Patents
Literature
2669 results about "Molten glass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cover glass for mobile terminals, manufacturing method of the same and mobile terminal device
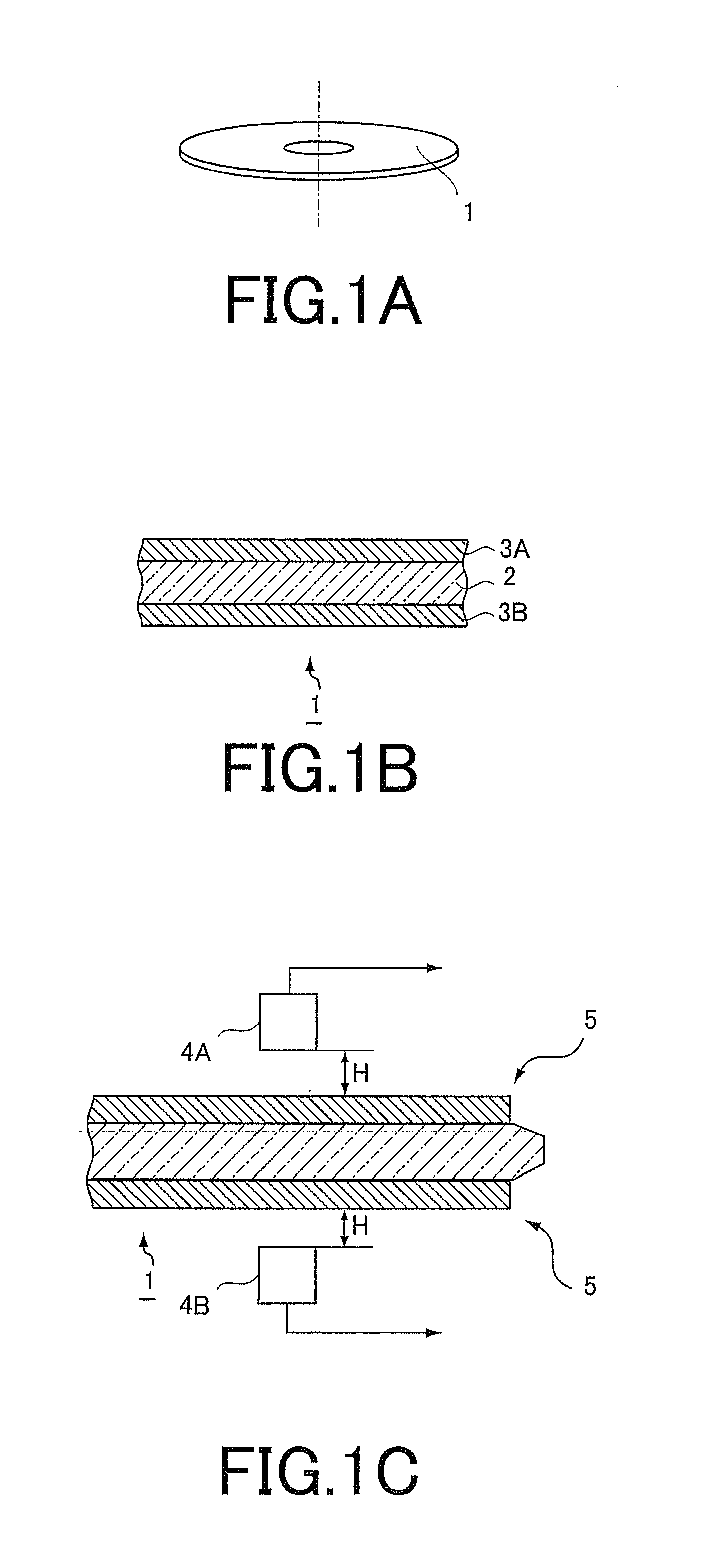
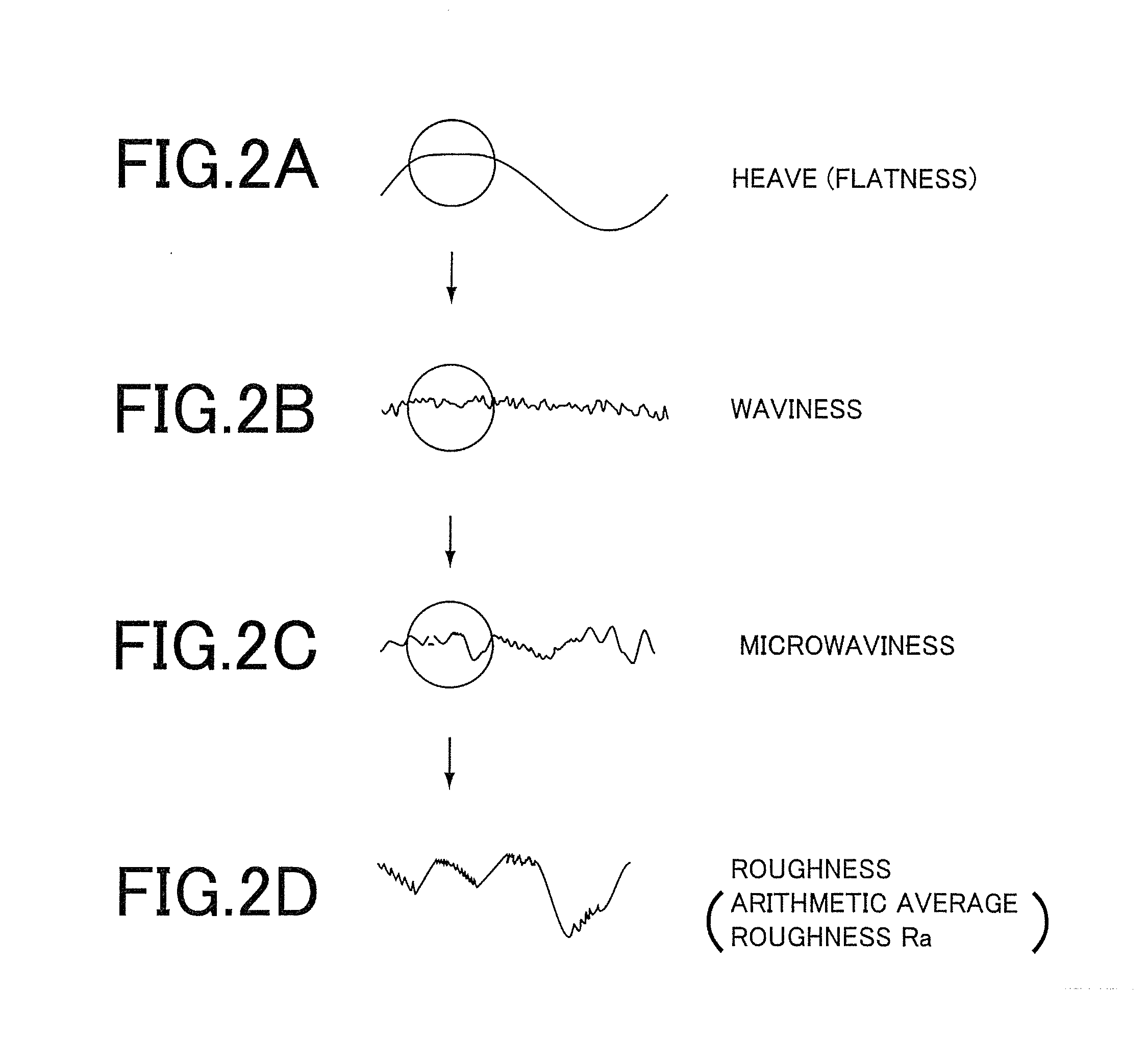
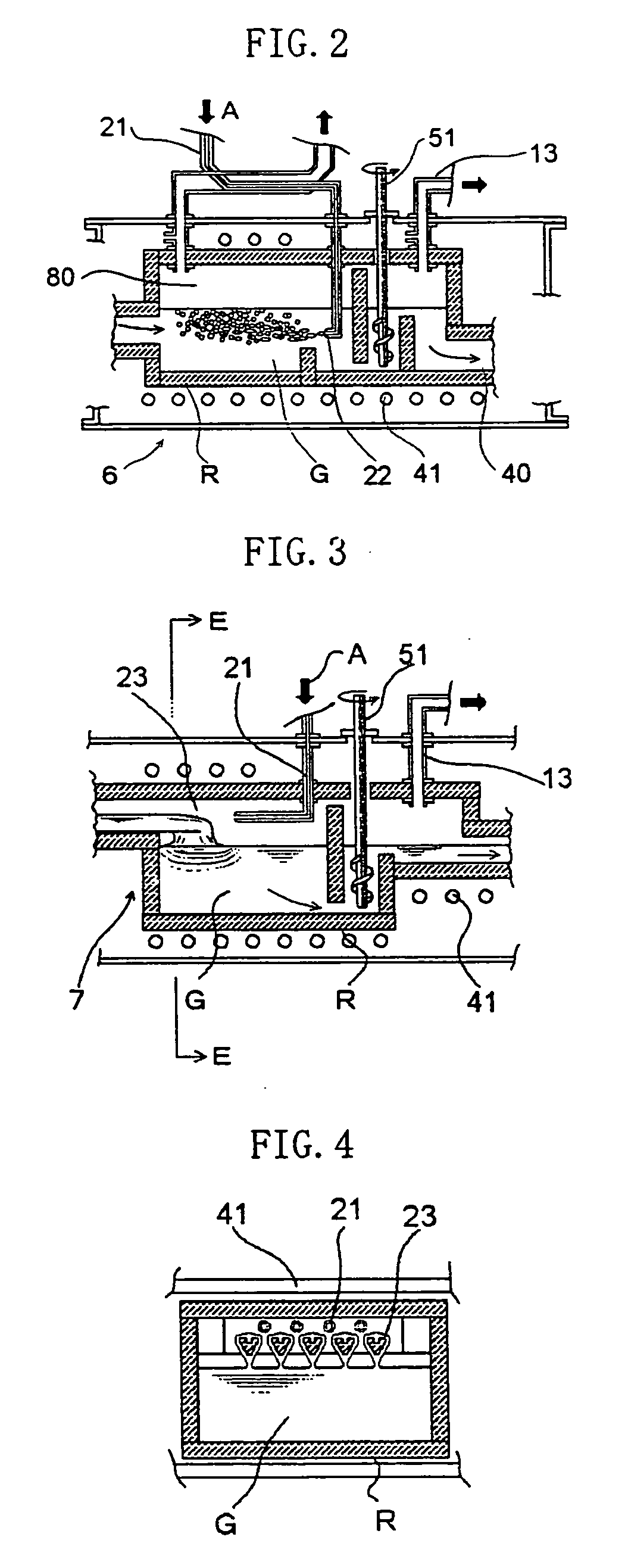
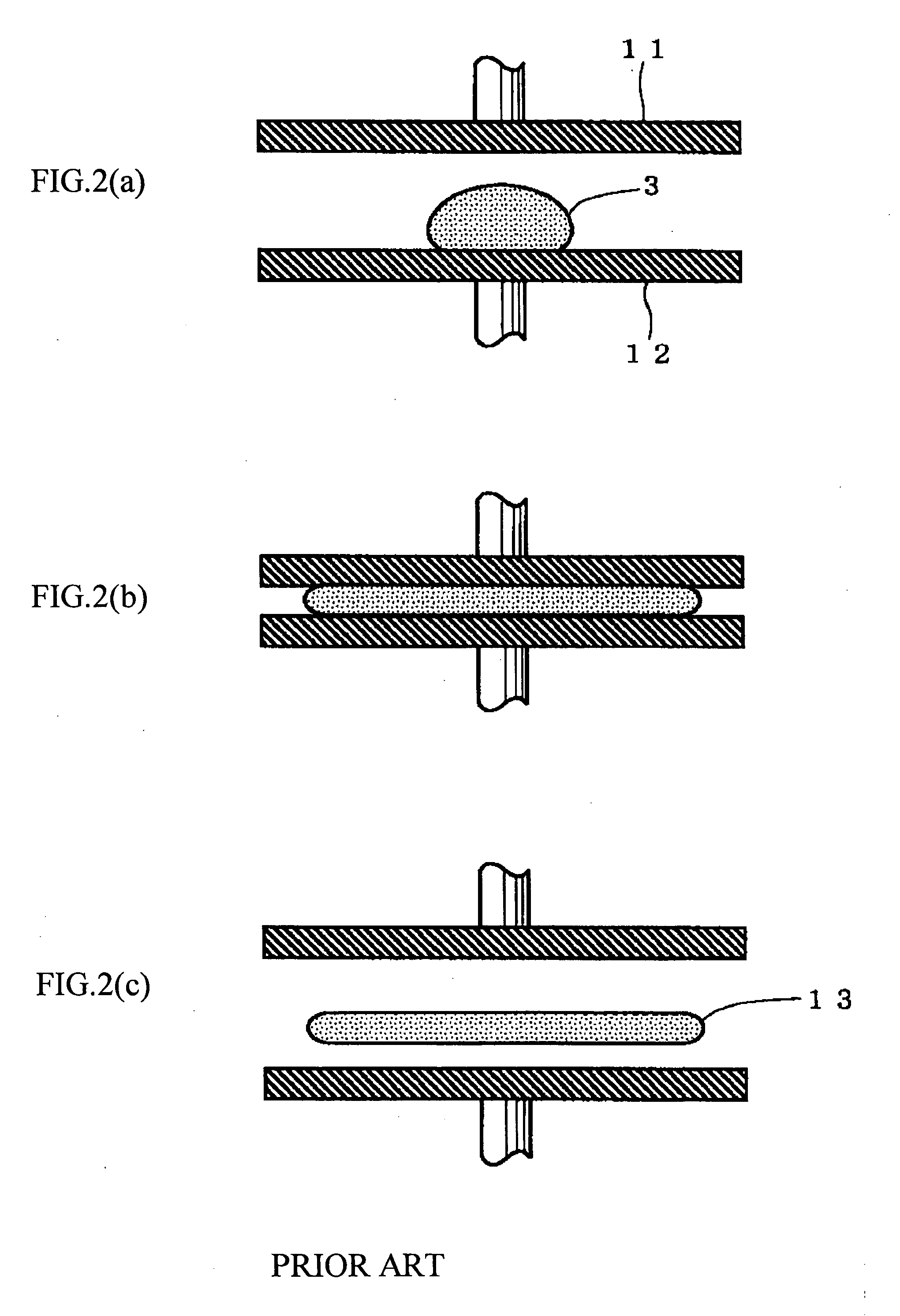
To provide cover glass for mobile terminals exhibiting high strength in a thin plate thickness state to enable reductions in thickness of apparatuses when inserted in the apparatuses, cover glass (1) for a mobile terminal of the invention is cover glass (1) that is obtained by forming a resist pattern on main surfaces of a plate-shaped glass substrate, then etching the glass substrate with an etchant using the resist pattern as a mask, and thereby cutting the glass substrate into a desired shape and that protects a display screen of the mobile terminal, where an edge face of the cover glass (1) is formed of a molten glass surface, and as surface roughness of the edge face, arithmetic mean roughness Ra is 10 nm or less.
Owner:HOYA CORP
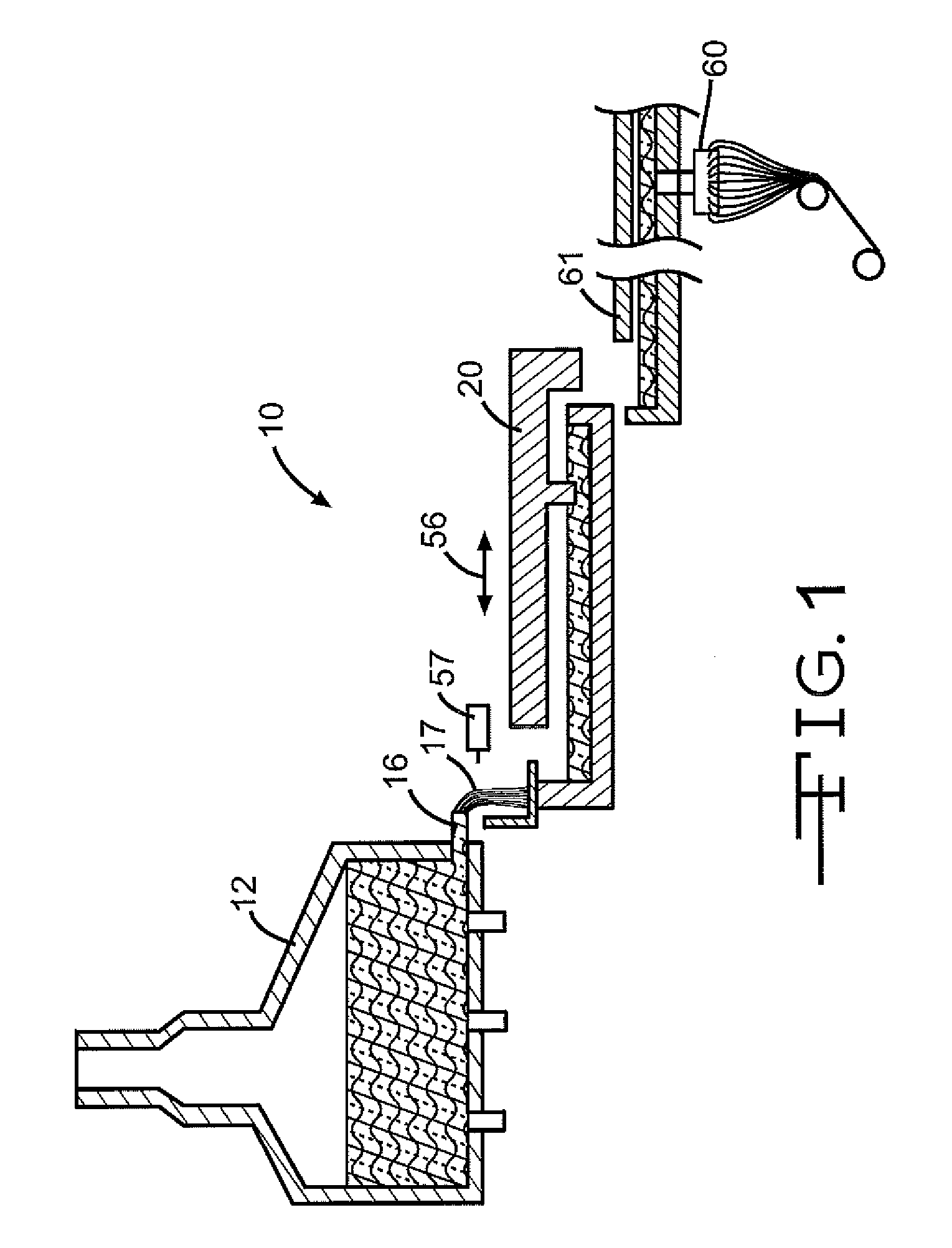
