Patents
Literature
102 results about "Optic disc" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
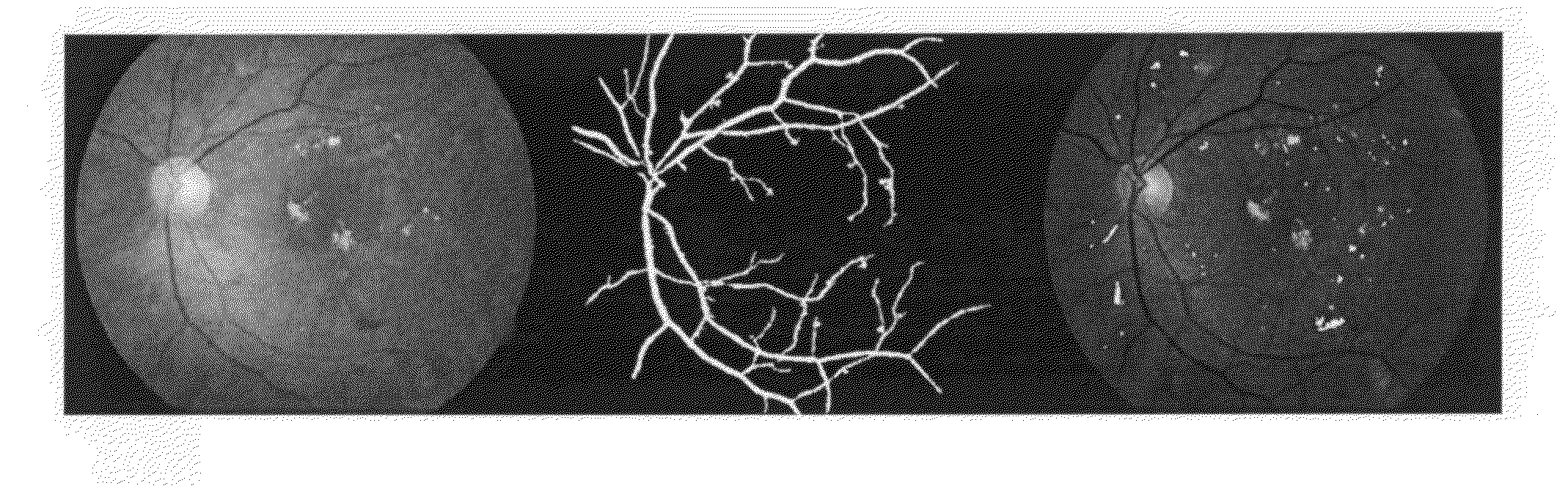
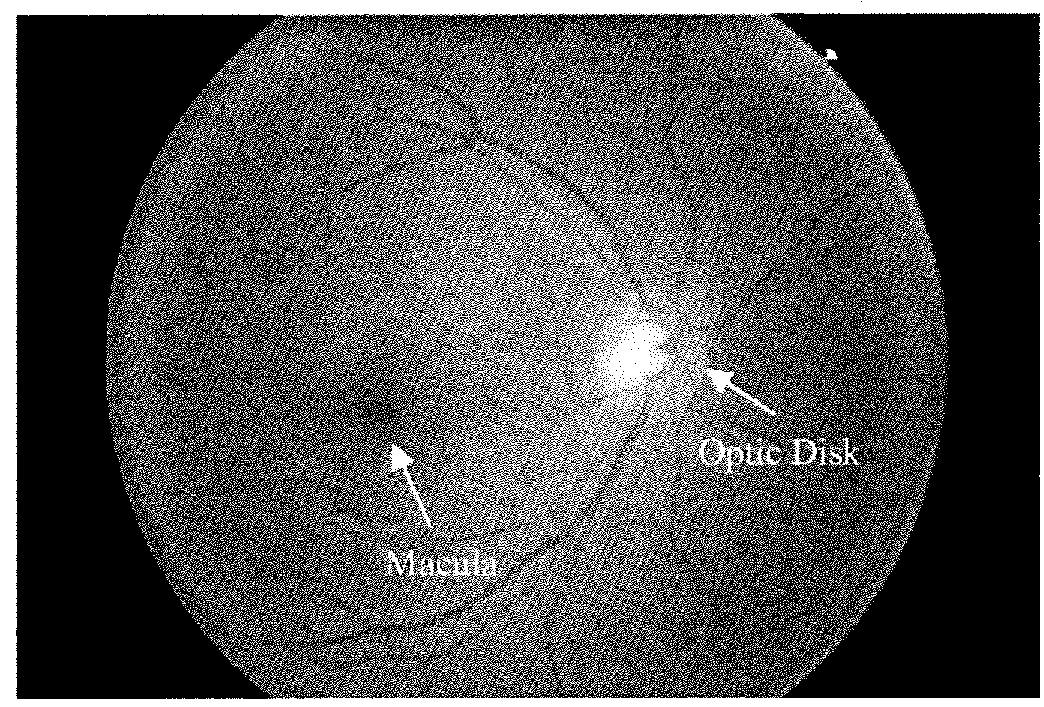
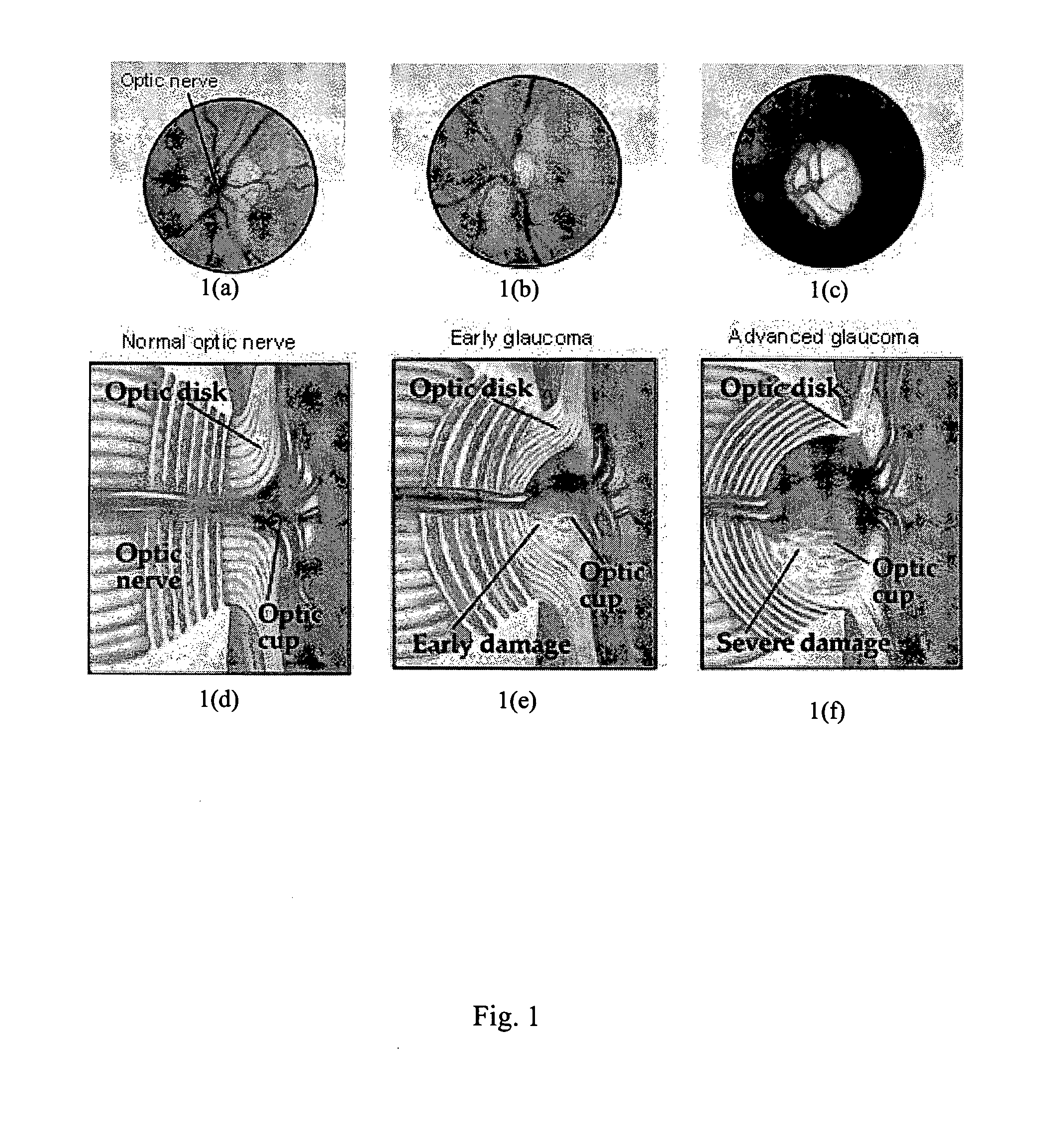
The optic disc or optic nerve head is the point of exit for ganglion cell axons leaving the eye. Because there are no rods or cones overlying the optic disc, it corresponds to a small blind spot in each eye.
Method of producing glass substrate for information recording medium
InactiveUS6332338B1Avoid deformationIncrease speedGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusProduction ratePoise
Disclosed is a process for producing a glass substrate for an information recording medium by press-shaping a molten glass which gives a glass containing 0.1 to 30 mol % of TiO2, 1 to 45 mol % of CaO, 5 to 40 mol % of total of MgO and the above CaO, 3 to 30 mol % of total of Na2O and Li2O, 0 to 15 mol % of Al2O3 and 35 to 65 mol % of SiO2 and having properties of a liquidus temperature of 1,360° C. or lower and a viscosity of at least 10 poise in a shaping-allowable temperature range, or by preparing a preform formed of a glass which contains 0.1 to 30 mol % of TiO2, 1 to 45 mol % of CaO, 5 to 40 mol % of total of MgO and the above CaO, 3 to 30 mol % of total of Na2O and Li2O, 0 to 15 mol % of Al2O3 and 35 to 65 mol % of SiO2 and has properties of a liquidus temperature of 1,360° C. or lower and shaping the preform in the form of a disc by a re-heat pressing method. According to the above process, there can be mass-produced, with high productivity, high-quality glass substrates to be used for information recording media such as a magnetic disc, an optical disc, a magneto-optic disc, and the like.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Method and apparatus to detect lesions of diabetic retinopathy in fundus images
InactiveUS20140314288A1Minimal run-time complexityFastImage enhancementImage analysisCotton wool patchesHard exudates
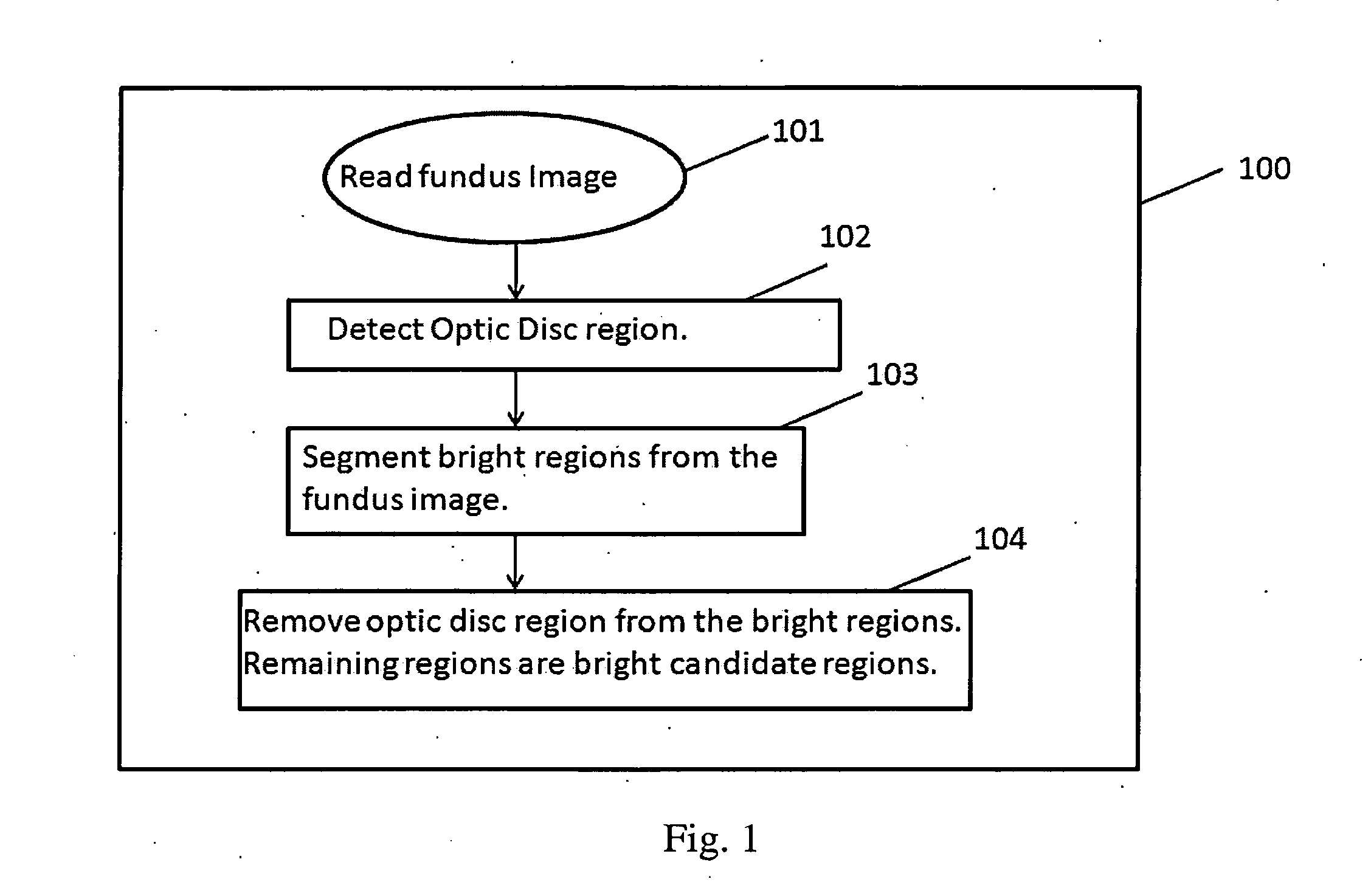
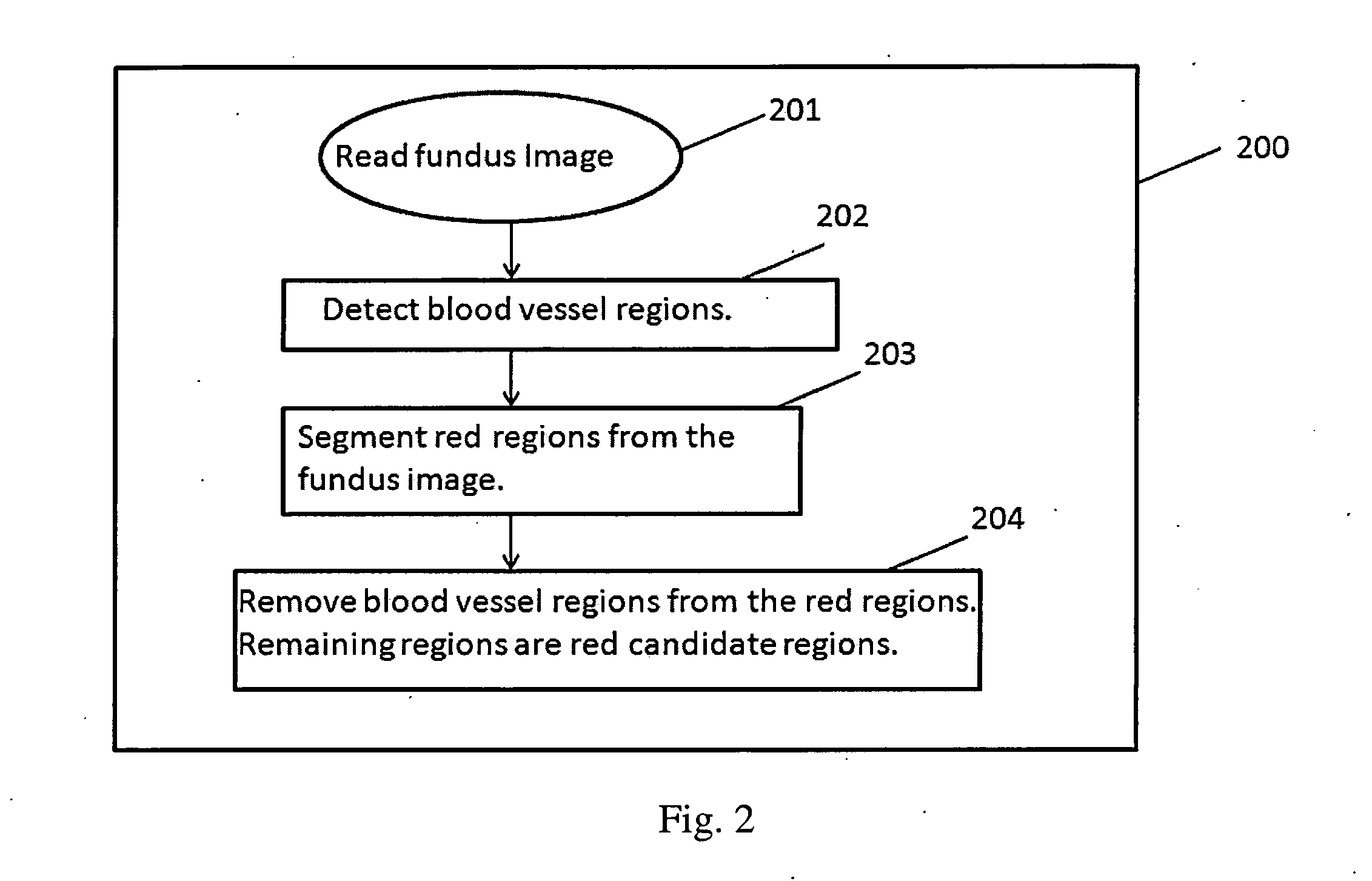
The present invention relates to the design and implementation of a three stage computer-aided screening system that analyzes fundus images with varying illumination and fields of view, and generates a severity grade for diabetic retinopathy (DR) using machine learning. In the first stage, bright and red regions are extracted from the fundus image. An optic disc has similar structural appearance as bright lesions, and the blood vessel regions have similar pixel intensity properties as the red lesions. Hence, the region corresponding to the optic disc is removed from the bright regions and the regions corresponding to the blood vessels are removed from the red regions. This leads to an image containing bright candidate regions and another image containing red candidate regions. In the second stage, the bright and red candidate regions are subjected to two-step hierarchical classification. In the first step, bright and red lesion regions are separated from non-lesion regions. In the second step, the classified bright lesion regions are further classified as hard exudates or cotton-wool spots, while the classified red lesion regions are further classified as hemorrhages and micro-aneurysms. In the third stage, the numbers of bright and red lesions per image are combined to generate a DR severity grade. Such a system will help in reducing the number of patients requiring manual assessment, and will be critical in prioritizing eye-care delivery measures for patients with highest DR severity.
