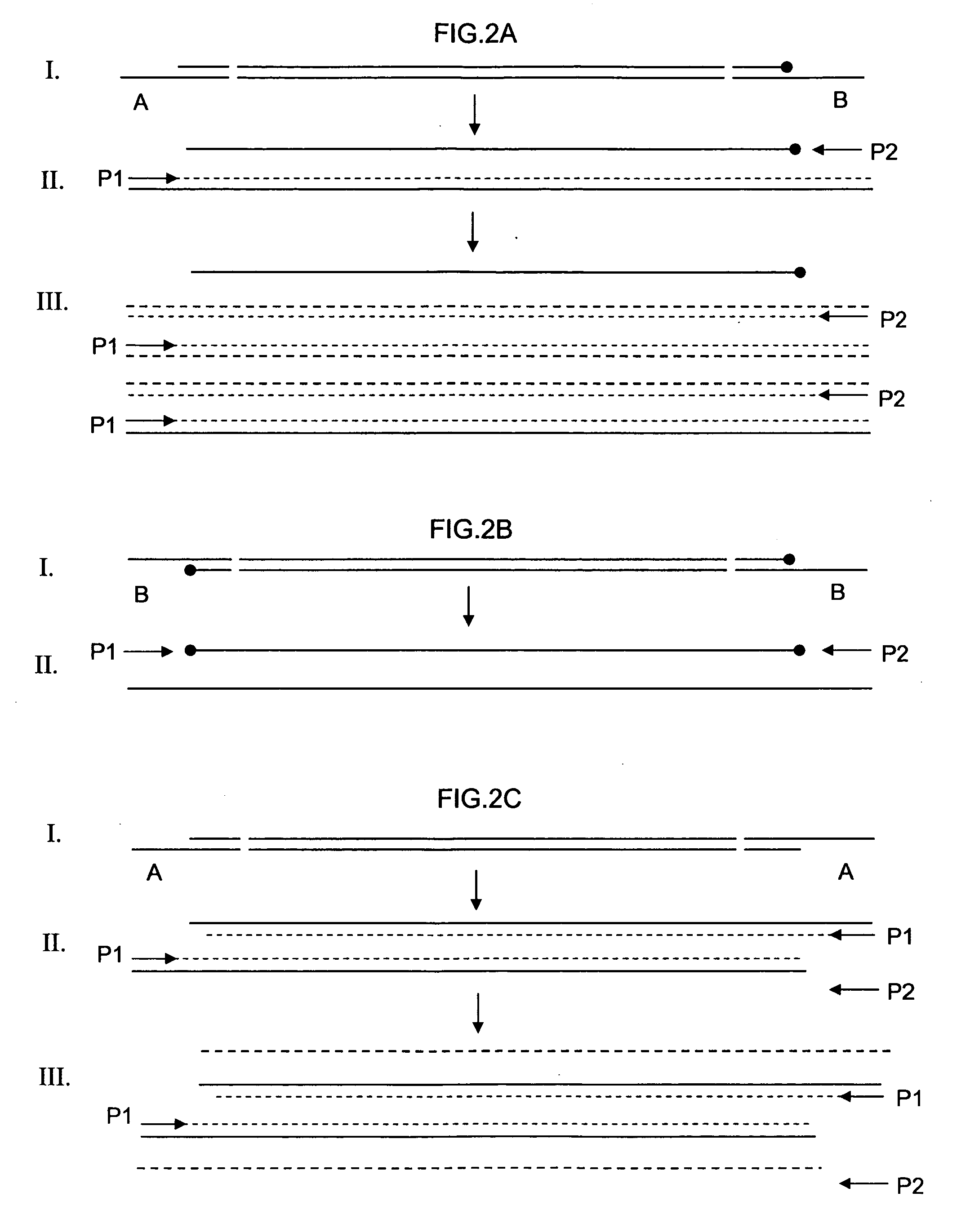
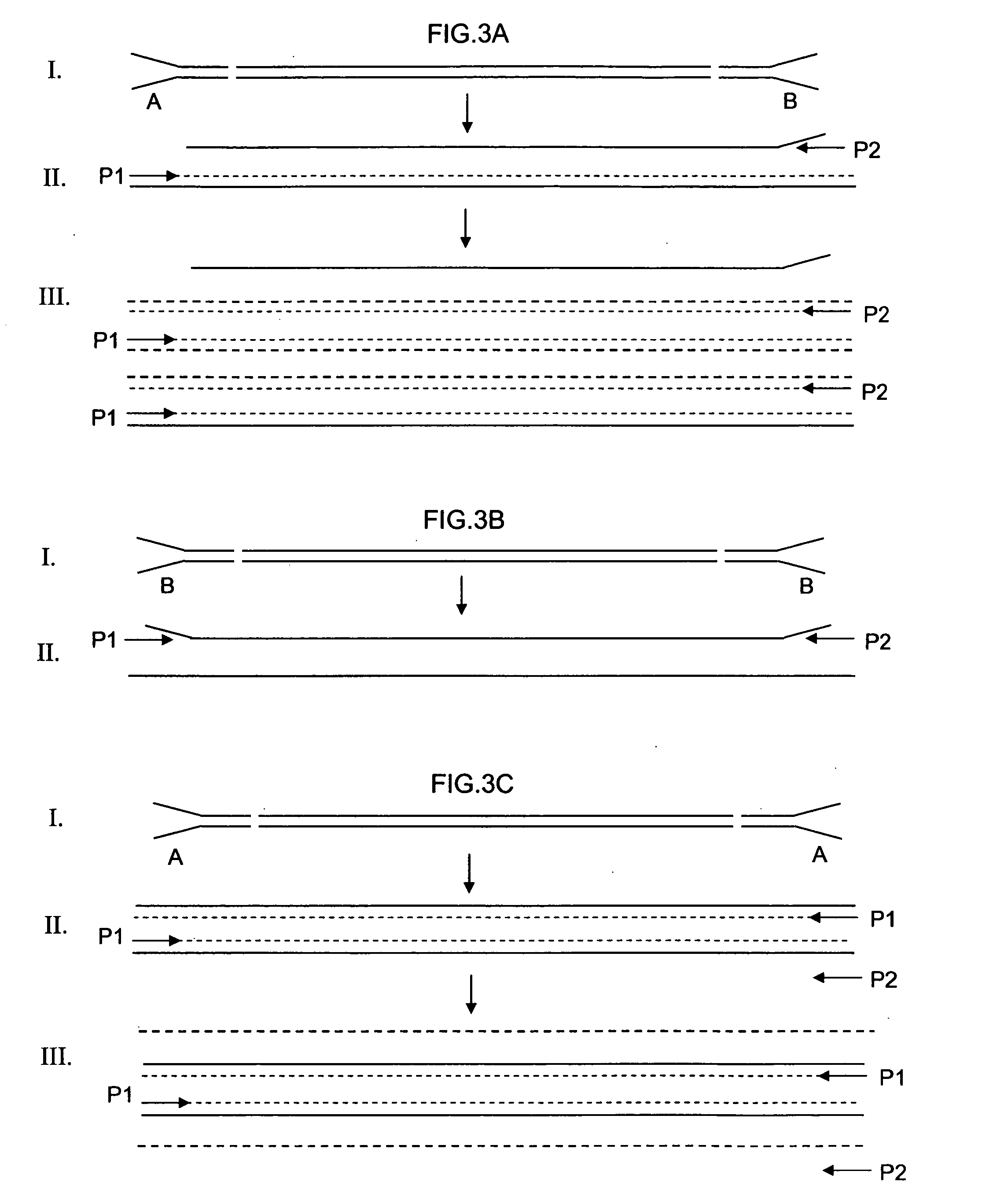
Patents
Literature
3247 results about "Single strand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
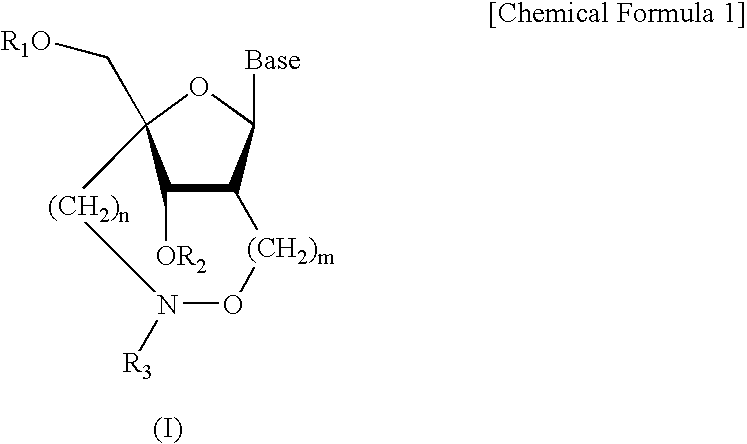
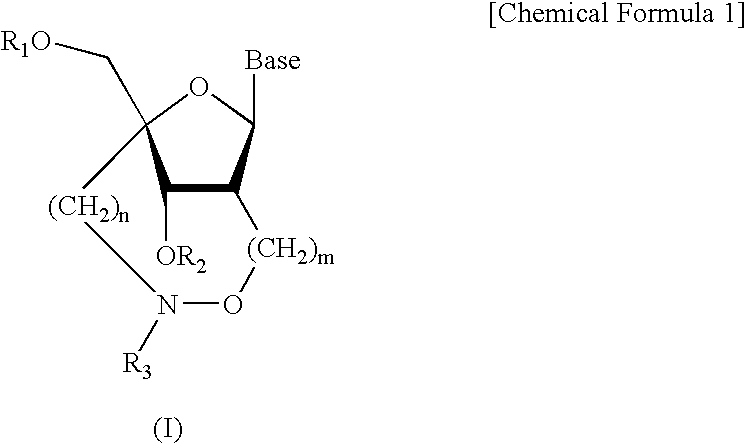
L-ribo-LNA analogues
Provided are L-ribo bicyclic nucleotide compounds as well as syntheses of such compounds. The nucleoside compounds of the invention are useful in forming oligonucleotides that can produce nucleobase specific duplexes with complementary single stranded and double stranded nucleic acids.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Artificial nucleic acids of n-o bond crosslinkage type
ActiveUS7427672B2High sensitivity analysisConfirmed its usefulnessBiocideSugar derivativesSingle strandDouble strand
Owner:RIKEN GENESIS
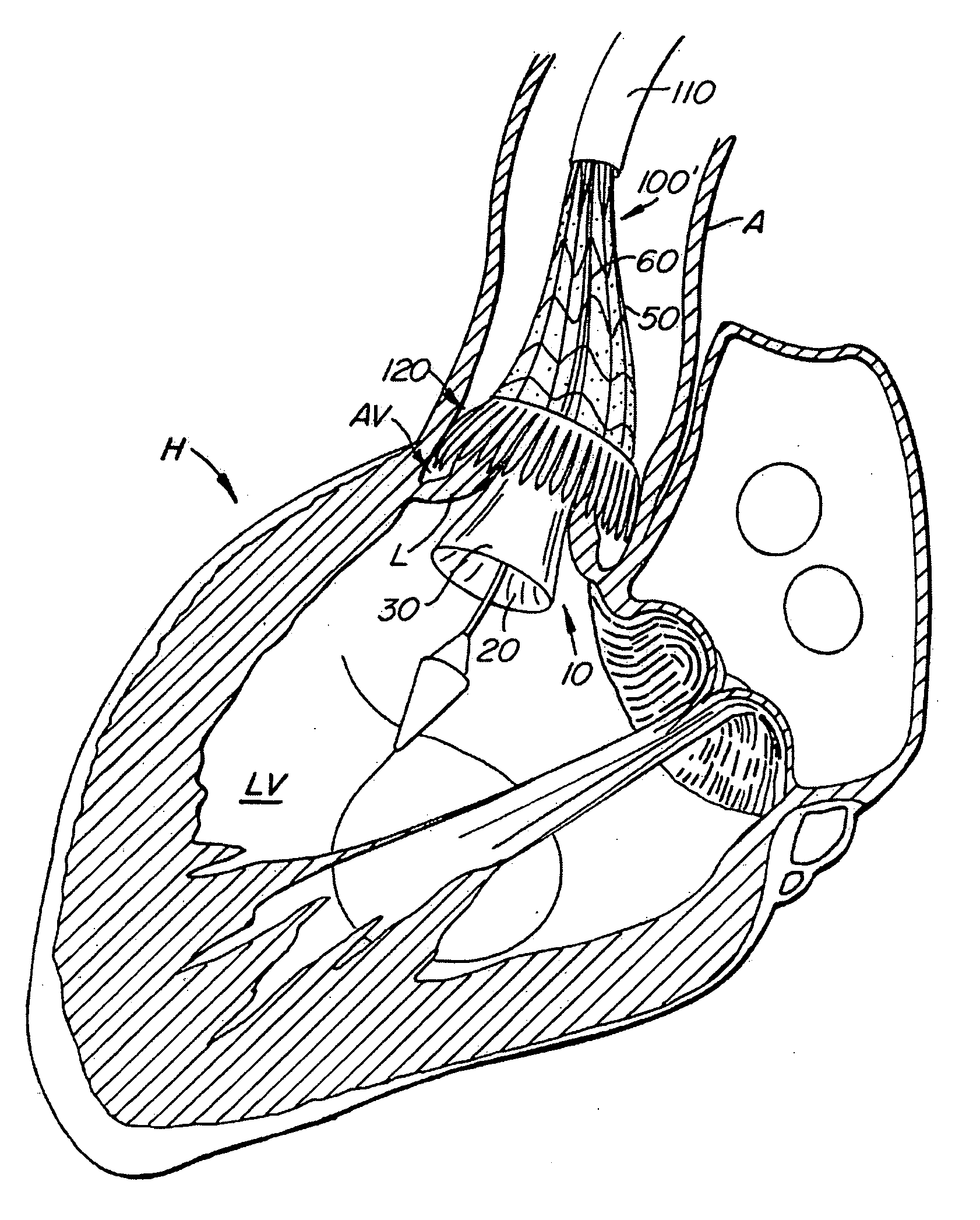
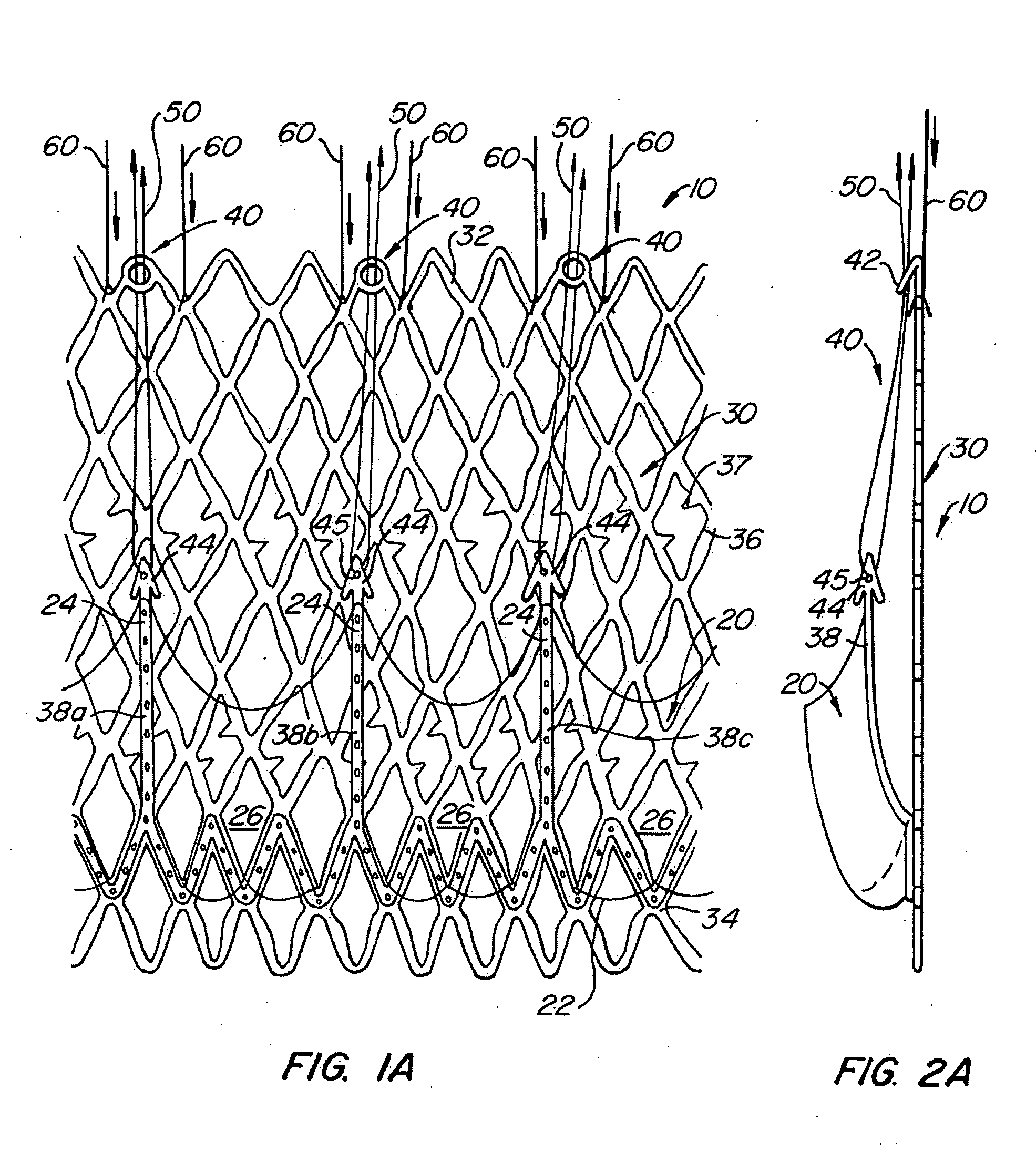
Everting heart valve
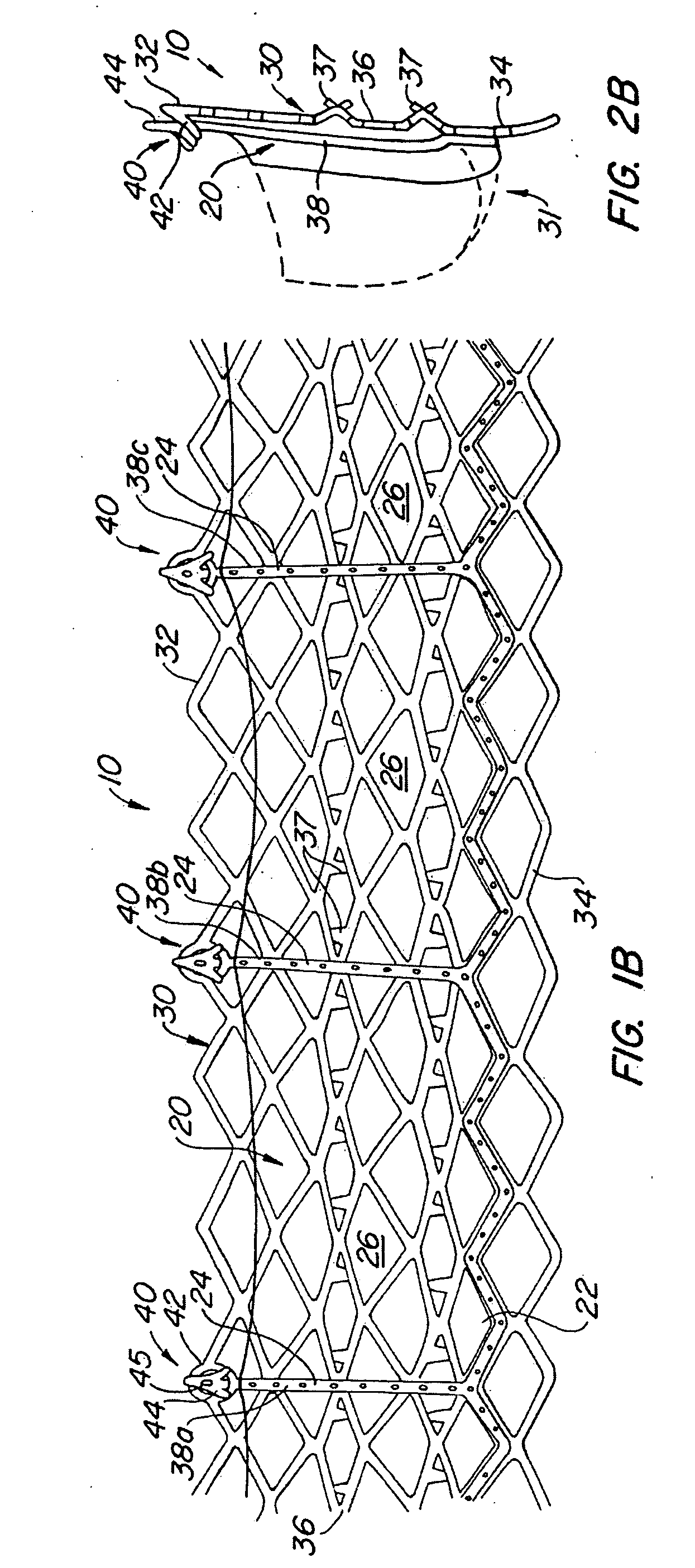
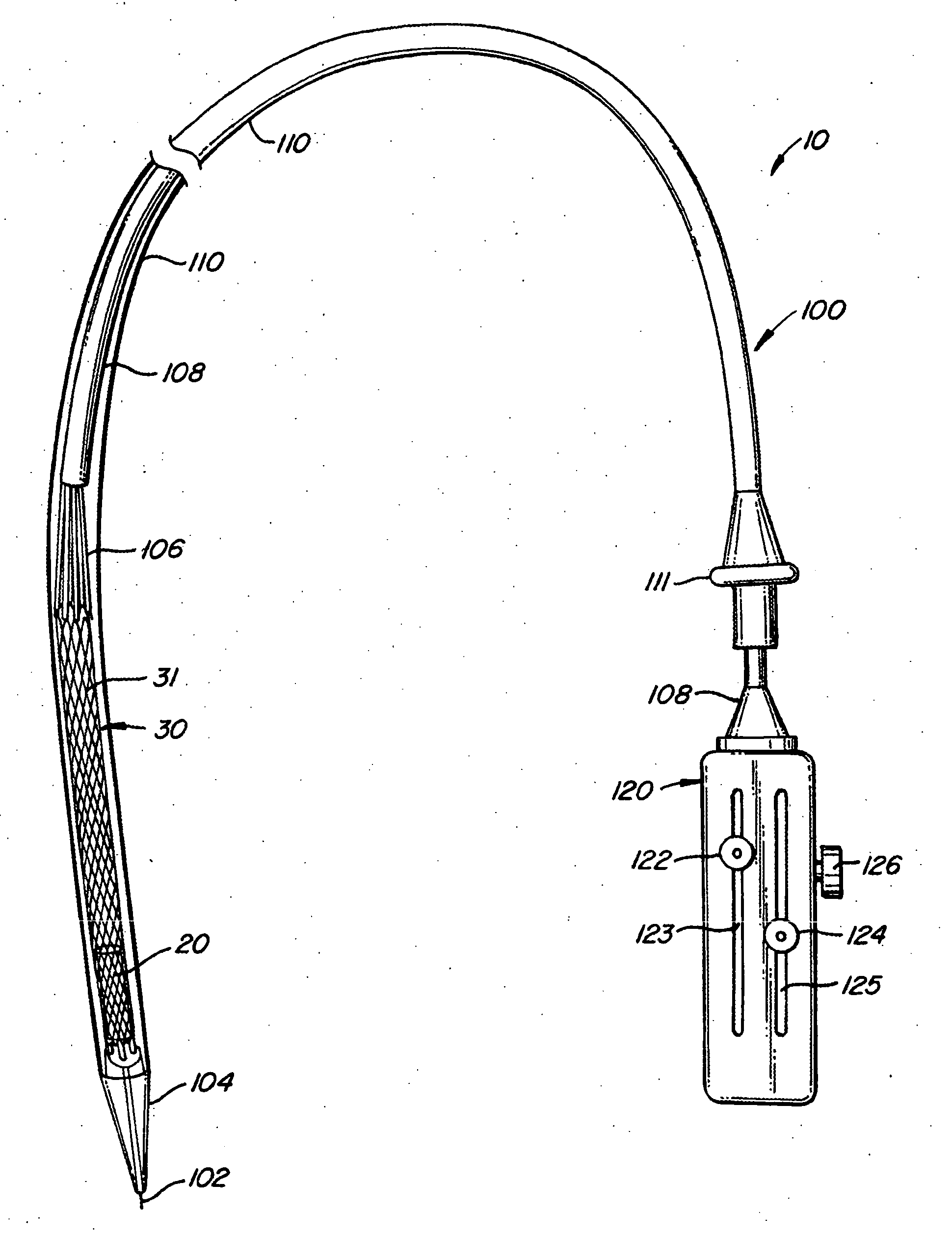
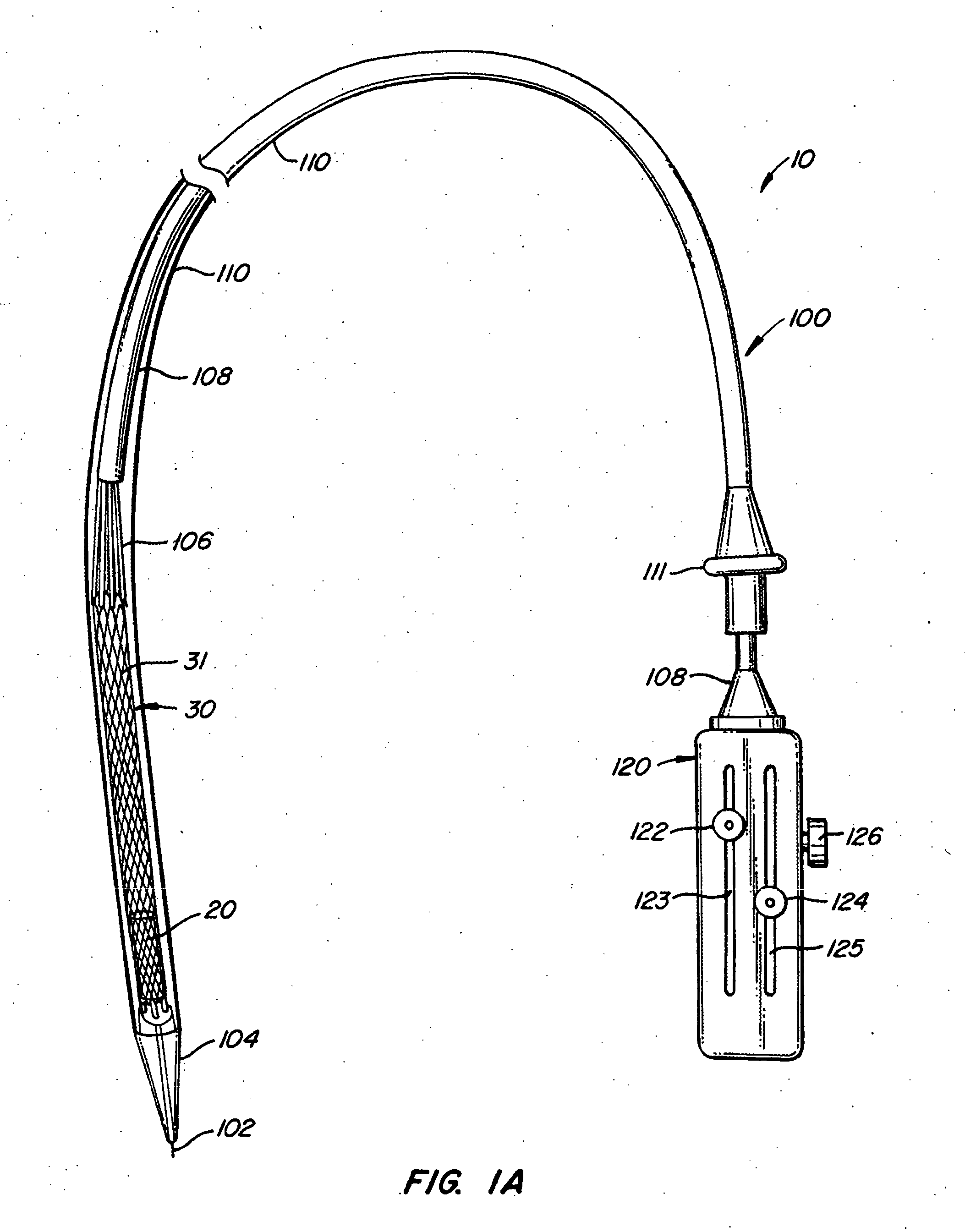
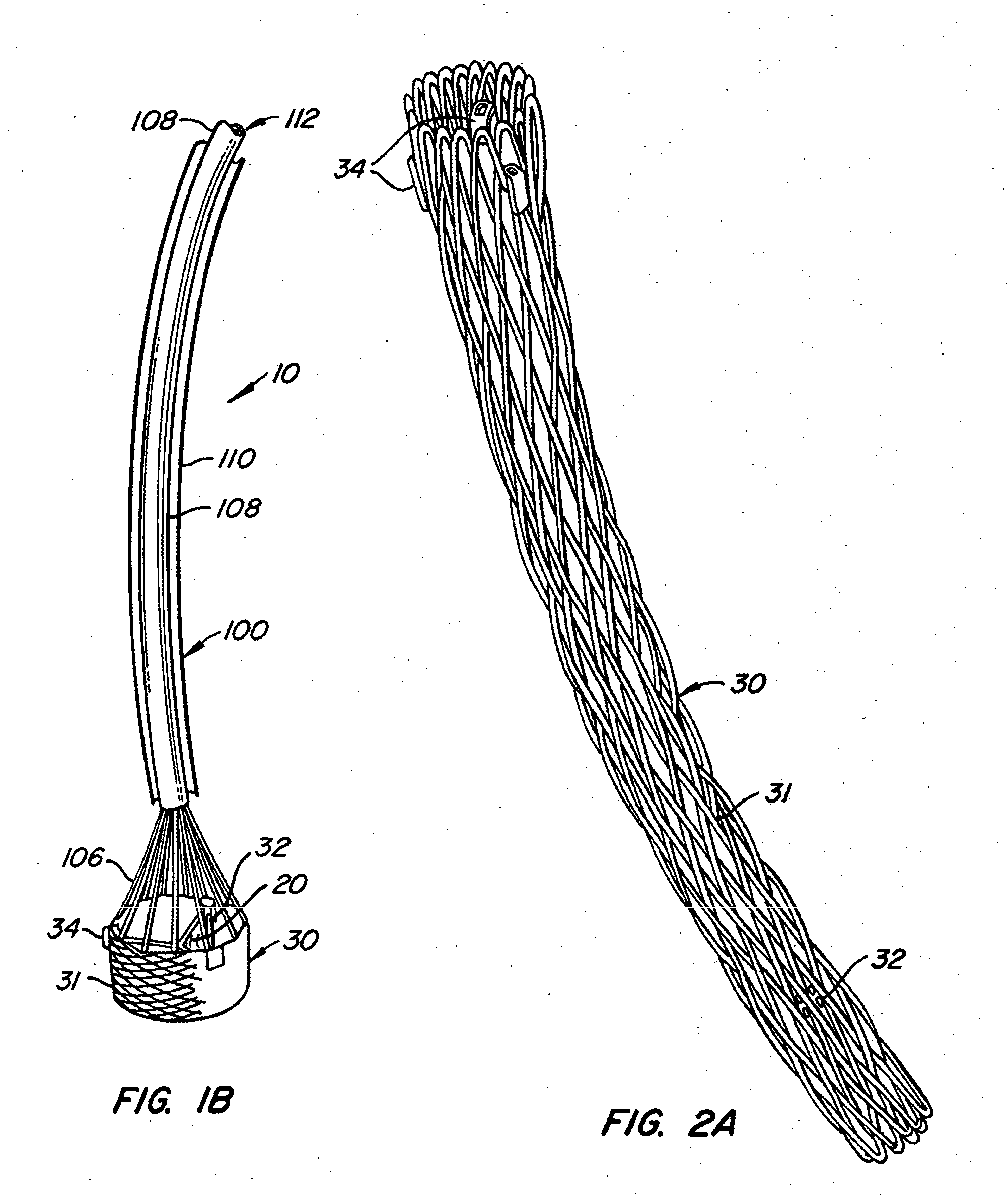
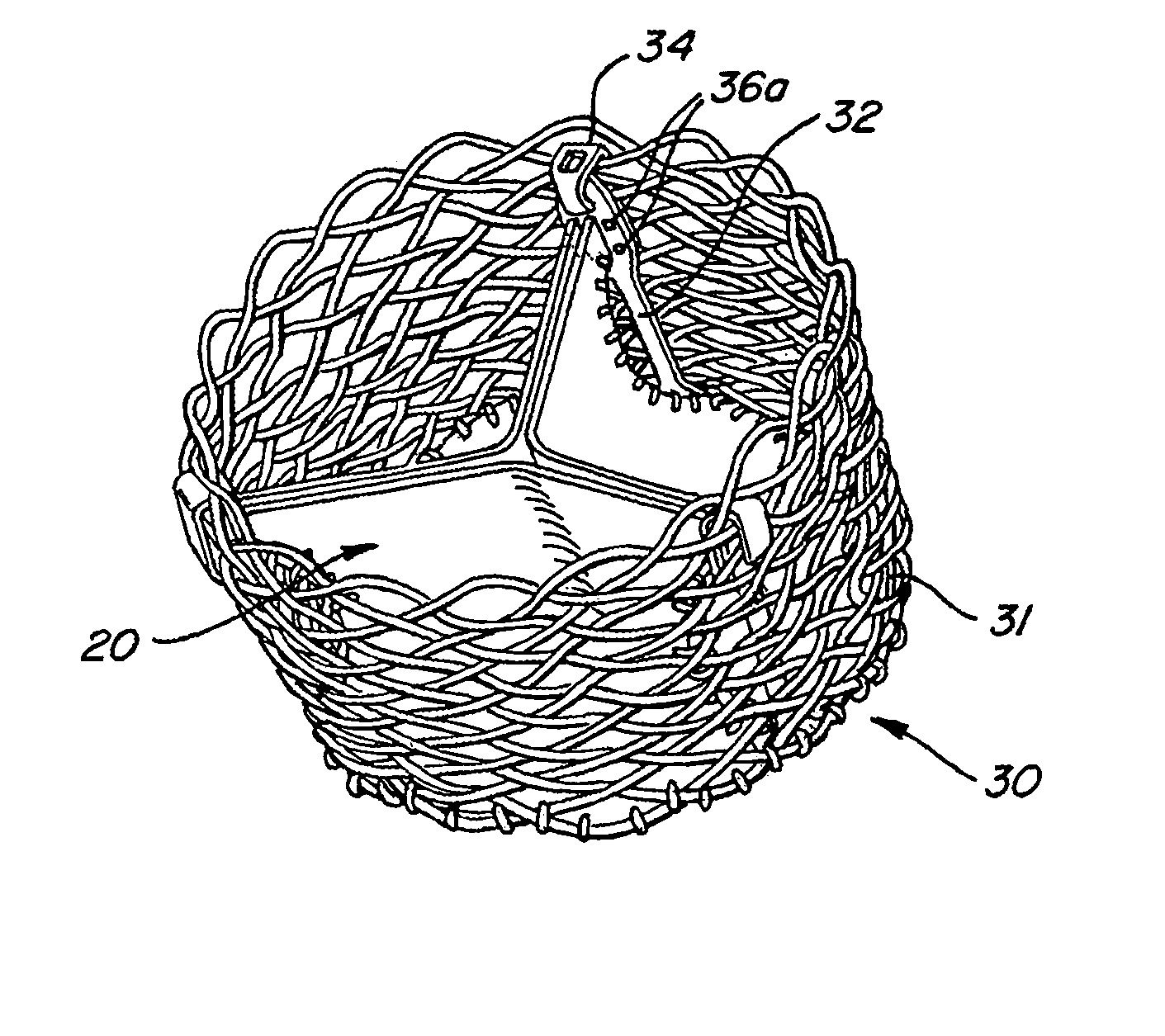
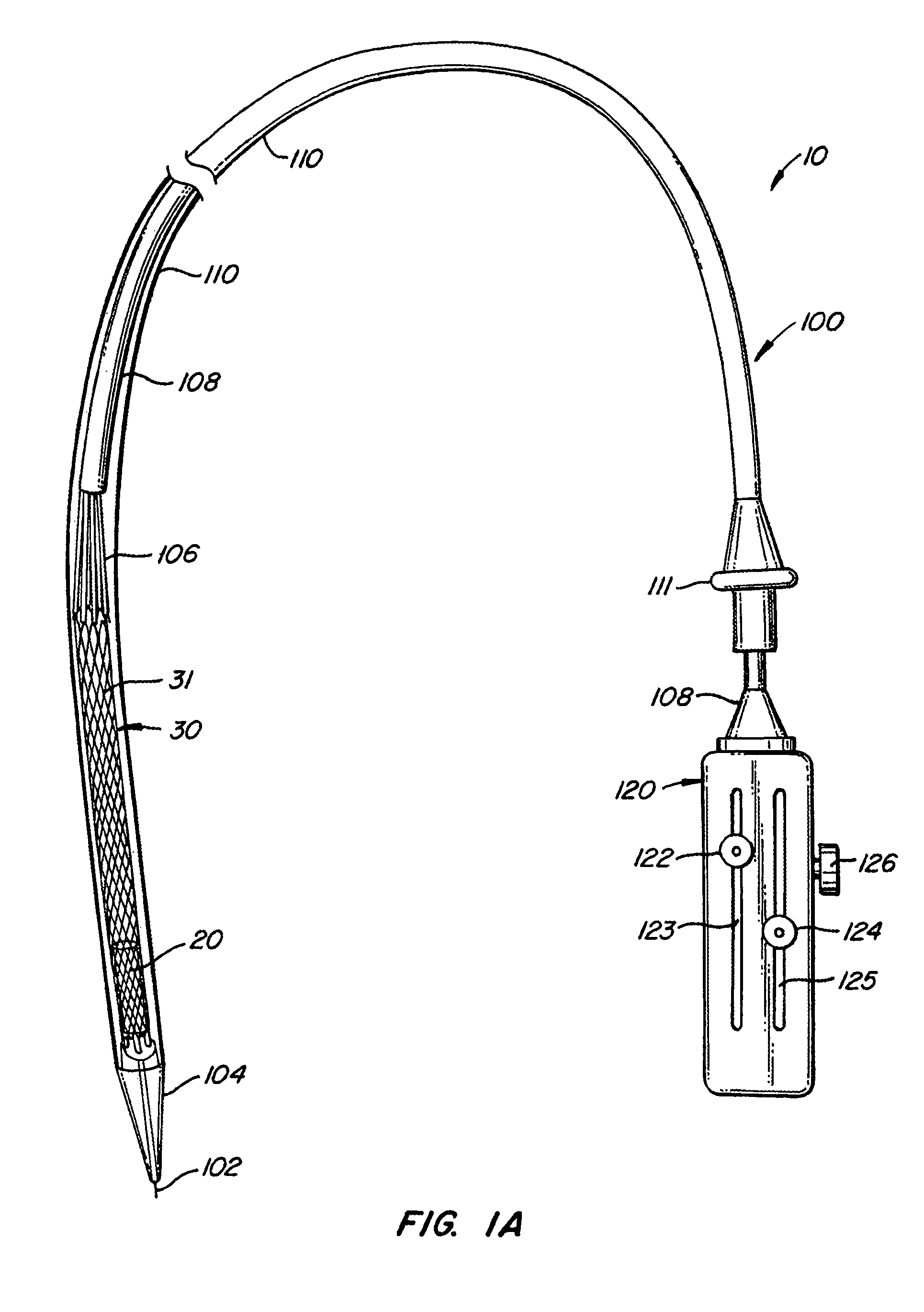
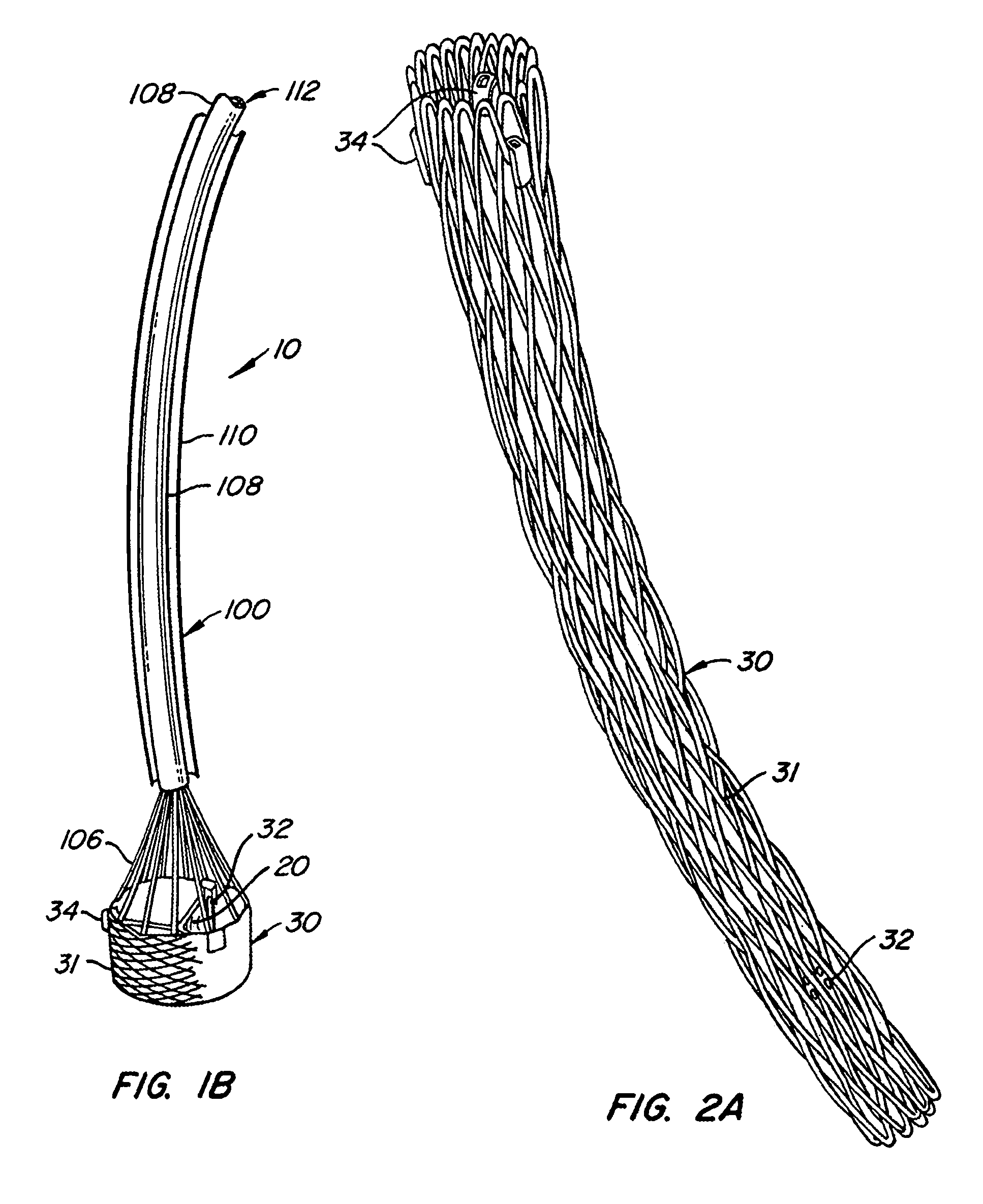
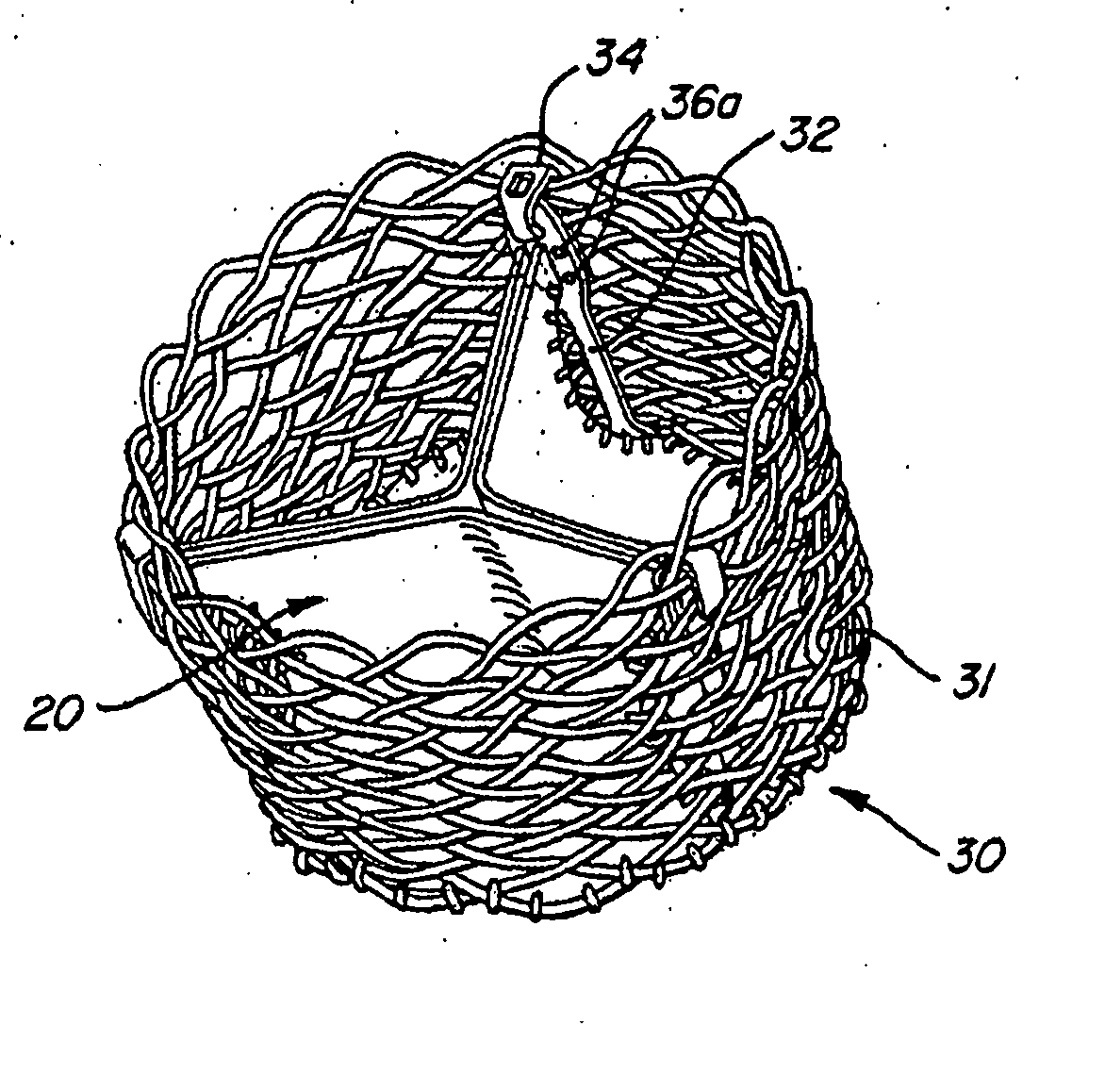
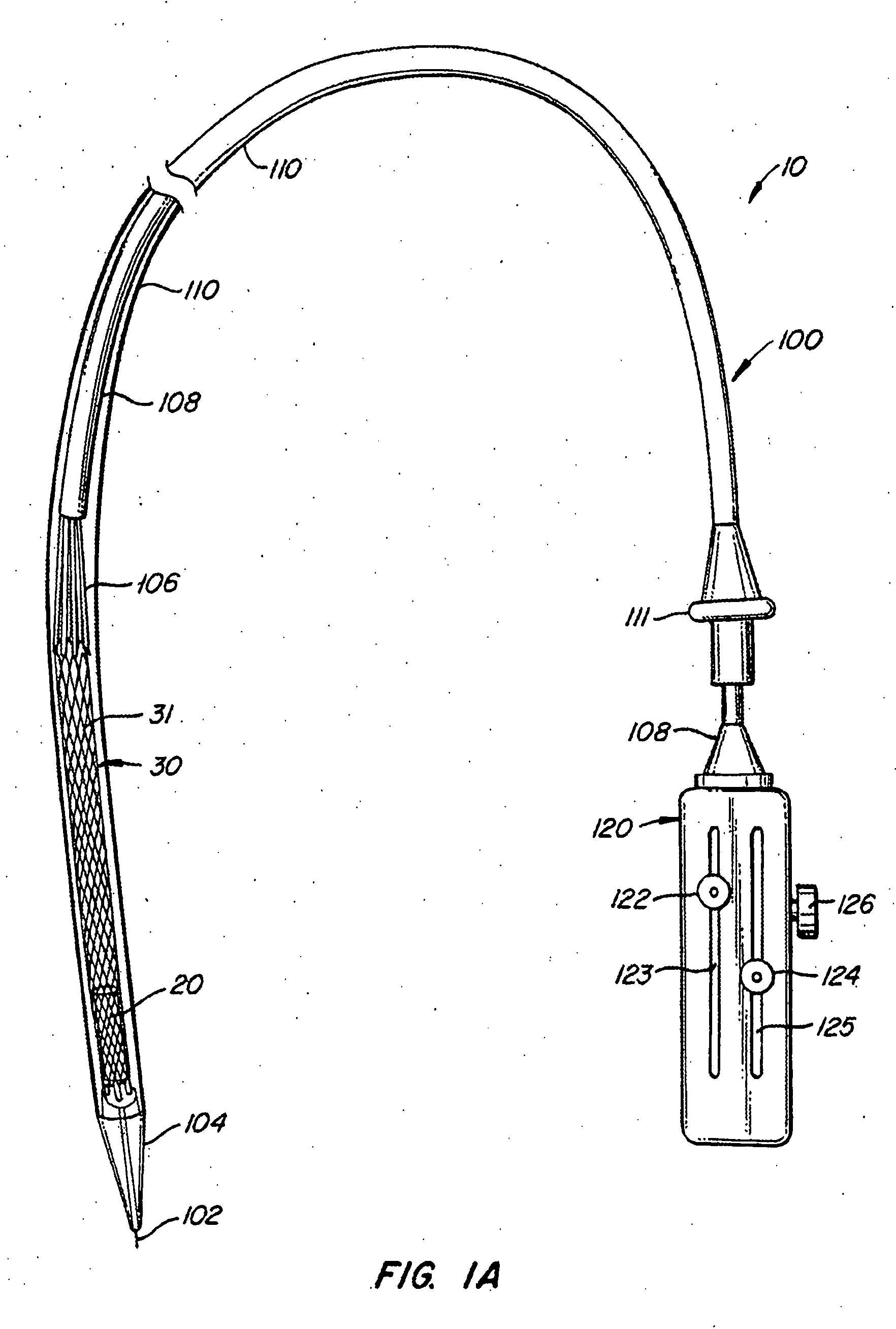
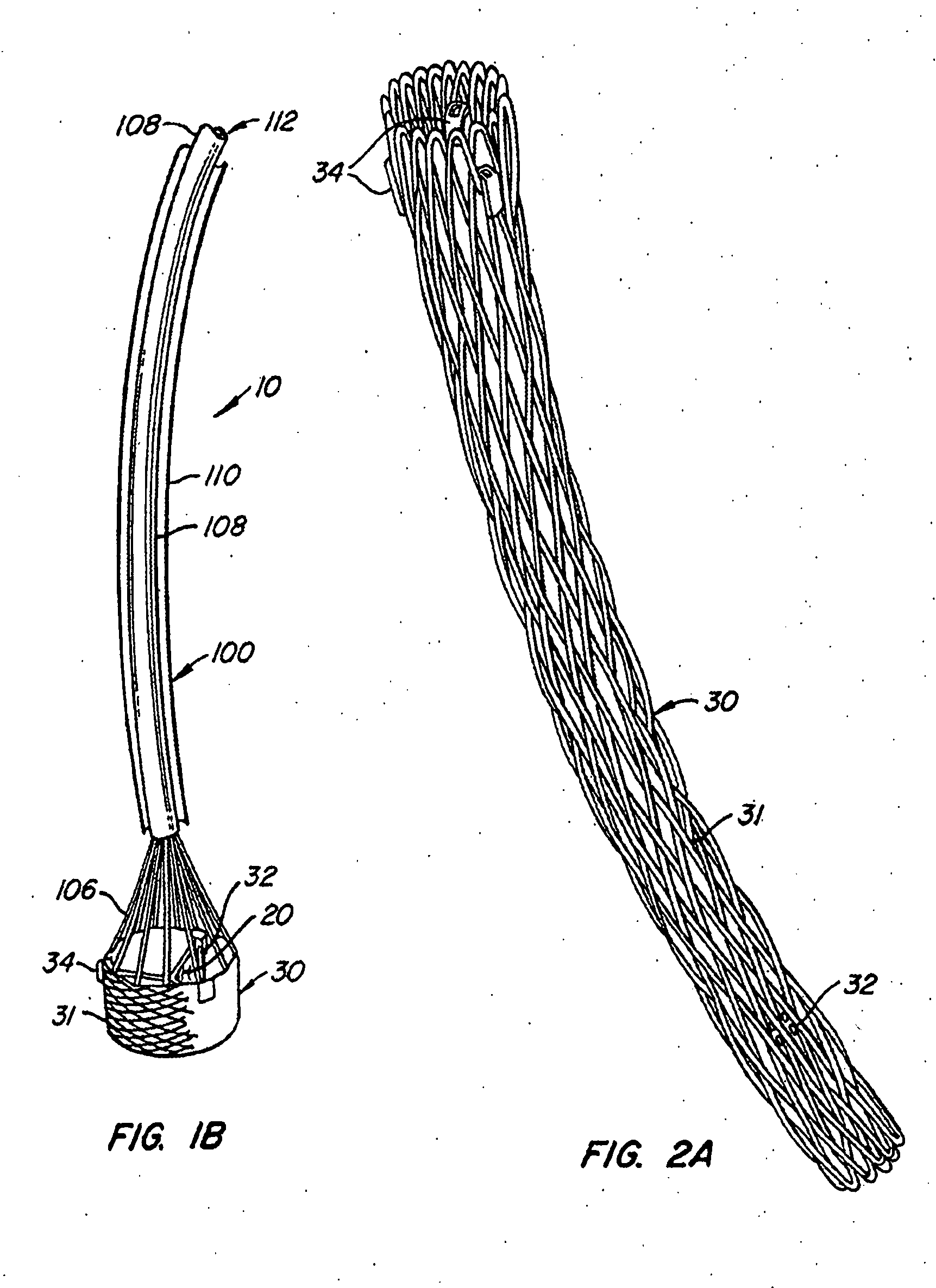
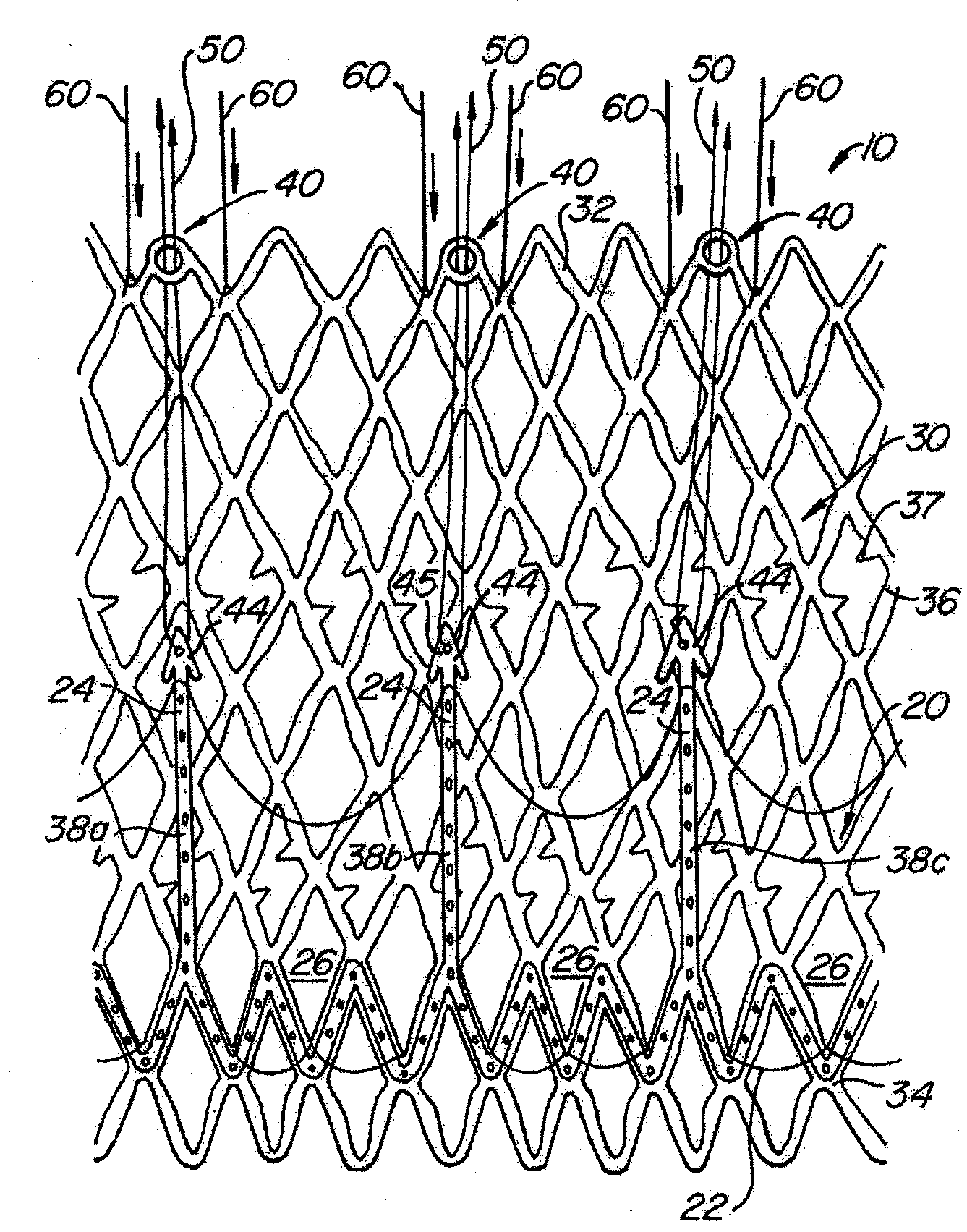
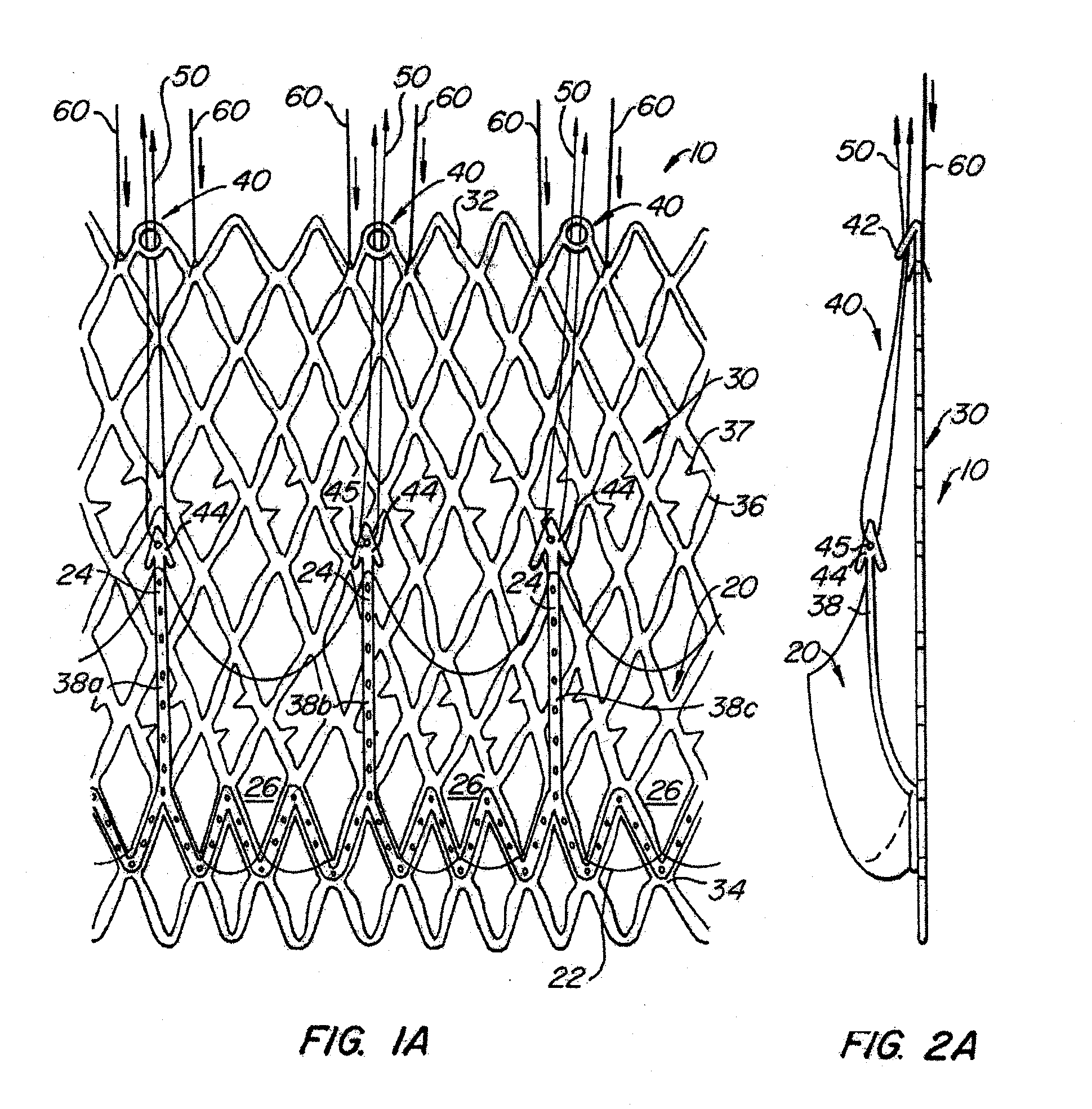
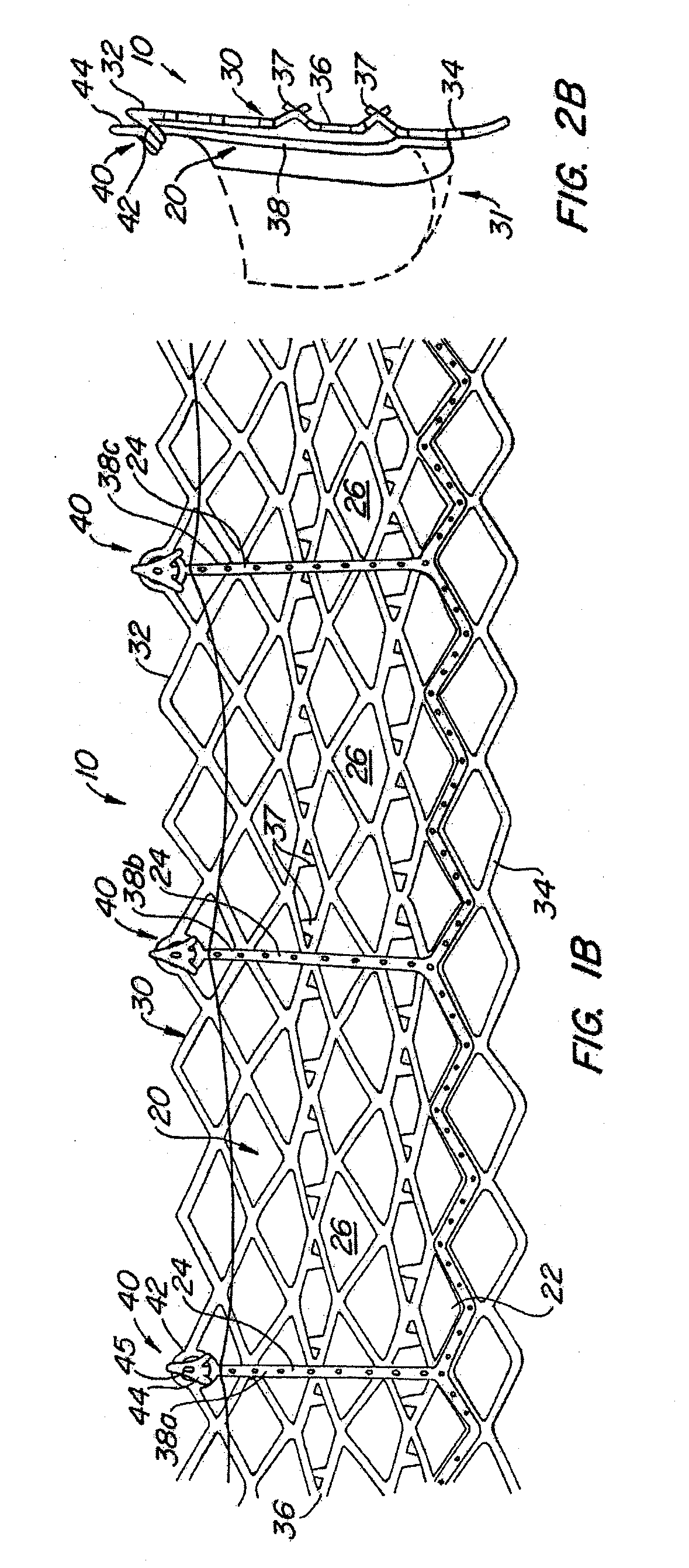
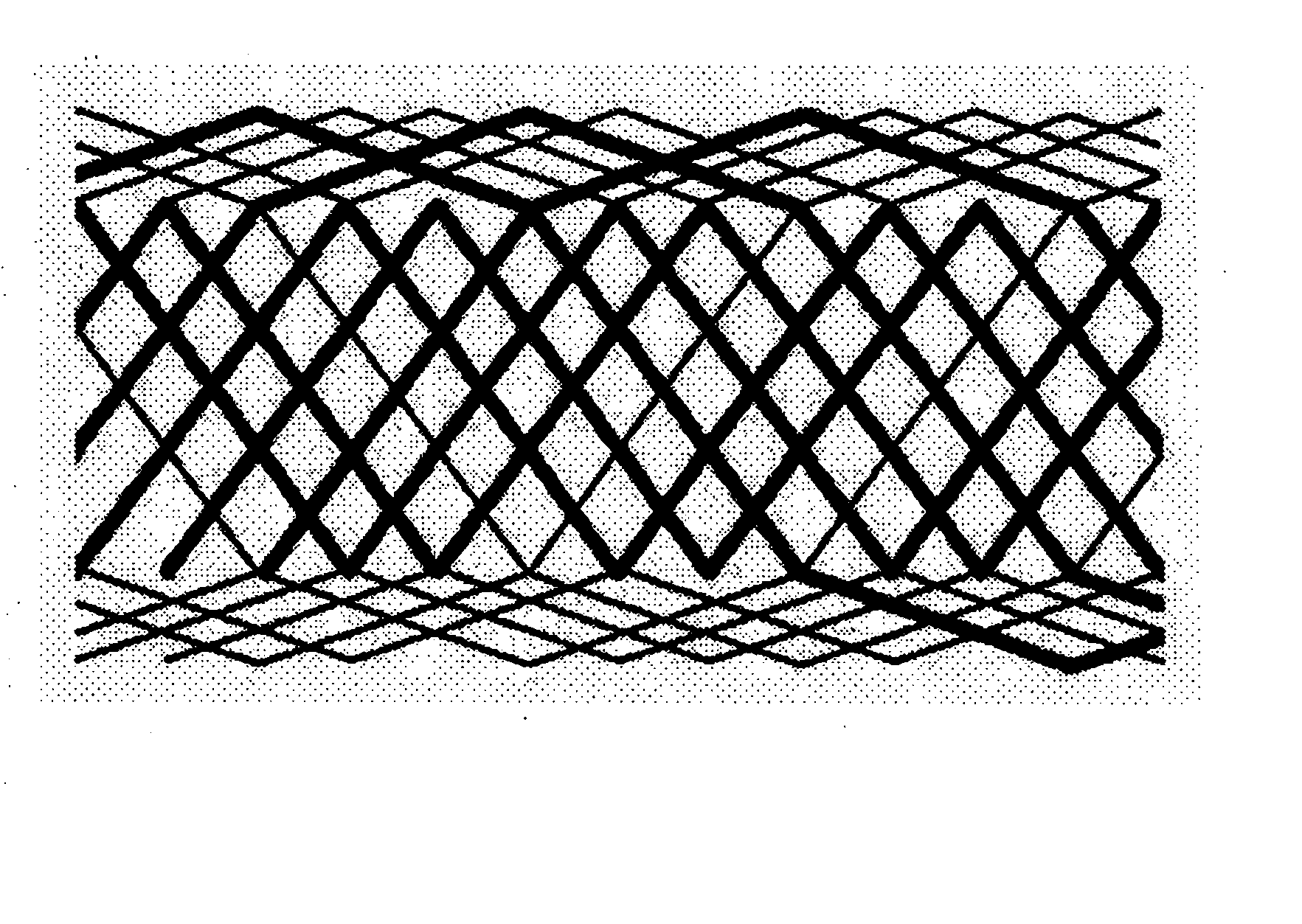
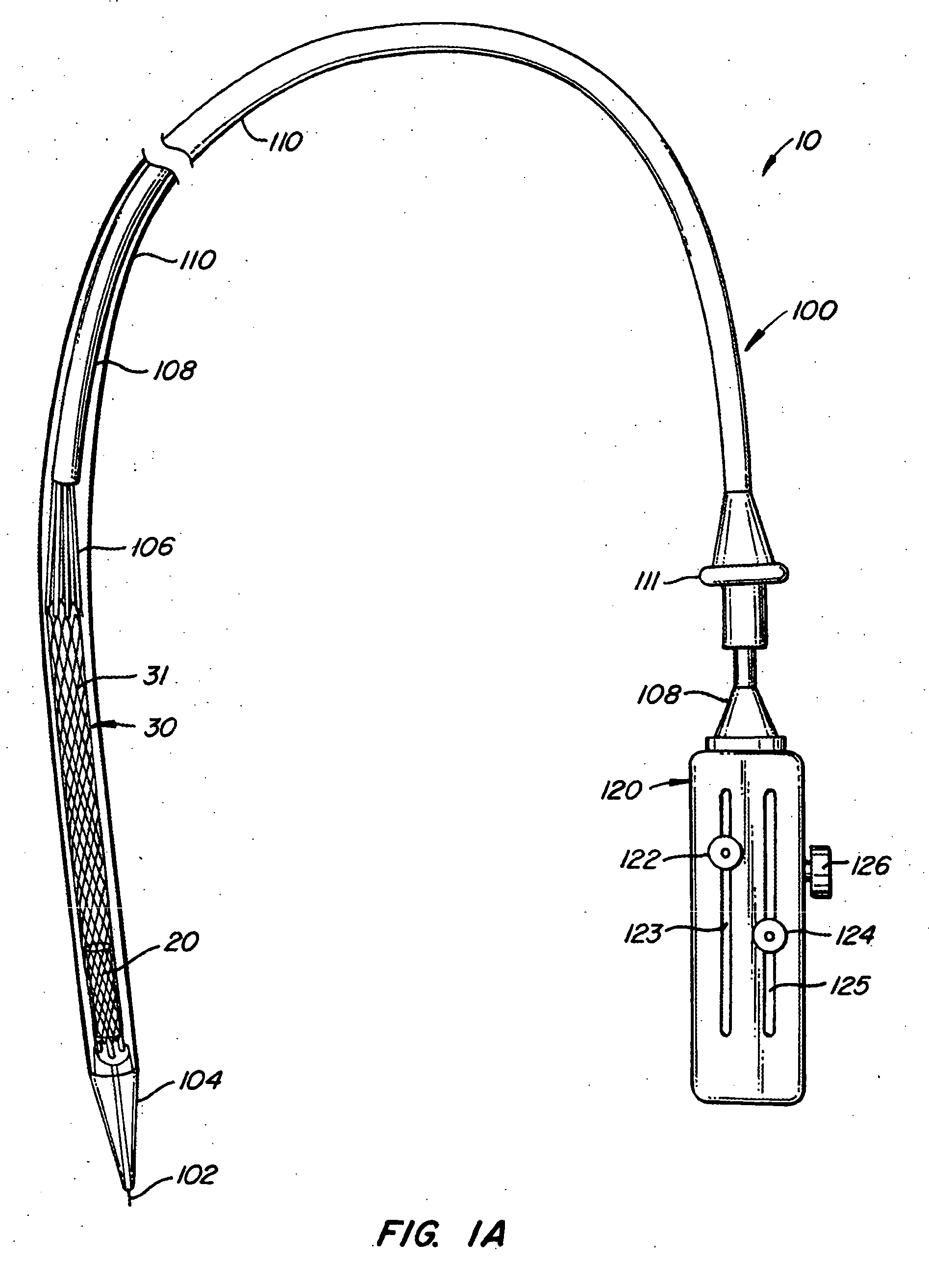
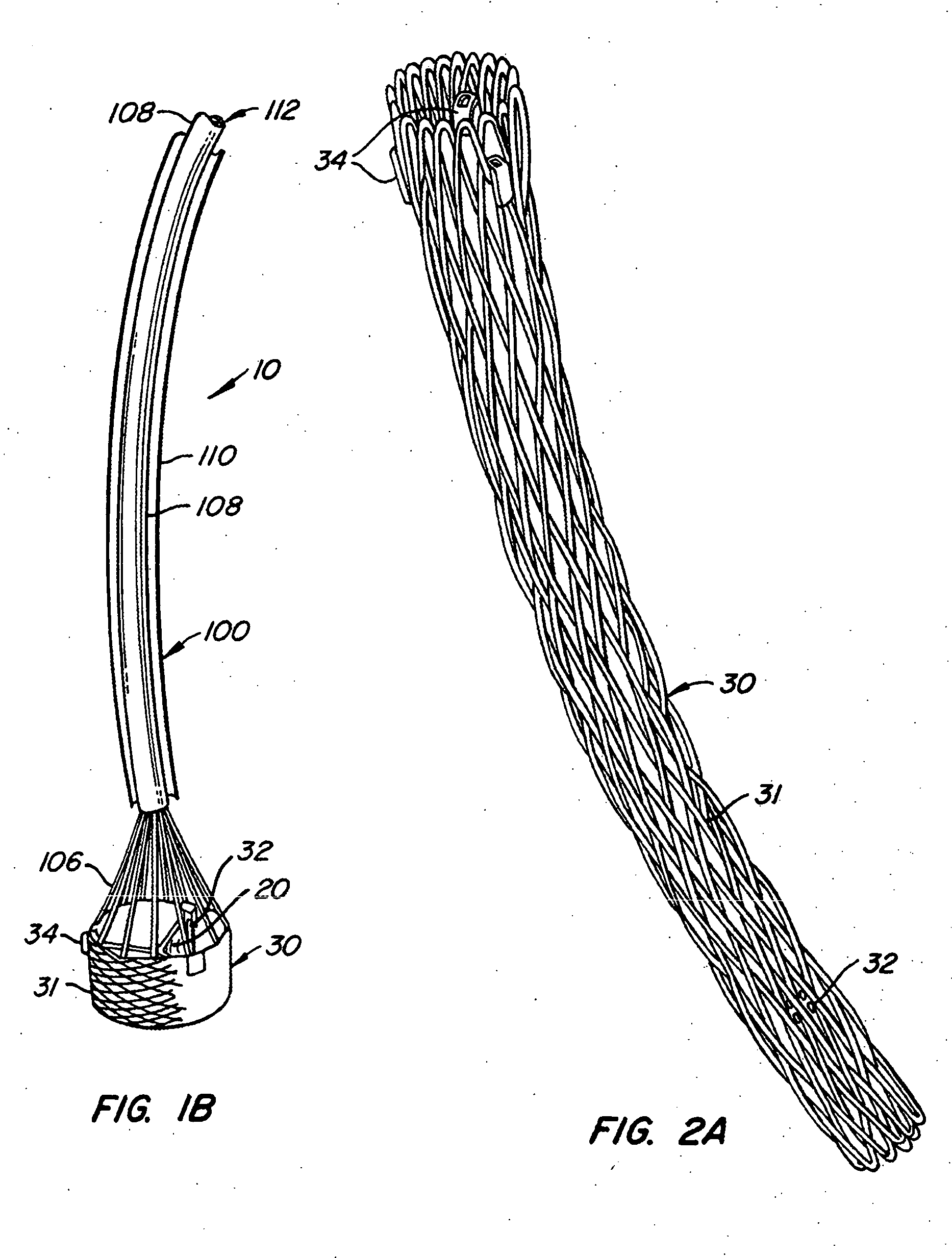
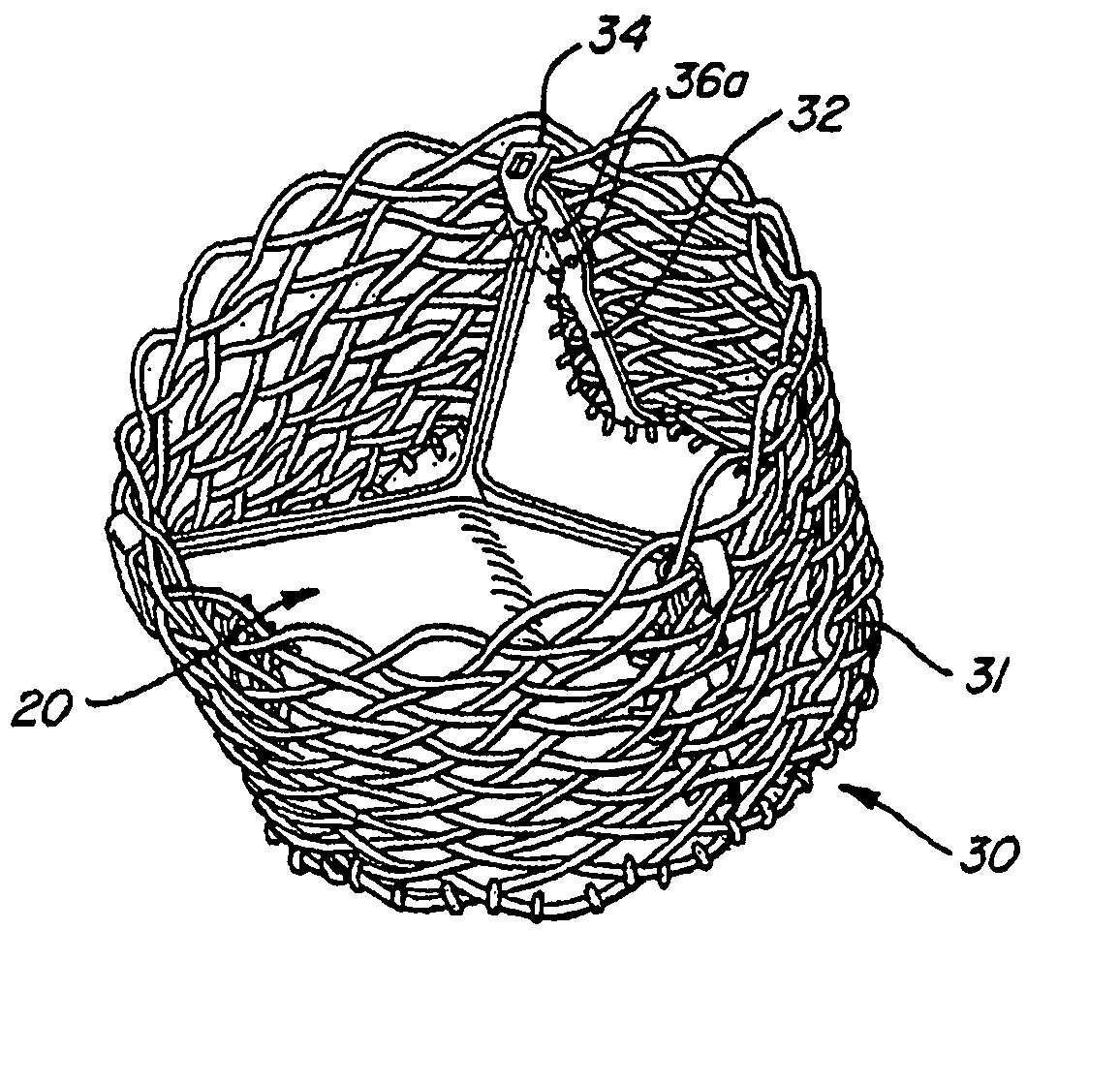
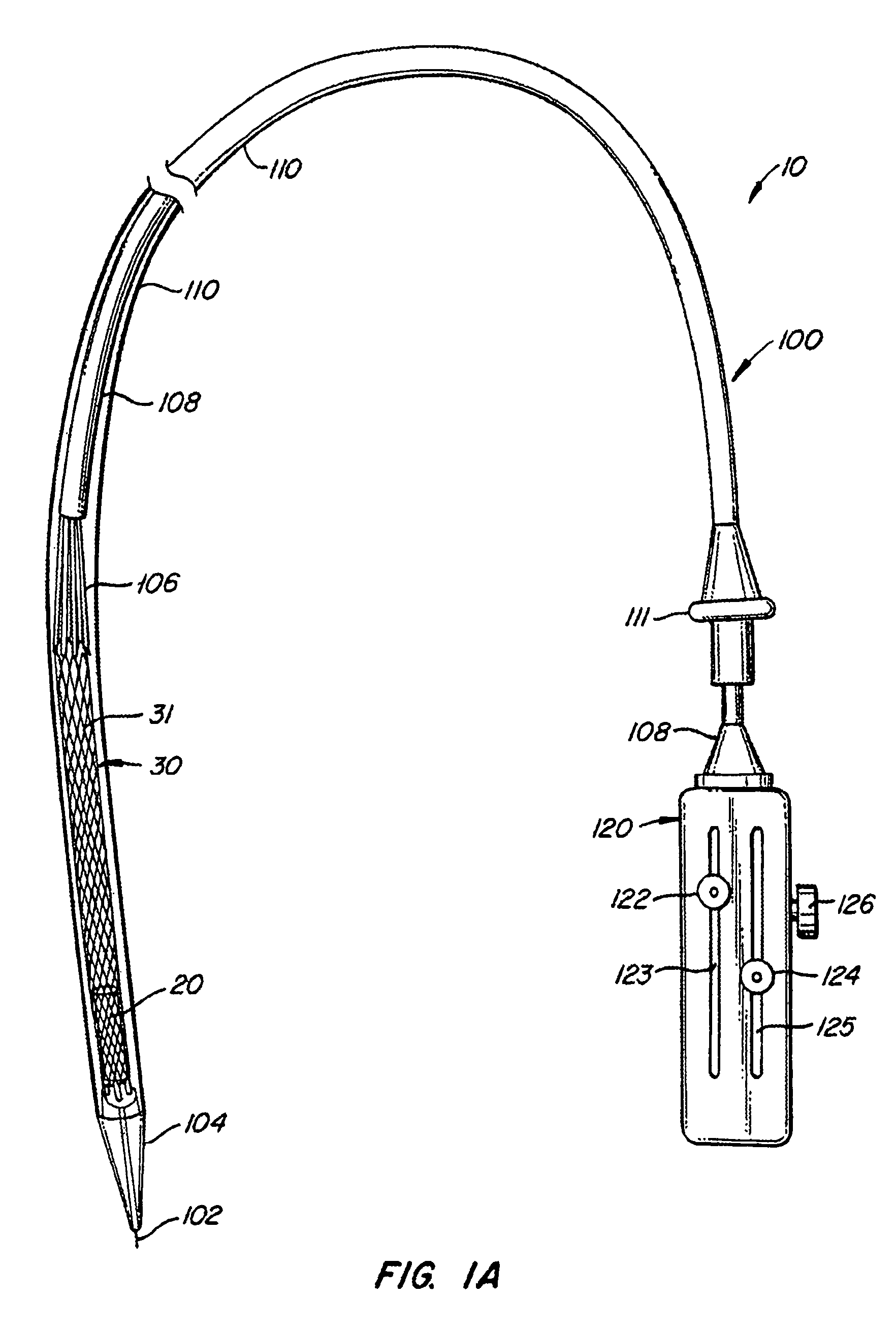
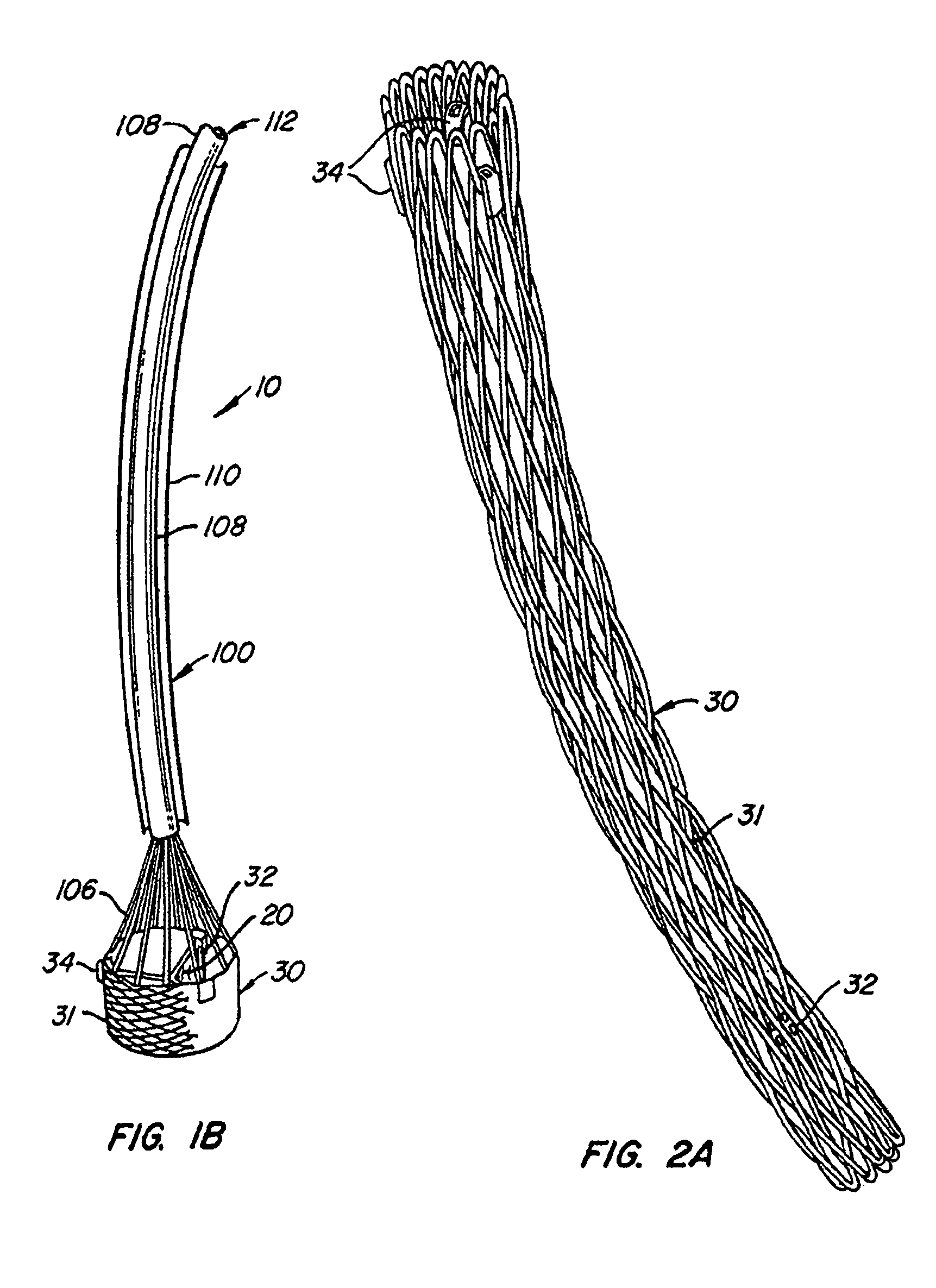
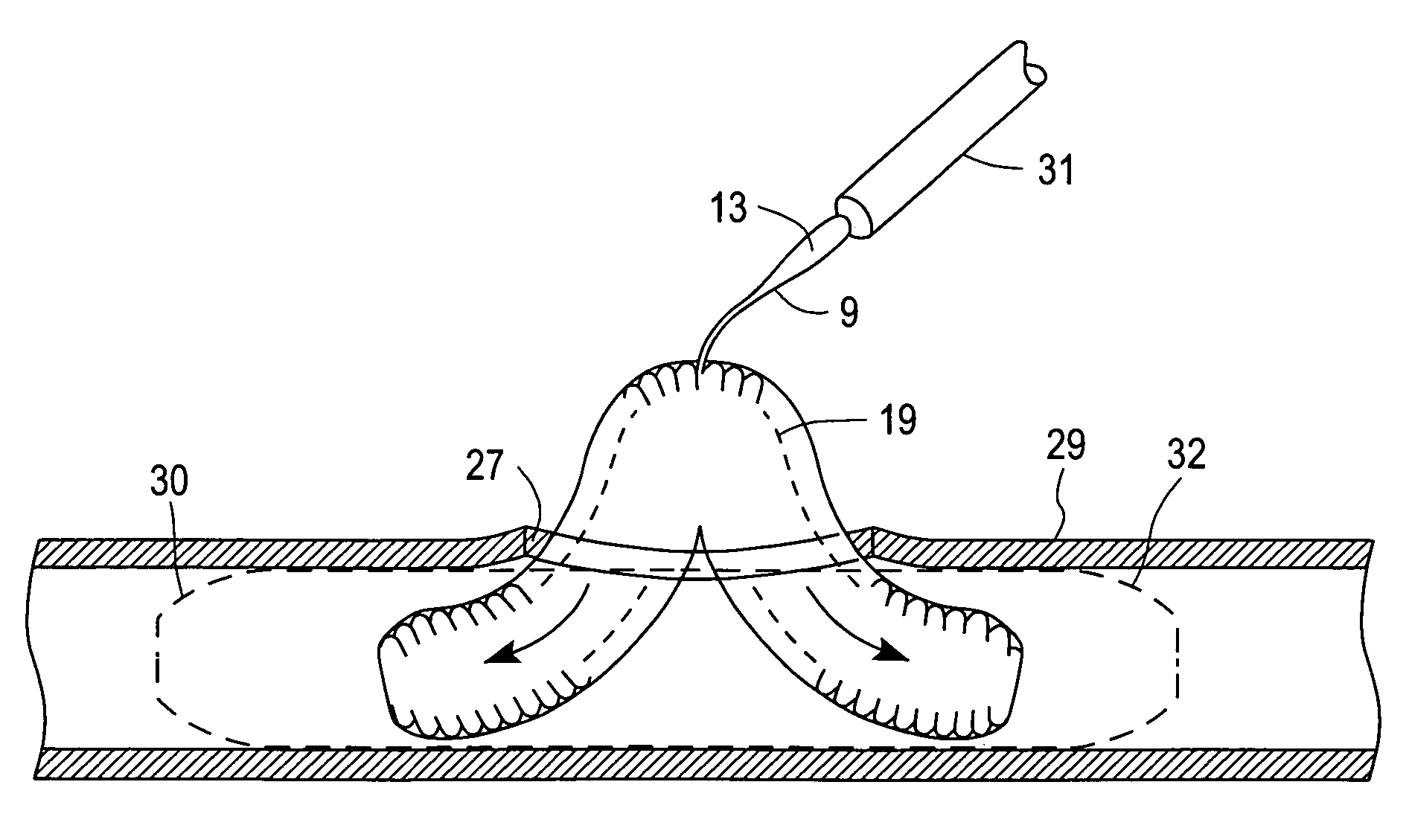
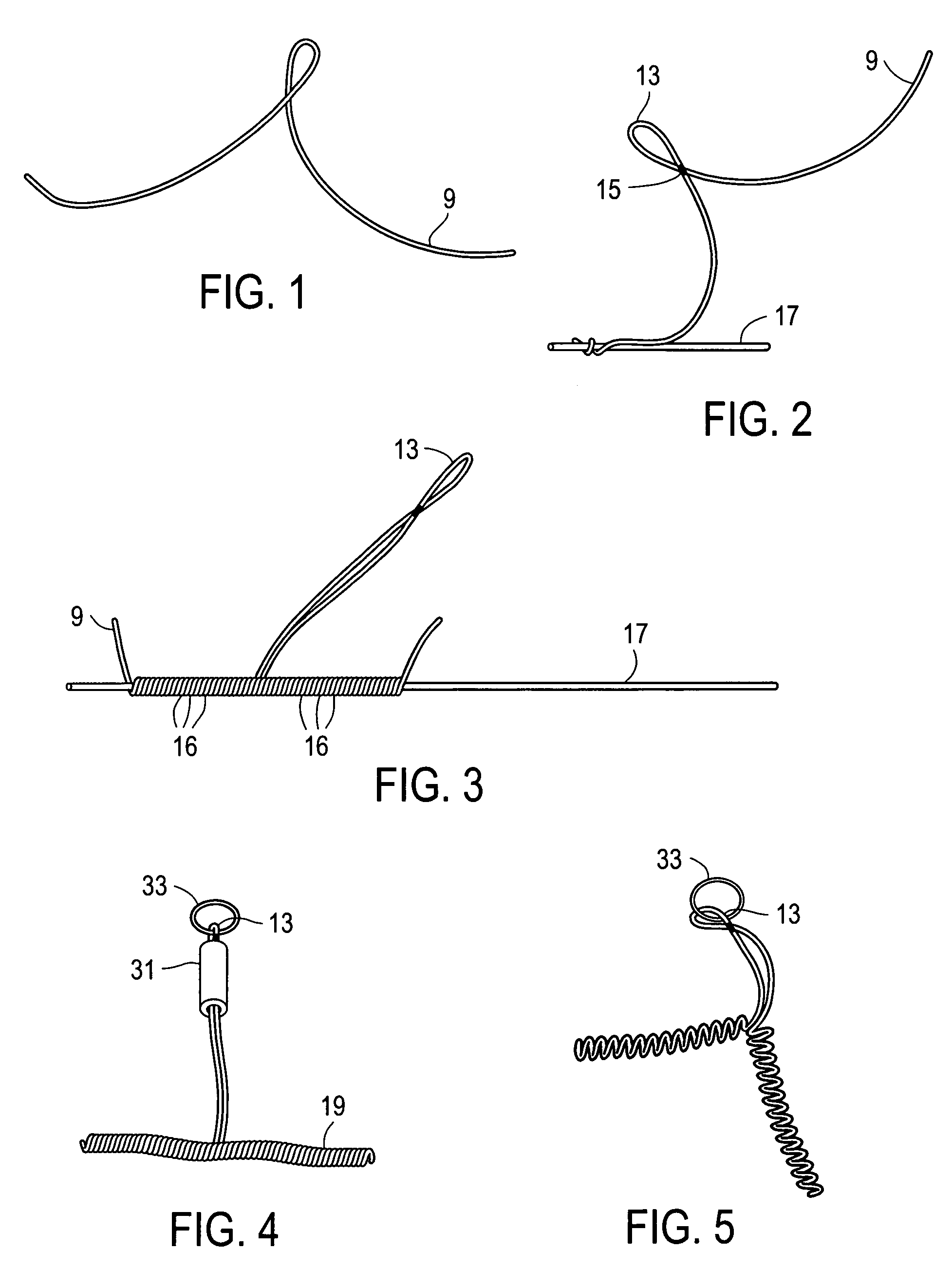
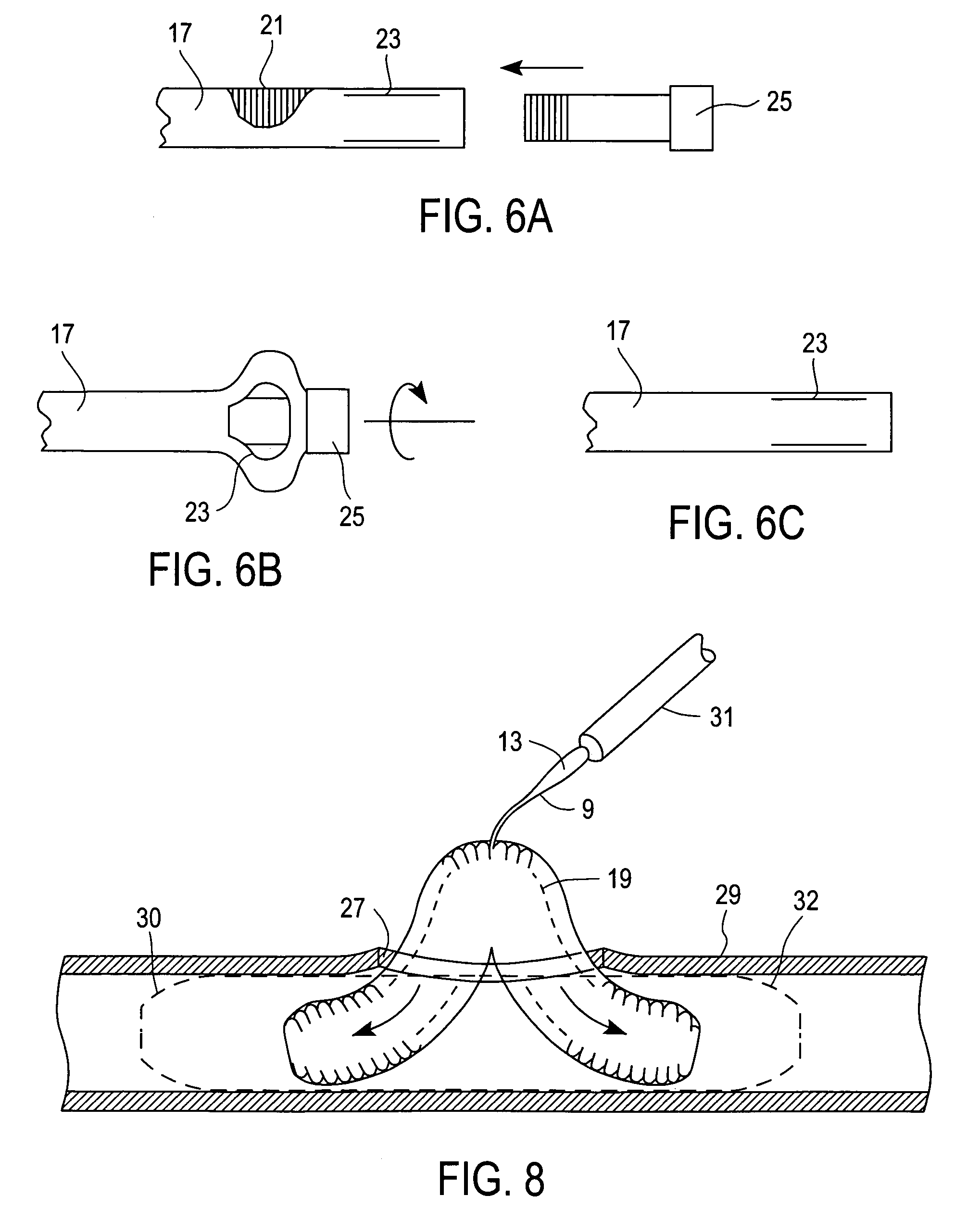
