Patents
Literature
617 results about "Color imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
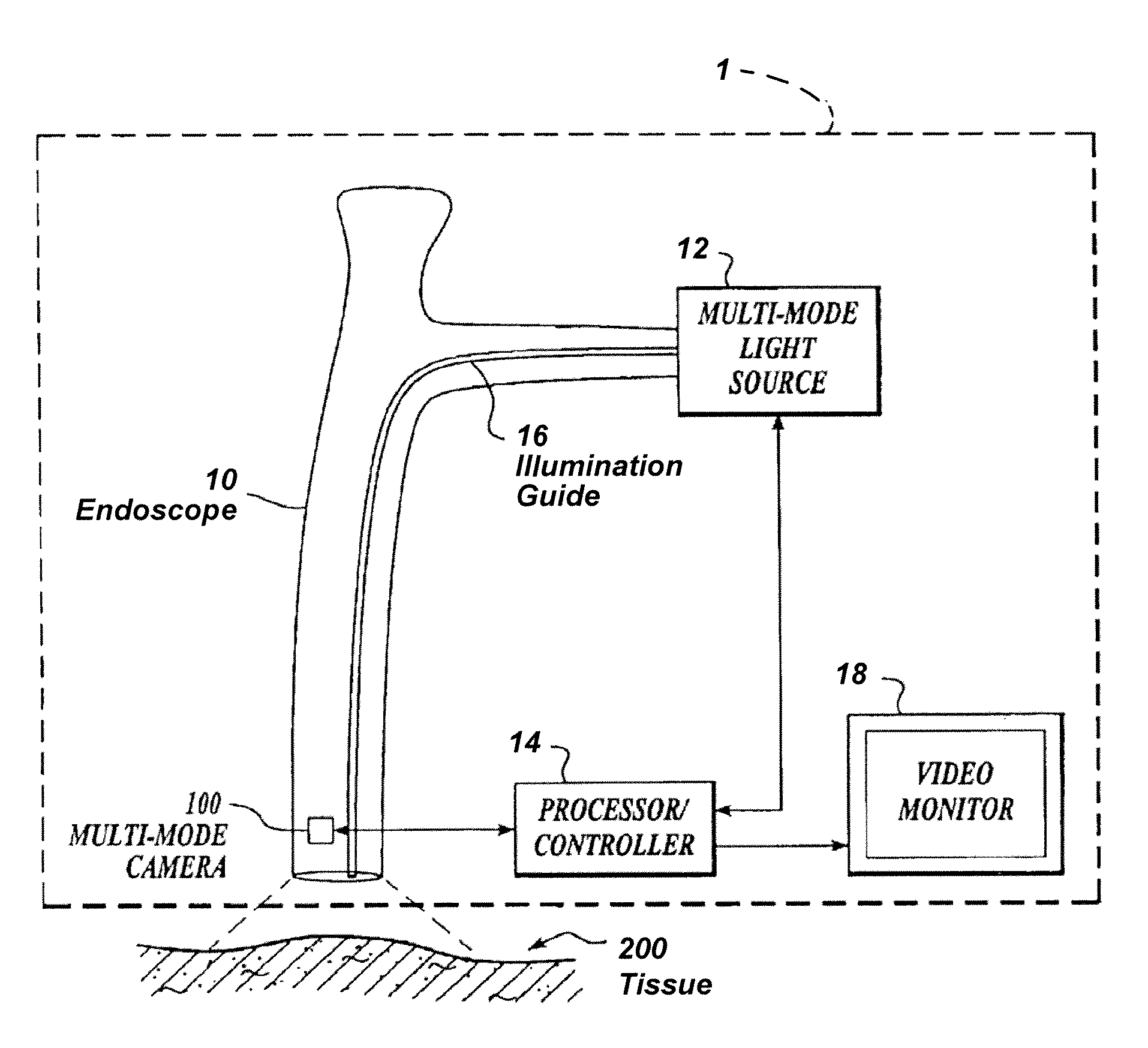
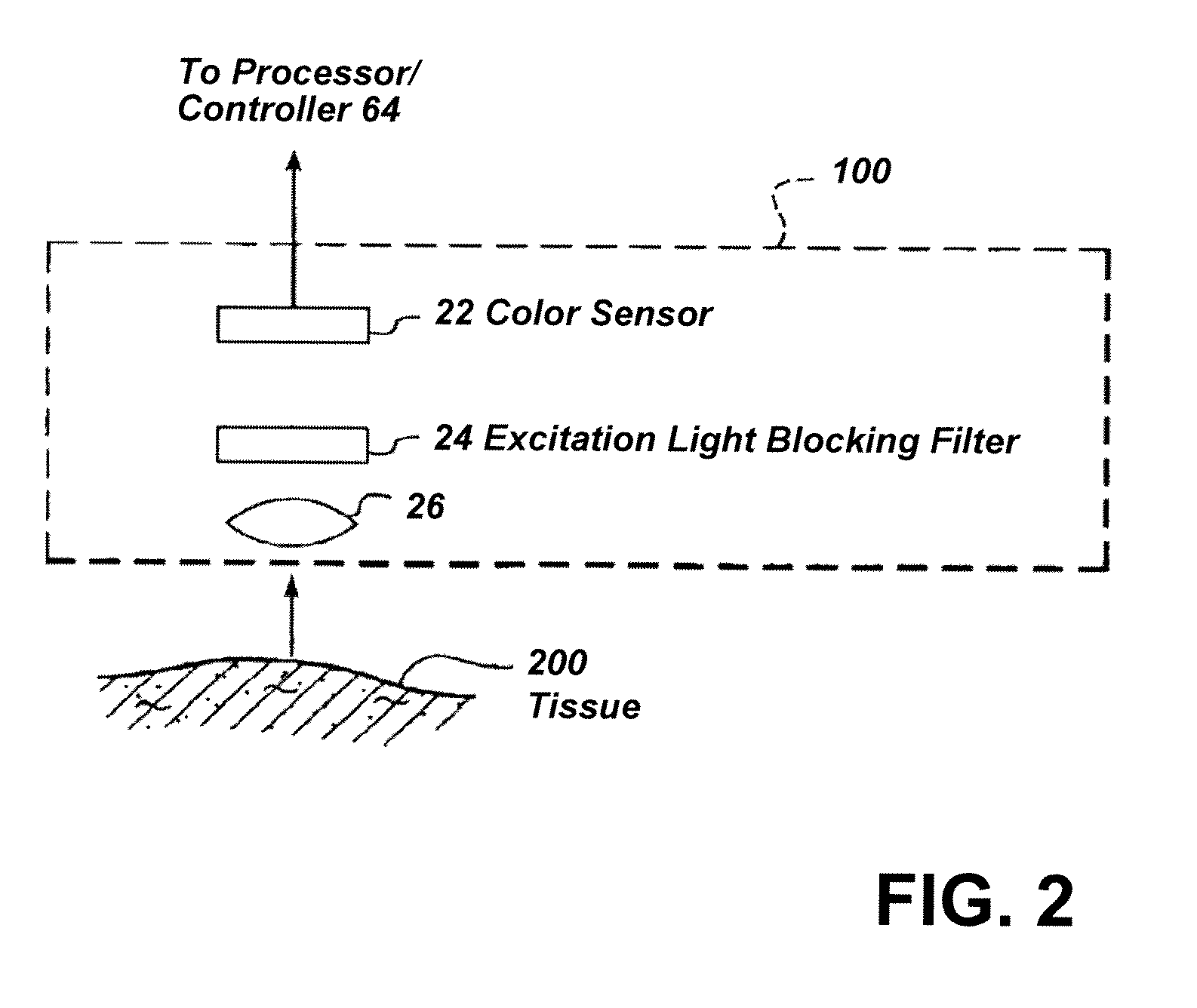
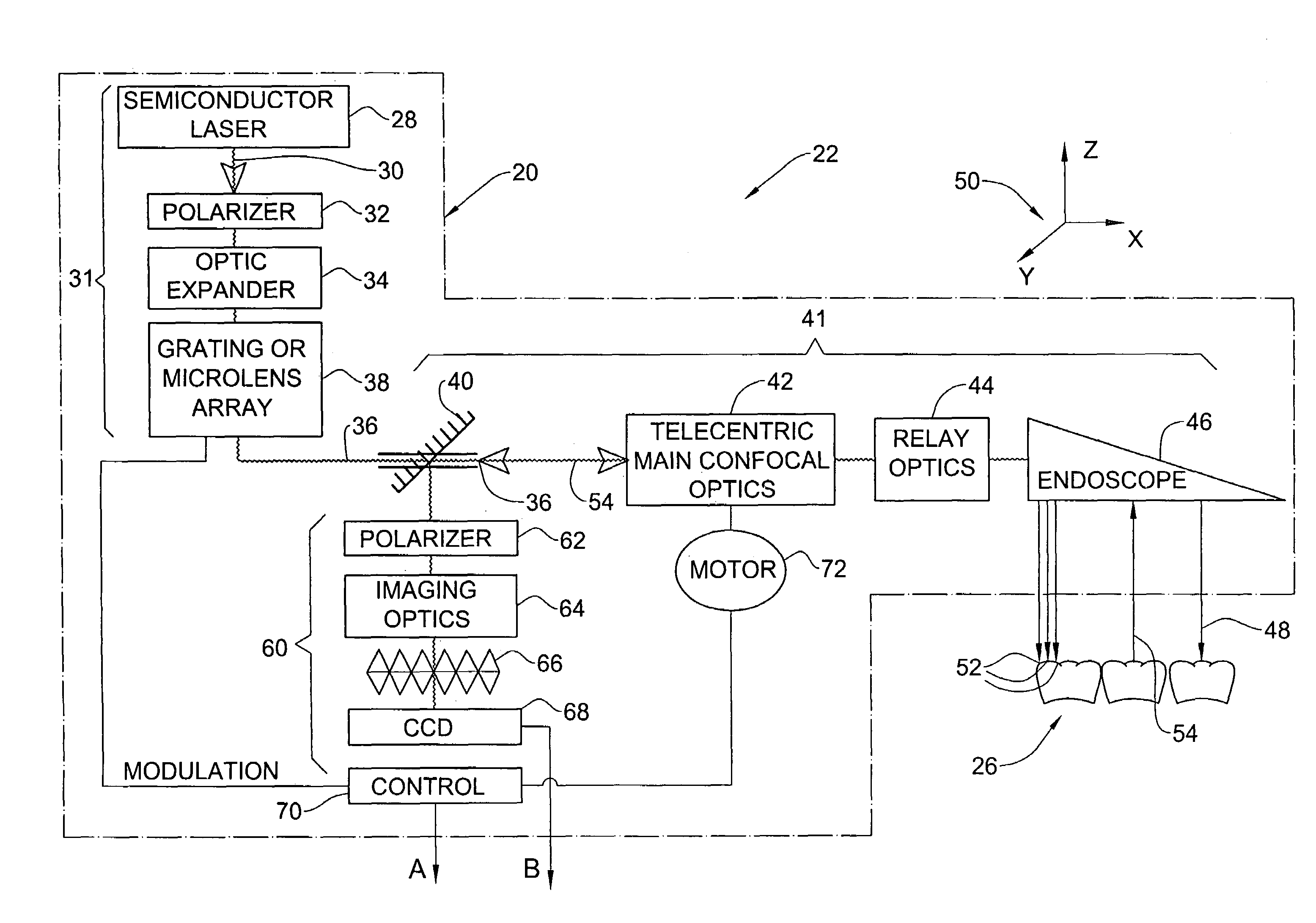
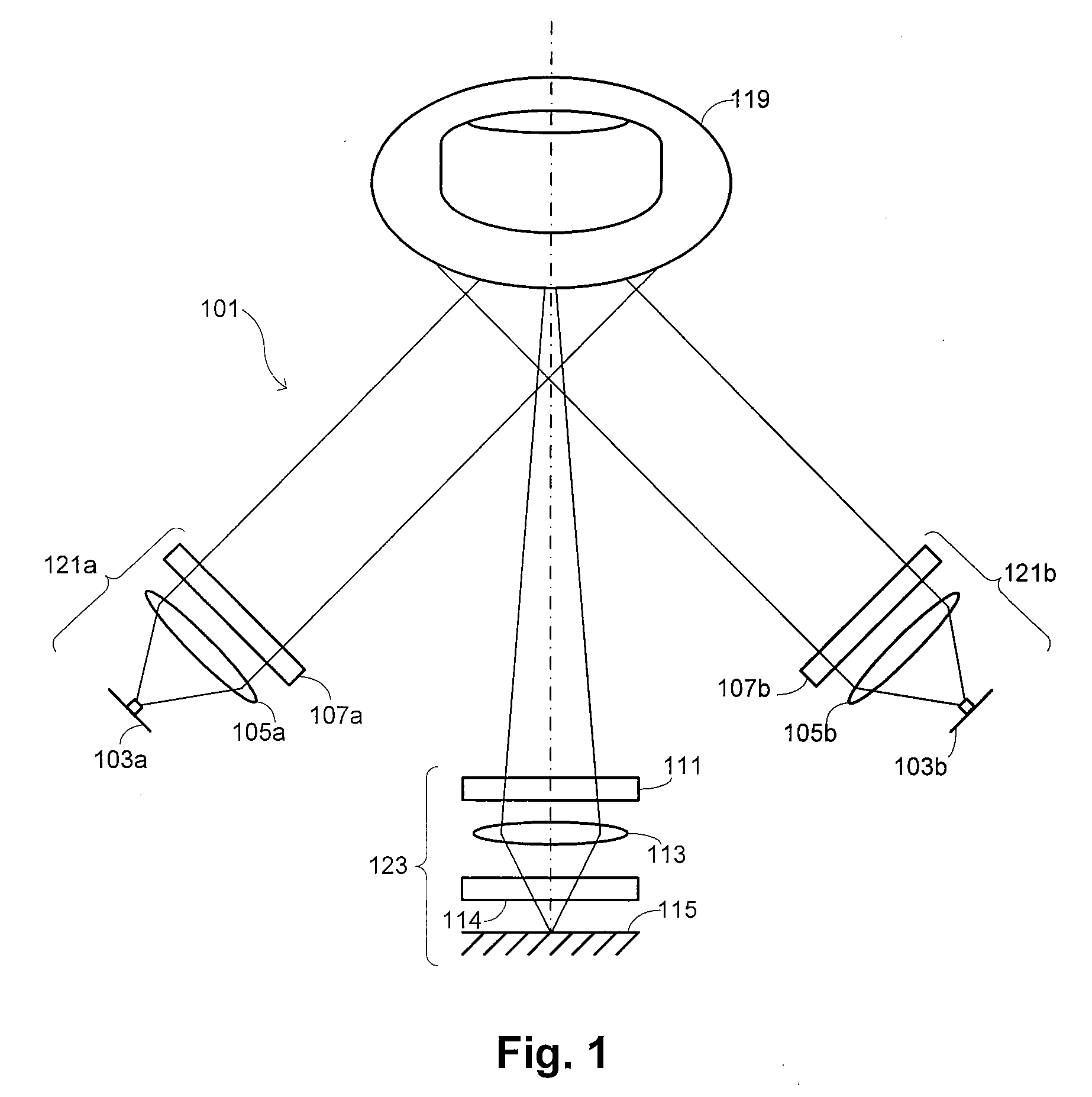
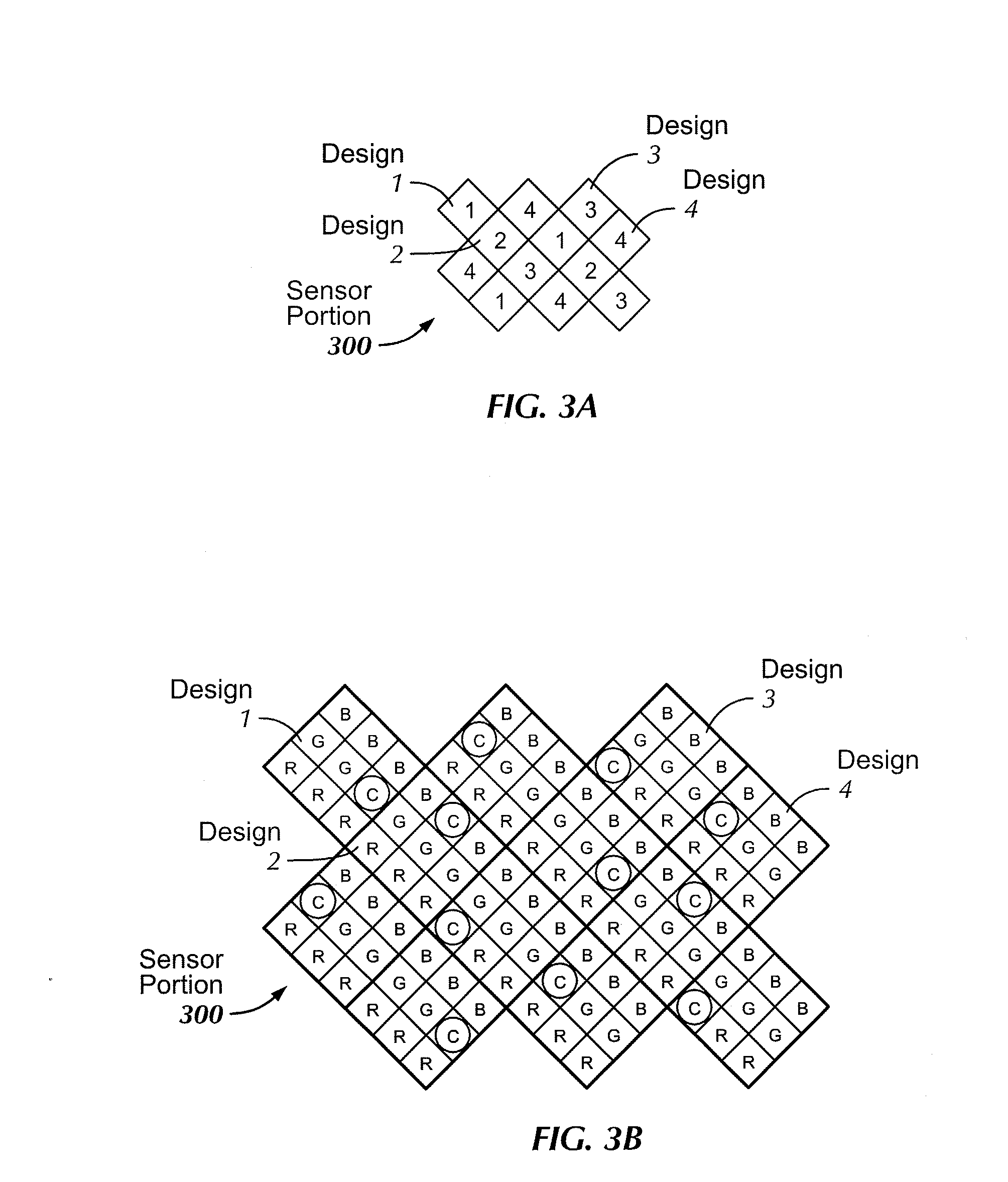
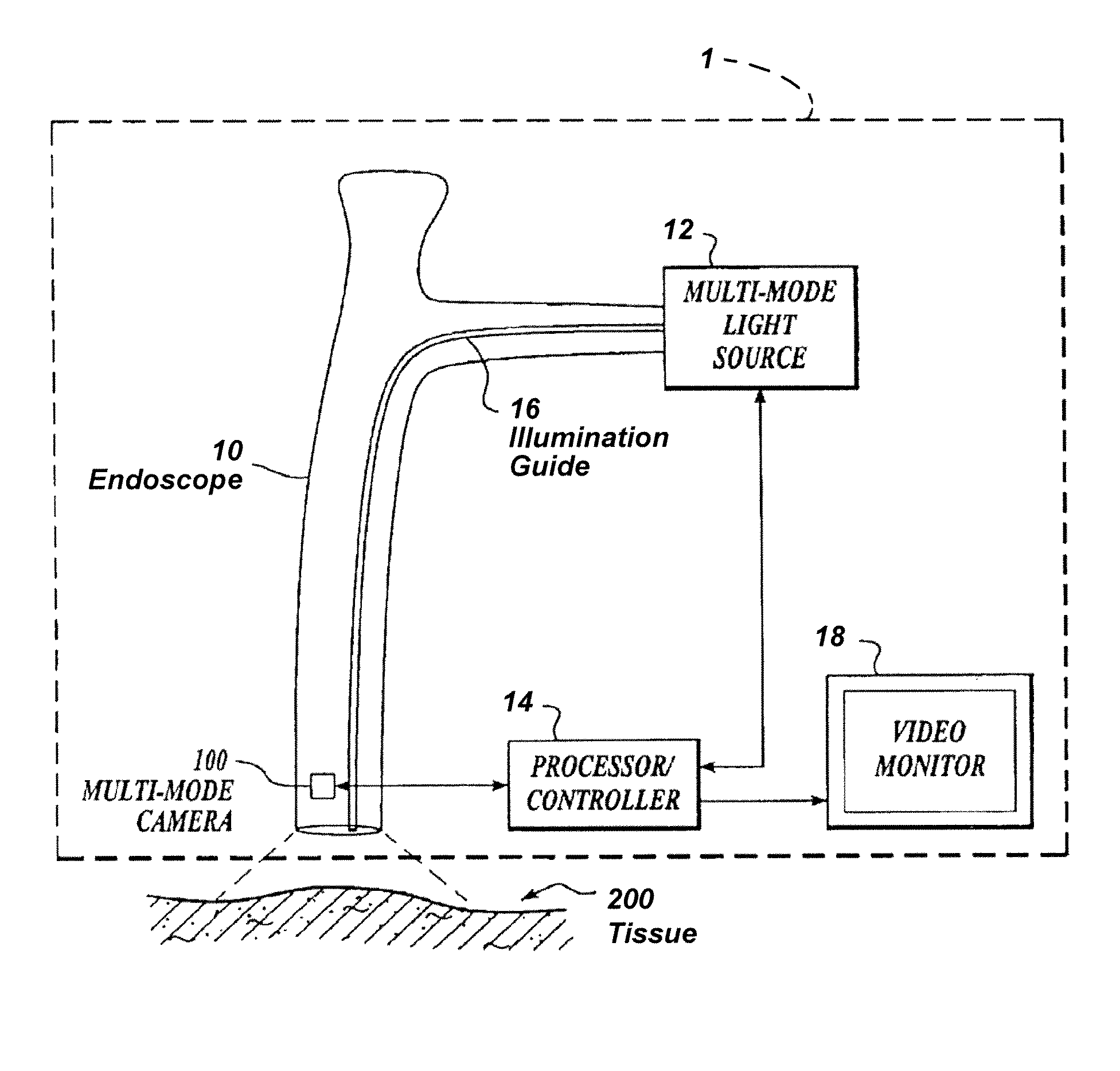
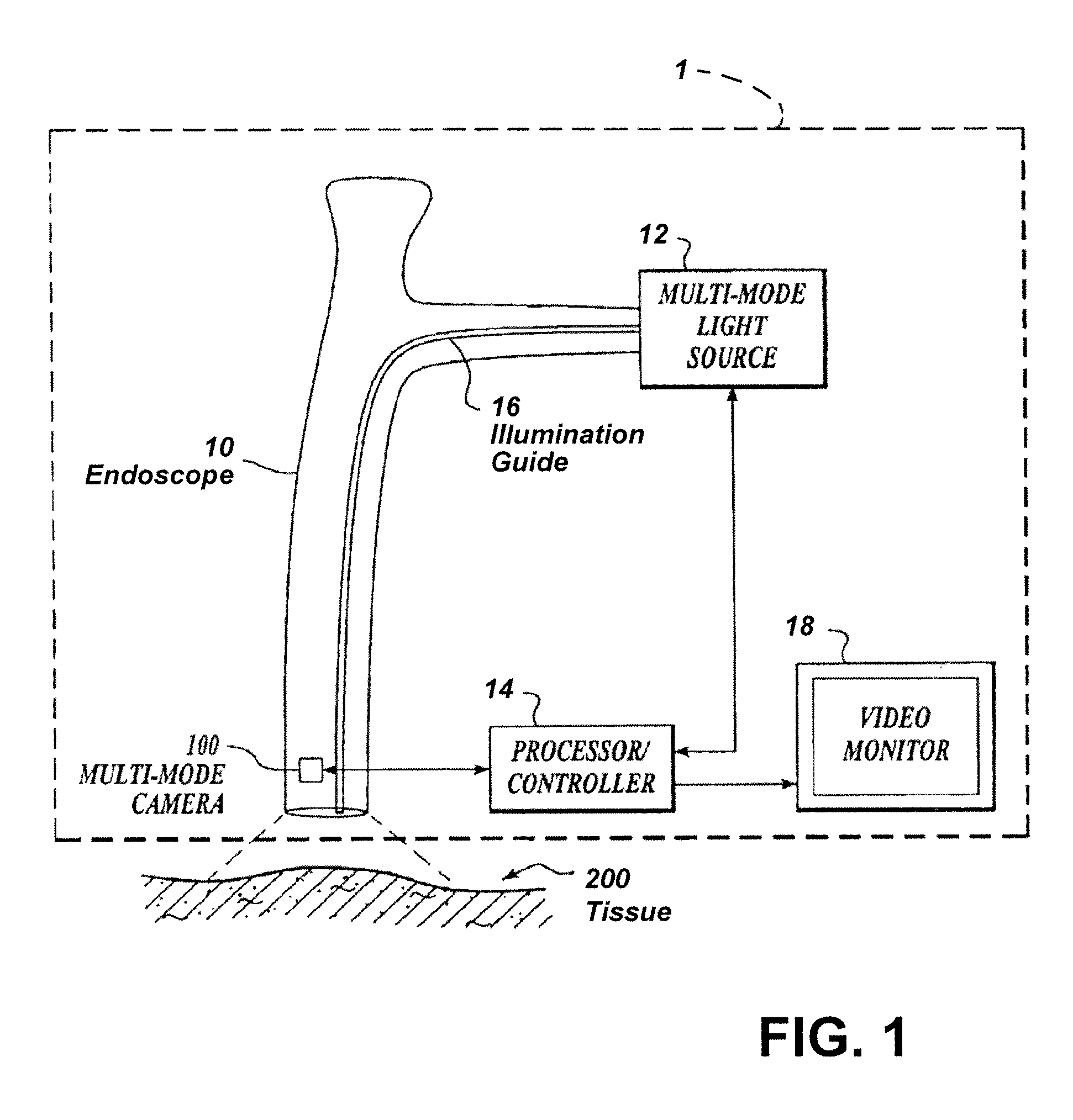
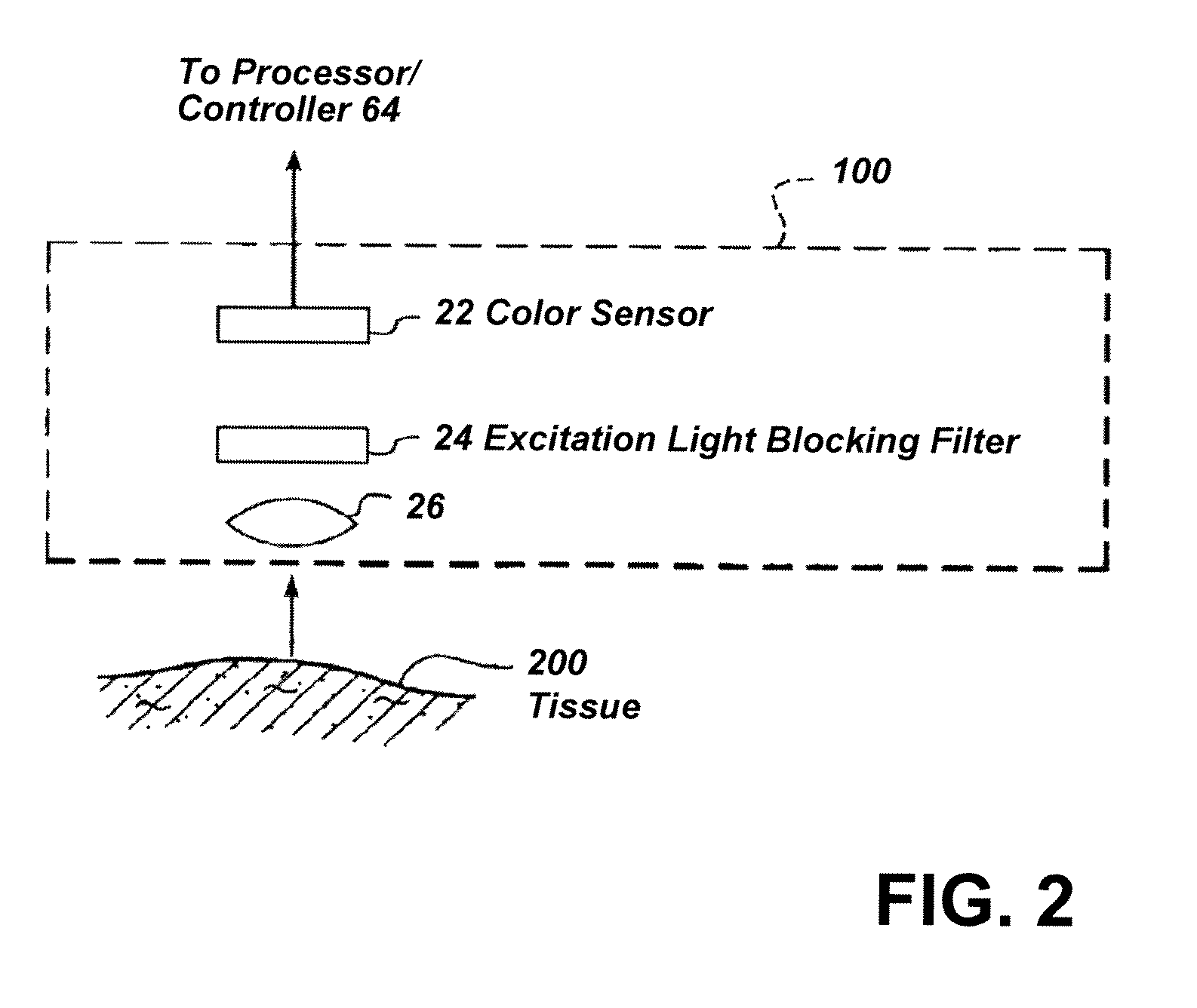
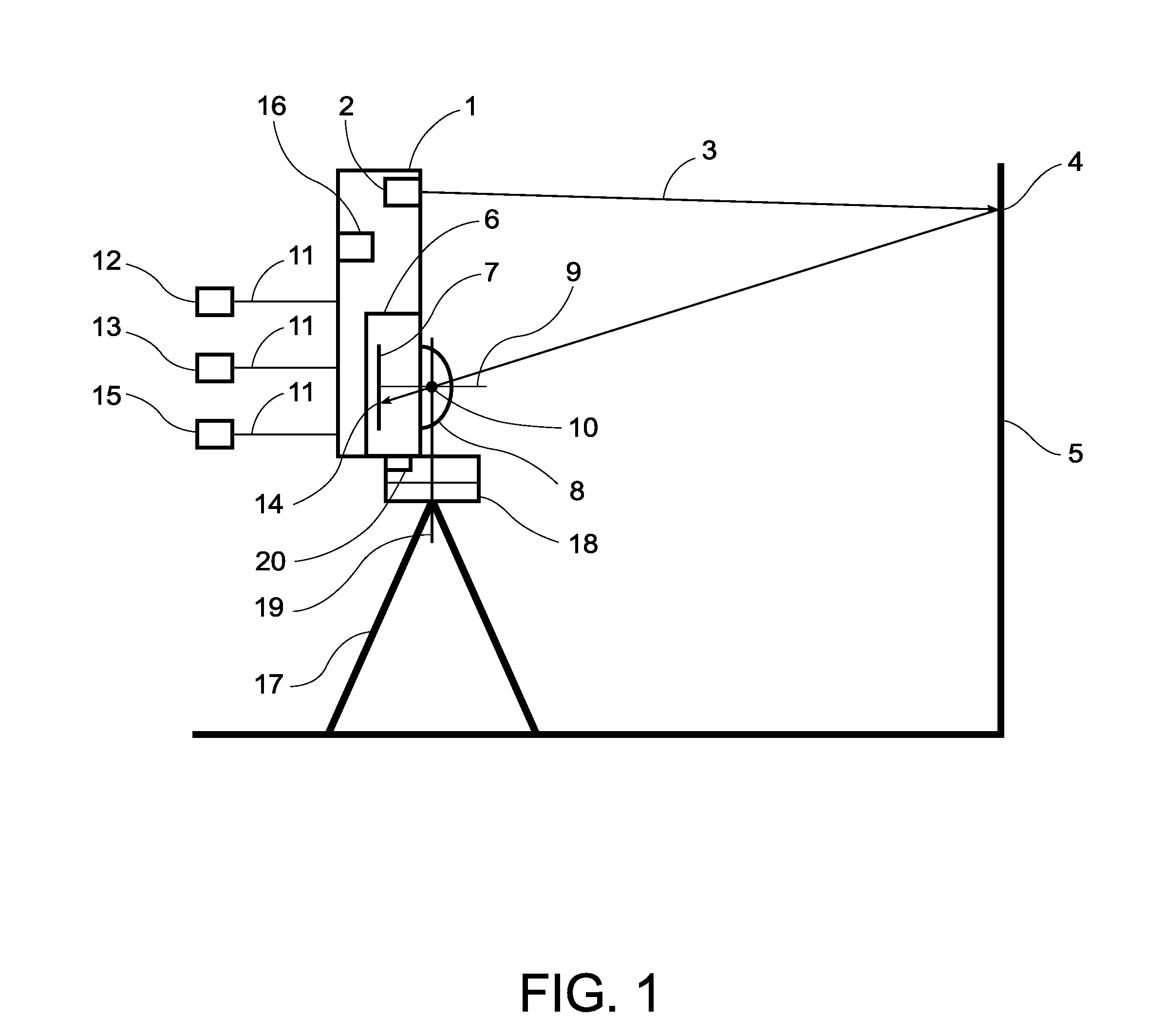
Imaging system with a single color image sensor for simultaneous fluorescence and color video endoscopy
ActiveUS20080239070A1Enhanced attainable spatial resolutionHigh-resolution imageTelevision system detailsSurgeryVideo rateMonochrome Image
An endoscopic video system and method using a camera with a single color image sensor, for example a CCD color image sensor, for fluorescence and color imaging and for simultaneously displaying the images acquired in these imaging modes at video rates in real time is disclosed. The tissue under investigation is illuminated continuously with fluorescence excitation light and is further illuminated periodically using visible light outside of the fluorescence excitation wavelength range. The illumination sources may be conventional lamps using filters and shutters, or may include light-emitting diodes mounted at the distal tip of the endoscope.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
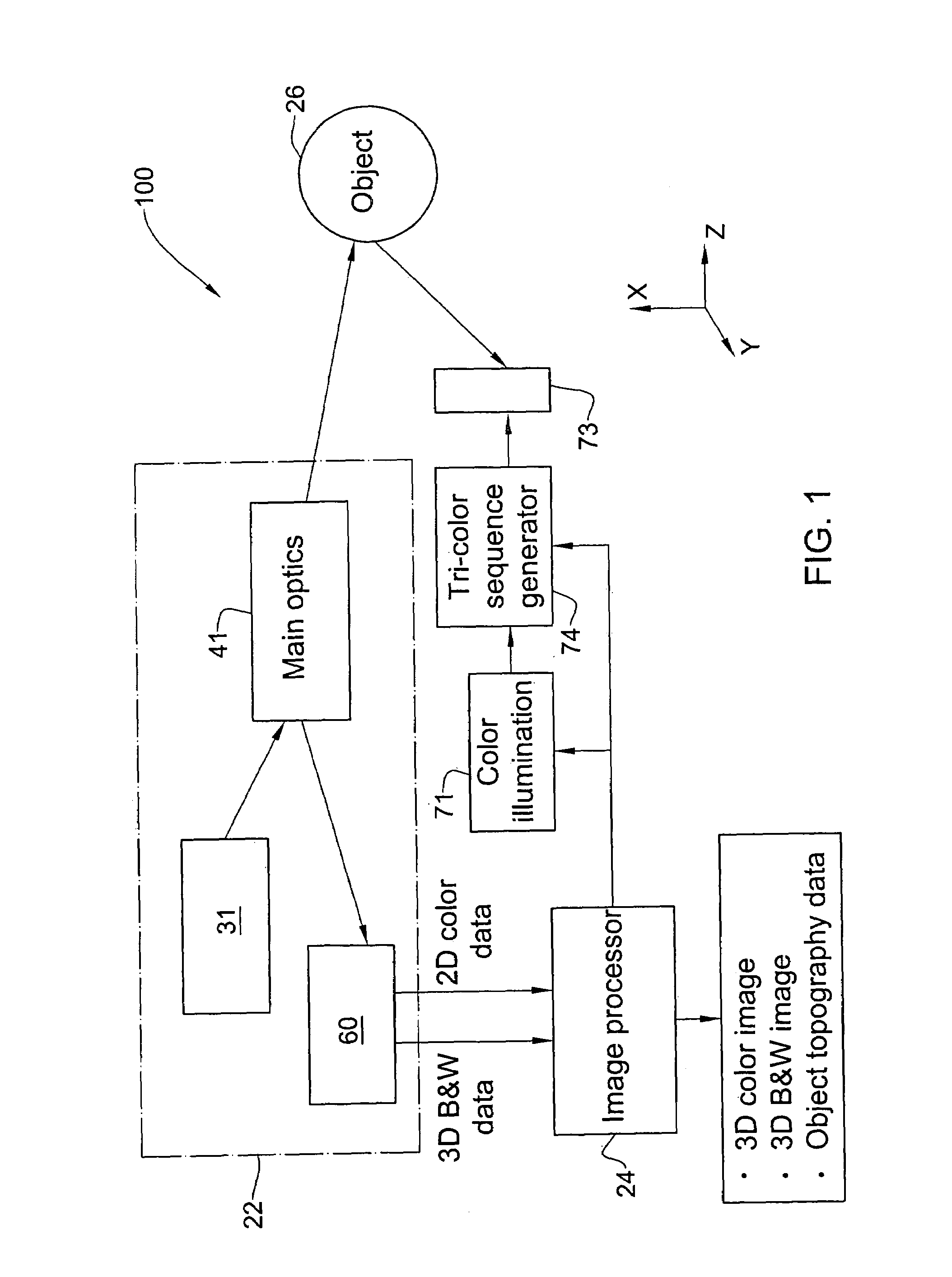
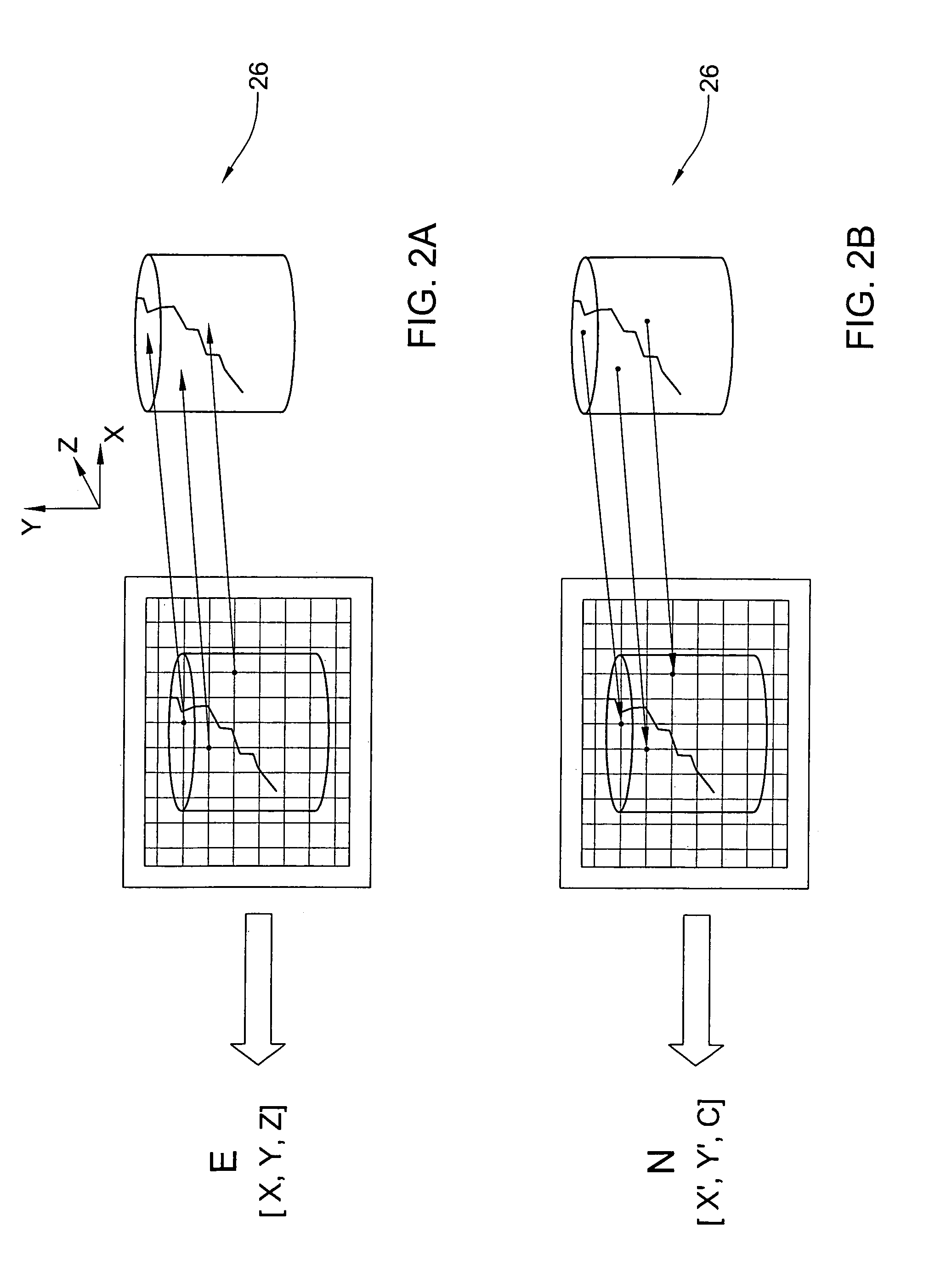
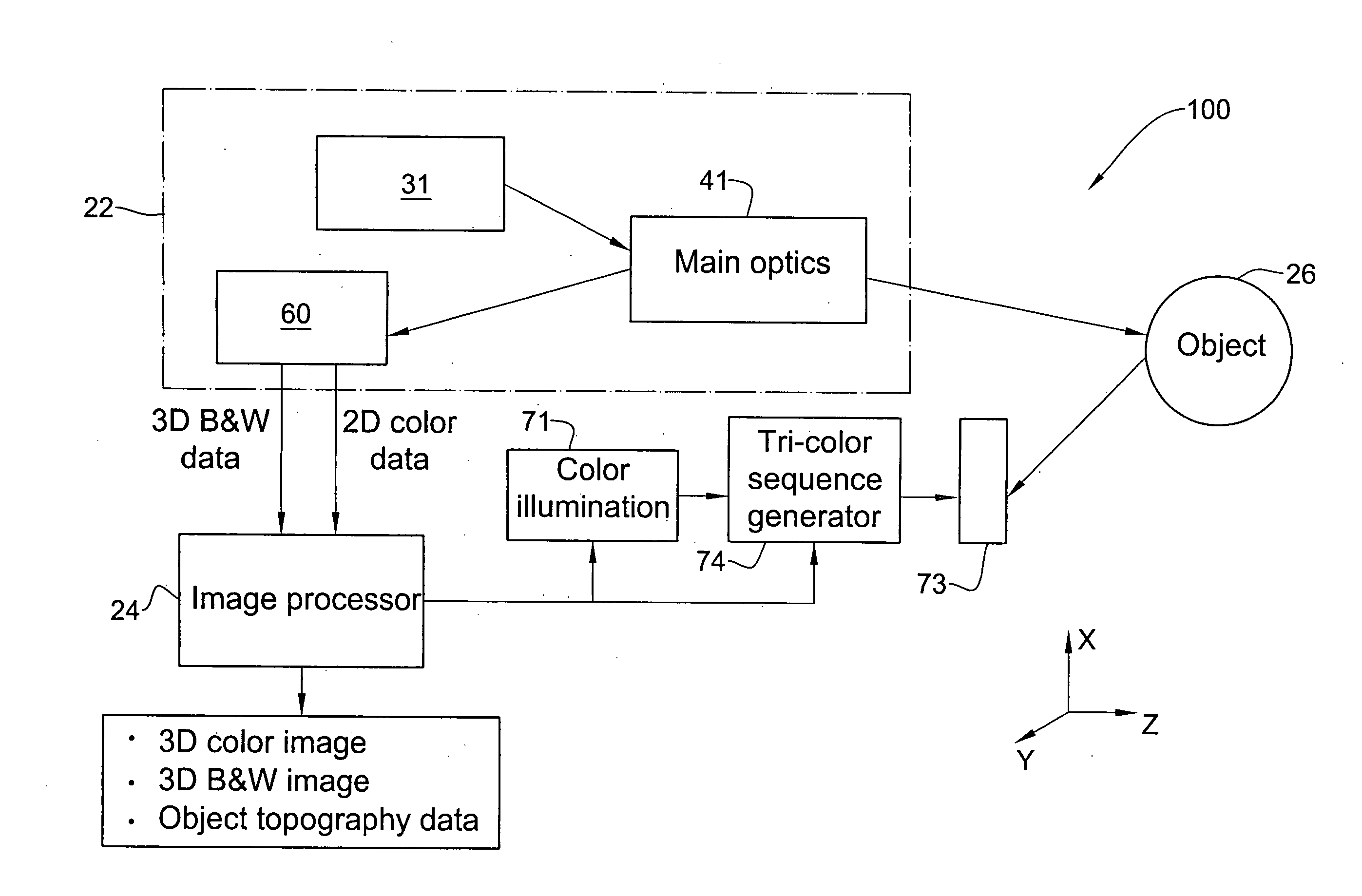
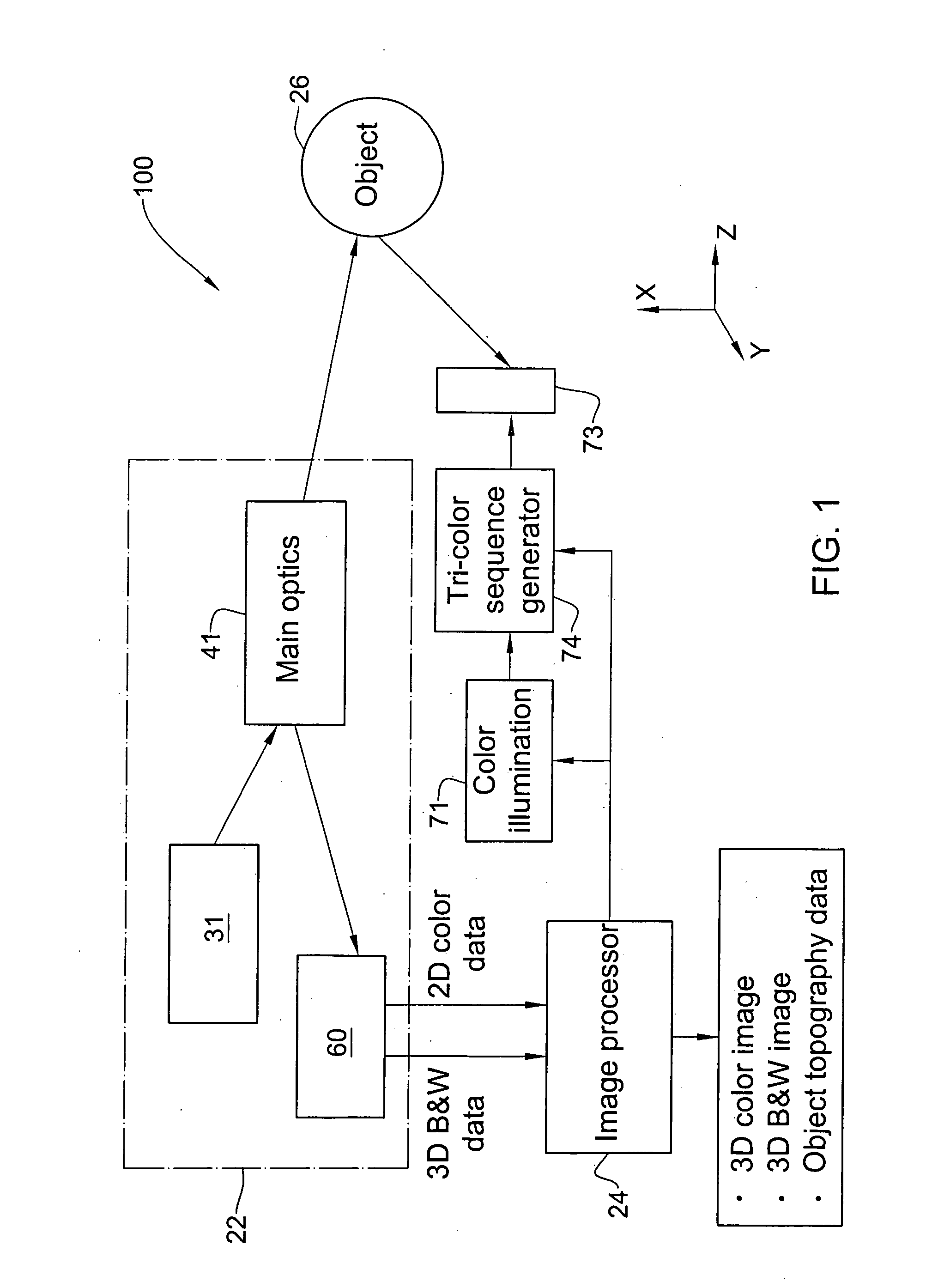
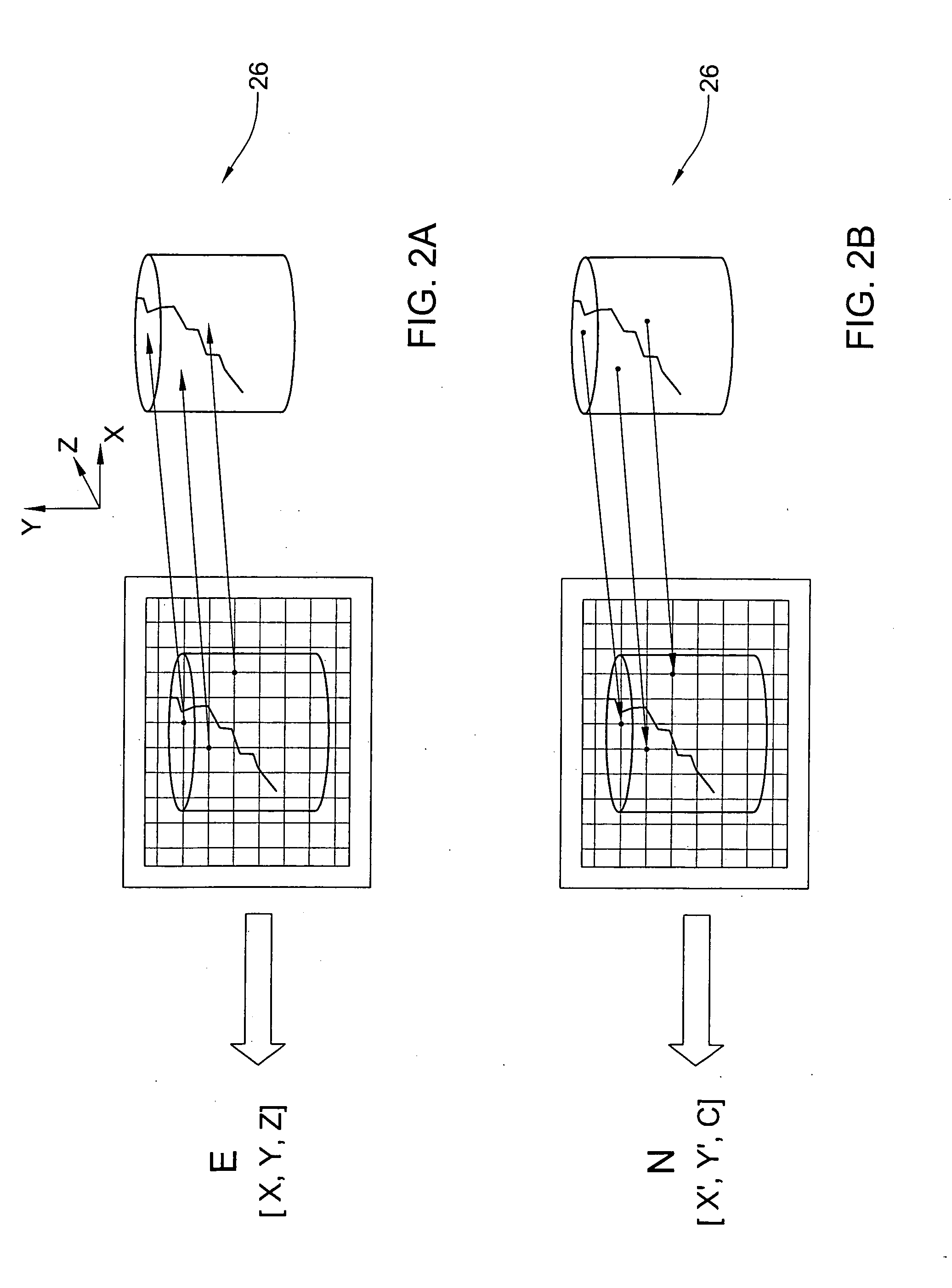
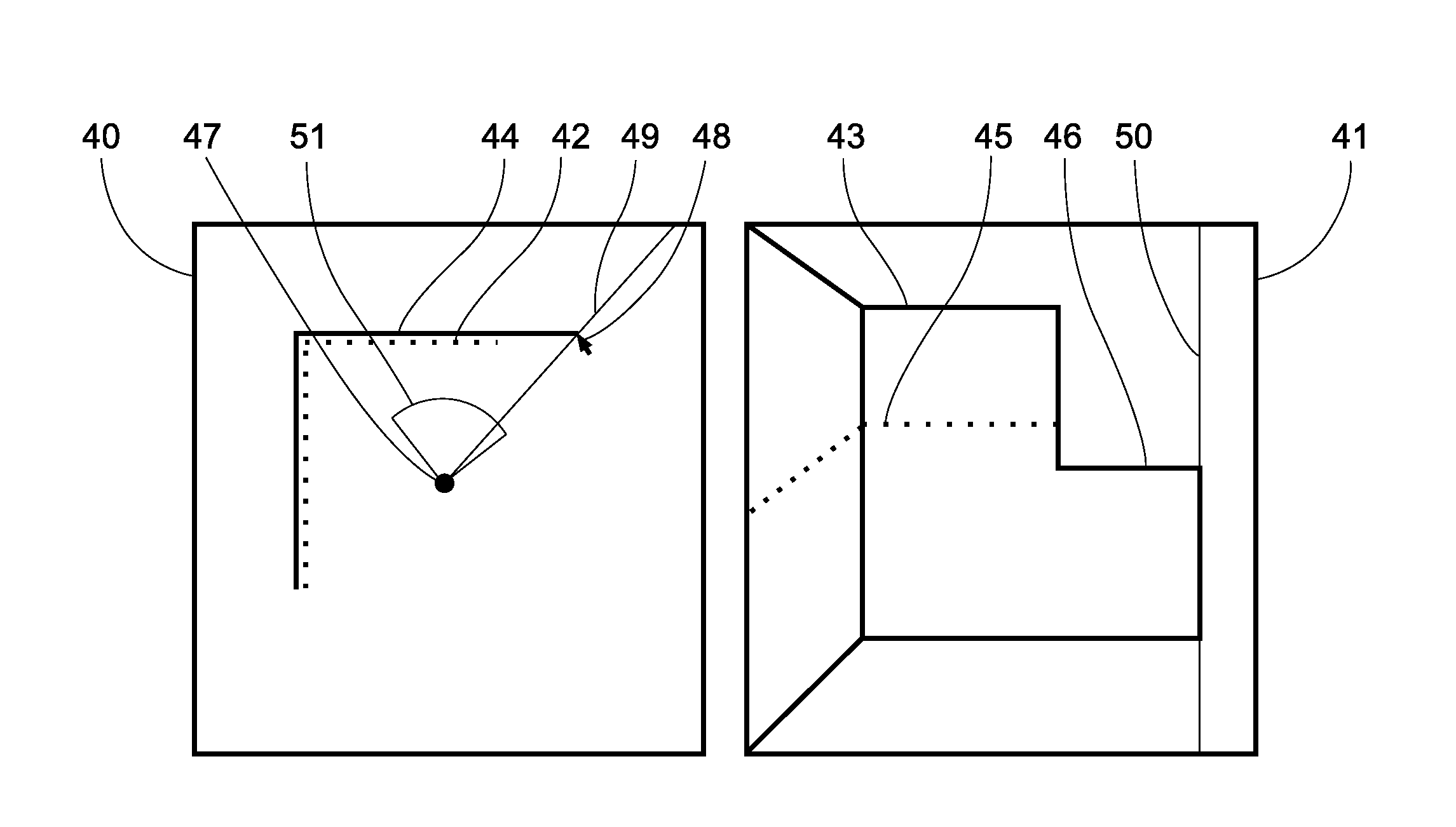
Method and apparatus for colour imaging a three-dimensional structure