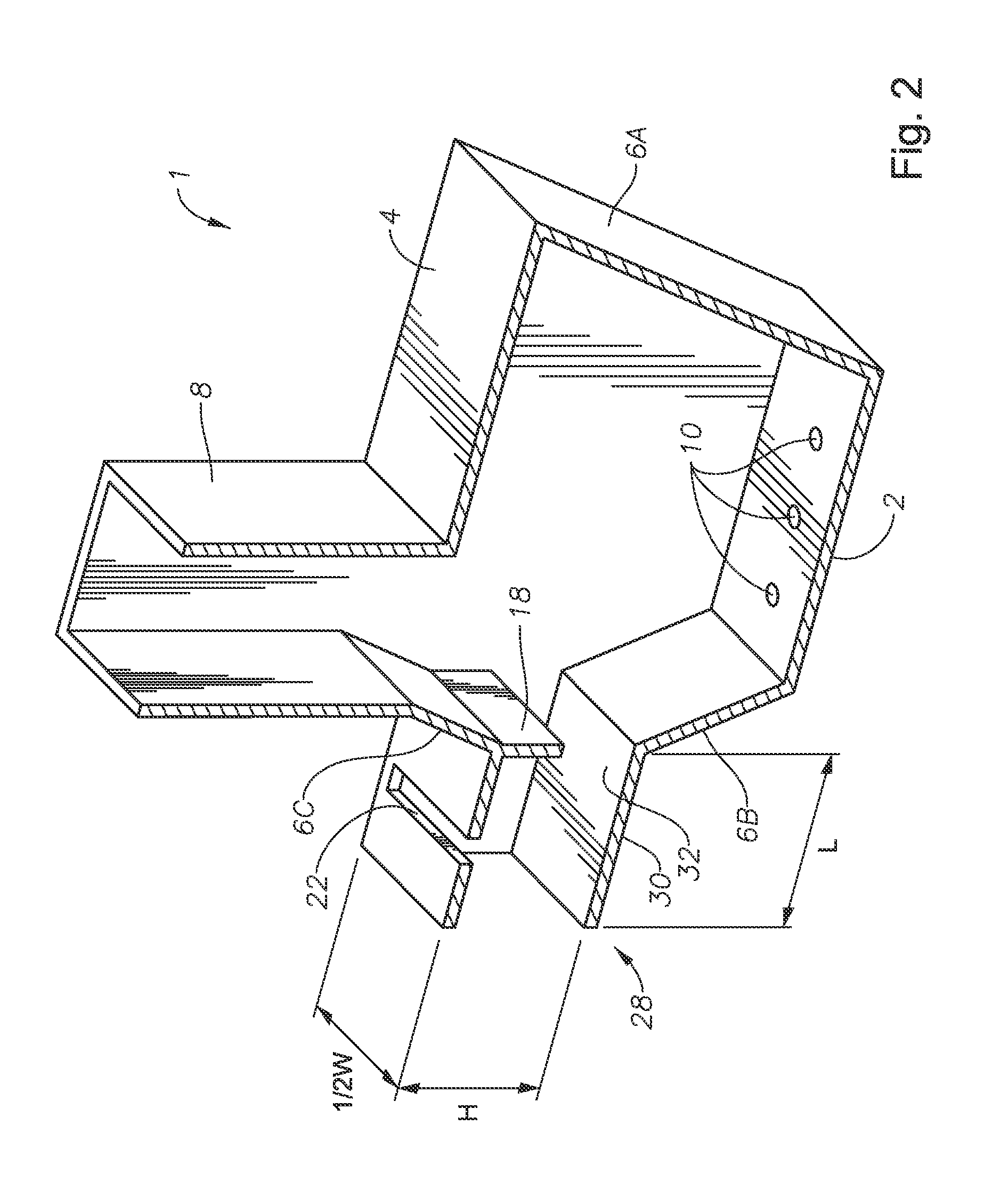
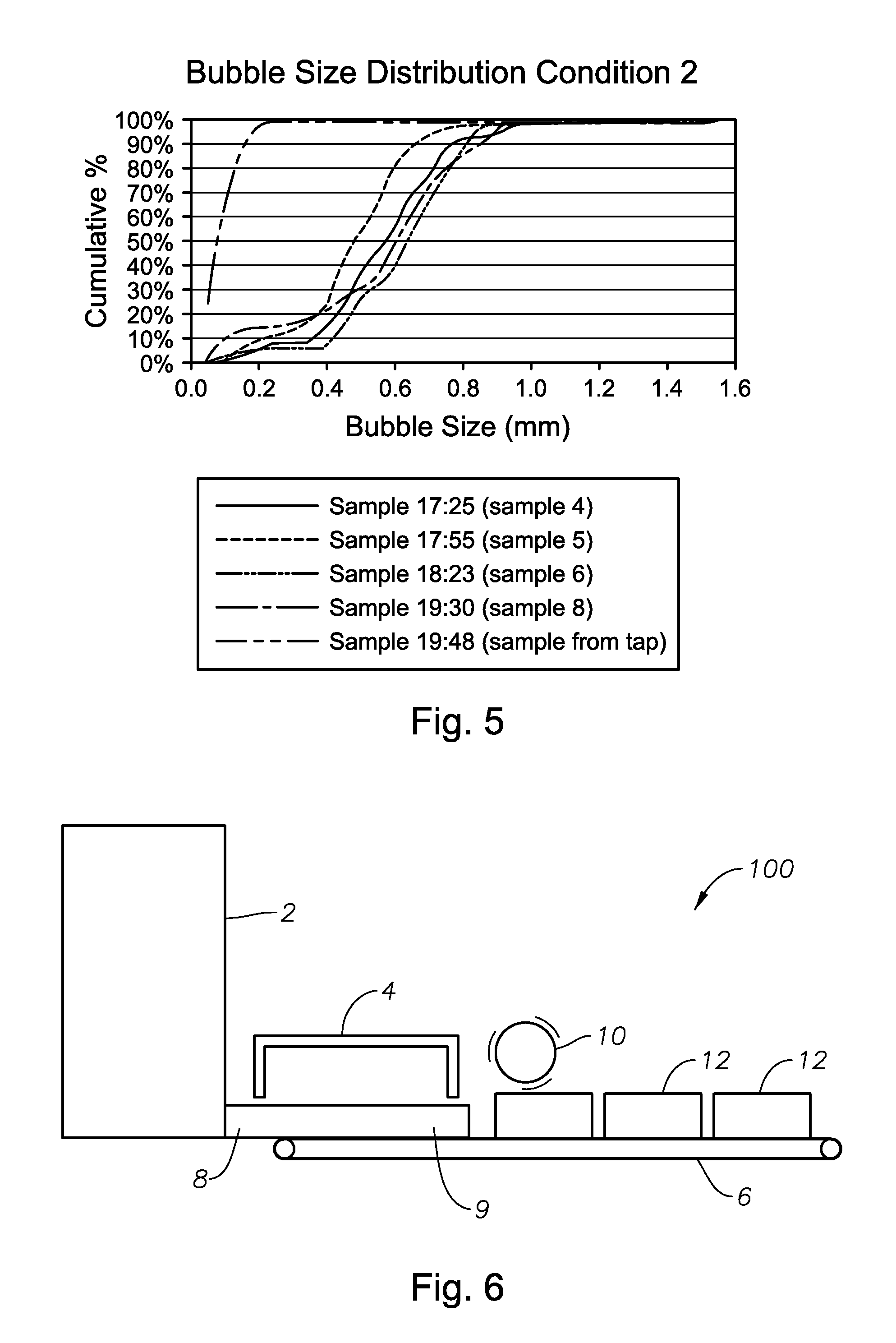
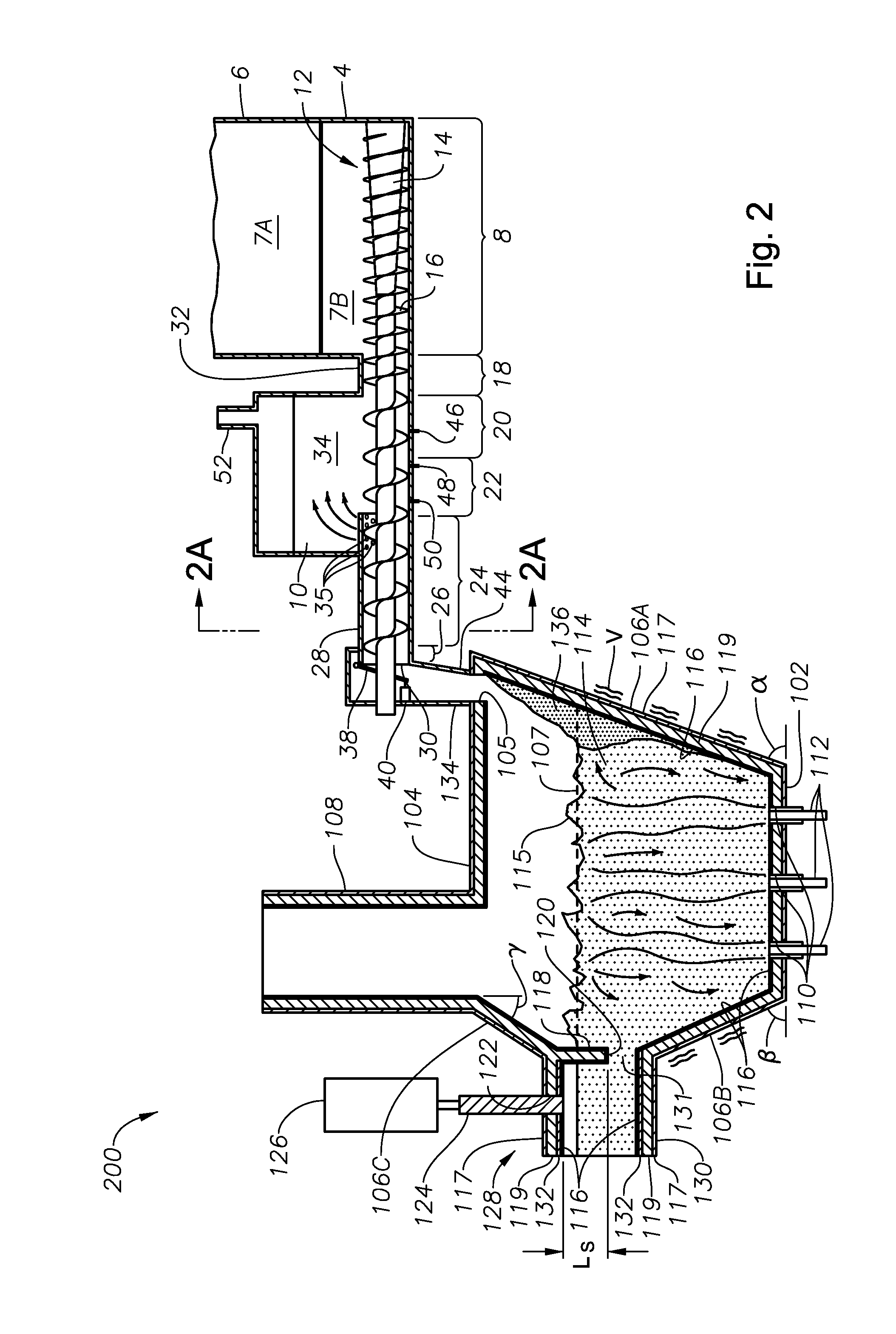
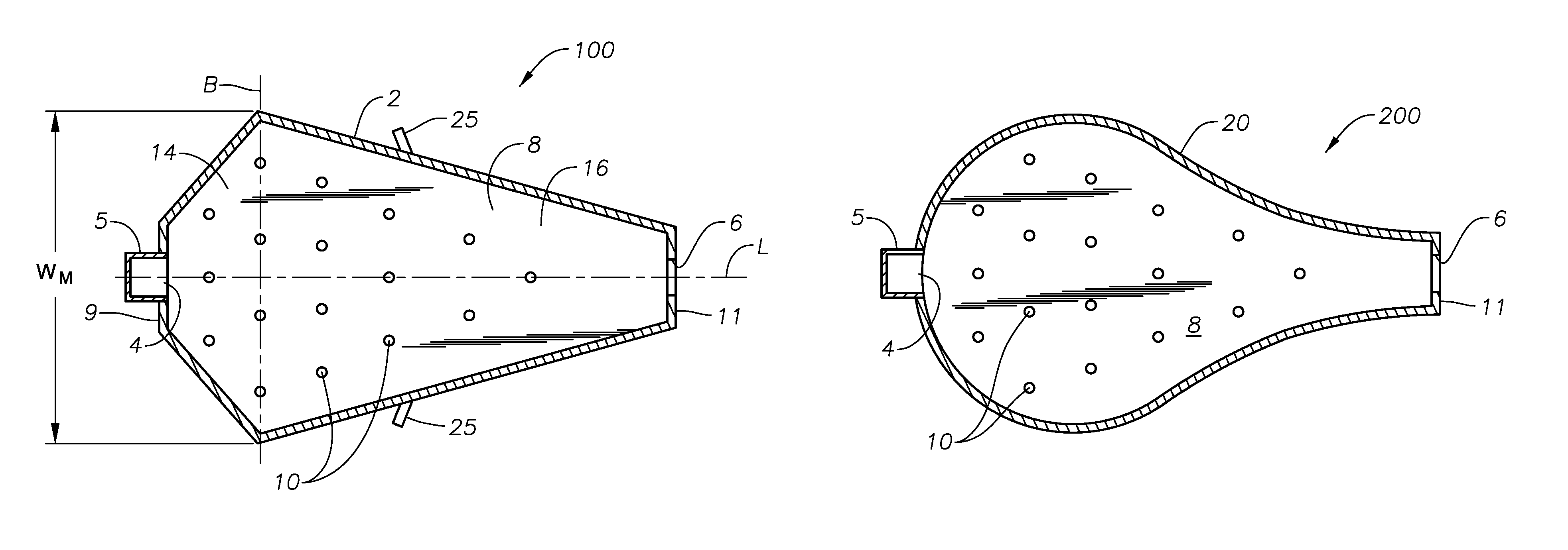
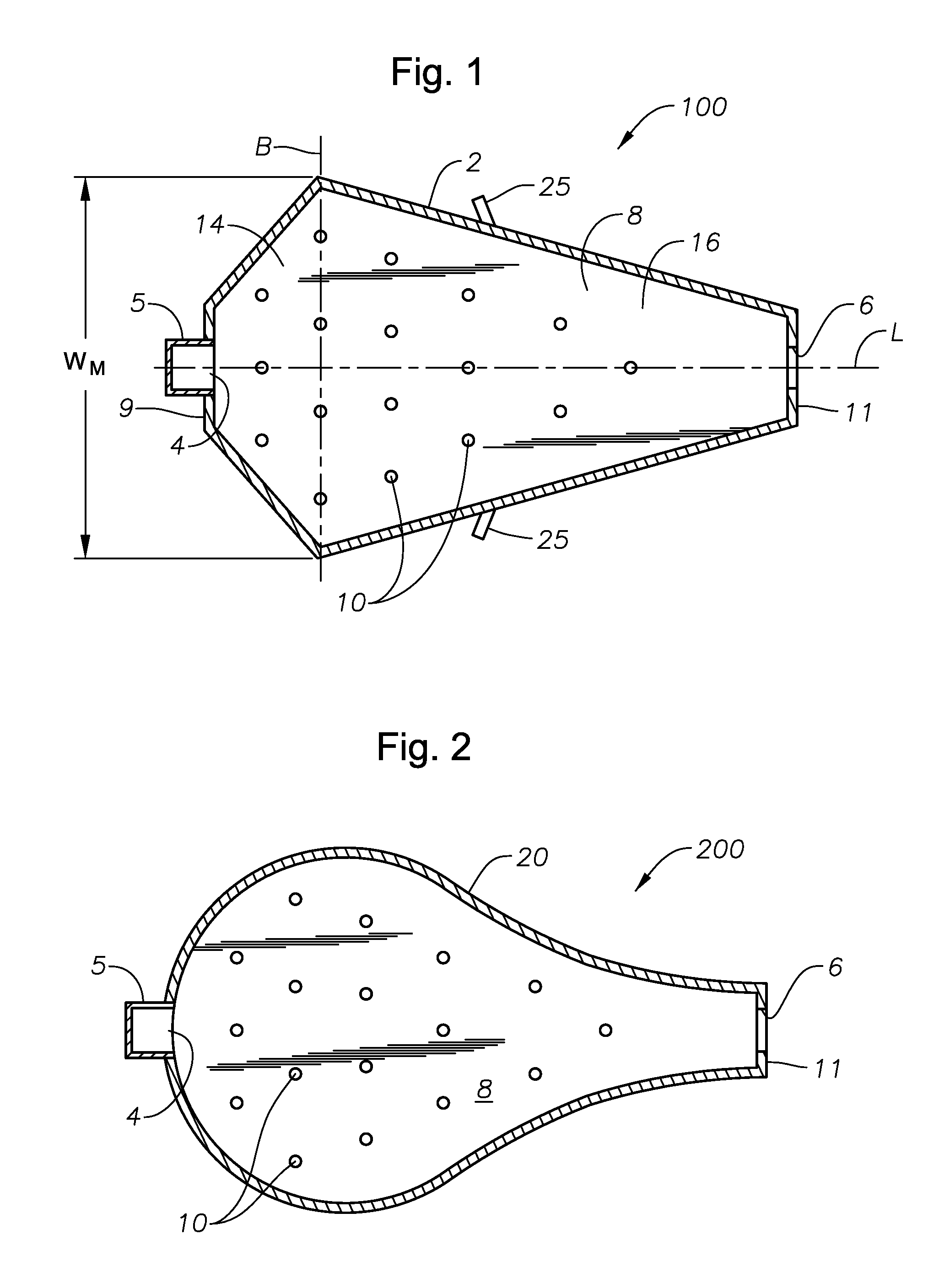
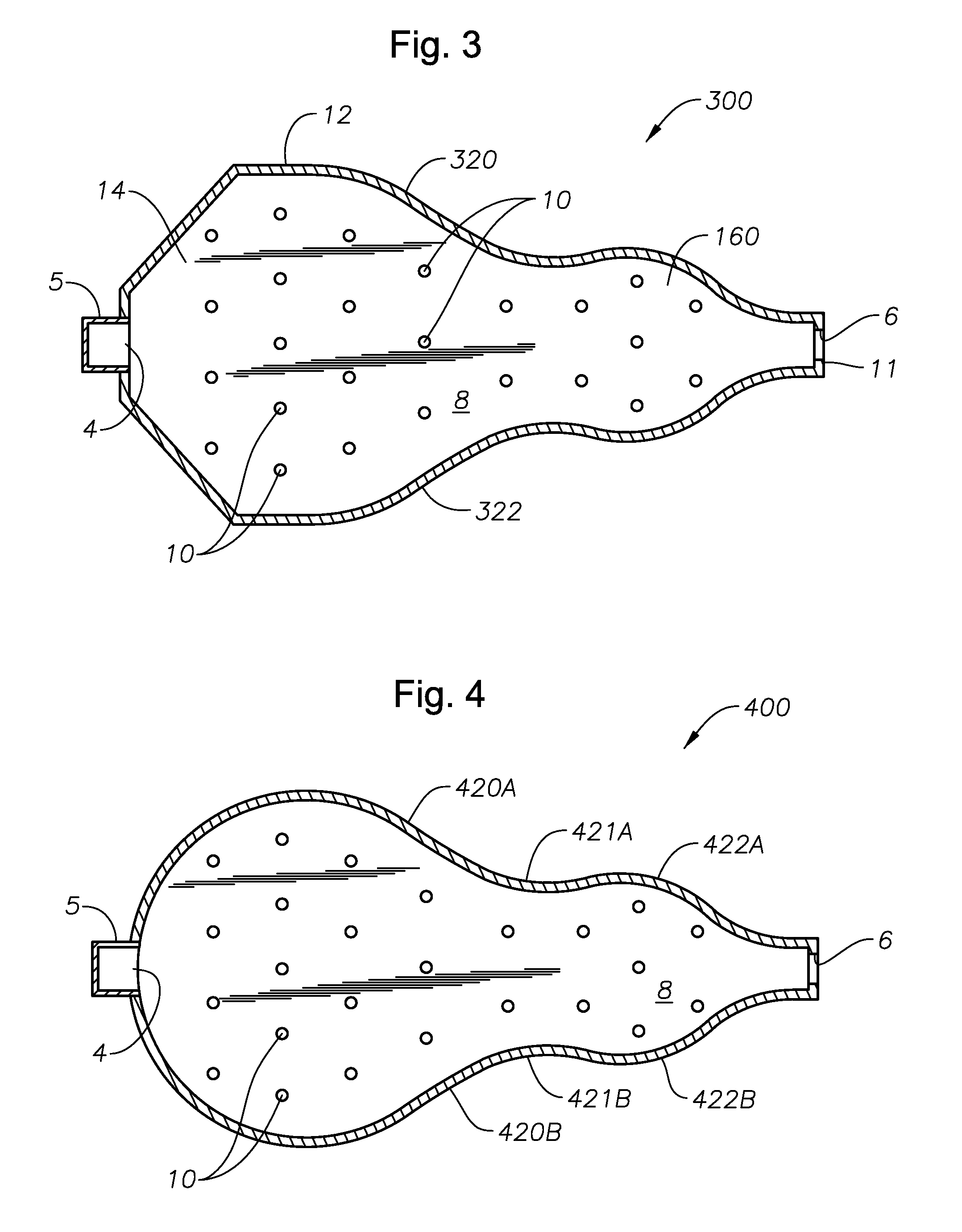
Panel-cooled submerged combustion melter geometry and methods of making molten glass
ActiveUS20110308280A1Reduce dead flow (stagnant) regionSmall sizePulsating combustionTank furnacesCombustorDirect combustion
A melter apparatus includes a floor, a ceiling, and a substantially vertical wall connecting the floor and ceiling at a perimeter of the floor and ceiling, a melting zone being defined by the floor, ceiling and wall, the melting zone having a feed inlet and a molten glass outlet positioned at opposing ends of the melting zone. The melting zone includes an expanding zone beginning at the inlet and extending to an intermediate location relative to the opposing ends, and a narrowing zone extending from the intermediate location to the outlet. One or more burners, at least some of which are positioned to direct combustion products into the melting zone under a level of molten glass in the zone, are also provided.