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve. The apparatus includes a replacement valve and an expandable anchor configured for endovascular delivery to a vicinity of the patient's heart valve. In some embodiments, the replacement valve is adapted to wrap about the anchor, for example, by everting during endovascular deployment. In some embodiments, the replacement valve is not connected to expandable portions of the anchor. In some embodiments, the anchor is configured for active foreshortening during endovascular deployment. In some embodiments, the anchor includes expandable lip and skirt regions for engaging the patient's heart valve during deployment. In some embodiments, the anchor comprises a braid fabricated from a single strand of wire. In some embodiments, the apparatus includes a lock configured to maintain anchor expansion. The invention also includes methods for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve. In some embodiments, the method includes the steps of endovascularly delivering a replacement valve and an expandable anchor to a vicinity of the heart valve, wrapping at least a portion of the replacement valve about the anchor, and expanding the anchor to a deployed configuration.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve. The apparatus includes a replacement valve and an anchor having an expandable braid. In some embodiments, the expandable braid is fabricated from a single strand of wire. In some embodiments, the expandable braid comprises at least one turn feature. The anchor and the valve preferably are configured for endovascular delivery and deployment.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve
Methods for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve. In some embodiments, the method includes the steps of endovascularly delivering a replacement valve and an anchor to a vicinity of the heart valve, the anchor having a braid, and expanding the braid to a deployed configuration against the patient's tissue. The braid may be fabricated from a single strand of wire and / or may comprise at least one the feature.