Patents
Literature
60 results about "Automated sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
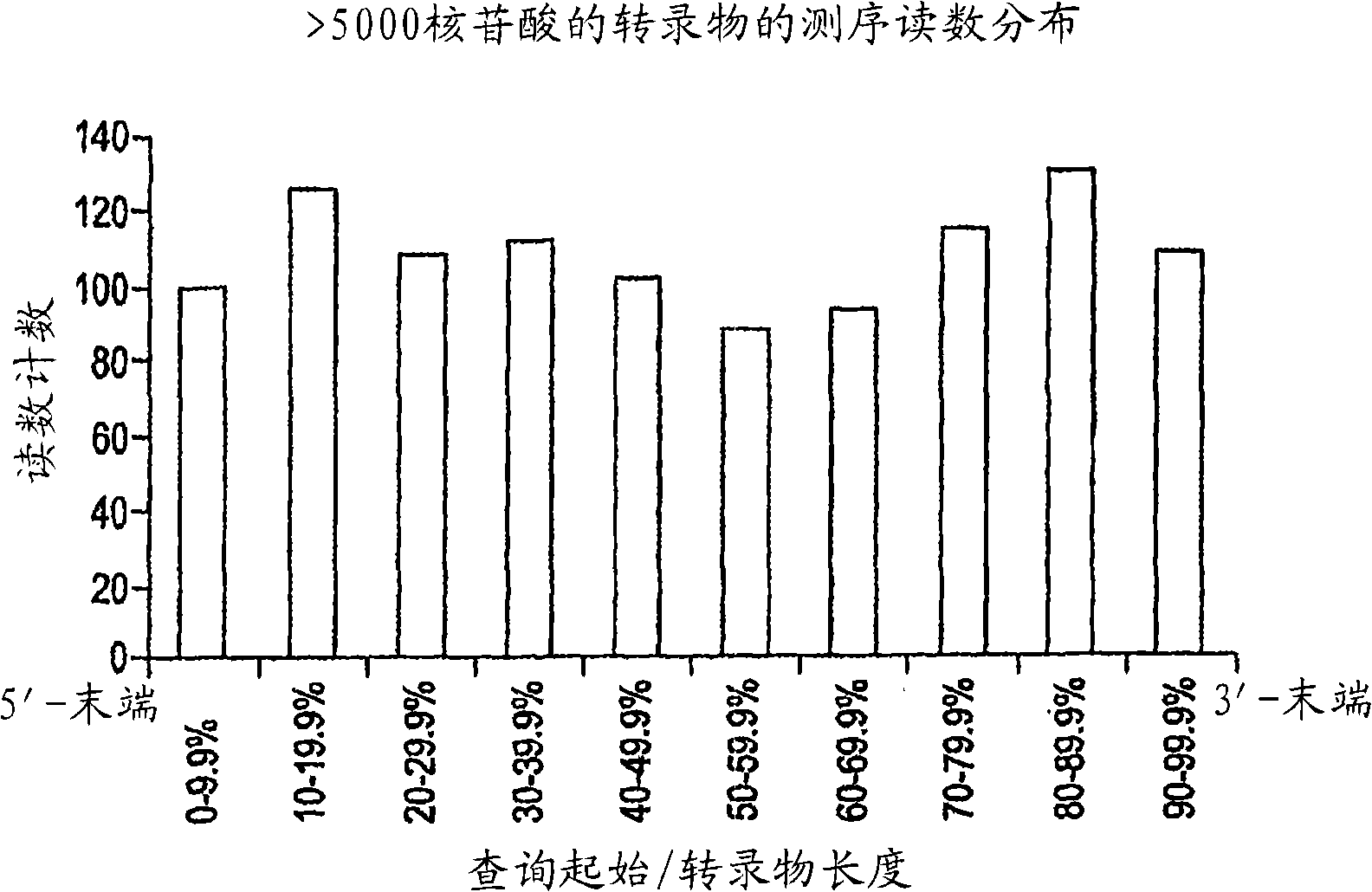
Automated Sequencing System. The massive amount of DNA sequencing necessary for the completion of the Human Genome Project and for the sequencing of other large genomes will require development of technology to increase sequencing throughput and to lower its cost.
High speed parallel molecular nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS6982146B1Minimize shearImprove automationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
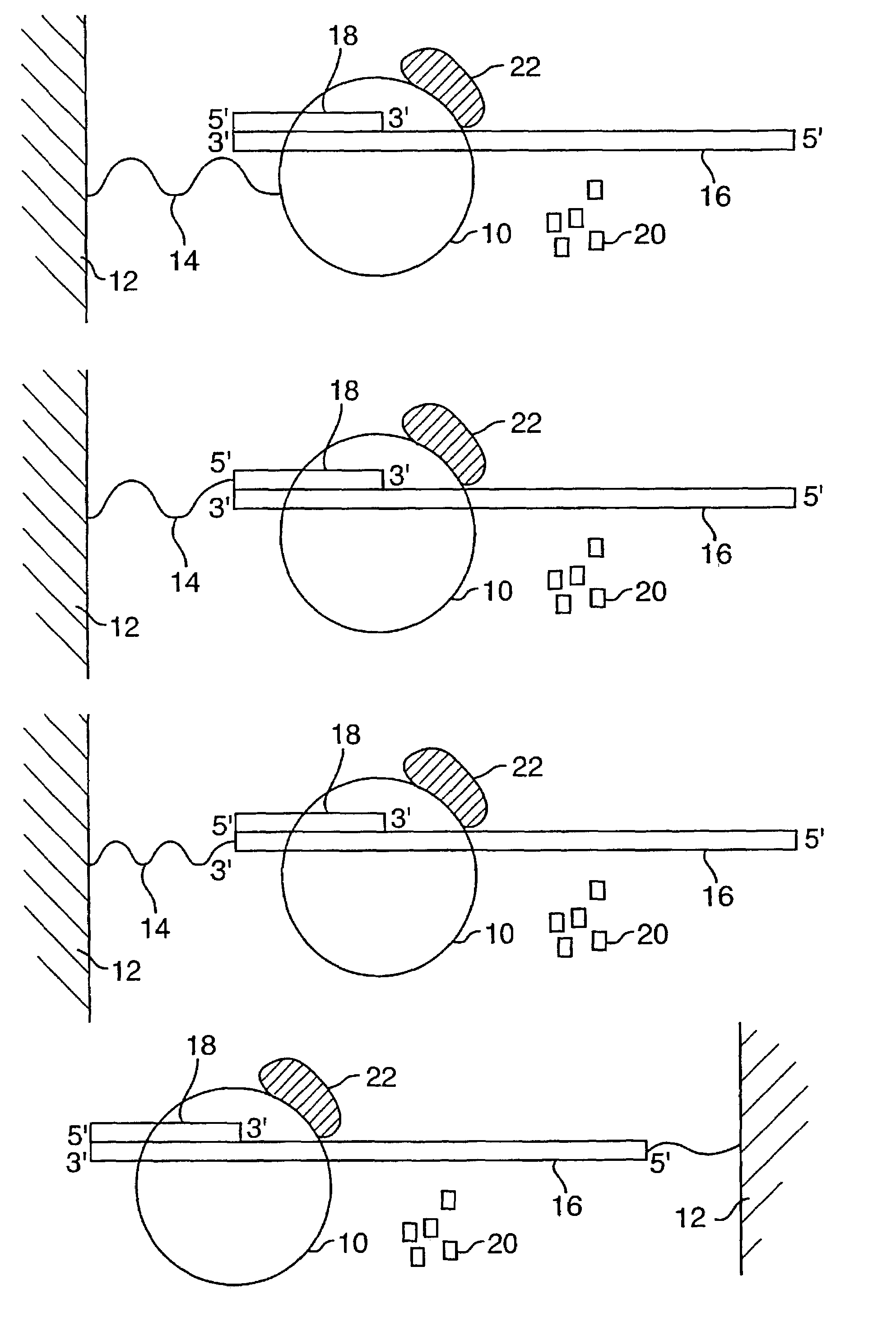
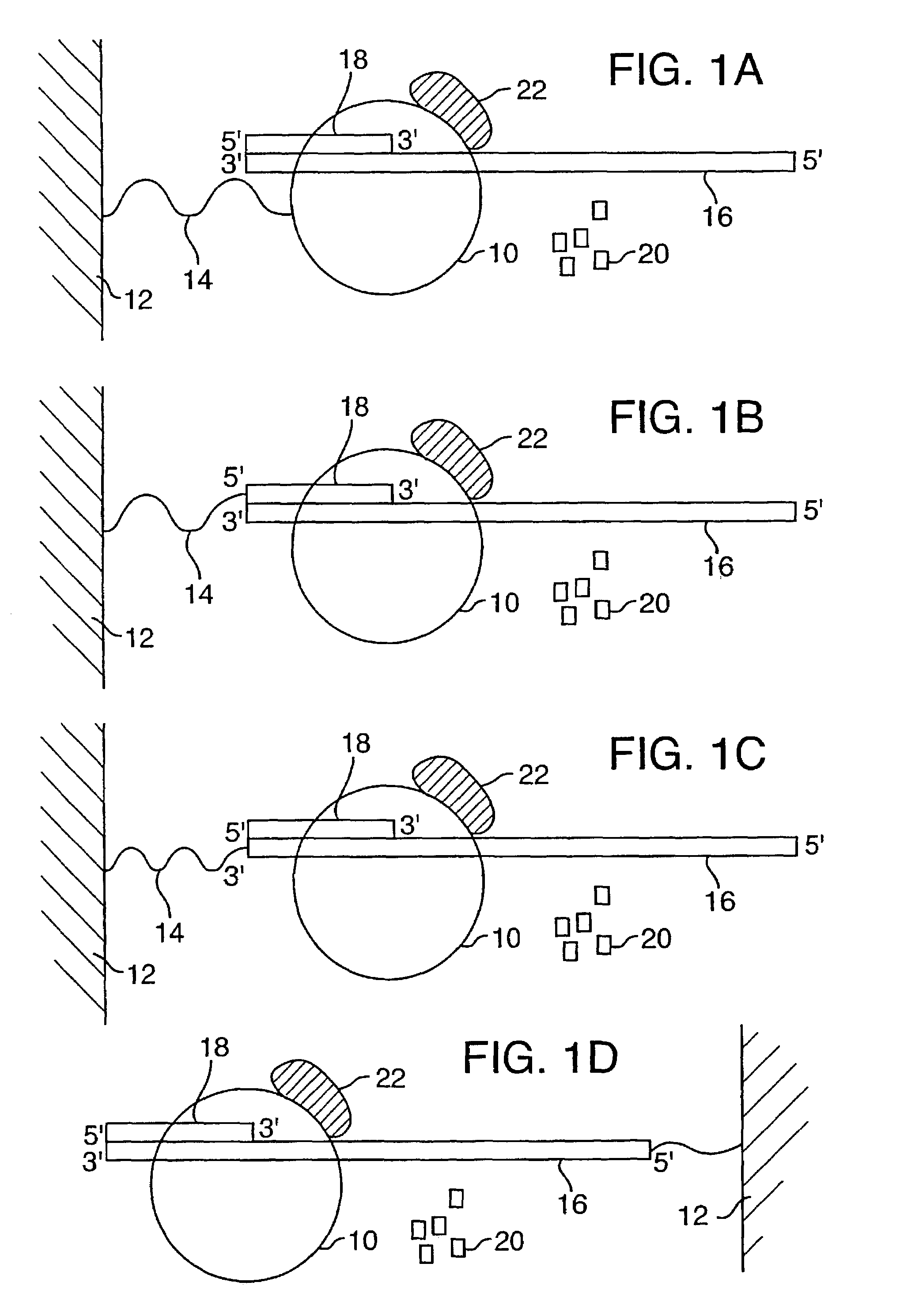
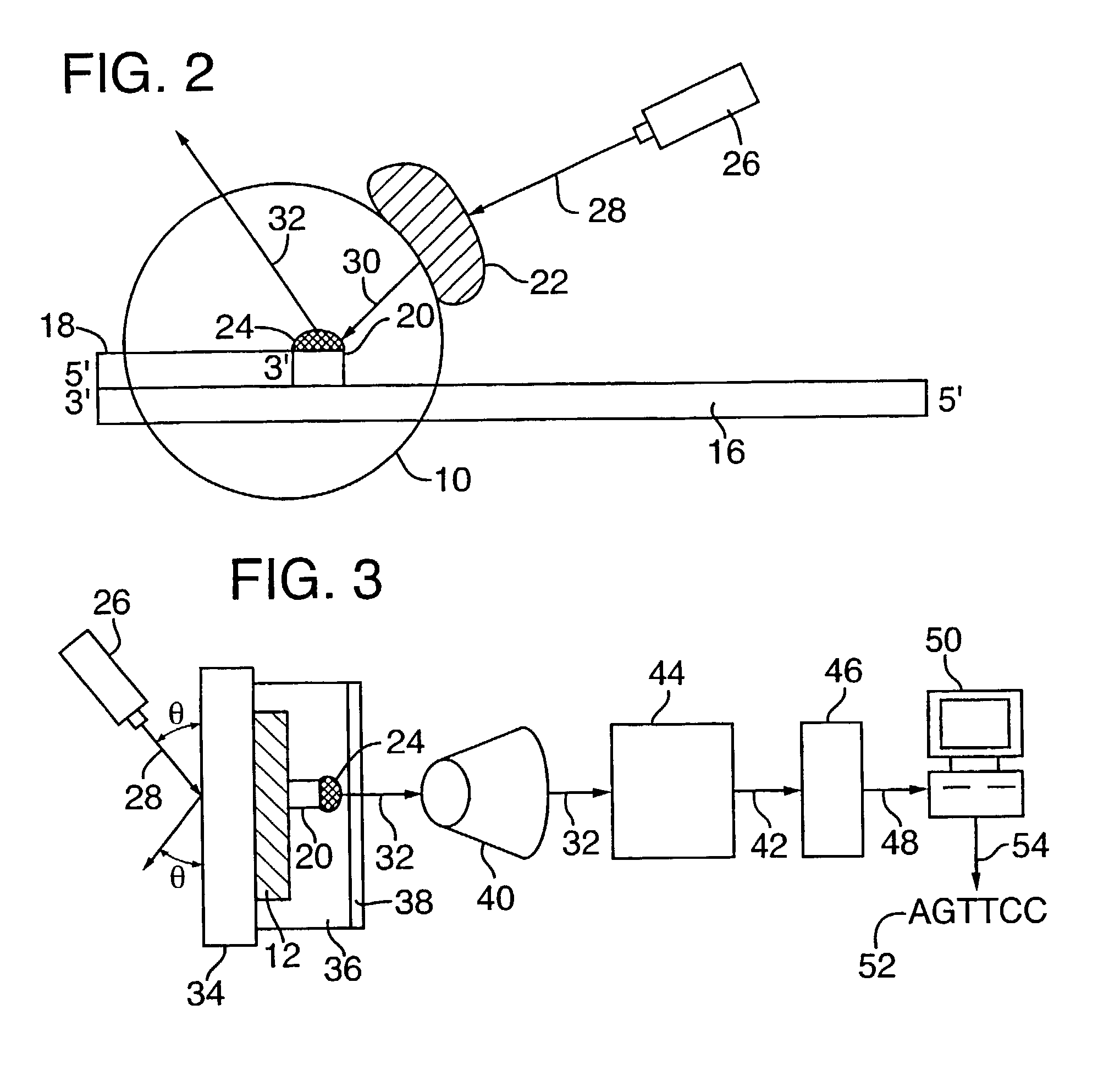
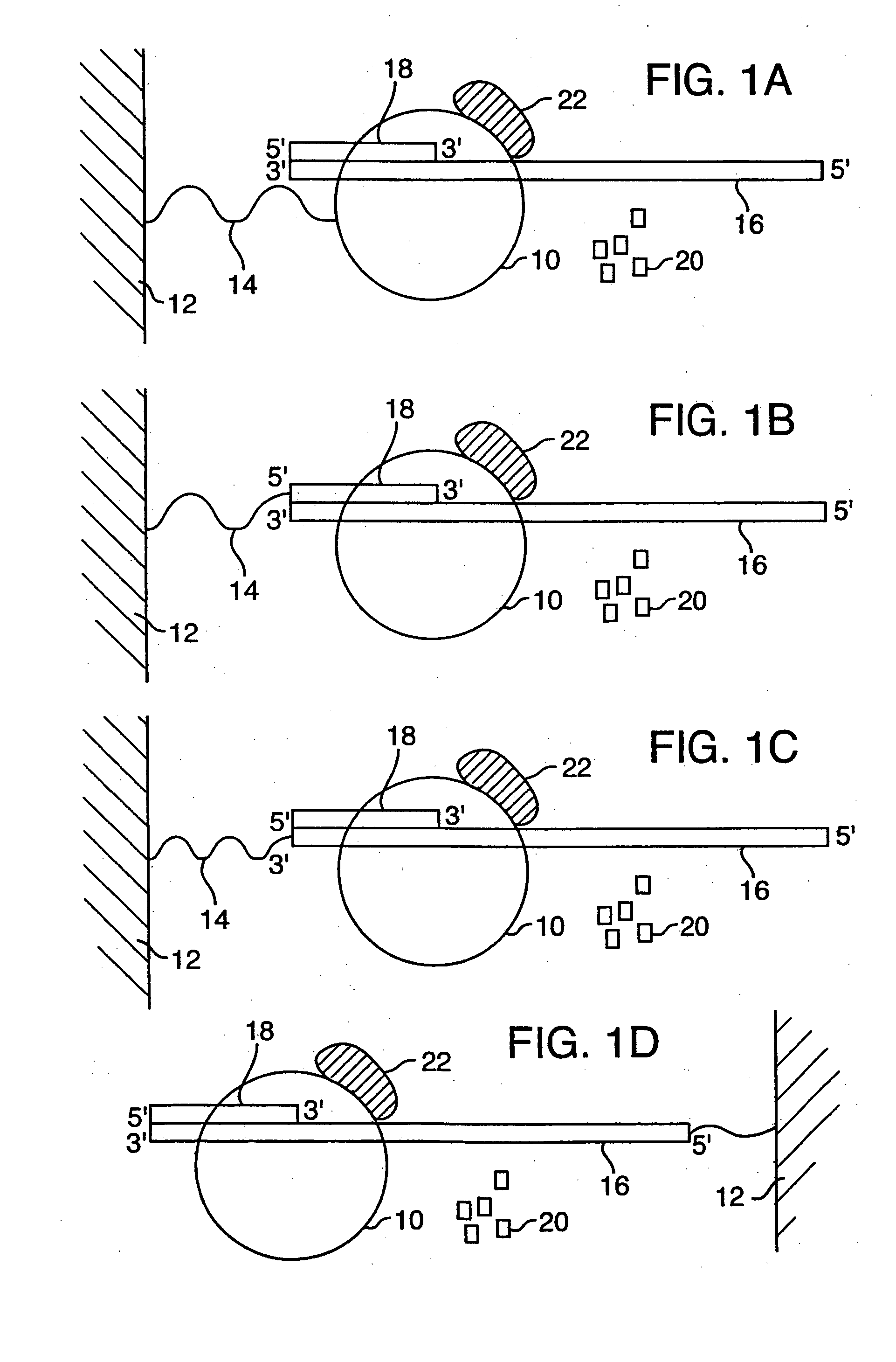
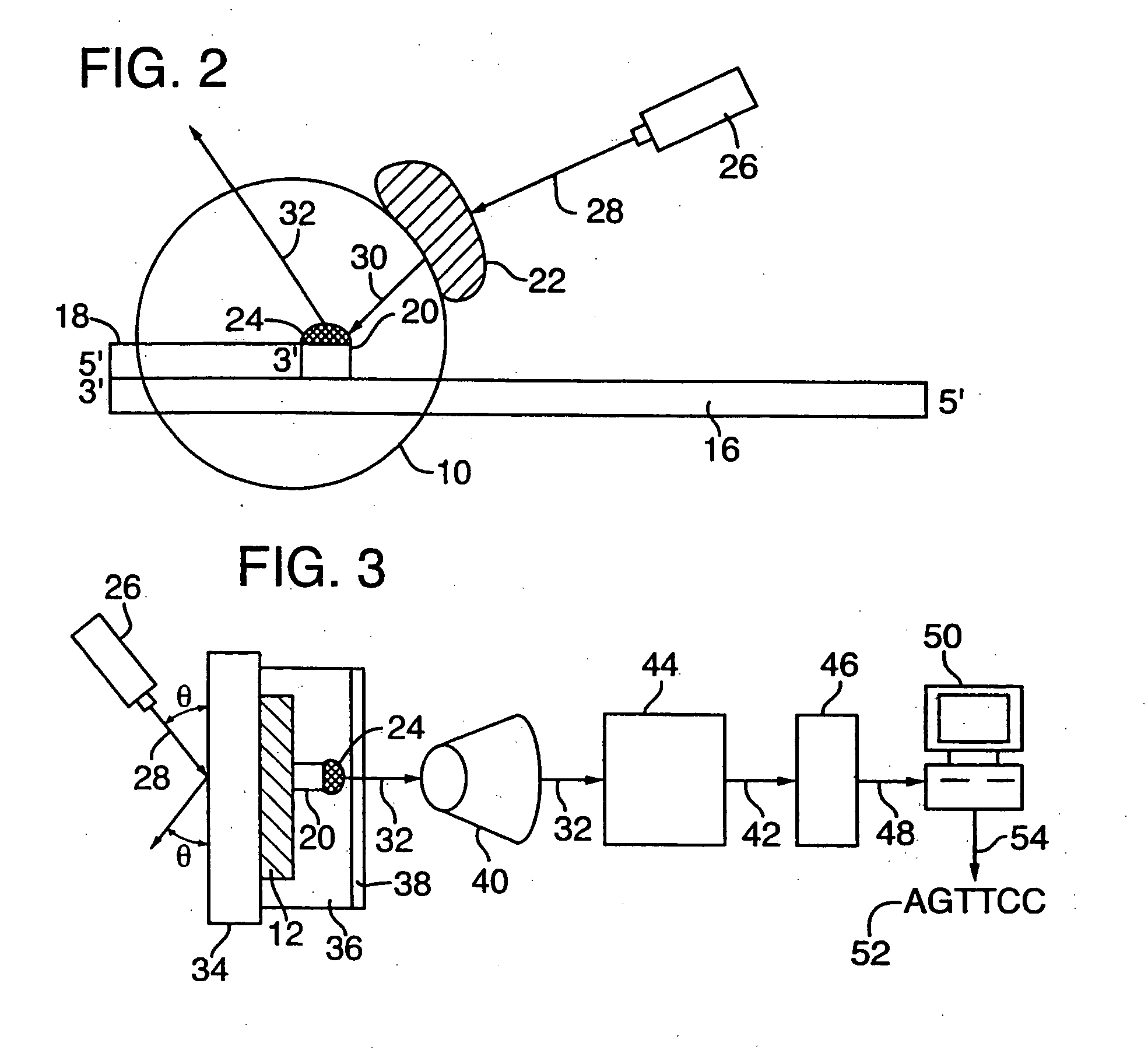
A method and device is disclosed for high speed, automated sequencing of nucleic acid molecules. A nucleic acid molecule to be sequenced is exposed to a polymerase in the presence of nucleotides which are to be incorporated into a complementary nucleic acid strand. The polymerase carries a donor fluorophore, and each type of nucleotide (e.g. A, T / U, C and G) carries a distinguishable acceptor fluorophore characteristic of the particular type of nucleotide. As the polymerase incorporates individual nucleic acid molecules into a complementary strand, a laser continuously irradiates the donor fluorophore, at a wavelength that causes it to emit an emission signal (but the laser wavelength does not stimulate the acceptor fluorophore). In particular embodiments, no laser is needed if the donor fluorophore is a luminescent molecule or is stimulated by one. The emission signal from the polymerase is capable of stimulating any of the donor fluorophores (but not acceptor fluorophores), so that as a nucleotide is added by the polymerase, the acceptor fluorophore emits a signal associated with the type of nucleotide added to the complementary strand. The series of emission signals from the acceptor fluorophores is detected, and correlated with a sequence of nucleotides that correspond to the sequence of emission signals.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF US SEC THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE
Reagents, methods, and libraries for gel-free bead-based sequencing
InactiveUS20090062129A1Efficient implementationHigh throughput sequencingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationImaging processingNucleic acid sequencing
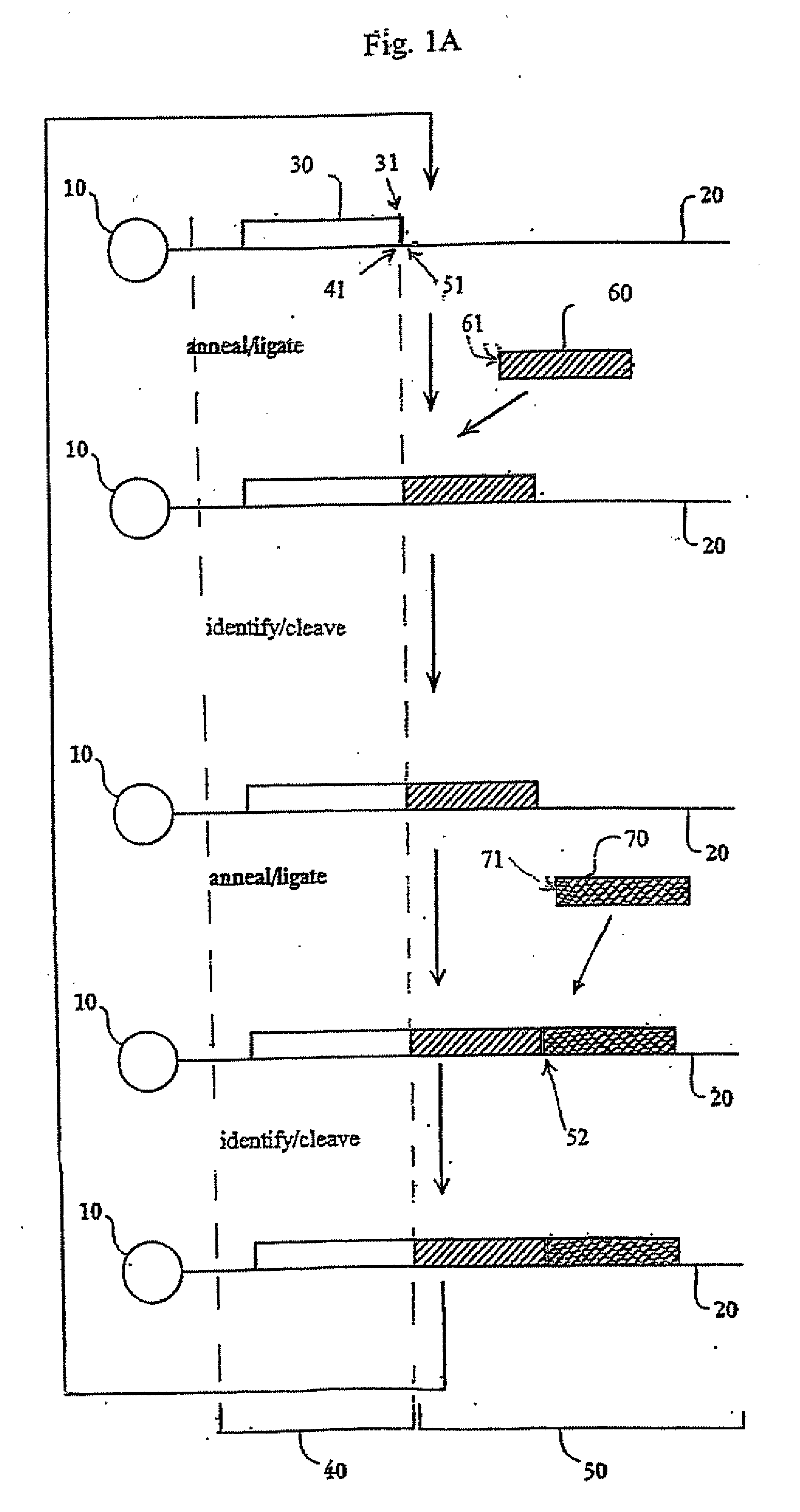
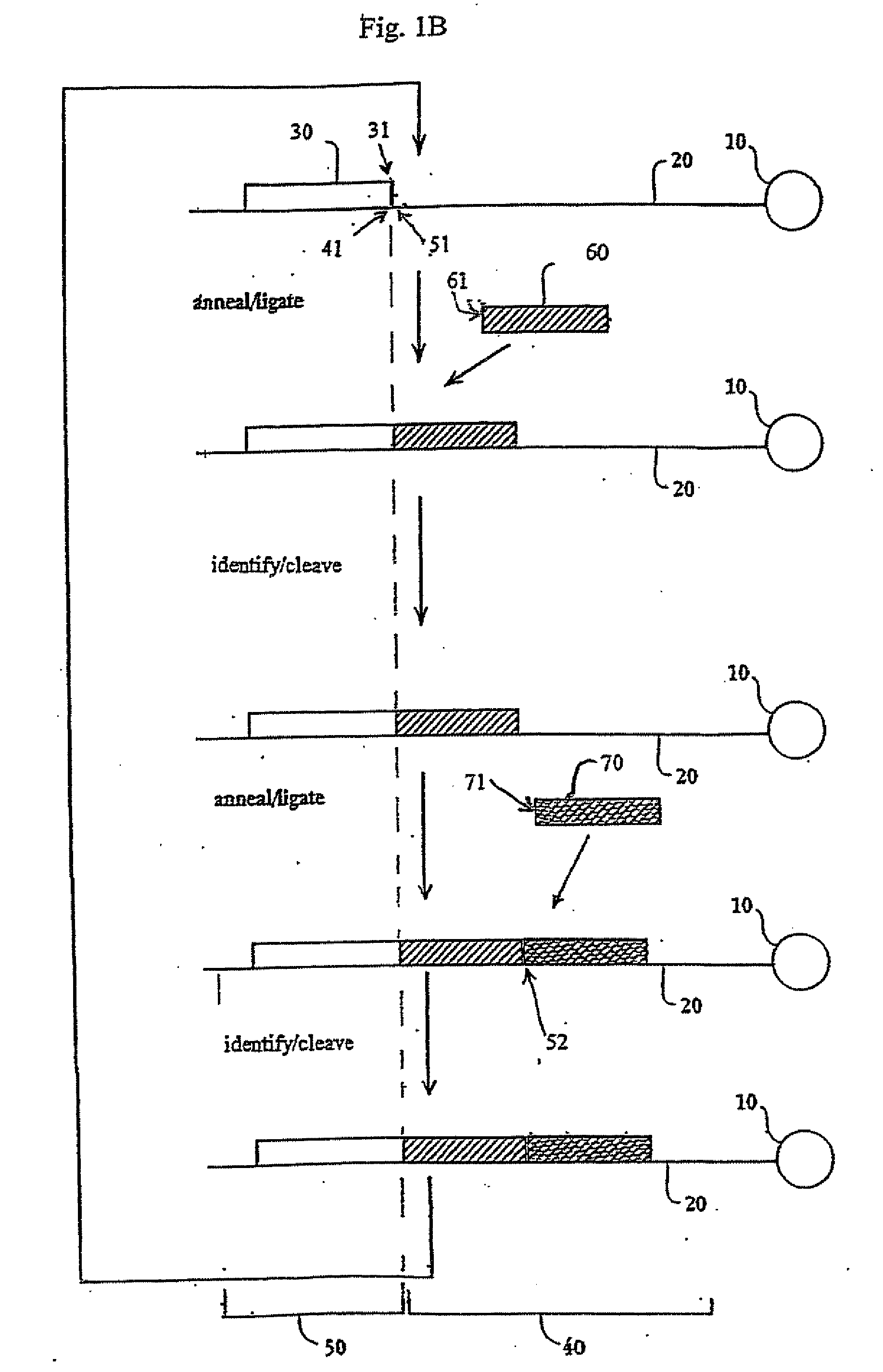
The present disclosure provides methods for determining a nucleic acid sequence by performing successive cycles of duplex extension along a single stranded template. The cycles typically comprise steps of extension, ligation, and cleavage. In certain embodiments, the methods make use of extension probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages and agents capable of cleaving such linkages. Methods of determining information about a sequence using at least two distinguishably labeled probe families are provided, as are methods of performing multiple sequencing reactions on a single template. Automated sequencing systems, flow cells, image processing methods, and computer-readable media that store computer-executable instructions and / or sequence information that can be used in accordance with such methods are also provided. In certain embodiments, blocking oligonucleotides are provided to facilitate sequencing using disclosed methods.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