Owner:MANVILLE JOHNS
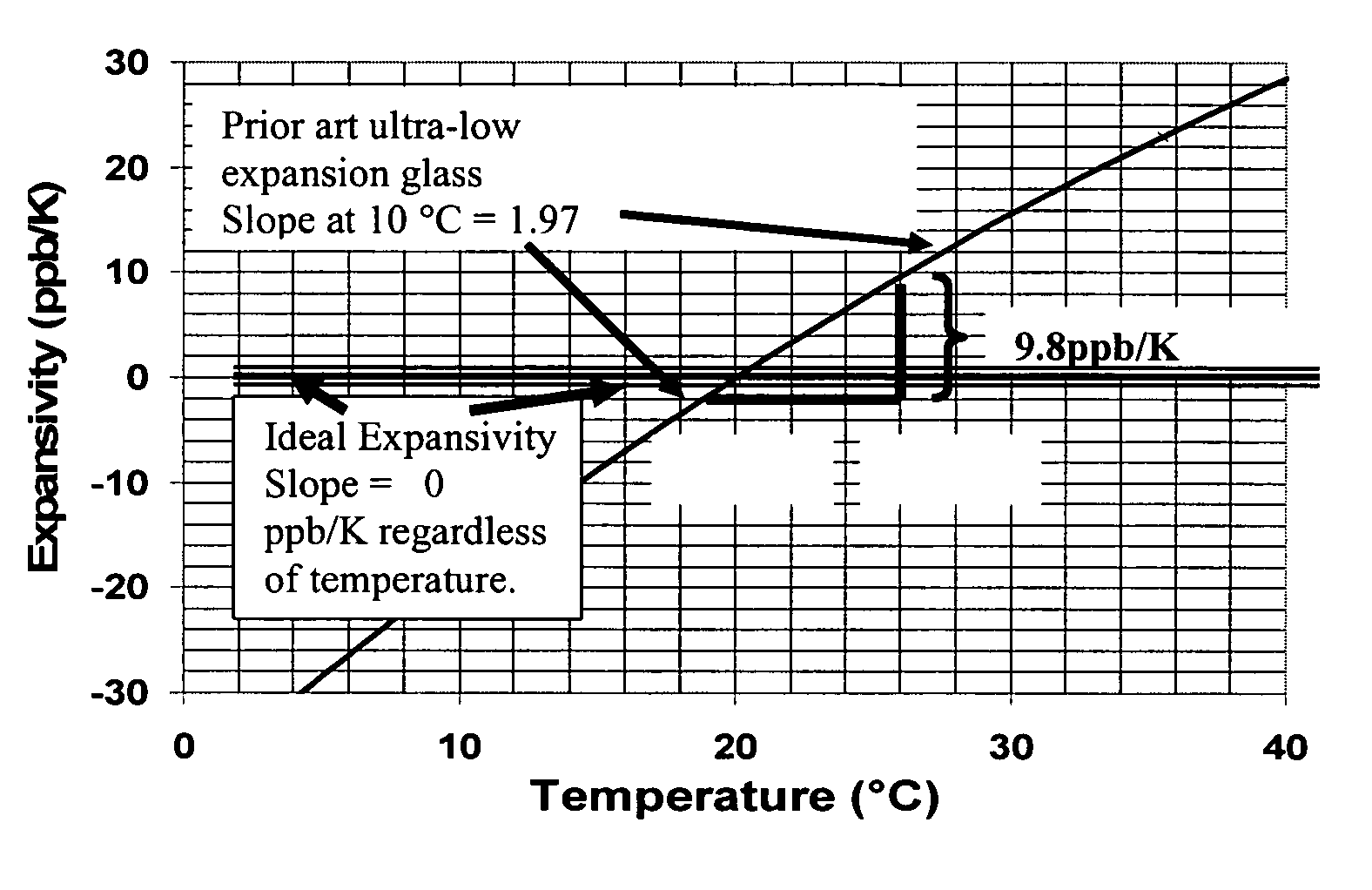
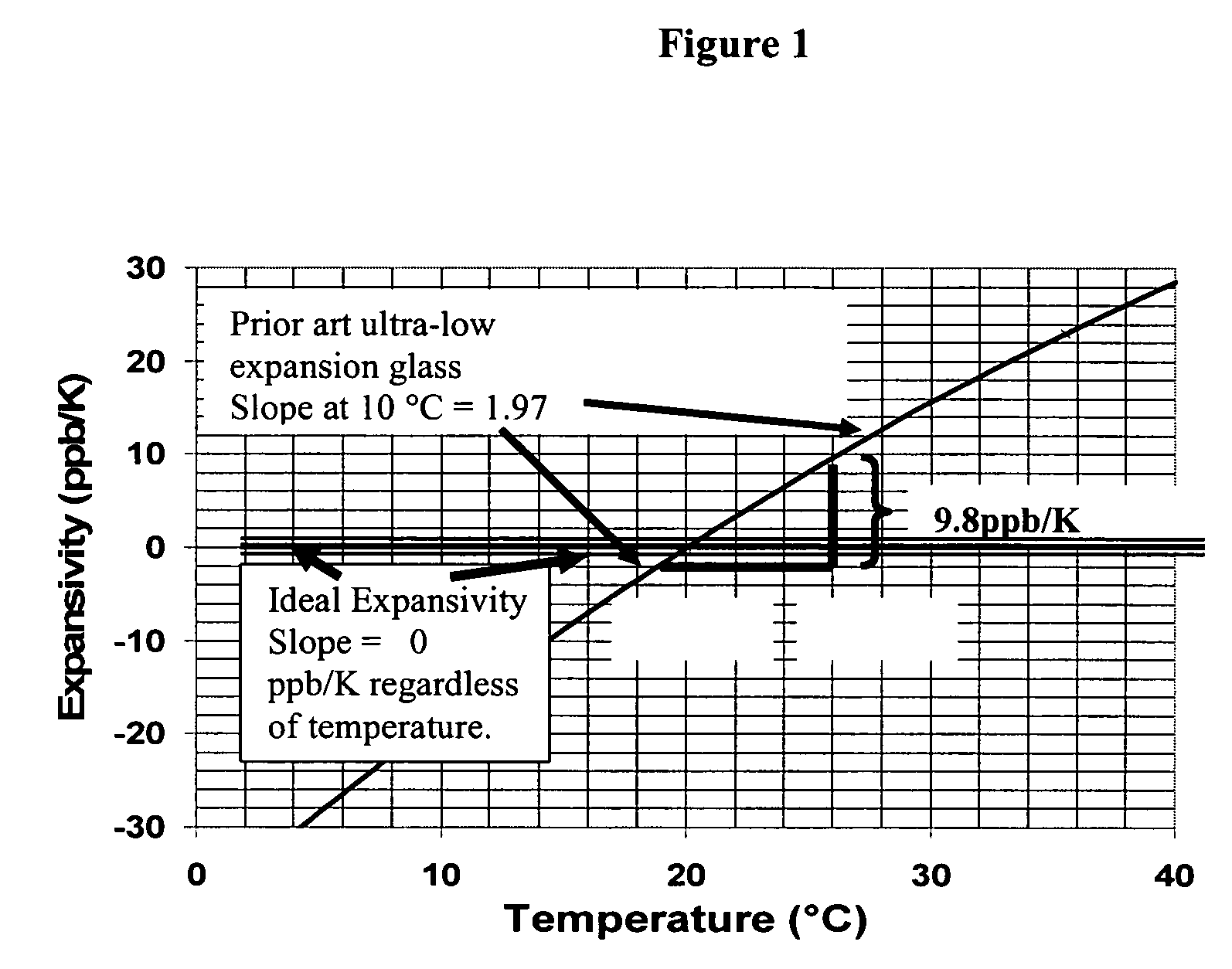
Adjusting expansivity in doped silica glasses
InactiveUS20060179879A1Low viscosityGlass shaping apparatusGlass deposition burnersDopantUltra low expansion glass
The invention is directed to ultra-low expansion glasses to which adjustments have been made to selected variables in order to improve the properties of the glasses, and particularly to lower the expansivity of the glasses. The glasses are titania-doped silica glasses. The variables being adjusted include an adjustment in β-OH level; an adjustment to the cooling rate of the molten glass material through the setting point; and the addition of selected dopants to impact the CTE behavior.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method and apparatus for drawing a low liquidus viscosity glass
InactiveUS20070130994A1Easy to understandGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusViscosityGlass sheet
A method of a drawing a glass ribbon from molten glass sheet via a downdraw process by creating a temperature drop across a thickness of the molten glass flowing over forming surfaces of a forming wedge. The forming wedge includes an electrically conductive material for heating the glass above the root.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of forming a glass melt
ActiveUS7454925B2Promote vigorous boilingReduce partial pressureCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusMolten glassExcessive Cooling
A method of forming a glass melt including heating a glass feed material in a first melting furnace to form a glass melt, flowing the glass melt into a second melting furnace through a refractory metal connecting tube, and further heating the glass melt in the second melting furnace. The refractory metal connecting tube is heated to prevent the molten glass from excessive cooling, and to ensure that the glass melt entering the second melting furnace is equal to or greater than the temperature of the glass melt in the second melting furnace. An apparatus for performing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
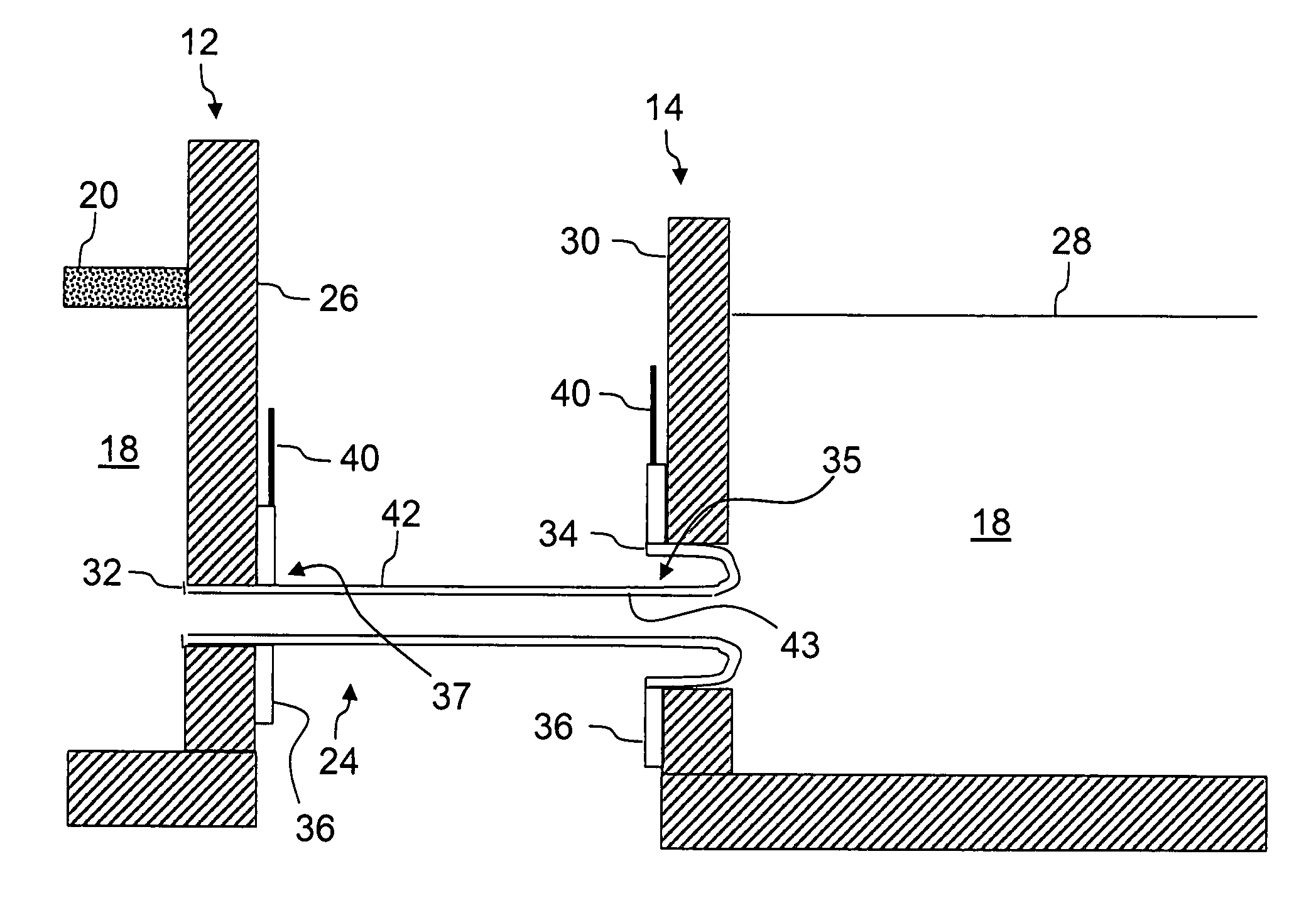
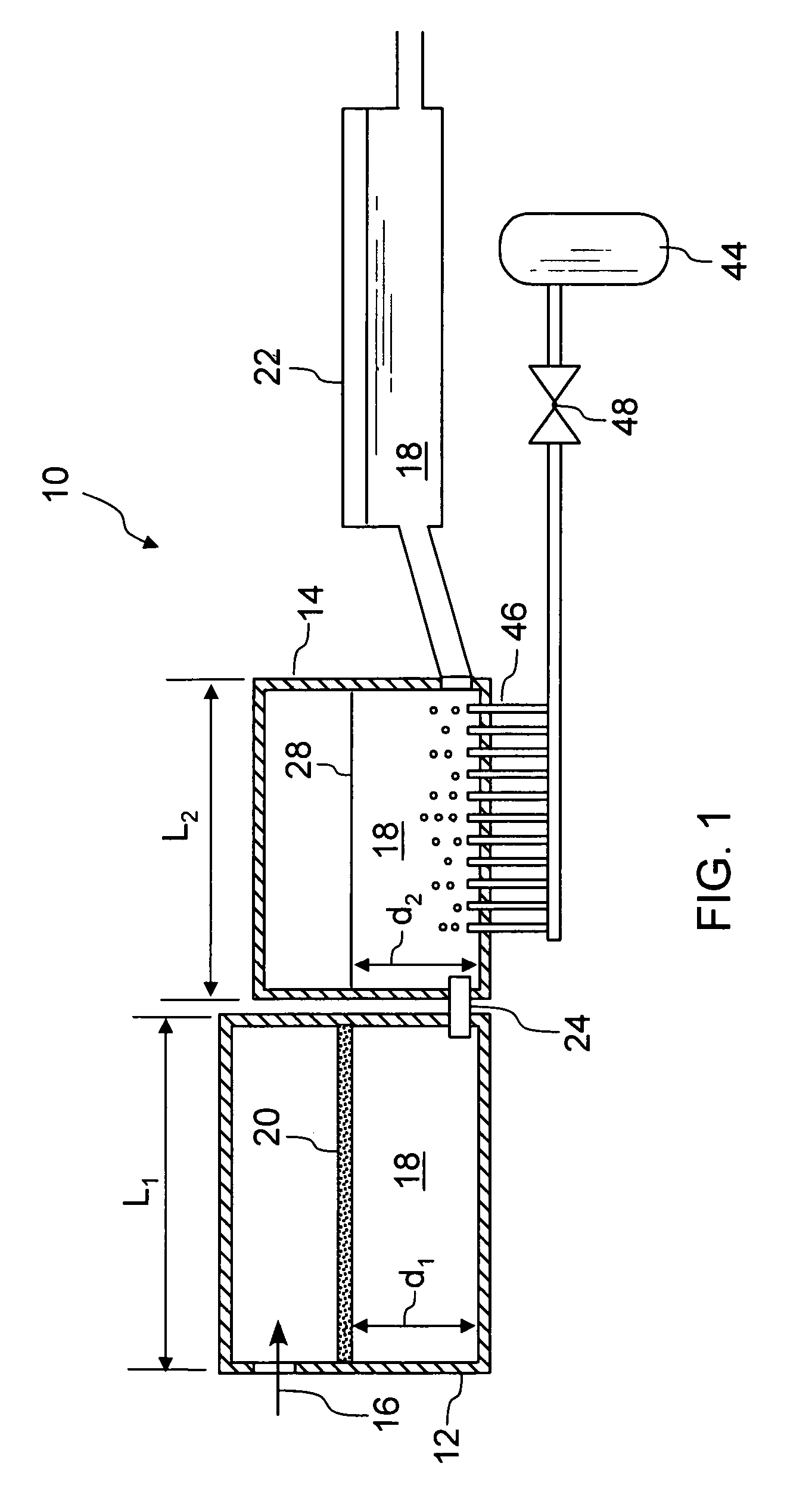
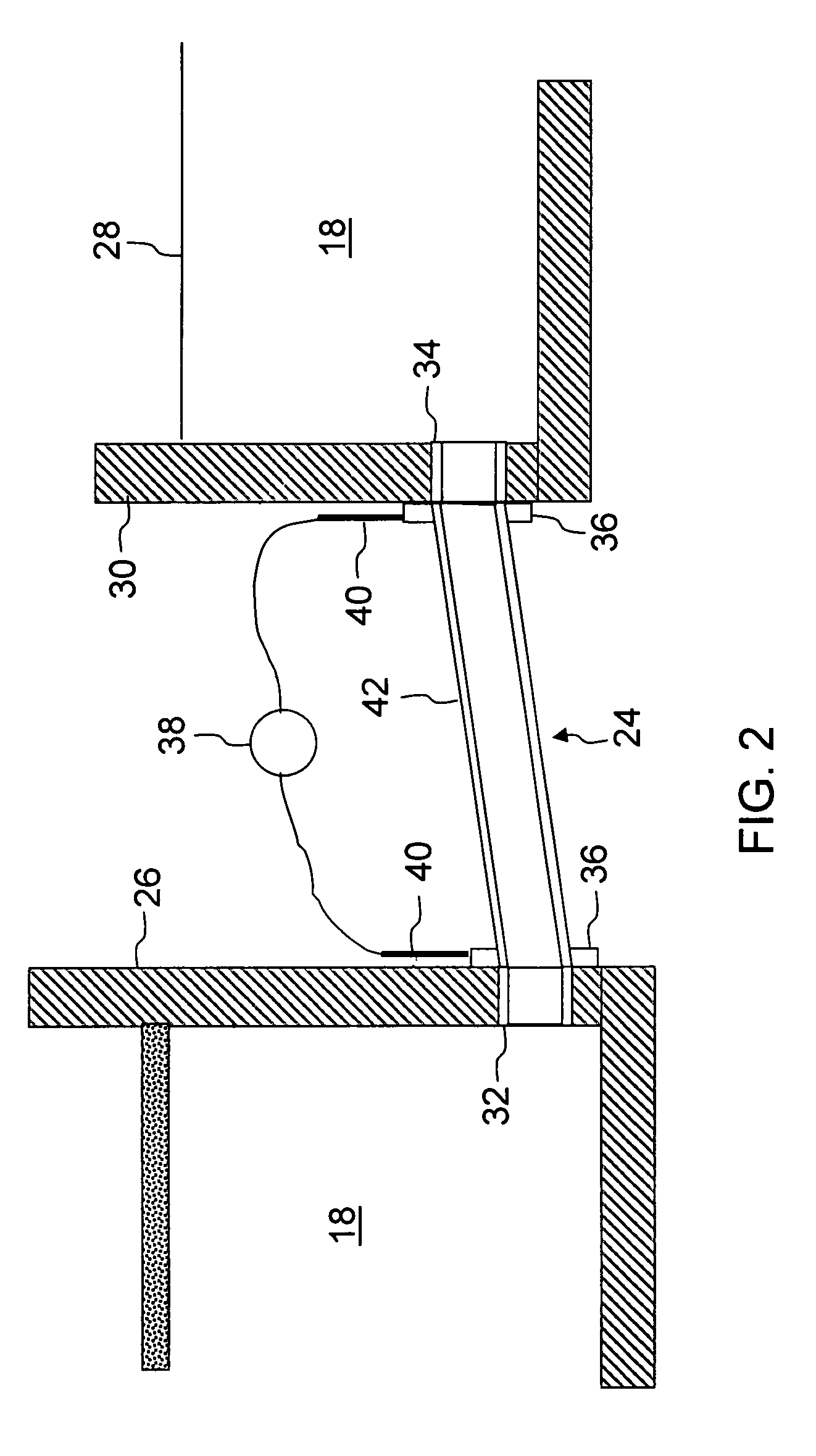
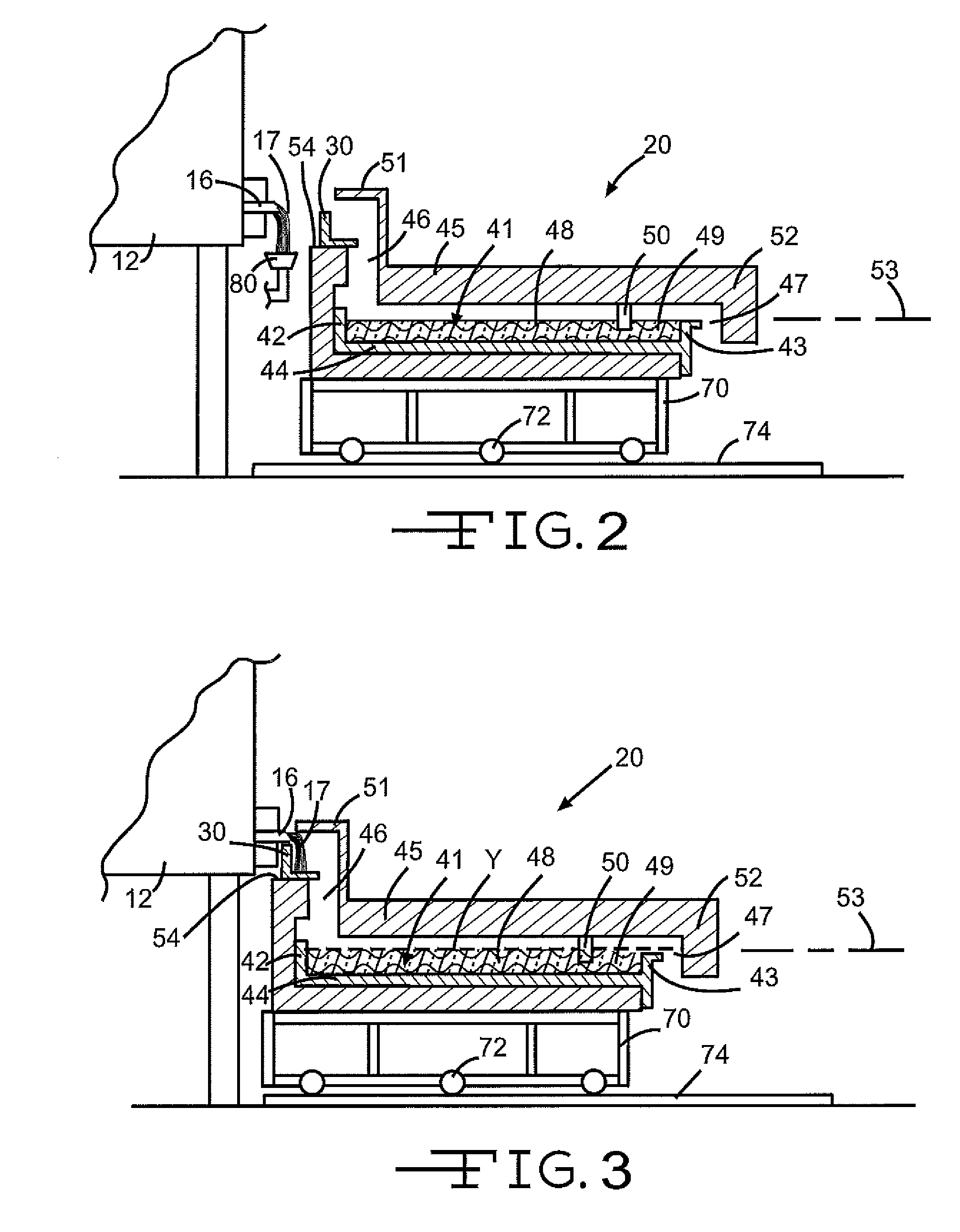
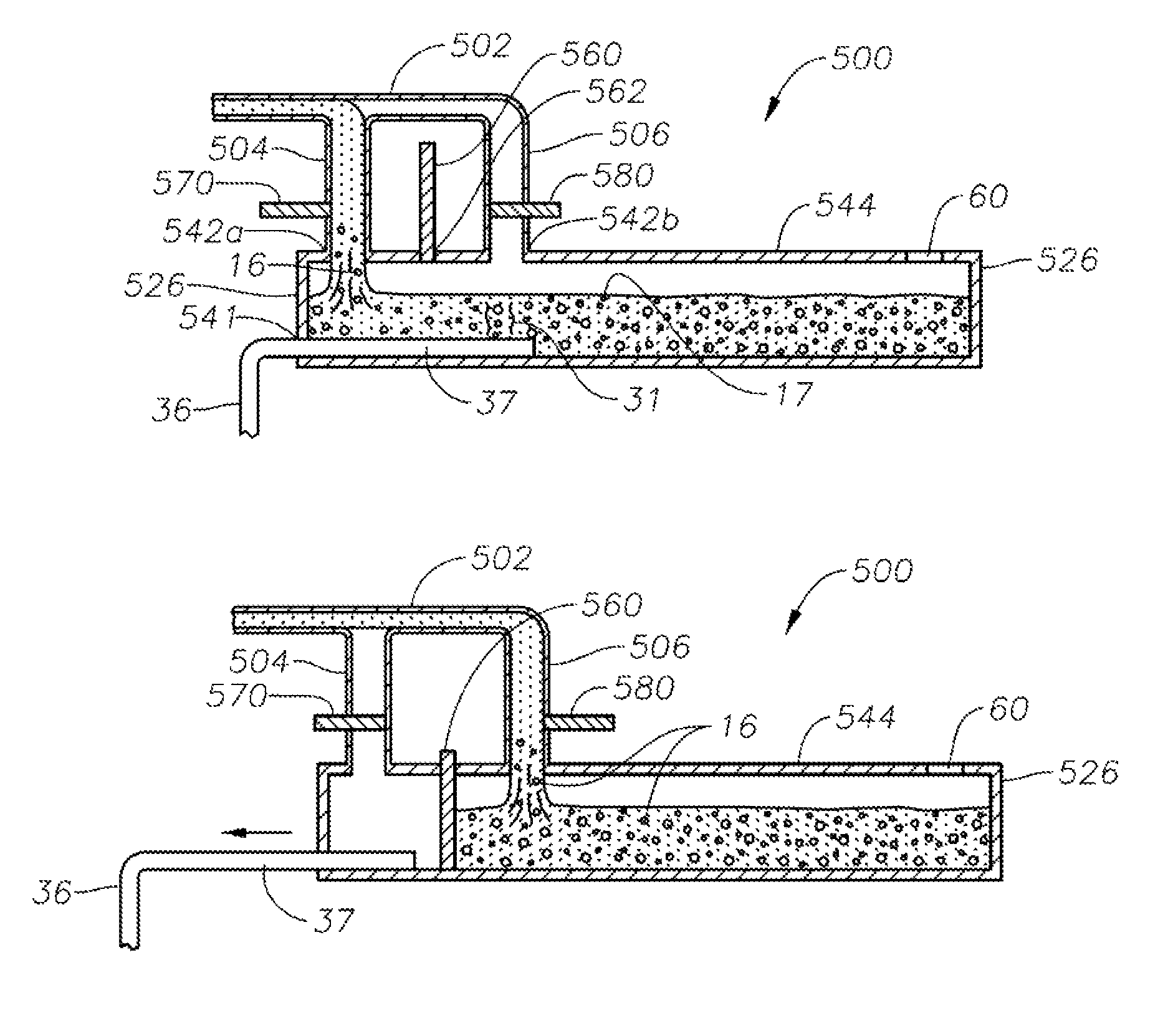
Molten glass delivery and refining system
Methods and apparatus for refining and delivering a supply of molten glass include melting a supply of glass in a melter and discharging a stream of molten glass. A refining section is provided to refine the molten glass discharged by the melter and to deliver the molten glass downstream to a glass forming apparatus. The refining section is mounted for movement into and out of contact with the stream of molten glass to connect and disconnect the glass forming apparatus with the stream of molten glass.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Submerged combustion melter comprising a melt exit structure designed to minimize impact of mechanical energy, and methods of making molten glass
A melter apparatus includes a floor, a ceiling, and a wall connecting the floor and ceiling at a perimeter of the floor and ceiling, a melting zone being defined by the floor, ceiling and wall, the melting zone having a feed inlet and a molten glass outlet positioned at opposing ends of the melting zone. Melter apparatus include an exit end having a melter exit structure for discharging turbulent molten glass formed by one or more submerged combustion burners, the melter exit structure fluidly and mechanically connecting the melter vessel to a molten glass conditioning channel. The melter exit structure includes a fluid-cooled transition channel configured to form a frozen glass layer or highly viscous glass layer, or combination thereof, on inner surfaces of the fluid-cooled transition channel and thus protect the melter exit structure from mechanical energy imparted from the melter vessel to the melter exit structure.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Methods of using a submerged combustion melter to produce glass products
A method comprises flowing an oxidant and a fuel into a submerged combustion burner in a glass tank furnace, the glass tank furnace receiving a feed of glass forming material and producing molten glass, the burner and furnace comprising a melting system. The melting system has a variable system vibration and / or oscillation due to the nature of submerged combustion. One method includes predicting a value of at least one property, such as viscosity, of the molten glass using the variable system vibration and / or oscillation.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Melting of glass
InactiveUS6715319B2Reduce the presence of air bubblesGlass furnace apparatusGlass rolling apparatusFlat glassMaterials science
A method of producing flat glass in which foam which appears on the surface of molten glass melted using oxy-fuel burners is dispersed by directing a diffuse, luminescent flame onto the surface of the glass carrying the foam.