Owner:PARHI KESHAB K +1
Macula lutea image detection method and equipment
ActiveCN108717696AEasy to identifyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImage detectionSample image
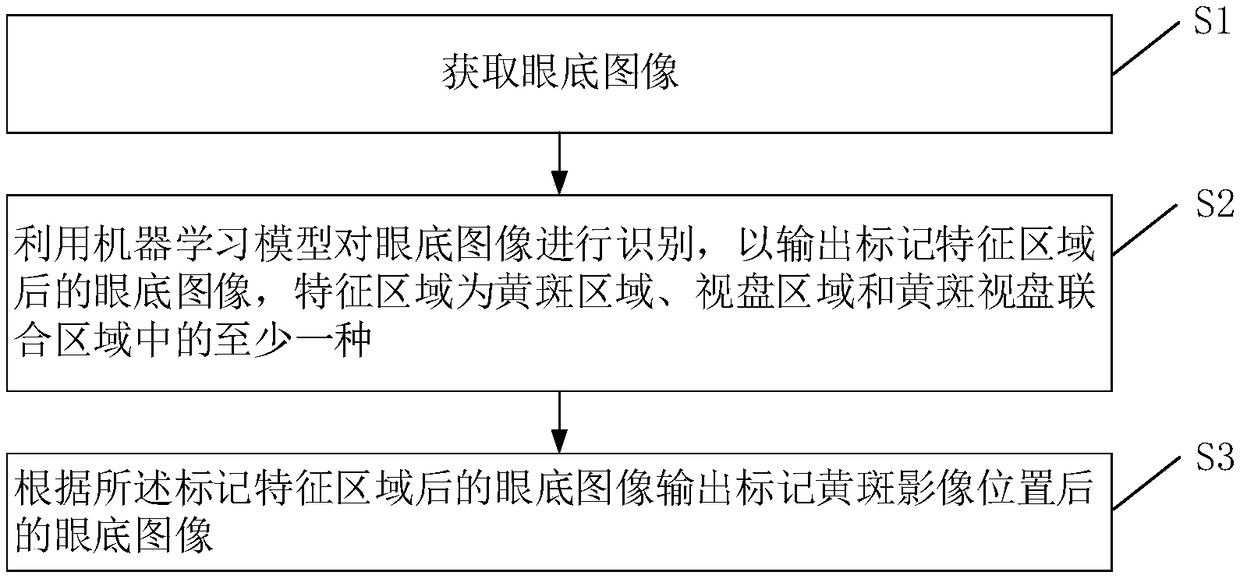
The invention provides a macula lutea image detection method and equipment. The macula lutea image detection method comprises the steps that a fundus image is acquired; a machine learning model is utilized to recognize the fundus image to output the fundus image obtained after feature regions are marked, wherein the feature regions are at least one of a macula lutea region, an optic disc region and a macula lutea and optic disc united region, and the machine learning model is obtained by performing training through sample images at the positions of the known feature regions; and according to the fundus image obtained after the feature regions are marked, the fundus image obtained after a macula lutea image position is marked is output.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAGLEVISION MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
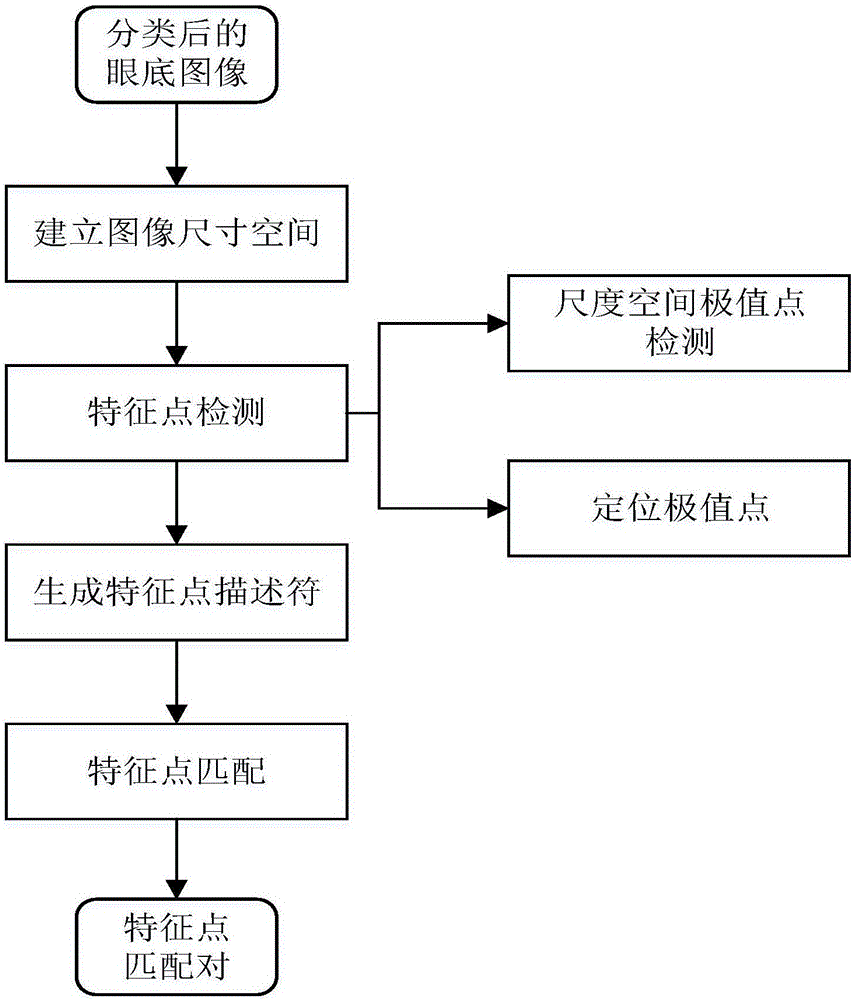
Fundus image registering method based on SIFT characteristics
ActiveCN106651827AImprove robustnessEliminate errorsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionFuzzy convergence
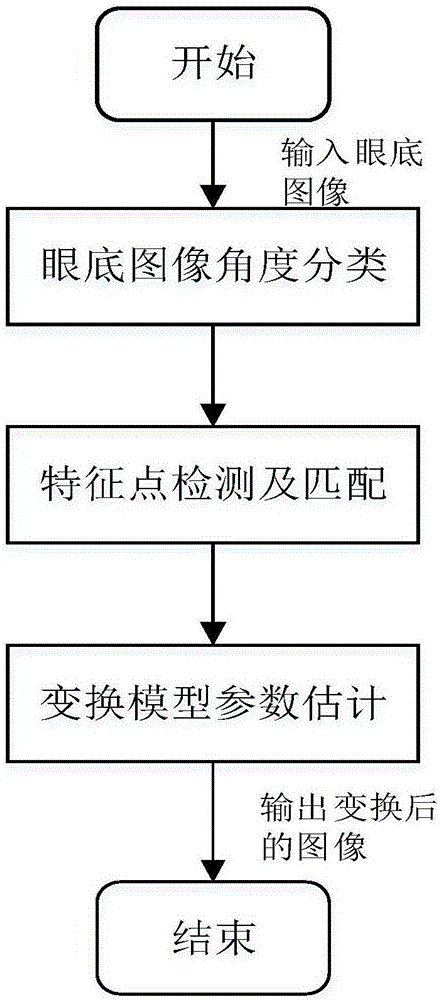
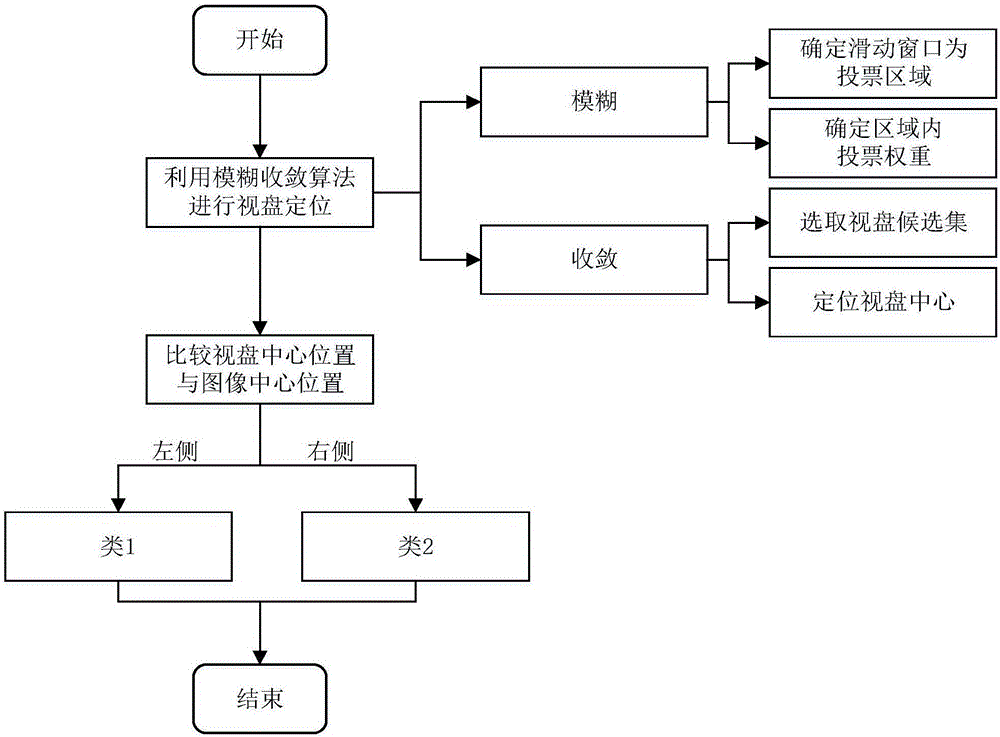
The invention discloses a fundus image registering method based on SIFT characteristics. The method comprises: conducting angle classification to a batch of inputted fundus images; calculating the transformative relationship among the images; converting the images onto the same background; and through the rapid switching of the images, finding out which parts of the fundus change. The invention mainly uses a fuzzy convergence optic disc positioning algorithm and conducts angle classification to the batch of inputted fundus images according to the position of the optic disc wherein the angle classification is referred as two types: the left side and the right side; and then in each image classification, a selected and uploaded first image is used as a reference for other images to register with; the SIFT characteristic points of all the images are extracted and the matching relation between every two points is calculated. Finally, the RANSAC algorithm is used to calculate the transformation model parameters between every two images. The images are converted onto the same background according to the transformation model; and an image switching interval is configured so that through the switching of the images, it is possible to find out the change among the images rapidly and accurately.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
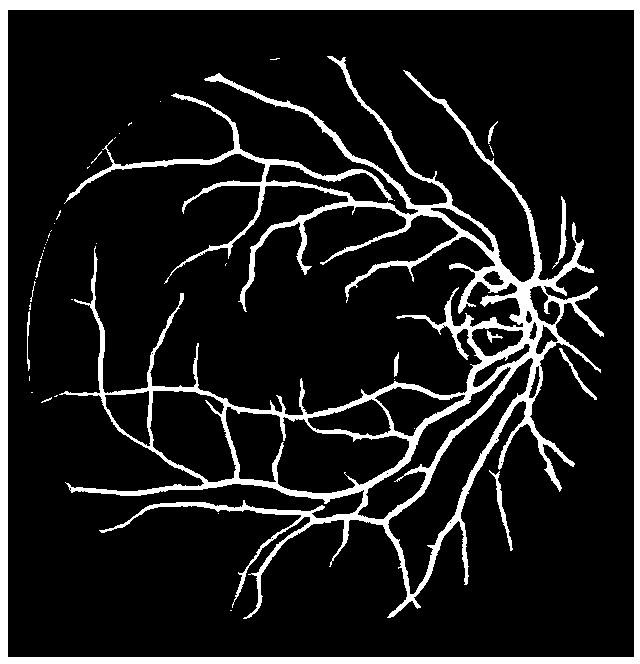
Automatic retinal blood vessel segmentation for clinical diagnosis of glaucoma
ActiveCN108986106AEliminate the effects ofGood segmentation resultImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseRetinal blood vessels
The invention provides an automatic retinal blood vessel segmentation method for clinical diagnosis of glaucoma. Through the method, the influence of bright regions such as optic disc and exudate is eliminated by fusing five models depending on different image processing technologies, namely a matched filter, a neural network, multi-scale line detection, scale space analysis and morphology. At thesame time, massive data is not needed to establish a retinal blood vessel segmentation model, so the method greatly reduces the amount and complexity of data to be processed, is easy to realize, andcan effectively improve the efficiency of retinal blood vessel segmentation. The method also utilizes the region growth method and the gradient information to carry out iterative growth on the background and the blood vessel region on the basis of a multimodal fusion result, the segmentation results exhibit better continuity and smoothness, more retinal vascular details and more complete retinal vascular network can be kept, and thus the method effectively assists ophthalmologists in diagnosing diseases and lightens the burden of ophthalmologists.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
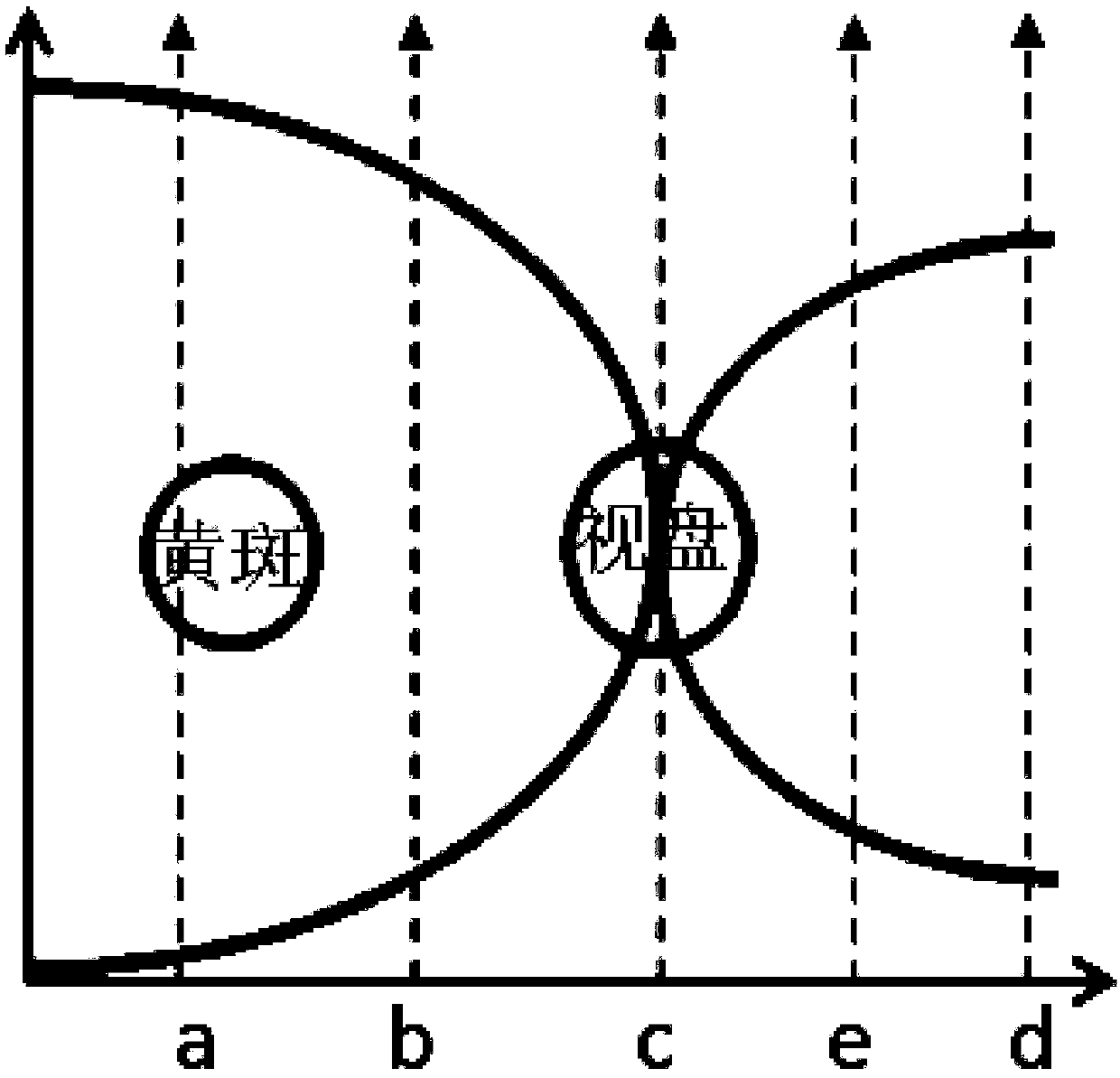
Quick optic disc positioning method based on multi-scale macula detection
InactiveCN104794721AReal-time detection effectSimple methodImage enhancementImage analysisData setBlob detection
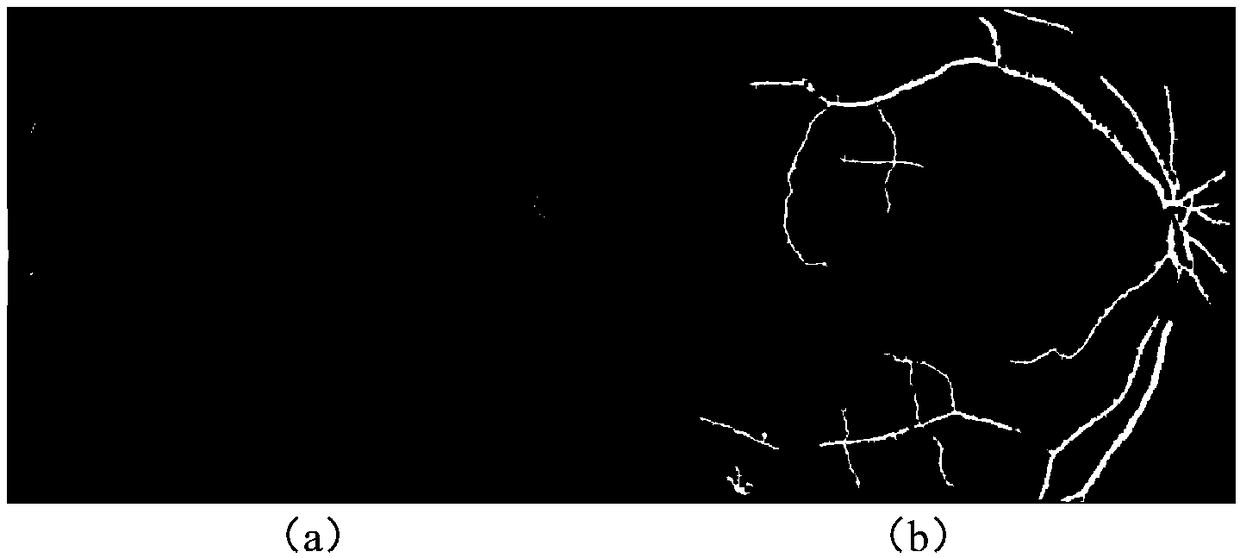
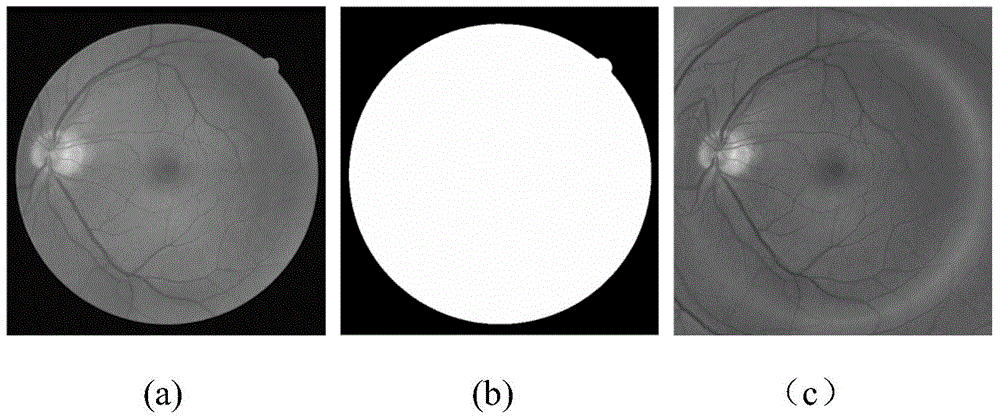
The invention discloses a quick optic disc positioning method based on multi-scale macula detection. The quick optic disc positioning method includes the steps of 1, masking fundus images; 2, performing boundary filling to the fundus images; 3, determining candidate regions of optic discs; 4, excluding boundary candidate positions; and 5, determining positions of the real optic discs. As the optic discs are represented by bright-yellow circular regions of different sizes, multiple candidate regions of optic discs are determined according to the multi-scale space theory and the LOG macula detection technology, and then the real optic discs are positioned on the basis of appearance characteristics of the candidate regions and local vasculature characteristics. By the quick optic disc positioning method, optic disc positioning is performed on the fundus images after the fundus image are reduced, and the real-time detection effect is achieved; due to the multi-scale detection capacity, the method is adaptable to different size of image data sets, and has the advantages easiness, high accuracy, quick positioning and the like.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Videodisc positioning method combining Gbvs model and phase consistency
ActiveCN106204555APrecise positioningInaccurate positioningImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionThree vessels
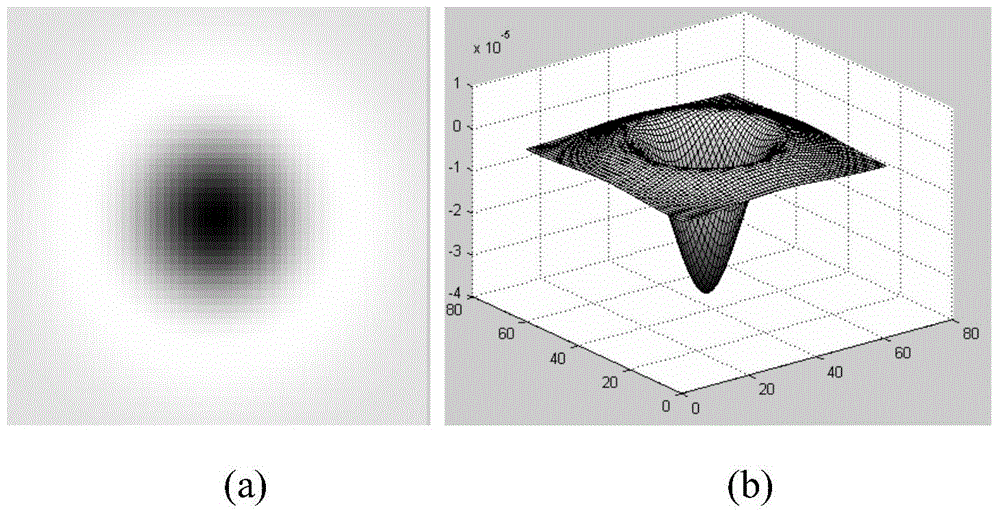
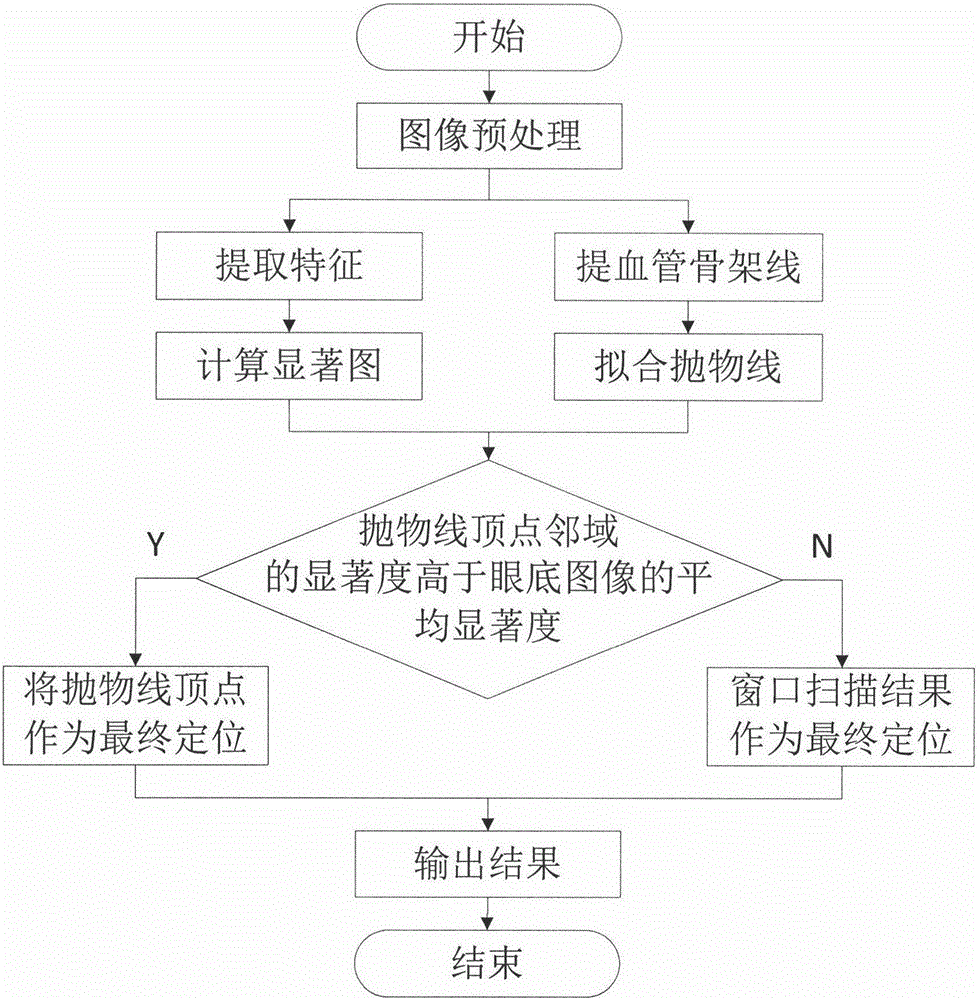
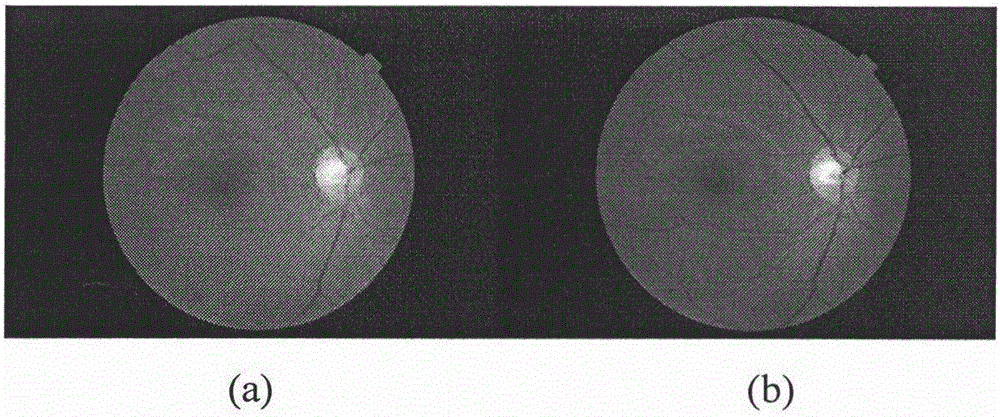
