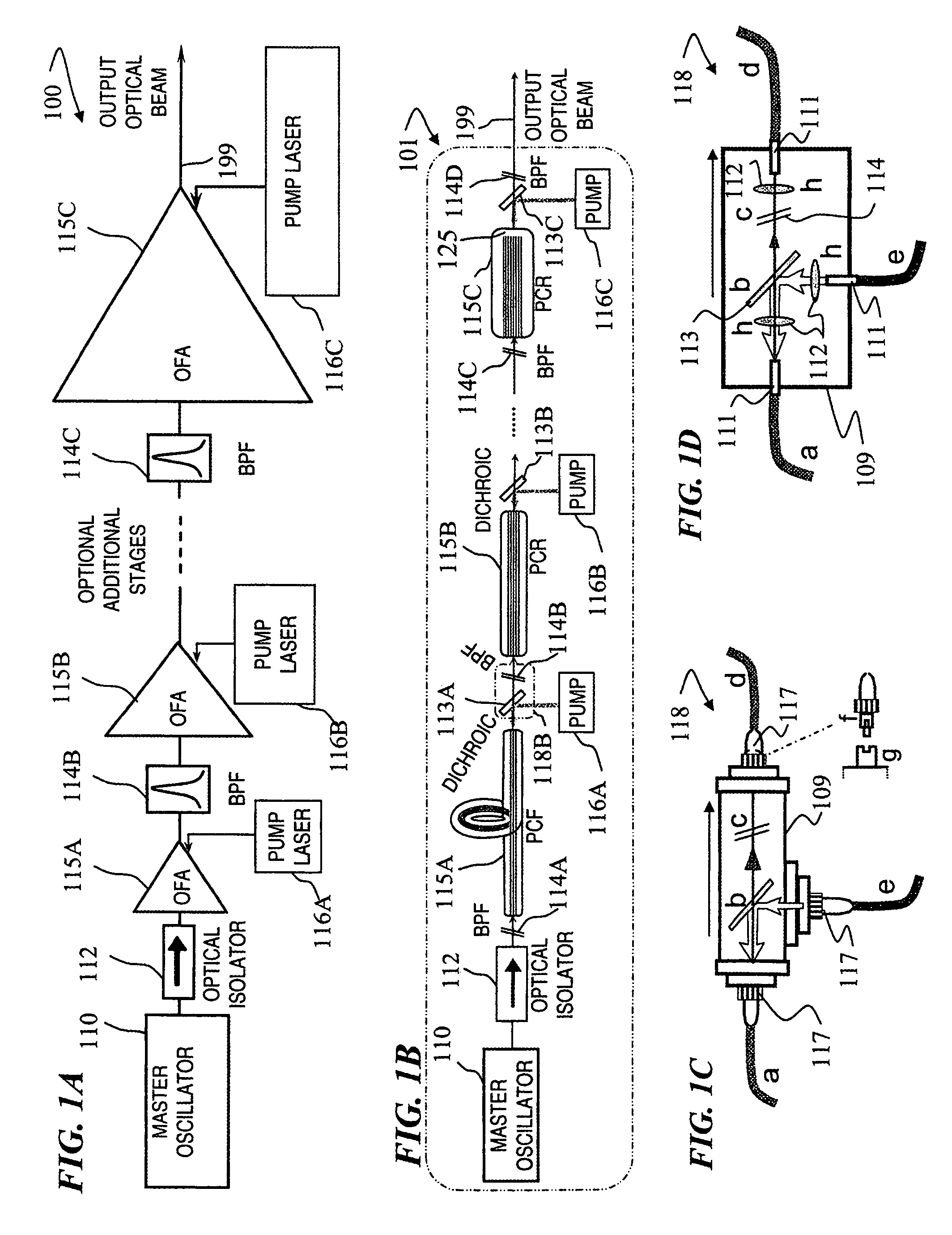
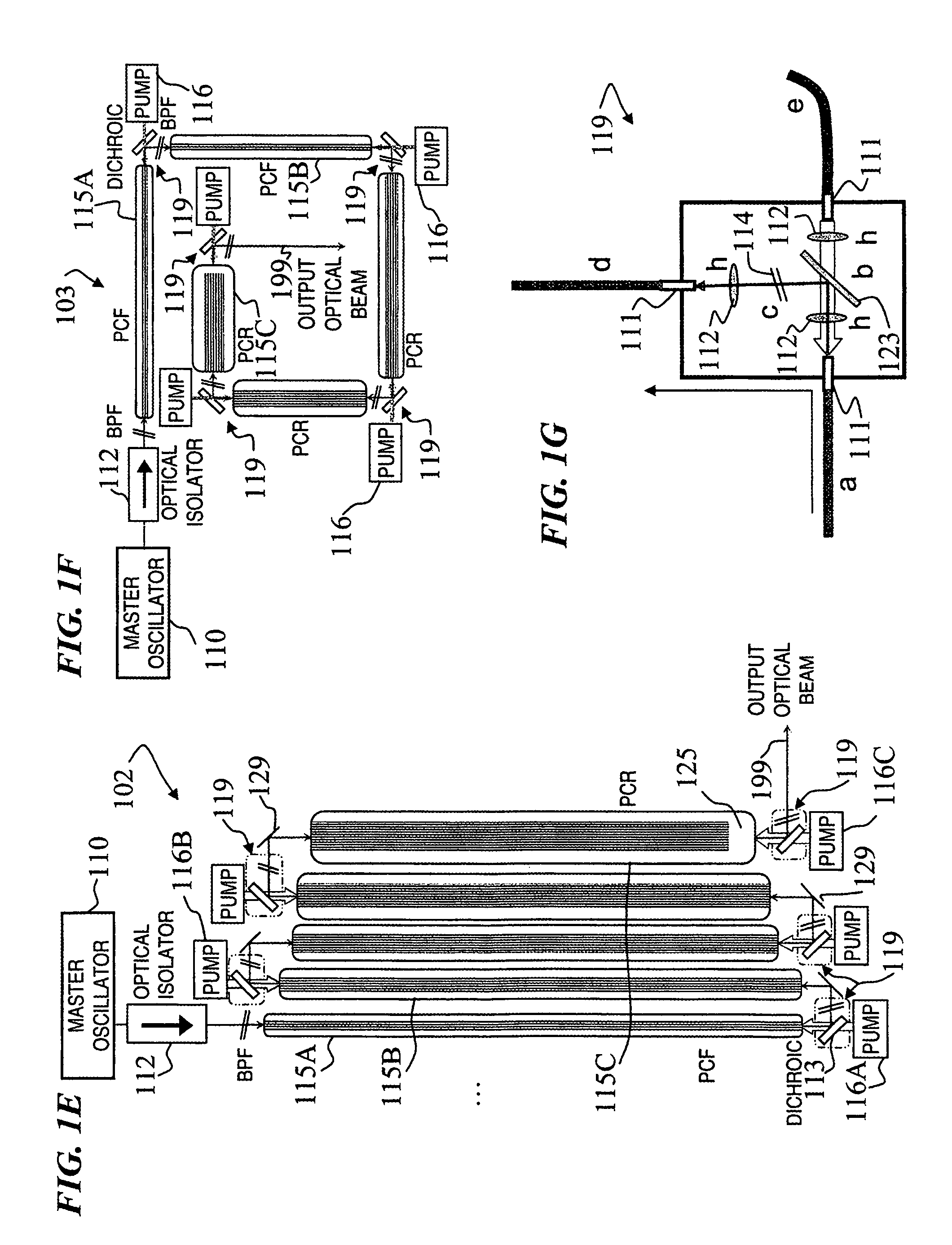
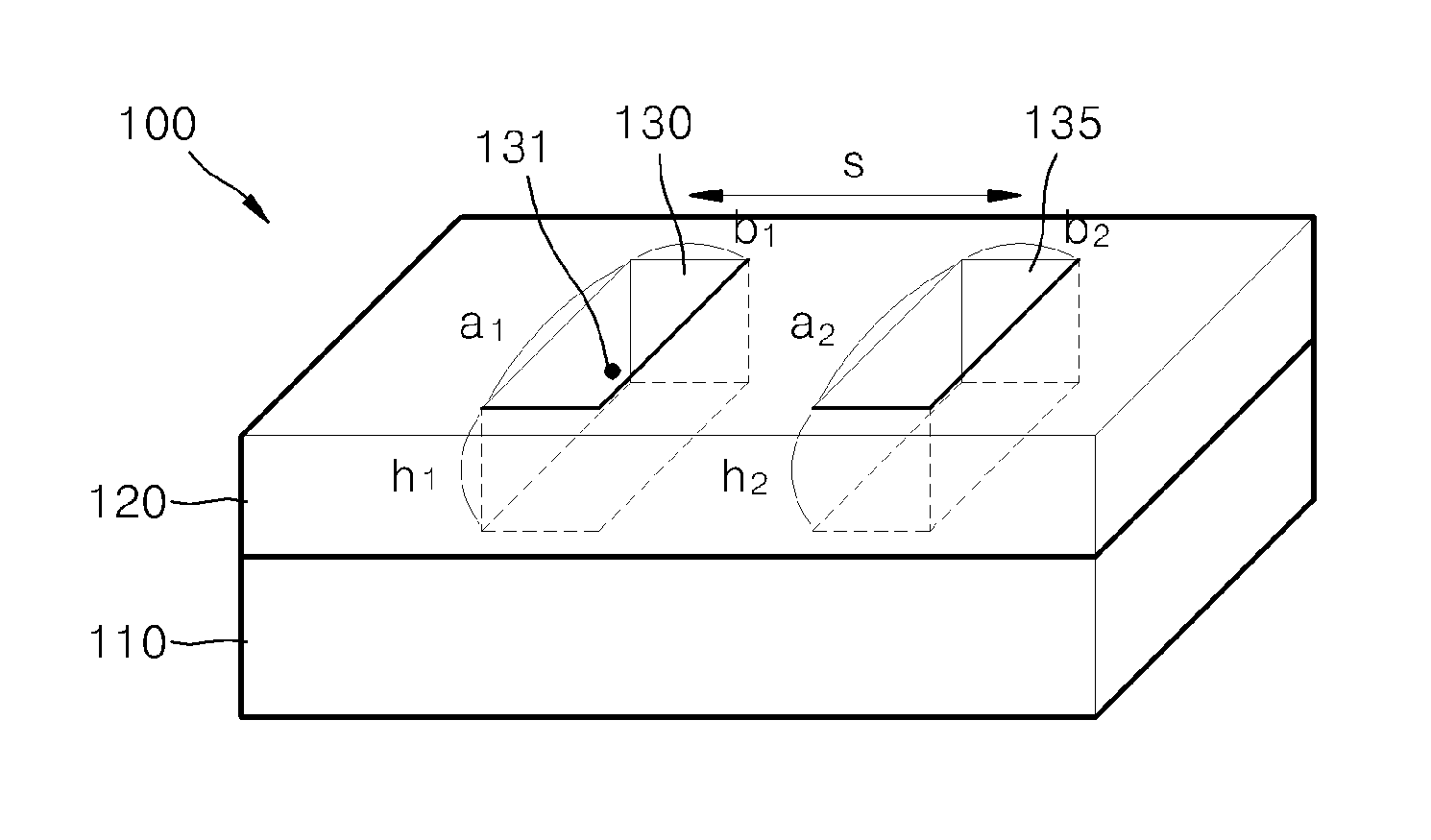
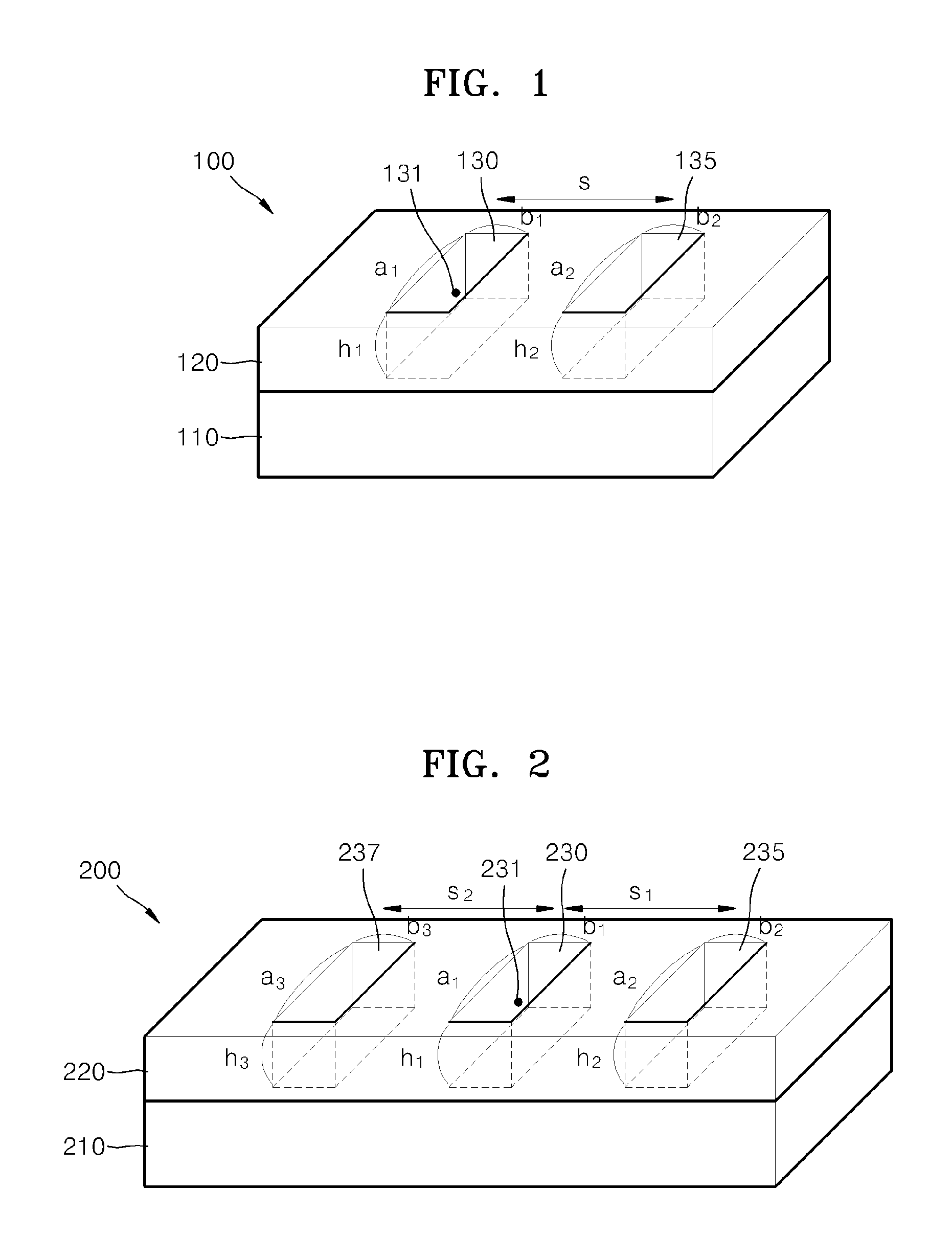
Patents
Literature
580results about "Laser constructional details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
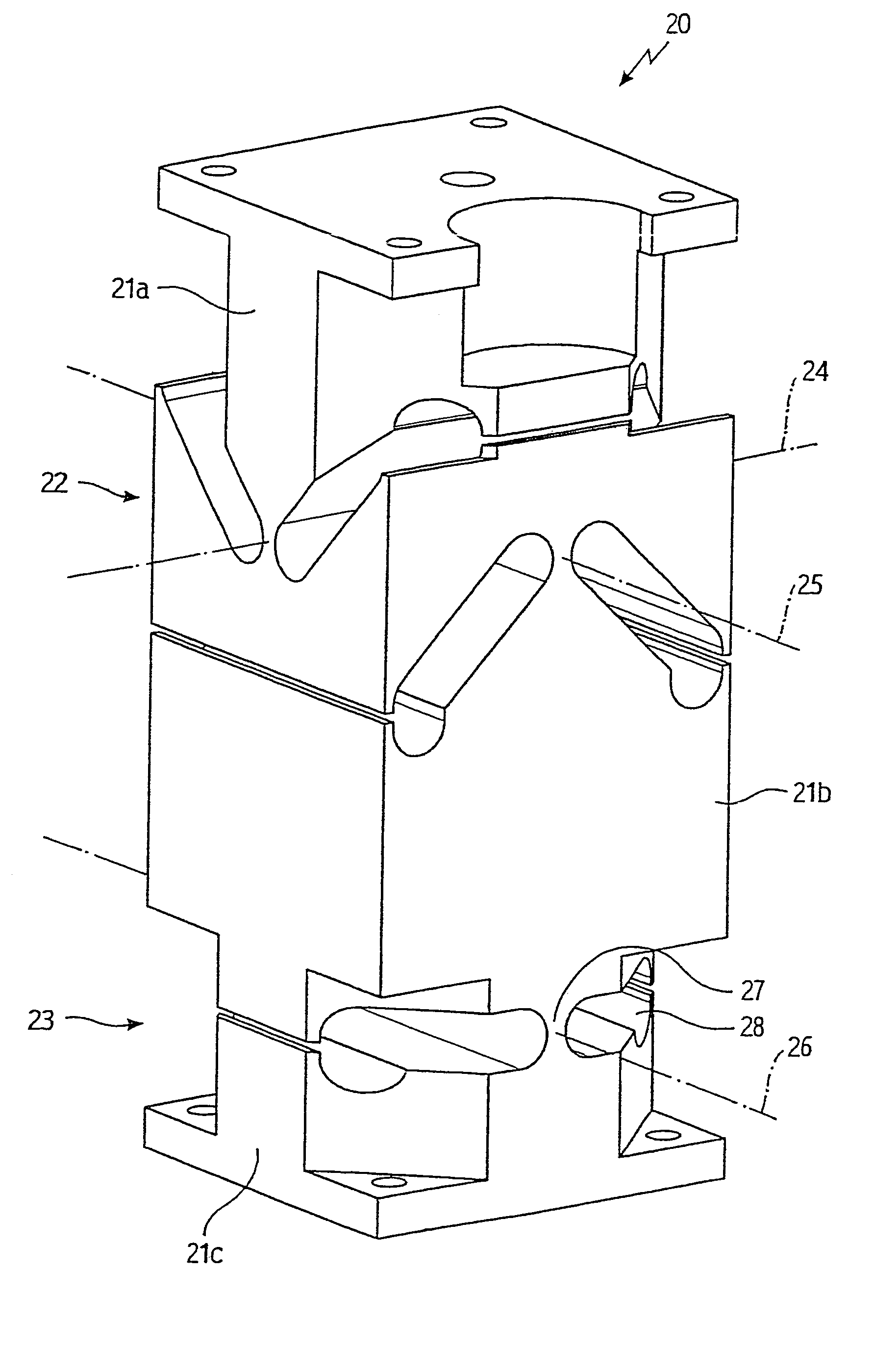
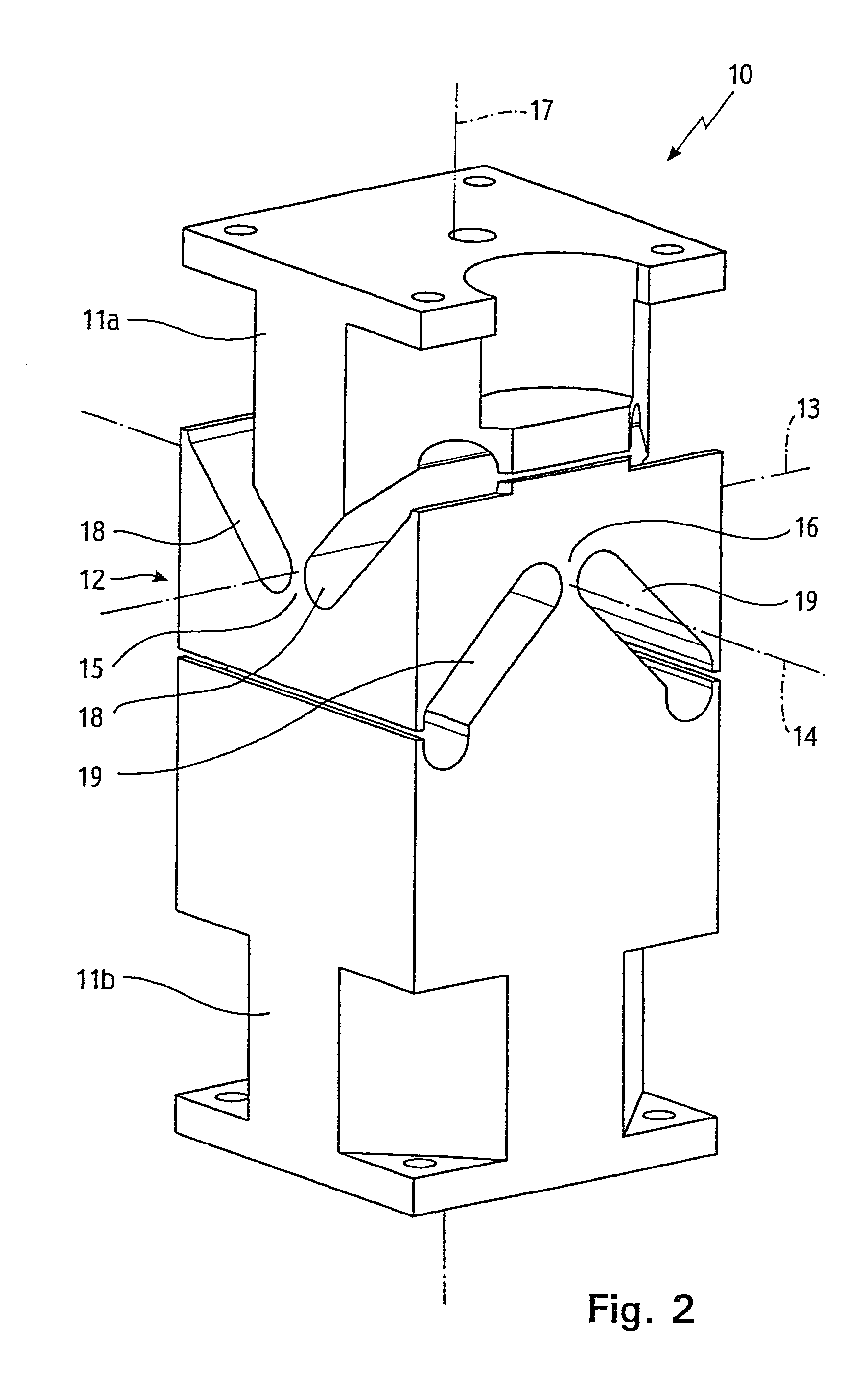
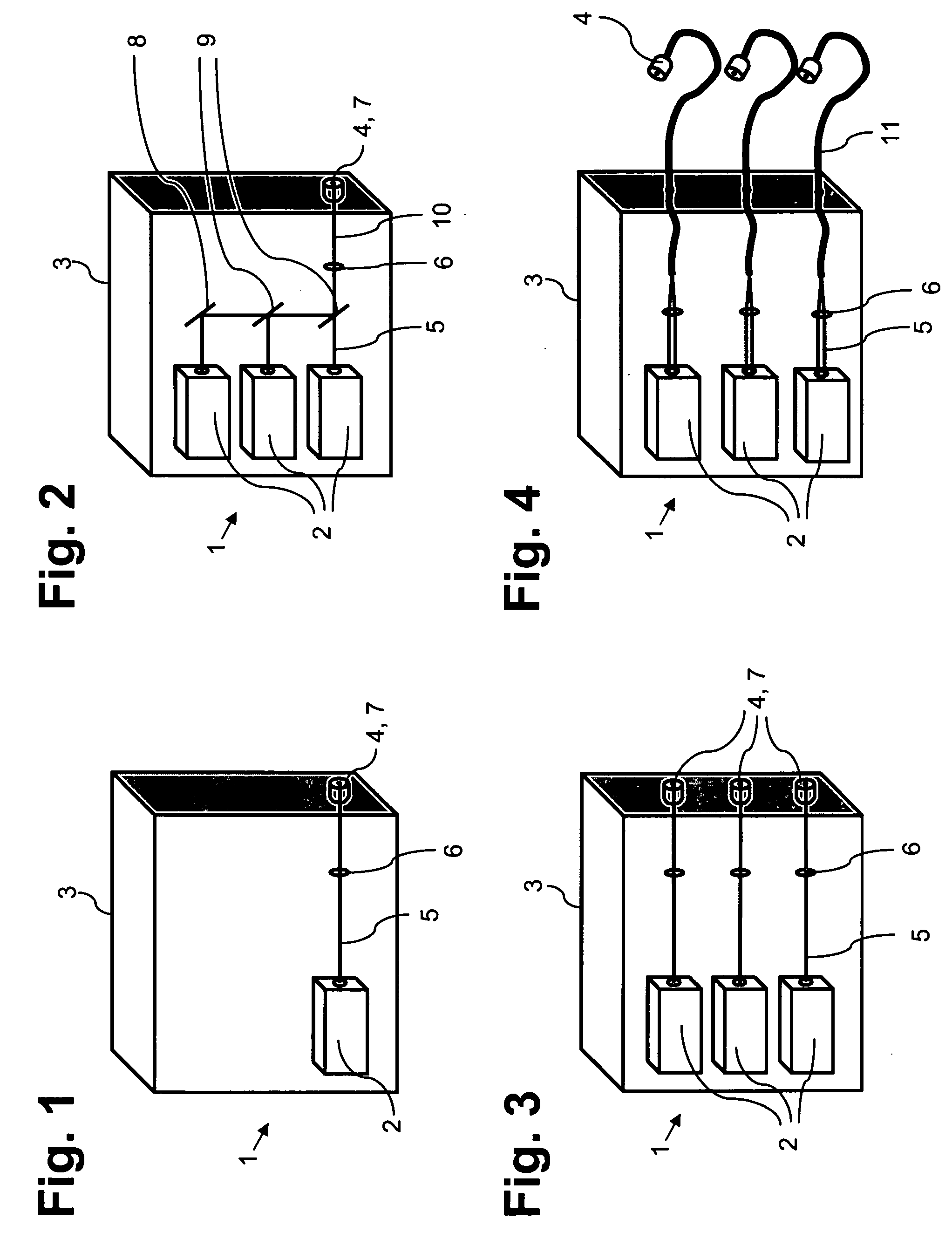
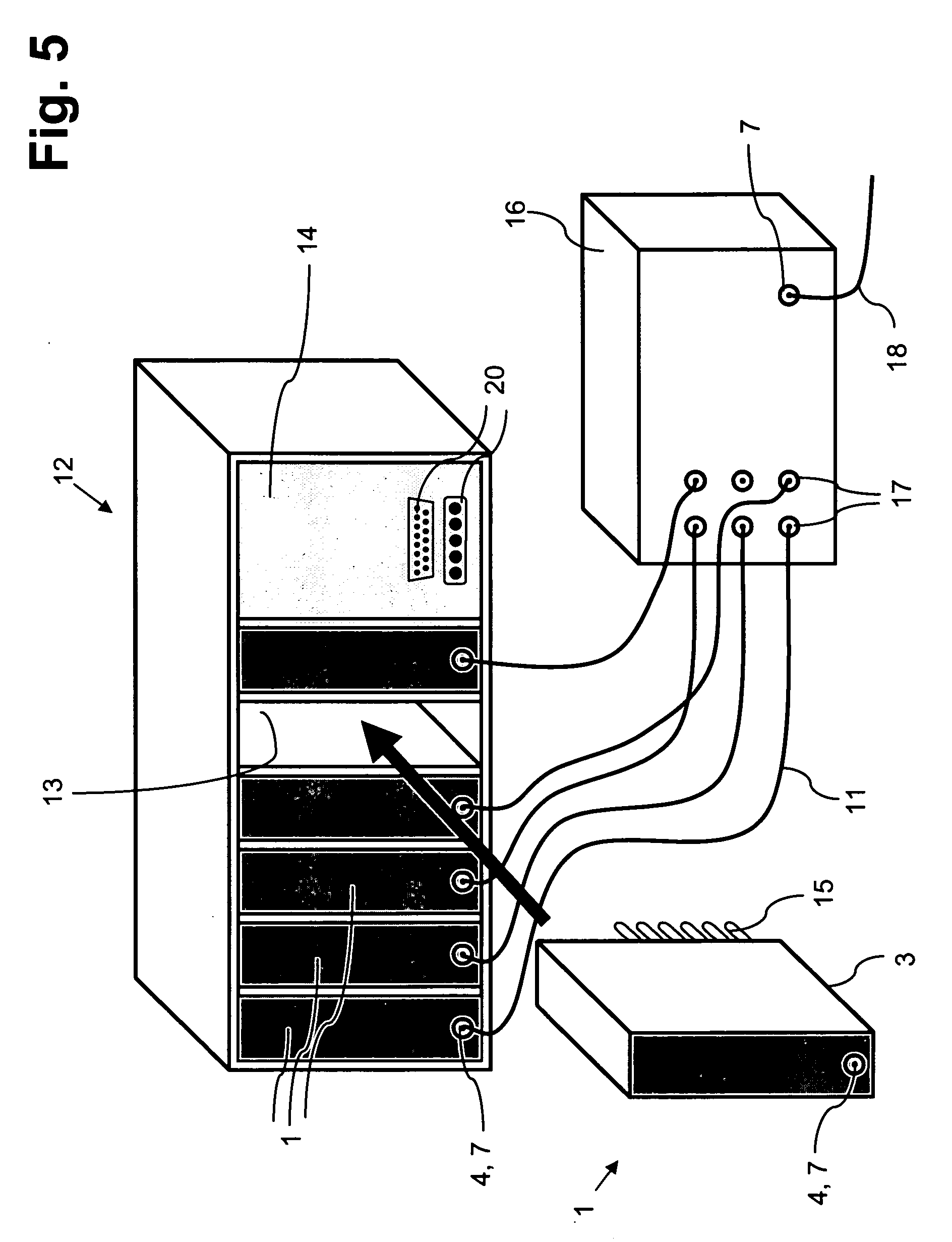
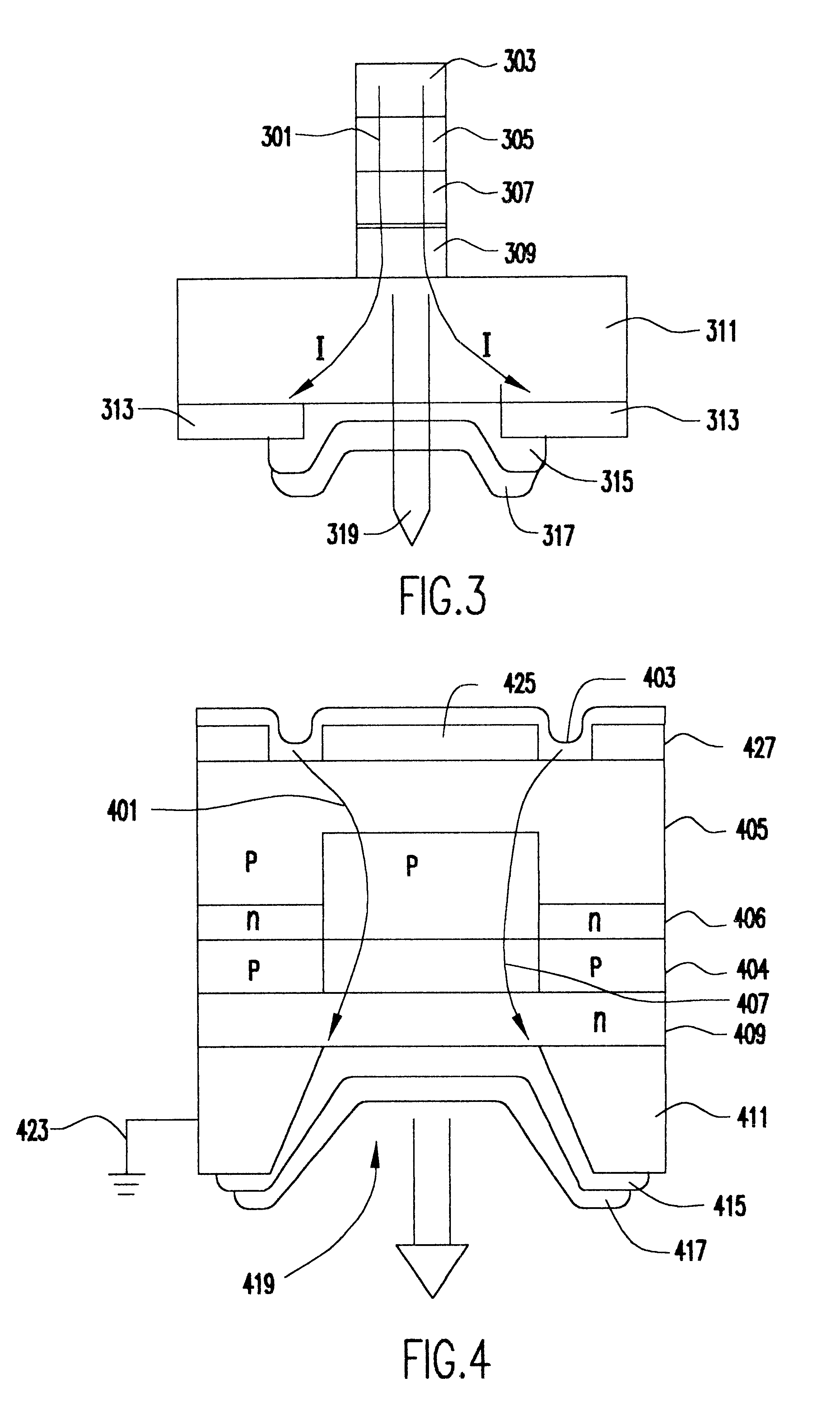
Articulated bearing supports for laser resonators
InactiveUS7316381B2Improve securityLow production costPortable framesLeaf springsMechanical engineeringResonator
In a bearing support (10) for a laser resonator, adjacent support sections (11a, 11b) are directly and undetachably connected to each other by an articulated deflectable joint (12). An additional vertical safety on the bearing support is no longer necessary since the two support sections (11a, 11b) are already held together in a vertically secure manner by the articulated joint (12).
