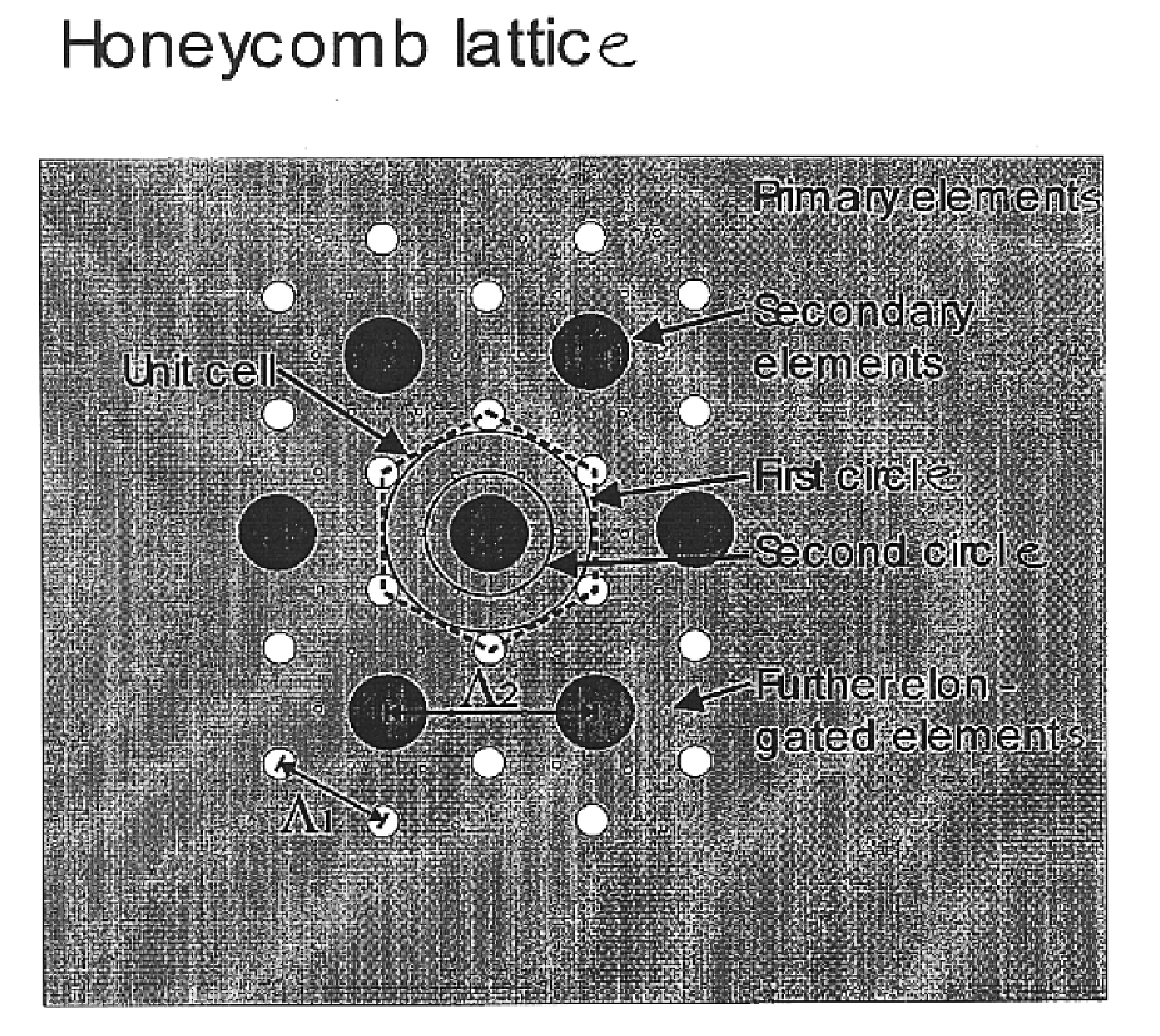
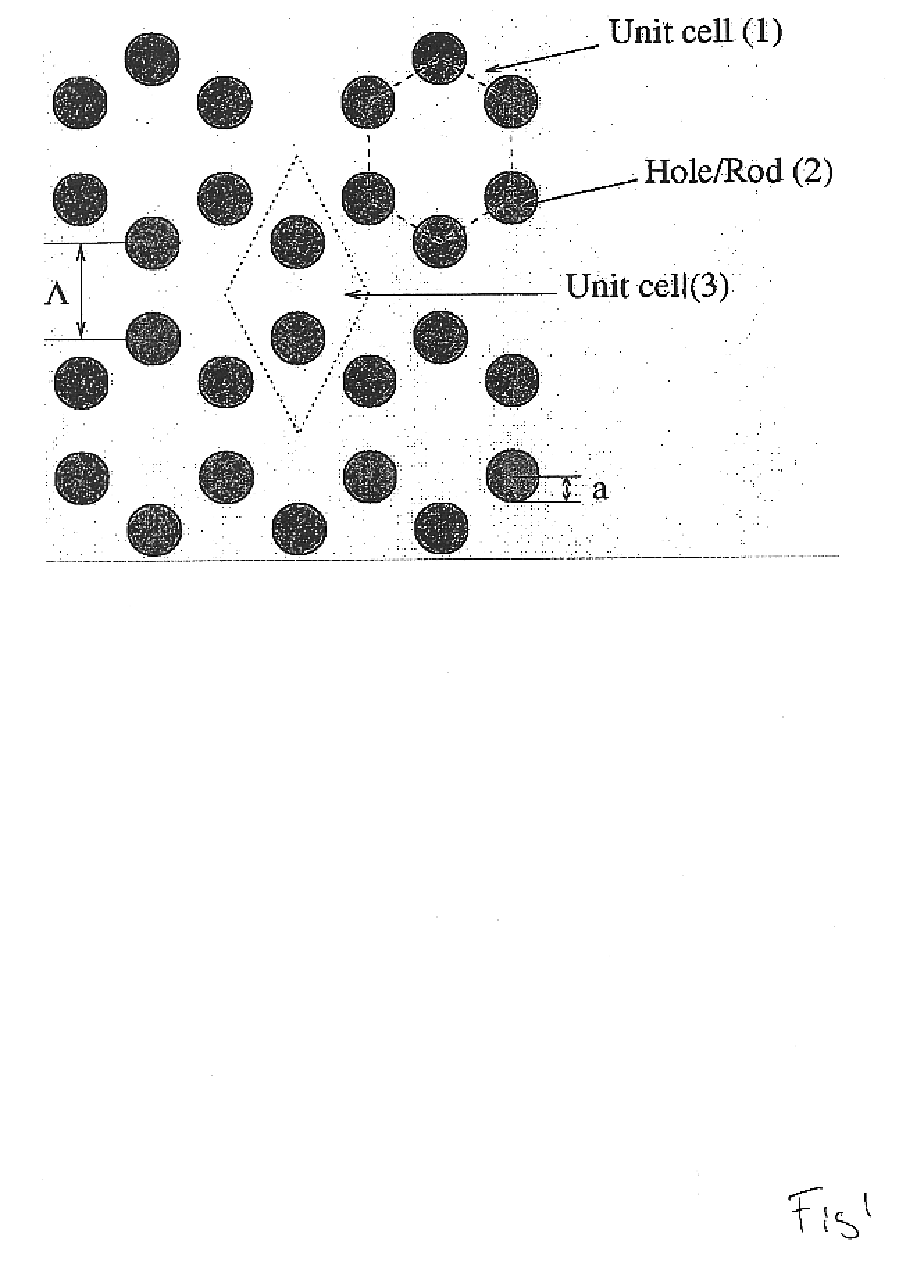
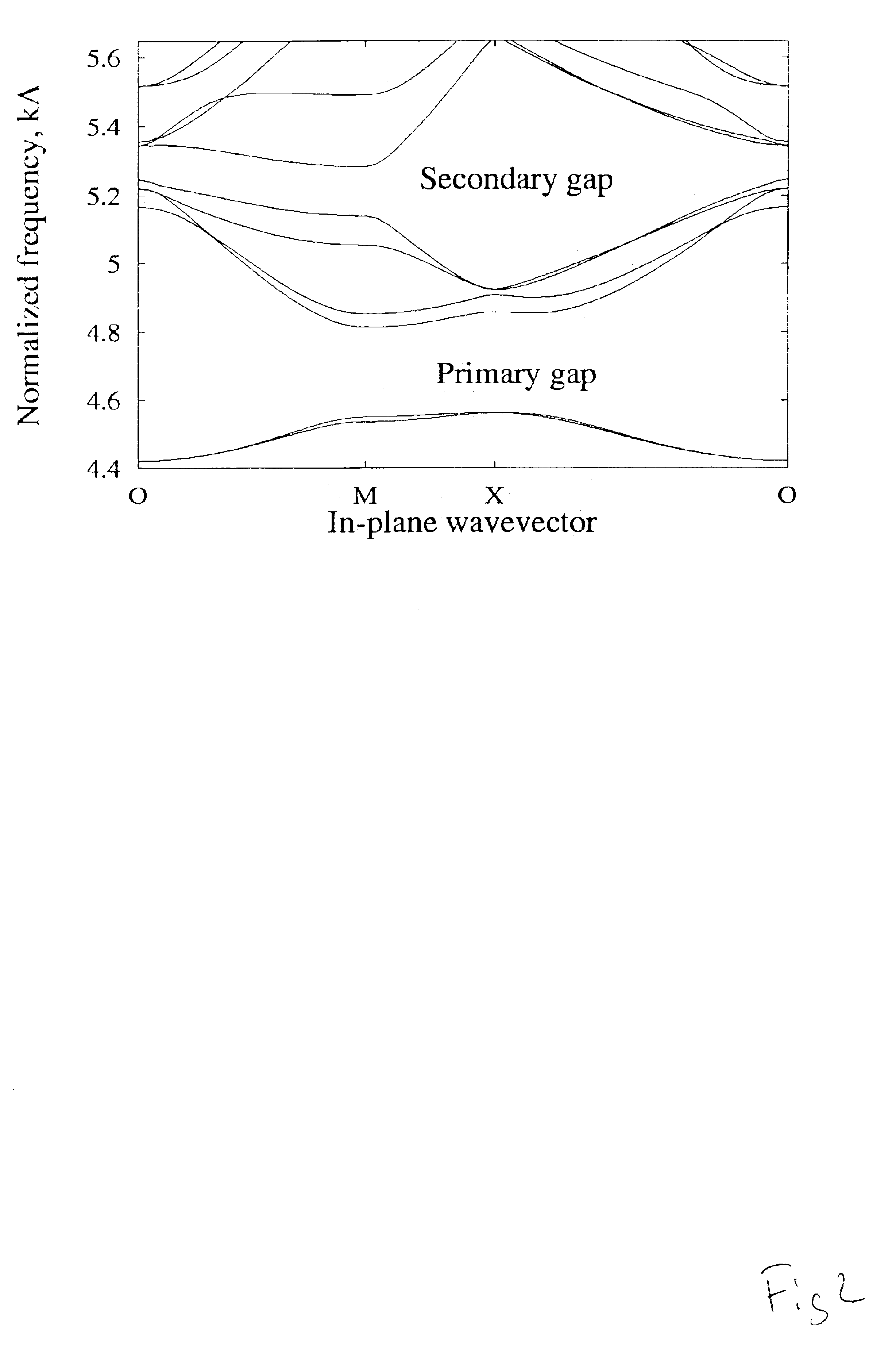
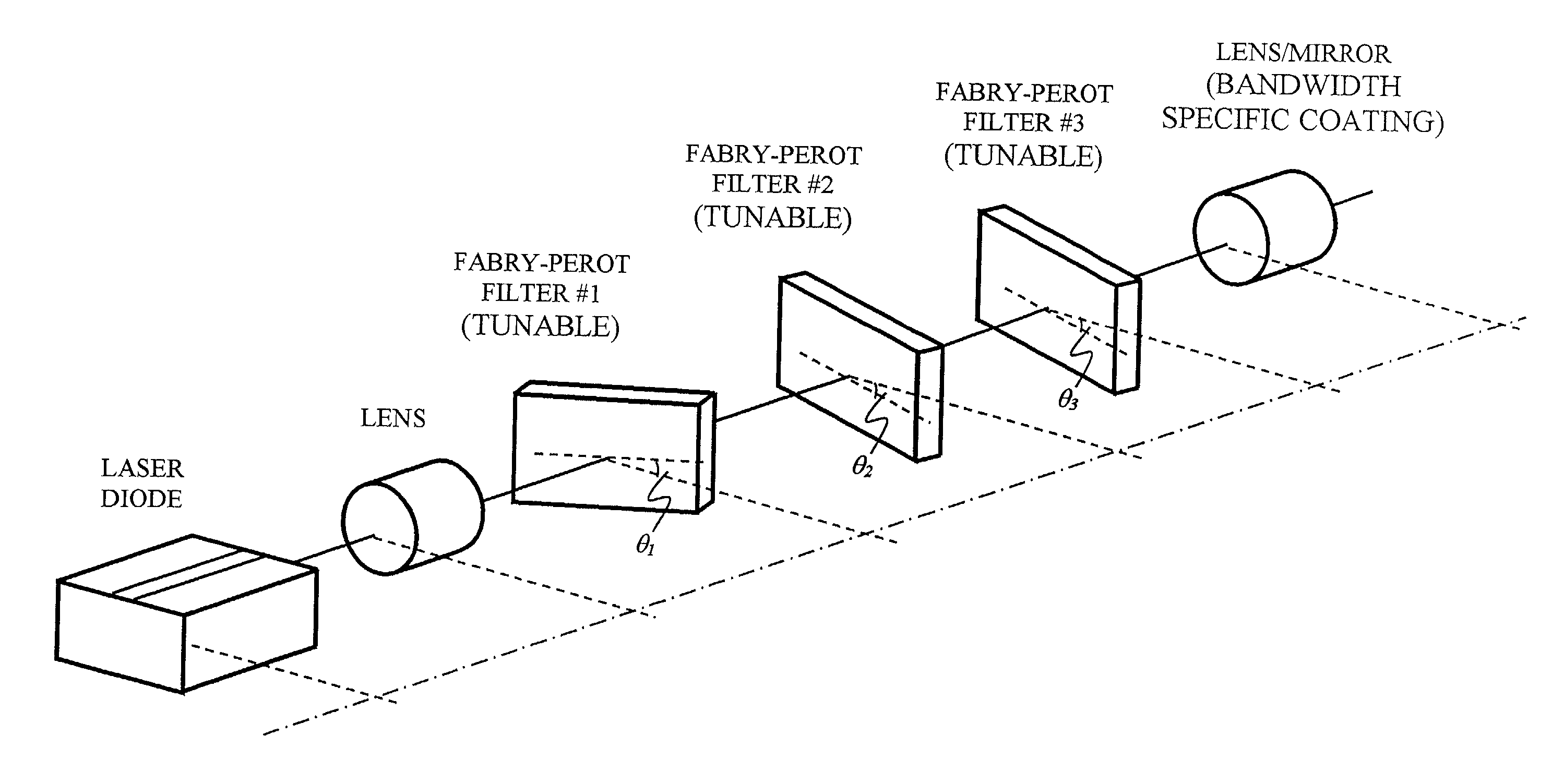
Patents
Literature
4794results about "Laser optical resonator construction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
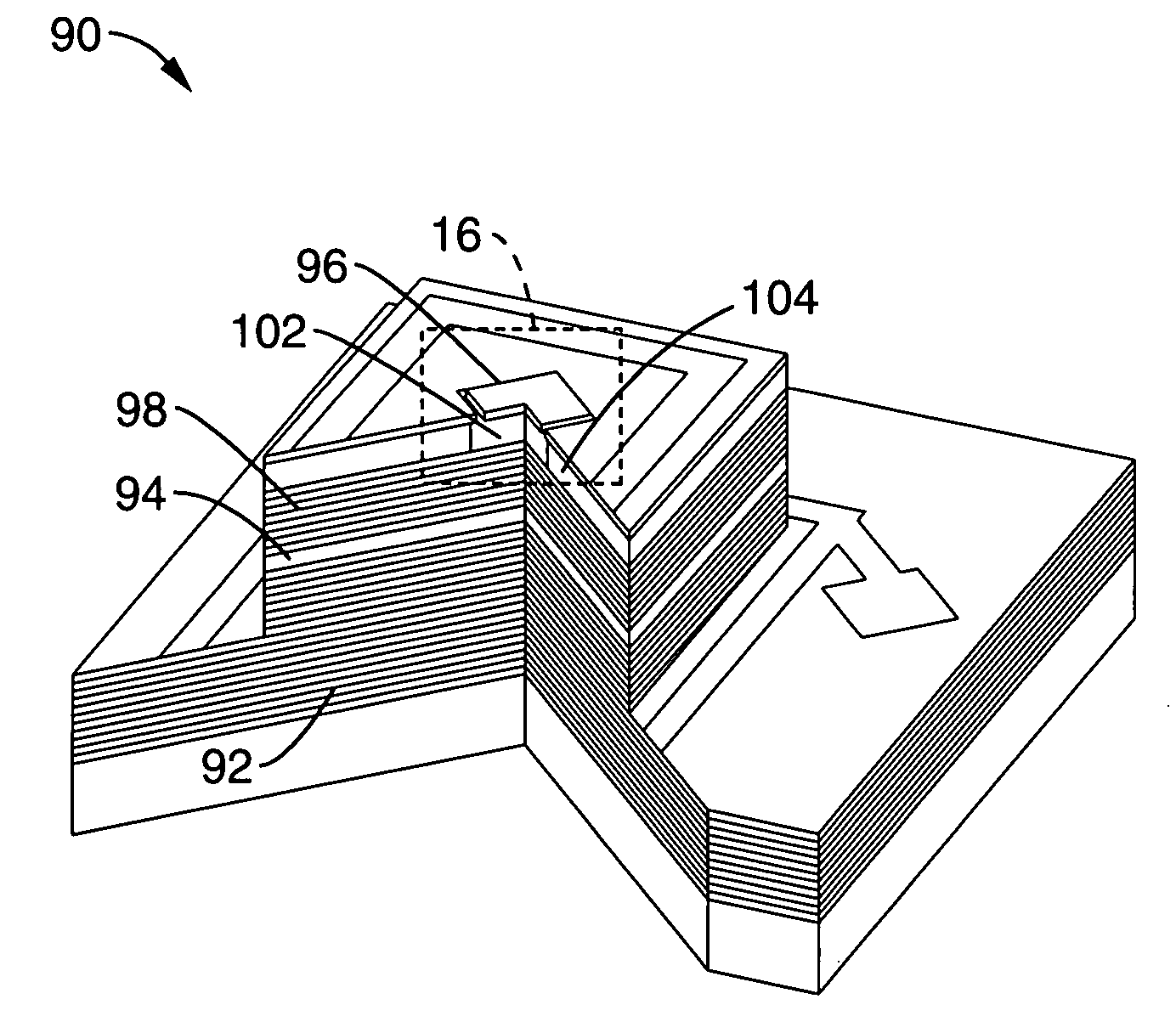
Resonator-enhanced optoelectronic devices and methods of making same
Optical resonators that are enhanced with photoluminescent phosphors and are designed and configured to output light at one or more wavelengths based on input / pump light, and systems and devices made with such resonators. In some embodiments, the resonators contain multiple optical resonator cavities in combination with one or more photoluminescent phosphor layers or other structures. In other embodiments, the resonators are designed to simultaneously resonate at the input / pump and output wavelengths. The photoluminescent phosphors can be any suitable photoluminescent material, including semiconductor and other materials in quantum-confining structures, such as quantum wells and quantum dots, among others.