A device for determining the surface topology and associated color of a structure, such as a teeth segment, includes a scanner for providing depth data for points along a two-dimensional array substantially orthogonal to the depth direction, and an image acquisition means for providing color data for each of the points of the array, while the spatial disposition of the device with respect to the structure is maintained substantially unchanged. A processor combines the color data and depth data for each point in the array, thereby providing a three-dimensional color virtual model of the surface of the structure. A corresponding method for determining the surface topology and associated color of a structure is also provided.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
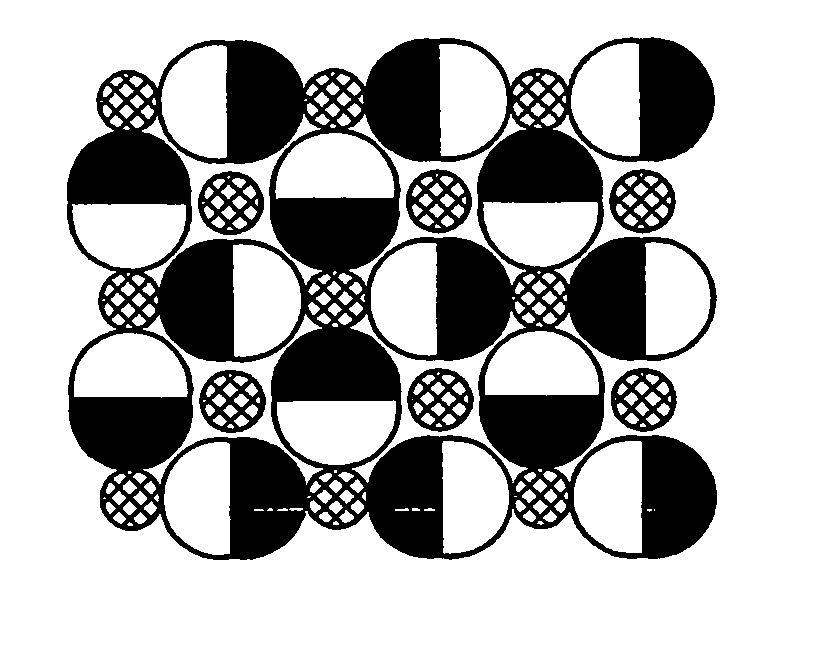
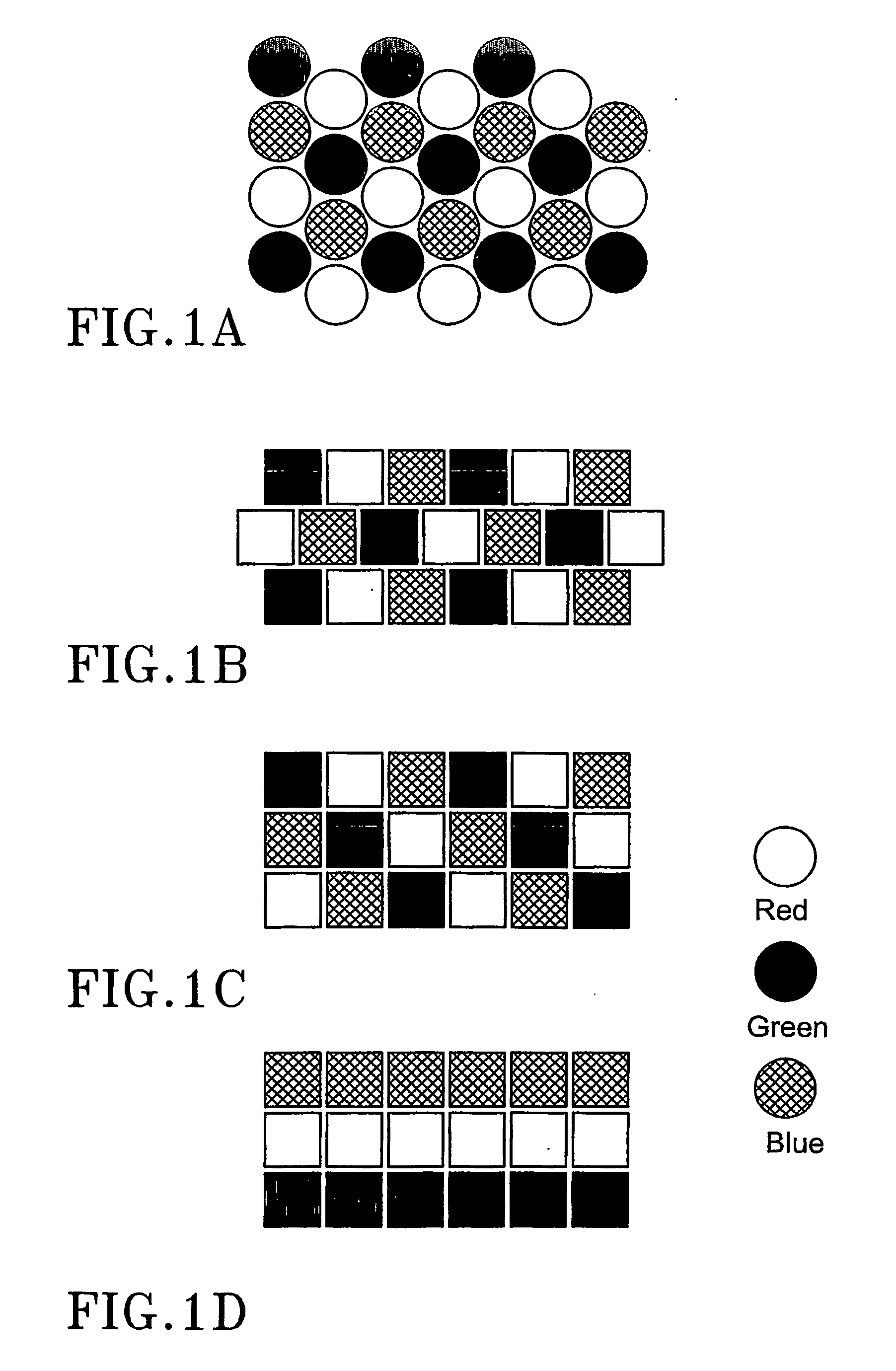
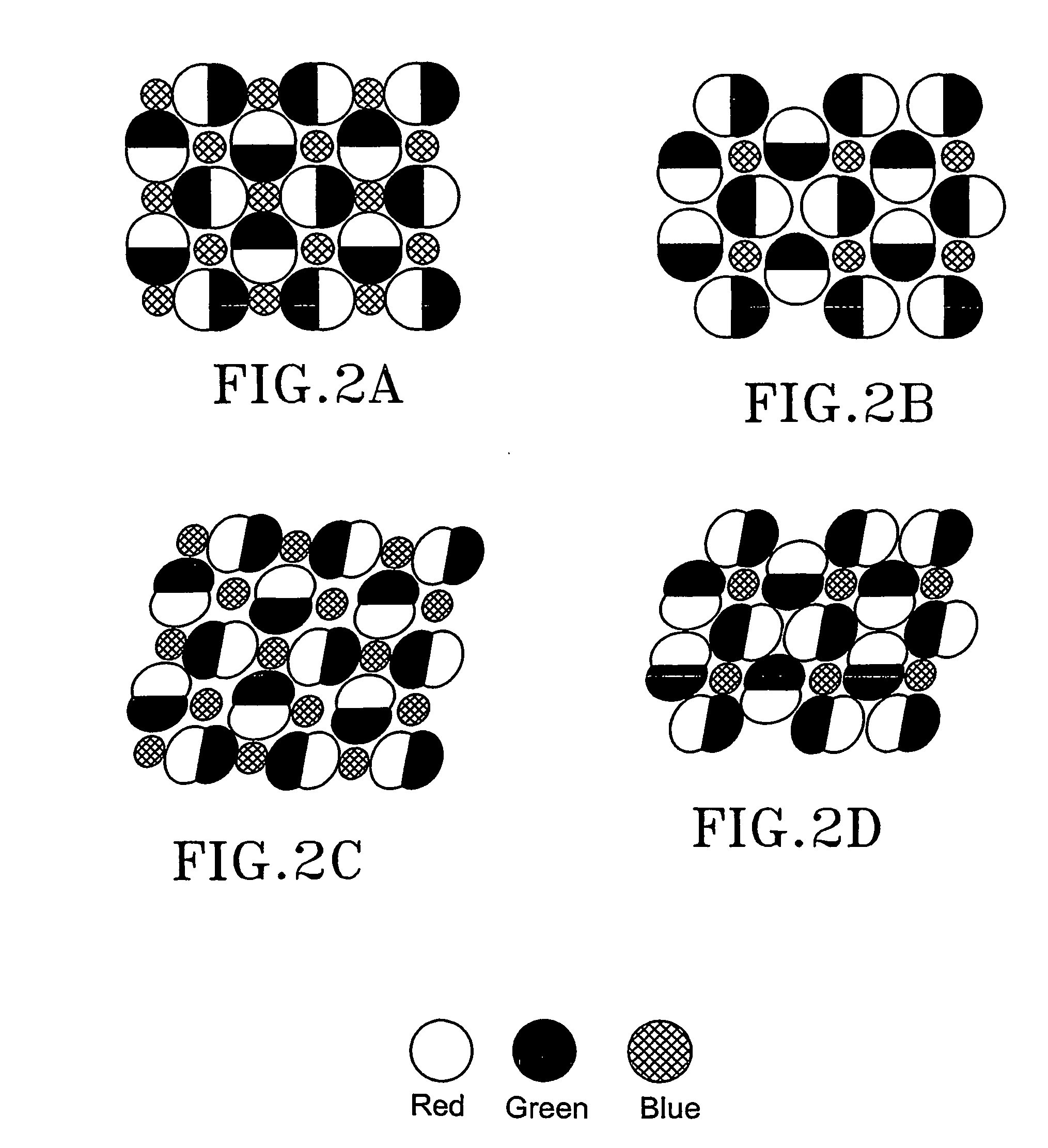
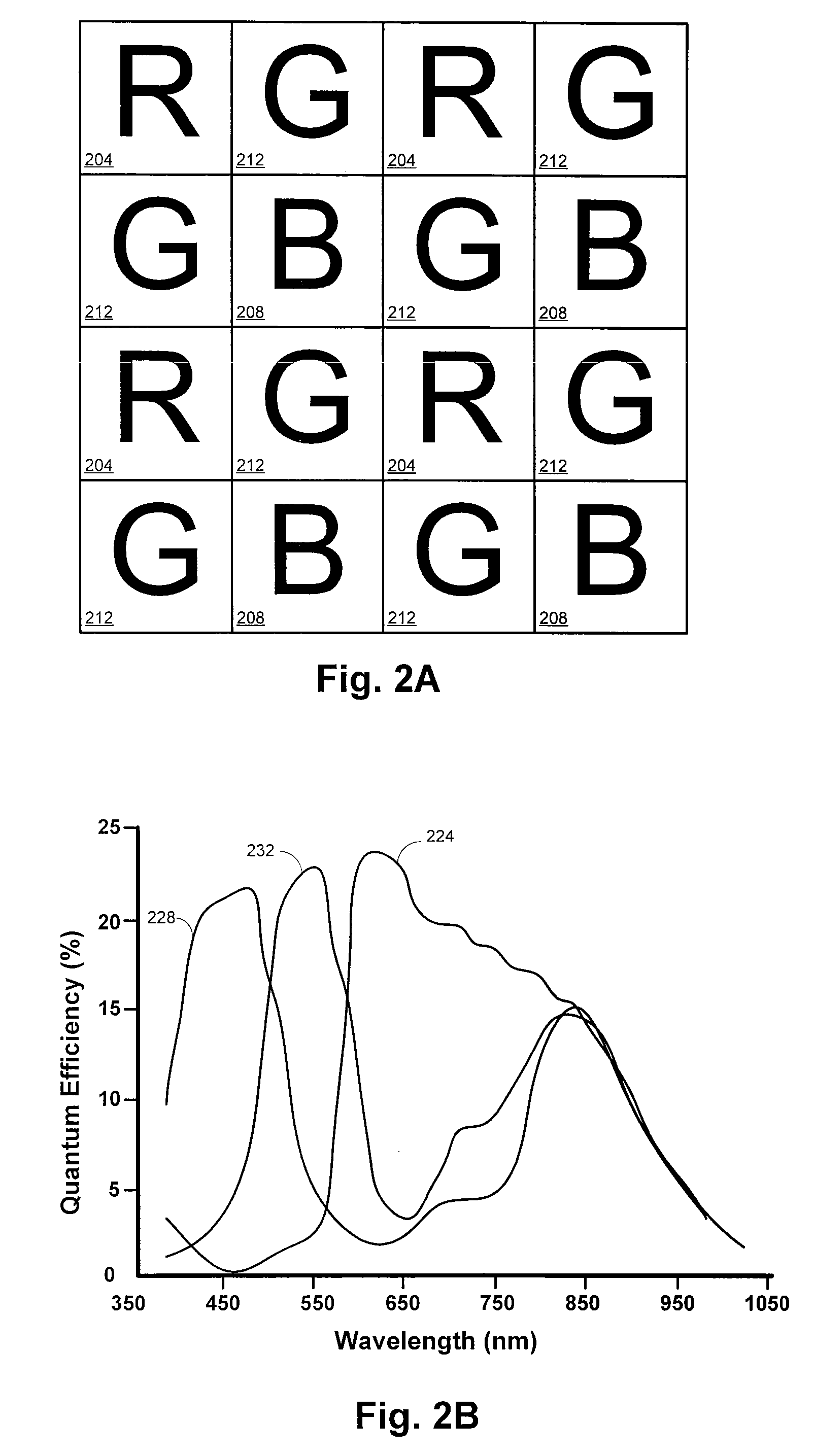
Pixel patterns
InactiveUS20070171290A1Risk minimizationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsHarmonicPixel matrix
The invention discloses an array of pixels to be arranged in electronic color imaging devices, where the risk of aliasing is reduced by arranging the pixels in the array according to irregular patterns. The array is provided with a first, a second and a third set of pixels representing a first, a second and a third color respectively. The pixels in the first set of pixels and / or the pixels in the second set of pixels are arranged in at least a first spatial frequency, and the pixels in the third set of pixels are arranged in at least a second spatial frequency. In addition, one of said first or second set of pixels may be arranged in at least a third spatial frequency. None of said first, second and third spatial frequencies are harmonics of each other. The array may be implemented in one or several different matrixes of pixels.
