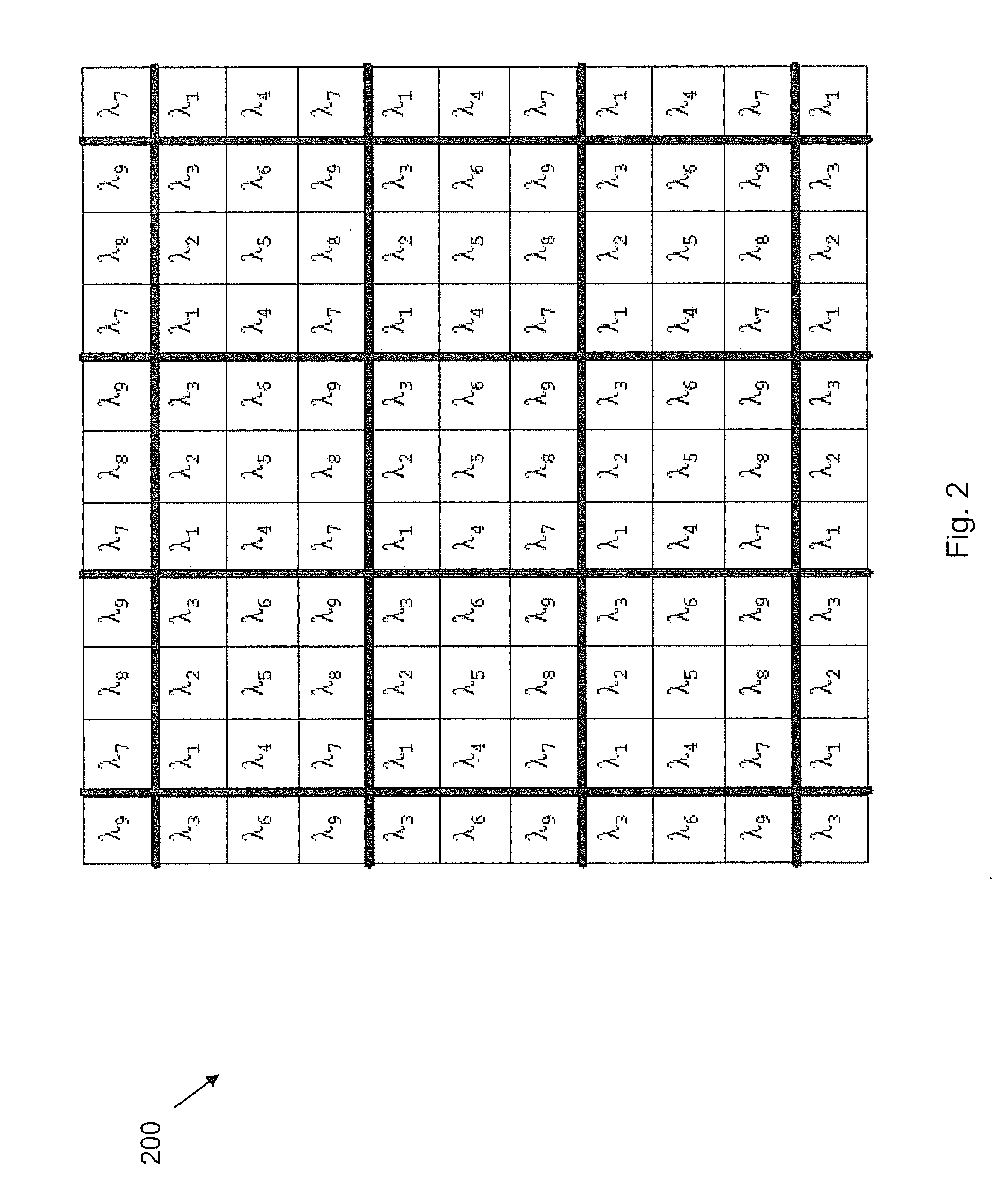
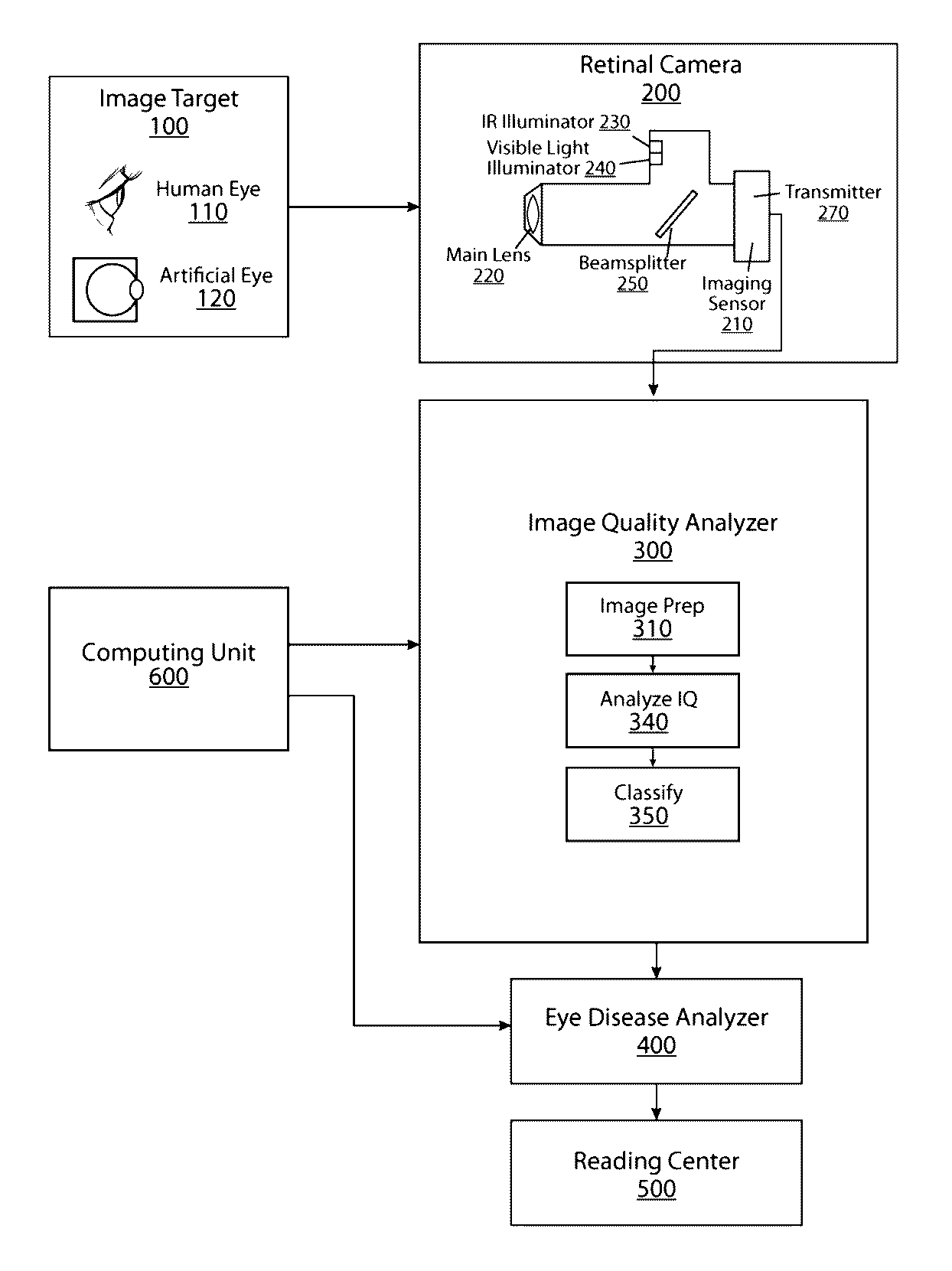
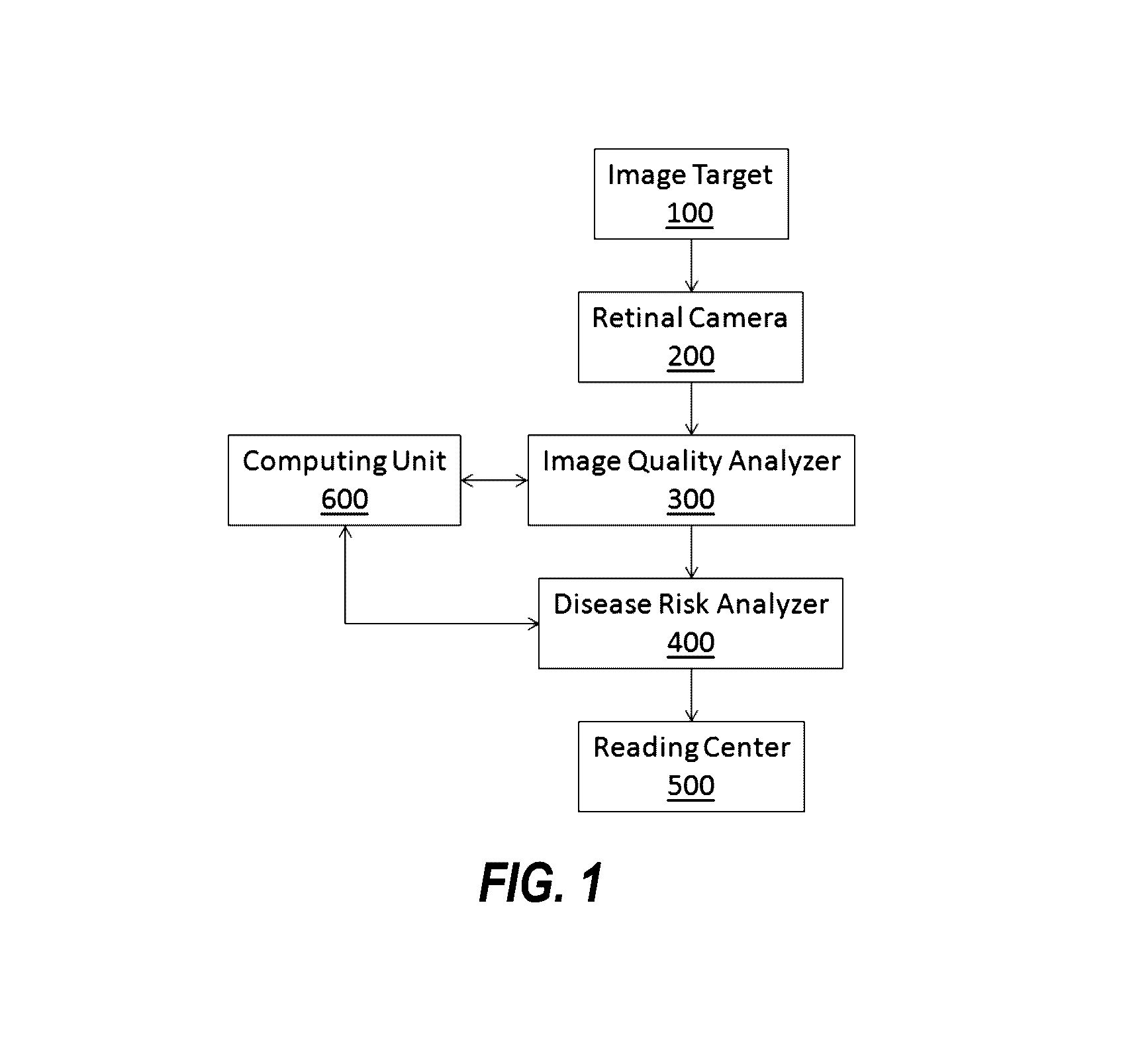
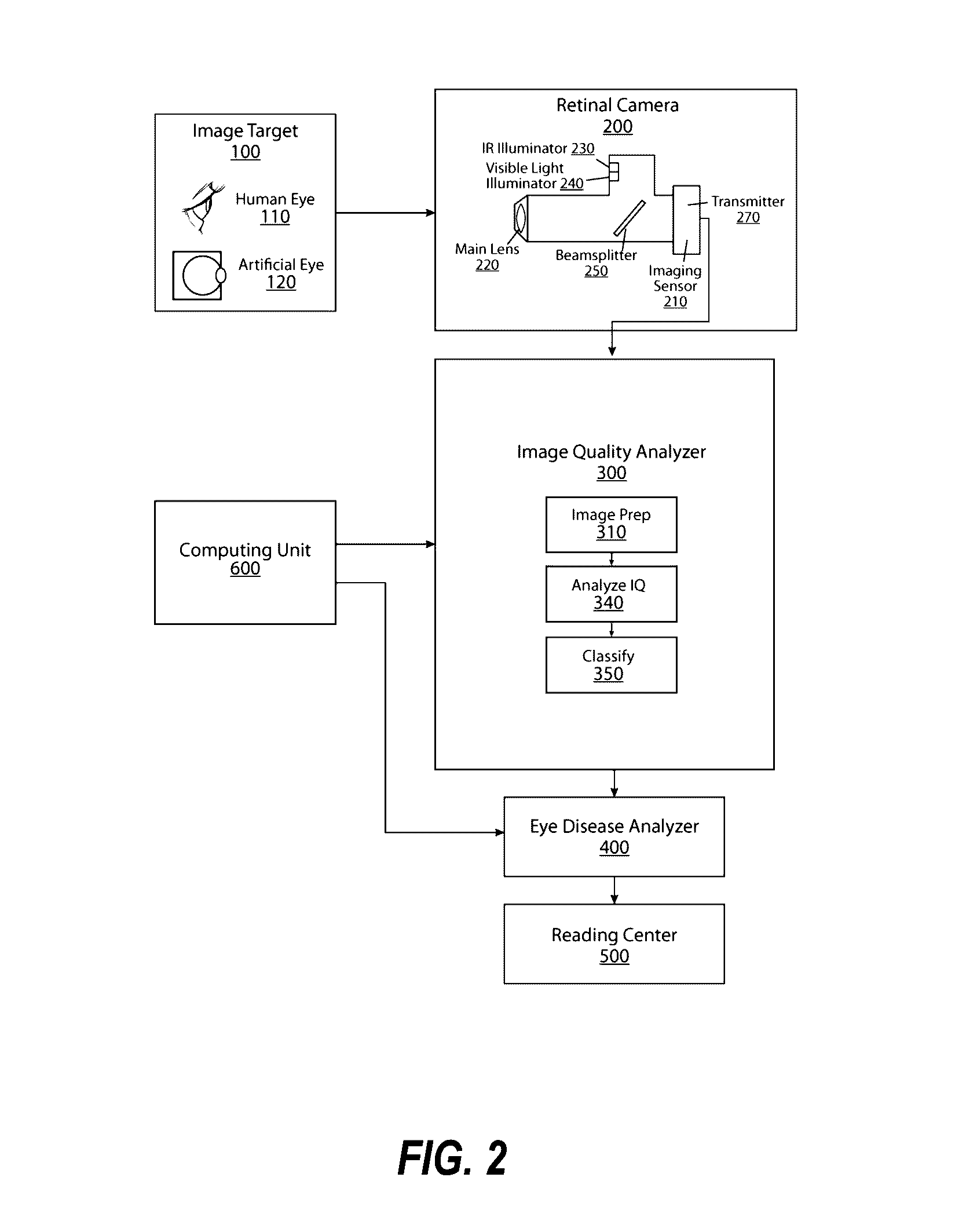
Patents
Literature
440 results about "Retinal image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
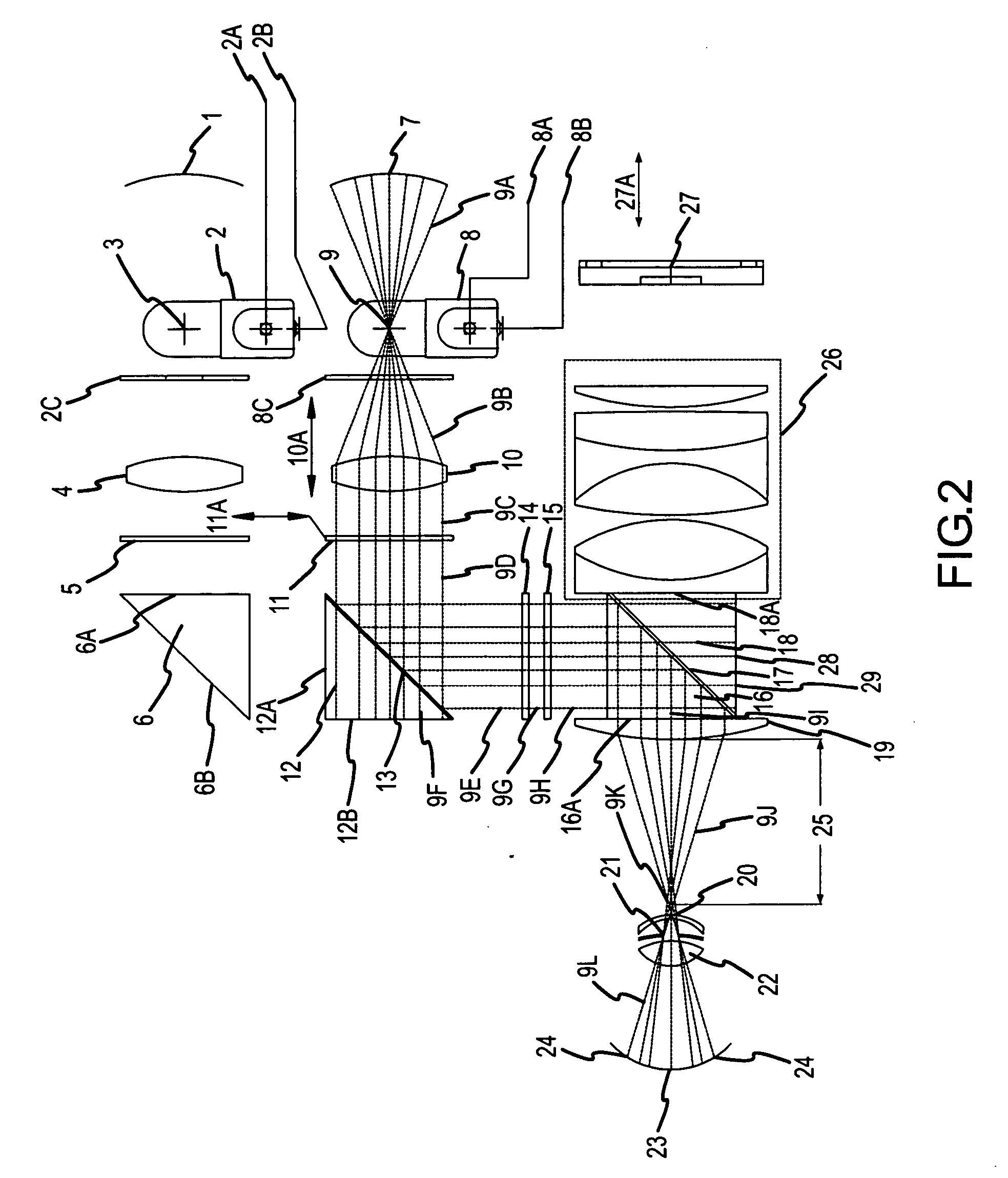
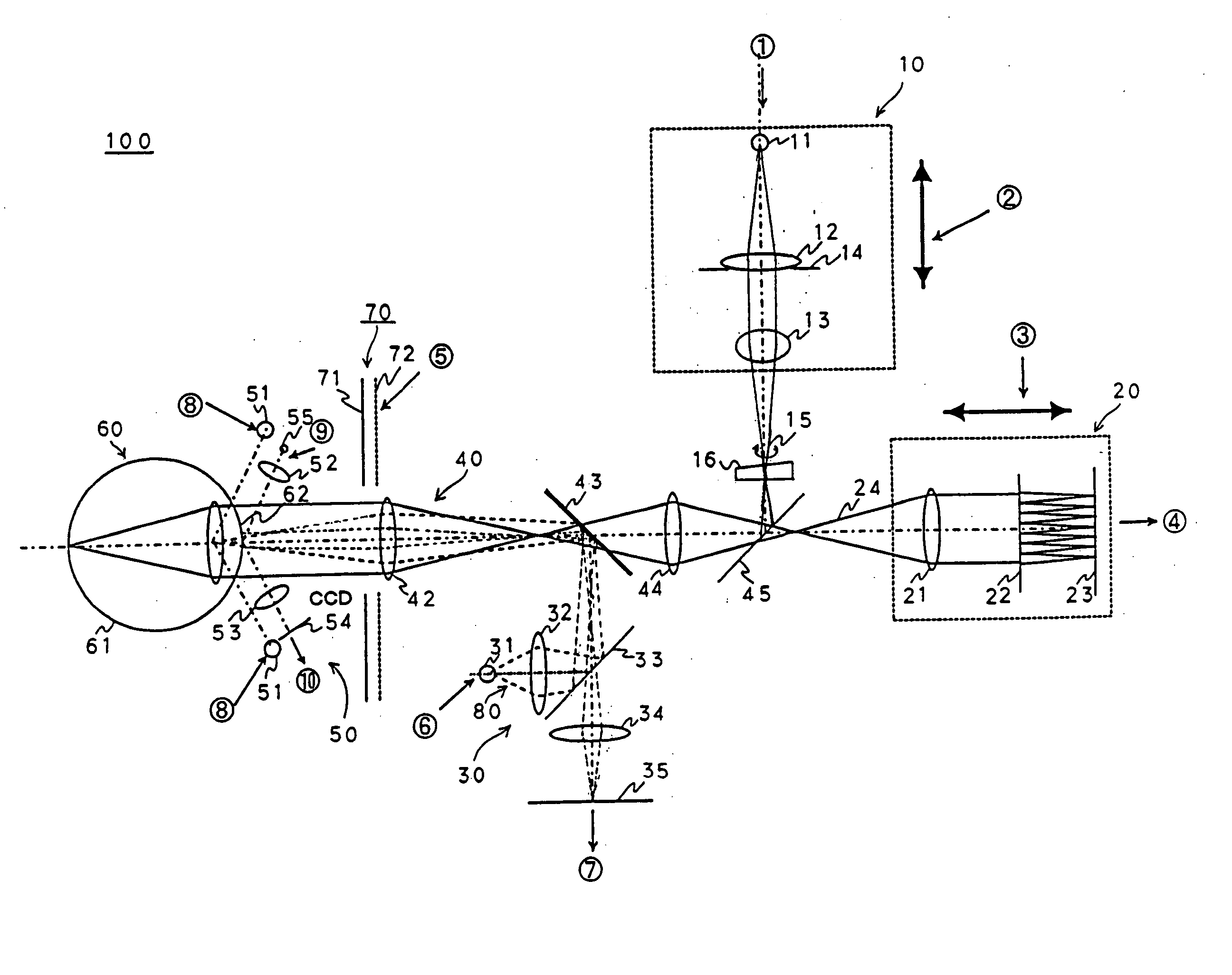
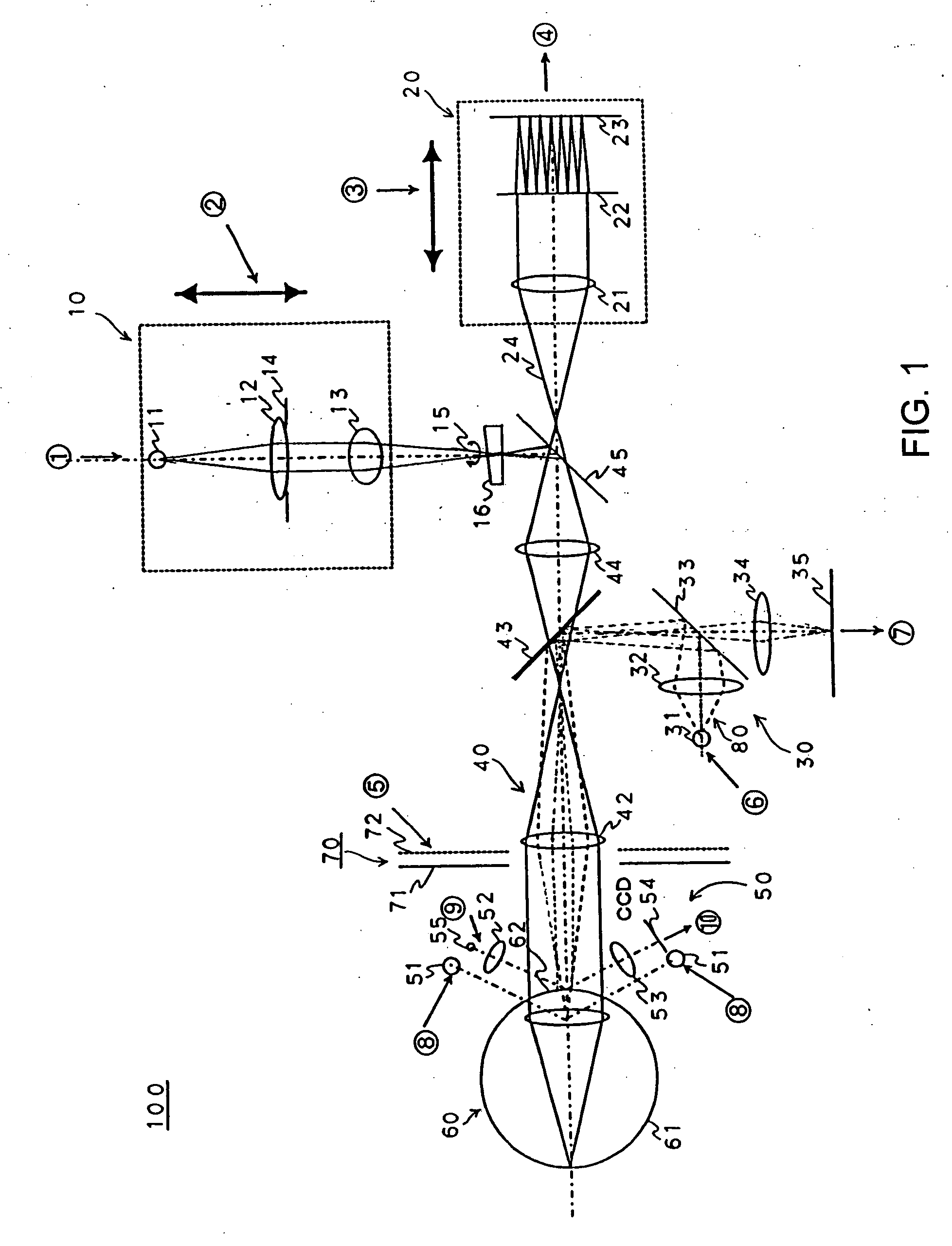
Scanning laser ophthalmoscope for selective therapeutic laser
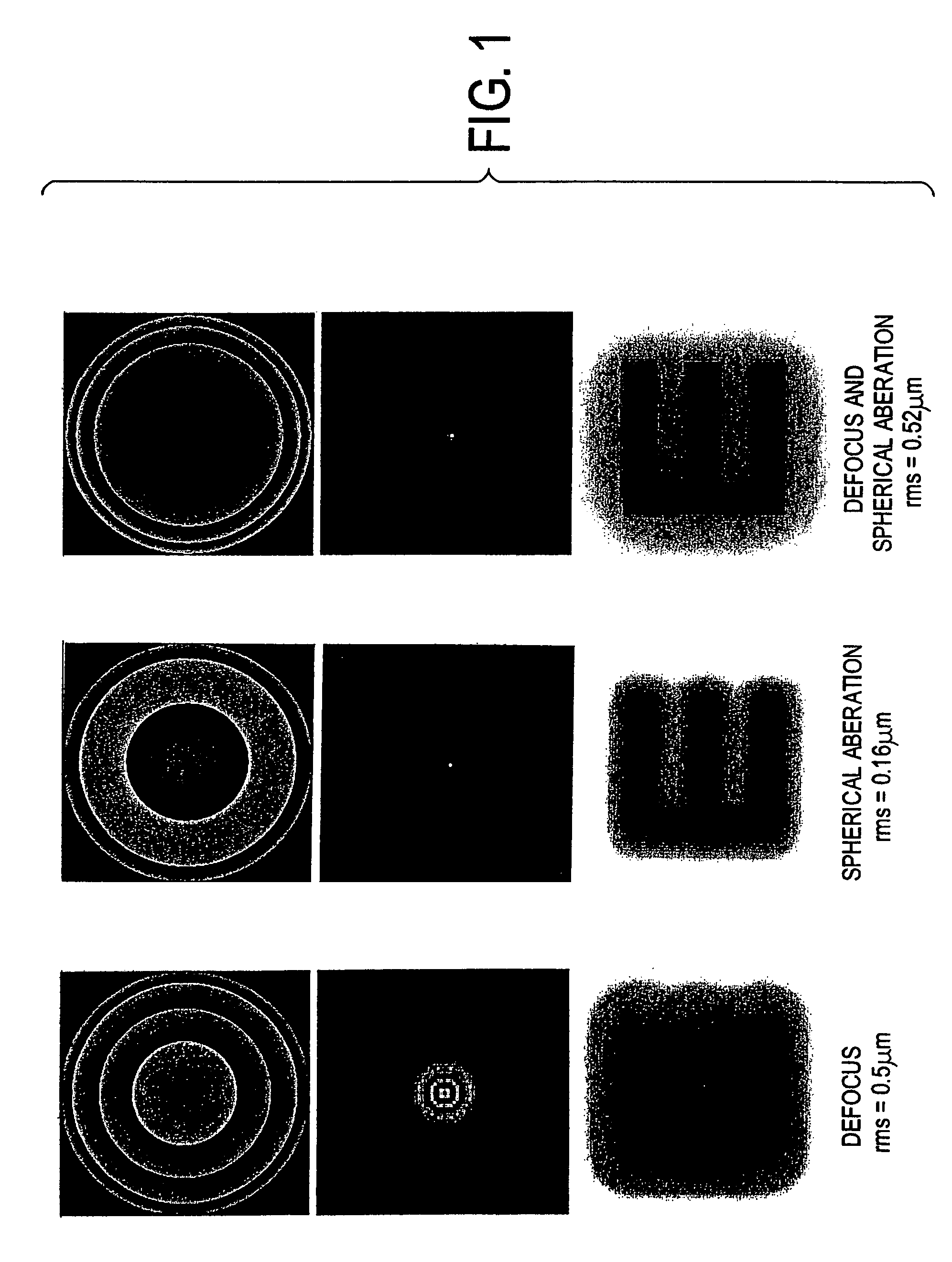
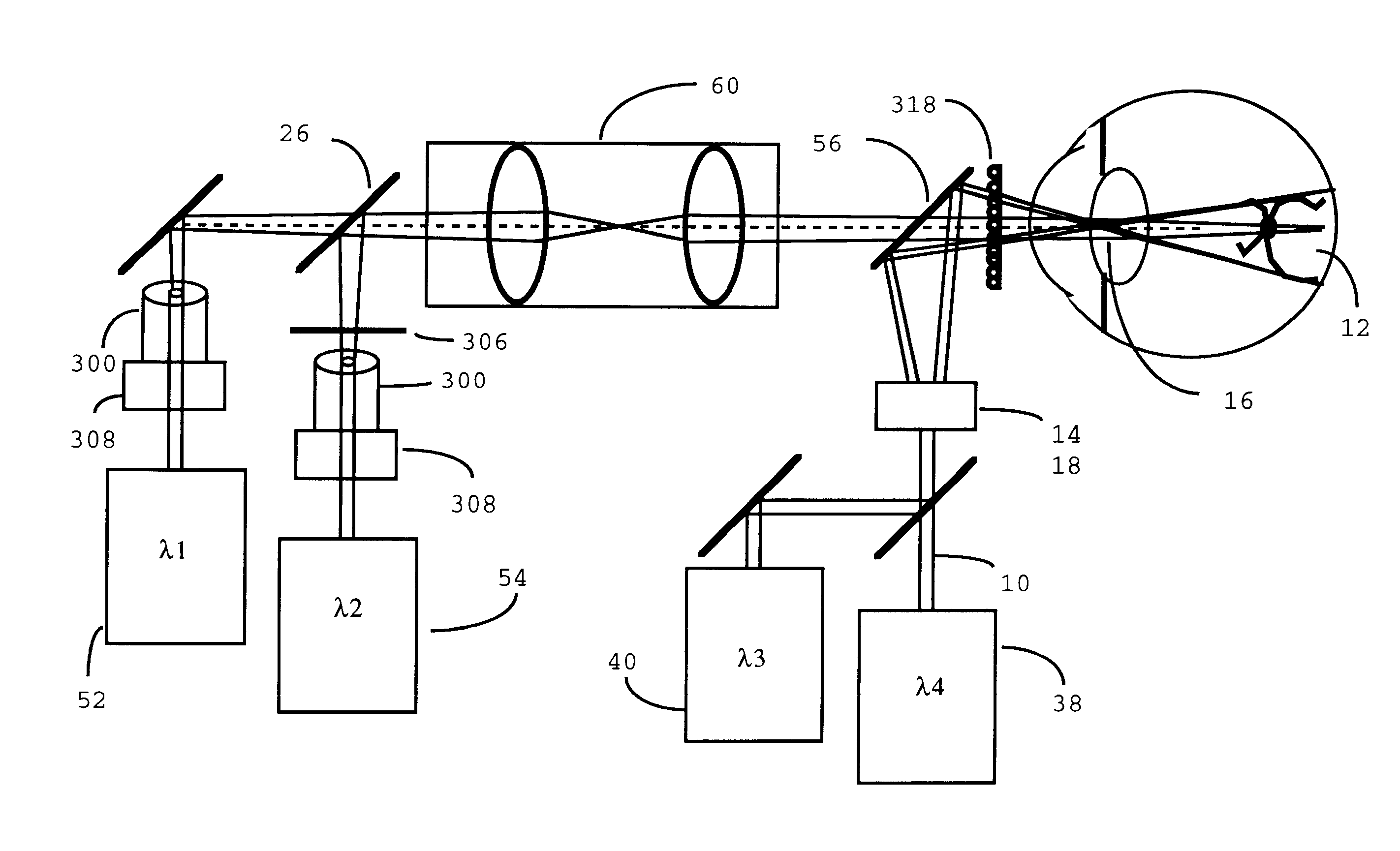
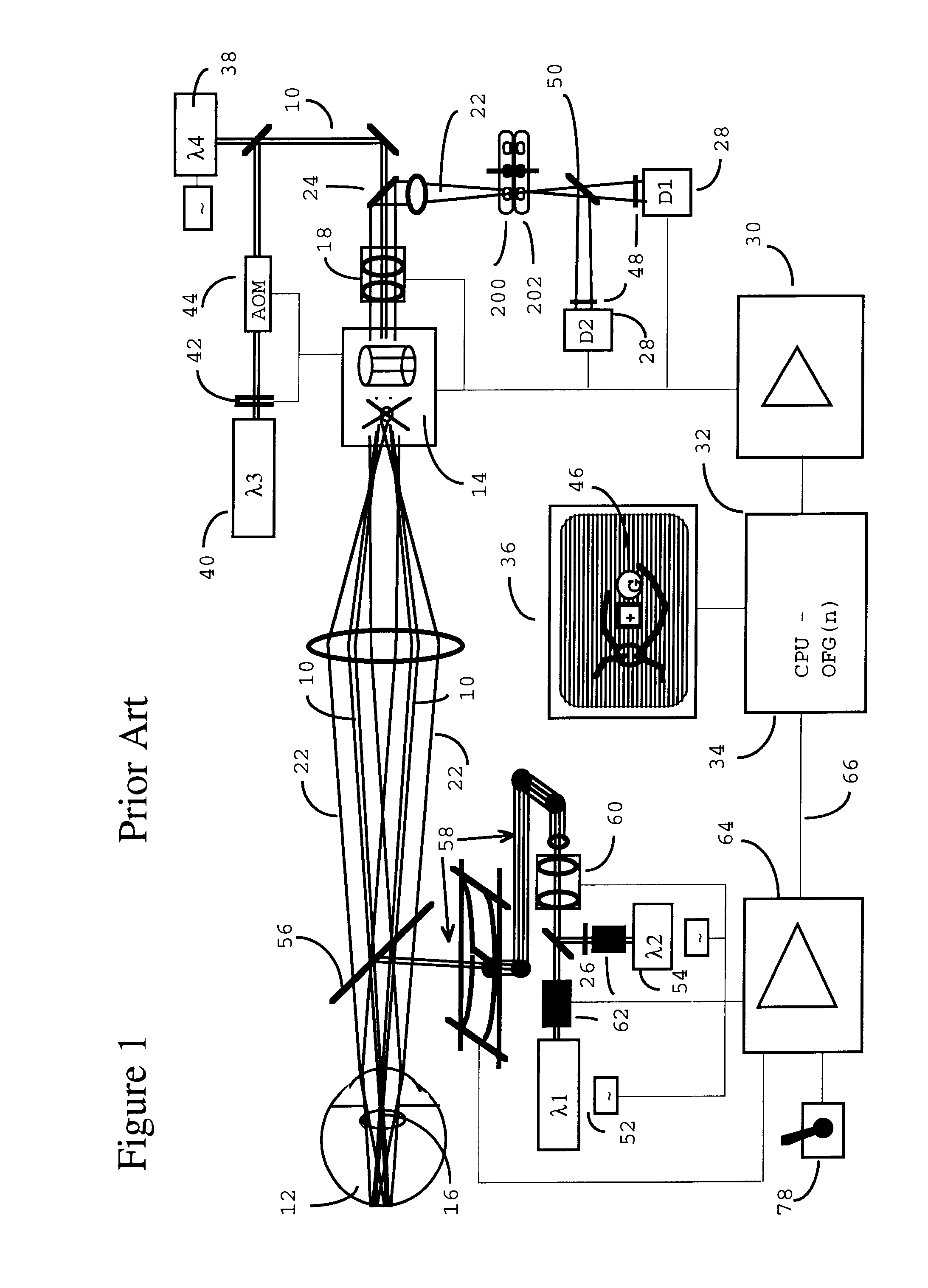
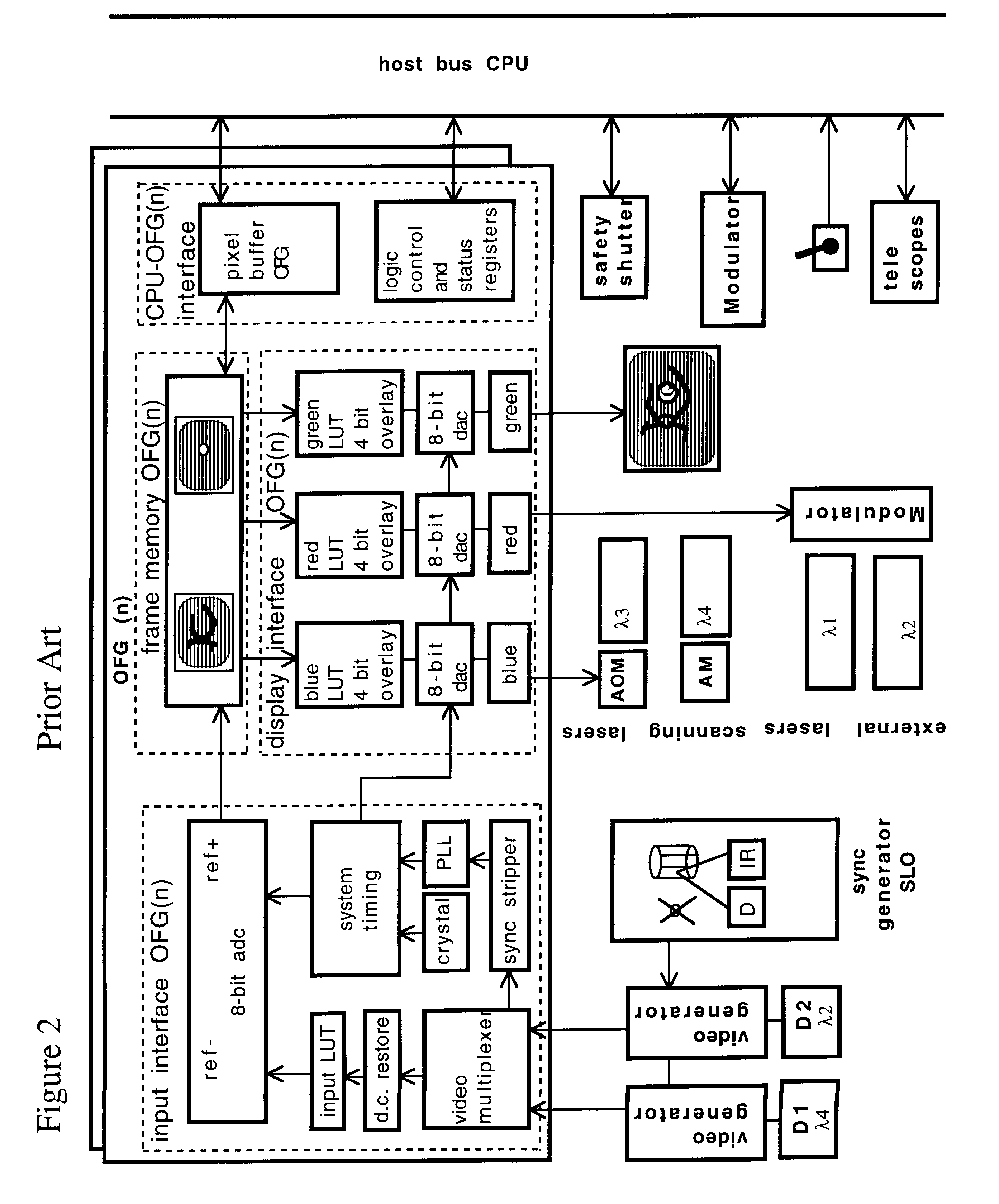
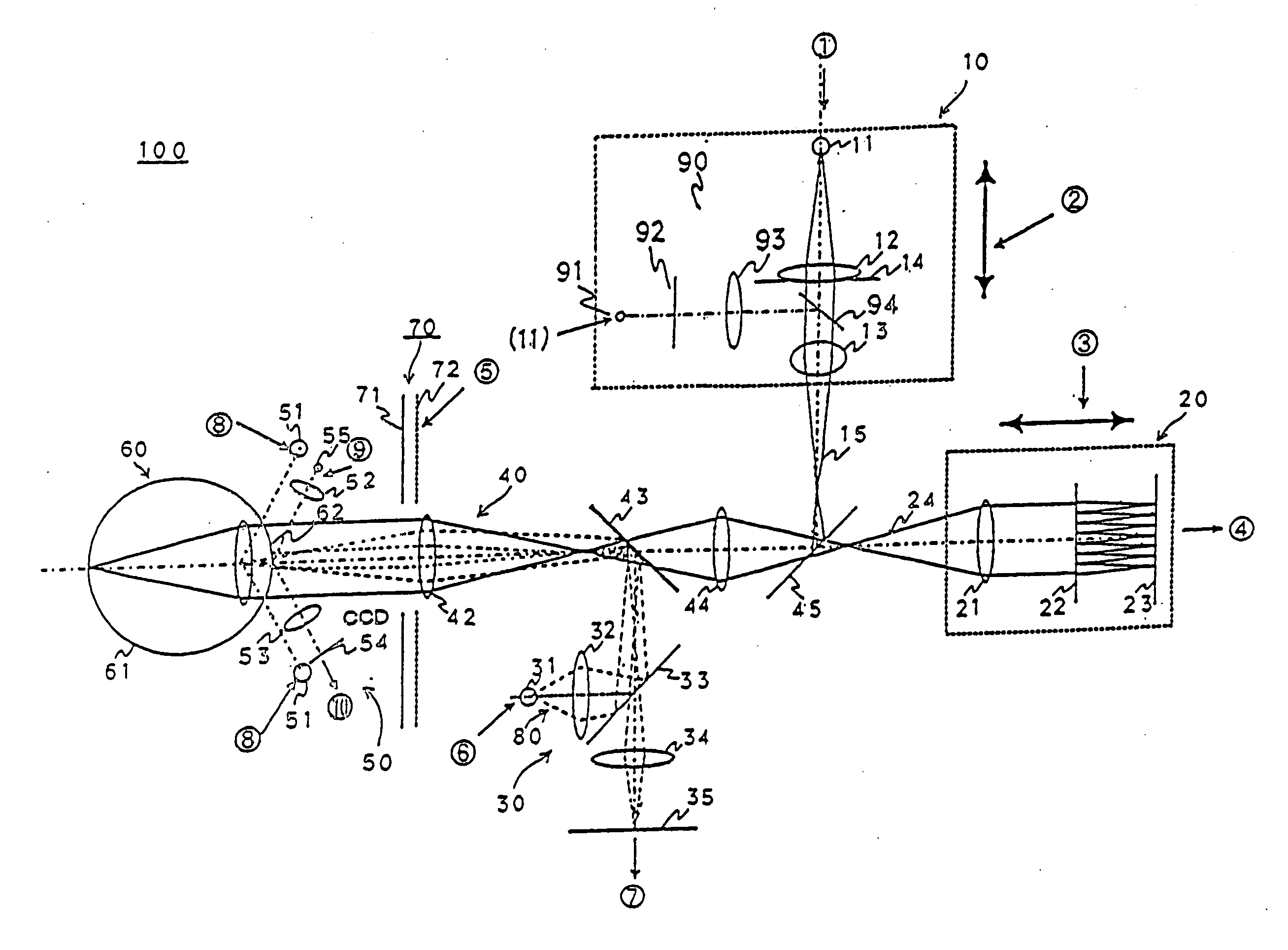
A combination of a scanning laser ophthalmoscope and external laser sources (52) is used for microphotocoagulation and photodynamic therapy, two examples of selective therapeutic laser. A linkage device incorporating a beamsplitter (56) and collimator-telescope (60) is adjusted to align the pivot point (16) of the scanning lasers (38, 40) and external laser source (52). A similar pivot point minimizes wavefront aberrations, enables precise focusing and registration of the therapeutic laser beam (52) on the retina without the risk of vignetting. One confocal detection pathway of the scanning laser ophthalmoscope images the retina. A second and synchronized detection pathway with a different barrier filter (48) is needed to draw the position and extent of the therapeutic laser spot on the retinal image, as an overlay (64). Advanced spatial modulation increases the selectivity of the therapeutic laser. In microphotocoagulation, an adaptive optics lens (318) is attached to the scanning laser ophthalmoscope, in proximity of the eye. It corrects the higher order optical aberrations of the eye optics, resulting in smaller and better focused applications. In photodynamic therapy, a spatial modulator (420) is placed within the collimator-telescope (60) of the therapeutic laser beam (52), customizing its shape as needed. A similar effect can be obtained by modulating a scanning laser source (38) of appropriate wavelength for photodynamic therapy.
Owner:VAN DE VELDE JOZEK F
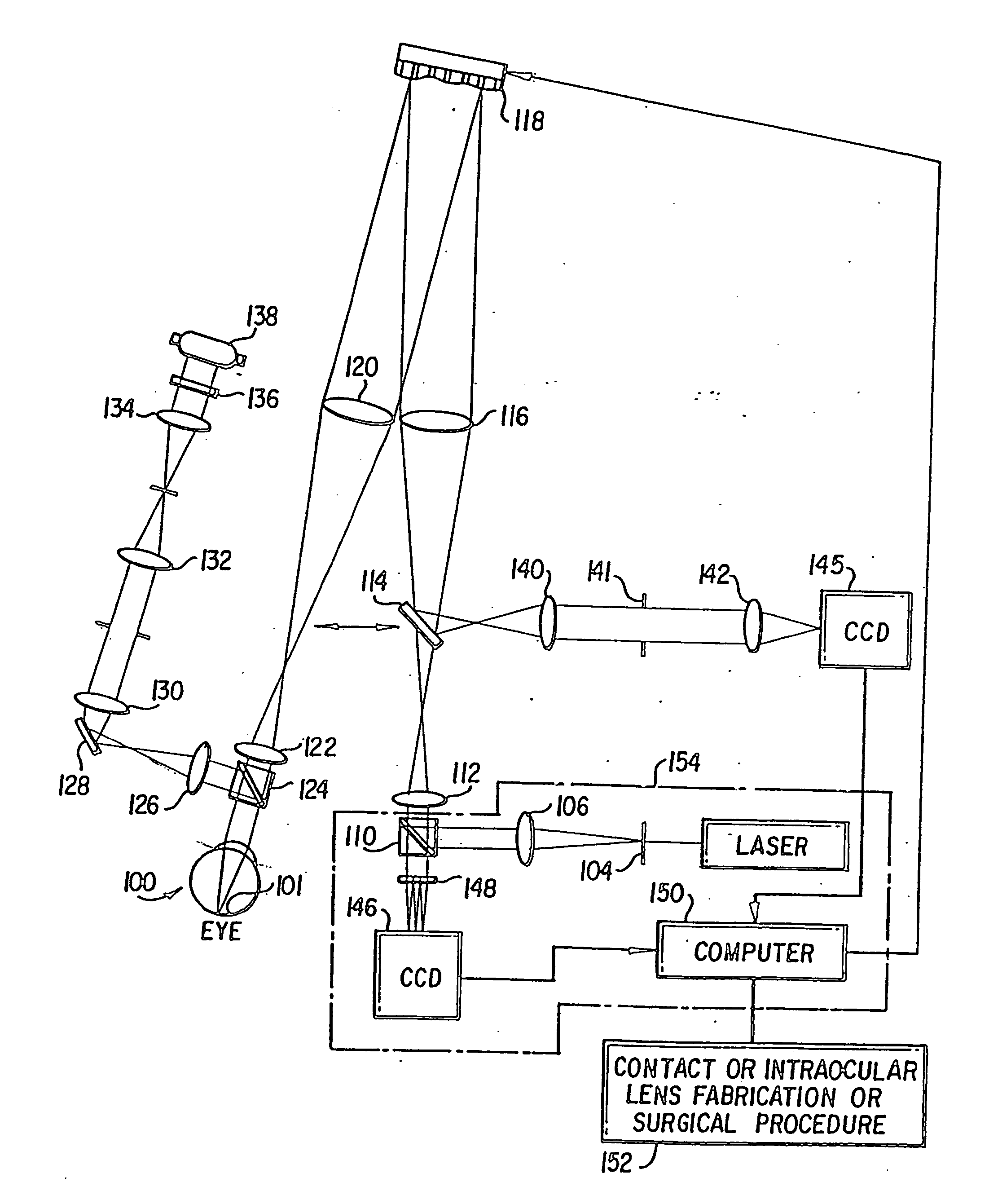
Method and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images