High speed parallel molecular nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20060292583A1Minimize shearImprove automationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolymerase LFluorophore
A method and device is disclosed for high speed, automated sequencing of nucleic acid molecules. A nucleic acid molecule to be sequenced is exposed to a polymerase in the presence of nucleotides which are to be incorporated into a complementary nucleic acid strand. The polymerase carries a donor fluorophore, and each type of nucleotide (e.g. A, T / U, C and G) carries a distinguishable acceptor fluorophore characteristic of the particular type of nucleotide. As the polymerase incorporates individual nucleic acid molecules into a complementary strand, a laser continuously irradiates the donor fluorophore, at a wavelength that causes it to emit an emission signal (but the laser wavelength does not stimulate the acceptor fluorophore). In particular embodiments, no laser is needed if the donor fluorophore is a luminescent molecule or is stimulated by one. The emission signal from the polymerase is capable of stimulating any of the donor fluorophores (but not acceptor fluorophores), so that as a nucleotide is added by the polymerase, the acceptor fluorophore emits a signal associated with the type of nucleotide added to the complementary strand. The series of emission signals from the acceptor fluorophores is detected, and correlated with a sequence of nucleotides that correspond to the sequence of emission signals.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
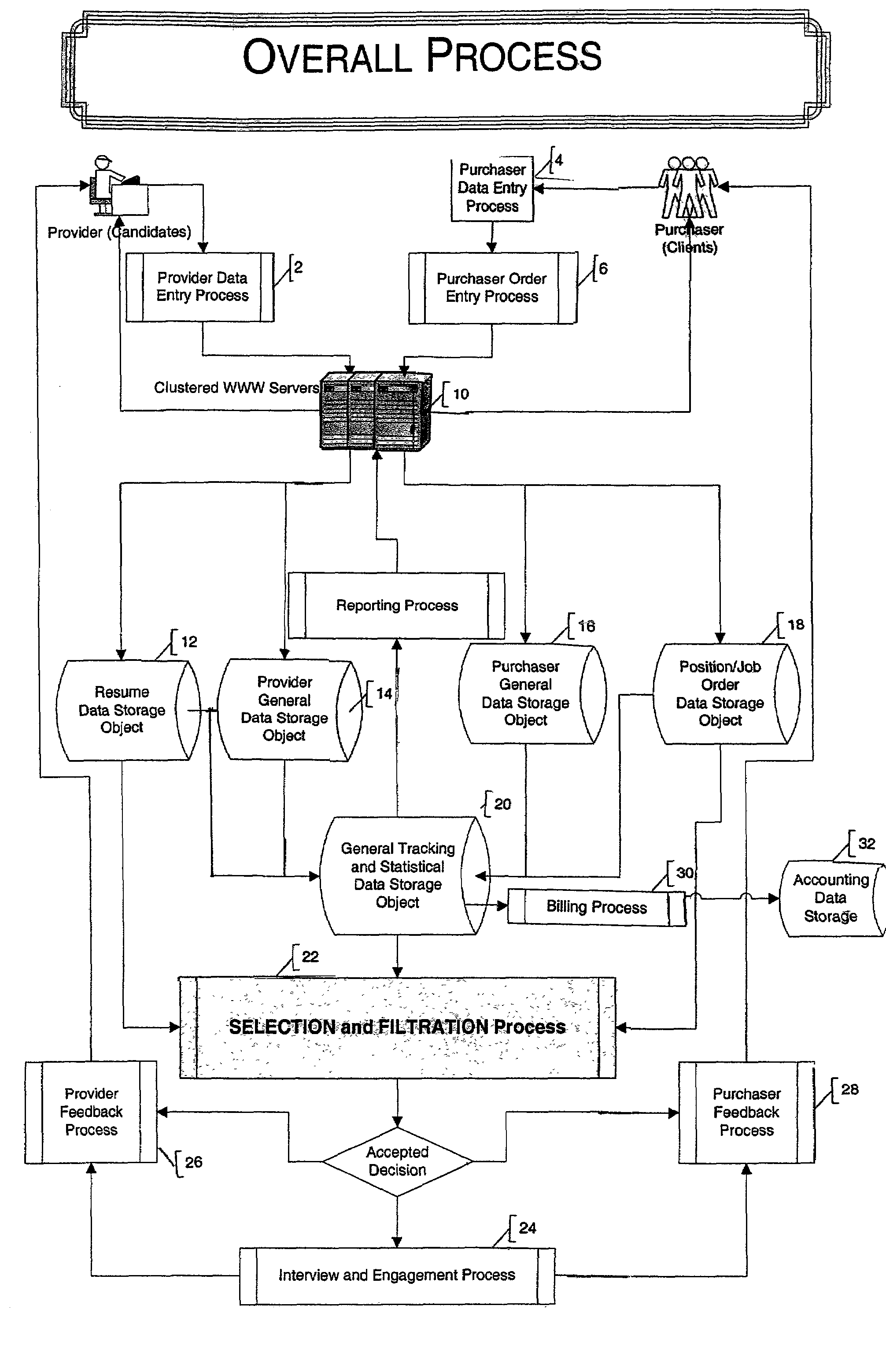
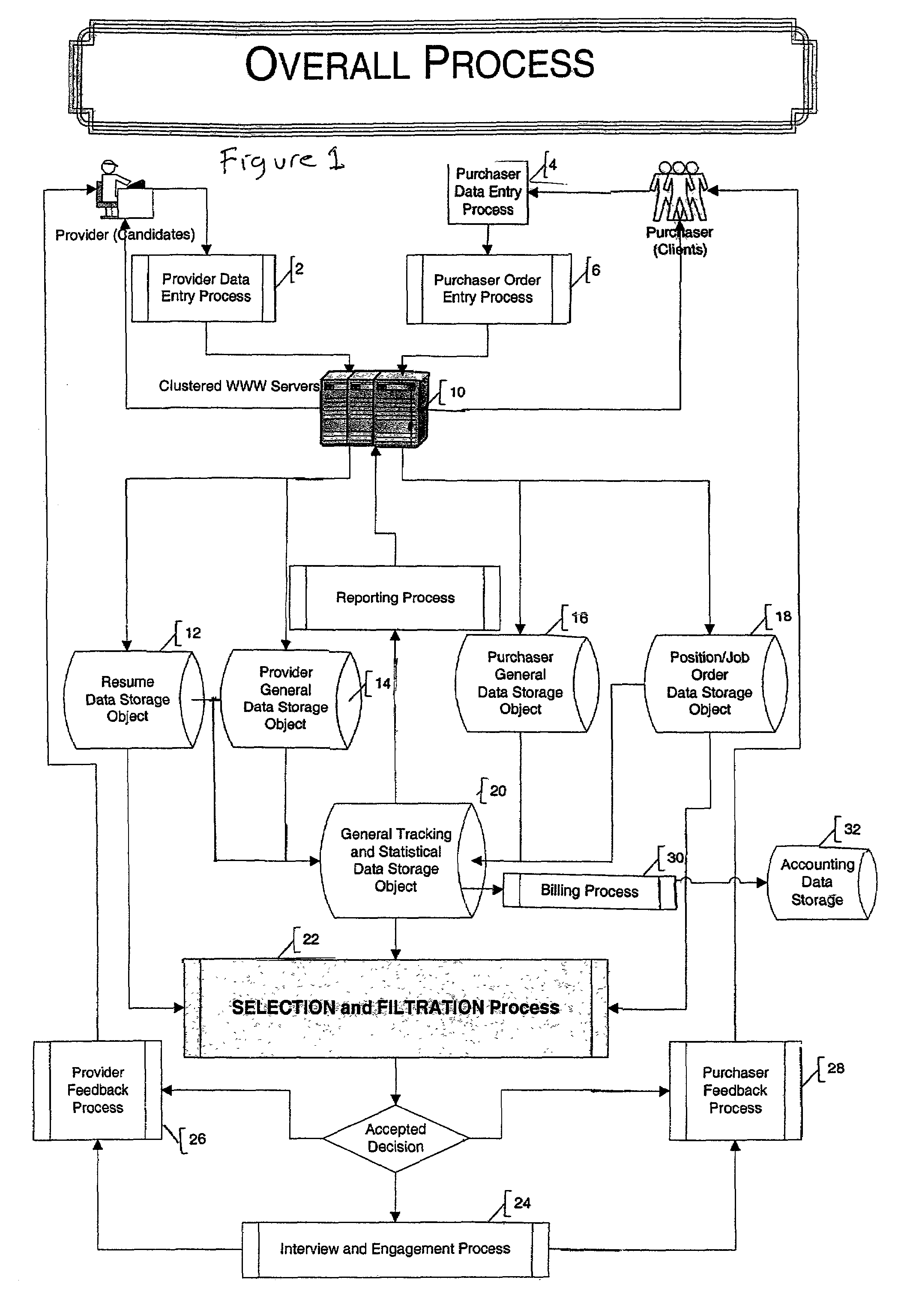
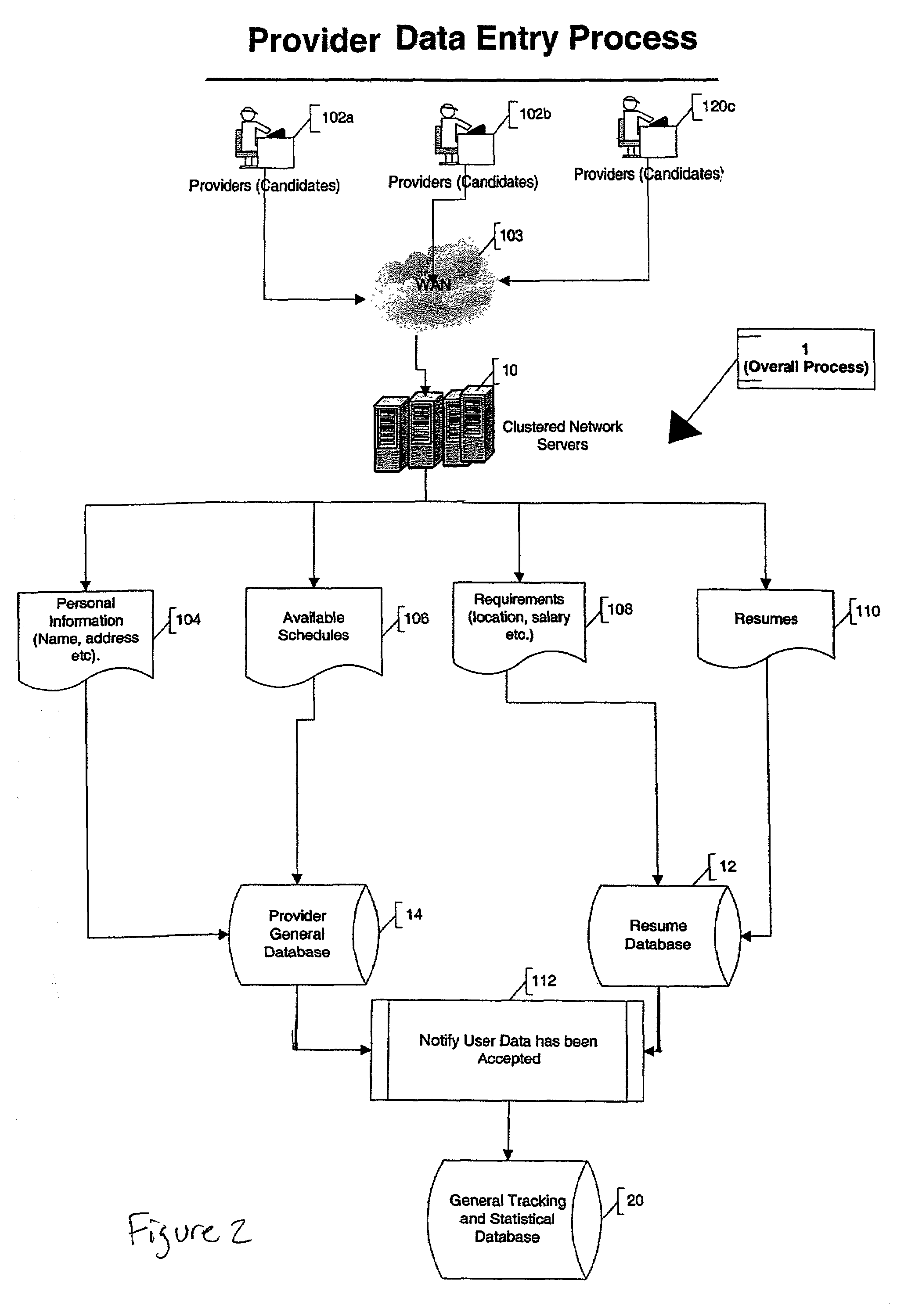
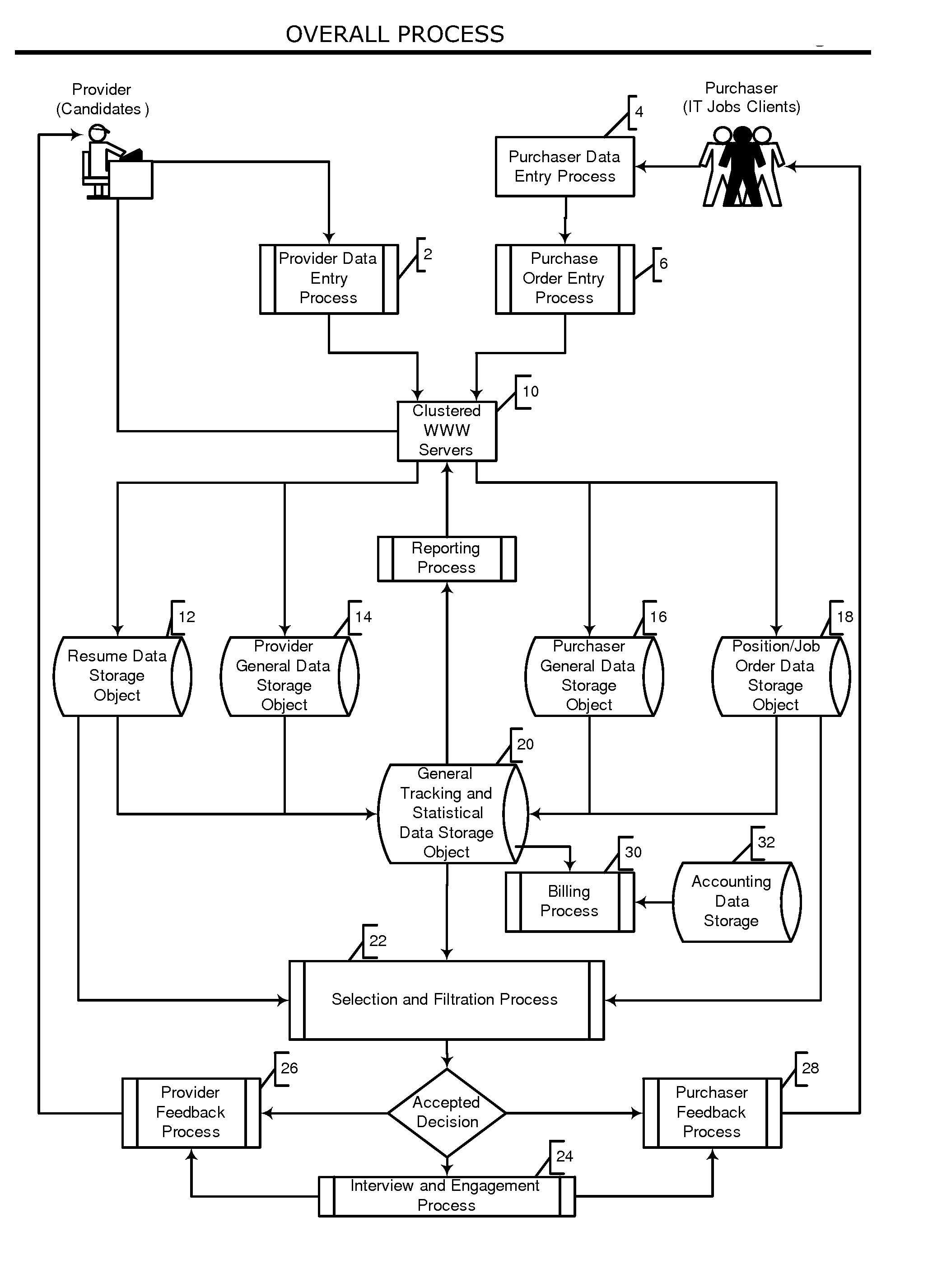
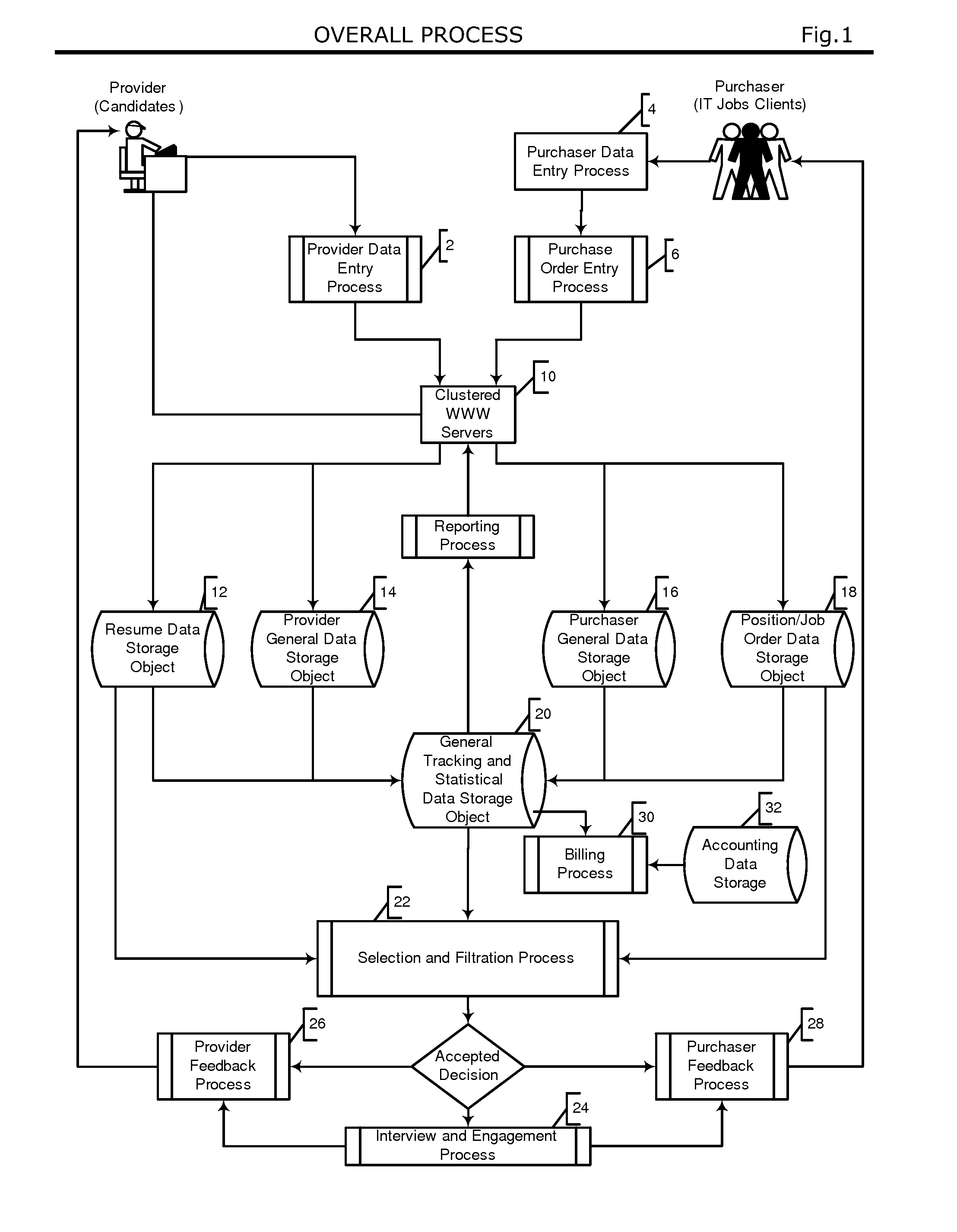
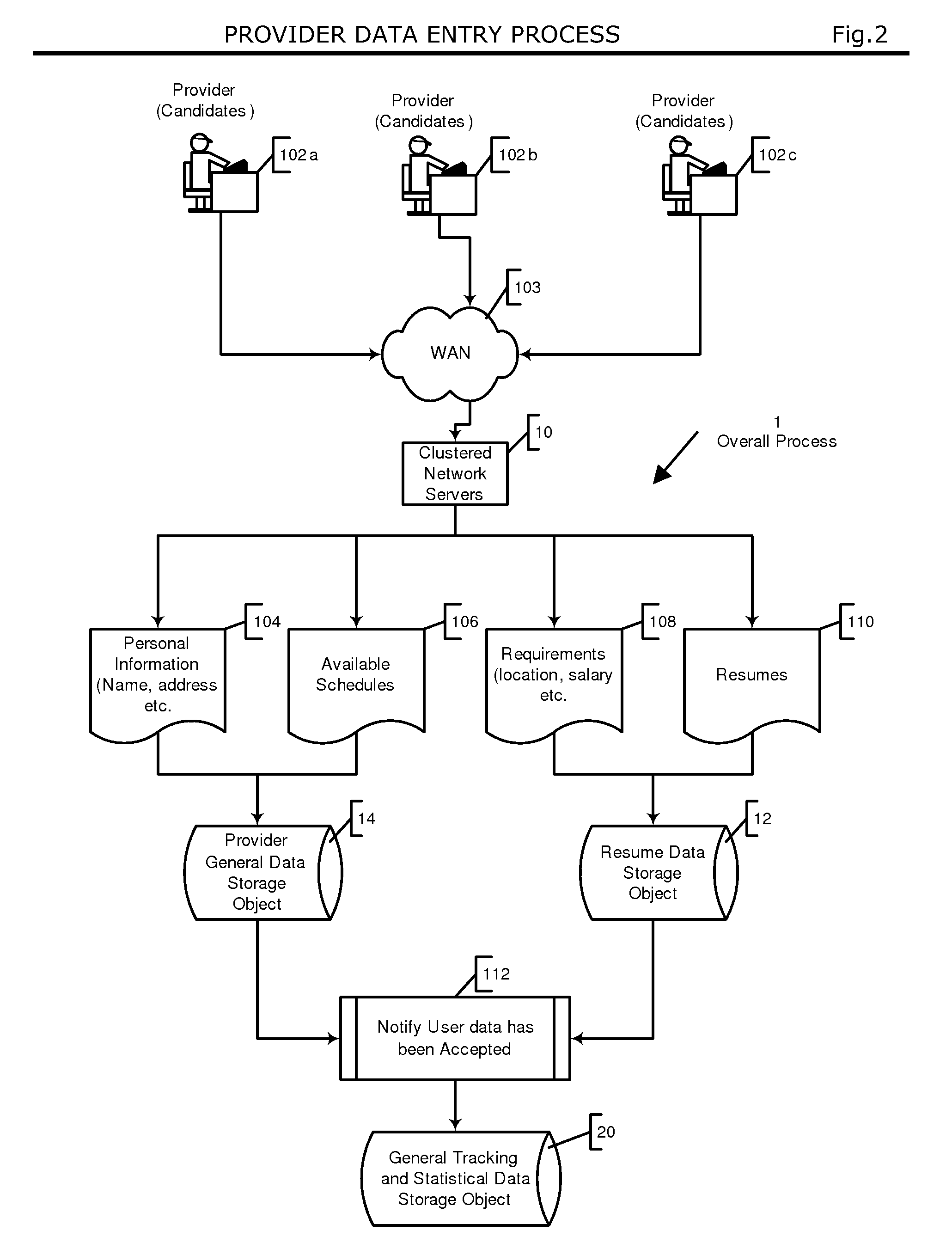
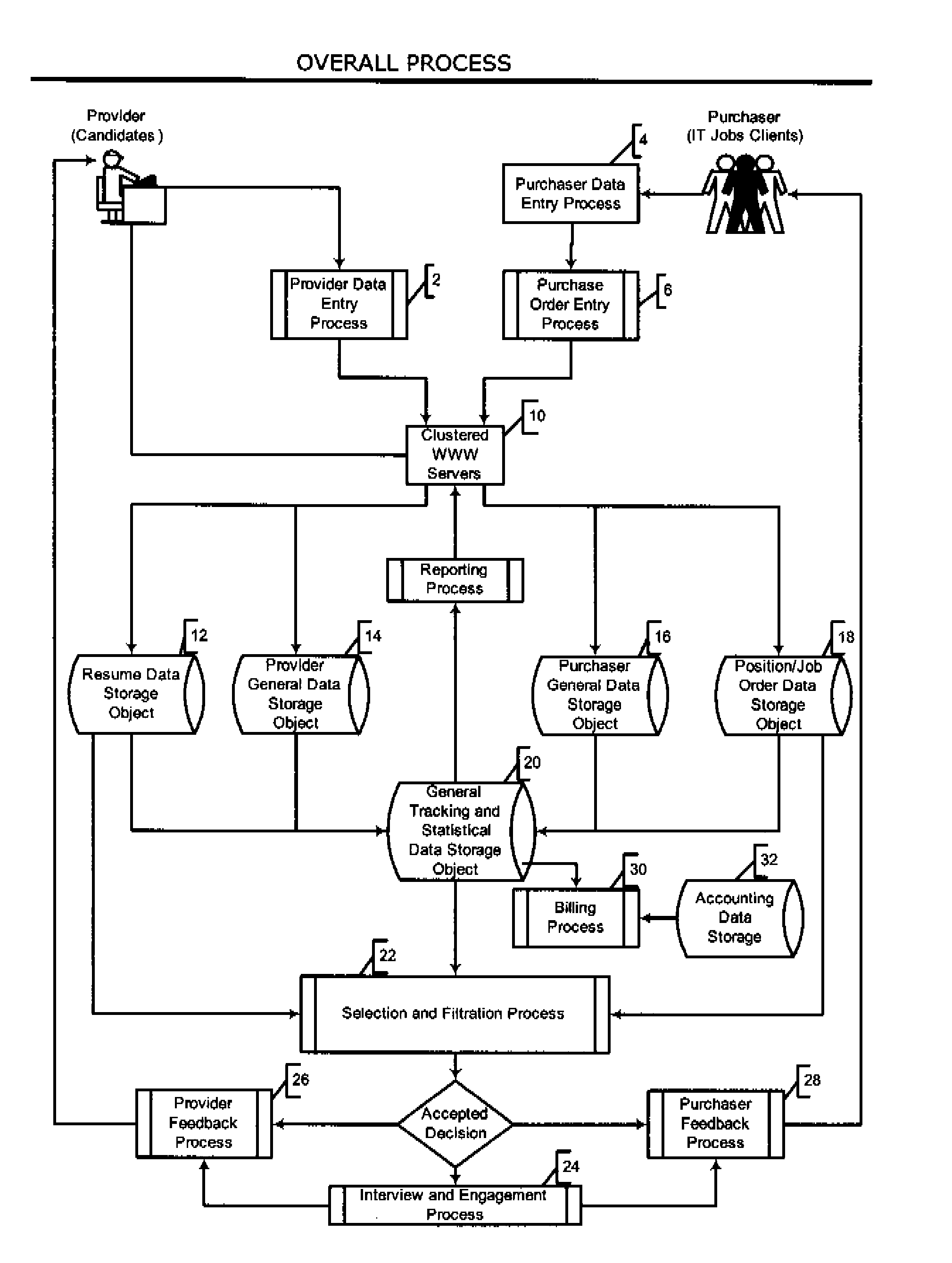
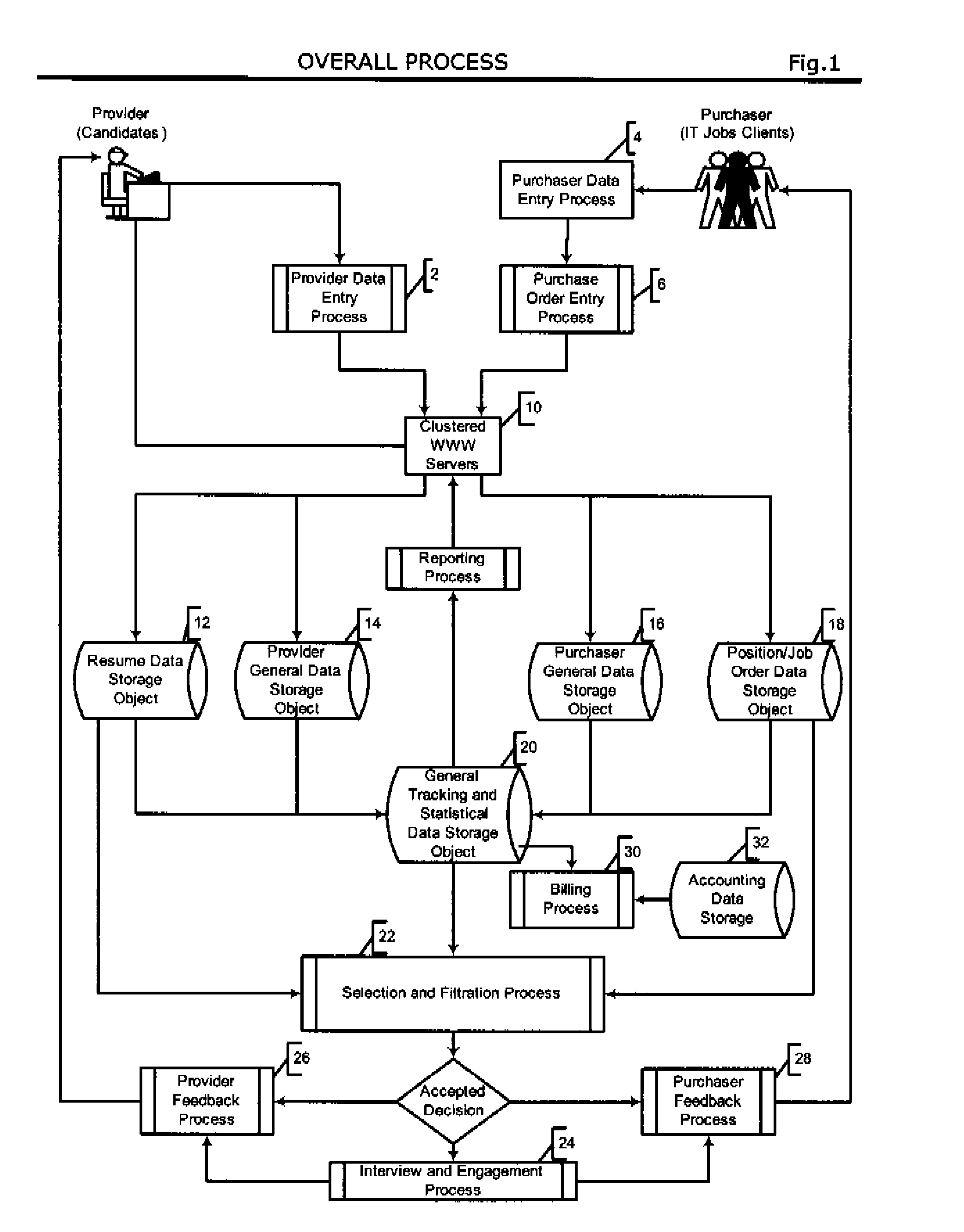
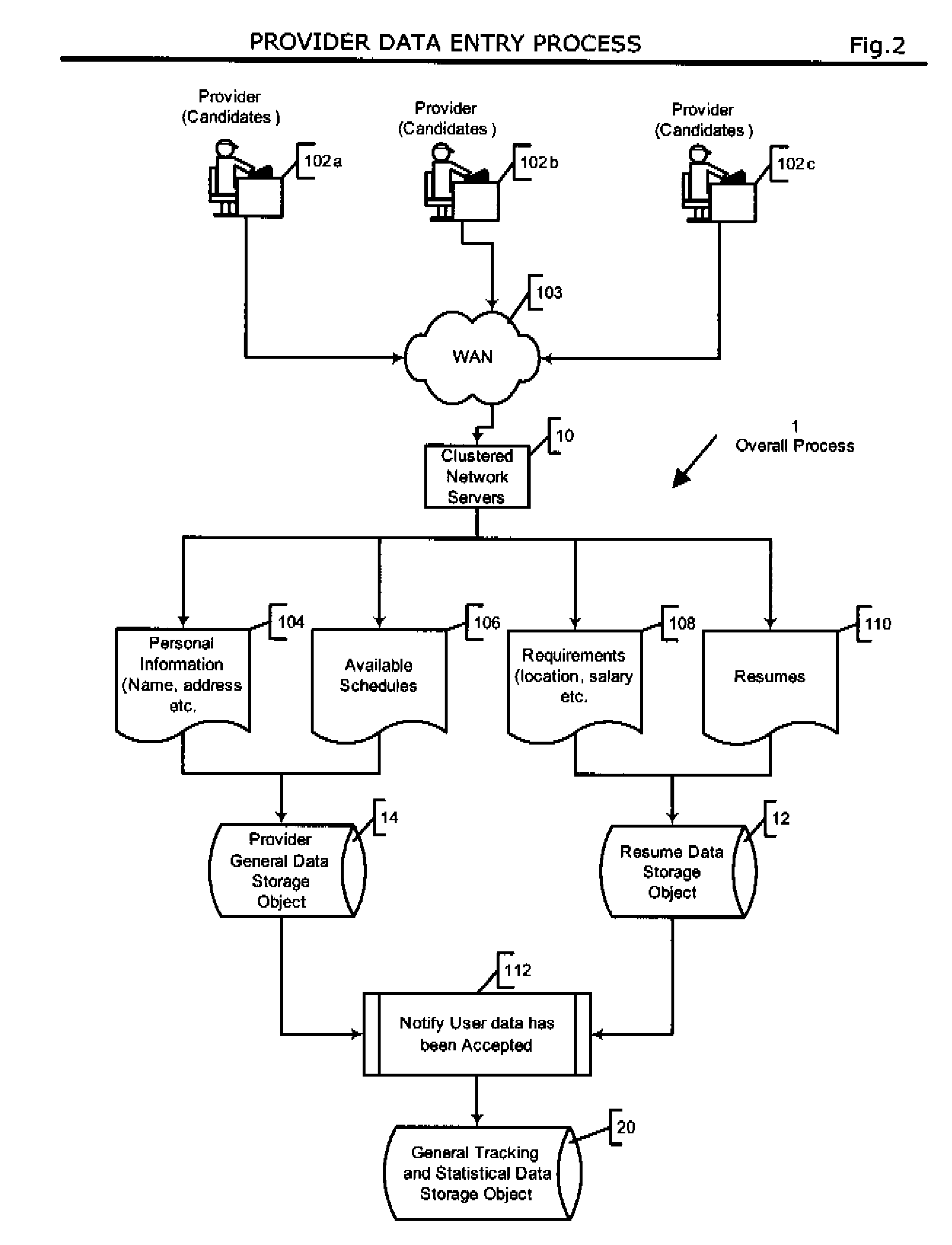
Automated system and method for managing a process for the shopping and selection of human entities
InactiveUS7212985B2Increase speedImprove efficiencyMarket predictionsOffice automationSelection criterionComputer science
This invention is a system and method for automatically managing a multi-step process in which human providers are selected for some purpose. Typical applications include the selection process associated with employment and dating services. The invention is directed to linking and coordinating the various steps of the selection process through automated sequencing, coordinating, tracking and status reporting processes. The interviewee answers questions that are printed, displayed, or spoken by an automated mechanism or questions are printed or displayed for use by a tester or interviewer. Answers can be written, spoken, or entered directly into a system by the interviewee.The invention provides a system and method for automatically scoring and ranking human providers with respect to selection criteria, making use of expert system concepts. Human shoppers are matched up and the usefulness of each match is scored on the basis of stated selection criteria of each human shopper.