Owner:PILKINGTON PLC
Cnt-infused glass fiber materials and process therefor
A composition includes a carbon nanotube (CNT)-infused glass fiber material, which includes a glass fiber material of spoolable dimensions and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) bonded to it. The CNTs are uniform in length and distribution. A continuous CNT infusion process includes: (a) disposing a carbon-nanotube forming catalyst on a surface of a glass fiber material of spoolable dimensions; and (b) synthesizing carbon nanotubes on the glass fiber material, thereby forming a carbon nanotube-infused glass fiber material. The continuous CNT infusion process optionally includes extruding a glass fiber material from a glass melt or removing sizing material from a pre-fabricated glass fiber material.
Owner:APPL NANOSTRUCTURED SOLUTIONS LLC
Downward Firing Oxygen-Fuel Burners for Glass Melting Furnaces
InactiveUS20100300153A1Maximize convective transferMaximize radiant heat transferCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusCombustorEngineering
This invention relates to a glass melting furnace with downward firing oxygen-fuel burners placed in the breast walls of the combustion space and adjacent to the skew block. The downward firing oxygen-fuel burner may be placed at an angle so that the oxygen-fuel flame from the downward firing oxygen-fuel burner impinges on the upper surface of the glass bath. The placement and angle of the downward firing oxygen-fuel burner may maximize the amount of heat transferred to the batch cover or the molten glass, ensure the formation of high quality glass products, and protect the integrity of the downward firing oxygen-fuel burners and the glass melting furnace.
Owner:ZHANG ZHIFA +1
Systems and methods for making foamed glass using submerged combustion
ActiveUS20130086944A1High densityLow densityRibbon machinesGlass furnace apparatusCombustion systemDownstream processing
Submerged combustion systems and methods of use to produce foamed glass. One system includes a submerged combustion melter having an outlet, the melter configured to produce an initial foamy molten glass having a density and comprising bubbles filled primarily with combustion product gases. The initial foamy molten glass is deposited directly onto or into a transport apparatus that transports the initial foamy molten glass to a downstream processing apparatus. An intermediate stage may be included between the melter and the transport apparatus. One intermediate stage is a channel that includes gas injectors. Another intermediate stage is a channel that produces an upper flow of a less dense glass and a relatively more dense glass lower flow. The upper flow may be processed into foamed glass products, while the more dense flow may be processed into dense glass products.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Glass substrate for display and display
ActiveUS20080206494A1Light weightImprove refining effectLiquid crystal compositionsAbsorbent padsDisplay deviceMetal
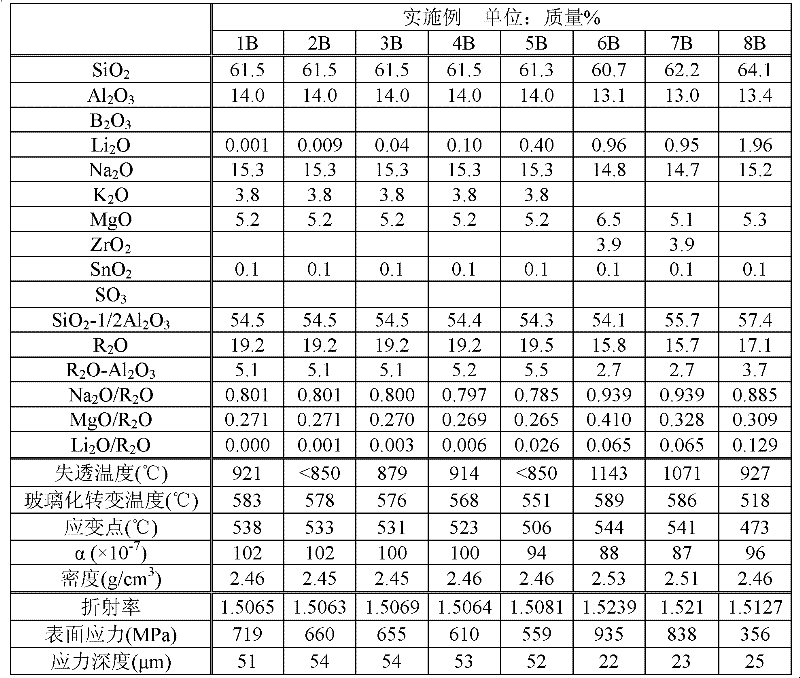
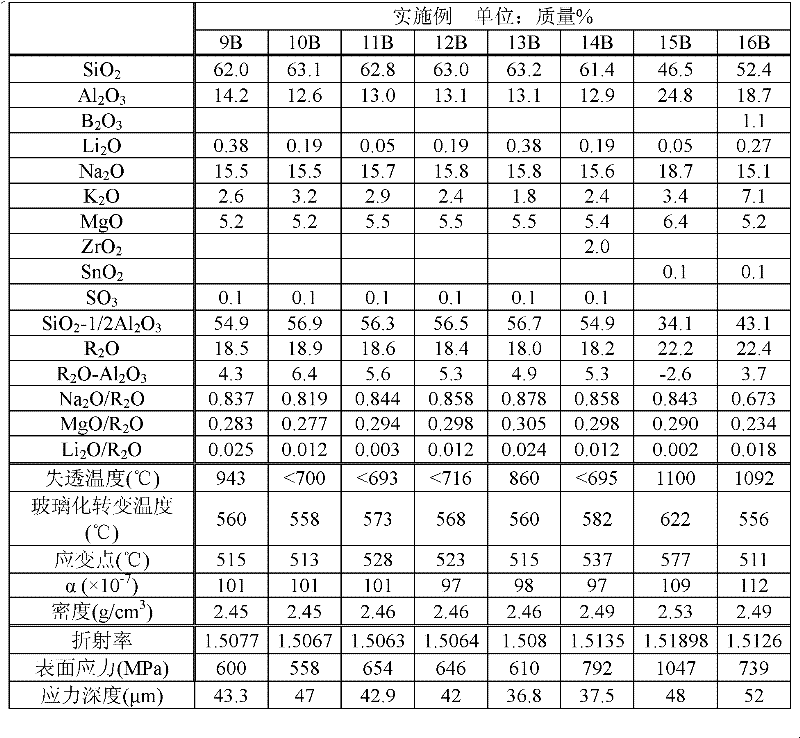
A glass substrate for a display, which is formed of a glass having a light weight and having high refinability with decreasing environmental burdens, the glass comprising, by mass %, 50 to 70% of SiO2, 5 to 18% of B2O3, 10 to 25% of Al2O3, 0 to 10% of MgO, 0 to 20% of CaO, 0 to 20% of SrO, 0 to 10% of BaO, 5 to 20% of RO (in which R is at least one member selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ca, Sr and Ba), and over 0.20% but not more than 2.0% of R′2O (in which R′ is at least one member selected from the group consisting of Li, Na and K), and containing, by mass %, 0.05 to 1.5% of oxide of metal that changes in valence number in a molten glass, and substantially containing none of As2O3, Sb2O3 and PbO.
Owner:AVANSTRATE INC
Submerged combustion melters having an extended treatment zone and methods of producing molten glass
A submerged combustion melter includes a floor, a roof, and a sidewall structure connecting the floor and roof defining an internal space. A first portion of the internal space defines a melting zone, and a second portion defines a fining zone immediately downstream of the melting zone. One or more combustion burners in either the floor, roof, the sidewall structure, or any combination of these, are configured to emit the combustion gases from a position under a level of, and positioned to transfer heat to and produce, a turbulent molten mass of glass containing bubbles in the melting zone. The fining zone is devoid of combustion burners or other apparatus or components that would increase turbulence above that in the melting zone. The melter may include a treating zone that stabilizes or destabilizes bubbles and / or foam. Processes of using the melters are a feature of the disclosure.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Method of producing glass substrate for information recording medium
InactiveUS6332338B1Avoid deformationIncrease speedGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusProduction ratePoise
Disclosed is a process for producing a glass substrate for an information recording medium by press-shaping a molten glass which gives a glass containing 0.1 to 30 mol % of TiO2, 1 to 45 mol % of CaO, 5 to 40 mol % of total of MgO and the above CaO, 3 to 30 mol % of total of Na2O and Li2O, 0 to 15 mol % of Al2O3 and 35 to 65 mol % of SiO2 and having properties of a liquidus temperature of 1,360° C. or lower and a viscosity of at least 10 poise in a shaping-allowable temperature range, or by preparing a preform formed of a glass which contains 0.1 to 30 mol % of TiO2, 1 to 45 mol % of CaO, 5 to 40 mol % of total of MgO and the above CaO, 3 to 30 mol % of total of Na2O and Li2O, 0 to 15 mol % of Al2O3 and 35 to 65 mol % of SiO2 and has properties of a liquidus temperature of 1,360° C. or lower and shaping the preform in the form of a disc by a re-heat pressing method. According to the above process, there can be mass-produced, with high productivity, high-quality glass substrates to be used for information recording media such as a magnetic disc, an optical disc, a magneto-optic disc, and the like.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Process for producing glass substrate and glass substrate
ActiveUS20090226733A1Easy to distortReadily warpedGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusBand shapeMolten glass
Provided are a process for producing a glass substrate usable for low-temperature p-SiTFT substrates directly in accordance with a down draw method, and the glass substrate obtained by the process. The process for producing a glass substrate includes a forming step of forming a molten glass into a ribbon shape in accordance with a down draw method, an annealing step of annealing the glass ribbon, and a cutting step of cutting the glass ribbon to give a glass substrate, in which, in the annealing step, an average cooling rate from the annealing point to the (annealing point −50° C.) is lower than an average cooling rate from the (annealing point +100° C.) to the annealing point.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
Glass substrate for magnetic disk and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20110159321A1Good surface irregularity accuracyImprove impact resistanceMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageFlat glassSurface roughness
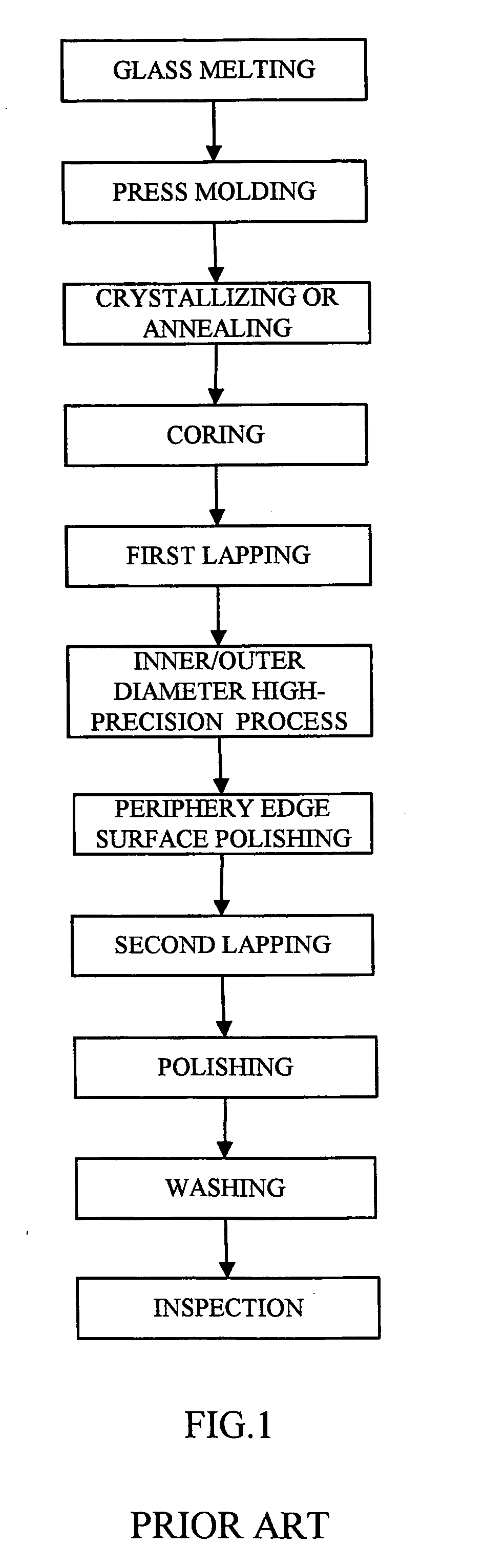
The present invention provides a method for efficiently manufacturing a glass substrate for magnetic disk having good accuracy of a surface irregularity and an impact resistance. The method includes the steps of: performing press forming to molten glass to prepare a sheet glass material, the sheet glass material having a roughness of the principal surface of 0.01 μm or less and target flatness of a glass substrate for magnetic disk; chemically strengthening the sheet glass material by dipping the sheet glass material in a chemically strengthening salt, thereby preparing a disk substrate; polishing the principal surfaces of the disk substrate. A thickness of the sheet glass material prepared in the press forming step is larger than a target thickness of the glass substrate for magnetic disk by a polishing quantity of the principal surface polishing step.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Processes for producing molten glasses from glass batches using turbulent submerged combustion melting, and systems for carrying out such processes
ActiveUS20140007622A1Reduce and eliminate batch lossCharging furnaceTank furnacesParticulatesCombustor
Processes and systems for producing molten glass using submerged combustion melters, including densifying an initial composition comprising vitrifiable particulate solids and interstitial gas to form a densified composition comprising the solids by removing a portion of the interstitial gas from the composition. The initial composition is passed from an initial environment having a first pressure through a second environment having a second pressure higher than the first pressure to form a composition being densified. Any fugitive particulate solids escaping from the composition being densified are captured and recombined with the composition being densified to form the densified composition. The densified composition is fed into a feed inlet of a turbulent melting zone of a melter vessel and converted into turbulent molten material using at least one submerged combustion burner in the turbulent melting zone.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Jade-type glass-ceramic and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a jade-type glass-ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The jade-type glass-ceramic contains a main crystal phase and can also contain a secondary crystal phase, wherein the maximum crystallite dimension of the secondary crystal phase is equal to or smaller than visible wavelength, the jade-type glass-ceramic contains the following components in percentage by weight: 45.0-75.0% of SiO2, 1.0-25.0% of Al2O3, 0-20.0% of alkaline earth metal oxide, 3.0-15.0% of alkali metal oxide, 0-4.0% of TiO2, 0-2.5% of ZrO2, 0-8.0% of F and the balance of flux and clarifier. The preparation method of the jade-type glass-ceramic comprises the steps that the main raw materials and the auxiliary materials are mixed uniformly and then are melted at high temperature to form molten glass, then the molten glass is thermally treated after being cooled and molded so as to form an organization structure beneficial to the penetration of the visible light part in molten glass, and after thermal treatment, the glass-ceramic is in a semitransparent neftdegil shape and becomes a jade-type glass-ceramic. The jade-type glass-ceramic has delicate texture, is translucent, can be widely used as a decorative plate, and can also be carved into handicrafts and prepared into tableware and sanitary ware.
Owner:香港福山实业有限公司
Panel-cooled submerged combustion melter geometry and methods of making molten glass
ActiveUS8769992B2Small sizeAllows more flexibility in the shape of the melterPulsating combustionGlass furnace apparatusThermodynamicsCombustor
A melter apparatus includes a floor, a ceiling, and a substantially vertical wall connecting the floor and ceiling at a perimeter of the floor and ceiling, a melting zone being defined by the floor, ceiling and wall, the melting zone having a feed inlet and a molten glass outlet positioned at opposing ends of the melting zone. The melting zone includes an expanding zone beginning at the inlet and extending to an intermediate location relative to the opposing ends, and a narrowing zone extending from the intermediate location to the outlet. One or more burners, at least some of which are positioned to direct combustion products into the melting zone under a level of molten glass in the zone, are also provided.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Process for producing glass/resin composite
InactiveUS20100192634A1High mechanical strengthReduce the possibilityLayered product treatmentLaminationCutting glassPolyresin
To provide a process for producing a glass / resin composite having a sufficient transportability, handling efficiency and processability, even though the thickness of the glass is very thin, without impairing excellent properties of glass.A process for producing a glass / resin composite, which comprises forming molten glass into a glass ribbon and forming a resin layer on at least one surface of the glass ribbon is provided. The resin layer is preferably formed by bonding to a glass ribbon, applying a heat melt resin or applying a curable resin. Further, a process for producing a glass / resin composite, wherein a cut glass substrate is bonded on a continuously supplied resin film is provided.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Overflow downdrawn glass forming method and apparatus
InactiveUS6889526B2Reduce unevennessEfficient degradationGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusThermal creepEngineering
Owner:CORNING INC
Process for the production of precision press-molding preform and process for the production of optical element
InactiveUS20050188724A1Highly producedReliably producedGlass drawing apparatusGlass pressing apparatusSurface layerOptical glass
A process for producing a precision press-molding preform having a predetermined weight from a molten glass, wherein the molten glass is shaped into a glass gob and the above glass gob is etched to remove a surface layer of the glass gob to produce the precision press-molding preform formed of an optical glass having said weight, and further wherein said surface layer has a thickness of 0.5 μm or more.
