circuit protection component and light
ActiveUS7586718B1Switch operated by earth fault currentsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionDimmerEngineering
An electrical wiring device includes a housing, and a circuit protection component and a light source operably mounted within the housing. In various aspects, the circuit protection component is a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) or an arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI). The light source can function to provide increased illumination in an environment surrounding the electrical wiring device (e.g., a darkened bathroom or a darkened kitchen), or to indicate the status of the circuit protection component (e.g., tripped or normal). The light source may be one or more LEDs, neon sources, incandescent sources, etc. Embodiments of the invention include, in addition, a sensor for controlling the on / off state of the light source and / or a trip indicator separate from the light Source for indicating a status condition of the circuit protection component. The device is illustratively represented by a grounded plug receptacle, but may be embodied in a switch, a dimmer, or other application device.
Owner:PASS SEYMOUR
Multi-color solid state light emitting device
InactiveUS20050242711A1Changeable colorSolution to short lifeDischarge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourceElectricityLight-emitting diode
A light emitting device for simulating neon light and method for doing the same. The light emitting device includes an elongated container having a combination of fluorescent pigment and phosphorescent pigment embedded therein. The light emitting device further includes a plurality of light emitting diodes aligned within the container. Finally, the light emitting device includes electrical means for providing electricity to the plurality of diodes.
Owner:BLOOMFIELD JOSEPH +2
Method for producing a nanostructured funcitonal coating and a coating that can be produced according to said method
InactiveUS20050011748A1Increase ion densityHigh materialPigmenting treatmentVacuum evaporation coatingOxygenNanostructure
A method for producing a nanostructured, in particular a ceramic-like functional coating on a substrate is described. To that end, using at least one plasma source, a pulsed plasma is produced with which a matrix phase and at least one nano-scale interstitial phase embedded in it are deposited on the substrate via a material input. Preferably a plurality of pulsed plasma sources that are time-correlated or synchronized with each other are used. Also proposed is a nanostructured functional coating, in particular one producible by this method, which is free of chlorine and / or sulfur, and which contains at least one metal and / or at least one element selected from the group oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon, helium, argon or neon.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
