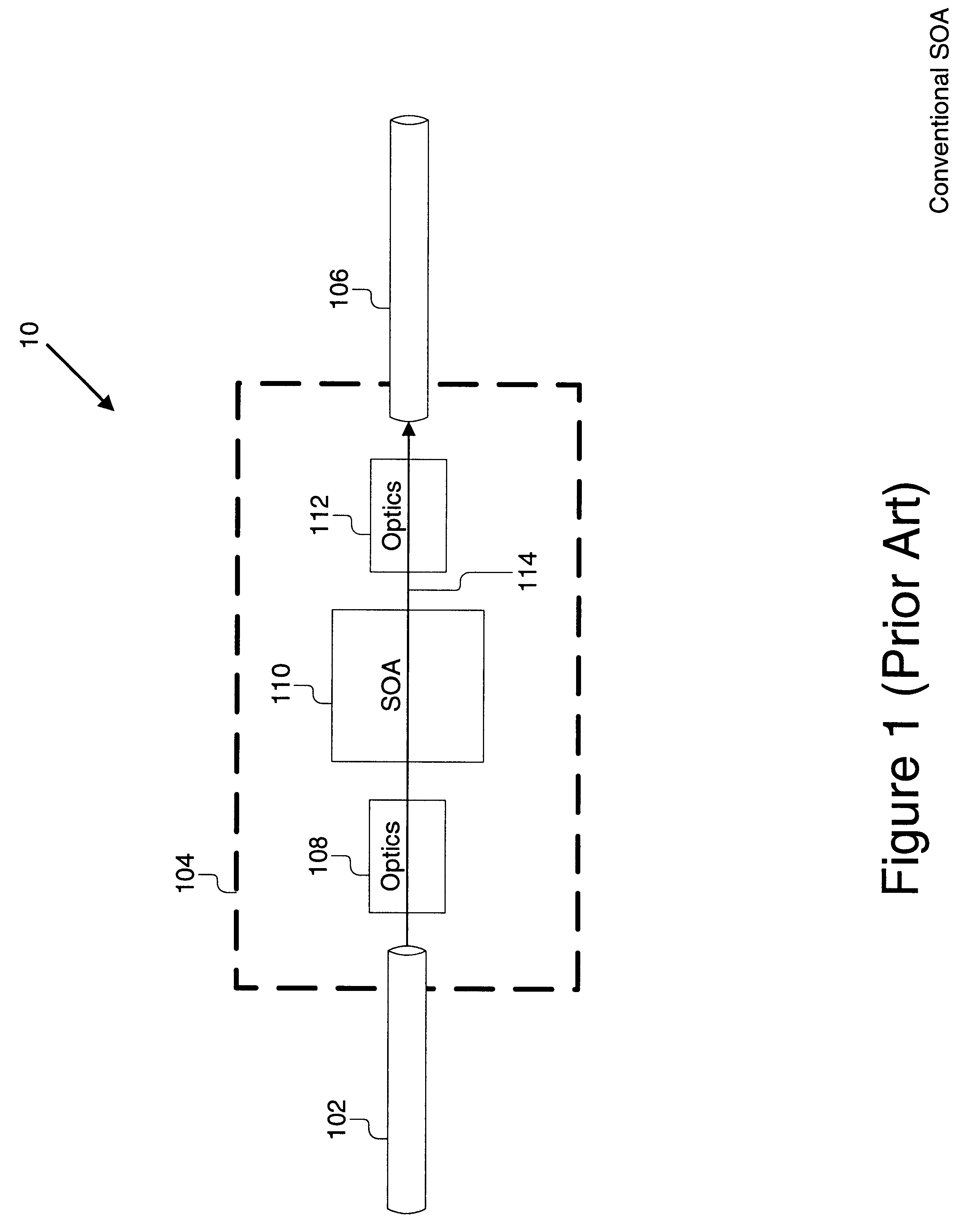
Patents
Literature
444 results about "Polarization dependent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polarization dependent loss is a measure of the peak-to-peak difference in Transmission of an optical component or system with respect to all possible states of polarization.
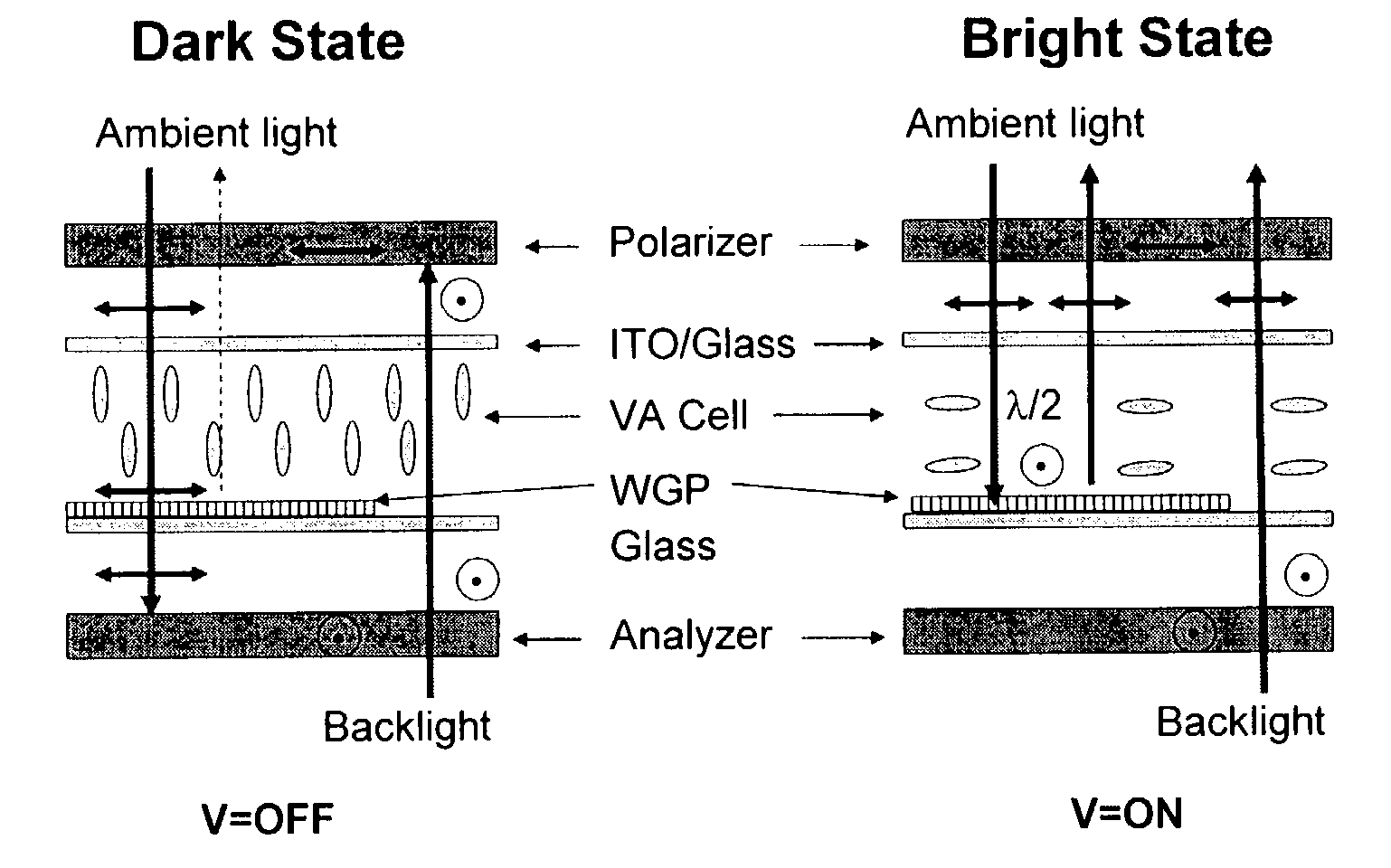
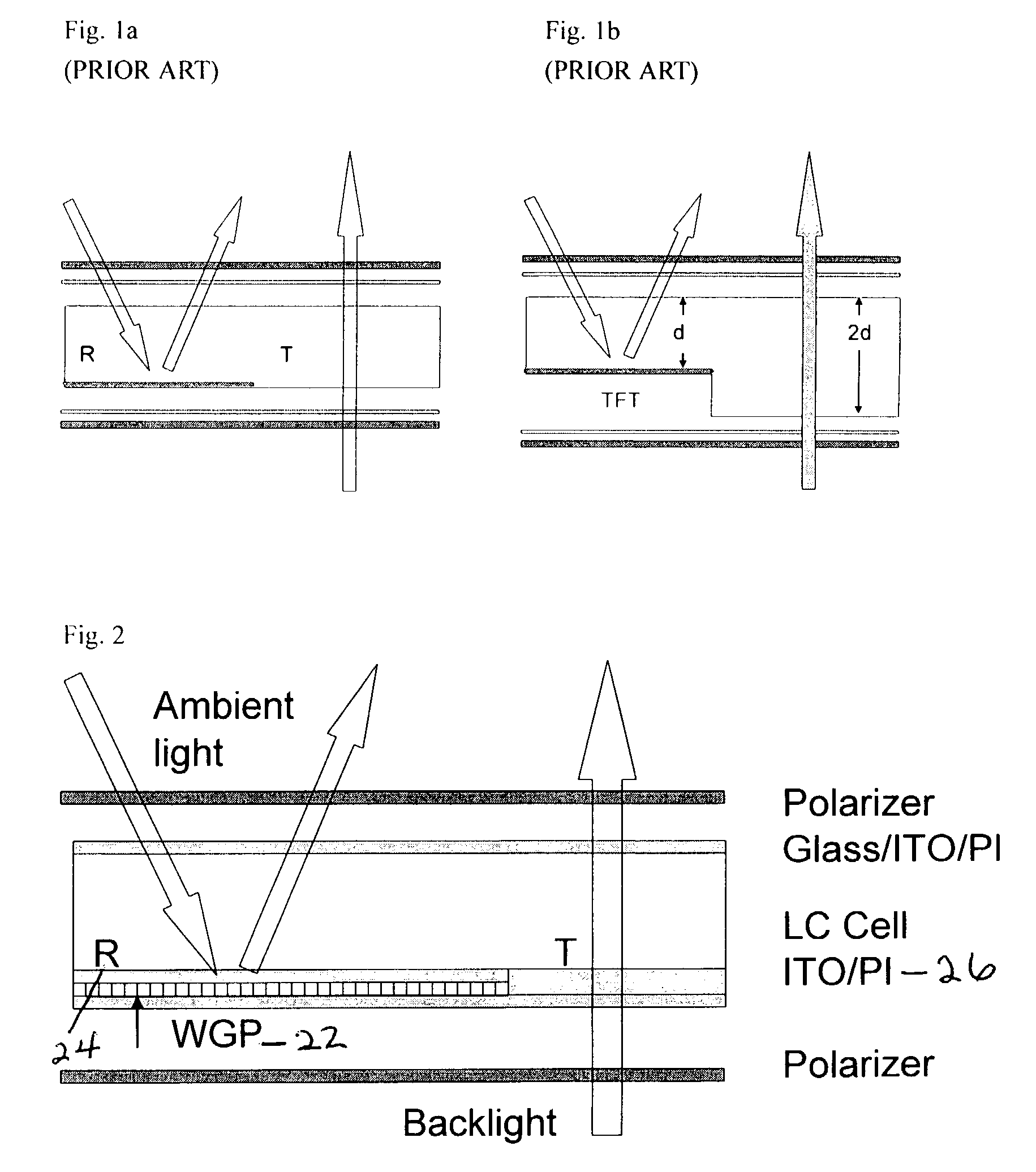
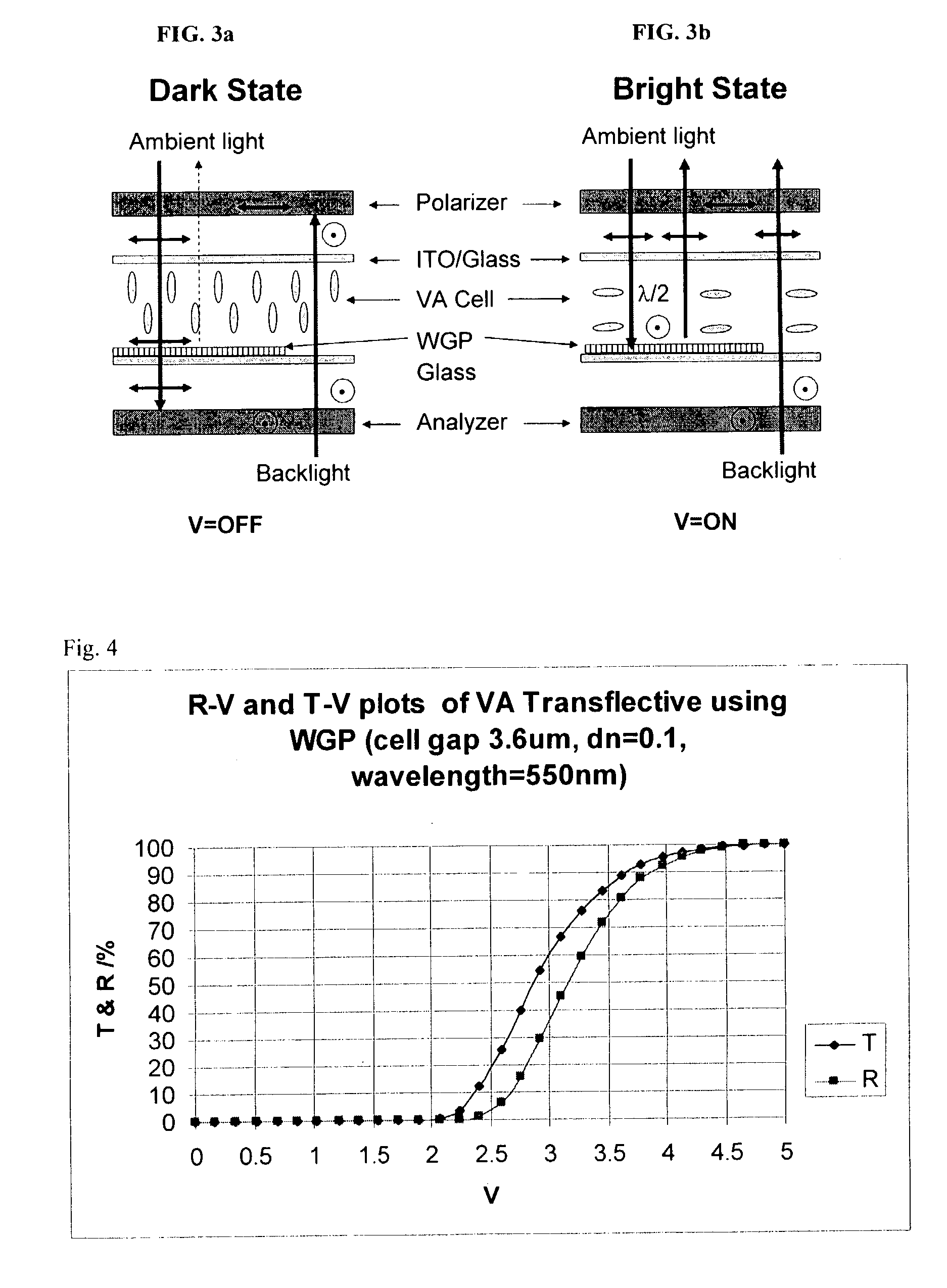
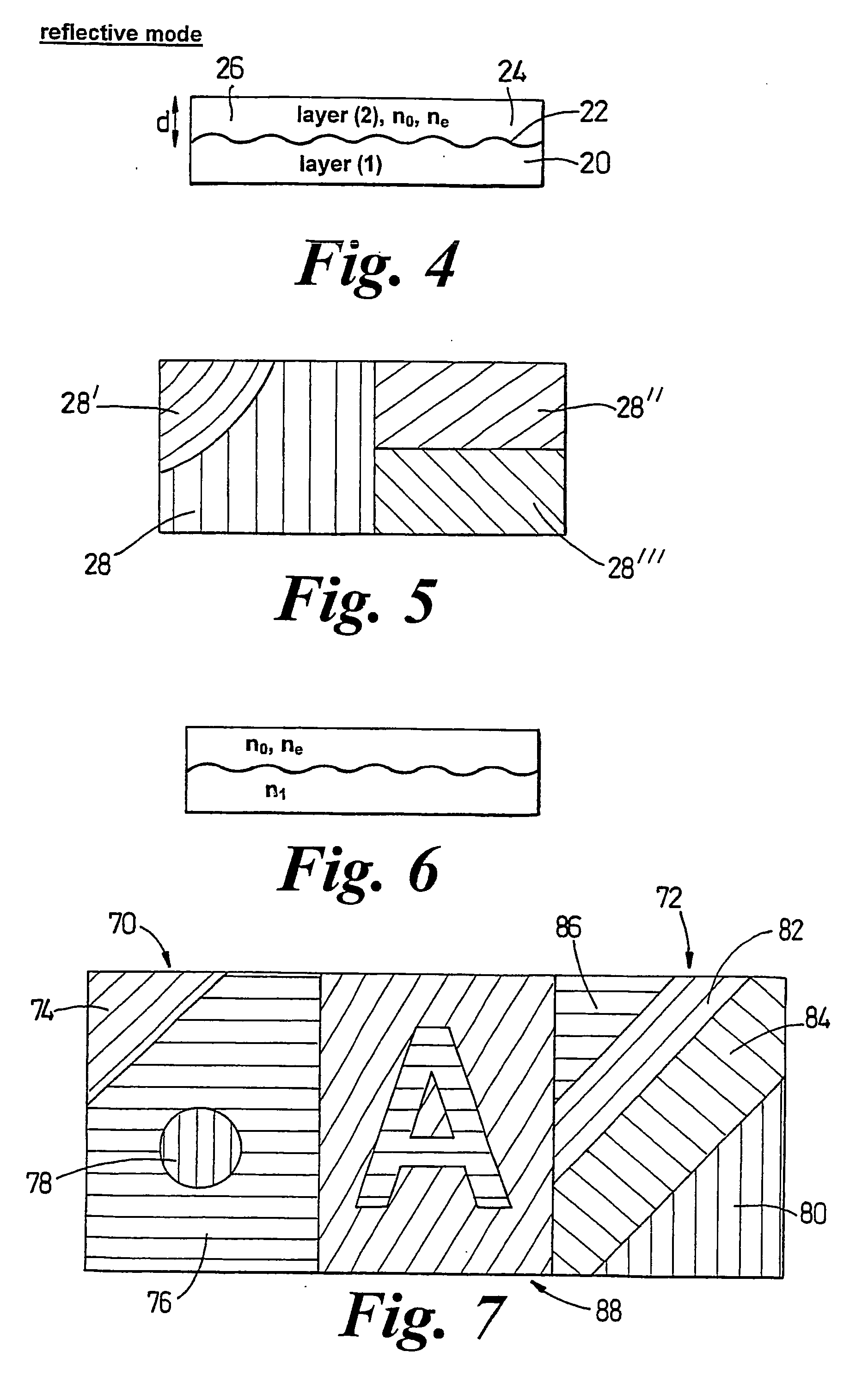
Reflective and transflective liquid crystal display using a wire grid polarizer
A device structure for single cell gap reflective and transflective liquid crystal displays (TF-LCDs). For an entirely reflective LCD, the imbedded wire-grid polarizer (WGP) serves as a polarization-dependent for the ambient light. For a transflective TF-LCD, the WGP only covers the reflective pixels. The disclosure also includes a method of using single cell gap liquid crystal displays (LCDs) without phase retardation films by providing a single cell gap LCD having reflective pixels and transmissive pixels, covering solely the reflective pixels, with at least one of: a wire grid polarizer and a broadband cholesteric reflector (BCR), reflecting ambient light off the reflective pixels; and passing back light through the transmissive pixels whereby the cell gap LCD obtains high contrast ratios without using phase retardation films.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
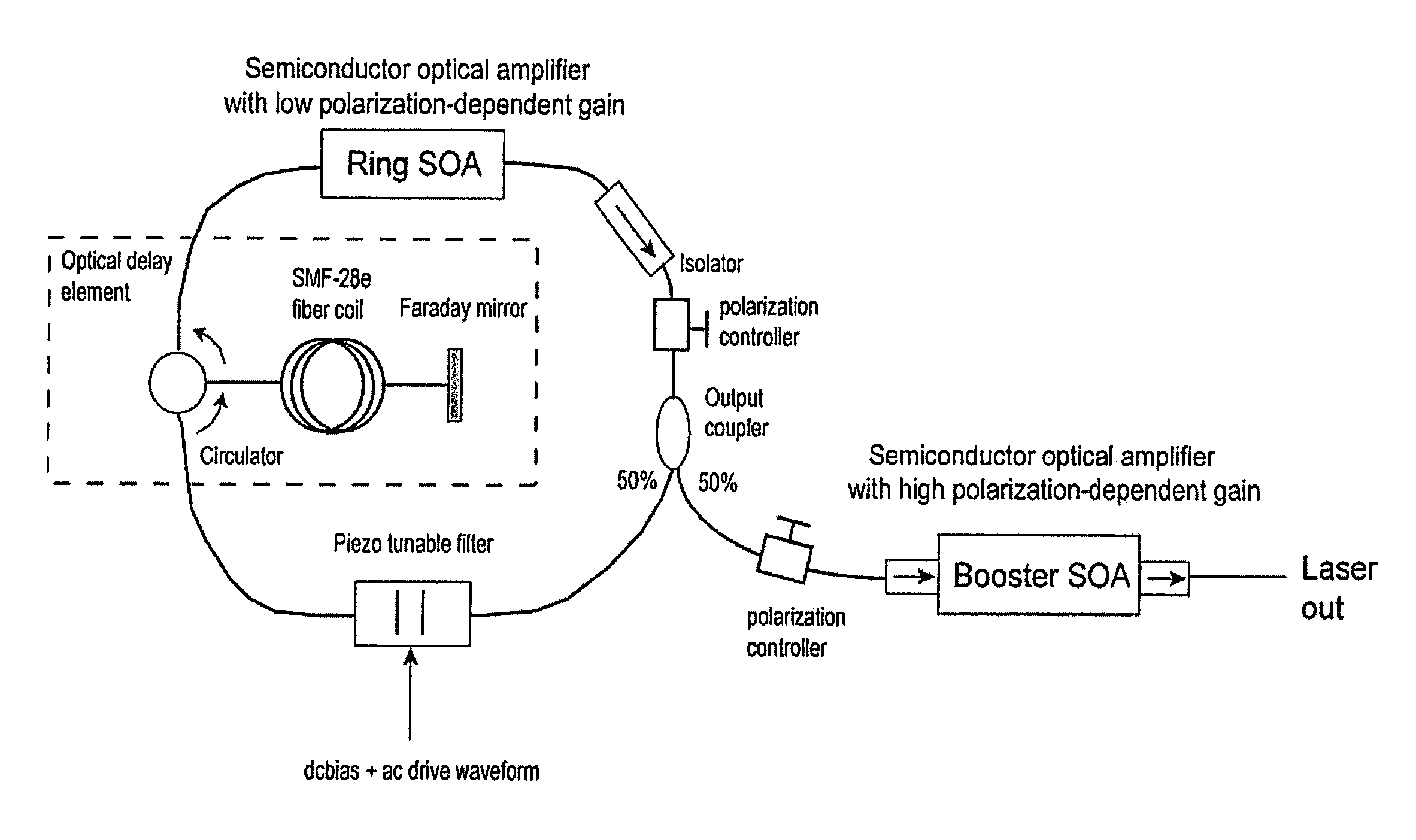
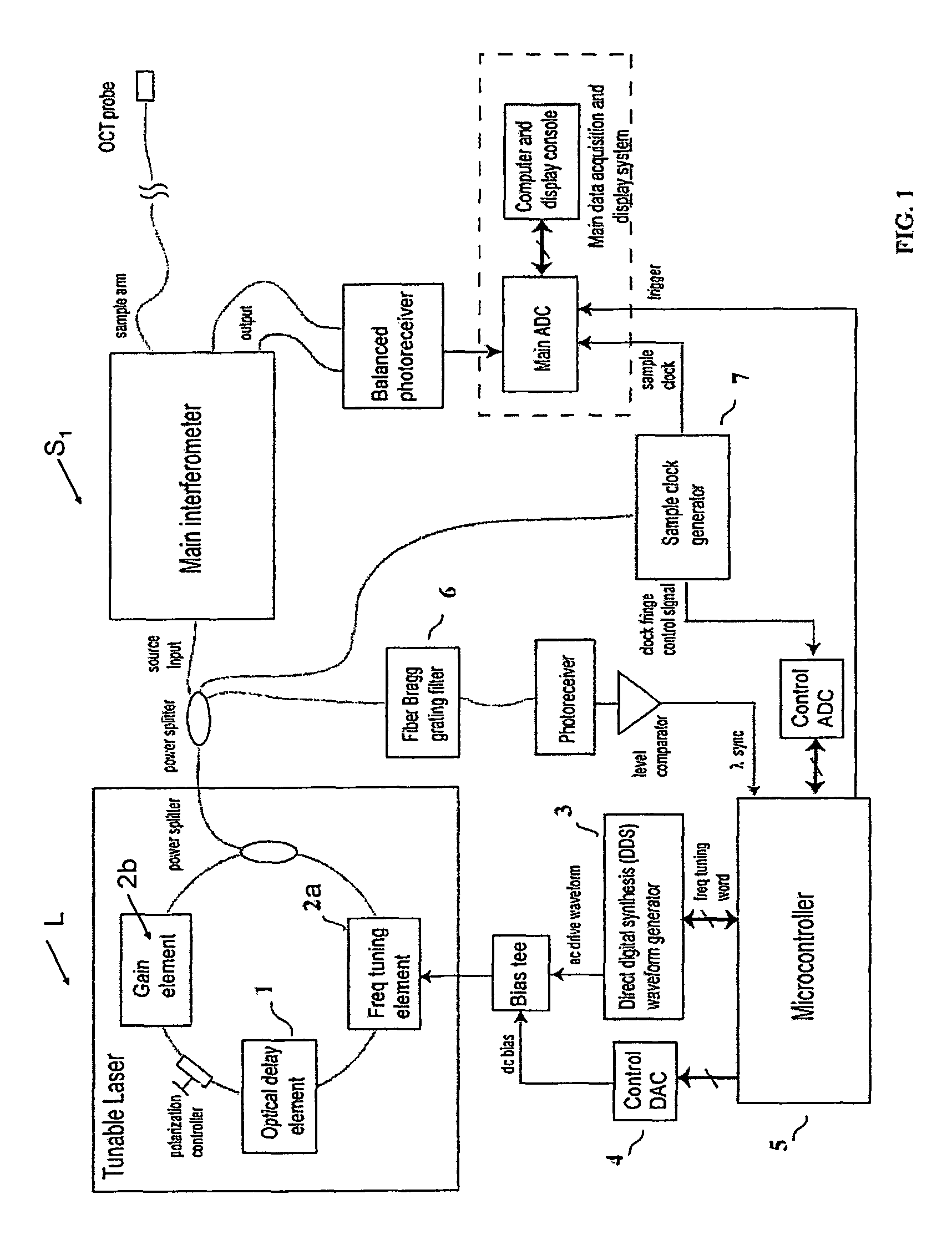
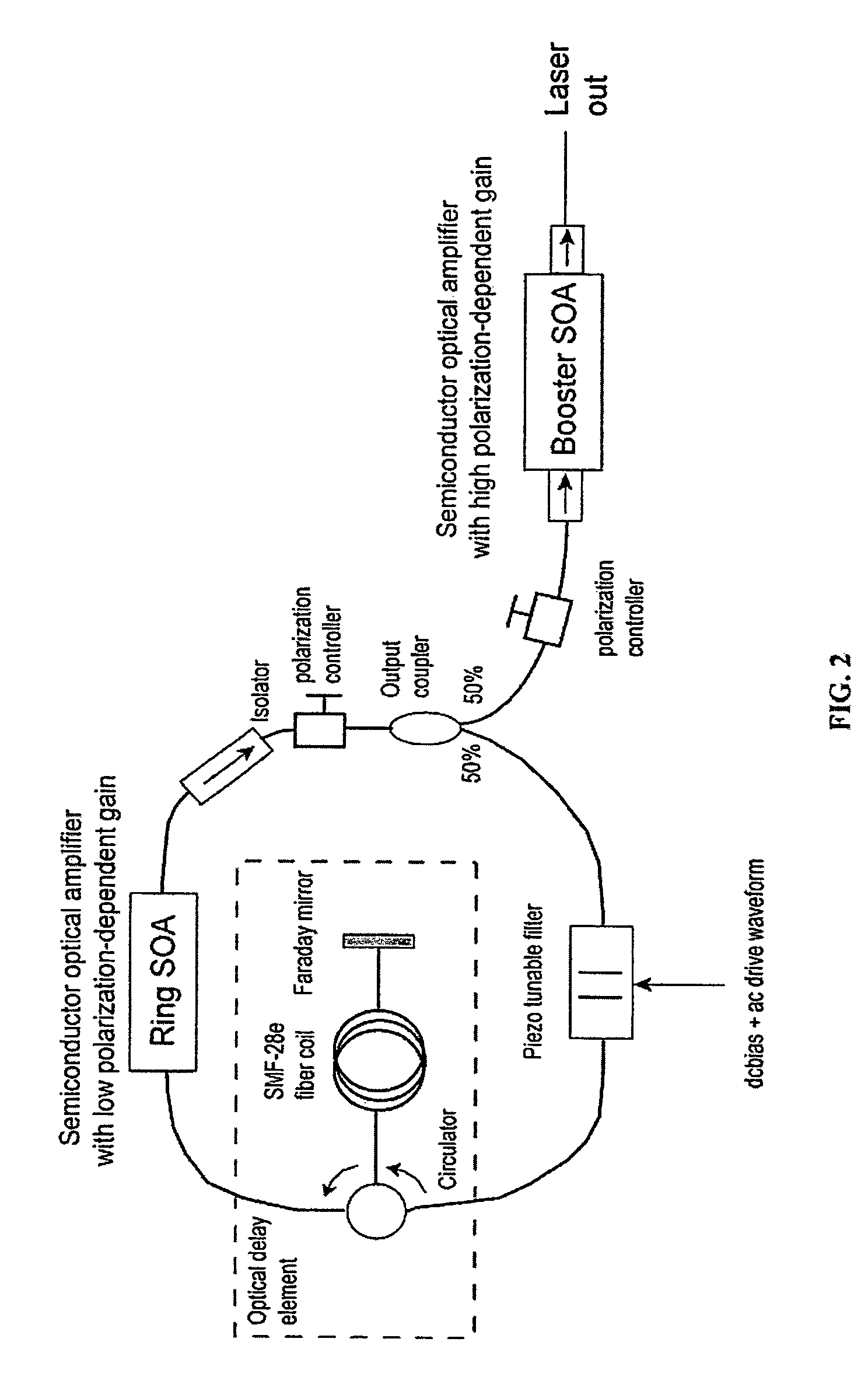
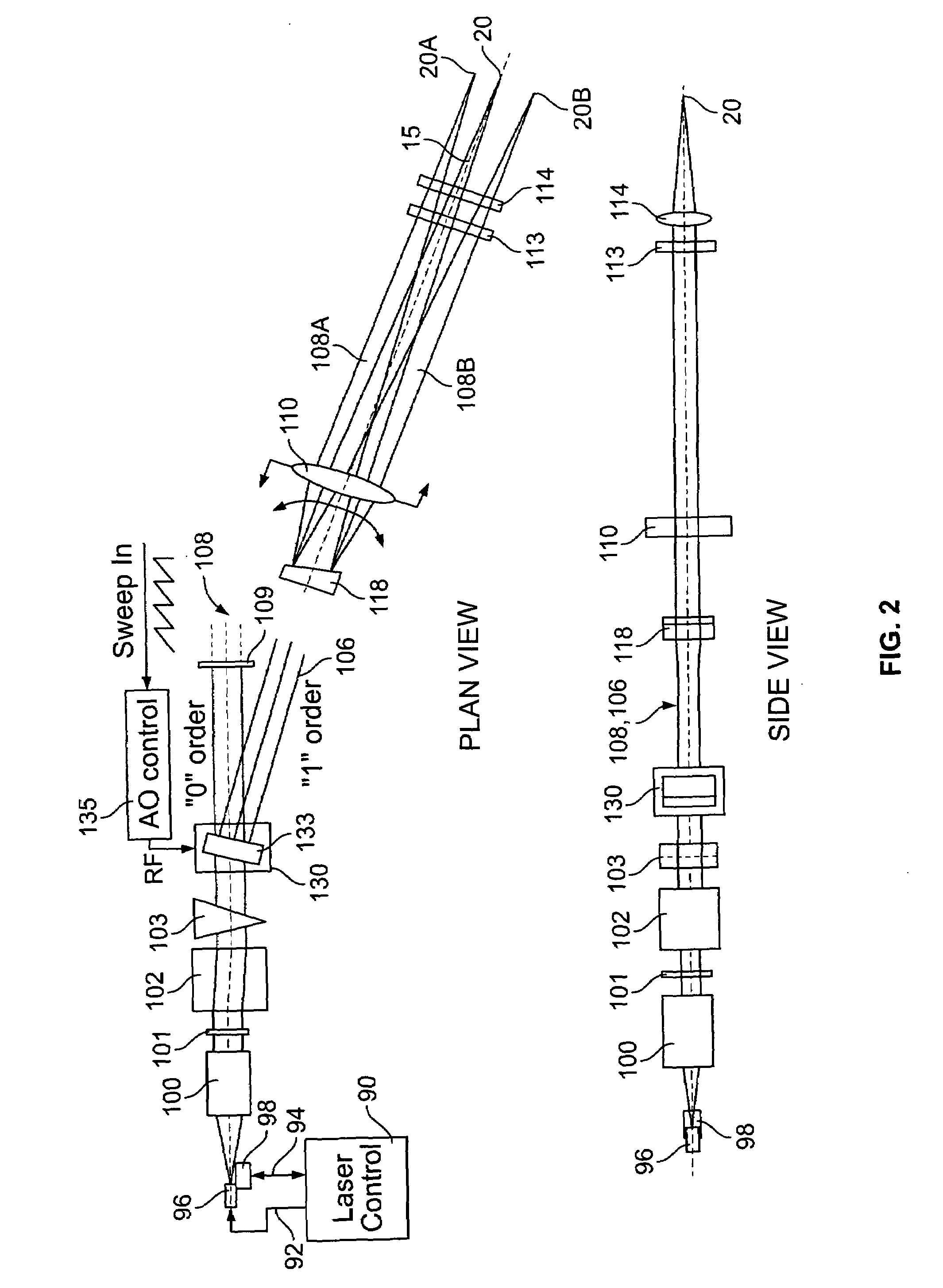
Methods and apparatus for swept-source optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS7916387B2Reduce impactValue maximizationLaser detailsInterferometersAudio power amplifierTomography
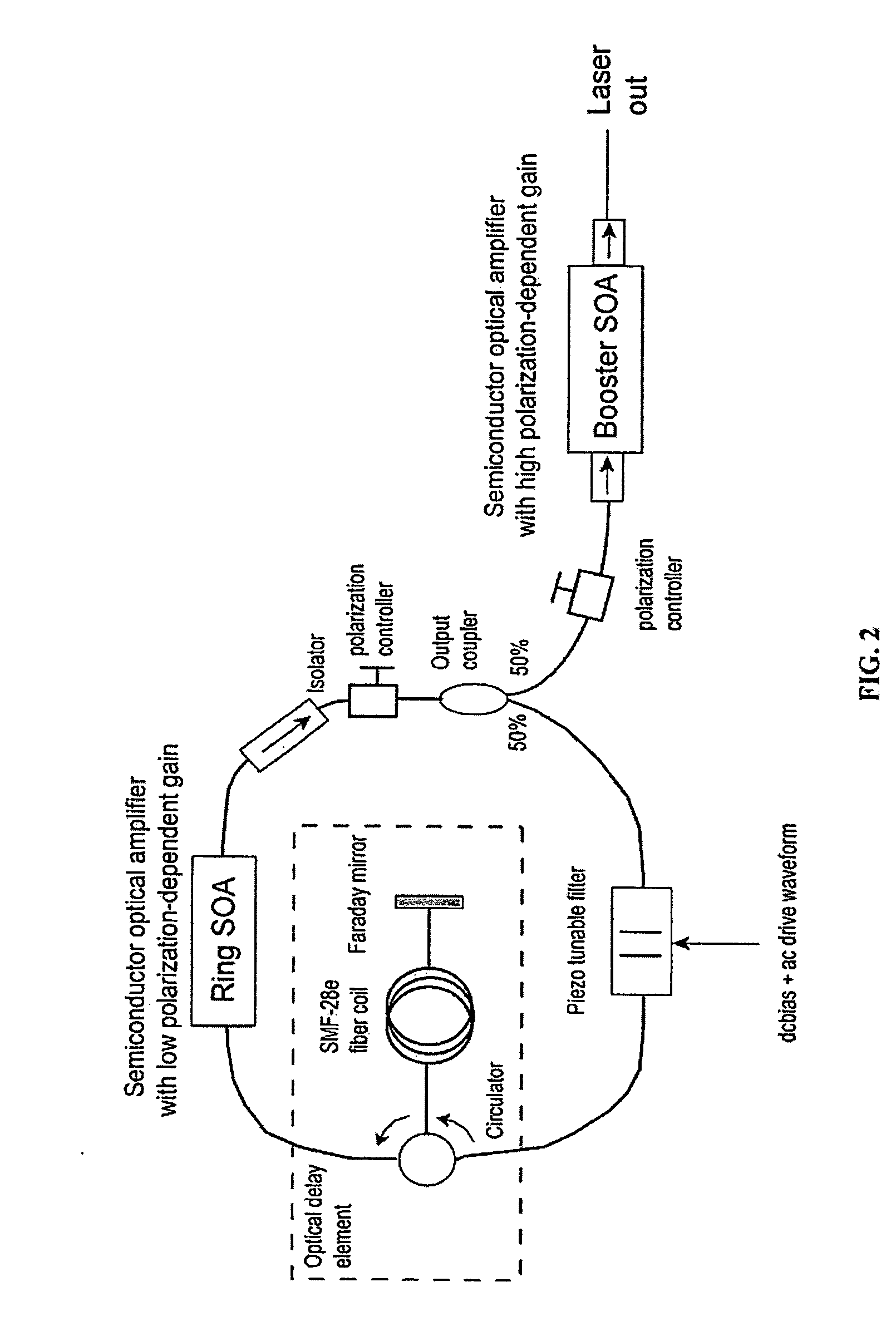
In one embodiment of the invention, a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) in a laser ring is chosen to provide low polarization-dependent gain (PDG) and a booster semiconductor optical amplifier, outside of the ring, is chosen to provide high polarization-dependent gain. The use of a semiconductor optical amplifier with low polarization-dependent gain nearly eliminates variations in the polarization state of the light at the output of the laser, but does not eliminate the intra-sweep variations in the polarization state at the output of the laser, which can degrade the performance of the SS-OCT system.