InactiveUS20060044510A1Accurate measurementHigh resolutionOptical measurementsEye surgeryCcd cameraLaser beams
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Multimodal ocular biometric system
ActiveUS20080044063A1Robust and accurateCharacter and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsBiometric dataIris image
A multimodal biometric identification system captures and processes images of both the iris and the retina for biometric identification. Another multimodal ocular system captures and processes images of the iris and / or the from both eyes of a subject. Biometrics based on data provided by these systems are more accurate and robust than using biometrics that include data from only the iris or only the retina from a single eye. An exemplary embodiment emits photons to the iris and the retina of both eyes, an iris image sensor that captures an image of the iris when the iris reflects the emitted light, a retina image sensor that captures an image of the retina when the retina reflects the emitted light, and a controller that controls the iris and the retina illumination sources, where the captured image of the iris and the captured image of the retina contain biometric data.
Owner:MORPHOTRUST USA
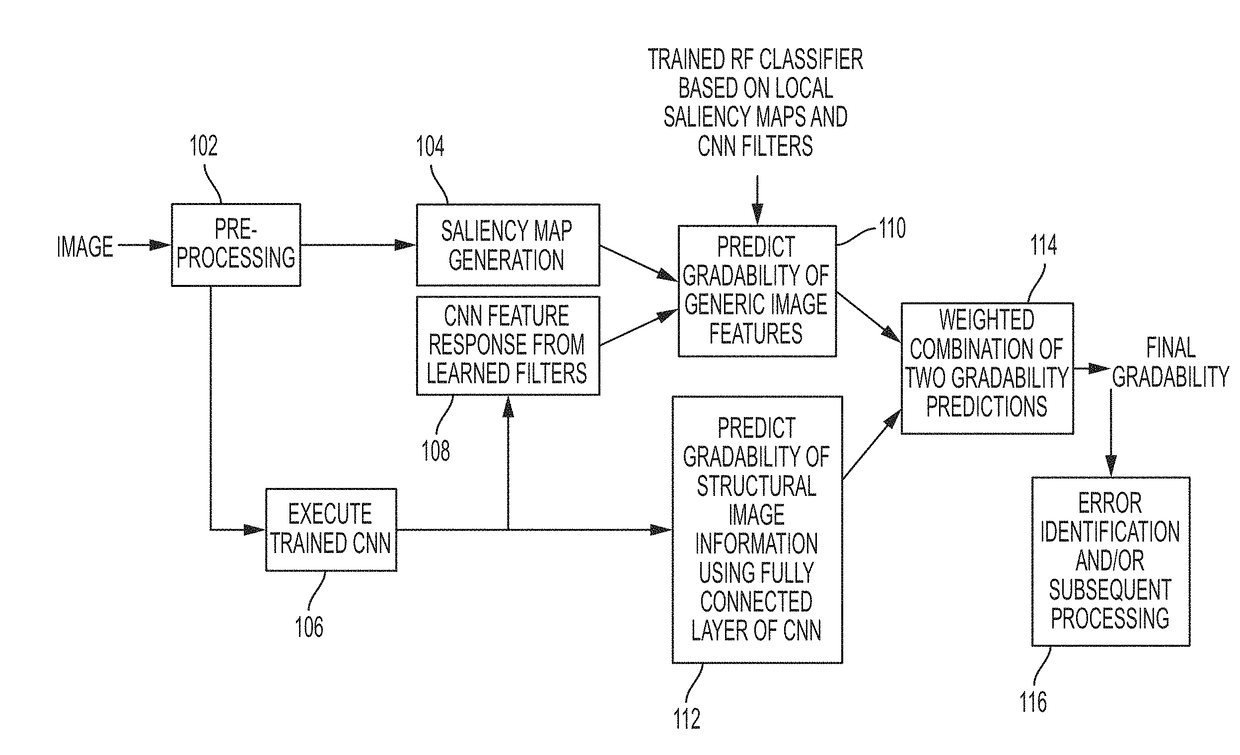
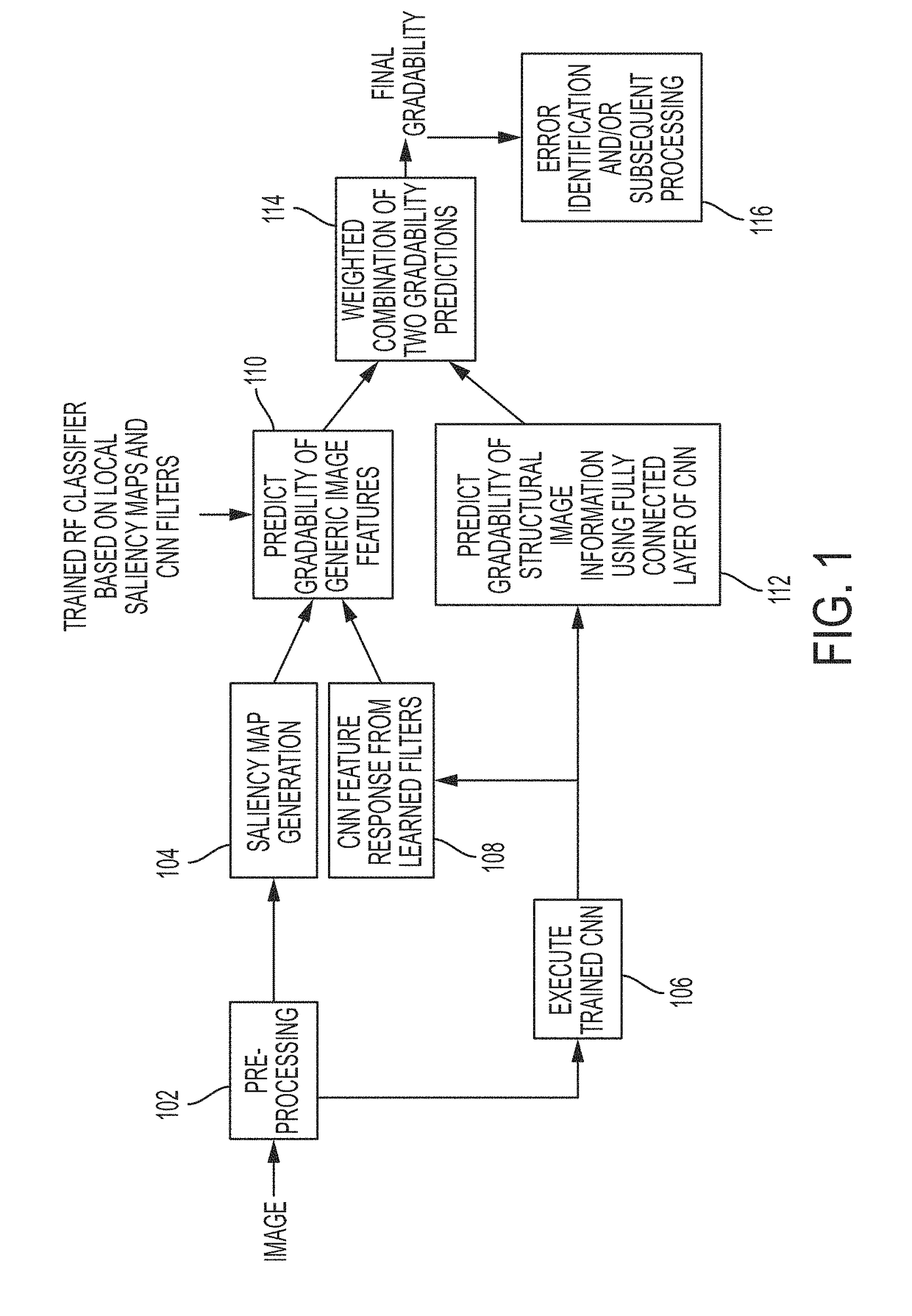
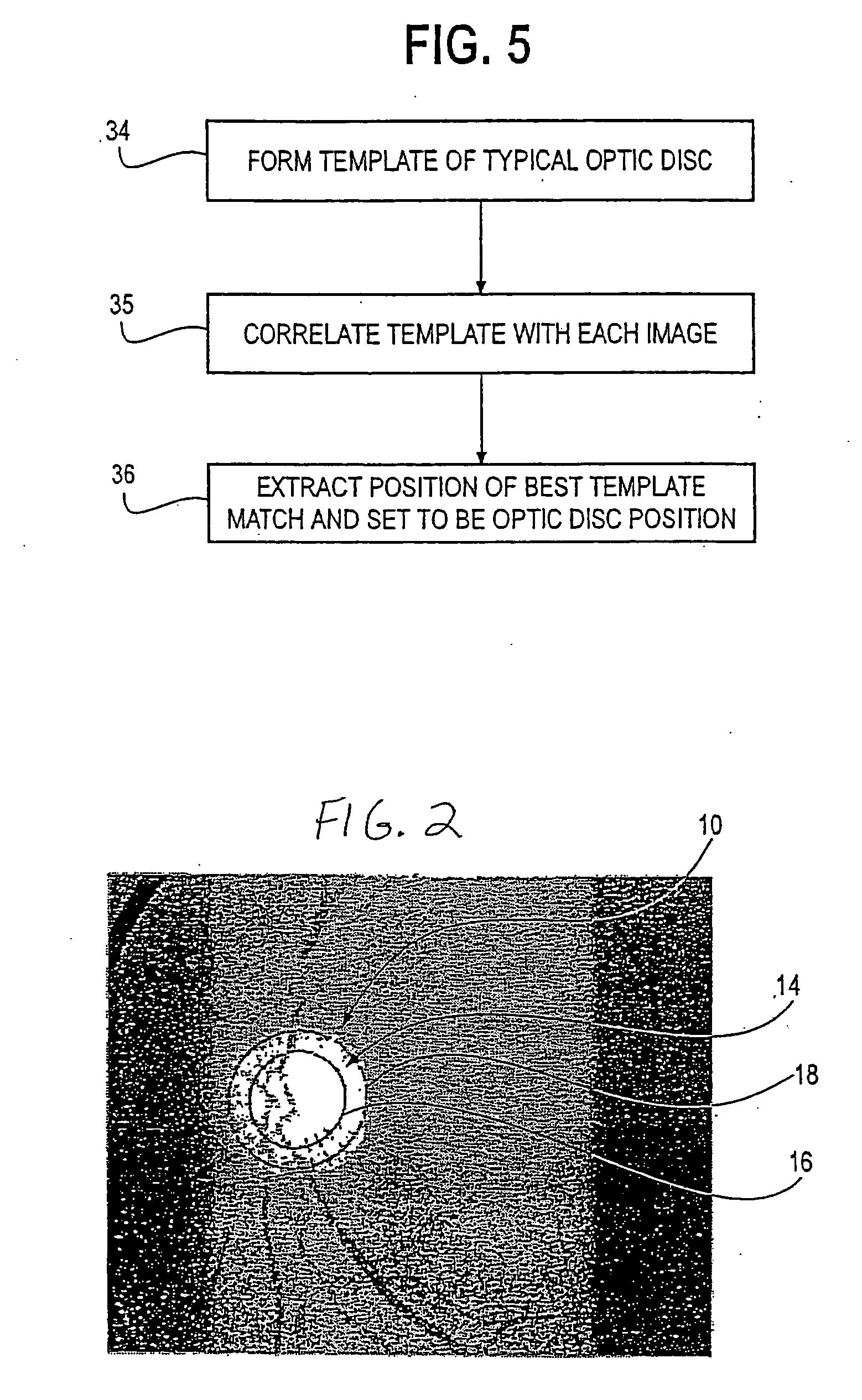
Retinal image quality assessment, error identification and automatic quality correction
Automatically determining image quality of a machine generated image may generate a local saliency map of the image to obtain a set of unsupervised features. The image is run through a trained convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract a set of supervised features from a fully connected layer of the CNN, the image convolved with a set of learned kernels from the CNN to obtain a complementary set of supervised features. The set of unsupervised features and the complementary set of supervised features are combined, and a first decision on gradability of the image is predicted. A second decision on gradability of the image is predicted based on the set of supervised features. Whether the image is gradable is determined based on a weighted combination of the first decision and the second decision.
