Patents
Literature
125 results about "Mode hopping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
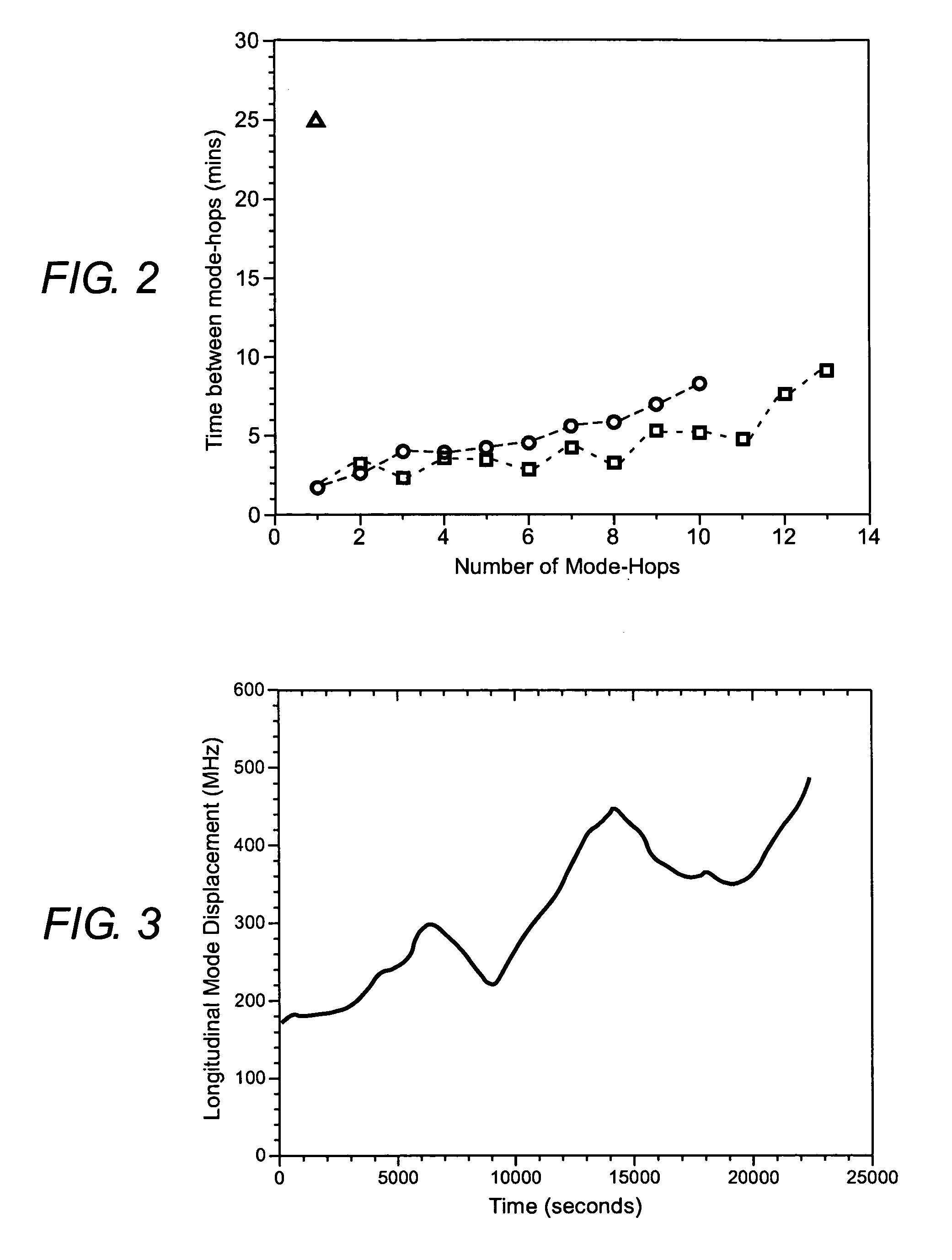
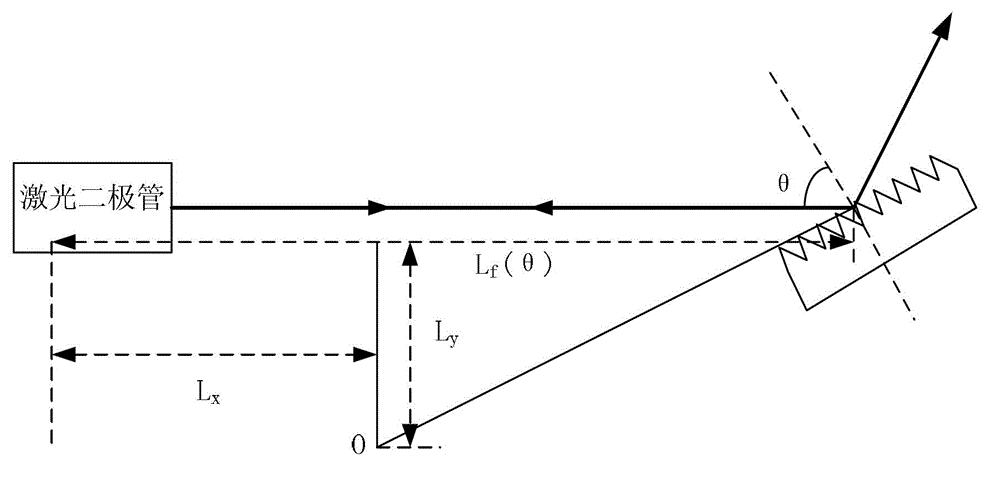
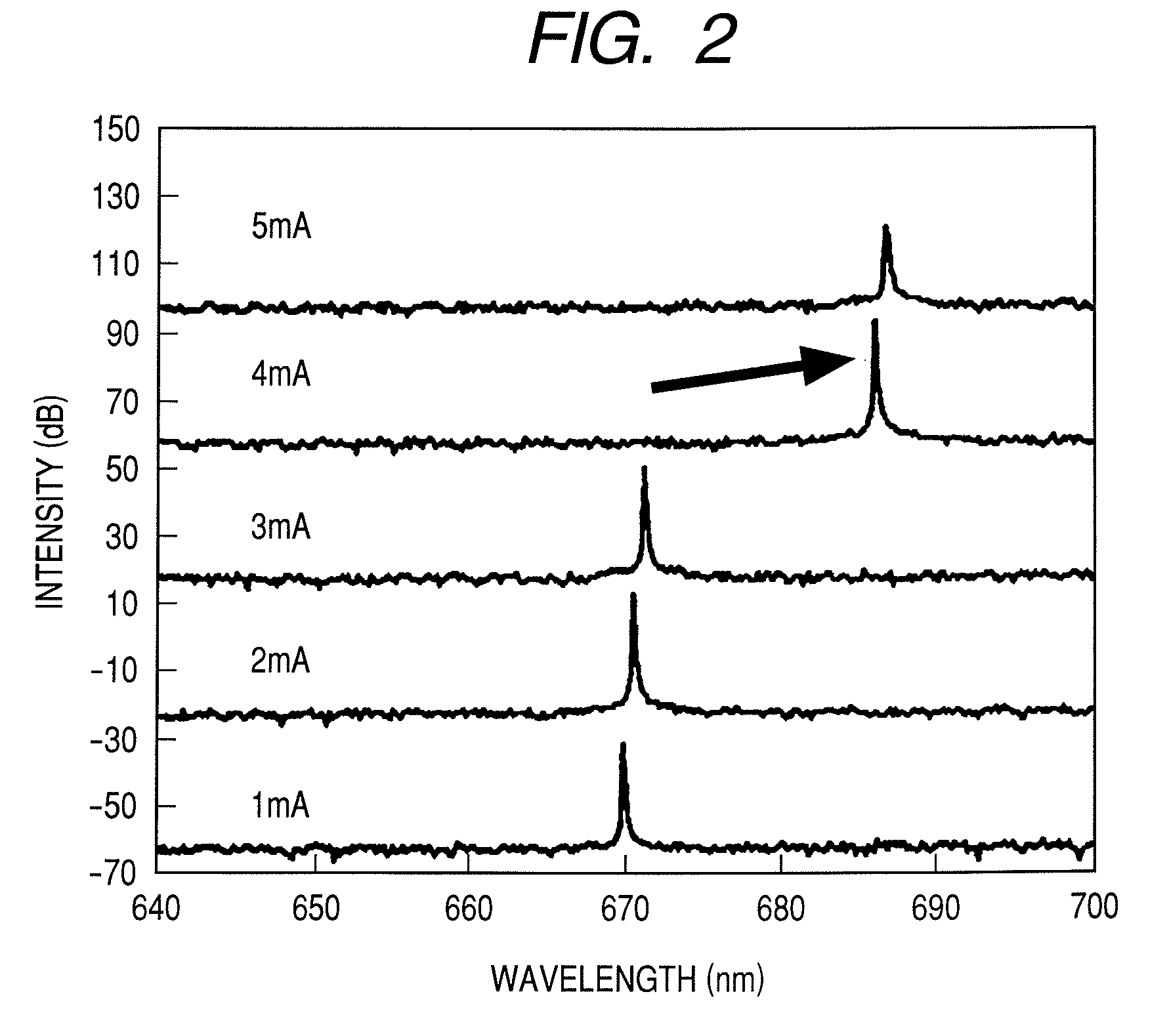
Mode hopping occurs for specific values of laser case temperature and injection current. This means that mode hopping can be eliminated by carefully controlling these two parameters. Mode hopping can be caused by other external influences.
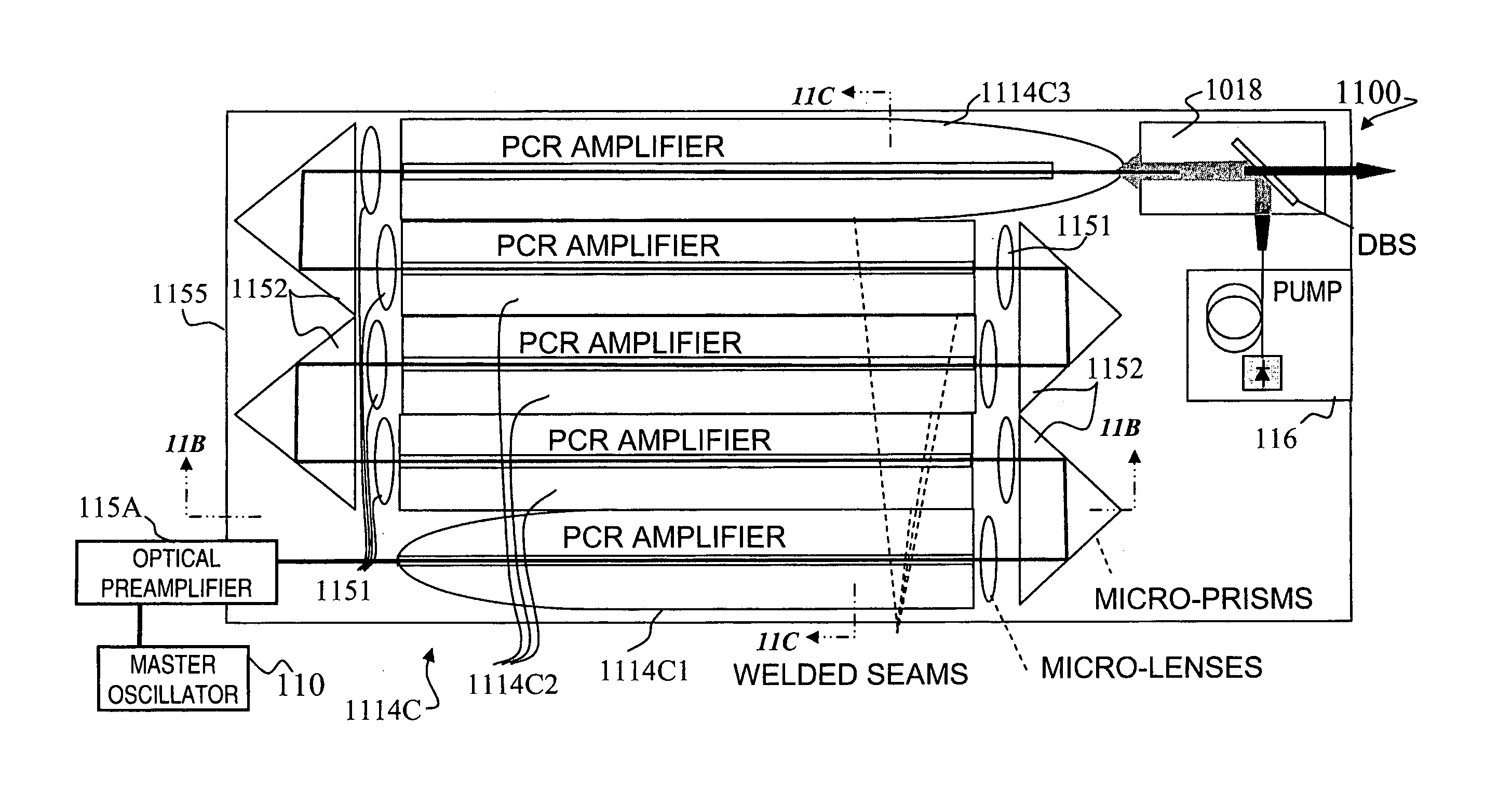
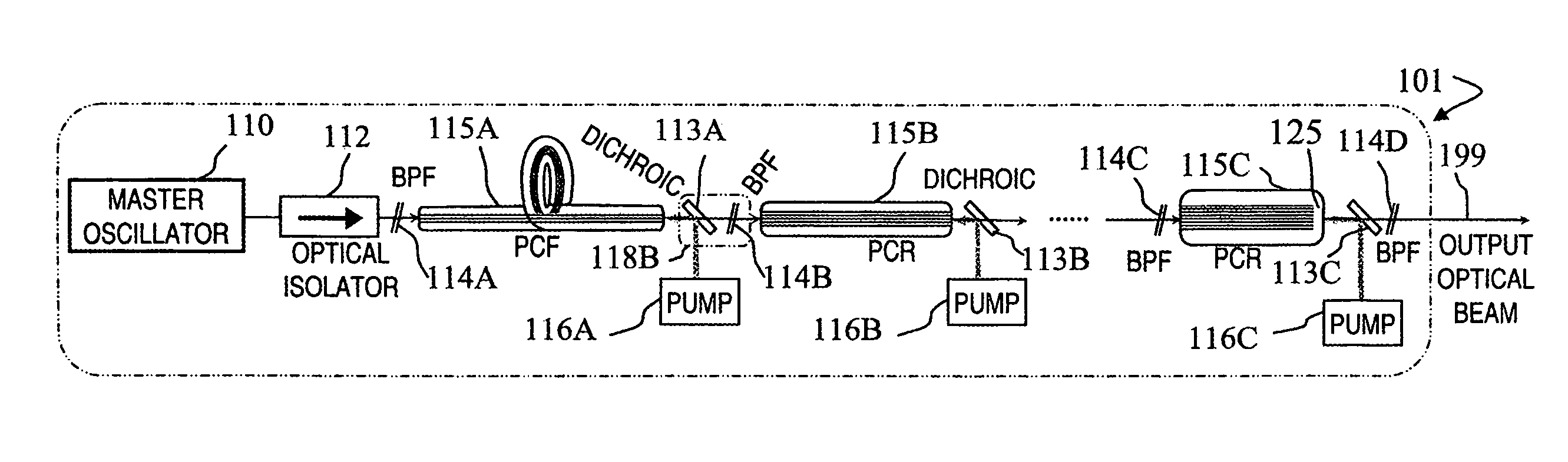
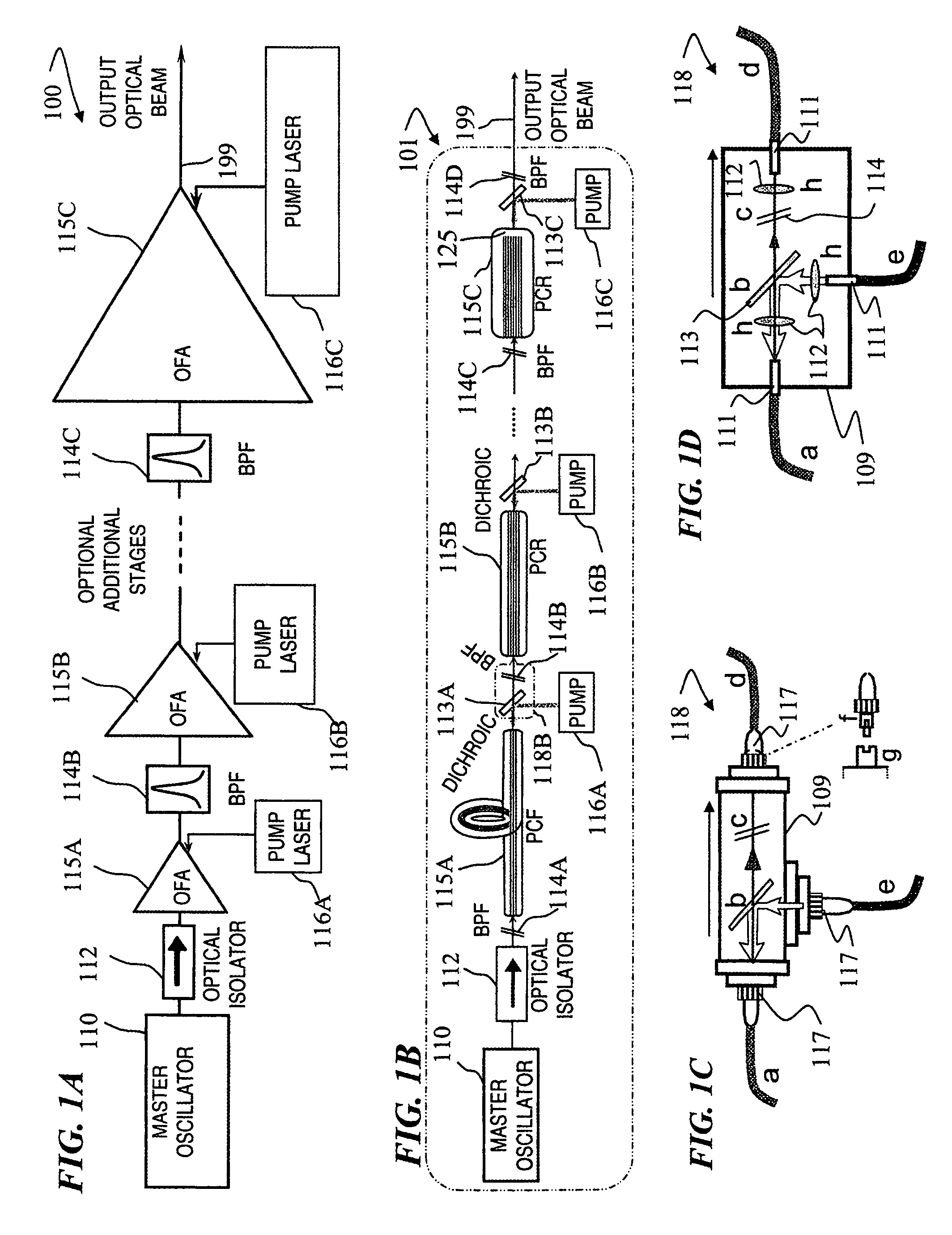
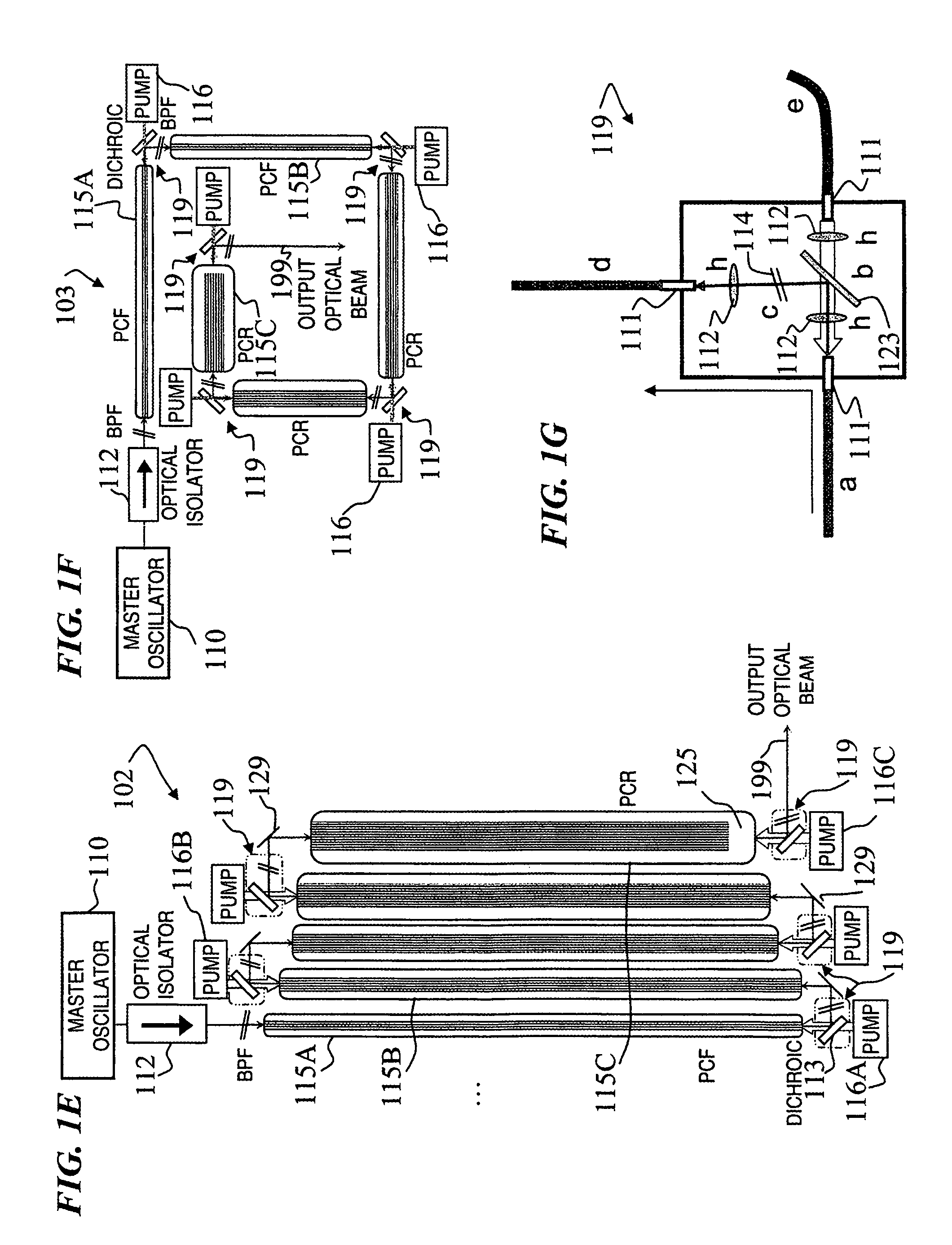
Fiber- or rod-based optical source featuring a large-core, rare-earth-doped photonic-crystal device for generation of high-power pulsed radiation and method
ActiveUS20070041083A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRare earthEngineering
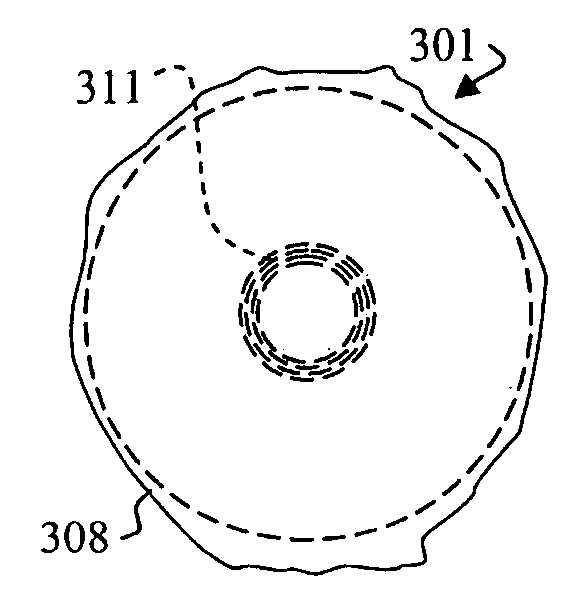
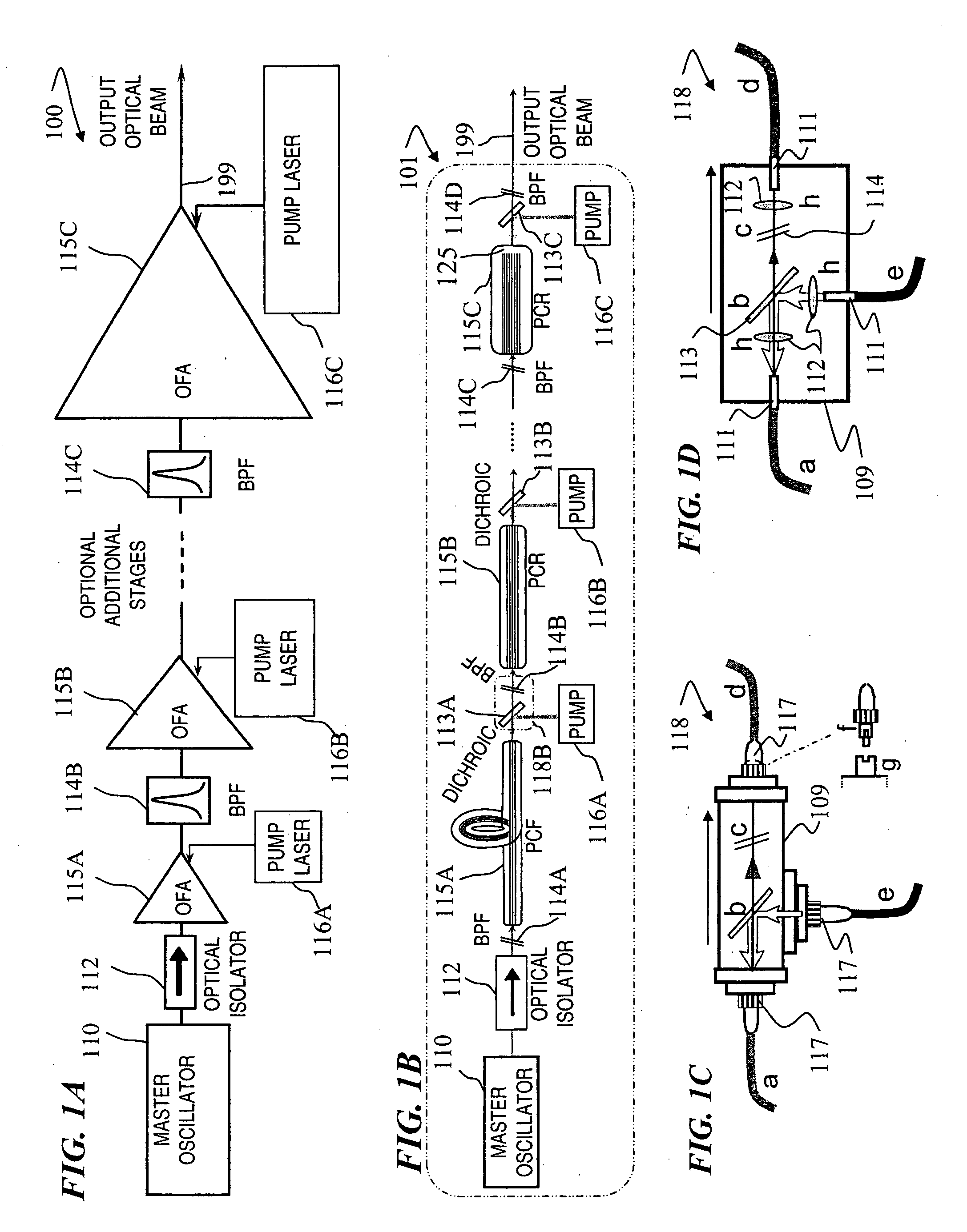
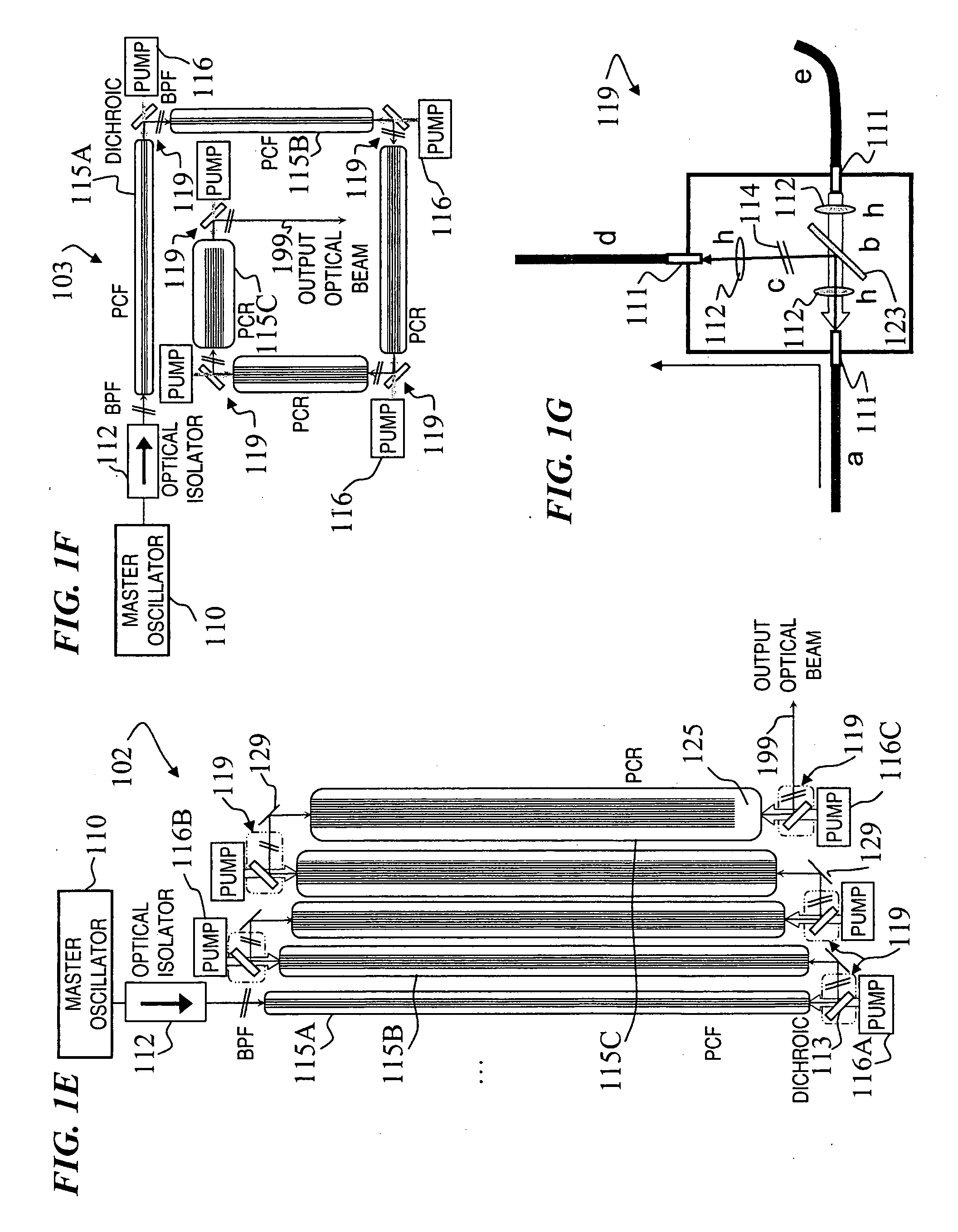
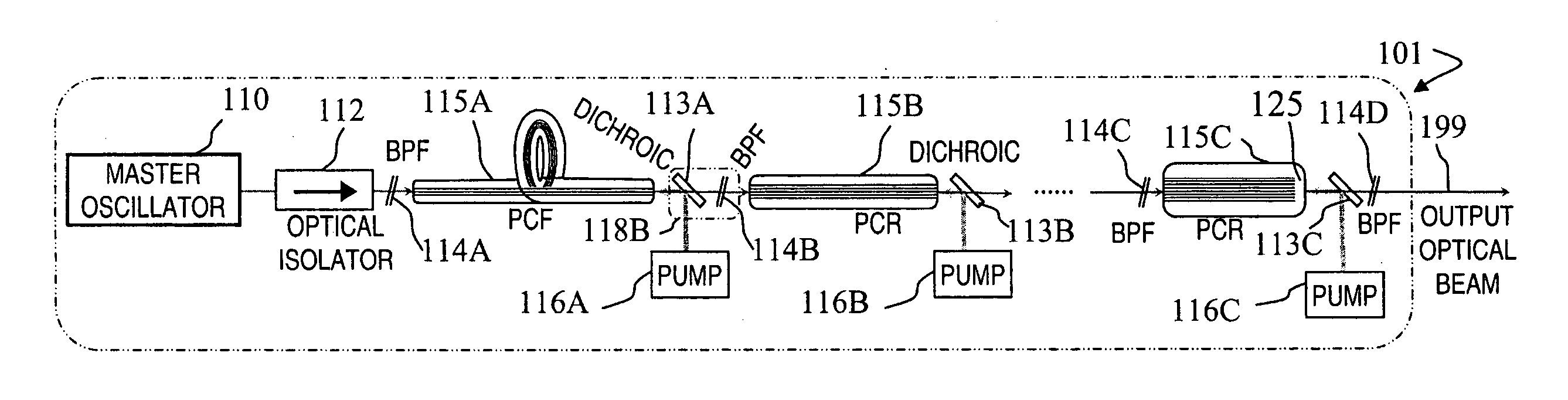
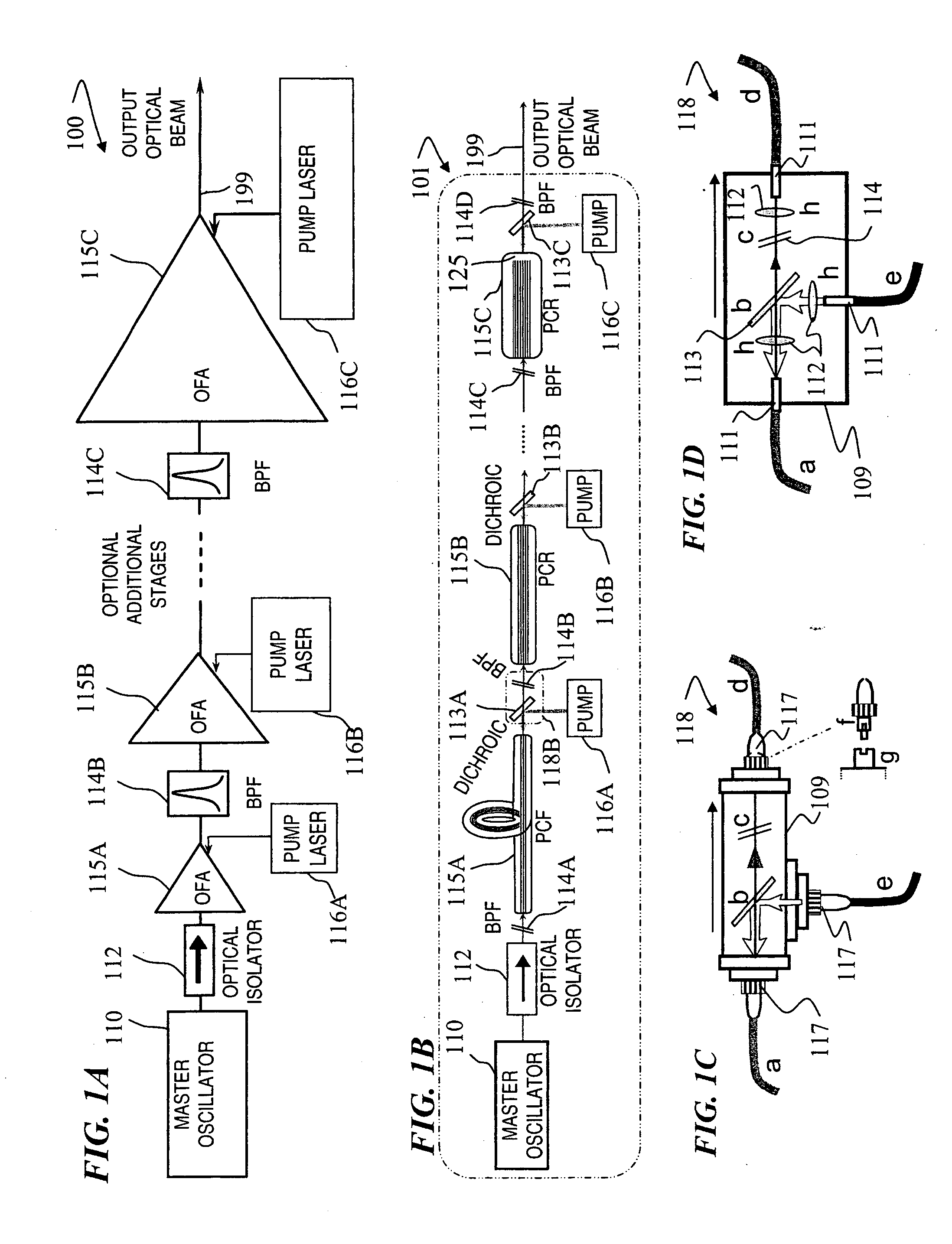
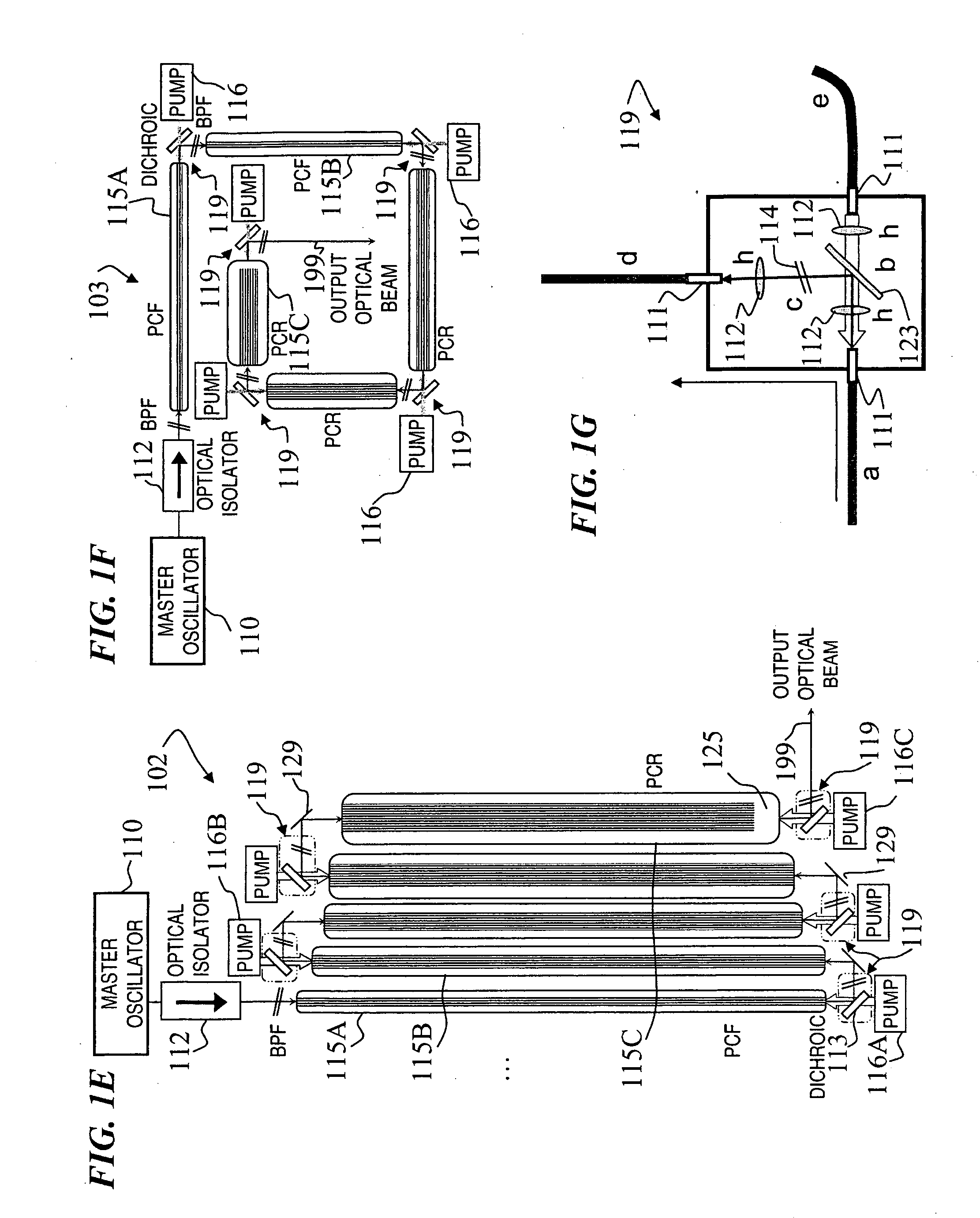
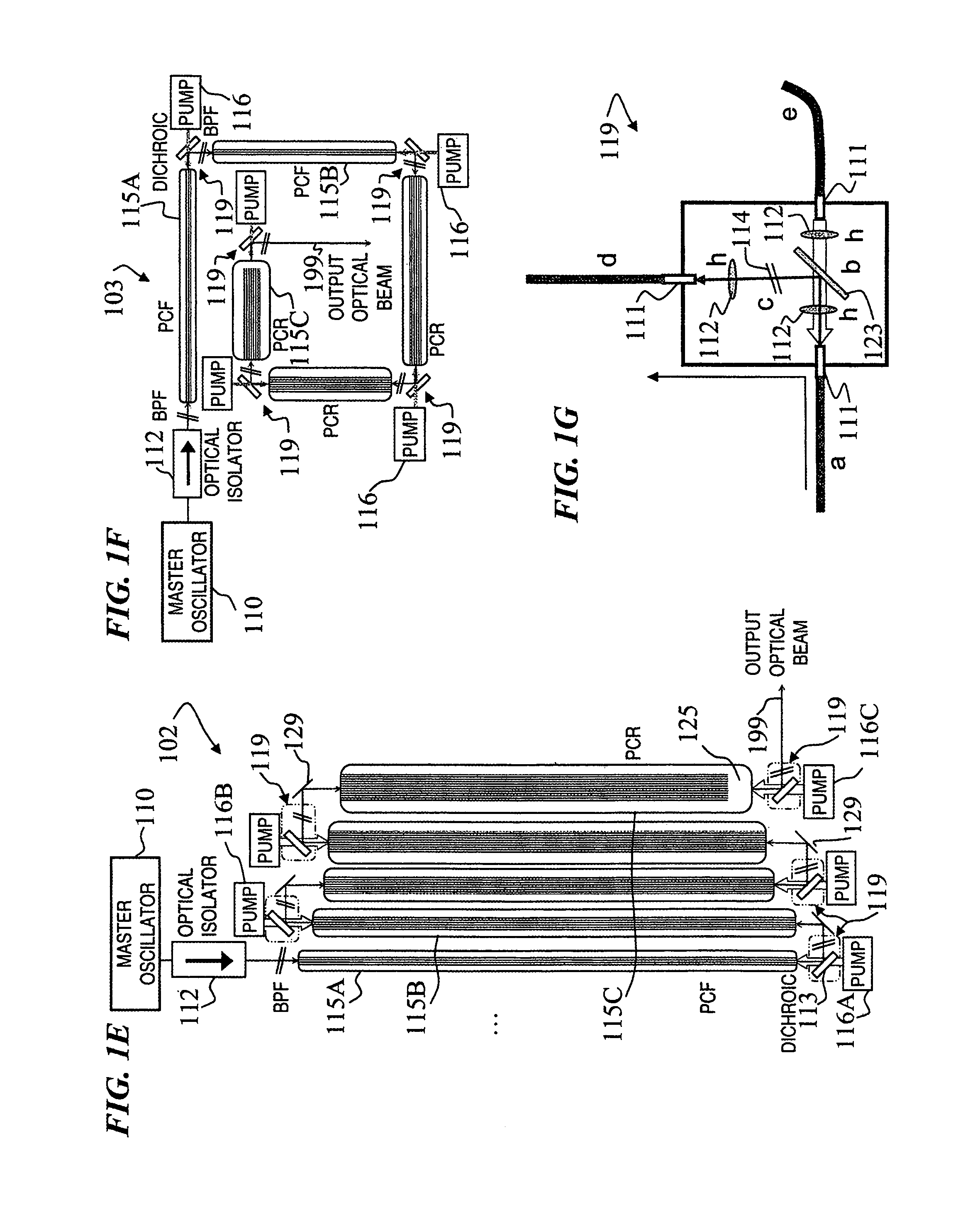
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
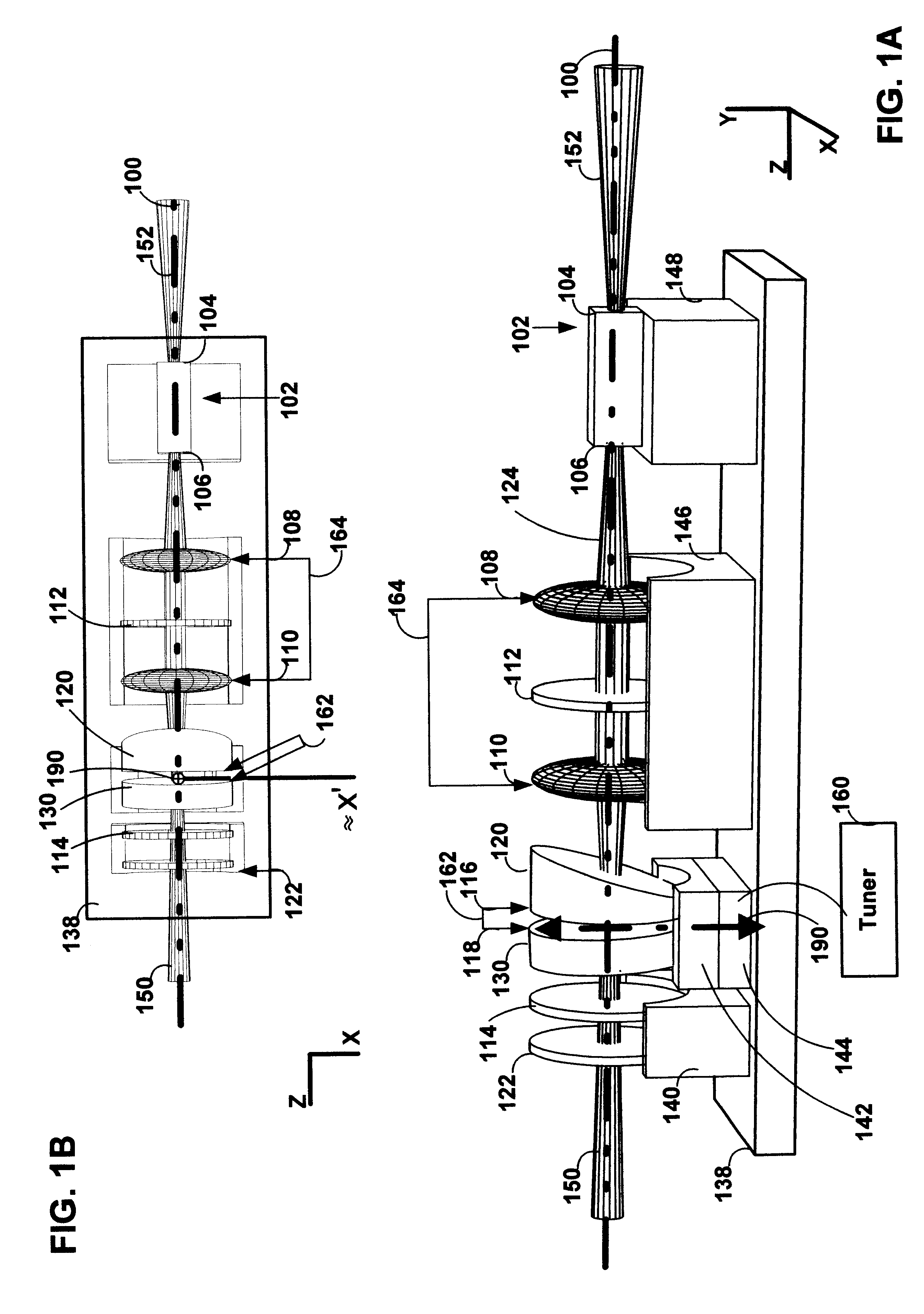
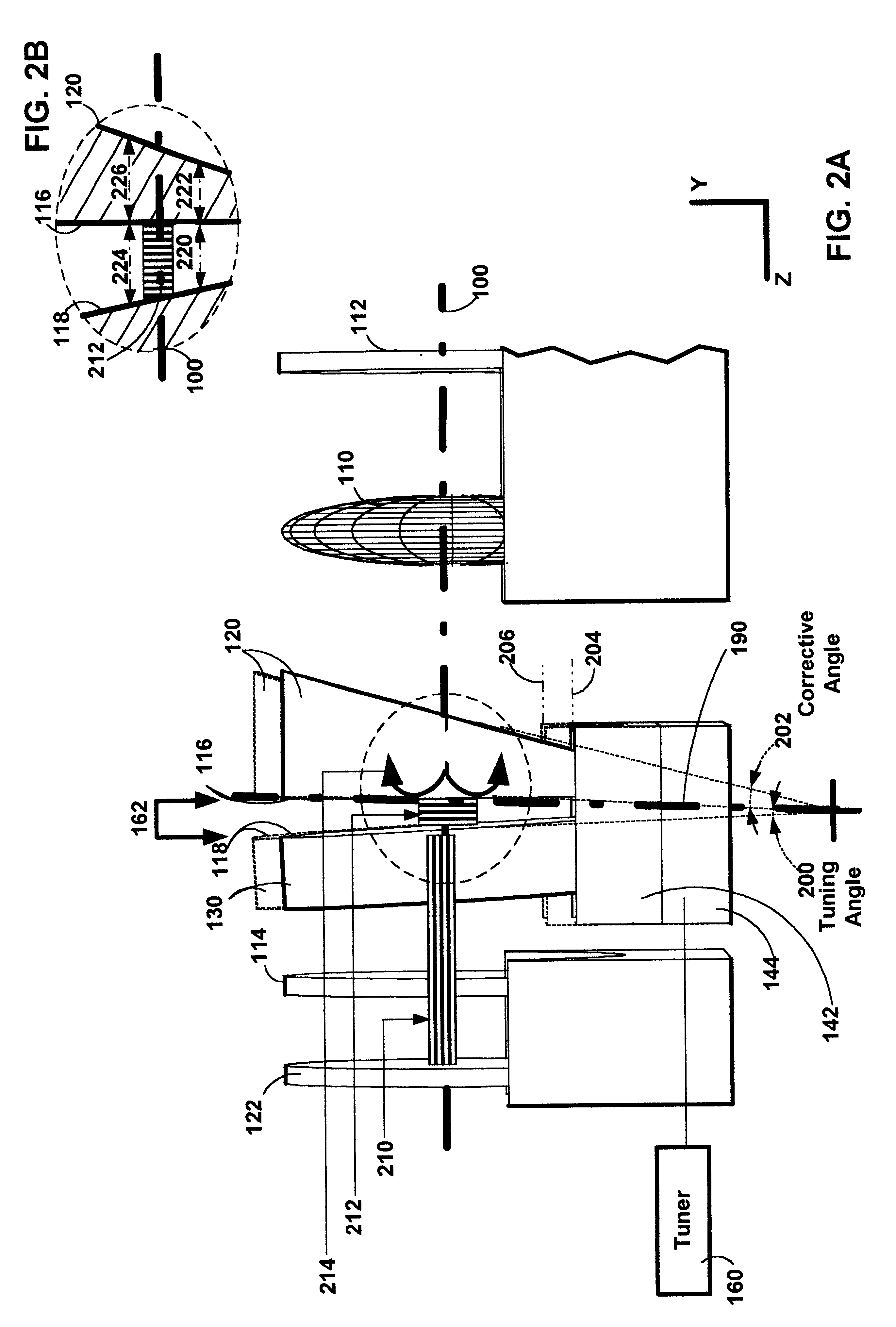
Continuously-tunable external cavity laser
InactiveUS6282215B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsExternal cavity laserClosed loop feedback