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
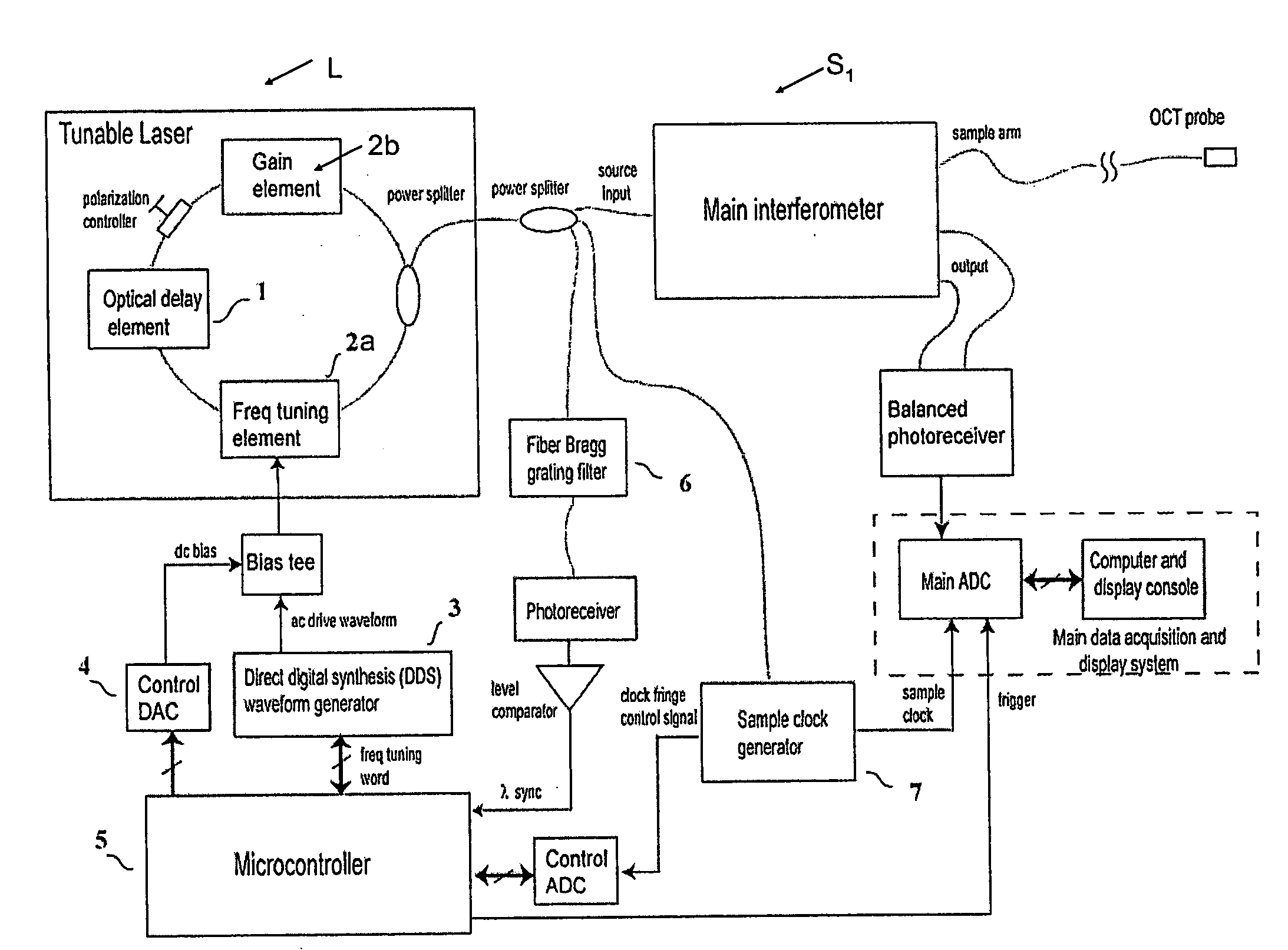
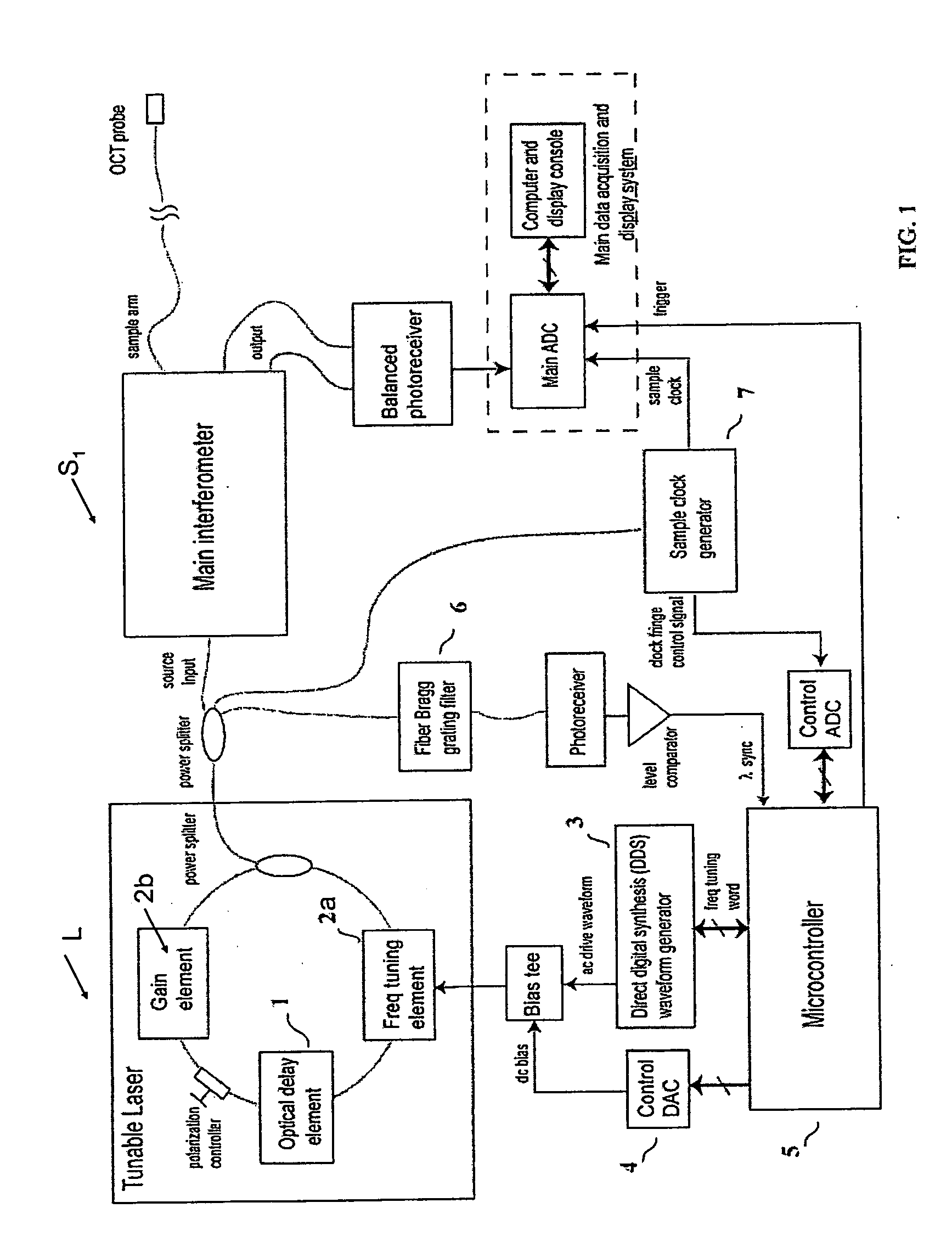
Methods and apparatus for swept-source optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20080165366A1Reduce impactValue maximizationLaser detailsInterferometersAudio power amplifierTomography
In one embodiment of the invention, a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) in a laser ring is chosen to provide low polarization-dependent gain (PDG) and a booster semiconductor optical amplifier, outside of the ring, is chosen to provide high polarization-dependent gain. The use of a semiconductor optical amplifier with low polarization-dependent gain nearly eliminates variations in the polarization state of the light at the output of the laser, but does not eliminate the intra-sweep variations in the polarization state at the output of the laser, which can degrade the performance of the SS-OCT system.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
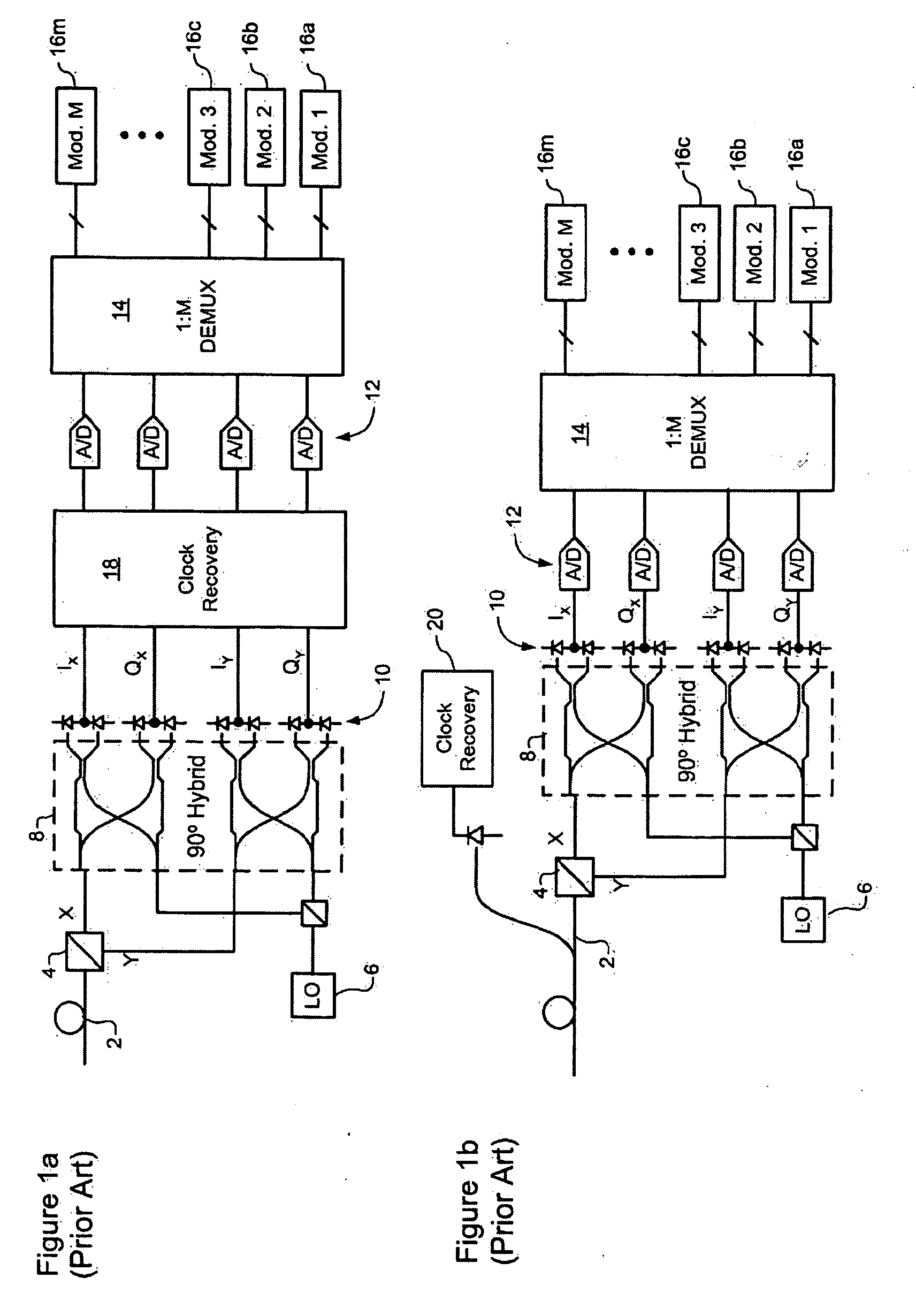
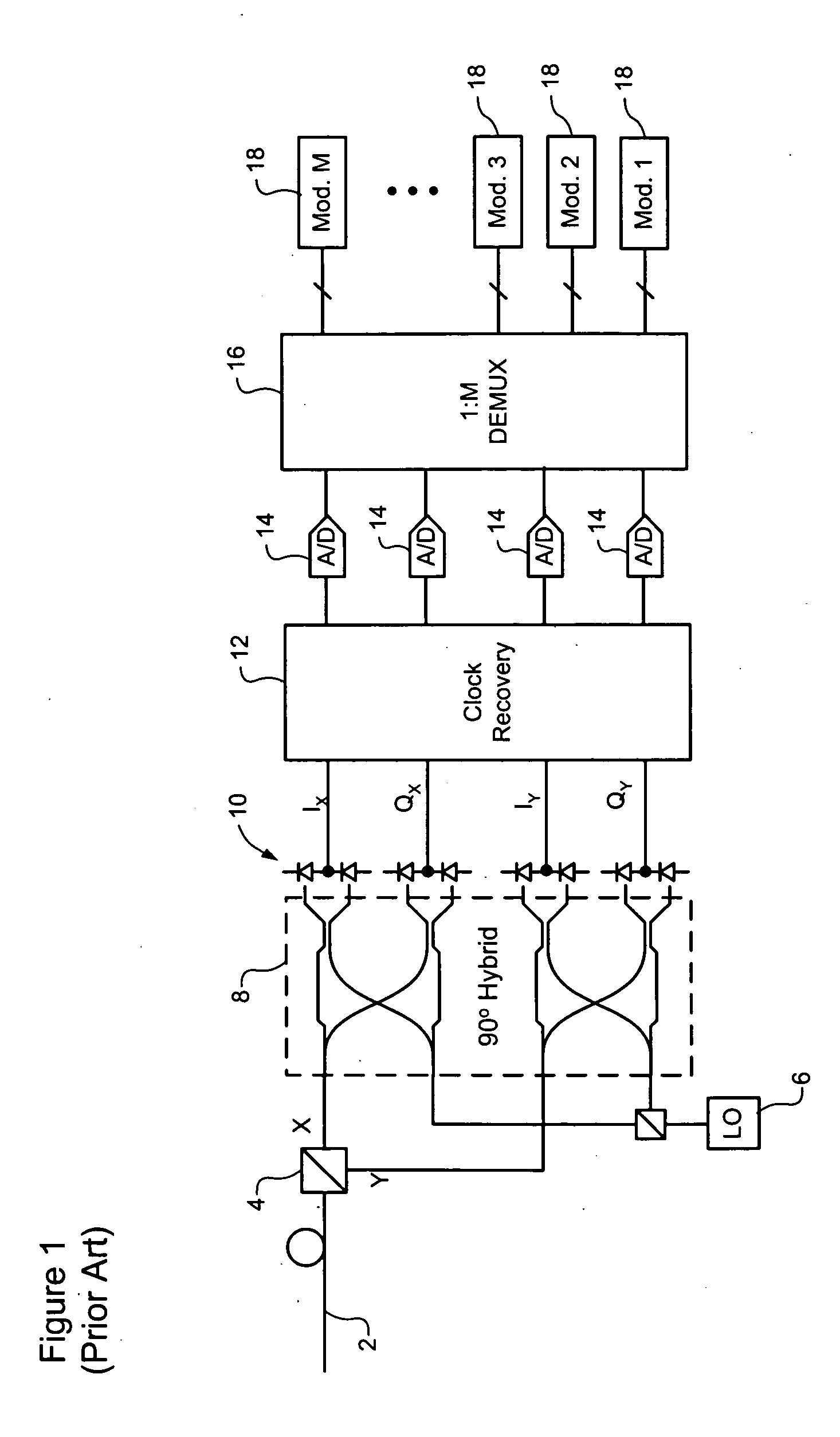
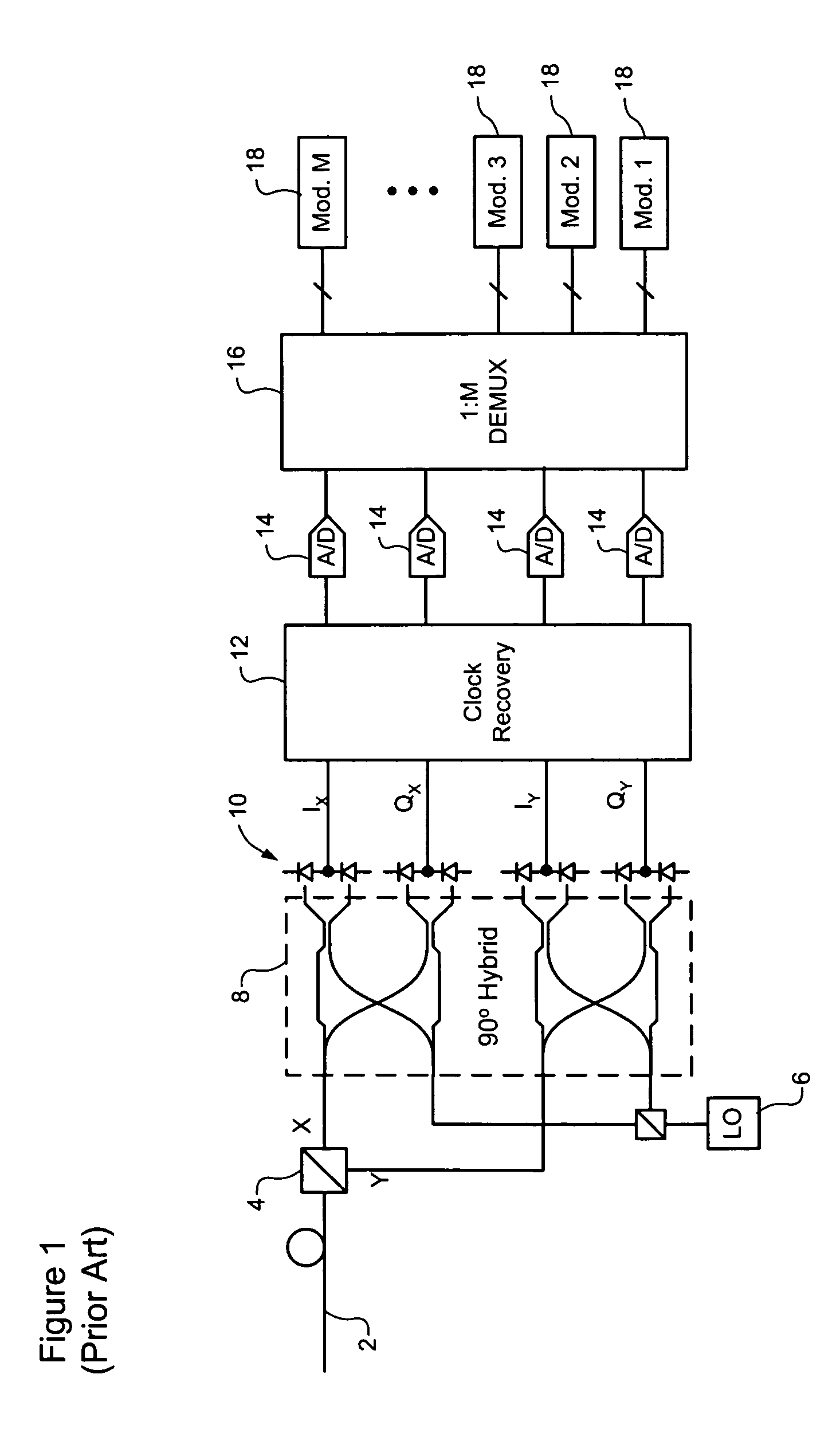
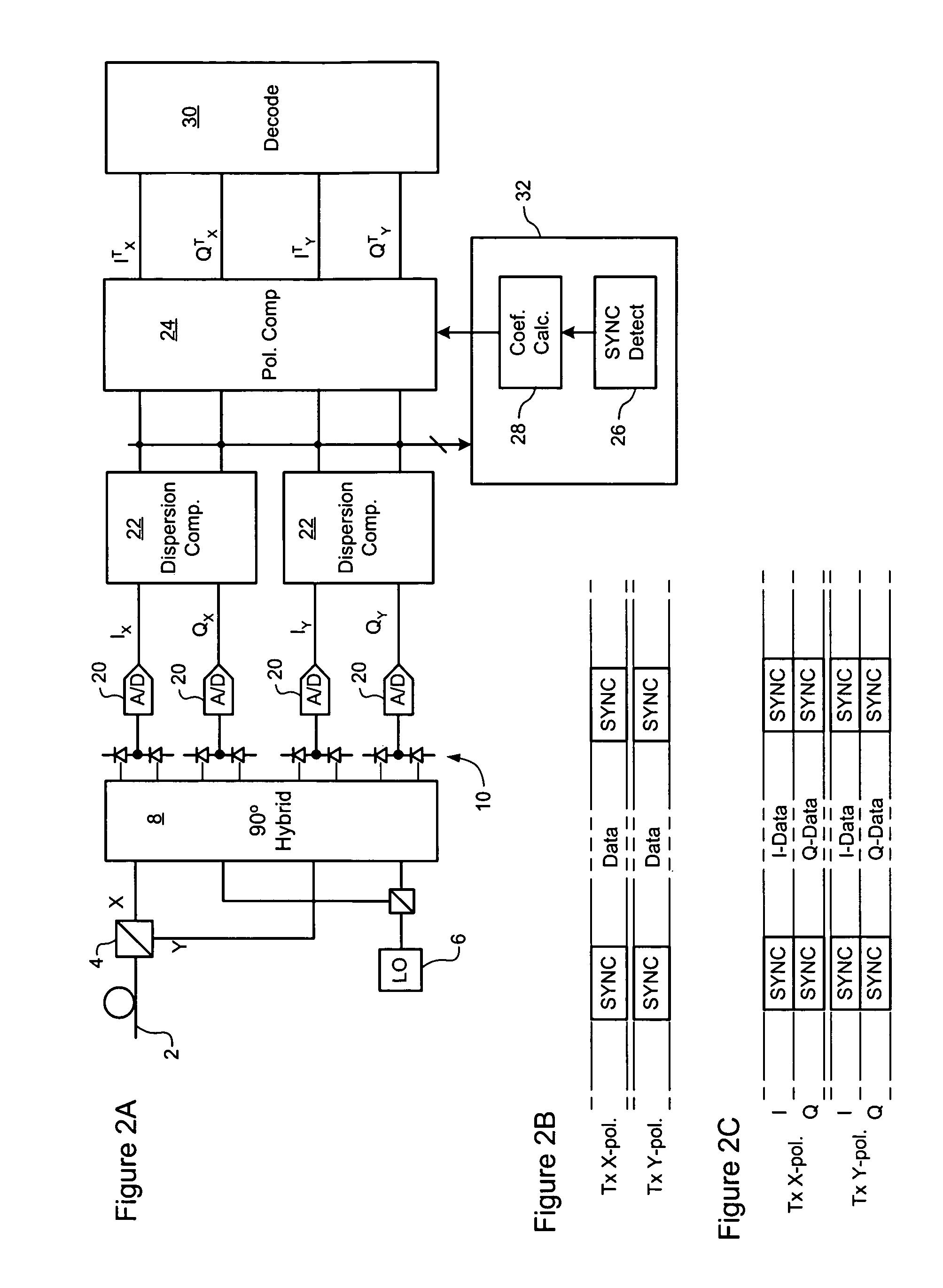
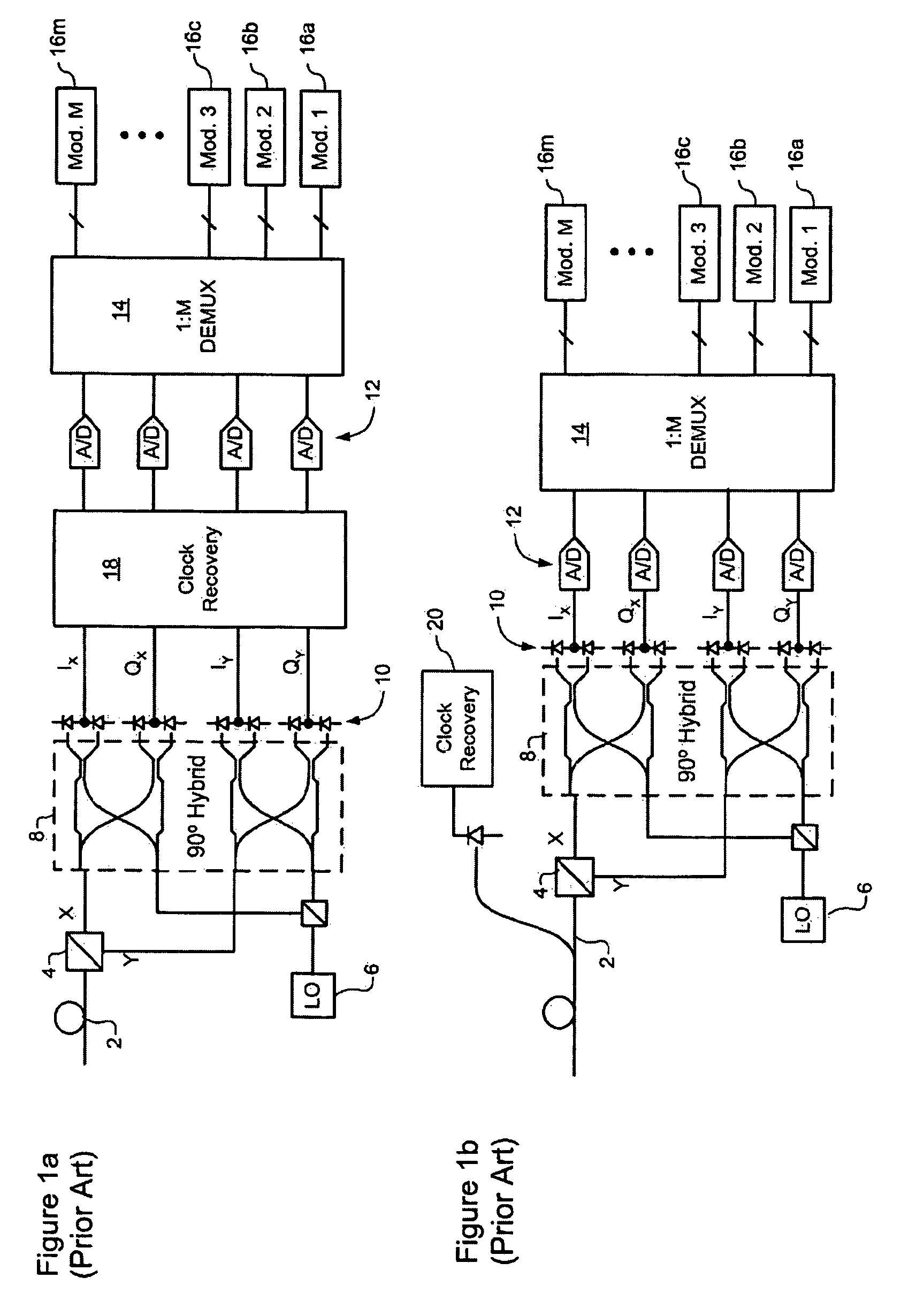
Clock recovery from an optical signal with polarization impairments
ActiveUS20060285855A1Pulse automatic controlPolarisation multiplex systemsCommunications systemClock recovery
A method of recovering a clock signal from an optical signal received through an optical communications system. A digital sample stream is processed to generate a dispersion compensated signal. The dispersion compensated signal is then tapped to obtain upper side band and lower side, band signals of each received polarization of the optical signal. The upper side band sand lower side band signals are then processed to compensate polarization dependent impairments and the clock recovered from the resulting optimized.
