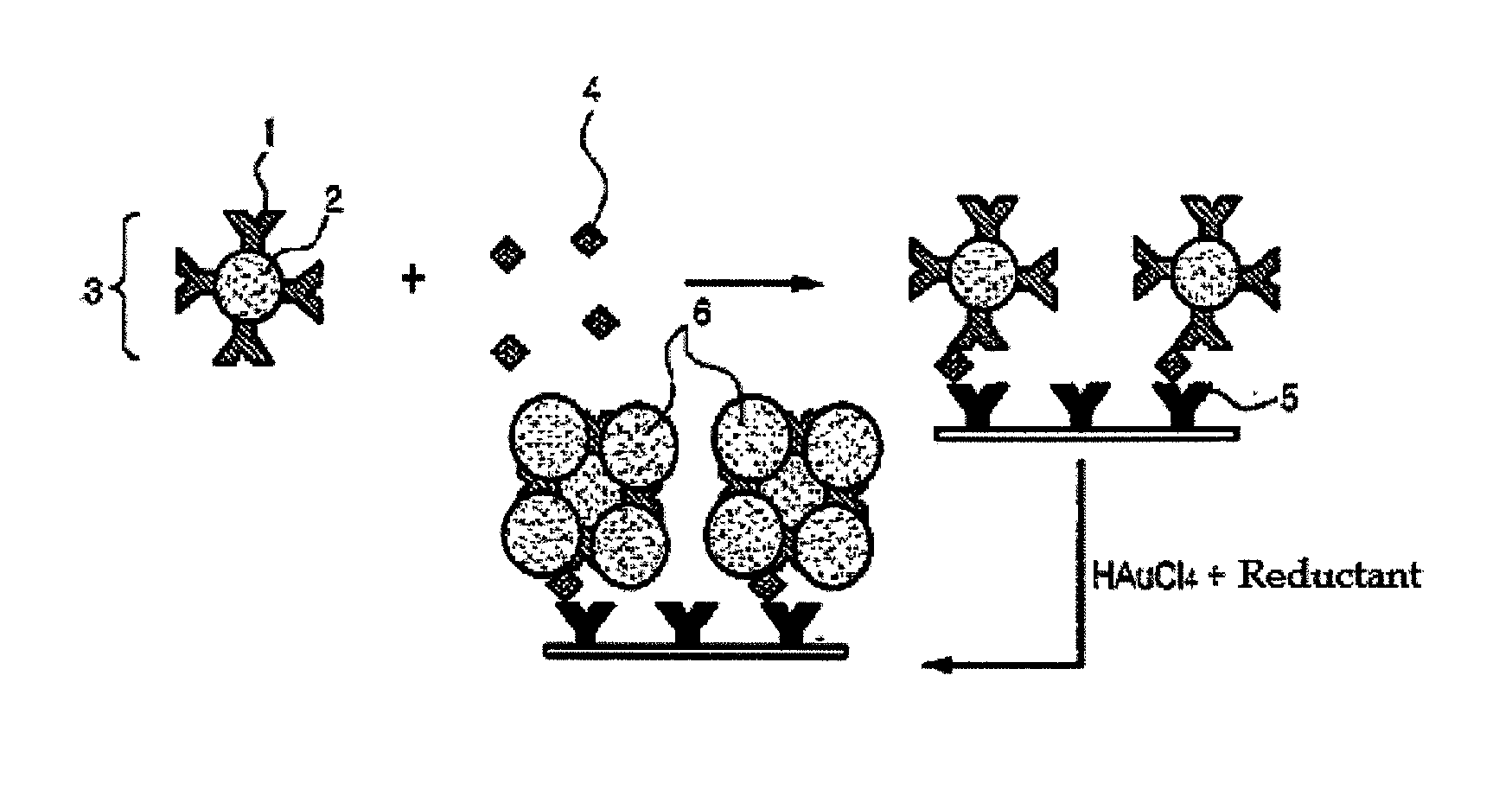
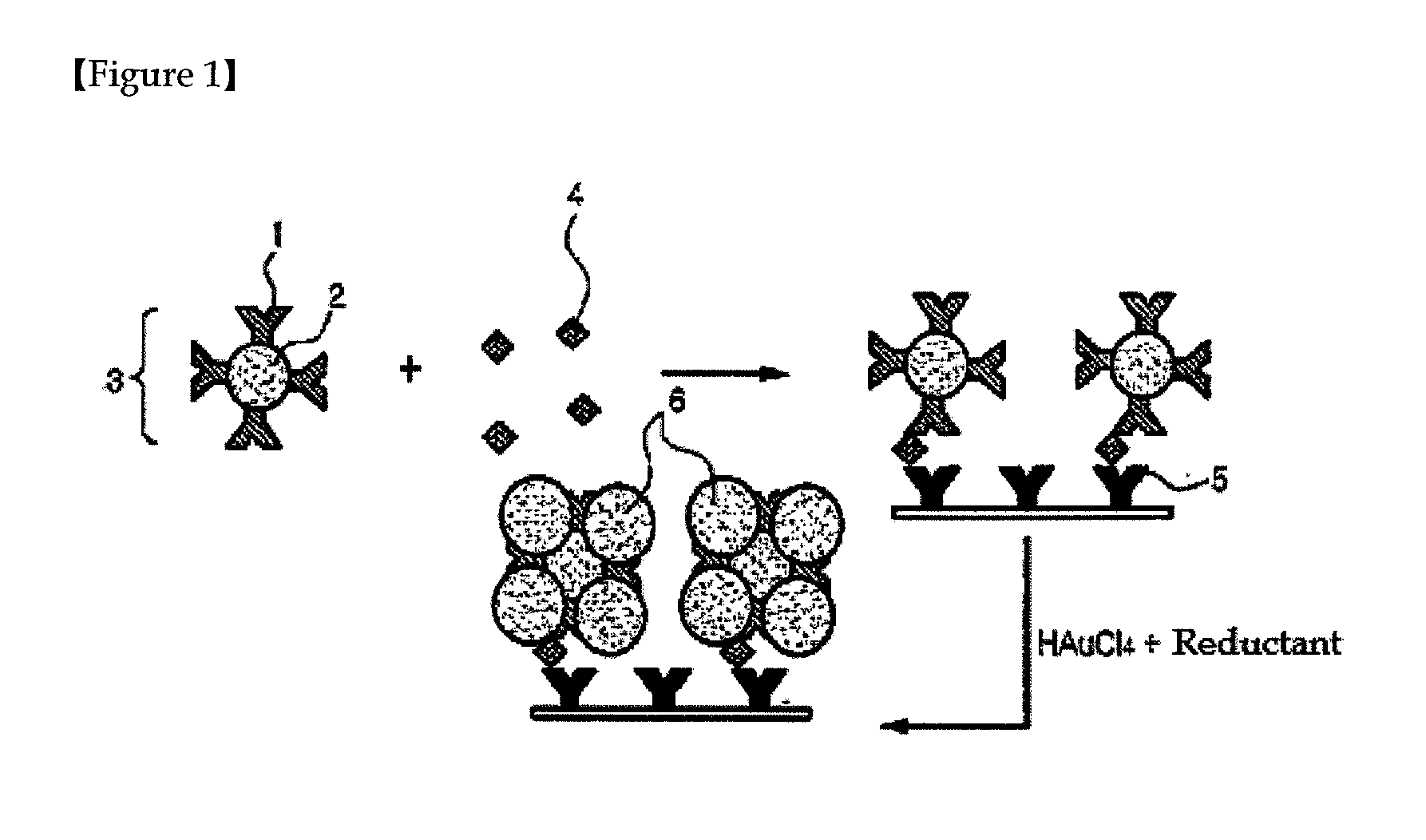
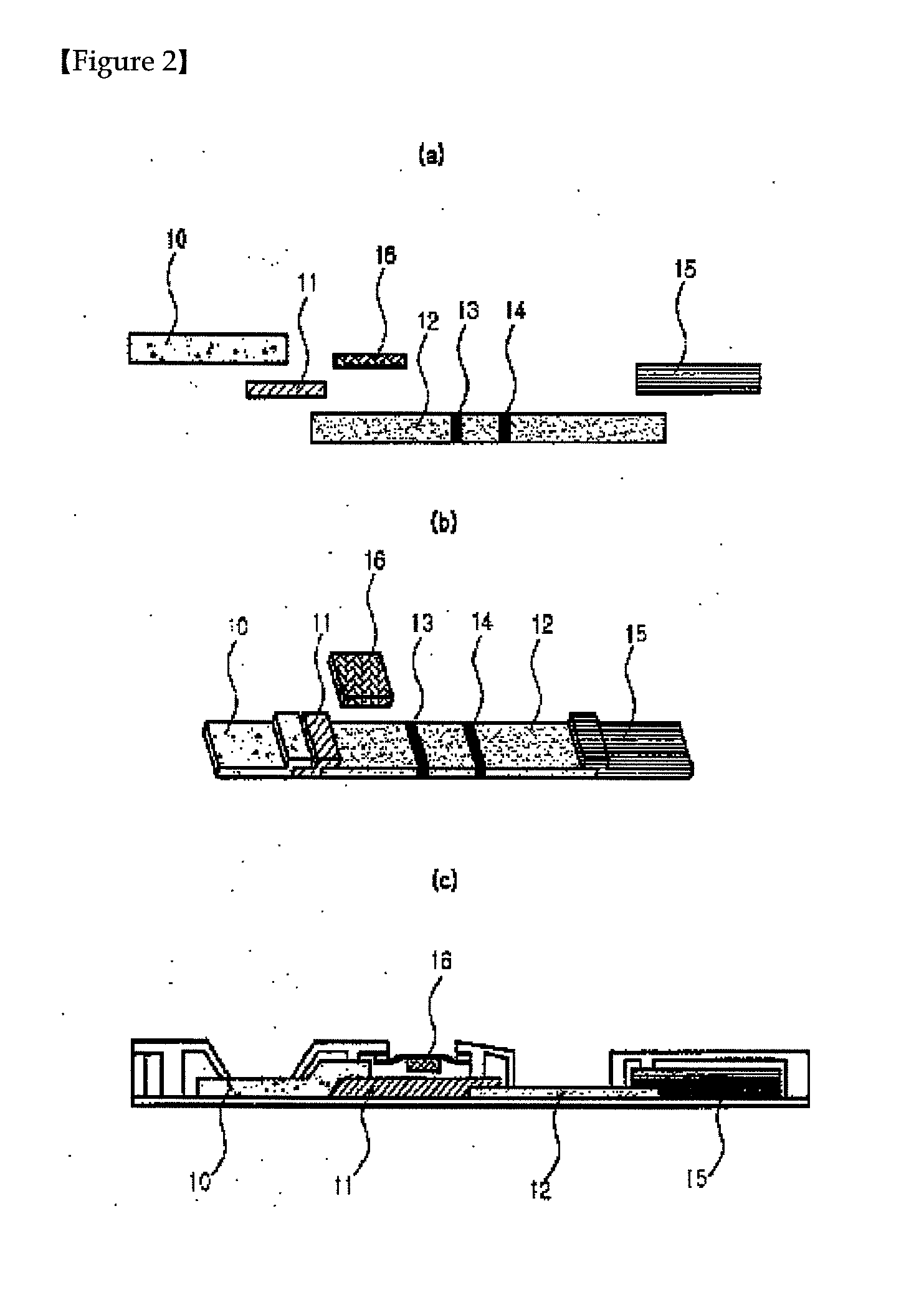
Patents
Literature
142results about How to "Good zoom effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
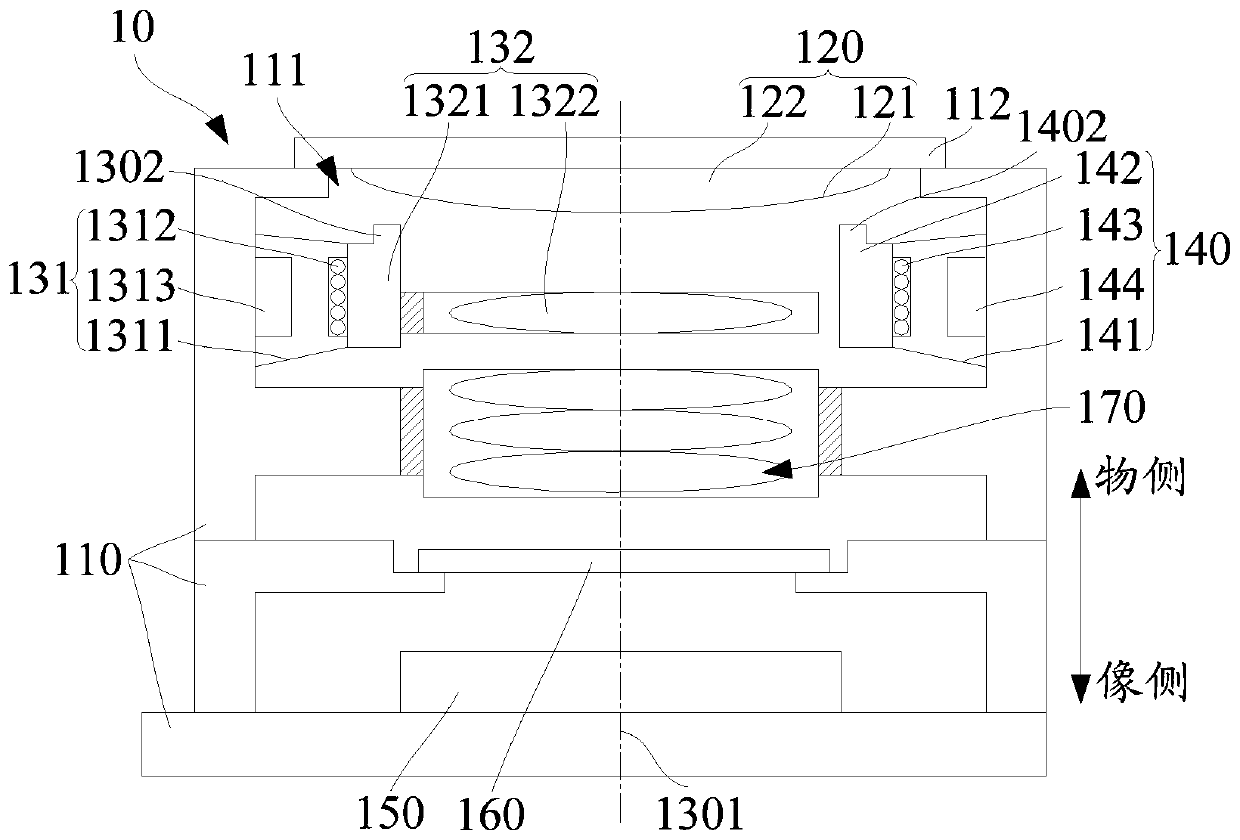
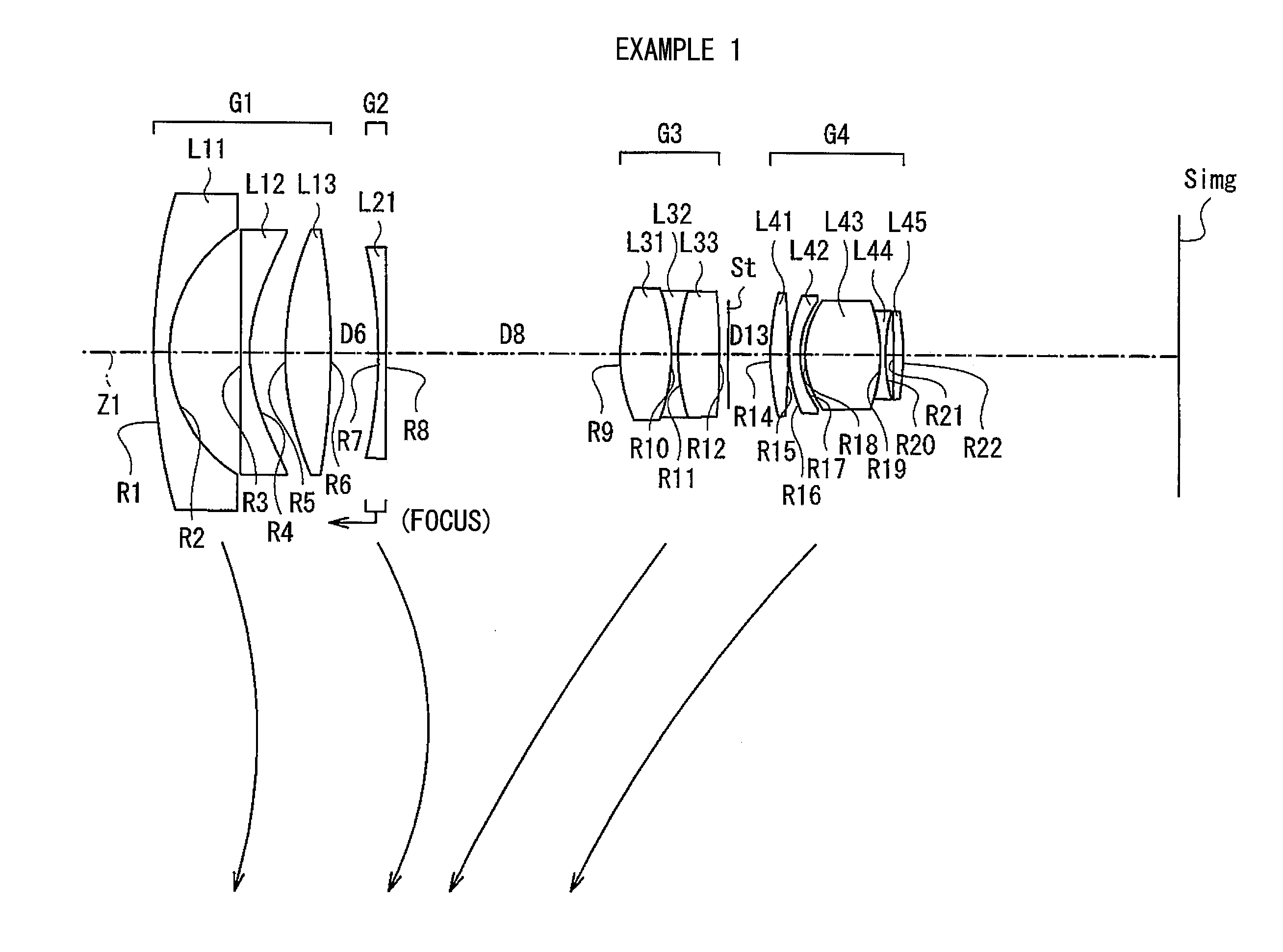
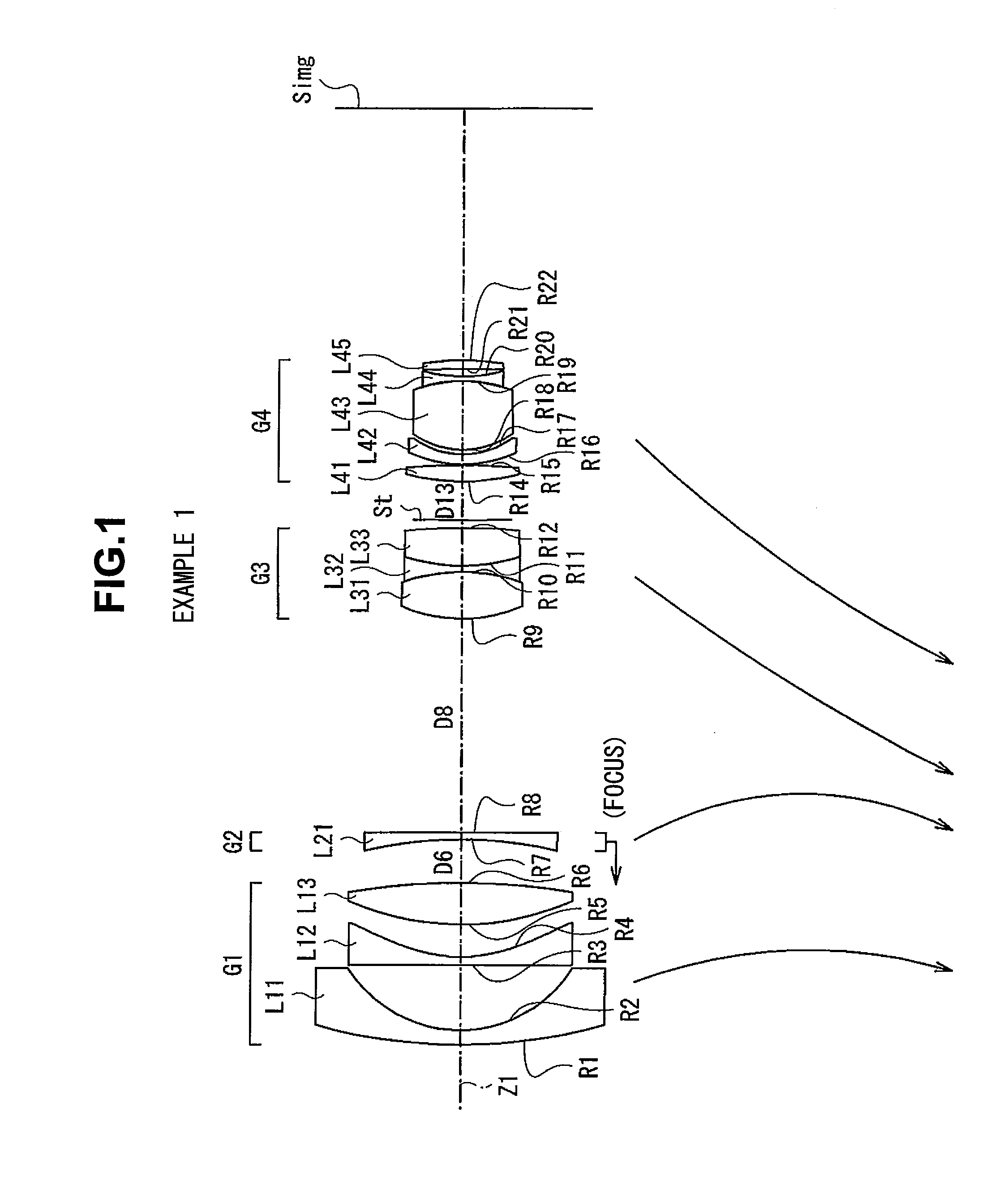
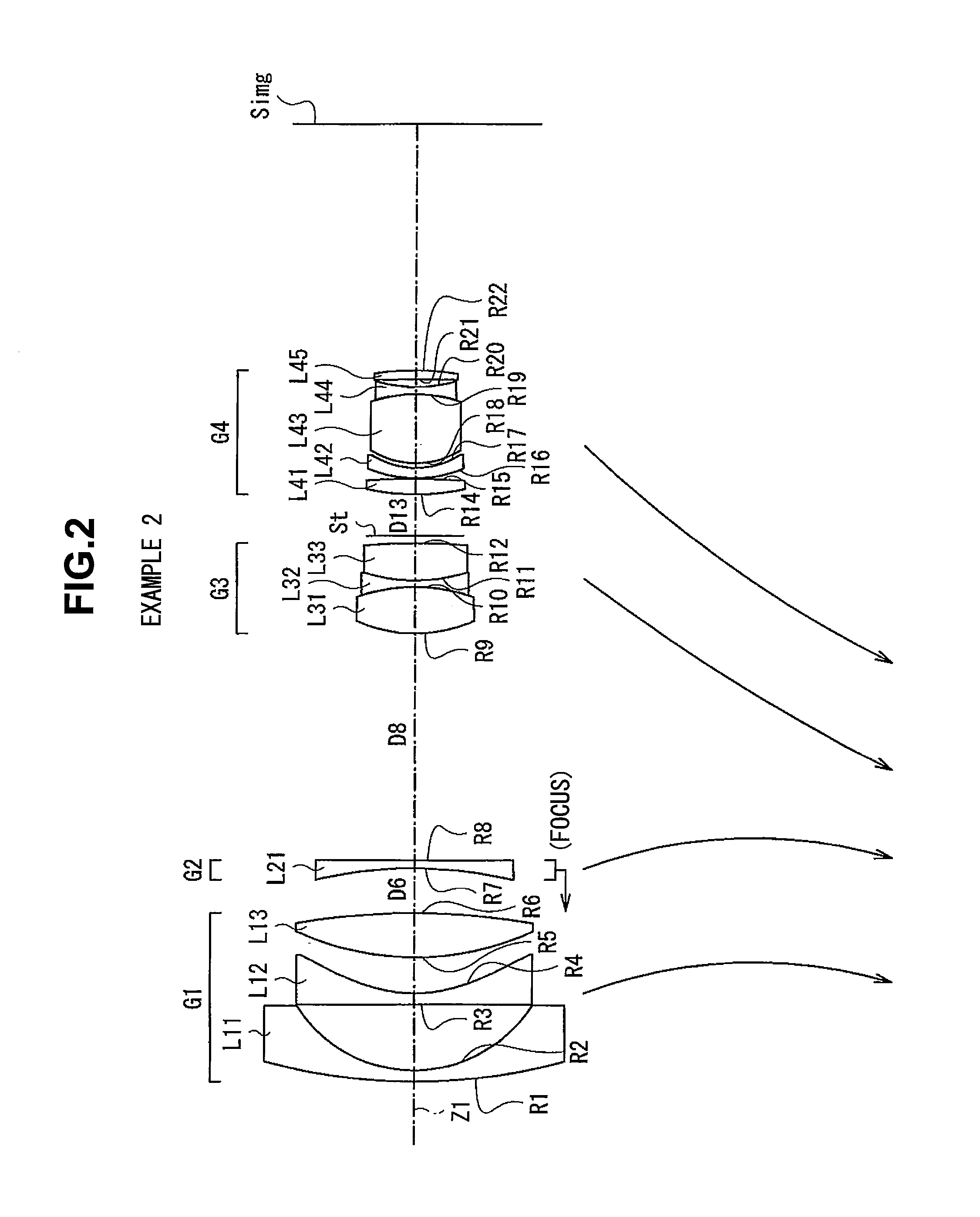
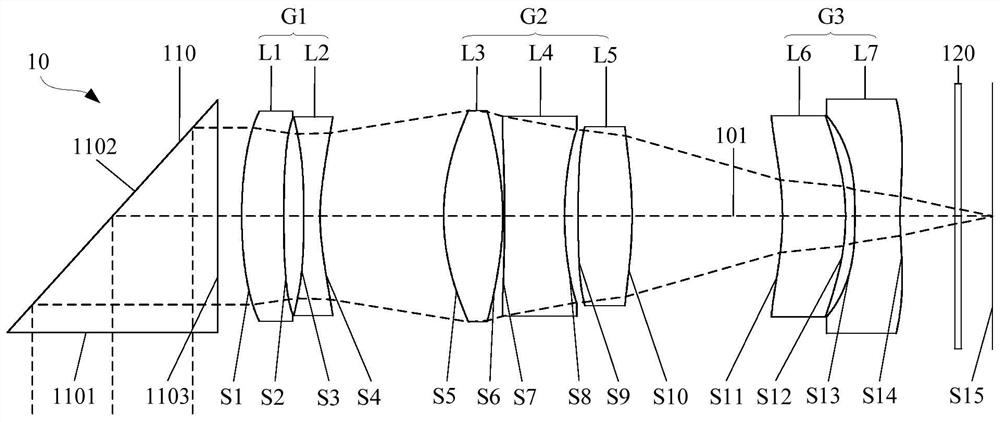
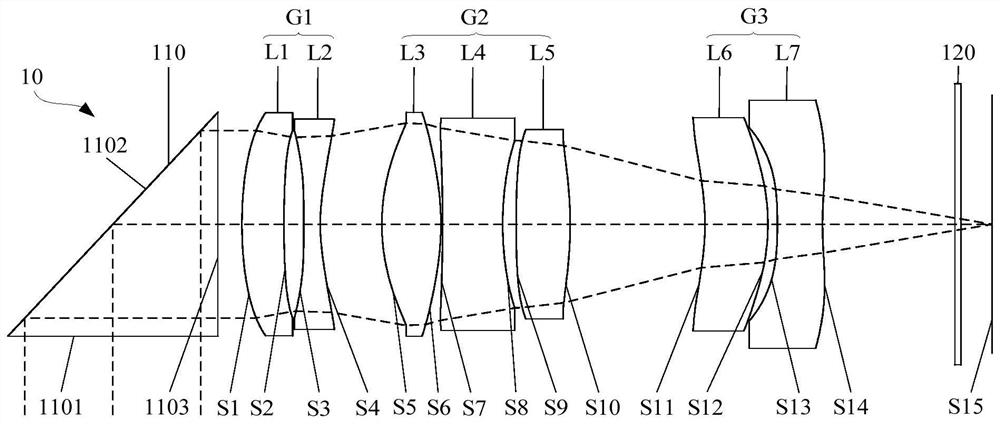
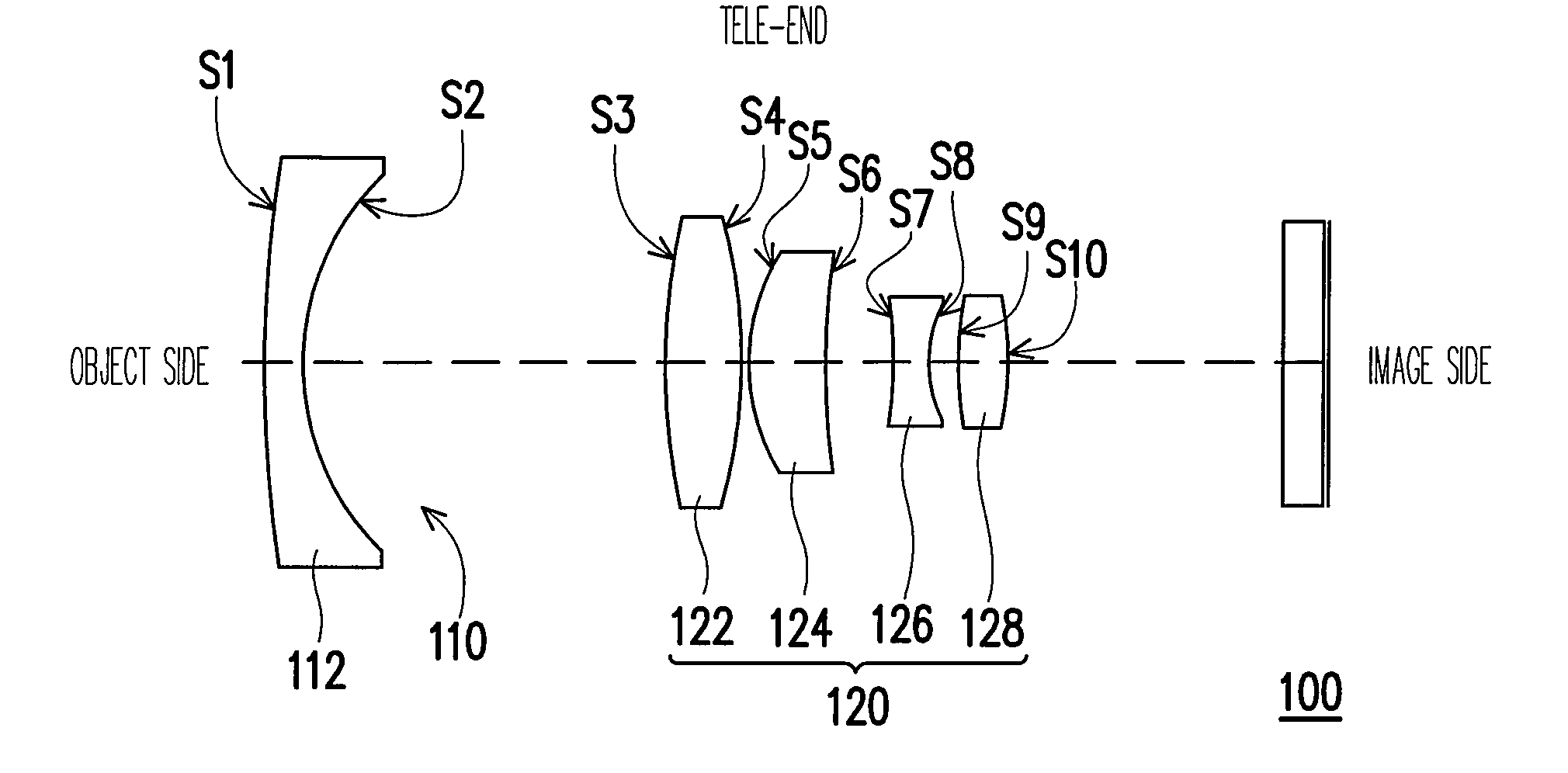
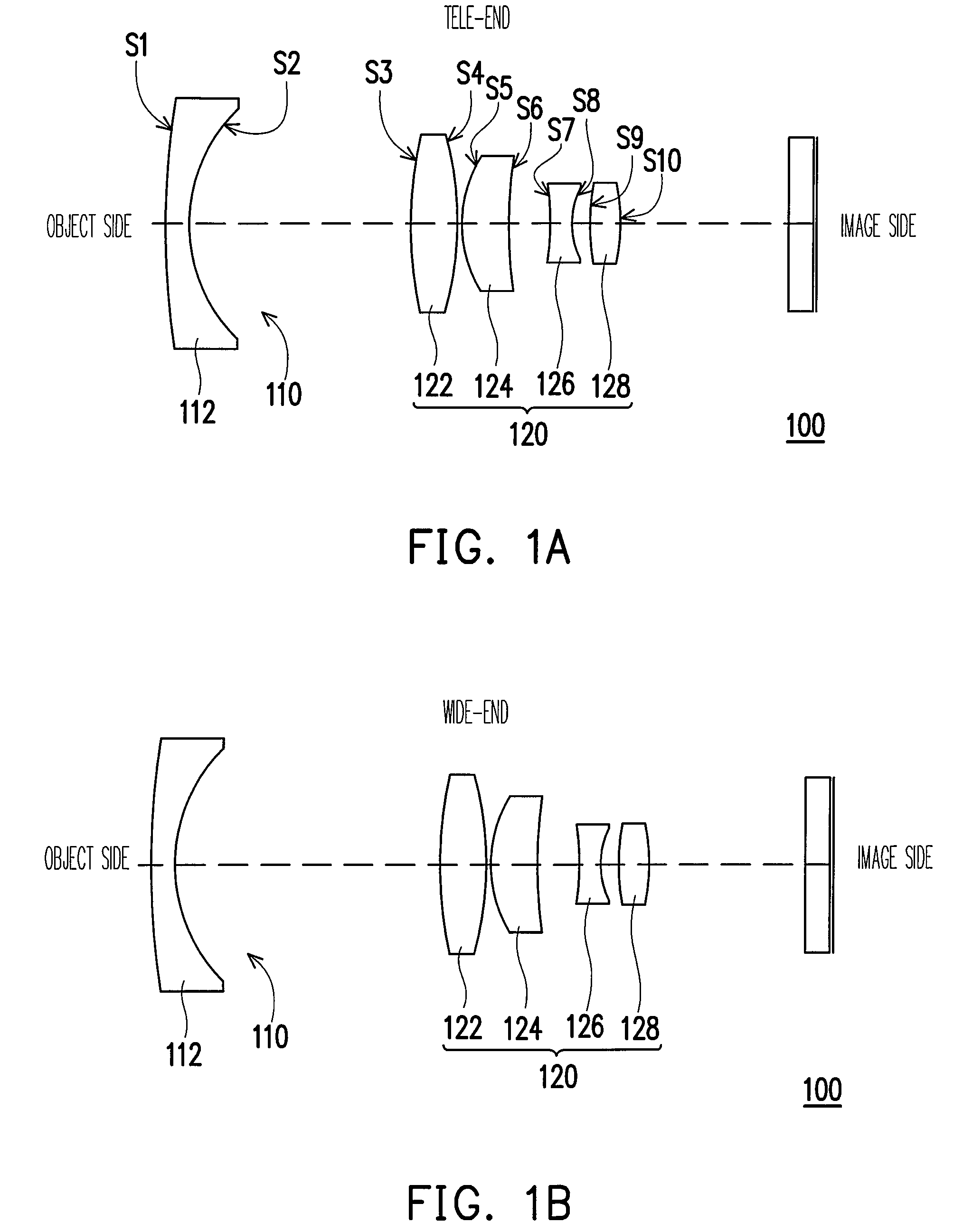
Optical image capturing lenses
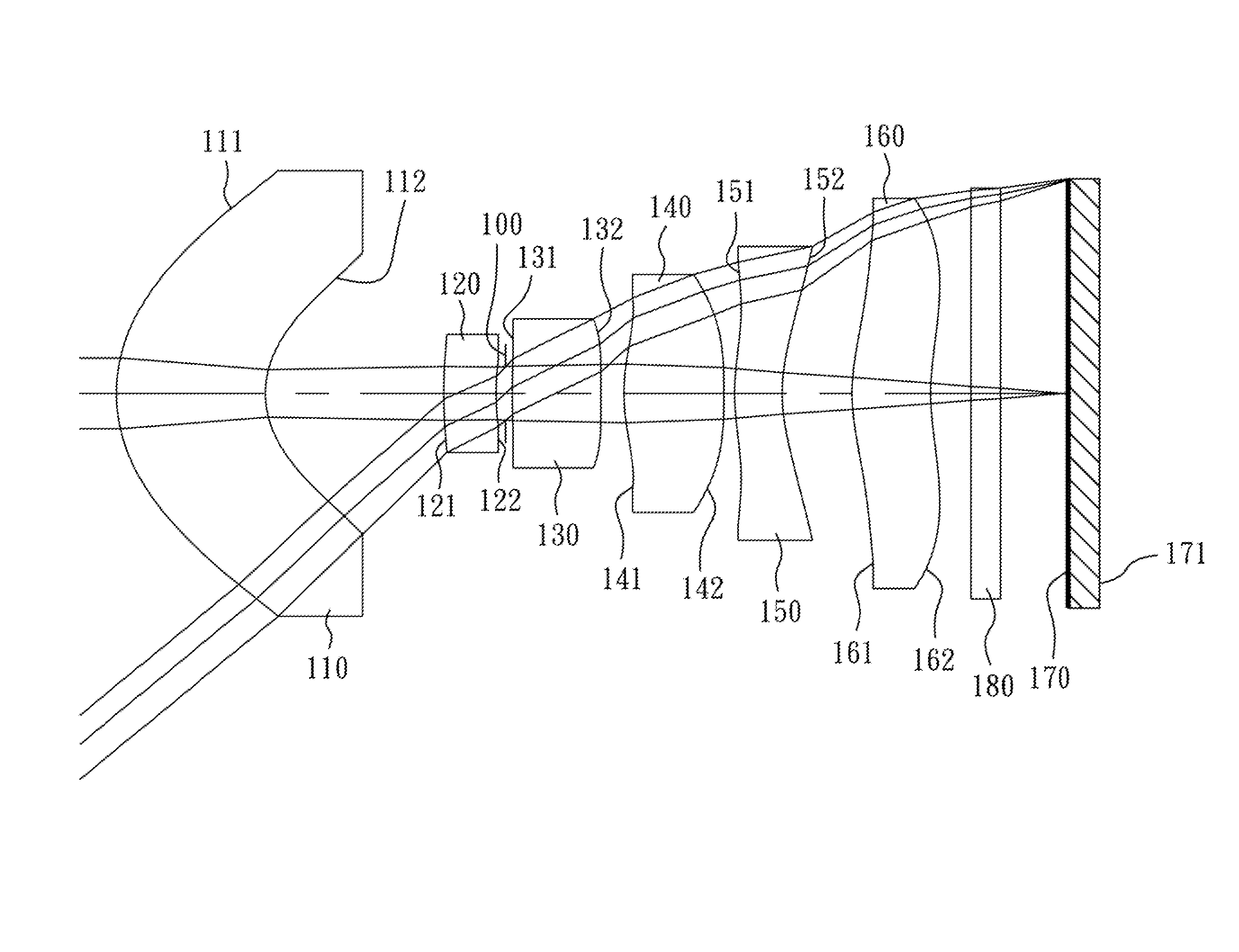
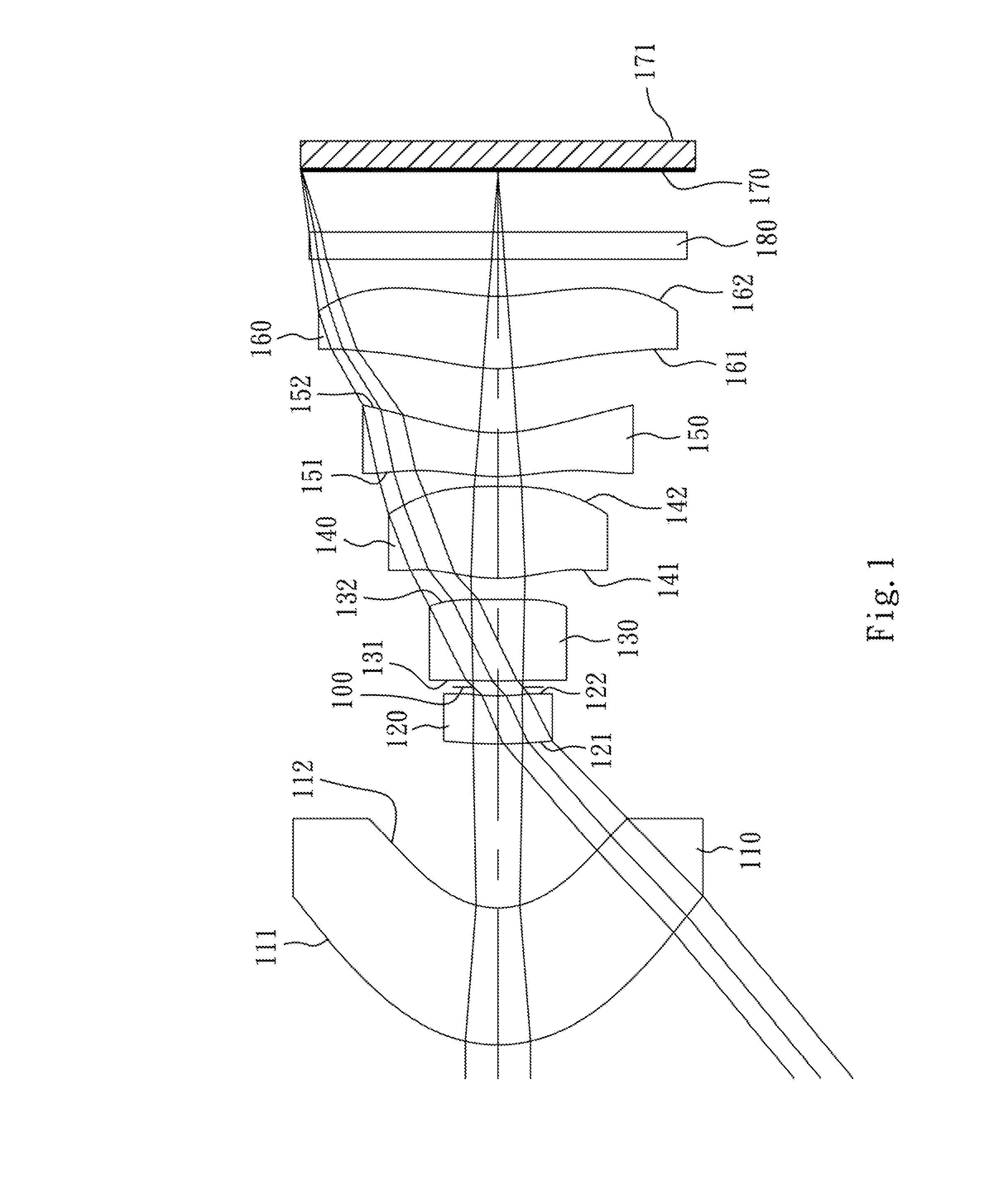
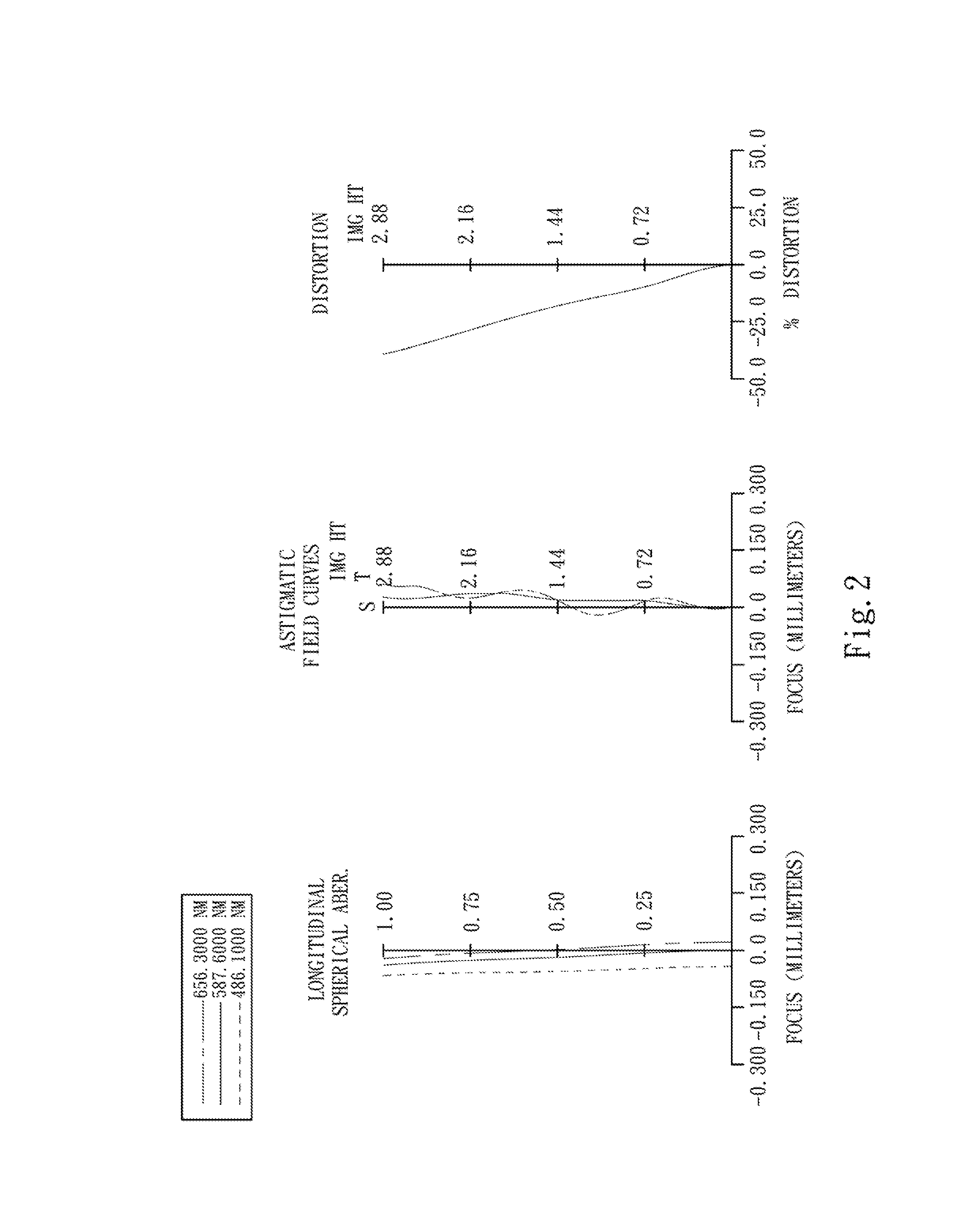
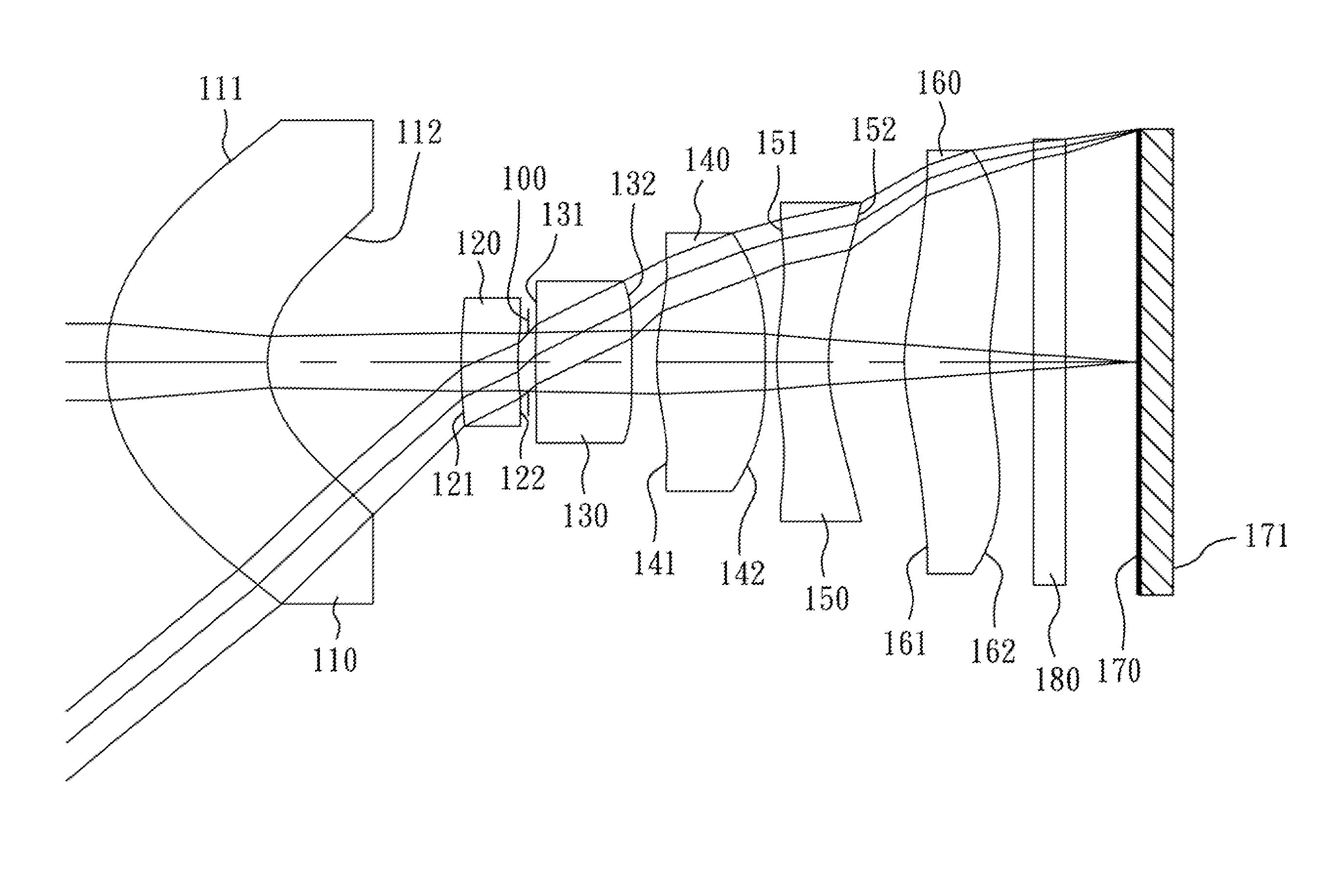
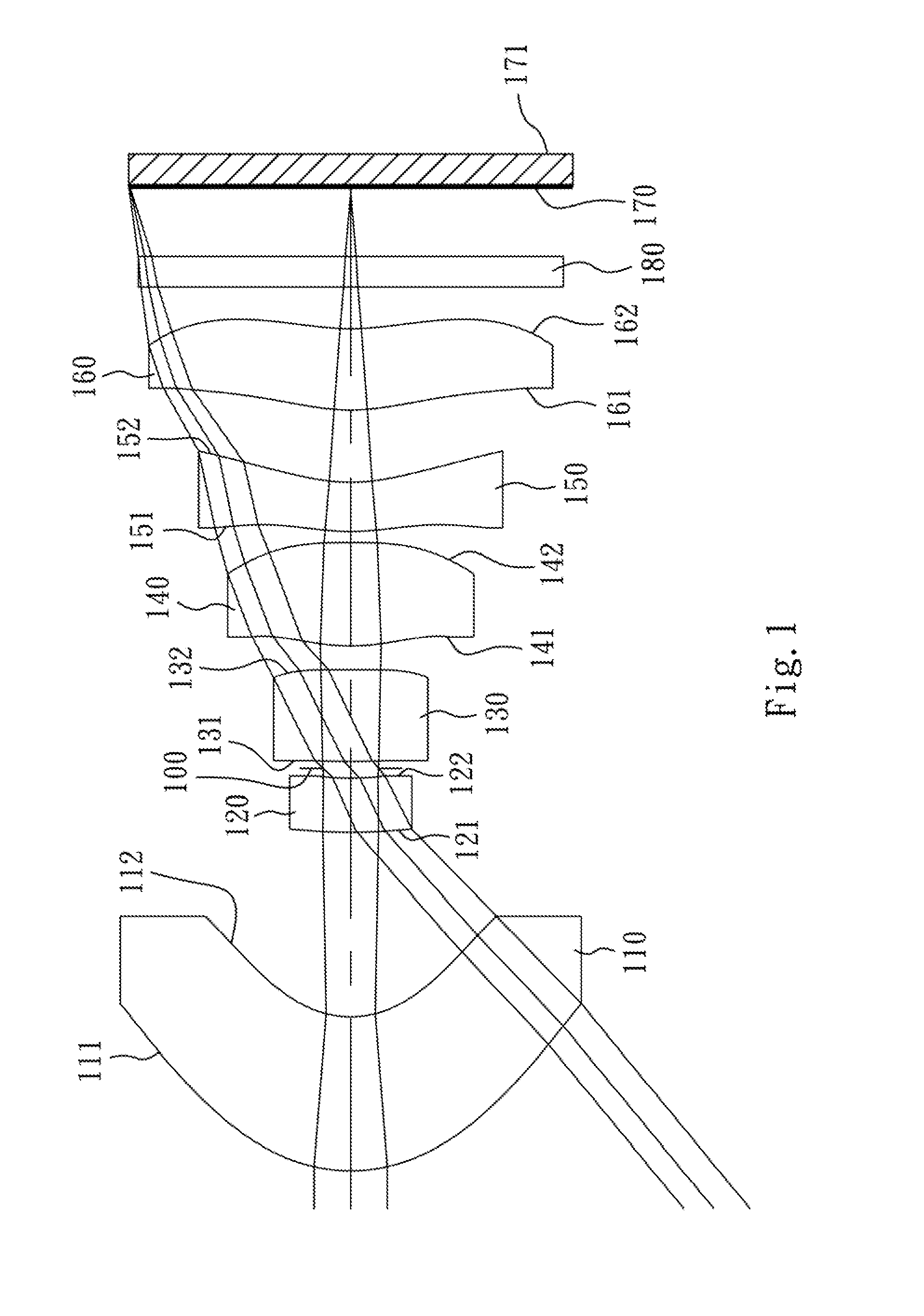
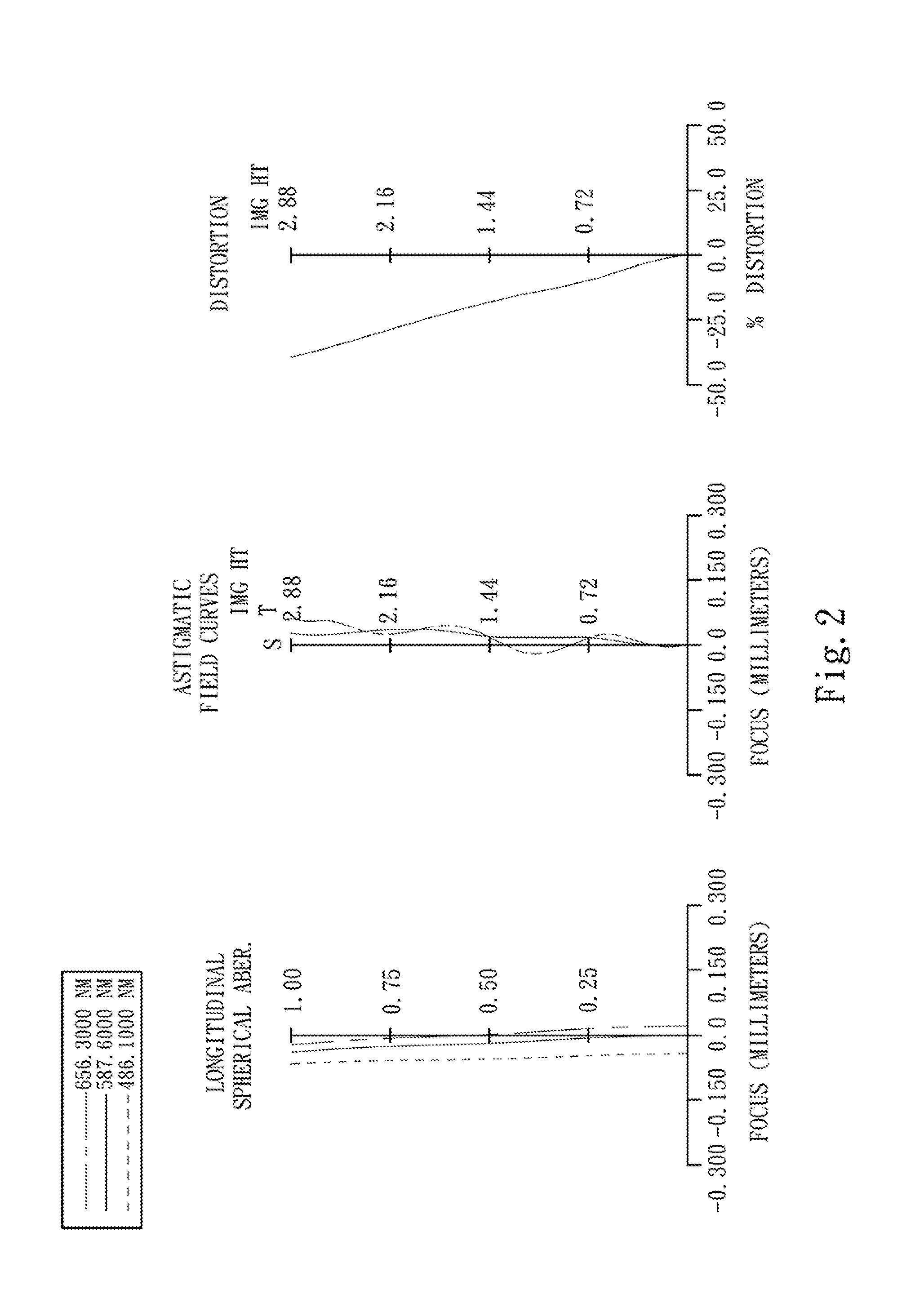
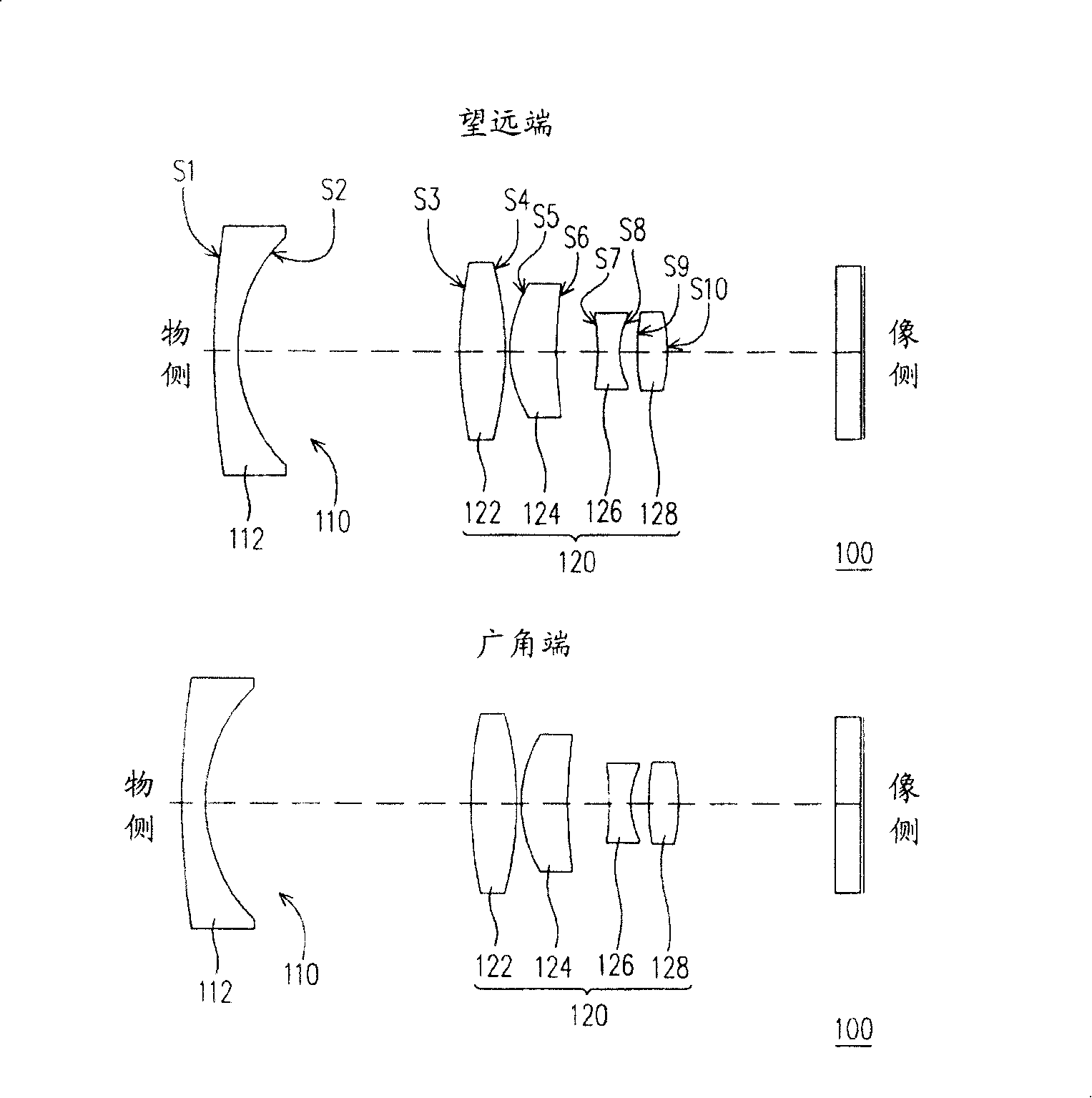
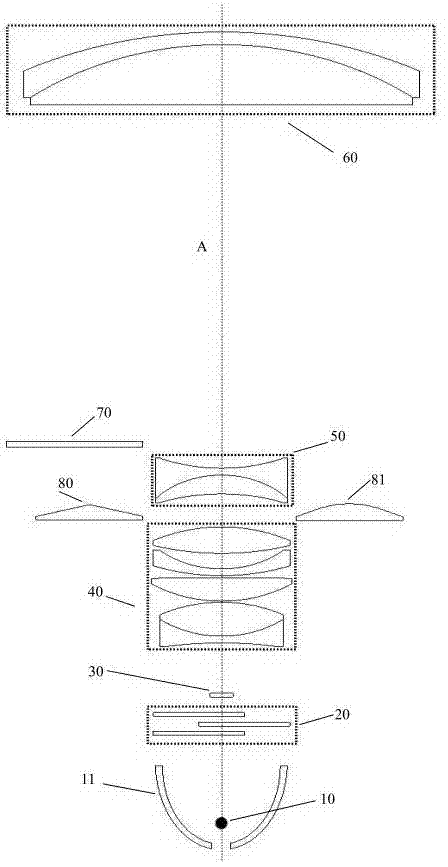