Owner:INTRAGROUP
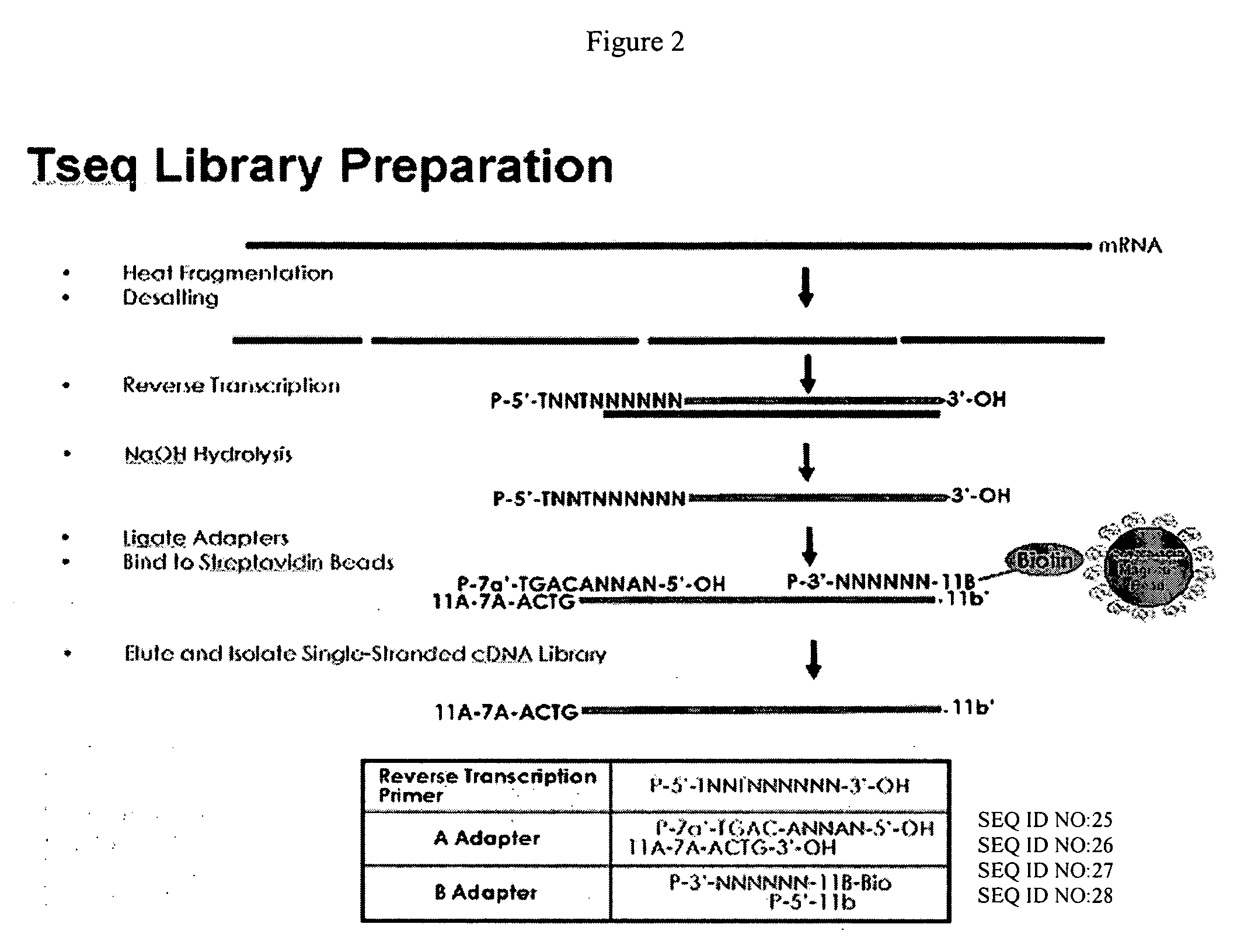
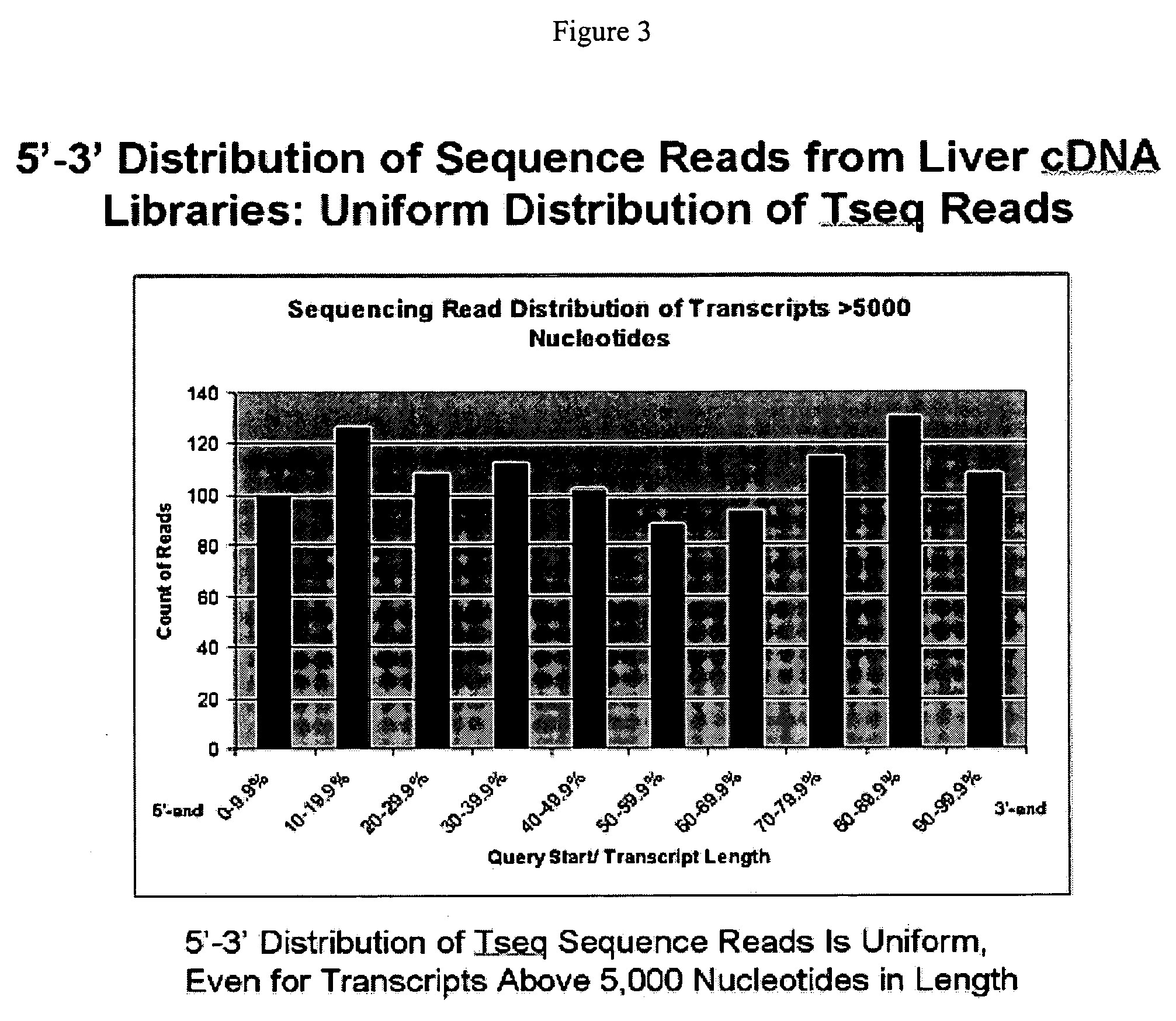
cDNA library preparation
InactiveUS20070117121A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCDNA libraryAutomated sequencing
New biochemical protocols for high throughput processing of mRNA samples into cDNA libraries with adaptor sequences compatible with automated sequencing systems are provided. The provided methods produces cDNA libraries which do not have 3′ bias associated with current cDNA library production methods. New methods for the production of DNA libraries from DNA are also provided.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
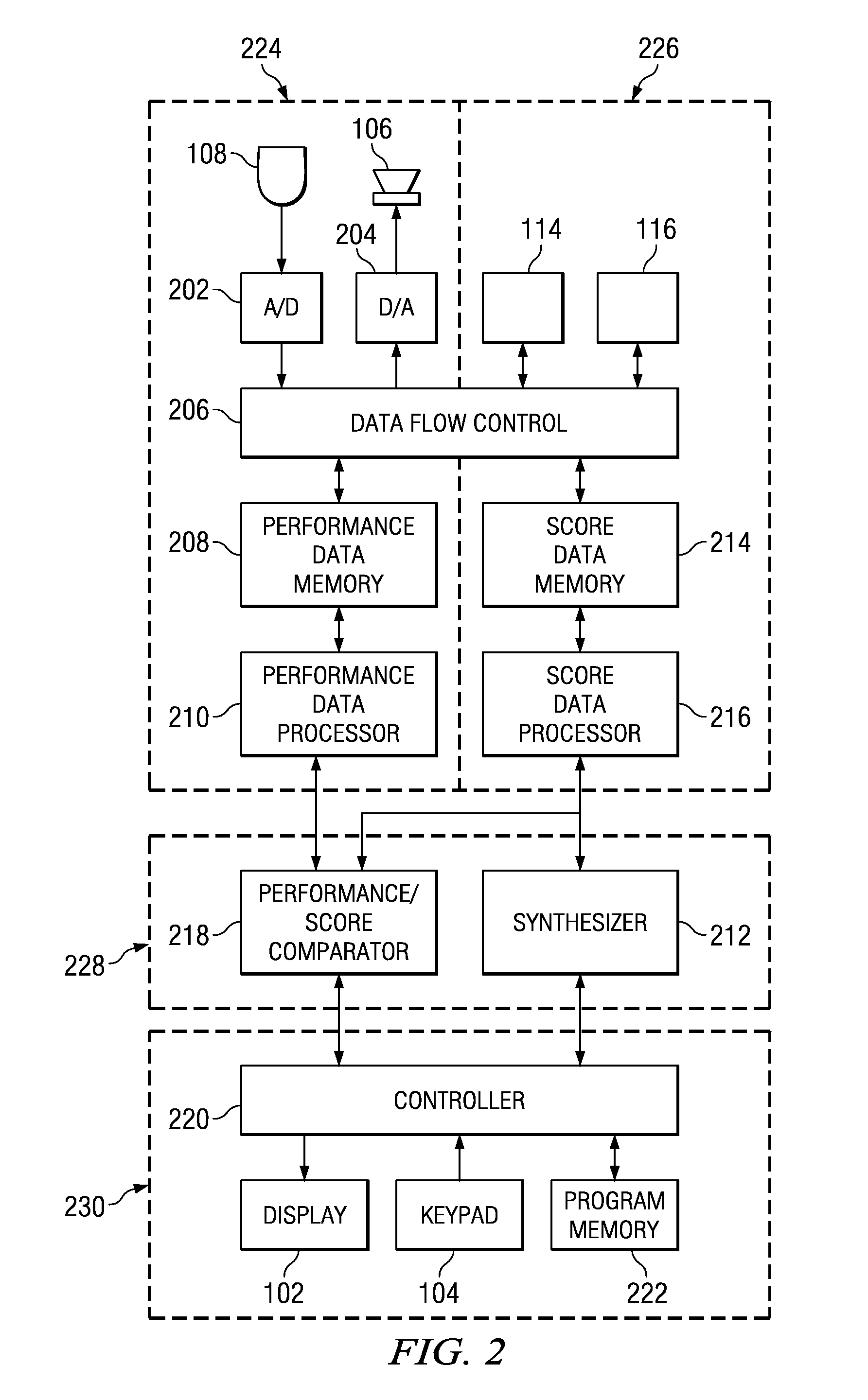
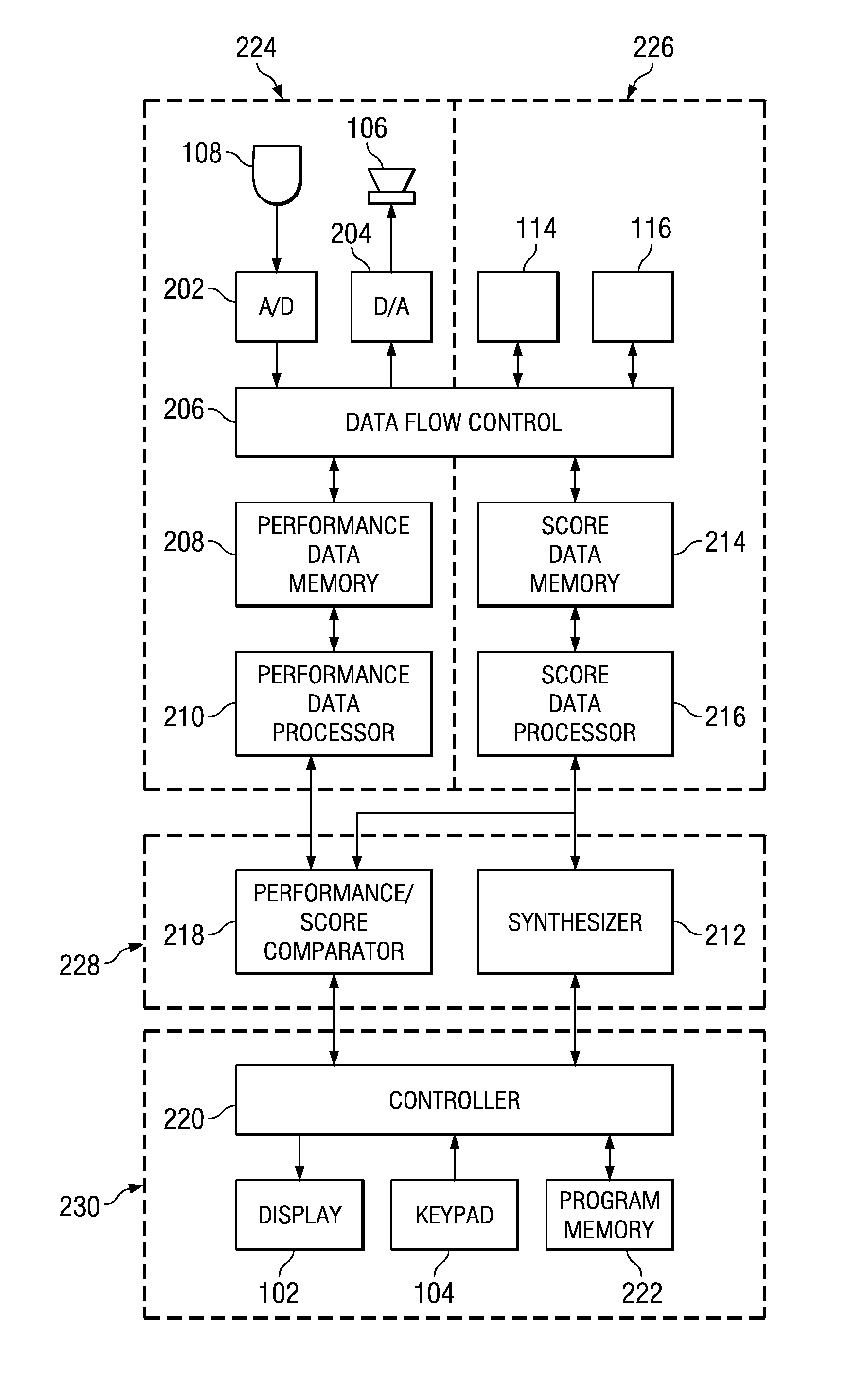
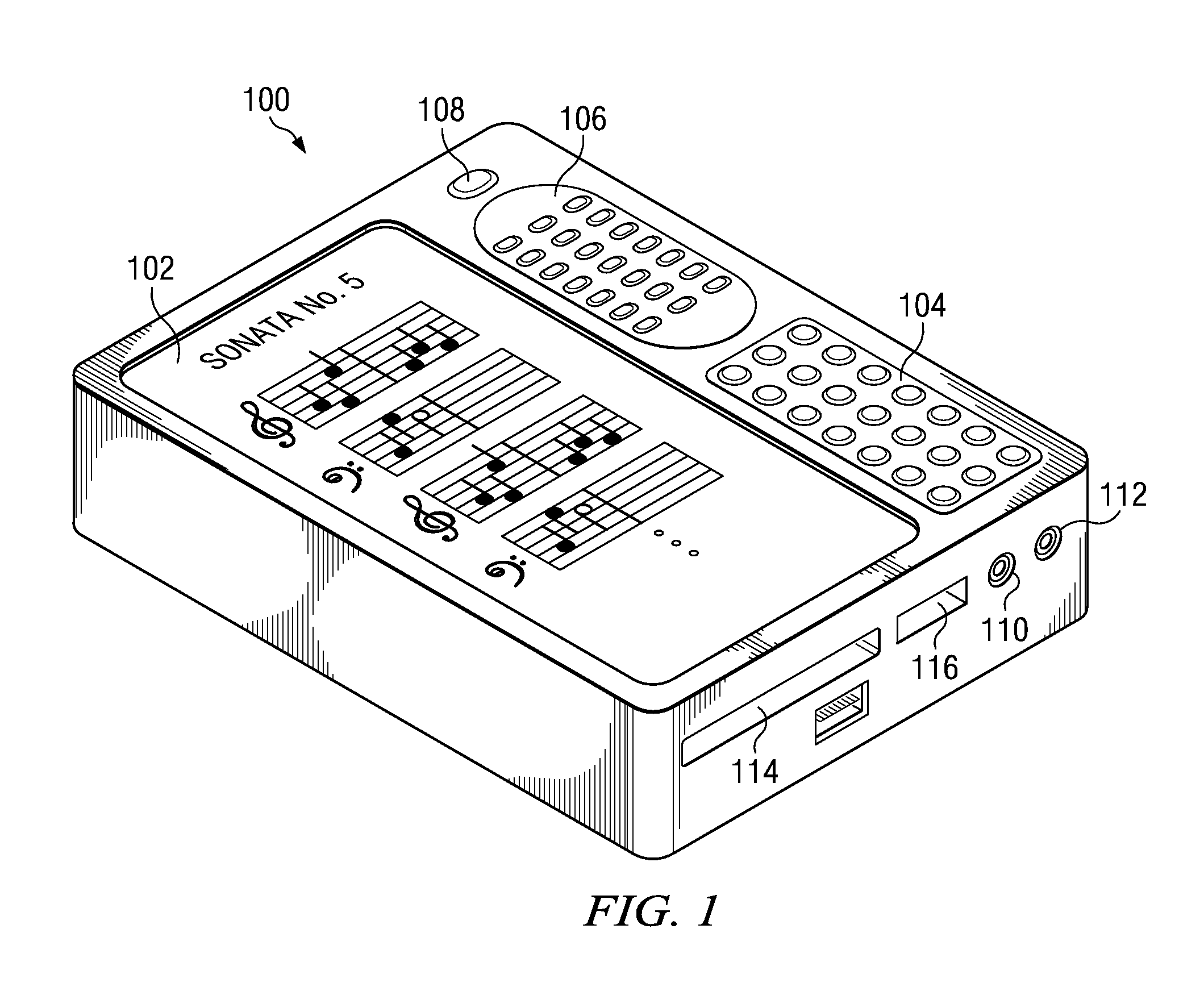
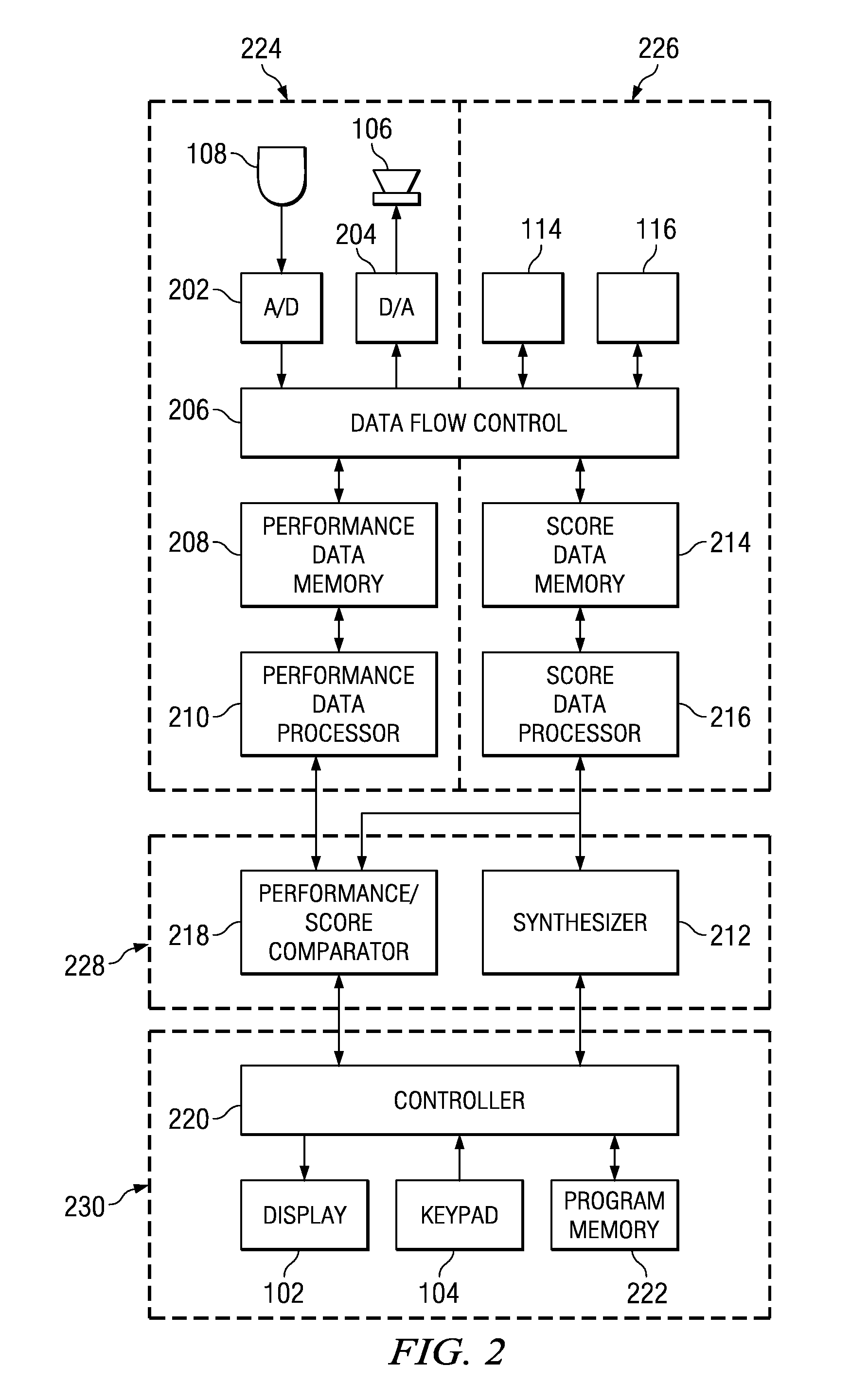
Automatic page sequencing and other feedback action based on analysis of audio performance data
Speech or musical performance is electronically analyzed using DSP techniques and is compared to a stored text script or musical score, to enable display of and automated sequencing through multiple pages of the stored script or score. The performer can modify timing of sequencing if desired, for example dependent on performance speed or musical complexity. Automated highlighting or marking of measures or text assists the performer in keeping track of progress through the performance. During or after the performance, electronic comparison of the performance to the score or script provides feedback to the performer, highlighting differences between the actual performance and the desired performance as described by the score or script. Additional capabilities enhancing the learning process include digital recording and playback of the actual performance, and / or accompaniment by synthesis or playback of digital recording of other performance parts (for example, other instruments in an ensemble or other actors in a play).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Automatic page sequencing and other feedback action based on analysis of audio performance data
Speech or musical performance is electronically analyzed using DSP techniques and is compared to a stored text script or musical score, to enable display of and automated sequencing through multiple pages of the stored script or score. The performer can modify timing of sequencing if desired, for example dependent on performance speed or musical complexity. Automated highlighting or marking of measures or text assists the performer in keeping track of progress through the performance. During or after the performance, electronic comparison of the performance to the score or script provides feedback to the performer, highlighting differences between the actual performance and the desired performance as described by the score or script. Additional capabilities enhancing the learning process include digital recording and playback of the actual performance, and / or accompaniment by synthesis or playback of digital recording of other performance parts (for example, other instruments in an ensemble or other actors in a play).