Patents
Literature
51 results about "Focal shift" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
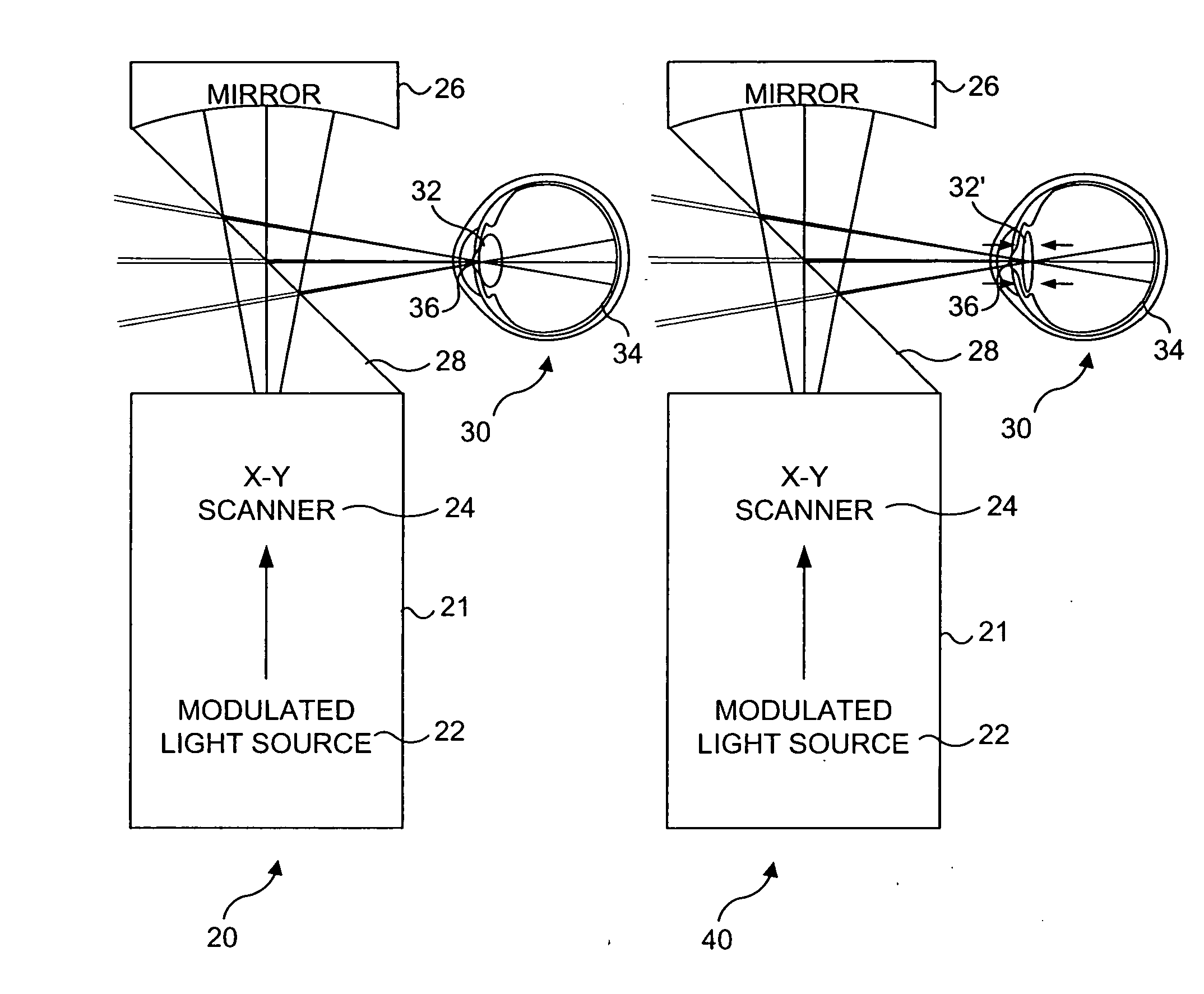
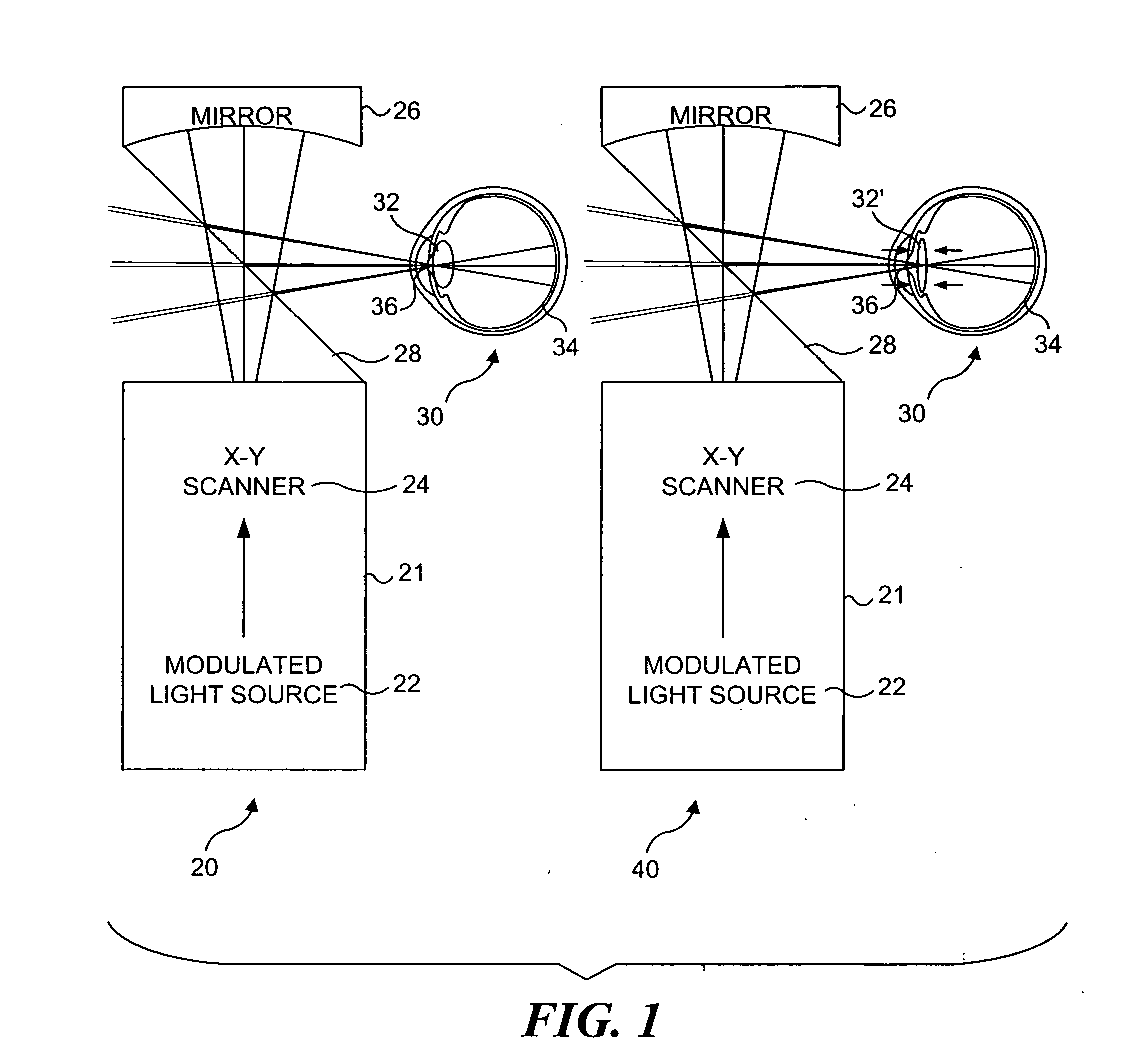
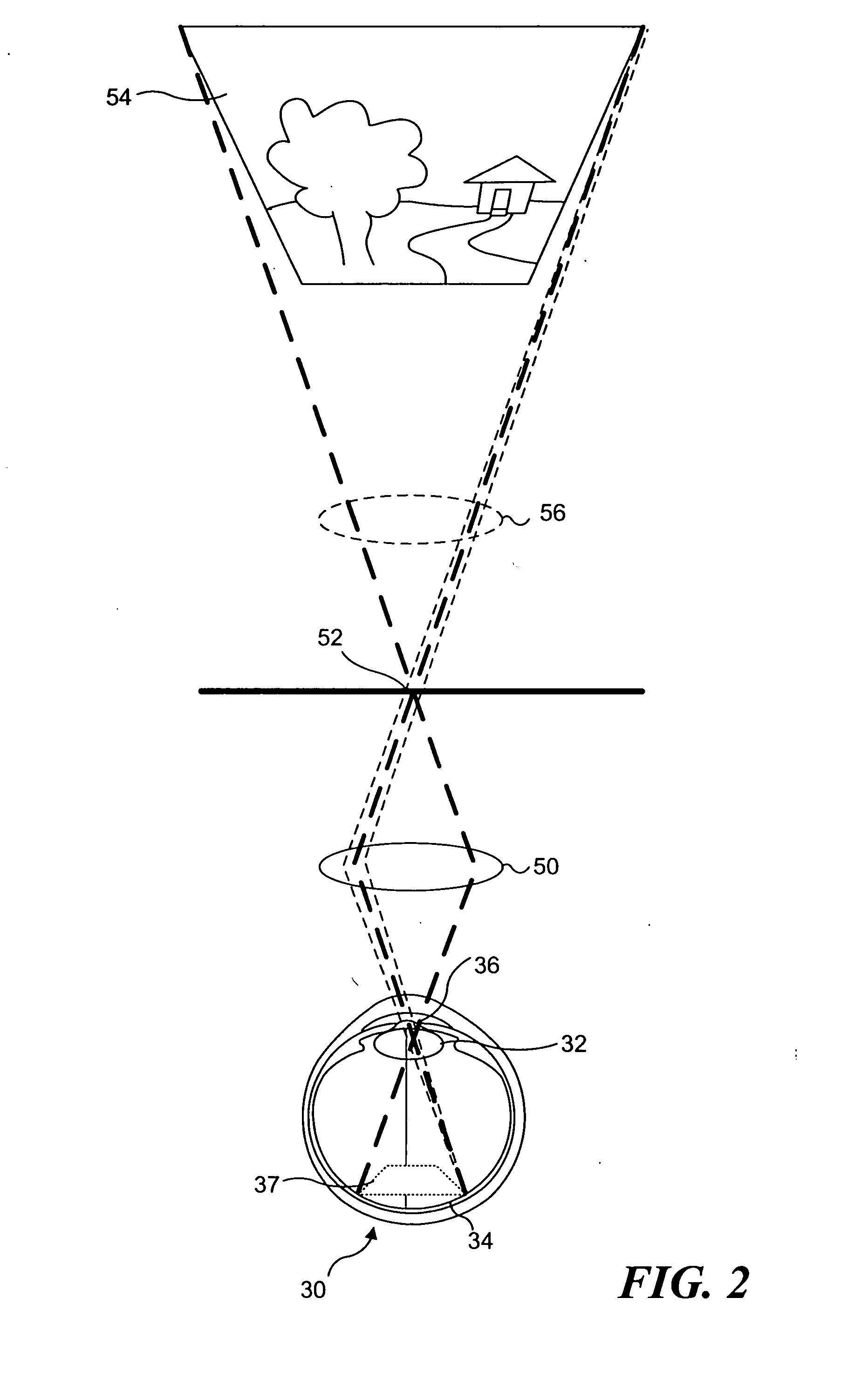
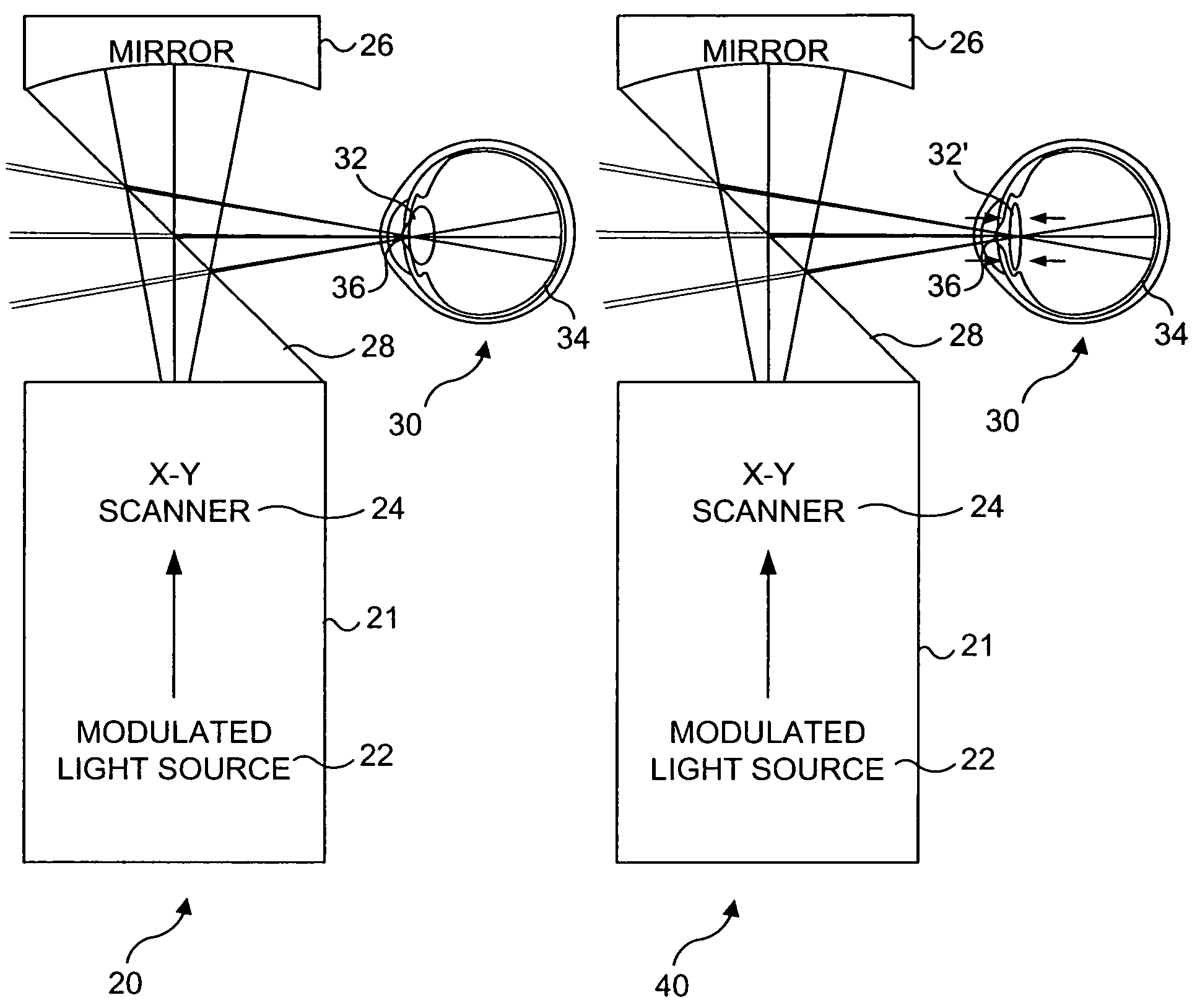
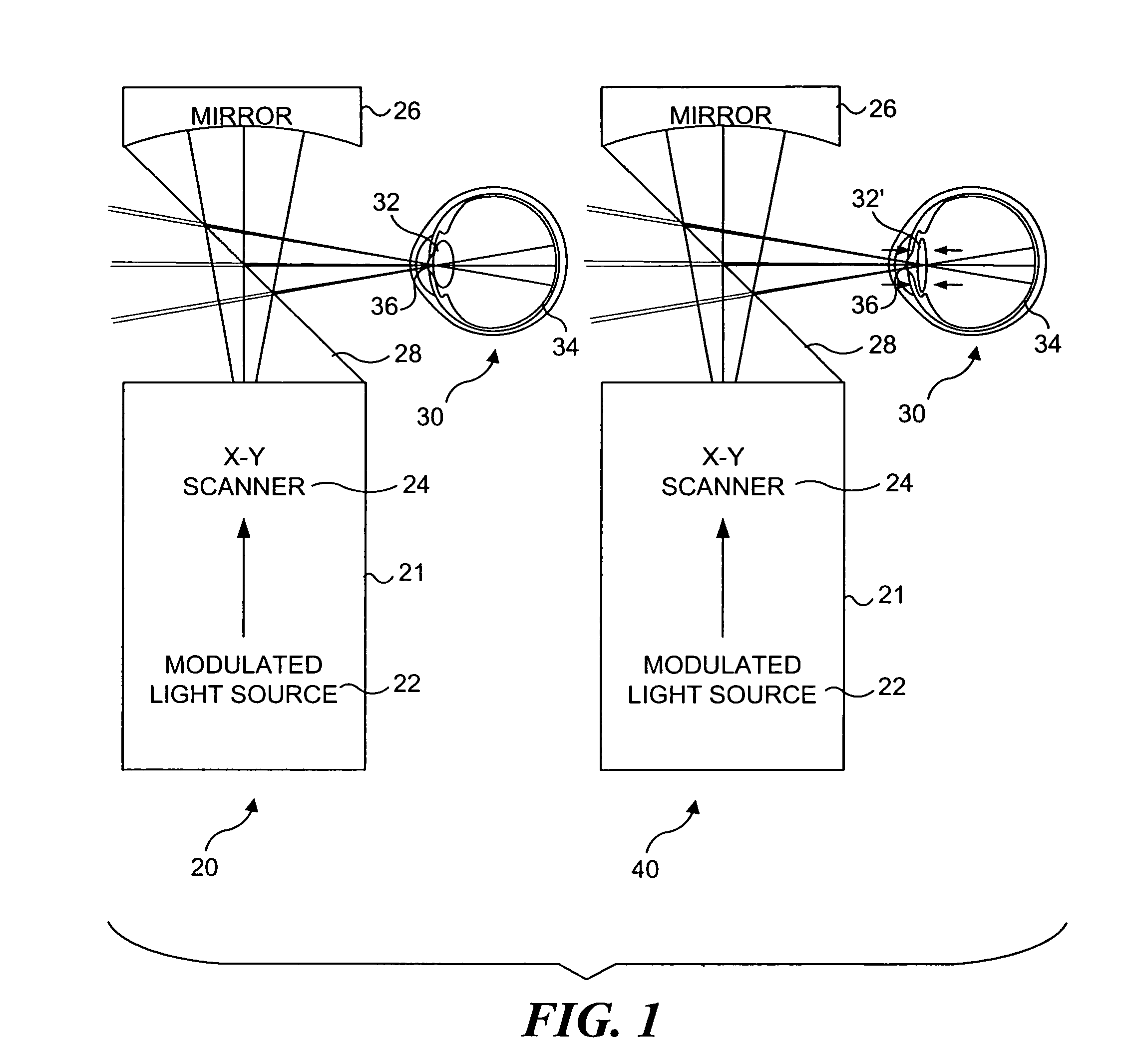
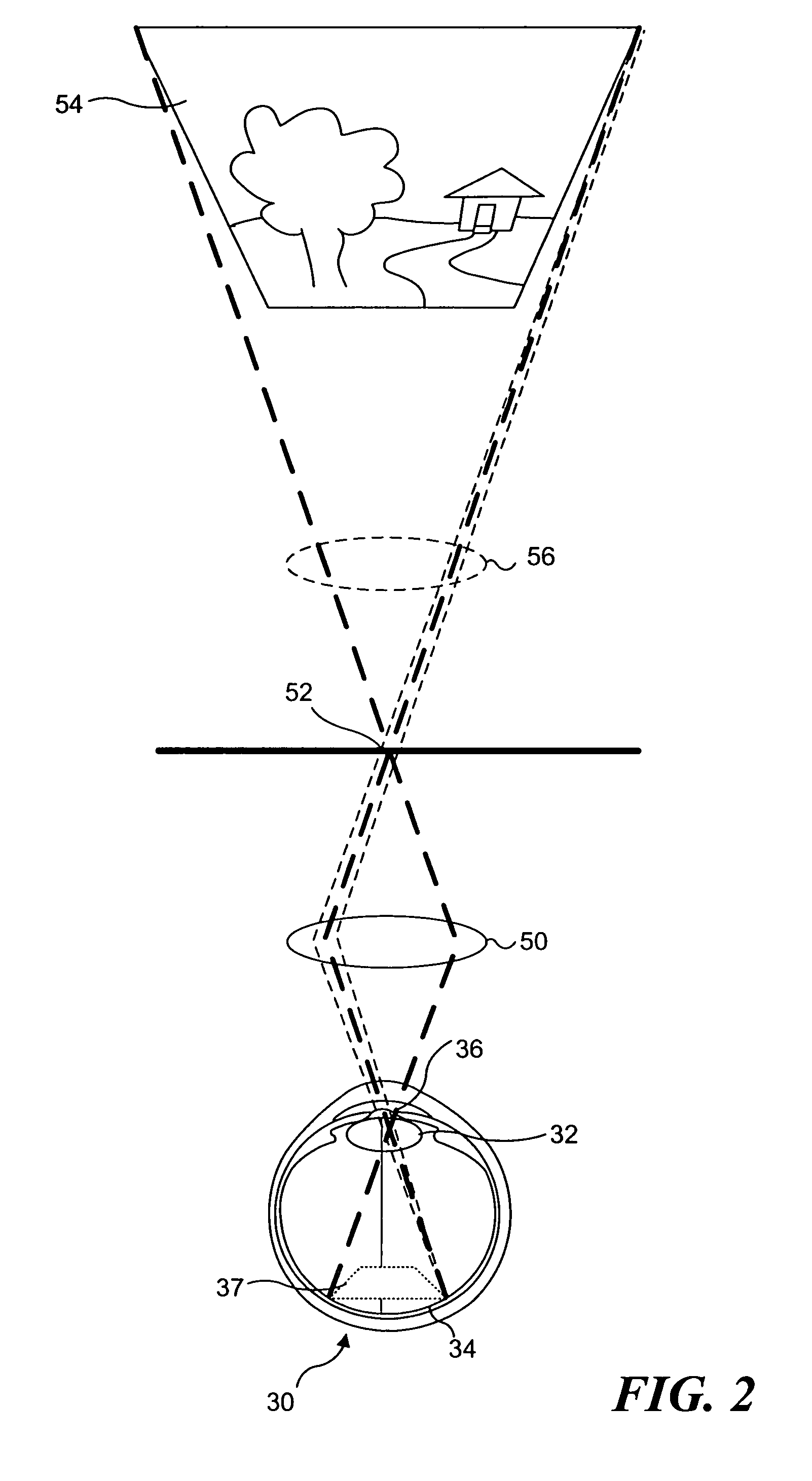
Materials and methods for simulating focal shifts in viewers using large depth of focus displays
ActiveUS20060232665A1Improve interactivityEnhances perceived realismTelevision system detailsSteroscopic systemsDisplay deviceDepth of field
A large depth of focus (DOF) display provides an image in which the apparent focus plane is adjusted to track an accommodation (focus) of a viewer's eye(s) to more effectively convey depth in the image. A device is employed to repeatedly determine accommodation as a viewer's gaze within the image changes. In response, an image that includes an apparent focus plane corresponding to the level of accommodation of the viewer is provided on the large DOF display. Objects that are not at the apparent focus plane are made to appear blurred. The images can be rendered in real-time, or can be pre-rendered and stored in an array. The dimensions of the array can each correspond to a different variable. The images can alternatively be provided by a computer controlled, adjustable focus video camera in real-time.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Materials and methods for simulating focal shifts in viewers using large depth of focus displays
InactiveUS7428001B2Improve interactivityEnhances perceived realismTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceDepth of focus
A large depth of focus (DOF) display provides an image in which the apparent focus plane is adjusted to track an accommodation (focus) of a viewer's eye(s) to more effectively convey depth in the image. A device is employed to repeatedly determine accommodation as a viewer's gaze within the image changes. In response, an image that