Owner:TRUMPF LASERTECHN
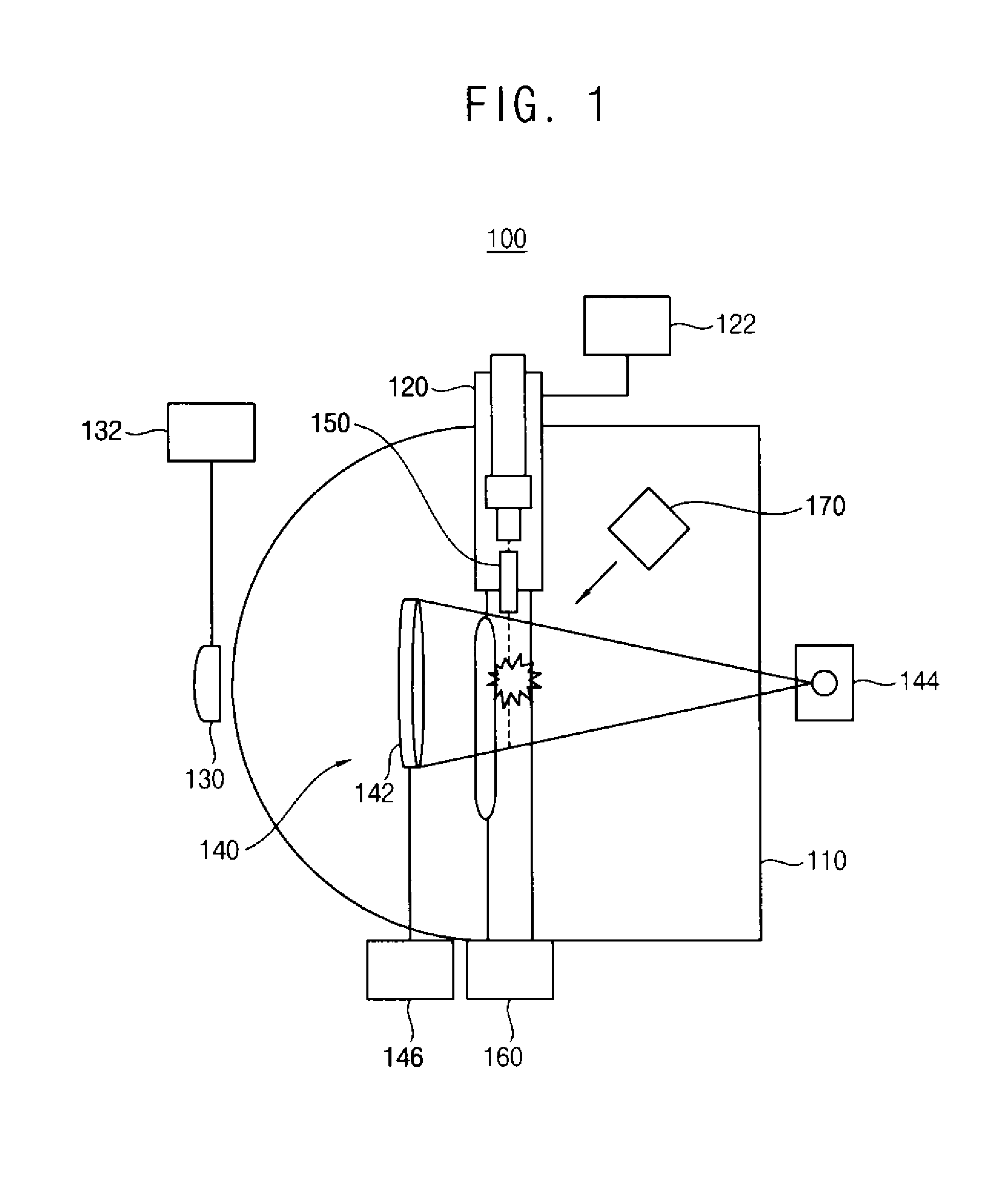
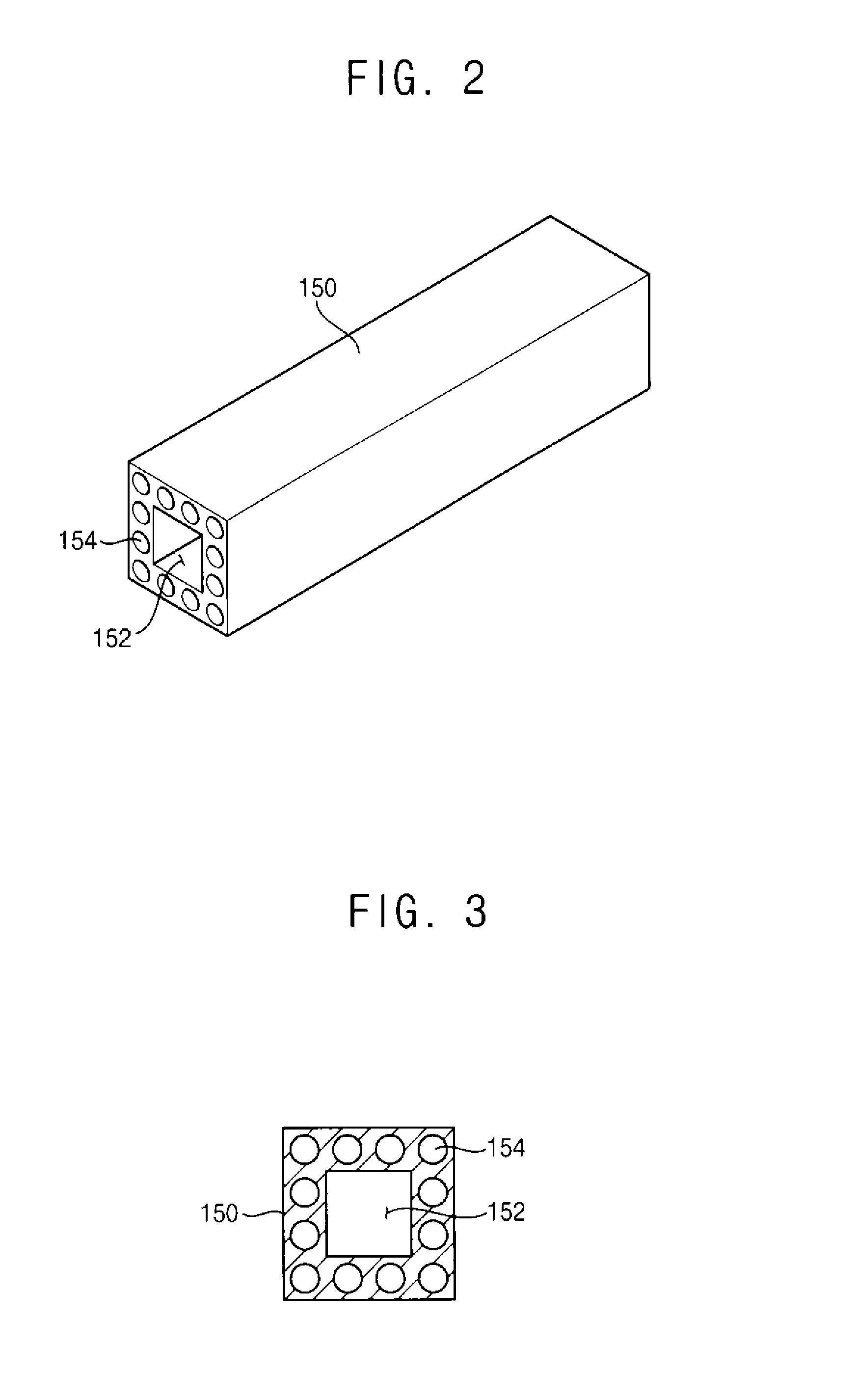
Laser irradiation apparatus, laser irradiation method, and insulating film forming apparatus
InactiveCN102441740AHigh quality formedSolid-state devicesLaser constructional detailsResistLight beam
The present invention provides a laser irradiation apparatus, a laser irradiation method and an insulating film forming apparatus, wherein a resist pattern is formed with high quality. The laser irradiating apparatus of the invention is provided with the following components: a laser source which sends out pulse laser beam; an object table which holds a substrate; a coating device which coats resist material on the substrate that is held on the object table; a first transmission optical system which focuses the pulse laser beam that is transmitted from the laser source on the resist material that is coated through the coating device for transmission and solidifying the resist material on the transmission position; a second transmission optical system which transmits the pulse laser beam that is sent out from the laser source to the resist material that is solidified by the pulse laser beam that is transmitted through the first transmission optical system and removes the resist material at a transmission position; and an optical path switching device which causes the pulse laser beam that is sent out from the laser source to selectively transmit to the first transmission optical system or the second transmission optical system.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
Laser beam machining apparatus
InactiveUS20050061778A1Laser constructional detailsLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingLaser beam machining
A laser beam machining apparatus includes a laser oscillator, a machining head which that machines a workpiece using the laser beam. An optical duct has an optical system to guide the laser beam form the laser oscillator to the machining head. Purge gas is supplied into the optical duct from a purge gas supply port, and the purge gas is output from a purge gas exhaust port. A detector detects presence of undesired gas in the optical duct.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Laser gas replenishment method
InactiveUS20060056478A1Improve performanceReduce turbulenceOptical resonator shape and constructionDiffraction gratingsVoltage rangeGas supply
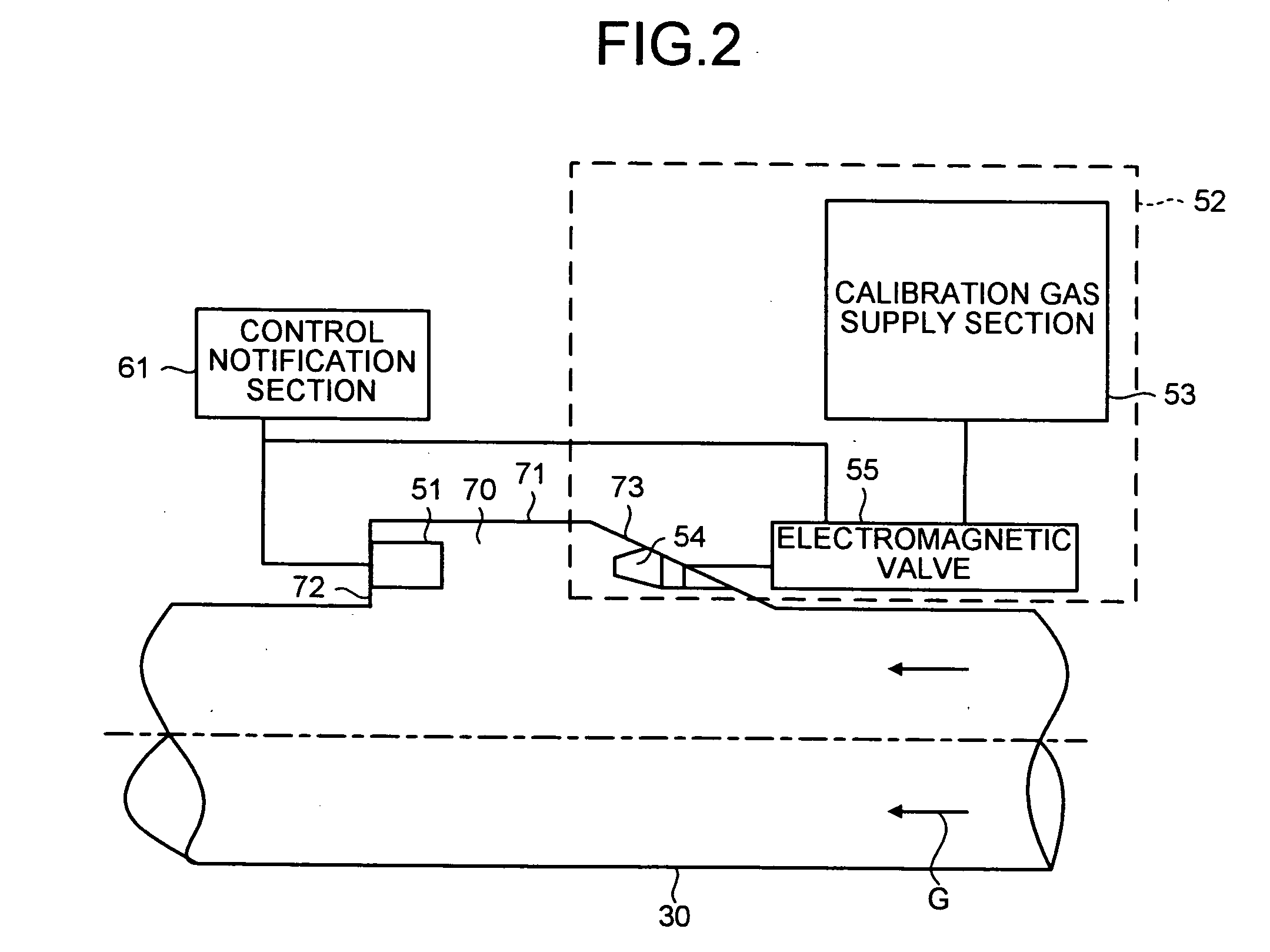
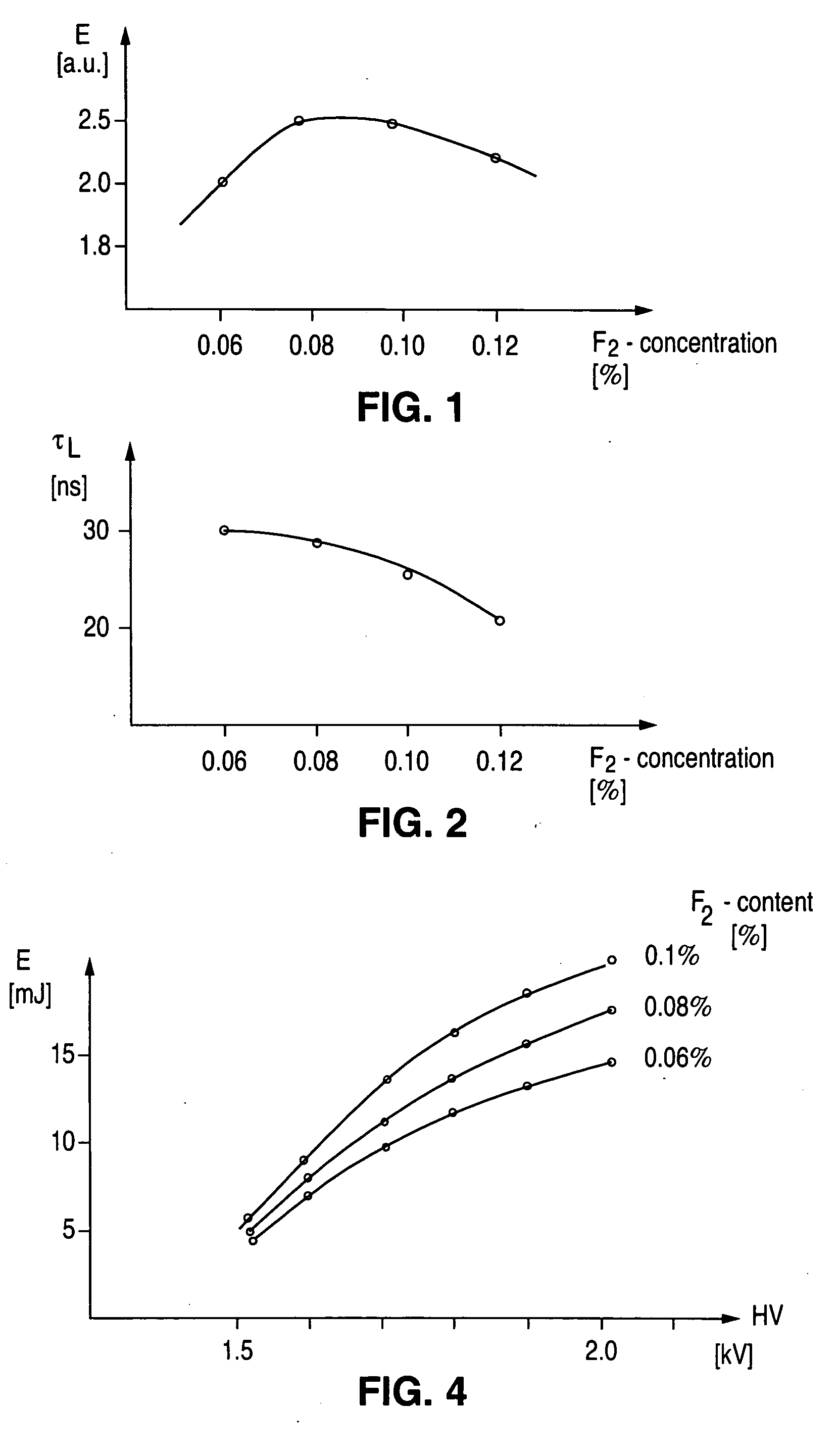
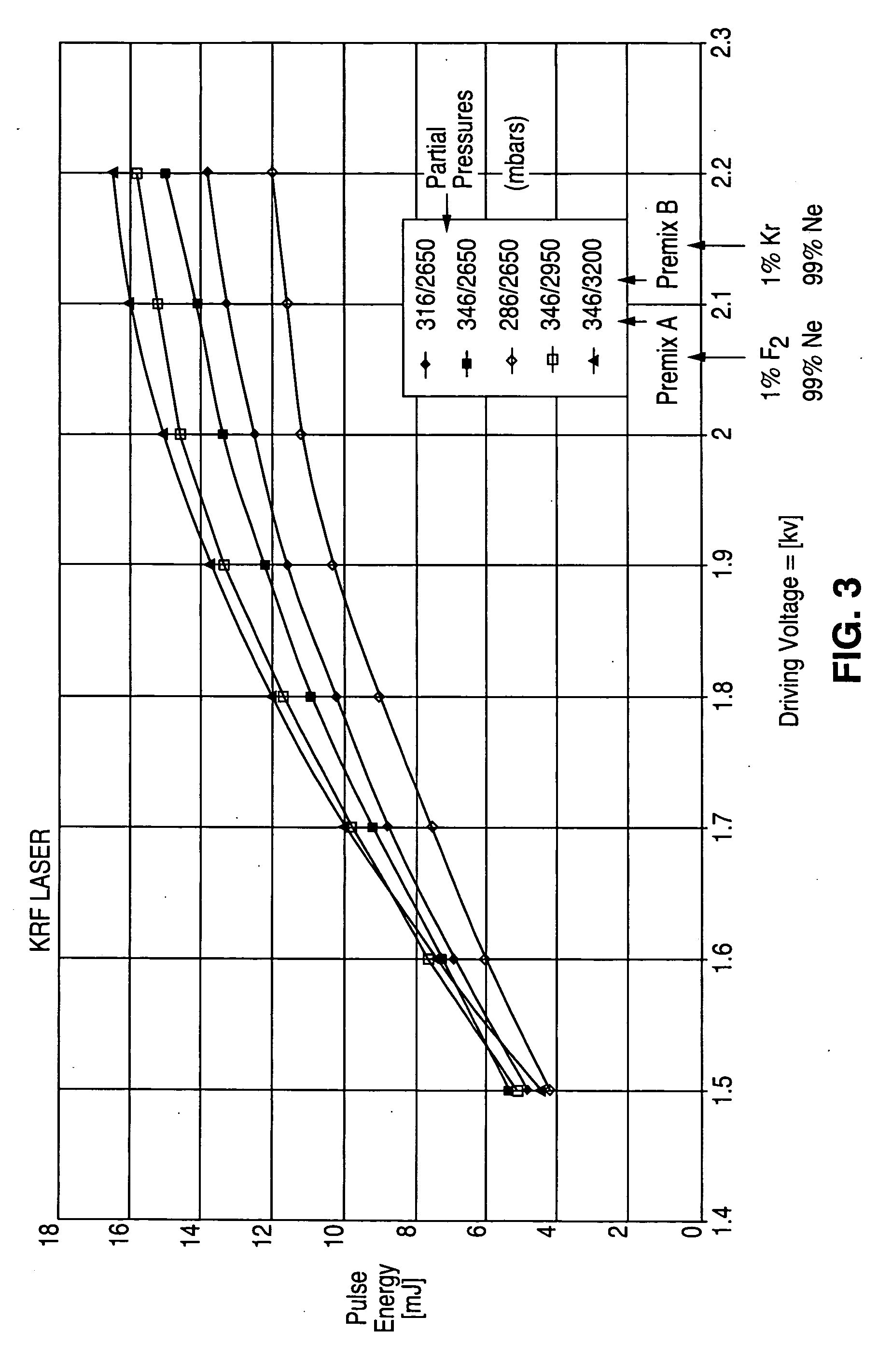
Output beam parameters of a gas discharge laser are stabilized by maintaining a molecular fluorine component at a predetermined partial pressure using a gas supply unit and a processor. The molecular fluorine is subject to depletion within the discharge chamber. Gas injections including molecular fluorine can increase the partial pressure of molecular fluorine by a selected amount. The injections can be performed at selected intervals to maintain the constituent gas substantially at the initial partial pressure. The amount per injection and / or the interval between injections can be varied, based on factors such as driving voltage and a calculated amount of molecular fluorine in the discharge chamber. The driving voltage can be in one of multiple driving voltage ranges that are adjusted based on system aging. Within each range, gas injections and gas replacements can be performed based on, for example, total applied electrical energy or time / pulse count.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
Optical regulation lens frame suitable for mobile process full-solid state high power laser
InactiveCN101470236AEasy to change the anglePrecise positioningLaser constructional detailsMountingsAll solid stateCamera lens
An optical adjusting mount capable of movably processing all-solid-state high power lasers comprises a frame, a support and a fine adjustment screw pair, wherein a lens hole of the frame is internally equipped with a baffle ring, a retainer ring is disposed on the front of the baffle ring, four tension spring holes are positioned on the frame, the back face of the frame is equipped with a V-type groove, a concave groove and a ball tapered-groove, the side face of the frame is equipped with a cooling water inlet and an outlet, the support is equipped with four tension spring holes, two holes for the fine adjustment screw pair and a ball tapered-groove which correspond to the frame, the frame and the support are connected through tension springs, each of the ball tapered-grooves of the frame and the support are inlaid with a ball, the fine adjustment screw pair is respectively mounted in the two holes for the fine adjustment screw pair of the support, the front ends of the fine adjustment screw pair are respectively located in the V-type groove and the groove. The optical adjusting mount has the advantages of scientific reasonable design, compact structure, low material consumption and low cost, further utilizes the baffle ring made of low-hardness fine heat conductivity red copper to press the lens on the end face, thereby effectively reducing the lens temperature, and utilizes the V-type groove and the ball for positioning, thereby realizing stable and reliable groove limiting.