Owner:HOYA CORP
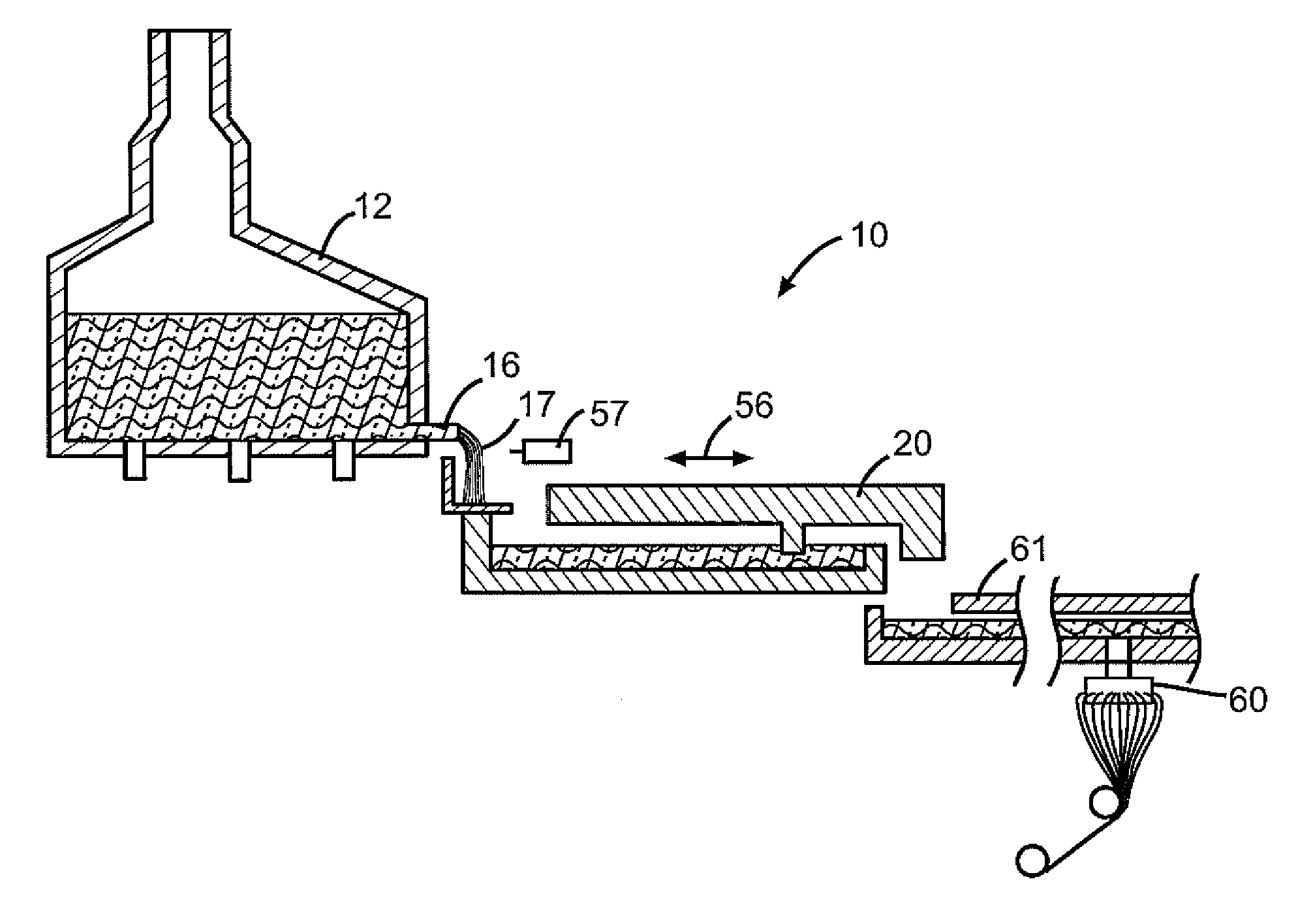
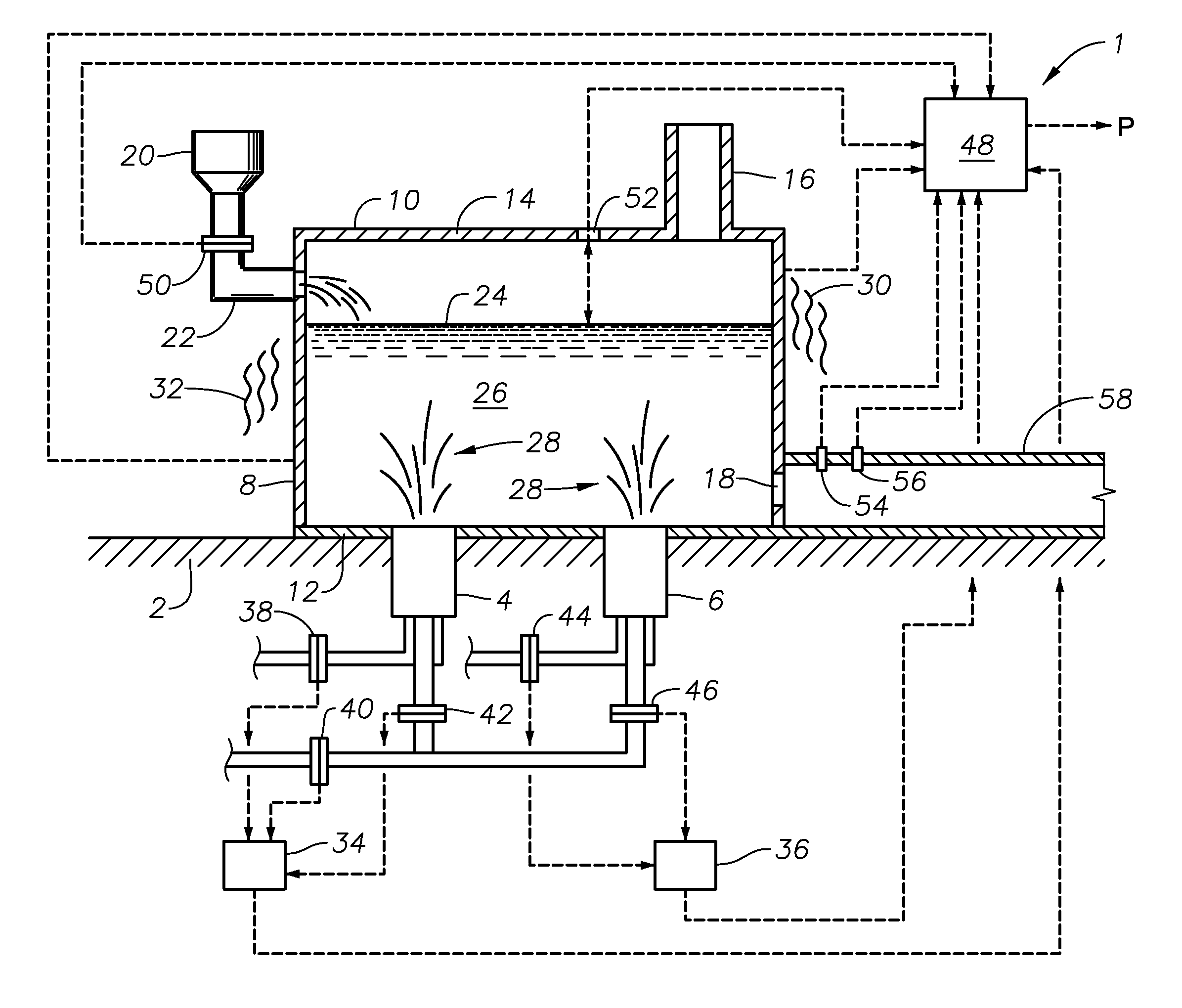
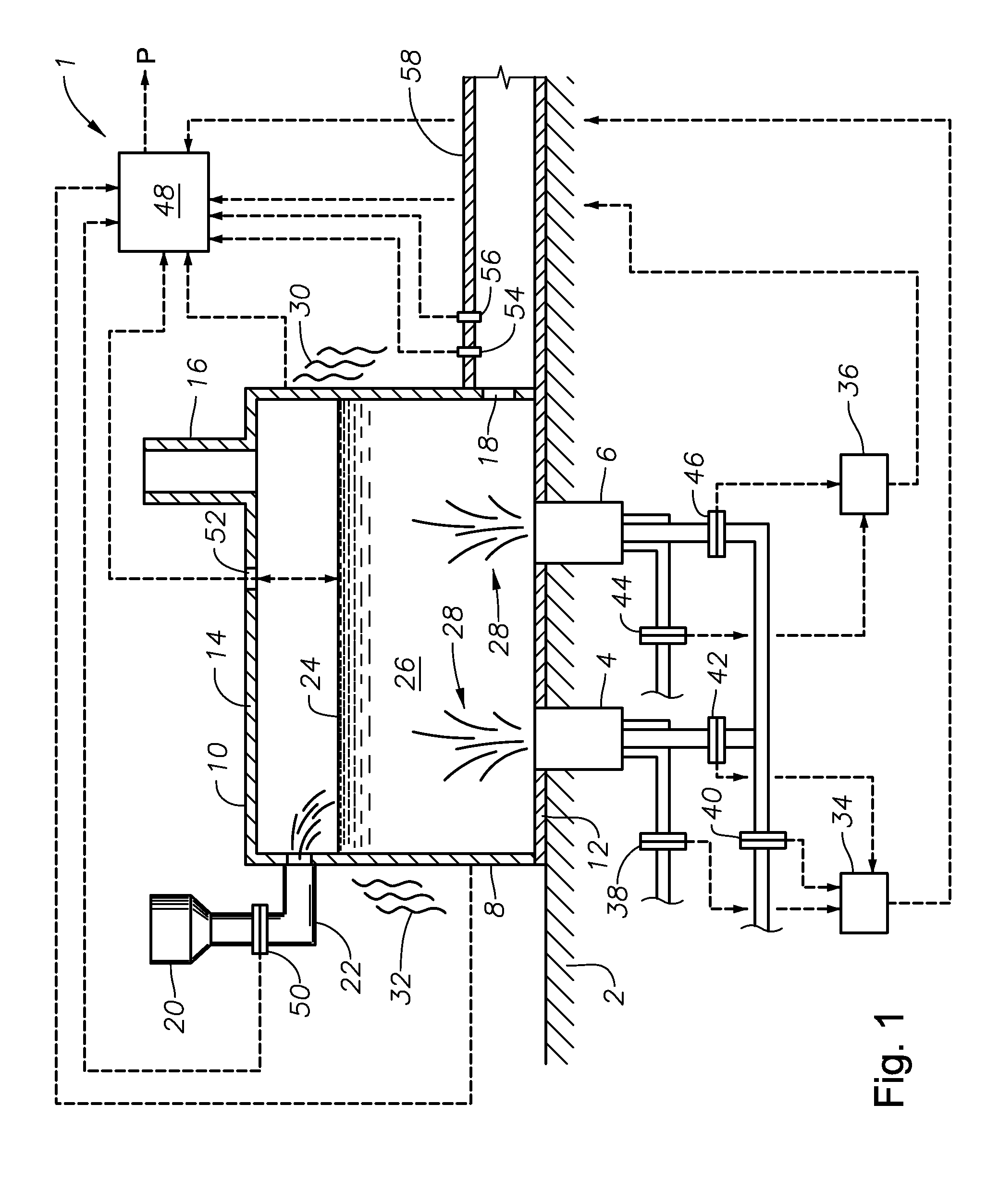
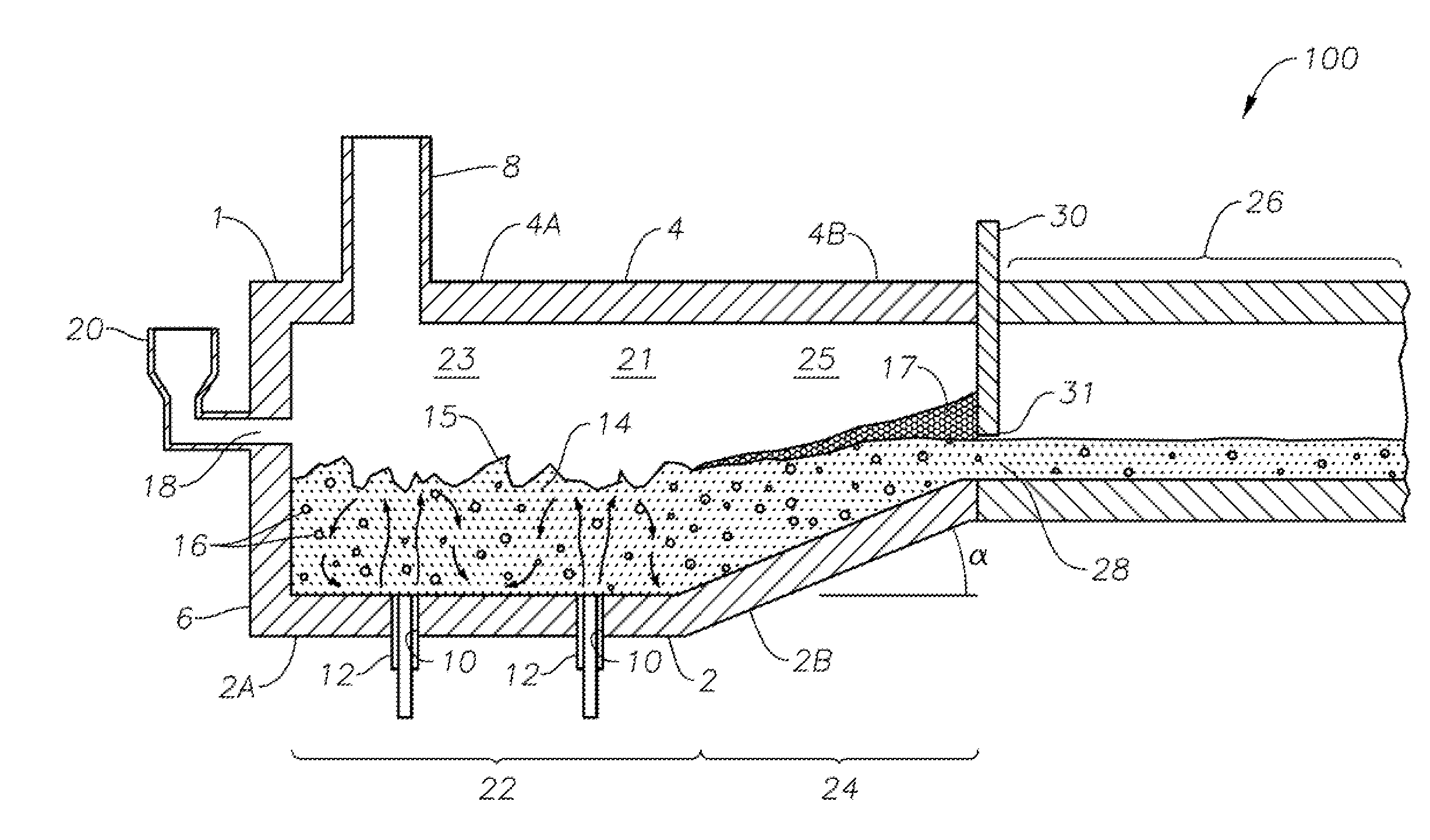
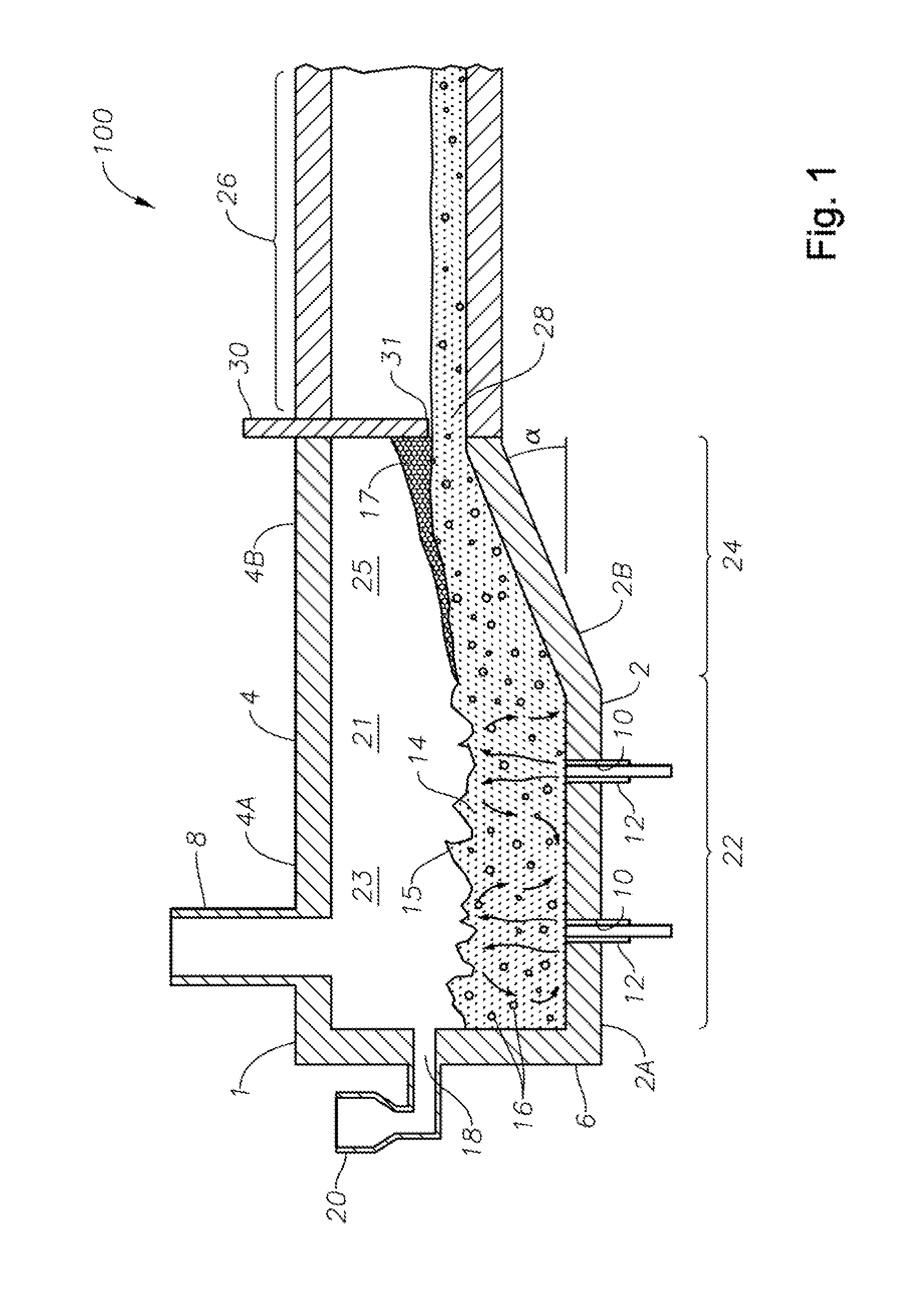
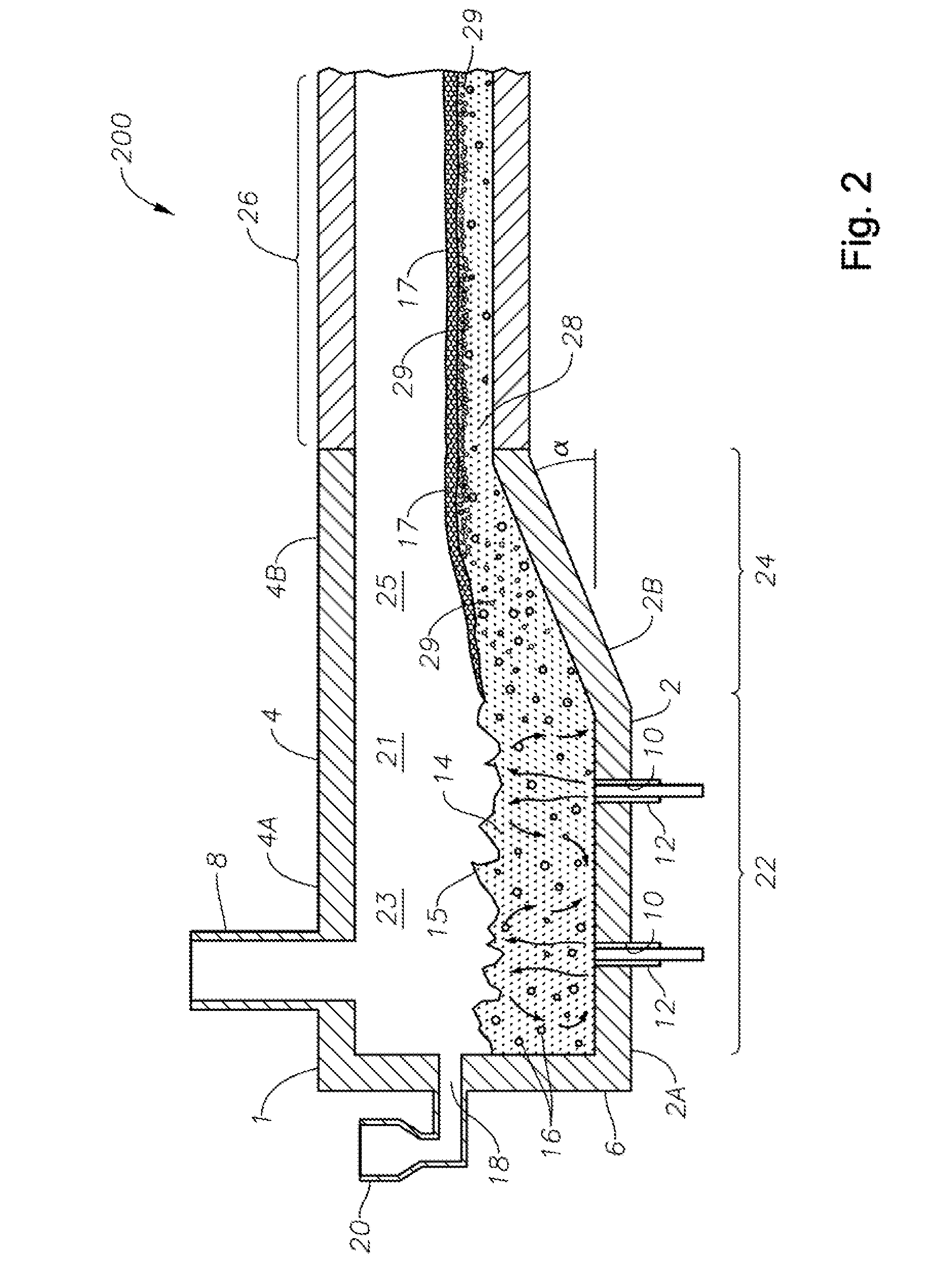
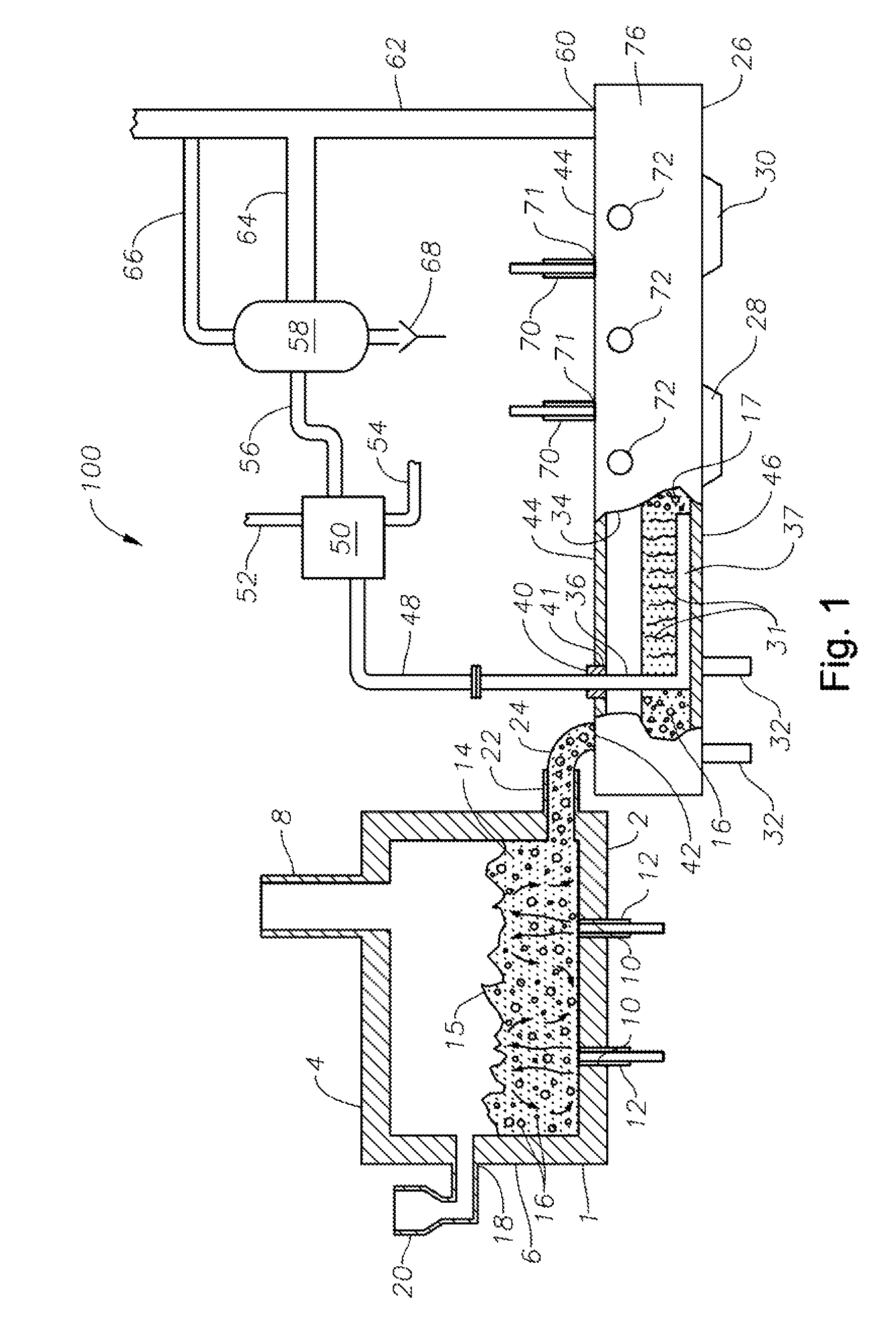
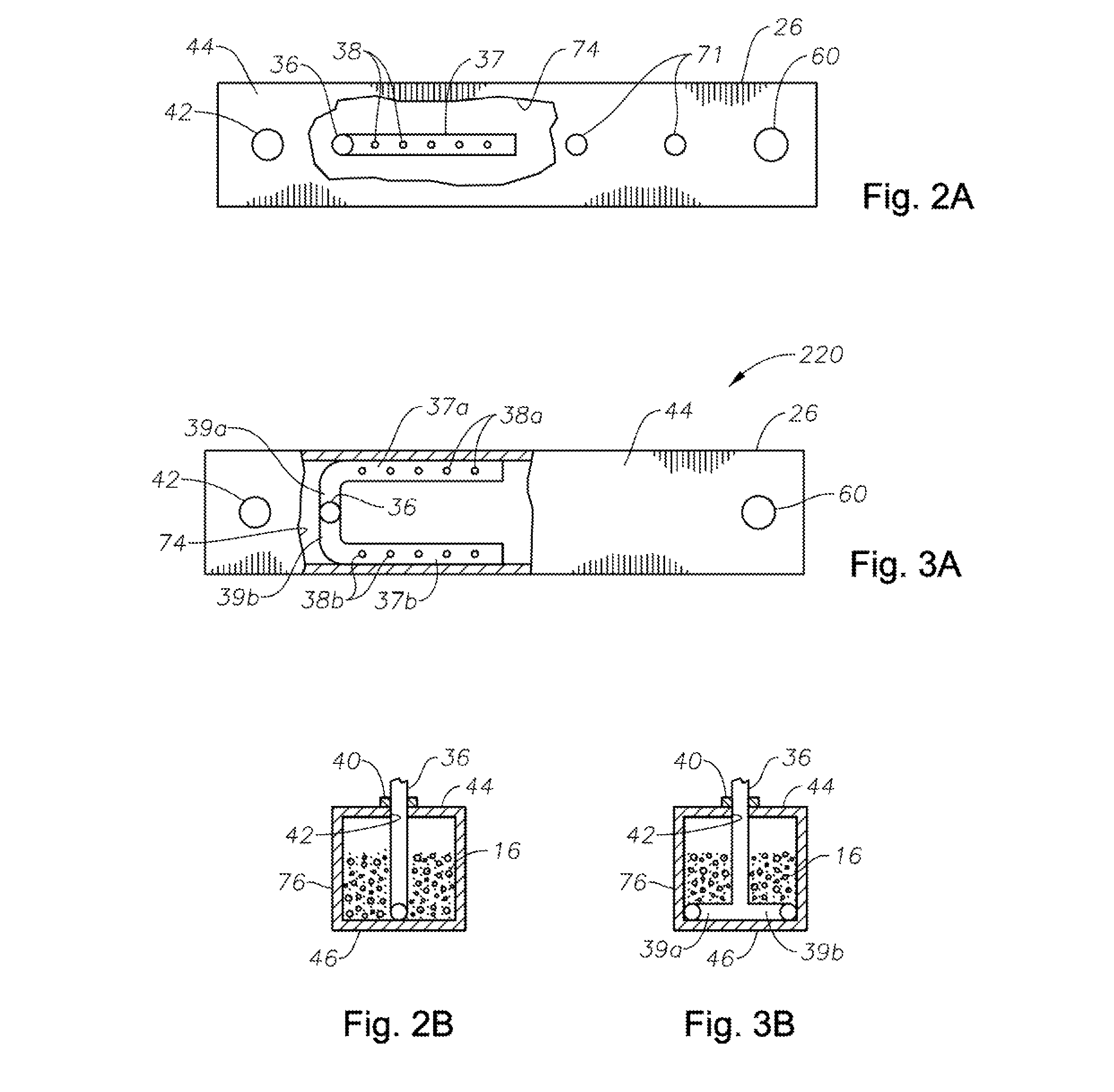
Apparatus, systems and methods for conditioning molten glass
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Cover glass and method for producing same
ActiveCN102531384AEfficient preparationHigh ion exchange capacityGlass forming apparatusGlass tempering apparatusCover glassMolten glass
Owner:AVANSTRATE INC +1
Glass melting gurnace and method for producing glass
InactiveUS20060101859A1Precise maintenanceReduce the environmentGlass furnace apparatusGlass pressing apparatusMelting tankNoble gas
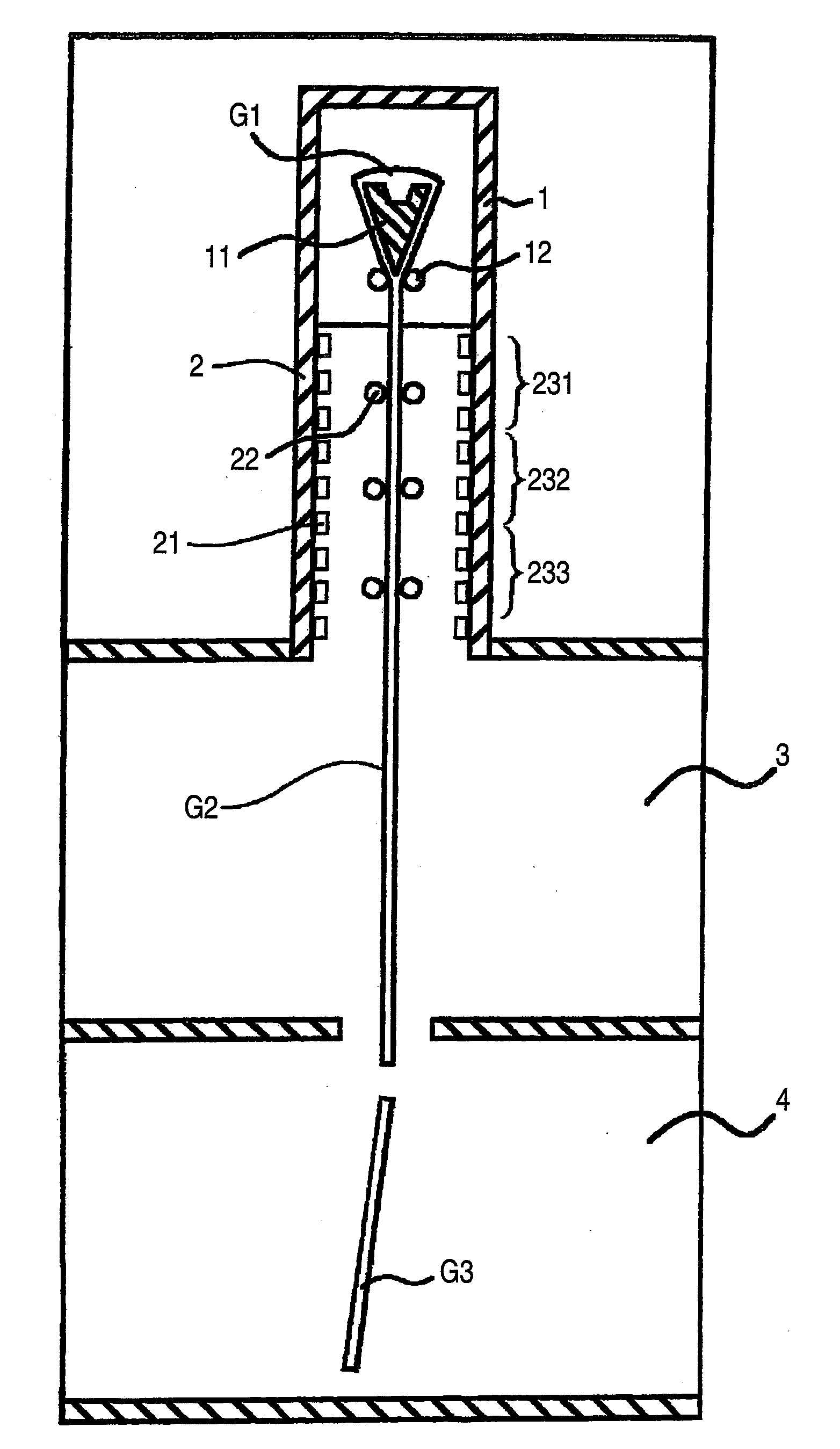
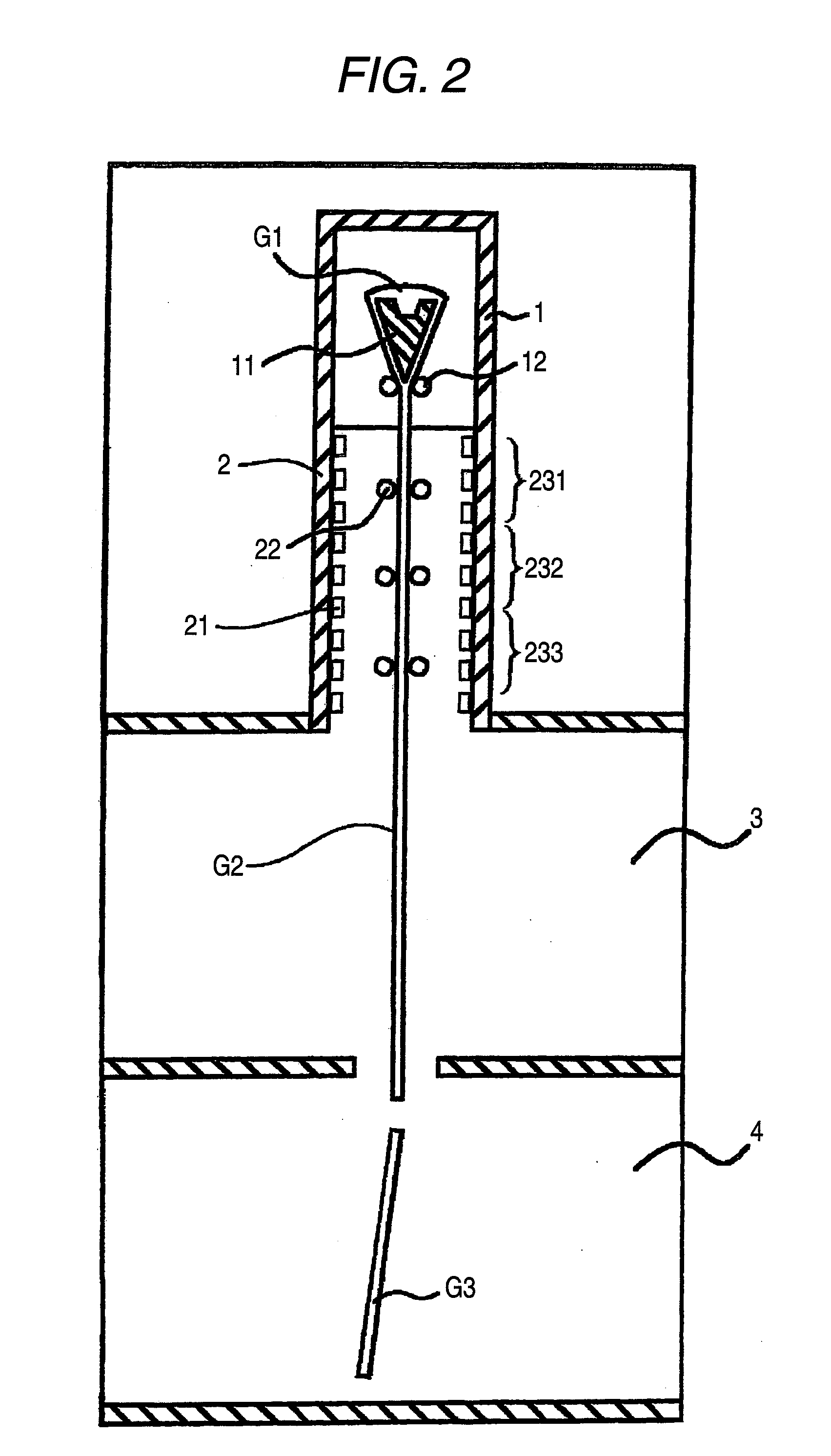
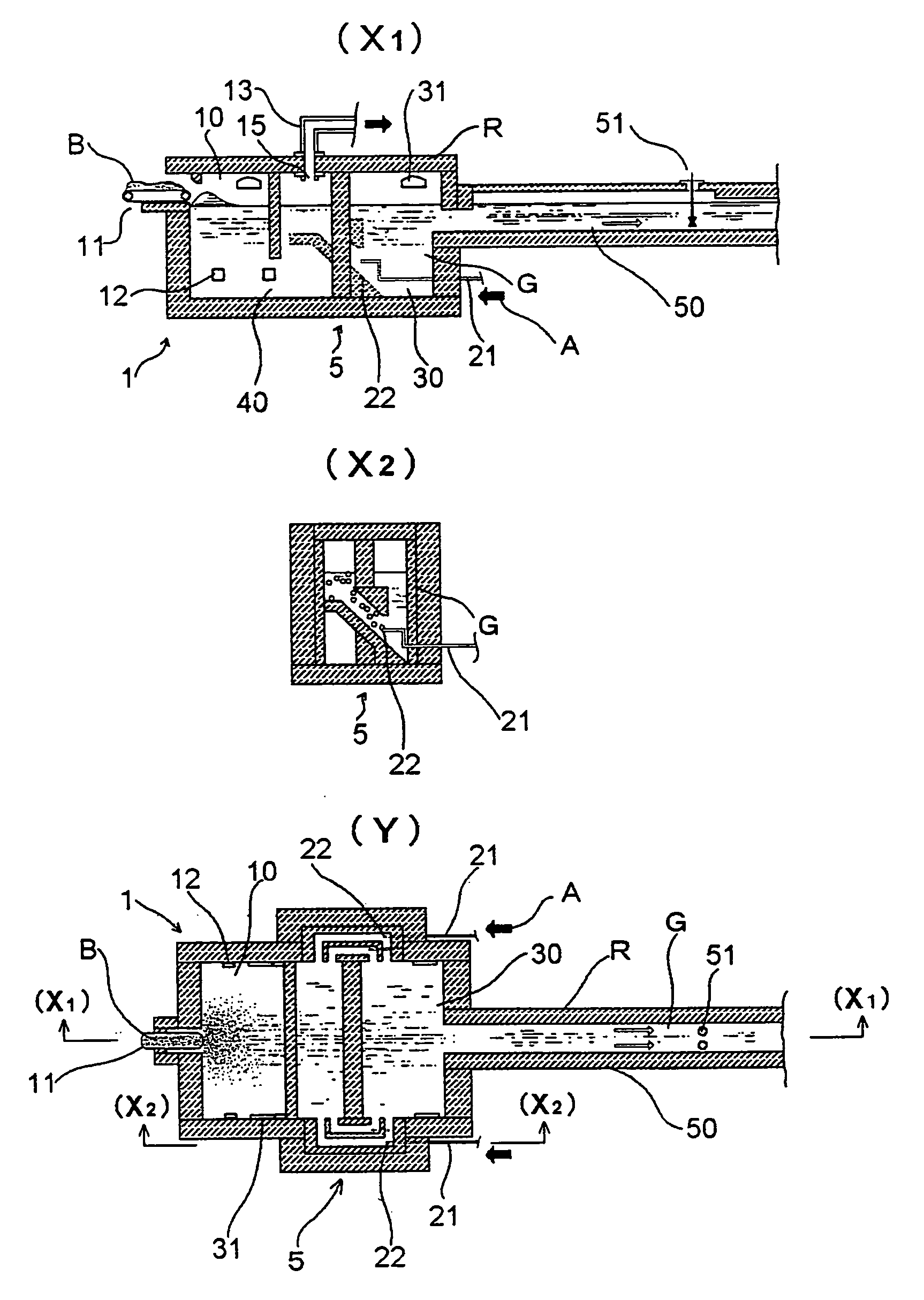
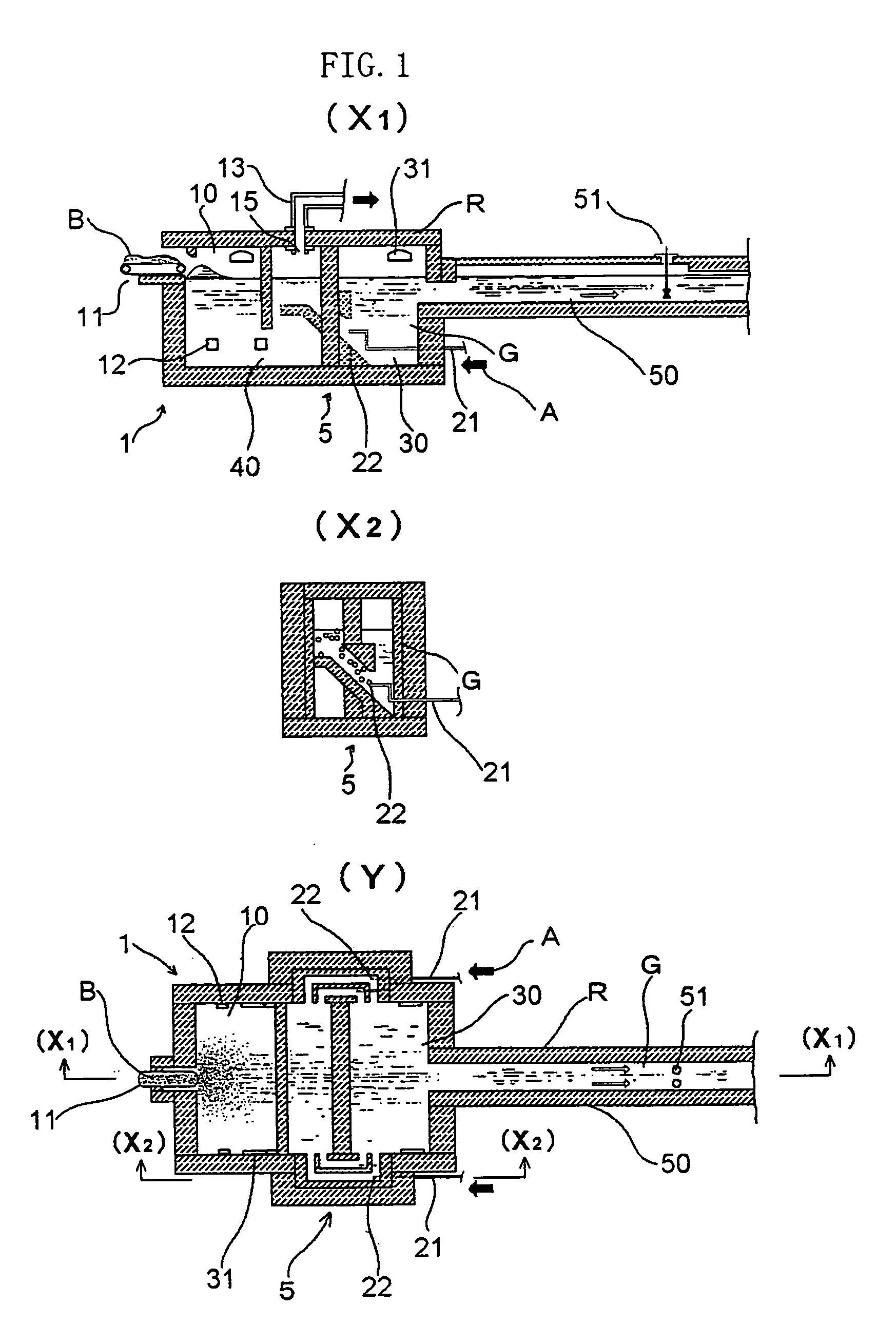
A charged glass raw material B is melted in a melting tank 10 by heating with a burner 31 and by heating with electrodes 12, to form molten glass G. Then, the molten glass G flows into a tank additionally provided as a noble gas dissolving tank 20 through a throat 40. The noble gas dissolving tank 20 is provided with a noble gas dissolving device 53, and the noble gas dissolving device 53 is provided with sixteen noble gas inlets 22 for