includes an apparent focus plane corresponding to the level of accommodation of the viewer is provided on the large DOF display. Objects that are not at the apparent focus plane are made to appear blurred. The images can be rendered in real-time, or can be pre-rendered and stored in an array. The dimensions of the array can each correspond to a different variable. The images can alternatively be provided by a computer controlled, adjustable focus video camera in real-time.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
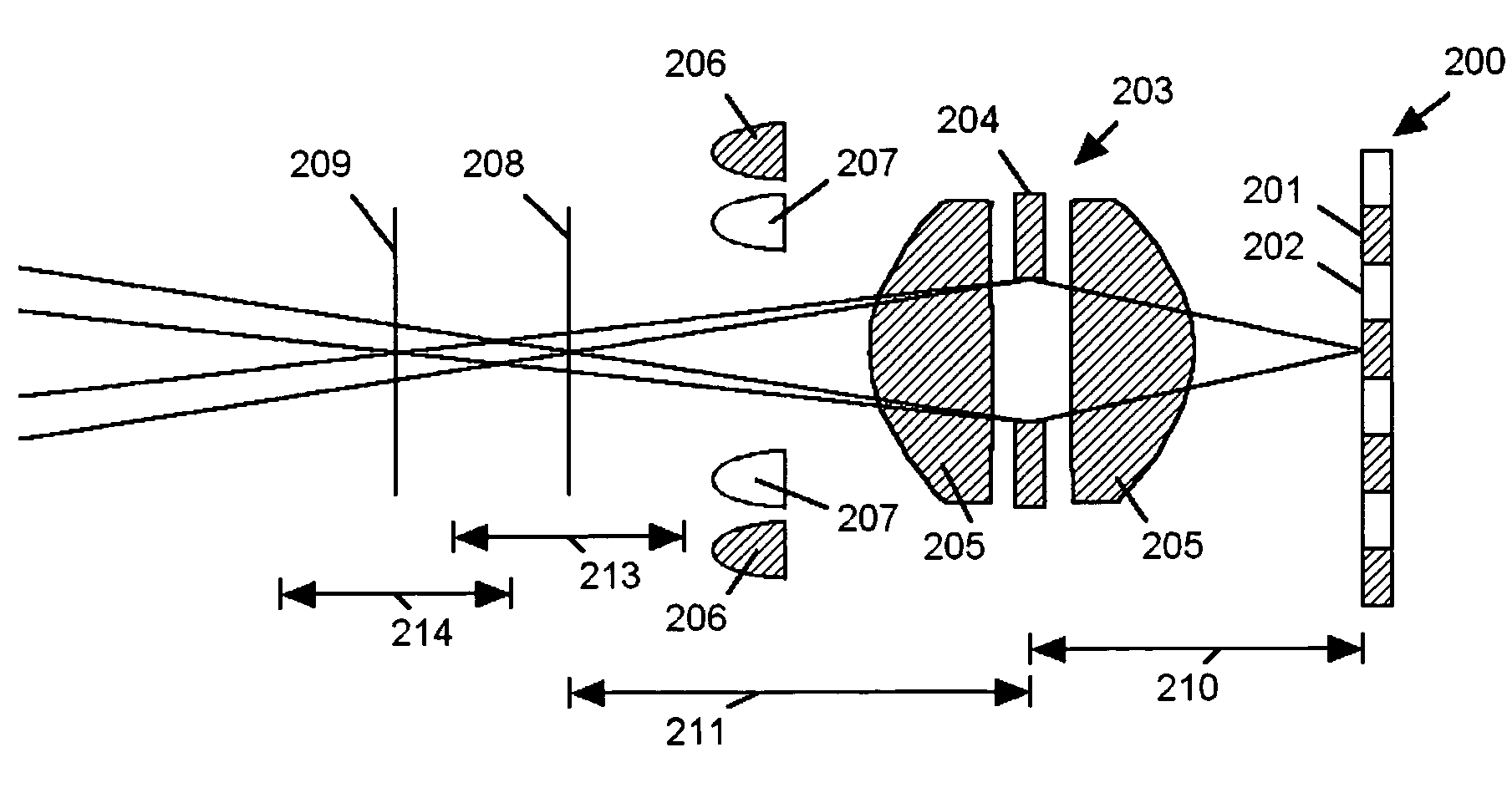
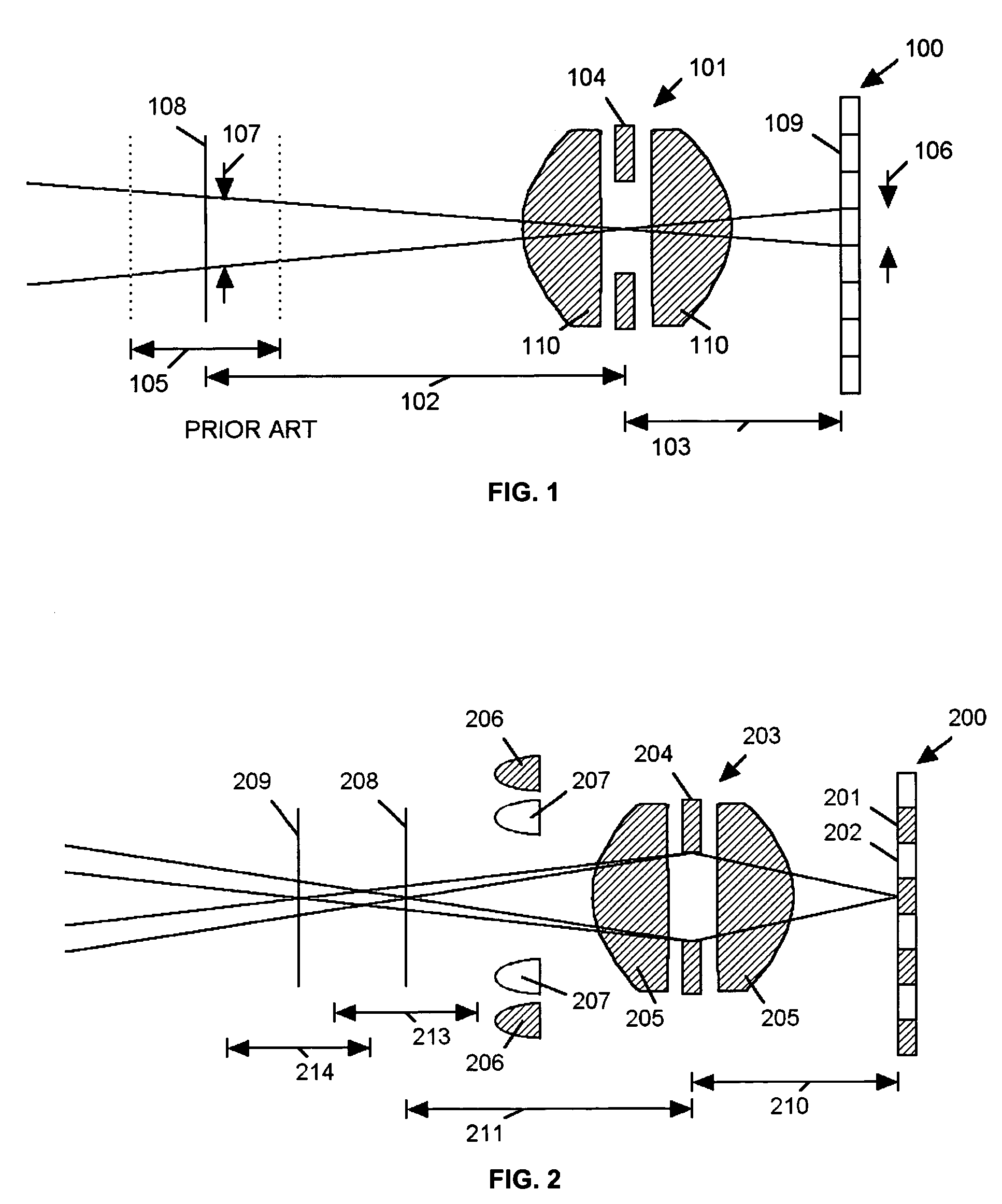
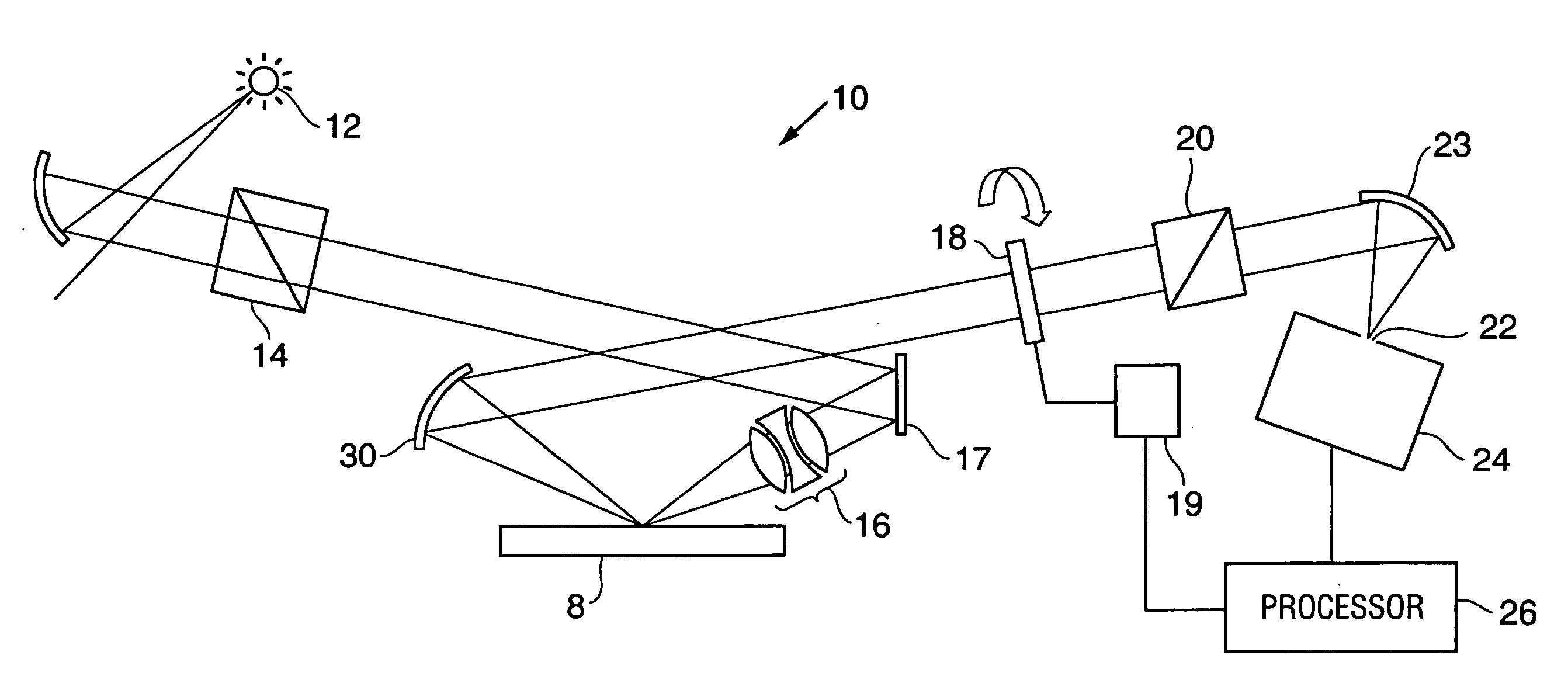
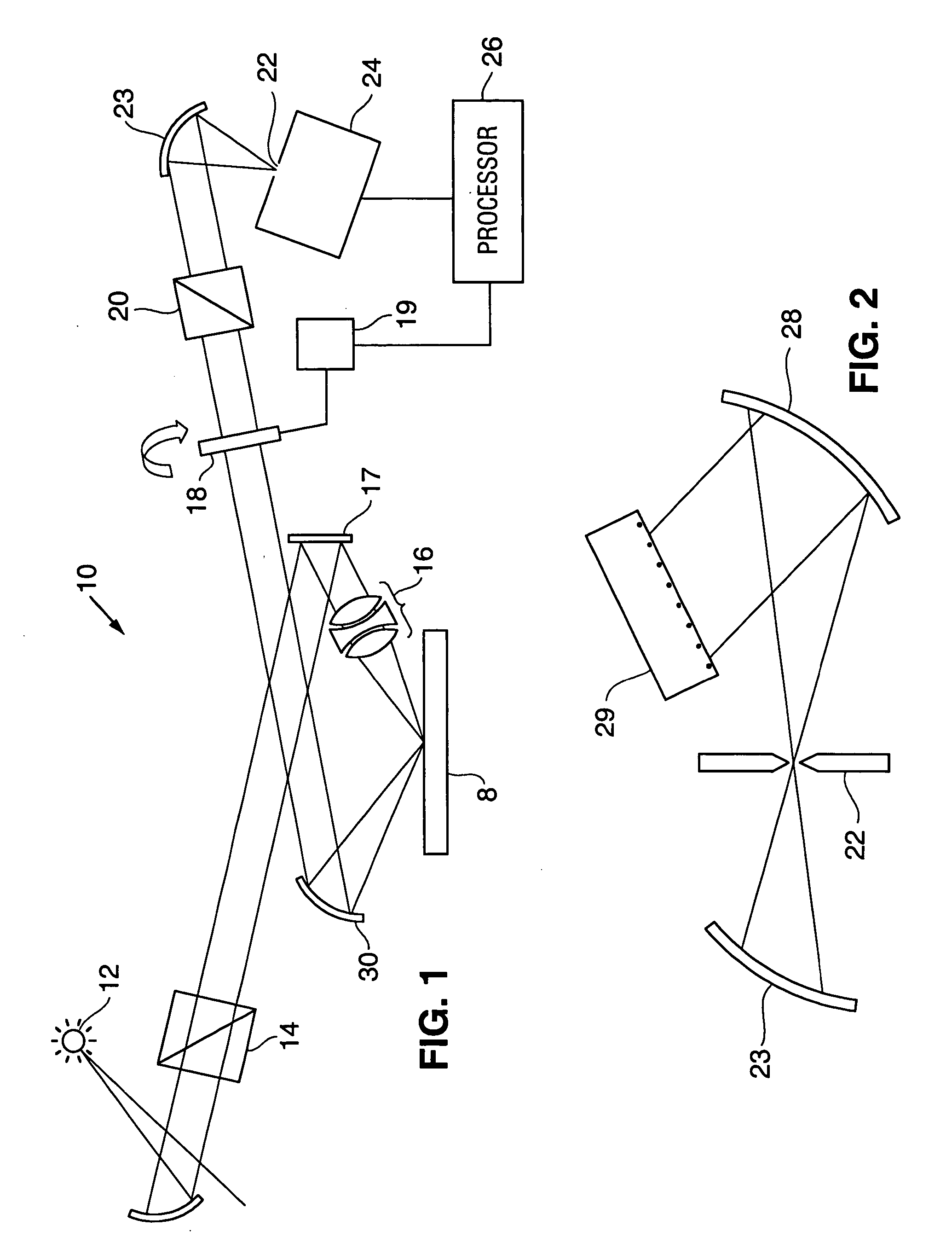
Extended depth of field imaging system using chromatic aberration
ActiveUS7224540B2Lower optical magnificationHigh intensity illuminationRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFocal positionDepth of field
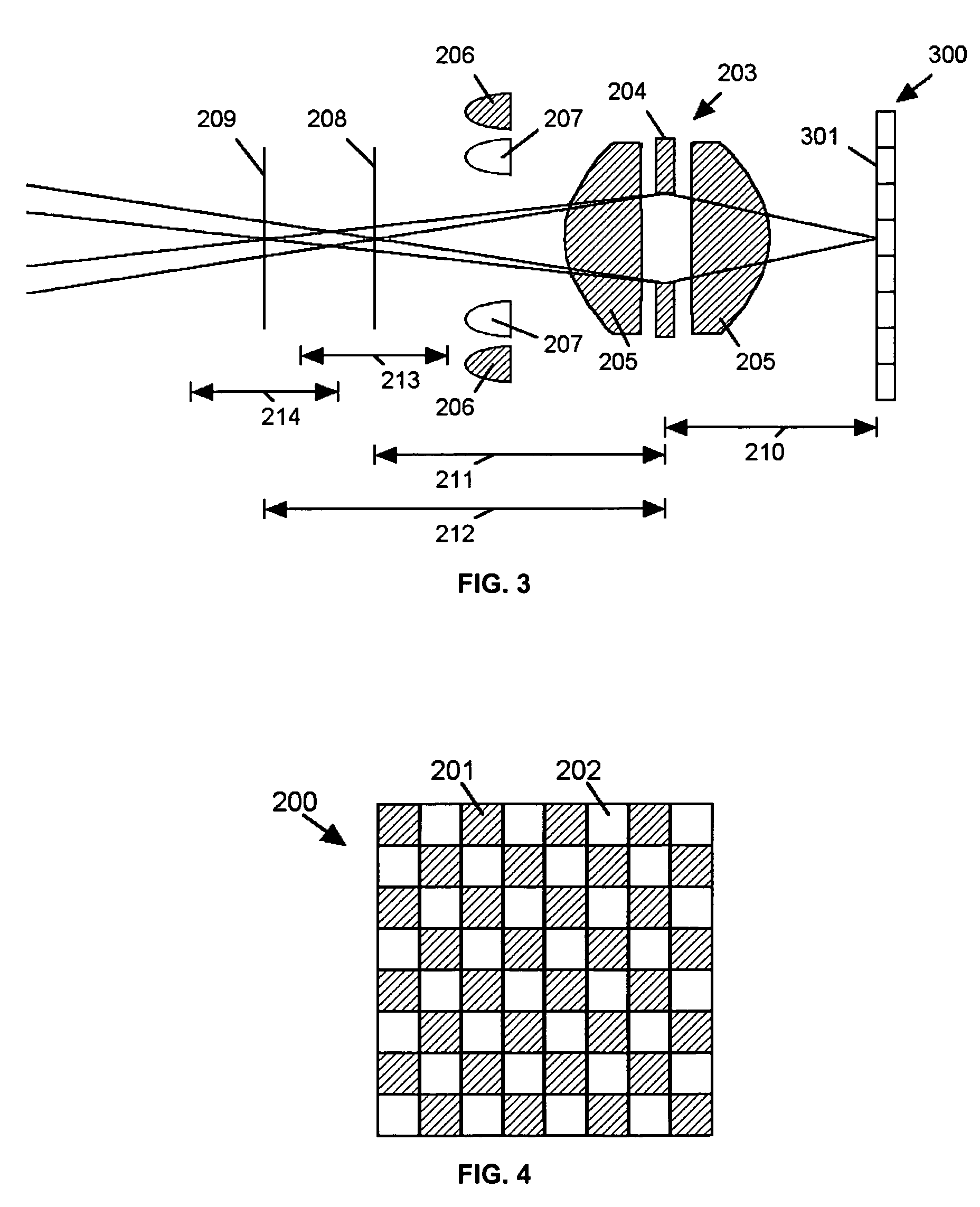
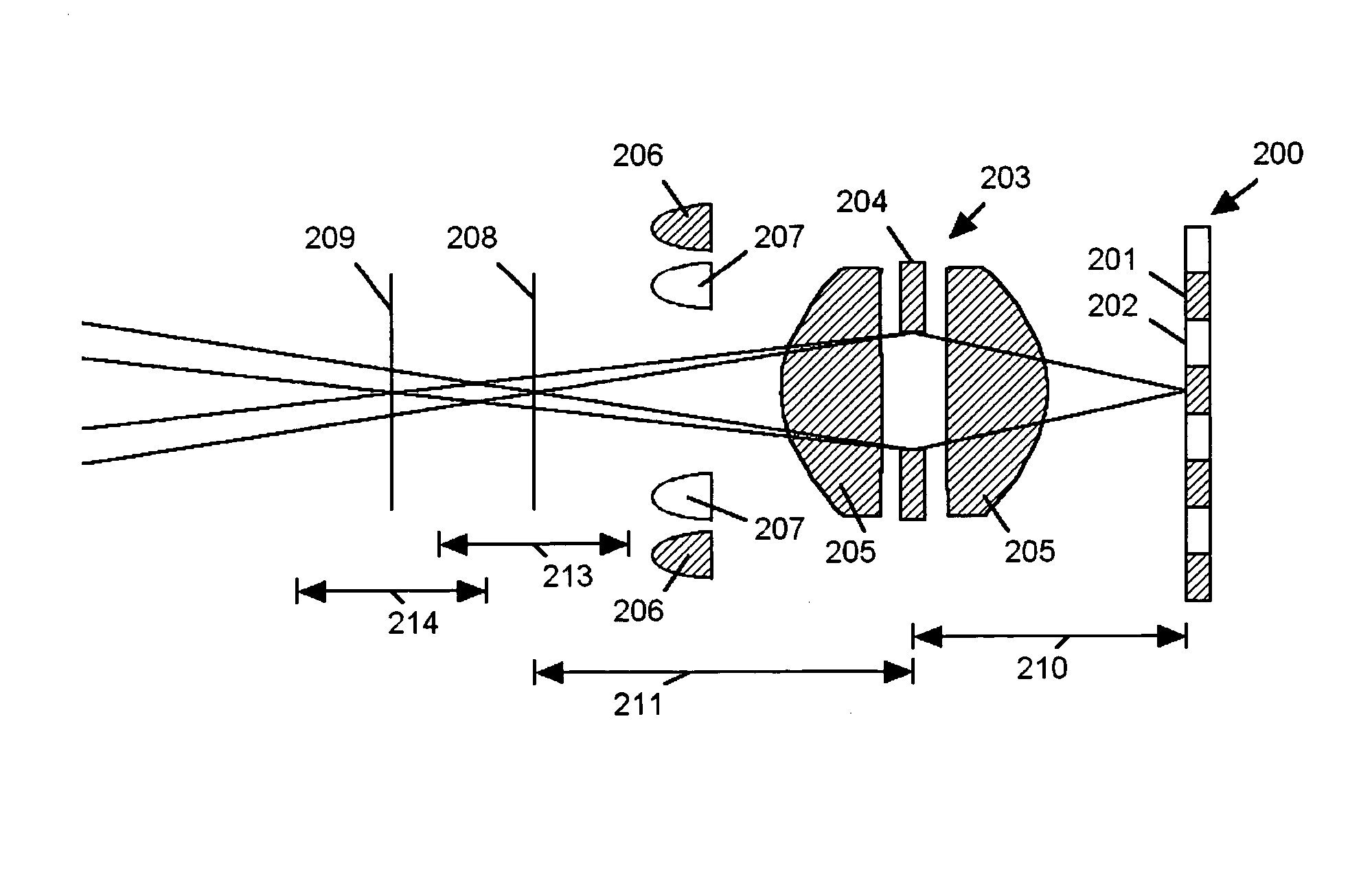
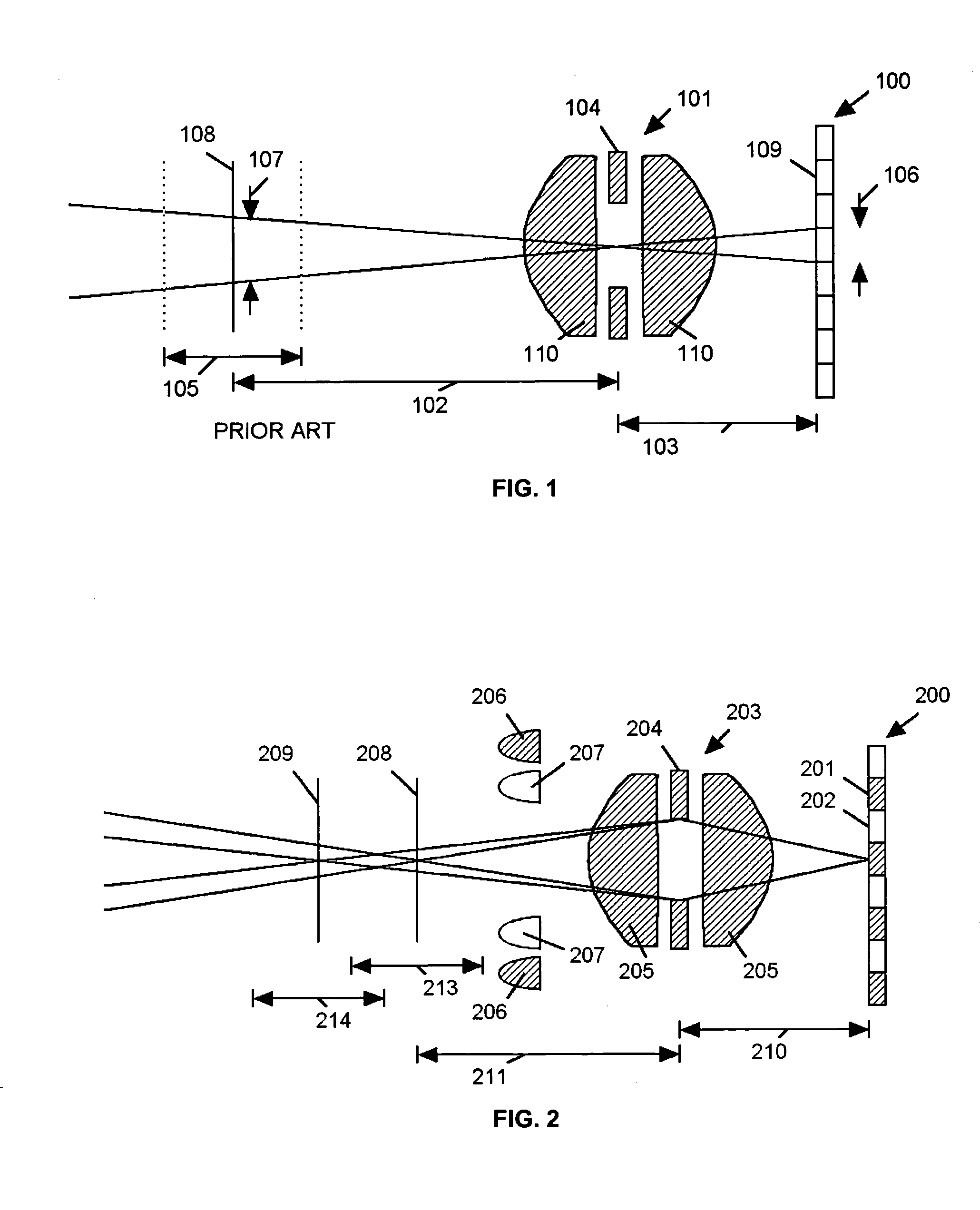
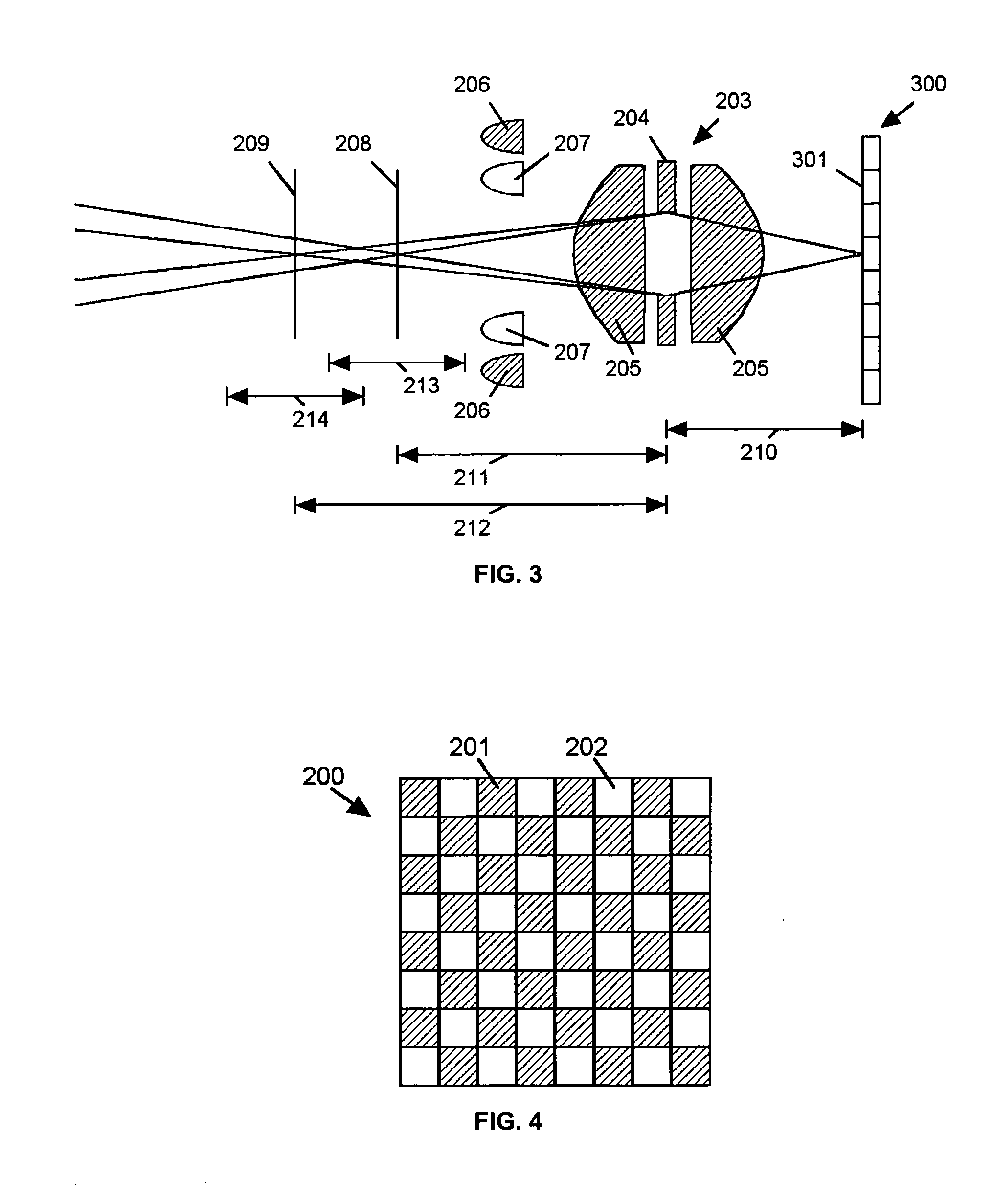
An imaging system (FIG. 3) is disclosed that has a wavelength dependent focal shift caused by longitudinal chromatic aberration in a lens assembly (203) that provides extended depth of field imaging due to focal shift (213,214) and increased resolution due to reduced lens system magnification. In use, multiple wavelengths of quasi-monochromatic illumination, from different wavelength LEDs (206,207) or the like, illuminate the target, either sequentially, or in parallel in conjunction with an imager (200) with wavelength selective (colored) filters. Images are captured with different wavelengths of illumination that have different focus positions (208,209), either sequentially or by processing the color planes of a color imager separately. Extended depth of field, plus high resolution are achieved. Additionally, information about the range to the target can be determined by analyzing the degree of focus of the various colored images.