Owner:DALU AUTOMATION TECH SHENYANG
Optical fibre gas laser and optical fiber type ring laser gyroscope possessing the laser
ActiveCN101165977AGood zoom effectSimple structureExcitation process/apparatusSagnac effect gyrometersFiber couplerRobotic systems
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Split type coaxial powder-feeding nozzle for laser fusion and coating
InactiveCN101138755AImprove cooling effectStable jobSpray nozzlesLaser constructional detailsLight spotShielding gas
The present invention belongs to the laser material processing technical field and is a multi-layer concentric conic cylinder, which consists of an internal conic cylinder, which comprises an optical path passage, a powder path passage, a protection gas passage, a cooling water path passage, all of which are coaxial, a middle conic cylinder, an external conic cylinder, a cooling water baffle, and a nozzle. The cooling water path comprises an internal conic cooling water path and an external cooling water path. The present invention is provided with the advantages of the simultaneous cooling of three conic cylinders, the flexible and convenient vertical unloading, the initiative homogenization of the powder flow, the flexible adjustment of the light spot diameter, the replaceable internal conic head, the laser reflection resistance of the end section, the recyclable powder, and so on. Moreover, the present invention is applicable in laser cladding, laser alloying, laser hardening, laser welding, and other occasions.
Owner:陈国雄
Scanning temporal ultrafast delay and methods and apparatuses therefor
InactiveUS20090296749A1Improving duty cycle of data acquisitionQuick scanLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsMetrologyLaser beams
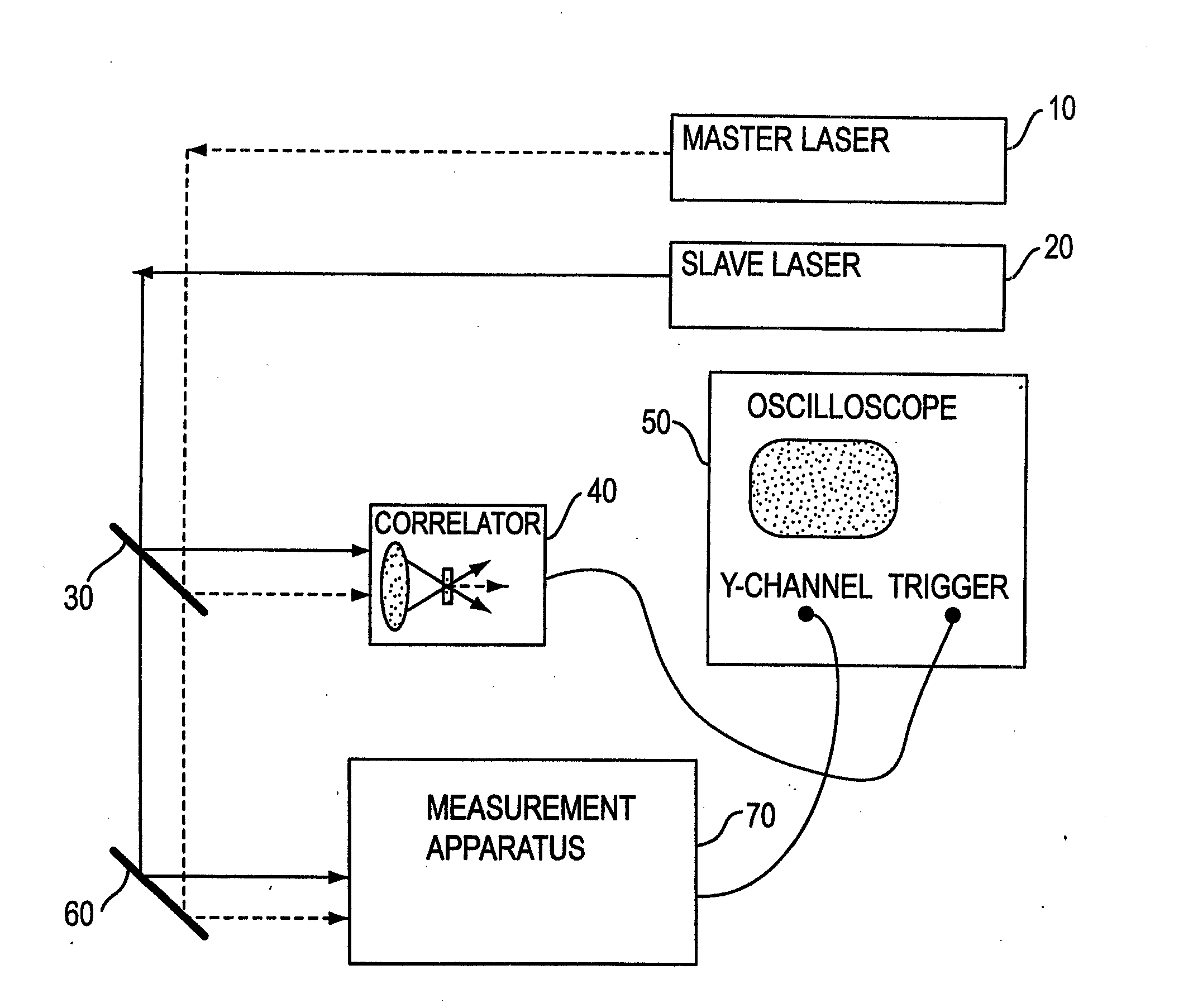
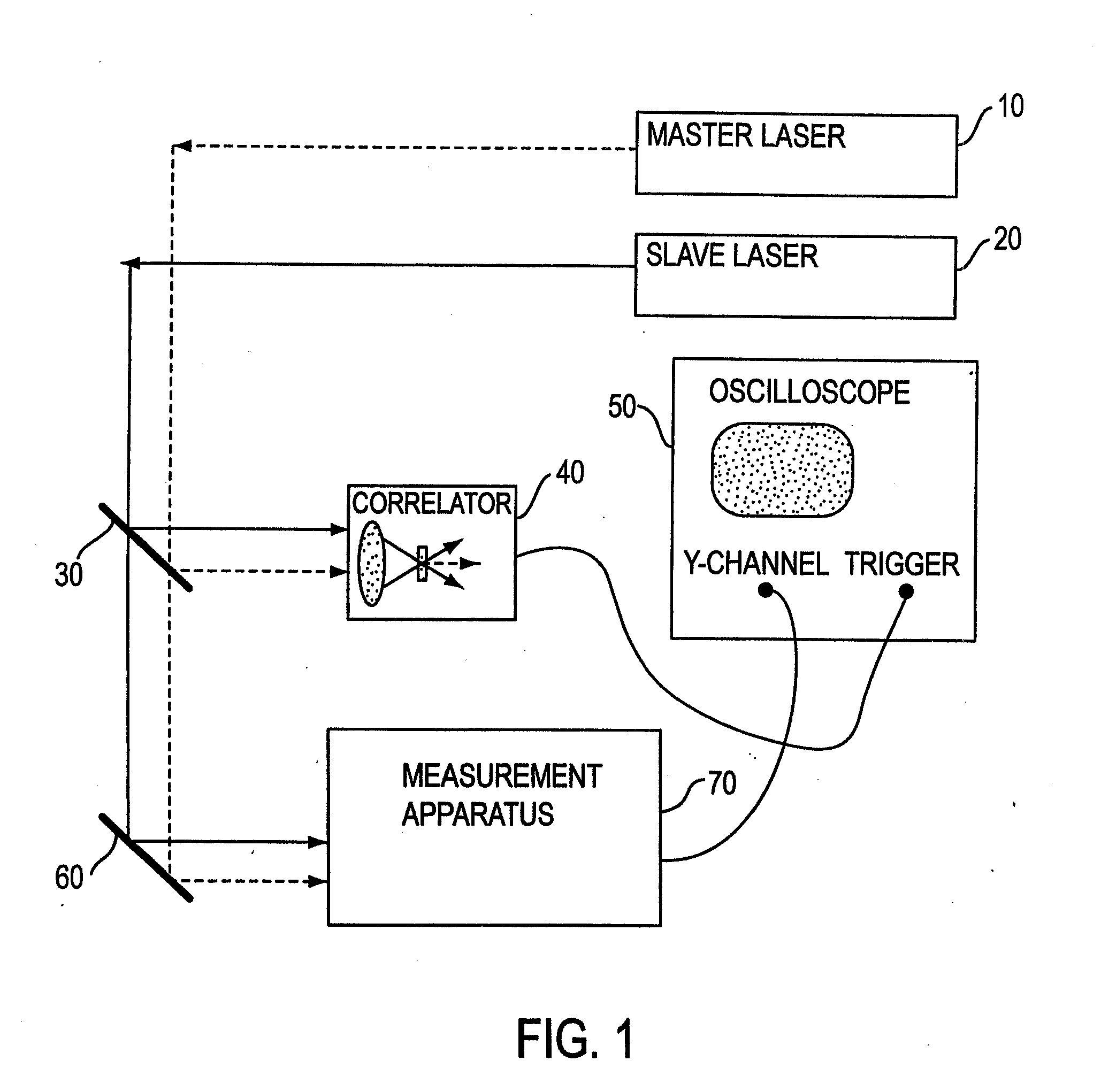
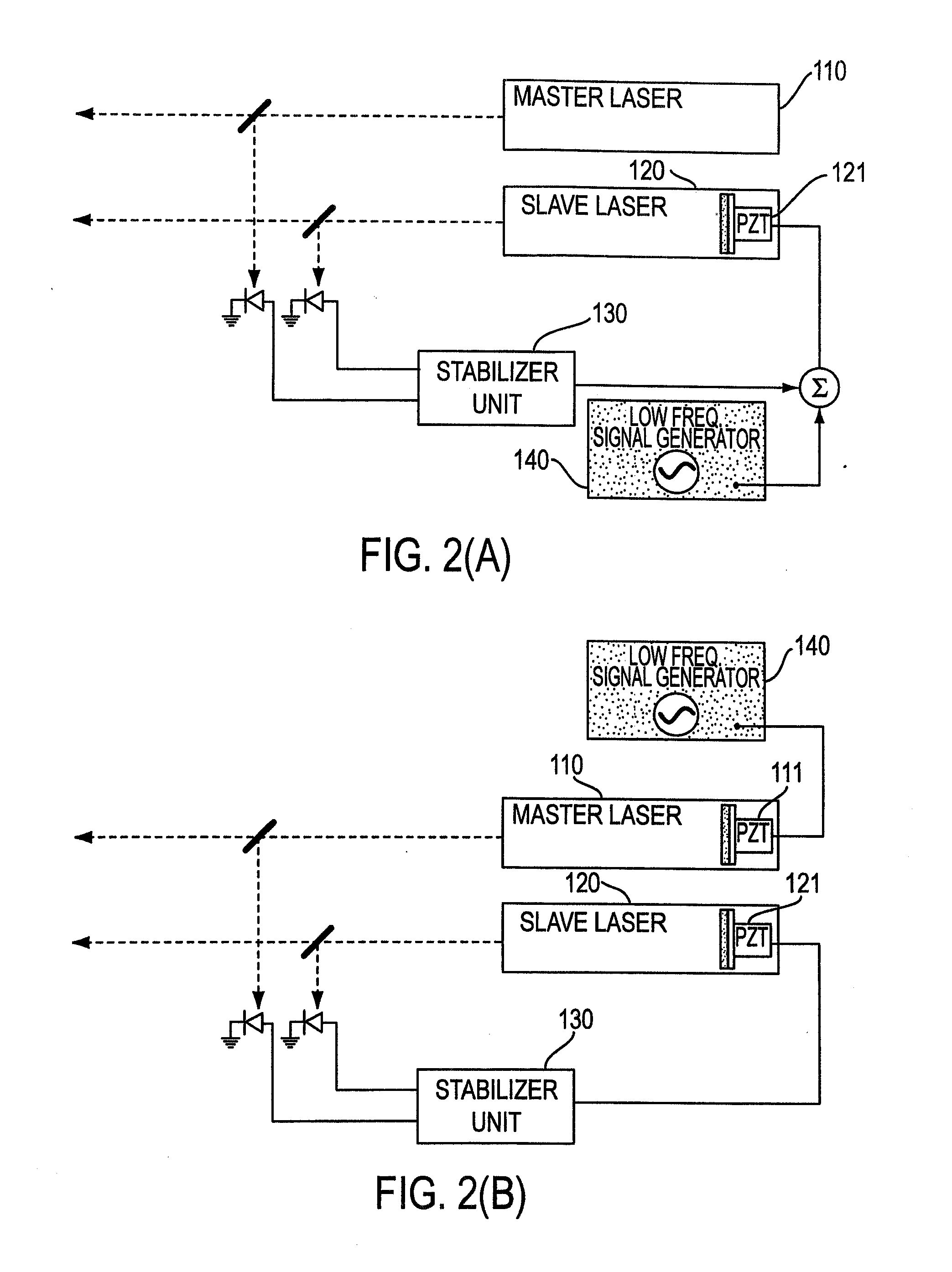
The present invention is directed to methods and apparatuses for performing temporal scanning using ultra-short pulsewidth lasers in which only minimal (micro-scale) mechanical movement is required. The invention also relates to methods for obtaining high-accuracy timing calibration, on the order of femtoseconds. A dual laser system is disclosed in which the cavity of one or more of the lasers is dithered, by using a piezoelectric element. A Fabry-Perot etalon is used to generate a sequence of timing pulses used in conjunction with a laser beam produced by the laser having the dithered laser cavity. A correlator correlates a laser pulse from one of the lasers with the sequence of timing pulses to produce a calibrated time scale. The methods and apparatuses of the present invention are applicable to many applications requiring rapid scanning and time calibration, including, but not limited to metrology, characterization of charge dynamics in semiconductors, electro-optic testing of ultrafast electronic and optoelectronic devices, optical time domain reflectometry, and electro-optic sampling oscilloscopes.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method and apparatus for long-range lidar and active imaging with optical output from a photonic-crystal rod
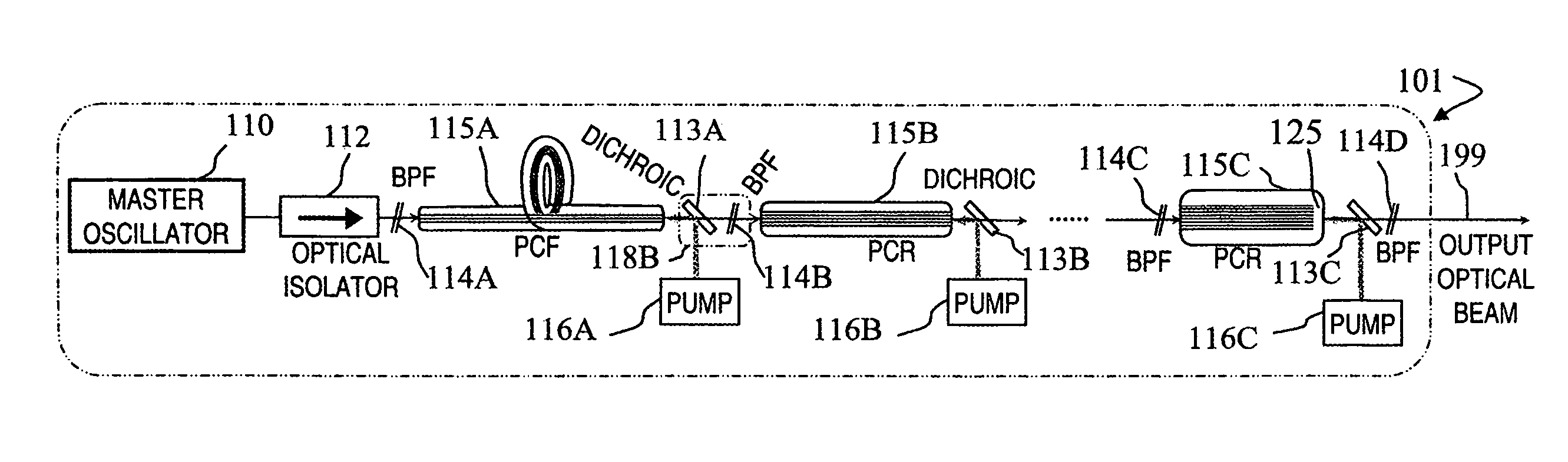
InactiveUS7375877B1High peak powerHigh pulse energyGlass making apparatusLaser constructional detailsEngineeringMultiple modes
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ACULIGHT CORP
Optical devices and methods of controlling propagation directions of light from the optical devices
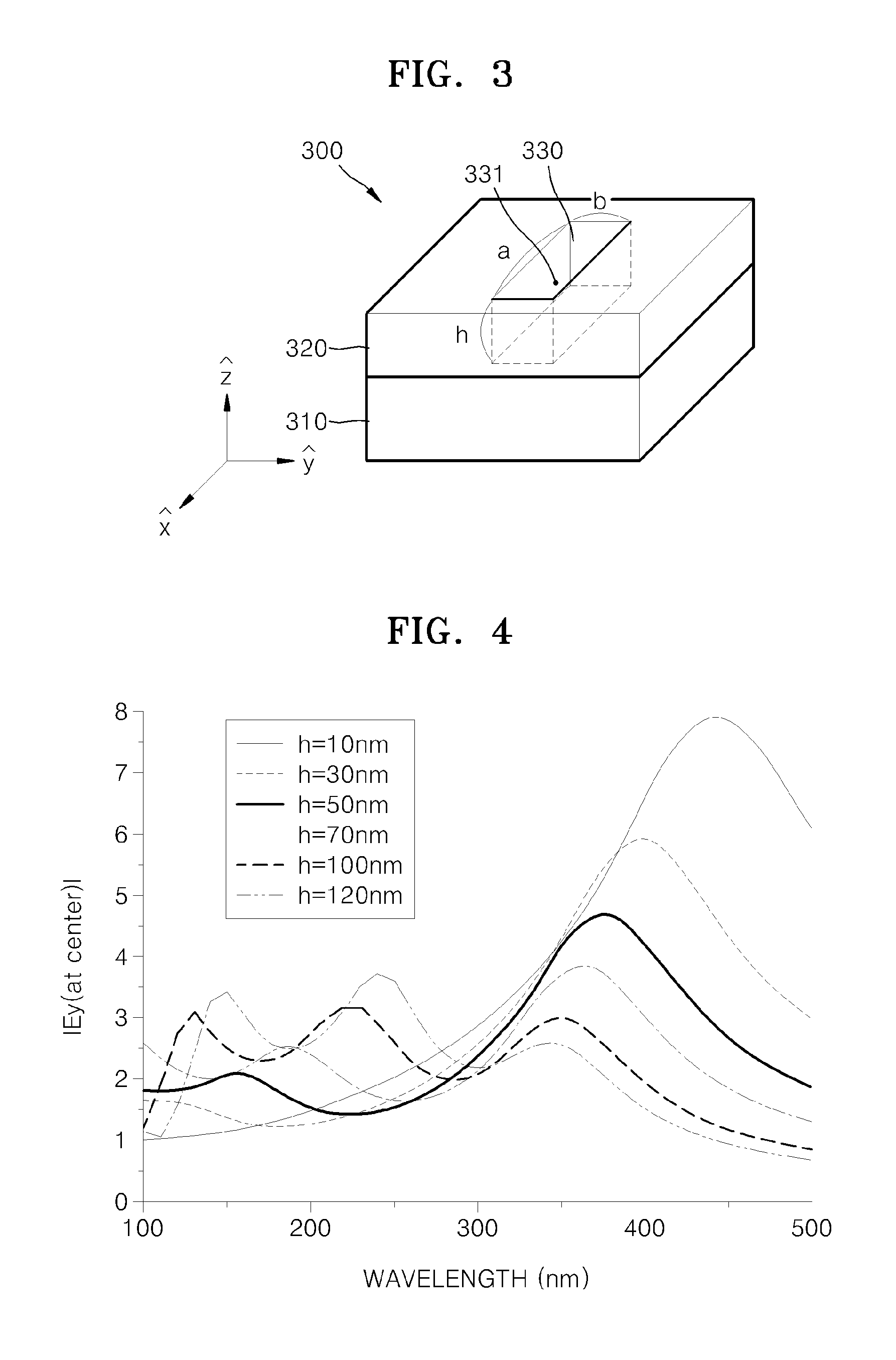
ActiveUS20130070459A1Constant maintenanceNanoopticsLaser constructional detailsOptoelectronicsNanostructure
An optical device may include a substrate, a metal layer on the substrate, at least one first nano-structure in the layer, and at least one second nano-structure in the layer. The at least one first nano-structure may include a light source. The at least one first and second nano-structures may be spaced apart. A method of controlling a propagation direction of light output from an optical device that includes a metal layer on a substrate may include disposing first and second nano-structures in the layer; disposing at least one light source in the first nano-structure; and controlling the propagation direction of the light output from the at least one light source by changing at least one of a shape of the first nano-structure, a shape of the second nano-structure, a size of the first nano-structure, a size of the second nano-structure, and an interval between the first and second nano-structures.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Fiber laser output head having light beam focusing characteristic and power monitoring function