Owner:VERLASE TECH
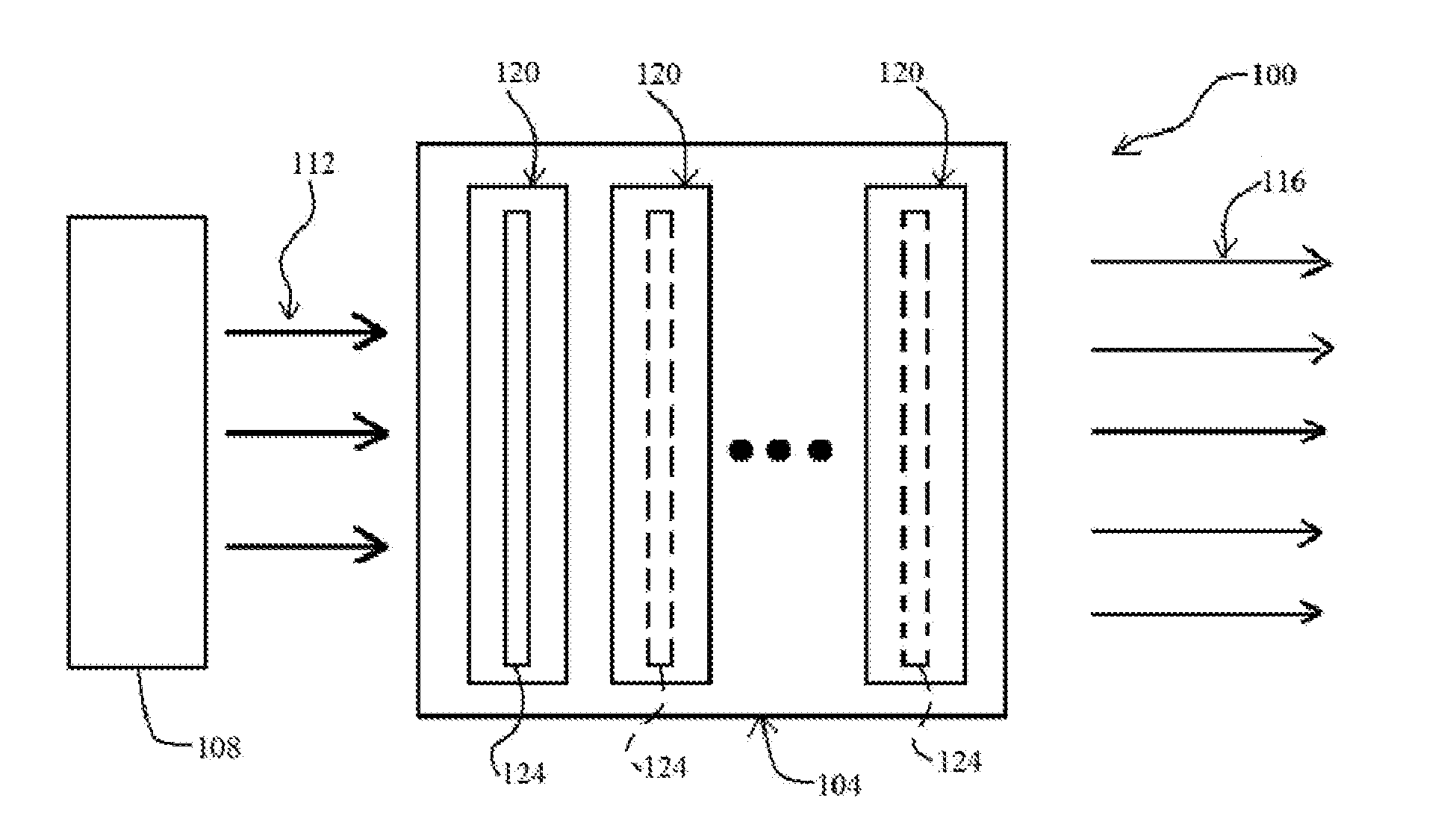
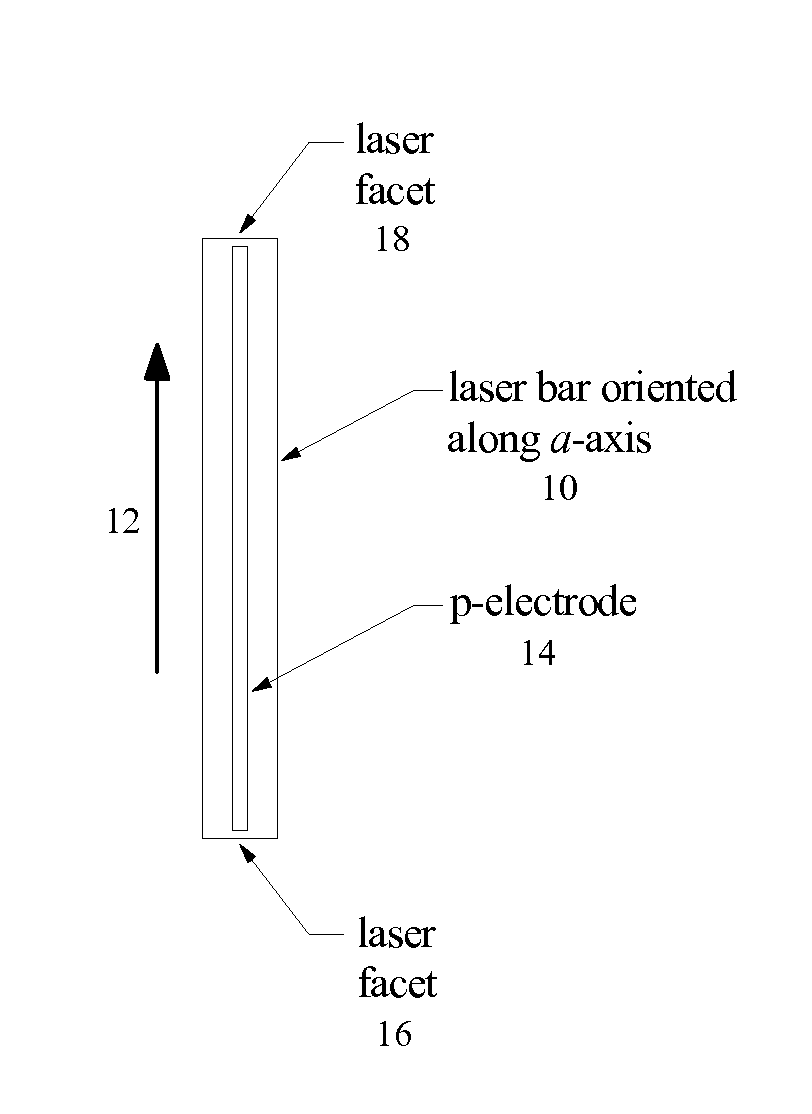
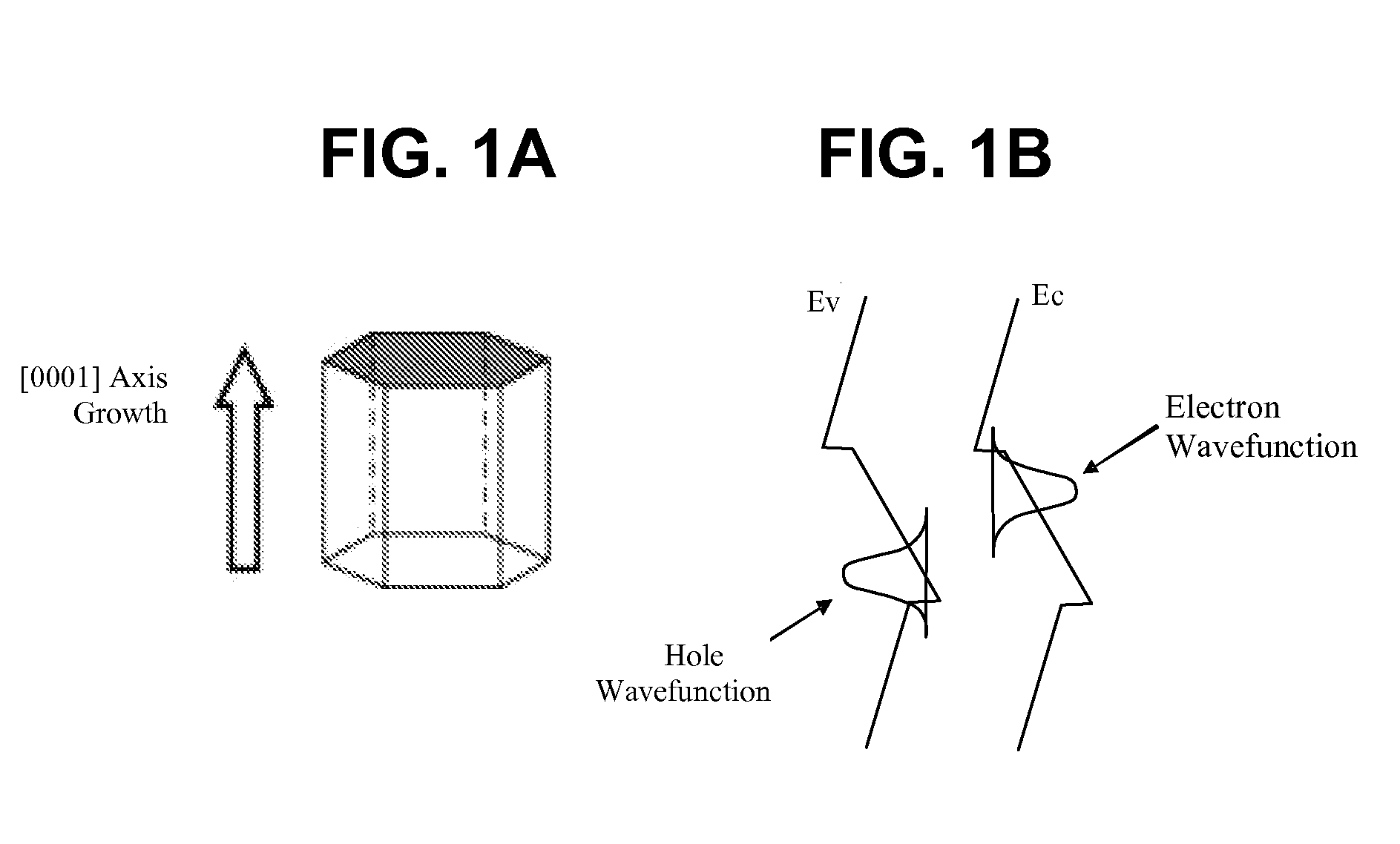
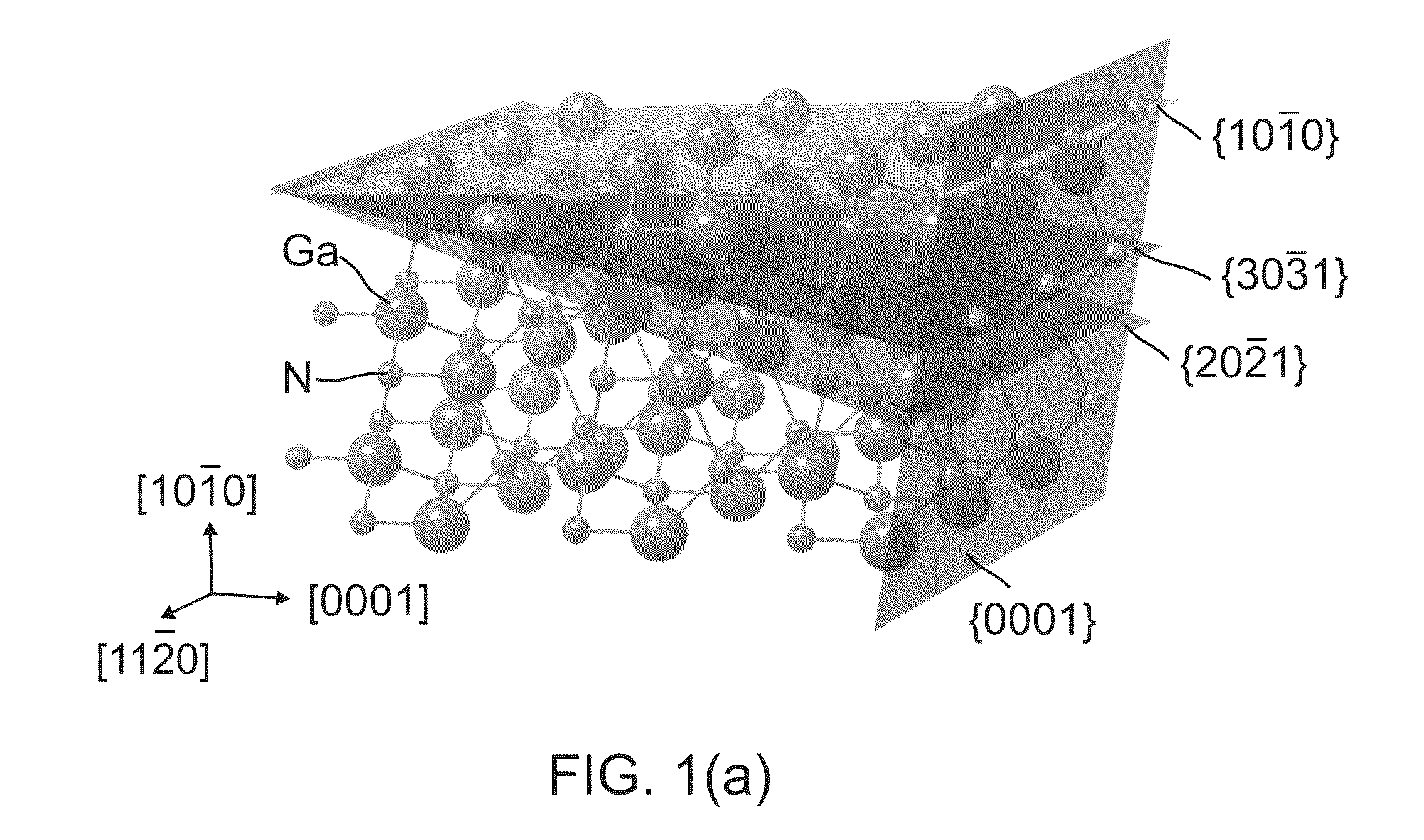
OPTIMIZATION OF LASER BAR ORIENTATION FOR NONPOLAR AND SEMIPOLAR (Ga,Al,In,B)N DIODE LASERS
ActiveUS20080198881A1Maximize optical gainOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsNitrideOptical polarization
Optical gain of a nonpolar or semipolar Group-III nitride diode laser is controlled by orienting an axis of light propagation in relation to an optical polarization direction or crystallographic orientation of the diode laser. The axis of light propagation is substantially perpendicular to the mirror facets of the diode laser, and the optical polarization direction is determined by the crystallographic orientation of the diode laser. To maximize optical gain, the axis of light propagation is oriented substantially perpendicular to the optical polarization direction or crystallographic orientation.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
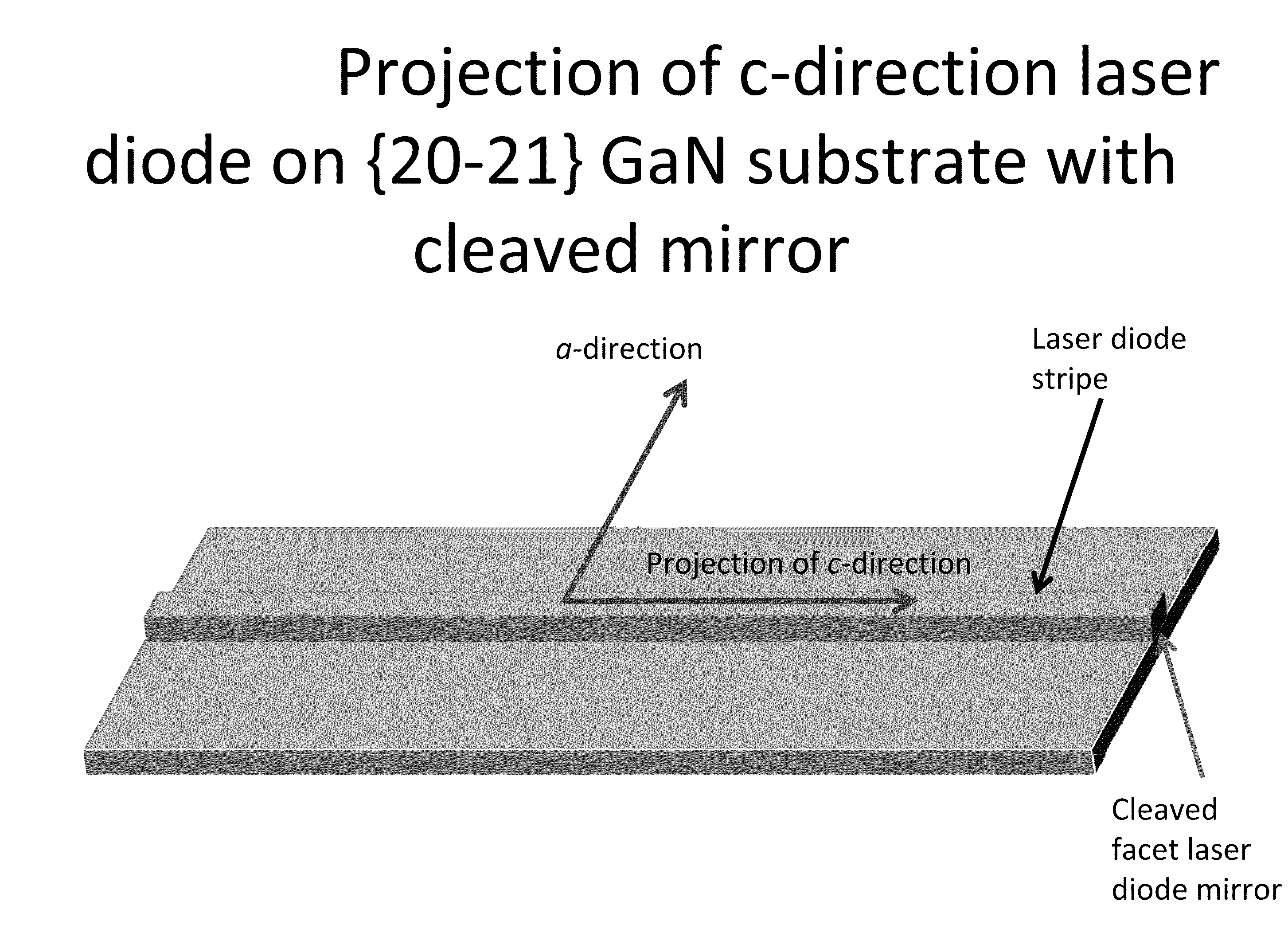
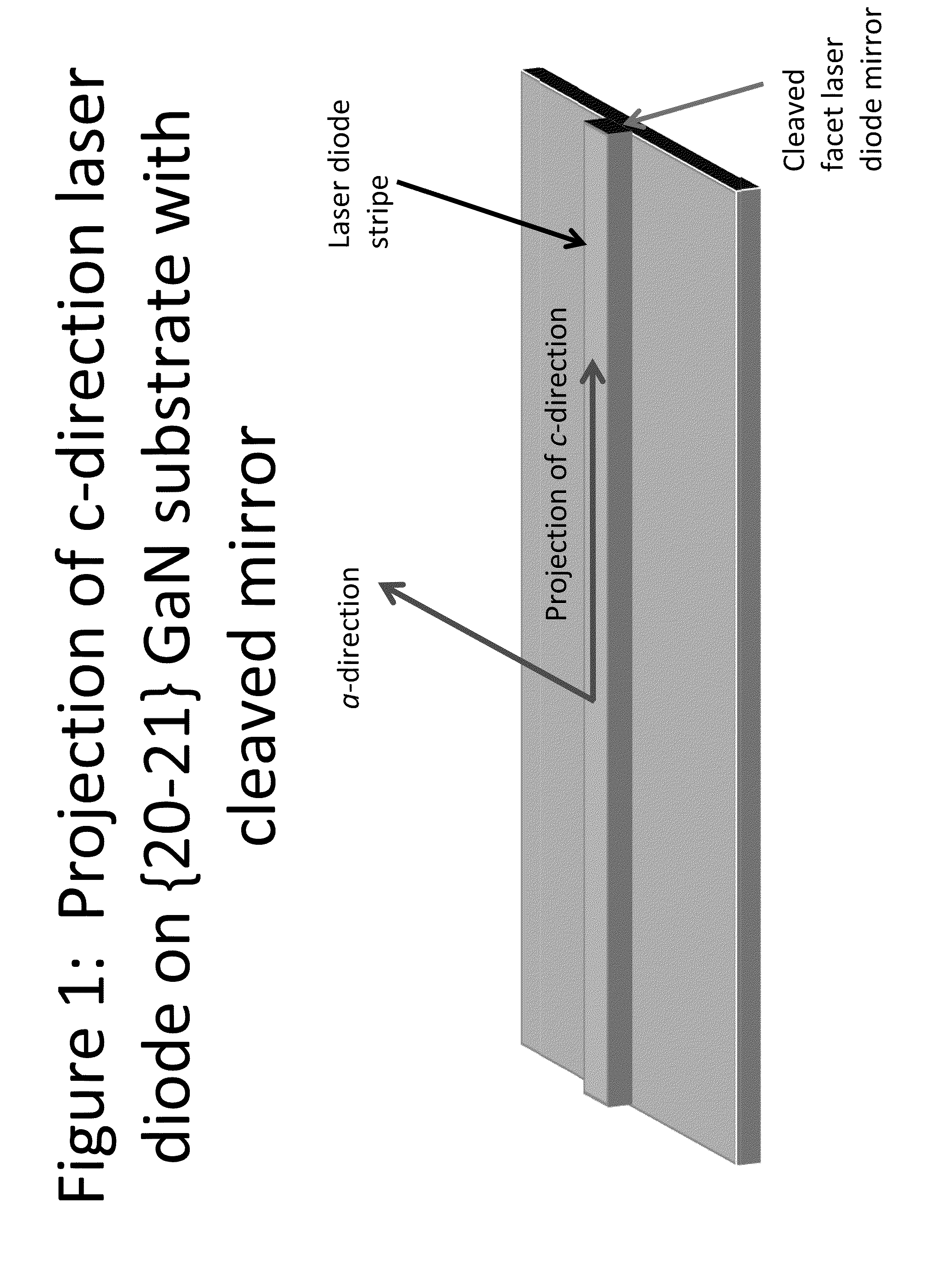
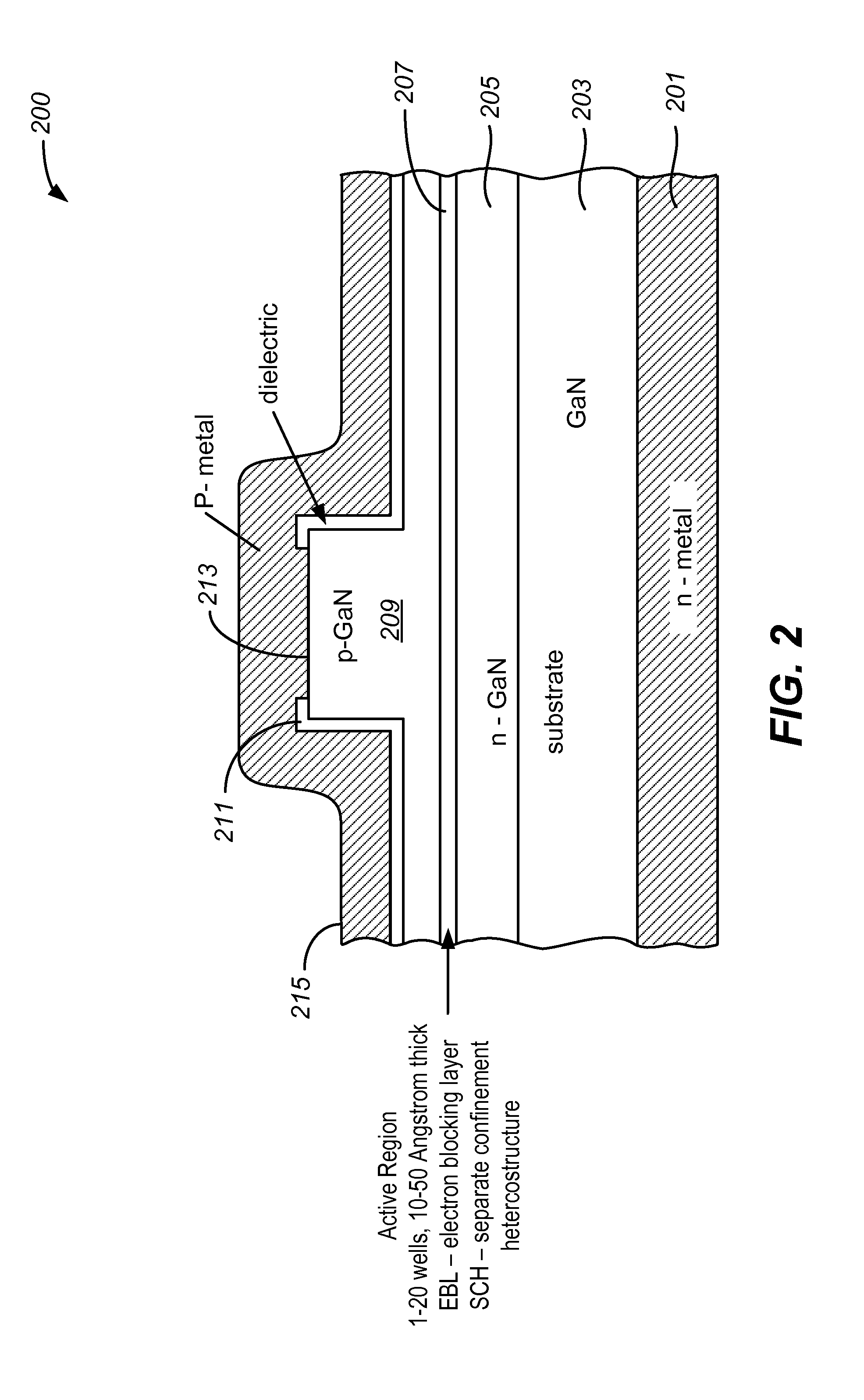
Growth Structures and Method for Forming Laser Diodes on or Off Cut Gallium and Nitrogen Containing Substrates
ActiveUS20110064100A1Improved cleavesCost-effectiveLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionNitrogenLength wave
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
Semiconductor light-emitting device
InactiveUS20060175624A1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorMaterials science
A semiconductor light-emitting diode, and method of fabricating same, wherein an indium (In)-containing light-emitting layer, as well as subsequent device layers, is deposited on a textured surface. The resulting device is a phosphor-free white light source.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Mach-Zehnder interferometer using photonic band gap crystals
InactiveUS6917431B2Small sizeLarge operating bandwidthLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonic crystalMach–Zehnder interferometer
A photonic crystal optical switch having a periodic dielectric structure including at least one input waveguide. First and second waveguide arms branch from the input waveguide in which the relative optical path lengths of electromagnetic radiation within the arms are controlled by stimuli. At least one output waveguide that combines the electromagnetic radiation propagating within the first and second waveguide arms.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
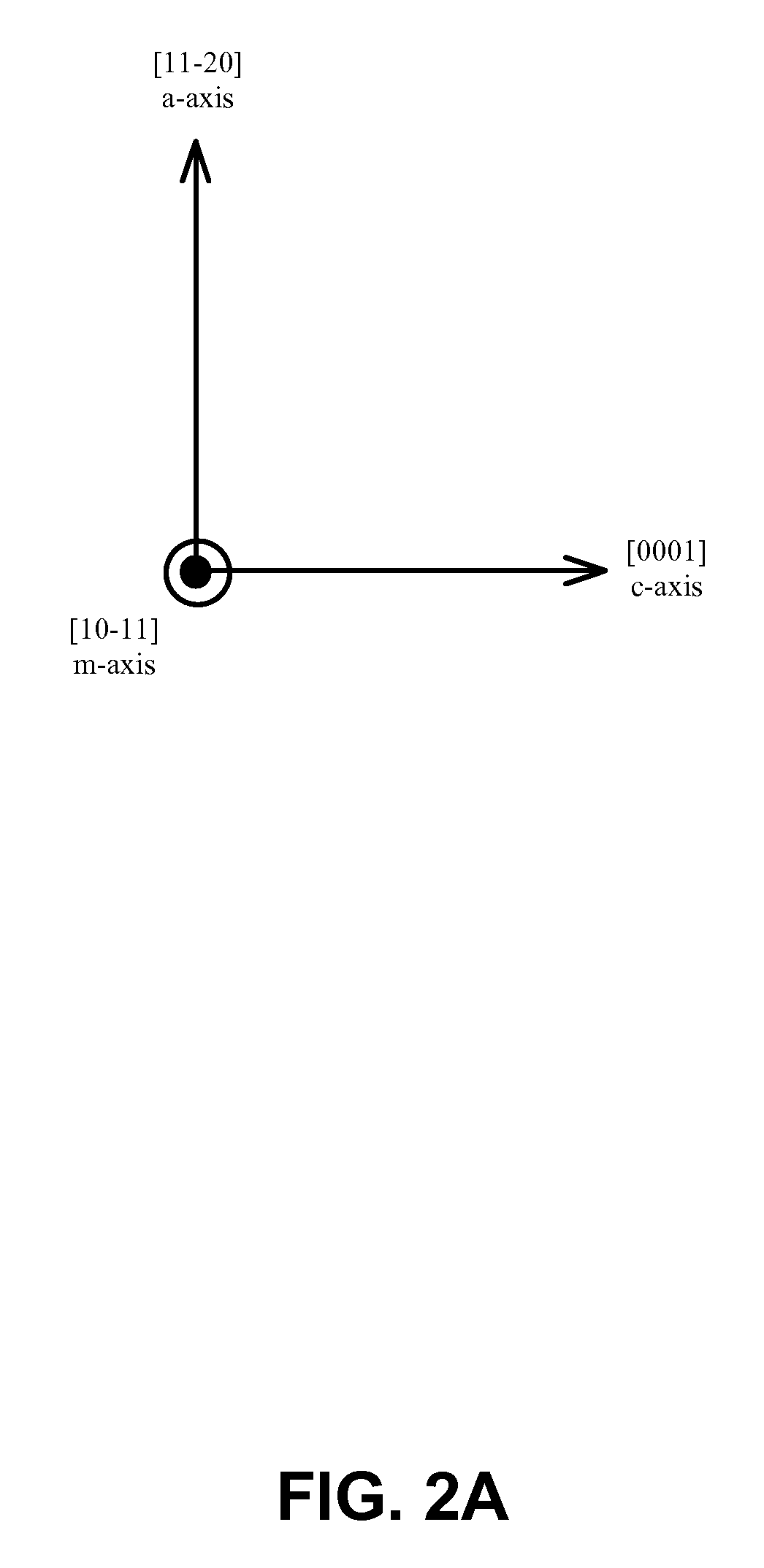
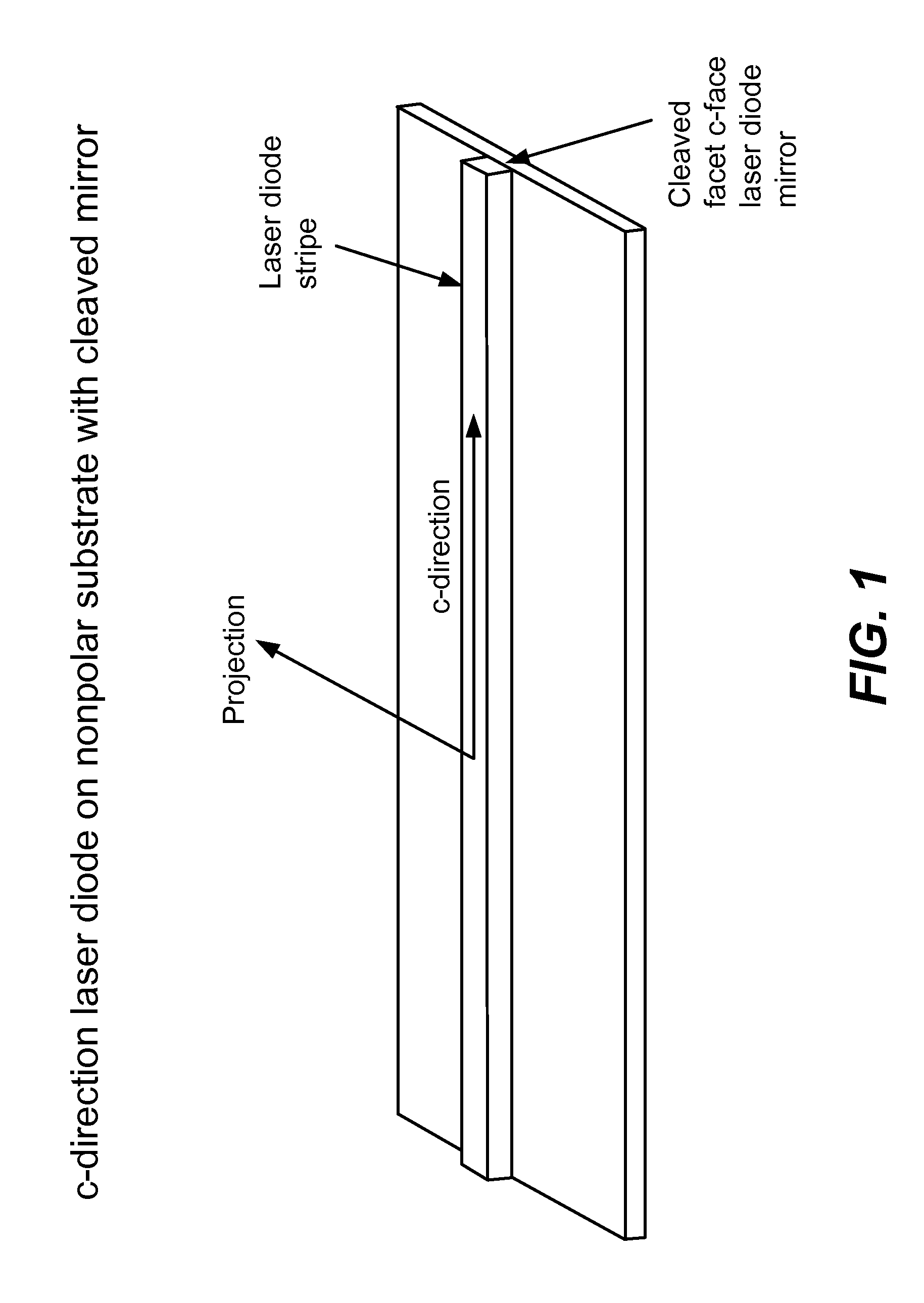
Optical Device Structure Using GaN Substrates for Laser Applications
ActiveUS20100316075A1Simple and cost-effectiveAchieve benefitsLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGallium nitrideLaser application
An optical device includes a gallium nitride substrate member having an m-plane nonpolar crystalline surface region characterized by an orientation of about −2 degrees to about 2 degrees towards (000-1) and less than about 0.5 degrees towards (11-20). The device also has a laser stripe region formed overlying a portion of the m-plane nonpolar crystalline orientation surface region. A first cleaved c-face facet is provided on one end of the laser stripe region, and a second cleaved c-face facet is provided on the other end of the laser stripe region.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
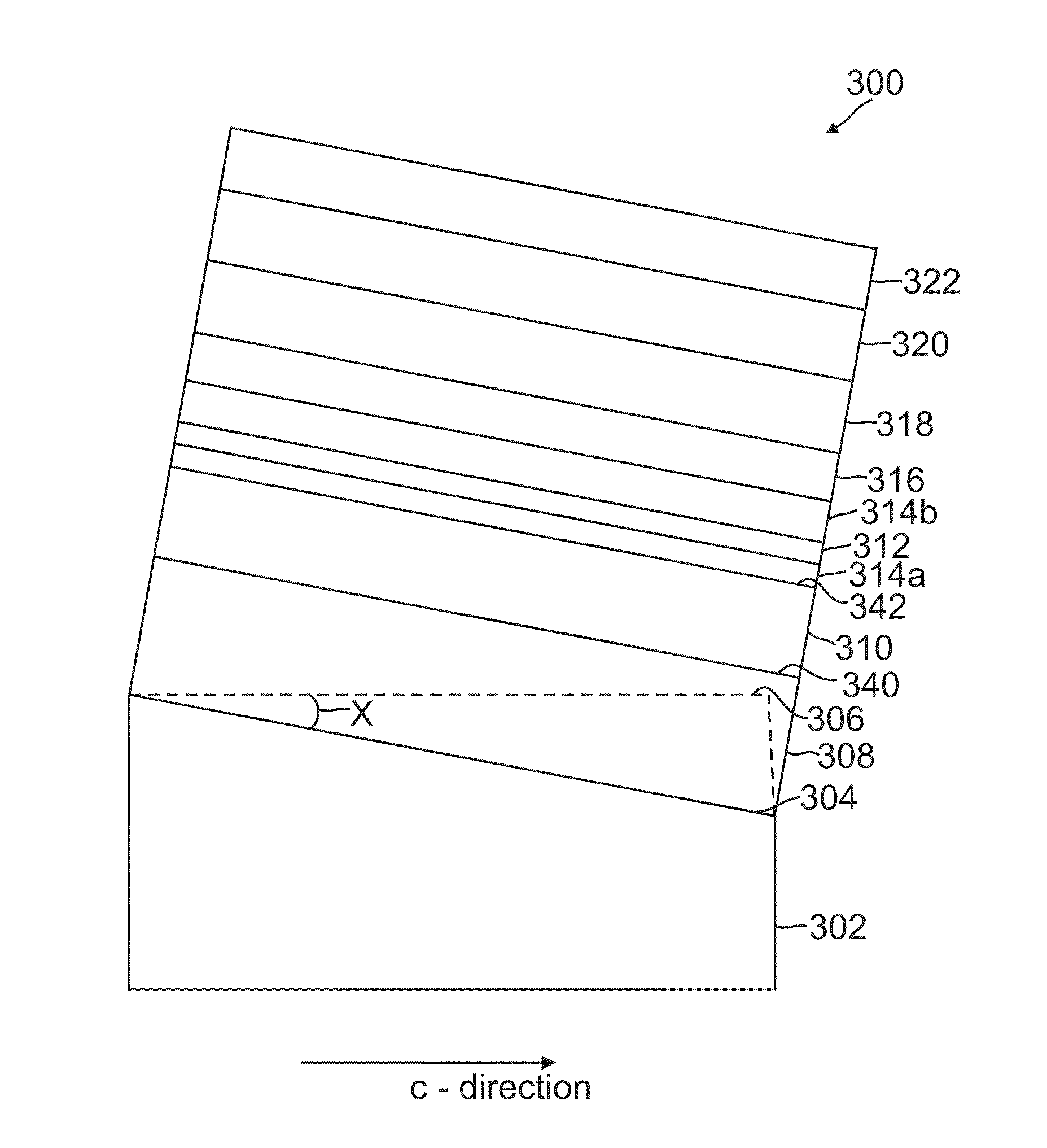
Semi-polar iii-nitride optoelectronic devices on m-plane substrates with miscuts less than +/-15 degrees in the c-direction
ActiveUS20110216795A1QCSE induced dependentIncrease oscillator strengthOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsCrystal planeNitride
An optoelectronic device grown on a miscut of GaN, wherein the miscut comprises a semi-polar GaN crystal plane (of the GaN) miscut x degrees from an m-plane of the GaN and in a c-direction of the GaN, where −15<x<−1 and 1<x<15 degrees.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
