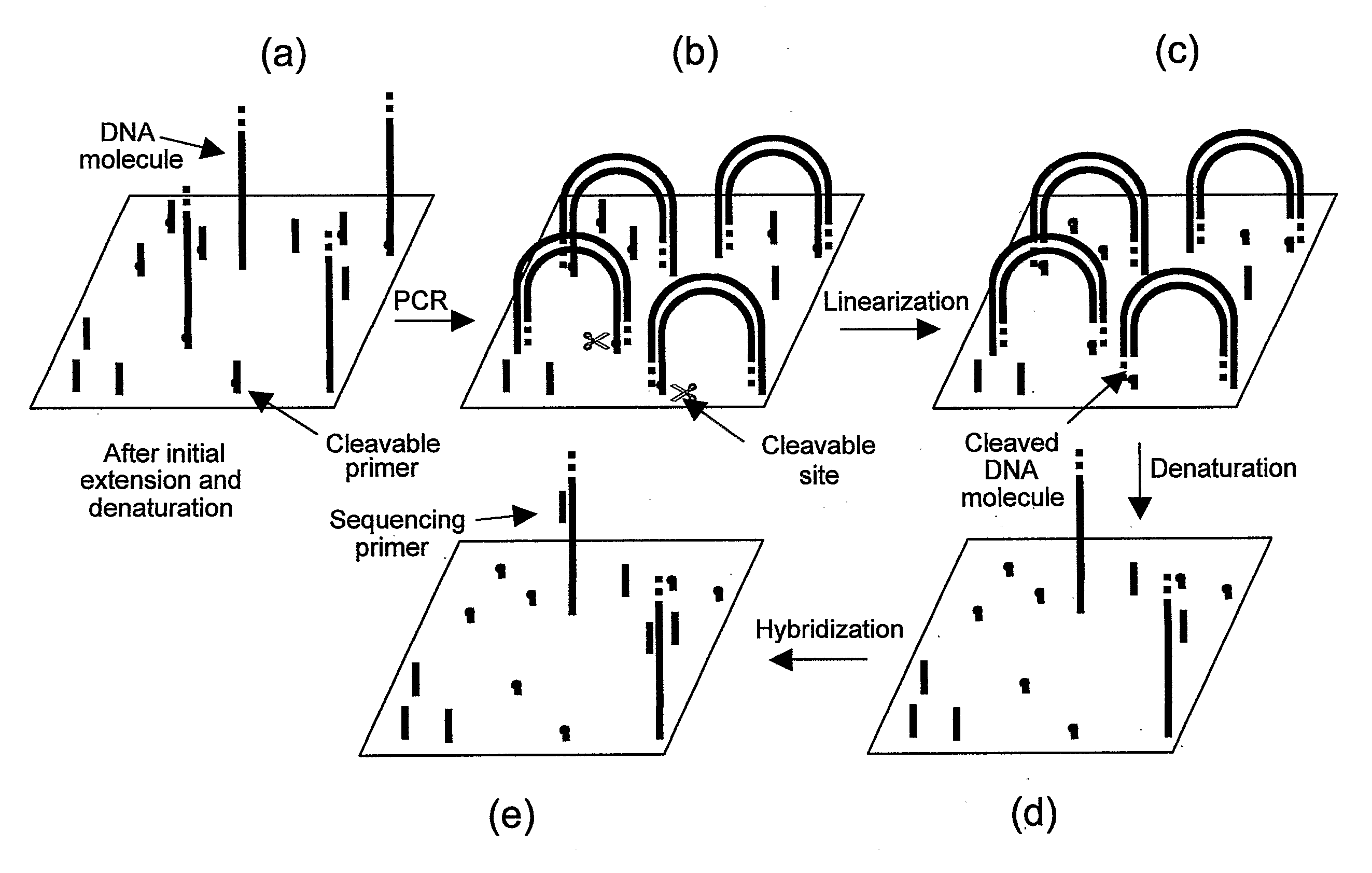
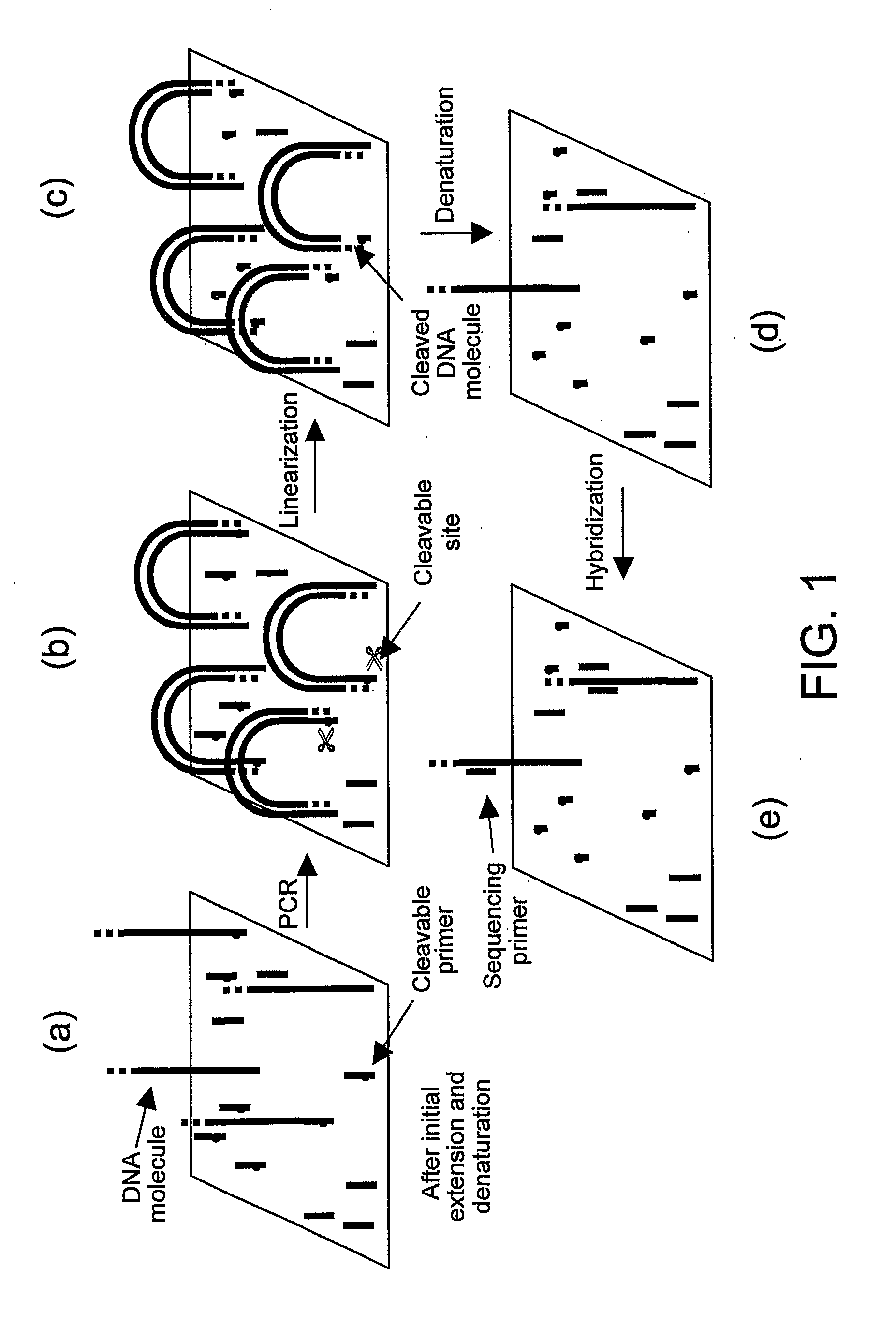
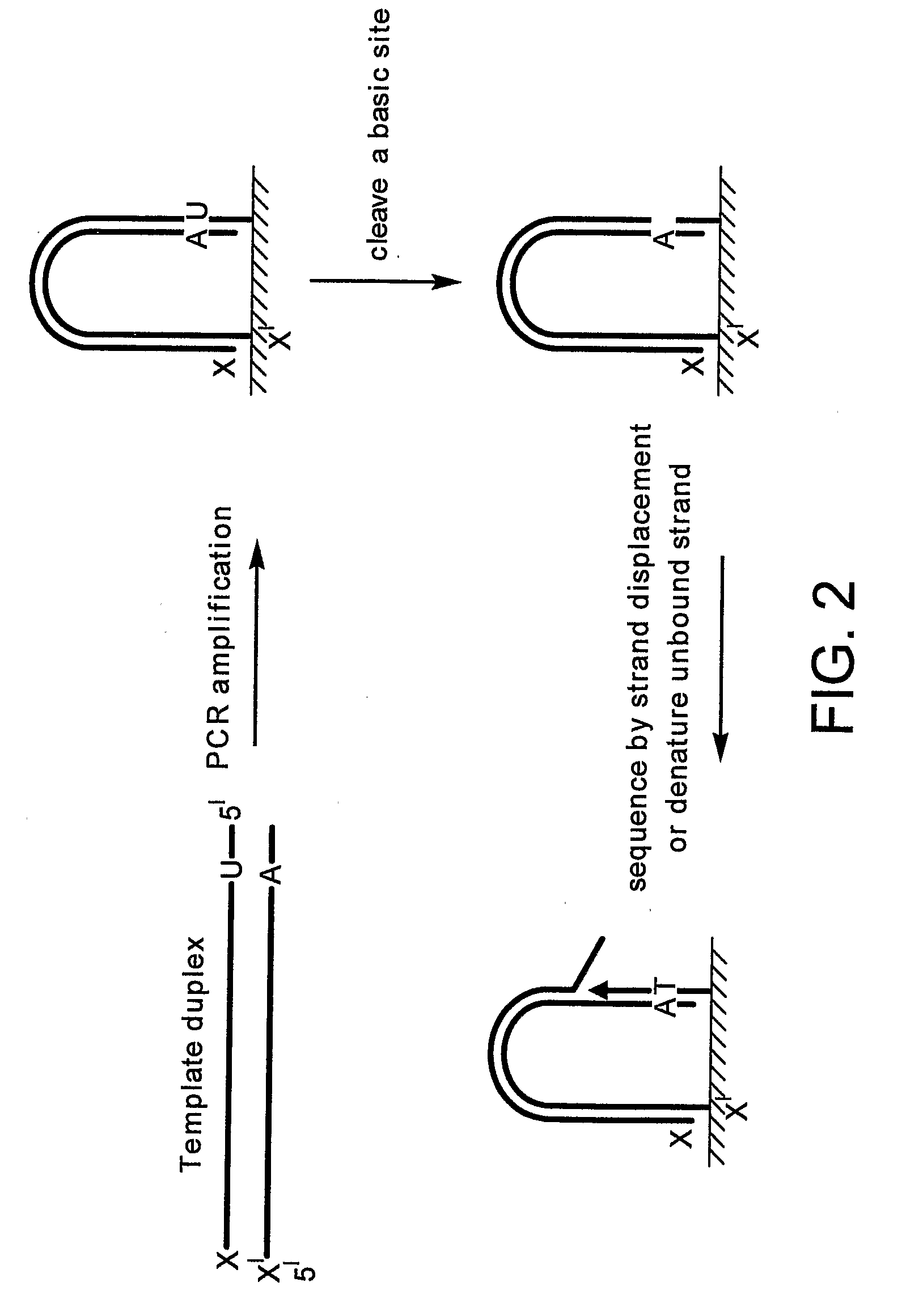
Preparation of templates for nucleic acid sequencing
a nucleic acid sequencing and template technology, applied in chemical libraries, sugar derivative preparation, combinational chemistry, etc., can solve the problem that the arrays comprised of such bridged structures provide inefficient templates for nucleic acid sequencing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Cleavage Evaluation of Diol Primer in 8 Channel (Baccarat) Chip
Oligonucleotides Used:
[0200]Labelled P5 complementary oligonucleotide (supplied by Eurogentec):
(SEQ ID NO:1)5′-Texas Red-TCGGTGGTCGCCGTATCATT-3′-OH
[0201]Grafting control primer (supplied by Eurogentec):
(SEQ ID NO:2)5′-phosphorothioate-GTAGACTGCATGACCTGTAG-3′-Cy3
[0202]P5 non-cleavable primer (supplied by Eurogentec):