The invention discloses a videodisc positioning method combining a Gbvs model and a phase consistency. The method comprises the following steps of (1) extracting a green channel of a color eye fundus image; (2) calculating a mask image of the fundus image and acquiring a region of interest (ROI) of the fundus image; (3) extracting three characteristics of brightness, a brightness contrast and the phase consistency; (4) using an improved significant model based on graph (graph based visual saliency, Gbvs) to construct a saliency graph; (5) extracting eye fundus image vein blood vessel skeleton lines and using a least square method to carry out parabola fitting; and (6) comparing significance in a parabola summit neighborhood and an average of significance of a whole eye fundus image and determining a videodisc position. During a process of calculating the saliency graph, according to a characteristic of a videodisc in the eye fundus image, the brightness, the brightness contrast and the phase consistency are extracted, the significant model based on the graph is improved, and during a process of positioning the videodisc, a structure characteristic of the vein blood vessel is used to assist accurate positioning. An experiment proves that the method possesses a good effect.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
An automatic analysis and comparison method of fundus images and a storage device
ActiveCN109166117AReduce brightnessShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisDiabetic retinopathyTherapeutic effect
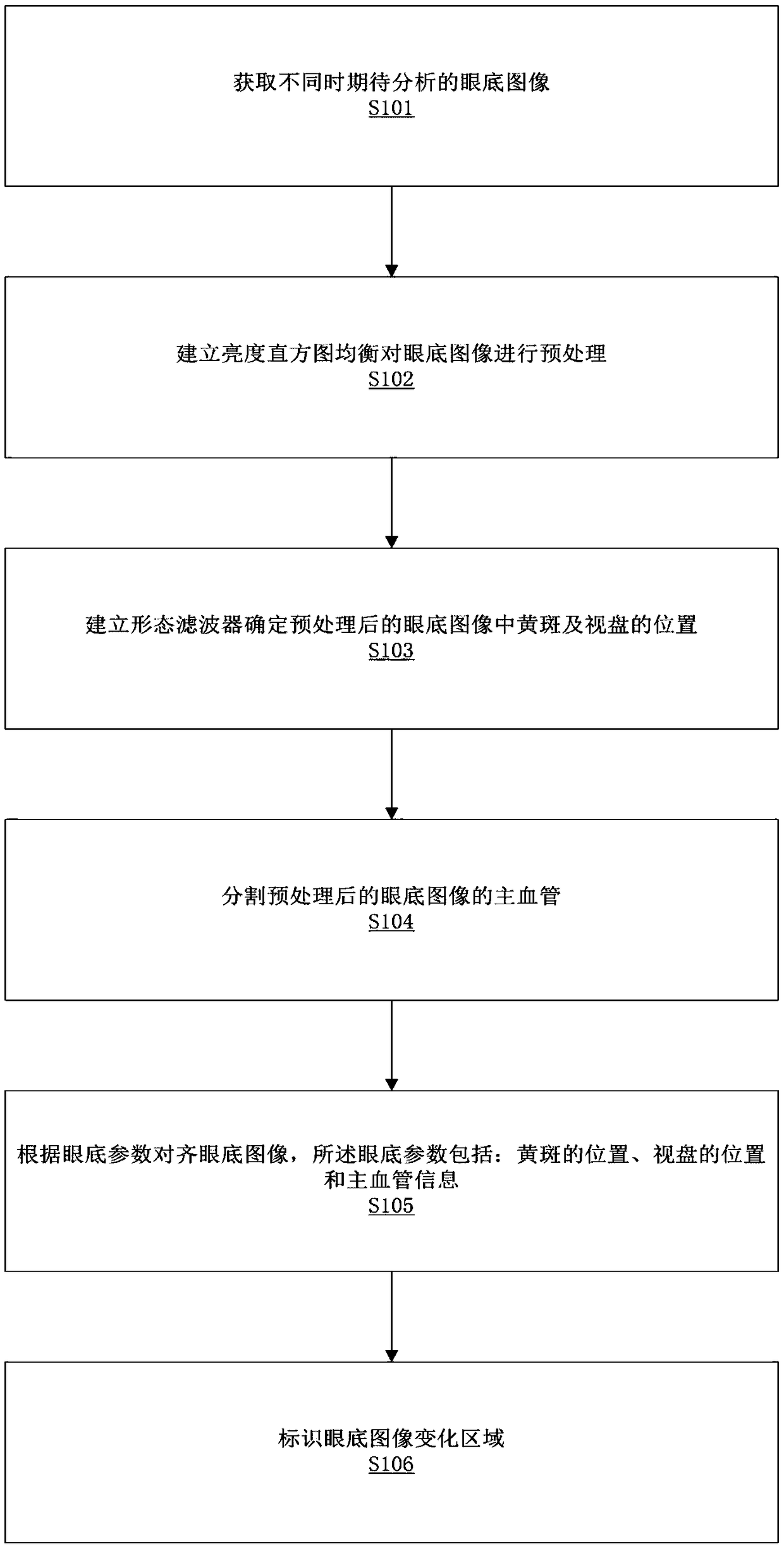
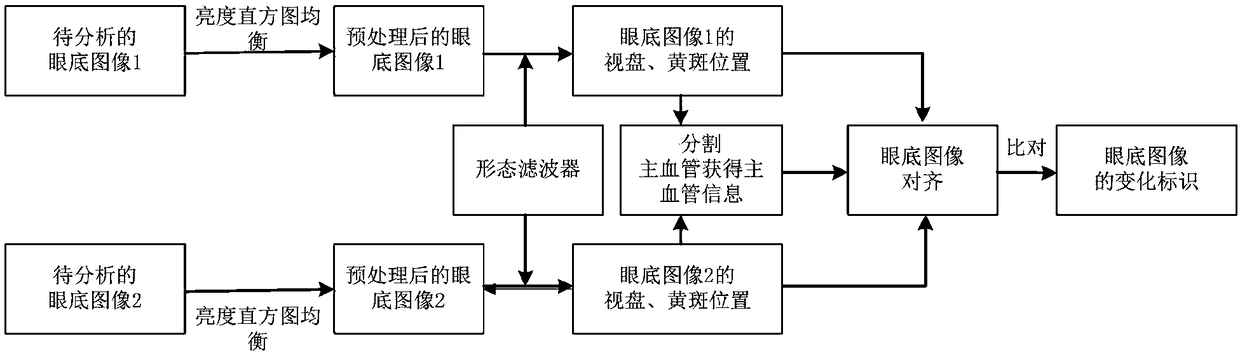
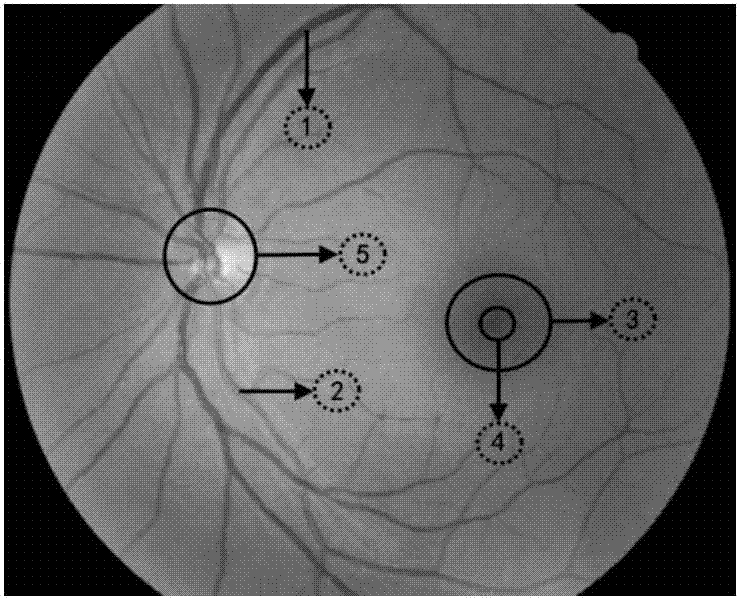
The invention relates to the field of image processing, in particular to an automatic analysis and comparison method of fundus images. The automatic analysis and comparison method of fundus image comprises the following steps: fundus images expect to be analyzed at different times are obtained; the brightness histogram equalization is established to preprocess the fundus image; a morphological filter is established to determine the position of macula and optic disc in the preprocessed fundus image; segmentation of the main vessels of the preprocessed fundus image is carried out; the fundus image is aligned according to fundus parameters, and the fundus image change area is identified. By changing the area, a person can visualize the changes in the health of the eye fundus at different times, so as to quickly judge whether the eye fundus of an individual has health problems, obtain valuable information favorable for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy (DR), glaucoma and vascular changes, and assist in detecting and evaluating the diagnosis and treatment effect of the related chronic diseases, wherein the whole process does not require manual comparison and treatment., Thus, time is greatly saved, workload is reduced and efficiency is improved.
Owner:FUZHOU YIYING HEALTH TECH CO LTD
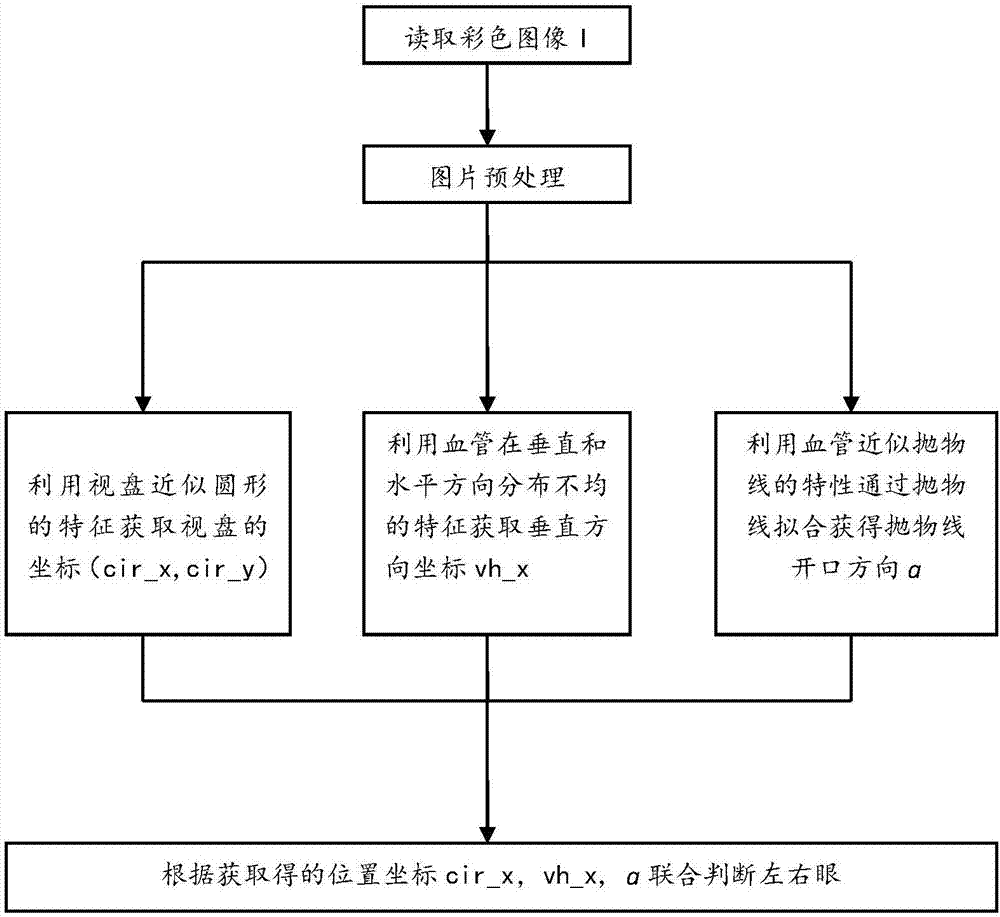
Left and right eye recognition method based on eye ground image features
ActiveCN107292877AReduce complexityHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging Feature
The invention provides a left and right eye recognition method based on eye ground image features, and belongs to the field of medical digital image processing. The method comprises the steps of firstly, processing the acquired eye ground image, then acquiring corresponding information from the processed image via three different methods according to different features of optic discs and blood vessels respectively, finally setting corresponding variables for the three methods and judging whether the methods can be used for judging left and right eyes, performing left and right eye recognition on the combination of the eye ground image according to the recognition result obtained by each method and outputting the recognition result.. The method can be used for quickly and accurately recognizing that the given eye ground image belongs to the left eye or the right eye, is high in recognition accuracy, simple and easy to operate, and has high application value.
Owner:BEIJING ZHENHEALTH TECH CO LTD
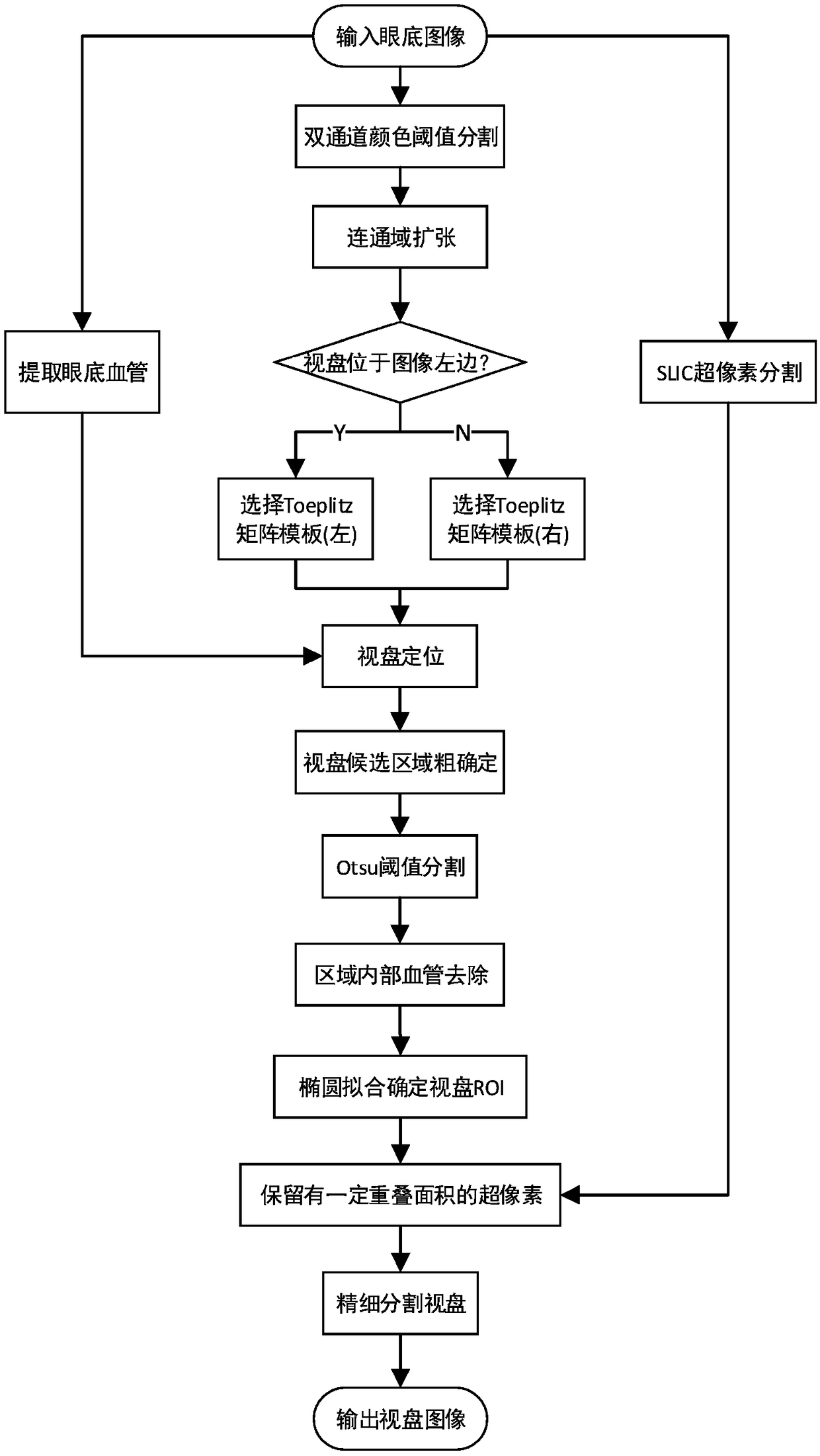
Method for fine segmentation of eye ground optic disc based on SLIC super-pixel segmentation
ActiveCN108961280AEasy to follow upTime consumingImage enhancementImage analysisEllipseMorphological processing
The invention discloses a method for fine segmentation of the eye ground optic disc based on SLIC super-pixel segmentation. The steps are as follows: super-pixel segmentation, vascular segmentation based on morphological processing and R-G double-channel color threshold segmentation are carried out on an input eye ground image, and after expansion of a connected region obtained from color threshold segmentation, a corresponding Toeplitz matrix template is selected according to the pixel coordinates of the connected region to filter an eye ground vascular image to obtain the center position ofthe optic disc; and then, a candidate area of the optic disc is extracted and the internal blood vessels are removed, threshold segmentation is carried out on the candidate area of the optic disc through a binarization method, the ROI (Region of Interest) of the optic disc ellipse is determined by using an ellipse fitting method based on least squares, super pixels with a certain overlapping areaare retained according to the SLIC super-pixel segmentation result, and thus, fine segmentation of the optic disc is completed. Through the method, automatic positioning and fine segmentation of the optic disc are realized, better contour information of the optic disc can be retained, less time is consumed, other follow-up processing of the eye ground image is facilitated, and assistant diagnosiscan be provided for ophthalmologists.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Glaucoma early stage screening method
InactiveCN106214120AImprove early detection rateAchieve early detectionTonometersOthalmoscopesThree levelComputer assistance
The invention relates to a glaucoma early stage screening method using a computer to carry out automatic analysis for eyeground photographs, thus fast calculating an eye cup-eye disk C / D ratio value in real time; the features are that the C / D value is compared with a set glaucoma risk value so as to determine the glaucoma existence possibility. The advantages are that the cup / disk ratio changes formed by glaucoma pathology optic nerve progressive damages are employed, thus carrying out automatic eyeground photograph reading analysis under computer assistance. Image fuzzy processing, OTSU algorithm and computer operation are introduced so as to greatly improve determination result accuracy and instantaneity when compared with a conventional diagnosis method singly using an eyeground photograph reading mode, and avoiding expensive and complex detection equipment; low cost high efficiency screening method can be carried out so as to realize glaucoma early discovery and early diagnosis; a database is built, and a screening and uploading step by step mode is employed, thus gradually improving a big data development system under a three-level networking system.