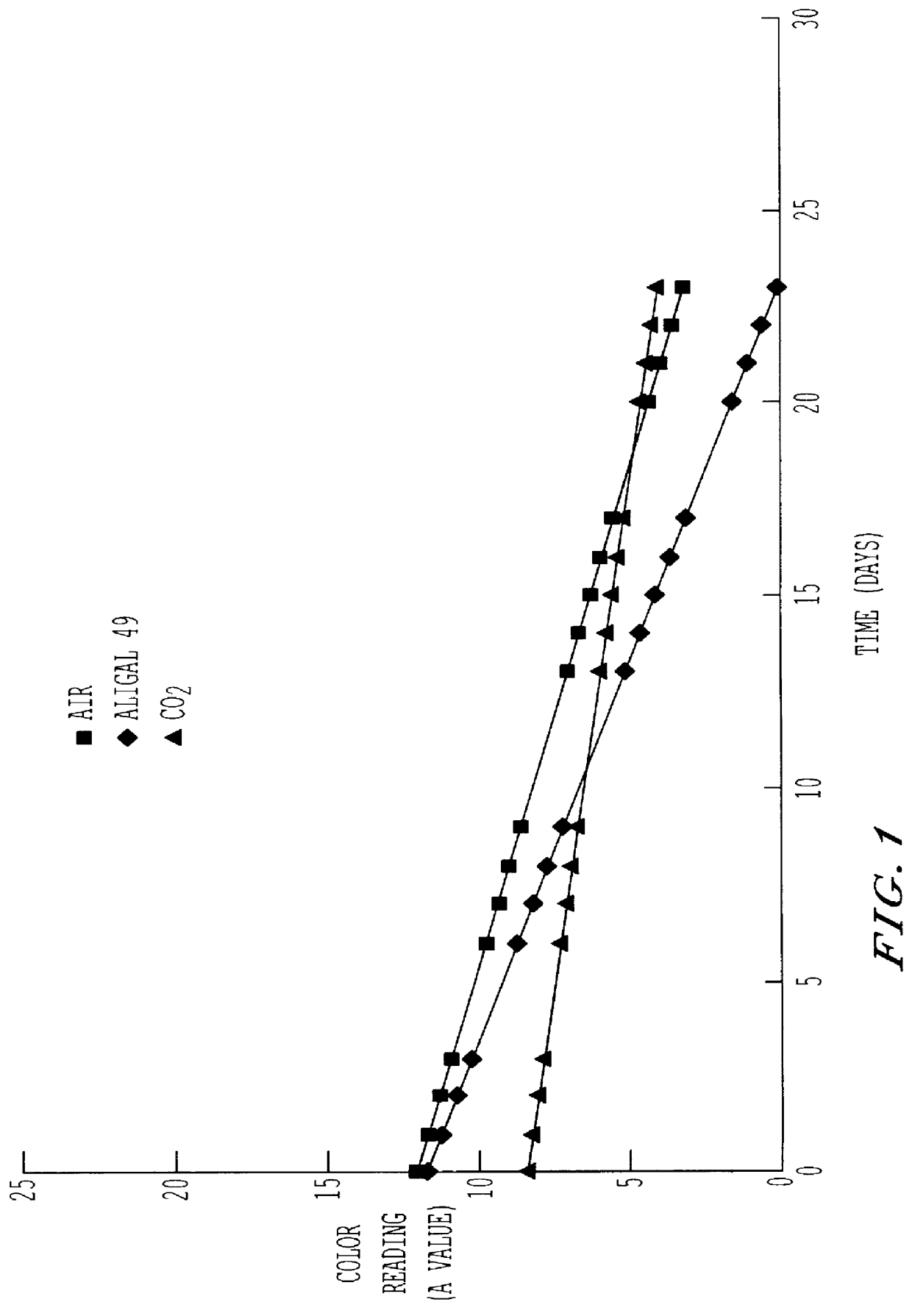
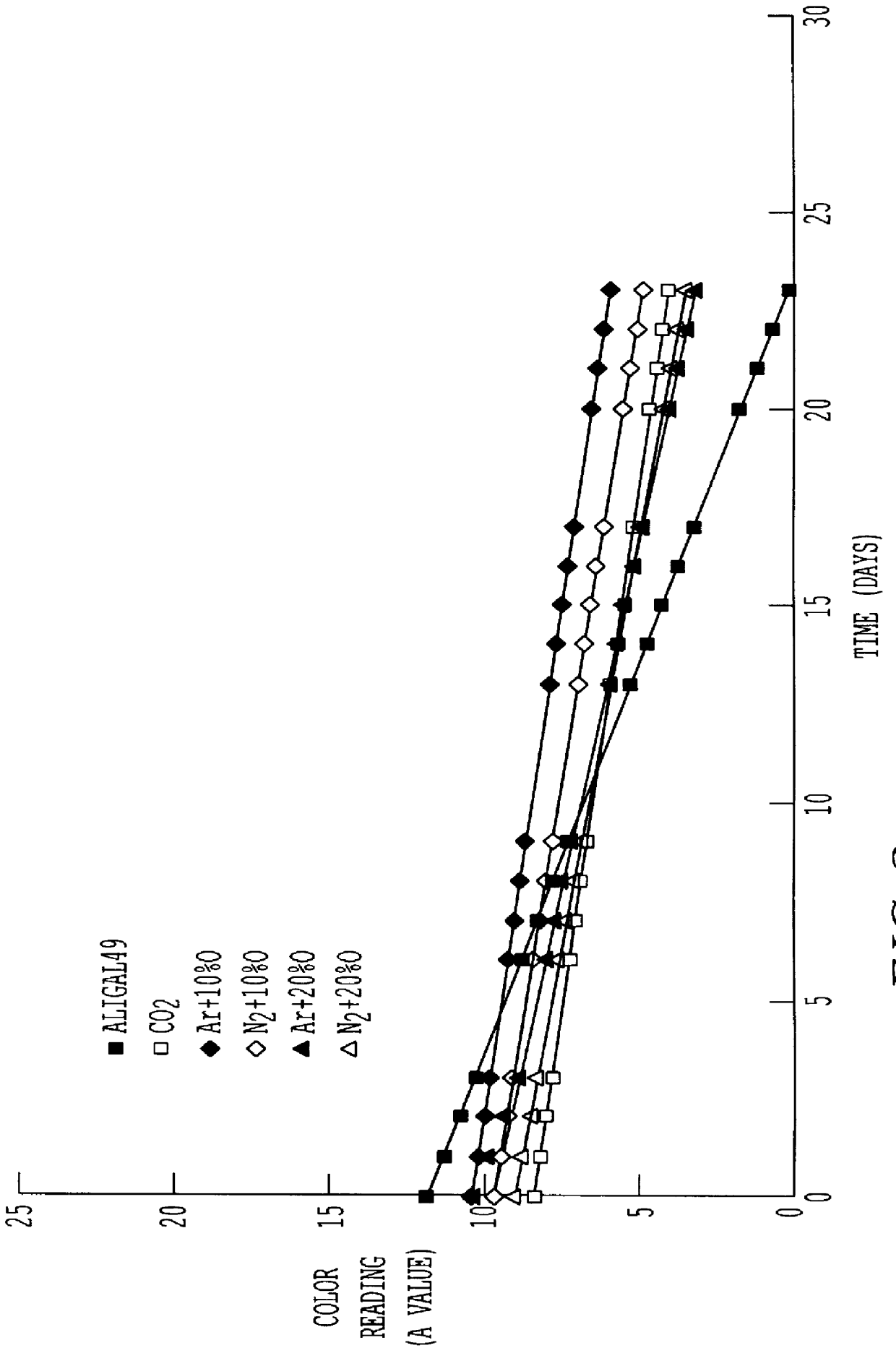
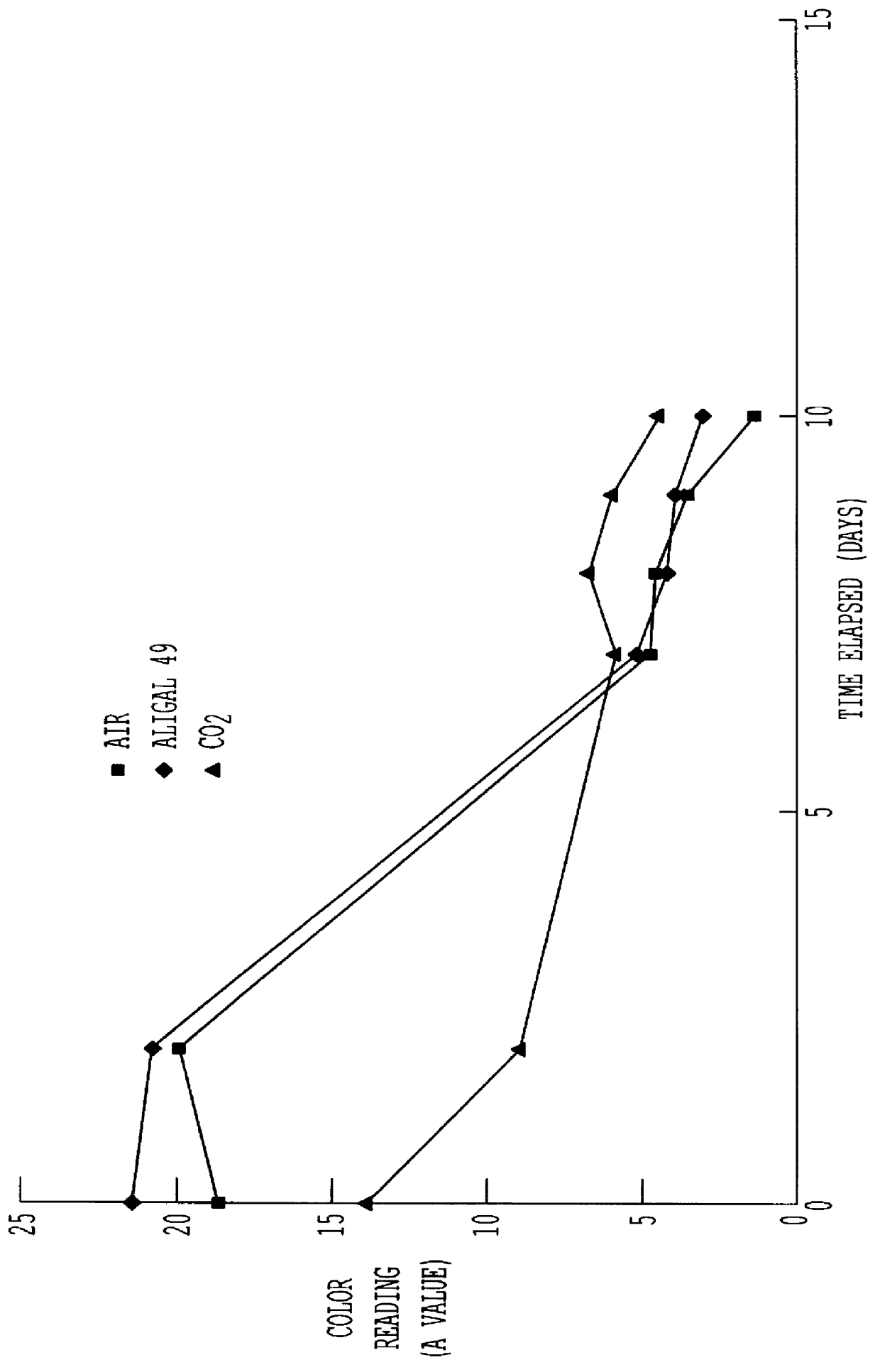
Preservation of color of stored meat using noble gases
A process for preserving the color of red meat, which entails contacting the meat with an effective amount of an atmosphere selected from the group consisting of a noble gas, a mixture of noble gases and a mixture containing at least one noble gas and a carrier gas, the noble gas in the mixture with the carrier gas being selected from the group consisting of argon, neon, xenon an krypton and being present in said mixture in an amount of greater than about 10% by volume.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC
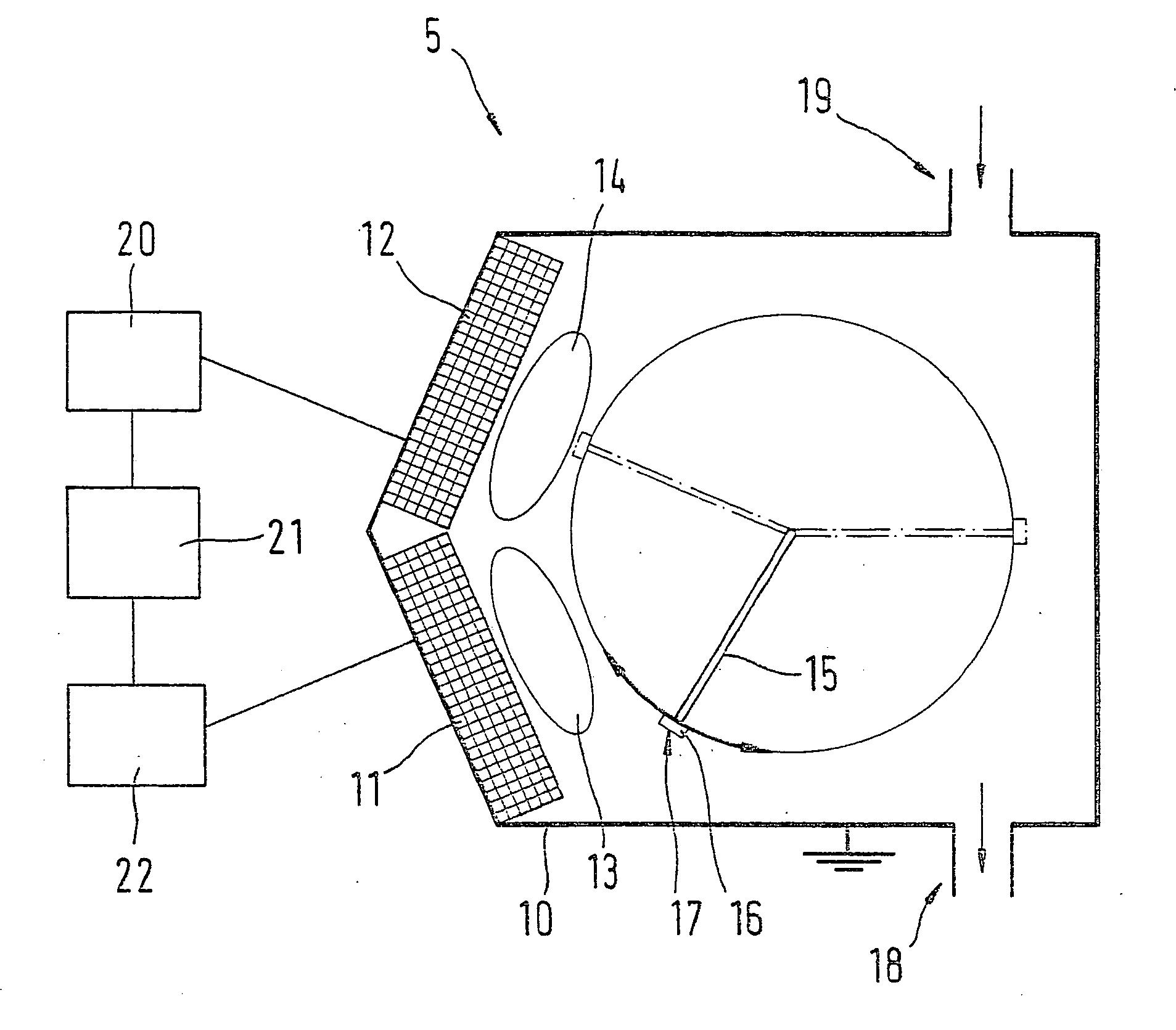
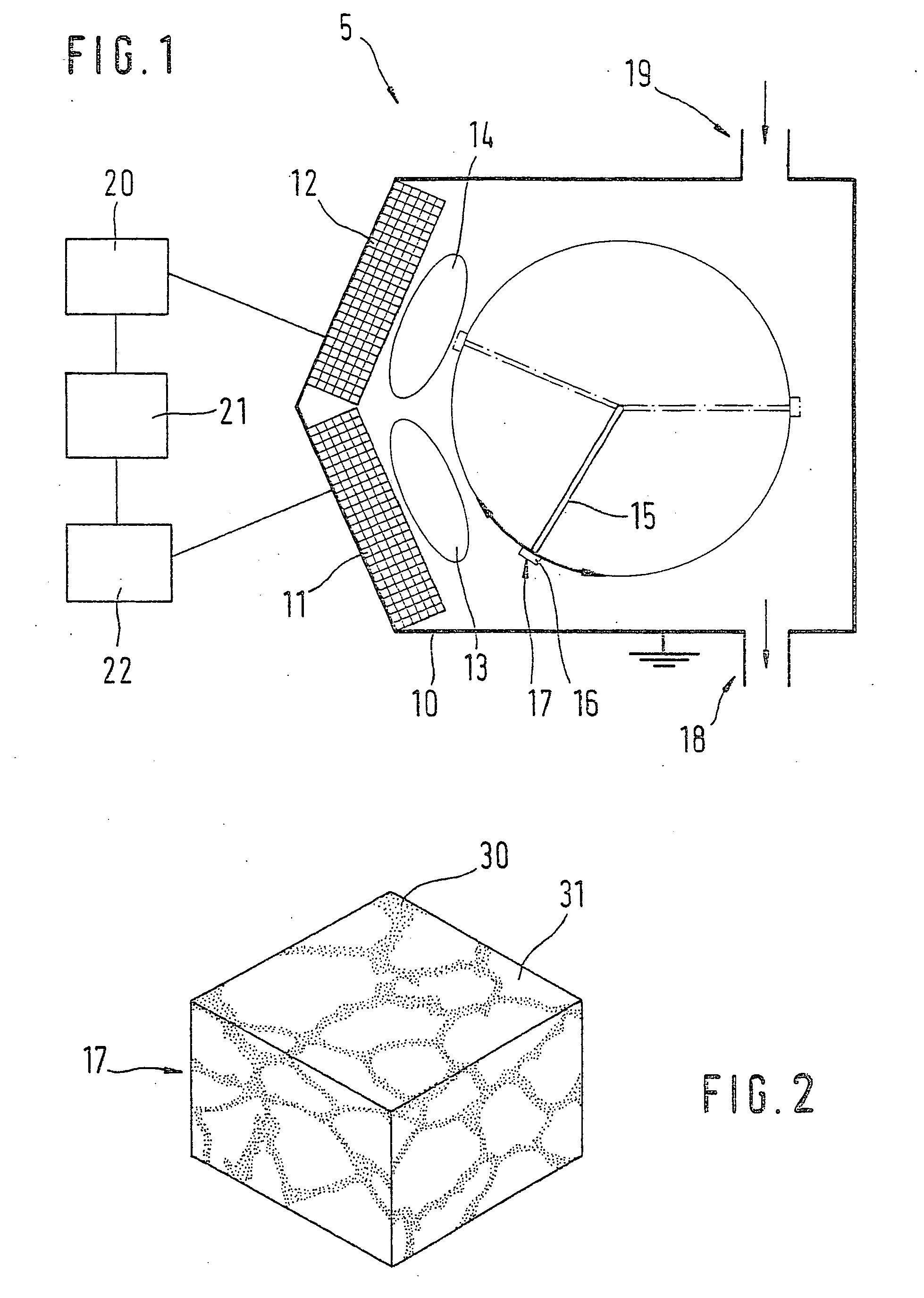
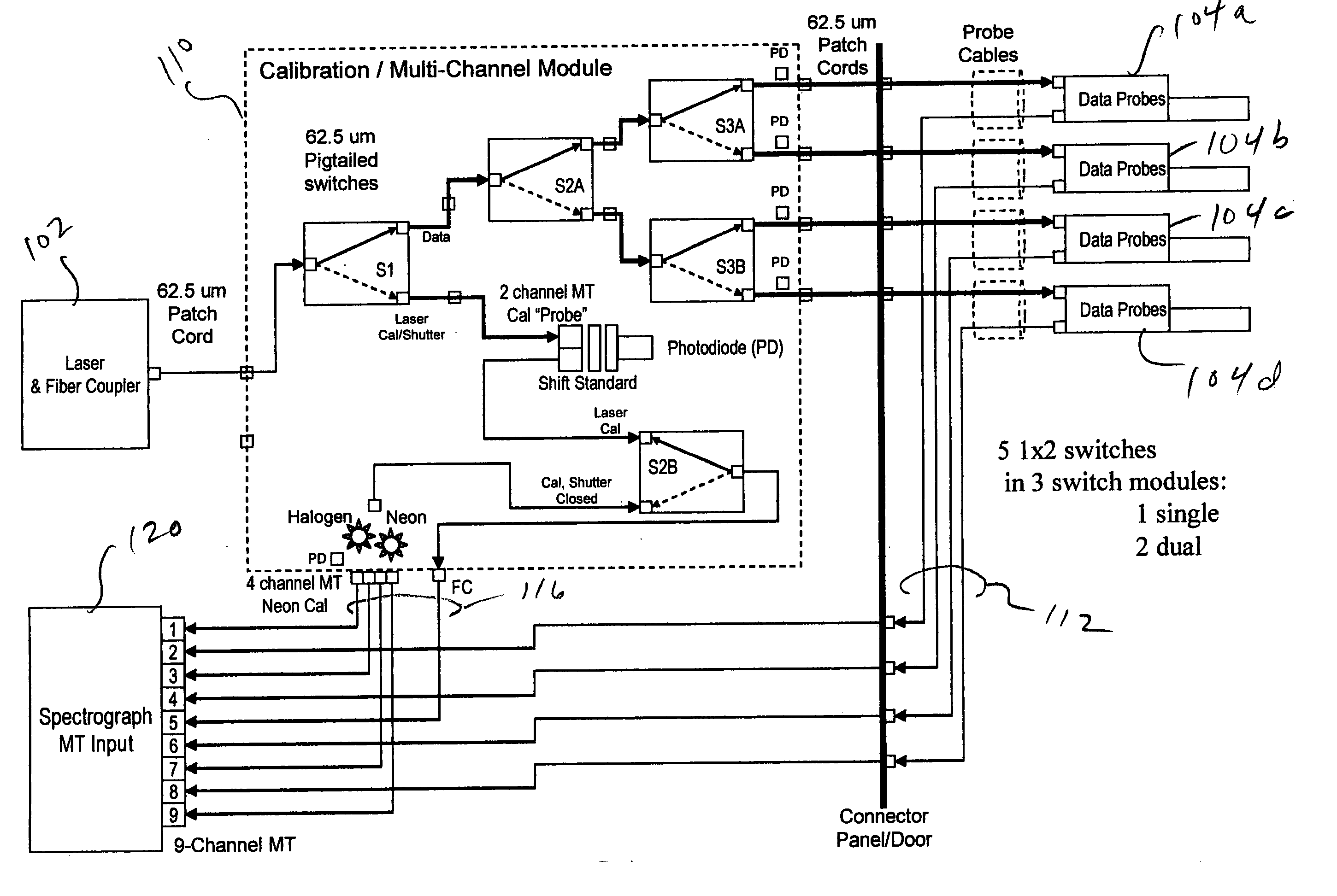
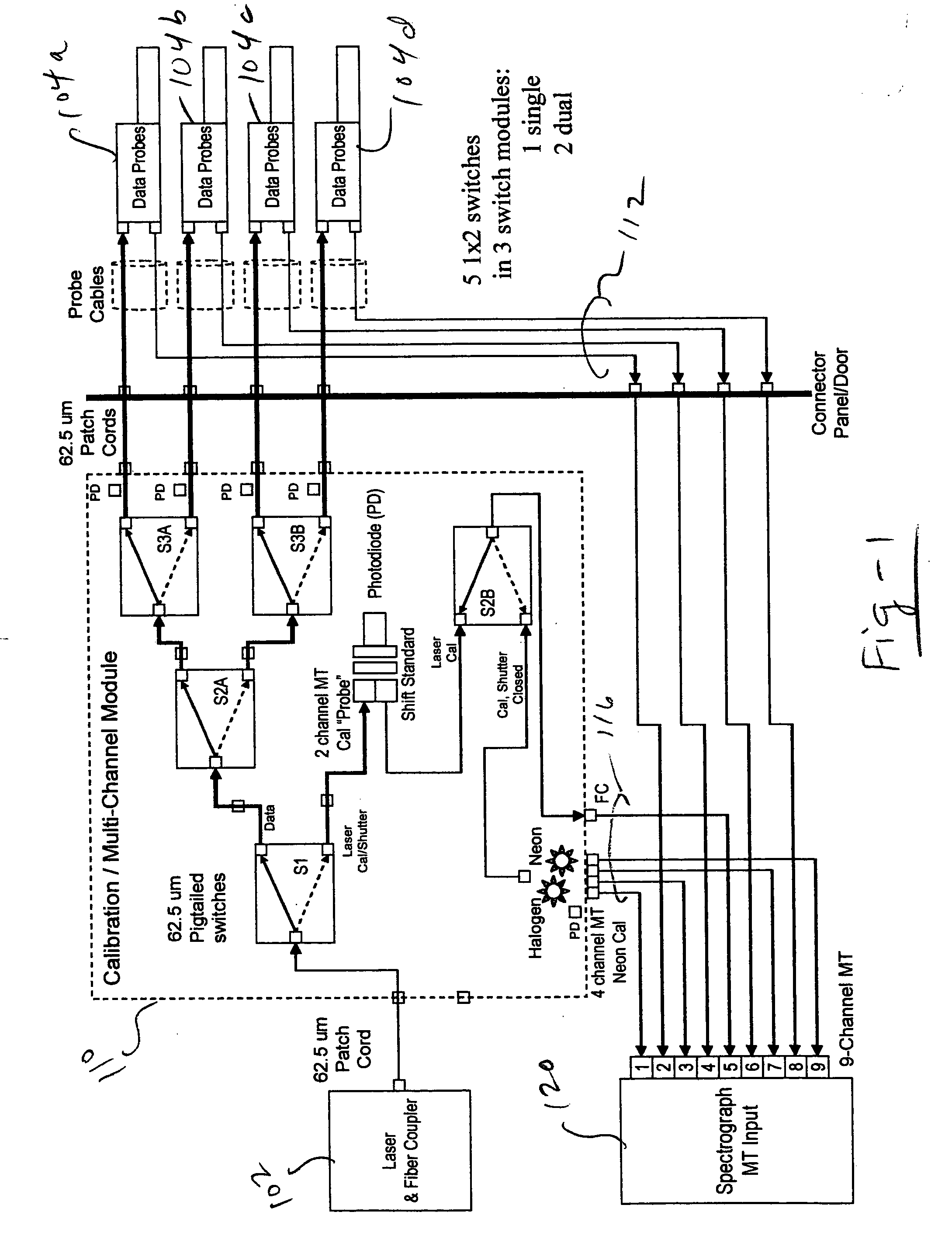
Multi-channel, self-calibrating fiber-coupled raman spectrometers including diagnostic and safety features
ActiveUS20050162646A1Facilitates quasi-simultaneousFacilitates sequential calibration/data acquisitionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationCircular discData acquisition
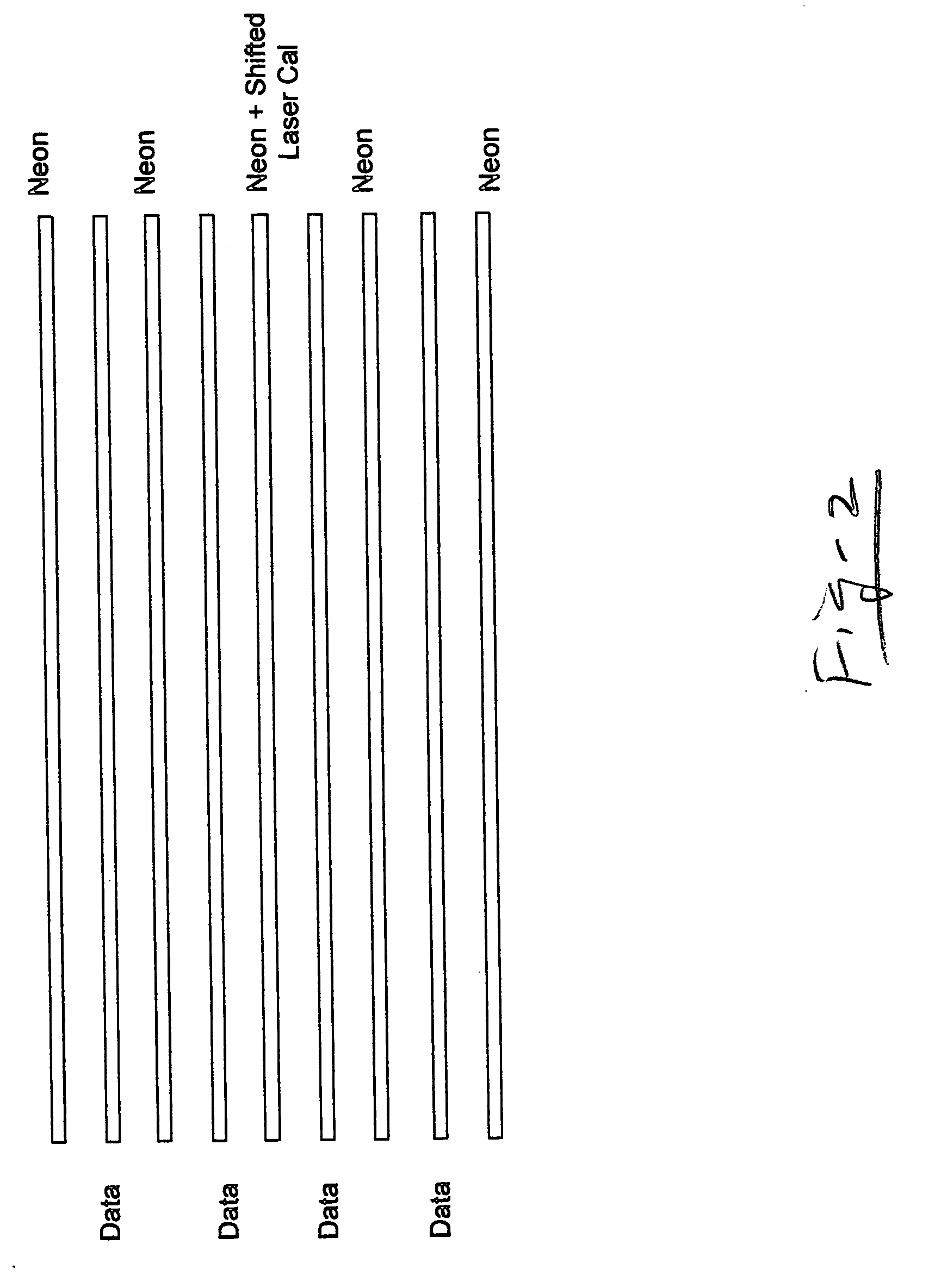
A multi-channel, reconfigurable fiber-coupled Raman instrument uses fiber optic switches for laser and calibration light routing to facilitate automated calibration, diagnosis and operational safety. The system allows wavelength axis calibration on all channels; laser wavelength calibration (including multiple and / or backup laser options); fiber coupling optimization; fault detection / diagnosis; and CCD camera binning setup. In the preferred embodiment, dedicated calibration channels surround data channels on a 2-dimensional CCD dispersed slit image implemented using a unique cabling architecture. This “over / under” calibration interpolation approach facilitates quasi-simultaneous or sequential calibration / data acquisitions. CCD binning between sequential calibration and data acquisitions enables higher density multi-channel operation with tilted images based upon a multiplexed grating configuration. A diamond sample is used as a Raman shift reference for laser calibration, preferably in the form of a small disc sampled with an edge-illuminating probe using two unfiltered fibers. Detection of beam transmitted through the diamond reference is also used to optimize laser coupling efficiency with motion servos. An “intrinsically safe” laser interlock circuit also serves as current source for probe head “laser on” diode indicator. The integrity of key components is monitored through strategically placed photodiodes positioned, for example, at fiber bends to detect light leakage from bent fiber as verification of commanded laser path through fiber switches and at neon and halogen lamp locations to verify lamp operation. The optical switches used for calibration may also be configured for use as a laser shutter.