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve. The apparatus includes a replacement valve and an anchor having an expandable braid. In some embodiments, the expandable braid is fabricated from a single strand of wire. In some embodiments, the expandable braid comprises at least one turn feature. The anchor and the valve preferably are configured for endovascular delivery and deployment.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Everting Heart Valve
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve. The apparatus includes a replacement valve and an expandable anchor configured for endovascular delivery to a vicinity of the patient's heart valve. In some embodiments, the replacement valve is adapted to wrap about the anchor, for example, by everting during endovascular deployment. In some embodiments, the replacement valve is not connected to expandable portions of the anchor. In some embodiments, the anchor is configured for active foreshortening during endovascular deployment. In some embodiments, the anchor includes expandable lip and skirt regions for engaging the patient's heart valve during deployment. In some embodiments, the anchor comprises a braid fabricated from a single strand of wire. In some embodiments, the apparatus includes a lock configured to maintain anchor expansion. The invention also includes methods for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve. In some embodiments, the method includes the steps of endovascularly delivering a replacement valve and an expandable anchor to a vicinity of the heart valve, wrapping at least a portion of the replacement valve about the anchor, and expanding the anchor to a deployed configuration.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
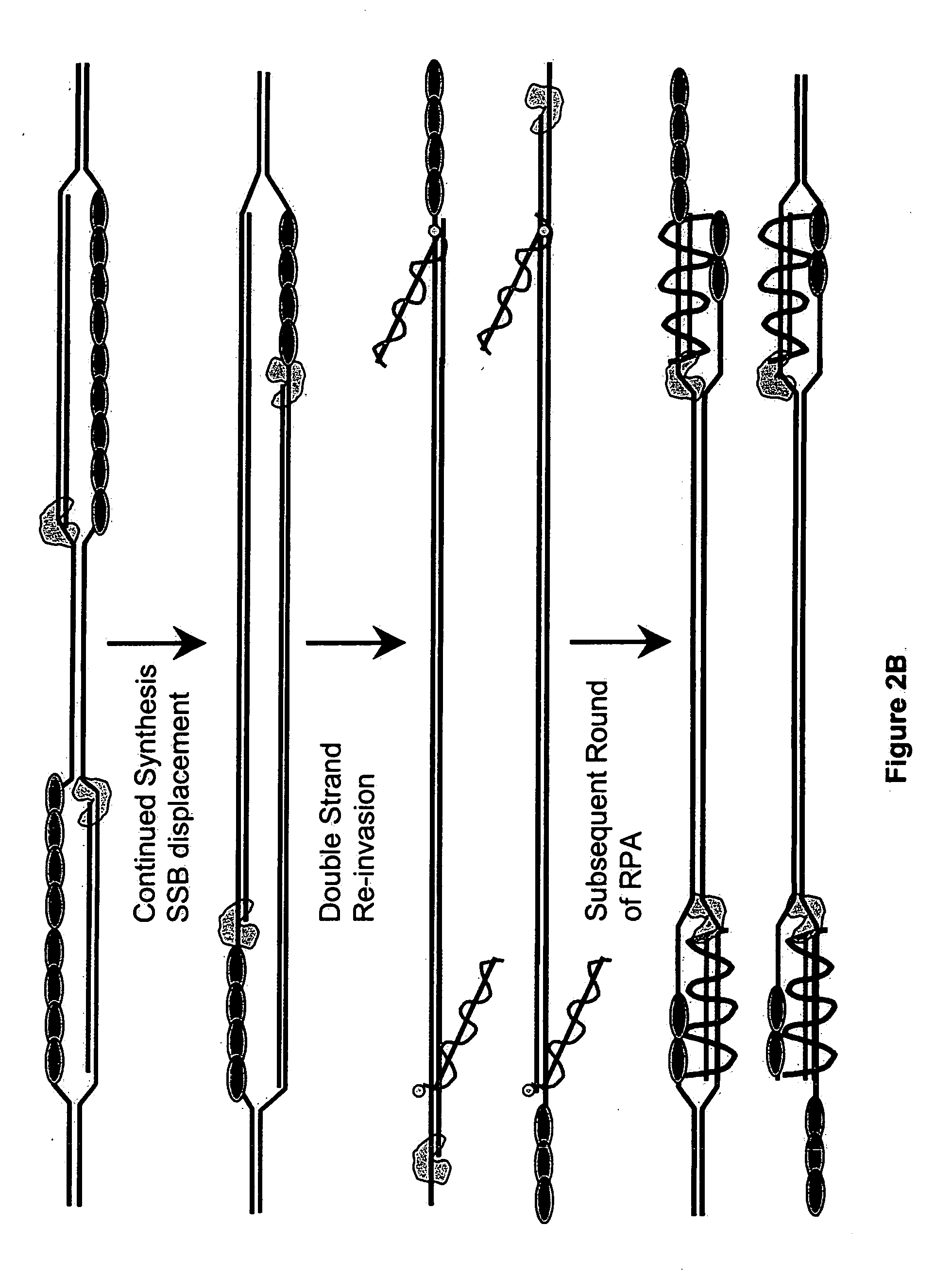
Recombinase polymerase amplification
ActiveUS7399590B2HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinase Polymerase AmplificationSingle strand
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
Methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve. The apparatus includes a replacement valve and an anchor having an expandable braid. In some embodiments, the expandable braid is fabricated from a single strand of wire. In some embodiments, the expandable braid comprises at least one turn feature. The anchor and the valve preferably are configured for endovascular delivery and deployment.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
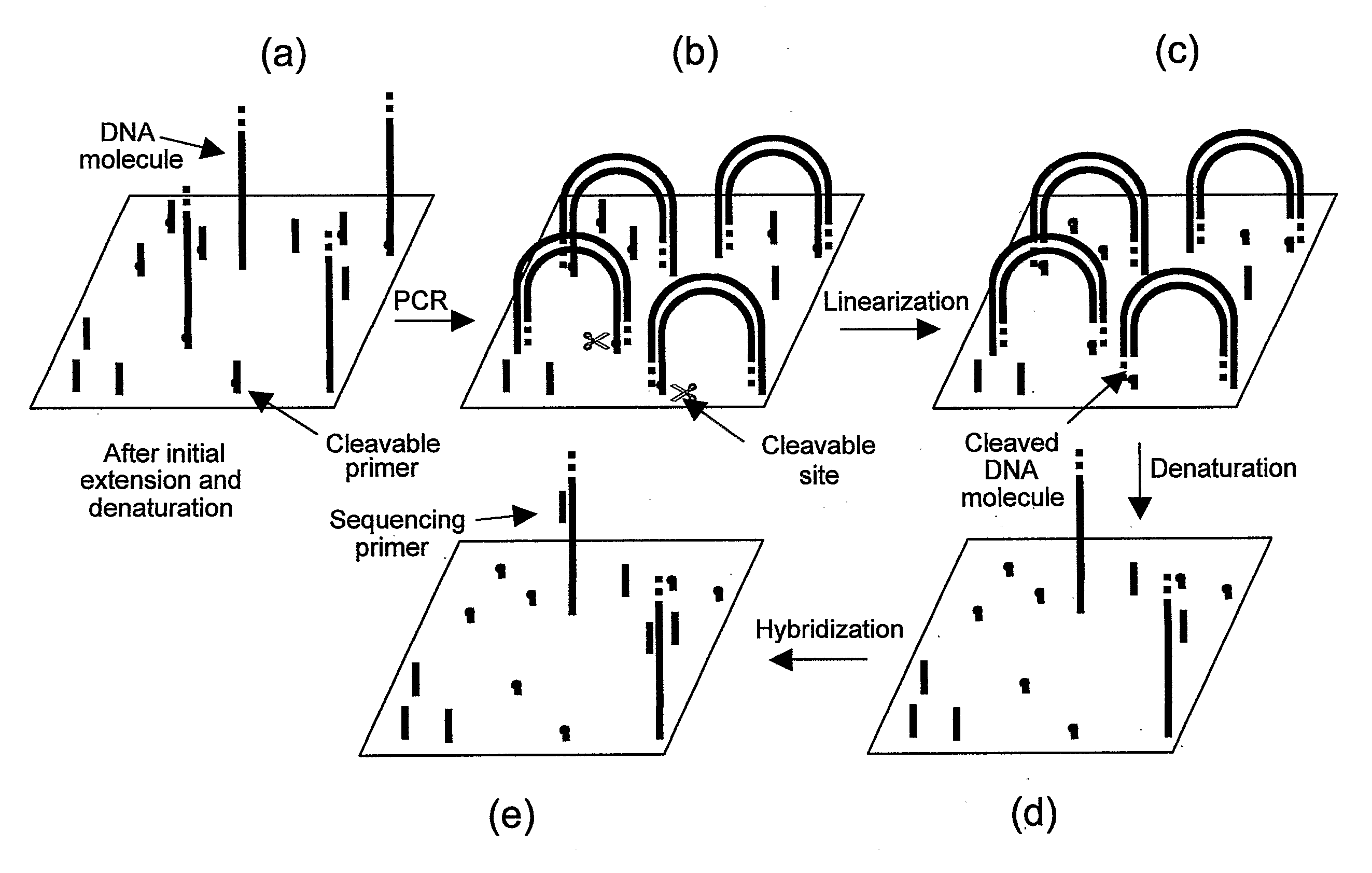
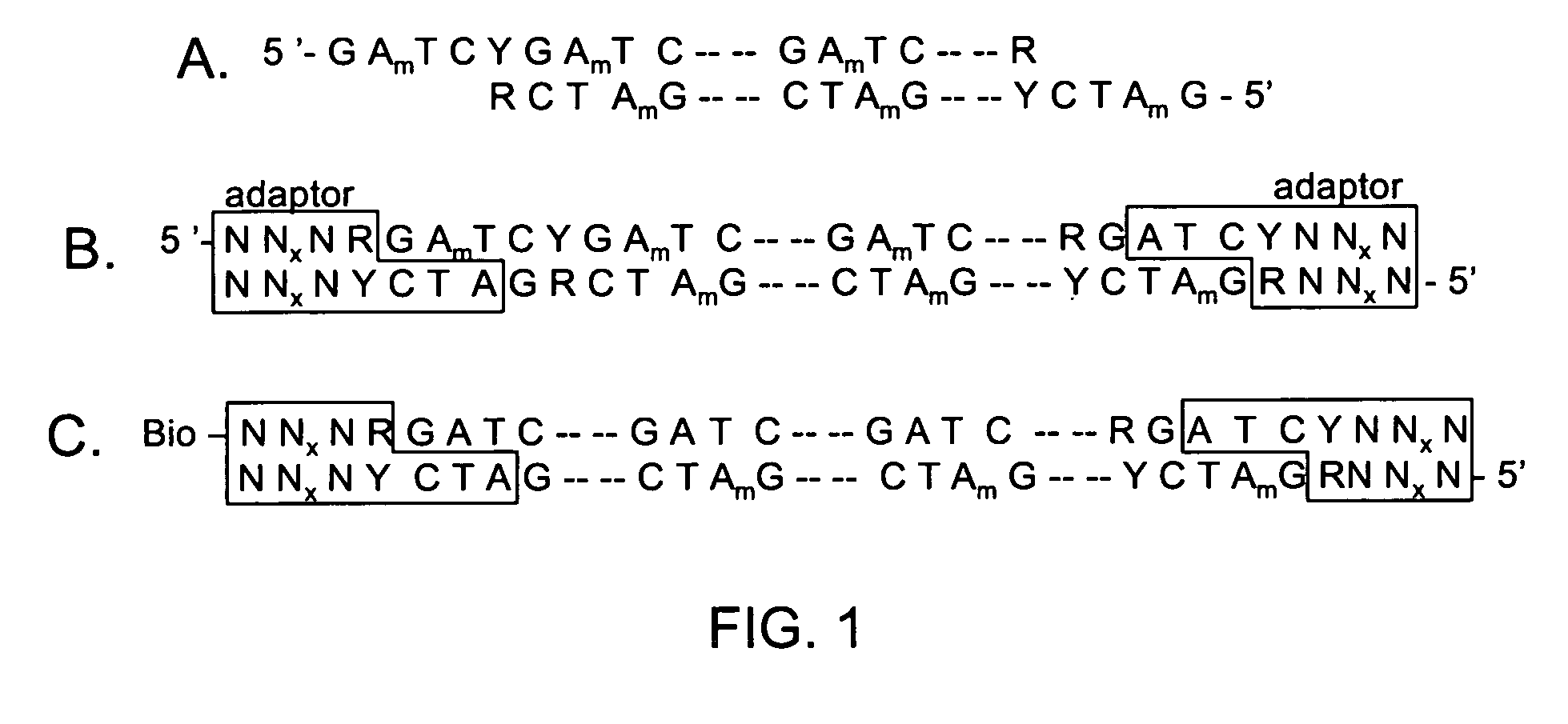
Method of sequencing genomes by hybridization of oligonucleotide probes
InactiveUS6018041ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalian genomeHomologous sequence
The conditions under which oligonucleotides hybridize only with entirely homologous sequences are recognized. The sequence of a given DNA fragment is read by the hybridization and assembly of positively hybridizing probes through overlapping portions. By simultaneous hybridization of DNA molecules applied as dots and bound onto a filter, representing single-stranded phage vector with the cloned insert, with about 50,000 to 100,000 groups of probes, the main type of which is (A,T,C,G)(A,T,C,G)N8(A,T,C,G), information for computer determination of a sequence of DNA having the complexity of a mammalian genome are obtained in one step. To obtain a maximally completed sequence, three libraries are cloned into the phage vector, M13, bacteriophage are used: with the 0.5 kb and 7 kbp insert consisting of two sequences, with the average distance in genomic DNA of 100 kbp. For a million bp of genomic DNA, 25,000 subclones of the 0.5 kbp are required as well as 700 subclones 7 kb long and 170 jumping subclones. Subclones of 0.5 kb are applied on a filter in groups of 20 each, so that the total number of samples is 2,120 per million bp. The process can be easily and entirely robotized for factory reading of complex genomic fragments or DNA molecules.