Owner:PSC SCANNING INC
Extended depth of field imaging system using chromatic aberration
ActiveUS20060171041A1Lower optical magnificationHigh intensity illuminationVisual representatino by photographic printingSensing by electromagnetic radiationImage resolutionDepth of field
An imaging system (FIG. 3) is disclosed that has a wavelength dependent focal shift caused by longitudinal chromatic aberration in a lens assembly (203) that provides extended depth of field imaging due to focal shift (213,214) and increased resolution due to reduced lens system magnification. In use, multiple wavelengths of quasi-monochromatic illumination, from different wavelength LEDs (206,207) or the like, illuminate the target, either sequentially, or in parallel in conjunction with an imager (200) with wavelength selective (colored) filters. Images are captured with different wavelengths of illumination that have different focus positions (208,209), either sequentially or by processing the color planes of a color imager separately. Extended depth of field, plus high resolution are achieved. Additionally, information about the range to the target can be determined by analyzing the degree of focus of the various colored images.
Owner:PSC SCANNING INC
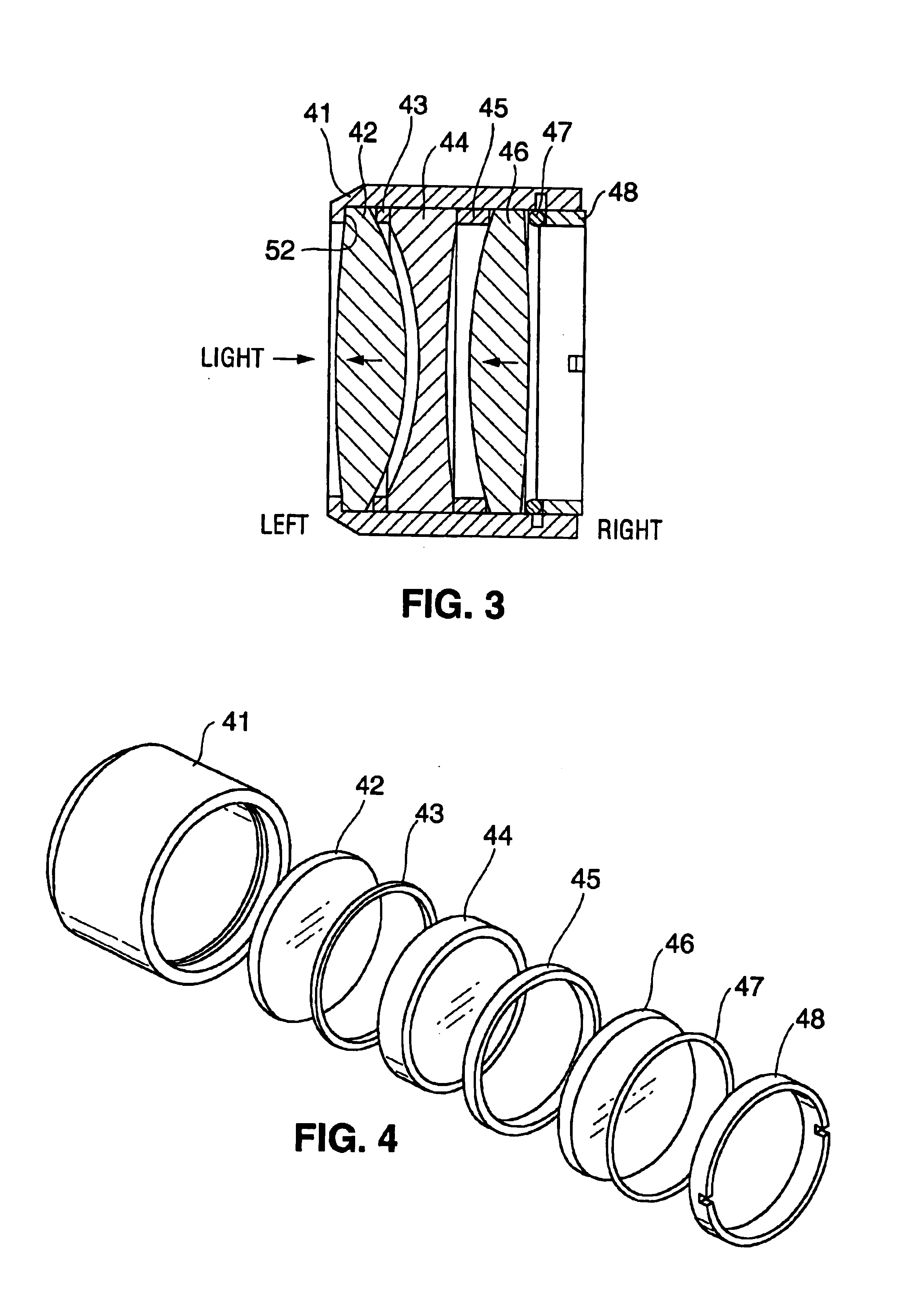
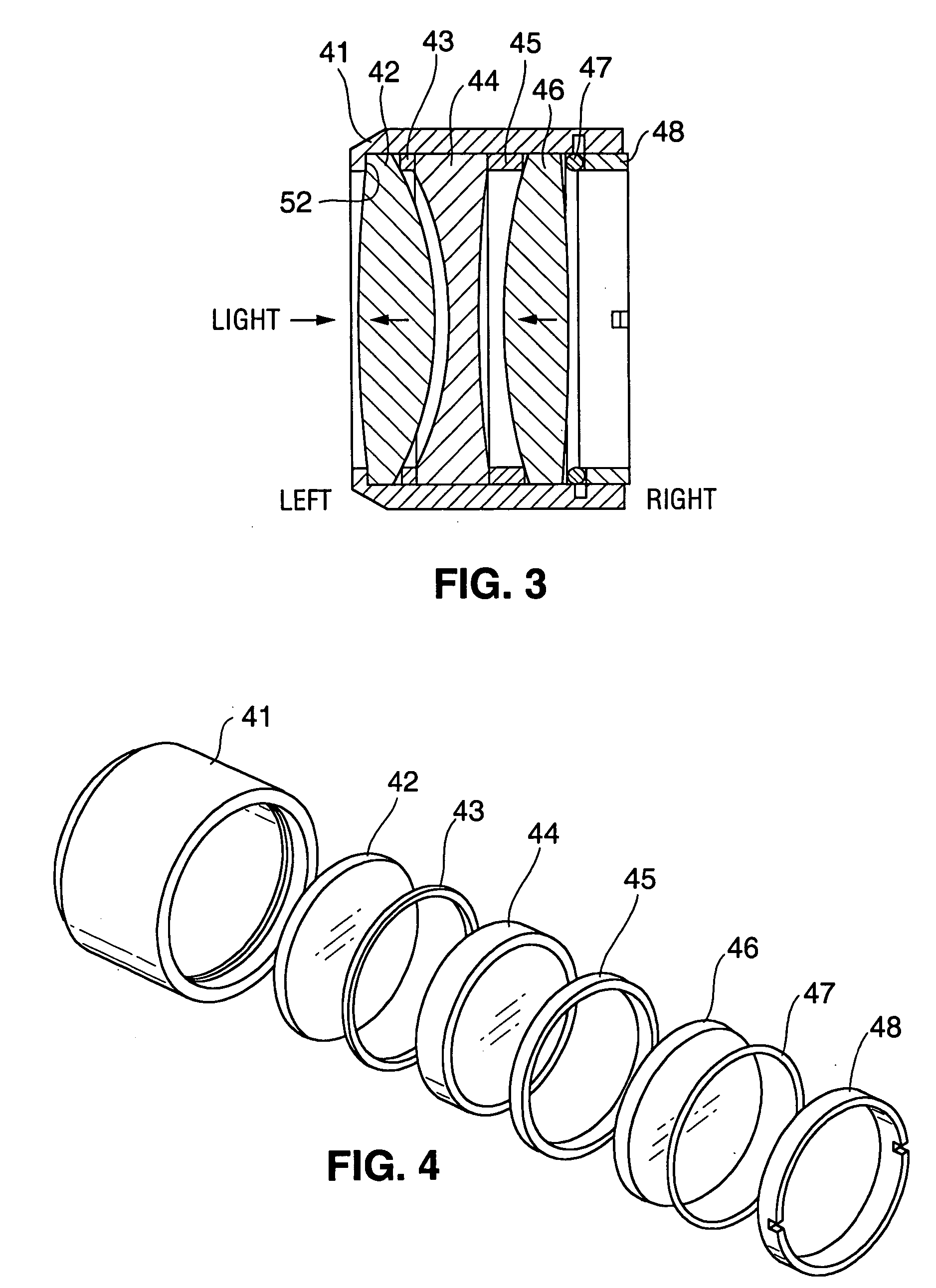
Lens unit and vehicle-mounted infrared lens unit
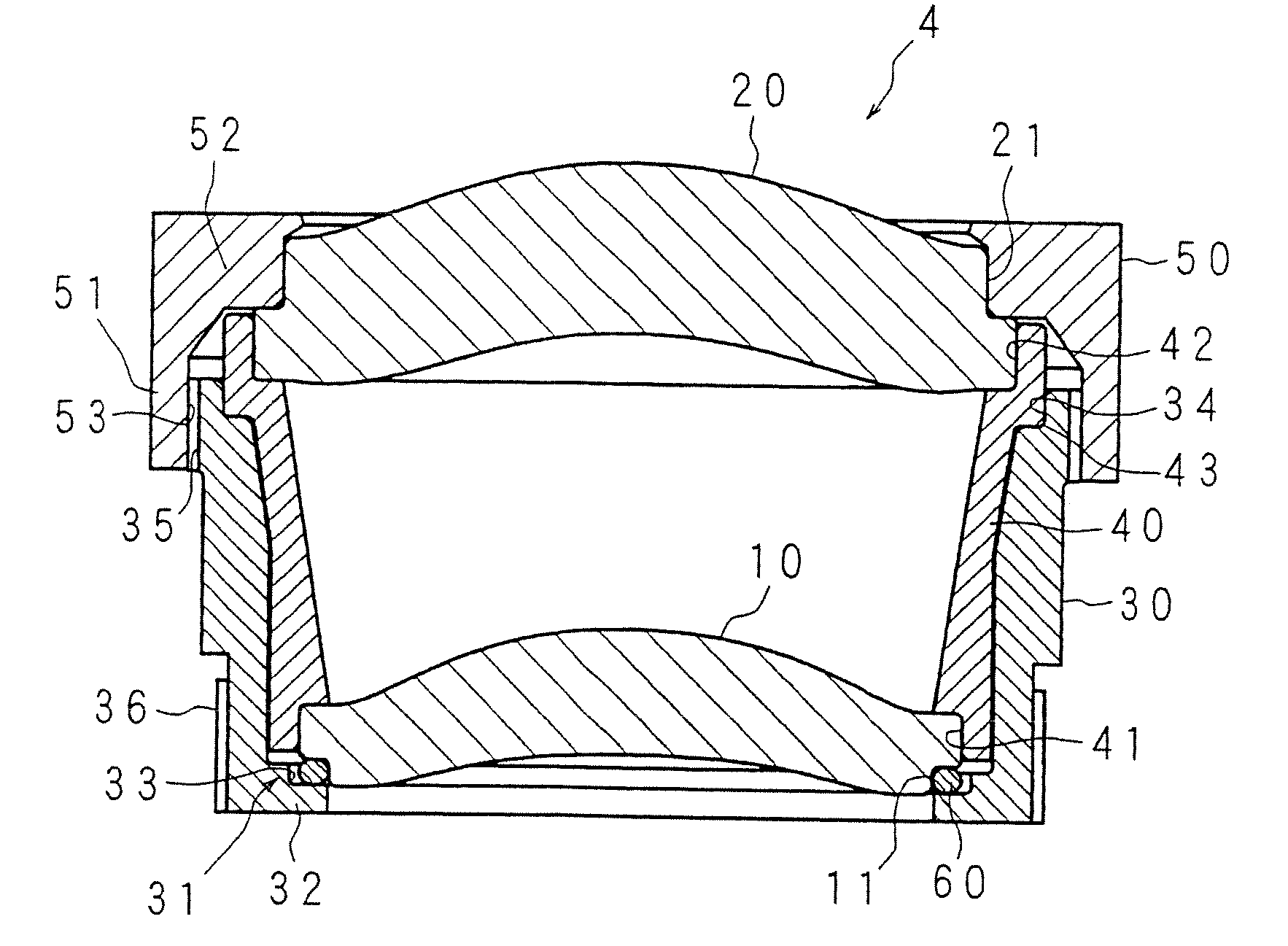
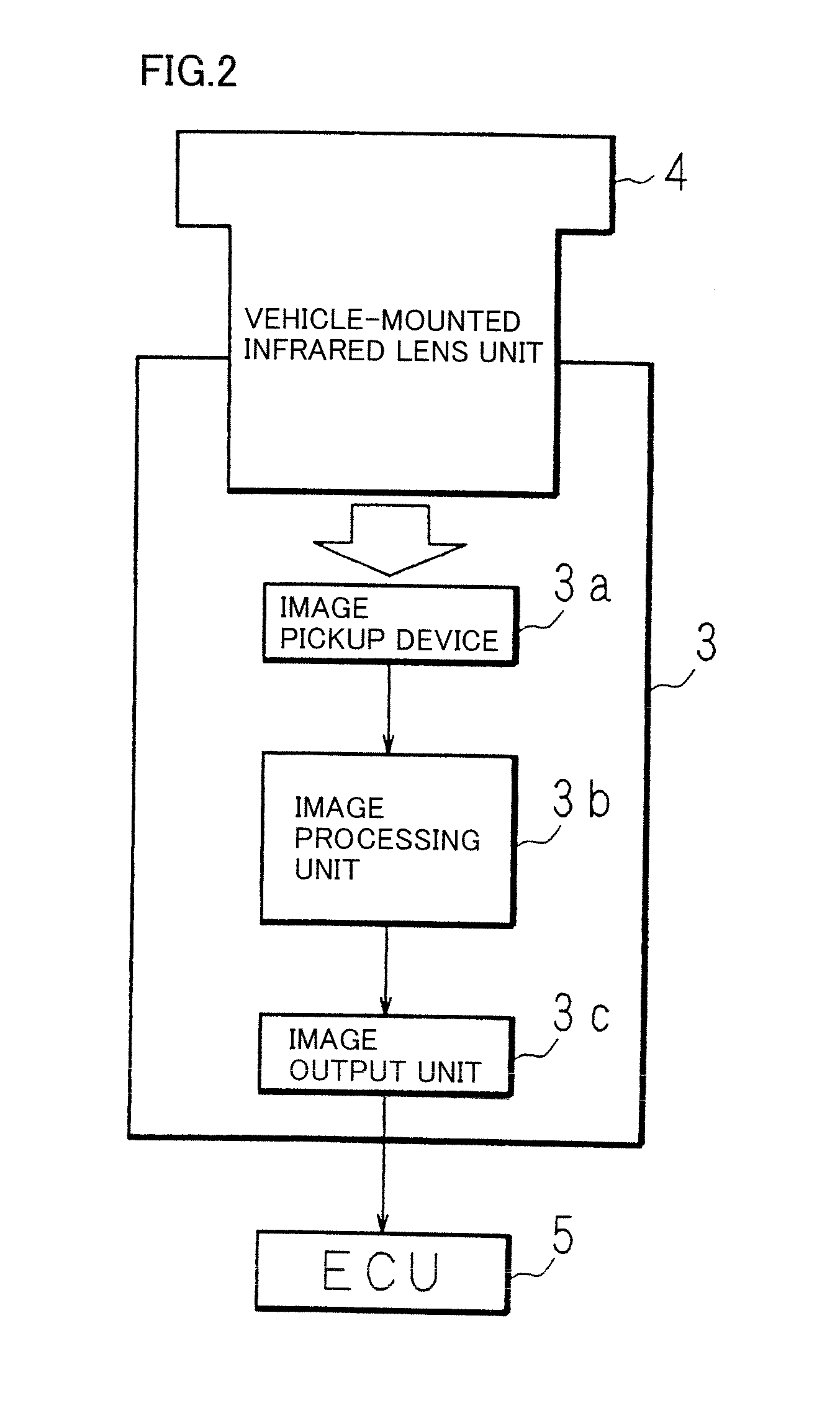
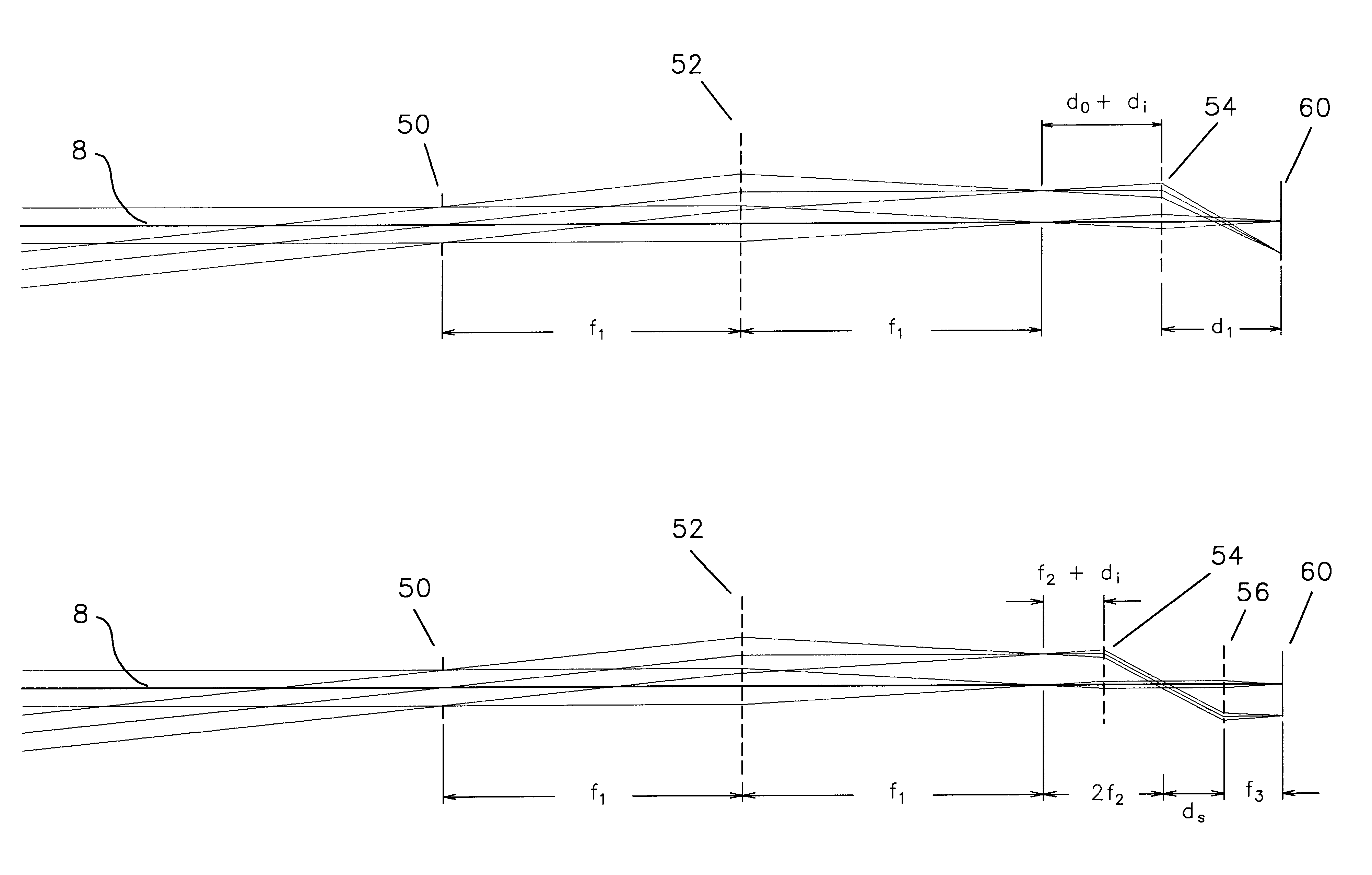
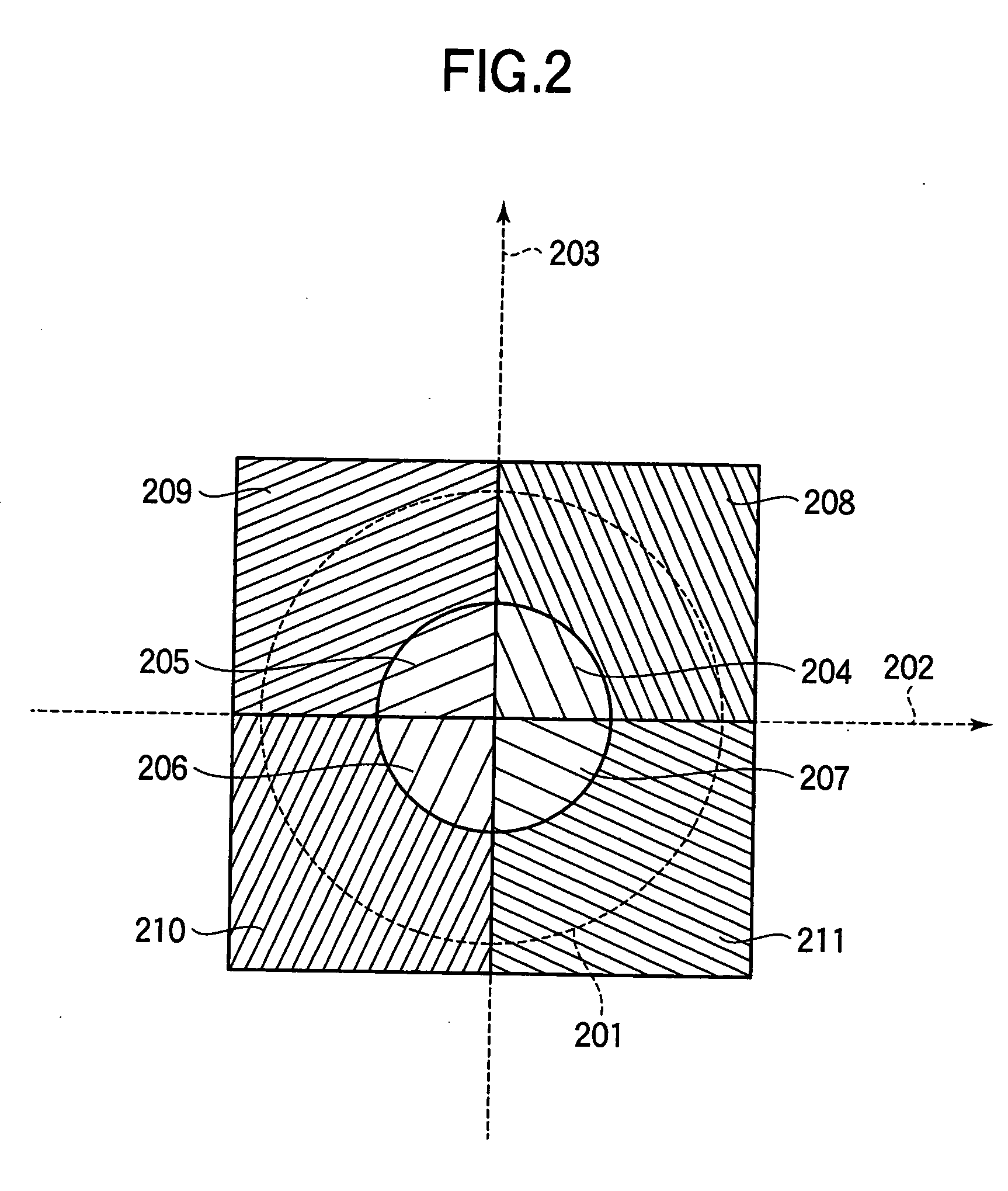
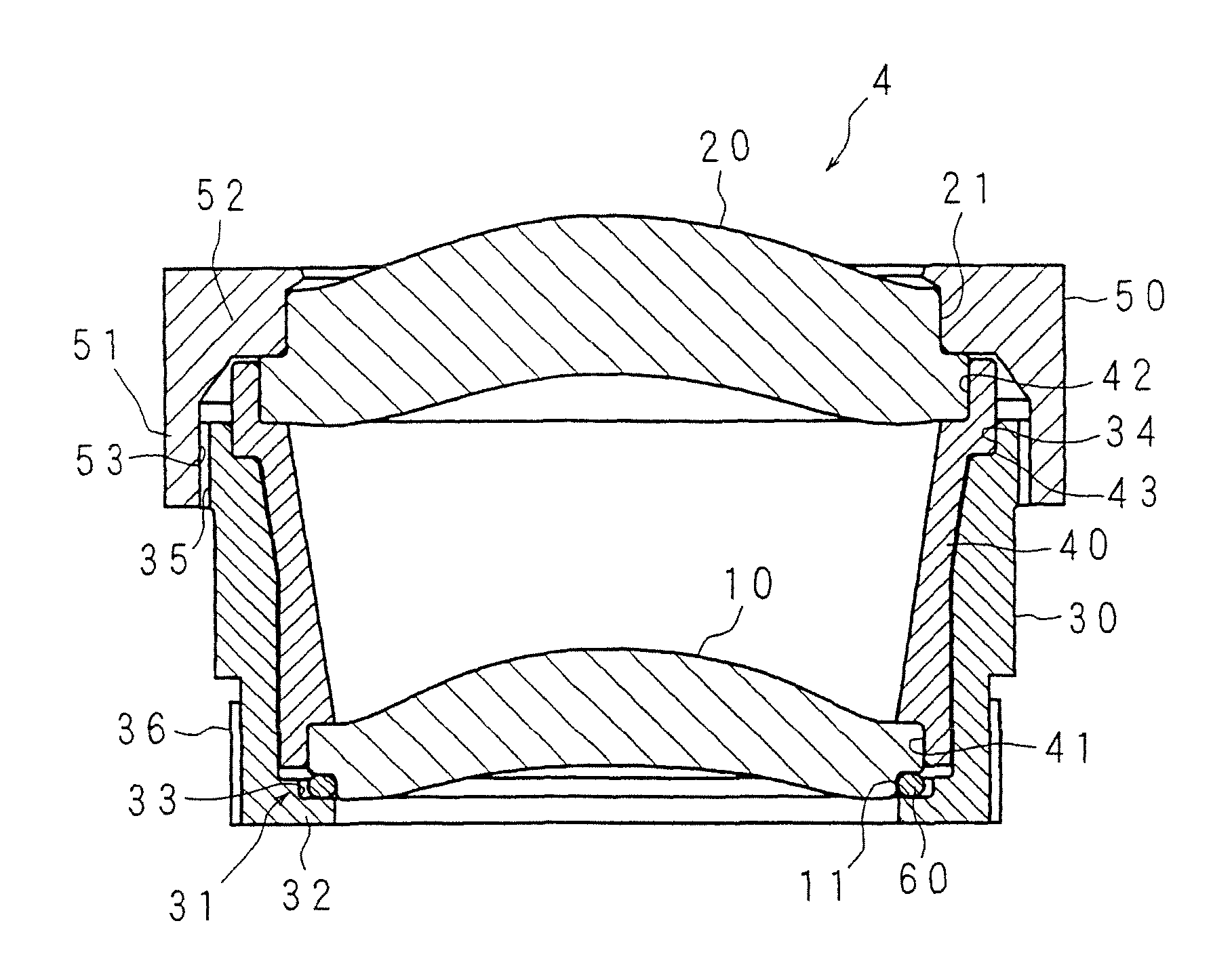
Provided are a lens unit and a vehicle-mounted infrared lens unit capable of correcting a focal shift due to a temperature change without increasing the apparatus size, complicating a production process, and increasing the costs. In a vehicle-mounted infrared lens unit 4 configured such that a plurality of infrared lenses are held by a barrel 30 and a spacer 40 is interposed between two infrared lenses, a first infrared lens 10 is held sandwiched between the spacer 40 and a lens holding portion 31 of the barrel 30. The spacer 40 and the barrel 30 are formed of materials having different thermal expansion coefficients. An O-ring 60 is interposed between a lock portion 32 of the lens holding portion 31 and the first infrared lens 10. Thermal expansion of the spacer 40 allows the first infrared lens 10 to move in the axial direction against the elastic force of the O-ring 60. When the spacer 40 is shrunken, the elastic force of the O-ring 60 allows the first infrared lens 10 to move in the opposite direction.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
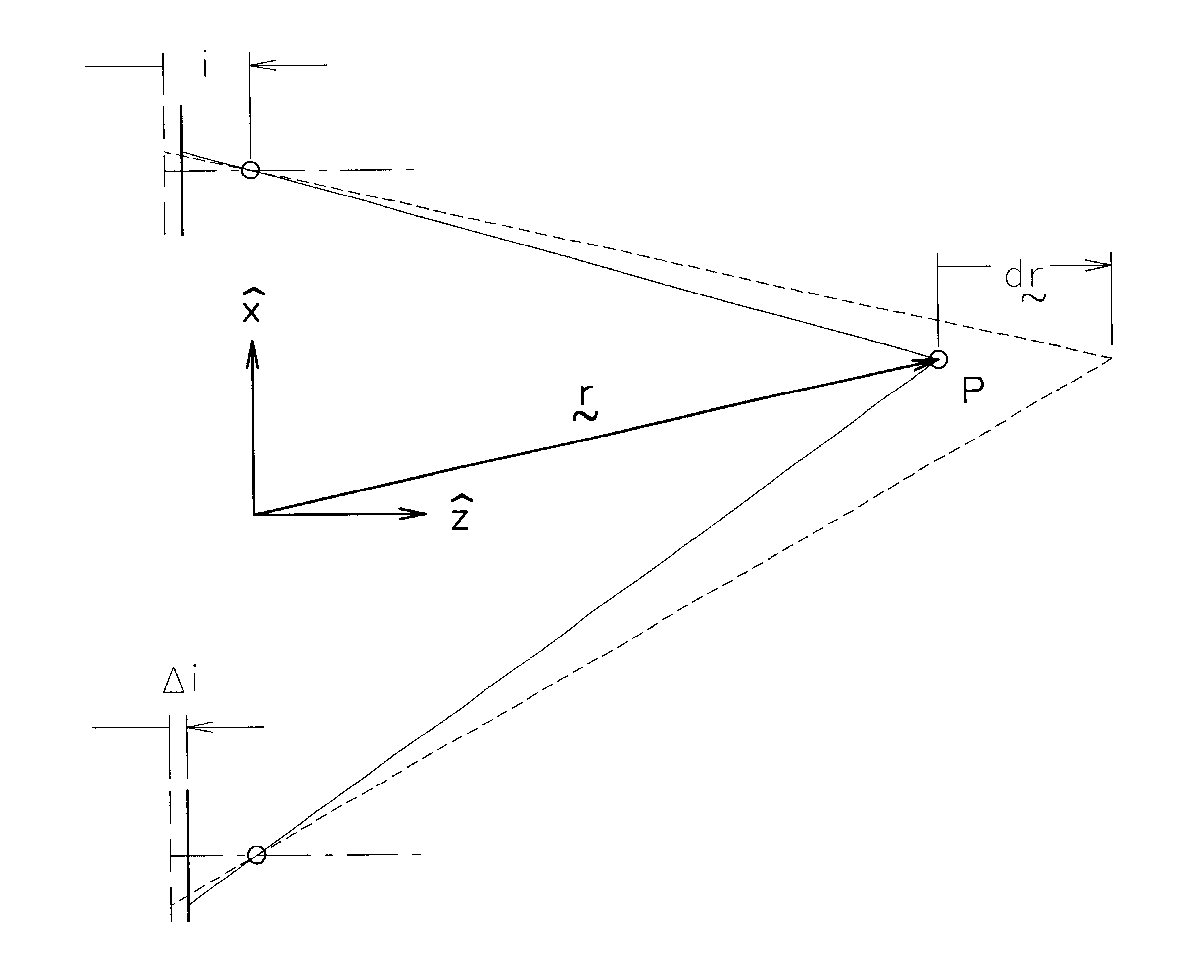
Focusing systems for perspective dimensional measurements and optical metrology
Focusing systems for which variation of magnification with focus is either inherently compensated, or is calibrated and corrected. The required conditions for inherent compensation are determined, and the desired state is called constant relative magnification. It is shown that telecentricity does not guarantee constant relative magnification. Both telecentric and non-telecentric accessory cameras for endoscopes are disclosed that have constant relative magnification, as are additional optical systems for general metrological purposes. Methods for calibrating change in relative magnification and deviation of the optical axis with focal shift are disclosed, as are methods for incorporating these changes into perspective dimensional measurements. Embodiments are disclosed in which only a single quantity need be measured to perform the correction, and these embodiments require only a low-resolution position transducer to provide accurate measurements. Apparatus is disclosed that enables an accessory camera to be aligned to an endoscope using only externally accessible adjustments. This apparatus also makes it possible to de-mount the camera from one endoscope and re-mount it to another without requiring any recalibration.