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
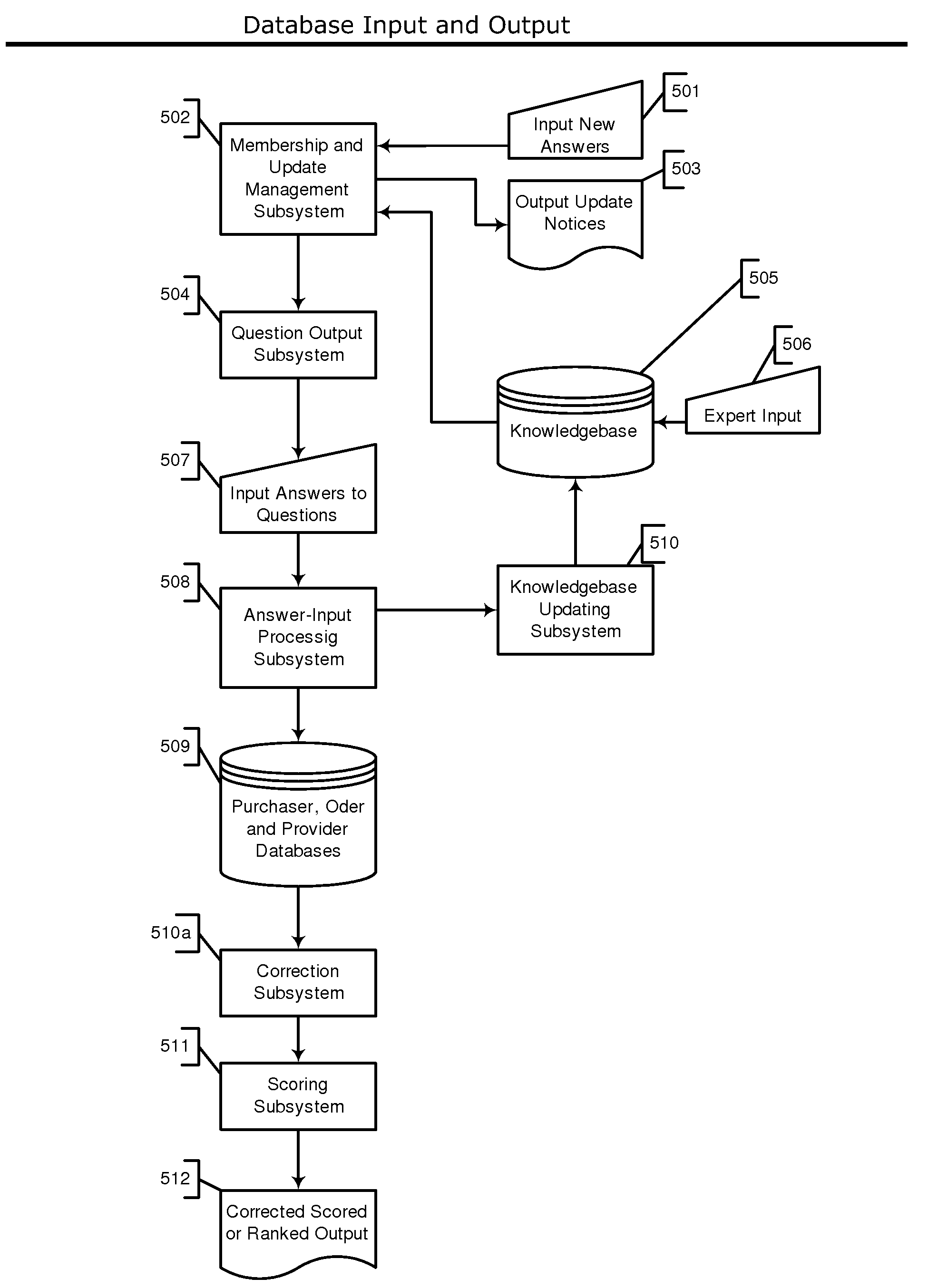
Automated system and method for managing a process for the shopping and selection of human entities
InactiveUS20070198319A1Improve effectivenessImprove accuracyMultiprogramming arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsQuestions and answersSelection criterion
A system and method for automatically managing a multi-step process in which human providers are selected, typically for employment and dating services. The selection process includes background checking, testing, interviewing, and acceptance by the provider and selecting entity, through automated sequencing, coordinating, tracking, status reporting, and an optional human intervention. The invention includes a system and method for automatically scoring and ranking human providers by a set of selection criteria, typically multiple choice options. The system determines the relevance of the questions and answers and stores it in a continuously updating Knowledge-base. The answers may be spoken, written, or entered directly into the system. The system includes testing and interviewing human providers with respect to the selection criteria; and the resulting scoring information is stored and may be used in future assessments. The system requires a charging process for updating information based on usage or subscription to the system.
Owner:INTRAGROUP
Automated system and method for managing a process for the shopping and selection of human entities
InactiveUS7487104B2Increase speedImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsMarket data gatheringSelection criterionQuestions and answers
A system and method for automatically managing a multi-step process in which human providers are selected, typically for employment and dating services. The selection process includes background checking, testing, interviewing, and acceptance by the provider and selecting entity, through automated sequencing, coordinating, tracking, status reporting, and an optional human intervention. The invention includes a system and method for automatically scoring and ranking human providers by a set of selection criteria, typically multiple choice options. The system determines the relevance of the questions and answers and stores it in a continuously updating Knowledge-base. The answers may be spoken, written, or entered directly into the system. The system includes testing and interviewing human providers with respect to the selection criteria; and the resulting scoring information is stored and may be used in future assessments. The system requires a charging process for updating information based on usage or subscription to the system.
