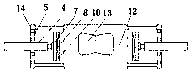Patents
Literature
231 results about "Eye surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
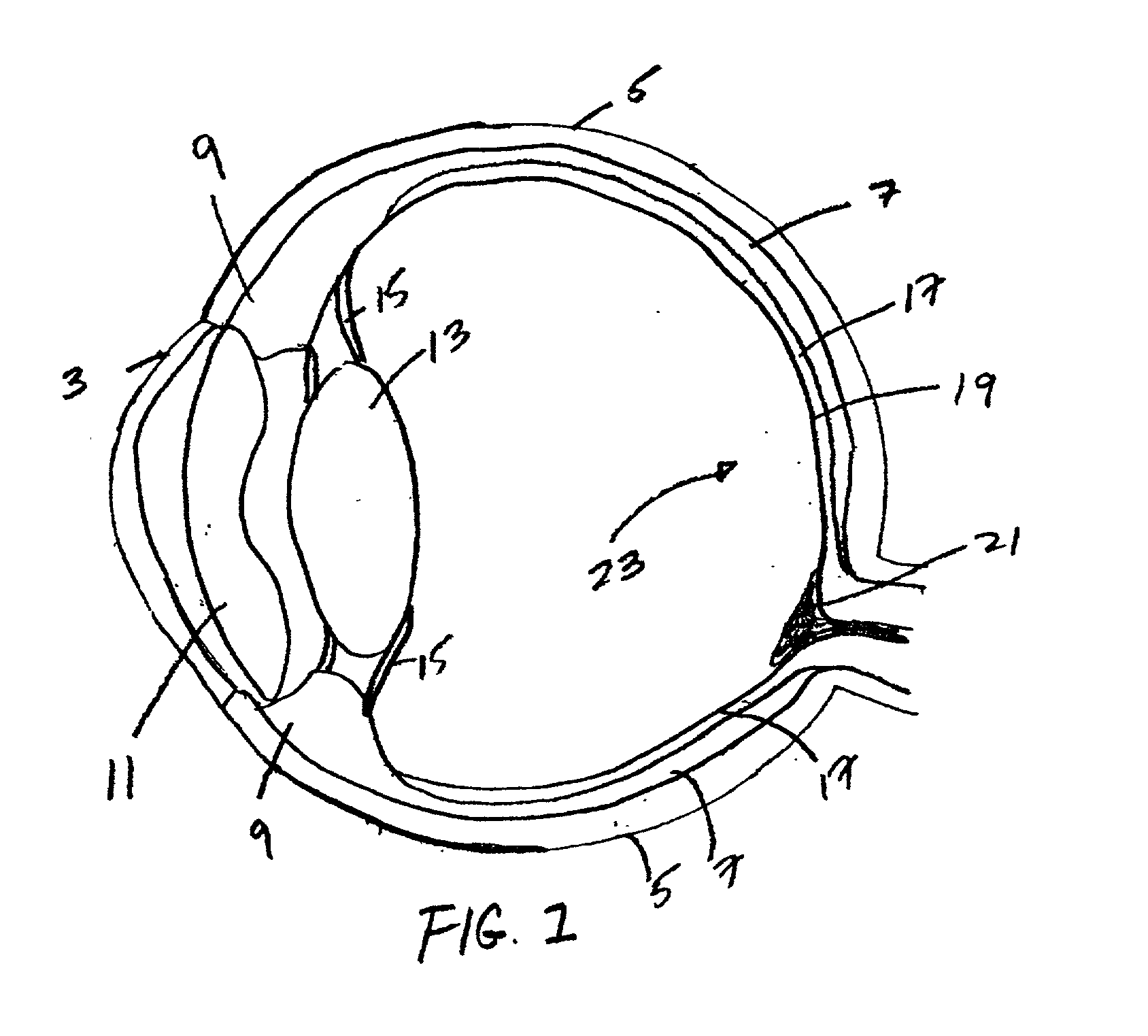
Eye surgery, also known as ocular surgery, is surgery performed on the eye or its adnexa, typically by an ophthalmologist. The eye is a very fragile organ, and requires extreme care before, during, and after a surgical procedure to minimise or prevent further damage. An expert eye surgeon is responsible for selecting the appropriate surgical procedure for the patient, and for taking the necessary safety precautions. Mentions of eye surgery can be found in several ancient texts dating back as early as 1800 BC, with cataract treatment starting in the fifth century BC. Today it continues to be a widely practiced type of surgery, having developed various techniques for treating eye problems.
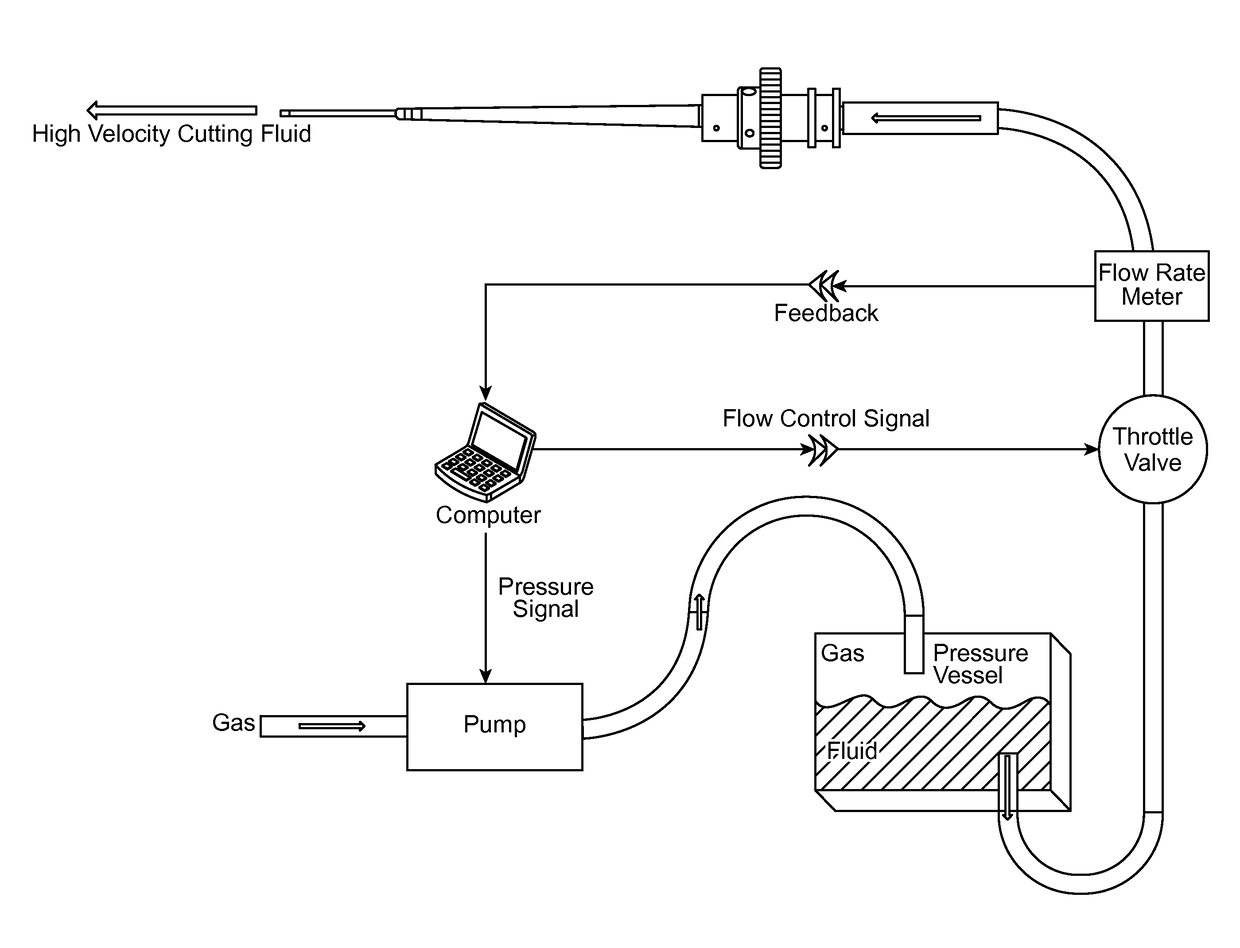
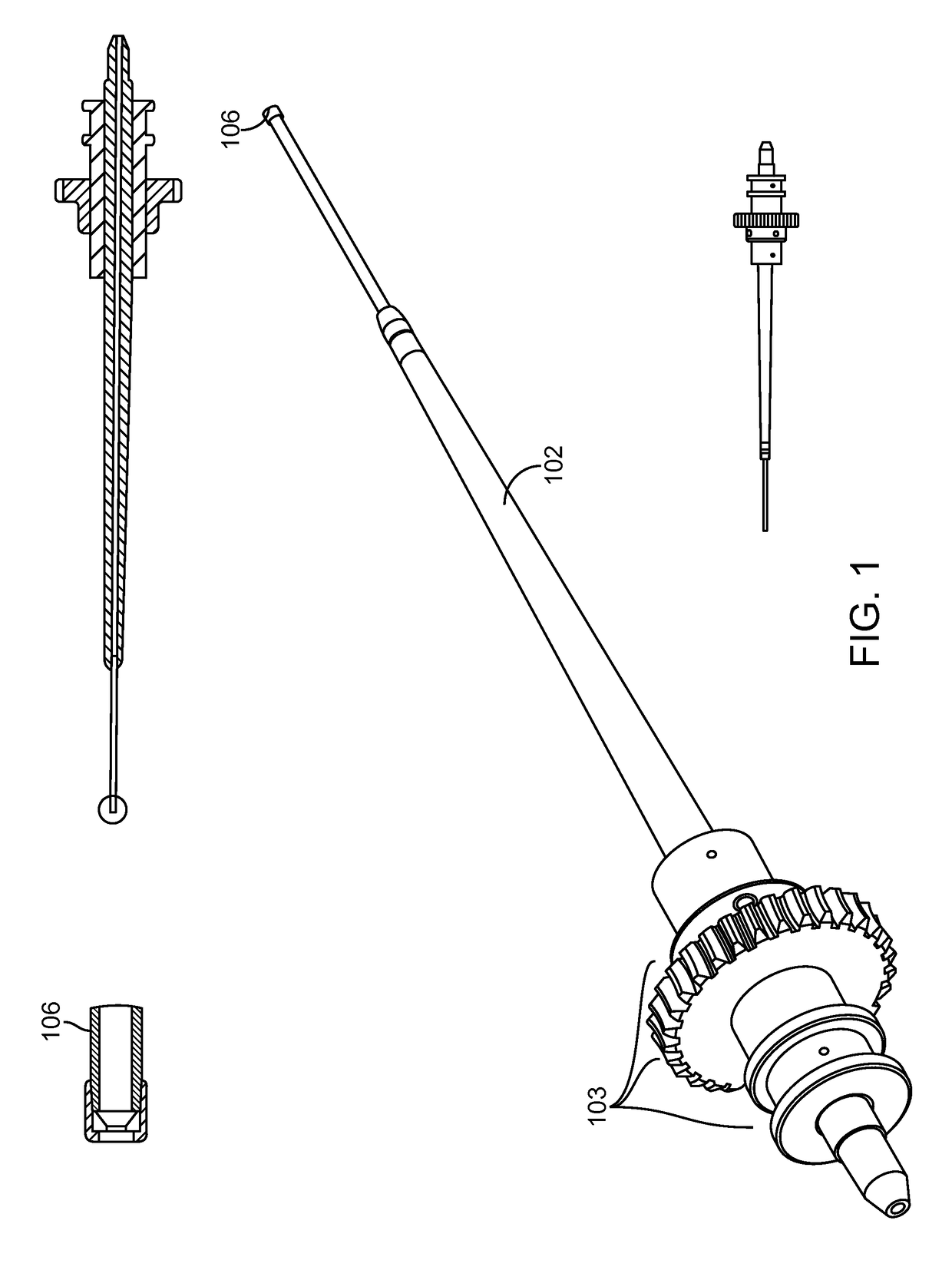
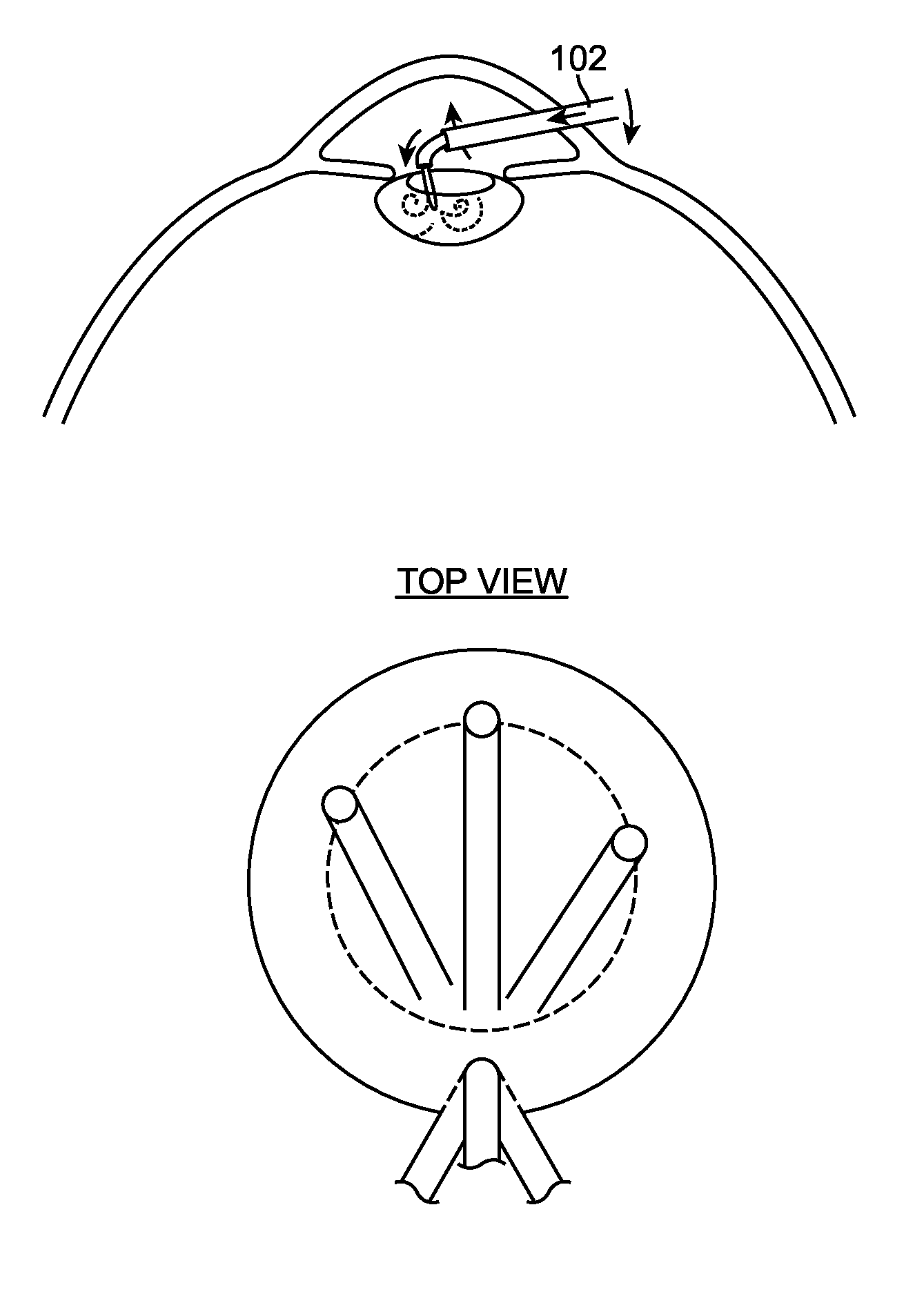
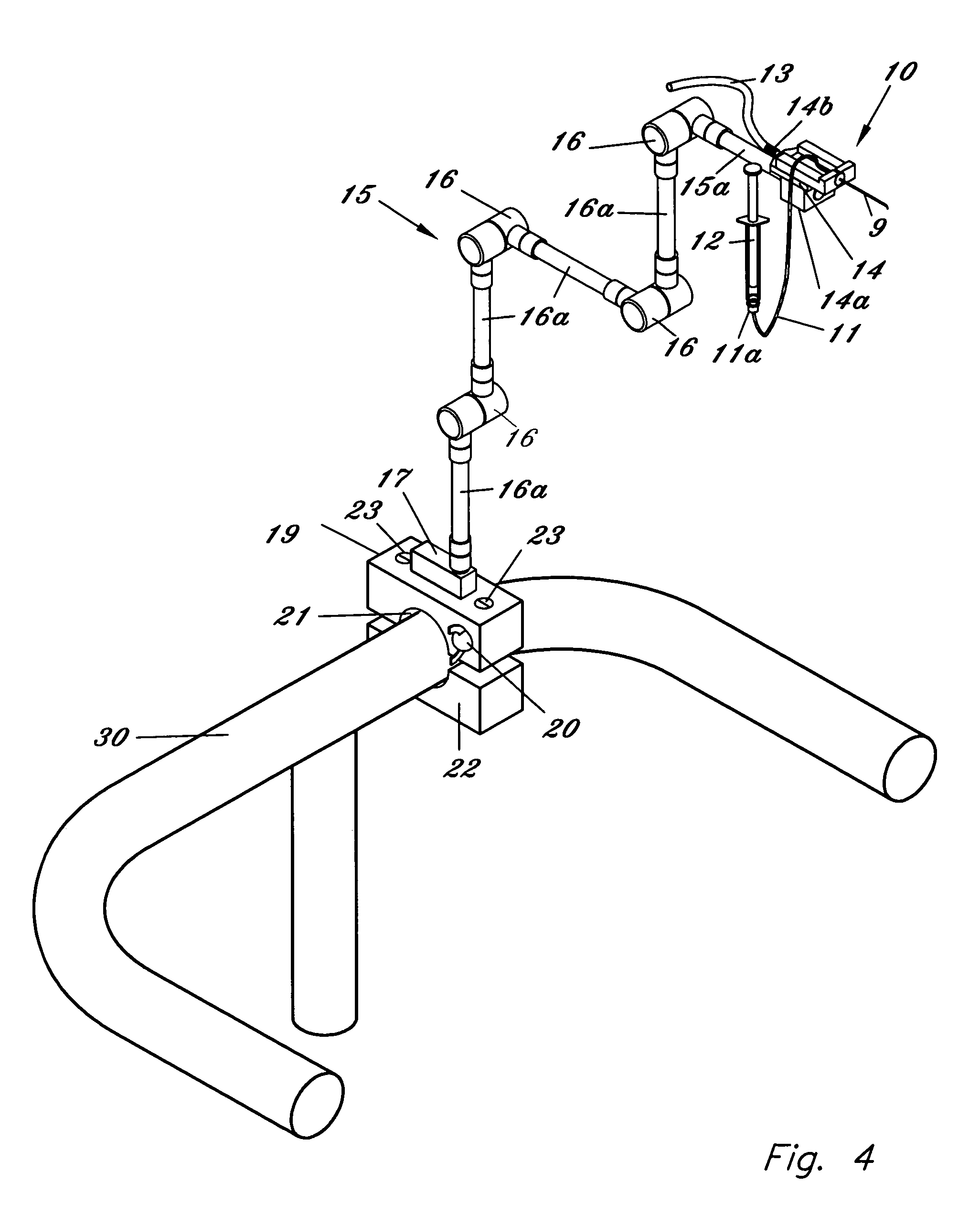
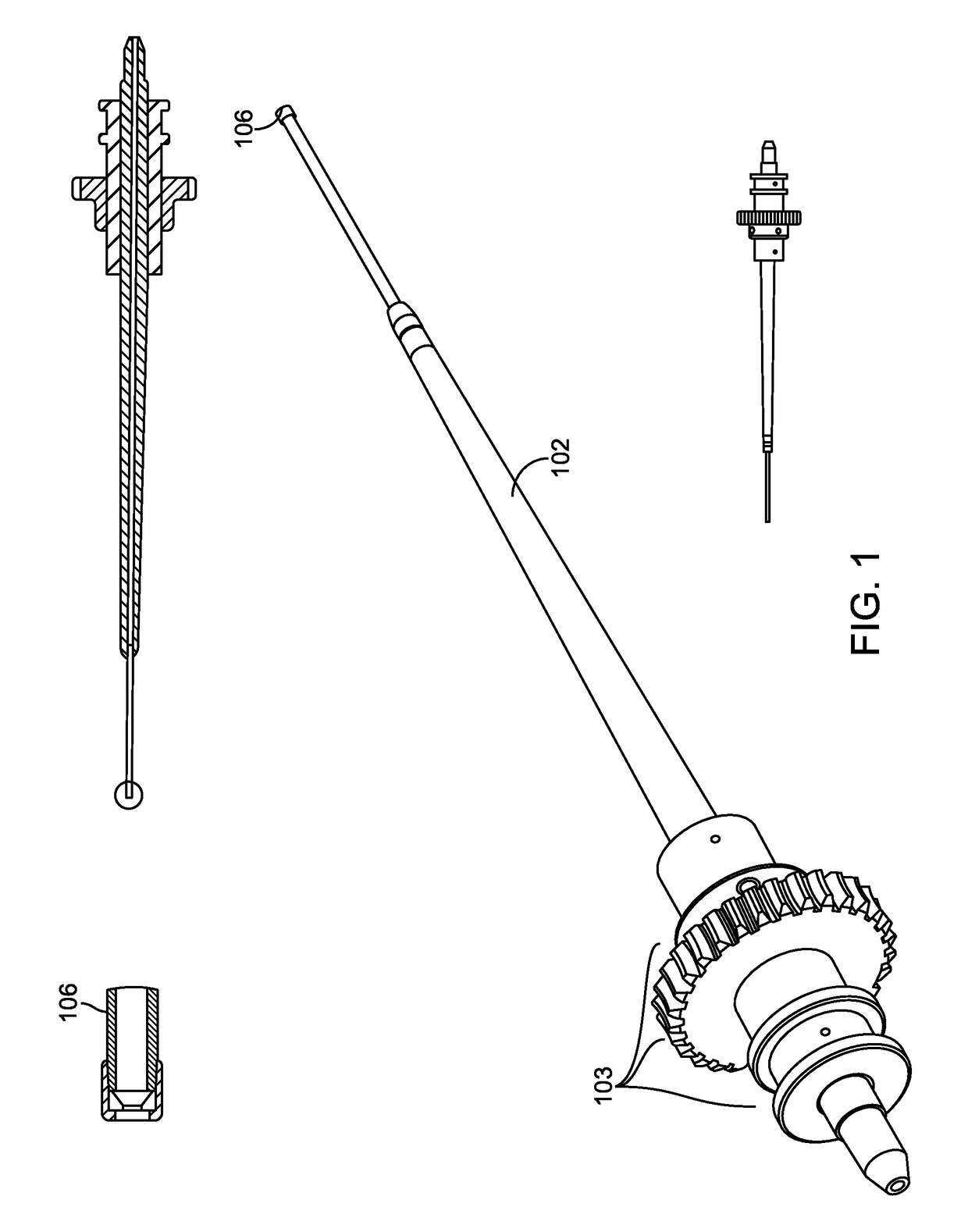
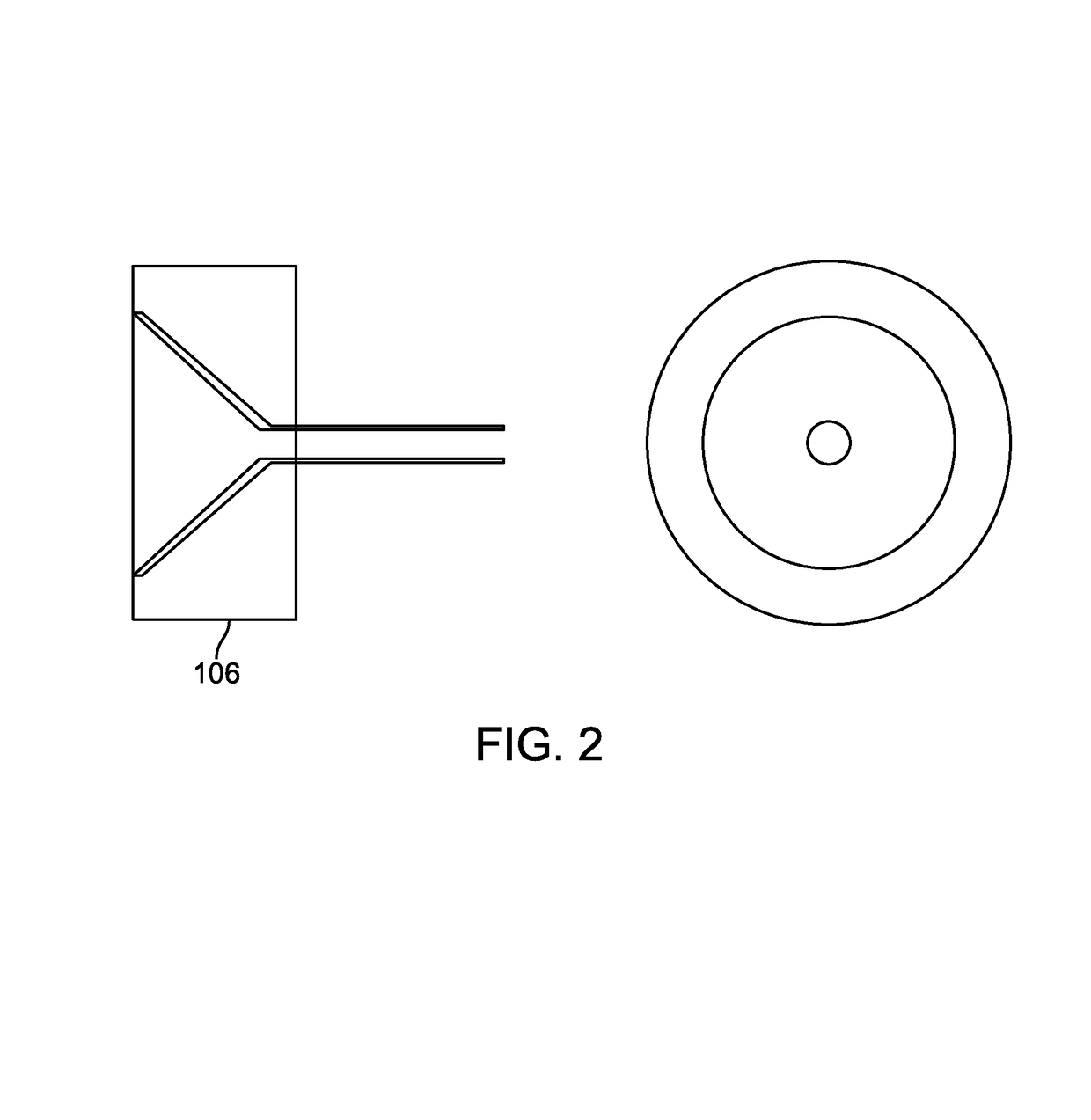
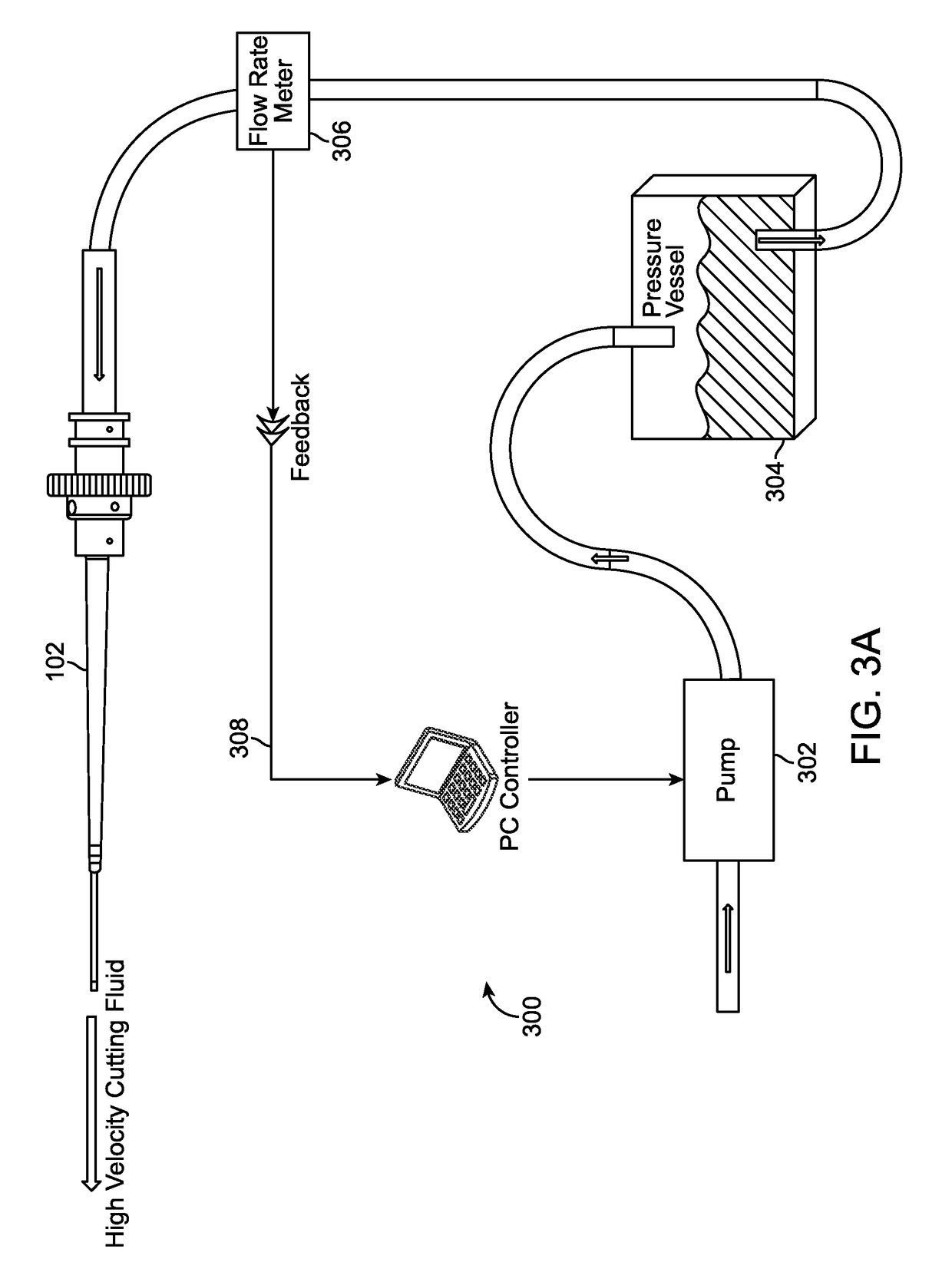
Method, apparatus and system for a water jet
A water jet instrument may be used for manually performing eye surgery such as, cataract, or perform micro-surgery (remove cartilage), or any emulsification technique. The water jet instrument may be manually controlled or controlled by a system with a robotic control. The water jet apparatus defines a jet cutting area that is based at least in part on a flow rate meter and a feedback loop.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
Method, apparatus and system for a water jet