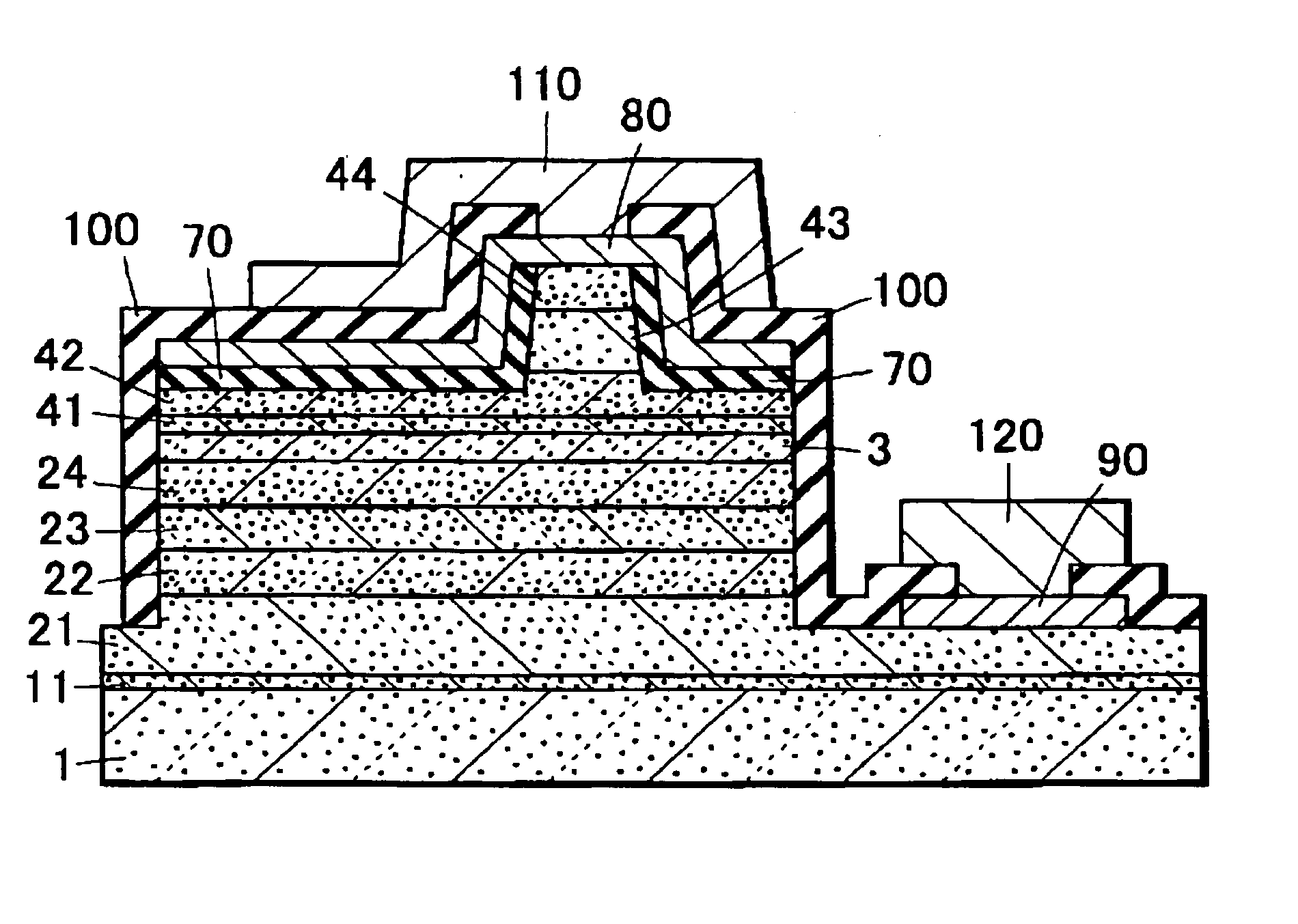
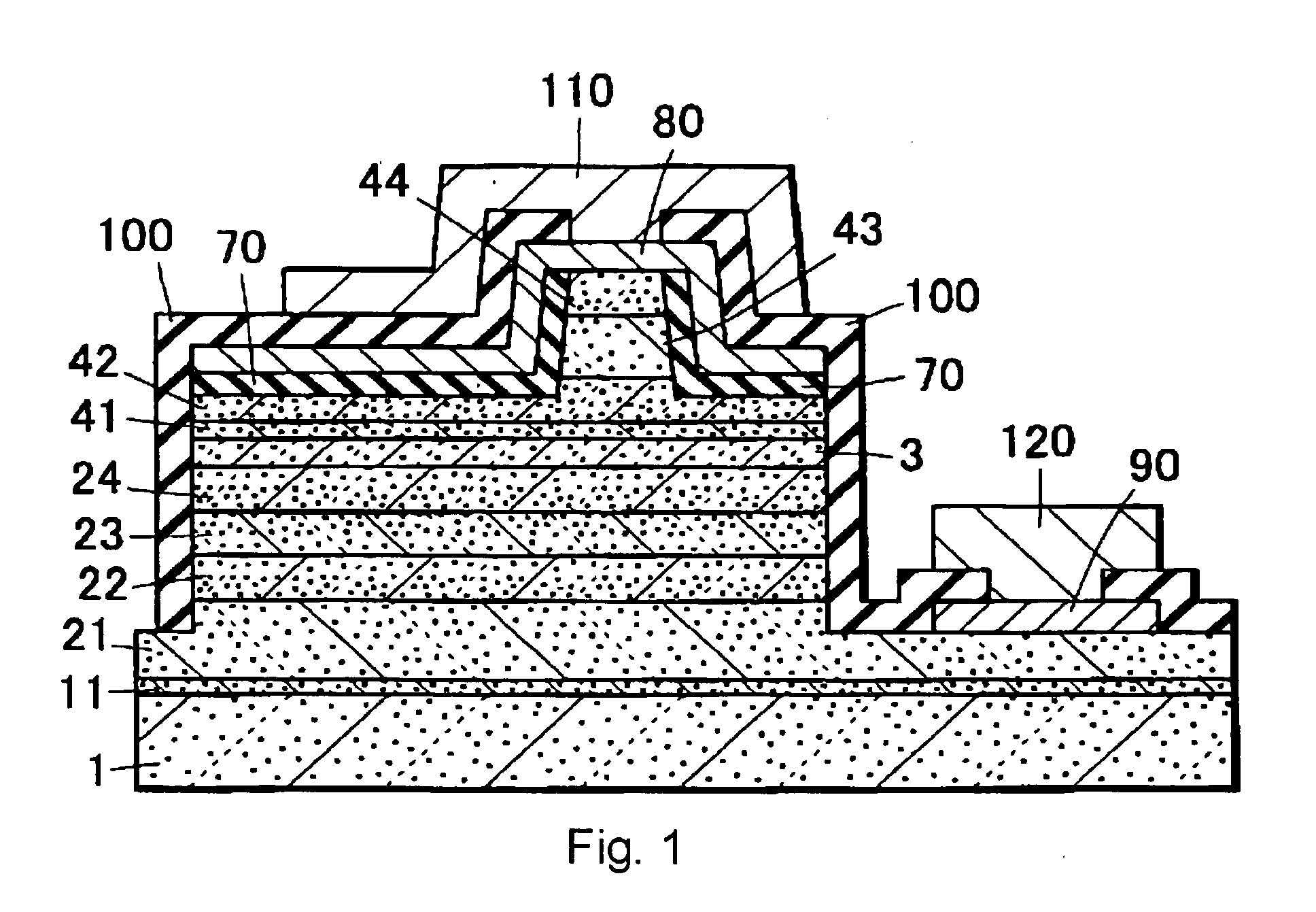
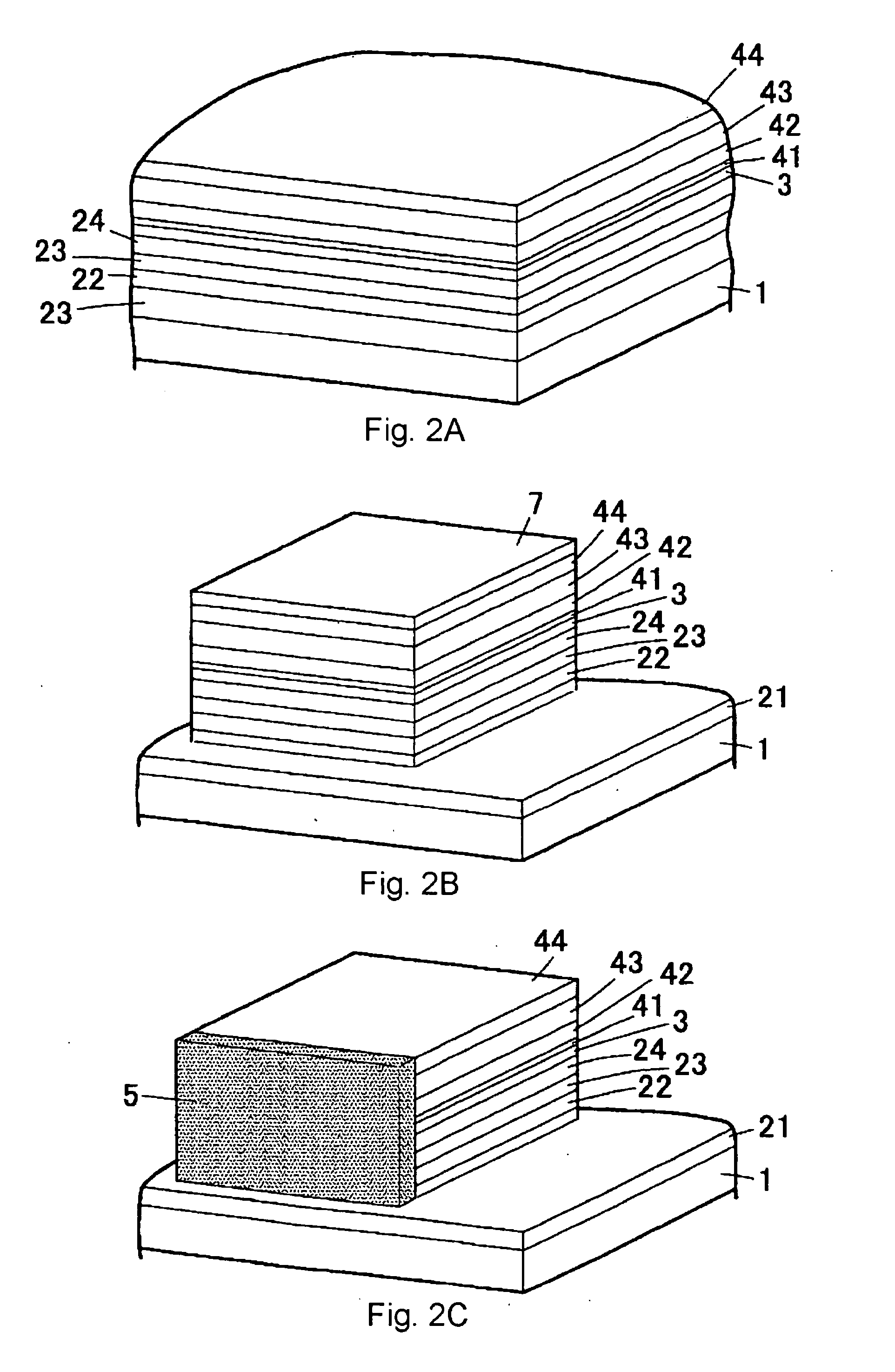
Light emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090078944A1High gainSimple stepsOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOptical cavityLight emitting device
This semiconductor light emitting device includes an optical cavity made of a group III nitride semiconductor having a major growth surface defined by a nonpolar plane and including a pair of cavity end faces parallel to c-planes, and a reflecting portion made of a group III nitride semiconductor having a major growth surface defined by a nonpolar plane and having a reflective facet opposed to one of the pair of cavity end faces and inclined with respect to a normal of the major growth surface. The optical cavity and the reflecting portion may be crystal-grown from the major surface of the substrate. The substrate is preferably a group III nitride semiconductor substrate having a major surface defined by a nonpolar plane.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Nanocomposites
ActiveUS7068898B2Increase percentageEfficiently waveguidedSolar heating energyMaterial nanotechnologyNanowireNanoparticle
This invention provides composite materials comprising nanostructures (e.g., nanowires, branched nanowires, nanotetrapods, nanocrystals, and nanoparticles). Methods and compositions for making such nanocomposites are also provided, as are articles comprising such composites. Waveguides and light concentrators comprising nanostructures (not necessarily as part of a nanocomposite) are additional features of the invention.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Semicondutor laser device and its manufacturing method
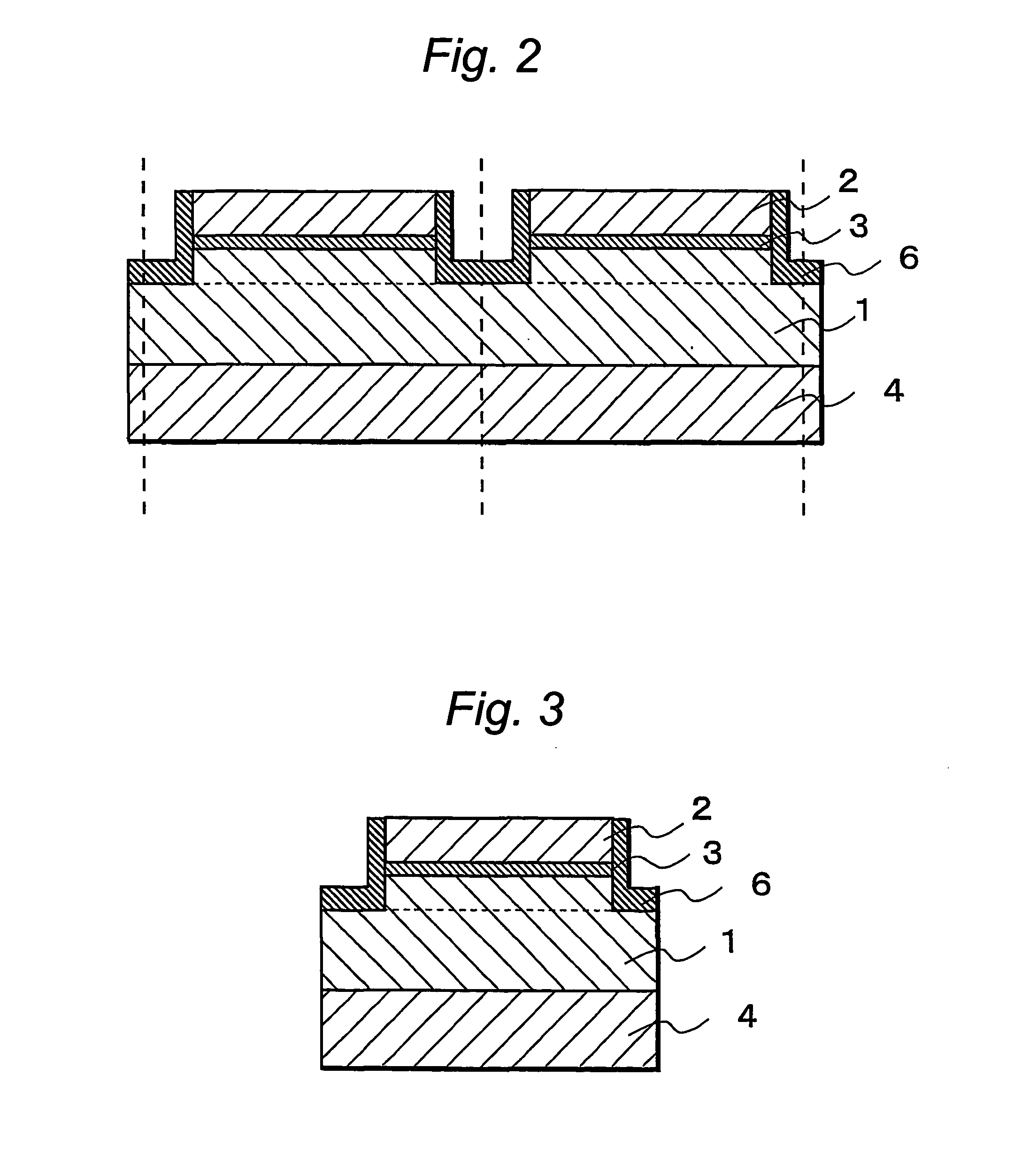
InactiveUS20040233950A1Efficient executionLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsTectorial membraneSemiconductor package
A semiconductor laser device have, on a substrate, a semiconductor layer including an active layer sandwiched between an n-type layer and a p-type layer, the semiconductor layer having a sonator face formed by etching and a projection projecting out in an emission direction relatively to the resonator face, wherein a protective film is formed to extend from the resonator face to an end face of the projection, and, an emission critical angle, which is the largest angle at which light emitted from the resonator face can be radiated without being blocked by the projection and the protective film formed on the projection, is larger than an emission half-angle of an emission distribution in a vertical direction of a laser beam emitted from the resonator face.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Light emitting element structure using nitride bulk single crystal layer
InactiveUS20040251471A1Improve crystal qualitySimple structureOptical wave guidancePolycrystalline material growthSingle crystalActive layer
The object of this invention is to provide a high-output type nitride light emitting device. The nitride light emitting device comprises an n-type nitride semiconductor layer or layers, a p-type nitride semiconductor layer or layers and an active layer therebetween, wherein a gallium-containing nitride substrate is obtained from a gallium-containing nitride bulk single crystal, provided with an epitaxial growth face with dislocation density of 10<5> / cm<2 >or less, and A-plane or M-plane which is parallel to C-axis of hexagonal structure for an epitaxial face, wherein the n-type semiconductor layer or layers are formed directly on the A-plane or M-plane. In case that the active layer comprises a nitride semiconductor containing In, an end face film of single crystal AlxGa1-xN (0<=x<=1) can be formed at a low temperature not causing damage to the active layer.
Owner:AMMONO SP Z O O (PL) +1
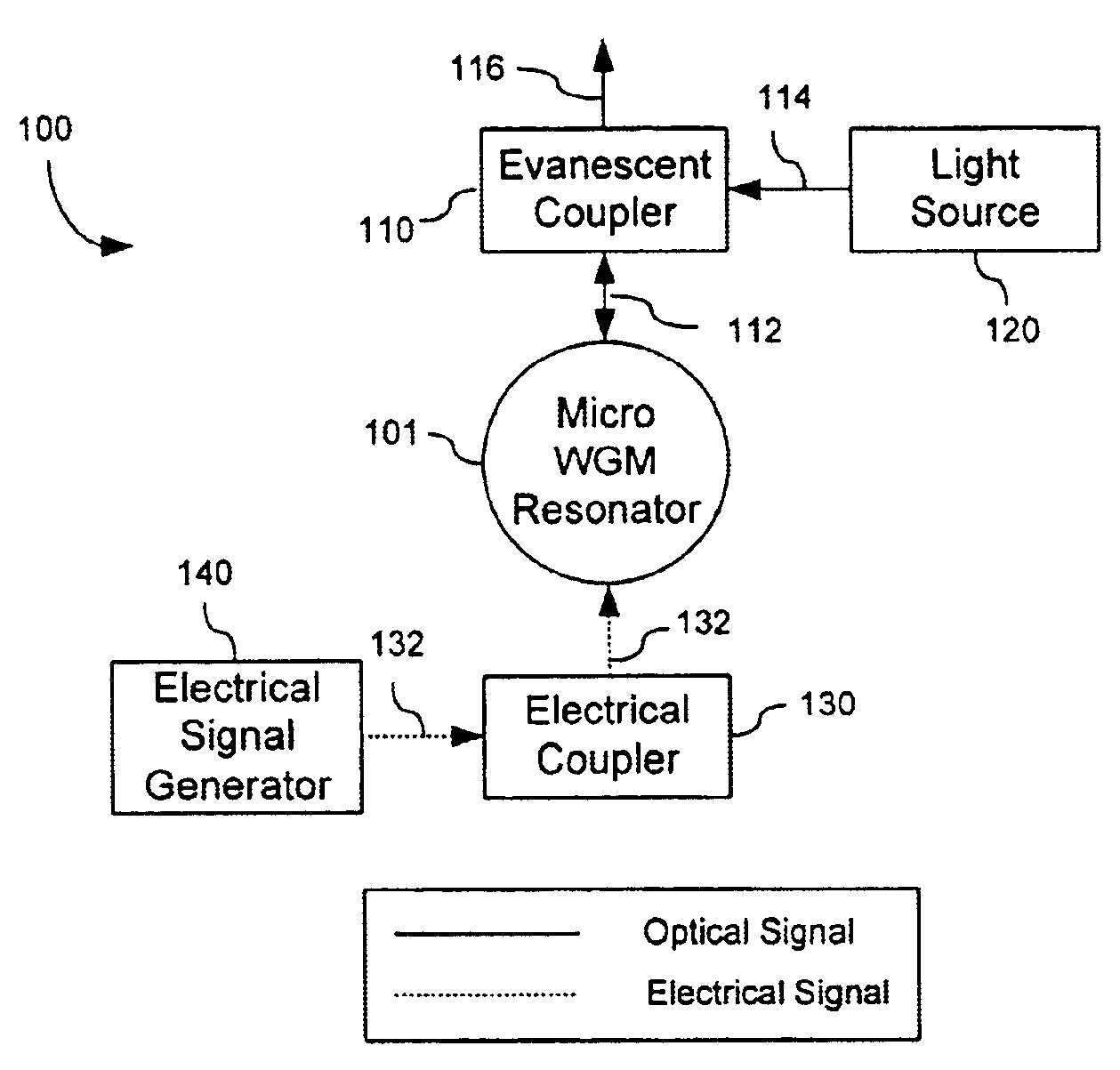
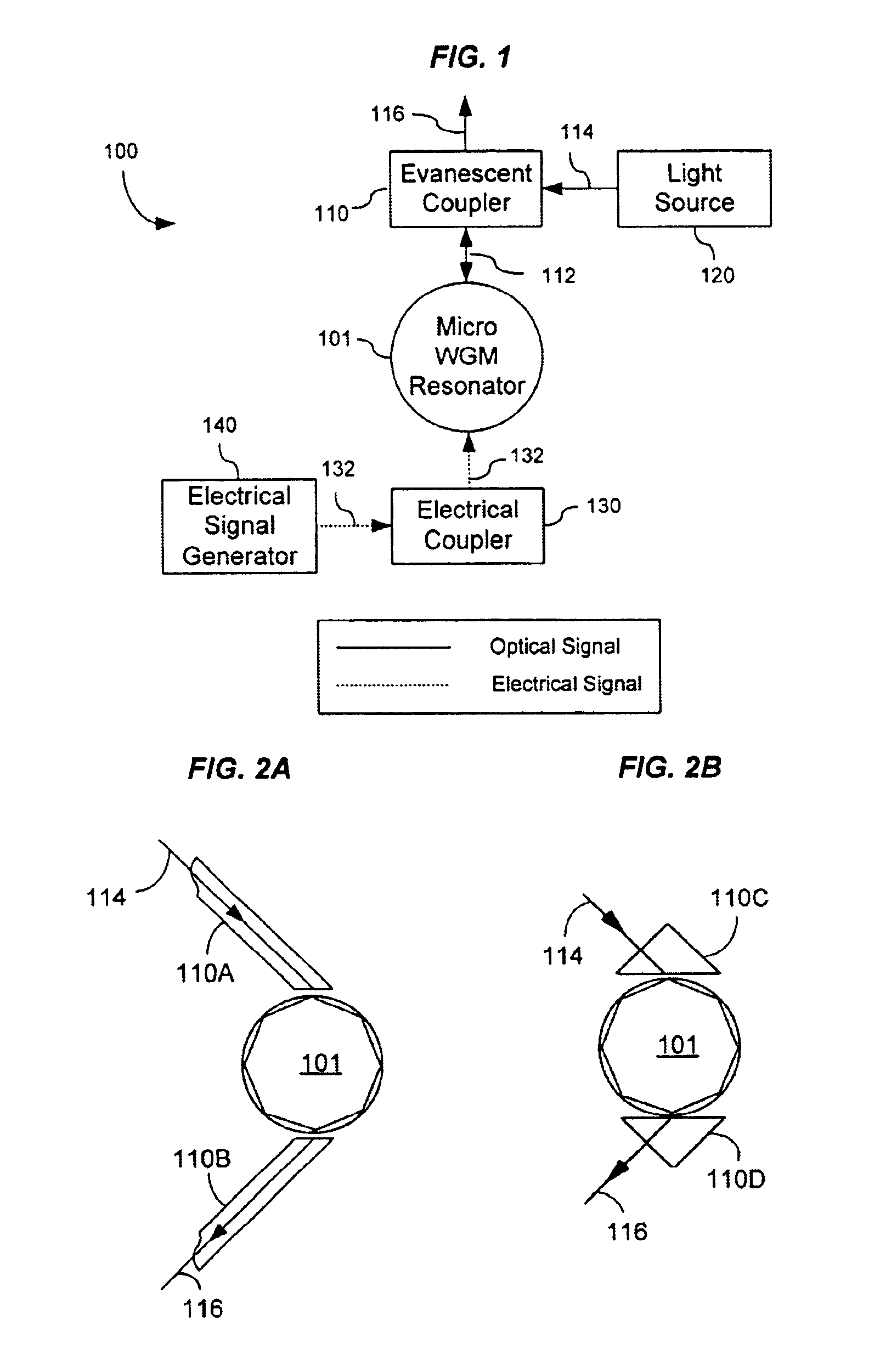