Owner:IBM CORP
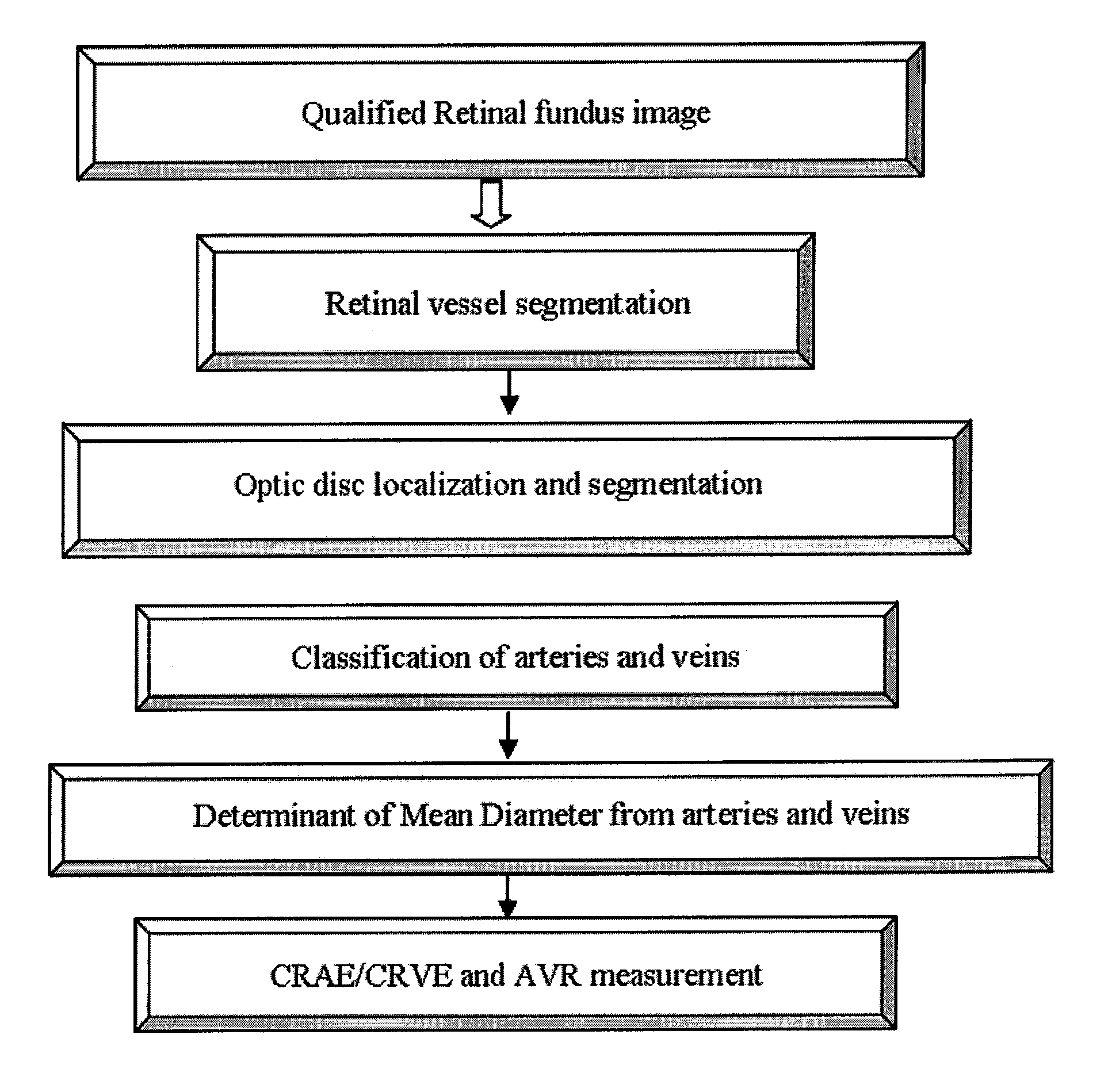
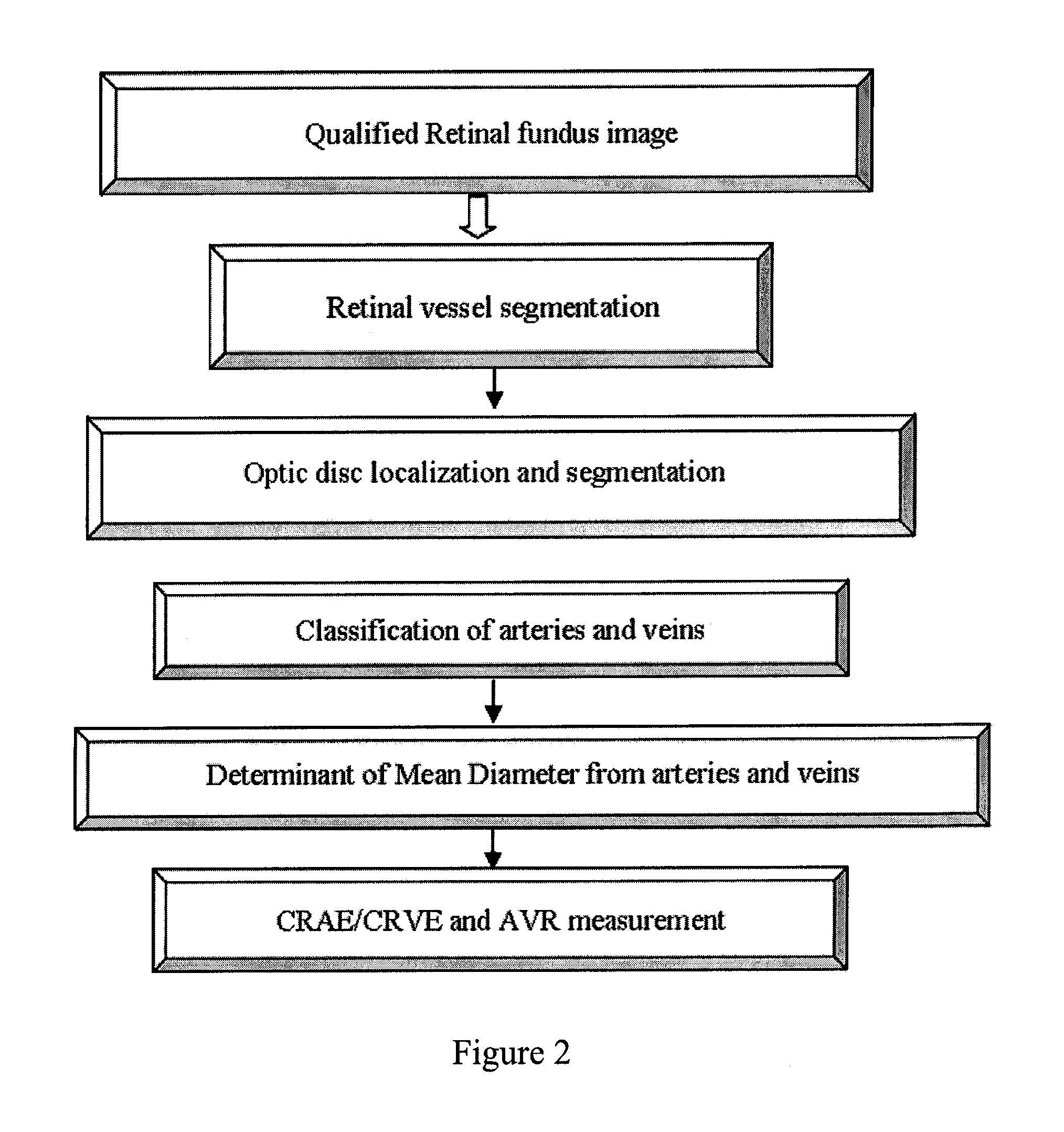
Method and device for retinal image analysis
The present application provides methods and devices for diagnosing and / or predicting the presence, progression and / or treatment effect of a disease characterized by retinal pathological changes in a subject.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
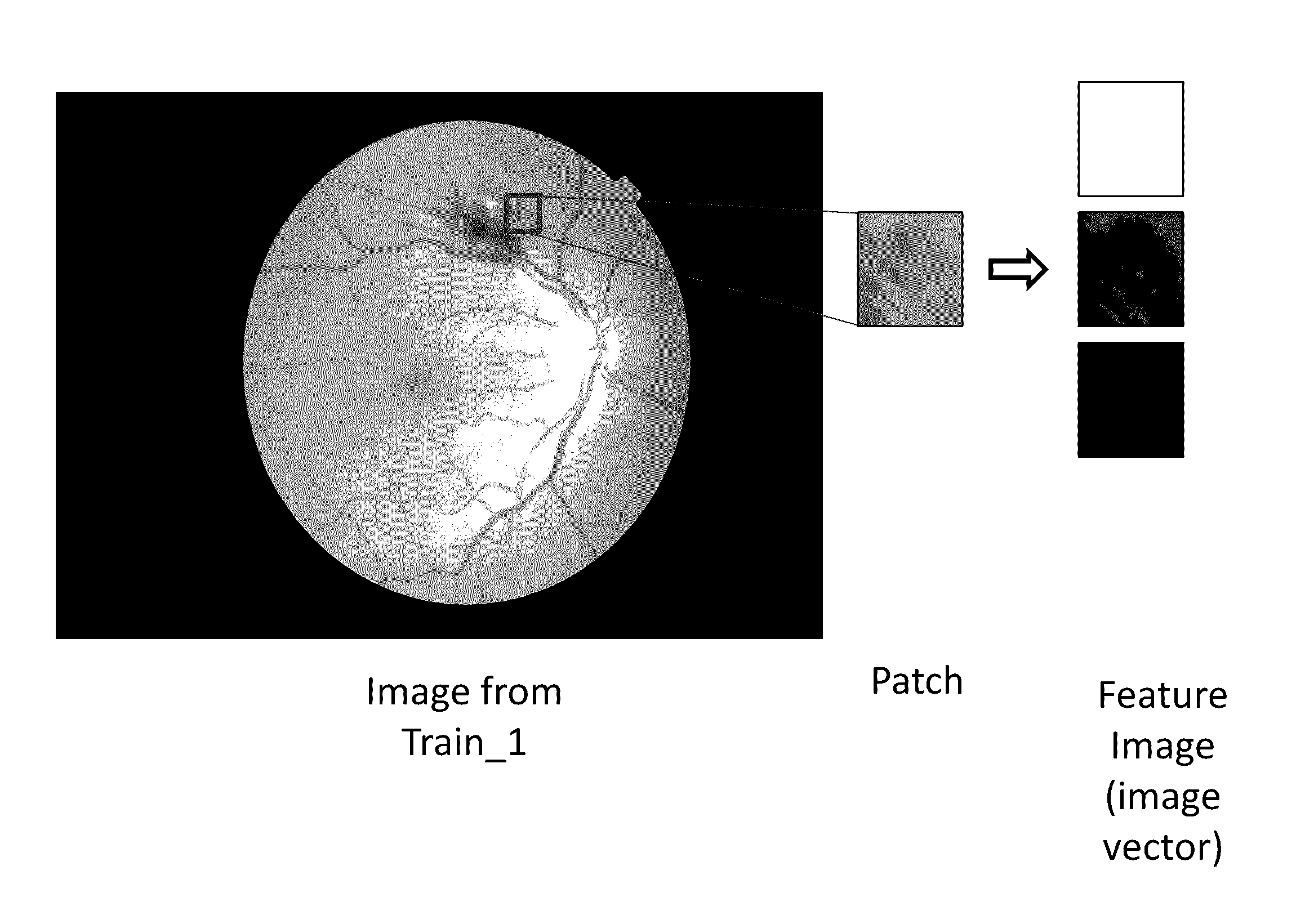
Systems and methods for feature detection in retinal images
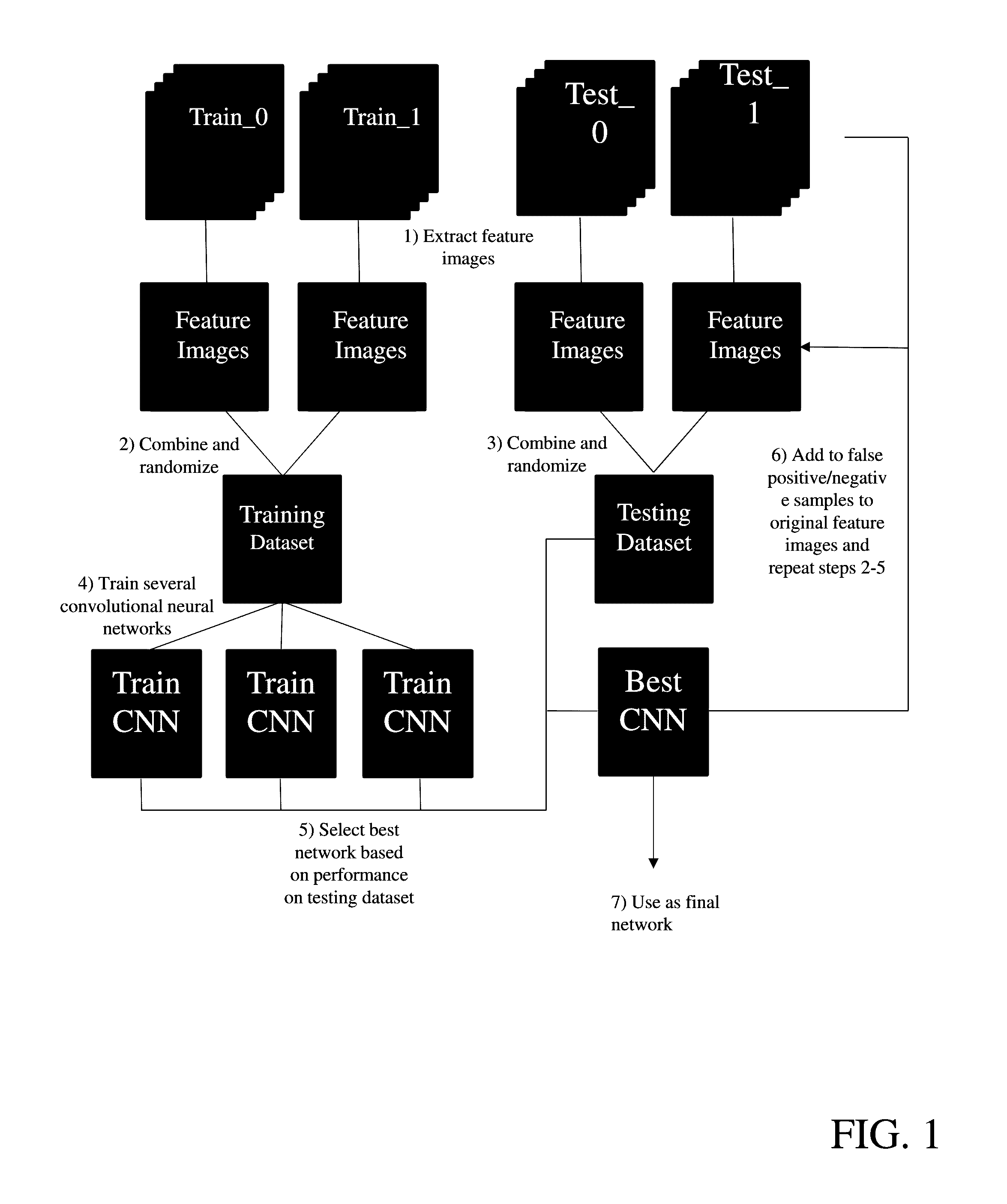
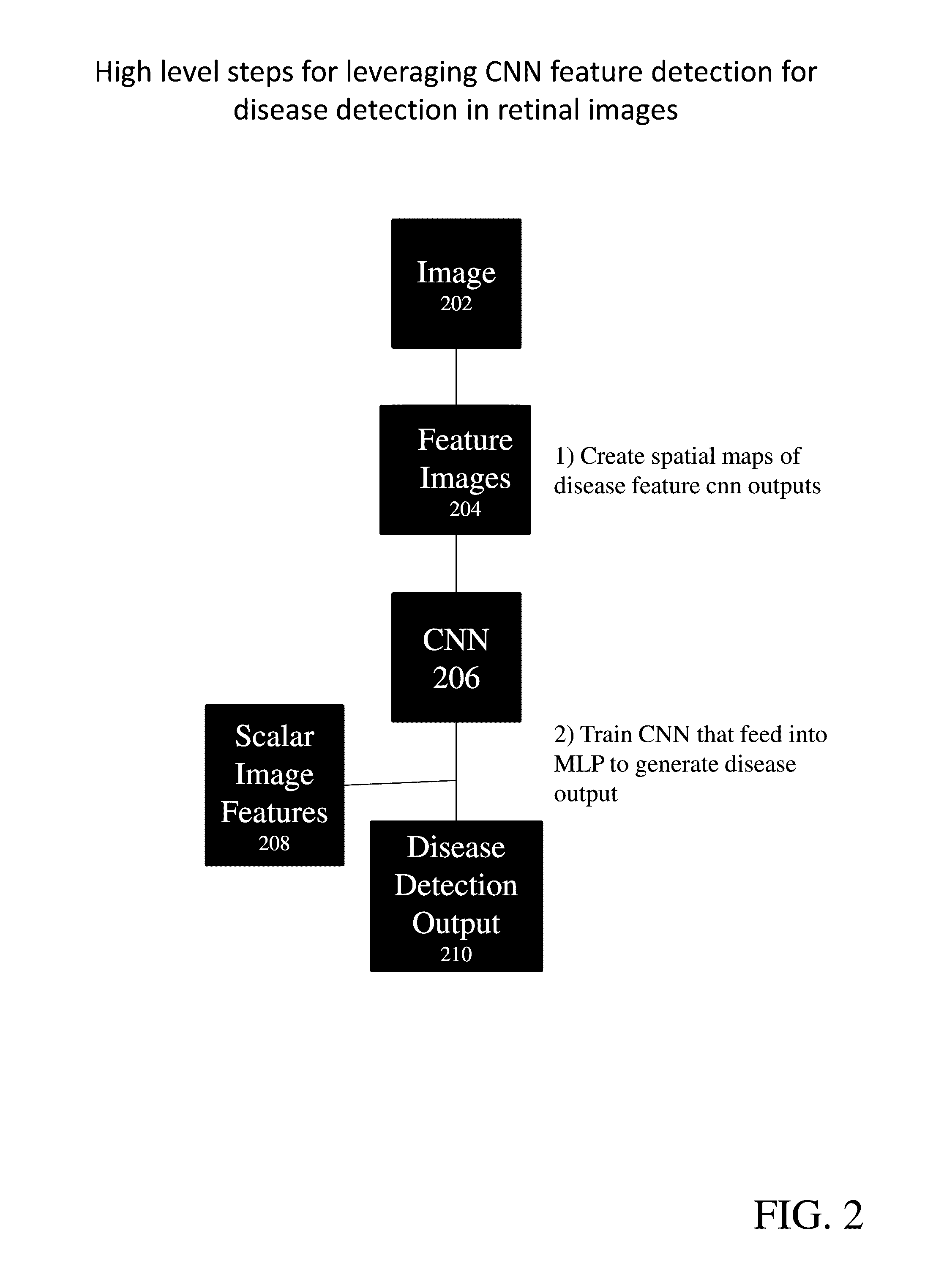
Provide are systems methods and devices for diagnosing disease in medical images. In certain aspects, disclosed is a method for training a neural network to detect features in a retinal image including the steps of: a) extracting one or more features images from a Train_0 set, a Test_0 set, a Train_1 set and a Test_1 set; b) combining and randomizing the feature images from Train_0 and Train_1 into a Training data set; c) combining and randomizing the feature images from Test_0 and Test_1 into a testing dataset; d) training a plurality of neural networks having different architectures using a subset of the training dataset while testing on a subset of the testing dataset; e) identifying the best neural network based on each of the plurality of neural networks performance on the testing data set; f) inputting images from Test_0, Train_1, Train_0 and Test_1 to the best neural network and identifying a limited number of false positives and false negative and adding the false positives and false negatives to the training dataset and testing dataset; and g) repeating steps d)-g) until an objective performance threshold is reached.
Owner:DIGITAL DIAGNOSTICS INC
Snapshot Spectral Imaging of the Eye
ActiveUS20090225277A1Minimizes problemStrong robustnessSpectrum investigationDiagnostic recording/measuringFundus cameraPupil
Obtaining spectral images of an eye includes taking an optical system that images eye tissue onto a digital sensor array and optically fitting a multi-spectral filter array and the digital sensor array, wherein the multi-spectral filter array is disposed between the digital sensor array and an optics portion of the optical system. The resulting system facilitates acquisition of a snap-shot image of the eye tissue with the digital sensor array. The snap shot images support estimation of blood oxygen saturation in a retinal tissue. The resulting system can be based on a non-mydriatic fundus camera designed to obtain the retinal images without administration of pupil dilation drops.
Owner:MERGE HEALTHCARE
System and methods for automatic processing of digital retinal images in conjunction with an imaging device
Systems and methods of obtaining and recording fundus images by minimally trained persons, which includes a camera for obtaining images of a fundus of a subject's eye, in combination with mathematical methods to assign real time image quality classification to the images obtained based upon a set of criteria. The classified images will be further processed if the classified images are of sufficient image quality for clinical interpretation by machine-coded and / or human-based methods. Such systems and methods can thus automatically determine whether the quality of a retinal image is sufficient for computer-based eye disease screening. The system integrates global histogram features, textural features, and vessel density, as well as a local non-reference perceptual sharpness metric. A partial least square (PLS) classifier is trained to distinguish low quality images from normal quality images.
Owner:VISIONQUEST BIOMEDICAL
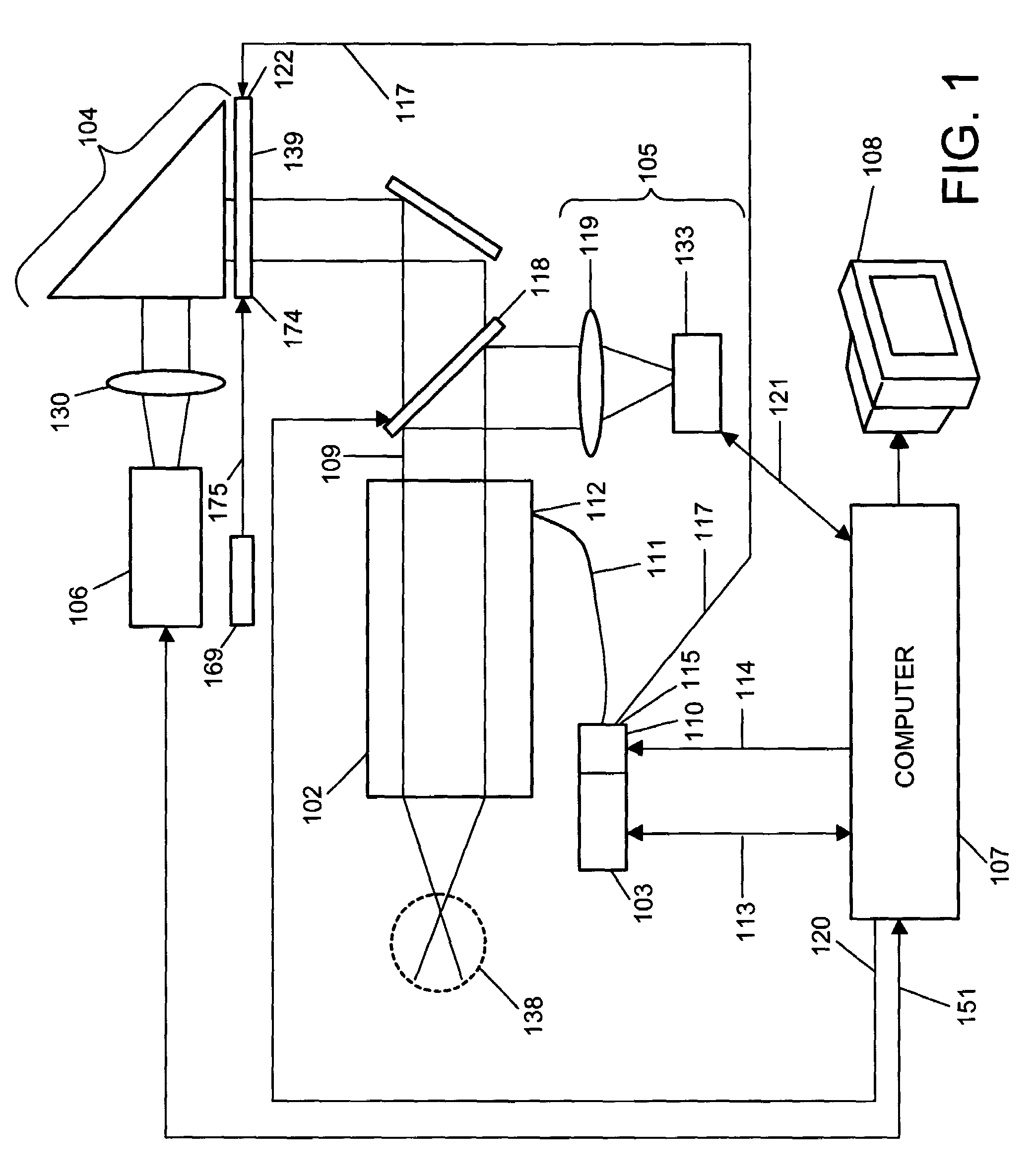
Automated fundus imaging system
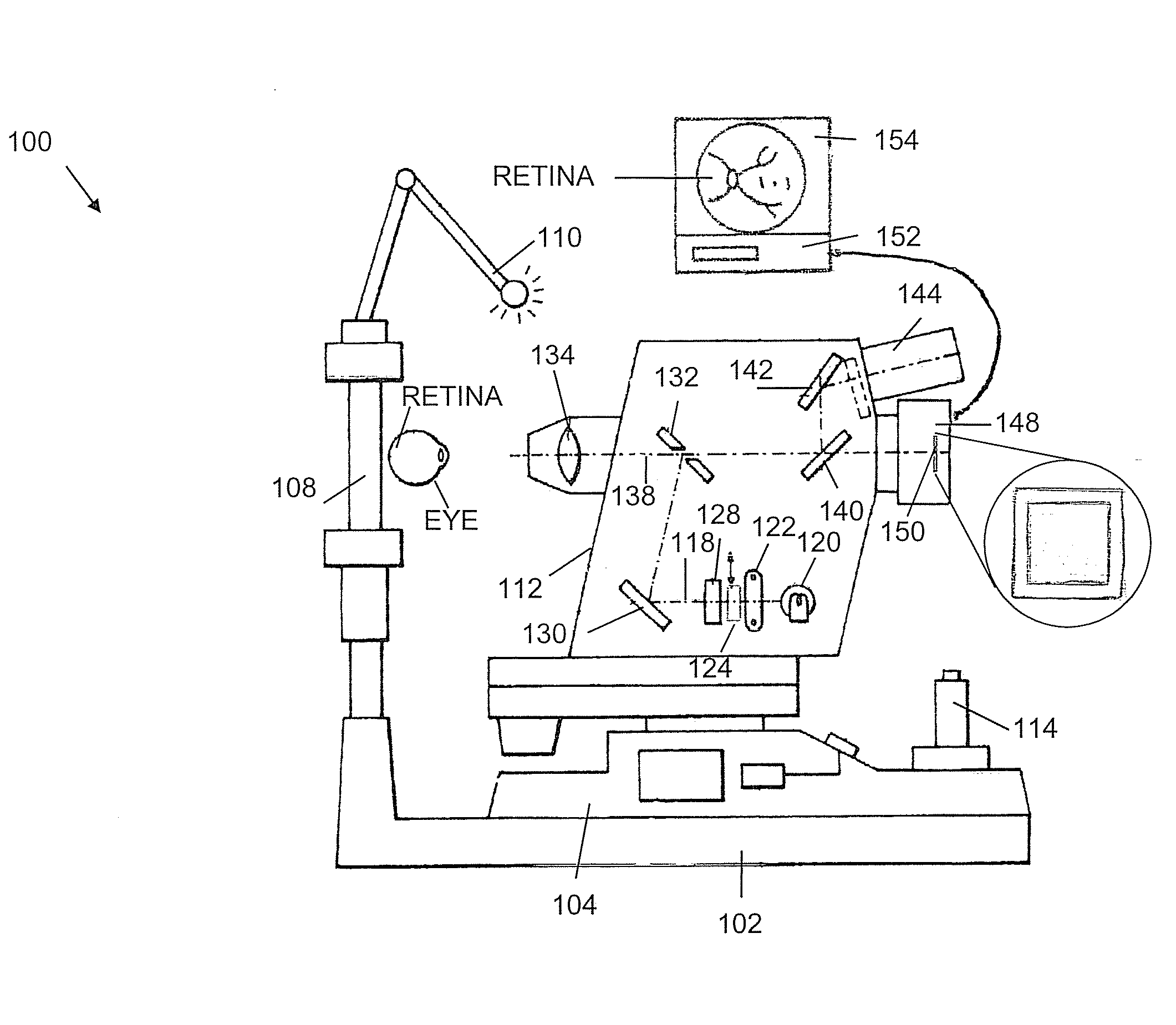
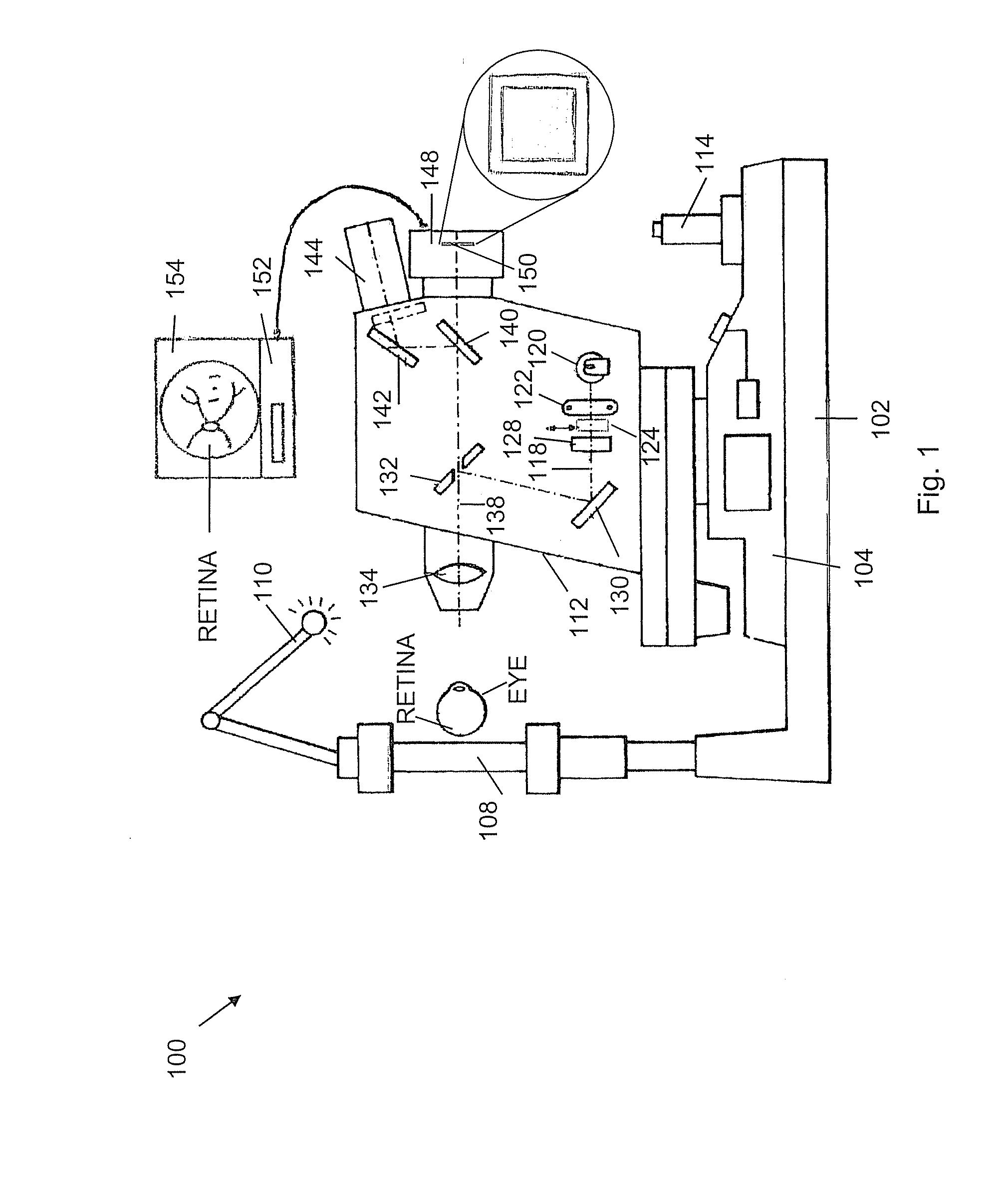
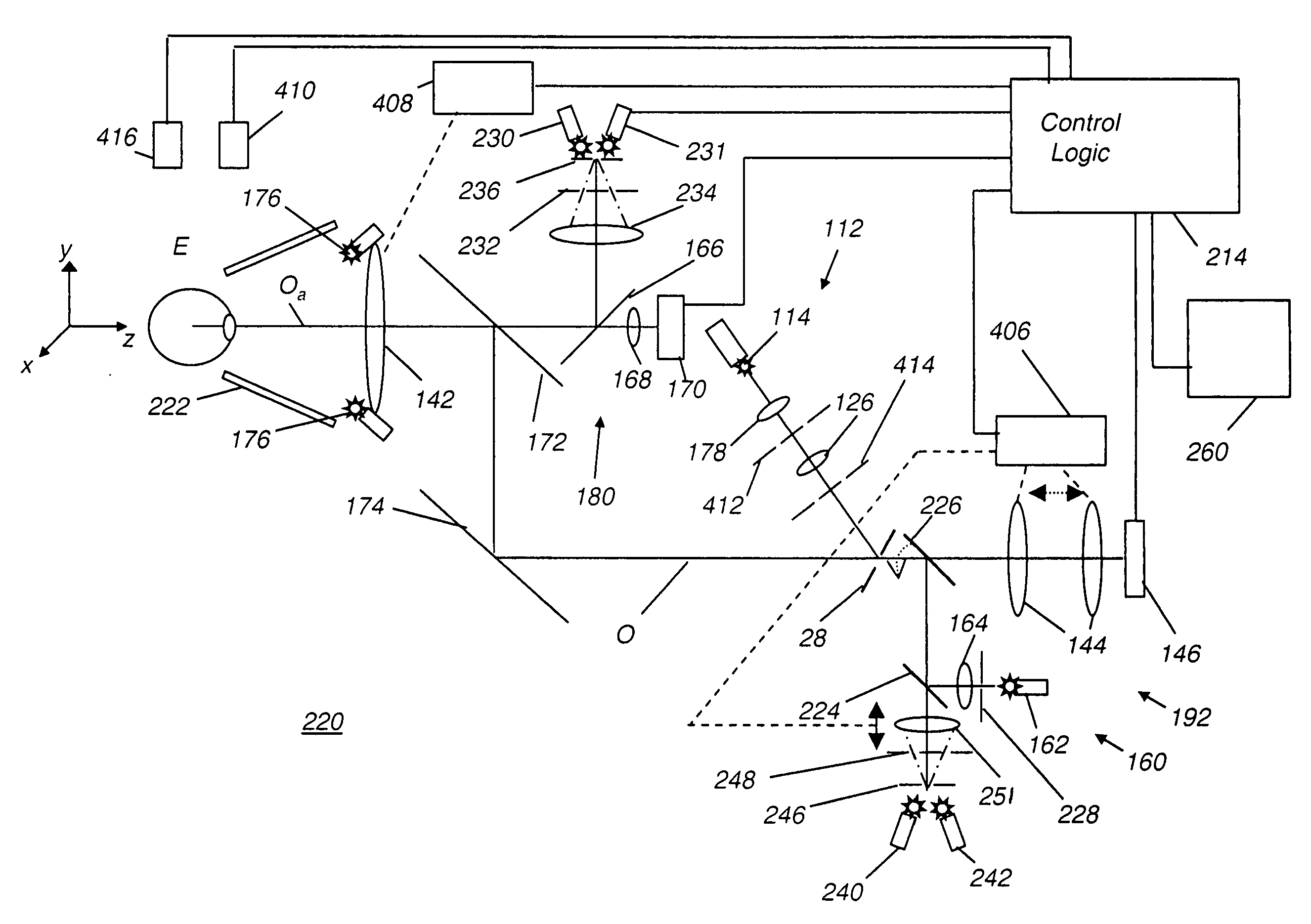
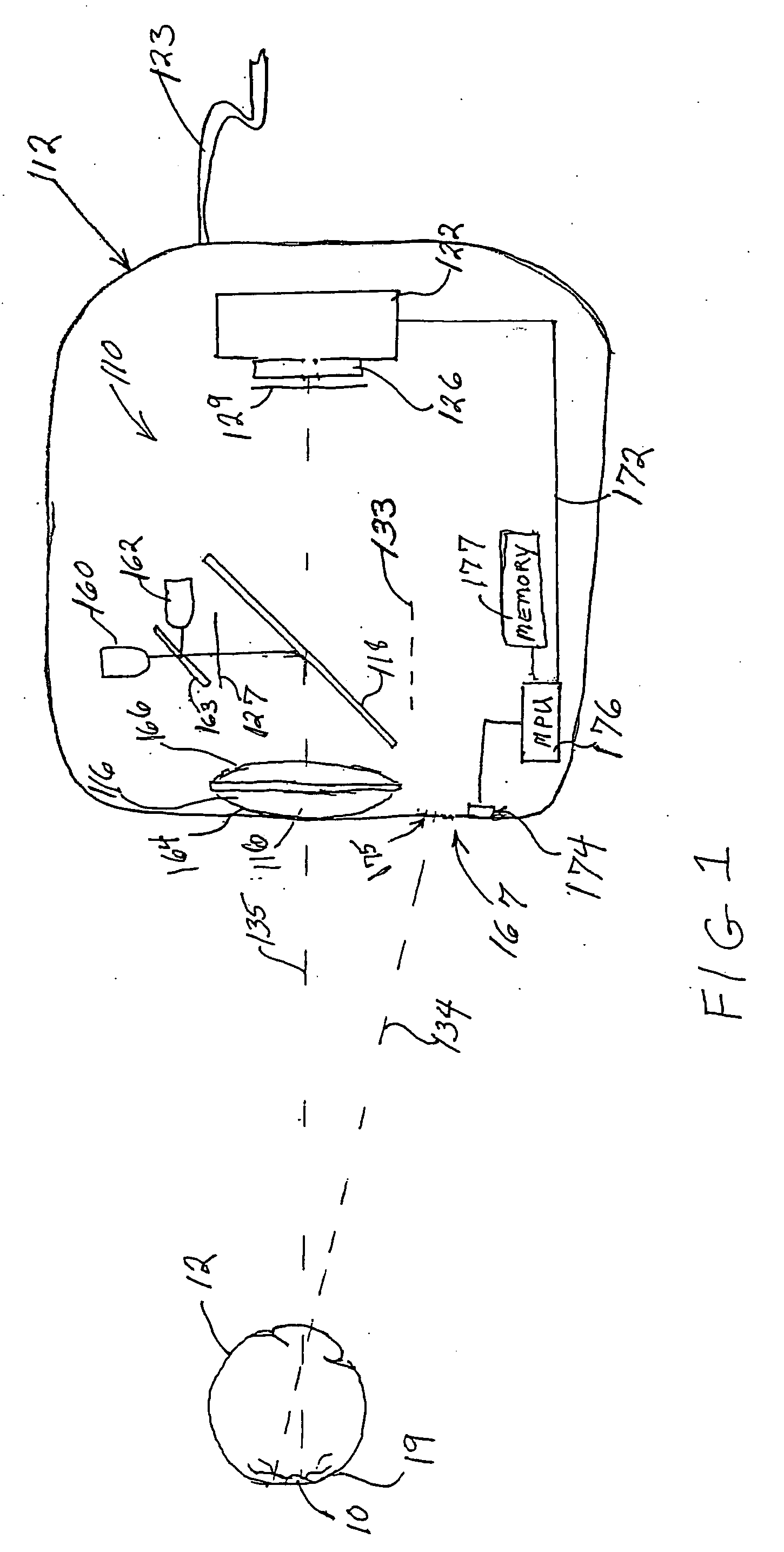
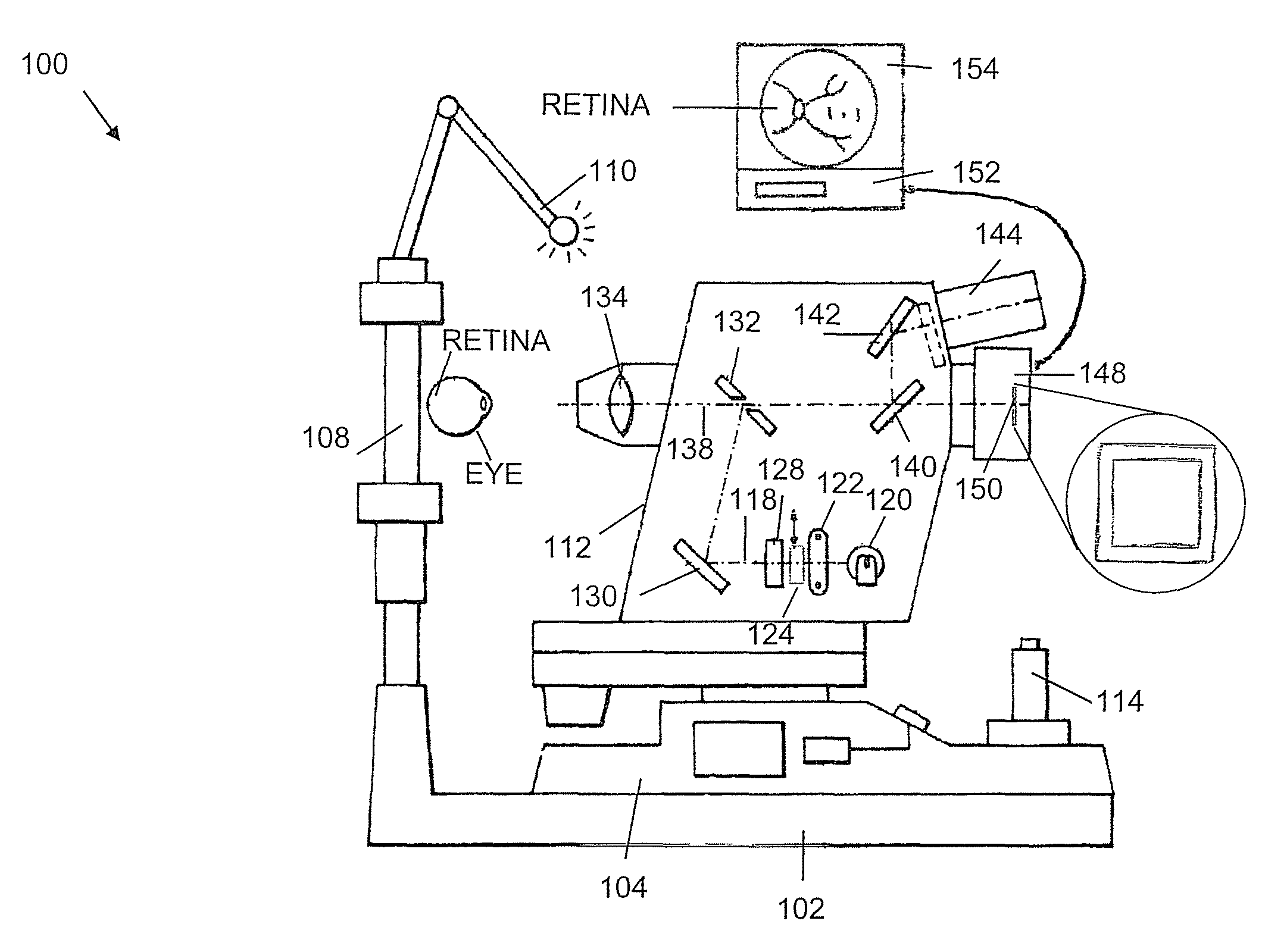
