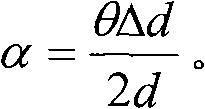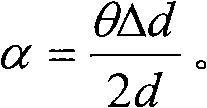Patents
Literature
458 results about "Birefringent crystal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
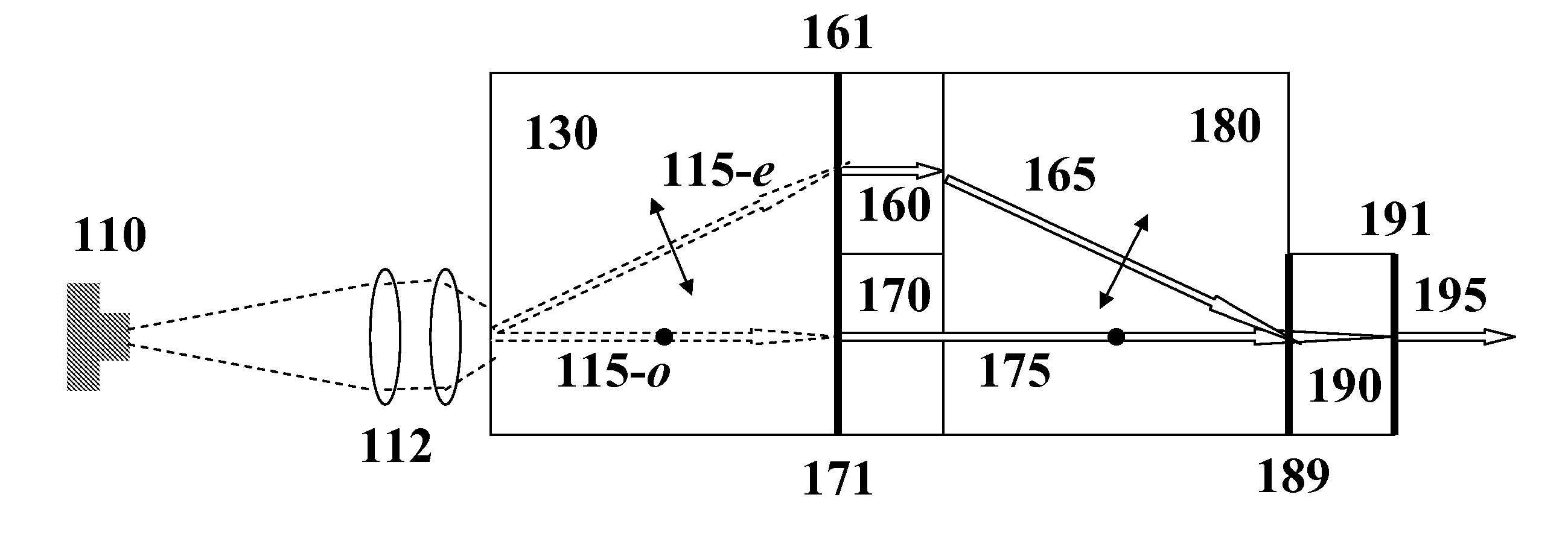
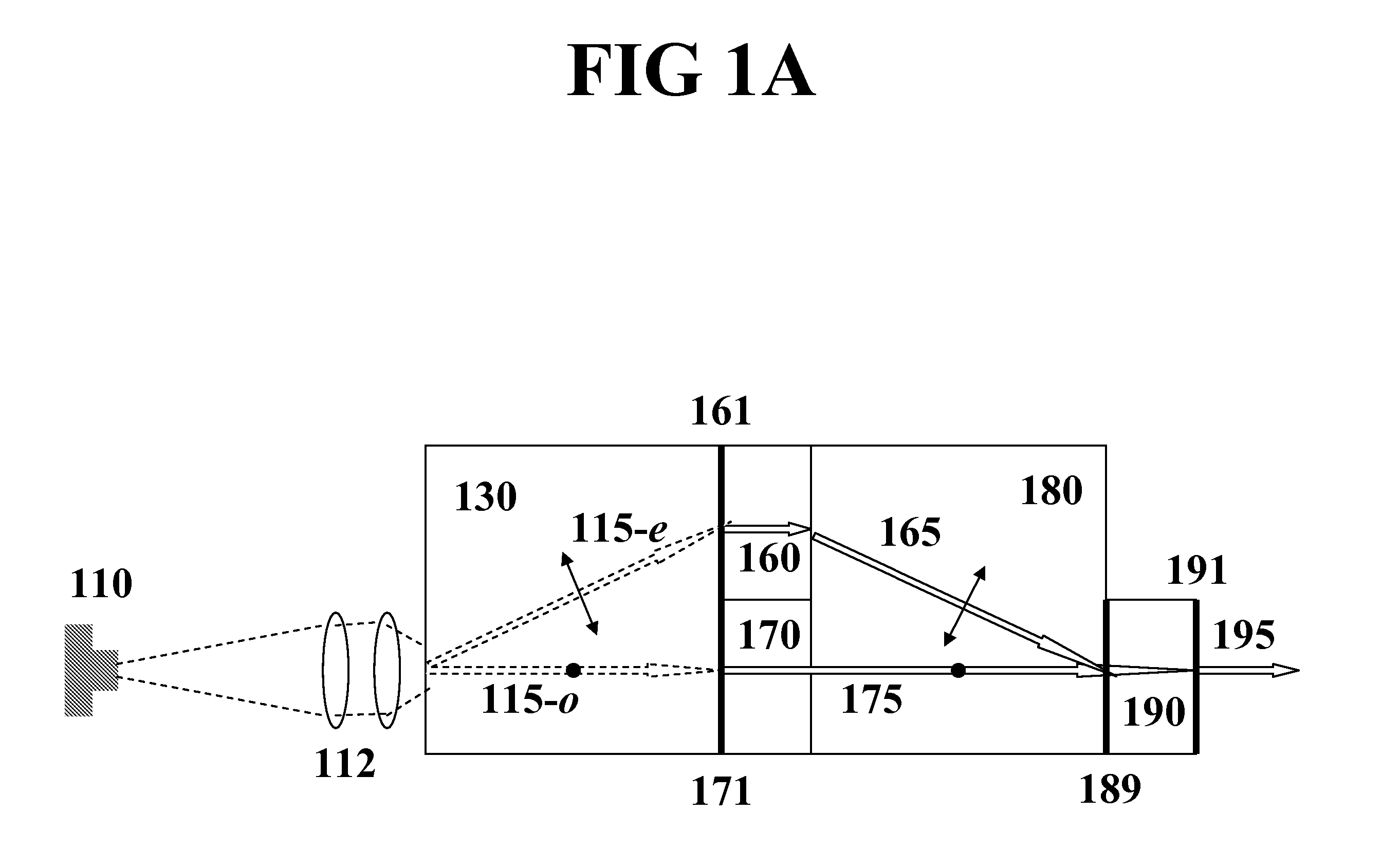
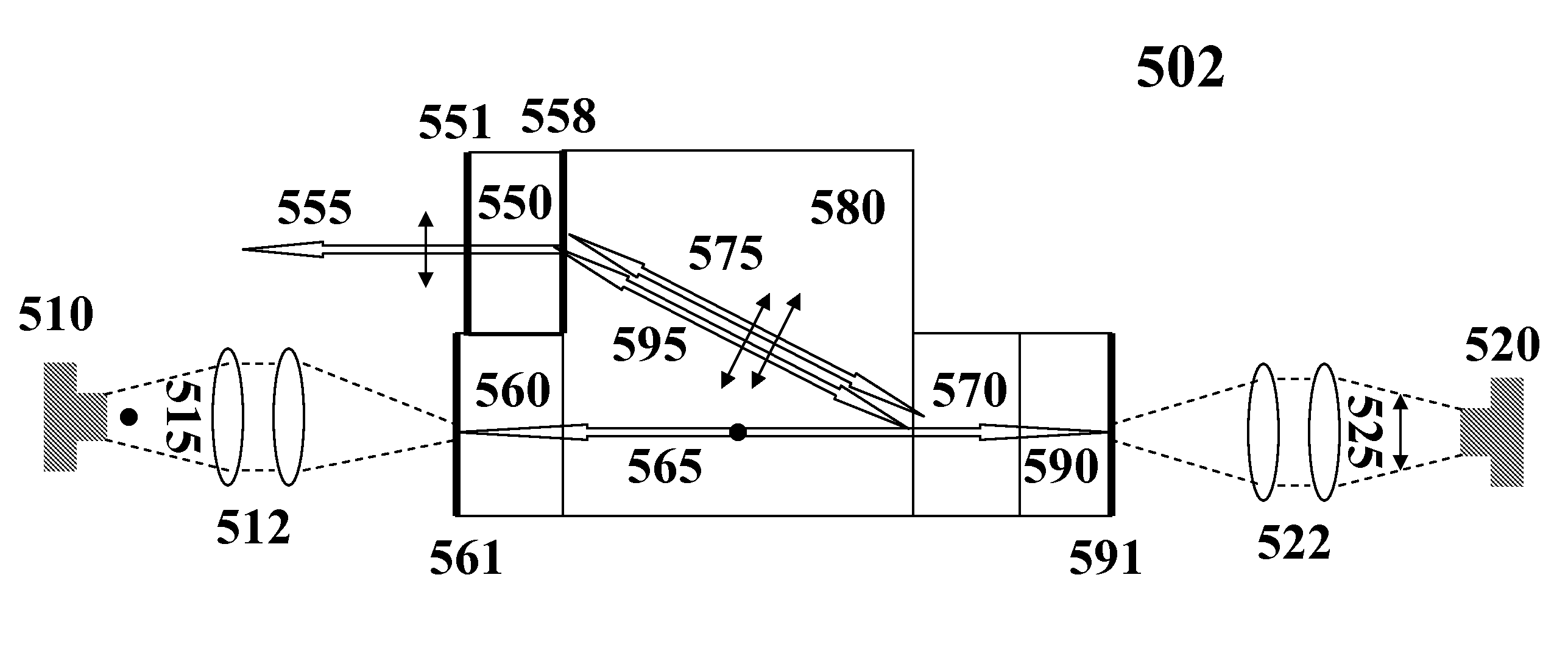
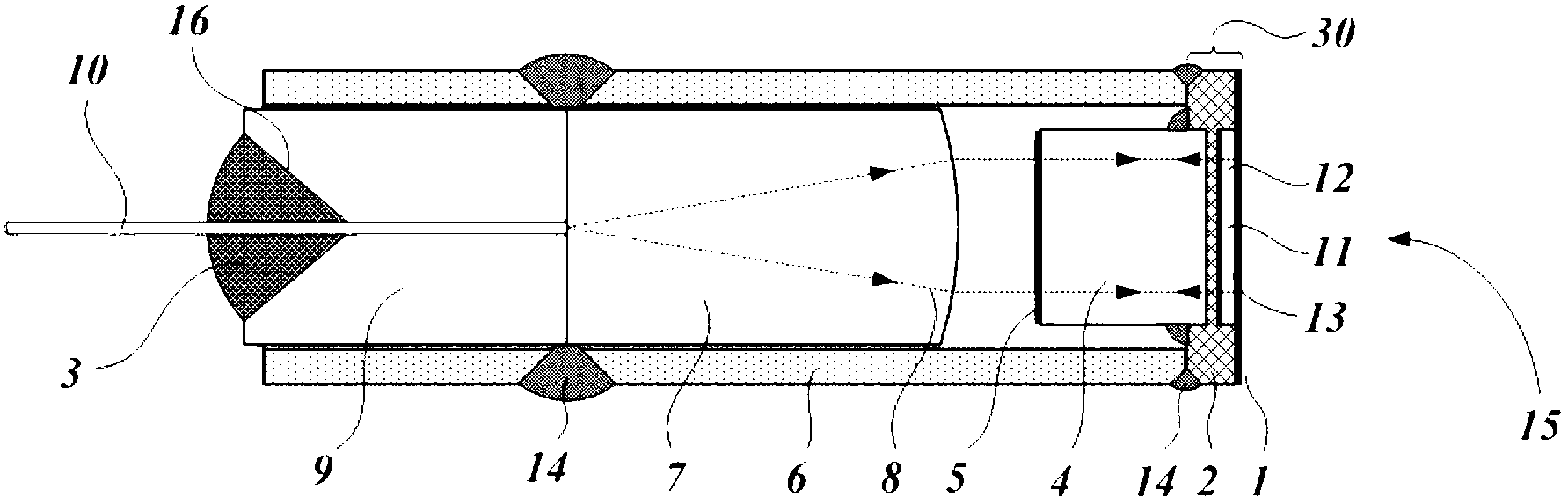
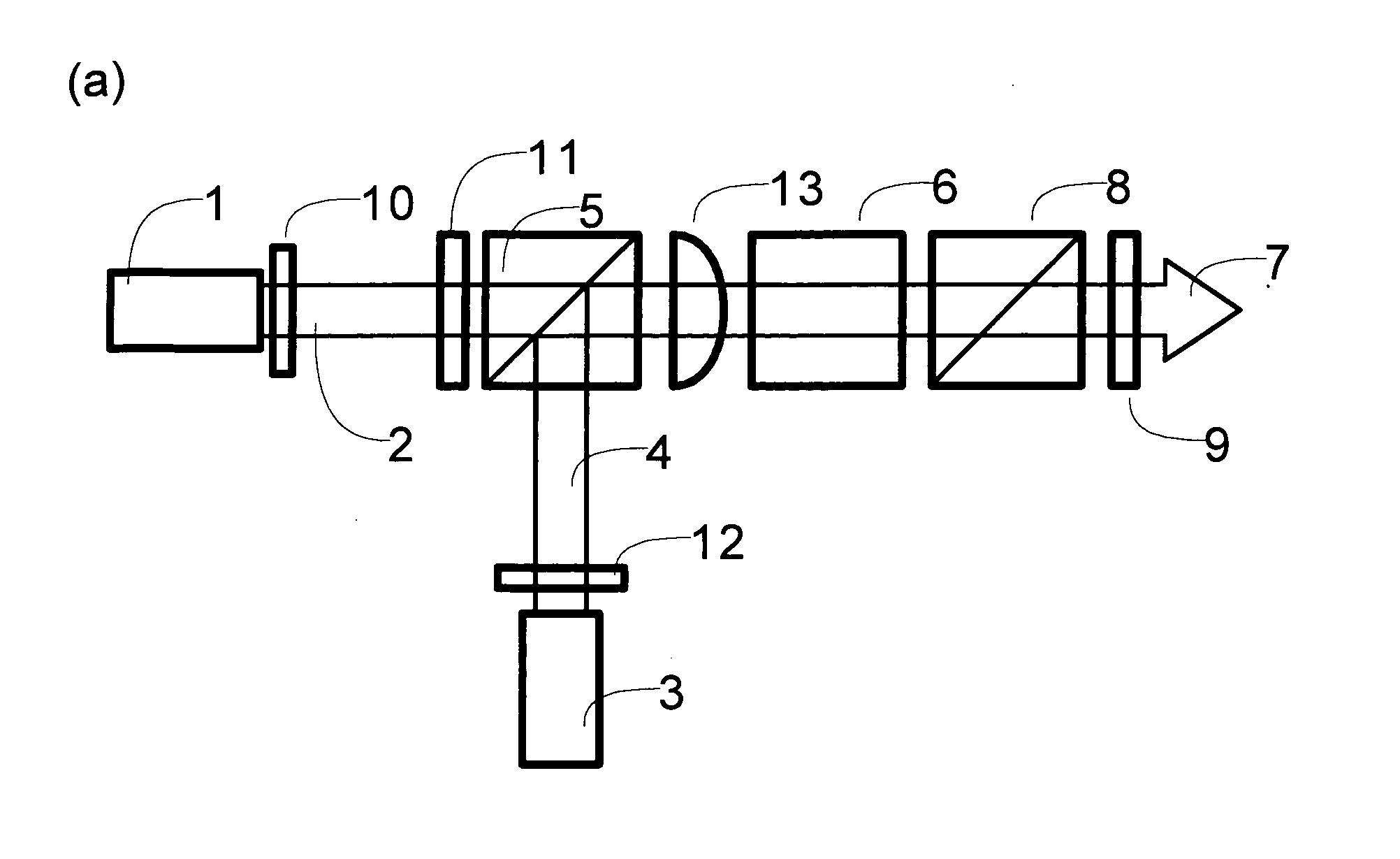
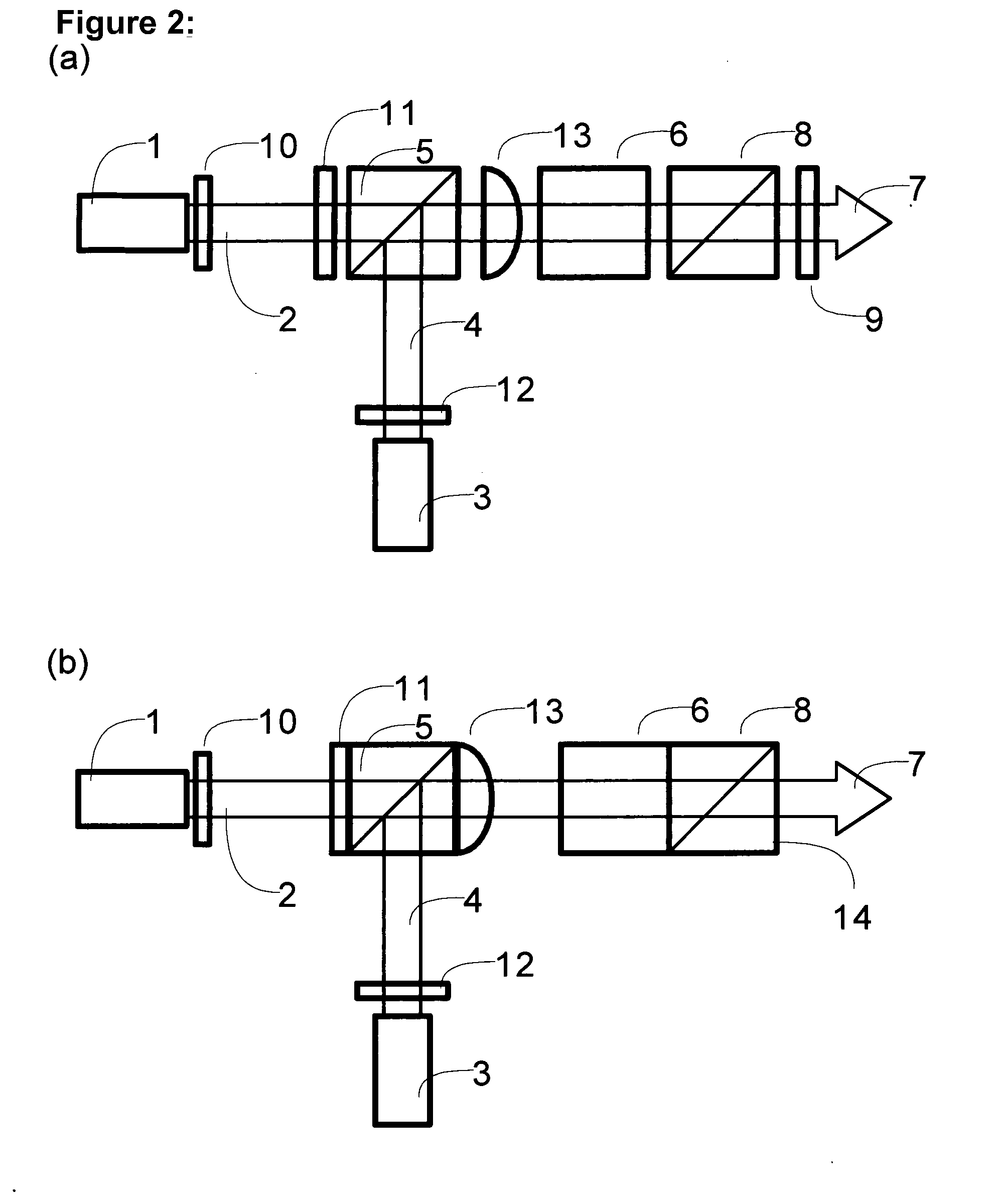
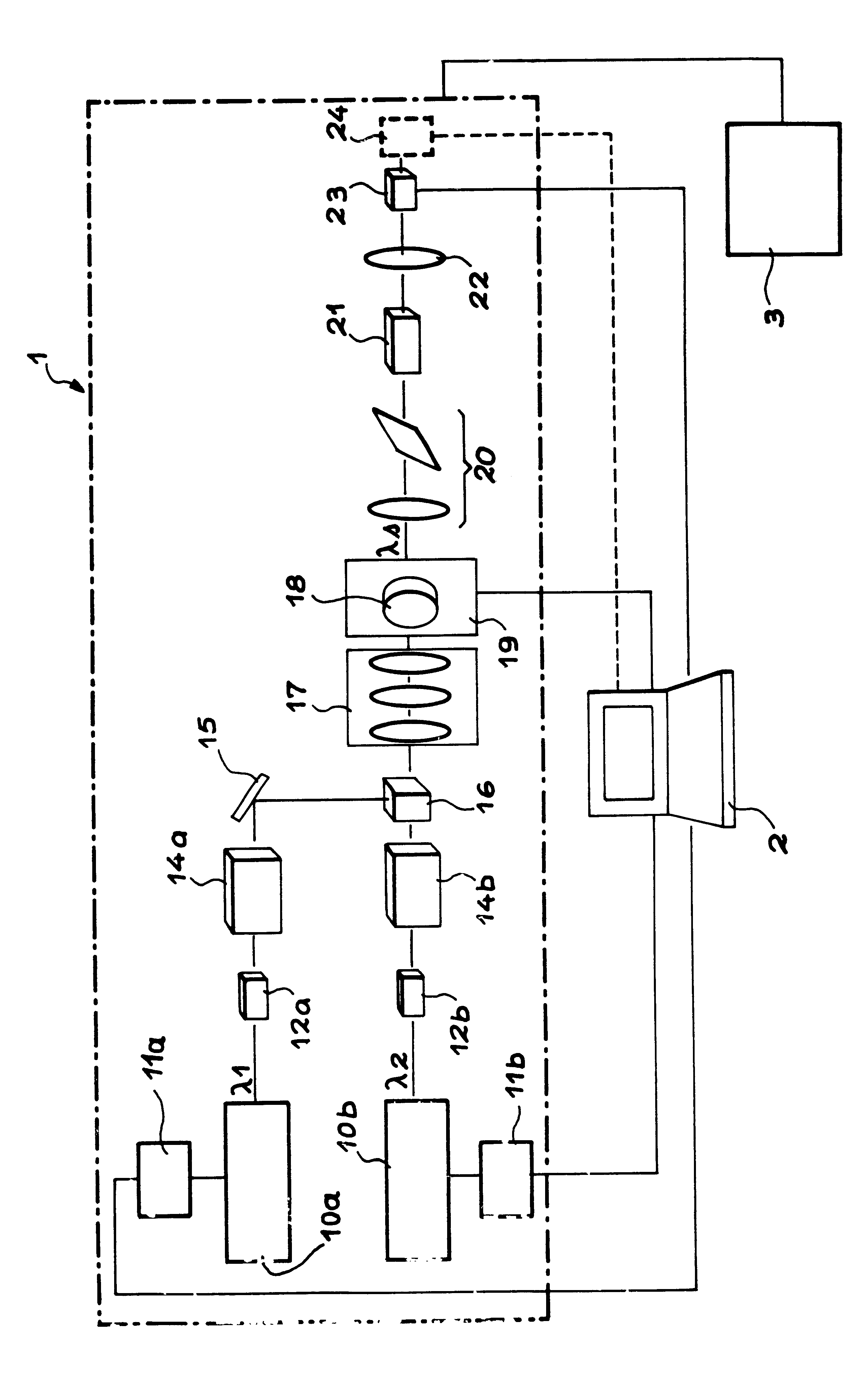
Low-Noise Monolithic Microchip Lasers Capable of Producing Wavelengths Ranging From IR to UV Based on Efficient and Cost-Effective Frequency Conversion
ActiveUS20070047600A1Efficient and cost-effective frequency conversionLow-noise laser outputOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionNonlinear optical crystalLow noise
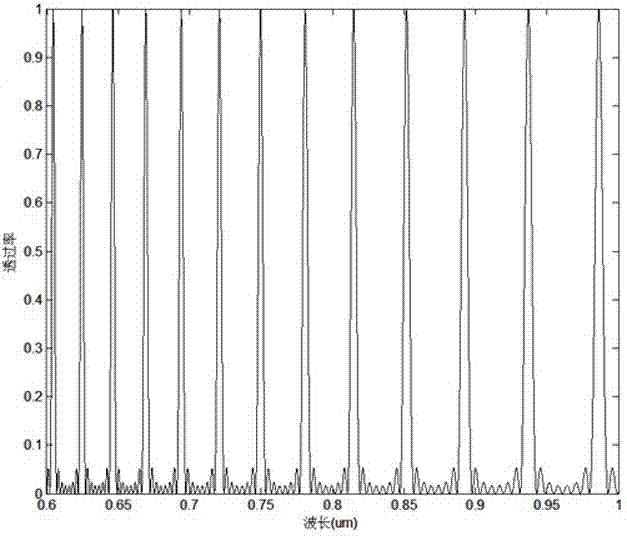
A method for producing low-noise laser output at wavelengths ranging from IR through visible to UV in various operation modes from a monolithic microchip laser comprises schemes of (1) generating one or two fundamental beam(s) from light source(s) selected upon the desired wavelength(s), polarization(s), and other features related to the desired laser output; (2) intracavity beam combination / separation due to the walk-off effect in one or more birefringent crystal(s) transparent to the propagating lights and highly anisotropic; (3) wavelength conversion in one or more nonlinear optical crystal(s); (4) compact and efficient pump source(s); and (5) minimization of intracavity loss / noise. One resonator cavity supports only one fundamental beam, which eliminates the green problem. The gain media can be selected from an extensive group of materials including isotropic and naturally birefringent crystals, with polarization dependent or independent laser emissions. Laser devices constructed in accordance with the inventive method are demonstrated with various configurations.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
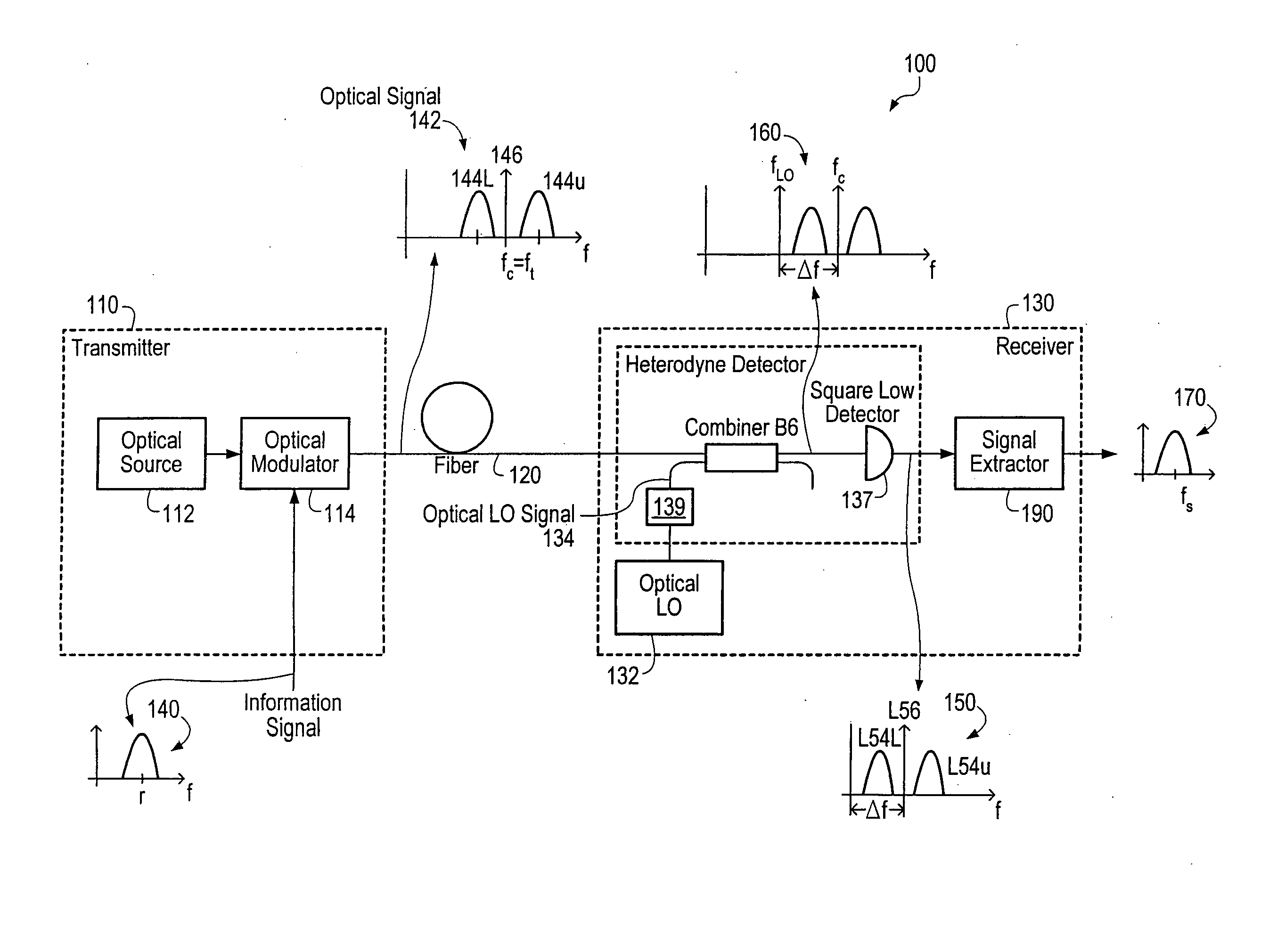
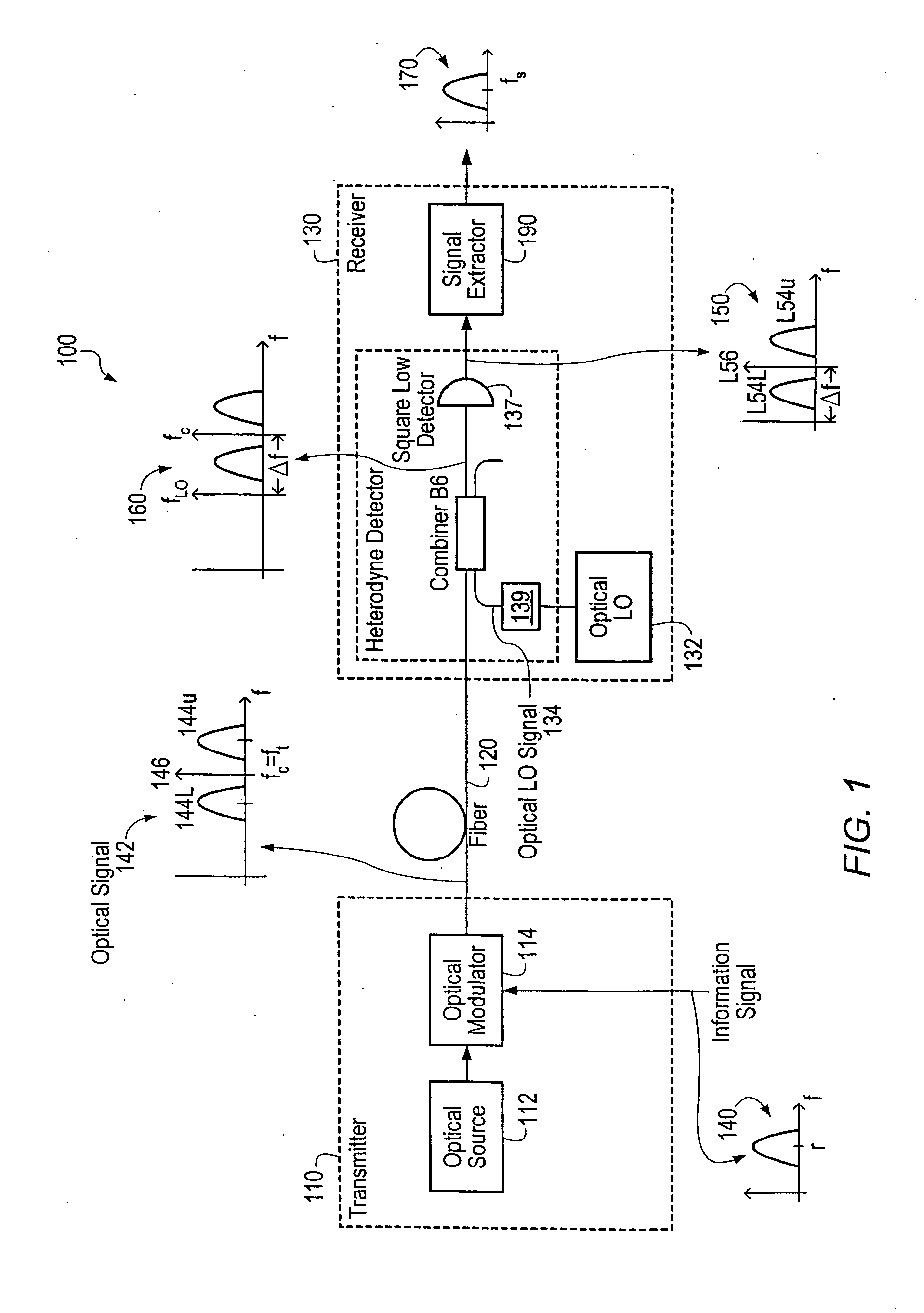
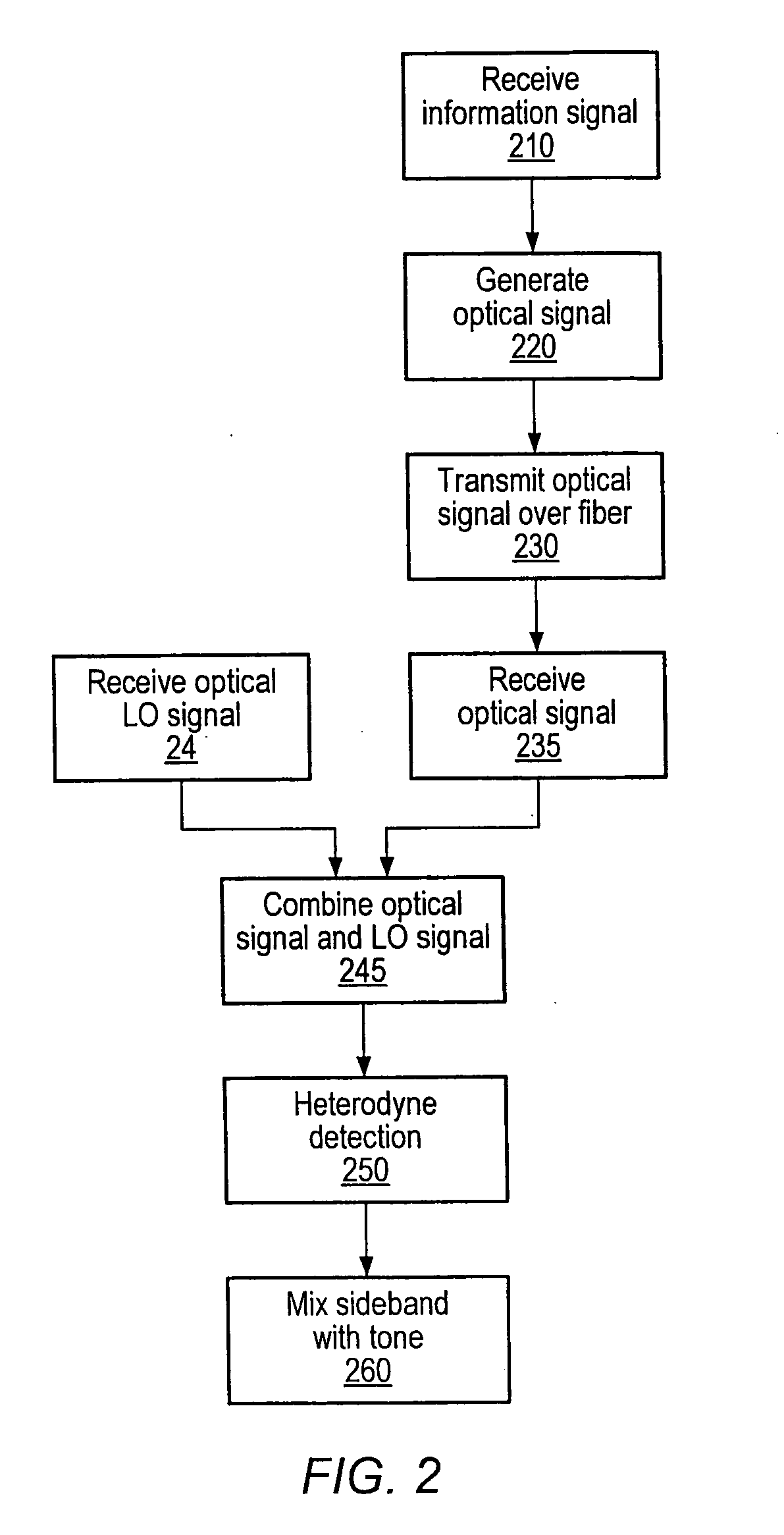
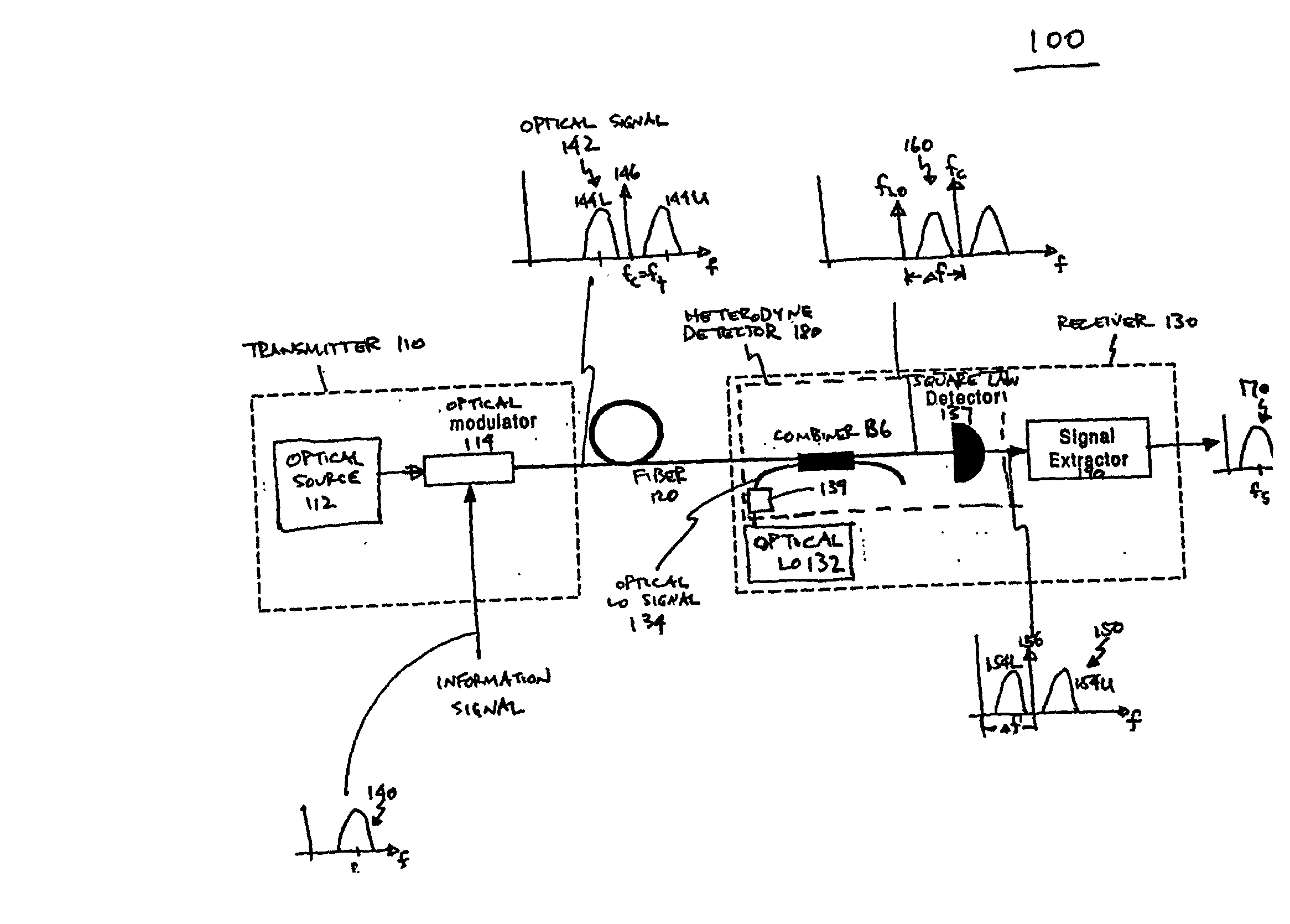
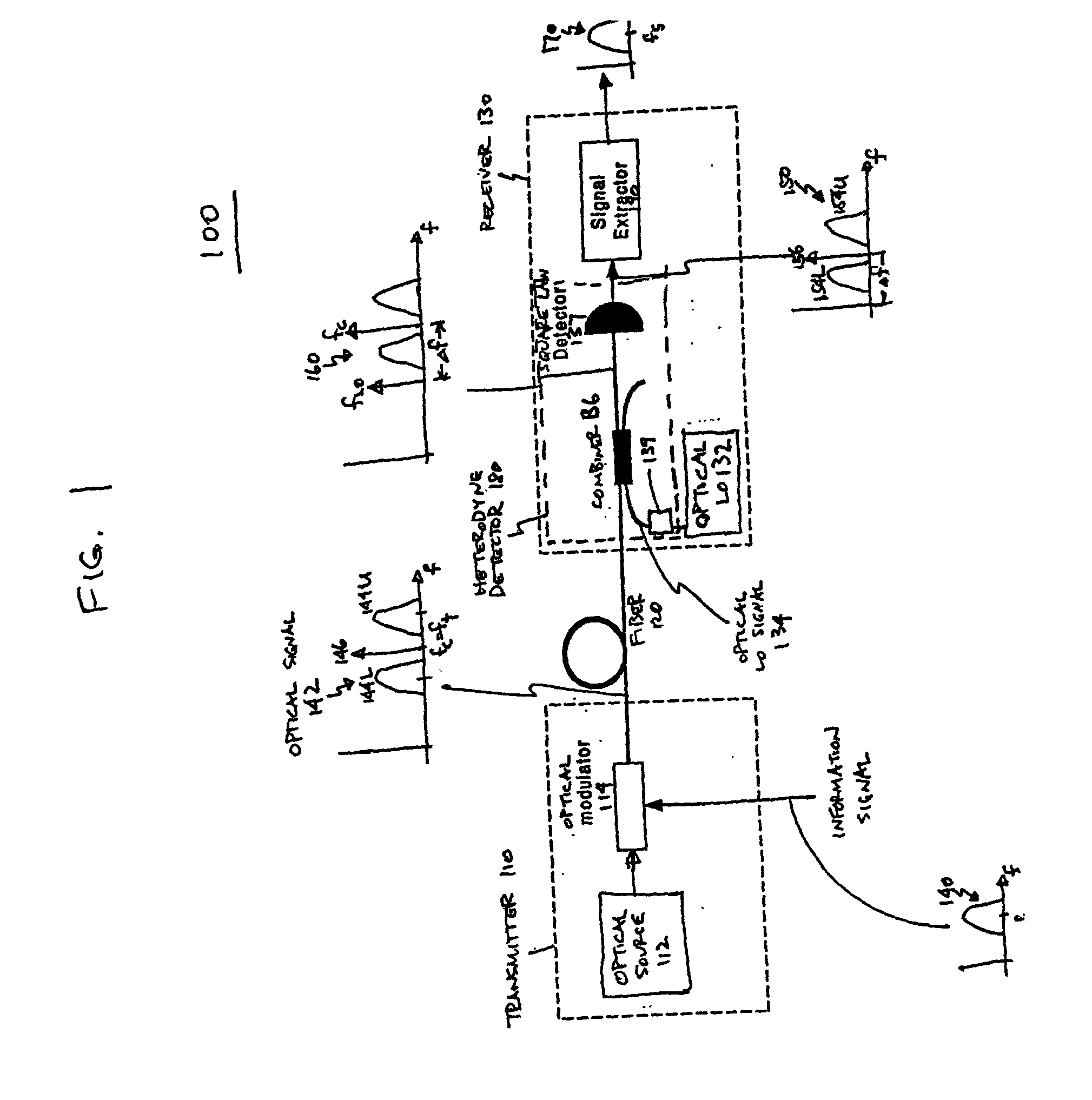
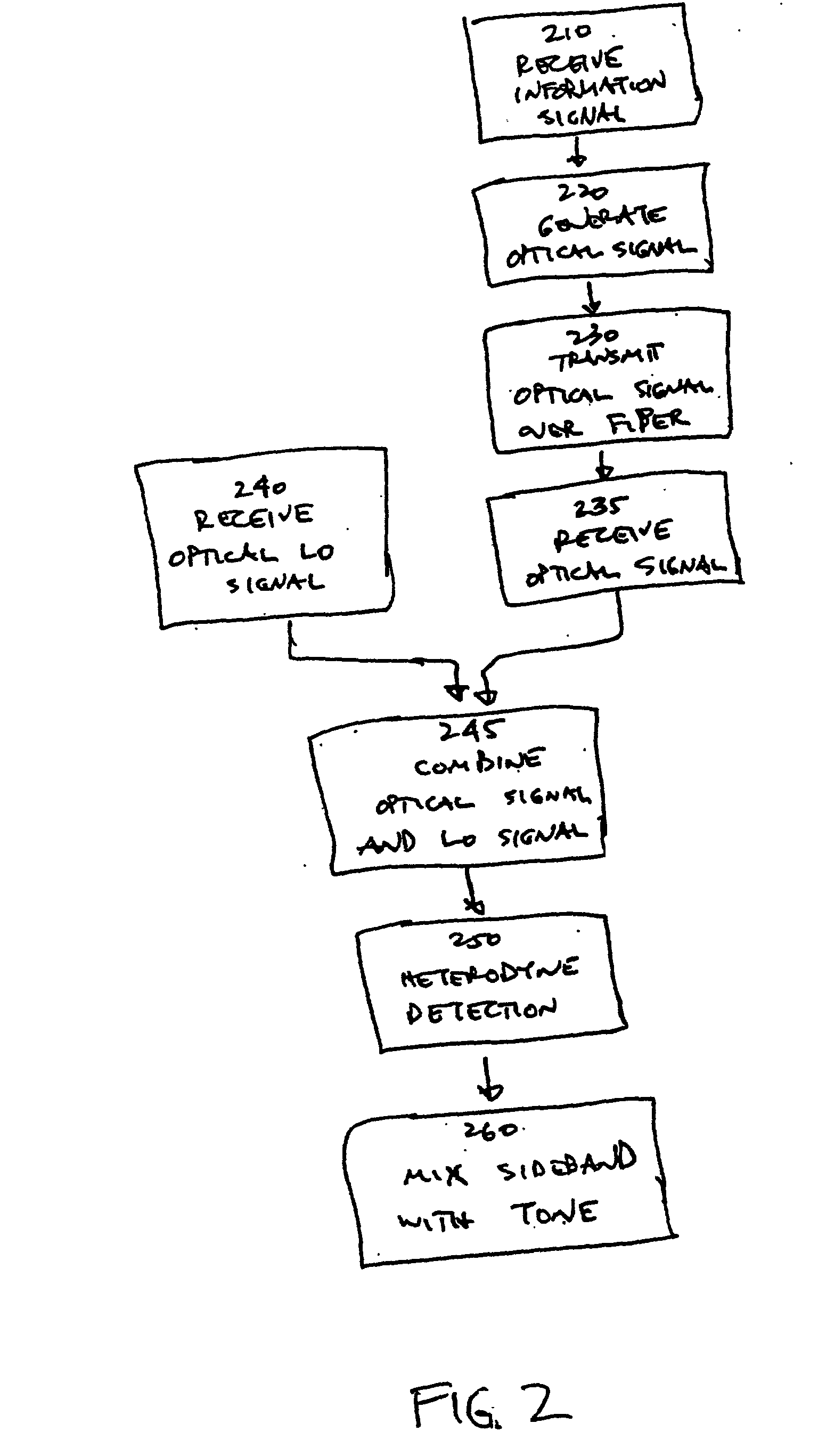
Optical communications using multiplexed single sideband transmission and heterodyne detection