The invention relates to a fiber laser output head having a light beam focusing characteristic and a power monitoring function. The fiber laser output head is composed of a laser power transmission device and an external packaging device. When myriawatt-level high-power laser passes through the laser output head, a mode stripper strips laser in forward transmission and residual pump light in a cladding layer; and a forward light detector in a photoelectric detection device detects a power of stripped scattered light. The laser is emitted by a quartz end cap; and because of increasing of an emitting end area, the emergent light power density is substantially reduced. The laser outputted by the quartz end cap is focused by a focusing lens and the size of the light spot is controlled by a focal length adjusting device. Besides, when the laser head is used for carrying out laser processing, the power of generated reflected return light is detected by a reverse light detector in the photoelectric detection device. And then a cooling device including a water flow guiding pipe, an inflow device, and a water outgoing device carries away lots of heat generated by working of the mode stripper.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
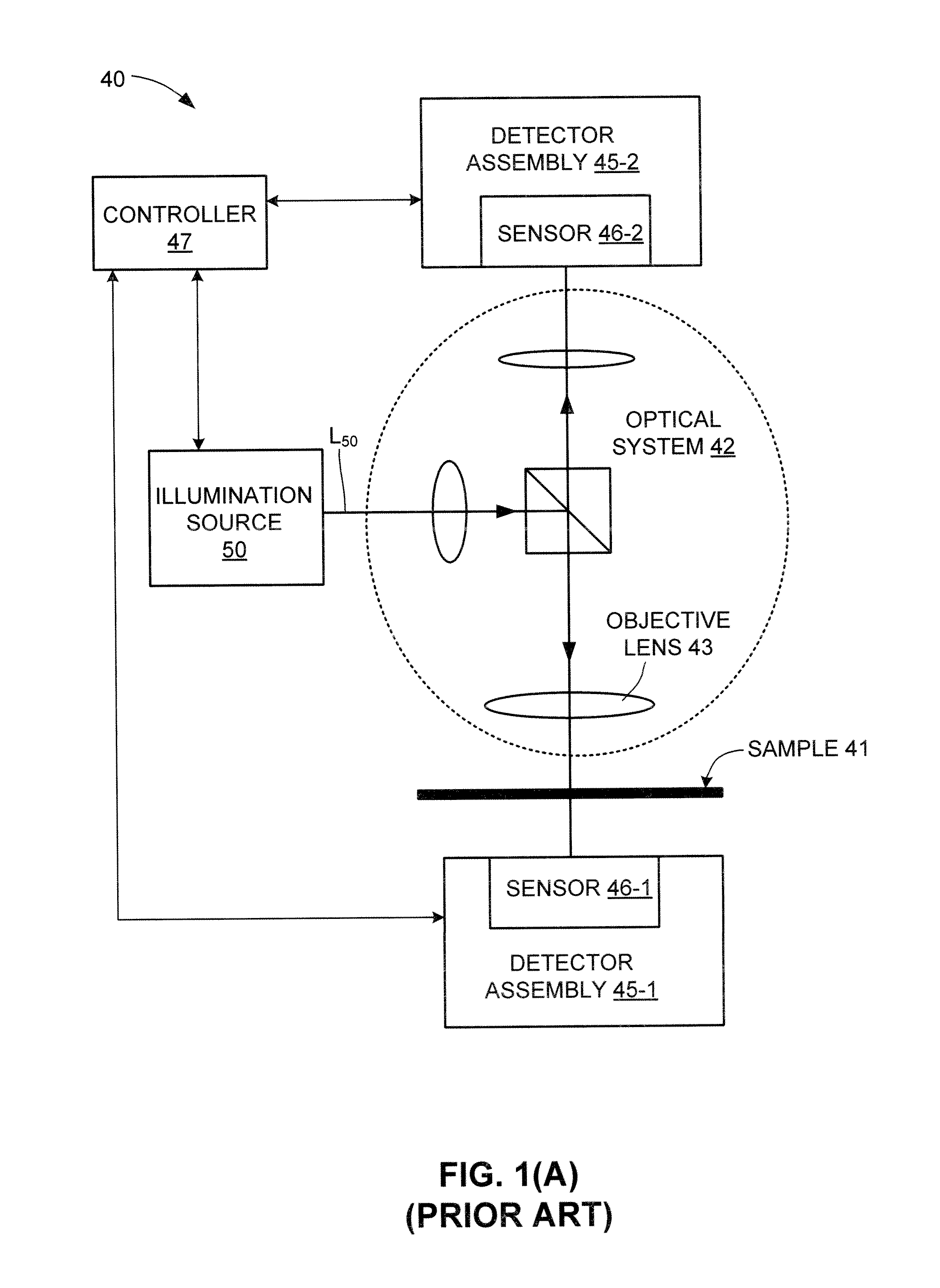
Device for generating a laser light beam
InactiveUS20050201441A1Increase flexibilityImprove adaptabilityExcitation process/apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansLaser lightLaser beams
A device for generating a laser light beam includes a module. The module includes at least one laser light source, and a mechanical, an electrical and / or an optical interface defined towards an outside of the module.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
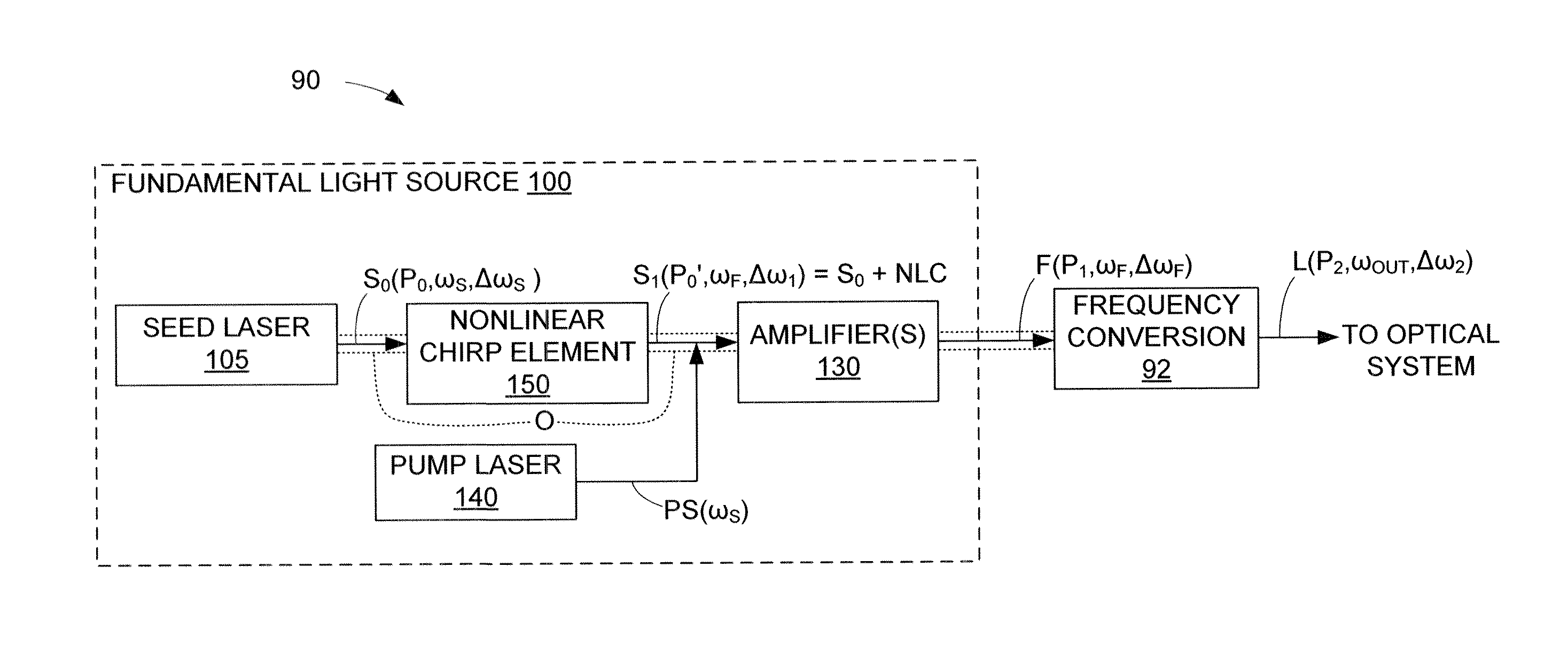
Reducing The Spectral Bandwidth Of Lasers
ActiveUS20140016655A1Power Loss MinimizationSimplifies compensating nonlinear chirp calculationLaser using scattering effectsMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberGrating
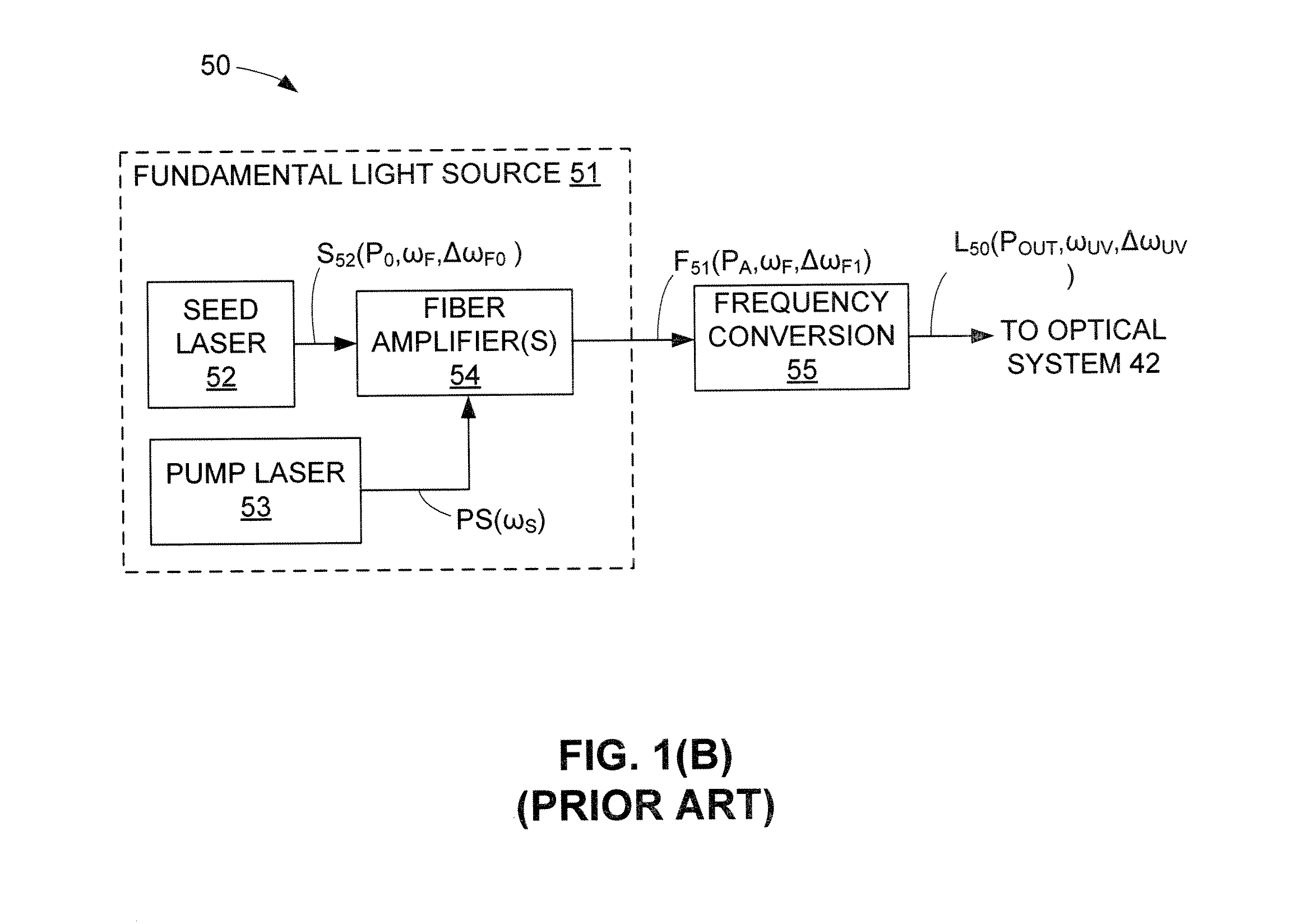
A laser system for semiconductor inspection includes a fiber-based fundamental light source for generating fundamental light that is then converted / mixed by a frequency conversion module to generate UV-DUV laser light. The fundamental light source includes a nonlinear chirp element (e.g., a Bragg grating or an electro-optic modulator) that adds a nonlinear chirp to the seed light laser system prior to amplification by the fiber amplifier(s) (e.g., doped fiber or Raman amplifiers). The nonlinear chirp includes an x2 or higher nonlinearity and is configured to compensate for the Self Phase Modulation (SPM) characteristics of the fiber-based amplifiers such that fundamental light is generated that has a spectral E95 bandwidth within five times that of the seed light. When multiple series-connected amplifiers are used, either a single nonlinear chirp element is provided before the amplifier string, or chirp elements are included before each amplifier.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Packaging structure of distributed feedback fiber laser
ActiveCN103887688ACompact structureEasy to integrateLaser constructional detailsActive medium shape and constructionGratingFiber Bragg grating
The invention discloses a packaging structure of a distributed feedback fiber laser. The packaging structure is characterized by comprising a quartz U-shaped groove and silicone grease or silicone oil with which the quartz U-shaped groove is filled, an active phase shift fiber bragg grating is immersed in the silicone grease or silicone oil in the quartz U-shaped groove, tail fibers at the two ends of the active phase shift fiber bragg grating are fixedly bonded to the quartz U-shaped groove through two pieces of parallel thermocuring glue respectively to enable the active phase shift fiber bragg grating to be kept in the free state under the condition that axial stress is not borne, the grating tail fibers located outside the quartz U-shaped groove are sleeved with plastic sleeves respectively, the two ends of the quartz U-shaped groove and the plastic sleeves on the two sides are jointly inserted into corresponding hot melting pipes respectively, the two hot melting pipes and the quartz U-shaped groove are integrally inserted into a heat shrink pipe, the two hot melting pipes and the heat shrink pipe are heated to be shrunk to enable the two plastic sleeves and the quartz U-shaped groove to be connected into a whole, and meanwhile the heat shrink pipe is shrunk to enable the silicone grease or silicone oil to be sealed in the quartz U-shaped groove.