Owner:CIENA
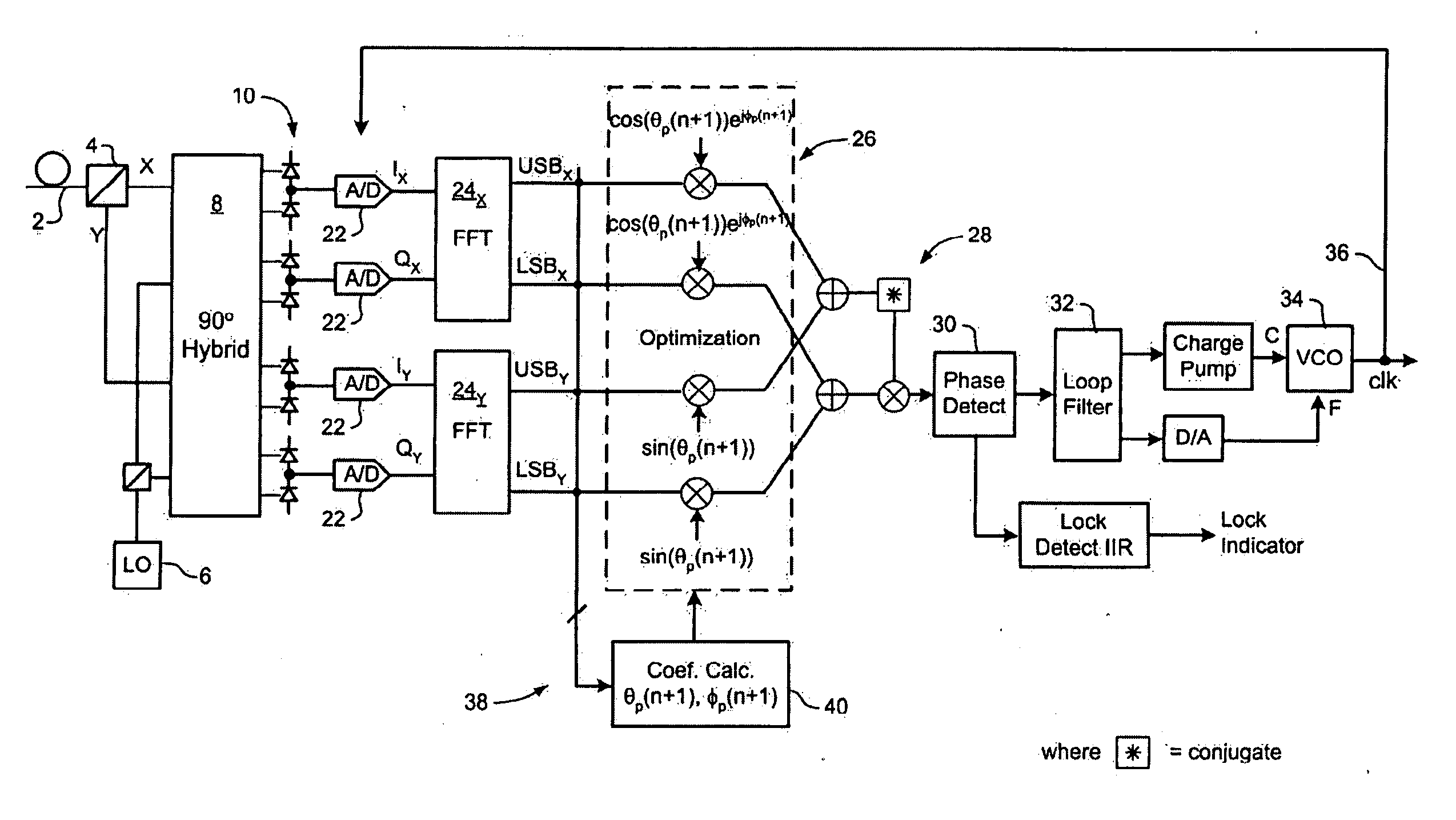
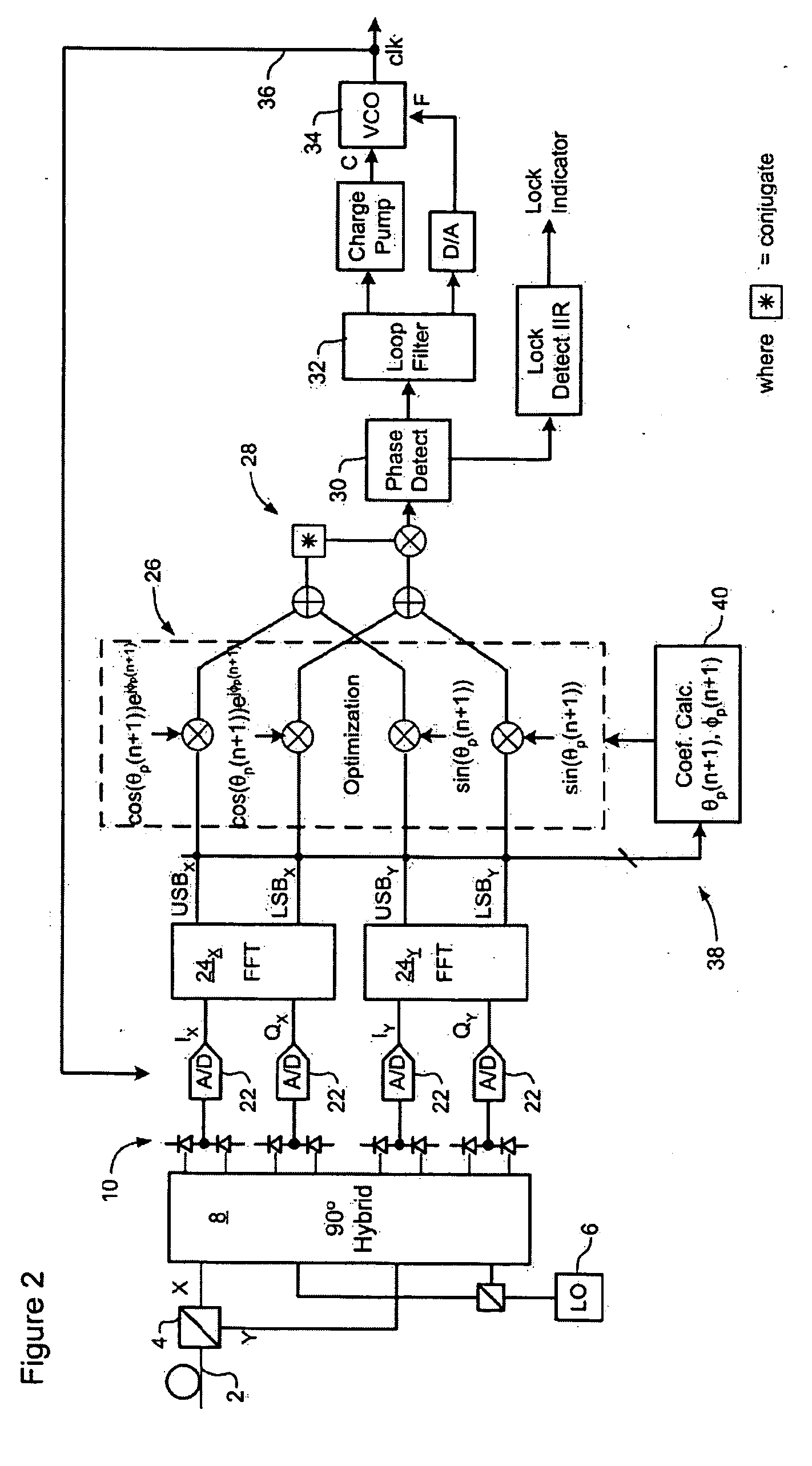
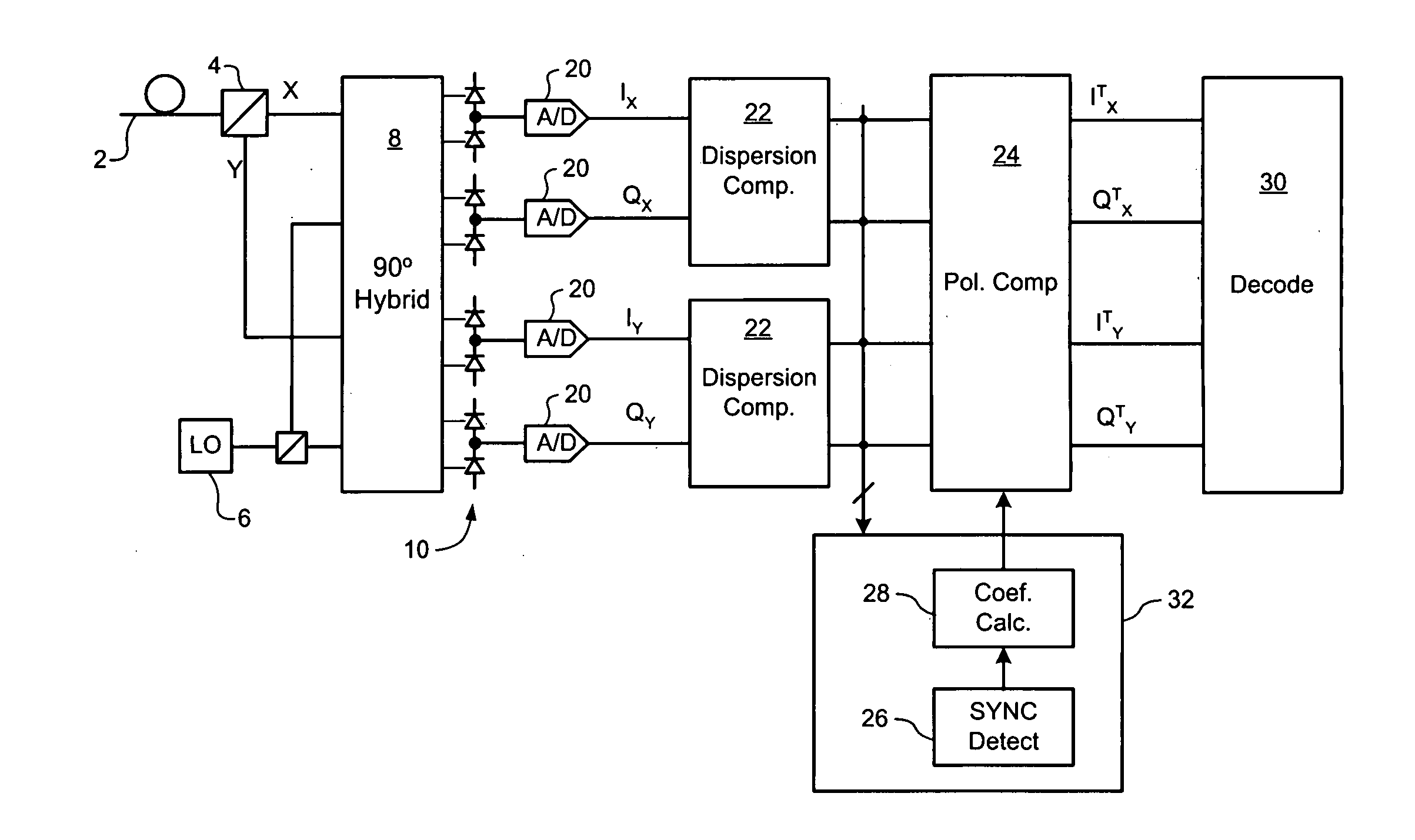
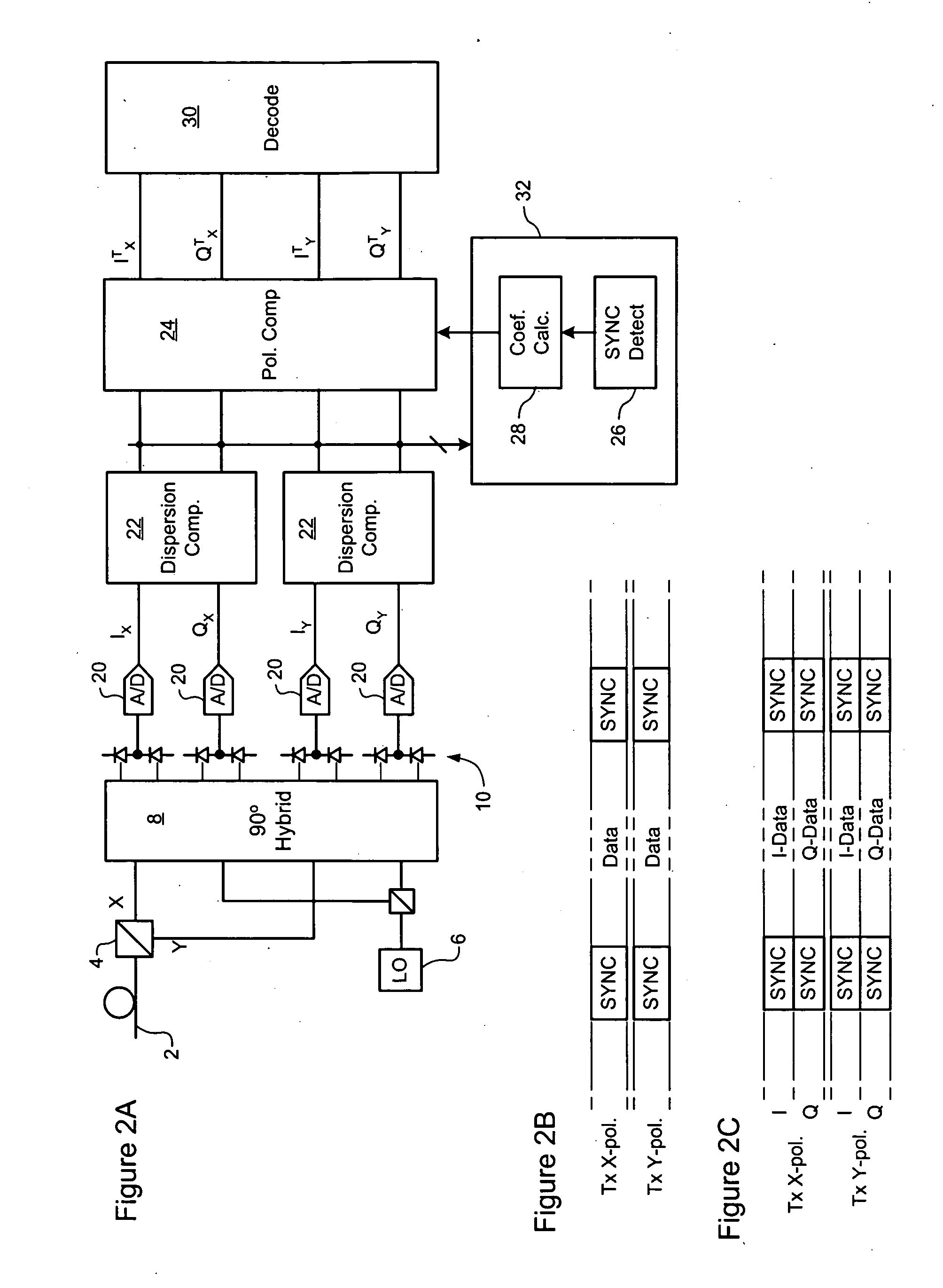
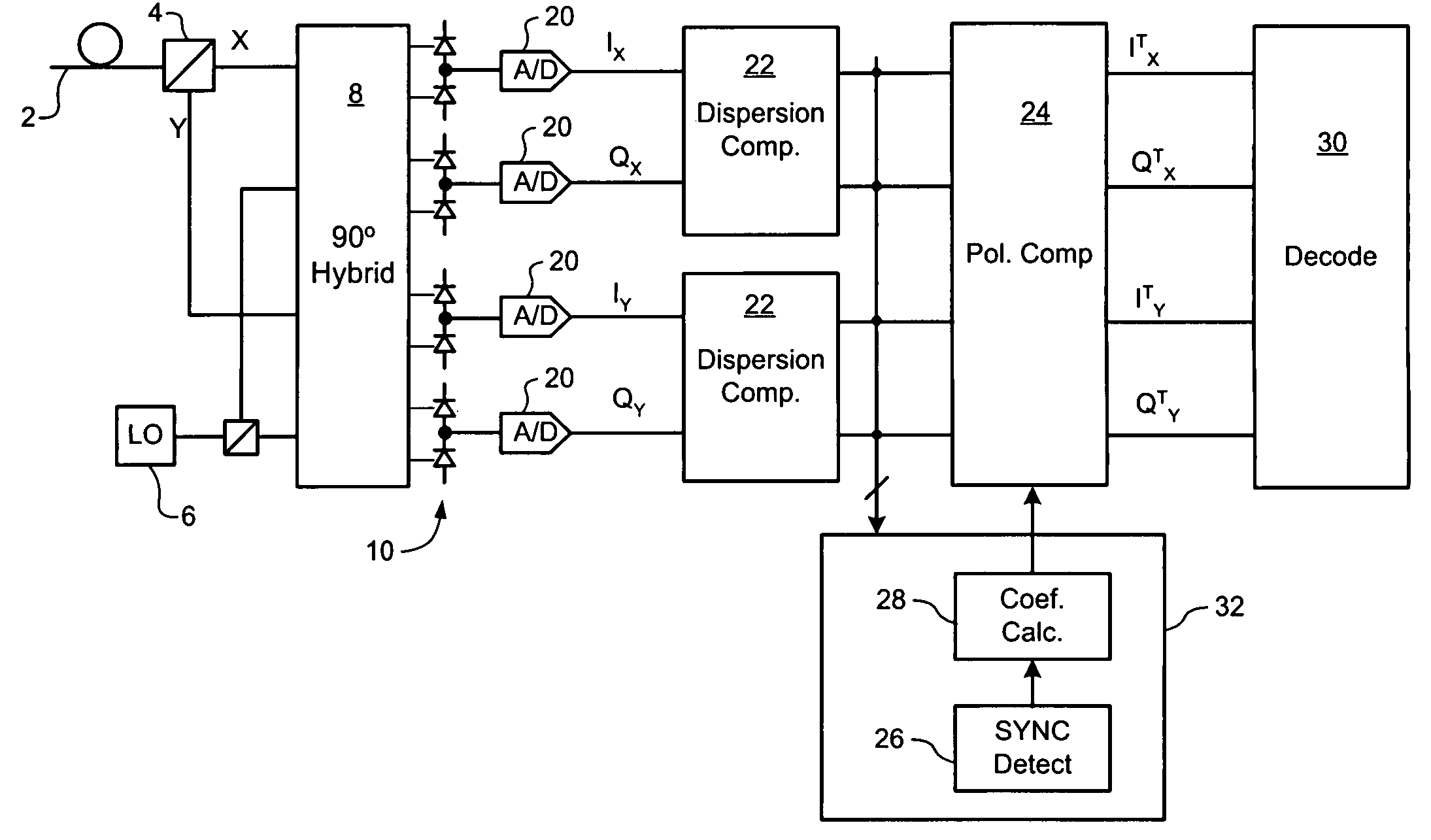
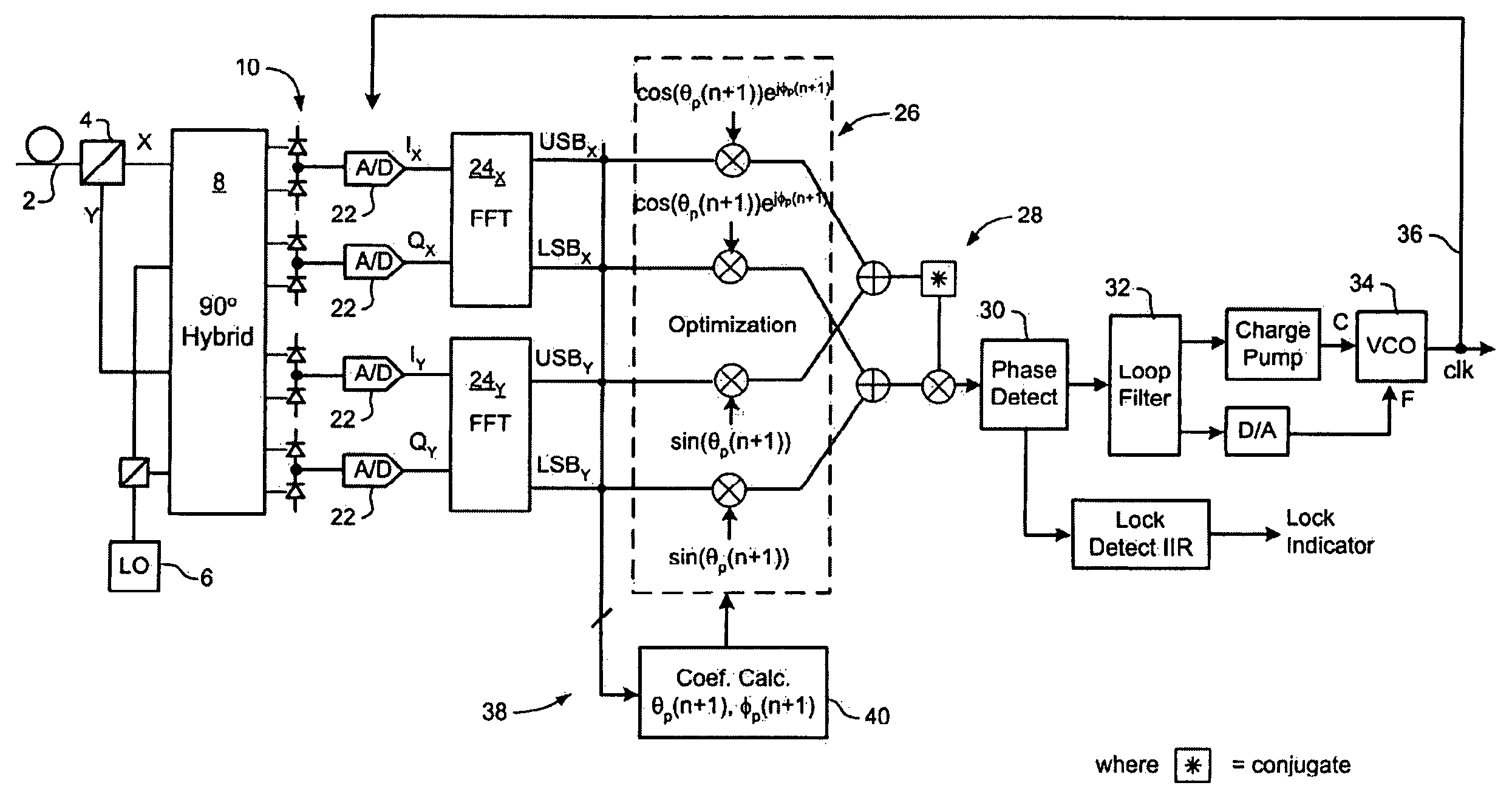
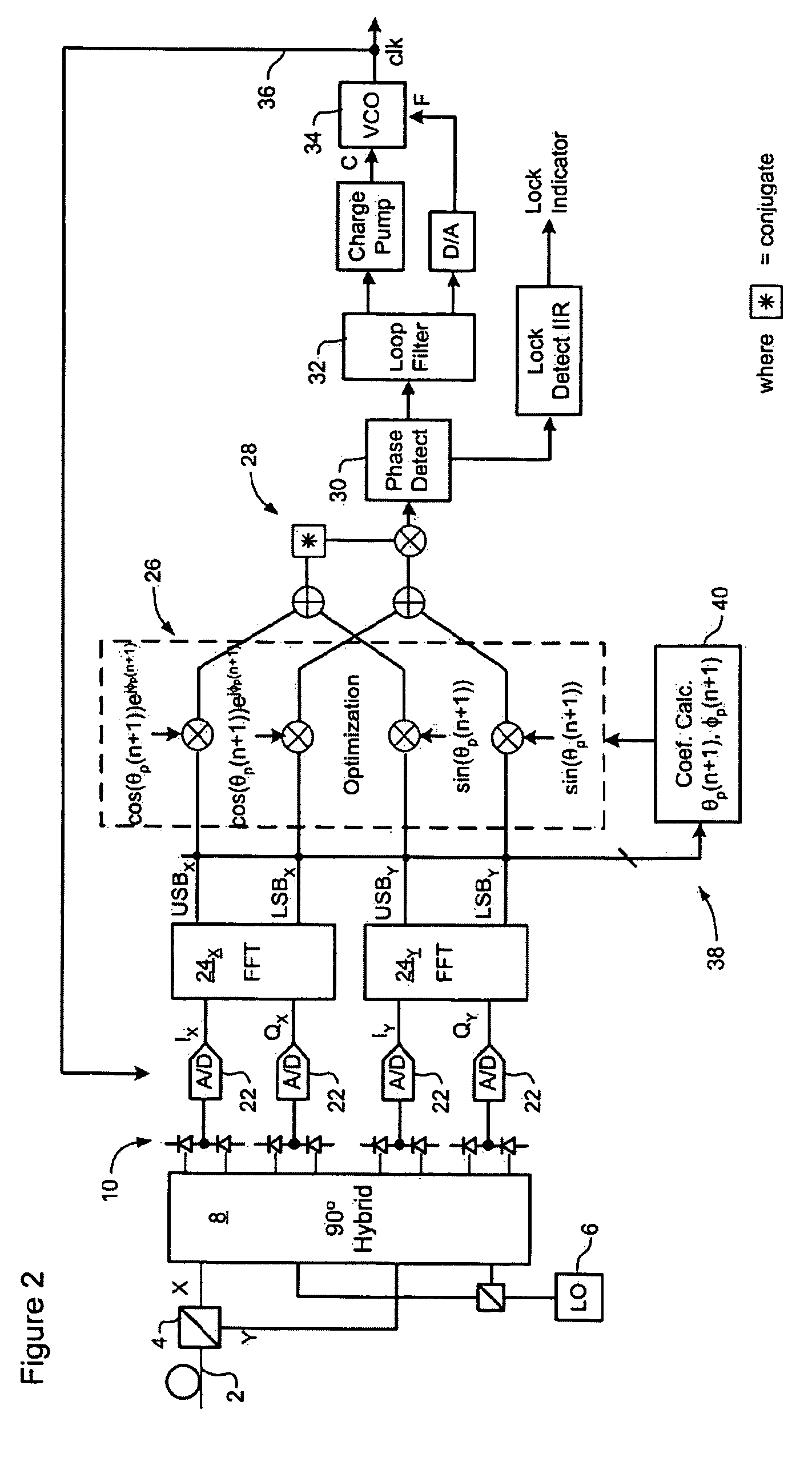
Polarization compensation in a coherent optical receiver
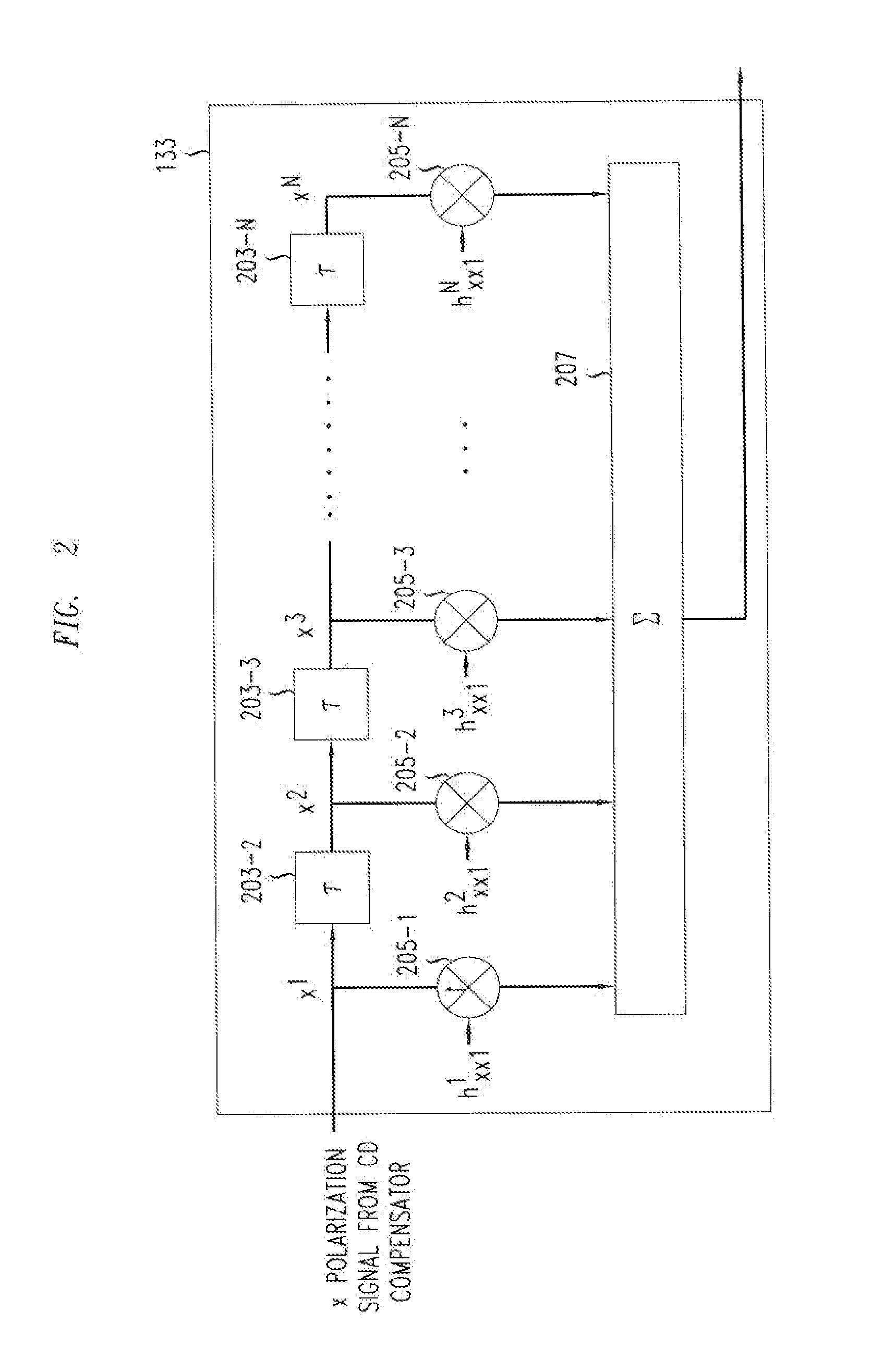
ActiveUS20070092259A1Polarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationPolarization dependentOptical receivers
A method of processing a stream of digital samples of an optical signal received by a coherent optical receiver. The digital sample stream is processed to generate a dispersion compensated sample stream. The dispersion compensated sample stream is then processed to compensate polarization dependent impairments of the optical signal.