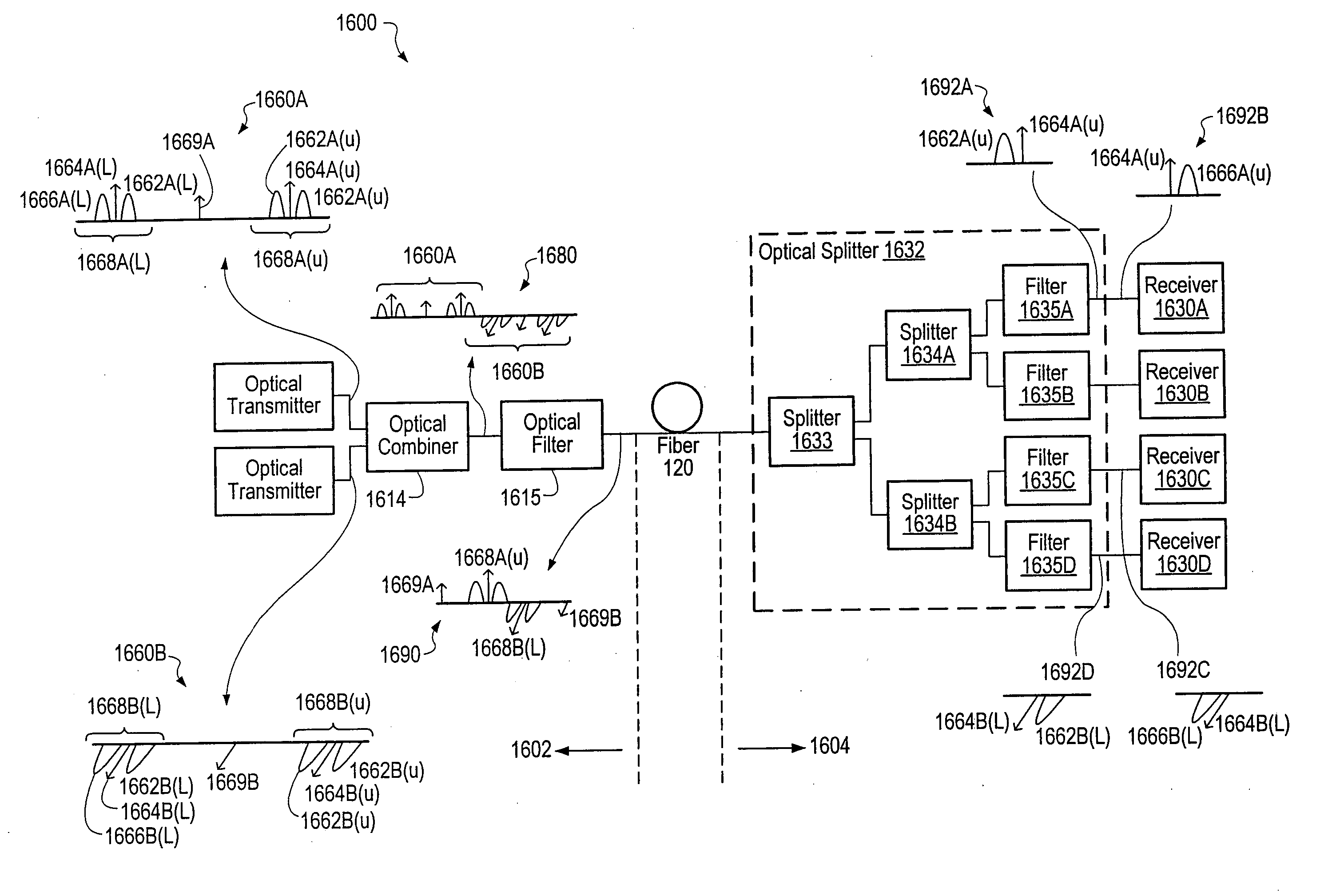
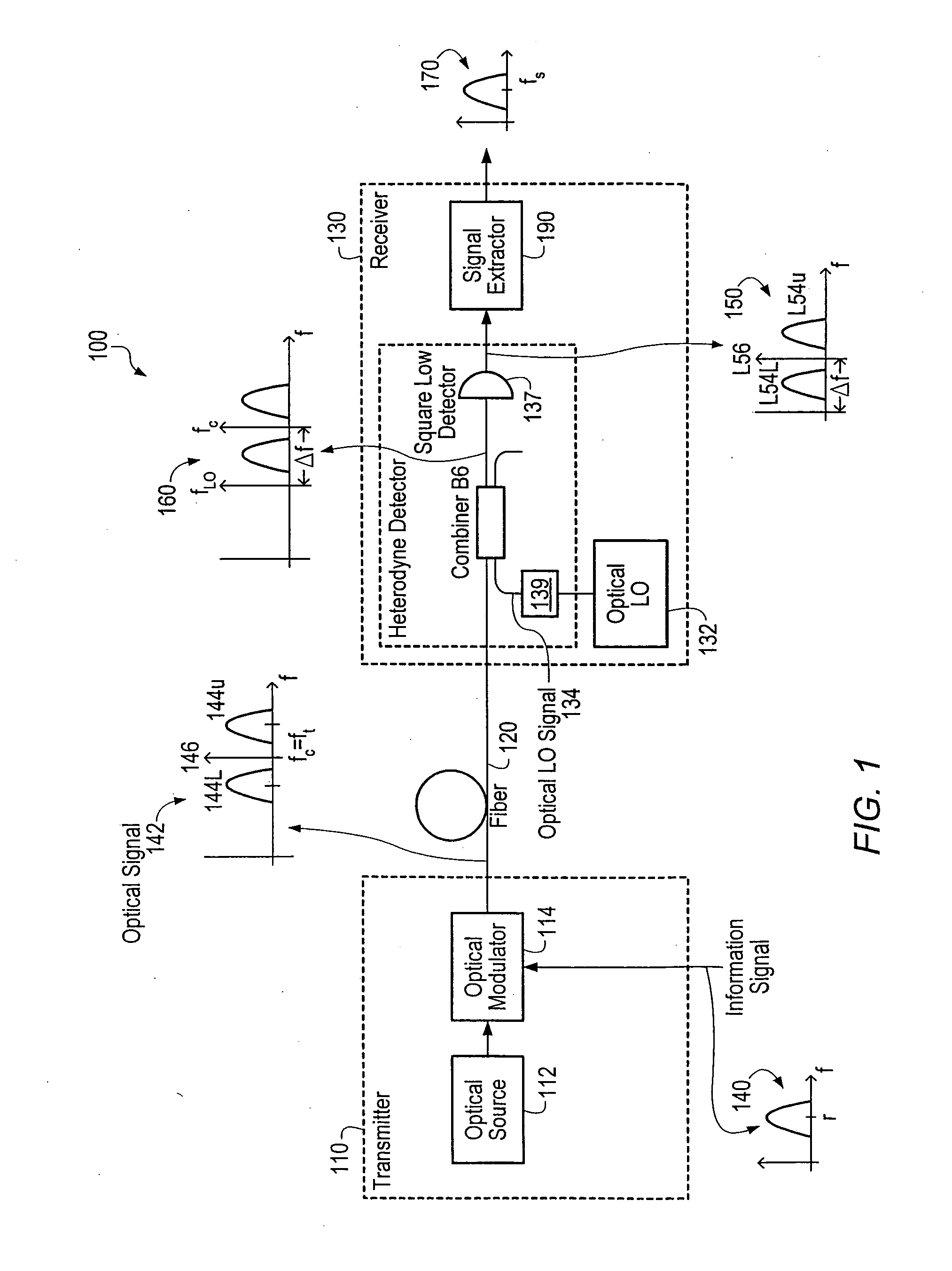
InactiveUS20060291868A1Less interactionUnwanted effectElectromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversMultiplexingBirefringent crystal
A transmitter subsystem generates an optical signal which contains multiple subbands of information. The subbands have different polarizations. For example, in one approach, two or more optical transmitters generate optical signals which have different polarizations. An optical combiner optically combines the optical signals into a composite optical signal for transmission across an optical fiber. In another approach, a single optical transmitter generates an optical signal with multiple subbands. The polarization of the subbands is varied, for example by using a birefringent crystal. In another aspect of the invention, each optical transmitter generates an optical signal containing both a lower optical sideband and an upper optical sideband (i.e., a double sideband optical signal). An optical filter selects the upper optical sideband of one optical signal and the lower optical sideband of another optical signal to produce a composite optical signal.
Owner:FORSTER ENERGY
Microlithography projection objective and projection exposure apparatus
The invention concerns a microlithography projection objective and a microlithographic projection exposure apparatus with a microlithography projection objective, having at least one lens of birefringent material. In accordance with an aspect of the invention, a microlithography projection objective has an optical axis and at least one lens of uniaxial birefringent crystal whose principal axis is oriented parallel to the optical axis, wherein all lenses of uniaxial birefringent crystal comprise the same crystal material, wherein light is tangentially polarised in the lens of uniaxial birefringent crystal and wherein the lens of uniaxial birefringent crystal has a diffractive power different from zero and has a plane exit face or a non-plane but refractive power-less exit face.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
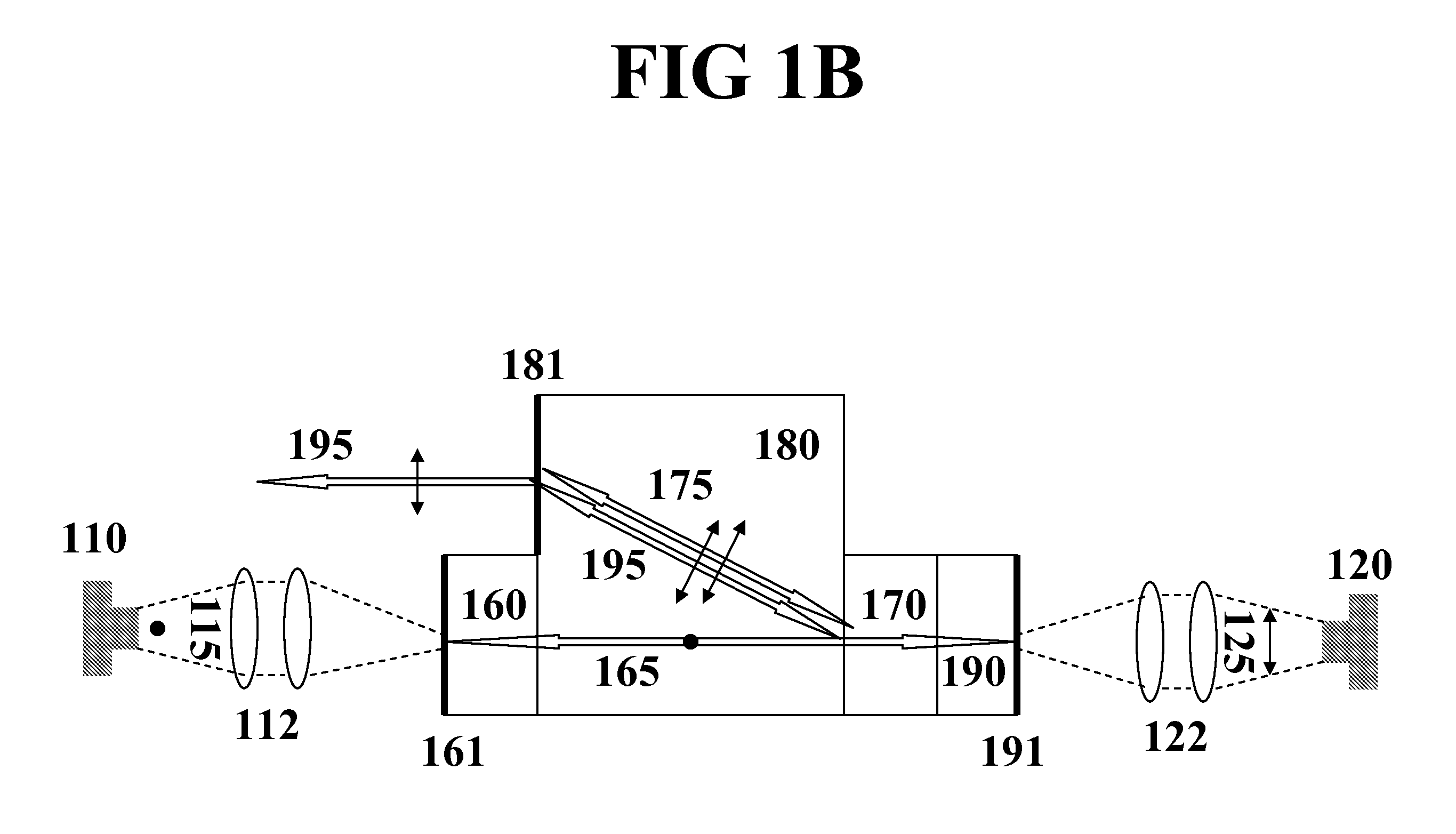
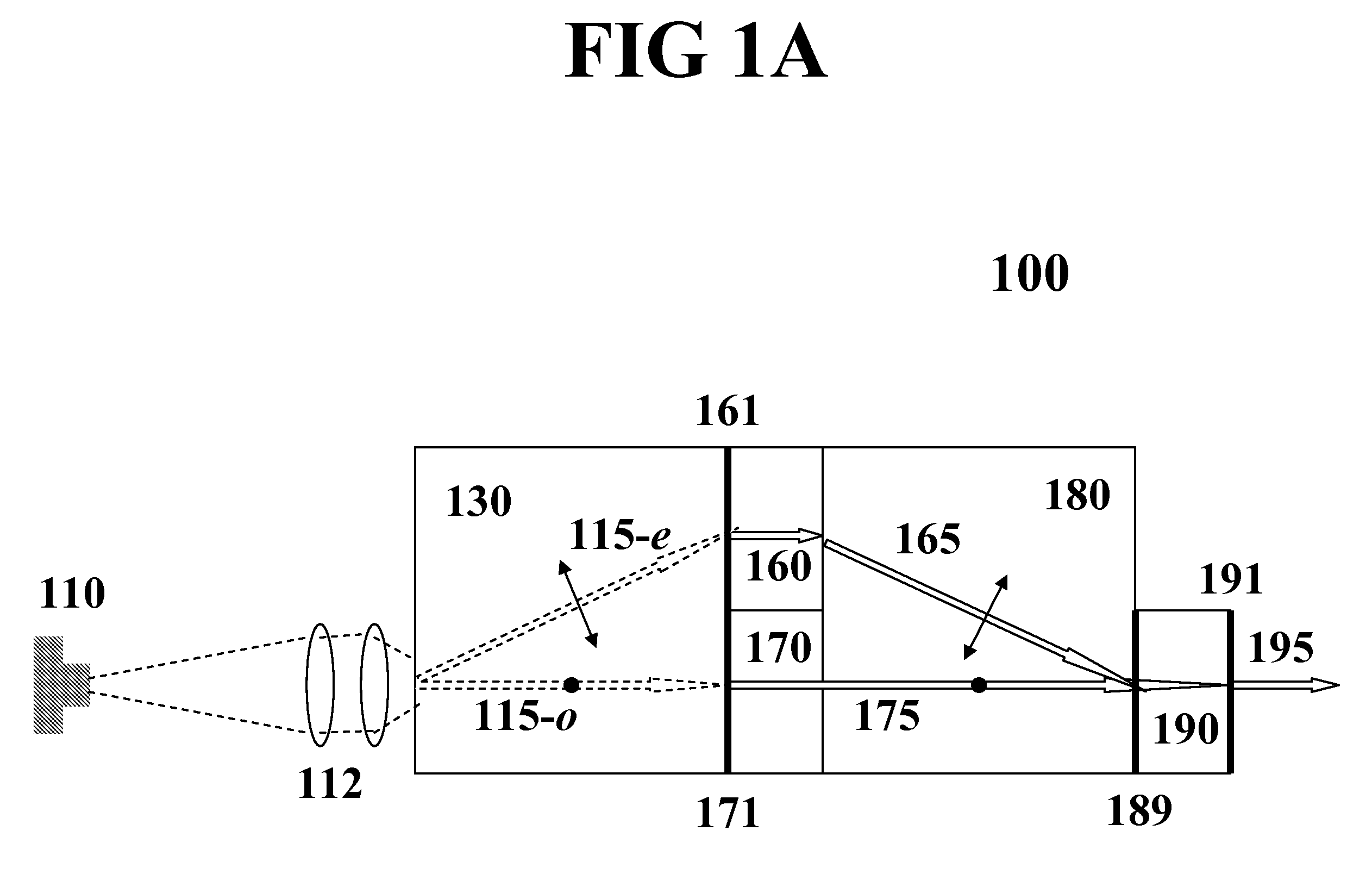
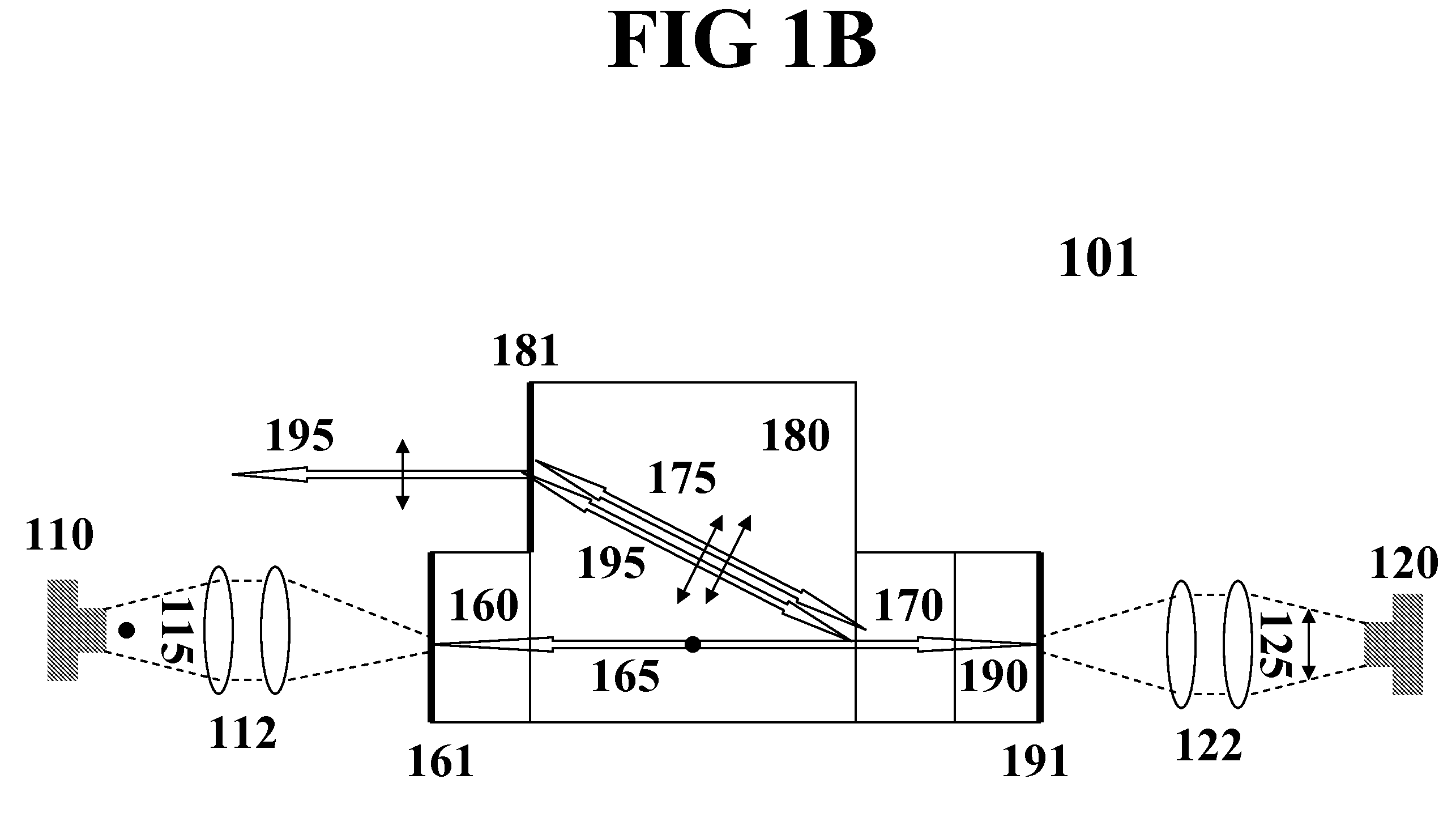
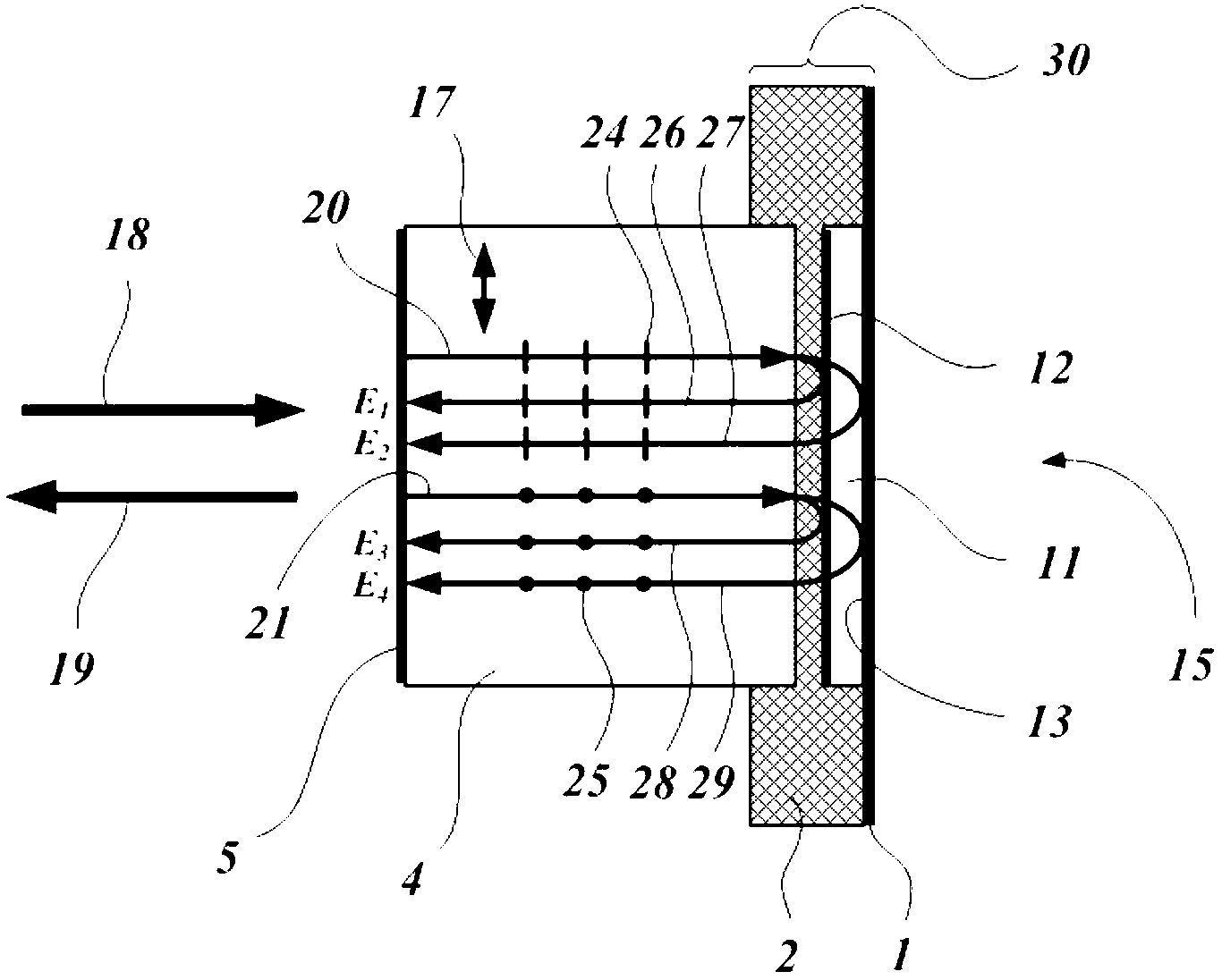