A water jet instrument may be used for manually performing eye surgery such as, cataract, or perform micro-surgery (remove cartilage), or any emulsification technique. The water jet instrument may be manually controlled or controlled by a system with a robotic control. The water jet apparatus defines a jet cutting area that is based at least in part on a flow rate meter and a feedback loop.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
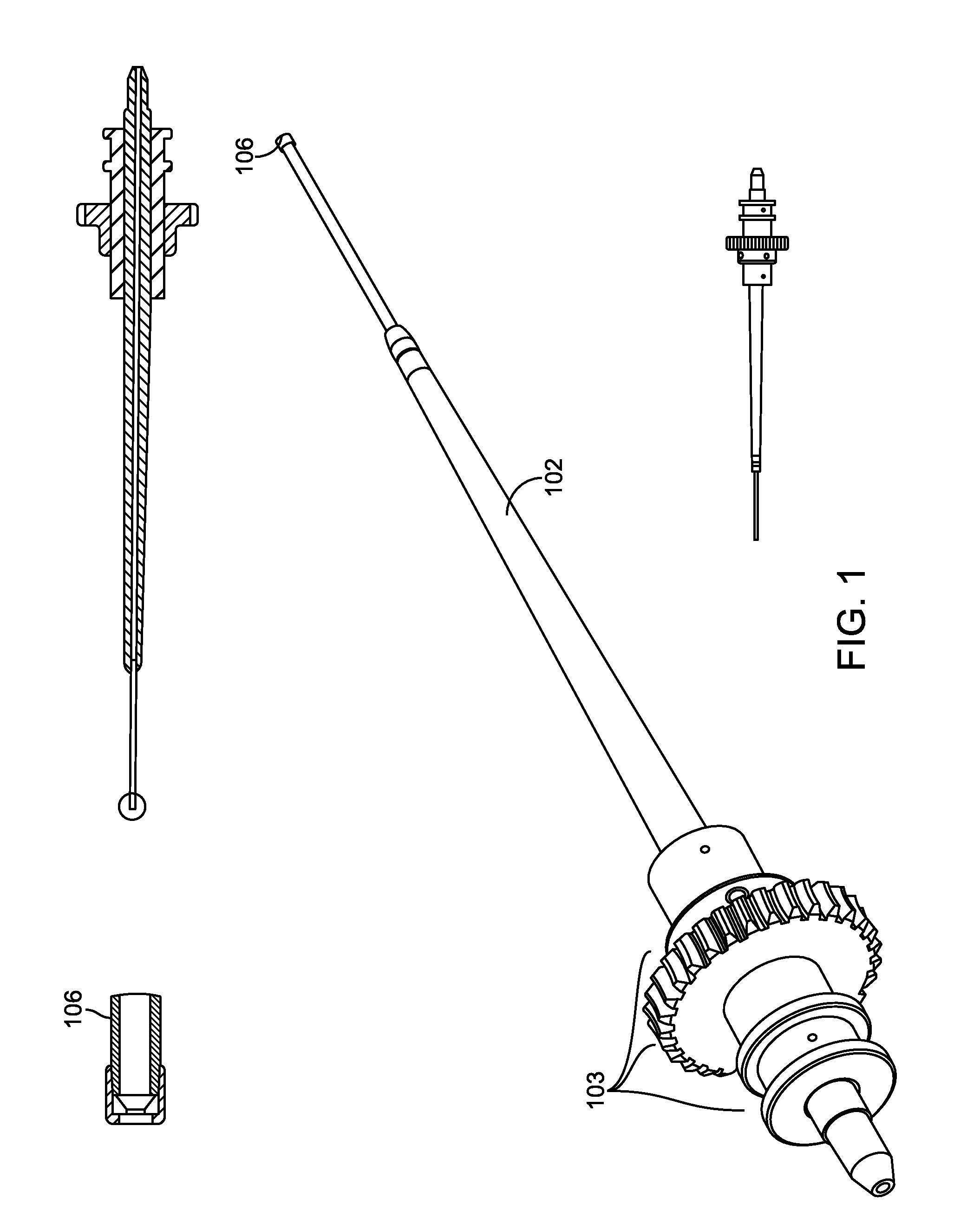
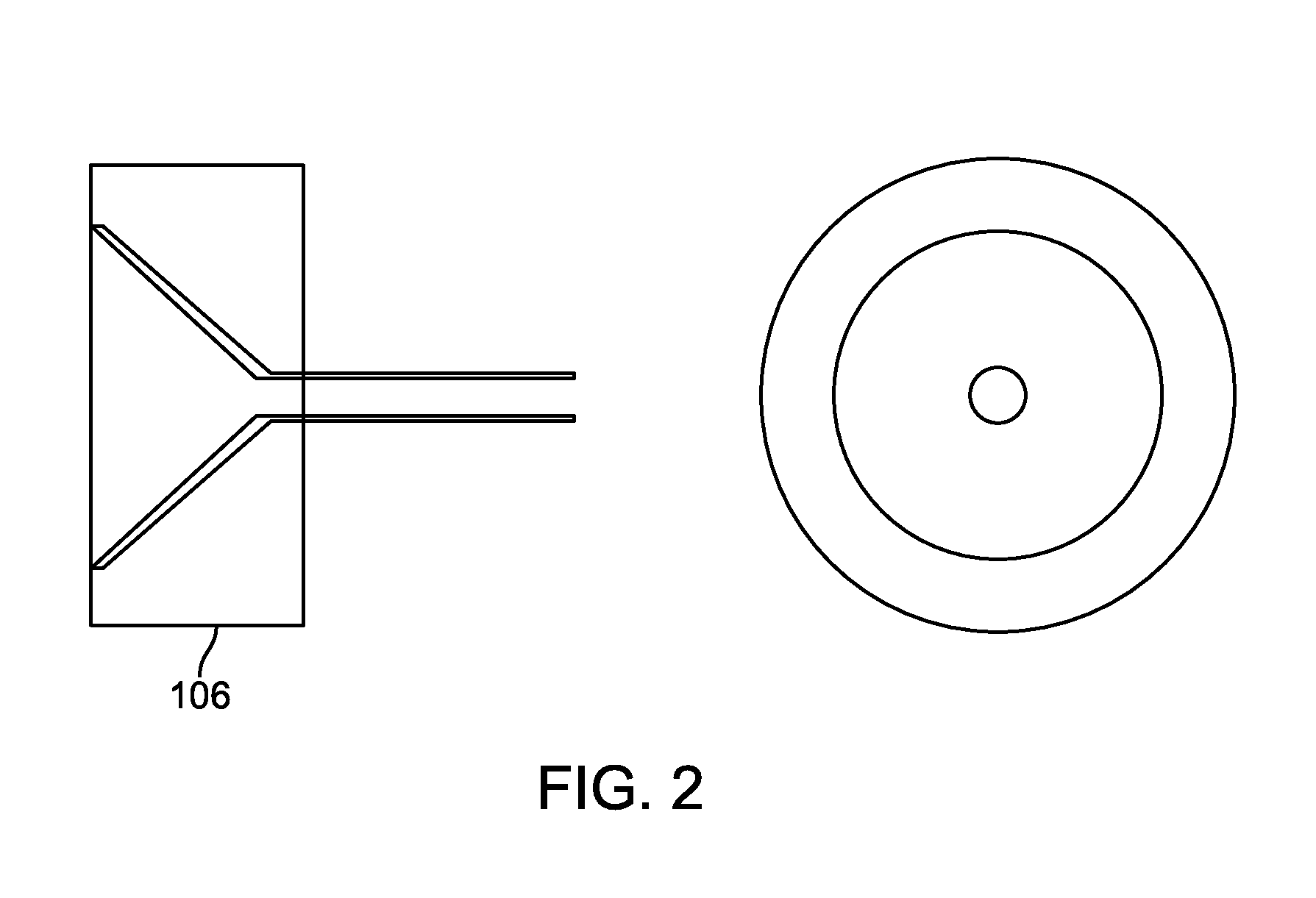
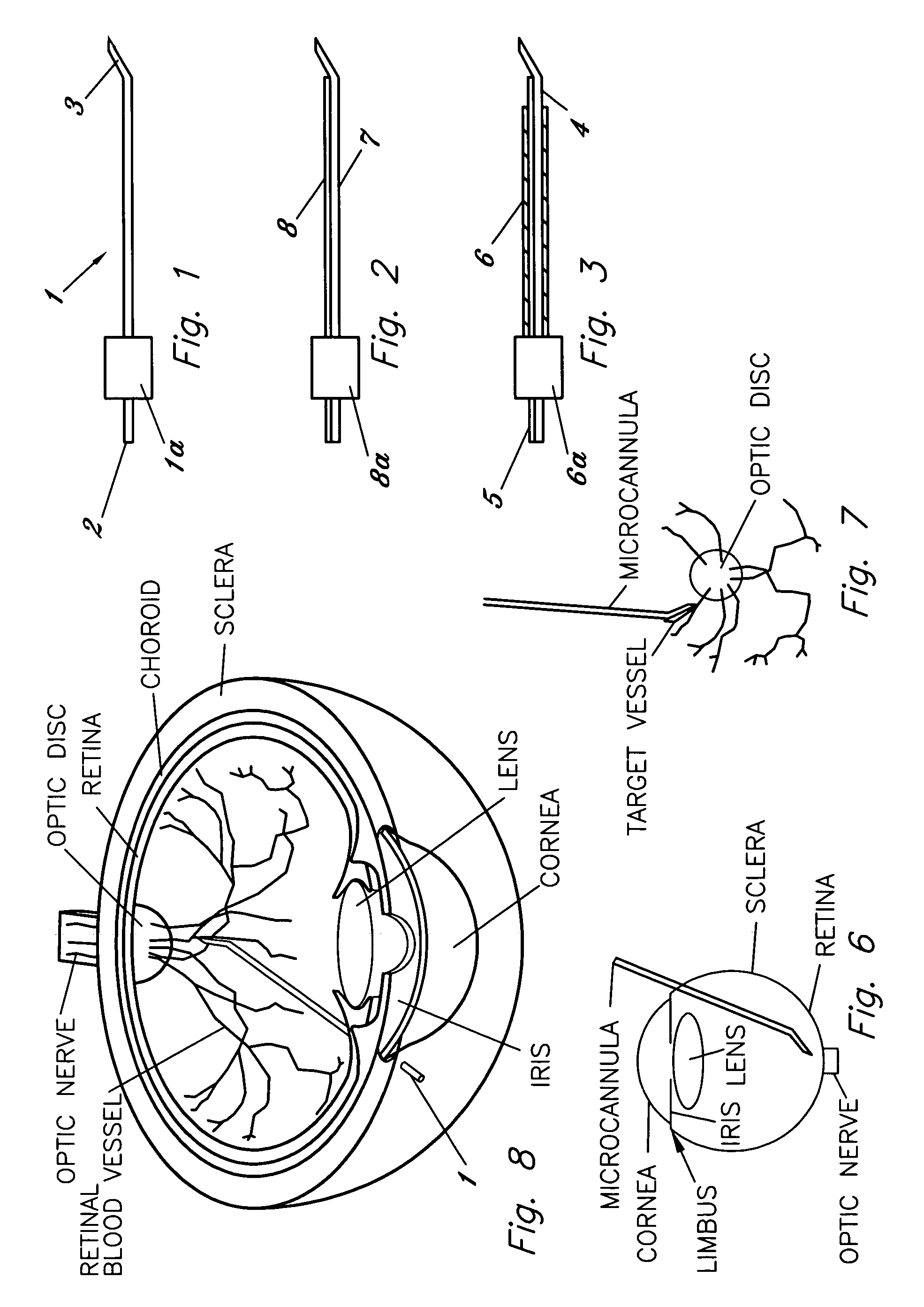
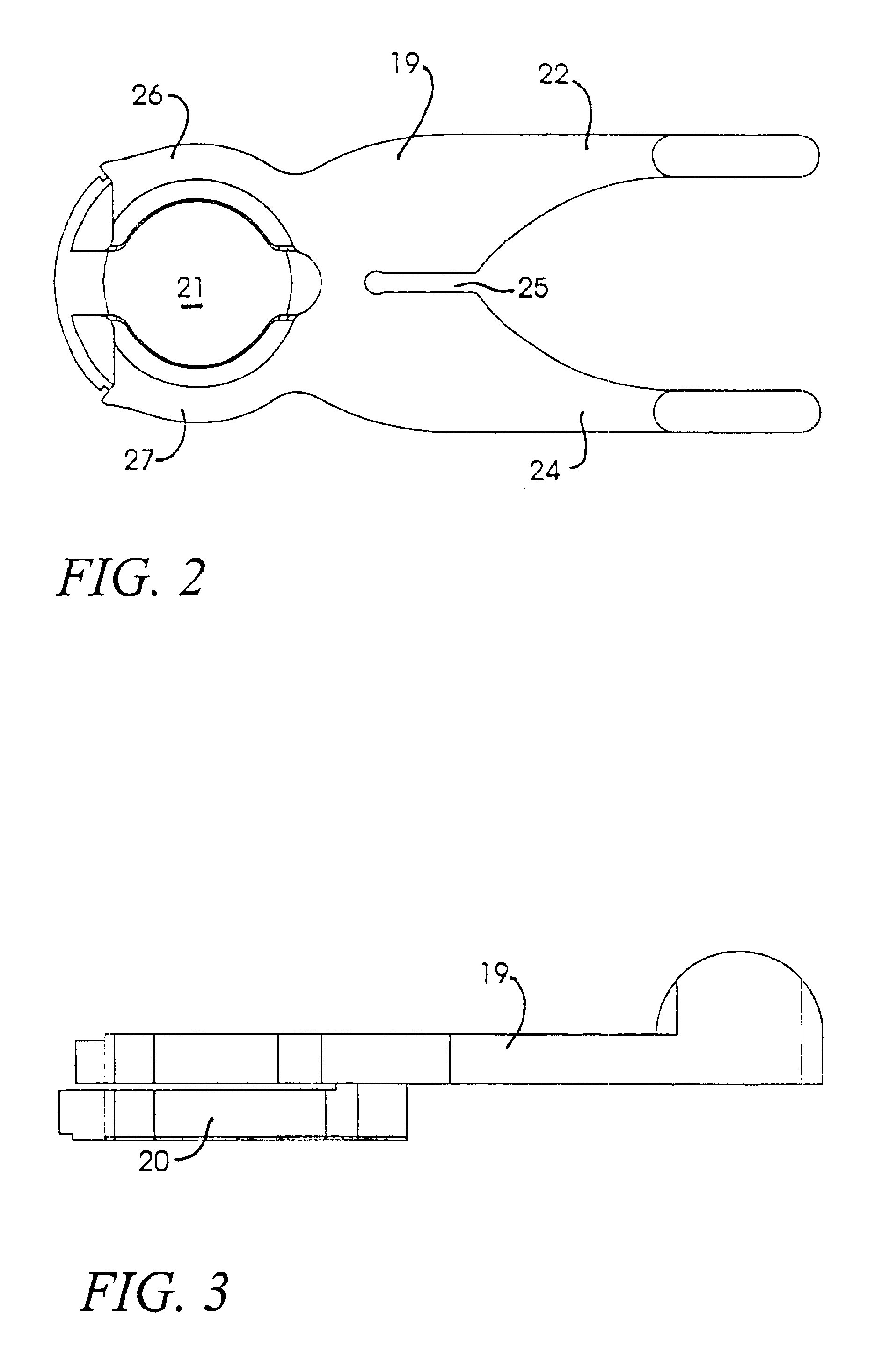
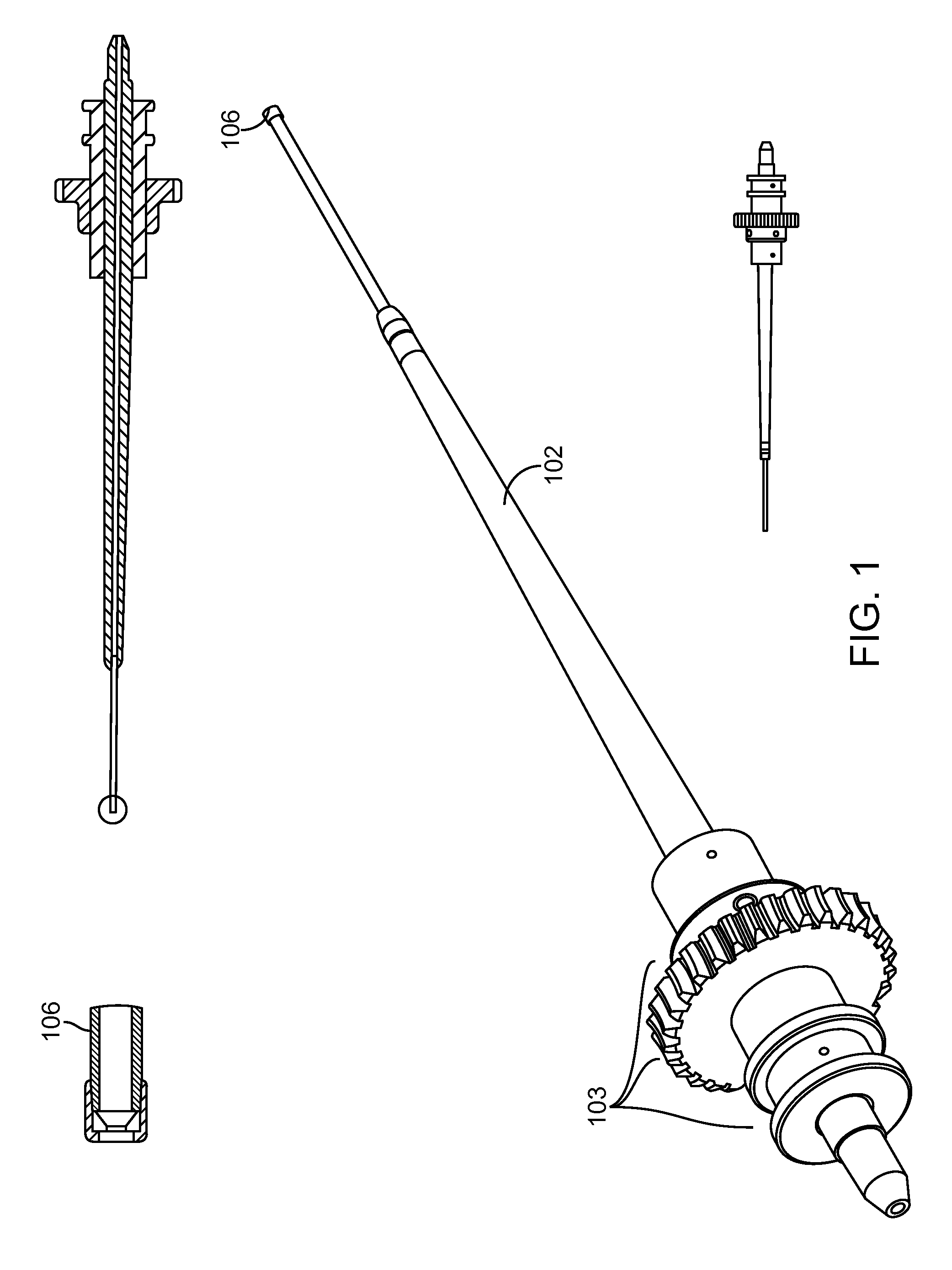
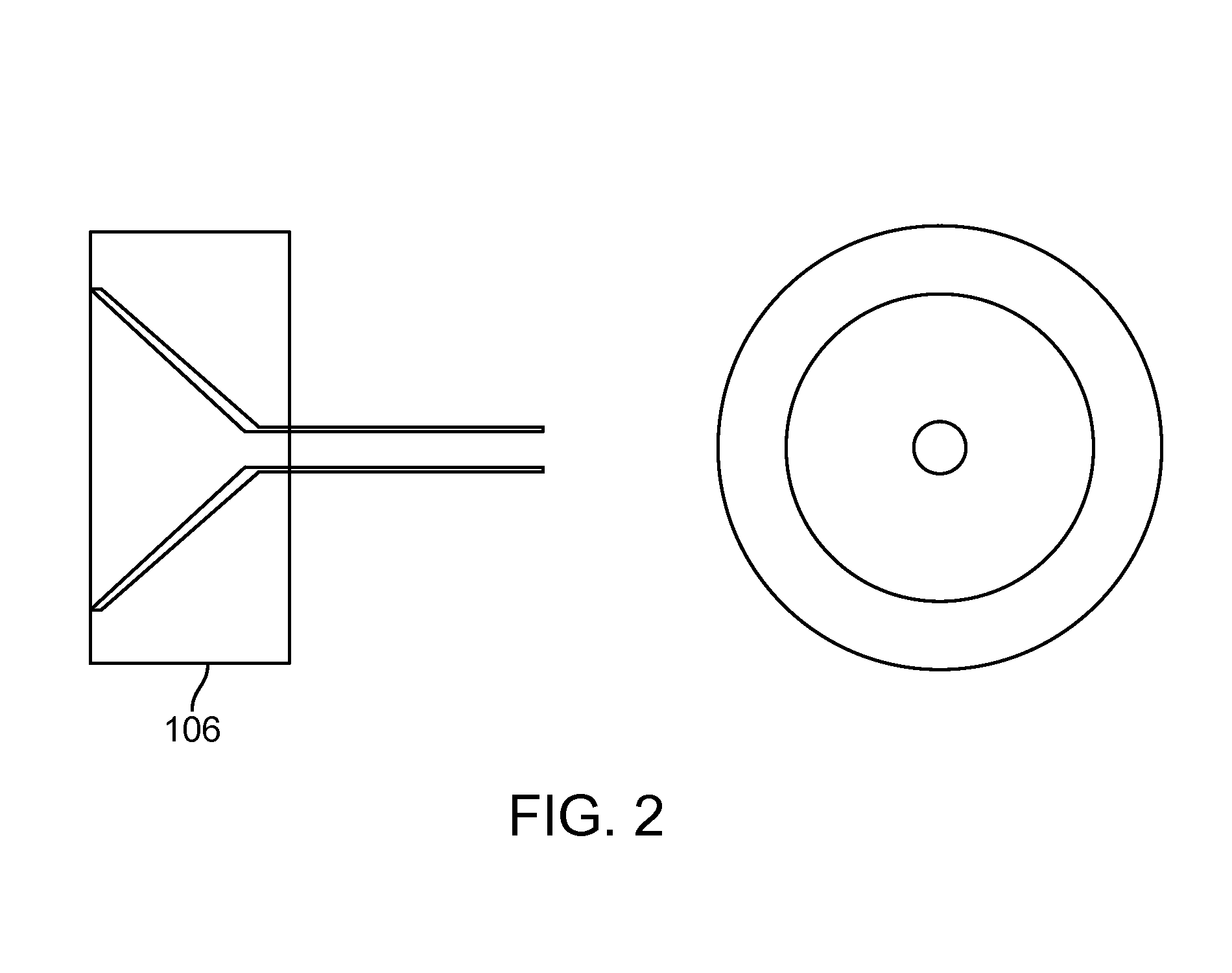
Ocular implant needle
InactiveUS6936053B1Easily perforate designated blood vesselMinimize bleedingStentsEye surgeryDiseaseOptic nerve
An apparatus and method for safely cannulating a blood vessels, including but not limited retinal blood vessels, is described. In one embodiment, the apparatus can consist of a micropipette / microcannula, micromanipulator and positioner mounted to a base, which is attached to a wrist rest commonly used in eye surgery. The micropipette / microcannula is connected to tubing such that a medication may be injected through the micropipette / microcannula into the blood vessel or conversely, a small quantity of material may be removed from a blood vessel. Alternatively, a catheter, wire or stent may be placed through the micropipette / microcannula to treat or diagnose an area remote from the insertion site. The ability to cannulate a retinal blood vessel should be efficacious in the treatment of vein and artery occlusion, ocular tumors and other retinal, vascular and optic nerve disorders that would benefit from diagnosis and / or treatment. In another embodiment, a self-sealing needle is provided which allows the perforation of a blood vessel or other structure and the minimization of hemorrhaging when the needle is withdrawn from the blood vessel / structure. Another embodiment discloses an ocular implant needle.