Direct electrical-to-optical conversion and light modulation in micro whispering-gallery-mode resonators
InactiveUS6871025B2Efficient couplingHigh quality factorLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionWhispering galleryLight modulation
Techniques for directly converting an electrical signal into an optical signal by using a whispering gallery mode optical resonator formed of a dielectric material that allows for direct modulation of optical absorption by the electrical signal.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Broadband light emitting device
ActiveUS7019325B2Increase heightBroad emission spectrumLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionStimulated emissionP–n junction
The invention concerns a superluminescent light emitting diode (SLED) comprising a semiconductor heterostructure forming a PN junction and a waveguide. The semiconductor heterostructure includes a gain region with a contact means for biasing the PN junction so as to produce light emission including stimulated emission from an active zone of the gain region, and in the active zone a plurality of quantum dot layers, each quantum dot layer made up of a plurality of quantum dots and a plurality of adjoining layers, each adjoining layer adjacent to one of said quantum dot layers. The material composition or a deposition parameter of at least two adjoining layers is different. This ensures an enhanced emission spectral width.
Owner:EXALOS
Surface plasmon devices
InactiveUS7010183B2Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionSoftware engineeringEngineering
A device including an input port configured to receive an input signal is described. The device also includes an output port and a structure, which structure includes a tunneling junction connected with the input port and the output port. The tunneling junction is configured in a way (i) which provides electrons in a particular energy state within the structure, (ii) which produces surface plasmons in response to the input signal, (iii) which causes the structure to act as a waveguide for directing at least a portion of the surface plasmons along a predetermined path toward the output port such that the surface plasmons so directed interact with the electrons in a particular way, and (iv) which produces at the output port an output signal resulting from the particular interaction between the electrons and the surface plasmons.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Use of volume Bragg gratings for the conditioning of laser emission characteristics
ActiveUS20050018743A1High damage thresholdLarge clear apertureLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsGratingLight emitting device
Apparatus and methods for altering one or more spectral, spatial, or temporal characteristics of a light-emitting device are disclosed. Generally, such apparatus may include a volume Bragg grating (VBG) element that receives input light generated by a light-emitting device, conditions one or more characteristics of the input light, and causes the light-emitting device to generate light having the one or more characteristics of the conditioned light.
Owner:NECSEL INTPROP
External cavity laser
InactiveUS6101210AAvoid disadvantagesEasy temperature controlLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsTemperature controlGrating
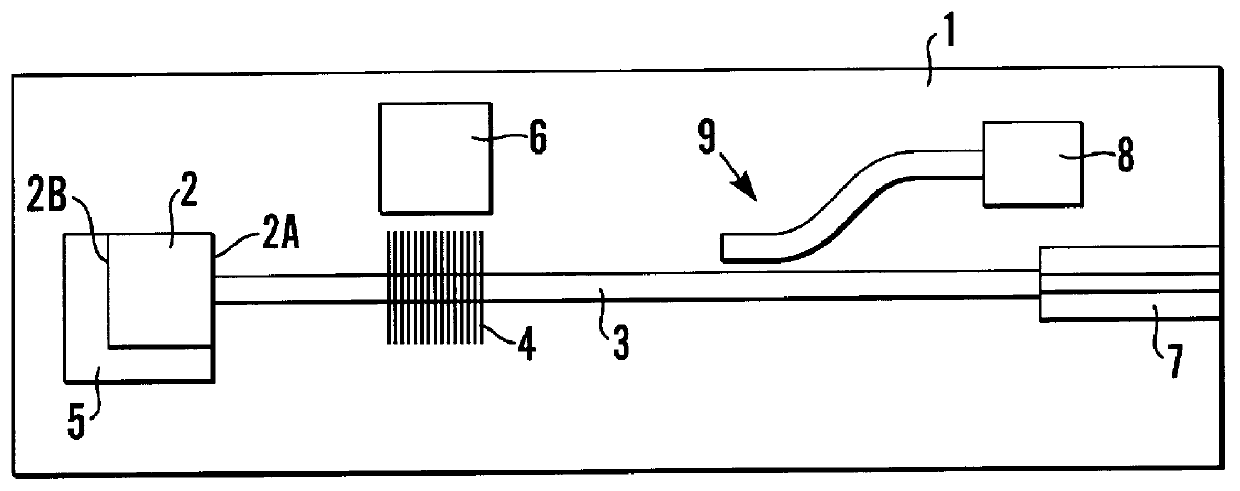
External Cavity Laser An external cavity laser comprising first and second feedback means with an optical gain medium (2) therebetween, one of the feedback means is provided by a grating (4) formed in a silicon waveguide and the other feedback means is provided by a reflective back facet (2B) of the optical gain medium (2). The output wavelength of the laser, at a given temperature, can thus be determined during its manufacture and the laser can be made by mass production techniques. The grating (4) may be thermally isolated to obviate the need for temperature control means (6) to control the temperature of the grating (4). An array of lasers may be provided on a single chip.