Owner:INTRAGROUP
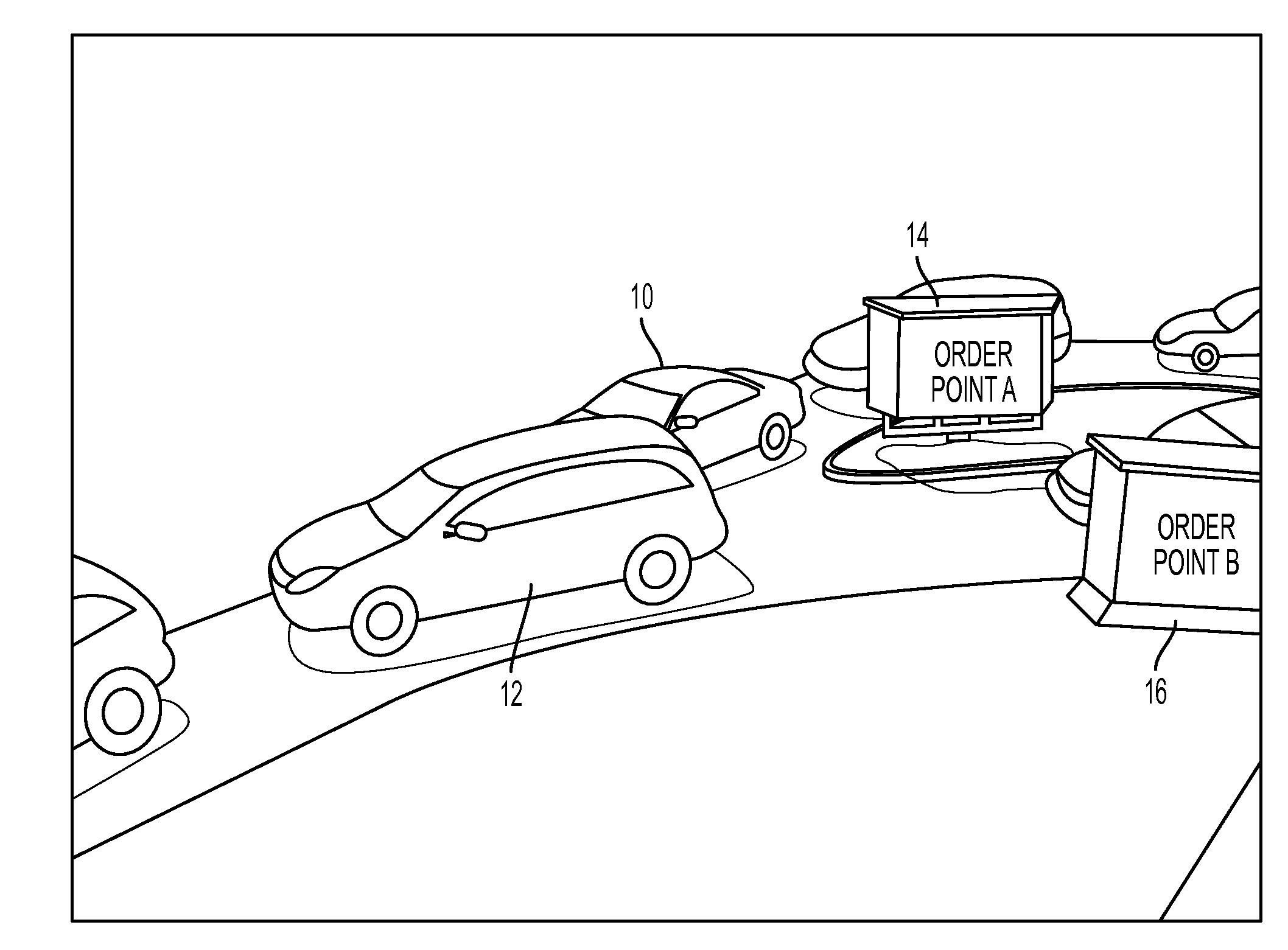
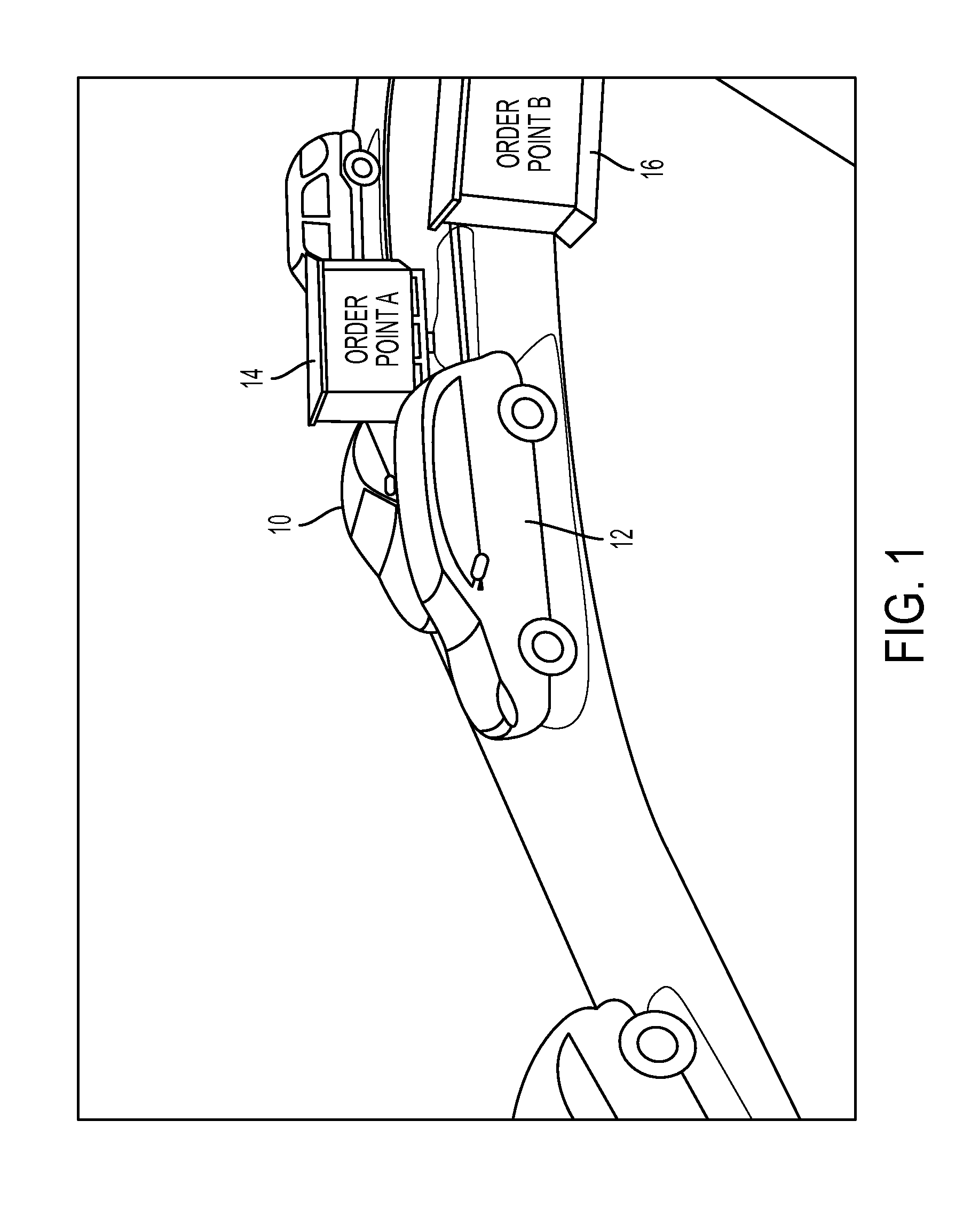
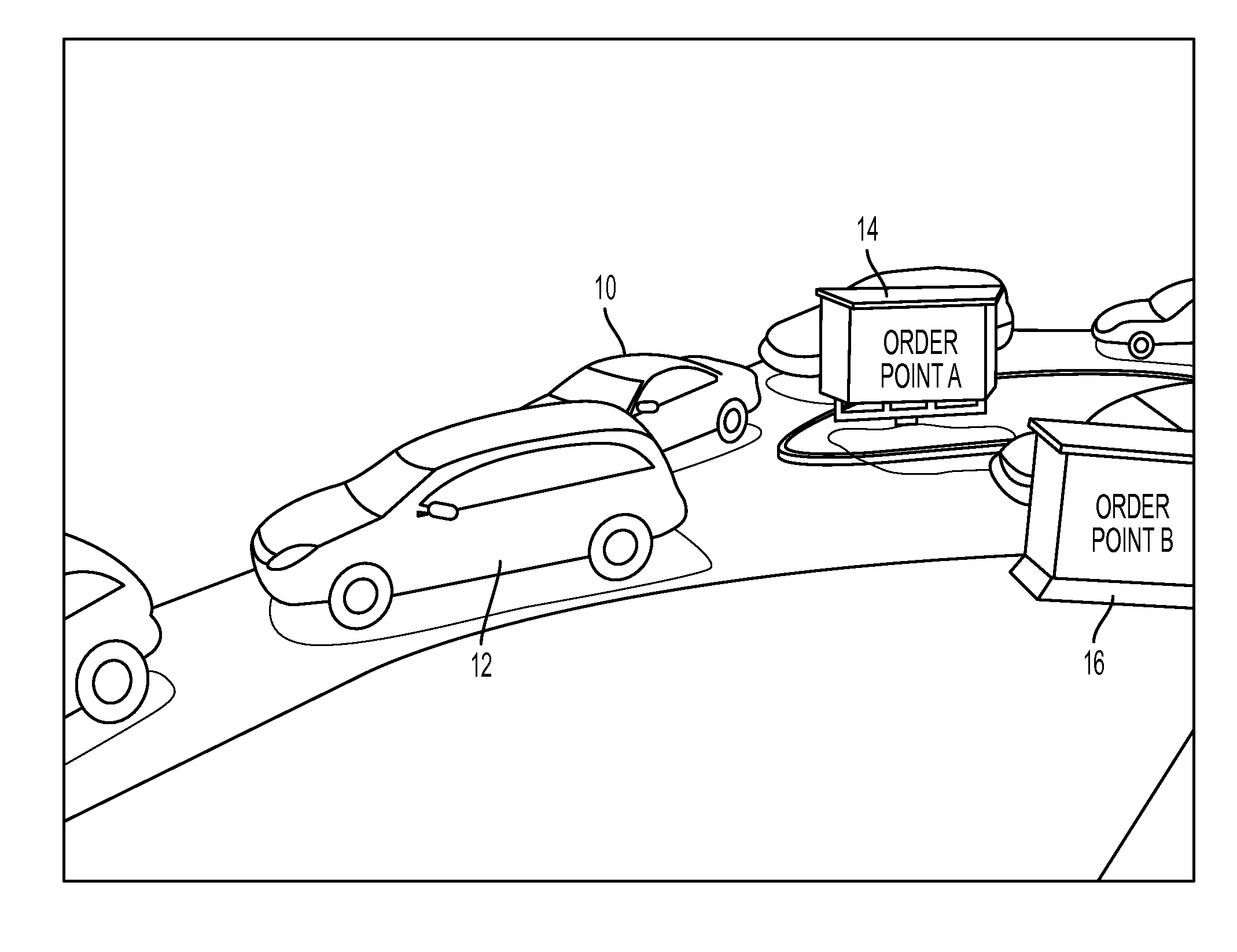
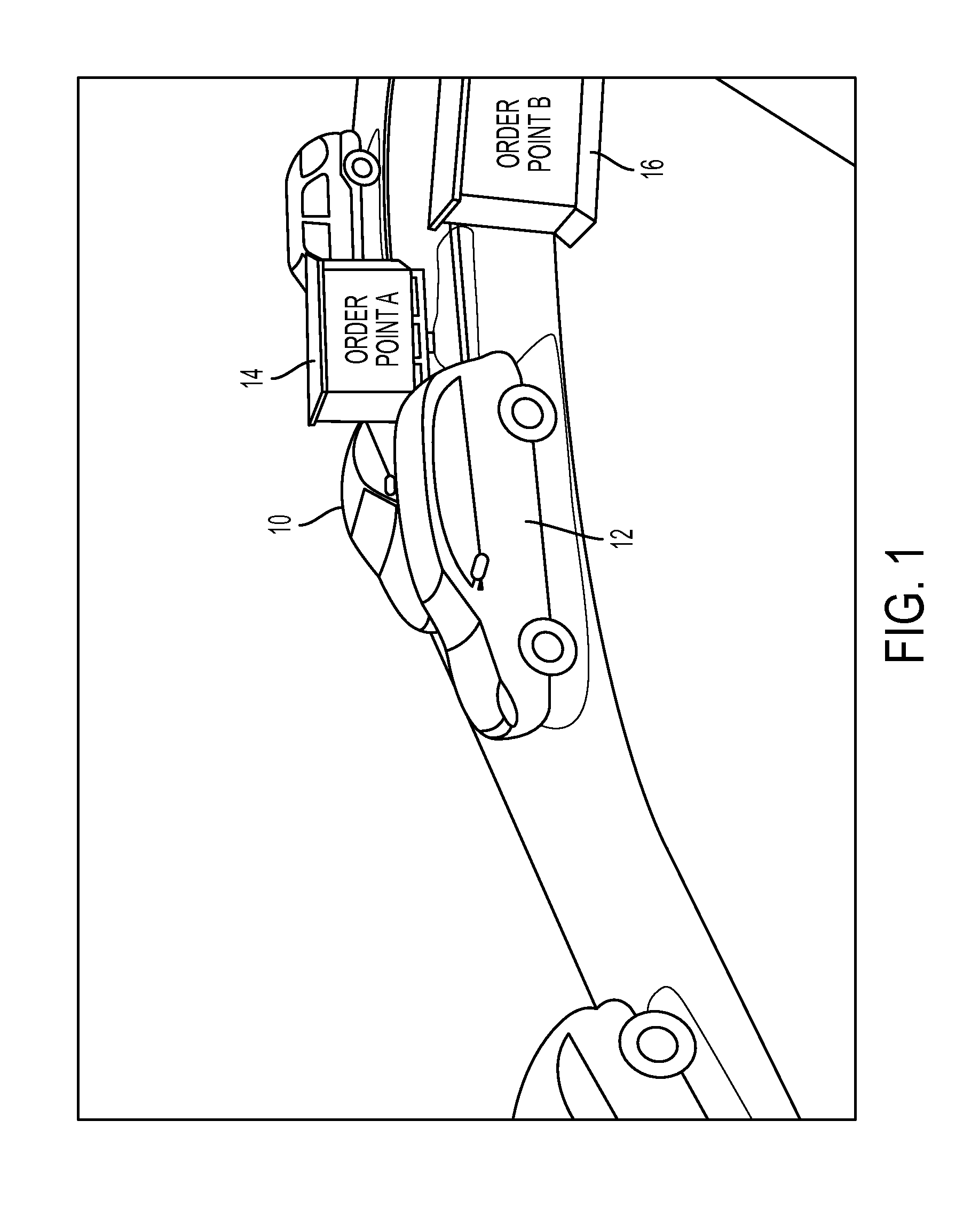
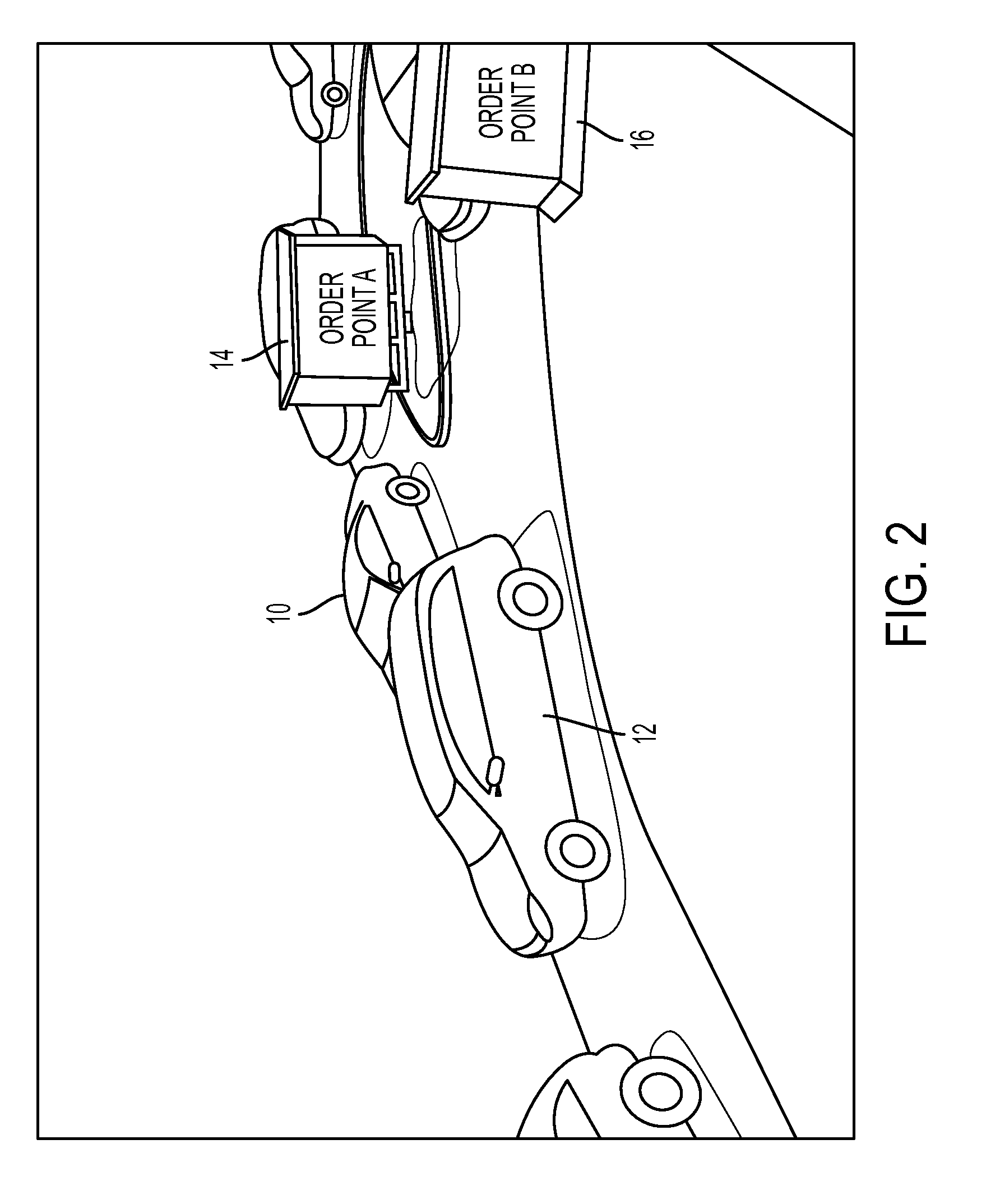
Method and system for automated sequencing of vehicles in side-by-side drive-thru configurations via appearance-based classification
This disclosure provides a method and system for automated sequencing of vehicles in side-by-side drive-thru configurations via appearance-based classification. According to an exemplary embodiment, an automated sequencing method includes computer-implemented method of automated sequencing of vehicles in a side-by-side drive-thru, the method comprising: a) an image capturing device capturing video of a merge-point area associated with multiple lanes of traffic merging; b) detecting in the video a vehicle as it traverses the merge-point area; c) classifying the detected vehicle associated with traversing the merge-point area as coming from one of the merging lanes; and d) aggregating vehicle classifications performed in step c) to generate a merge sequence of detected vehicles.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
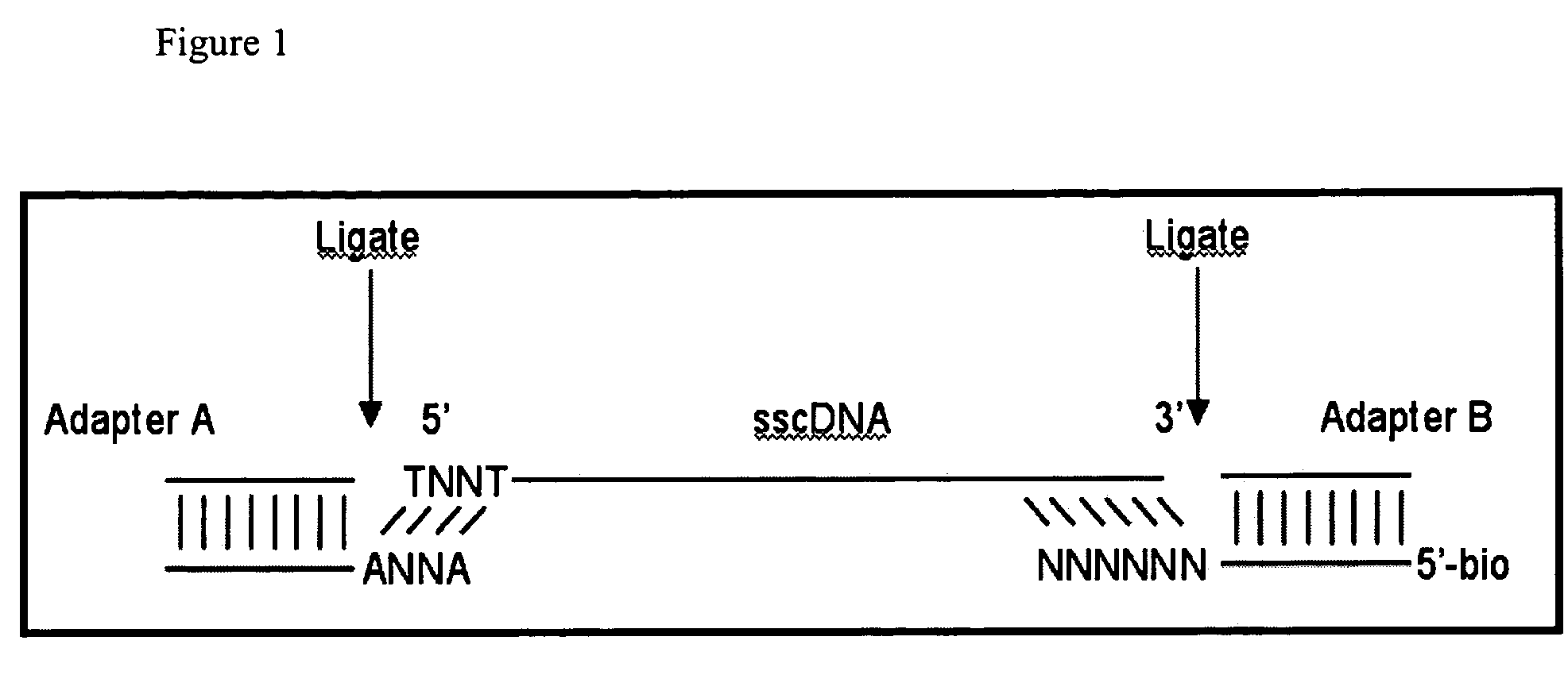
Reagents, methods, and libraries for bead-based sequencing
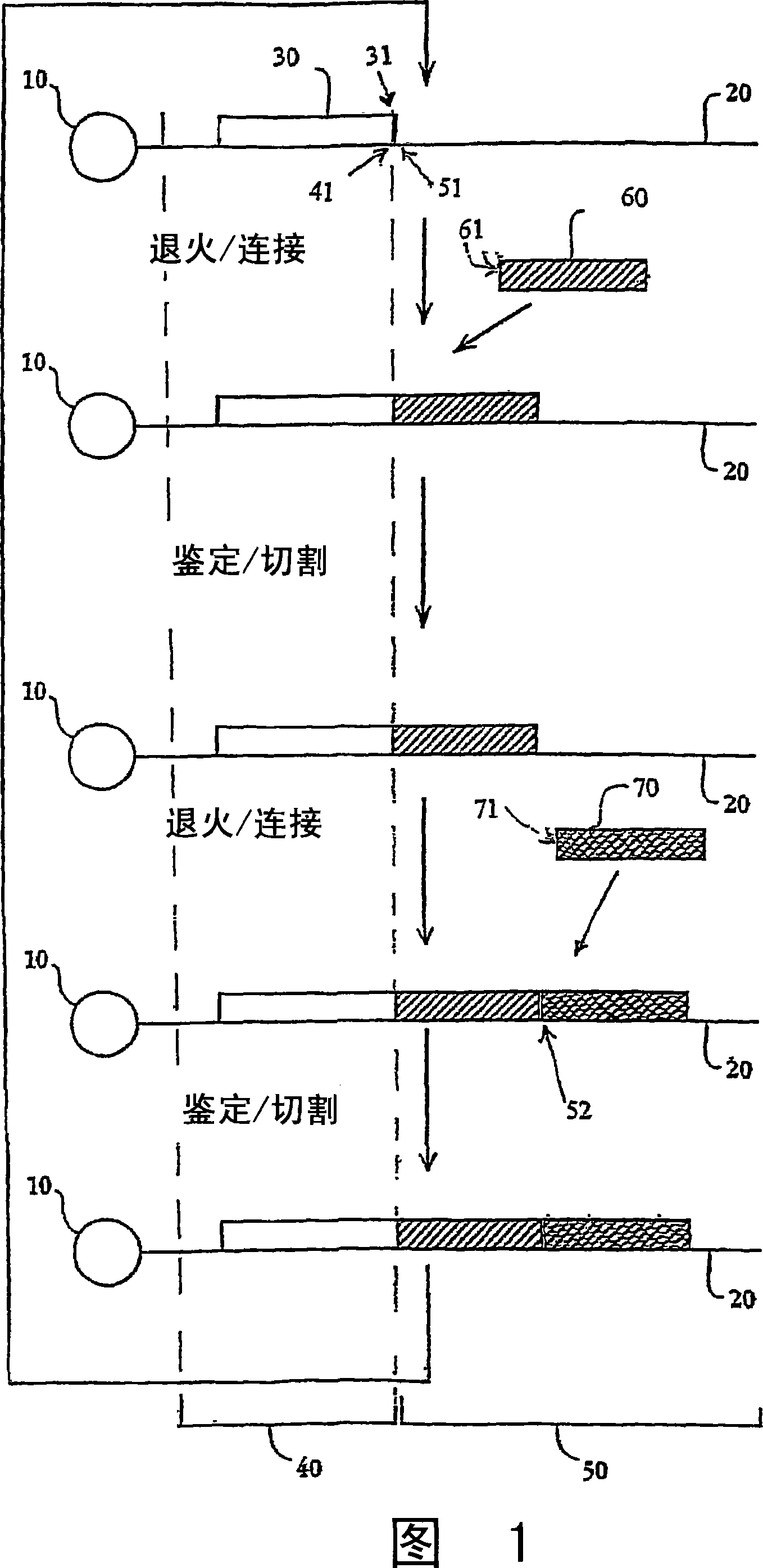
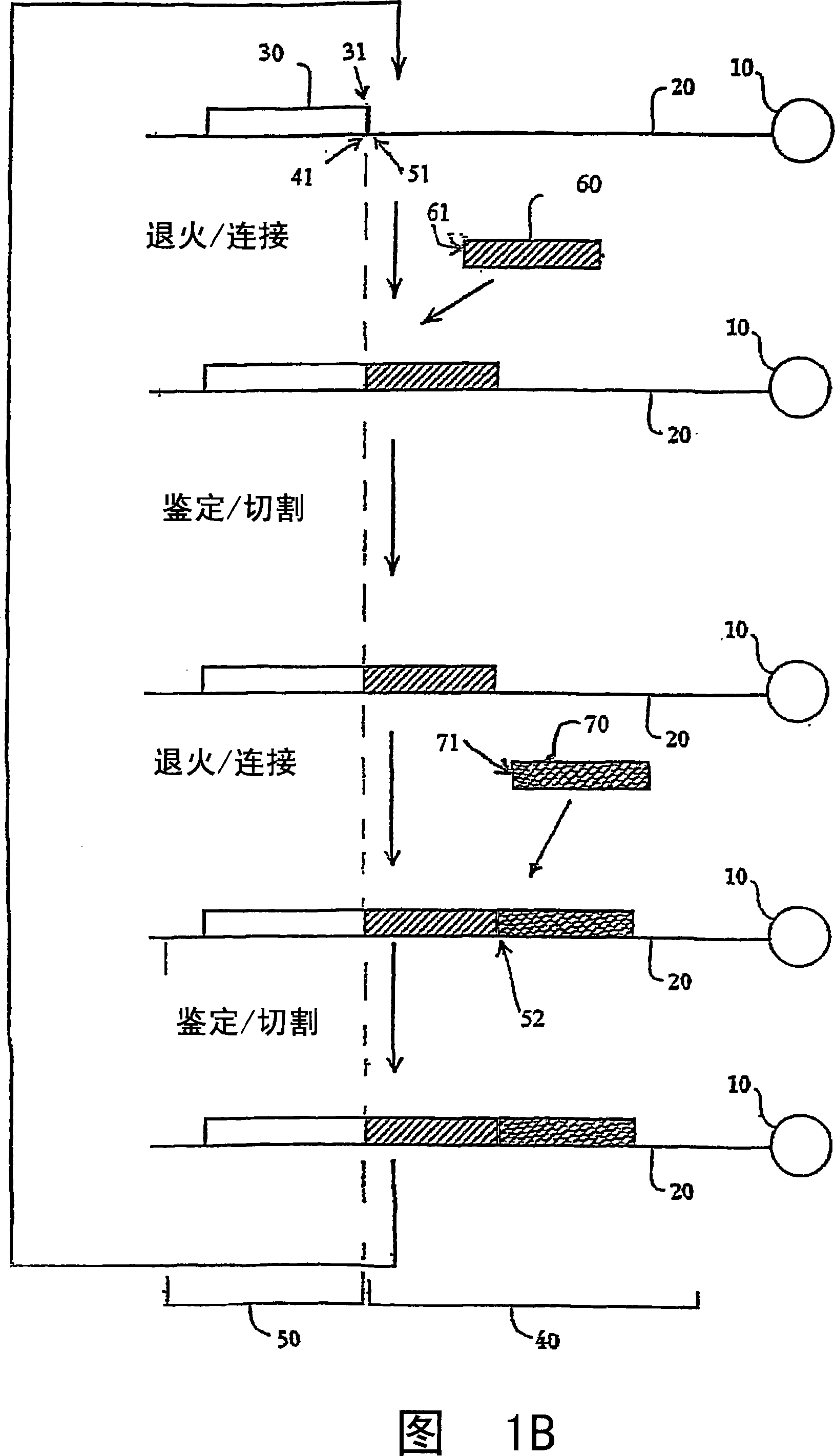
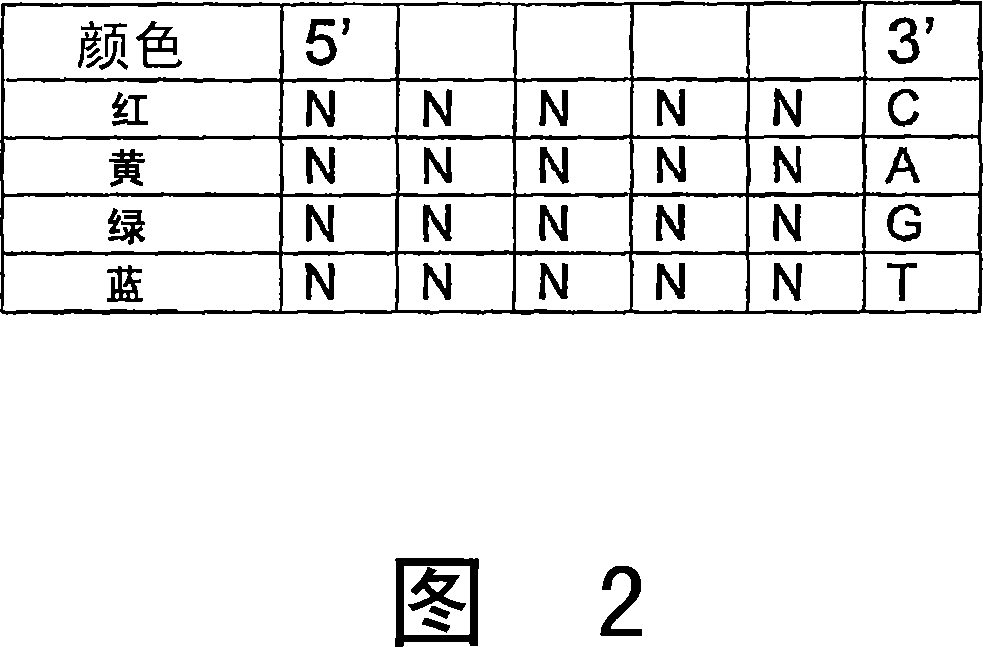
The present invention provides a method for determining the sequence of a nucleic acid by successive cycles of duplex extension along a single-stranded template. This cycle includes the steps of: extension, ligation, preferably cleavage. In certain embodiments, the method utilizes an extension probe containing a phosphorothioate linkage and utilizes a substance suitable for cleaving such linkage. In certain embodiments, the method utilizes extension probes containing abasic residues or damaged bases, and utilizes substances suitable for cleaving linkages between nucleosides and abasic residues and / or suitable for Removes substances that damage bases in nucleic acids. The present invention provides methods for determining sequence information using at least two differentially labeled probe families. In certain embodiments, the method obtains less than 2 bits of information per cycle from each of the plurality of nucleotides of the template. In certain embodiments, the sequencing reaction is performed on templates attached to beads immobilized in or on a semi-solid support. The invention also provides labeled extension probe sets containing phosphorothioate linking or priming residues suitable for use in this method. In addition, the present invention includes removing the starting oligonucleotide and the extending strand and performing subsequent reactions with different starting oligonucleotides, thereby performing multiple sequencing reactions on one template. The invention also provides an effective method for preparing templates, especially for parallel sequencing of multiple different templates. The invention also provides methods for performing ligation and cleavage. The invention also provides novel libraries of nucleic acid fragments containing paired tags, methods for preparing microparticles to which multiple different templates (eg, containing paired tags) are attached, and for individually sequencing these templates. The invention also provides automated sequencing systems, flow chambers, image processing methods, and computer-readable media storing computer-executable instructions (such as performing image processing methods) and / or sequence information. In certain embodiments, sequence information is stored in a database.
