Patents
Literature
252 results about "Complementary DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA synthesized from a single-stranded RNA (e.g., messenger RNA (mRNA) or microRNA) template in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. cDNA is often used to clone eukaryotic genes in prokaryotes. When scientists want to express a specific protein in a cell that does not normally express that protein (i.e., heterologous expression), they will transfer the cDNA that codes for the protein to the recipient cell. cDNA is also produced naturally by retroviruses (such as HIV-1, HIV-2, simian immunodeficiency virus, etc.) and then integrated into the host's genome, where it creates a provirus.
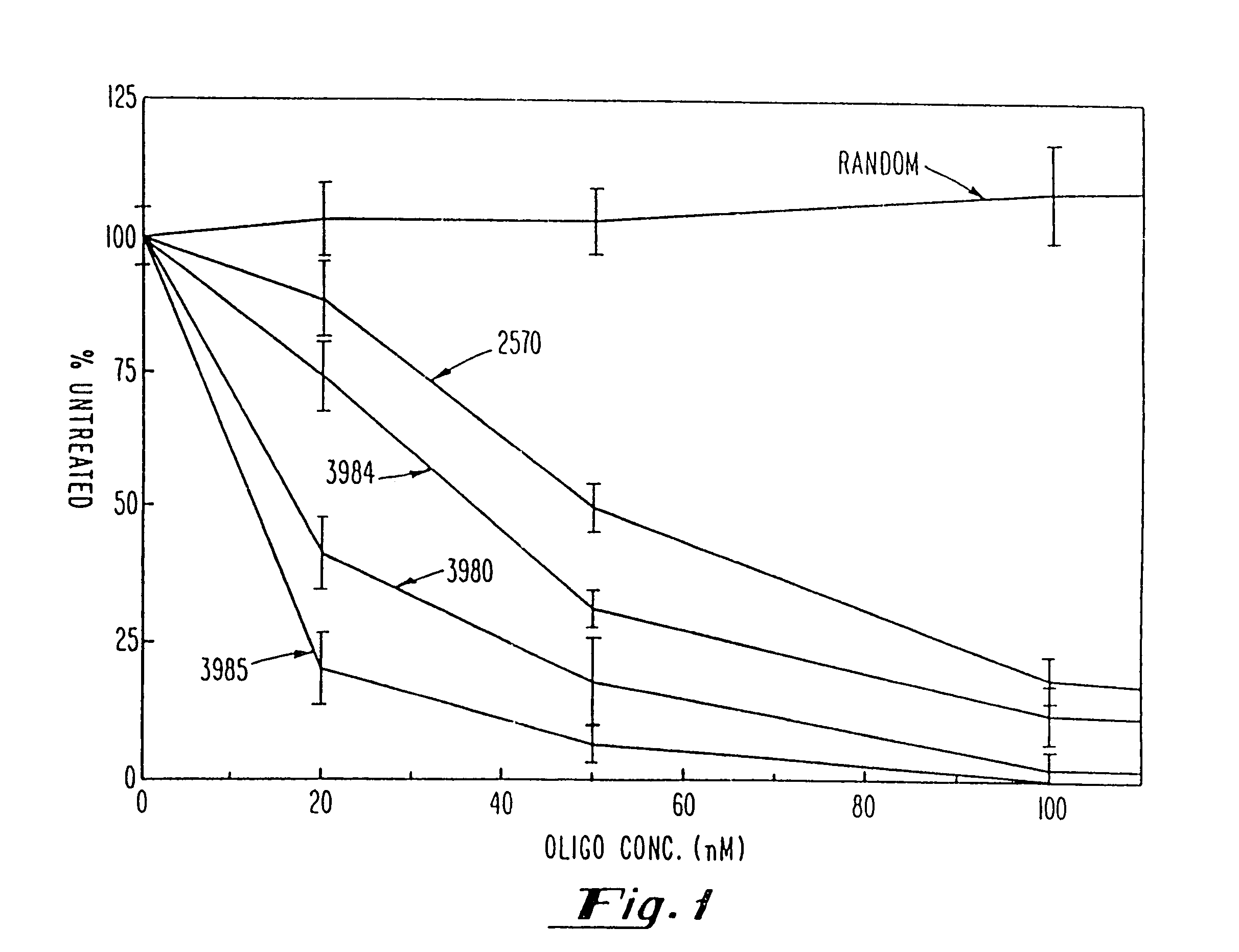
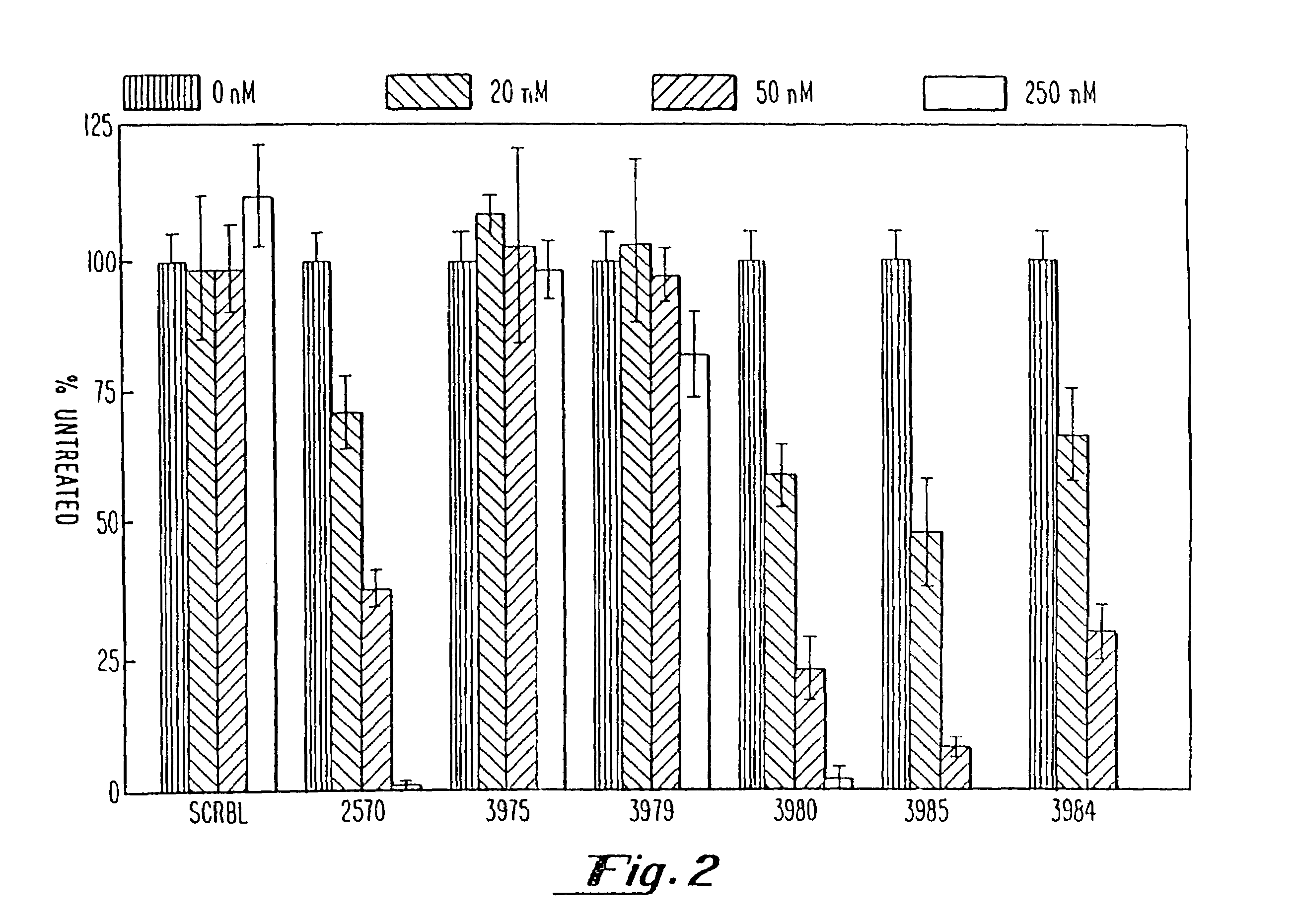
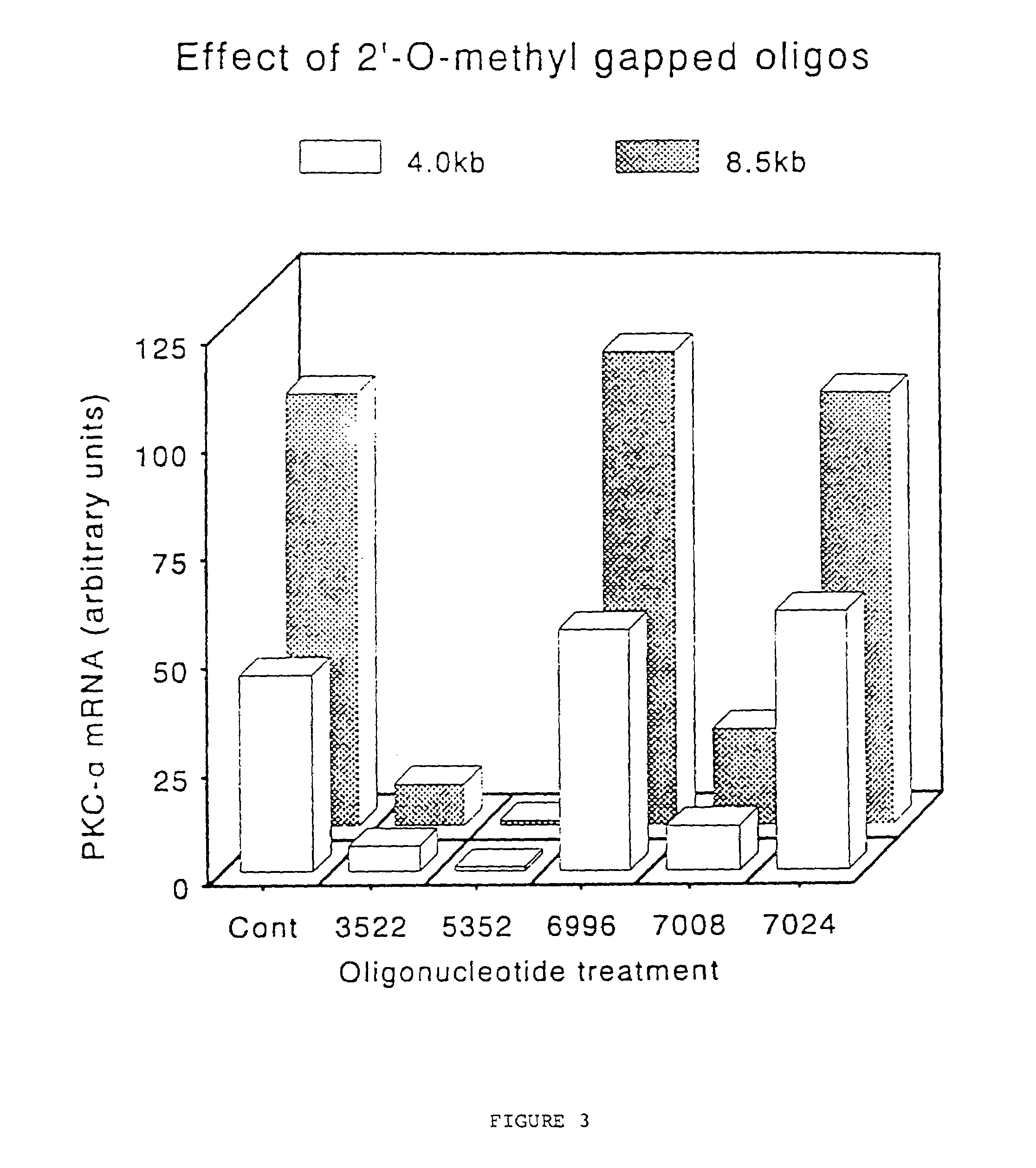
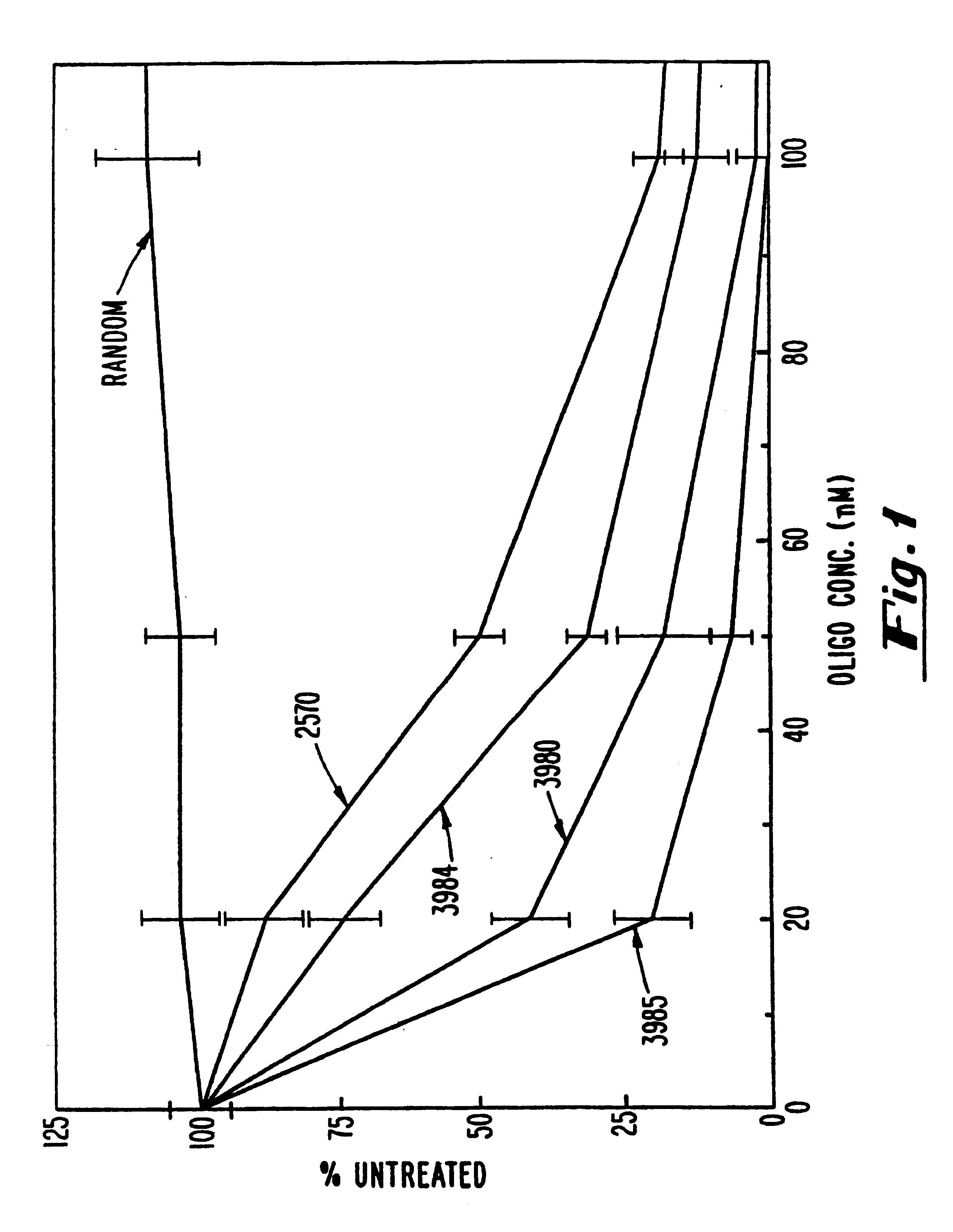
Gapped oligonucleotides
InactiveUS7015315B1Increased nuclease resistanceHigh binding affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsNuclease
Oligonucleotides and other macromolecules are provided which have increased nuclease resistance, substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary strand, and subsequences of 2′-deoxy-erythro-pentofuranosyl nucleotides that activate RNase H. Such oligonucleotides and macromolecules are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Gapped 2' modified oligonucleotides
InactiveUS6326199B1High affinityAvoid degradationHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideNuclease
Oligonucleotides and other macromolecules are provided that have increased nuclease resistance, substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary strand, and sub-sequences of 2'-deoxy-erythro-pentofuranosyl nucleotides that activate RNase H enzyme. Such oligonucleotides and macromolecules are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to antisense therapeutics.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
High speed parallel molecular nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS6982146B1Minimize shearImprove automationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