The present invention provides a continuously-tunable external cavity laser (ECL) with a compact form factor and precise tuning. A novel interference filter which may be used to tune the ECL provides an absence of mode-hopping and reduced feedback from both spurious interference and reflections in the external cavity. A novel tuning mechanism is disclosed which provides for mechanical FM tuning of a wide range ECL tuning elements such as: an interference filter, a diffraction element, and a retroreflector. A novel feedback circuit is disclosed which provides closed loop feedback for selecting output wavelength in a laser.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
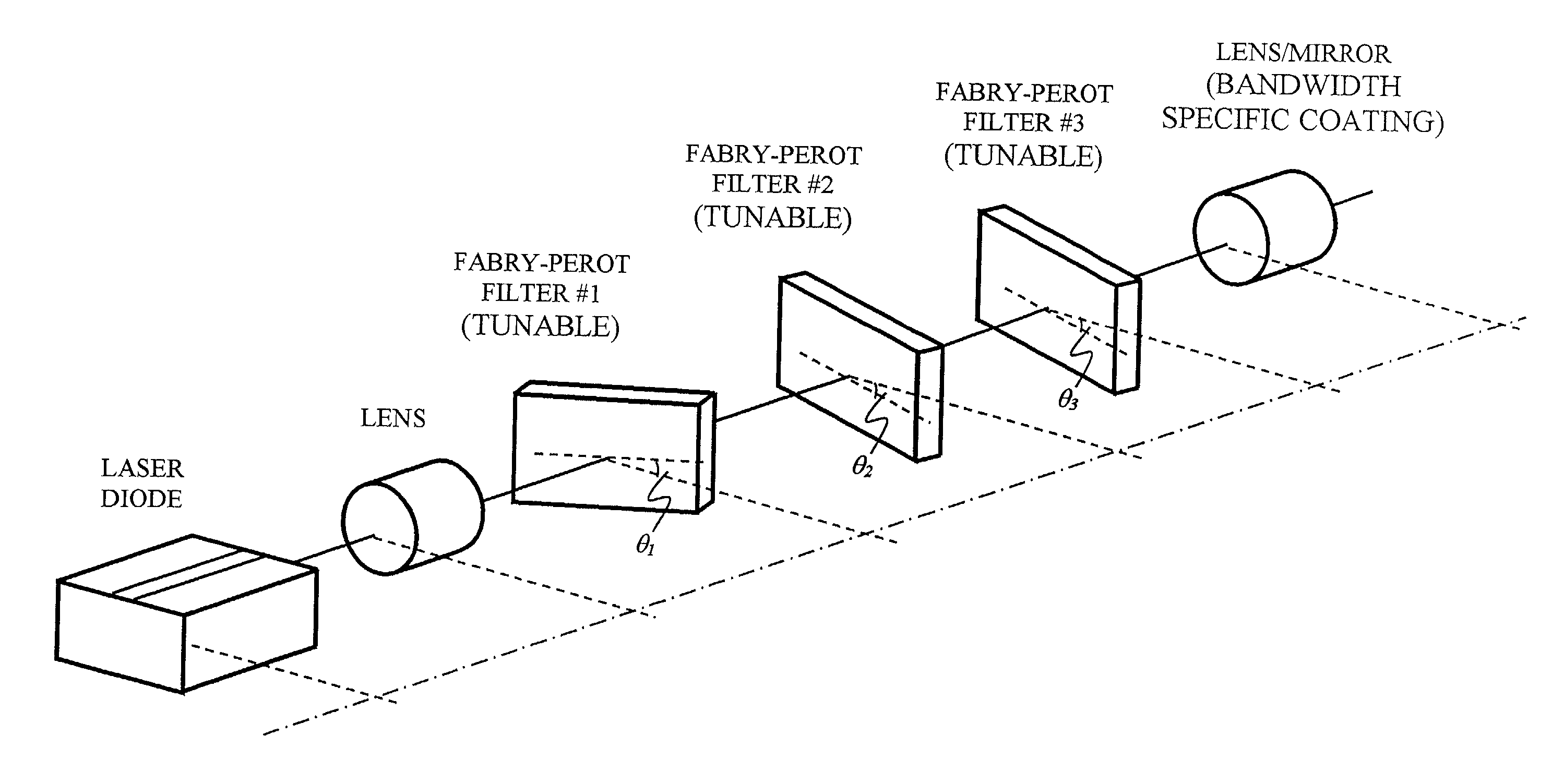
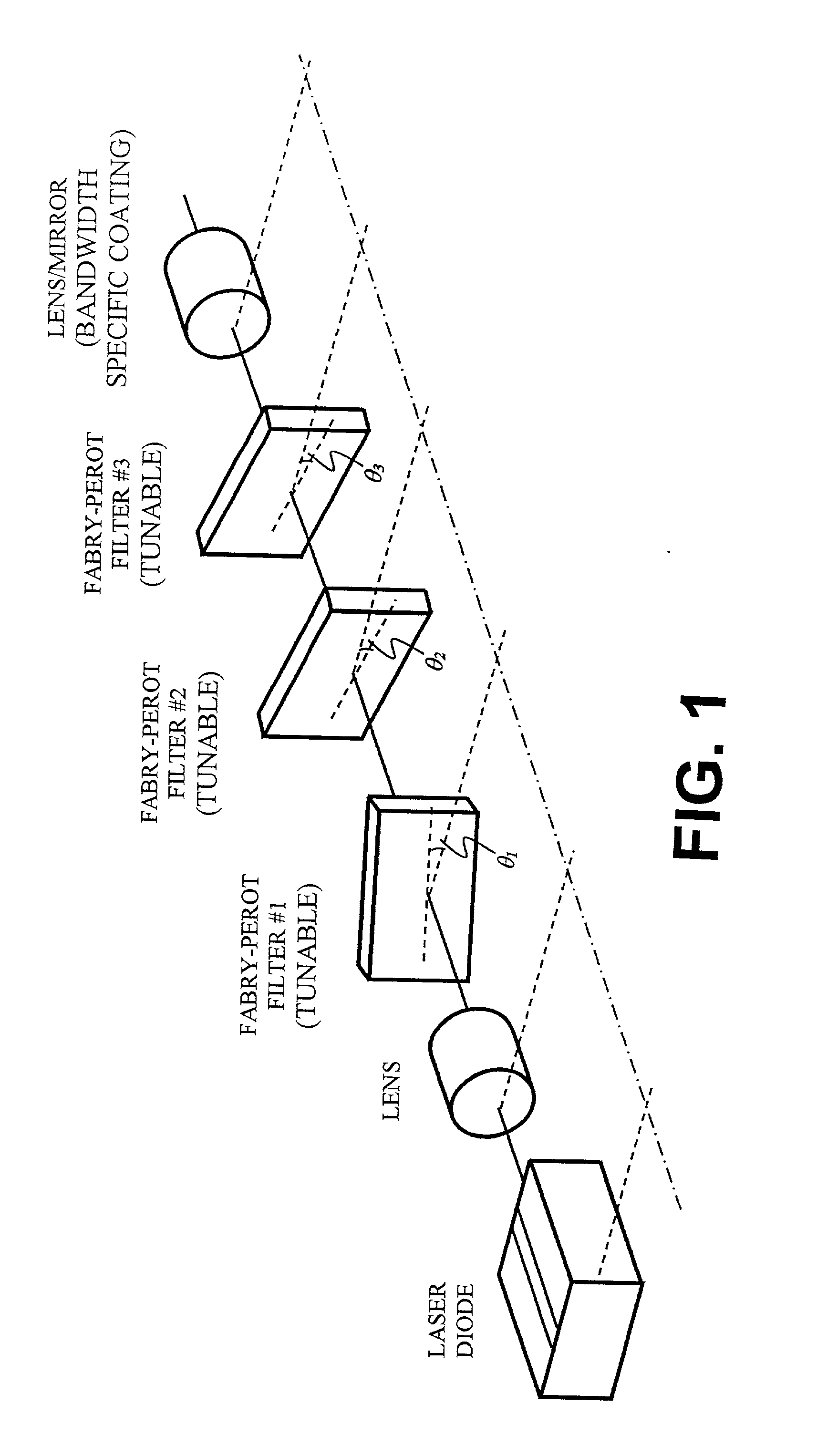
Wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20020054614A1Increase output powerFast switching timeLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionWedge filter (device)Switching time
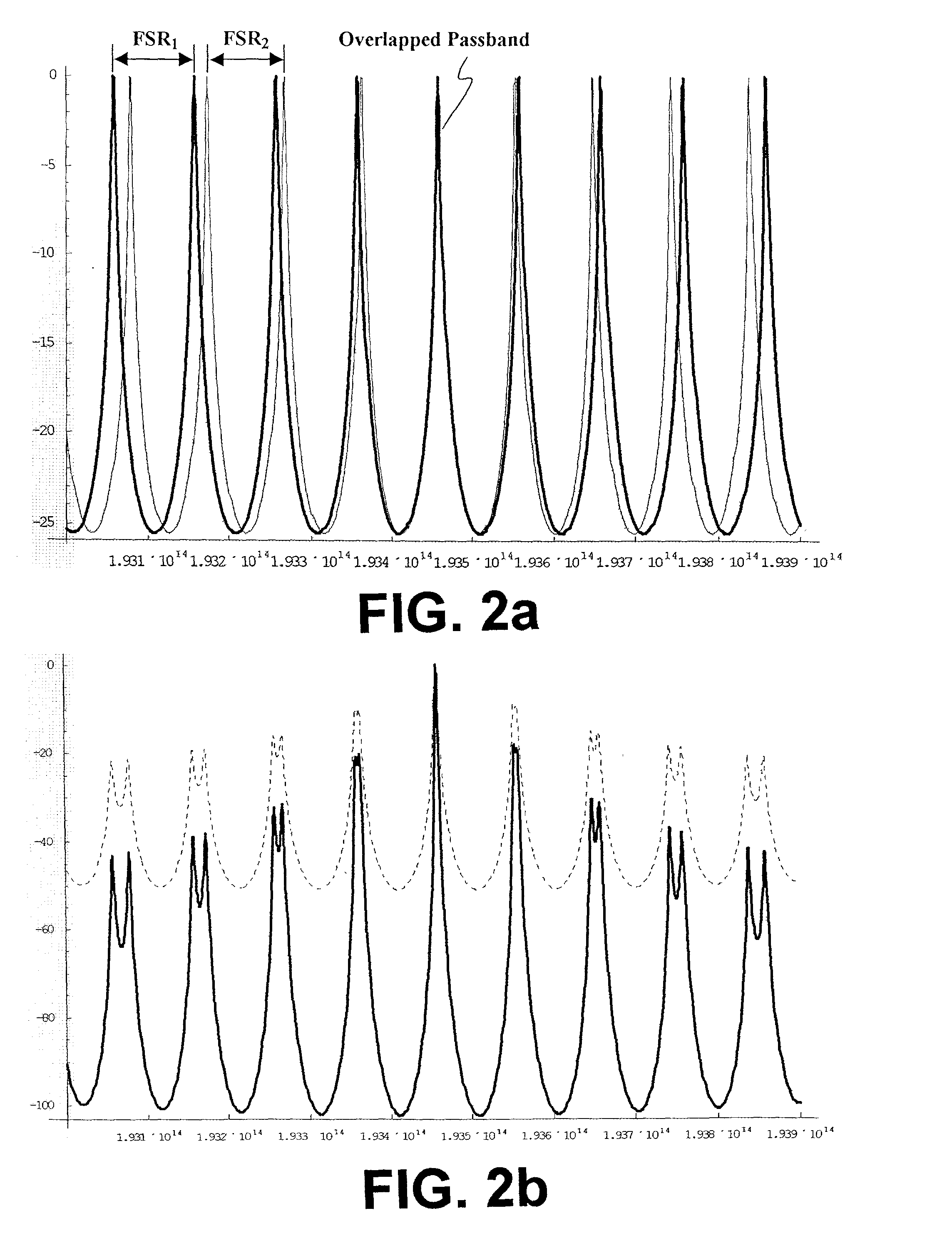
A wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser that addresses wide wavelength tuning range, is mode hopping free, has high output power, has fast wavelength switching time, is wavelength locking free and is relatively simple. Four exemplary embodiments disclosed herein utilize a wavelength discretely tunable semiconductor laser that comprises a discretely tunable filter and laser amplifier. In the first embodiment, the tuning element comprises a pair of cascade Fabry-Perot filters, each having a plurality of characteristic narrow transmission passbands that pass only the cavity mode under the passband. The spacing between the narrow transmission passbands are slightly different in one filter from the other filter so that only one passband from each filter can be overlapped in any given condition over the entire active element gain spectral range, thereby permitting lasing only at a single cavity mode passed by the cascade double filters. One of the two etalon filters can be made with a plurality of transmission passbands predetermined by industry, application and international standards, making this element an intra-cavity wavelength reference and eliminating further wavelength locking needs for the tunable laser. In a second embodiment, one of the two etalons is replaced by a wedge filter. The filter optical path change and thus the transmission passband shift are achieved by translating the wedge filter in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis. In a third embodiment, one of the two etalon filters is replaced by a polarization interference filter. The polarization interference filter consists of an electro-optically-tunable birefringent waveplate, a fixed birefringent waveplate, the laser cavity and T.E. polarization light emitted from the laser diode. In a fourth embodiment, the laser and wavelength tuning structure are integrated on a semiconductor substrate by epitaxy processes.