Owner:SCHAACK DAVID F
Optical disk apparatus using focal shift signals to control spherical aberration
InactiveUS7012875B2Suppress lightIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical detectorsComputational physicsLuminous flux
In the past there has been a problem that on a detection surface the influence of interference causes a defocusing signal to degrade, narrowing the range in which spherical aberration can be stably detected. Accordingly, a diffraction grating is used to focus the inner and outer sides of luminous flux on separate optical detectors before the optical flux is focused on an optical detector and defocusing signals are independently calculated to find the difference therebetween, thereby providing a spherical aberration signal. This makes it possible to detect spherical aberation signals more stably.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Focusing systems for perspective dimensional measurements and optical metrology
InactiveUS6806899B1Accurate measurementColor television detailsBuilding rescueImage resolutionOptical axis
Focusing systems for which variation of magnification with focus is either inherently compensated, or is calibrated and corrected. The required conditions for inherent compensation are determined, and the desired state is called constant relative magnification. It is shown that telecentricity does not guarantee constant relative magnification. Both telecentric and non-telecentric accessory cameras for endoscopes are disclosed that have constant relative magnification, as are additional optical systems for general metrological purposes. Methods for calibrating change in relative magnification and deviation of the optical axis with focal shift are disclosed, as are methods for incorporating these changes into perspective dimensional measurements. Embodiments are disclosed in which only a single quantity need be measured to perform the correction, and these embodiments require only a low-resolution position transducer to provide accurate measurements. Apparatus is disclosed that enables an accessory camera to be aligned to an endoscope using only externally accessible adjustments. This apparatus also makes it possible to de-mount the camera from one endoscope and re-mount it to another without requiring any recalibration.
Owner:SCHAACK DAVID F
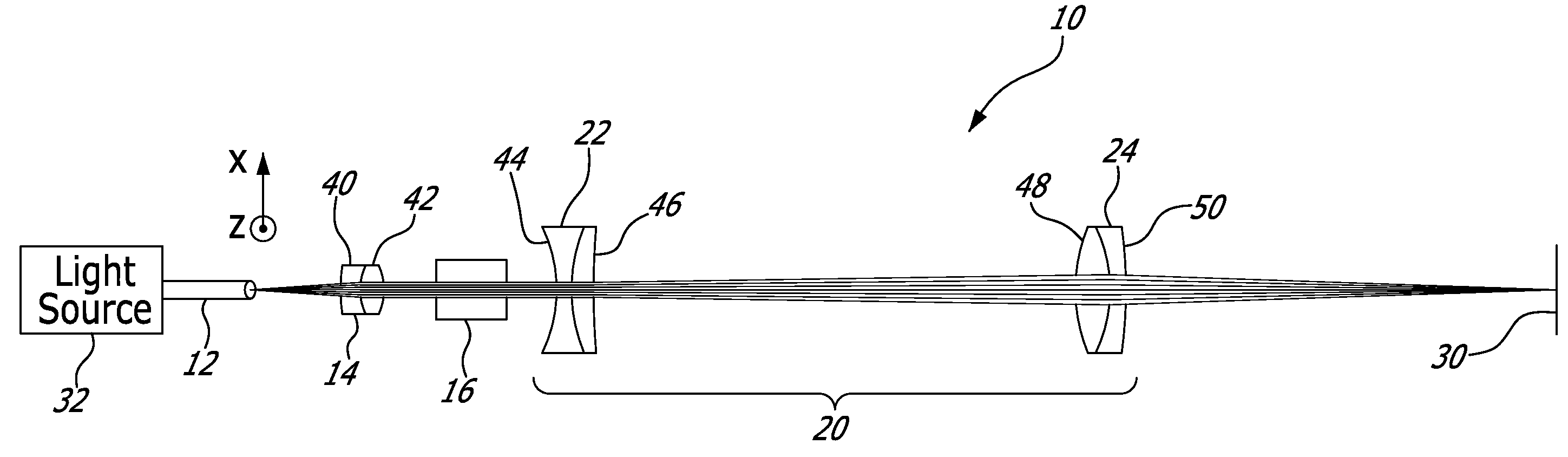
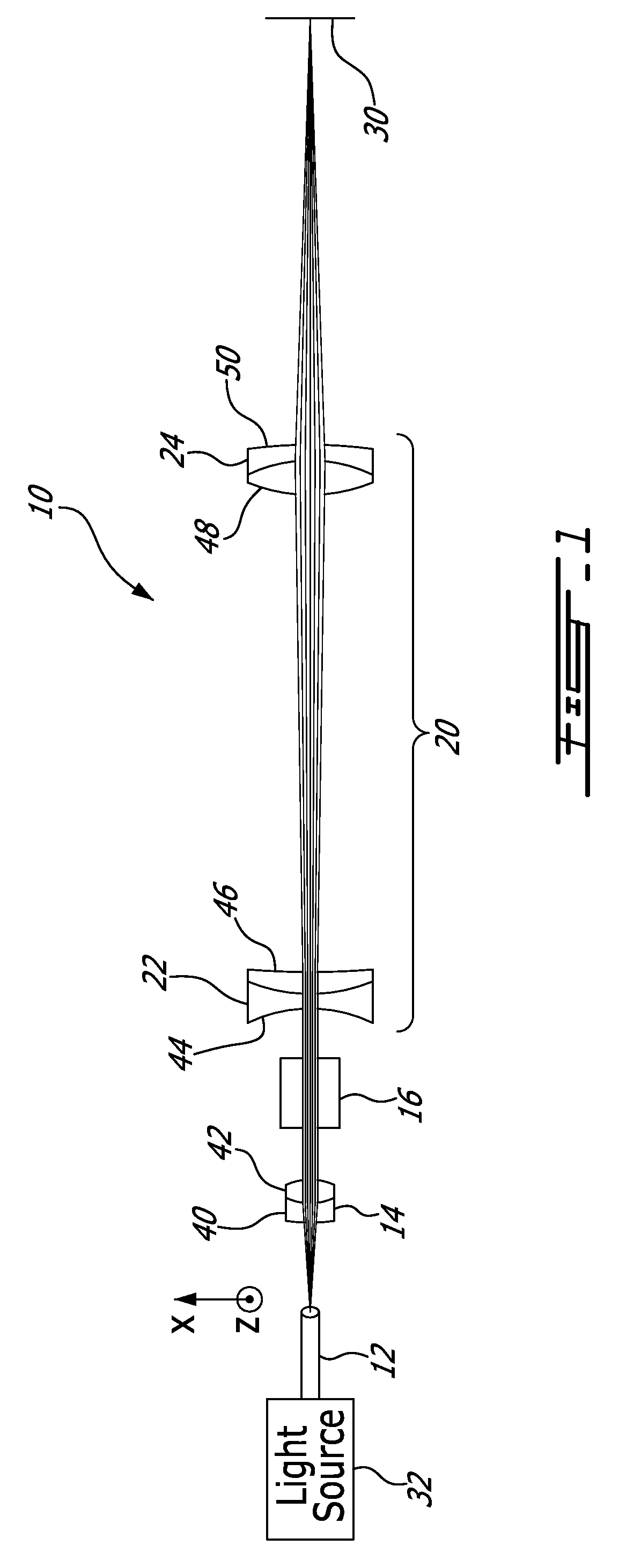
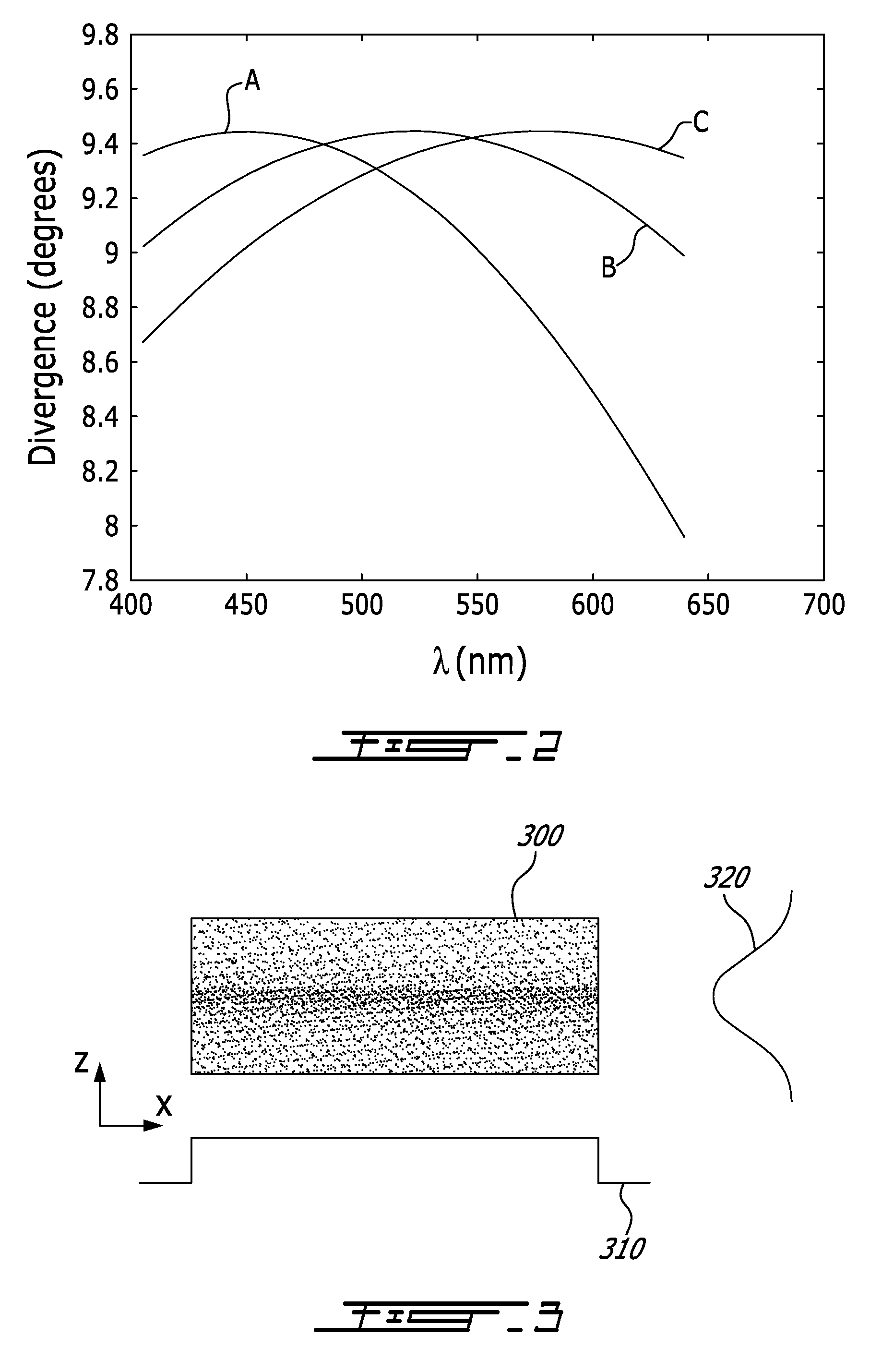
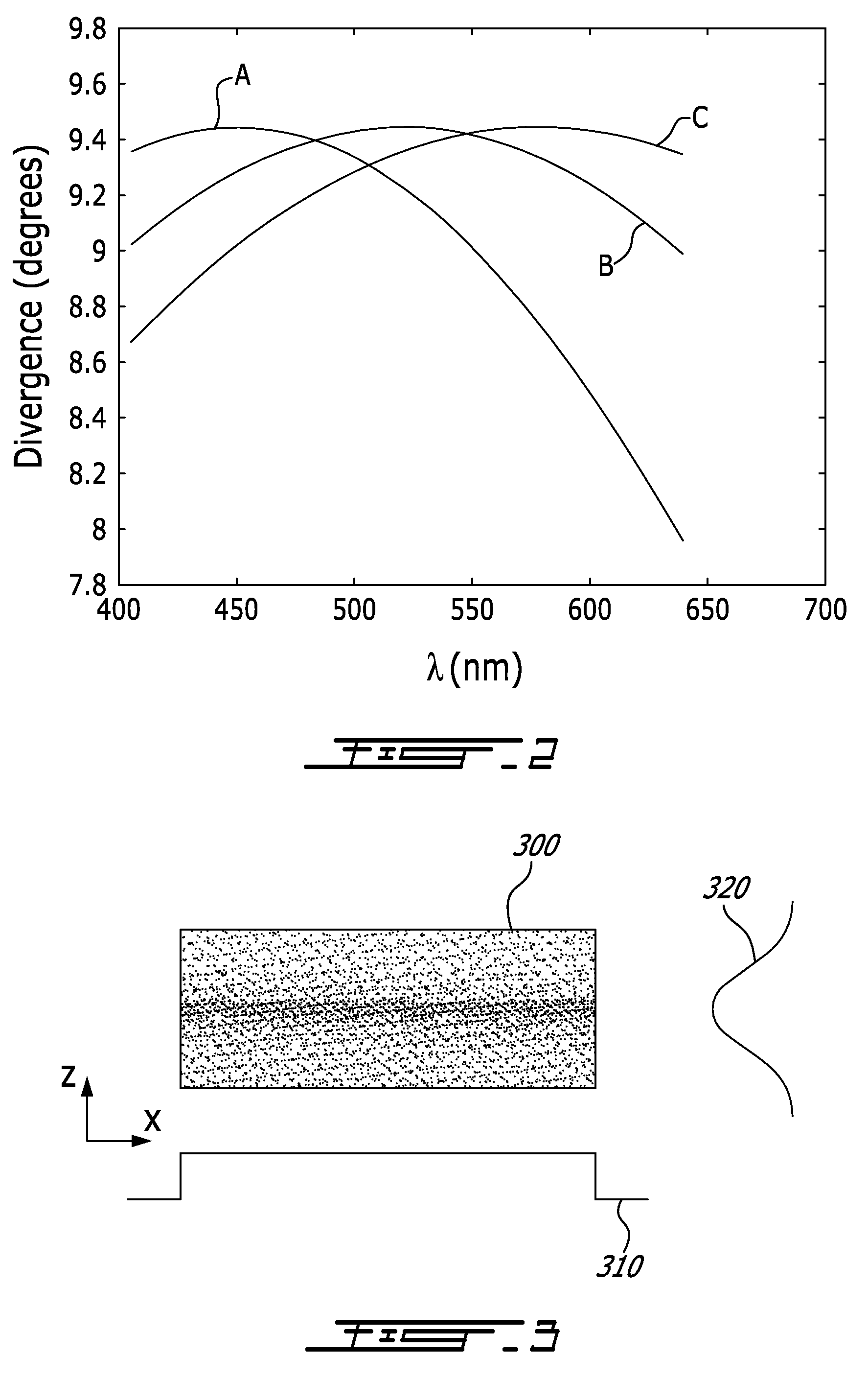
Achromatic flat top beam shaping
ActiveUS20100208356A1Reduce deviation from uniformityUniform strengthLensRefractorsShaped beamLight beam
There is provided an optical system and method for shaping a polychromatic light into a substantially uniform profile beam along a first axis. A polychromatic divergent light with having multiple wavelength components is provided with a dispersion of divergence. A collimation optic collimates the polychromatic divergent light. A shaping lens shapes the collimated beam into a shaped beam with a nearly uniform profile along the first axis, the dispersion of divergence causing a deviation from uniformity of the nearly uniform profile. A focusing optic focuses the shaped beam. A combination of the collimation and focusing optics shows a chromatic focal shift that compensates for said dispersion of divergence, so as to reduce the deviation from uniformity to obtain a profile with a substantially uniform intensity along the first axis, for all of said multiple wavelength components.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Focusing systems for perspective dimensional measurements and optical metrology
InactiveUS7161741B1Maintain measurement accuracyReduce in quantityTelescopesMountingsOptical axisImage resolution
Focusing systems for which variation of magnification with focus is either inherently compensated, or is calibrated and corrected. The required conditions for inherent compensation are determined, and the desired state is called constant relative magnification. It is shown that telecentricity does not guarantee constant relative magnification. Both telecentric and non-telecentric accessory cameras for endoscopes are disclosed that have constant relative magnification, as are additional optical systems for general metrological purposes. Methods for calibrating change in relative magnification and deviation of the optical axis with focal shift are disclosed, as are methods for incorporating these changes into perspective dimensional measurements. Embodiments are disclosed in which only a single quantity need be measured to perform the correction, and these embodiments require only a low-resolution position transducer to provide accurate measurements. Apparatus is disclosed that enables an accessory camera to be aligned to an endoscope using only externally accessible adjustments. This apparatus also makes it possible to de-mount the camera from one endoscope and re-mount it to another without requiring any recalibration.
Owner:SCHAACK DAVID F
Imaging apparatus and method for controlling same
ActiveUS20140284449A1Reduce adverse effectsLow reliabilityTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansPhase differenceImage signal
An imaging element includes pixel portions each having a first sub-pixel and a second sub-pixel and outputs a phase difference detection-type focus detecting signal. An image signal A includes information for the first sub-pixel and an image signal AB includes information for the second sub-pixel. A level determining unit compares the image signal A with a threshold value SHA and compares the image signal AB with a threshold value SHAB. A correlation calculation processing unit performs correlation calculation for a signal excluding the image signal A having a level exceeding the threshold value SHA and the image signal AB having a level exceeding the threshold value SHAB so as to output the result of calculation to a CPU. The CPU calculates a focal shift amount in accordance with the result of calculation and performs a focus adjusting operation by drive-controlling a focus lens.
Owner:CANON KK
Power scalable multi-pass faraday rotator
InactiveUS20140218795A1Reduce thermal gradientReduce gradientPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsOptical isolatorLight beam
Transparent heat-conductive layers of significant thickness are bonded or adhered to opposing optical faces of a Faraday optic to form a Faraday optic structure that can be used with beam-folding mirrors and an external magnetic field to form a multi-pass Faraday rotator with minimal thermal gradient across the beam within the Faraday optic. The transparent heat conductive layers conduct heat through the Faraday optic substantially parallel to the beam propagation axis for each pass through the Faraday optic structure and thereby reduce thermal gradients across the beam cross section that would otherwise contribute to thermal lens focal shifts and thermal birefringence in the Faraday optic structure. The multi-pass Faraday rotator of this invention is suitable for use with any device based upon the Faraday effect such as optical isolators, optical circulators and Faraday mirrors that are scalable with beam size to power levels in excess of 2 kW.