Owner:ENDRESS + HAUSER OPTICAL ANALYSIS INC
Illumination device for simulating neon or similar lighting in the shape of a toroid
Owner:ILIGHT TECH INC
Glass melting gurnace and method for producing glass
InactiveUS20060101859A1Precise maintenanceReduce the environmentGlass furnace apparatusGlass pressing apparatusMelting tankNoble gas
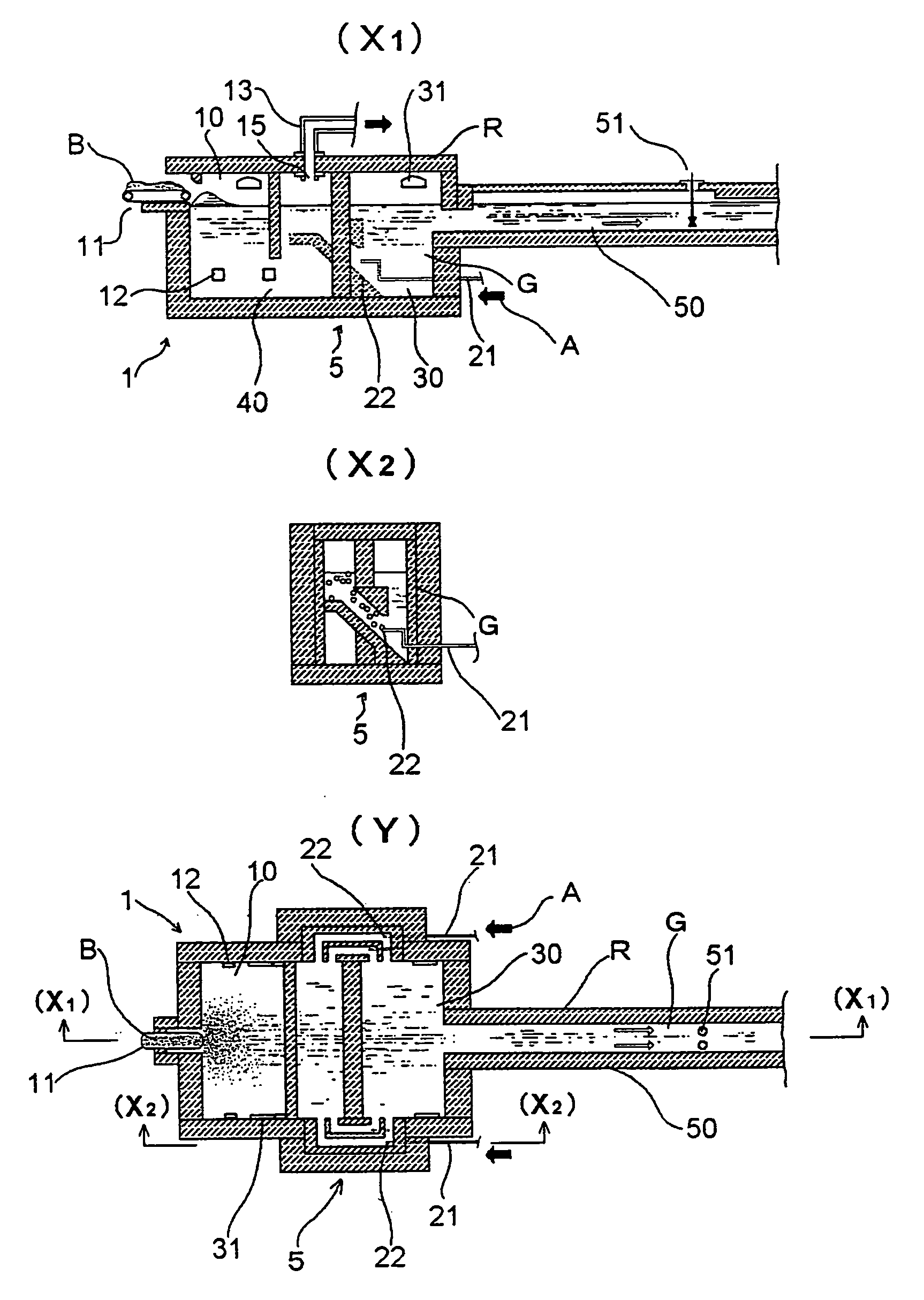
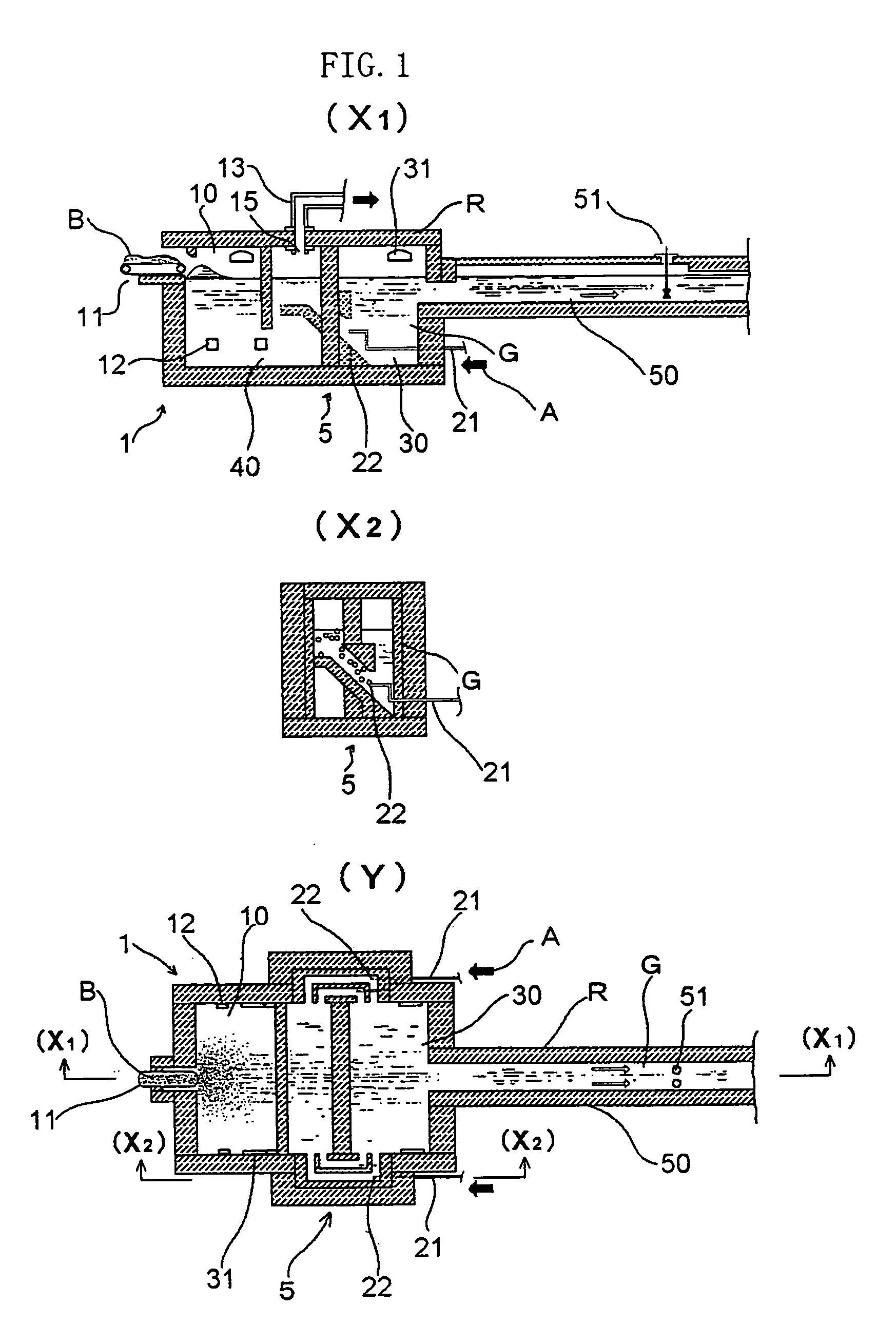
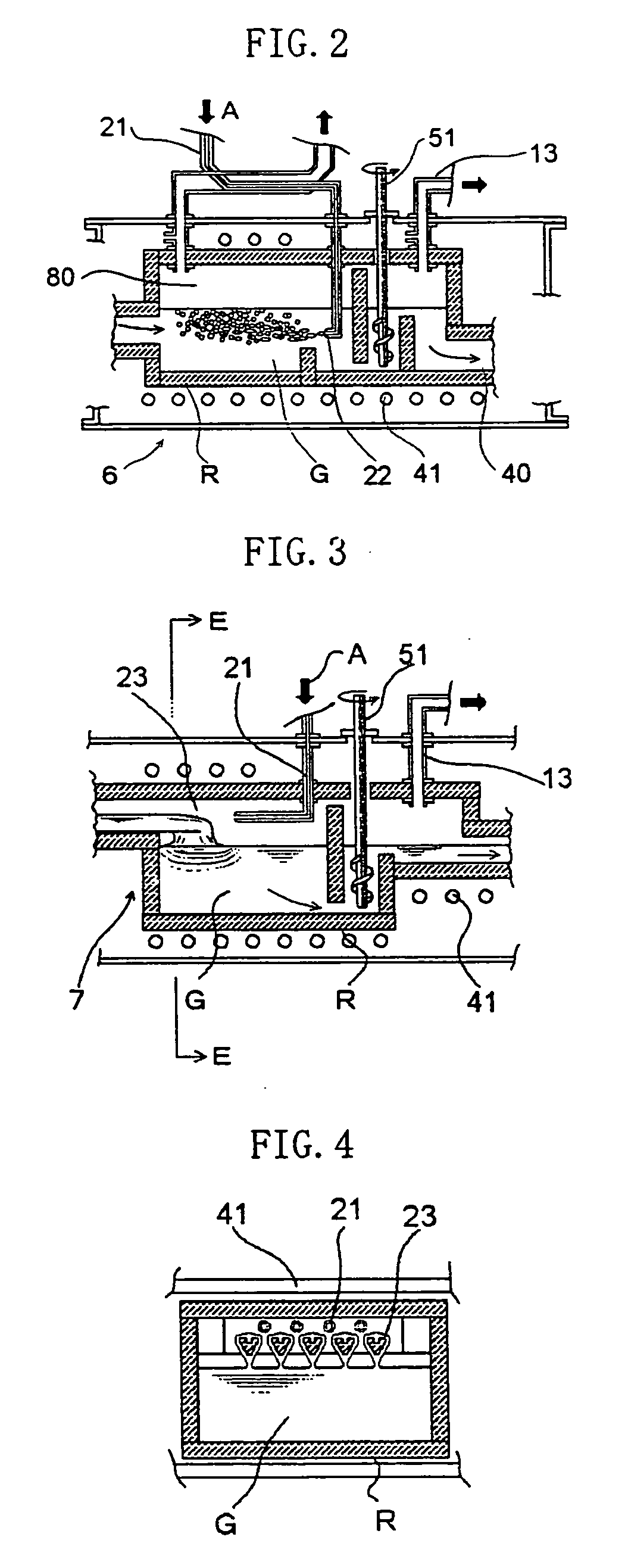
A charged glass raw material B is melted in a melting tank 10 by heating with a burner 31 and by heating with electrodes 12, to form molten glass G. Then, the molten glass G flows into a tank additionally provided as a noble gas dissolving tank 20 through a throat 40. The noble gas dissolving tank 20 is provided with a noble gas dissolving device 53, and the noble gas dissolving device 53 is provided with sixteen noble gas inlets 22 for introducing a helium or neon gas supplied to a hearth through heat resistant gas introduction tubes 21 into the noble gas dissolving tank 20. Bubbles of a helium gas A having a purity of 99% are blown out from the noble gas inlets 22 in volumes such that the bubbles have an average diameter of 80 mm or less in the molten glass G.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
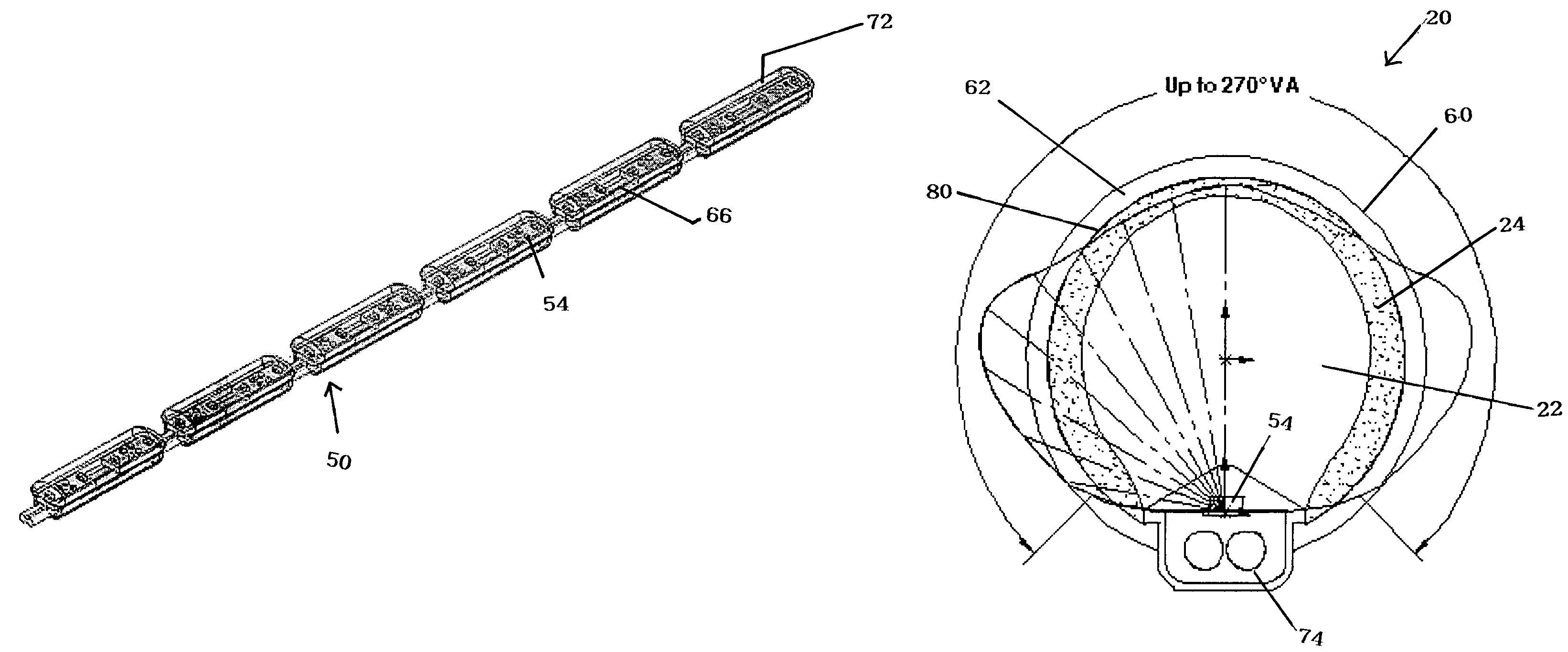
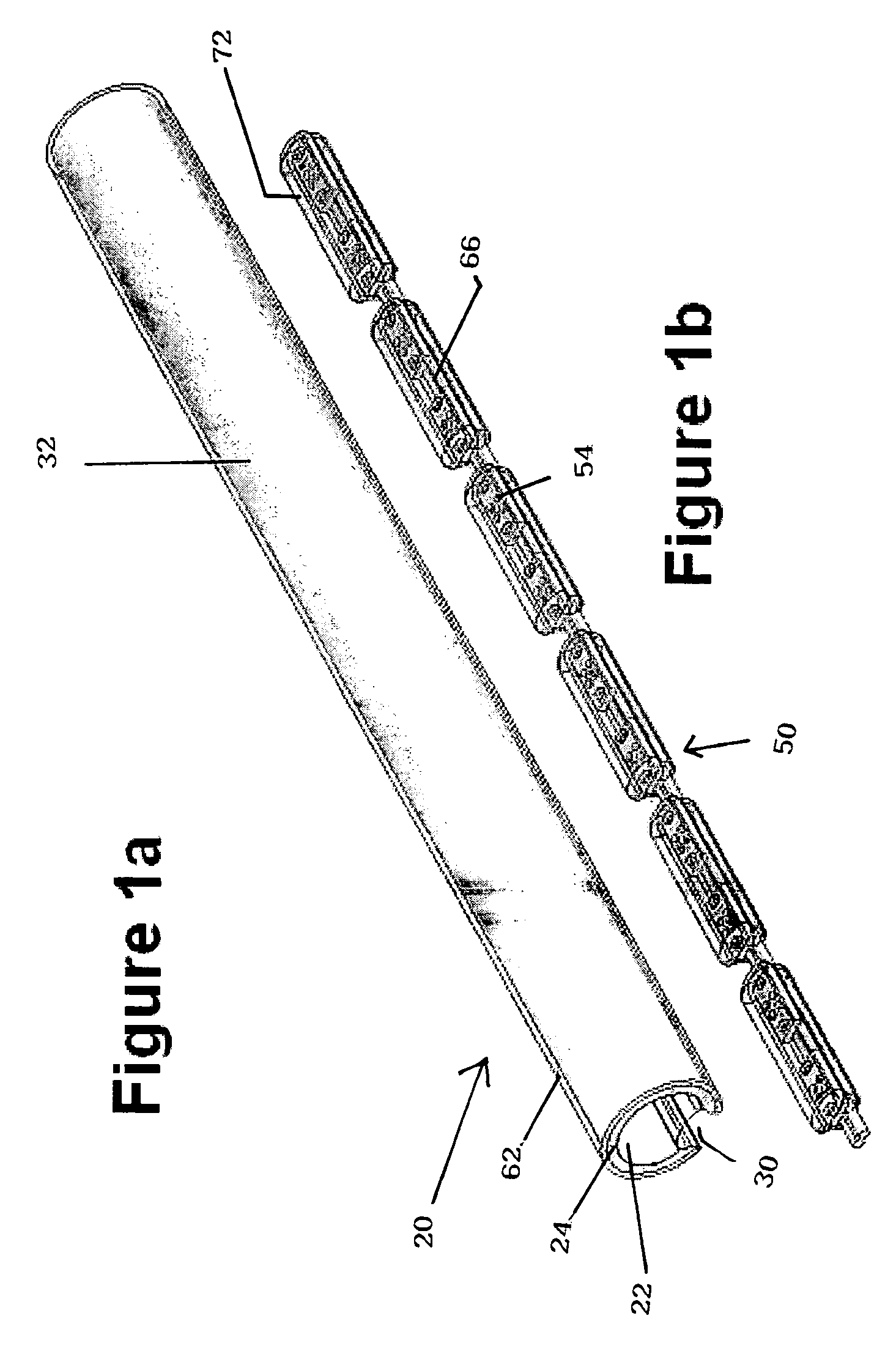
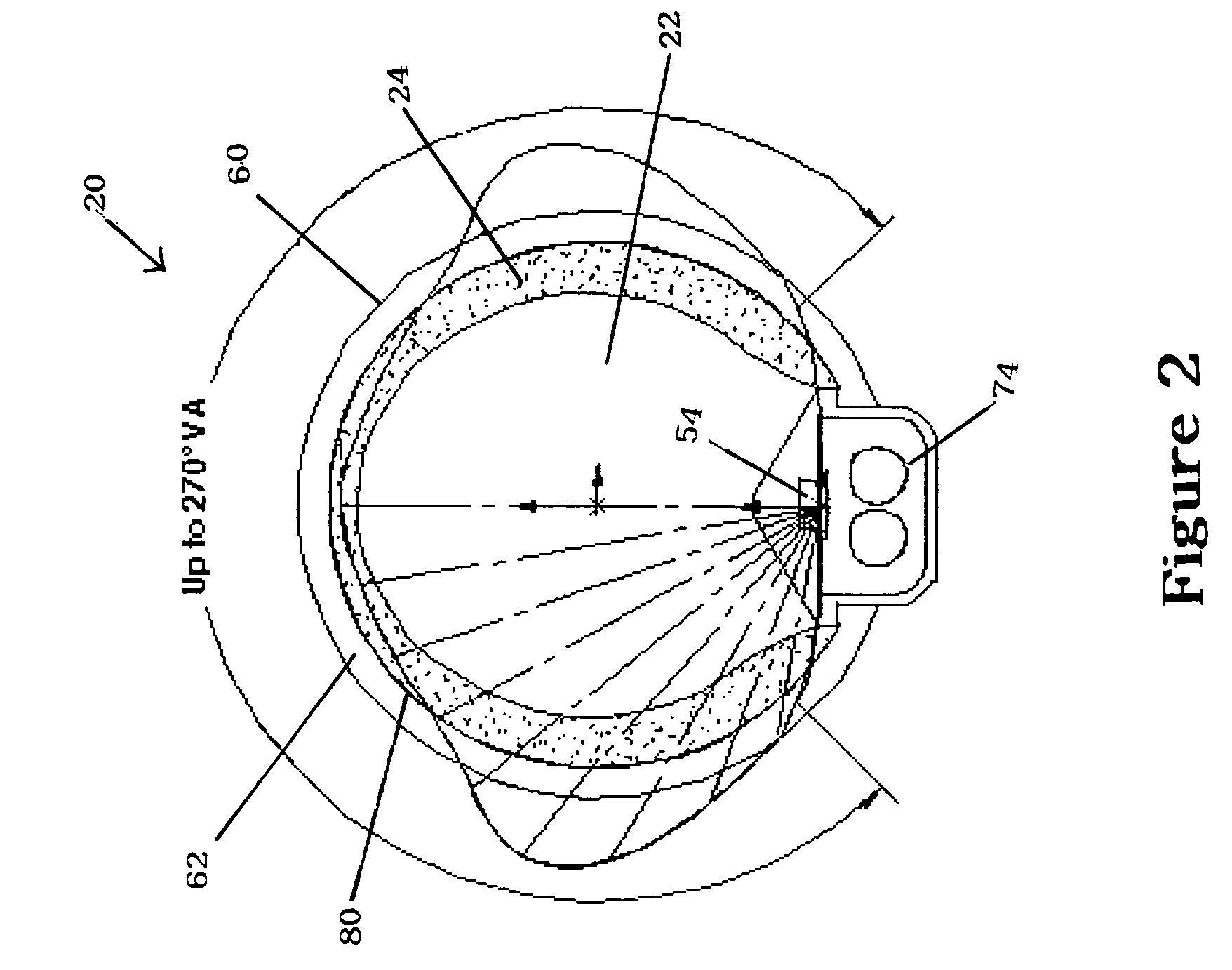
Illumination device for simulating neon or fluorescent lighting including a waveguide and a scattering cap
ActiveUS7008097B1Effective lightingProduced cost-effectivelyNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceDistribution patternEffect light
An illumination device includes: an optical waveguide having a first lateral surface for emitting light and a second lateral surface for receiving light; a scattering cap secured to the first lateral surface of and extending substantially the length of the waveguide; and a light source (e.g., a plurality of LEDs spaced a predetermined distance from one another) positioned adjacent to the light-receiving surface of the waveguide. Light entering the waveguide is efficiently transmitted to the scattering cap and is then preferentially scattered so as to exit with a broad elongated light intensity distribution pattern being formed along a lateral surface of the scattering cap.