Owner:JNW PARTNERS
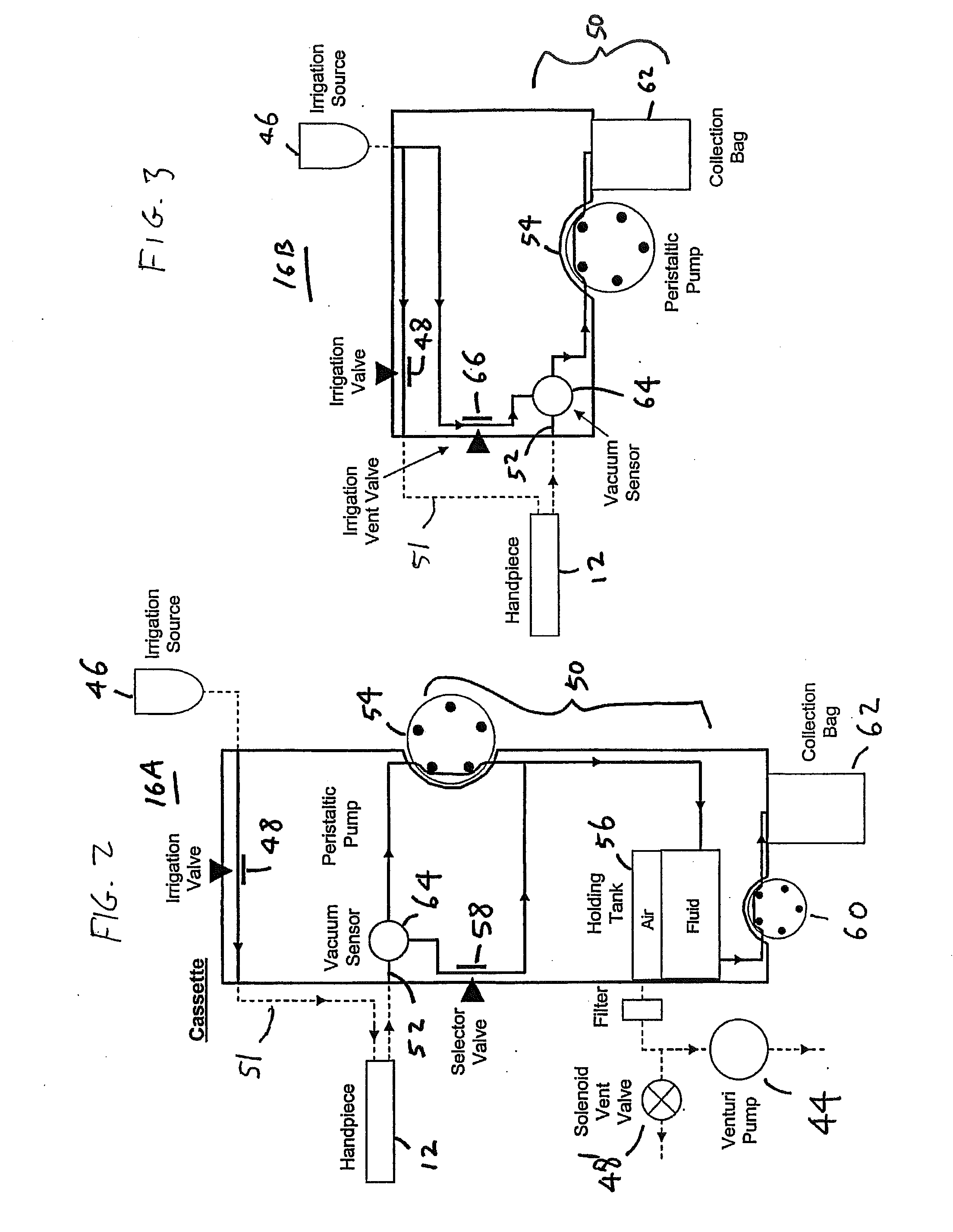
Reversible peristaltic pump and other structures for reflux in eye surgery
Devices, systems, and methods for treatment of an eye alter aspiration flow from the eye in response to an occlusion of the aspiration conduit pathway. Where aspiration is drawn from the eye using a volumetric pump, the pump can be reversed so as to induce fluid reflux from the aspiration conduit pathway into the eye to help clear the occlusion. The pump may vary the reverse flow in response to sensed aspiration pressure or the like, and the reverse flow may be halted before the pressure within the aspiration conduit pathway adjacent the eye significantly exceeds the irrigation fluid pressure and / or the pressure within the eye. Reflux may alternatively be generated by modulating a vent valve disposed between an irrigation conduit pathway and the aspiration conduit pathway.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Method, apparatus and system for a water jet
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
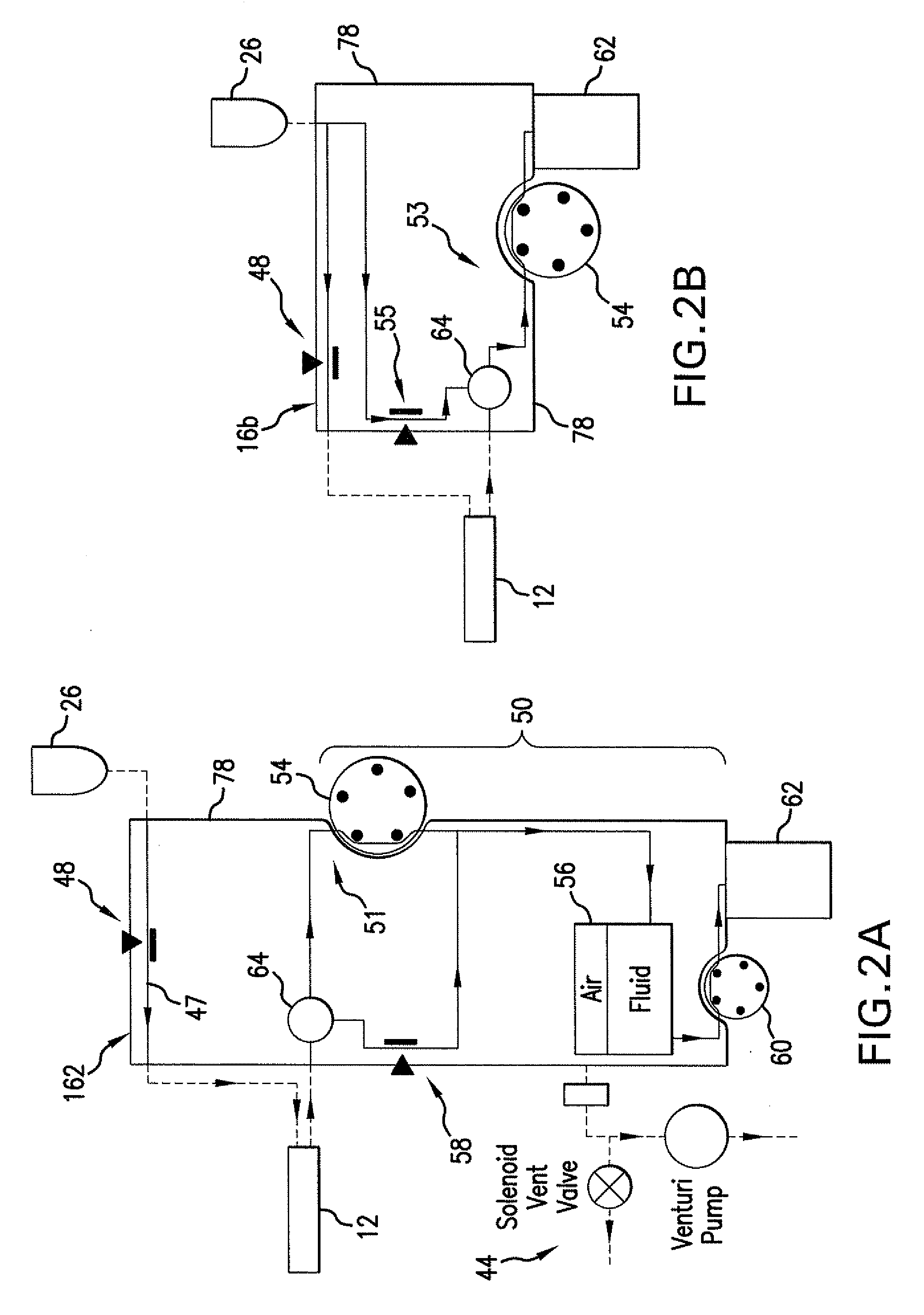
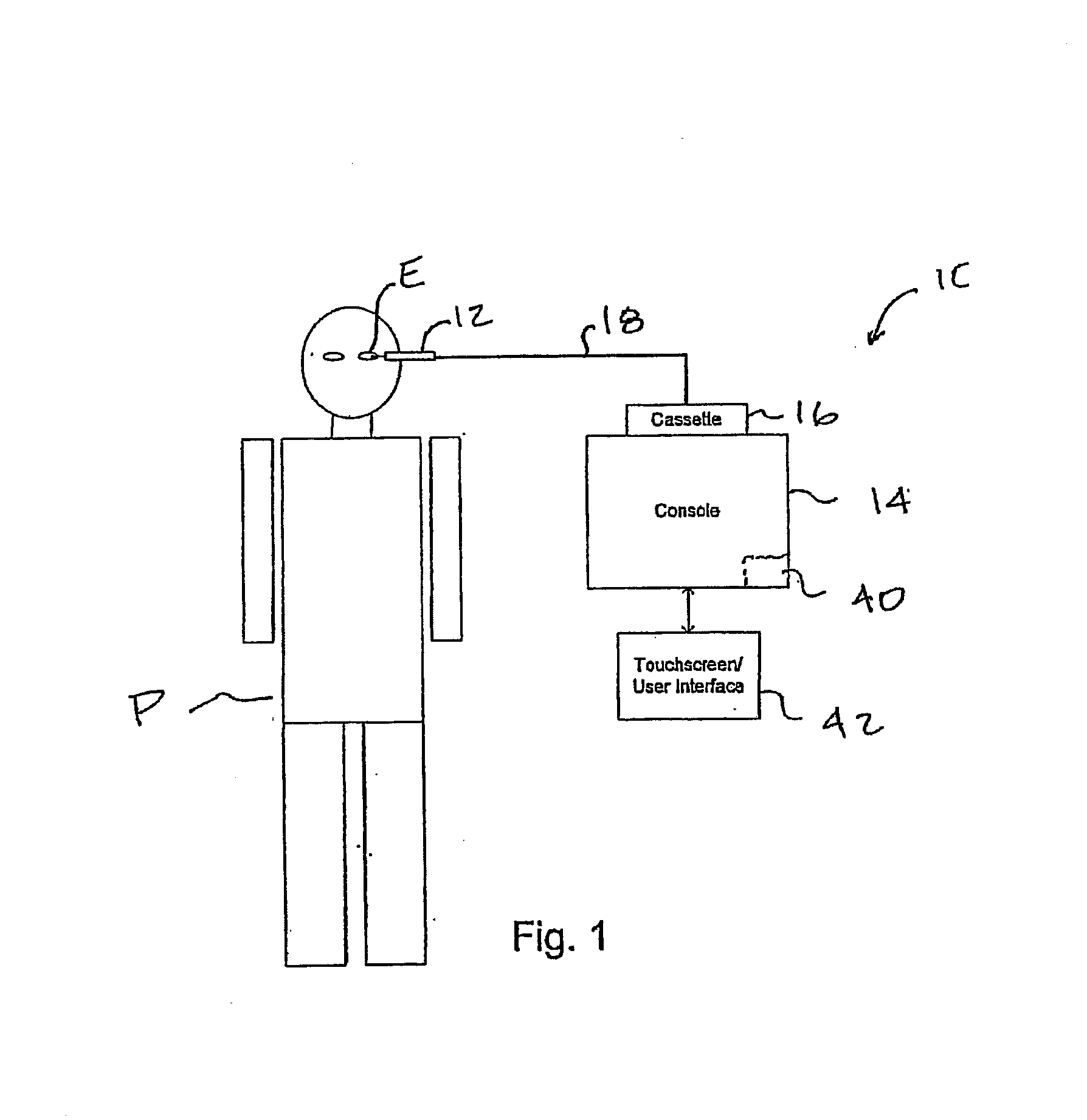
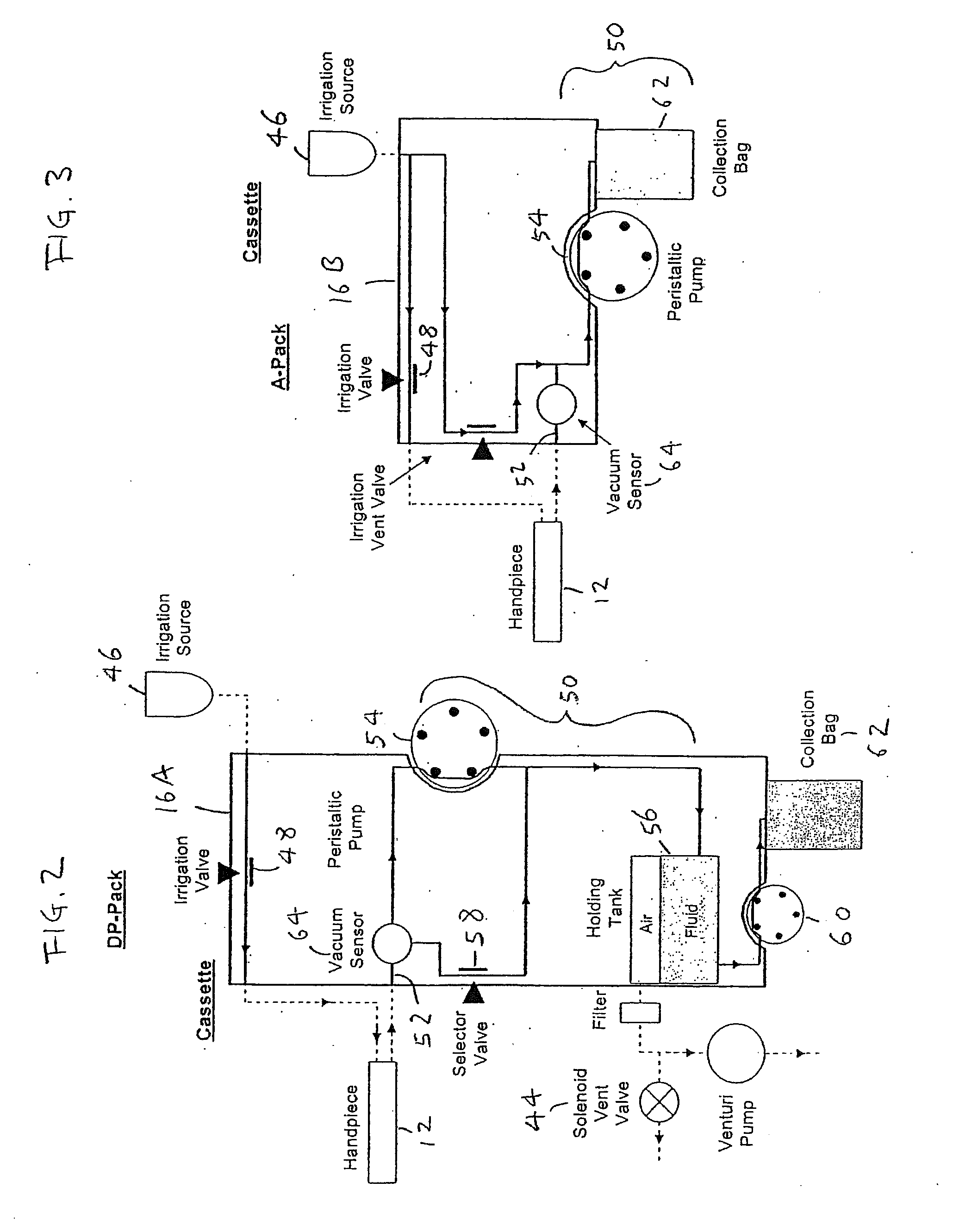
Fluidics cassette for ocular surgical system
Methods, devices, and systems for laser eye surgery generally make use of a console that interchangeably accepts multiple types of eye treatment cassettes. The cassettes enable one or both of displacement-based or vacuum-based aspiration. The console and the cassette may communicate to establish the functionality of the installed cassette by utilizing a component indigenous to the operation of the cassette. A dual-mode cassette may include a separable holding tank for enabling vacuum-based aspiration. A displacement-based pump may be provided to drain the holding tank while the vacuum system continues to aspirate fluids. A vacuum sensor for controlling the flow of aspirated fluids may have three ports for communicating with a handpiece, a displacement-based pump, a vacuum-based pump, or an irrigation source. The handpiece may be vented during vacuum-based aspiration by opening a vent valve interposed between the handpiece and the vacuum source.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Applanation lens and method for ophthalmic surgical applications
InactiveUS6899707B2Guaranteed stable engagementResist discolorationLaser surgeryDiagnosticsHigh energyTransmittance
An improved applanation lens and method for use in an interface between a patient's eye and a surgical laser system does not discolor or lose light transmittance when subjected to gamma radiation. The improved applanation lens has an applanation surface configured to contact the eye upon application of a pressure. The lens is formed of high purity silicon dioxide (SiO2) with purity great enough to resist discoloration upon prolonged irradiation by high-energy radiation such as UV, x-rays, gamma rays or neutrons, and is preferably a fused silica.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
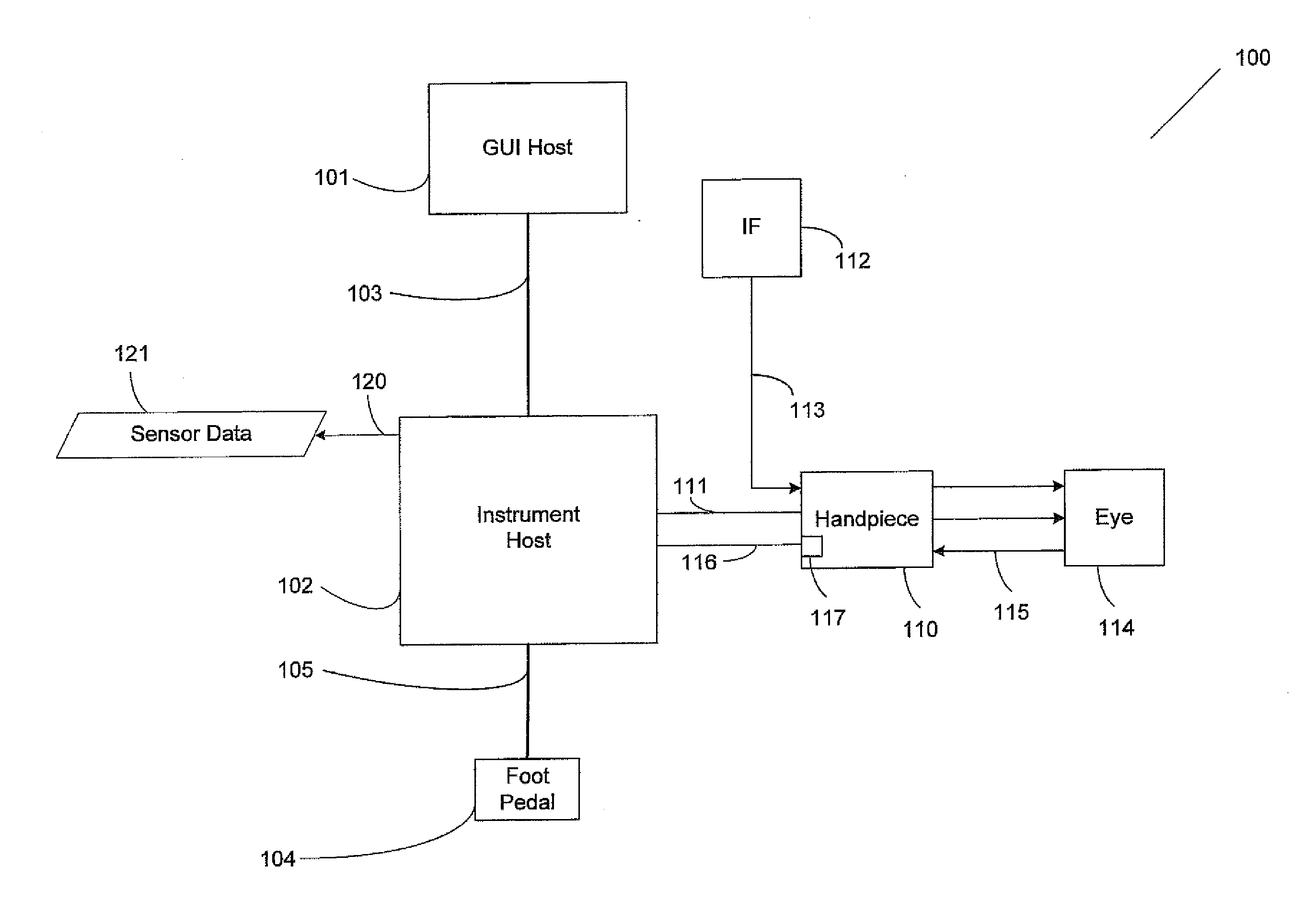
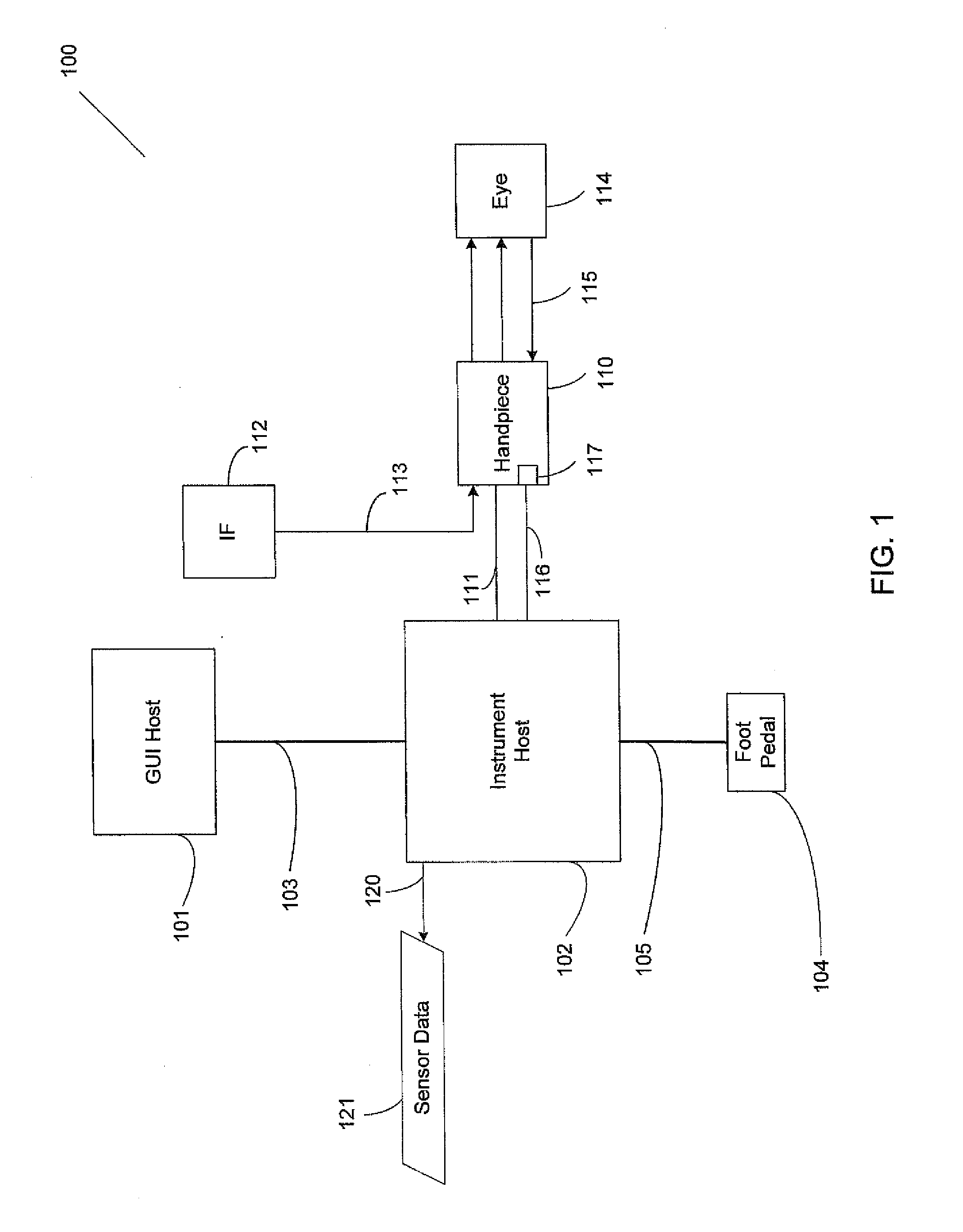
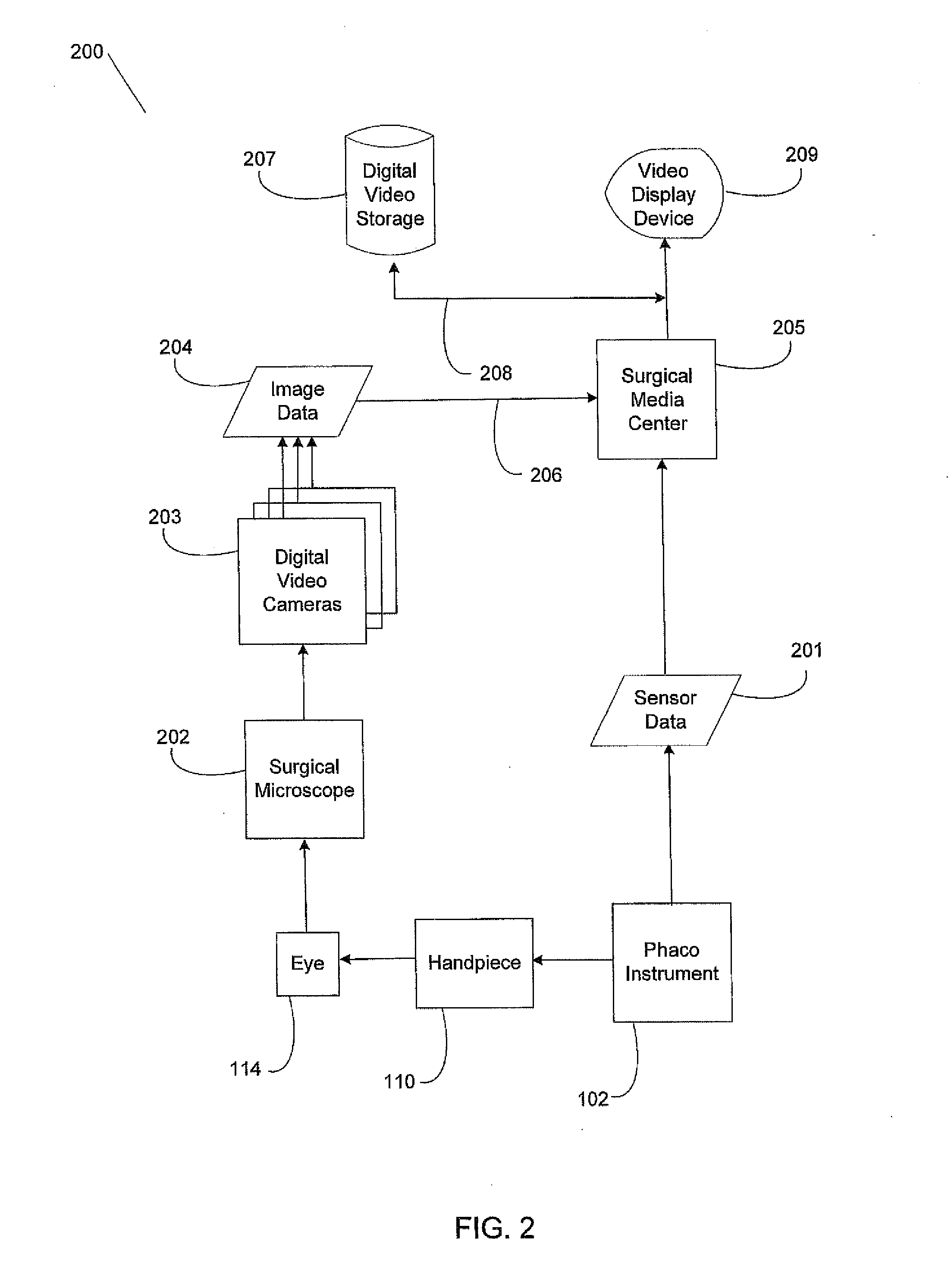
Controlling a phacoemulsification system based on real-time analysis of image data
A design for dynamically adjusting parameters applied to a surgical instrument, such as an ocular surgical instrument, is presented. The method includes detecting surgical events from image data collected by a surgical microscope focused on an ocular surgical procedure, establishing a desired response for each detected surgical event, delivering the desired response to the ocular surgical instrument as a set of software instructions, and altering the surgical procedure based on the desired response received as the set of software instructions.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Illuminated infusion cannula
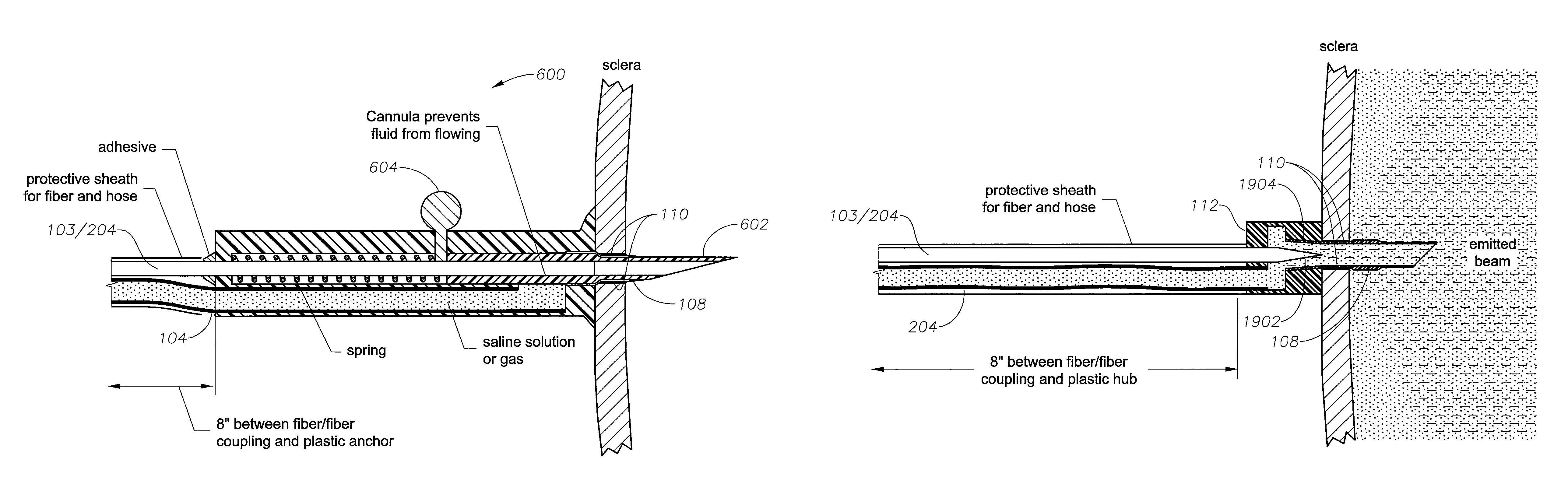
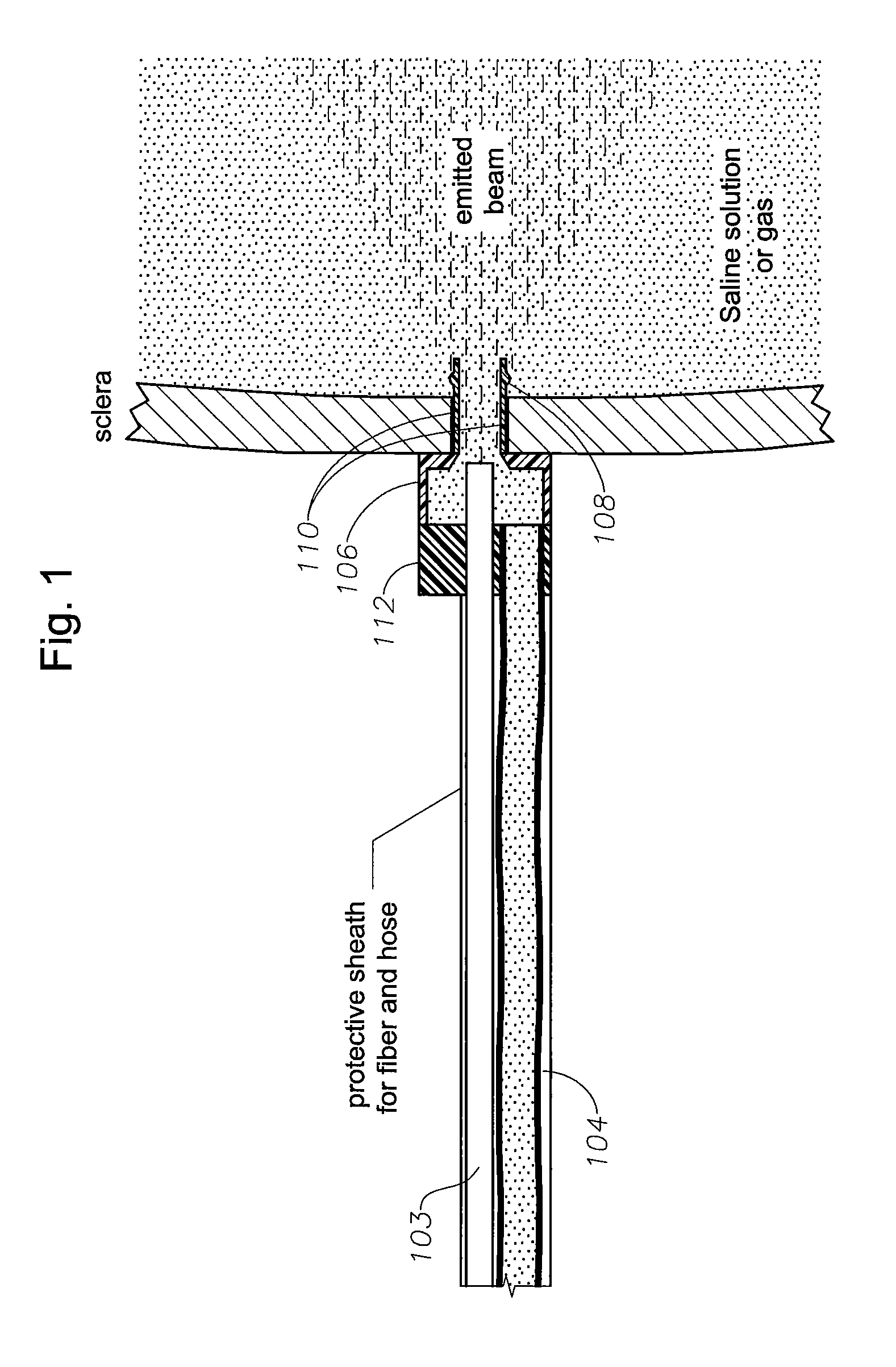
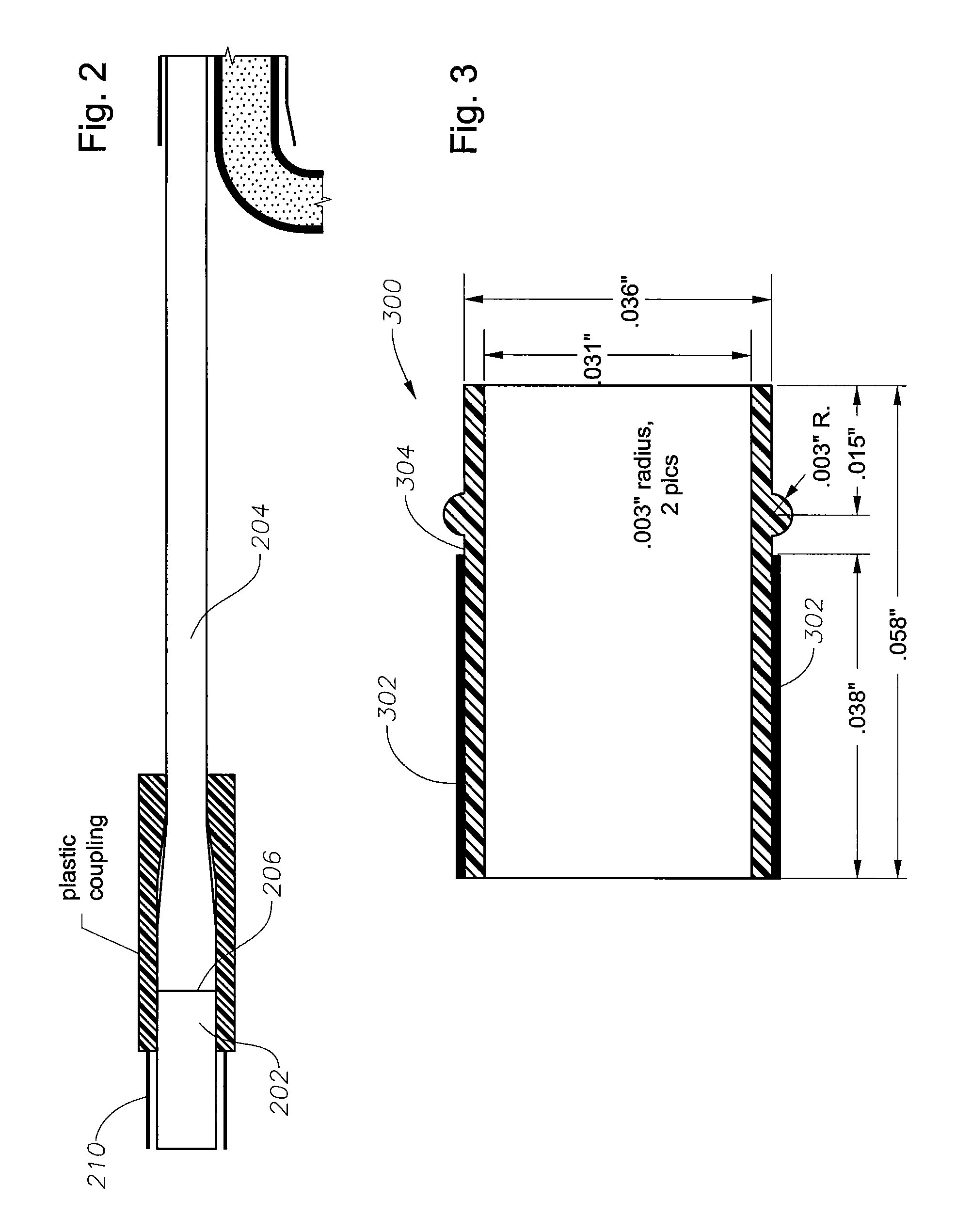
ActiveUS7783346B2Increase flow rateHigh light transmittanceElectrotherapyEye surgeryFiberTransmittance
A transparent illuminated infusion cannula is provided for illuminating an area during eye surgery. An optical fiber may be spaced a certain distance away from the cannula such that fluid flow around the distal end of the fiber and into the transparent cannula may occur with a much higher flow rate than what had previously been possible. The fiber cannula airspace may be optimized so that the cross-sectional area of the fluid conduit remains substantially constant in order to achieve a best compromise between high light transmittance and high fluid flow rate.