Owner:TRANSPACIFIC INTELLIGENCE
Color imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20120293695A1Accurate estimateSuppress generationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageAverage filter
A color imaging apparatus comprising: a single-plate color imaging element including color filters arranged on pixels arranged in horizontal and vertical directions where all colors are arranged in each line in the directions; weighted average filters with filter coefficients set in a local area extracted from a mosaic image acquired from the color imaging element corresponding to the weighted average filters so that proportions of sums of the filter coefficients of each color in the lines in the horizontal and vertical directions are equal; a weighted average calculation unit that calculates weighted average values of each color; a demosaicking processing unit that calculates a pixel value of another color at a pixel position of a target pixel of demosaicking processing and that interpolates a pixel value of the target pixel based on a color ratio or a color difference of the calculated weighted average values to calculate the pixel value.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method and apparatus for colour imaging a three-dimensional structure
ActiveUS20060001739A1Accurate mappingImage enhancementImpression capsComputer graphics (images)Tooth segment
A device for determining the surface topology and associated color of a structure, such as a teeth segment, includes a scanner for providing depth data for points along a two-dimensional array substantially orthogonal to the depth direction, and an image acquisition means for providing color data for each of the points of the array, while the spatial disposition of the device with respect to the structure is maintained substantially unchanged. A processor combines the color data and depth data for each point in the array, thereby providing a three-dimensional color virtual model of the surface of the structure. A corresponding method for determining the surface topology and associated color of a structure is also provided.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
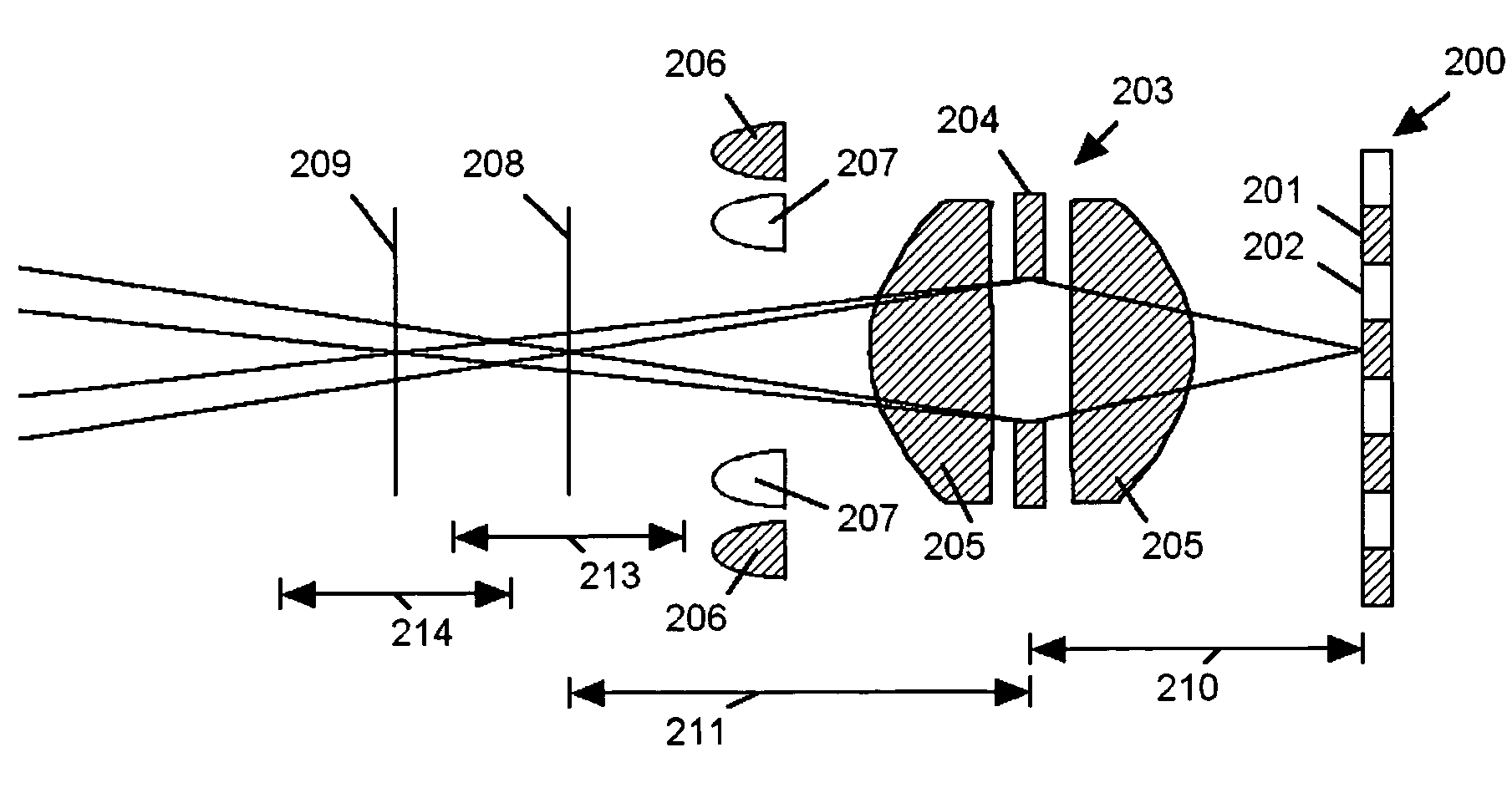
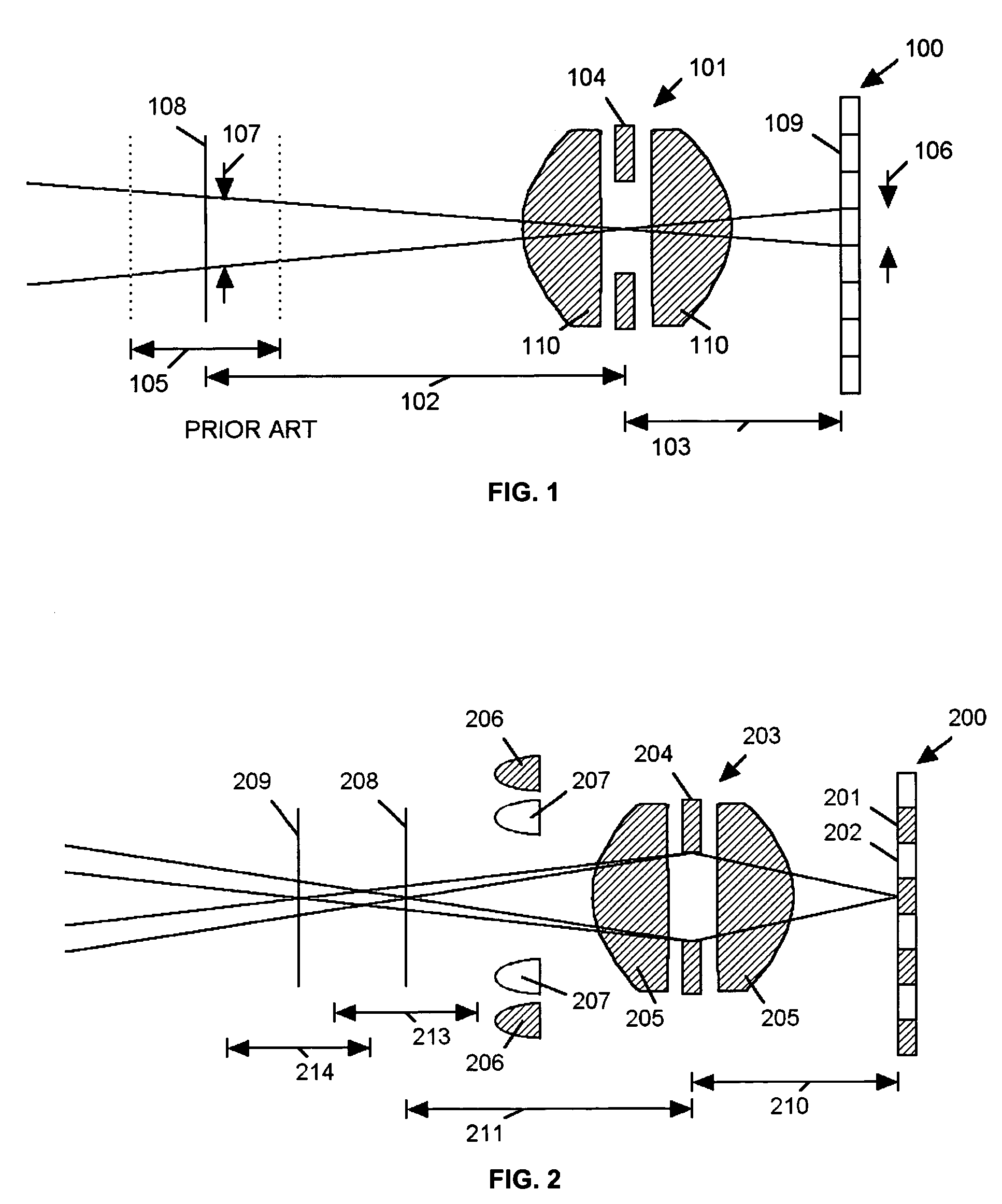
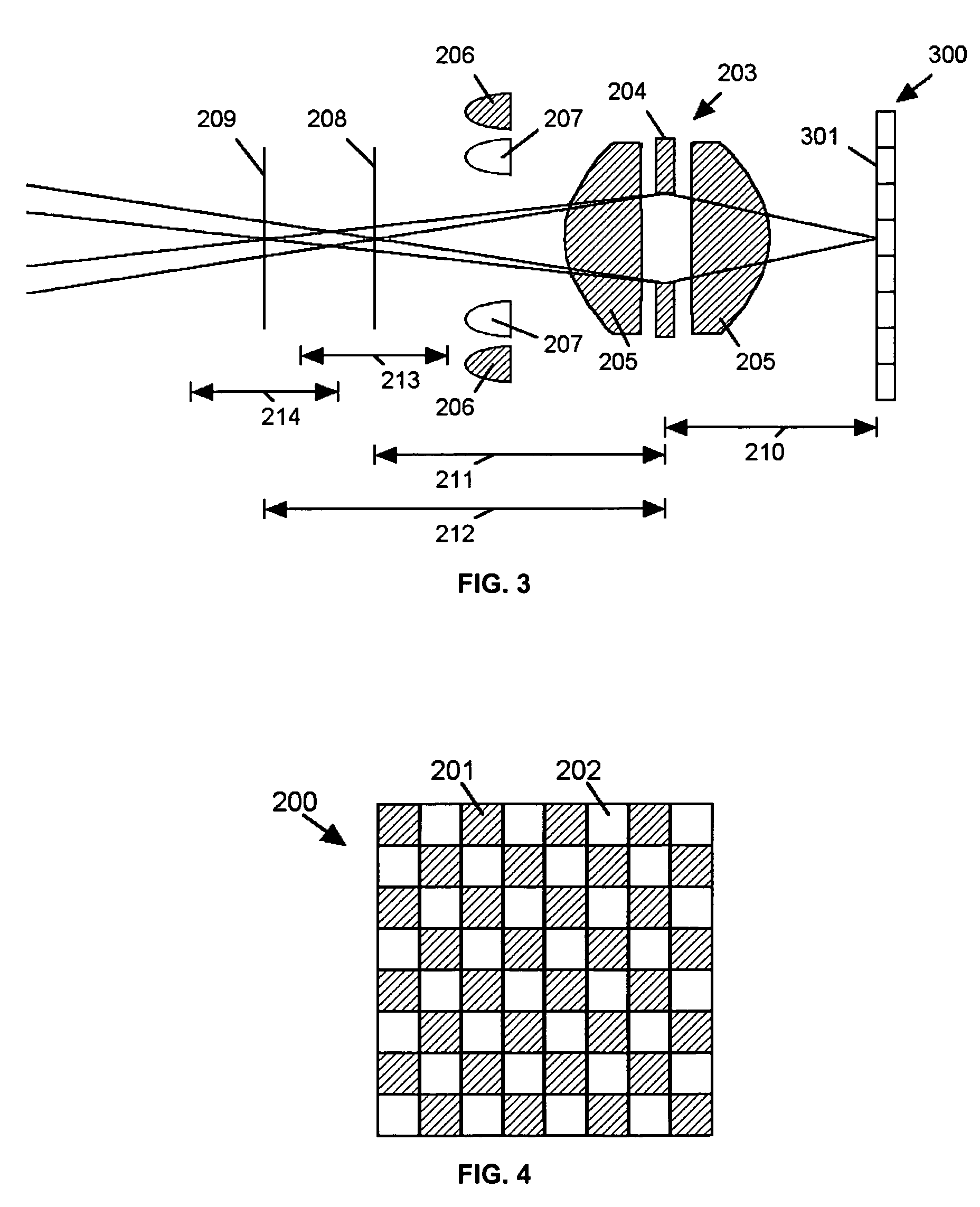
Extended depth of field imaging system using chromatic aberration
ActiveUS7224540B2Lower optical magnificationHigh intensity illuminationRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFocal positionDepth of field
An imaging system (FIG. 3) is disclosed that has a wavelength dependent focal shift caused by longitudinal chromatic aberration in a lens assembly (203) that provides extended depth of field imaging due to focal shift (213,214) and increased resolution due to reduced lens system magnification. In use, multiple wavelengths of quasi-monochromatic illumination, from different wavelength LEDs (206,207) or the like, illuminate the target, either sequentially, or in parallel in conjunction with an imager (200) with wavelength selective (colored) filters. Images are captured with different wavelengths of illumination that have different focus positions (208,209), either sequentially or by processing the color planes of a color imager separately. Extended depth of field, plus high resolution are achieved. Additionally, information about the range to the target can be determined by analyzing the degree of focus of the various colored images.
Owner:PSC SCANNING INC
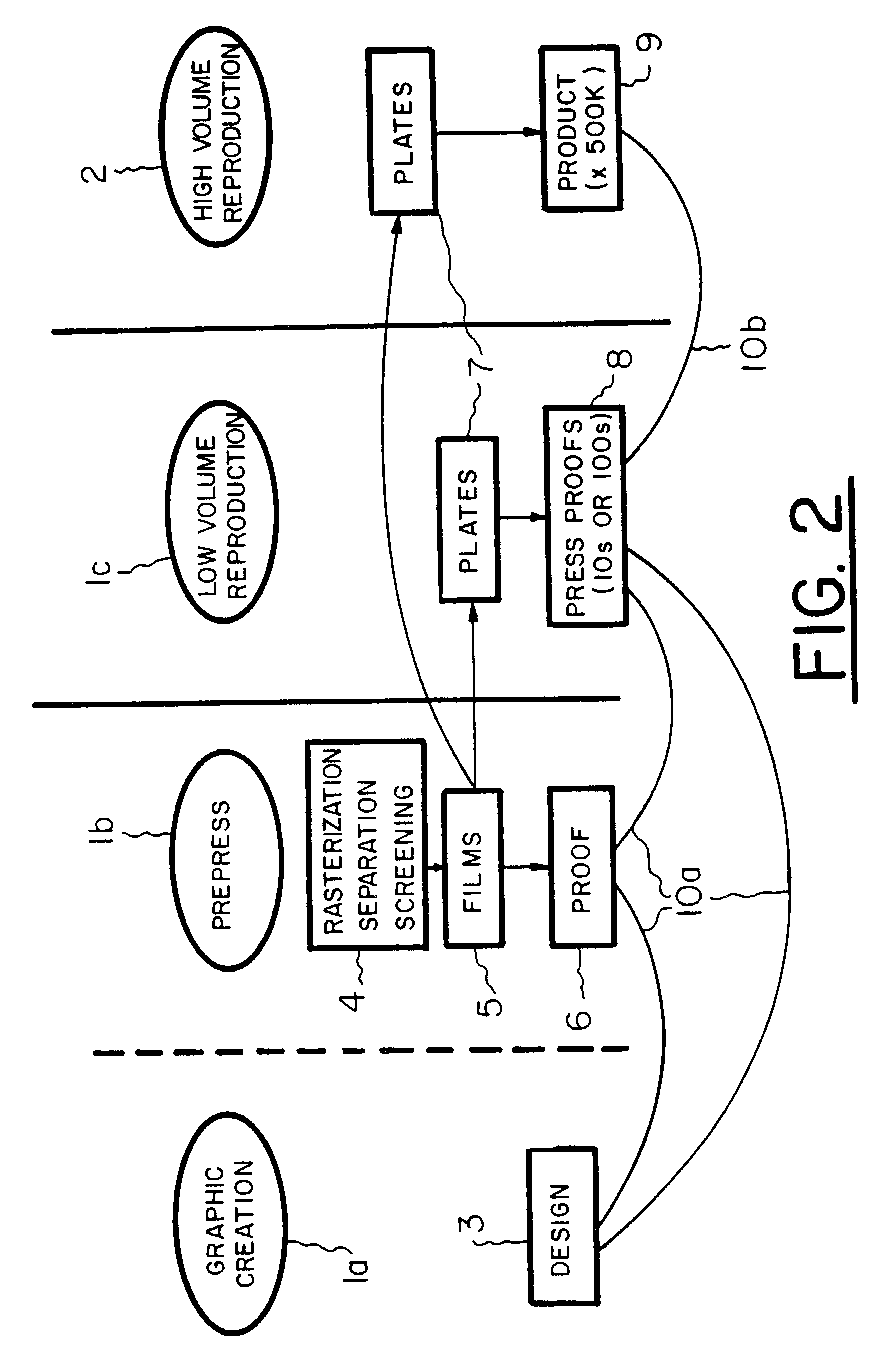
System for distributing and controlling color reproduction at multiple sites
InactiveUS7075643B2Provide accuratelyMinimize involvementImage enhancementRadiation pyrometryMeasuring instrumentSpectrograph
In the color imaging system, multiple rendering devices are provided at different nodes along a network. Each rendering device has a color measurement instrument for calibrating the color presented by the rendering device. A rendering device may represent a color display in which a member surrounds the outer periphery of the screen of the display and a color measuring instrument is coupled to the first member. The color measuring instrument includes a sensor spaced from the screen at an angle with respect to the screen for receiving light from an area of the screen. A rendering device may be a printer in which the measuring of color samples on a sheet rendered by the printer is provided by a sensor coupled to a transport mechanism which moves the sensor and sheet relative to each other, where the sensor provides light from the sample to a spectrograph. The color measuring instruments provide for non-contact measurements of color samples either displayed on a color display, or printed on a sheet, and are self-calibrating by the use of calibration references in the instrument.
Owner:RAH COLOR TECH
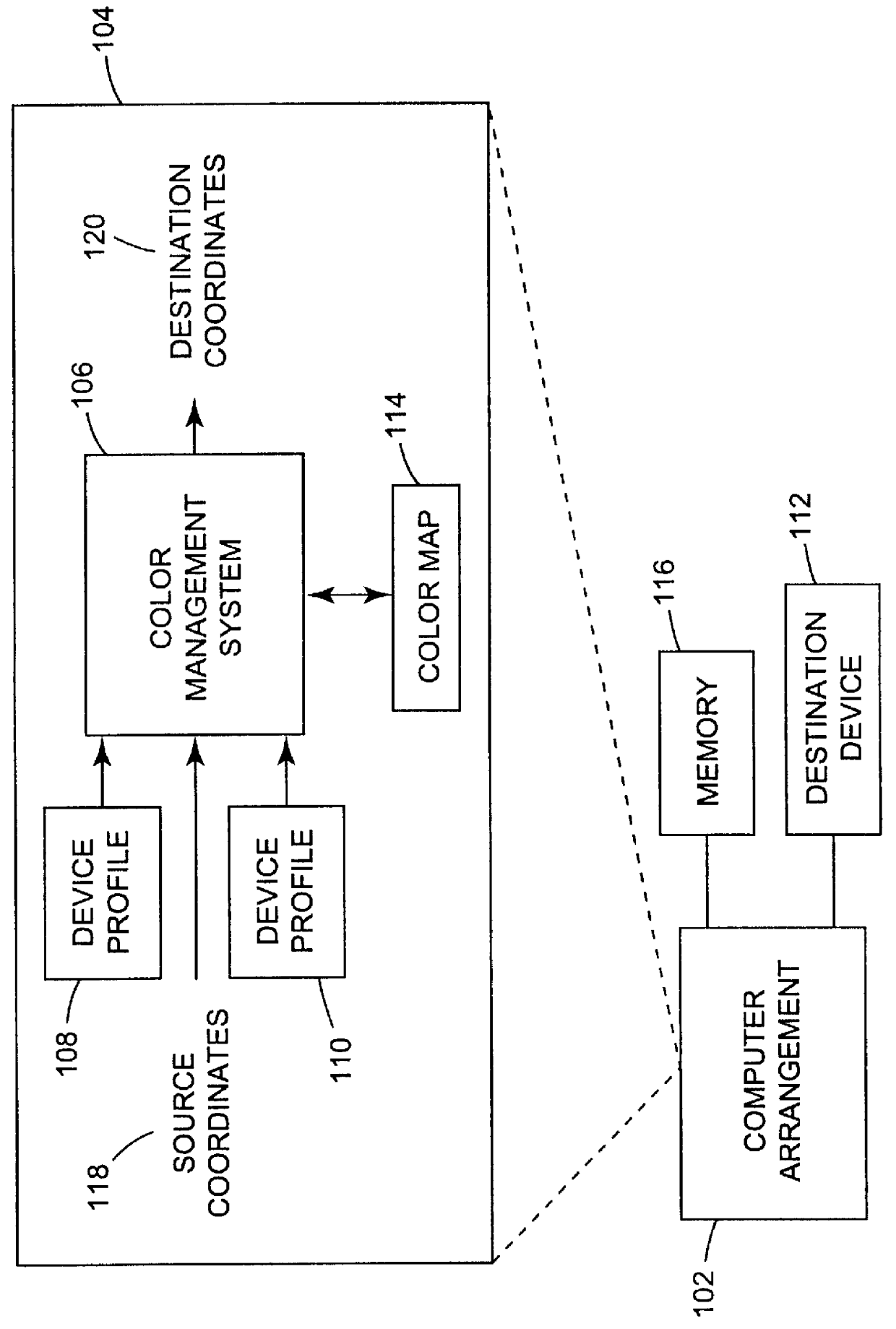
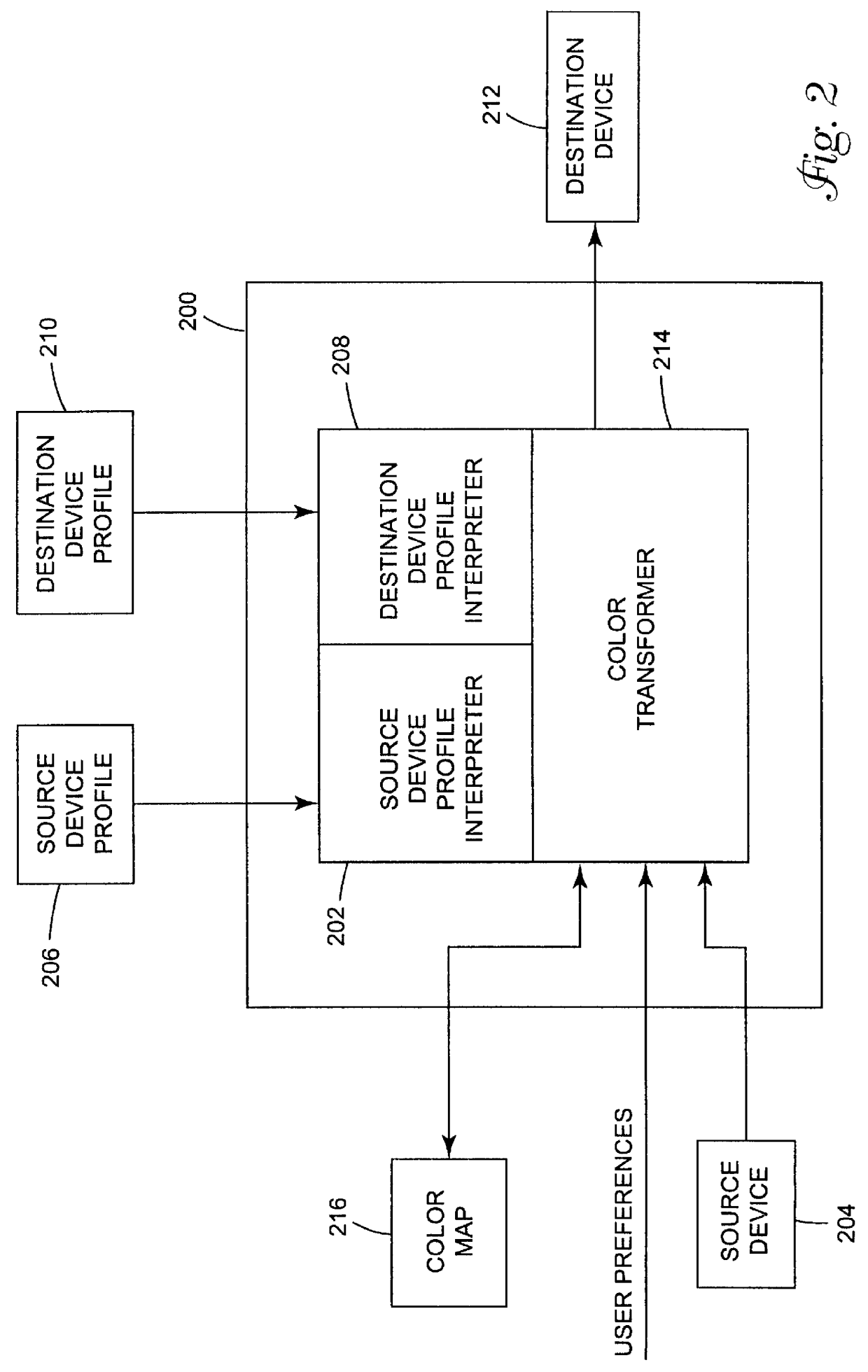