(SEQ ID NO:3)5′-phosphorothioate-TTTTTTTTTTAATGATACGGCGACCACCGA-3′OH
[0203]P5 cleavable primer (supplied by Fidelity systems):
(SEQ ID NO:4)5′-phosphorothioate-arm 26-diol22A-AATGATACGGCGACCACCGA-3′OH
[0204]The structures of the arm26 and diol22A components were as follows:
[0205]Grafting was performed according to the procedure described under general methods. Channels 1 and 2 of an 8 channel chip were grafted using the non-cleavable primer, channels 5, 6 and 7 using the cleavable diol linker and channel 8 using the grafting control.
[0206]A first hybridization using the complementary P5 oligonucleotide (SEQ ID NO...
example 2
Nucleic Acid Colony Formation on Acrylamide (SFA) Coated 8 Channel (Baccarat) Chips Using Diol Primer
Oligonucleotides Used:
[0209]PS non-cleavable primer (supplied by Eurogentec):
(SEQ ID NO:3)5′-phosphorothioate-TTTTTTTTTTAATGATACGGCGACCACCGA-3′OH
[0210]P7 non-cleavable primer (supplied by Eurogentec):
(SEQ ID NO:5)5′-phosphorothioate-TTTTTTTTTTCAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGA-3′OH
[0211]P5 cleavable primer (supplied by ATD):
5′-phosphorothioate-TTTTTTTTTT-(diol)X3-AATGATACGGCGACCACCGA-3′OH
(equivalent to SEQ ID NO:3 but including diol linkage)
[0212]The structure of the “diol” linker incorporated into the cleavable primer was as follows:
[0213]It will be noted that the linker unit is incorporated with the diol in a protected OAc form during oligonucleotide synthesis. The free diol is released by ammonia treatment during oligonucleotide cleavage / deprotection. Therefore, the primers used in the grafting reaction contain the free diol.
[0214]Grafting was performed according to the procedure described in ...
example 3
Cleavage and Subsequent Hybridization of Nucleic Acid Colonies Generated on Diol Cleavable Primer
Olionucleotide Used:
[0217]A594 sequencing primer (supplied by Eurogentec):
(SEQ ID NO:6)5′-A594-CTGGCACGACAGGTTTCCCGACTGGAAAGCGGGCAGTG-3′-OH
[0218]Channels to be cleaved were treated with a solution of 0.1M of sodium periodate and 0.1M ethanolamine in water for 1 hour at room temperature. All the other channels were washed with milliQ water. All channels were then washed for 30 minutes with milliQ water at room temperature.
[0219]Hybridization was carried out using the sequencing primer (SEQ ID NO:6) labelled with A594 to evaluate the percentage of non-cleaved oligonucleotide. The sequencing primer was hybridised to the linearised clusters prepared as described above at 500 nM, using standard conditions for hybridisation as described under the general methods. The chip was then imaged using an orange filter with an exposure time of 1 s.
Results
[0220]As expected, the channels grafted with the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com