Owner:靳晓亮 +2
Image processing device and method, eye fundus image processing device, image photographing method, and eye fundus image photographing device and method
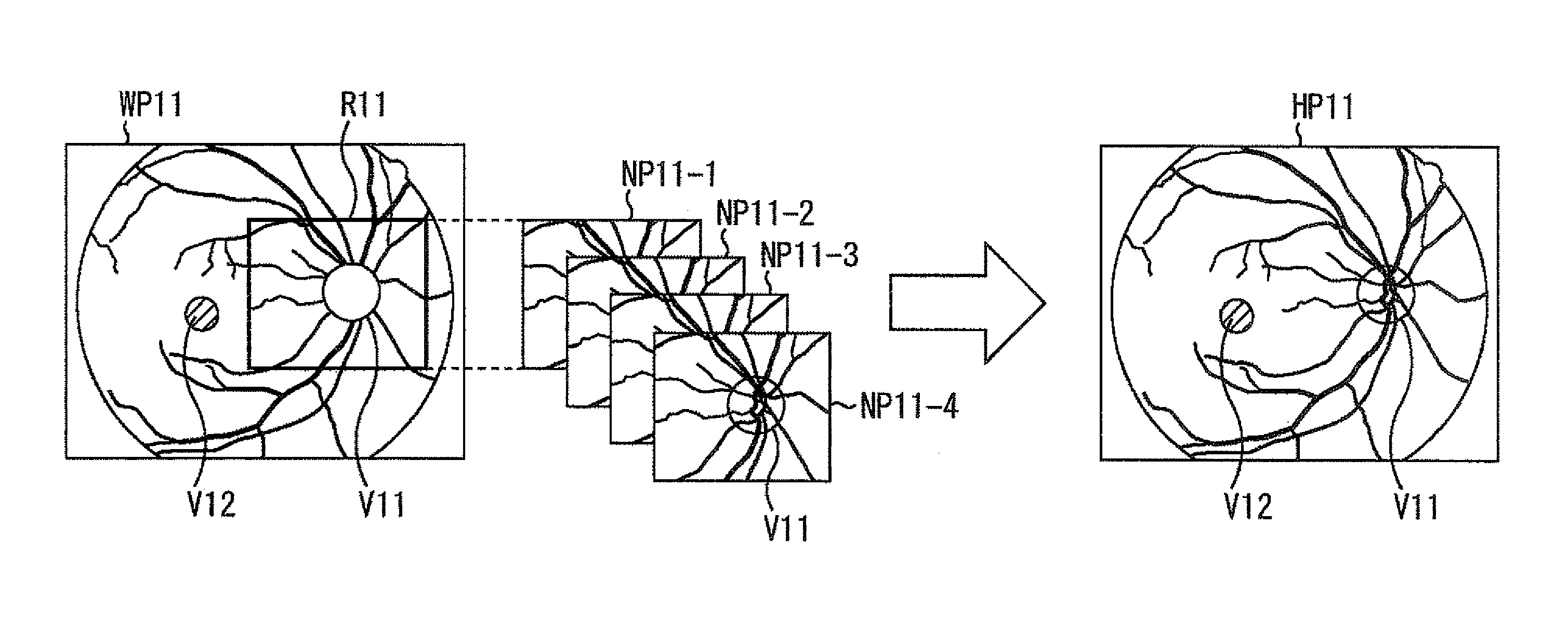
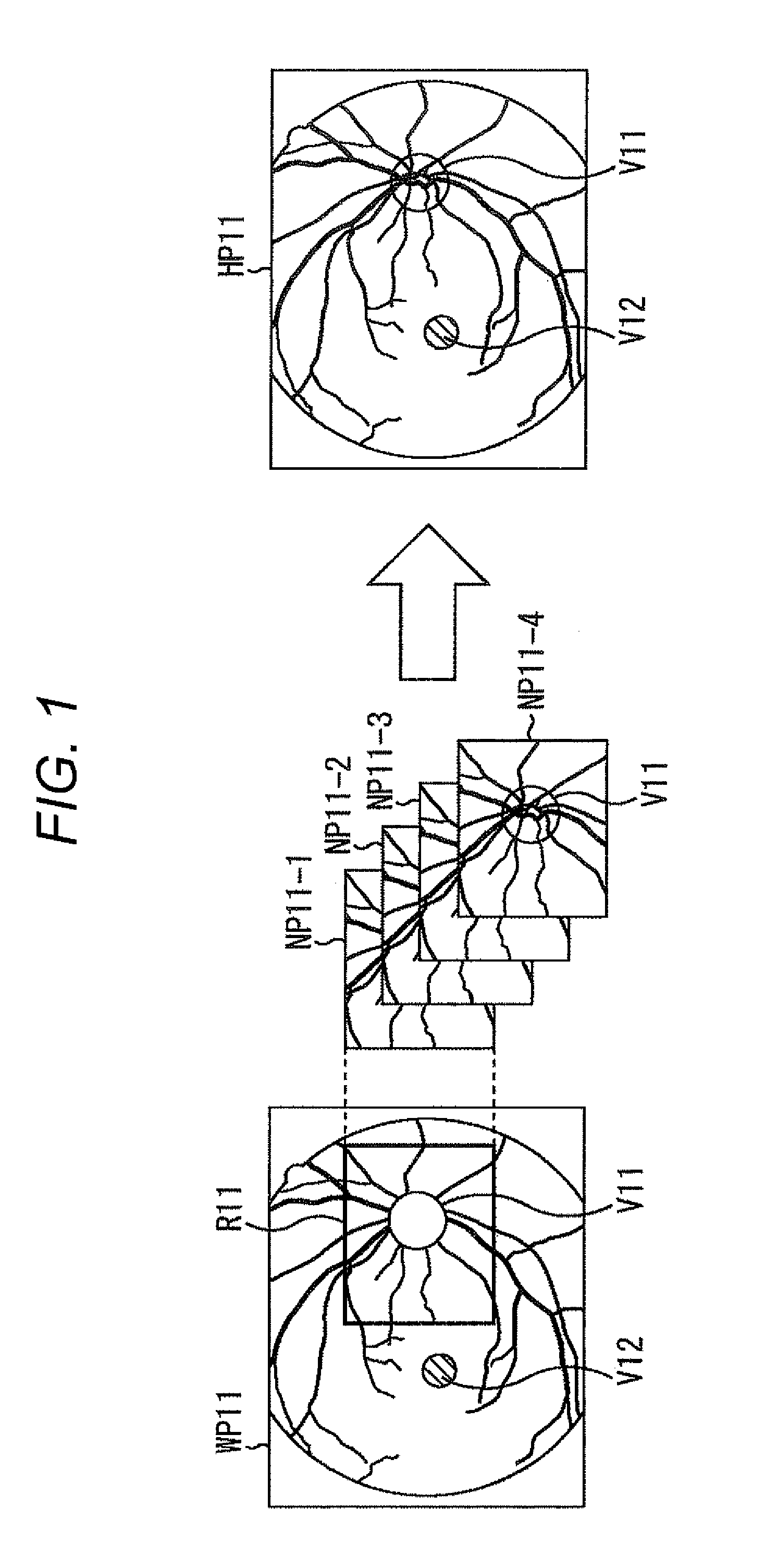
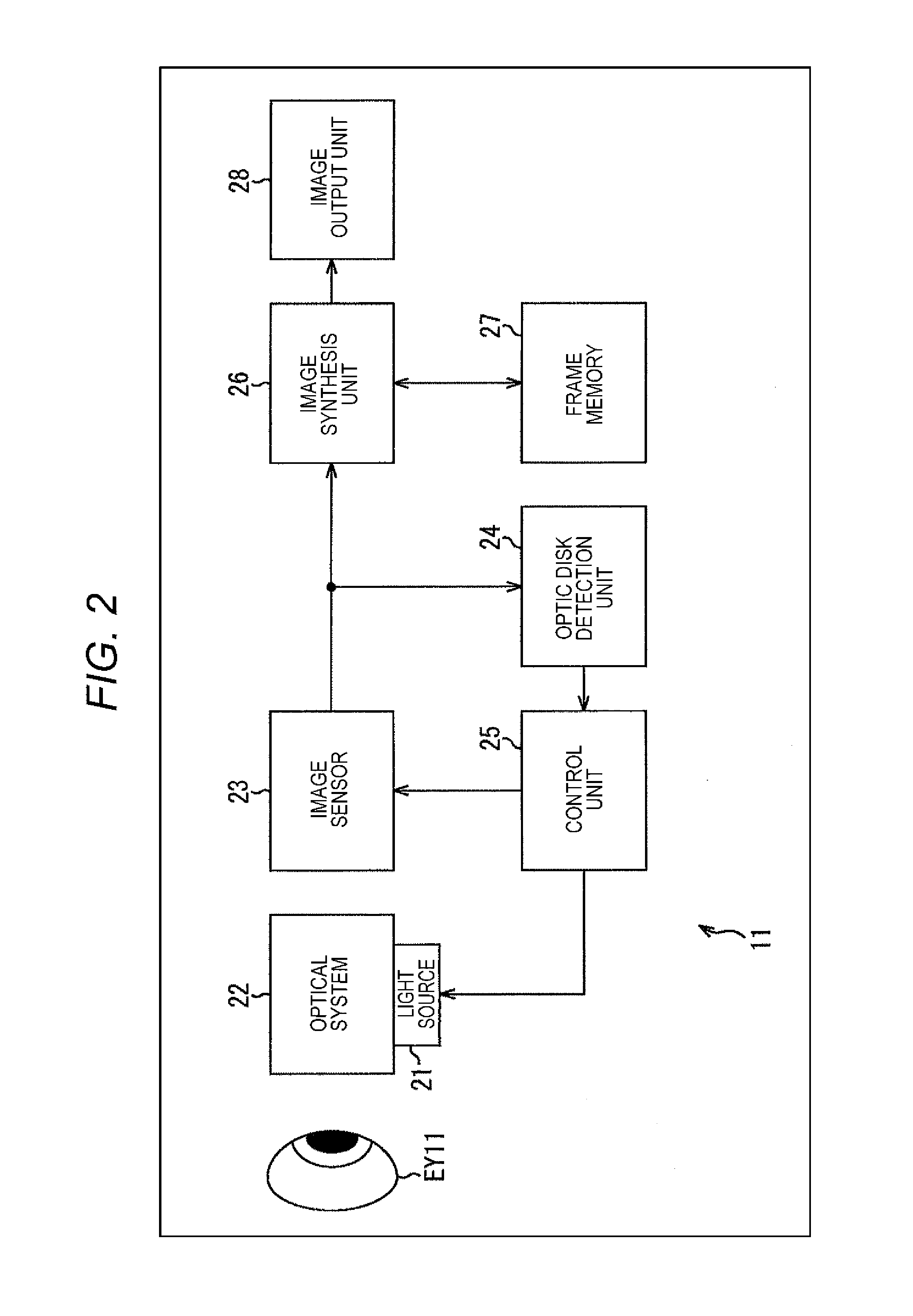
An eye fundus image photographing device and method that can acquire images of higher quality. The eye fundus image photographing device photographs a wide-angle eye fundus image on an appropriate exposure condition with respect to a peripheral area different from an optic disk region of an eye fundus area and detects the optic disk region from the wide-angle eye fundus image. Moreover, based on the detection result of the optic disk region, the eye fundus image photographing device photographs a narrow-angle eye fundus image which assumes an area of the optic disk region as an object, on an appropriate exposure condition with respect to the area of the optic disk region. Further, the eye fundus image photographing device generates a synthetic eye fundus image of a high dynamic range by synthesizing the wide-angle eye fundus image and the narrow-angle eye fundus image.
Owner:SONY CORP
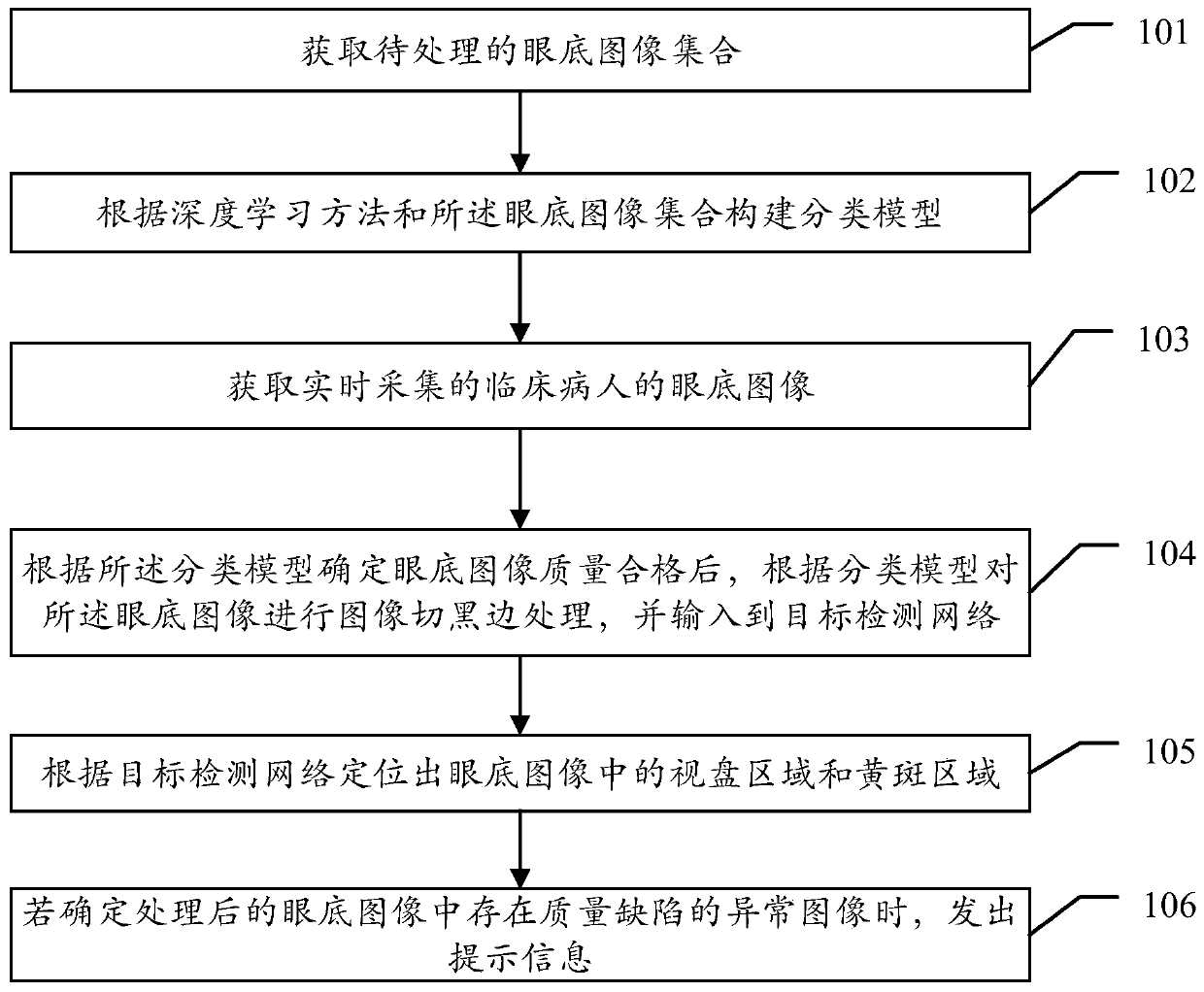
Eye fundus image quality evaluation method and device and storage medium
The invention relates to the technical field of image detection, and provides an eye fundus image quality evaluation method and device, and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a to-be-processed eye fundus image set; constructing a classification model according to a deep learning method and the fundus image set; acquiring an eye fundus image of the clinical patient acquired in real time; after determining that the fundus image is qualified according to the classification model, performing image black edge cutting processing on the fundus image according to the classification model, and inputting the image black edge cutting processing into a target detection network; positioning a optic disc area and a macular area in the fundus image according to the target detection network; and if it is determined that there is an abnormal image with a quality defect in the processed fundus image, sending prompting information, wherein the prompting information is used for prompting a collection part corresponding to the abnormal image to be collected again. By adopting the scheme, the collection quality of the fundus image can be fed back in real time, and the quality stability of the fundus image is ensured.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Optic disc positioning method for retina image
InactiveCN103971369ARapid positioningPrecise positioningImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionBlood vessel featureRetina
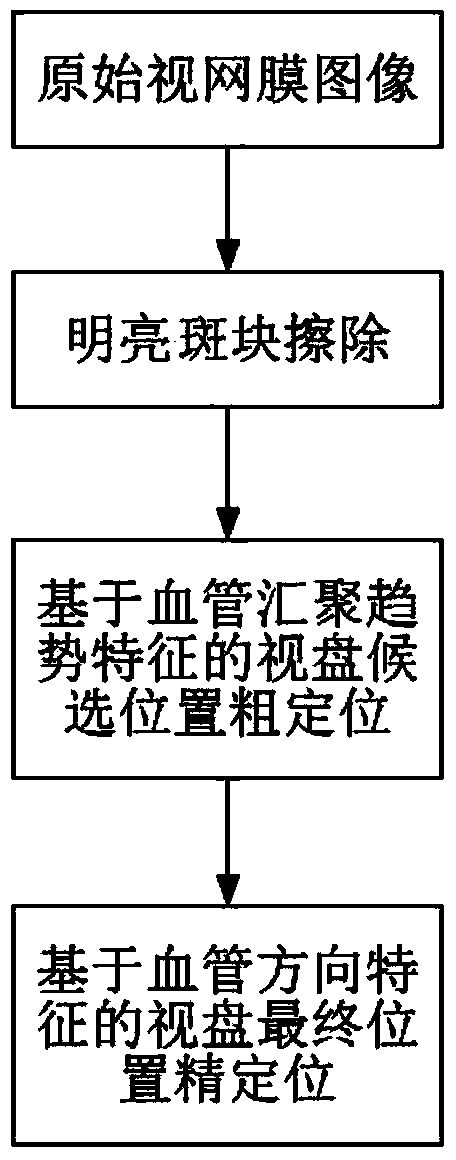
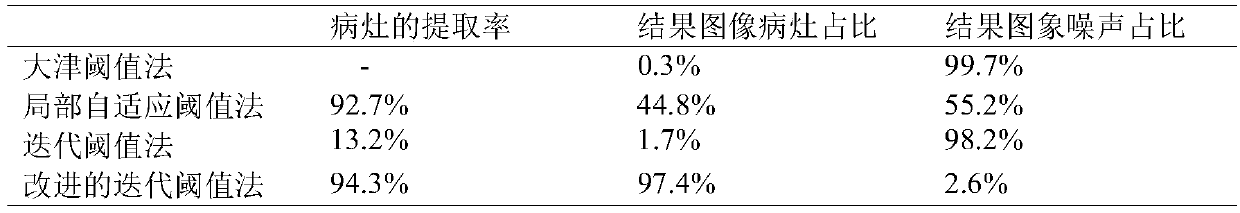
The invention discloses an optic disc positioning method for a retina image. The optic disc positioning method for the retina image comprises the following steps that (a) bright plaques in the background are erased, and meanwhile blood vessel features are reserved; (b) candidate positions of the center of the optic disc are determined based on blood vessel convergence tendency features; (c) the finial position of the center of the optic disc is determined from the candidate positions of the center of the optic disc based on blood vessel direction features. The optic disc positioning method for the retina image can solve the problem that the positioning of the optic disc is prone to interference brought by various lesions and other noise in the background, and the accuracy and the speed of the positioning of the optic disc under the complex background can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN ACAD OF METROLOGY & QUALITY INSPECTION
An diabetic retina image quality detection method based on an image analysis technology
ActiveCN109544540AImprove visibilityEasy diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityEqualization
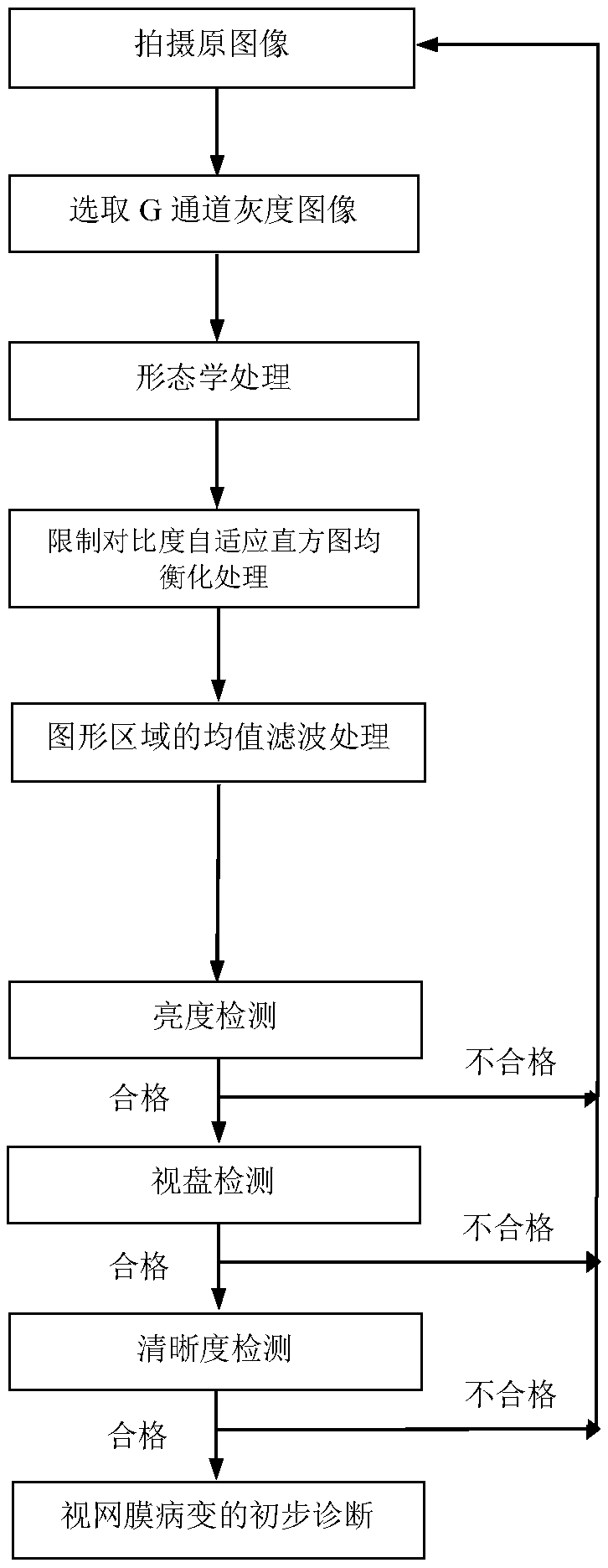