Owner:JIN HONG
Multi-segment photonic-crystal-rod waveguides for amplification of high-power pulsed optical radiation and associated method
InactiveUS20070104431A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyLaser detailsCladded optical fibreOptical radiationPromiscuous behaviour
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
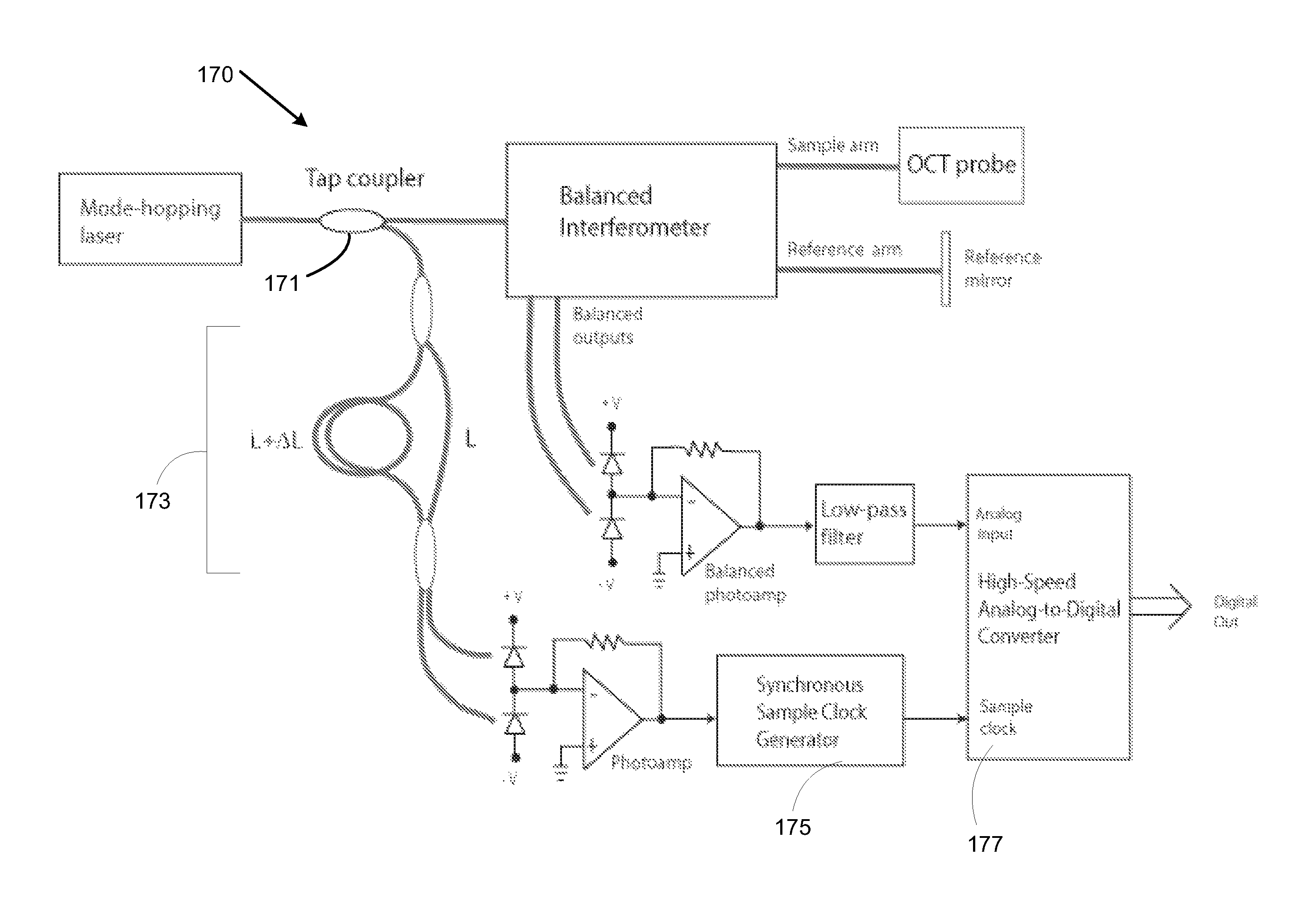
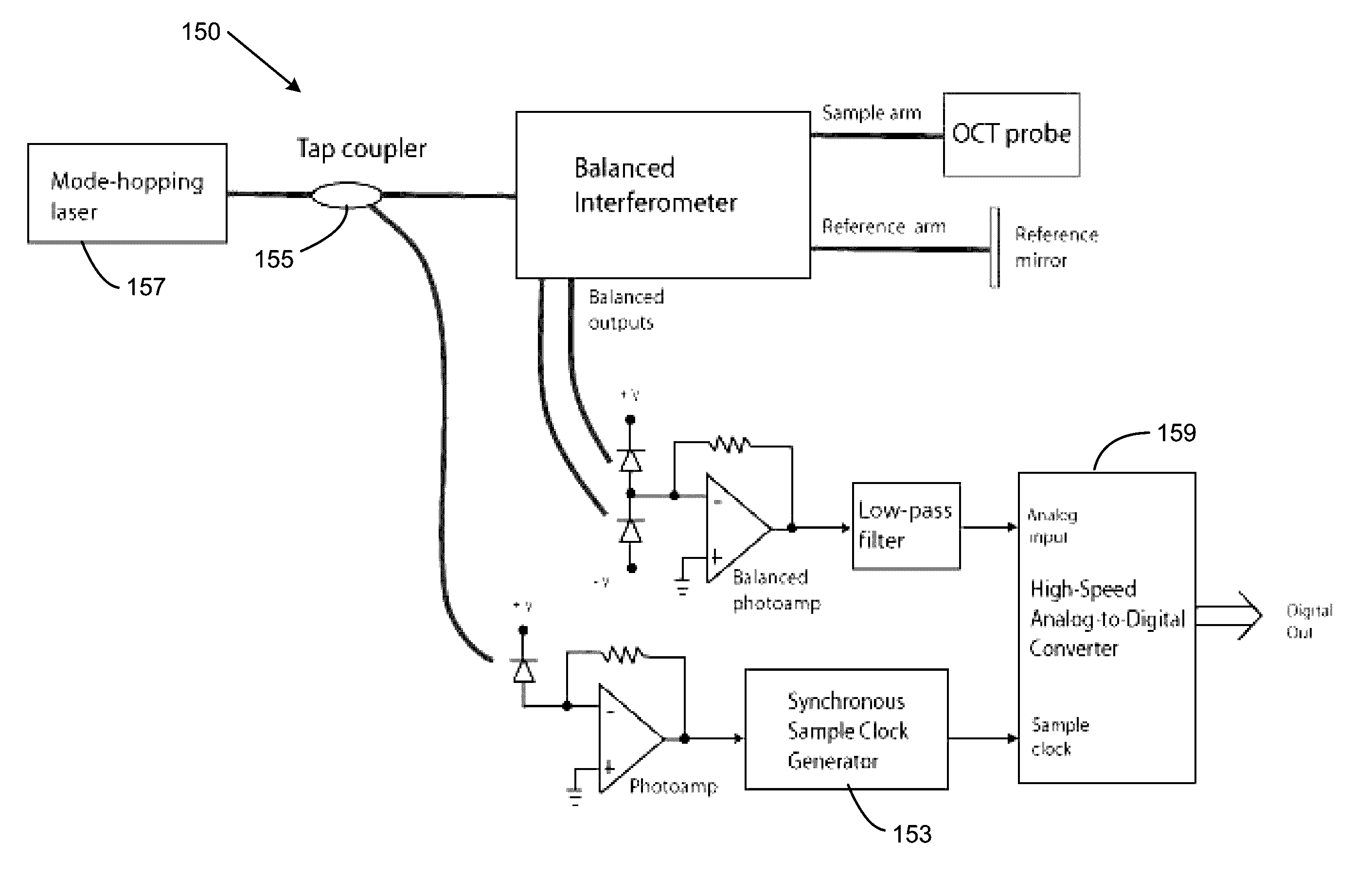
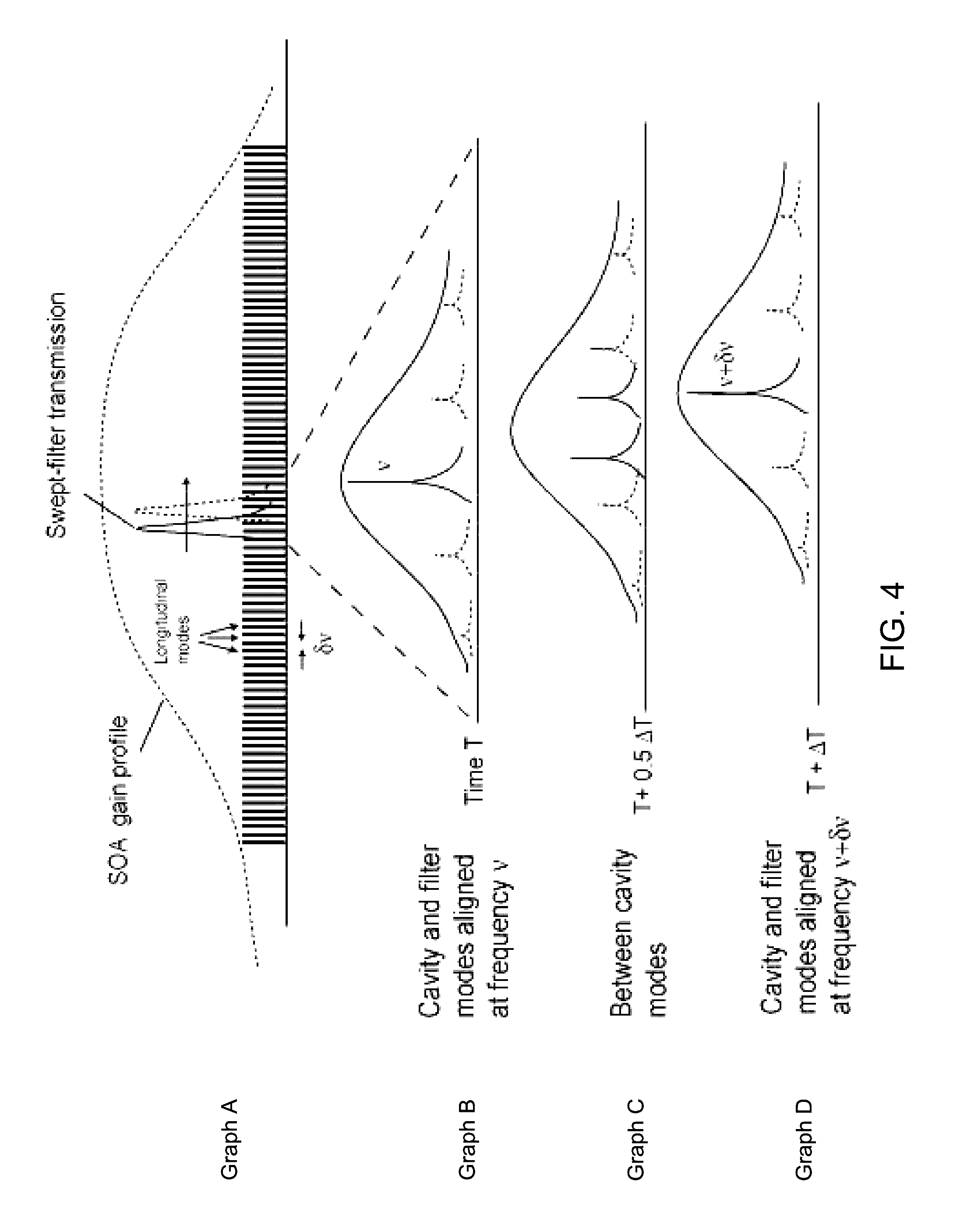
Swept mode-hopping laser system, methods, and devices for frequency-domain optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS8582109B1Intensity fluctuationShort transition timeLaser detailsUsing optical meansLaser lightOptical communication
In part, the invention relates to frequency-domain optical coherence tomography system. The system includes a tunable laser comprising a laser output for transmitting laser light and a laser cavity having a length L, a gain element disposed within the laser cavity; a tunable wavelength selective element disposed within the laser cavity; a reference reflector disposed outside of the laser cavity; an interferometer in optical communication with the laser output and the reference reflector, wherein the interferometer is configured to transmit a portion of the laser light to a sample and combine light scattered from the sample with light scattered from the reference reflector; and a detector in optical communication with the interferometer that receives the combination of light scattered from the sample and the light scattered from the reference reflector and transforms the combination of light into an electronic signal comprising measurement data with respect to the sample.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
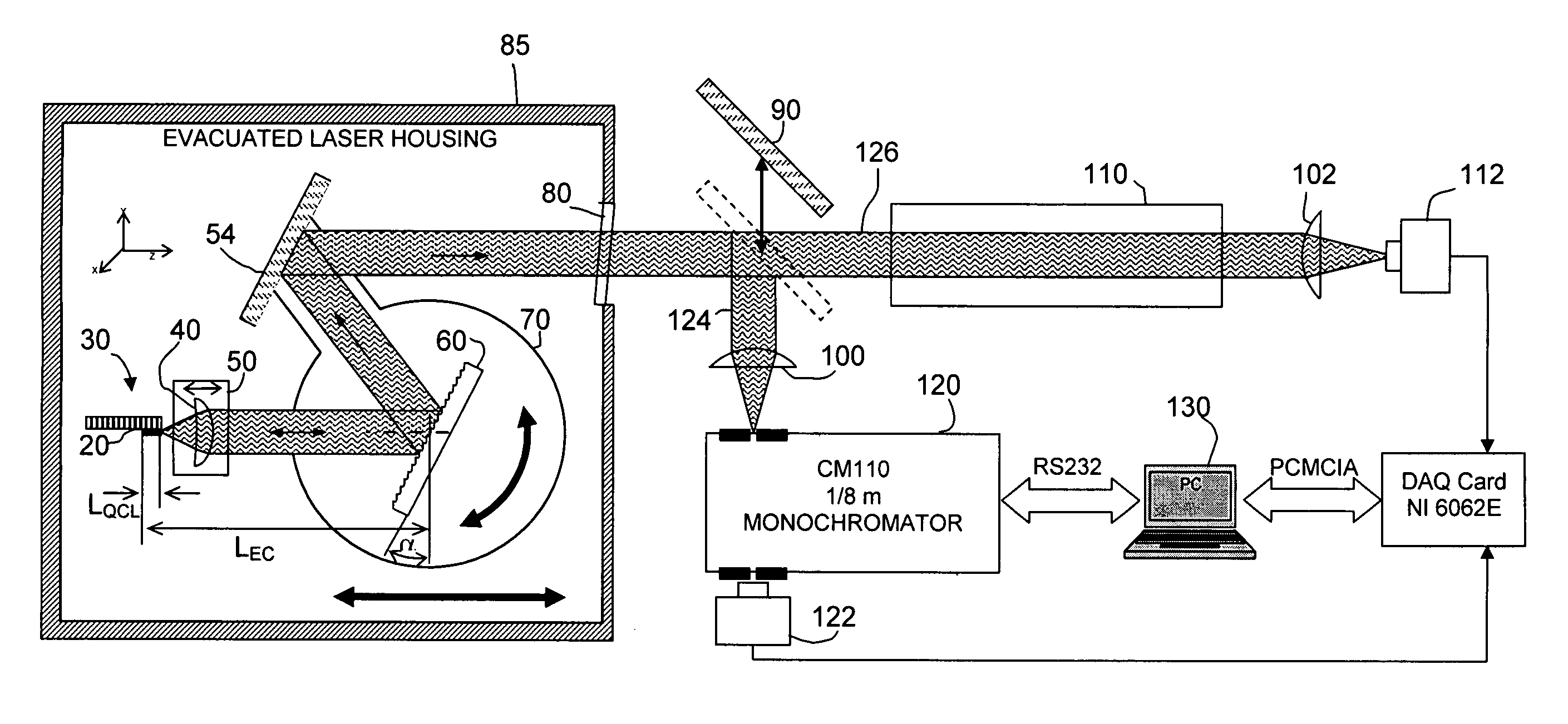
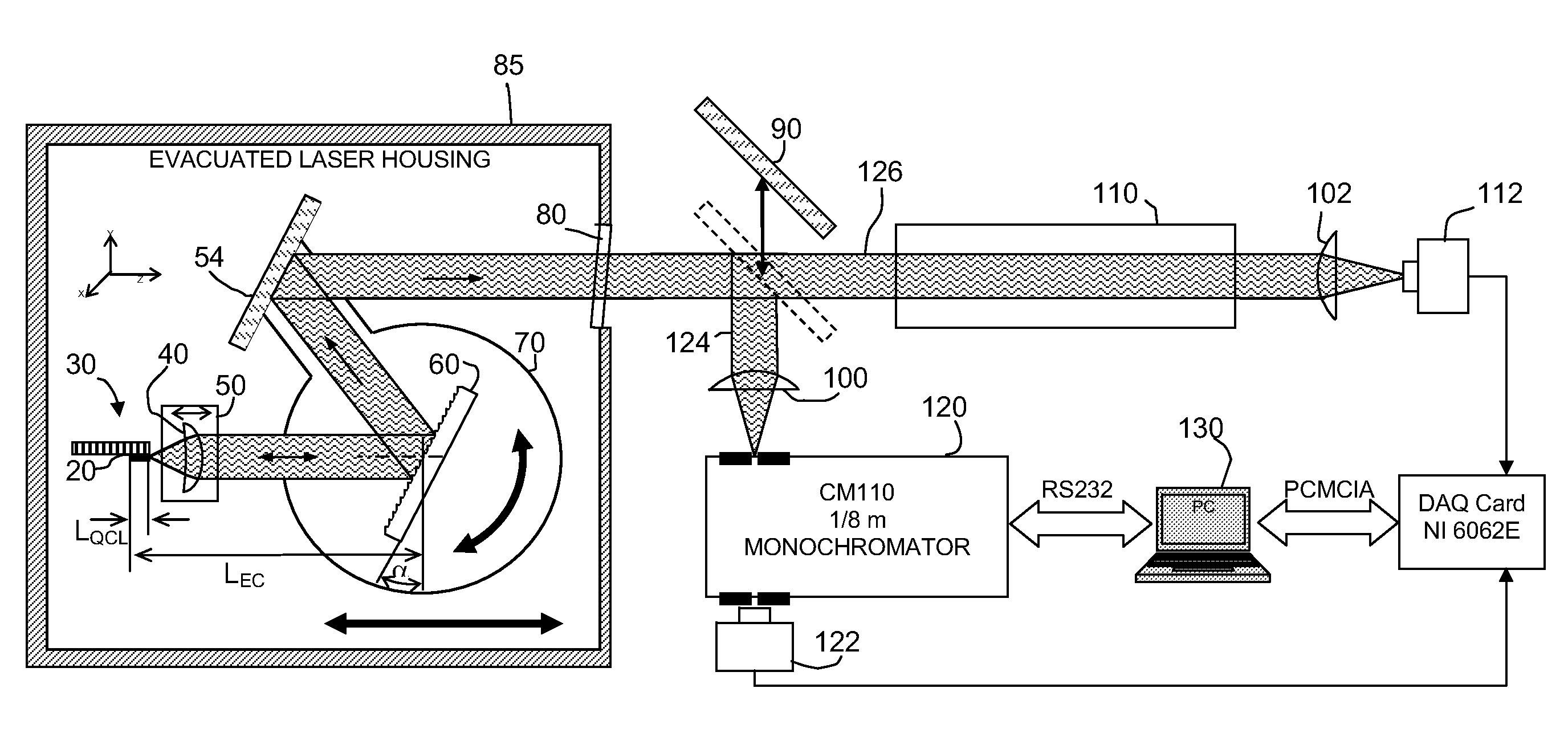
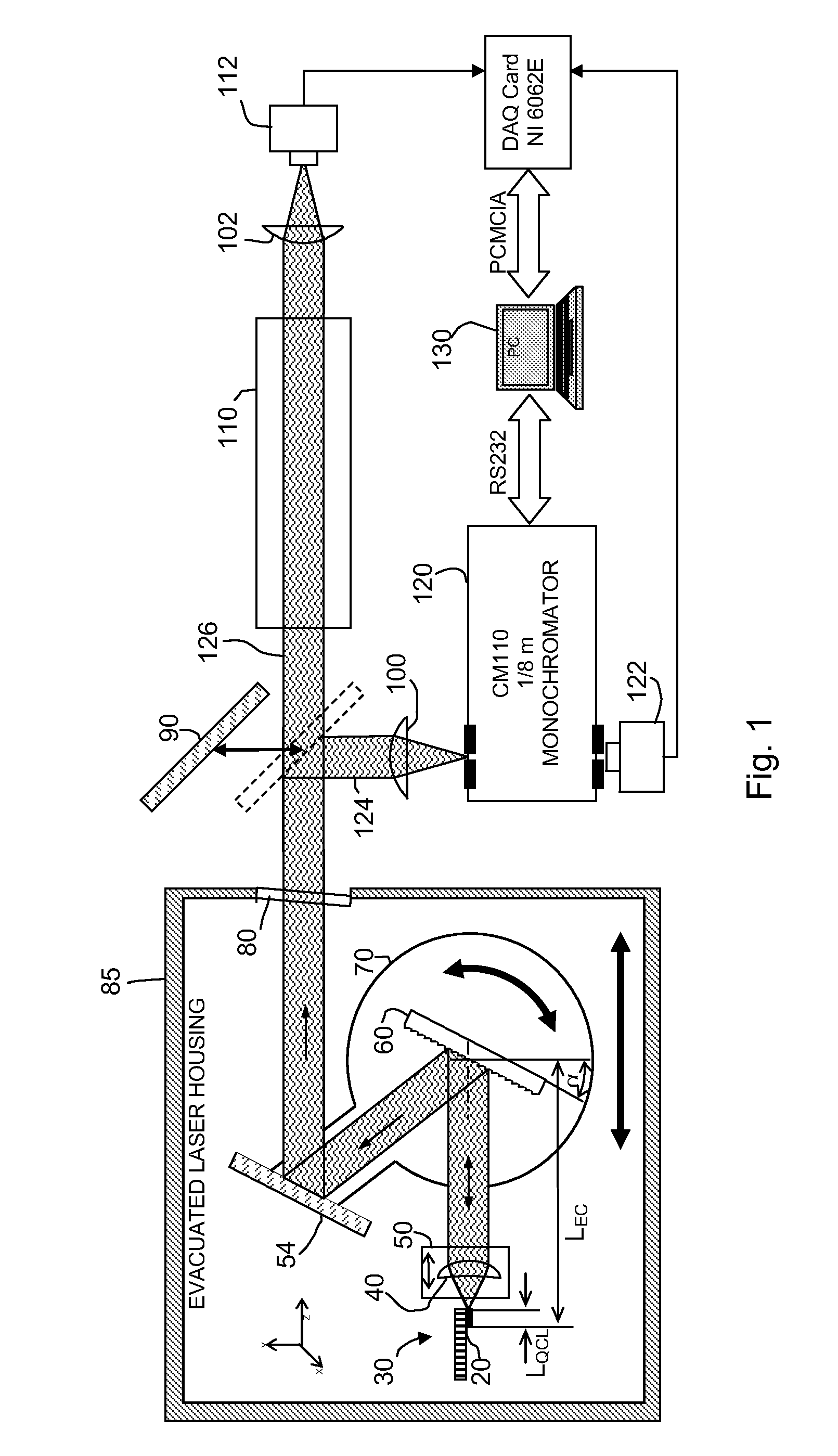
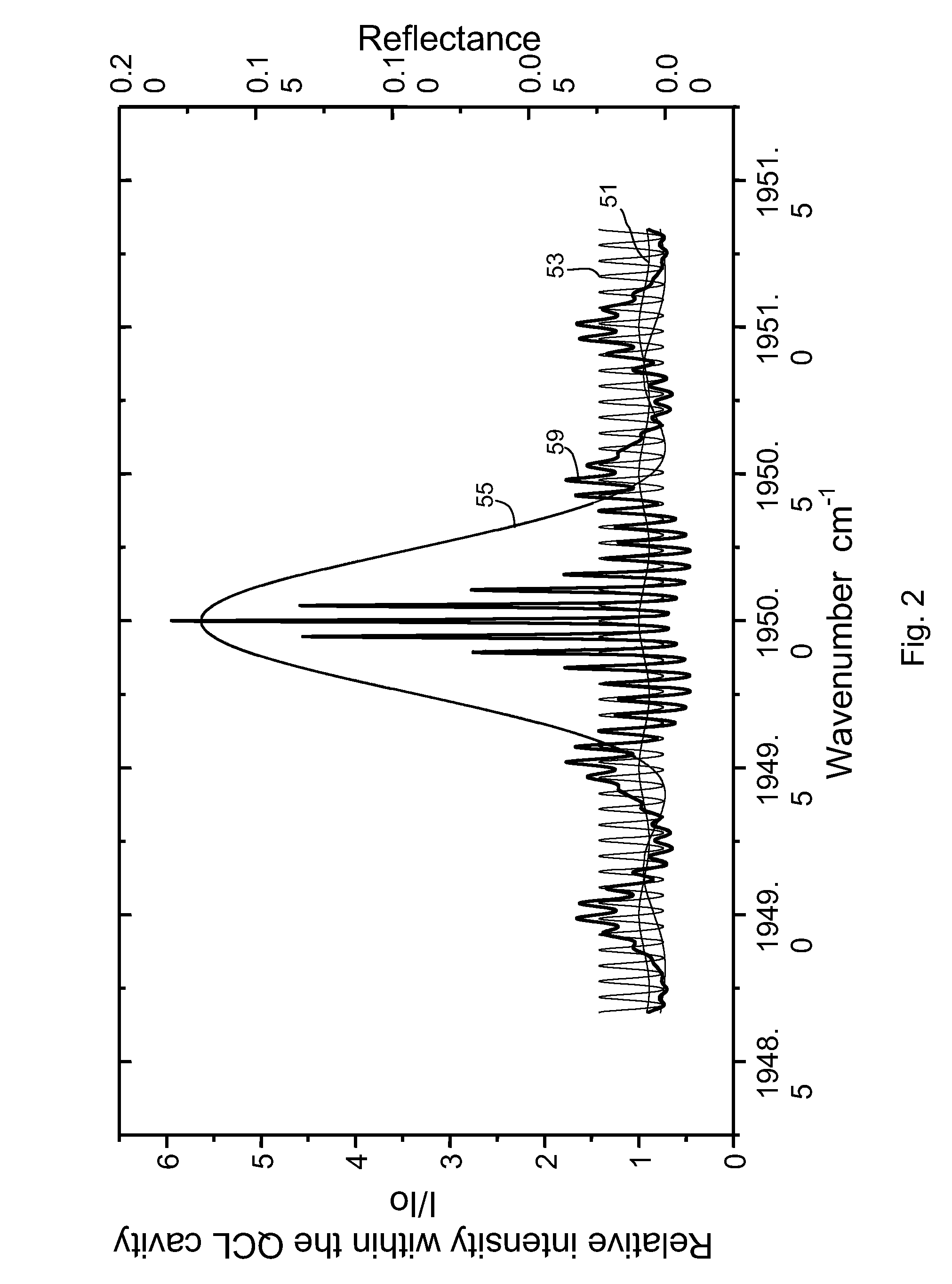
Piezo activated mode tracking system for widely tunable mode-hop-free external cavity mid-IR semiconductor lasers
InactiveUS20070047599A1High resolutionWide tunabilityOptical resonator shape and constructionNanoopticsAnti-reflective coatingSemiconductor
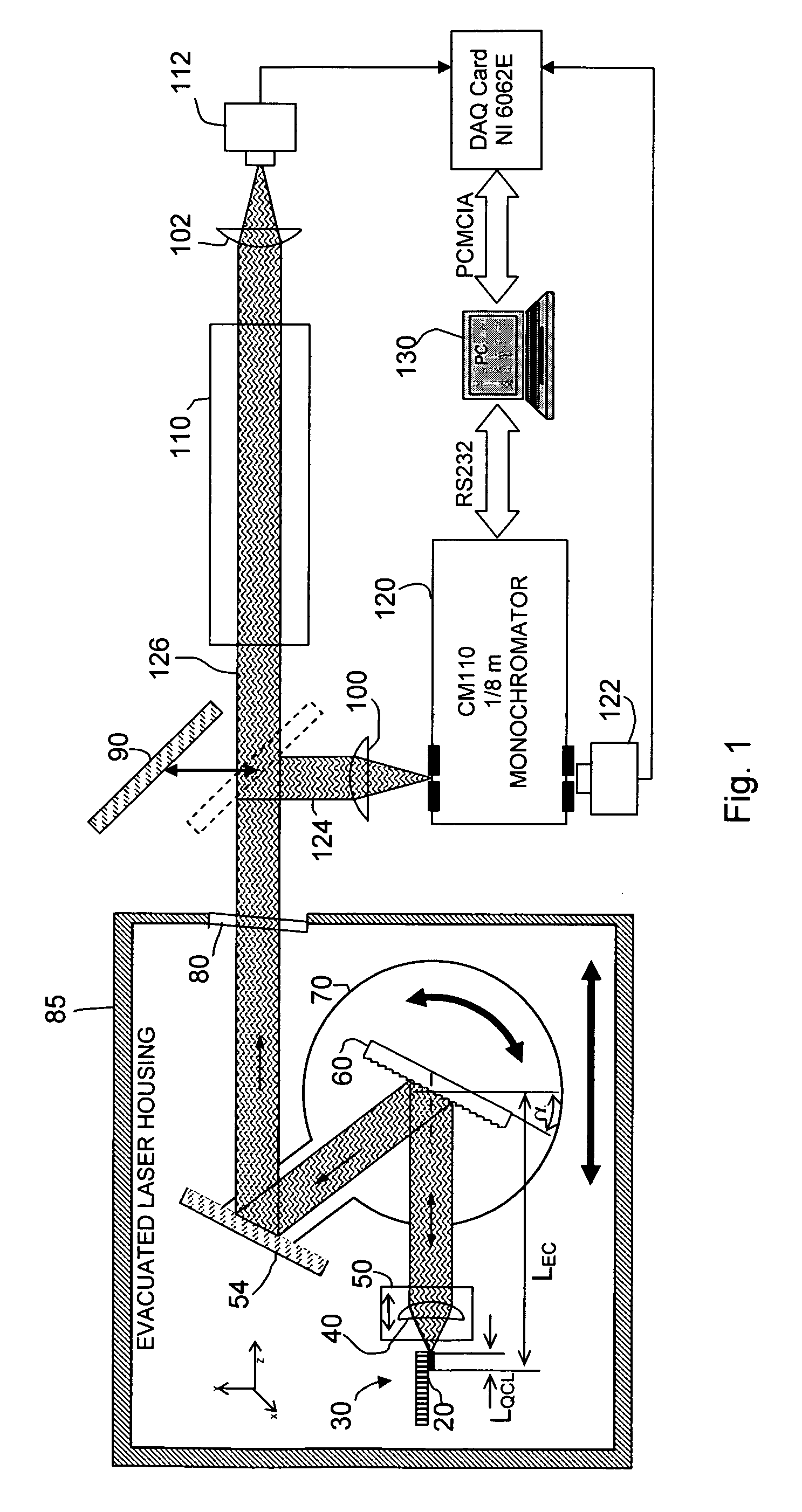
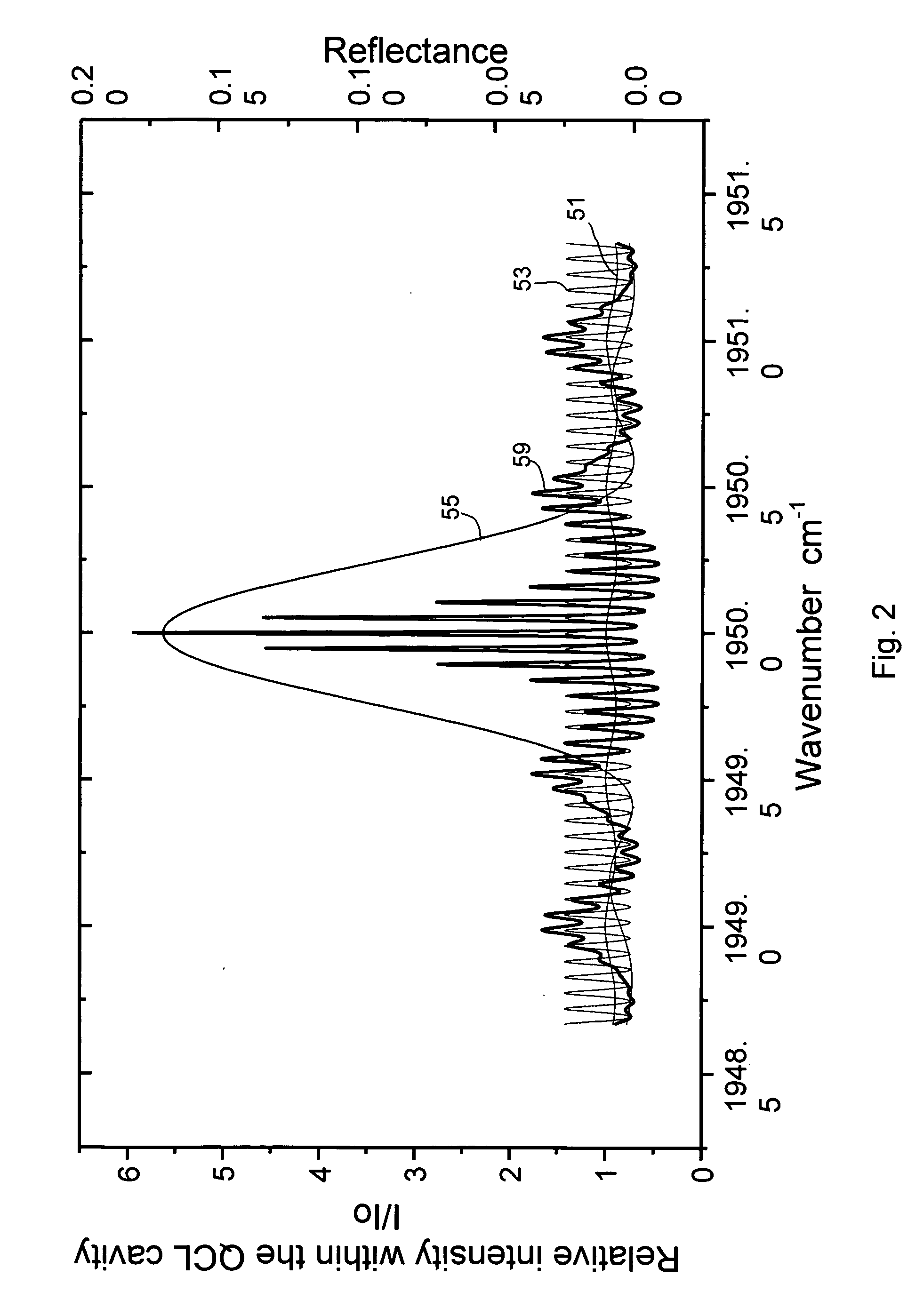
A widely tunable, mode-hop-free semiconductor laser operating in the mid-IR comprises a QCL laser chip having an effective QCL cavity length, a diffraction grating defining a grating angle and an external cavity length with respect to said chip, and means for controlling the QCL cavity length, the external cavity length, and the grating angle. The laser of claim 1 wherein said chip may be tuned over a range of frequencies even in the absence of an anti-reflective coating. The diffraction grating is controllably pivotable and translatable relative to said chip and the effective QCL cavity length can be adjusted by varying the injection current to the chip. The laser can be used for high resolution spectroscopic applications and multi species trace-gas detection. Mode-hopping is avoided by controlling the effective QCL cavity length, the external cavity length, and the grating angle so as to replicate a virtual pivot point.