Owner:KOTURA
Coolerless photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for WDM transmission networks and PICs operable with a floating signal channel grid changing with temperature but with fixed channel spacing in the floating grid
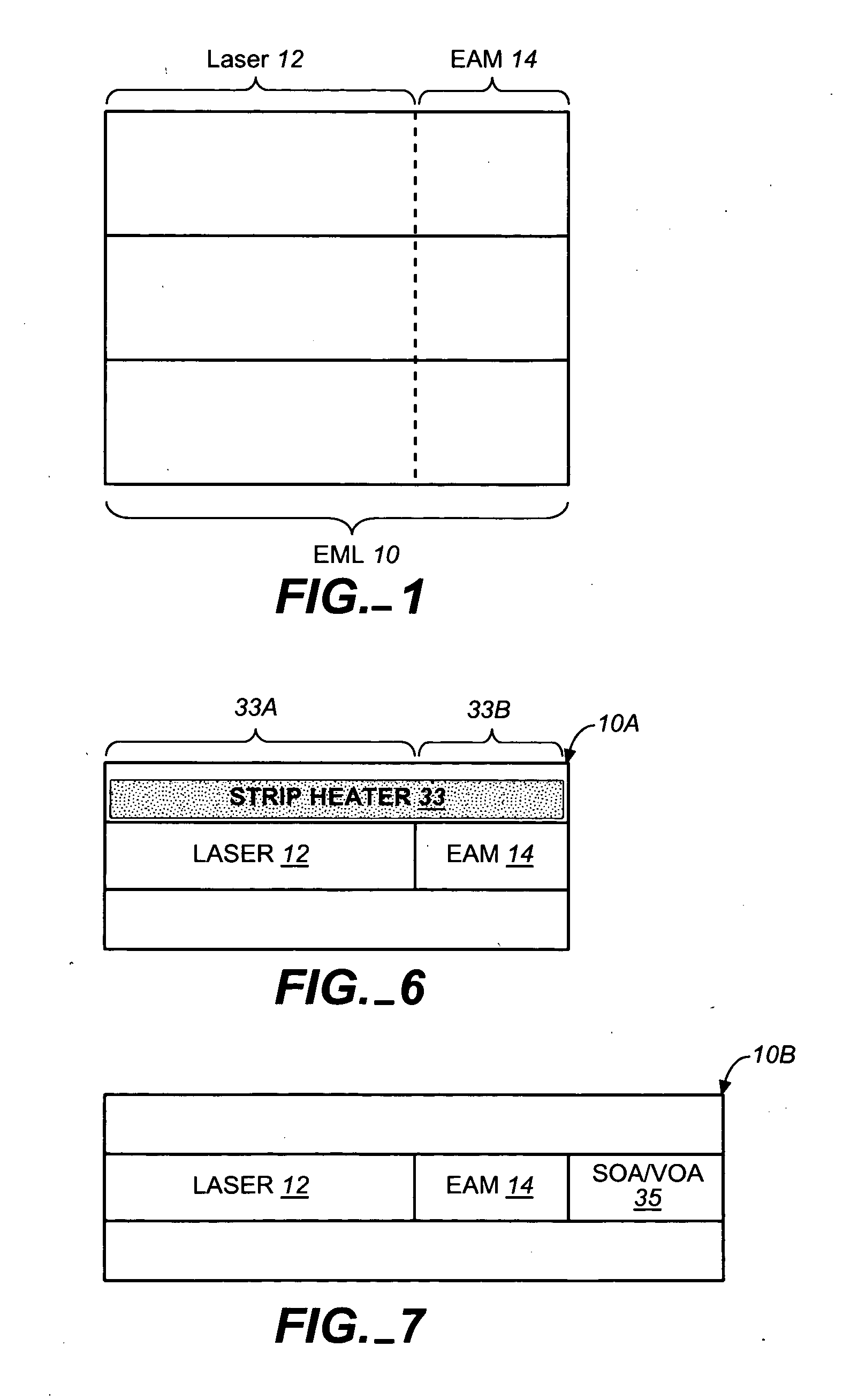
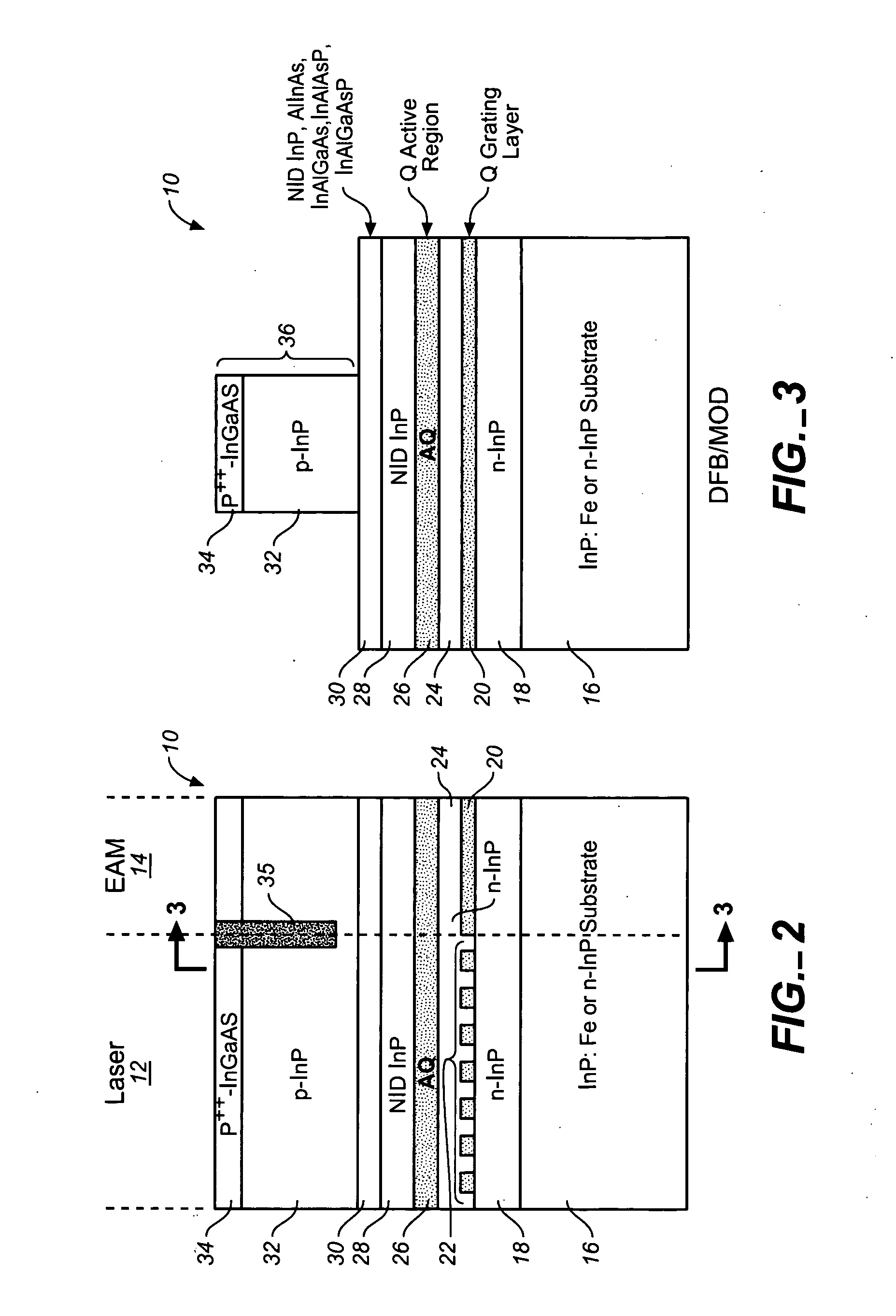
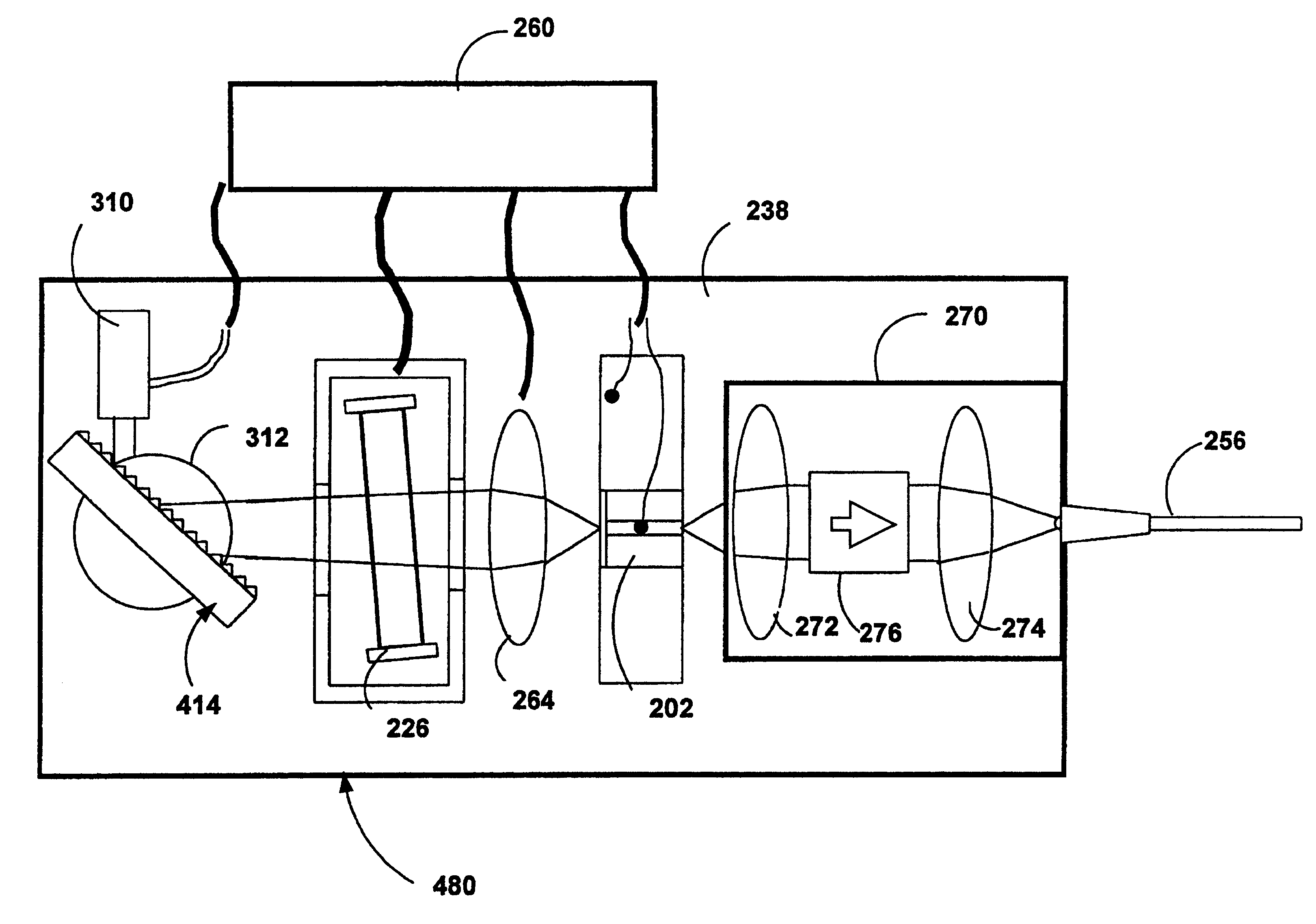
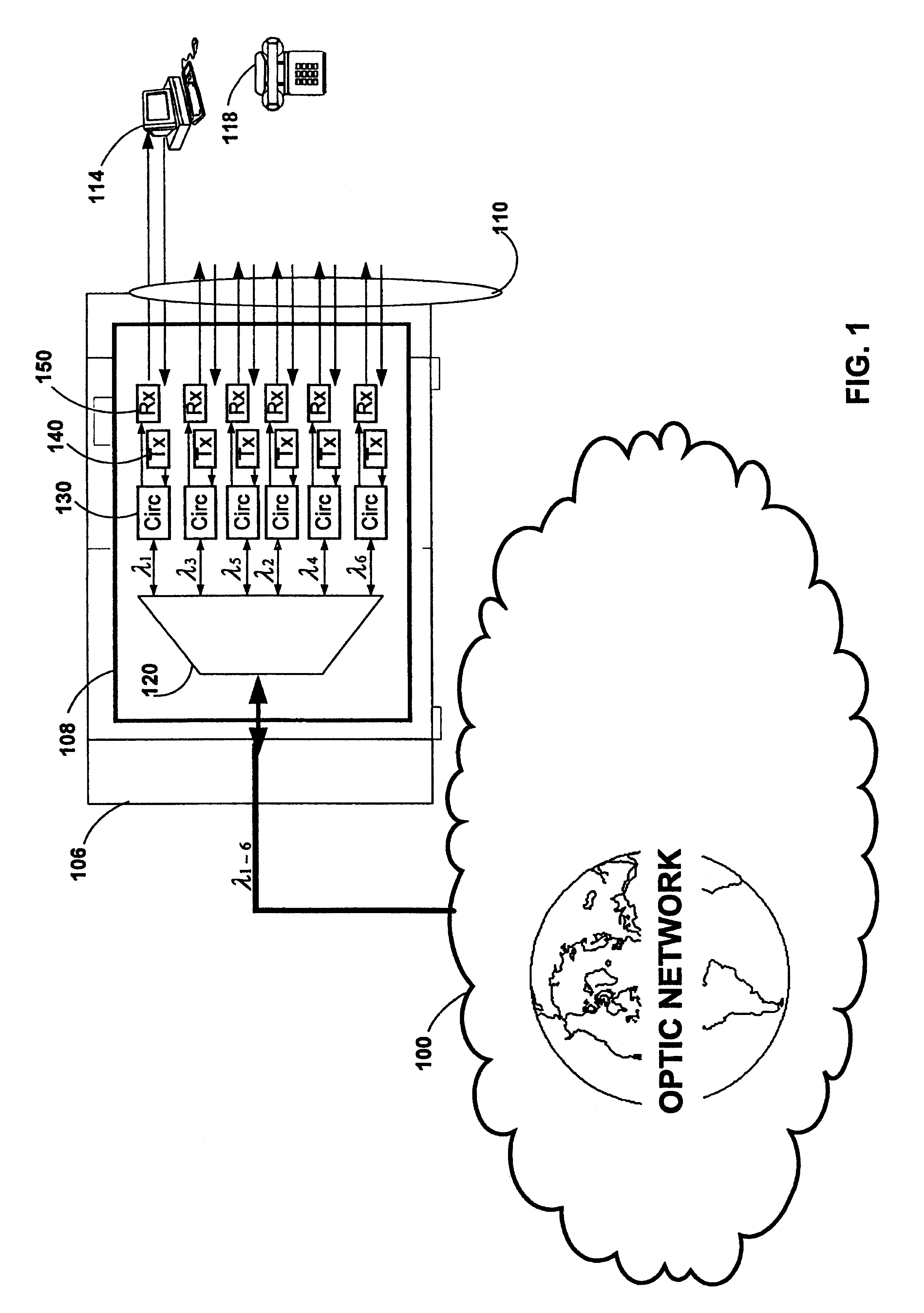
ActiveUS20050249509A1Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedEasy to controlLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorHermetic packaging
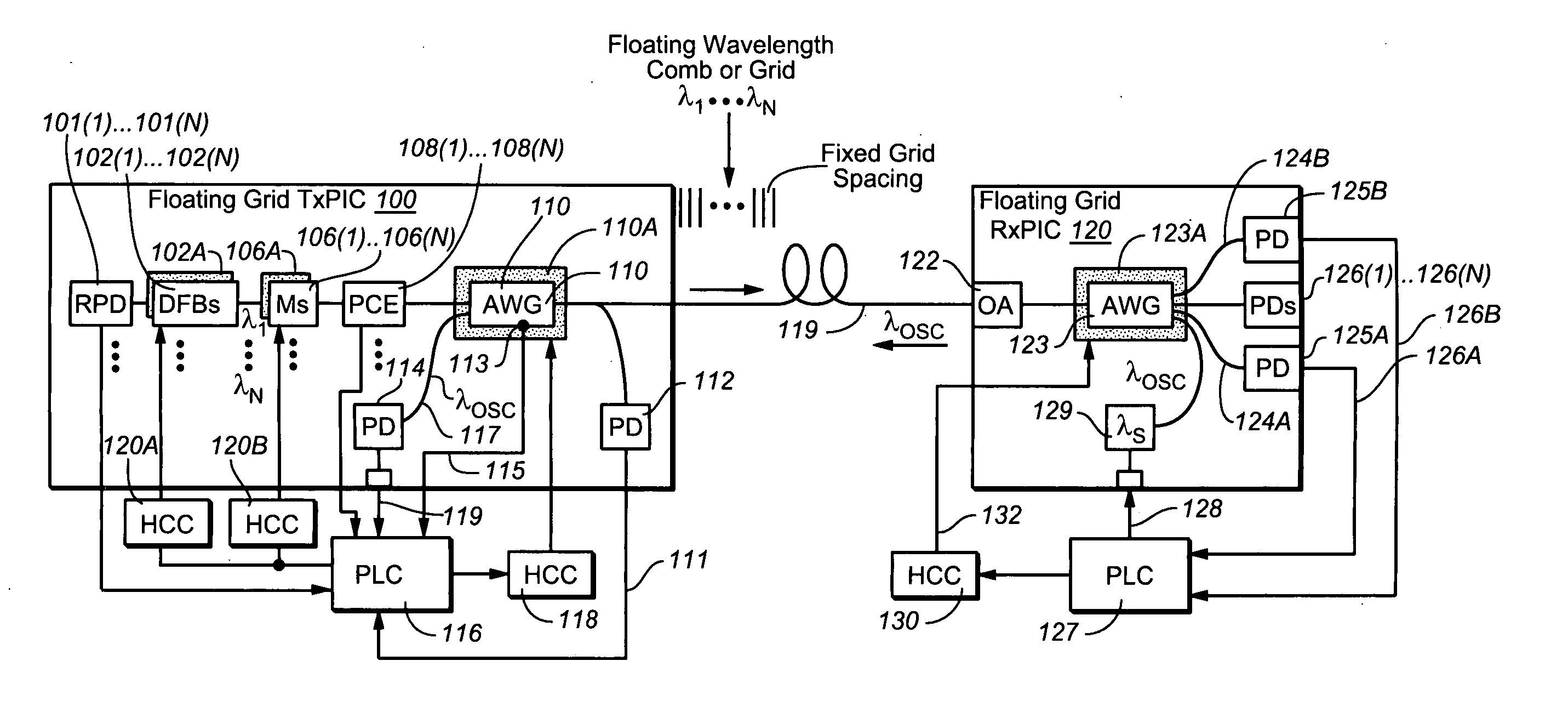
A coolerless photonic integrated circuit (PIC), such as a semiconductor electro-absorption modulator / laser (EML) or a coolerless optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC), may be operated over a wide temperature range at temperatures higher then room temperature without the need for ambient cooling or hermetic packaging. Since there is large scale integration of N optical transmission signal WDM channels on a TxPIC chip, a new DWDM system approach with novel sensing schemes and adaptive algorithms provides intelligent control of the PIC to optimize its performance and to allow optical transmitter and receiver modules in DWDM systems to operate uncooled. Moreover, the wavelength grid of the on-chip channel laser sources may thermally float within a WDM wavelength band where the individual emission wavelengths of the laser sources are not fixed to wavelength peaks along a standardized wavelength grid but rather may move about with changes in ambient temperature. However, control is maintained such that the channel spectral spacing between channels across multiple signal channels, whether such spacing is periodic or aperiodic, between adjacent laser sources in the thermally floating wavelength grid are maintained in a fixed relationship. Means are then provided at an optical receiver to discover and lock onto floating wavelength grid of transmitted WDM signals and thereafter demultiplex the transmitted WDM signals for OE conversion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Tunable laser transmitter with internal wavelength grid generators
InactiveUS6526071B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsCapacitanceLaser transmitter
The present invention provides a continuously tunable external cavity laser (ECL) with a compact form factor and precise tuning to a selected center wavelength of a selected wavelength grid. The ECL may thus be utilized in telecom applications to generate the center wavelengths for any channel on the ITU or other optical grid. The ECL does not require a closed loop feedback. A novel tuning mechanism is disclosed which provides for electrical or mechanical tuning to a known position or electrical parameter, e.g., voltage, current or capacitance, with the required precision in the selected center wavelength arising as a result of a novel arrangement of a grid generator and a channel selector. The grid generator exhibits first pass bands which correspond to the spacing between individual channels of the selected wavelength grid and a finesse which suppresses side band modes of the laser. The channel selector exhibits second pass bands that are wider than the first pass bands. In an embodiment of the invention the second pass bands have a periodicity substantially corresponding with the separation between the shortest wavelength channel and the longest wavelength channel of the selected wavelength grid and a finesse which suppresses channels adjacent to the selected channel. The broad second pass bands of the channel selector reduce the sensitivity of the ECL to tuning variations about the selected channel, thus avoiding the requirement of a closed loop feedback system to control the channel selector.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Projection display apparatus, system, and method
An apparatus, system, and method for generating a projected display is disclosed. A light source generates red, green, and blue light using arrays of extended cavity surface emitting semiconductor lasers. The beams of individual lasers overlap and have a distribution of optical attributes selected to reduce speckle on a display surface.