introducing a helium or neon gas supplied to a hearth through heat resistant gas introduction tubes 21 into the noble gas dissolving tank 20. Bubbles of a helium gas A having a purity of 99% are blown out from the noble gas inlets 22 in volumes such that the bubbles have an average diameter of 80 mm or less in the molten glass G.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
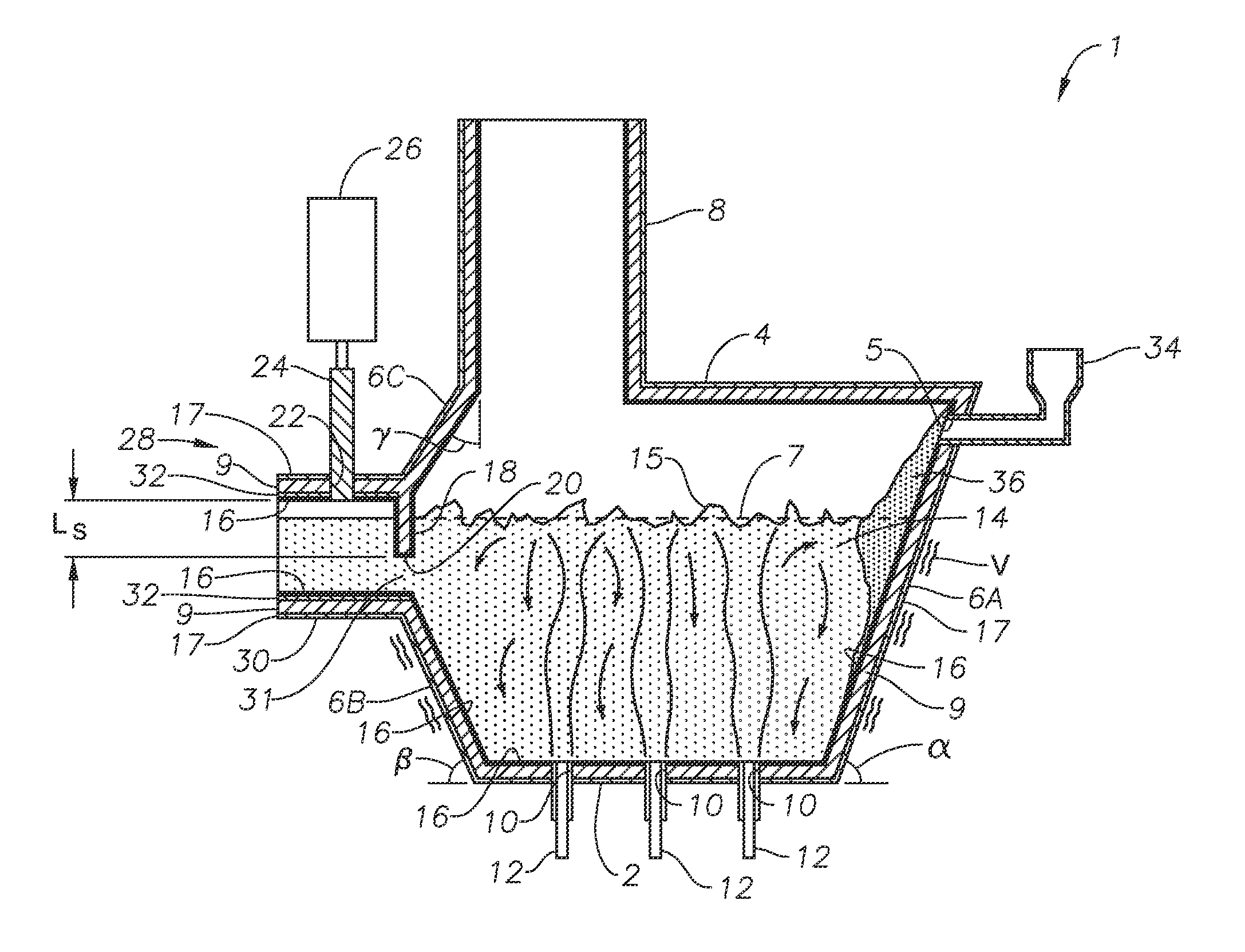
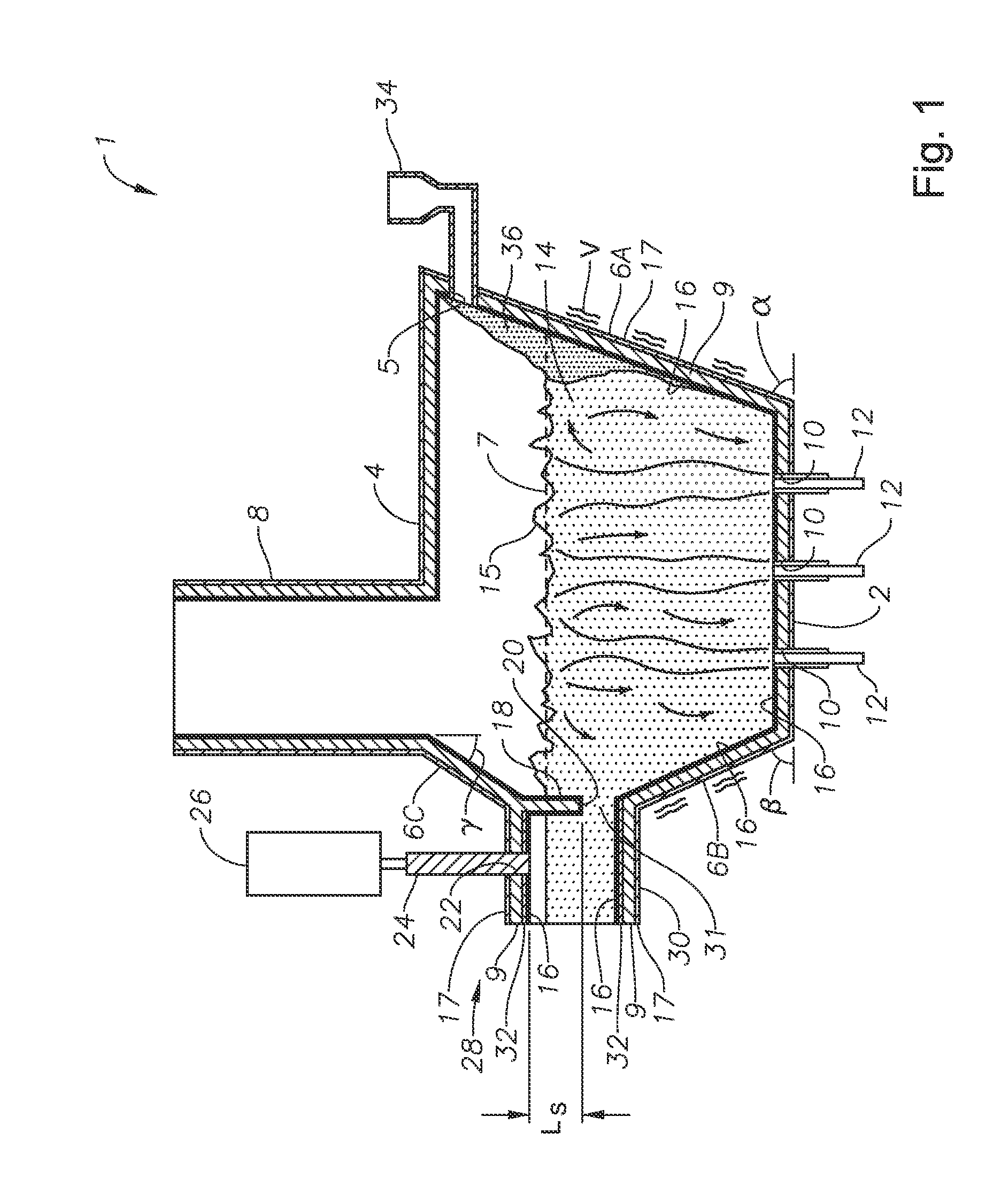
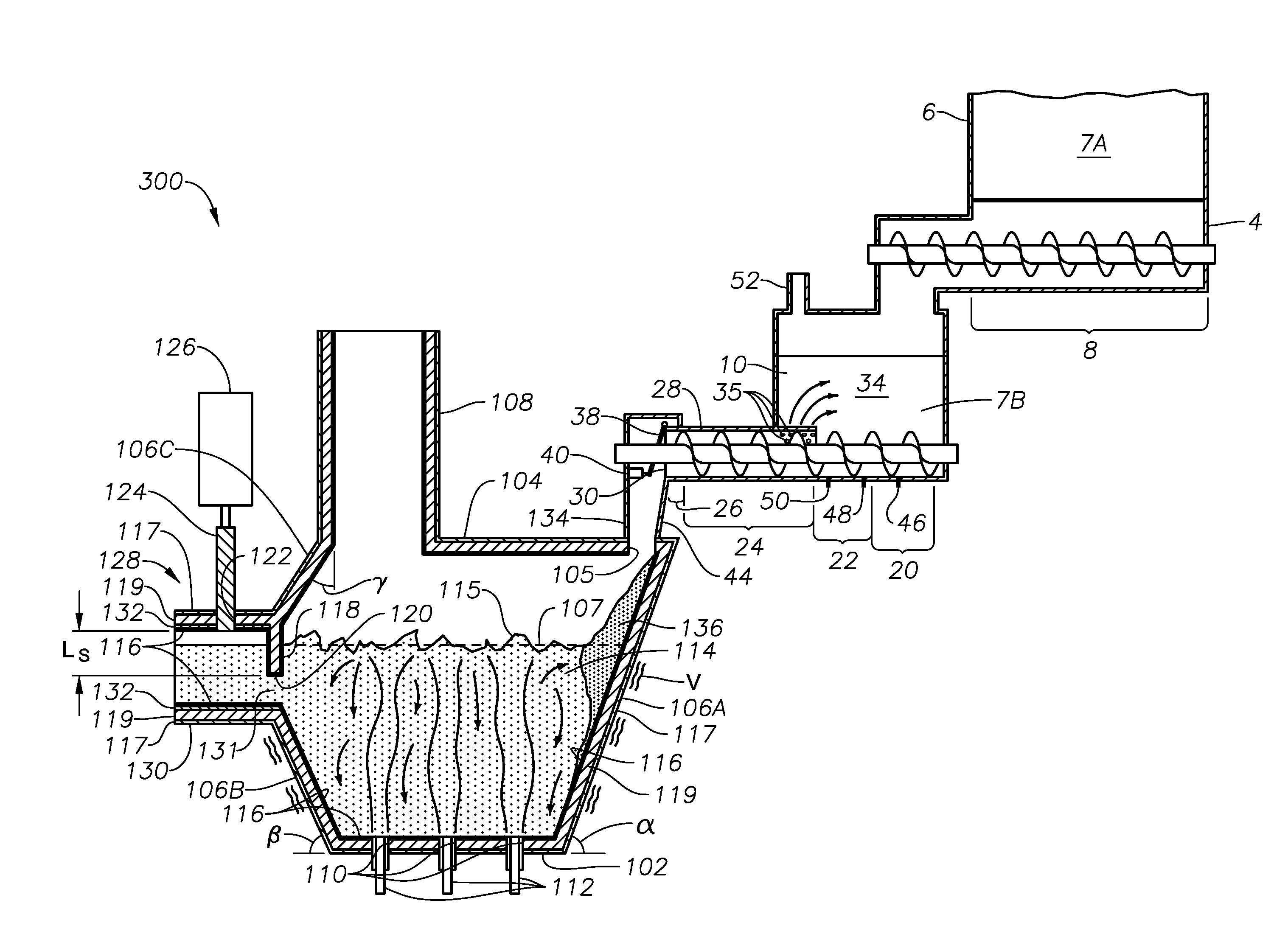
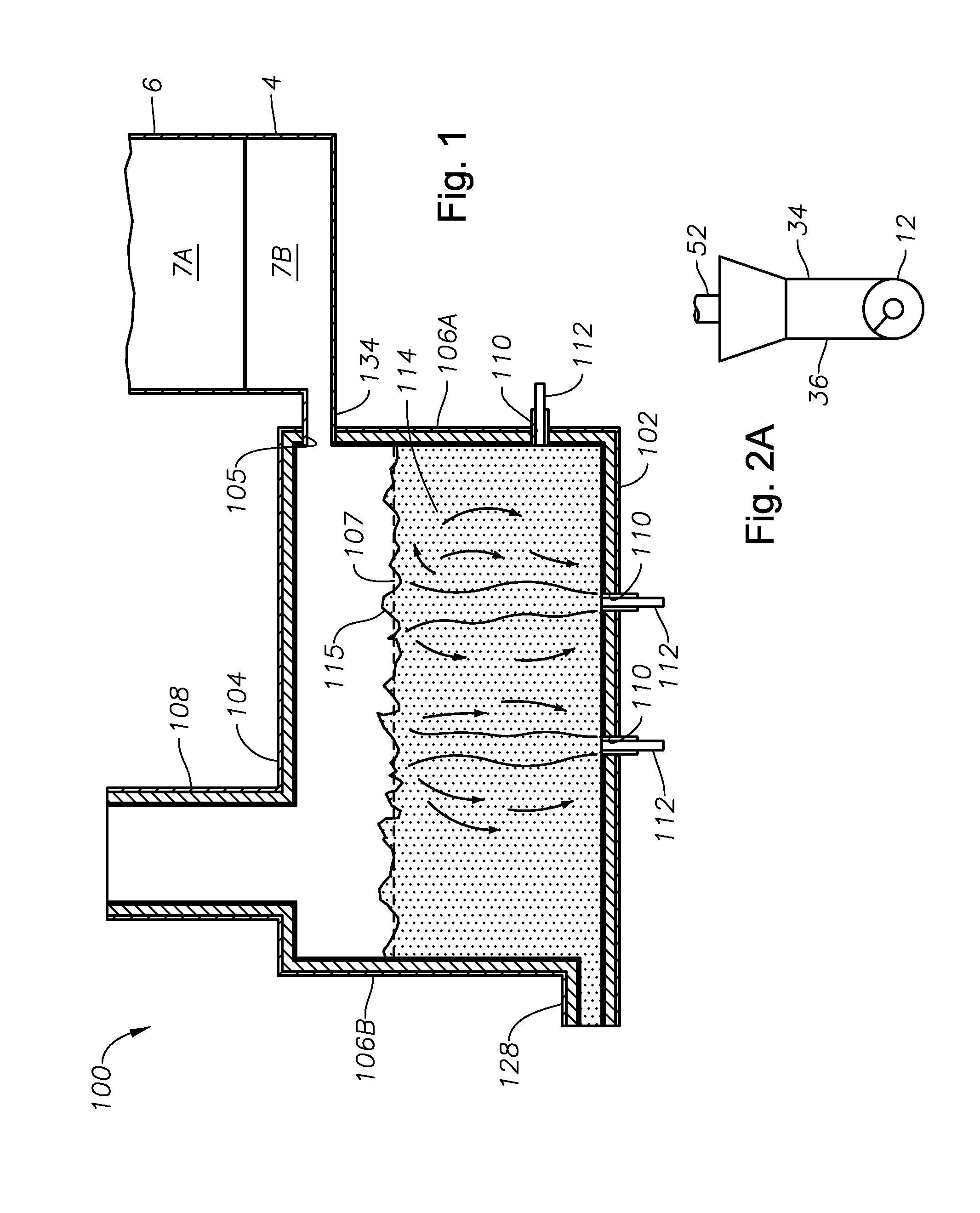
Apparatus, systems and methods for reducing foaming downstream of a submerged combustion melter producing molten glass
Apparatus including a flow channel defined by a floor, roof, and sidewall structure connecting the floor and roof. One or more combustion burners is positioned in either the roof, the sidewall structure, or both, and transfer heat to a molten mass of glass containing bubbles having a bubble atmosphere flowing through the flow channel. The burners contribute to formation of a channel atmosphere above the molten glass. Apparatus includes a device, at least a portion of which is positionable under a level of the molten glass in the flow channel, configured to emit a composition into the molten glass under the level to intimately contact the composition with the molten glass and bubbles therein. The composition diffuses into the bubbles to form modified atmosphere bubbles sufficiently different from the channel atmosphere to increase diffusion of a species in the channel atmosphere into the modified atmosphere bubbles.