Owner:RICE UNIV
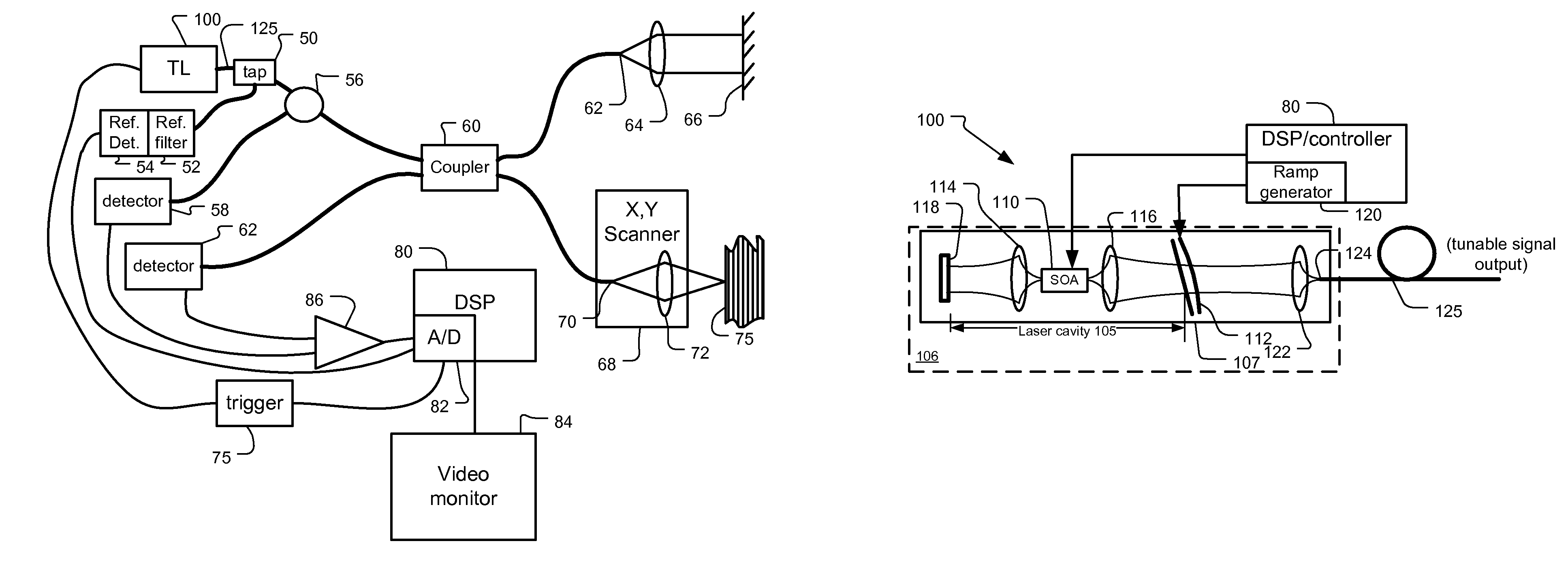
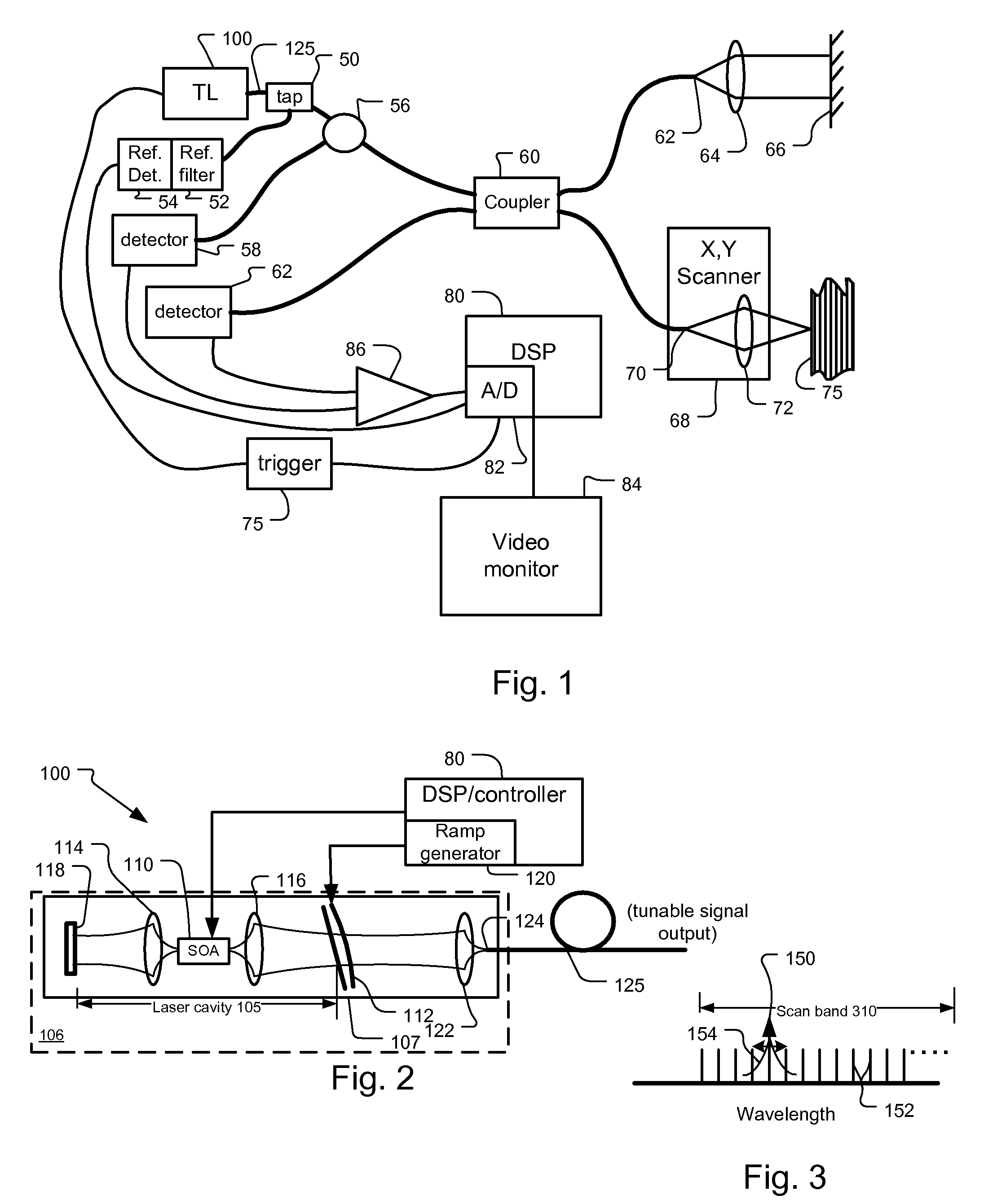
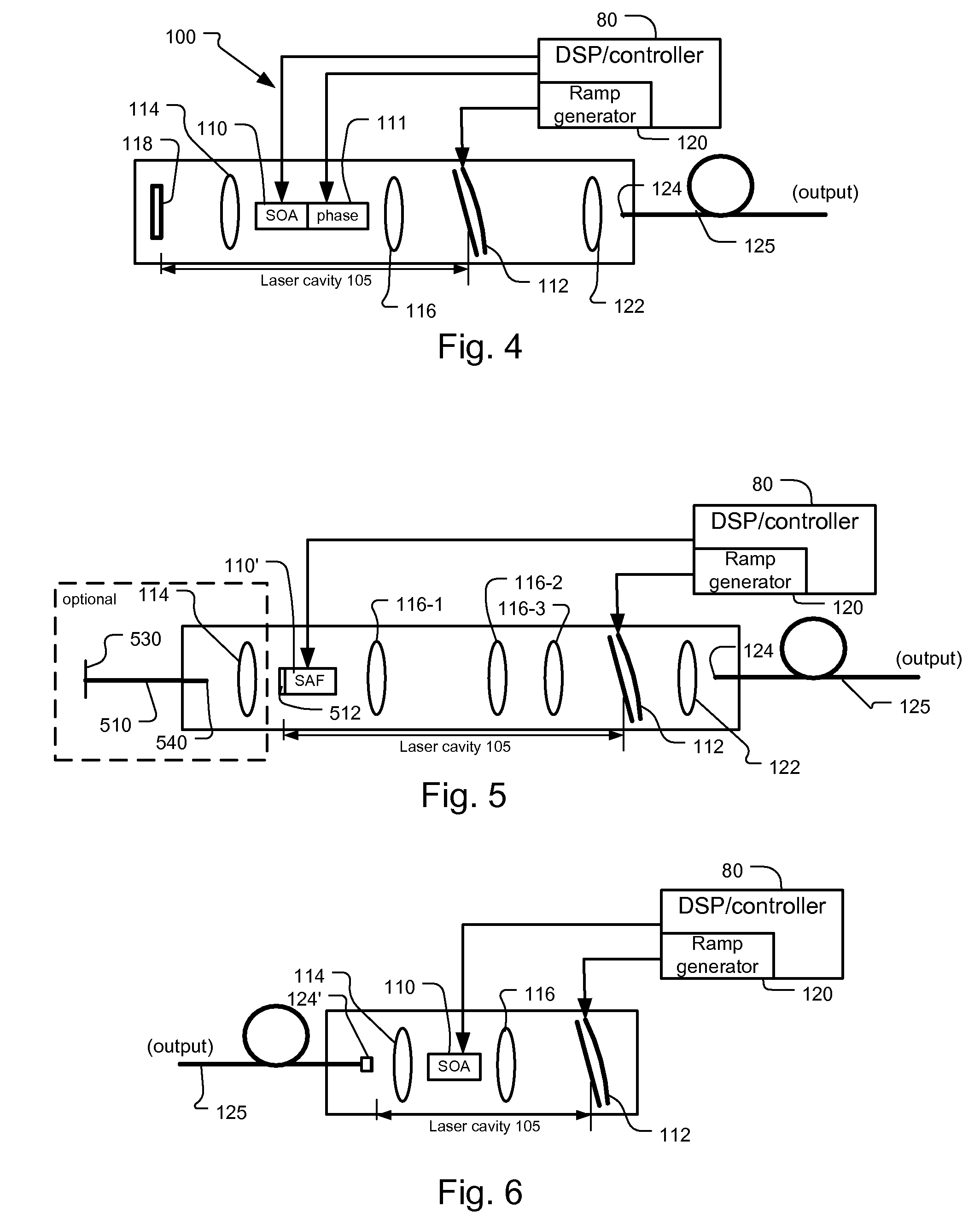
Mode Hopping Swept Frequency Laser for FD OCT and Method of Operation
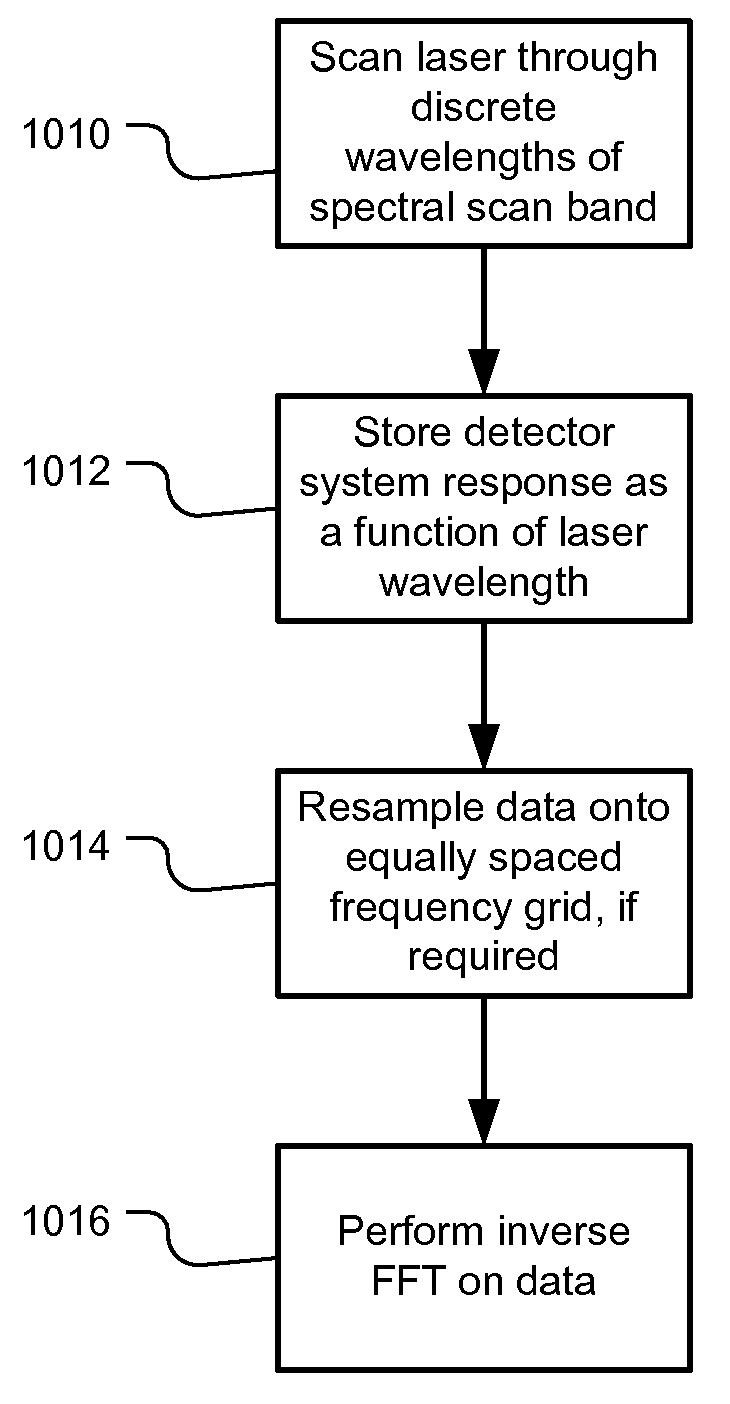
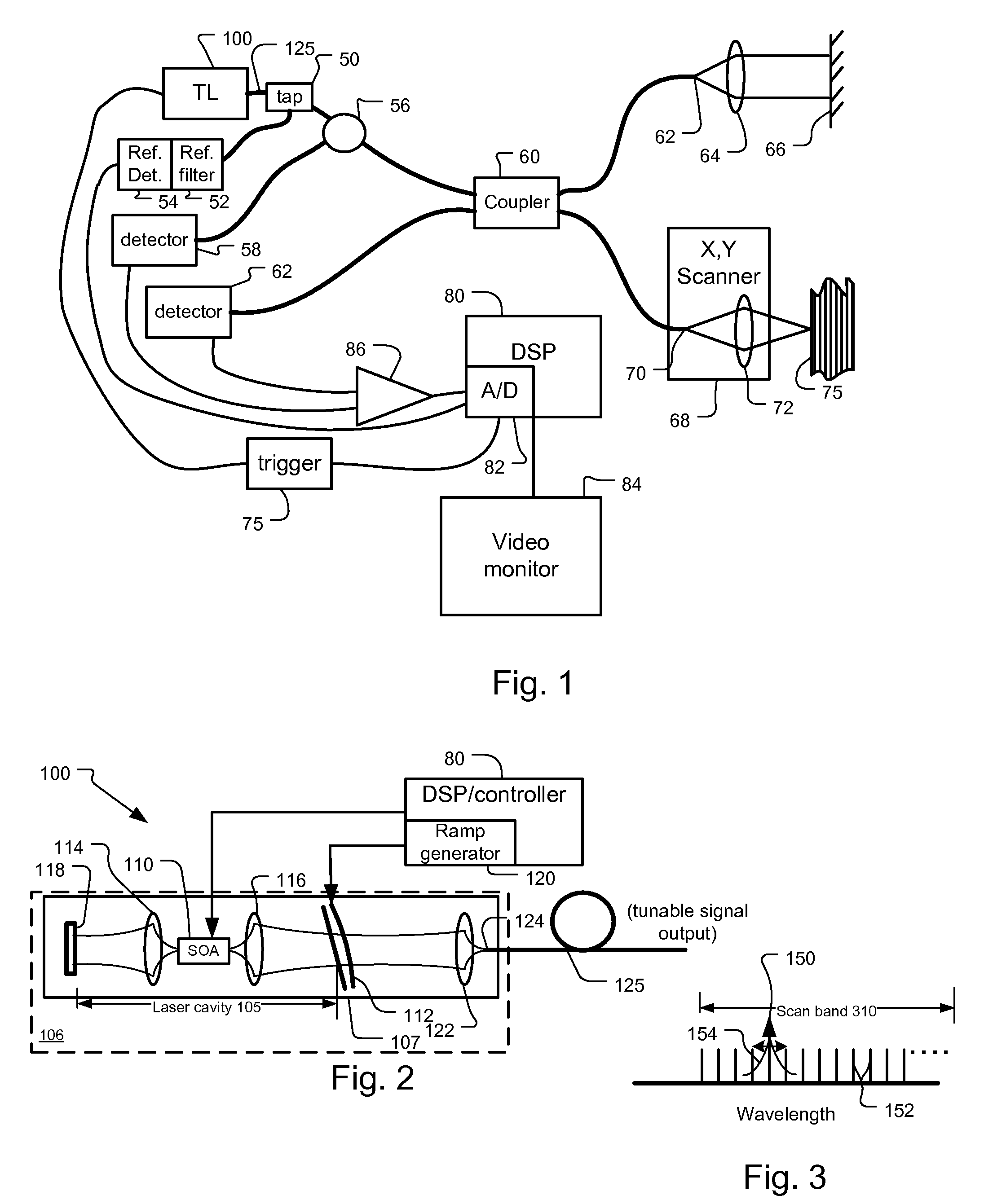
ActiveUS20090059970A1Dwell timeIncrease tuning speedLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansBeam splitterLength wave
A frequency swept laser source that generates an optical signal that is tuned over a spectral scan band at single discrete wavelengths associated with longitudinal modes of the swept laser source. Laser hopping over discrete single cavity modes allows long laser coherence length even under dynamic very high speed tuning conditions. A ramp drive to the laser is used to linearize laser frequency tuning. A beam splitter is used to divide the optical signal between a reference arm leading to a reference reflector and a sample arm leading to a sample. A detector system detects the optical signal from the reference arm and the sample arm for generating depth profiles and images of the sample.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Surface-emitting laser and optical apparatus formed by using surface-emitting laser
InactiveUS20090135876A1Suppress longitudinal mode hoppingStable beam spotMirrorsOptical filtersDistributed Bragg reflectorOptoelectronics
A surface-emitting laser has an active layer between a first distributed Bragg reflector and a second distributed Bragg reflector. The first distributed Bragg reflector is formed so as to have a resonant mode and a first longitudinal mode different from the resonant mode included in the reflectivity stop band and a second longitudinal mode different from the resonant mode and the first longitudinal mode excluded from the reflectivity stop band. Oscillation is suppressed in the first longitudinal mode and in the second longitudinal mode. As a result, the surface-emitting laser can oscillate in a single longitudinal mode, suppressing longitudinal mode hopping.