Owner:CIENA
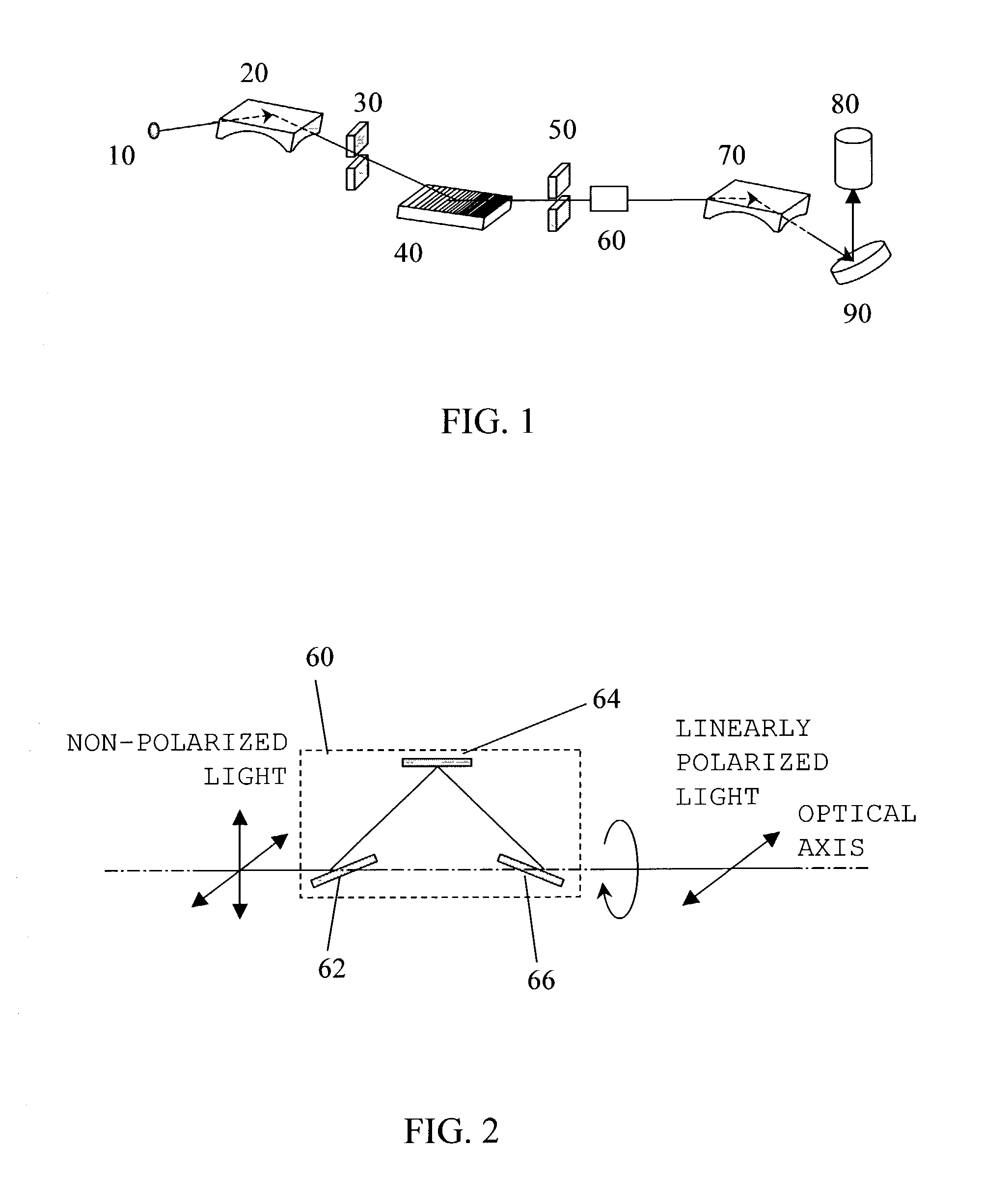
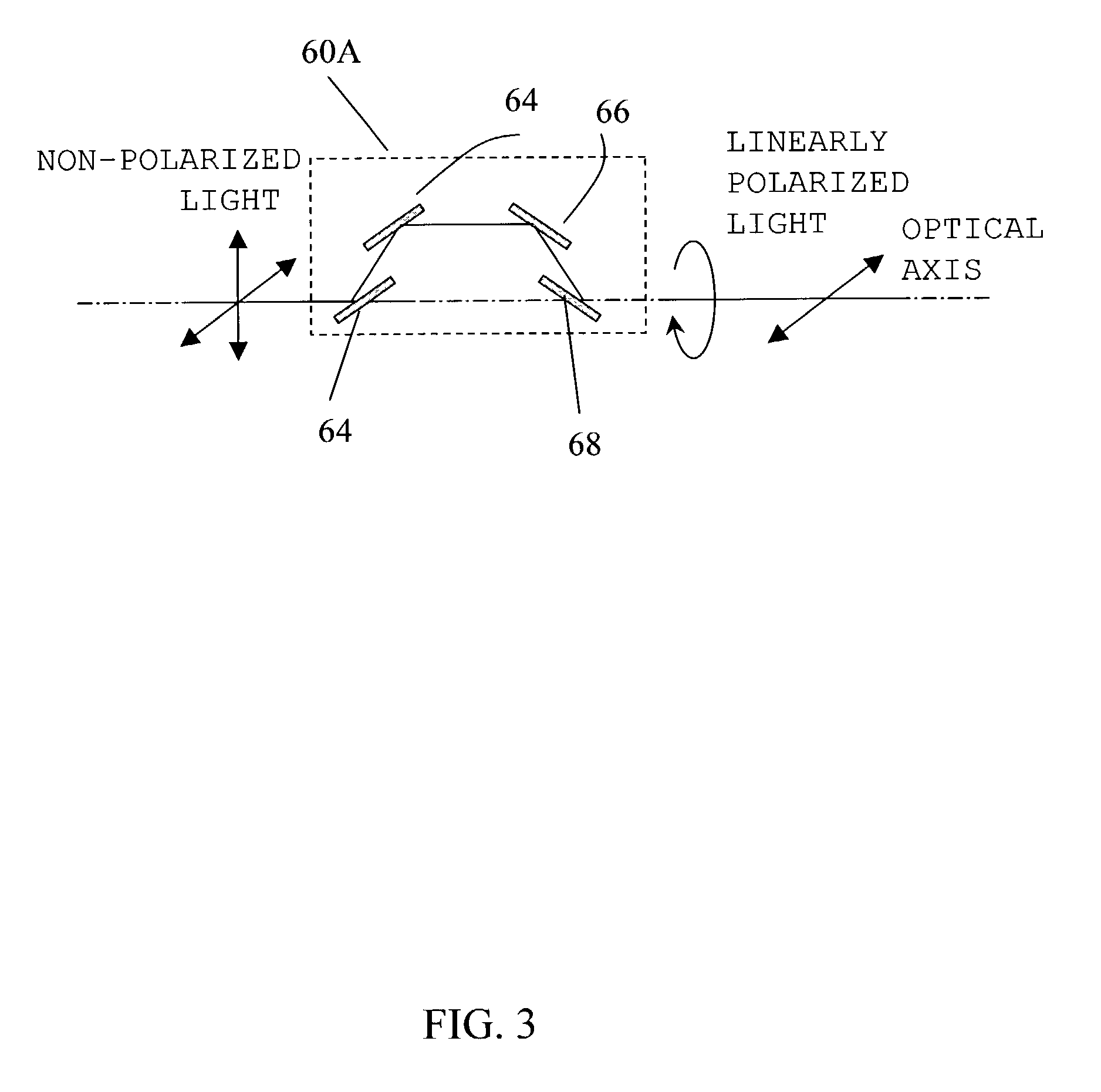
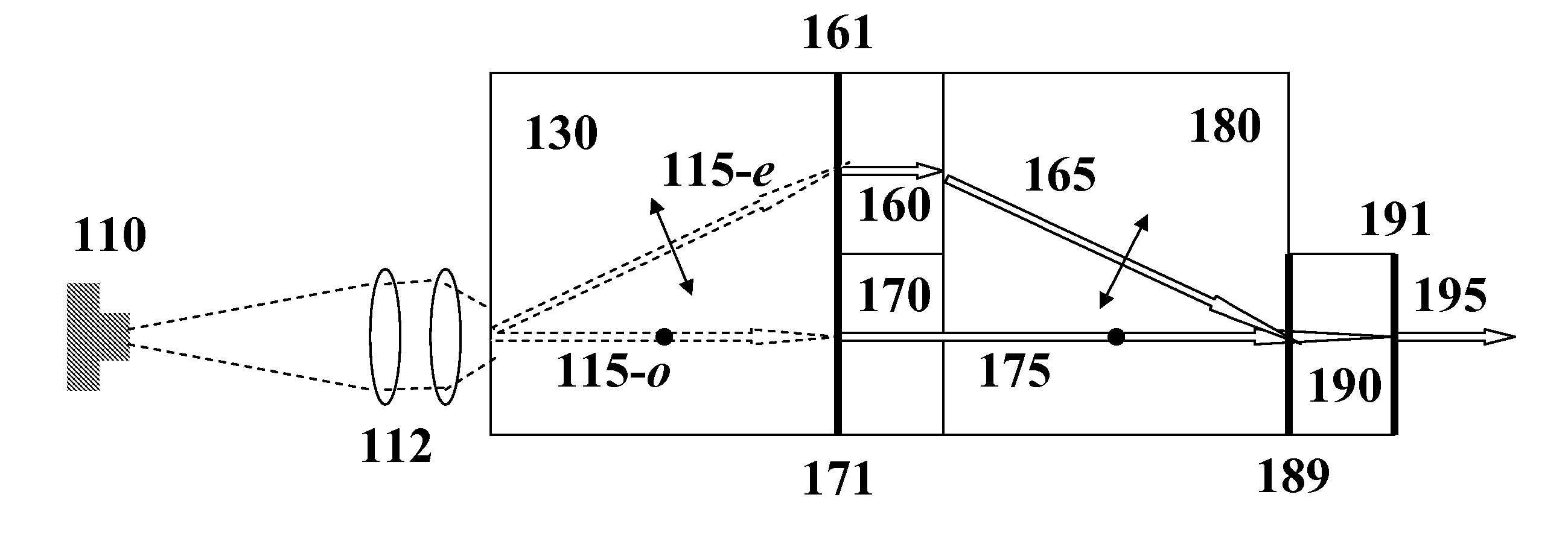
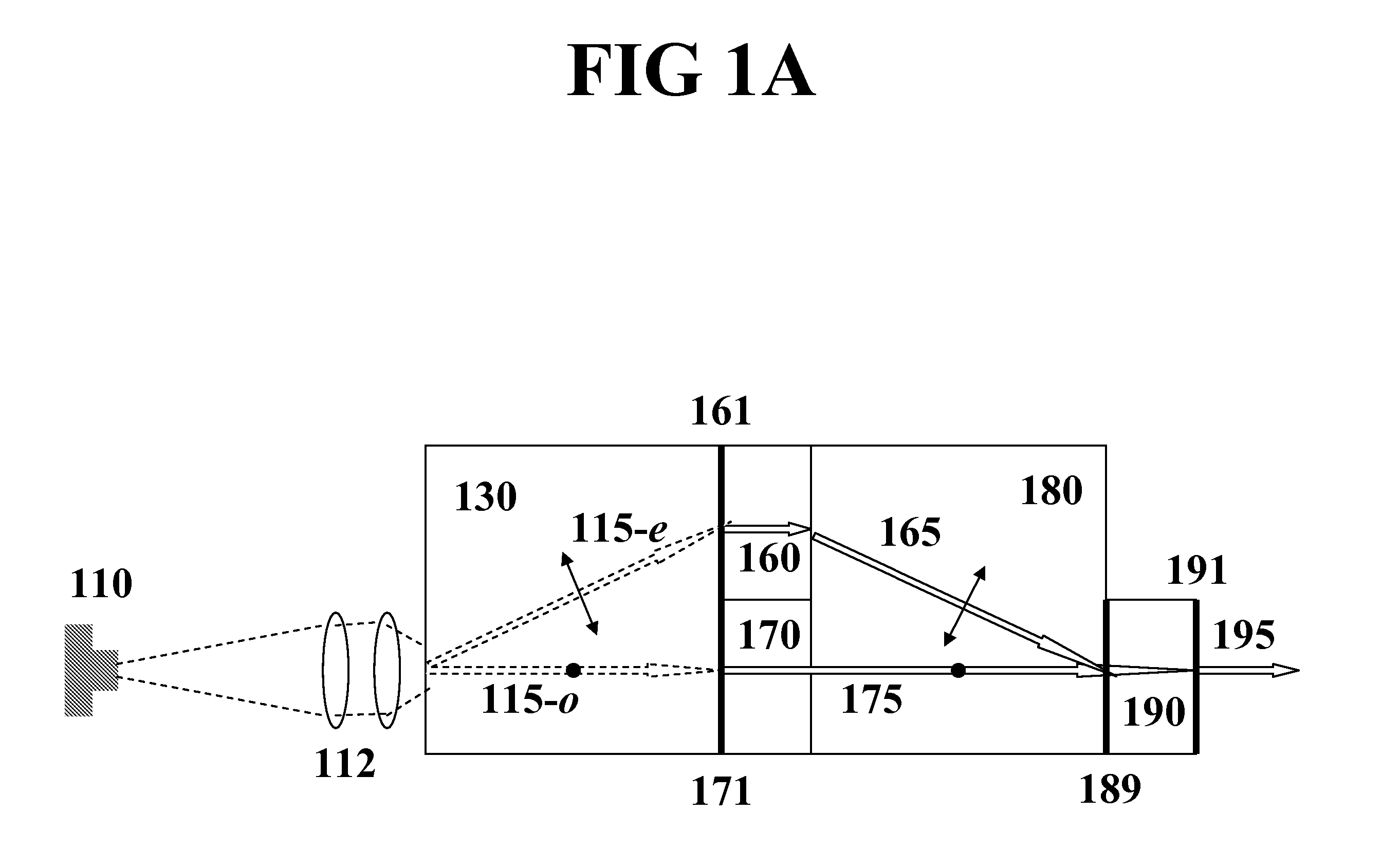
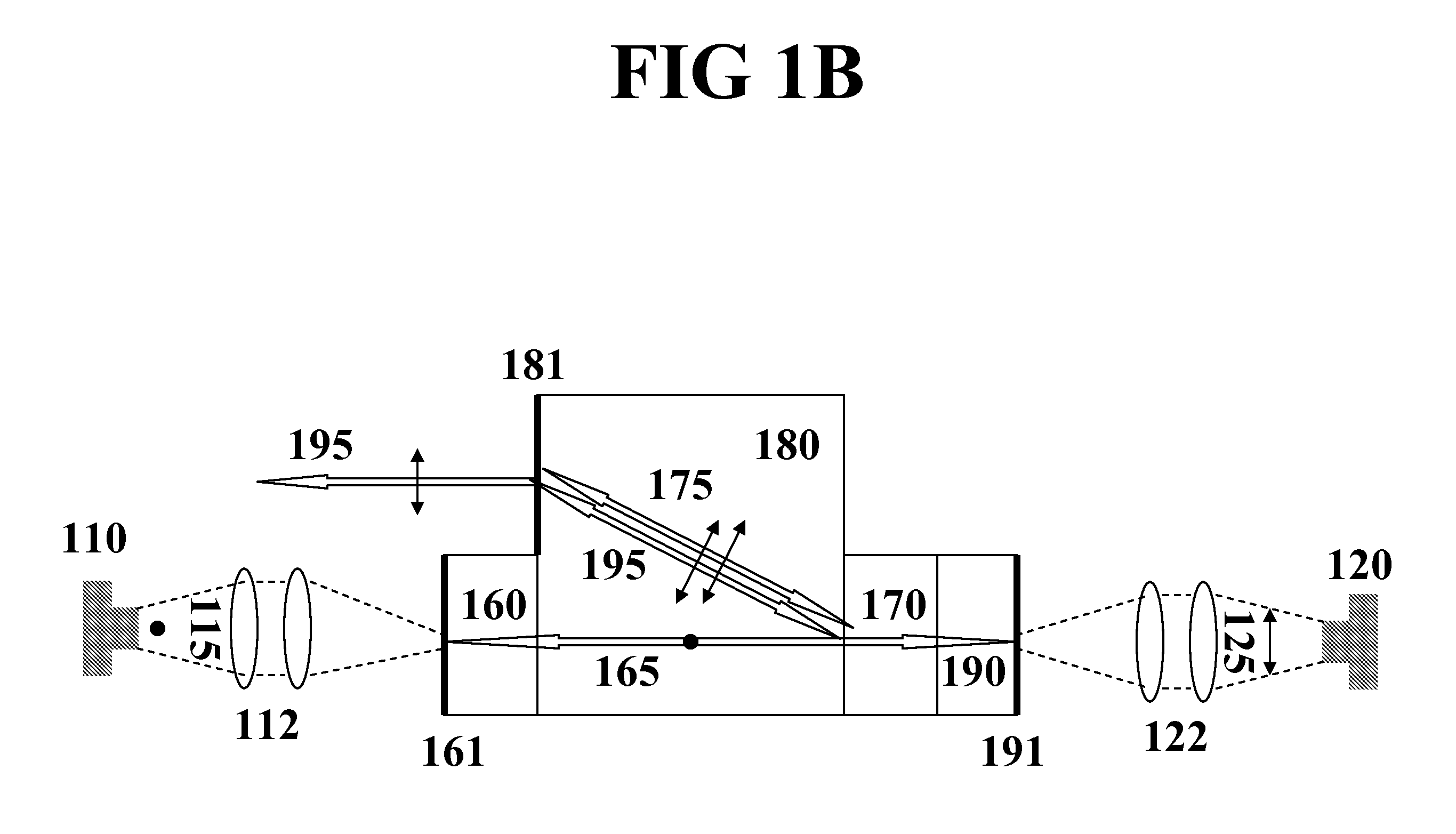
Optical apparatus
InactiveUS6999172B2Easily polarization planeImprove polarizationPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsOptical axisX-ray
Owner:CANON KK
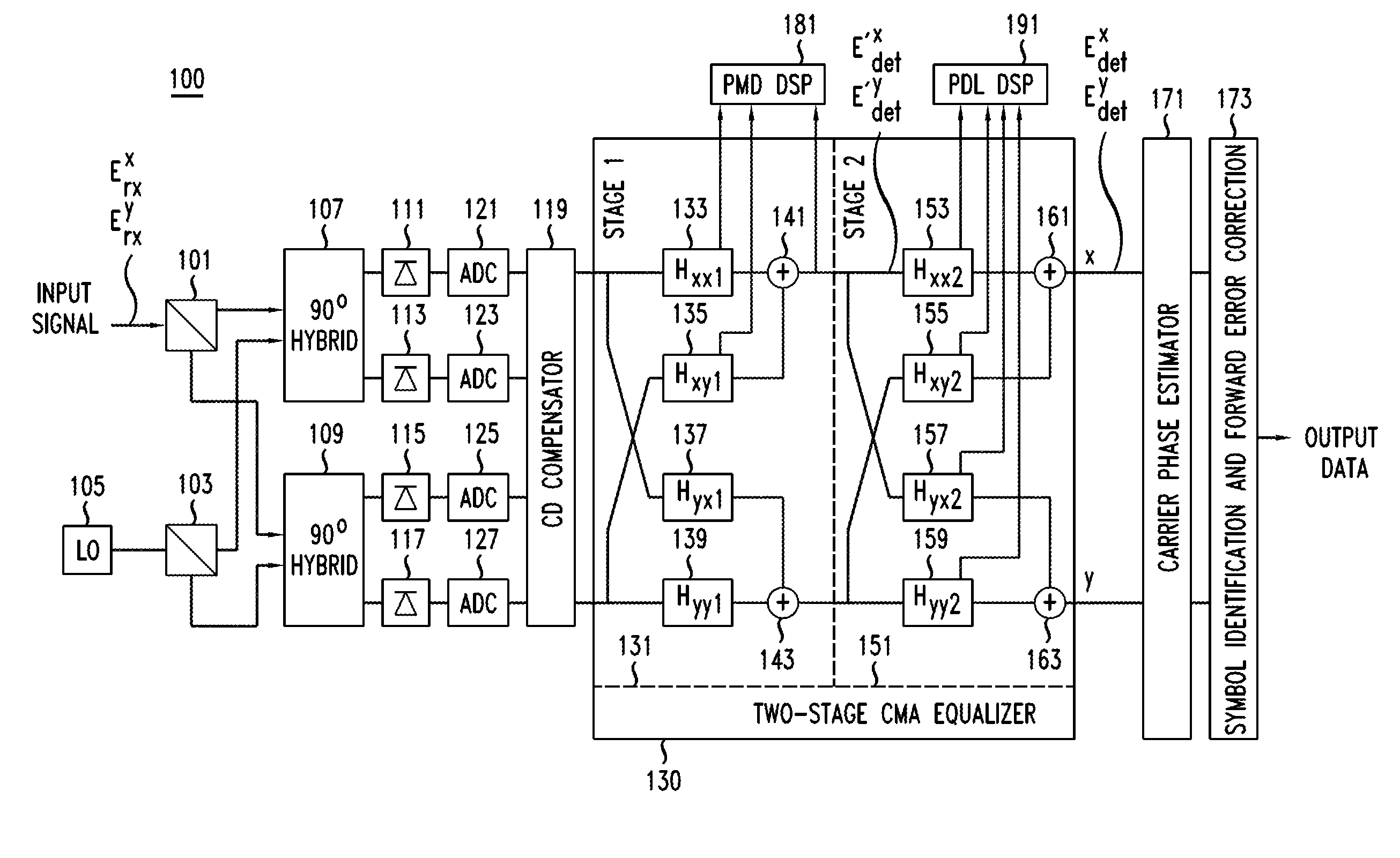
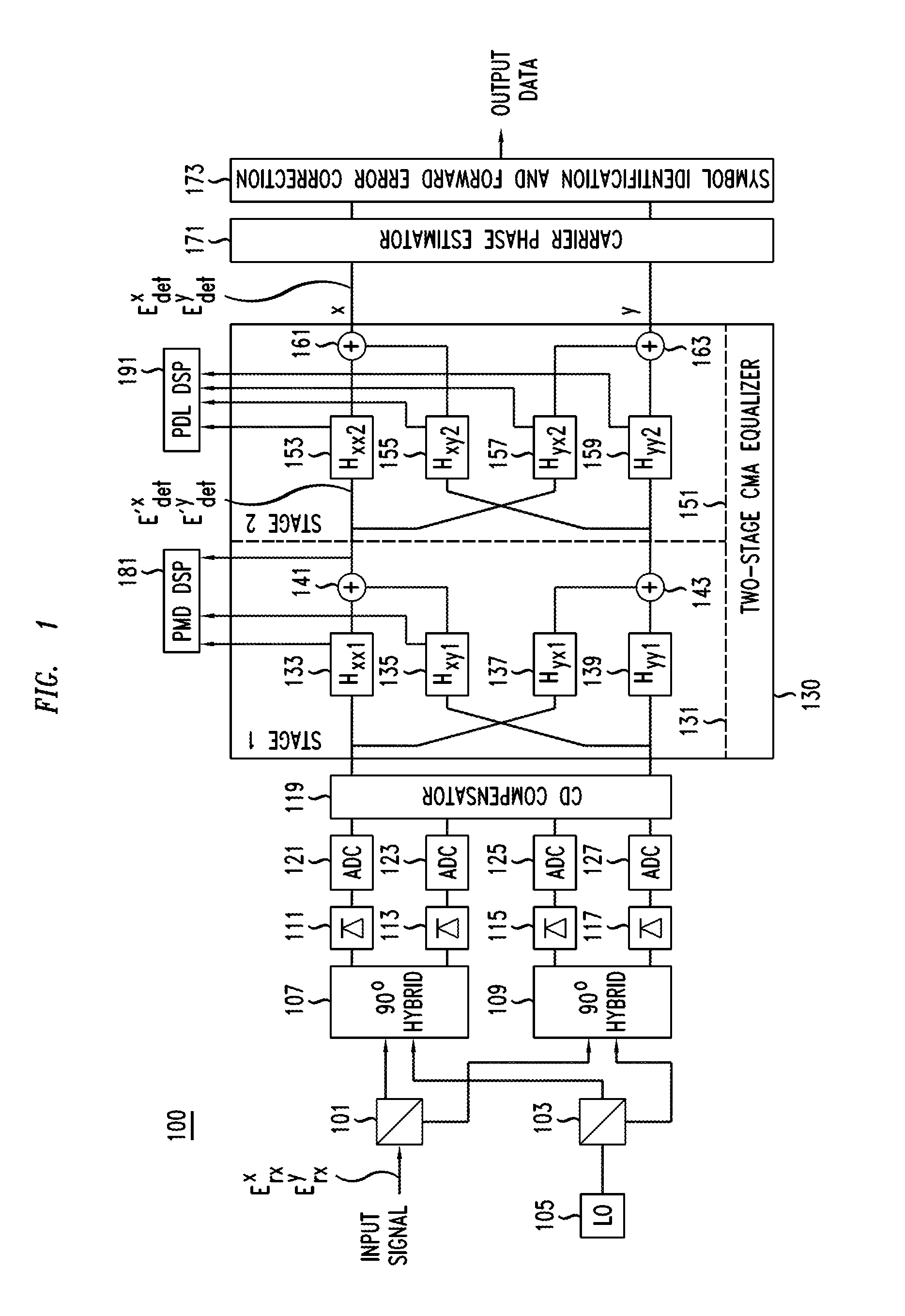
Method And Apparatus For Polarization-Division-Multiplexed Optical Receivers
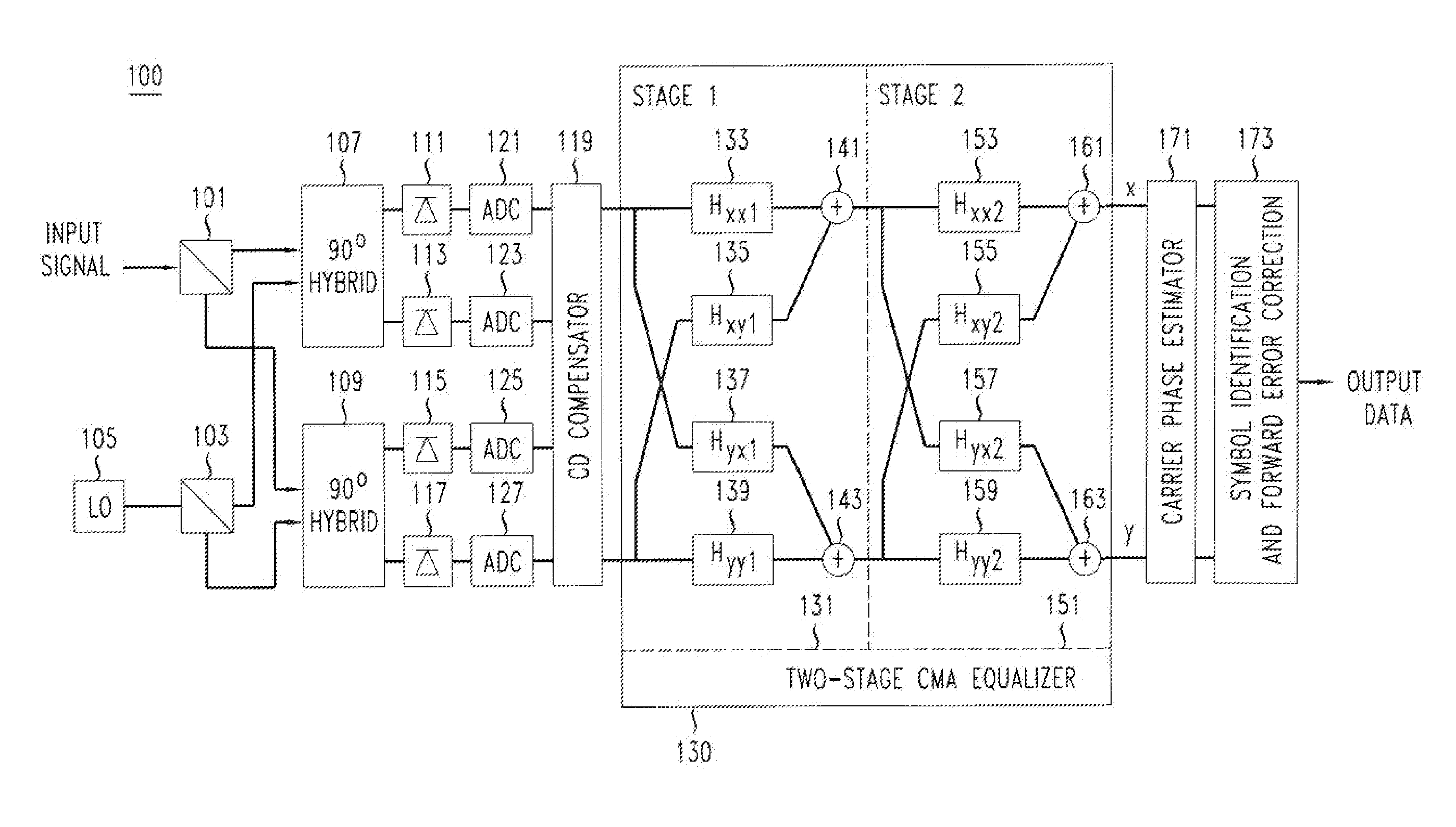
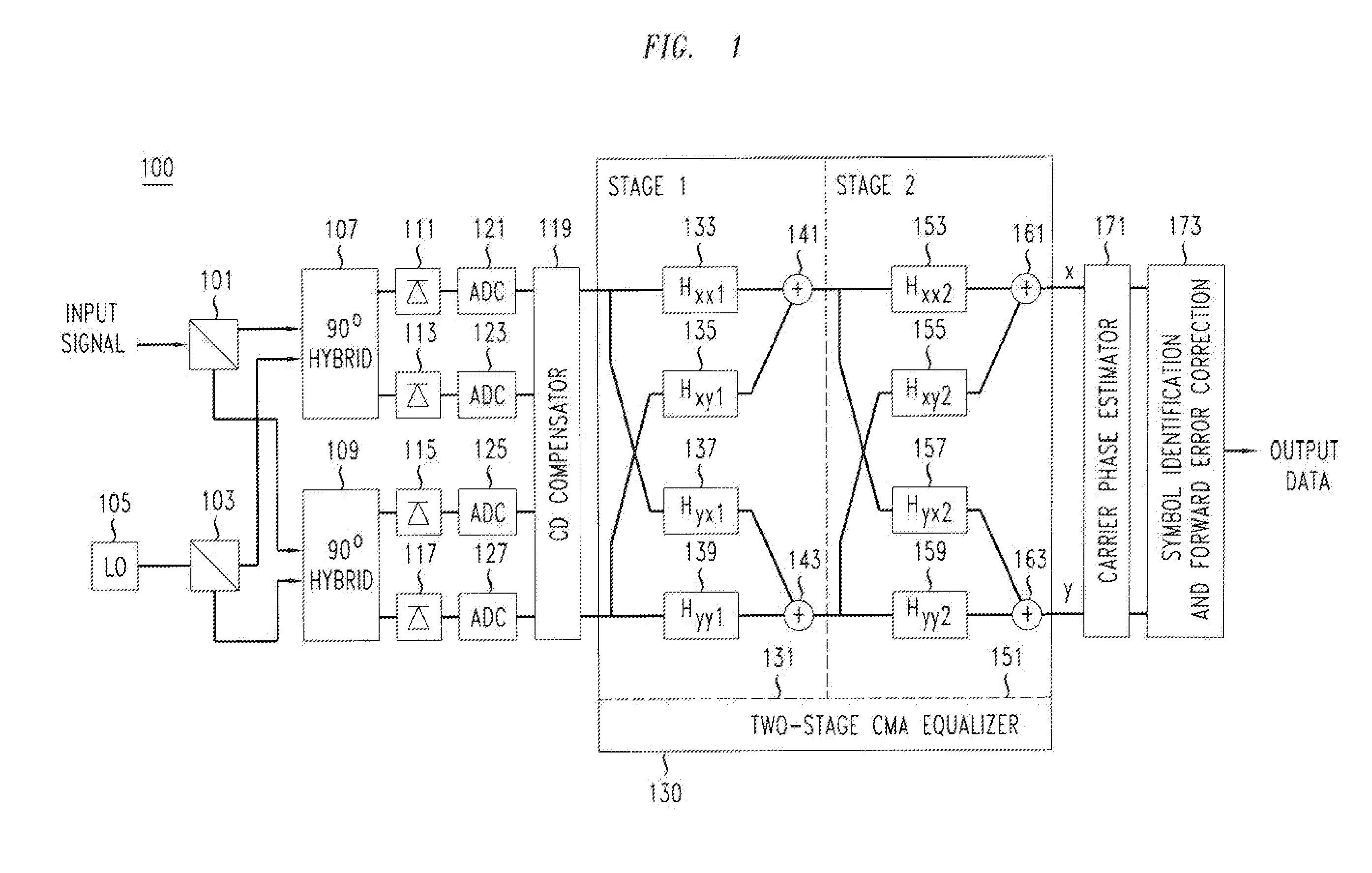
ActiveUS20120002979A1Effective wayEliminate the problemElectromagnetic receiversEqualizationPolarization mode dispersion
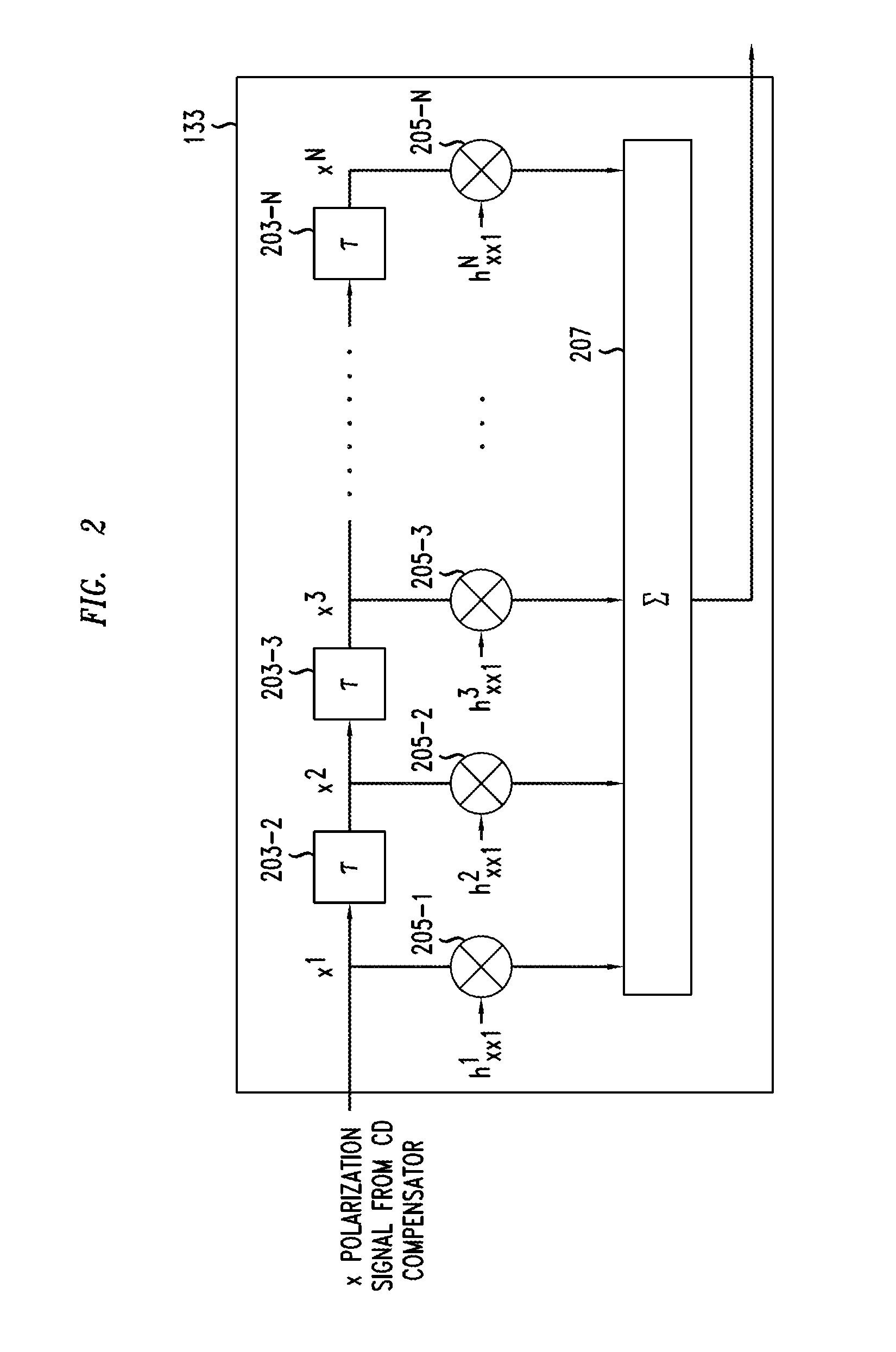
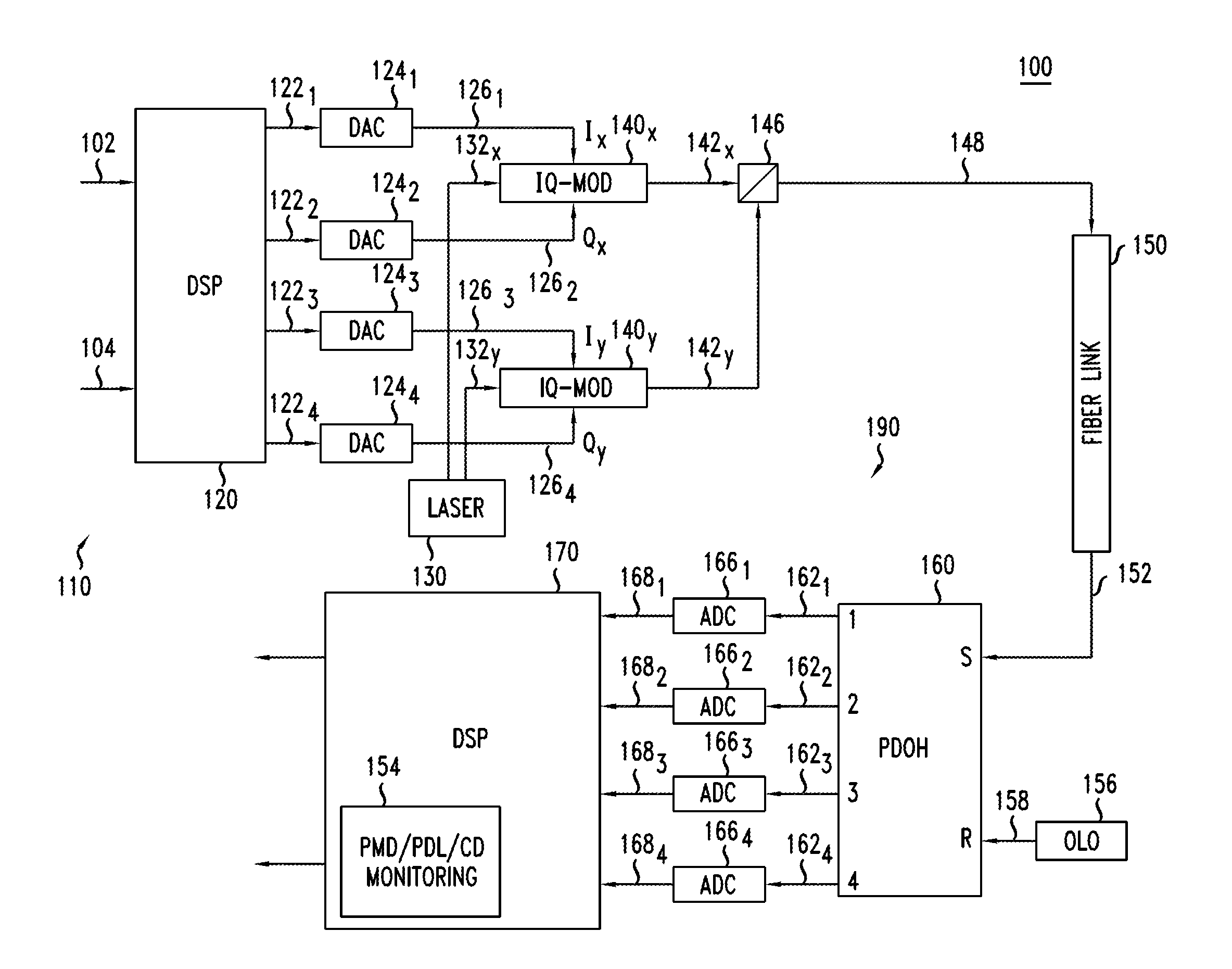
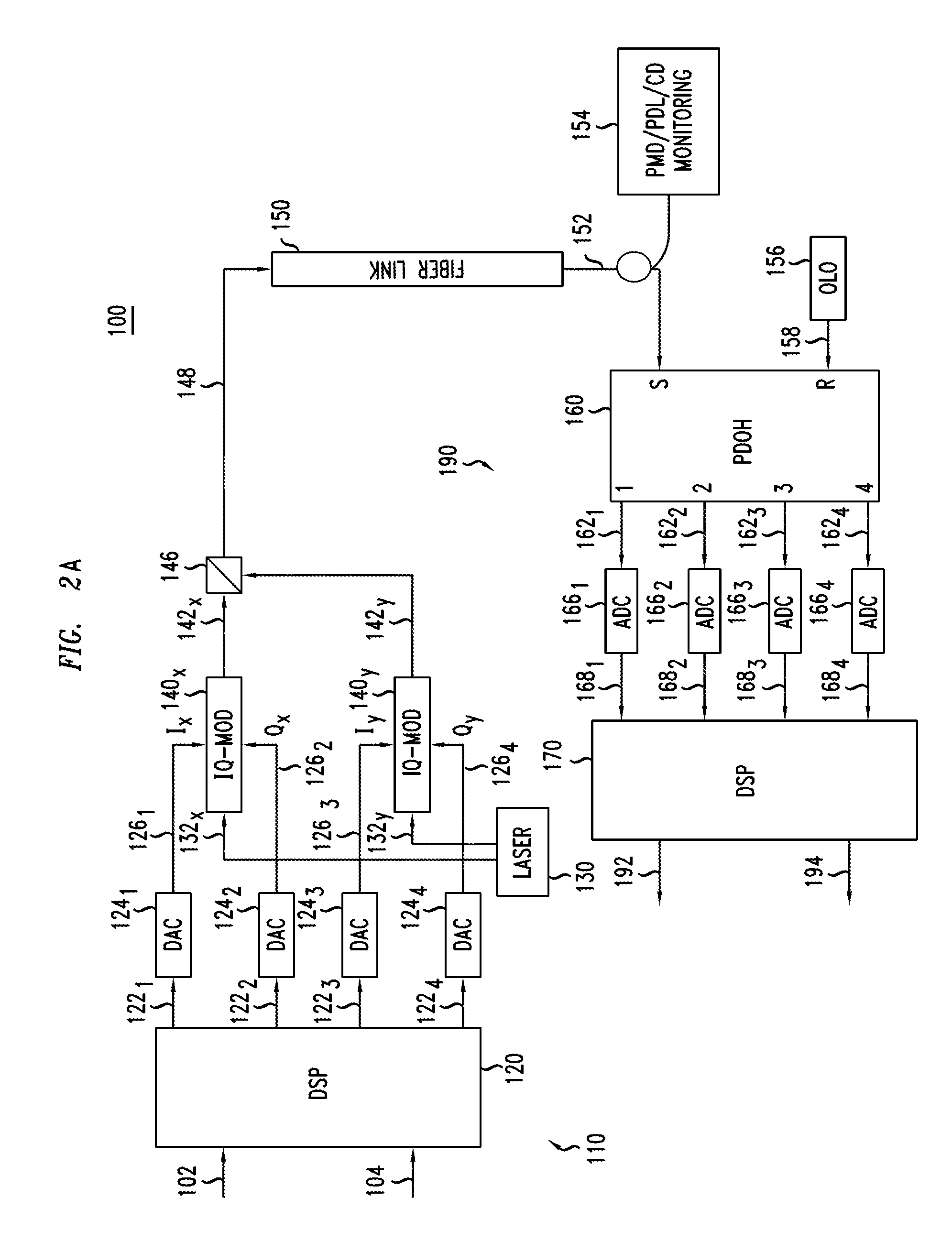
An optical receiver includes a two-stage constant modulus algorithm (CMA) equalizer. The first stage is a modified version of a CMA equalizer and the second stage is a conventional CMA equalizer. The first stage may be made up of four sub-equalizers, of which only two of the sub-equalizers are independent, i.e., uncorrelated to each other. This first stage equalizer compensates for polarization-mode dispersion (PMD). The second stage equalizer is a conventional CMA equalizer made up of four sub-equalizers that are adjusted independently. This second stage equalizer may compensate for polarization-dependent loss (PDL). The receiver includes a first processor that determines PMD information based on a plurality of transfer function parameters