Method for signal amplification and detection of dna target sequences
A target sequence and signal amplification technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, material stimulation analysis, etc., can solve problems such as low detection temperature, loss of probe discrimination ability, and limited application range, and achieve detection low limit effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1
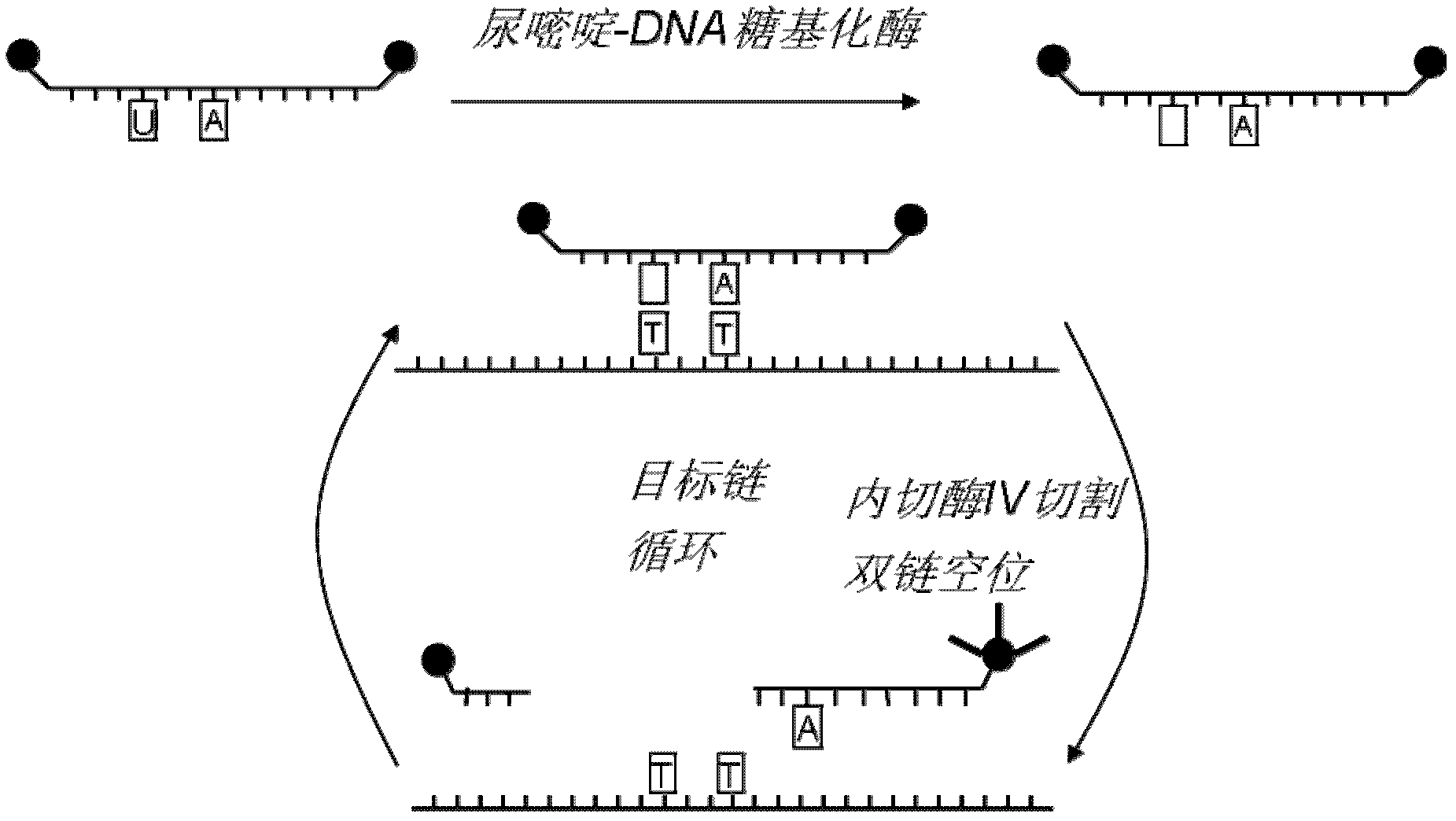
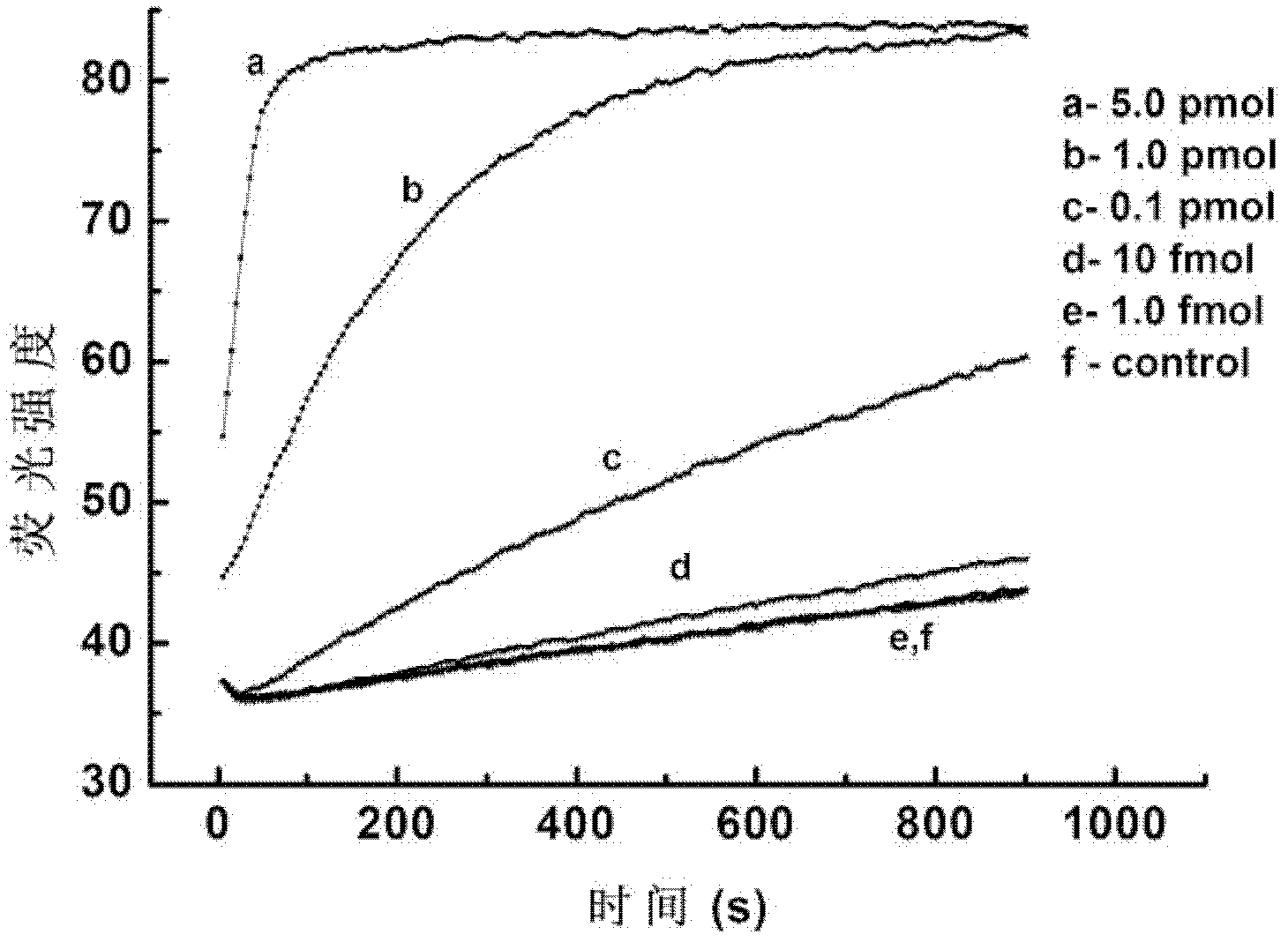
[0031]In this embodiment, the target is a perfectly matched DNA single strand, and a series of concentration gradients of the DNA single strand are set in the experiment, hoping to detect as few target strands as possible. For detection principle see figure 1 ,Specific steps are as follows:
[0032] 1. Use UDG enzyme to treat double-labeled fluorescent probes containing uracil deoxynucleotide residues to obtain single abasic probes;
[0033] 2. Mix the obtained single abasic probe with different concentrations of target DNA sequences, then add endonuclease IV, and quickly measure the change of fluorescence value of endonuclease IV in the mixed solution over time.