Owner:CANON KK
Multi-segment photonic-crystal-rod waveguides coupled across a free-space gap and associated method
ActiveUS7260299B1High peak powerHigh pulse energyLaser detailsCladded optical fibreEngineeringMulti segment
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
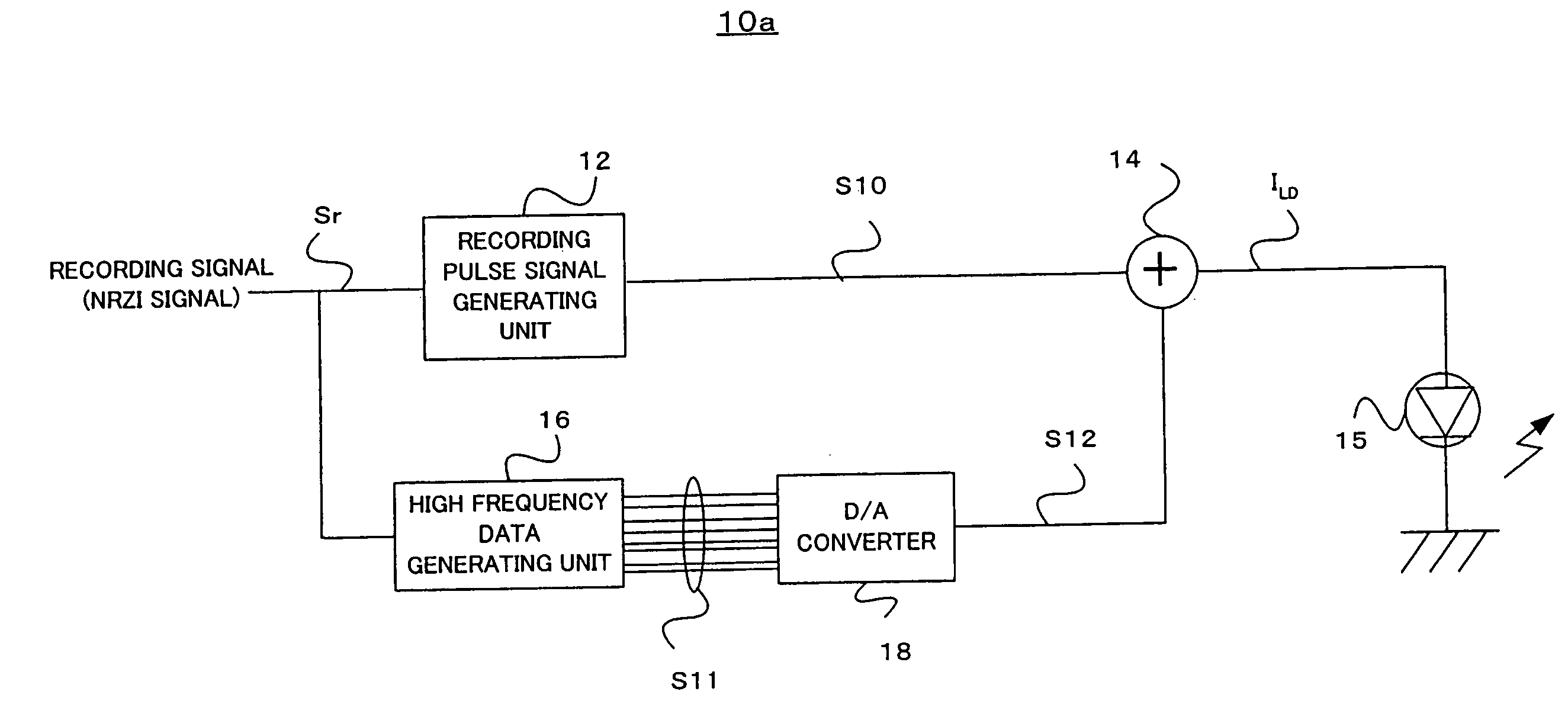
Information recording apparatus and information recording method
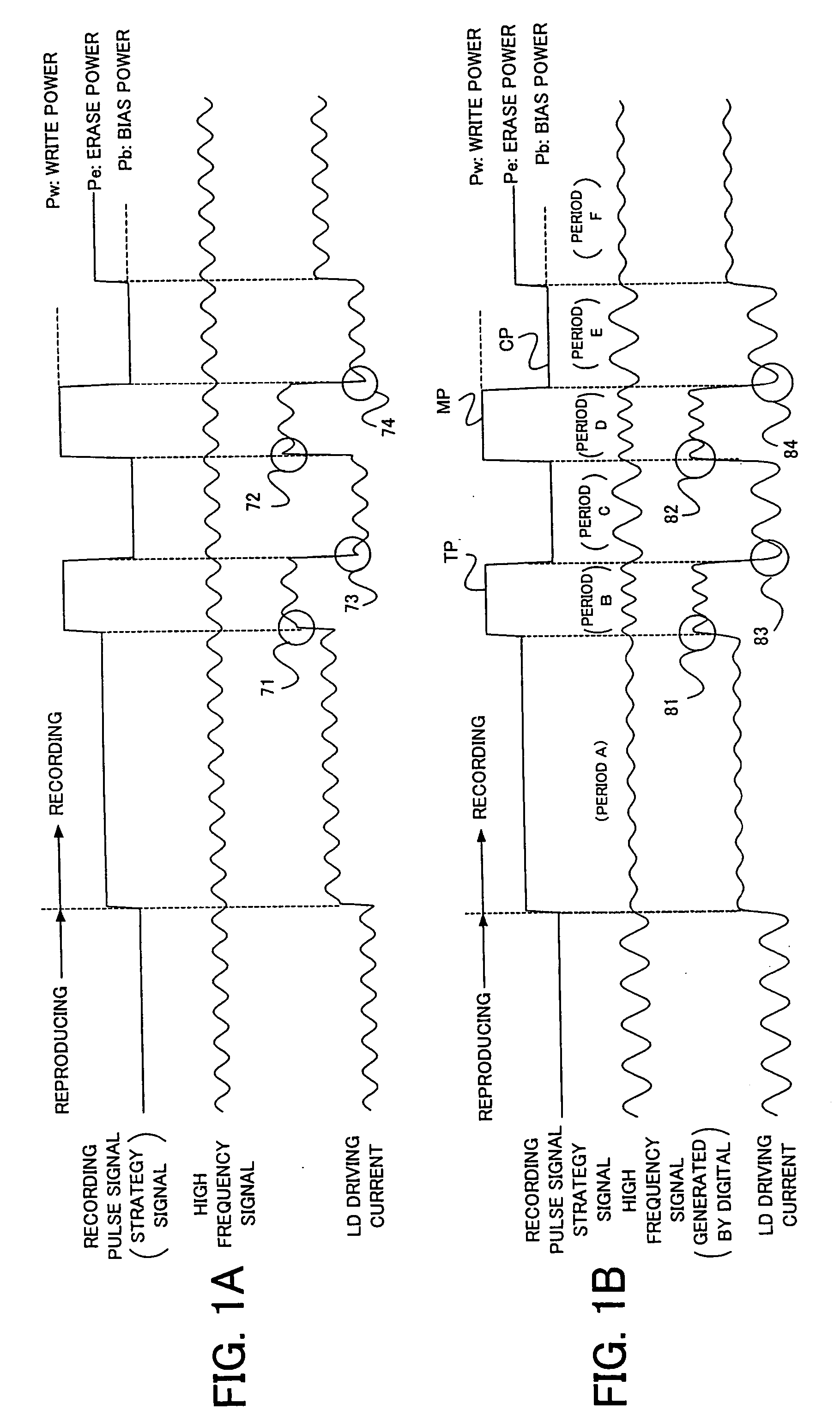
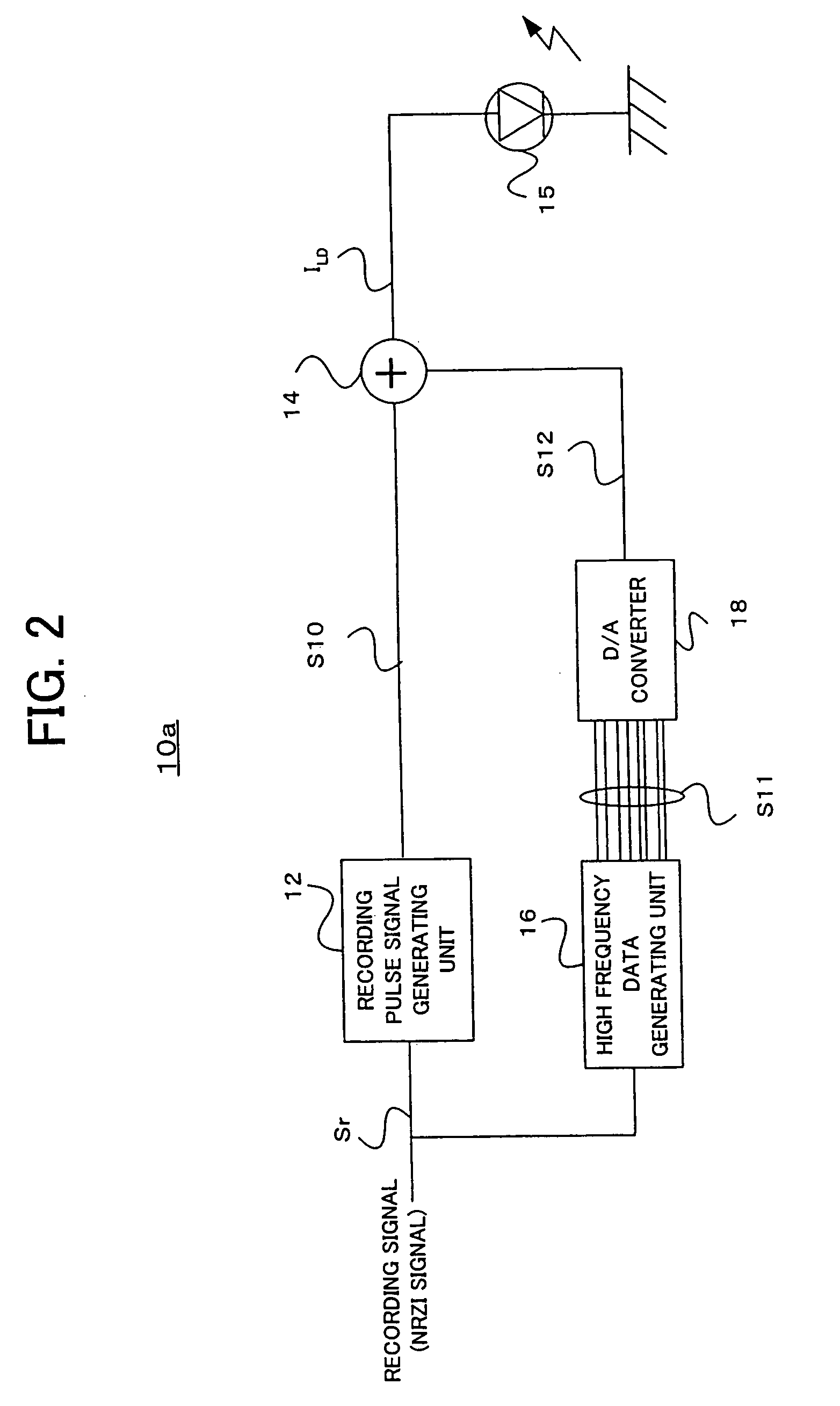
InactiveUS20050030871A1Quality improvementReduce impactTelevision system detailsRecording strategiesOptoelectronicsLaser light
An information recording apparatus irradiates a recording light, such as a laser light, on a recording medium, such as various kinds of optical discs, and records information. A recording pulse signal is generated based on a recording signal corresponding to the information to be recorded. The recording pulse signal is also called “strategy signal”, and the signal includes driving pulses which drive a light source for forming a recording mark on the recording medium. As to the recording light such as the laser light, the high frequency signal is superimposed for decreasing occurrence of noise due to mode hopping. The high frequency signal is generated as a digital signal, and the signal is added to the recording pulse signal to generate a driving pulse signal. Then, the light source is driven and the recording light is emitted. By generating the high frequency signal as the digital signal, it is possible to control a frequency and a phase thereof with high accuracy.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Swept mode-hopping laser system, methods, and devices for frequency-domain optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS9488464B1Intensity fluctuationShort transition timeLaser detailsUsing optical meansLaser lightOptical communication
In part, the invention relates to frequency-domain optical coherence tomography system. The system includes a tunable laser comprising a laser output for transmitting laser light and a laser cavity having a length L, a gain element disposed within the laser cavity; a tunable wavelength selective element disposed within the laser cavity; a reference reflector disposed outside of the laser cavity; an interferometer in optical communication with the laser output and the reference reflector, wherein the interferometer is configured to transmit a portion of the laser light to a sample and combine light scattered from the sample with light scattered from the reference reflector; and a detector in optical communication with the interferometer that receives the combination of light scattered from the sample and the light scattered from the reference reflector and transforms the combination of light into an electronic signal comprising measurement data with respect to the sample.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Method and apparatus for long-range lidar and active imaging with optical output from a photonic-crystal rod
InactiveUS7375877B1High peak powerHigh pulse energyGlass making apparatusLaser constructional detailsEngineeringMultiple modes
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ACULIGHT CORP
Fiber bragg grating temperature/strain sensing system and demodulation method thereof
ActiveCN108120525AReduced Power RequirementsSolve the problem of deterioration of strain accuracyThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansInjection lockedPhase noise
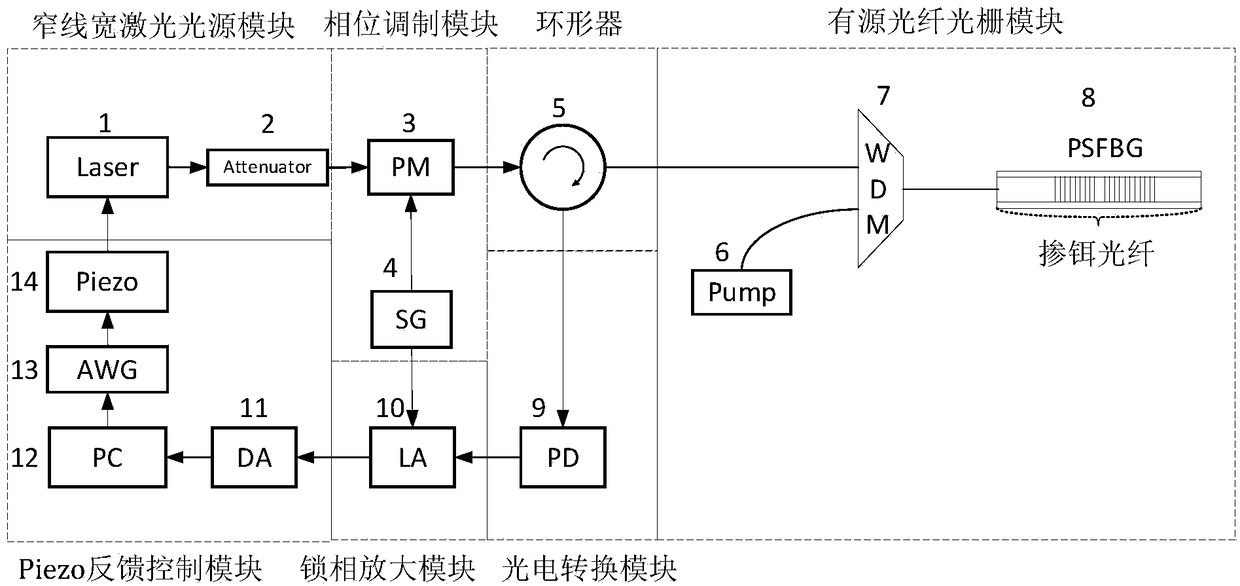
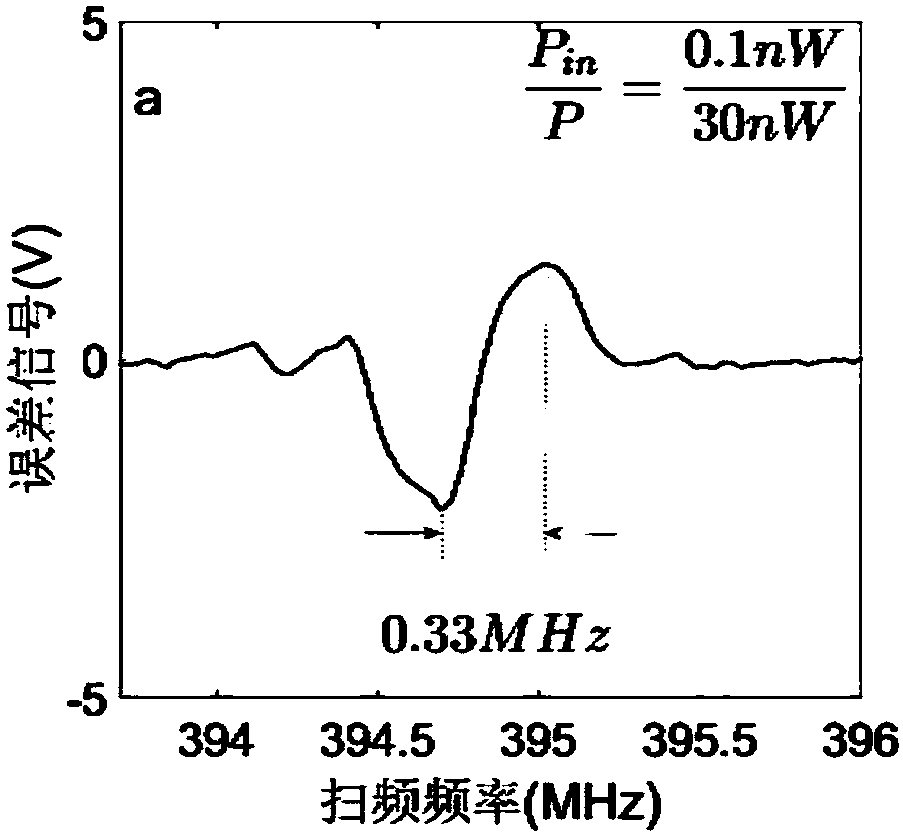
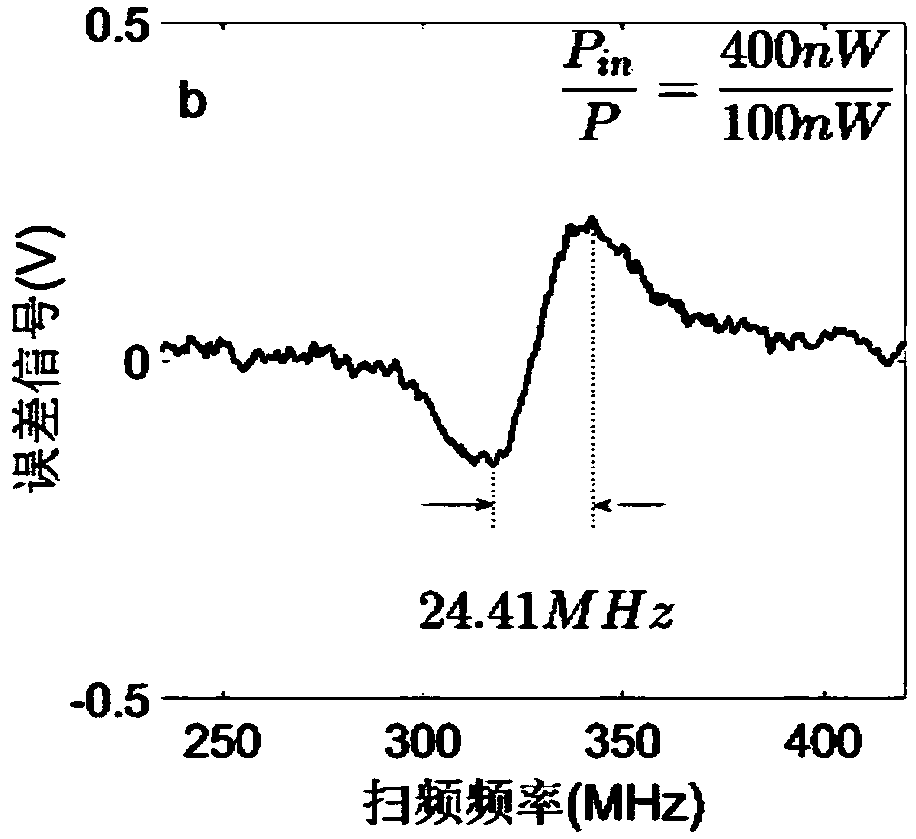
The invention relates to a fiber bragg grating temperature / strain sensing system and a demodulation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: after seed layer generated by a narrow linewidth laser light source module generates a sideband through a phase modulation module, injecting into active fiber grating stimulated by pump light through a circulator and a wavelength division multiplexer in an active fiber grating module; and performing photovoltaic conversion on return light and a photoelectric detector connected with the circulator to acquire a beat frequency signal, extracting a component, namely an error signal reflecting the center frequency deviation between the narrow linewidth laser and the active fiber grating, at the phase modulation frequency position by a phase-locked amplifier, and generating a feedback voltage signal by a feedback control module by virtue of the error signal to control the center frequency of the narrow linewidth laser so as to realize injection locking between the narrow linewidth laser and the active fiber grating. The quasi-static accuracy of p-epsilon can be achieved; the characteristic of adjustable strain sensitivity is achieved; and the problems of mode jump, relaxation shock and low-frequency phase noise in a fiber laser sensor can be effectively solved.