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Method for treating waste incineration fly ash by using plasmas
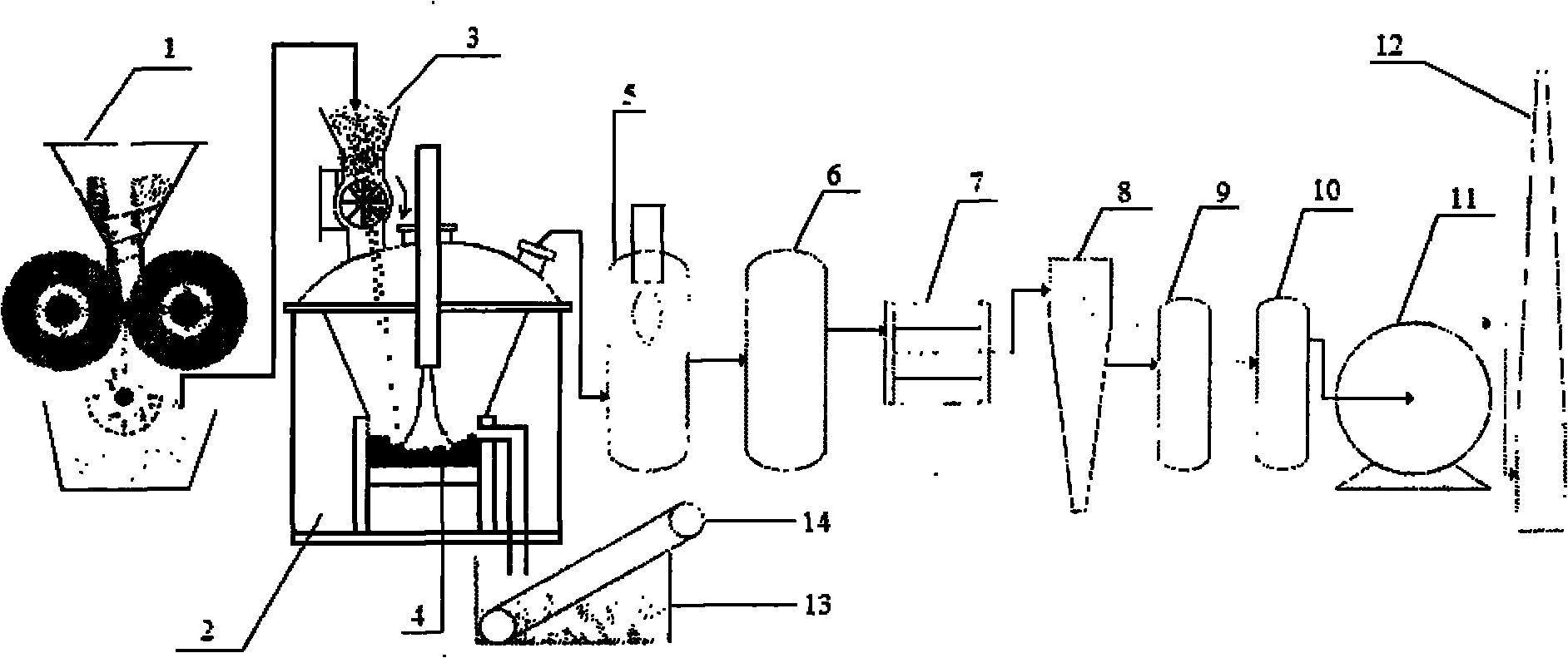
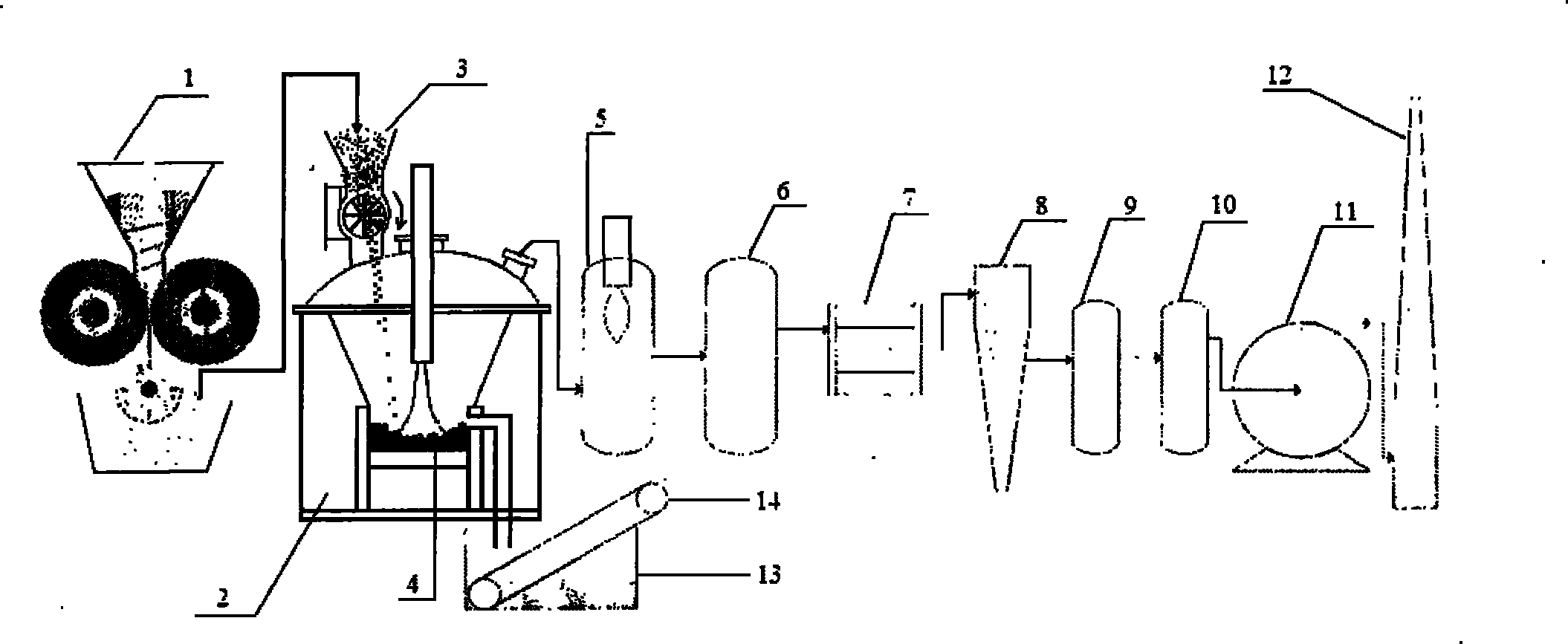
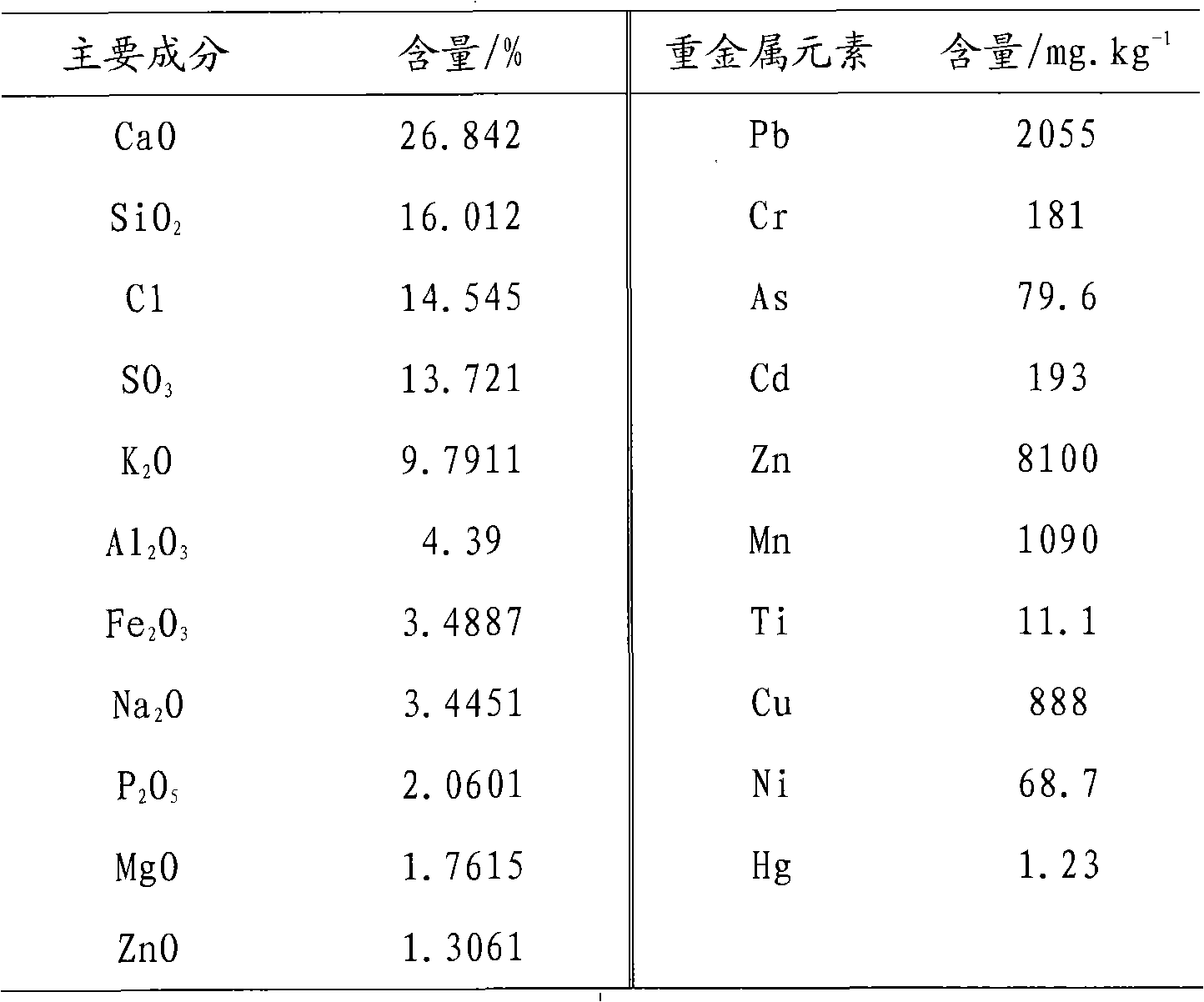
InactiveCN101797572APromote vitrificationSolve the "bridge" problemSolid waste disposalMelting tankVitrification
Owner:安徽中科华炬环保科技有限公司
Method of manufacturing glass substrate for information recording medium
InactiveUS20050204777A1Reduce in quantityEfficient preparationGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusMetalMolten glass
Molten glass is press-molded by a metallic die in which a cylindrical body is provided in a vertically standing manner at a central part of a bottom surface of a bottomed hole and a molding surface corresponding to a chamfering shape of an outer peripheral edge surface of a glass substrate is consecutively formed in an inner peripheral wall, and a glass substrate precursor provided with the chamfering shape axially consecutive on an outer peripheral surface thereof and a through hole formed at a central part thereof is thereby formed. The glass substrate precursor is cut perpendicular to an axial direction to be separated into respective glass substrates. Next, the respective glass substrates are subjected to a lapping process