The invention relates to the technical field of image processing, in particular to a diabetic retina image quality detection method based on an image analysis technology. The method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing the fundus image, performing morphological treatment, equalization treatment and filtering treatment on the fundus image during the pretreatment process, performing brightness detection, optic disc detection and definition detection after the pretreatment, and finally obtaining the fundus image to be diagnosed, and diagnosing diabetic retinopathy. The preprocessing operation in the method greatly improves the visibility of the retinal fundus image, It is more advantageous for doctors to diagnose and analyze the patients' condition, and the quality inspection operation can greatly reduce the occurrence of the unqualified fundus images taken at the census spots. The fundus images which pass the quality inspection can be used for the preliminary diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
A method for detecting the rigid exudate lesion in a fundus image based on a convolution neural network
InactiveCN109447962AAchieve high-precision detection of lesionsIncrease contrastImage enhancementImage analysisHard exudatesNetwork model
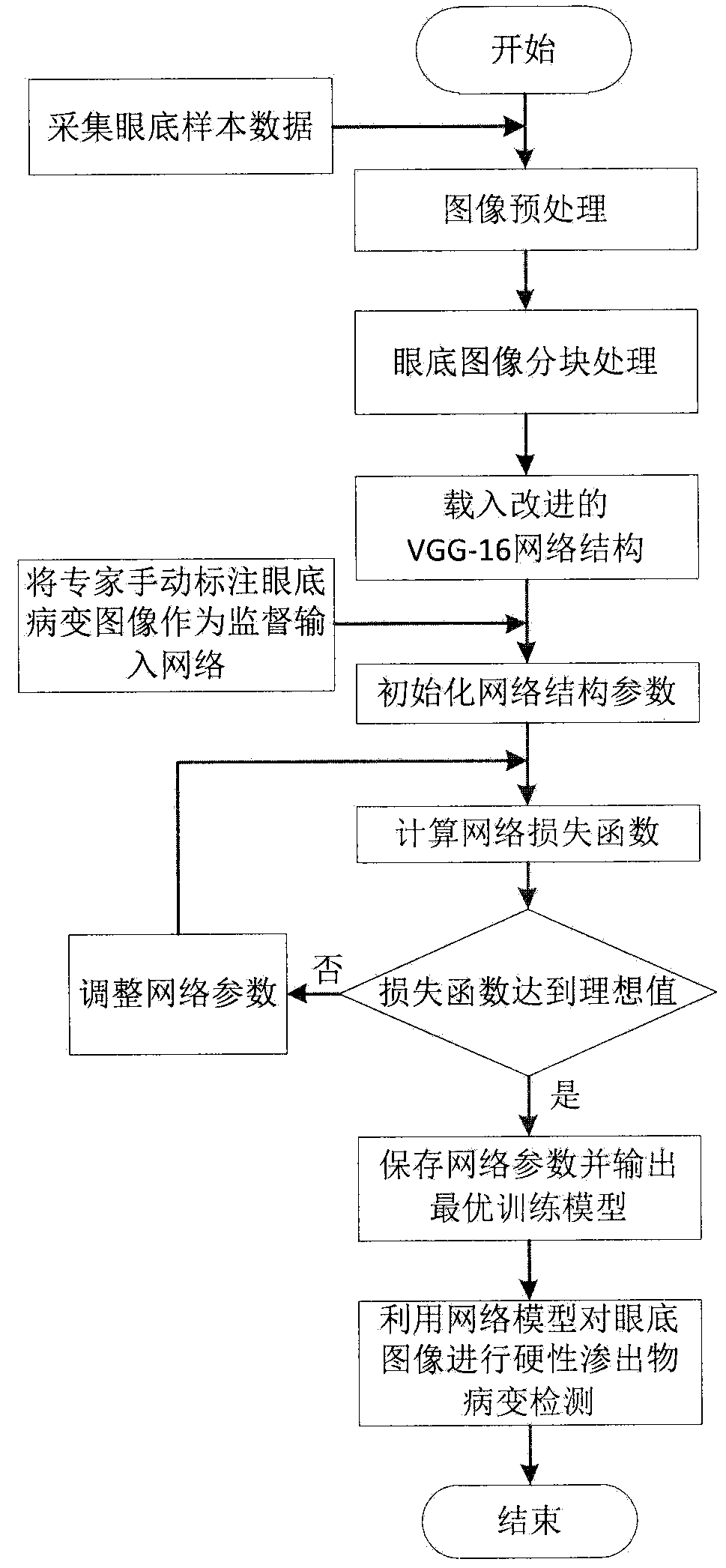
The invention provides a method for detecting the rigid exudate lesion in a fundus image based on a convolution neural network. The method comprises the following steps of 1) preprocessing the fundusimage and enhancing image contrast through Gamma correction algorithm; 2) carrying out block processing on that image to expand the data; 3) using the lesion results manually annotated by experts in DRIVE, MESSIDOR database as the monitoring data, using the adjusted VGG-16 network to train the block image and introducing the channel weighting module to establish the dependency of the feature channel explicitly by learning; 4) using the trained network model to detect the hard exudate lesion in the fundus image. Compared with the traditional scheme, the method of the invention avoids the complicated image processing process, is not affected by the fundus optic disc and cotton floc spots on the hard exudate lesion, realizes the high-precision detection of the hard exudate lesion, and can bewidely used in the field of automatic screening of the fundus rigid exudate.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
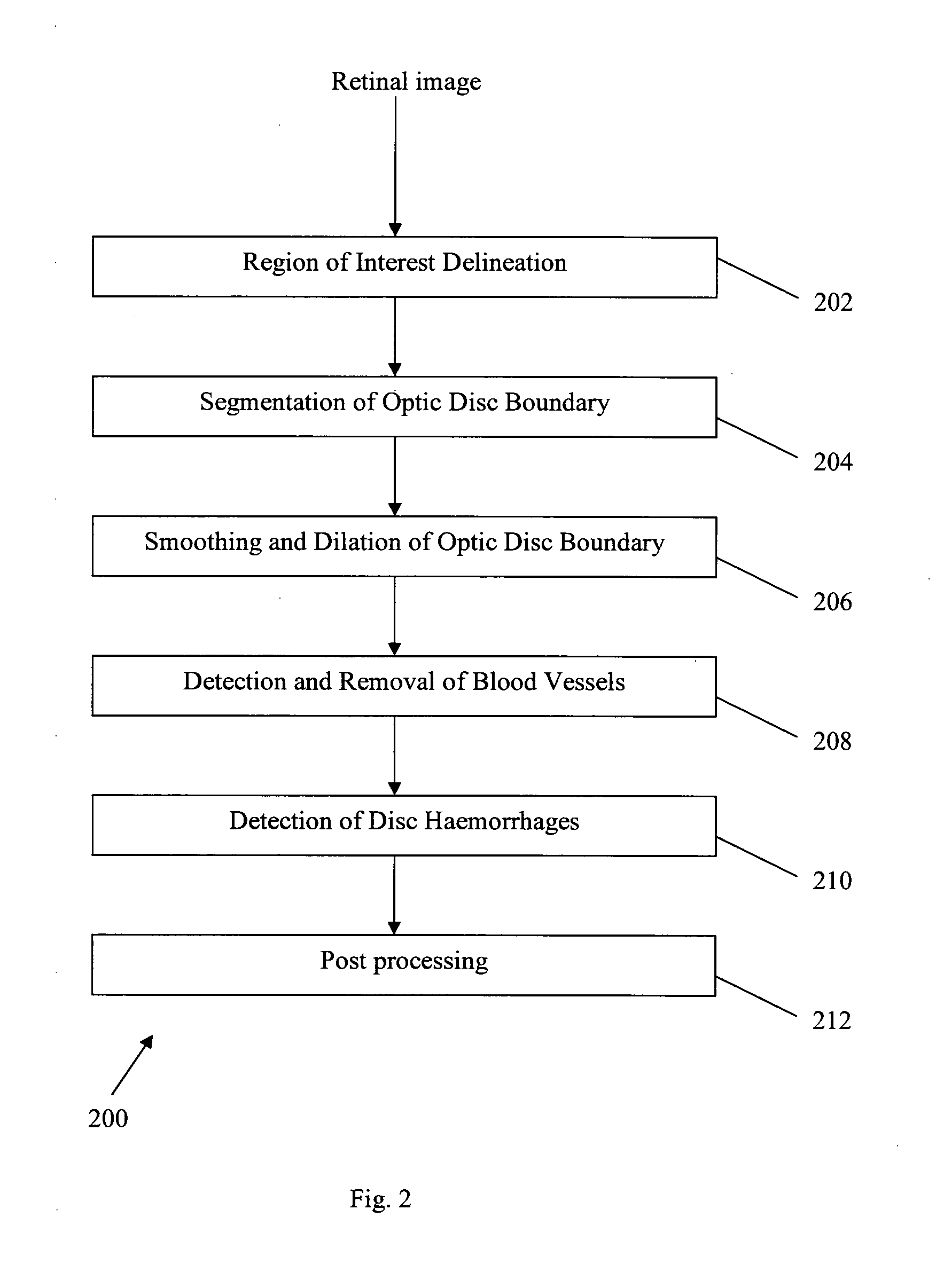
Method and system for detecting disc haemorrhages
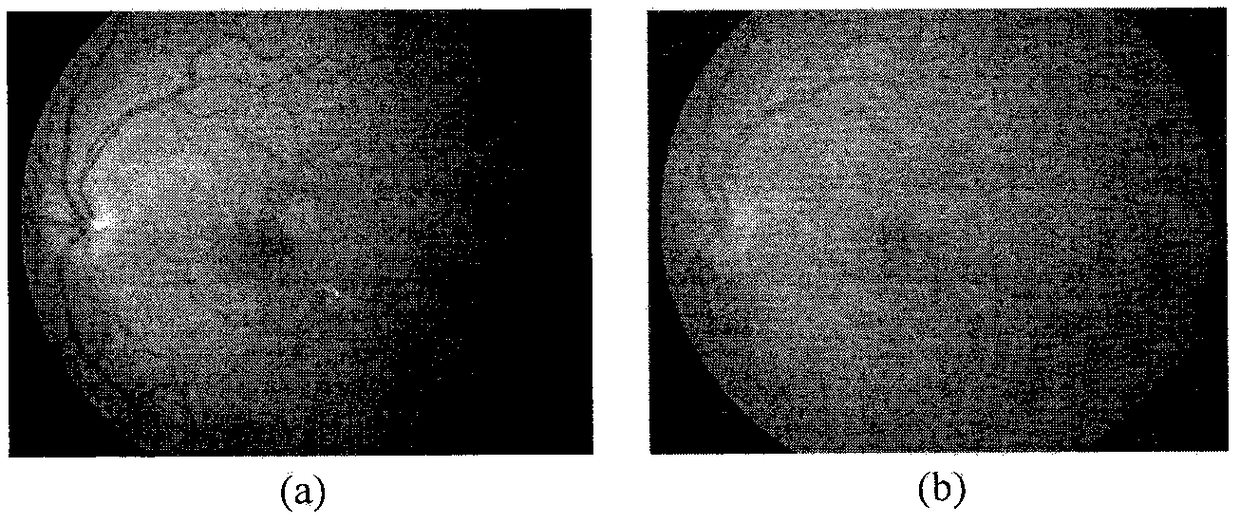
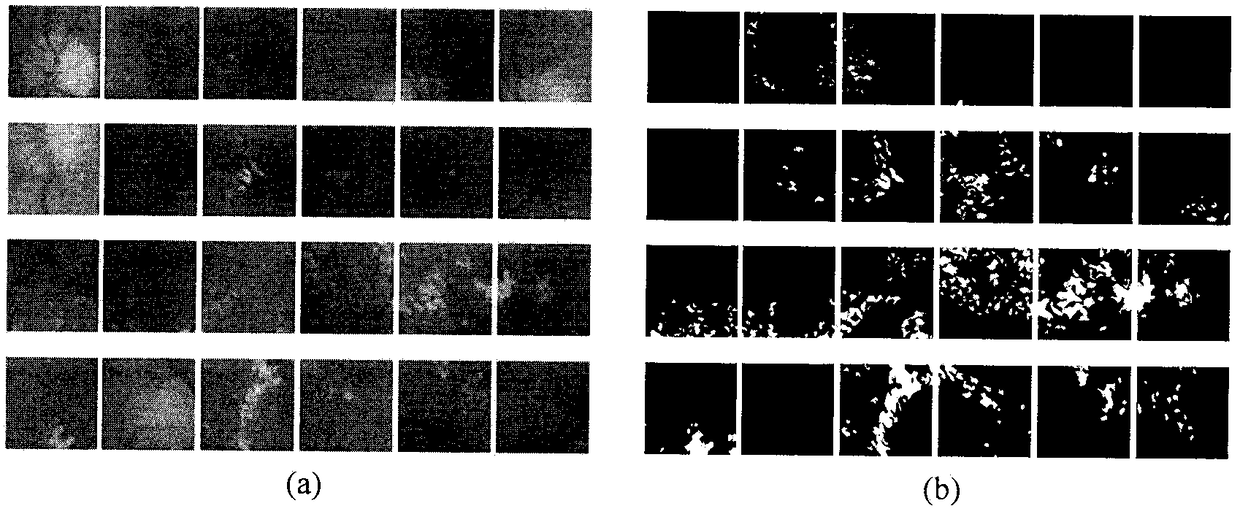
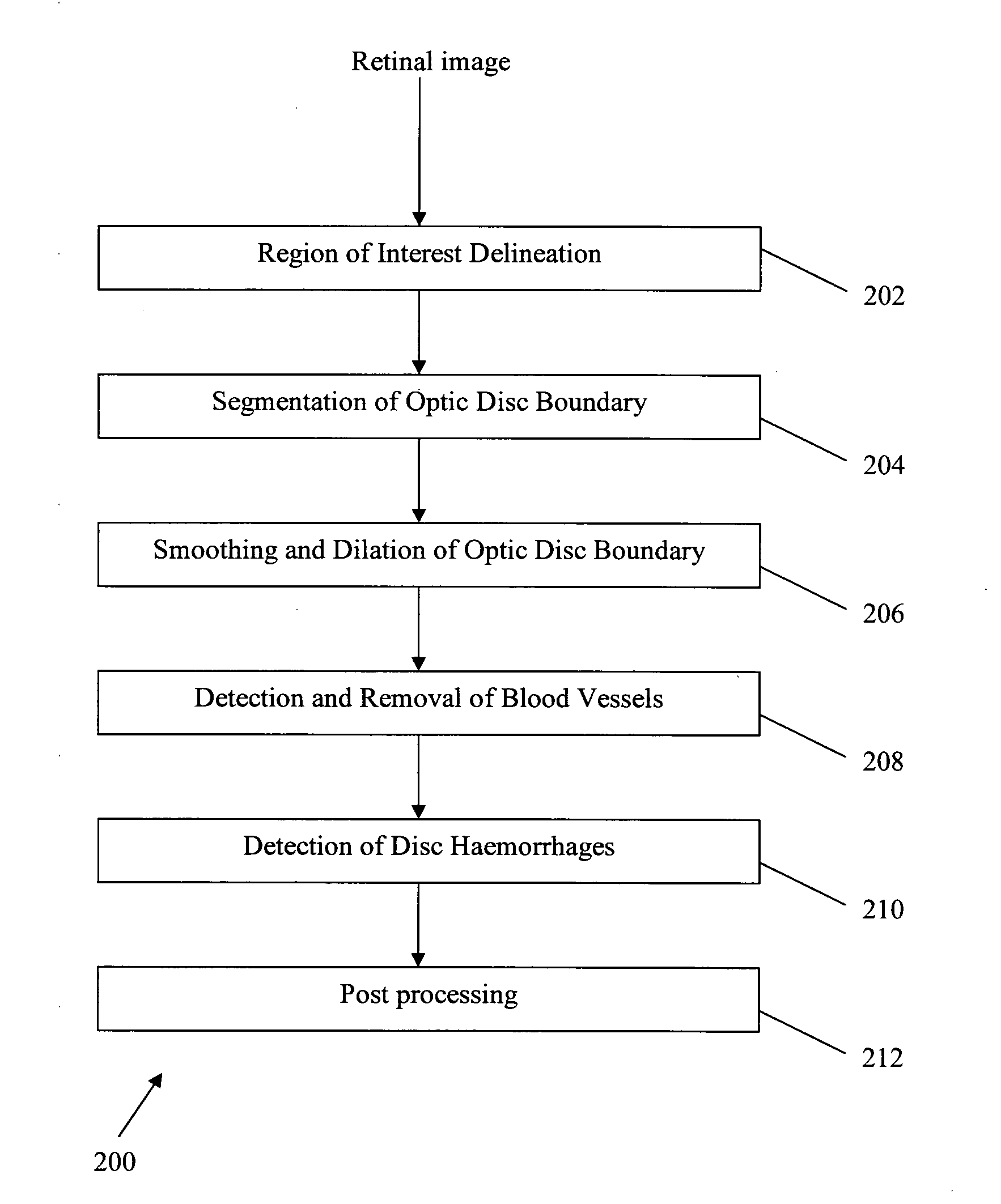
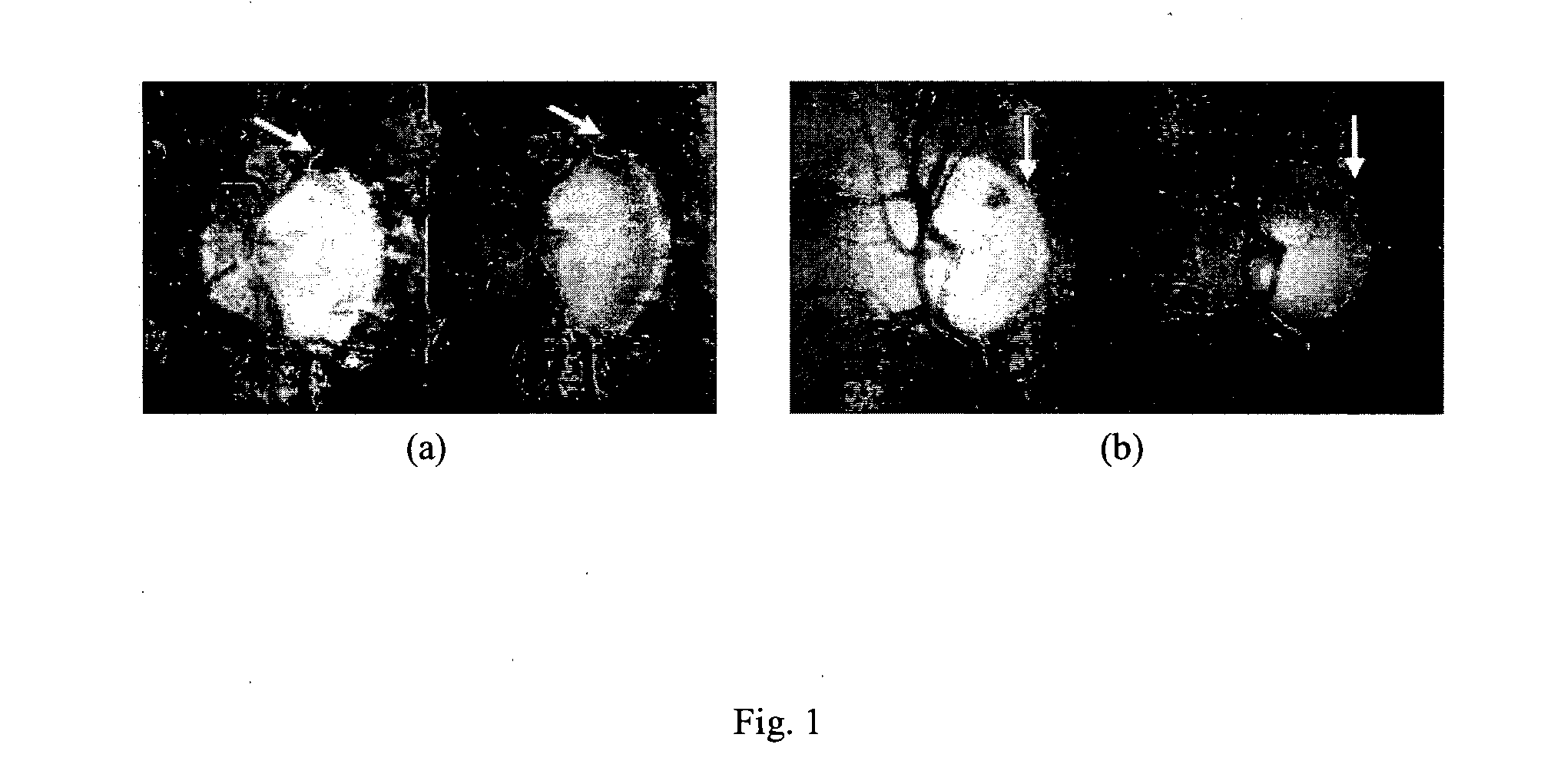
A method for detecting disc haemorrhages in a retinal fundus image. The method includes (a) identifying a ring-shaped region of interest in the retinal fundus image encompassing the optic disc boundary; (b) removing blood vessel regions in the identified region of interest; (c) detecting candidate disc haemorrhages from the removed blood vessels regions in the identified region of interest; and (d) screening the candidate disc haemorrhages. The detected disc haemorrhages may be used to aid in the detection of glaucoma.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERIVICES PTE LTD A COMPANY ORGANIZED & EXISTING UNDER THE LAWS OF SINGAPORE +2
Retina image analysis method and device, and calculation equipment
ActiveCN107123124AIncrease contrastEliminate negative effectsImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisRetina
The invention discloses a retina image analysis method applied to calculation equipment. The method comprises steps that a to-be-analyzed retina image is acquired, and the to-be-analyzed retina image is pre-processed to acquire an enhanced image; the enhanced image is filtered to extract a background image; a bright region image and a dark region image are determined according to RGB color values of pixels of the enhanced image and the background image; a videodisc region and a bright noise region are determined, and the videodisc region and the bright noise region are removed from the bright region image to acquire an exudation region; a blood vessel region and a dark noise region are determined, and the blood vessel region and the dark noise region are removed from the dark region image to acquire a hemorrhage region. The invention further discloses a retina image analysis device of the retina image analysis method, and the calculation equipment equipped with the retina image analysis device. The method is advantaged in that the exudation region and the hemorrhage region of the retina image can be rapidly acquired through segmentation.