Owner:LUMINII PURCHASER LLC
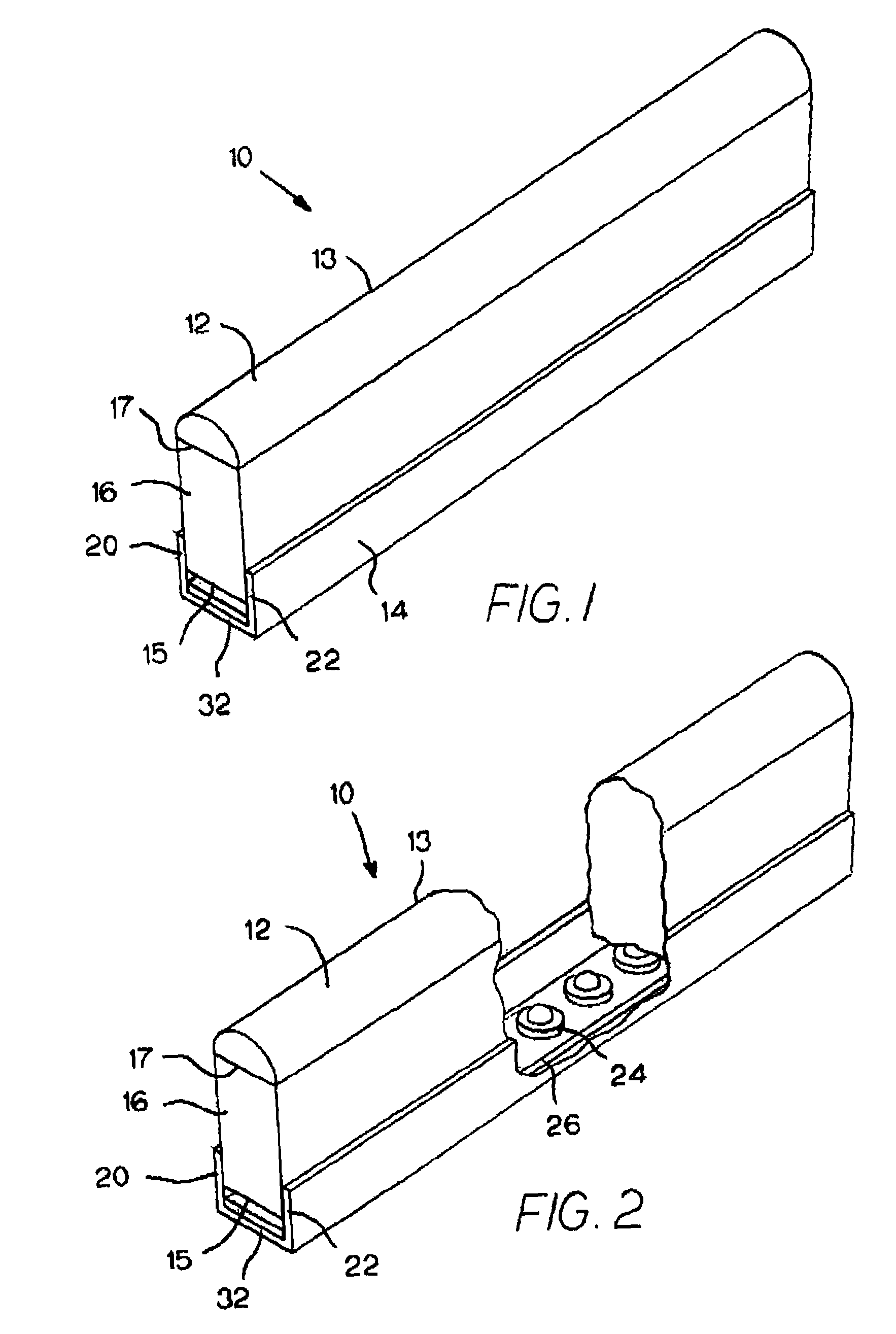
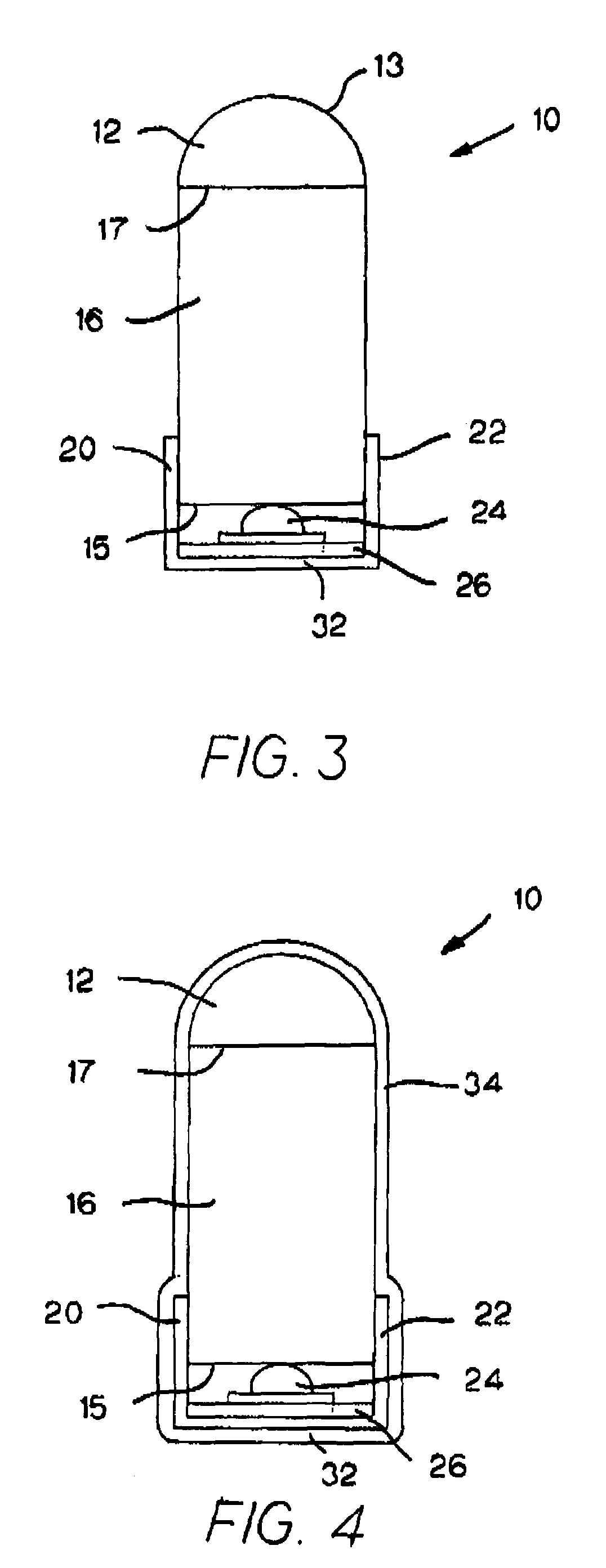
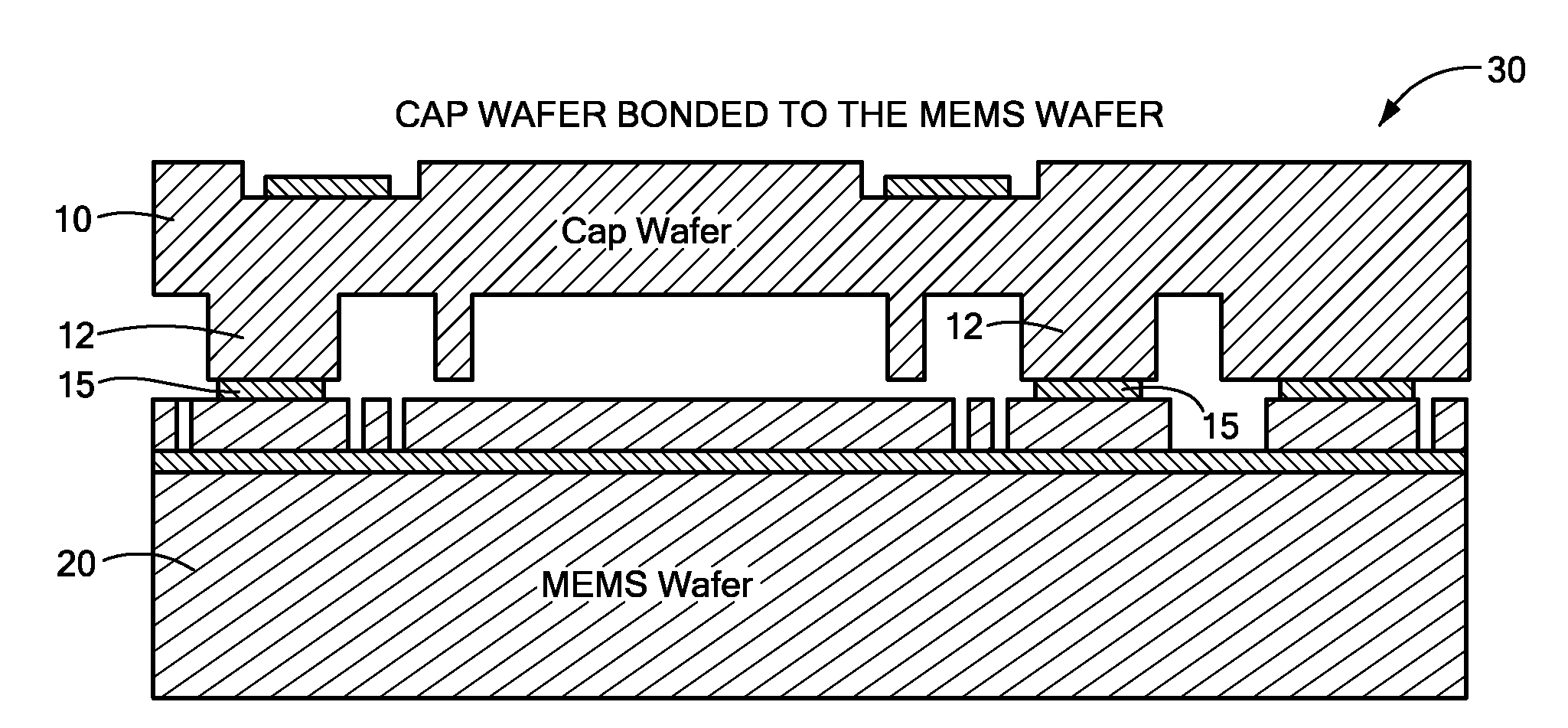
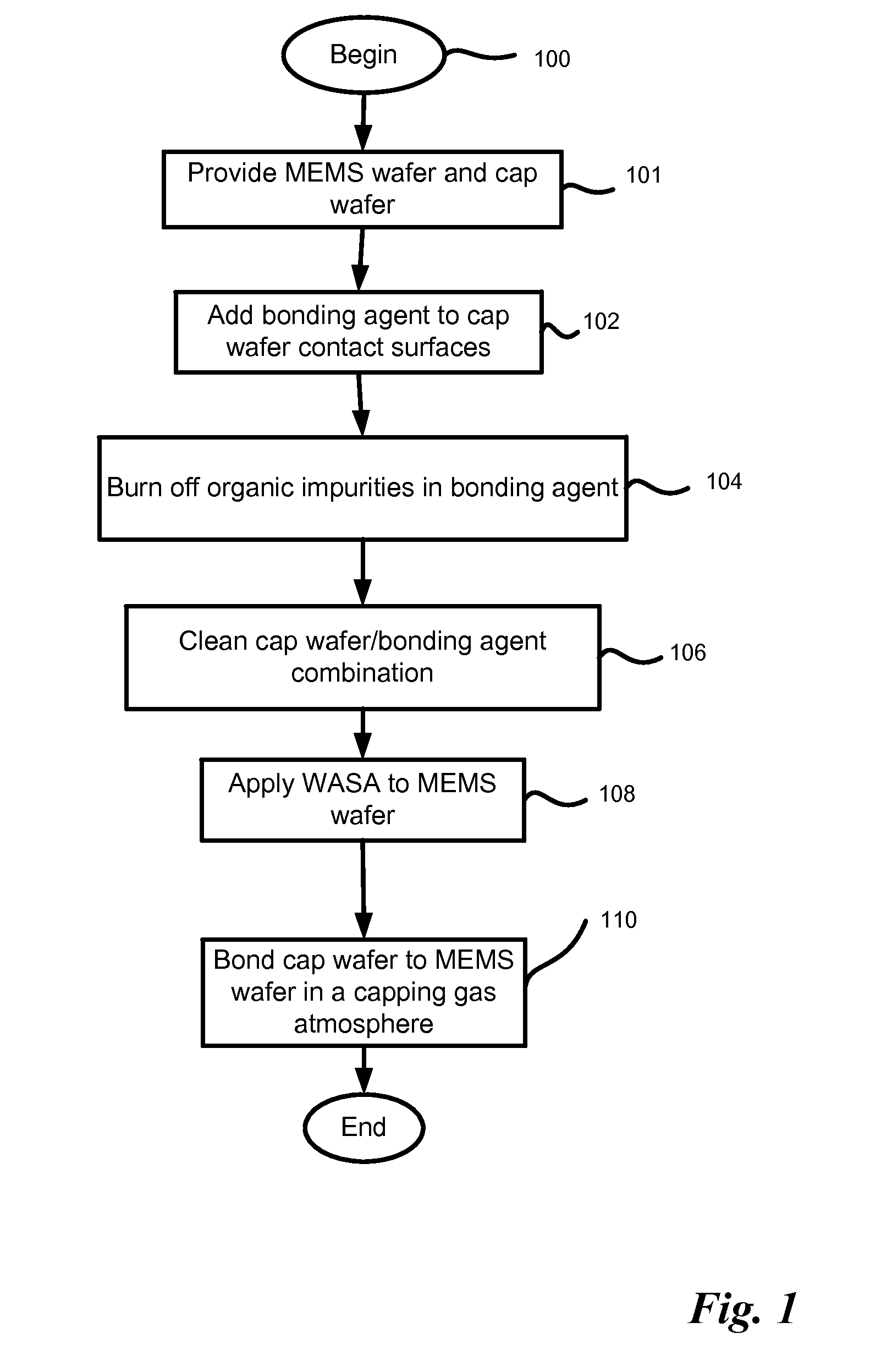
Method for Capping a MEMS Wafer
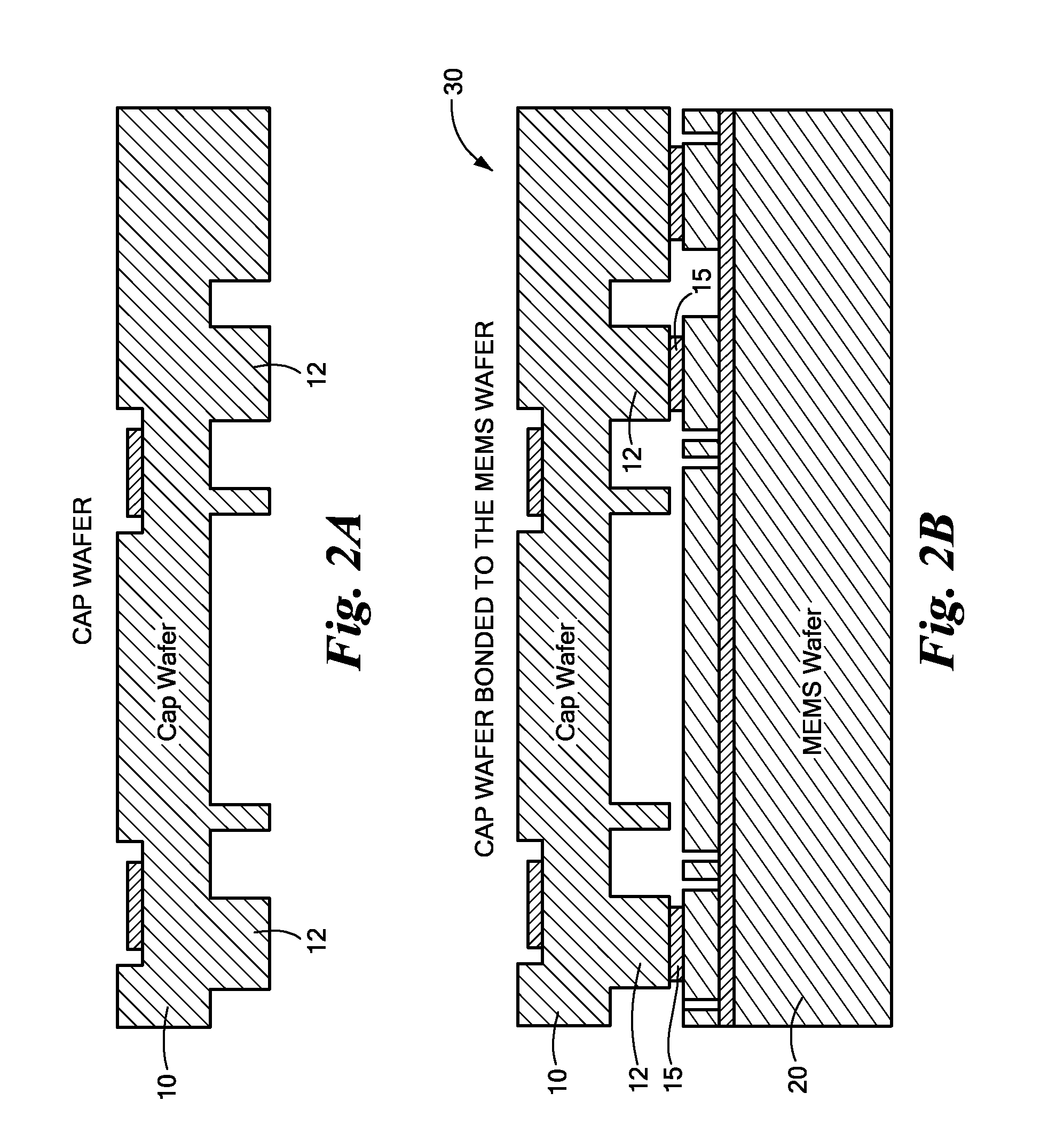
ActiveUS20090294879A1Reduce static frictionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNeonEngineering
A method for capping a MEMS wafer to form a hermetically sealed device. The method includes applying a glass bonding agent to the cap wafer and burning off organic material in the glass bonding agent. The cap wafer / glass bonding agent combination is then cleaned to reduce lead in the combination. The cleaning is preferably accomplished using an oxygen plasma. The MEMS device is coated with a WASA agent. The cap wafer is then bonded to the MEMS wafer by heating this combination in a capping gas atmosphere of hydrogen molecules in a gas such as nitrogen, argon or neon. This method of capping the MEMS wafer can reduce stiction in the MEMS device.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Method and equipment for selectively collecting process effluent
An apparatus and process for recovering a desired gas such as xenon difluoride, xenon, argon, helium or neon, from the effluent of a chemical process reactor that utilizes such gases alone or in a gas mixture or in a molecule that becomes decomposed wherein the chemical process reactor uses a sequence of different gas composition not all of which contain the desired gas and the desired gas is captured and recovered substantially only during the time the desired gas is in the effluent.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
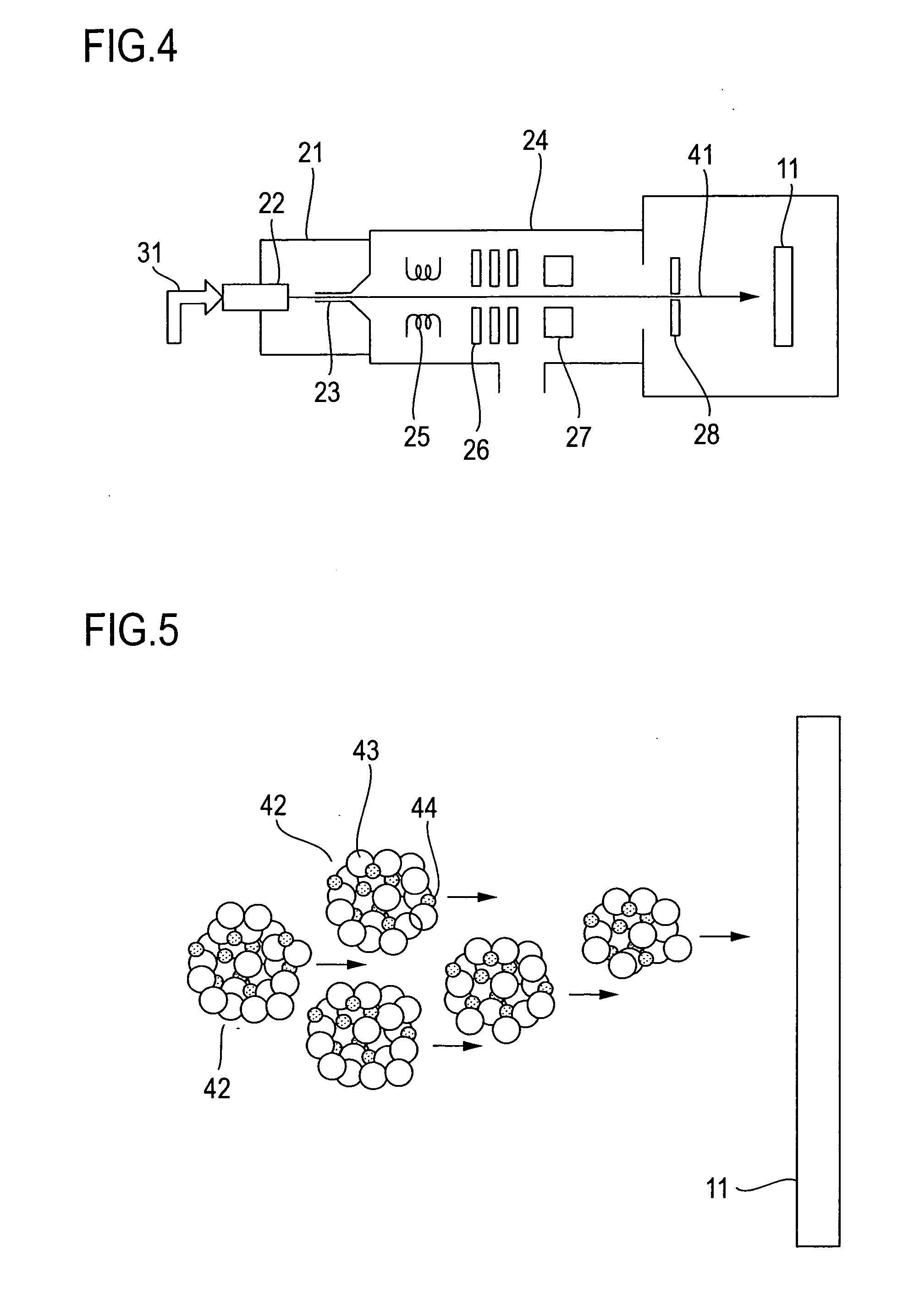
Dry etching method and photonic crystal device fabricated by use of the same
InactiveUS20050155951A1Minimize surface roughnessReduce roughnessElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsKryptonPhotonic crystal