Owner:HYSEQ
RNA preparations comprising purified modified RNA for reprogramming cells
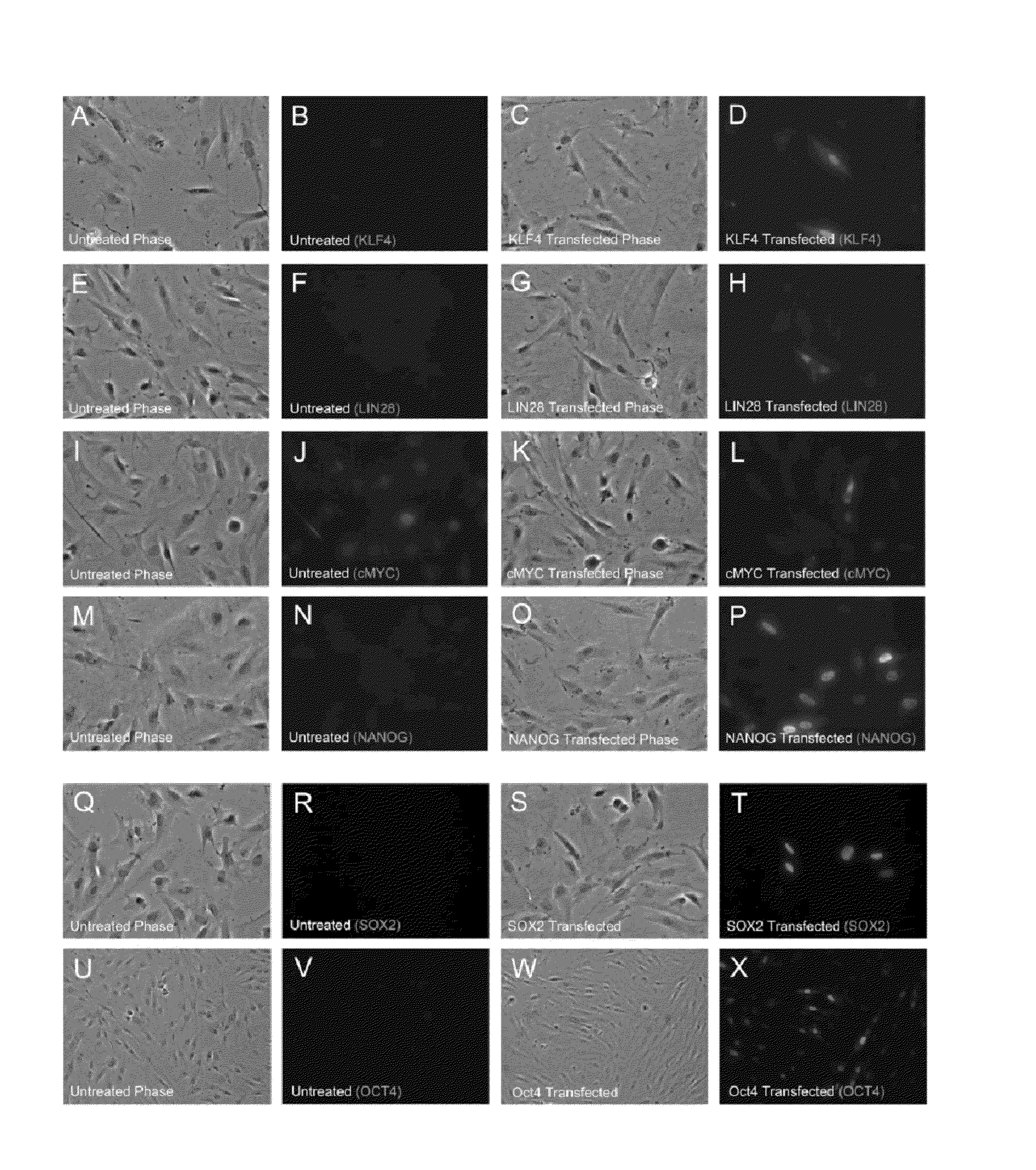
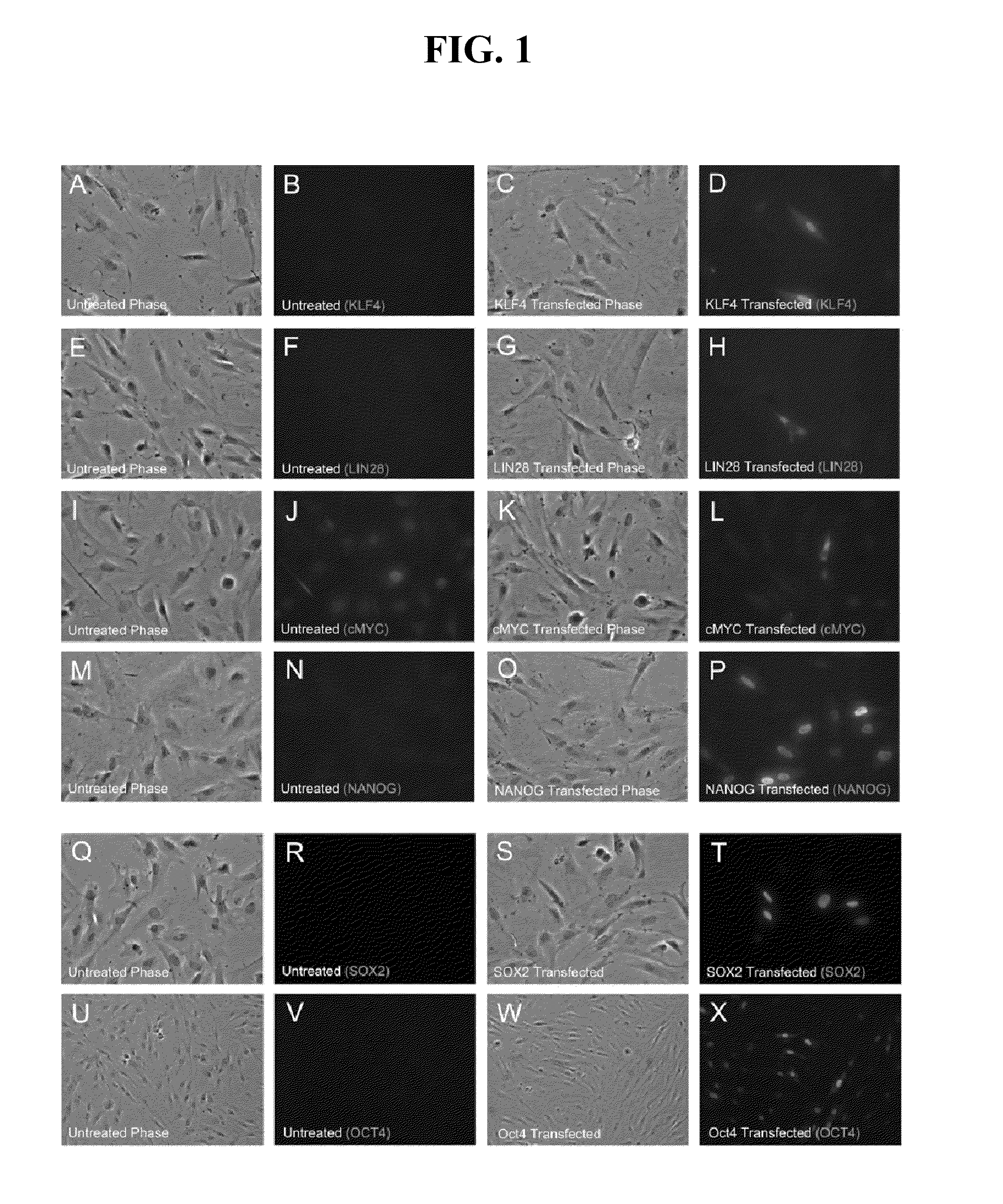
ActiveUS20110143397A1Promote growthArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsSingle strandSomatic cell
The present invention provides compositions and methods for reprogramming somatic cells using purified RNA preparations comprising single-strand mRNA encoding an iPS cell induction factor. The purified RNA preparations are preferably substantially free of RNA contaminant molecules that: i) would activate an immune response in the somatic cells, ii) would decrease expression of the single-stranded mRNA in the somatic cells, and / or iii) active RNA sensors in the somatic cells. In certain embodiments, the purified RNA preparations are substantially free of partial mRNAs, double-stranded RNAs, un-capped RNA molecules, and / or single-stranded run-on mRNAs.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Use of single-stranded nucleic acid binding proteins in sequencing
InactiveUS20060024678A1Stabilizing sequencingIncrease speedMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid sequencingSingle strand
The invention provides methods for stabilizing a nucleic acid sequencing reaction. Generally, methods of the invention include exposing a target nucleic acid to a single-stranded nucleic acid binding protein and performing a sequencing reaction.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Method for determining relative abundance of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS6897023B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeFluorescence
Disclosed are methods for identifying nucleic acid sequences which are of different abundances in different nucleic acid source populations, e.g. differentially expressed genes or genomic variations among individuals or populations of individuals. In one embodiment, probes derived from the source nucleic acid populations are derivatized with a terminal sample ID (SID) sequence characteristic of that population. Upon competitive hybridization of the probes to a reference or index nucleic acid library containing all the sequences in the populations being compared, the SID tags remain single stranded, and those from the different sources are then annealed to one another. Unhybridized (remainder) SID sequences are then quantified. By labeling such remainder SID sequences with a fluorescent dye, FACS sorting of beads containing the hybridized probes can be carried out. The signal ratio upon which such sorting is based is enhanced compared to competitive hybridization using labeled probes without SID sequences.
Owner:THE MOLECULAR SCI INST +1
Characterization of individual polymer molecules based on monomer-interface interactions
InactiveUS7189503B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologySingle strandDouble strand
The invention relates to a method for detecting a double-stranded region in a nucleic acid by (1) providing two separate, adjacent pools of a medium and a interface between the two pools, the interface having a channel so dimensioned as to allow sequential monomer-by-monomer passage of a single-stranded nucleic acid, but not of a double-stranded nucleic acid, from one pool to the other pool; (2) placing a nucleic acid polymer in one of the two pools; and (3) taking measurements as each of the nucleotide monomers of the single-stranded nucleic acid polymer passes through the channel so as to differentiate between nucleotide monomers that are hybridized to another nucleotide monomer before entering the channel and nucleotide monomers that are not hybridized to another nucleotide monomer before entering the channel.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Recombinase polymerase amplification
ActiveUS7270981B2Web data indexingMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandRecombinase Polymerase Amplification
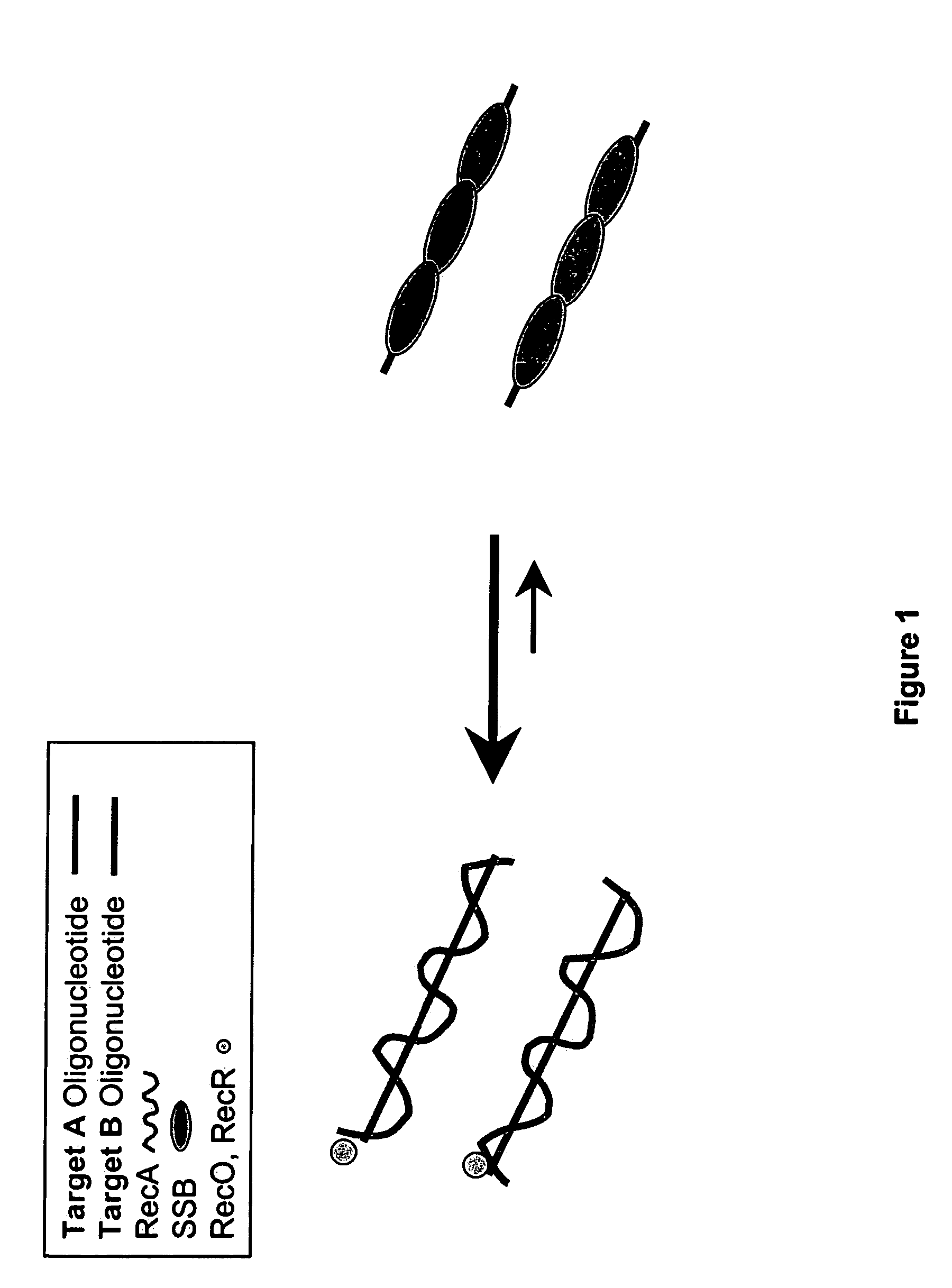
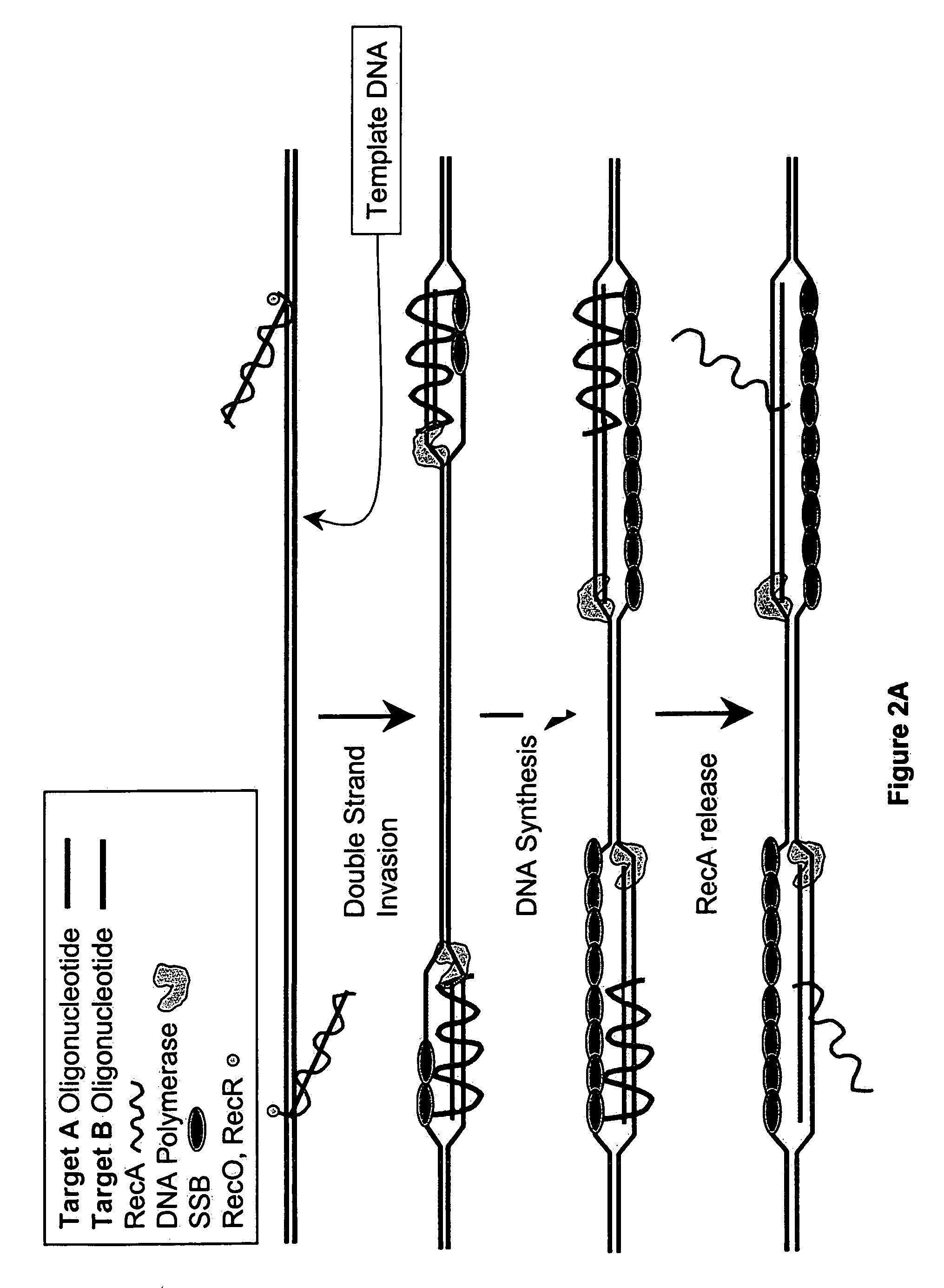
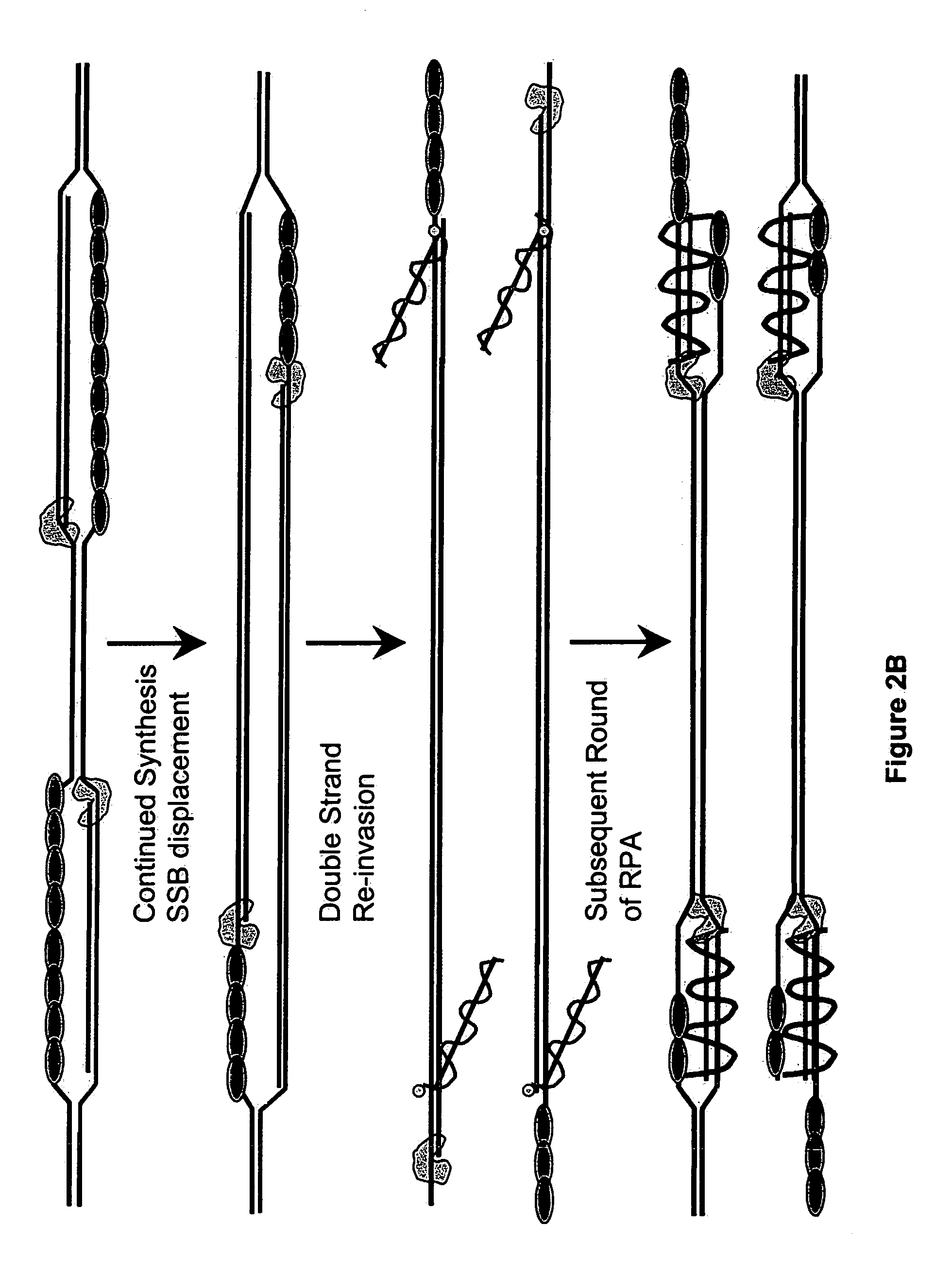
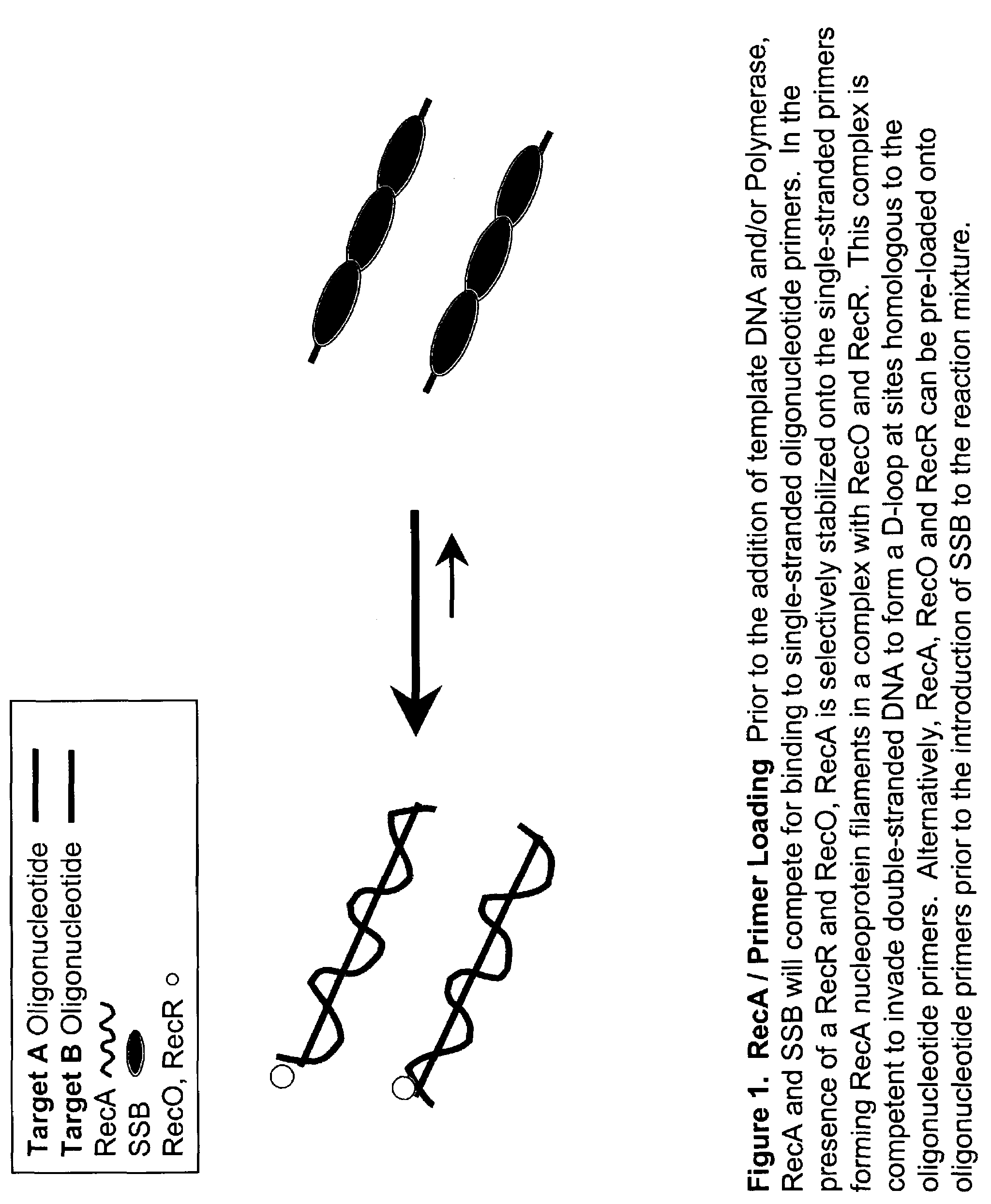
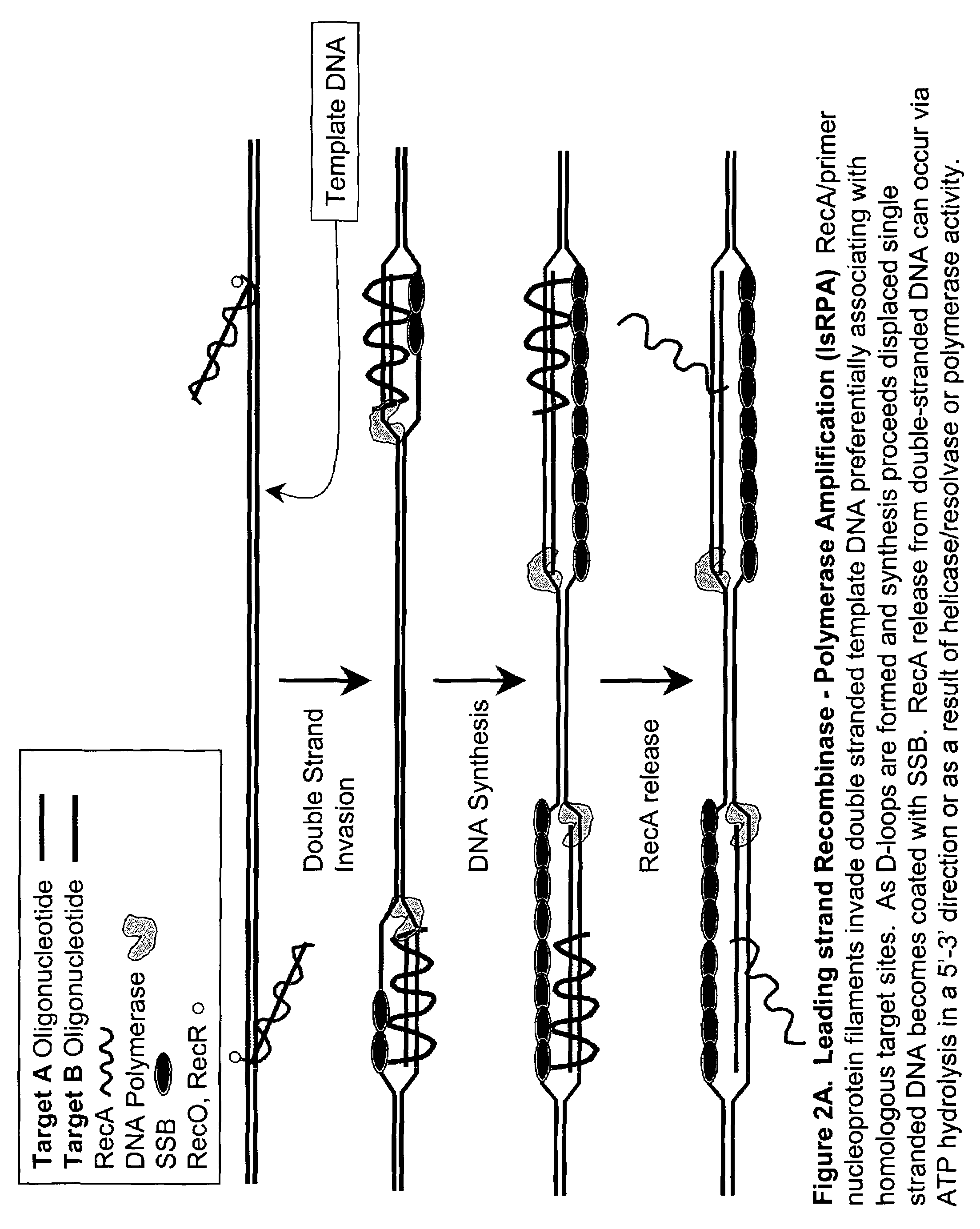
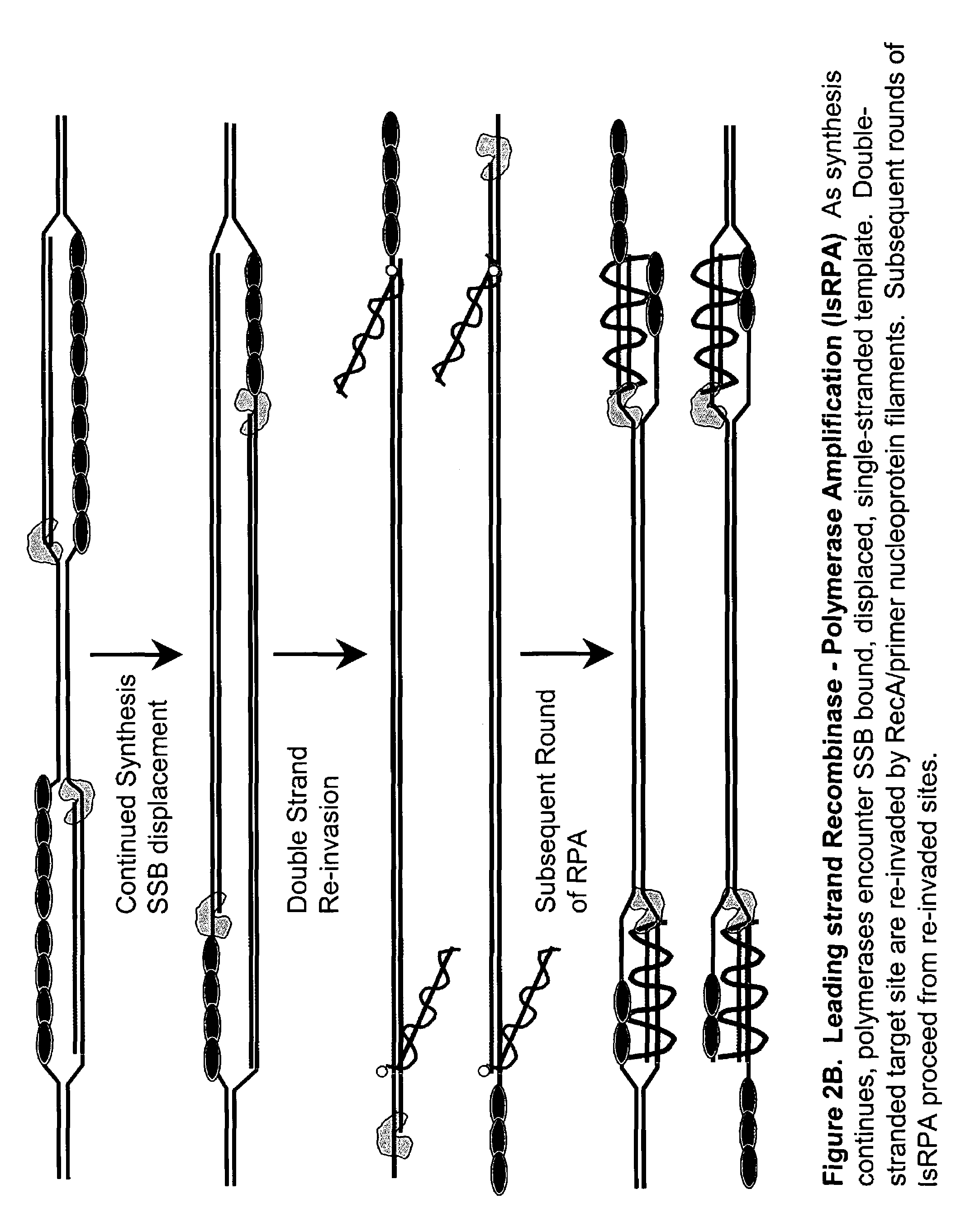
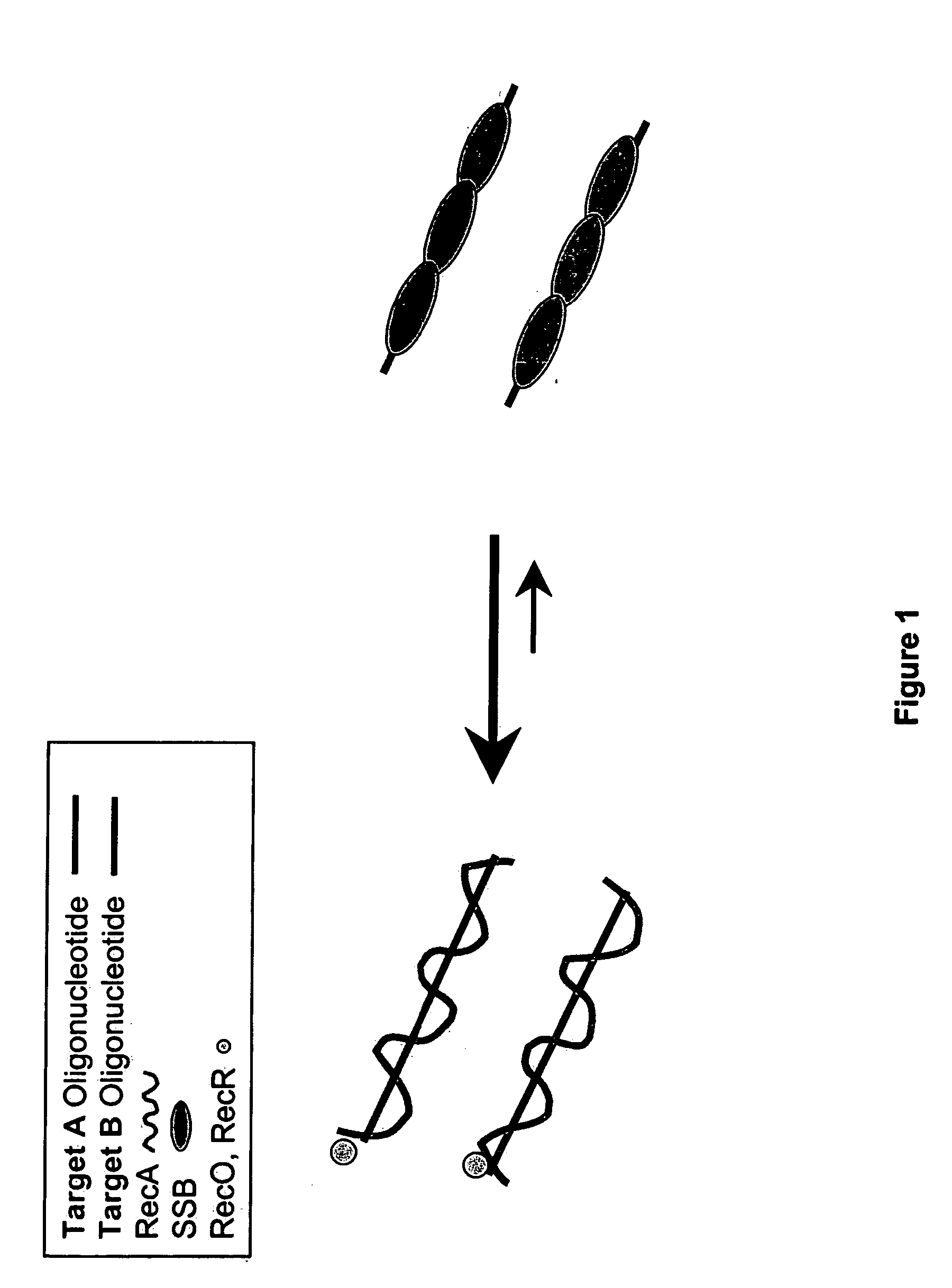
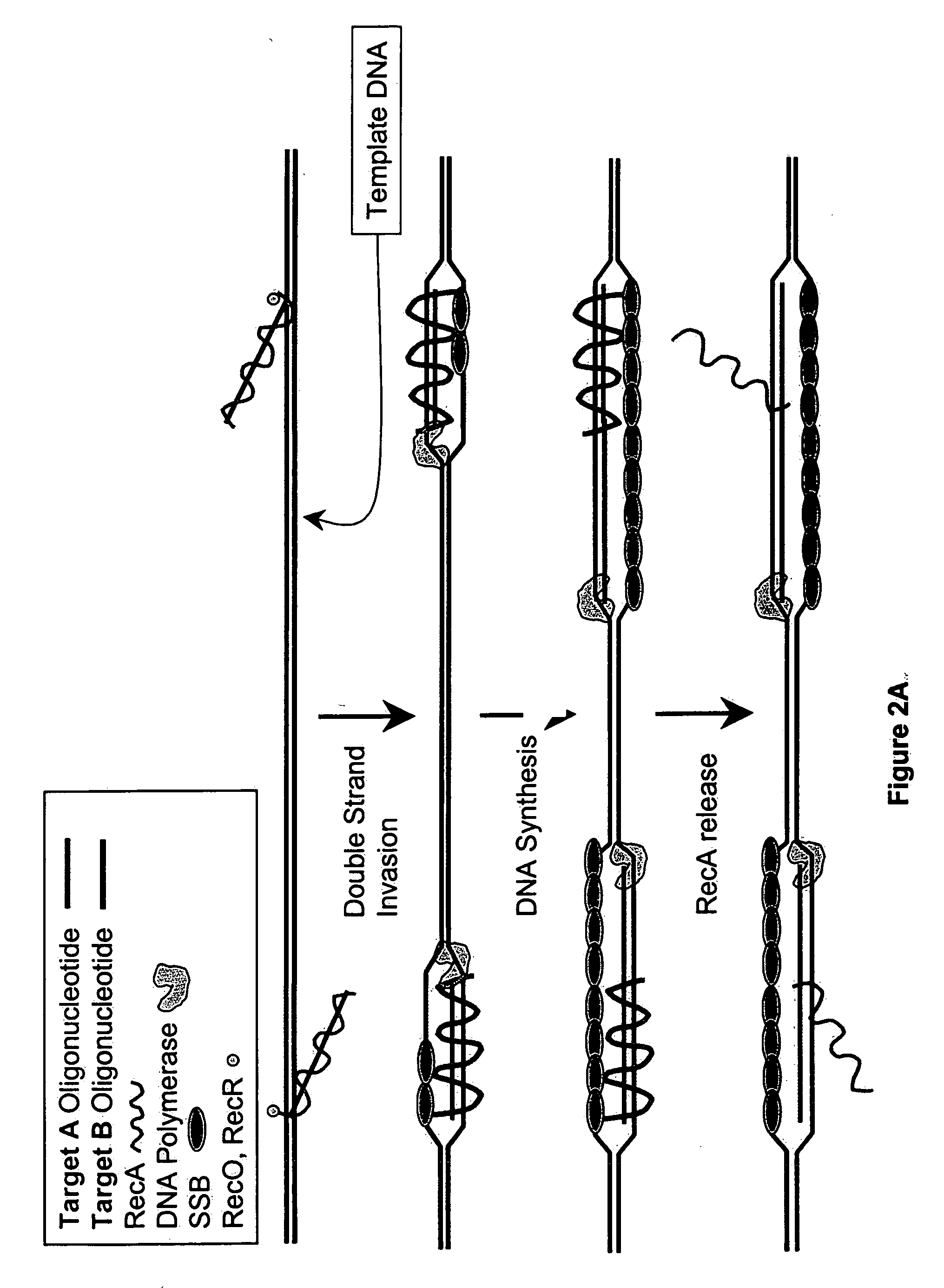
This disclosure describe three related novel methods for Recombinase-Polymerase Amplification (RPA) of a target DNA that exploit the properties of the bacterial RecA and related proteins, to invade double-stranded DNA with single stranded homologous DNA permitting sequence specific priming of DNA polymerase reactions. The disclosed methods has the advantage of not requiring thermocycling or thermophilic enzymes. Further, the improved processivity of the disclosed methods allow amplification of DNA up to hundreds of megabases in length.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
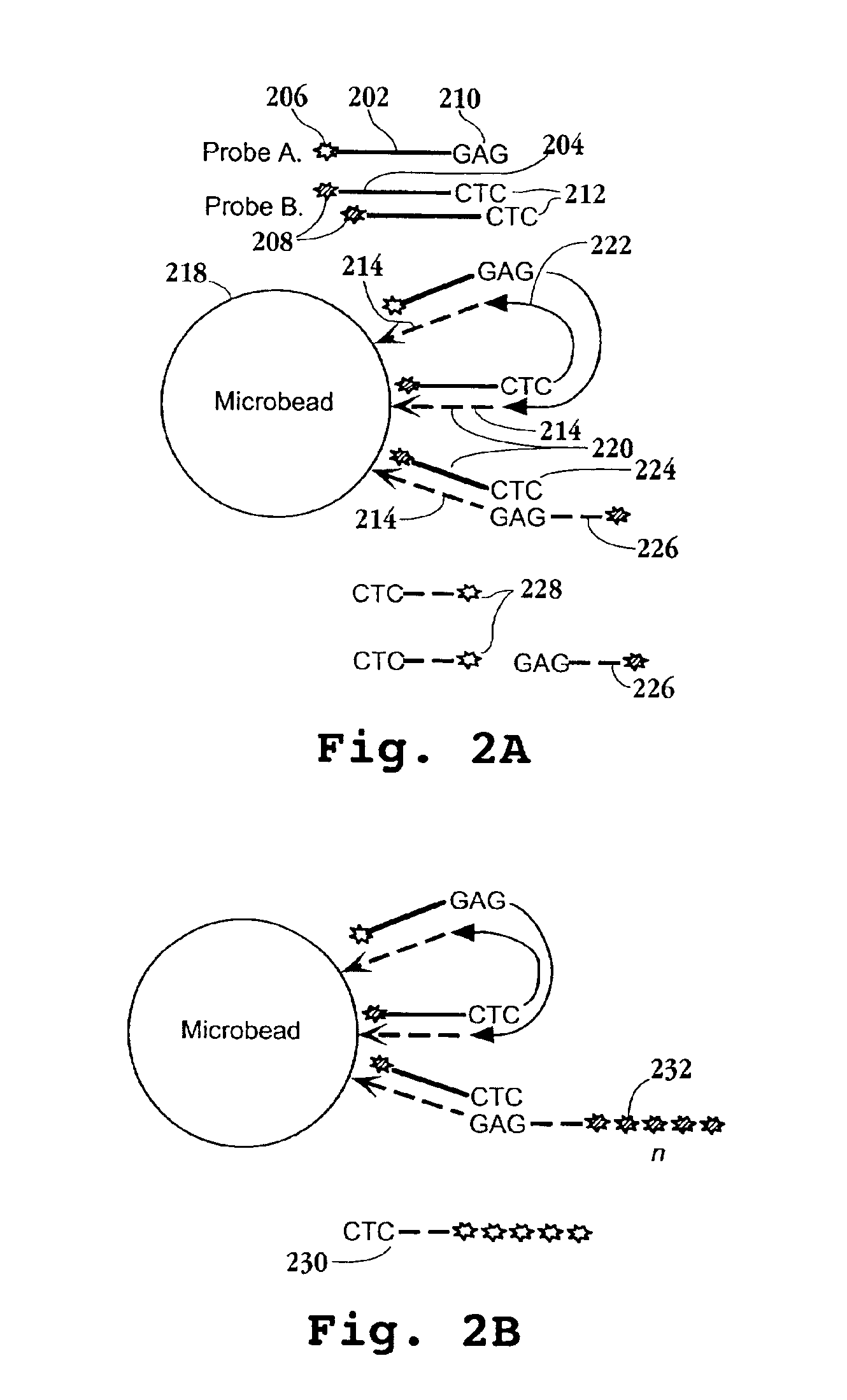
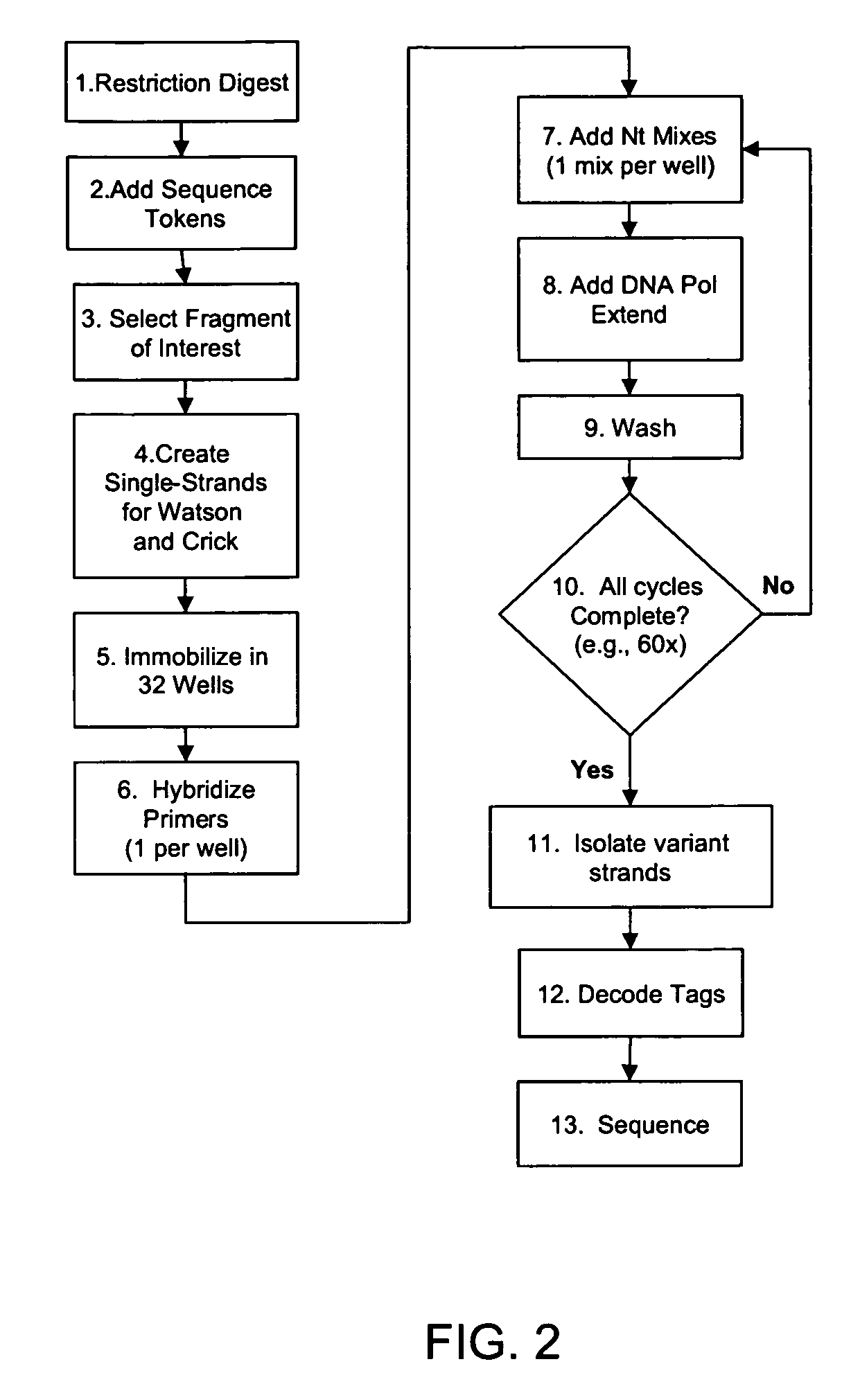
Reagents, methods, and libraries for bead-based sequencing
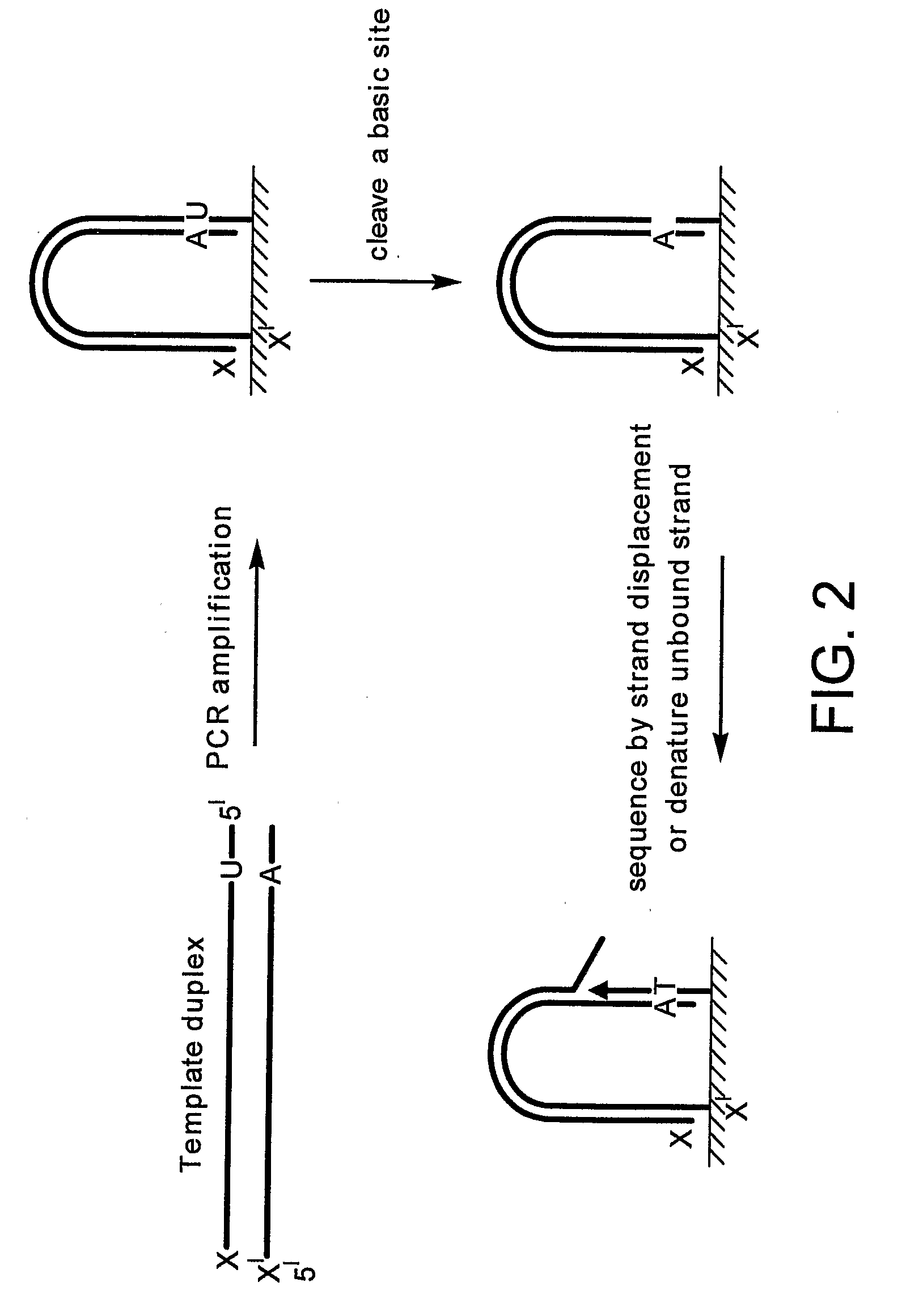
InactiveUS20080003571A1Efficient methodEfficient implementationMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