Owner:NECSEL INTPROP +1
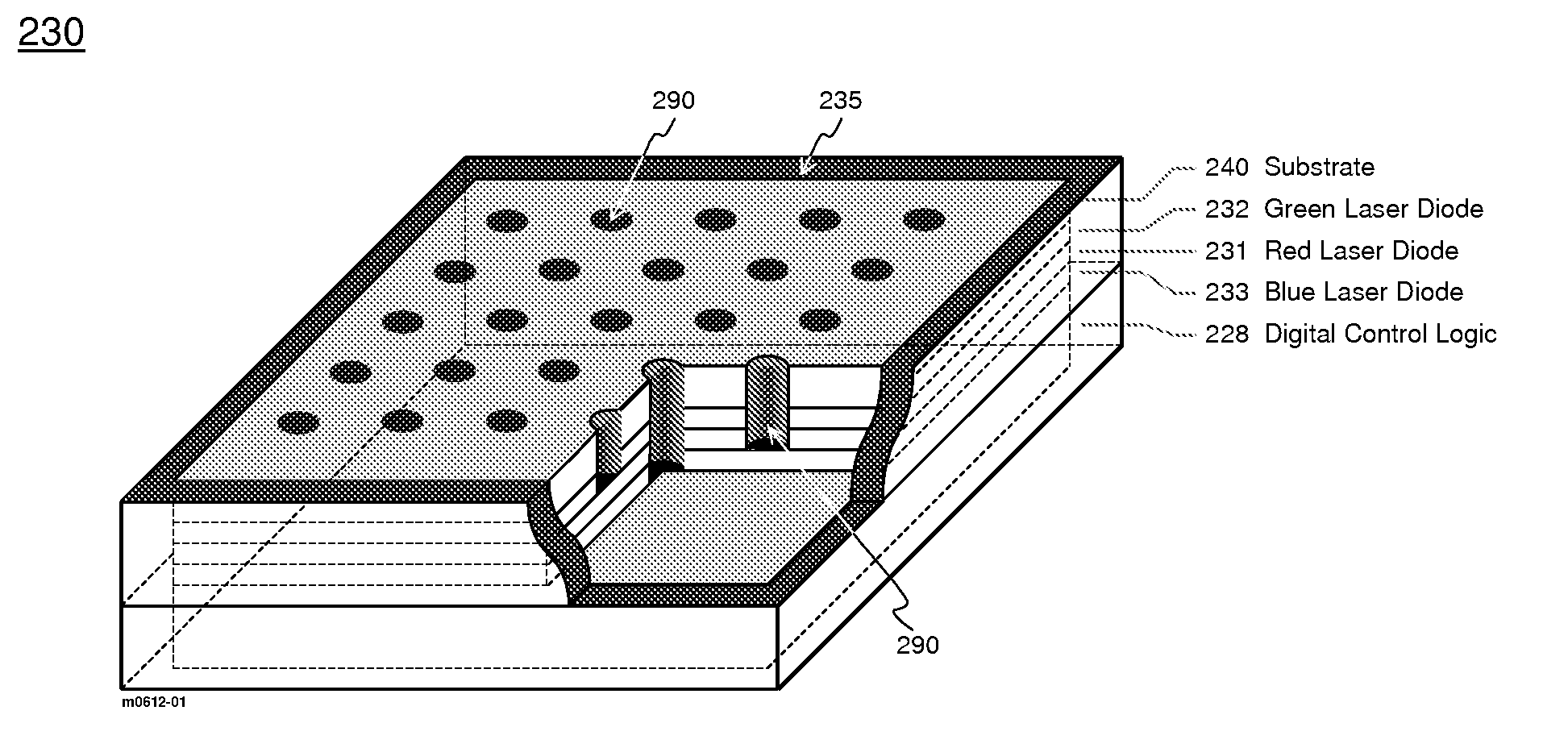
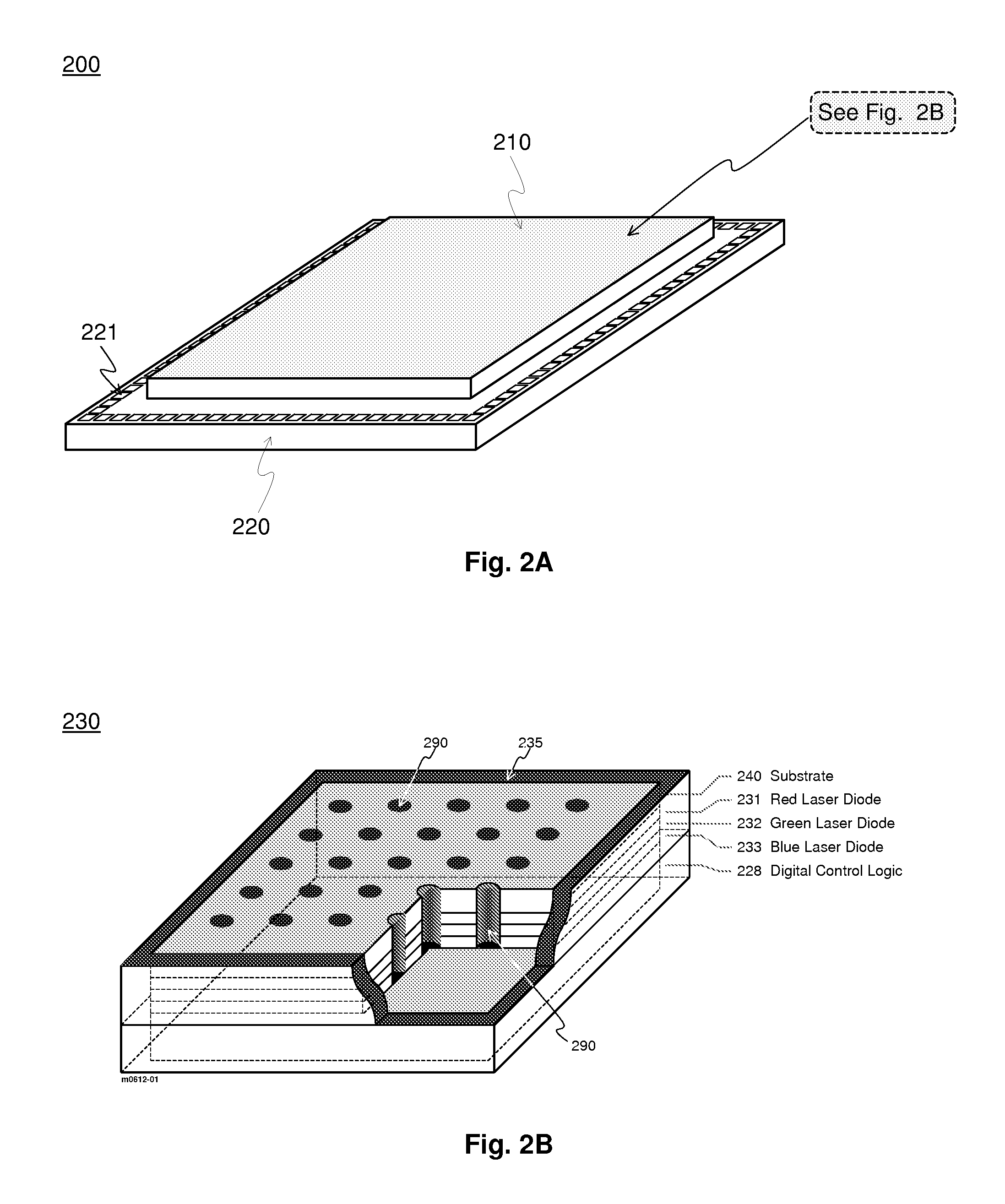
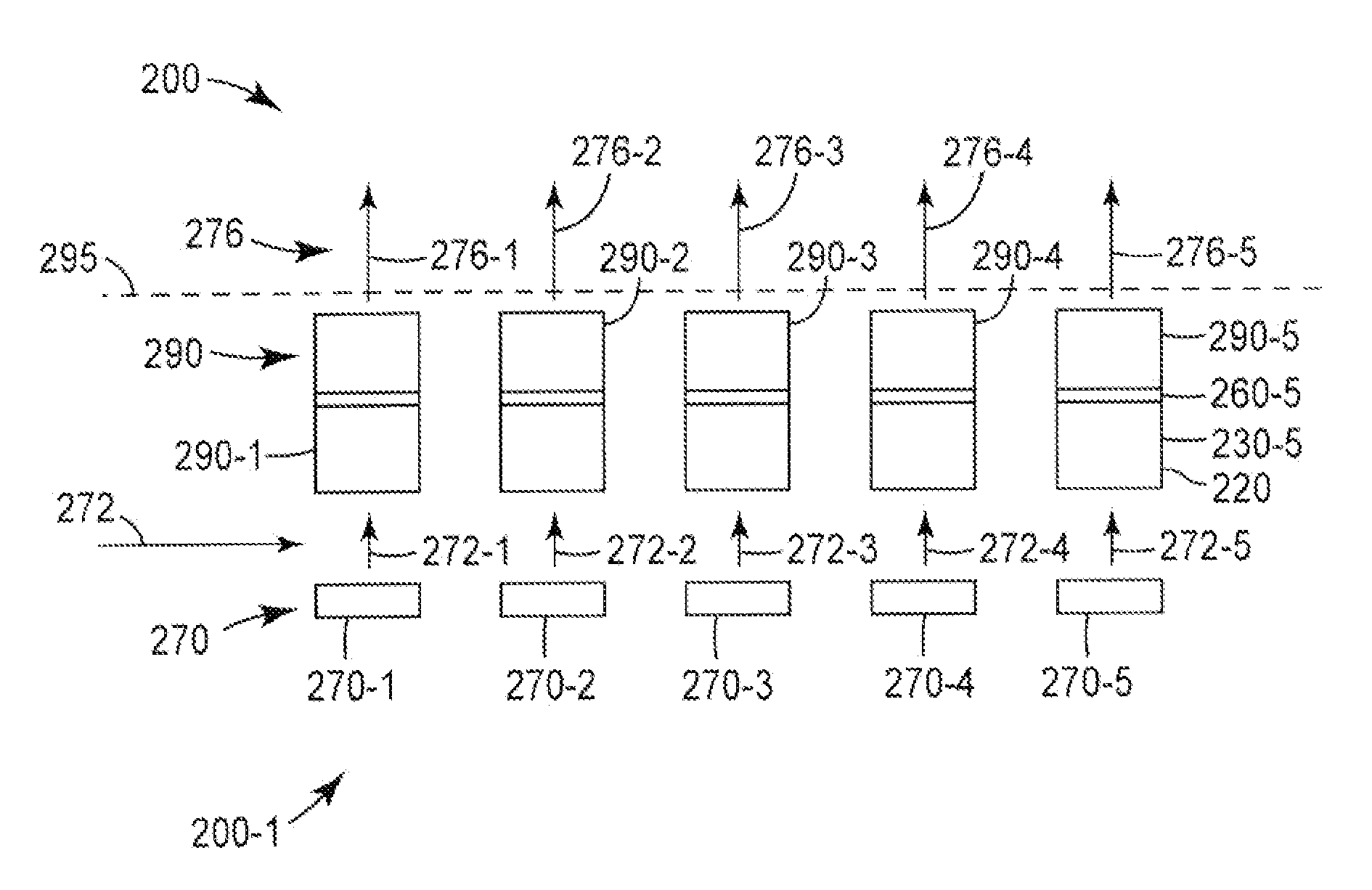
Quantum Photonic Imagers and Methods of Fabrication Thereof
ActiveUS20090086170A1Reduce power consumptionImprove efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionStatic indicating devicesPhotonicsLaser light
Emissive quantum photonic imagers comprised of a spatial array of digitally addressable multicolor pixels. Each pixel is a vertical stack of multiple semiconductor laser diodes, each of which can generate laser light of a different color. Within each multicolor pixel, the light generated from the stack of diodes is emitted perpendicular to the plane of the imager device via a plurality of vertical waveguides that are coupled to the optical confinement regions of each of the multiple laser diodes comprising the imager device. Each of the laser diodes comprising a single pixel is individually addressable, enabling each pixel to simultaneously emit any combination of the colors associated with the laser diodes at any required on / off duty cycle for each color. Each individual multicolor pixel can simultaneously emit the required colors and brightness values by controlling the on / off duty cycles of their respective laser diodes.
Owner:OSTENDO TECH INC
Sub-wavelength grating integrated VCSEL
InactiveUS20070153860A1Good optical performanceEasy to manufactureLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserGrating
A vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is described using a sub-wavelength grating (SWG) structure that has a very broad reflection spectrum and very high reflectivity. The grating comprises segments of high and low refractive index materials with an index differential between the high and low index materials. By way of example, a SWG reflective structure is disposed over a low index cavity region and above another reflective layer (either SWG or DBR). In one embodiment, the SWG structure is movable, such as according to MEMS techniques, in relation to the opposing reflector to provide wavelength selective tuning. The SWG-VCSEL design is scalable to form the optical cavities for a range of SWG-VCSELs at different wavelengths, and wavelength ranges.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Continuously-tunable external cavity laser
InactiveUS6282215B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsExternal cavity laserClosed loop feedback
The present invention provides a continuously-tunable external cavity laser (ECL) with a compact form factor and precise tuning. A novel interference filter which may be used to tune the ECL provides an absence of mode-hopping and reduced feedback from both spurious interference and reflections in the external cavity. A novel tuning mechanism is disclosed which provides for mechanical FM tuning of a wide range ECL tuning elements such as: an interference filter, a diffraction element, and a retroreflector. A novel feedback circuit is disclosed which provides closed loop feedback for selecting output wavelength in a laser.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