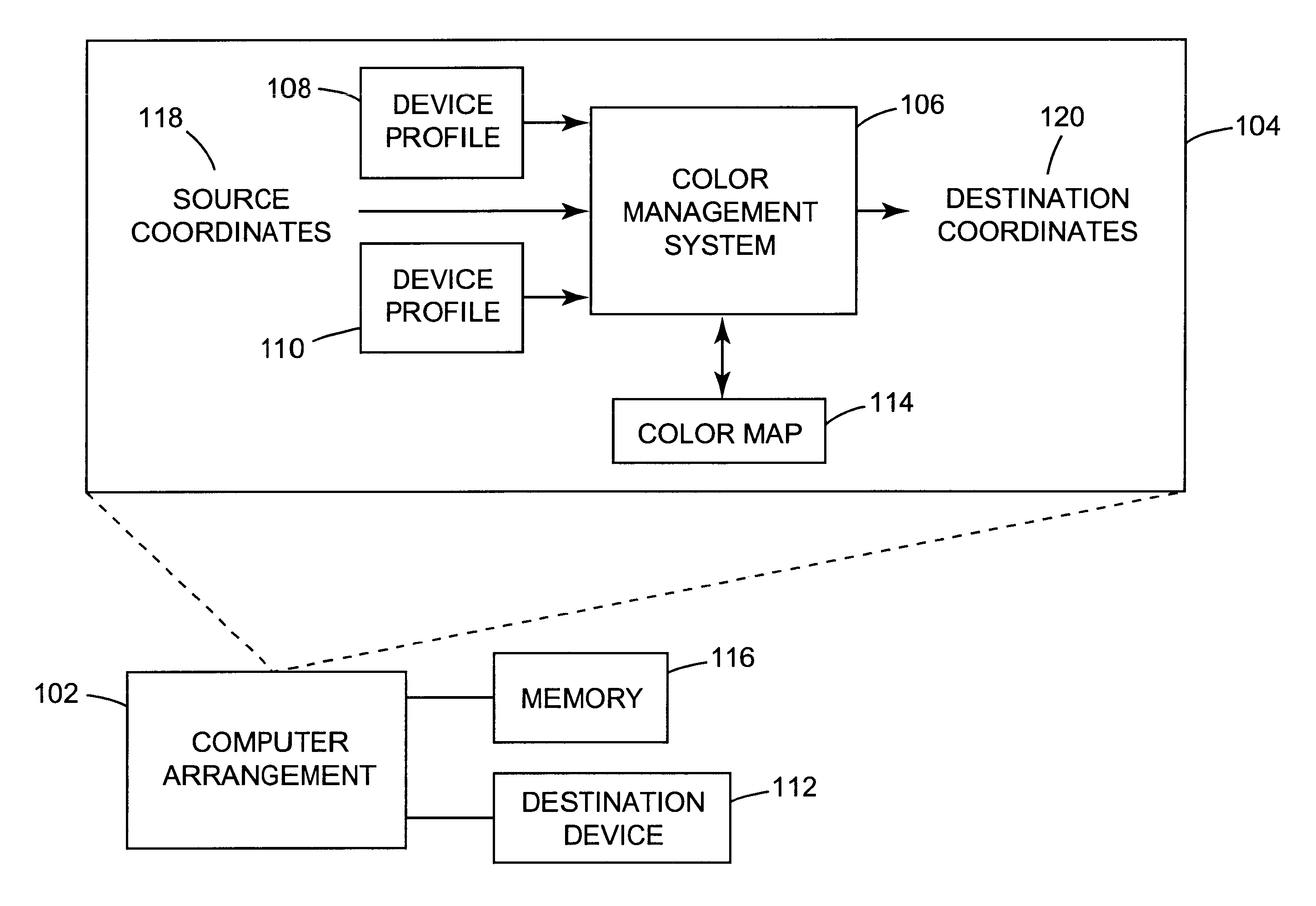
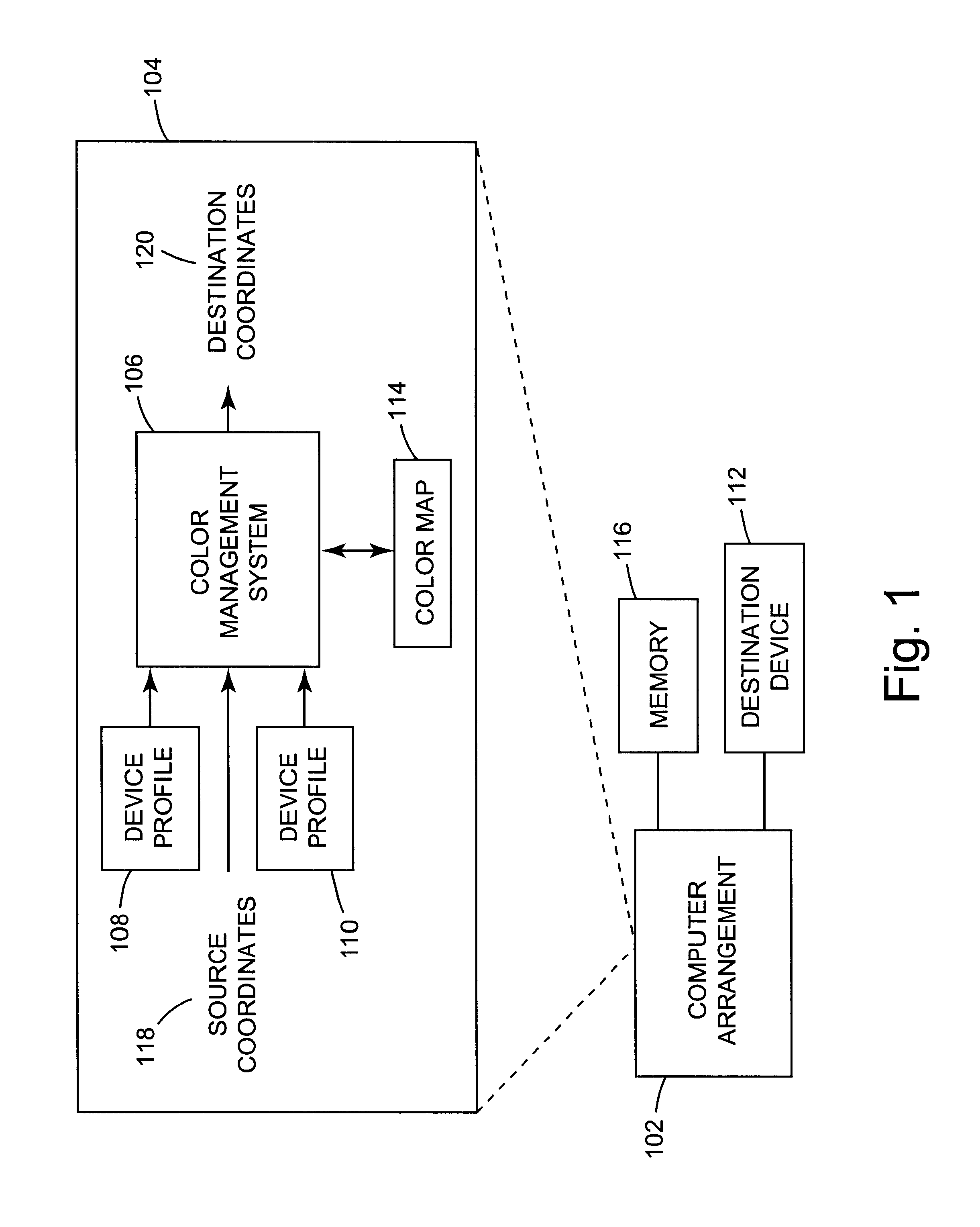
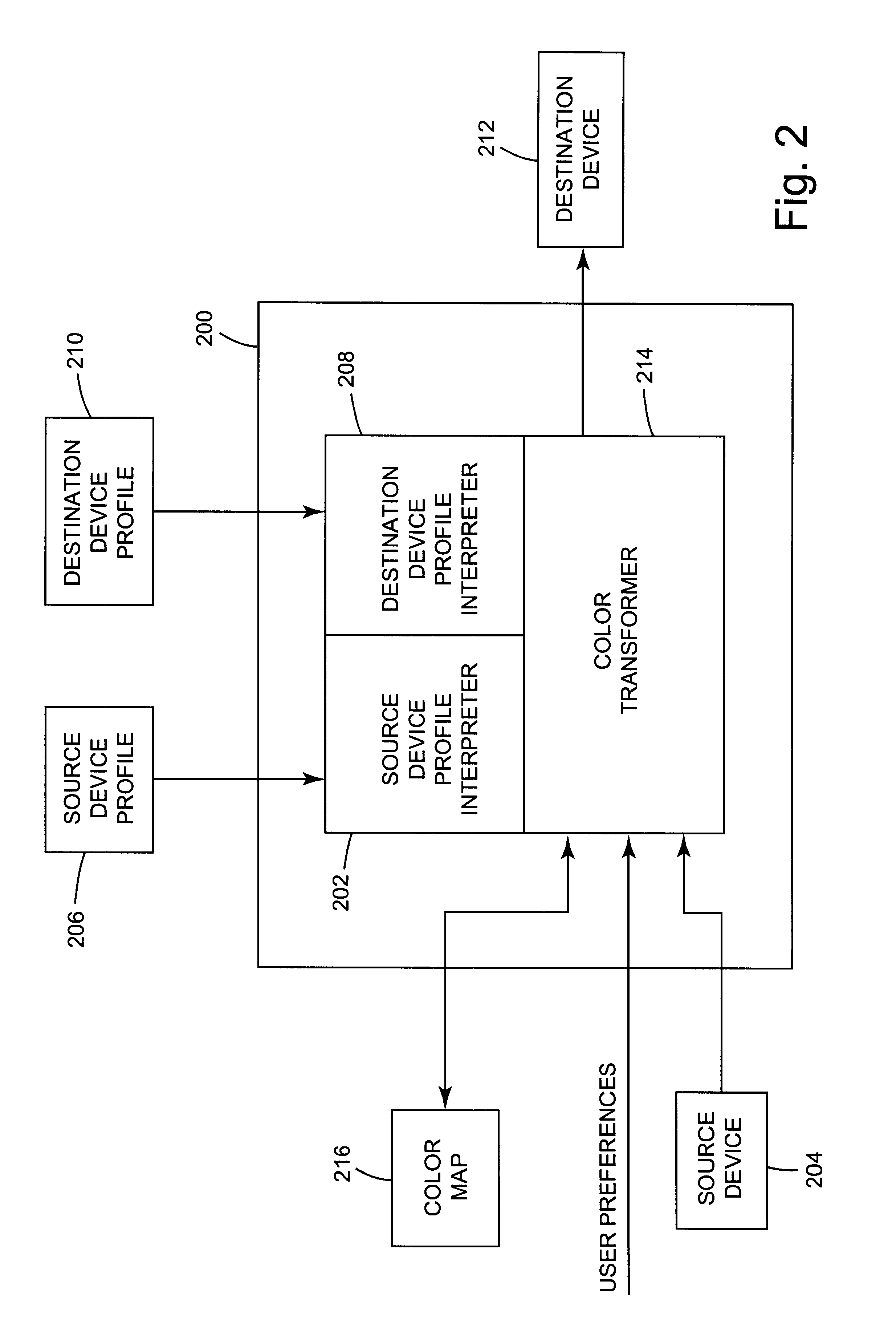
Arrangement for mapping colors between imaging systems and method therefor
A color mapping method is used in transforming colors between color imaging systems. The method includes using forward transformation profiles that characterize the color imaging systems to generate respective sets of device-independent color values for the color imaging systems. Color conversions are calculated by recursively reducing differences between the respective sets of device-independent color values. Based on these color conversions, a color map is constructed that describes a relationship between the color imaging systems.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
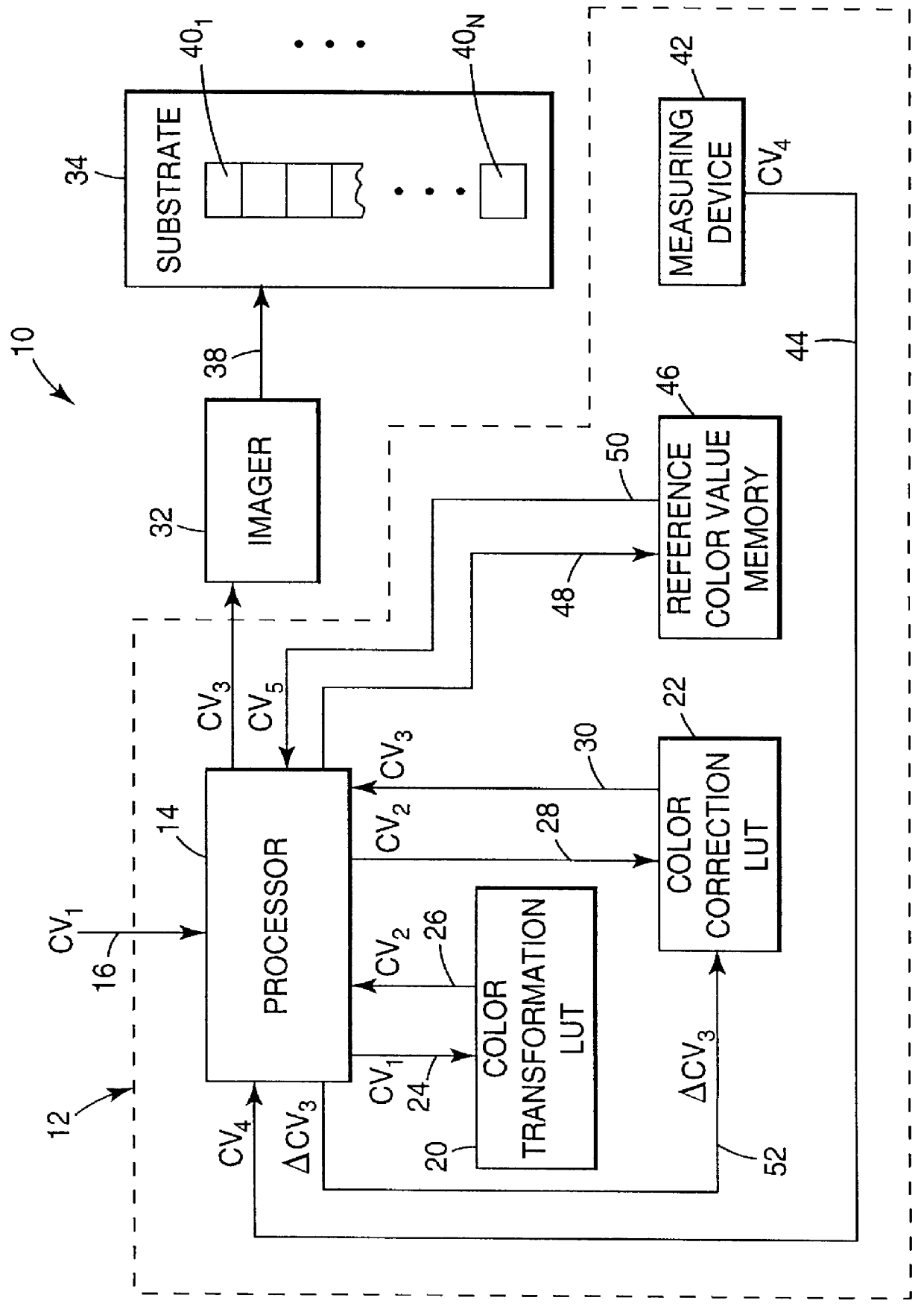
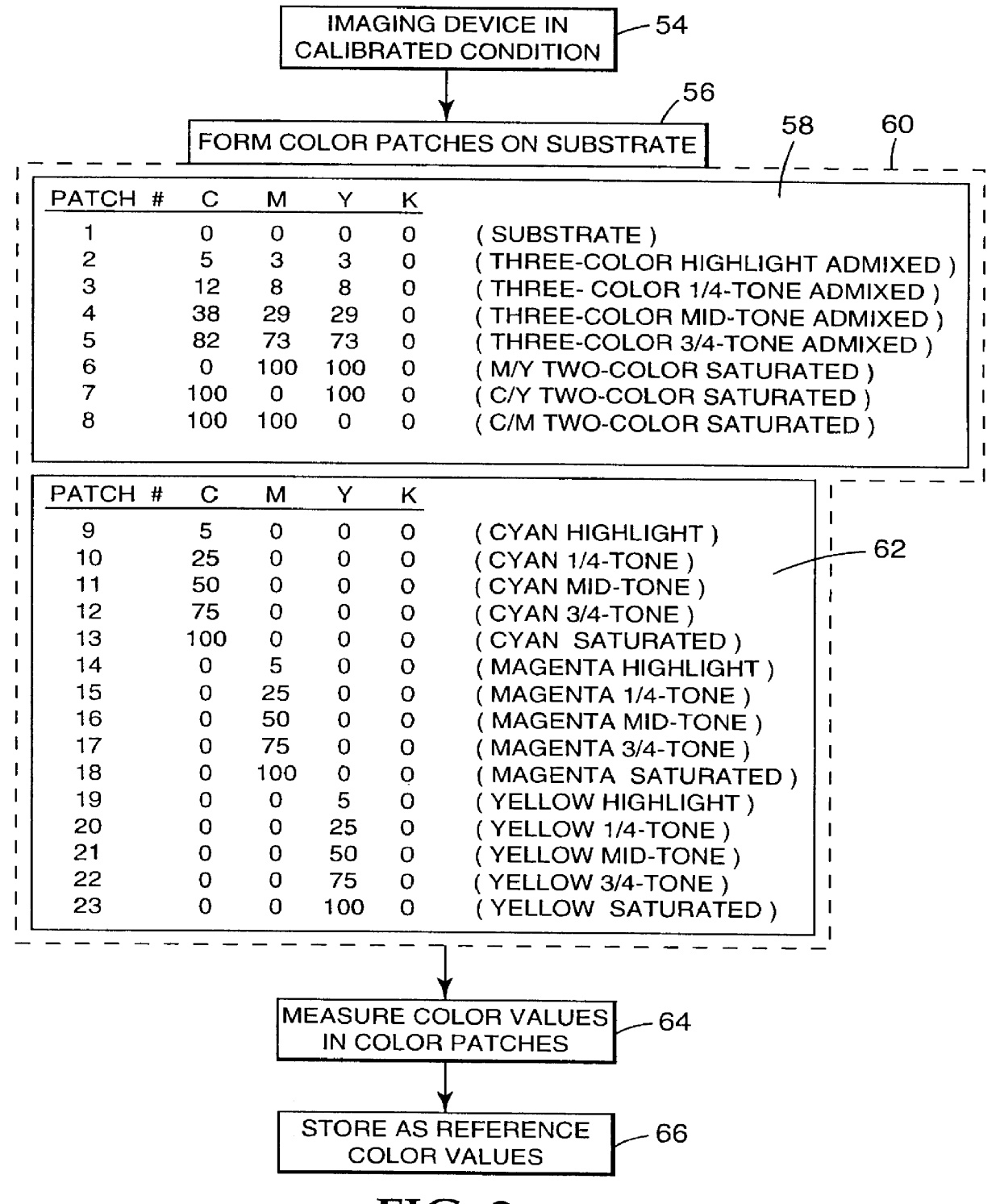
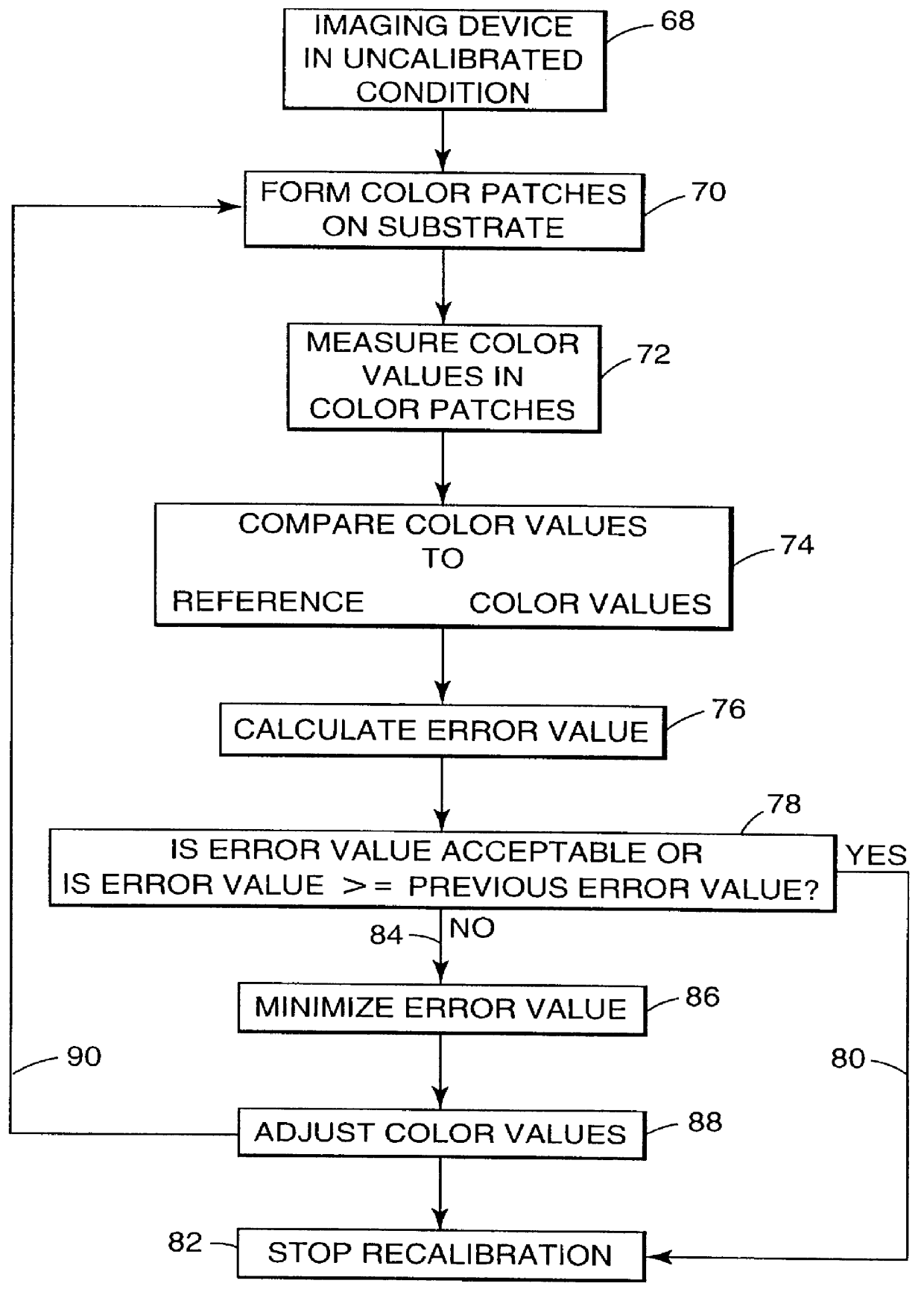
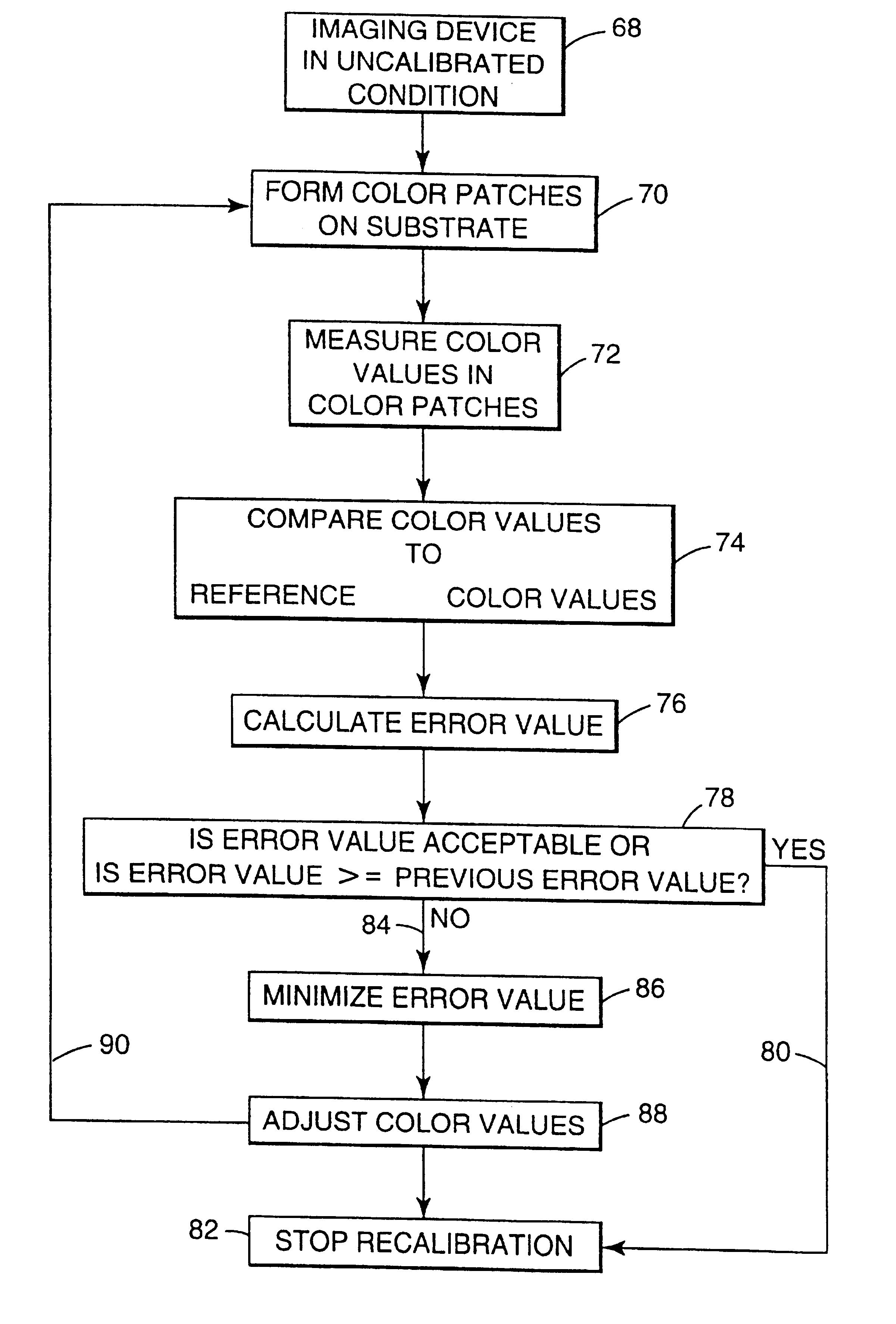
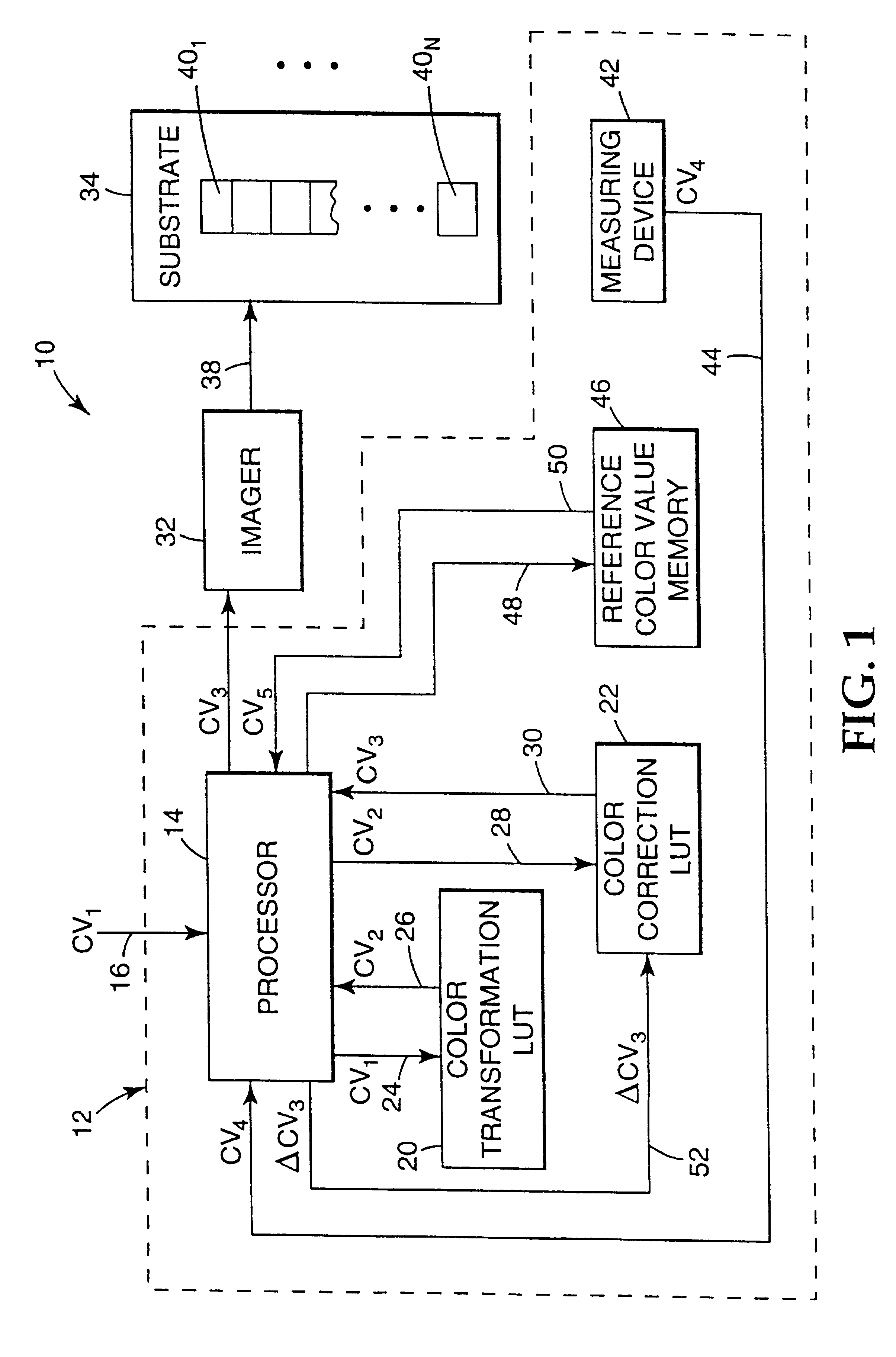
Recalibrating a multi-color imaging system
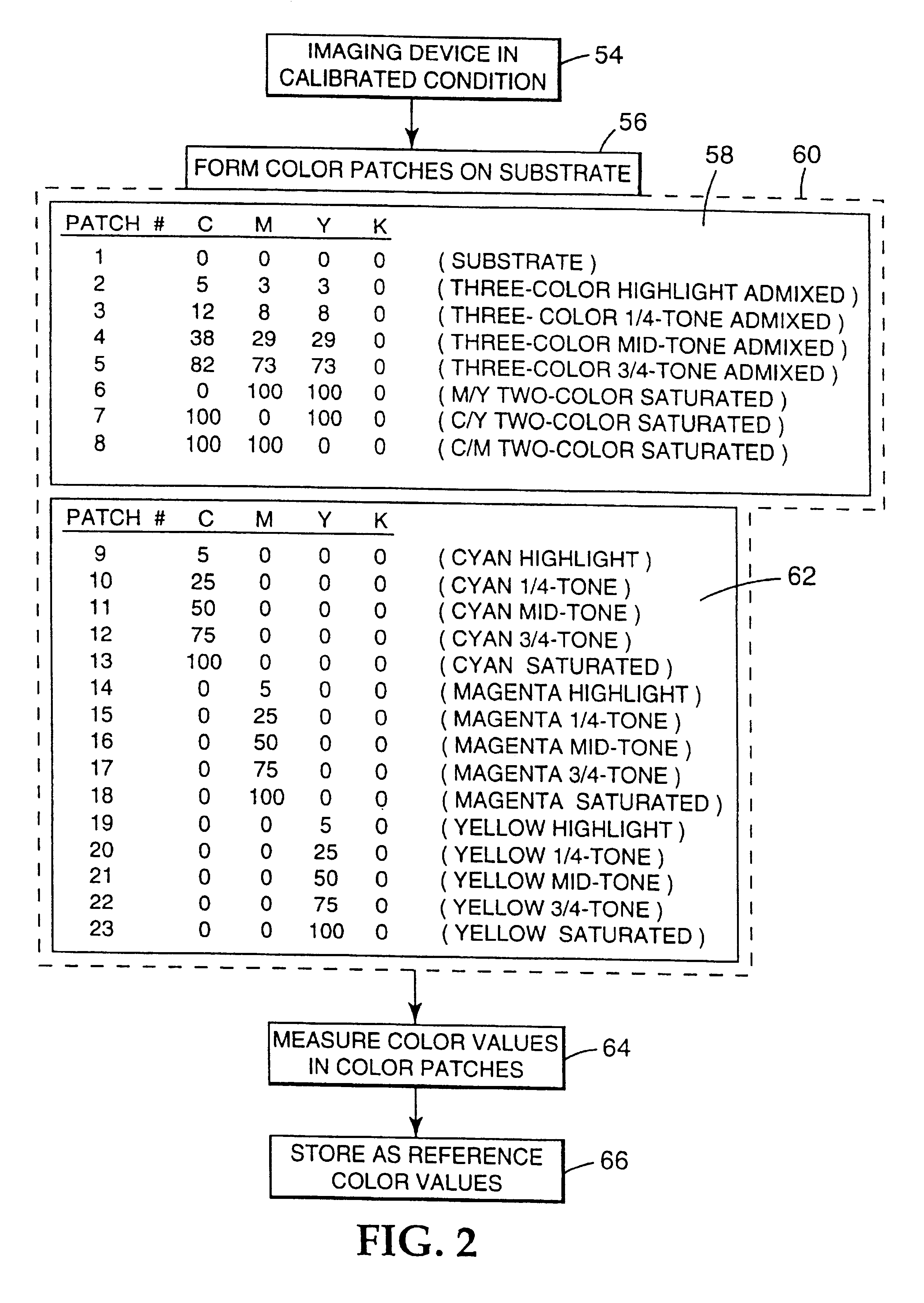
An apparatus and method for recalibrating a multi-color imaging system are provided. The multi-color imaging system is capable of applying different colorants to a substrate based on a plurality of input color values. The input color values control amounts of the colorants to be applied to the substrate by the imaging system. A subset of the input color values is selected and used to control the imaging system to apply one or more of the different colorants to the substrate, thereby forming a plurality of different color patches on the substrate. The subset of input color values is selected such that one or more of the different color patches is formed by application of a combination of at least two of the different colorants to the substrate. Color values are measured for each of the different color patches, and compared to reference color values, representing a calibrated condition of the imaging system. An error value is calculated. The error value represents a deviation of the measured color values from the reference color values. The input color values for each colorant then are independently adjusted to reduce the error value to a predetermined degree.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Arrangement for mapping colors between imaging systems and method therefor
InactiveUS6362808B1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsColor transformationColor mapping
A color mapping method is used in transforming colors between color imaging systems. The method includes using forward transformation profiles that characterize the color imaging systems to generate respective sets of device-independent color values for the color imaging systems. Color conversions are calculated by reducing differences between the respective sets of device-independent color values. Based on these color conversions, a color map is constructed that describes a relationship between the color imaging systems.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
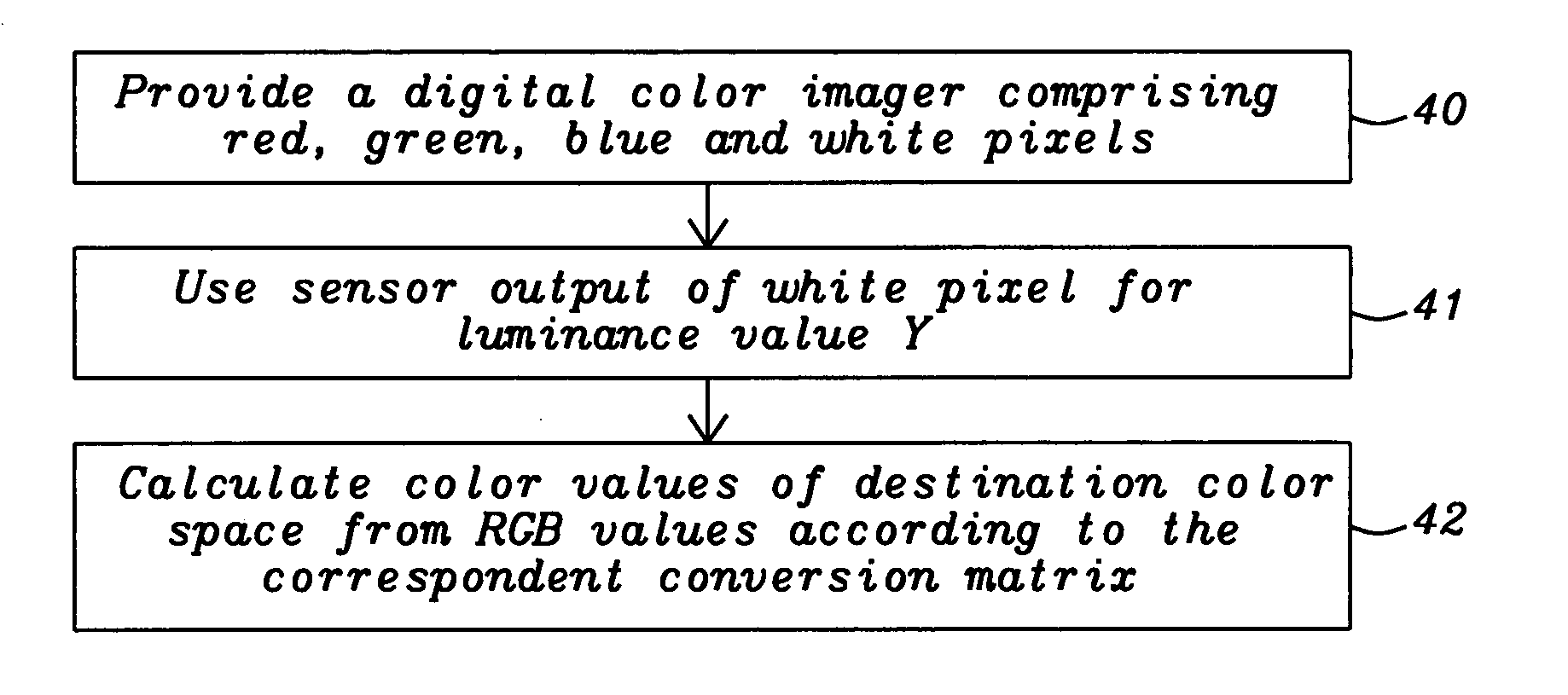
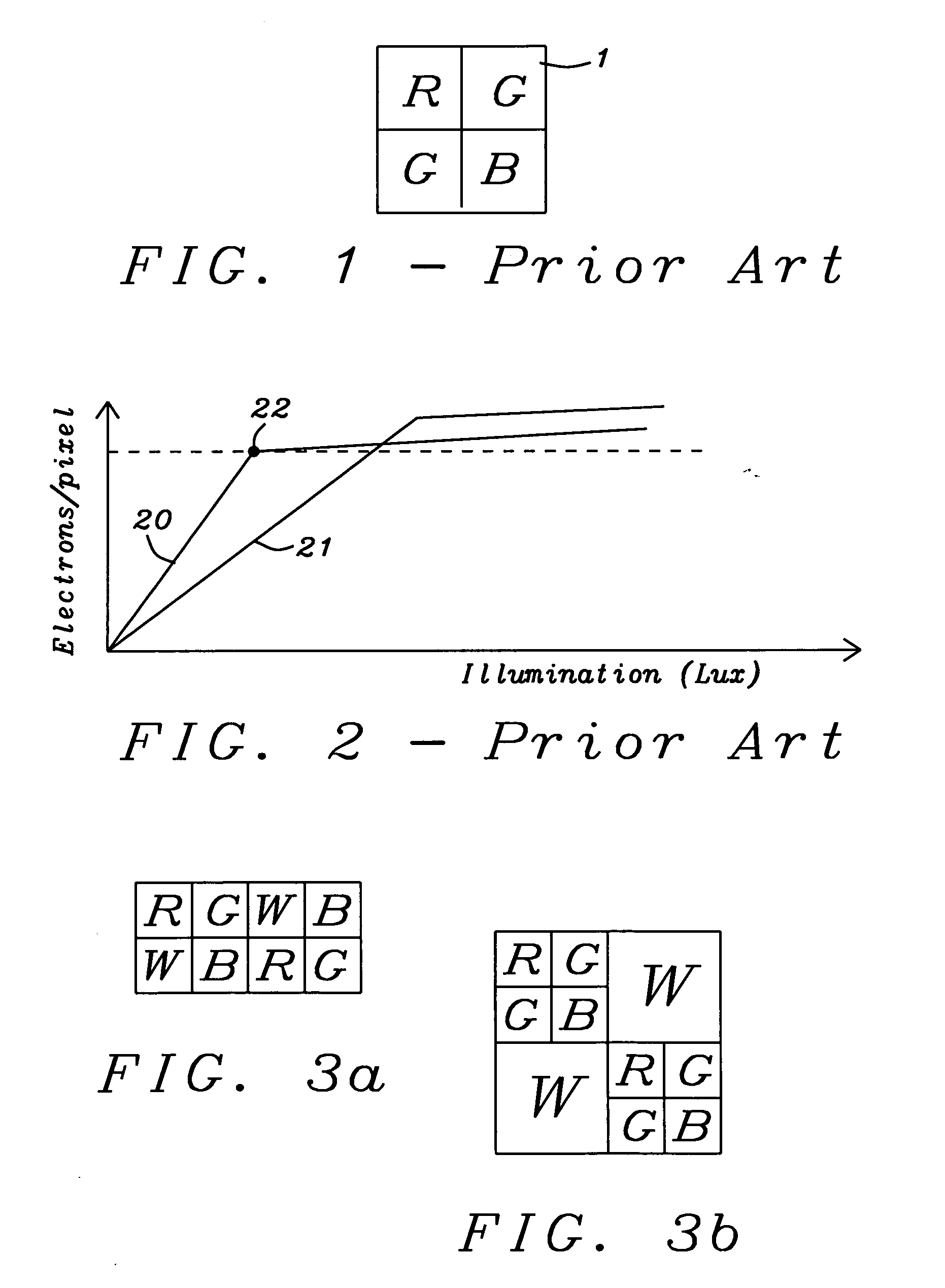
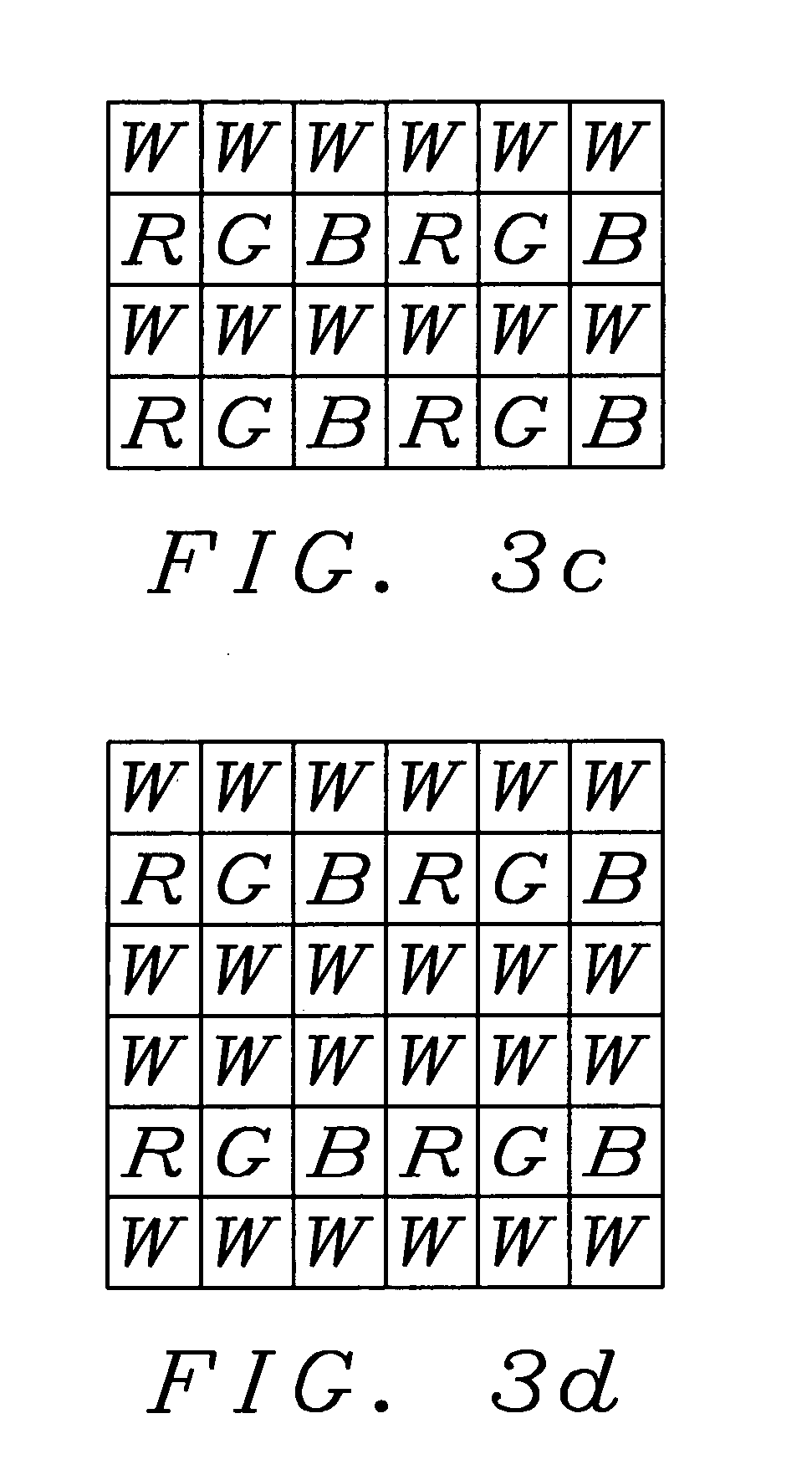
Extended dynamic range in color imagers
ActiveUS20050248667A1Increase the luminous rangeGood colorTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsYcbcr color spaceLarge size
A digital color imager providing an extended luminance range, an improved color implementation and enabling a method for an easy transformation into another color space having luminance as a component has been achieved. Key of the invention is the addition of white pixels to red, green and blue pixels. These white pixels have either an extended dynamic rang as described by U.S. patent (U.S. Pat. No. 6,441,852 to Levine et al.) or have a larger size than the red, green, or blue pixels used. The output of said white pixels can be directly used for the luminance values Y of the destination color space. Therefore only the color values and have to be calculated from the RGB values, leading to an easier and faster calculation. As an example chosen by the inventor the conversion to YCbCr color space has been shown in detail.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Convergent parameter instrument
InactiveUS20120078113A1Advanced technologyLow-cost and robust and portableMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringControl setImaging technique
The present invention relates to a convergent parameter instrument and method for performing real-time imaging using multiple imaging techniques. More particularly, the present invention relates to a handheld convergent parameter instrument providing some or preferably all of real-time imaging, including surface mapping, color imaging, perfusion imaging, thermal imaging, and near infrared spectroscopy, and including a common control set and a common display.