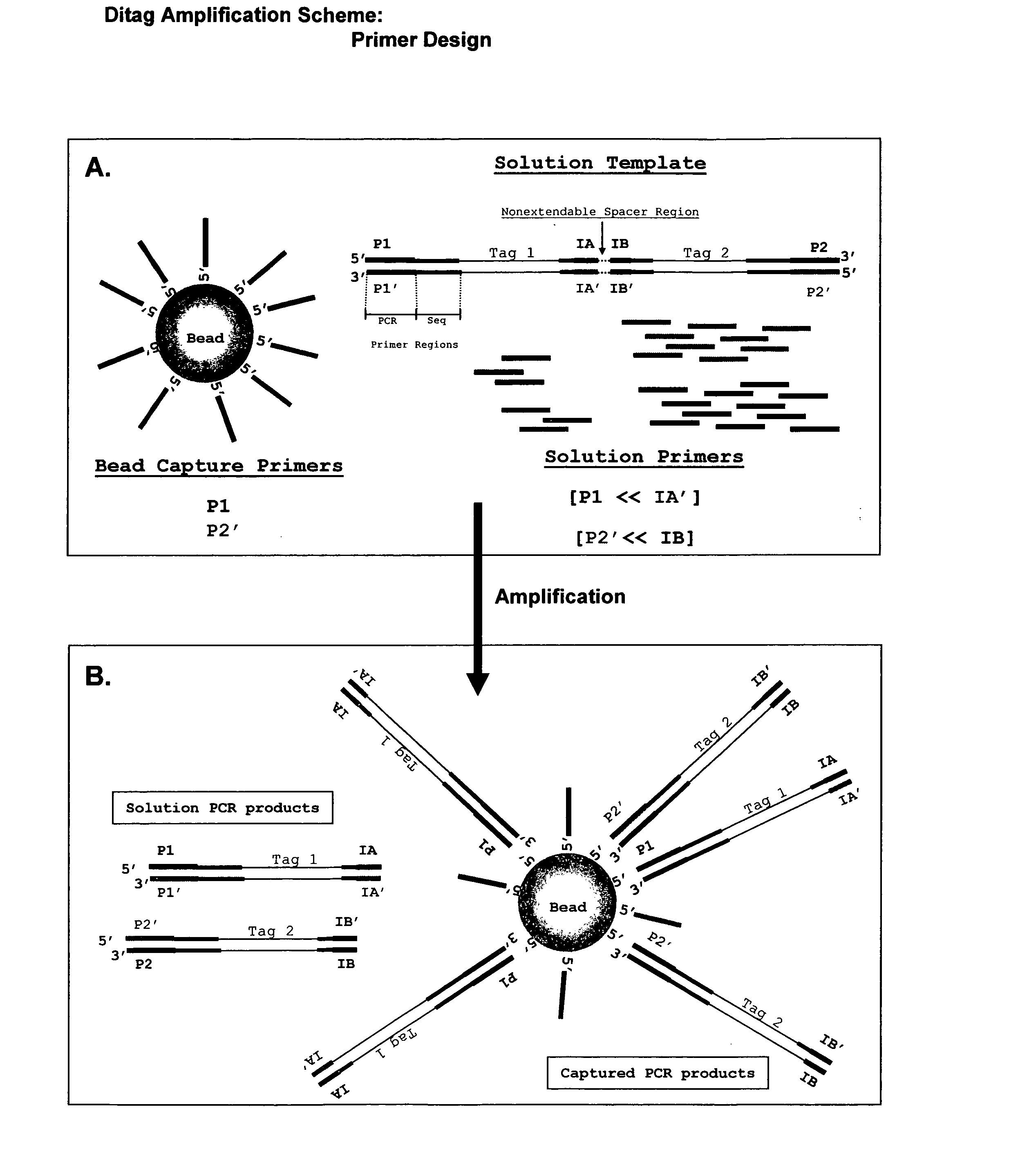
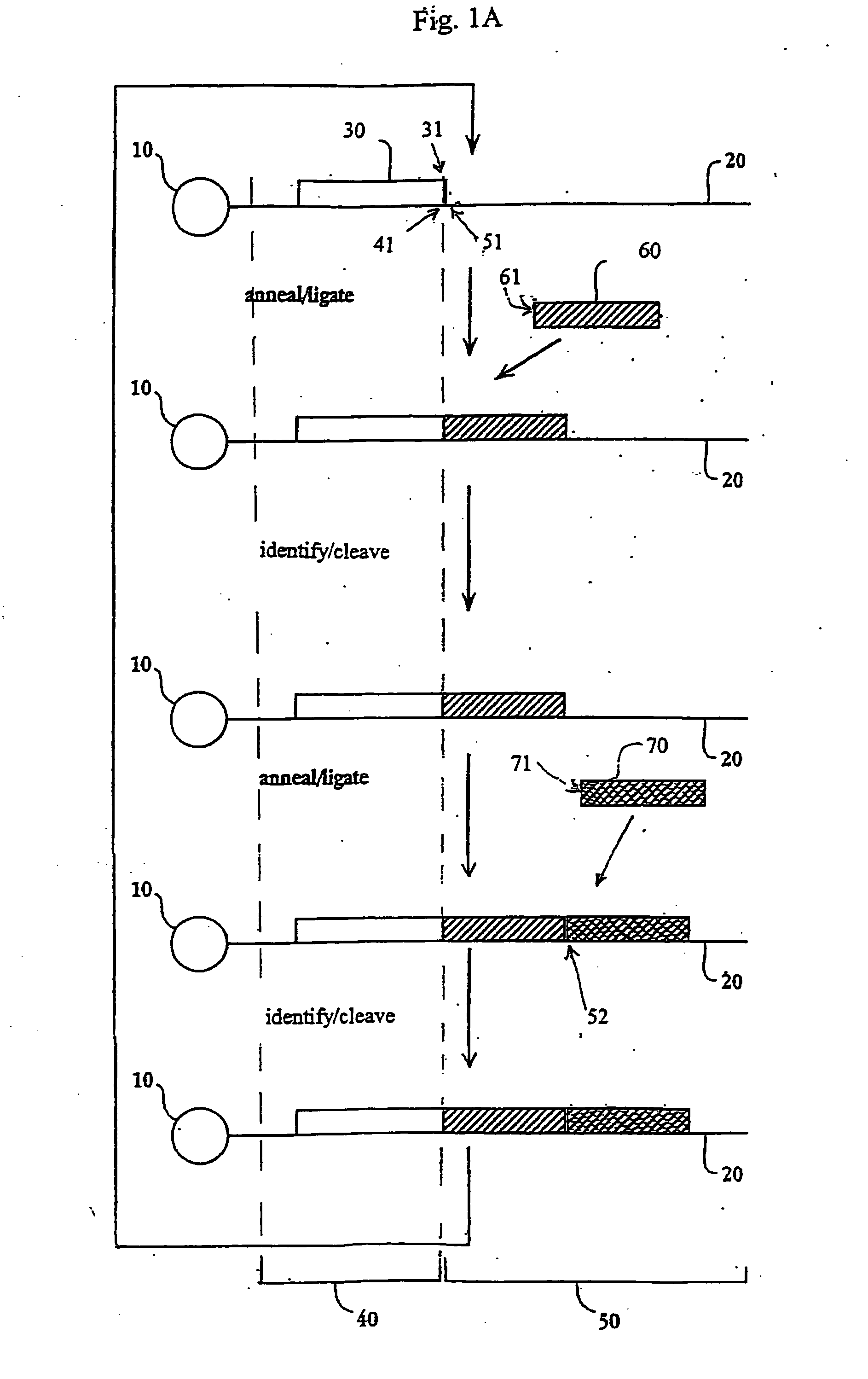
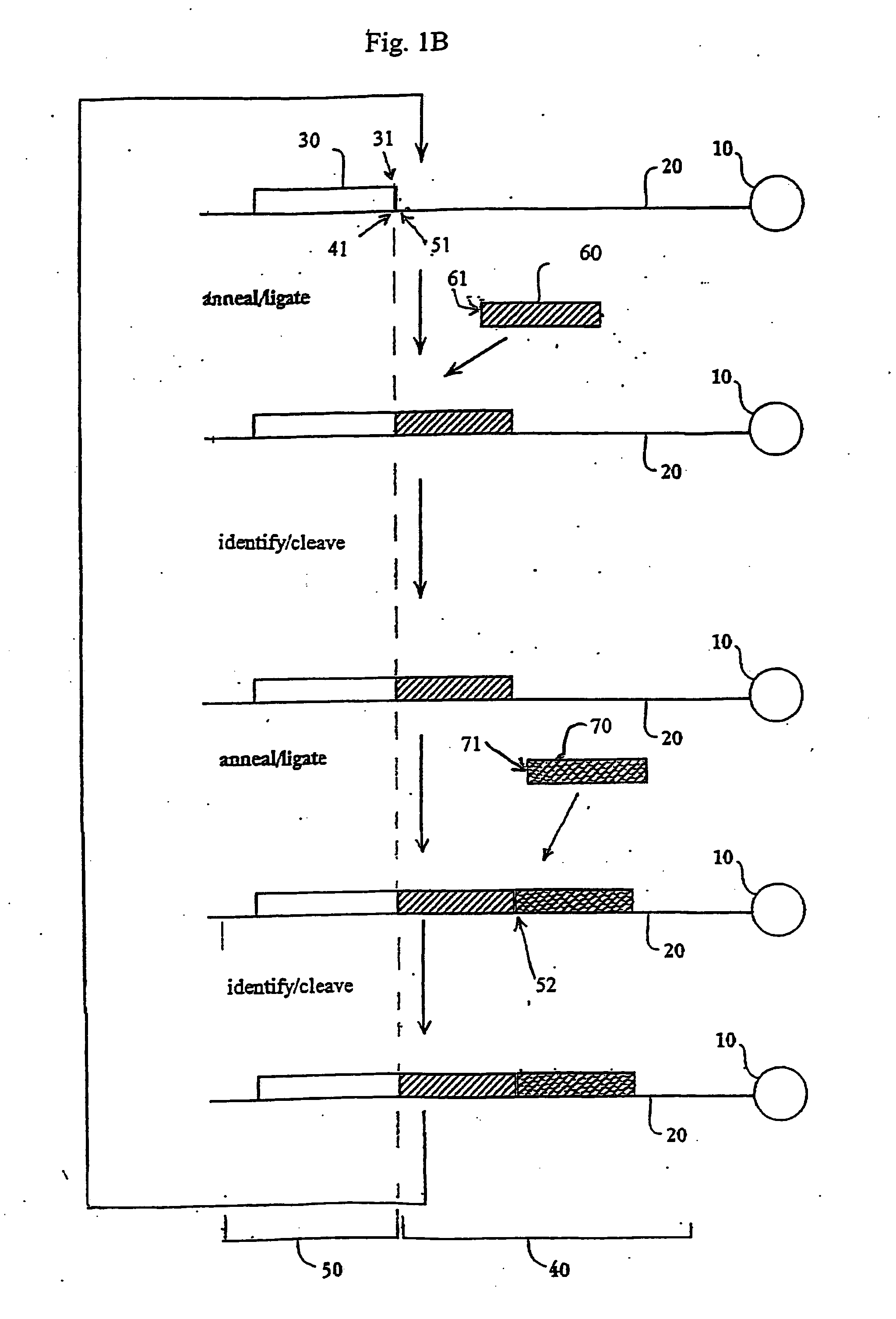
The present invention provides methods for determining a nucleic acid sequence by performing successive cycles of duplex extension along a single stranded template. The cycles comprise steps of extension, ligation, and, preferably, cleavage. In certain embodiments the methods make use of extension probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages and employ agents appropriate to cleave such linkages. In certain embodiments the methods make use of extension probes containing an abasic residue or a damaged base and employ agents appropriate to cleave linkages between a nucleoside and an abasic residue and / or agents appropriate to remove a damaged base from a nucleic acid. The invention provides methods of determining information about a sequence using at least two distinguishably labeled probe families. In certain embodiments the methods acquire less than 2 bits of information from each of a plurality of nucleotides in the template in each cycle. In certain embodiments the sequencing reactions are performed on templates attached to beads, which are immobilized in or on a semi-solid support. The invention further provides sets of labeled extension probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages or trigger residues that are suitable for use in the method. In addition, the invention includes performing multiple sequencing reactions on a single template by removing initializing oligonucleotides and extended strands and performing subsequent reactions using different initializing oligonucleotides. The invention further provides efficient methods for preparing templates, particularly for performing sequencing multiple different templates in parallel. The invention also provides methods for performing ligation and cleavage. The invention also provides new libraries of nucleic acid fragments containing paired tags, and methods of preparing microparticles having multiple different templates (e.g., containing paired tags) attached thereto and of sequencing the templates individually. The invention also provides automated sequencing systems, flow cells, image processing methods, and computer-readable media that store computer-executable instructions (e.g., to perform the image-processing methods) and / or sequence information. In certain embodiments the sequence information is stored in a database.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve. The apparatus includes a replacement valve and an anchor having an expandable braid. In some embodiments, the expandable braid is fabricated from a single strand of wire. In some embodiments, the expandable braid comprises at least one turn feature. The anchor and the valve preferably are configured for endovascular delivery and deployment.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Recombinase polymerase amplification
ActiveUS20050112631A1HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinase Polymerase AmplificationSingle strand
This disclosure describe three related novel methods for Recombinase-Polymerase Amplification (RPA) of a target DNA that exploit the properties of recombinase and related proteins, to invade double-stranded DNA with single stranded homologous DNA permitting sequence specific priming of DNA polymerase reactions. The disclosed methods have the advantage of not requiring thermocycling or thermophilic enzymes. Further, the improved processivity of the disclosed methods may allow amplification of DNA up to hundreds of megabases in length.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS SCARBOROUGH INC
Double-Stranded Ribonucleic Acid with Increased Effectiveness in an Organism
ActiveUS20070275465A1Improve stabilityGreat to enzymatic digestionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandDouble strand
The invention concerns a method for the targeted selection of a double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) consisting of two single strands that exhibits increased effectiveness in inhibiting the expression of a target gene by means of RNA interference, whereby the sequences of the single strands of the dsRNA are selected in such a way that on both ends of the dsRNA the last complementary nucleotide pair is a G-C, or at least two of the last four complementary nucleotide pairs are G-C pairs; whereby the dsRNA exhibits a single-stranded overhang consisting of 1 to 4 unpaired nucleotides at the first end, and no overhang at the second end; whereby the unpaired nucleotide of the single-stranded overhang that is directly adjacent to the last complementary nucleotide pair contains a purine base.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
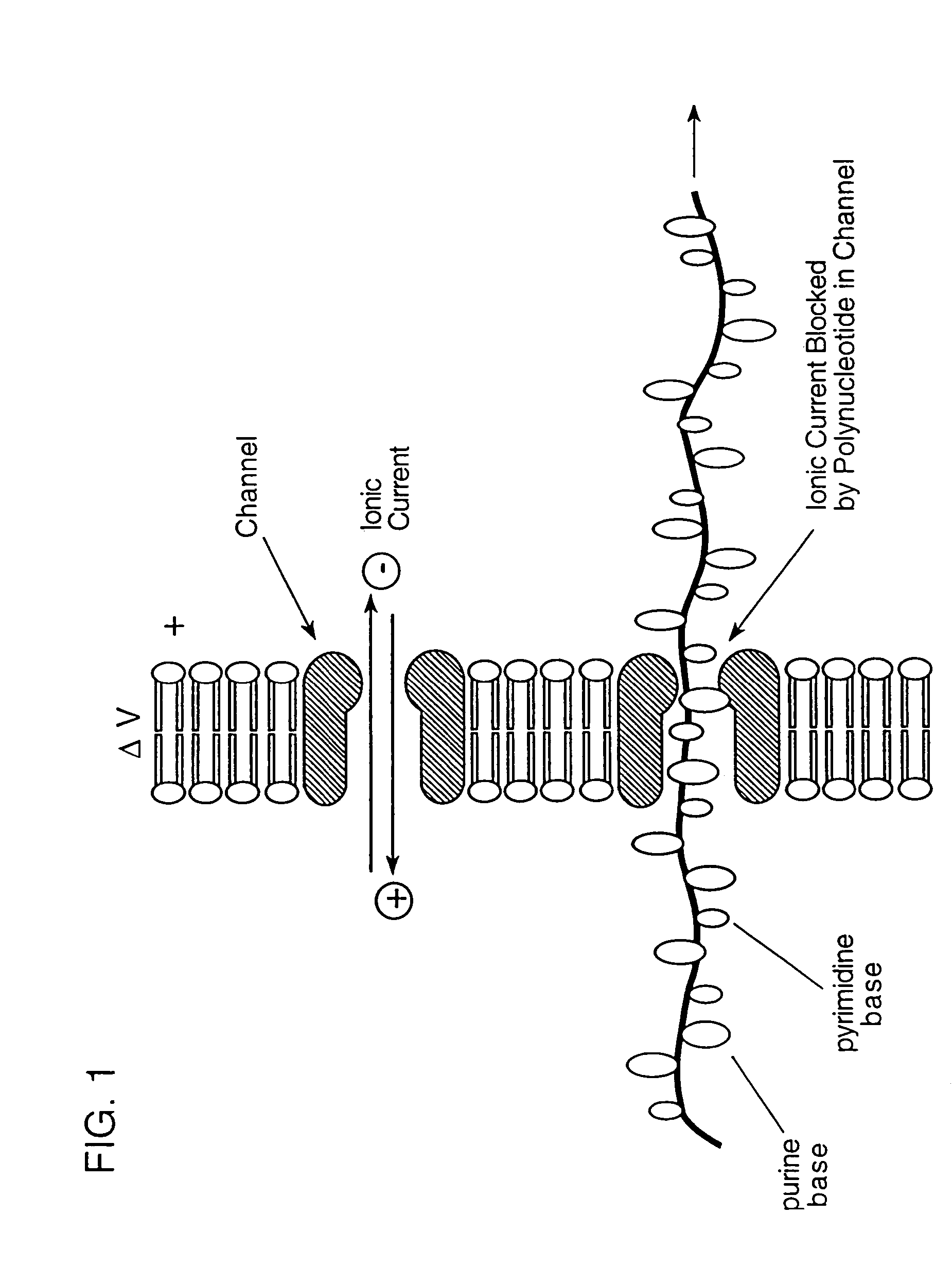
Hybridization assisted nanopore sequencing
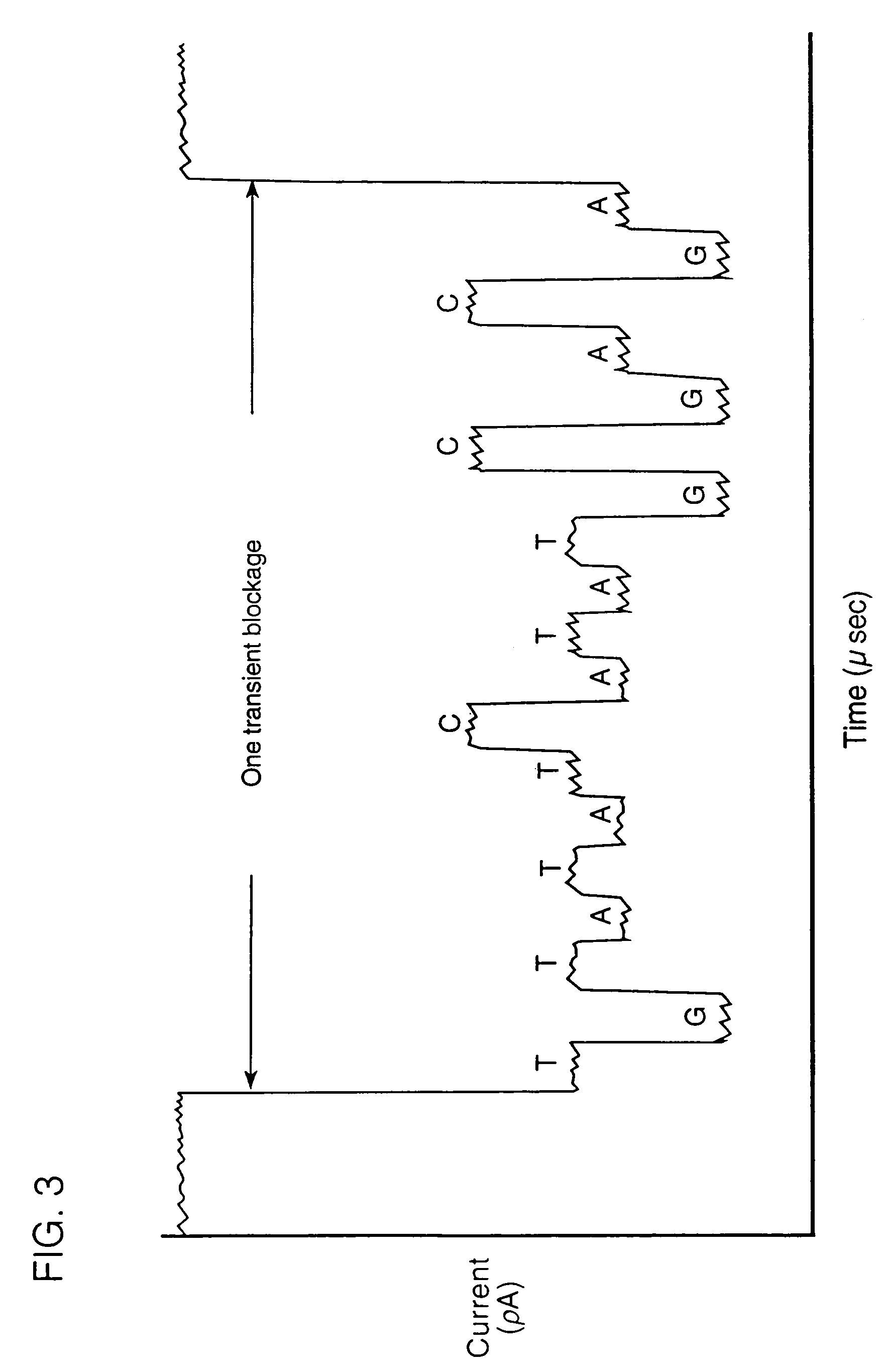
InactiveUS20070190542A1Eliminate needEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresHybridization probeNucleic Acid Probes