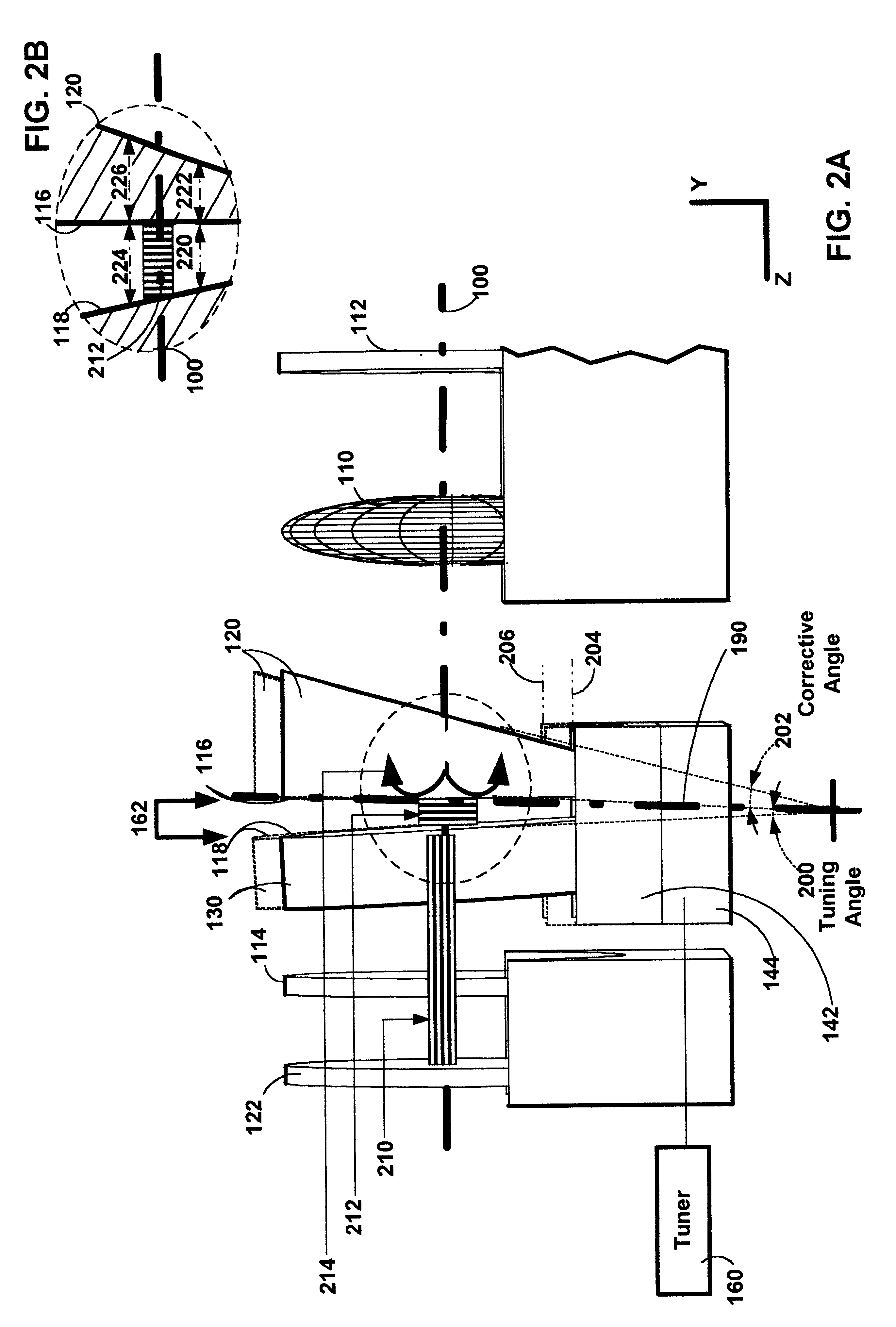
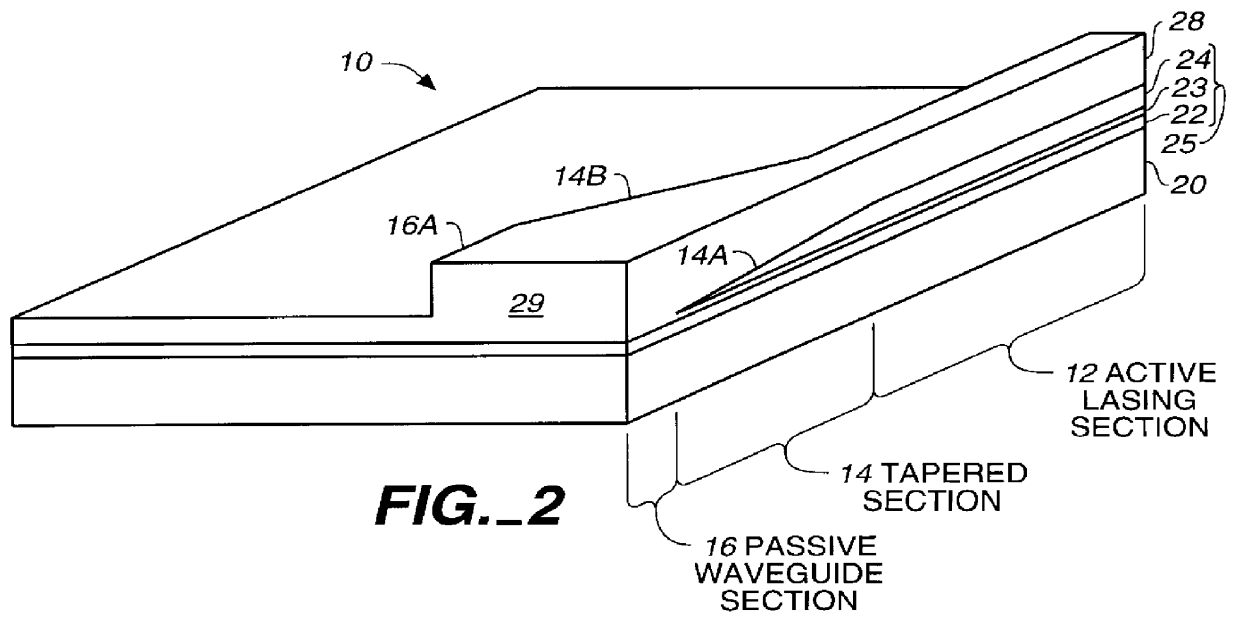
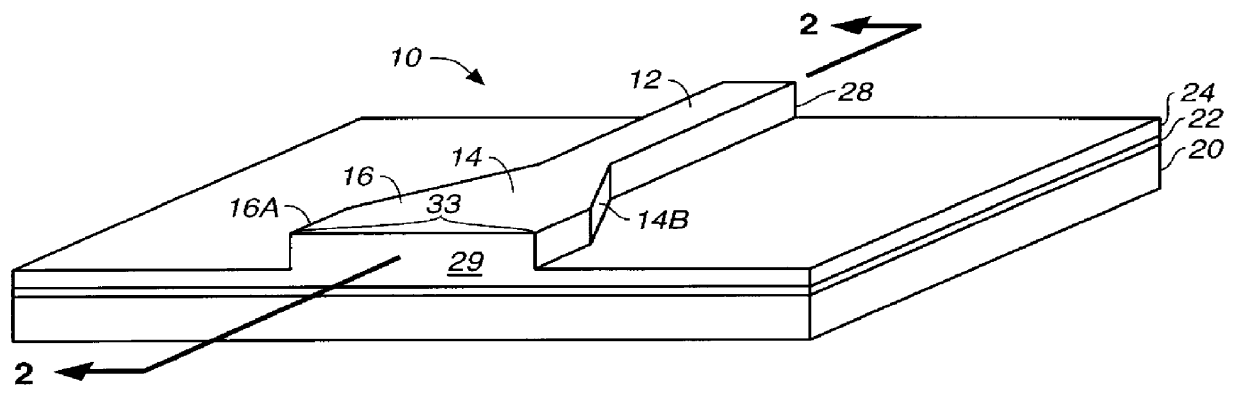
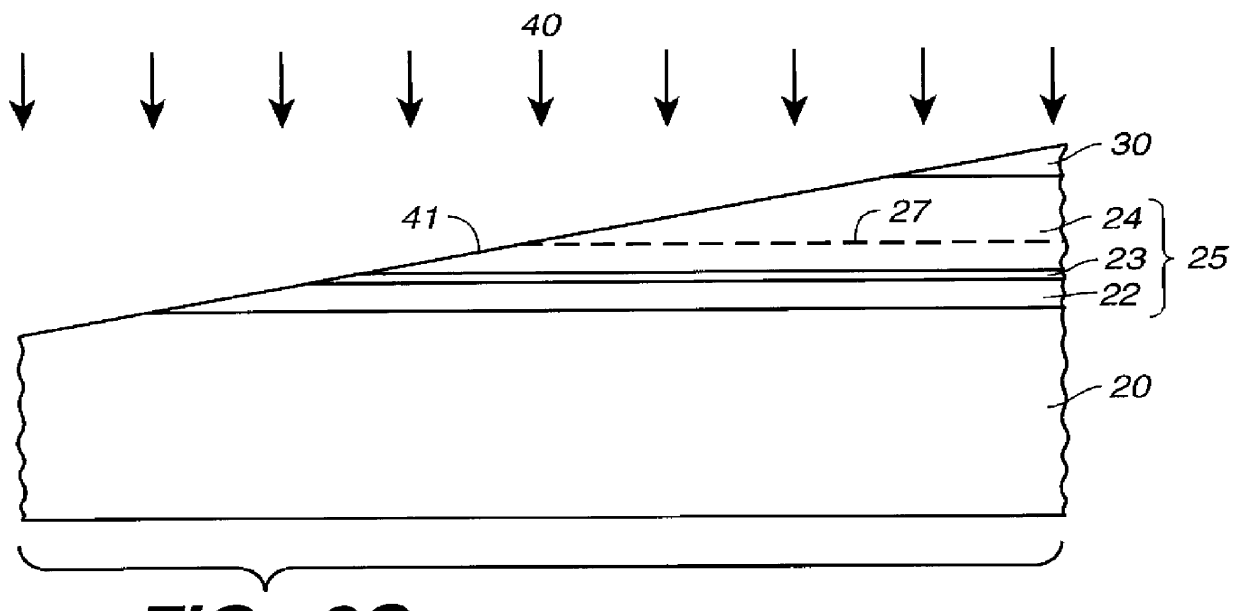
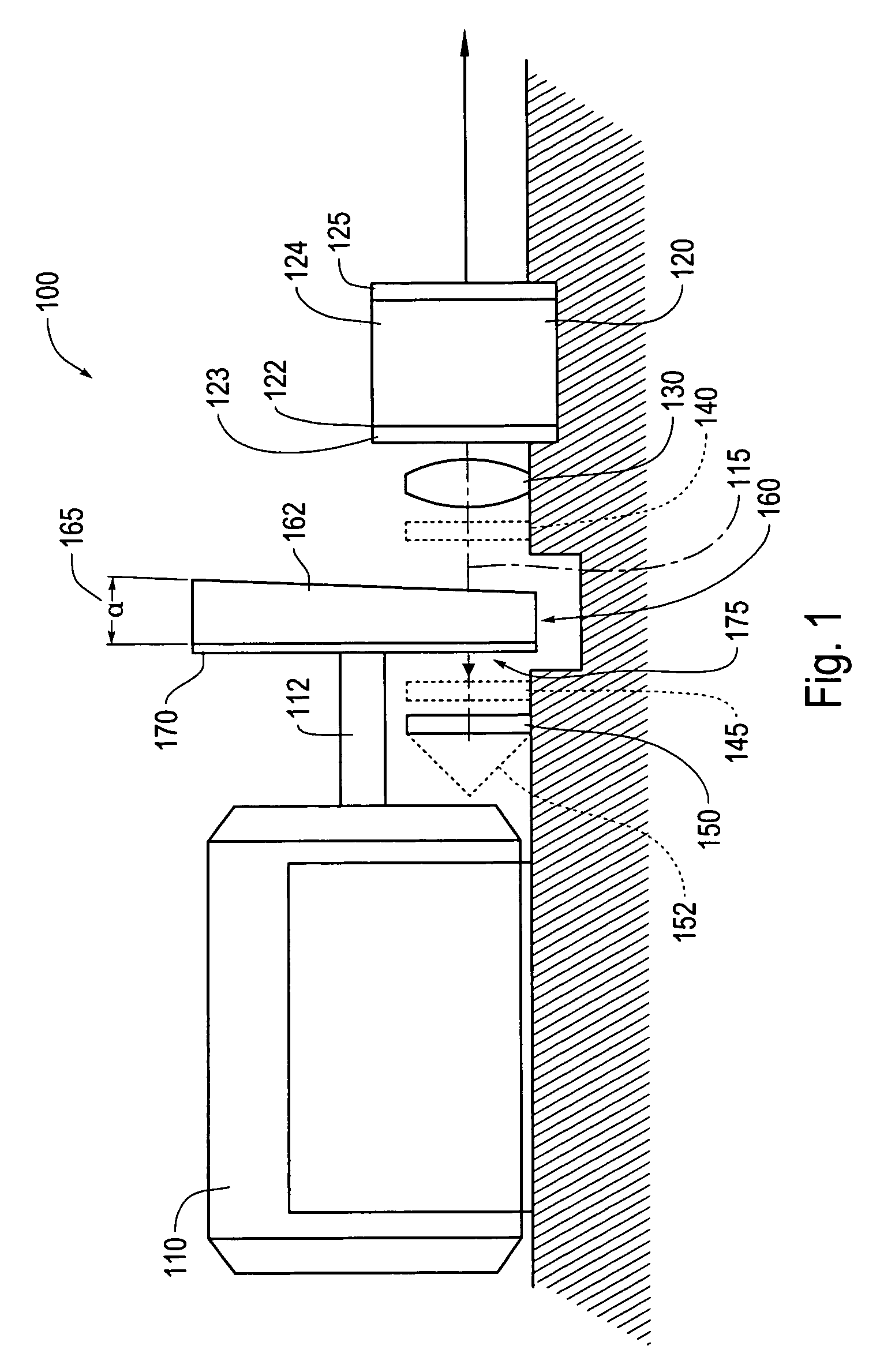
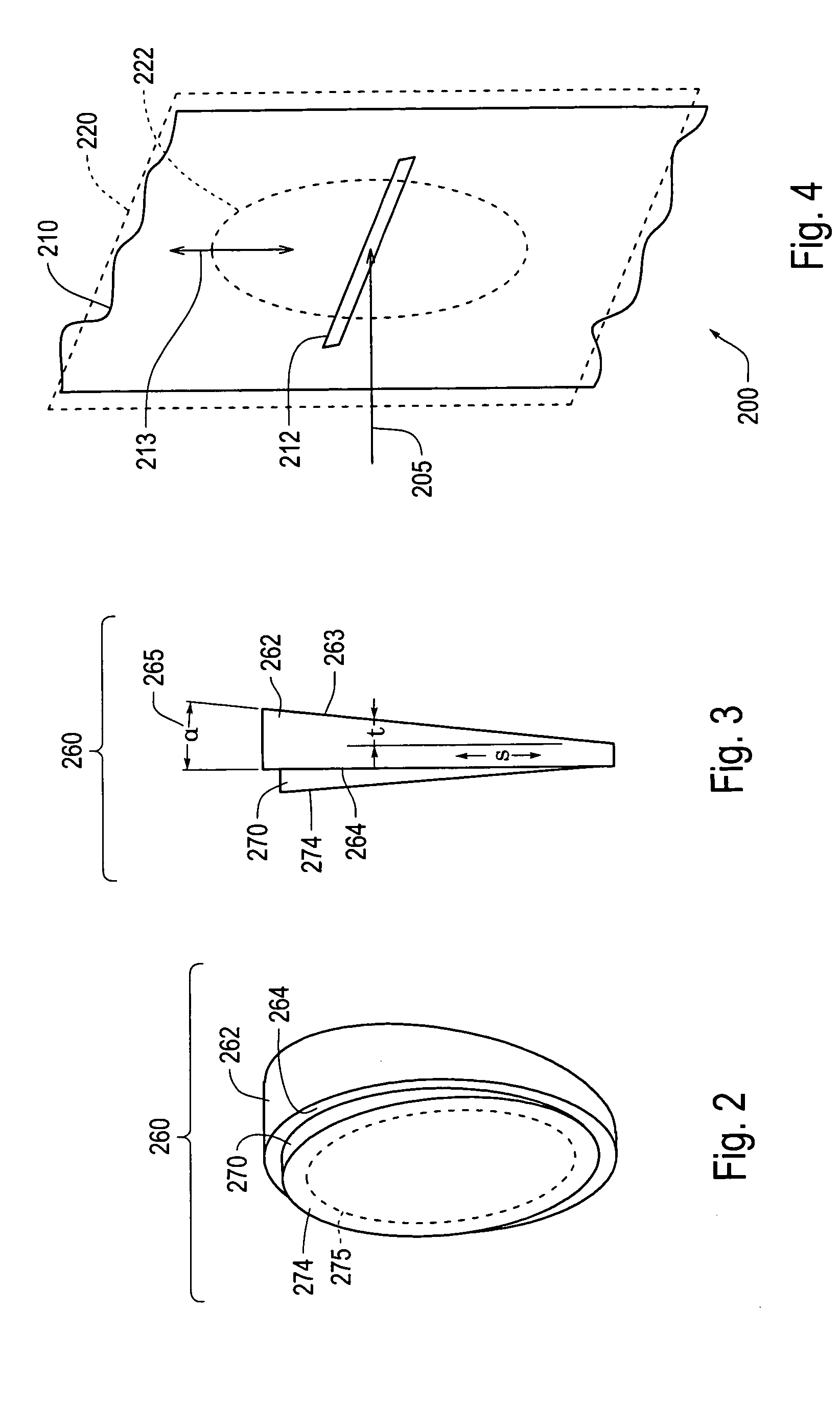
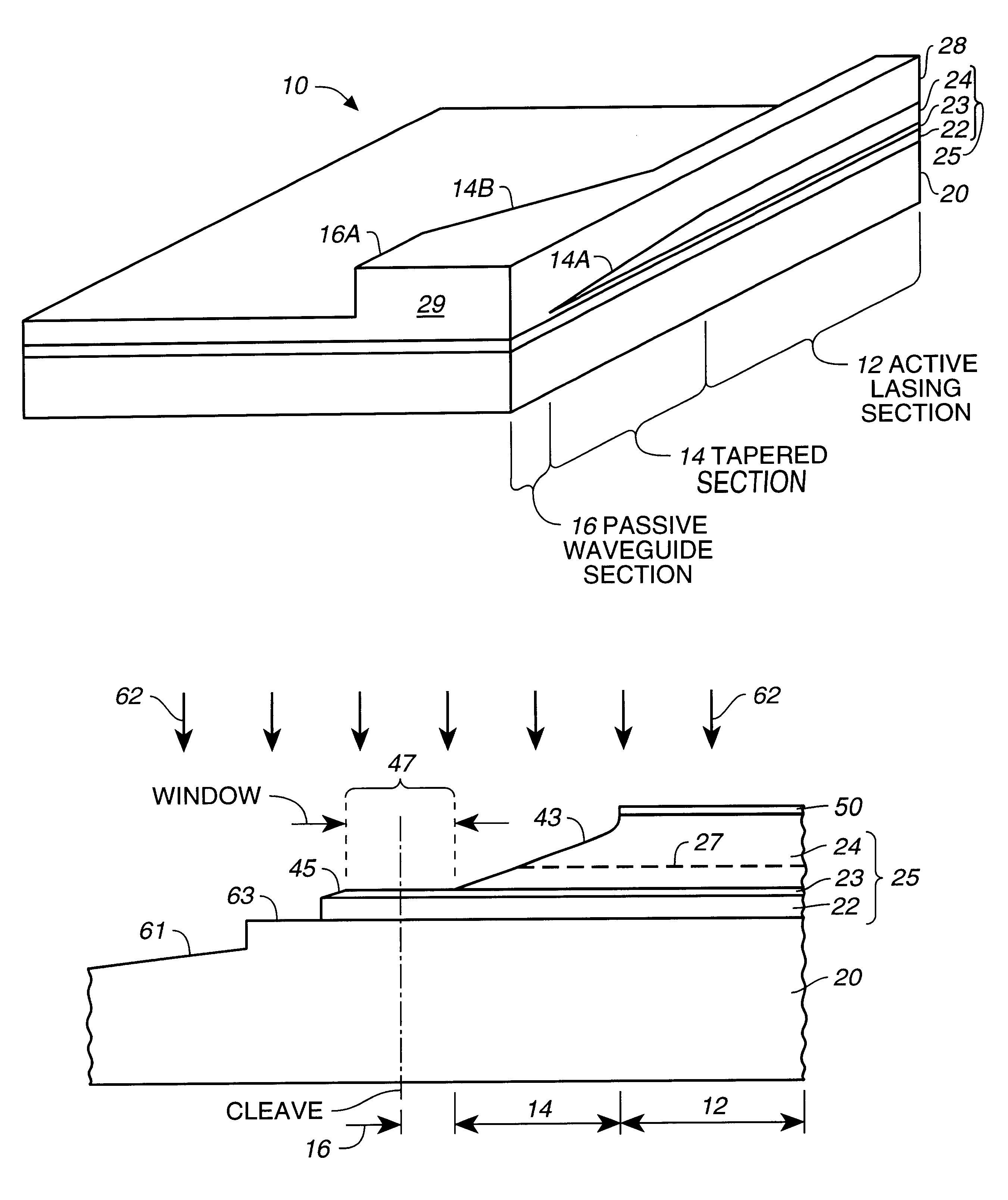
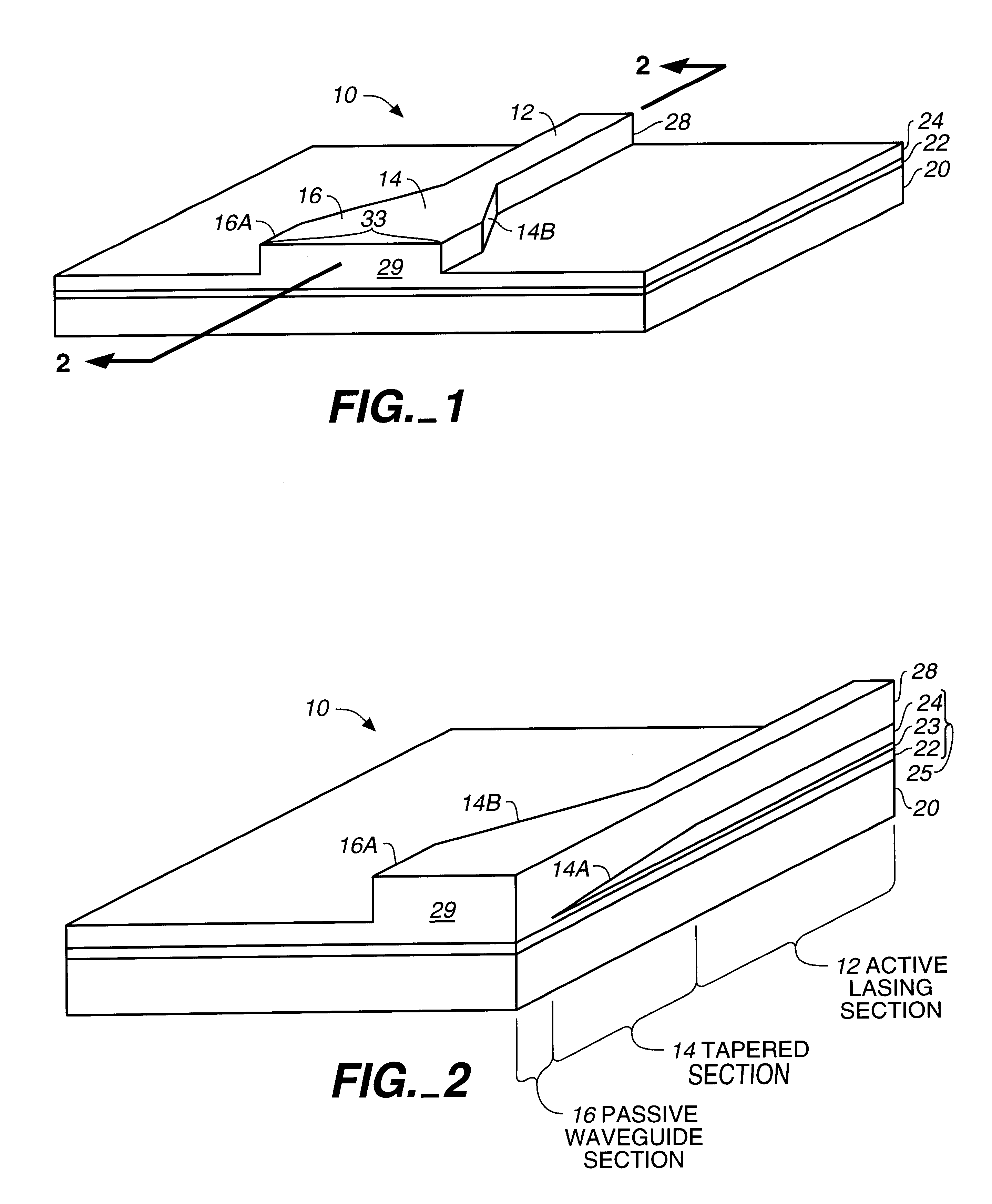
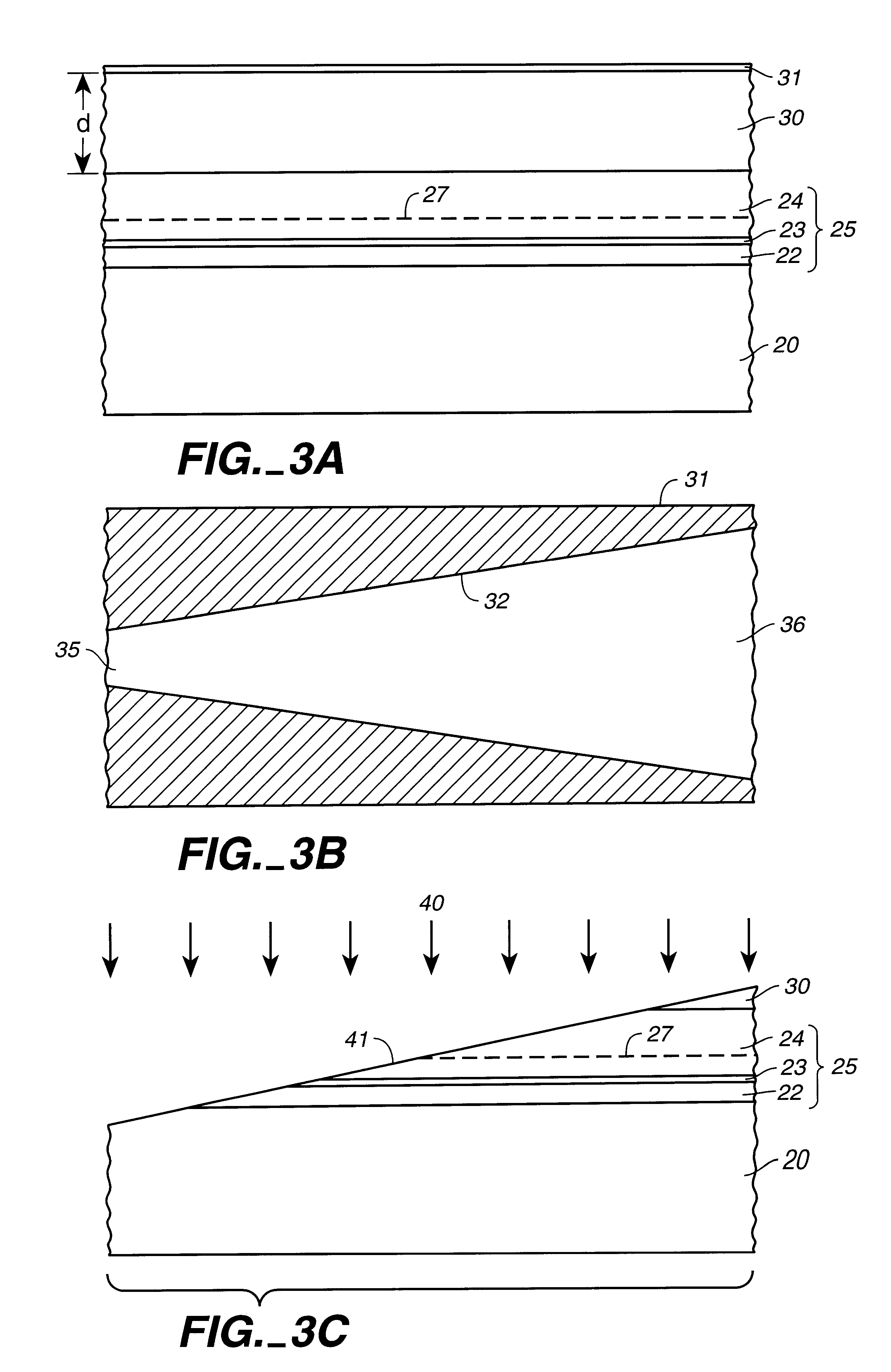
Laser diode device having a substantially circular light output beam and a method of forming a tapered section in a semiconductor device to provide for a reproducible mode profile of the output beam
InactiveUS6052397AEasy to makeGood reproducibilityLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionHigh power lasersCoupling
A device and method for fabricating a high power laser diode device with an output emission with a nearly circular mode profile for efficient coupling into an optical fiber. A vertical taper waveguide and a window tolerance region are formed in a base structure of the device employing successive etching steps. Further regowth completes the device structure. The resultant laser device has a vertical and lateral tapered waveguide that adiabatically transforms the highly elliptical mode profile in an active gain section of the device into a substantially circular mode profile in a passive waveguide section of the device.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Optoelectronic device incorporating an interference filter
InactiveUS20050117623A1Optical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionOptical cavityResonance
A novel class of optoelectronic devices incorporate an interference filter. The filter includes at least two optical cavities. Each of the cavities localizes al least one optical mode. The optical modes localized at two cavities are at resonance only at one or at a few discrete selective wavelengths. At resonance, the optical eigenmodes contain one mode having a zero intensity at a node position between the two cavities, where this position shifts as a function of the wavelength. A non-transparent element, which is preferably an absorbing element, a scatterer, or a reflector, is placed between two cavities. At a discrete selective wavelength, when the node of the optical mode matches with the non-transparent element, the filter is transparent for light. At other wavelengths, the filter is not transparent for light. This allows for the construction of various optoelectronic devices showing a strongly wavelength-selective operation.