Owner:宁波联河光子技术有限公司
A method of producing stable full-time low-noise laser output
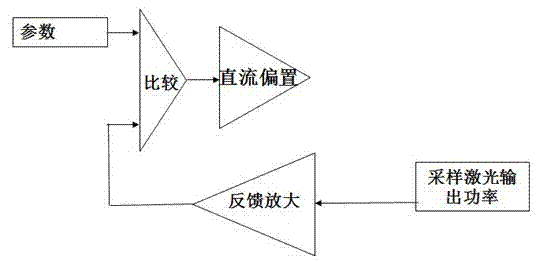
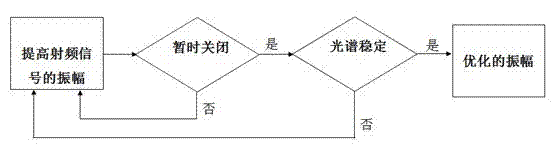
ActiveCN102290706AIncrease amplitudeOptimizing RF modulationLaser detailsLaser output parameters controlLow noiseImpedance matching
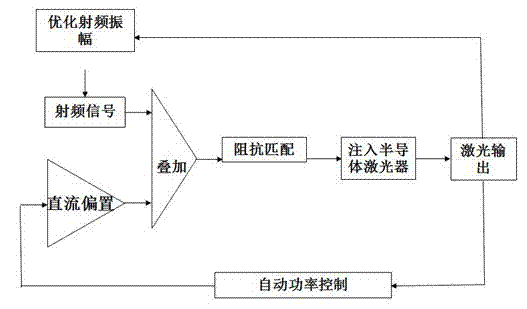
The invention discloses a method for generating stable, full-time low noise laser output. The method includes the following steps: regulating and maintaining a semiconductor laser operating temperature by means of a thermoelectric controller (TEC) attached on the laser; generating a direct-current bias from a direct-current generator; generating an amplitude-modulatable radio frequency signal from a local oscillator; superposing the radio frequency signal onto the direct-current bias to generate amplitude-modulatable drive current; injecting the amplitude-modulatable drive current into the semiconductor laser by way of input-coupled impedance matching; regulating the direct-current bias by means of an automatic power control circuit; and optimizing the amplitude of the radio frequency signal. By modulating the driving of the semiconductor laser diode, the method effectively overcomes the mode hopping phenomenon, the method is applicable to laser diodes with various wavelengths, the generated laser output has the advantages of low coherence, low noise, little speckles, long-time stable output power and long-time uniform beam illumination, and the method is particularly suitable forbiomedicine and medical diagnosis and clinic.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION CORP SUZHOU
Photonic-crystal-rod amplifiers for high-power pulsed optical radiation and associated method
InactiveUS7379237B1High peak powerHigh pulse energyGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical radiationEngineering
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
External cavity laser with reduced optical mode-hopping
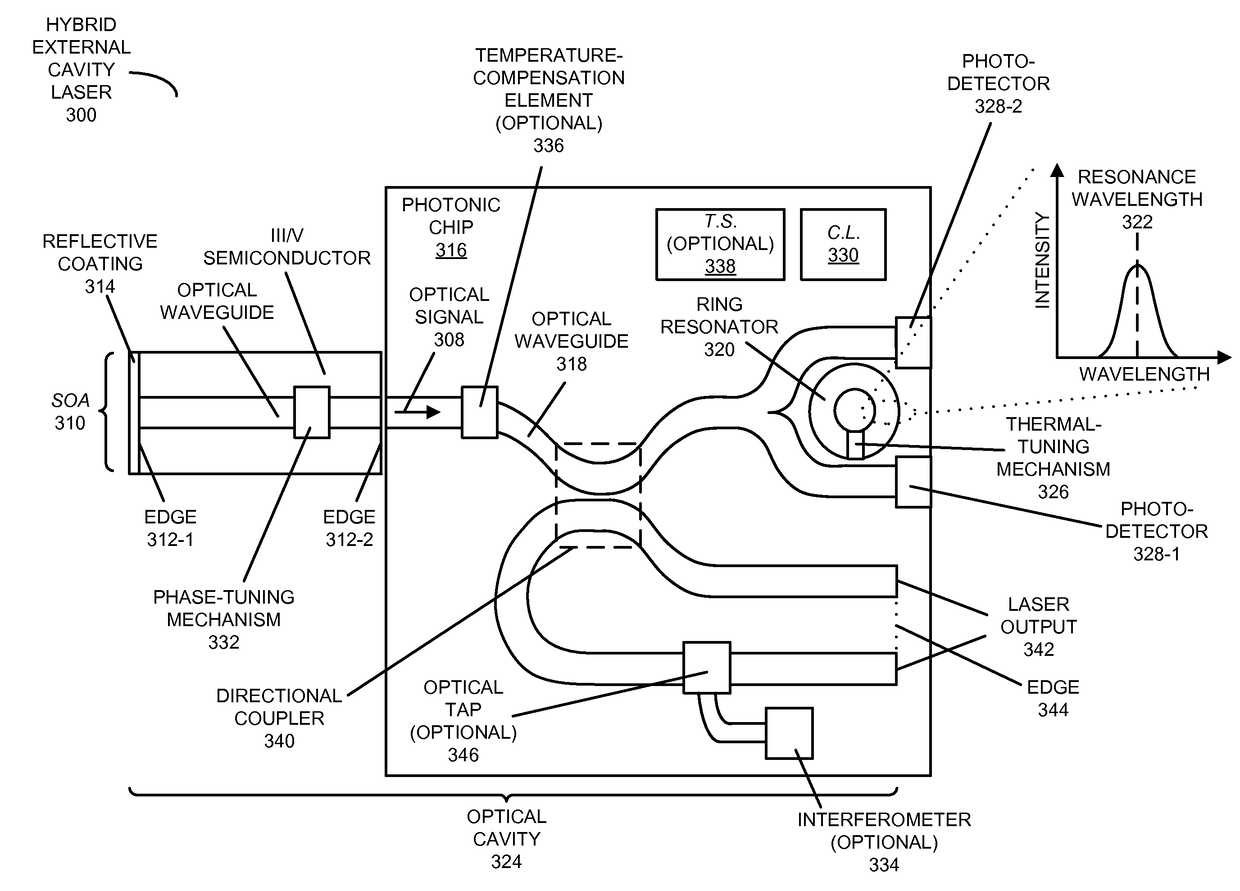
ActiveUS20170324218A1Minimize measured optical powerLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionExternal cavity laserCarrier signal
An optical source is described. This optical source includes a semiconductor optical amplifier (with a semiconductor other than silicon) that provides an optical gain medium and that includes a reflector. Moreover the hybrid external cavity laser includes a photonic chip with: an optical waveguide that conveys an optical signal output by the semiconductor optical amplifier; and a ring resonator, having a resonance wavelength, which reflects at least a resonance wavelength in the optical signal, where the reflector and the ring resonator define an optical cavity. Furthermore, the photonic chip includes: a thermal-tuning mechanism that adjusts the resonance wavelength; a photo-detector that measures an optical power output by the ring resonator; and control logic that adjusts the temperature of the ring resonator based on the measured optical power to lock a cavity mode of the optical cavity to a carrier wavelength.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Mode hopping swept frequency laser for FD OCT and method of operation
InactiveUS8059277B2Increase speedDwell time highLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansBeam splitterLength wave
A frequency swept laser source that generates an optical signal that is tuned over a spectral scan band at single discrete wavelengths associated with longitudinal modes of the swept laser source. Laser hopping over discrete single cavity modes allows long laser coherence length even under dynamic very high speed tuning conditions. A ramp drive to the laser is used to linearize laser frequency tuning. A beam splitter is used to divide the optical signal between a reference arm leading to a reference reflector and a sample arm leading to a sample. A detector system detects the optical signal from the reference arm and the sample arm for generating depth profiles and images of the sample.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Stabilized near-infrared laser
InactiveUS20100027571A1Minimizing mode-hoppingActive medium shape and constructionNear infrared laserOptical pumping
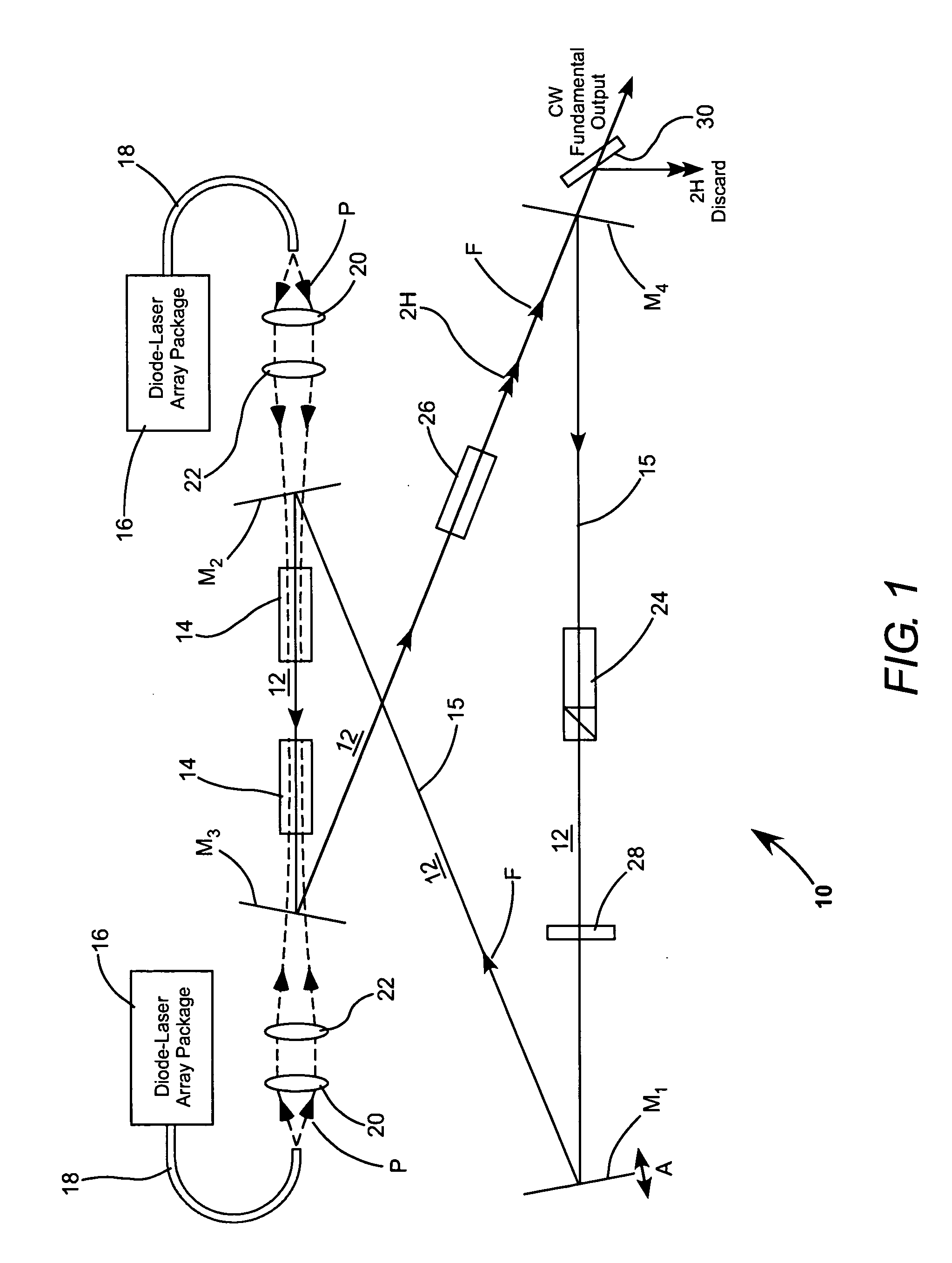
A traveling wave ring-resonator is configured to deliver CW single-longitudinal-mode radiation having a fundamental wavelength characteristic of an optically pumped gain-element in the resonator. The delivered fundamental-wavelength radiation is the output-radiation of the resonator. An optically nonlinear crystal is located in the resonator and arranged to convert a fraction of fundamental-wavelength radiation into second harmonic radiation. The conversion of this fraction of fundamental-wavelength radiation to second-harmonic radiation minimizes mode-hopping in the output radiation.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Semiconductor laser all-fiber frequency stabilizing system
InactiveCN101694921AGuaranteed Polarization CharacteristicsImprove anti-interference abilityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersFrequency stabilizationFinesse
The invention discloses a semiconductor laser all-fiber frequency stabilizing system, which belongs to the field of laser frequency-sweeping interferometery. The frequency stabilizing system consists of a non-mode-hopping frequency scanning semiconductor laser, an all-fiber reference interferometer, a high-finesse fiber ring resonator and a data acquisition processing and controlling system. In the semiconductor laser all-fiber frequency stabilizing system, the all-fiber reference interferometer is used for monitoring frequency changes of an external-cavity semiconductor laser, and frequency of the laser is stabilized to be equal to resonance frequency of the fiber ring resonator by using a feed back method when the laser frequency approaches resonance frequency of the fiber ring resonator after scanning. The semiconductor laser all-fiber frequency stabilizing system has the advantages of small volume, light weight, high precision and fine stabilizing degree and is adaptable to laser frequency-sweeping interferometering systems.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Gas concentration detection method and device
InactiveCN1908624AMeasurement accuracy is irrelevantColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsAudio power amplifierGas detector
The gas detector device comprises at least a VCSEL source and at least a light sensor for detecting a light beam having passed through a sample chamber containing a given gas to be detected. The detection signal of the sensor directly provided to or is time derivated by an electronic derivator and then provided to respective lock-in amplifiers in order to generate a two different 2f-detection, f being the frequency of a wavelength modulation of the source, and thus to provide two corresponding measuring signals the division of which gives a precise value of the gas concentration. The invention uses at least a first modulation reference signal at twice and a second modulation reference signal at twice of the modulation frequency of the laser source. Providing at least a first 2f modulation reference signal has advantages over the prior art, because by using such a reference modulation signal it is possible measure the absolute intensity and therefore to receive the same result at different temperatures or at mode hopping of the laser. A further advantage is that the measurement accuracy is independent from the gas concentration.
Owner:IR MICROSYST
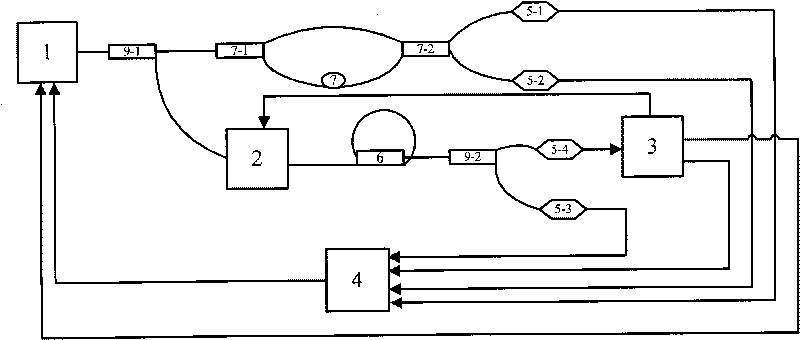
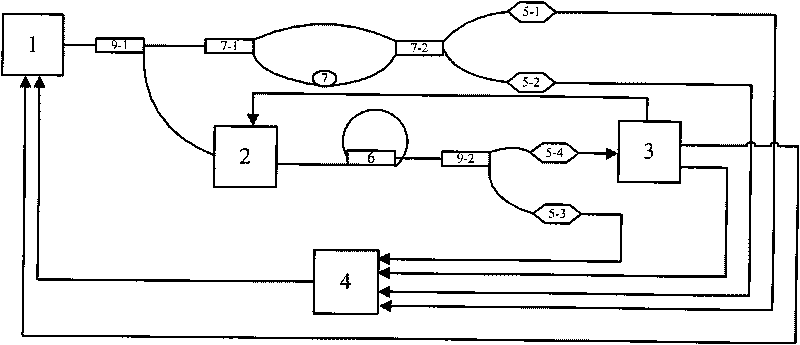
Littrow-structure tunable external-cavity laser and mode-hopping-free sweep-frequency regulation method thereof
ActiveCN103151703AOptical cavity length compensationAchieve mode-hop-free tuningLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlGratingExternal cavity laser
The invention relates to a Littrow-structure tunable external-cavity laser and a mode-hopping-free sweep-frequency regulation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of laser tuning. The problem that the existing Littrow-structure external-cavity laser cannot realize large-scale mode-hopping-free tuning is solved. The Littrow-structure tunable external-cavity laser comprises a semiconductor laser, a liquid crystal spatial light modulator and a blazed grating. The mode-hopping-free sweep-frequency regulation method comprises the steps that laser beams which are emitted by the semiconductor laser are enabled to pass through the liquid crystal spatial light modulator and then to be incident onto the blazed grating, first-order diffracted light which passes through the blazed grating and returns back along the original path forms resonance between the inner cavity and the outer cavity of the tunable external-cavity laser, and finally the light emerges from the zero order of the blazed grating; and the blazed grating is rotated around an axis point O, the voltage of the liquid crystal spatial light modulator is changed at the same time to change the refractive index of the liquid crystal spatial light modulator and the mode-hopping-free sweep-frequency regulation of the tunable external-cavity laser is realized during tuning by rotating the blazed grating. The mode-hopping-free sweep-frequency regulation method is applicable to the regulation of lasers.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Manufacturing method of multi-color and multi-functional EVA sports and leisure sole
InactiveCN106750871AImprove seismic performanceAvoid crackingDomestic footwearEngineeringWear resistance
The invention relates to the technical fields of shoes and particularly relates to a manufacturing method of a multi-color and multi-functional EVA sports and leisure sole. The method comprises the following steps of manufacturing first EVA particles and second EVA particles according to the formula separately; injecting the two EVA particles into a mold corresponding to an injection device for prefabricating and molding; cooling and opening the mold so as to obtain a pre-foamed sole base of a sole main body and a pre-foamed sole base of a functional part separately; putting the two sole bases into different positions in a foaming mold separately, and carrying out foam molding to obtain a crude foamed sole product; and carrying out mode hopping on the crude foamed sole product and then carrying out gradient cooling, setting by cooling and trimming to obtain the multi-color and multi-functional EVA sports and leisure sole. The manufacturing method is simple in process, low in production cost, high in production efficiency and low in defect rate; the prepared multi-color and multi-functional EVA sports and leisure sole has the advantages of being light, good in damping property, good in elasticity, good in wear resistance and good in slip resistance, and is convenient to wear; and the functional part does not easily fall off from the sole main body.