A method of employing a nanopore structure in a manner that allows the detection of the positions (relative and / or absolute) of nucleic acid probes that are hybridized onto a single-stranded nucleic acid molecule. In accordance with the method the strand of interest is hybridized with a probe having a known sequence. The strand and hybridized probes are translocated through a nanopore. The fluctuations in current measured across the nanopore will vary as a function of time corresponding to the passing of a probe attachment point along the strand. These fluctuations in current are then used to determine the attachment positions of the probes along the strand of interest. This probe position data is then fed into a computer algorithm that returns the sequence of the strand of interest.
Owner:NABSYS 2 0 +1
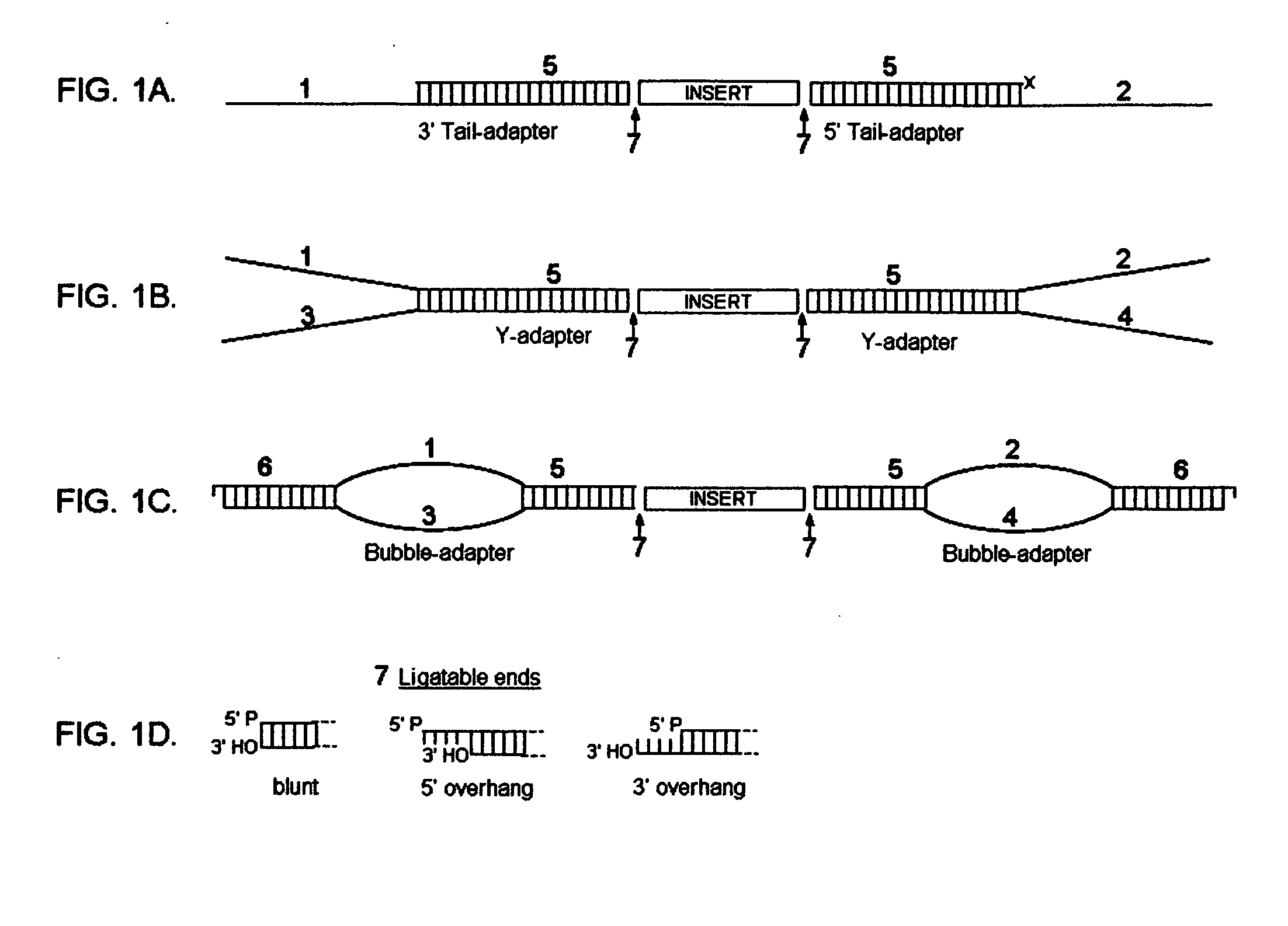
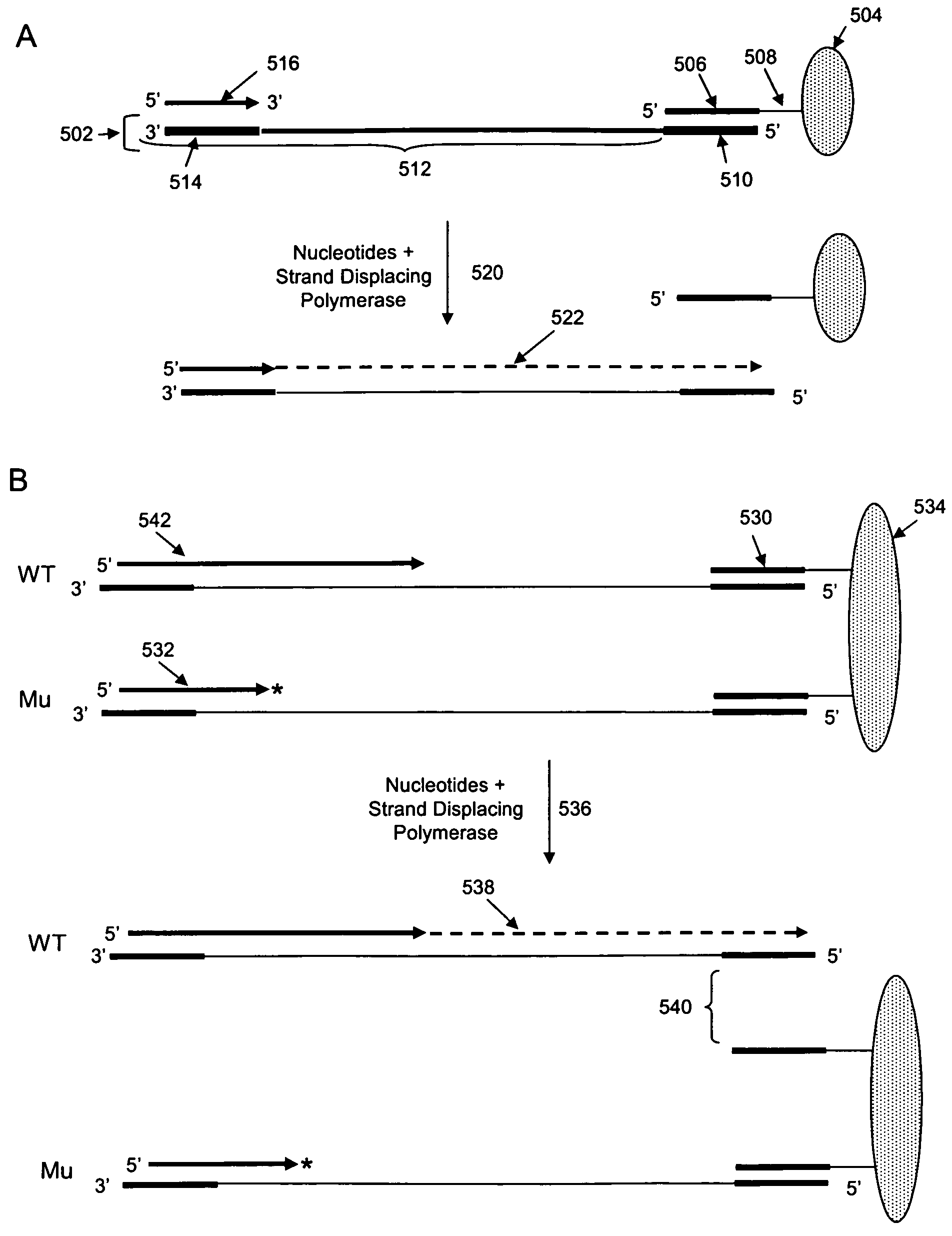
Asymmetrical adapters and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070172839A1Improve fidelityEasy to zoom inSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingSingle strand
A pair of asymmetrical, partially double-stranded oligonucleotide adapters are provided wherein the pair of adapters comprise a first asymmetrical oligonucleotide adapter comprising a single-stranded 3′ overhang and a second asymmetrical double-stranded oligonucleotide adapter comprising a single-stranded 5′ overhang and at least one blocking group on the strand of said second asymmetrical oligonucleotide adapter that does not comprise the 5′ overhang. Also provided are a pair of double-stranded Y oligonucleotide adapters and a pair of double-stranded bubble oligonucleotide adapters and methods of using said asymmetrical adapters for amplification of at least one double stranded nucleic acid molecule, wherein the amplification produces a plurality of amplified nucleic acid molecules having a different nucleic acid sequence at each end are also described. Also provided is a method for exponentially amplifying one strand in a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule. Also provided are methods for preparing libraries of paired tags using COS-linkers. Also provided are cleavable adapters comprising an affinity tag and a cleavable linkage, wherein cleaving the cleavable linkage produces two complementary ends. Methods of using the cleavable adapters to produce a paired tag library are also described.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Single-stranded and double-stranded oligonucleotides comprising a 2-arylpropyl moiety
ActiveUS20060008822A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderNucleotidePhosphate
One aspect of the present invention relates to a double-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one aralkyl ligand. In certain embodiments, an aralkyl ligand is bound to only one of the two oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, an aralkyl ligand is bound to both of the oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide strands comprise at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, at least one phosphate linkage in the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the aralkyl ligand is naproxen or ibuprofen. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a single-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one aralkyl ligand. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide comprises at least one modified sugar moiety. In certain embodiments, at least one phosphate linkage in the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate linkage. In a preferred embodiment, the aralkyl ligand is naproxen or ibuprofen. The aralkyl ligand improves the pharmacokinetic properties of the oligonucleotide.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Method of analyzing DNA sequence using field-effect device, and base sequence analyzer
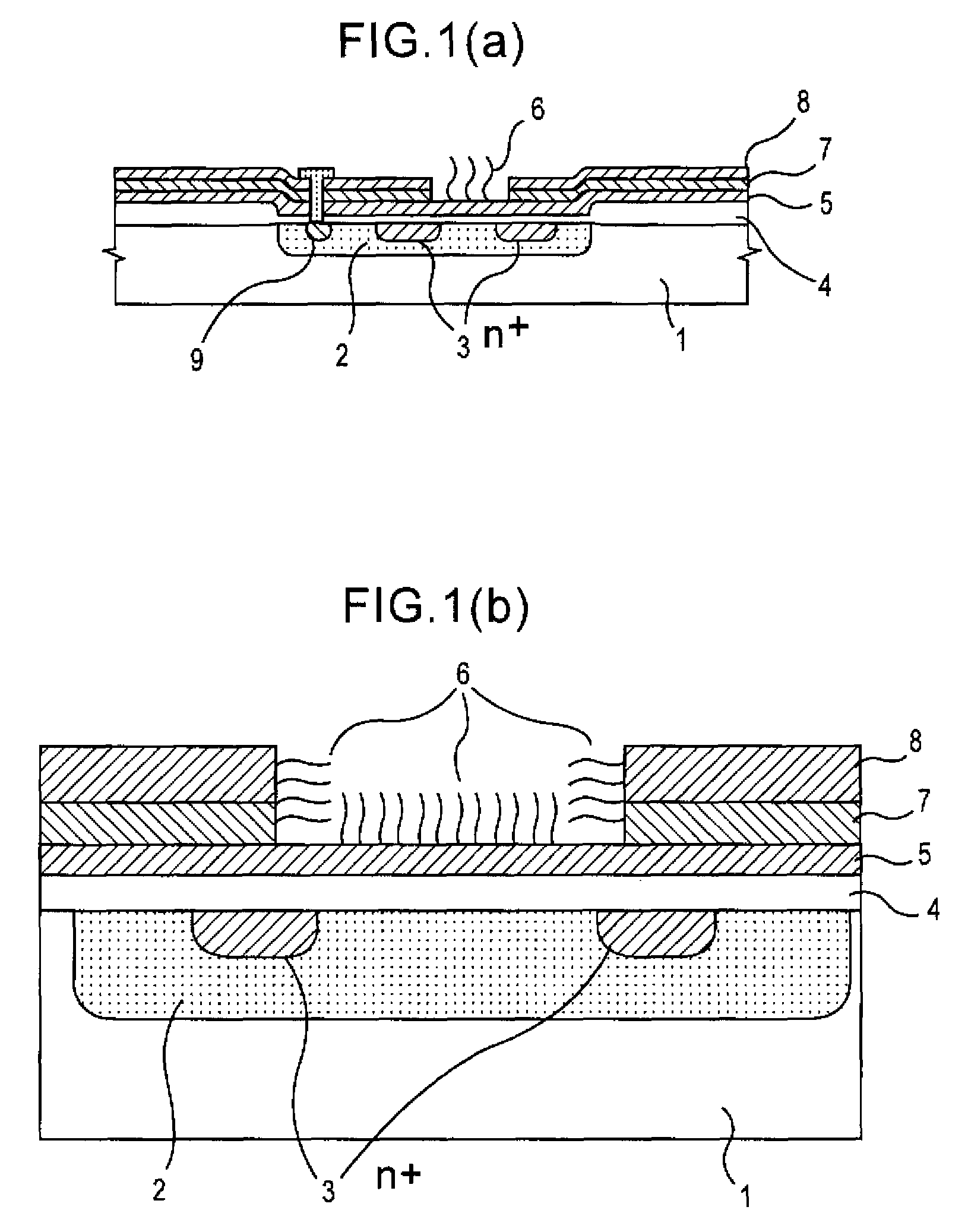
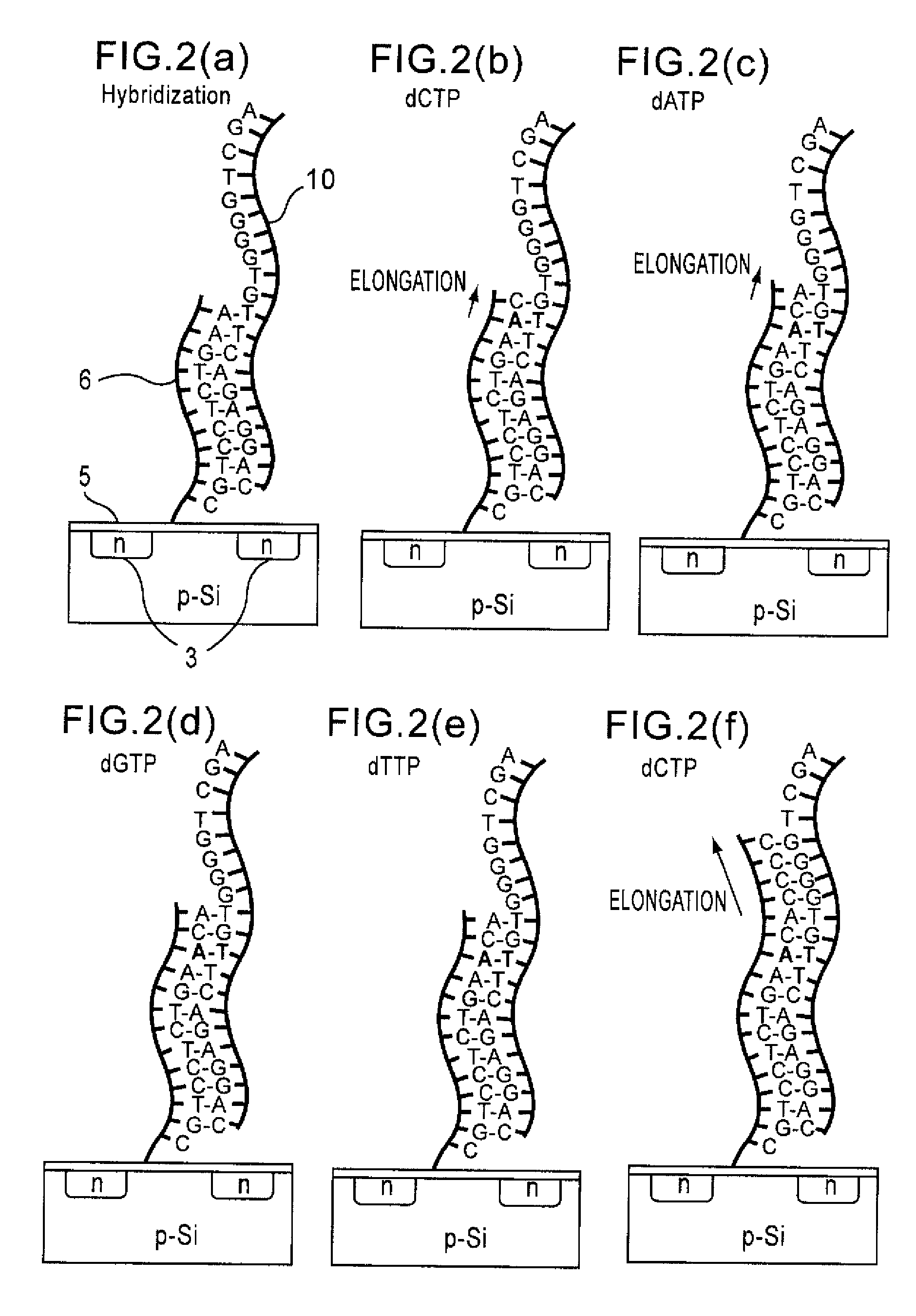
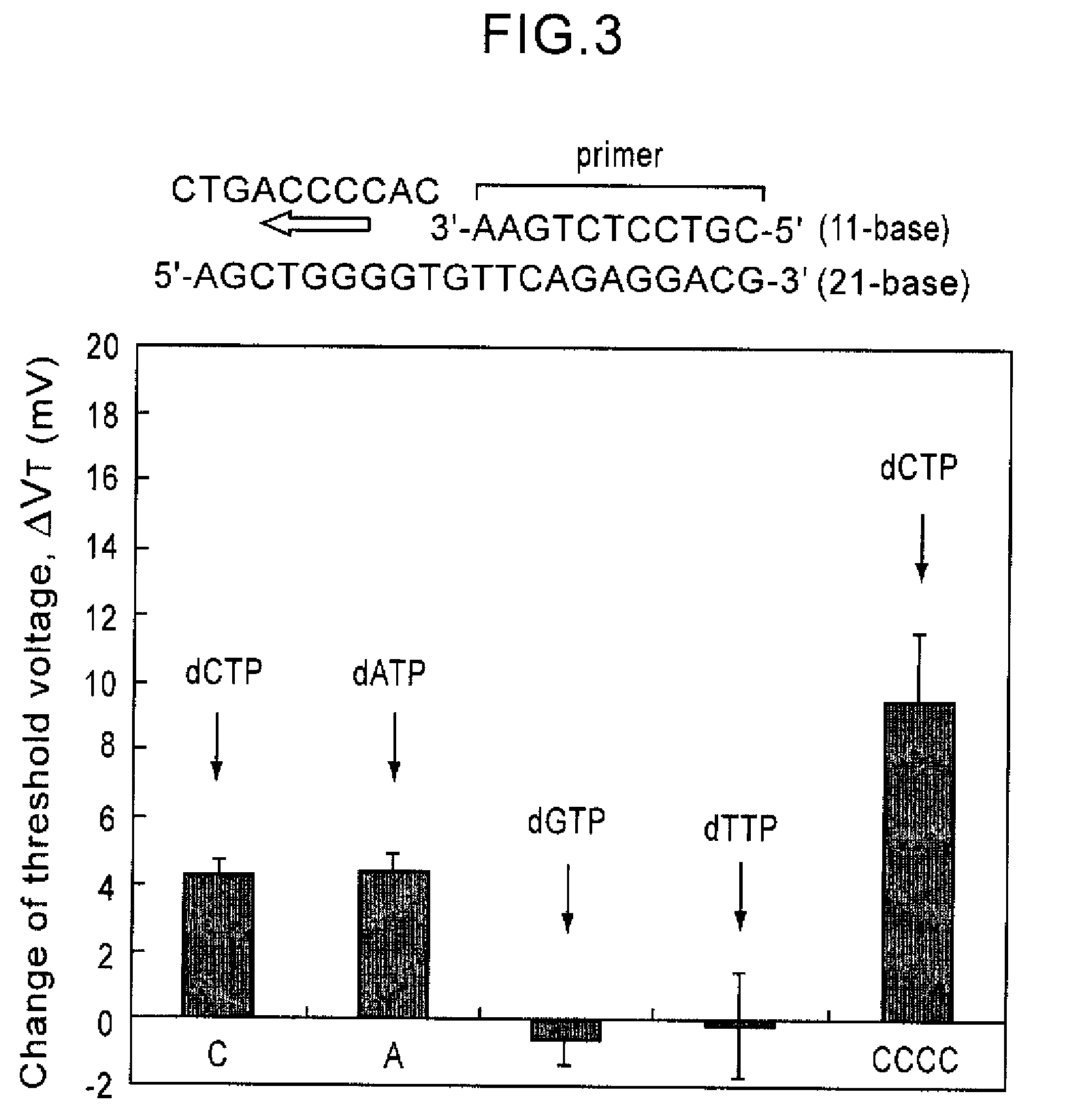
ActiveUS7888013B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalysis dnaFluorescence
Since conventional DNA sequence analyzing technologies are based on the fundamental principle of fluorescent detection, expensive, complex optical systems and laser sources have been necessary.A field-effect device for gene detection of the present invention analyzes a base sequence by immobilizing a single-strand nucleic acid probe at a gate portion, inducing hybridization at the gate portion to form a double-stranded DNA, inducing elongation reaction by adding a DNA polymerase and one of the substrates, and measuring the electrical characteristic of the field-effect device caused by elongation reaction.Since the elongation reaction of one base induced at the gate portion can be directly converted to an electrical signal, expensive lasers or complex optical systems are not needed. Thus, a small gene polymorphism detection system that can conduct measurement at high precision can be provided.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
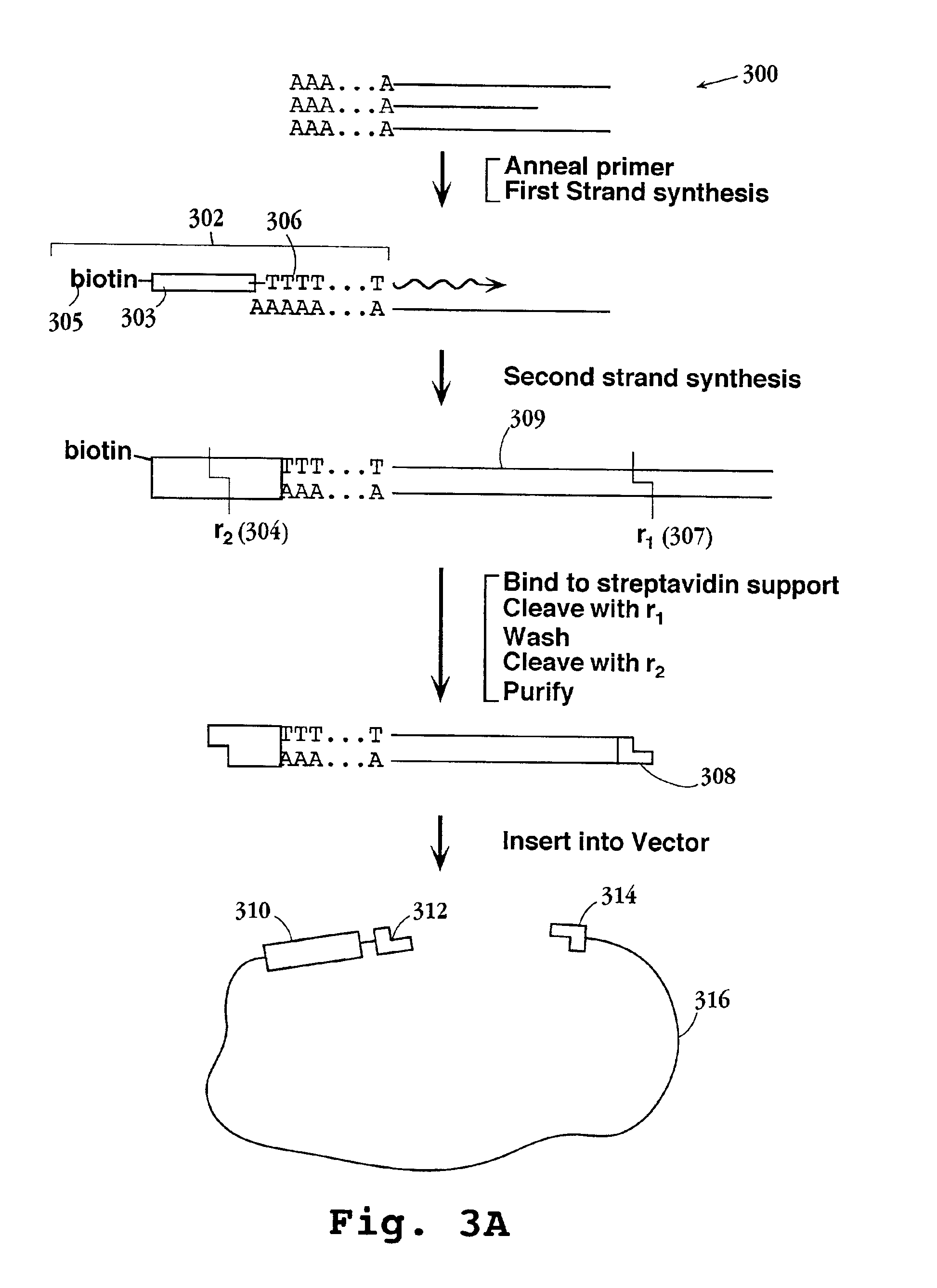
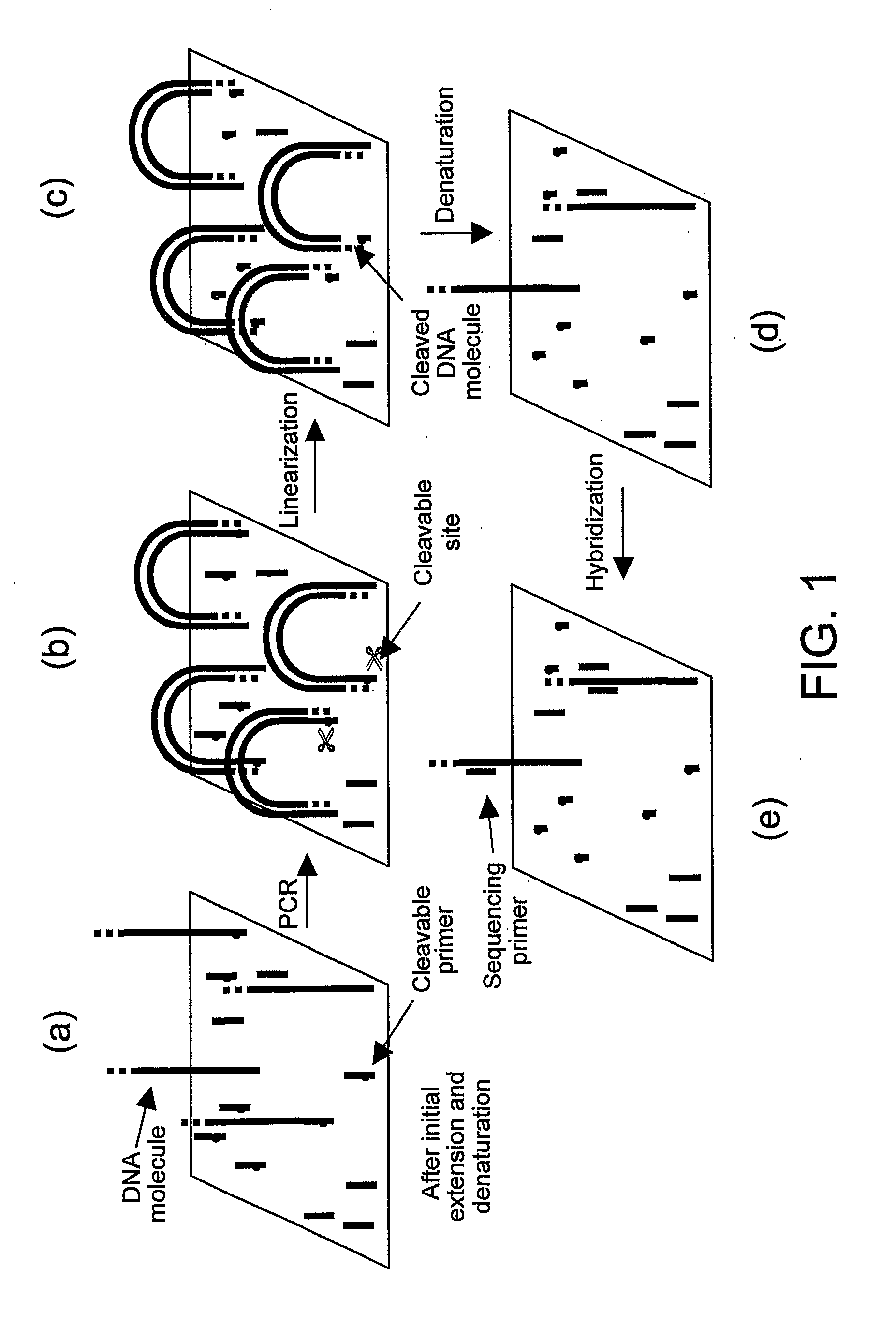
Preparation of templates for nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20090118128A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsSugar derivativesNucleic acid sequencingDouble strand