Owner:POINT OF CONTACT
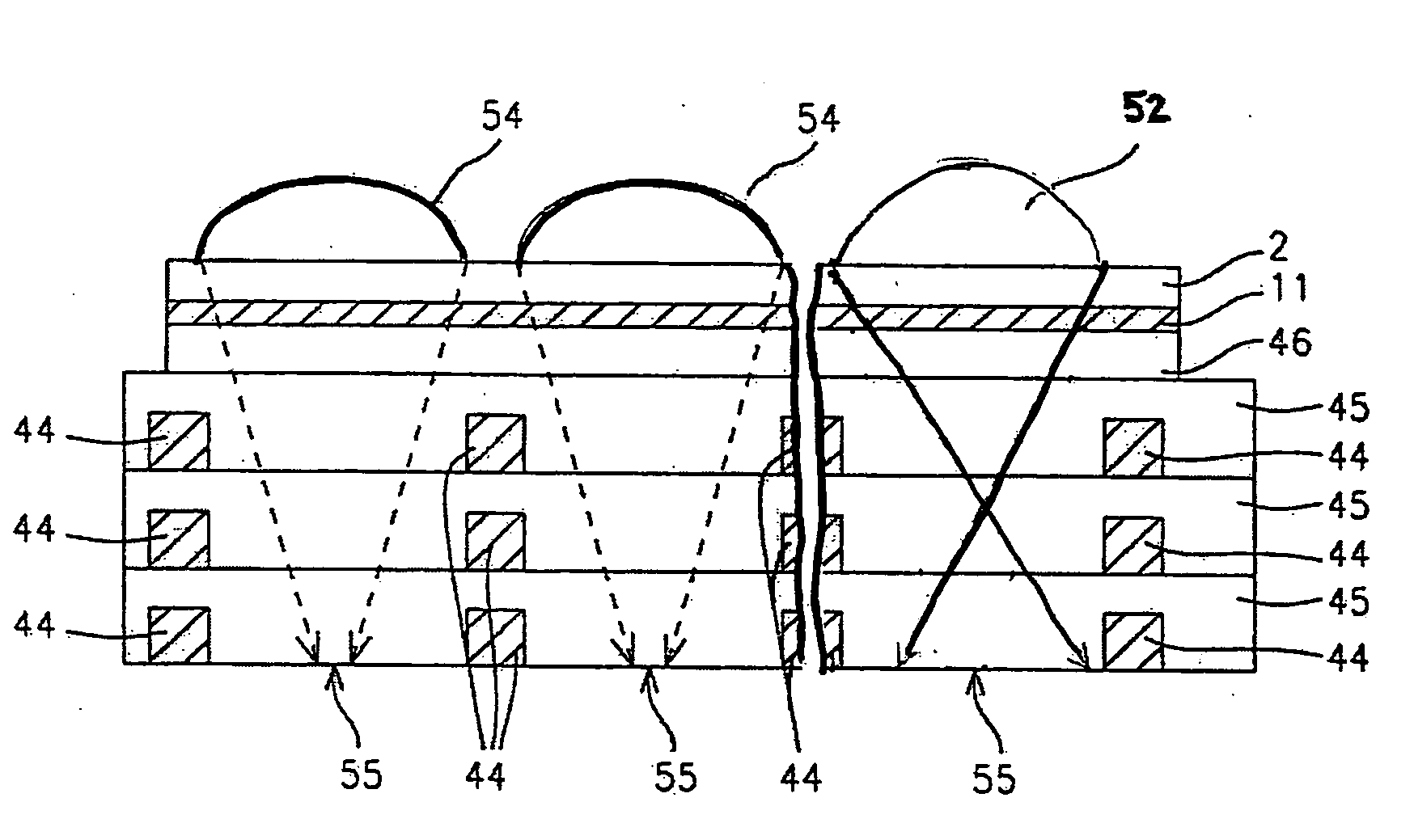
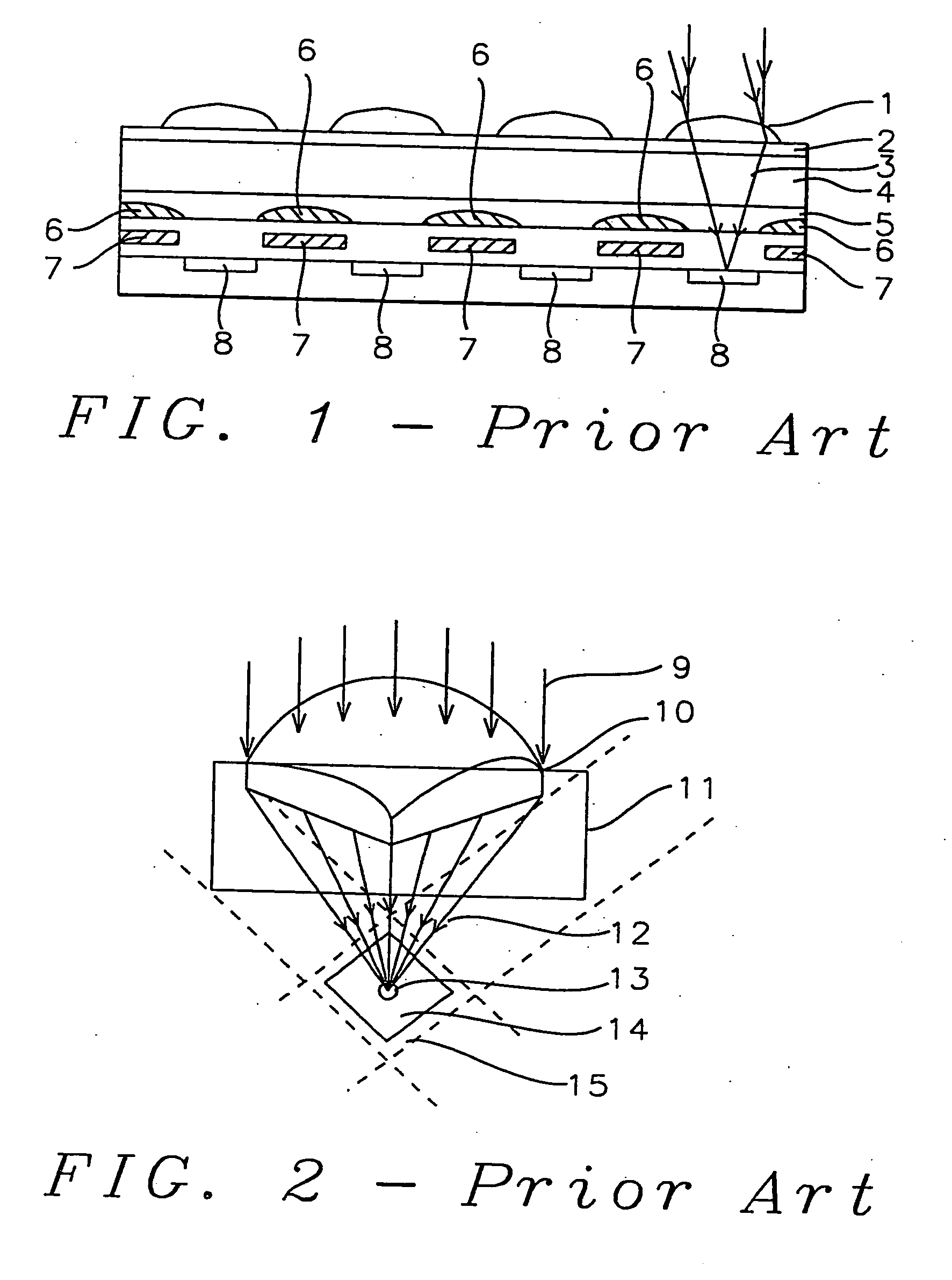
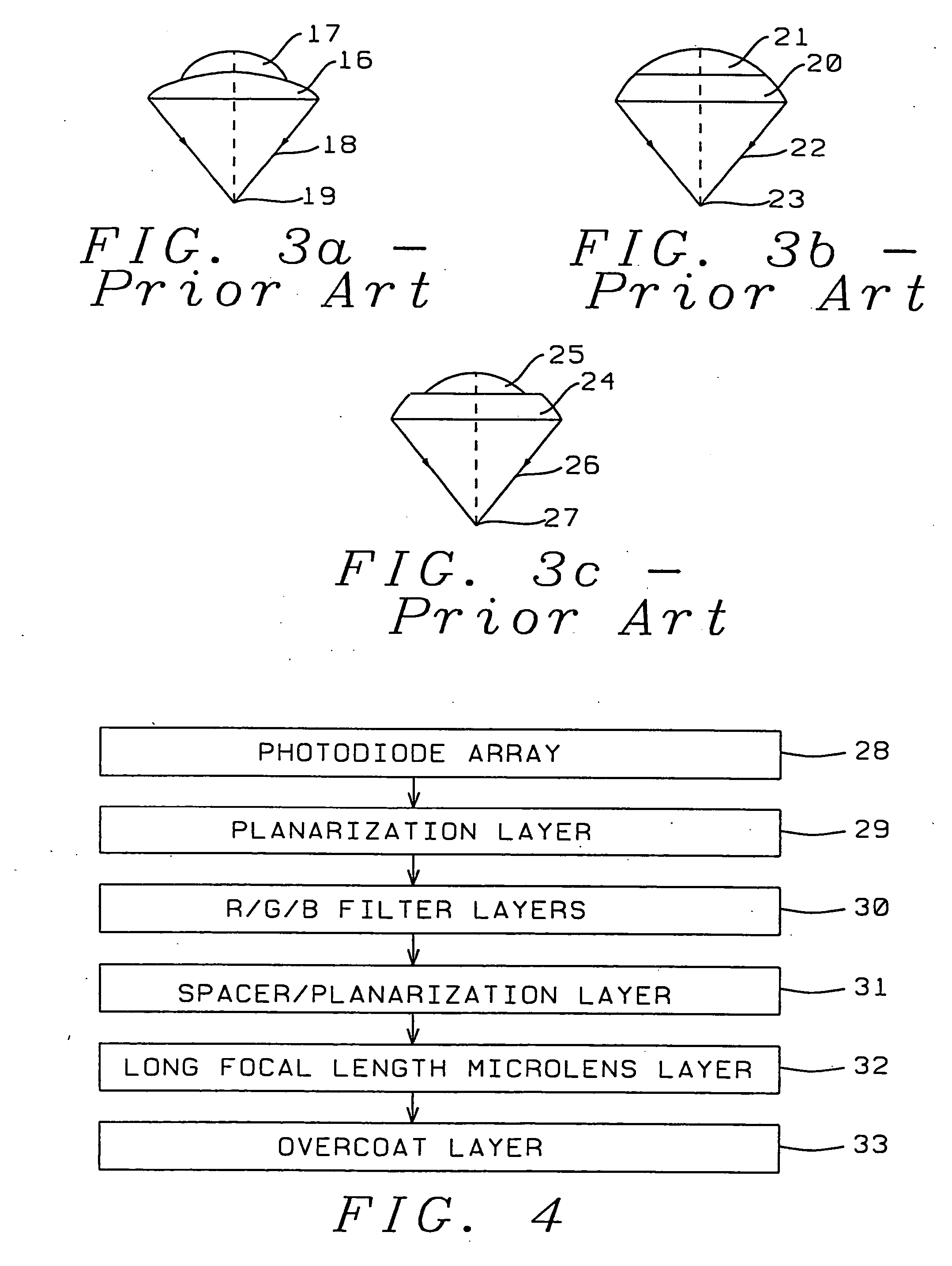
High transmittance overcoat for microlens arrays in semiconductor color imagers
InactiveUS20050041296A1Improve focus performanceHigh light transmittanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSHigh volume manufacturing
A transmittance overcoat with effectively planar top surface and specified optical and materials properties is applied above a microlens layer to extend the focal length and enhance the performance of long focal length microlenses for semiconductor array color imaging devices. The geometrical optics design factors and microelectric fabrication sequence to achieve optimized long focal length microlens performance are disclosed. The principal advantages of the adaptive process taught in the present invention is shown to enable real-time compensation adjustments for process and material variations. The overcoat process enables simplified single-layer integrated microlens optics for low-cost, high volume manufacturing of CMOS and CCD color video cameras.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
White-light spectral biometric sensors
Methods and systems are provided for performing a biometric function. A purported skin site of an individual is illuminated with white light. Light scattered from the purported skin site is received with a color imager on which the received light is incident. Spatially distributed images of the purported skin site are derived and correspond to different volumes of illuminated tissue of the individual. The images are analyzed to perform the biometric function.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
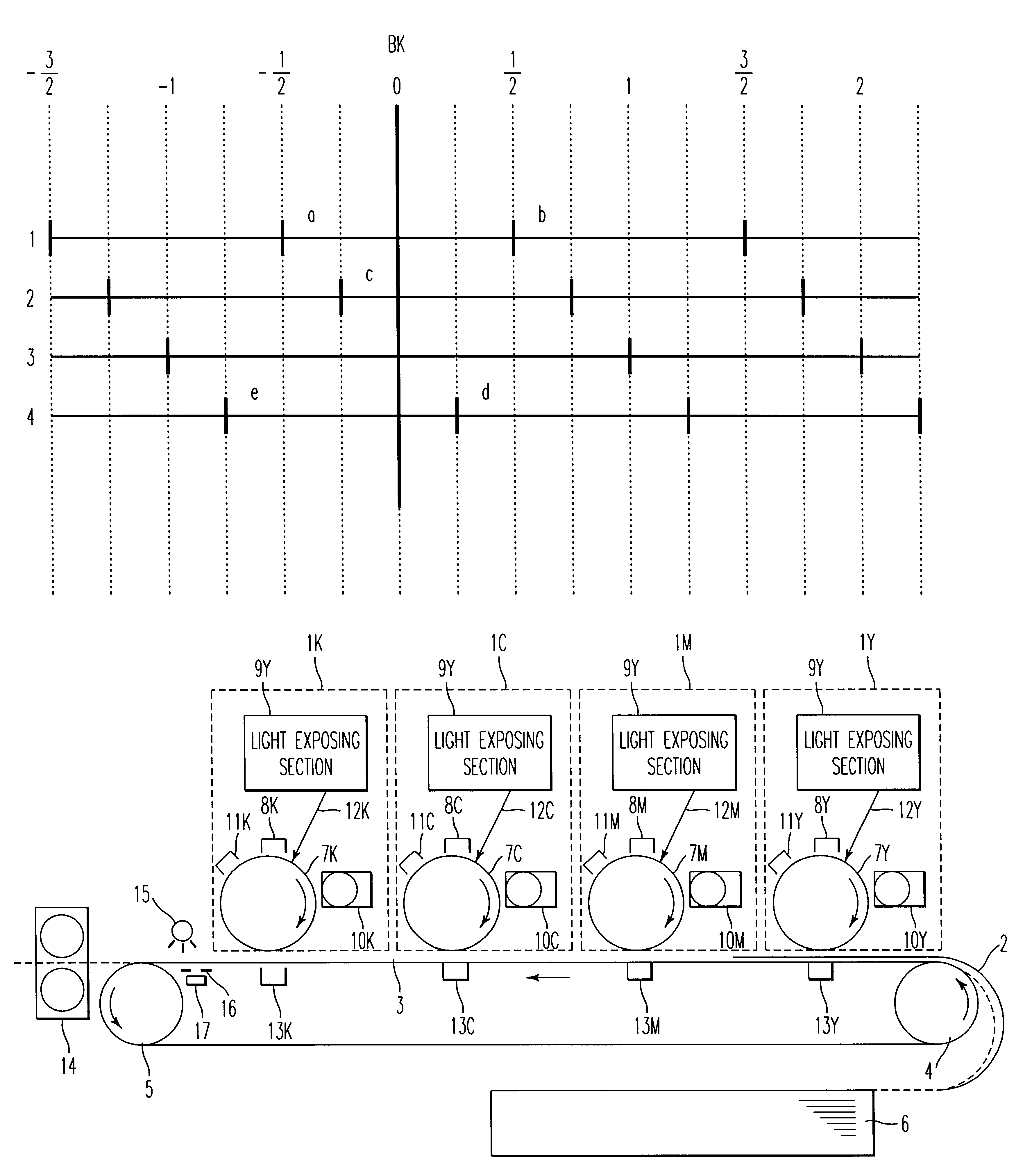
Dot position correcting apparatus, optical scanning apparatus, imaging apparatus, and color imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20060285186A1Without costAccurate lightingPrintingPictoral communicationOptoelectronicsOptical scanning
An optical scanning apparatus is disclosed that includes a light source unit having plural main light sources that are two-dimensionally arranged in the main scanning direction and the sub scanning direction, and plural sub light sources that are arranged between rows of the main light sources aligned in the main scanning direction. The optical scanning apparatus also includes an optical system configured to scan light emitted from the light source unit on a scanning object to form an image on the scanning object, and a control apparatus configured to adjust a main scanning direction image position by controlling two of the main light sources that are juxtaposed to each other with respect to the main scanning direction and adjust a sub scanning direction image position by controlling a main light source and a sub light source that are adjacent to each other.
Owner:RICOH KK
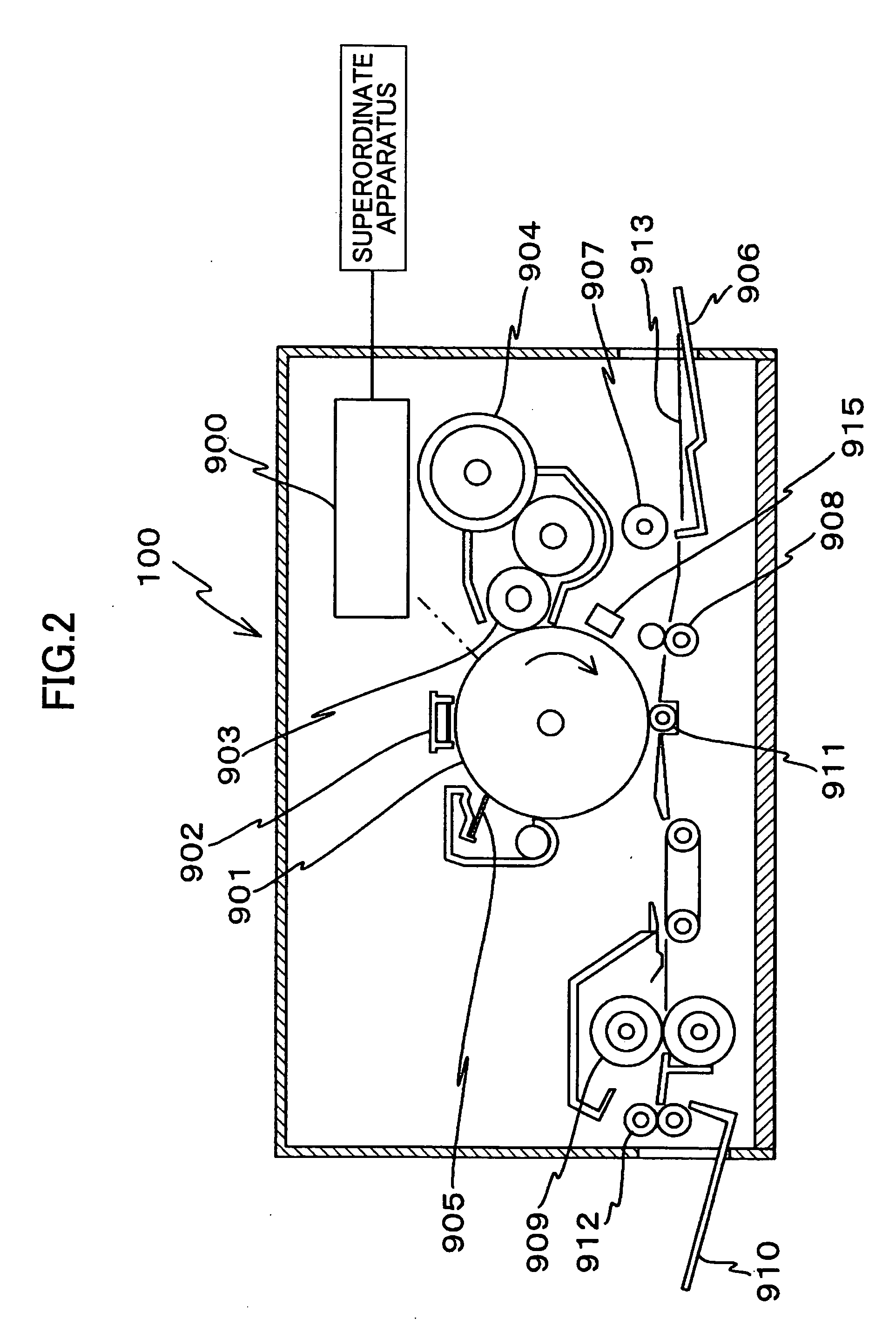
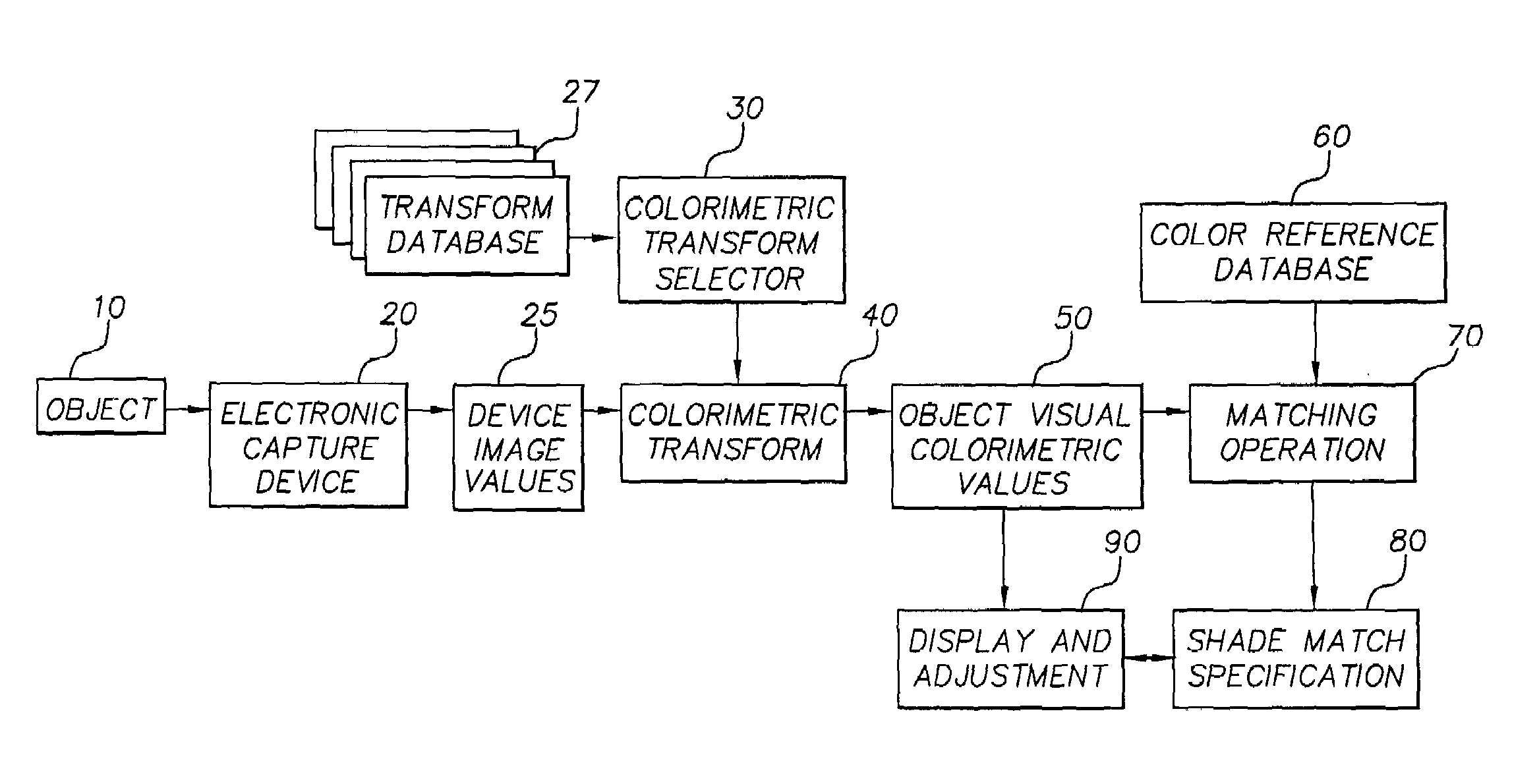
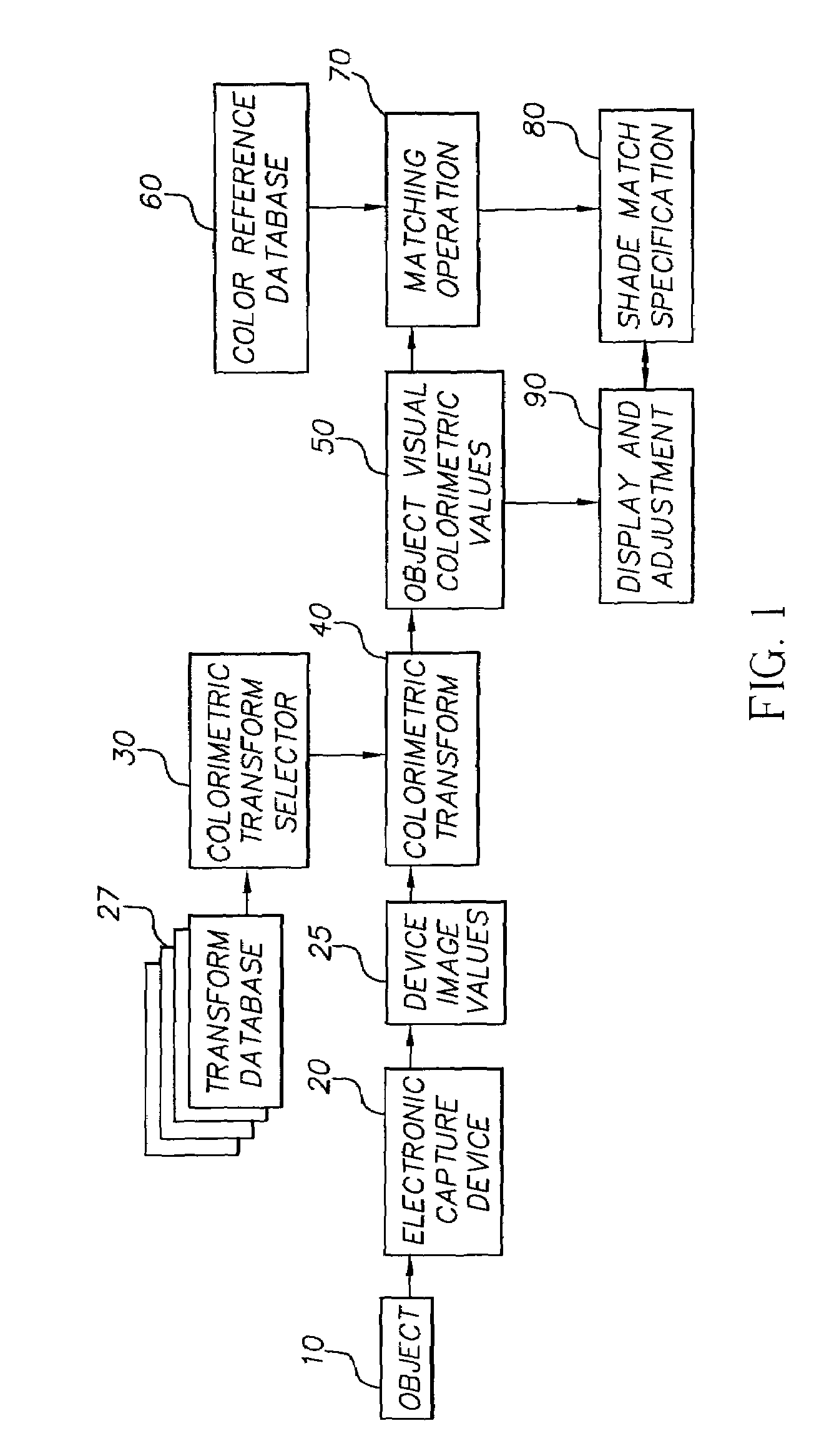
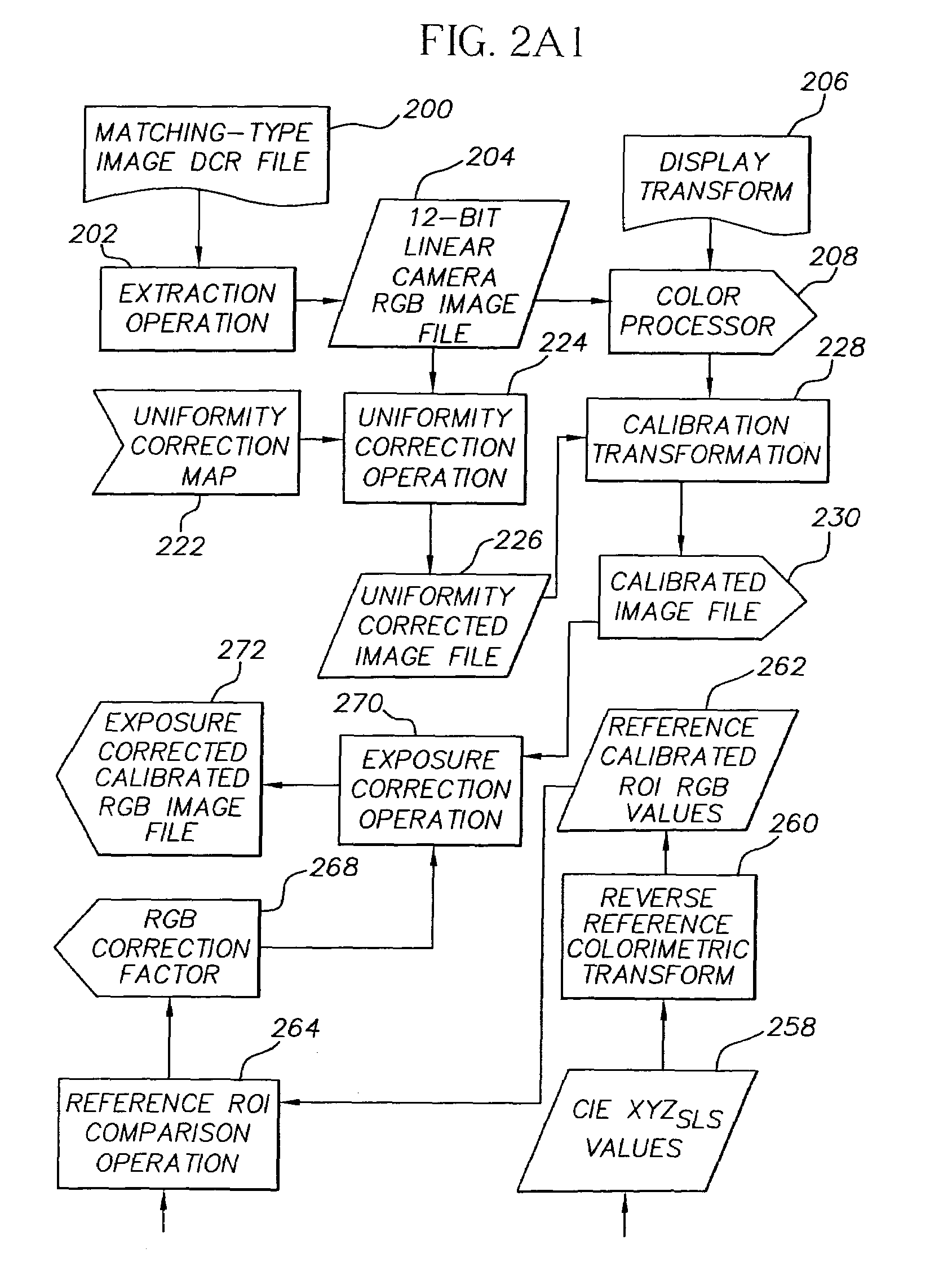
Dental color imaging system
ActiveUS7064830B2Accurately determineAccurate specificationsRadiation pyrometryImpression capsVisual perceptionImage capture
A method for determining visual calorimetric values for an object having particular spectral reflectance characteristics comprises the steps of: (a) photographing an object with an electronic image capture device to form device image values; (b) selecting a transform from a plurality of transforms for converting device image values to visual colorimetric values, wherein the selection of the transform is based on the particular spectral reflectance characteristics of the object; and (c) applying the selected transform to the device image values to determine the visual colorimetric values for the object.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
Imaging device and method, computer program product on computer-readable medium, and imaging system
InactiveUS20060266942A1Prevent large relative motionTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansColor imageDisplay device
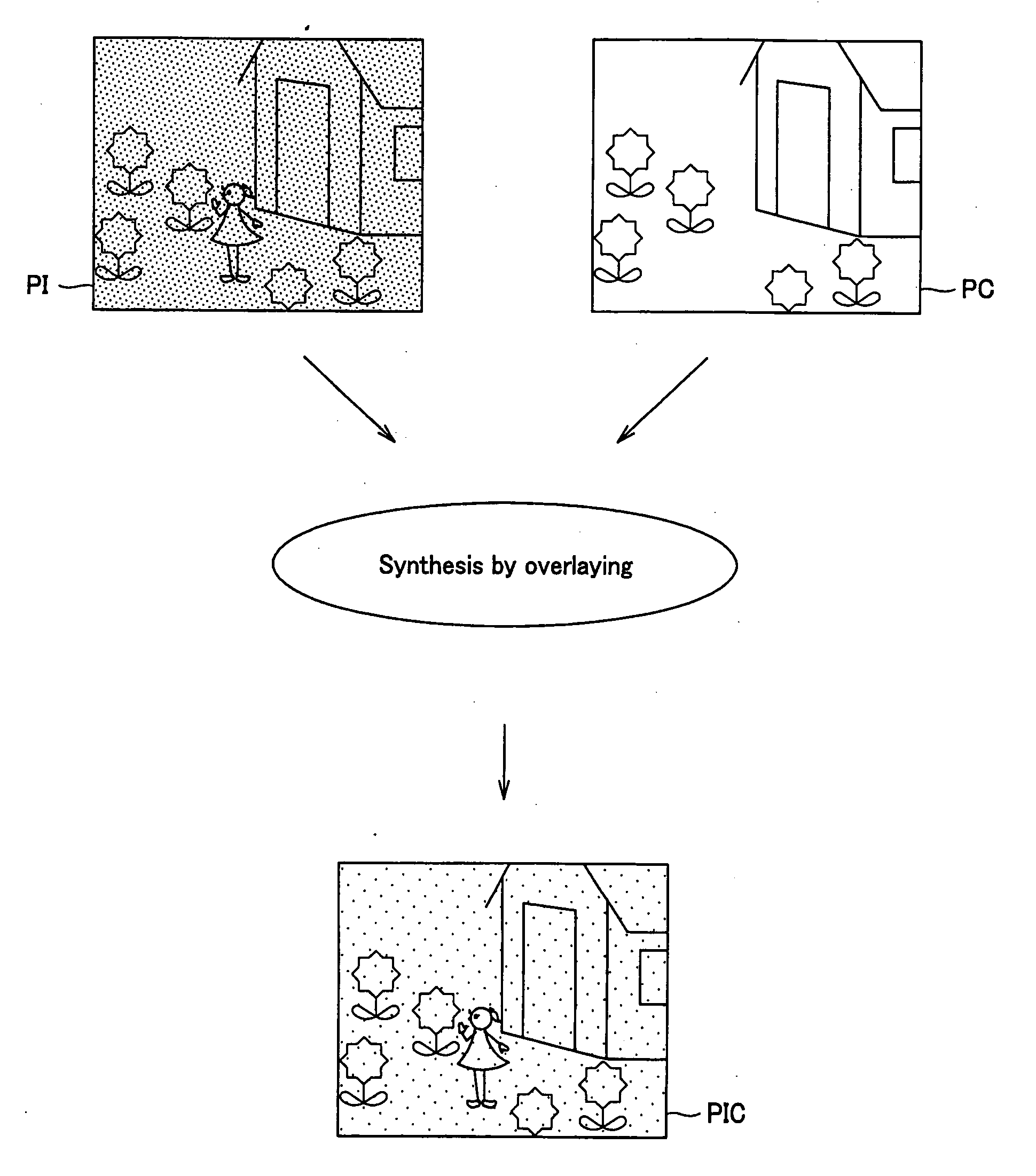
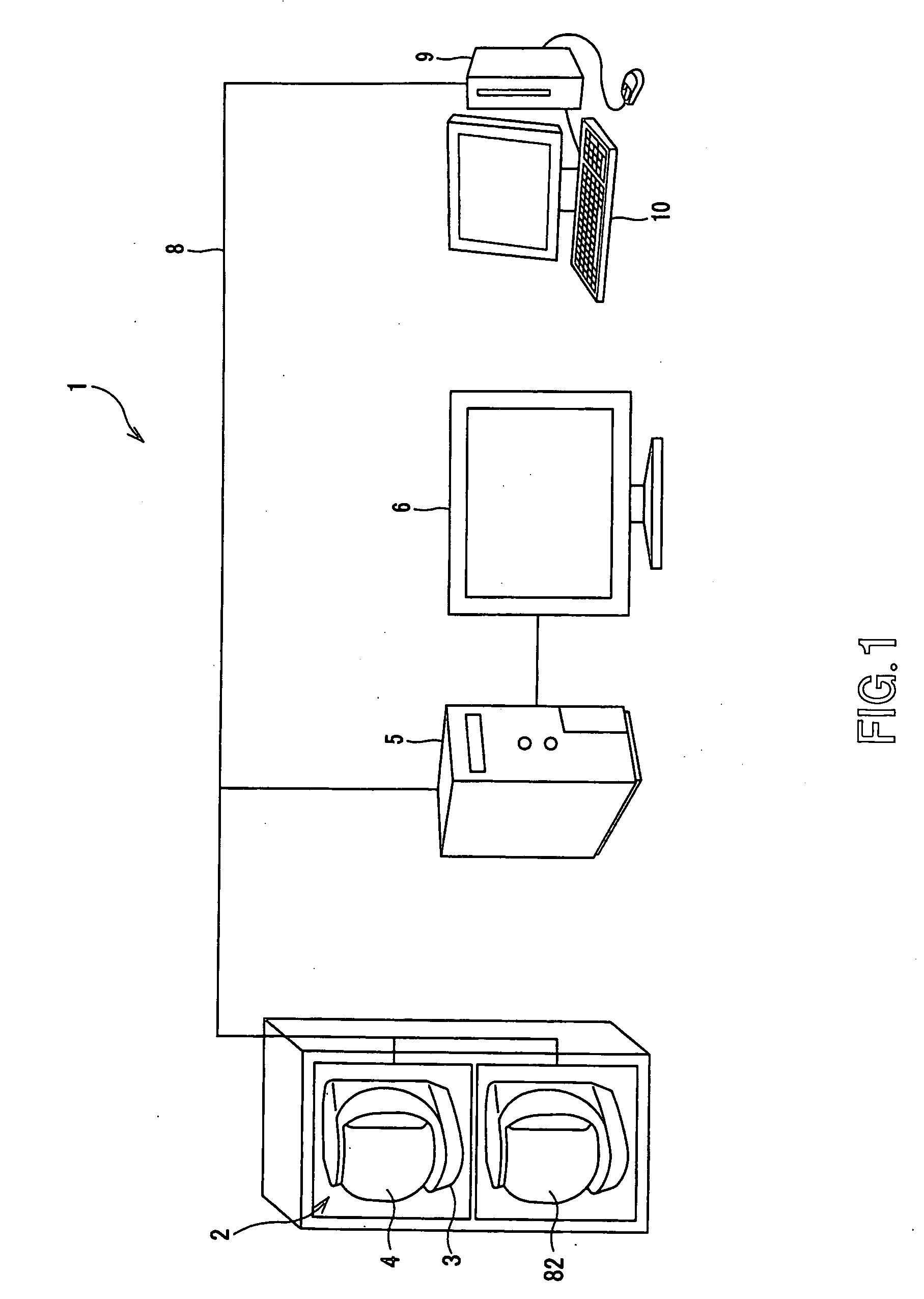
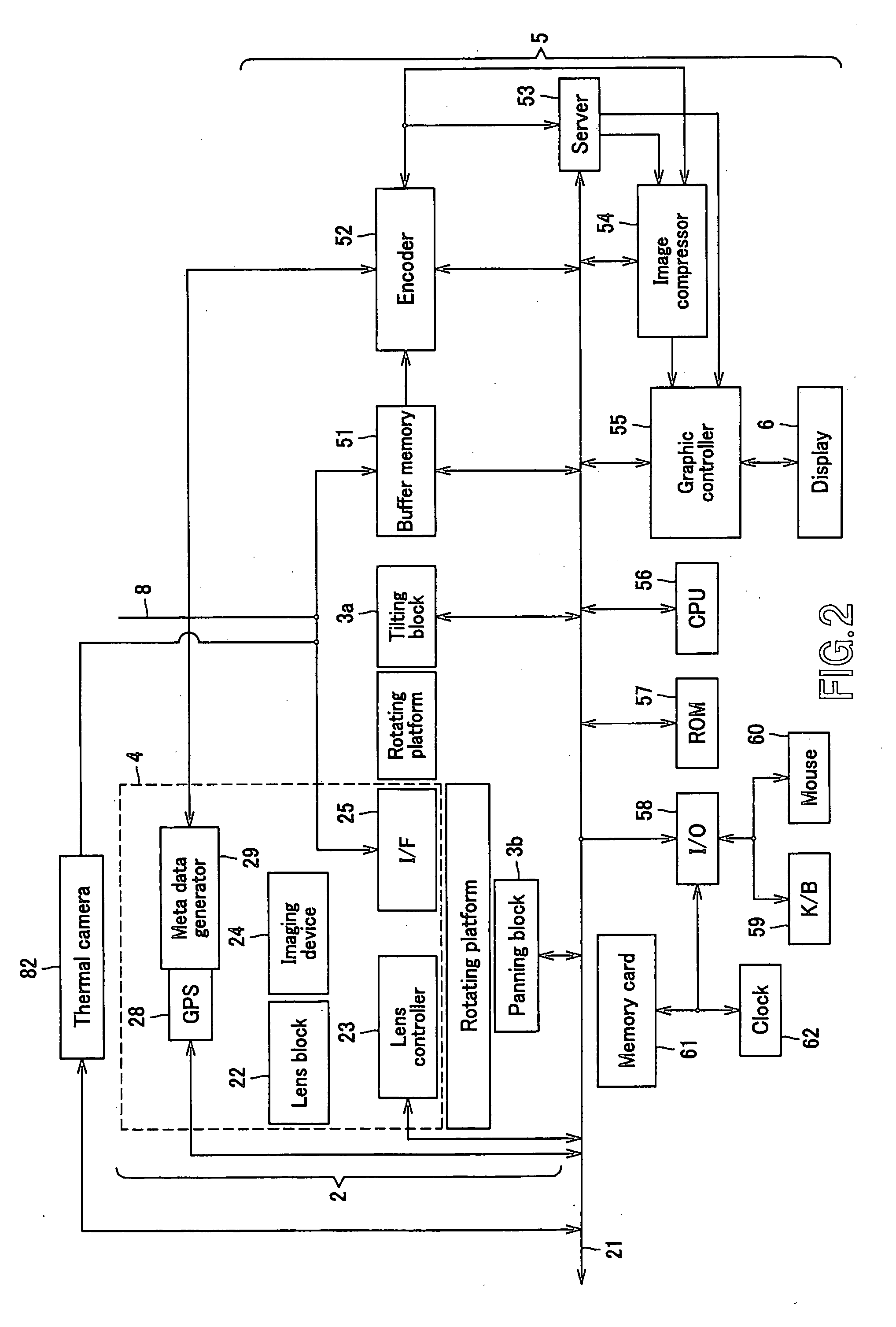
A specific object such as a human body can be visualized in a wide range in a relation to its background night and day to definitely identify a location of the object in relation to the background as well in the infrared image captured by the infrared camera. The present invention provides an imaging device including a color camera unit for making color imaging with the imaging direction being sequentially adjusted for each of unit images forming together a panoramic image, an infrared camera for imaging by infrared radiation measurement with the imaging direction being sequentially adjusted for each of unit images forming together a panoramic infrared image, a server for storing / managing a panoramic color image produced by overlaying a plurality of unit images captured in colors by the color camera unit one on the other and a panoramic infrared image produced by overlaying a plurality of unit images captured by infrared radiation measurement by the infrared camera one on the other, an image synthesizer for overlaying, on an image of an object imaged by controlling the direction of imaging by the infrared camera to a desired one in a range of the imaging, a color image corresponding to a location, where the object has been imaged by the infrared camera, in a panoramic color image stored / managed in the server, and an image display for displaying an image produced by the overlaying by the image synthesizer.