A method and device is disclosed for high speed, automated sequencing of nucleic acid molecules. A nucleic acid molecule to be sequenced is exposed to a polymerase in the presence of nucleotides which are to be incorporated into a complementary nucleic acid strand. The polymerase carries a donor fluorophore, and each type of nucleotide (e.g. A, T / U, C and G) carries a distinguishable acceptor fluorophore characteristic of the particular type of nucleotide. As the polymerase incorporates individual nucleic acid molecules into a complementary strand, a laser continuously irradiates the donor fluorophore, at a wavelength that causes it to emit an emission signal (but the laser wavelength does not stimulate the acceptor fluorophore). In particular embodiments, no laser is needed if the donor fluorophore is a luminescent molecule or is stimulated by one. The emission signal from the polymerase is capable of stimulating any of the donor fluorophores (but not acceptor fluorophores), so that as a nucleotide is added by the polymerase, the acceptor fluorophore emits a signal associated with the type of nucleotide added to the complementary strand. The series of emission signals from the acceptor fluorophores is detected, and correlated with a sequence of nucleotides that correspond to the sequence of emission signals.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF US SEC THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE
Methods for localized in situ detection of mRNA
ActiveUS8551710B2Easy to detectHigh affinitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
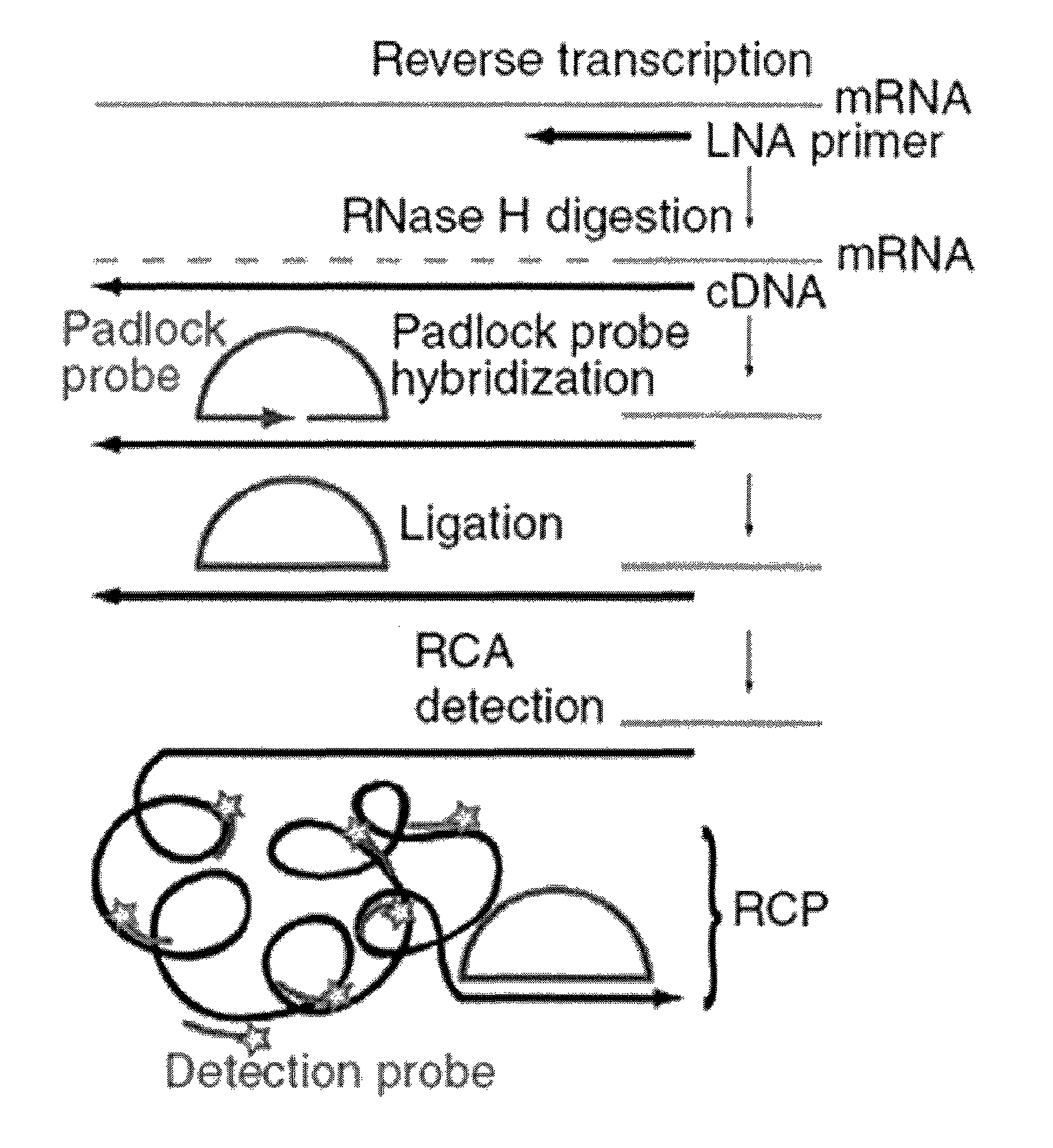
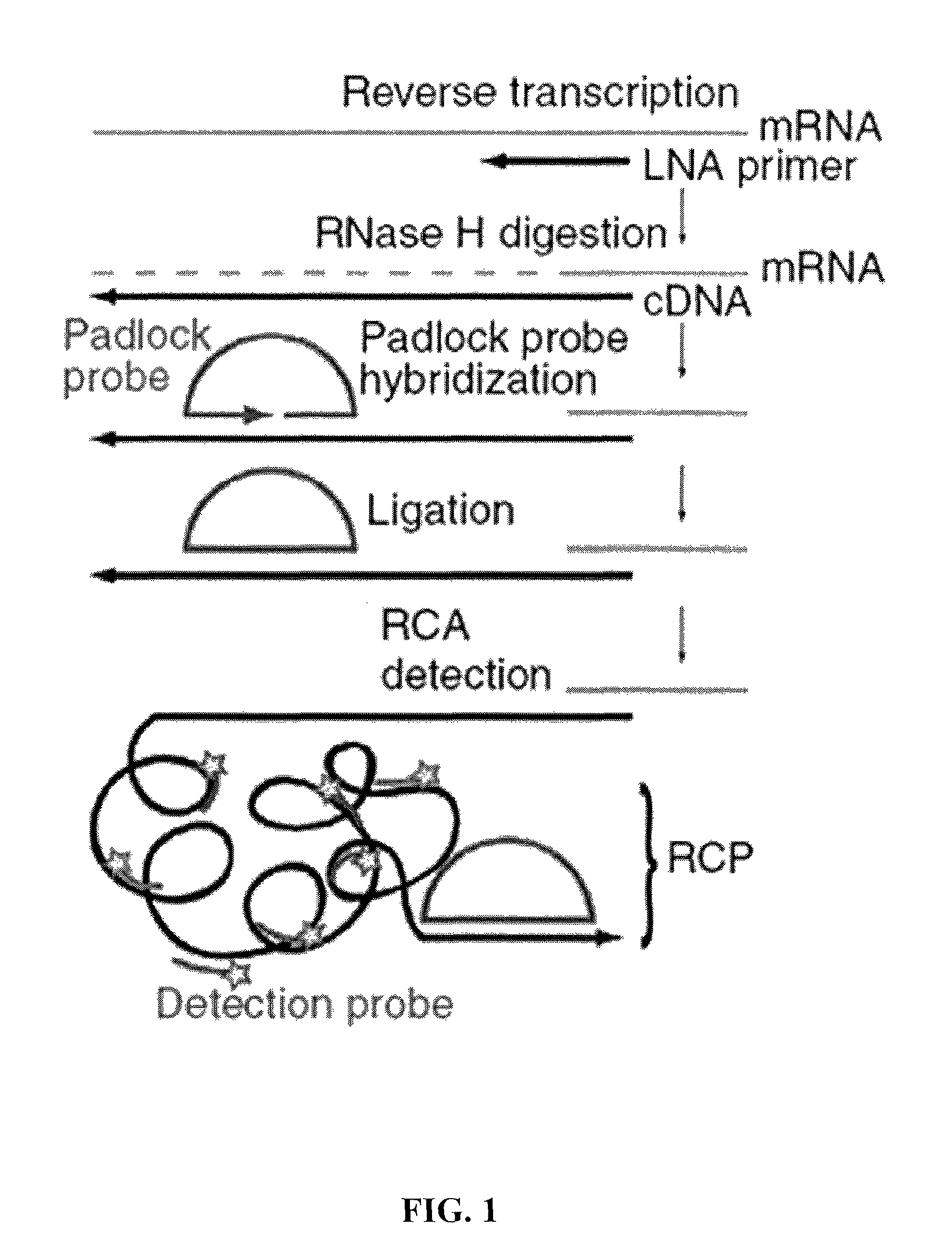
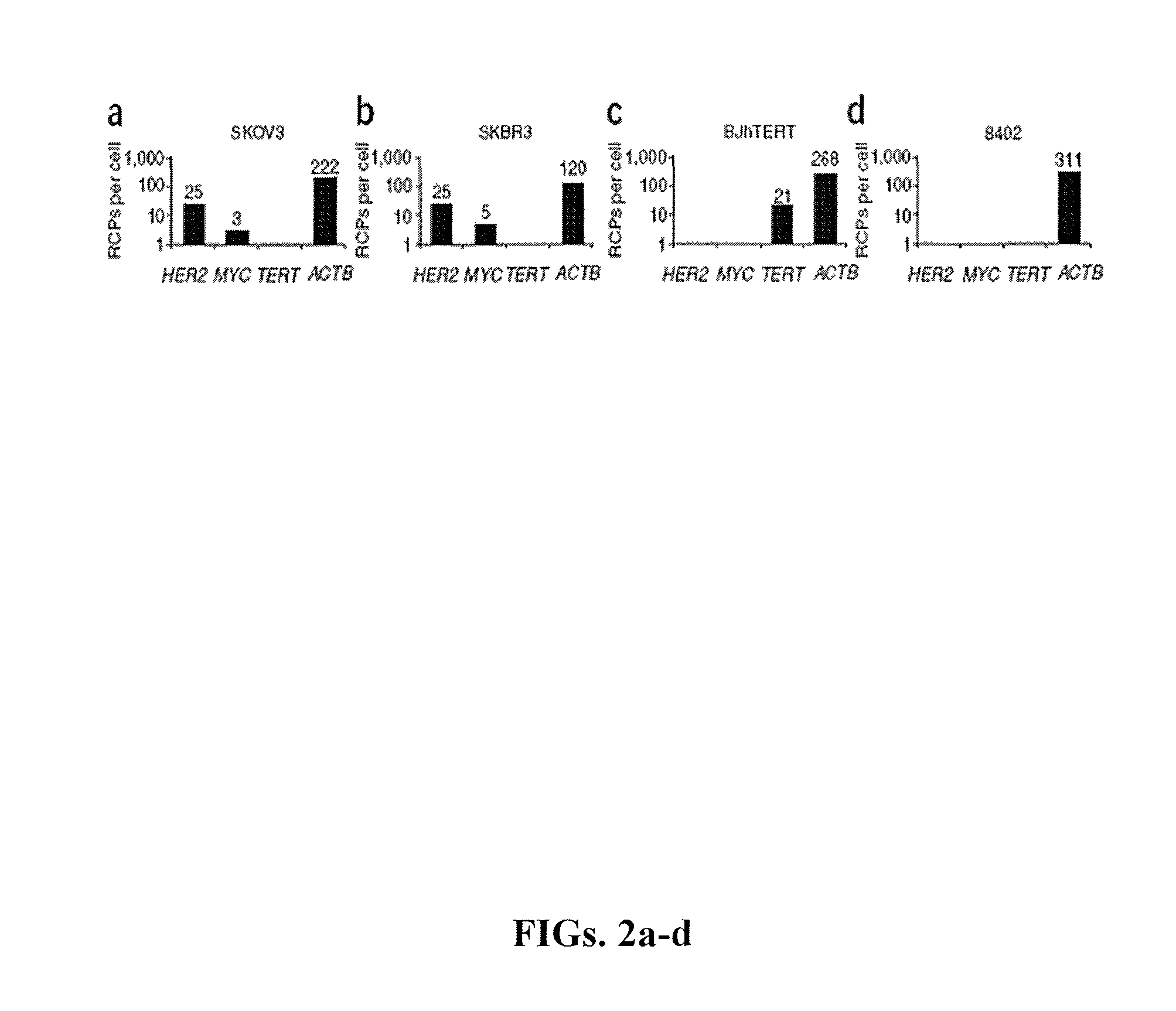
The present invention relates to the detection of RNA in a sample of cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to the localized detection of RNA in situ. The method relies on the conversion of RNA to complementary DNA prior to the targeting of the cDNA with a padlock probe(s). The hybridization of the padlock probe(s) relies on the nucleotide sequence of the cDNA which is derived from the corresponding nucleotide sequence of the target RNA. Rolling circle amplification of the subsequently circularized padlock probe produces a rolling circle product which may be detected. Advantageously, this allows the RNA to be detected in situ.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST NEWCASTLE
Gapped 2' modified oligonucleotides
InactiveUS6146829AHigh affinityAvoid degradationSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleaseOrganism
Oligonucleotides and other macromolecules are provided that have increased nuclease resistance, substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary strand, and sub-sequences of 2'-deoxy-erythro-pentofuranosyl nucleotides that activate RNase H enzyme. Such oligonucleotides and macromolecules are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to antisense therapeutics.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
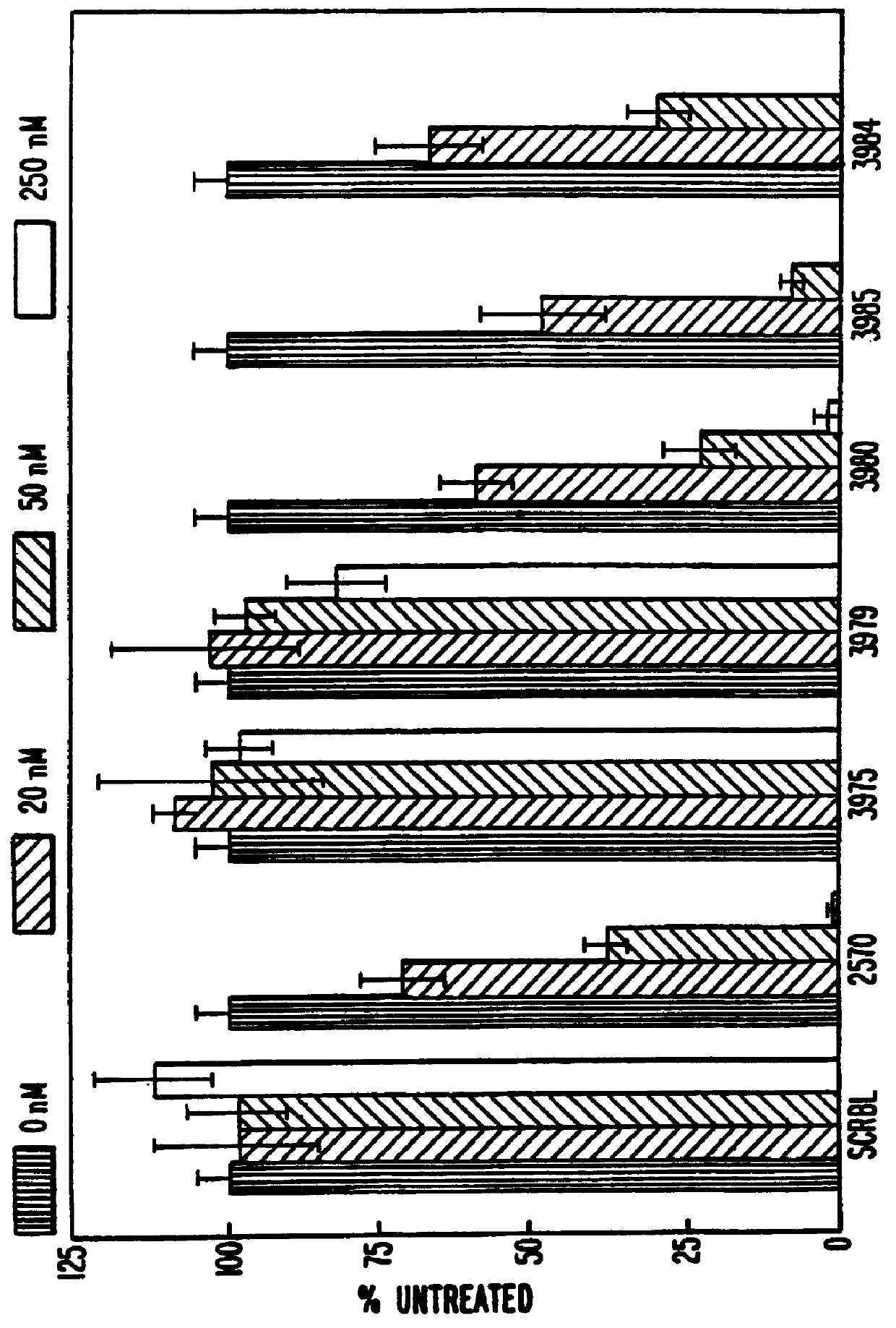
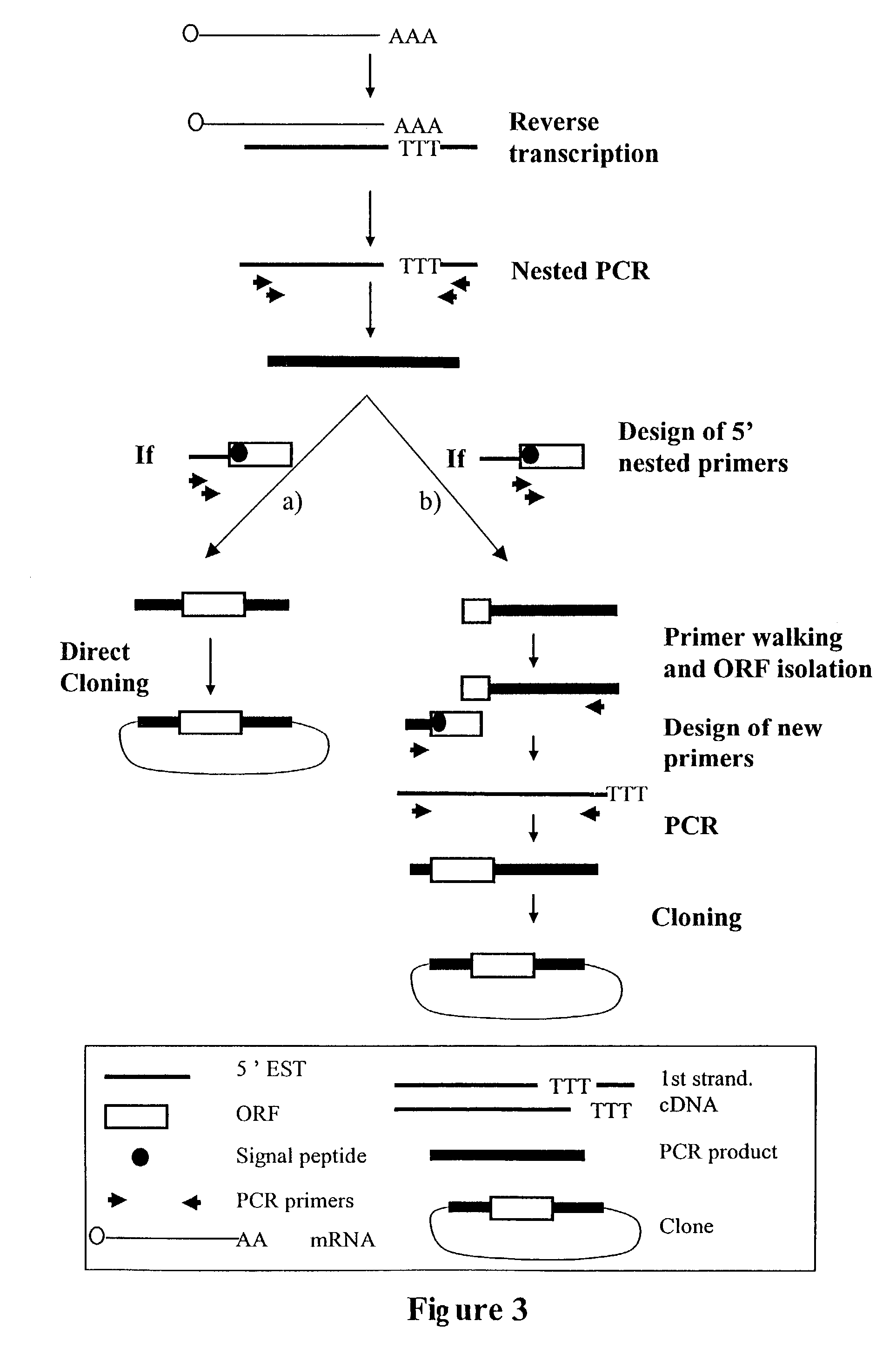
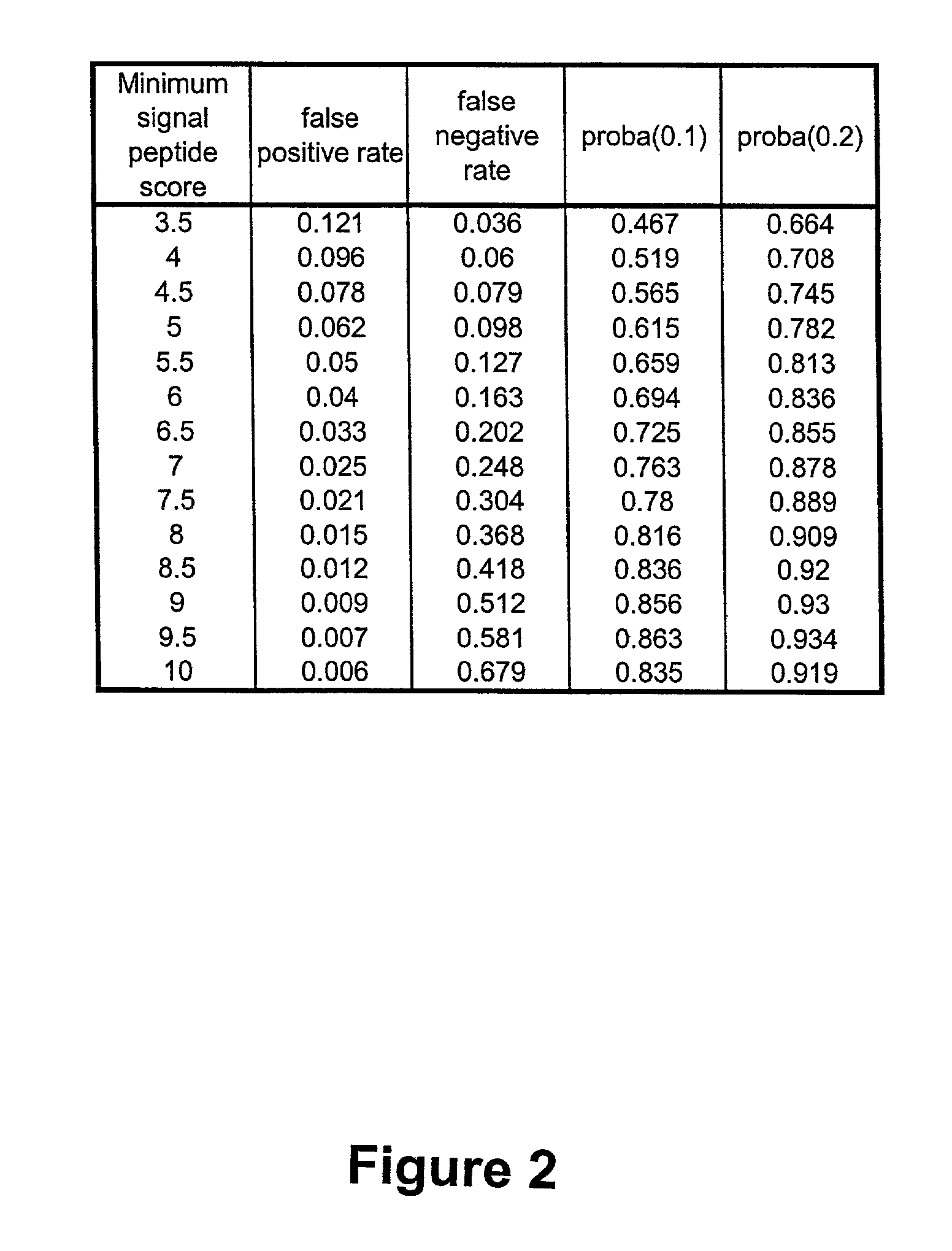
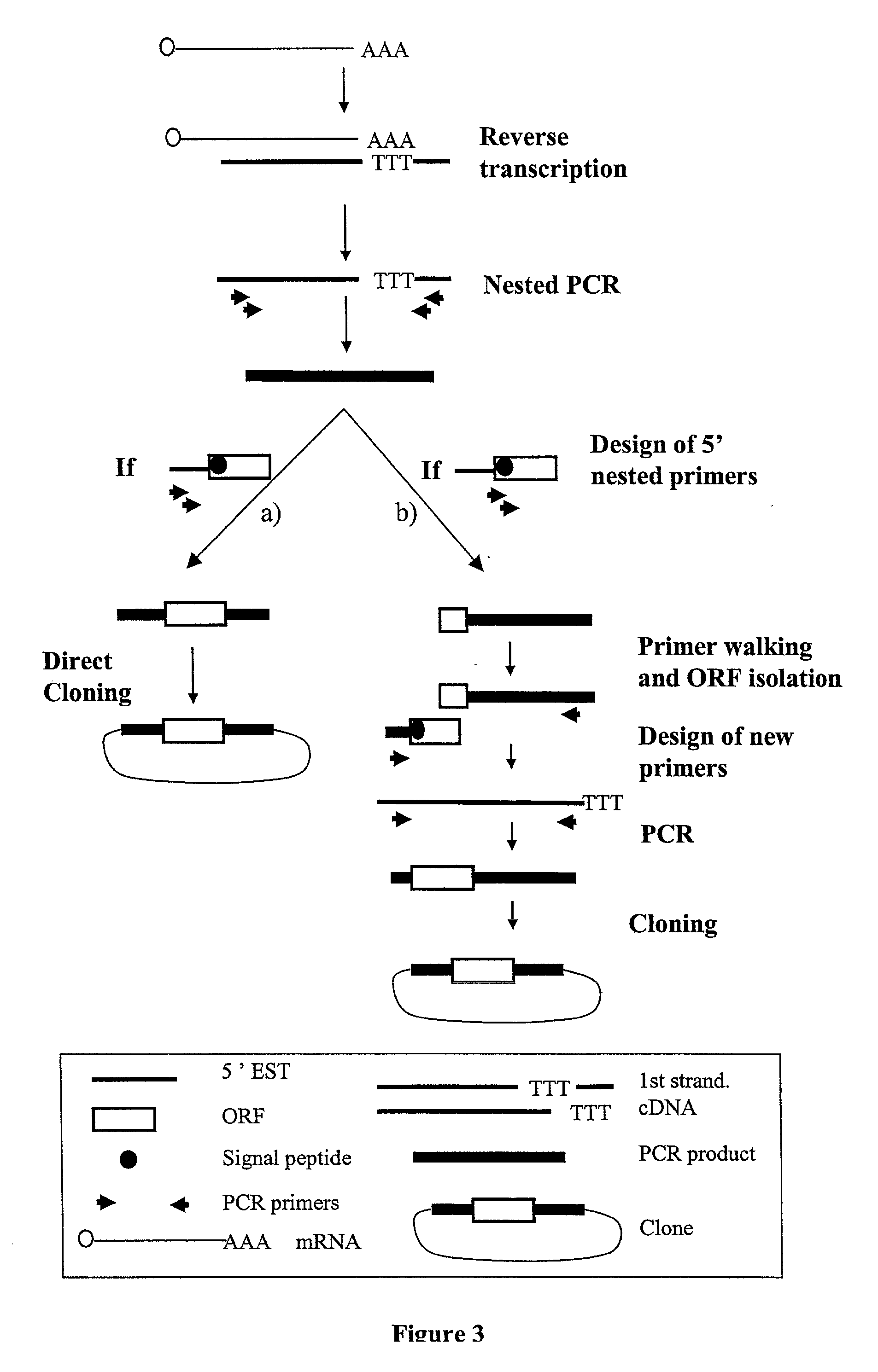
Complementary DNAs encoding proteins with signal peptides
InactiveUS7385034B2Improve purification effectSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsSecretory protein
The sequences of cDNAs encoding secreted proteins are disclosed. The cDNAs can be used to express secreted proteins or fragments thereof or to obtain antibodies capable of specifically binding to the secreted proteins. The cDNAs may also be used in diagnostic, forensic, gene therapy, and chromosome mapping procedures. The cDNAs may also be used to design expression vectors and secretion vectors.
Owner:SERONO GENETICS INST SA
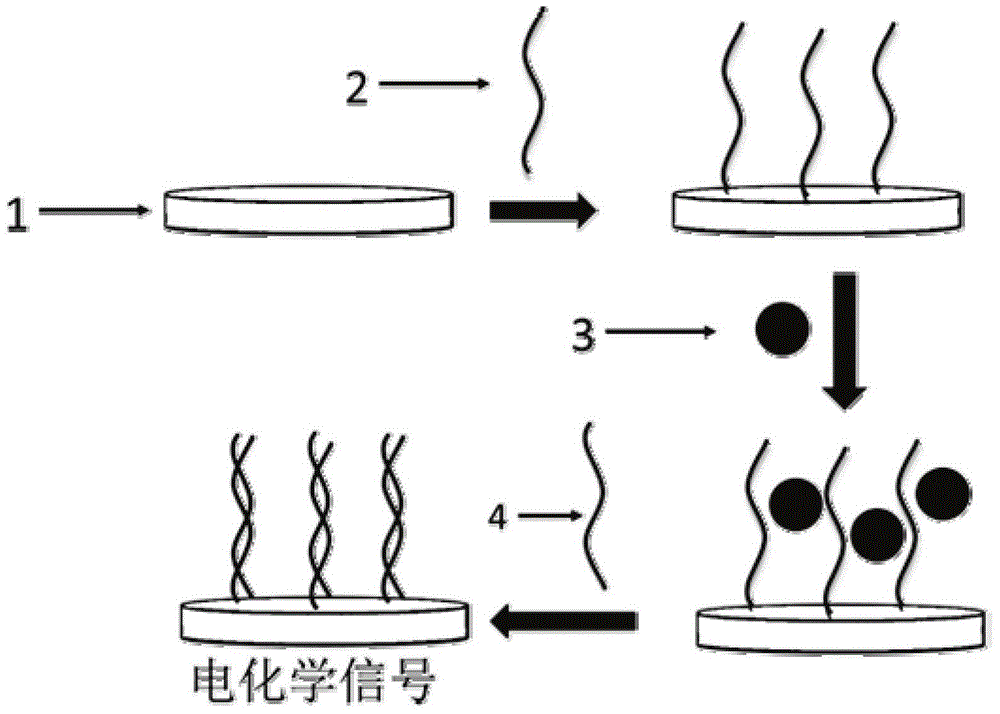
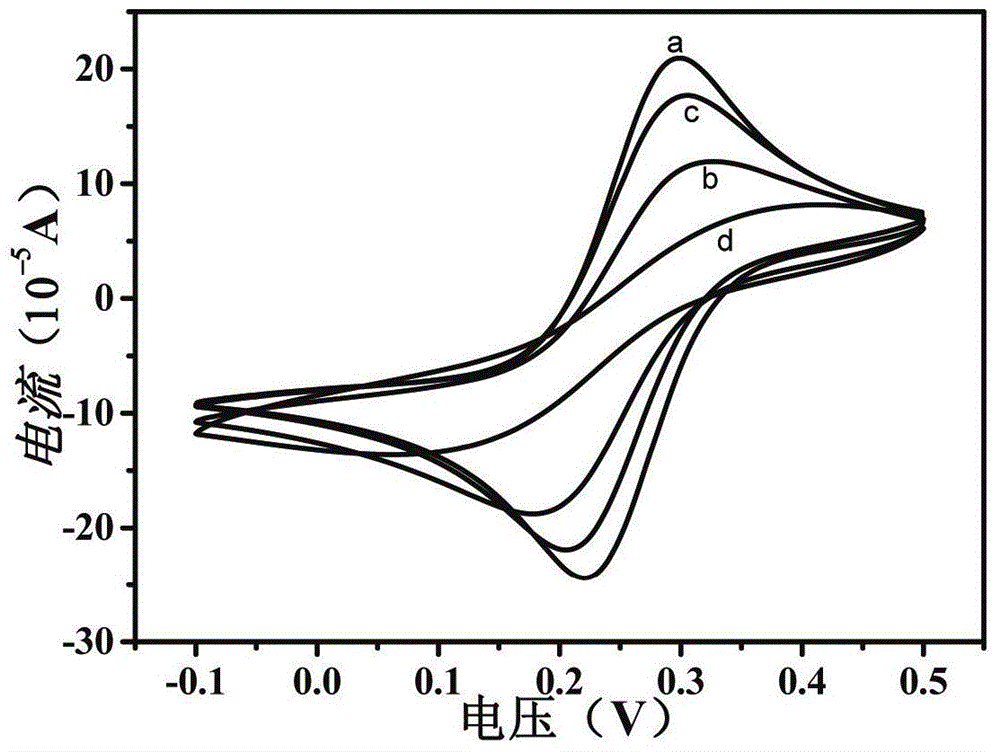
DNA electrochemical sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101078026AHigh densityStrong Mismatch CapabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization reactionElectrochemistry
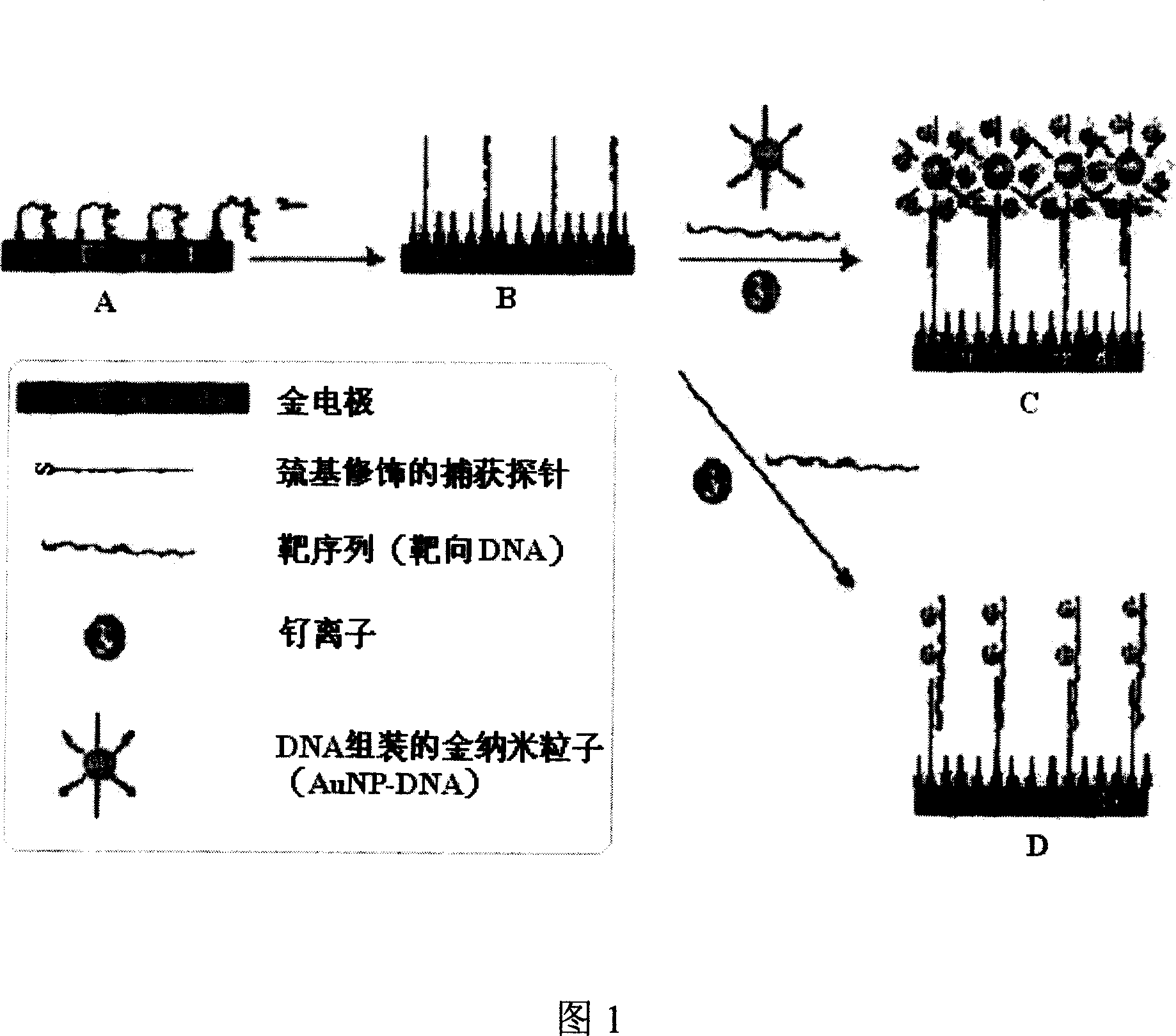
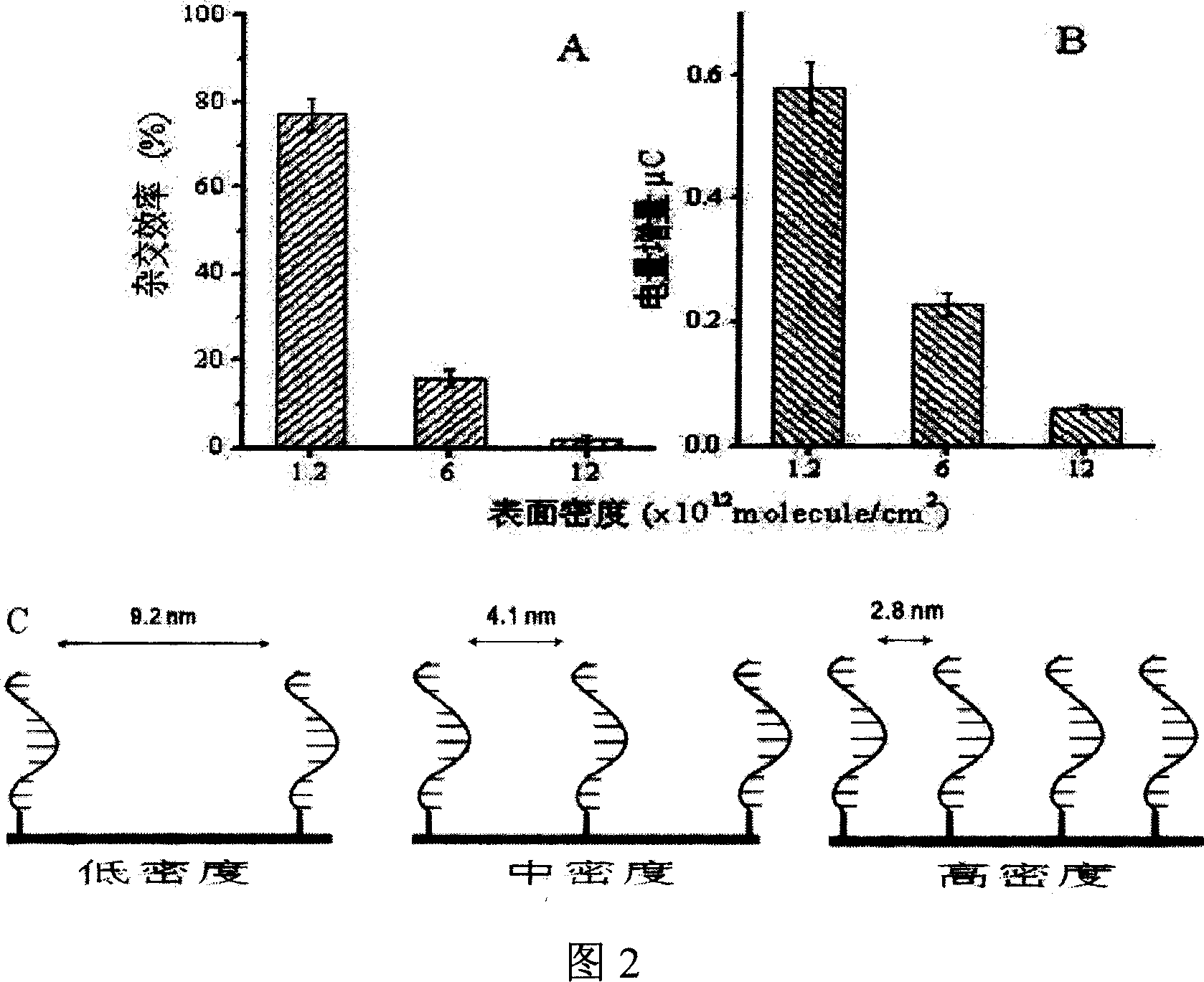
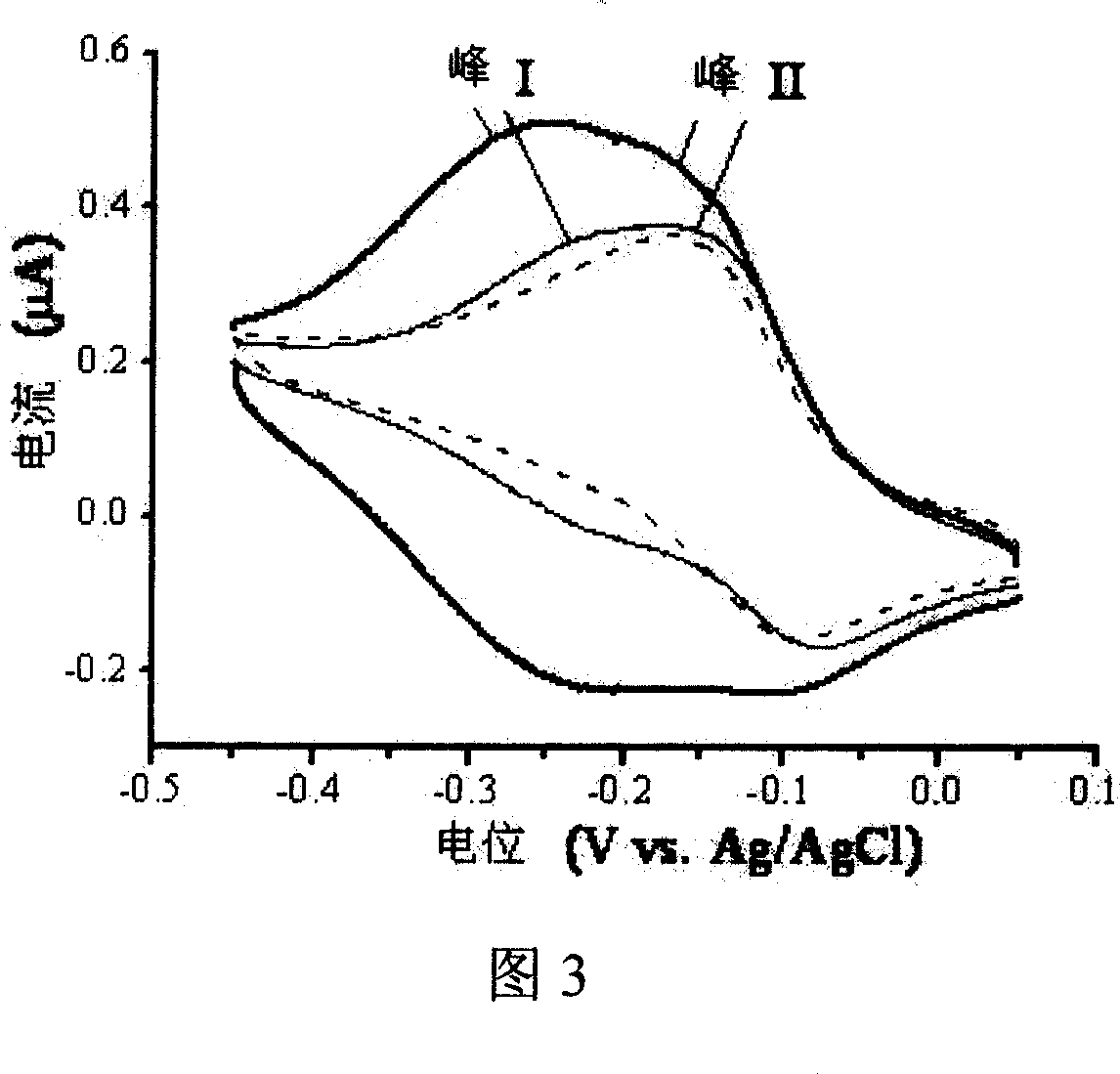
The invention describes a kind of DNA electrochemistry sensor, which comprises gold pole, complementary DNA, gold nano-particles and electrochemistry indicator. It is characterized in that one segment of complementary DNA is assembled onto the gold pole as capture probe, and the other segment as detection probe is integrated with the gold nano-particles to be the carrier of electrochemistry indicator. The preparation method is disclosed. By means of 'sandwich' hybridization method, the surface of the pole has high DNA chains with negative charge and The VIII family transition metal ions with positive charge was introduced to combine with DNA as electrochemistry indicator. The DNA hybridization reaction is indicated by detecting the electrochemistry numerical change (electric current or quantity) of the pole surface. Because of the amplification effect of the gold nano-particles, the sensor can detect trace DNA with high selectivity and the gold pole modified with DNA can be used repeatedly.