The invention relates to methods of generating templates for a nucleic acid sequencing reaction which comprise:providing at least one double-stranded nucleic acid molecule, wherein both strands of the double-stranded nucleic acid molecule are attached to a solid support at the 5′ end,cleaving one or both strands of the double-stranded nucleic acid molecule, andsubjecting the cleaved strand(s) to denaturing conditions to remove the portion of the cleaved strand(s) not attached to the solid support, thereby generating a partially or substantially single-stranded template for a nucleic acid sequencing reaction.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Methods and compositions for isolating nucleic acid sequence variants
The invention is drawn to isolating sequence variants of a genetic locus of interest using a modified iterative primer extension method. The nucleic acids analyzed are generally single stranded and have a reference sequence which is used as a basis for performing iterative single nucleotide extension reactions from a hybridized polymerization primer. The iterative polymerization reactions are configured such that polymerization of the strand will continue if the sequence of the nucleic acid being analyzed matches the reference sequence, whereas polymerization will be terminated if the nucleic acid being analyzed does not match the reference sequence. Nucleic acid strands that have mutations can be isolated using a variety of methods and sequenced to determine the precise identity of the mutation / polymorphism. By performing the method on both strands of the nucleic acid being analyzed, virtually all possible mutations can be identified.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
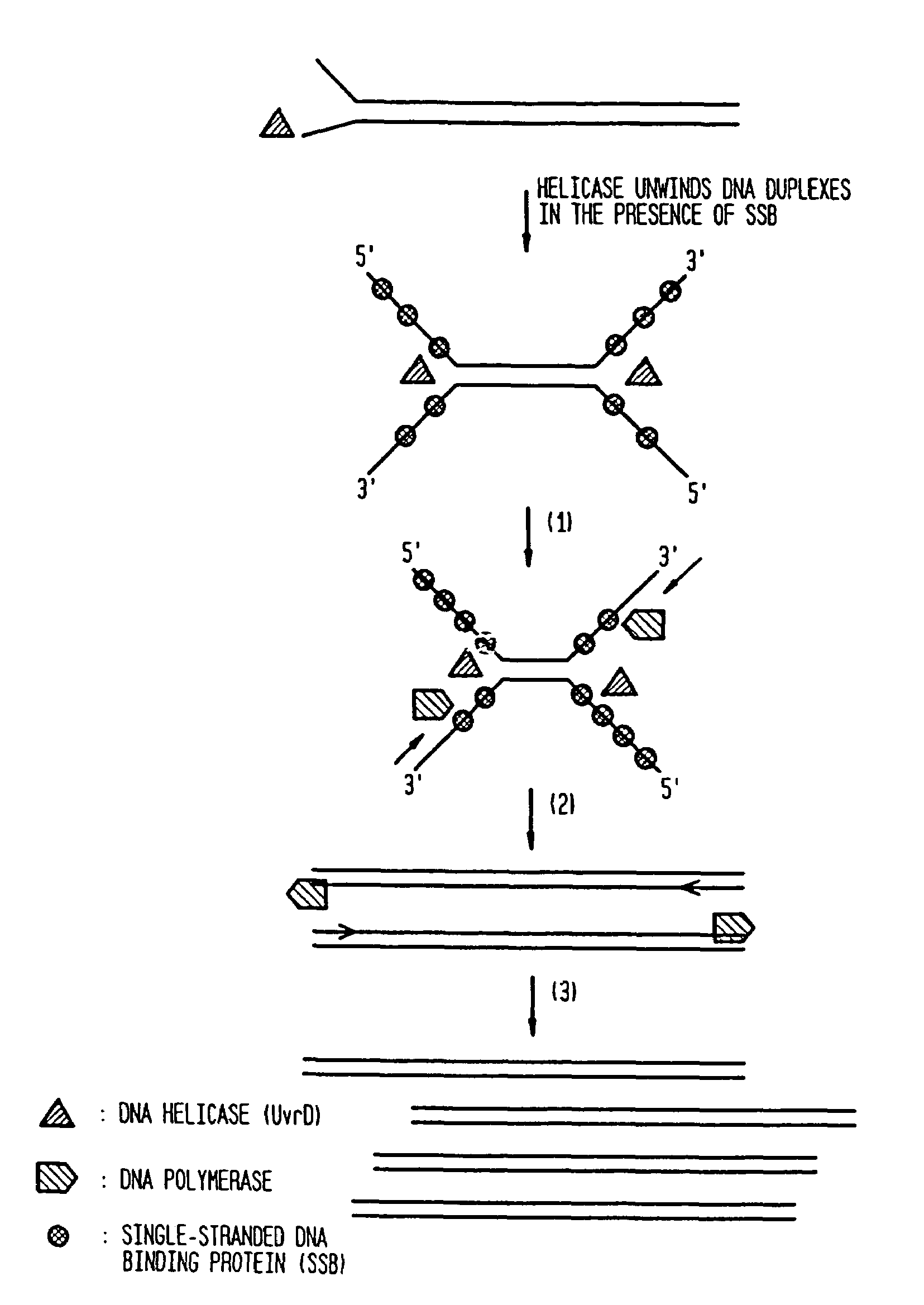
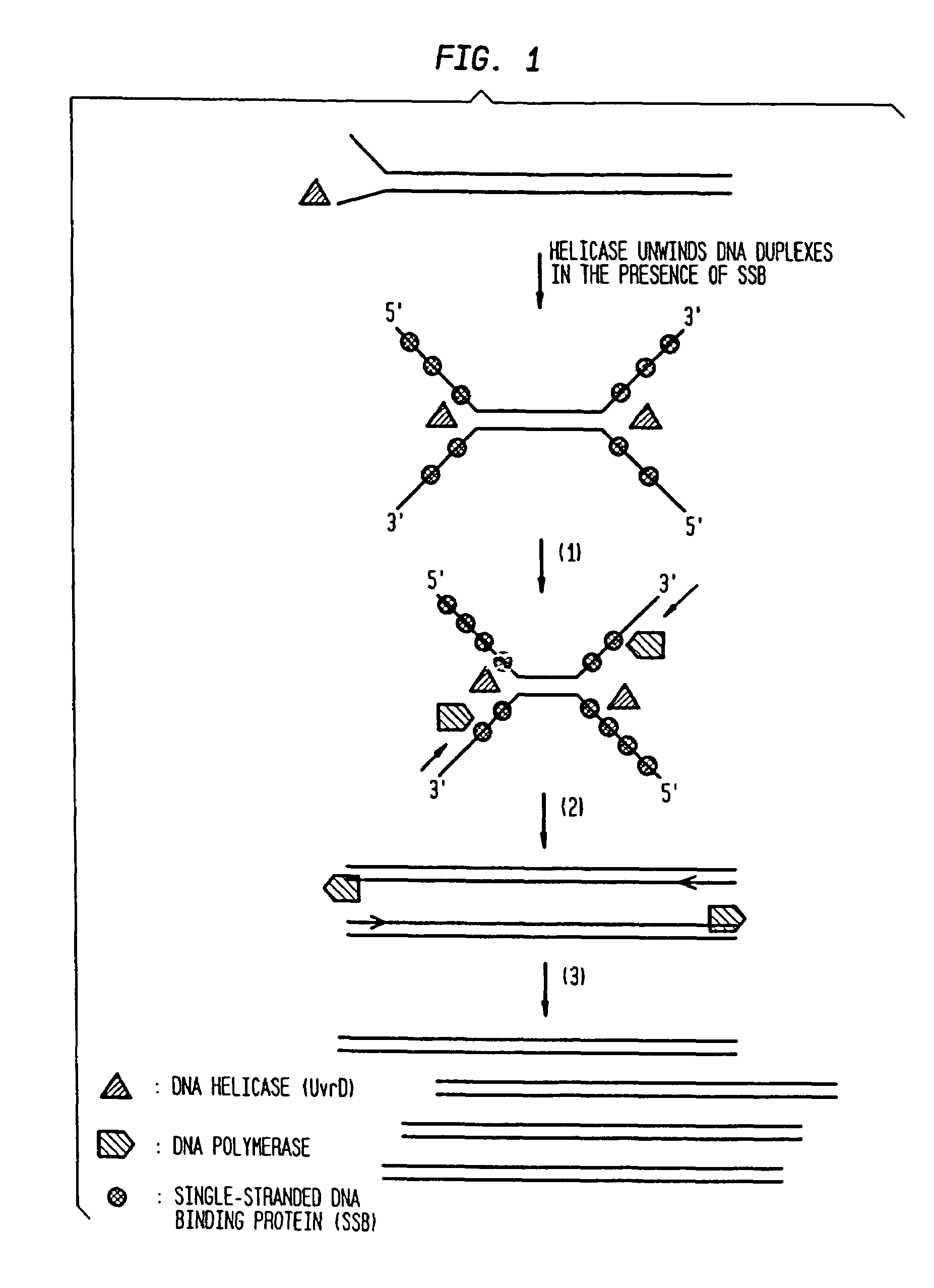
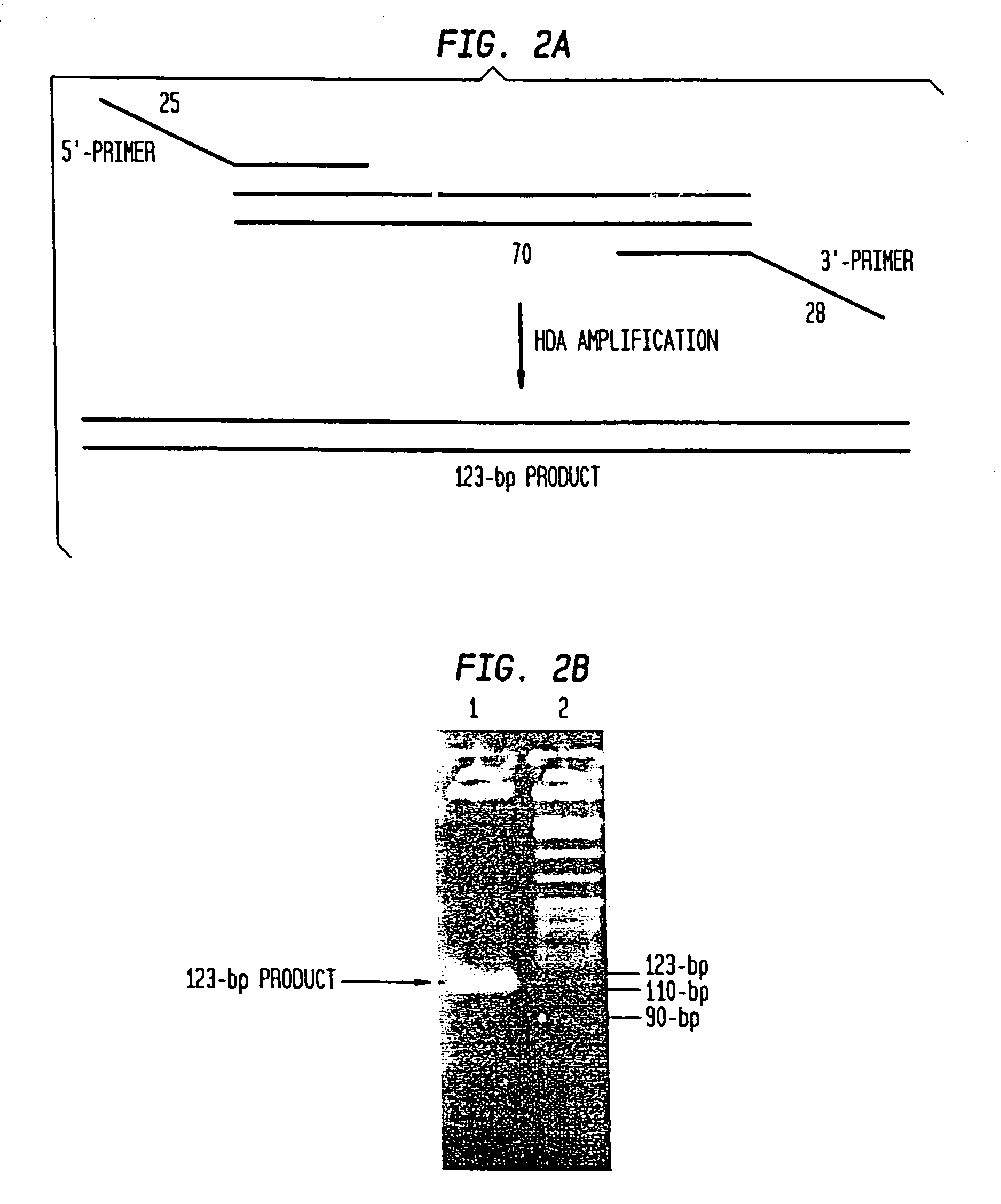
Helicase-dependent amplification of RNA
Owner:BIOHELIX CORP
Crispr/cas system-based novel fusion protein and its applications in genome editing
An inactive CRISPR / Cas system-based fusion protein and its applications in gene editing are disclosed. More particularly, chimeric fusion proteins including an inCas fused to a DNA modifying enzyme and methods of using the chimeric fusion proteins in gene editing are disclosed. The methods can be used to induce double-strand breaks and single-strand nicks in target DNAs, to generate gene disruptions, deletions, point mutations, gene replacements, insertions, inversions and other modifications of a genomic DNA within cells and organisms.
Owner:SAGE LABS
Temporary arterial shunt and method
Surgical construction or bypass grafting of a target vessel includes method and instrumentation and apparatus for forming and inserting a fluid-impervious tubular conduit including a central protrusion through an aperture in the vessel to form a fluid-conducting shunt past the aperture. An anastomosis over the aperture is partially completed with the protrusion of the tubular conduit extending through the partial anastomosis. A removal tube is disposed over the protrusion for applying tensile force thereto relative to the tubular conduit for dissembling the tubular conduit along a continuous path for removal as a single strand from the vessel through the tube and aperture and the partial anastomosis prior to completion of the procedure.
Owner:ORIGIN MEDSYST +1
Methods and systems for manufacturing a structure having organized areas
A beaded preform includes a plurality of adjacently positioned beads for forming a plurality of voids in an engineered material. The beaded preforms may be comprised of a filaments (single strand of beads) and mats (two-dimensional and three dimensional arrays of beads). The filaments and mats may be coated to become tows and laminates, respectively, which may then be assembled into composite materials. The preforms may be produced using novel manufacturing apparatuses and methods, and incorporated into known manufacturing processes to produce porous structures, including stress-steering structures, in any material including metals, plastics, ceramics, textiles, papers, and biological materials, for example. Permanent bead material is preferably made of polyacrylonitrile, carbon fiber, or graphite.
Owner:HEX
2'-f modified RNA interference agents
InactiveUS20110269814A1Inhibit expressionSuppress gene expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleotideSense strand
This invention relates to a method of modulating the expression of a target gene in an organism comprising administering an iRNA agent, wherein the iRNA comprises at least one 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro (2′-F) nucleotide in the antisense strand and at least one modified nucleotide in the sense strand. The invention also relates to compositions comprising a single-stranded oligonucleotide that contains at least one 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro (2′-F) nucleotide. siRNA molecule containing these oligonucleotides have decreased immunogenicity.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com