In a dry etching method in which clusters formed by agglomeration of atoms or molecules are ionized and accelerated as a cluster ion beam for irradiation of an object surface to etch away therefrom its constituent atoms, the clusters are mixed clusters 42 formed by agglomeration of two or more kinds of atoms or molecules, and the mixed clusters 42 contain atoms 43 of at least one of argon, neon, xenon and krypton, and a component 44 that is deposited on the object surface to form a thin film by reaction therewith. With this method, it is possible to provide an extremely reduced sidewall surface roughness and high vertical machining accuracy.
Owner:JAPAN AVIATION ELECTRONICS IND LTD
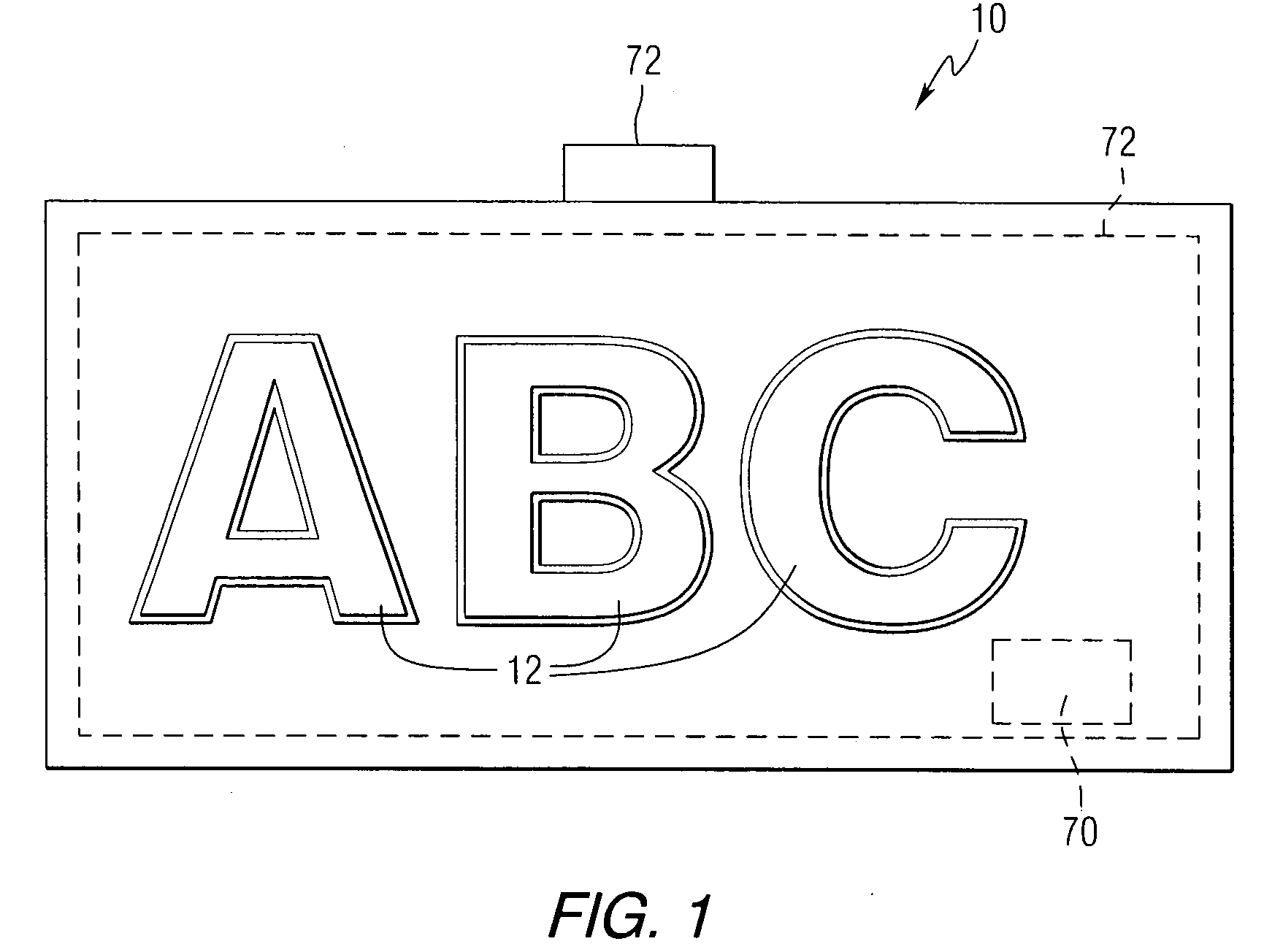
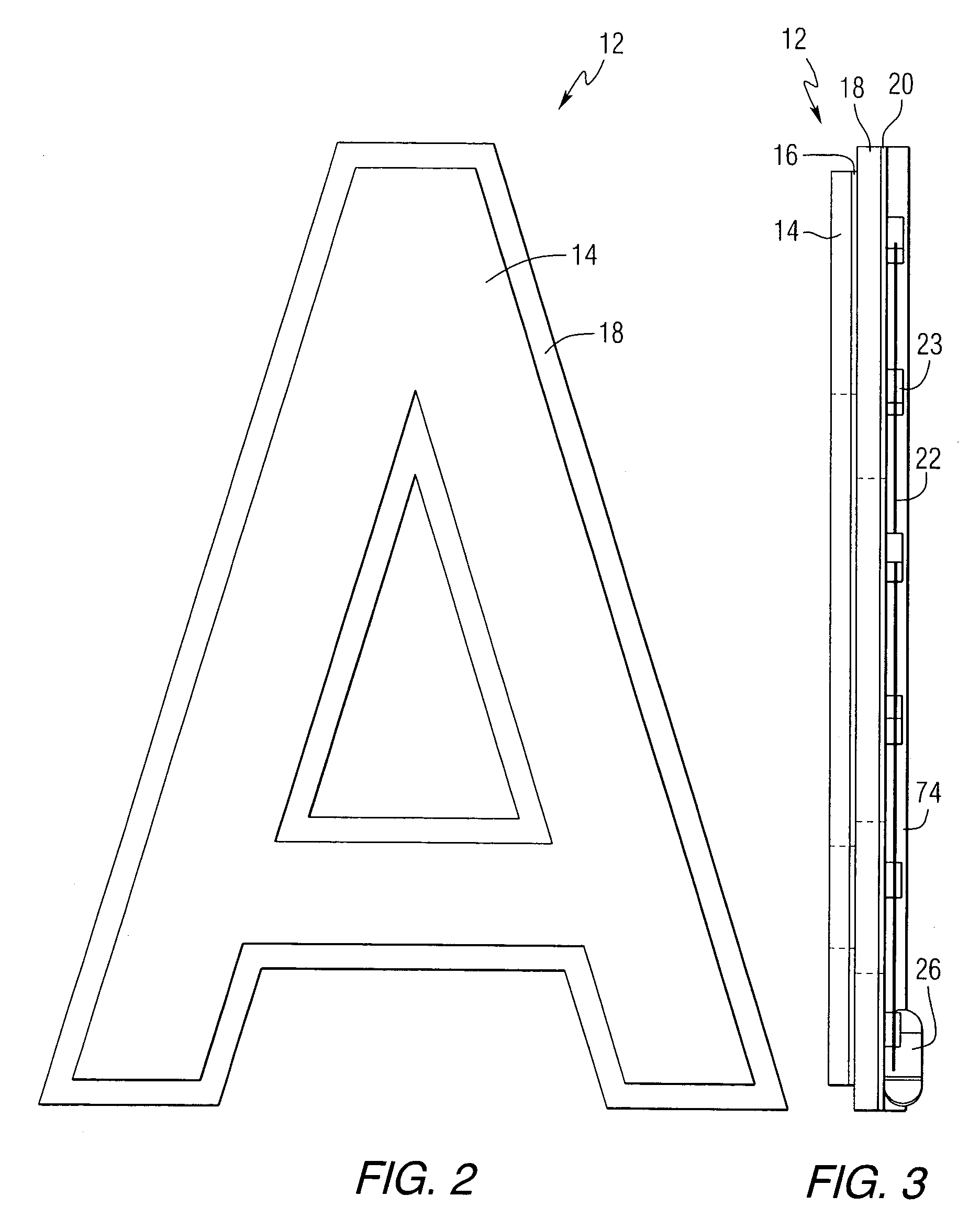
Illuminated sign
InactiveUS7162821B2Enhances formed outline and contourEasily and accurately reproducedMobile visual advertisingIlluminated signsElectromagnetic radiationReflective layer
An illuminated sign or nametag achieving the even glow and brightness of neon light displays without neon light tubes. Each character or symbol of the sign or nametag contains a plurality of light emitting members. Each such indicia comprises a light diffusion layer illuminated by light emitting members disposed on, near or in the light diffusion layer. A permanent or temporary masking layer partially covers the light diffusion layer to form a glowing border around the masking layer. Reflective layers covering either or both faces of the light diffusion layer may be used to intensify the light emitted therefrom. By the particular arrangement of the reflective surfaces relative to the light diffusion layer, electromagnetic radiation in the form of visible light from the light emitting members is controlled to provide an aura that enhances formed outlines or contours of light around the indicia making up the sign.