Owner:珠海全一科技有限公司
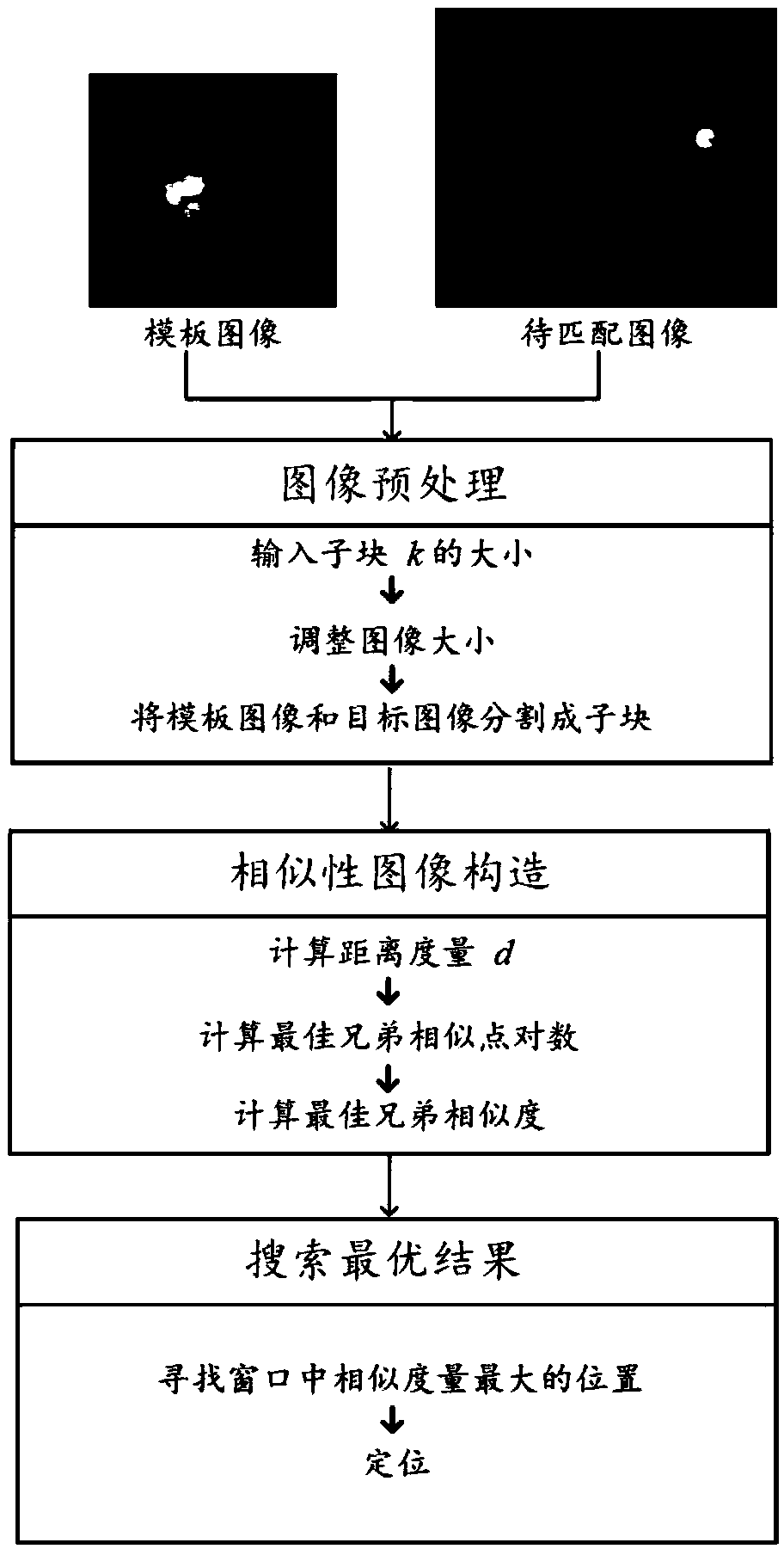
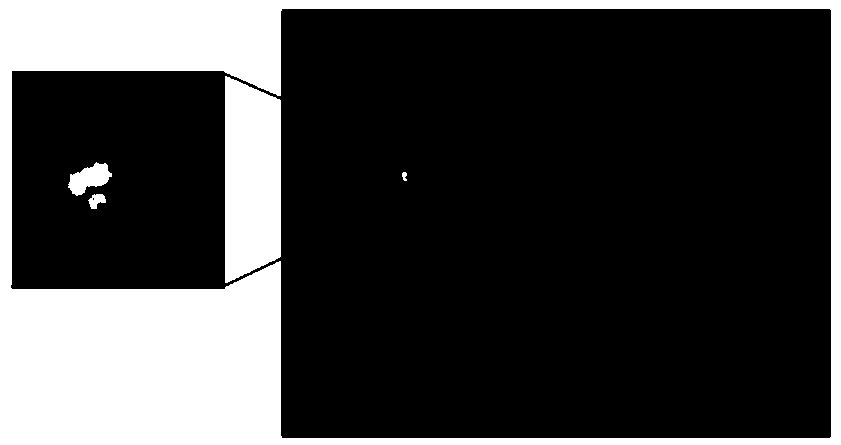
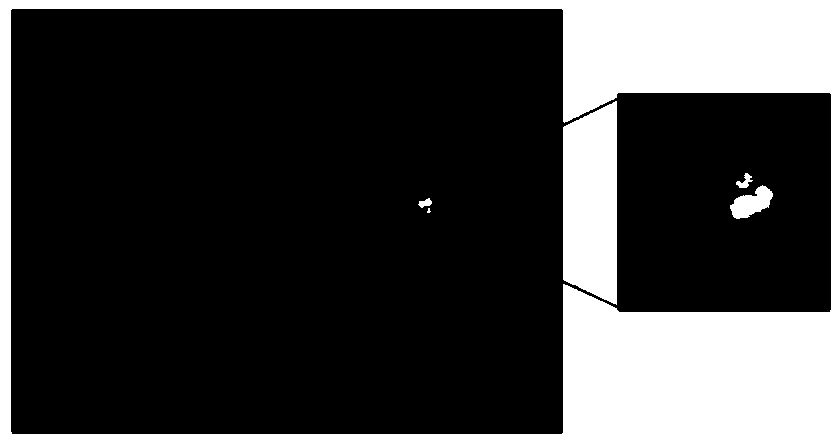
Optimal sibling similarity-based fundus image optic disc positioning method and system
ActiveCN108629769AImprove robustnessOvercome clutterImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMinimum bounding rectangle
The invention discloses an optimal sibling similarity-based fundus image optic disc positioning method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a healthy fundus image, and extracting an image in a minimum circumscribed rectangle as a template image, wherein the minimum circumscribed rectangle is in the healthy fundus image and contains an optic disc region; (2)preprocessing the template image and a to-be-matched image; (3) calculating an optimal sibling similarity between the template image and the to-be-matched image; (4) searching in the to-be-matched image, and determining a region corresponding to the maximum value of the optimal sibling similarity as a final positioning result. According to the invention, a new concept is provided for the positioning work of the fundus image optic disc, and a good effect is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
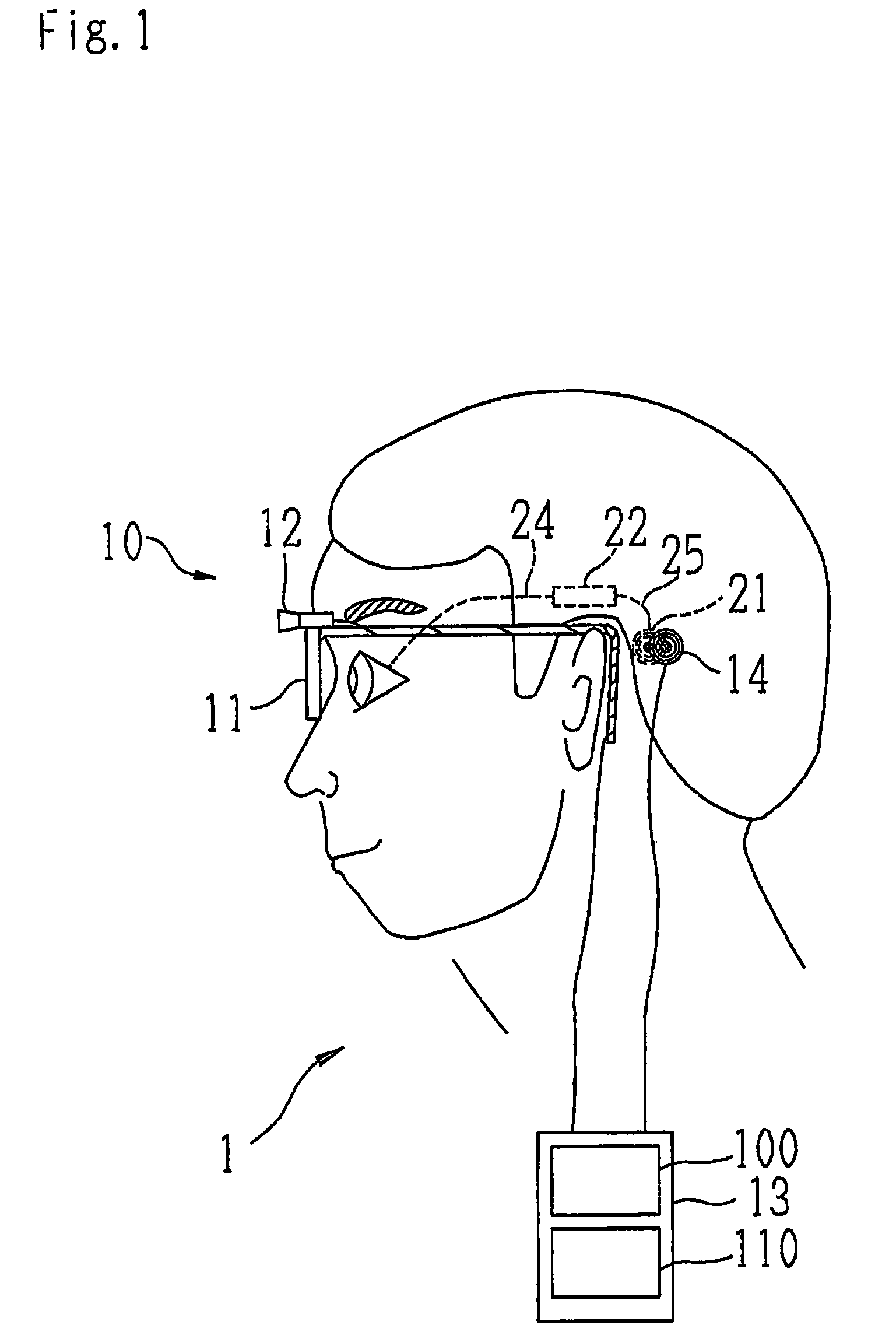
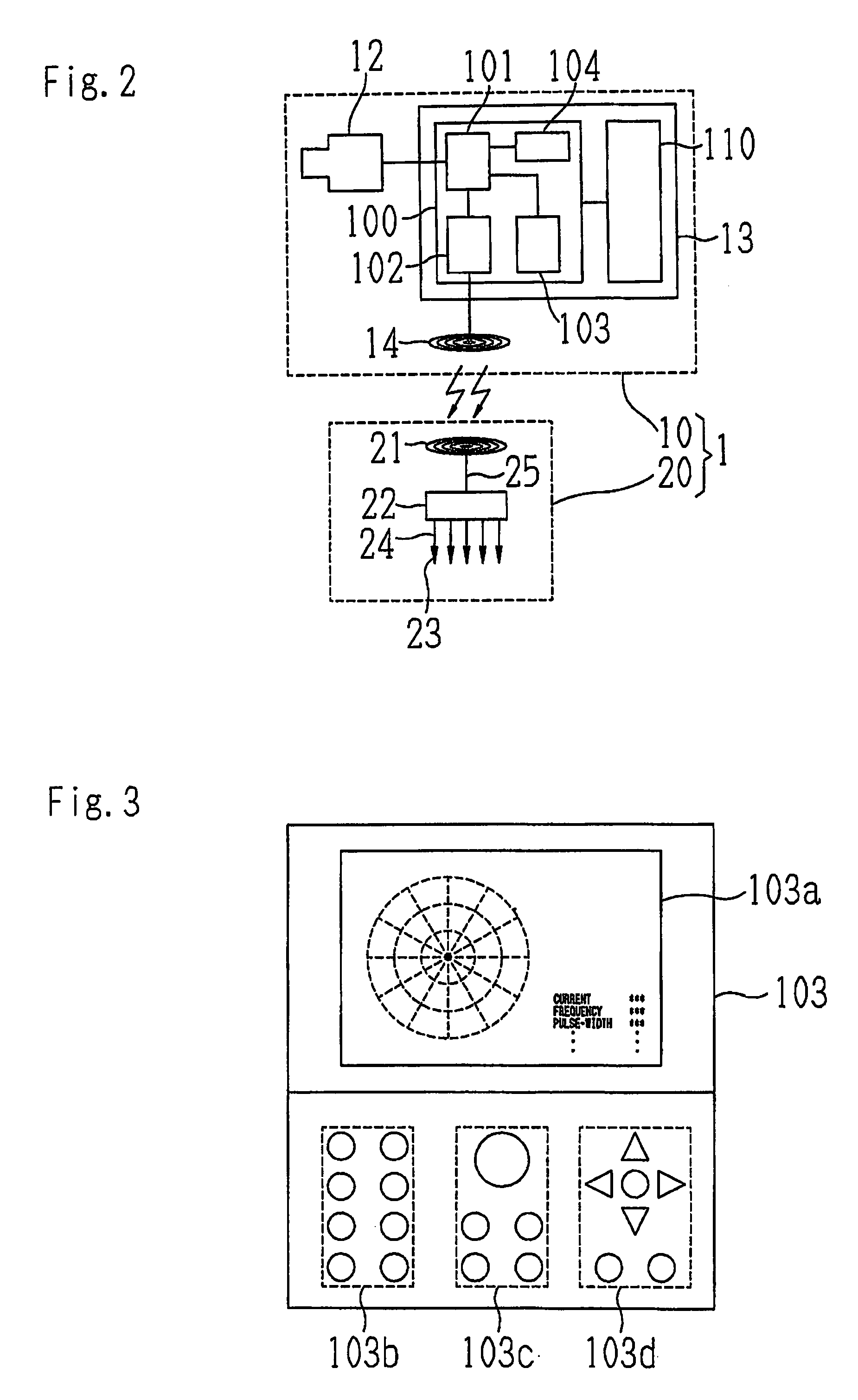
Vision regeneration assisting device
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Methods and systems for assessing retinal images, and obtaining information from retinal images
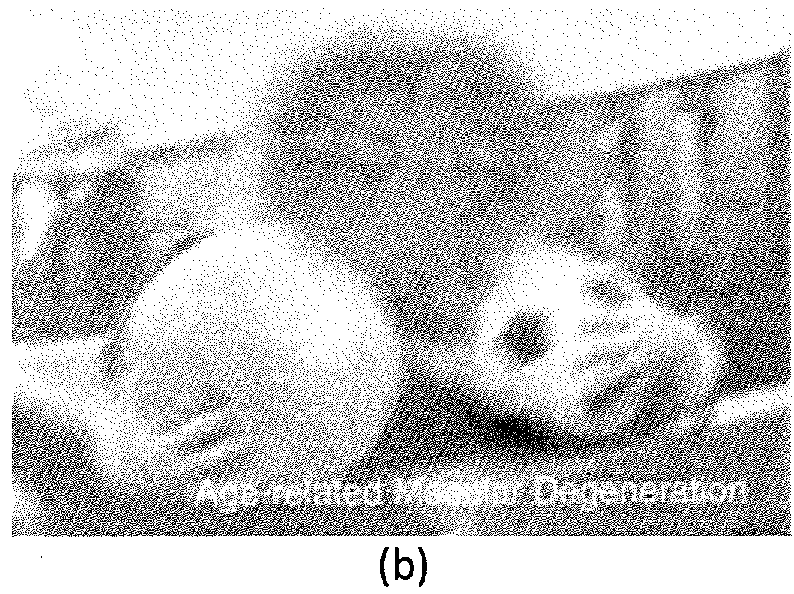
ActiveUS20180181833A1Easy to useImprove reliabilityImage enhancementMedical imagingPathology diagnosisRetinal image
A method of assessing the quality of an retinal image (such as a fundus image) includes selecting at least one region of interest within a retinal image corresponding to a particular structure of the eye (e.g. the optic disc or the macula), and a quality score is calculated in respect of the, or each, region-of-interest. Each region of interest is typically one associated with pathology, as the optic disc and the macula are. Optionally, a quality score may be calculated also in respect of the eye as a whole (i.e. over the entire image, if the entire image corresponds to the retina).
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
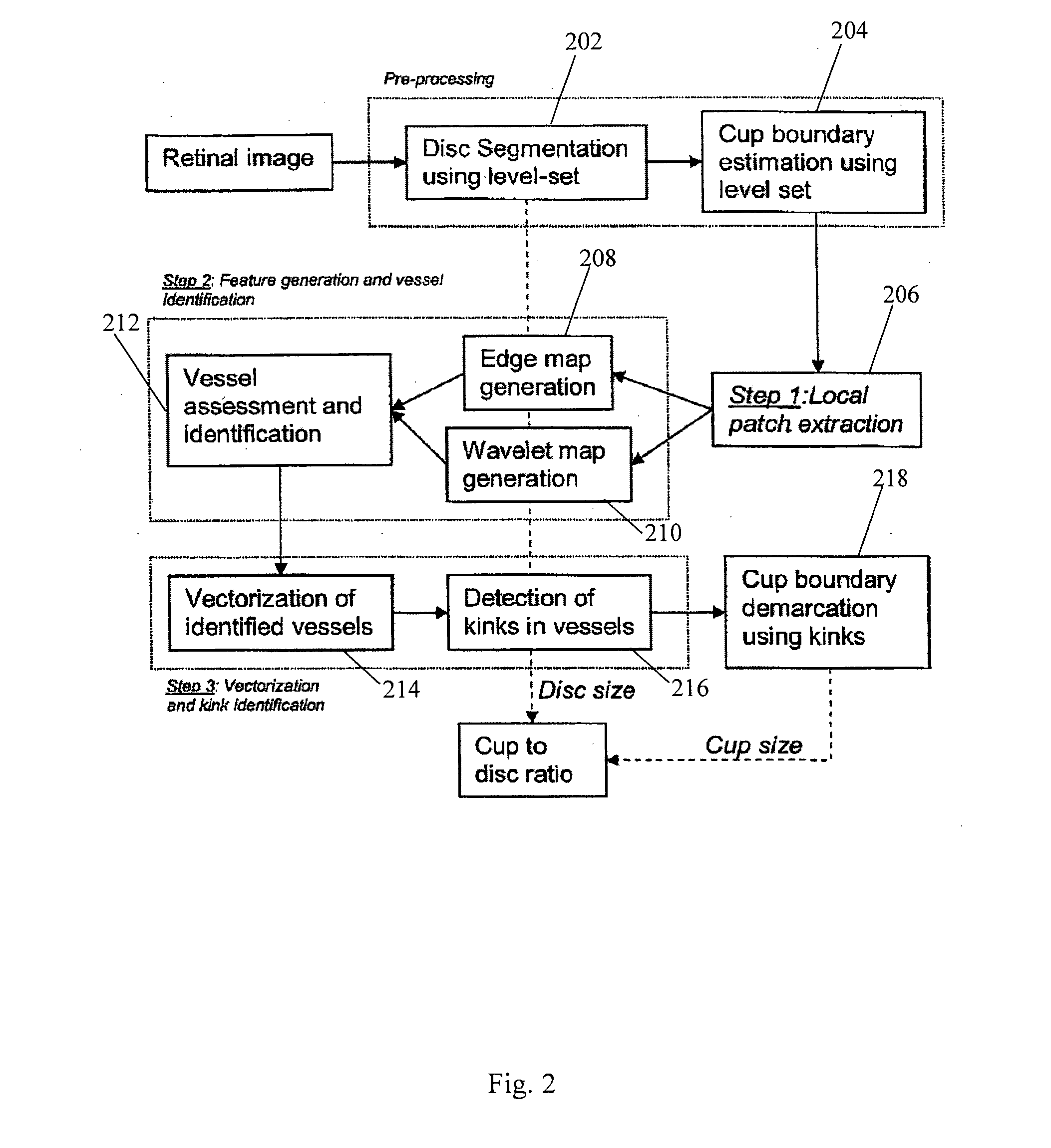
Method and system for determining the position of an optic cup boundary
A method for determining the position of an optic cup boundary in a 2D retinal image. The method includes detecting kinks in blood vessels at an estimated boundary of the optic cup and the optic disc, and determining the position of the optic cup boundary in the 2D retinal image based on the detected kinks. The determined optic cup boundary may be used for determining a CDR which may in turn be used for determining a risk of contracting glaucomatous.