Owner:ELECTRO OPTICS TECH
Wavelength scanning confocal micro-displacement measurement device and method
ActiveCN106767431AAvoid mechanical propertiesAvoid disturbanceUsing optical meansAxial displacementMeasurement device
The invention provides a wavelength scanning confocal micro-displacement measurement device and a method. In a confocal microscope optical path system, a wavelength tunable laser is used for carrying out illumination; a Fresnel zone plate is used for carrying out focus point illumination; according to the axial color difference focal shift characteristic, axial scanning of focus light spots is achieved through wavelength scanning; a confocal pinhole photoelectric detection unit is used for detecting confocal axial optical chromatography response output; for the disperse wavelength lambda<n> = lambda<min> + (n-)deltalambda, n = 1, 2, ..., 11, obtaining the axial optical chromatography displacement-intensity response, wherein the lambda<min> is the wavelength lower limit, the wavelength upper limit is lambda<max> = lambda<min> + 10deltalambda, and the deltalambda is the wavelength stepping interval; peak value positions of the optical chromatography response curves form a linear calibration relation searching table of illumination wavelengths and axial displacement; and fine wavelength scanning is executed for each characteristic point of a to-be-measured sample for once, and actual displacement of each point is calculated according to the peak value of each response curve and the searching table. Thus, measurement of micro-displacement or relative height is finished, and the method is suitable for precise measurement of micro displacement, film thickness, nano steps and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
X-Ray CT device
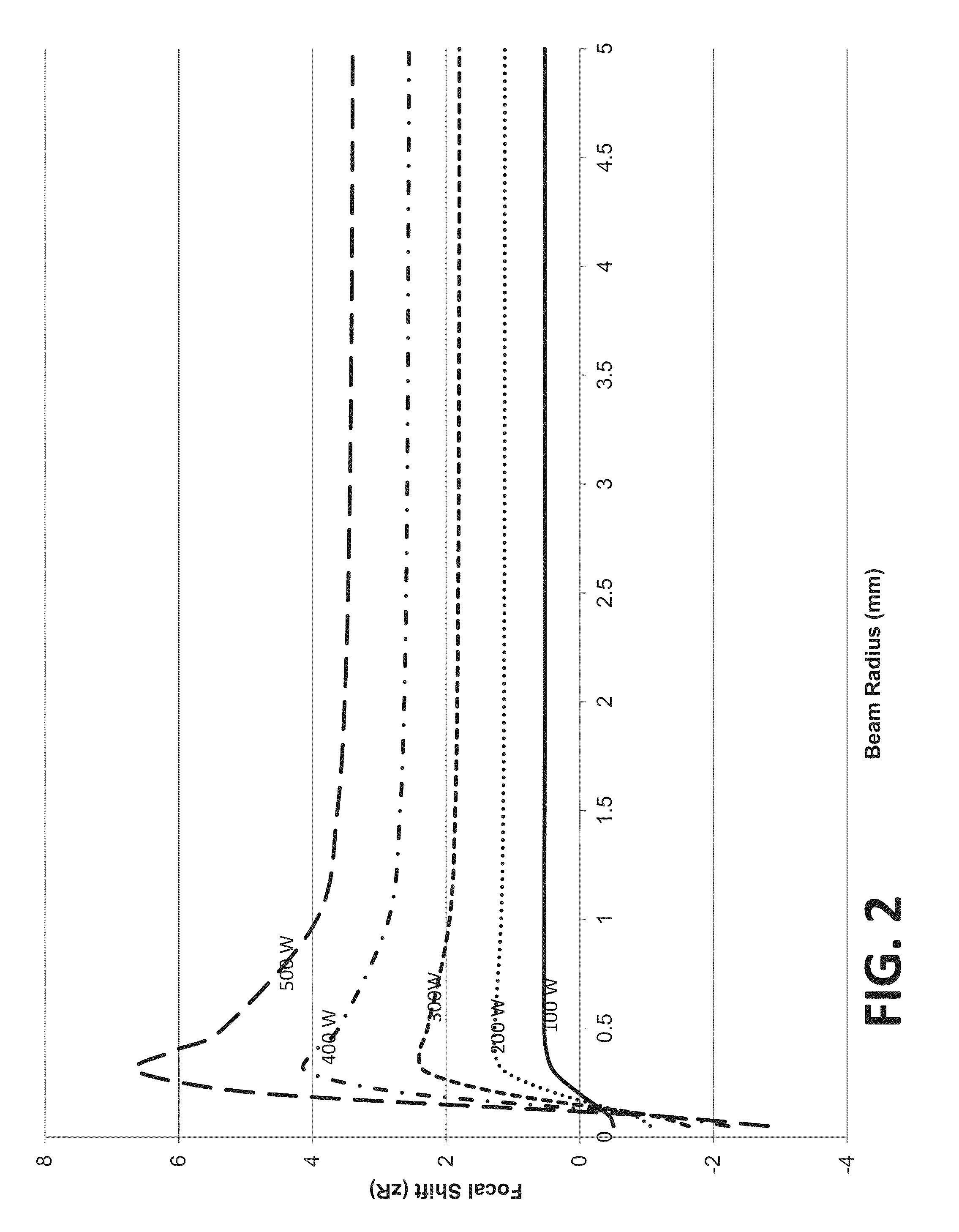
ActiveCN102639060ARemove and suppress artifactsRemove and suppress image quality degradation such as quantitative reductionComputerised tomographsTomographySoft x rayX-ray
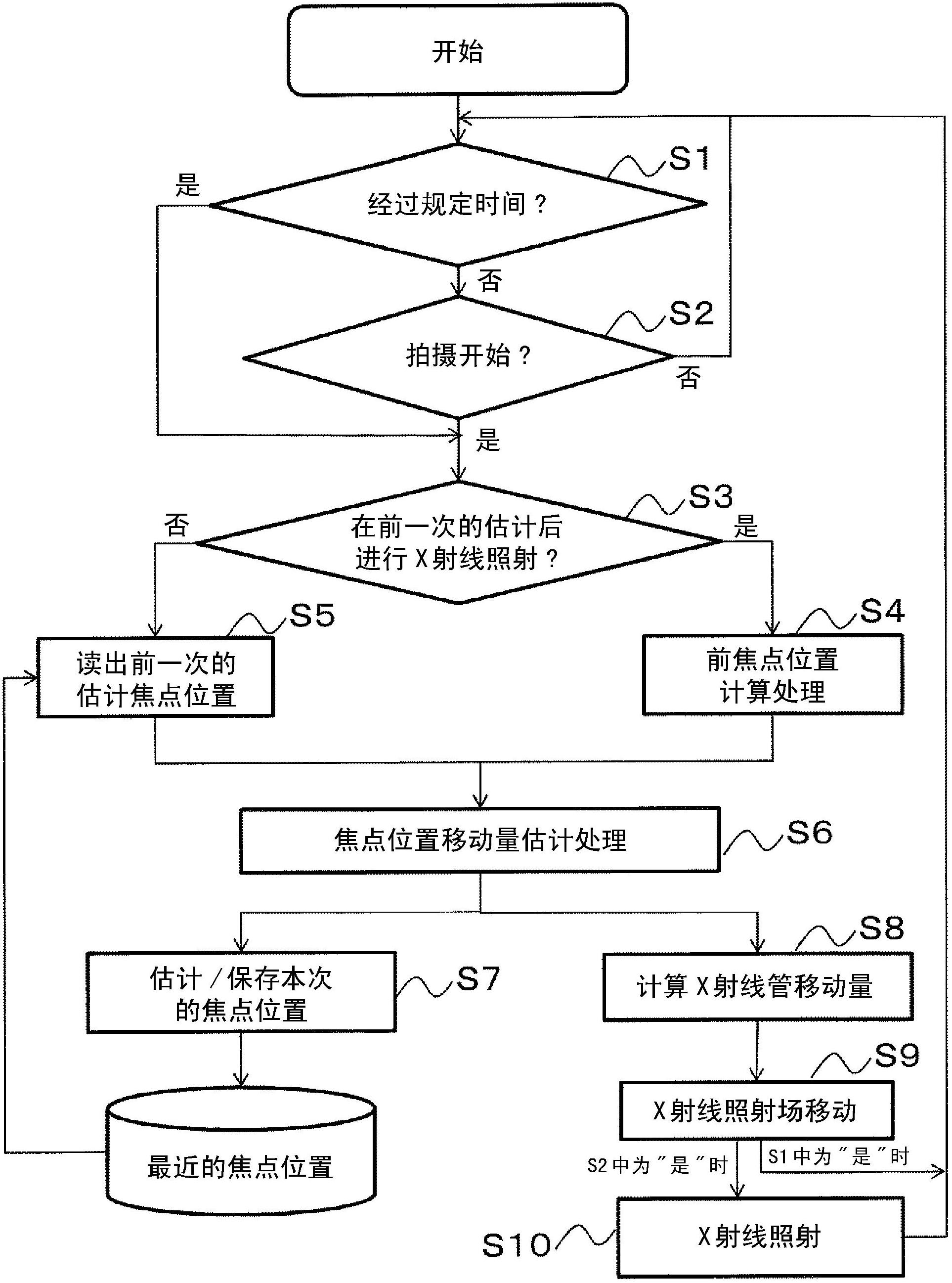
In order to eliminate and suppress image quality degradation including the occurrence of an artifact and the deterioration of quantitative performance caused by a focal shift, without delaying a photographing timing by accurately estimating the shift amount of a focal position without x-ray irradiation for detecting the focal position and by changing the x-ray irradiation field, disclosed is an X-ray CT device provided with: an X-ray generation means (100); an X-ray detection means (104); an X-ray collimator means (303); a reconstruction processing means (105); an irradiation field change drive means (200, 301, 302) which controls and moves at least one of the X-ray generation means (100), the X-ray detection means, and the X-ray collimator means (303); and a shift amount calculation means (105) which estimates the focal position of the X-ray generation means at an estimation time (S2, S4), and using the result of the estimation, calculates the shift amount, which is needed to keep the X-ray incident position in the X-ray detection means constant, of the irradiation field change drive means (S6). When a predetermined time has passed since a time at which the focal position is estimated in the most recent past, or when a photographing start instruction signal is inputted, the shift amount calculation means calculates the shift amount (S8), and the irradiation field change drive means performs the control and shift corresponding to the shift amount before the next estimation time or X-ray irradiation (S9).
Owner:HITACHI HEALTHCARE MFG LTD
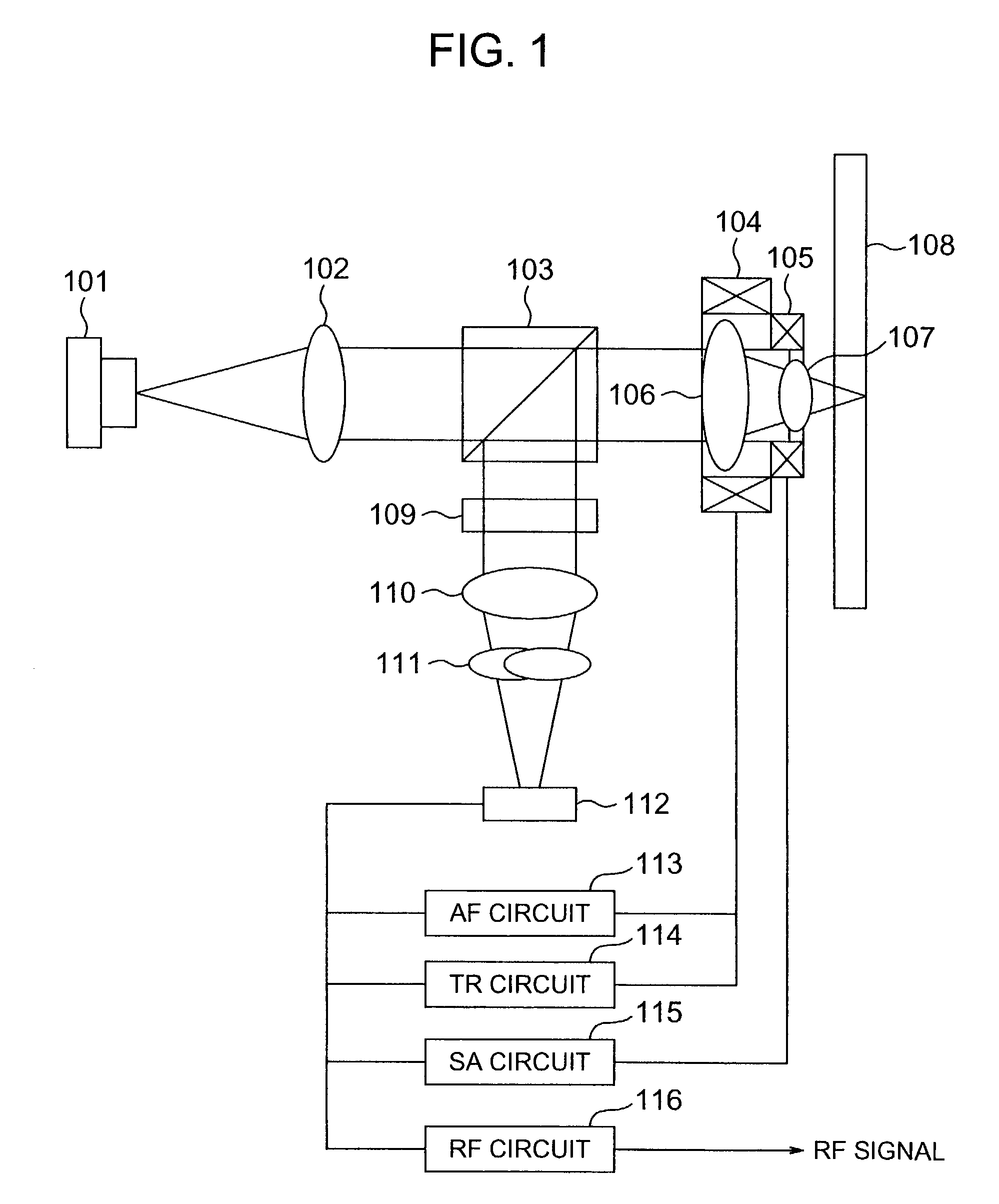
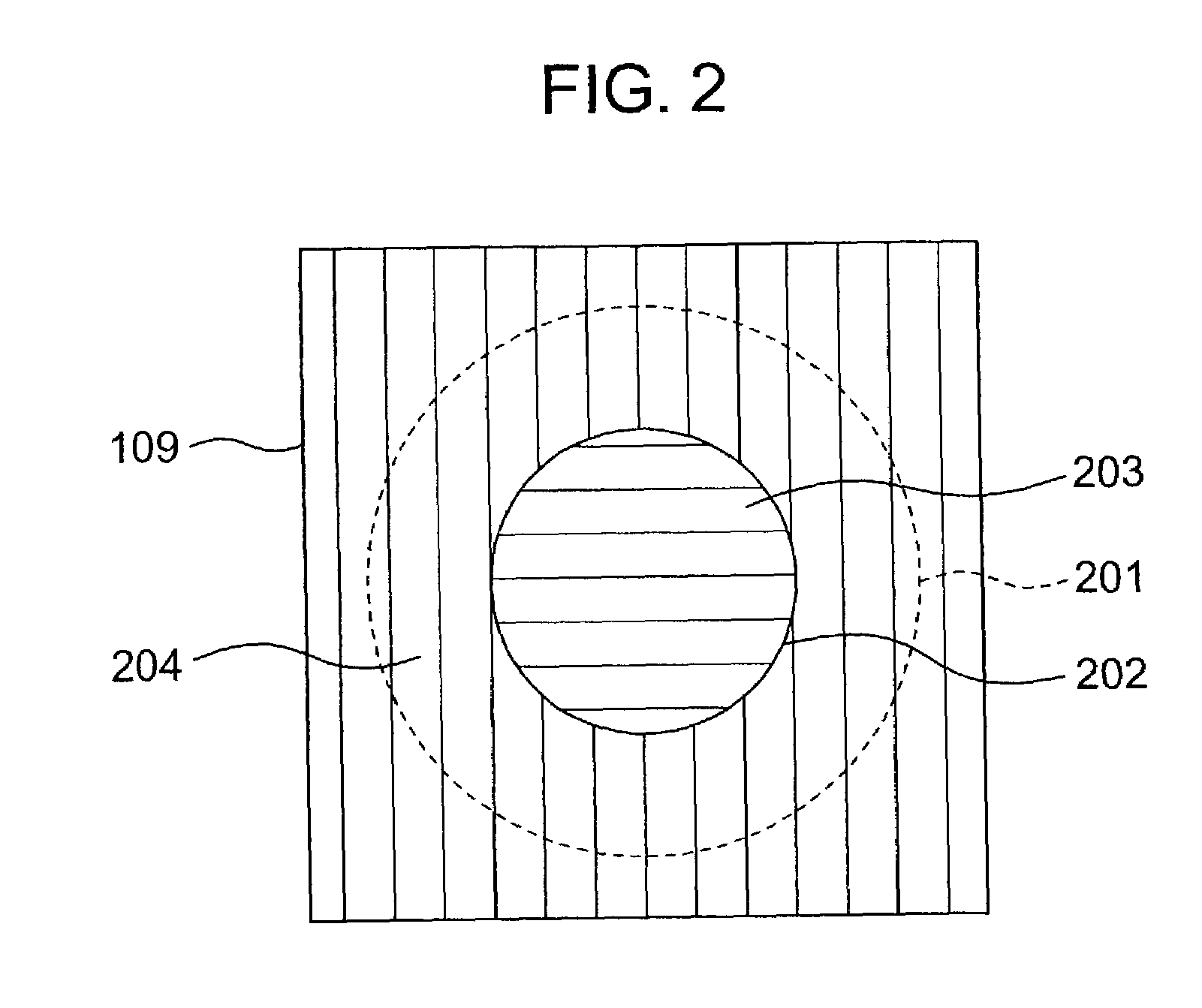
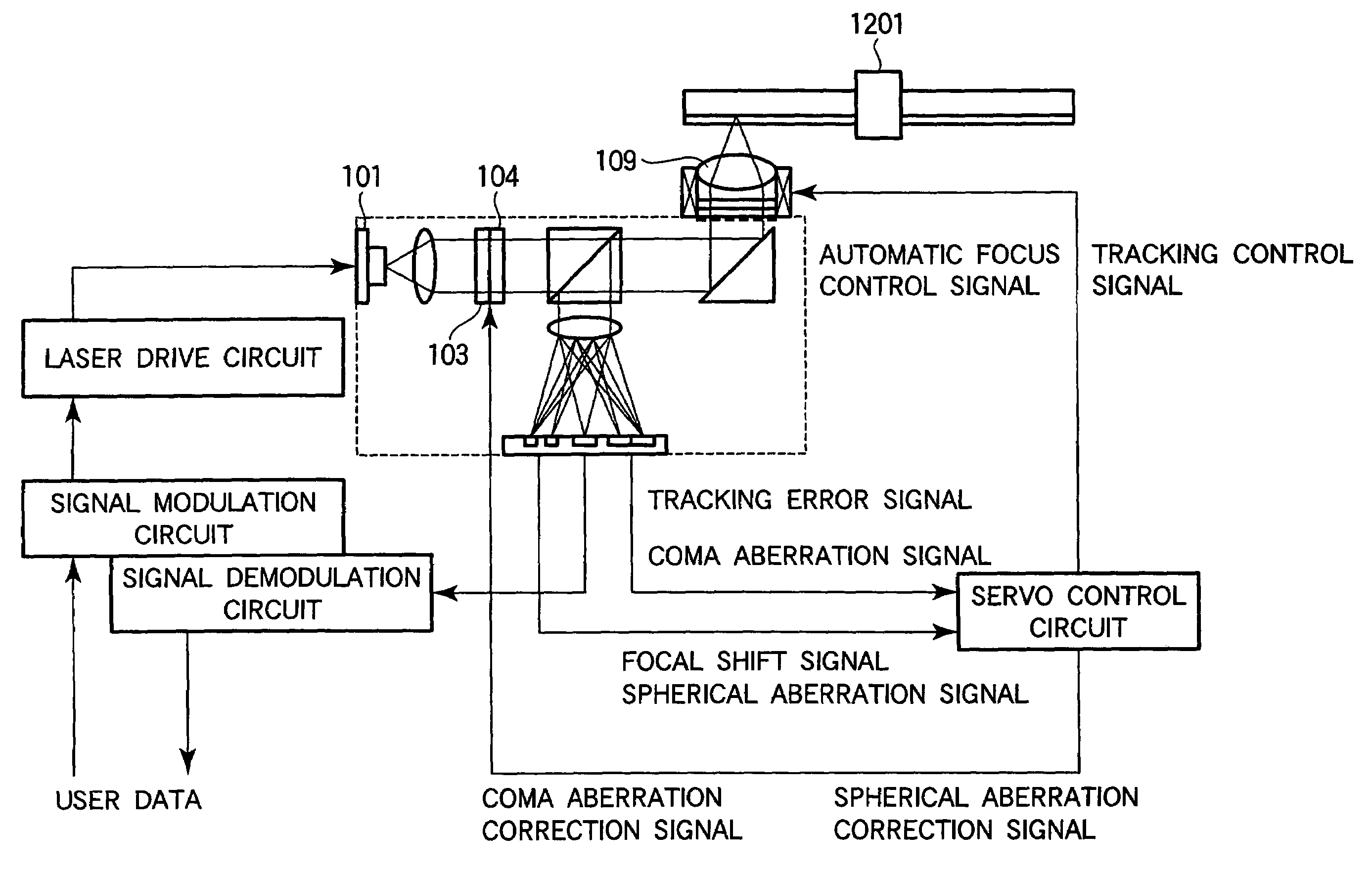
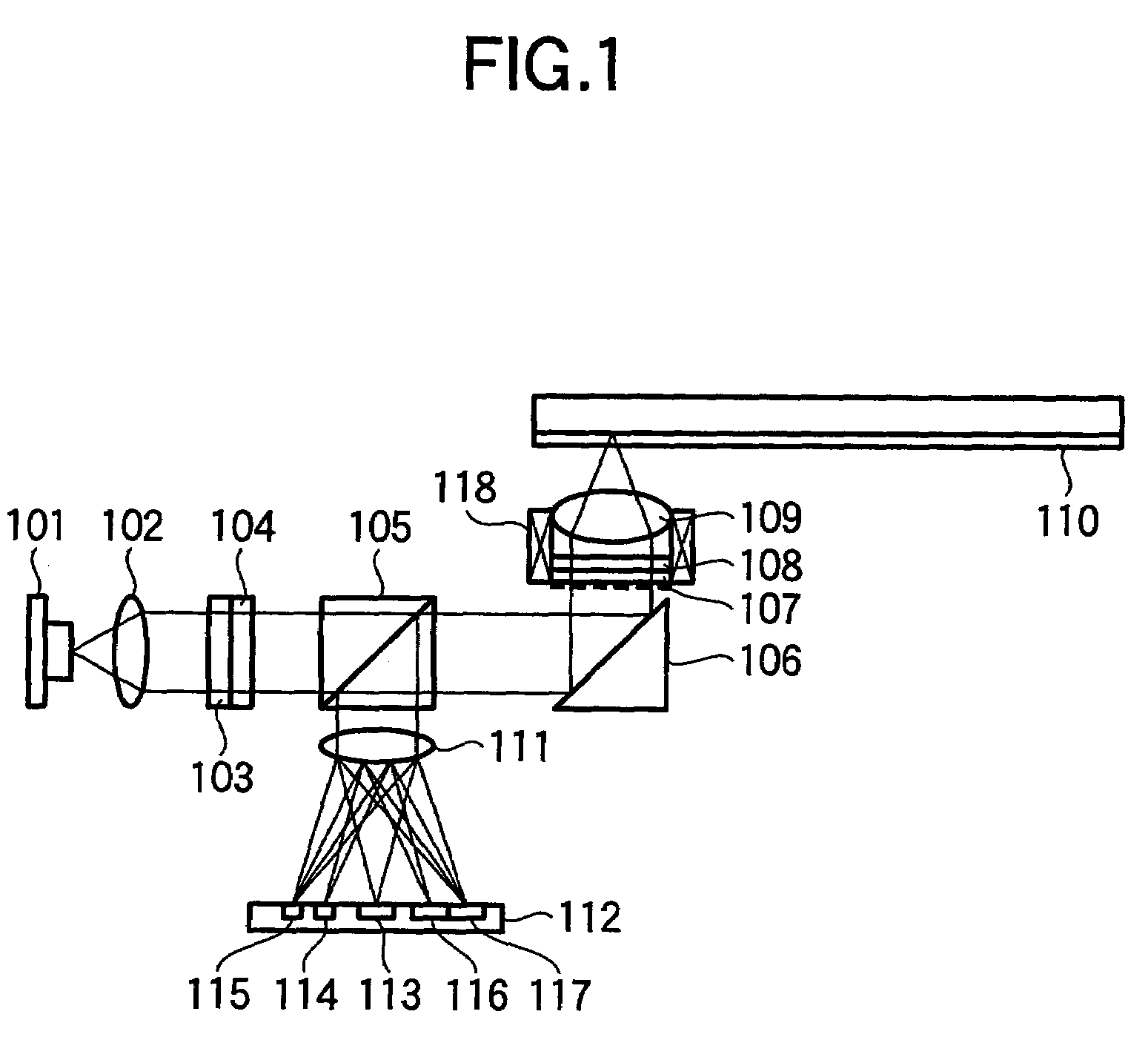
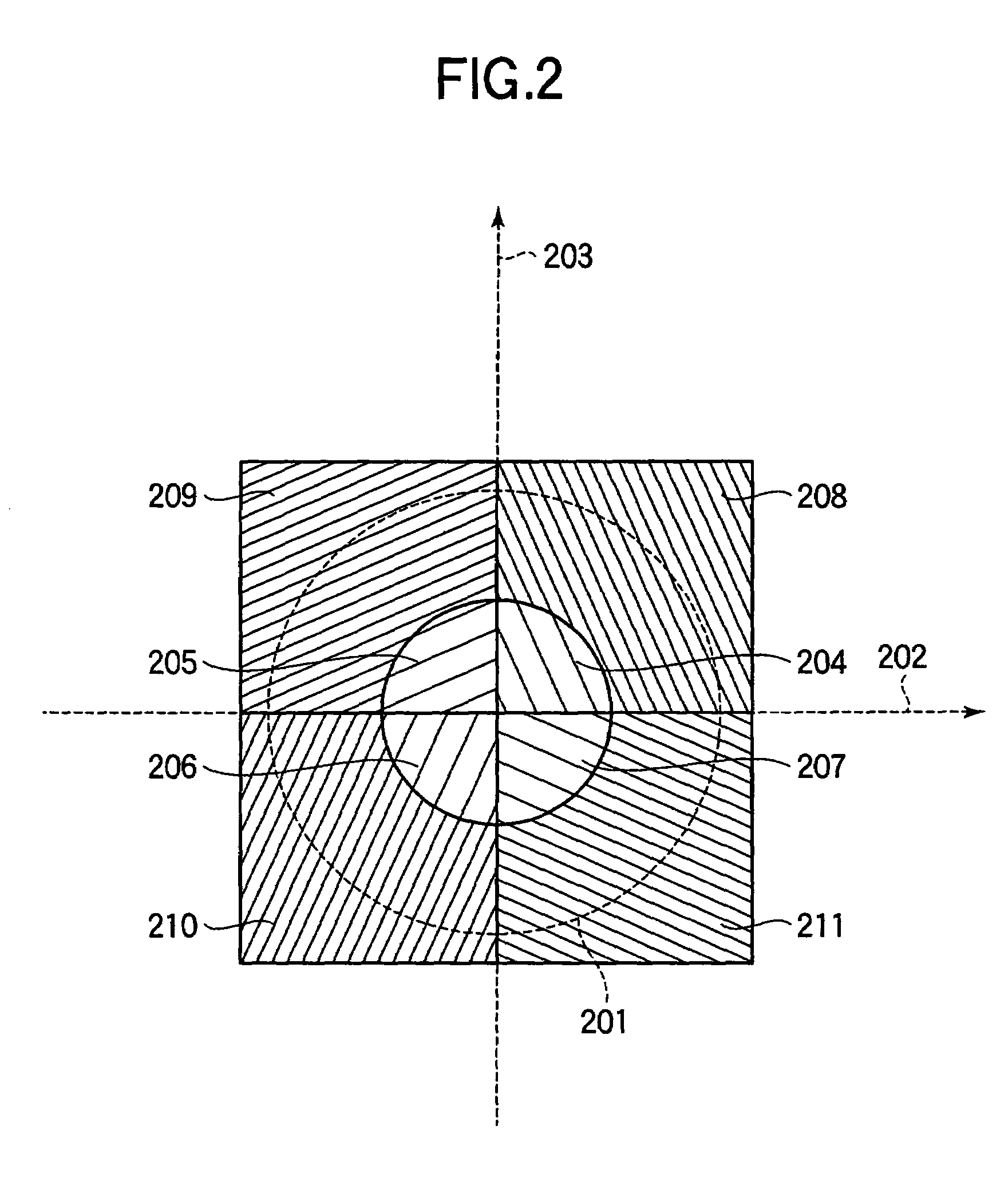
Optical head and optical disk apparatus
InactiveUS20050025000A1Low costIncrease speedIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical detectorsHigh densityLight flux
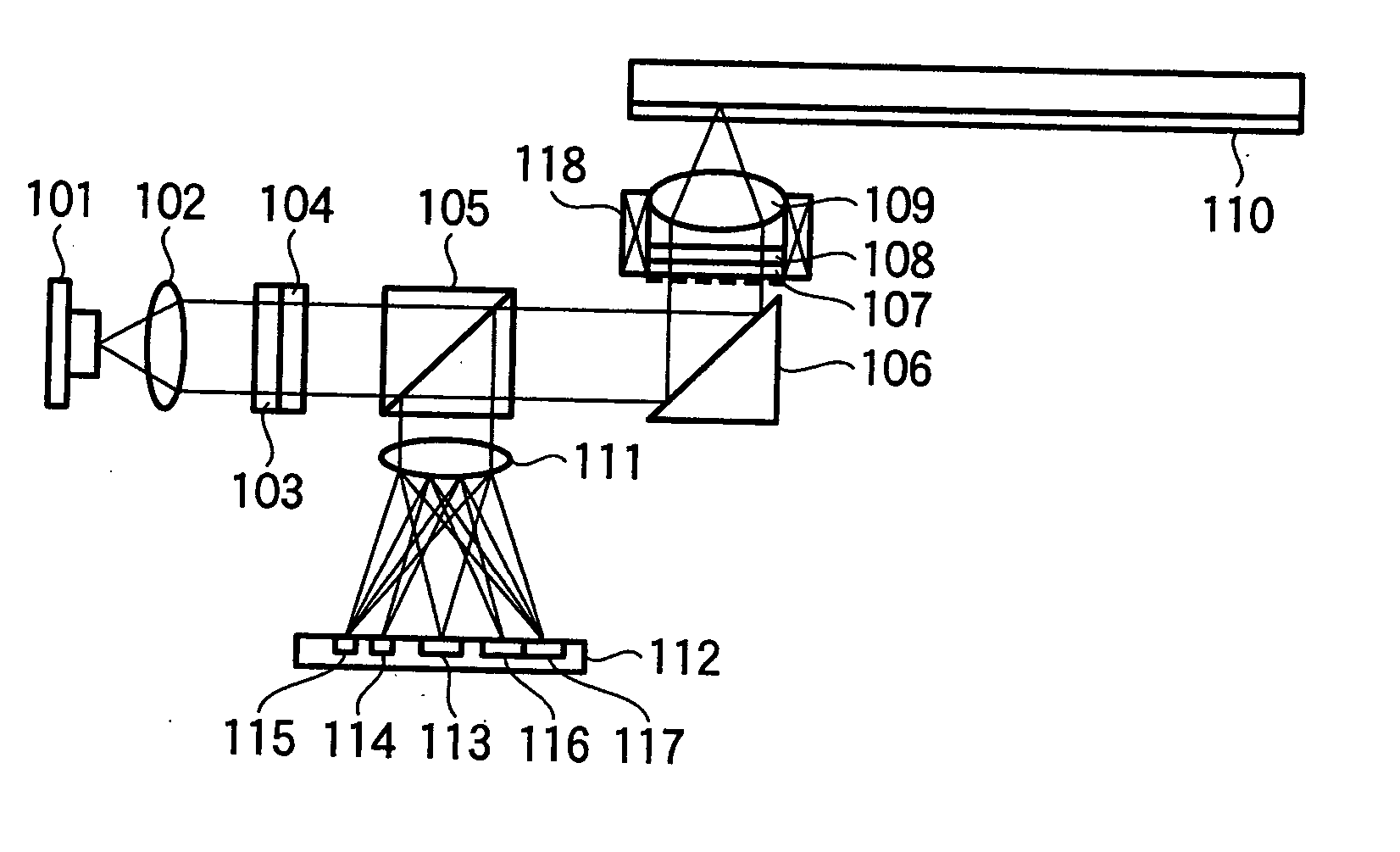
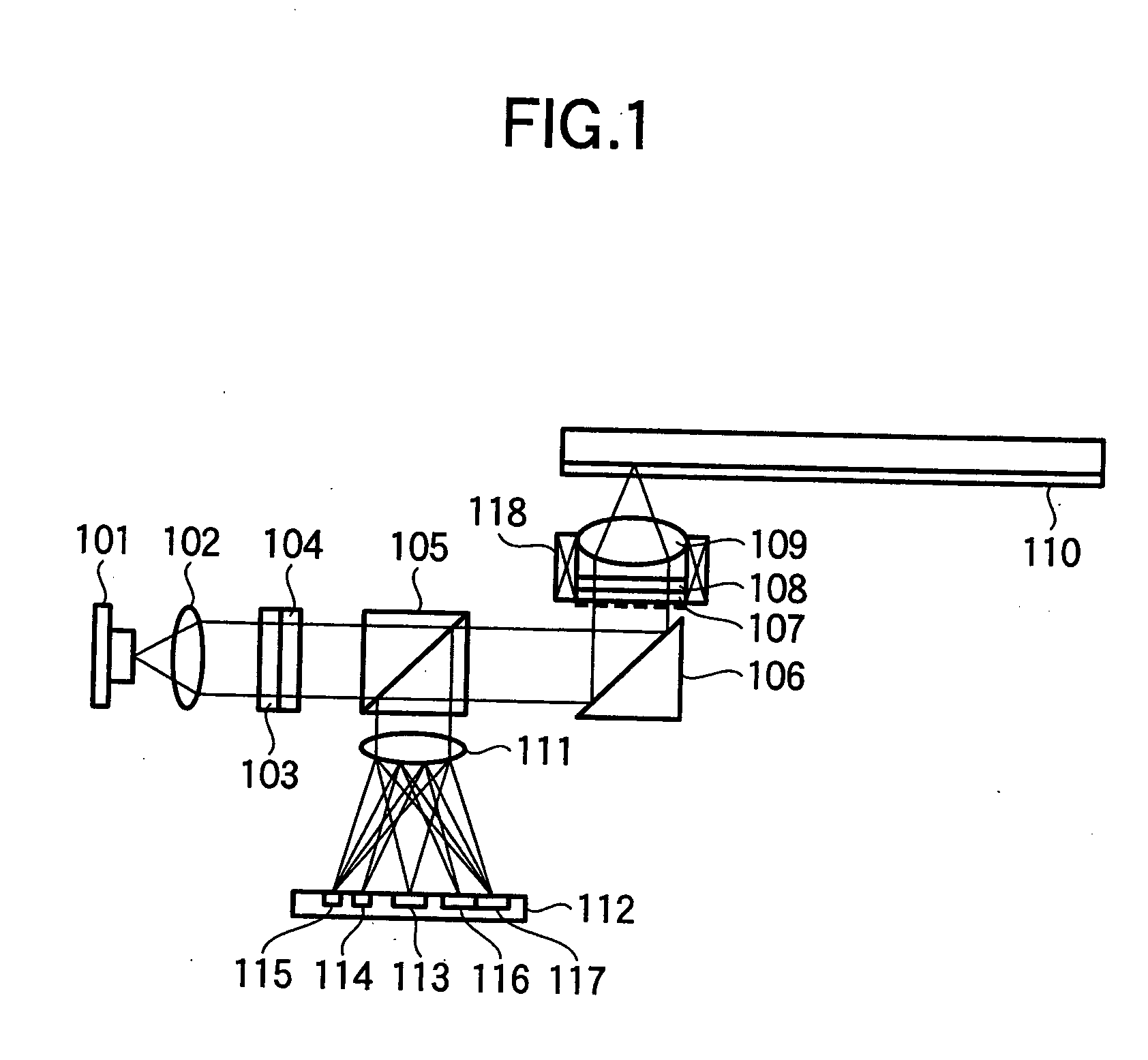
To stably carry out recording and reproducing to and from a high density optical disk without using a double servo in the optical disk using a high NA objective lens. A detection of a spherical aberration and a detection of a coma aberration in a radial direction are simultaneously performed, and the coma aberration generated with the offset of an objective lens 109 is corrected in real time, thus enlarging an allowable offset amount of the objective lens. In order to simultaneously detect the spherical aberration and the coma aberration, focal shift and tracking shift signals in an inside region and outside region of reflected light flux are detected respectively, and the differential signals are set as spherical aberration and coma aberration signals.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Lens unit and vehicle-mounted infrared lens unit
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Integrated Sensor and Lens Assembly with Post-tuning Optical Alignment
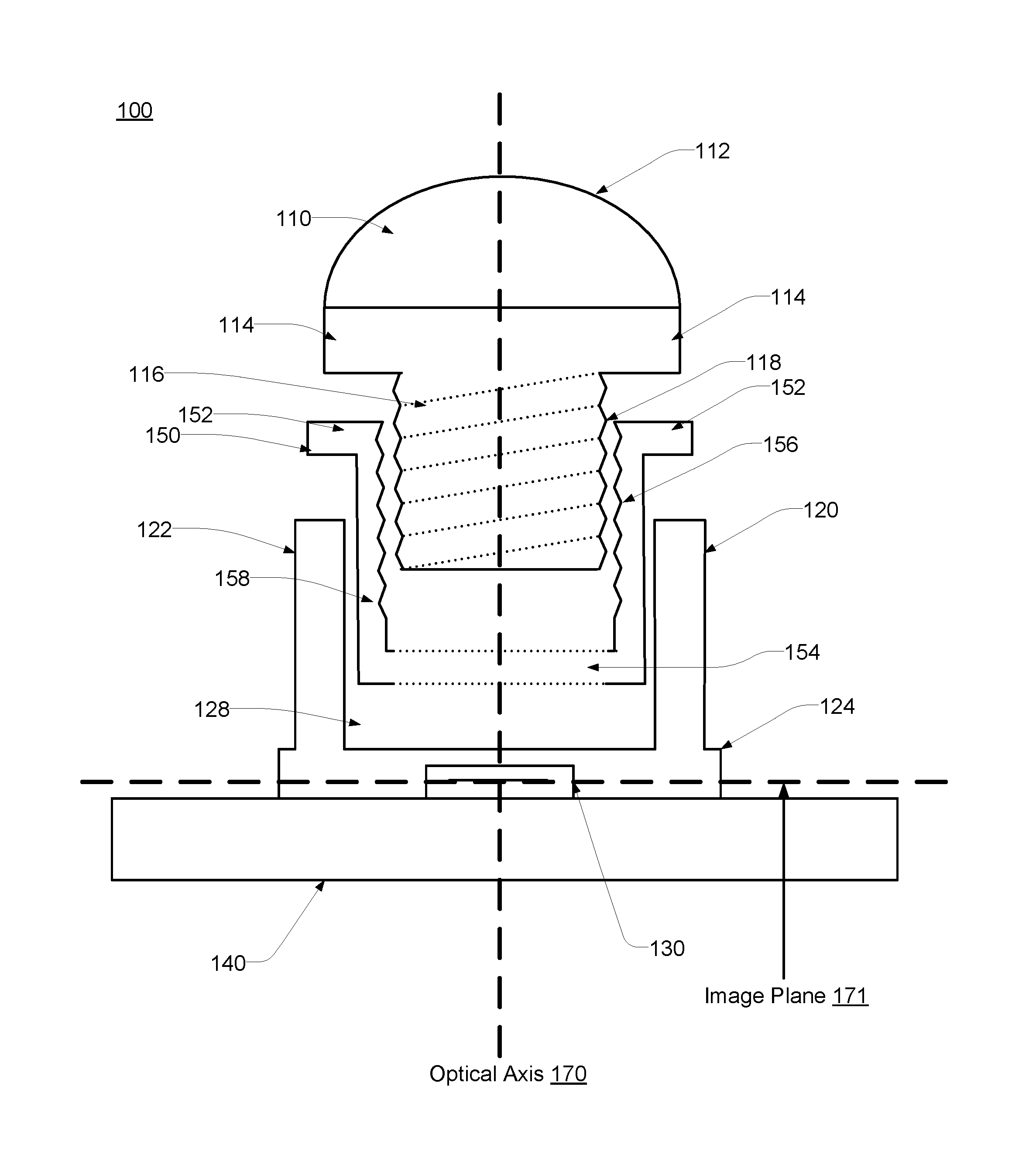
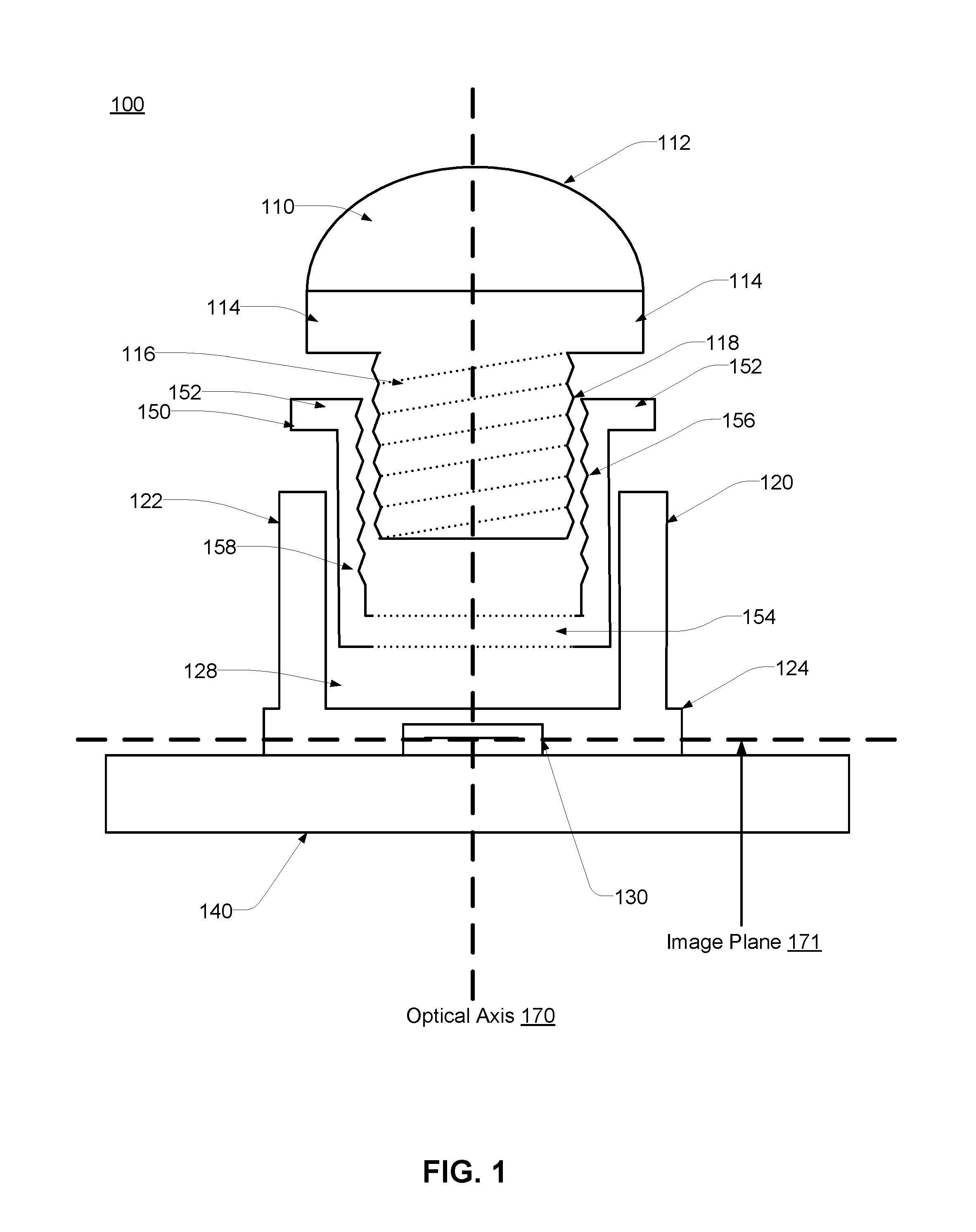
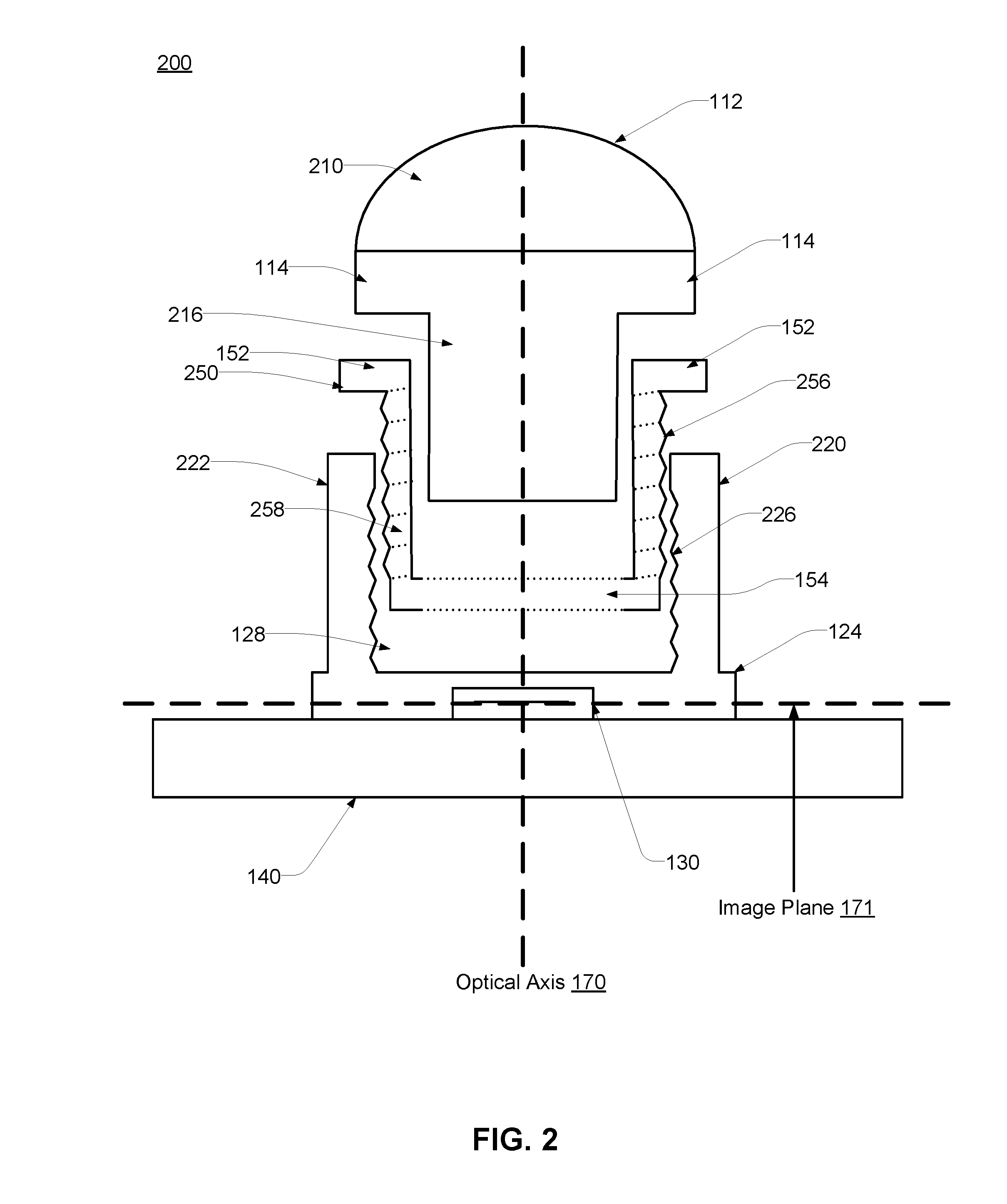