of the modified CMA equalization of the first stage equalizer and the modified-equalized output and a second processor that determines PDL based on a plurality of transfer function parameters of the CMA equalization of the second stage equalizer.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
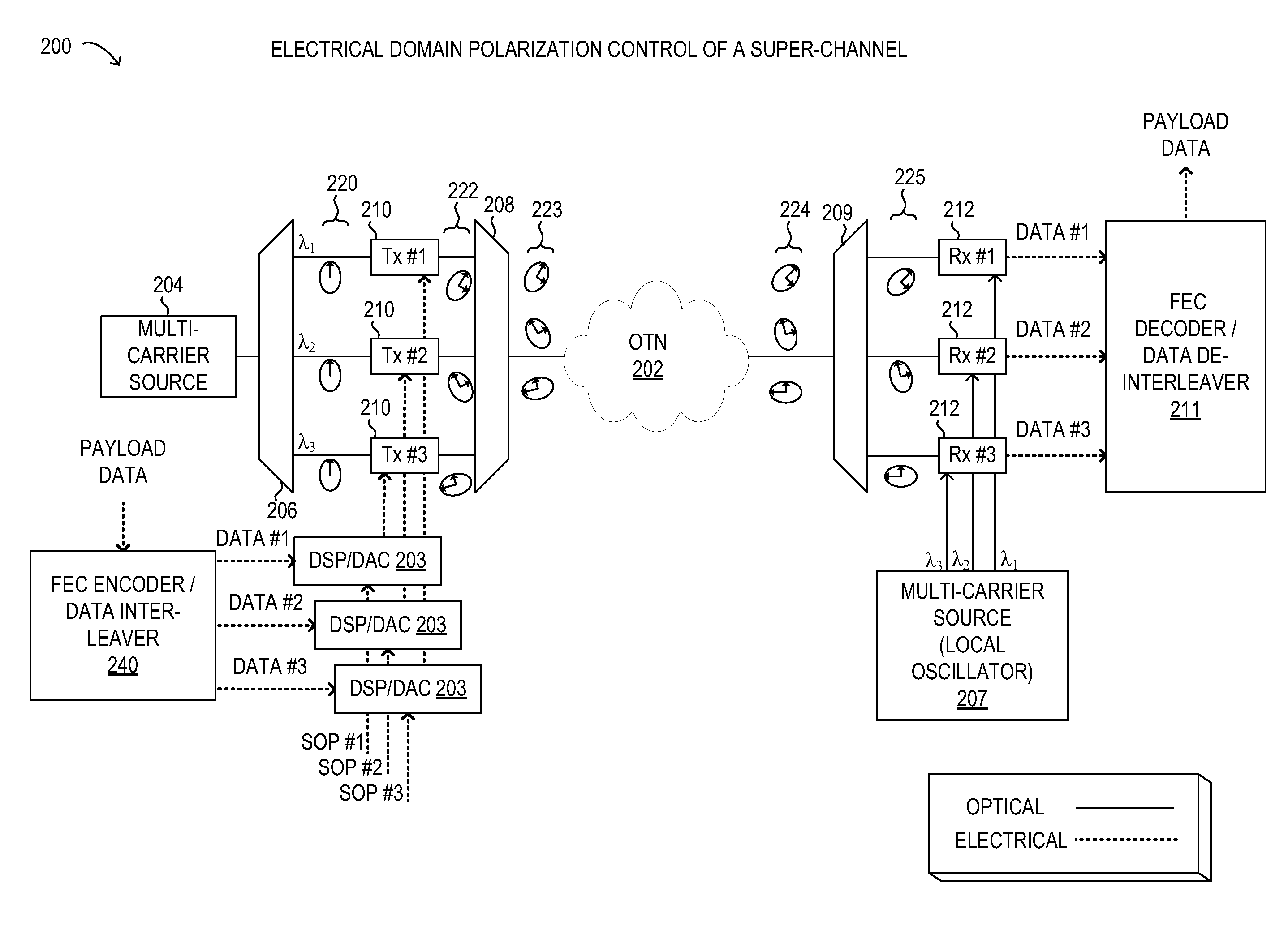
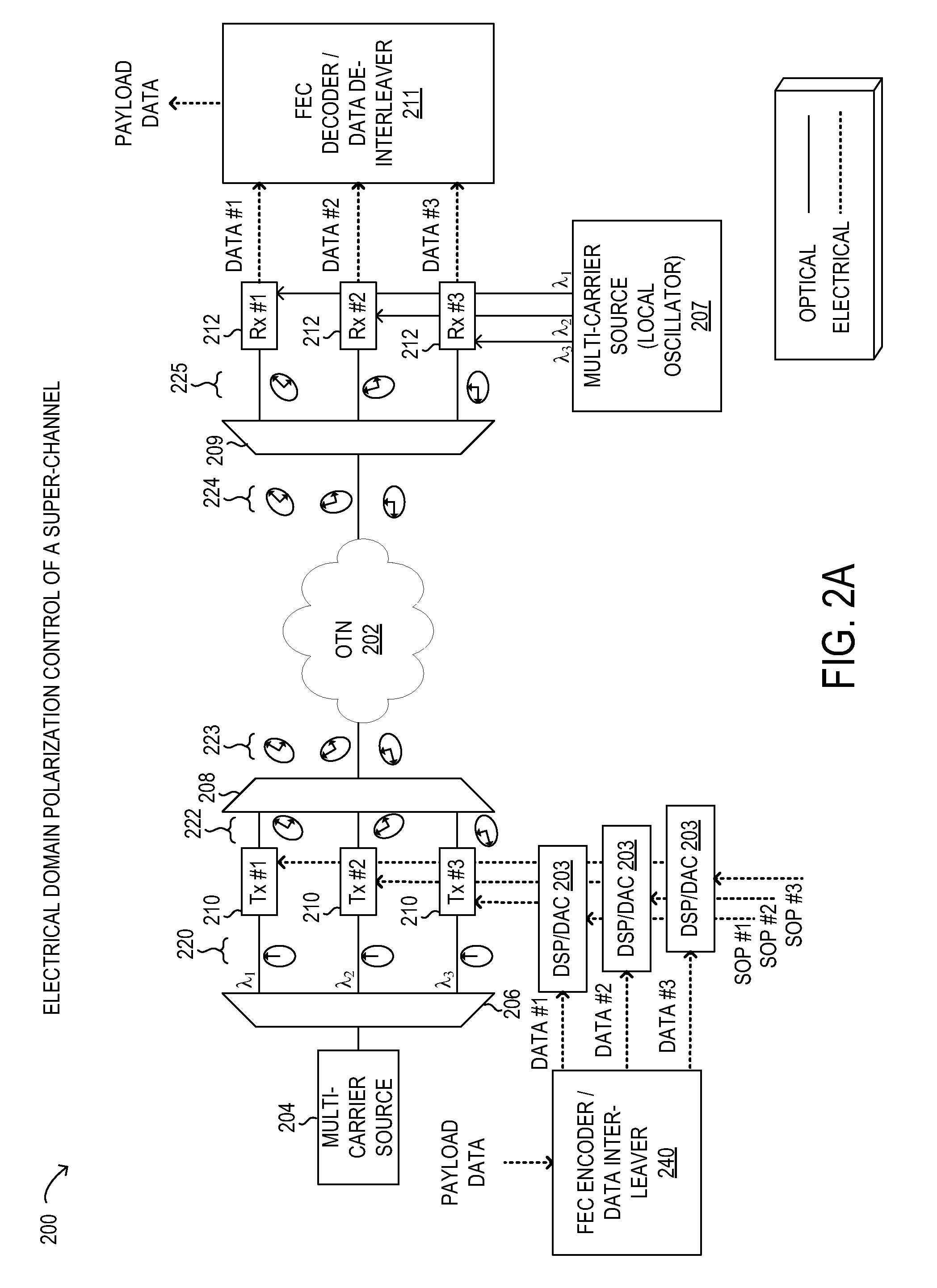
Electrical domain mitigation of polarization dependent effects in an optical communications system
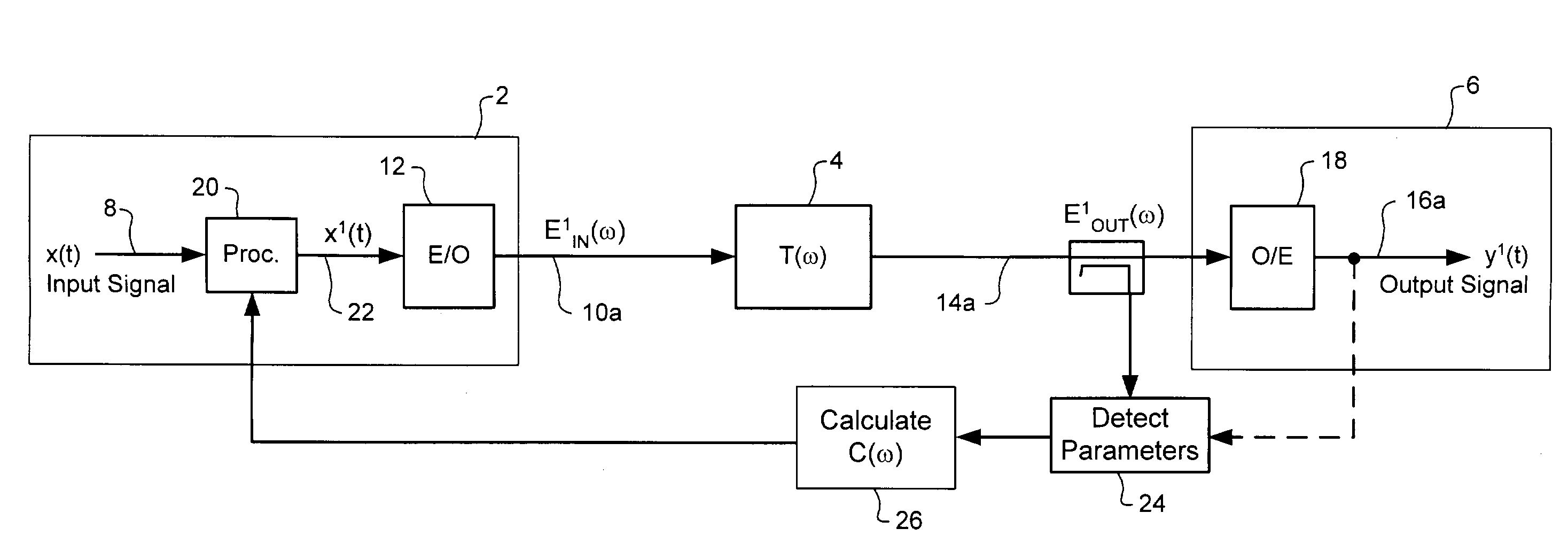
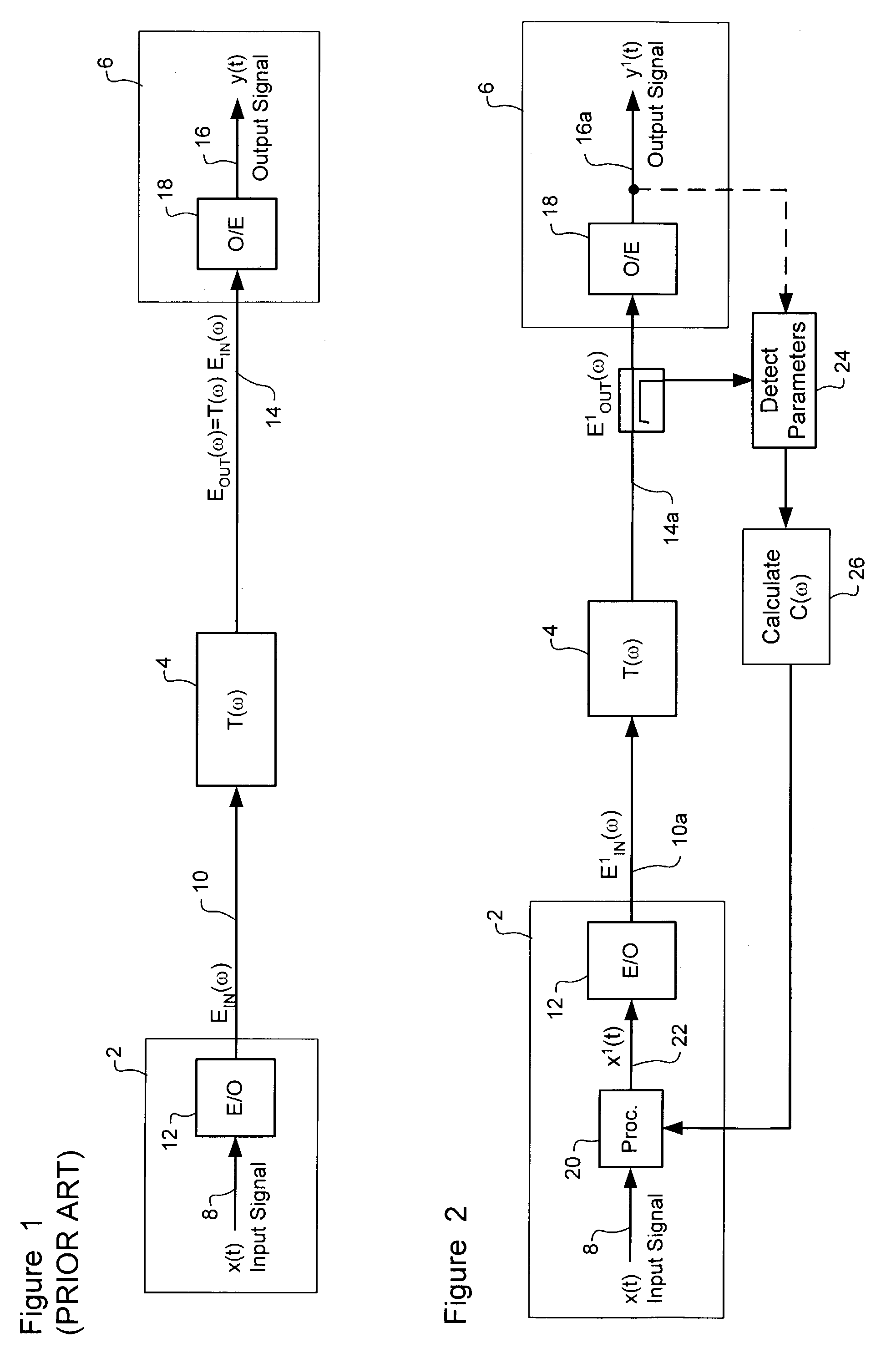
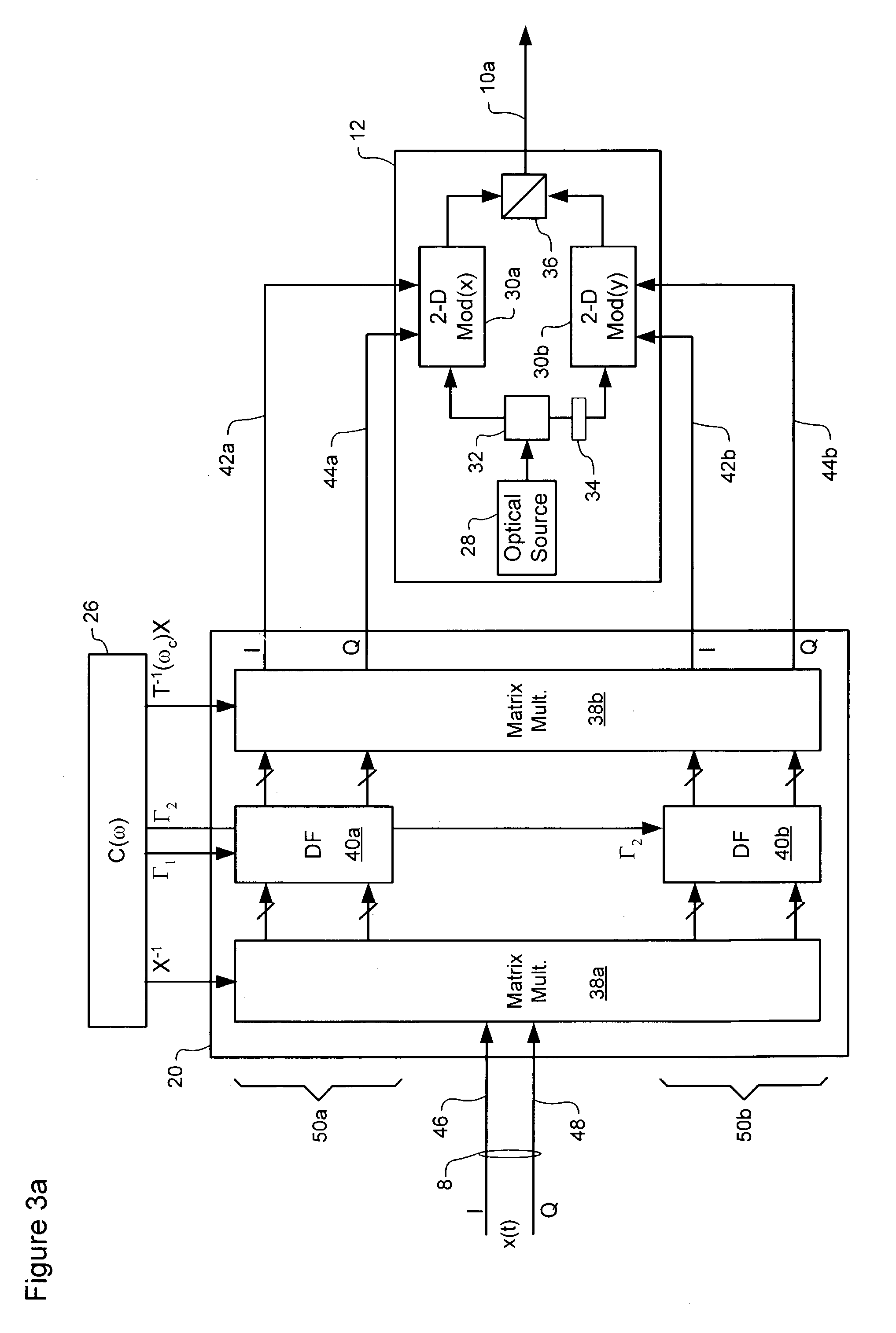
ActiveUS7382985B2Reduce impactCost-effectiveDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersCommunications systemPolarization mode dispersion
Polarization Dependent Effects (PDEs), including Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) and Polarization Dependent Loss (PDL) imposed on optical signals conveyed through an optical link are compensated by processing an input signal in the electrical domain prior to transmission. A compensation function is derived that at least partially compensates the PDEs. The communications signal is then processed in the electrical domain using the compensation function to generate an electrical predistorted signal. The electrical predistorted signal is then used to modulate an optical source to generate a corresponding predistorted optical signal for transmission through the optical link. The PDEs of the optical link operate of the predistorted optical signal such at that substantially undistorted optical signal is received at a receiving end of the link.