Owner:ALCON INC
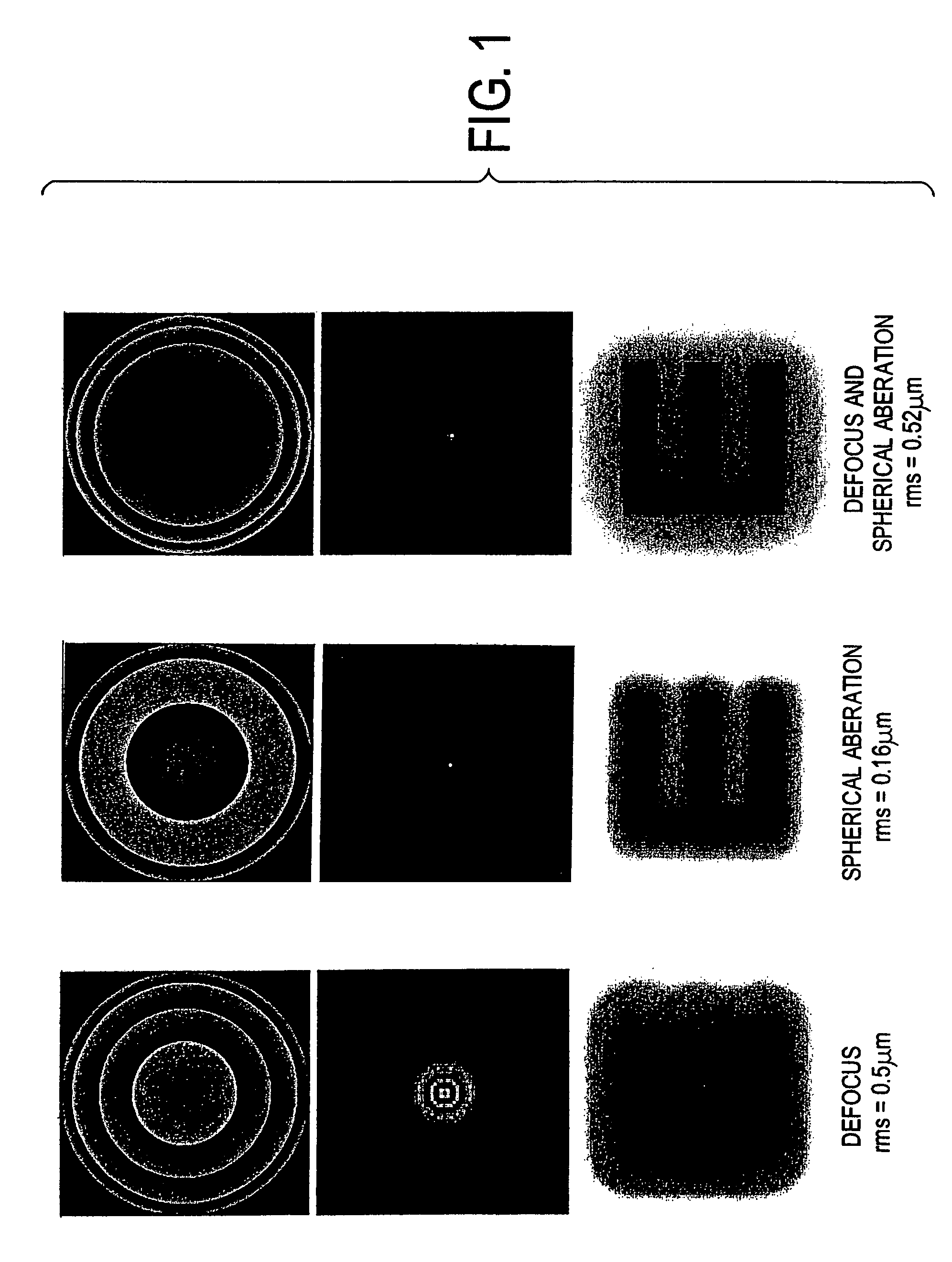
Sharpness metric for vision quality
InactiveUS7077522B2Remove wave aberrationSubjective blurRefractometersSkiascopesQuality of visionPoint spread function
A vision metric, called the sharpness metric, indicates the subjective sharpness of a patient's vision by taking into account both the wavefront aberration and the retinal response to the image. A retinal image quality function such as the point spread function is convolved by a neural quality function, and the maximum of the convolution over the retinal plane provides the sharpness metric. The sharpness metric can be used to control eye surgery or the fabrication of a lens.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Diode-laser-pumped ultraviolet and infrared lasers for ablation and coagulation of soft tissue
Method and systems for eye surgery for the treatment of presbyopia, ocular hypertension and glaucoma and other soft tissue surgeries are disclosed. System design parameters of lasing crystals (Nd:YAG, Nd:YLF, Er:YAG and Er:YSGG), nonlinear crystals (KTP, BBO, LBO), laser cavity configuration and energy delivery means are disclosed for diode-laser-pumped lasers with output wavelength at UV (263 or 266 nm), green (527 or 523 nm), and mid-IR (2.78 or 2.94 microns). Dual function of ablation and coagulation is proposed by a mode control means. The preferred diode-laser includes a wavelength at about 0.75 to 0.98 microns with power about 15 to 40 W and used in a side-pumping configuration to generate UV or IR having an energy per pulse about 3 to 30 mJ, power of about 0.1 to 1.5 W and operated at free running mode (IR laser) or pulsed mode (UV laser).
Owner:NEW VISION
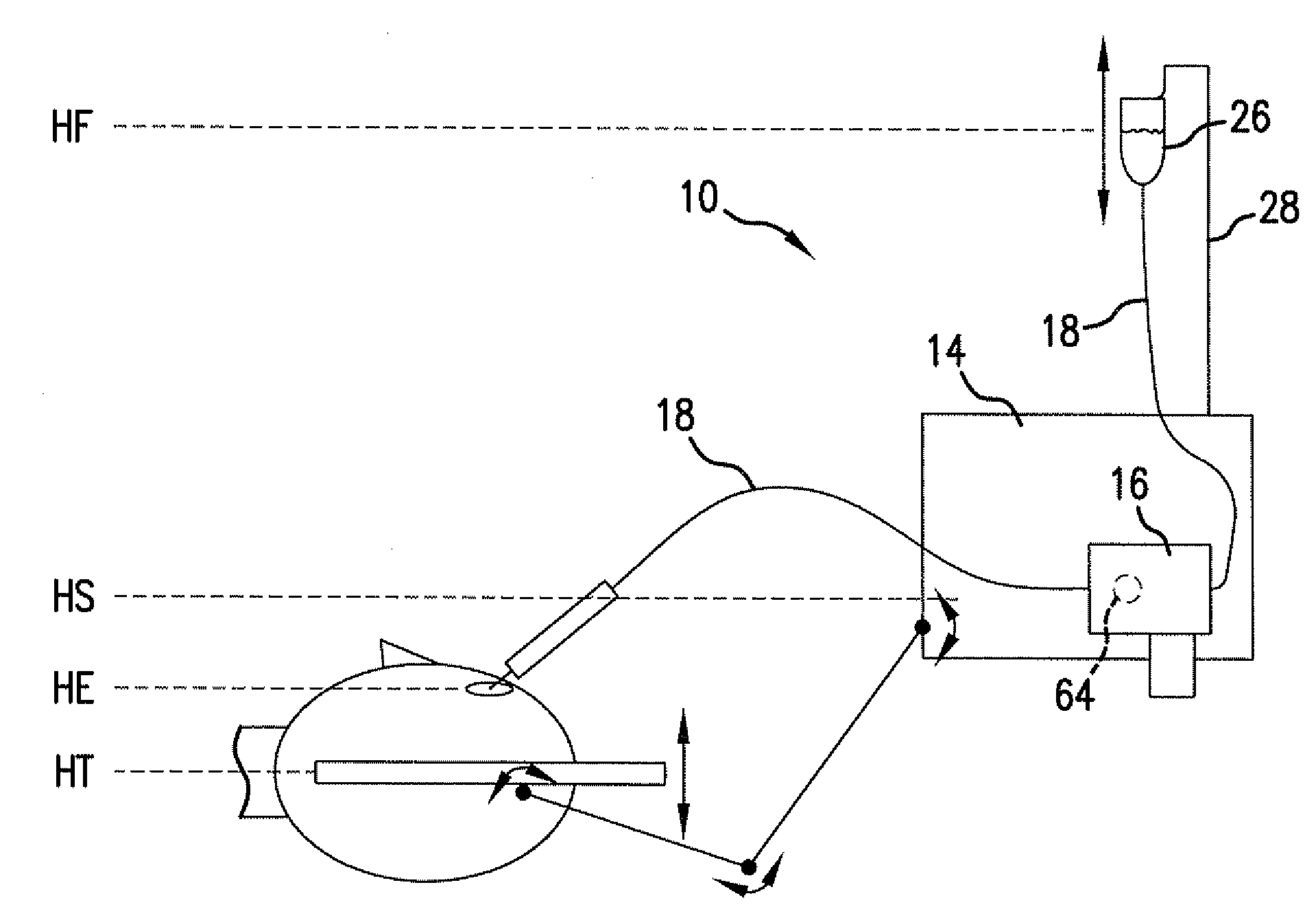
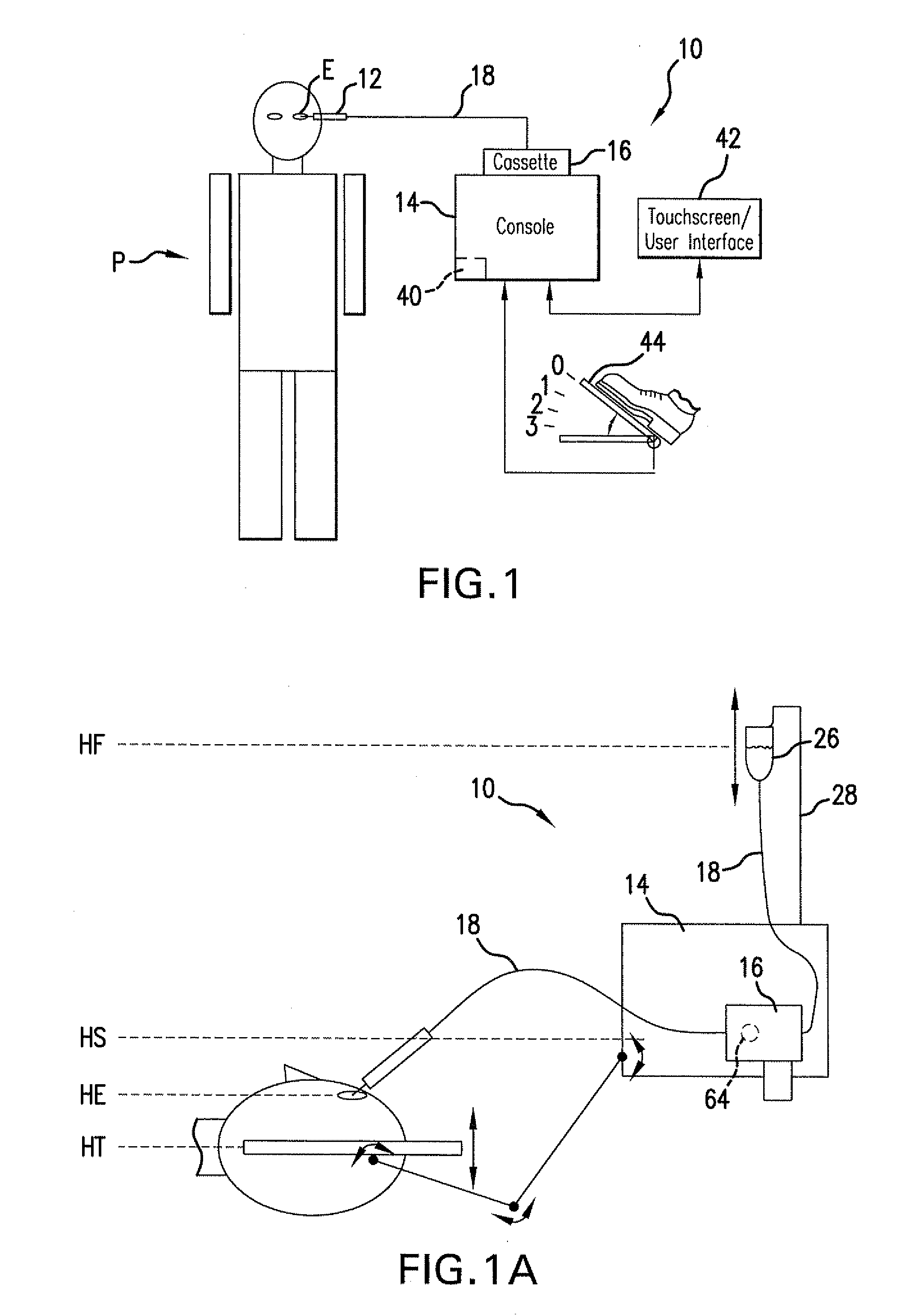
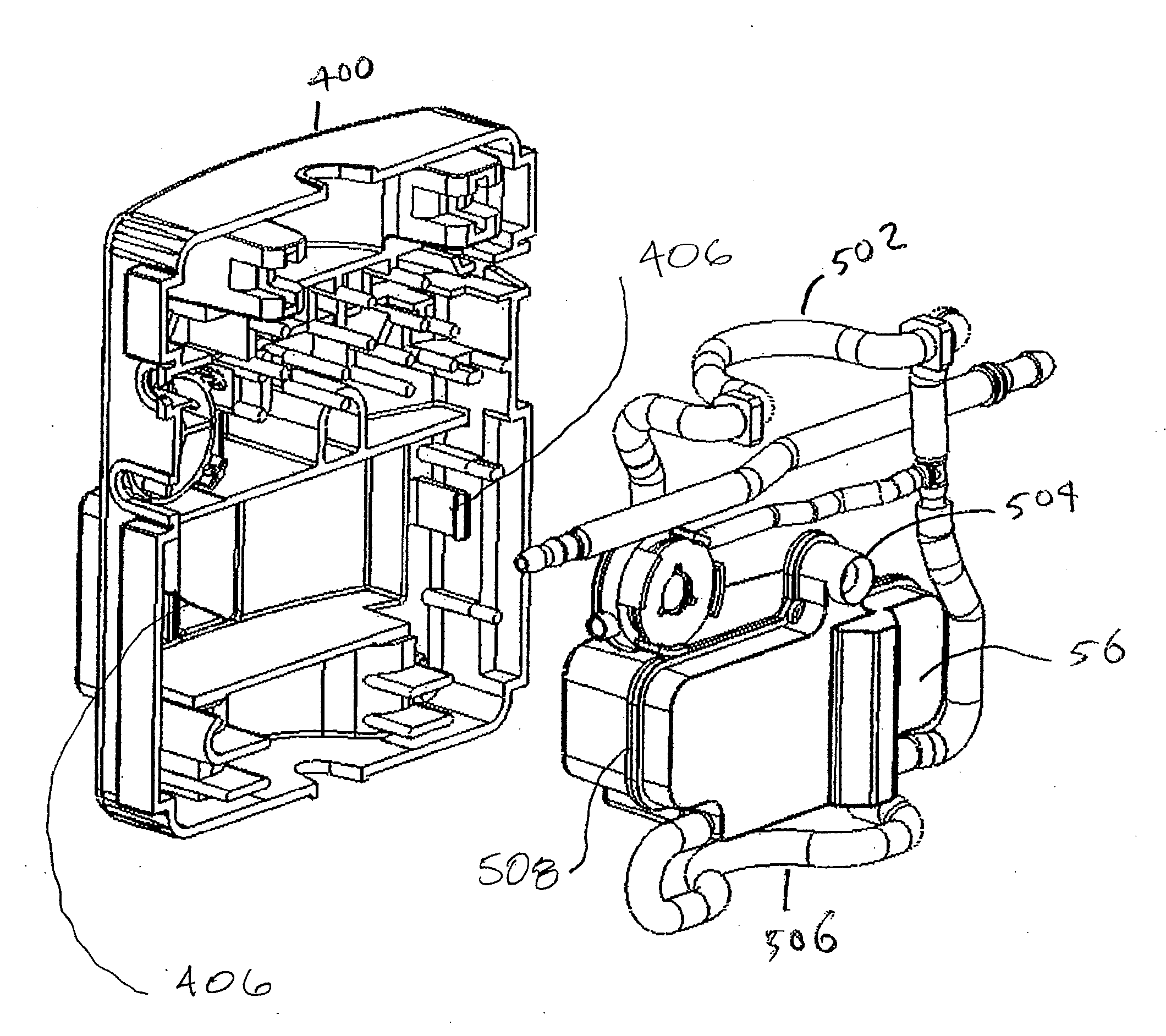
Holding tank devices, systems, and methods for surgical fluidics cassette
The present invention is generally directed to improved methods, devices, and systems for eye surgery. In some embodiments, the invention may provide new and / or improved devices, systems, and methods for detecting surgical fluids in a fluidics cassette, particularly cassettes which are used to couple an eye treatment probe to an eye treatment console. Rather than relaying on internal reflection by a gas-liquid interface, the fluid detection techniques described herein may make use of the changes in propagation of light through a portion of the holding tank when the portion varies between empty and full. For example, light may propagate directly through the holding tank portion when there is no surgical fluid, but may be directed away from a light detector when the portion of the holding tank is filled with surgical fluid. As the light may be controllably refracted using the interface between the transparent holding tank material and the surgical fluid, the propagation properties of the light may be more reliably predicted and controlled. While the sensor may not determine the actual liquid level within the holding tank, a plurality of individual liquid detectors may be sufficient to determine when it is appropriate to (for example) turn drain pumps on and off, when the holding tank is in danger of being overfilled, and the like. Other aspects of the invention may provide devices, systems, and methods for producing different types of fluidics cassette using a single cassette body type.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Method, apparatus and system for a water jet
A water jet instrument may be used for manually performing eye surgery such as, cataract, or perform micro-surgery (remove cartilage), or any emulsification technique. The water jet instrument may be manually controlled or controlled by a system with a robotic control. The water jet apparatus defines a jet cutting area that is based at least in part on a flow rate meter and a feedback loop.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
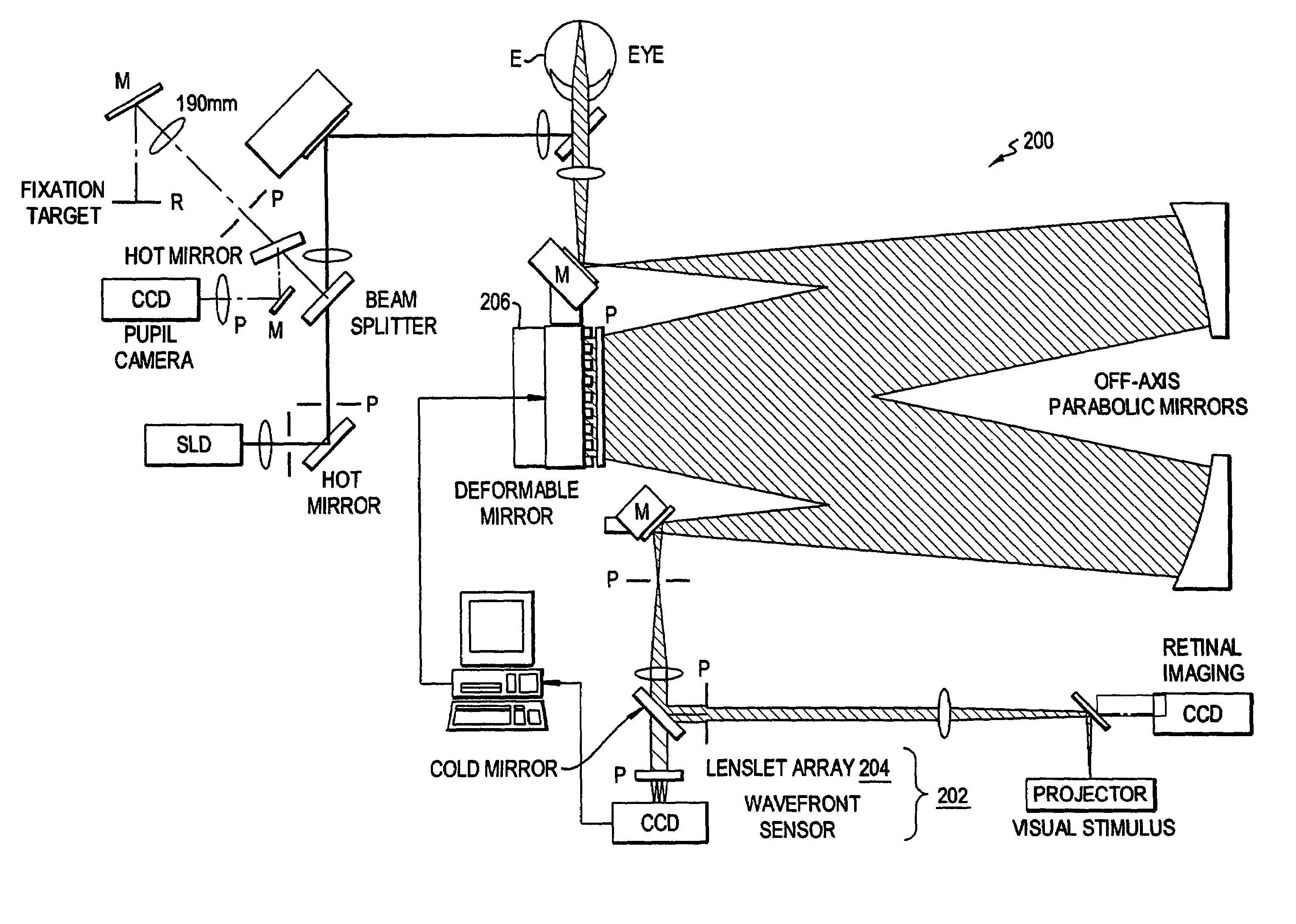
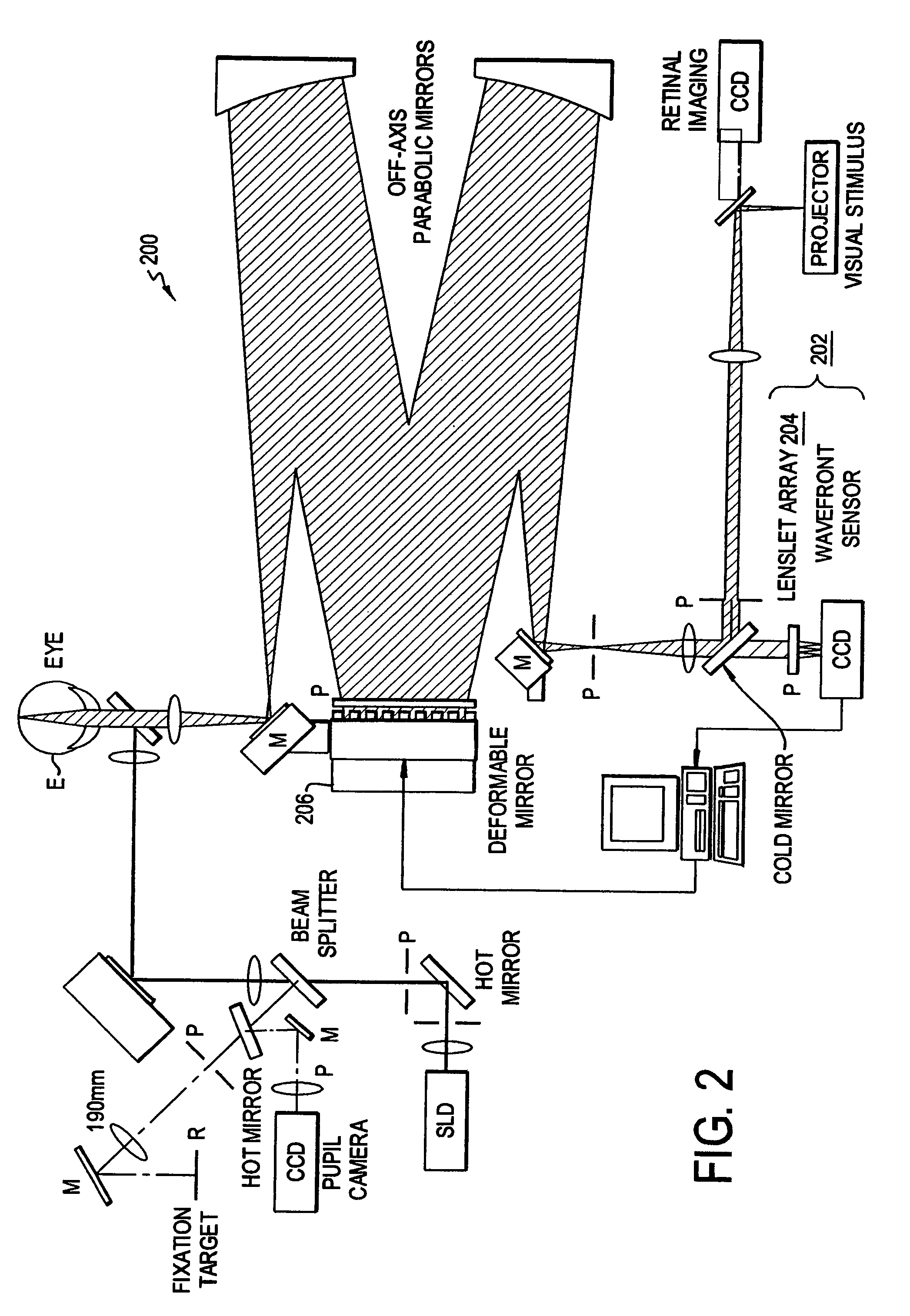
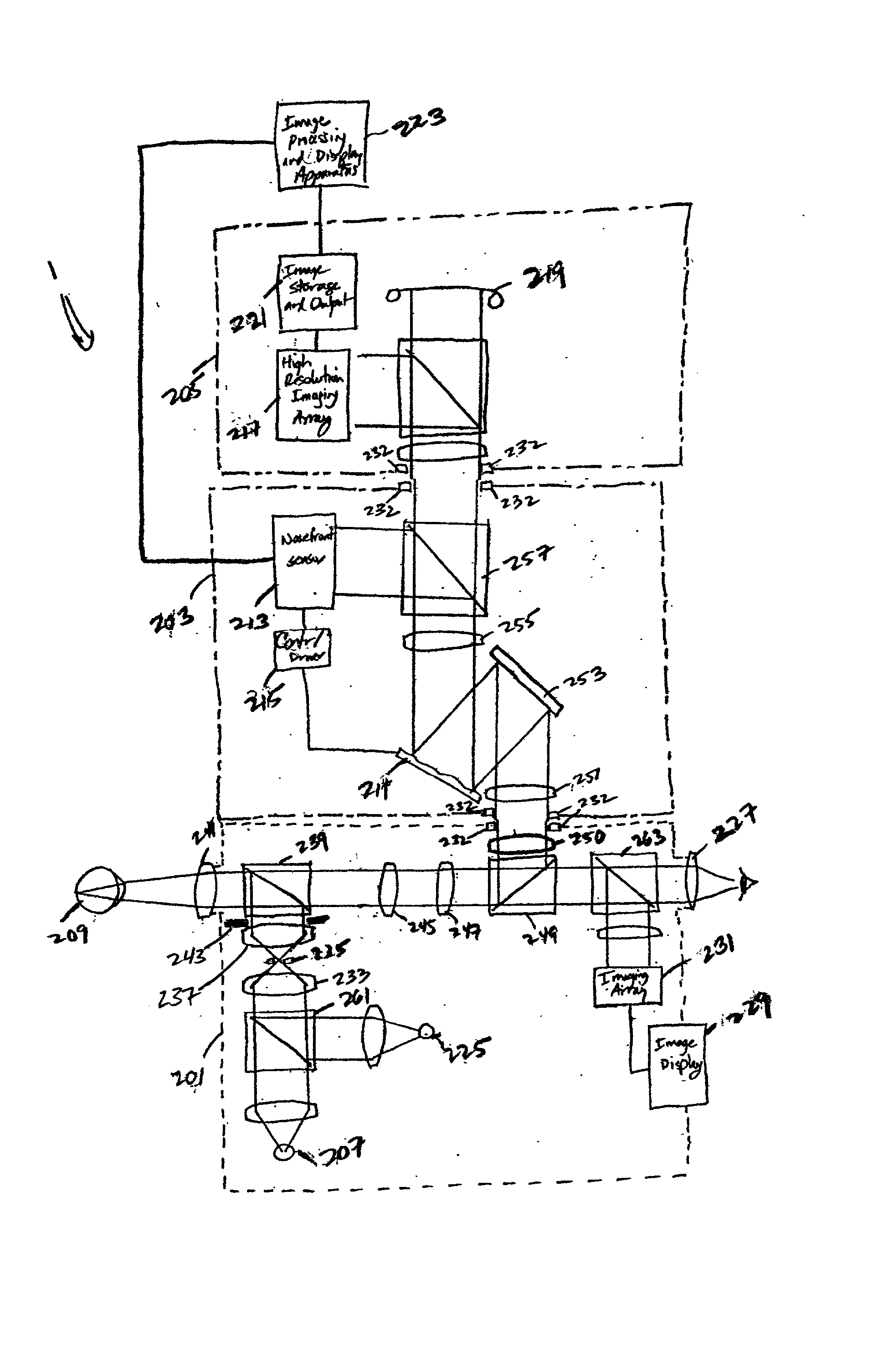
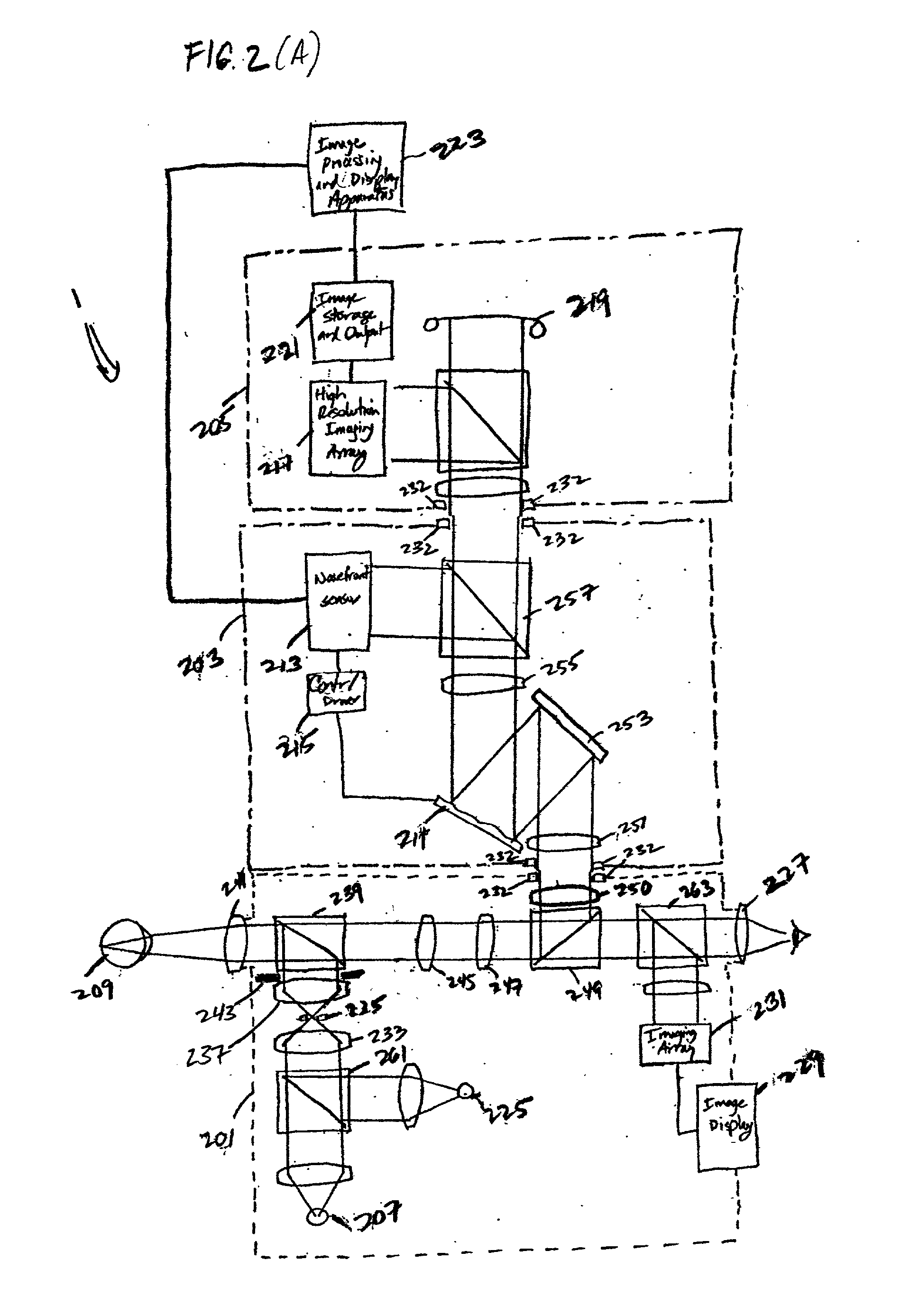
Ophthalmic imaging instrument having an adaptive optical subsystem that measures phase aberrations in reflections derived from light produced by an imaging light source and that compensates for such phase aberrations when capturing images of reflections derived from light produced by the same imaging light source