Owner:INNOLUME
External cavity laser with rotary tuning element
InactiveUS7130320B2Improve economyImprove reliabilityLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionVariable thicknessExternal cavity laser
An external cavity laser has a wavelength of the laser output that is tuned by a rotary tuning element mounted on the axle of a motor. The rotary tuning element includes a variable thickness interference film for wavelength selection, and a variable thickness compensation prism to adjust the cavity length appropriately for the selected wavelength, to stable wavelengths and mode-hop-free tuning ranges as the tuning element is rotated.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
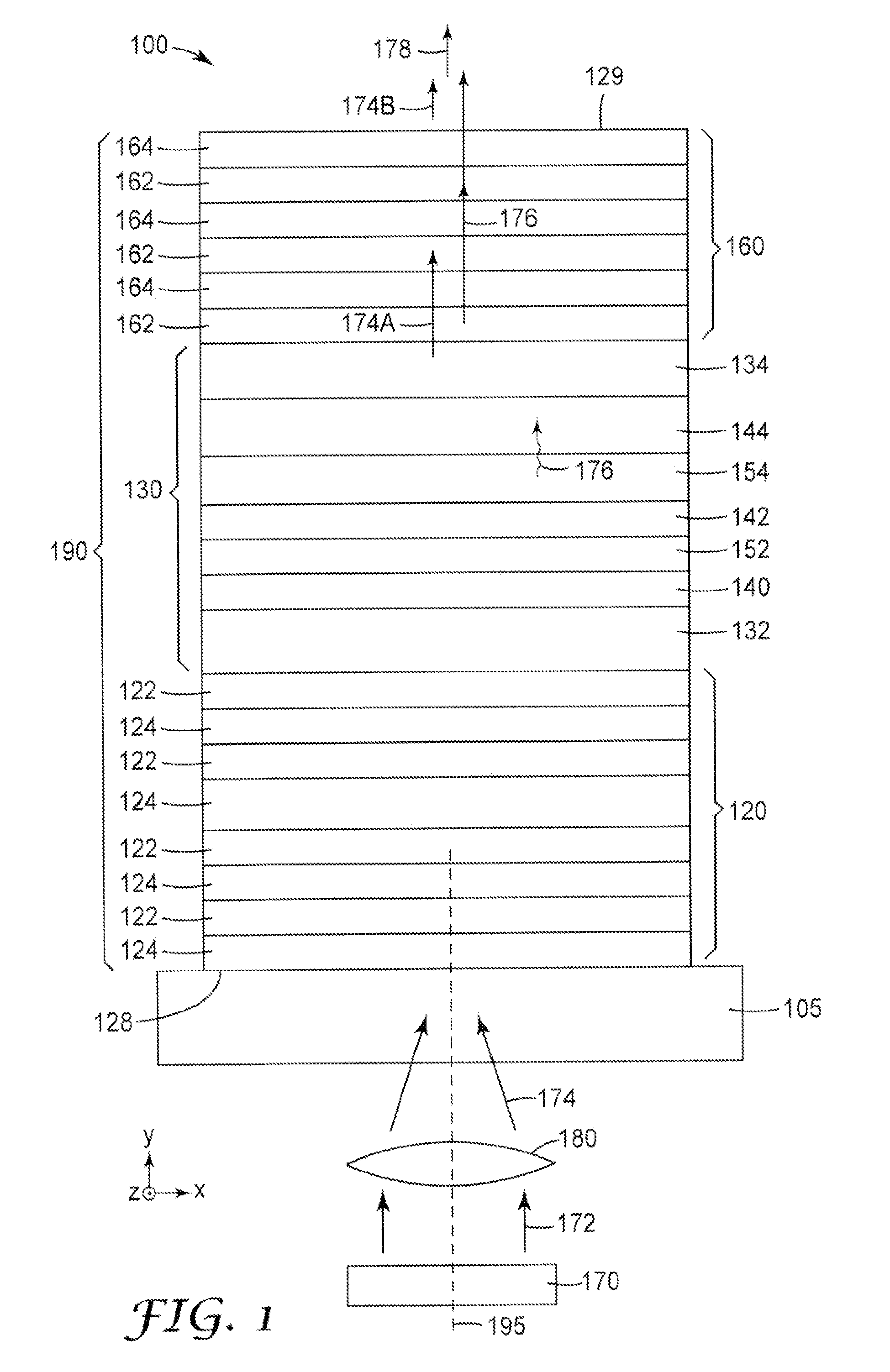
Ii-vi mqw vscel on a heat sink optically pumped by a GAN ld
InactiveUS20110150020A1Improved light emissionSuppress luminescenceLaser optical resonator constructionNanoopticsVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserOptical cavity
Light sources are disclosed. A disclosed light source includes a III-V based pump light source (170) that includes nitrogen and emits light at a first wavelength. The light source further includes a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) that converts at least a portion of the first wavelength light (174) emitted by the pump light source (170) to at least a partially coherent light at a second wavelength (176). The VCSEL includes first and second mirrors (120, 160) that form an optical cavity for light at the second wavelength. The first mirror (120) is substantially reflective at the second wavelength and includes a first multilayer stack. The second mirror (160) is substantially transmissive at the first wavelength and partially reflective and partially transmissive and the second wavelength. The second mirror includes a second multilayer stack. The VCSEL further includes a semiconductor multilayer stack (130) that is disposed between the first and second mirrors and converts at least a portion of the first wavelength light to the second wavelength light. The semiconductor multilayer stack (130) includes a quantum well that includes a Cd(Mg)ZnSe alloy.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method of forming a tapered section in a semiconductor device to provide for reproducible mode profile of the output beam
InactiveUS6174748B1Easy to makeGood reproducibilityLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionHigh power lasersCoupling
A method for fabricating a high power laser diode device with an output emission with a nearly circular mode profile for efficient coupling into an optical fiber. A vertical taper waveguide and a window tolerance region are formed in a base structure of the device employing successive etching steps. Further regrowth completes the device structure. The resultant laser device has a vertical and lateral tapered waveguide that adiabatically transforms the highly elliptical mode profile in an active gain section of the device into a substantially circular mode profile in a passive waveguide section of the device.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Photonic band gap fiber
InactiveUS6845204B1Lower areaHigh refractive indexGlass making apparatusLaser optical resonator constructionFiberMulti method
An optical fiber having a periodical cladding structure providing an photonic band gap structure with superior qualities. The periodical structure being one wherein high index areas are defined and wherein these are separated using a number of methods. One such method is the introduction of additional low index elements, another method is providing elongated elements deformed in relation to a circular cross section. Also described is a cladding structure comprising elongated elements of a material having an index of refraction higher than that of the material adjacent thereto. Using this additional material, prior art structures may obtain much better qualities.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20020054614A1Increase output powerFast switching timeLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionWedge filter (device)Switching time
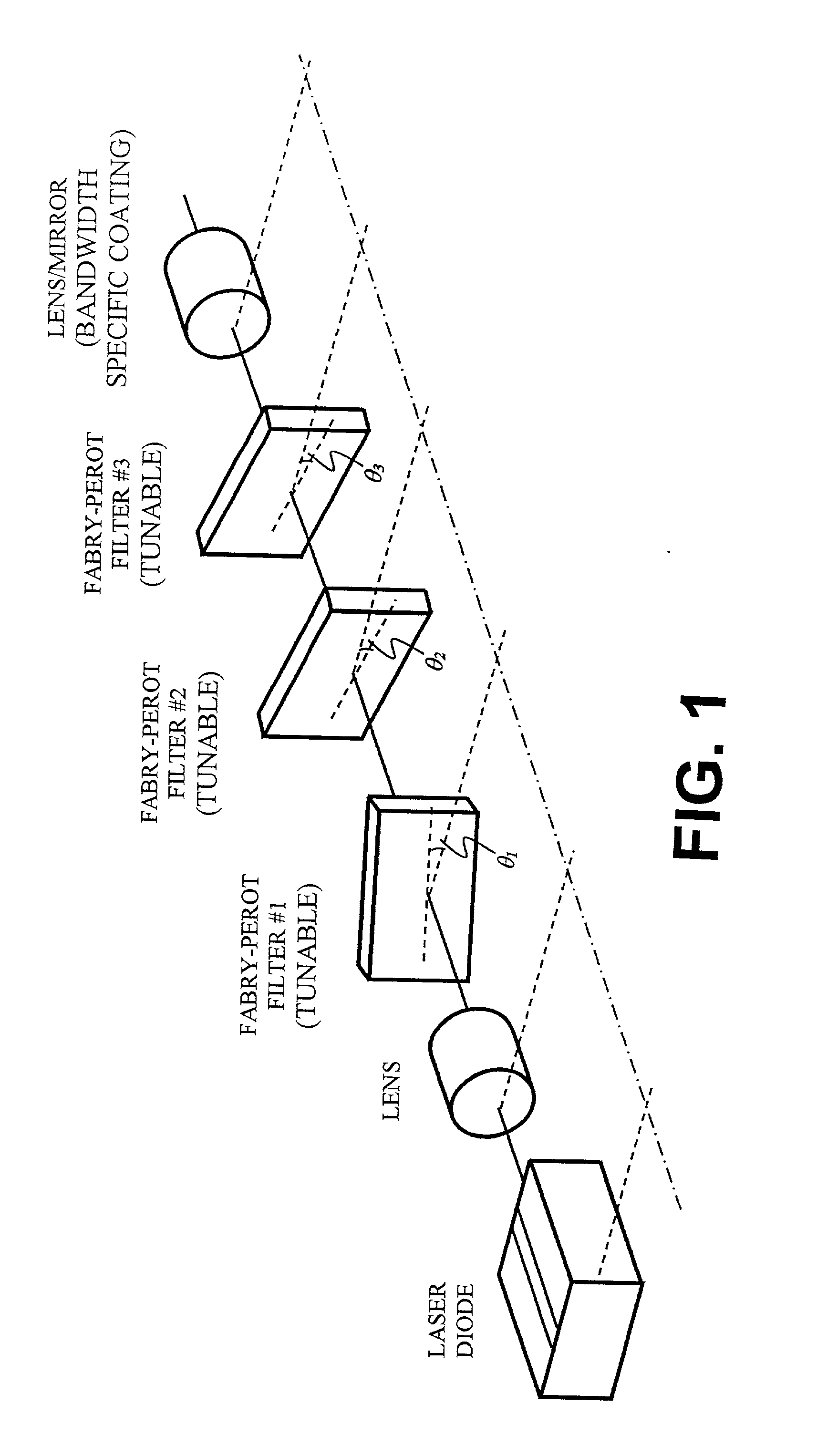
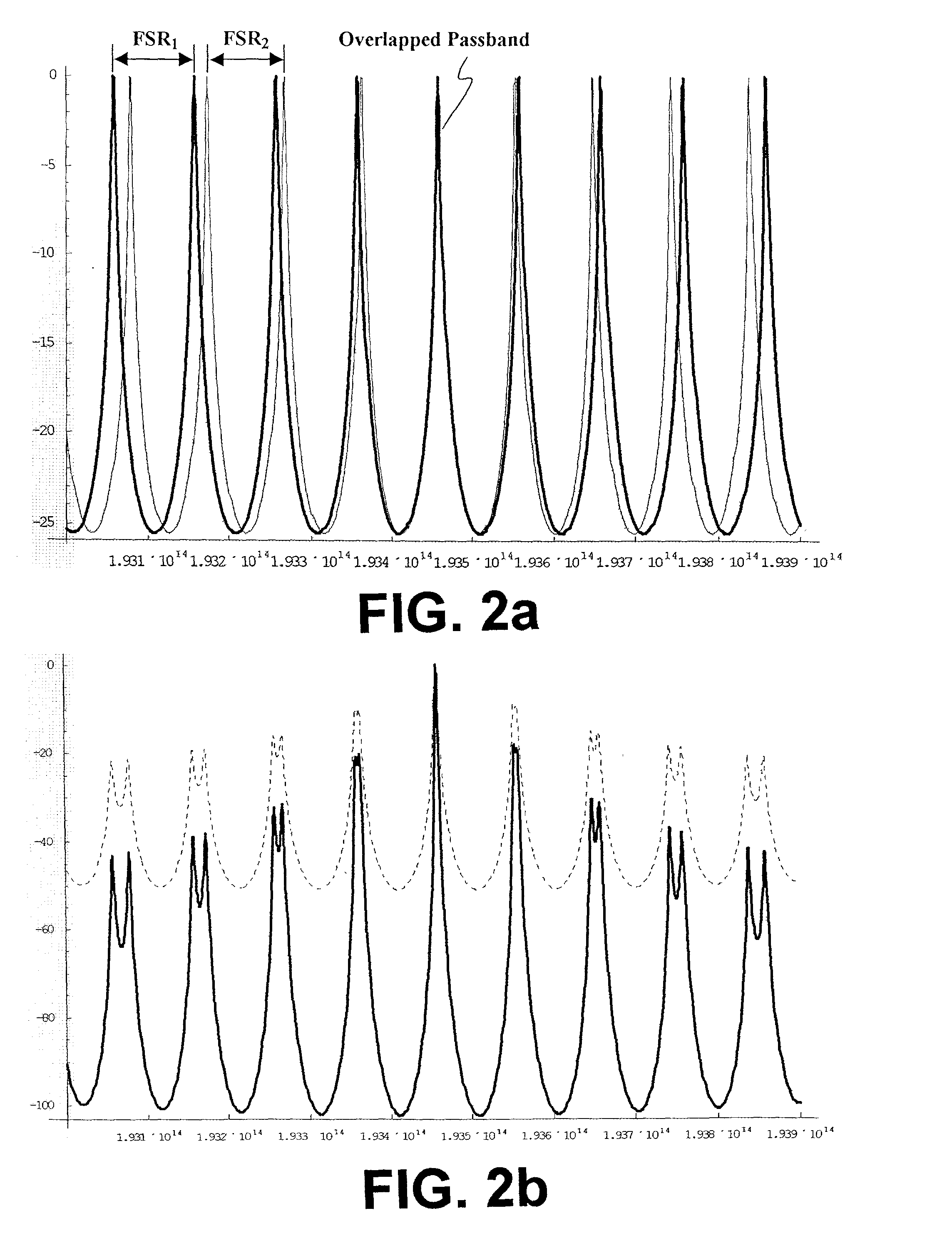
A wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser that addresses wide wavelength tuning range, is mode hopping free, has high output power, has fast wavelength switching time, is wavelength locking free and is relatively simple. Four exemplary embodiments disclosed herein utilize a wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser that comprises a discretely tunable filter and laser amplifier. In the first embodiment, the tuning element comprises a pair of cascade Fabry-Perot filters, each having a plurality of characteristic narrow transmission passbands that pass only the cavity mode under the passband. The spacing between the narrow transmission passbands are slightly different in one filter from the other filter so that only one passband from each filter can be overlapped in any given condition over the entire active element gain spectral range, thereby permitting lasing only at a single cavity mode passed by the cascade double filters. One of the two etalon filters can be made with a plurality of transmission passbands predetermined by industry, application and international standards, making this element an intra-cavity wavelength reference and eliminating further wavelength locking needs for the tunable laser. In a second embodiment, one of the two etalons is replaced by a wedge filter. The filter optical path change and thus the transmission passband shift are achieved by translating the wedge filter in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis. In a third embodiment, one of the two etalon filters is replaced by a polarization interference filter. The polarization interference filter consists of an electro-optically-tunable birefringent waveplate, a fixed birefringent waveplate, the laser cavity and T.E. polarization light emitted from the laser diode. In a fourth embodiment, the laser and wavelength tuning structure are integrated on a semiconductor substrate by epitaxy processes.
Owner:JIN HONG
Wavelength-locked external cavity lasers with an integrated modulator
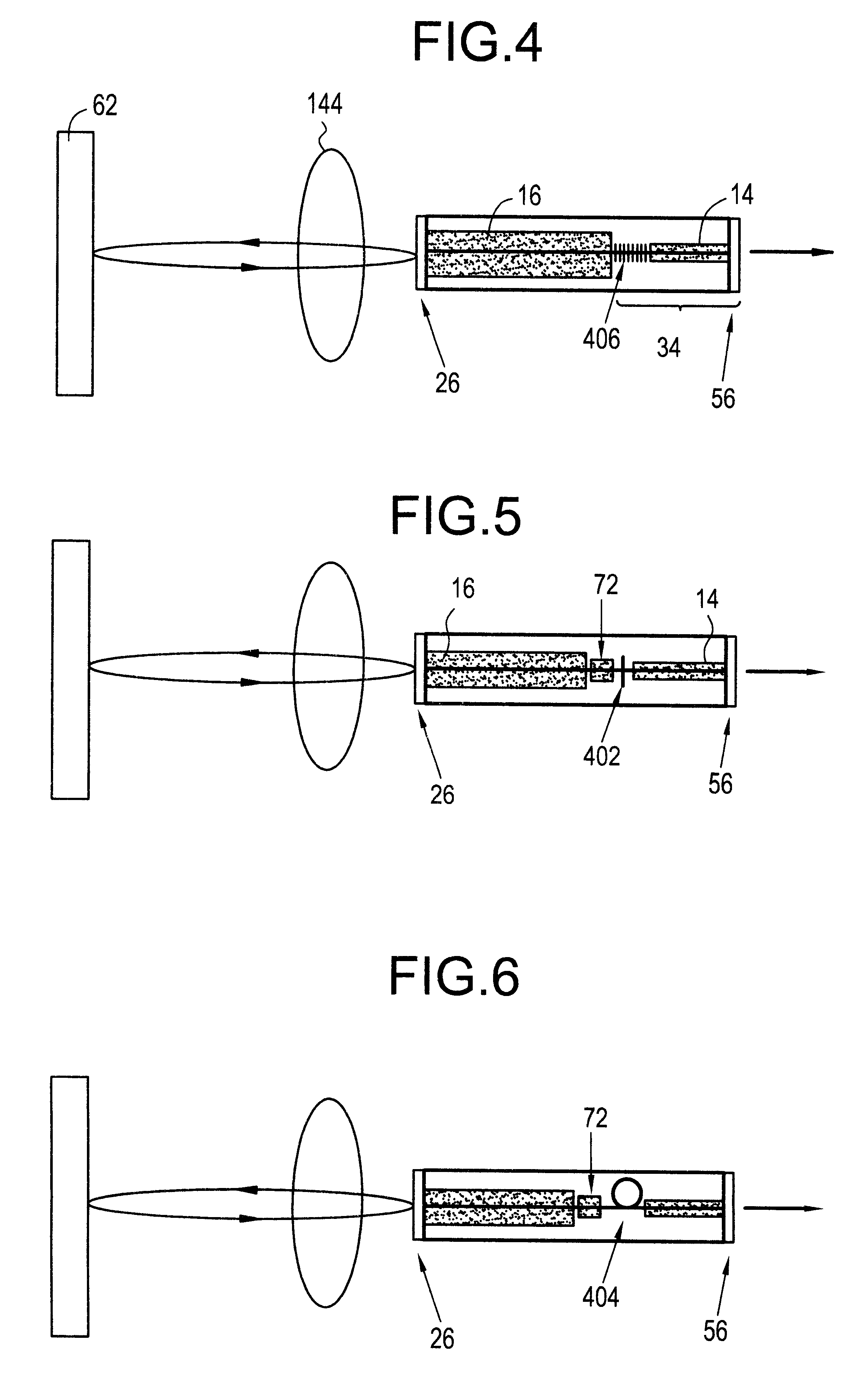
InactiveUS6295308B1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionExternal cavity laserLength wave
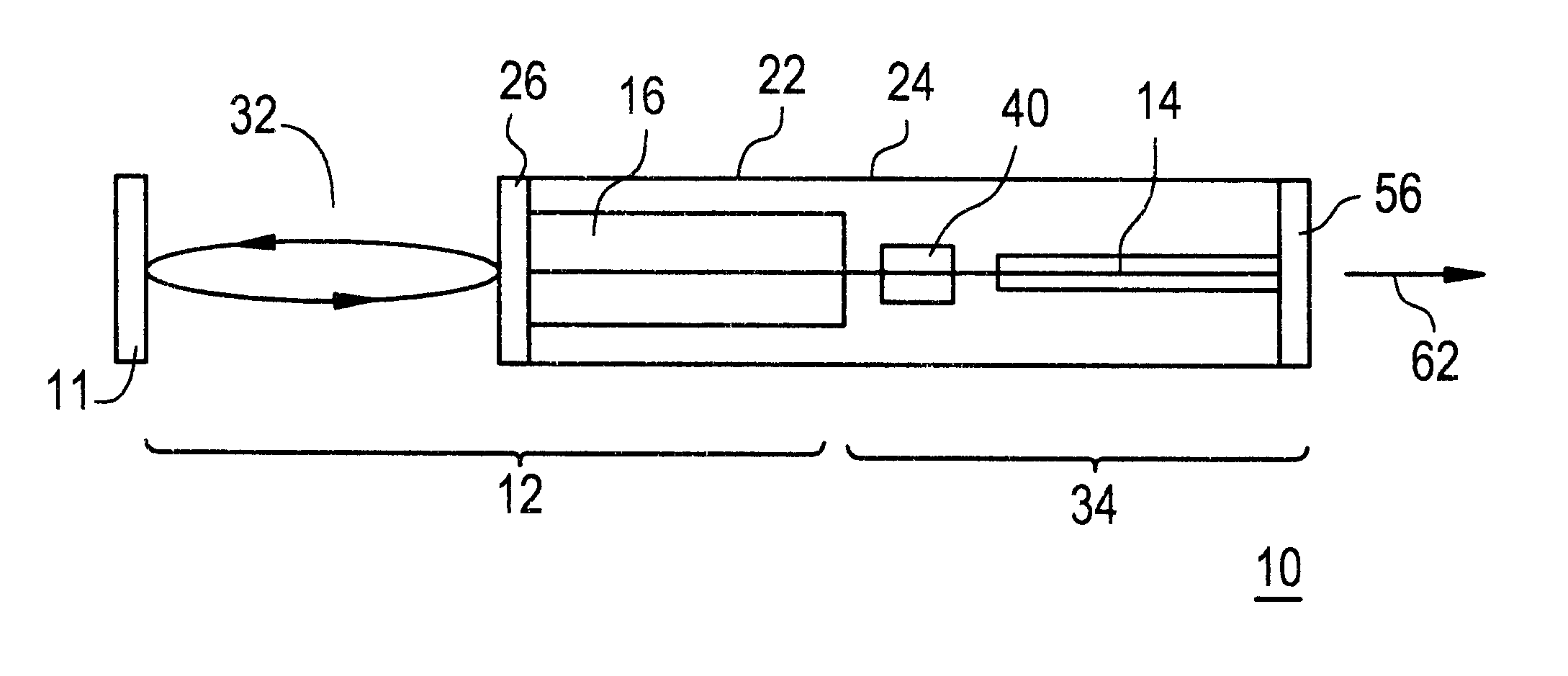
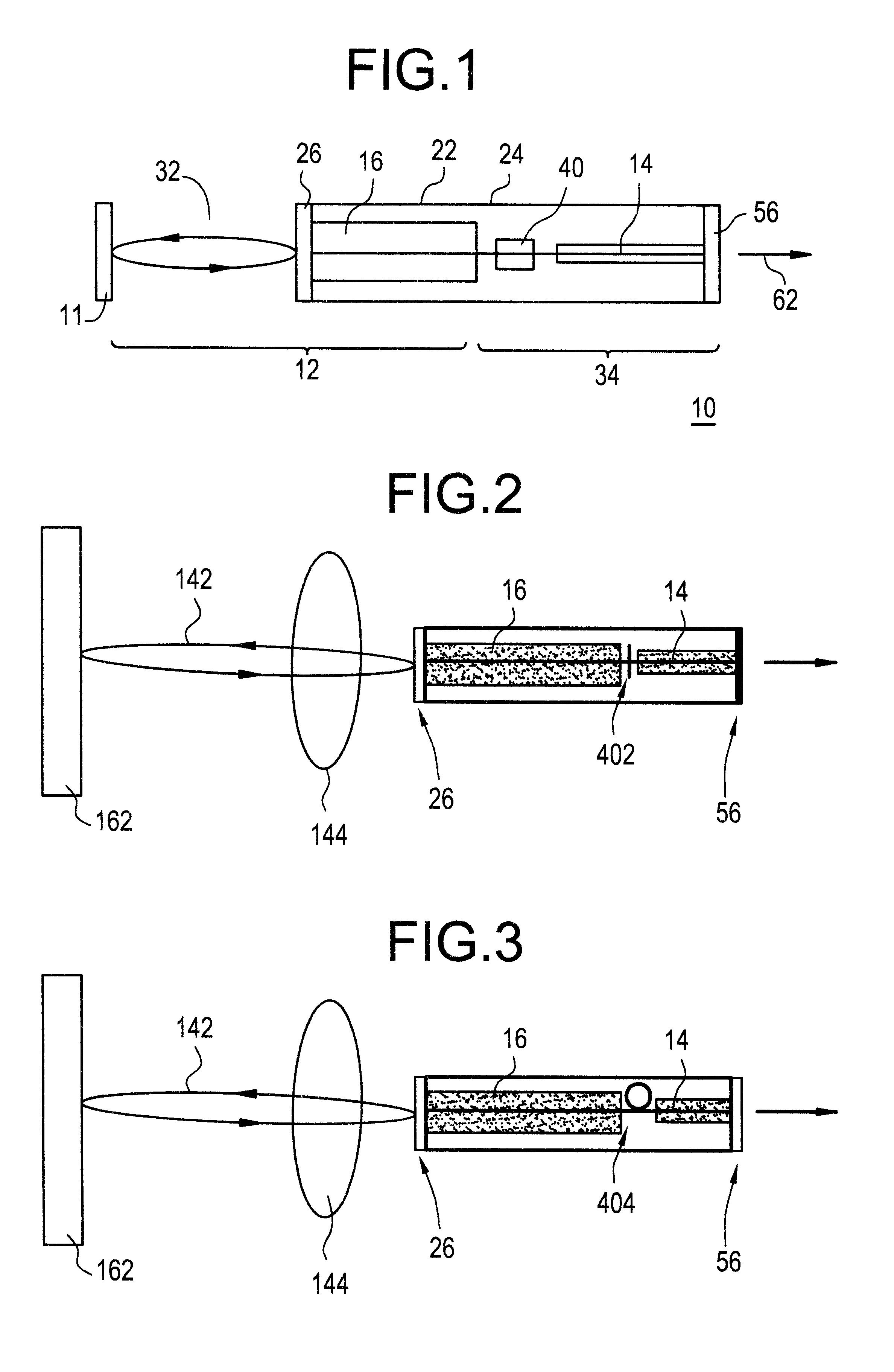
An optical transmitter providing the benefits of both filter-locked and wavelength-locked lasers is disclosed by modifying an external cavity (32) for the integration of an optical modulator (14). The external cavity (32) provides a round-trip path for light travel. A substrate (24) is connected to the external cavity (32) where at least one gain element (16) and the optical modulator (14) are integral with the substrate (24). A partial reflector (40) is also integral with the substrate (24) and couples the at least one gain element (16) with the optical modulator (14).
Owner:OCLARO NORTH AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com