Owner:山东飞博赛斯光电科技有限公司
Apparatus for creating an extreme ultraviolet light, an exposing apparatus including the same, and electronic devices manufactured using the exposing apparatus
ActiveUS20140078480A1Accurate irradiationAvoid pollutionRadiation pyrometryLaser constructional detailsEngineeringIrradiation
An apparatus for creating an EUV light may include a droplet-supplying unit, a laser-irradiating unit, a light-concentrating unit and a guiding unit. The droplet-supplying unit may supply a droplet from which the EUV light may be created. The laser-irradiating unit may irradiate a laser to the droplet supplied from the droplet-supplying unit to create the EUV light. The light-concentrating unit may concentrate the EUV light created by the laser-irradiating unit. The guiding unit may guide the droplet to a position at which the laser may be irradiated. The guiding unit may have at least one gas-spraying hole for spraying a gas to a space between the droplet-supplying unit and the laser irradiation position to form a gas curtain configured to surround the droplet.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
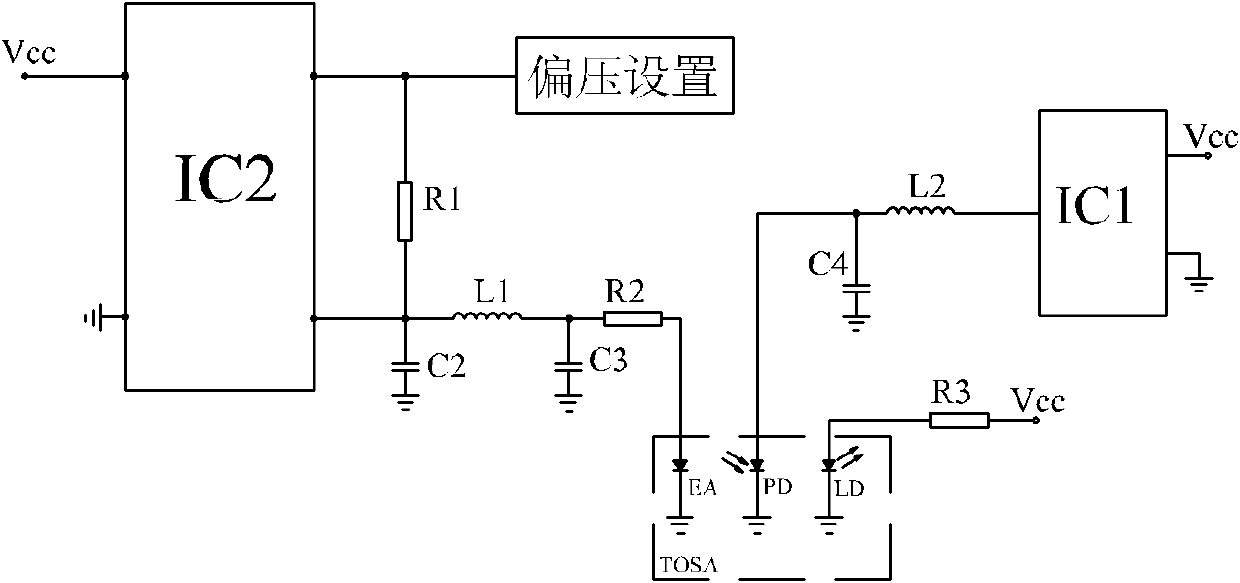
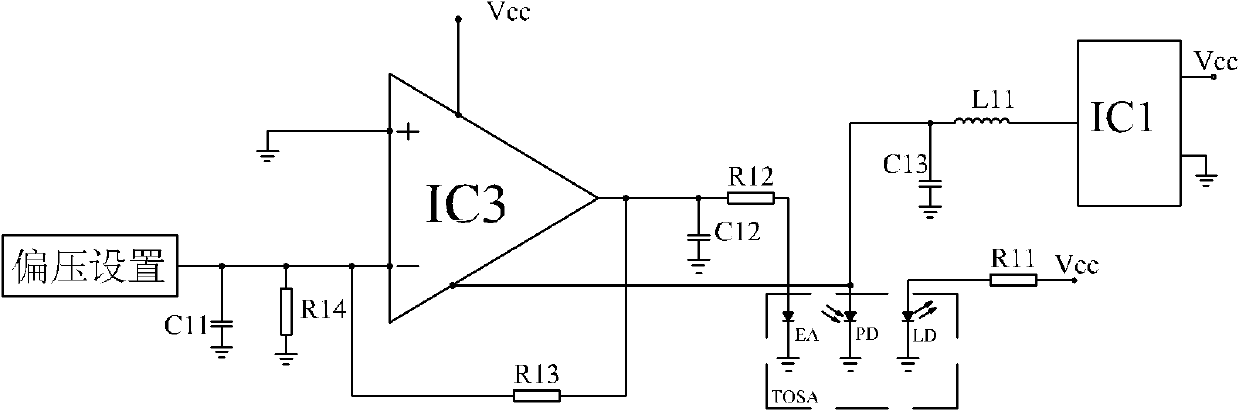
Bias circuit of electroabsorption modulated laser
ActiveCN102571003AImprove work performanceLow costLaser constructional detailsDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceElectro-absorption modulator
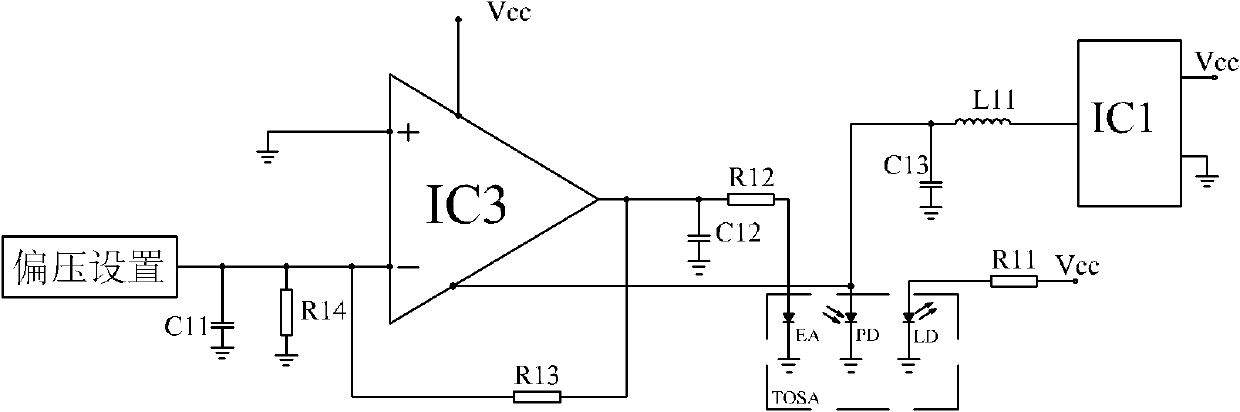
The invention provides a bias circuit of an electroabsorption modulated circuit. The bias circuit comprises a light emitting assembly TOSA (Transmitter Optical Sub Assembly), a conversion charge pump with nonadjustable output voltage or a switch tube chip, an operation amplifier, and a feedback resistor, wherein the light emitting assembly TOSA is composed of an electroabsorption modulator EA, a semiconductor laser LD and a monitor diode PD, which have a common grounded cathode; the anode of the semiconductor laser LD is connected with a power supply Vcc through a first current limiting resistor; the conversion charge pump or the switch tube chip has a positive power pin connected with the power supply Vcc, a grounded negative power pin, and an output pin connected with one end of a first inductor; the other end of the inductor is connected with the anode of the monitor diode PD and with one end of a third filter capacitor; the other end of the capacitor is grounded; the operation amplifier has a positive power pin connected with the power supply Vcc, a negative power pin connected with the anode of the monitor diode PD, a grounded positive input pin, a negative input pin connected with an external bias unit through a loop resistor, and an output pin connected with the anode of the electroabsorption modulator EA; and the feedback resistor is connected between the negative input pin and the output pin of the operation amplifier.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEOPHOTONICS TECH
Device and method of generating high-speed picosecond narrow pulse laser
InactiveCN104134923AConstant outputStable outputExcitation process/apparatusLaser constructional detailsTemperature controlPicosecond
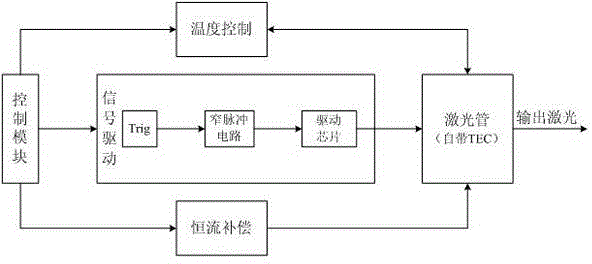
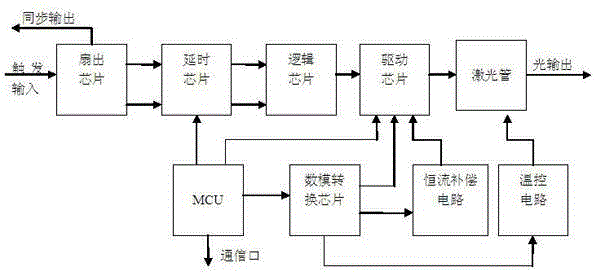
The invention discloses a device of generating high-speed picosecond narrow pulse laser. A control module is electrically connected with a signal driving module, a constant current compensation module and a temperature control module respectively; the signal driving module, the constant current compensation module and the temperature control module are electrically connected with a laser tube; the control module converts an input triggering signal into a radio frequency driving signal by the signal driving module, and outputs the radio frequency driving signal to the laser tube to drive a laser device to work at a constant temperature to output laser; the control module controls the working temperature of the laser tube by the temperature control module to allow the laser device to work at a constant temperature; and the control module controls the magnitude of compensation current by the constant current compensation module to allow the laser device to output at constant current. The invention further discloses a method of generating the high-speed picosecond narrow pulse laser. The device is stable in output, can be suitable for a quantum key distribution system with quantum light and synchronous light multiplexing an optical fiber, and has the characteristics of concision, convenience and low cost.
Owner:ANHUI QASKY QUANTUM SCI & TECH CO LTD
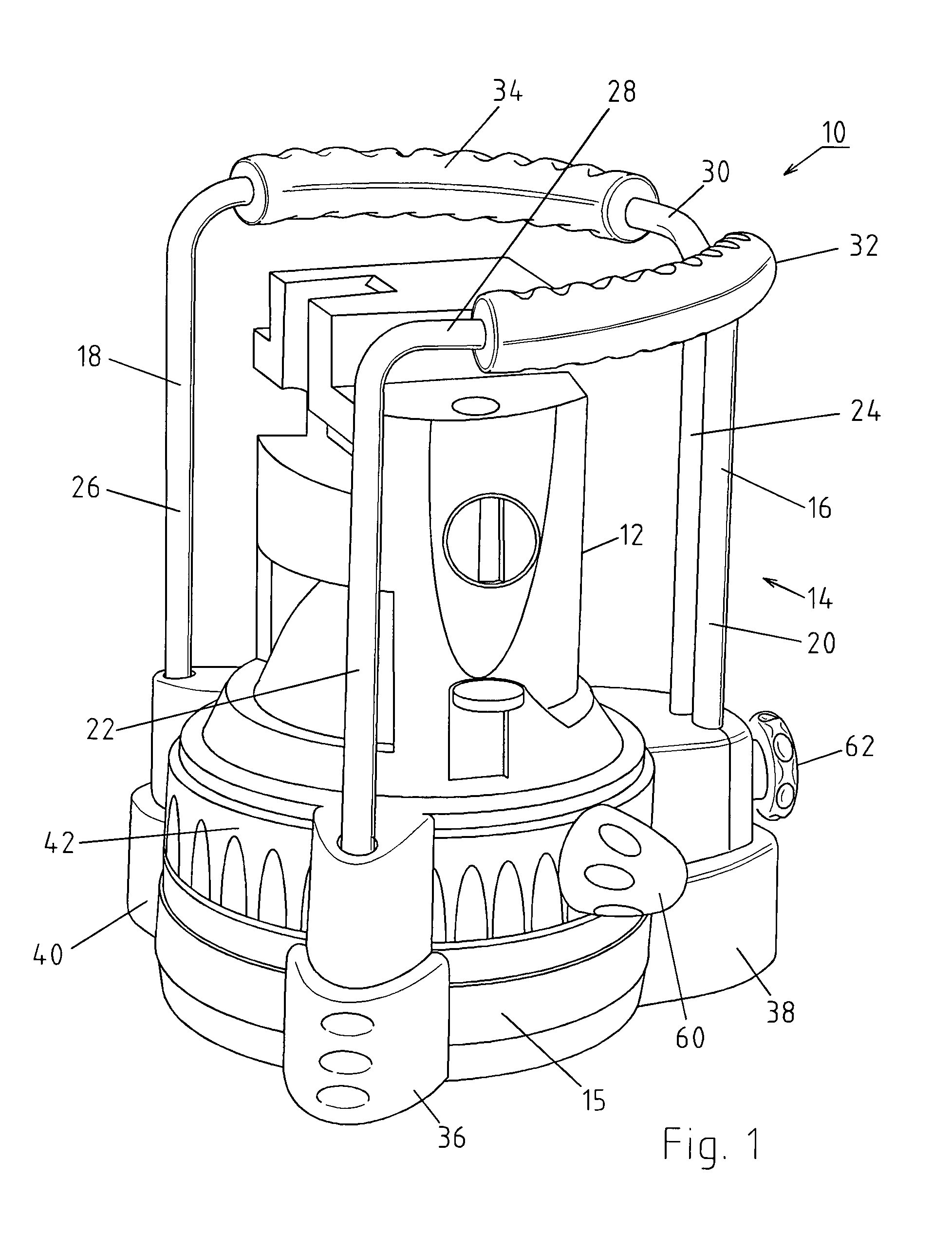
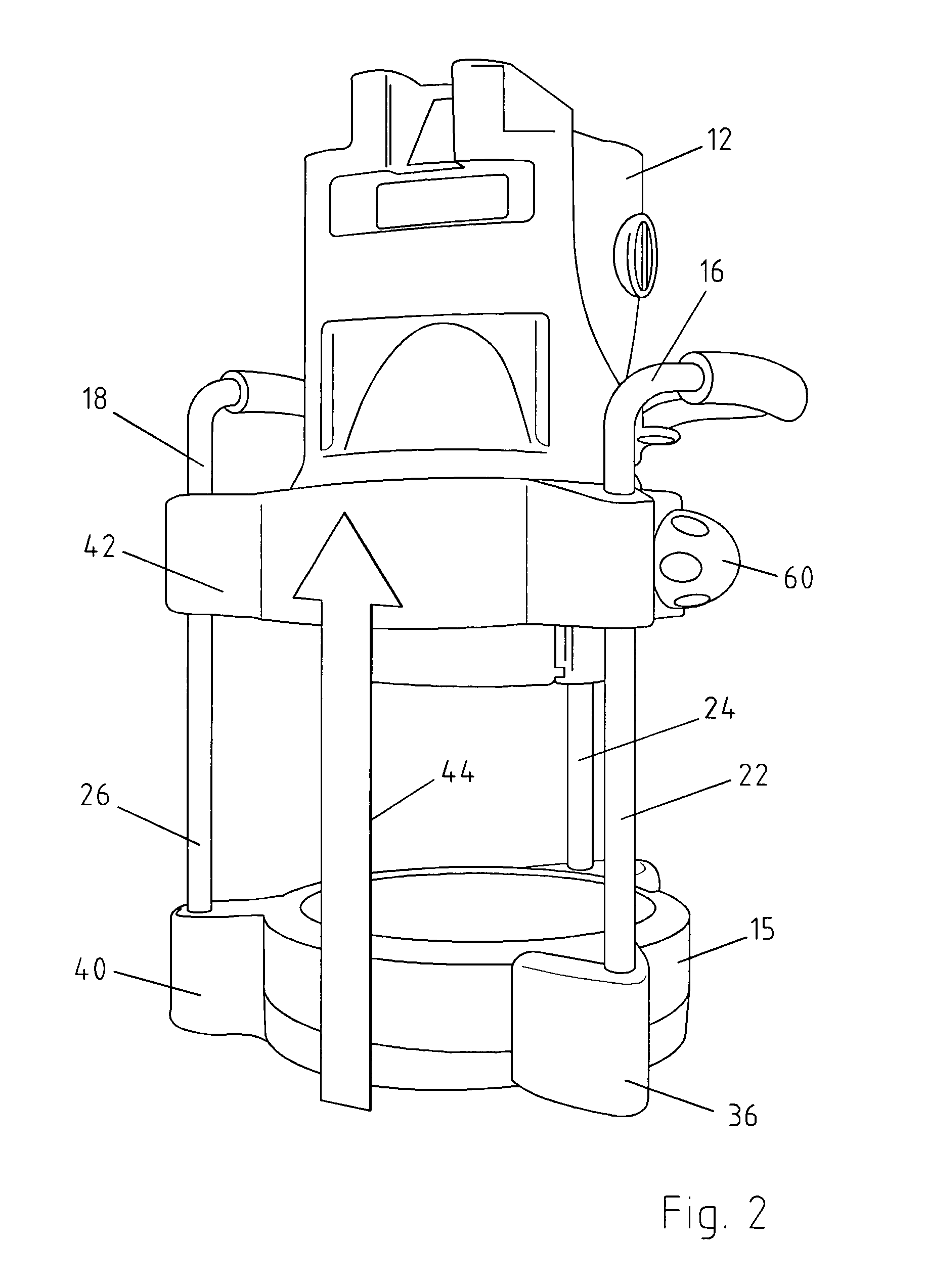
Laser apparatus such as a construction laser apparatus
ActiveUS7167500B2Improve protectionOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser constructional detailsEngineeringLight source
The invention relates to a laser apparatus as construction laser apparatus (10) comprising a light source accommodated inside a housing (12). For providing an increased protection of the apparatus and for adjusting the housing and thus the laser plane to the desired extent with constructive simple measurements, it is suggested that the housing (12) is enclosed by a receiving means (14), along which said housing (12) of the laser is arranged in adjustable manner.