Owner:JIANGSU WUZHONG HIGH & NEW TECH IND
Mammalian cell surface DNA receptor
The present invention relates to novel mammalian DNA-R proteins and genes that encode such proteins. The invention is directed toward the isolation and characterization of mammalian DNA-R proteins. The invention specifically provides isolated complementary DNA copies of mRNA corresponding to rat and human homologues of a mammalian DNA-R gene. Also provided are recombinant expression constructs capable of expressing the mammalian DNA-R genes of the invention in cultures of transformed prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as such cultures of transformed cells that synthesize the mammalian catecholamine receptor proteins encoded therein. The invention also provides methods for screening compounds in vitro that are capable of binding to the mammalian DNA-R proteins of the invention, and further characterizing the binding properties of such compounds in comparison with known DNA-R agonists and antagonists. Improved methods of pharmacological screening are provided thereby.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
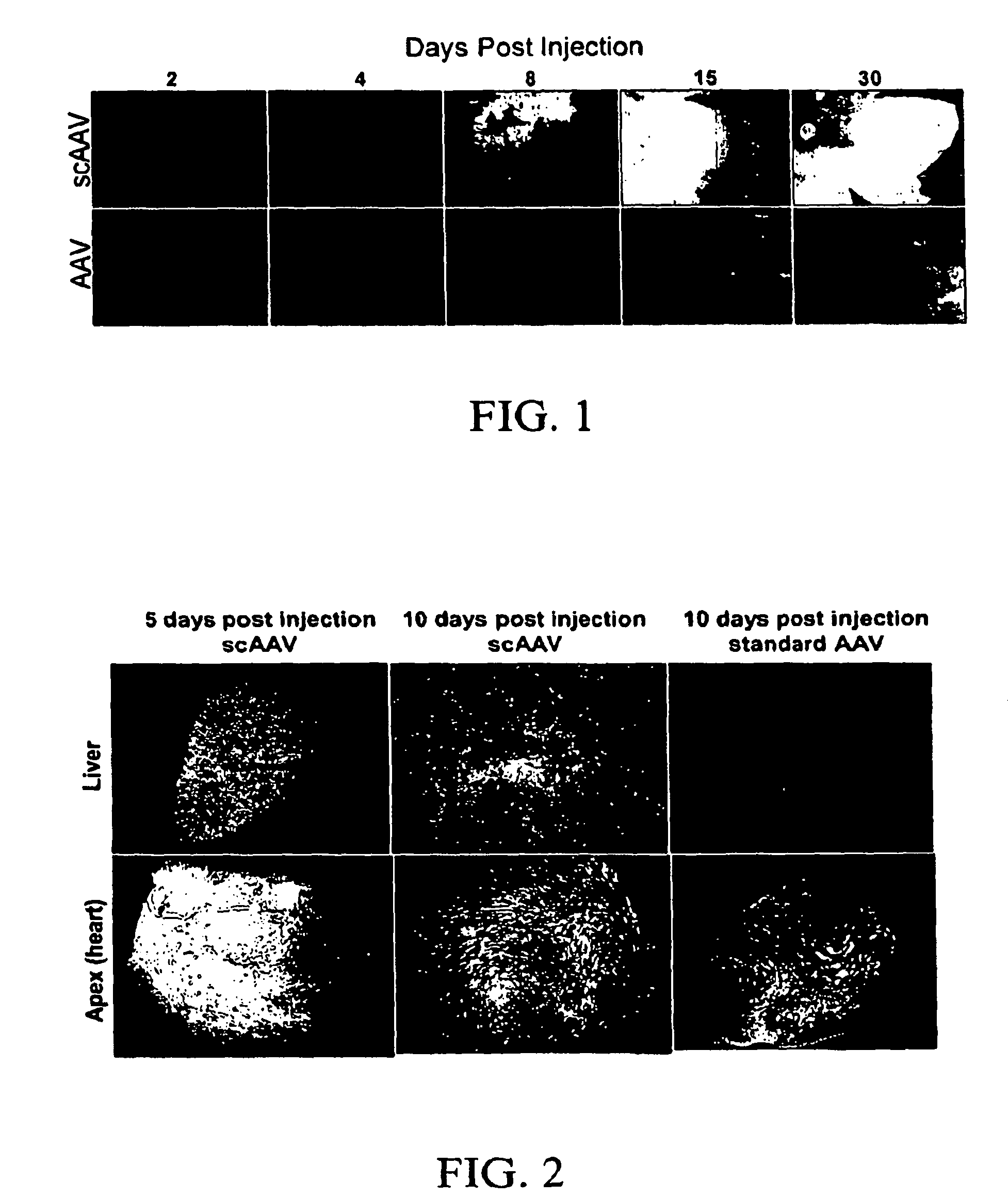
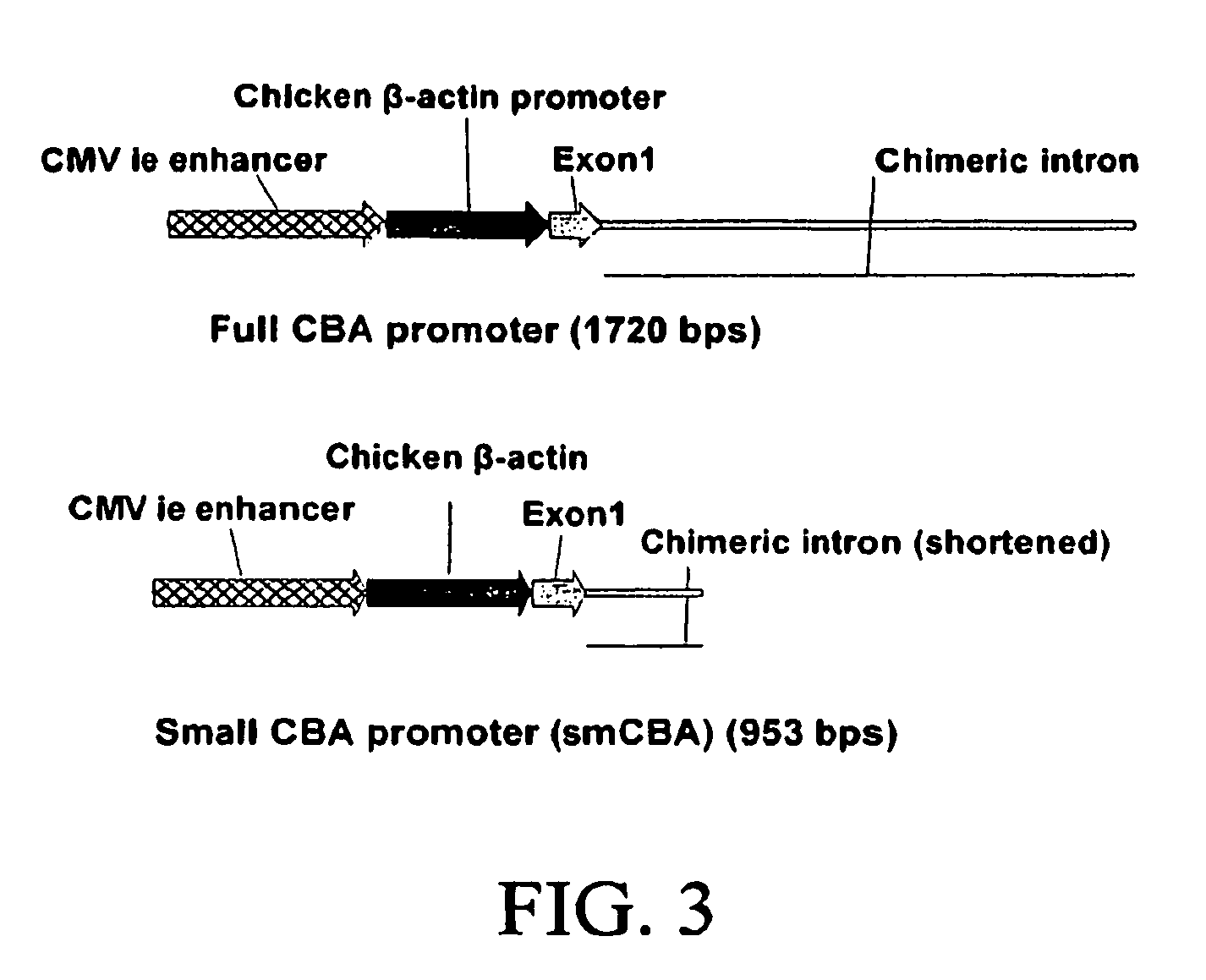
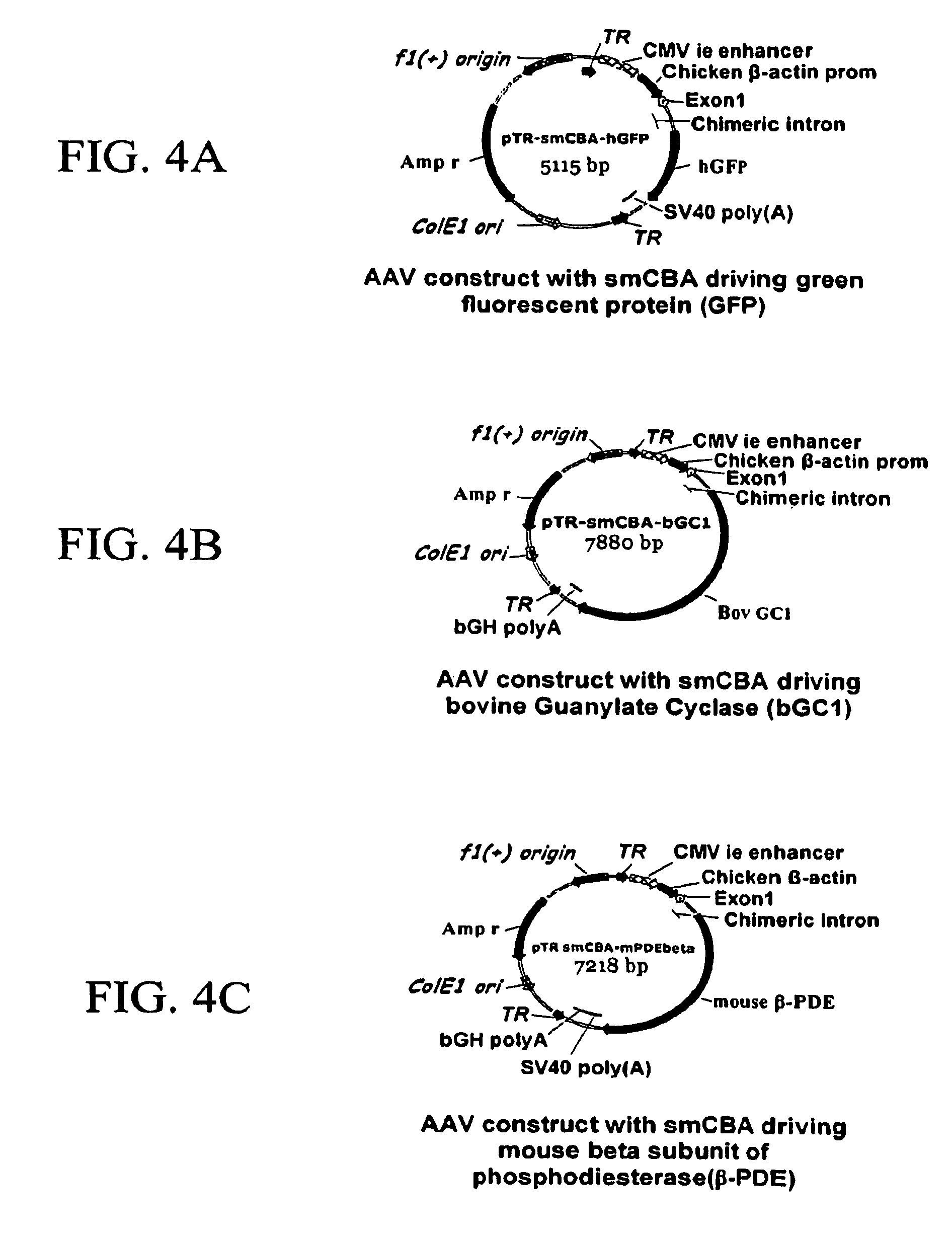
Self-complementary adeno-associated virus having a truncated CMV-chicken β-actin promoter
The present inventors concerns vectors carrying a truncated chimeric CMV-chicken β-actin (smCBA) promoter in which the hybrid chicken β-actin / rabbit β-globin intron is greatly shortened, and their use to deliver to an operatively linked polynucleotide to host cells in vitro or in vivo, resulting in expression of the polynucleotide in the host cells. In one embodiment, the vector carrying the smCBA promoter is administered to the eye. In another embodiment, the vector carrying the smCBA promoter is a self-complementary adeno-associated virus (AAV). The AAV vector may be of any serotype (e.g., type 1, type 2, type 3, type 4, type 5, type 6, type 7, type 8, type 9, type 10). In another embodiment, a self-complementary vector carrying the smCBA promoter is administered to the eye. Another aspect of the invention concerns host cells carrying a vector of the invention. Another aspect of the invention concerns pharmaceutical composition comprising the vectors or host cells of the invention, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Bioelectrochemical sensor for detecting tumor markers and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102262118AMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDNA/RNA fragmentationProtein targetBioelectrochemistry
The invention relates to a bioelectrochemical sensor for detecting tumor markers and a preparation method thereof. It is a three-electrode system sensor, which is characterized in that the counter electrode in the three electrodes is a platinum electrode, the reference electrode is a saturated calomel electrode, and the working electrode is a gold electrode, and the gold electrode is decorated with two tumor markers The complementary DNA strand of the DNA aptamer, that is, the cDNA strand, is labeled with an electrochemical probe ferrocene molecule at the end of the cDNA strand. The novel bioelectrochemical sensor for detecting tumor markers of the present invention combines the characteristics of highly specific binding of DNA aptamers to target proteins and high sensitivity of electrochemical detection methods, making early diagnosis of cancer possible.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
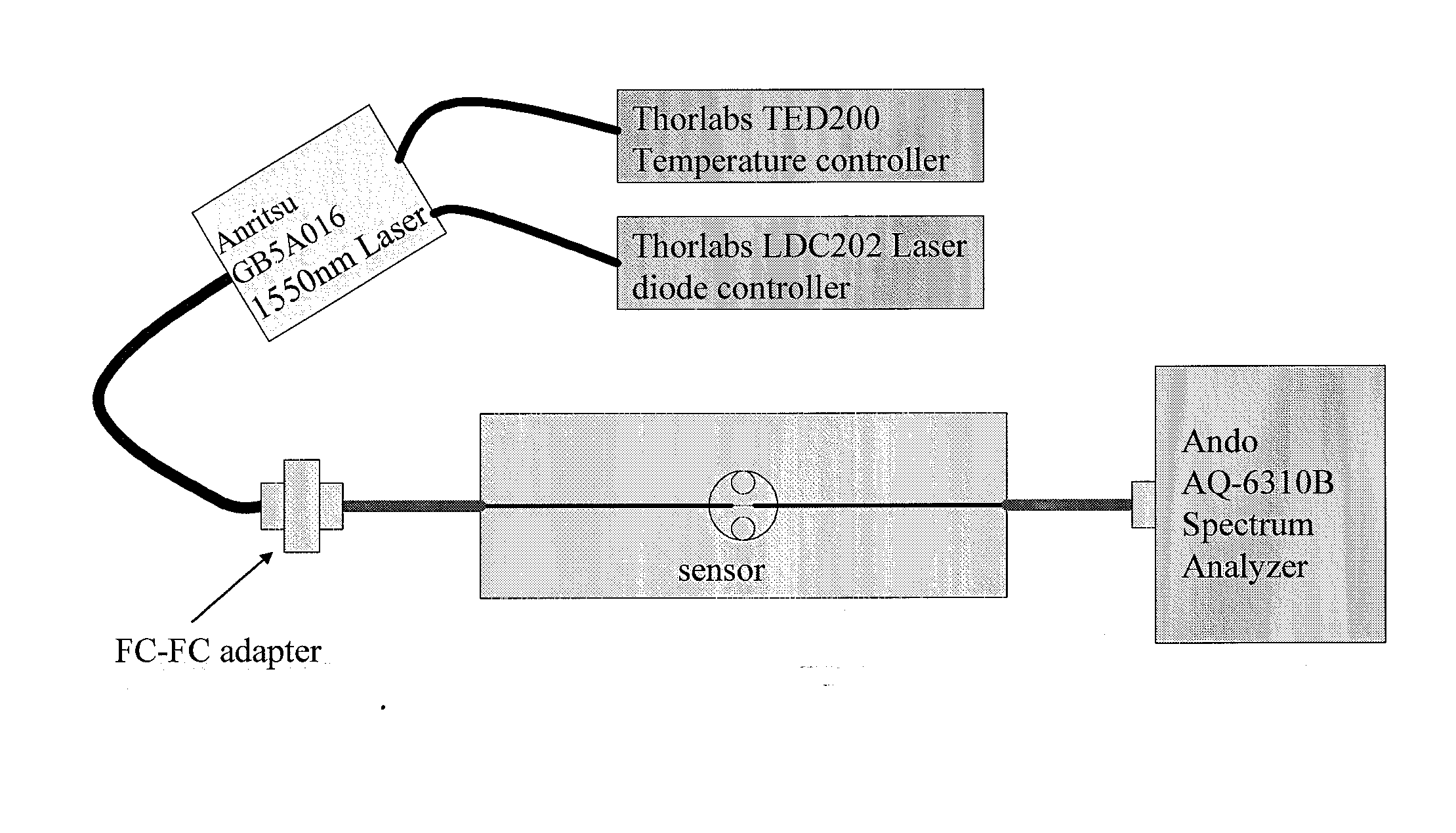
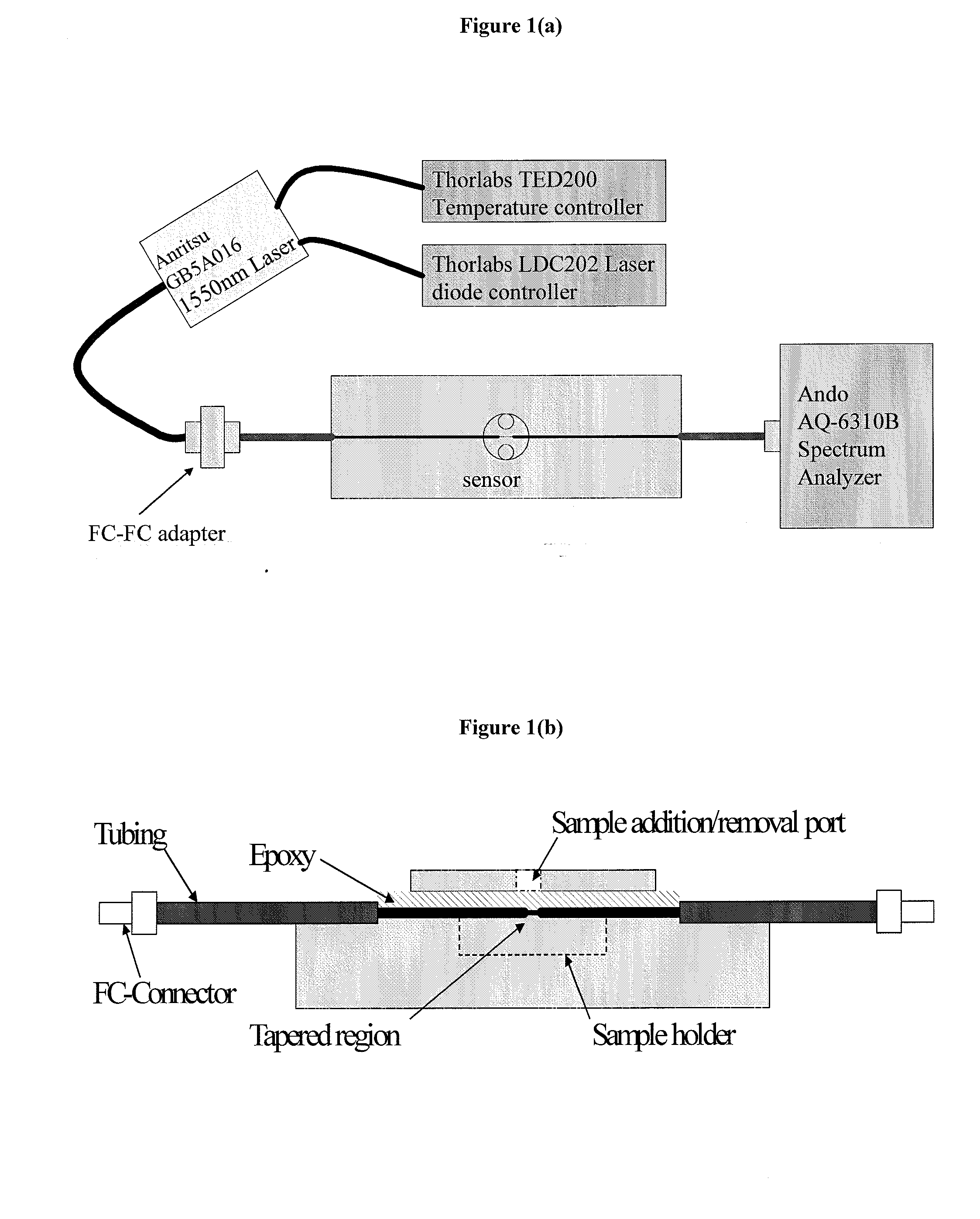
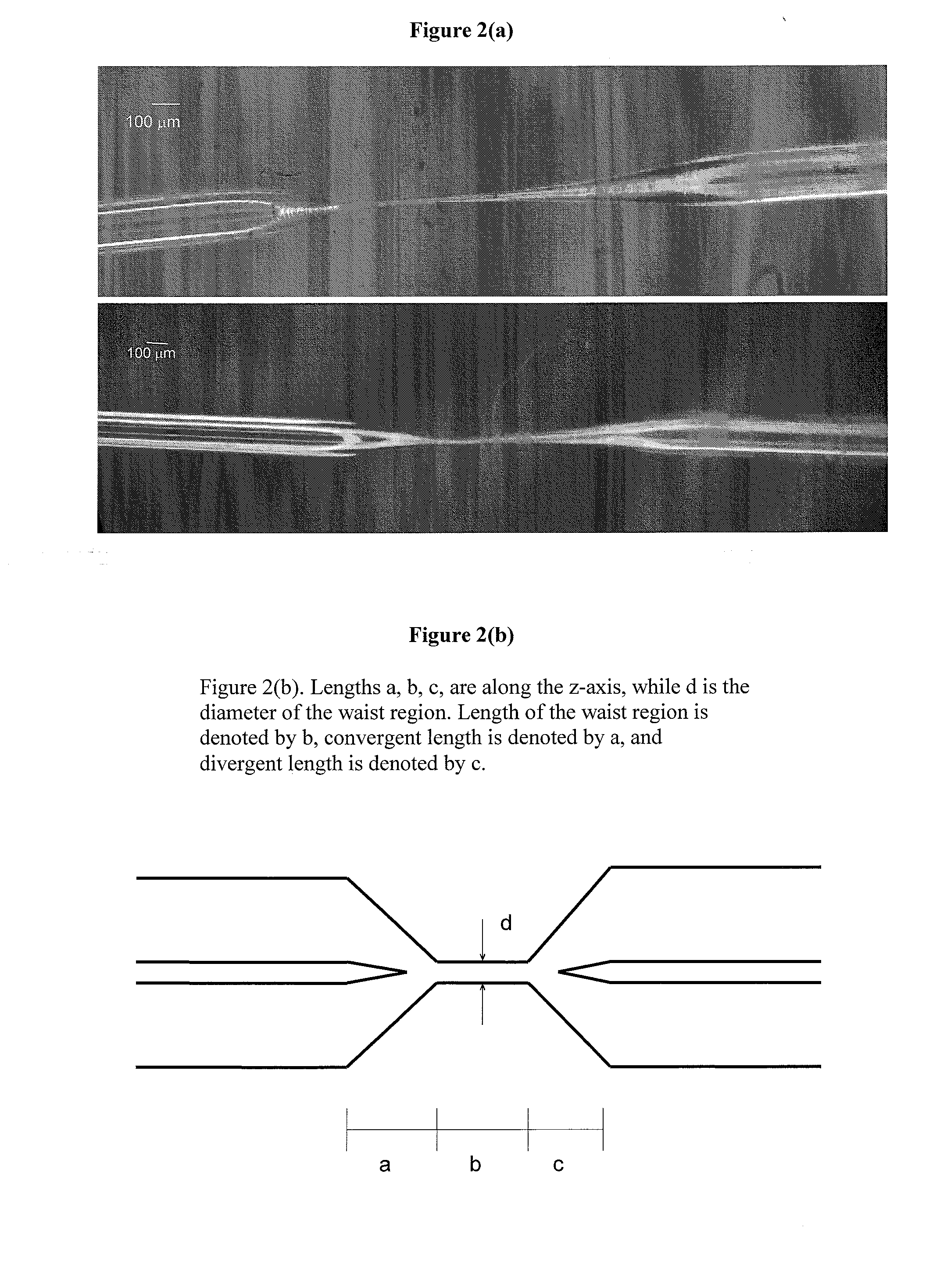
Ultra Sensitive Tapered Fiber Optic Biosensor For Pathogens, Proteins, and DNA
InactiveUS20090304551A1Improve abilitiesSmall amount of sampleMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFiberProtein insertion