An improved ophthalmic imaging instrument including a wavefront sensor-based adaptive optical subsystem that measures phase aberrations in reflections derived from light produced by an imaging light source and compensates for such phase aberrations when capturing images of reflections derived from light produced by the same imaging light source. The high-resolution image data captured by the improved ophthalmic imaging instrument can be used to assist in detection and diagnosis (such as color imaging, fluorescein angiography, indocyanine green angiography) of abnormalities and disease in the human eye and treatment (including pre-surgery preparation and computer-assisted eye surgery such as laser refractive surgery) of abnormalities and disease in the human eye.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
Microscope magnification sensor
InactiveUS20050094262A1Maintain positionLaser surgeryDiagnosticsMicroscopic observationDisplay device
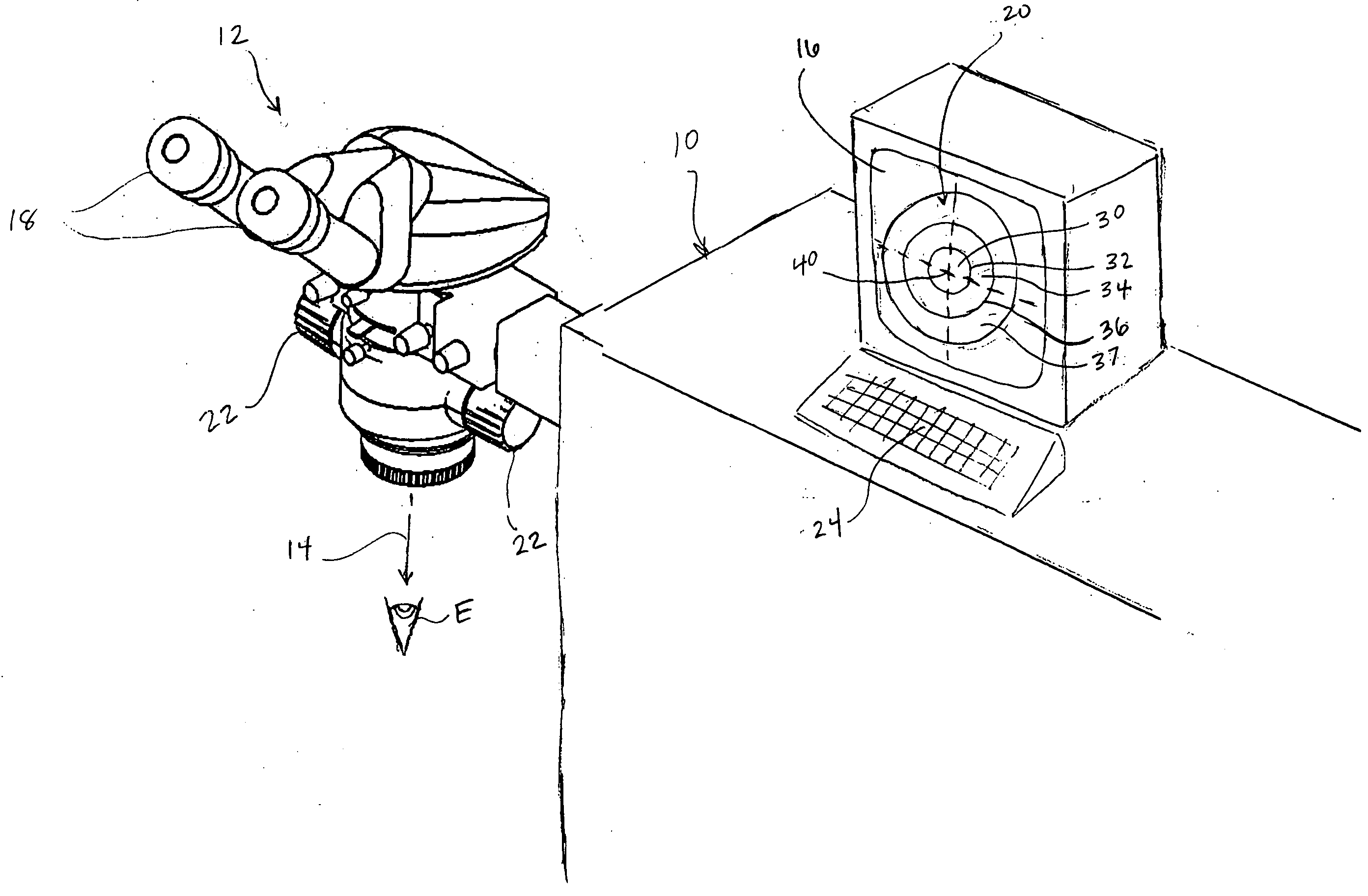
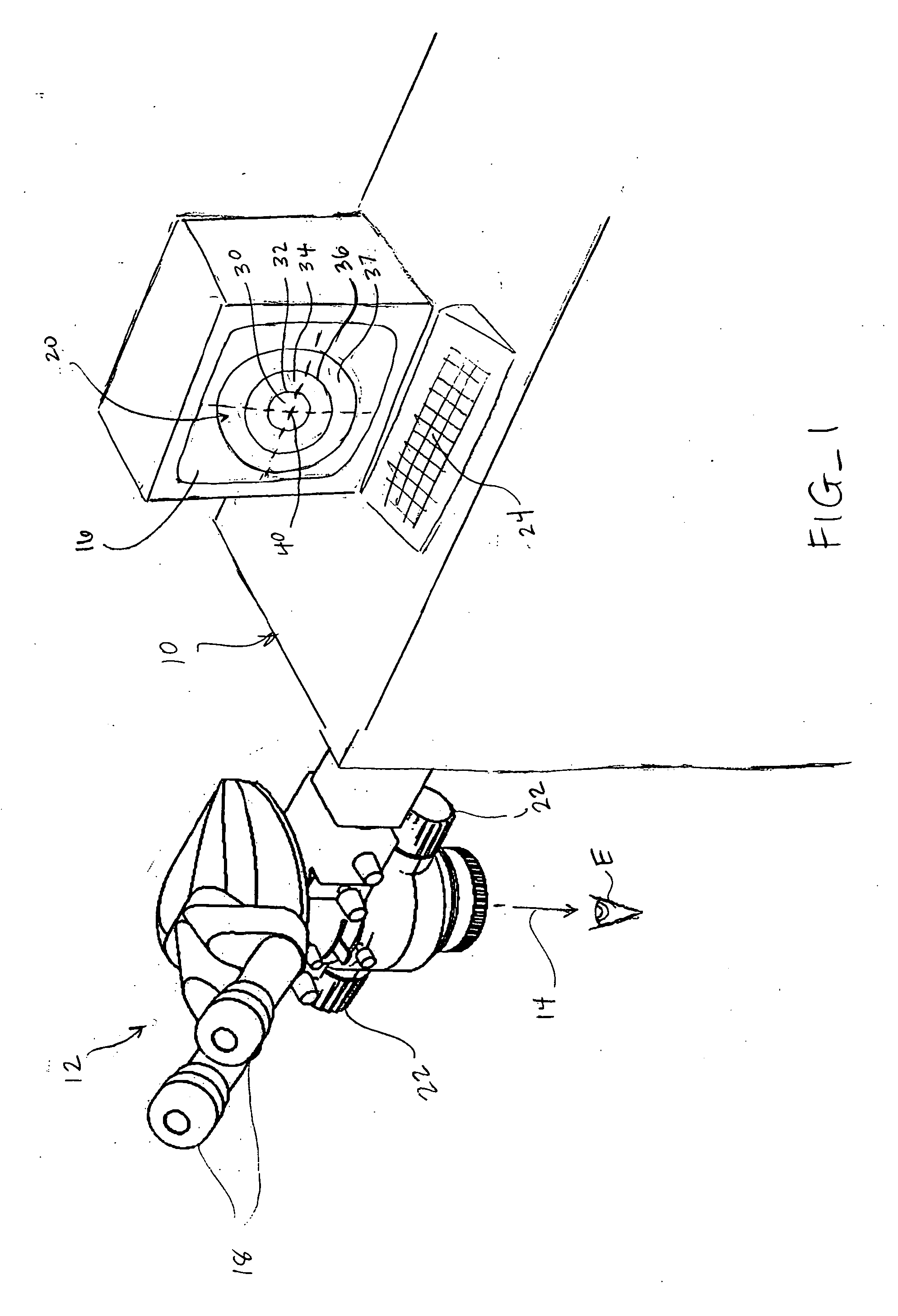
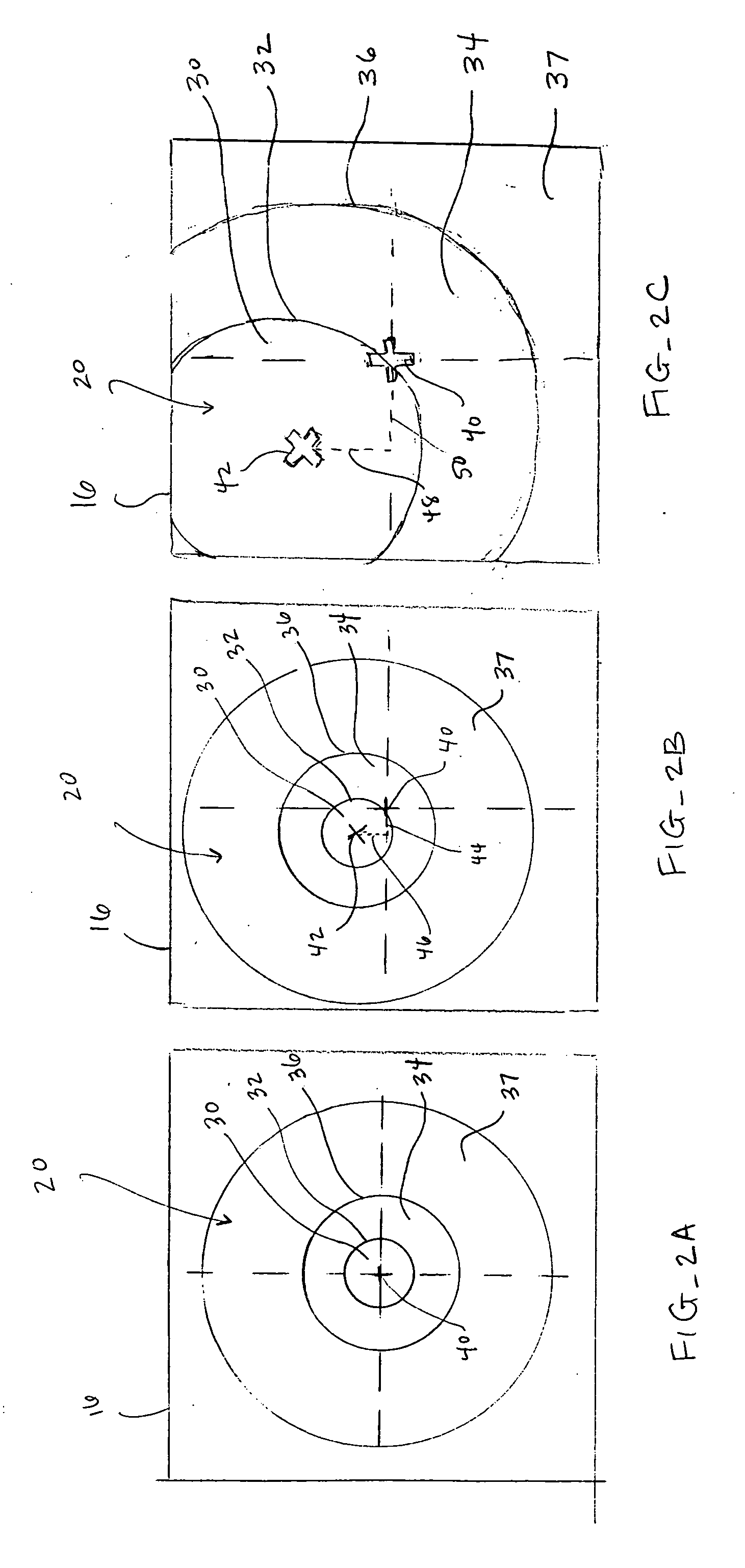
Devices, systems and methods for scaling the size and / or position of a marker on a magnified image of an object. In preferred embodiments, the object is an eye that is undergoing laser eye surgery. The eye is viewed through a magnification system or microscope and an image of the eye is presented on a display. One or more markers are present on the image, each identifying a specific target location or landmark on the eye. When a desired magnification setting is selected, the image is scaled accordingly. In addition, one or more of the markers is scaled in size and / or position to reflect the magnification setting. This allows the marker to maintain identification of the target location while reflecting the selected magnification level.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Beam position monitoring for laser eye surgery
InactiveUS6864478B2Improve safety and successInhibit unwanted ablationLaser surgeryPhotometry using reference valueLight beamImproved method
Improved methods, apparatus and systems for monitoring laser beam position enhance the safety and efficacy of laser eye surgery systems. The present invention will advantageously be used in laser eye surgery where accurate control of the laser beam is crucial for patient safety and successful vision correction. In one embodiment, a first beam of laser energy is directed through a scanning mechanism toward an eye to ablate the eye, and a second beam of laser energy is directed through the scanning mechanism toward a sensor. When the scanning mechanism is moved by a laser eye surgery system to move the first beam across the eye, the scanning mechanism also moves the second beam across the sensor. Movement of the beam across the sensor can be used to monitor movement of the first beam across the eye. If actual movement of the first beam across the eye does not match desired movement of the beam, one or more components of the laser surgery system will shut down in order to stop the laser eye surgery procedure, thus preventing undesirable ablation of the eye.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Intrastromal Refractive Correction Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20070219543A1Quickly and accurately inciseSignificant changeLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorTarget surface
Devices, systems, and methods for laser eye surgery selectively ablate tissues within the cornea of an eye along one or more target surfaces, so that corneal tissue bordered by the laser incision surface(s) can be mechanically removed. An appropriate tissue-shaping surface can be selected based on the regular refractive error of the eye, and a shape of the target laser surface(s) can be calculated so as to correct irregular refractive errors of the eye, impose desired additional sphero-cylindrical and / or irregular alterations.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
System and method for corneal astigmatic axis marking
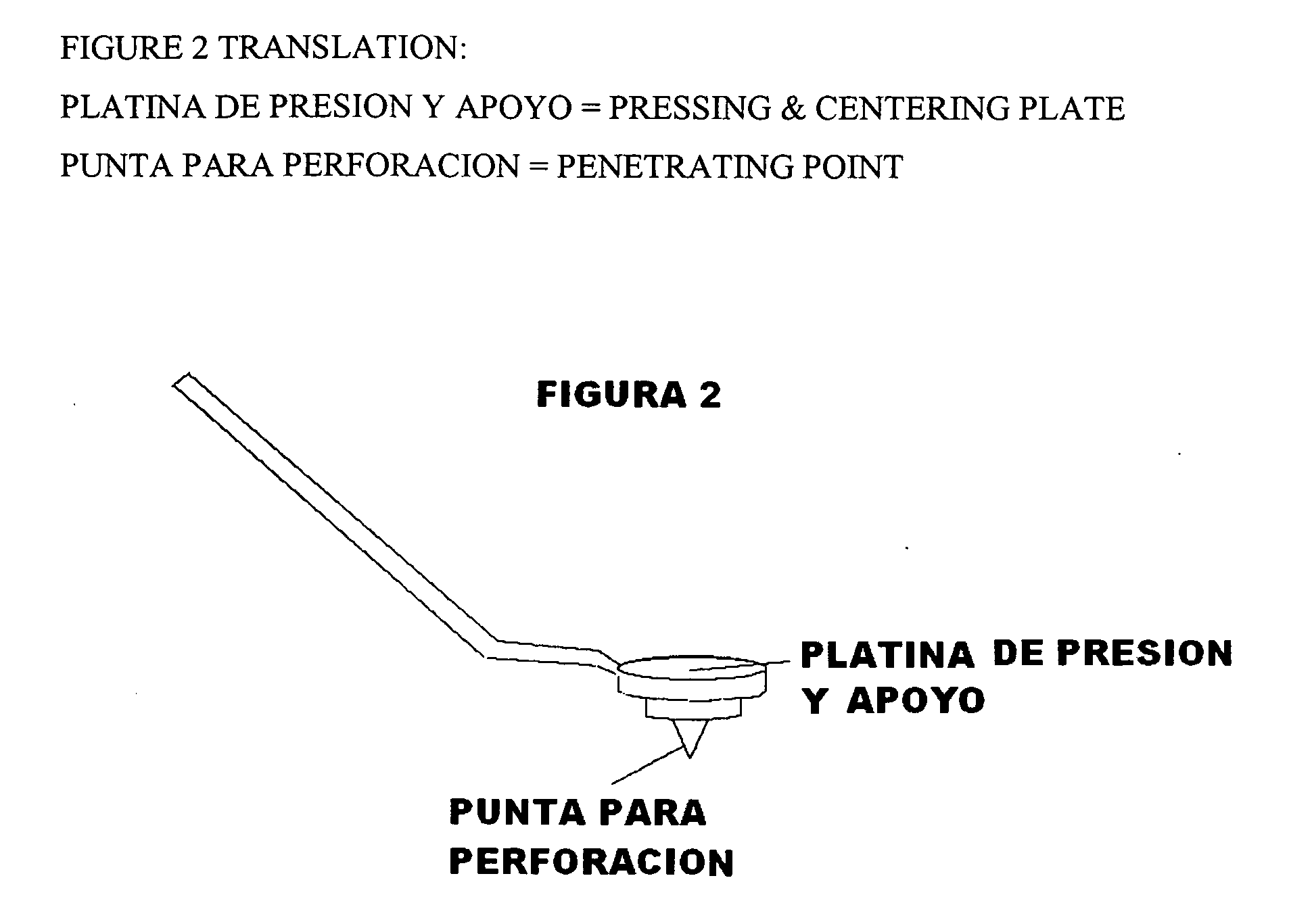
The present invention includes a corneal marker having an adjustable element providing for orientation of the marker to the astigmatic axis of a patient's eye under examination, a handle secured to the corneal marker and a stem secured to and extending below the handle. The stem is weighted to facilitate alignment of the corneal marker to the corneal surface of the patient's eye under examination during corrective eye surgery according to the corneal light reflex from the eye in response to an illumination source.