Owner:CIENA
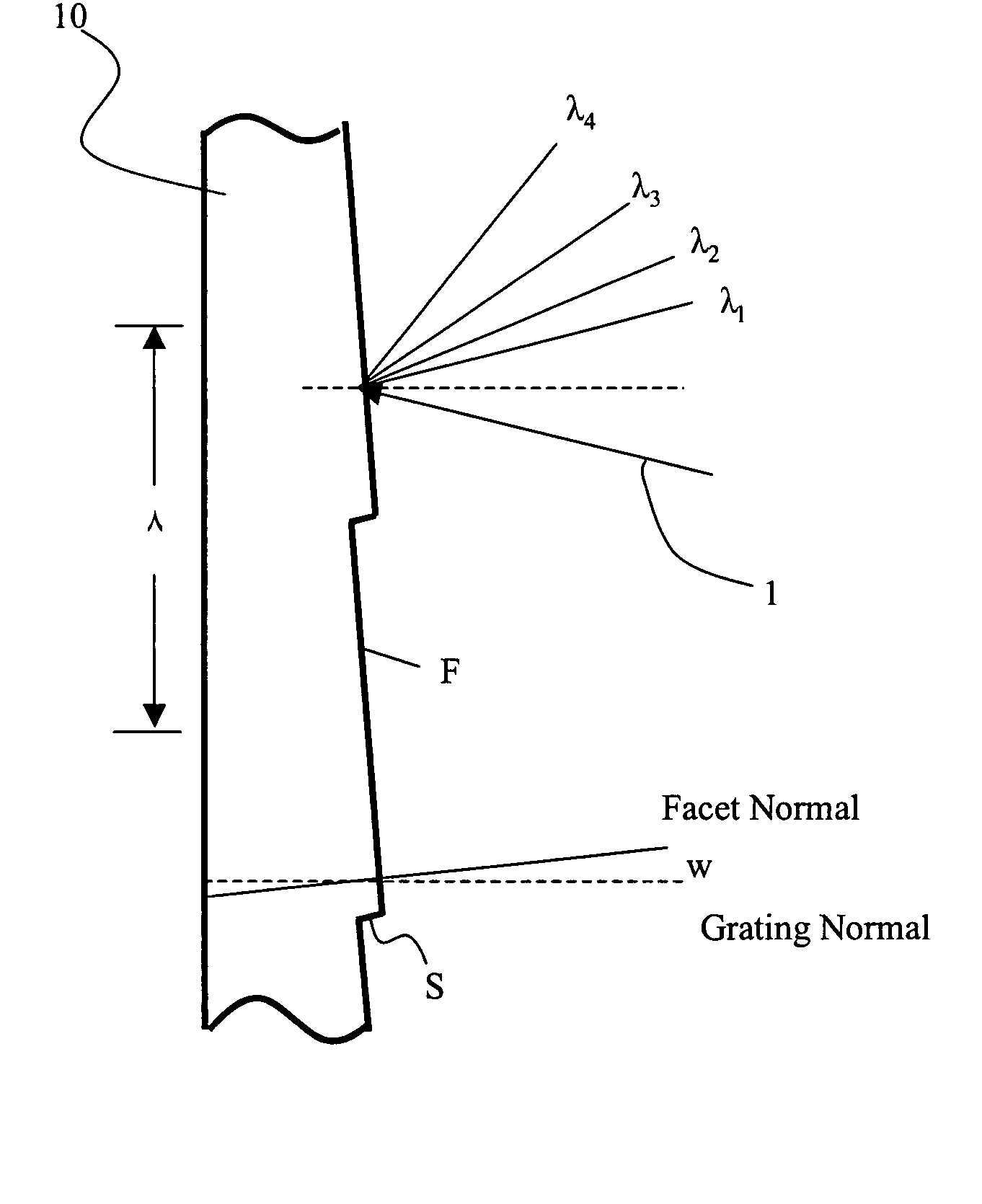
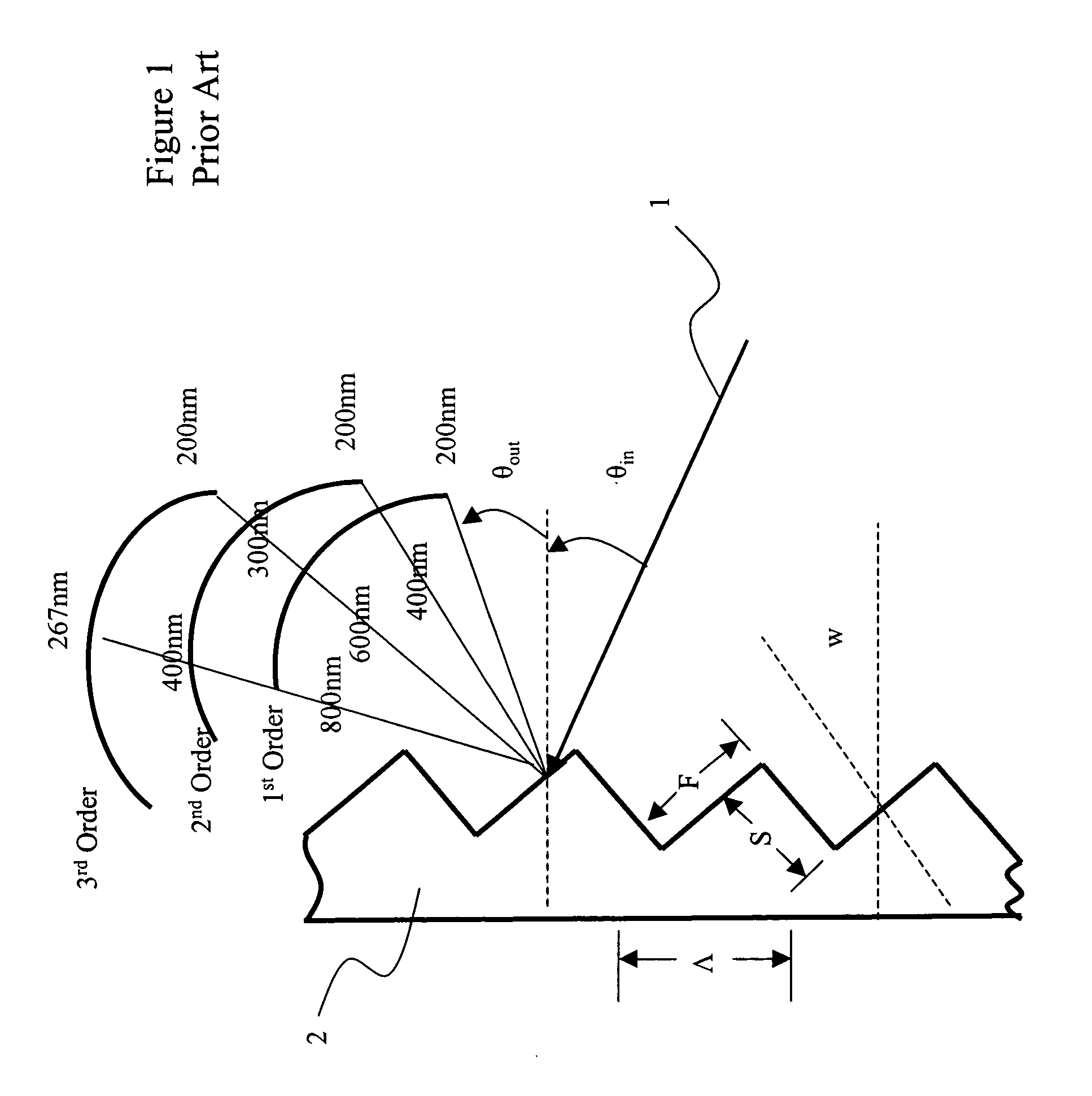
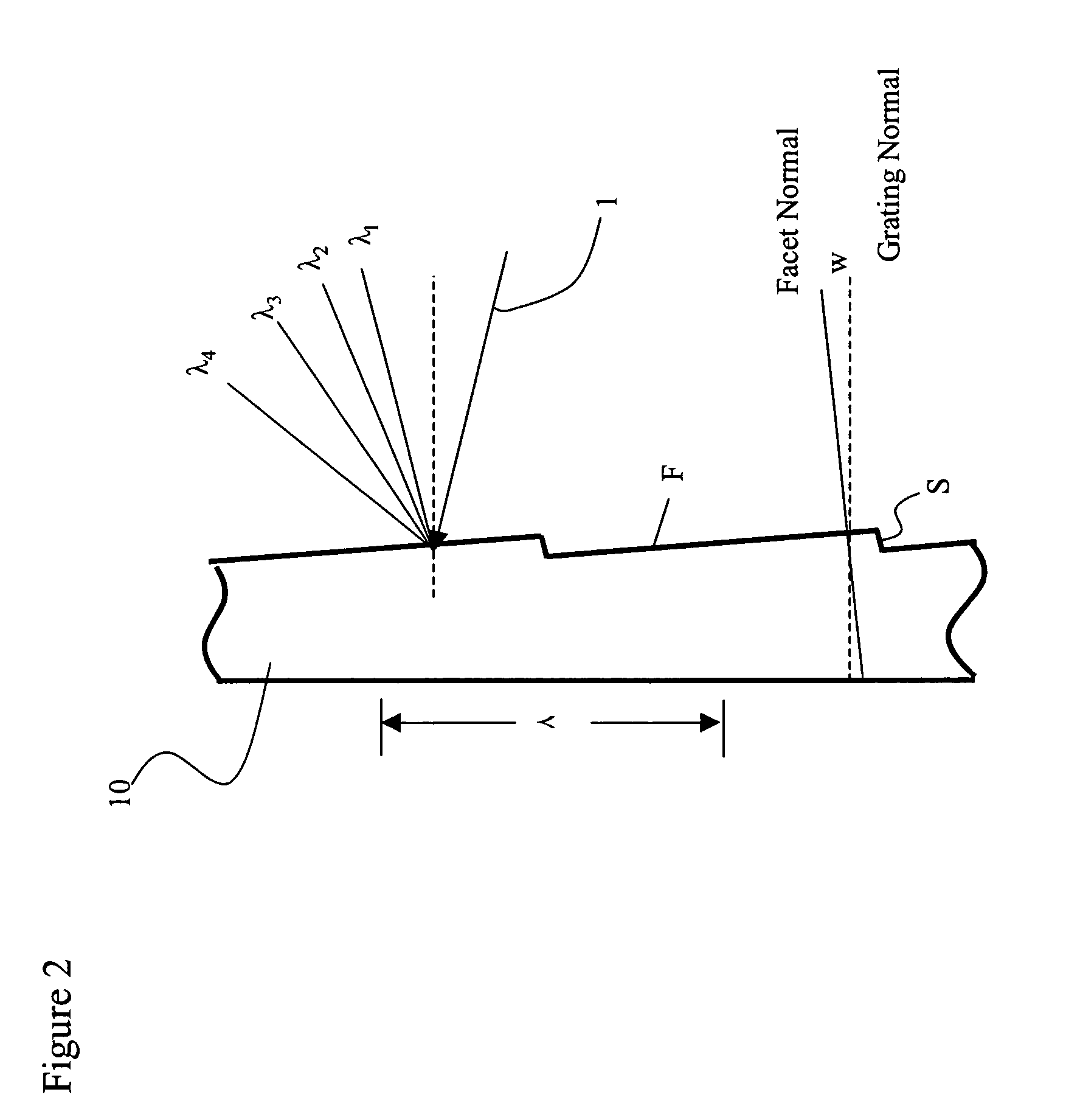
Planar waveguide reflective diffraction grating
Owner:ENABLENCE
Polarization compensation in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS7555227B2Polarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationPolarization dependentOptical receivers
A method of processing a stream of digital samples of an optical signal received by a coherent optical receiver. The digital sample stream is processed to generate a dispersion compensated sample stream. The dispersion compensated sample stream is then processed to compensate polarization dependent impairments of the optical signal.
Owner:CIENA
Method and system for providing a high definition triangulation system
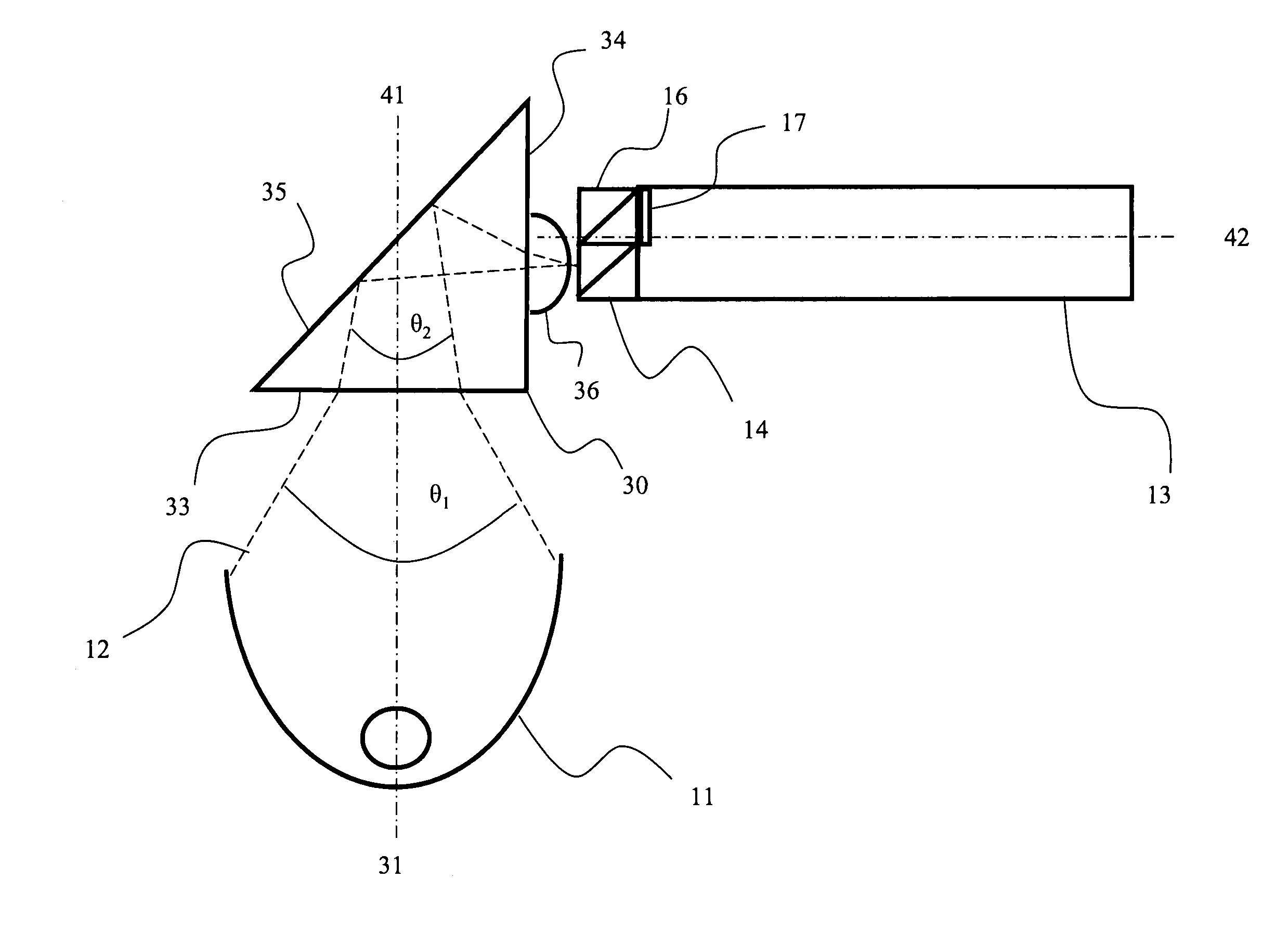
ActiveUS20080165357A1Precise positioningSmall spot sizeScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansOphthalmologyTriangulation
A triangulation system including a laser beam, optics focusing the laser beam on an object, a light detection unit detecting light reflected from the object due to impingement of the beam on the object, and an arrangement for determining, based on the detected light, object feature dimensions. The wavelength of the laser beam may be shorter than of infrared radiation, which allows for a reduced spot size without significant loss of depth of field. So as to reduce aberrations or a sensitivity to aberrations due to the shortened wavelength, the system may include (i) a polarization dependent coating matching the index of refraction of an element of the light detection unit to that of air for a range of angles, (ii) tilted projection optics, (iii) a prism wavefront corrector, and / or (iv) a positioning assembly, which provides for increased precision in positioning the laser diode with respect to a collimator lens.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Low-Noise Monolithic Microchip Lasers Capable of Producing Wavelengths Ranging From IR to UV Based on Efficient and Cost-Effective Frequency Conversion
ActiveUS20070047600A1Efficient and cost-effective frequency conversionLow-noise laser outputOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionNonlinear optical crystalLow noise
A method for producing low-noise laser output at wavelengths ranging from IR through visible to UV in various operation modes from a monolithic microchip laser comprises schemes of (1) generating one or two fundamental beam(s) from light source(s) selected upon the desired wavelength(s), polarization(s), and other features related to the desired laser output; (2) intracavity beam combination / separation due to the walk-off effect in one or more birefringent crystal(s) transparent to the propagating lights and highly anisotropic; (3) wavelength conversion in one or more nonlinear optical crystal(s); (4) compact and efficient pump source(s); and (5) minimization of intracavity loss / noise. One resonator cavity supports only one fundamental beam, which eliminates the green problem. The gain media can be selected from an extensive group of materials including isotropic and naturally birefringent crystals, with polarization dependent or independent laser emissions. Laser devices constructed in accordance with the inventive method are demonstrated with various configurations.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Mitigation of polarization dependent loss in optical multi-carrier/super-channel transmission
ActiveUS9112609B2Polarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationSuper-channelCarrier signal
Methods and systems for mitigating effects of polarization dependent loss (PDL) in an optical network transmitting a multi-carrier optical signal comprising a plurality of subcarriers may involve assigning and modifying a state of polarization to each subcarrier prior to transmission. An assigned state of polarization for each subcarrier may be modified for the subcarrier in the digital domain and / or the optical domain. Various specific assignment methods may be used, including individual subcarrier assignment, subcarrier set assignment, arbitrary subcarrier group assignment, random assignment, and / or combinations thereof. The assigned states of polarization may be selected based on a resulting minimum PDL-induced peak-to-peak power variation over a sum of the subcarriers for all orientations of a principal axis of PDL.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
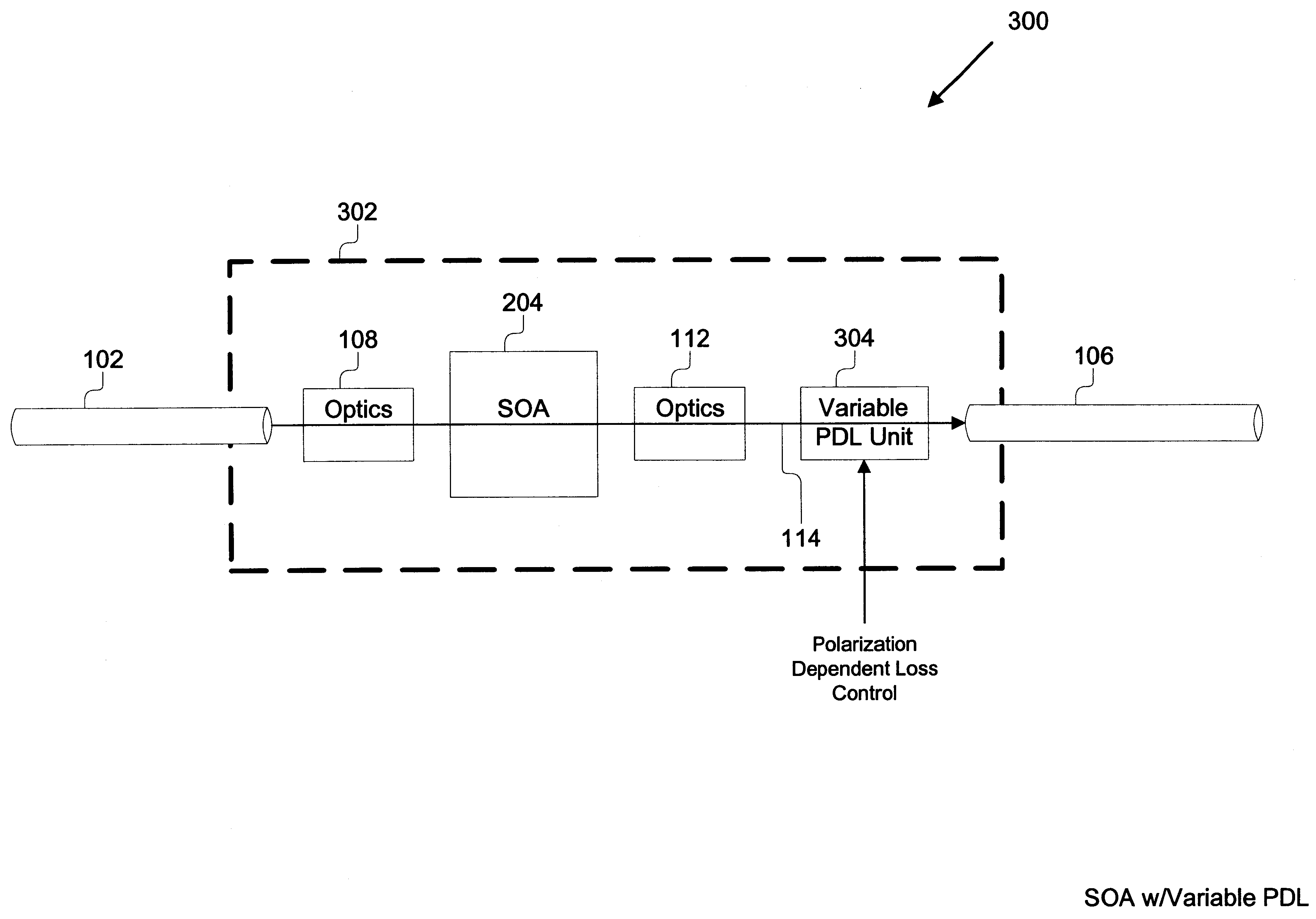
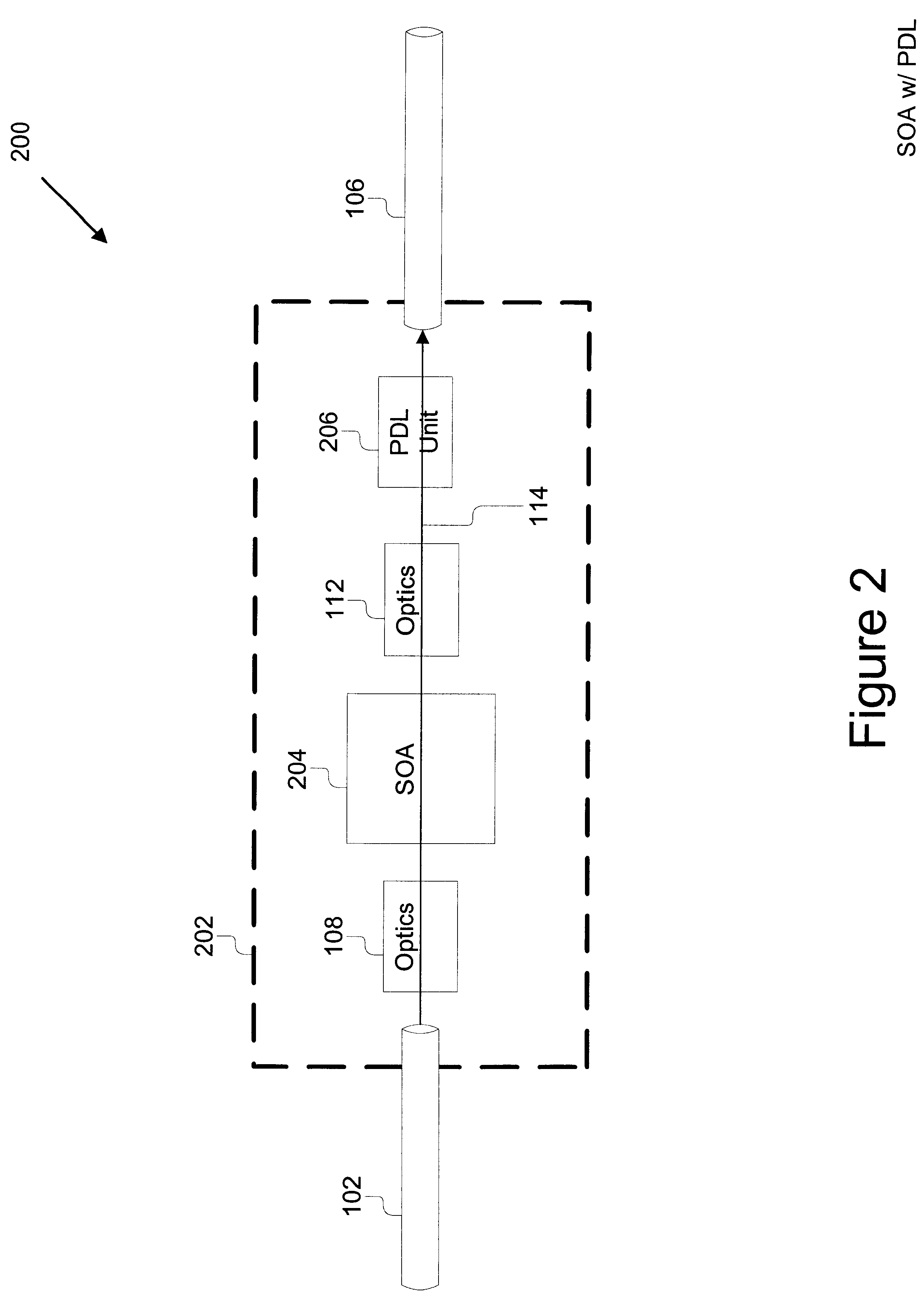
Polarization insensitive semiconductor optical amplifier
An optical amplifier module that is insensitive to polarization comprises a first fiber, a second fiber, a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA), and a polarization dependent loss (PDL) unit. The first fiber provides for optical input to the SOA. The SOA amplifies the optical signal received and outputs the amplified signal. The output of the SOA is optically coupled to the unit. The PDL unit provides polarization dependent loss and the loss is preferably selected to match the polarization dependent gain of the SOA such that when two are coupled there is no overall polarization dependence. The output of the PDL is optically coupled to the fiber for transmission output. The present invention also comprises a method for manufacturing an optical amplifier module that comprises the steps of: determining the polarization dependent gain of an SOA, determining the polarization dependent loss of a plurality of PDL units, selecting a PDL unit such that the polarization dependent loss when coupled to the SOA is reduced, and packaging the SOA and the PDL unit as an optical amplifier module.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
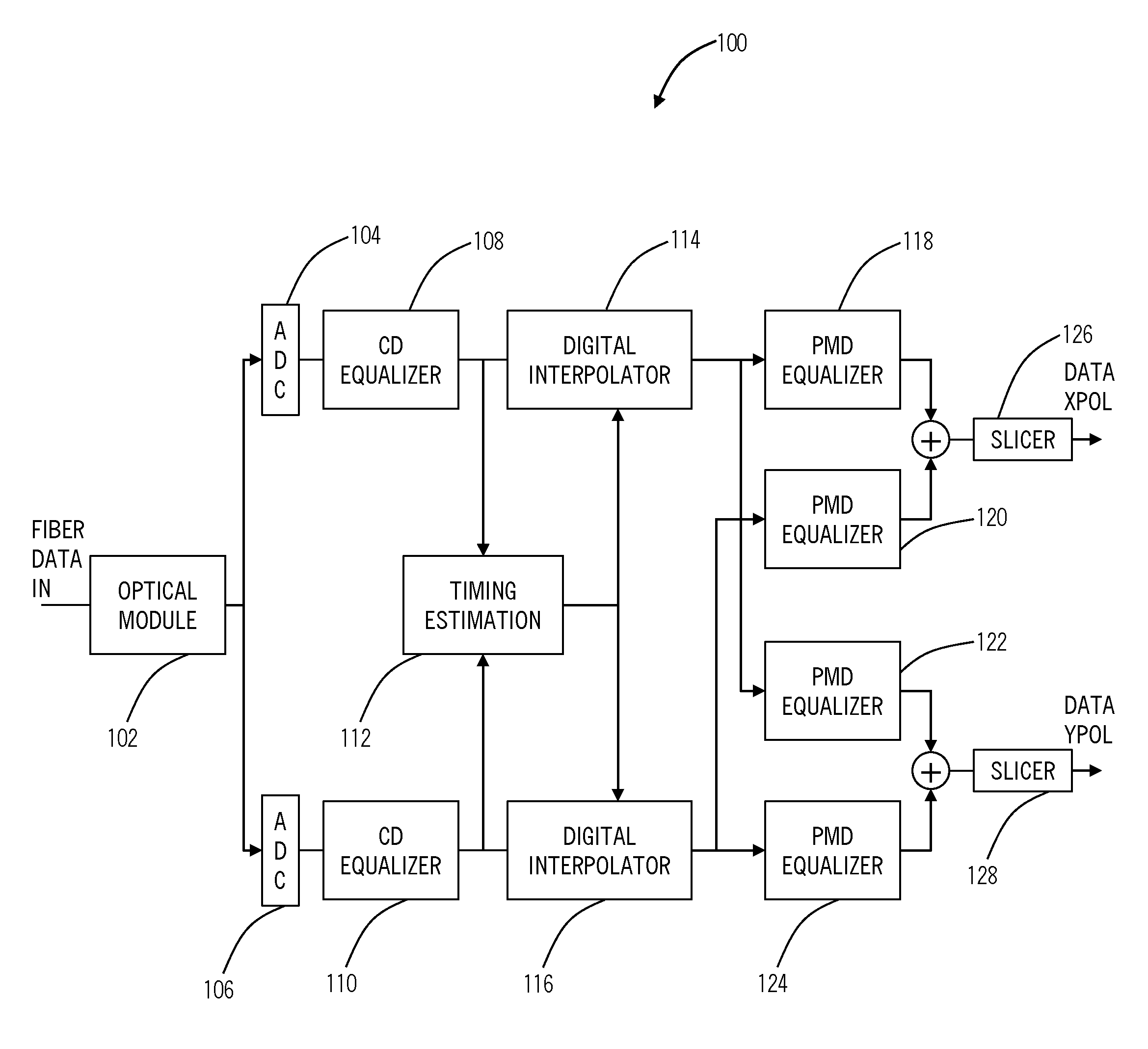
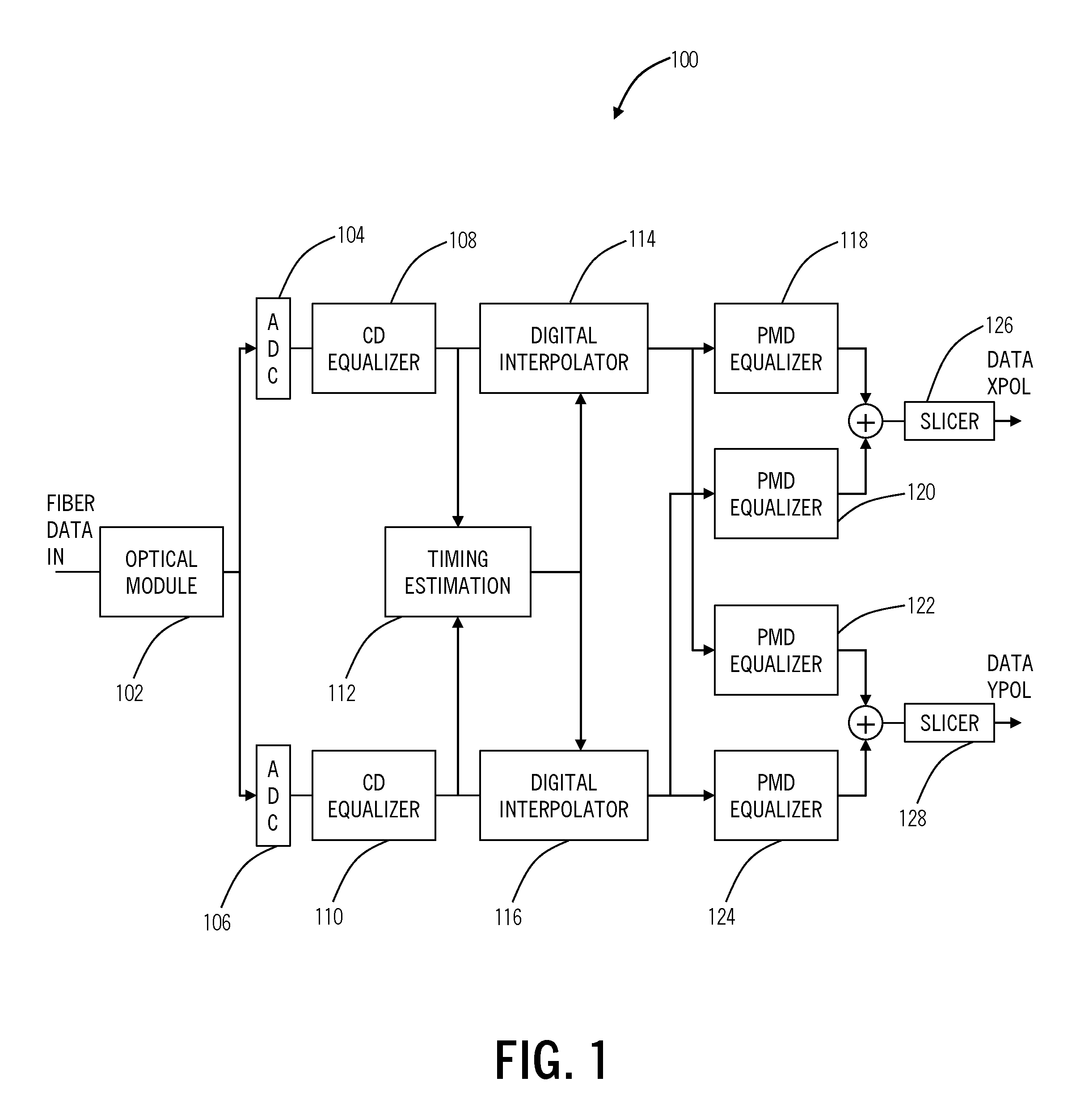
Timing recovery in presence of optical impairments and optimization of equalization based on timing recovery moment strengths
ActiveUS20110268459A1Minimizing hardwarePolarisation multiplex systemsSynchronisation error detectionTransceiverEngineering
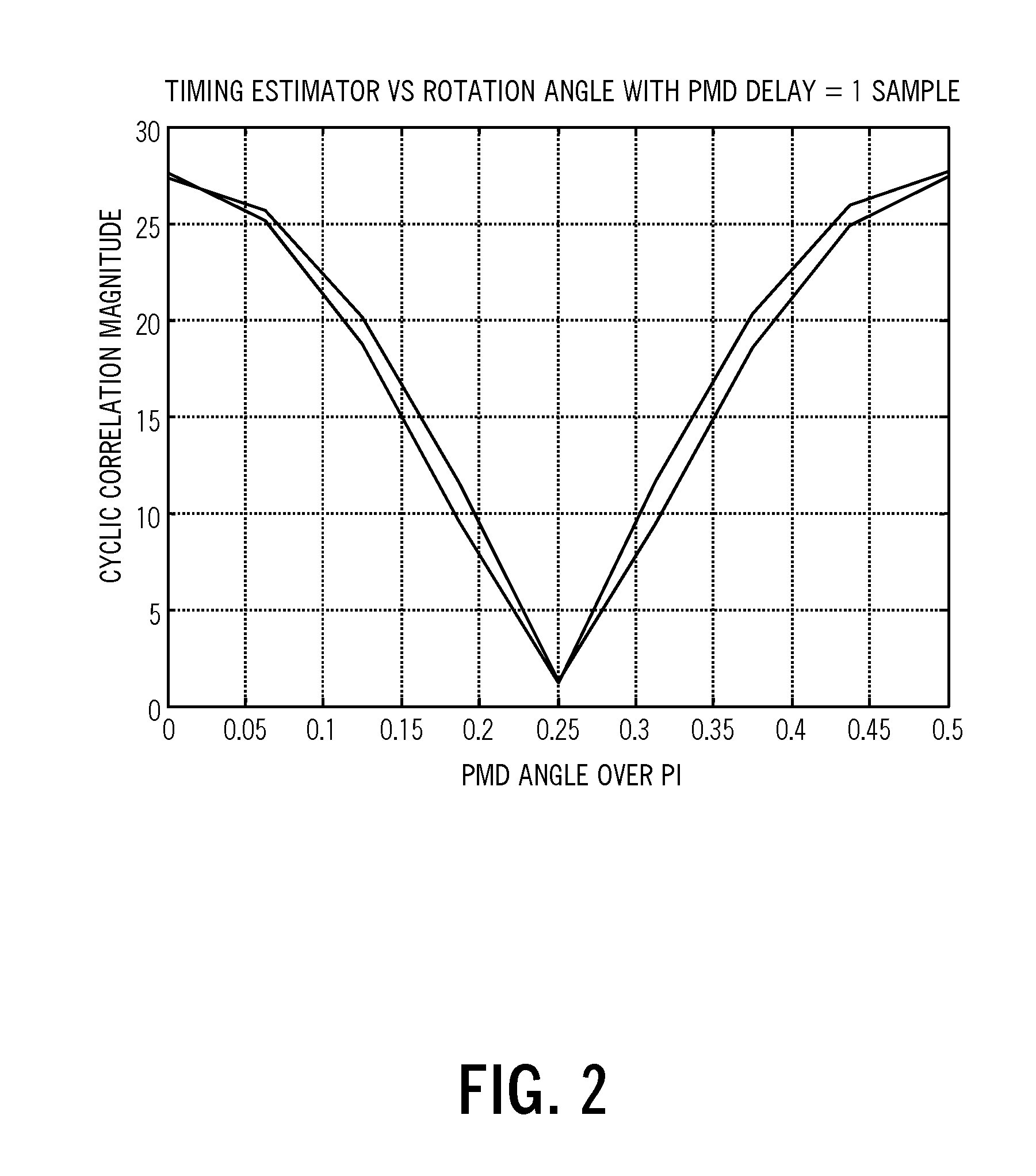
The present disclosure provides timing recovery in optical systems in the presence of chromatic dispersion (CD), polarization mode dispersion (PMD), and polarization dependent loss (PDL) and to optimization of equalization settings based upon timing recovery moment strengths. A stable timing point may be determined in the presence of PMD and PDL impairments, even when the direct estimate of timing becomes unreliable. This determination may be performed entirely in the digital domain providing precise, predictable performance. Also, the present invention utilizes a monotonic relationship between the timing metric and CD setting error to provide directed search in setting the CD equalizer thereby reducing significantly the overall search effort in optimizing CD equalizer settings. This utilizes computations already performed by the transceiver for timing recovery function yielding a computational advantage over competing methods.
Owner:CIENA
Multipurpose testing system for optical cross connect devices
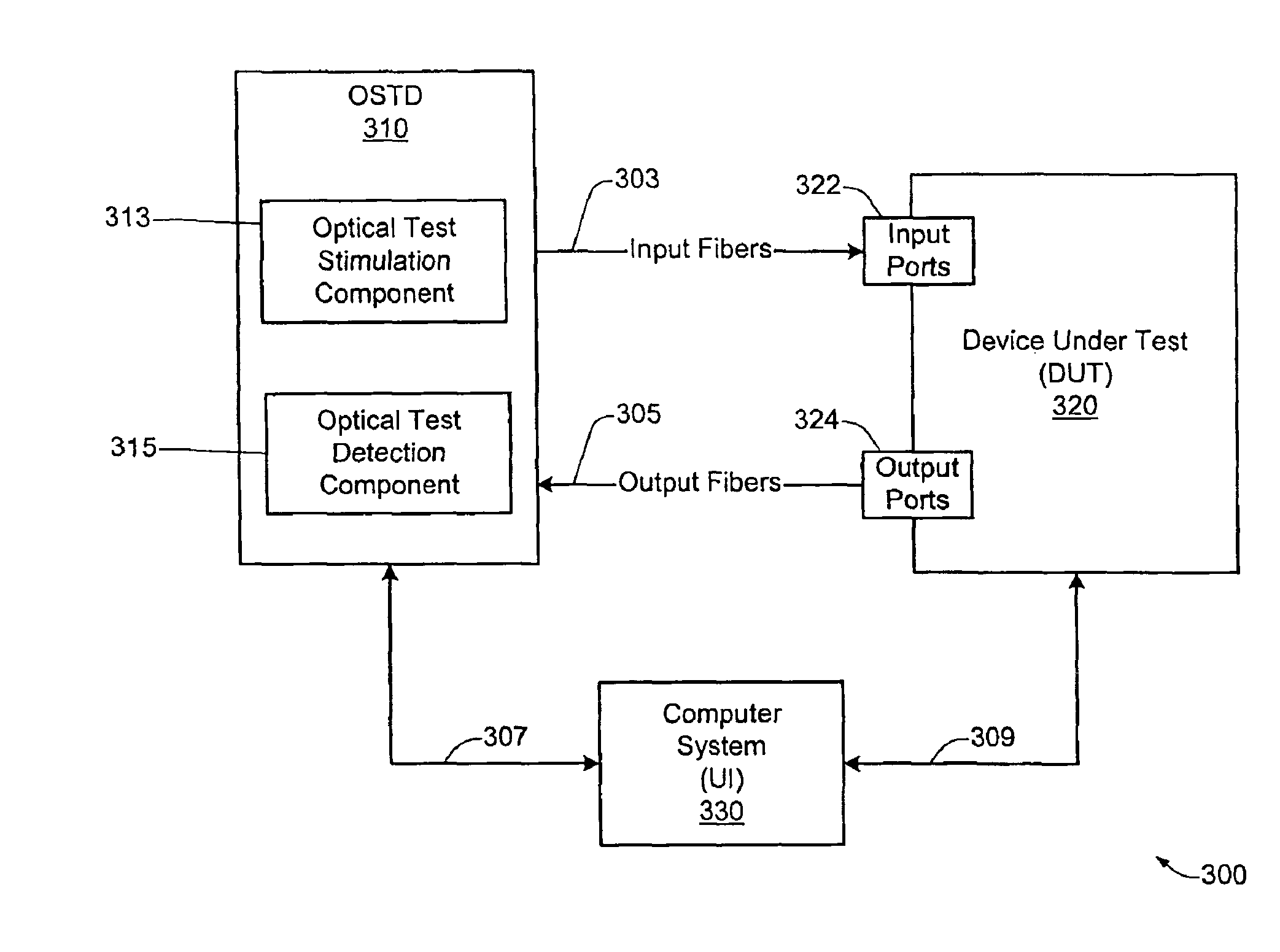