A biconically tapered optical fiber serves as a biosensor at all optical wavelengths of interest ranging from UV to far IR at subfemtogram per mL sensitivity. The biconically tapered sensor detects biomaterials such as pathogenic species, proteins and DNA and others biological analytes. Although it uses the principles of evanescent fields, absorption, adsorption, fluorescence capture and retransmission through the fiber, the detection at the sub-nanogram per mL level is achieved primarily by adsorption or a surface activity due to a refractive index change. The geometry of the biconically tapered optical sensor affects its performance. The sensing modality is achieved in situ with a source connected at one end of a tapered fiber and a suitable detector at the other end. The tapered region is optionally immobilized with a recognition molecule such as an antibody to the target antigen or a complementary DNA strand. The sample is brought in contact with the tapered region either in batch mode or in a flow mode.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Complementary DNAs encoding proteins with signal peptides
InactiveUS20060009633A9Improve purification effectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementADAMTS ProteinsSecreted substance
The sequences of cDNAs encoding secreted proteins are disclosed. The cDNAs can be used to express secreted proteins or fragments thereof or to obtain antibodies capable of specifically binding to the secreted proteins. The cDNAs may also be used in diagnostic, forensic, gene therapy, and chromosome mapping procedures. The cDNAs may also be used to design expression vectors and secretion vectors.
Owner:SERONO GENETICS INST SA
Gene chip and kit for detecting common pathogen in dairy products
ActiveCN101240335AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsKlebsiella oxytocaStaphylococcus aureus
The present invention provides a gene chip for detecting common pathogen in dairy, which comprises a solid-phase vector and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid-phase vector, wherein the oligonucleotide probe includes DNA fragment or its complementary DNA or RNA sequence selected from E. sakazakii, streptococcus pyogenes, staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Listeria monocytogenes, salmonella and 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer region of Bacillus cereus, as well as ipaH gene of Shigella or gyrB gene of citrobacter freundii. The invention further provides a reagent box which uses the gene chip to detect pathogen in dairy. The gene chip and the reagent box of the invention for detecting pathogen in dairy are easy to operate, highly precise and greatly repeatable.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD +1
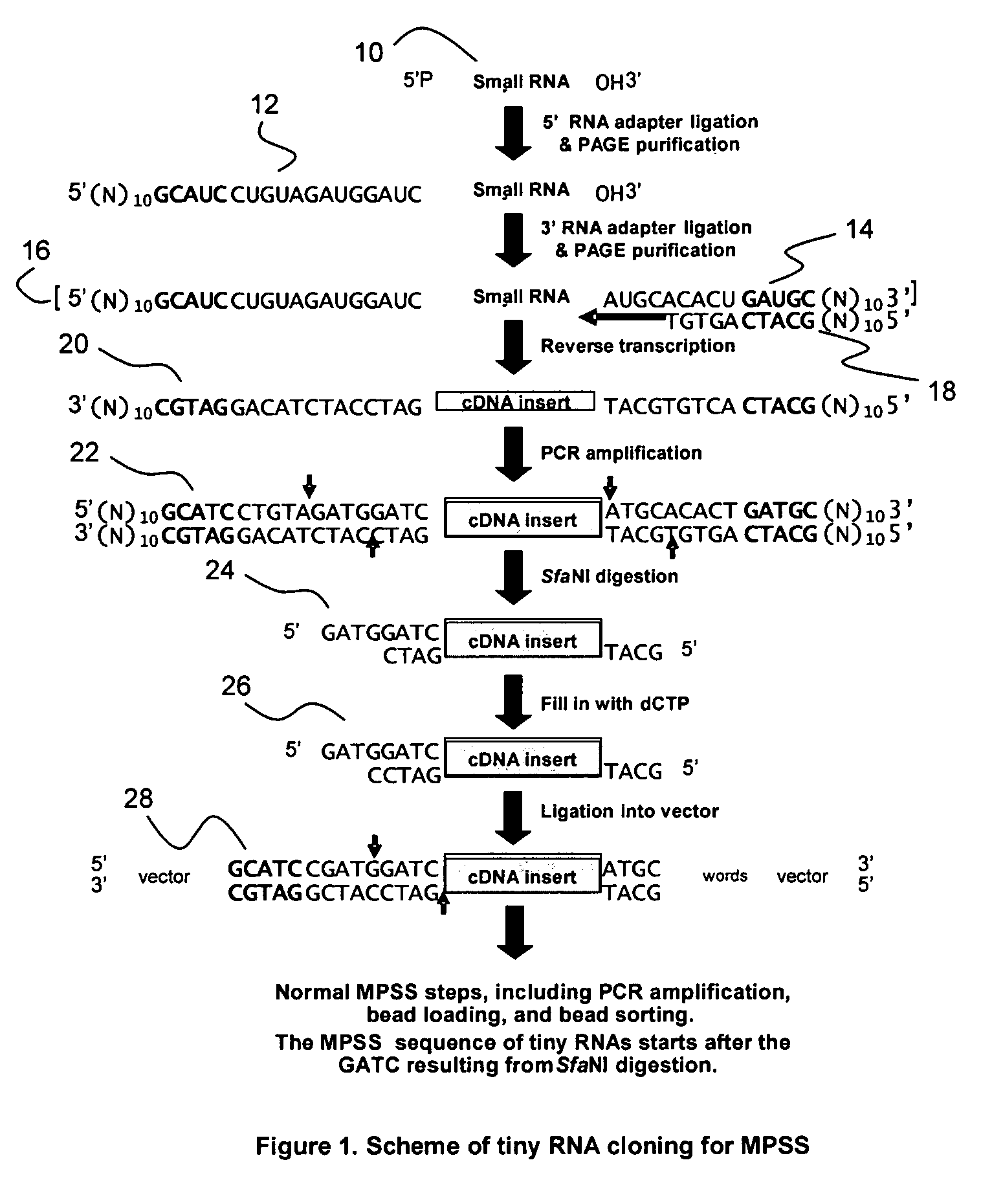
Method for identification and quantification of short or small RNA molecules
InactiveUS20060063181A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationComplementary DNABioinformatics
A method of identifying and quantifying small RNA molecules comprising a) isolating RNA molecules; b) ligating RNA adapter molecules onto the isolated RNA molecules to form RNA template molecules; c) forming complementary DNA molecules by transcribing the RNA template molecules; d) amplifying the complementary DNA molecules; e) obtaining sequence information of the complementary DNA molecules (and thereby the RNA from which it was derived); and f) obtaining quantity information of the complementary DNA molecules, wherein the quantity information of the DNA molecules reflects the quantity of the isolated RNA molecules is provided. Included in the invention is the identification of RNA molecules between 15 and 30 nucleotides in length.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE +1
Process for producing the enzyme D-amino acid oxidase of Rhodotorula gracilis in host cells
Process for producing the enzyme D-amino acid oxydase of Rhodotorula gracilis in host cells. The process for the expression of the enzyme comprises isolating the complementary DNA corresponding to the messager RNA of the gene which codes for the D-amino acid oxydase of any strain of Rhodotorula gracillis producing said enzyme; fusing the fragment of DNA which codes for D-amino acid oxydase of Rhodotorula gracillis with a DNA sequence which contains a site of union to the ribosome and a high efficiency promoter sequence for the express of genes in host cells; inserting the DNA fragment into a plasmid appropriate for the host cell; cultivating the host cells transformed with said plasmid; and collecting the enzyme.