and a polishing process, if necessary, to produce a glass substrate as a final product. According to the manufacturing method, a glass substrate for information recording medium whose inner and outer peripheral edge surfaces are chamfered can be manufactured with an improved efficiency. Further, a glass substrate having a small diameter can be manufactured with a high efficiency.
Owner:HOYA CORP
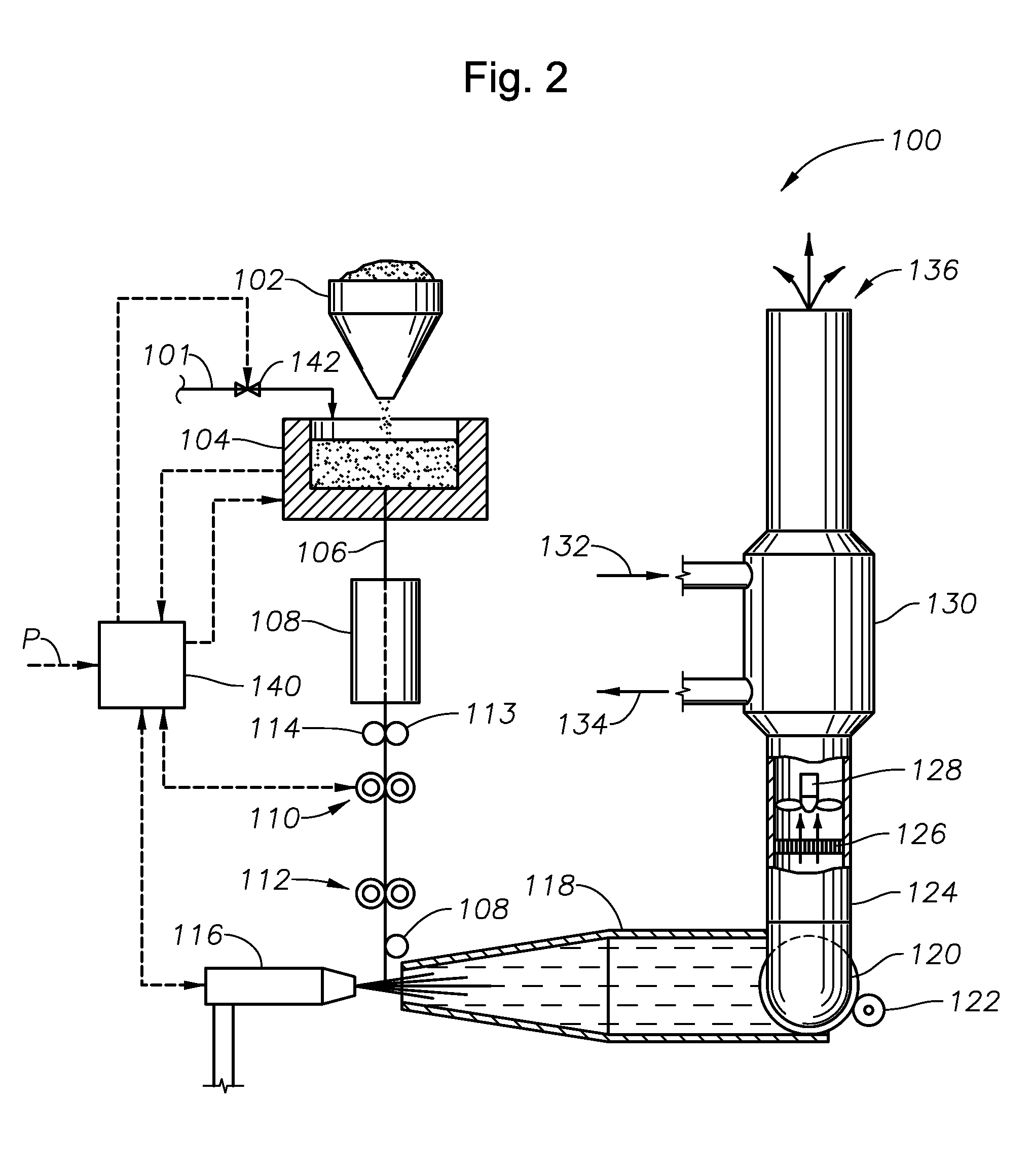
Manufacturing method of glass molded body, manufacturing apparatus of glass molded body, and glass molded body
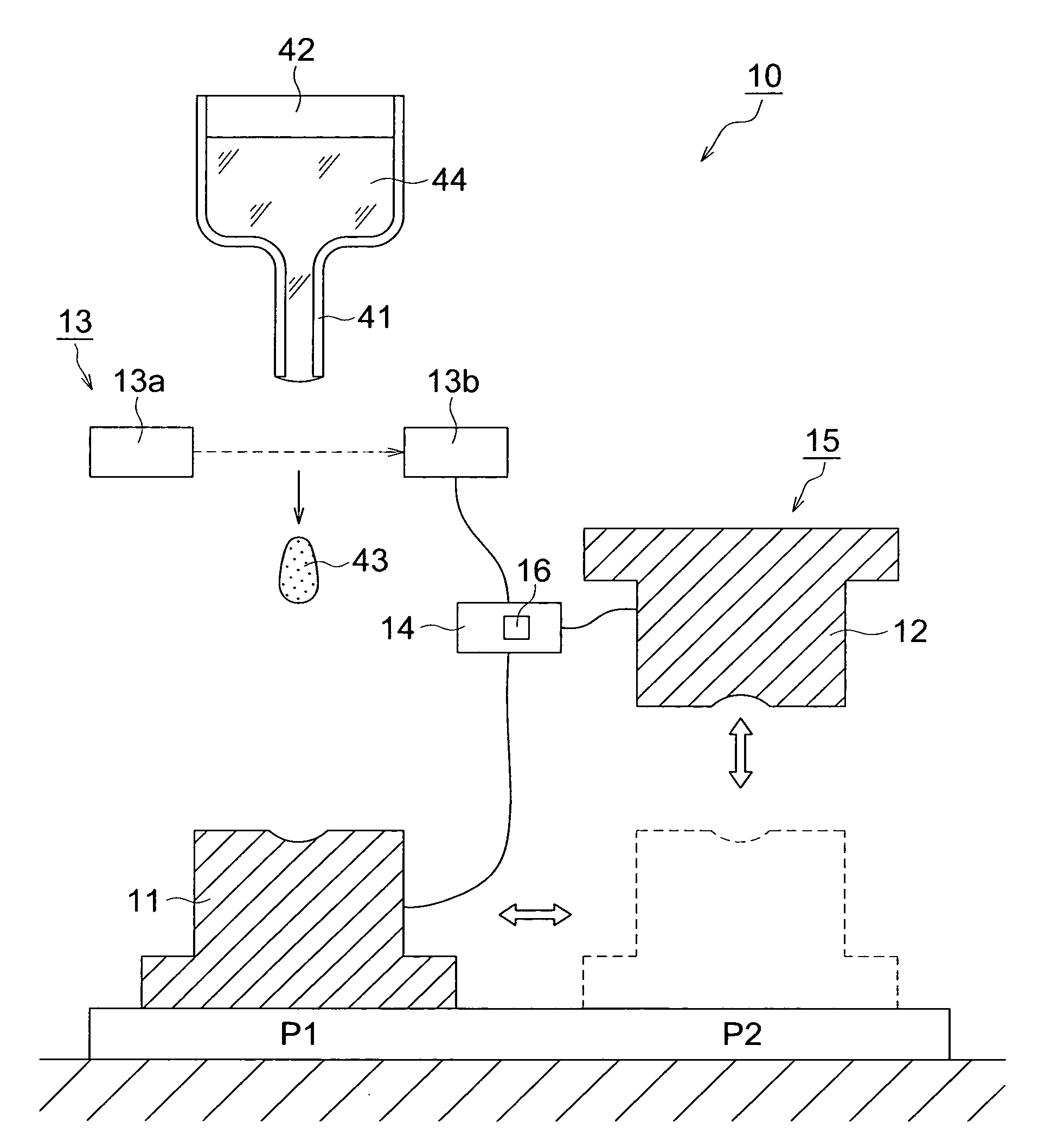
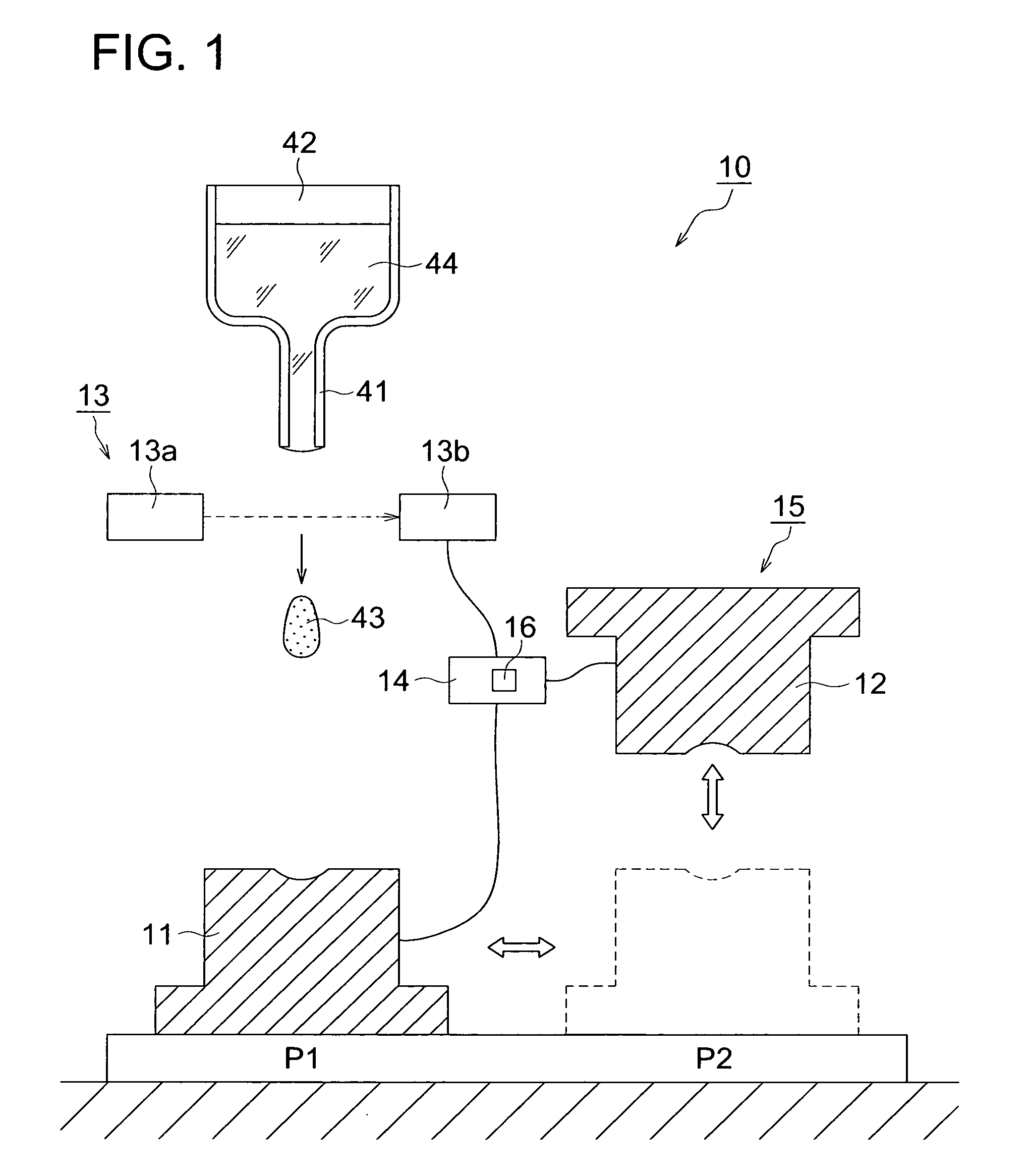
InactiveUS20100120601A1Quality improvementImprove accuracyGlass pressing apparatusSensitive elementsShell moldingManufactured apparatus
A process for producing a glass molding, in which a glass molding of stable quality can be efficiently produced through minimizing of temperature fluctuation of molten glass drops at pressure molding operation; and an apparatus for production of a glass molding used in this process. Molten glass drops are fed into an inferior die by causing the molten glass drops to fall from above toward the inferior die. The arrival of molten glass drops having fallen at a given location is detected, and pressurization of the molten glass drops by means of molding dies is initiated upon the passage of a given time since the detection.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com