An optical image capturing lenses includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a front lens group, a stop, and a rear lens group. The front lens group includes, in order from the object side to the image side, at least a first lens element and a second lens element. The first lens element has a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface. The rear lens group includes, in order from the object side to the image side, at least a third lens element, a fourth lens element, a fifth lens element, and a sixth lens element. The sixth lens element is made of plastic material. The object-side surface and the image-side surface of the sixth lens are aspheric. The sixth lens element has at least one inflection point formed on at least one of the object-side surface and the image-side surface thereof.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical image capturing lenses
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Gene detecting methods without using PCR
ActiveUS8704165B2Enhanced signalHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementParticle spectrometer methodsMicroparticleBiology
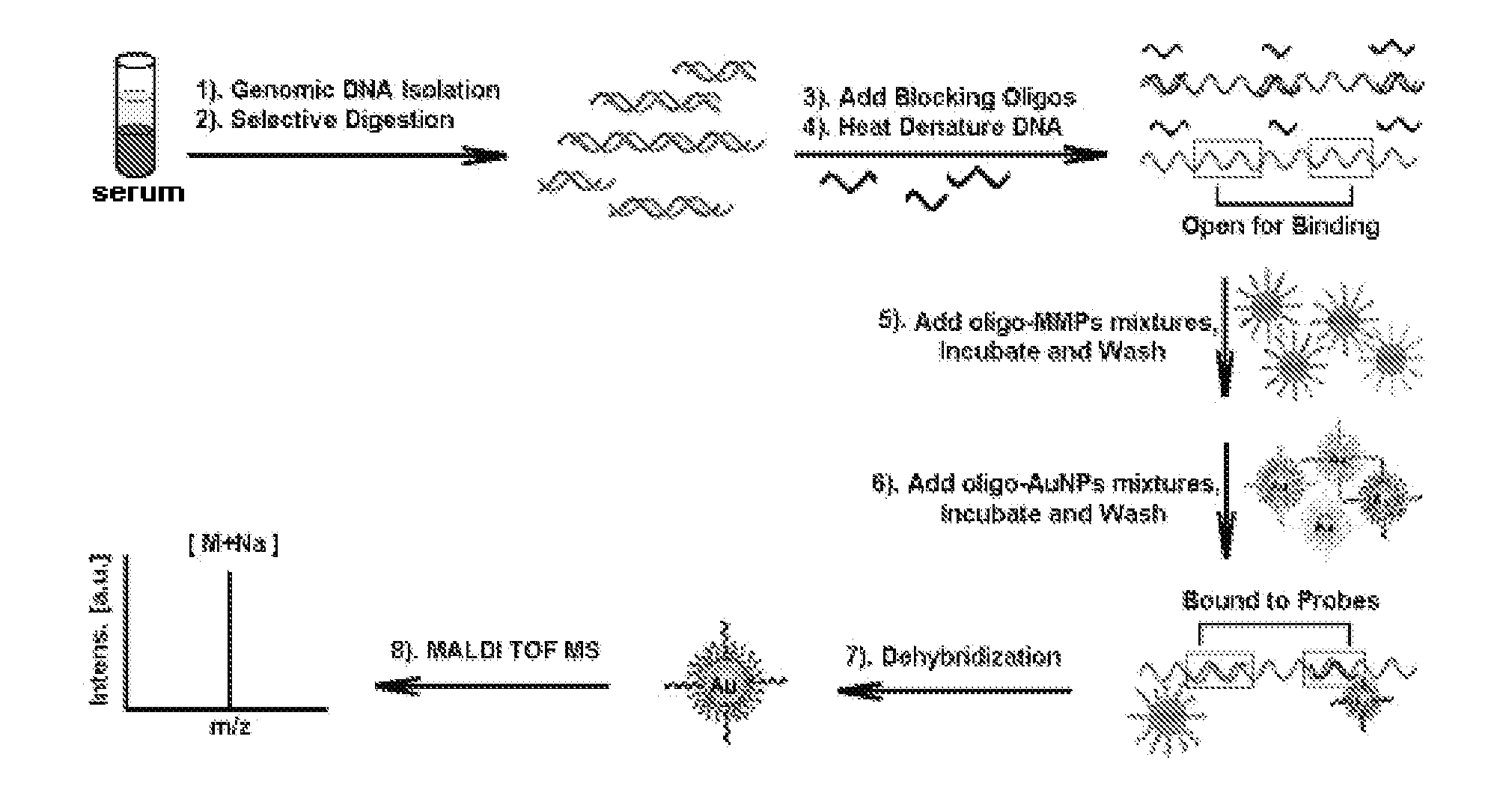
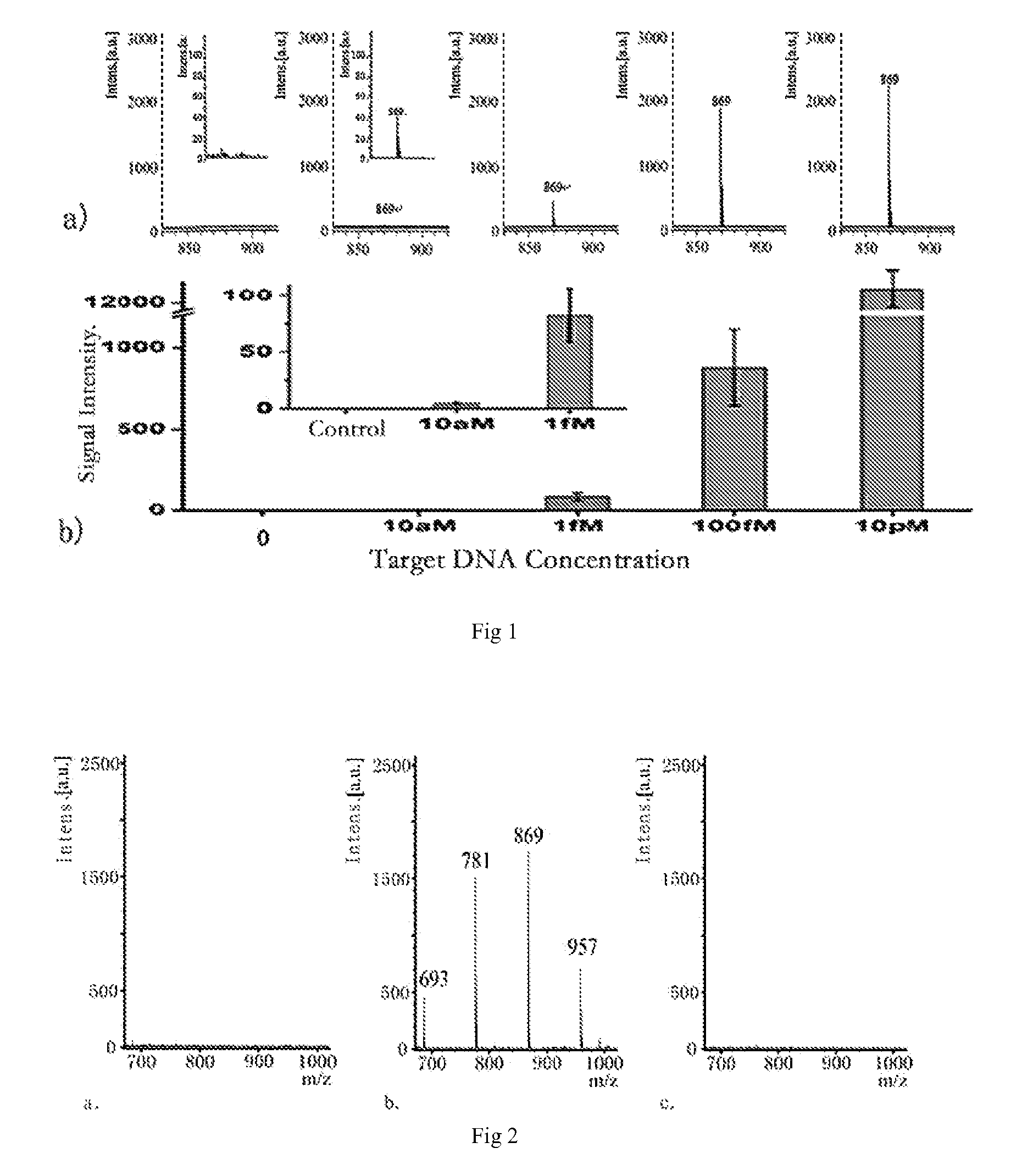
Gene detecting methods without using PCR are disclosed. The methods comprise forming sandwich complexes by target genes with nano-probes and capture probes, wherein nano-probes are modified with recognition molecules and magnetic microparticles modified with capture molecules; then separating the sandwich complexes; releasing the nano-probes; and detecting molecular ion peaks of encoding molecules on the surface of nano-probes by mass spectrometric detection directly, characterized in that the proportions of recognition molecules and encoding molecules on the nano-probes are 300-2000:1.