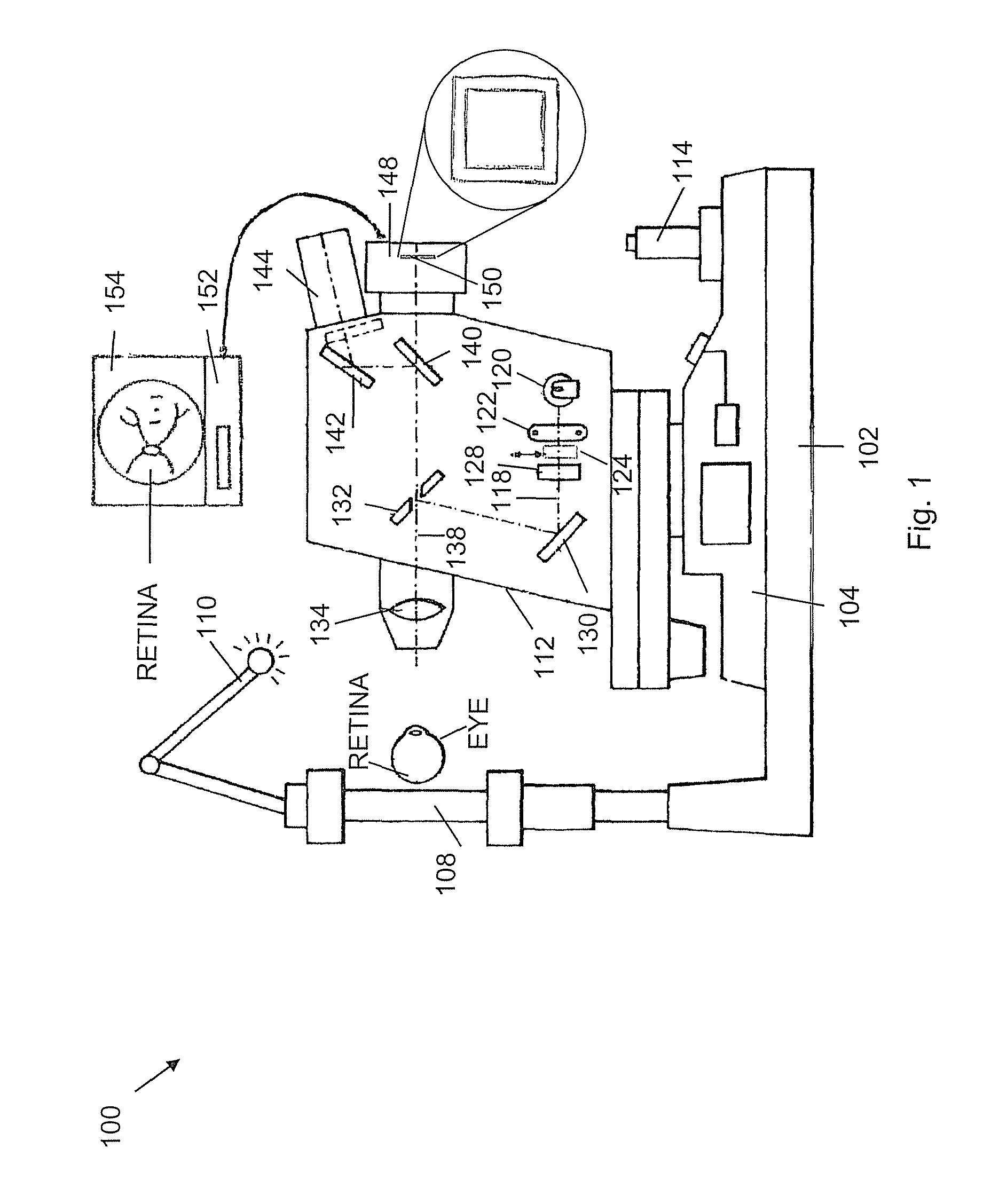
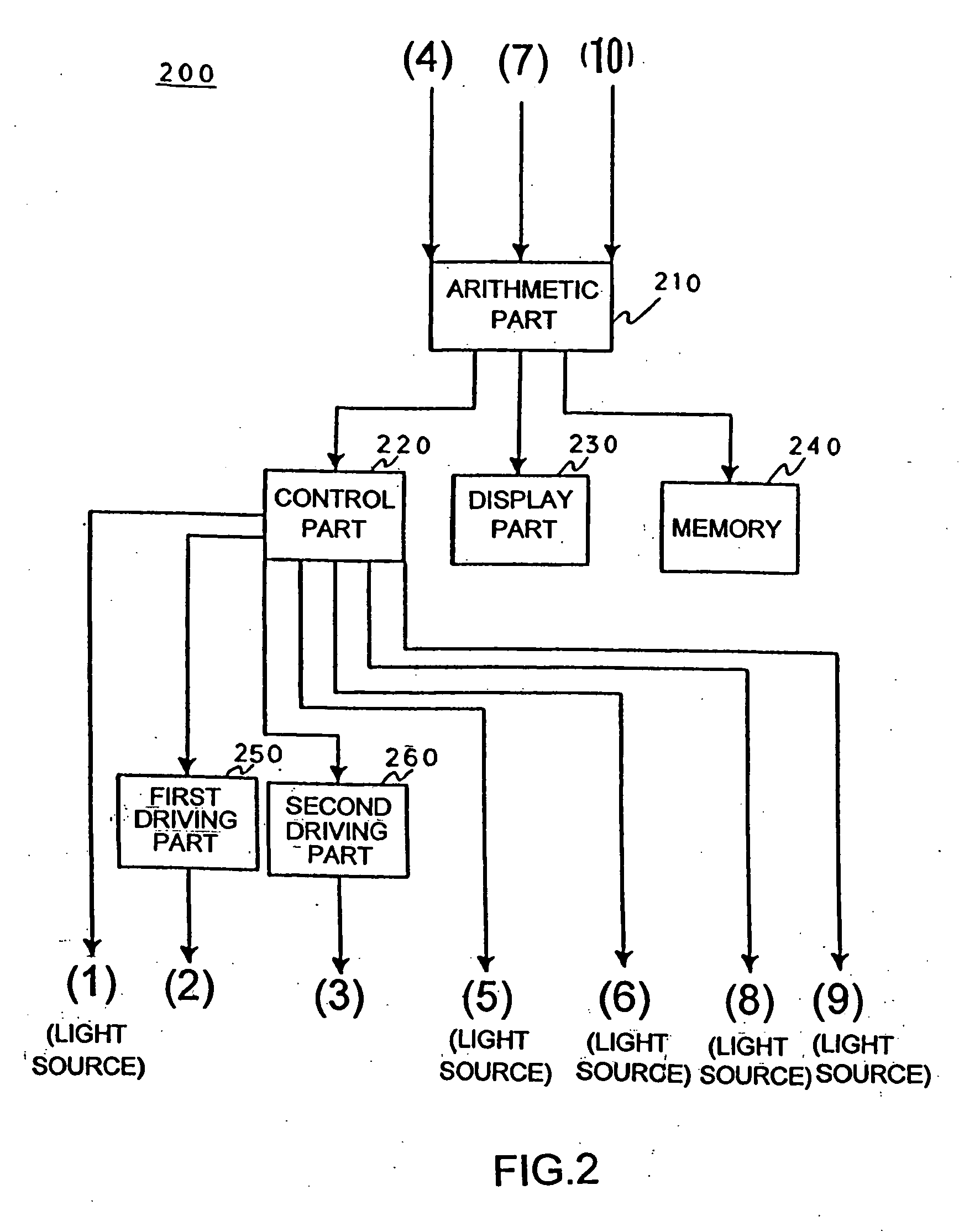
An apparatus for obtaining a retinal image of an eye has a control logic processor (214) for executing a sequence of operations for obtaining the image. A visual target (162) orients the eye of a patient when viewed. An indicator element (410) provides a signal that indicates that the patient is in position. A cornea focus detection section (450) indicates cornea focus, in cooperation with the control logic processor (214). An alignment actuator aligns the optical path according to a signal obtained from the cornea focus detection section (450). A retina focus detection section (452) detects retina focus in cooperation with the control logic processor (214). A focusing actuator (406) is controlled by instructions from the control logic processor (214) according to a signal obtained from the retina focus detection section (452). An image capture light source is energized by the control logic processor (214) for illuminating the retina.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
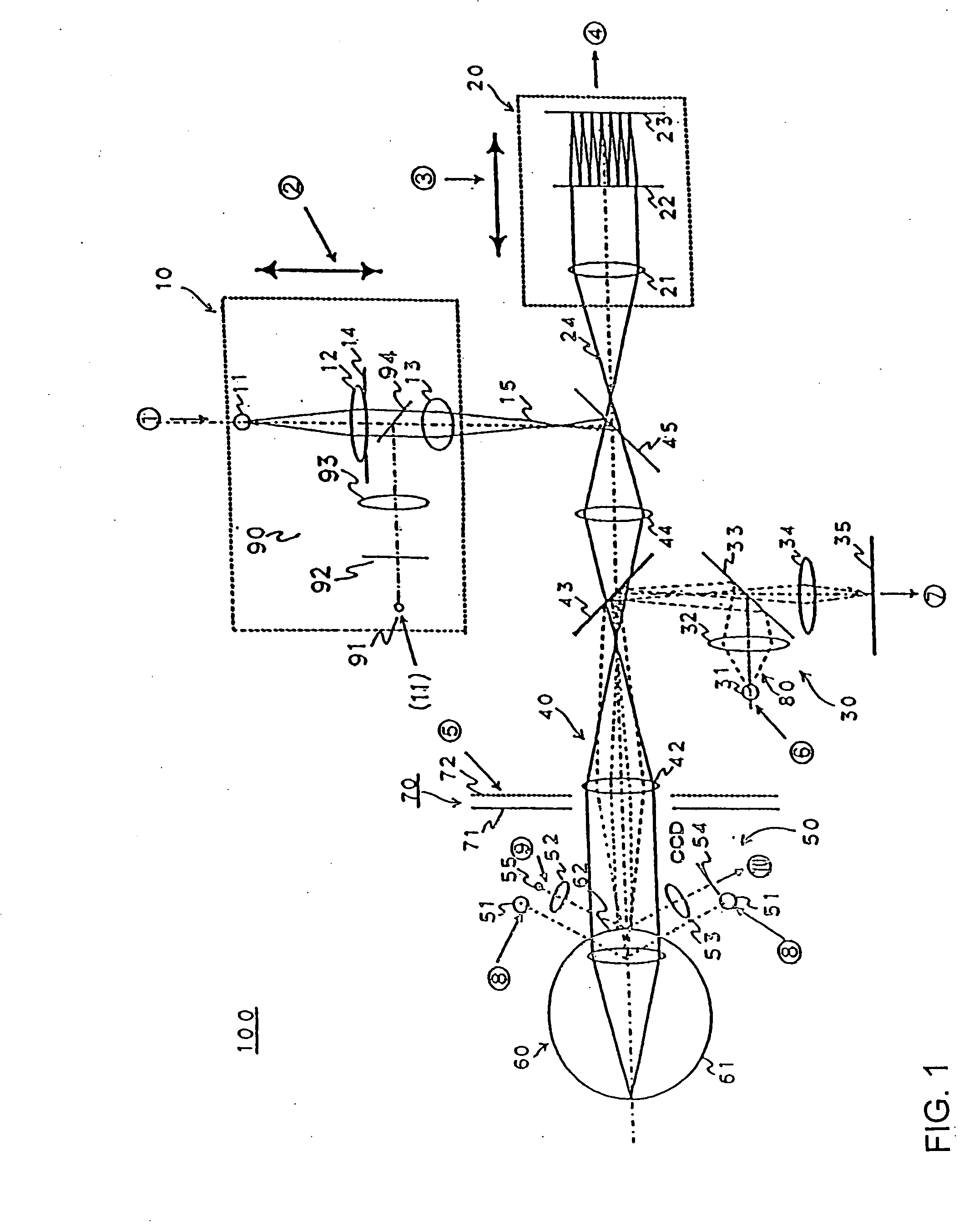
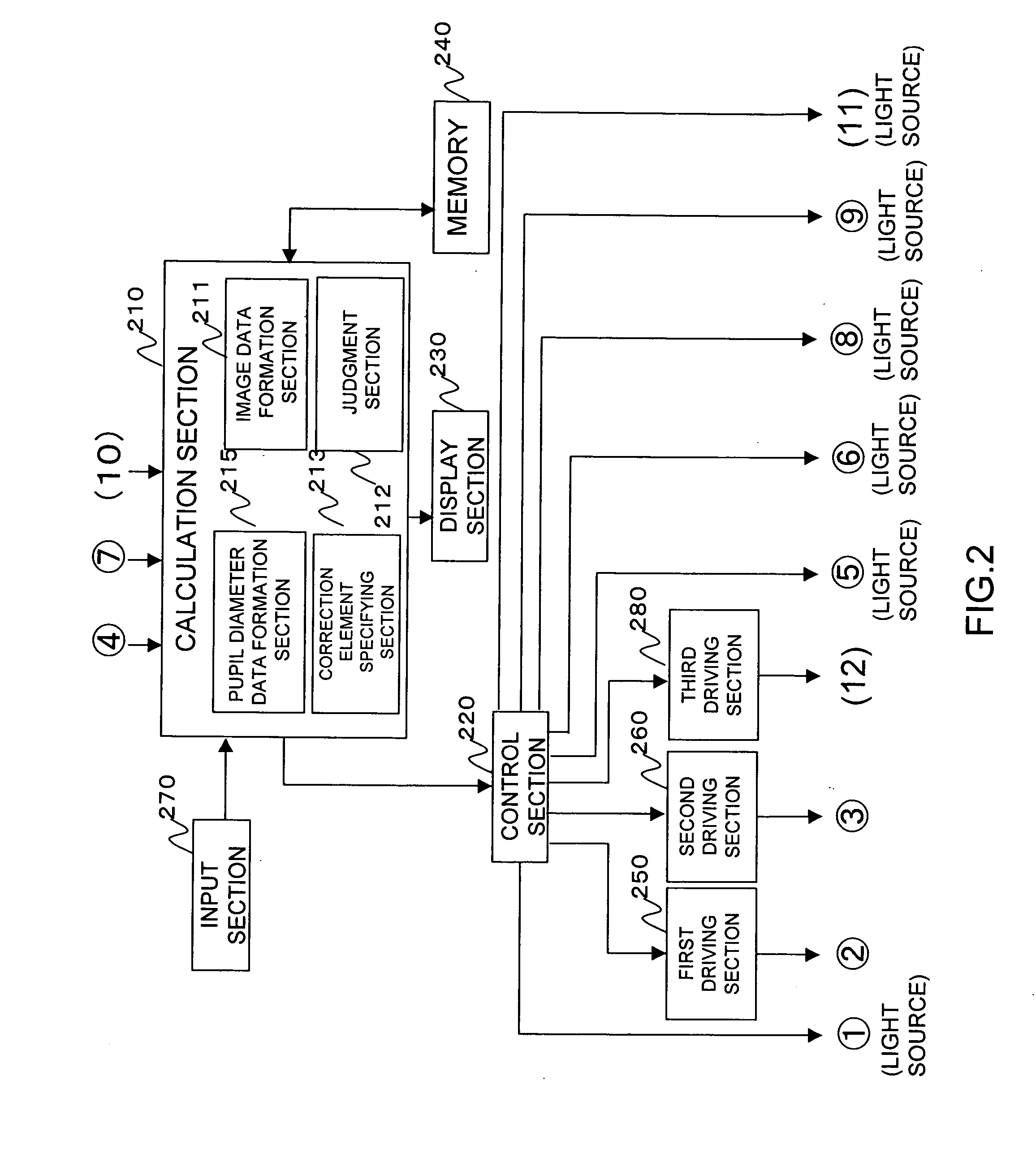
Ophthalmic data measurement device, ophthalmic data measurement program, and eye characteristic measurement device
InactiveUS20060170865A1Predict contrast sensitivityAccurate measurementRefractometersSkiascopesPupil diameterOphthalmology department
It is possible to estimate optical characteristic according to a pupil diameter in daily life of an examinee, correction data near to the optimal prescription value, eyesight, and sensitivity. A calculation section receives measurement data indicating refractive power distribution of an eye to be examined and pupil data on the eye and calculates lower order and higher order aberrations according to the measurement data and the pupil data (S101 to 105). For example, a pupil edge is detected from the anterior ocular segment image and a pupil diameter is calculated. By using this pupil diameter, lower order and higher order aberrations are calculated. According to the lower order and higher order aberrations obtained, the calculation section performs simulation of a retina image by using high contrast or low contrast target and estimates the eyesight by comparing the result to a template and / or obtains sensitivity (S107). Alternatively, according to the lower order and the higher order aberraations obtained, the calculation section calculates an evaluation parameter indicating the quality of visibility by the eye to be examined such as the Strehl ratio, the phase shift (PTF), and the visibility by comparison of the retina image simulation with the template. According to the evaluation parameter calculated, the calculation section changes the lower order aberration amount so as to calculate appropriate correction data for the eye to be examined (S107). The calculation section outputs data such as the eyesight, sensitivity, correction data, and the simulation result to a memory or a display section (S109).
Owner:KK TOPCON
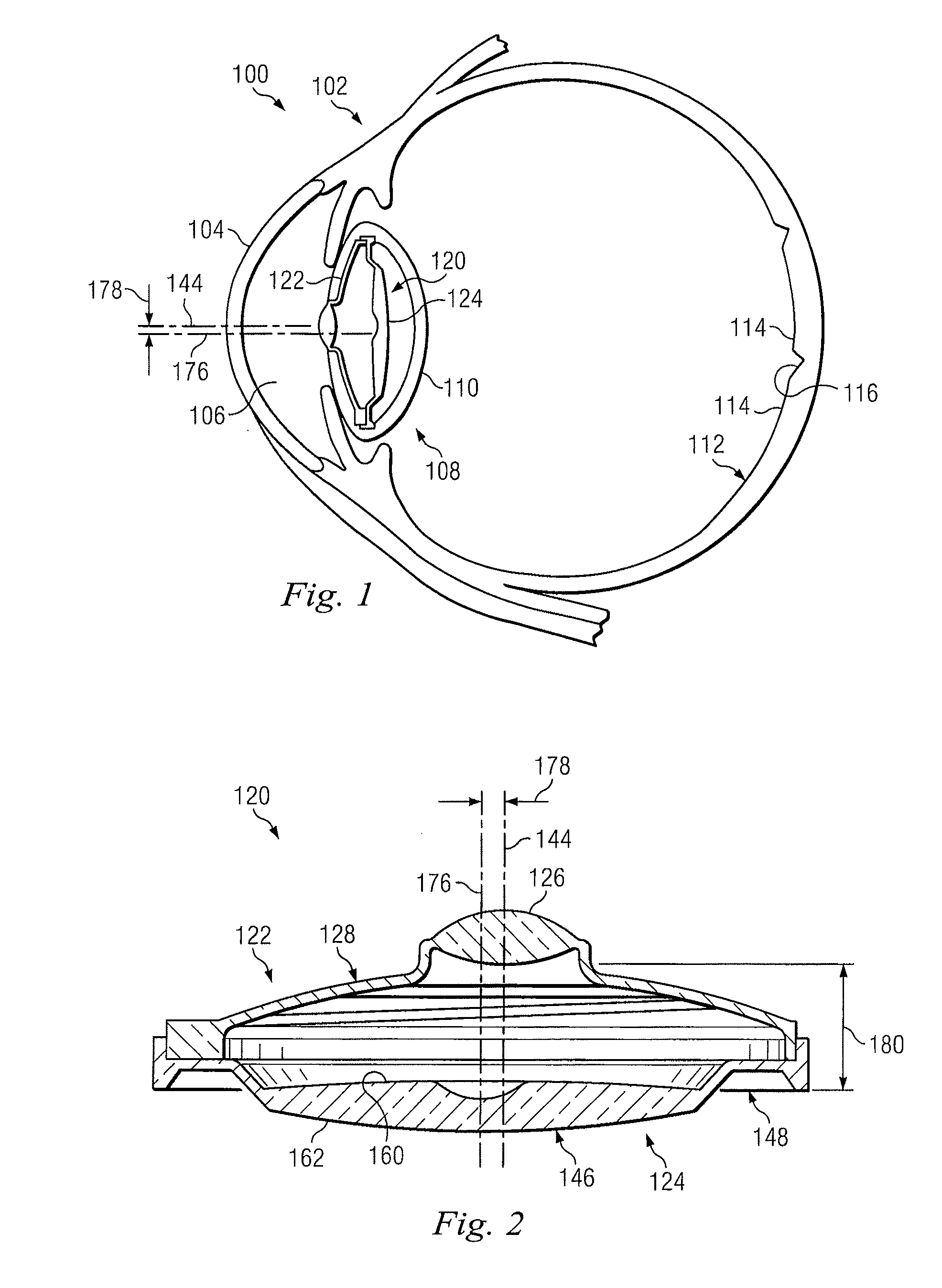
Intraocular devices and associated methods
Visual aids and associated methods for improving the eye sight of low vision patients are provided. Generally, the devices of the present disclosure address the needs of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and other low vision patients by providing a magnified retinal image while keeping a large visual field of view. Further, the devices of the present disclosure allow direction of the magnified retinal image away from damaged portions of the retina and towards healthy, or at least healthier, portions of the retina. The devices of the present disclosure are also configured for implantation within the eye using minimally invasive surgical procedures. Methods of utilizing the devices of the present disclosure, including surgical procedures, are also provided.