An integrated image sensor and lens assembly may include a lens barrel, a collet, and a lens mount. The lens barrel may be coupled to the collet which is coupled to the lens mount. The lens barrel and the collet may each include a fastening structure reciprocal to each other. Alternatively, the collet and the lens mount may each include a fastening structure reciprocal to each other. The optical distance between the set of lenses and the image sensor may be tuned such that the focal plane of the lenses coincides with the image plane. The fastening structures allow the lens barrel to be adjusted relative to the lens mount in order to shift the focal plane in a direction along the optical axis to compensate for focal shifts occurring during assembly / cure and / or temperature cycling.
Owner:GOPRO
Electric-controlled focal shift ultra-resolved iris filter
InactiveCN101178485AEasy to controlAchieving lateral super-resolutionPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsBirefringent crystalPolarizer
A super resolution pupil filter with focus movement controlled by electricity belongs to the optical super resolution technical field, which comprises a polarizer (1), an Lambada / 4 delay wave plate (2) of Lambada Pi / 4 azimuth angle, an electro-optic crystal (3), a radial symmetry doubly refracting crystal (4), an Lambada / 4 delay wave plate (5) of 3 Pi / 4 azimuth angles, and an analyzer (6). The polarizer (1) is parallel to a euphotic shaft of the analyzer (6), and the azimuth angle of the electro-optic crystal (3) is defined according to the position of an electric induction main shaft, and an electric induction slow shaft is consistent with an euphotic shaft of the polarizer (1). The slow shaft direction of the radial symmetry doubly refracting crystal (4) has an included angle of Pi / 4 with the euphotic shaft of the polarizer (1). The size of an electric field size added outside of the electro-optic crystal (3) is defined according to a half wave voltage of the electro-optic crystal, and the voltage change range is between the half wave voltage of o to 2 times. The invention can synchronously realize the electric control of transverse super resolution and radial focus moving effect by conducting electro-optic modulation to the electro-optic crystal.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Refractive focusing element for spectroscopic ellipsometry
InactiveUS6940596B2Eliminate the problemPolarisation-affecting propertiesLight polarisation measurementSpectroscopic ellipsometryEmission spectrum
A broadband ellipsometer is disclosed with an all-refractive optical system for focusing a probe beam on a sample. The ellipsometer includes a broadband light source emitting wavelengths in the UV and visible regions of the spectrum. The change in polarization state of the light reflected from the sample is arranged to evaluate characteristics of a sample. The probe beam is focused onto the sample using a composite lens system formed from materials transmissive in the UV and visible wavelengths and arranged to minimize chromatic aberrations. The spot size on the sample can be less than 3 mm and the aberration is such that the focal shift over the range of wavelengths is less than five percent of the mean focal length of the system.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
Refractive focusing element for spectroscopic ellipsometry
InactiveUS20050046842A1Eliminate the problemPolarisation-affecting propertiesLight polarisation measurementUltravioletSpectroscopic ellipsometry
A broadband ellipsometer is disclosed with an all-refractive optical system for focusing a probe beam on a sample. The ellipsometer includes a broadband light source emitting wavelengths in the UV and visible regions of the spectrum. The change in polarization state of the light reflected from the sample is arranged to evaluate characteristics of a sample. The probe beam is focused onto the sample using a composite lens system formed from materials transmissive in the UV and visible wavelengths and arranged to minimize chromatic aberrations. The spot size on the sample can be less than 3 mm and the aberration is such that the focal shift over the range of wavelengths is less than five percent of the mean focal length of the system.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
An infrared induction switching zoom lens and its imaging monitoring method
InactiveCN102269855AAvoid IR TransmittanceHigh infrared transmittanceMountingsCamera body detailsNight visionCamera lens
The invention discloses an infrared induction switching zoom lens and an imaging monitoring method thereof. The lens includes a mechanically connected infrared filter, a switching device, and a focusing lens group; in the visible light mode, the infrared filter is moved into the optical system of the lens through the switching device , used to block infrared light; in the infrared light mode, the infrared filter moves out of the optical system of the lens through the switching device; the focusing lens group is associated with the infrared filter, and is used to correct the optical system for focus shift. Due to the use of the focusing lens group to switch the optical system where the focal point shifts, only one infrared filter can be used to switch between the visible light mode and the infrared light mode, thereby avoiding the problem caused by the characteristics of crystal and other materials. The infrared transmittance of the optical system in night vision is only 90%, which improves the infrared light transmittance of the optical system at night; increases the brightness of the imaging monitoring screen, reduces image noise, and makes the screen clearer and cleaner.