Owner:JIANGSU SINOBIOPHARMA
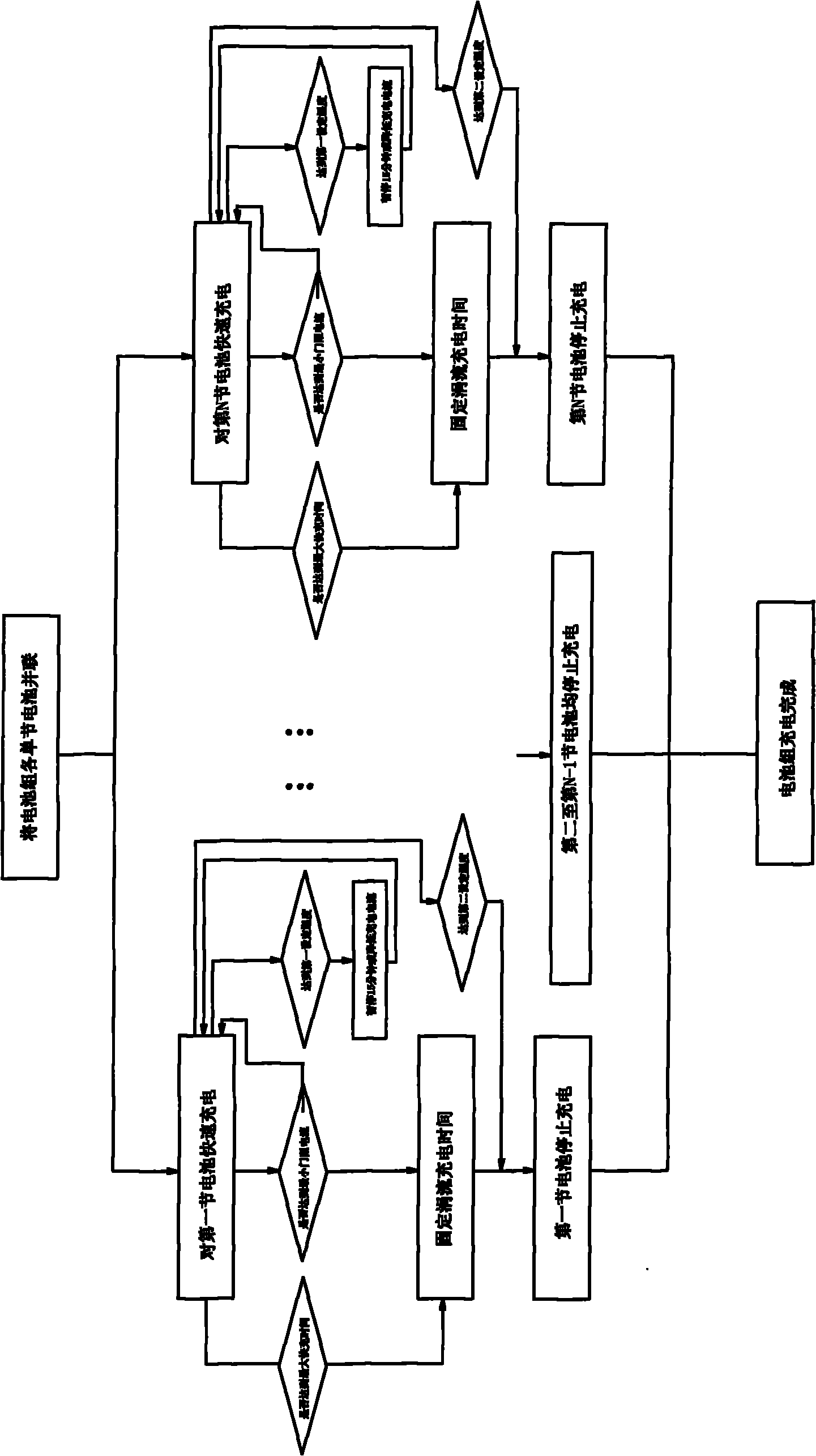
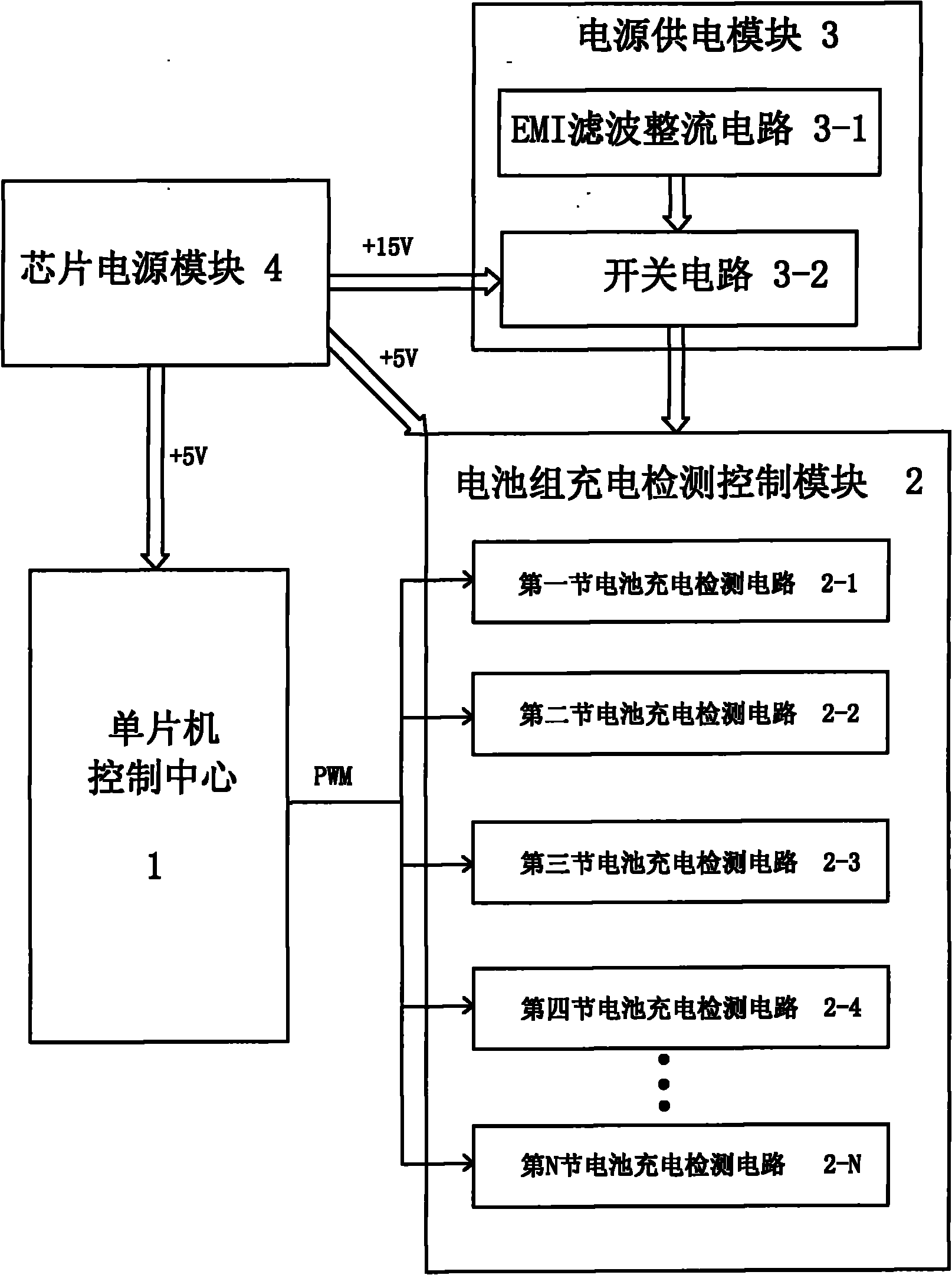
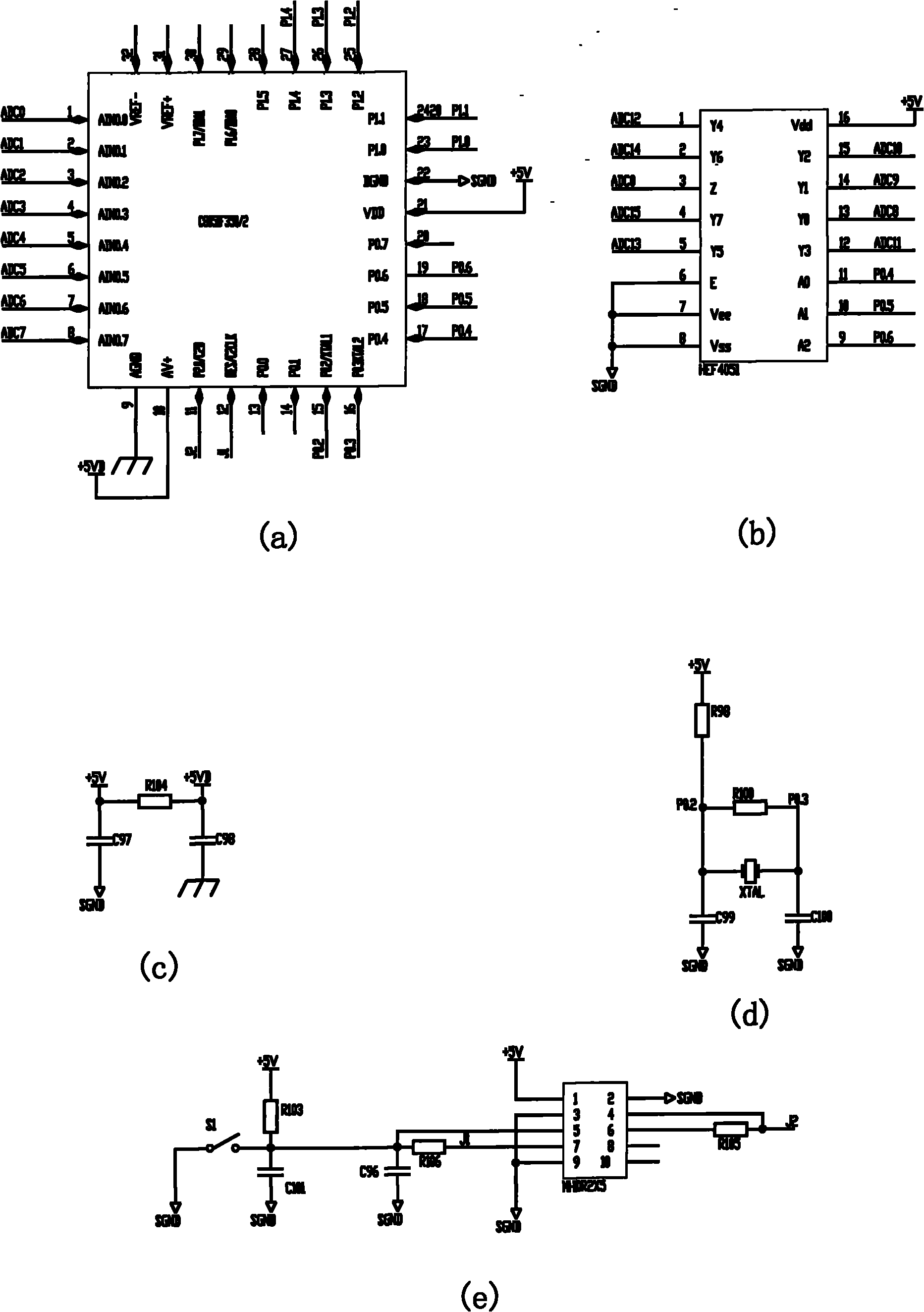
Equalizing charge method and equalizing charger
InactiveCN101777675ABalanced chargingEnsure consistencyBatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingSingle chipBattery charger
The invention discloses an equalizing charge method and an equalizing charger. The equalizing charge method comprises the following steps: (1) connecting N (N is integer and is more than or equal to 2) single batteries in a battery pack in parallel; (2) independently and quickly charging the N single batteries at the same time; and (3) after the single batteries meet the charge requirement, finishing charging the battery pack. The equalizing charge method of the invention changes the series discharge mode of the single batteries of the battery pack into a parallel mode to independently charge the batteries of the battery pack, thus independently controlling the charge process of the single batteries to ensure equalizing charge for the single batteries. The charger of the invention uses a single chip control center as the core, and simply and precisely realizes independent charge and independent control of the single batteries.
Owner:常州黄海麦科卡电动汽车有限公司
Photovoltaic generation capacity prediction method based on particle swarm algorithm wavelet neural network
InactiveCN105139264AEfficient extractionApproximate strongData processing applicationsTechnical supportPrediction system
The invention relates to a photovoltaic generation capacity prediction method based on a particle swarm algorithm wavelet neural network. Prediction of solar photovoltaic generation capacity is realized, and organic combination between the particle swarm algorithm and a wavelet neural network learning nervous system is realized. A prediction system comprises a module for optimizing model parameters of a wavelet neural network through the particle swarm algorithm, a wavelet neural network learning training module after optimization, and a wavelet neural network prediction module after training. The prediction method integrates the advantages of the particle swarm algorithm and the advantages of the wavelet neural network. Therefore, the prediction accuracy is improved effectively, the prediction error is reduced, and technical support can be provided for large-scale connection of photovoltaic generated power to the grid. Moreover, the method is portable, and can provide generation capacity prediction for wind and other new energy through simple modification.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
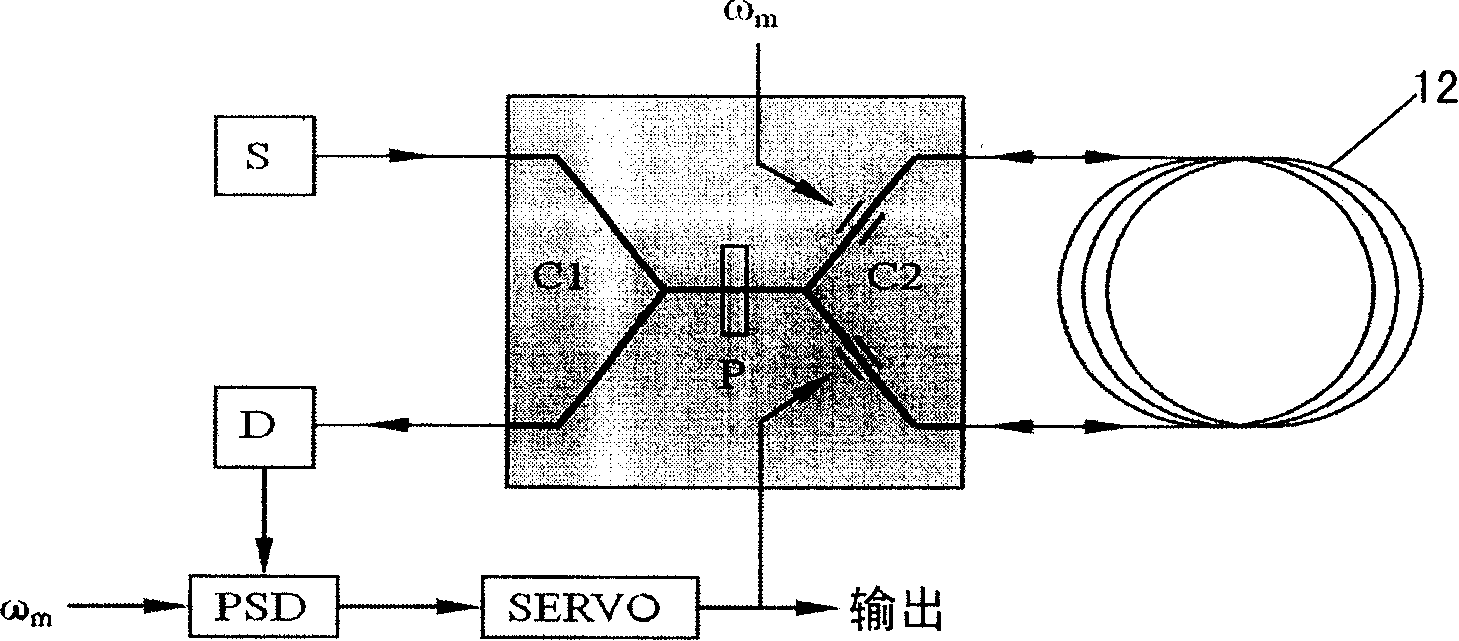
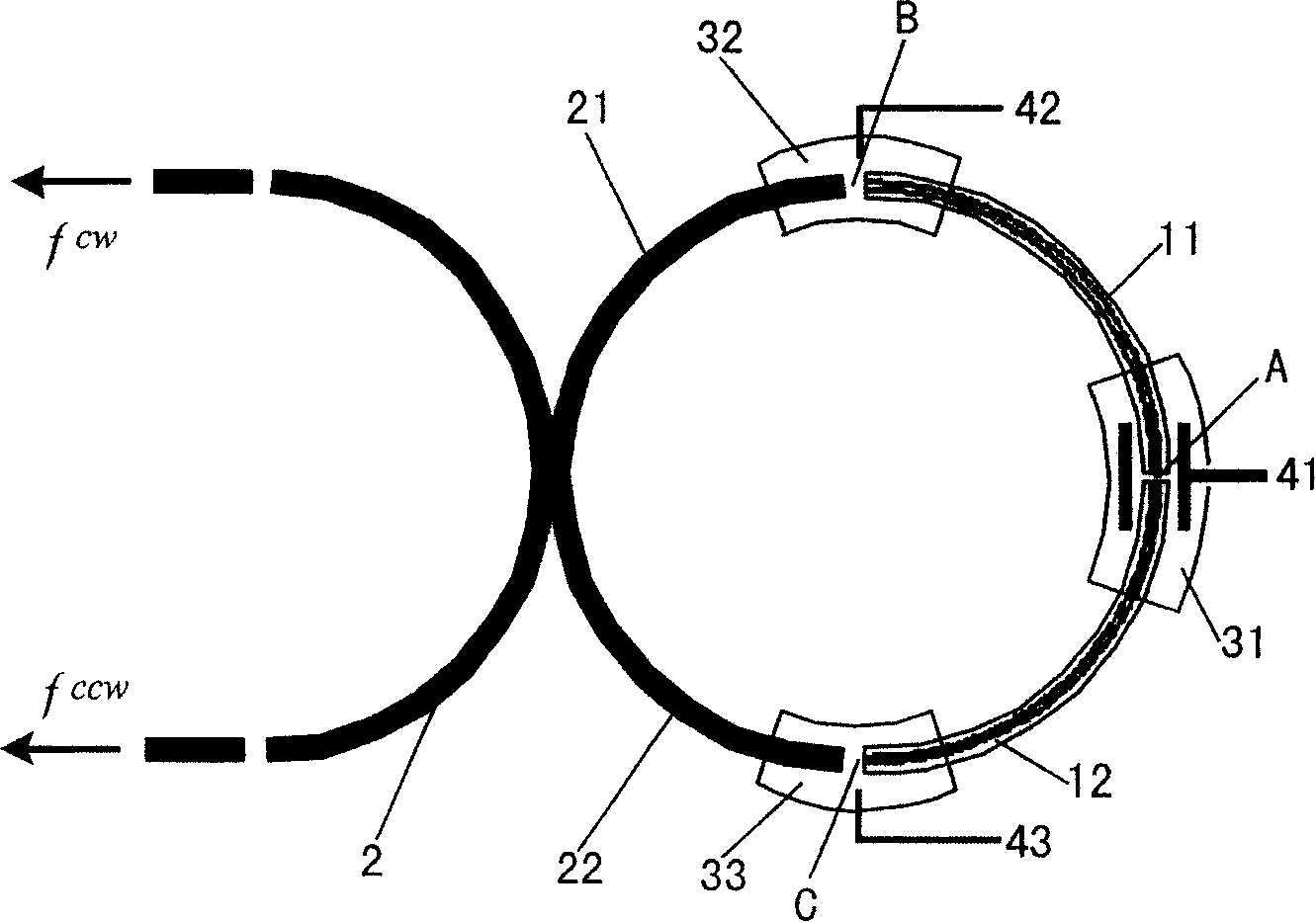
Optical fibre gas laser and optical fiber type ring laser gyroscope possessing the laser
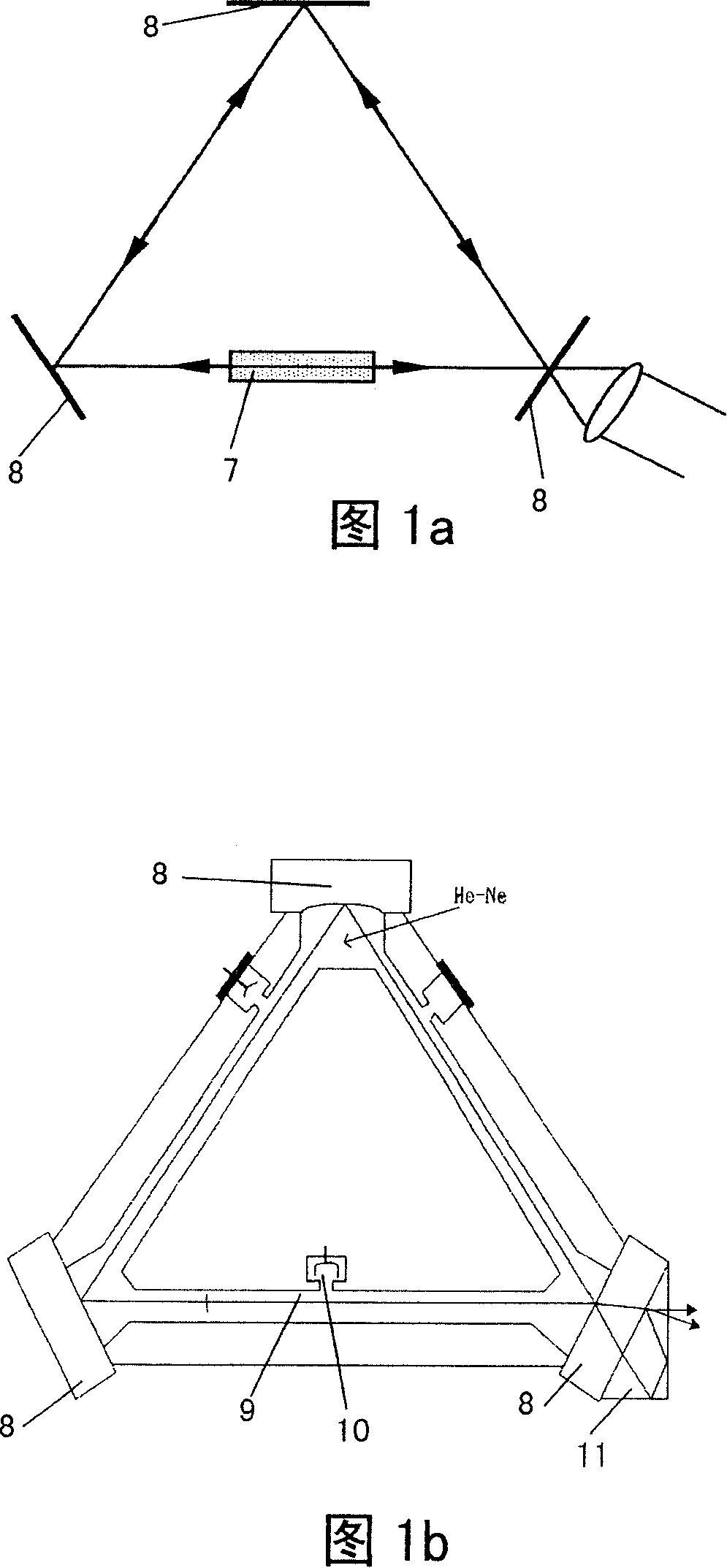
ActiveCN101165977AGood zoom effectSimple structureExcitation process/apparatusSagnac effect gyrometersFiber couplerRobotic systems
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
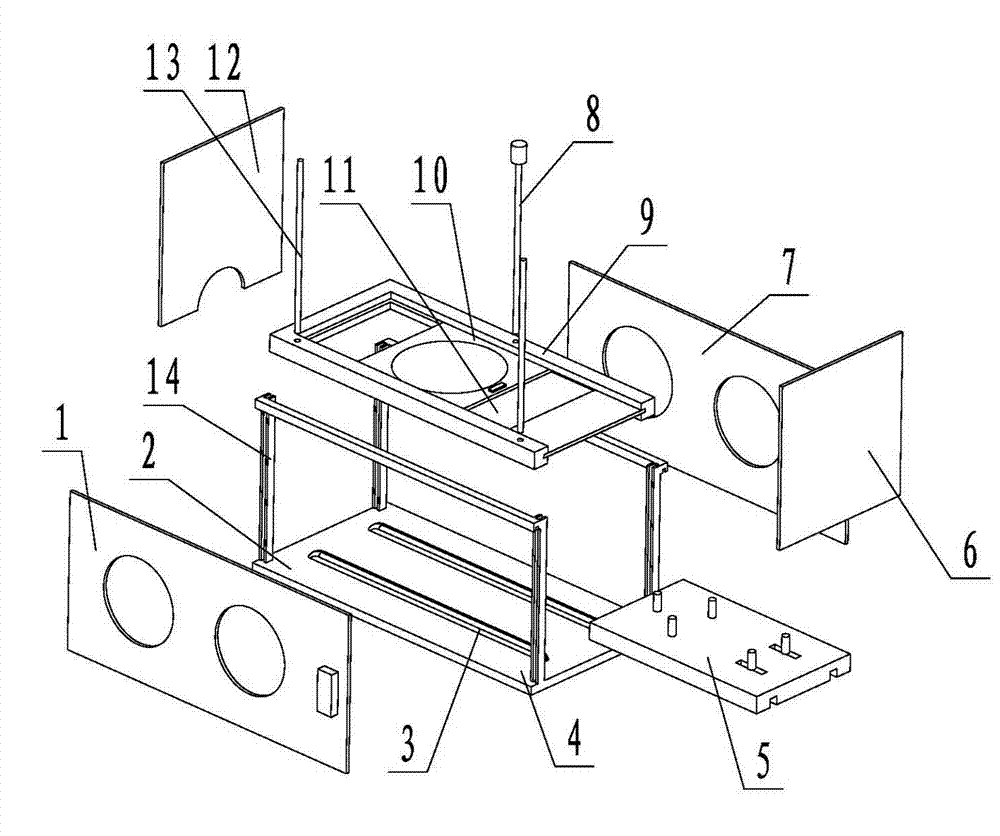
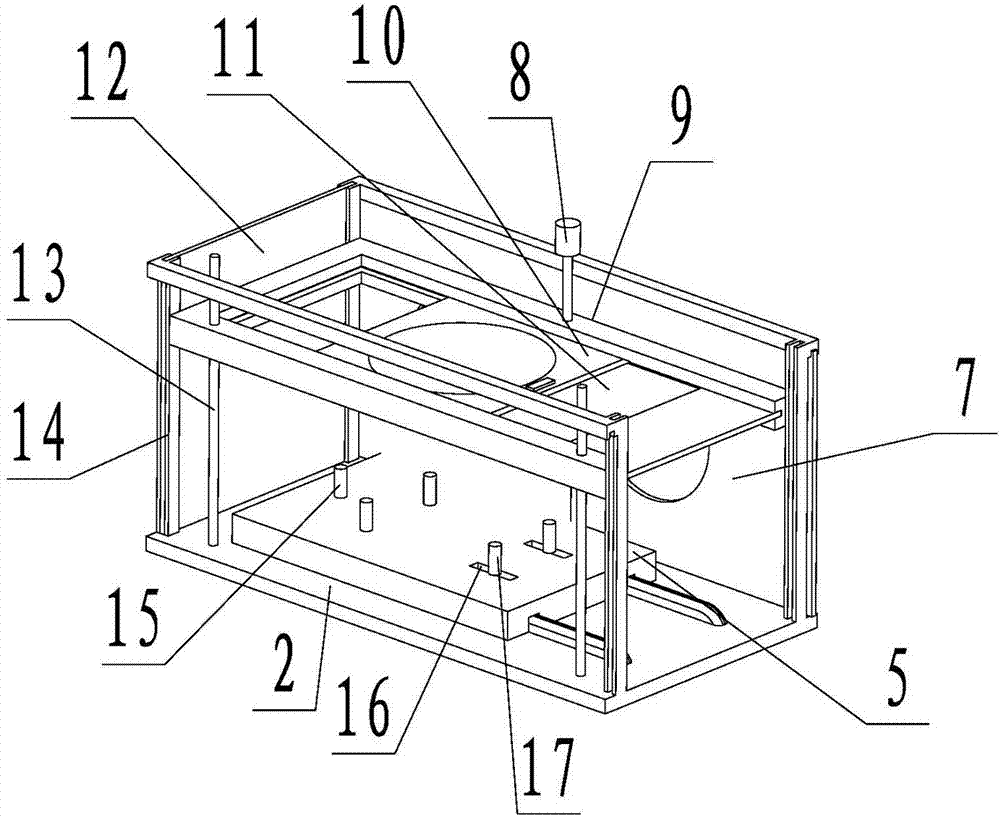
Enclosed animal experiment operation box
InactiveCN104257439AAvoid contamination and damage to equipmentProtect physical and mental healthAnimal fetteringAnimal scienceEngineering
The invention relates to an enclosed animal experiment operation box and aims to solve the problems that the conventional pharmacological animal experiment causes environmental pollution which causes damage to instruments and equipment and influences experimenters' health, the operation view is not clear, and the light is insufficient. The enclosed animal experiment operation box comprises a box body and an operational table assembled inside the box body and used for fixing an experimental animal, and is characterized in that the box body comprises a base, a frame, a front baffle, a back baffle, a left baffle, a right baffle and an erector, fixed limiting posts and adjustable limiting posts are arranged on the operational table and limited to the rails of the base, guiding rods and an adjusting screw rod used for controlling the erector to move are arranged on the base, and a magnifier is arranged in the picture frame of the erector. According to the invention, the enclosed animal experiment operation box has the advantages of being simple in operation, convenient to adjust and the like, and provides modern experimental equipment with a clean and excellent working environment; the view is clean and the light is sufficient when experiments are carried out; the accuracy and the success rate of the experiments are significantly improved, and the experimental appropriation expenditure is reduced.
Owner:SHENYANG MEDICAL COLLEGE
Phase type laser distance measuring system
ActiveCN105093233AIncreaseImprove ranging accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingPulse voltage
The invention discloses a phase type laser distance measuring system. The system comprises a laser for generating laser signals; an emission signal unit for generating emission signals and sending the emission signals to the laser after amplitude adjustment and power amplification are successively performed on the emission signals; a returning light receiving unit for receiving reflection signals of laser signals; a bias driving unit for providing offset voltages for driving the laser to emit the laser signals; and a controller for outputting PWM pulse voltage signals with an adjustable duty ratio to the bias driving unit to form the offset voltages and receive the emission signals. When the controller receives that the emission signals involves weak reflection, the controller reduces the duty ratio of the PWM pulse voltage signals and improves the amplitude of the emission signals in a linkage mode; and when the controller receives that the emission signals involves strong reflection, the controller increases the duty ratio of the PWM pulse voltage signals and reduces the amplitude of the emission signals in a linkage mode. The system provided by the invention has the advantages of simple system, high anti-interference capability and high distance measuring accuracy.
Owner:SUZHOU YISEN PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
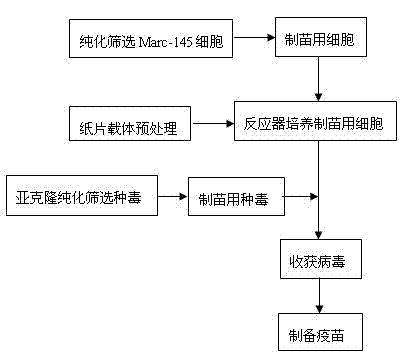
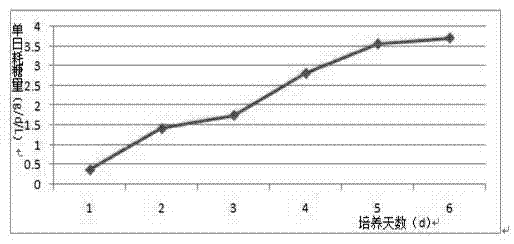
Preparation method of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome vaccines by utilizing bioreactor
ActiveCN102552896AUniform stateSmall batch-to-batch varianceViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsImmune effectsTGE VACCINE
A preparation method of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome vaccines by utilizing a bioreactor utilizes a stream perfusion type bioreactor as a cultivation tool. The preparation method comprises the steps of a cultivating cells for preparing the vaccines; b vaccinating and cultivating viruses; c harvesting virus liquor; d preparing the vaccines and the like. The preparation method has the advantages that the preparation method is simple and convenient in operation, low in contamination probability and capable of remarkably reducing preparation cost, the vaccines are large in yield, uniform and stable in quality and good in immune effect, and the like. The whole preparation process does not involve other problems of biological safety and public hygiene so that the preparation method is suitable for large-scale preparation of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome vaccines.