Owner:STABILA MESSGERATE GUSTAV ULLRICH GMBH & CO KG
Attenuated strain of Leishmania
Differentially expressed Leishmania genes and proteins are described. One differentially expressed gene (A2) is expressed at significantly elevated levels (more than about 10 fold higher) in the amastigote stage of the life cycle when the Leishmania organism is present in macrophages than in the free promastigote stage. The A2 gene encodes a 22 kD protein (A2 protein) that is recognized by kala-azar convalescent serum and has amino acid sequence homology with an S-antigen of Plasmodium falcilparum Vietnamese isolate VI. Differentially expressed Leishmania genes and proteins have utility as vaccines, diagnostic reagents, as tools for the generation of immunological reagents and the generation of attenuated variants of Leishmania.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Method for modularizing crystal and heat sink in laser diode pumped solid laser
InactiveCN101958506AReduce the difficulty of assemblyReduce thermal resistanceLaser constructional detailsActive medium materialOptoelectronicsHeat sink
The invention relates to a laser diode pumped solid laser, in particular to a method for modularizing crystal and heat sink in laser diode pumped solid laser. The method is characterized in that the crystal and the crystal heat sink are welded into a whole at high temperature; the crystal heat sink comprises an upper crystal heat sink component and a lower crystal heat sink component; the crystal, the upper crystal heat sink component and the lower crystal heat sink component are assembled together, are closely pressed together by two large parallel free copper, are put into a vacuum furnace together, and then are heated until a silver layer is melted; the crystal, the upper crystal heat sink component and the lower crystal heat sink component are welded together to form a whole; and the welded crystal and the crystal heat sink are plated integrally to obtain an integral element which can be directly used. The method improves the heat conduction efficiency of the crystal side wall, reduces the influence of heat effect, improves the system reliability and the environmental adaptability, and is convenient for batch production of products.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Apparatus for distributed feedback optical fiber laser frequency modulation and denoising
InactiveCN101425655AHigh precisionLow costLaser constructional detailsNon-linear opticsElectrical conductorGrating
The invention relates to a frequency modulation and noise reduction device for a distributed feedback fiber laser. The frequency modulation and noise reduction device comprises a semiconductor laser, a first wavelength division multiplexer, a first optical isolator, an active phase-shifted grating, a second optical isolator, a second wavelength division multiplexer, a polarization controller, a measuring feedback part and a control part, wherein the 980 end of the first wavelength division multiplexer is connected with the output end of the semiconductor laser; the input end of the first optical isolator is connected with the 1550 end of the first wavelength division multiplexer; one end of the phase-shifted grating is connected with the coupled end of the wavelength division multiplexer; the input end of the second optical isolator is connected with the other end of the active phase-shifted grating; the coupled end of the second wavelength division multiplexer is connected with the output end of the second optical isolator; one end of the polarization controller is connected with the 1550 end of the second wavelength division multiplexer; the measuring feedback part is connected with the other end of the polarization controller; and the input end of the control part is connected with the output end of the measuring feedback part. The device is used to realize frequency modulation and noise reduction for the DFB optical fiber laser.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Encapsulating structure of distributed feedback (DFB) fiber laser
InactiveCN102035125AHighly integratedImprove performanceLaser constructional detailsActive medium shape and constructionFiber disk laserEngineering
The invention discloses an encapsulating structure of a distributed feedback (DFB) fiber laser. The encapsulating structure comprises a rectangular base, an outer encapsulating layer, a sound insulating board, an inner encapsulating layer and strip-shaped piezoelectric ceramic, wherein the outer encapsulating layer is an inwardly-concave rectangle and is buckled on the base so as to form an accommodating space between the base and the outer encapsulating layer; two opposite side walls of the outer encapsulating layer are concentrically provided with two first circular holes; the sound insulating board is attached to an inner wall between the base and the outer encapsulating layer and provided with two second circular holes corresponding to the two circular holes on the outer encapsulating layer; the inner encapsulating layer is a hollow rectangular shell fixed on the sound insulating board on the base and provided with two third circular holes corresponding to the two circular holes on the sound insulating board; the strip-shaped piezoelectric ceramic is fixed on the bottom surface of the inner encapsulating layer on the sound insulating board on the base; the DFB fiber laser is fixed on the upper two sides of the strip-shaped piezoelectric ceramic by bonding; and the two ends of the DFB fiber laser pass through the first, second and third circular holes.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus and method for repairing liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN1790103ADefect rate minimizationImprove yieldLaser constructional detailsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The present invention relates to a device and method for repairing a liquid crystal display panel, which can minimize the defect rate of the liquid crystal display panel by dimming bright spots, thereby increasing its yield. An apparatus for repairing a liquid crystal display panel according to the present invention includes: a liquid crystal display panel including a repair film formed on any one of a first substrate and a second substrate facing each other, and a liquid crystal layer is located between the two substrates and a laser irradiating device for irradiating laser light to the repair film to darken a specific area of the repair film corresponding to the area where bright spots appear in the liquid crystal display panel.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Fiber cutting mechanism and laser light source application apparatus comprising the mechanism