Owner:ALCON INC
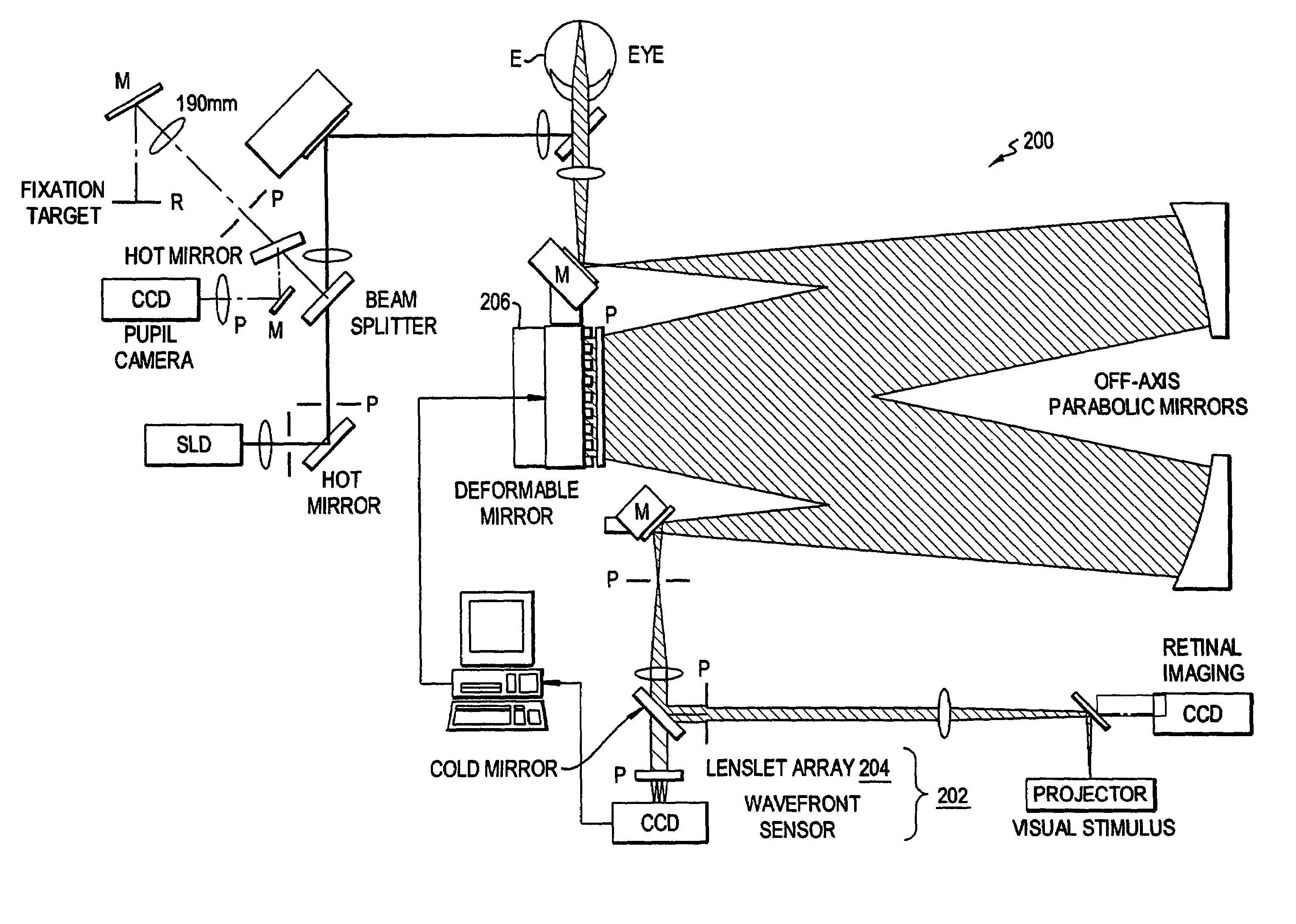
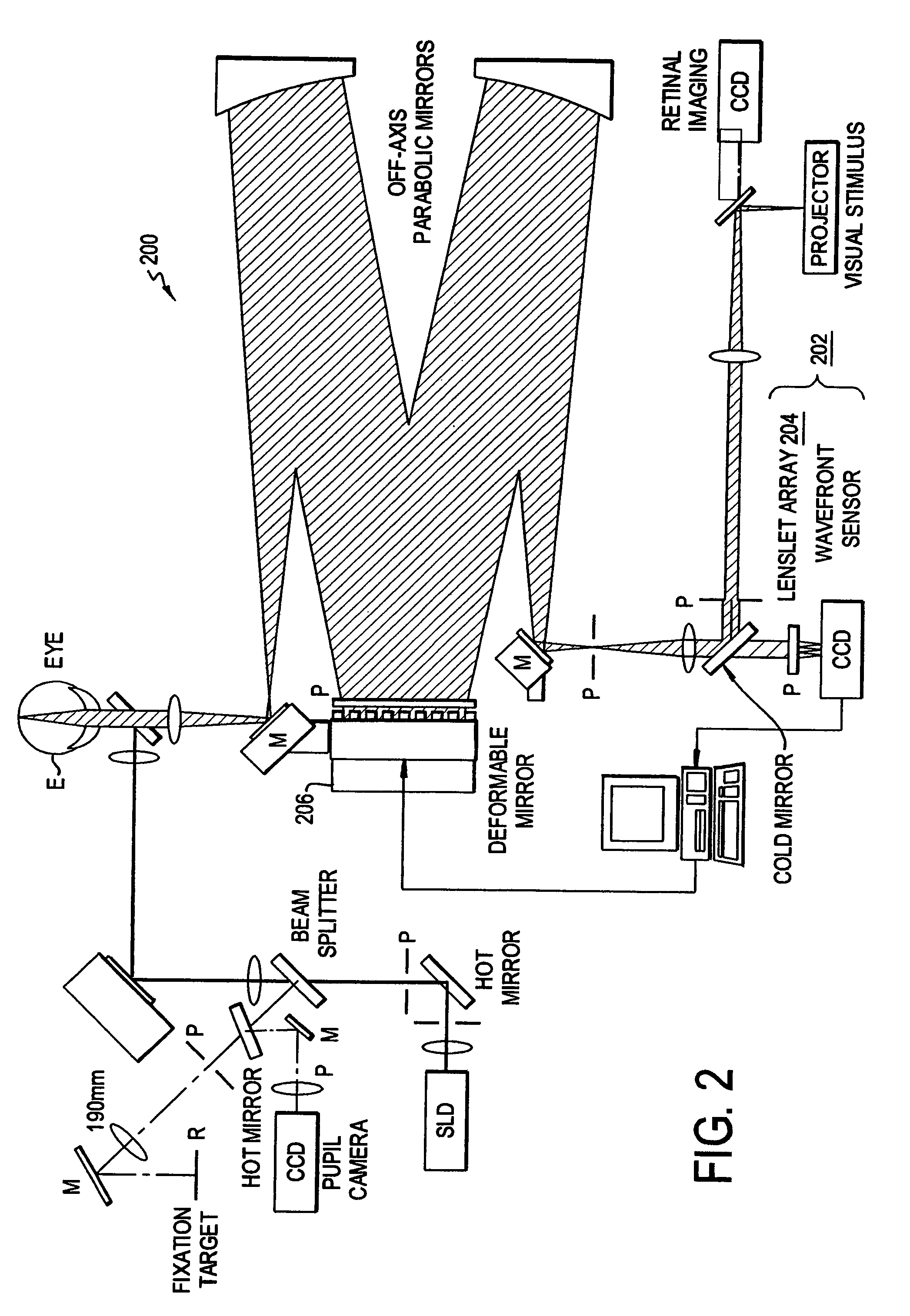
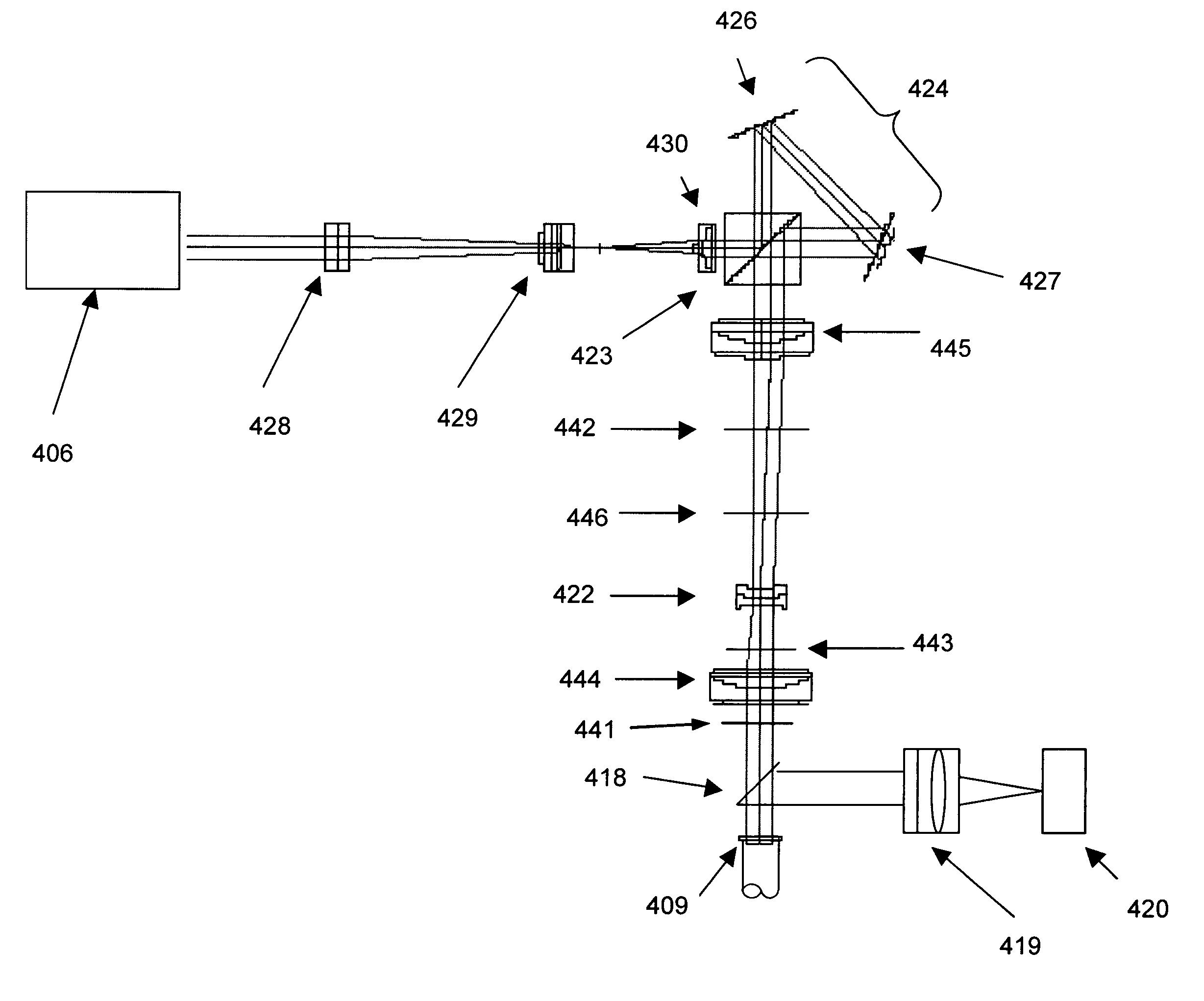
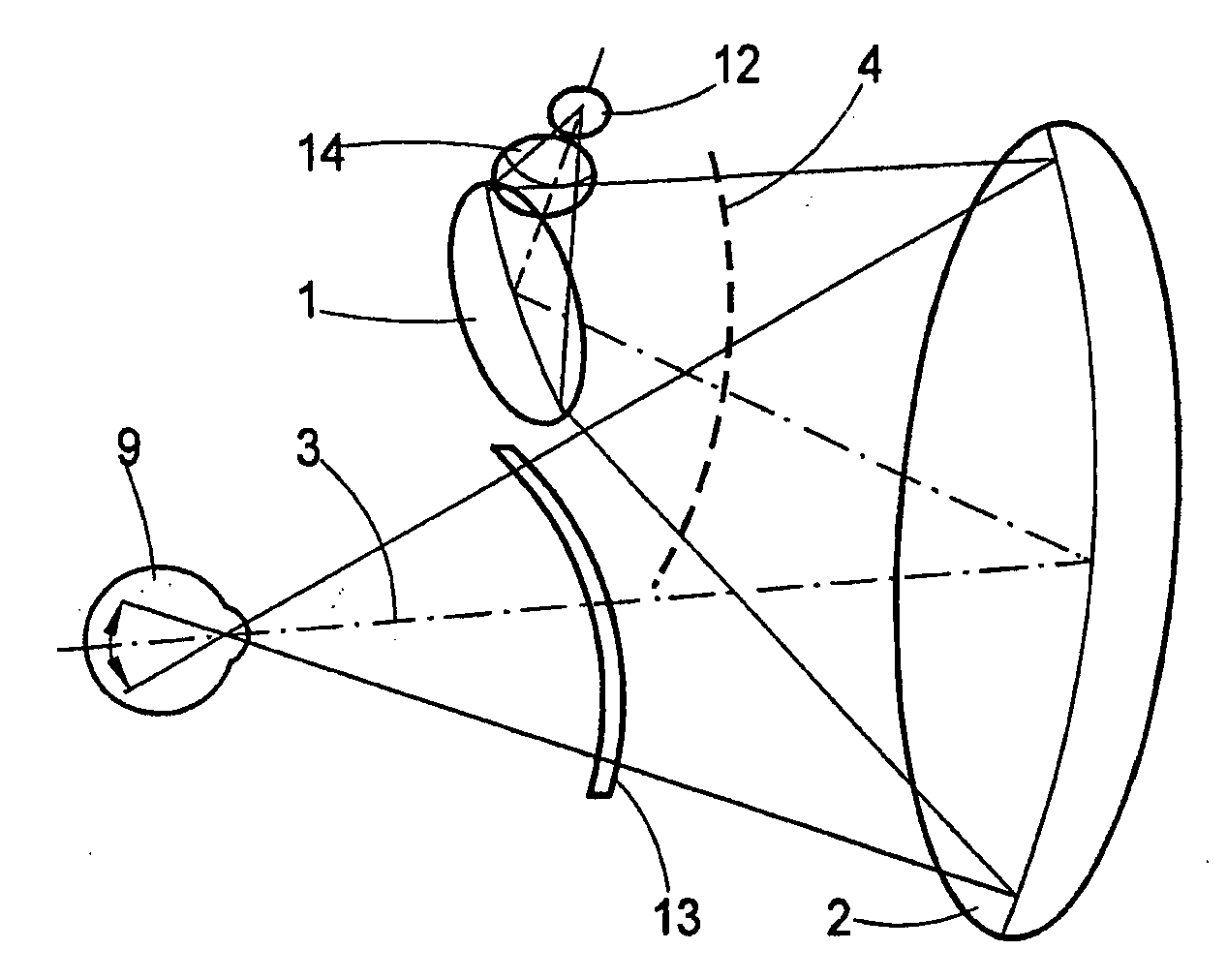
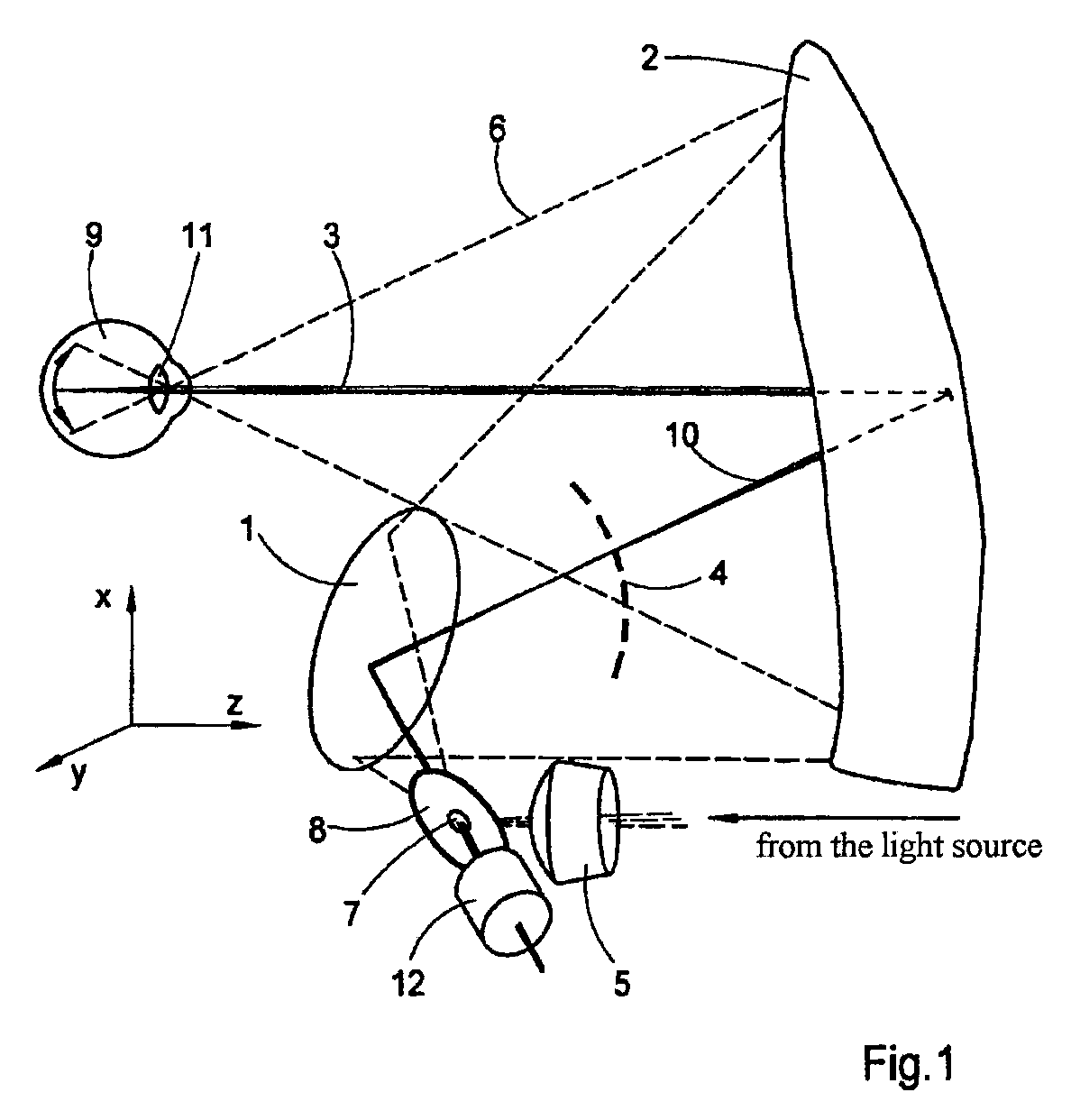
High resolution, multispectral, wide field of view retinal imager
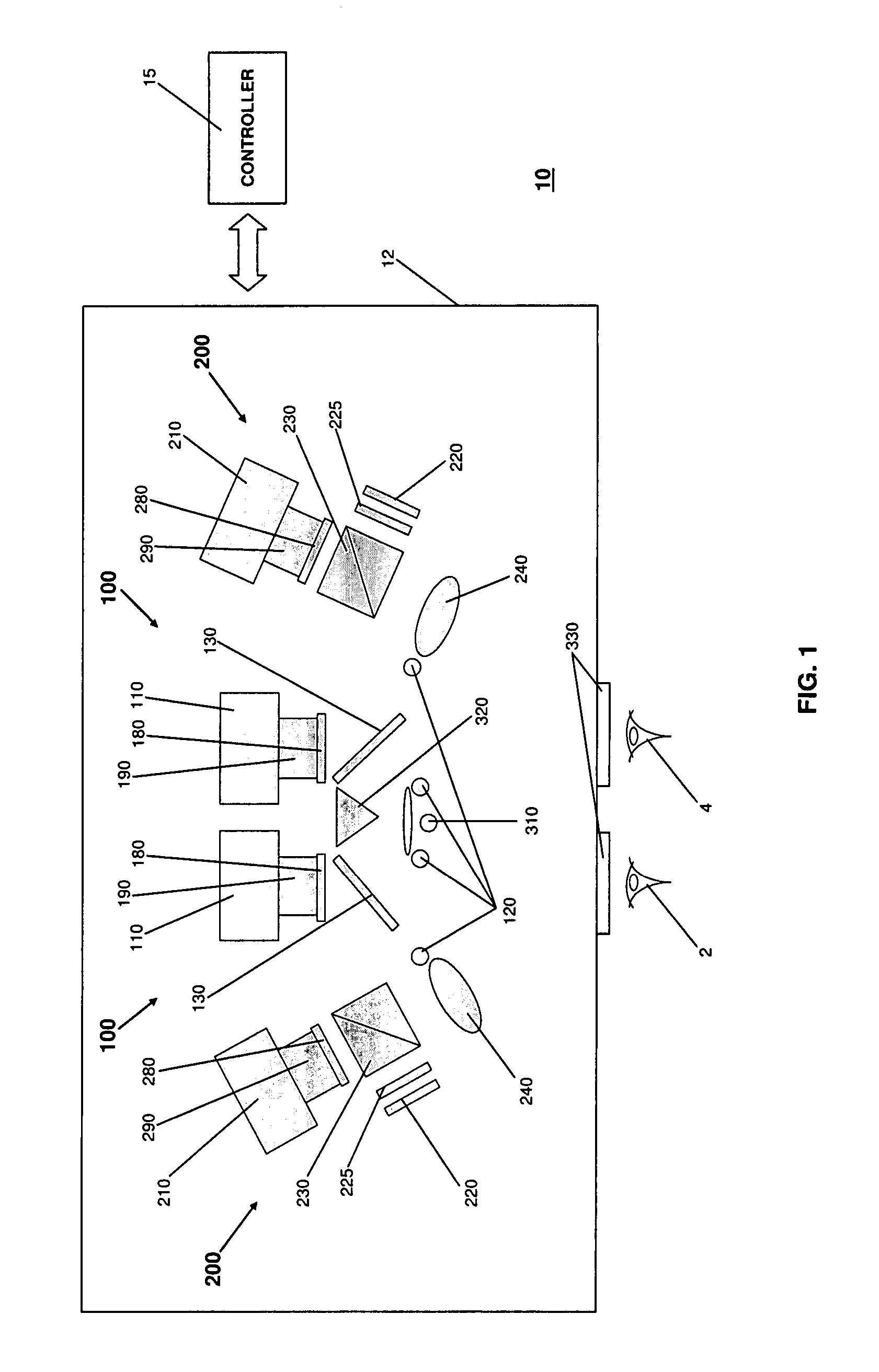
An ophthalmic instrument (for obtaining high resolution, wide field of area multi-spectral retinal images) including a fundus retinal imager, (which includes optics for illuminating and imaging the retina of the eye); apparatus for generating a reference beam coupled to the fundus optics to form a reference area on the retina; a wavefront sensor optically coupled to the fundus optics for measuring the wavefront produced by optical aberrations within the eye and the imager optics; wavefront compensation optics coupled to the fundus optics for correcting large, low order aberrations in the wavefront; a high resolution detector optically coupled to the imager optics and the wavefront compensation optics; and a computer (which is connected to the wavefront sensor, the wavefront compensation optics, and the high resolution camera) including an algorithm for correcting, small, high order aberrations on the wavefront and residual low order aberrations.
Owner:KESTREL CORP
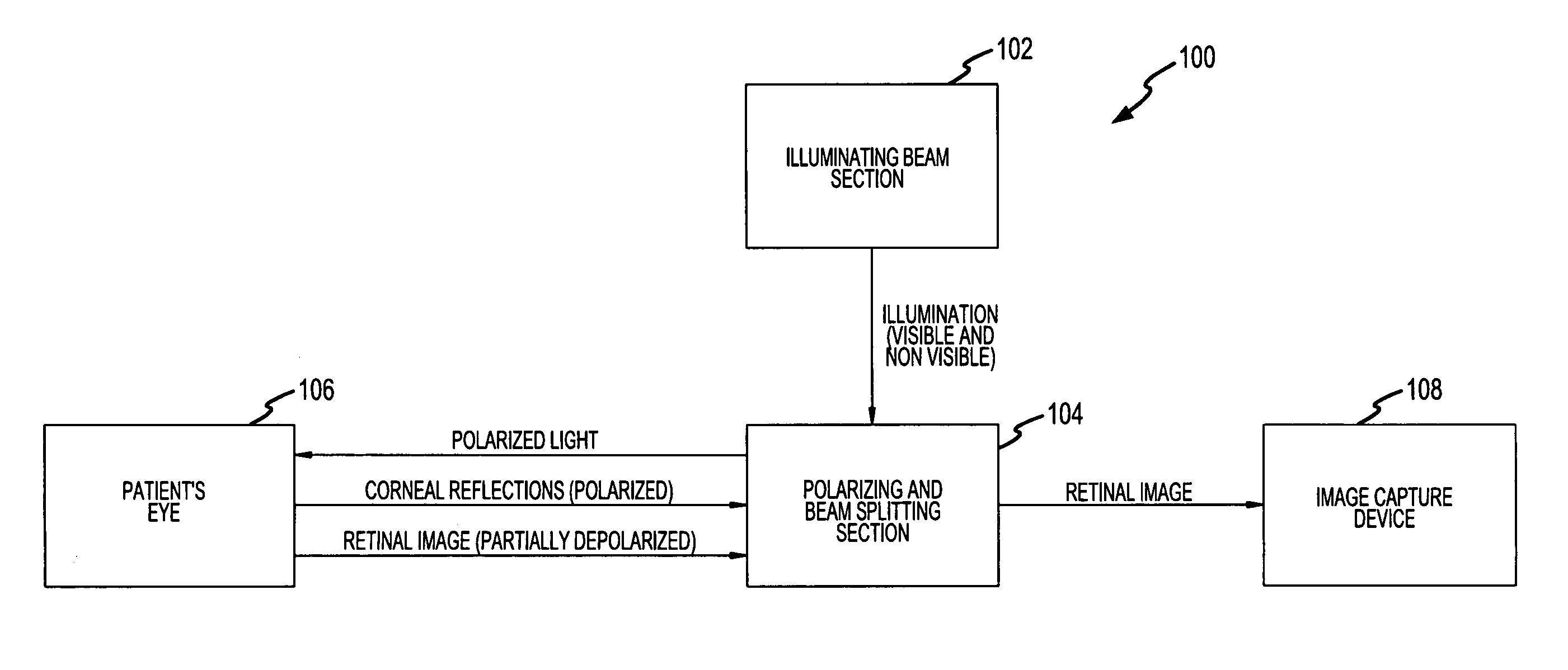
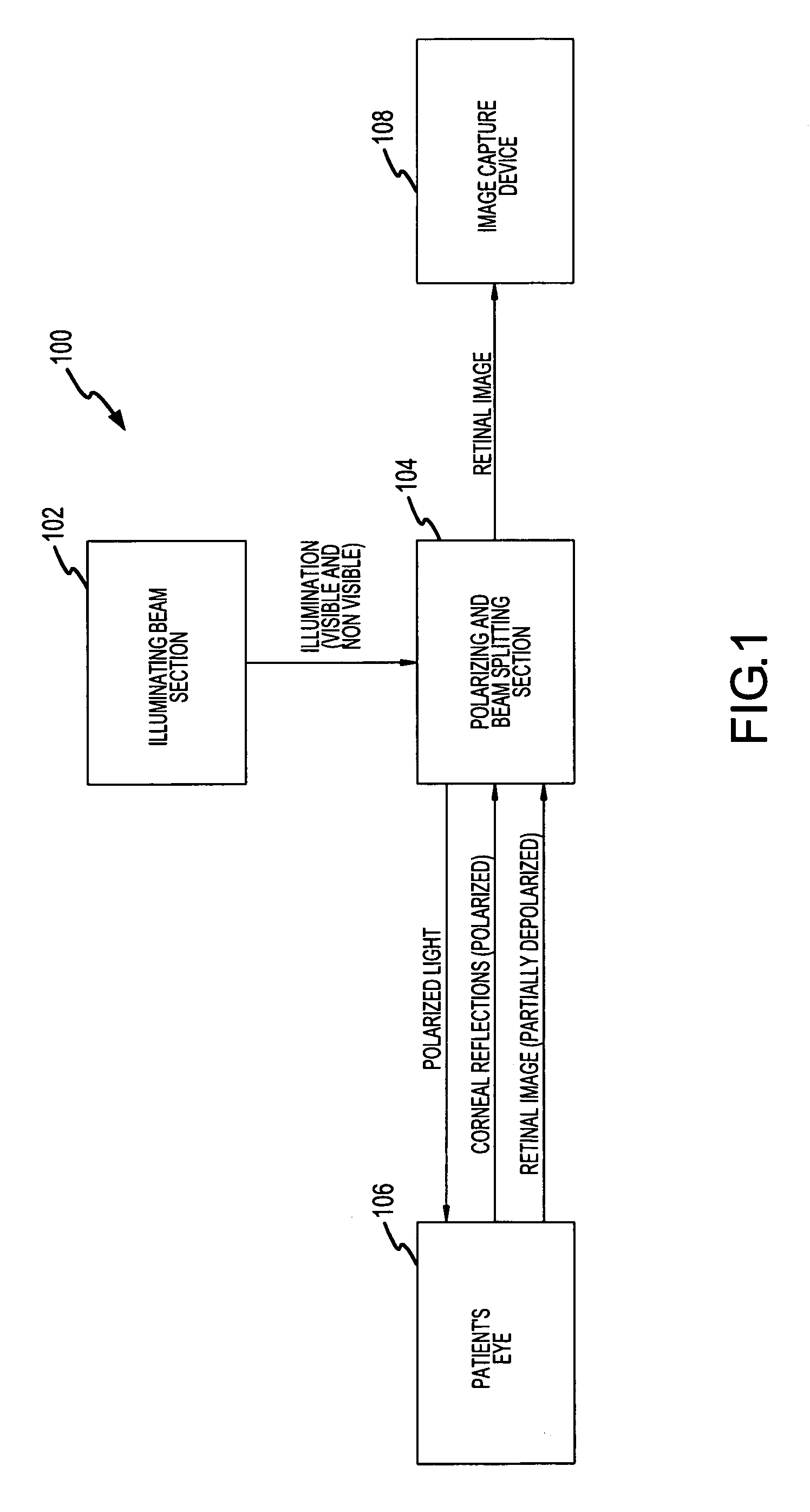
Hand held device and methods for examining a patient's retina
A hand held device for examining a patient's retina. In one example, the device generates visible or non-visible illuminating beams having desired spectral content. The illuminating beams are then polarized to generate polarized light beam(s) that are directed towards the patient's retina. At the patient's eye, a portion of the polarized beam is partially reflected by the cornea and travels back to the device, and another portion of the polarized beam enters the eye through the undilated pupil, illuminates the patient's retina, and generates a reflected retinal image (generally de-polarized) which also travels back to the device. The device receives the retinal image and transmits certain portions of the retinal image on through to an image detector (i.e., CCD or CMOS); and the device deflects the received polarized corneal reflections away from the image capture device. Hence, the image capture device receives retinal images but does not receive the polarized corneal reflected light.