Owner:RINGPU (BAODING) BIOLOGICAL PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Porous building decoration material capable of adjusting humidity, reducing harm and releasing negative ions
A porous building decoration material capable of adjusting humidity, reducing harm and releasing negative ions is characterized by comprising a sintered functional layer, and the functional layer comprises 1-65 wt% of a negative-ion powder capable of releasing the negative ions and 0.1-60 wt% of a humidity-adjusting harm-reducing material, wherein the humidity-adjusting harm-reducing material is one or two or more of porous materials comprising zeolite, diatomite, allophane, vitreous trass, meerschaum, acidic white clay, active carbon, silica gel, white carbon black, active alumina and aluminium hydroxide. Compared with the prior art, the porous building decoration material of the invention has the advantage of releasing a large number of the negative ions.
Owner:堆龙德庆绿家科技有限公司
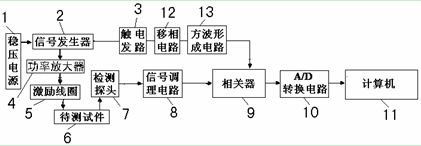
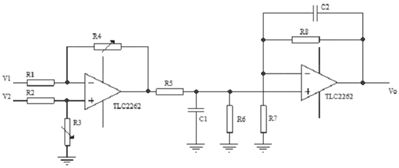
Circuit device based on disturbed magnetic field detection instrument
InactiveCN102520059AGood zoom effectEnhanced inhibitory effectMaterial magnetic variablesLabview softwareSoftware engineering
The invention relates to a circuit device based on a disturbed magnetic field detection instrument and discloses a circuit system based on the disturbed magnetic field detection instrument. A total circuit of the detection system mainly consists of an excitation source module, a sensor module, a signal modulation circuit, a phase shifting circuit, a correlator circuit, an analog-to-digital (A / D) conversion circuit and a computer display system. The visual detection system capable of obtaining detection signal amplitude values and phase information is designed on the basis of unique advantages of Labview software in the respects of value analysis, image display, programming and the like by utilizing mutual correlation principles and an A / D data collecting card. The detection circuit has a good amplification effect on weak signals and simultaneously has a good inhibition effect on the noise. The circuit also has the advantages that the amplitude value and the phase of the defect signals can also be simultaneously detected, and the detection and characterization on the metal surface crack defect characteristics can be perfectly realized.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Cushioning mechanism
ActiveCN107489093AAvoid failureAvoid destructionInertia force compensationVibration dampersReciprocating motionBall screw
The invention provides a cushioning mechanism comprising a base, an equal-width cam mechanism, a limiting bracket, a ball screw, two groups of energy dissipaters and energy dissipater fixing bases, wherein the equal-width cam mechanism, the limiting bracket, the ball screw, the two groups of energy dissipaters and the energy dissipater fixing bases are mounted on the base. The equal-width cam mechanism comprises a quadrilateral frame and a cam mounted in the quadrilateral frame. The cam is connected with a nut of the ball screw. The two groups of energy dissipaters are mounted on the energy dissipater fixing bases on the two sides of the equal-width cam mechanism separately. The ends, away from the energy dissipater fixing bases, of the two groups of energy dissipaters are connected with the two sides of the quadrilateral frame separately. The limiting bracket is mounted on the periphery of the equal-width cam mechanism. The cam mechanism performs linear reciprocating motions between the two groups of energy dissipaters under the limit of the limiting bracket. The end, away from the equal-width cam mechanism, of the ball screw is provided with a spring latch assembly used for being connected with a building structure or a bridge structure. The cushioning mechanism is low in cost and has a good damping limiting function.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
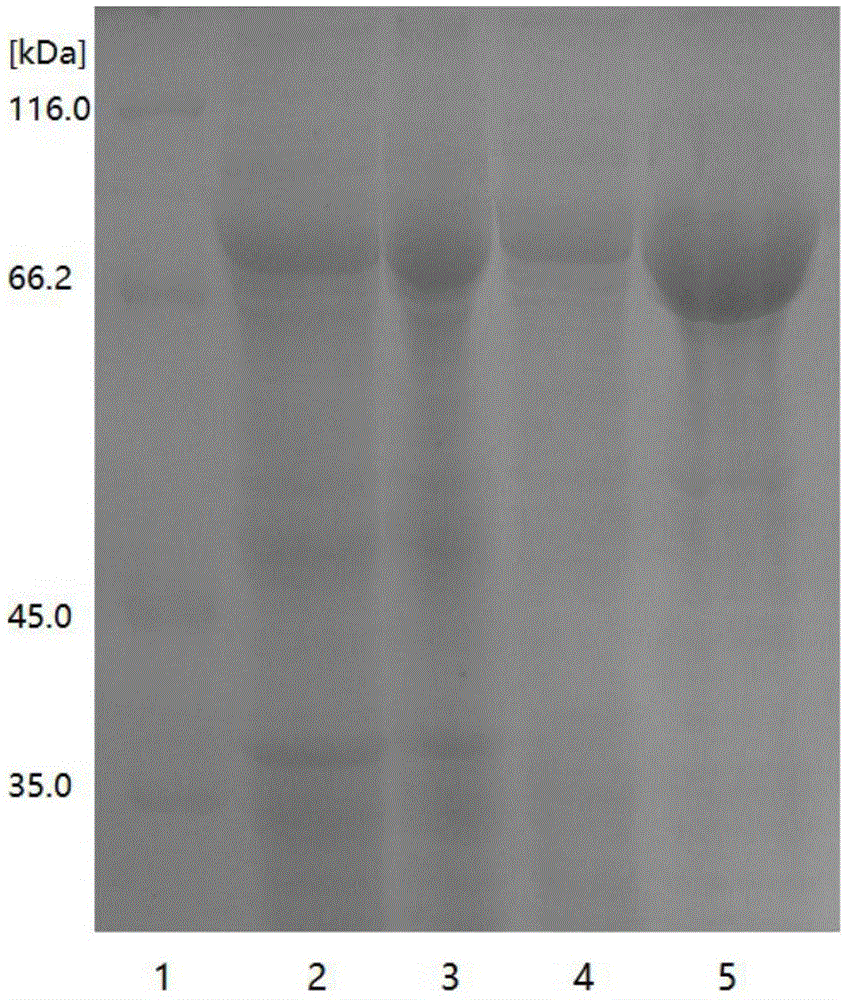
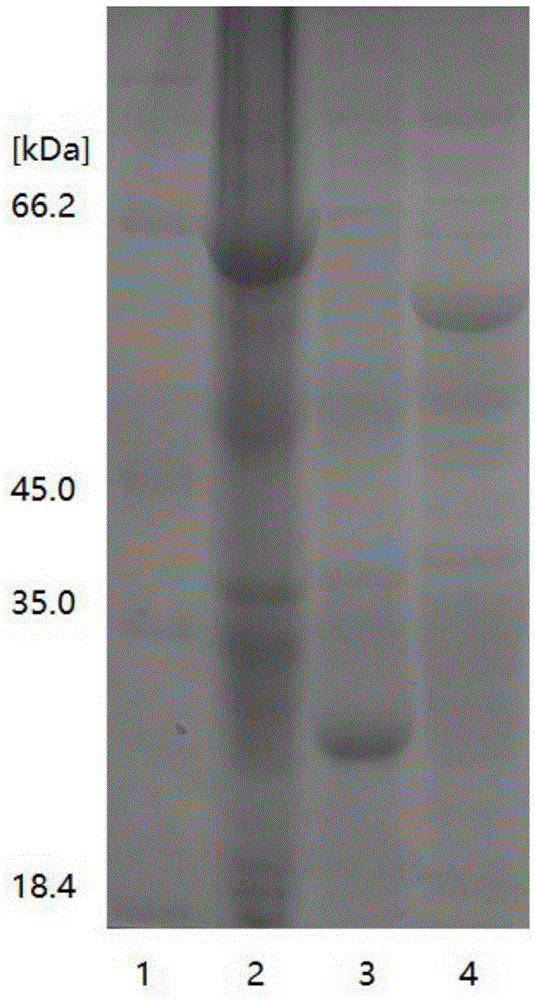
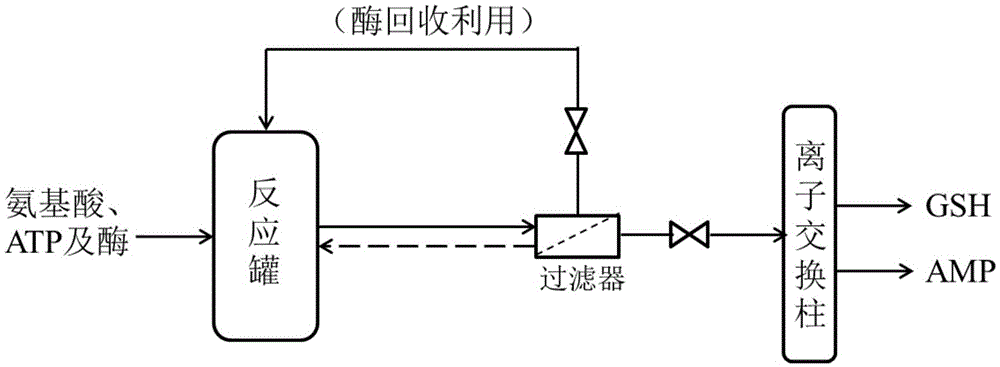
Enzymic method for simultaneously preparing glutathione and adenylate
ActiveCN105603028ASimple reaction conditionsIncrease concentrationPeptidesFermentationEnzymeAmino acid
The invention discloses an enzymic method for simultaneously preparing glutathione and adenylate. The enzymic method comprises the following steps: (1) generating glutathione and adenylate from GshF enzyme and Adk enzyme in a reaction tank; (2) separating the immobilized GshF enzyme and Adk enzyme in the reaction tank, or separating the free GshF enzyme and Adk enzyme by virtue of filtering equipment; and (3) separating products GSH and AMP. By virtue of the preparation method, the reaction condition in production of the GSH is optimized, the generation concentration of GSH reaches 30g / L-50g / L, and the utilization rate of amino acid is relatively high; meanwhile, by carrying out partial regeneration on ATP consumed in reaction by virtue of the Adk enzyme, the consumption of the ATP is reduced; and furthermore, the GSH and the AMP can be simultaneously prepared by virtue of the preparation method.
Owner:BEIJING TIANKAI YIDA BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Camera module and electronic equipment
ActiveCN111308833ALarge zoom rangeReduce axial sizeTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementImage sensorEngineering
The invention relates to a camera module and electronic equipment. The camera module comprises a lens seat; a liquid lens which is connected with the lens base and comprises a closed bag body and liquid arranged in the closed bag body; a first pressing element which comprises a first driving piece and a first lens group, a second pressing element which is connected to the lens seat, and an image sensor which is arranged on one side, far away from the liquid lens, of the first pressing element and is connected with the lens seat, wherein the first driving piece is connected with the lens seat and the first lens group; the first lens group comprises a first pressing part and at least one lens arranged on the first pressing part, the optical axis of the first lens group is a first optical axis, the liquid lens is arranged on an object side of the first lens group along the direction of the first optical axis, the first driving piece can drive the first lens group to move along the direction of the first optical axis so as to enable the first pressing element to press the liquid lens, the second pressing element and the first pressing element are arranged at intervals, and the second pressing element can press the liquid lens in the direction of the first optical axis. The camera module has a large zoom range and can realize miniaturized design.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Zoom lens
A zoom lens includes a first lens group with negative diopter and a second lens group with a positive diopter; wherein, the second lens group is arranged between the first lens group and an image side; and the first lens group and the second lens group are suitable for moving between an object side and the image side. Besides, the first lens group includes a first lens with negative diopter; while the first lens is a meniscus lens with a convex surface facing to the object side and an Abbe number larger than 50. Furthermore, the focus of the zoom lens is F, the focus of the first lens group is F1, a curvature radius of the first lens facing to the surface of the second lens group is R2 and F / F1 is more than 0.6 below zero and less than 0.2 below zero and R2 / F is more than 0.7 and less than 1.8.