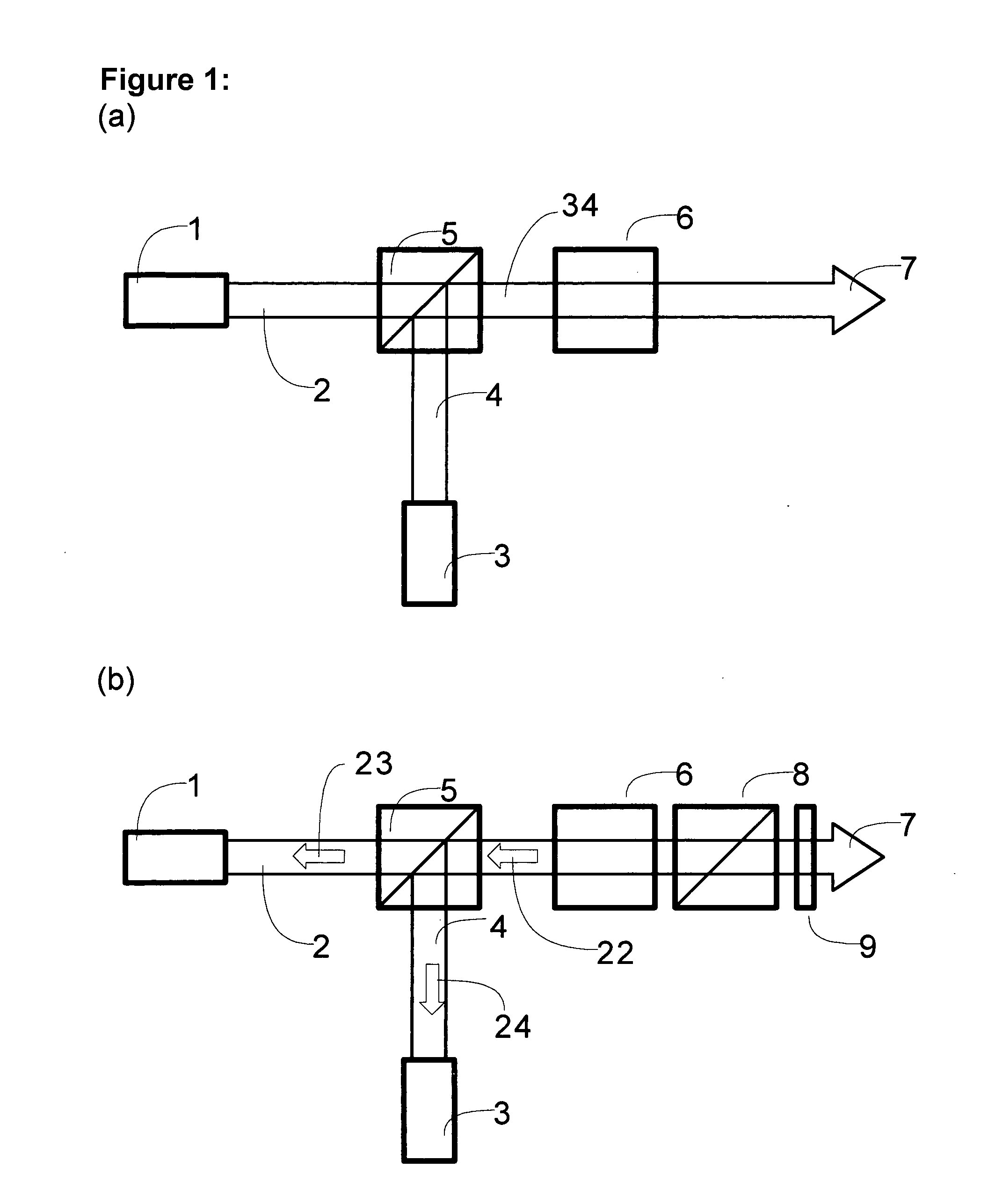
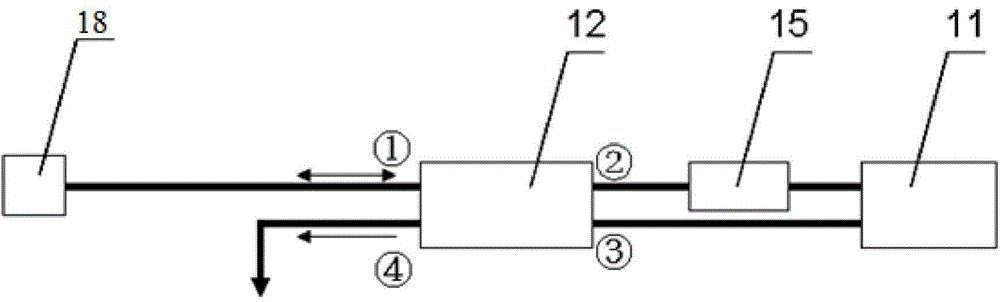
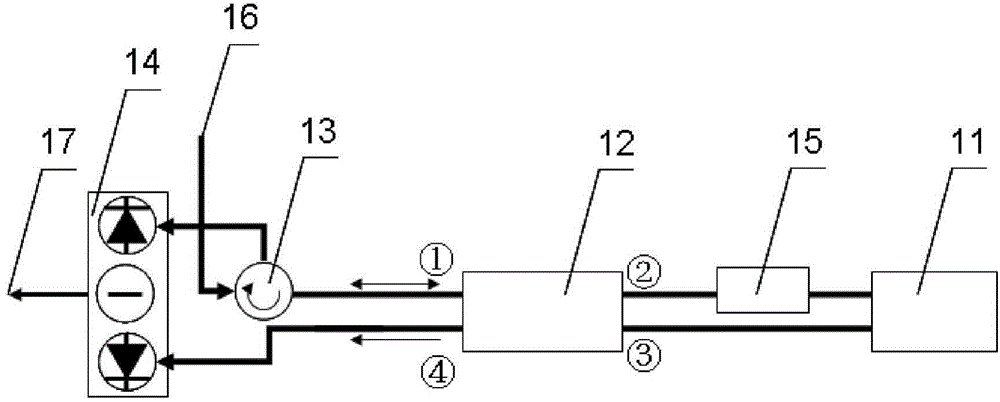
Monolithic microchip laser with intracavity beam combining and sum frequency or difference frequency mixing
ActiveUS20060209912A1Avoid polarizationLasing suppressionOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionLow noiseNonlinear optical crystal
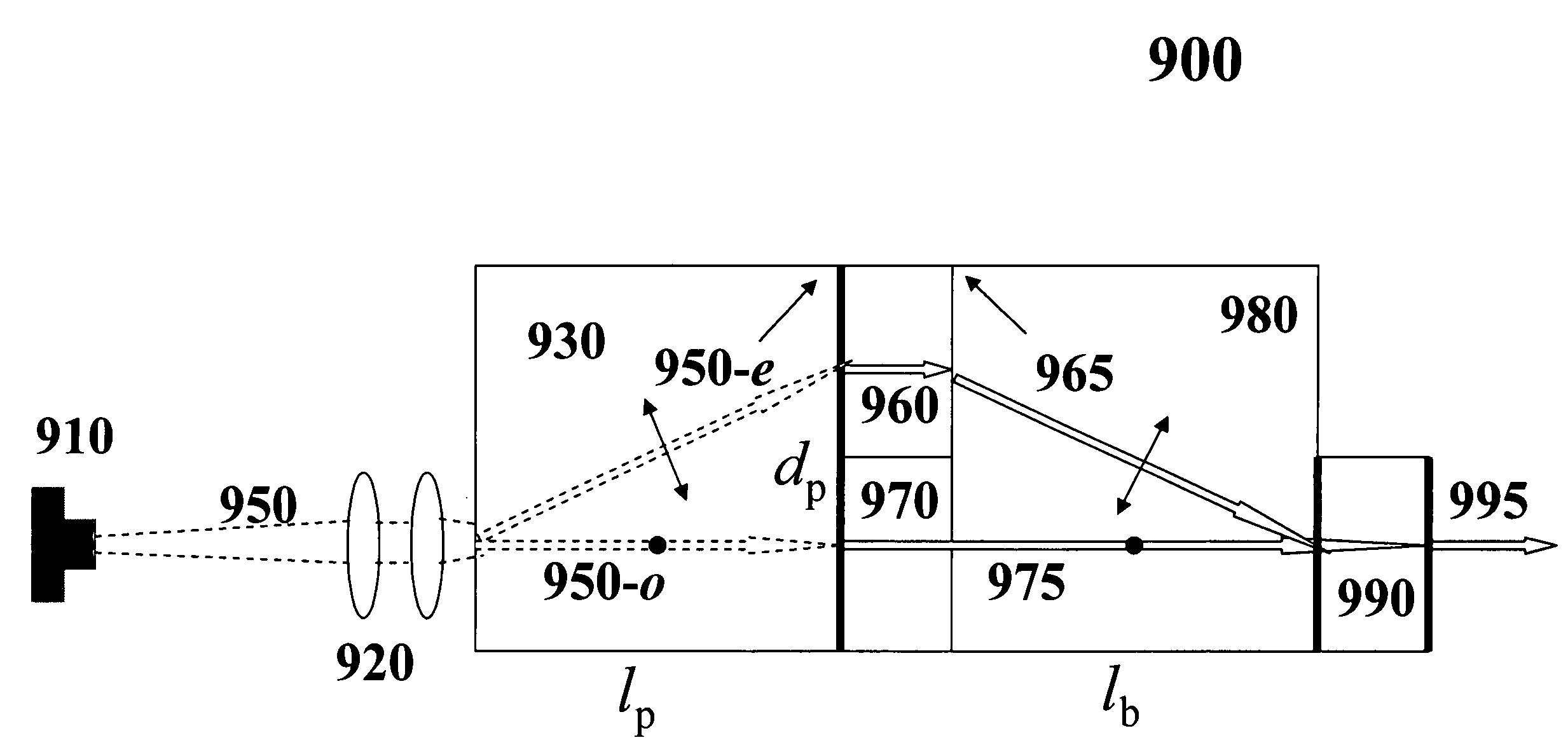
A method for producing low-noise laser output at various wavelengths and / or in various operation modes in a monolithic microchip laser comprises schemes of generating two fundamental beams in separate cavities, precise intracavity beam combination based on the walk-off effect in birefringent crystal, and wavelength conversion in nonlinear optical crystals. The fundamental beams are produced from light sources selected upon the desired wavelengths, polarizations, and other features related to the laser output. Low-noise laser devices operated in SLM or with spectra of flat-top or desired bandwidths are constructed according to the method. High-volume fabrication is feasible. Apparatus of compact size and efficient frequency conversion is demonstrated with various configurations including those for generating low-noise 491 nm laser, as a replacement of Argon ion laser.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Integrated optical isolator array
InactiveUS7263247B1High gainReduce noiseCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideFiberBirefringent crystal
An integrated isolator array is provided having a plurality of waveguides fabricated in a planar optical substrate, each waveguide having input and output sections. An isolator subassembly is received within a transverse trench formed in the substrate between the input and output sections such that it intersects the optical paths of the waveguides. The isolator subassembly, which may consist of layers of Faraday rotator material sandwiched between layers of birefringent crystal material, permits the forward passage of light from the input sections to the output sections of the waveguides while preventing the backward passage of light from the output to the input sections. Each waveguide input section is preferably adapted with a mode-expanding input taper to collimate light propagating through the waveguide. Similarly, each output section is preferably adapted with a mode-reducing output taper to reduce the mode size of forward-traveling light to match that of an output fiber, as well as to collimate light traveling backward within the output section.