Owner:OCUTRONICS
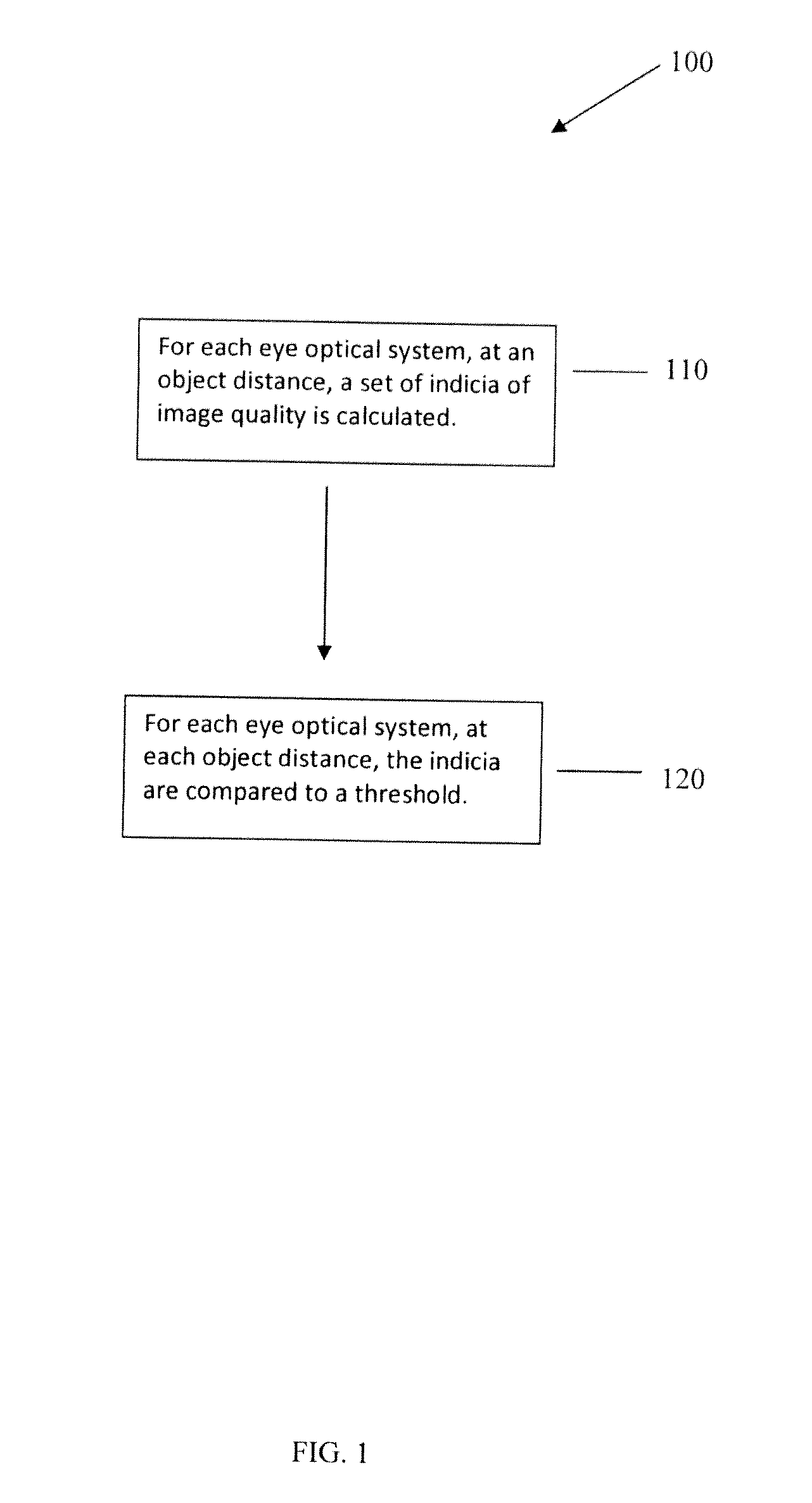
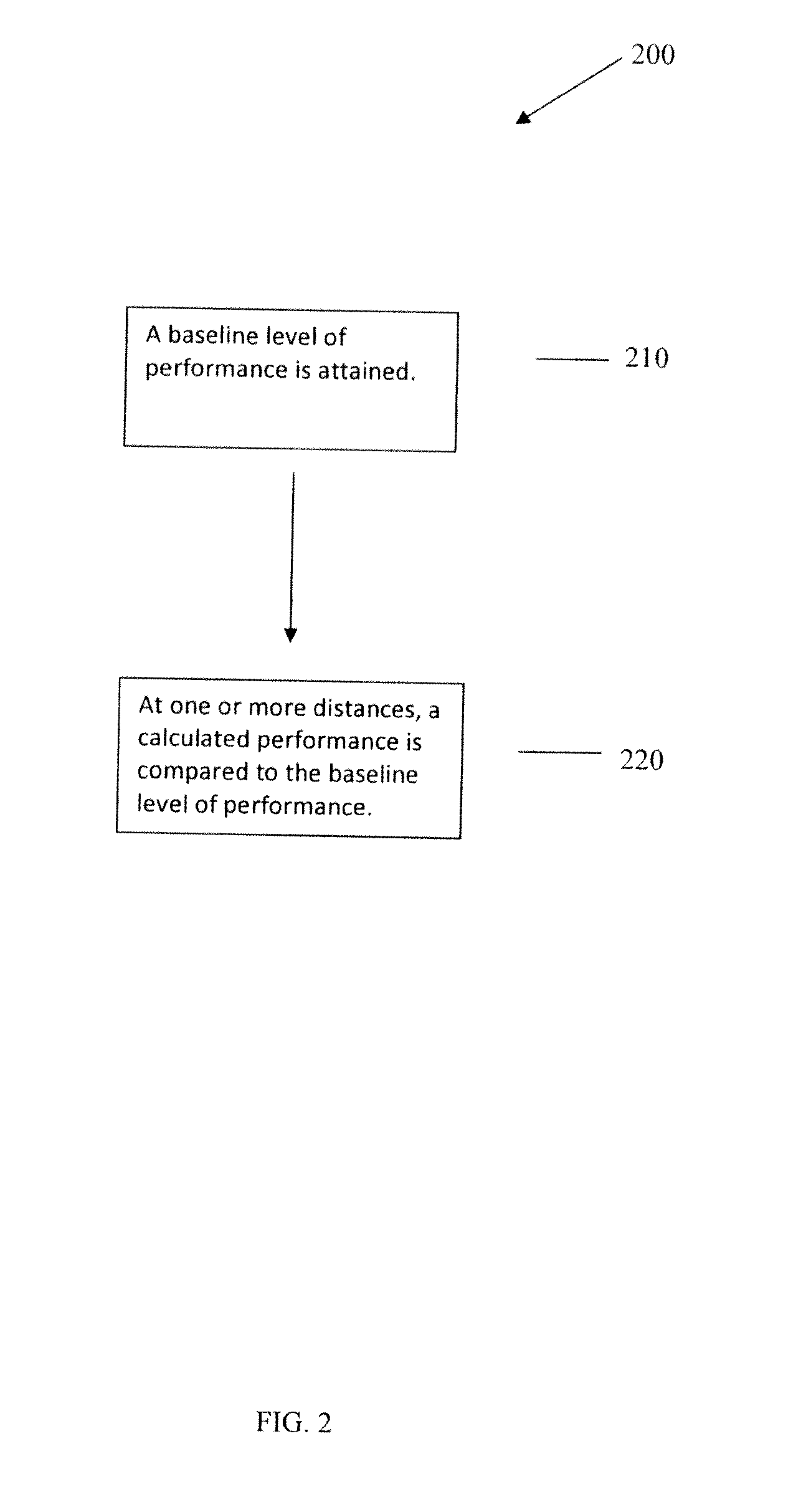
Use of an optical system simulating behavior of human eye to generate retinal images and an image quality metric to evaluate same
A method of predicting clinical performance of an ophthalmic optical correction using simulation by imaging a series of objects of different sizes by each of a plurality of eye optical systems, each of the eye optical systems including the ophthalmic optical correction, the method providing an output value representing the resolution and contrast performance of the optical design at that vergence for the eye optical systems.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
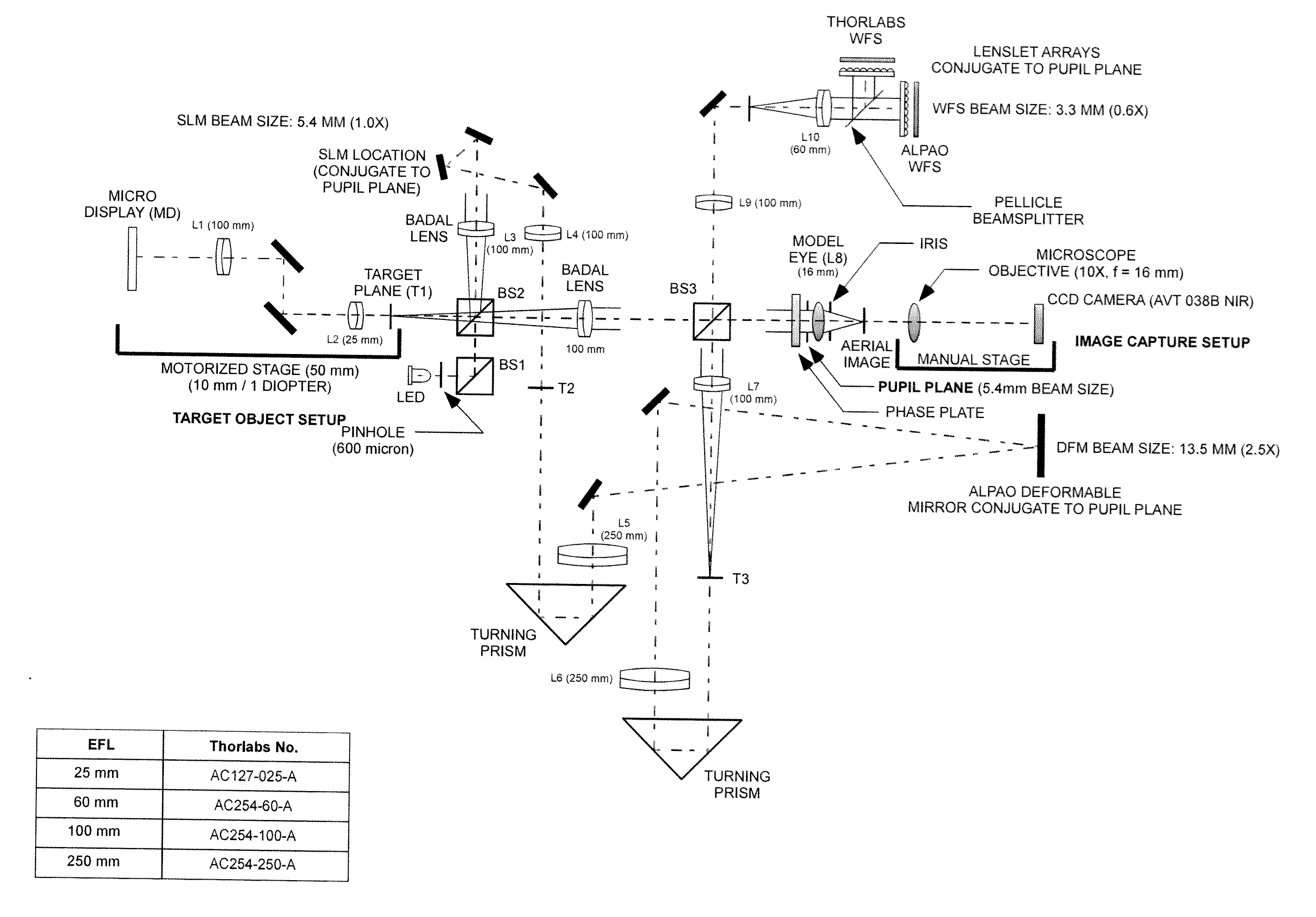
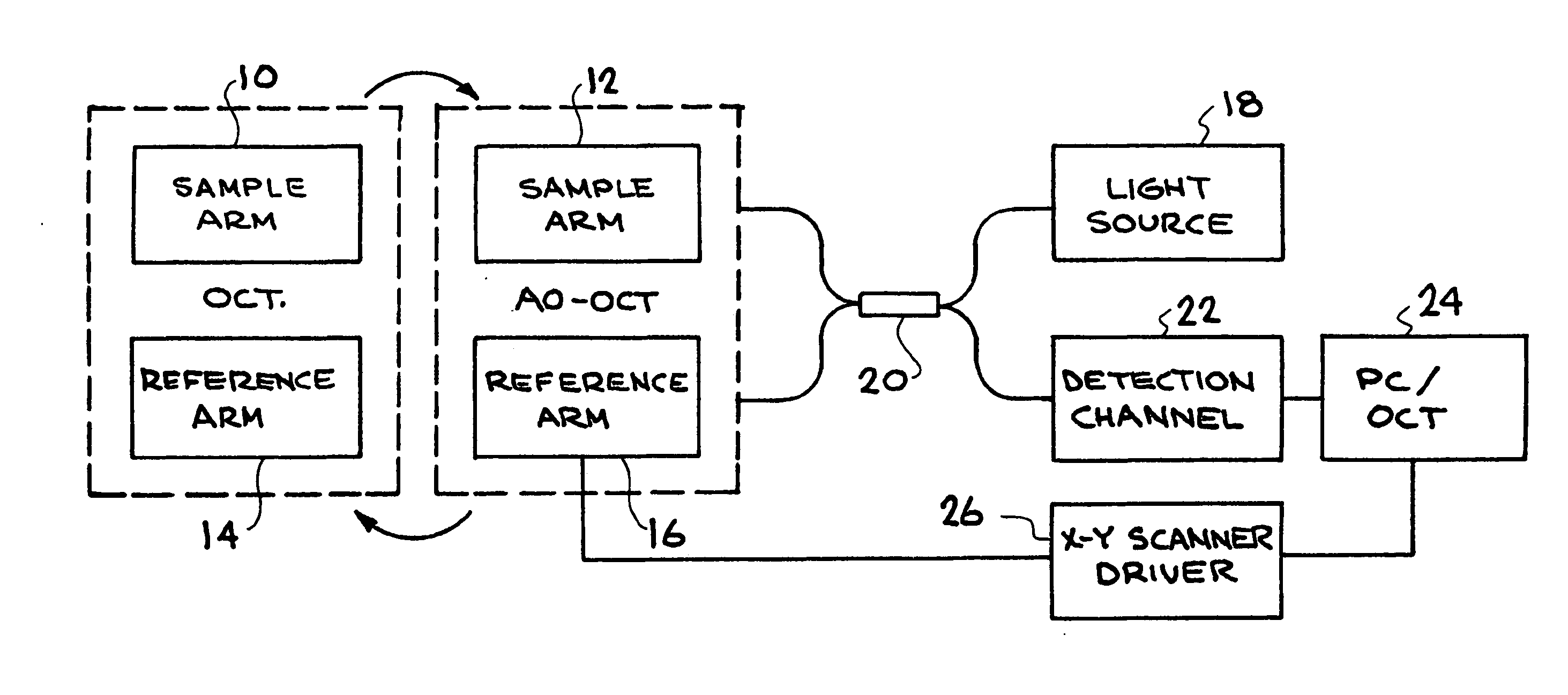
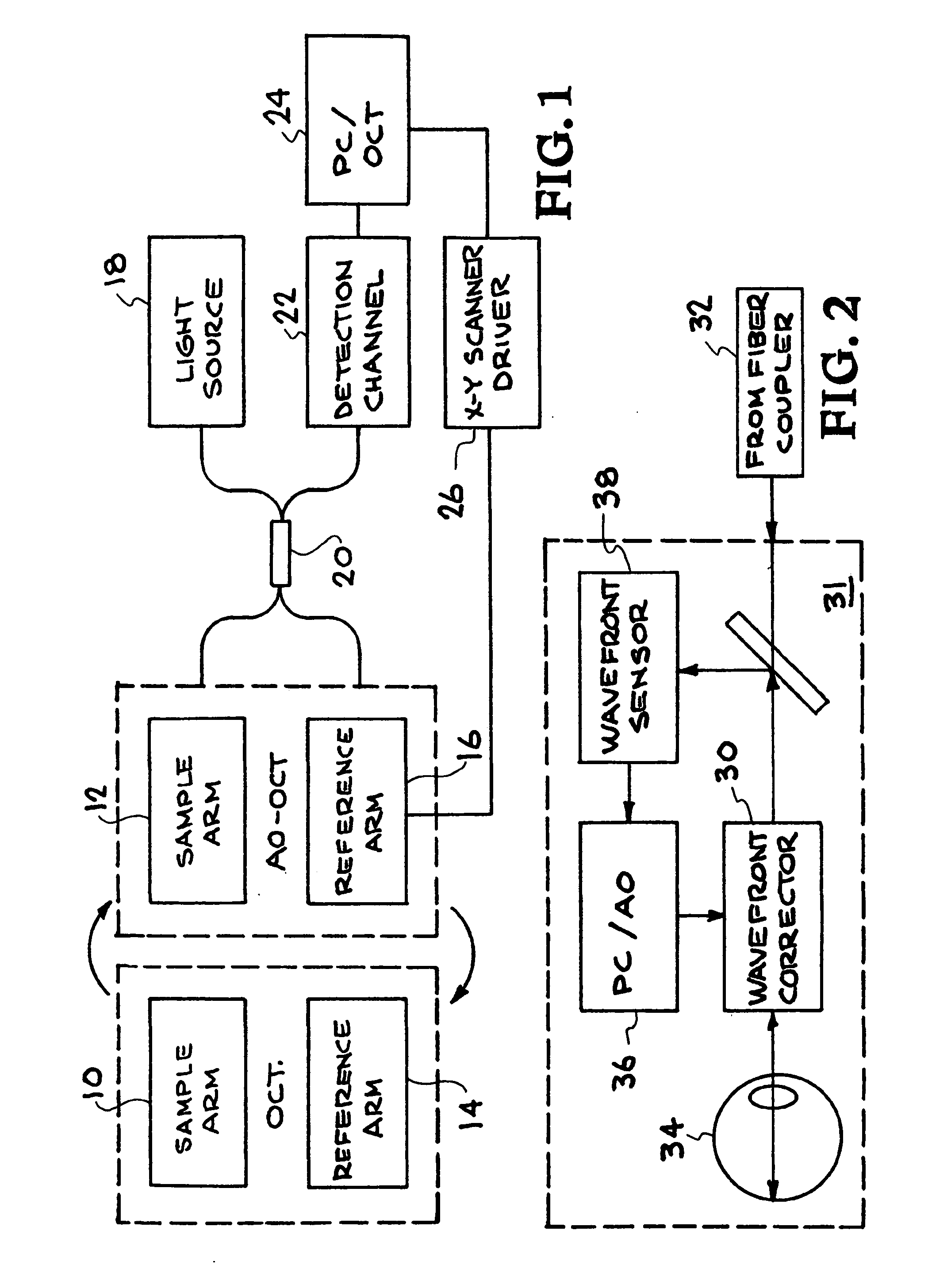
High-resolution retinal imaging using adaptive optics and fourier-domain optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20070258095A1Precise positioningMinimize eye motionUsing optical meansOthalmoscopesMicroscopic blood vesselHuman eye
This invention permits retinal images to be acquired at high speed and with unprecedented resolution in three dimensions (4×4×6 μm). The instrument achieves high lateral resolution by using adaptive optics to correct optical aberrations of the human eye in real time. High axial resolution and high speed are made possible by the use of Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography. Using this system, we have demonstrated the ability to image microscopic blood vessels and the cone photoreceptor mosaic.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Sharpness metric for vision quality
InactiveUS7077522B2Remove wave aberrationSubjective blurRefractometersSkiascopesQuality of visionPoint spread function
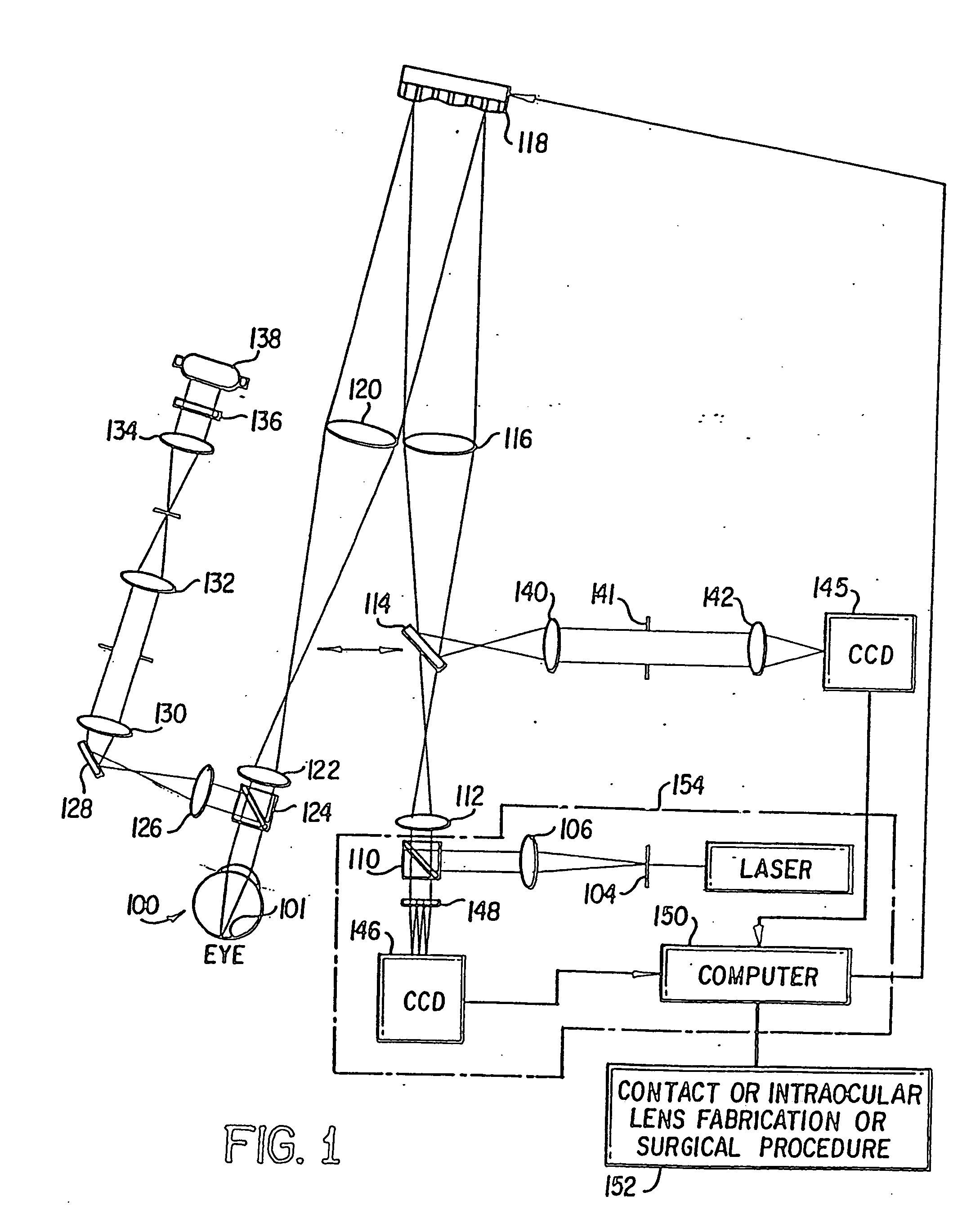
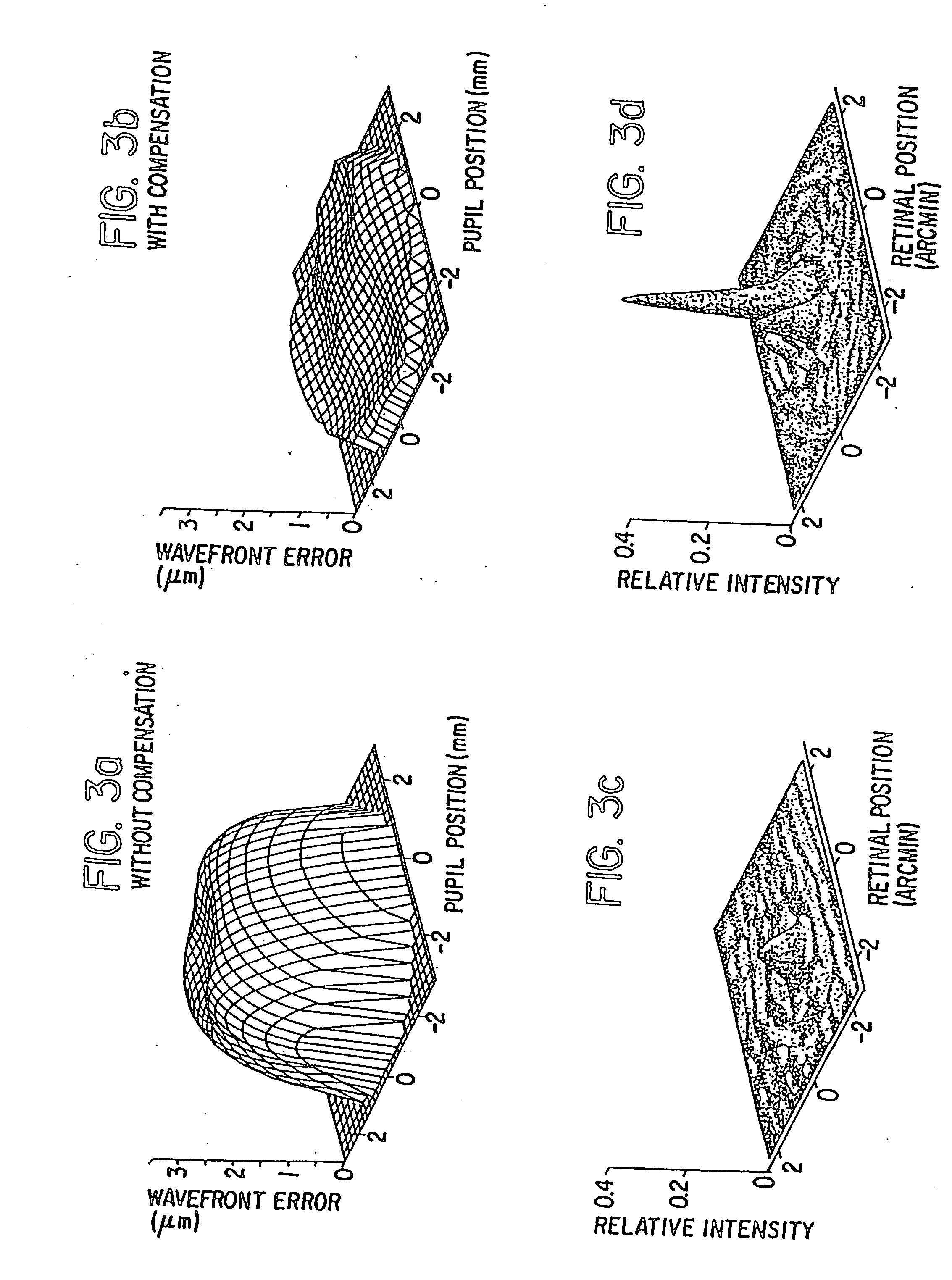
A vision metric, called the sharpness metric, indicates the subjective sharpness of a patient's vision by taking into account both the wavefront aberration and the retinal response to the image. A retinal image quality function such as the point spread function is convolved by a neural quality function, and the maximum of the convolution over the retinal plane provides the sharpness metric. The sharpness metric can be used to control eye surgery or the fabrication of a lens.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Ocular-performance-based head impact measurement applied to rotationally-centered impact mitigation systems and methods
ActiveUS20190167095A1Reduce chanceDiagnostic recording/measuringEye diagnosticsHertzVisual perception
A system or method for measuring human ocular performance can be implemented using an eye sensor, a head orientation sensor, and an electronic circuit. The device is configured for measuring vestibulo-ocular reflex, pupillometry, saccades, visual pursuit tracking, vergence, eyelid closure, dynamic visual acuity, retinal image stability, foveal fixation stability, focused position of the eyes or visual fixation of the eyes at any given moment and nystagmus. The eye sensor comprises a video camera that senses vertical movement and horizontal movement of at least one eye. The head orientation sensor senses pitch and yaw in the range of frequencies between 0.01 Hertz and 15 Hertz. The system is implemented as part of an impact reduction helmet that comprises an inner frame having interior pads configured to rest against a person's head and one or more shock absorption elements attached between the inner frame and the spherical shell that couple the spherical shell to the inner frame. The spherical shell has a circular geometry, that when viewed horizontally at its horizontal midplane, includes a center point that is the rotational center of the spherical shell. The one or more shock absorption elements are sized to provide greater spacing between the inner frame and the spherical shell at the sides and rear of the spherical shell than at the front of the spherical shell. The one or more shock absorption elements are sized to configure the alignment of the rotational center of the spherical shell with the proximate rotational center of the wearer's head.