Owner:IDG
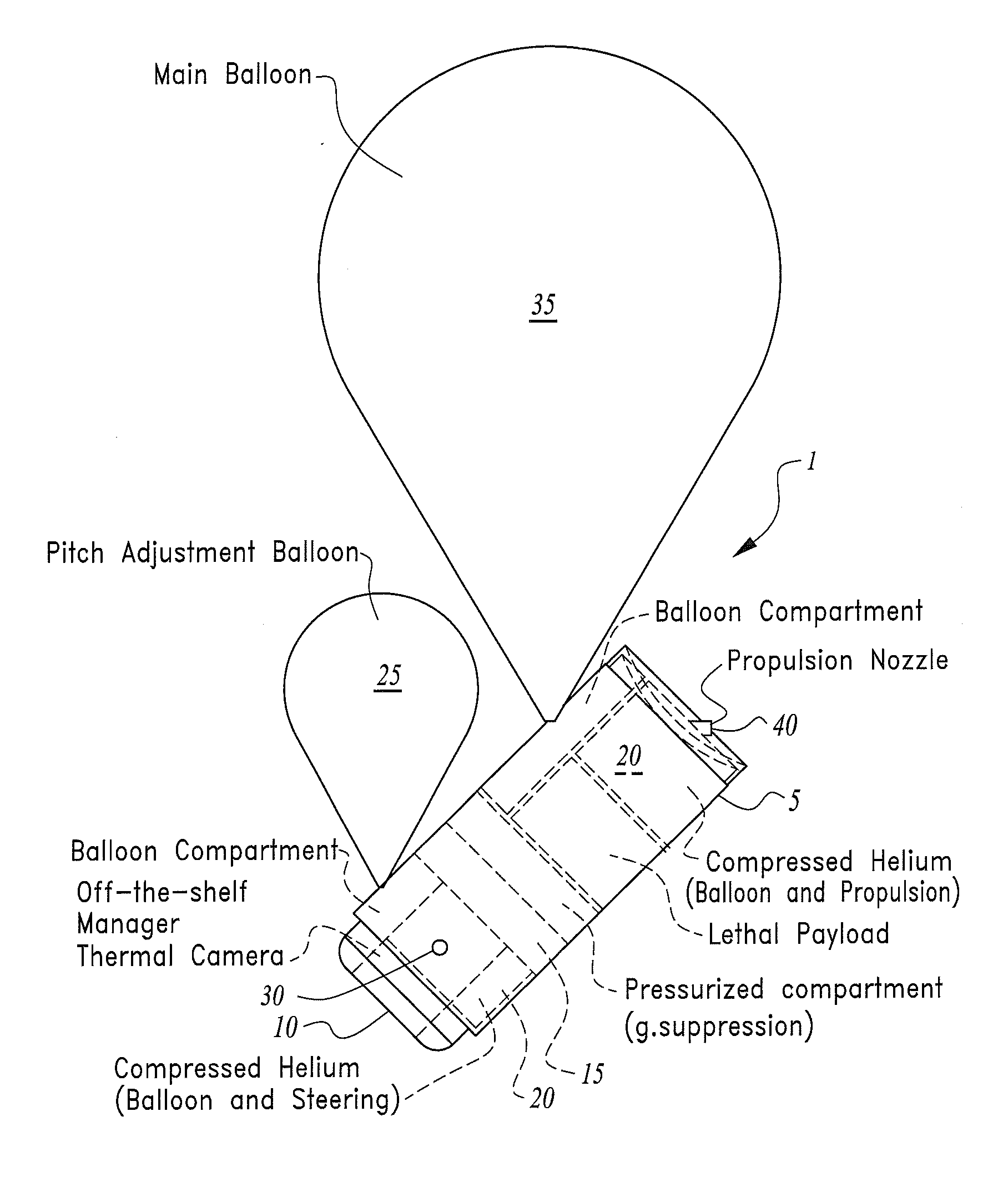
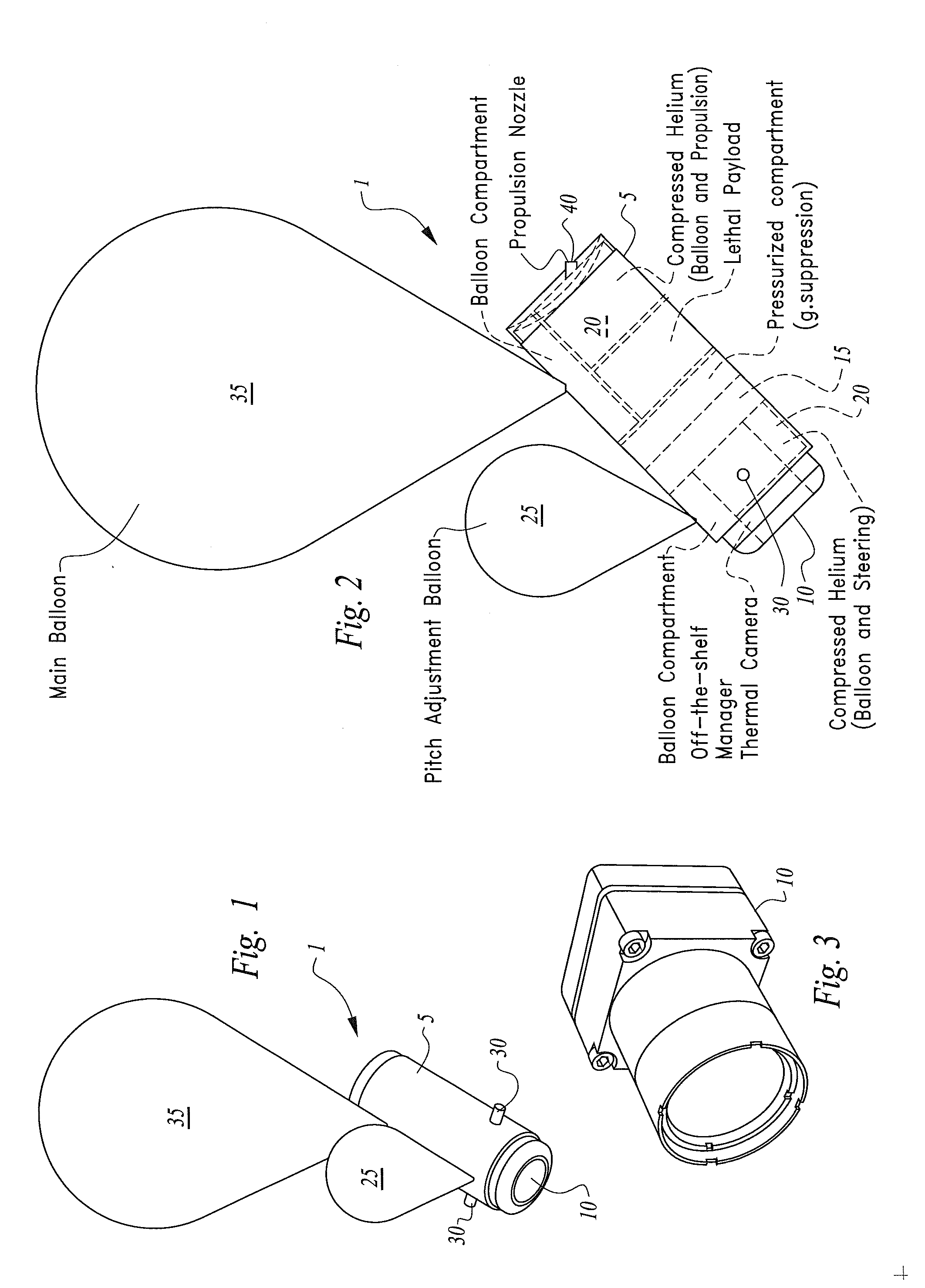
Hovering Surveillance Air Vehicle
A hovering surveillance device. An electronic imaging device is disposed on a housing having a primary lift element, at least one compressed lighter-than-air gas element, a pitch adjustment element, and, a steering element. The compressed lighter-than-air gas is channeled to the primary lift element and the pitch adjustment element to selectively vary the altitude and angle for the housing such that scene of interest may be imaged. The lighter-than-air gas may be selected from the group of helium, hydrogen, heated air, neon, ammonia, and methane.
Owner:PFG IP
Heat sink with helical fins and electrostatic augmentation
InactiveUS20100181889A1Improve cooling effectImprove performancePoint-like light sourceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAir pumpEngineering
A heat sink for an LED downlight utilizes tilted fins forming helical air passages that can enhance thermal performance by 30% over conventional fins. To overcome the thermal challenge of installation within the stagnant hot air of insulated ceiling cans, a heat sink has an integral electrostatic air pump on its exterior, to move hot air downwards and drain the stagnant air from the can by establishing a chimney-like circulation up through the heat sink and back down around the outside of the heat sink. The air mover can be powered by a compact high-voltage, low-current power supply similar to those of neon signs. An embodiment of the heat sink is also revealed that is suitable for cooling an LED replacement for standard screw-in or equivalent light bulbs. This device can perform well in variety of orientations (horizontal, vertical, etc.) and fixtures.
Owner:LIGHT PRESCRIPTIONS INNOVATORS
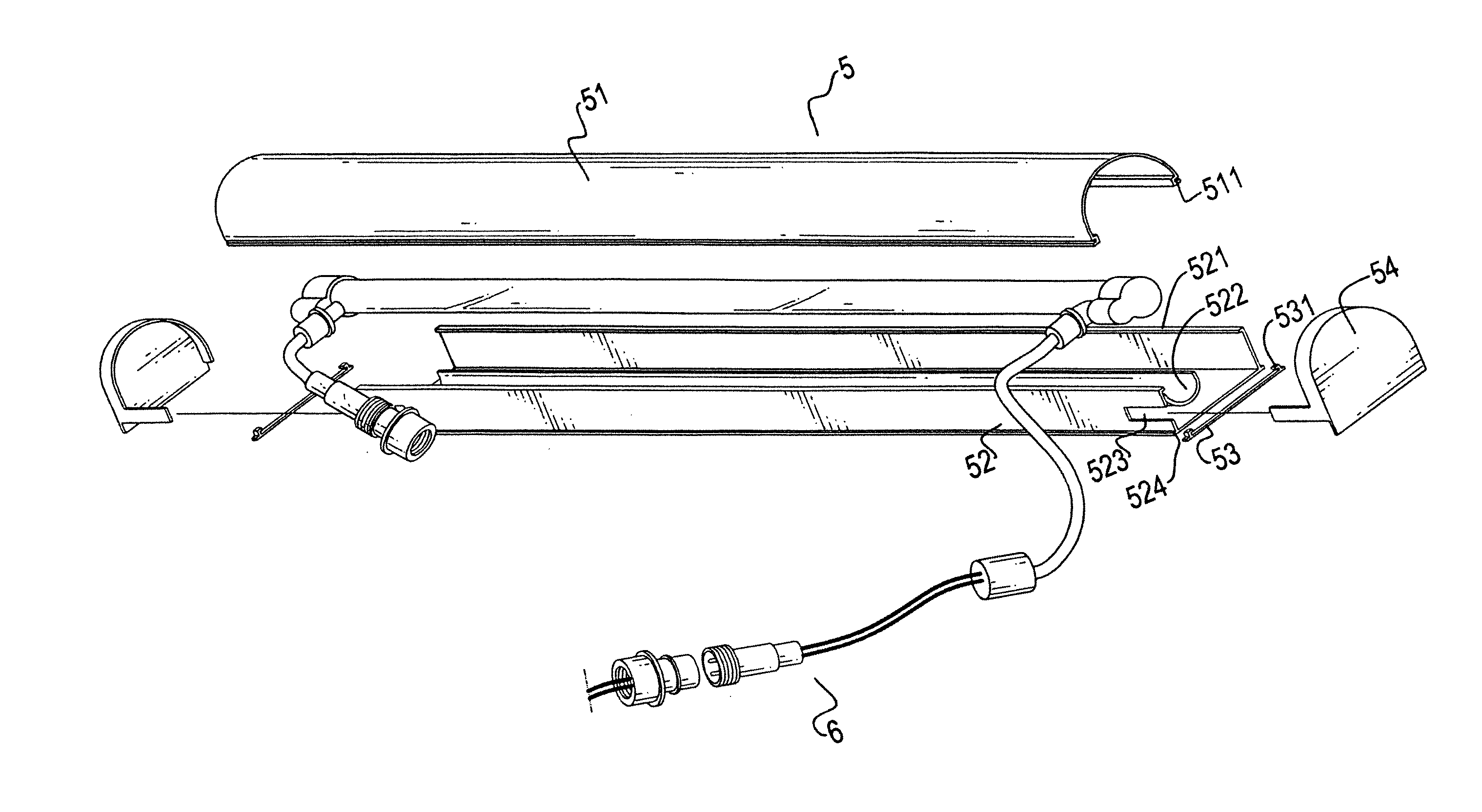
Improved structure of soft tube lamp
InactiveCN1641260AUniform continuous light effectLarge production batchPoint-like light sourceProtective devices for lightingContinuous lightSource lines
The invention discloses an improved structure of a soft tube lamp, including a core line, a plurality of LEDs arranged in the core line, a diffusing body with a length equal to the core line and provided above the LEDs, an envelopping layer with a length equal to the core line and envelopping the core line and the diffusing body, a joint for connecting the soft tube lamp with a power source line. The improved structure of the soft tube lamp according to the invention has an even and continuous light effect of an analog neon light, achieves an object desired and seeked in a soft tube lamp industry for a long time, realizes continuous and automatic mass-production of analog neon lights at the same time, thereby compared with the analog neon lights and soft tube lamps having other sturectures, the soft tube lamp of the invention has advantages of mass-production and low producing cost.
Owner:HE SHAN LIDE ELECTRONICS ENTERPRISE CO LTD
All solid-state omni directional luminary and flashlight
InactiveUS20010015893A1Guaranteed normal transmissionLight source combinationsPoint-like light sourceCamera lensAll solid state