Owner:BROADEX TECH UK LTD
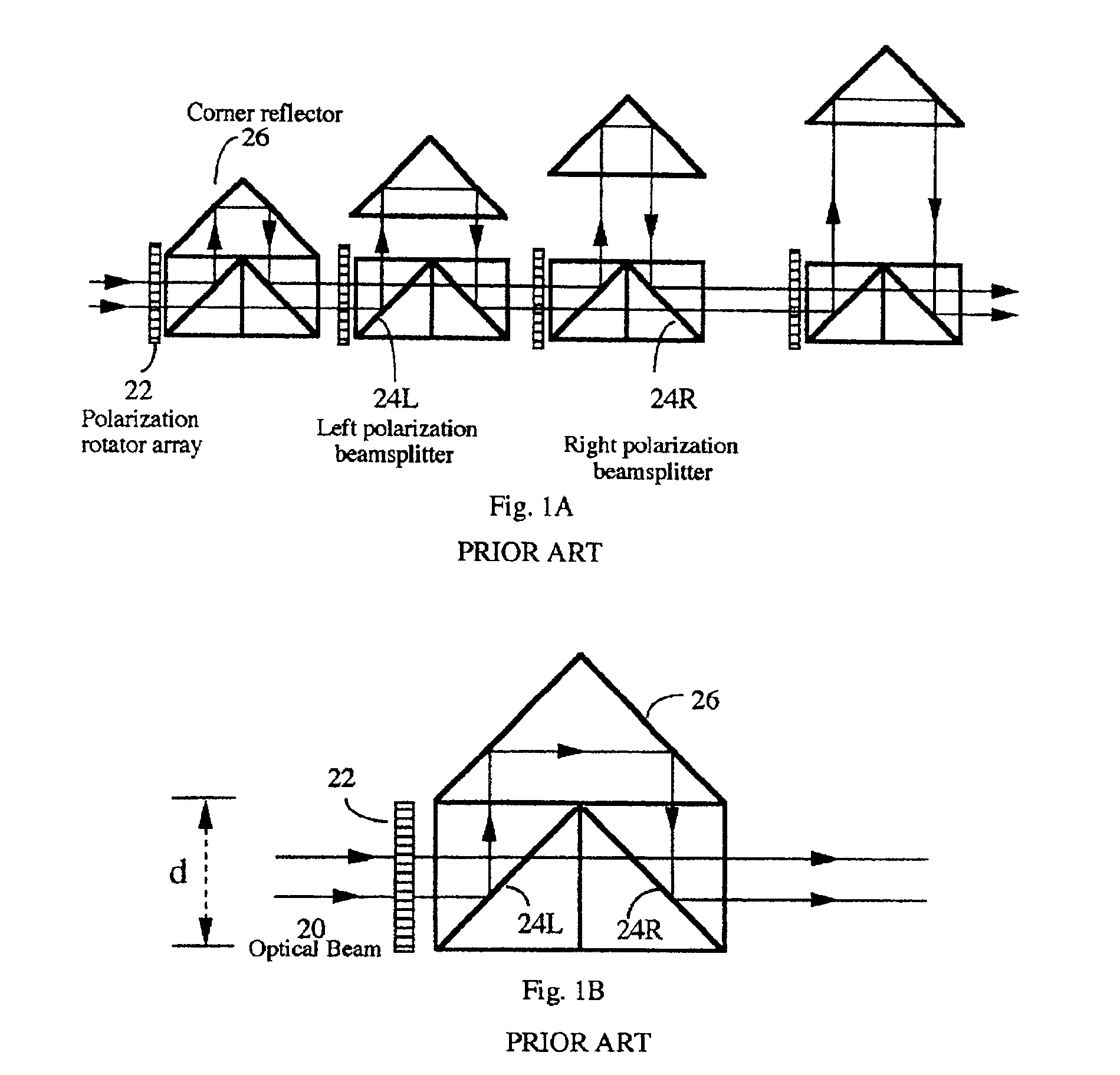
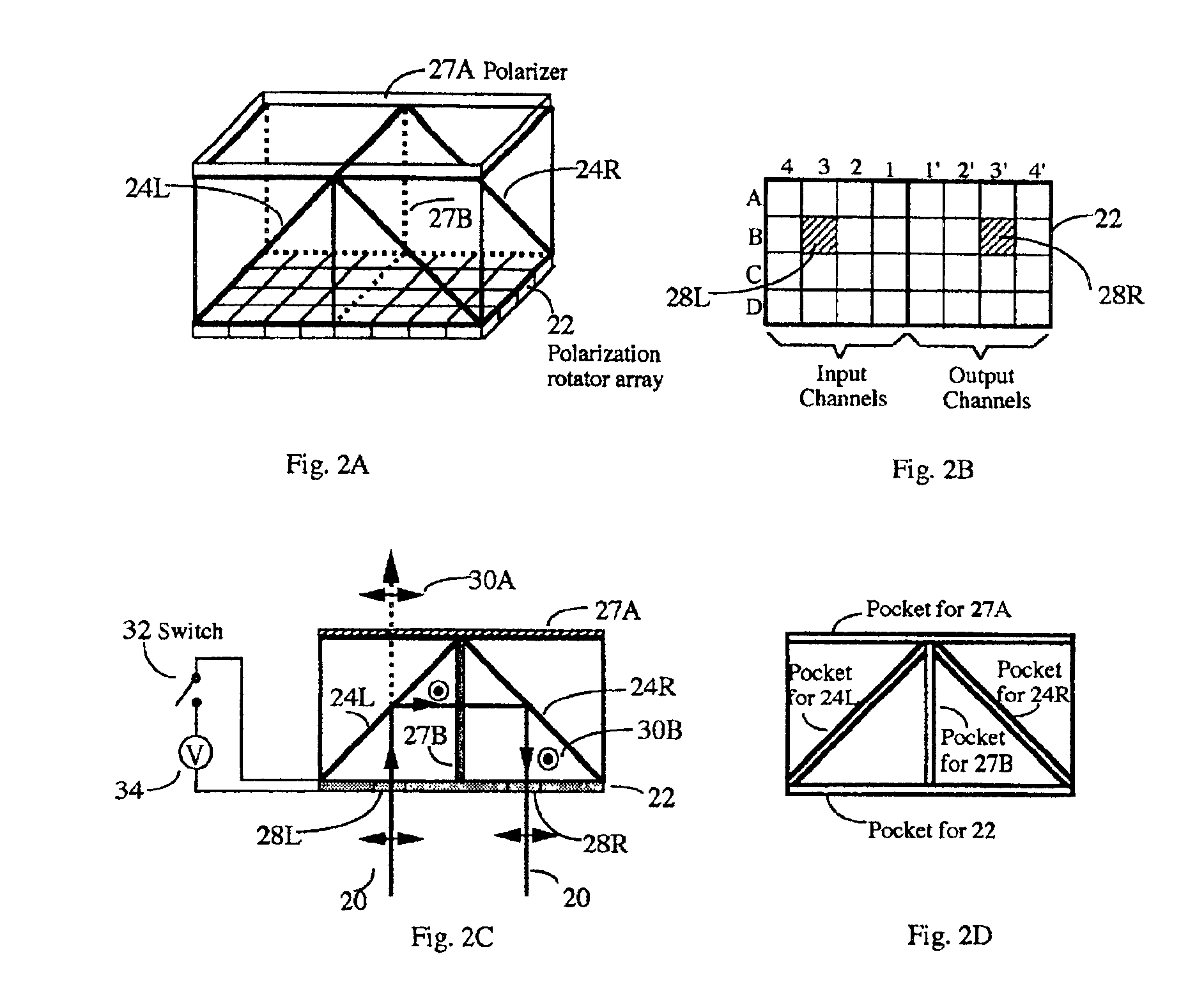
Photonic variable delay devices based on optical birefringence
Optical variable delay devices for providing variable true time delay to multiple optical beams simultaneously. A ladder-structured variable delay device comprises multiple basic building blocks stacked on top of each other resembling a ladder. Each basic building block has two polarization beamsplitters and a polarization rotator array arranged to form a trihedron; Controlling an array element of the polarization rotator array causes a beam passing through the array element either going up to a basic building block above it or reflect back towards a block below it. The beams going higher on the “ladder” experience longer optical path delay. An index-switched optical variable delay device comprises of many birefringent crystal segments connected with one another, with a polarization rotator array sandwiched between any two adjacent crystal segments. An array element in the polarization rotator array controls the polarization state of a beam passing through the element, causing the beam experience different refractive indices or path delays in the following crystal segment. By independently control each element in each polarization rotator array, variable optical path delays of each beam can be achieved. Finally, an index-switched variable delay device and a ladder-structured variable device are cascaded to form a new device which combines the advantages of the two individual devices. This programmable optic device has the properties of high packing density, low loss, easy fabrication, and virtually infinite bandwidth. The device is inherently two dimensional and has a packing density exceeding 25 lines / cm2. The delay resolution of the device is on the order of a femtosecond (one micron in space) and the total delay exceeds 10 nanosecond. In addition, the delay is reversible so that the same delay device can be used for both antenna transmitting and receiving.