[0034] In this embodiment, the designed probe sequence is as follows:
[0035] 5'-FAM-TCGTCTCCACUGAAACATACTCCATAA-TAMRA-3' (SEQ ID No.1)
[0036] The base composition of the target sequence is as follows:
[0037] 5'-GTTTTAAATTATGGAGTATGTTTCTGTGGAGACGAGAGTAAG-3' (SEQ ID No. 2)
[0038] In 5...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2
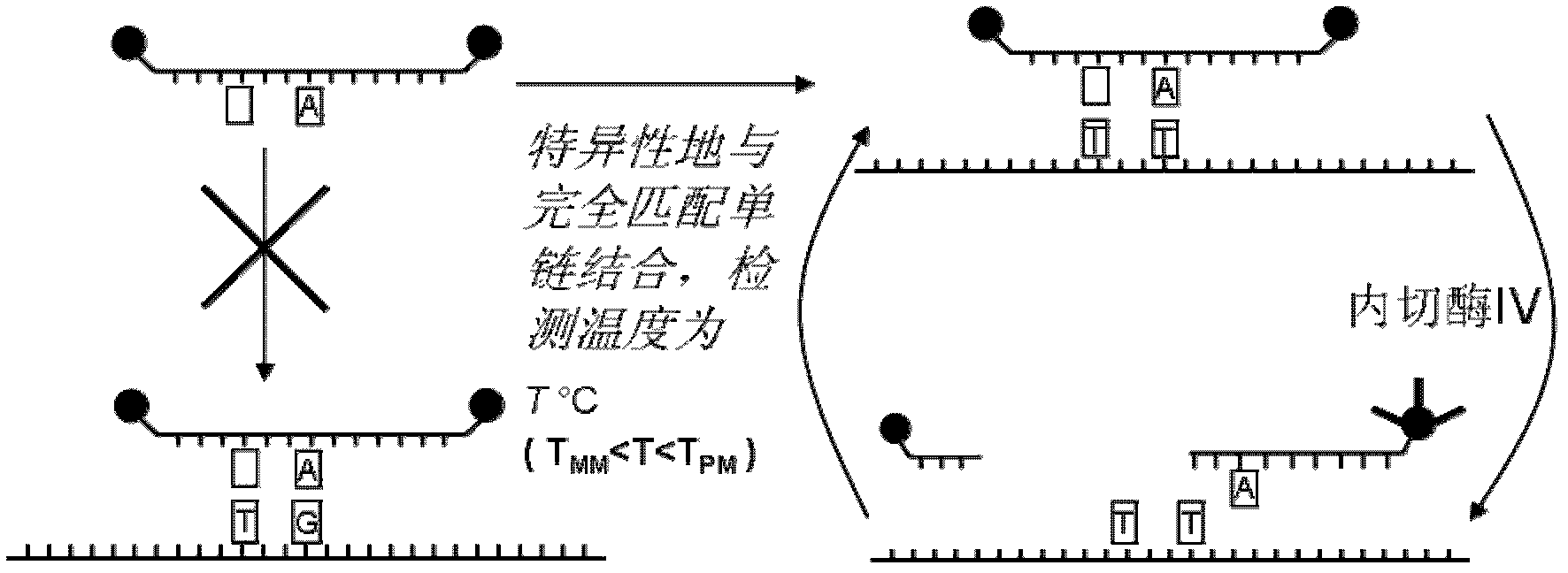
[0044] In this example, the system to be tested is a mixed system of the wild chain and the mutant chain, and the total amount of the two chains is 5 pmol, but a series of different mutation ratios are set, hoping to detect as low a mutation ratio as possible. For detection principle see image 3 , the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0045] 1. Prepare a single abasic probe, the method is the same as step 1 in Example 1;
[0046] 2. Measure the melting temperature of the double strand formed by the single abasic probe, the wild strand and the mutant strand respectively, and determine the appropriate detection temperature;
[0047] 3. Mix the single abasic probe with the mixed target system containing different proportions of mutant chains, add endonuclease IV, rapidly raise the temperature to the detection temperature determined in step 2, and measure the change of fluorescence value with time.
[0048] In this embodiment, the designed prob...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com