Owner:YOUNG OPTICS KUSN
Method for detecting photolithography equipment exhaust system and judging product CPK
InactiveCN101377622AGood zoom effectPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusHuman powerPhotolithography
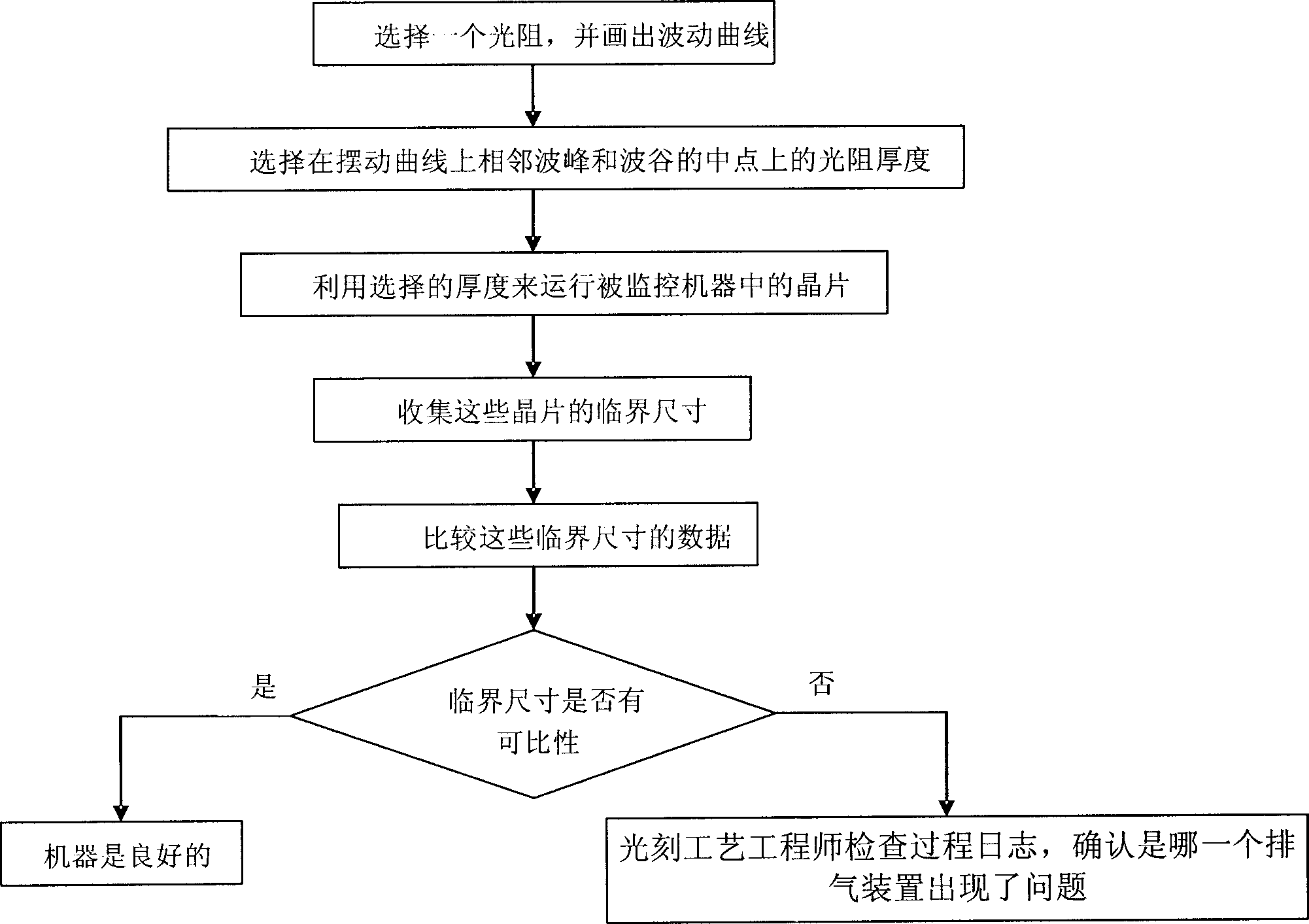
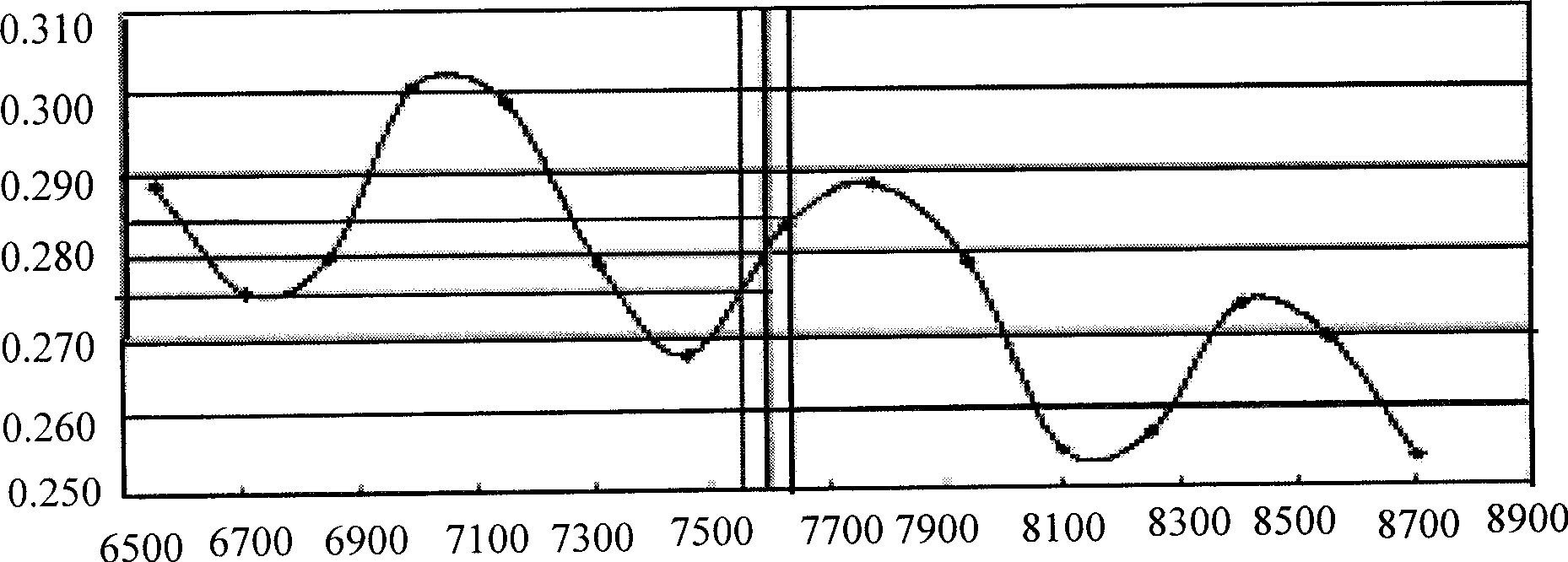
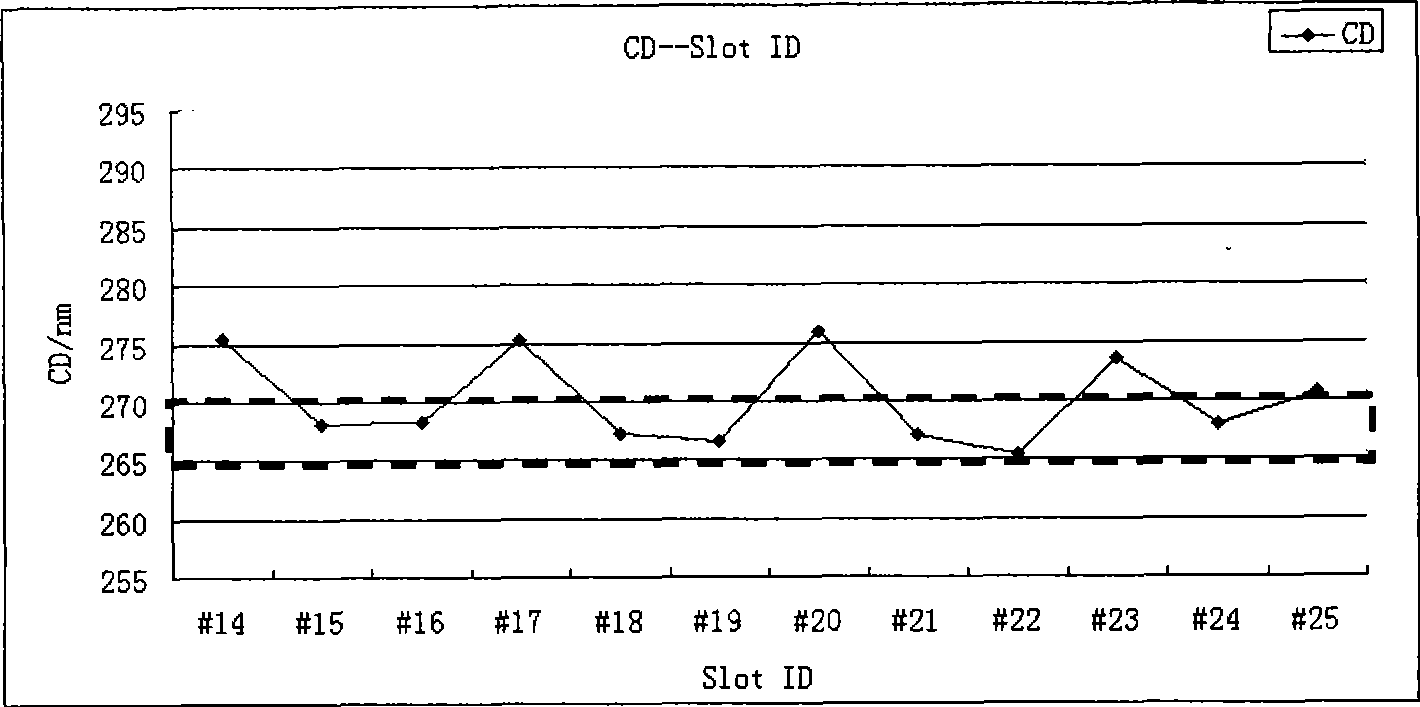
The present invention relates to a method for detecting the exhaust system of a machine in the lithographic field. The method mainly comprises the following steps: selecting an optical resistance and mapping out the swinging curve; selecting a point on the swinging curve at random as detection point, and finding out the thickness of the optical resistance at the point; coating the optical resistances with the thickness on wafers; summarizing the characteristic sizes of the wafers; and comparing the data of the characteristic sizes of the wafers. If the data is within the standard variance range, the exhaust system of the machine equipment is proved to be excellent; if the data is not within the standard variance range, the process log is required to be detected to determine the exhaust device with a failure; and then the equipment engineer detects the exhaust system of the equipment. The present invention can be used for detecting whether the exhaust system has the failure without stopping the machine, so the present invention can not only improve the operation efficiency of the machine, but also save the labor.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Zoom lens and imaging apparatus
A zoom lens includes a first negative lens group, a second negative lens group, a third positive lens group, an aperture diaphragm, and a fourth positive lens group arranged in this order from an object side. When power varies from a wide angle end to a telephoto end, the first and second lens groups are moved to an image surface along an optical axis and then moved to the object side. The third and fourth lens groups are moved to only the object side along the optical axis. The first lens group includes at least one aspheric lens, and the aspheric lens has an aspheric shape in which a positive refractive power is increased toward the periphery of the lens when a paraxial refractive power is positive and a negative refractive power is decreased toward the periphery of the lens when the paraxial refractive power is negative.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
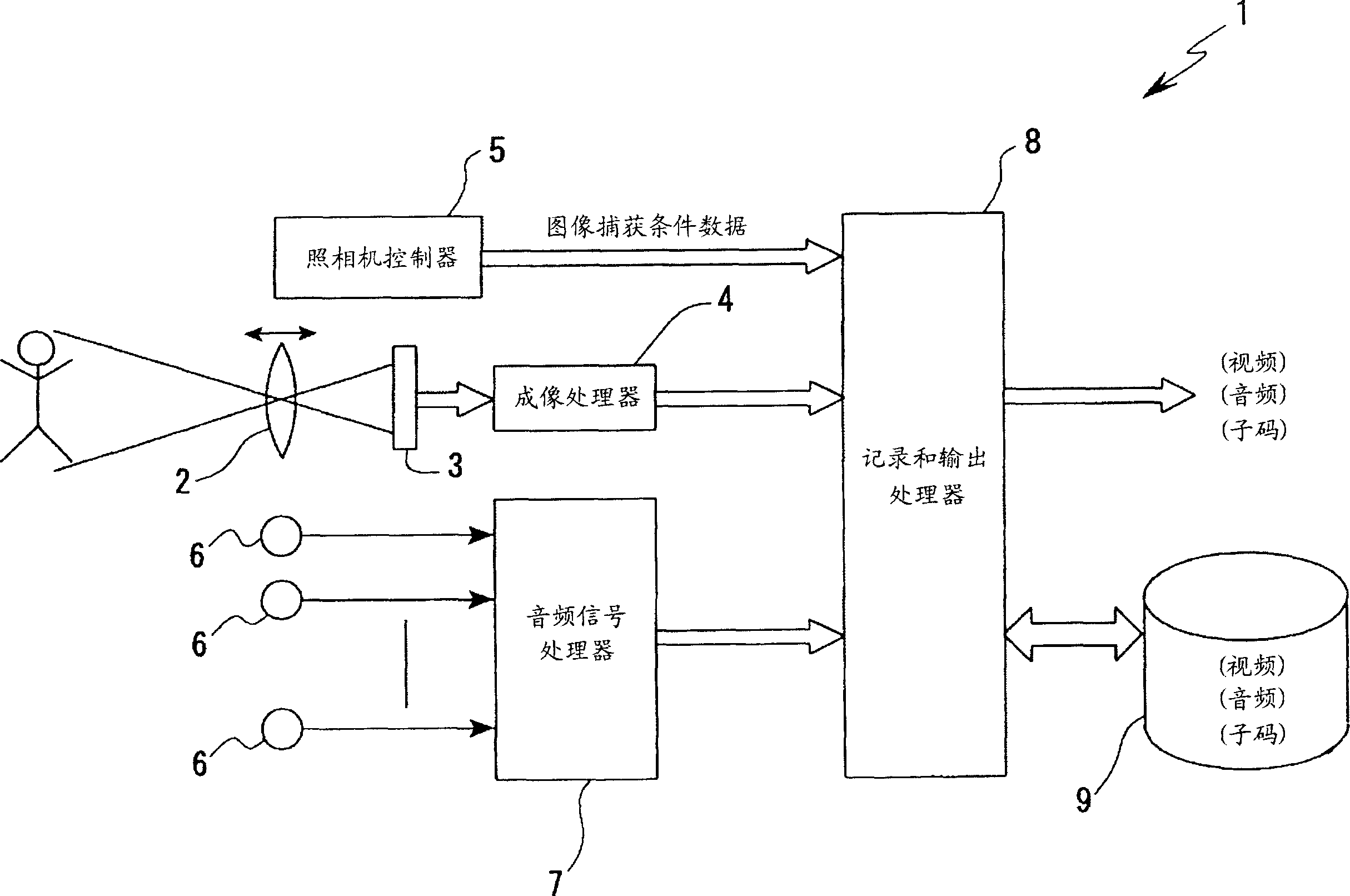
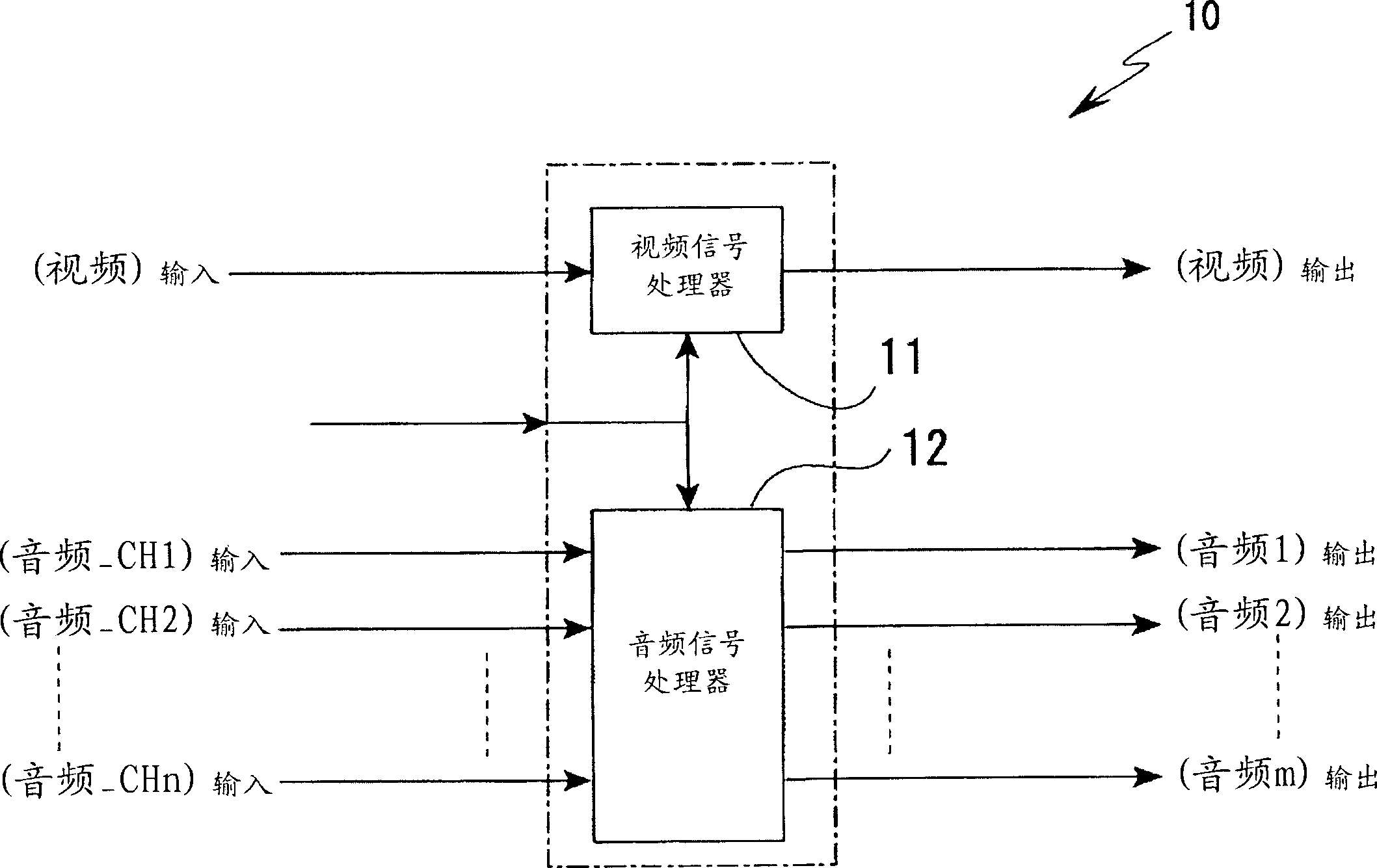
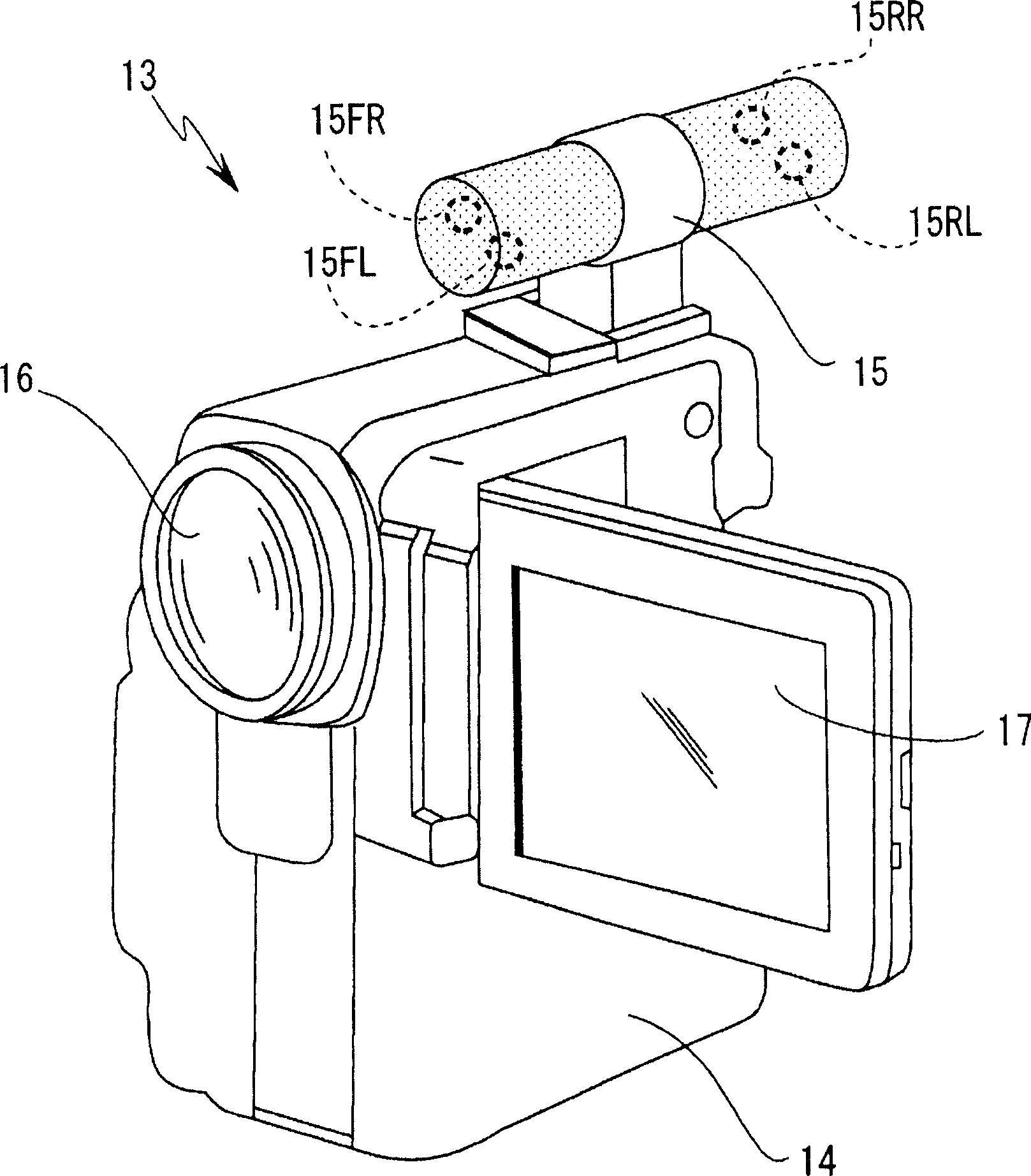
Information processing apparatus, imaging apparatus, information processing method, and program
InactiveCN1691765ARealistic sound effectsProduces a zoom (distance) effectSievingTelevision system detailsInformation processingSignal correlation
An information processing apparatus has a function of processing plural-channel audio signals associated with a video signal. The information processing apparatus includes an audio converting unit for generating a plurality of audio signals by converting the levels of the plural-channel audio signals in accordance with an adjusting parameter defined depending on information of image-capturing conditions concerning the video signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical zoom system, camera module and electronic equipment
PendingCN112684599AGood zoom effectImprove image qualityOptical elementsOphthalmologyImaging quality
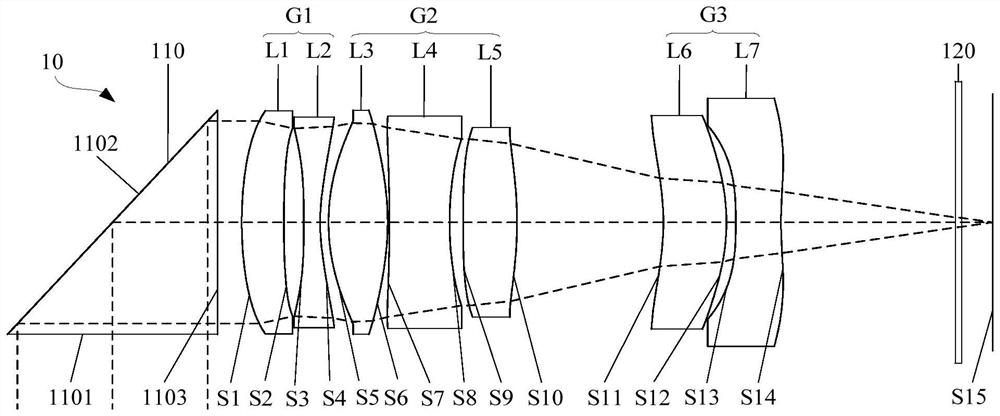
The invention relates to an optical zoom system, a camera module and electronic equipment. The optical zoom system includes: a first lens group having negative refractive power and including a first lens and a second lens; a second lens group having positive refractive power and including a third lens, a fourth lens, and a fifth lens; and a third lens group having negative refractive power and including a sixth lens and a seventh lens. In the zooming process from the short-focus end to the long-focus end, the distance between the first lens group and the second lens group is reduced, and the distance between the third lens group and the imaging surface is increased; the system satisfies the following relationship: 0.2 < (R5-R6) / R8 < 3; and R5 is the curvature radius of the object side surface of the third lens at the optical axis, R6 is the curvature radius of the image side surface of the third lens at the optical axis, and R8 is the curvature radius of the image side surface of the fourth lens at the optical axis. The optical zoom system satisfying the above relationship is beneficial for enabling the aberration component between the lens groups to reach a balanced state, thereby being beneficial for improving the imaging quality.