Owner:GENERAL PHOTONICS CORP
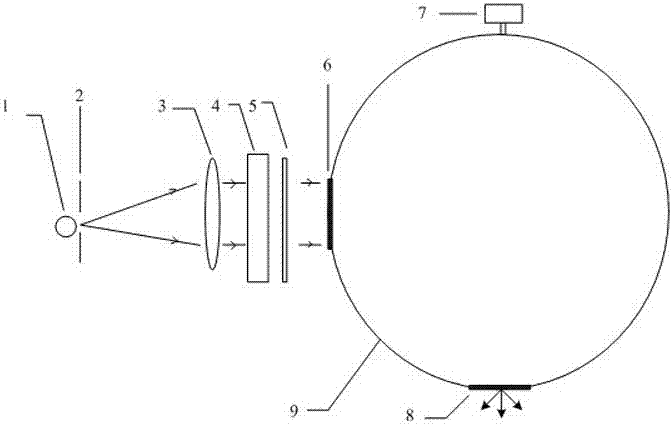
Spectrum scaling apparatus used for spectrum imager
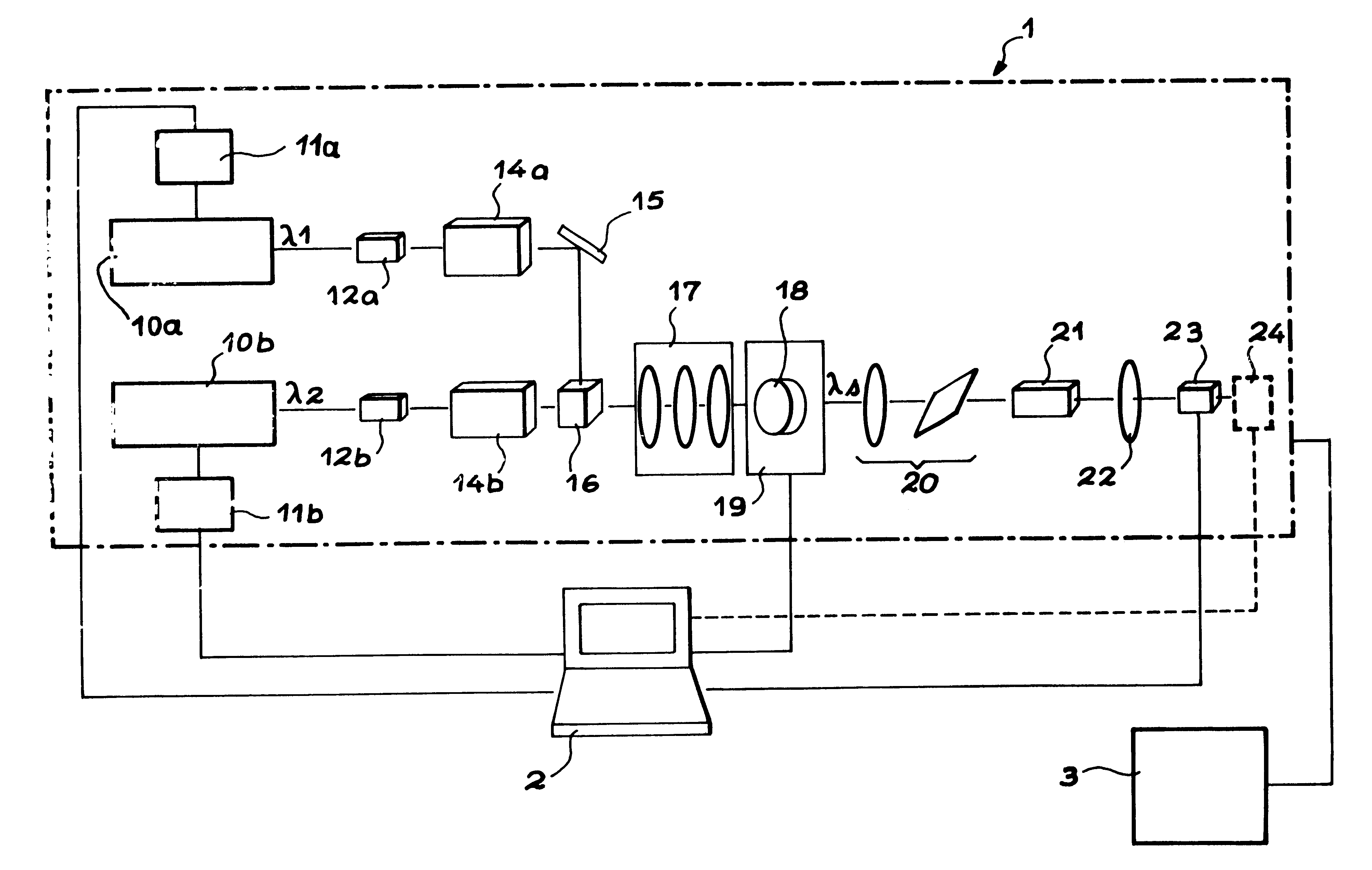
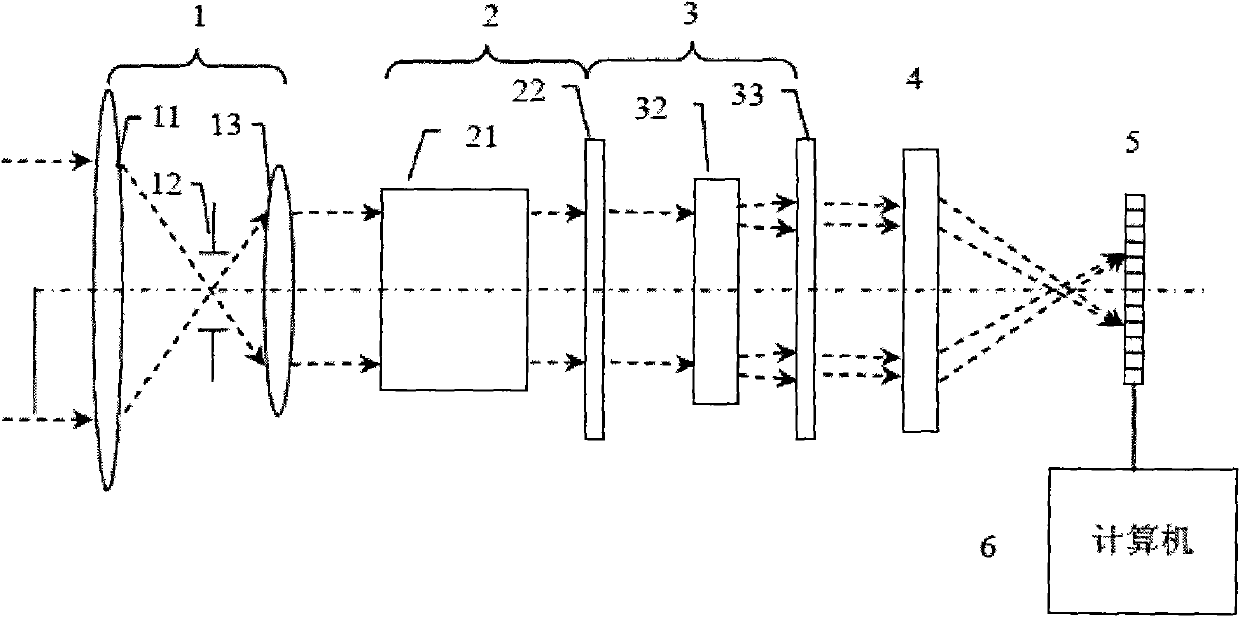
InactiveCN102353447ARadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using refracting elementsBirefringent crystalEngineering
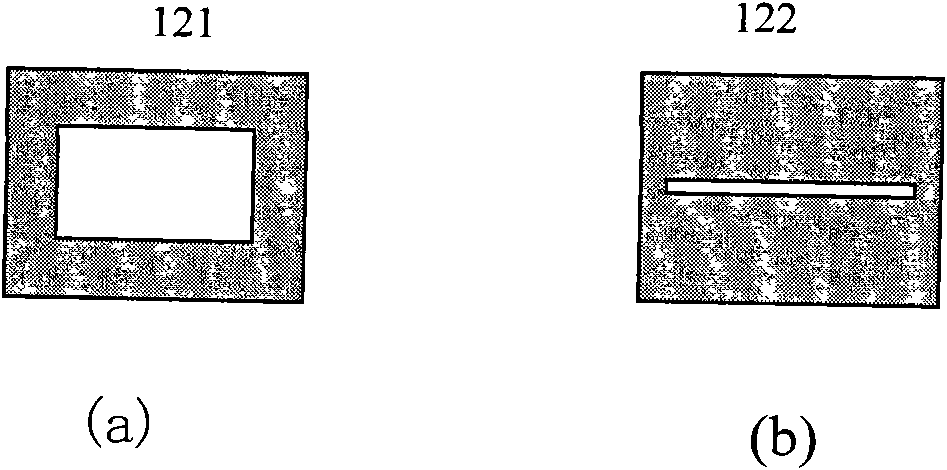
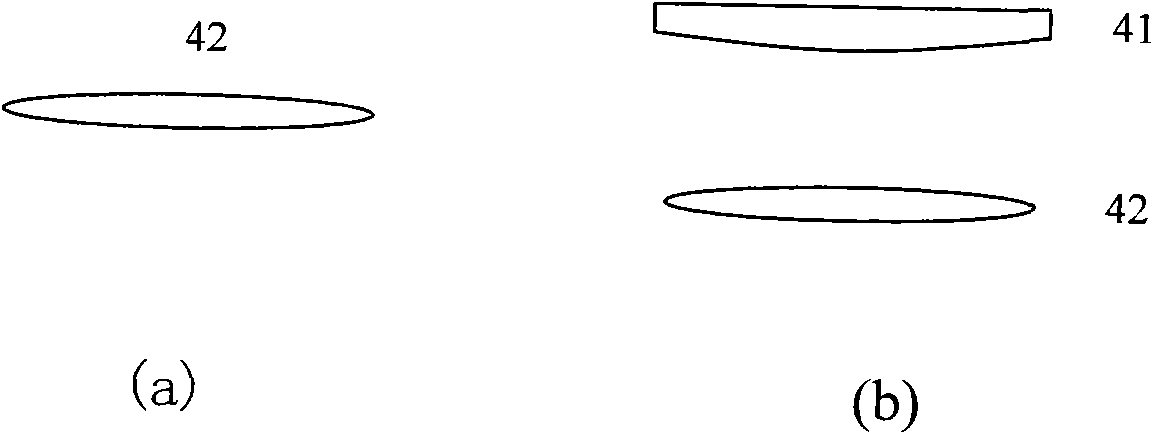
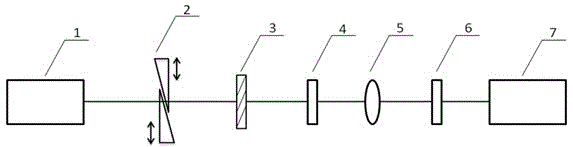
The invention discloses a spectrum scaling apparatus used for a spectrum imager. The apparatus is characterized in that: a light beam which is emitted by a broadband light source (1) goes through a diaphragm (2) and a collimating lens (3) and irradiates a wavelength tuning optical filter (4), a plurality of narrowband optical signals which are distributed in a comb-shaped mode and have different wavelengths are outputted, after light intensity adjusting by a broadband bandpass optical filter (5), the signals enter into an integrating sphere (9) from an integrating sphere incident light hole (6) for depolarization and space uniformity processing, and an integrating sphere light extraction hole (8) outputs a surface light source. A spectrum imager to be measured is placed on the light extraction hole (8) for spectrum scaling. According to the apparatus, a birefringence crystal is utilized to carry out light transmission rate modulation, a passband peak value position and a bandwidth size can be adjusted, a plurality of narrowband light intensity signals changing with a wavelength are provided in a broadband range, wavelength scanning is not needed when carrying out spectrum scaling on the spectrum imager, wavelength scaling with one-time imaging is realized, and the apparatus is suitable for scaling a large field of view and large caliber spectrum imager.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
Monolithic microchip laser with intracavity beam combining and sum frequency or difference frequency mixing
ActiveUS7535937B2Enhances efficiency and compactnessLow intracavity lossOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionNonlinear optical crystalLow noise
A method for producing low-noise laser output at various wavelengths and / or in various operation modes in a monolithic microchip laser comprises schemes of generating two fundamental beams in separate cavities, precise intracavity beam combination based on the walk-off effect in birefringent crystal, and wavelength conversion in nonlinear optical crystals. The fundamental beams are produced from light sources selected upon the desired wavelengths, polarizations, and other features related to the laser output. Low-noise laser devices operated in SLM or with spectra of flat-top or desired bandwidths are constructed according to the method. High-volume fabrication is feasible. Apparatus of compact size and efficient frequency conversion is demonstrated with various configurations including those for generating low-noise 491 nm laser, as a replacement of Argon ion laser.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Low-noise monolithic microchip lasers capable of producing wavelengths ranging from IR to UV based on efficient and cost-effective frequency conversion
ActiveUS7535938B2Low-noise laser outputEfficient and cost-effective frequency conversionActive medium shape and constructionNonlinear optical crystalLow noise
A method for producing low-noise laser output at wavelengths ranging from IR through visible to UV in various operation modes from a monolithic microchip laser comprises schemes of (1) generating one or two fundamental beam(s) from light source(s) selected upon the desired wavelength(s), polarization(s), and other features related to the desired laser output; (2) intracavity beam combination / separation due to the walk-off effect in one or more birefringent crystal(s) transparent to the propagating lights and highly anisotropic; (3) wavelength conversion in one or more nonlinear optical crystal(s); (4) compact and efficient pump source(s); and (5) minimization of intracavity loss / noise. One resonator cavity supports only one fundamental beam, which eliminates the green problem. The gain media can be selected from an extensive group of materials including isotropic and naturally birefringent crystals, with polarization dependent or independent laser emissions. Laser devices constructed in accordance with the inventive method are demonstrated with various configurations.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Birefringent crystal temperature compensation based optic fiber pressure sensor and production method thereof
ActiveCN103234672ARealize two-parameter measurementRealize high-precision measurementForce measurement by measuring optical property variationFluid pressure measurement by optical meansFiberBirefringent crystal
The invention discloses a birefringent crystal temperature compensation based optic fiber pressure sensor and a production method thereof. The sensor comprises a Fabry-Perot pressure sensing head chip, a birefringent crystal, a grin lens, a glass capillary, a quartz glass tube and a multimode optical fiber. Optical signals sequentially pass the birefringent crystal and an optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensing head, then optical path difference is modulated, and double-parameter measurement of pressure and temperature is achieved by detecting variation of the optical path difference of the birefringent crystal and the optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensing head. Comparing with the prior art, the optic fiber pressure sensor has the advantages that high-precision pressure measurement sensing are achieved by introducing temperature measuring result as reference quantity and correcting pressure measurement result, besides, a demodulation instrument achieves synchronous demodulation of temperature and pressure, a demodulation system is simple, data processing is accurate, system cost is low, and practical operation is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
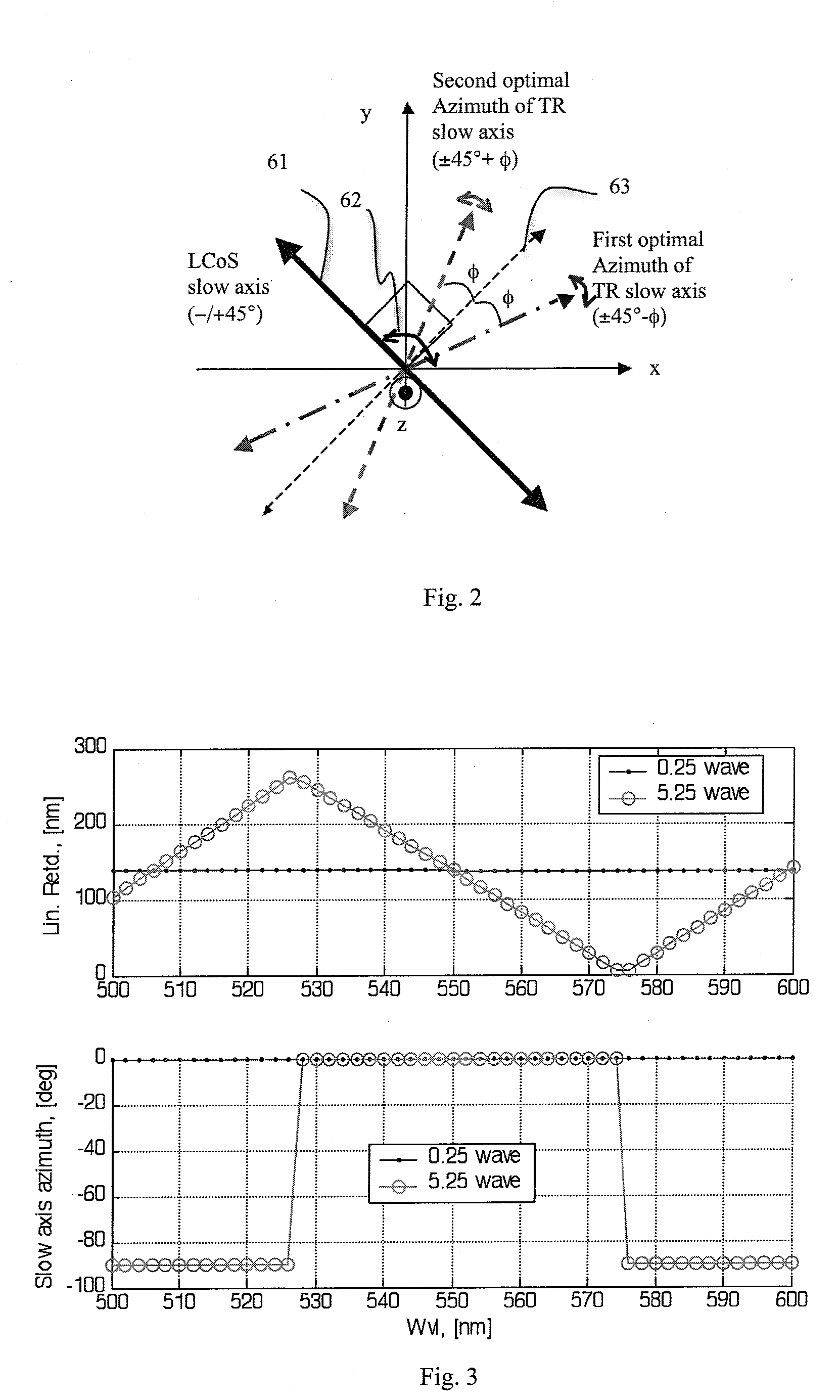
Near Halfwave Retarder For Contrast Compensation
InactiveUS20090002579A1Increase contrastOptimal polarization outputTelevision system detailsNon-linear opticsIn planeLiquid-crystal display
Contrast compensation for a liquid crystal display projection system is provided with a trim retarder that includes a single-layer retarder element that has an in-plane retardance that is shifted from a zero-order half-wave at a predetermined wavelength by a predetermined amount. This near half-wave plate provides similar contrast compensation and azimuthal angle sensitivity to conventional relatively low-magnitude trim retarders, yet is readily fabricated with inorganic birefringent crystals with a manageable thickness tolerance.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
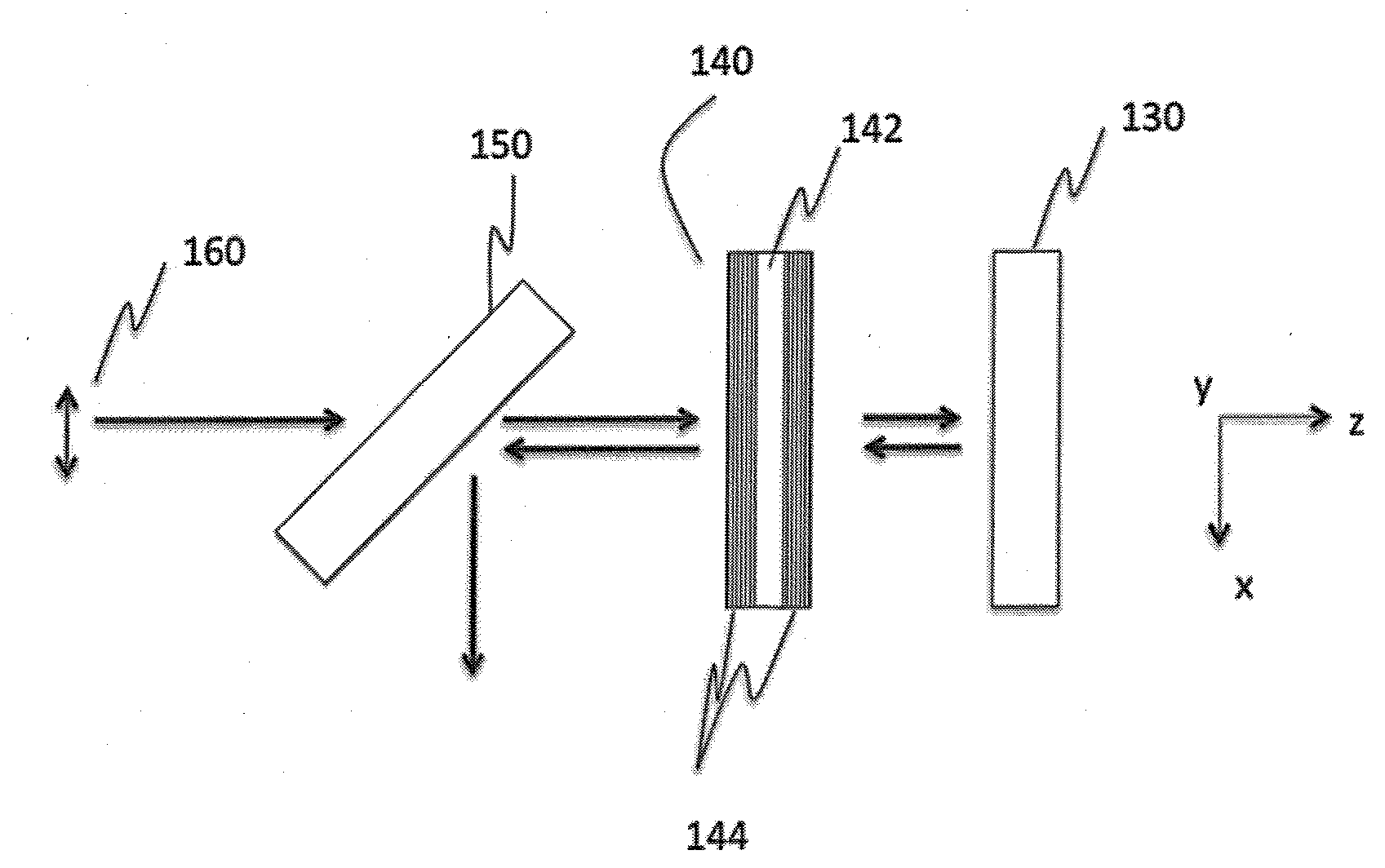
Polarization coupler
InactiveUS20110261456A1Increase output powerMore couplingLaser optical resonator constructionPolarising elementsBeam splitterBirefringent crystal
The invention comprises an assembly (a) by which two polarized beam sources (1) and (2) of different wavelength by means of polarizing beam splitters (5) can be superimposed. By means of a dispersively birefringent crystal (6) both beams are rectified to reconstitute the linear polarization.If, as assumed in (b), the beam sources can react spectrally to feedback, an additional polarization filter (8) and a partially reflecting coating (9) can ensure that suitable wavelengths are established automatically.This assembly can be scaled as depicted in (b). By help of further dispersively birefringent crystals (6) and birefringent displacers more beams can be combined into a single beam, eight sources in the given setup.