Owner:ANTIBIOTICOS SA
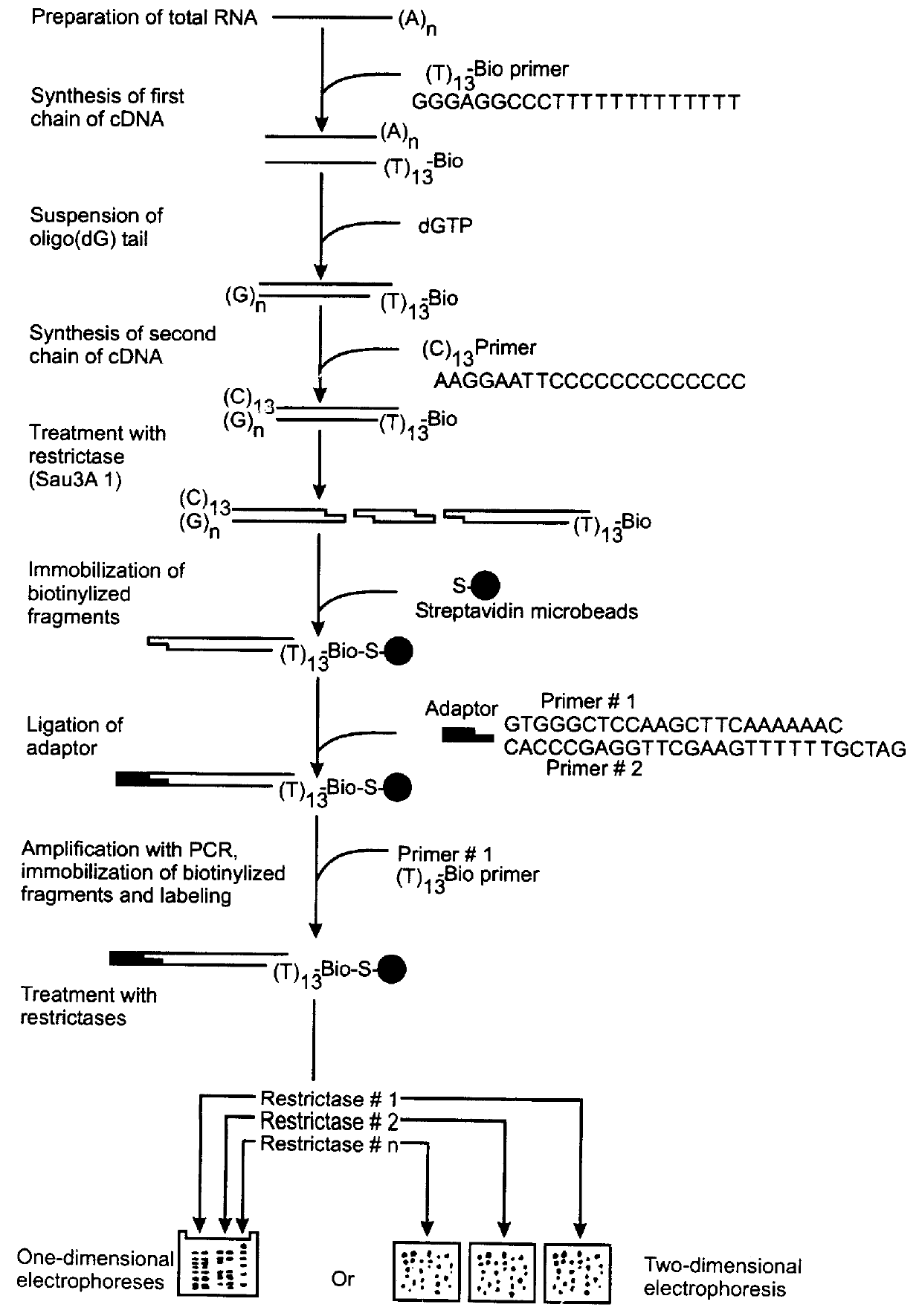
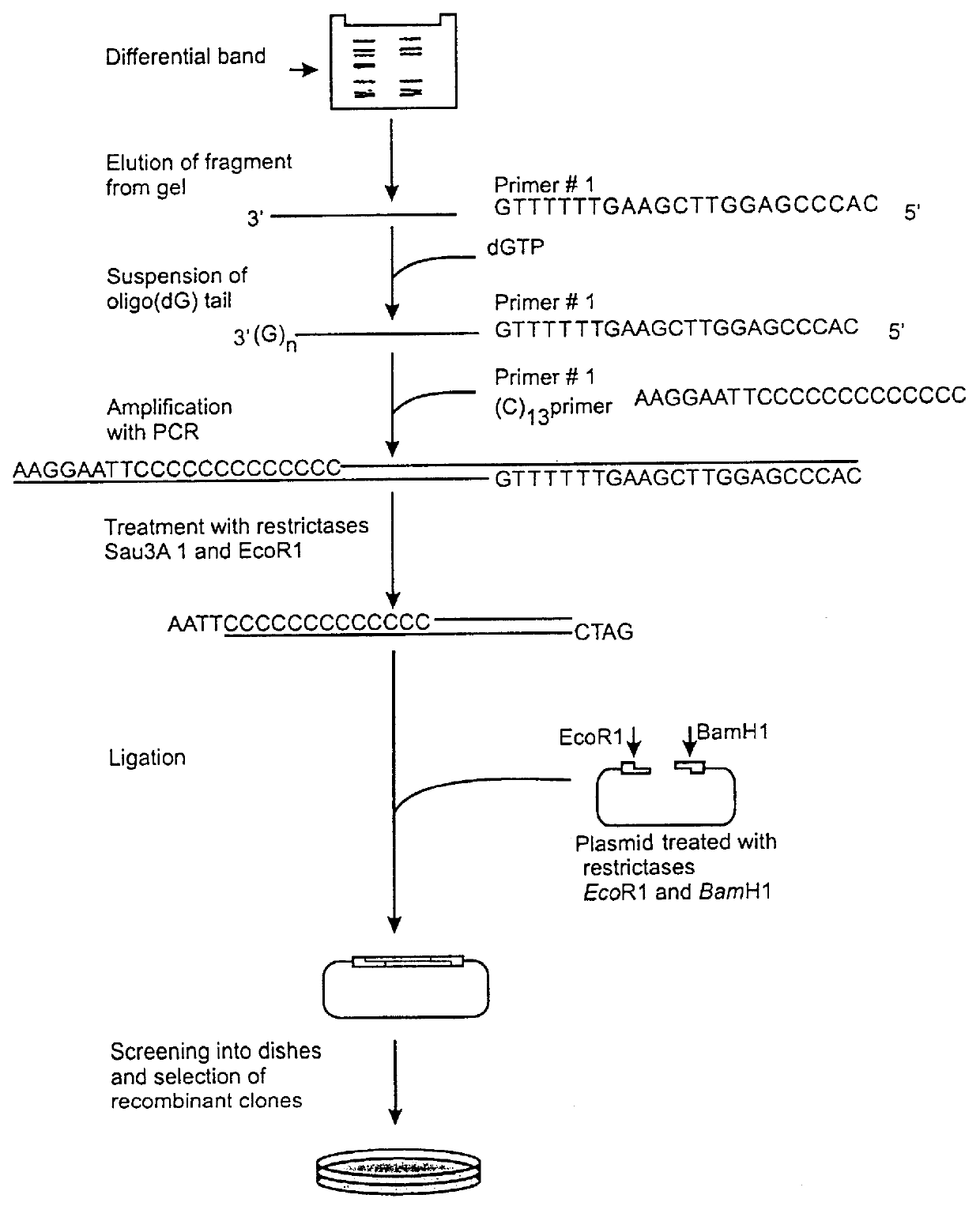
Method of identification and cloning differentially expressed messenger RNAs
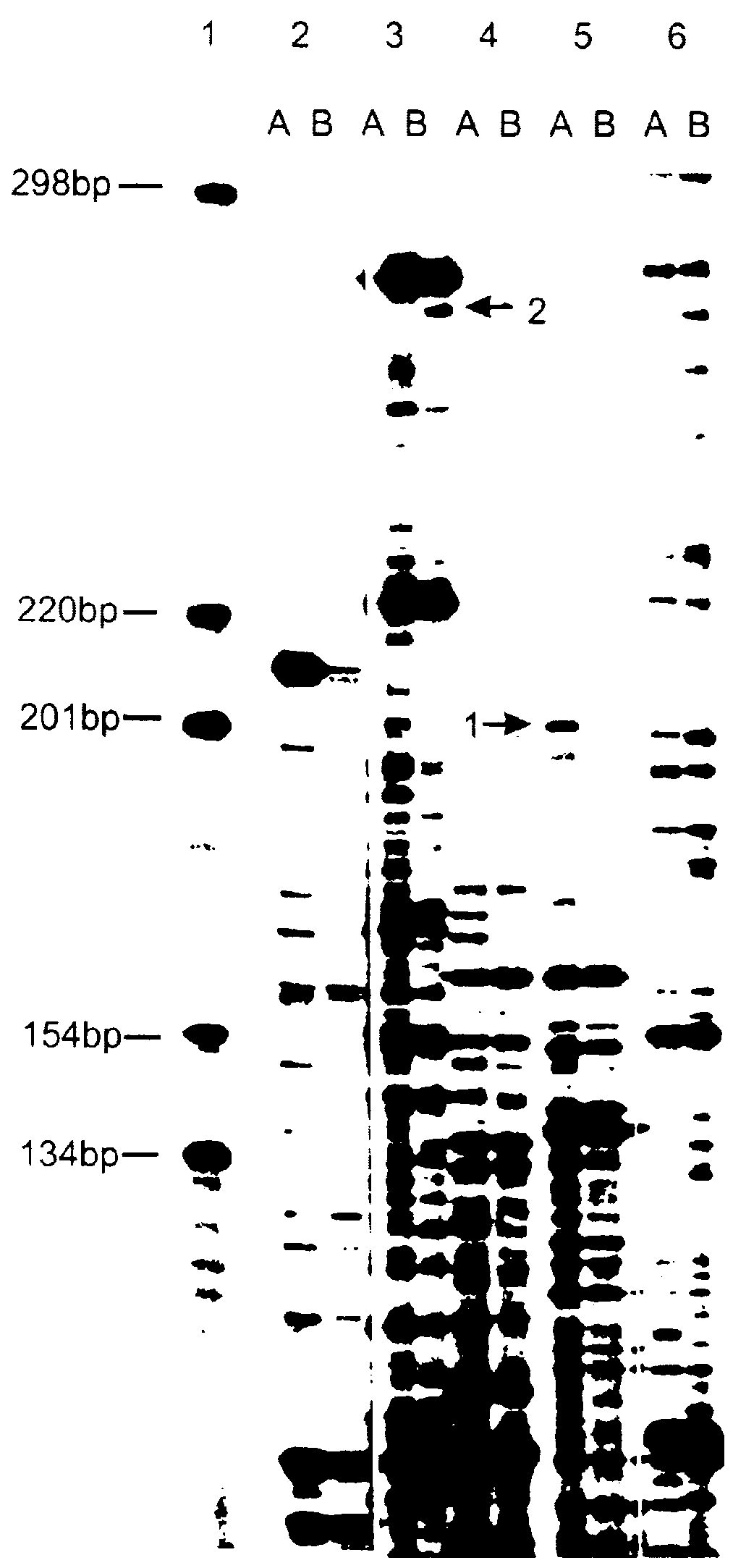
A method of identification of differentially expressed messenger RNA (mRNA) which consists of synthesizing from a set of sequences of mRNA sets of fragments of complementary DNA (cDNA), which are separated with the aid of gel electrophoresis and the pictures of separation of the cDNA from different types of cells are compared and fragments with differential signal intensity are identified. For formation of the set of fragments the cDNA is cleaved with the aid of restriction nucleases. A method of cloning of differentially expressed mRNAs consists of synthesizing from sets of sequences of mRNAs from different types of cells sets of fragments of complementary DNA (cDNA) which are separated with the aid of gel electrophoresis, the pictures of the separation of the cDNA from different types of cells are compared, fragments of cDNA with different signal intensities are separated from the gel, amplified with the aid of a polymerase chain reaction and cloned to a plasmid or phage vector. For the formation of the set of fragments one carries out cleavage of the cDNA with the aid of restriction endonucleases and uses only those fragments of cDNA that correspond to the 3' or 5' end regions of the mRNAs.
Owner:NEW YORK BLOOD CENT
Gene chip of main pathogenic microorganism in drinking water and testing kit
InactiveCN101748192ALow costImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention provides a gene chip of main pathogenic microorganism in drinking water and a testing kit, which mainly aims at 11 kinds of bacteria of colibacillus / Shigella, salmonella, vibrio cholera, vibrio parahaemolyticus, staphylococcus aureus, enterococcus faecails, pseudomonas aeruginosa, legionella pneumophilia, pneumobacillus, yersinia enterocolitica and the like, and L.interrogans. The gene chip comprises a solid phase carrier and a oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid phase carrier, wherein the oligonucleotide probe contains gyrB gene with tremendous evolutionary advantage, ITS gene and DNA segment selected from 16srRNA gene or complementary DNA segment. The gene chip and the testing kit of the invention can test the main pathogenic microorganism in drinking water, and has the characteristics of simple operation, high throughput, high accuracy, strong repeatability and the like, and can be used for clinical test for the water quality monitoring department.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Linker for detecting low-frequency variation, linker mixture and corresponding method
InactiveCN109439729AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInformation analysisLibrary preparation
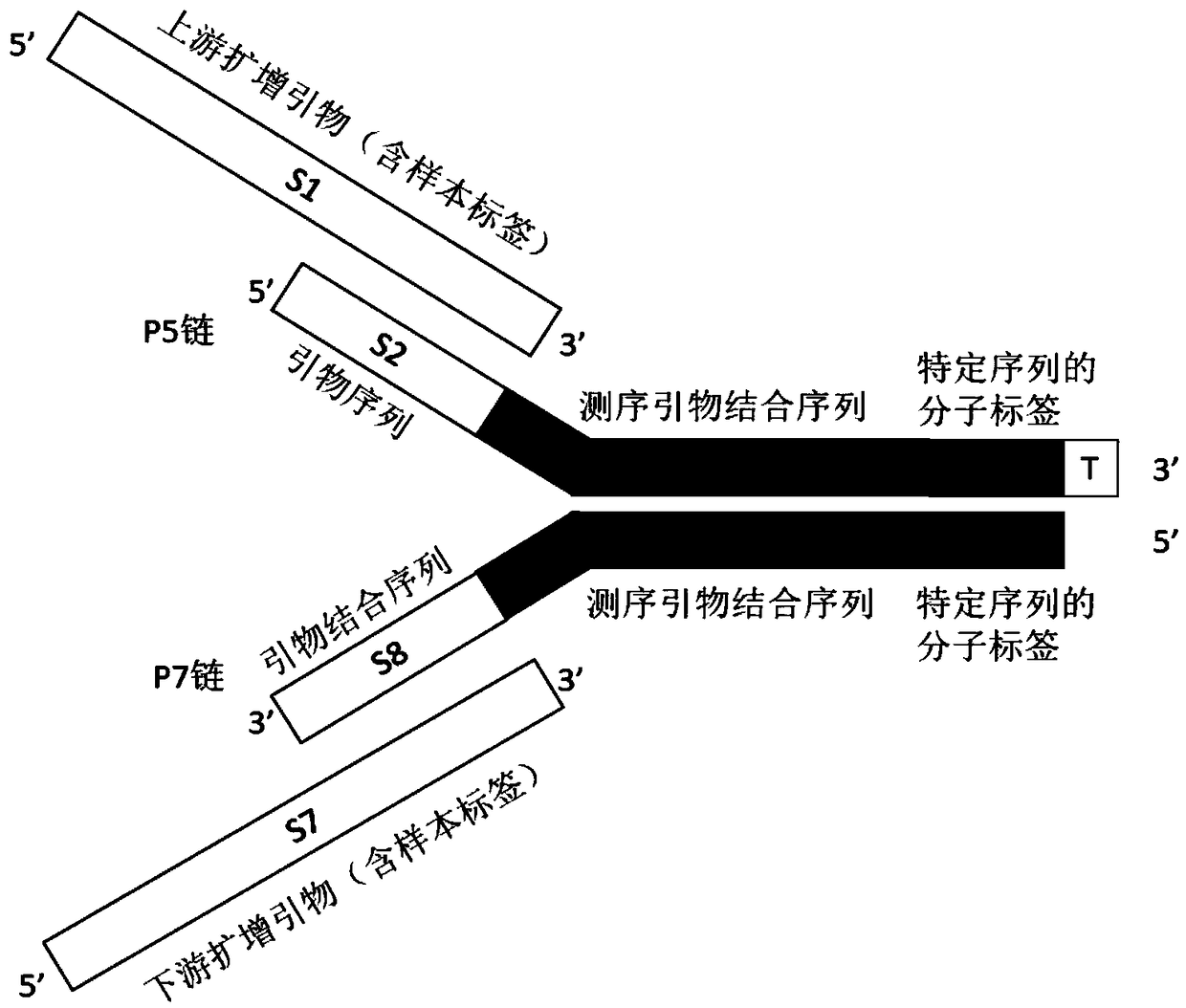
The invention relates to a linker for detecting low-frequency variation. The linker comprises two complementary DNA single chains, wherein one chain P5 comprises a sequence locally coincided with an upstream amplification primer, a sequence combined with an upstream sequencing primer, a molecular label of a specific nucleotide sequence combination and a bulged base T in turn from 5' end to 3' end;and the other chain P7 comprises the following three parts in turn from 5' end to 3' end: a molecular label reversely complementing to the molecular label in the chain P5, a sequence combined with adownstream sequencing primer and a sequence combined with a downstream amplification primer. The invention also relates to a linker mixture for detecting low-frequency variation and a corresponding method. The linker mixture provided by the invention is used for performing library preparation and high-throughput sequencing on the samples containing low-frequency variation and with damaged single chains, and the biological information analysis process and algorithm disclosed by the invention are adopted for effectively increasing the accuracy of variation detection.