Owner:JIANGXI JINGCHAO OPTICAL CO LTD
Hybrid laser radar for Mars atmosphere detection
PendingCN112924985AImplement type detectionRealize gas content detectionScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsParticulatesTransceiver
The invention relates to a hybrid laser radar for Mars atmosphere detection. The hybrid laser radar comprises a single set of optical transceiver module for obtaining back scattering signals from Mars atmosphere molecules and dust; a coherent balance detection module which mixes the local oscillation light and the atmospheric echo signal into an intermediate frequency electric signal and converts the intermediate frequency electric signal into a high-speed analog electric signal, so a Mars atmospheric wind field is obtained through data processing; a single-photon direct detection module which is used for measuring photon electric signals of each channel to obtain photon count of each channel; and a data processing module which obtains the concentration of polarized light and Mars aerosol particles. The laser power and the echo signal stability are calibrated by using the signal-to-noise ratio of coherent detection and the photon number of direct detection, and the method is used for detecting the content of carbon dioxide gas. The hybrid laser radar has the advantages of large dynamic range and small data processing calculation amount by using single photon direct detection, and also has the advantages of high coherent detection sensitivity and good weak signal amplification performance, and the problem of multi-atmosphere parameter detection of the Mars atmosphere detection laser radar is solved under the condition that the load weight and complexity are not increased.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
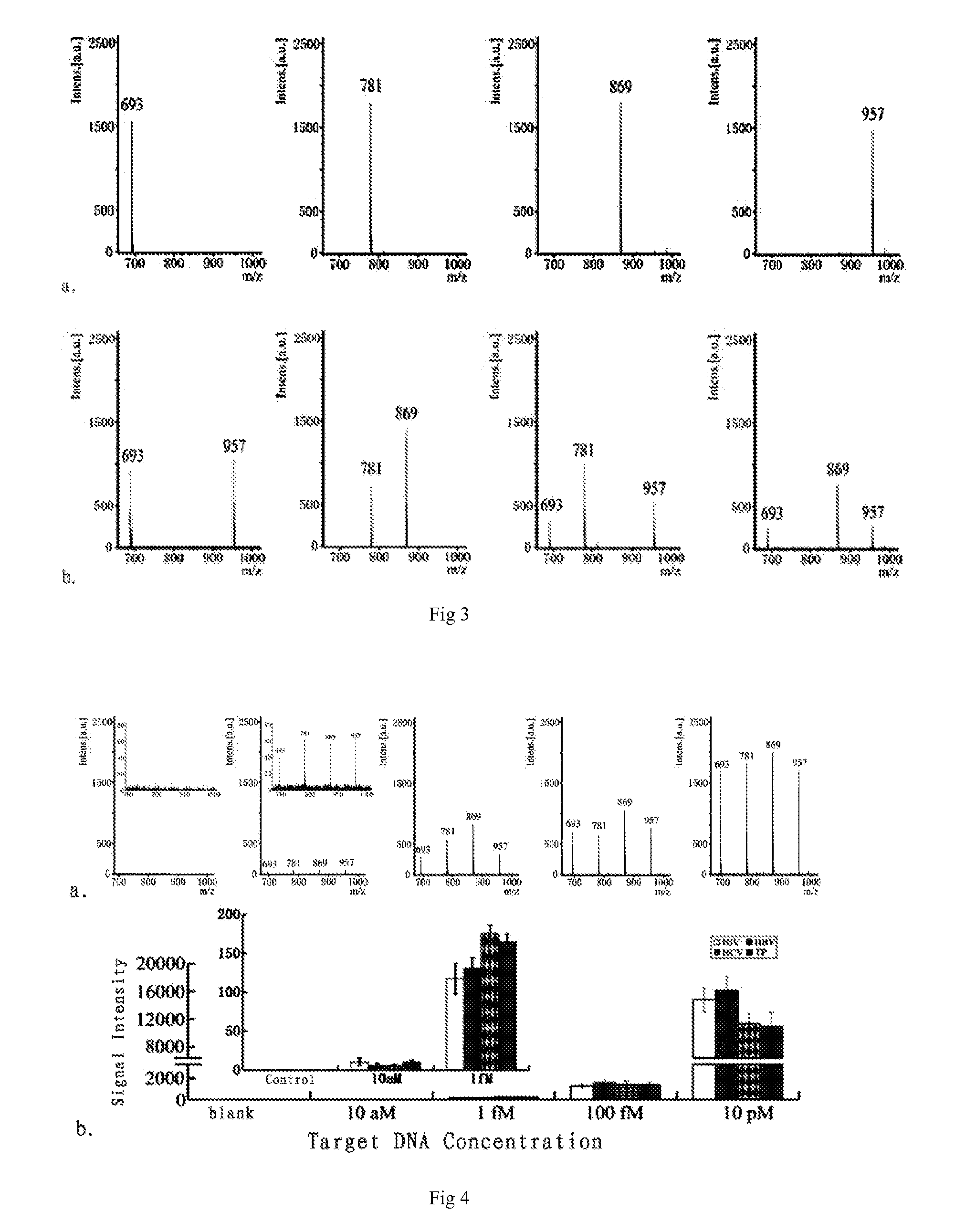
Method for signal amplification and detection of dna target sequences
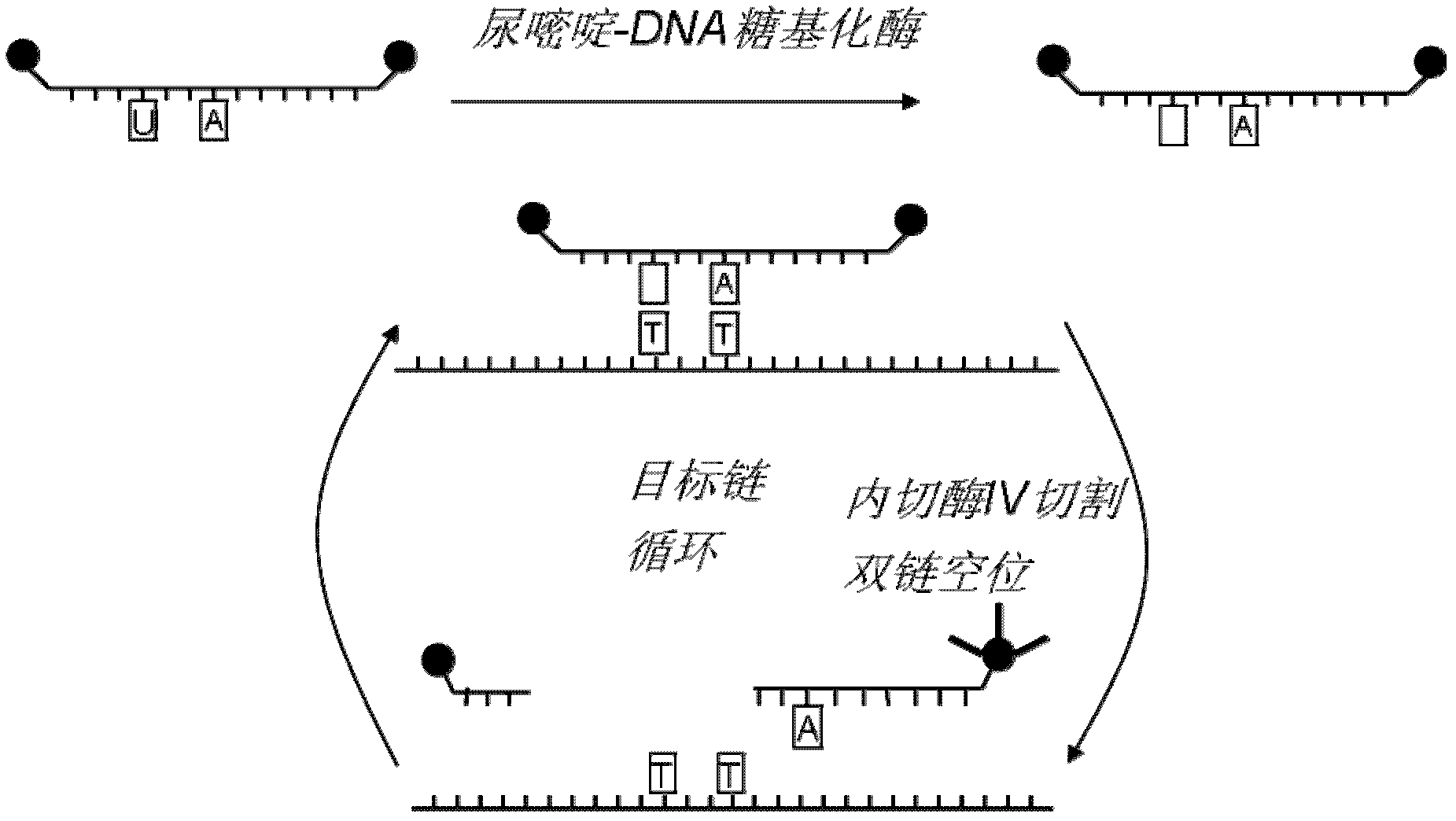
InactiveCN102296116AGood zoom effectHigh selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceExact matchTarget signal
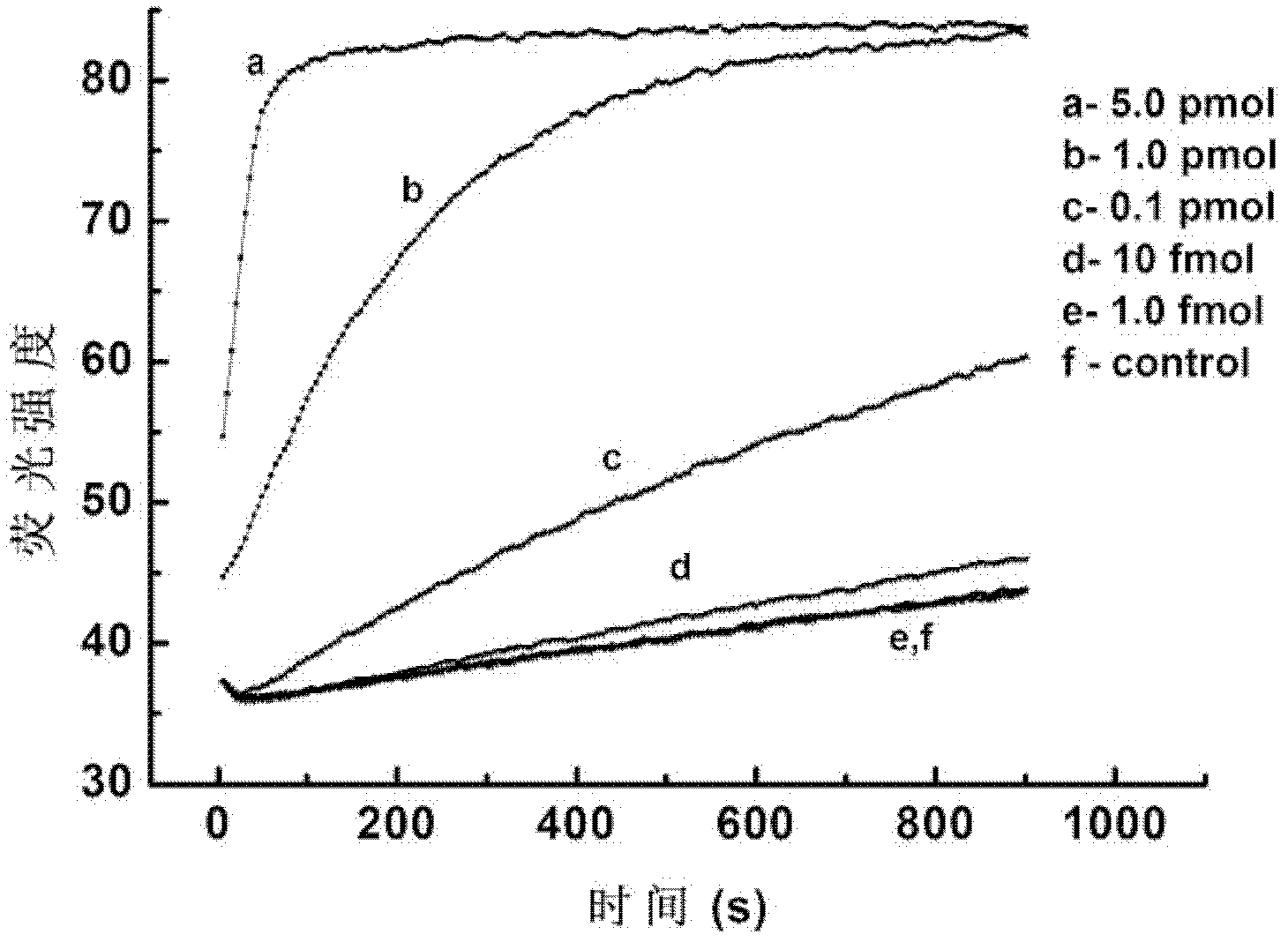
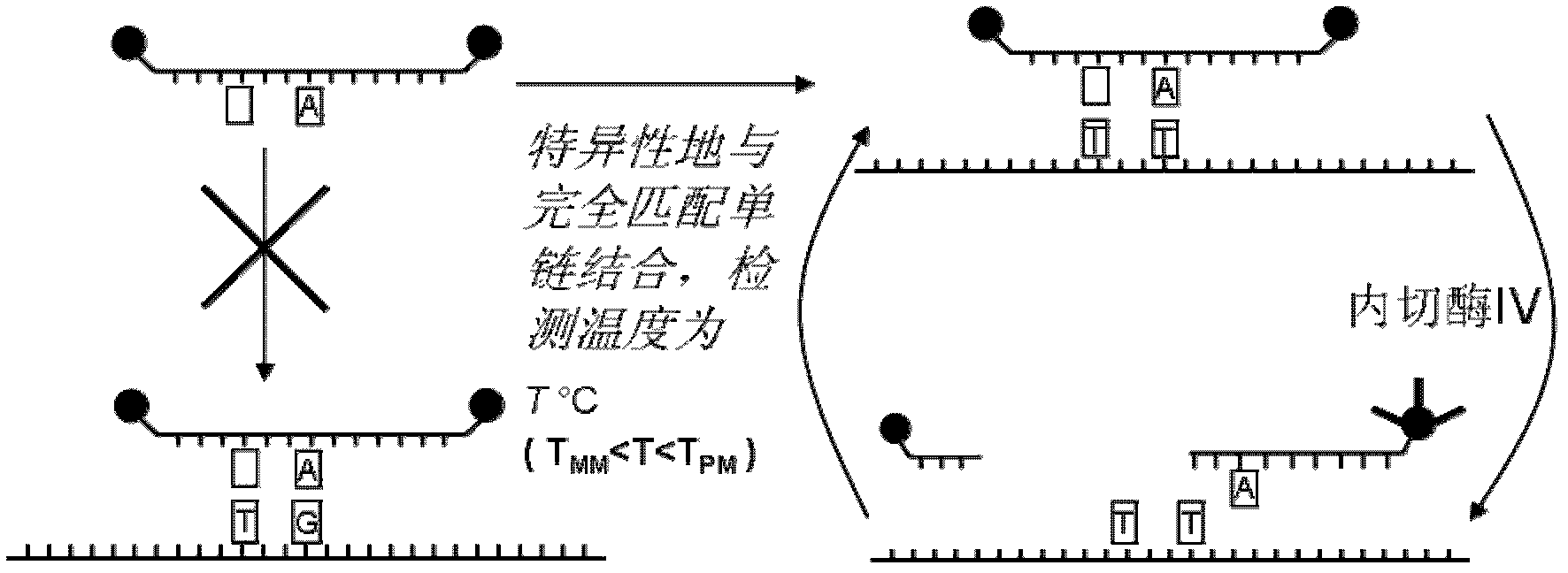
The invention discloses a method for signal amplification and detection of a DNA target sequence, and prepares a single abasic double-labeled fluorescent probe. One end of the probe is labeled with a fluorescent group, and the other end is labeled with a quenching group. Outside the base site, its sequence completely matches the DNA target sequence; at a certain detection temperature, the probe specifically combines with the target sequence to form a double-strand gap, and the endonuclease IV is used to recognize and cut the double-strand gap, and the cleaved Probe fragments dissociate from the target sequence to generate fluorescent signals, and the target sequence released by dissociation can continue to bind to another probe, repeating the above process, thereby achieving signal amplification and detection of the target sequence. The method of the invention can realize high selectivity and high sensitivity low-abundance gene mutation detection.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Internet of Things low power consumption radio frequency circuit and terminal
ActiveCN108631800AGood frequency selection functionReduce entryTransmissionLow noiseSignal processing circuits
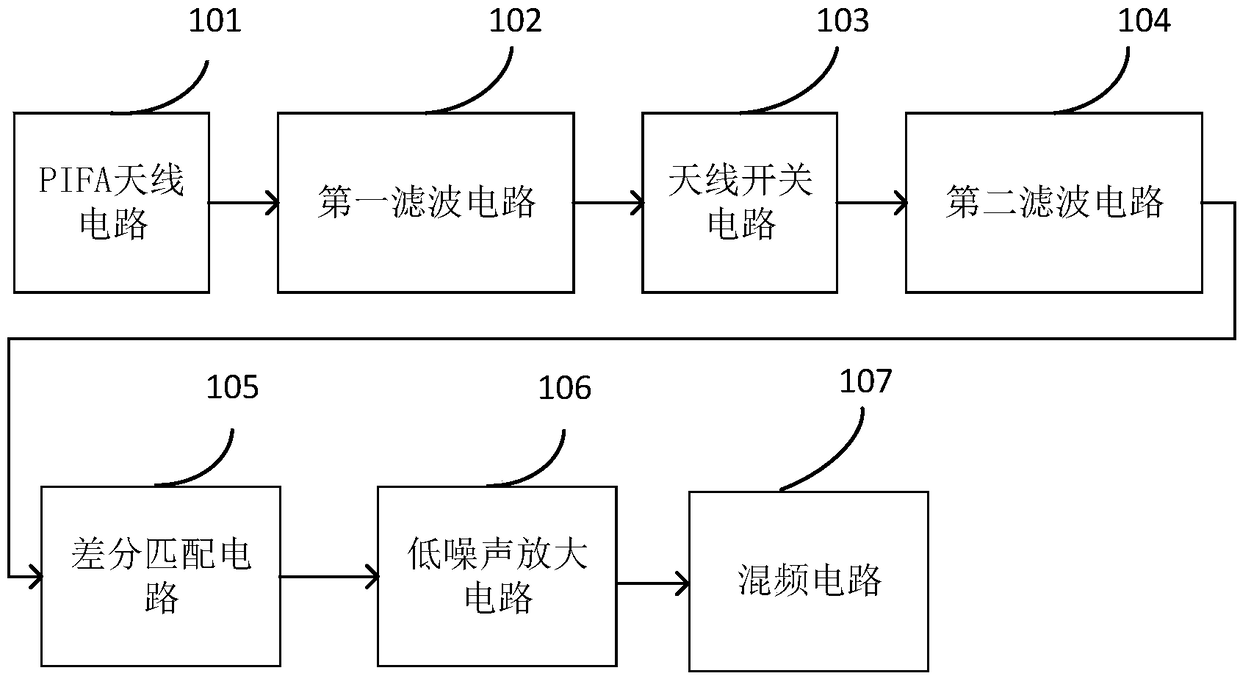
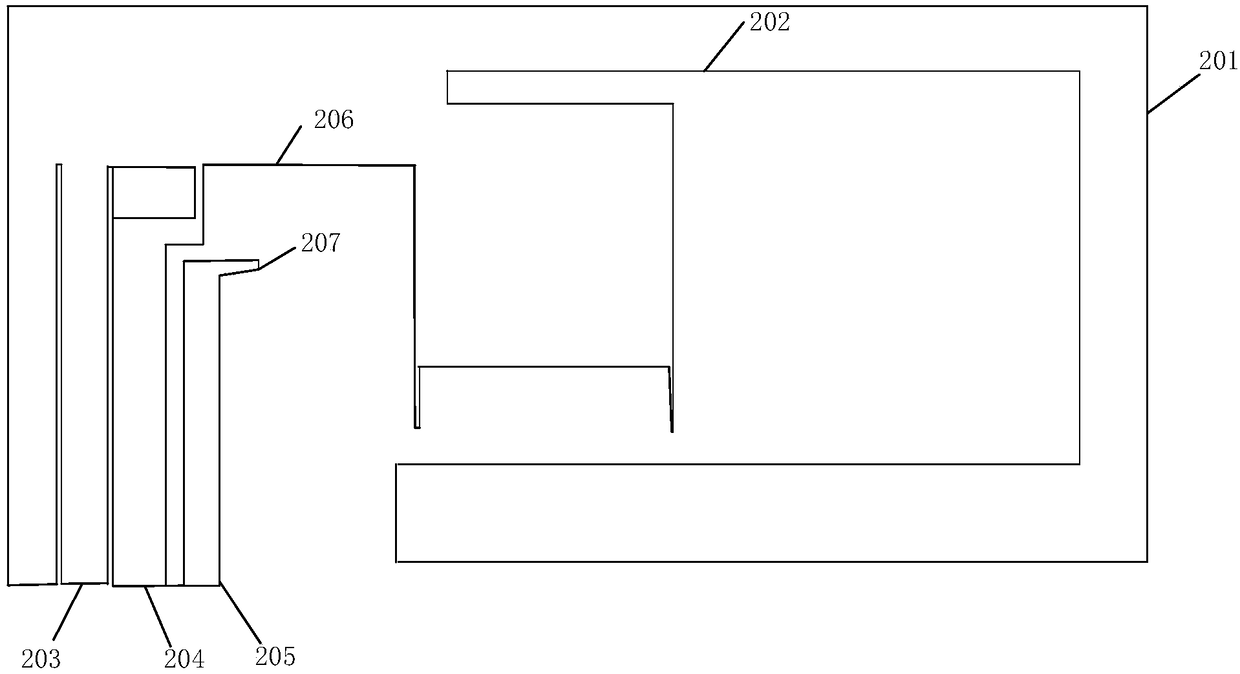
The embodiments of the invention disclose a signal processing circuit, which is applied to an Internet of Things terminal. The Internet of Things terminal comprises a main board. The circuit comprises: a PIFA antenna, a first filter circuit, an antenna switch circuit, a second filter circuit, a differential matching circuit, a low noise amplifying circuit and a mixing circuit; the PIFA antenna comprises an outer strip wire, a radiator, a grounding bending wire, a feeding plate, a grounding point and a short-circuit probe, the outer strip wire encircles a rectangle with an opening, the openingis located at the outer strip wire and the grounding point, the radiator is arranged inside the rectangle and connected to the grounding bending wire, the grounding bending wire is connected to the grounding point, the end of the grounding bending wire is connected to the short-circuit probe, and the feeding plate is arranged between the grounding point and the outer strip wire. By serially connecting the surface acoustic filter, the differential matching circuit and the low noise amplifier, secondary reflection signals can be reduced to enter the inside of a chip, so that the signal-to-noiseratio of useful signals is improved, and the sensitivity of a receiver is enhanced.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHENGLU IOT COMM TECH CO LTD
Piezoelectric-hydraulic control type dispensing device
InactiveCN103433178APrevent leakageGood zoom effectLiquid surface applicatorsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesBolt connectionFiring pin
The invention provides a dispensing device which is suitable for the field of dispensing. The dispensing device comprises a power system, a displacement amplifying system, a glue feeding system and an injection system, which are connected with one another through bolts, wherein a piezoelectric stack is used for powering the whole device; the displacement amplifying system is used for amplifying the displacement of the piezoelectric stack through an L-shaped hydraulic amplifying cavity, and a firing pin of the injection system impacts a nozzle under the displacement so as to jet a glue solution supplied by the glue feeding system. The dispensing device is dedicated to solving the problems that a current dispensing device cause large noise, and is not high in stability and low in frequency, the universality of the dispensing device is improved, and a good practical effect is achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
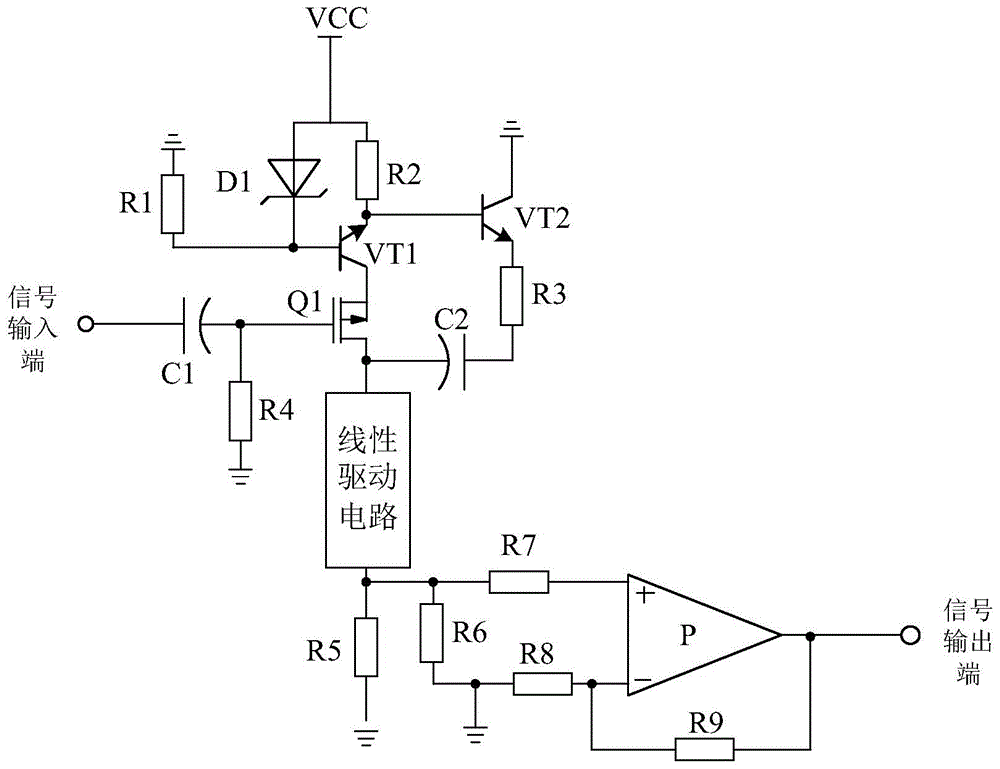
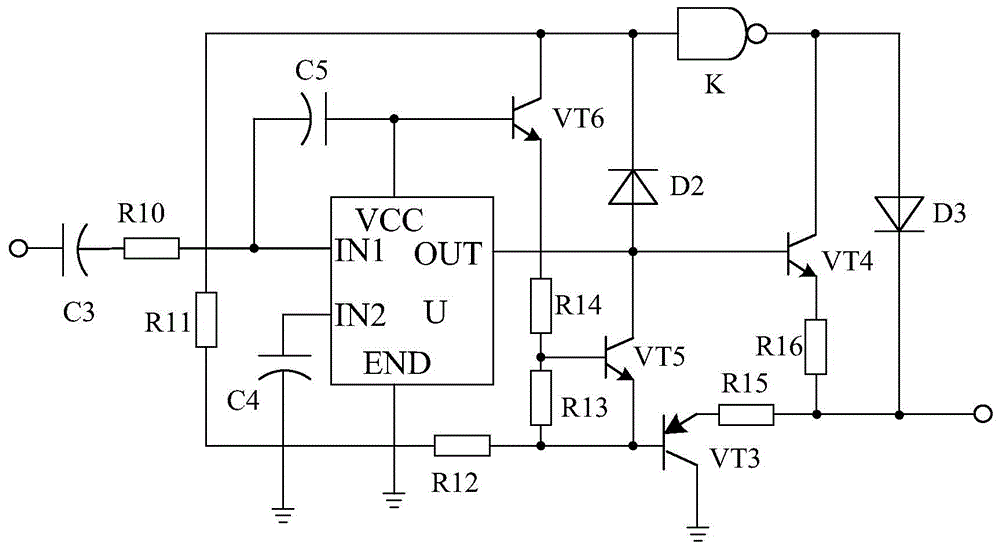
Linear drive based bias current source amplifier system
InactiveCN104467697AGood zoom effectDrive stabilityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a linear drive based bias current source amplifier system. The linear drive based bias current source amplifier system mainly consists of a field-effect tube Q1, a polar capacitor C1, a resistor R4, a current source circuit and an amplification circuit, wherein the negative pole of the polar capacitor C1 is connected with the grid electrode of the field-effect tube Q1, the positive pole of the polar capacitor C1 serves as a signal input end, one end of the resistor R4 is connected with the grid electrode of the field-effect tube Q1, the other end of the resistor R4 is grounded, and the current source circuit is connected with the source electrode of the field-effect tube Q1. The linear drive based bias current source amplifier system is characterized in that a linear drive circuit is further connected between the drain electrode of the field-effect tube Q1 and the amplification circuit and consists of a drive chip U, an audion VT3, an audion VT4, an audion VT5, an audion VT6 and the like. The linear drive circuit of the linear drive based bias current source amplifier system can stably drive the amplifier system, and accordingly the amplification effect of an amplifier is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU SIMAO TECH