Owner:ADVANCED GENETIC ANALYSIS CORP
Auto-sequencing multi-directional inline processing apparatus
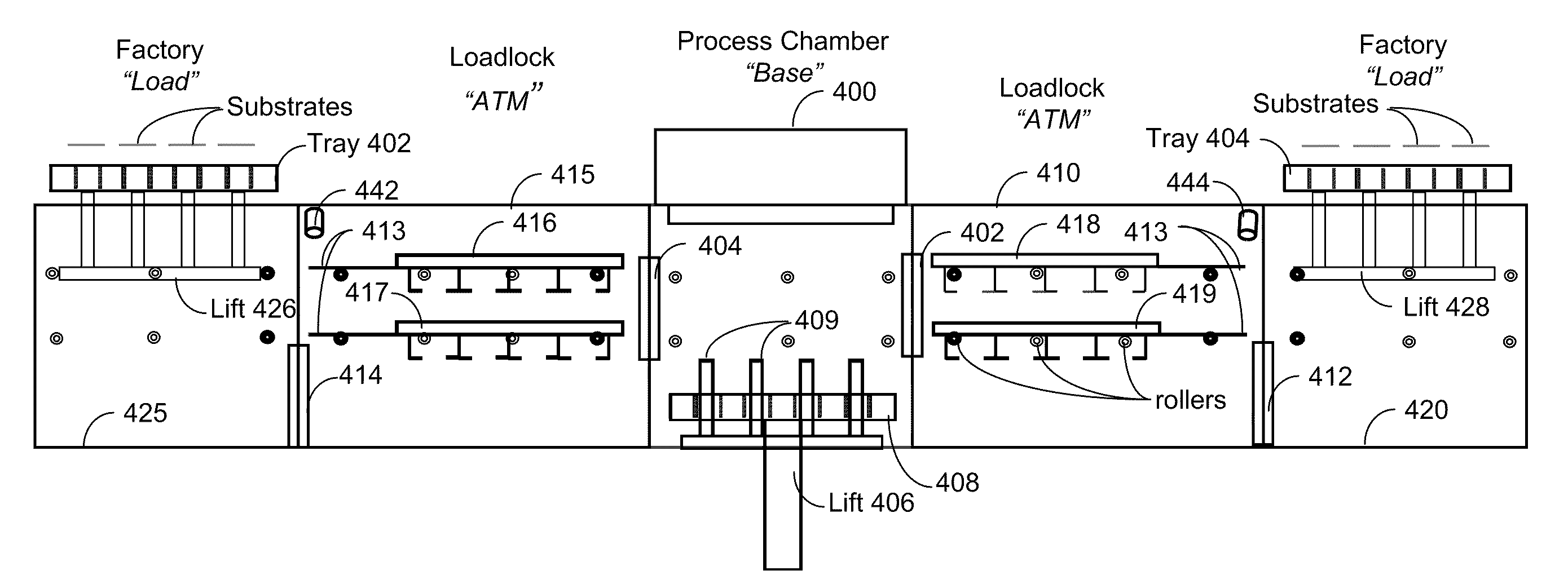
ActiveUS8444364B2Improve throughputImprove accuracyImage analysisElectric discharge tubesSequence processingEngineering
An apparatus and method for concurrent processing of several substrates. The system employs a novel architecture which, while being linear, may autonomously sequence processing and move substrates in different directions as necessary. The system moves several substrates concurrently; however, unlike the prior art it does not utilize trays.
Owner:KLA CORP
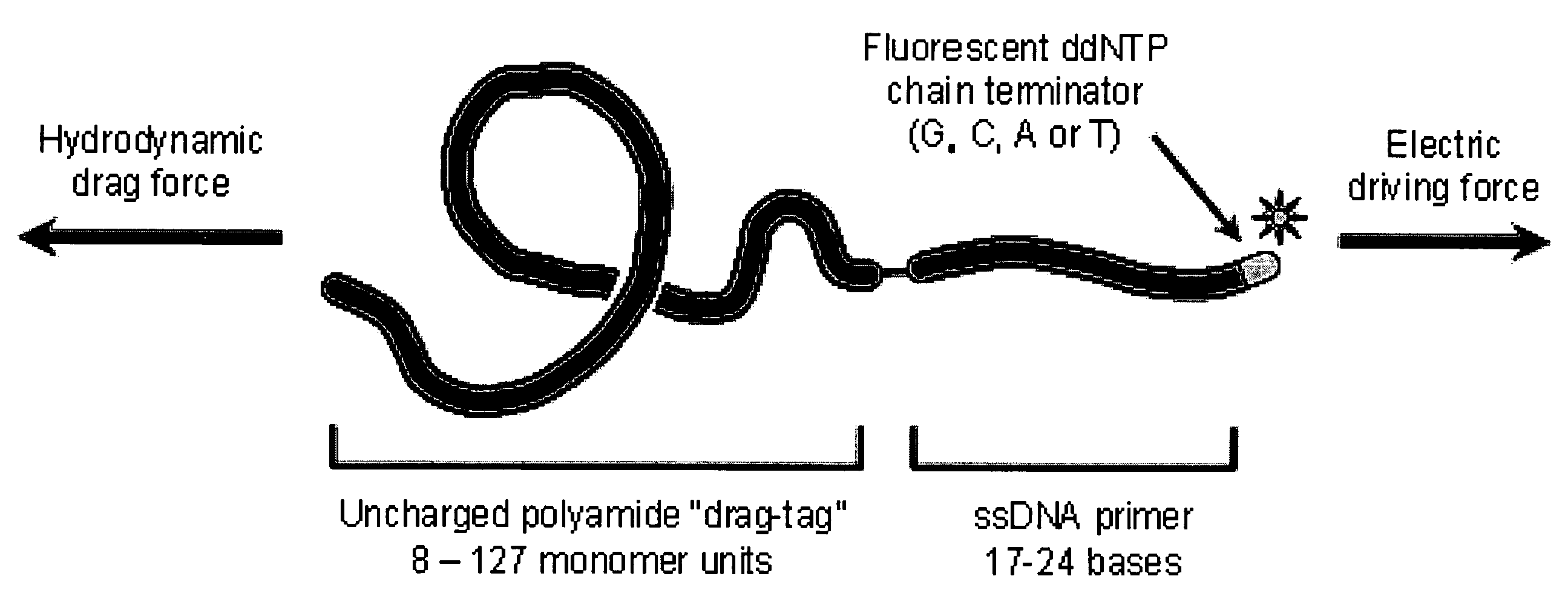
Nucleic Acid Sequencing In Free Solution Using Protein Polymer Drag-Tags
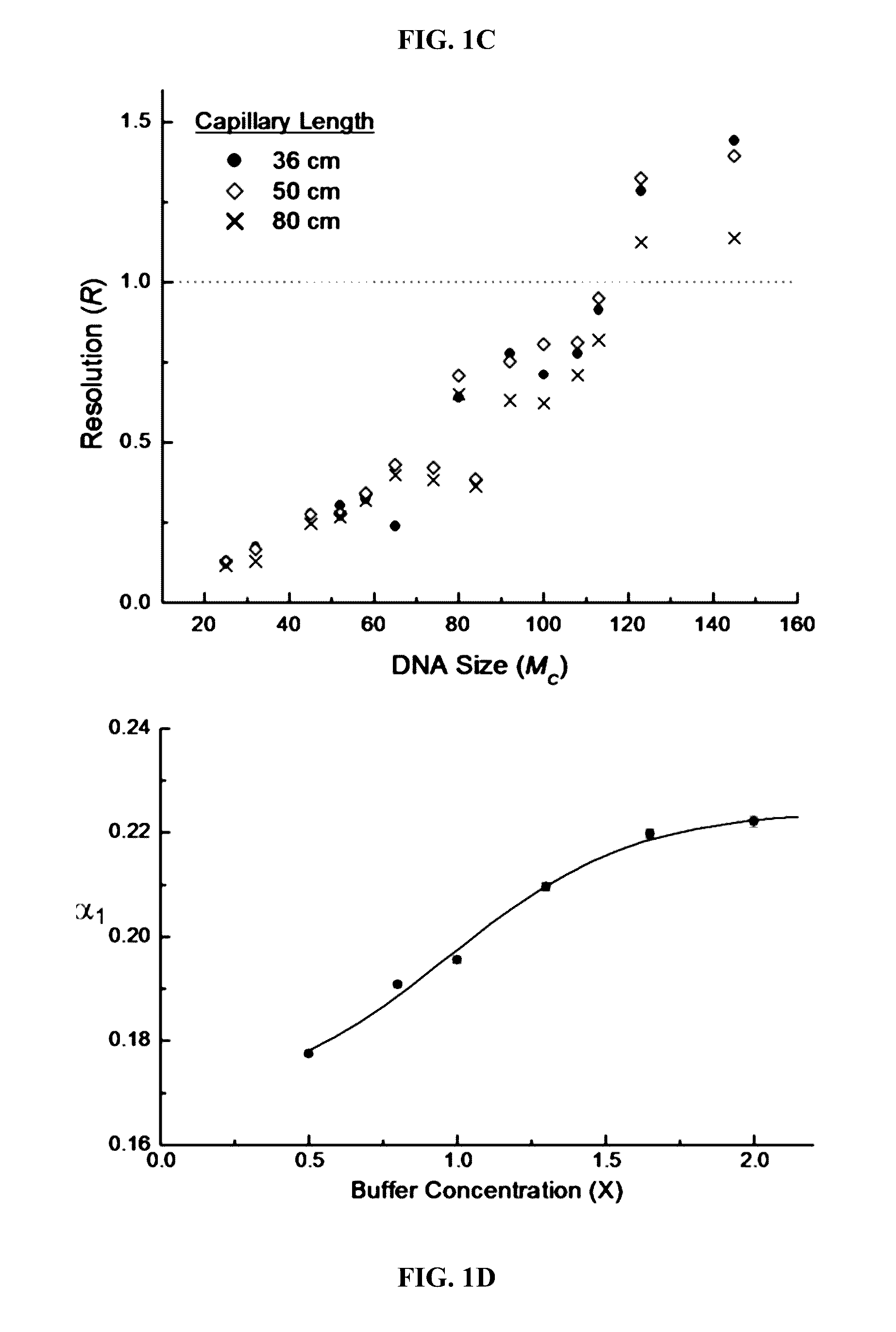
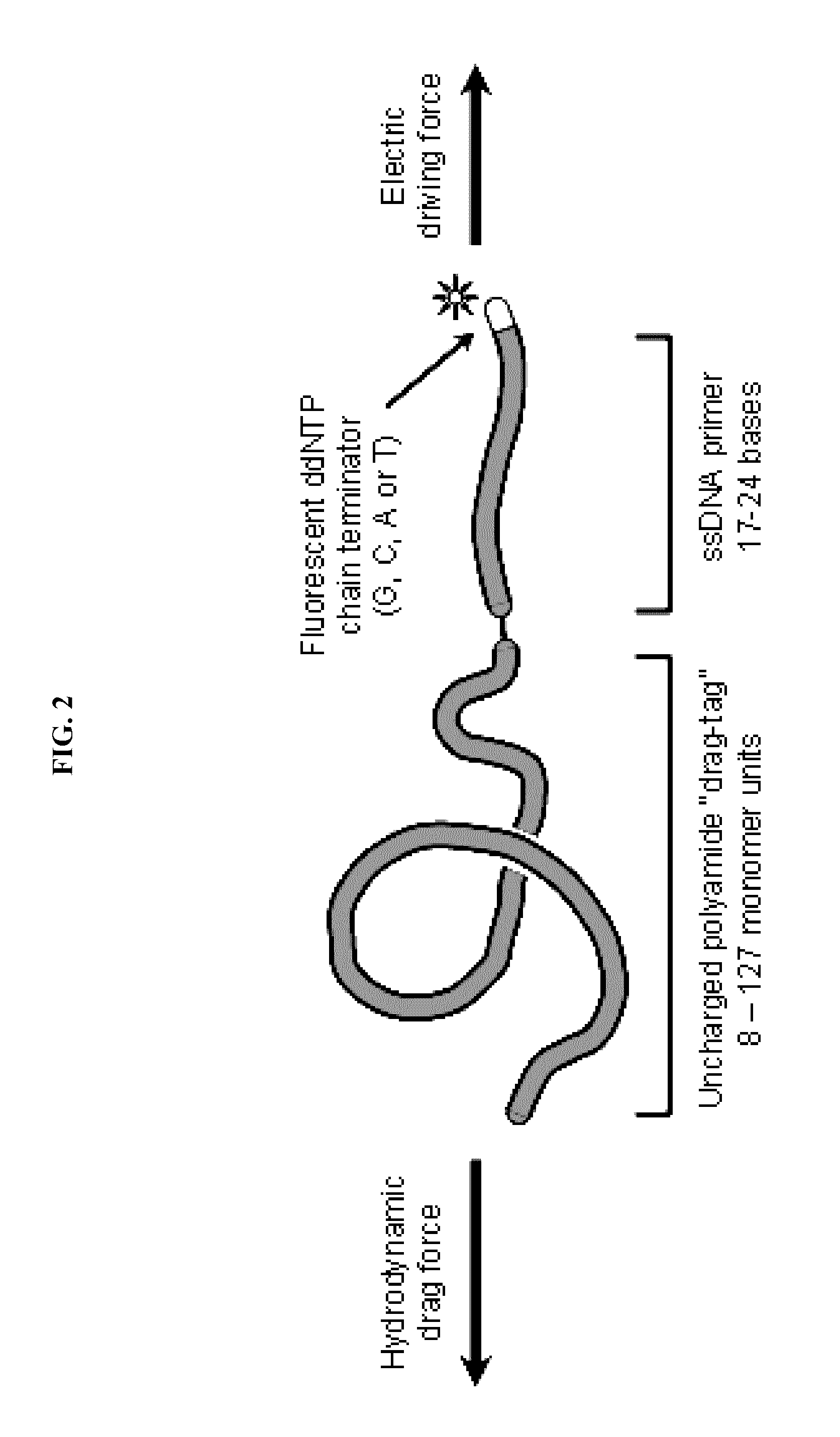
InactiveUS20080241950A1High resolutionCleaner resultMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMolecular compositionProtein insertion
The present invention relates to systems, compositions, and methods for nucleic acid sequencing and analysis in free-solution using protein polymer drag-tags. As such, the present invention provides protein-based molecular compositions that find use as drag-tags for use in sequencing and nucleic acid analysis methods and provides systems and methods for automated sequencing and analysis of nucleic acids in free solution.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
CDNA library preparation
InactiveCN101263227AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationCDNA libraryAutomated sequencing
New biochemical protocols for high throughput processing of mRNA samples into cDNA libraries with adaptor sequences compatible with automated sequencing systems are provided. The provided methods produces cDNA libraries which do not have 3' bias 5 associated with current cDNA library production methods. New methods for the production of DNA libraries from DNA are also provided.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Automated system and method for managing a process for the shopping and selection of human entities
InactiveUS8229777B2Increase speedImprove efficiencyComplete banking machinesTelephonic communicationSelection criterionComputer science
Owner:INTRAGROUP
Method for identifying designations
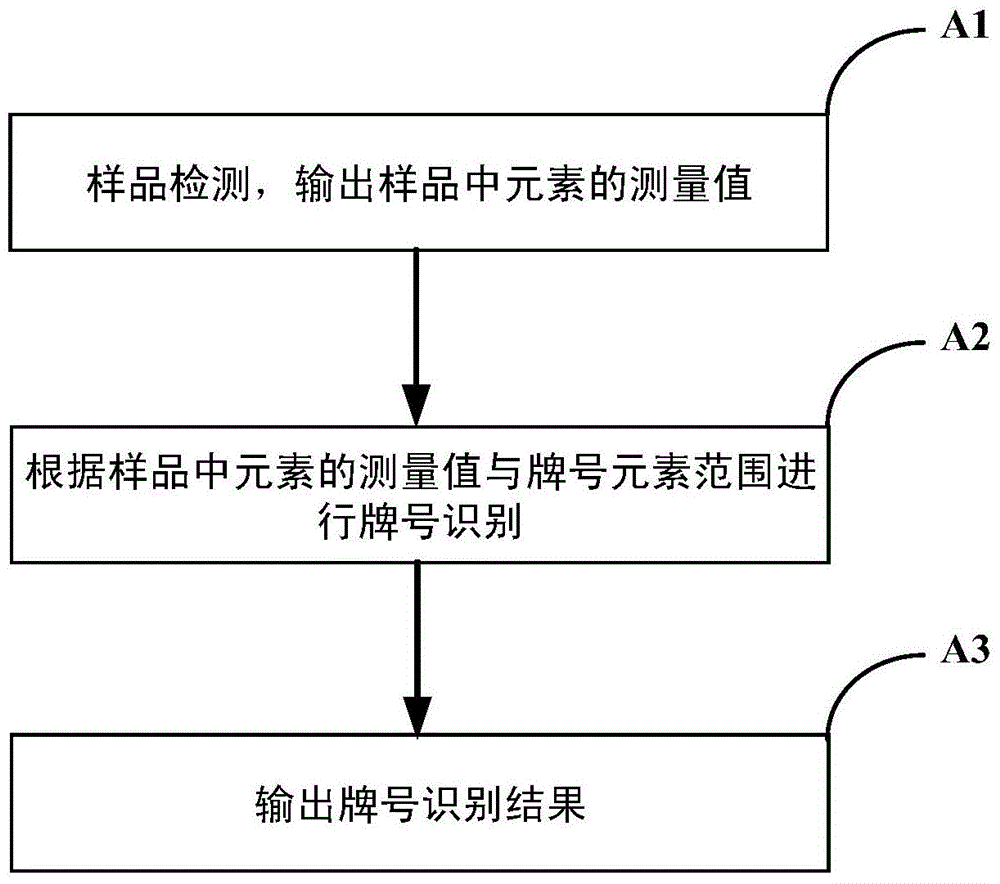
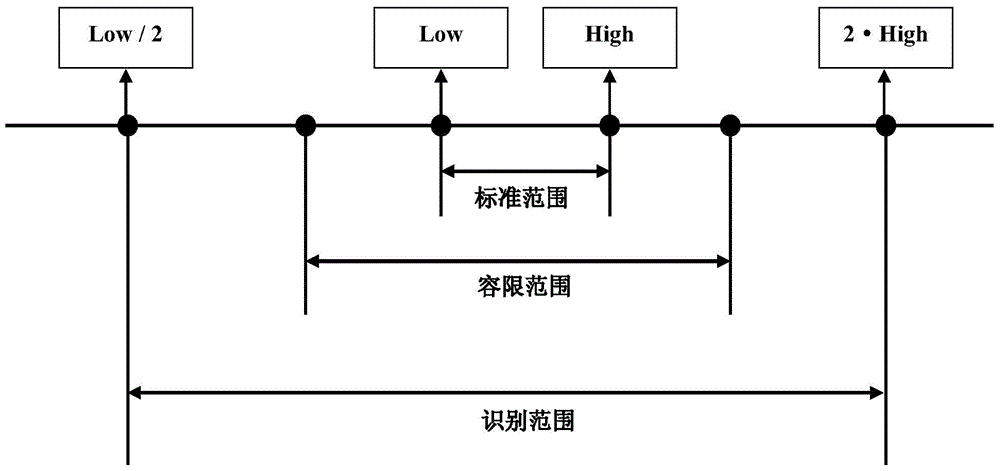
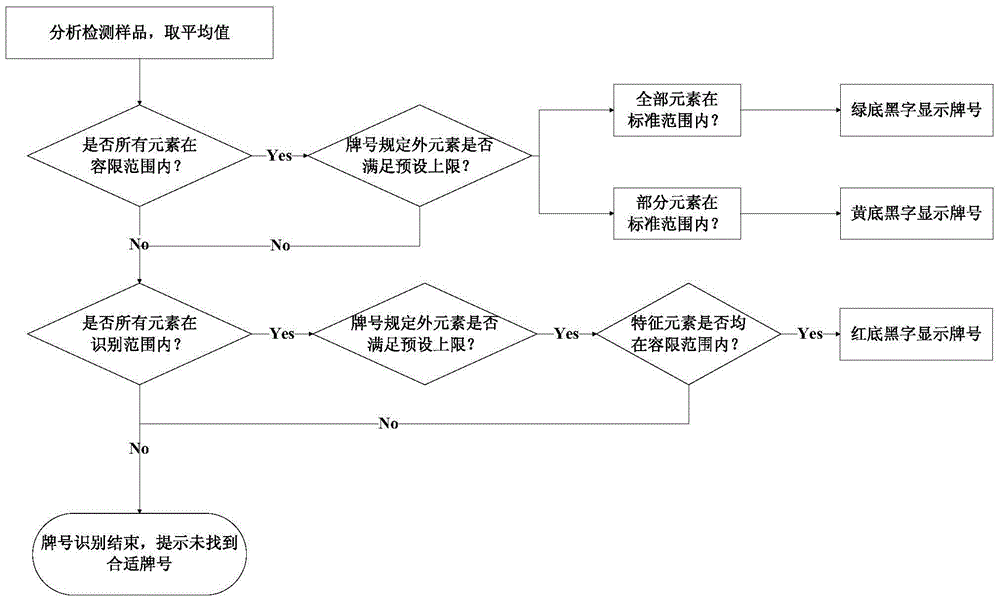
InactiveCN105678329ARealize automatic queryAchieving identifiabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringData mining
The invention relates to a method for identifying designations. The method for identifying designations comprises following steps: (A1) detecting samples and outputting measurement values of elements of the samples; (A2) identifying designations according to the measurement values of elements in the samples and a designation element range; (A3) outputting designation identification results. The method has advantages such as automatic query and automatic ranking of designations.