Owner:RAAB VOLKER
Optical communications using multiplexed single sideband transmission and heterodyne detection
InactiveUS20020097469A1Less interactionImprove bandwidth utilizationWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationMultiplexingBirefringent crystal
A transmitter subsystem generates an optical signal which contains multiple subbands of information. The subbands have different polarizations. For example, in one approach, two or more optical transmitters generate optical signals which have different polarizations. An optical combiner optically combines the optical signals into a composite optical signal for transmission across an optical fiber. In another approach, a single optical transmitter generates an optical signal with multiple subbands. The polarization of the subbands is varied, for example by using a birefringent crystal. In another aspect of the invention, each optical transmitter generates an optical signal containing both a lower optical sideband and an upper optical sideband (i.e., a double sideband optical signal). An optical filter selects the upper optical sideband of one optical signal and the lower optical sideband of another optical signal to produce a composite optical signal.
Owner:XYLON LLC
System for detection and measurement of one or several gases in a gas mix
InactiveUS6344648B1Easy to moveHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsBirefringent crystalFluorescence
A portable system for the real time detection and measurement of one or several gases is a gaseous mixture is disclosed. Such systems can be applied to industrial domains in which gases are to be measured and particularly toxic, dangerous, or polluting gases are generated. The system uses absorption spectrometry of a gas from a gaseous medium of interest. The optical means is at least two laser diodes with matchable cavities to generate a first and second wavelength, a light beam mixer prism, a double refraction crystal rotating on a controlled table. The tuned beam causes the gas to be measured to fluoresce and emit a signal to an infrared radiation detector which can indicate the identity and magnitude of the gas being measured.
Owner:AEROSPATIALE MATRA
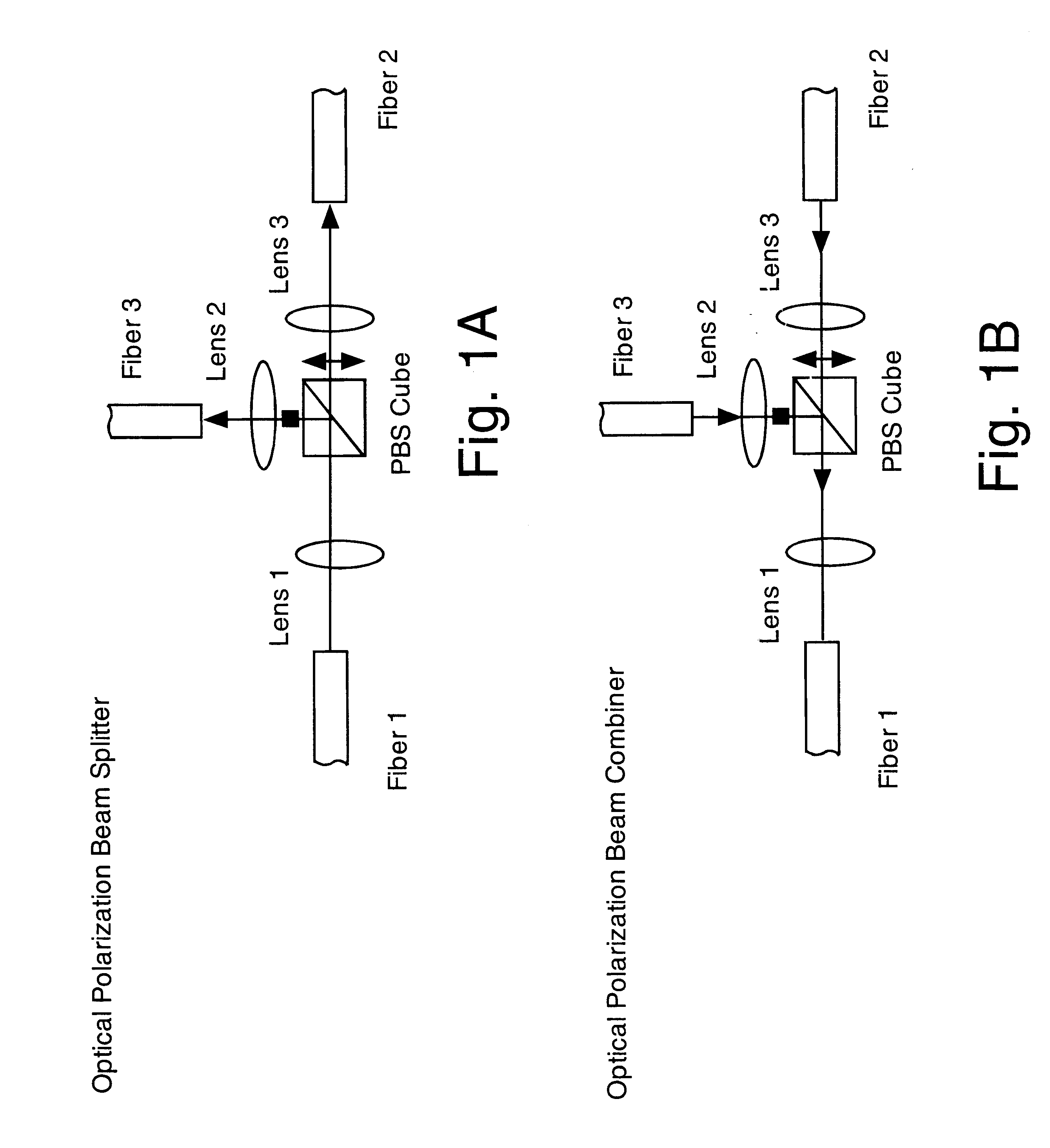
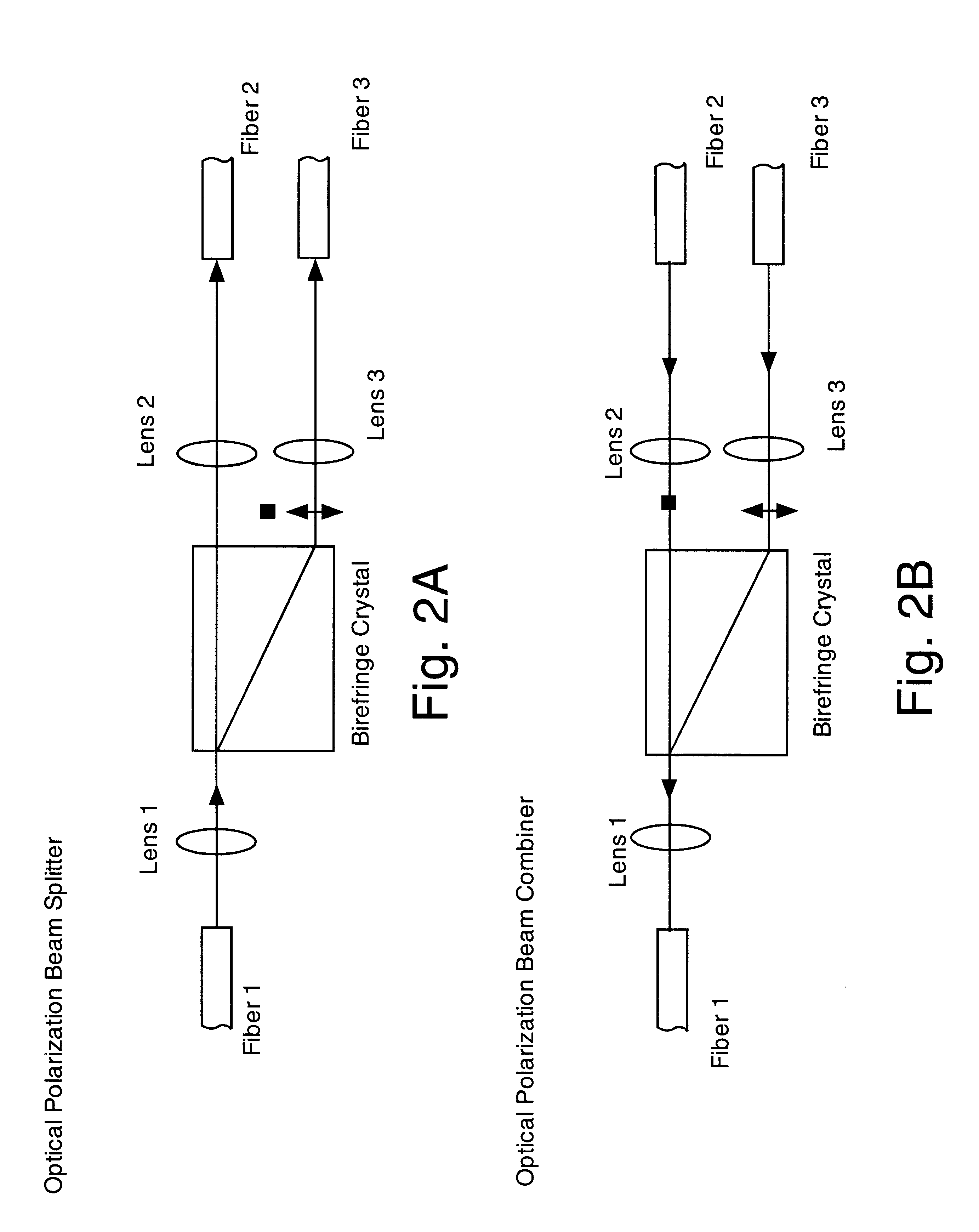
Optical polarization beam combiner/splitter
An optical polarization beam splitter comprises a first optical fiber having an end defining a first optical axis, a second optical fiber having an end defining a second optical axis, and a third optical fiber having an end defining a third optical axis parallel to and spaced apart from the second optical axis. A collimating lens is disposed along the first optical axis positioned to form a collimated optical beam from the first optical fiber. A focussing lens is disposed along a path of the collimated optical beam. A birefringent walk-off crystal has a first face adjacent to the focussing lens and a second face located at a focal plane of the focussing lens and in contact with the ends of the second and third optical fibers. The birefringent crystal is oriented such that and has a thickness between its first and second faces selected such that a first component of the optical beam having a first polarization exits the crystal at its second face and enters the end of the second optical fiber along the second optical axis and a second component of the optical beam having a second polarization orthogonal to the polarization of the first polarization exits the crystal at its second face and enters the end of the third optical fiber along the third optical axis.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
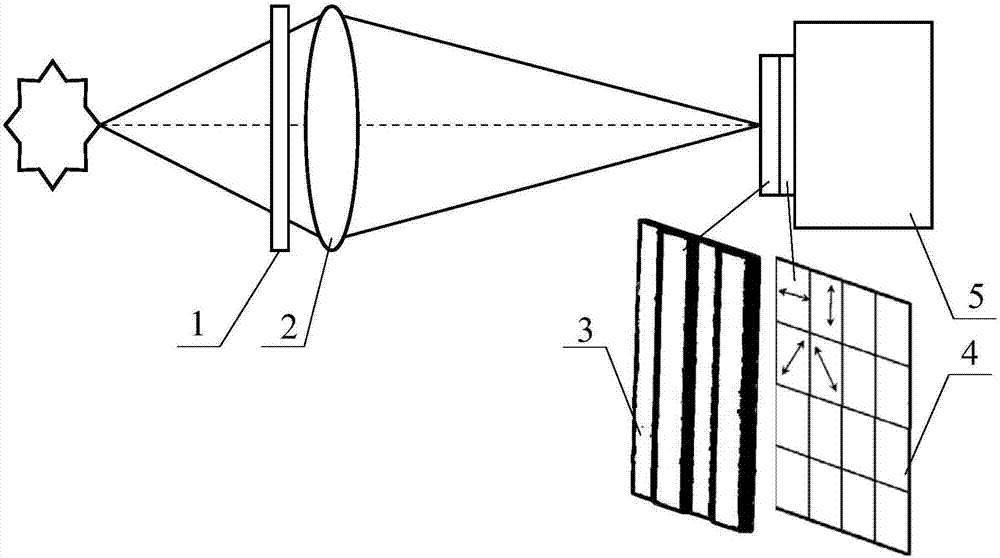
Light and small interference imaging spectrum full-polarized detection device
ActiveCN101793559AHigh resolution imagingStrong vibration resistanceInterferometric spectrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesBirefringent crystalLuminous flux
The invention discloses a light and small interference imaging spectrum full-polarized detection device comprising a preposed optics looking-out system, a static full-light modulation module, an angle shearing static interference imaging spectrometer, an imaging mirror set and a detector which are coaxially and successively arranged in sequence, wherein the detector is connected with a signal obtaining and processing system; after being collected, collimated and performed with stray light elimination by the preposed optics looking-out system, irradiation light emitted by a target source enters the static full-light modulation module; after passing through an angle shearing birefringent crystal set, one beam of modulation line polarized light is sheared into polarization light at an angle; after passing through an analyzer, the polarization light is divided into two beams of line polarized lights; the two beams of the line polarized lights are gathered in the detector after passing through the imaging mirror set; and the received signal is processed by the signal obtaining and processing system to obtain a target image, hyperspectral information and full-polarized information. The invention has the characteristics of compact and simple structure, no moving components and large luminous flux, can obtain a target two-dimensional space image, one-dimensional hyperspectral information and integral polarization information in one time.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method capable of adjusting polarization and intensity of terahertz wave rapidly and continuously
ActiveCN102882107AEasy to adjustContinuous regulationSolid masersNon-linear opticsHigh resistanceBirefringent crystal
The invention relates to a method capable of adjusting the polarization and the intensity of a terahertz wave rapidly and continuously. According to the method, a focusing lens is arranged at the outlet of a femto-second laser; incident laser passes through the focusing lens and a doubling frequency crystal in sequence to generate frequency doubled light; the frequency doubled light and remaining fundamental frequency laser pass through a uniaxial birefringent crystal wafer together; according to the principle that the refractive indexes of the fundamental frequency laser and the frequency doubled light in a uniaxial birefringent crystal are different, the optical path difference, namely the time delay, between the fundamental frequency laser and the frequency doubled light can be changed by adjusting the thickness of the uniaxial birefringent crystal wafer and the spatial included angle between a glass piece and an incident light beam, so that the relative phase between the fundamental frequency laser and the frequency doubled light is changed; and therefore, the polarization and the intensity of the finally generated terahertz wave are adjusted. Finally, the generated terahertz wave enters a terahertz wave detection system after being filtered by a high-resistance silicon wafer. By the method, the polarization and the intensity of the terahertz wave can be adjusted rapidly and continuously; and the operation is simple, rapid and effective.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Optical communications using multiplexed single sideband transmission and heterodyne detection
InactiveUS20070133993A1Less interactionImprove bandwidth utilizationWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersMultiplexingBirefringent crystal
A transmitter subsystem generates an optical signal which contains multiple subbands of information. The subbands have different polarizations. For example, in one approach, two or more optical transmitters generate optical signals which have different polarizations. An optical combiner optically combines the optical signals into a composite optical signal for transmission across an optical fiber. In another approach, a single optical transmitter generates an optical signal with multiple subbands. The polarization of the subbands is varied, for example by using a birefringent crystal. In another aspect of the invention, each optical transmitter generates an optical signal containing both a lower optical sideband and an upper optical sideband (i.e., a double sideband optical signal). An optical filter selects the upper optical sideband of one optical signal and the lower optical sideband of another optical signal to produce a composite optical signal.
Owner:XYLON LLC
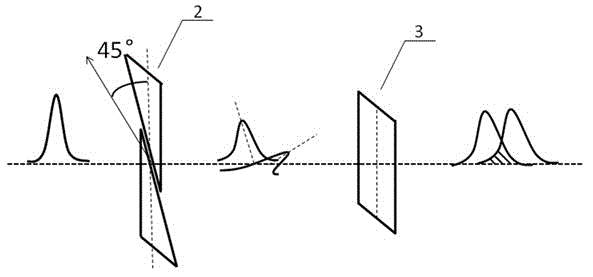
Method utilizing polarization-controllable T-Hz wave to measure optical axis direction of birefringent crystal
InactiveCN101813619AEasy and accurate measurementPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhase retardationBirefringent crystal
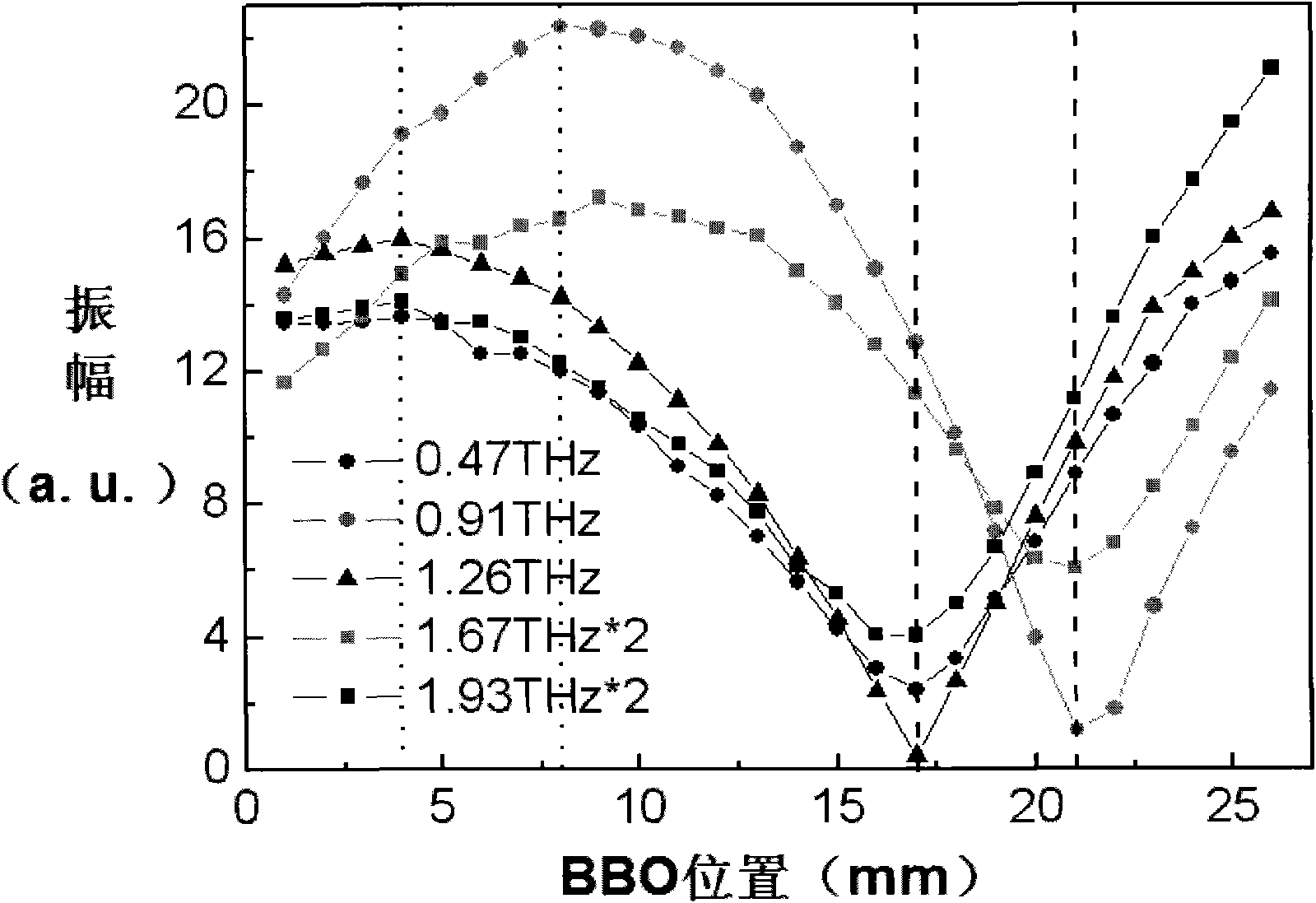
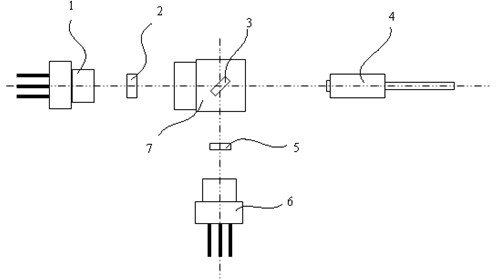
The method of the invention comprises the following steps: (1) moving a BBO crystal to change the distance from the BBO crystal to a plasma to obtain the relationship between the angle theta of the polarization direction of T-Hz wave relative to horizontal direction and the distance d from the BBO crystal to the plasma; (2) substituting the refractive indexes of T-Hz wave under different frequencies to a formula for calculating phase delay, thus obtaining the relationship of phase delay between the two axes of the birefringent crystal along with frequency change; (3) respectively selecting a corresponding T-Hz wave frequency f1 when the phase delay is odd times of pi and a corresponding T-Hz wave frequency f2 when the phase delay is even times of pi, moving the BBO crystal, and measuring the motion distance delta d of the BBO crystal corresponding to the T-Hz waves of frequency f1 and f2 at the nearest neighbor part with the minimum amplitude; and (4) calculating the included angle alpha between the birefringent crystal optical axis and the horizontal direction. Therefore, the invention can measure the optical axis direction of the birefringent crystal without rotating the birefringent crystal, thereby ensuring the measurement along the optical axis direction of the birefringent crystal to be more convenient and accurate.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A single fibre bi-directional assembly
InactiveCN102183828AReasonable structureReduce manufacturing costCoupling light guidesBirefringent crystalSingle fibre
The invention relates to a single fibre bi-directional assembly comprising a TO tube seat, a laser, an isolating part, a 45-degree optical filter, a 0-degree optical filter, a fiber connector and a probe, wherein the laser is encapsulated in the TO tube seat. An isolator system and a wavelength division multiplexing system in the single fibre bi-directional component share one 45-degree multifunctional optical filter, which saves a popolaroid or a birefringent crystal in the isolator so that the assembly is more reasonable in structure, besides, the cost for producing the BOSA is reduced either.