Owner:GUANGDONG GUOLI SCI & TECH CO LTD
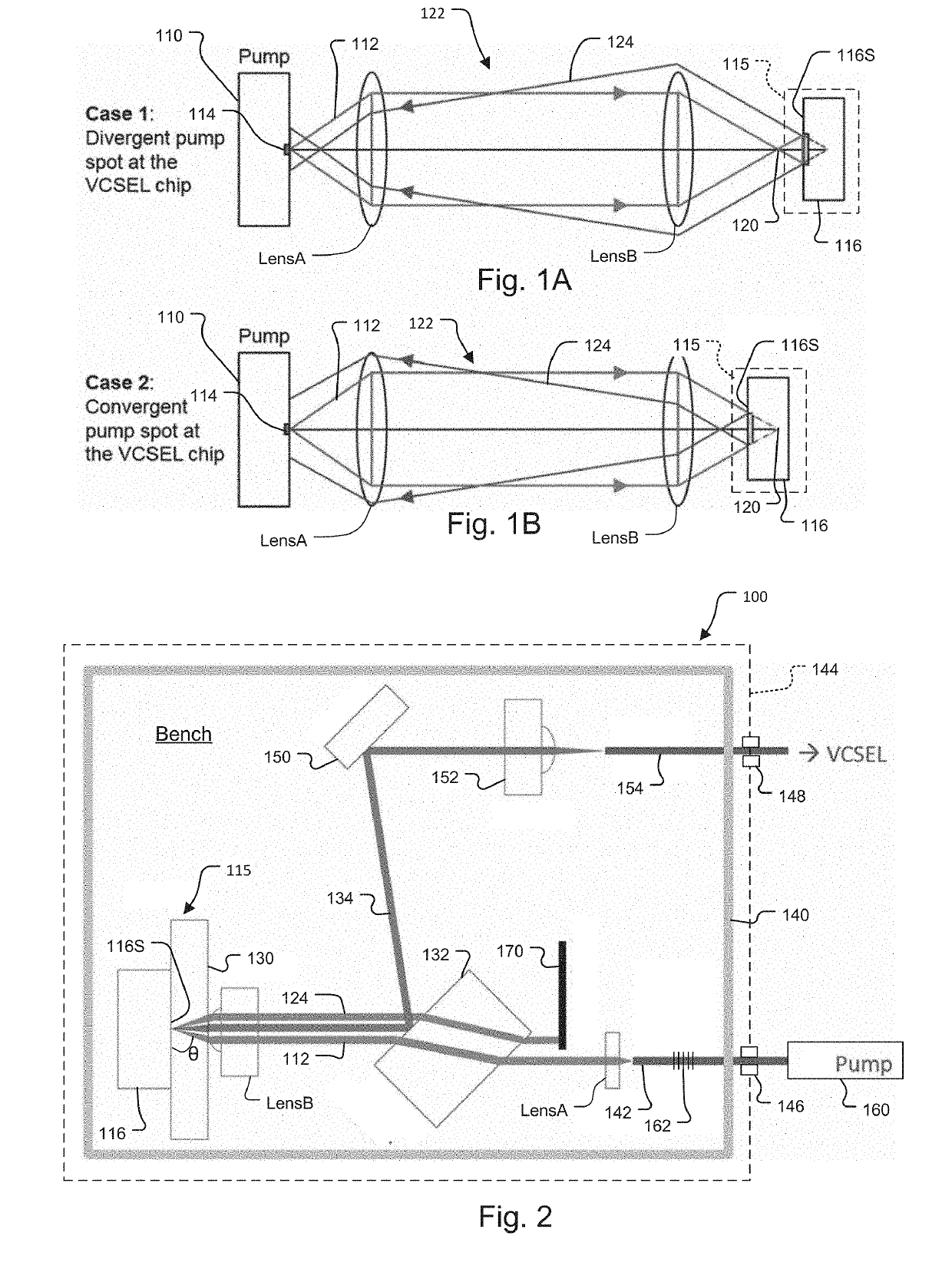
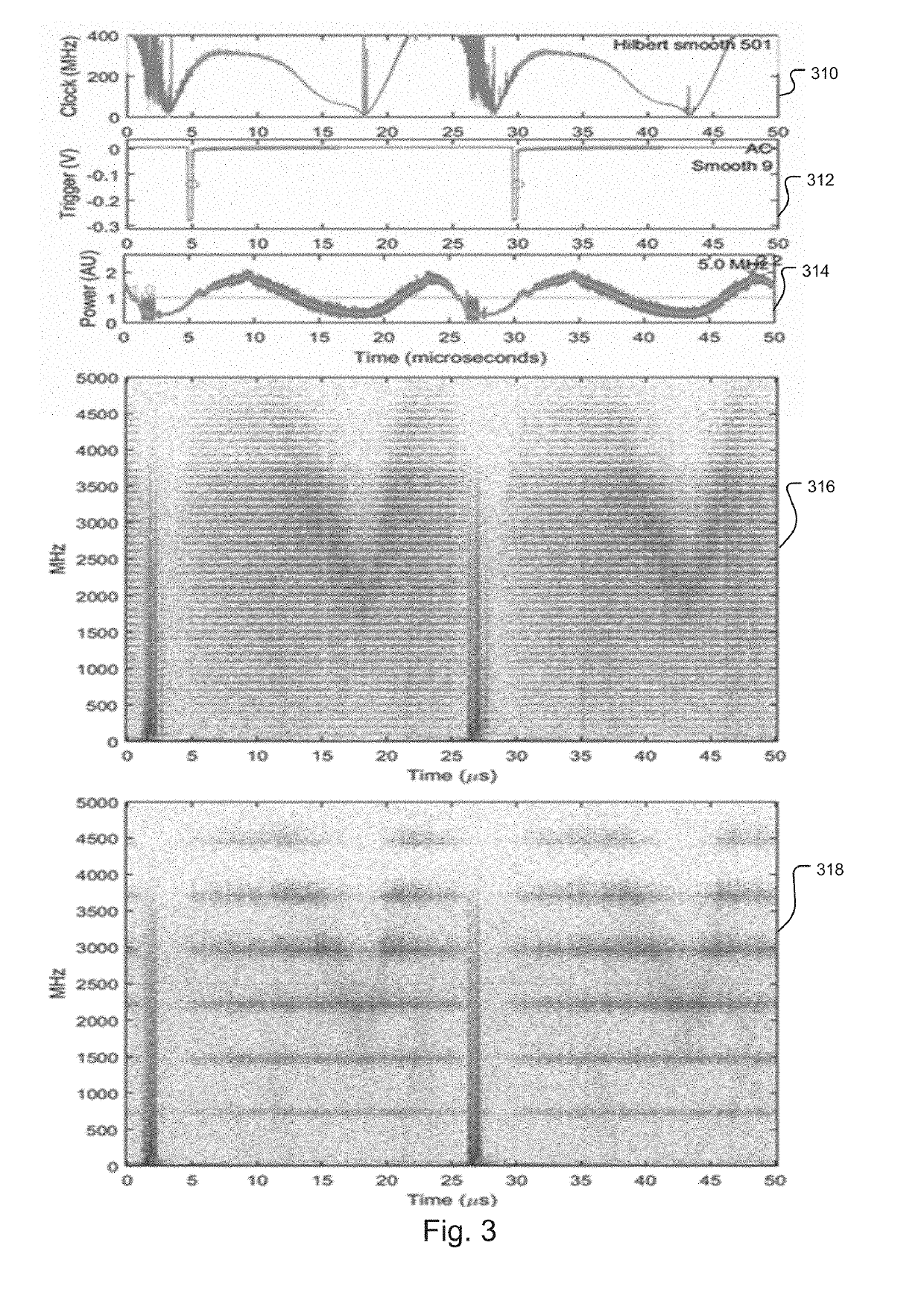
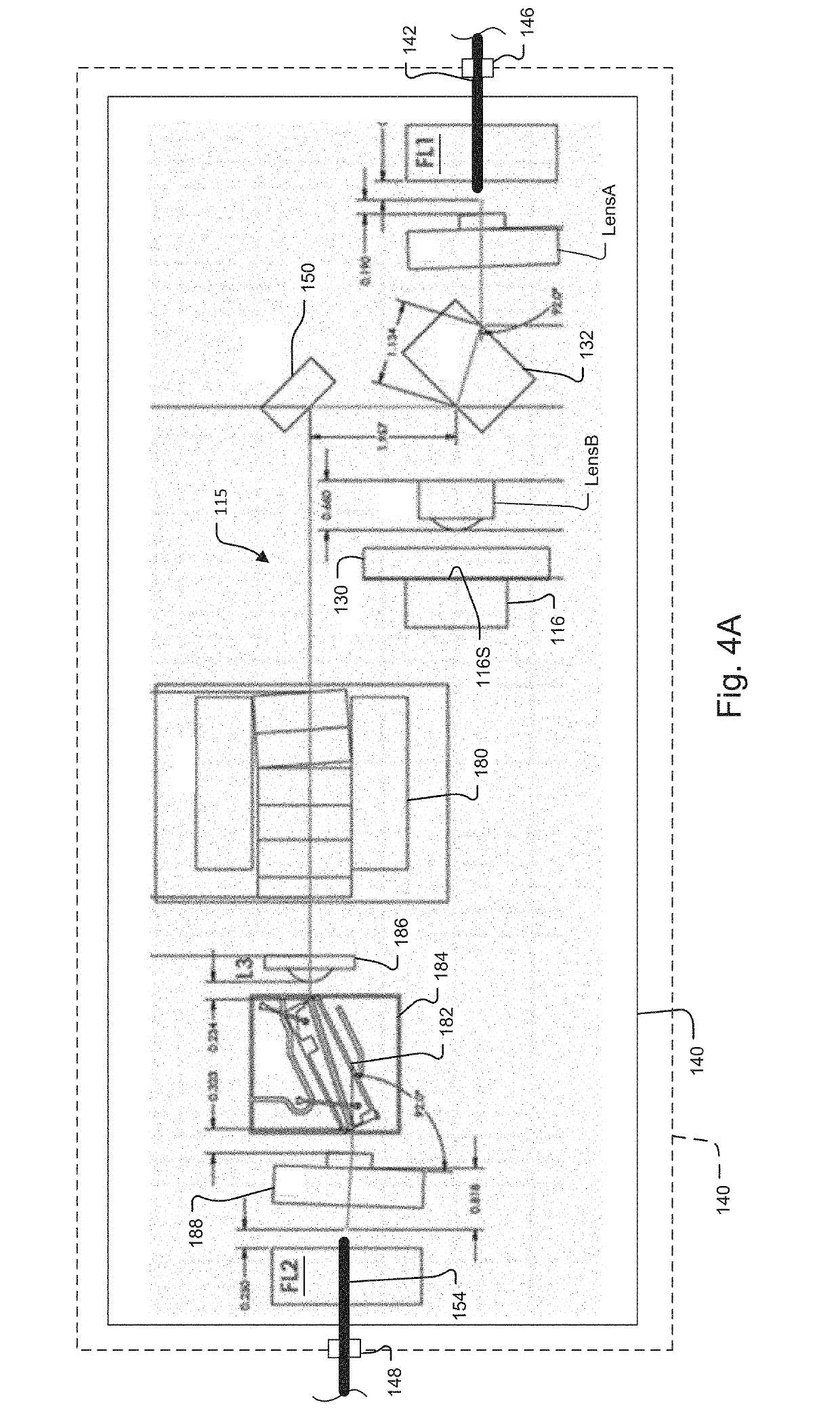
Optically pumped tunable VCSEL employing geometric isolation
ActiveUS20190348813A1Reduce feedbackRemove noiseOptical wave guidanceExcitation process/apparatusDistributed feedback laserDistributed Bragg reflector laser
An optically pumped tunable VCSEL swept source module has a VCSEL and a pump, which produces light to pump the VSCEL, wherein the pump is geometrically isolated from the VCSEL. In different embodiments, the pump is geometrically isolated by defocusing light from the pump in front of the VCSEL, behind the VCSEL, and / or by coupling the light from the pump at an angle with respect to the VCSEL. In the last case, angle is usually less than 88 degrees. There are further strategies for attacking pump noise problems. Pump feedback can be reduced through (1) Faraday isolation and (2) geometric isolation. Single frequency pump lasers (Distributed feedback lasers (DFB), distributed Bragg reflector lasers (DBR), Fabry-Perot (FP) lasers, discrete mode lasers, volume Bragg grating (VBG) stabilized lasers can eliminate wavelength jitter and amplitude noise that accompanies mode hopping.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Control method and control device for single-mode stability of laser
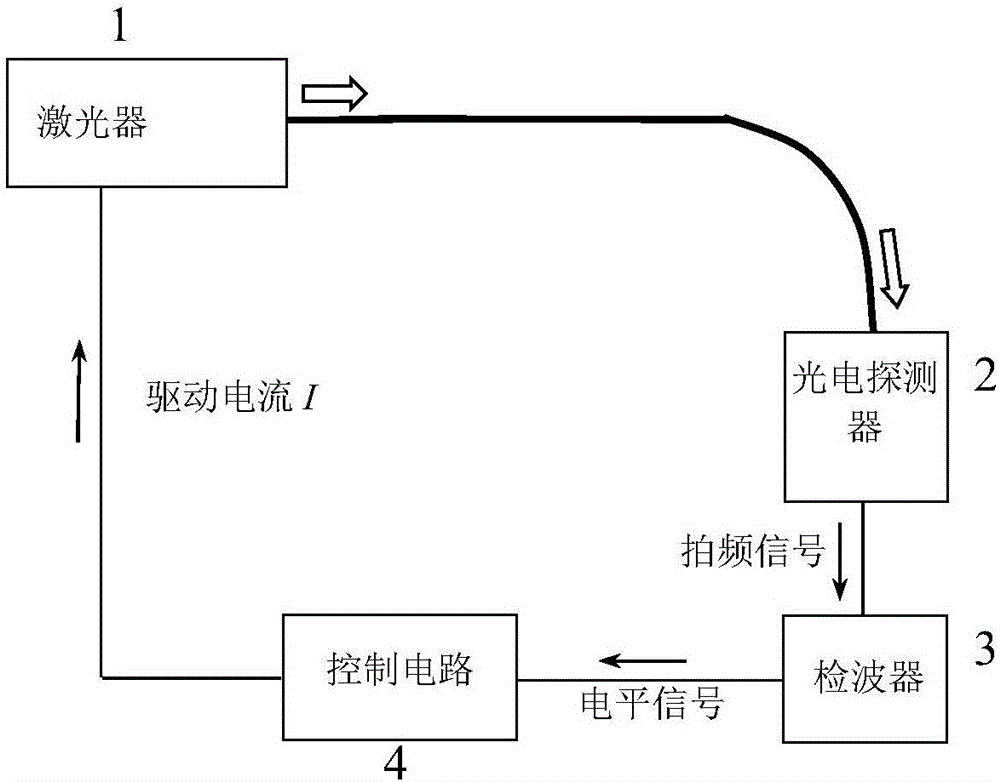
InactiveCN106451059AImprove stabilityEliminate coexistenceLaser detailsDriving currentPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention provides a control device and a control method for the single-mode stability of a laser. The control device comprises the laser, a photoelectric detector, a detector and a control circuit, wherein the photoelectric detector is used for detecting a laser signal generated by the laser and performing frequency beating on a main mode and a side mode in the laser signal to generate a frequency beating signal; the detector is used for measuring the power of the frequency beating signal, and transmitting a level signal corresponding to the frequency beating signal in power to the control circuit; the control circuit is used for adjusting driving current of the laser according to the level signal until the level signal reaches a preset threshold range. According to the control device and the control method provided by the invention, the laser is enabled to always work in a better single-mode state, the side mode is suppressed, and the phenomena of coexistence of dual modes and mode hopping are eliminated, thereby improving the stability of single-mode working of the laser.
Owner:THE 44TH INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Tunable semiconductor laser with Littman-structured outer cavity
InactiveCN105932541AGuaranteed stretching in a straight lineNo assembly errorsLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionArchitectural engineeringFrequency modulation
The invention discloses a tunable semiconductor laser with a Littman-structured outer cavity. The tunable semiconductor laser comprises a base, a supporting base, an optical path adjustment accessory, a raster base, a reflecting mirror base, a sleeve base, a one-dimensional flexible platform and a flexible hinge, wherein the supporting base is fixed on the horizontally-arranged base; the supporting base comprises a bottom plate and a supporting table, wherein the cantilever of the supporting table is arranged on the bottom plate; the optical path adjustment accessory, the raster base and the flexible hinge are fixed on the bottom plate; a vertical mounting plane is arranged on the supporting table; the one-dimensional flexible platform is mounted on the vertical mounting plane; the one-dimensional flexible platform is provided with a mounting part used for mounting the sleeve base; the sleeve base is mounted on the mounting part through a semiconductor cooler; the flexible hinge is hinged with the cantilever; a PZT used for pushing the cantilever to swing around the hinge is also mounted on the flexible hinge; the reflecting mirror base is fixed at the tail end of the cantilever; and a reflecting mirror mounting part is arranged at the upper part of the reflecting mirror base in a cantilever-shaped manner. The tunable semiconductor laser with the Littman-structured outer cavity can realize large-range frequency modulation without mode hopping.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Surface-emitting laser and optical apparatus formed by using surface-emitting laser
InactiveUS7830944B2Improve light outputMirrorsOptical filtersDistributed Bragg reflectorOptoelectronics
A surface-emitting laser has an active layer between a first distributed Bragg reflector and a second distributed Bragg reflector. The first distributed Bragg reflector is formed so as to have a resonant mode and a first longitudinal mode different from the resonant mode included in the reflectivity stop band and a second longitudinal mode different from the resonant mode and the first longitudinal mode excluded from the reflectivity stop band. Oscillation is suppressed in the first longitudinal mode and in the second longitudinal mode. As a result, the surface-emitting laser can oscillate in a single longitudinal mode, suppressing longitudinal mode hopping.
Owner:CANON KK
Single chip integrated semiconductor laser with tunable wavelength and without mode hopping
The invention discloses a monolithic integrated mode-hop-free wavelength tunable semiconductor laser which comprises an optical cavity consisting of a waveguide end surface and a wavelength dispersive diffraction grating, an active waveguide arranged at one side of the optical cavity and providing gains and a wavelength dispersive diffraction grating arranged at the other side of the optical cavity and applied as a filter to select lasing wavelength; a planar waveguide area and a wavelength tuning area are arranged between the active waveguide and the wavelength dispersive diffraction grating and the wavelength tuning area is clamped between a pair of electrodes. Effective refractive index of the wavelength tuning area is changed by an electric effect so as to adjust the wavelength of a grating filter as well as the length of the optical cavity, so that the adjustment of the laser mode wavelength is synchronous with that of wavelength of the grating filter, thus realizing mode-hop-free continuous tuning. The design structure can be used for multiband integrated tunable lasers and multi-wavelength tunable laser array.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Piezo activated mode tracking system for widely tunable mode-hop-free external cavity mid-IR semiconductor lasers
InactiveUS7733924B2High resolutionWide tunabilityOptical resonator shape and constructionNanoopticsAnti-reflective coatingSemiconductor
A widely tunable, mode-hop-free semiconductor laser operating in the mid-IR comprises a QCL laser chip having an effective QCL cavity length, a diffraction grating defining a grating angle and an external cavity length with respect to said chip, and means for controlling the QCL cavity length, the external cavity length, and the grating angle. The laser of claim 1 wherein said chip may be tuned over a range of frequencies even in the absence of an anti-reflective coating. The diffraction grating is controllably pivotable and translatable relative to said chip and the effective QCL cavity length can be adjusted by varying the injection current to the chip. The laser can be used for high resolution spectroscopic applications and multi species trace-gas detection. Mode-hopping is avoided by controlling the effective QCL cavity length, the external cavity length, and the grating angle so as to replicate a virtual pivot point.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Wavelength tunable semiconductor laser apparatus
InactiveUS20060203858A1Increase distanceHigh precisionLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersGratingLength wave
The present invention relates to wavelength tunable DBR semiconductor laser devices in which light waves generated from a plurality of laser portions (or laser channels) are combined. This type of semiconductor laser device requires that the laser channels together cover an entire desired wavelength range, allowing the oscillation wavelength to be continuously varied over this range. However, to accomplish this, it is necessary to employ highly accurate crystal growth and process techniques. Furthermore, the length of the gain region must be reduced to increase the range over which the oscillation wavelength can be continuously varied, making it difficult to achieve laser oscillation. Two laser channels operate in combination, and a combiner combines the light waves emitted from these laser portions (or laser channels) so as to cover one entire wavelength range. Specifically, an inter-grating element distance Lgrt1 of the first laser portion is set larger or smaller than an inter-grating element distance Lgrt2 of the second laser portion by one half of the grating pitch. This allows these laser portions to exhibit different mode-hopping DBR current values appropriately adjusted against each other and thereby together cover a desired wavelength range.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
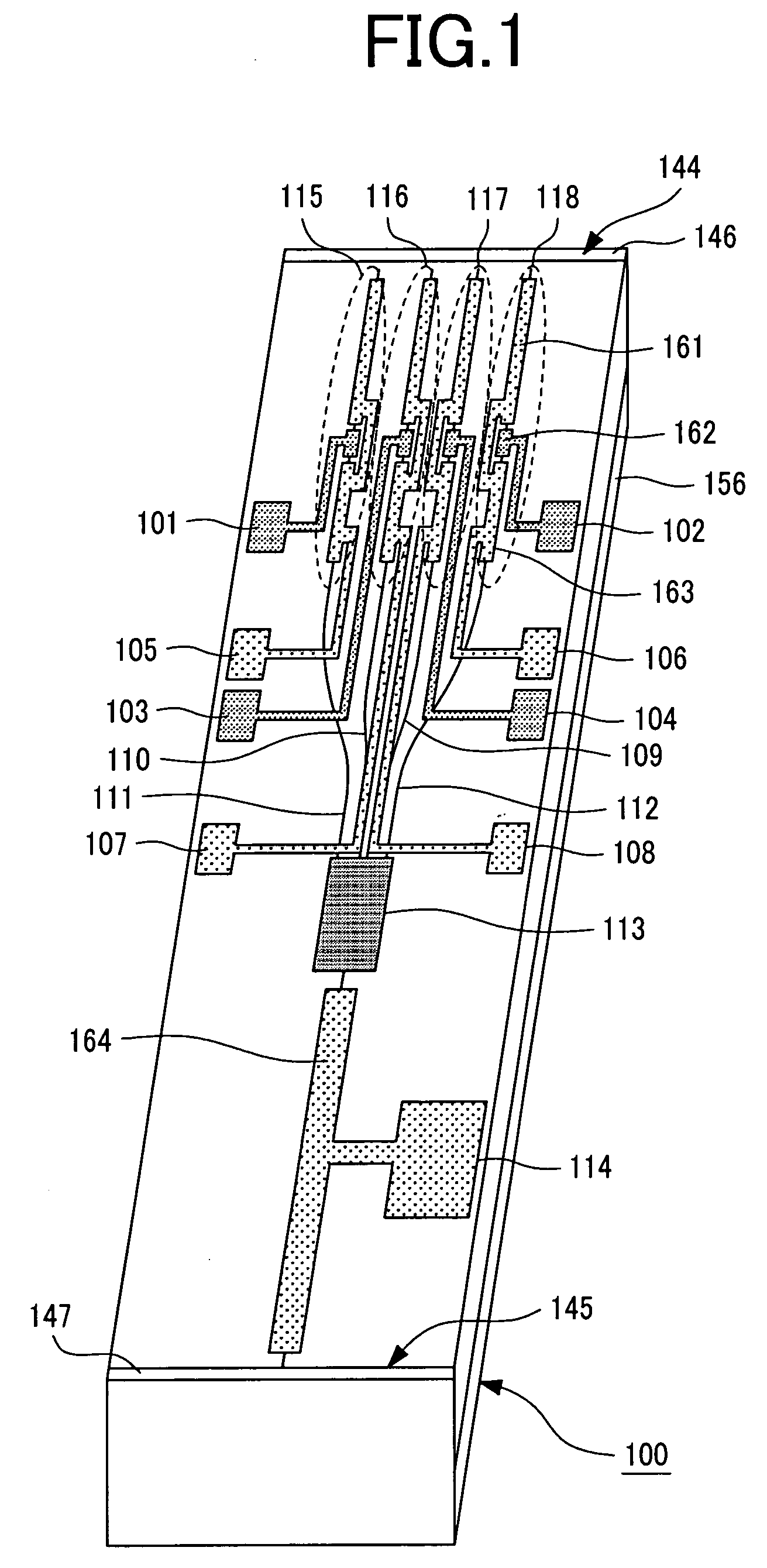
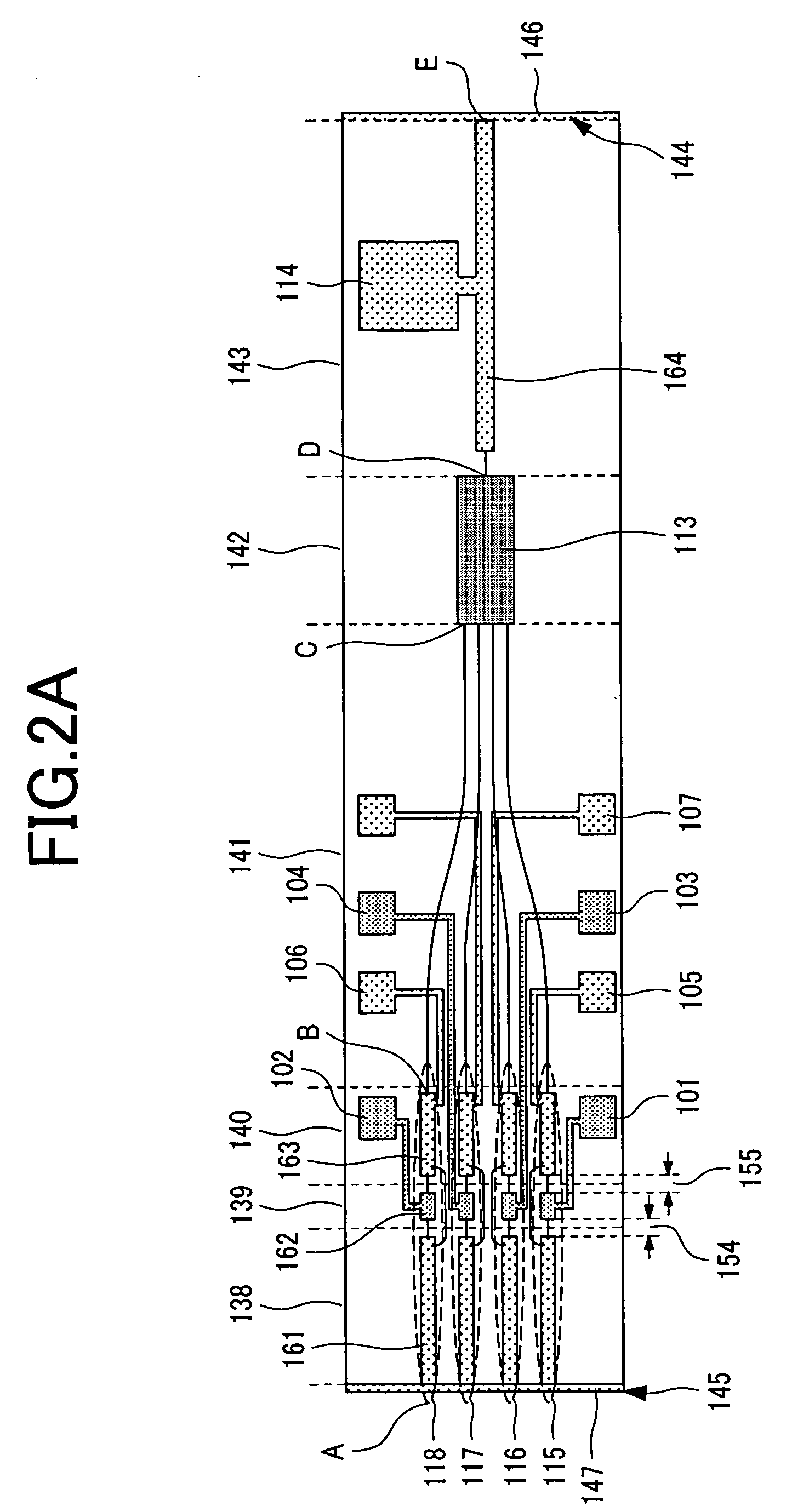
Super-high spectral resolution gas medium wave infrared spectrum measurement system
InactiveCN103091283AMeasurement applicableDuring the measurement, the measurement appliesColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectrometerLongitudinal mode
The invention discloses a super-high spectral resolution gas medium wave infrared spectrum measurement system which is composed of a no-longitudinal mode broadband medium wave infrared laser source, a gas absorption tank and a super-high resolution spectrograph, wherein the no-longitudinal mode broadband medium wave infrared laser source directly spatially enters the gas absorption tank by virtue of an optical system and enters the super-high resolution spectrograph to obtain a to-be-measured gas absorption spectrum after exiting from the gas absorption tank. By adopting the no-longitudinal mode broadband medium wave infrared laser source, an incident light source has the characteristics that spectral components are continuous and spectrum is stable among different laser pulses, and spectrum measurement of the super-high resolution spectrograph can not be affected by mode jump. Therefore, the super-high spectral resolution gas medium wave infrared spectrum measurement system has sky-high spectral resolution, can be used for measuring slight change of the gas absorption spectrum, and is suitable for measurement of a trace gas.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com