Owner:FOCUSED PHOTONICS
Method and system for automated sequencing of vehicles in side-by-side drive-thru configurations via appearance-based classification
This disclosure provides a method and system for automated sequencing of vehicles in side-by-side drive-thru configurations via appearance-based classification. According to an exemplary embodiment, an automated sequencing method includes computer-implemented method of automated sequencing of vehicles in a side-by-side drive-thru, the method comprising: a) an image capturing device capturing video of a merge-point area associated with multiple lanes of traffic merging; b) detecting in the video a vehicle as it traverses the merge-point area; c) classifying the detected vehicle associated with traversing the merge-point area as coming from one of the merging lanes; and d) aggregating vehicle classifications performed in step c) to generate a merge sequence of detected vehicles.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
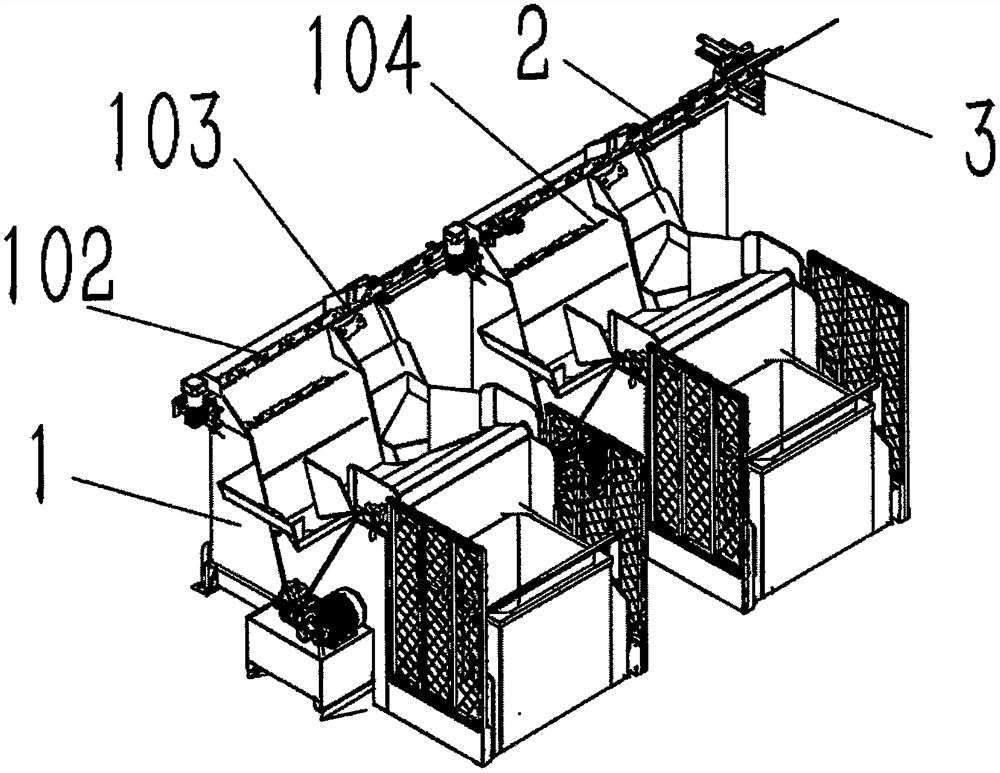
Automatic production line for steel backing surface treatment
ActiveCN113086543AImplement sortingImplement automatic classificationLiquid surface applicatorsControl devices for conveyorsProduction lineSand blasting
The invention discloses an automatic production line for steel backing surface treatment. The automatic production line is used for transforming an existing steel backing surface treatment production line and comprises a steel backing cleaning machine, a steel backing sand blasting machine and a steel backing glue spraying machine and further comprises an automatic feeding and conveying device, a cleaning, sequencing and conveying device, a cleaning, discharging and conveying device, a sand blasting, feeding and conveying device, a sand blasting, discharging and conveying device, a transferring, sequenching and conveying device, a sorting, overturning and conveying device, a glue spraying and sequencing device and a drying, discharging and sorting device according to the production sequence. The automatic production line for steel backing surface treatment has the beneficial effects that full automation, automatic feeding, automatic sequenching, automatic transferring, automatic glue spraying, automatic drying and automatic sorting of steel backing surface treatment are achieved.
Owner:RIZHAO POLYTECHNIC
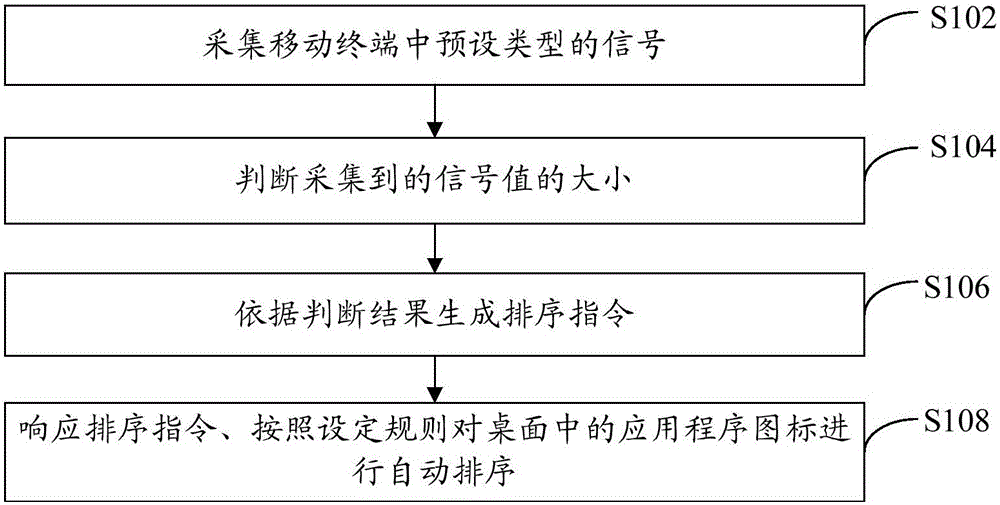
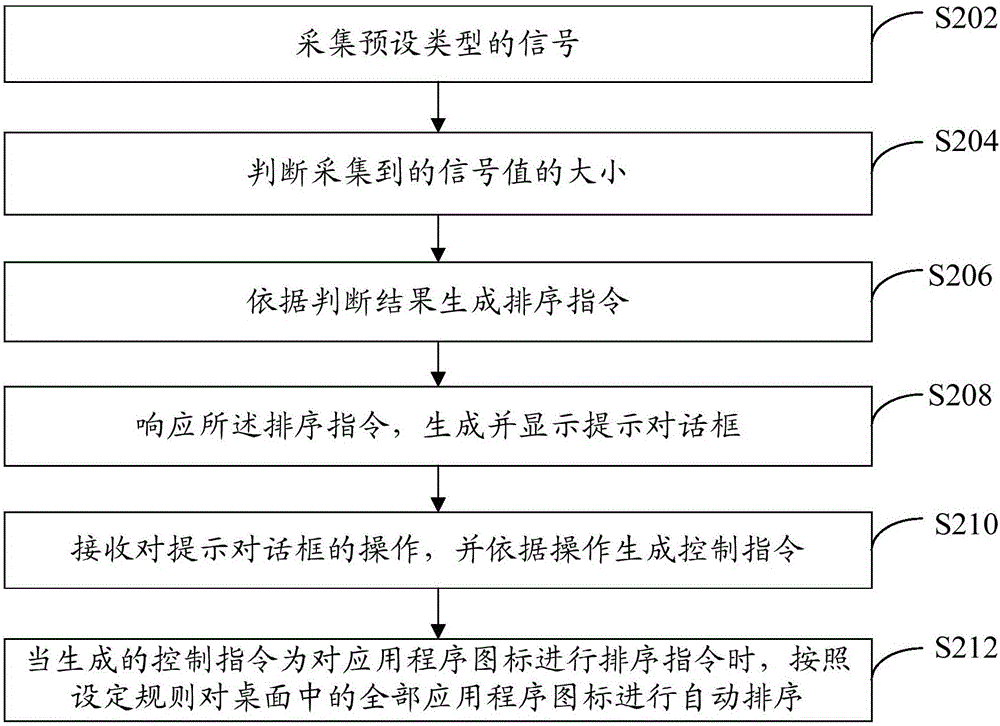
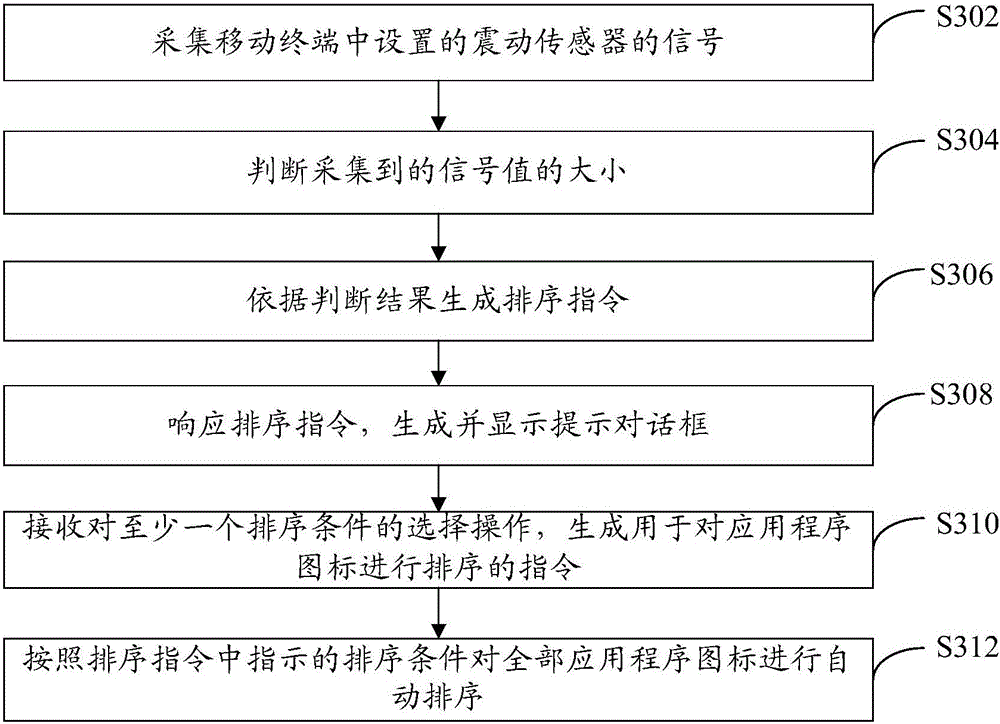
Application program icon sequencing method and mobile terminal
InactiveCN105824504AEasy to operateShort timeExecution for user interfacesInput/output processes for data processingProgramming languageAutomated sequencing
The invention provides an application program icon sequencing method and a mobile terminal, wherein the method comprises the following steps of collecting a signal in a preset type in the mobile terminal; judging the size of the collected signal value; generating a sequencing instruction according to the judging result; responding to the sequencing instruction; performing automatic sequencing on the application program icons in the desktop according to the set rule. By using the application program icon sequencing scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the mobile terminal can automatically sequence the application program icons according to the preset rule according to the generated instruction; the operation by a user is convenient; the time consumption is short.
Owner:LETV INFORMATION TECH BEIJING
A design system and method
InactiveCN108604356ABuying/selling/leasing transactionsInput/output processes for data processingGraphical user interfaceSoftware engineering
Provided is a computer-implemented method (400) for product design, the method (400) generally comprising a first step (402) of providing a graphical user interface (GUI) to a user for inputting product specifications, said GUI including a plurality of design modules each providing specific product specification customization options. Once the GUI has been provided (402), a user is able to provideproduct specifications, which is then received (404) by the system (300). The method (400) then provides a substantially real-time user-operable visualization of the specified product via the GUI. Inaddition, the GUI generally further also includes a pricing engine configured to provide substantially real- time product pricing information (410) according to the selected product specifications. Once the product has been finalized, in response to receiving a final product approbation via the GUI (indicated by block 412), the method (400) includes the step of automatically sequencing the product specifications required for manufacturing the final product. In addition, the method further includes the step (418) of outputting such manufacturing sequence in a predetermined format.
Owner:THE STAINLESS STEEL MONUMENT CO PTY LTD
Elevator
PendingCN113526083AImplement automatic sortingEasy to removeConveyor partsStructural engineeringMachining
The invention provides an elevator, and belongs to the technical field of machining and manufacturing equipment. The problems that an existing elevator cannot achieve automatic sequencing and is low in feeding efficiency are solved. The elevator comprises a shell with a material groove, a step-shaped base is arranged in the material groove, a guide rail is arranged at the top of the base and distributed in the length direction of the top face, a through groove with an upward notch and penetrating through the two ends of the guide rail is formed in the guide rail in the length direction, the long edge of the lowest position of the base is close to the notch of the through groove, and one end of the guide rail is connected to the shell in a hinged mode, and the other end can be lifted when the guide rail rotates. When workpieces fall into the guide rail, the smaller-diameter ends of the workpieces can fall into the through groove, the larger-diameter ends of the workpieces can be clamped at the notch positions of the through groove, automatic sorting of the workpieces is achieved, the guide rail can rotate around a hinge point under the ejecting pressure of an air cylinder, the workpieces clamped on the guide rail can slide towards the lower side along with rotation of the guide rail, the workpieces can be conveniently taken down by people, and the feeding efficiency is further improved.
Owner:浙江云强智能装备有限公司
System and method for automatic sequencing of shipments
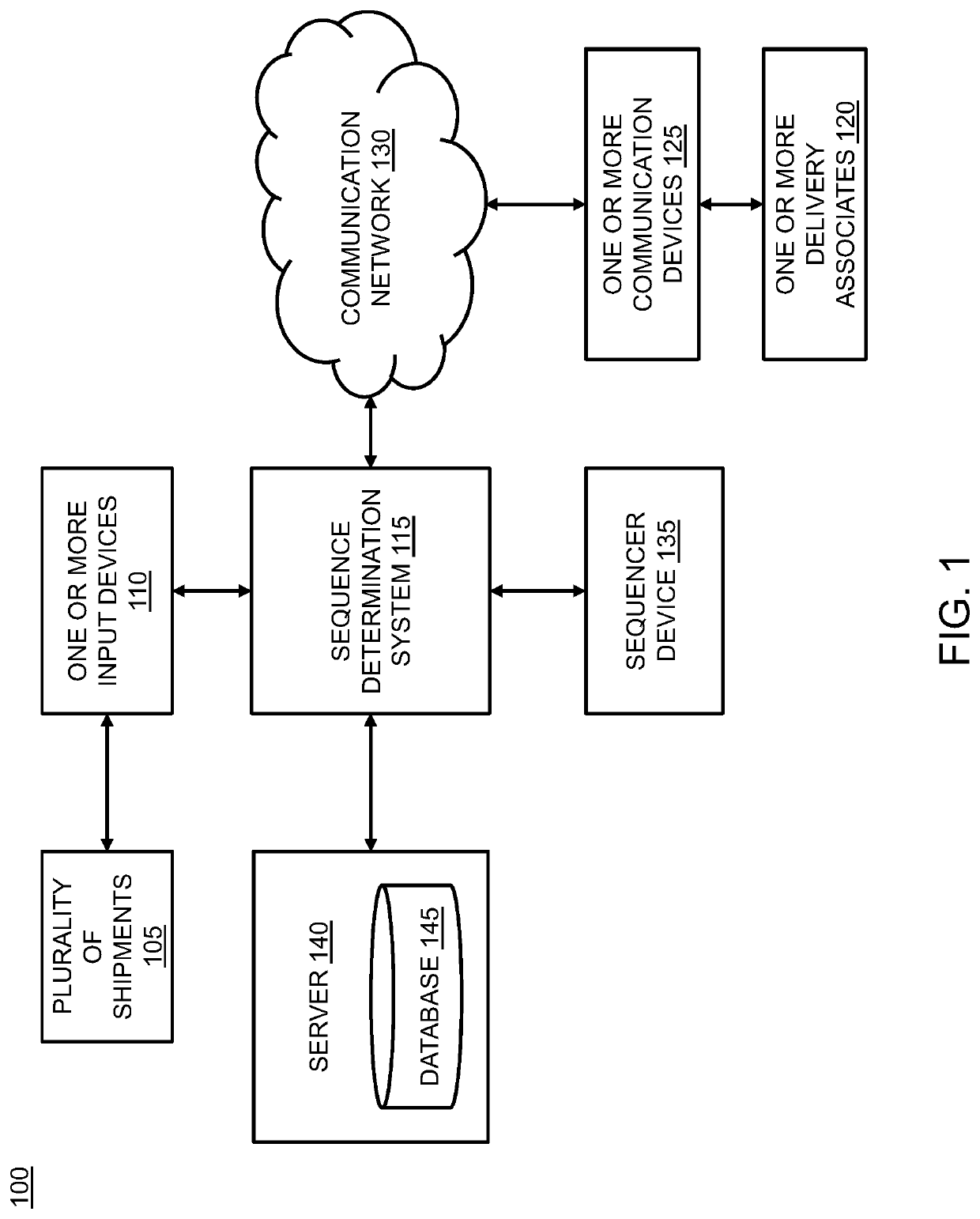
InactiveUS20200184418A1Reduce dependenceEfficient deliveryRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsEngineeringData mining
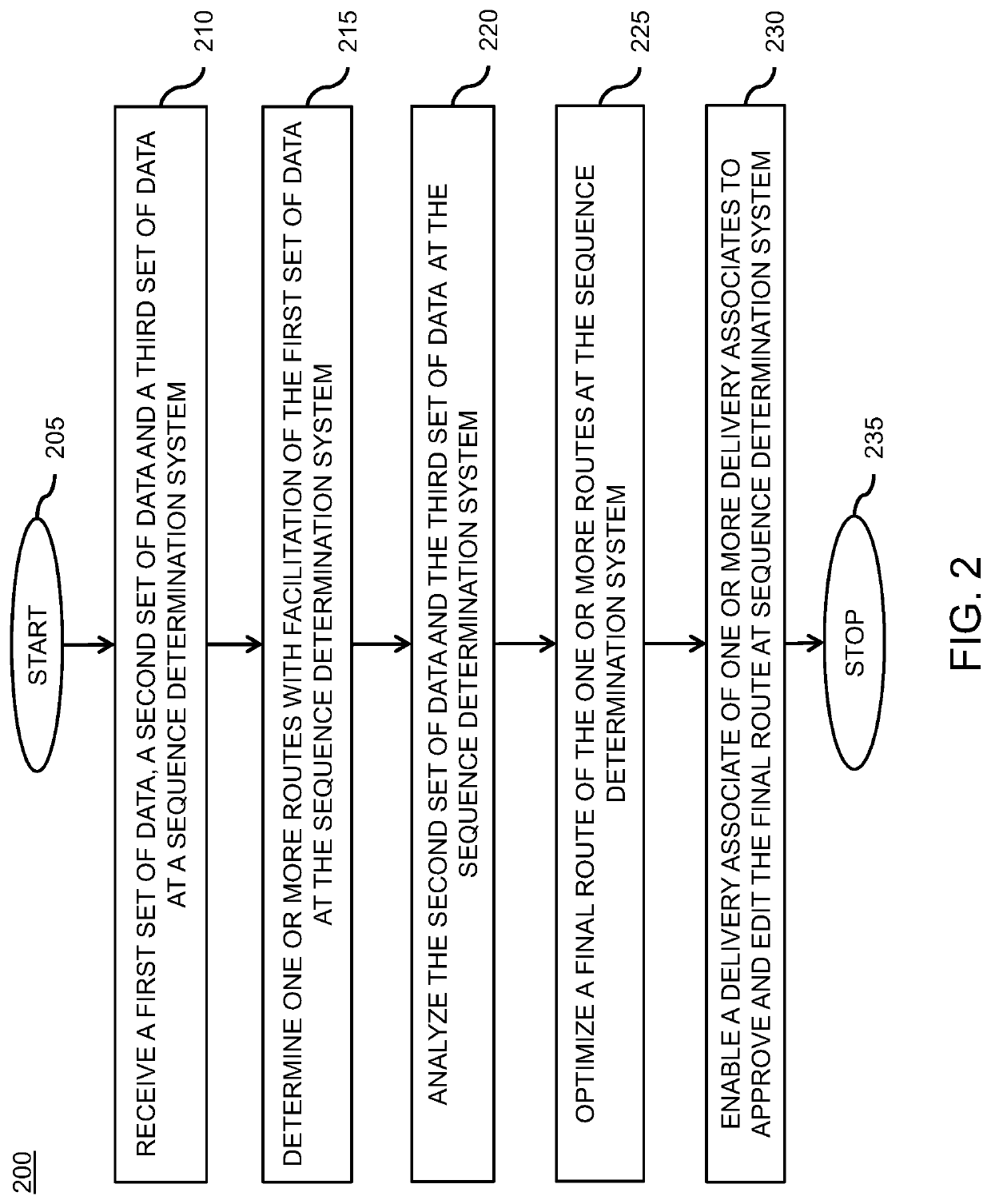
The present disclosure provides a computer-implemented method and system for sequencing of a plurality of shipments in order of delivery. The method includes a first step of receiving a first set of data, a second set of data and a third set of data at sequence determination system. The method includes another step of determining one or more routes with facilitation of the first set of data at the sequence determination system. The method includes yet another step of analyzing the second set of data and the third set of data at the sequence determination system. The method includes yet another step of optimizing a final route form the one or more routes at the sequence determination system. The method includes yet another step of enabling a delivery associate of the one or more delivery associate to edit and approve the final route.
Owner:NTEX TRANSPORTATION SERVICES PVT LTD
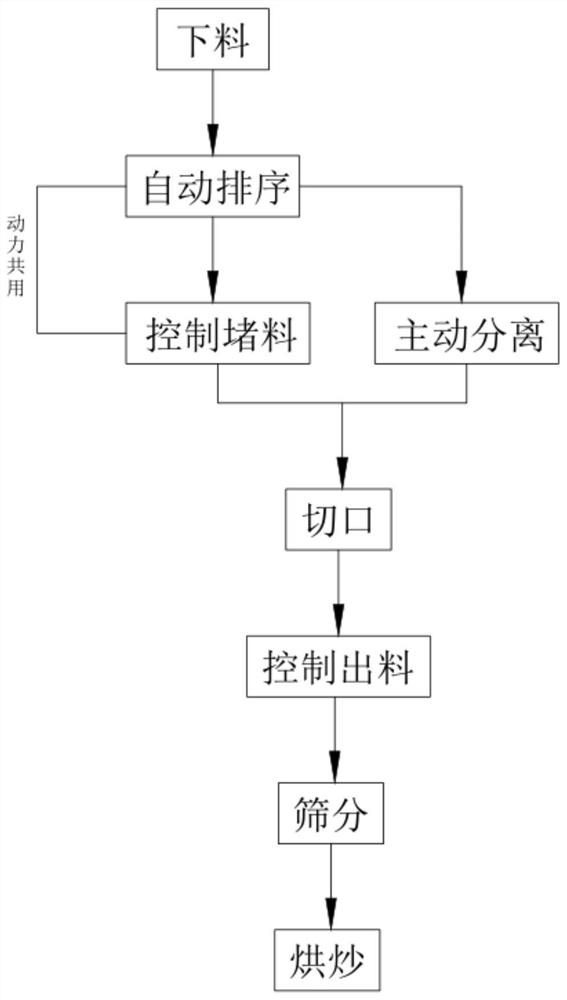
Processing technology of stir-fried pumpkin seeds convenient to shell
The present invention relates to a processing technology of stir-fried pumpkin seeds convenient to shell. The processing technology comprises the following steps: step one, feeding; step two, automatic sequencing; step three, controlling material blocking; step four, active separation, wherein in synchronization with the step three, a material blocking assembly drives a transmission assembly to synchronously transmit, the transmission transmission assembly drives a supporting rod to move, and inserting assemblies move towards gaps between two adjacent pumpkin seeds and realize separation of the integrally bonded pumpkin seeds in the moving process; step five, cutting, wherein a translation process of the inserting assemblies drives an opening mechanism to synchronously move to complete anautomatic cutting operation of middle parts of the pumpkin seeds; step six, discharging controlling; step seven, screening; and step eight, baking and frying. The processing technology solves technical problems that partial pumpkin seeds are adhered together under adhesion of the pulp and not separated thoroughly due to incomplete cleaning, and the targeted single cutting operation of the pumpkinseeds cannot be realized during the cutting operation.