Owner:XUKANG MEDICAL SCI & TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
DNA electrochemical biosensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104569101AEnables electrochemical signal conversionHigh binding specificityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical responseA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA electrochemical biosensor and a preparation method thereof. The DNA electrochemical biosensor comprises a gold electrode, a complementary DNA complementary with a target DNA sequence, conductive nanoparticles, and a soluble electrochemical active reagent, wherein a complementary single chain DNA, as a capturing probe, is assembled on the gold electrode; the single chain DNA and the conductive nanoparticles are combined as an electrochemical signal conversion unit for realizing electrochemical response to a DNA hybridizing event. By the preparation method, the sulfhydrylated DNA modified gold electrode adsorbed with the conductive nanoparticles is used as a signal conversion electrode, and through electrode reaction of the soluble electrochemical active reagent, based on base complementing and pairing between the DNA sequences, electrochemical response and detection of the target DNA is realized. The DNA electrochemical biosensor is simple in structure, simple and convenient in preparation process and high in sensibility, can be applied to quick detection of DNA molecules, and has the characteristic of reusability.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
A sandwich-type electrochemical sensor for detection of ovarian skov-3 cancer cells
InactiveCN102288656AHigh sensitivityHighly selective assayMaterial electrochemical variablesAntigenCancer cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry and a chemical sensor, and discloses an electrochemical sensor for diagnosis of an ovarian SKOV-3 cancer cell, relating to a preparation method of a sandwich-type immunosensor based on graphene and a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) marker and application of the same in medical diagnosis. Antigens (human ovarian cancer) are indirectly tested with a glassy carbon electrode modified by graphene / antibody / antigen / DNA-labeled antibody / complementary DNA through catalytic oxidation based on guanine bases and adenine bases. The high electronic conductivity of the graphene is adopted, and the cost of the antibody marker is reduced. The immunosensor prepared based on the technical scheme can also be applied in detection of other types of cells has a wide scope of application. The sensor has high sensitivity, can be prepared simply, can be applied in detection any cancer cell, and has good prospects of application in medical diagnosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Pixel and DNA cross dynamic chaotic cipher-based image encryption method and device
The present invention relates to a pixel and DNA cross dynamic chaotic cipher-based image encryption method and device. The method comprises the following processing of ranking the pixels of a plaintext image to obtain a first index matrix, and carrying out the first chaotic coding on the plaintext image according to the first index matrix to obtain a first intermediate image; ranking the rows andthe columns of the first intermediate image separately to obtain a row index matrix and a column index matrix, and scrambling the first intermediate image according to the row and column index matrixes to obtain a second intermediate image; converting each pixel in the second intermediate image into a 4-base DNA sequence, selecting eight kinds of coding rules satisfying a Watson-Crick complementrule according to the second chaotic coding, adopting the above eight kinds of coding rules to carry out the complementary DNA coding on each DNA sequence in the second intermediate image to obtain athird intermediate image, and then carrying out the DNA subtraction, add operation and xor operation on the third intermediate image to obtain a fourth intermediate image; carrying out the adjacent DNA coding on the fourth intermediate image to obtain a final ciphertext image.
Owner:SHANDONG ZHENGZHONG COMP NETWORK TECH CONSULTING
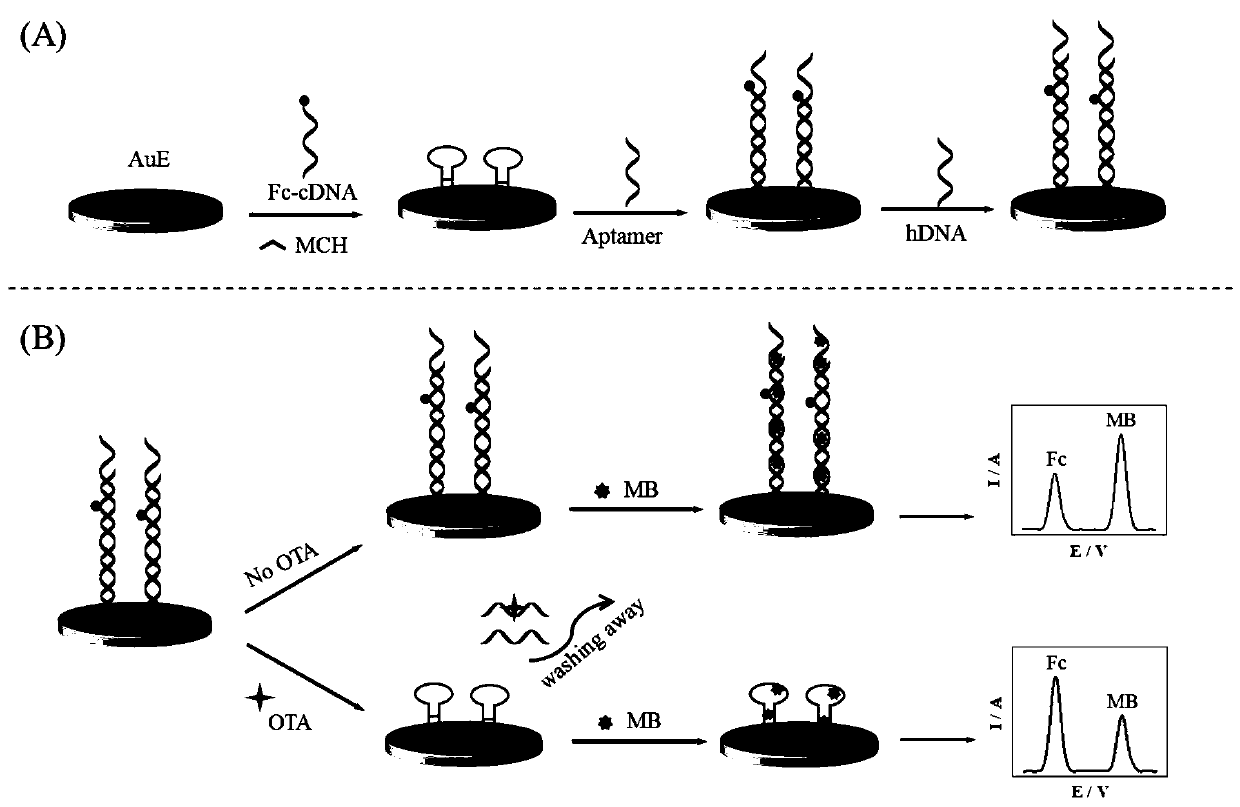
Ratio electrochemical detection method of ochratoxin A
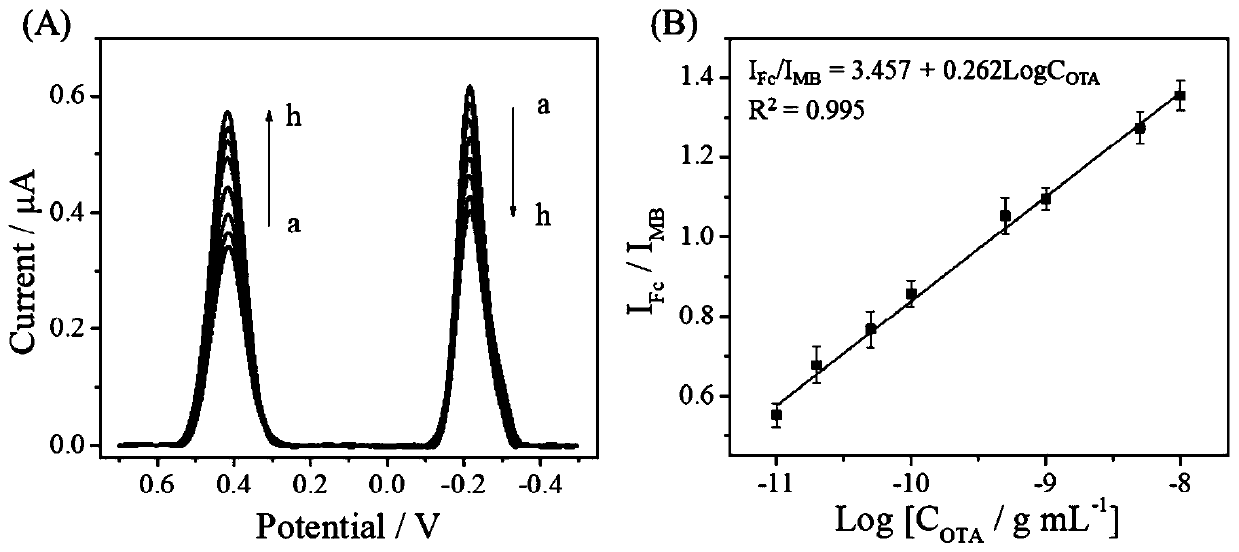
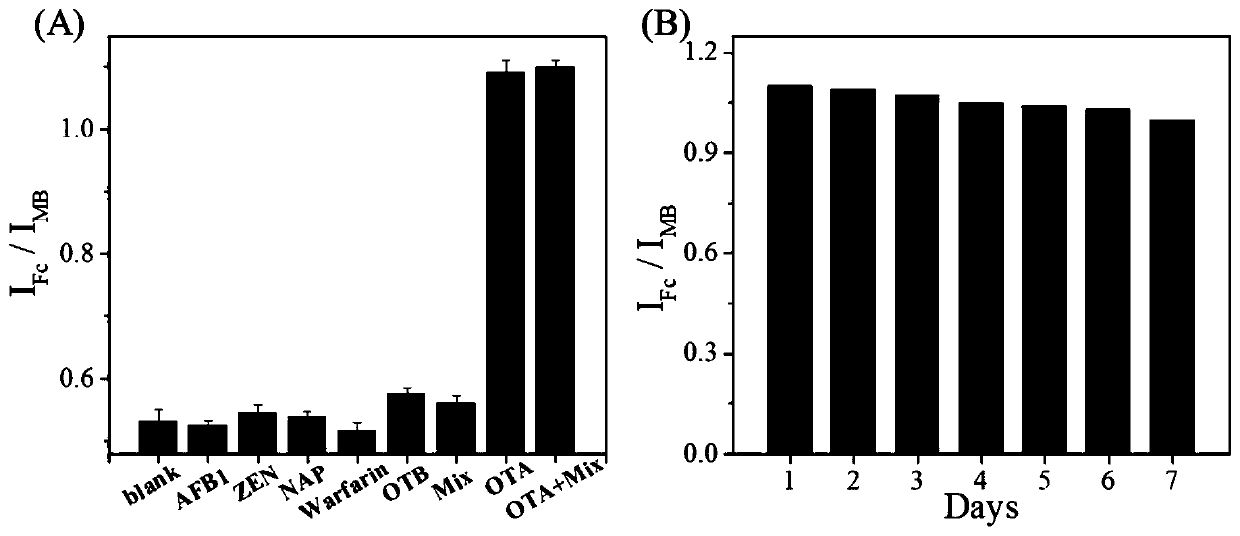
ActiveCN110618185AImprove reliabilityImprove accuracyMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerPower flow
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Process for improving DNA detecting sensitivity
InactiveCN1464070AIncrease the degree of fixationImprove adsorption capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementGold particlesSingle strand
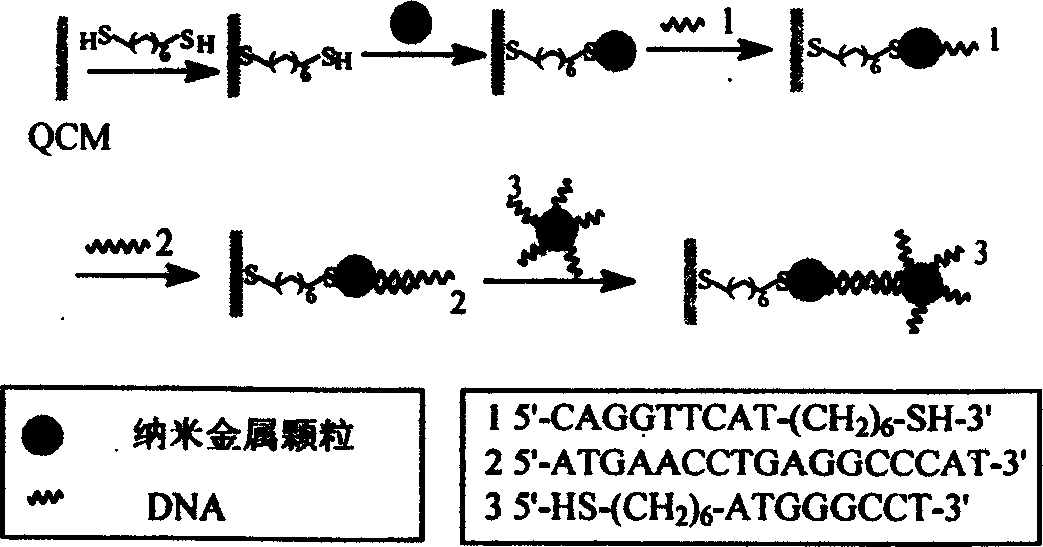
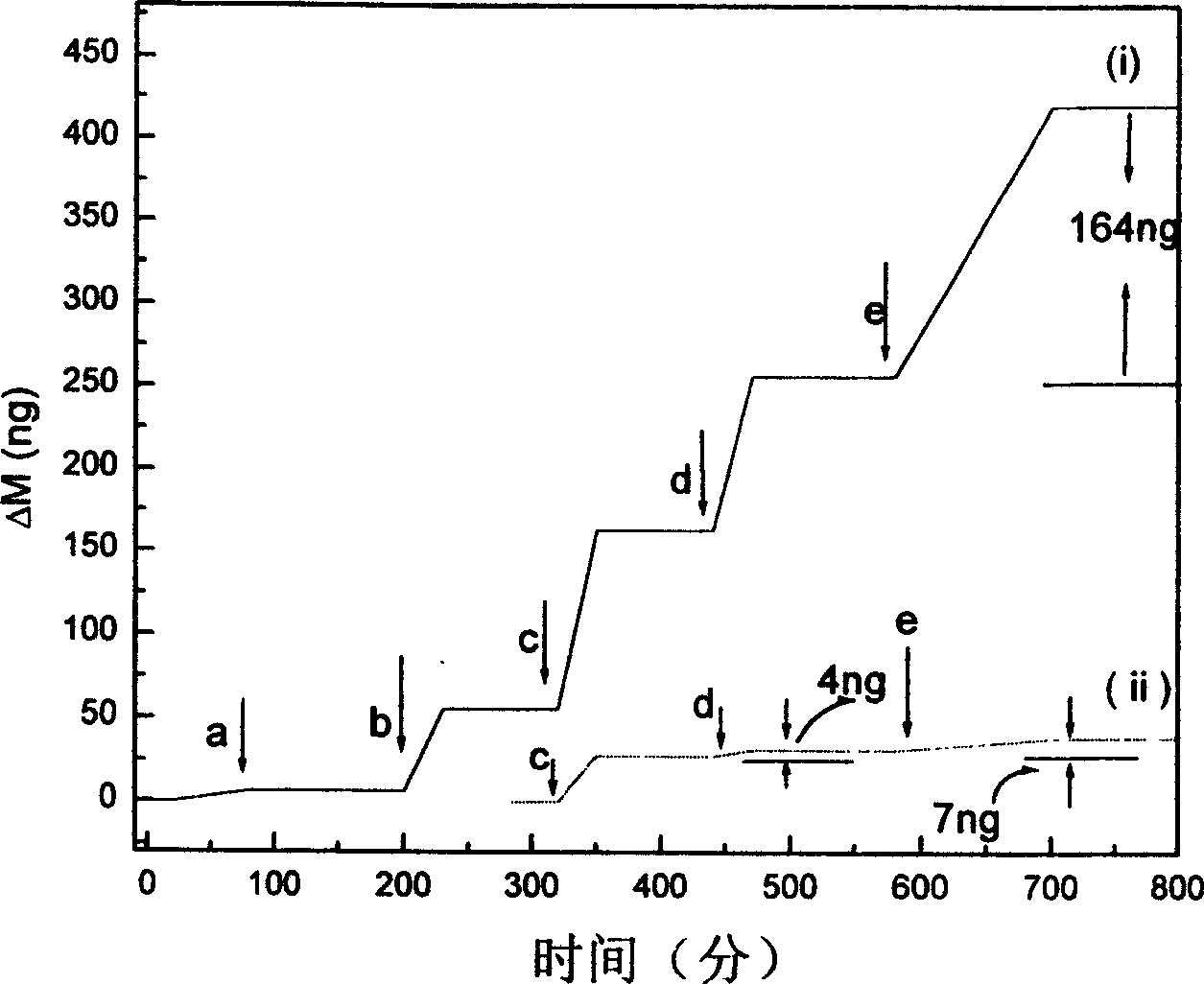
The present invention relates to one kind of method of detecting DNA crossbreeding and mispairing in raised sensitivity based on DNA base pairing principle. Nano gold particles in different sizes are used separately as the surfactant of quartz crystal microbalance and distinguishing amplifier as DNA detector. By means of the decoration of the metal surface of the quartz crystal microbalance with double-functional radical connecting agent, nano metal particles are fixed to the quartz crystal microbalance. Single-strand DNA probe is then fixed onto the nano metal decorated surface, and the DNA probe and the target DNA single strand to be detected are made to crossbred. The relatively longer target DNA has one part complementary with the probe DNA via being fixed onto the quartz crystal microbalance and the other part paired with the complementary DNA single strand connected to nano metal particles to raise the detection sensitivity to 10E(-16).