A technique is disclosed for performing testing of an optical device under test (DUT). According to a specific embodiment, the DUT includes a plurality of DUT optical input ports and a plurality of DUT optical output ports. The testing may be performed by an optical switching testing system (OSTS) which includes a plurality of OSTS output ports optically connected to a plurality of DUT input ports, and a plurality of OSTS input ports optically connected to a plurality of DUT output ports. Components of the OSTS are configured in order to perform a specific test on the DUT. A first test scenario is configured at the DUT. At least one optical test signal is transmitted to at least one DUT input port. Test results may then be obtained by monitoring at least one DUT output port for the presence or absence of light. The test results are then analyzed for specific characteristics. According to a specific embodiment, the OSTS of the present invention may be adapted to automatically perform a plurality of testing operations on a selected plurality of different optical paths associated with the DUT. Such testing operations may include, for example, transmitting a plurality of optical test signals to a plurality of DUT input ports during a given test scenario, and / or monitoring a plurality of DUT output ports for test results during a given test scenario. According to a specific embodiment, the optical switch testing system of the present invention may be used to measure and verify selected characteristics associated with a device under test (DUT) or a system under test (SUT). Such characteristics may include, for example, optical cross talk, insertion loss, polarization dependent loss, path switching time, data integrity, optical path verification, optical path stability, etc.
Owner:CALIENT TECH
Methods and apparatus for ophthalmic devices including cycloidally oriented liquid crystal layers
ActiveUS20150081016A1Effect be causeAlters a focal characteristic of the lensSpectales/gogglesOptical articlesElectricityLiquid-crystal display
This invention discloses methods and apparatus for providing a variable optic insert into an ophthalmic lens. A liquid crystal layer may be used to provide a variable optic function and in some examples, an alignment layer for the liquid crystal layer may be patterned in a cycloidally dependent manner. The patterning may allow for a polarization dependent lens in some examples. An energy source is capable of powering the variable optic insert included within the ophthalmic lens. In some examples, an ophthalmic lens is cast-molded from a silicone hydrogel. The various ophthalmic lens entities may include electroactive liquid crystal layers to electrically control optical characteristics.
Owner:BEAM ENG FOR ADVANCED MEASUREMENTS +1
Clock recovery from an optical signal with polarization impairments
ActiveUS7532822B2Pulse automatic controlPolarisation multiplex systemsCommunications systemClock recovery
A method of recovering a clock signal from an optical signal received through an optical communications system. A digital sample stream is processed to generate a dispersion compensated signal. The dispersion compensated signal is then tapped to obtain upper side band and lower side band signals of each received polarization of the optical signal. The upper side band sand lower side band signals are then processed to compensate polarization dependent impairments and the clock recovered from the resulting optimized.
Owner:CIENA
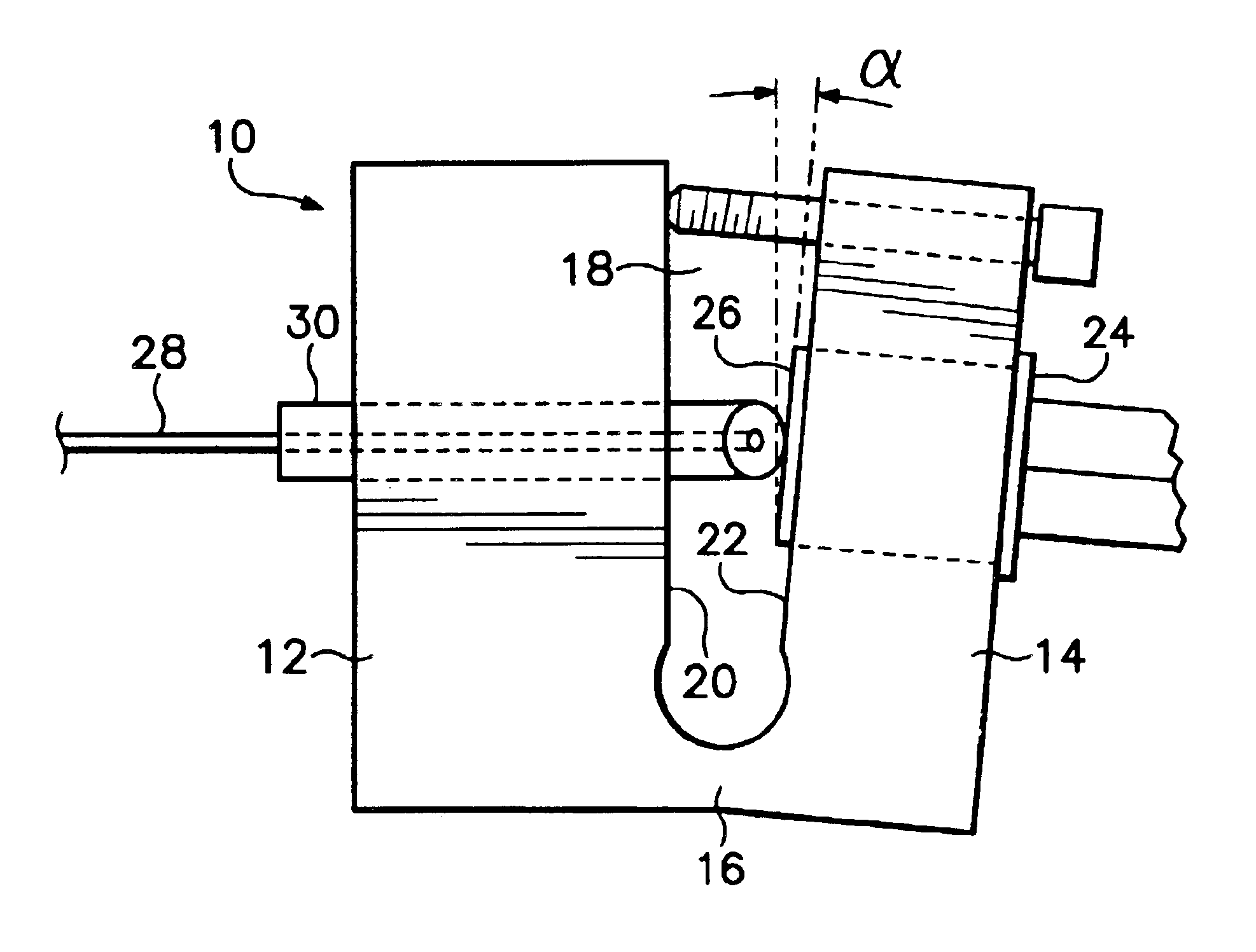
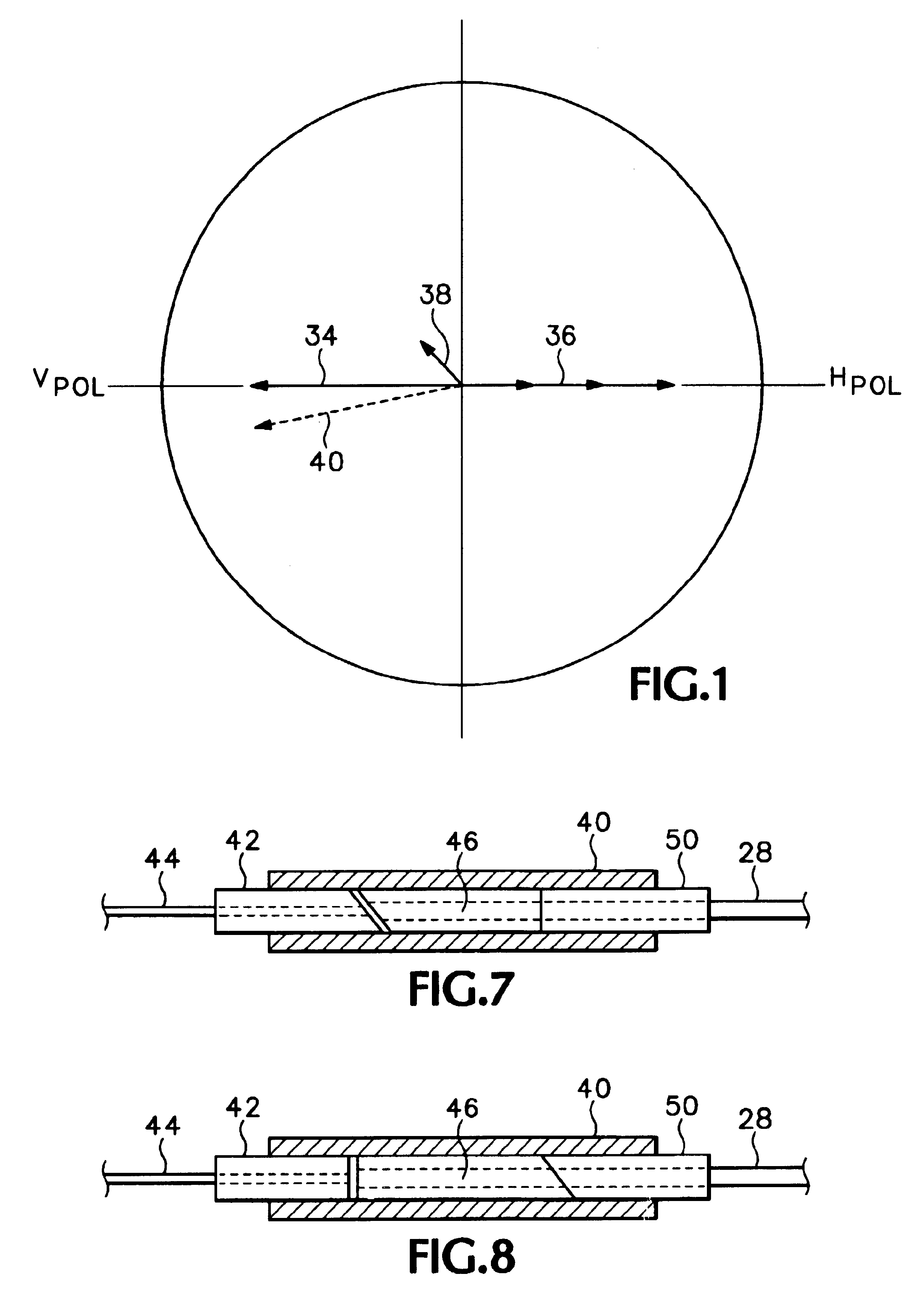
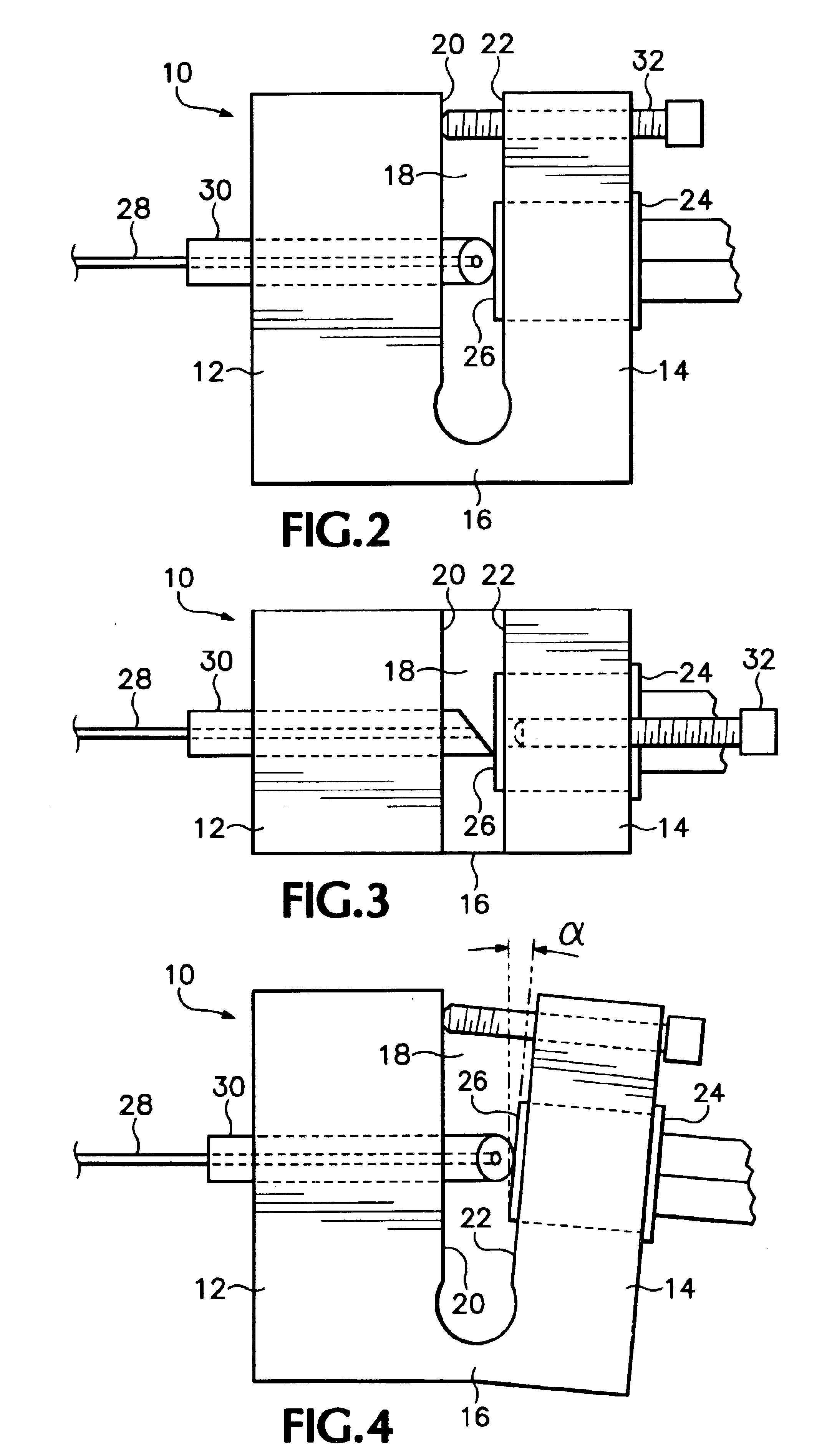
Fiber-pigtailed assembly
A fiber-pigtailed assembly for an optical detector with low back reflection and minimal polarization-dependent responsivity has a detector surface mounted adjacent a beveled end of a fiber pigtail such that the detector surface is tilted and rotated with respect to the beveled end of the fiber pigtail. Also an external optical fiber may be coupled to the fiber pigtail with low back reflection and minimal polarization-dependent responsivity by having an input ferrule at the end of the external optical fiber, the end being beveled; by having an intermediate ferrule at a coupling end of the fiber pigtail, the coupling end being beveled while the other end of the ferrule is beveled by the same amount but approximately orthogonal to the coupling end; and by having an output ferrule on the fiber pigtail adjacent to the intermediate ferrule, the end of the output ferrule adjacent to the intermediate ferrule being beveled. The ferrules are maintained in position so that the beveled ends of the intermediate ferrule are parallel to the corresponding beveled ends of the input and output ferrules and there is a gap between the input and intermediate ferrules. The beveled ends of the ferrules at both the coupler and detector ends of the fiber pigtail introduce fixed amounts of polarization-dependent responsivity while reducing back reflection, while the tilt of the detector surface at the detector end and the opposite approximately orthogonal bevel of the intermediate ferrule at the coupler end compensate and essentially eliminate such polarization-dependent responsivity.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Polarization insensitive microbend fiber gratings and devices using the same
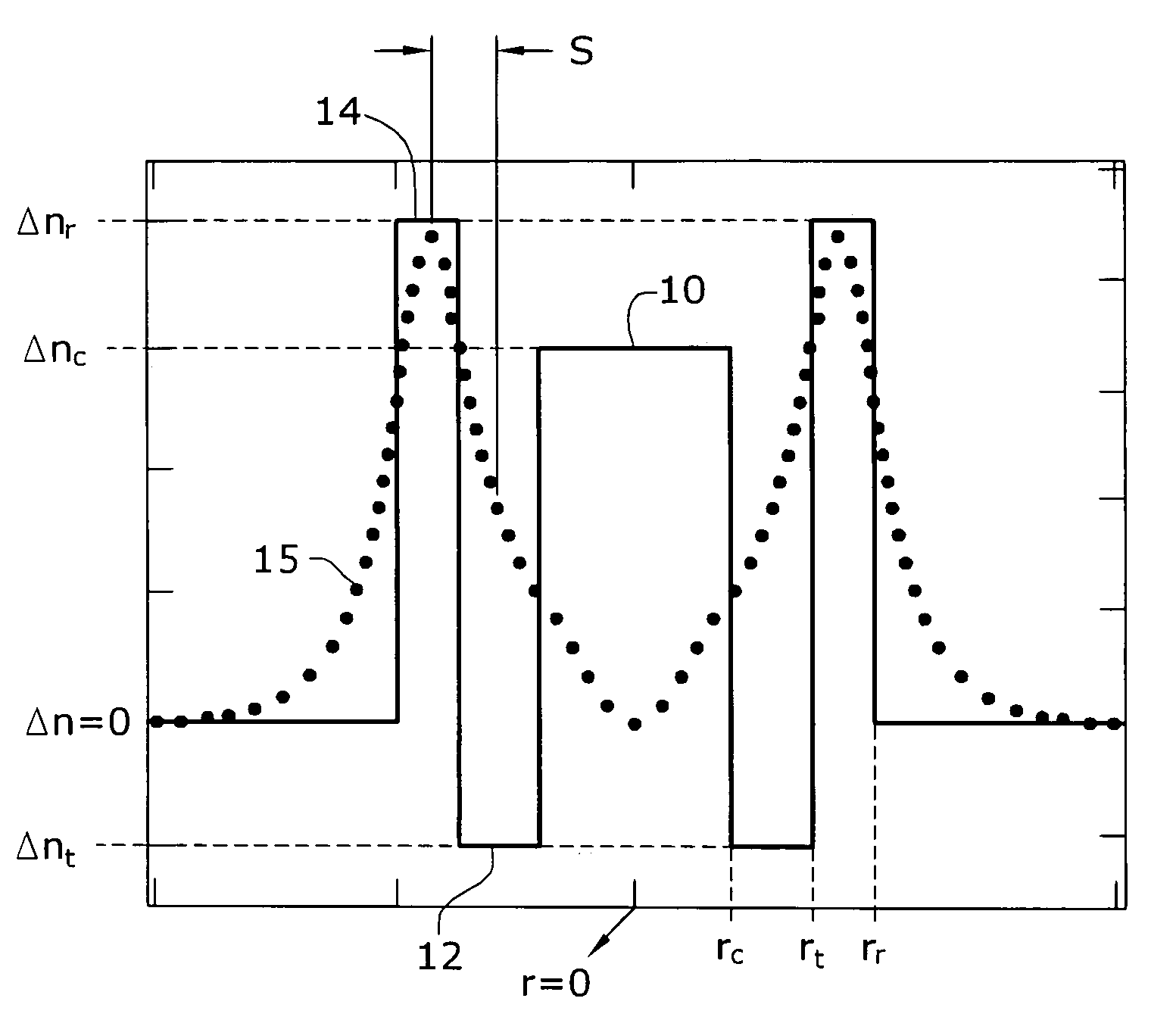
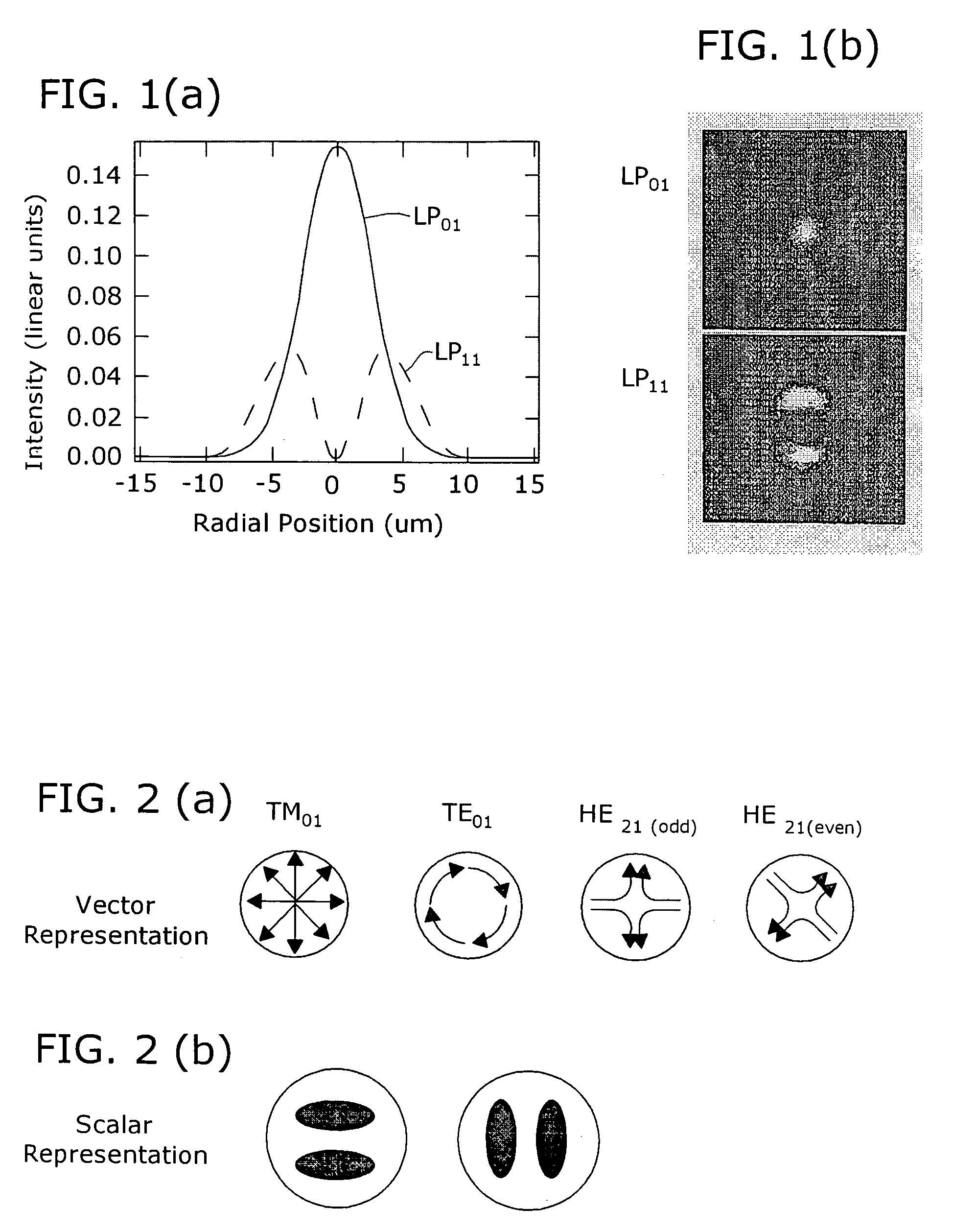
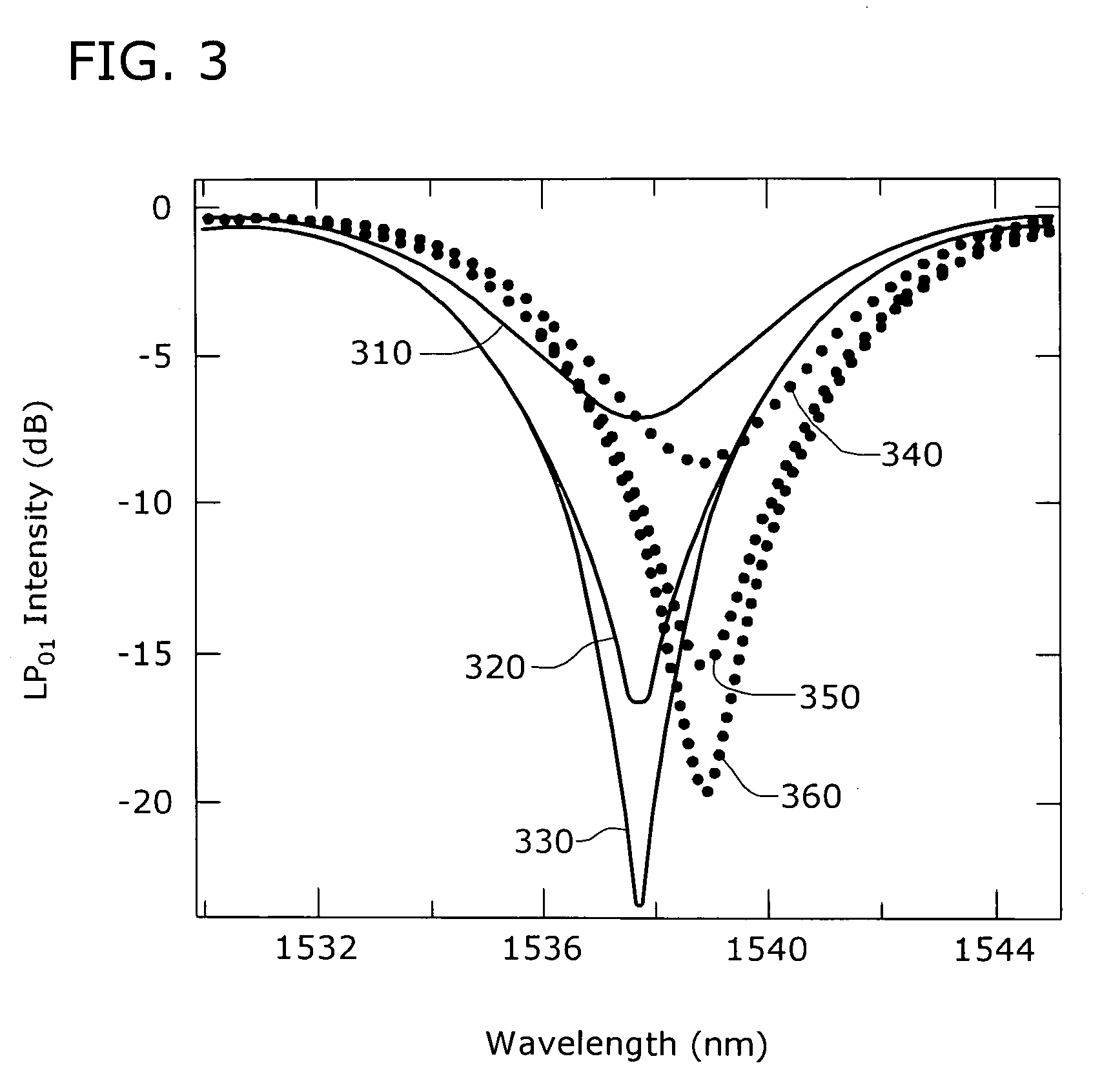
ActiveUS7177510B2Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberGrating
A microbend-induced fiber grating is formed from a section of optical fiber configured to exhibit “splitting” between the resonant wavelengths supported by the TE and TM components of the LP1m mode and the resonant wavelength supported by the odd / even HE2m components of the LP1m mode. Since only the TE and TM components are polarization dependent, by splitting and shifting the resonant wavelengths for these modes away from a system-desired wavelength(s) supported by the odd / even HE modes, a polarization insensitive microbend-induced fiber grating can be formed. A fiber core configuration including a central core region, trench and ring is formed to exhibit a large radial gradient in core refractive index profile, with a significantly steep transition between the ring index and the trench index, to provide the desired splitting between the (undesired, polarization sensitive) TE / TM modes and the HE mode.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Enhanced light absorption of solar cells and photodetectors by diffraction
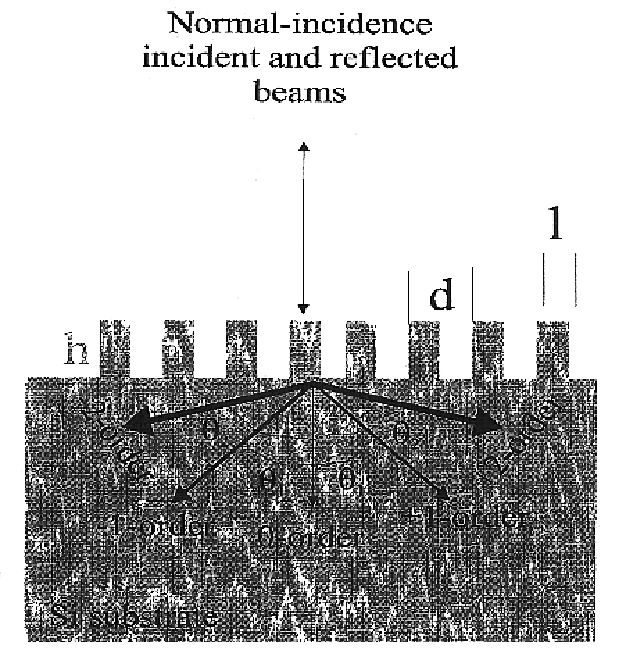
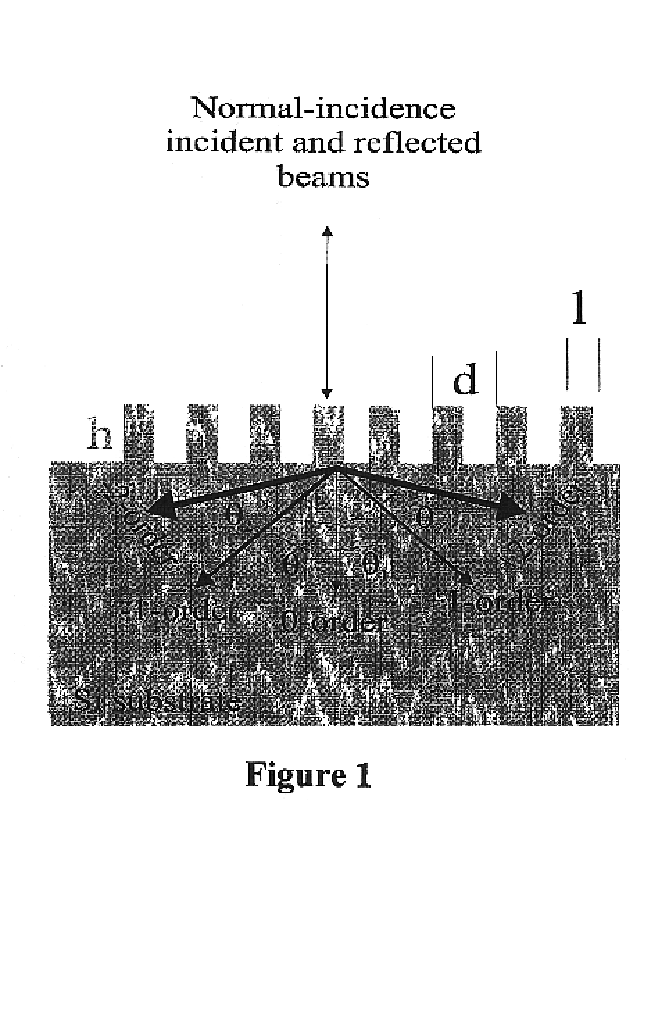
InactiveUS6858462B2Promote absorptionImprove performanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction orderGrating
Enhanced light absorption of solar cells and photodetectors by diffraction is described. Triangular, rectangular, and blazed subwavelength periodic structures are shown to improve performance of solar cells. Surface reflection can be tailored for either broadband, or narrow-band spectral absorption. Enhanced absorption is achieved by efficient optical coupling into obliquely propagating transmitted diffraction orders. Subwavelength one-dimensional structures are designed for polarization-dependent, wavelength-selective absorption in solar cells and photodetectors, while two-dimensional structures are designed for polarization-independent, wavelength-selective absorption therein. Suitable one and two-dimensional subwavelength periodic structures can also be designed for broadband spectral absorption in solar cells and photodetectors. If reactive ion etching (RIE) processes are used to form the grating, RIE-induced surface damage in subwavelength structures can be repaired by forming junctions using ion implantation methods. RIE-induced surface damage can also be removed by post RIE wet-chemical etching treatments.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Mode and polarization control in vcsels using sub-wavelength structure
InactiveUS20070242715A1Degradation minimizedDiffraction minimizedLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserWavelength
This invention relates to a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) comprising a bottom mirror structure, a top mirror structure, an active layer sandwiched between the top mirror structure and the bottom mirror structure; and at least one asymmetric sub-wavelength structure arranged in on or at least adjacent to the mirror structure of said VCSEL so as to create a polarization dependent mirror reflectivity from said mirror structure.
Owner:GUSTAVSSON JOHAN +3
Method And Apparatus For Polarization-Division-Multiplexed Optical Coherent Receivers
ActiveUS20110142449A1Avoid problemsPolarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversSingle stageEngineering
The singularity problem of the constant modulus algorithm (CMA) equalizer may be overcome by implementing the CMA equalizer as a two-stage equalizer, with the first stage being a modified version of a CMA equalizer and the second stage being a conventional CMA equalizer. The first stage may be made up of four sub-equalizers, of which only two of the sub-equalizers are independent, i.e., uncorrelated to each other. This first stage equalizer may compensate for PMD. The second stage equalizer is a conventional CMA equalizer made up of four sub-equalizers that are adjusted independently. This second stage equalizer may compensate for polarization-dependent loss (PDL) and any residual CD that is not fully compensated for by a CD compensator before the two-stage equalizer. Advantageously, as the determinant of the first stage never approaches zero, the singularity problem of a conventional CMA single-stage-only equalizer is avoided by the two-stage equalizer.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Polarization Independent Birefringent Tunable Filters
InactiveUS20090284708A1Compact designImprove efficiencyPolarising elementsNanoopticsBeam splitterGrating
Novel, polarization-insensitive, birefringent, broadband tunable filter arrangements that allow high throughput, based on a combination of tunable birefringent layers or polarization dependent filters, in combination with one or more of the following components (i) thin film achromatic quarter waveplates based on the form birefringence of dielectric subwavelength grating structures, (ii) nano wire-grid polarizers made of metallic wire grids; (iii) omnidirectional dielectric mirrors, (iv) polarization conversion mirrors, (v) reflective polarized beam splitters for circularly polarized light, (vi) metallic subwavelength gratings with lines having Gaussian profile, and (vii) Faraday mirror. All of these components may be implemented in thin film form on one or more substrates, such that a compact and cost effective filter can be produced. The birefringent layers can be any birefringent or magneto-optic layer but especially liquid crystals. The use of novel polarization conversion disposition of the components of the filter results in a filter having high throughput.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
Folding converging light into a lightpipe
InactiveUS7252399B2Raise the ratioEffectively provides extra distance between the light source and the lightpipeLighting support devicesProjectorsRefractive indexLight beam
The present invention relates to a folded front end unit used in a light engine of a projection display device. The front end unit comprises a light source for generating a beam of light, and a lightpipe for providing spatial uniformity to the beam of light. Polarization-dependent front end units include polarization beam splitters for separating the light into orthogonally polarized sub-beams, and a polarization rotating element, e.g. a waveplate, for rotating the polarization of one of the sub-beams. In accordance with the present invention, a prism is positioned between the light source and the lightpipe for reflecting the light into the lightpipe. The difference in refractive index between the air and the prism decreases the cone angle of the beam of light enough to effectively increase the distance between the light source and the lightpipe to compensate for the added distance required to fold the light.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
In-guide control of optical propagation
InactiveUS6859567B2Improve efficiencyCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsOptical propagationRefractive index
We propose a dynamically tunable electro-optic cladding using our proprietary electro-optic material, applied to various circular and planar wave-guides along with specific electrode configuration and excitation electric field format appropriate to that material. Based on the evanescent field coupling phenomena, the proposed device may be used in variable optical attenuators, tunable filters and couplers, etc. Different design of applied electrodes and optical properties of controllable refractive index materials allow polarization dependent or independent, as well as direct or inverse operation regimes of proposed devices.
Owner:PHOTINTECH
Diffractive, polarization modulating optical devices
InactiveUS20070053028A1Little and no diffractive effectImprove securityPaper-money testing devicesPolarising elementsOptical polarizationPolarization dependent
An optical device includes an encoding surface having a micro-relief pattern (22) over at least part thereof designed to produce a predetermined diffracted first image when illuminated in use, and an optically anisotropic layer (26) such as a polymerized liquid crystal provided whereby at least part of the micro-relief pattern (22) induces local orientation of the optically anisotropic layer (26) thereby to impose a predetermined polarization modulation, thereby to produce a predetermined polarization dependent second image when illuminated in use.
Owner:DE TECH
Folding converging light into a lightpipe
InactiveUS20050036203A1Increasing focal ratioSufficient distanceLighting support devicesProjectorsRefractive indexLight beam
The present invention relates to a folded front end unit used in a light engine of a projection display device. The front end unit comprises a light source for generating a beam of light, and a lightpipe for providing spatial uniformity to the beam of light. Polarization-dependent front end units include polarization beam splitters for separating the light into orthogonally polarized sub-beams, and a polarization rotating element, e.g. a waveplate, for rotating the polarization of one of the sub-beams. In accordance with the present invention, a prism is positioned between the light source and the lightpipe for reflecting the light into the lightpipe. The difference in refractive index between the air and the prism decreases the cone angle of the beam of light enough to effectively increase the distance between the light source and the lightpipe to compensate for the added distance required to fold the light.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Apparatus And Method For Monitoring An Optical Coherent Network
InactiveUS20120170929A1Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsPolarization mode dispersionComputer science
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
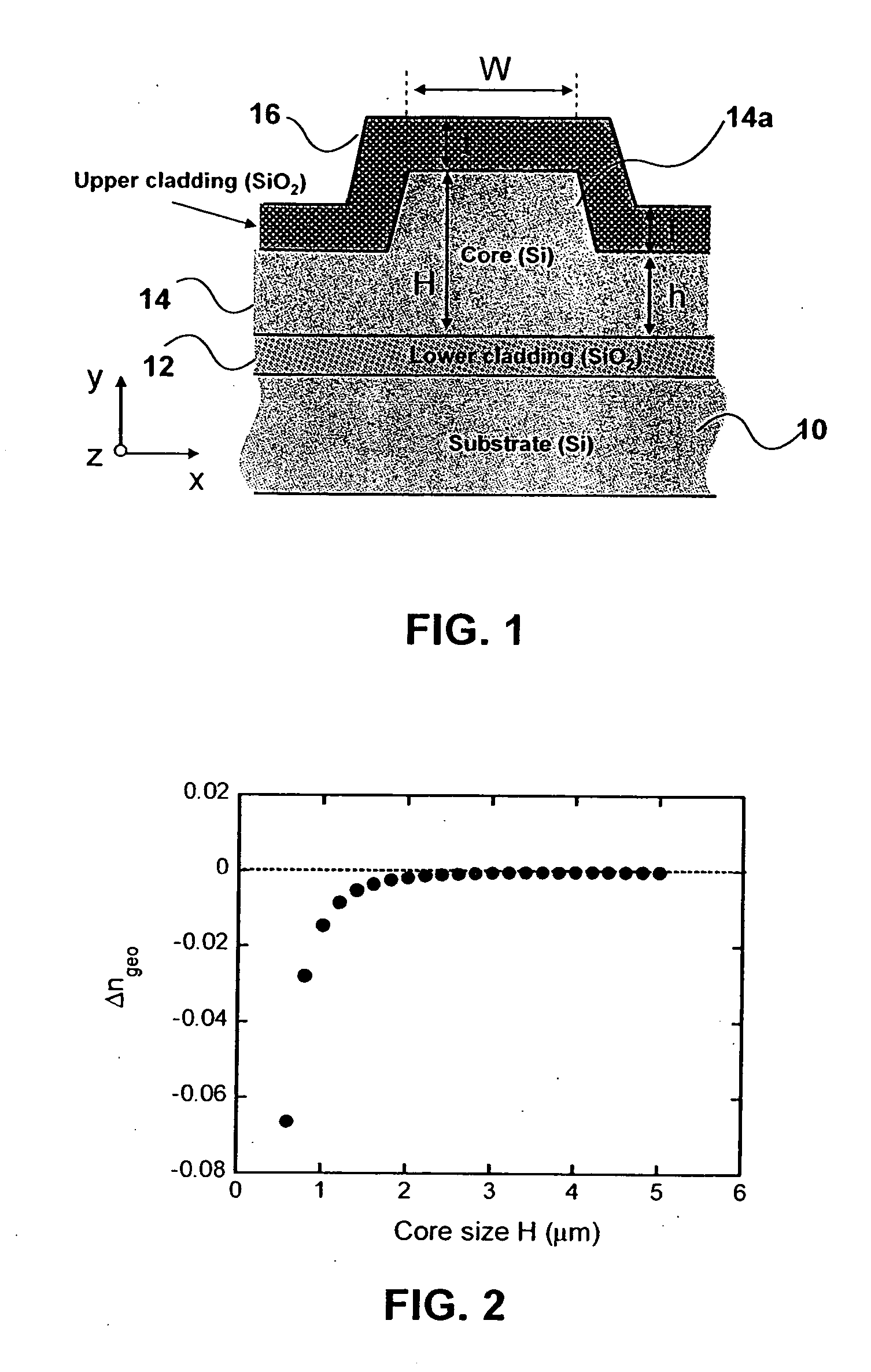
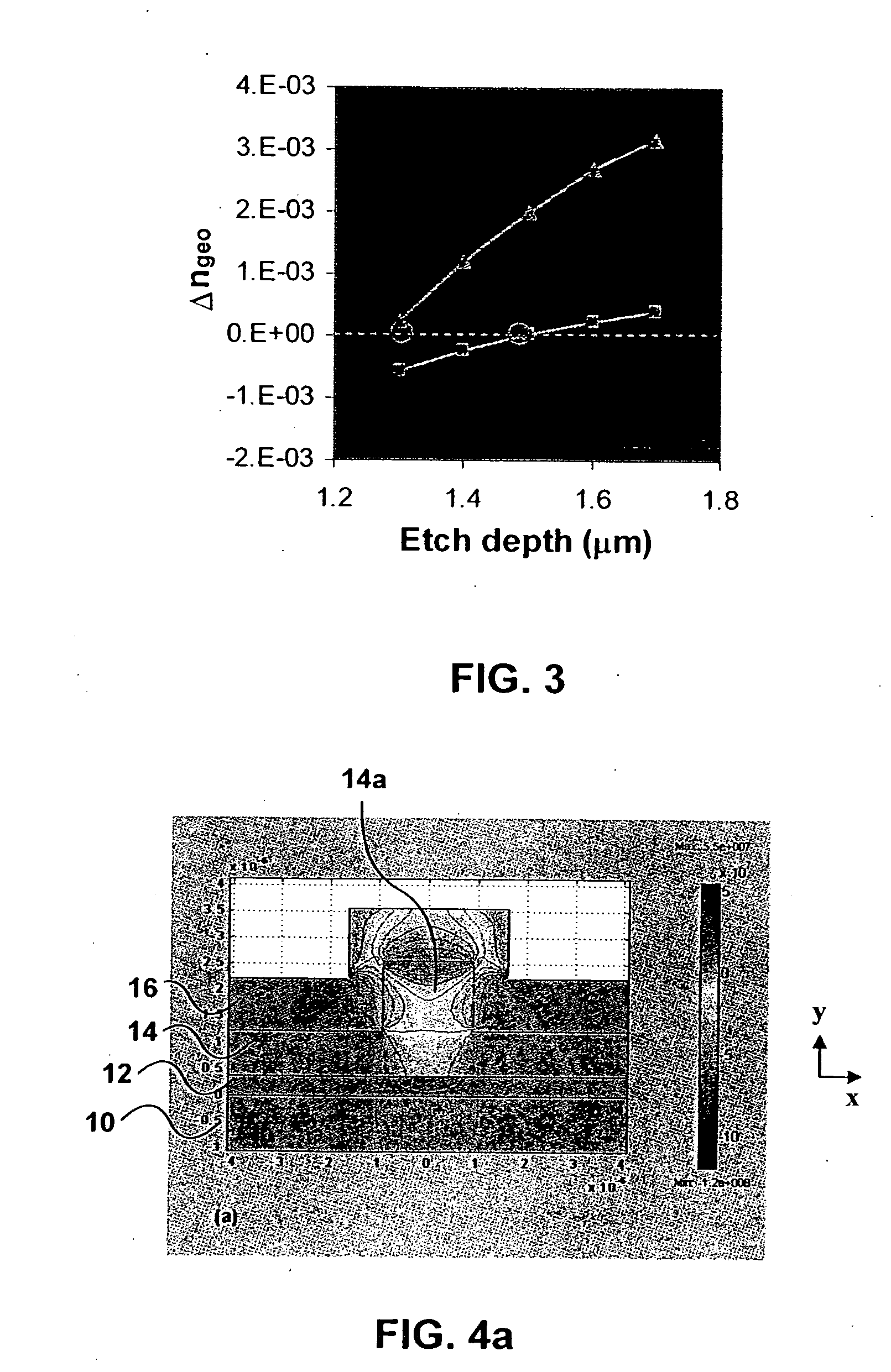
Stress-induced control of polarization dependent properties in photonic devices
InactiveUS20050196114A1Simple designGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreStress inducedPhotonics
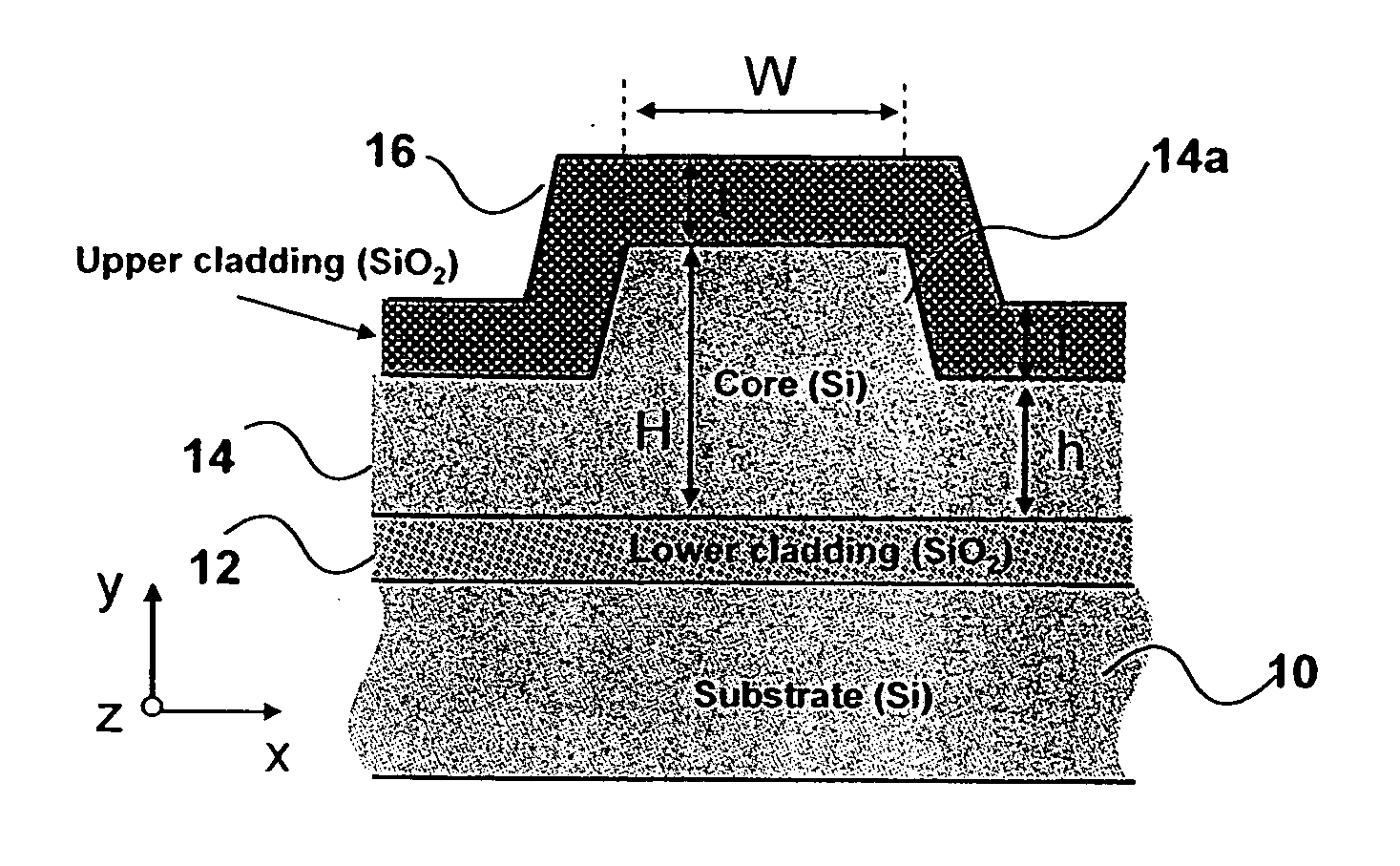
In order to make a photonic device incorporating a waveguide, a waveguide is formed with a predetermined geometry. Birefringence is then controlled by determining the amount of stress induced within the waveguide.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com