Owner:阜阳运筹生产力促进中心有限公司
Multi-stage self-sequencing liquid-controlled fracturing ball throwing device
ActiveCN107476795AGuarantee continuous fracturing constructionImprove the efficiency of fracturing constructionFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsSequence controlElectric machinery
The invention relates to a multi-stage self-sequencing liquid-controlled fracturing ball throwing device. The device includes a cover plate, a base, a seal cover, a rotary disk and a motor. The cover plate and the base are internally provided with conductive circuits, small fracturing balls are put in from the top, the weight of the balls are tested through a gravity sensor, a second hydraulic push mechanism pushes the balls to a ball delivery channel, the balls are sequentially located at the position of a baffle arranged in the radial direction of the rotary disk and located on the upper portion of a ball-throwing guide channel, according to the weight of the small fracturing balls, sequencing is conducted through the recursive algorithm, according to the sequence, the rotation angle of the motor is controlled so as to make the ball-throwing guide channel coincided with the axis of a ball throwing channel, and the small fracturing balls are pushed to the ball throwing channel through a first hydraulic push mechanism and enter a fracturing channel under the combined action of the high-pressure fluid negative pressure effect and the self gravity. According to the device, the several small fracturing balls can be automatically and sequentially thrown after being loaded at a time, the single-well multi-section continuous fracturing construction is effectively ensured, the safety risk of fracturing construction is reduced, and great engineering and economic benefits are generated.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
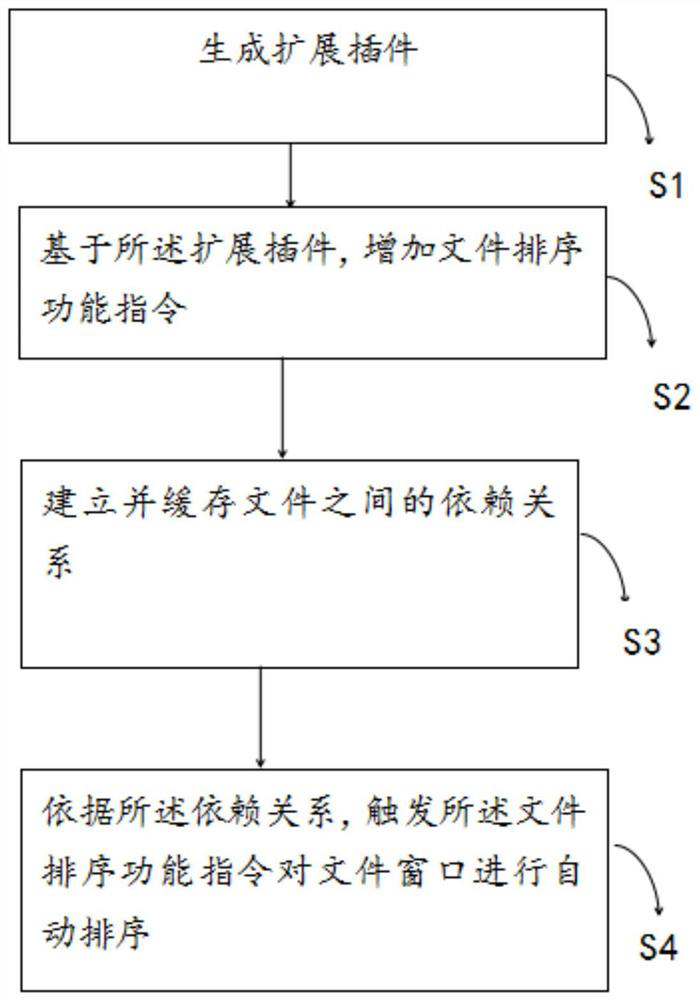
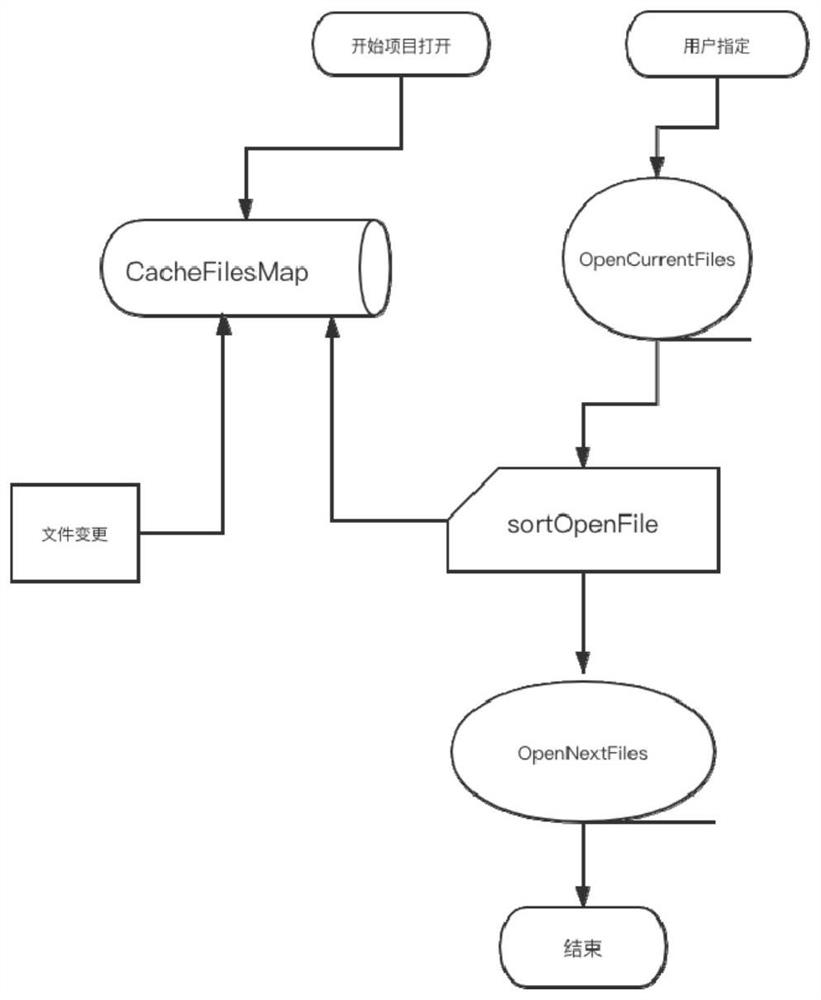
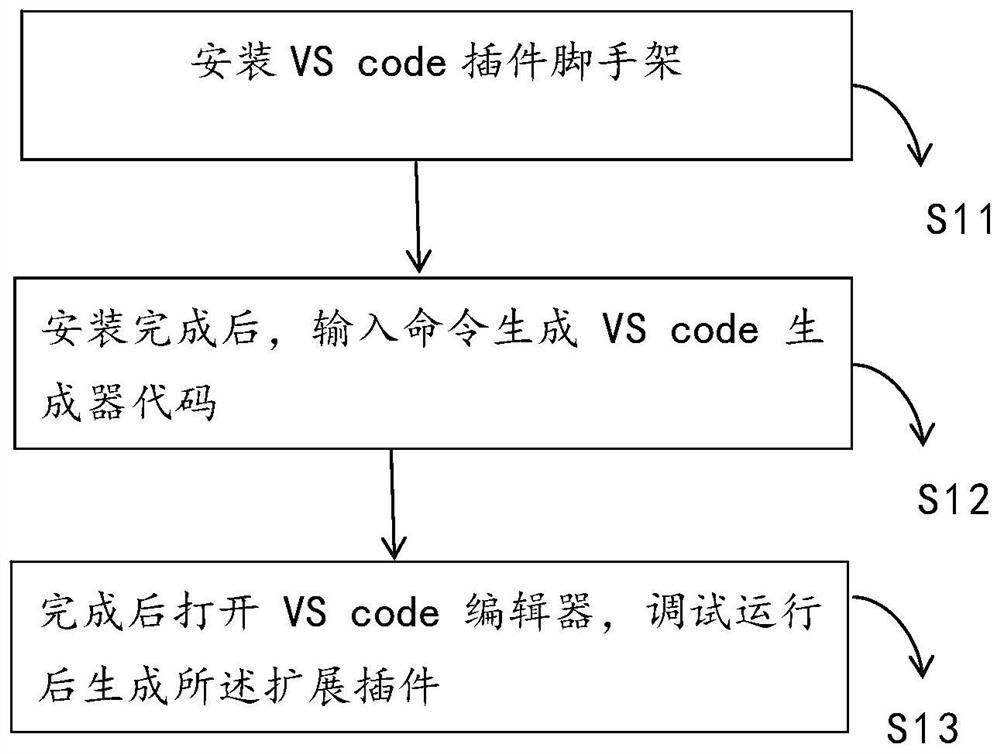
Method and system for automatically adjusting file window sequence based on file dependency relationship
PendingCN112486470ARealize the function of sorting and displaying from left to rightReduce dead timeIntelligent editorsVisual/graphical programmingCode editorParallel computing
The invention discloses a method and a system for automatically adjusting a file window sequence based on a file dependency relationship. Based on a VS code editor, the method comprises the followingsteps of generating an extension plug-in, adding a file sorting function instruction based on the extension plug-in, establishing and caching a dependency relationship between the files, and triggering the file sorting function instruction to automatically sort the file windows according to the dependency relationship. Through the method and the system, the function of sequencing and displaying the files from left to right according to the dependency relationship can be realized, and the coding experience is improved.
Owner:恩亿科(北京)数据科技有限公司
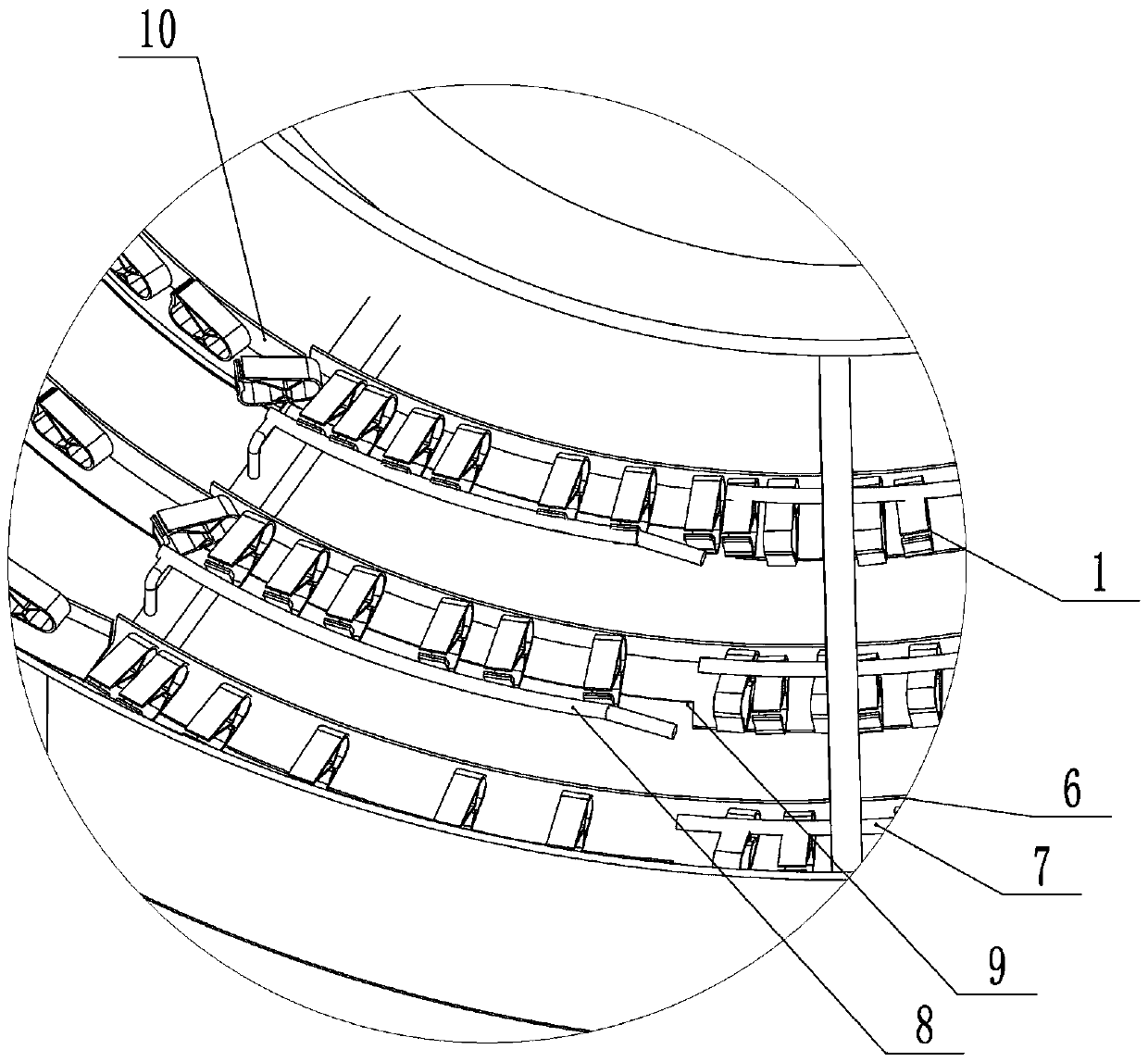
Automatic sequencing device for cut-off valves
ActiveCN107720182AGuaranteed stabilityImprove operational efficiencyConveyorsConveyor partsBiotechnologyAutomated sequencing
The invention provides an automatic sequencing device for cut-off valves. The automatic sequencing device comprises a vibrating disc. The vibrating disc is internally provided with a helical materialconveying way. The tail end of the helical material conveying way is provided with a plurality of sets of sliding ways. The tail end of the vibrating disc is provided with a feeding way. The tail endsof the sliding ways are provided with material passing ways. The tail ends of the material passing ways are provided with original material dosing ways. Screening openings are formed in the rear halfends of the original material dosing ways. The outer sides of the original material dosing ways are provided with steering material ways. The lower ends of the steering material ways are provided with overturning material ways. The material passing ways are provided with material passing rods and material passing openings. The material passing rods are arranged at the upper ends of the material passing openings, and a 35-degree angle is formed between the material passing rods and the material passing ways. The height of the lowest point of the material passing rods and the height of the material passing ways are 2mm higher than the height of the cut-off valves. The outer sides of the original material dosing ways are provided with original dosing sliding guiding rods. The original dosingsliding guiding rods are fixed on supporting rods. According to the automatic sequencing device for the cut-off valves, multiple direction decomposing and sorting and filtering are conducted on the material ways, sequencing and feeding of the cut-off valves are completed finally, and an on-line work original end is formed, so that smooth carrying out of automatic assembling equipment is facilitated, and the production efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:YANTAI KAIBO AUTOMATION TECH
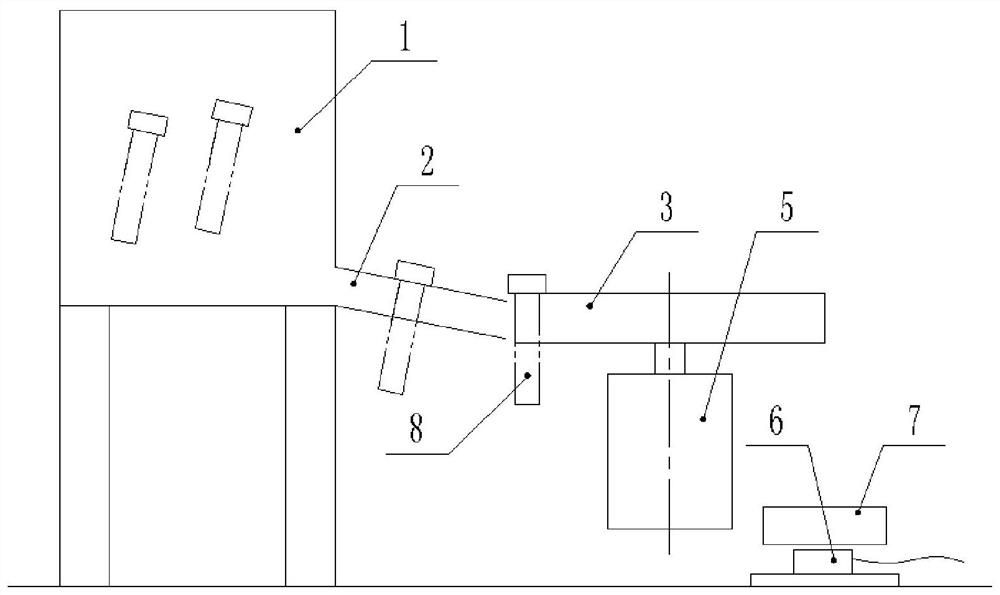
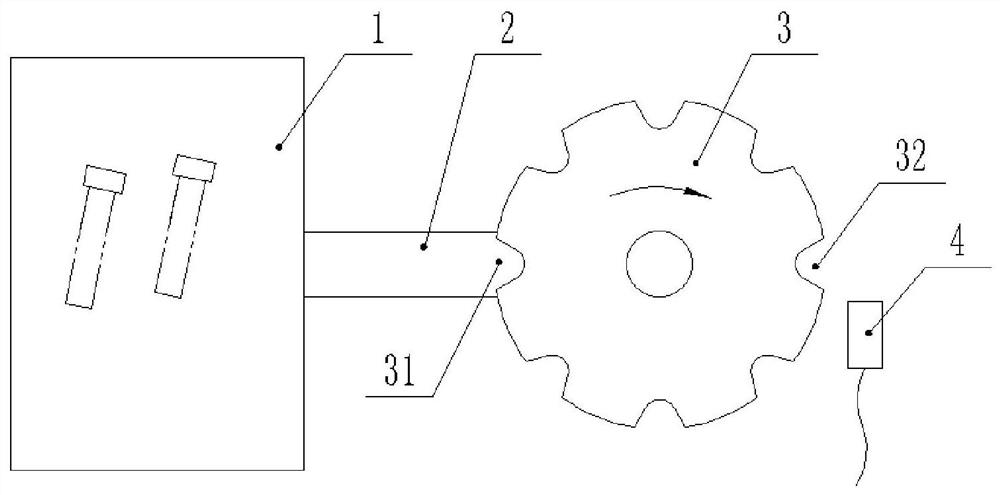
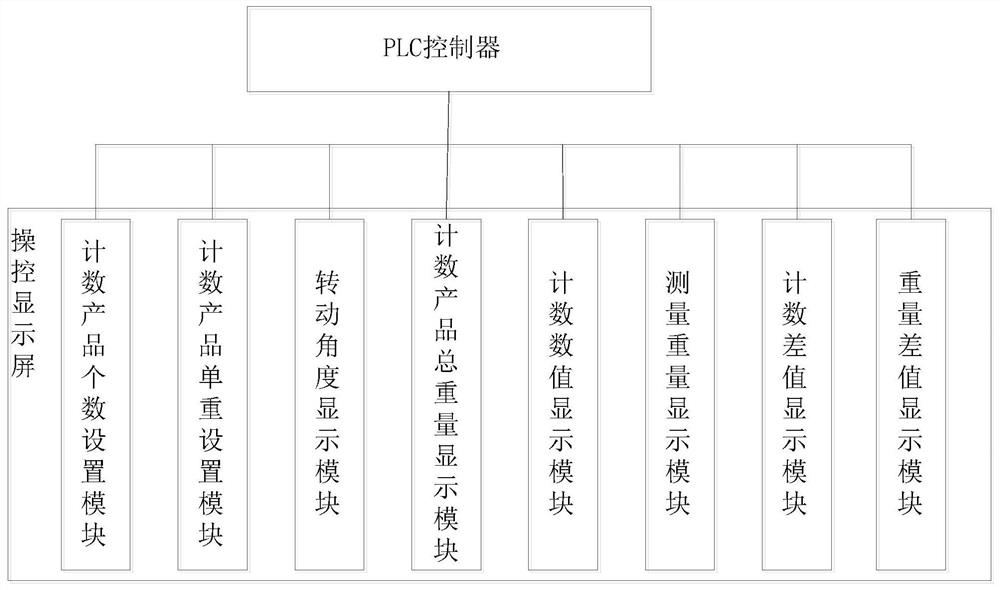
Counting device and method with automatic complementing and checking functions
PendingCN111924190AImprove Counting AccuracyImprove efficiencyPackaging automatic controlEmbedded systemAutomated sequencing
The invention discloses a counting device and method with automatic complementing and checking functions. The device comprises a PLC, a control display screen, an automatic sequencing device, a conveying device, an indexing rotating disc, a counting sensor, a servo motor, a weighing sensor and a weighing platform, wherein the indexing rotating disc is provided with a feeding port and a falling port; the automatic sequencing device is connected with the input end of the conveying device, and the output end of the conveying device is connected with the feeding port of the indexing rotating disc;the weighing sensor and the weighing platform are arranged below the falling port of the indexing rotating disc, the counting sensor is arranged at the falling port of the indexing rotating disc, andthe servo motor is connected with the indexing rotating disc; and the control display screen, the automatic sequencing device, the conveying device, the counting sensor, the servo motor and the weighing sensor are electrically connected with the PLC. The device has the advantages of being simple in structure, high in automation degree and high in counting accuracy.
Owner:刘思睿
Automatic identification machine for image recognition spring, and working method thereof
PendingCN112919080ASolve puzzlesLow costLiquid surface applicatorsRotary pressesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an automatic identification machine for image recognition spring, and a working method thereof. The automatic identification machine is composed of a spring density ring automatic sequencing unit, a spring translation unit, a spring end face automatic locating unit, a spring automatic identification unit, a spring drying unit and a spring conveying unit. Springs are input through the spring density ring automatic sequencing unit, the front and back positions of spring density rings are judged through a pitch measuring camera, and the springs which do not meet the requirements are turned over through a spring density ring turnover mechanism; the sequenced springs are conveyed to the spring end face automatic locating unit through the spring translation unit; the position of an end face notch is measured through an end face notch measuring camera, and the springs are conveyed to the spring automatic identification unit through a spring pushing mechanism for identification; and the spring drying unit is used for drying, and the marked springs are conveyed through the spring conveying unit. According to the automatic identification machine, the problems that manual identification is slow, low in efficiency, prone to making mistakes, and not standard are solved, the cost is reduced, and the efficiency and quality are improved.
Owner:北京金维畅想科技有限公司
Nucleic acid sequencing in free solution using protein polymer drag-tags
InactiveUS20160376646A1High resolutionCleaner resultMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoassaysMolecular compositionFree solution
The present invention relates to systems, compositions, and methods for nucleic acid sequencing and analysis in free-solution using protein polymer drag-tags. As such, the present invention provides protein-based molecular compositions that find use as drag-tags for use in sequencing and nucleic acid analysis methods and provides systems and methods for automated sequencing and analysis of nucleic acids in free solution.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
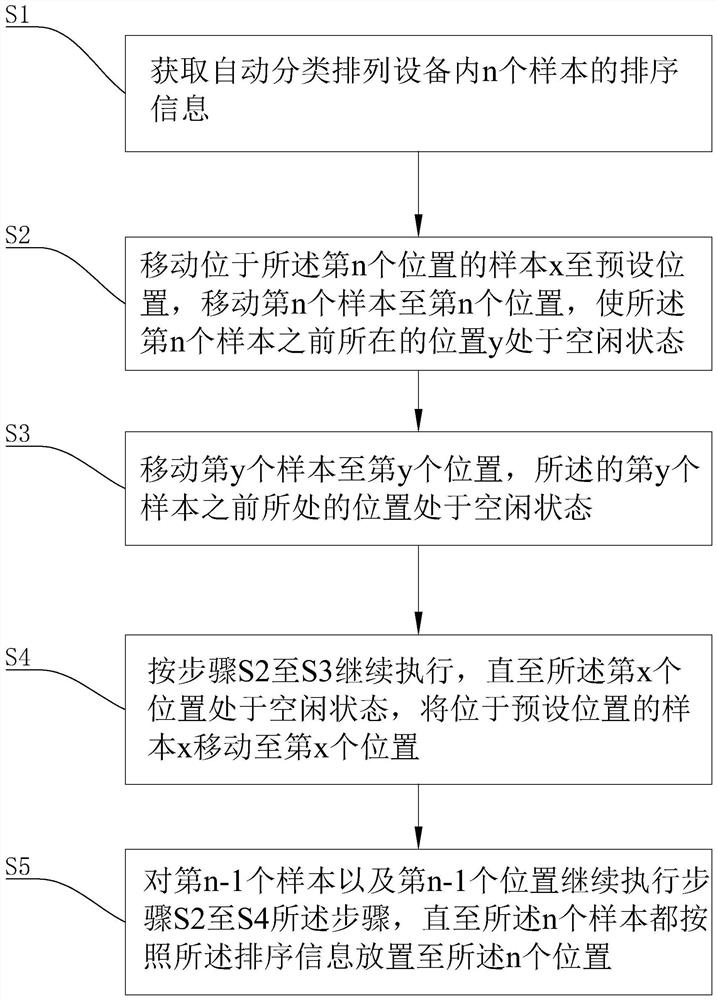
Automatic classification and arrangement method and equipment applied to pathological tissue slices
PendingCN112986599AImprove the efficiency of position adjustmentAvoid problems with inaccurate sort orderMaterial analysisRadiologyComputer science
The invention discloses an automatic classification and arrangement method and equipment applied to pathological tissue slices, and belongs to the technical field of automatic classification of the pathological tissue slices. According to the method and the device, the plurality of samples in the automatic classification and arrangement equipment are automatically sorted according to the sorting information through the obtained sorting information, so that not only is the position adjustment efficiency of the plurality of samples improved, but also the problem of inaccurate sorting sequence caused by manual sorting is avoided.
Owner:HANGZHOU HEALTHSKY BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com