Owner:SONY CORP
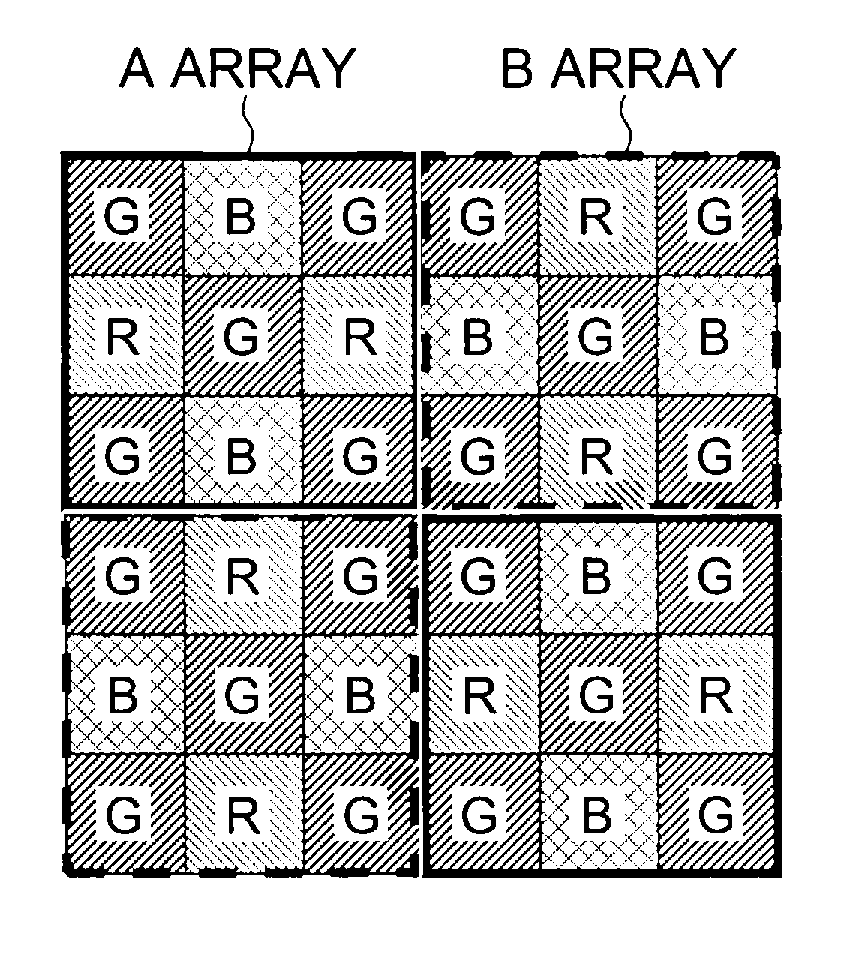
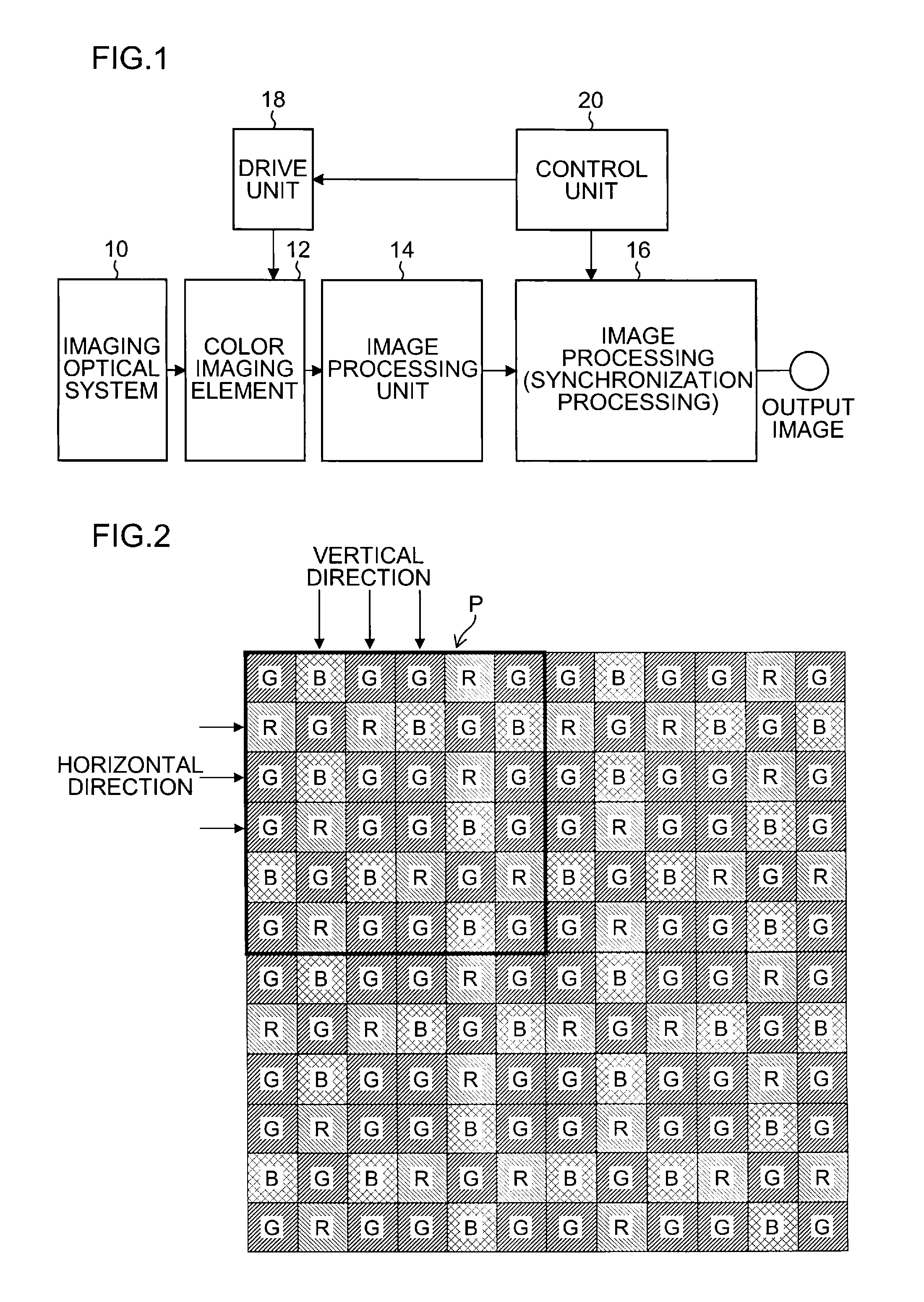
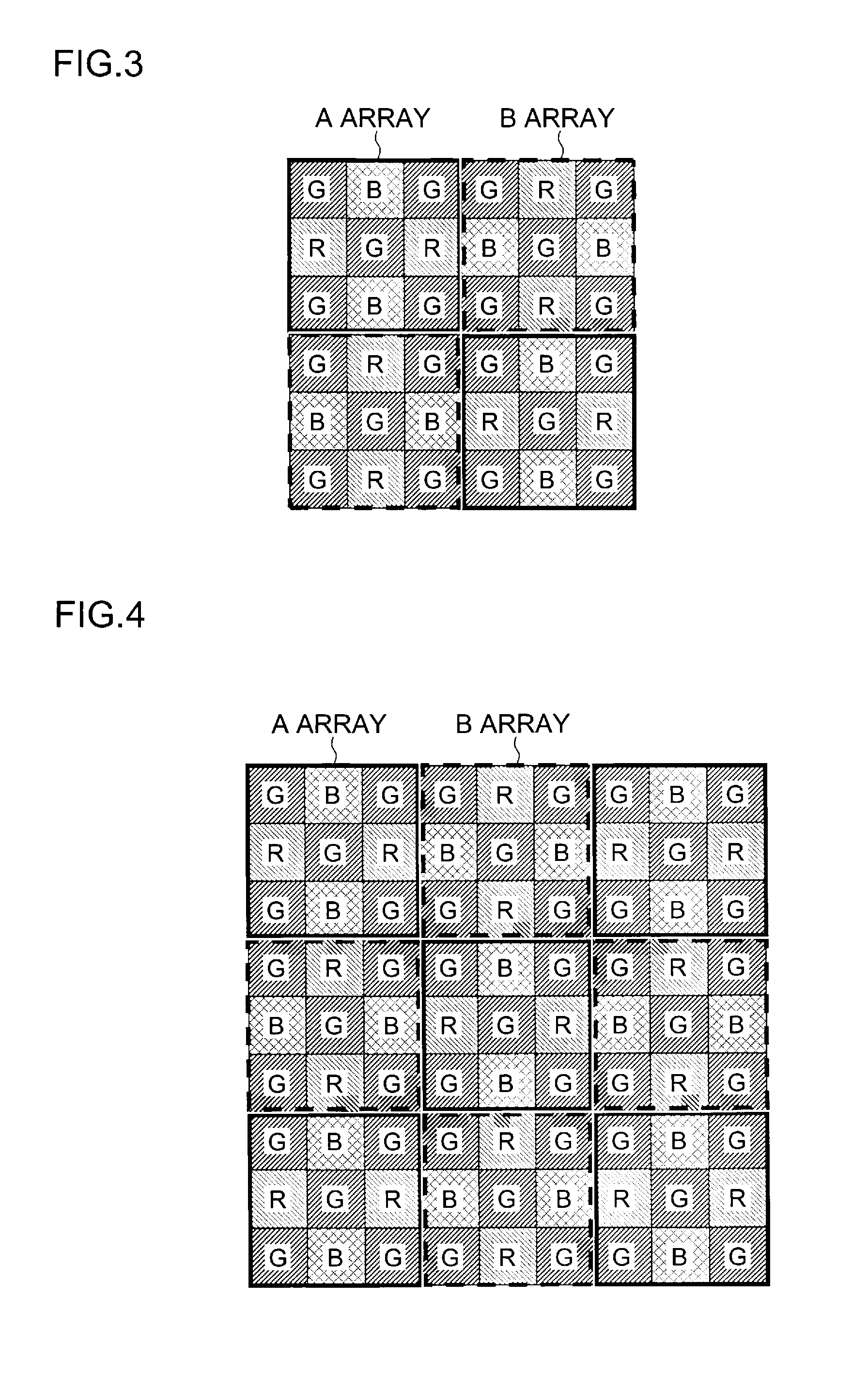
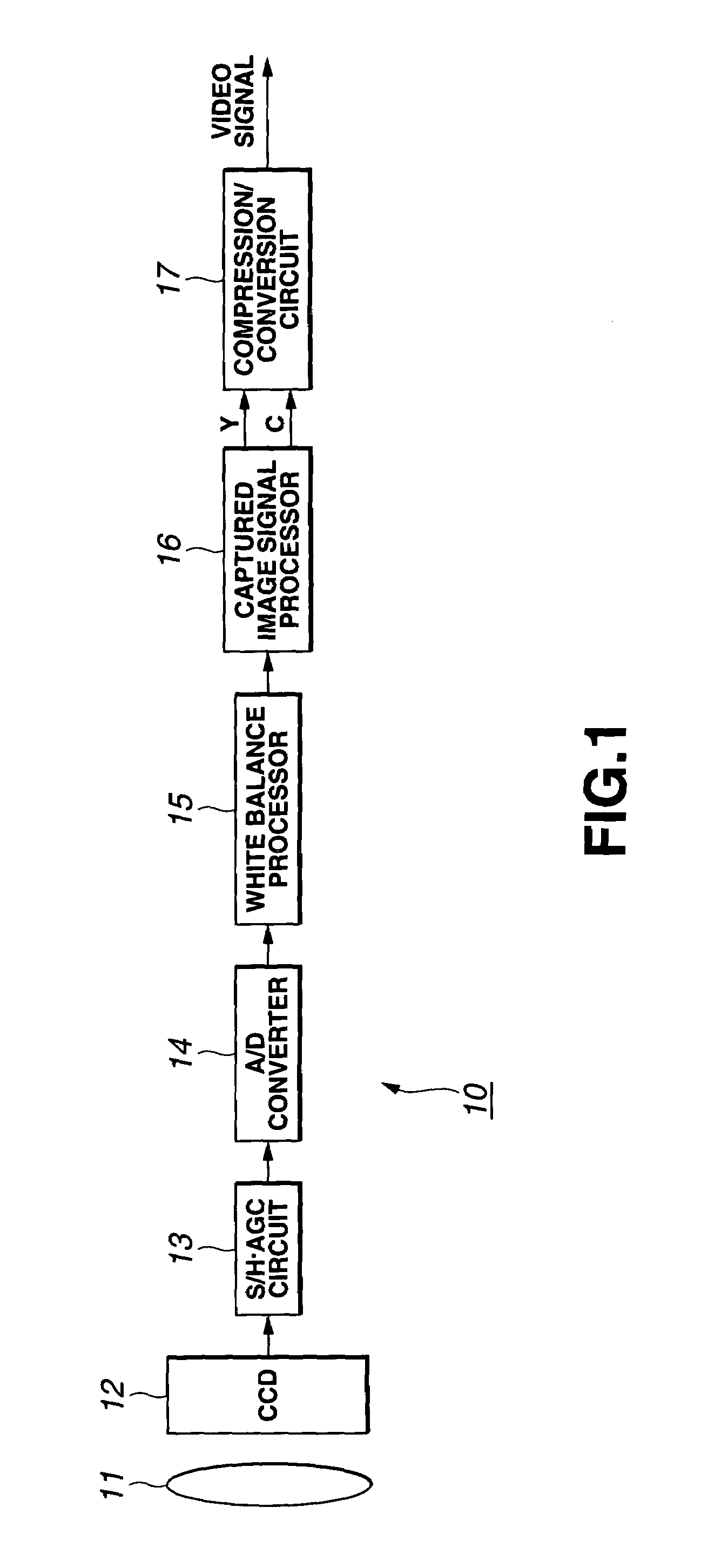
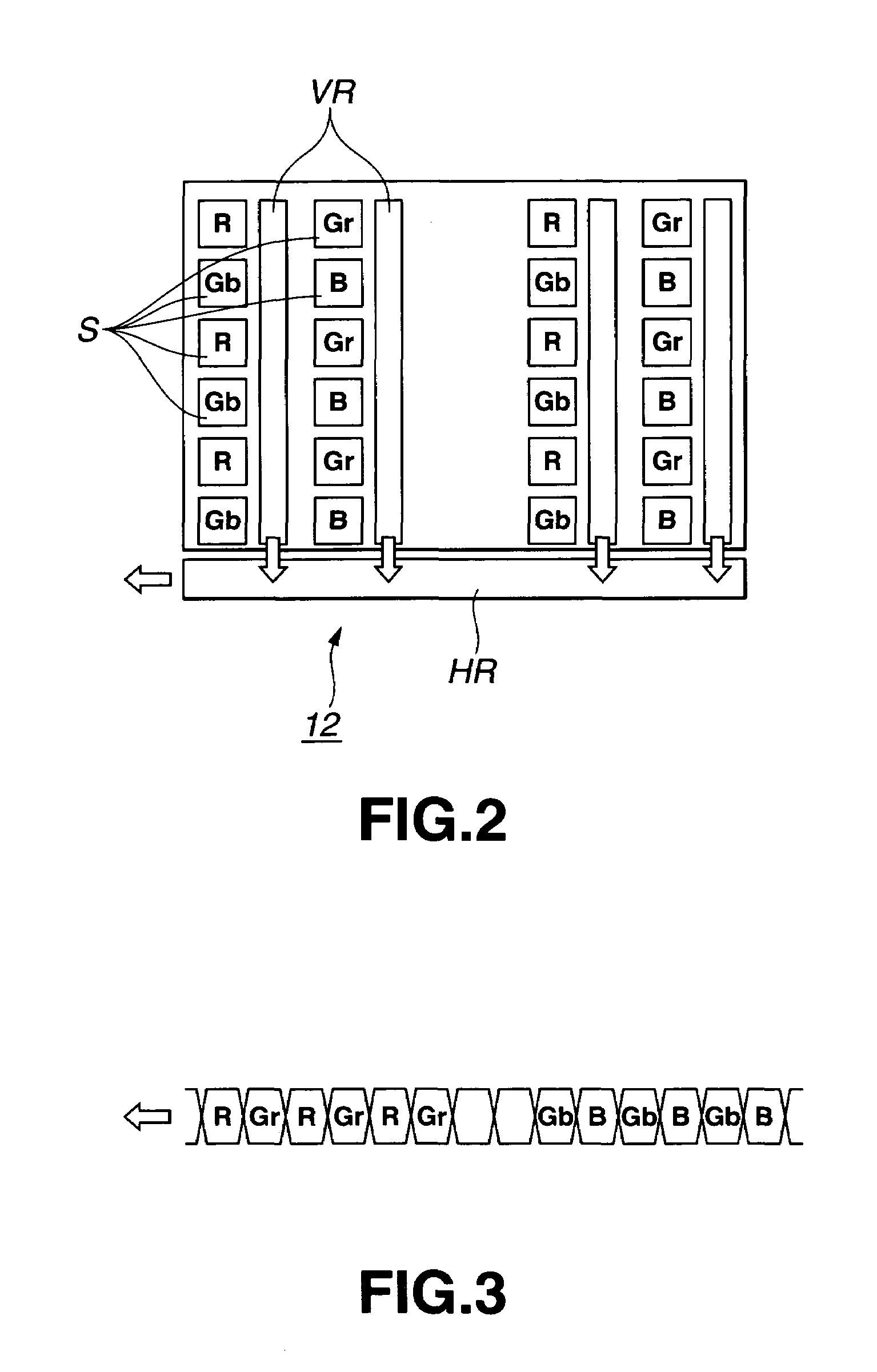
Color imaging by independently controlling gains of each of R, Gr, Gb, and B signals
InactiveUS7009639B1Reduce noiseImage degradationTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor imageBalanced amplifier
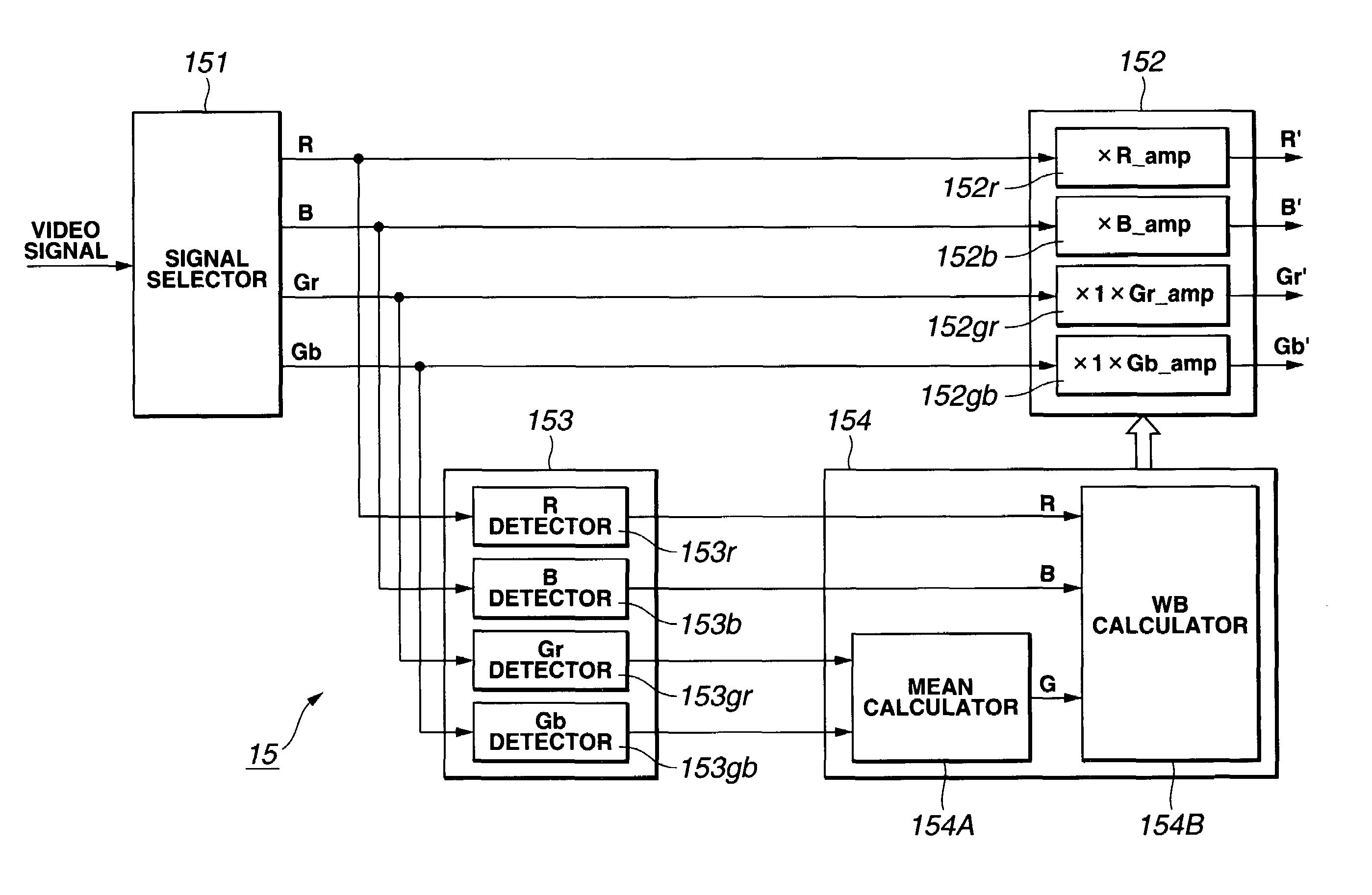
To eliminate an amplitude difference between luminance signals from pixels included in horizontal lines of color filters, caused by a sensitivity difference from one photosensor to another in a CCD, and reduce a horizontal stripe-like noise appearing in a monitoring image and captured image, there is provided an arithmetic circuit to calculate an amplitude difference in Gr and Gb signals based on an output from a four-channel detector to set gains multiplied by compensation factors, respectively, with which the white balance-processed Gr and Gb signals are equal in amplitude to each other, thereby controlling the gain of a while balance amplifier.
Owner:SONY CORP
Recalibrating a multi-color imaging system
An apparatus and method for calibrating a multi-color imaging system are provided. The multi-color imaging system is capable of applying different colorants to a substrate based on a plurality of input color values. The input color values control amounts of the colorants to be applied to the substrate by the imaging system. A subset of the input color values is selected and used to control the imaging system to apply one or more of the different colorants to the substrate, thereby forming a plurality of different color patches on the substrate. The subset of input color values is selected such that one of more of the different color patches is formed by application of a combination of at least two of the different colorants to the substrate. Color values are measured for each of the different color patches, and compared to reference color values, representing a calibrated condition of the imaging system. An error value is calculated. The error value represents a deviation of the measured color values from the reference color values. The input color values for each colorant then are independently adjusted to reduce the error value to a predetermined degree.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
High-resolution optical code imaging using a color imager
ActiveUS20100200658A1Easy to optimizeCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationColor imageSensor array
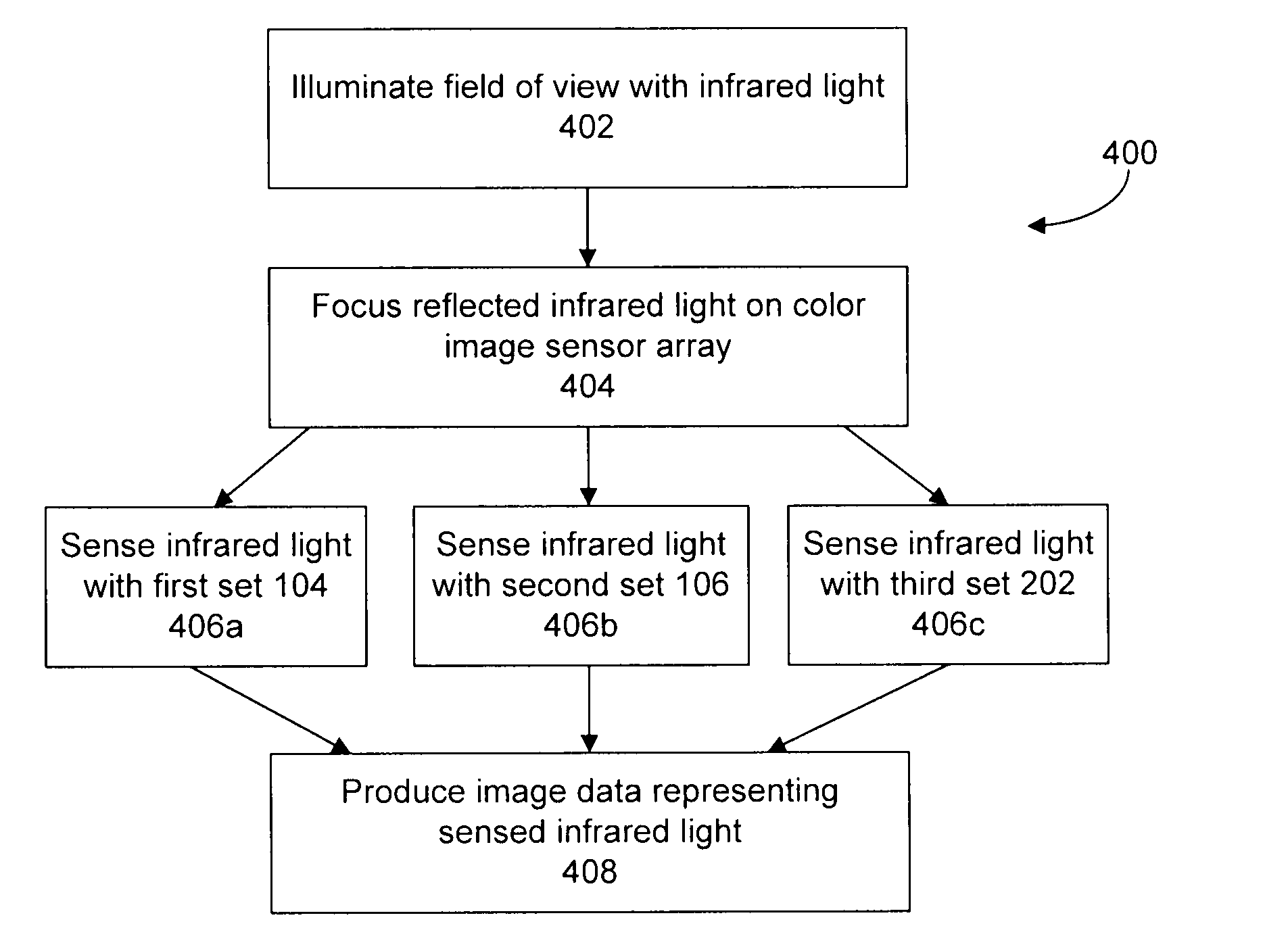
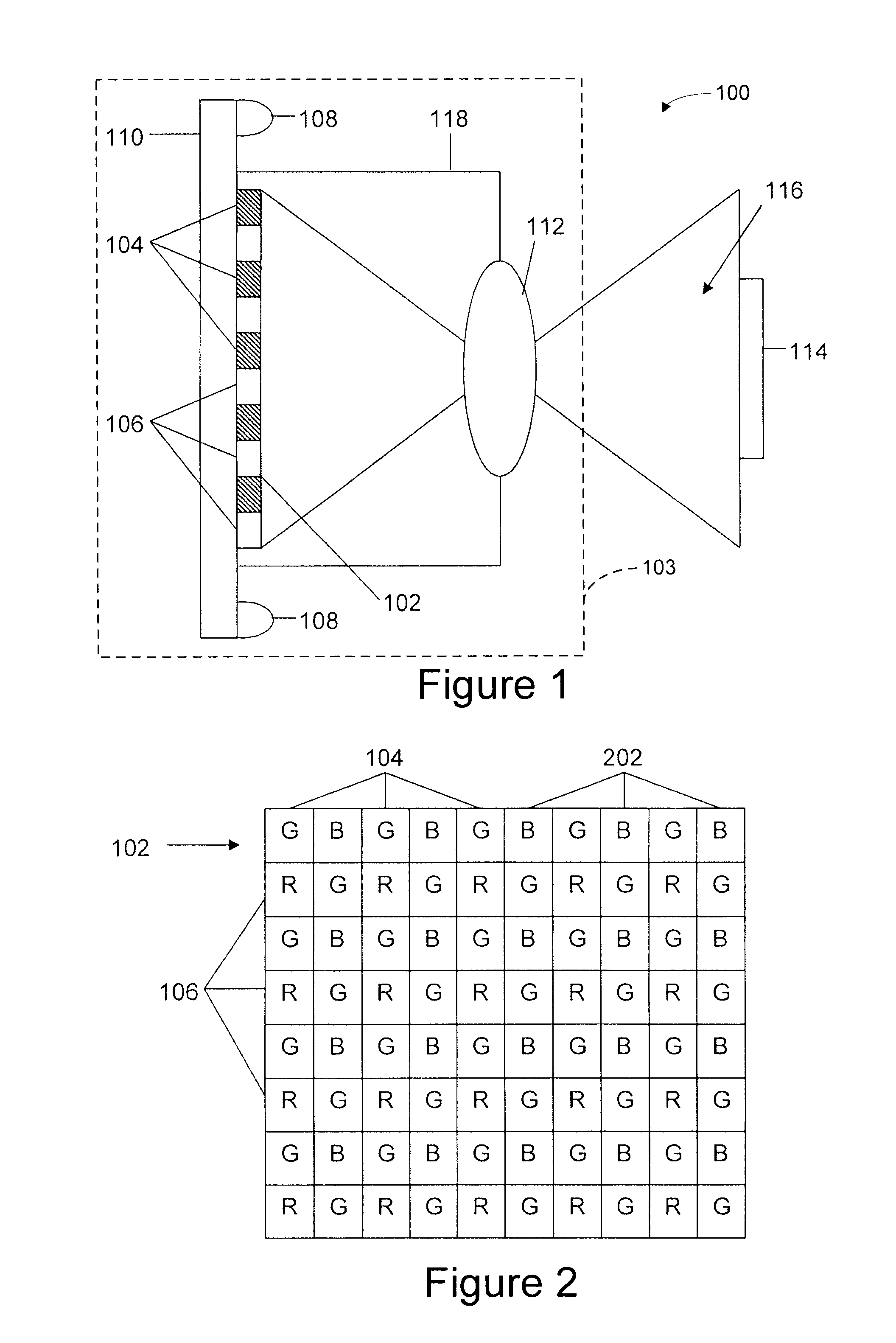
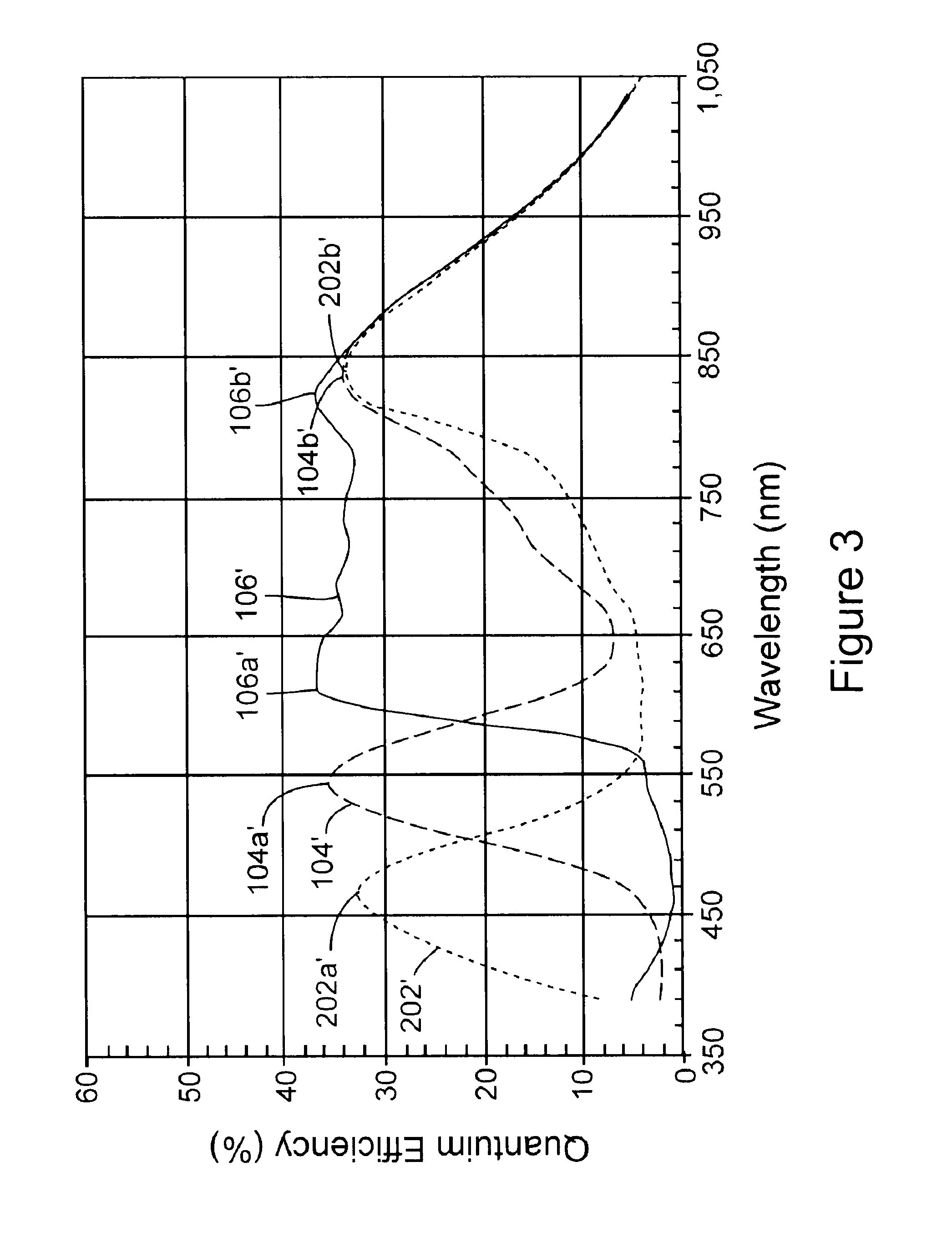
An optical code or other data reading device includes a color image sensor array positioned to sense light reflected from an object, and to produce image data. In one configuration, the color image sensor array has multiple sets (e.g., first and second sets) of sensor elements that are sensitive to corresponding visible wavelength bands of light (e.g., first and second wavelength bands), the sets also being sensitive to light within an infrared wavelength band. An artificial illumination source is positioned to illuminate the field of view with light that is reflected off an object in the field of view toward the image sensor array, the illumination source being operable to produce infrared light having wavelengths within the infrared wavelength band so that, upon illumination, at least some sensor elements of each of the sets are sensitive to the infrared light and contribute to production of the image data.