Owner:DAVIS ANDREW
Intrastromal refractive correction systems and methods
InactiveUS20090234335A1Quickly and accurately inciseSignificant changeLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorTarget surface
Devices, systems, and methods for laser eye surgery selectively ablate tissues within the cornea of an eye along one or more target surfaces, so that corneal tissue bordered by the laser incision surface(s) can be mechanically removed. An appropriate tissue-shaping surface can be selected based on the regular refractive error of the eye, and a shape of the target laser surface(s) can be calculated so as to correct irregular refractive errors of the eye, impose desired additional sphero-cylindrical and / or irregular alterations.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
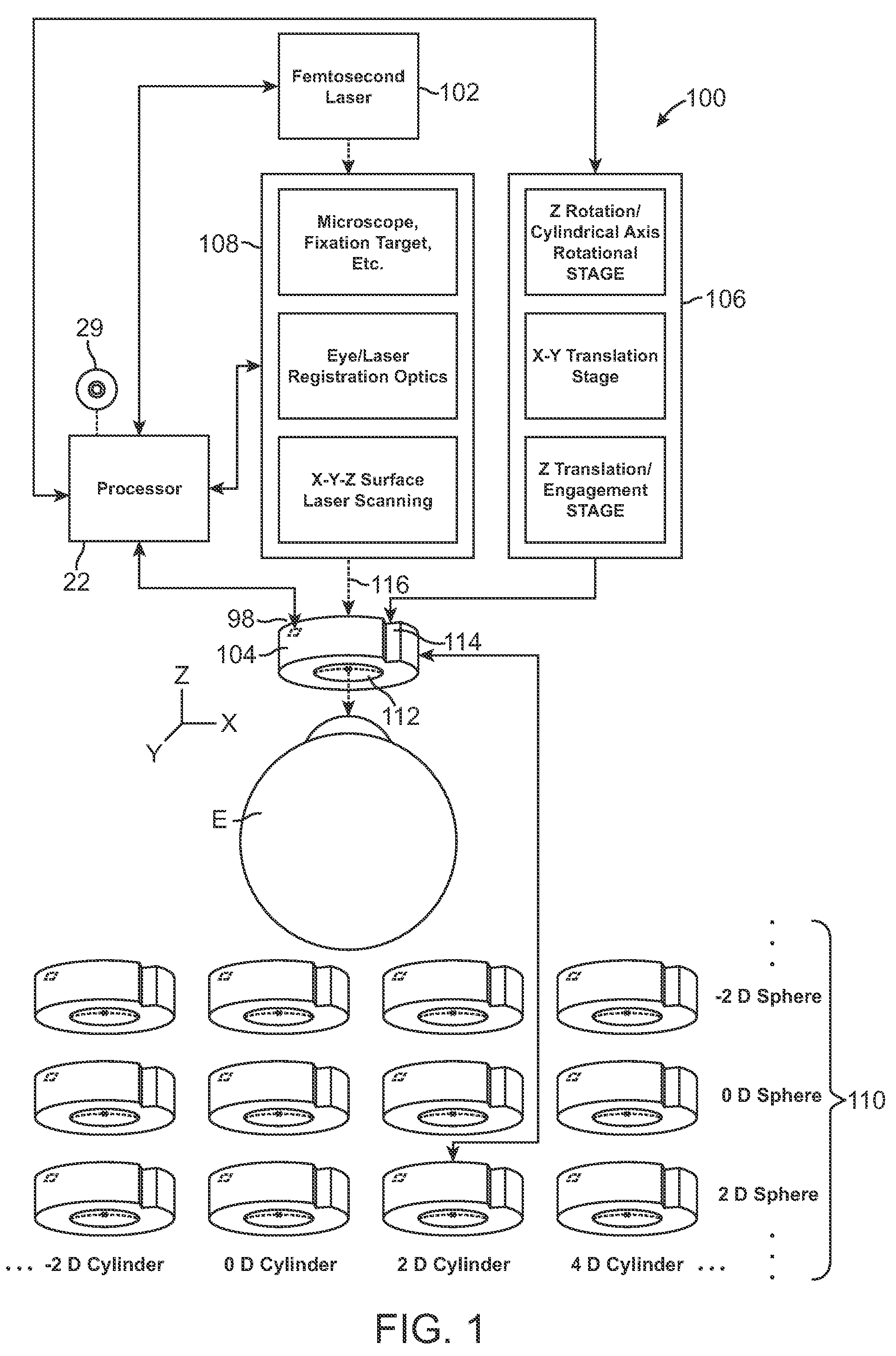
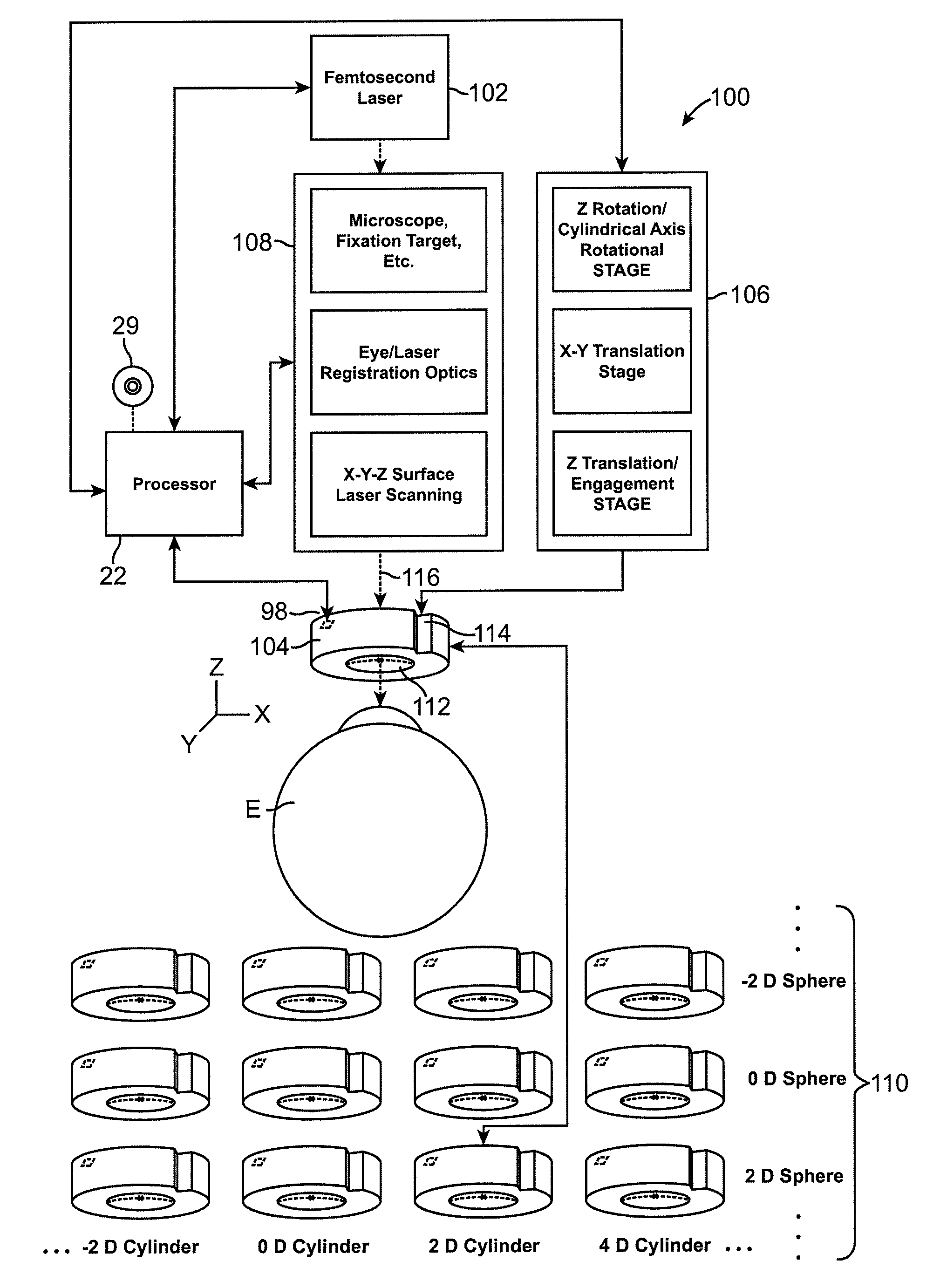
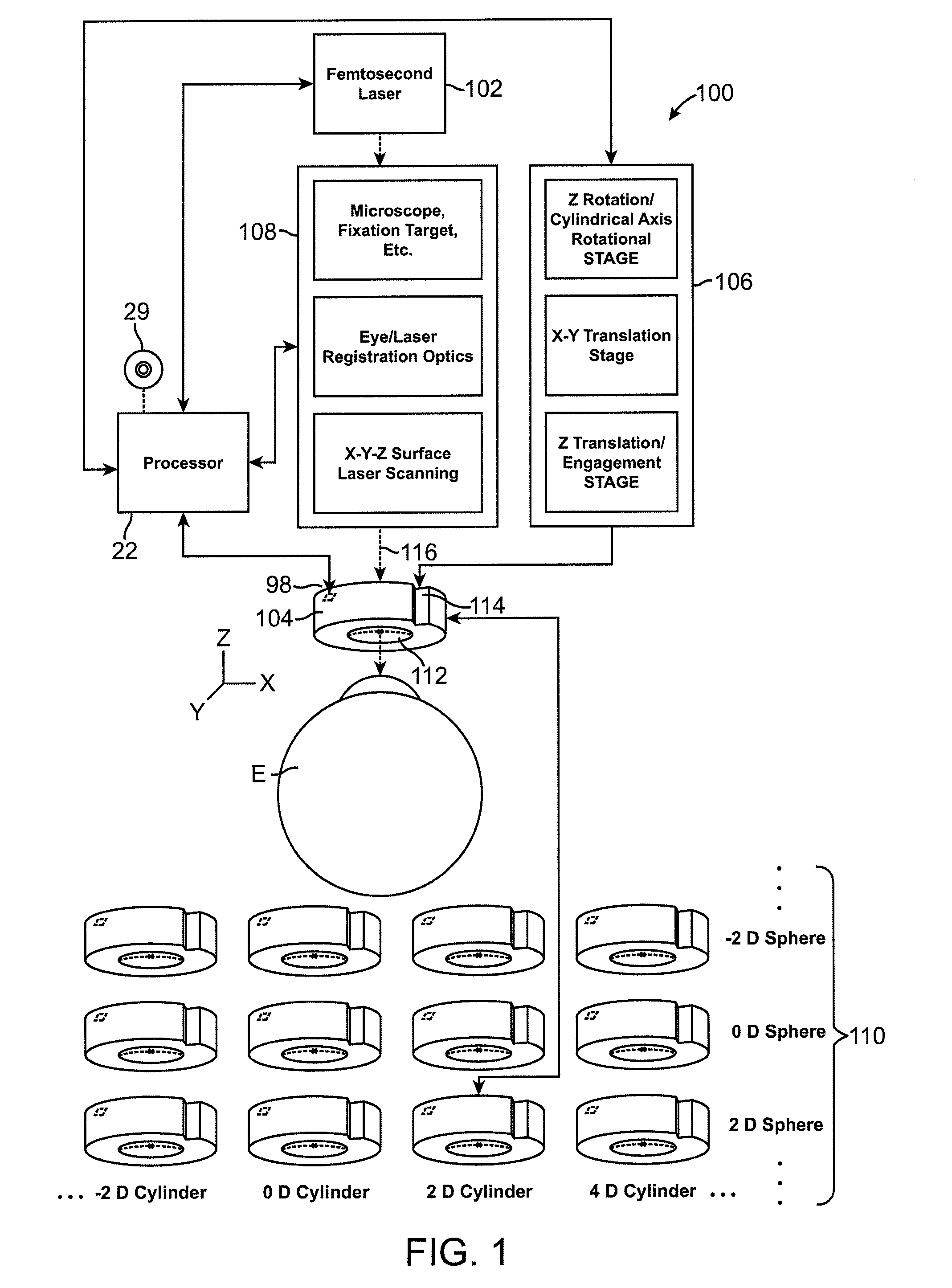
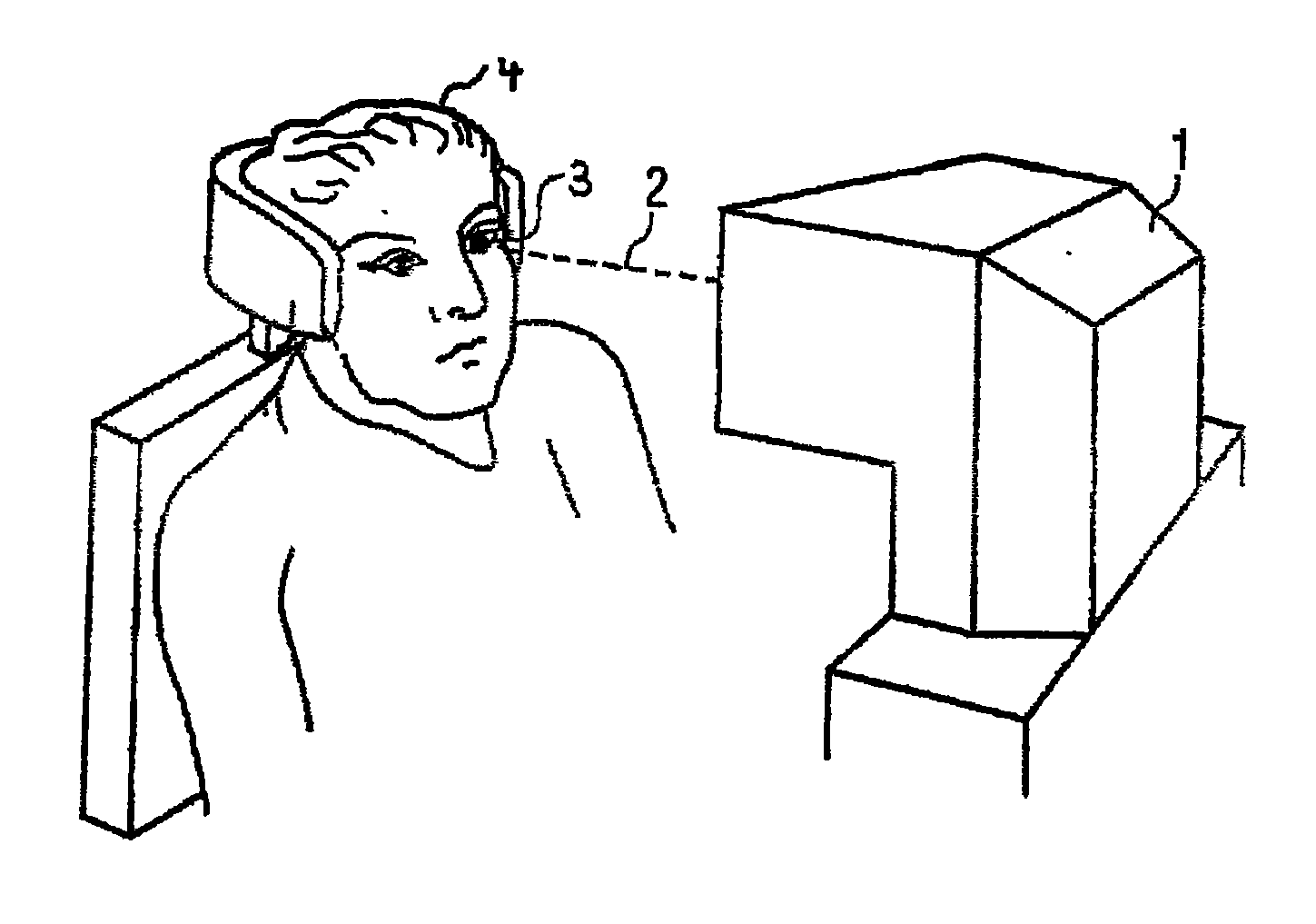
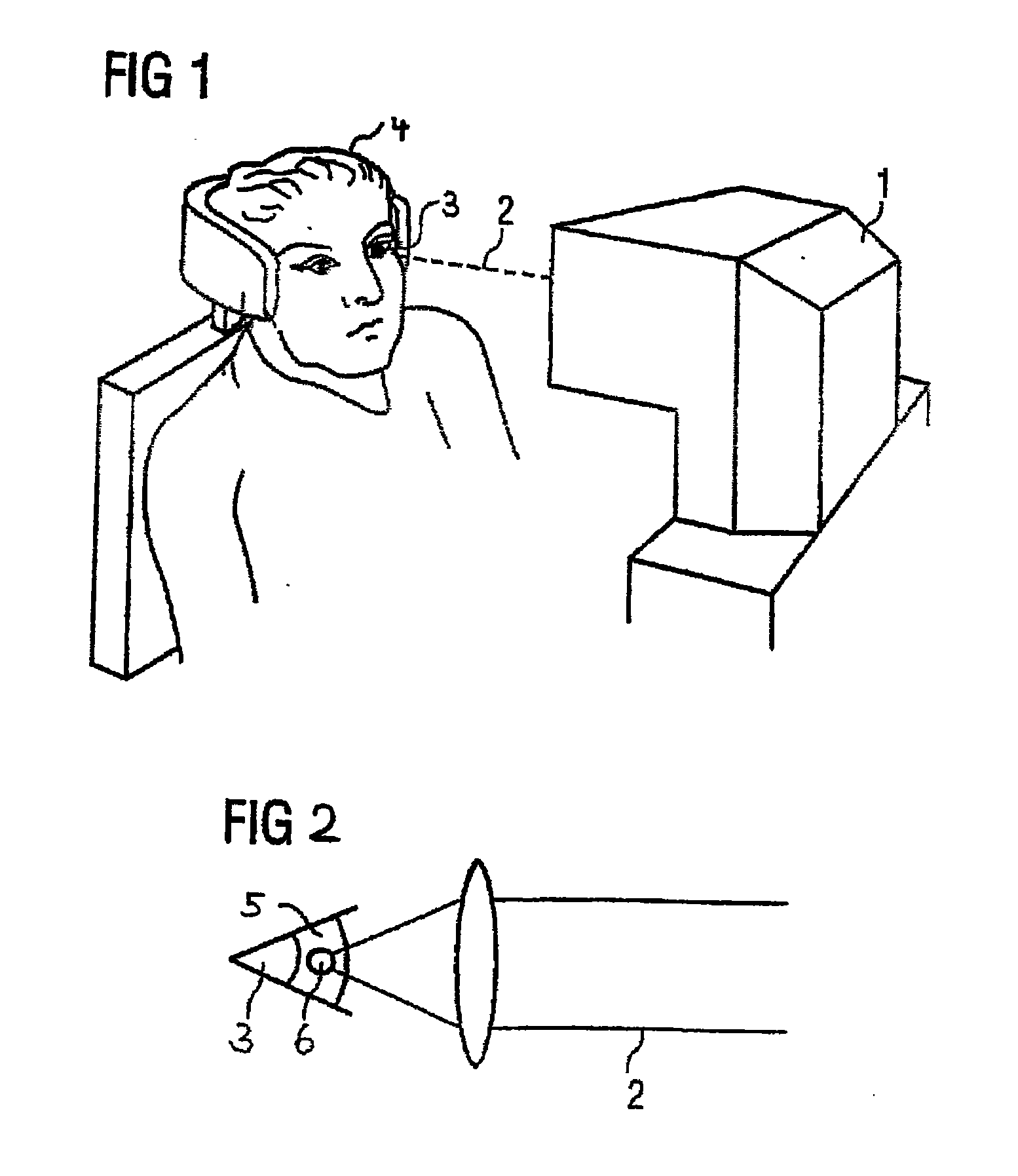
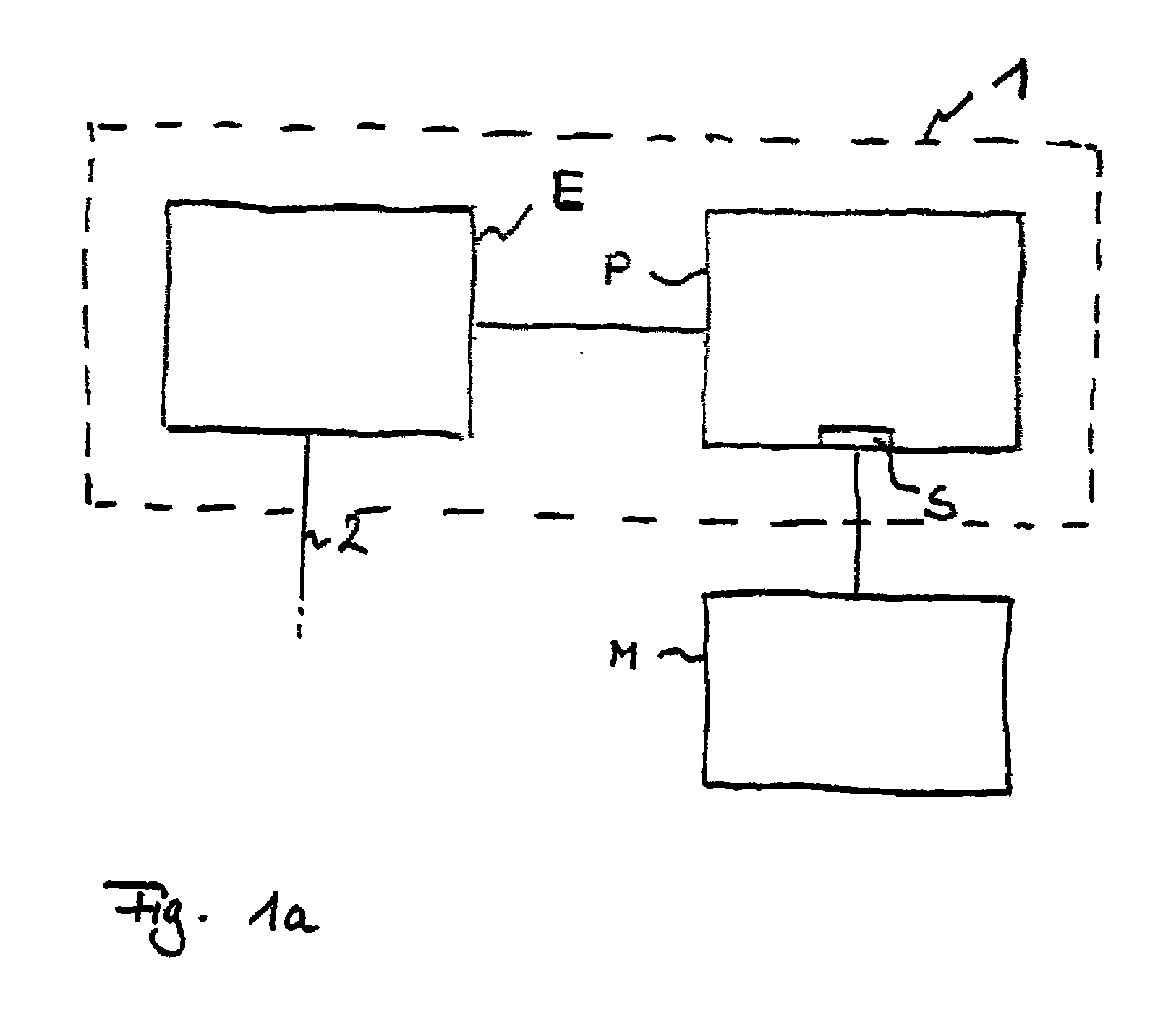
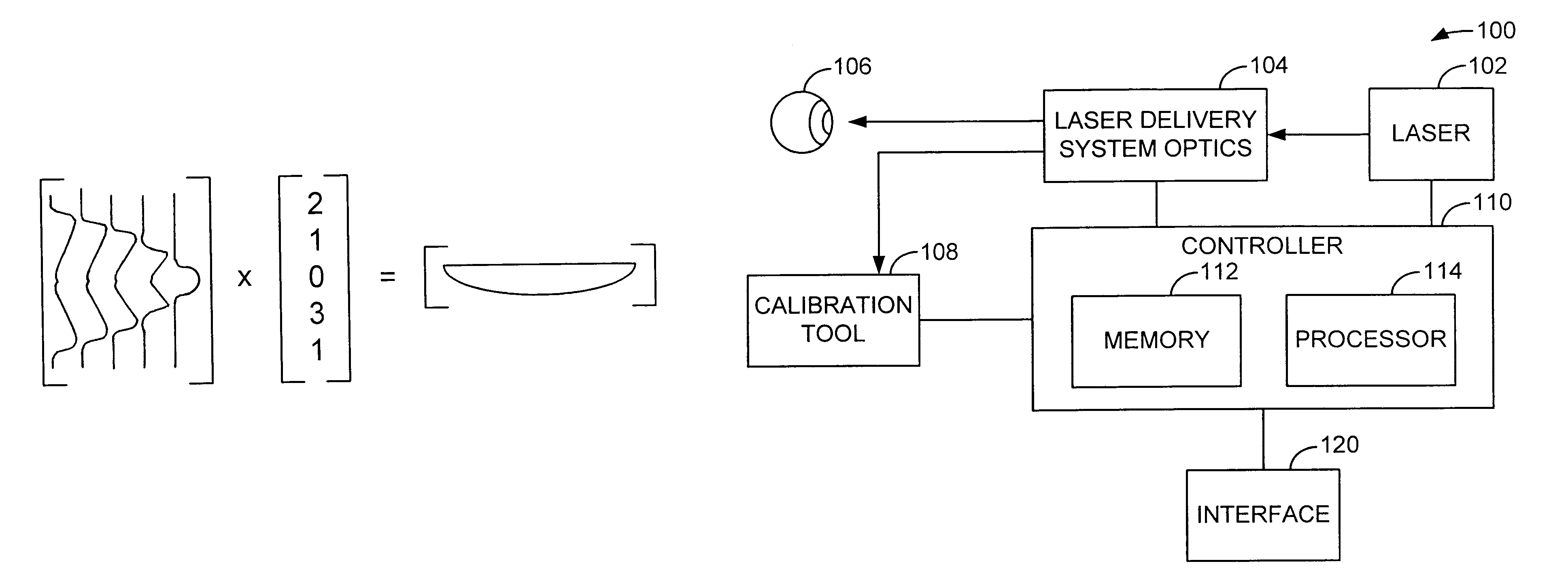
Method for generating control data for eye surgery, and eye-surgical treatment device and method
ActiveUS20110034911A1Precise laser-surgery operation resultConsiderable deformationLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsSurgical operationSurgical treatment
A method for generating control data for an eye-surgical treatment device, which separates tissue layers in the eye cornea by application of a laser device, wherein a contact glass having a contact surface deforms the cornea to conform to the shape of the contact surface during the operation of the laser device. The contact surface is first placed on a cornea apex at a contact surface apex and is then pressed against the same for deforming the cornea. The method includes: generating the control data of the laser device such that the data specifies coordinates of target points located in the cornea for the laser device, and upon generation of the target point coordinates the deformation of the cornea which is present during the operation of the laser device as a result of the contact glass is taken into consideration. The invention provides that the several steps are carried out in consideration of the deformation in order to determine a displacement of a point P in the undeformed cornea caused by the deformation.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
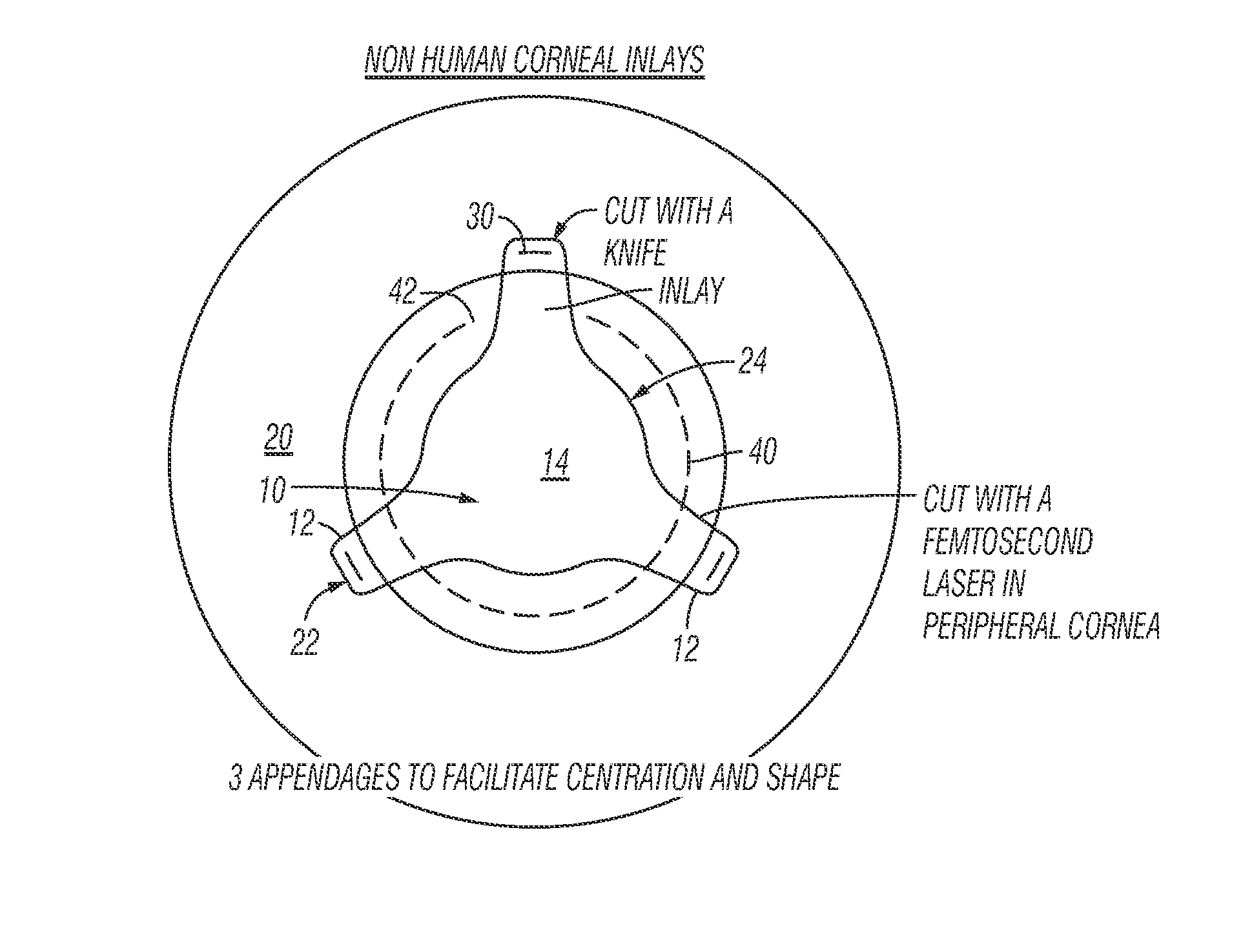
Method for preparing corneal donor tissue for refractive eye surgery utilizing the femtosecond laser
InactiveUS20140155871A1High precisionKeep clearLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFiberCross-link
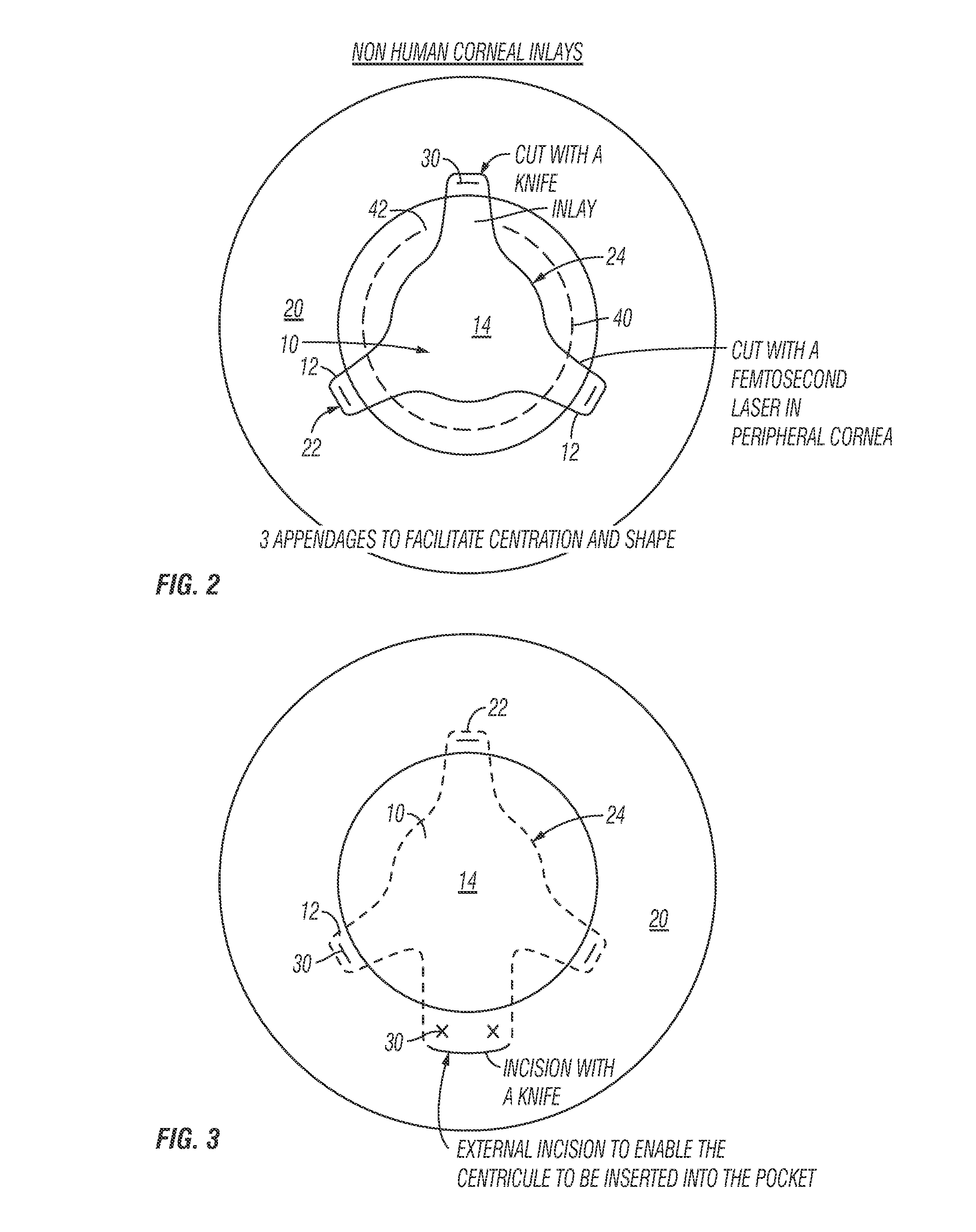
A method of accurately fabricating a non-human donor corneal tissue for implantation into a recipient human cornea, the method comprising the steps of: removing corneal tissue from a donor with a femtosecond laser; placing the corneal tissue in a fixative solution for a selected time interval to cross-link the collagen fibrils in the tissue and prevent swelling of the corneal tissue; and shaping the tissue to provide a conical inlay of a selected shape and thickness having one or more radial extensions. The method is such that the corneal inlay may be attached to the peripheral corneal and / or the sclera. The method is such that the corneal inlay may be stored for a period of up to two years prior to attachment.