Owner:PINGHU ZHONGTIAN HEBO COMM TECH
Method for preparing two-dimensional metallic photonic crystal structure in large area through femtosecond laser direct writing
InactiveCN105108342AAvoid complicated proceduresThe technical method is simpleLaser beam welding apparatusBirefringent crystalTime delays
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Device and method for converting an optical frequency
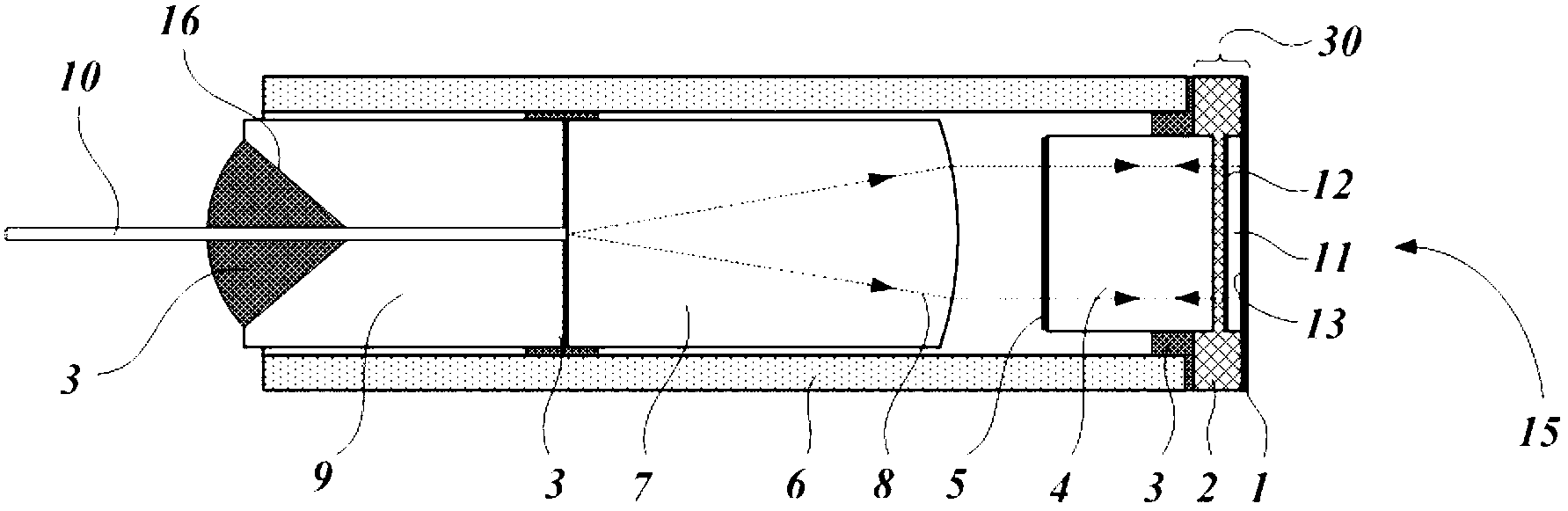
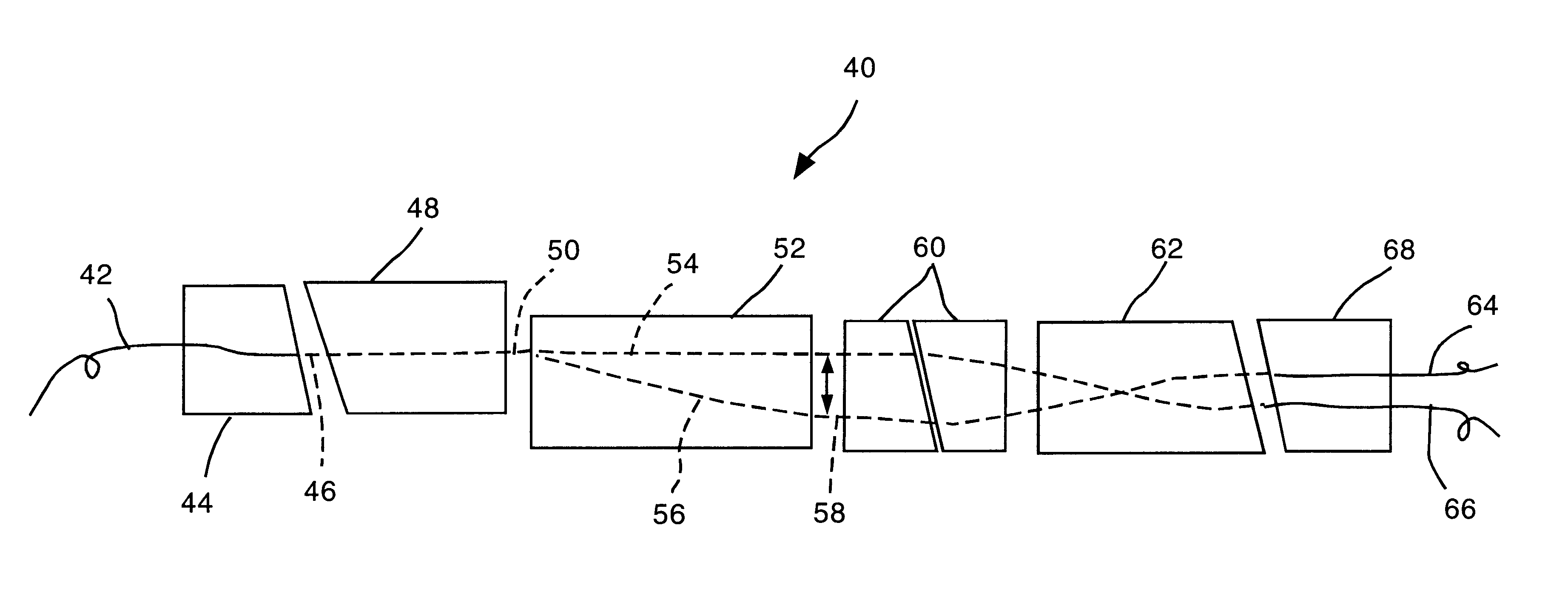
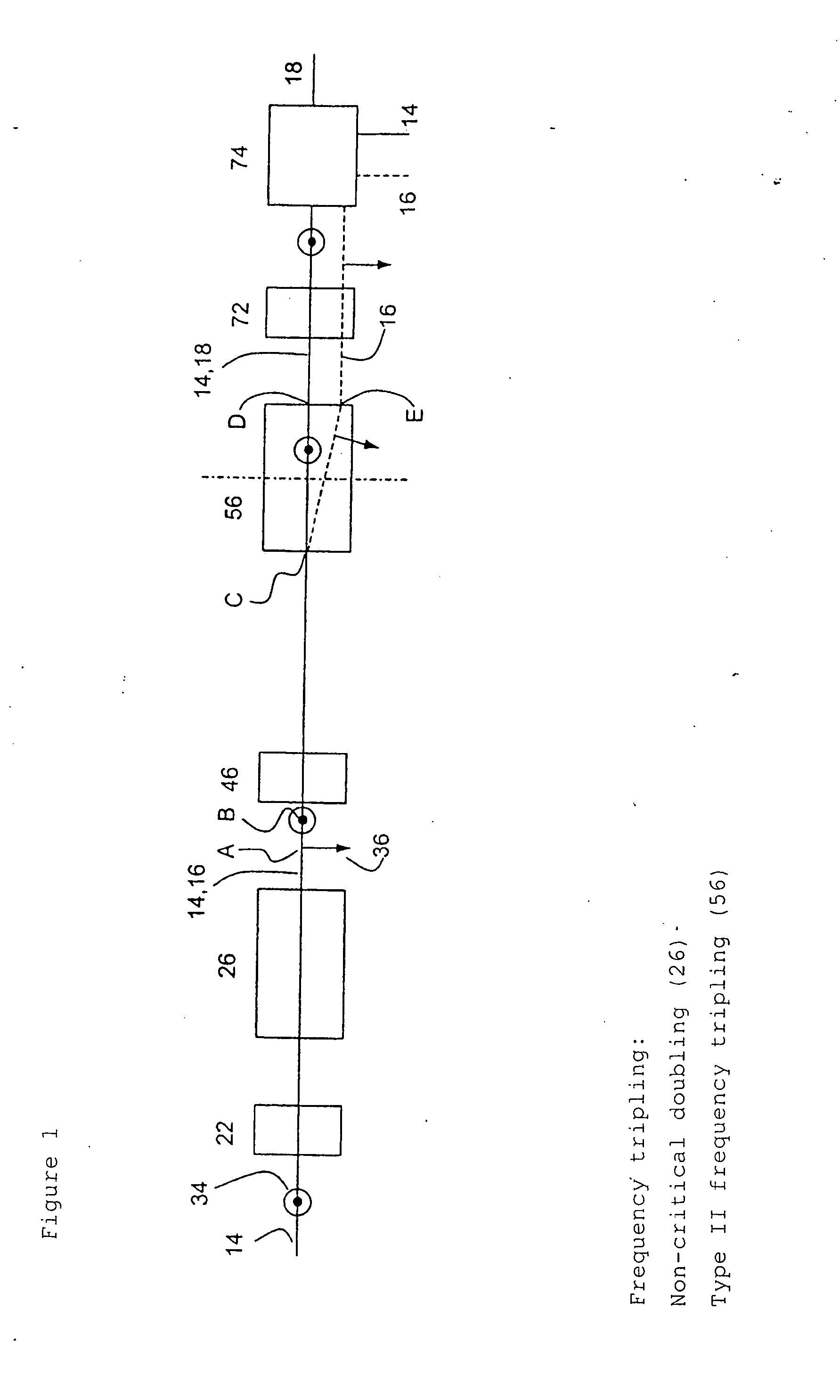
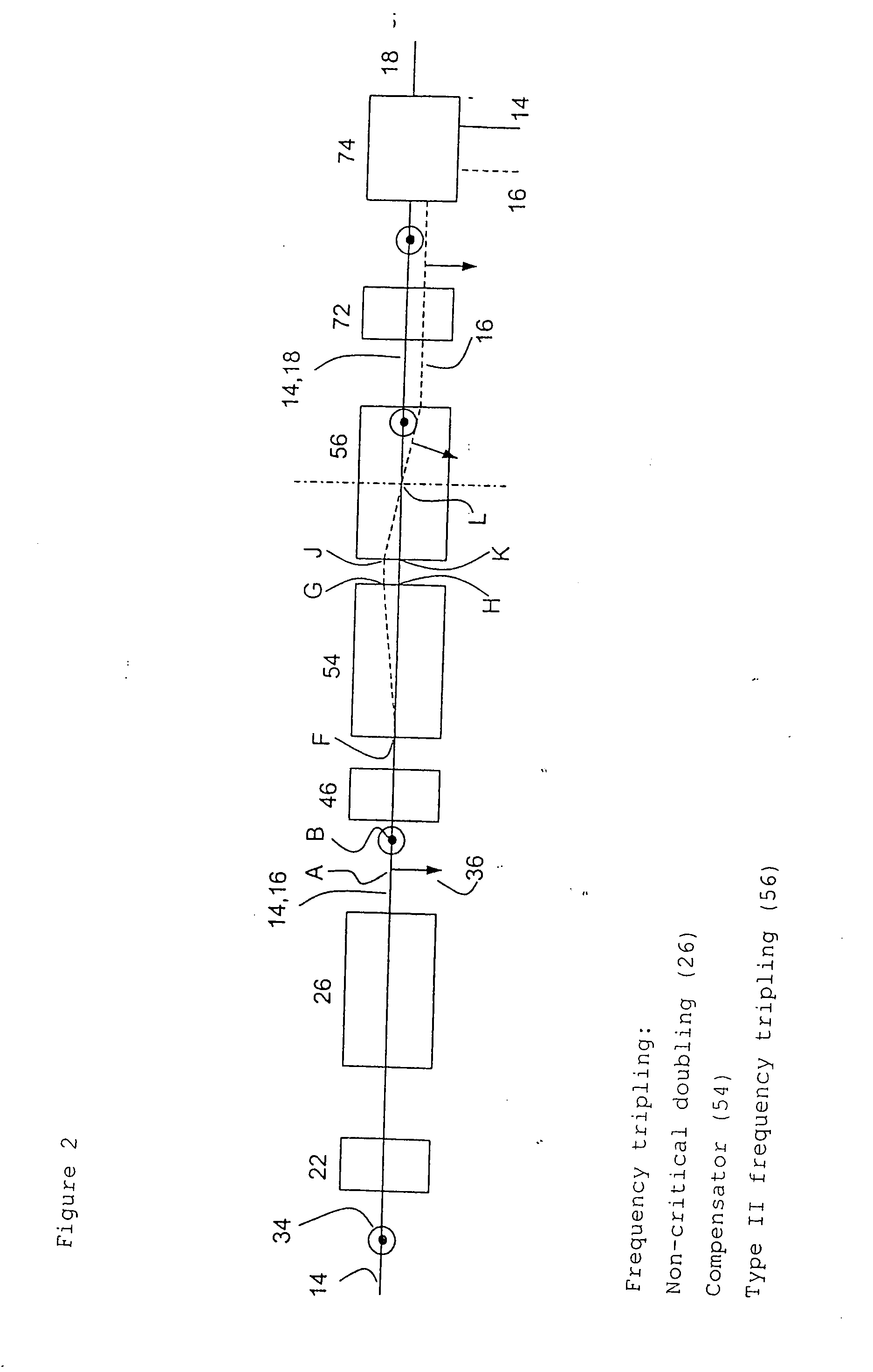
InactiveUS20040240491A1Improve conversion efficiencyIncrease spacingOptical resonator shape and constructionLight demodulationBirefringent crystalOptical frequencies
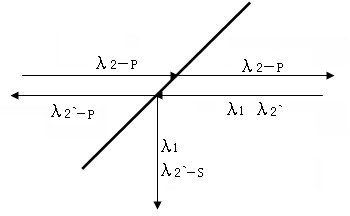
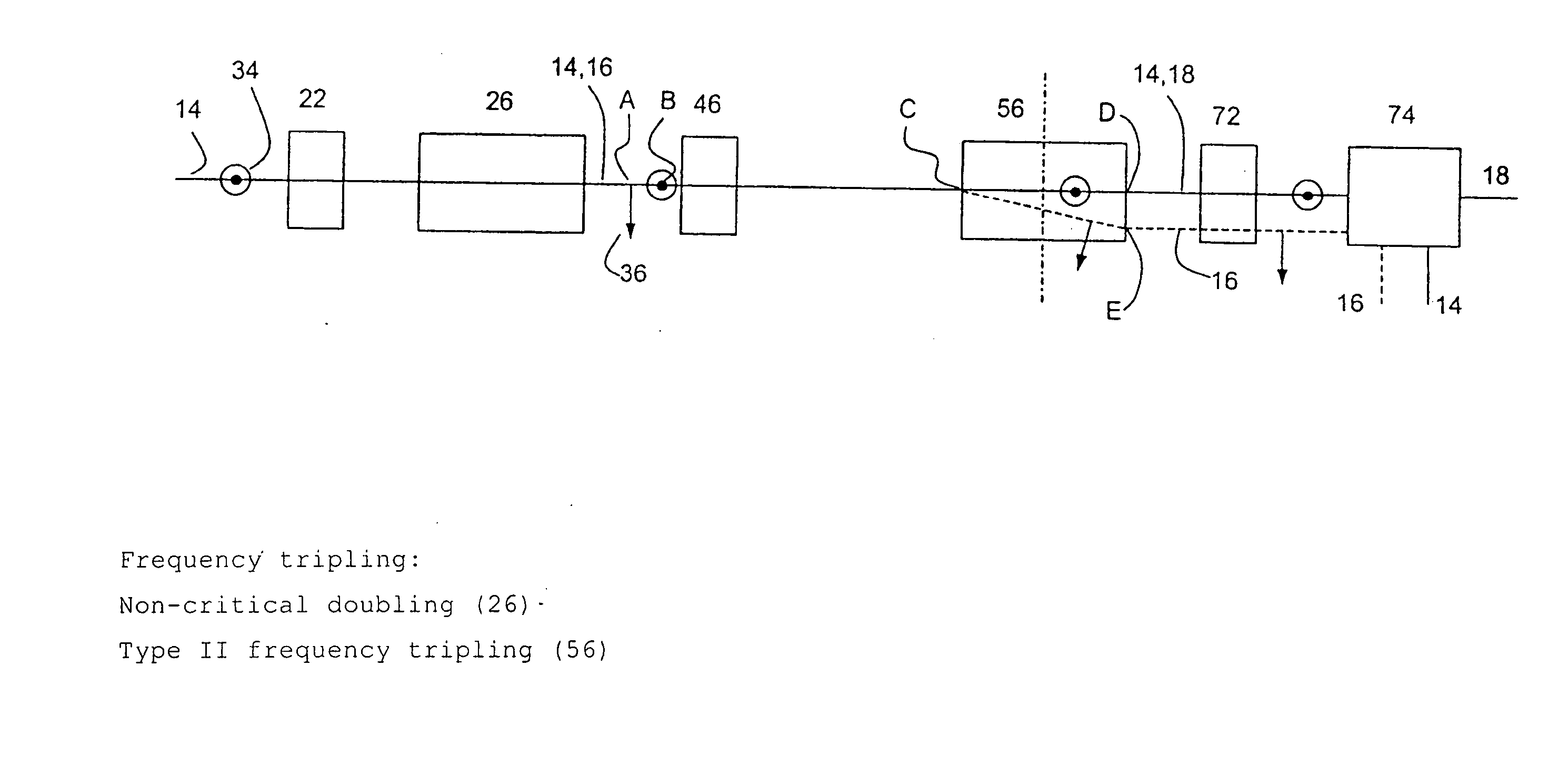
To optimise the transformation rate (efficiency) in the optical frequency conversion of laser beams of ultra-short light pulses in optically non-linear media such as a crystal (56), a double refracting crystal (54) is arranged in the beam path before the optically non-linear medium (56). The length of the double refracting crystal (54) is selected and the orientation of its optical crystal axis in relation to the propagation direction of the laser beams involved in the frequency conversion is set such that the change caused by the double refracting crystal (54) in the location, time and direction of incidence of the laser pulses (14) and (16) on the optically non-linear medium (56) and the resulting change in the spatial and temporal overlap of the laser pulses in the optically non-linear medium (56) for optical frequency conversion in the crystal (56) give a conversion efficiency which is higher than the conversion efficiency which would be achieved without the double refracting crystal (54).
Owner:LUMERA LASER
High-temperature-phase tellurium barium molybdate crystal as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN102031563AEasy to implementEasy to operatePolycrystalline material growthPolarising elementsNonlinear optical crystalCrystal system
The invention relates to a high-temperature-phase tellurium barium molybdate crystal as well as a preparation method and the applications thereof. The high-temperature-phase tellurium barium molybdate crystal belongs to an orthorhombic system, a space group is Pca21, a=14.8683 (2), b=5.66360 (10), c=17.6849 (3), ultraviolet-visible-near-infrared light is displayed through a light spectrum, intermediate infrared light is displayed through the light spectrum, the crystal permeates the wavelength range of 380-5530 nm, and infrared laser of 1064 nm is incident into the crystal at a room temperature to generate green light with the wavelength of 532 nm. A fluxing agent method is adopted for growth. The invention also provides the applications of the high-temperature-phase tellurium barium molybdate crystal as a nonlinear optical crystal, a birefringent crystal, a piezoelectric crystal, a ferroelectric crystal, a pyroelectric crystal or a laser substrate material.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Optical mixer of free space
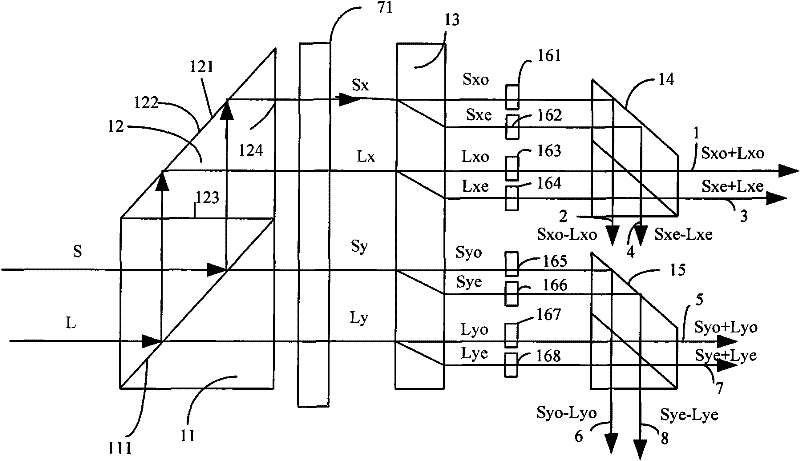
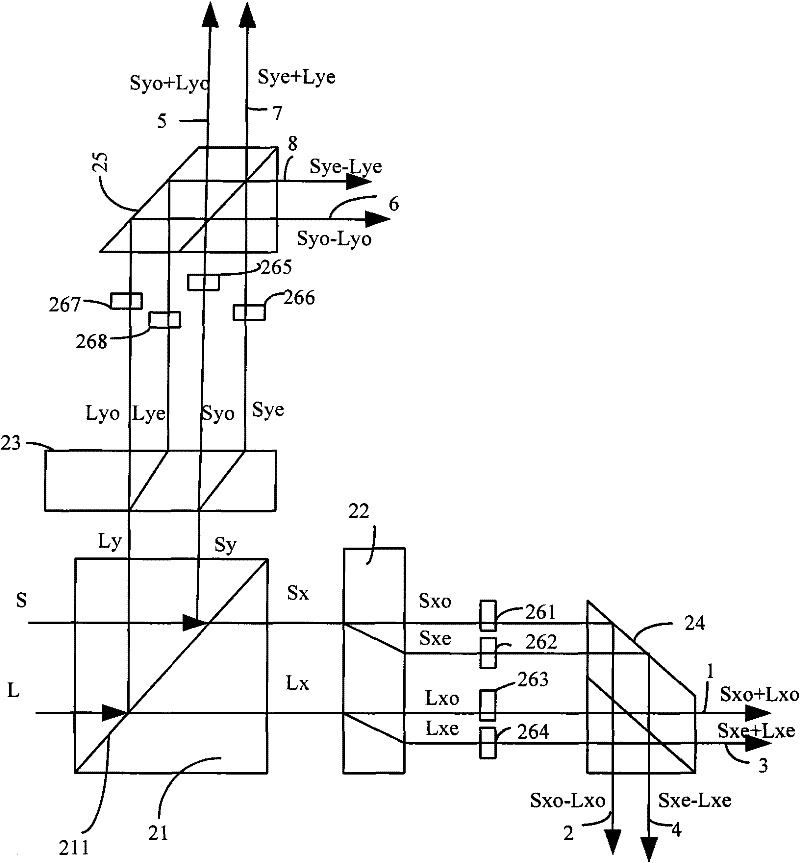
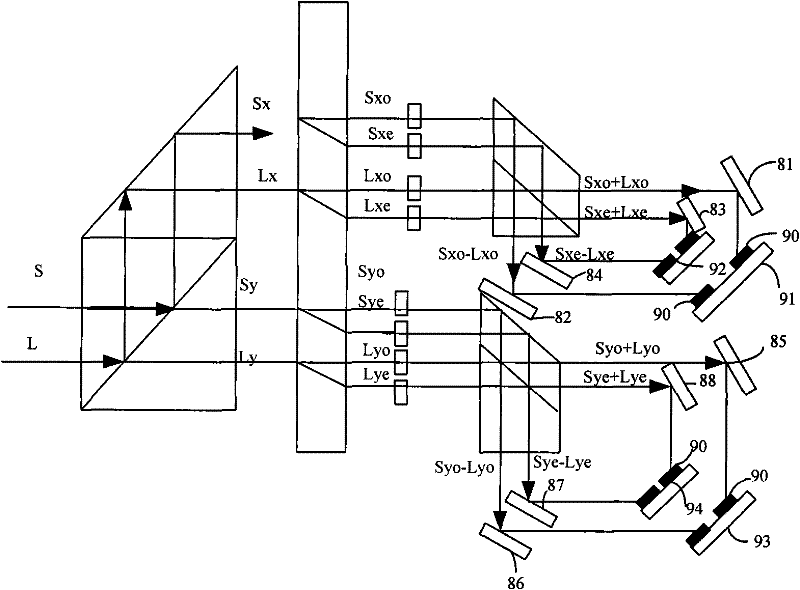
ActiveCN102221728ACompact structureImprove stabilityCoupling light guidesBirefringent crystalLight beam
The invention provides an optical mixer of free space. The optical mixer is characterized in that: a polarizing splitter respectively separates beam S and beam L into horizontal polarization beams Sx and Lx as well as vertical polarization beams Sy and Ly; at least one birefringence crystal divides the horizontal polarization beams Sx and Lx as well as the vertical polarization beams Sy and Ly into beams Sxo, Sxe, Lxo, Lxe, Syo, Sye, Lyo, and Lye; and then beam Sxo+Lxo, beam Sxo-Lxo, beam Sxe+jLxe, beam Sxe-jLxe, beam Syo+Lyo, beam Syo-Lyo, beam Sye+jLye, beam Sye-jLye are combined by a light combiner and are output by a port. The advantages of the invention are as follows: an optical mixer of free space is allowed by utilizing a birefringence crystal, so that beams with different polarization can be separated well in free space; and the optical mixer has a compact structure and good stability.