Owner:DATALOGIC ADC
Color image forming method and color image forming device
InactiveUS6904255B2Improve transmission efficiencyReduce voltageElectrographic process apparatusColor imageEngineering
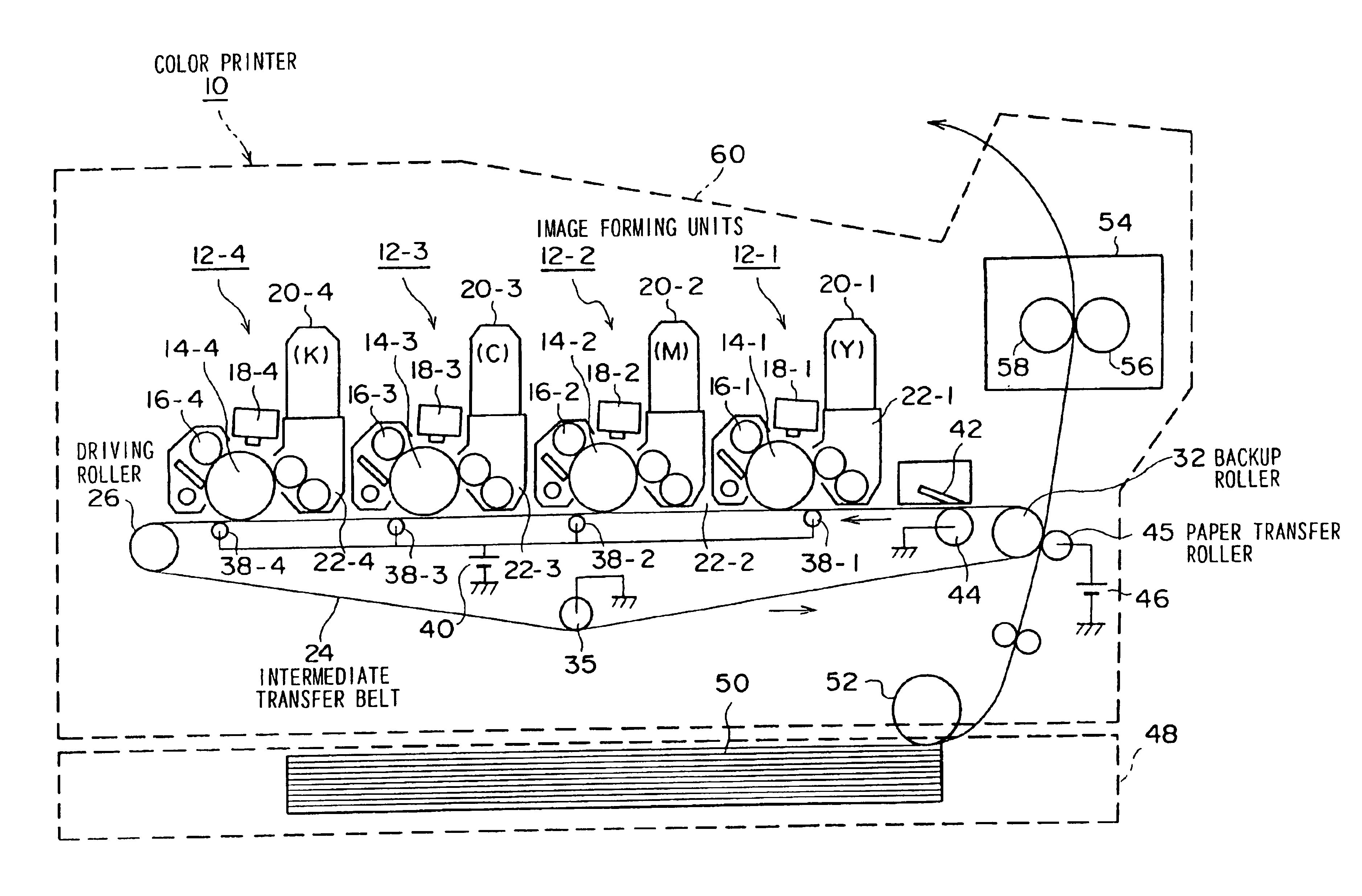
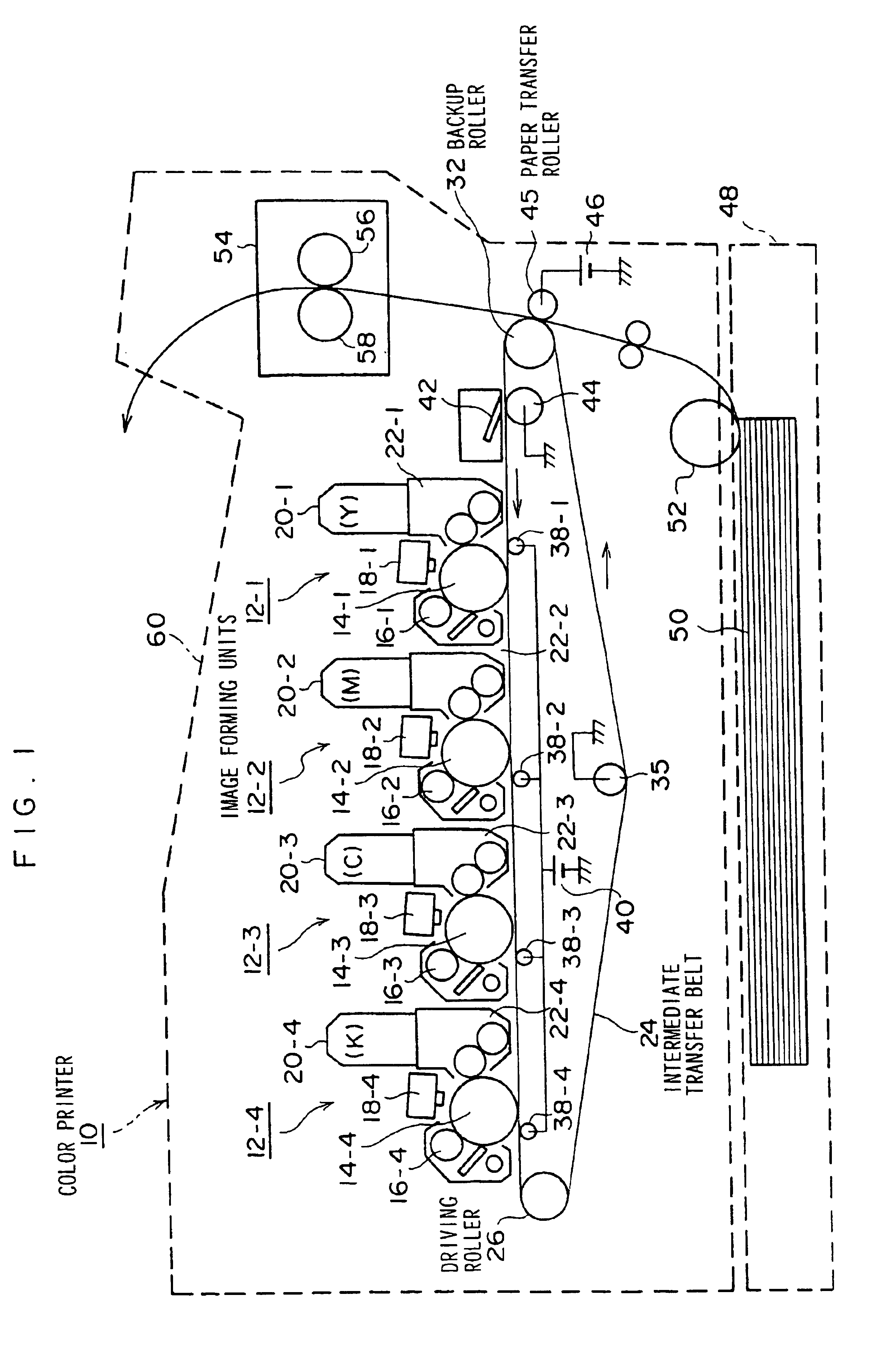
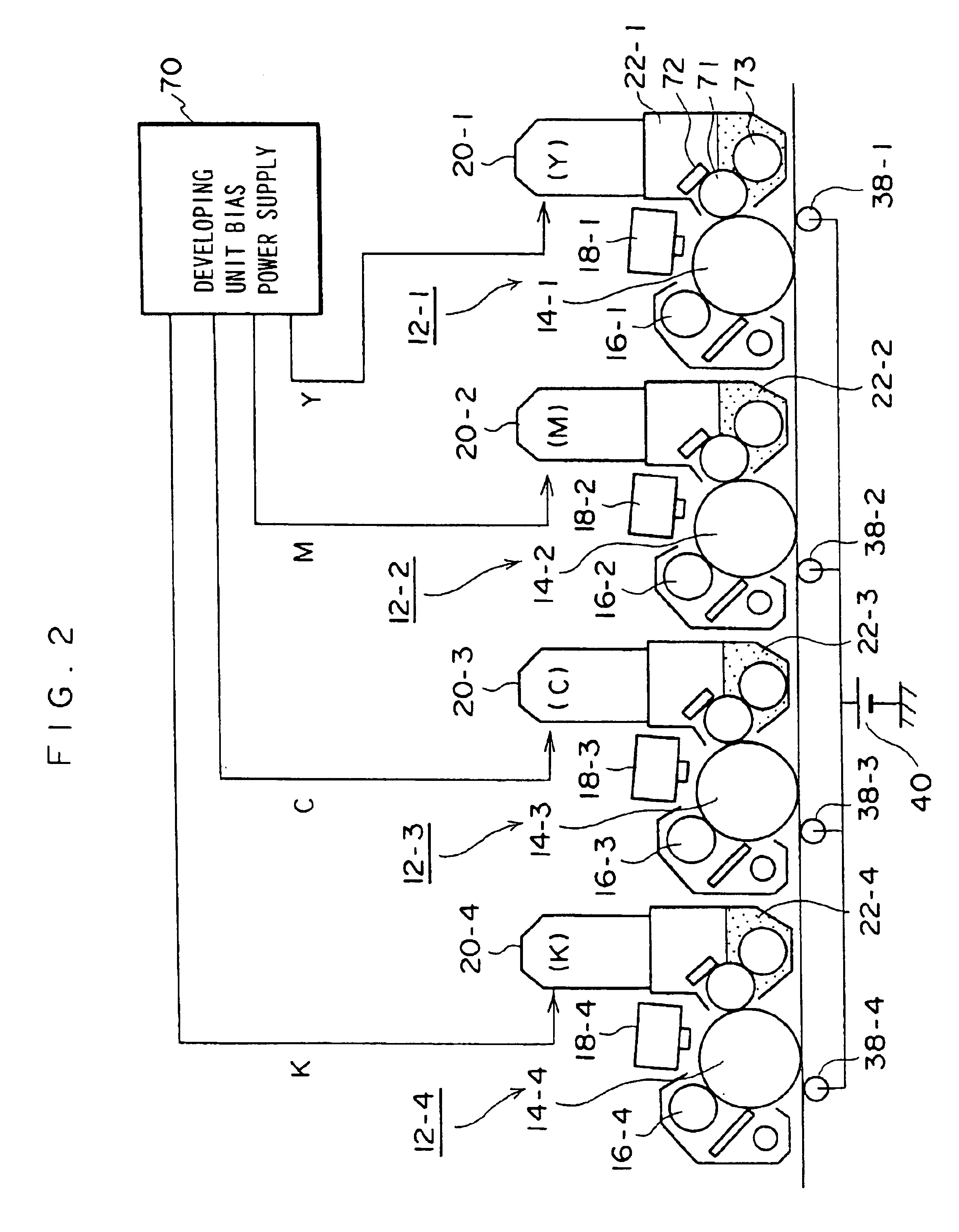
The present invention relates to a color image forming device for forming toner images of a plurality of colors on a medium, and is for improving second transfer efficiency from an intermediate transfer body to the medium. The device has image forming units (12-1 to 12-4) for forming the toner images of the plurality of colors on at least one image bearing body (14-1 to 14-4) by a plurality of developing units (22-1 to 22-4) respectively accommodating toner of different colors; an intermediate transfer body (24); primary transfer means (38-1 to 38-4) for primary transferring the toner images of the plurality of colors onto the intermediate transfer body sequentially for the respective colors; and secondary transfer means (45) for secondary transferring the toner images of the plurality of colors on the intermediate transfer body onto the medium. The image forming units form the toner images of the plurality of colors so that the potentials of toner layers transferred onto the intermediate transfer body (24) are progressively lower in the order in which the plurality of colors are transferred. Since the potential of the toner layer directly adhered to the intermediate transfer body is higher, the directly adhered toner layer becomes easier to be secondary-transferred, and thereby, the secondary transfer efficiency is improved and the reproducibility of the secondary color is improved.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Desktop color image forming apparatus and method of making the same
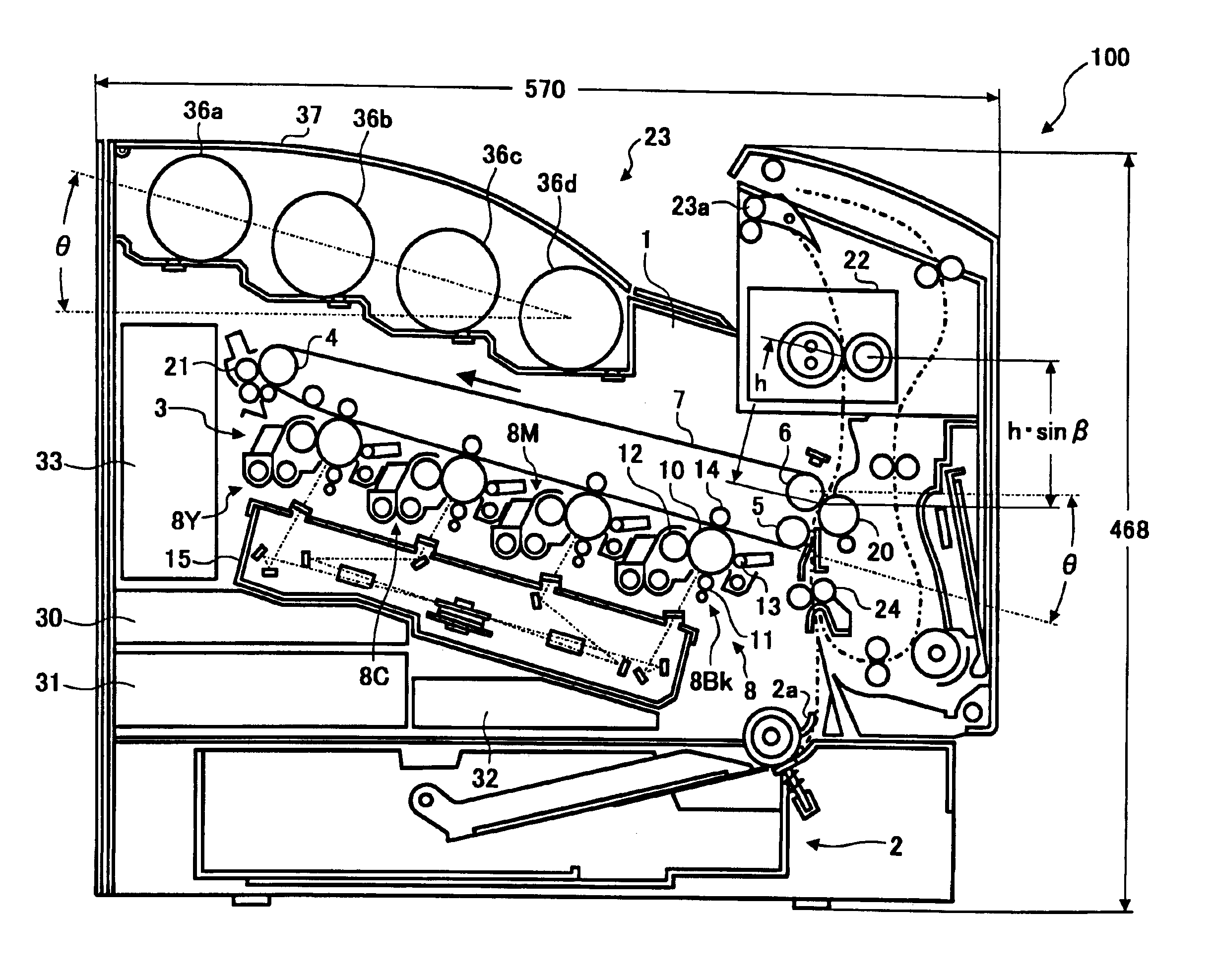
ActiveUS6898407B2Compact profileAvoid insufficient lengthElectrographic process apparatusColor imageIntermediate image
The present invention relates to an electrophotographic color image forming apparatus using a tandem-drum development, an indirect image-transfer method, and a vertical sheet supply path. An intermediate image-transfer member is angled relative to a horizontal line such that a rear side of the intermediate image-transfer member away from a recording sheet is lifted and a front side of the intermediate image-transfer member closer to the recording sheet is lowered. Further, image creating mechanisms of the tandem-drum development are aligned and arranged in parallel to a moving image transfer bed of the intermediate image-transfer member, such that one of the image creating mechanisms firstly forming an image faces the rear side of the moving image transfer bed and another one of the image creating mechanisms lastly forming an image faces the front side.
Owner:RICOH KK
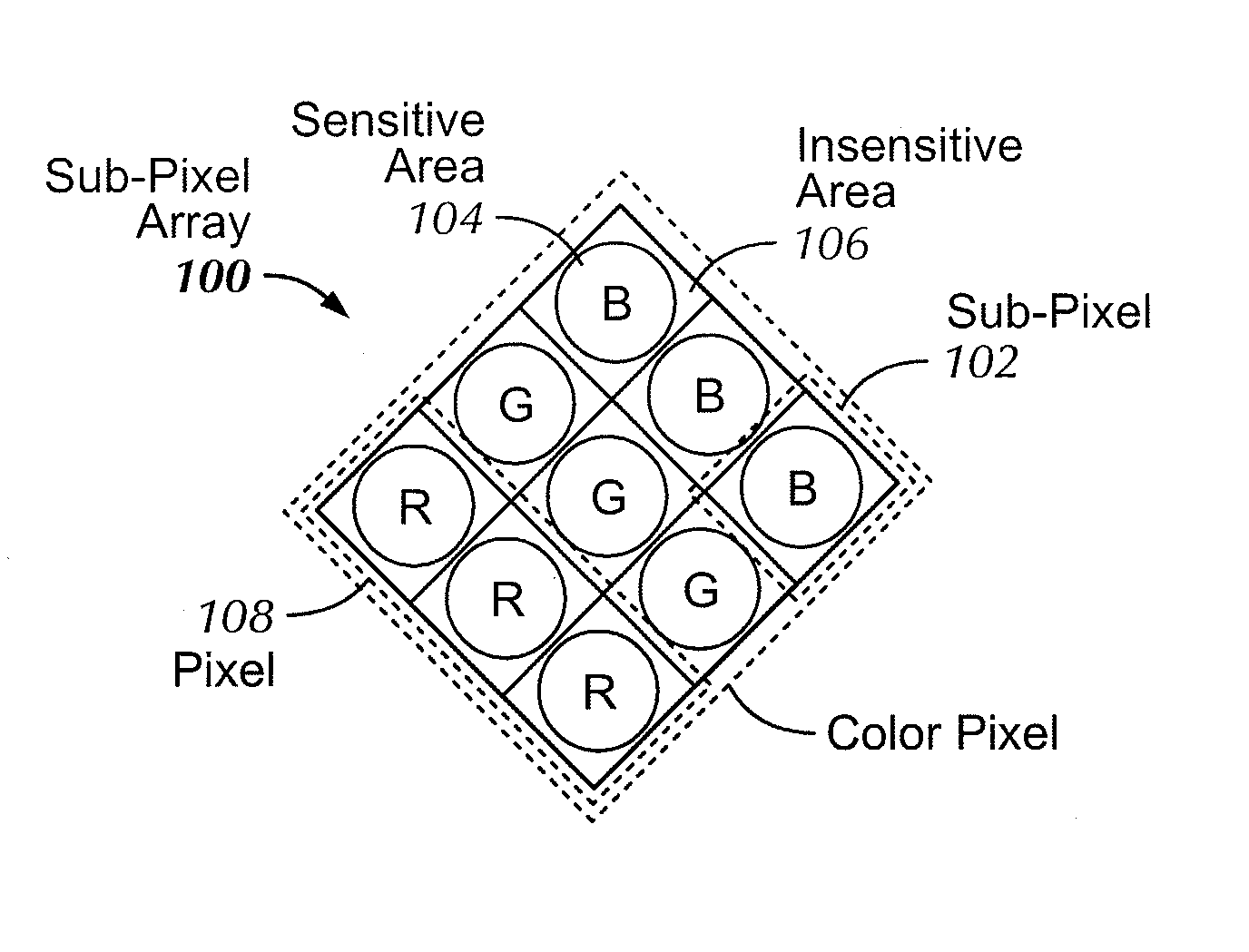
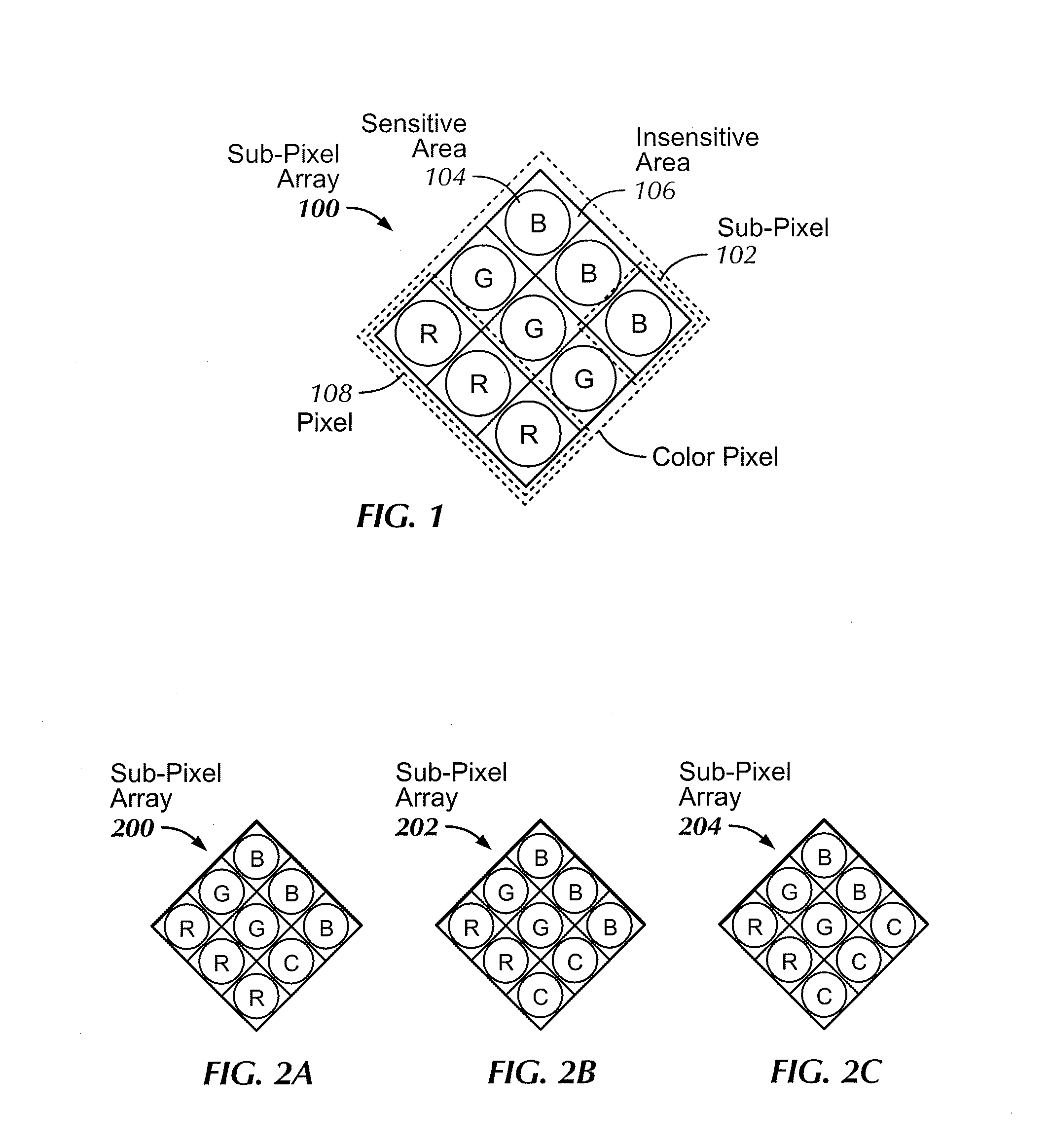
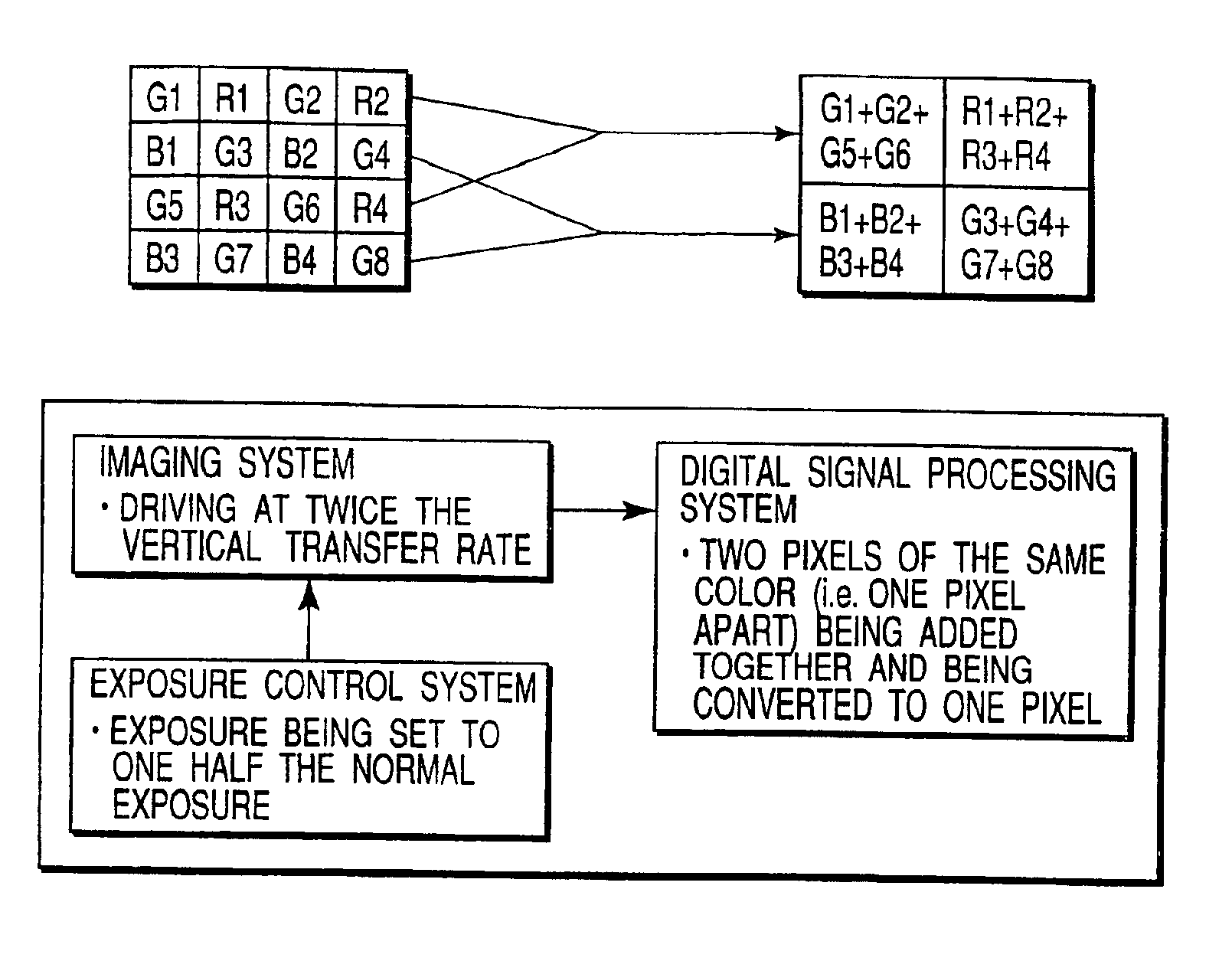
Increasing the resolution of color sub-pixel arrays
InactiveUS20100149393A1Improve dynamic rangeIncrease exposureTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital imagingImage resolution
Increasing the resolution of digital imagers is disclosed by sampling an image using diagonally oriented color sub-pixel arrays, and creating missing pixels from the sampled image data. A first method maps the diagonal color imager pixels to every other orthogonal display pixel. The missing display pixels can be computed by interpolating data from adjacent color imager pixels, and averaging color information from neighboring display pixels. This averaging can be done either by weighting the surrounding pixels equally, or by applying weights to the surrounding pixels based on intensity information. A second method utilizes the captured color imager sub-pixel data instead of interpolation. Missing color pixels for orthogonal displays can be obtained directly from the sub-pixel arrays formed between the row color pixels in the imager.
Owner:PANAVISION IMAGING LLC
Imaging system with a single color image sensor for simultaneous fluorescence and color video endoscopy
An endoscopic video system and method using a camera with a single color image sensor, for example a CCD color image sensor, for fluorescence and color imaging and for simultaneously displaying the images acquired in these imaging modes at video rates in real time is disclosed. The tissue under investigation is illuminated continuously with fluorescence excitation light and is further illuminated periodically using visible light outside of the fluorescence excitation wavelength range. The illumination sources may be conventional lamps using filters and shutters, or may include light-emitting diodes mounted at the distal tip of the endoscope.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
Indoor surveying apparatus and method
InactiveUS20150116691A1Optical rangefindersActive open surveying meansSurveyorCalibration coefficient
An indoor surveying apparatus comprises a light source, a color imaging system, a memory storing calibration coefficients, and a computing device for determining coordinates of 3D intersection points of the emitted light with objects using calibration coefficients and images captured by the imaging system. A method of using the surveying apparatus comprises the steps of capturing first image of a scene illuminated by the light source, capturing second image of the scene without the illumination by the light source, comparing the two images to identify locations of the 3D intersection points in the first image, using the set of calibration coefficients and the locations of the 3D intersection points in the first image to compute 3D coordinates of the intersection points, whereby surveying information collected by the apparatus comprises the coordinates of 3D intersection points and the color photographic images captured from known poses relative to the 3D intersection points.
Owner:PLANITAR INC
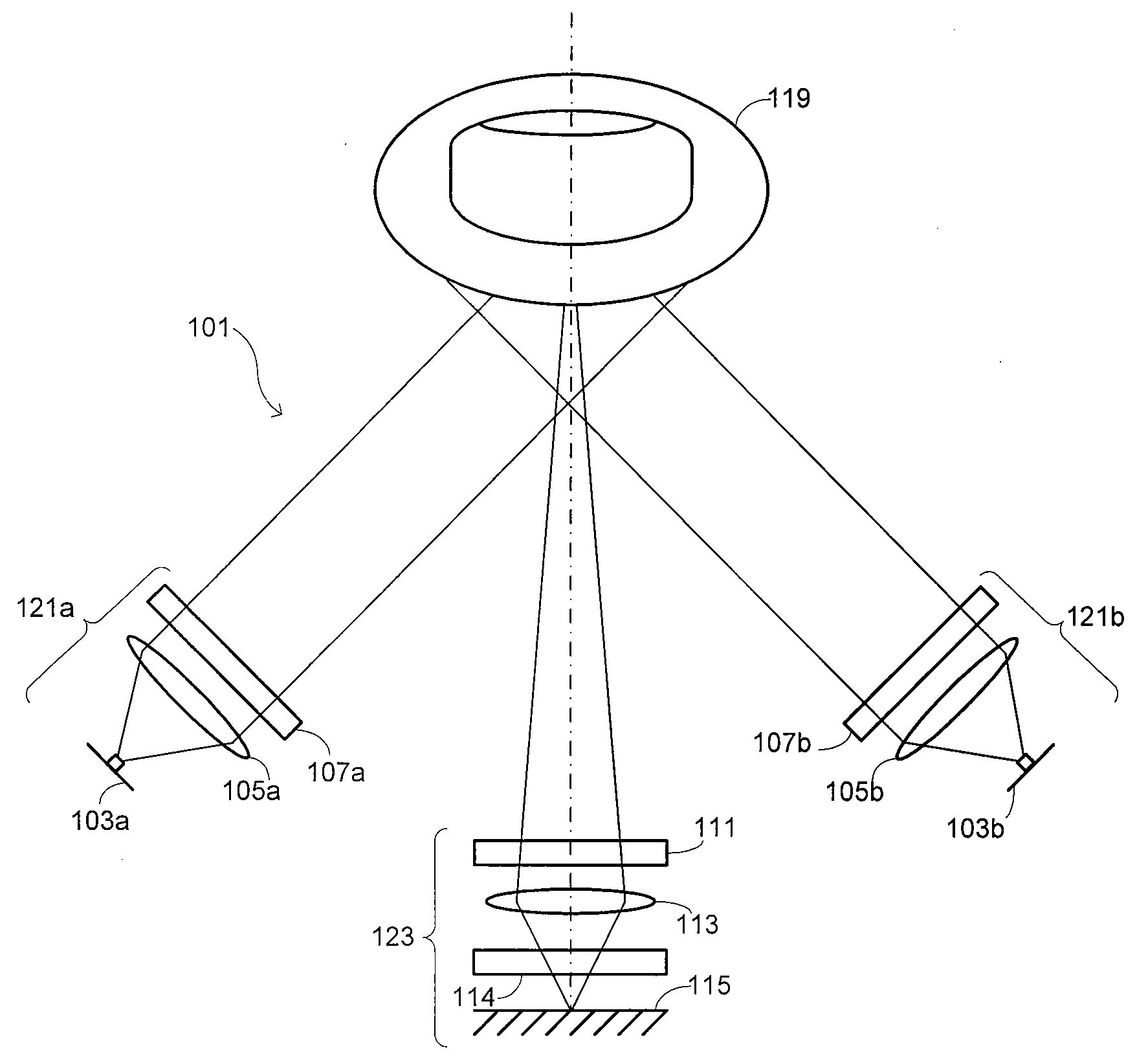
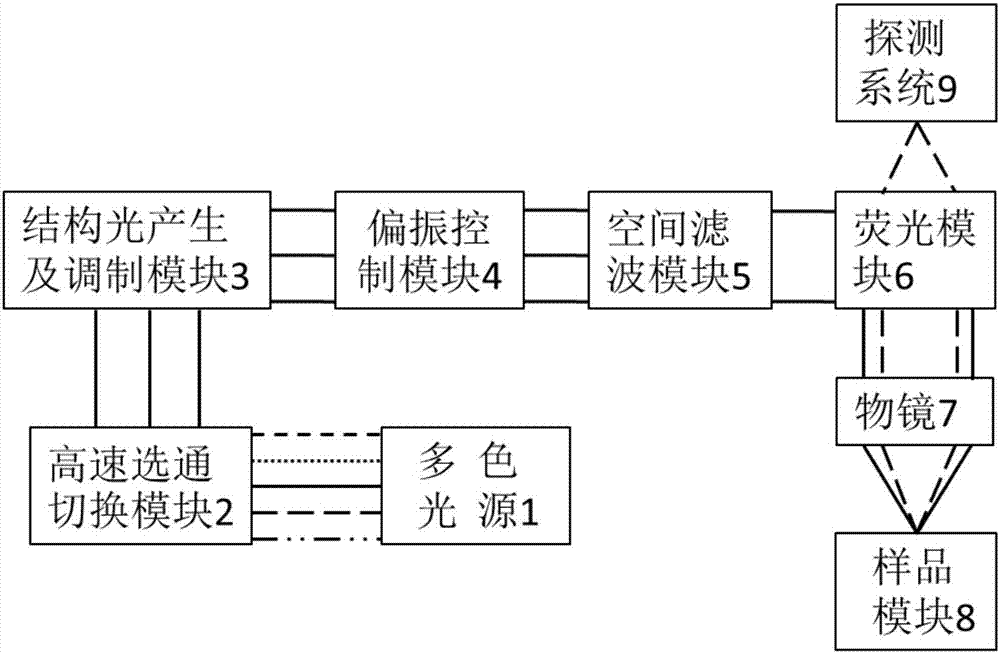
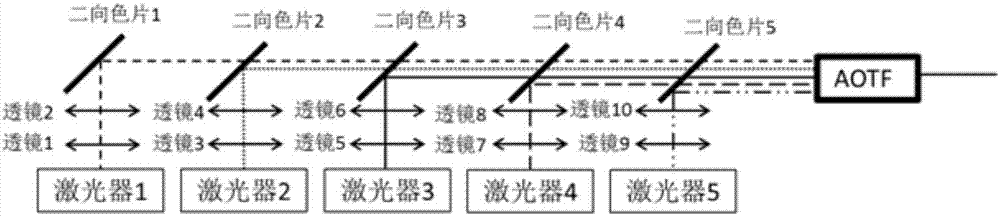
High-speed multicolor and multimode structured light illumination super-resolution microimaging system and method thereof
ActiveCN107389631AIncrease contrastFast imagingFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingFluorescence
The invention discloses a high-speed multicolor and multimode structured light illumination super-resolution microimaging system. Laser generated by a multicolor light source is incident into a high-speed gating switching module; the high-speed gating switching module selects the laser in one or multiple colors and enables the laser to irradiate a structured light generation and modulation module; the structured light generation and modulation module generates periodically modulated structured light and controls the direction and the phase of the structured light; the modulated laser is transmitted to a polarization control module; the polarization control module adjusts the polarization direction of the laser, so that the structured light illumination stripe is high in contrast, and the laser is transmitted to a space filter module; the space filter module filters out redundant stray light, and then emits the laser to a sample module through a fluorescence module and an objective lens in sequence; signal light emitted by the sample module is collected by the objective lens, and then the fluorescence module separates exciting light from the signal light; finally the signal light is received by a detection module. The system is high in structured light illumination stripe contrast and high in imaging speed, and meanwhile at least 5-color imaging can achieve the optimal performance.