Owner:CUMMING JAMES STUART
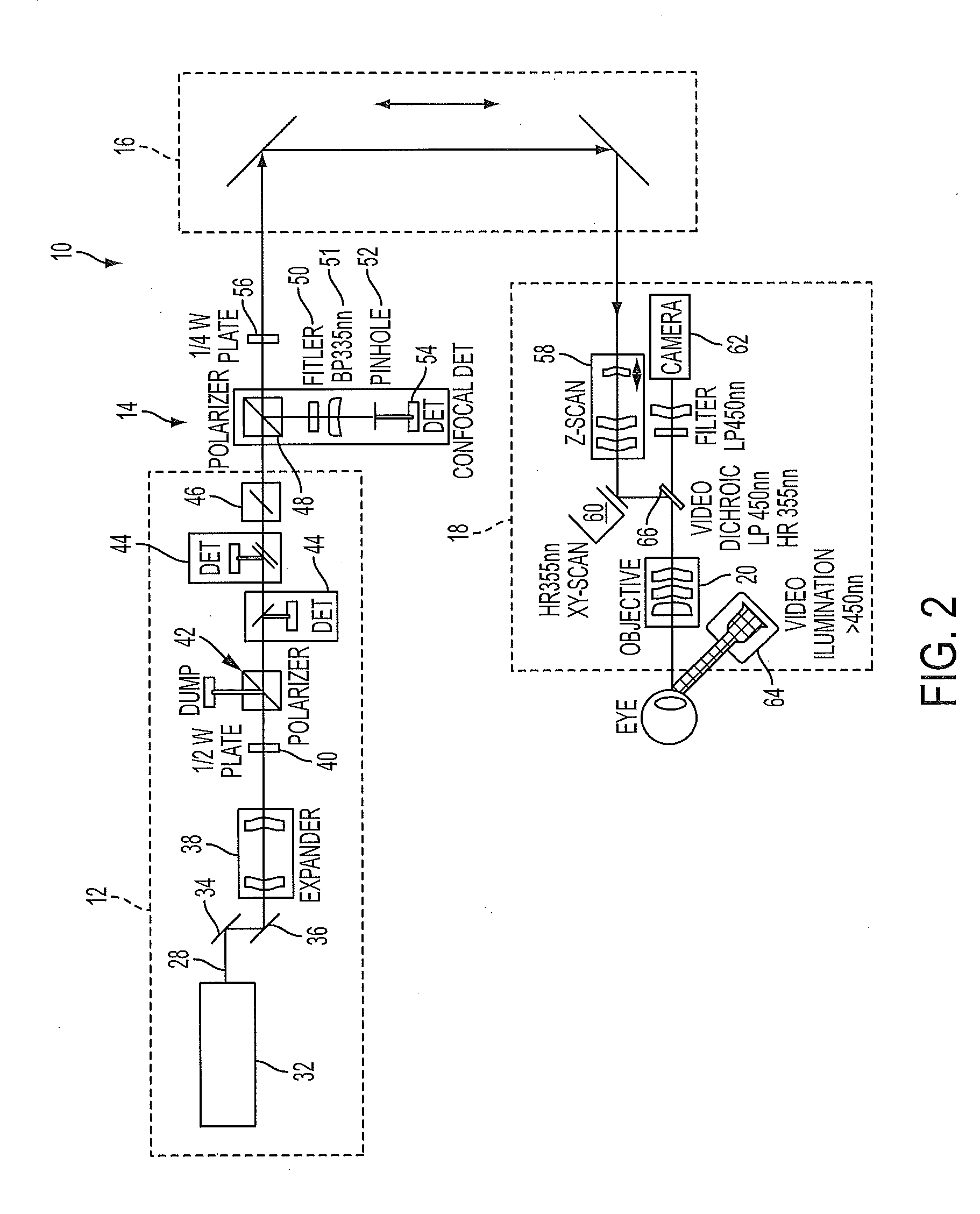
Confocal laser eye surgery system
ActiveUS20150272782A1Increase power levelReduce power levelLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLaser surgeryElectromagnetic radiation
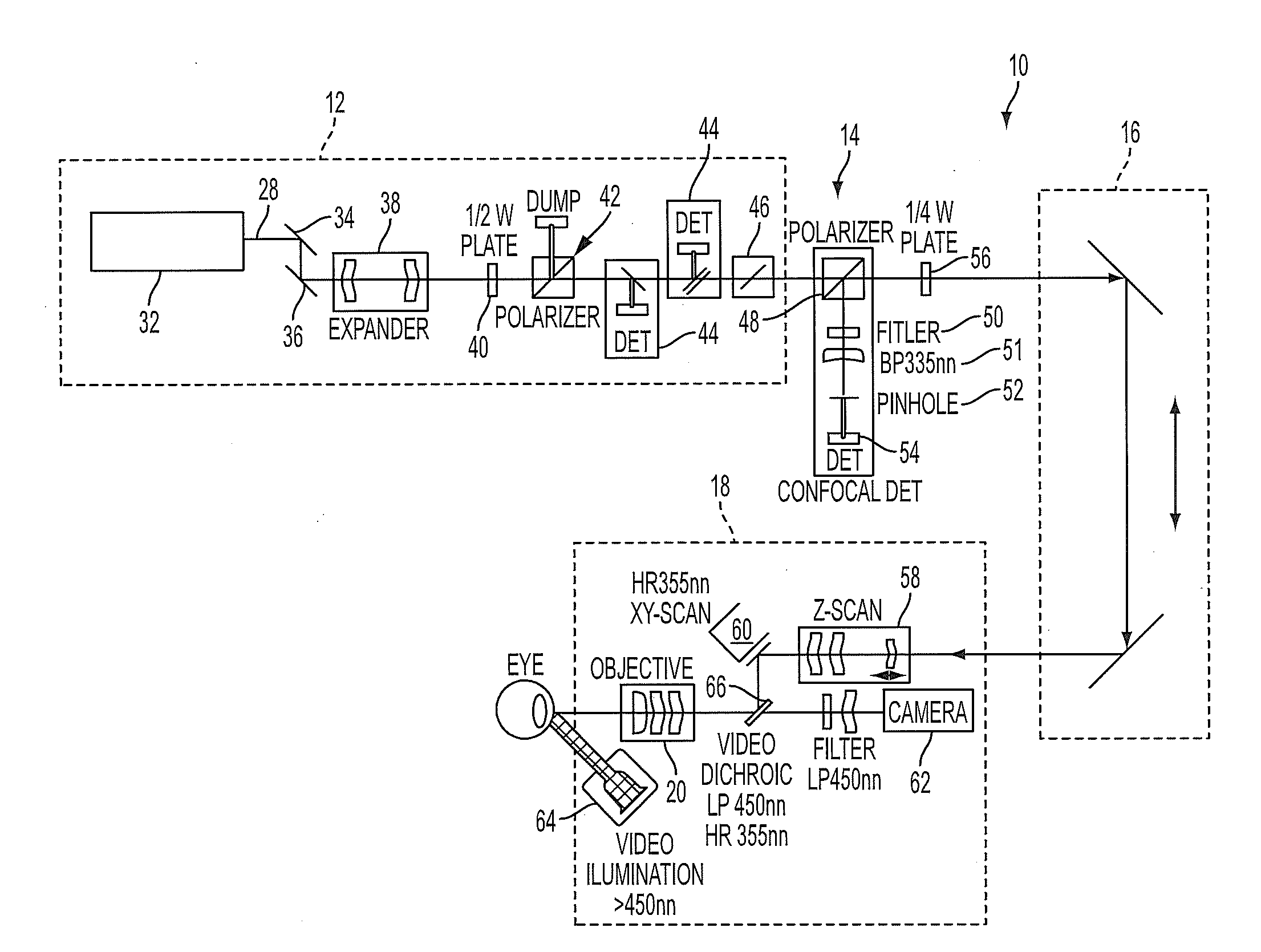
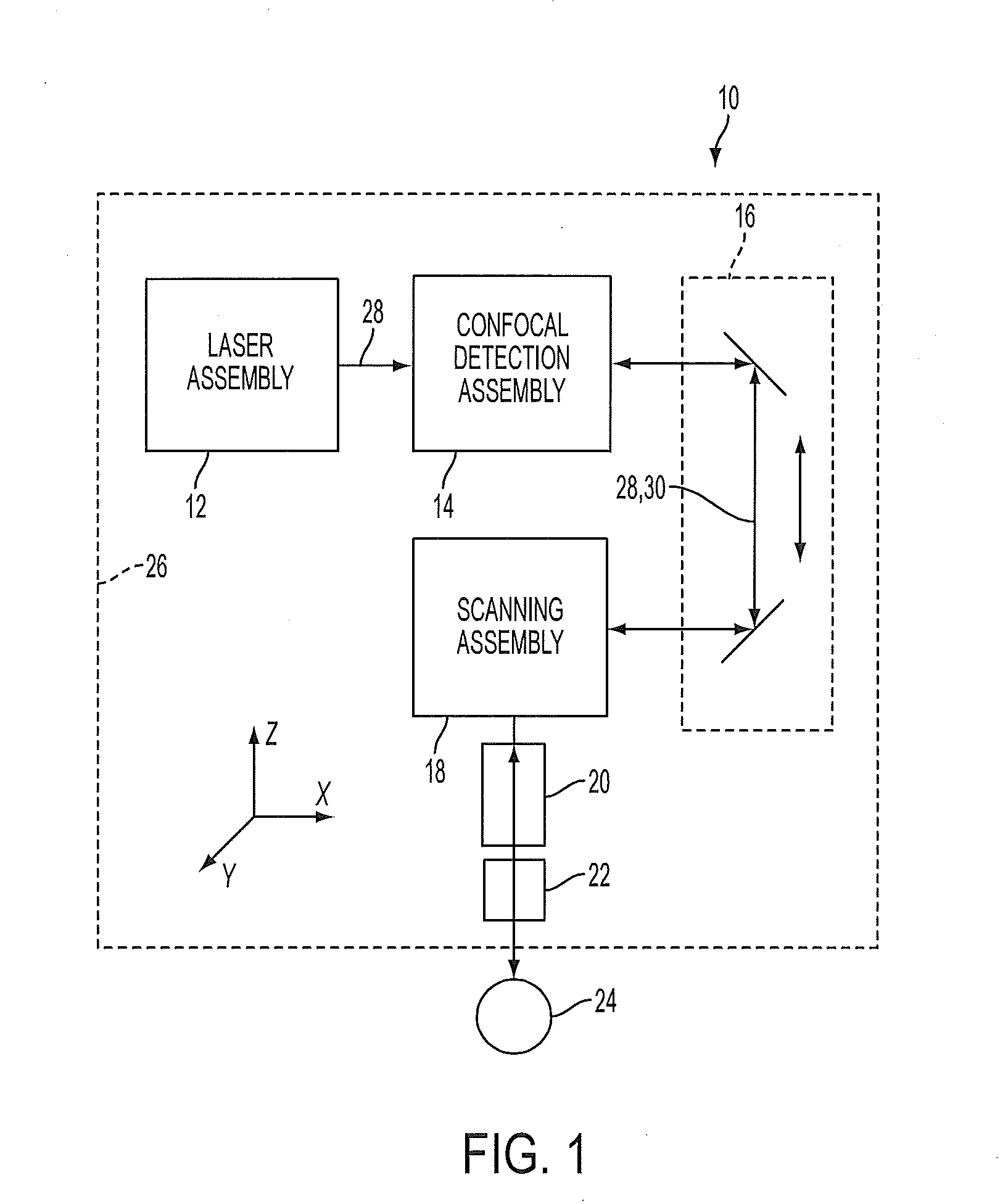
A laser surgery system includes a light source, an eye interface device, a scanning assembly, a confocal detection assembly and preferably a confocal bypass assembly. The light source generates an electromagnetic beam. The scanning assembly scans a focal point of the electromagnetic beam to different locations within the eye. An optical path propagates the electromagnetic beam from a light source to the focal point, and also propagates a portion of the electromagnetic beam reflected from the focal point location back along at least a portion of the optical path. The optical path includes an optical element associated with a confocal detection assembly that diverts a portion of the reflected electromagnetic radiation to a sensor. The sensor generates an intensity signal indicative of intensity the electromagnetic beam reflected from the focal point location. The confocal bypass assembly reversibly diverts the electromagnetic beam along a diversion optical path around the optical element.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Generating scanning spot locations for laser eye surgery
InactiveUS7008415B2Easy to analyzeVariable shapeLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFar-sightednessLens plate
Scanning spot locations are generated for ablating tissue using a scanning laser beam over a treatment region by taking a target function representing a desired lens profile of ablation with a basis function representing a treatment profile produced by overlapping scanning spots in a particular treatment pattern. In some embodiments, the basis function is a two-dimensional function representing a two-dimensional section of a three-dimensional treatment profile, which has symmetry with respect to the two-dimensional section extending along the treatment pattern. For example, the treatment pattern is generally straight for myopic and hyperopic cylinders, and is generally circular for myopia and hyperopia. The fit produces ablation depths for discrete scanning spots, which are used to calculate the number of pulses at each reference position along the two-dimensional section. The pulses are distributed along the treatment pattern to produce the desired overlapping effect.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
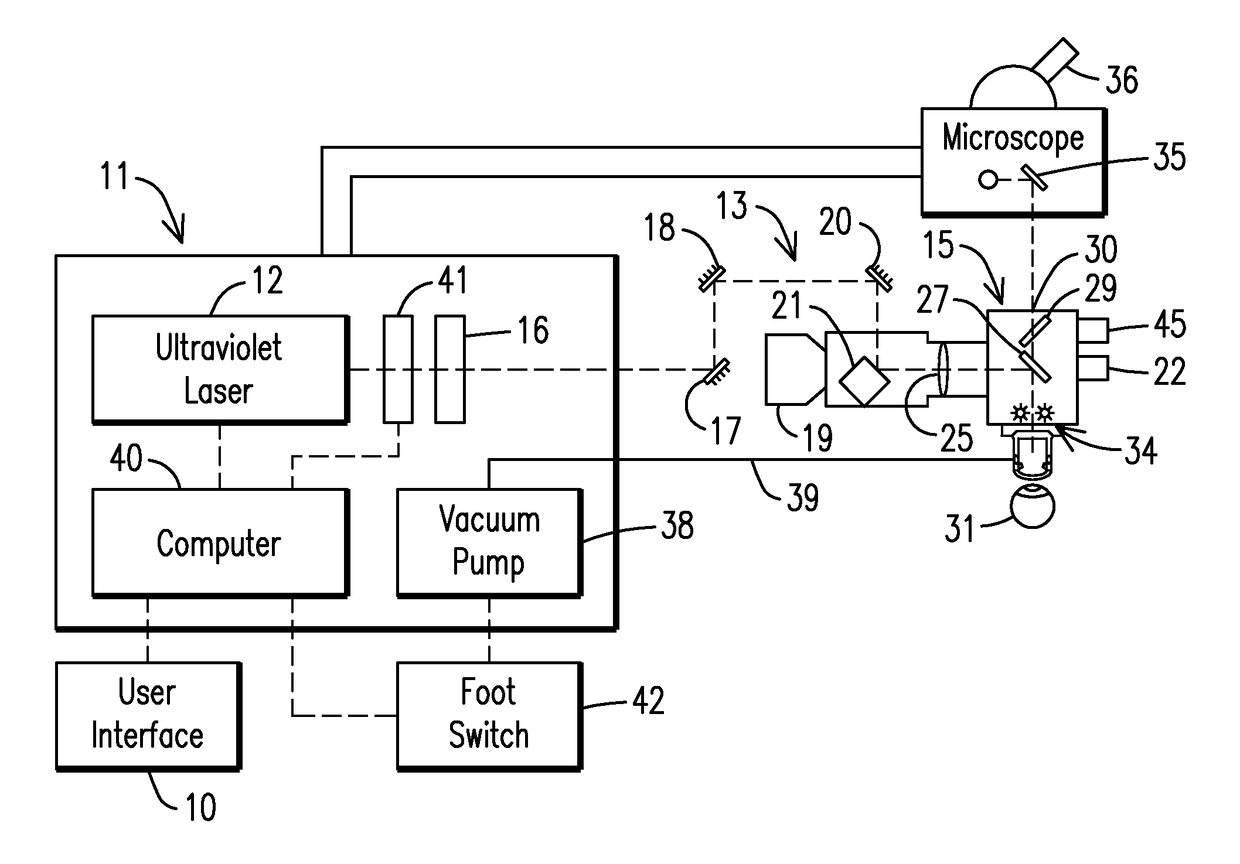
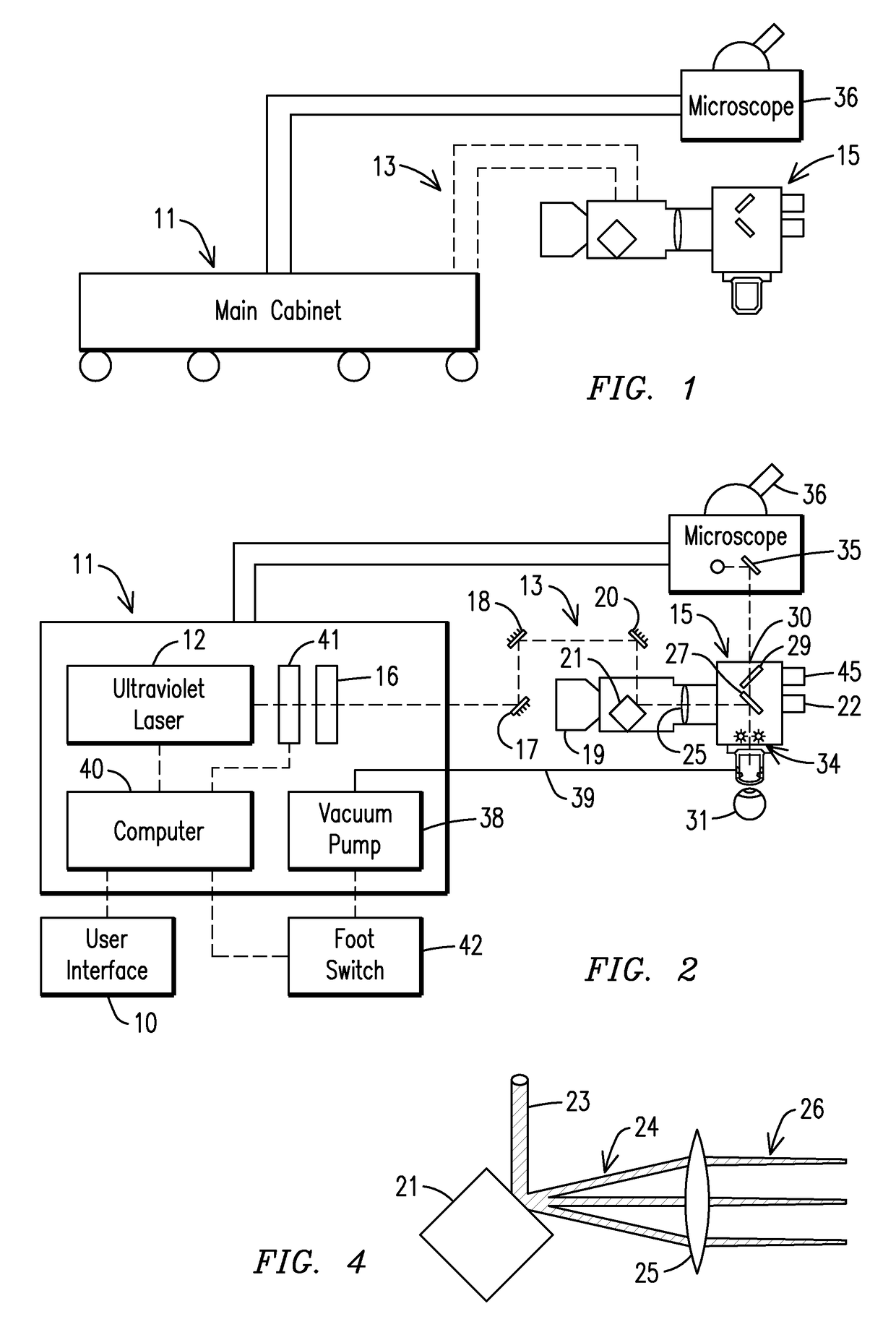
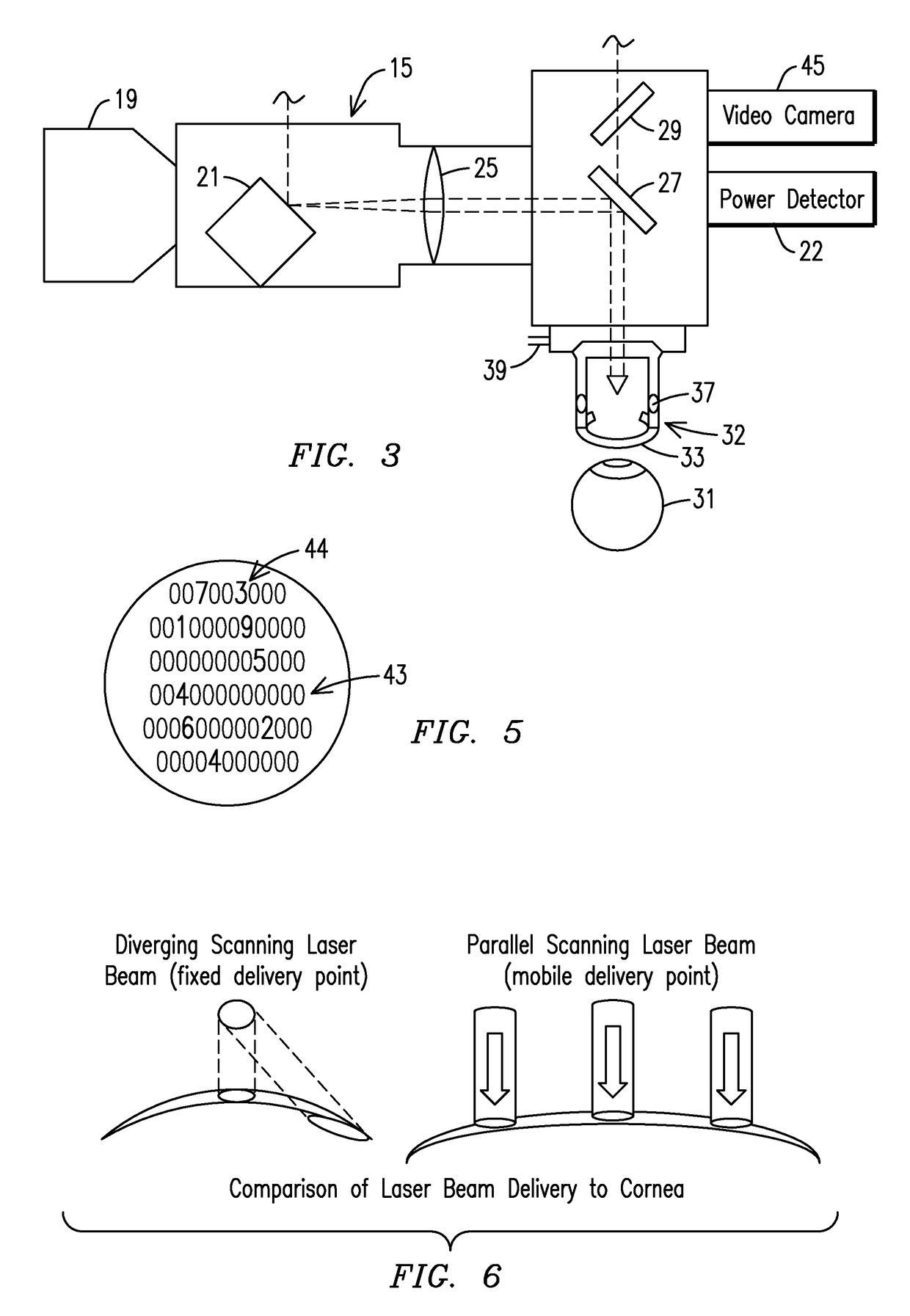
Laser beam ophthalmological surgery method and apparatus
This invention is related to refractive eye surgery and specifically regarding guiding a laser beam through free space using a set of rotatable mirrors to guide said laser beam into a hand piece module that converts the laser beam into a two dimensional random overlapping scanning parallel laser beam that is delivered to the eye for ablation of cornea tissue to reshape the cornea of the eye. The rotating mirror set module allows a hand piece having an eye stabilization and distance control unit to be positioned by the surgeon onto a patient's eye for performing the surgery.
Owner:EXCELSIUS MEDICAL CO LTD
Surgical auxiliary support frame for ophthalmologists
InactiveCN108042306AEasy to useQuick installation and fixingOperating tablesEye treatmentMental stateMusic player
The invention belongs to the technical field of surgical auxiliary tools, and particularly discloses a surgical auxiliary support frame for ophthalmologists. By the aid of the surgical auxiliary support frame, the problem of easiness in shaking due to the sense of fear of patients in eye surgery can be solved. The scheme includes that the surgical auxiliary support frame comprises a bottom plate;a headrest is connected with the center of the top of the bottom plate by bolts, side plates are vertically arranged at two ends of the bottom plate, fixing plates are welded at two ends of the bottoms of certain sides of the two side plates, the certain sides of the two side plates are far away from each other, and electric push rods which are horizontally arranged are connected with the centersof the tops of the two side plates by bolts. The surgical auxiliary support frame has the advantages that the heads of patients can be fixedly clamped by the two electric push rods by the aid of memory sponge mats and can be prevented from shaking in surgery procedures; music can be played by a music player in the surgery procedures, accordingly, nervous mental states of the patients can be eased,and the surgical auxiliary support frame is beneficial to smoothly carrying out surgery on the patients; the eyes of the patients can be illuminated by supplement light by the aid of illumination lamps, accordingly, the surgery can be conveniently smoothly carried out by the ophthalmologists, and eye surgery risks of the ophthalmologists can be reduced.
Owner:赵金亮
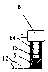
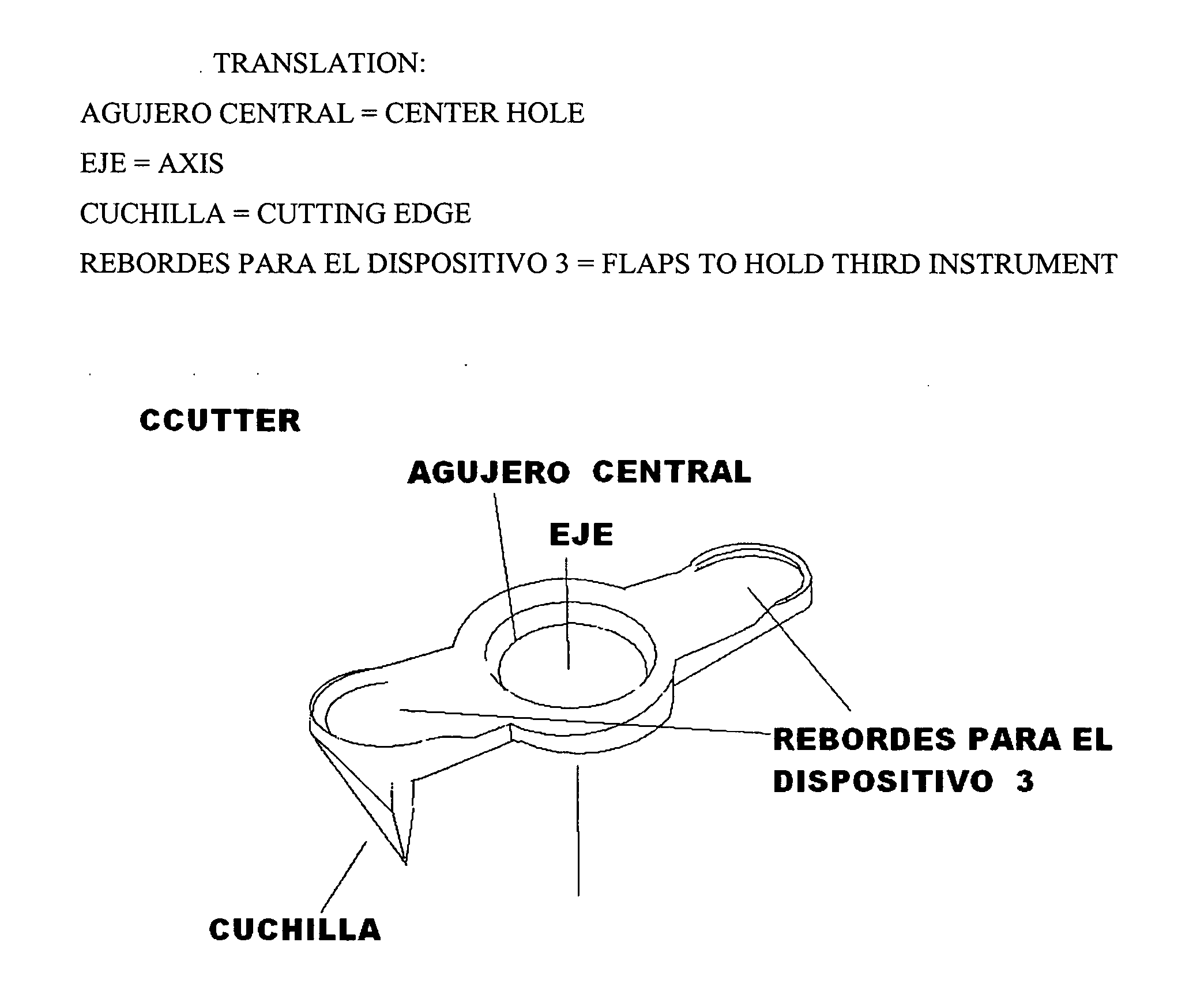
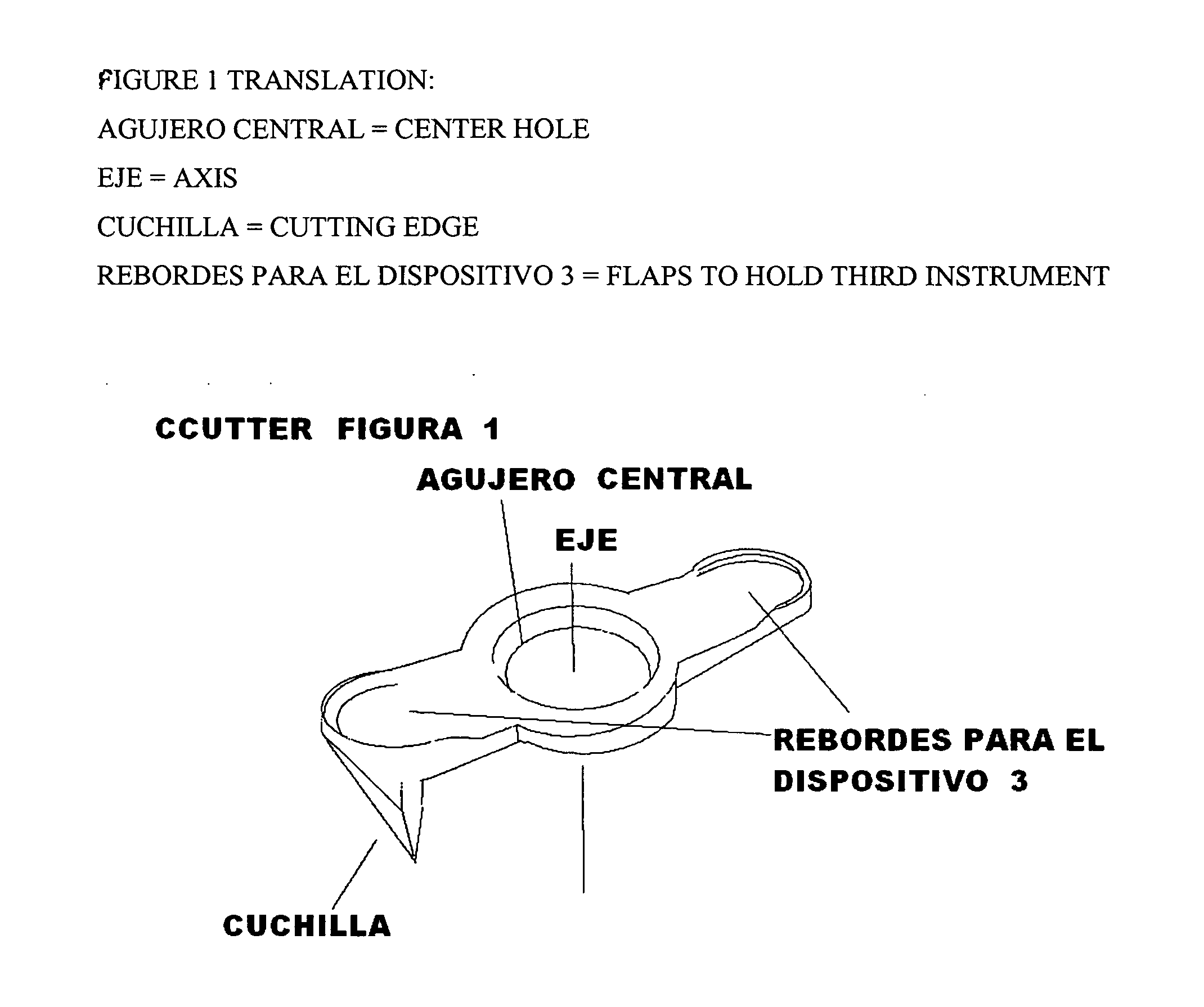
Ccutter
The CCUTTER is an innovative ophthalmologic surgical instrument that greatly facilitates the performance of cataract surgery. Cataract surgery is the most frequently performed surgery in the United States, with over one million cataract surgeries done each year. A cataract is a clouding of the eye's internal lens, which interferes with the individual's ability to see clearly. During surgery, a continuous circular tear (called capsulorhexis) is made in the anterior capsule of the crystalline lens of the eye, and the front surface of the cataract is opened to allow access to the clouded tissue inside. The cloudy portion is then removed, leaving the thin clear back surface of the lens (called the posterior capsule) in place. A lens implant is then placed in the shell of the natural lens, and the incision is closed. The CCUTTER is designed to improve the predictability and consistency of performing the capsulorhexis during cataract surgery.