Owner:NOVUTZ LLC
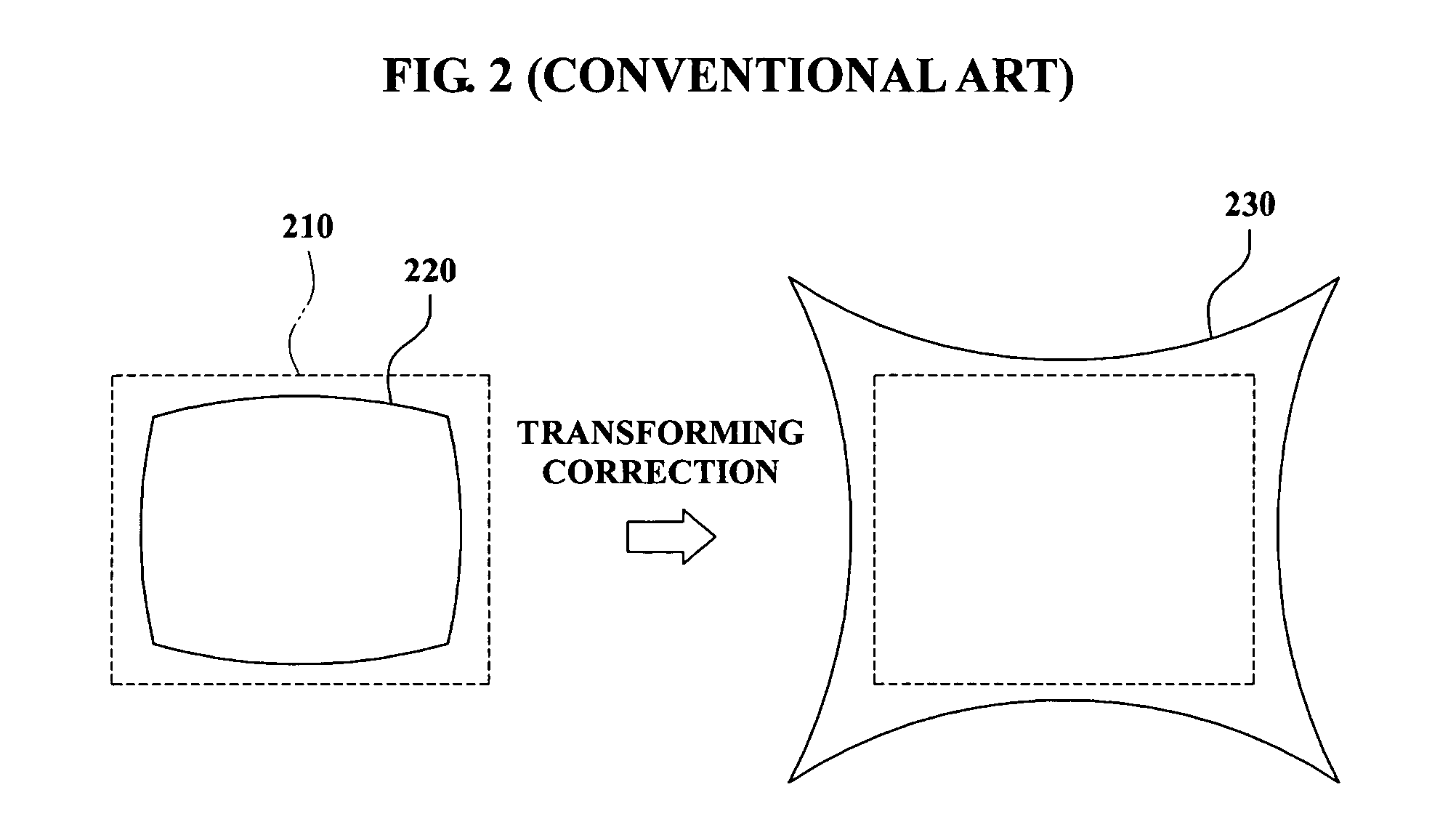
Method and apparatus for providing panoramic view with geometric correction
InactiveUS20070159527A1Accurate correctionTelevision system detailsImage enhancementGround planeDepth direction
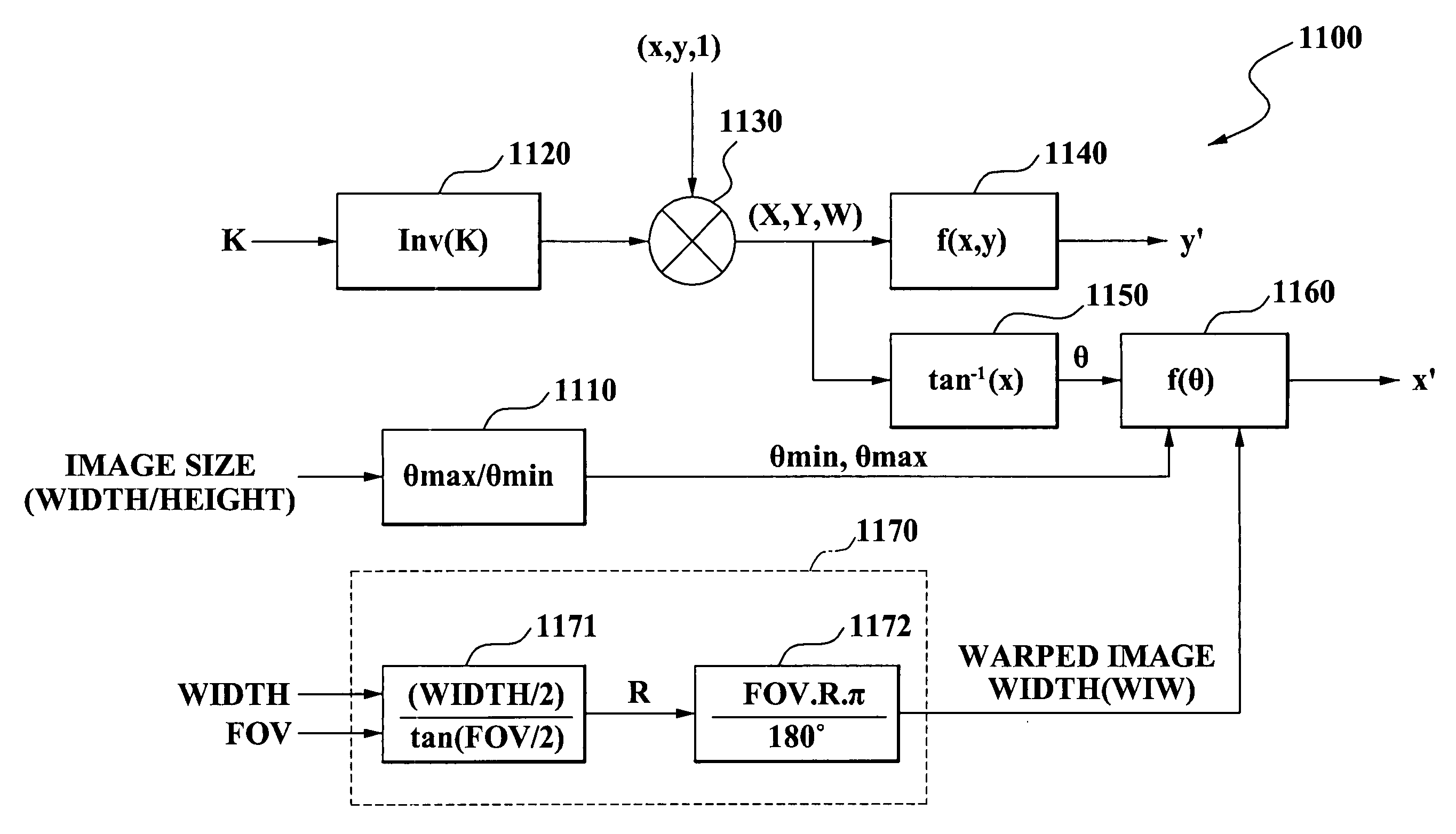
A method and apparatus of correcting geometric information and providing a panoramic view. In the method of providing a panoramic view, a tilting vector (X′, Y′) is generated by applying matrices H(a,b) and HF to a source image vector (X,Y). The matrix H(a,b) is defined by distortion angles “b” towards a plane direction and a distortion angle “a” towards a depth direction of the source image, and the matrix HF is defined according to a camera parameter matrix K. Also, a two-dimensional vector (x,y) of a source image is converted into a three-dimensional vector (X,Y,W) on a retinal image plane having a unit radial distance from an origin of a ground plane. Also, a warped image width (WIW) is estimated from a width and a field of view (FOV) of the source image. A warping vector (x′,y′) is generated based on the converted vector (X,Y,W) and the WIW.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
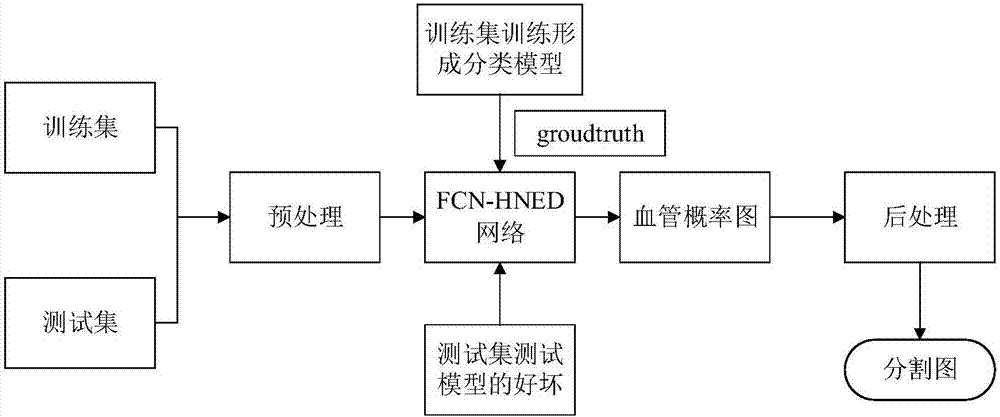
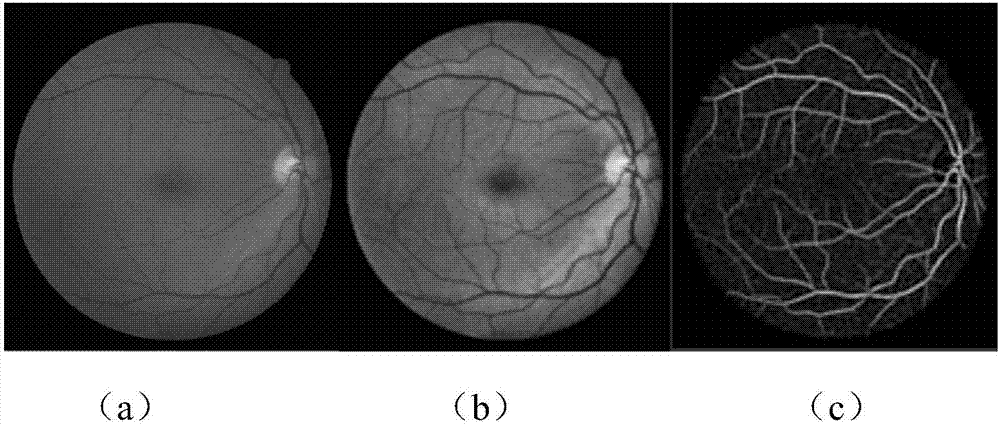
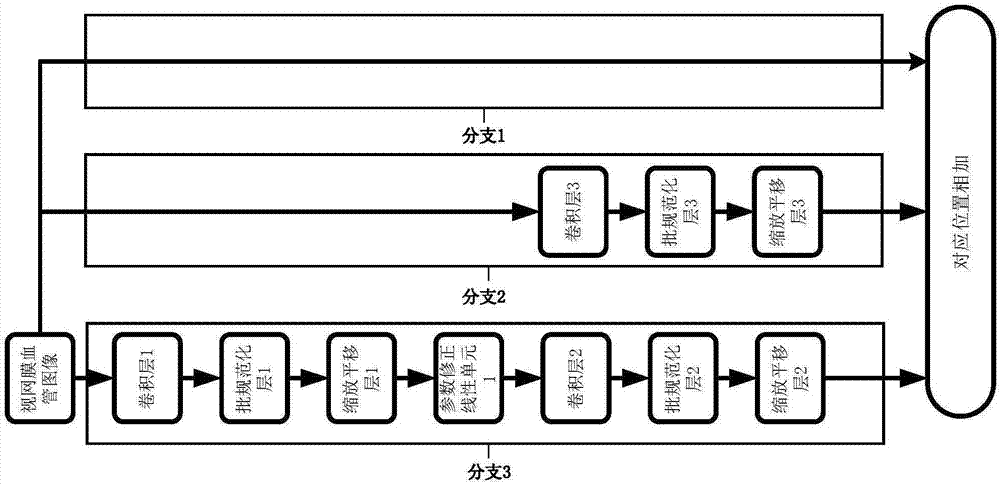
Retinal vessel segmentation method based on combination of deep learning and traditional method
ActiveCN106920227AImprove robustnessImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisRobustificationPattern recognition
The invention discloses a retinal vessel segmentation method based on combination of deep learning and a traditional method and relates to the fields of computer vision and mode recognition. According to the method, two grayscale images are both used as training samples of a network, corresponding data amplification, including elastic deformation, smooth filtering, etc., is done against the problem of less retinal image data, and wide applicability of the method is improved. According to the method, an FCN-HNED retinal vessel segmentation deep network is constructed, an autonomous learning process is realized to a great extent through the network, convolutional features of a whole image can be shared, feature redundancy can be reduced, the category of multiple pixels can be recovered from the abstract features, a CLAHE graph and a gauss matched filtering graph of the retinal vessel image are input into the network, an obtained vessel segmentation graph is subjected to weighted average, and therefore a better and more intact retinal vessel segmentation probability graph is obtained. Through the processing mode, the robustness and accuracy of vessel segmentation are improved to a great extent.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Hyperspectral retinal imager
InactiveUS6992775B2High resolutionImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFourier transform on finite groupsInstrumentation
An ophthalmic instrument (for obtaining high resolution, wide field of area hyperspectral retinal images for various sized eyes) includes a fundus retinal imager, (which includes optics for illuminating and imaging the retina of the eye); apparatus for generating a real time image of the area being imaged and the location of the hyperspectral region of interest; a high efficiency spatially modulated common path Fourier transform hyperspectral imager, a high resolution detector optically coupled to the hyperspectral and fundus imager optics; and a computer (which is connected to the real time scene imager, the illumination source, and the high resolution camera) including an algorithm for recovery and calibration of the hyperspectral images.
Owner:KESTREL CORP
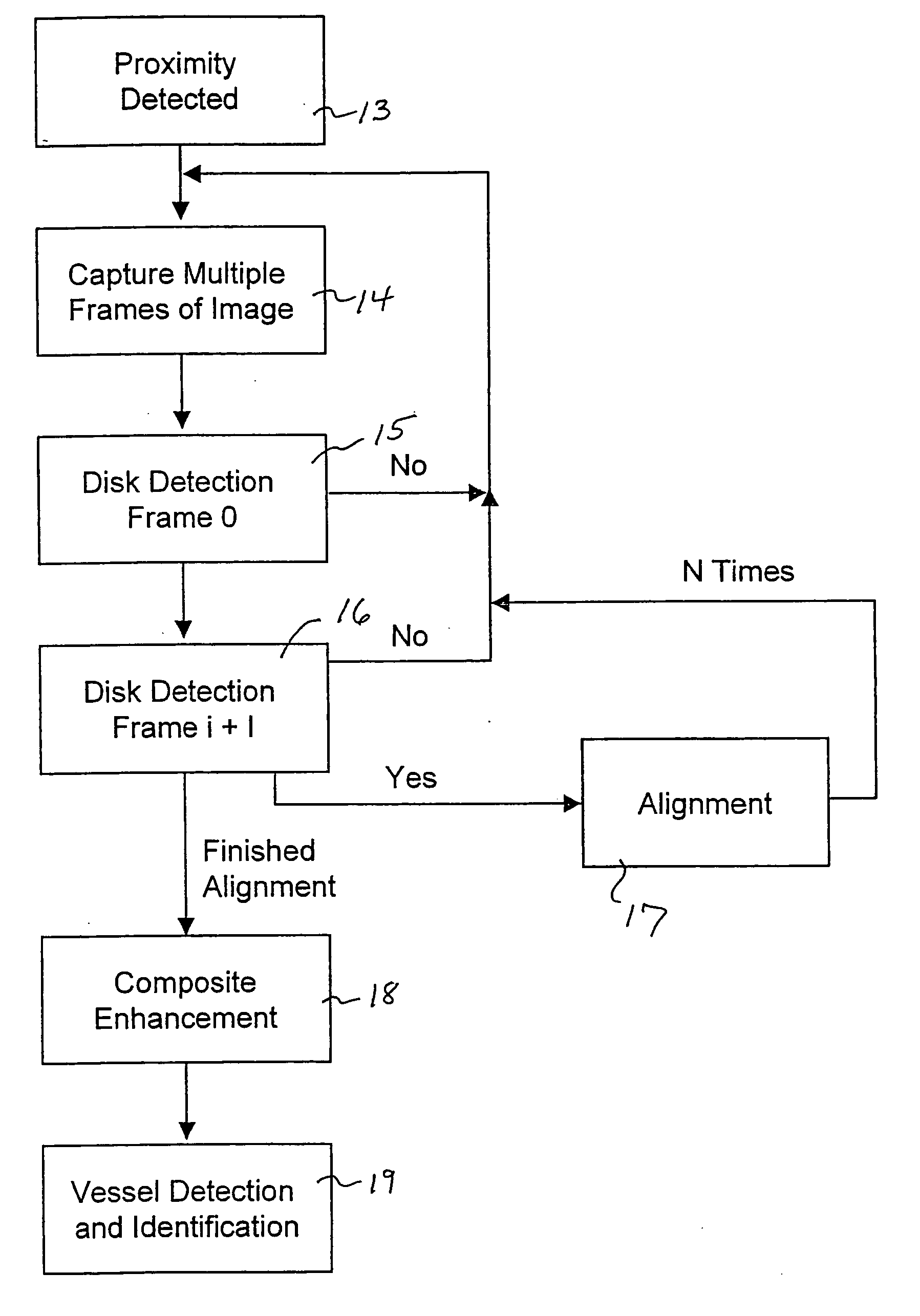
Method and system for automatically capturing an image of a retina
A method and system capture an image of the interior of the eye, for example the retina and determine whether the captured image is sufficient to provide data for identifying an individual or animal before attempting to generate the identification data. If the captured image is not sufficient, the method and system automatically capture another image of the interior of the eye.
Owner:IDENTIX
Optical system for a fundus camera
InactiveUS20100014052A1Suppression of blurDimension of can be minimizeEye diagnosticsOptical elementsCatoptricsDioptre
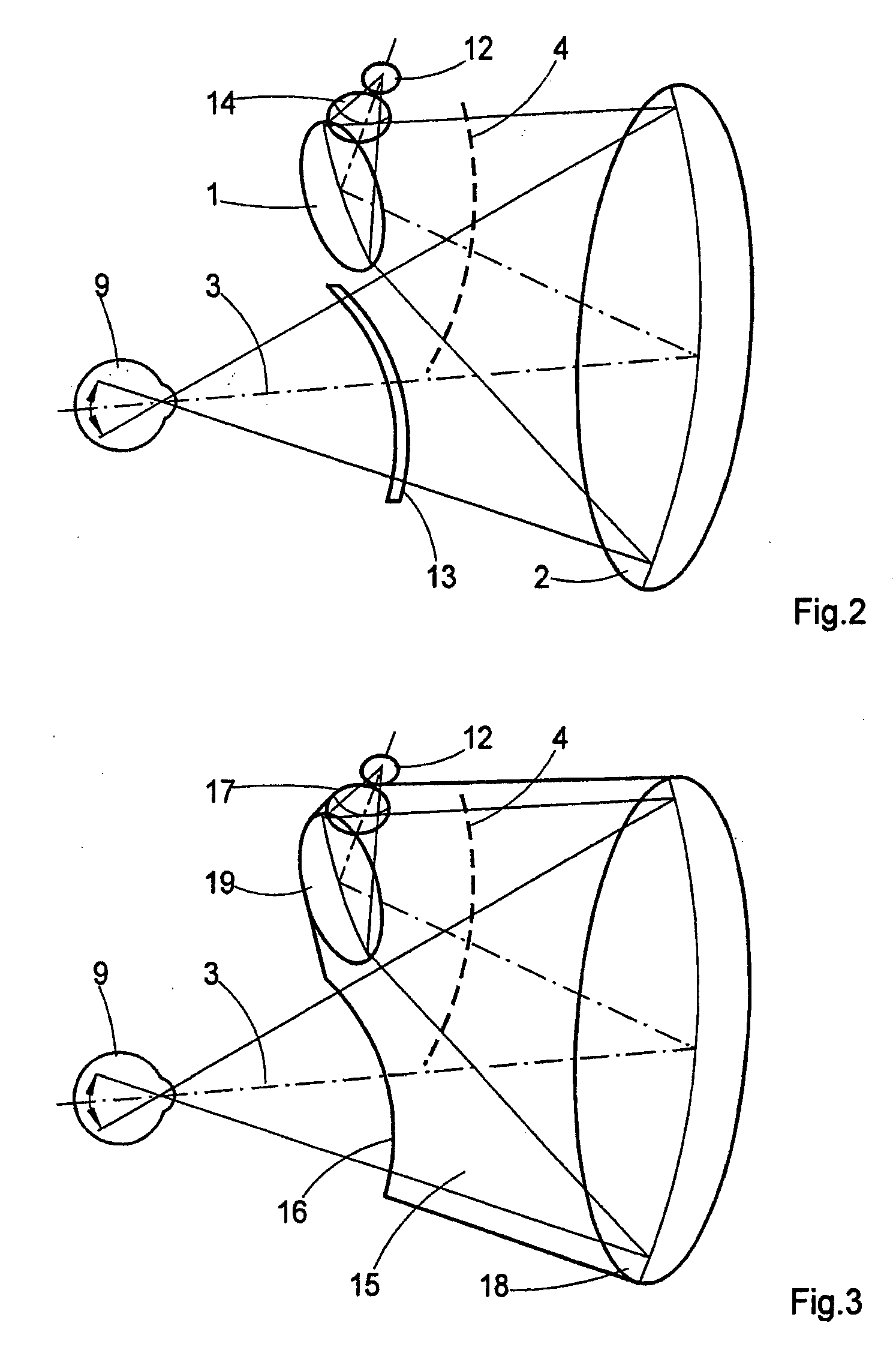
The invention is directed to an optical system for a fundus camera for reflection-free opthalmoscopy having a beam path with refractive and reflective optical elements which are used substantially in common for illumination and observation or recording. An imaging mirror system substantially comprising a plurality of reflecting optical elements in the form of mirrors and is provided for illuminating and imaging the fundus. At least one optical element, for example, mirror, is formed as a freeform mirror with an imaging, reflecting freeform surface. The optical elements are arranged in a housing in a precisely defined position and attitude relative to one another in such a way that an imaging of the reflecting surfaces of the optical elements on the image of the imaged retina is prevented within a wide diopter range of the patient's eye to be examined.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Snapshot spectral imaging of the eye
ActiveUS8109634B2Strong robustnessWithout reducing effective resolutionSpectrum investigationDiagnostic recording/measuringFundus cameraPupil
Obtaining spectral images of an eye includes taking an optical system that images eye tissue onto a digital sensor array and optically fitting a multi-spectral filter array and the digital sensor array, wherein the multi-spectral filter array is disposed between the digital sensor array and an optics portion of the optical system. The resulting system facilitates acquisition of a snap-shot image of the eye tissue with the digital sensor array. The snap shot images support estimation of blood oxygen saturation in a retinal tissue. The resulting system can be based on a non-mydriatic fundus camera designed to obtain the retinal images without administration of pupil dilation drops.
Owner:MERGE HEALTHCARE
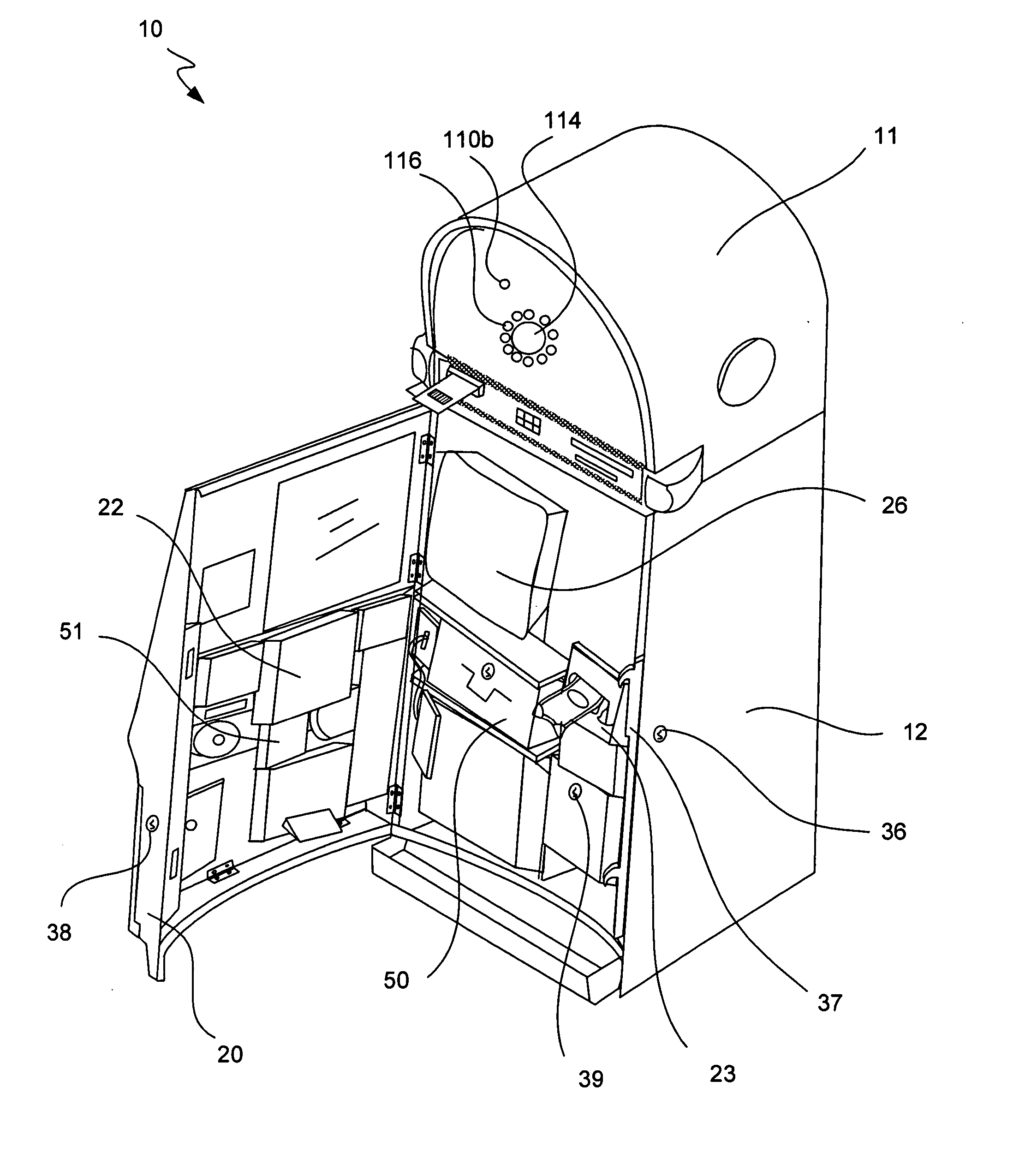
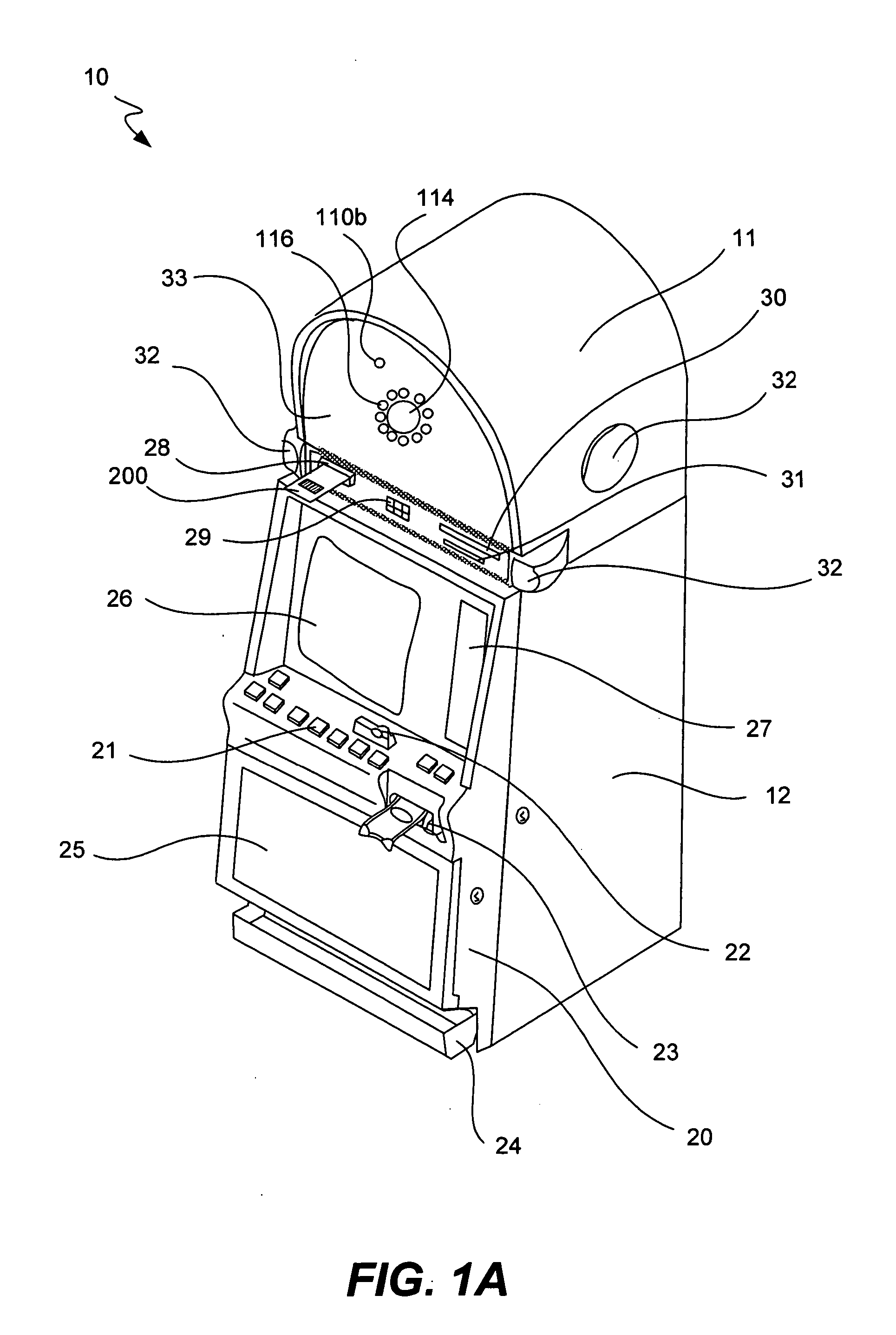
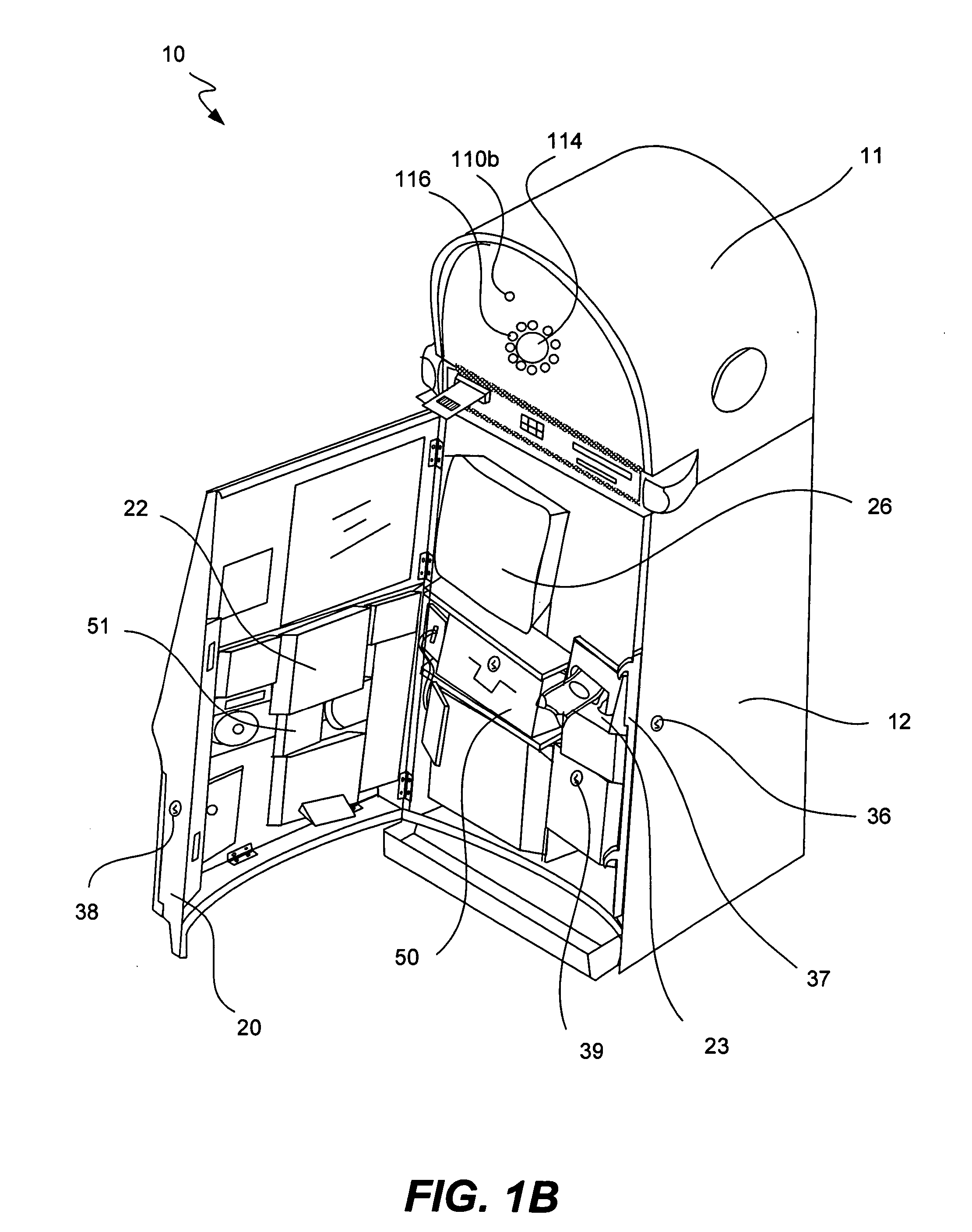
Gaming machine with scanning 3-D display system
ActiveUS20070060390A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingComputer scienceRetinal image
The present invention provides systems and methods that cast an image into a person's eye from a retinal image system included with a gaming machine. The gaming machine includes a retinal image system located within or about the external cabinet and configured to cast an image toward an eye of a person near the gaming machine. The gaming machine also includes an eye detection system configured to locate the eye relative to a position of a projection component of the retinal image system.
Owner:IGT
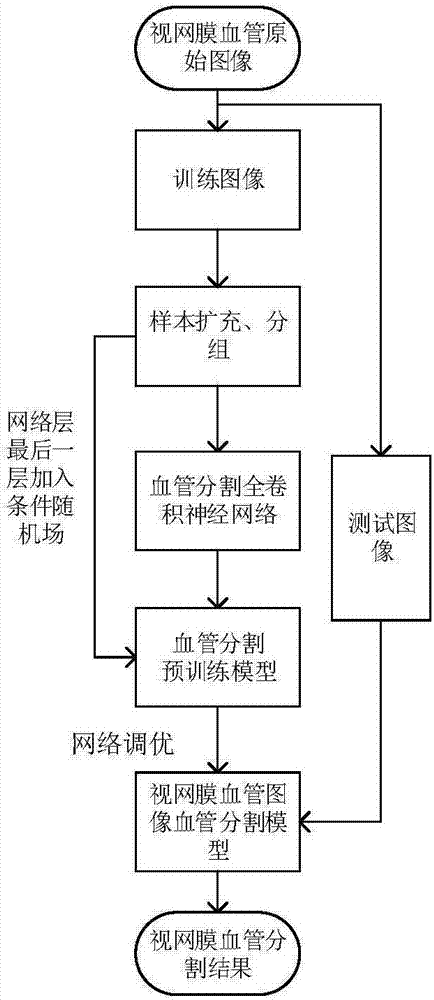
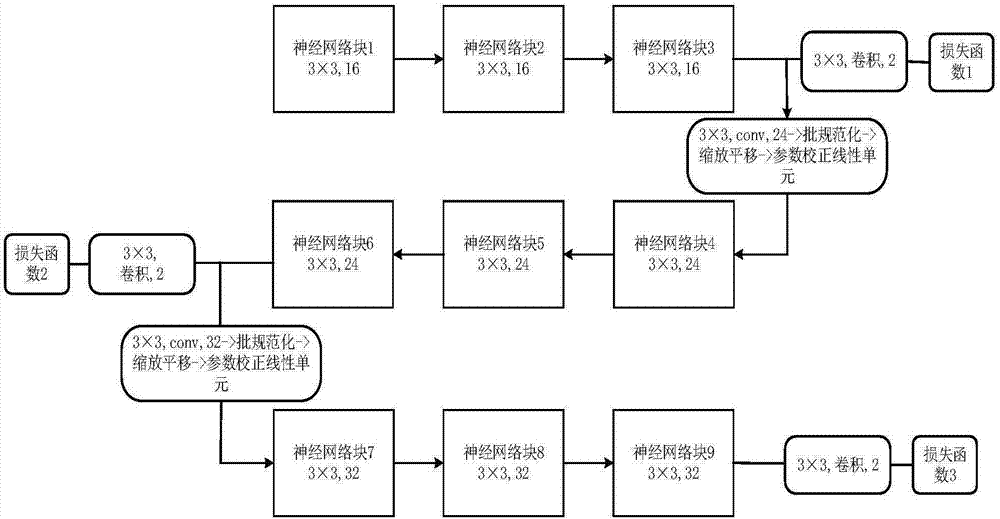
Retinal blood vessel segmentation method based on deep-learning adaptive weight
ActiveCN107292887AFast convergenceEliminate class imbalance problemsImage enhancementImage analysisConditional random fieldRetinal blood vessels
The invention discloses a retinal blood vessel segmentation method based on the deep-learning adaptive weight, comprising: performing sample expansion on retinal blood vessel images and grouping the samples; constructing a full-convolution neural network for blood vessel segmentation; pre-training the network through the training samples; performing the global adaptive weight segmentation on the retinal blood vessel images; obtaining the initial model parameters for retinal blood vessel segmentation; adding a conditional random field layer to the last network layer and optimizing the network; using the rotation test method to input the testing samples to the network; and obtaining the retinal blood vessel segmentation result. The blood vessel segmentation full-convolution neural network structure and the adaptive weight method proposed by the invention can realize the human-eye level image segmentation and can test on two internationally published retinal image databases DRIVE and CHASE_DB1 with the average accuracy of 96.00 % and 95.17% respectively, both higher than the latest algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Opthalmological apparatus
In an ophthalmological apparatus, how scattering at an eye under measurement and a contact lens affects how the eye sees is shown by measuring scattering when the contact lens is worn and by comparing a retinal image obtained with aberration and the scattering taken into account and a retinal image obtained with only the aberration taken into account. An aberration measurement section obtains the aberration of the eye under measurement. An other-components measurement section obtains other components other than the aberration component based on a point light-source image caused by each Hartmann plate. A scattering-level calculation section obtains a coefficient expressing the level of scattering based on the other components and the aberration. A simulation section generates a retinal image or data indicating how the eye under measurement sees with the measured aberration and the other components taken into account, based on the aberration and the coefficient.