InactiveUS20100183037A1Avoid utilizationLaser using scattering effectsFibre light guidesGratingLaser light
Provided is a fiber cutting mechanism that prevents secondary utilization of a fiber laser light source incorporated in a device that uses a laser light. With a characteristic fiber cutting mechanism, when a laser device is separated from a laser light source application apparatus, at least a fiber 26 is cut in an specific area from a point within a fiber grating 29 to a connection point between the fiber grating 29 and the fiber 26 containing a laser activating substance (cutting position area (1)).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Variable reflectivity mirror for increasing available output power of a laser
InactiveUS6351482B1Increase productionImprove reflectivityOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser constructional detailsElectrical conductorTransmittance
Output for a laser is greatly increased by altering the transmitivity of a superconductor layer which serves as one of the mirrors of the laser cavity. The superconductor layer is switched between a superconductive state, having reflectivity of one, and a non-superconductive state, having a reflectivity of less than one. When the mirror is in its superconducting state, output power is decreased and power in the cavity is increased, and when the mirror is in its non-superconducting state, output power of the laser is increased and power in the cavity decreases.
Owner:TERRACOMM RES
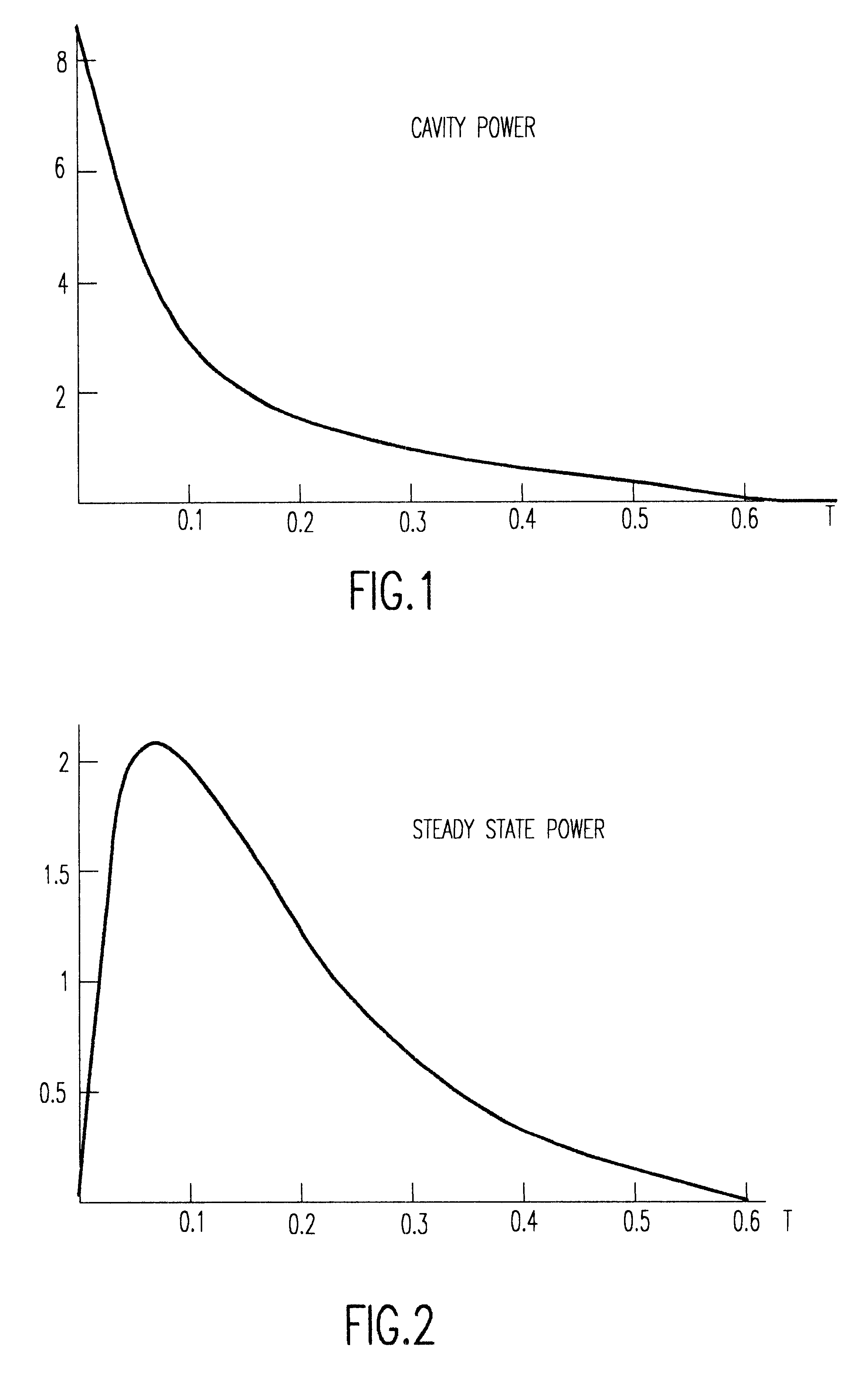
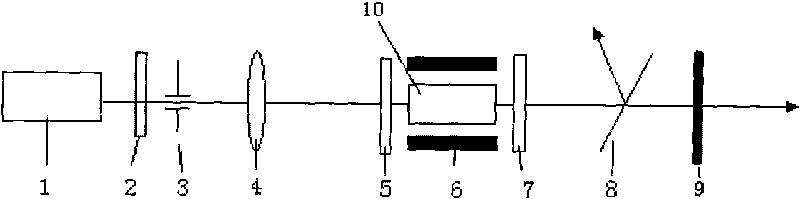
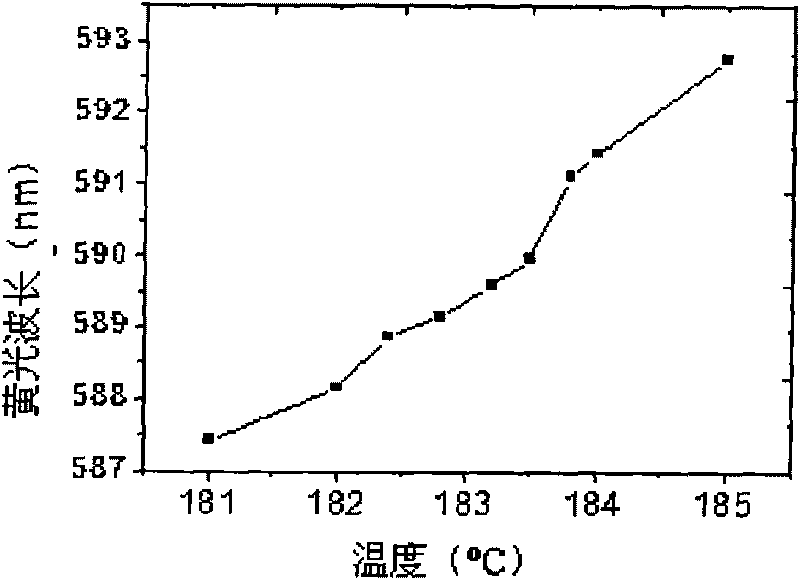
Yellow light laser using cascading superlattice as frequency changer crystal
InactiveCN101741000ACompact structureEasy to integrateOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser constructional detailsFrequency changerTemperature control
The invention provides a yellow light laser using a cascading superlattice as frequency changer crystal. The laser comprises a pumping light source, a resonant cavity formed by front and back cavity mirrors, a temperature control furnace and a two-segment cascading optical superlattice, wherein the cascading optical superlattice is used as the non-linear frequency changer crystal; and the light emitted by the pumping light source enters the resonant cavity and then passes the cascading optical superlattice, and finally the yellow light, of which the wavelength is 590nm, is outputted from the back cavity mirror. The first-segment structure of the cascading superlattice is used for realizing an oscillatory process of light parameters, and the second-segment structure of the cascading superlattice is used for generating the double frequency yellow light. The yellow light laser has the advantages that: the design is flexible; both the cascading periodic structure and the pseudo periodic, aperiodic or double periodic structure can be used to simultaneously realize the phase matching of two non-linear processes; a plurality of structures can be integrated on one chip, the structure is compact; the integrated property of the system is improved; the broad tuning yellow light output is realized; and the laser output is stably achieved, and the highly efficient and stable full solid-state yellow light laser is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Fiber holder and fiber laser apparatus
ActiveUS20120301097A1Wound easily and accuratelyOptical fibre/cable installationLaser constructional detailsBobbinEngineering
A fiber holder which can wind an optical fiber easily and accurately, and hold an optical fiber in a wound state is provided. The optical fiber is accommodated in the groove (introduction portion) formed on the fiber bobbin, after that, the bobbin cover is rotated in the rotational direction of the helical groove while the optical fiber is kept in contact with the cutout formed in the bobbin cover. With this, the optical fiber can be accommodated in the groove. Thus, the optical fiber can be wound easily and accurately, and the optical fiber can be held on the fiber bobbin.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Master oscillator system and laser apparatus
A master oscillator system may include a grating that functions as one of a plurality of resonator mirrors in an optical resonator, an optical element disposed within an optical path between the plurality of resonator mirrors, and an attitude control mechanism that adjusts an angle at which laser light traveling within the optical resonator is incident on the grating by adjusting the attitude of the optical element.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
Method and apparatus for controlling output power levels of a laser used for optical data transmission based on data rate-speed optical feedback
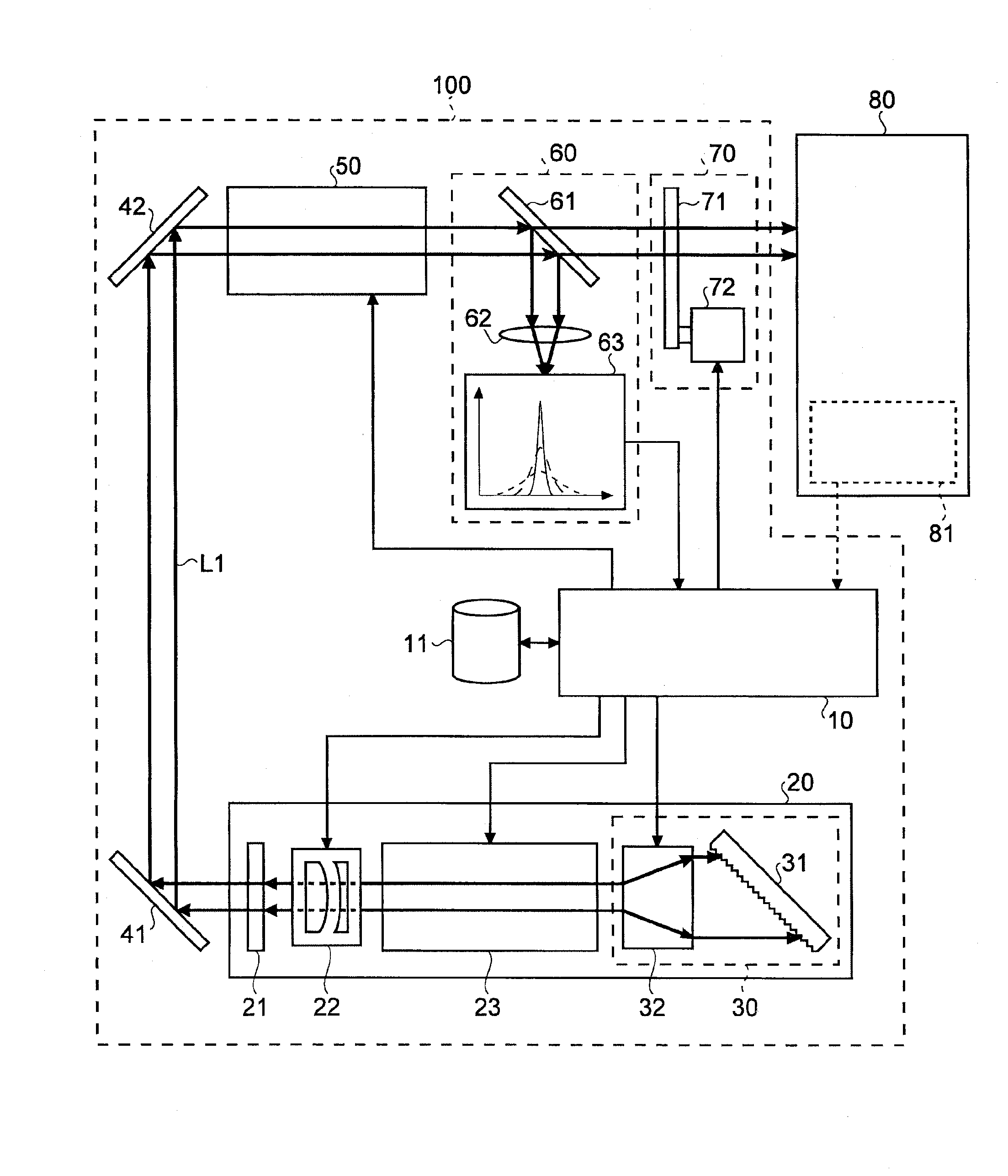
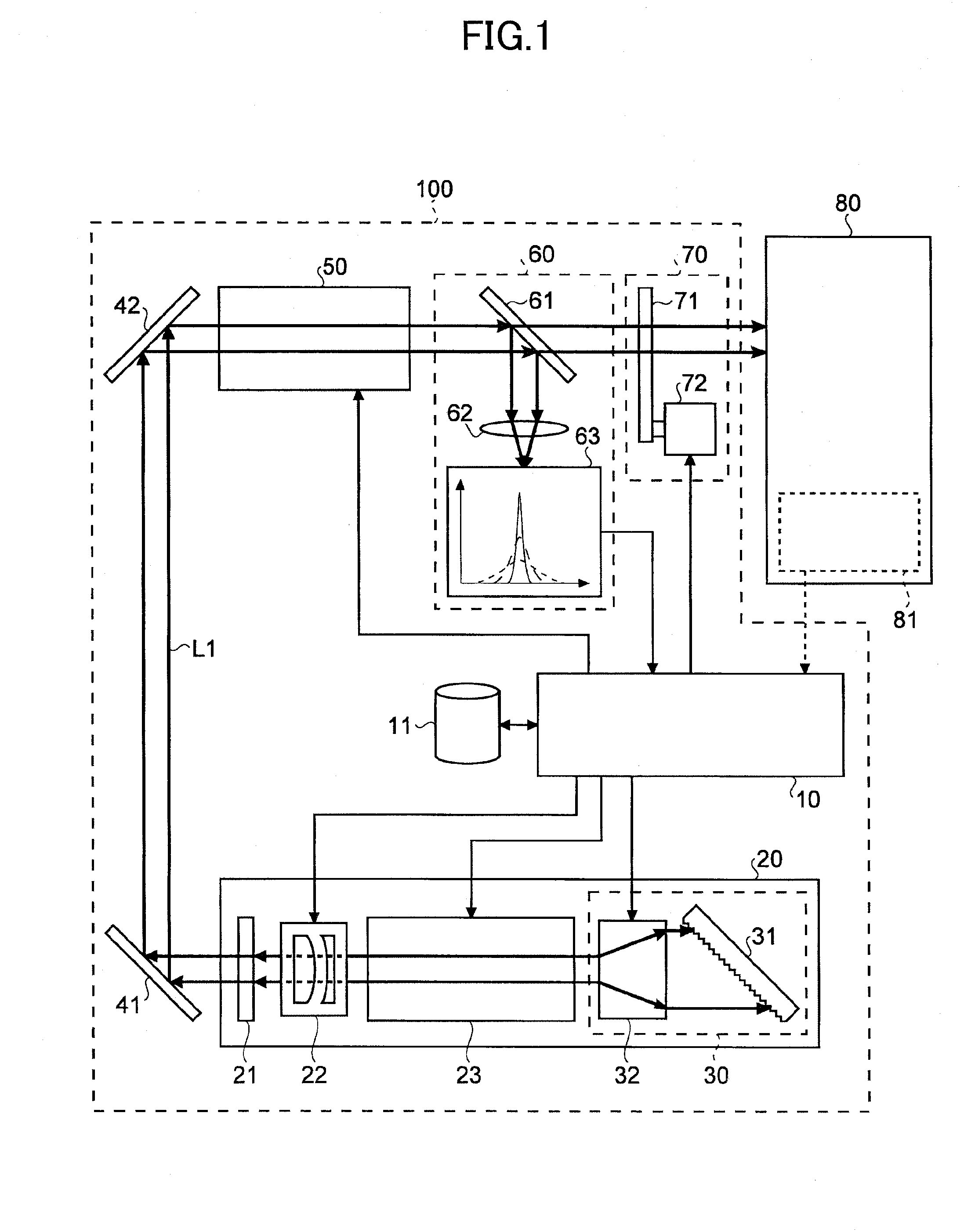
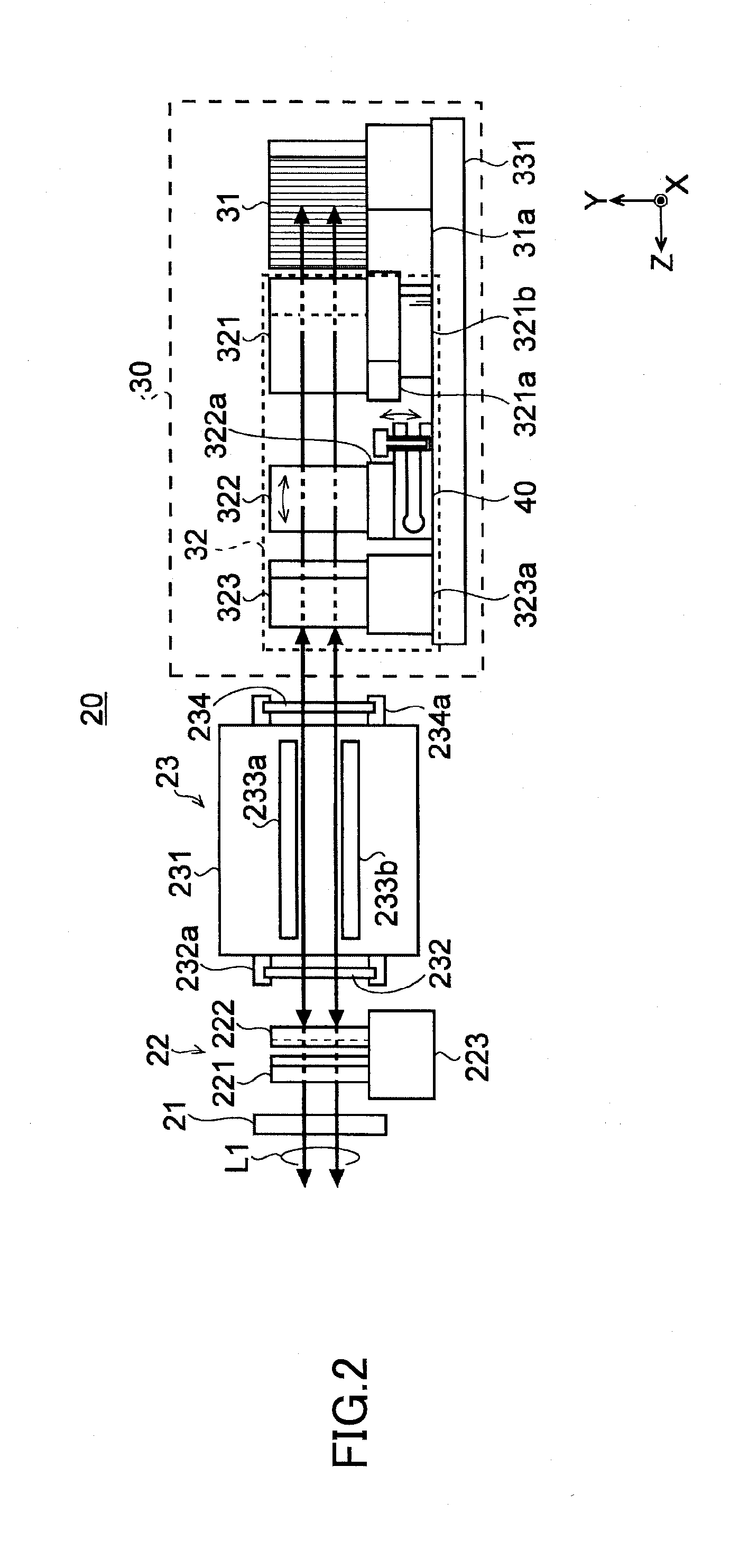
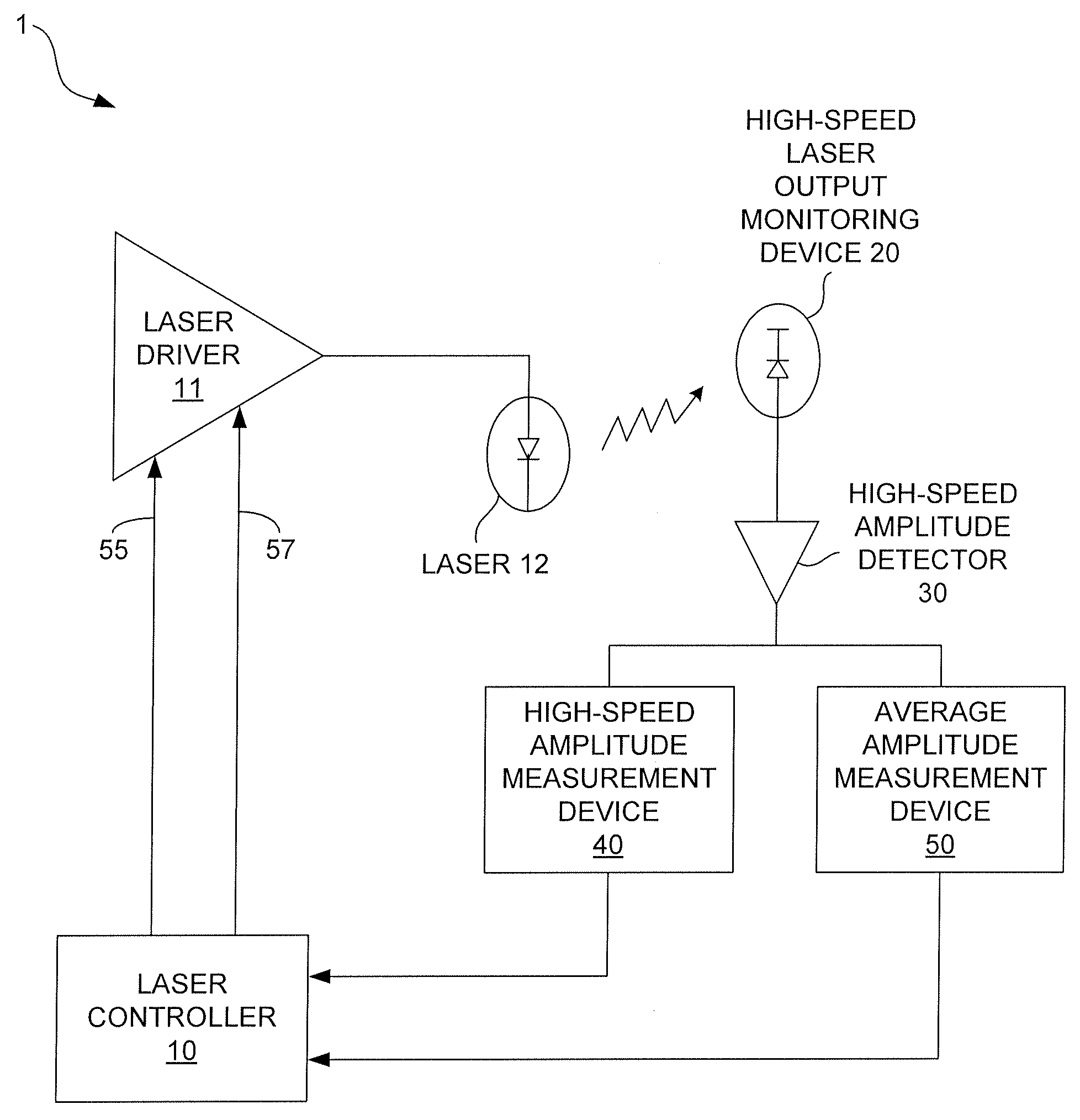
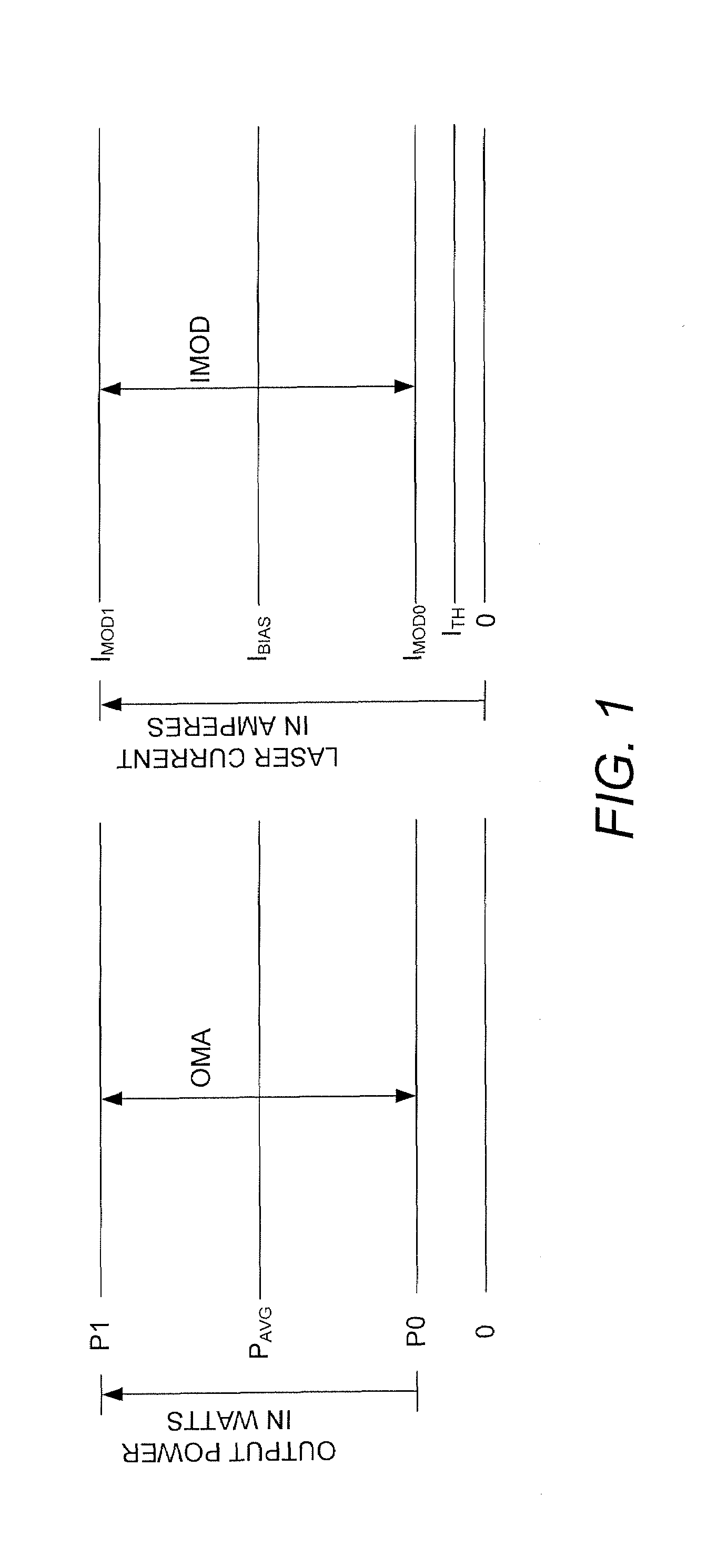
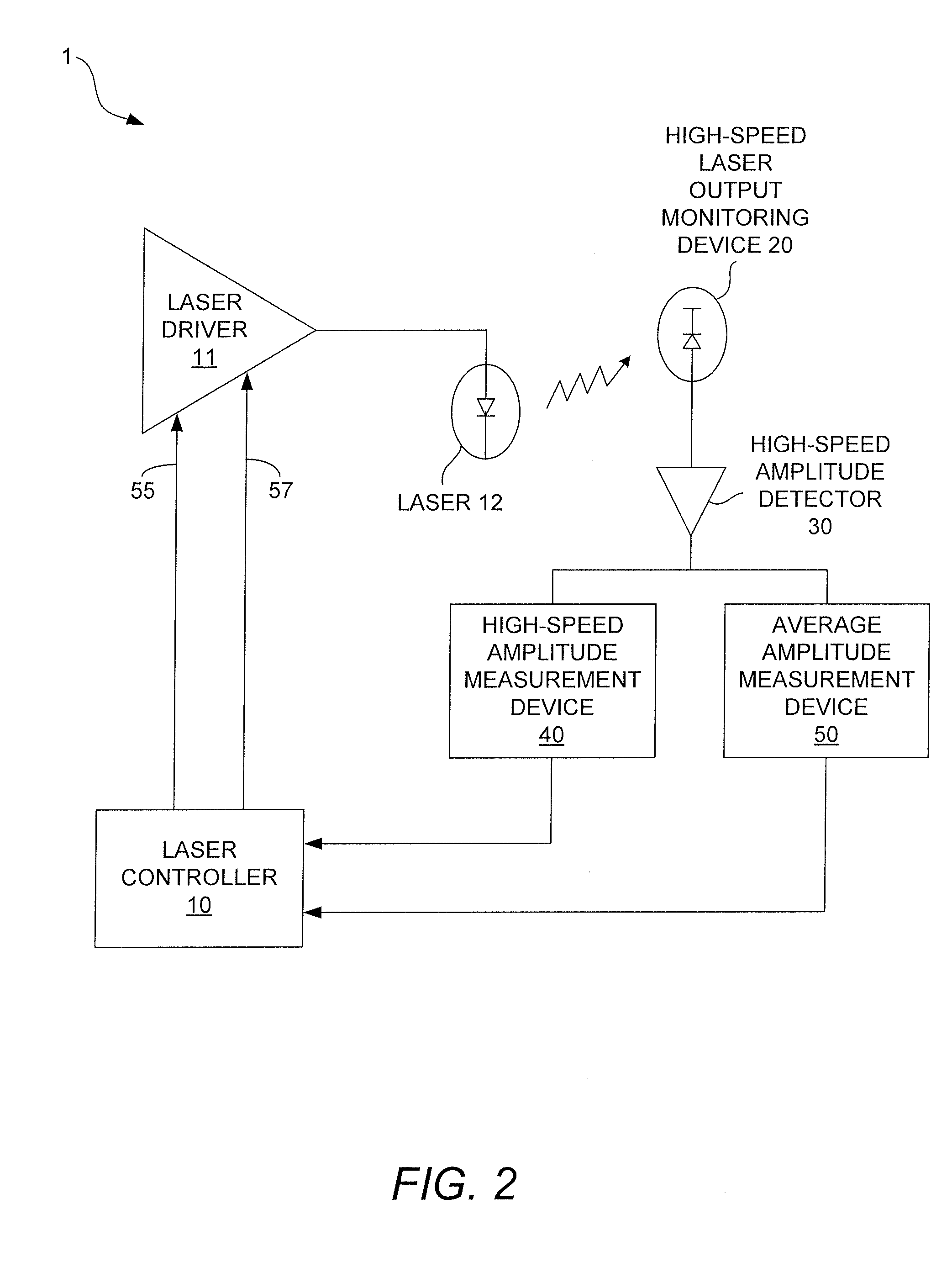
InactiveUS20080181272A1Laser constructional detailsSemiconductor lasersMeasurement deviceControl signal
High-speed measurements of the output power level of a laser are obtained by using a high-speed laser output power monitoring device that is capable of producing an electrical feedback signal having an amplitude that varies as the output power level of the laser varies. A high-speed amplitude detector receives the electrical feedback signal and detects the amplitude of the feedback signal and produces an optical modulation amplitude (OMA) detection signal. The OMA detection signal is received in a high-speed amplitude measurement device that measures the OMA and produces an OMA measurement value. The OMA measurement value is then processed by the laser controller to obtain a modulation current control signal, which is then output to the laser driver to cause the laser driver to adjust the laser modulation current to obtain a desired or optimum laser output power level. An average amplitude measurement value may also be obtained using an average amplitude measurement device that processes the OMA detection signal produced by the high-speed amplitude detector to obtain the average amplitude measurement value. The laser controller receives the average amplitude measurement value and processes it to obtain a bias current control signal, which is then output to the laser driver to cause it to adjust the amplitude of the bias current to obtain a desired or optimum average laser output power level.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com