A laser lens glow baton is a hand held, dual purpose, visual signaling baton. This device can be used as a flashlight that projects a well-defined beam of light via its laser lens and assembly or as a highly visible luminary that radiates an intense flux of light similar to neon tube. The laser lens glow baton is useful as a visual-signaling device because the colors of the main body and the colors of the projected beam emitted from the laser lens assembly are easily changed. The laser lens glow baton may be easily fabricated in different lengths because of its compartmentalization of the components.
Owner:GRACE INDS
Process For Preserving Biological Materials For Extended Periods Of Time
The present invention provides for a process for preserving biological material. The process comprises subjecting the biological material to a fixation process and then packaging the biological material in a container under a controlled atmosphere of noble gas. In the process, the controlled atmosphere of noble gas utilized comprises one or more noble gases selected from argon, xenon, helium, neon, krypton and radon. The process optionally also utilizes one or more additional gases selected from nitric oxide, hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and oxygen. This process allows for the long term storage of the biological material.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE HEALTHCARE AMERICA CORP +1
Color-changing illumination device
An illumination device for simulating neon or similar lighting is generally comprised of a rod-like member, a housing, a light source, and an intermediate light-transmitting medium extending along and positioned adjacent the light source with a light-receiving surface for receiving light emitted from said light source and a light-emitting surface for emitting light into the rod-like member. This intermediate light-transmitting medium is preferably composed of a matrix of a substantially translucent acrylic, polyurethane, or similar material tinted with a predetermined combination of one or more fluorescent and / or phosphorescent dyes. The intermediate light-transmitting medium is subdivided into independent sections, each of which is provided with differing combinations of fluorescent dye, phosphorescent dye, and / or no dye at all.
Owner:ILIGHT TECH INC
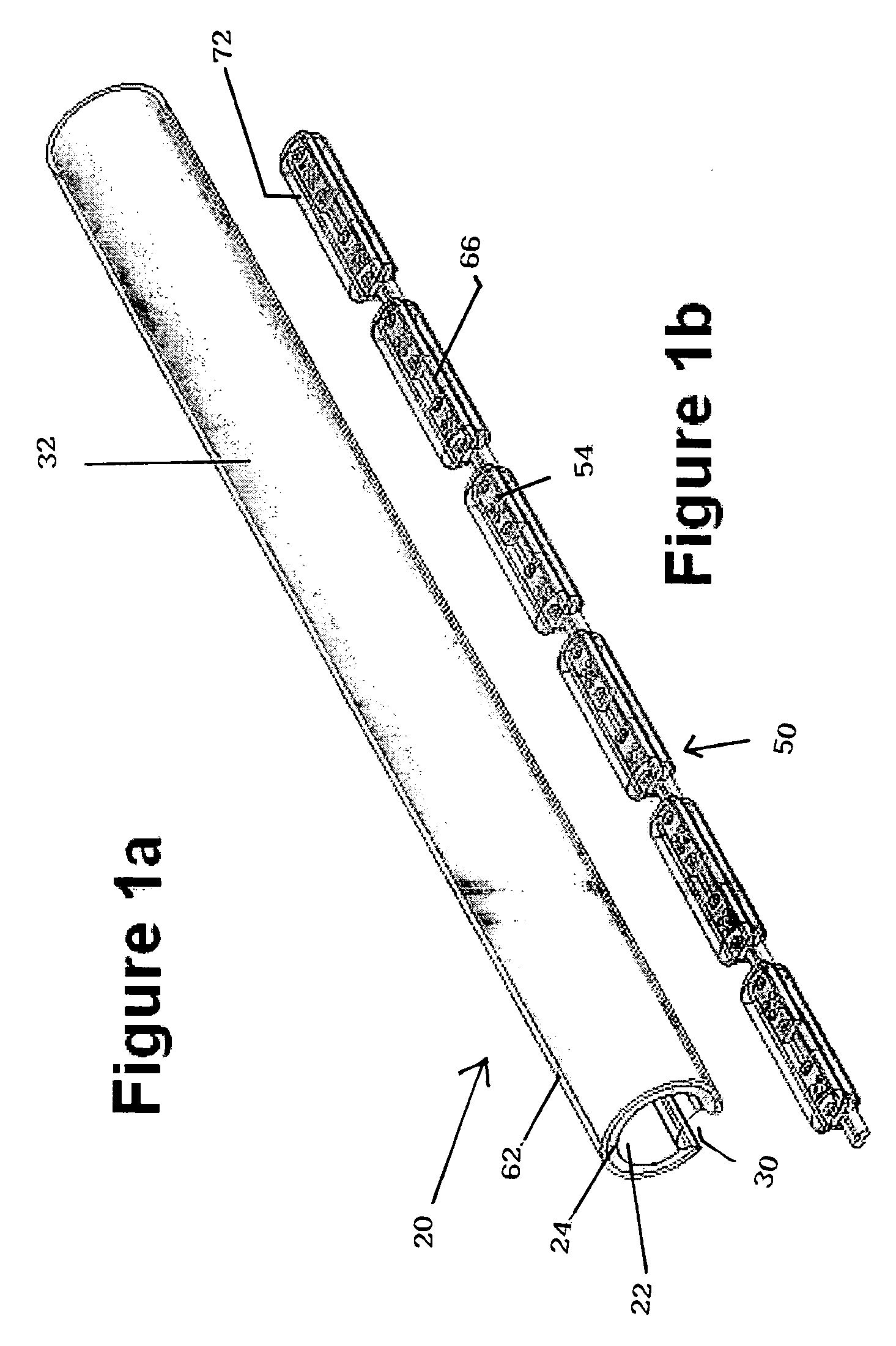
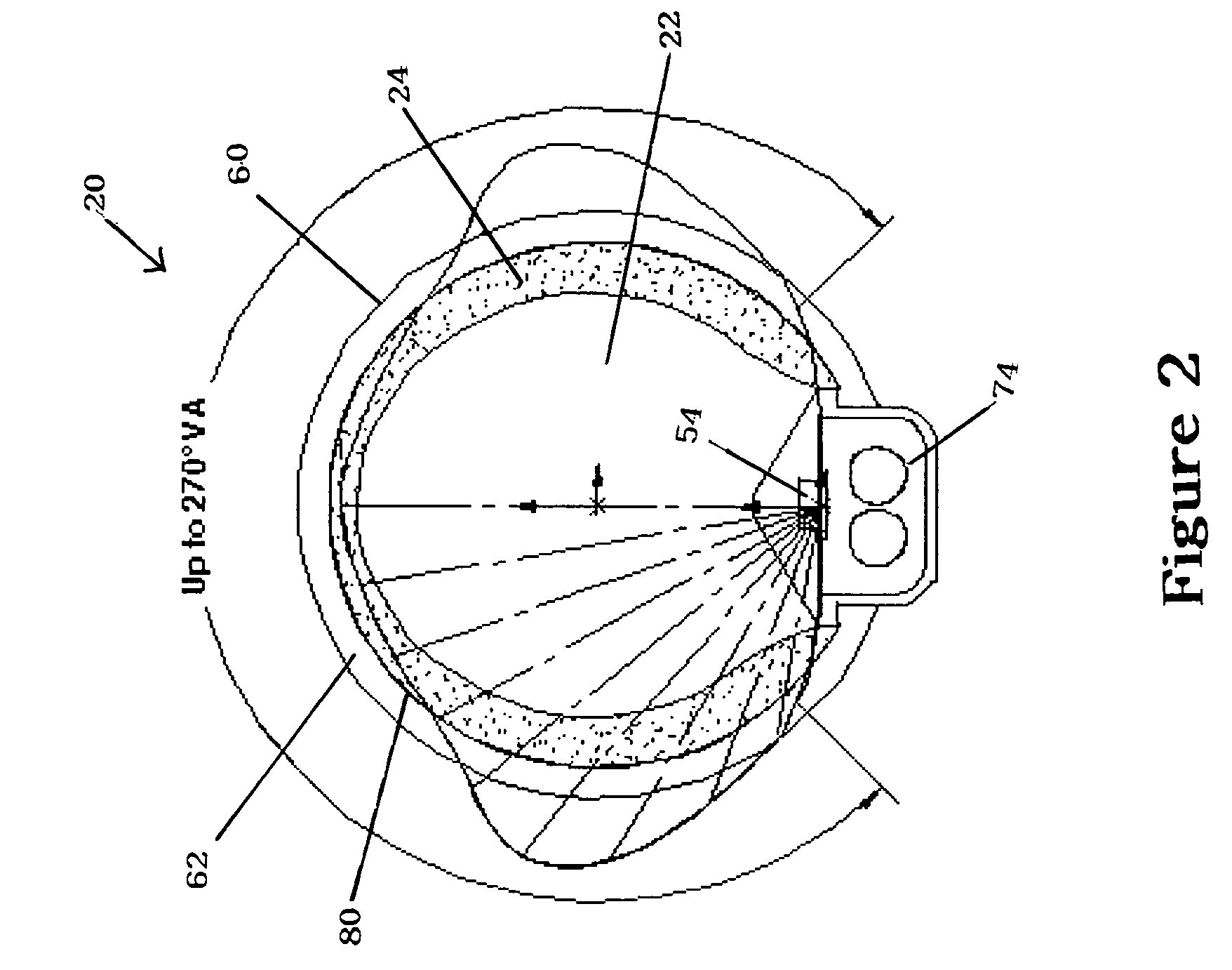
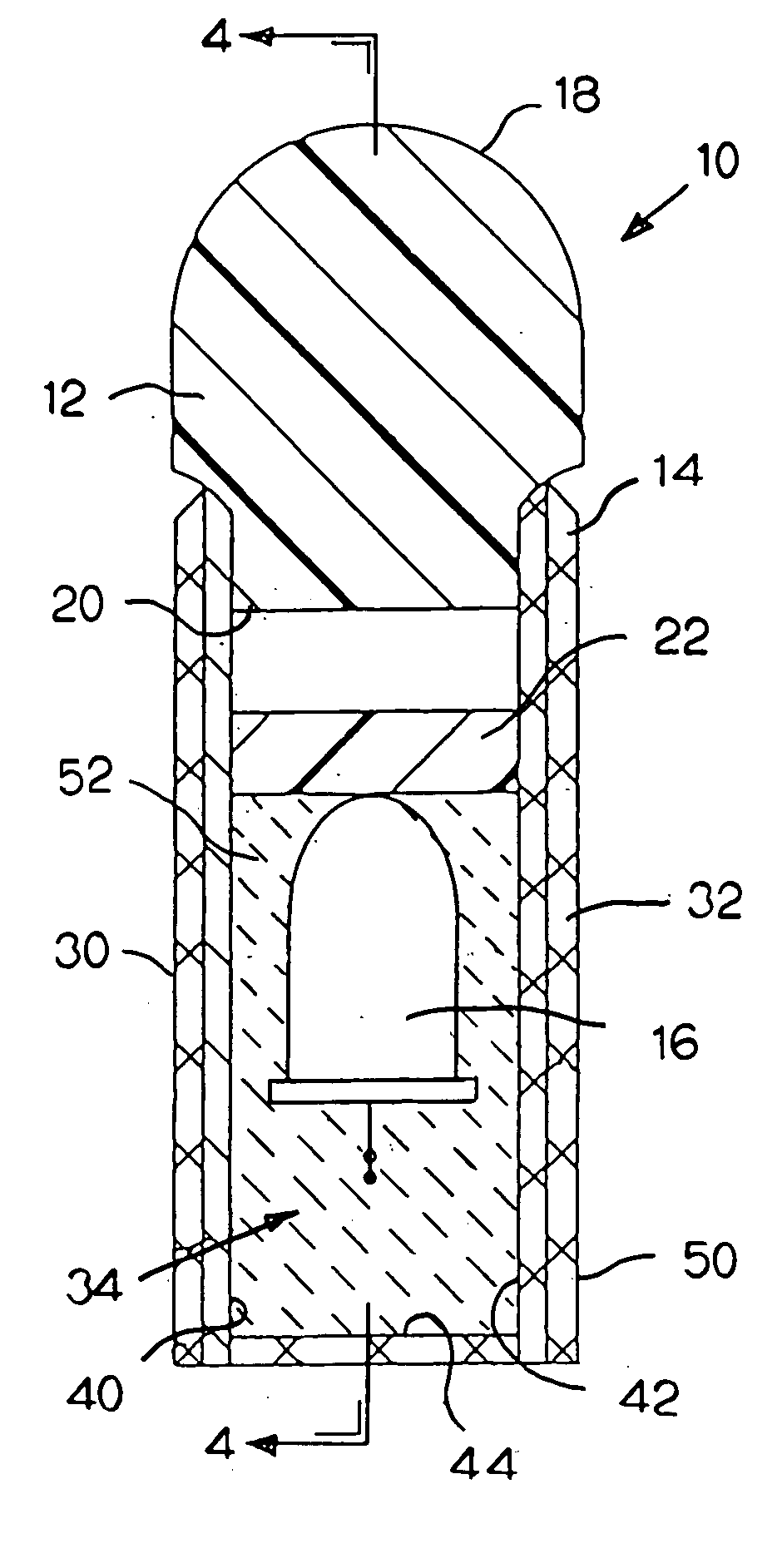
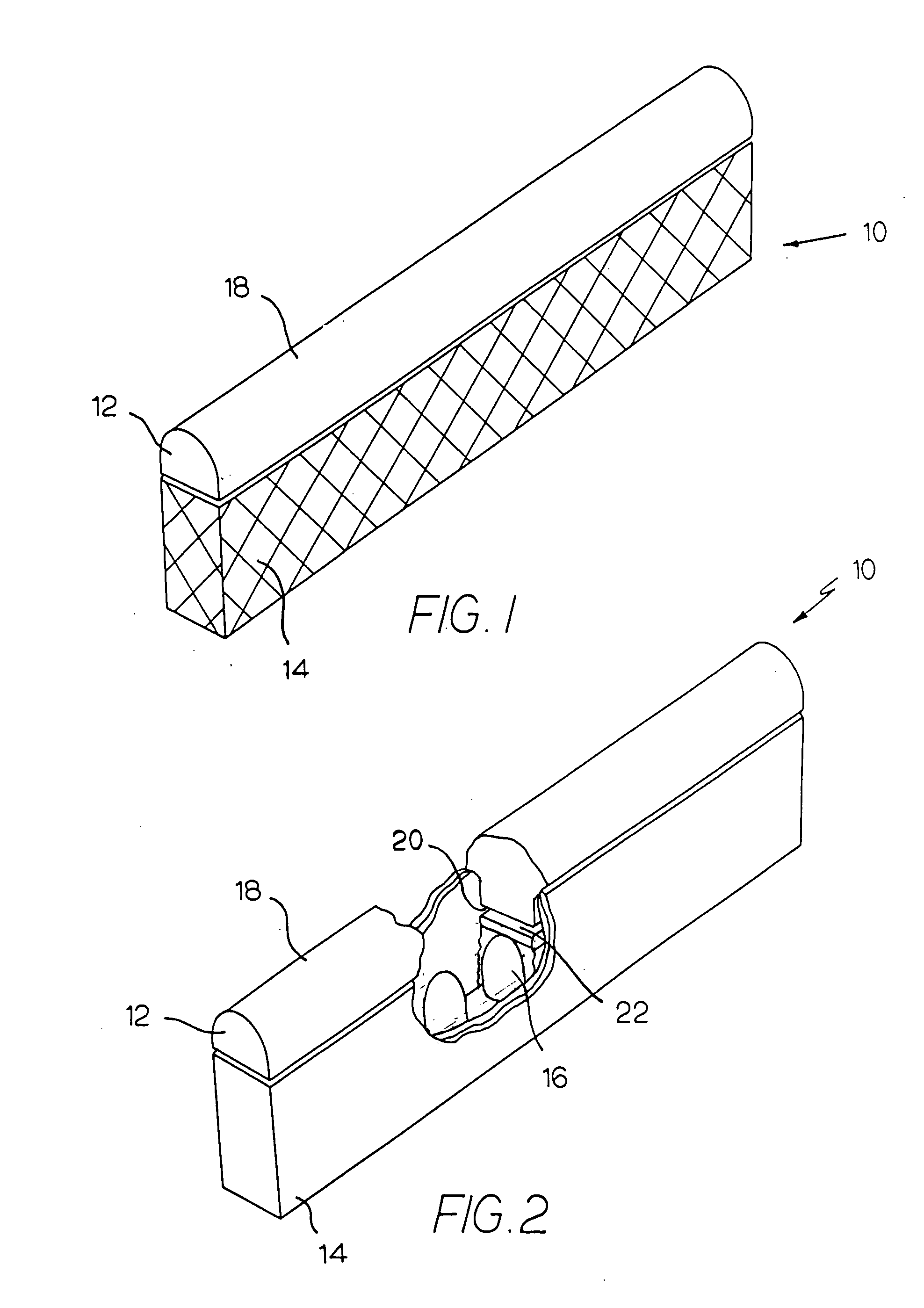
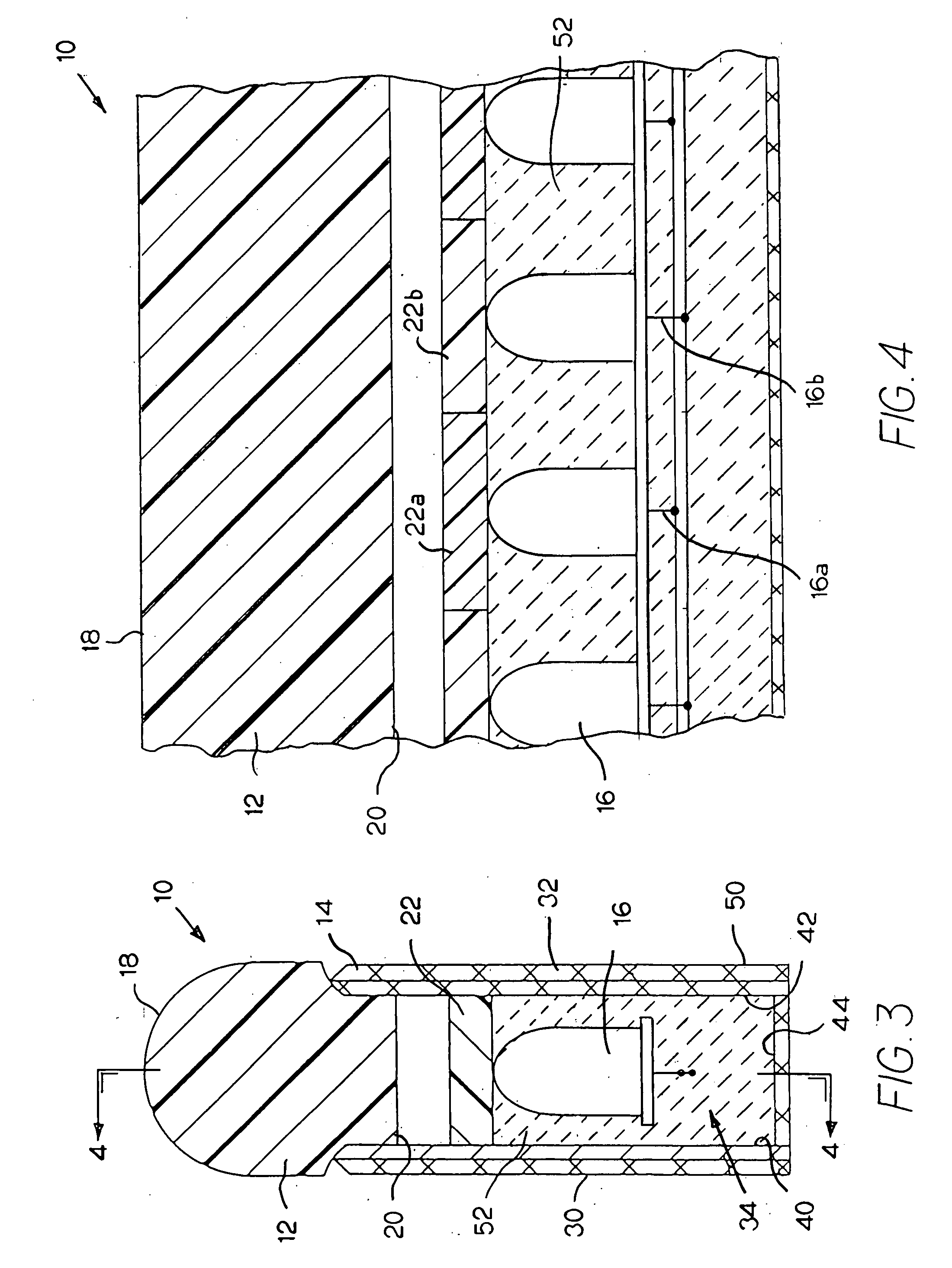
Neon light using a rope light as a light source
InactiveUS20050041418A1Improve waterproof performanceLow maintenanceNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceRope lightEngineering
A neon light includes a cover and a rope light. The cover is composed of a milky colored U-shaped cover and a base connected to the U-shaped cover. A ledge is formed on two free sides of the U-shaped cover to correspond to two ribs formed on two upright side walls on a top face of the base. An arcuate seat is formed between the two side walls to receive thereon the rope light. Two end caps are provided to seal two open ends defined by combination between the U-shaped cover and the base.