Owner:SINGAPORE HEALTH SERVICES PTE +2
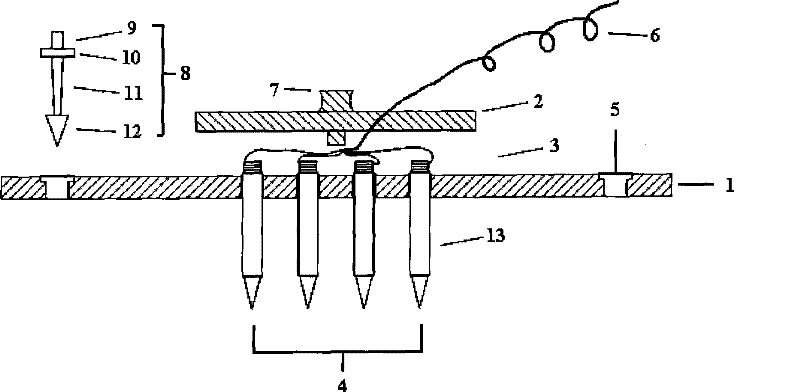
Retinal prosthesis, implanting device and flexible cable
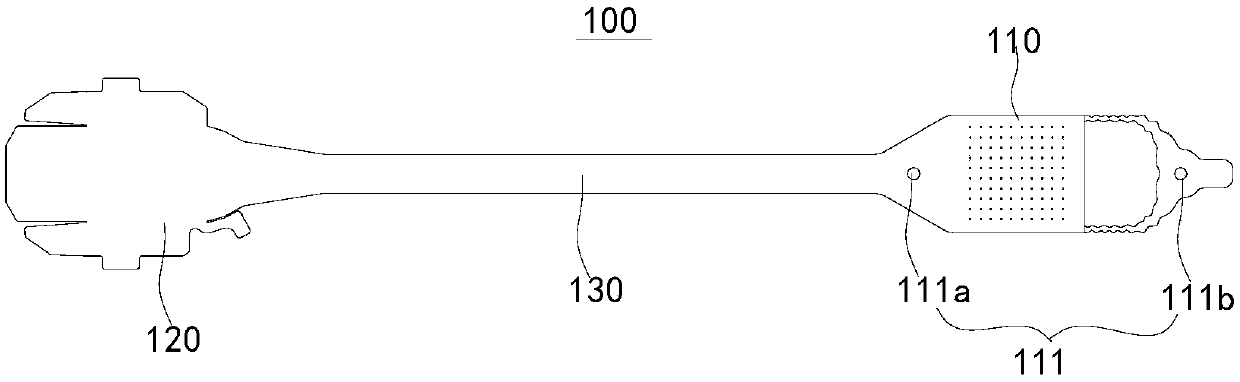
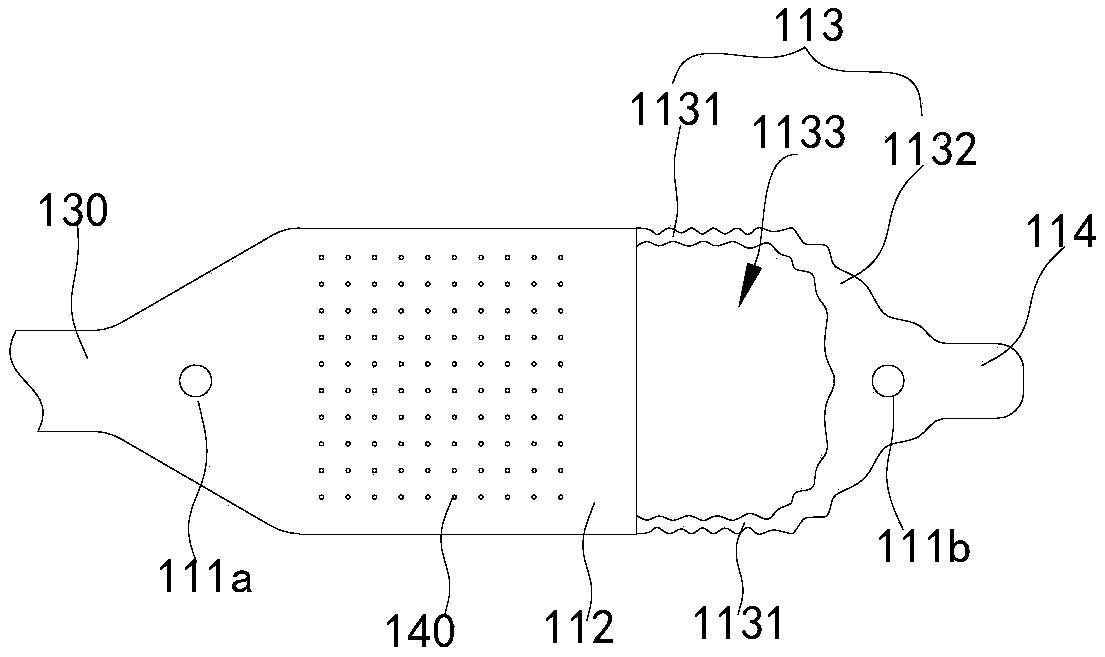
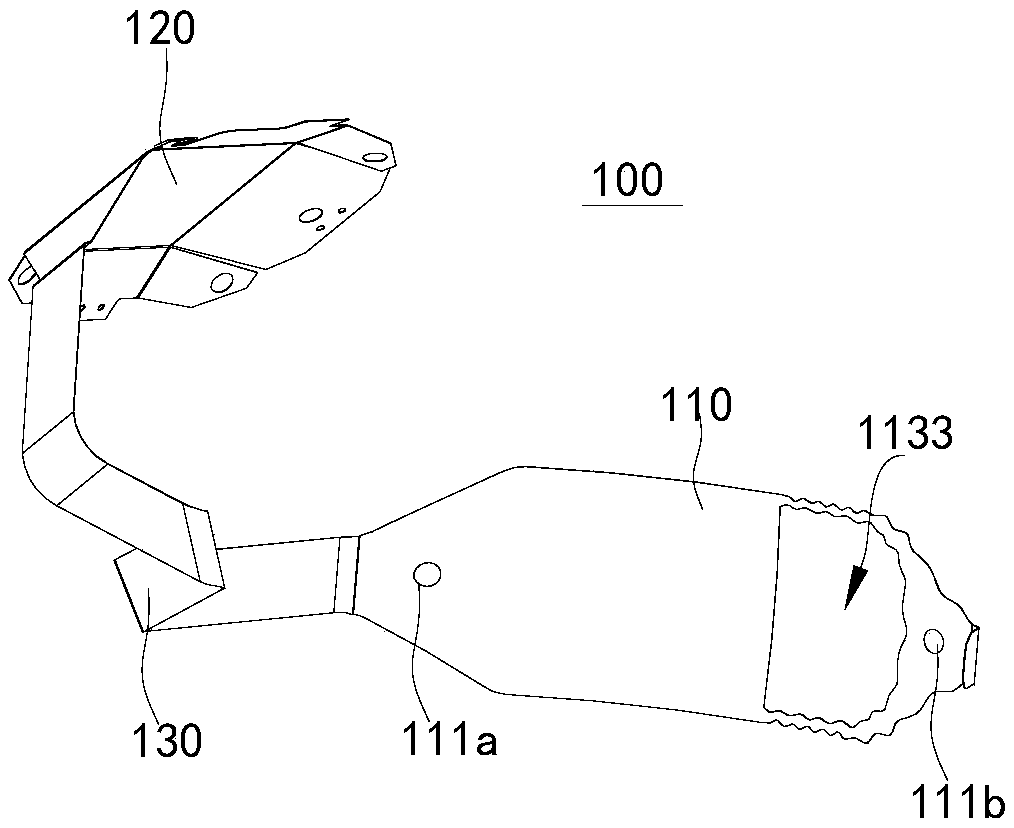
PendingCN109621195AEven by forceUniform distanceEye implantsHead electrodesImplanted deviceProsthesis
The invention discloses a flexible cable for a retinal prosthesis. The flexible cable comprises a microelectrode with two mounting holes corresponding to two sides of the optic disc during implantingof the retina, wherein the microelectrode comprises an electrode area located between the two mounting holes and an elastic portion connected to the electrode area, the elastic portion is deformable and stretchable at least in a longitudinal direction of a connection line of the two mounting holes, and the electrode area is provided with a plurality of stimulation electrodes; a leading portion connected with an electronic device; a connection portion connected between the microelectrode and the leading portion and including a plurality of wires respectively connected to the plurality of stimulation electrodes. The flexible cable enables the microelectrode to be uniformly stressed and better attached to the retina to obtain a more effective stimulating effect. The invention also discloses an implanting device for the retina and the retinal prosthesis.
Owner:INTELLIMICRO MEDICAL CO LTD
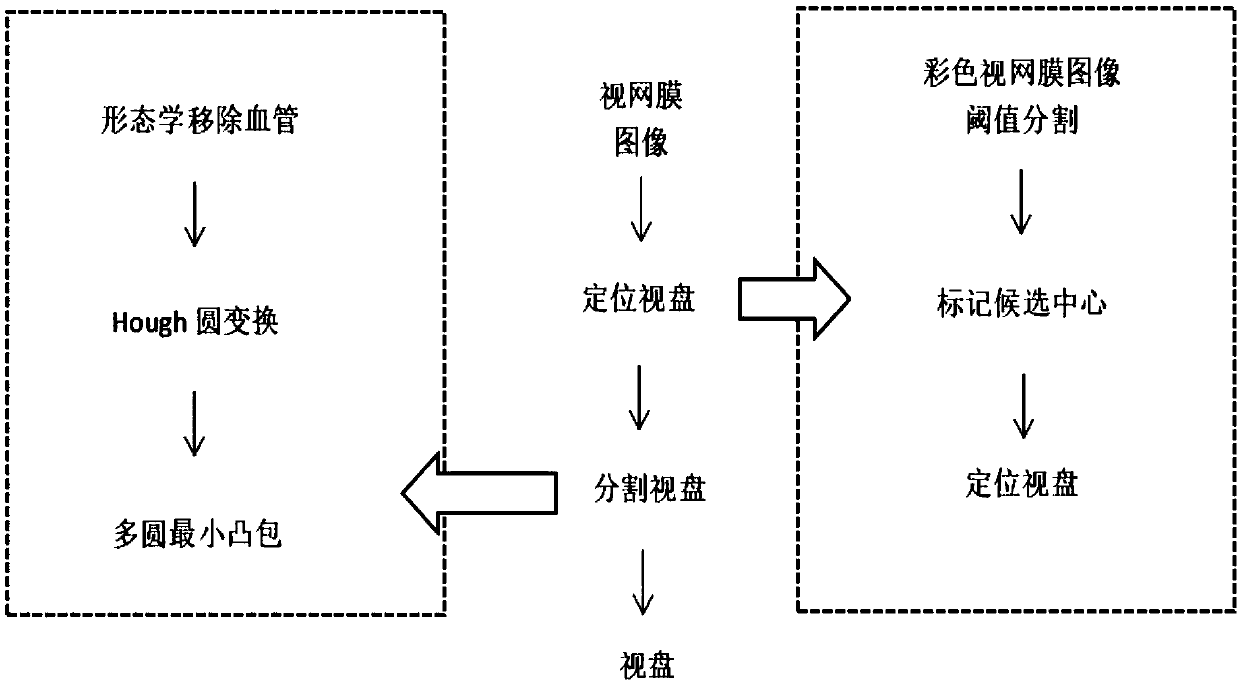
Method for rapidly segmenting fundus optic disc based on multiple circles
The present invention relates to the technical field of computers and particularly relates to a method for rapidly segmenting a fundus optic disc based on multiple circles. The method comprises a stepof (1) determining a disc center based on high brightness and blood vessel characteristics including the steps of (1.1) color retinal image threshold segmentation, (1.2) candidate center marking and(1.3) positioning to a disc center, and a step of (2) the segmentation of the optic disc based on a multi-circle minimum convex hull operation including the steps of (2.1) morphological removal of blood vessels by using an expansion operation, (2.2) Hough circle transformation, and the segmentation of an optic disc area after the expansion of the optic disc by using canny operator double thresholds to obtain a binarized edge image E, and (2.3) a multi-circle minimum convex hull operation. The method for segmenting the optic disc by the multiple circles is used, the convex hull operation is carried out on a plurality of circles detected inside the optic disc, and the speed and precision of the segmentation can be effectively improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
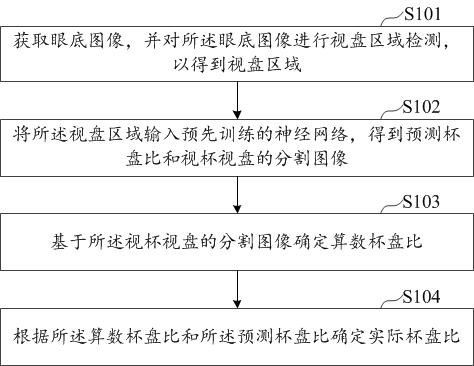
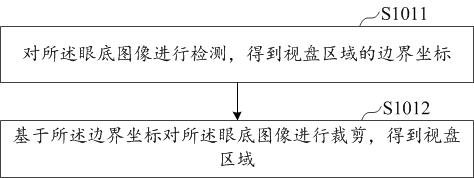
Cup-to-disk ratio determination method and device based on neural network, equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN111862187AImprove accuracyReduce dependenceImage enhancementImage analysisComputer hardwareAlgorithm
The invention relates to the field of artificial intelligence, specifically uses a neural network, and discloses a cup-to-disk ratio determination method, device and equipment based on the neural network, and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: obtaining an eye fundus image, and carrying out the optic disk region detection of the eye fundus image, so as to obtain an optic disk region; inputting the optic disk area into a pre-trained neural network to obtain a predicted cup-to-disk ratio and a segmented image of the optic cup and the optic disk; determining an arithmetic cup-to-disk ratio based on the segmented image of the optic cup and the optic disk; and determining an actual cup-to-disk ratio according to the arithmetic cup-to-disk ratio and the predicted cup-to-disk ratio. The accuracy of the determined cup-to-disk ratio is improved, and the situations of multiple screening and screening omission in the disease screening process are reduced. The invention is applicable to the field of smart medical treatment.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Retina vessel curvature determination method
ActiveCN109685770AAutomatic determination of curvatureImprove the efficiency of bending recognitionImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineRetina
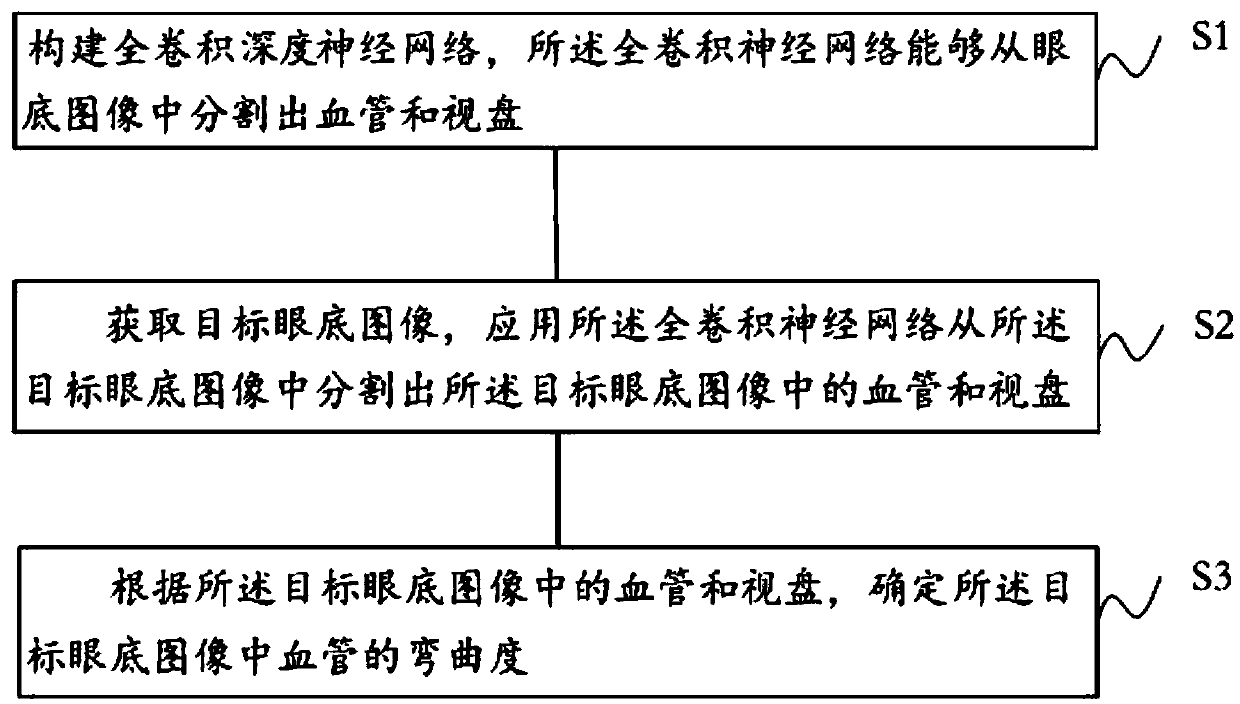
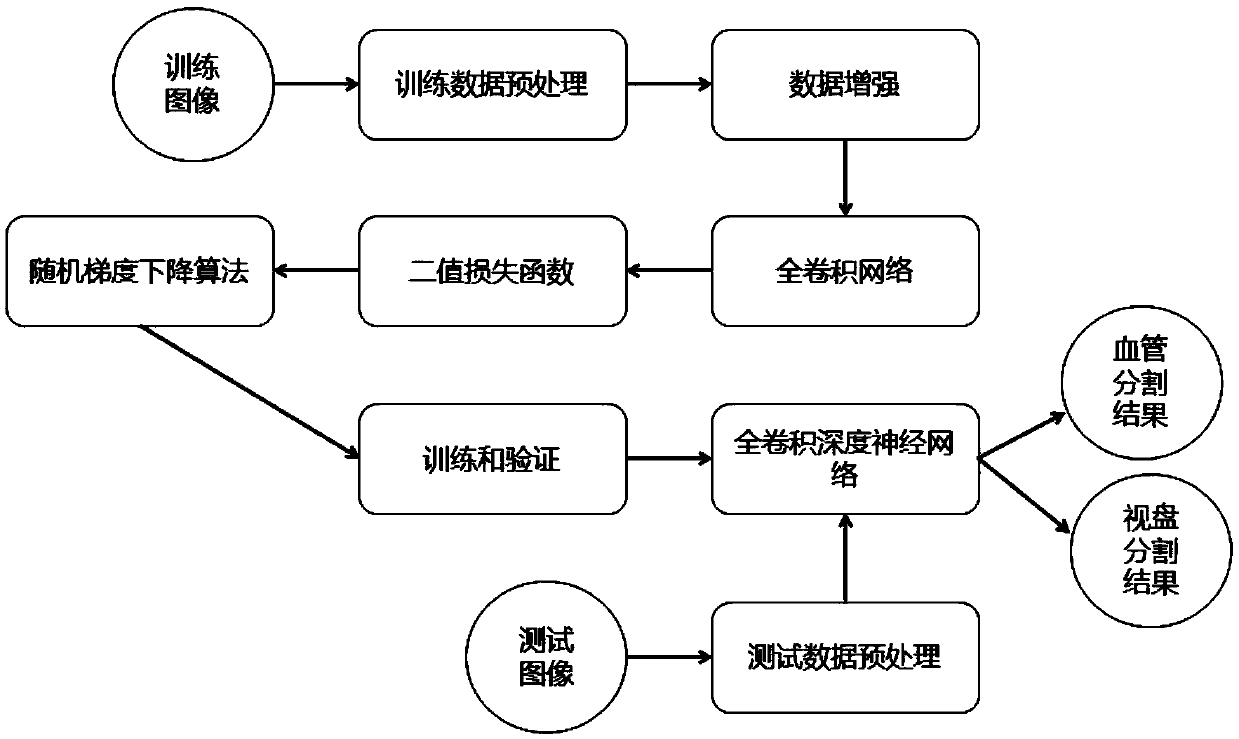
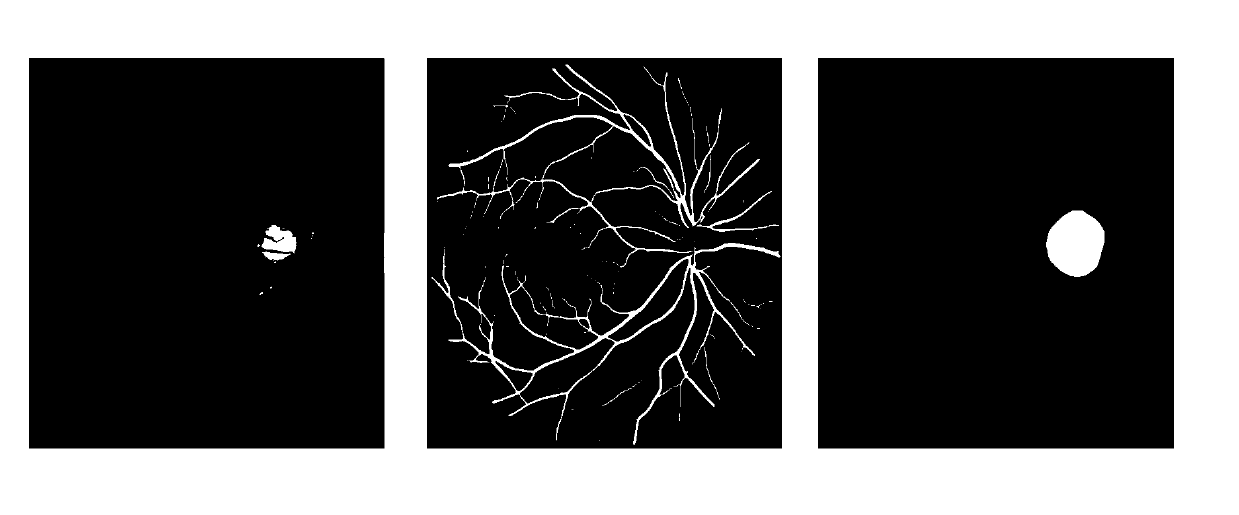
The embodiment of the invention discloses a retinal vessel curvature determination method, which comprises the following steps of: constructing a full convolutional deep neural network, and segmentinga vessel and an optic disc in a target fundus image from an acquired target fundus image by applying the full convolutional deep neural network. According to the blood vessel and the optic disc in the target fundus image, the bending degree of the blood vessel in the target fundus image is determined, the retinal vessel bending degree is automatically determined based on the full convolution depth neural network, and therefore the retinal vessel bending degree recognition efficiency can be improved.