Owner:O NET COMM (SHENZHEN) LTD
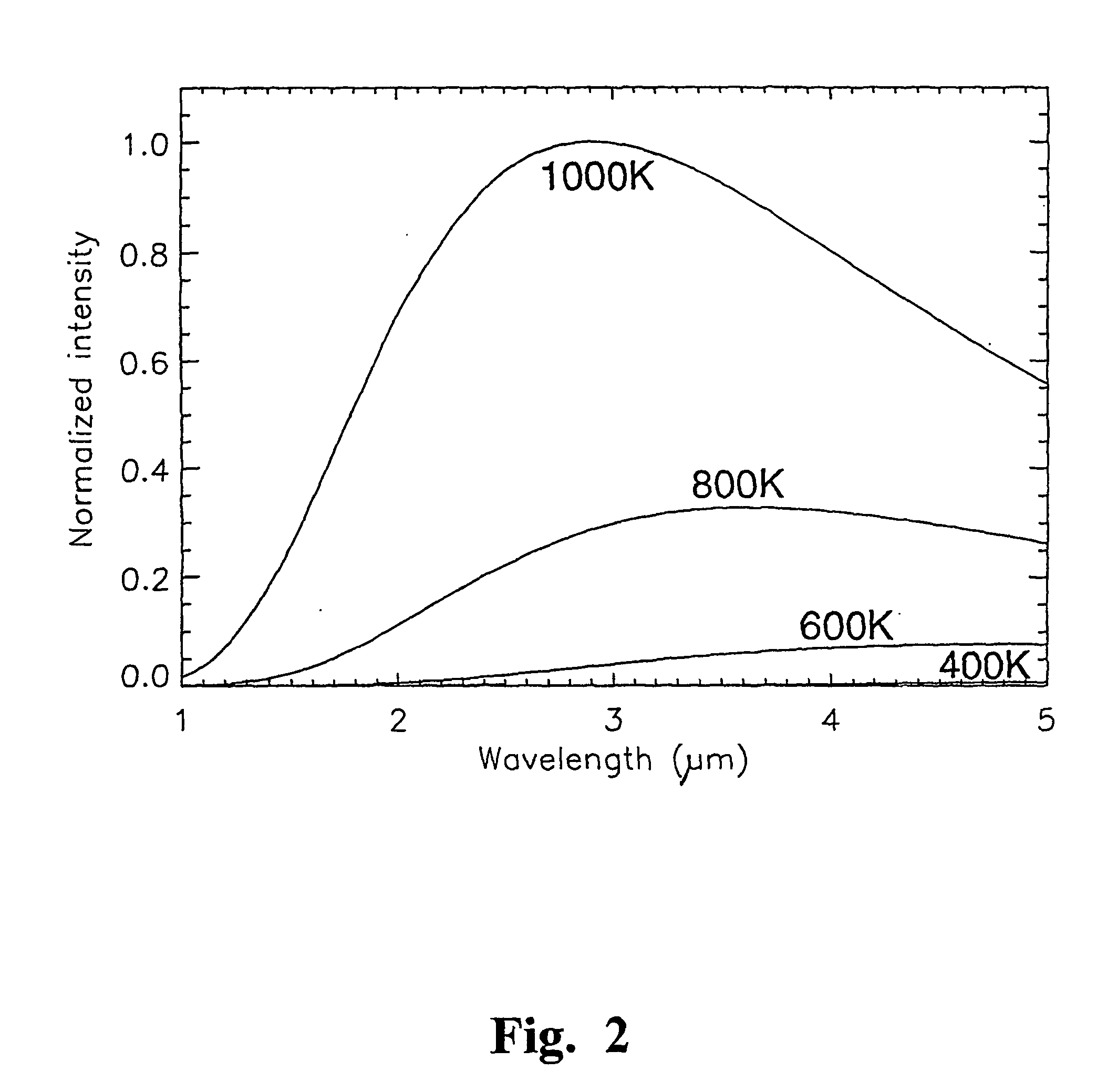
Method and apparatus for the estimation of the temperature of a blackbody radiator
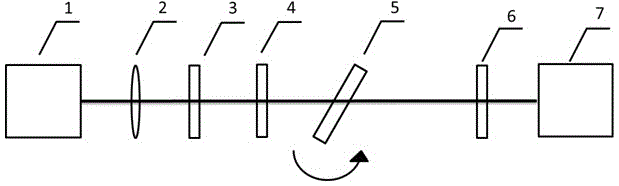
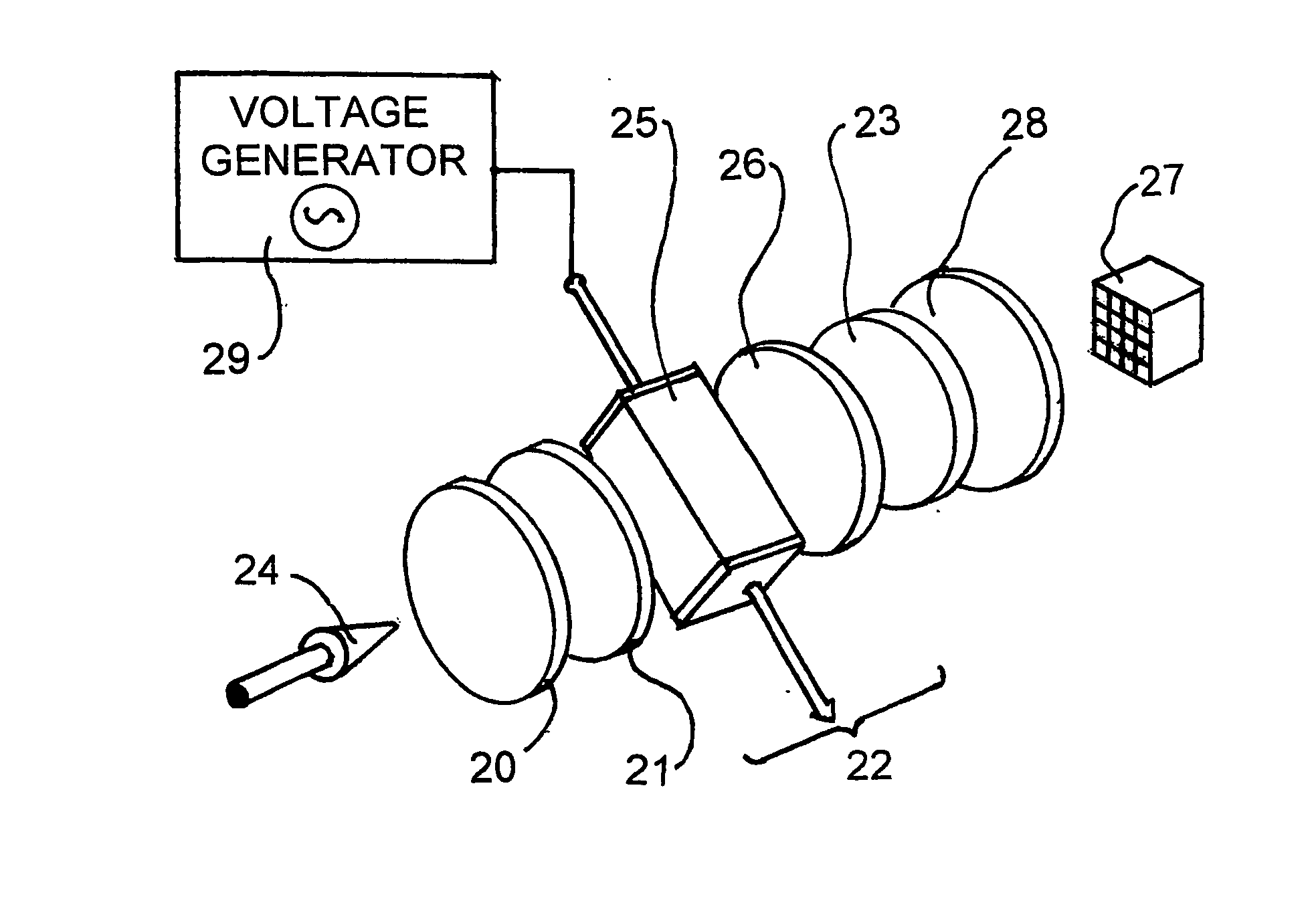
InactiveUS20040240517A1Enhanced signalRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBirefringent crystalBand-pass filter
Remote sensing of the temperature of a greybody or blackbody radiator is effected by passing its radiation (24) through a modulated infrared filter spectrometer. The infrared filter comprises, in sequence, a band pass filter (20), a first polariser (21) which polarises the radiation, an electro-optical element (22) which splits the polarised radiation into two orthogonally polarised components, and a second polariser (23). A lens (28) images the radiation leaving the second polariser onto a detector (27). The electrical signal from the detector (27) is input to a numerical analyser. The electro-optical element (22), typically comprising a birefringent crystal assembly (25) and a birefringent trim plate (26), is configured so that the net optical delay of the orthogonally polarised components passed through it is such that the recombined components are at or near a peak or trough in their interferogram. A sinusoidally varying voltage is applied to the electro-optical element to modulate the net delay of the components passed through the electro-optical element. The numerical analyser is programmed to compute the harmonic amplitude ratio (the ratio of signal amplitudes at the fundamental and second harmonic of the frequency of the modulating voltage) of the signal that it receives from the detector (27). The harmonic amplitude ratio is a function of the temperature of the radiator, which can be estimated by reference to a calibration look-up table.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
Method for continuously regulating central frequency and spectrum width of THz (terahertz) wave
ActiveCN102879971AAdjust the center frequencyAdjustable widthNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumBirefringent crystal
The invention relates to a method for continuously regulating central frequency and spectrum width of THz (terahertz) wave. A bundle of ultrafast laser pulse passes through a movable birefringence crystal oblique split pair and a zero-order quarter wave plate to generate a novel specially-polarized light field by a polarizing gate method. The novel light field passes through a polarizer to obtain laser pulse with width of narrow pulse with linear polarization. Laser pulses different in width are obtained by controlling inserting quantity of the birefringence crystal oblique split pair, and accordingly the function of regulating central frequency and spectrum width of the THz wave is achieved. A device is simple and easy to operate, the width of the novel laser pulse can be changed only two crystals of the birefringence crystal oblique split pair simultaneously move oppositely at equal distance, and accordingly the central frequency and the spectrum width are adjusted. The method is suitable for light sources of various pulse widths and wavelengths.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
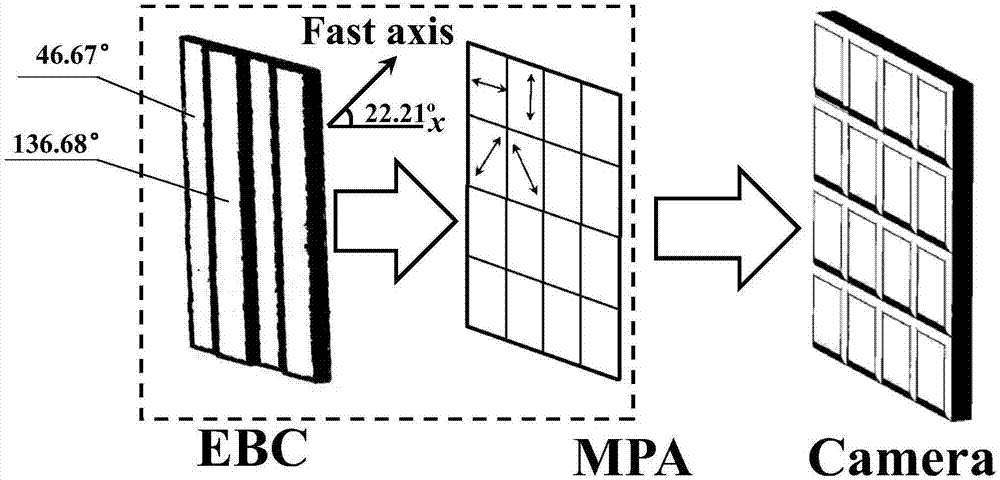
Miniaturized full Stokes vector polarization imaging device based on binary digital coded birefringent crystal
InactiveCN108007575AStrong real-timeCompact structureLight polarisation measurementCamera lensBirefringent crystal
The invention discloses a miniaturized full Stokes vector polarization imaging device based on a binary digital coded birefringent crystal, including a spectral filter (1), an imaging lens (2), a binary digital coded birefringent crystal sheet (3), a micro polarizer array (4), and a light intensity detector (5). Binary digital coding is carried out on the birefringent crystal sheet by making use of the birefringence effect of a birefringent crystal and using a micro sodium optical processing method, and the birefringent crystal sheet is integrated with the micro polarizer array and the light intensity detector to form a compact and fully-functional full Stokes vector polarization imaging device. A full Stokes vector can be acquired through only one exposure, and the real-time performance is good. The device has a compact structure and a stable system. The micro optical structure is large, the requirement on precision is low, the cost is low, and the device can be mass produced. The device has low requirement on environment, and has stable performance. The device can be widely used in important areas such as astronomical polarization imaging, biological tissue detection and medicinediagnosis, remote sensing imaging, and target detection.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tunable periodic filter
InactiveUS6370286B1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsPolarising elementsBeam splitterBirefringent crystal
A polarization-interferometry based tunable periodic filter includes polarization defining components such as polarizing beam splitters or polarizing beam displacers located on the input and output sides of a phase retarder such as a birefringent crystal. A polarization independent input consisting of multiple optical channels having a periodic frequency spacing is converted to a branched output of optical channels in which each branch has a periodic frequency spacing that is different from that of the input, and which are interleaved with each other. The output period is tunable by adjusting the phase delay of orthogonal polarization components. A contrast ratio of >=20 dB can be realized. The device allows the mux / demux of up to 200 WDM channels with a 50 GHz frequency spacing. Applications of the device include a band splitter, a wavelength selective cross-connect, and a wavelength monitor.
Owner:CORNING INC
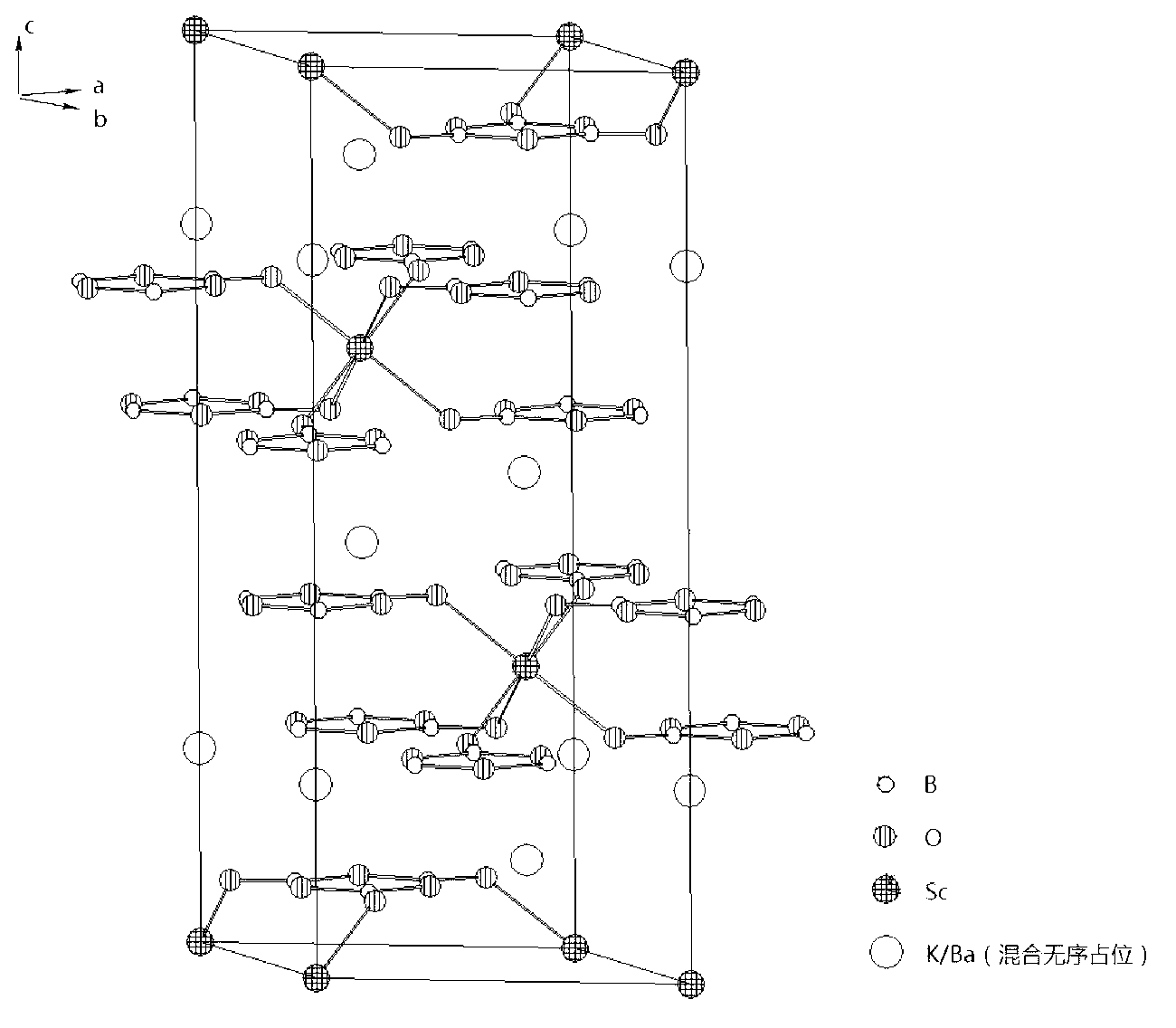
Borate birefringent crystal for ultraviolet band as well as growing method and purpose of same
InactiveCN103074684ACut wellGood groundingPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltSpace groupFlux growth
The invention relates to a borate birefringent crystal for an ultraviolet band. The chemical formula of the borate birefringent crystal is KBaSc(B3O6)2 and belongs to a trigonal system; an atom K and an atom Ba in a crystal structure are in disordered mixed occupation; a space group is R-3 and a cell parameter Z is 3; the transmission range is 184-3000 nm; a calculated value n0 of the refractive index at gamma of 589 nm is 1.6168, ne is 1.5079 and delta n is 0.1089; the crystal grows by using a self-melting and spontaneous crystallization method or a flux growth method; the crystal is easy to grow, cut, grind, polish and preserve, is stable in the air, is uneasy for deliquescence and is insoluble in water; the crystal can be used for making polarization beam splitters such as Glan prisms, Wollaston prisms, Rochon prisms or beam splitting polarizers; and the crystal is importantly applied to the optical and communication fields.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Integrated reflective phase bias device, fiber laser and light wave and microwave phase detector
ActiveCN104979747AUndisturbedReduce volumeActive medium shape and constructionPhase detectorMicrowave
The present invention discloses an integrated reflective phase bias device, a fiber laser and a light wave and microwave phase detector. The phase bias device comprises a fiber holder, a collimation lens, a polarizing prism, a Faraday rotator, a birefringent crystal and a mirror. According to the device, the fiber laser and the light wave and microwave phase detector, two polarization-maintaining fibers with mutually vertical directions are fixed in the fiber holder, the light with mutually vertical polarization directions are separated by the polarizing prism, only one collimator, one Faraday rotator, one birefringent crystal and one mirror are needed, the size is small, the stability is high, the price is low, and no any adjustment is needed. The phase bias device is used in the fiber laser, a self started mode-locked pulse train can be obtained, the characteristic of the pulse train is not interfered by an external environment, and the phase bias device can be applied to various complex environments with high noise, heavy pollution or emission. The phase bias device is used in the light wave and microwave phase detector, thus the light wave and microwave phase detector is compact and is not interfered by the outside, and the working is more reliable.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com