Owner:FAN BEN
High pressure processing of a substance utilizing a controlled atmospheric environment
InactiveUS20030170356A1Slow growth ratePrevent spoilageFatty acid hydrogenationFood preservationKryptonNitric oxide
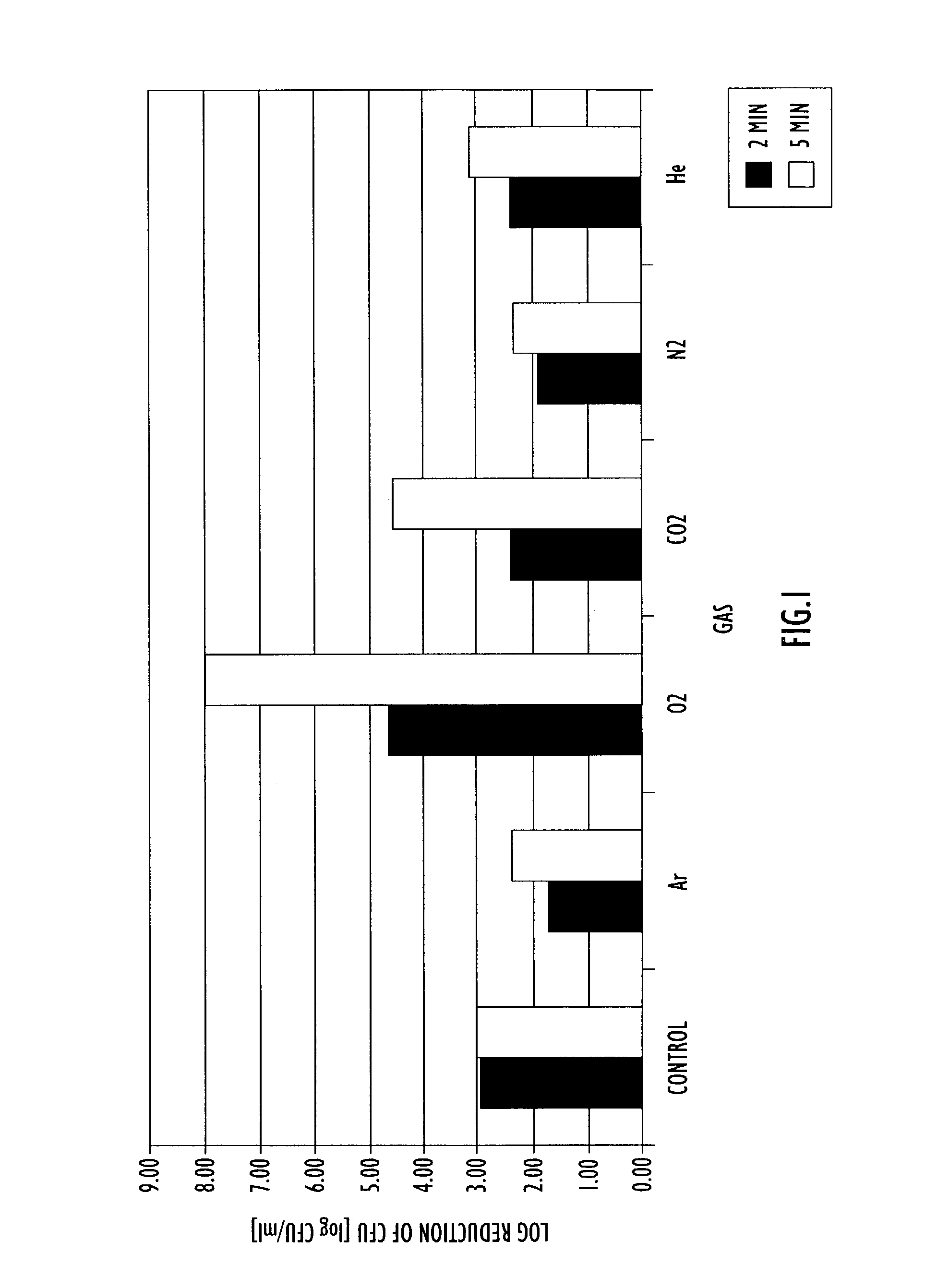
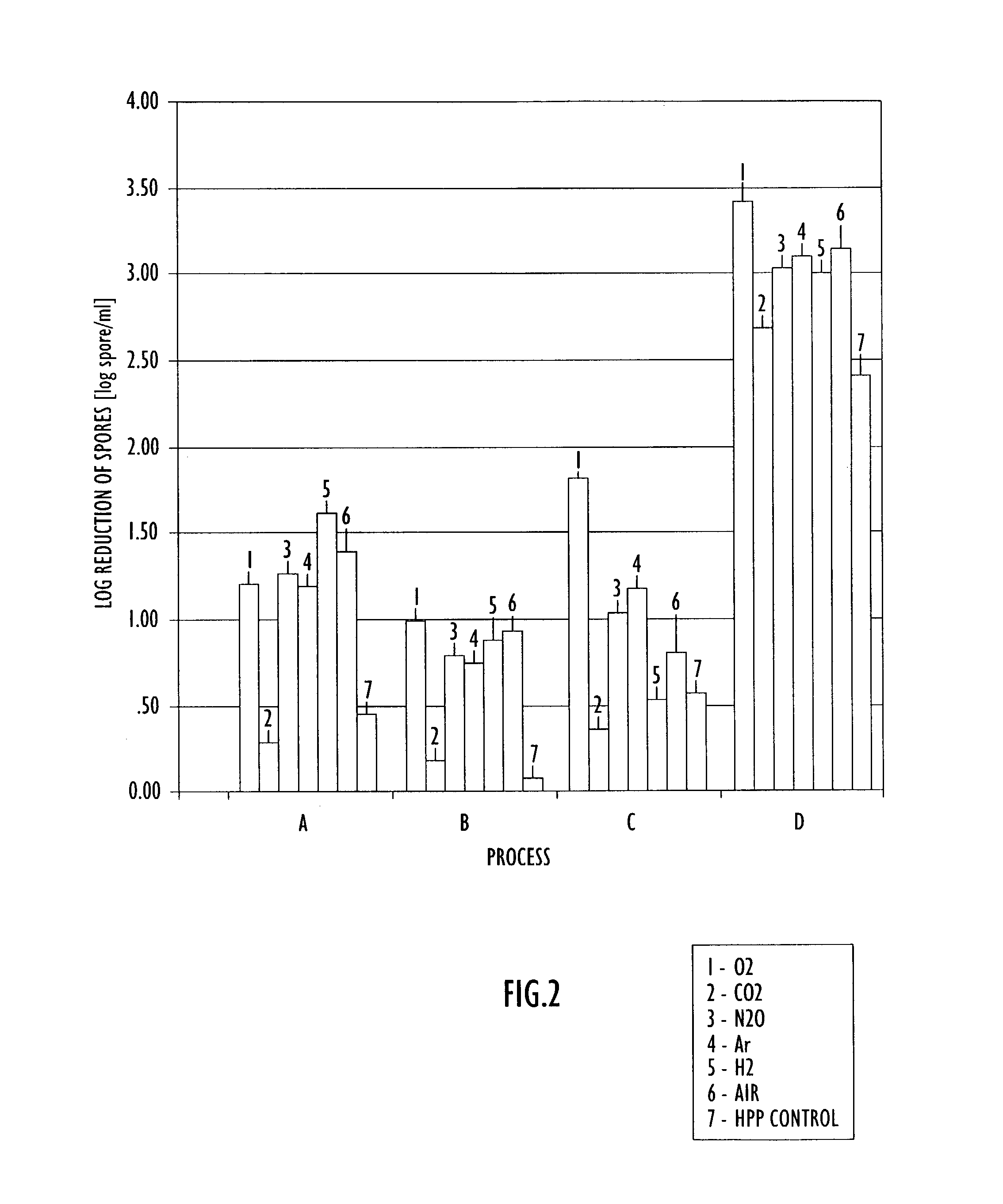
A method of processing a substance, such as a food item, utilizing high pressure processing includes providing an enclosed environment including the substance and one or more of the following gases: carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, nitric oxide, nitrous oxide, hydrogen, oxygen, helium, argon, krypton, xenon and neon. The enclosed environment including the substance and at least one gas is subjected to high pressure processing and sealed in a container. The high pressure processing may occur prior to or after sealing the substance in the container. Control of the amount and type of gases in the enclosed environment including the substance enhances the biocidal efficacy of high pressure processing as well as ensuring desirable sensory qualities of the substance during storage.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC +1
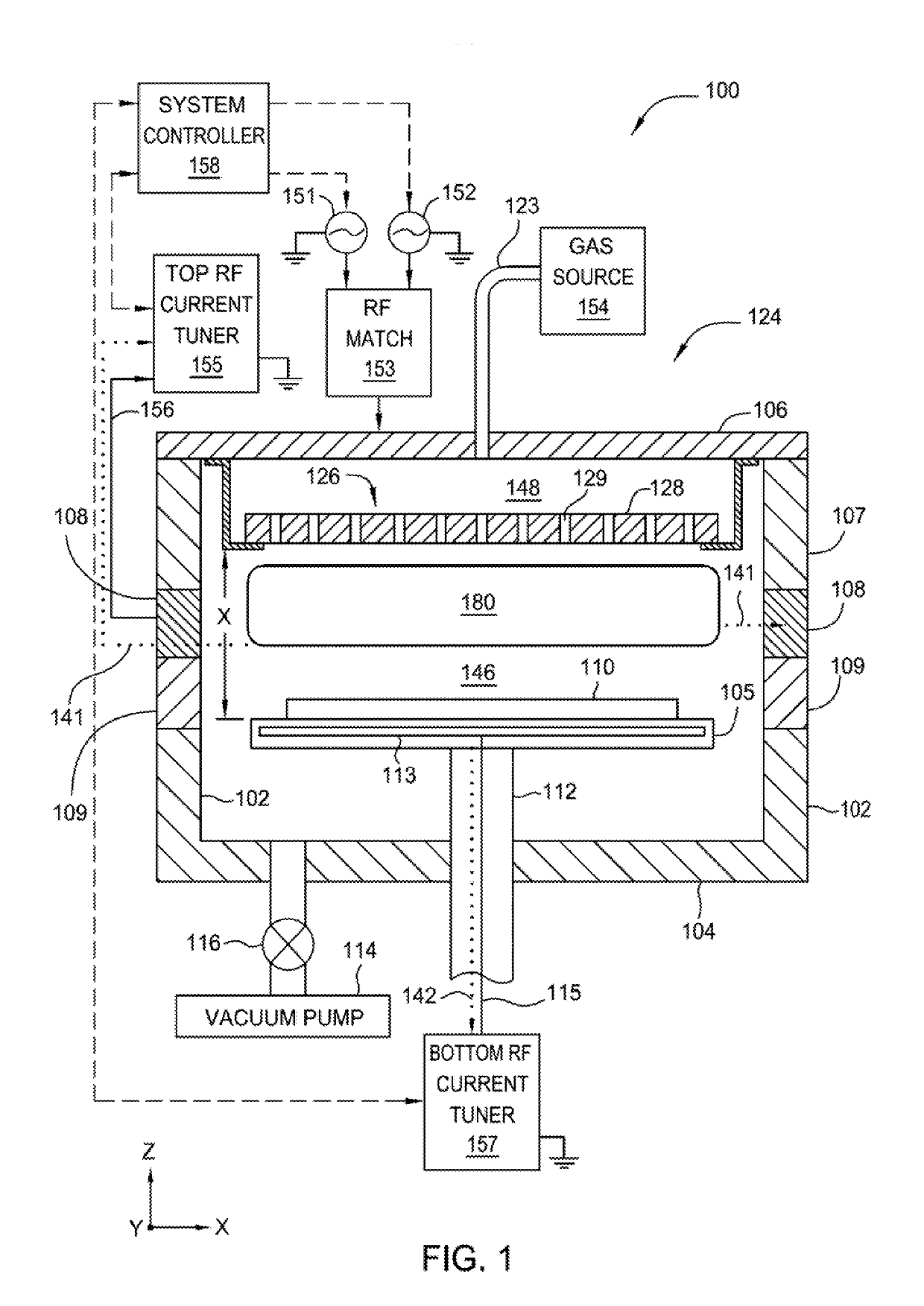
CMOS sion gate dielectric performance with double plasma nitridation containing noble gas
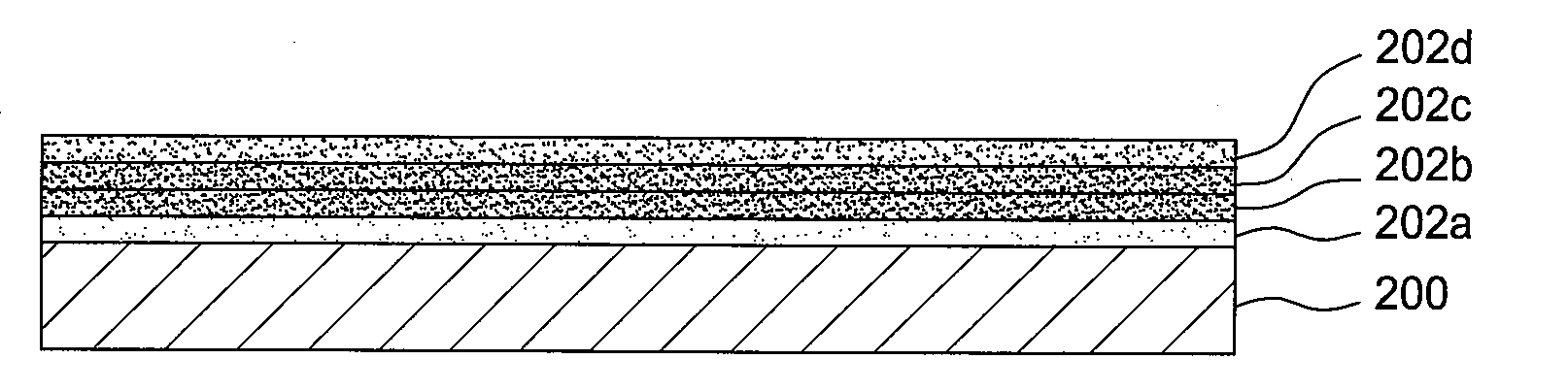
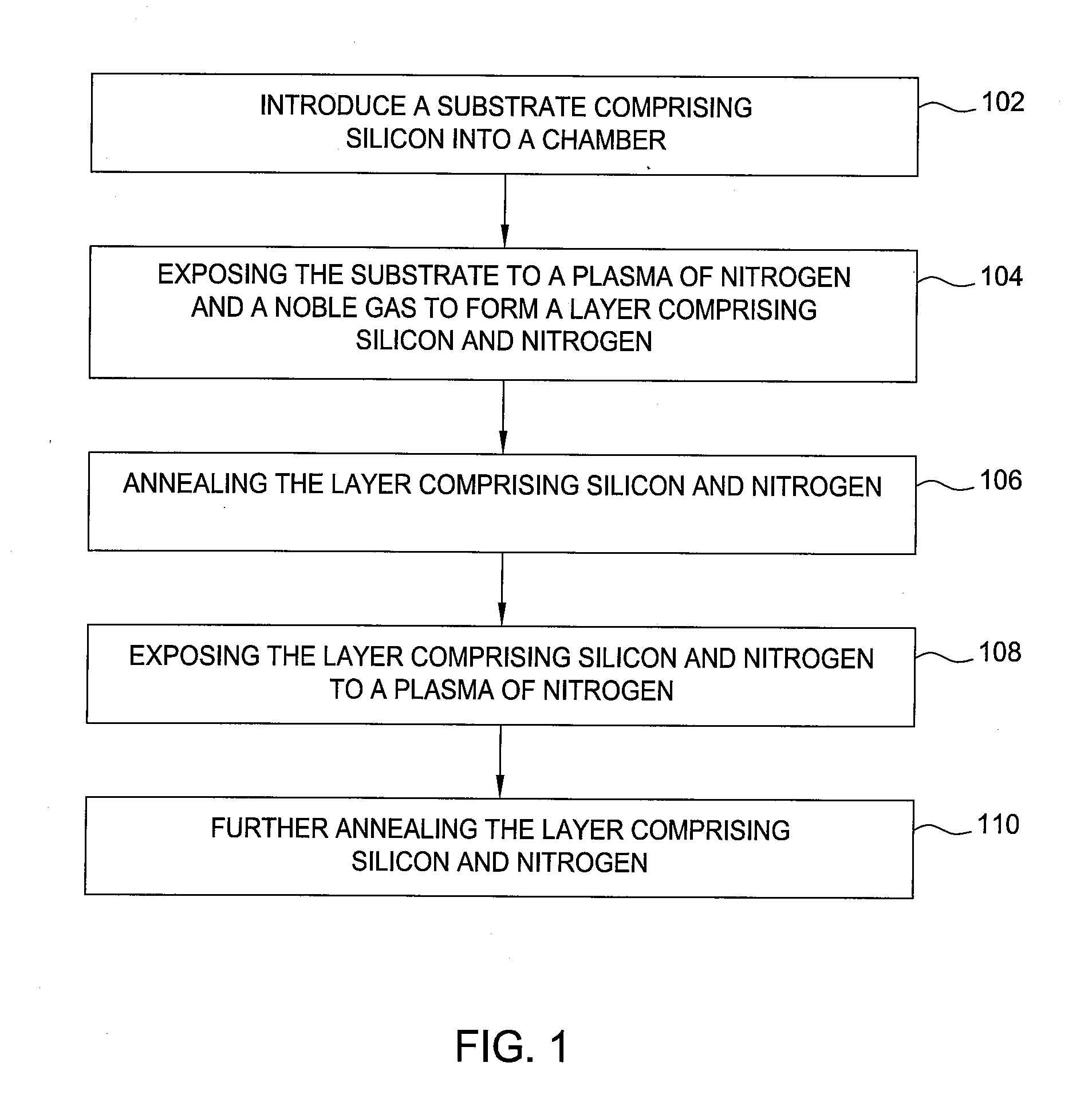
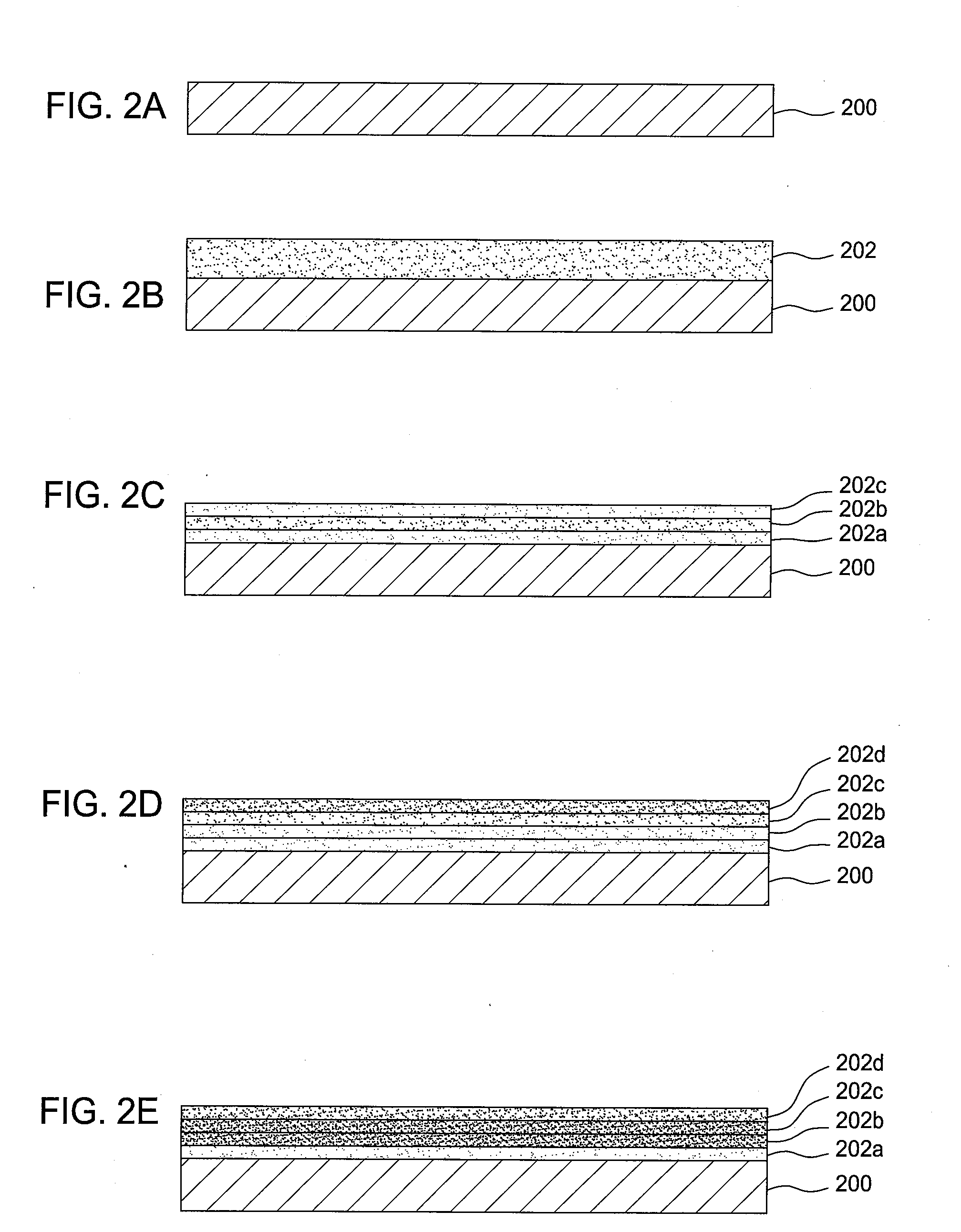
A method of forming a layer comprising silicon and nitrogen on a substrate is provided. The layer may also include oxygen and be used as a silicon oxynitride gate dielectric layer. In one aspect, forming the layer includes exposing a silicon substrate to a plasma of nitrogen and a noble gas to incorporate nitrogen into an upper surface of the substrate, wherein the noble gas is argon, neon, krypton, or xenon. The layer is annealed and then exposed to a plasma of nitrogen to incorporate more nitrogen into the layer. The layer is then further annealed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Light string using a cladding to scatter light from light emitting diodes to present a neon light effect
A light string includes a core made of a soft material and having multiple axial holes defined in one side of the core, two connection wires received in the other side of the core to be opposite to positions of the axial holes, multiple light emitting diodes (LEDs) respectively received in the axial holes and connected to the two connection wires for electrical connection with one another, a scattering body formed on top of the core and on top of the LEDs for scattering light beams from the LEDs and a cladding enclosing the scattering body and the core and having an arcuate top face for emission of light beams of the LEDs. Due to the addition of the scattering body and the cladding, the light beams from the LEDs are refracted and scattered to present a soft and continuous lighting effect.
Owner:GUANGDONG TONGFANG ILLUMINATIONS CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com