Owner:SHENZHEN PROTRULY ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Focus measurement method and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
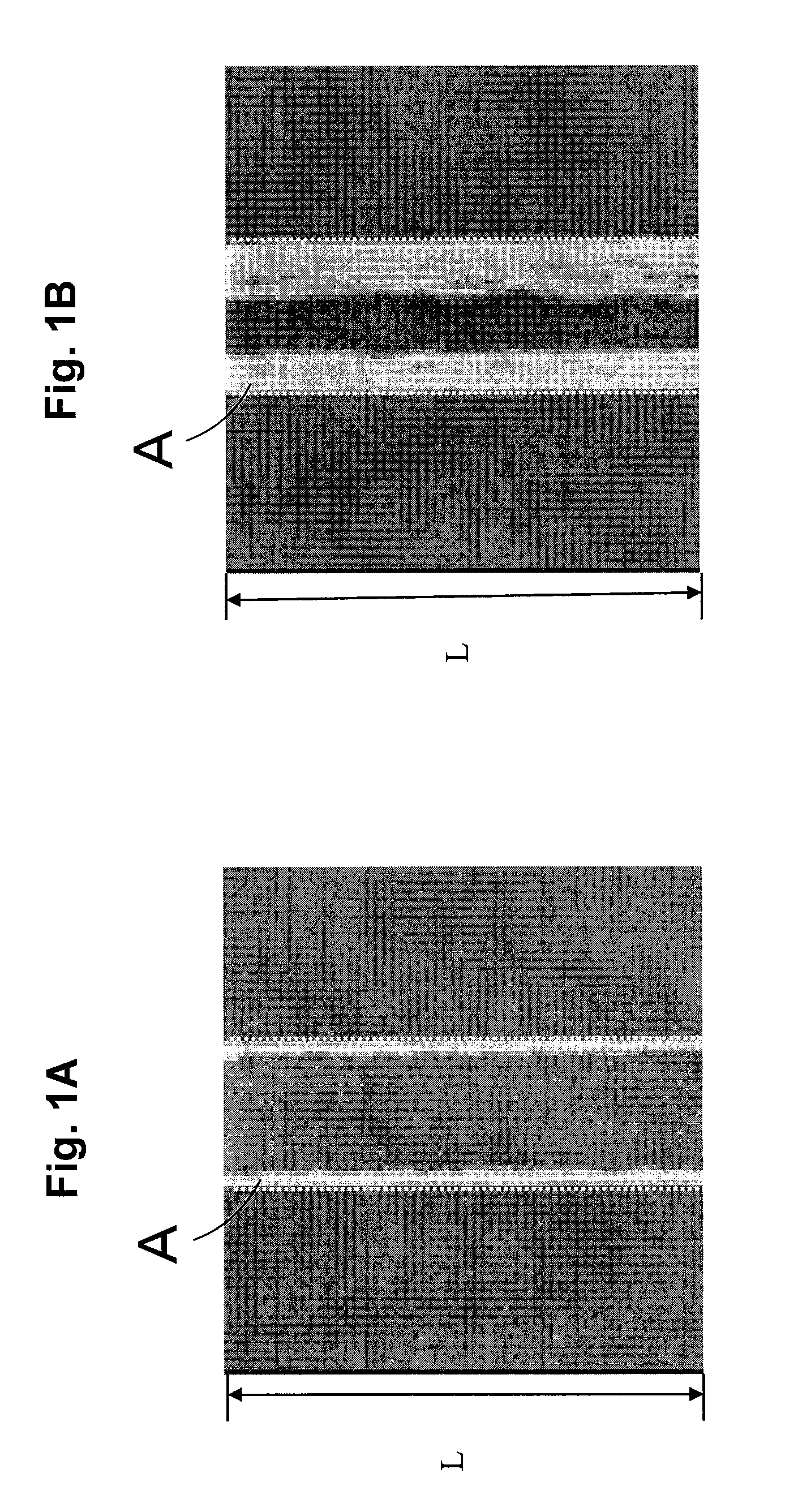
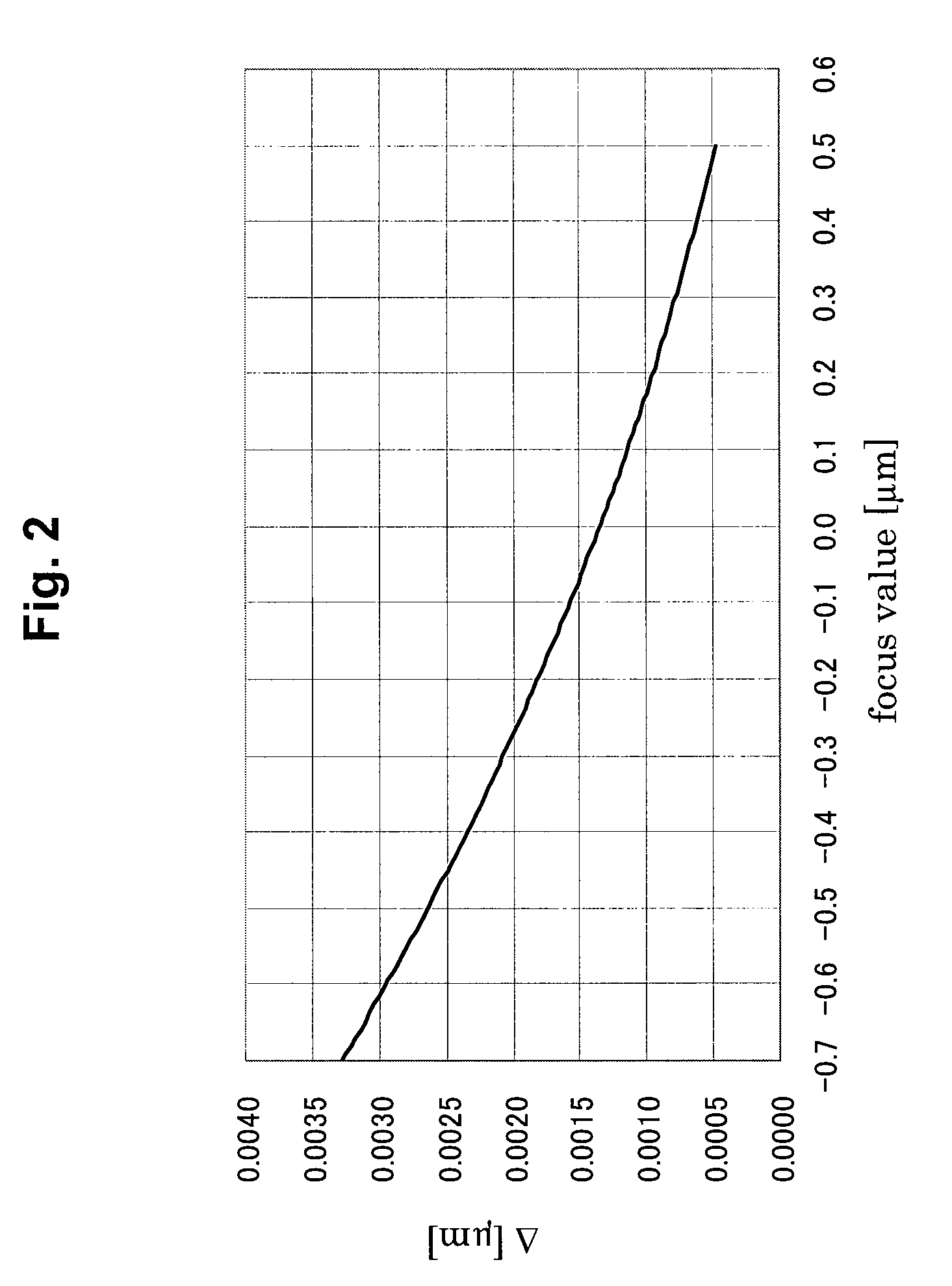
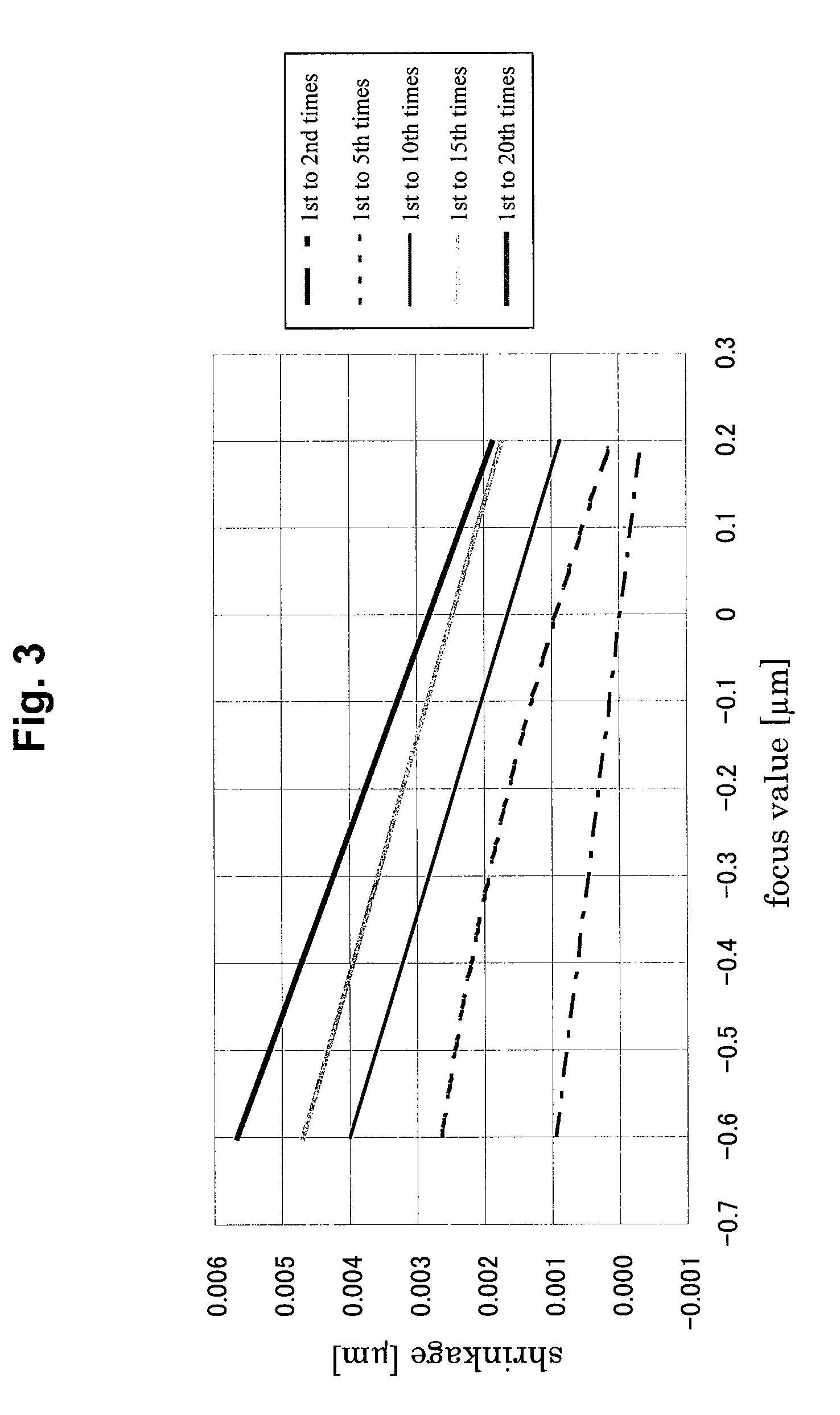
ActiveUS20090197189A1Accurate and easy focusHigh product yieldElectric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsResistSemiconductor
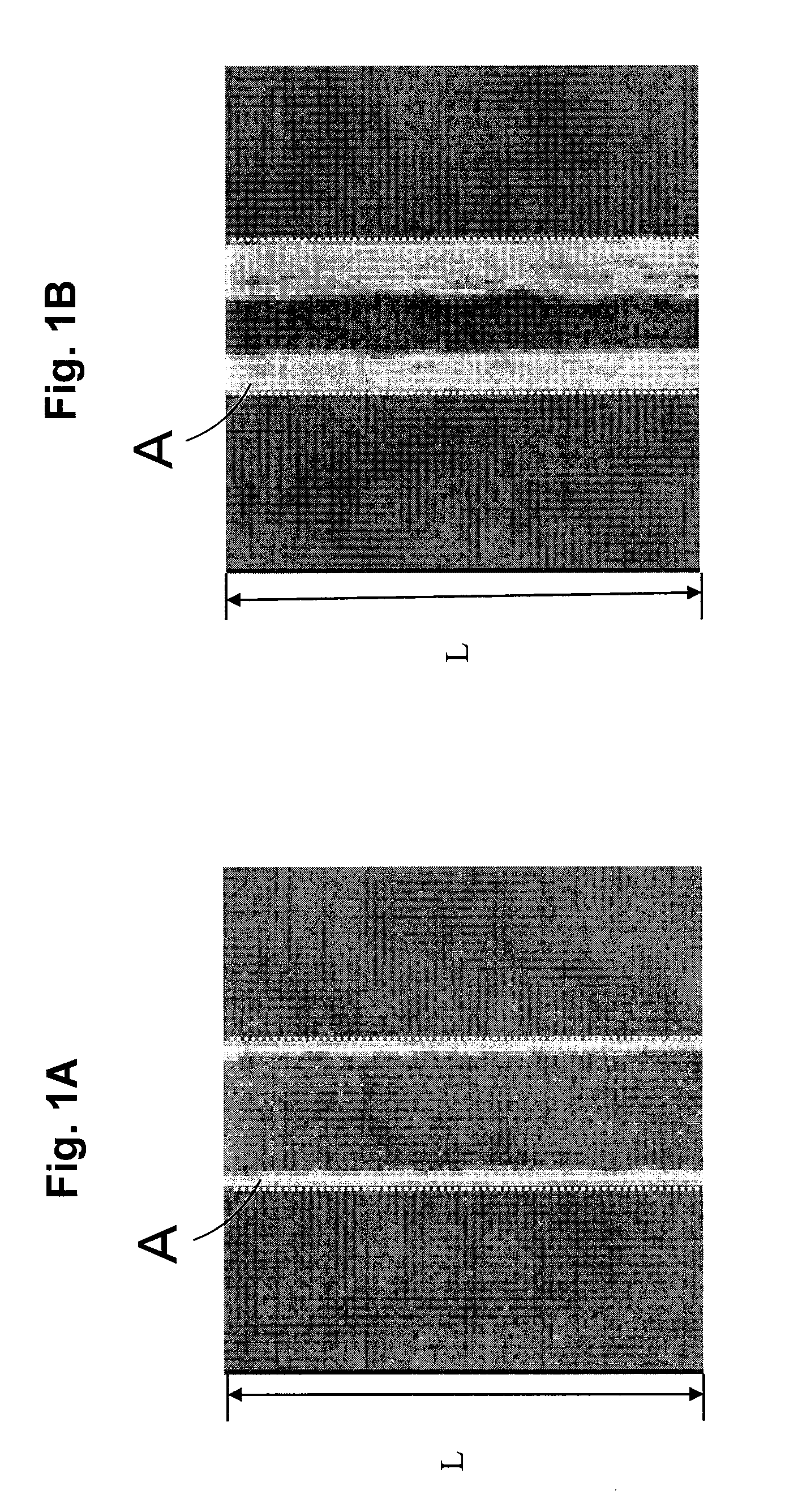
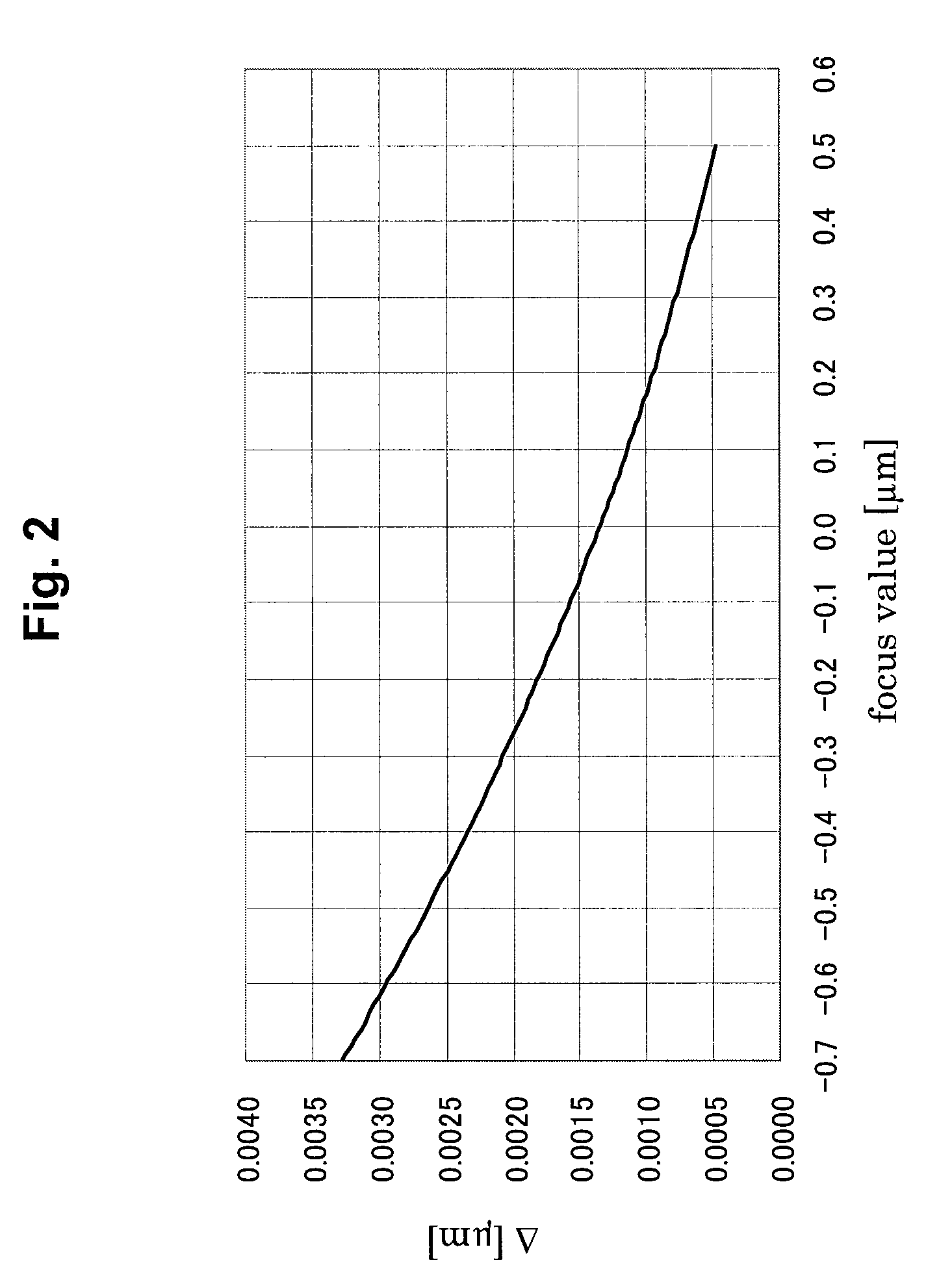
In a focus measurement method and a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device relating to the present invention, a focus value is obtained by using a fluctuation where shrinkage of a resist pattern by an electron beam irradiation depends upon the focus value. In the case of obtaining the focus value, the shrinkage of the resist pattern for a focus measurement formed by exposure to be subject for a focus value measurement is measured. The focus value corresponding to the shrinkage is obtained from the pre-obtained focal dependency of the shrinkage. A focal shift length can be defined from a difference between the focus value and a predetermined best focus value.
Owner:PANNOVA SEMIC
Achromatic flat top beam shaping
There is provided an optical system and method for shaping a polychromatic light into a substantially uniform profile beam along a first axis. A polychromatic divergent light with having multiple wavelength components is provided with a dispersion of divergence. A collimation optic collimates the polychromatic divergent light. A shaping lens shapes the collimated beam into a shaped beam with a nearly uniform profile along the first axis, the dispersion of divergence causing a deviation from uniformity of the nearly uniform profile. A focusing optic focuses the shaped beam. A combination of the collimation and focusing optics shows a chromatic focal shift that compensates for said dispersion of divergence, so as to reduce the deviation from uniformity to obtain a profile with a substantially uniform intensity along the first axis, for all of said multiple wavelength components.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Optical head and optical disk apparatus
InactiveUS7068572B2Increase speedLow costIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical detectorsHigh densityLight flux
To stably carry out recording and reproducing to and from a high density optical disk without using a double servo in the optical disk using a high NA objective lens. A detection of a spherical aberration and a detection of a coma aberration in a radial direction are simultaneously performed, and the coma aberration generated with the offset of an objective lens 109 is corrected in real time, thus enlarging an allowable offset amount of the objective lens. In order to simultaneously detect the spherical aberration and the coma aberration, focal shift and tracking shift signals in an inside region and outside region of reflected light flux are detected respectively, and the differential signals are set as spherical aberration and coma aberration signals.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
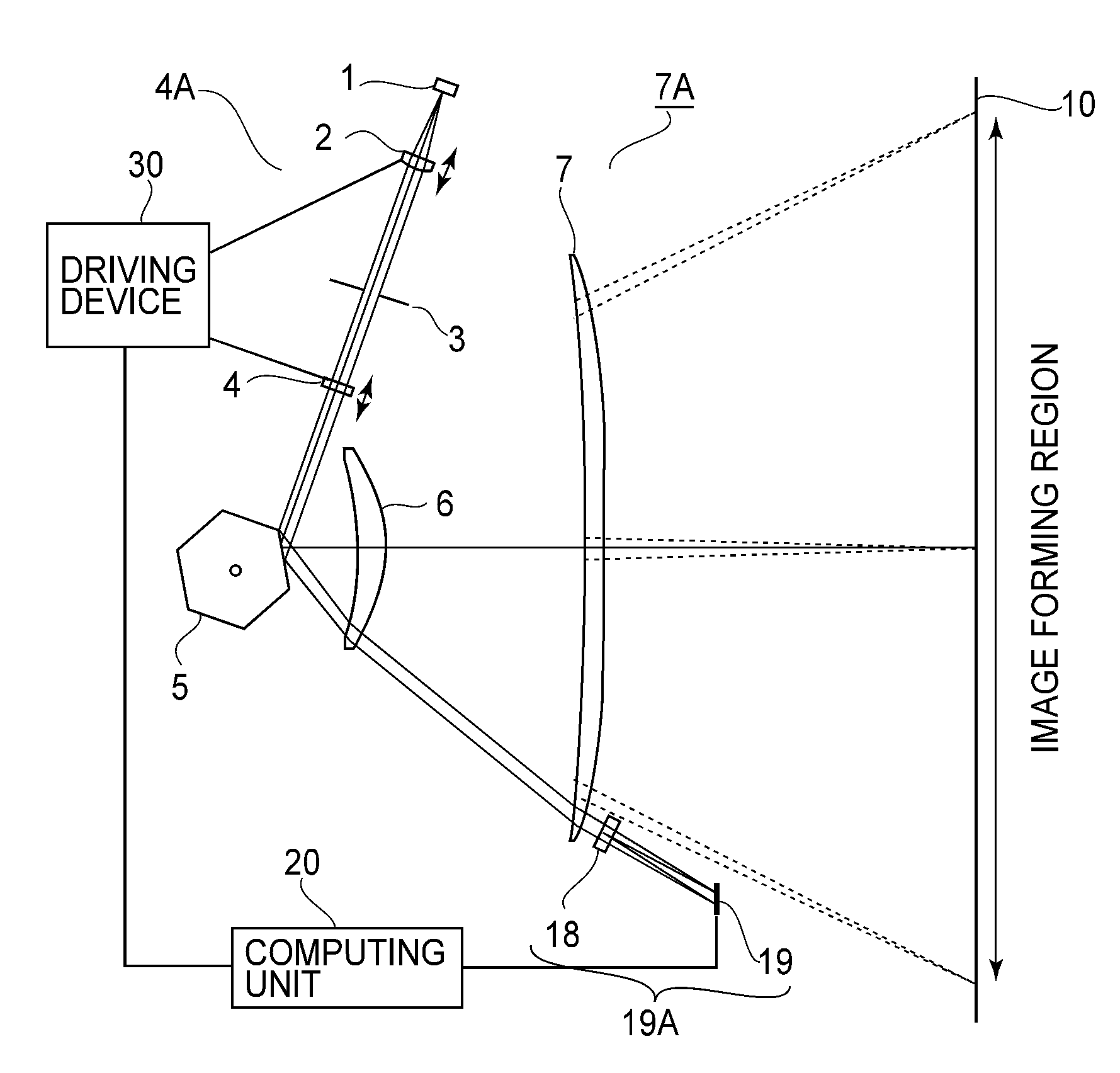
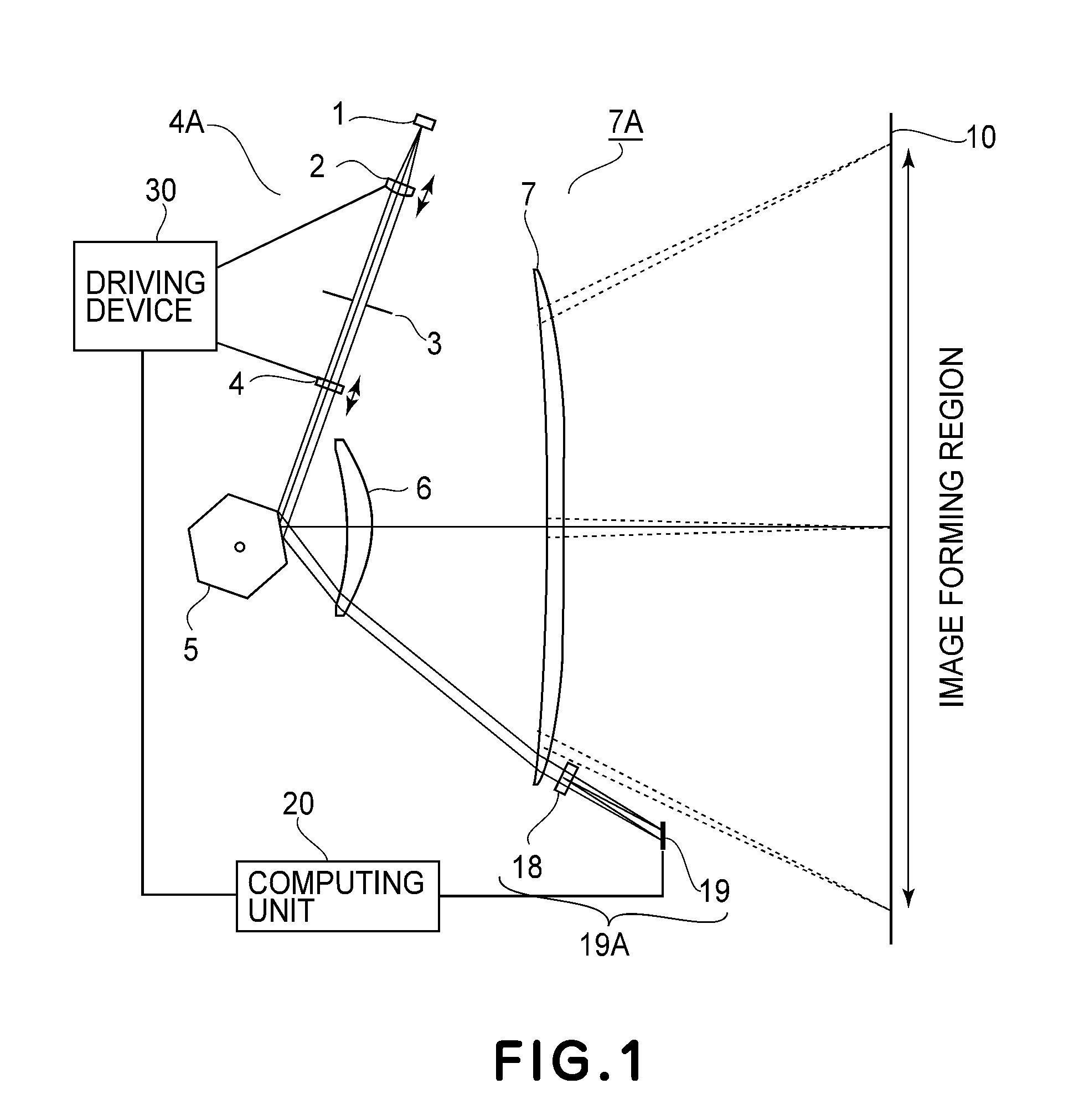
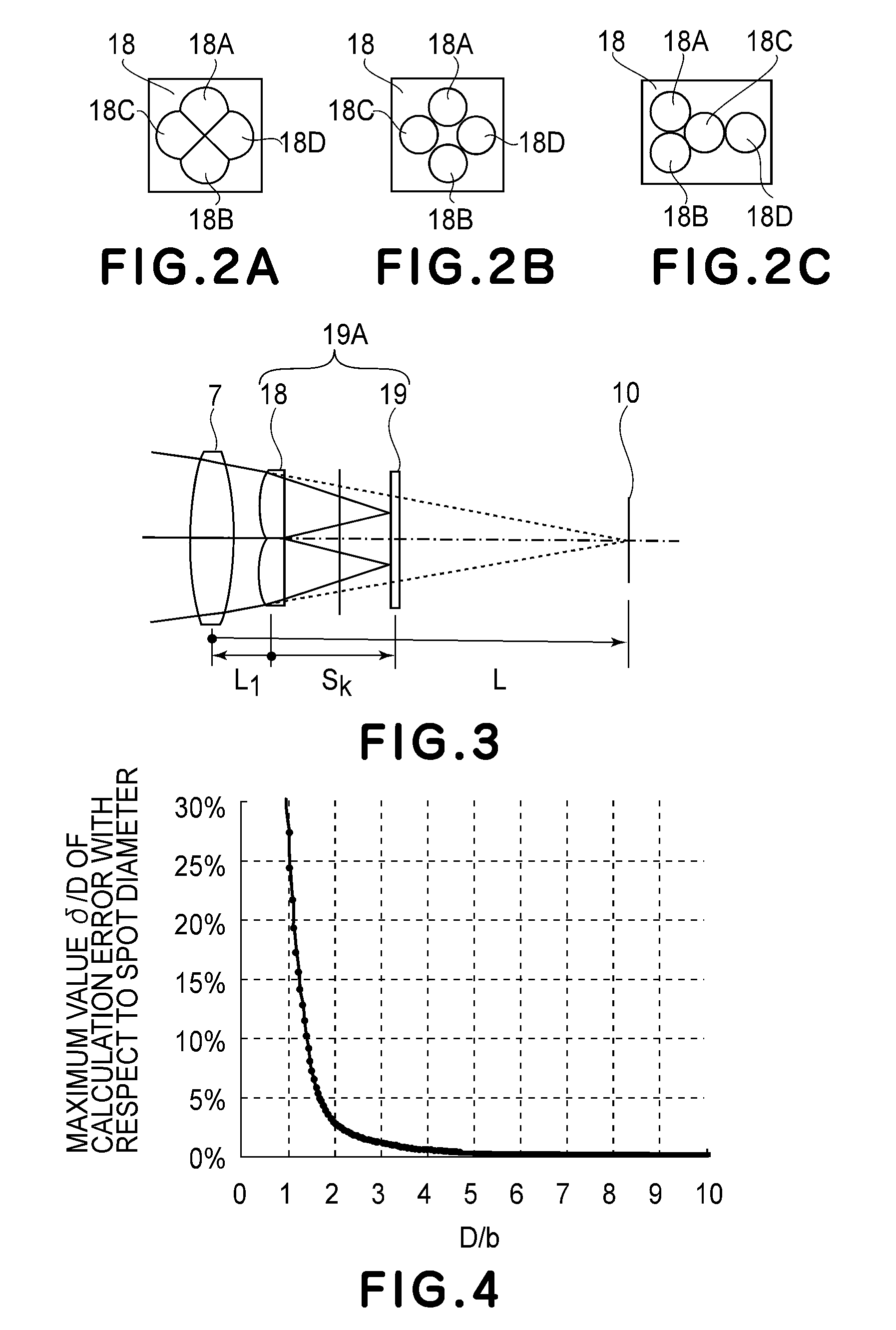
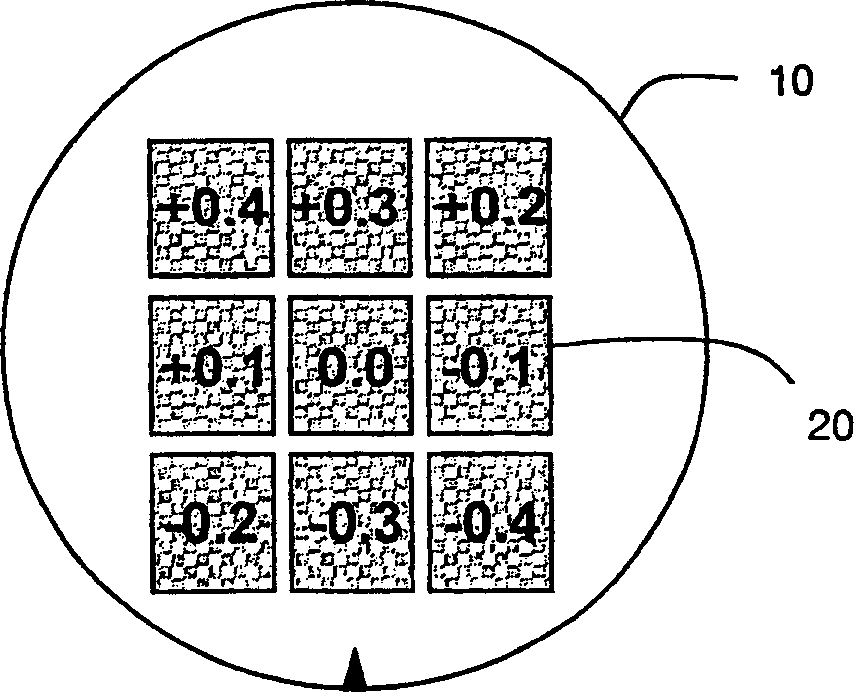
Scanning optical device and image forming apparatus using the same
A scanning optical device wherein, on the basis of positional information concerning a spacing in a main-scan direction between imaging positions of a plurality of light beams passed through resin-made imaging optical elements and detected by a photodetecting device and a spacing between the imaging positions in a sub-scan direction of the plurality of light beams, a focal shift direction and a focal shift amount in the main-scan direction as well as a focal shift direction and a focal shift amount in the sub-scan direction are determined, and wherein an optical element of an input optical system is moved in an optical axis direction based on the determination, to correct the focal shift in the main-scan direction and the focal shift in the sub-scan direction.