Owner:北京纳析光电科技有限公司
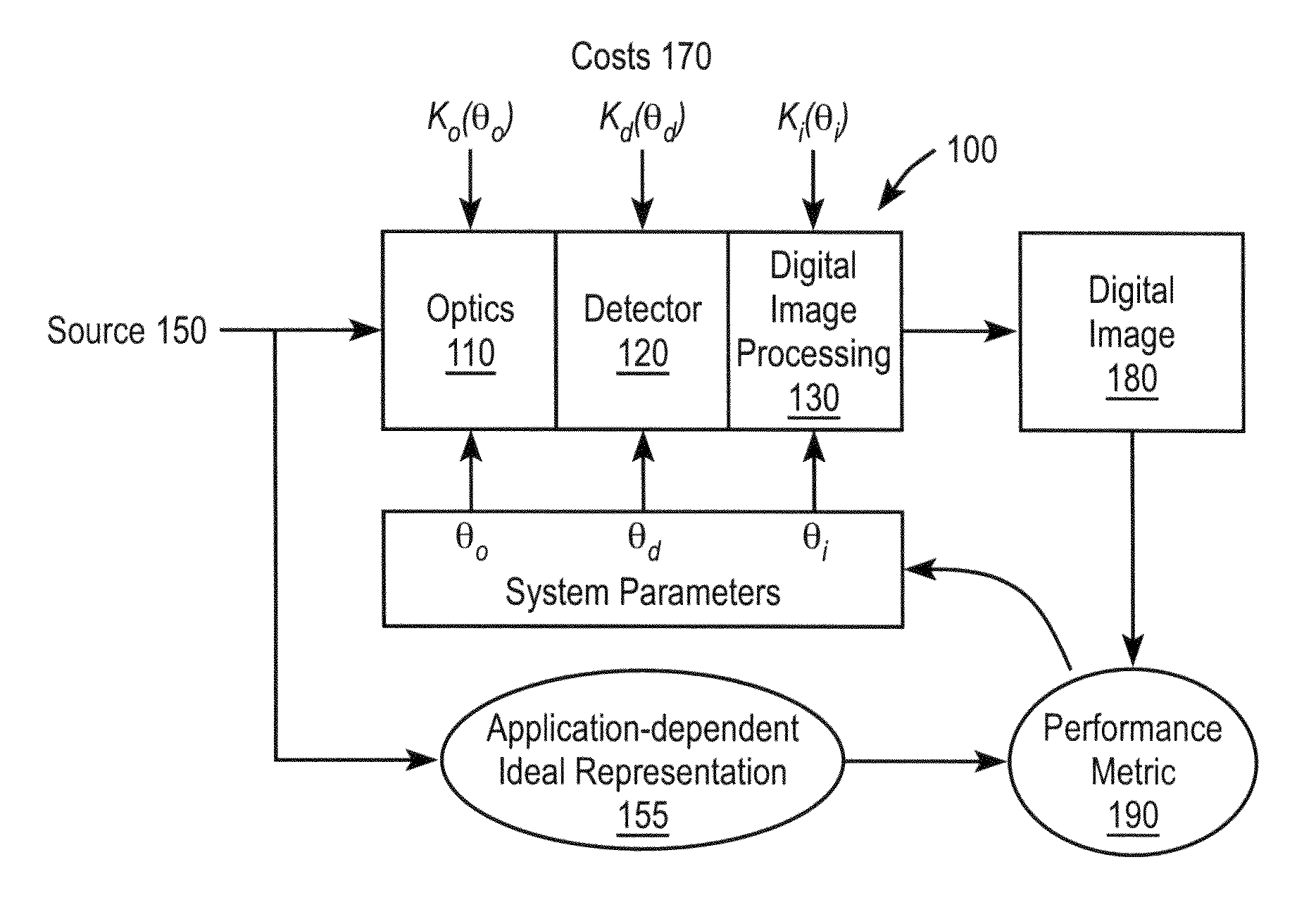
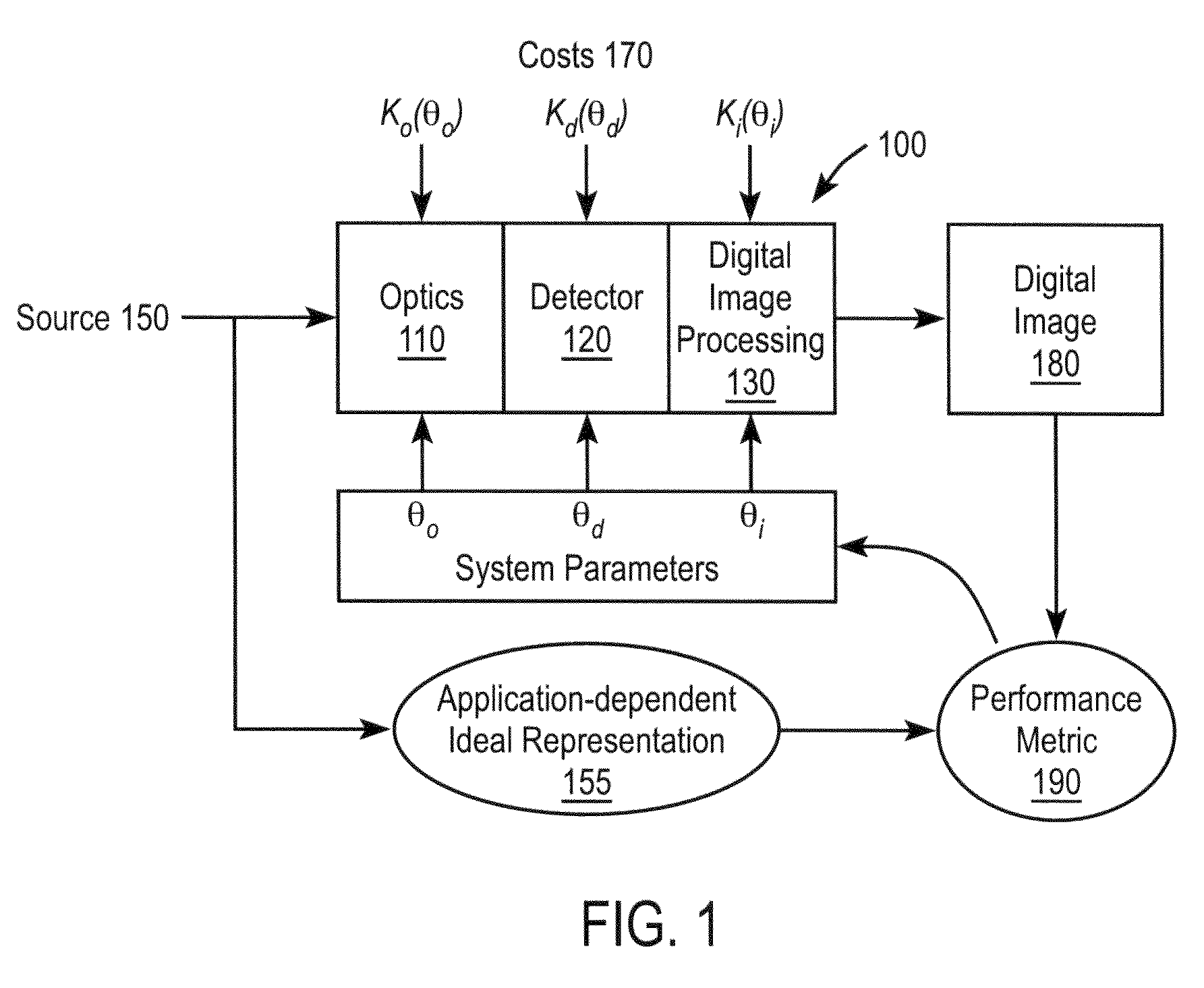
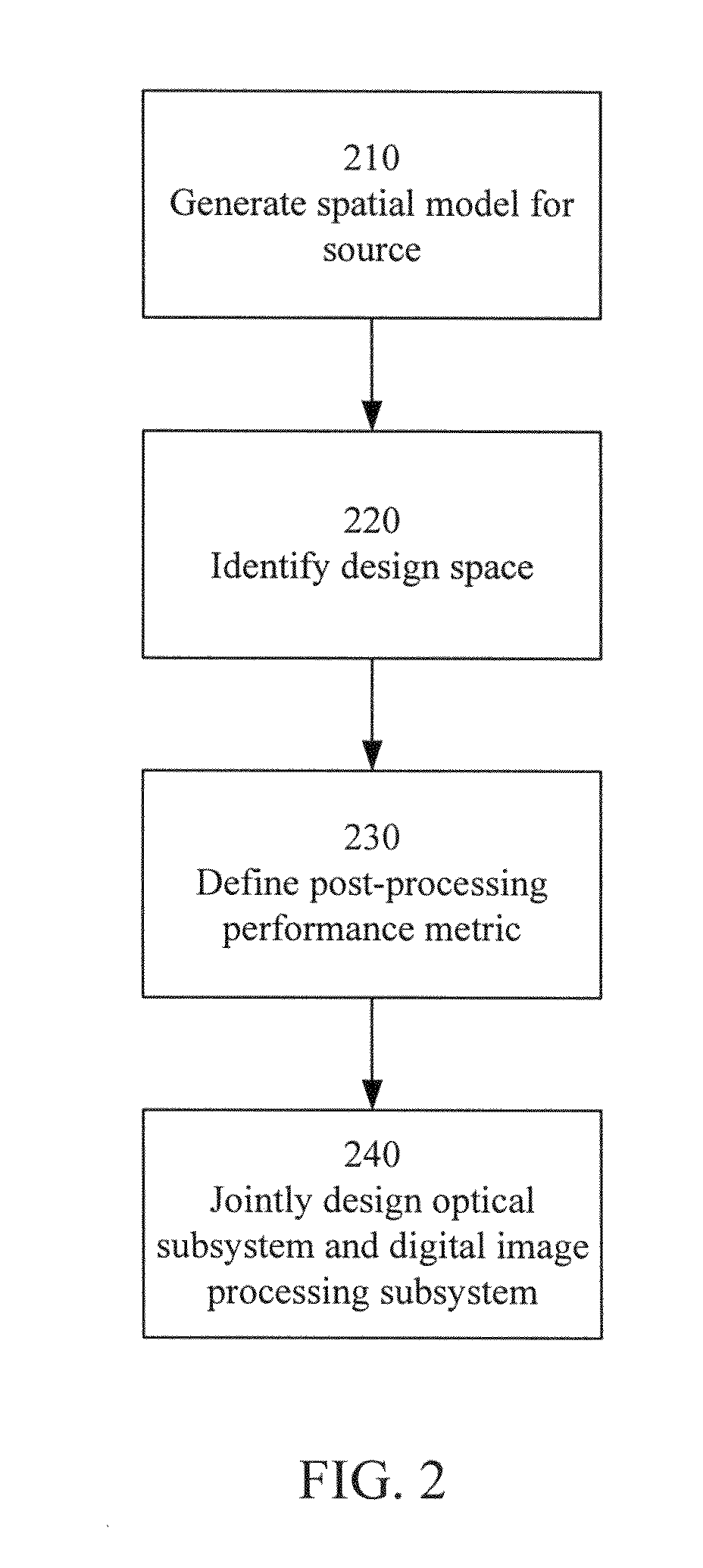
End-to-end design of electro-optic imaging systems for color-correlated objects
InactiveUS20090141140A1Overcome limitationsAdd depthImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingPerformed Imaging
An electro-optic color imaging system includes an optical subsystem, a detector subsystem and a digital image processing subsystem. The system is used to image a color-correlated object. In the optical subsystem, the image surfaces for different color channels of the object are substantially separated. Thus, one color channel may be in focus while others are out of focus. The detector subsystem is located at a fixed image distance from the optical subsystem and captures the different color channel images of the object. The image processing subsystem estimates the image of the object by combining the captured color channel images based at least in part on an a priori estimate of the correlation between the color channels.
Owner:RICOH KK
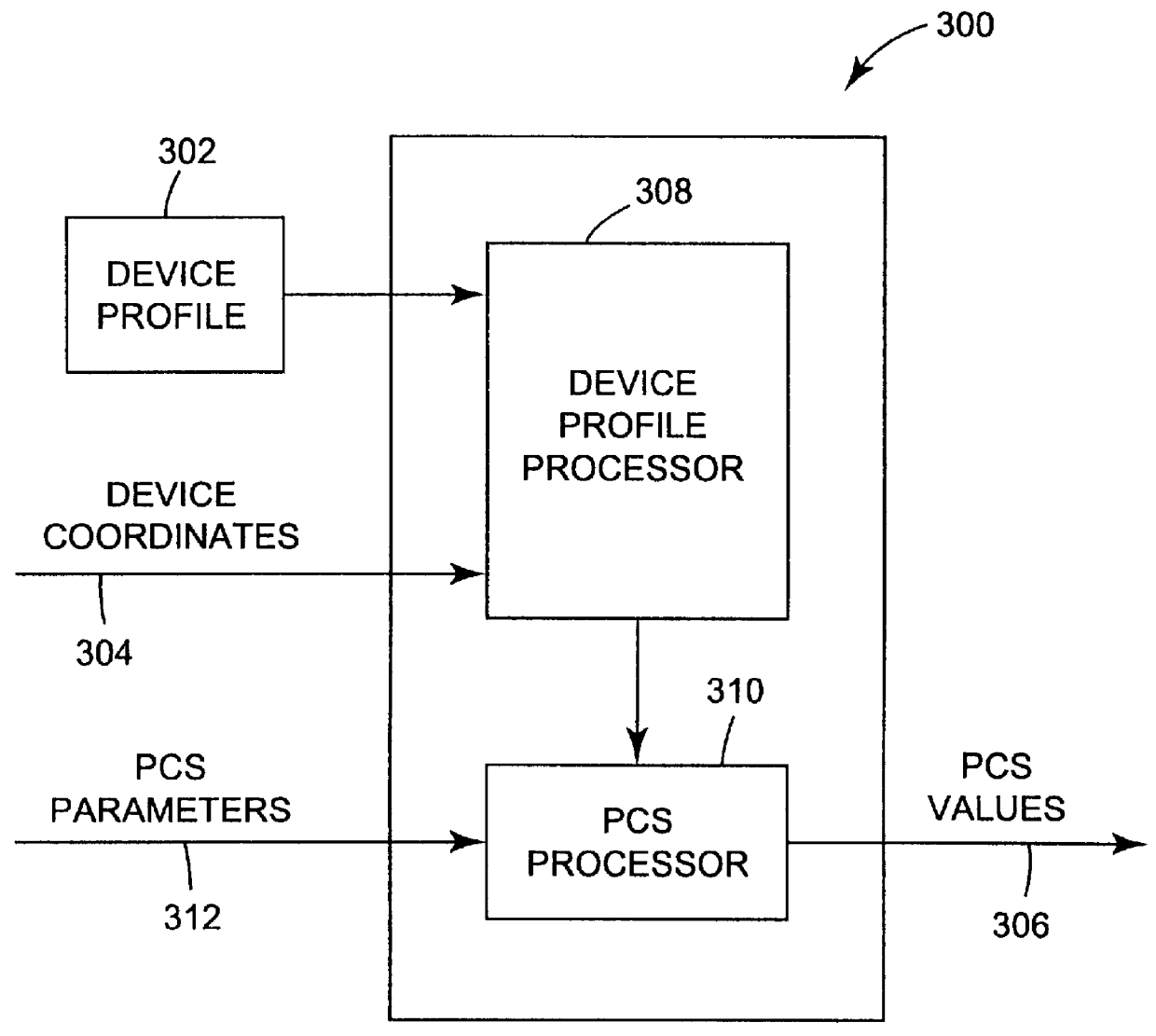
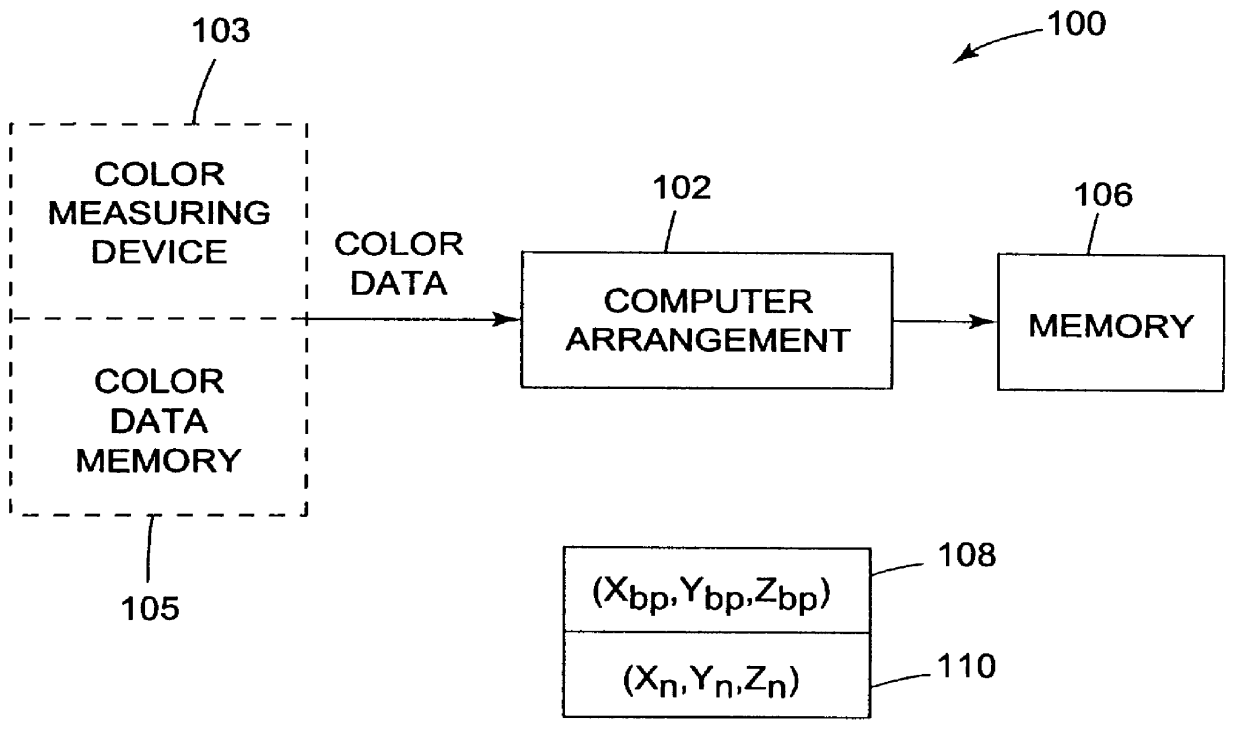
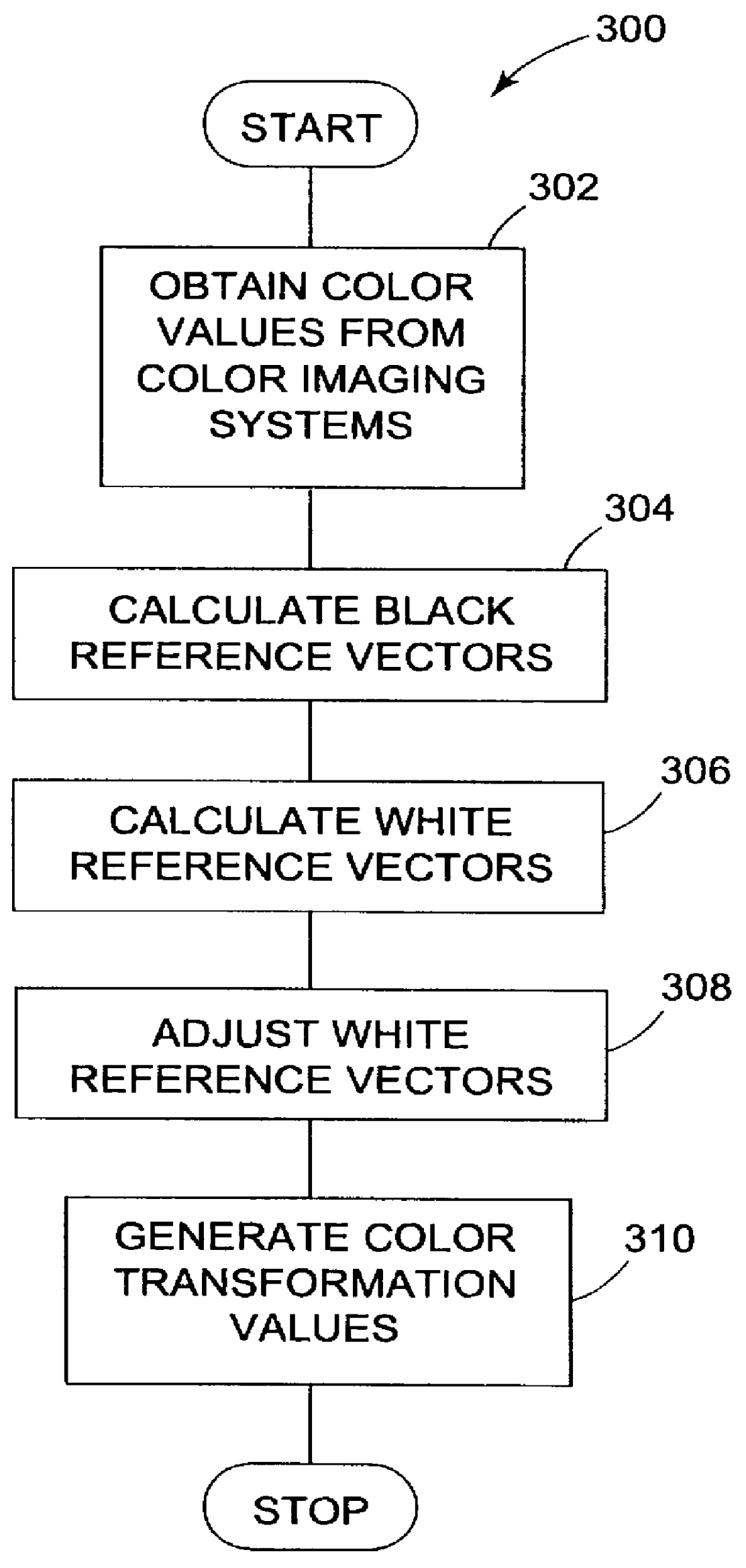
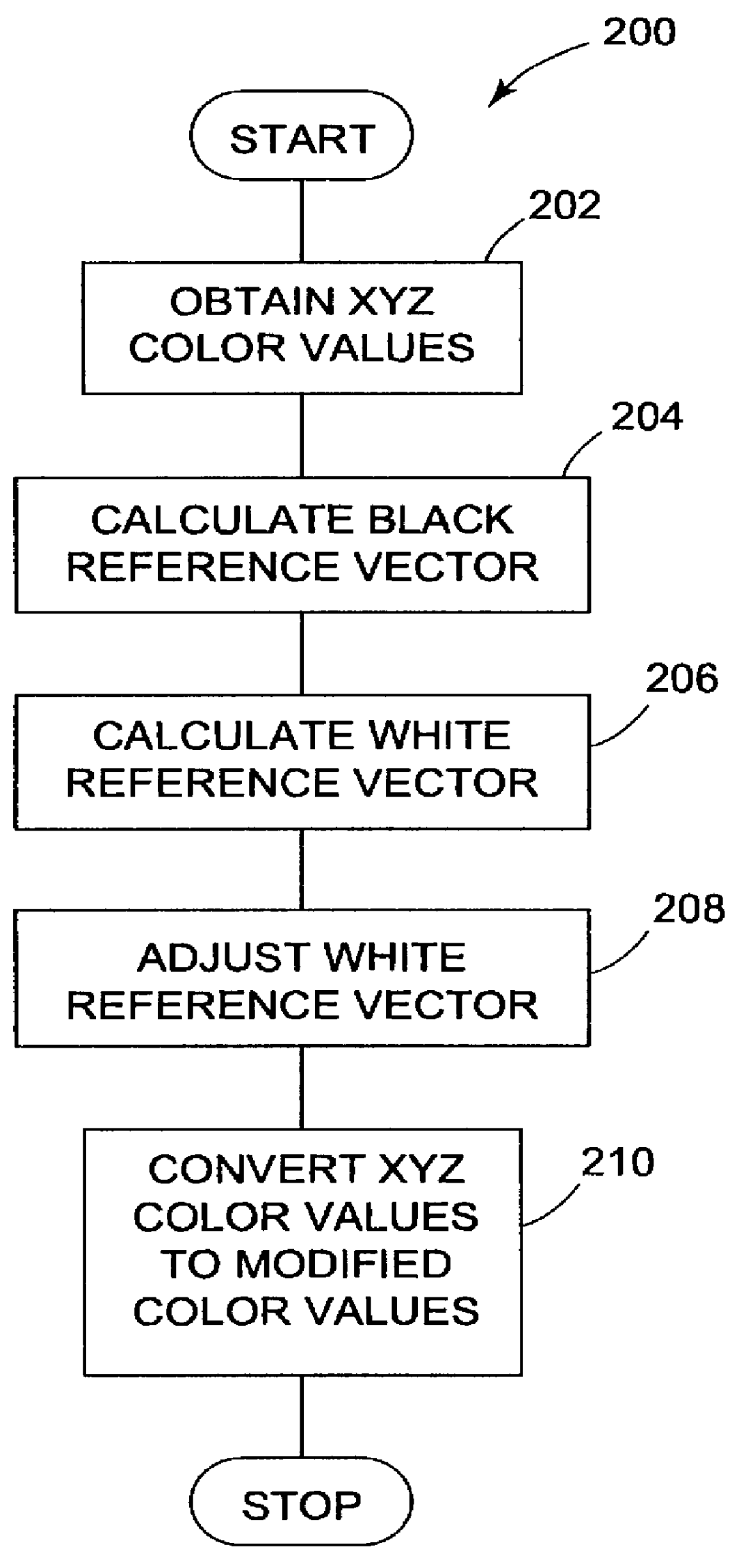
Characterization of color imaging systems
InactiveUS6108442AColor measuring devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionReference vectorColor coordinates
Characterizing a color imaging system involves generating color values representing colors of output samples of the color imaging system. The color values are converted into a device-independent color coordinate system using an adjustable white reference vector and a black reference vector. The white reference vector is calculated using the black reference vector. Color values can be transformed between color imaging systems using the device-independent color coordinate system.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Color image forming apparatus with position compensation
A full-color image forming apparatus, in which an image formed by plural electrophotographic processing portions arranged along a conveying belt is superposedly transferred in order onto a recording medium conveyed by the conveying belt, and thereby the color image is obtained on the recording medium, is capable of obtaining high-quality output and suppressing the positional displacement of the respective colors. When the adjustment of the positioning is performed between the n (n>=2) colors, the calculation and the compensation of the positional displacement is performed such that the displacement amount of the respective n colors falls in the area within (n-1).R / n by use of the CPU 121.
Owner:RICOH KK
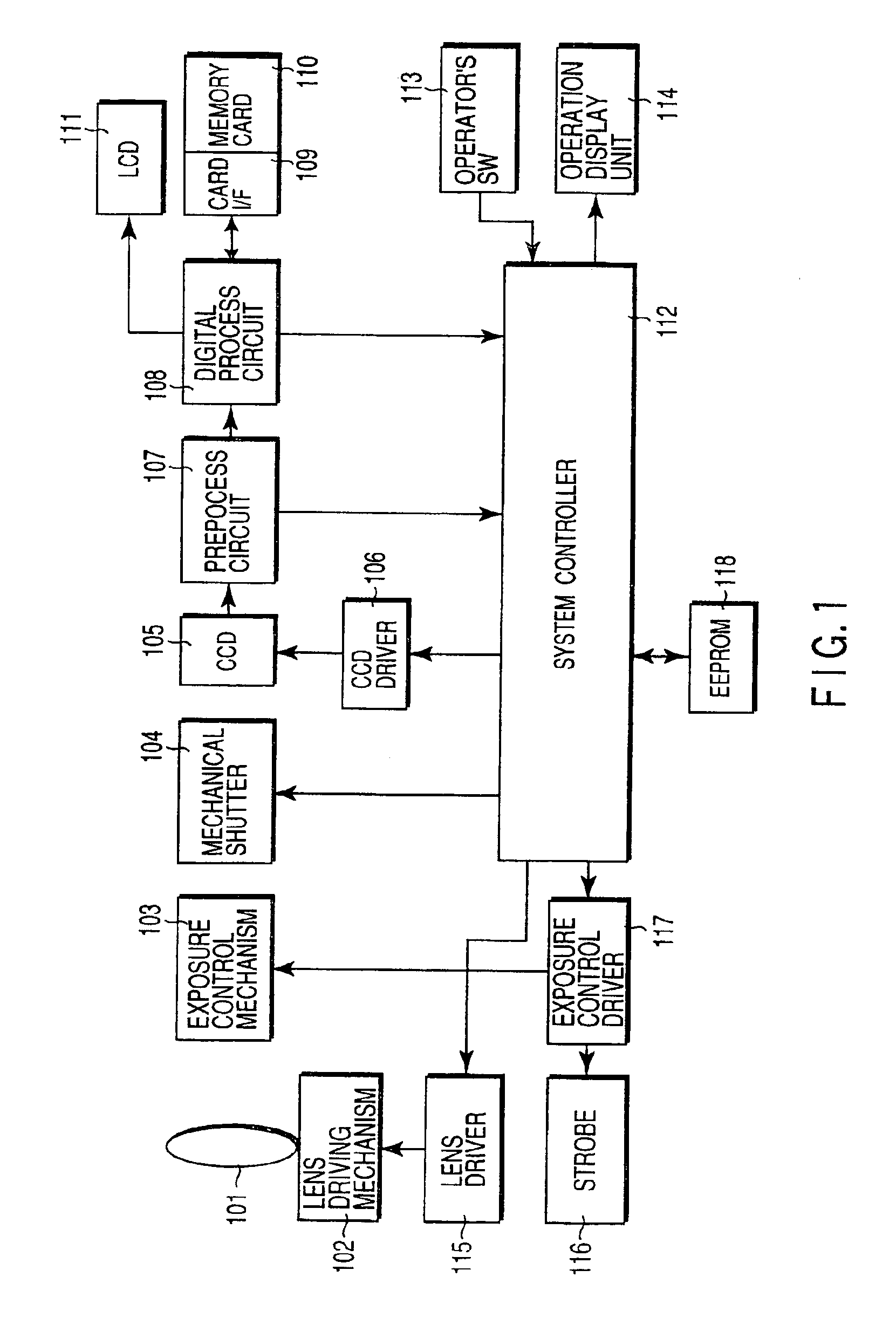
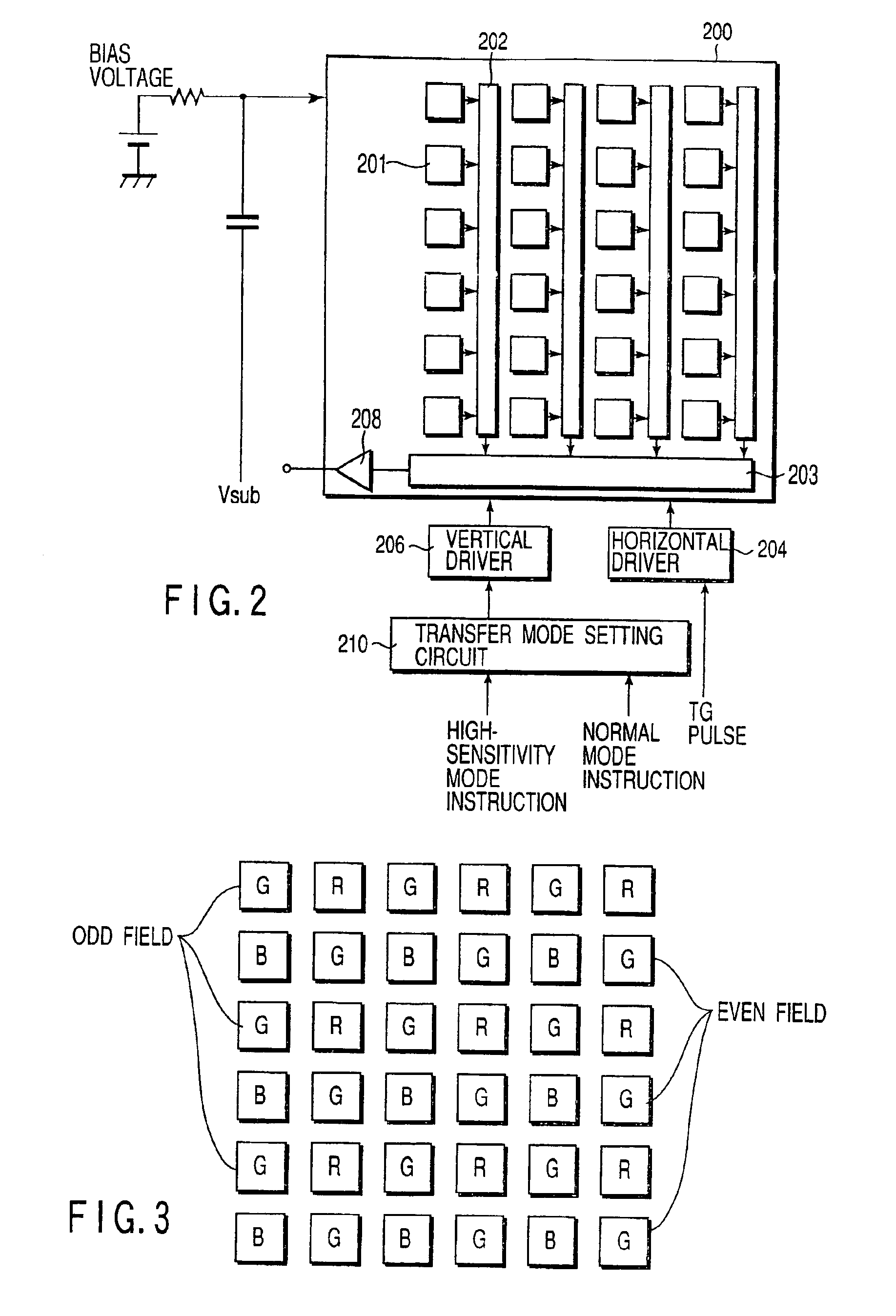
Imaging apparatus capable of adding together signal charges from pixels and reading out the added pixel signals
InactiveUS6930716B2High sensitivityIncrease frame rateTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageNormal mode
A color imaging apparatus includes a CCD imaging device having interline transfer charge transfer paths adapted for interlaced reading and a Bayer-arranged color filter. The apparatus can be put in either of normal shooting mode and high-sensitivity shooting mode. In the high-sensitivity mode, pixel signals from two pixels arranged in the vertical direction in each photosensitive CCD array are transferred by a corresponding vertical transfer path at two times the rate in the normal mode to a horizontal transfer path where they are added together. A line of pixel signals from the horizontal transfer path is output to a preprocess circuit where pixel signals separated by one pixel in the horizontal direction are added together. This process produces a line of image signal.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com