Zoom lens
Owner:YOUNG OPTICS
Light scattering layer for electronic device comprising nano-particles, junction structure for thin film transistor comprising light scattering layer, and methods of forming the same
InactiveUS20070134516A1Reduce thicknessPromote generationNatural mineral layered productsSemiconductor devicesNanoparticleCarbide
A light scattering layer for an electronic device comprising nano-particles, a junction structure for a thin film transistor comprising the light scattering layer, and methods of forming the same are provided. The light scattering layer for the electronic device comprises a carbide-semimetal or a carbide-metal comprising nano-particles comprising Si or a metal. In the junction structure for a thin film transistor according to an embodiment of the present invention, the light scattering layer is interposed between a first protective layer and a second protective layer comprising (ZnS)1-x(SiC)x, W1-xCx, Ta1-xCx, and Mo1-xCx, wherein 0<x<1. First and second capping layers comprising M1-y((ZnS)1-x(SiC)x)y, M1-y(W1-xCx)y, M1-y(Ta1-xCx)y, and M1-y(Mo1-xCx)y, wherein 0<x<1, 0<y<1, and M is Si, Ta, W or Mo, may be interposed between the first protective layer and the light scattering layer, and between the light scattering layer and the second protective layer, respectively. The layers are sequentially formed in-situ, without breaking a vacuum state after the process of forming each layer is performed.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
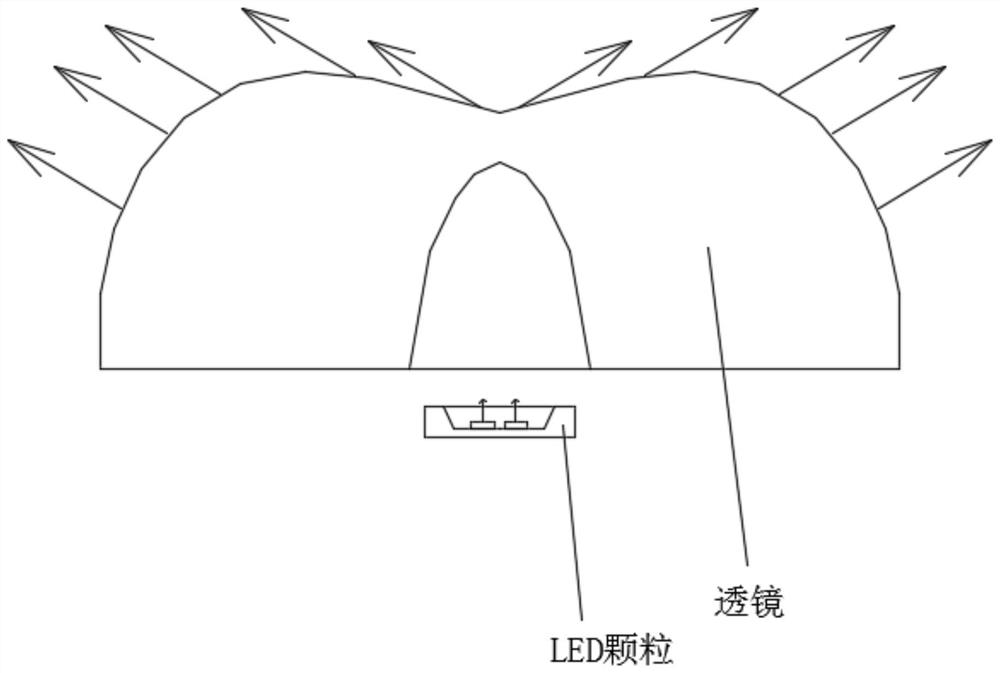
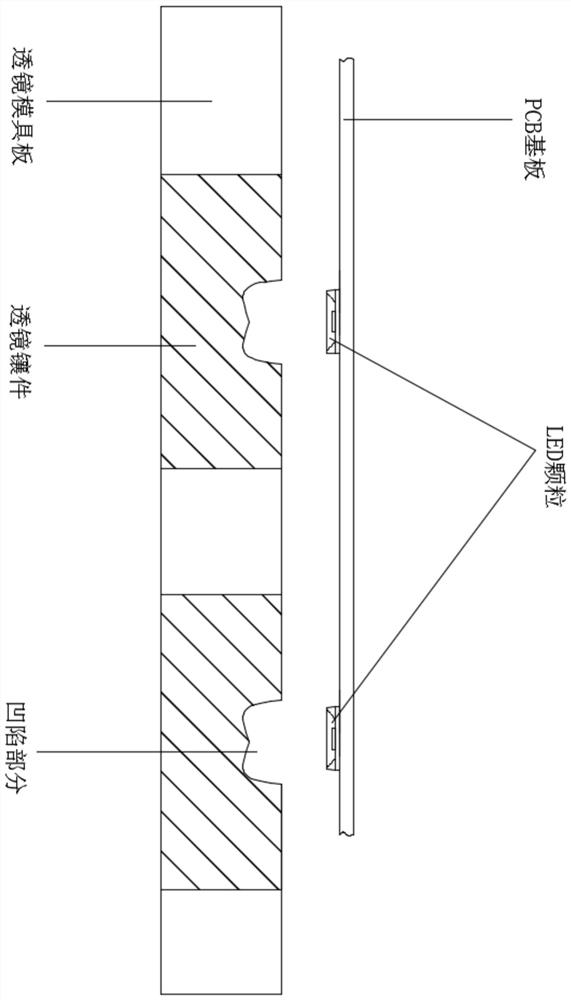
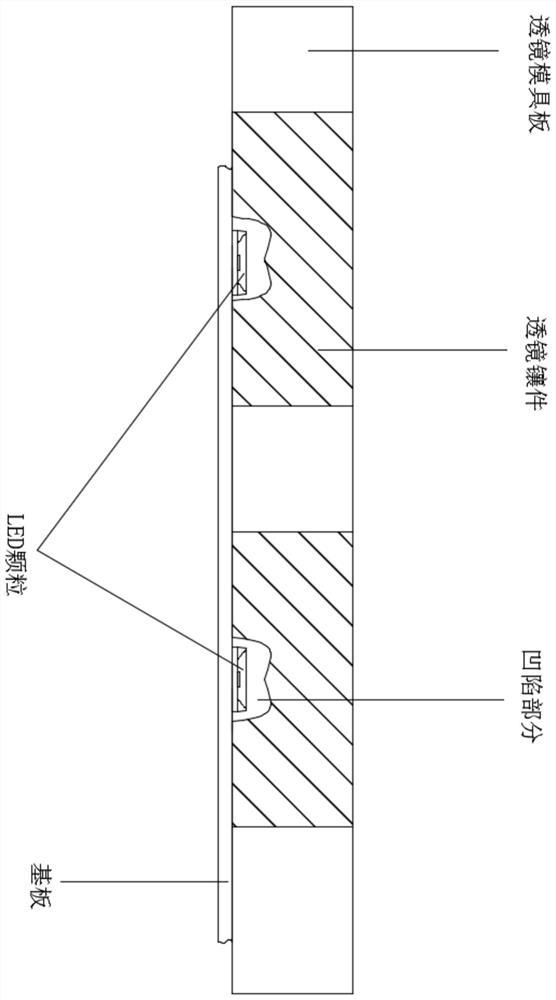
Preparation method of LED light-emitting device, and LED light-emitting device
InactiveCN112259660AIncrease productivityGood zoom effectNon-linear opticsSemiconductor devicesCompression moldingMaterials science
The invention provides a preparation method of an LED light-emitting device. The preparation method comprises the steps that S1, LED particles or LED chips are attached to a substrate of a LED light-emitting device; S2, the concave part of a lens insert on a lens mold plate is filled with a curing glue; S3, the substrate obtained in the step S1 is inversely pressed on the lens mold plate obtainedin the step S2, wherein the positions of the LED particles or the LED chips correspond to about the middle position of the concave part of the lens insert; and S4, the substrate and the lens mold plate which are pressed together in the step S3 are cured, after the curing glue is cured, the curing glue, the LED particles or the LED chips and the substrate are fixed together, and after mold opening,a LED light-emitting device is obtained. The invention further provides an LED light-emitting device, which is characterized in that LED particles or LED chips are located at the position about the middle of a lens, the lens is only provided with one optical face, and the lens is directly formed in a compression molding mode through a curing glue.
Owner:苏州东岩电子科技有限公司
Non-Invasive pipeline pressure detection mechanism based on fiber grating
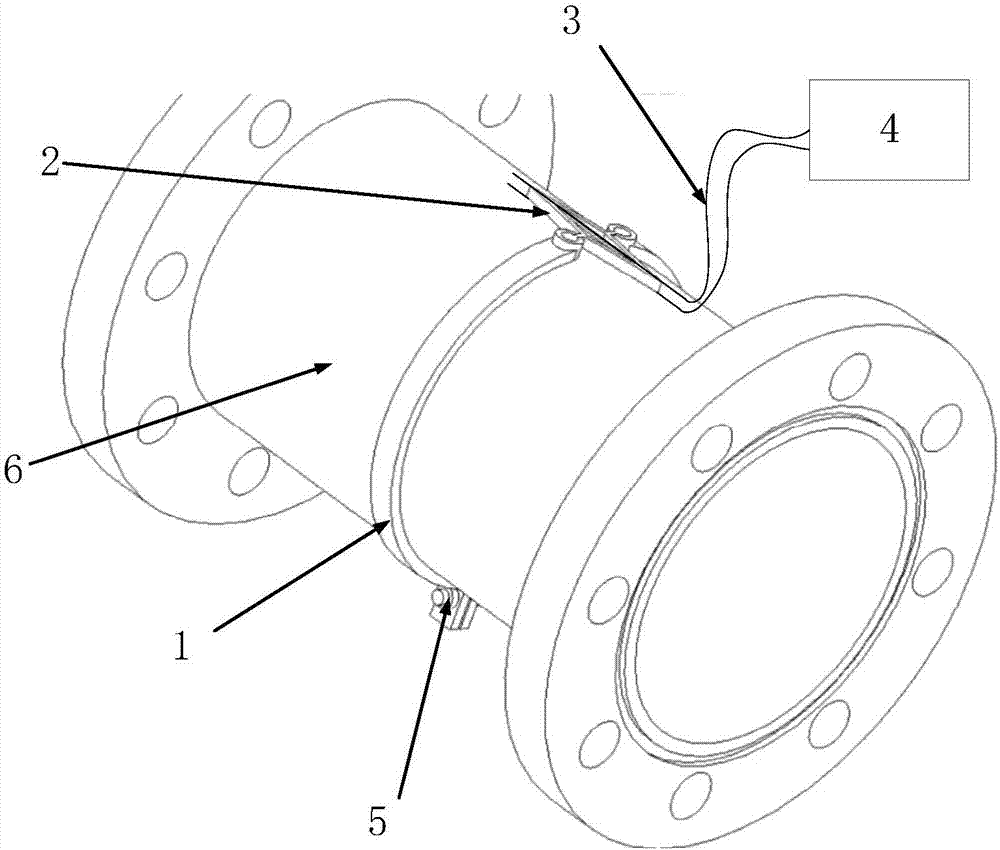
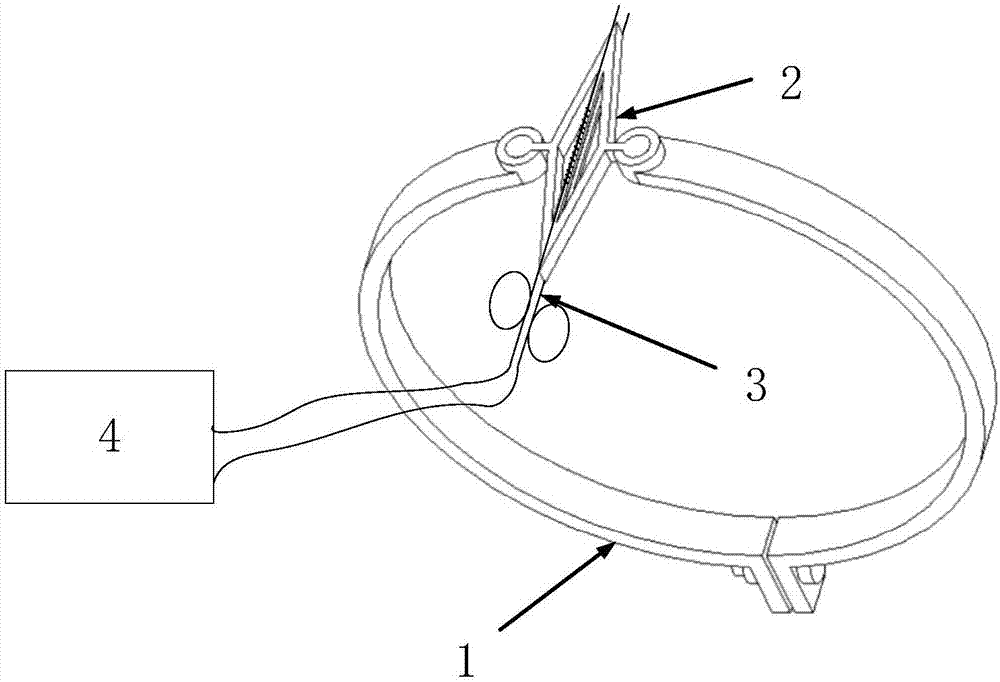
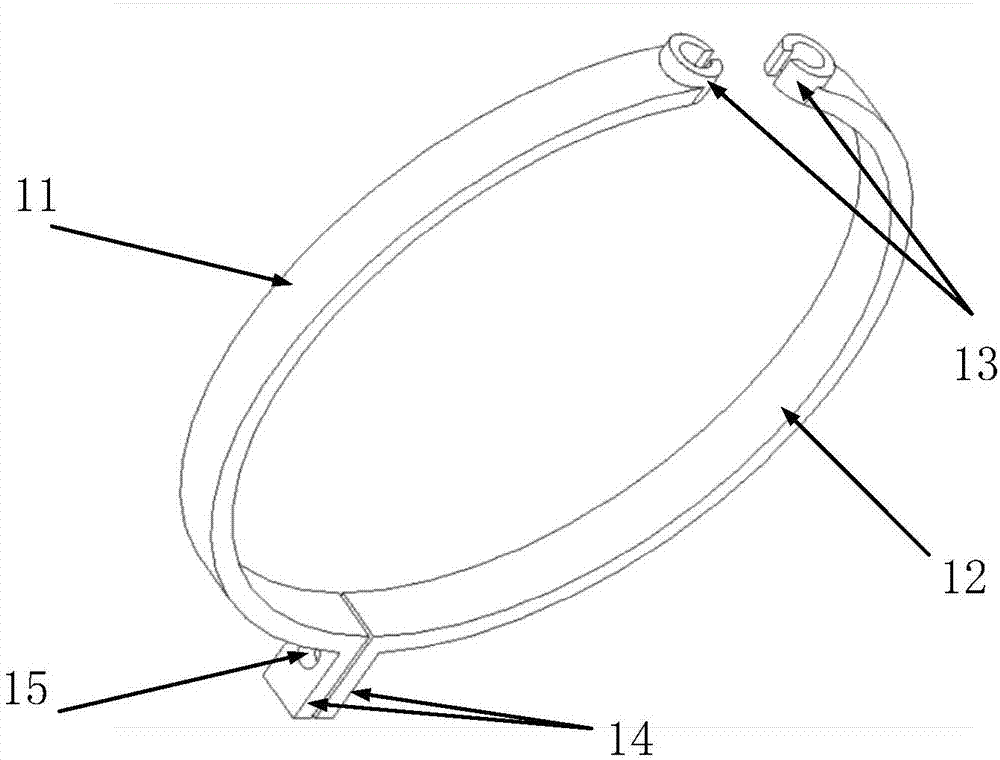
ActiveCN107884114AEnables non-intrusive detectionSimple structureForce measurement by permanent gauge deformationFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesInternal pressureGrating
The present invention relates to a non-Invasive pipeline pressure detection mechanism based on fiber grating. The mechanism comprises a clamp ring body clinging to an outer wall of a pipeline, a rhombic detection unit and a fiber grating; the clamp ring body comprises a first clamp body and a second clamp body which are two symmetrical semicircular structures, two opposite ends of the first clampbody and the second clamp body are provided with clamp rings connected with the rhombic detection unit, the other ends of the first clamp body and the second clamp body are provided with ear portionsconfigured to perform connection and fastening of the first clamp body and the second clamp body, each ear portion is provided with one through hole, and each through hole is internally provided withone fastener. The non-Invasive pipeline pressure detection mechanism based on fiber grating is simple in structure and convenient to mount and dismount, the clamp ring body clings to the outer wall ofthe measurement pipeline when measurement is performed, and the clamp ring body is in buckle connection with the rhombic detection unit; and moreover, the mechanism provided by the invention has goodtransmission and amplification effects on pipeline wall strain on the premise without damaging the measured pipeline wall so as to achieve an enhanced sensitivity effect, and can achieve non-Invasivedetection of internal pressure of the pipeline based on features of the high resolution and high sensitivity of the fiber grating.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Stage lamp optical system having soft light and light beam effects
ActiveCN104266109AGood effectSharp edgeLighting applicationsMechanical apparatusCamera lensOptical axis
The invention relates to a stage lamp optical system having soft light and light beam effects. The stage lamp optical system having the soft light and light beam effects comprises a light source assembly, a light collecting device, an effect assembly and an imaging light path system which are sequentially arranged along a light path; the imaging light patch system comprises a focusing lens assembly, a magnifying lens assembly and a fixed lens assembly which are sequentially arranged along a light path; a soft light transformation assembly which can move front and back along the optical axis direction is arranged inside the imaging light path system; the soft light transformation assembly is arranged between the magnifying lens assembly and the fixed lens assembly; the soft light transformation assembly and the magnifying lens assembly are connected with a first driving mobile mechanism; the first driving mobile mechanism drives the soft light transformation assembly and the magnifying lens assembly to move front and back along the optical axis direction to adjust zoom ranges under a soft light mode. The stage lamp optical system having the soft light and light beam effect achieving switching of a soft light effect and a light beam effect, is good in effect under the light beam effect and meanwhile the zoom ranges can achieve 6 to 12 times under the soft light mode.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HAOYANG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for signal amplification during lateral-flow analysis
InactiveUS20120070822A1Good signal amplificationHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologySignal amplification
Owner:INFOPIA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com