Owner:BENITEZ PEDRO +1
Eye registration and astigmatism alignment control systems and method
InactiveUS6866661B2Precise positioningAvoid placingLaser surgeryImage analysisControl systemStigmatism
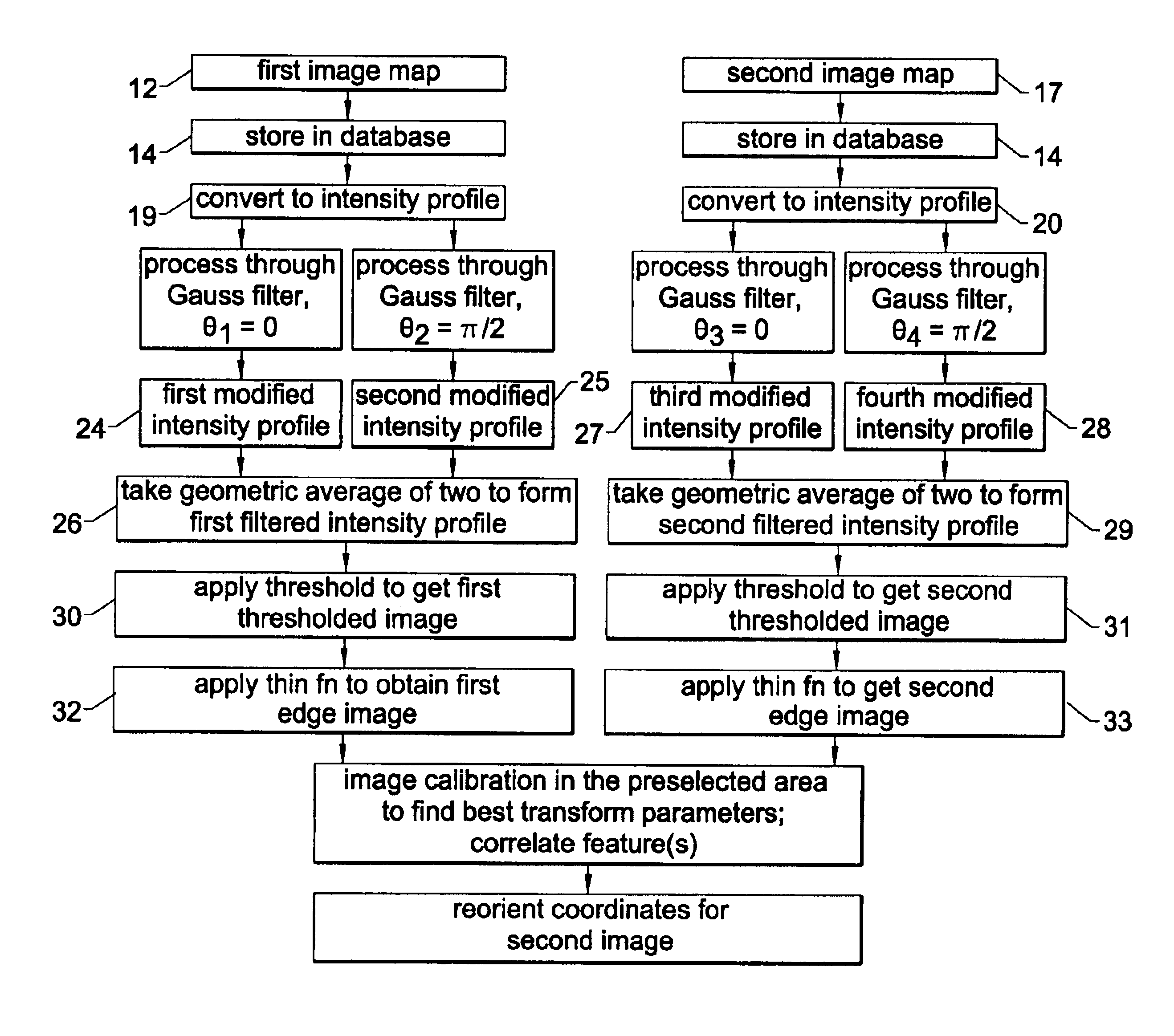
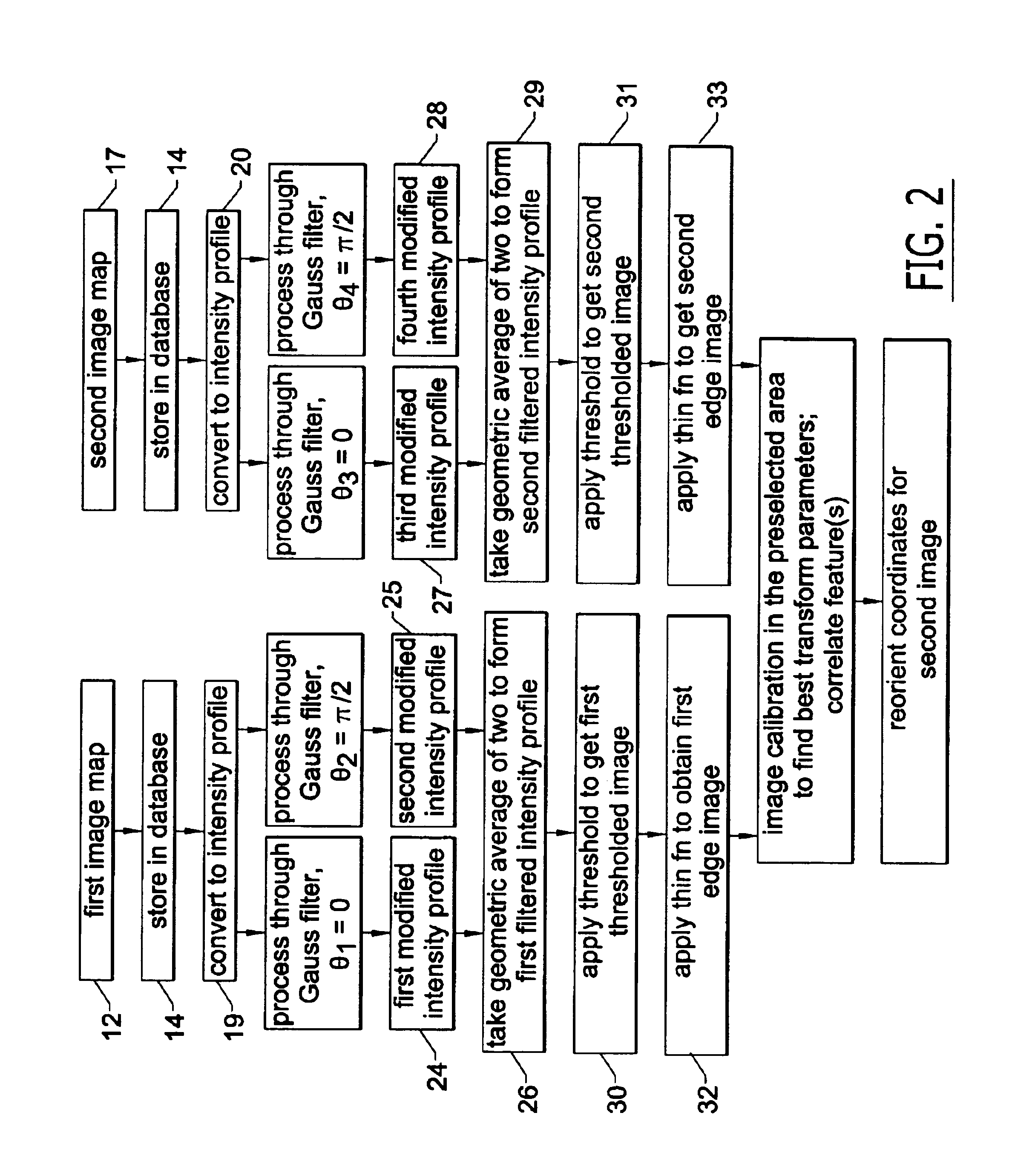
An orientation system for corrective eye surgery includes a camera for performing a first image mapping of a patient's eye using a predetermined eye feature and software for processing the first image map to determine an edge location of the feature. A second image mapping of the eye is performed with the patient in a different position. The second image map is processed to locate the predetermined eye feature. Correlation of the mappings is used to calculate an orientational change of the eye between the two positions. The data are used to calculate an adjustment to be applied to a corrective prescription for application by the surgical procedure.
Owner:ALCON INC
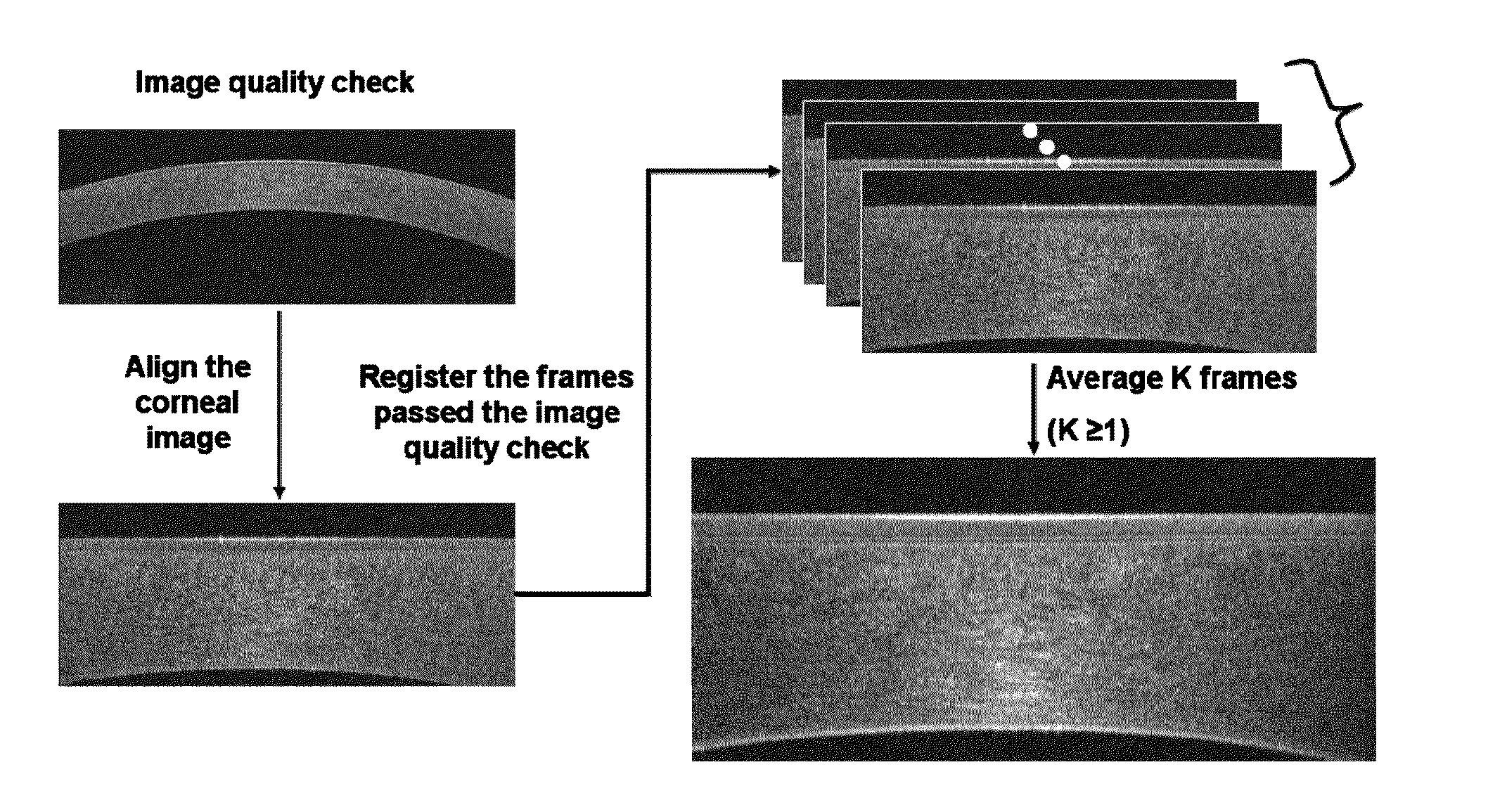
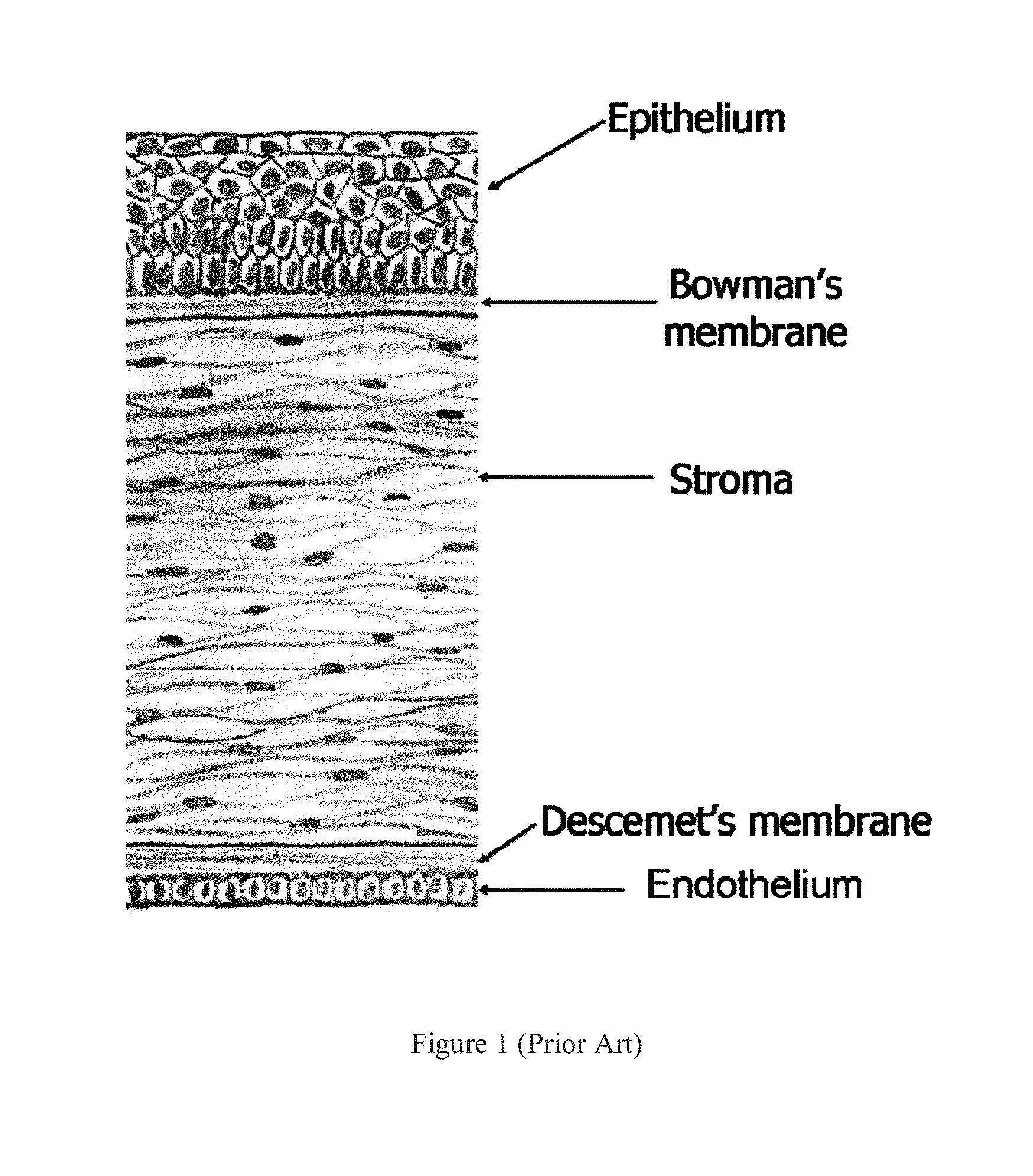
Methods and Systems to Measure Corneal Epithelial Thickness and Power, Stromal Thickness, Subepithelial Corneal Power and Topography for Disease Diagnosis
ActiveUS20130128222A1Improve image qualityReliably determinedImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseOptical tomography
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
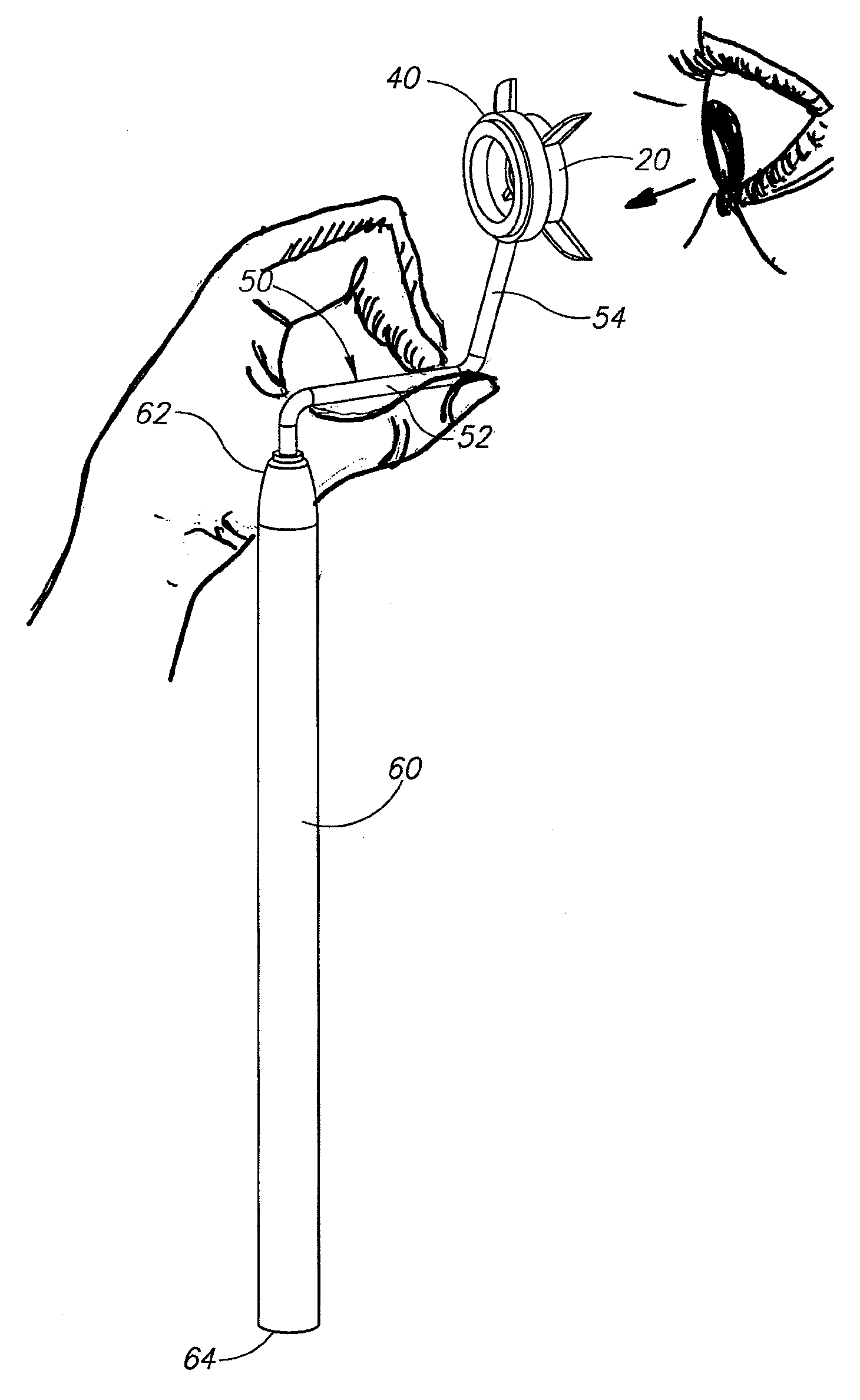
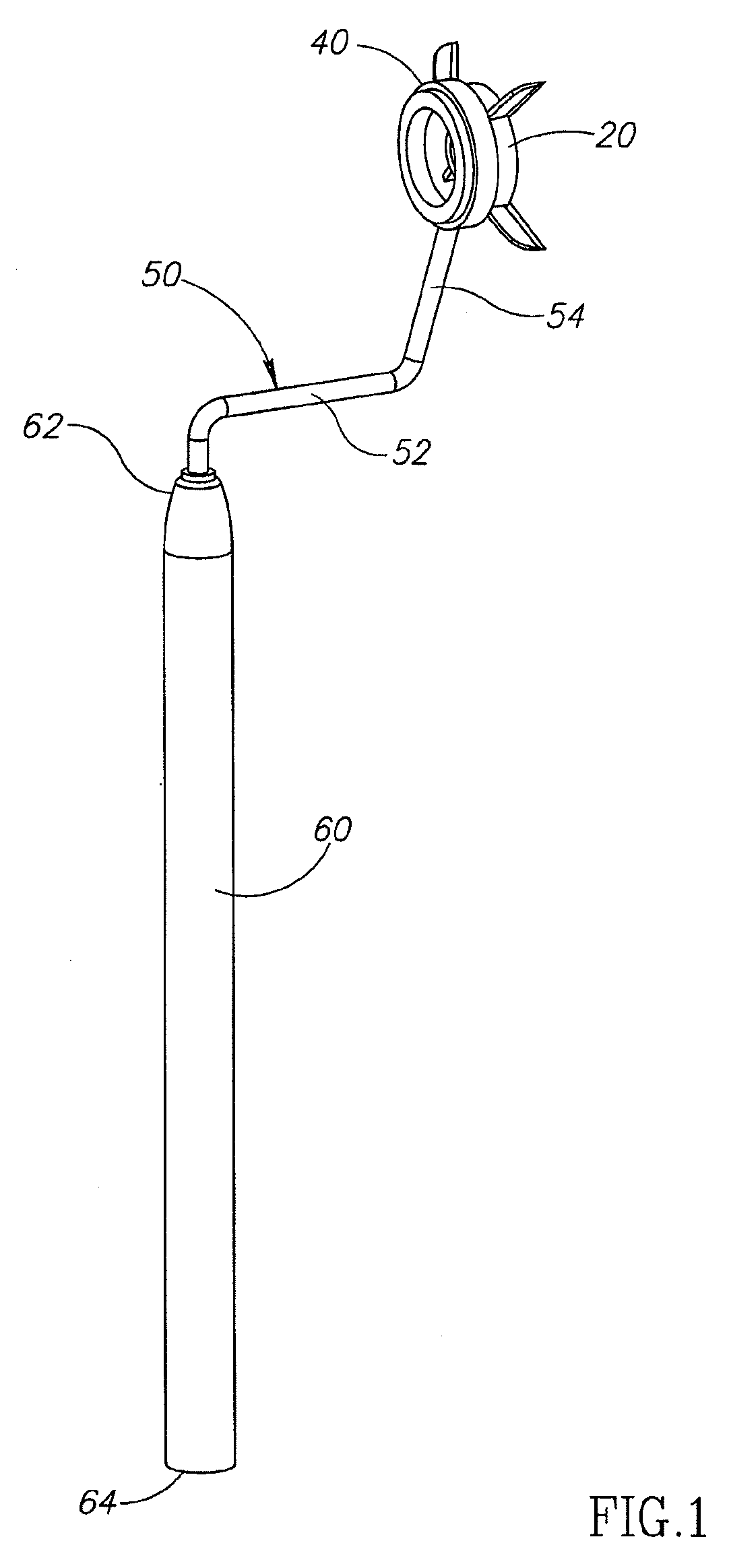
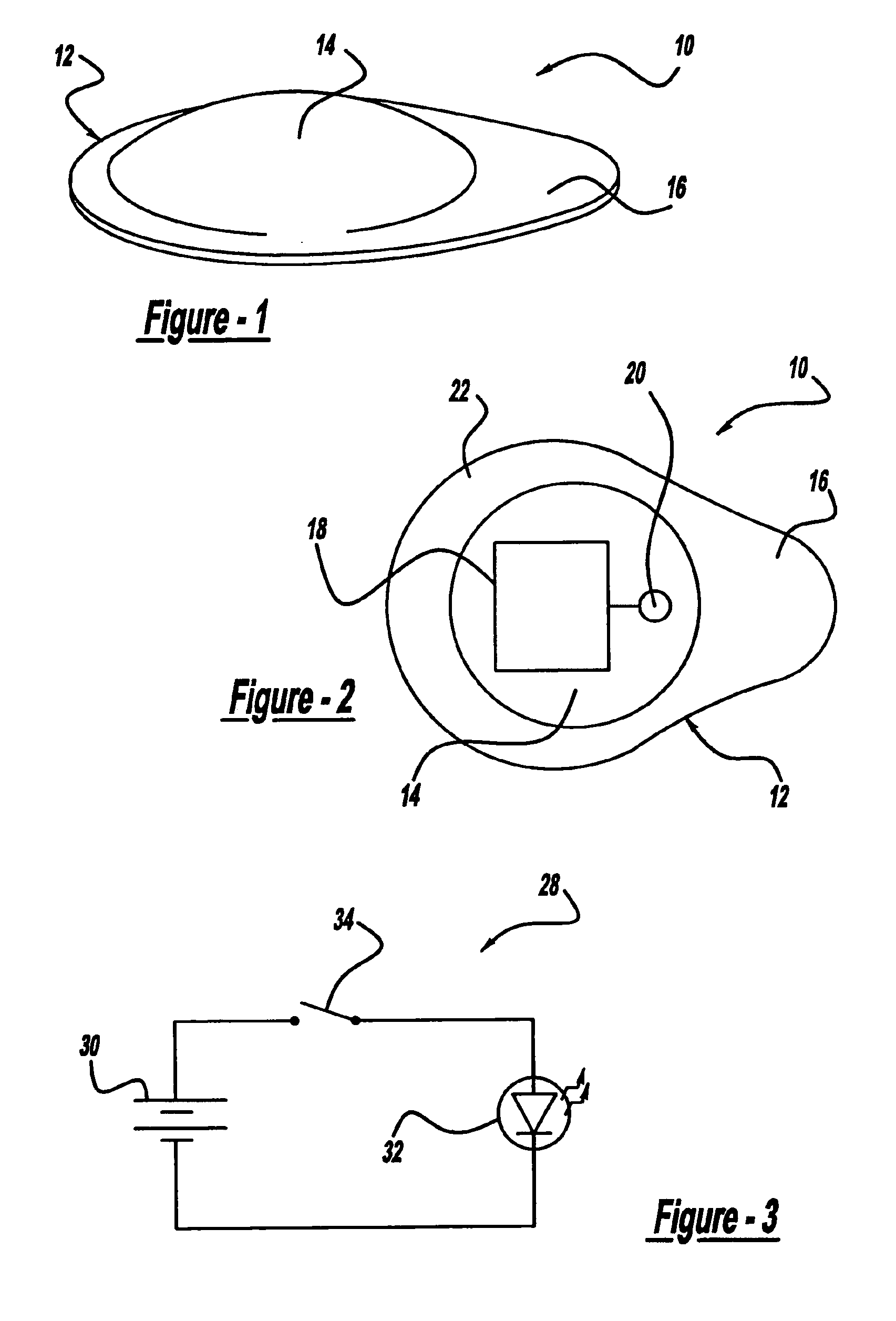
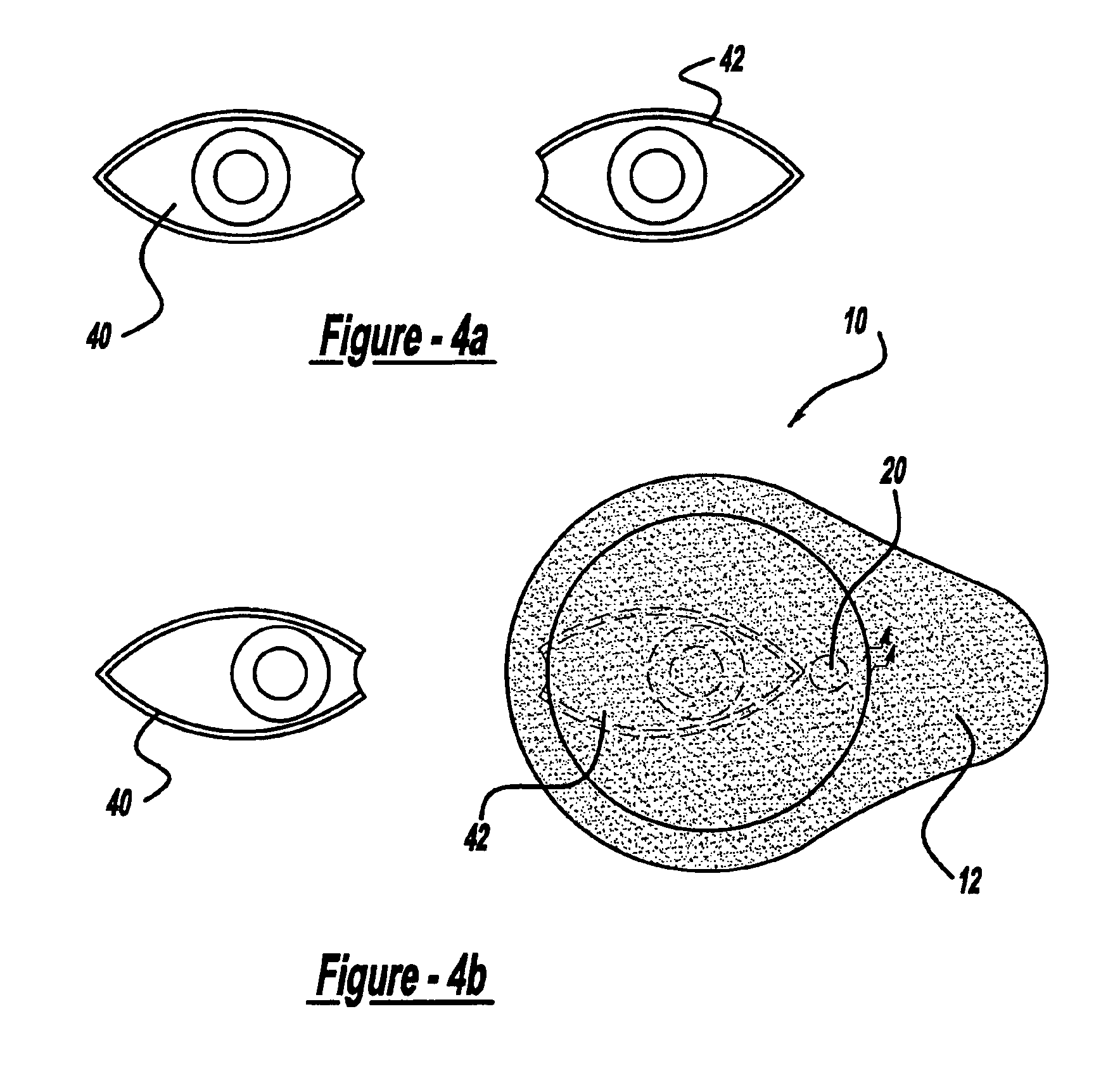
LED fixation device for topical anesthesia eye surgery
InactiveUS6869427B1Reduces and eliminates eye movementEliminate needElectrotherapyEye surgeryEye closureSurgical department
An LED fixation device that is secured to a patient's face and covers the patient's fellow eye during eye surgery to provide a lighted fixation target. The fixation device includes an eye shield, a battery, a switch and an LED light source secured to the eye shield. The light source is switched on, and the patient is directed to look at the light source during the surgical procedure. The eye shield can be made of any suitable material, such as plastic and paper, and can be disposable.
Owner:SHOKOOHI KAMRAN K
Occlusion-activated heat supression infusion sleeve
InactiveUS20150038894A1Constant pressureImprove fluid flowEye surgeryCannulasIrrigation fluidsEye surgery
Described is a phacoemulsification device for eye surgery that generally comprises an ultrasonically vibrating aspiration needle that withdraws ocular material from inside of the eye. The ocular material withdrawn from the eye is equally replaced with irrigation fluid provided through irrigation ports in an irrigation sleeve surrounding the aspiration needle. In the event the aspiration needle stops withdrawing ocular material, such as if it becomes occluded with a chunk of ocular material, irrigation fluid is directed to the outside of the eye via at least one irrigation aperture to keep the eye cool where the needle is ultrasonically vibrating.
Owner:URICH ALEX +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com