Owner:合肥奥比斯科技有限公司
An optic disc positioning method and a storage device based on main blood vessel fitting
PendingCN109101950AReduce complexityShort timeImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineImaging analysis
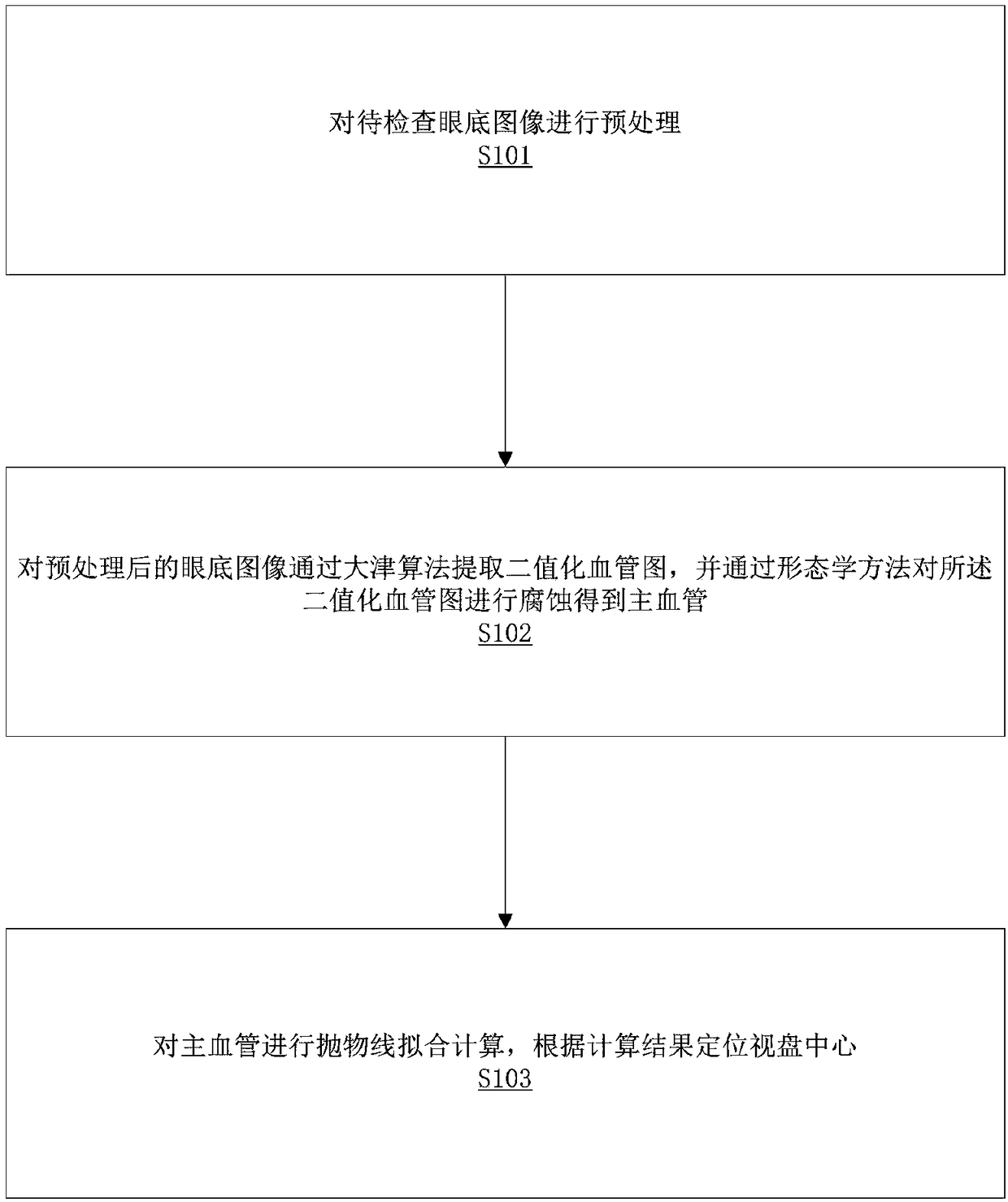
The invention relates to the field of image analysis, in particular to an optic disc positioning method and a storage device based on main blood vessel fitting. The optic disc positioning method basedon the main blood vessel fitting comprises the following steps: the image of the fundus to be examined is preprocessed; the binary angiogram is extracted from the preprocessed fundus image by a Otsualgorithm, and the main blood vessel is obtained by eroding the binary angiogram by morphological method; the main blood vessel is calculated by parabola fitting, and the center of optic disc was located according to the result of calculation. The whole method has low complexity, small time consuming and strong practicability, and even if the optic disc appearance changes due to the lesion, or there are some large areas of bright lesion interference, it will not affect the localization results, and the whole method has high efficiency and high accuracy.
Owner:FUZHOU YIYING HEALTH TECH CO LTD
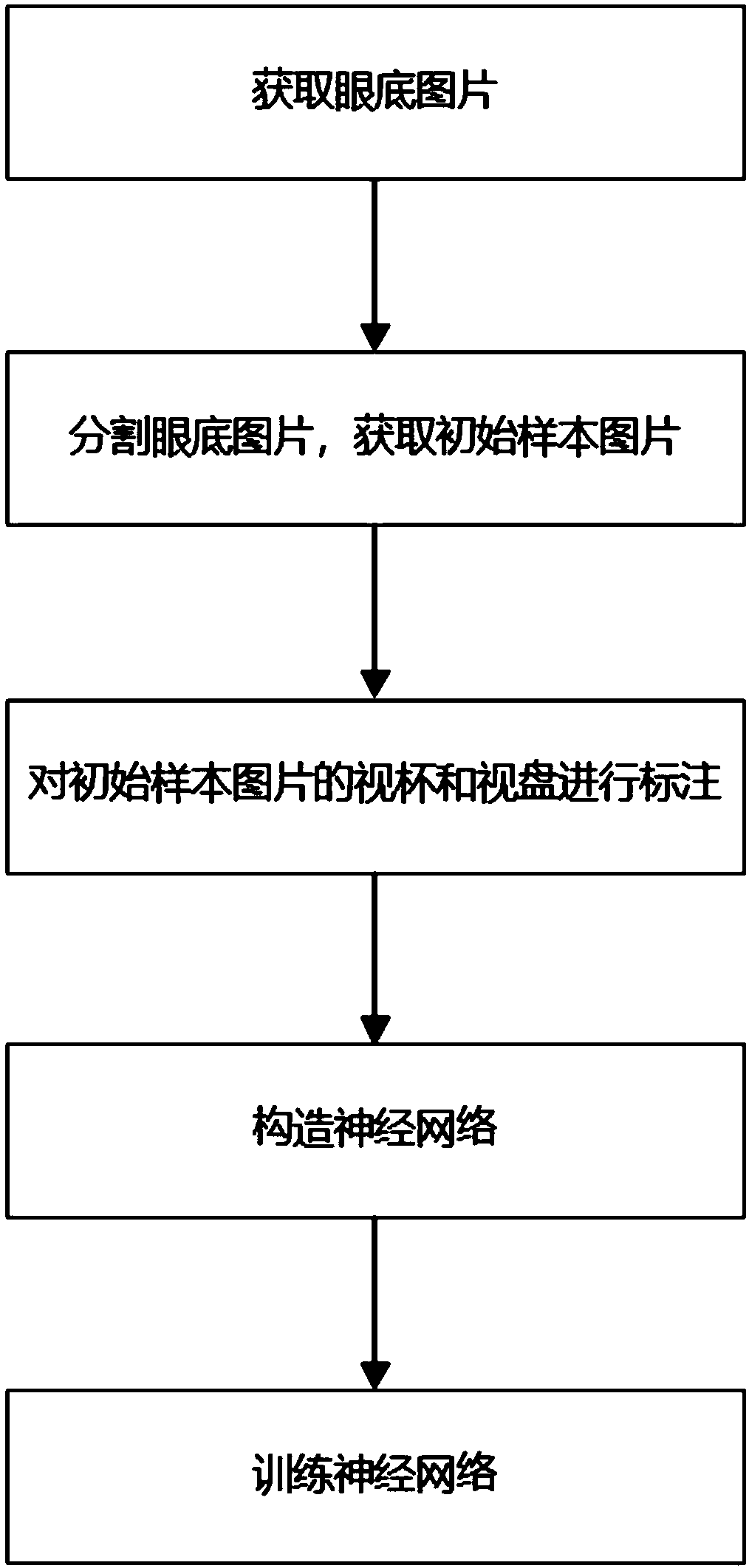
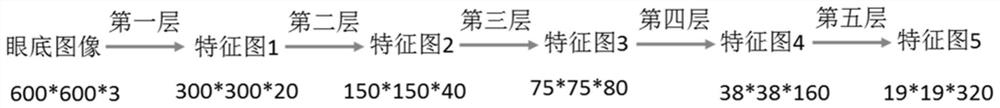
A processing method of fundus picture based on neural network
ActiveCN109215039AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionInitial sample
The invention provides an eyeground picture processing method based on a neural network, comprising the following steps: S1, acquiring a plurality of eyeground pictures through shooting by a camera; S2, detecting an area including an optic disc and an optic cup in the fundus picture, and cutting the area including the optic disc and the optic cup from the fundus picture to obtain an initial samplepicture; 3, circling an optic disc region and an optic cup region on the initial sample picture and filling the optic disc region and the optic cup region with different color respectively to obtaina training sample picture; S4, constructing a neural network; 5, training the neural network through a plurality of pictures of the train samples, and determining the parameters of the neural network;this method can help doctors and nurses to judge the cup-to-dish ratio of fundus picture efficiently and accurately, and improve the efficiency and accuracy of glaucoma diagnosis.
Owner:CHANGZHOU IND TECH RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV
Eye fundus image analysis system and method and electronic equipment
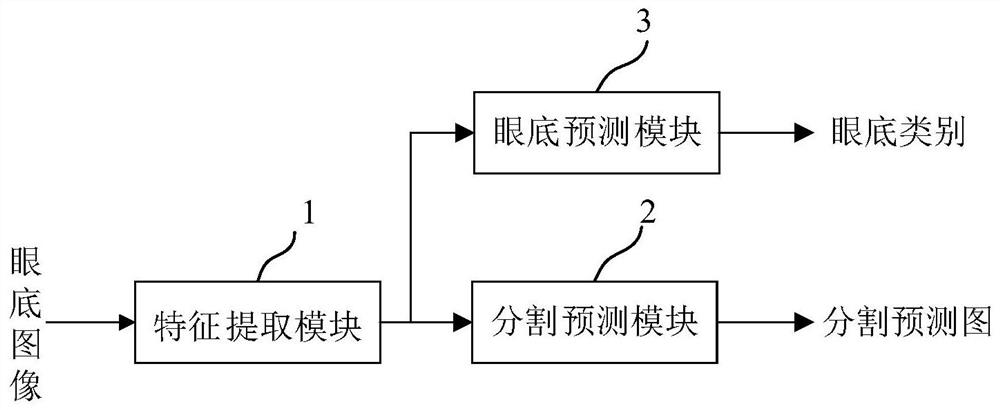
PendingCN113768460AGive full play to the advantagesAccurate responseImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionImage pair
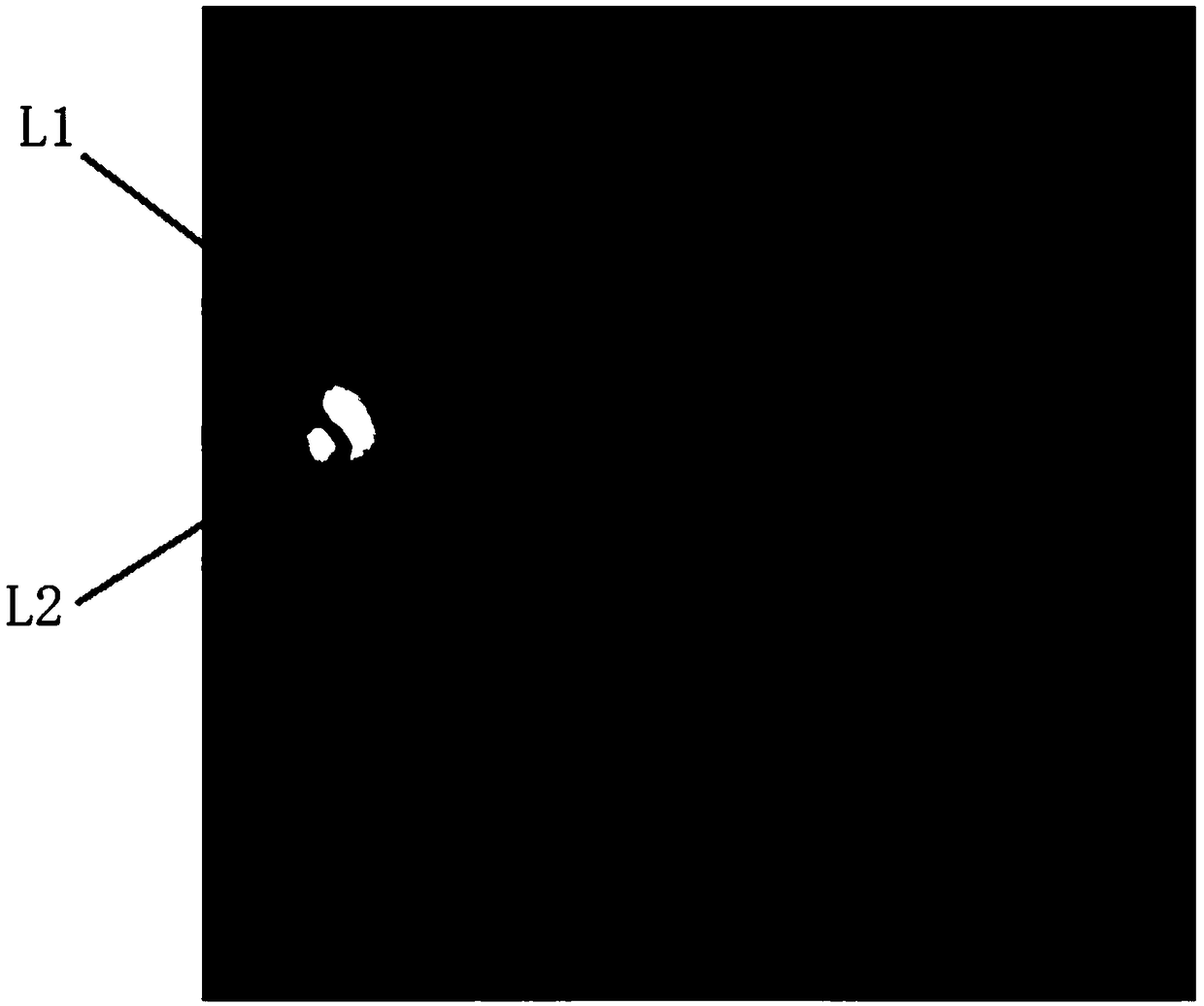
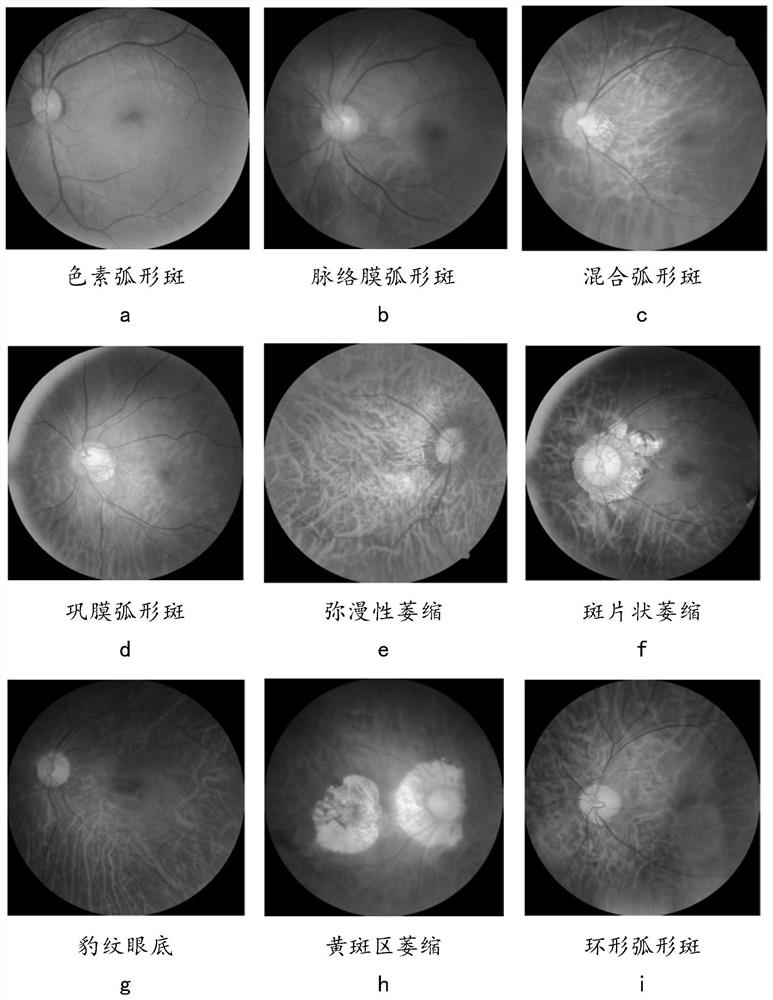
The embodiment of the invention provides an eye fundus image analysis system and method and electronic equipment. The system comprises a feature extraction module, an eye fundus prediction module and a segmentation prediction module, wherein the feature extraction module samples an eye fundus image to be analyzed to extract an eye fundus feature map; The eye fundus prediction module analyzes eye fundus categories corresponding to the eye fundus image according to the eye fundus feature map, wherein the eye fundus categories comprise normal eye fundus and various myopia associated eye fundus; and the segmentation prediction module samples the eye fundus feature map to analyze a segmentation prediction map corresponding to the eye fundus image, and indicates the category of each pixel in the eye fundus image, and the categories of the pixels comprise a background pixel category, an optic disk pixel category, a plurality of arc spot pixel categories and a plurality of atrophic spot pixel categories. According to the method, a machine learning technology is utilized to solve the problem that traditional classification of the myopia eye fundus is only rough categories related to pathological myopia, so that better diagnosis and treatment or daily eye using suggestions are provided for detected personnel.
Owner:BEIJING AIRDOC TECH CO LTD +1
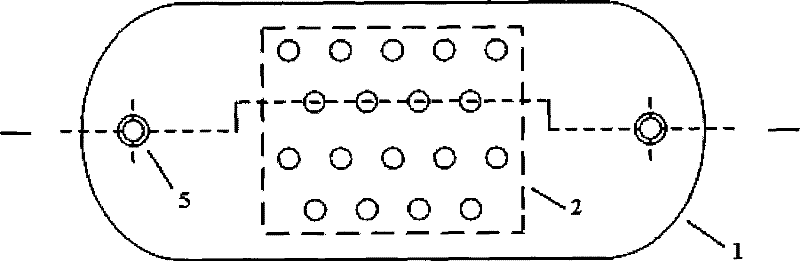
Vision prosthesis device based on optical-disc micro-electrode array
InactiveCN101396583BAvoid damageRepair visual functionEye treatmentArtificial respirationProsthesisMicroelectrode
A visual prosthetic device is based on videodisc microelectrode array, belonging to the technical field of medical appliance. The device comprises a microelectrode array substrate, a microelectrode array and an electrode cable, and is characterized by further comprising a cover board and a retina nail; wherein, the two ends of the microelectrode array substrate are respectively provided with a through hole of the retina nail, the middle of microelectrode array substrate is provided with 18 electrode through holes, and the retina nail passes through the through hole of the retina nail to fix the microelectrode array substrate on a videodisc of the retina; the microelectrode array consists of 18 wire electrodes which are fixed in the electrode through holes that are arranged in the center of the microelectrode array substrate, one ends of the wire electrodes are connected in vitro by the electrode cables, and the cover board covers above the electrode through holes of the microelectrodearray substrate to fix the microelectrode array. The visual prosthetic device is applied for generating artificial vision and is the medical device for helping the retina blindness patients to gain brightness and vision again.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com