Owner:KK TOPCON
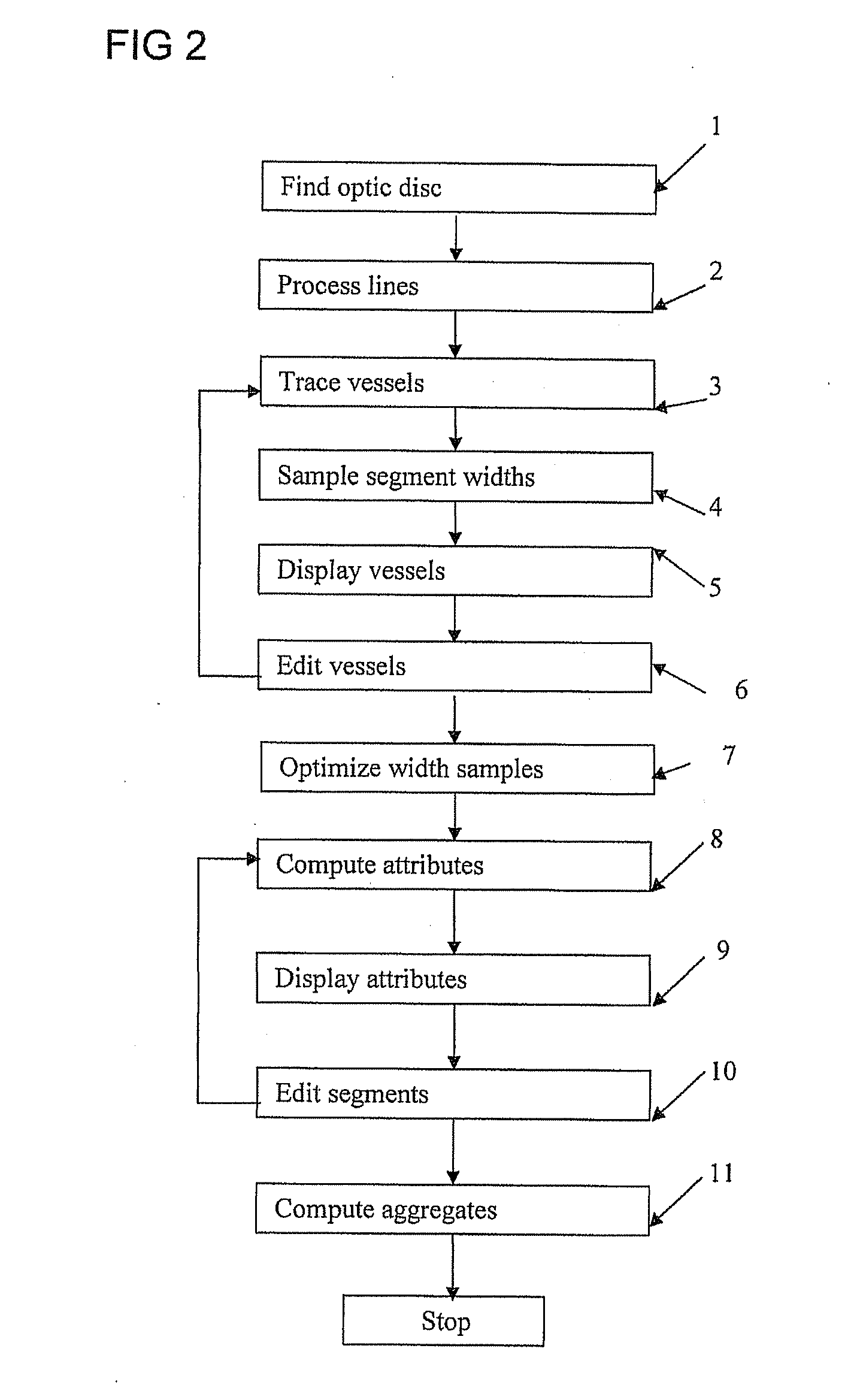
Retinal image analysis systems and methods
InactiveUS20110026789A1Simple methodImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisVascular diseaseDiabetes mellitus
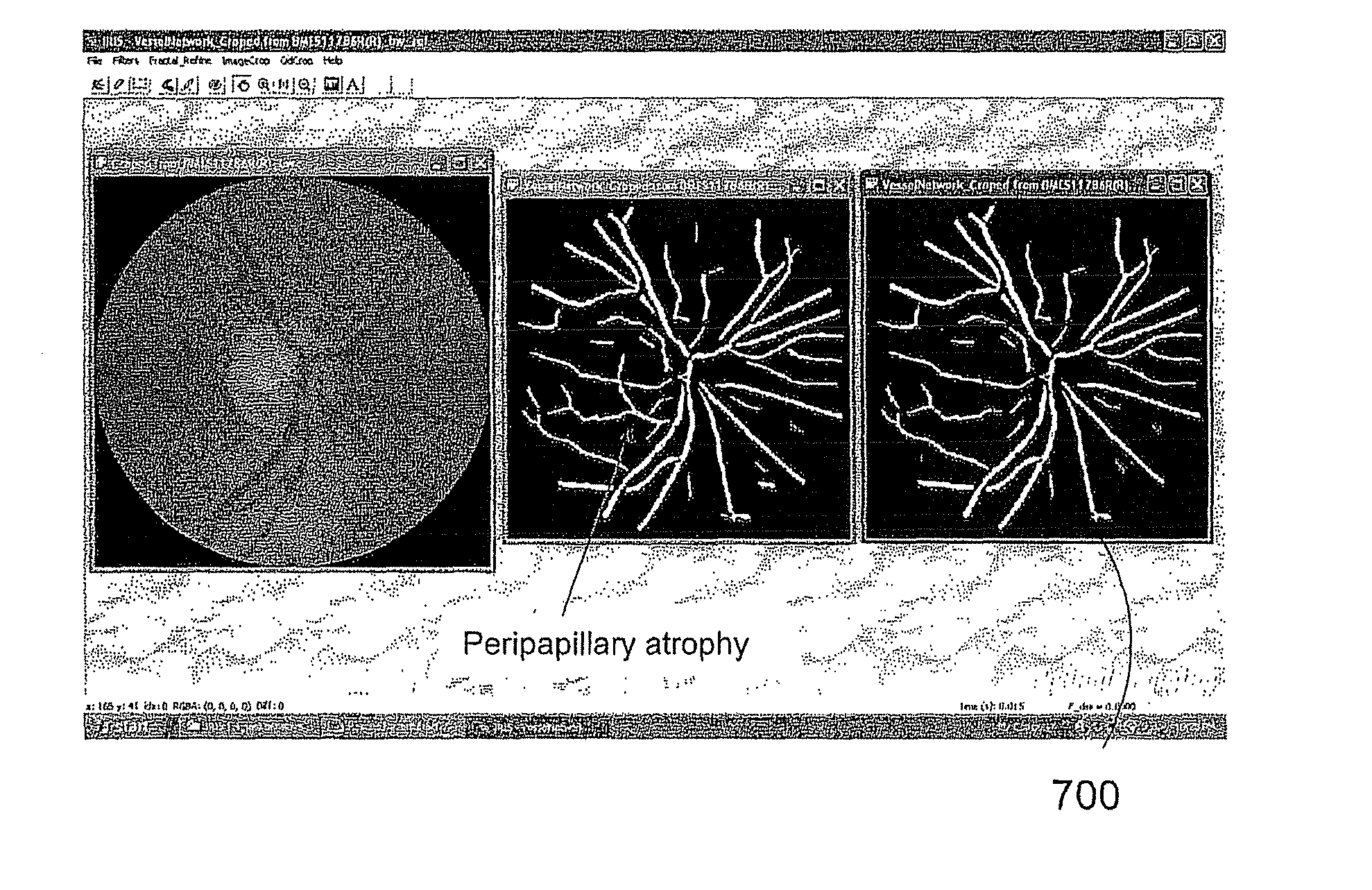
A platform is proposed for automated analysis of retinal images, for obtaining from them information characterizing retinal blood vessels which may be useful in forming a diagnosis of a medical condition. A first aspect of the invention proposes that a plurality of characteristics of the retina are extracted, in order to provide data which is useful for enabling an evaluation of cardiovascular risk prediction, or even diagnosis of a cardiovascular condition. A second aspect uses fractal analysis of retinal images to provide vascular disease risk prediction, such as, but not limited to, diabetes and hypertension.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
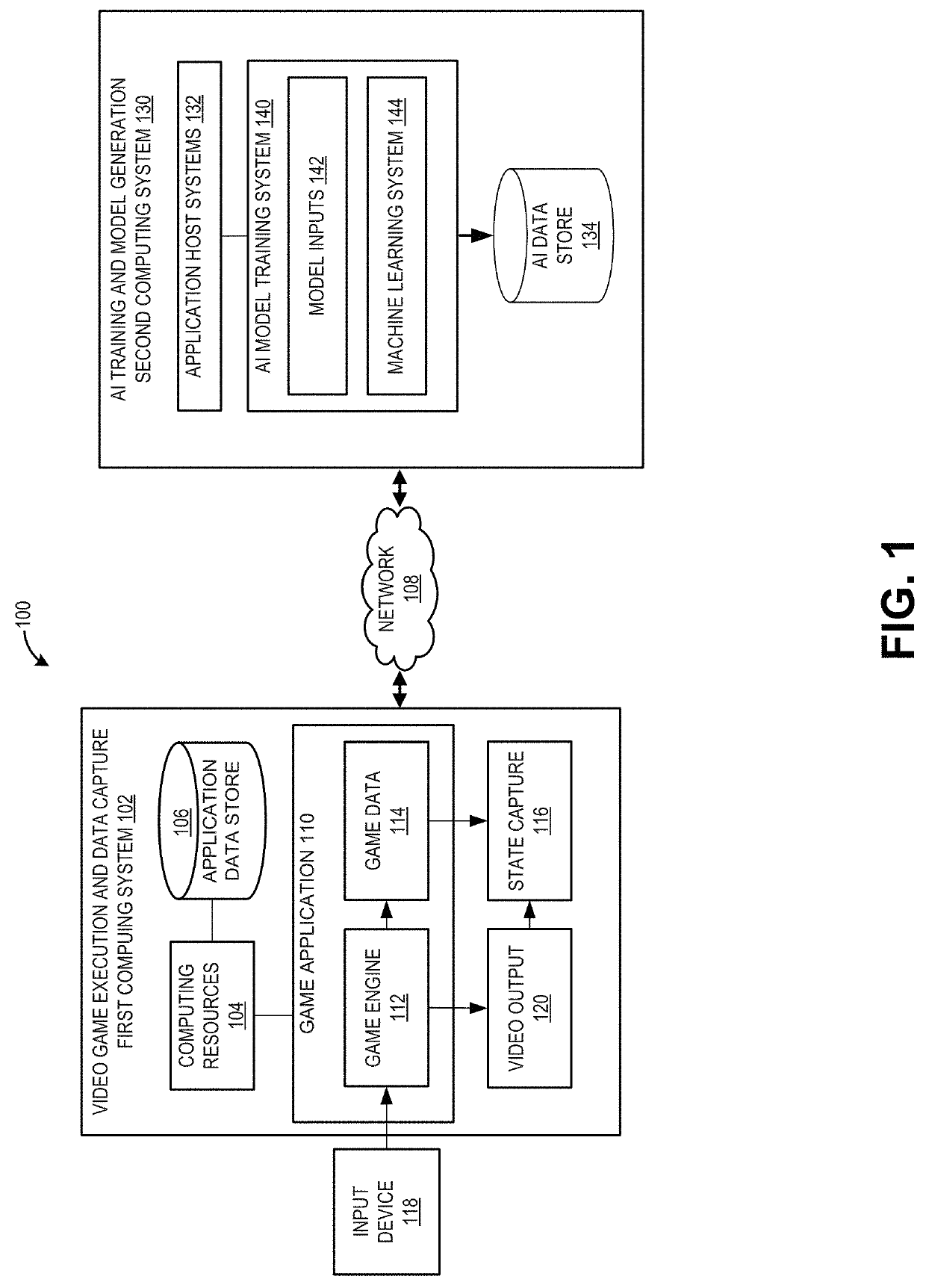
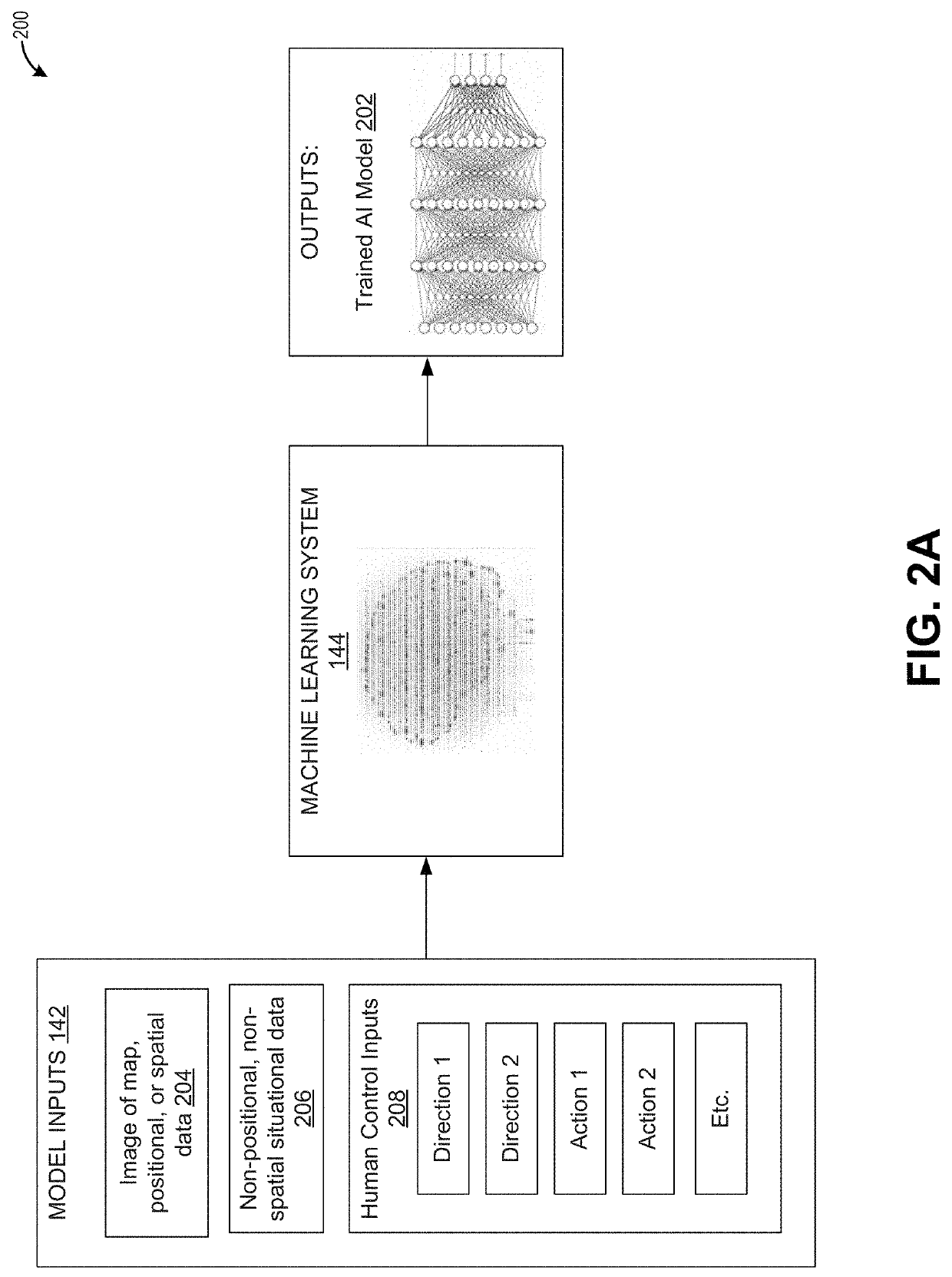
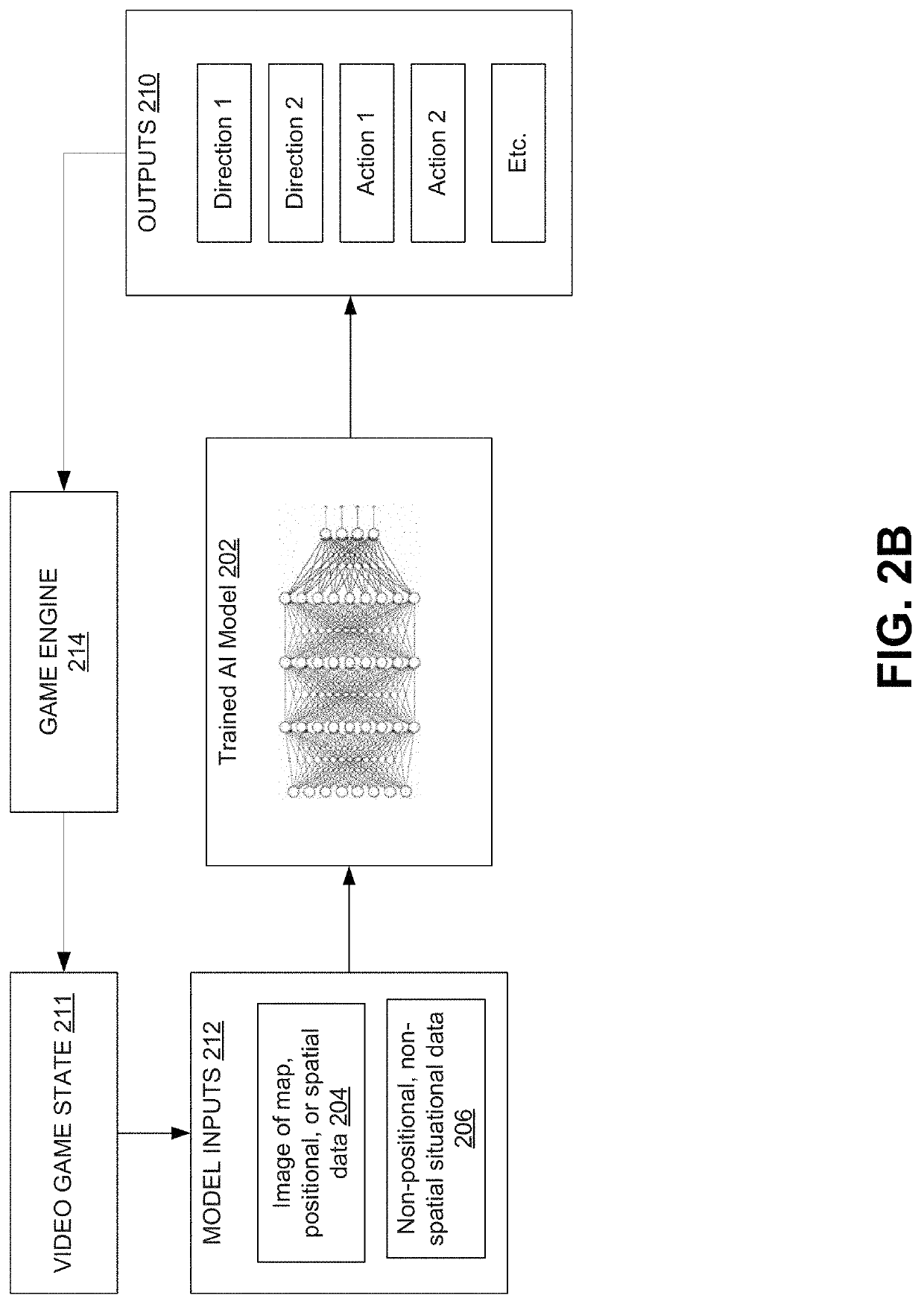
Artificial intelligence for emulating human playstyles
An artificially intelligent entity can emulate human behavior in video games. An AI model can be made by receiving gameplay logs of a video gameplay session, generating, based on the gameplay data, first situational data indicating first states of the video game, generating first control inputs provided by a human, the first control inputs corresponding to the first states of the video game, training a first machine learning system using the first situational data and corresponding first control inputs, and generating, using the first machine learning system, a first artificial intelligence model. The machine learning system can include a convolutional neural network. Inputs to the machine learning system can include a retina image and / or a matrix image.
Owner:ELECTRONICS ARTS INC
Fundus scanning imaging device
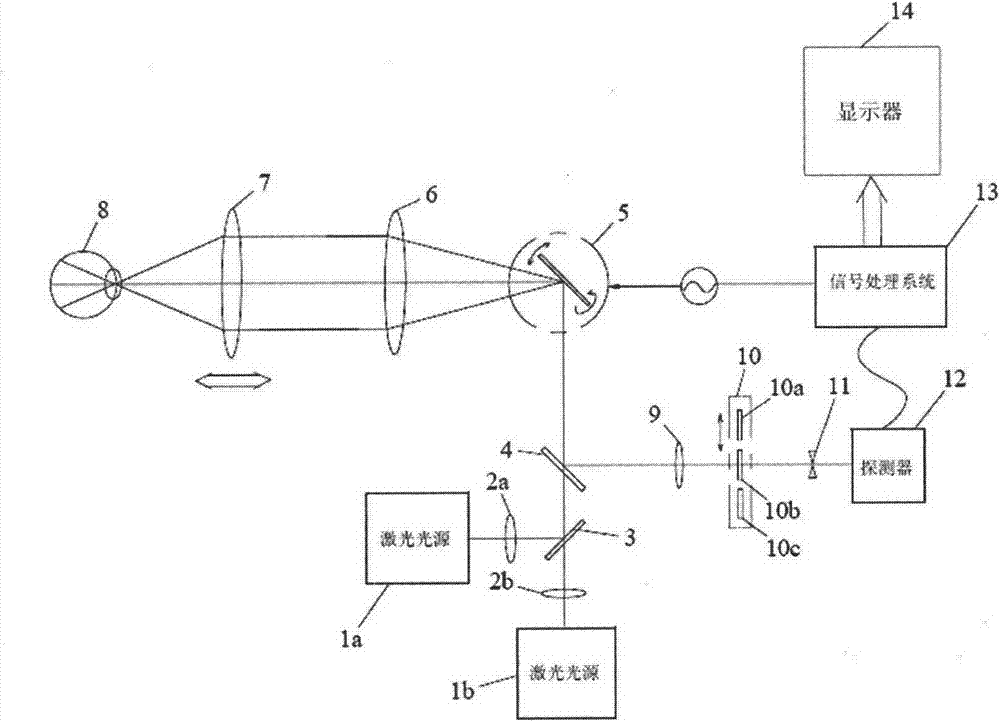
ActiveCN103750814AGet a pseudo-color imageRealize the function of fluorescence contrastOthalmoscopesColor imageFluorescence
The invention discloses a fundus scanning imaging device which is used for fundus examination of a human eye medically. A human eye fundus image is obtained through a confocal scanning technology to judge the fundus pathology and focus. The fundus scanning imaging device adopts laser as a lighting source. A scanning galvanometer achieves two-dimensional scanning of the human eye fundus. A high-sensitivity photodiode is used for detecting light signals returned from the human eye fundus, the collected signals are subjected to signal conversion and image reconstruction to obtain a large-view-field high-resolution fundus retina video image. The fundus scanning imaging device adopts a single galvanometer to replace a traditional orthogonal double-galvanometer module and acquires high-frame-frequency video image outputting through low galvanometer scanning frequency. A single detector is adopted, and a motor is utilized to switch an optical filter to achieve an FFA and ICGA fluorescent radiography function. Two kinds of retina images of light sources with different wavelengths can be utilized to combine a pseudo color image by synchronously controlling the image collection sequence, and two functions of video and camera shooting can be achieved simultaneously.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROCLEAR MEDICAL INSTR
Method and apparatus for eye-scan authentication using a liquid lens
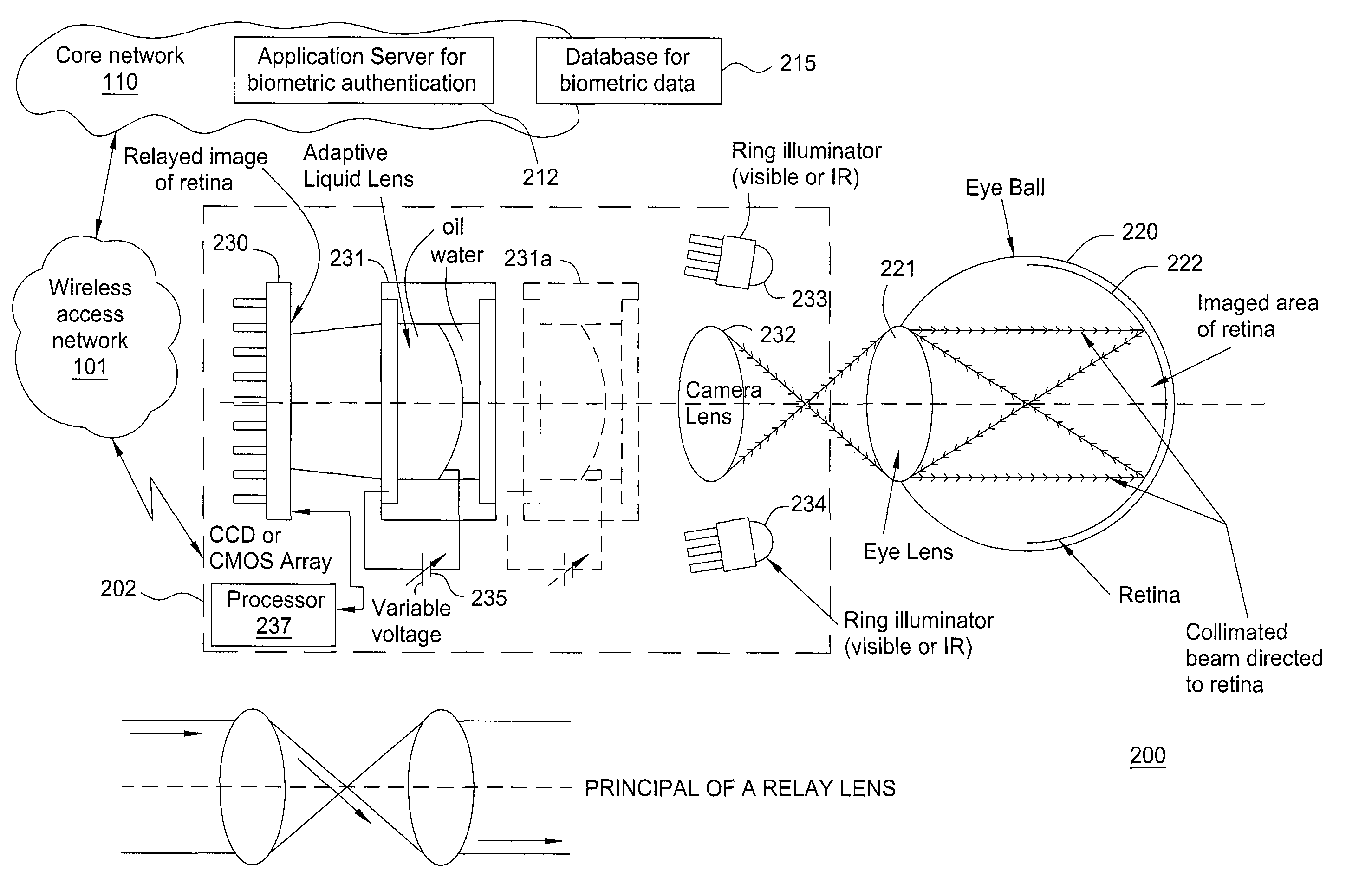
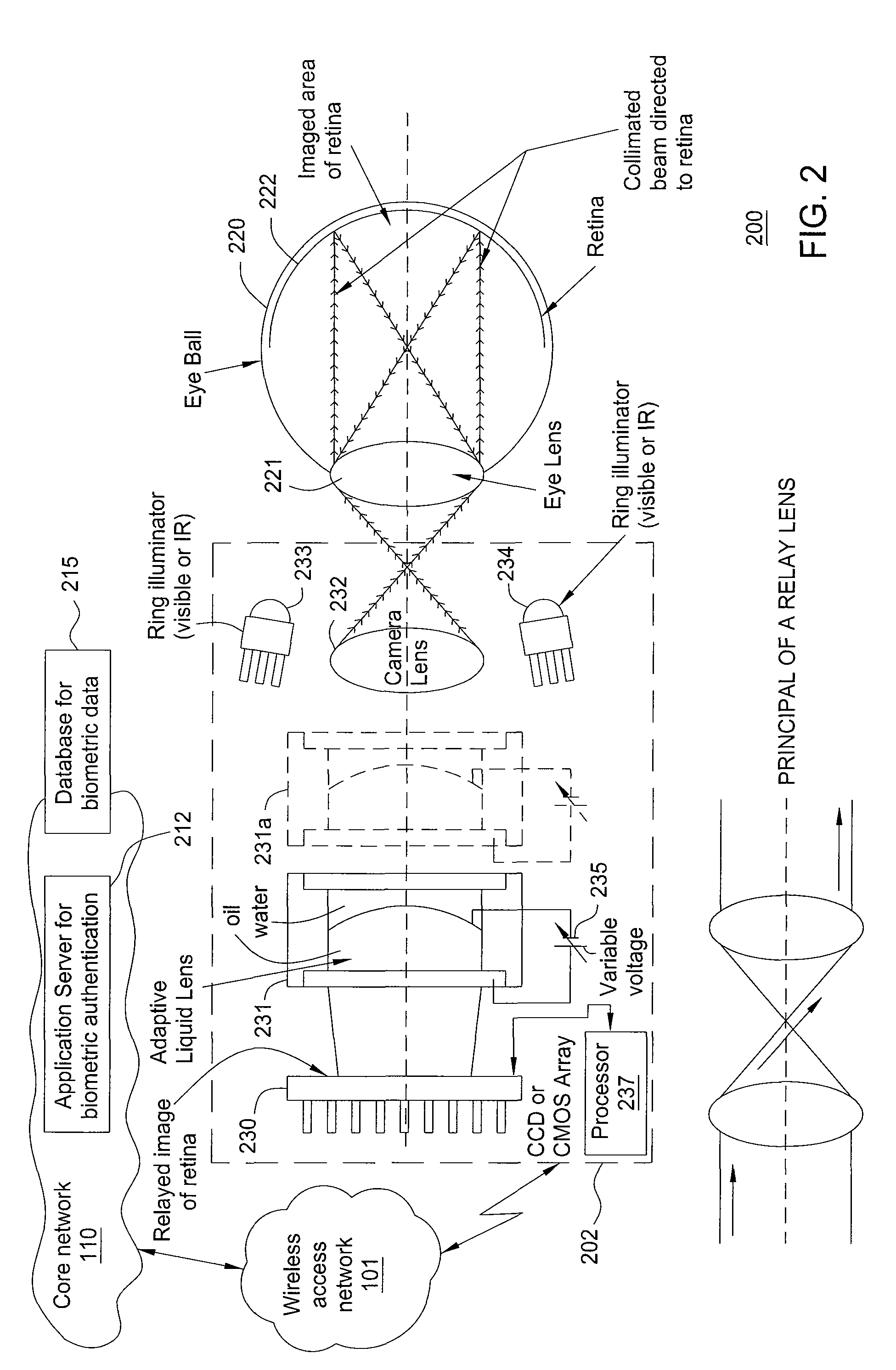
ActiveUS8233673B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationRetinaComputer science
A method and apparatus for providing eye-scan authentication using an adaptive liquid lens are disclosed. For example, in one embodiment, the method receives a request for eye-scan authentication from a mobile endpoint device of a user, wherein the request comprises a first retinal image of the user captured using an adaptive liquid lens of the mobile endpoint device. The method obtains a second retinal image of the user, wherein the second retinal image is a stored retinal image of the user. The method authenticates the first retinal image against the second retinal image. In another embodiment, the method captures a first retinal image of a user via a mobile endpoint device of the user, wherein the mobile endpoint device comprises an adaptive liquid lens. The method then sends a request for eye-scan authentication from the mobile endpoint device over a network, wherein the request comprises the first retinal image.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com