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gene chip for detecting pathogens of lower respiratory tract and reagent kit
ActiveCN101748193AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesK pneumoniaeStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a gene chip for detecting pathogens of lower respiratory tract, which comprises a solid phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid phase carrier, wherein the oligonucleotide probe comprises a sequence selected from one or more DNA sequences of staphylococcus aureus, 16s-23s rDNA intergenic spacer region of Klebsiella pneumoniae or Acinetobacter baumannii, 16S gene of pseudomonas aeruginosa or haemophilus influenzae, gyrB gene of streptococcus pneumoniae or legionella pneumophila and copB gene of moraxella catarrhalis or the complementary DNA or RNA sequence. The invention further provides a reagent kit containing the gene chip. The utilization of the gene chip and the reagent kit can detect the pathogens of the lower respiratory tract; furthermore, the operation is simple, the accuracy is high and the repeatability is strong.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Gene treatment to enhance feed efficiency and growth rate of livestock
InactiveUS20020137701A1Improve feed conversion efficiencyPromote growth rateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyLivestock
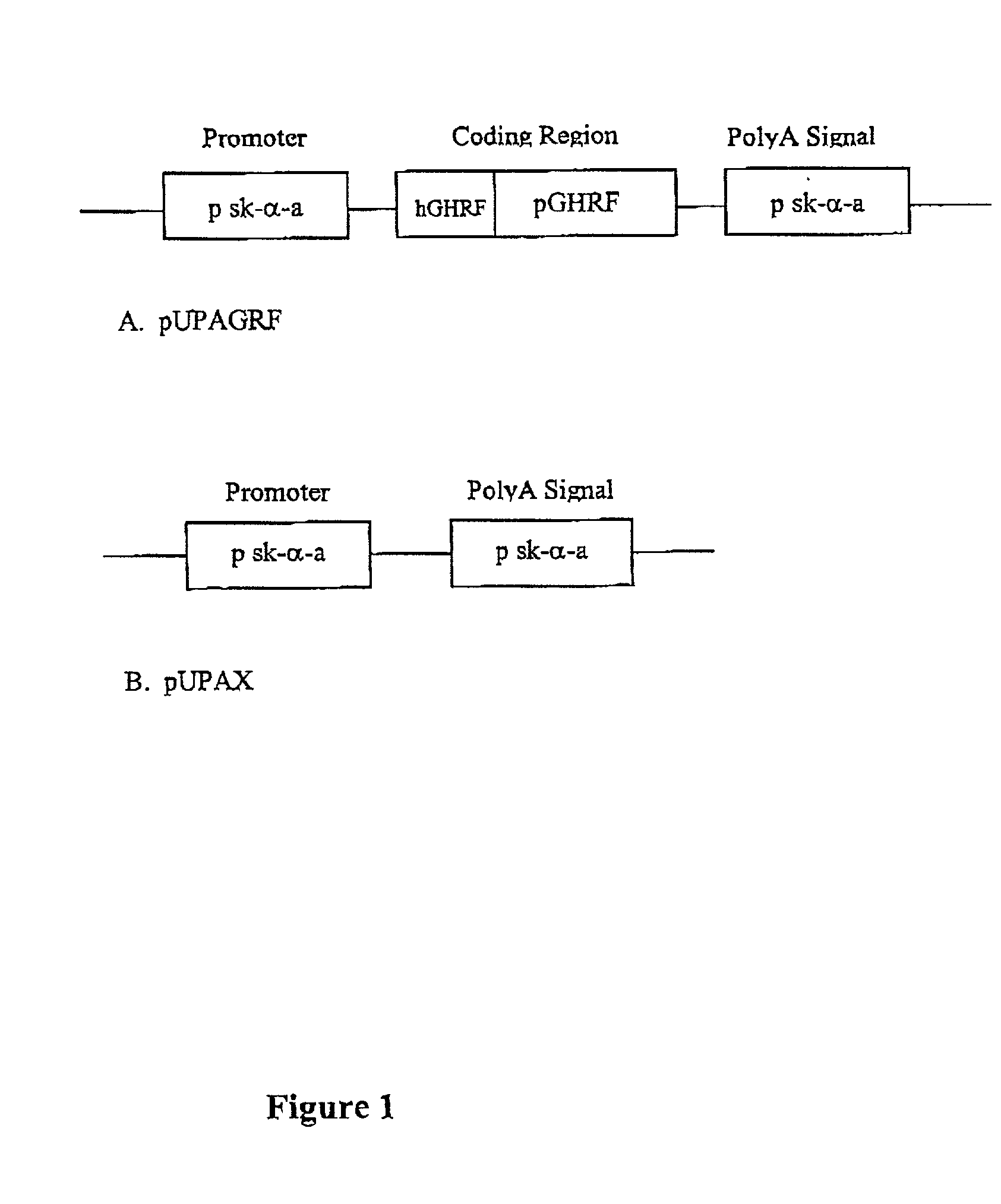
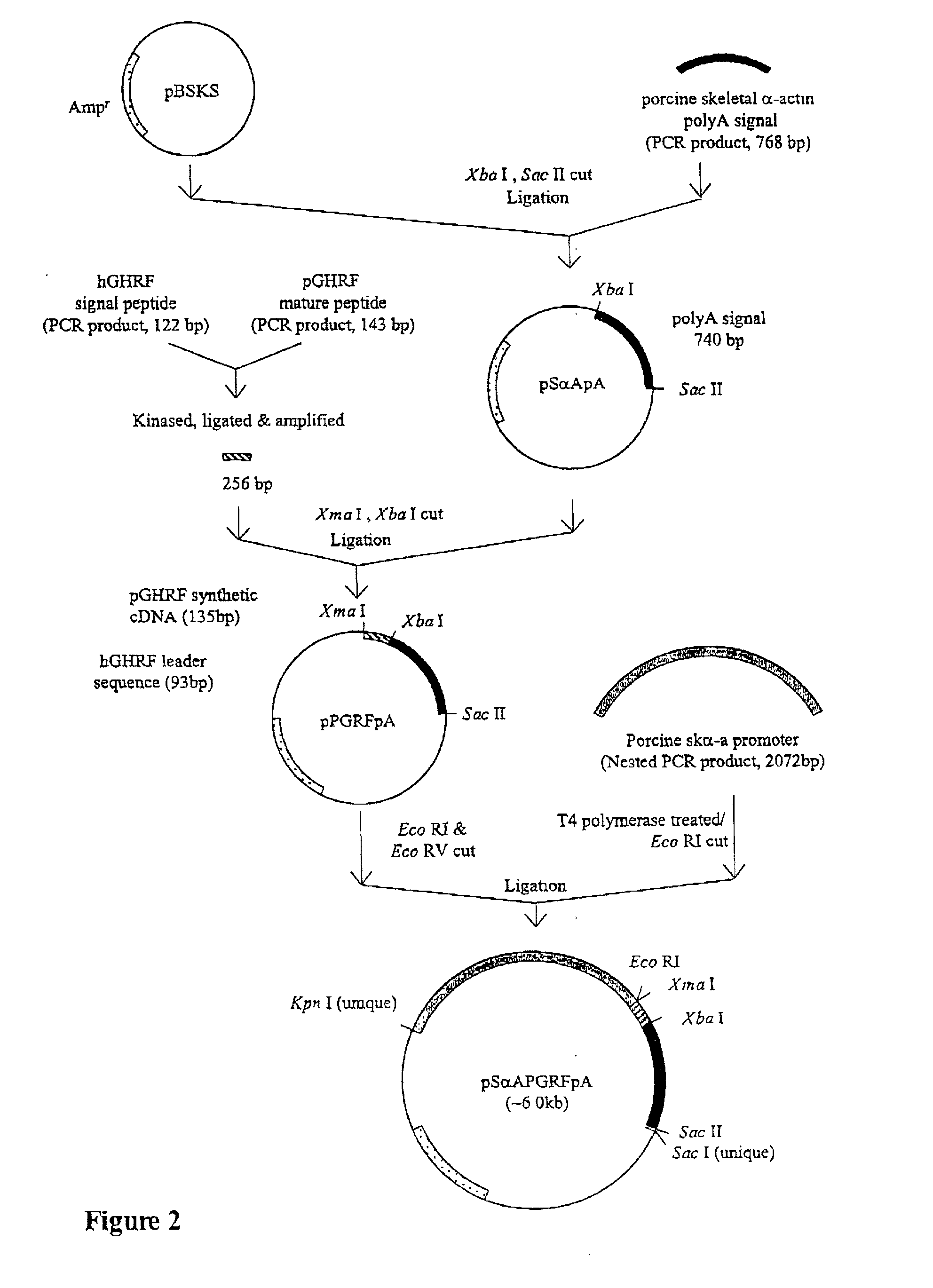
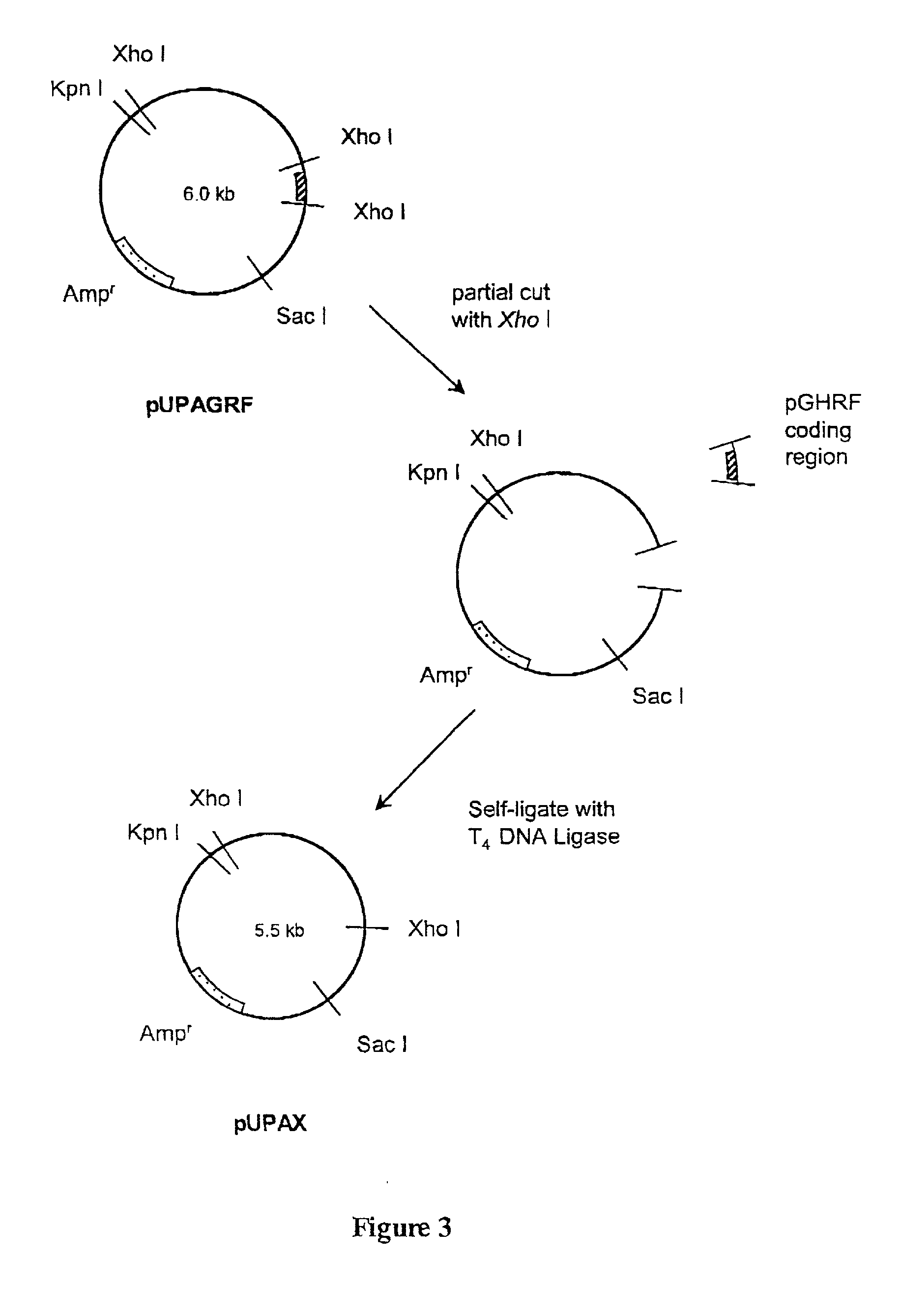
This invention relates to the enhancement of feed efficiency and growth rate, and the reduction of fit accumulation to produce better quality meat by administration of an exogenous gene sequence comprising the complementary DNA sequence of growth hormone releasing factor to stimulate the production of the endogenous hormone peptide growth hormone. This invention further relates to methods for producing such gene sequence.
Owner:LEADERGENE
SPR (Surface Plasmon Resonance) sensor made with graphene/gold/D-type plastic optical fiber and preparation method thereof
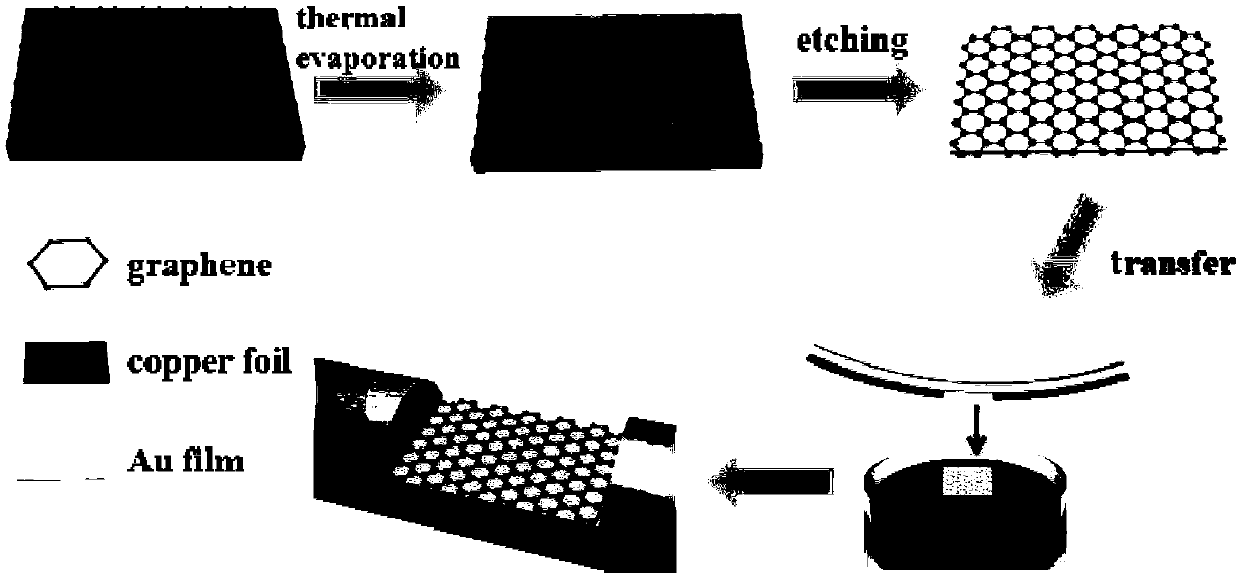
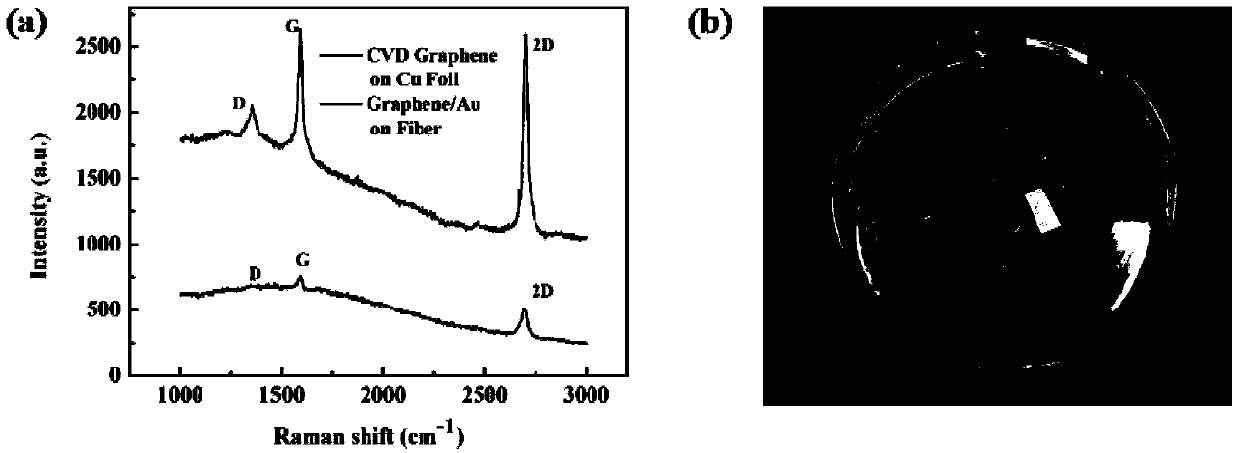
ActiveCN109540847AAffect functionQuality improvementMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberEvaporation
The invention belongs to the technical field of SPR sensors, and particularly relates to a SPR sensor made with a graphene / gold / D-type plastic optical fiber and a preparation method. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) forming a groove shaped sensing area in the fiber, and preparing a D-type fiber; (2) growing the graphene on a copper foil by using a chemical vapor deposition method,and directly evaporating a gold film onto the graphene through a thermal evaporation method, to obtain a gold / graphene / copper foil composite layer; (3) corroding the copper foil in the gold / graphene / copper foil composite layer, and moving the obtained graphene / gold film to a D-type optical fiber, to obtain the sensor. According to the preparation method, the gold is directly evaporated onto the graphene through the thermal evaporation method, so that the graphene and the gold film are perfectly laminated; and then the graphene / gold etched off the copper foil is moved to the D-type plastic optical fiber, so that the structure of the gold plus graphene is realized on the plastic optical fiber. The prepared SPR sensor made with the graphene / gold / D-type plastic optical fiber has the characteristic of a high recognition sensitivity of complementary and non-complementary DNA strands.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Detection genetic chip and detection kit for infectious diarrhea
InactiveCN102140507ALow costImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesEscherichia coli
The invention provides a genetic chip and a detection kit related to major pathogenic microorganisms causing infectious diarrhea of human beings, which are mainly specific to 13 types of bacteria including lapactic bacillus coli / shigella, salmonella, comma bacillus, vibrio parahemolyticus, aeromona hydrophila, plesiomonas, virio hollisae, vibrio fluvialis, vibrio mimicus, Wauter's strains, vibriodamsela and vibrio furnissii. The genetic chip comprises a solid-phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid-phase carrier, wherein the oligonucleotide probe comprises DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) fragments selected from genes including a gyrB gene, an ITS gene, a dnaJ gene, a toxR gene and the like with remarkable biological evolution advantages or complementary DNA fragments. By adopting the genetic chip and the detection kit provided by the invention, major pathogenic microorganisms causing infectious diarrhea of human beings can be detected. The genetic chip and the detection kit have the characteristics of easiness and convenience for operation, high flux, high accuracy, high repeatability and the like, and can be applied to clinical detection of inspection departments in hospitals.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Gene chip for detecting nine pathogenicity vibrios in marine products
InactiveCN103820558AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesMicrobiologyComplementary DNA
The invention relates to a gene chip for detecting nine pathogenicity vibrios in marine products and a kit thereof. The gene chip comprises a solid phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe, wherein the oligonucleotide probe includes one or more selected from the following nucleotide sequences: 1) DNA sequences selected from genes of a vibrio hollisae, a vibrio vulnificus, a vibrio cholera, a vibrio parahemolyticus, a vibrio harveyi, a vibrio alginolyticus, a vibrio furnissi, a vibrio mimicus and a vibrio damsel, 2) complementary DNA sequences of the DNA sequences selected in the DNA sequences in 1), 3) complementary RNA sequences of the selected DNA sequences in 1) or 2). The kit comprises the gene chips. The gene chip for detecting nine pathogenicity vibrios in marine products and the kit thereof provided by the invention are used for detecting the nine pathogenicity vibrios in marine products, and have the advantages of simplicity in operation, good sensitivity and strong repeatability.
Owner:ZHOUSHAN INST OF CALIBRATION & TESTING FOR QUALITY & TECHNICAL SUPERVISION
Preparation method of nanostar dimmer with surface raman strengthening activities
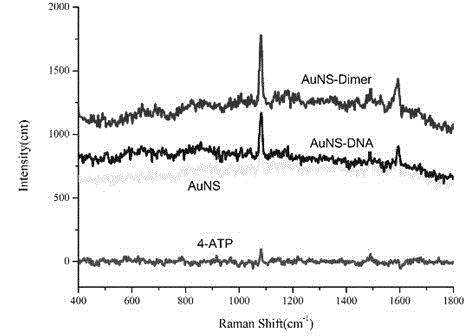
ActiveCN102875626AUniform structureSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationCouplingStrengthening activity
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nanostar dimmer with surface raman strengthening activities and belongs to the technical field of materials chemistry. The method includes synthesizing gold seeds, synthesizing gold nanostars which modify deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) 1 and DNA 2 respectively, and assembling gold nanostars modified by the DNA 1 and the DNA 2. The synthesized gold nanostars are plasma resonators and form a gold nanostar dimmer structure by means of coupling of complementary DNA chains. According to the method, self-assembly of the plasma gold nanostars is achieved, and the prepared gold nanostar dimmer is uniform in structure.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Pseudosciaena crocea interferon (IFN) gene and cloning method thereof
InactiveCN102559695AActivate immune responseNo pollution in the processFermentationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyDisease
The present invention discloses a Pseudosciaena crocea interferon gene, which is characteristics in that: the cDNA (complementary DNA) sequence of the coding region of the interferon protein has the base sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and the amino acid sequence shows in SEQ ID NO.2 in the sequence list; as well as a cloning method thereof. The Pseudosciaena crocea interferon gene disclosed by the invention has a good application prospect in prevention and control of Pseudosciaena crocea disease and further development of biological fish drugs, and lays the foundation for Pseudosciaena crocea molecular marker-auxiliary disease resistance breeding and detection of health status of fishes.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com