Owner:CANON KK
Determination of center of focus by parameter variability analysis
InactiveCN1771464AUsing optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLithographic artistDirect analysis
A method for judging the center of focus and process control of a lithography tool. Diffractive features are obtained from multiple diffractive structures located within multiple different focus setting fields. The variability of the diffraction characteristics of each field is determined by direct analysis or comparison with a database. The variability or uniformity can be represented by any measurement, including the standard deviation or range of values of selected features of a database of theoretical diffraction structures or the variability or uniformity of the diffractive features themselves, as represented by RMS differences or intensity ranges. These methods can be used to process control and monitor focus shift by determining the internal field variation of the diffractive features of multi-diffractive structures in a series of wafers.
Owner:ACCENT OPTICAL TECH
Low focal shift kW class optical isolator
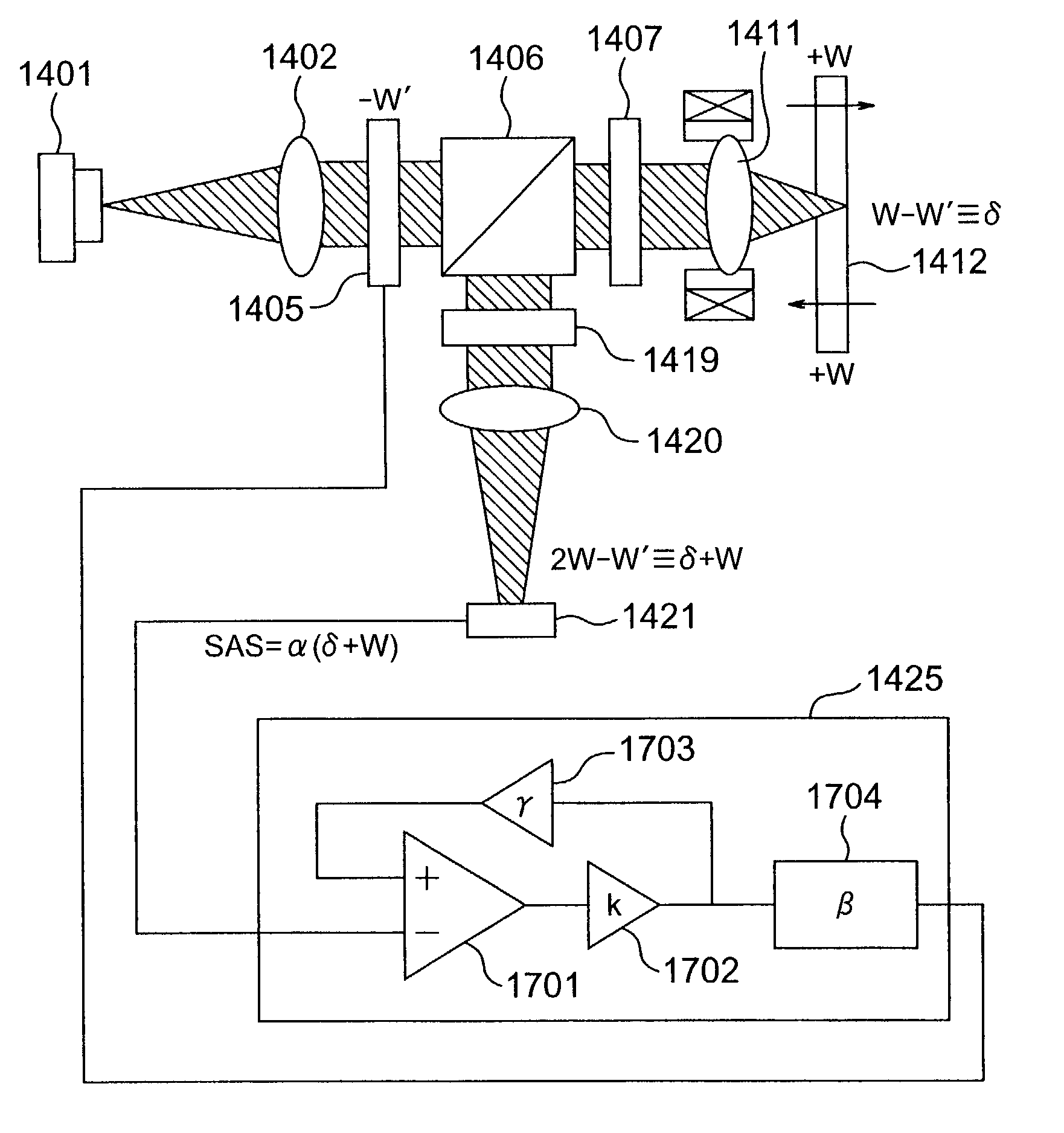
ActiveUS9268159B2Low birefringenceEasy to useCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsNegative feedbackOptical isolator
A kW Class optical isolator employs negative feedback to yield low focal shift over dynamically changing power levels. The isolator is useful as a kW fiber laser output isolator.
Owner:ELECTRO OPTICS TECH
X-ray CT apparatus and image reconstruction method
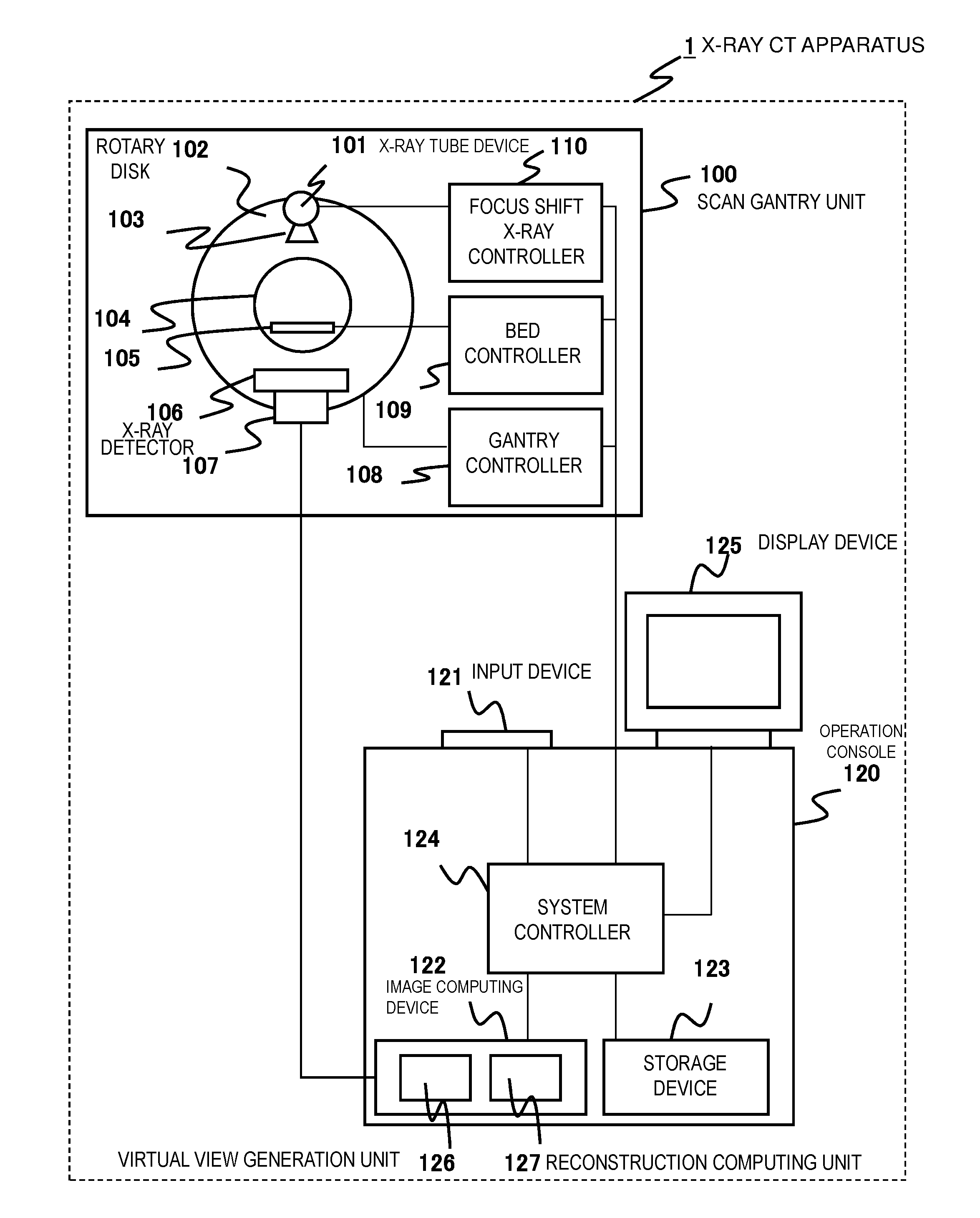
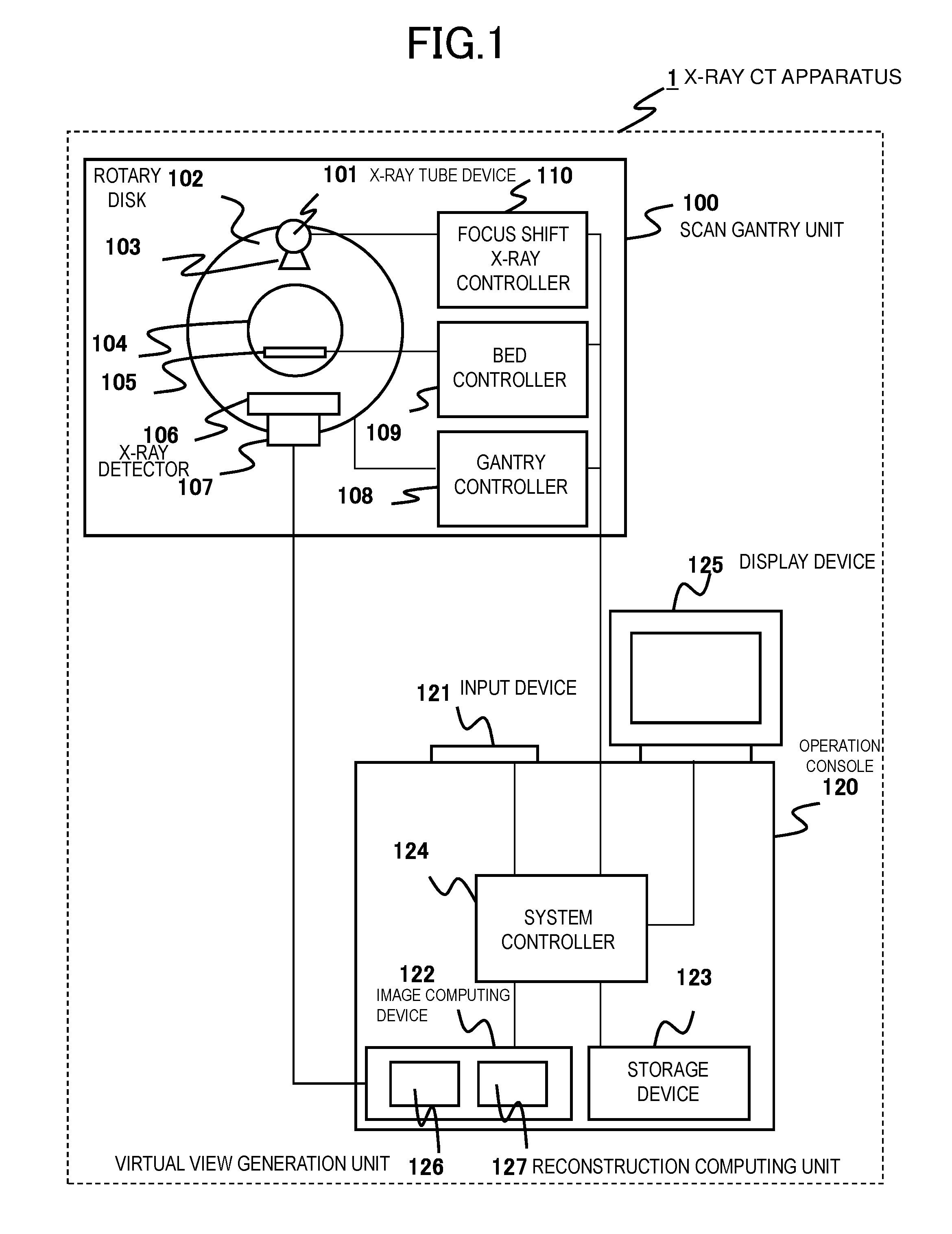
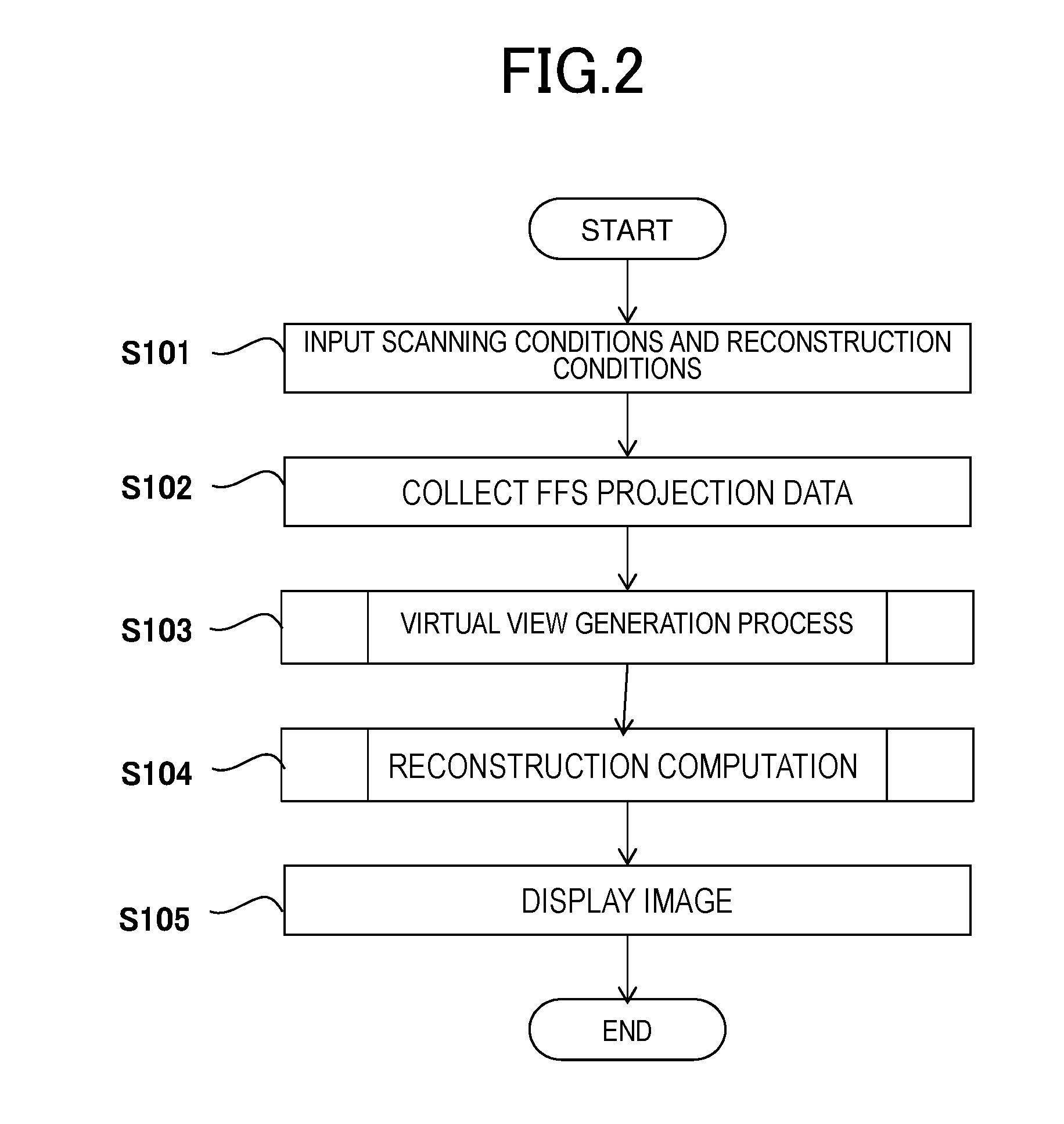
ActiveUS20160183900A1Improve spatial resolutionReduce speedReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayImage resolution
In an FFS method that improves spatial resolution by moving an X-ray focal spot to multiple positions to acquire projection data, in order to provide an X-ray CT apparatus and an image reconstruction method that enables to improve spatial resolution of the entire effective field of view without reducing a rotational speed, the X-ray focal spot in the X-ray tube device 101 is shifted to acquire focal shift projection data (FFS projection data), the virtual view generation unit 126 up-samples the FFS projection data (generates a virtual view) in the view direction, and the reconstruction computing unit 127 reconstructs an image using actual data of the FFS projection data in the central region 604 closer to the image center than a predetermined boundary and using the up-sampled projection data in the peripheral region 603 outside the boundary in an image reconstruction computing process.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Focus measurement method and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
ActiveUS7838185B2Accurate and easy focusHigh product yieldElectric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsResistSemiconductor
In a focus measurement method and a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device relating to the present invention, a focus value is obtained by using a fluctuation where shrinkage of a resist pattern by an electron beam irradiation depends upon the focus value. In the case of obtaining the focus value, the shrinkage of the resist pattern for a focus measurement formed by exposure to be subject for a focus value measurement is measured. The focus value corresponding to the shrinkage is obtained from the pre-obtained focal dependency of the shrinkage. A focal shift length can be defined from a difference between the focus value and a predetermined best focus value.
Owner:PANNOVA SEMIC
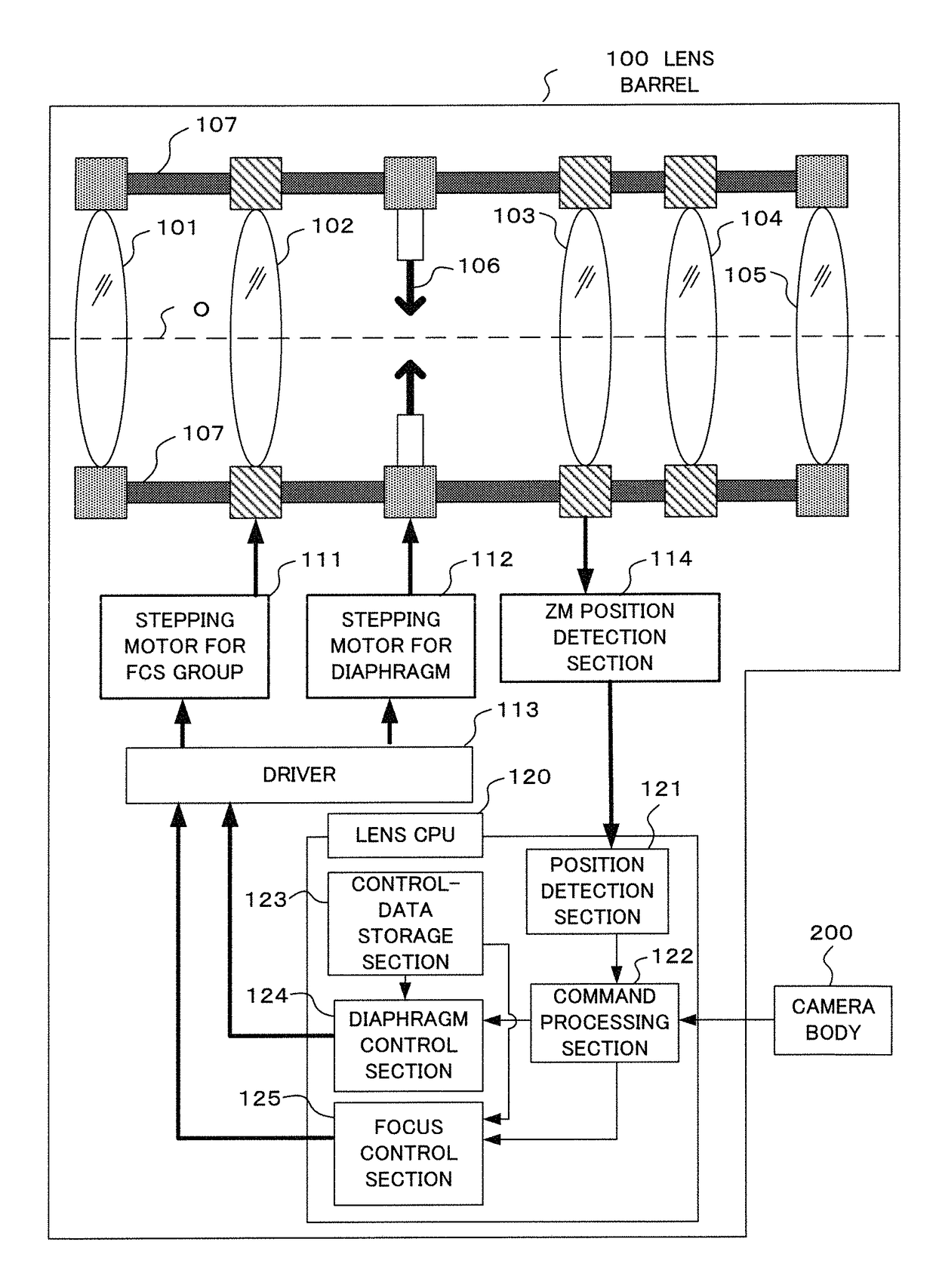
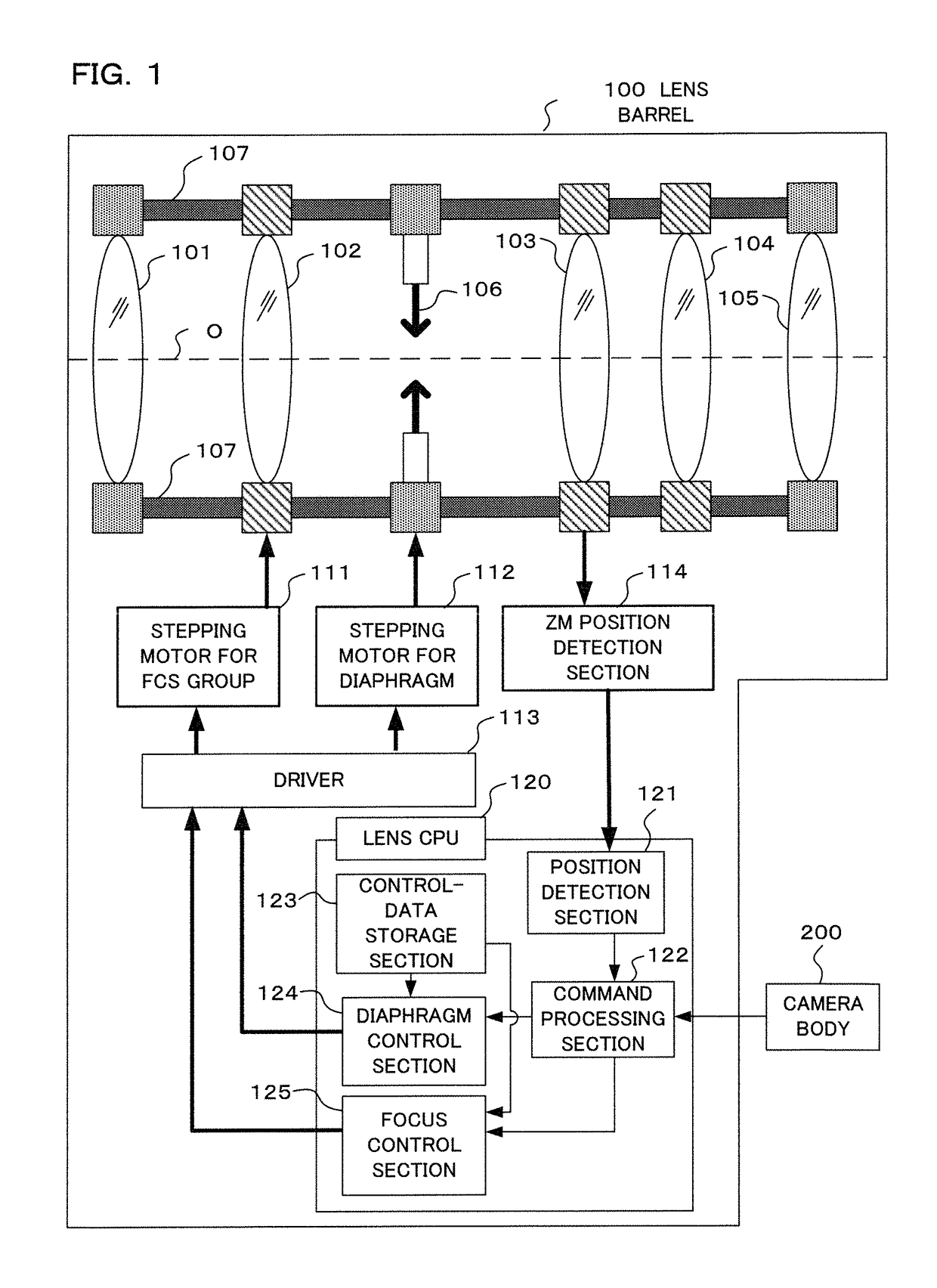
Shooting apparatus including a diaphragm
ActiveUS9756259B2Reduce exerciseImprove usabilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage signalImaging Signal
A shooting apparatus comprising: a photographing optical system having a variable aperture diaphragm; an imaging section that outputs an image signal; a diaphragm position detection section that detects a diaphragm position; a lens control section that controls movement of a focus lens; a storage section that stores an amount of focal shift corresponding to the diaphragm position; a focus detection section that detects a peak of a contrast value based on the image signal, wherein the lens control section, while moving the focus lens to a focusing position based on a position at which the contrast value indicates the peak, corrects a position of the focus lens to be moved, on the basis of a diaphragm position when the position at which the contrast value indicates the peak is detected, a diaphragm position while moving the focus lens, and the amount of focal shift stored in the storage section.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com